Low complex degree equalization method based on iteration jam deleting in spread spectrum communication system
A technology of interference cancellation and spread spectrum communication, which is applied in transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the influence of receiving performance, the decrease of signal-to-noise ratio, and unbearable computational complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
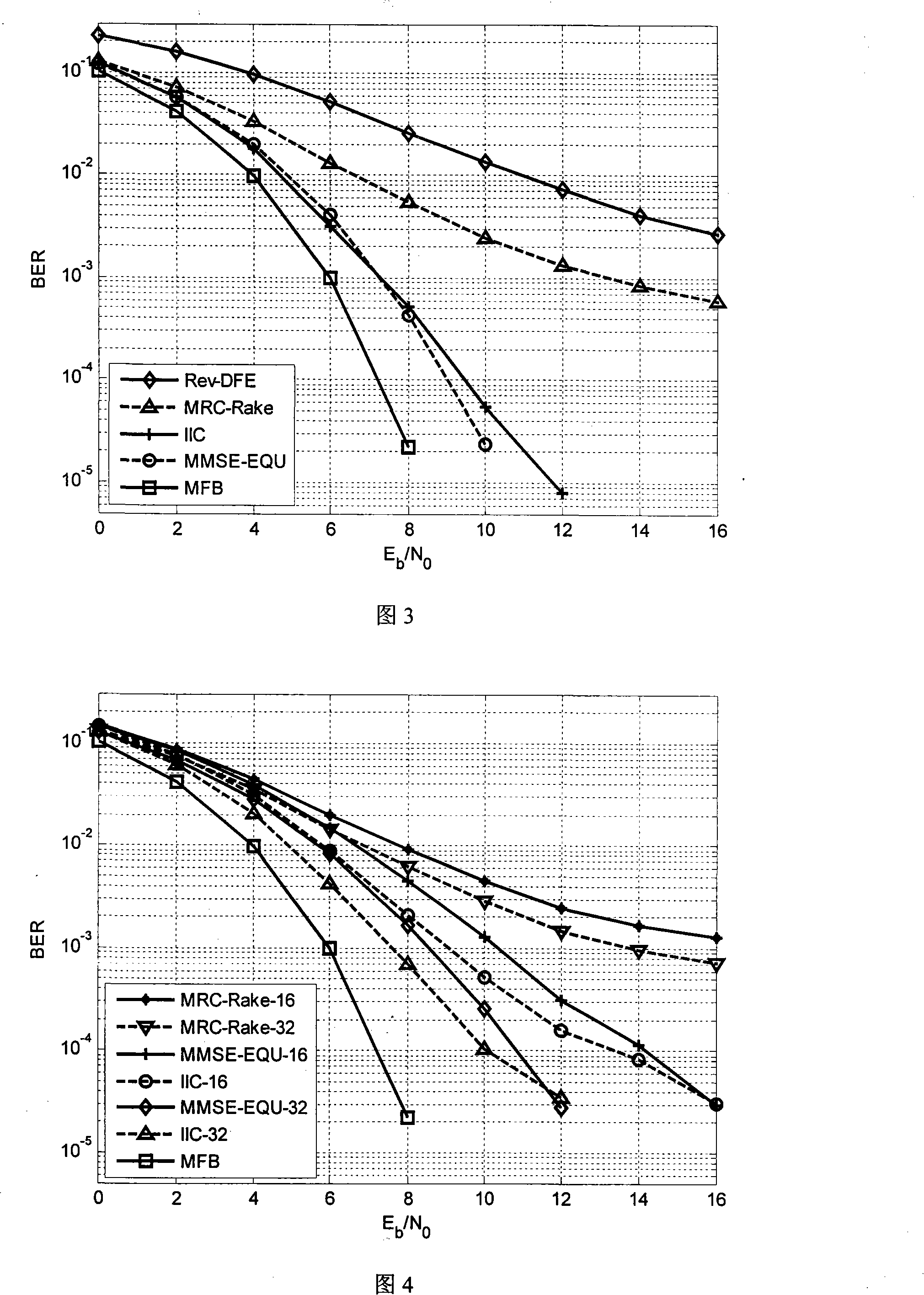
[0055] The low-complexity equalization method based on iterative interference deletion in the spread spectrum communication system proposed by the present invention is described in detail as follows with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0056] The inventive method comprises the following steps:
