Patents
Literature
4345 results about "Low complexity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
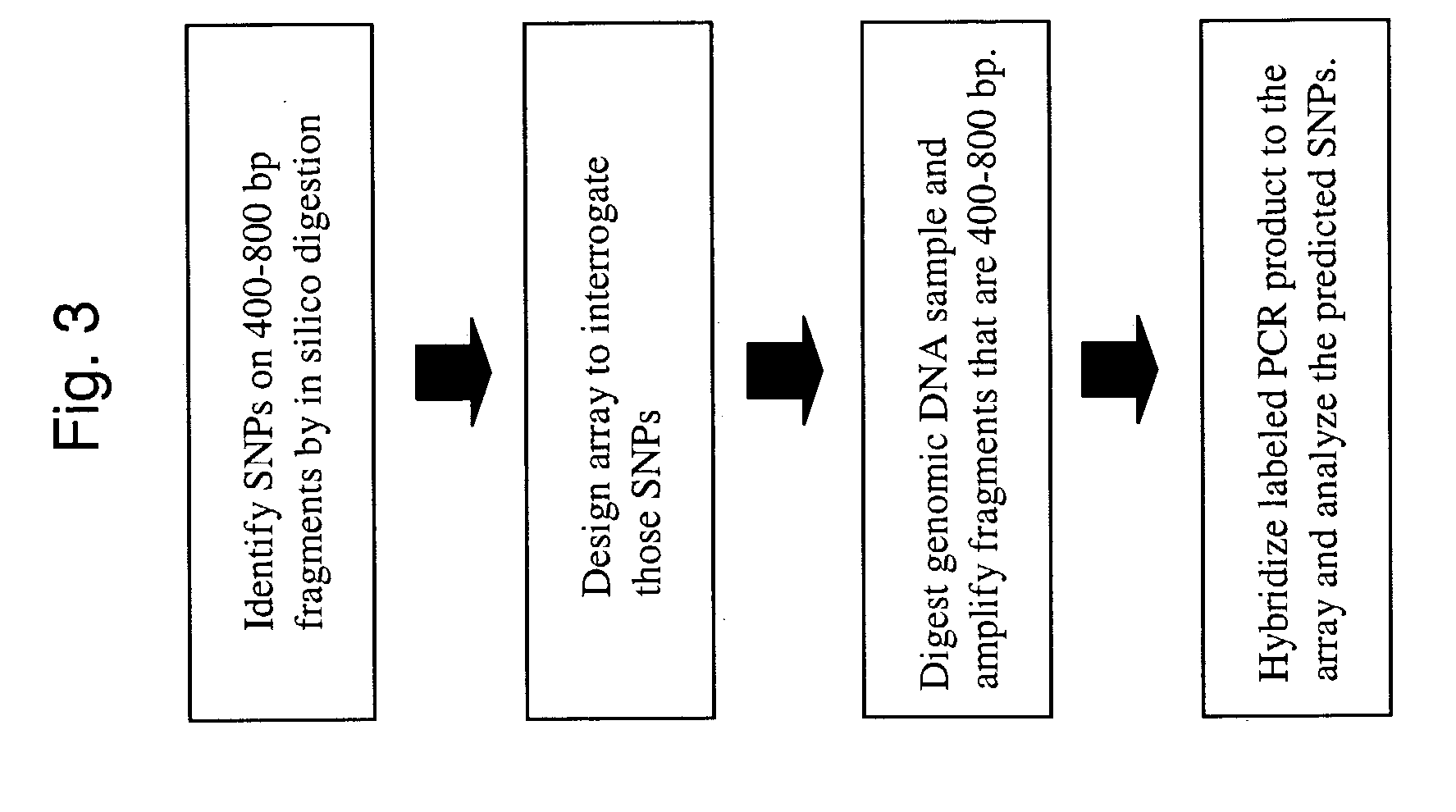
Low complexity. medical decision - making. Low Complexity Medical Decision-Making requires only slightly more intellectual energy than straightforward MDM. The acuity of care remains minimal. For example, this level of MDM is required for a level 3 office visit (99213) or a level 3 office consult (99243).
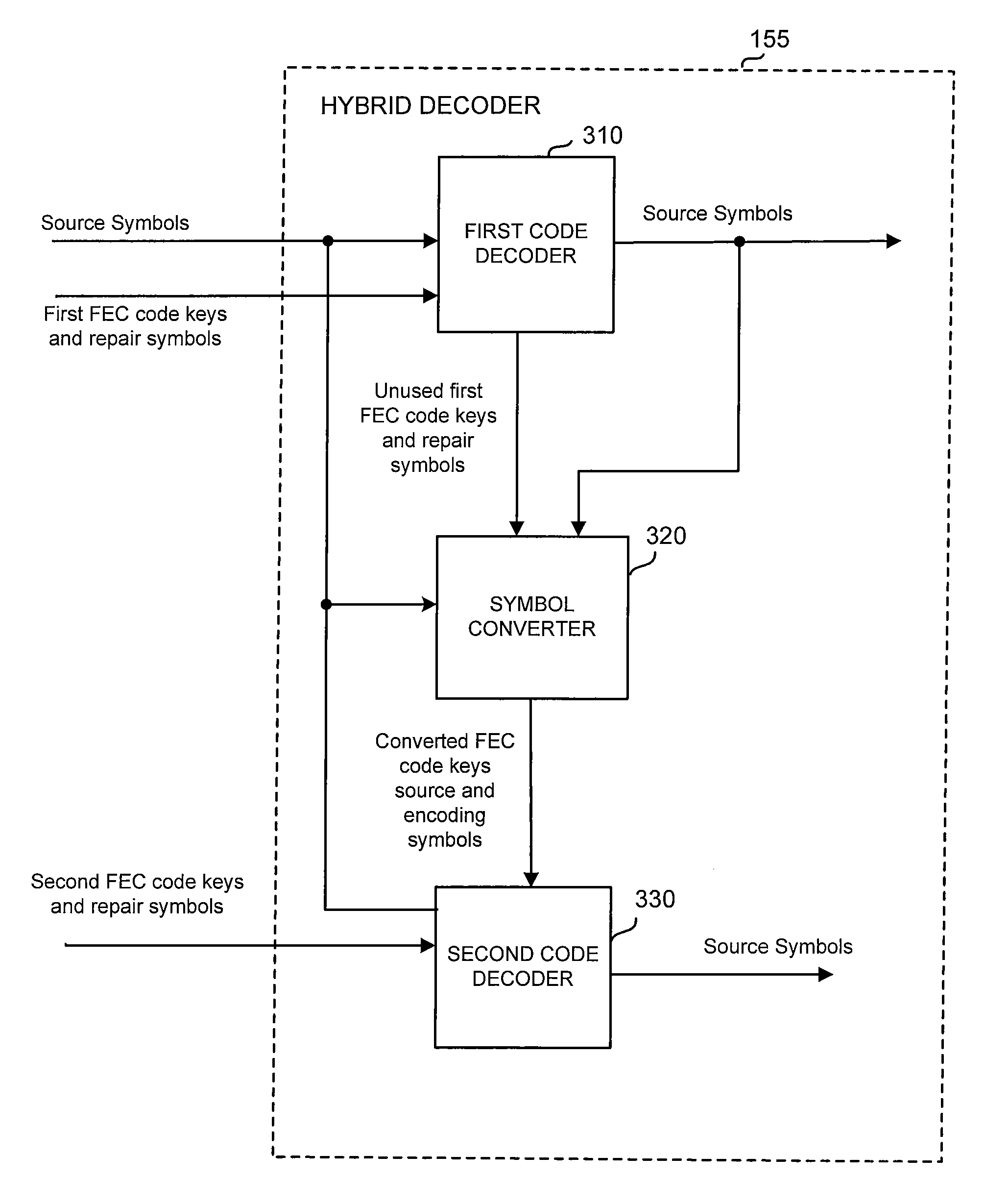
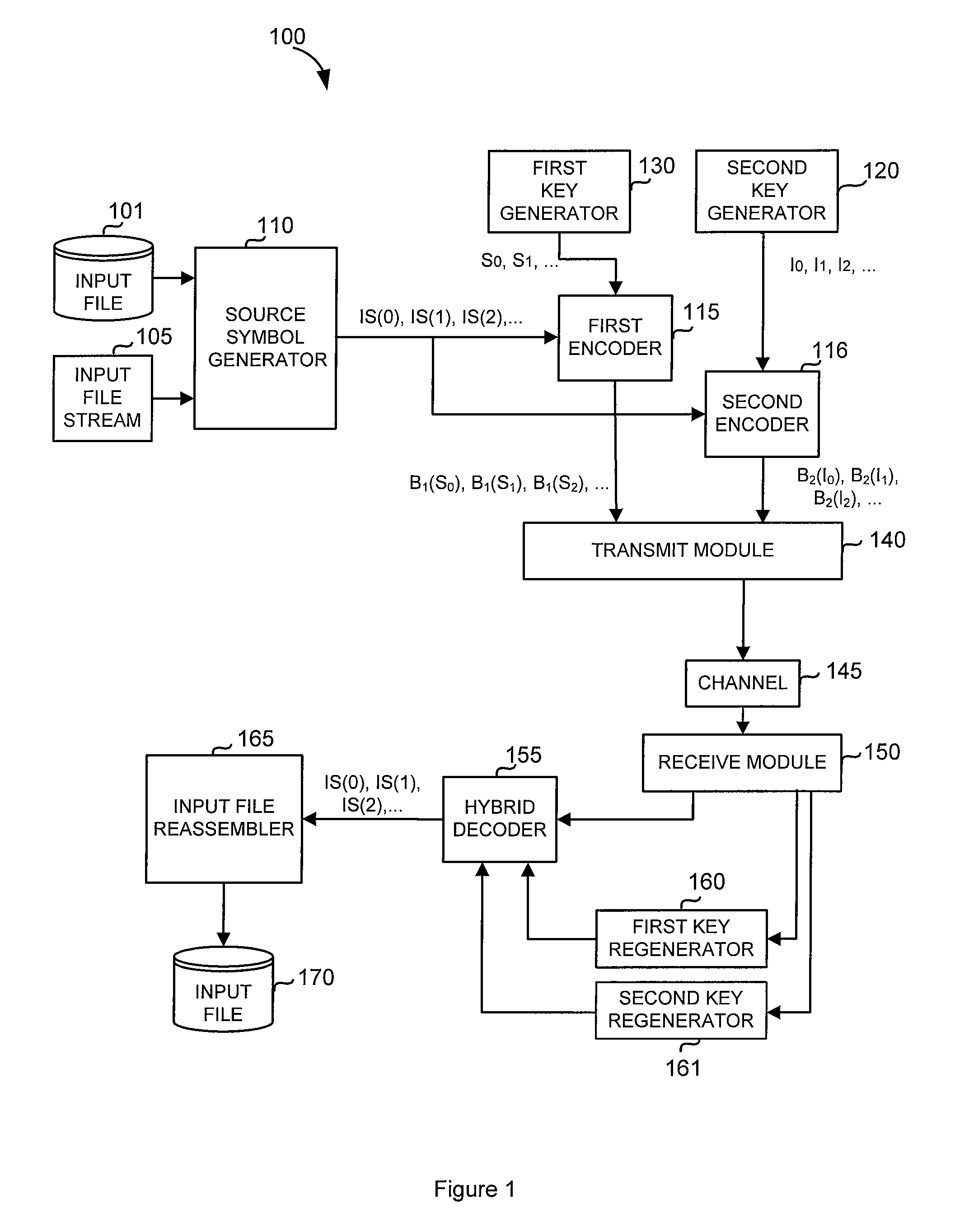
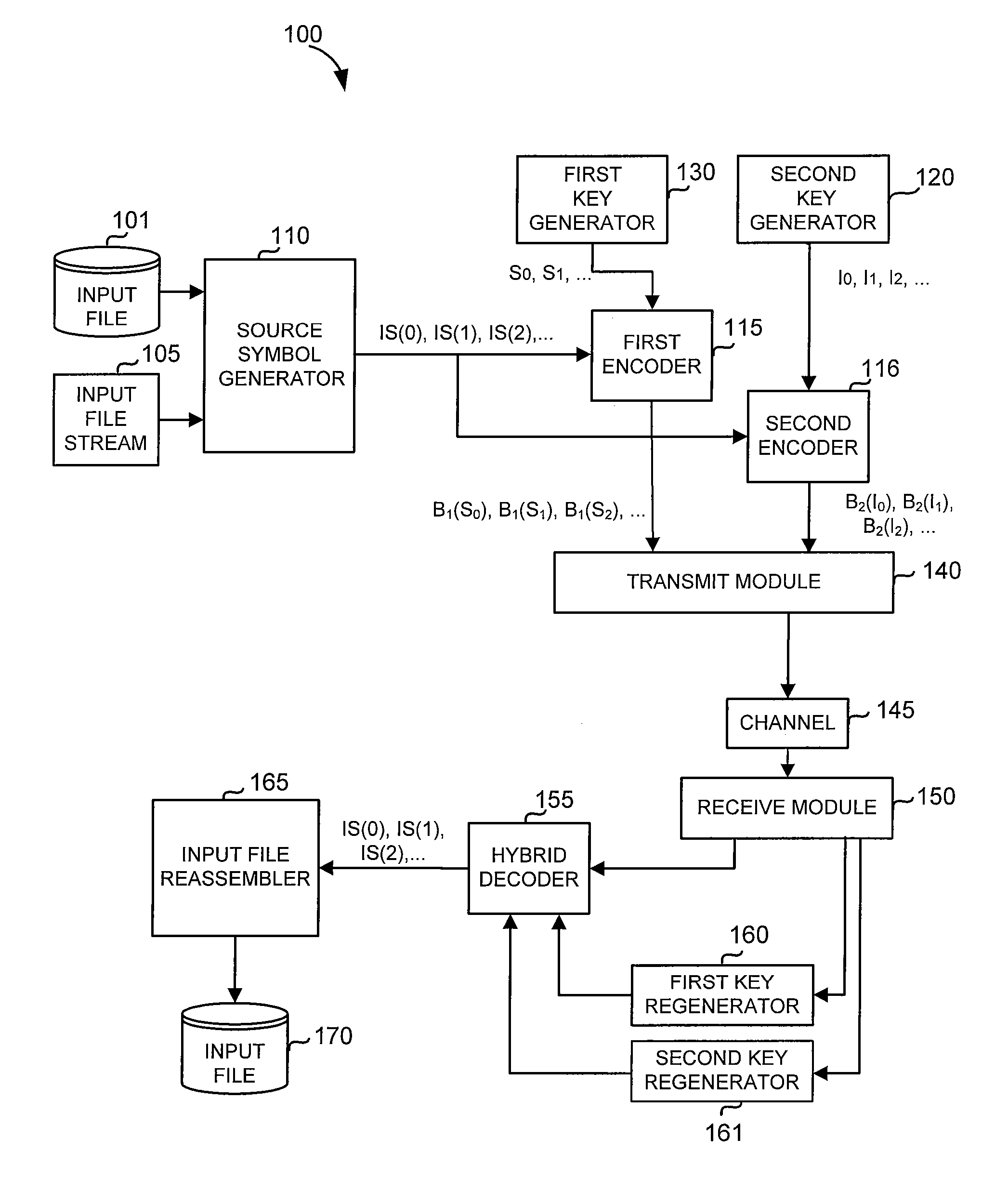
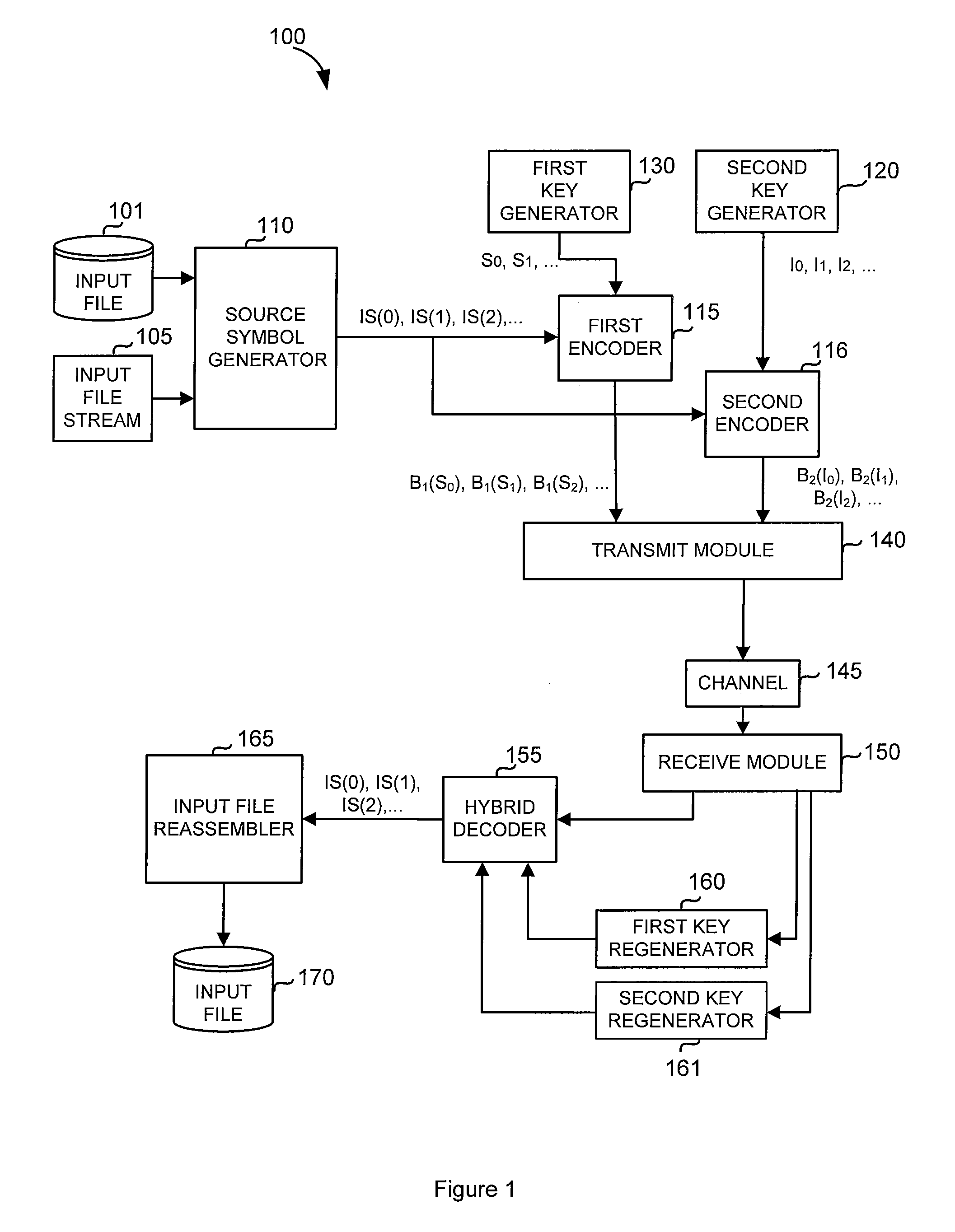
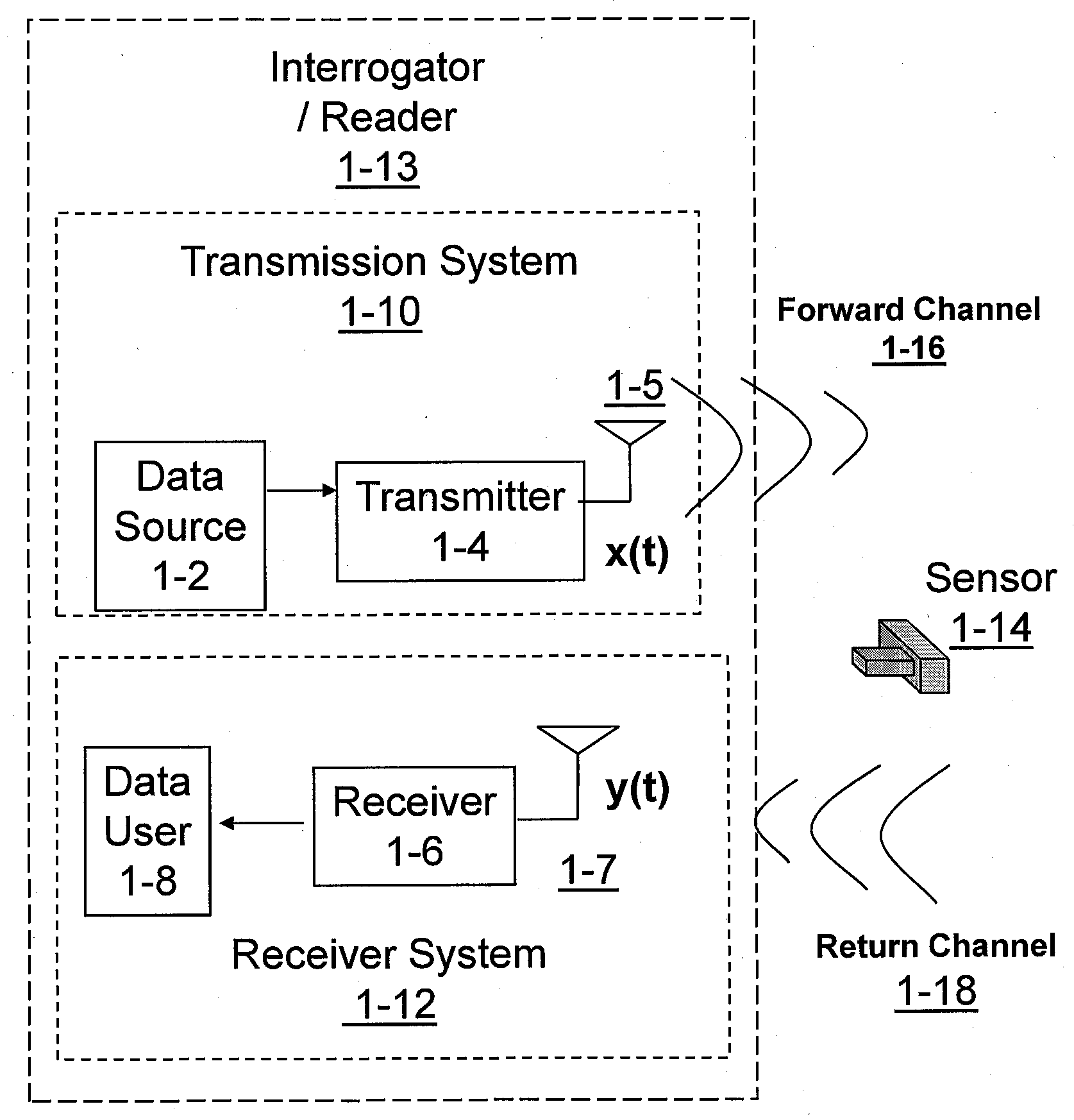
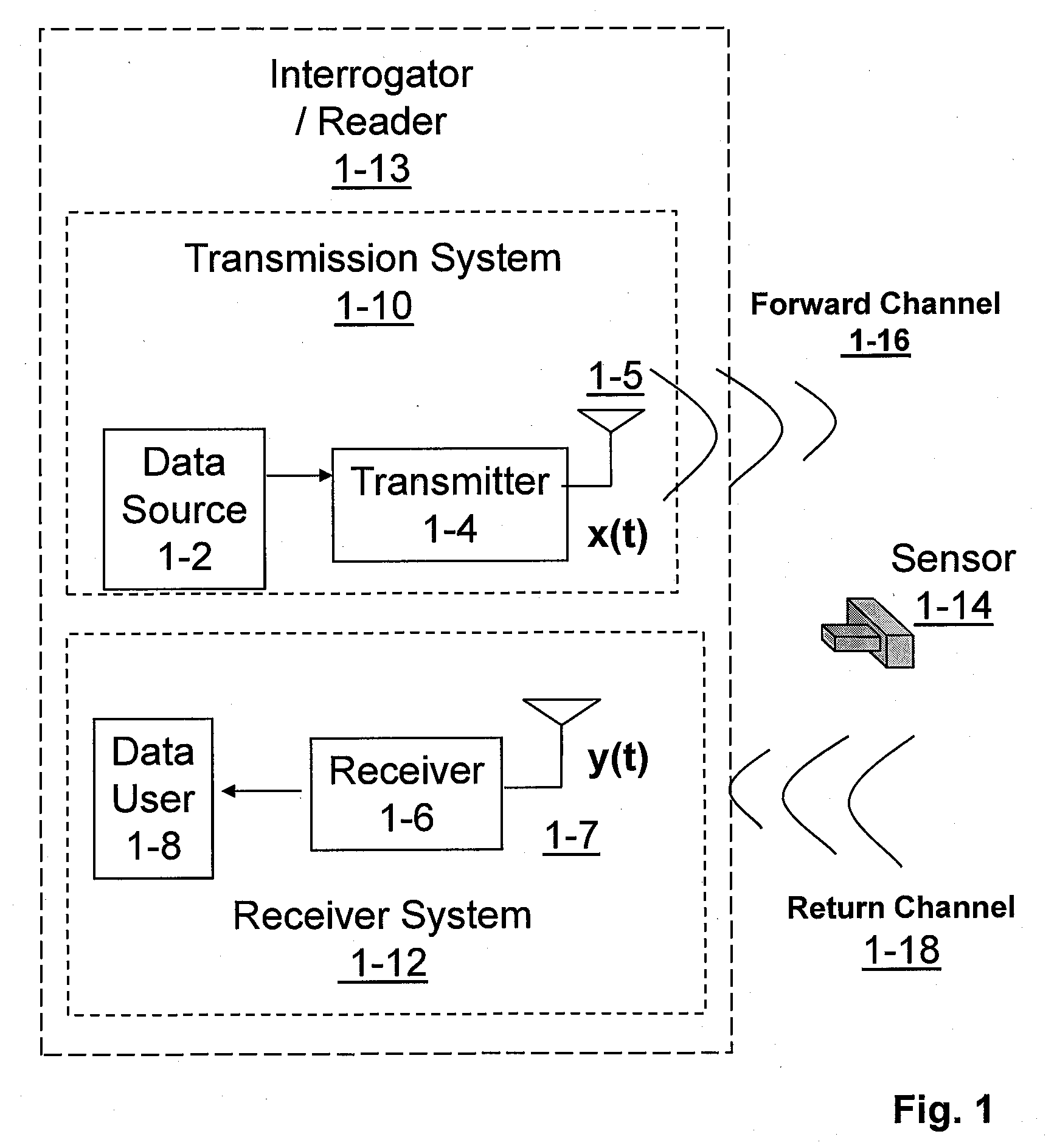
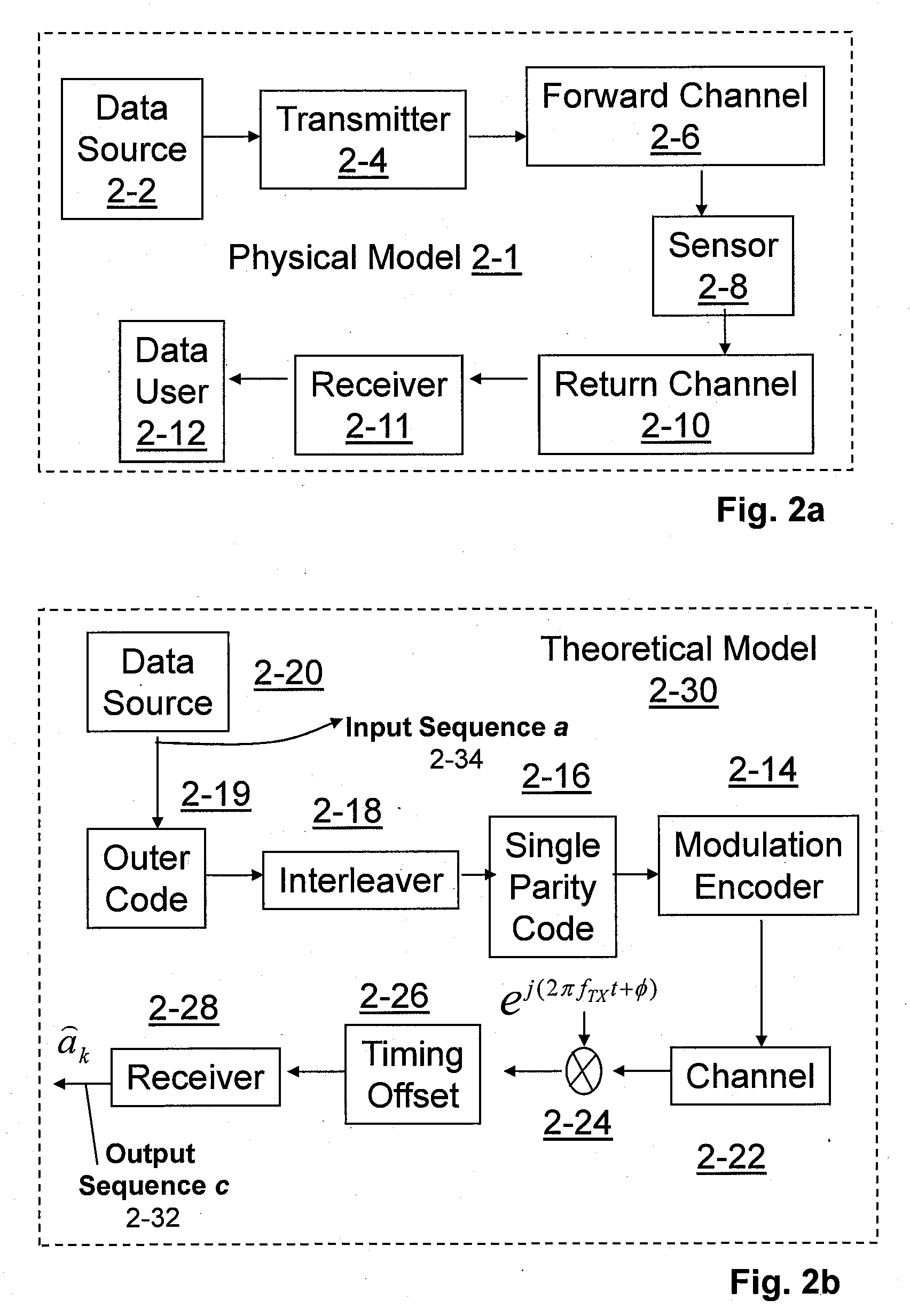
Code generator and decoder for communications systems operating using hybrid codes to allow for multiple efficient users of the communications systems
InactiveUS7971129B2Error protectionImprove errorData representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
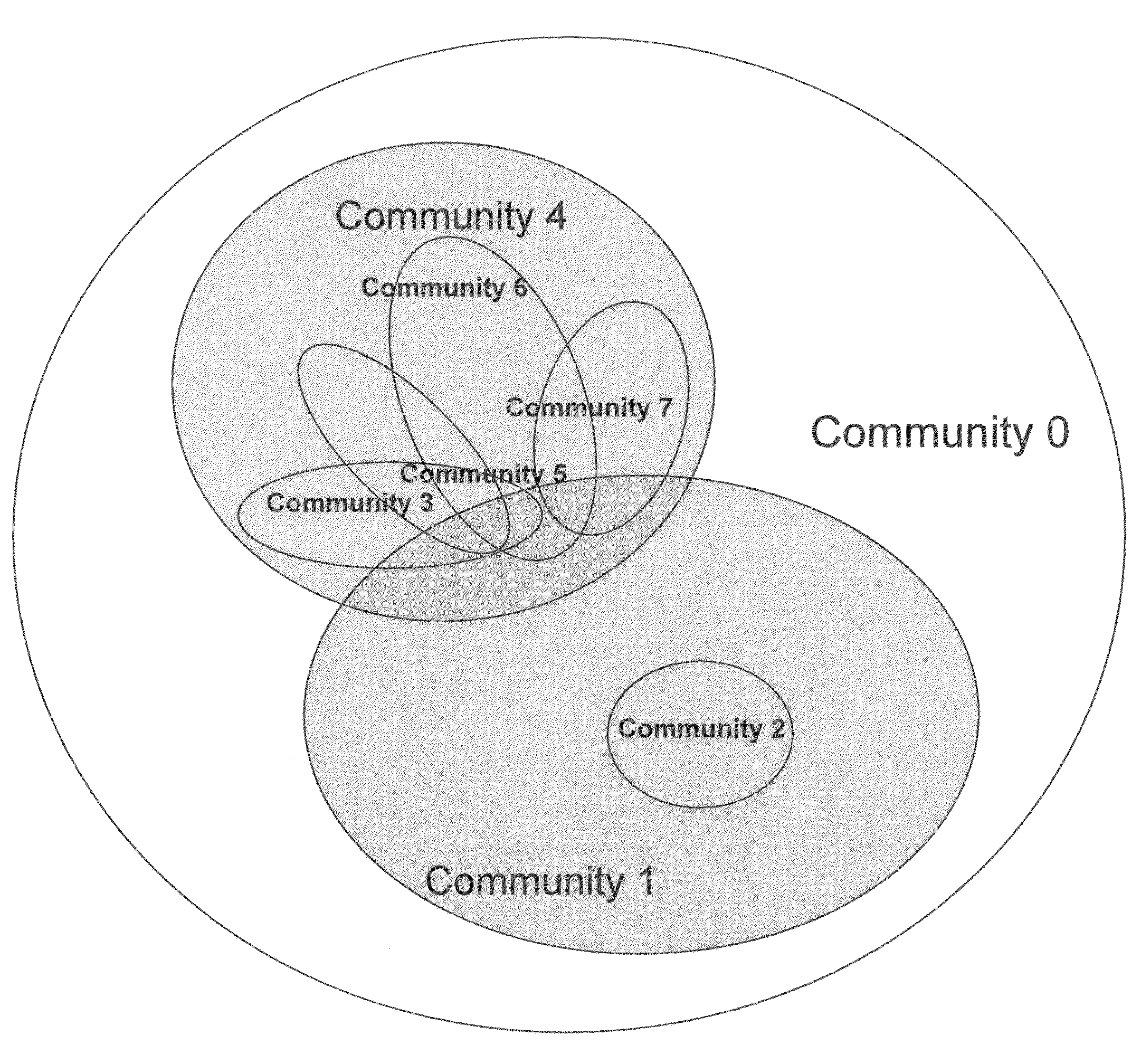
Method and apparatus for distributed community finding
ActiveUS7958120B2New informationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsDiffusion
Methods and apparatus for a new approach to the problem of finding communities in complex networks relating to a social definition of communities and percolation are disclosed. Instead of partitioning the graph into separate subgraphs from top to bottom a local algorithm (communities of each vertex) allows overlapping of communities. The performance of an algorithm on synthetic, randomly-generated graphs and real-world networks is used to benchmark this method against others. An heuristic is provided to generate a list of communities for networks using a local community finding algorithm. Unlike diffusion based algorithms, The provided algorithm finds overlapping communities and provides a means to measure confidence in community structure. It features locality and low complexity for exploring the communities for a subset of network nodes, without the need for exploring the whole graph.
Owner:NETABEER +1
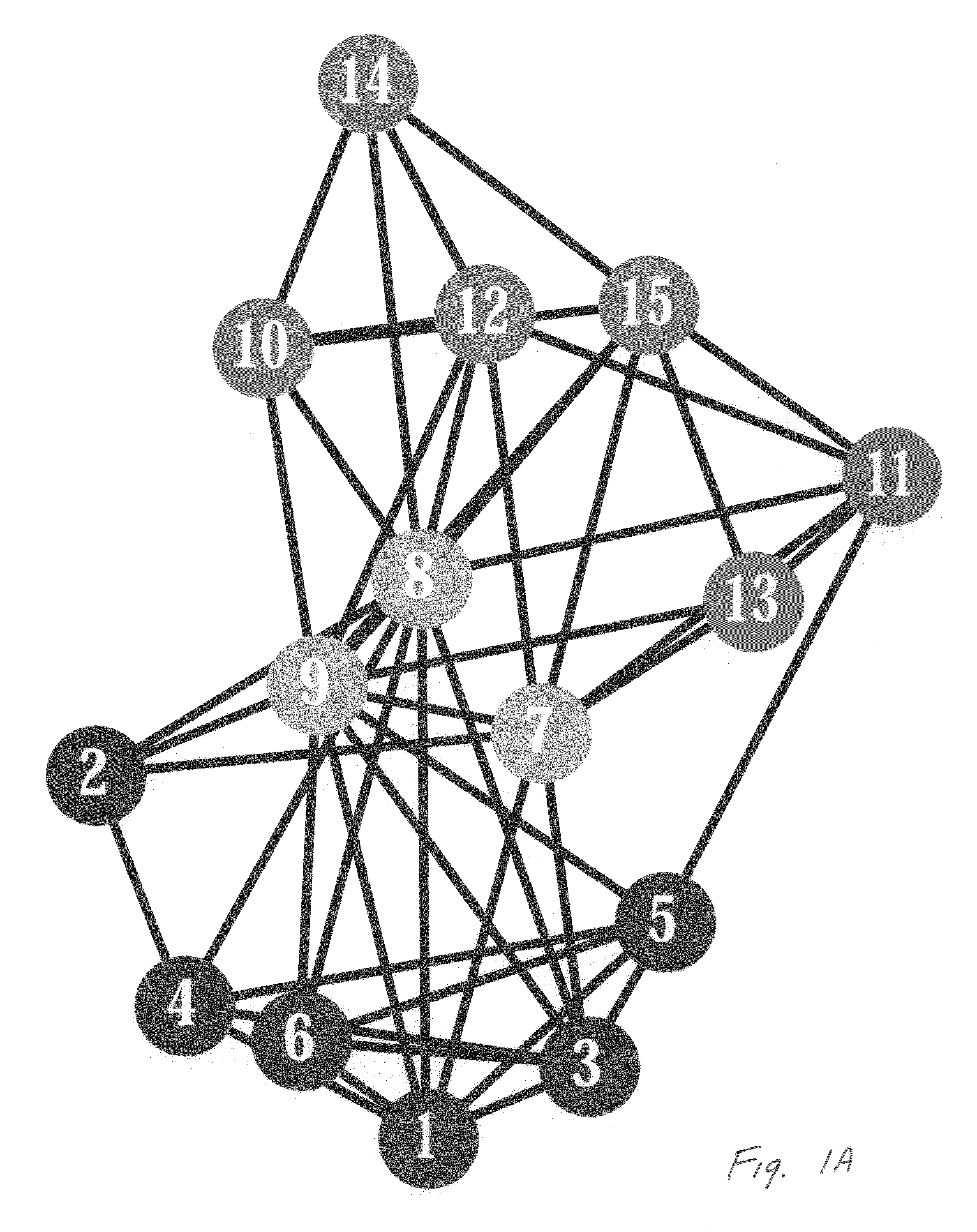
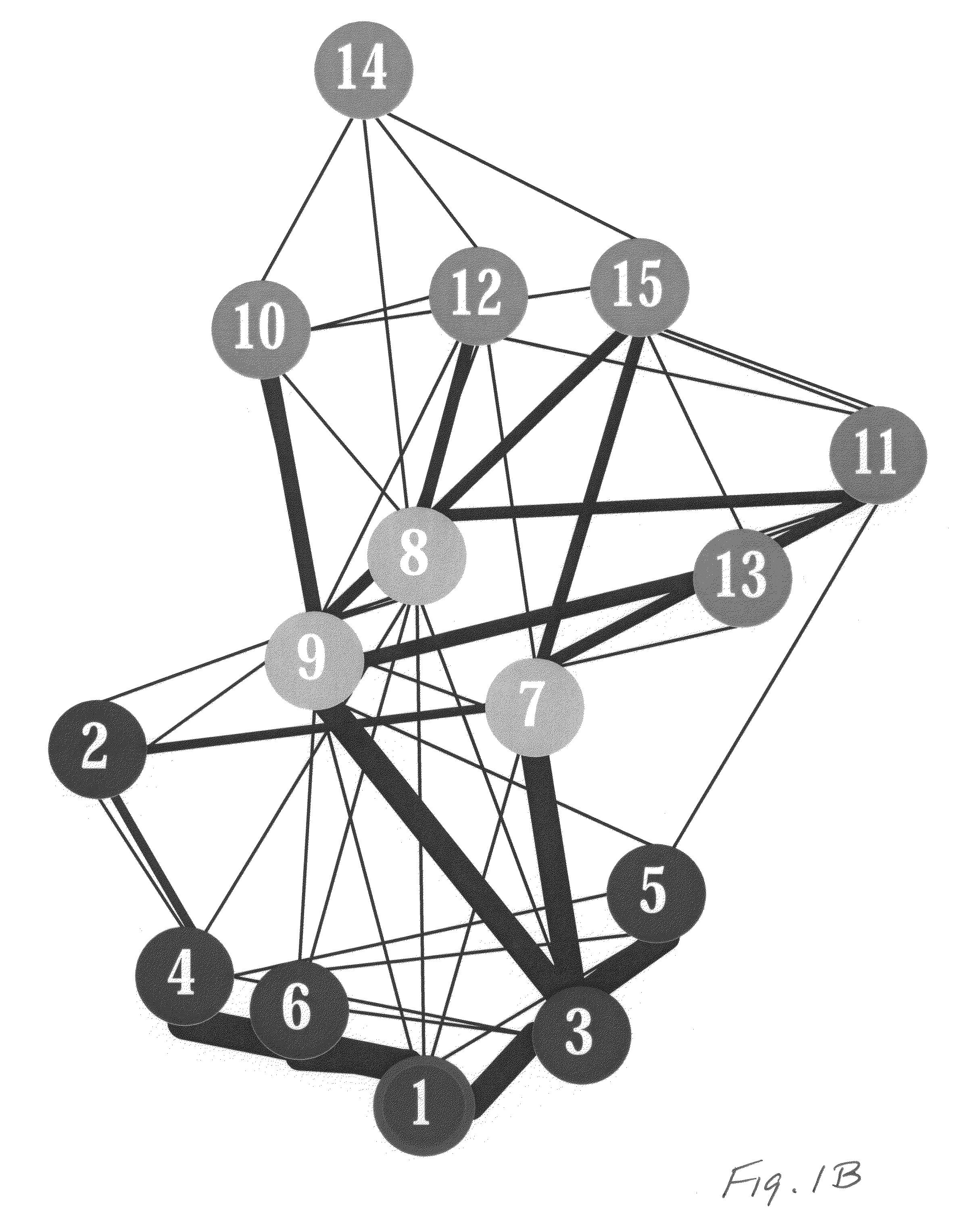
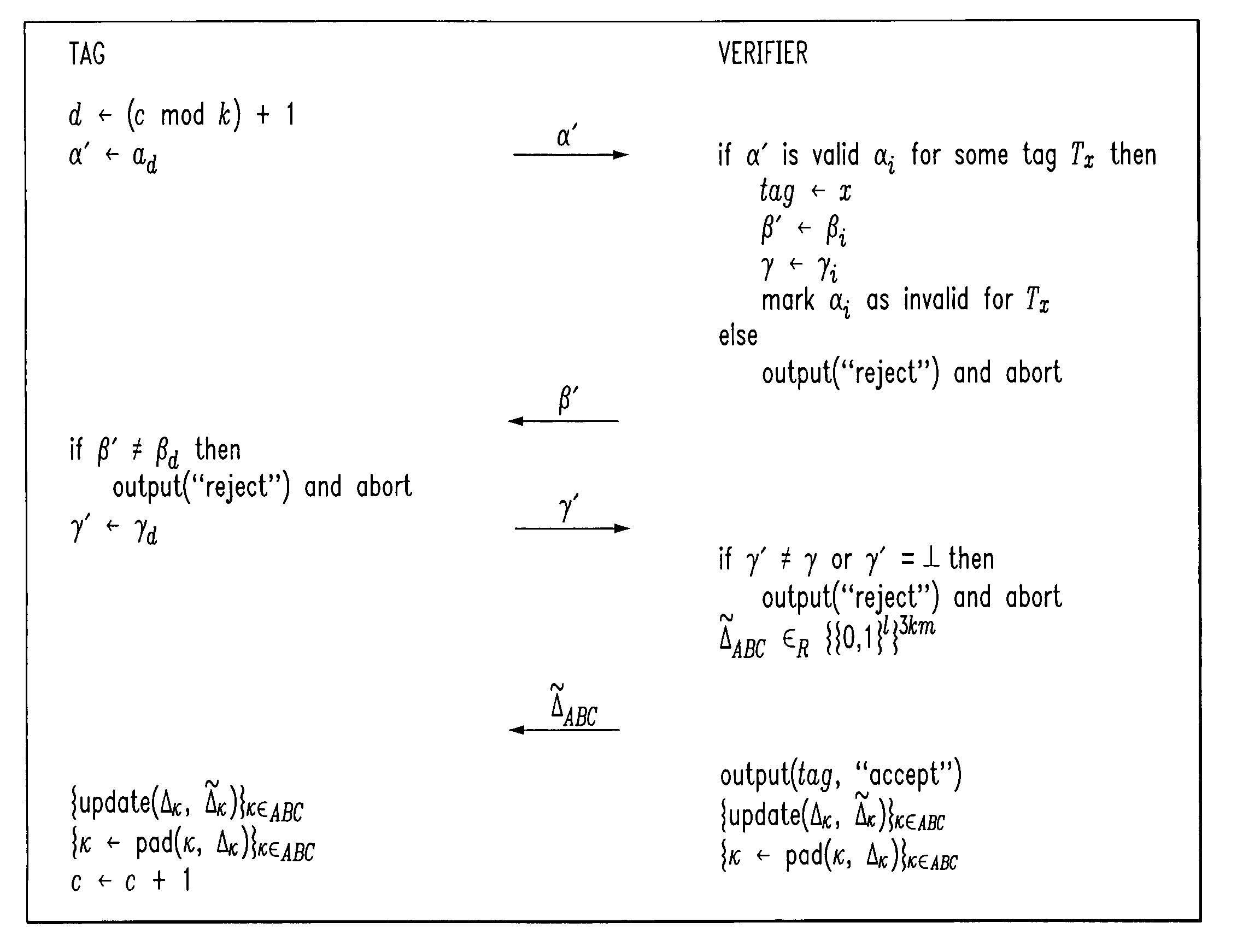
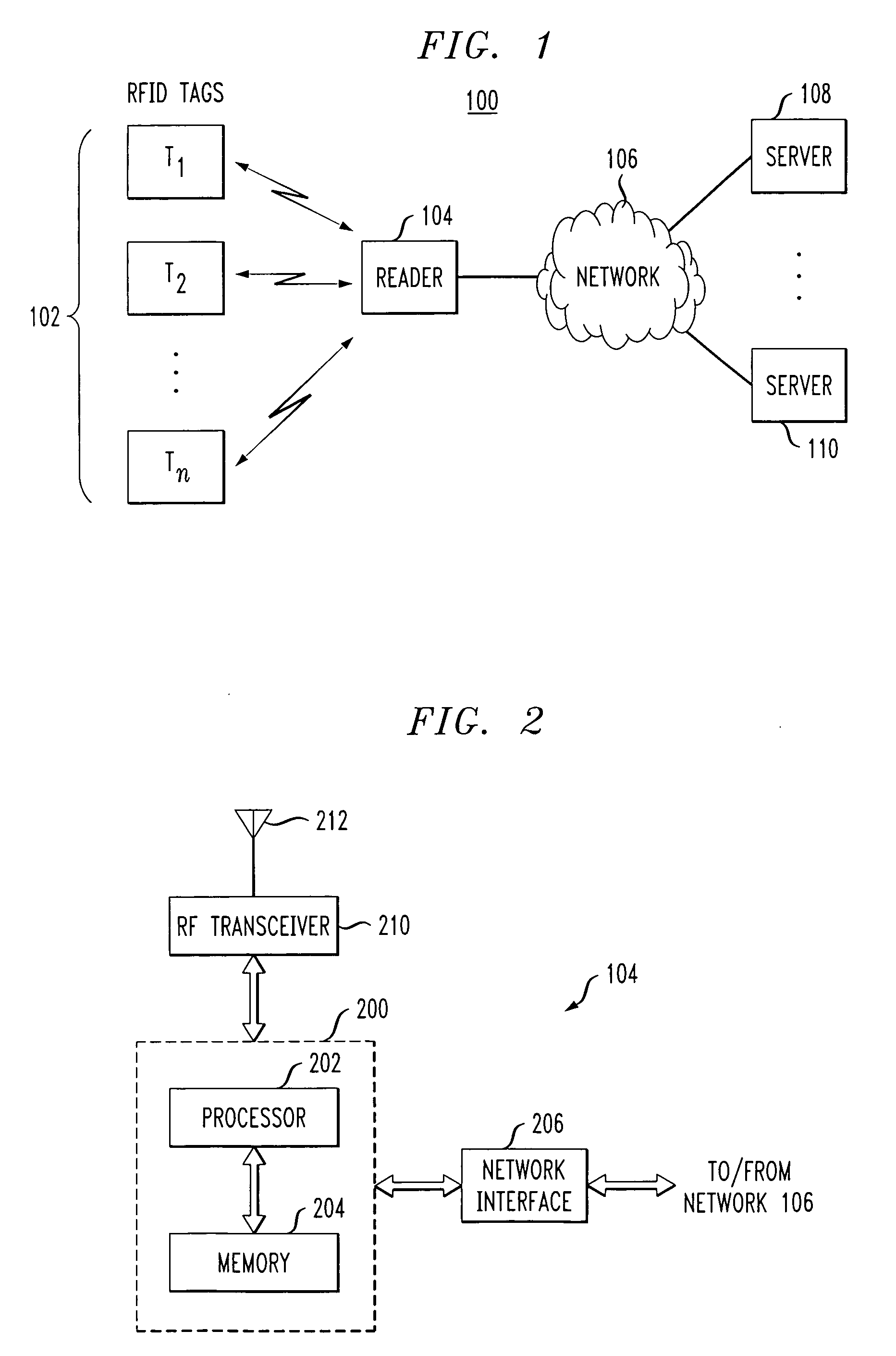
Low-complexity cryptographic techniques for use with radio frequency identification devices
ActiveUS7532104B2Easy authenticationElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareRadio frequency
Cryptographic techniques are provided having a complexity level which permits their implementation in inexpensive radio frequency identification (RFID) tags or other RFID devices. In an RFID system comprising one or more RFID devices and at least one reader that communicates with the devices, a plurality of pseudonyms is associated with a given one of the RFID devices. The RFID device transmits different ones of the pseudonyms in response to different reader queries, and an authorized verifier is able to determine that the different transmitted pseudonyms are associated with the same RFID device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Low-complexity deblocking filter
InactiveUS7050504B2Minimizing introductionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionCoding artifacts
A method of filtering to remove coding artifacts introduced at block edges in a block-based video coder, the method having the steps of: checking the content activity on every line of samples belonging to a boundary to be filtered and where content activity is based on a set of adaptively selected thresholds determined using Variable-Shift Table Indexing (VSTI); determining whether the filtering process will modify the sample values on that particular line based on said content activity, and selecting a filtering mode between at least two filtering modes to apply on a block boundary basis, implying that there would be no switching between the two primary modes on a line by line basis along a given block boundary. The two filtering modes include a default mode based on a non-recursive filter, and a strong filtering mode which features two strong filtering sub-modes and a new selection criterion that is one-sided with respect to the block boundary to determine which of the two strong filtering sub-modes to use. The two strong filtering sub-modes include a new 3-tap filter sub-mode and a 5-tap filter sub-mode that permits a more efficient implementation of the filter.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
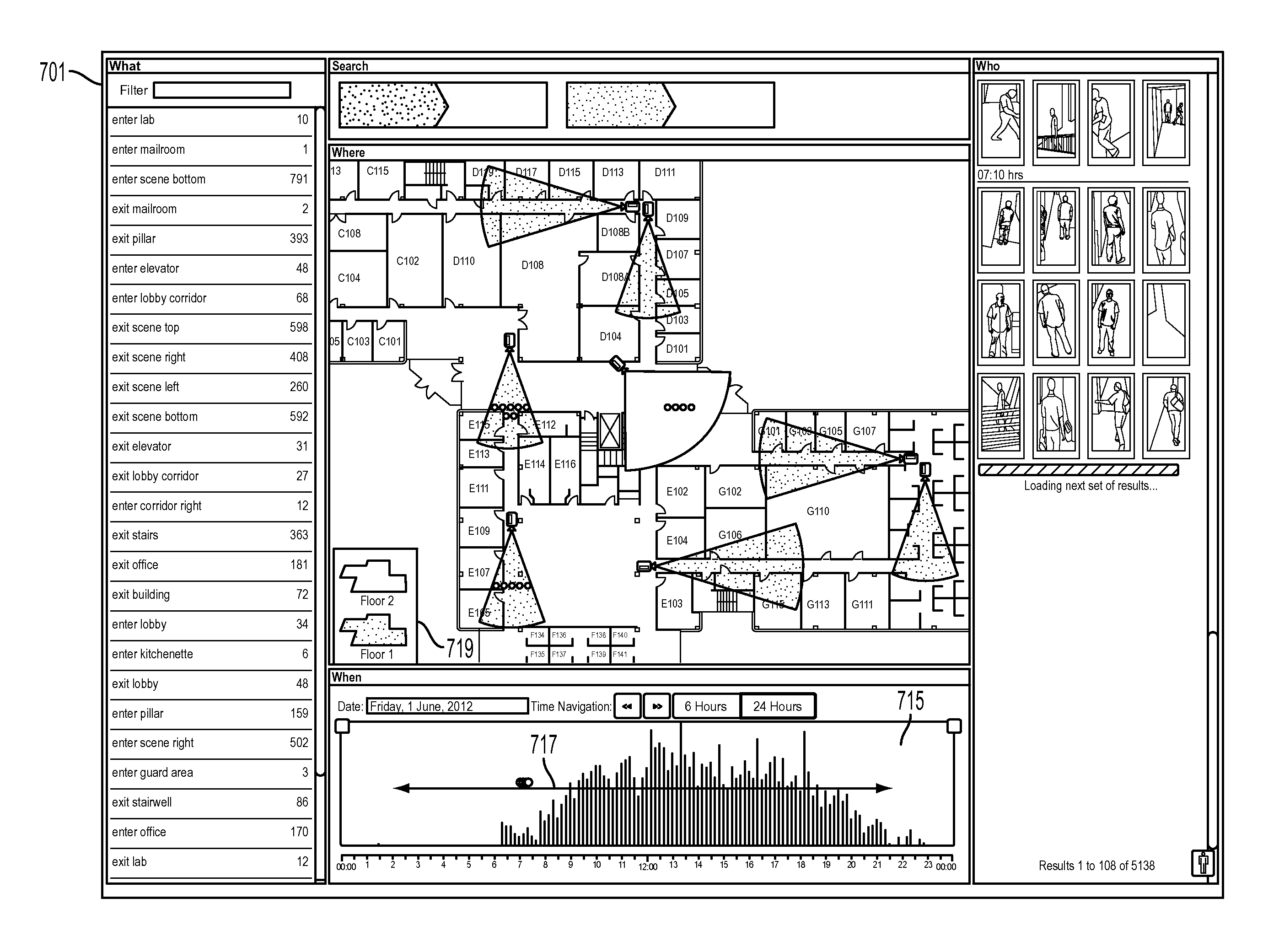
Method and user interface for forensic video search
ActiveUS20130091432A1Easy searchVideo data queryingVideo data browsing/visualisationComputer graphics (images)Low complexity
A forensic video search user interface is disclosed that accesses databases of stored video event metadata from multiple camera streams and facilitates the workflow of search of complex global events that are composed of a number of simpler, low complexity events.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
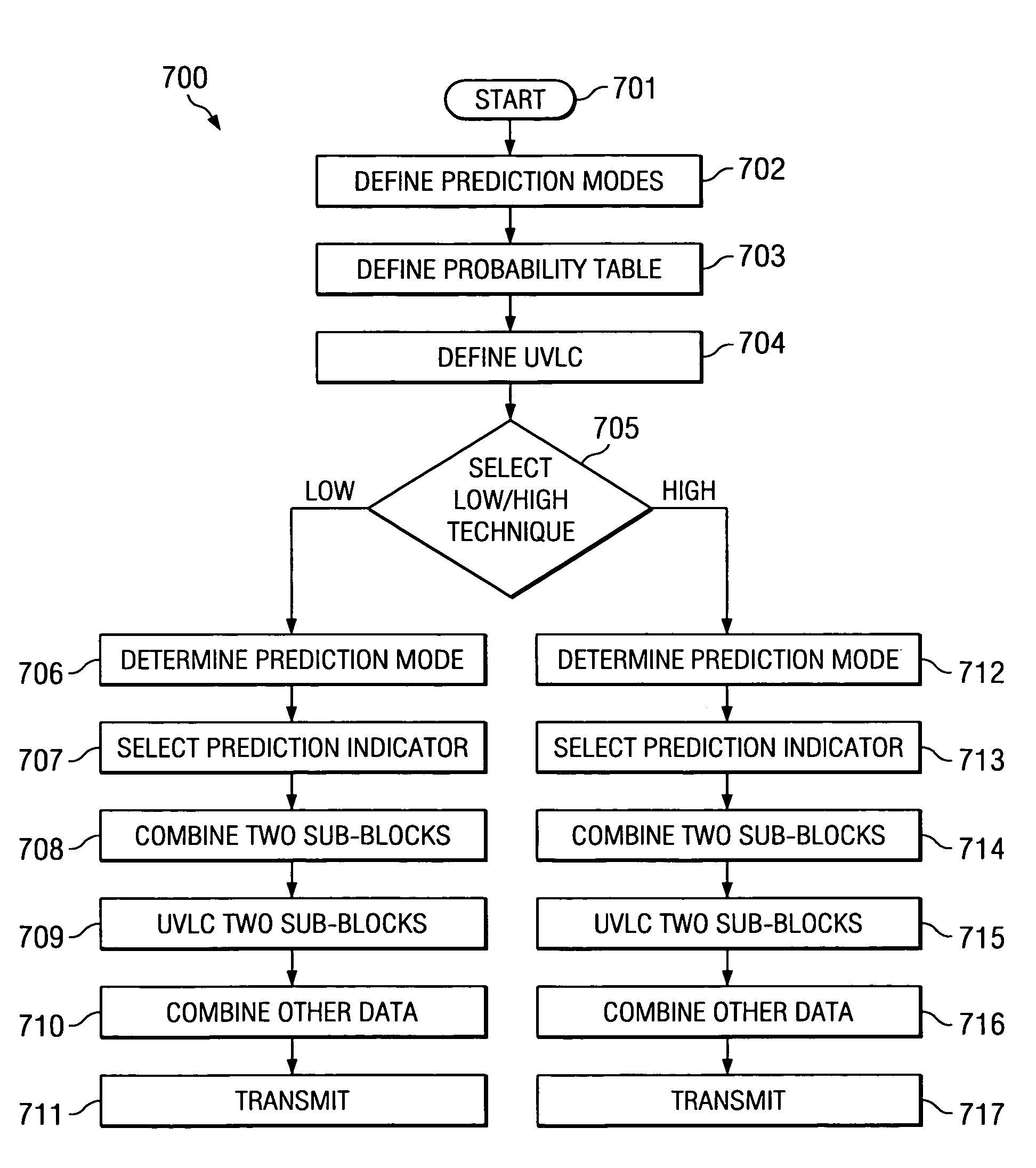
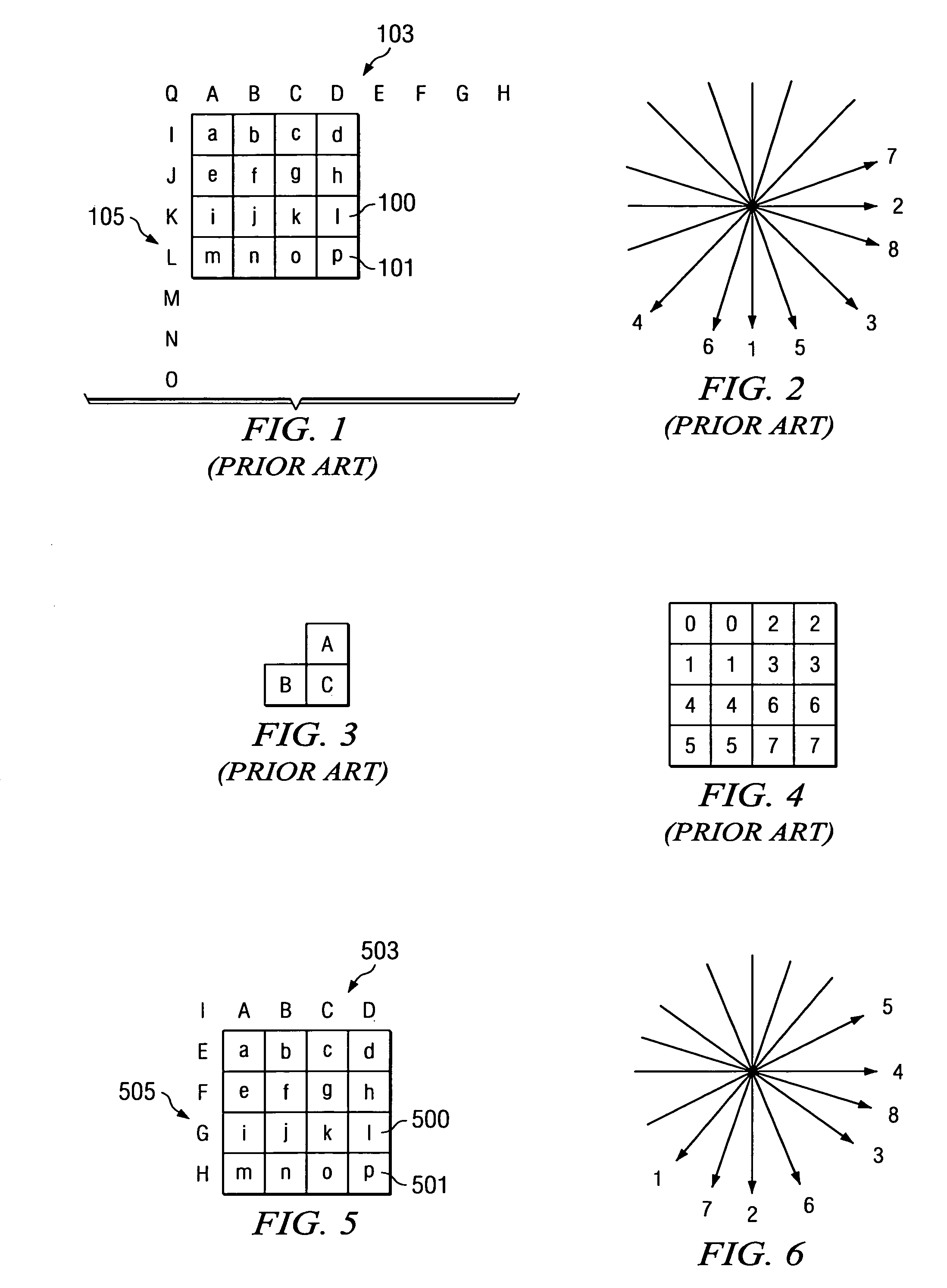
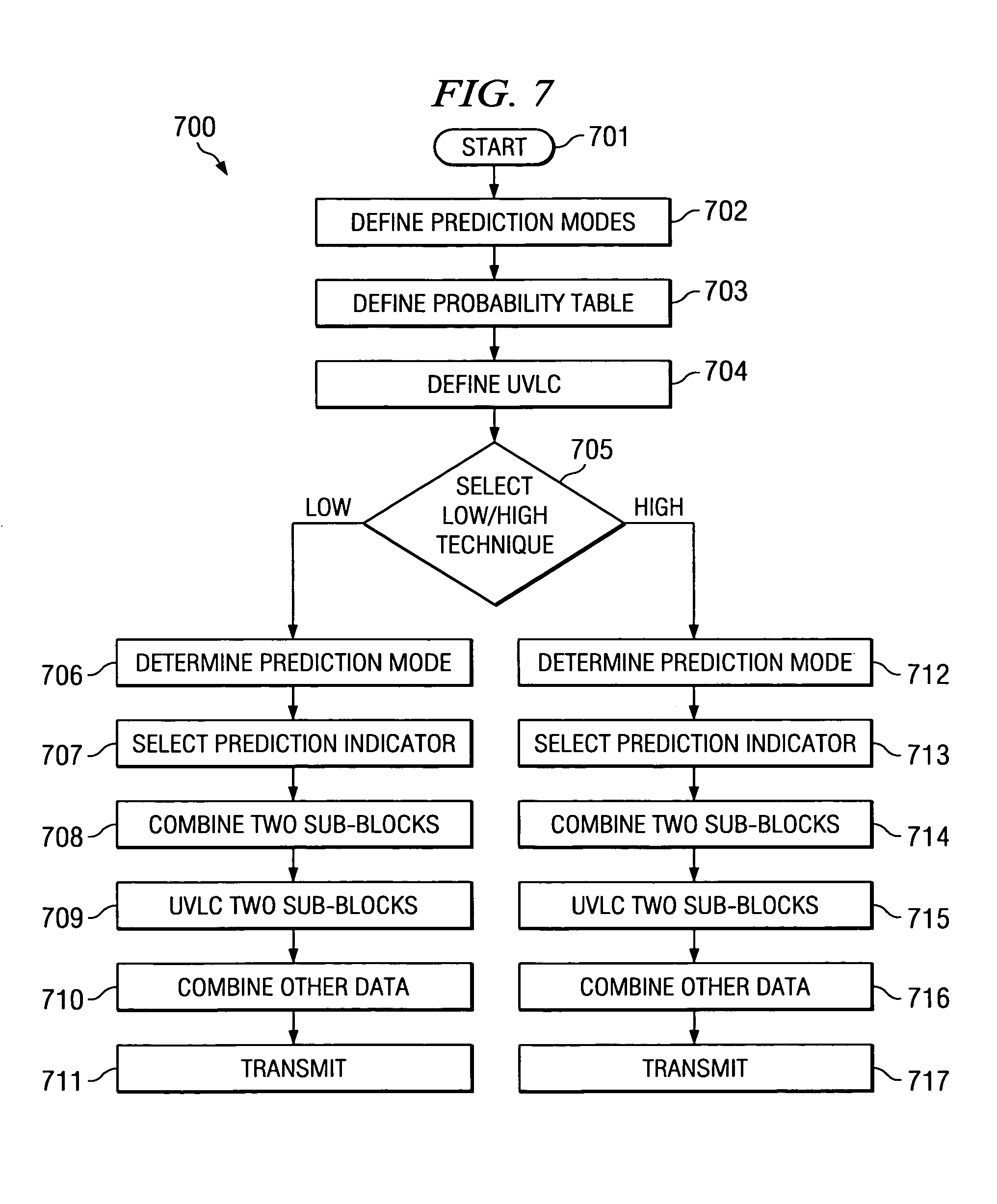
Complexity-scalable intra-frame prediction technique
ActiveUS7170937B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceIntra-frame