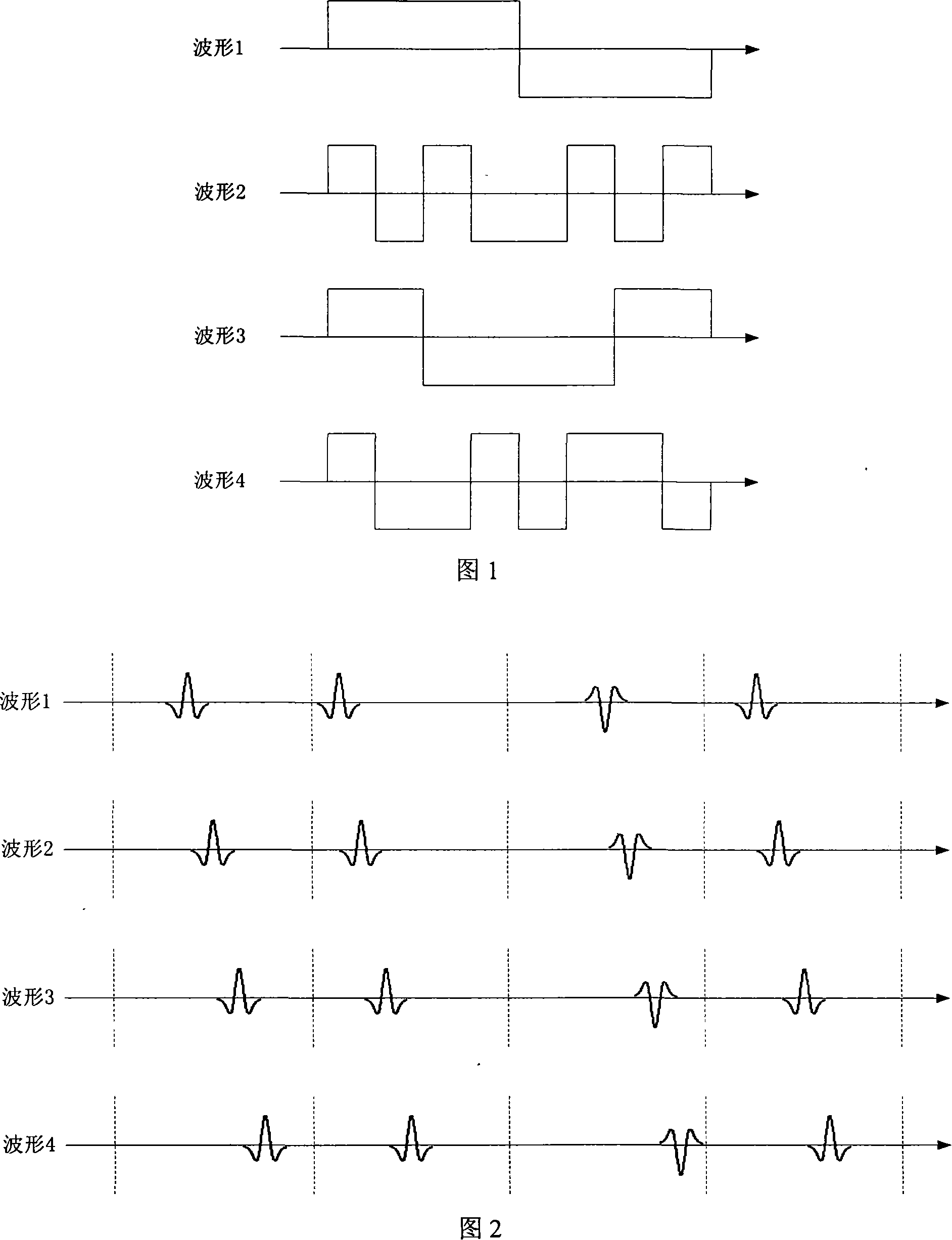
[0057] Firstly, in the pilot phase of the received signal, channel estimation is performed using methods such as sliding correlation or least squares, and the estimated value h of the composite channel response is obtained m [i], m=0, 1, ..., M-1, i = 0, 1, ..., KN c -1, where M represents the number of spread spectrum waveforms used by the communication system, K represents the number of symbols covered by the composite channel response, N c Indicates the number of sampling points in a symbol period;
[0058] For each composite channel response h m [i], i=0, 1, ..., KN c -1, from KN c Select the L diameter with the largest amplitude among the diameters, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com