This invention is a method of encoding intra frames when encoding a motion picture. A set of intra frame prediction modes includes a low-complexity subset. A probability table relates the prediction mode of adjacent sub-blocks to the prediction mode of the current sub-block. For each combination of adjacent sub-blocks, the probability table includes a list of prediction modes in order of expected occurrence. The probability table is adjusted so that each list for prediction modes within the low-complexity subset include initial prediction modes of the low-complexity subset. Individual sub-blocks of intra frames are predictively coded in a low-complexity encoding the using the low-complexity subset or in a high-complexity encoding using any prediction mode. This permits a low-complexity decoder responsive to only the low-complexity subset.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
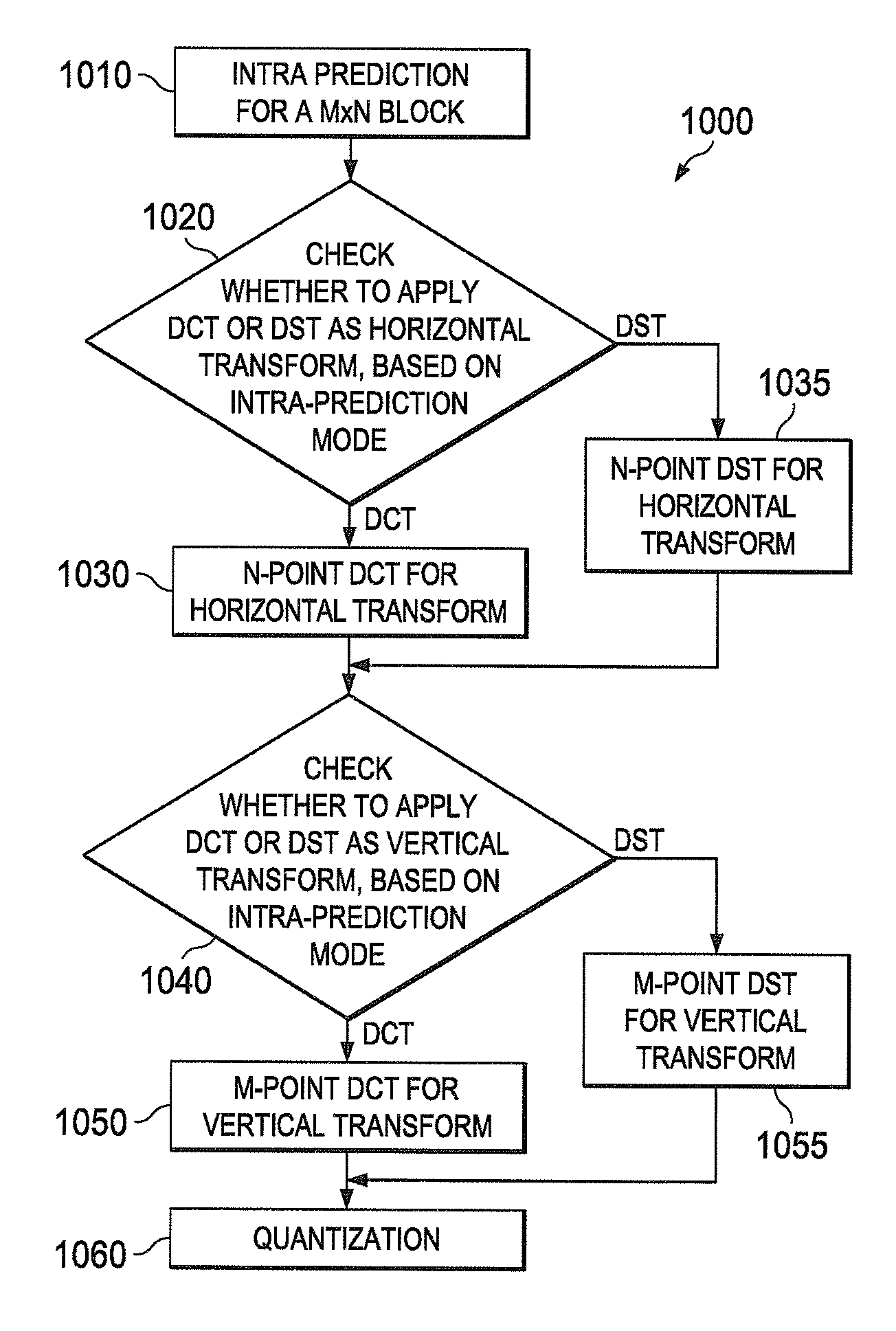
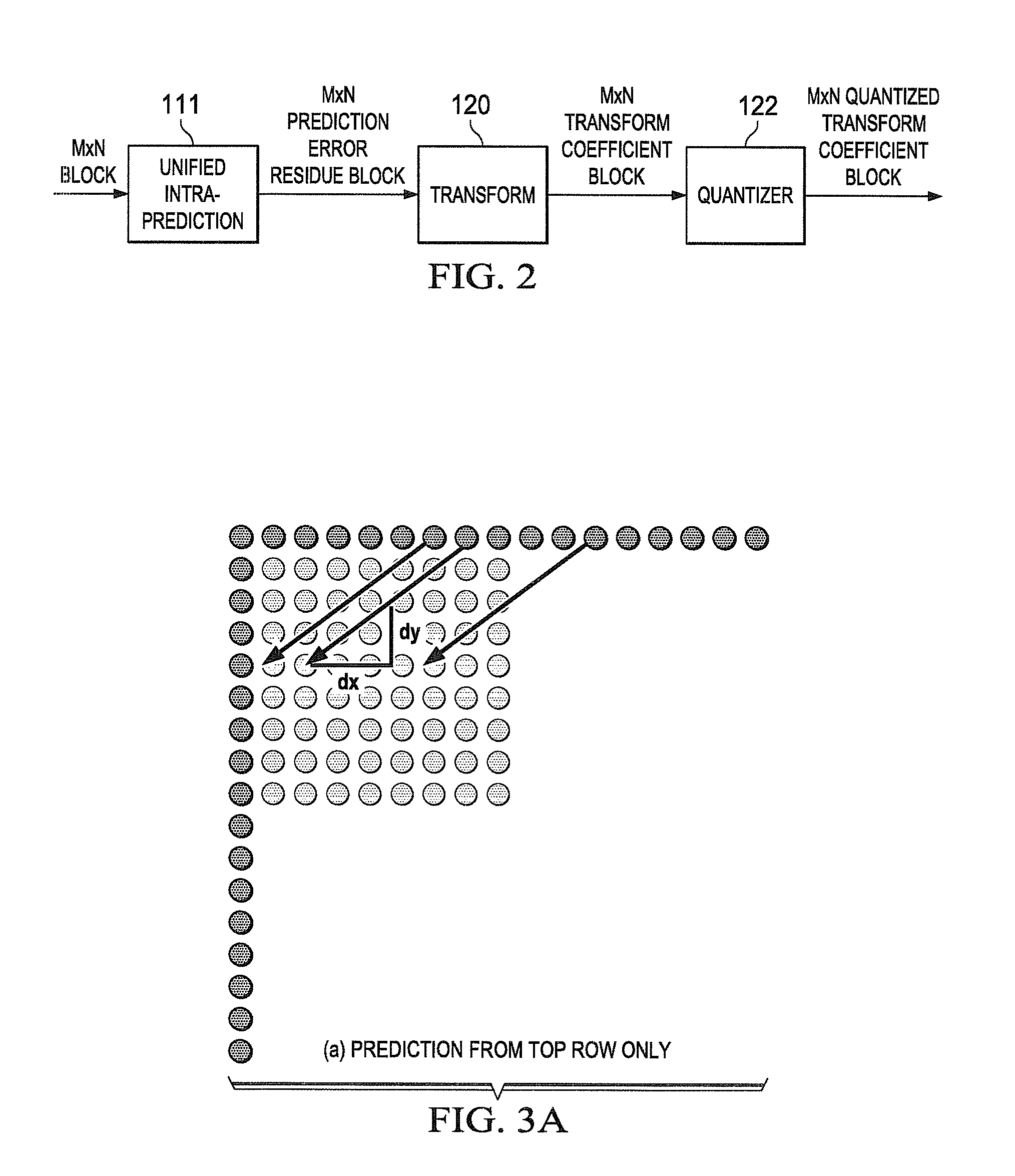
Low complexity transform coding using adaptive dct/dst for intra-prediction
InactiveUS20120057630A1Reduce complexityQuick implementationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus encode and decode video by determining whether to use discrete cosine transform (DCT) and DST for each of the horizontal and vertical transforms. During encoding, an intra-prediction is performed based on an intra-prediction mode determined for an M×N input image block to obtain an M×N intra-prediction residue matrix (E). Based on the intra-prediction mode, each of a horizontal transform and a vertical transform is performed using one of DCT and DST according to the intra-prediction mode. During decoding, the intra-prediction mode is determined from an incoming video bitstream. The M×N transformed coefficient matrix of the error residue is obtained from the video bitstream using an inverse quantizer. Based on the intra prediction mode, one of DCT and DST is performed for each of an inverse vertical transform and an inverse horizontal transform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
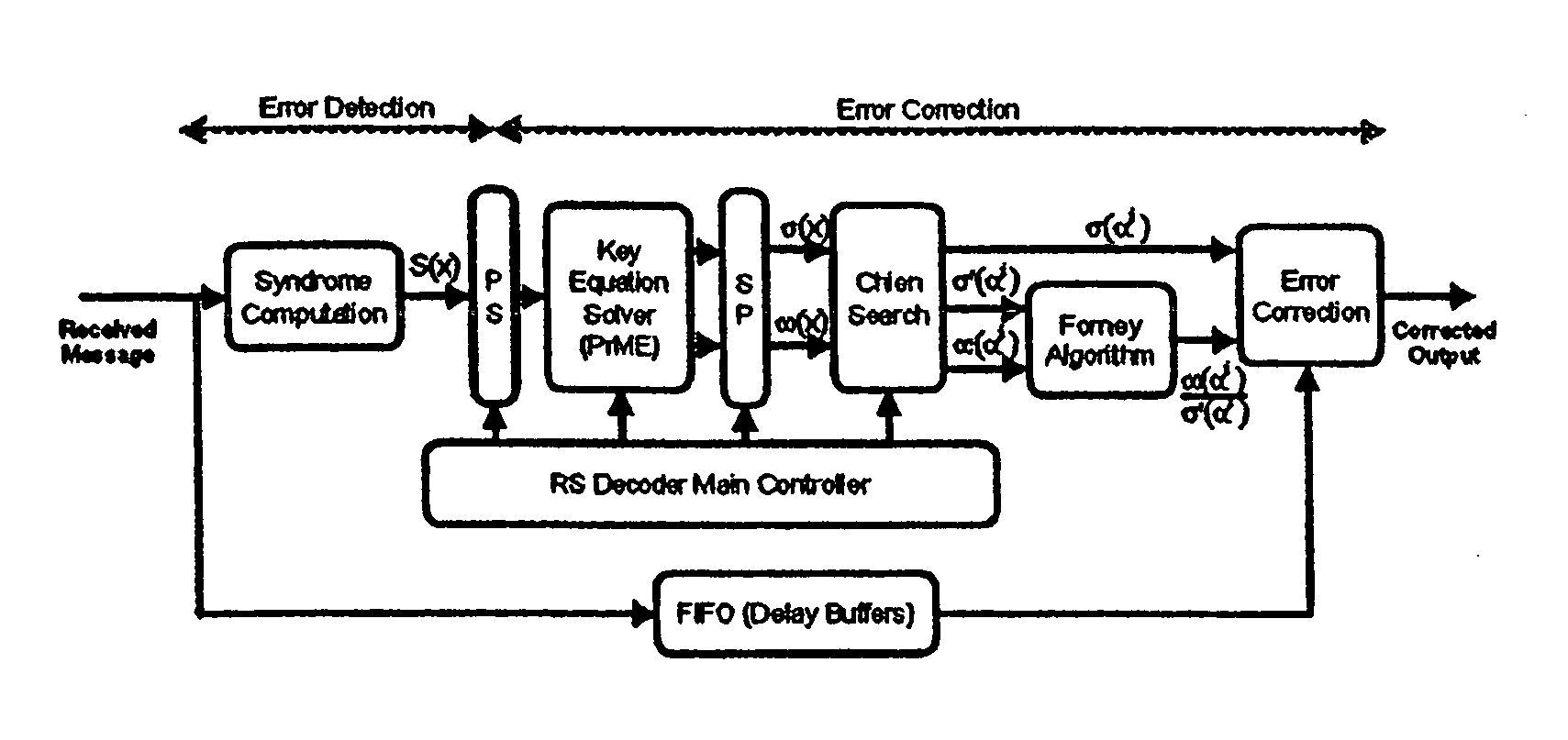
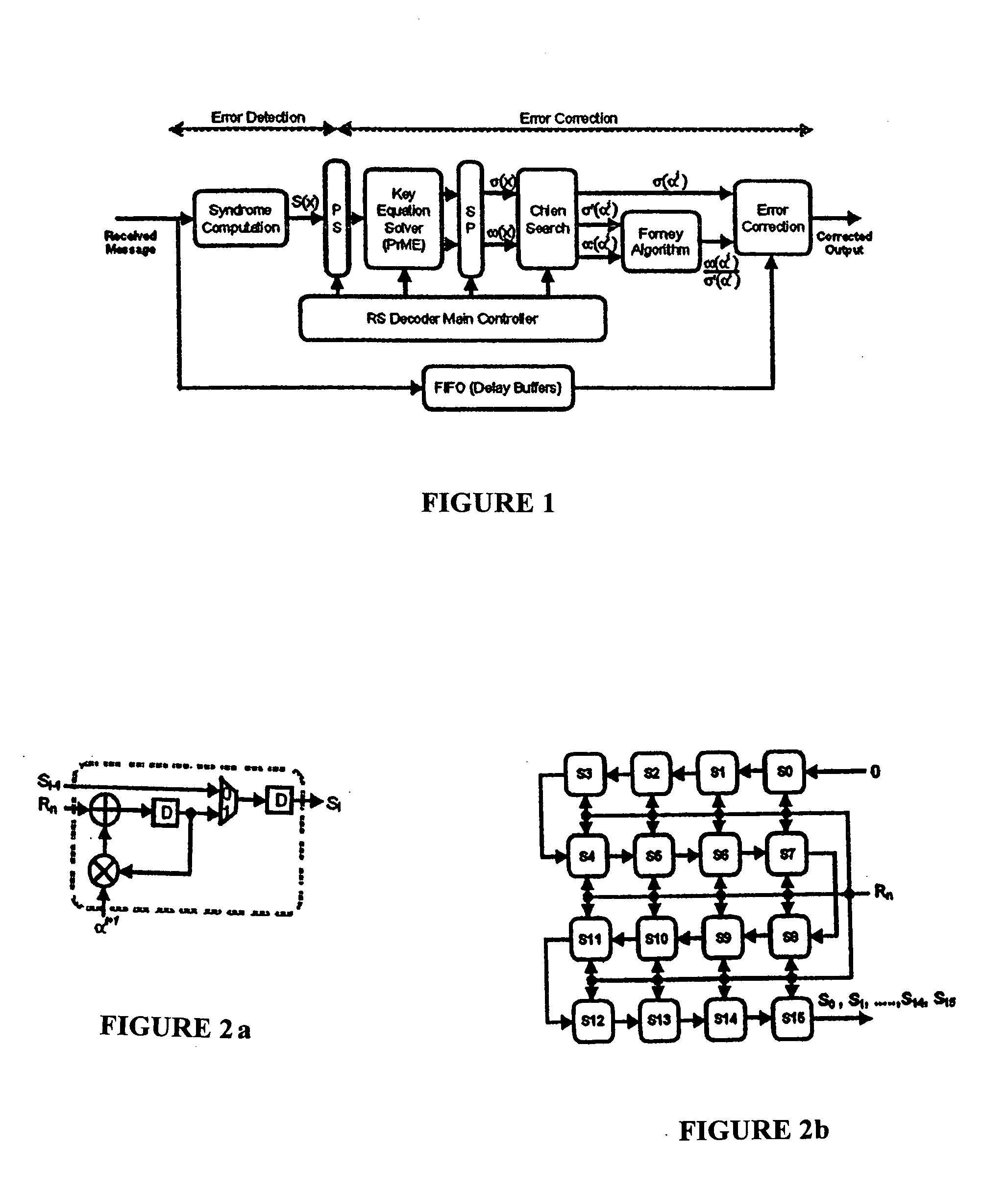
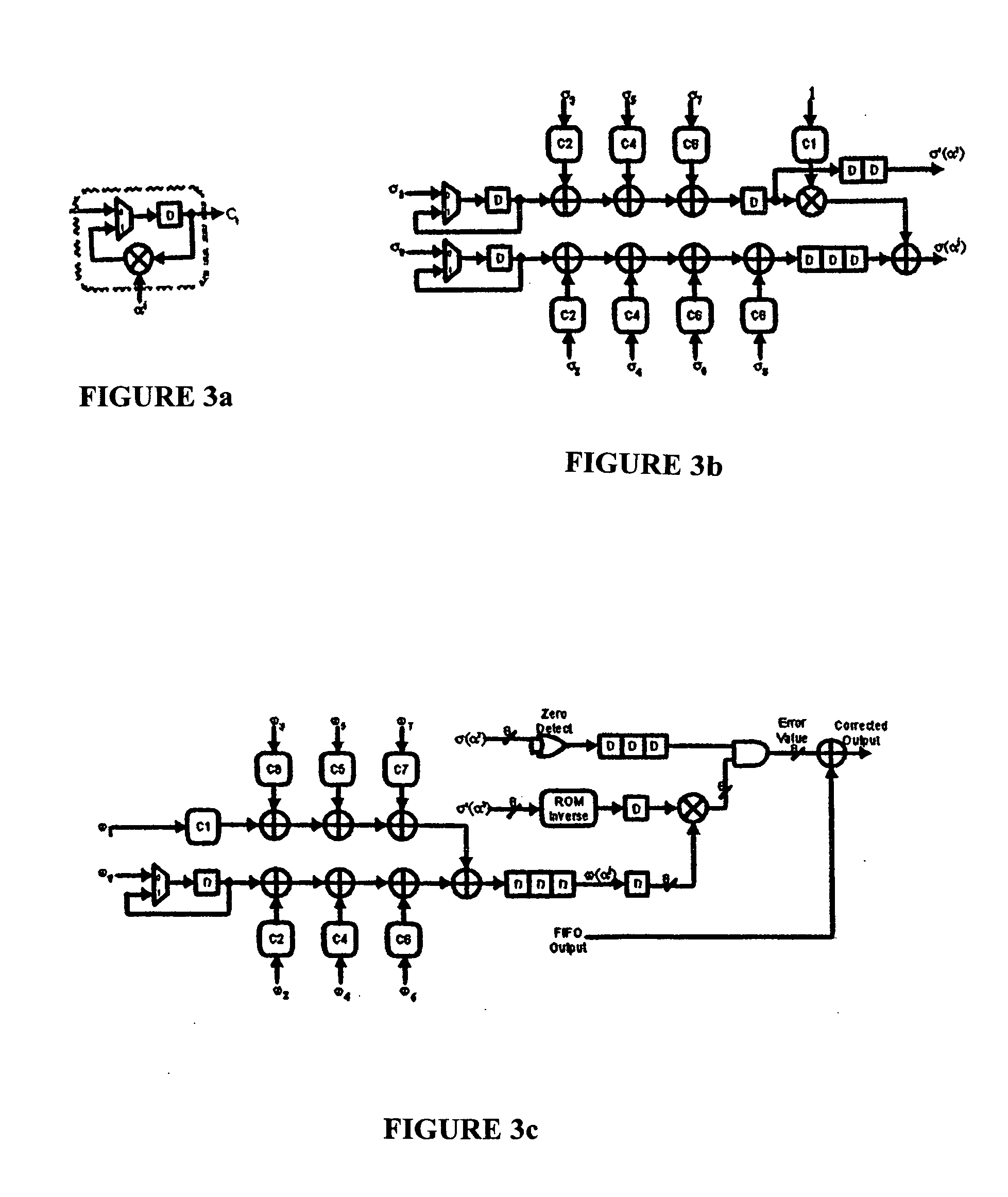
Reed-solomon decoder systems for high speed communication and data storage applications
InactiveUS20060059409A1Effective and reliable error correction functionalityReduce complexityCode conversionCoding detailsModem deviceHigh rate
A high-speed, low-complexity Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder architecture using a novel pipelined recursive Modified Euclidean (PrME) algorithm block for very high-speed optical communications is provided. The RS decoder features a low-complexity Key Equation Solver using a PrME algorithm block. The recursive structure enables the low-complexity PrME algorithm block to be implemented. Pipelining and parallelizing allow the inputs to be received at very high fiber optic rates, and outputs to be delivered at correspondingly high rates with minimum delay. An 80-Gb / s RS decoder architecture using 0.13-μm CMOS technology in a supply voltage of 1.2 V is disclosed that features a core gate count of 393 K and operates at a clock rate of 625 MHz. The RS decoder has a wide range of applications, including fiber optic telecommunication applications, hard drive or disk controller applications, computational storage system applications, CD or DVD controller applications, fiber optic systems, router systems, wireless communication systems, cellular telephone systems, microwave link systems, satellite communication systems, digital television systems, networking systems, high-speed modems and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Low complexity high-speed communications transceiver
InactiveUS7590168B2Improve data transfer rateReduce interferenceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationTransceiverCommunications system
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Multicode direct sequence spread spectrum
InactiveUSRE37802E1Improve throughputReduce ICISecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumDirect-sequence spread spectrum
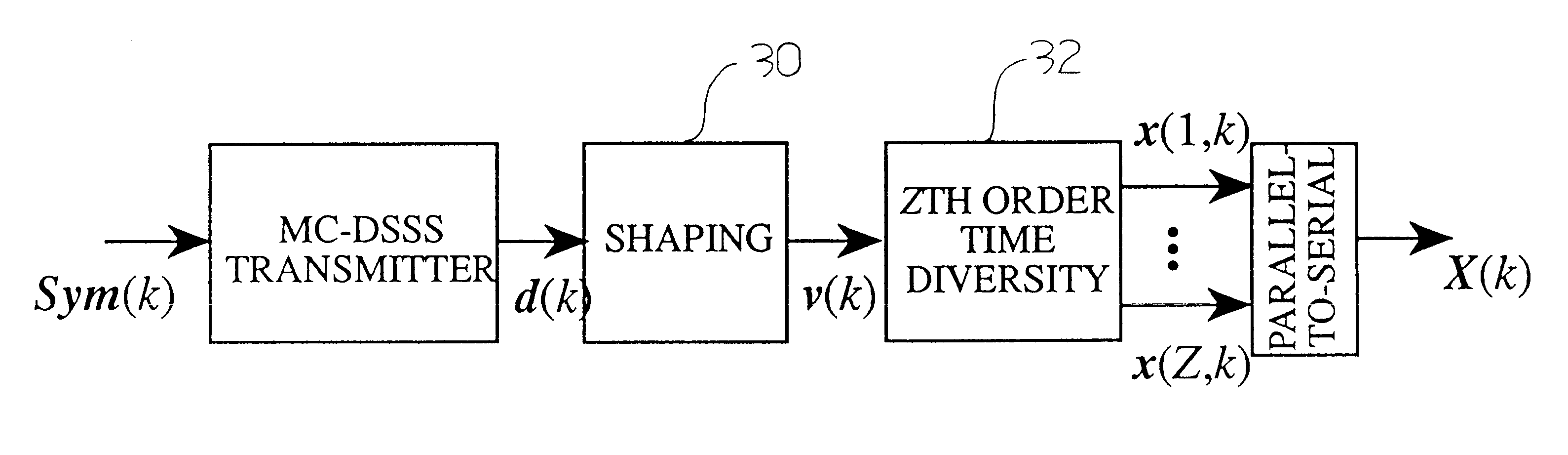
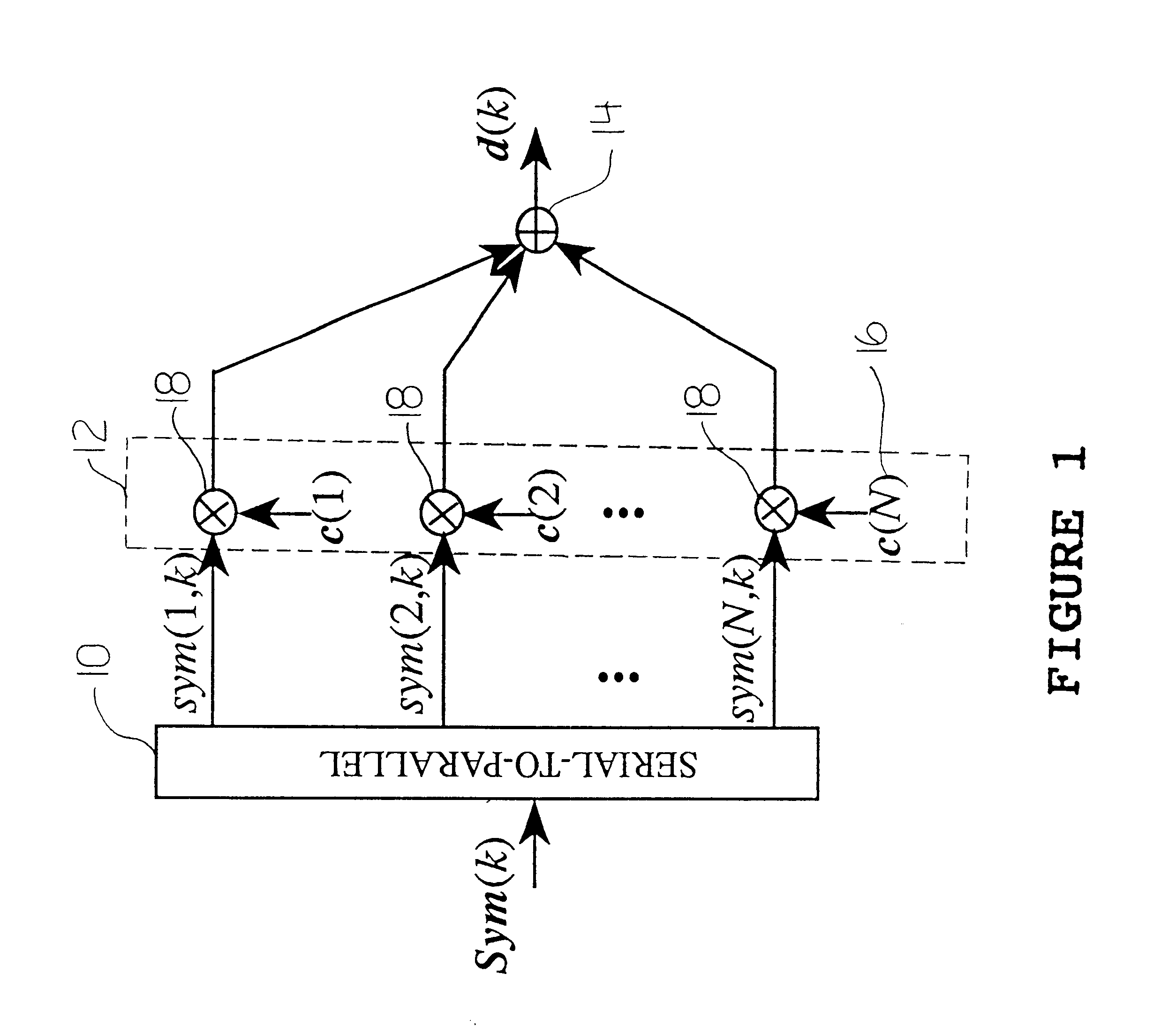
In this patent, we present MultiCode Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (MC-DSSS) which is a modulation scheme that assigns up to N DSSS codes to an individual user where N is the number of chips per DSSS code. When viewed as DSSS, MC-DSSS requires up to N correlators (or equivalently up to N Matched Filters) at the receiver with a complexity of the order of N2 operations. In addition, a non ideal communication channel can cause InterCode Interference (ICI), i.e., interference between the N DSSS codes. In this patent, we introduce new DSSS codes, which we refer to as the "MC" codes. Such codes allow the information in a MC-DSSS signal to be decoded in a sequence of low complexity parallel operations which reduce the ICI. In addition to low complexity decoding and reduced ICI. MC-DSSS using the MC codes has the following advantages: (1) it does not require the stringent synchronization DSSS requires, (2) it does not require the stringent carrier recovery DSSS requires and (3) it is spectrally efficient.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Methods for genotyping
InactiveUS20070065816A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneLow complexity
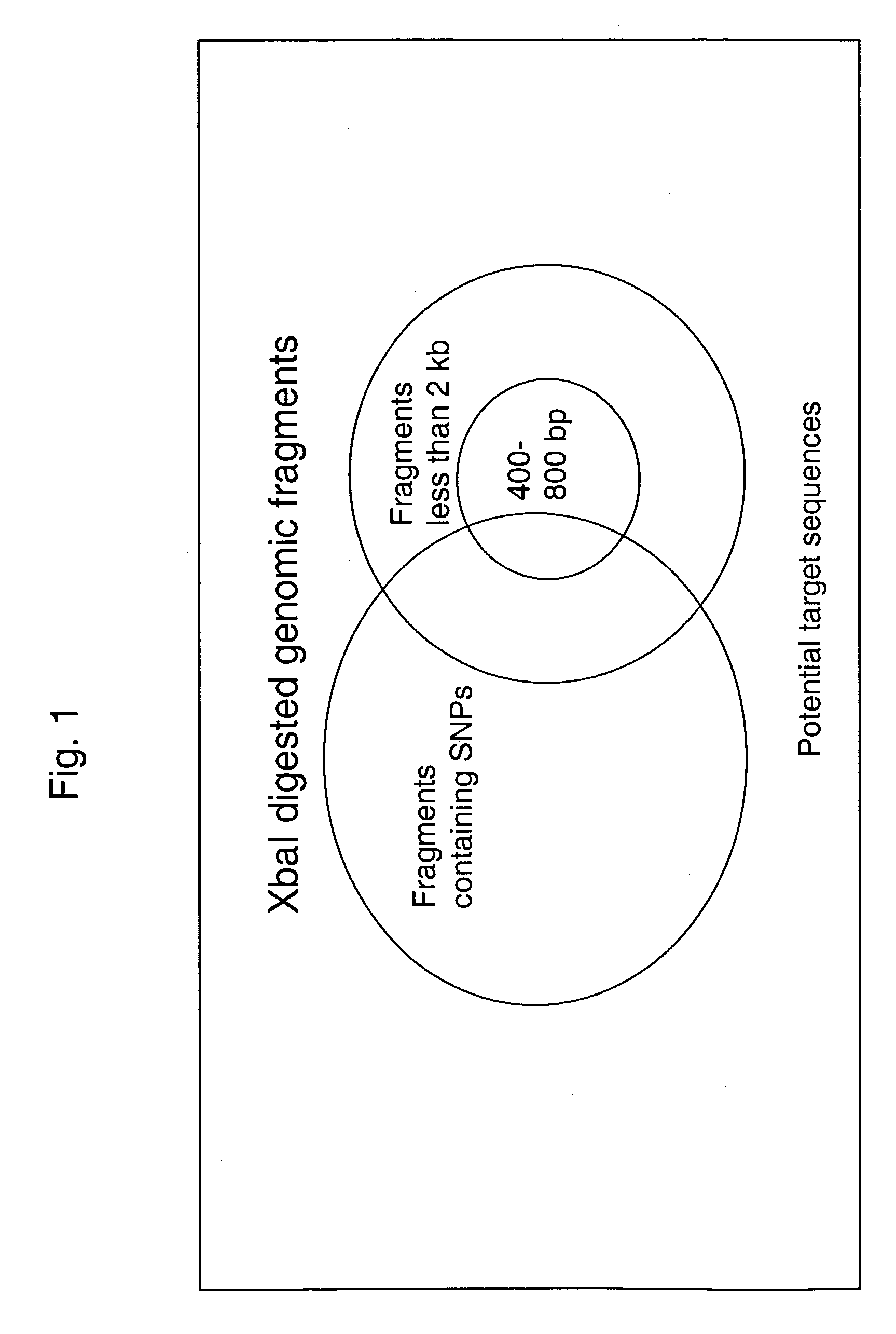
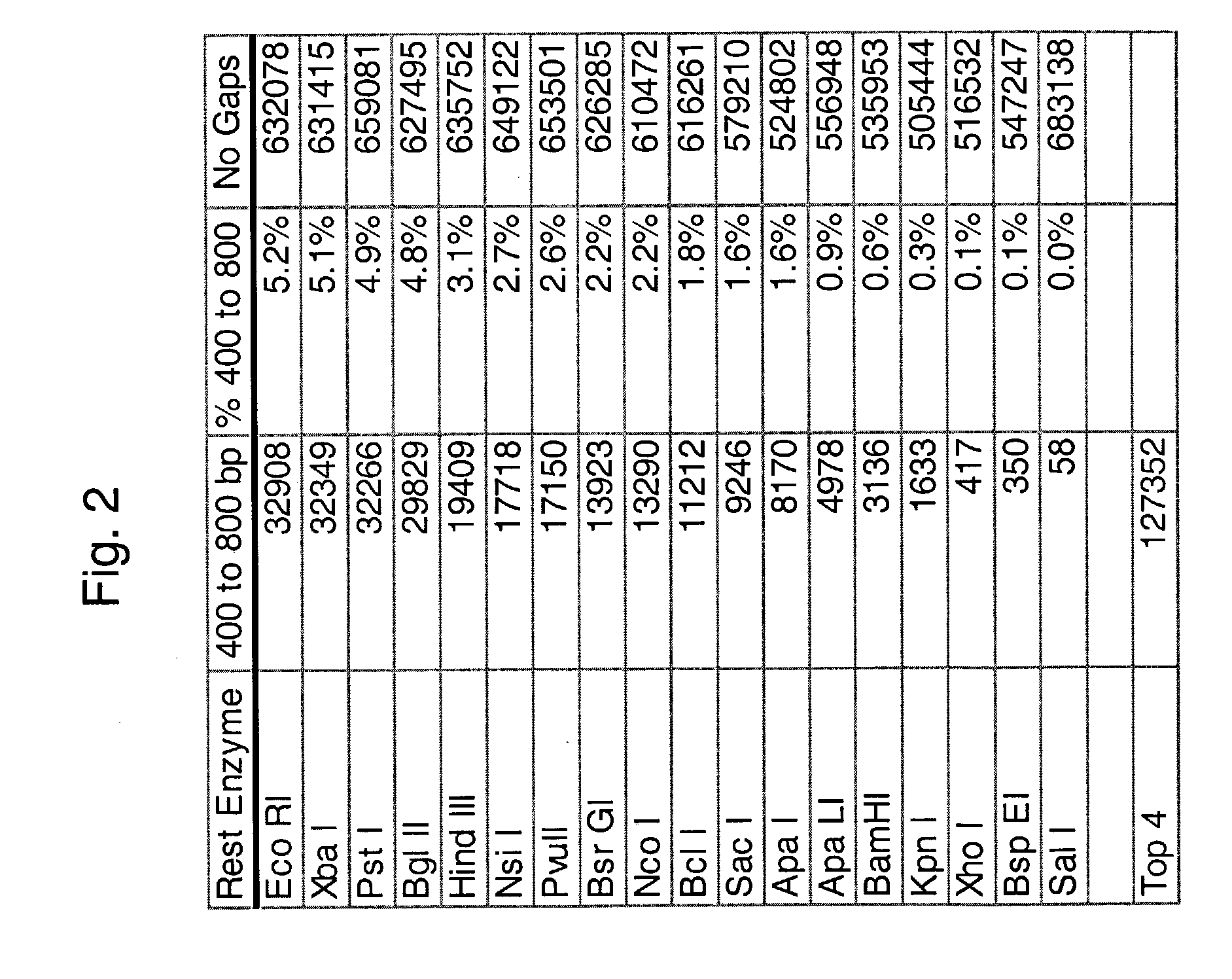
Novel methods and kits for analyzing a collection of target sequences in a nucleic acid sample are provided. A reduced complexity sample is generated and then analyzed. A sample is amplified under conditions that enrich for a subset of fragments that includes a collection of target sequences. The invention further provides for analysis of the above sample. Analysis may be by hybridization to an array, which may be specifically designed to interrogate the collection of target sequences for particular characteristics, such as, for example, the presence or absence of one or more polymorphisms.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
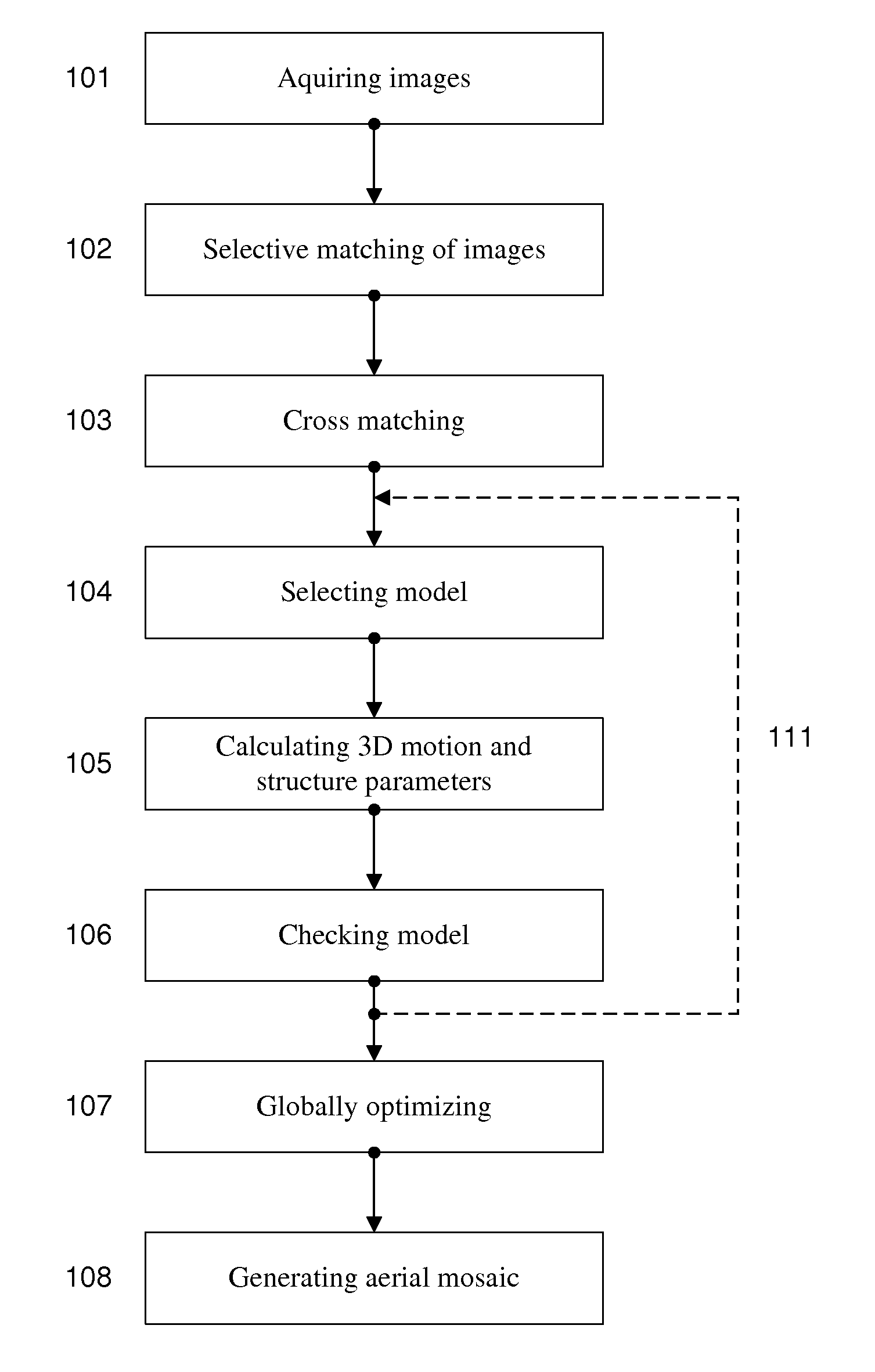
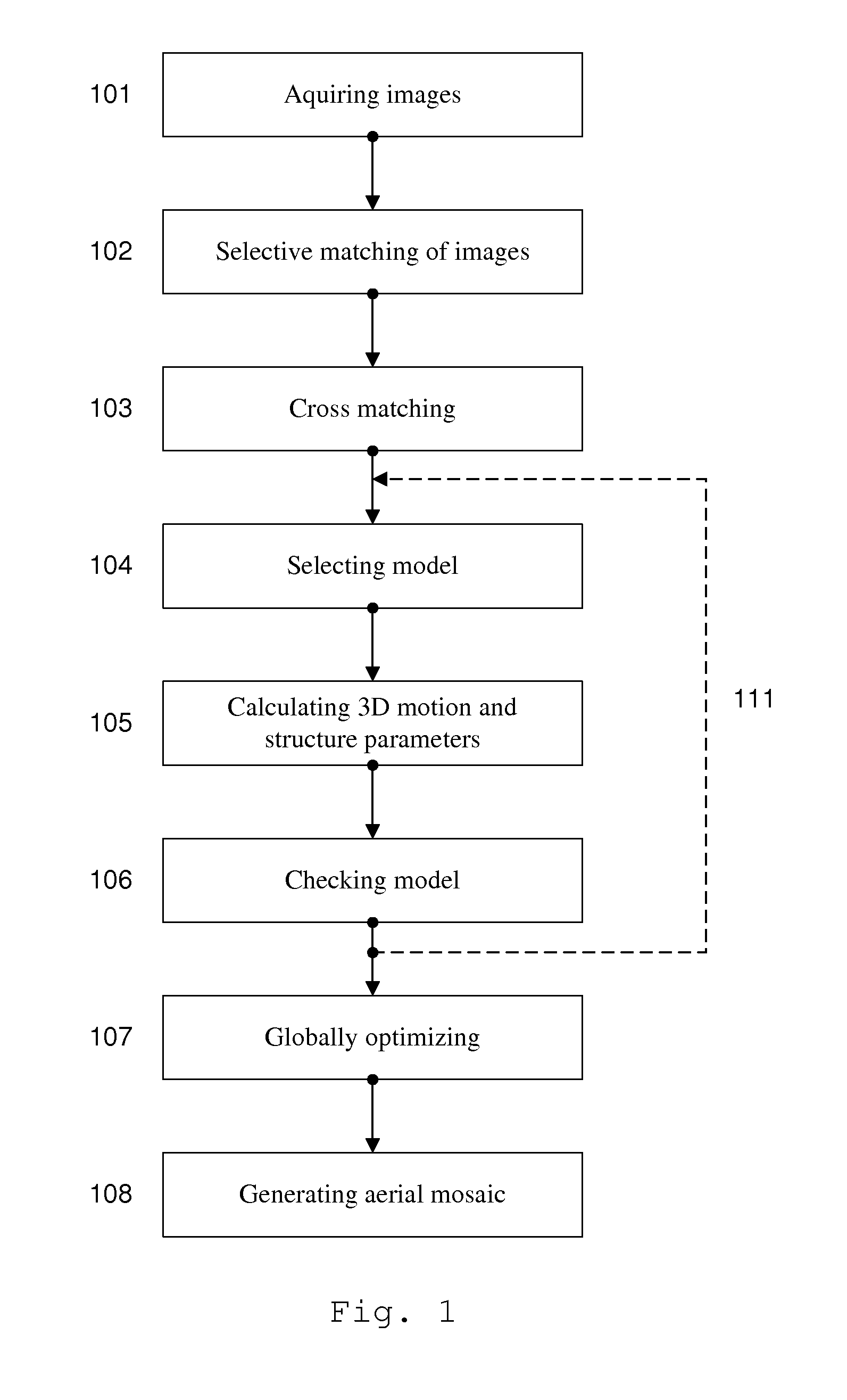
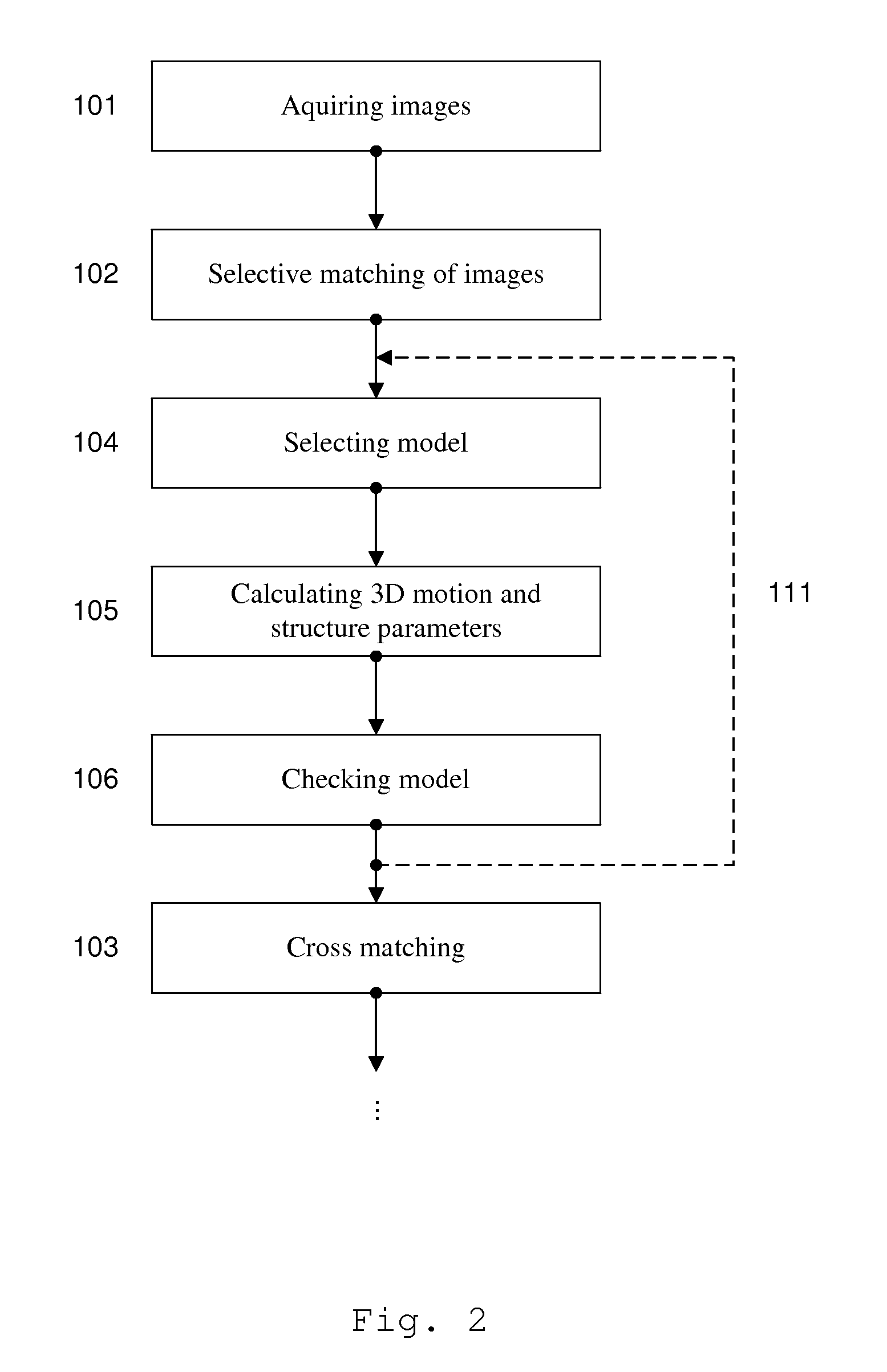
Generation of aerial images
ActiveUS20110090337A1Quality improvementRobust and cheap and lightPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryColor television detailsSingle imageAerial photography
The method according to the invention gene rates an aerial image mosaic viewing a larger area than a single image from a camera can provide using a combination of computer vision and photogrammetry. The aerial image mosaic is based on a set of images acquired from a camera. Selective matching and cross matching of consecutive and non-consecutive images, respectively, are performed and three dimensional motion and structure parameters are calculated and implemented on the model to check if the model is stable. Thereafter the parameters are globally optimised and based on these optimised parameters the serial image mosaic is generated. The set of images may be limited by removing old image data as new images are acquired. The method makes it is possible to establish images in near real time using a system of low complexity and small size, and using only image information.
Owner:IMINT IMAGE INTELLIGENCE AB
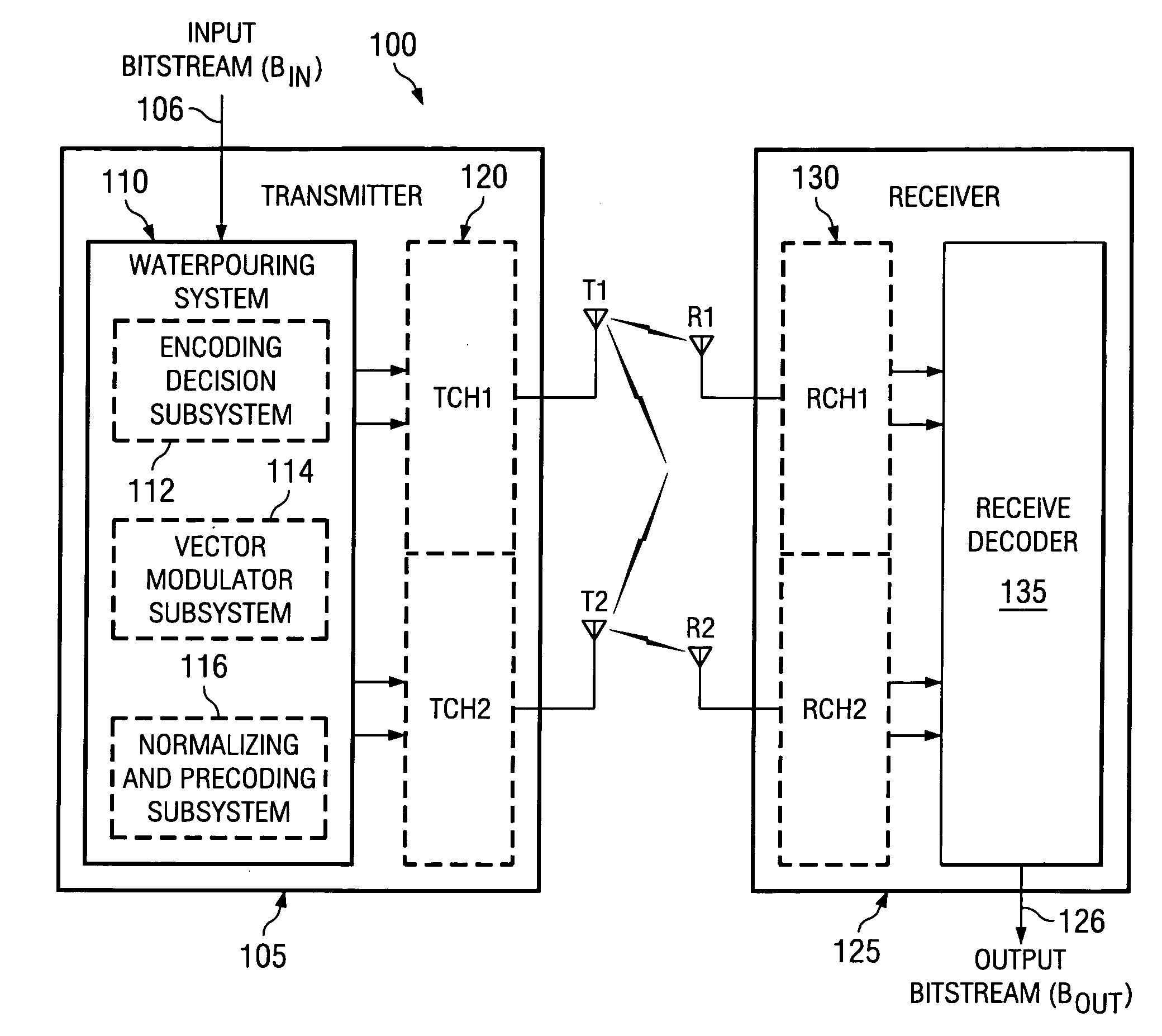
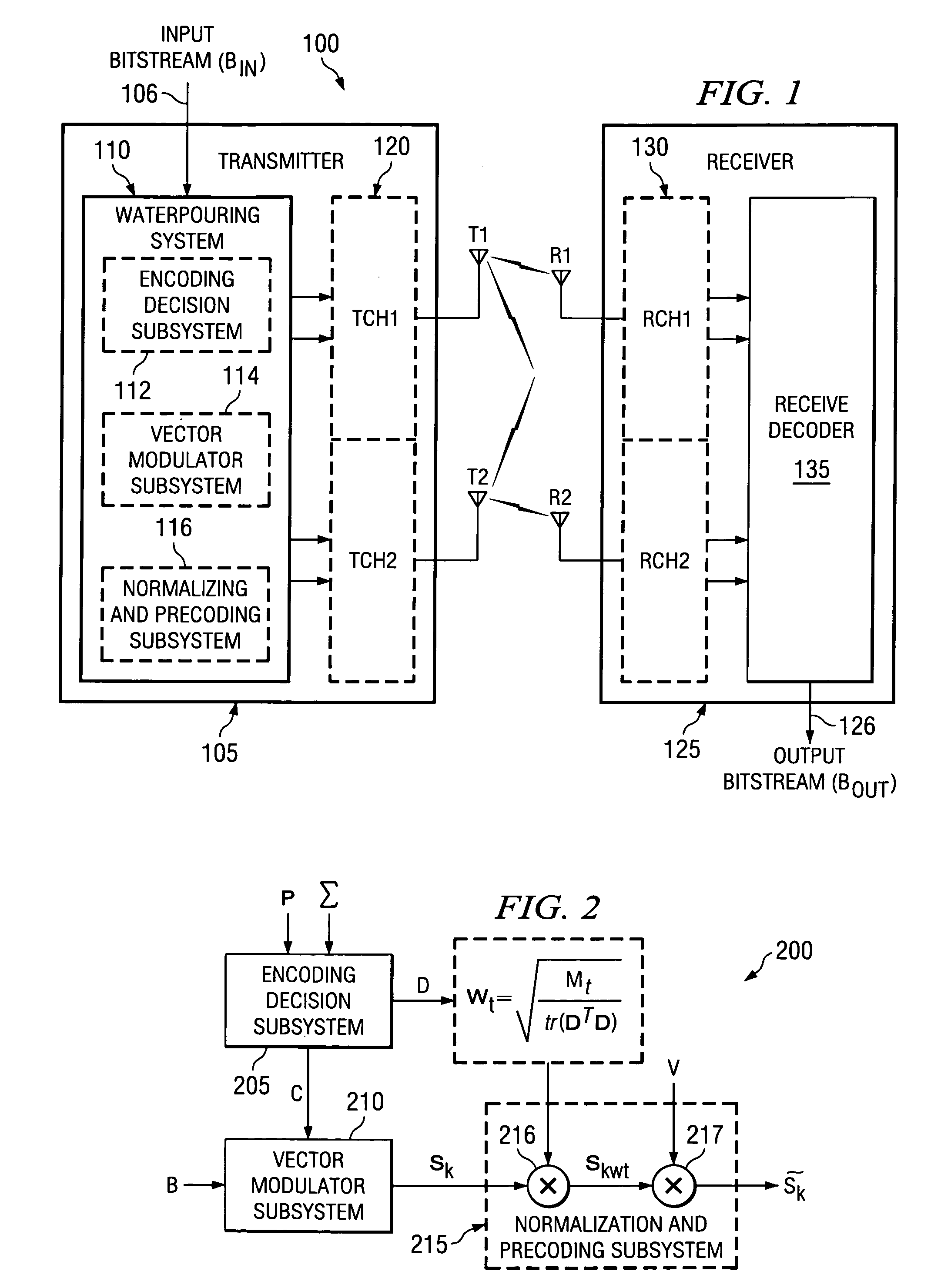
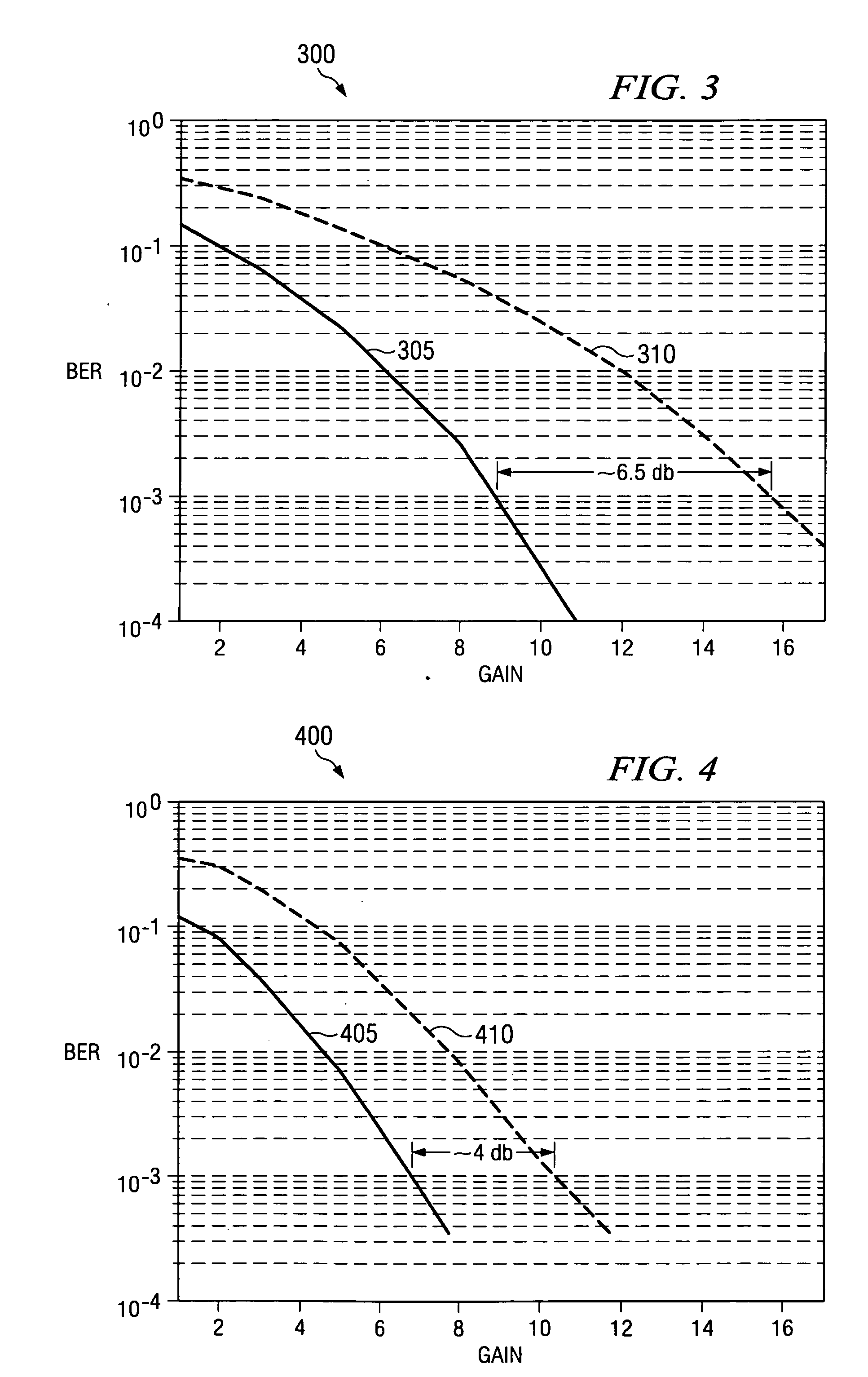
Reduced complexity transmit spatial waterpouring technique for multiple-input, multiple-output communication systems
A waterpouring system and method for use with a multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) transmitter. In one embodiment, the waterpouring system includes an encoding decision subsystem that selects a constellation combination based on gains in channels of the MIMO transmitter, and a vector modulator subsystem, coupled to the encoding decision system, that modulates a fixed number of bits in a bitstream with the constellation combination to generate a symbol vector. The waterpouring system also includes a normalization and precoding subsystem, coupled to the vector modulator subsystem, that weights the symbol vector based on the gains to yield a weighted symbol vector and distributes the weighted symbol vector among the channels.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Entropy coding supporting mode switching
ActiveUS20140140400A1Increase spectral resolution of spectralImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareData stream
A decoder for decoding a data stream into which media data is coded has a mode switch configured to activate a low-complexity mode or a high-efficiency mode depending on the data stream, an entropy decoding engine configured to retrieve each symbol of a sequence of symbols by entropy decoding using a selected one of a plurality of entropy decoding schemes, a desymbolizer configured to desymbolize the sequence of symbols to obtain a sequence of syntax elements, a reconstructor configured to reconstruct the media data based on the sequence of syntax elements, selection depending on the activated low-complexity mode or the high-efficiency mode. In another aspect, a desymbolizer is configured to perform desymbolization such that the control parameter varies in accordance with the data stream at a first rate in case of the high-efficiency mode being activated and the control parameter is constant irrespective of the data stream or changes depending on the data stream, but at a second lower rate in case of the low-complexity mode being activated.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
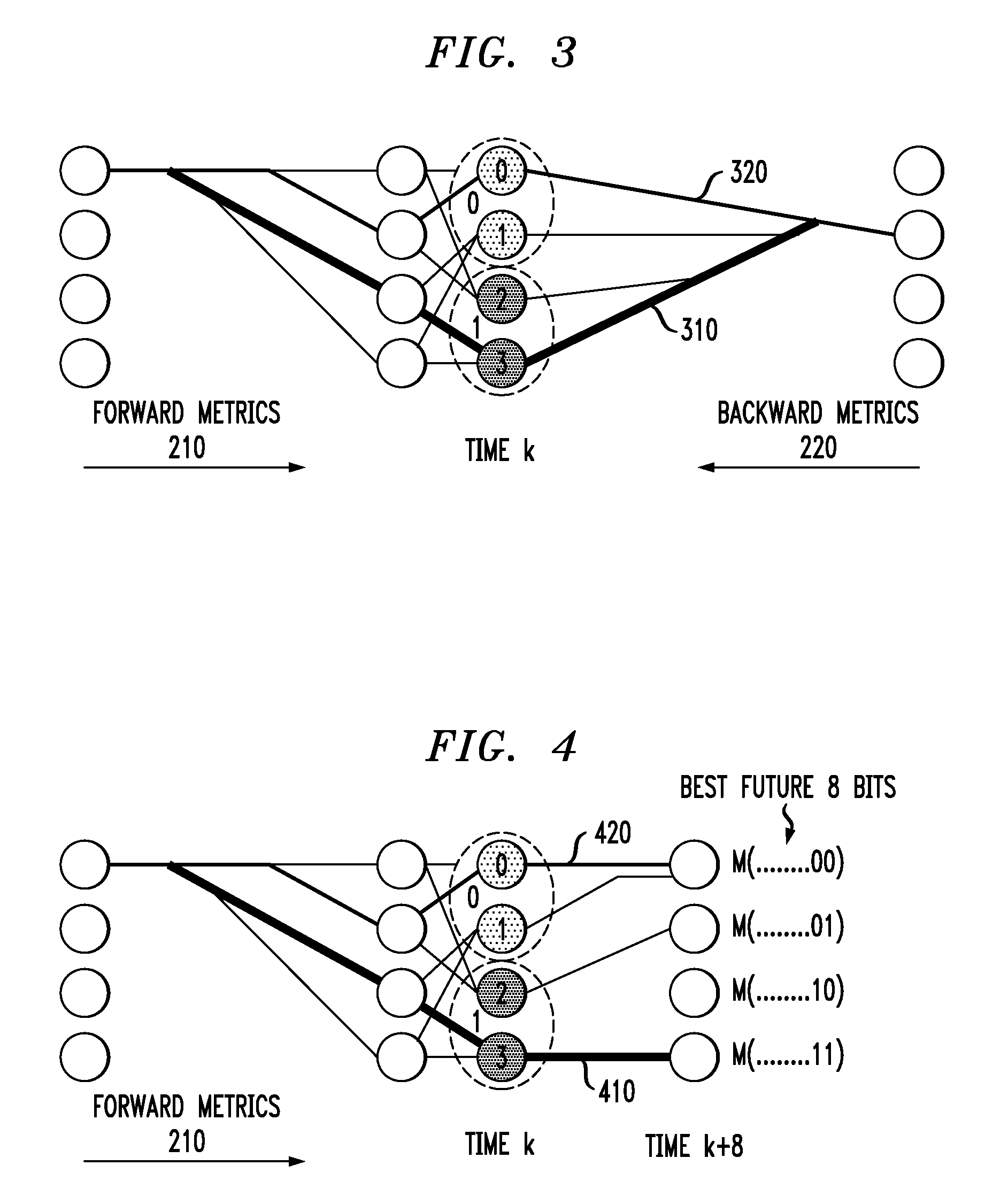
Methods and Apparatus for Map Detection with Reduced Complexity
ActiveUS20090185643A1Reduce complexityDependence moreDriving/moving recording headsError preventionLog likelihoodComputer science
Methods and apparatus are provided for high-speed, low-power, high-performance channel detection. A soft output channel detector is provided that operates at a rate of 1 / N and detects N bits per 1 / N-rate clock cycle. The channel detector comprises a plurality, D, of MAP detectors operating in parallel, wherein each of the MAP detectors generates N / D log-likelihood ratio values per 1 / N-rate clock cycle and wherein at least one of the plurality of MAP detectors constrains each of the bits. The log-likelihood ratio values can be merged to form an output sequence. A single MAP detector is also provided that comprises a forward detector for calculating forward state metrics; a backward detector for calculating backward state metrics; and a current branch detector for calculating a current branch metric, wherein at least two of the forward detector, the backward detector and the current branch detector employ different trellis structures.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
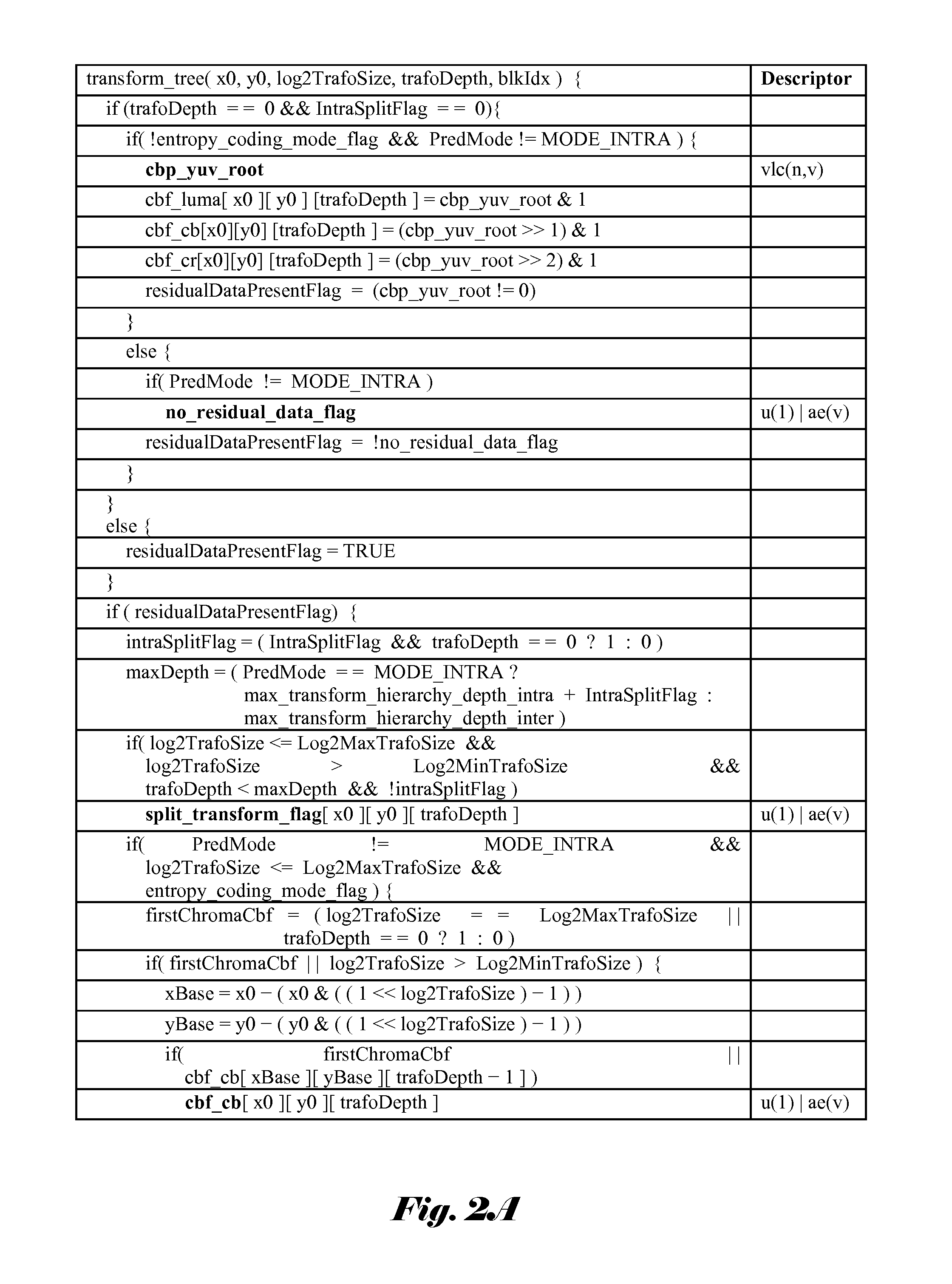
Method and Apparatus of Transform Unit Partition with Reduced Complexity
ActiveUS20120230411A1Reduced encoding computational complexitySmall motion estimation costColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRound complexityMotion vector
Three block concepts are introduced in HEVC: coding unit (CU), prediction unit (PU), and transform unit (TU). The overall coding structure is characterized by the various sizes of CU, PU and TU in a recursive fashion. For transform processing in current HEVC, a hierarchy RQT (Residual Quad Tree) is used and the TU size is related to the CU size, but independent of the PU size. This results in high encoding complexity and also causes increased processing time to process the syntax of residual quad tree. Accordingly a modified transform unit partition with reduced complexity is disclosed. According to an embodiment, the TU size may be restricted to the minimum of PU width and height, except for a 2N×2N coding unit with the 2N×2N partition type. In another embodiment, the maximum TU size equals to maximum of PU width and height, and the minimum TU size equals to minimum of the PU width and height, except for a 2N×2N coding unit with the 2N×2N partition type. In yet another embodiment, the TU size is selected between 2N×2N and N×N for the 2N×2N, 2N×N, N×2N and N×N partition types. The syntax element, split_transform_flag, is used to indicate the selection of 2N×2N or N×N TU size when needed. Furthermore, a method with reduced complexity of selecting the best merge candidate for the 2N×2N CU merge mode is disclosed. The method relies on R-D cost associated with the motion vector of merge candidate to reduce required computation.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
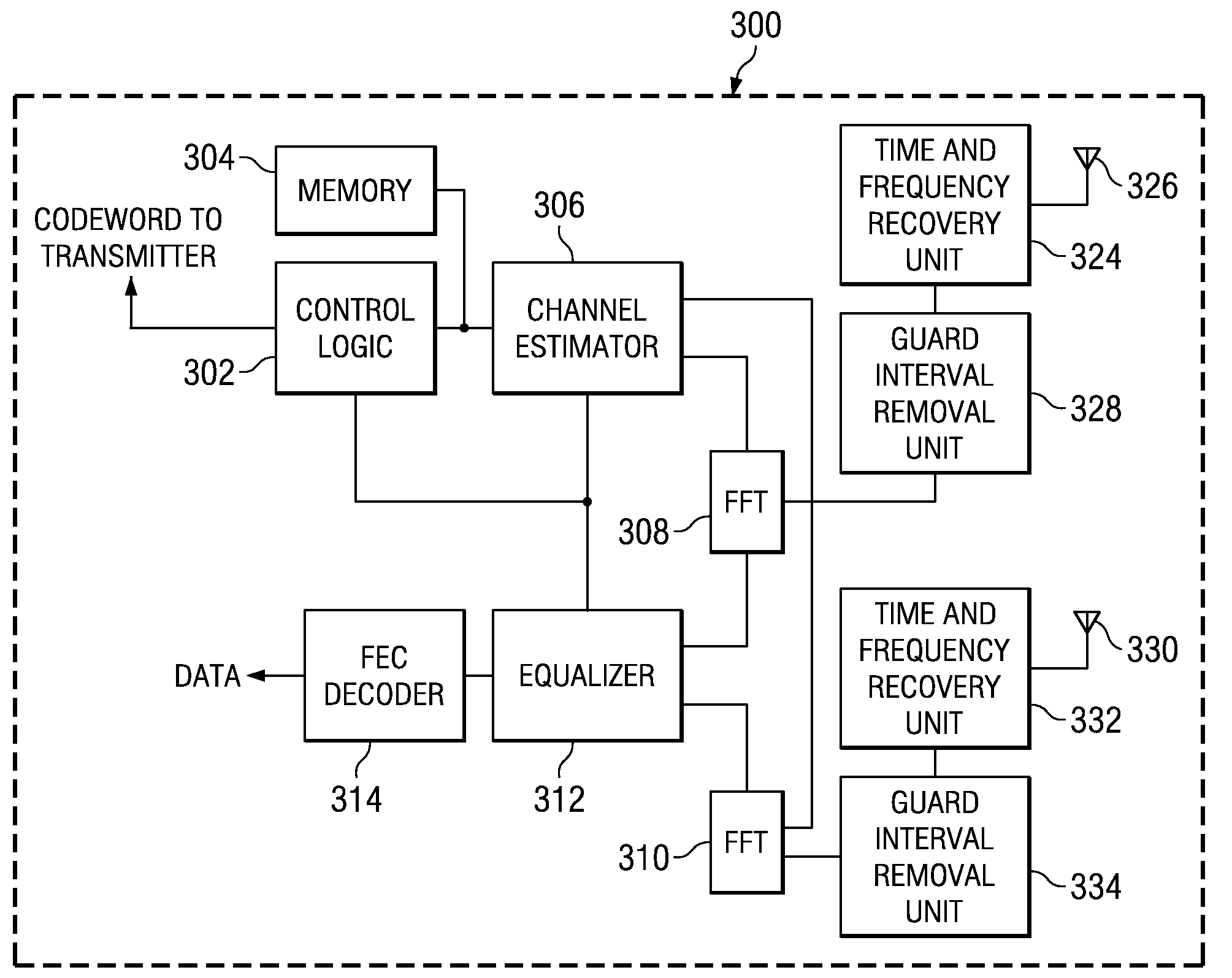
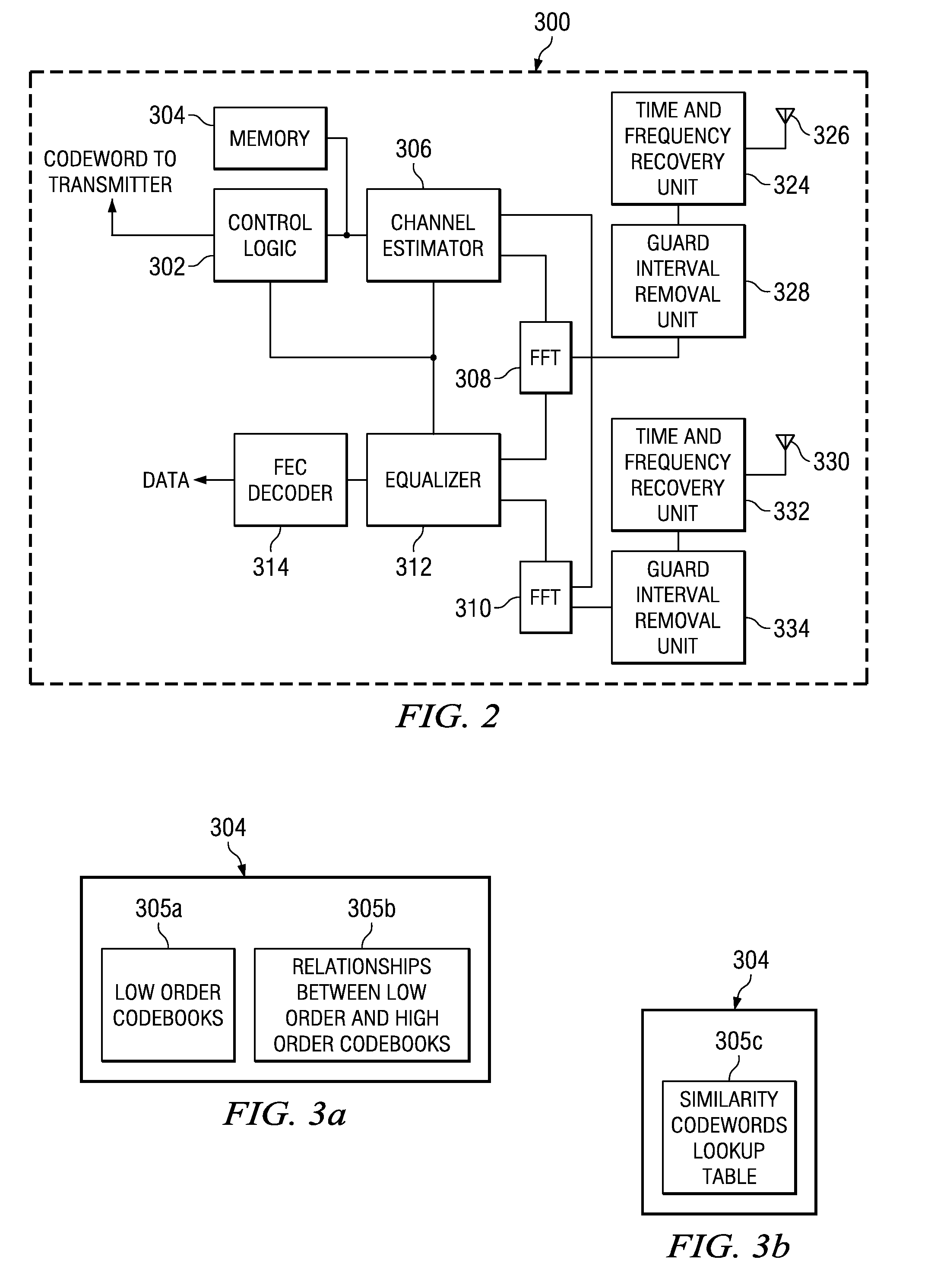
Low complexity precoding matrix selection
ActiveUS20080304464A1Transmission path divisionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsLow complexityTransmitter
A method of determining indices for matrix codewords in a matrix codeword codebook. The matrix codewords are adapted for communicating information between a transmitter and a receiver. The method includes retrieving from temporary storage, an eigenmode representation for a communications channel, where the eigenmode representation is based upon on a received signal precoded by a first matrix codeword. The method also includes performing a test on multiple vector codewords to identify a first vector codeword among the multiple vector codewords, where the test includes determining a relationship between the first vector codeword and the representation of an eigenmode. The first vector codeword is associated with a first vector codeword index that identifies the first vector codeword. The method also includes generating a matrix codeword index associated with a second matrix codeword in the matrix codeword codebook. The matrix codeword index is based upon the first vector codeword index, and the order of the first vector codeword is different from the order of the second matrix codeword.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for generating a binaural audio signal
ActiveUS20100246832A1Improved binauralReduce complexitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsMultiplexerAudio frequency
An apparatus for generating a binaural audio signal includes a de-multiplexer and decoder which receives audio data comprising an audio M-channel audio signal which is a downmix of an N-channel audio signal and spatial parameter data for upmixing the M-channel audio signal to the N-channel audio signal. A conversion processor converts spatial parameters of the spatial parameter data into first binaural parameters in response to at least one binaural perceptual transfer function. A matrix processor converts the M-channel audio signal into a first stereo signal in response to the first binaural parameters. A stereo filter generates the binaural audio signal by filtering the first stereo signal. The filter coefficients for the stereo filter are determined in response to the at least one binaural perceptual transfer function by a coefficient processor. The combination of parameter conversion / processing and filtering allows a high quality binaural signal to be generated with low complexity.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
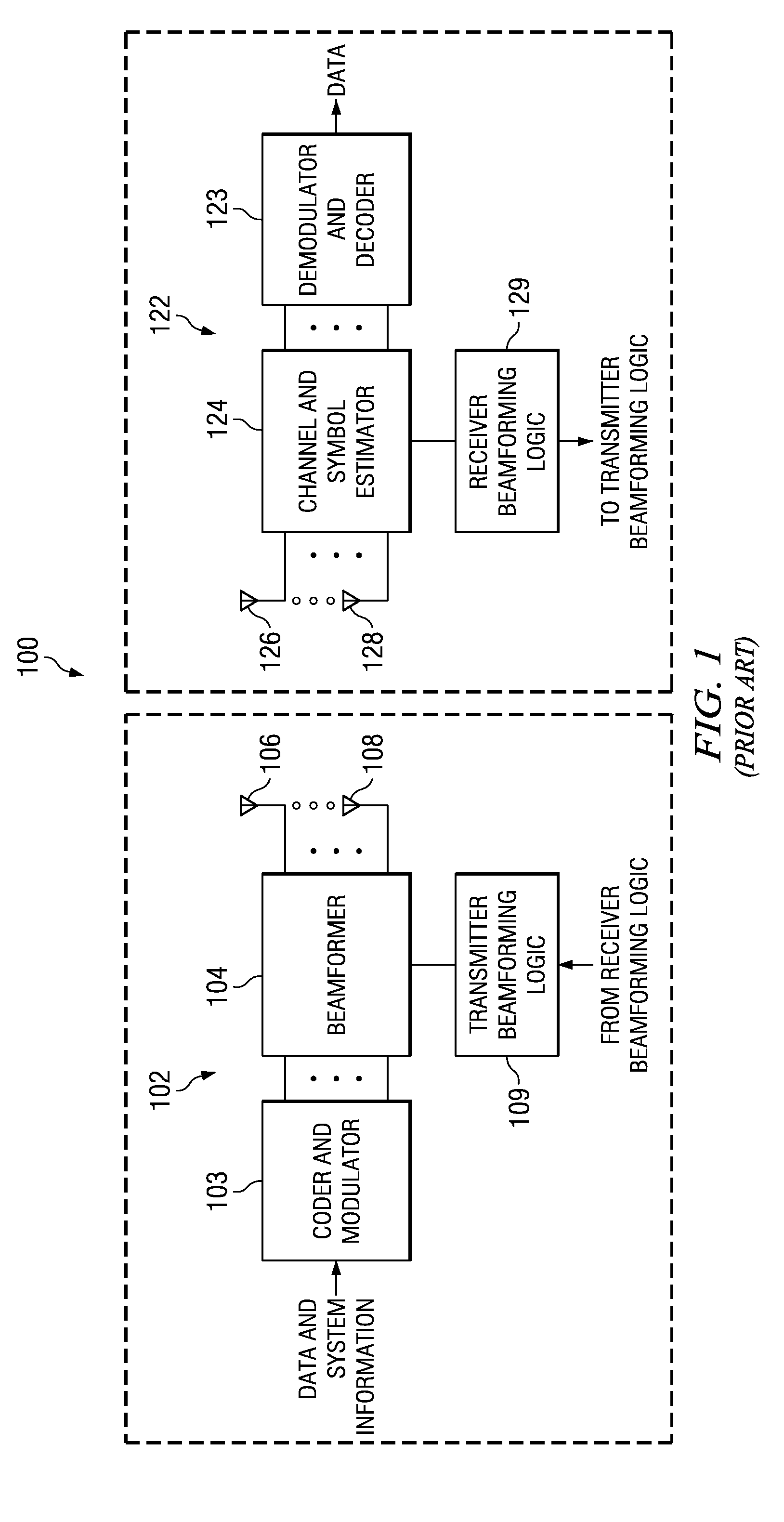
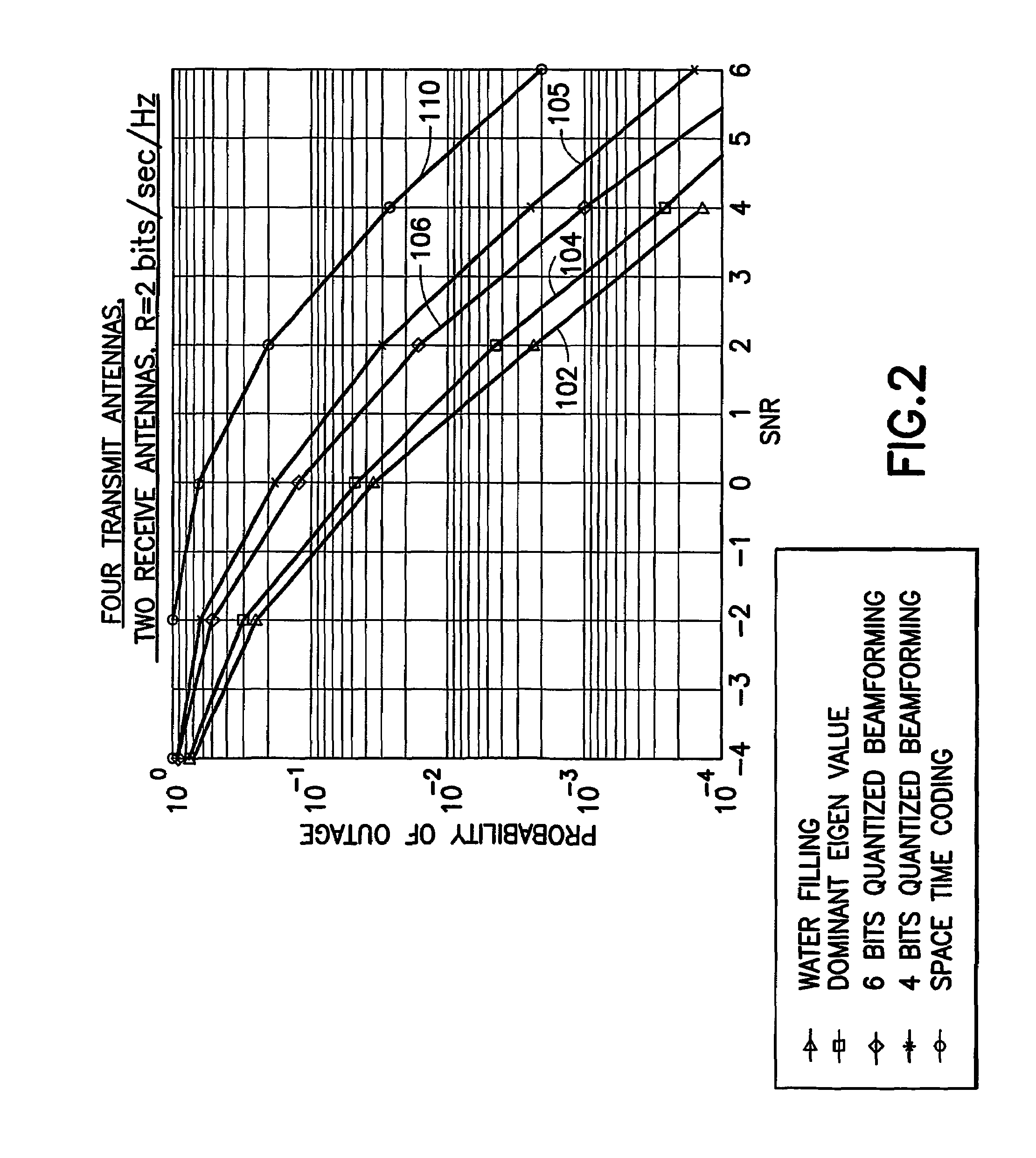
Low complexity beamformers for multiple transmit and receive antennas
InactiveUS7330701B2Power managementSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationRound complexity
Beamforming systems having a few bits of channel state information fed back to the transmitter benefit from low complexity decoding structures and performances gains compared with systems that do not have channel state feedback. Both unit rank and higher rank systems are implemented. Substantial design effort may be avoided by following a method of using functions formulated for space-time systems with the change that the channel coherence time is equated to the number of transmit antennas and the number of antennas in the space-time formulation is fixed at one.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
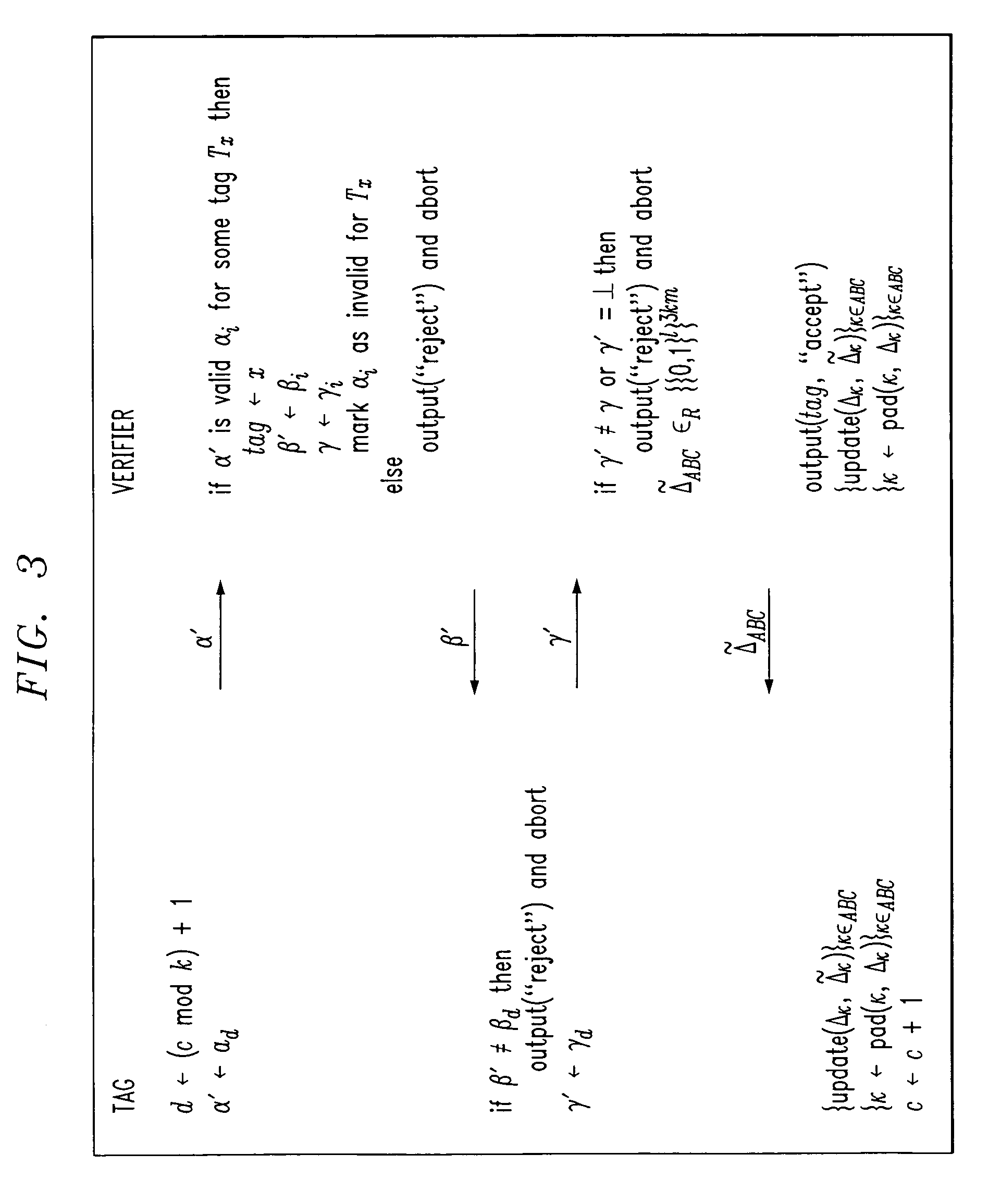
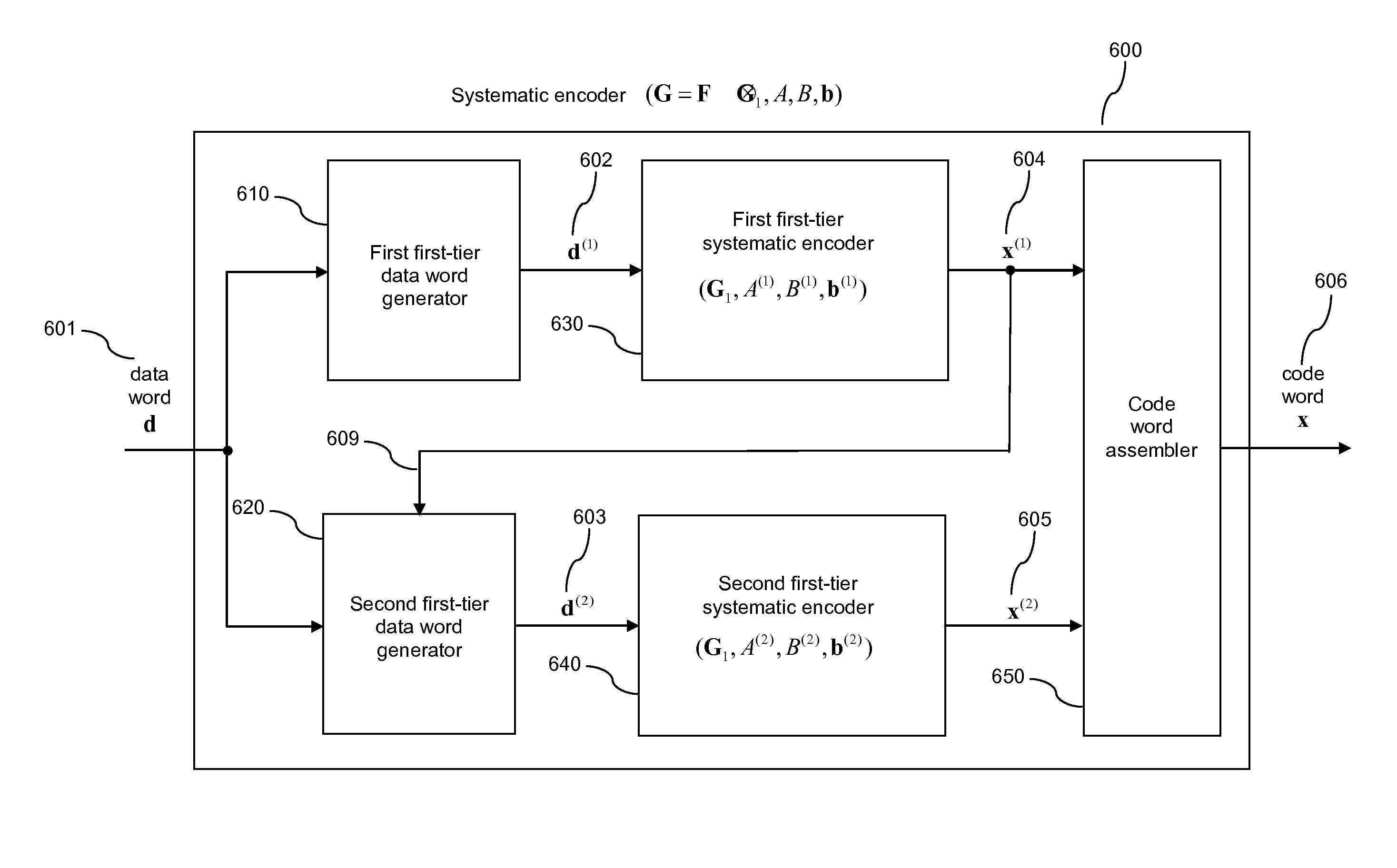
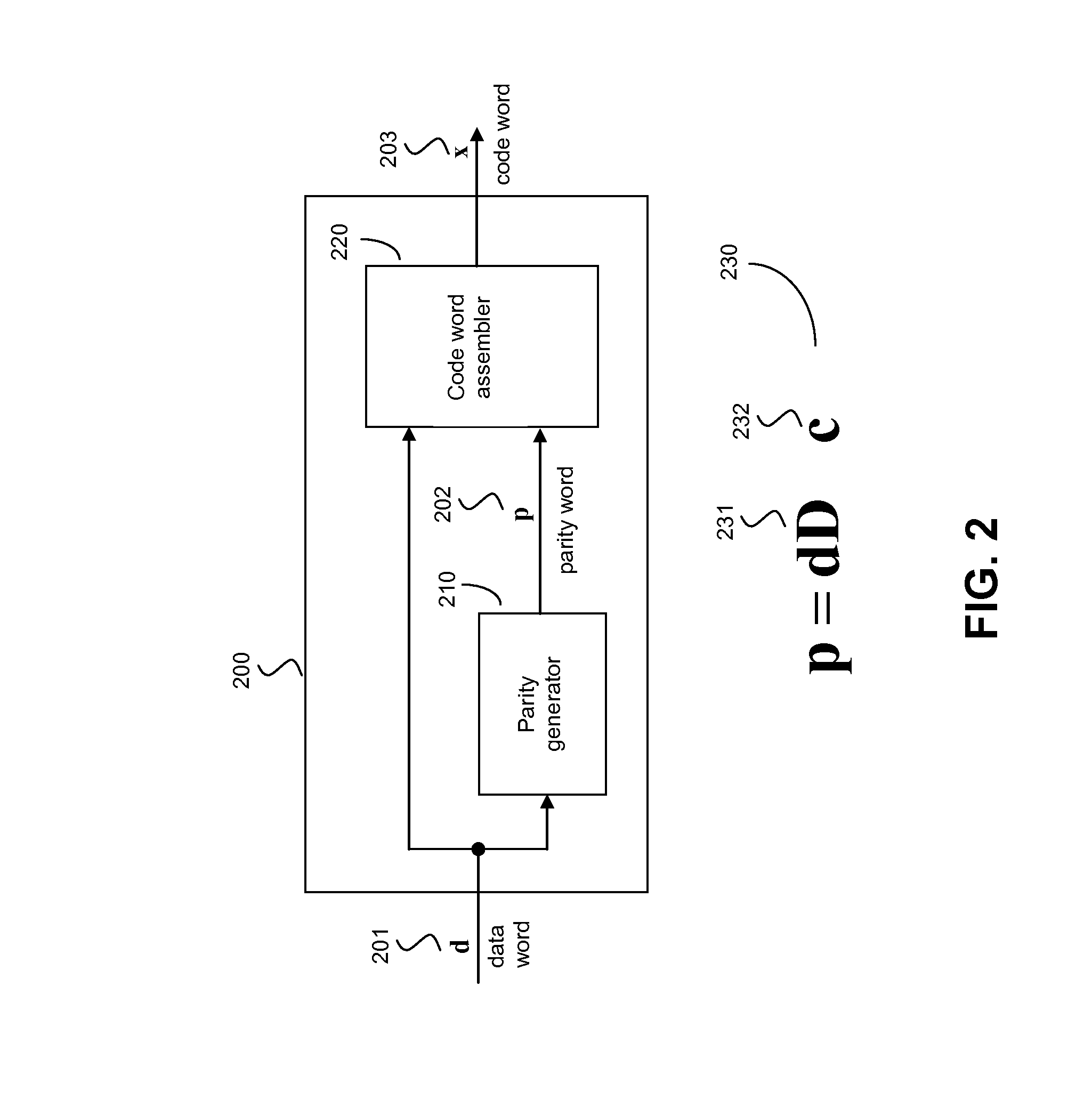
Method and system for error correction in transmitting data using low complexity systematic encoder
ActiveUS8347186B1Improve performanceImprove Noise PerformanceCode conversionChannel coding adaptationTransmission channelComputer science
A systematic encoder such as a systematic polar encoder for channel encoding to ameliorate the effects of noise in a transmission channel. The codeword carries a data word to be transmitted transparently, and also carries a parity part derived from the data word and a fixed word. Implementations advantageously reduce coding complexity to the order of N log(N), wherein N is the dimension of a matrix of the nth Kronecker power associated with a matrix effectively employed by the encoder.
Owner:POLARAN YAZILIM BILISIM DANISMANLIK ITHALAT IHRACAT SANAYI TICARET SIRKETI
Dynamic GOP system and method for digital video encoding
InactiveUS6959044B1Improve performanceTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoVideo quality
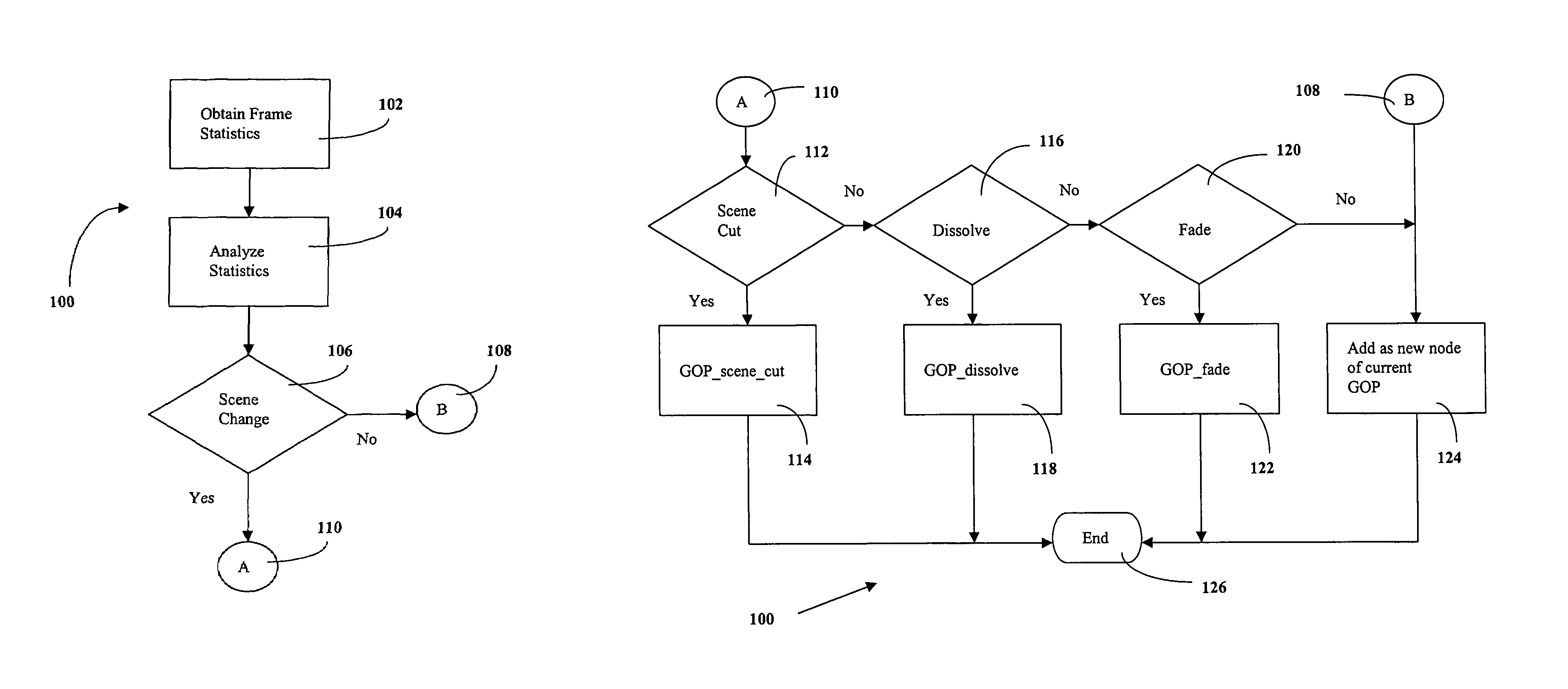
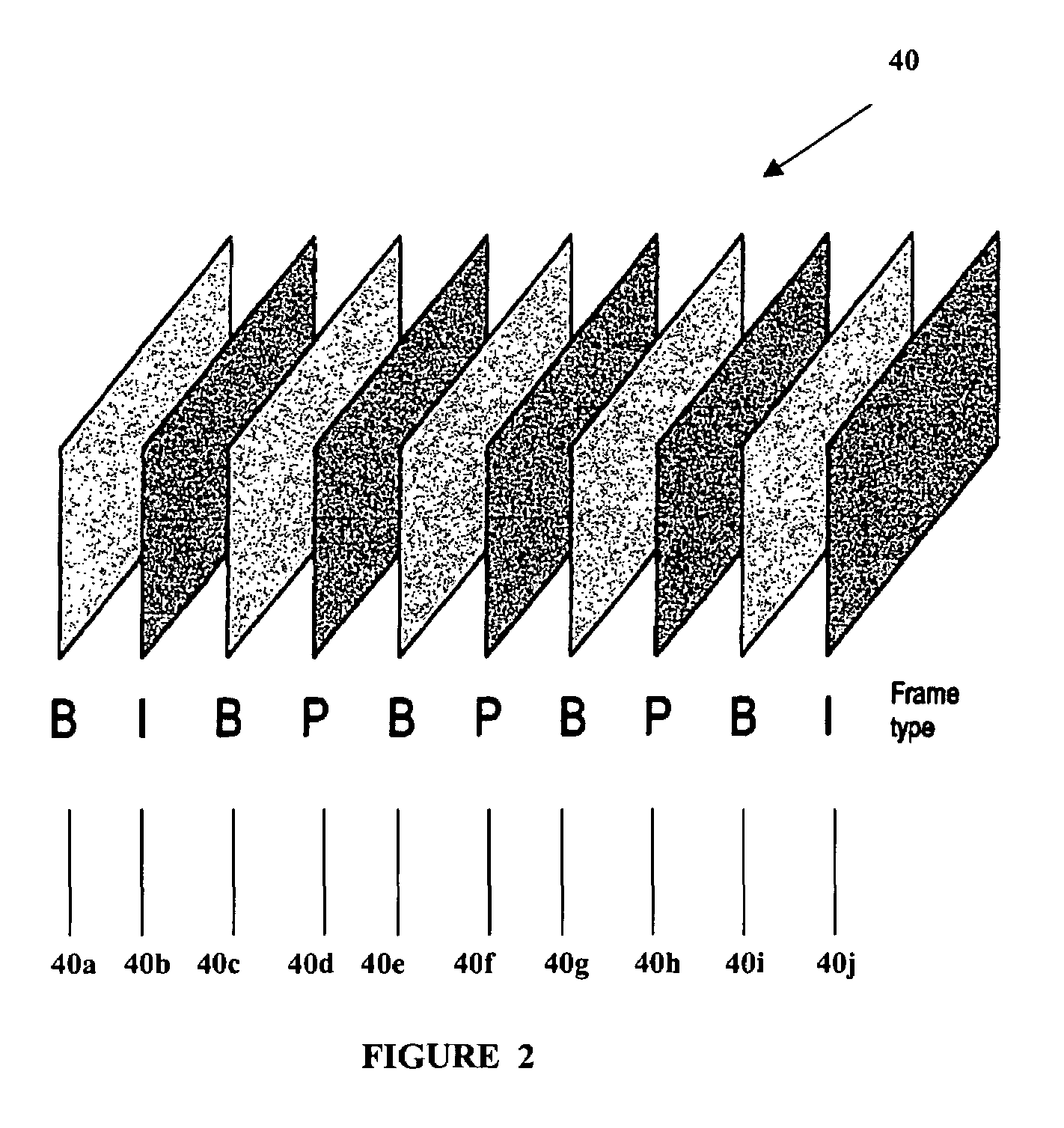
This invention discloses an intra-frame complexity based dynamic GOP system and method for the encoding of MPEG-2 video streams. The present invention may be used as a rate control tool to improve video quality. The selective insertion of low complexity I frames in scene changes such as fades is disclosed. It is disclosed that the selective use of I frames in certain scene change situations can improve encoder performance, particularly when encoding at a low bit rate.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
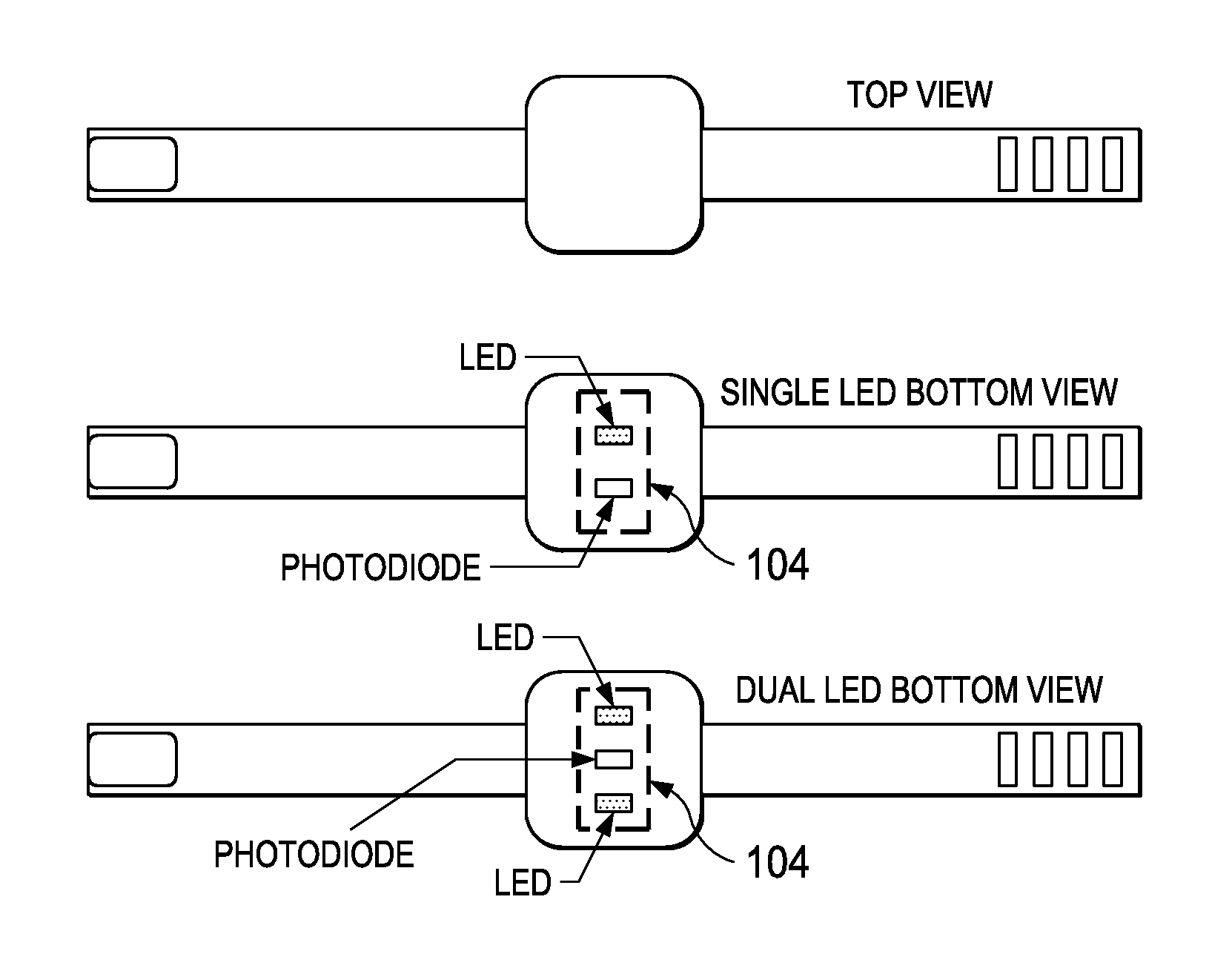
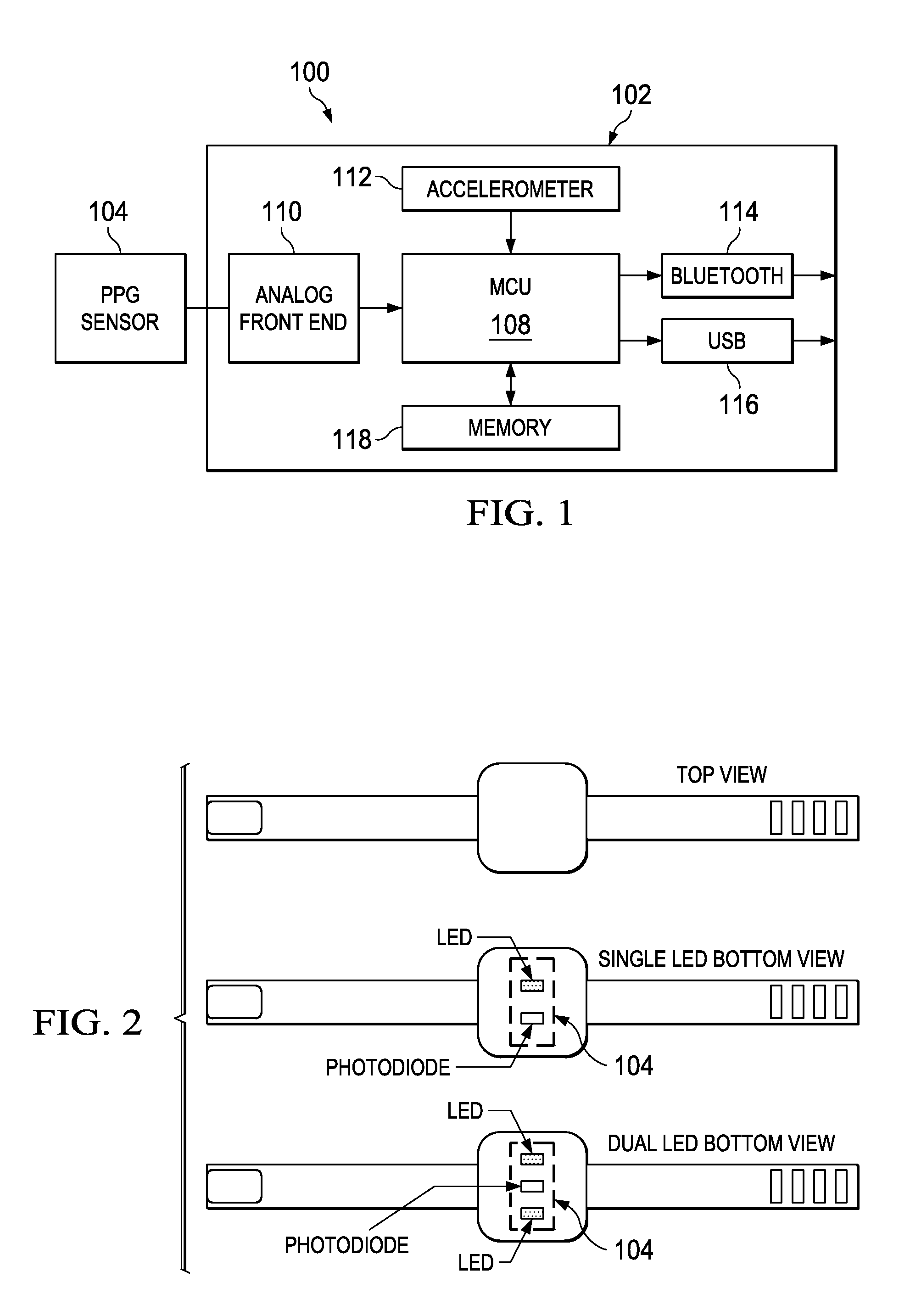
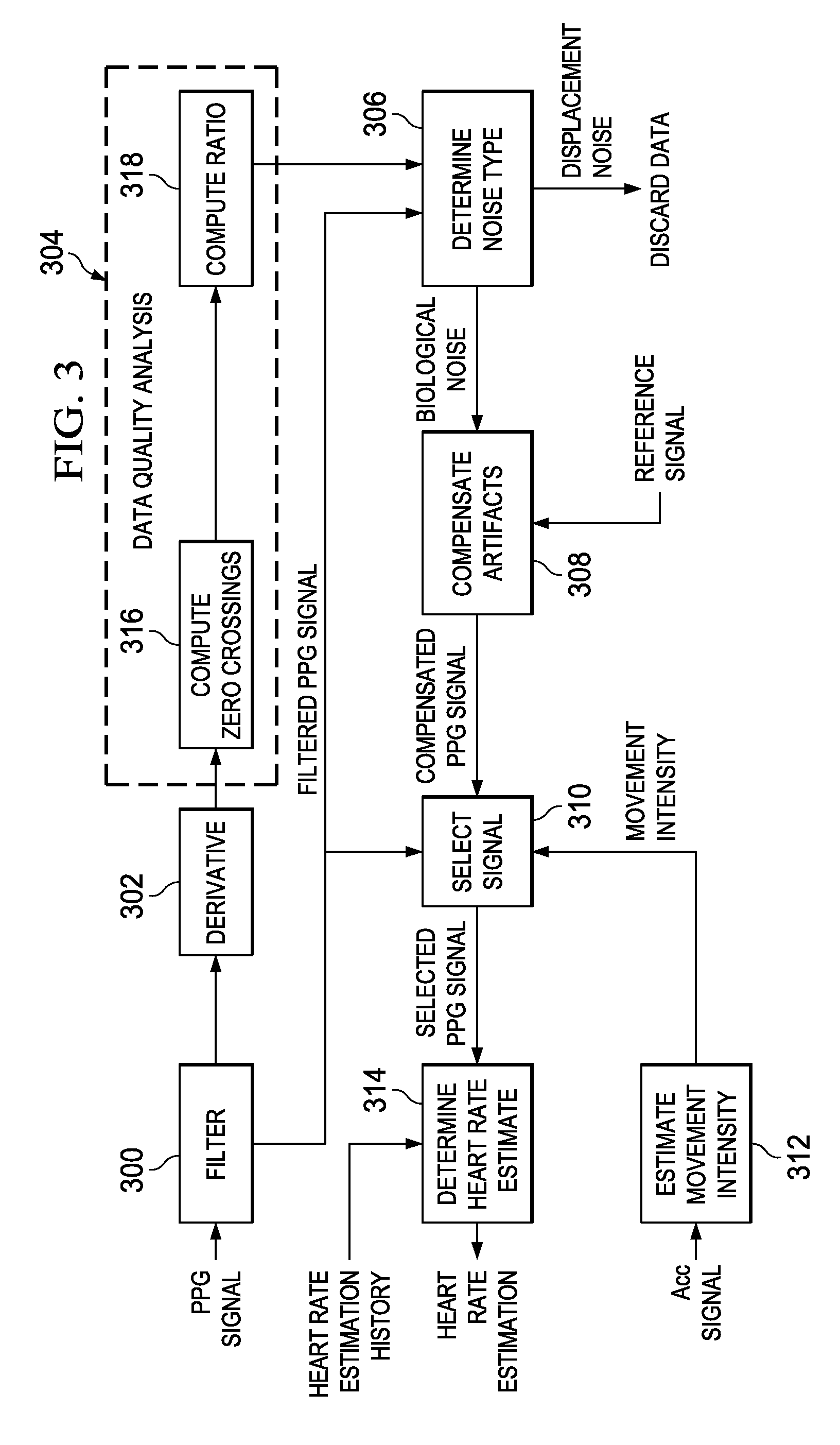
Low-Complexity Sensor Displacement Tolerant Pulse Oximetry Based Heart Rate Measurement
ActiveUS20140213863A1SensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateRelative displacementHeart rate measurement
Methods for heart rate measurement based on pulse oximetry are provided that can tolerate some degree of relative displacement of a photoplethysmograph (PPG) heart rate monitor device. In some methods, artifact compensation based on a reference signal is performed on the PPG signal data to remove artifacts in the signal that may be caused, for example, by changes in ambient light and / or motion of a person wearing the monitor device. The reference signal used for artifact compensation may be generated using an LED of a complementary wavelength to that of the LED used to generate the PPG signal, or by driving an LED at a lower current than the current applied to generate the PPG signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
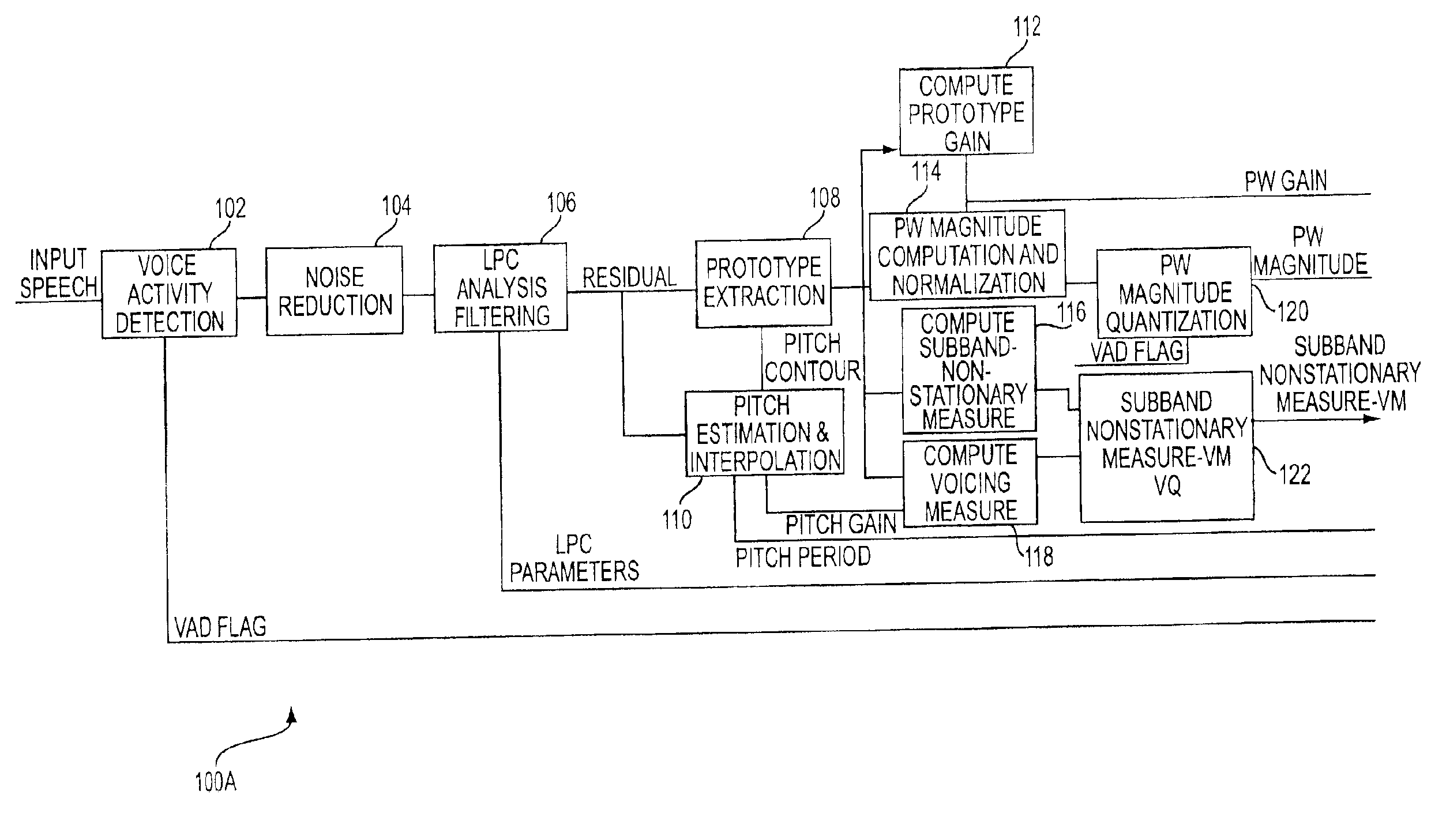
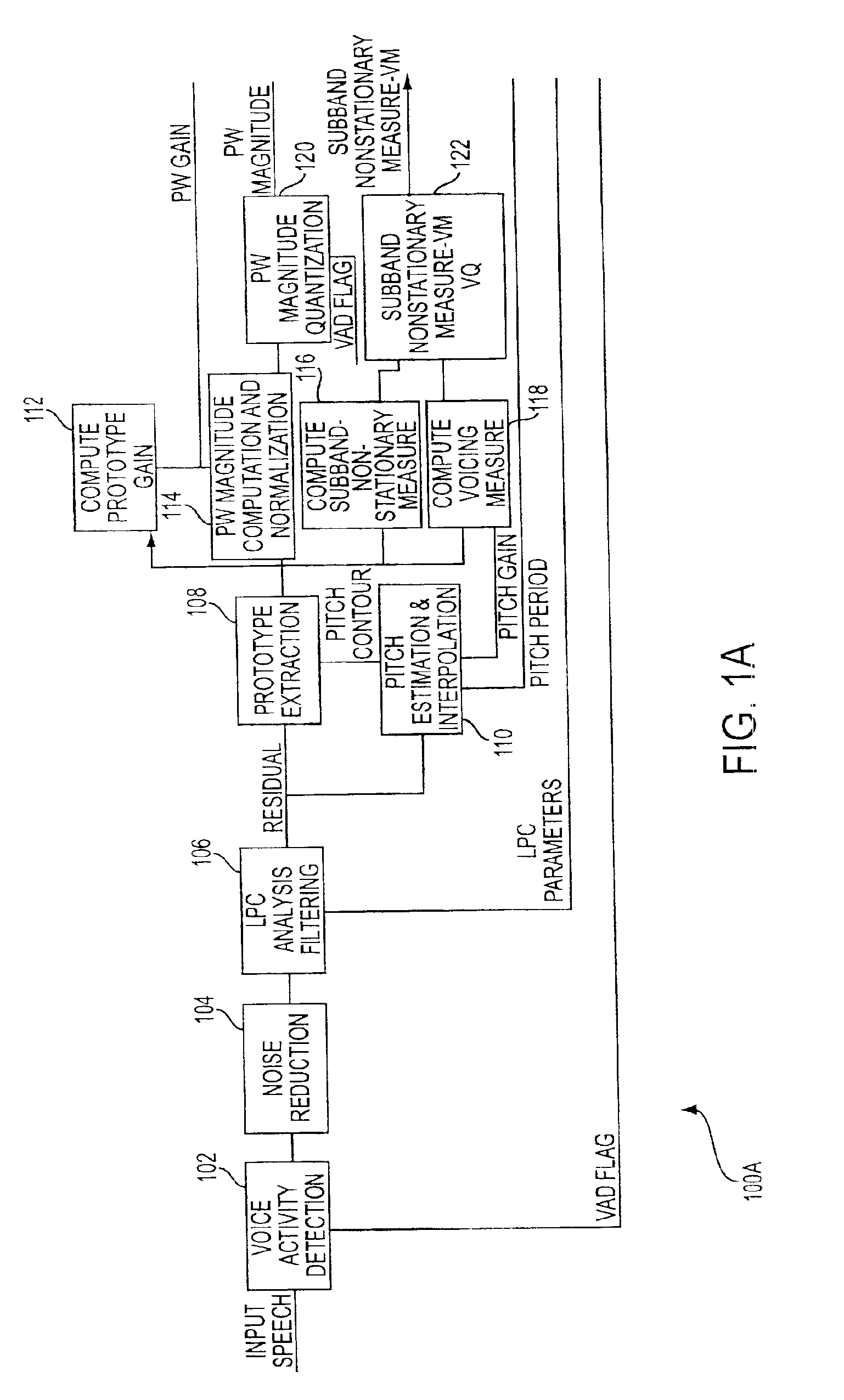
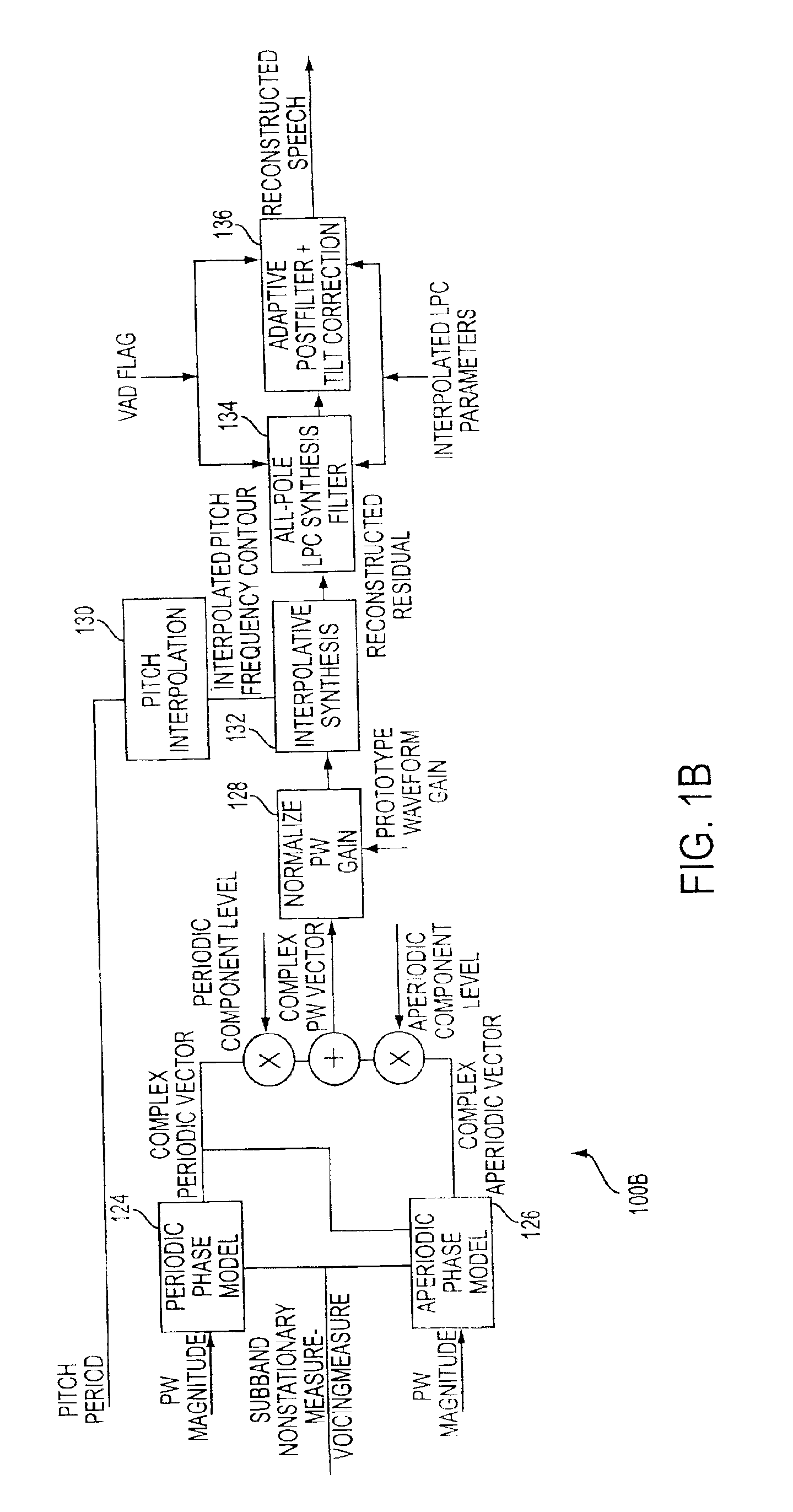
Prototype waveform phase modeling for a frequency domain interpolative speech codec system
A system and method is provided that employs a frequency domain interpolative CODEC system for low bit rate coding of speech which comprises a linear prediction (LP) front end adapted to process an input signal that provides LP parameters which are quantized and encoded over predetermined intervals and used to compute a LP residual signal. An open loop pitch estimator adapted to process the LP residual signal, a pitch quantizer, and a pitch interpolator and provide a pitch contour within the predetermined intervals is also provided. Also provided is a signal processor responsive to the LP residual signal and the pitch contour and adapted to perform the following: provide a voicing measure, where the voicing measure characterizes a degree of voicing of the input speech signal and is derived from several input parameters that are correlated to degrees of periodicity of the signal over the predetermined intervals; extract a prototype waveform (PW) from the LP residual and the open loop pitch contour for a number of equal sub-intervals within the predetermined intervals; normalize the PW by a gain value of the PW; encode a magnitude of the PW; and separate stationary and nonstationary components of the PW using a low complexity alignment process and a filtering process that introduce no delay. The ratio of the energy of the nonstationary component of the PW to that of the stationary component of the PW is averaged across 5 subbands to compute the nonstationarity measure as a frequency dependent vector entity. A measure of the degree of voicing of the residual is also computed using openloop pitchgain, pitch variance, relative signal power, PW correlation and PW nonstationarity in low frequency subbands. The nonstationarity measure and voicing measure are encoded using a 6-bit spectrally weighted vector quantization scheme using a codebook partitioned based on a voiced / unvoiced decision. At the decoder, a stationary component of PW is reconstructed as a weighted combination of the previous PW phase vector, a random phase perturbation and a fixed phase vector obtained from a voiced pitch pulse.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
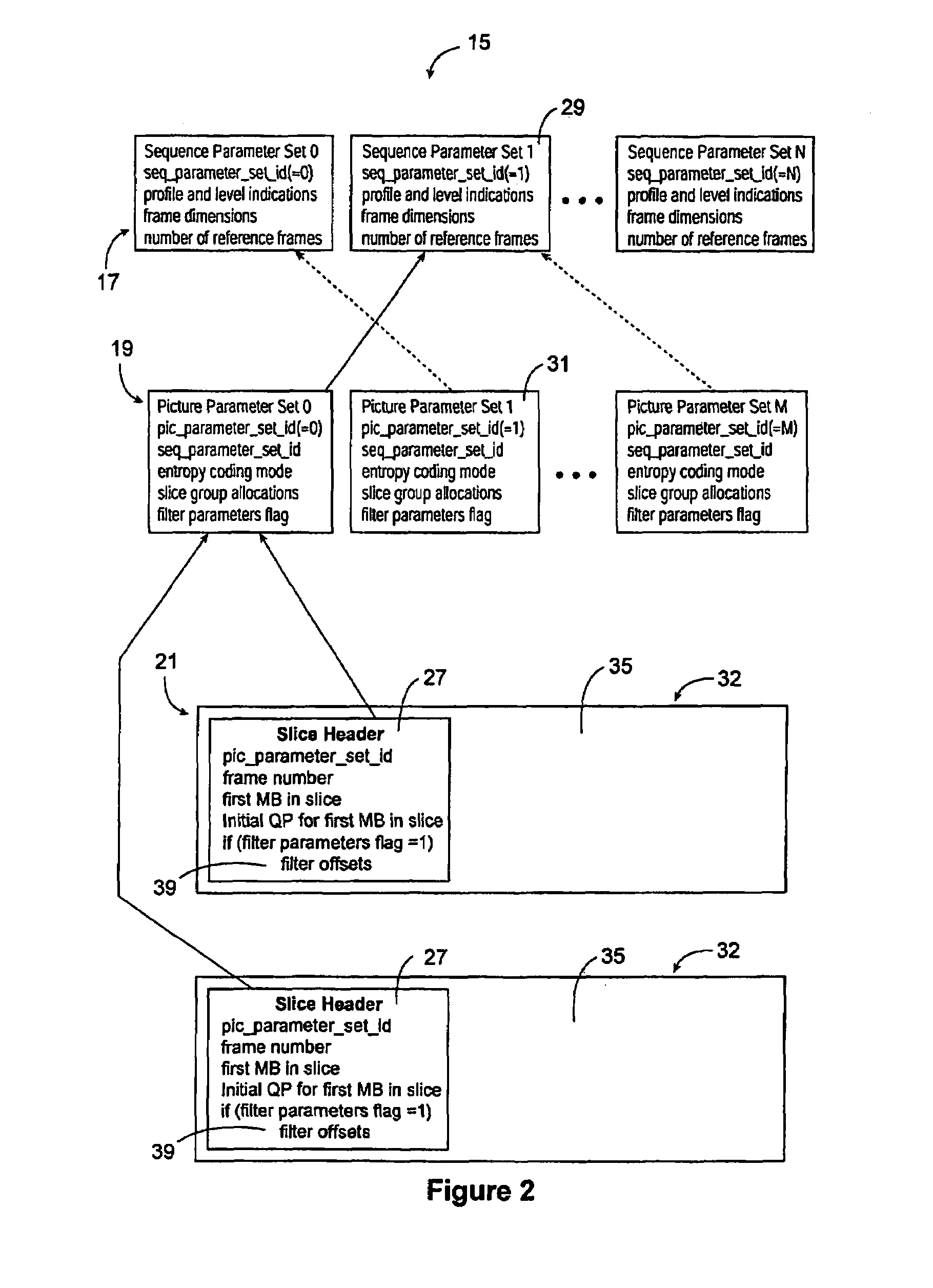
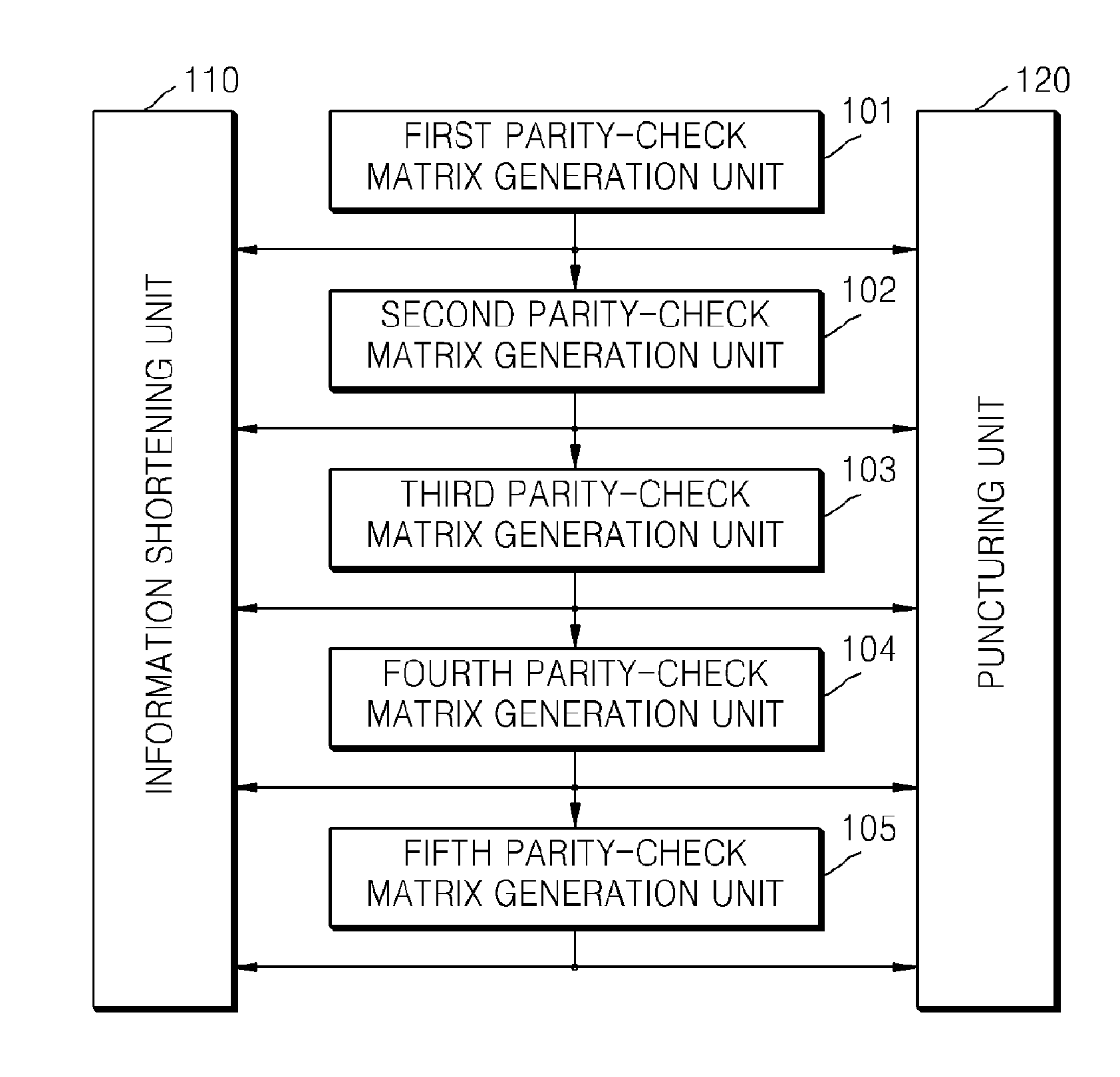
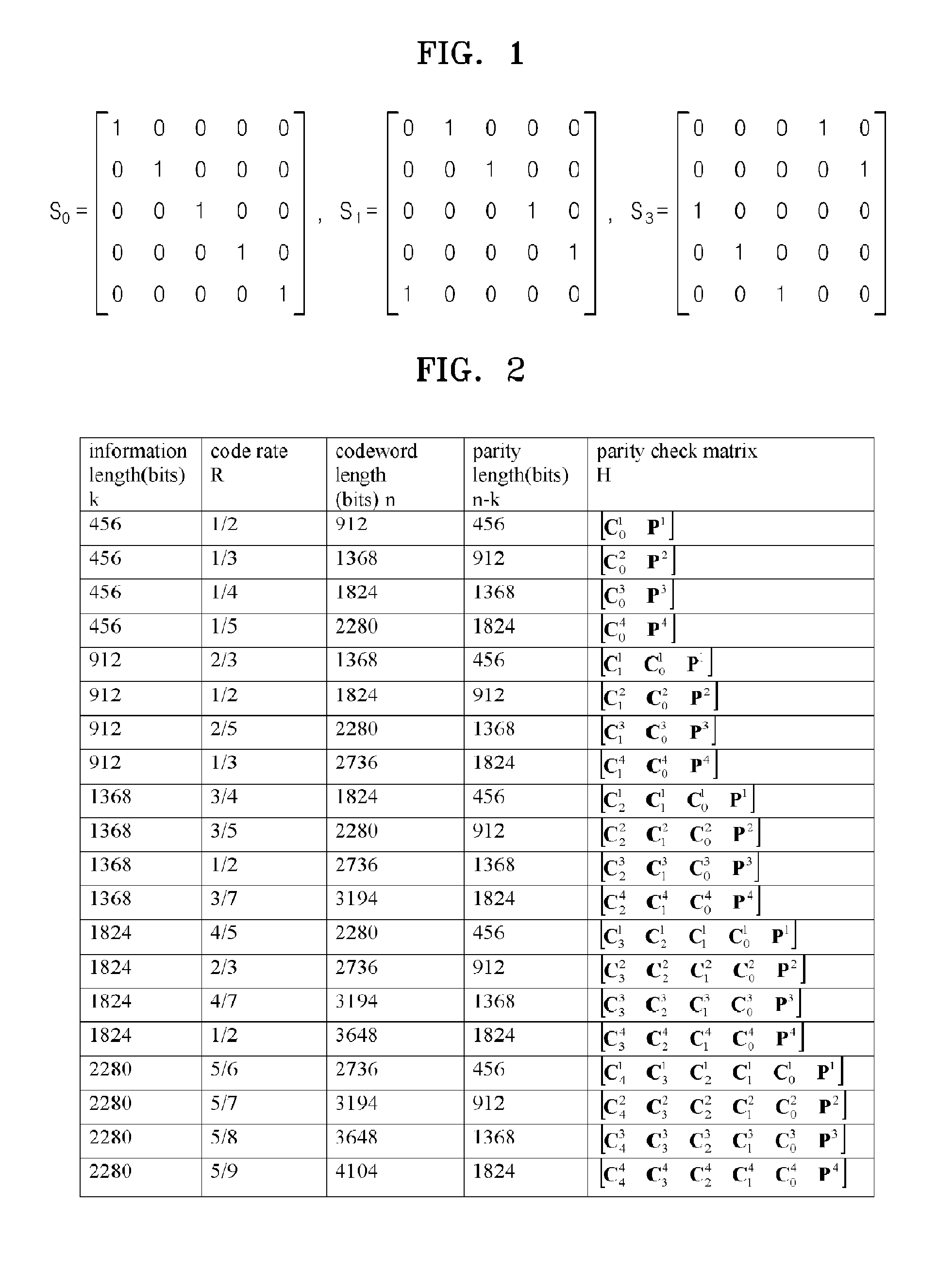
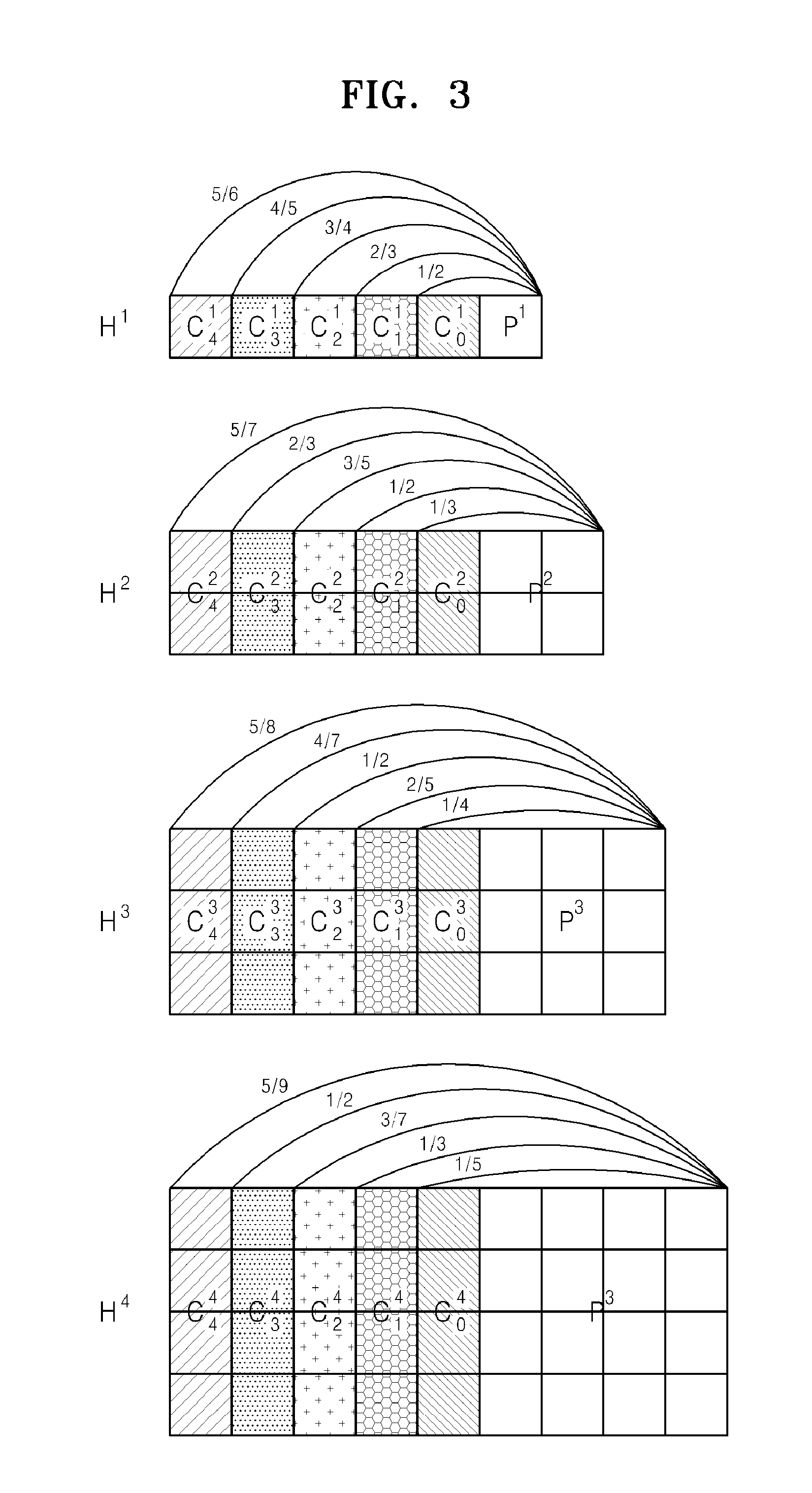
Method of generating parity-check matrix, encoding/decoding method for low density parity-check code with variable information length and variable code rate and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20100325511A1Easily embodiedIncrease speedError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionGeneration processParity-check matrix
A method of generating a parity-check matrix of a low density parity-check (LDPC) code with a variable information length and a variable code rate, an encoding / decoding method, and an apparatus using the same are provided. The method of generating a parity-check matrix of an LDPC code includes: a first parity-check matrix generation process of generating a first parity-check matrix constructed with a first information block and a parity block; and an m-th parity-check matrix generation process of generating an m-th parity-check matrix by an m-th information block to a generated (m−1)-th parity-check matrix (1<m≦M, where M is a natural number equal to or greater than two). Accordingly, it is possible to provide an LDPC code with a variable information length and a variable code rate which has a low complexity for encoding / decoding and a high quality of correction and detection of errors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Code generator and decoder for communications systems operating using hybrid codes to allow for multiple efficient users of the communications systems
InactiveUS20070300127A1Error protectionImprove errorError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method of encoding data for transmissions from a source to a destination over a communications channel is provided. The method operates on an ordered set of source symbols and may generate zero or more redundant symbols from the source symbols, wherein data is encoded in a first step according to a simple FEC code and in a second step, data is encoded according to a second FEC code, more complex than the first FEC code. The first FEC code and / or the second FEC code might comprise coding known in the art. These steps result in two groups of encoded data in such a way that a low-complexity receiver may make use of one of the groups of encoded data while higher complexity receivers may make use of both groups of encoded data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Low-complexity motion vector prediction for video codec with two lists of reference pictures
ActiveUS7400681B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo encoding
A method of motion vector prediction for use in differential motion vector coding within a block motion-compensation-based video coder. The video coder employs a generalized multiple reference picture buffer which may contain multiple reference pictures in both the forward and backward temporal direction from the current picture. For the purpose of coding selections of reference pictures within the buffer, the pictures are organized into two, potentially overlapping, lists of reference pictures. The prediction of a motion vector that selects a reference picture using a given reference picture list is not dependent upon any motion vectors that select their reference pictures using the other reference picture list. The values of spatially neighbouring motion vectors that use the same list of reference pictures as the notion vector being predicted are used for prediction, regardless of the relative temporal direction of the current and neighbouring motion vectors.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
Methods and devices for optical aberration correction
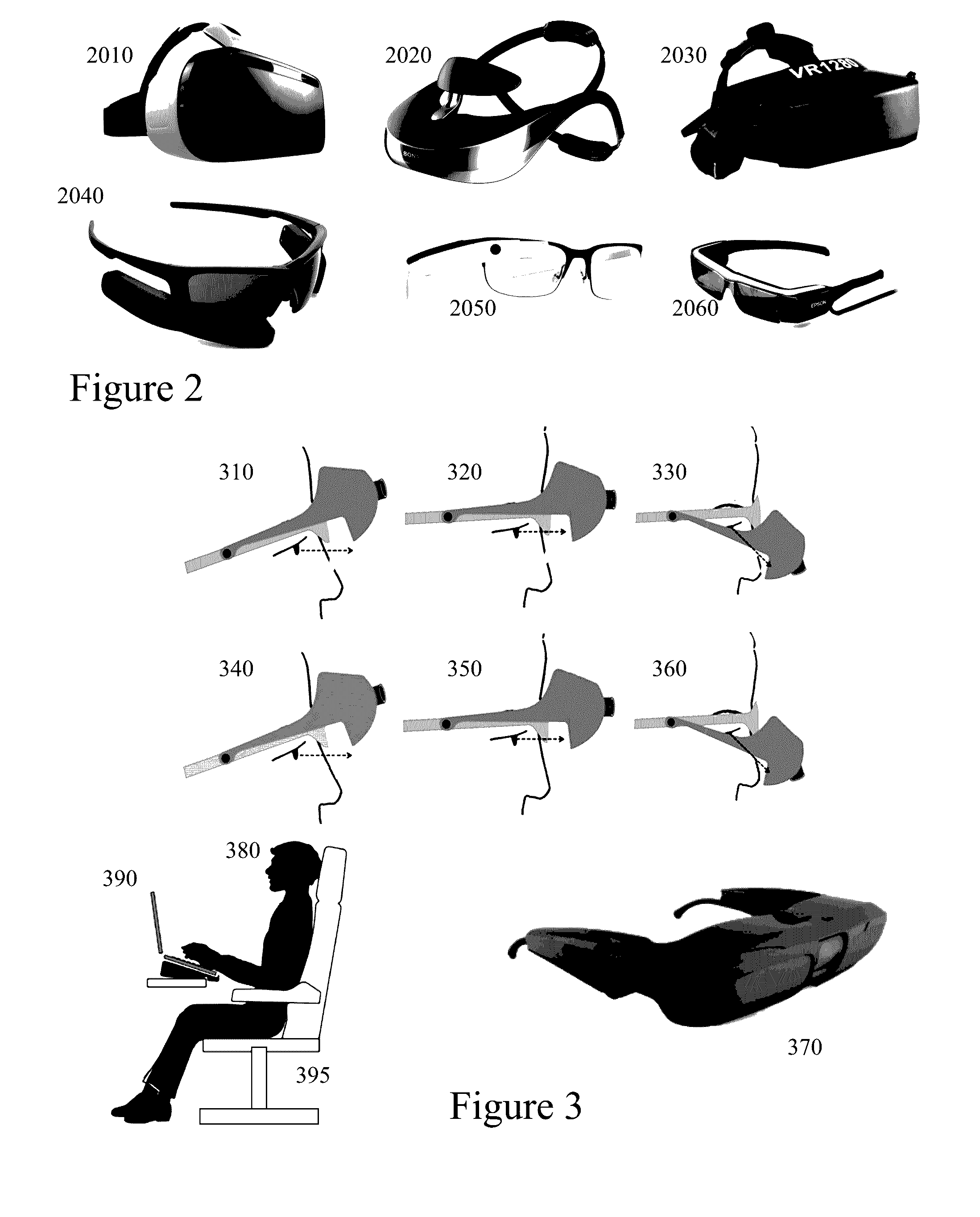
ActiveUS20160314564A1Reduce restrictionsSpectales/gogglesImage enhancementSide effectOptical Obstruction
Near-to-eye displays within head mounted devices offer both users with and without visual impairments enhanced visual experiences either by improving or augmenting their visual perception. Unless the user directly views the display without intermediate optical elements then the designer must consider chromatic as well as other aberrations. Within the prior art the optical train is either complex through additional corrective elements adding to weight, cost, and size or through image processing. However, real time applications with mobile users require low latency to avoid physical side effects. Accordingly, it would be beneficial to provide near-to-eye displays mitigating these distortions and chromatic aberrations through pre-distortion based electronic processing techniques in conjunction with design optimization of the optical train with low weight, low volume, low complexity, and low cost. Further, it would be beneficial to exploit consumer grade low cost graphics processing units rather than application specific circuits.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
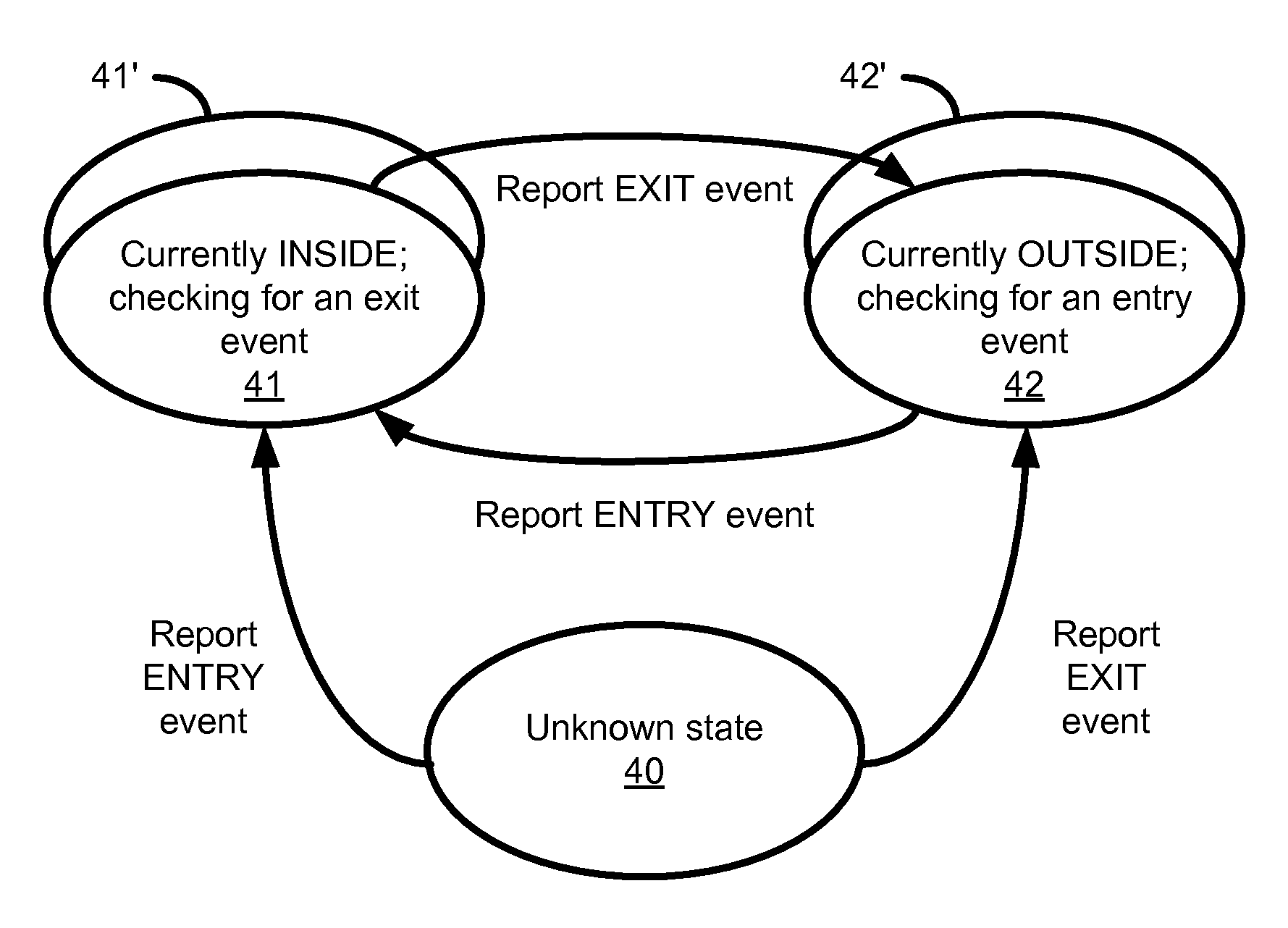
Geographical boundary based tracking
An apparatus, method and system for geographical tracking entry and / or exiting of an asset into and / or out of a defined geographical boundary and reporting the same. Entry and exit tests compare position fixes with various thresholds and parameters to determine if the asset has entered or exited the geographical boundary. Tests are sequenced such that tests having lower levels of complexity (lower order) are performed before tests having higher levels of complexity (higher order). In this way, most position fixes are processed using computations having a lower order of mathematical complexity than conventionally implemented.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
RFID system with low complexity implementation and pallet coding error correction
InactiveUS20080197982A1Reduce frequency differenceSource can be removedElectric signal transmission systemsError preventionCarrier signalData signal
Systems and methods for decoding data transmitted by RFID tags are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention includes an analyzer and equalizer configured to filter an input signal, an estimation block configured to obtain a baseband representation of the modulated data signal by mixing the filtered input signal with the carrier wave, and a coherent detector configured to perform phase and timing recovery on the modulated data signal in the presence of noise and to determine a sequence of data symbols.
Owner:MOJIX
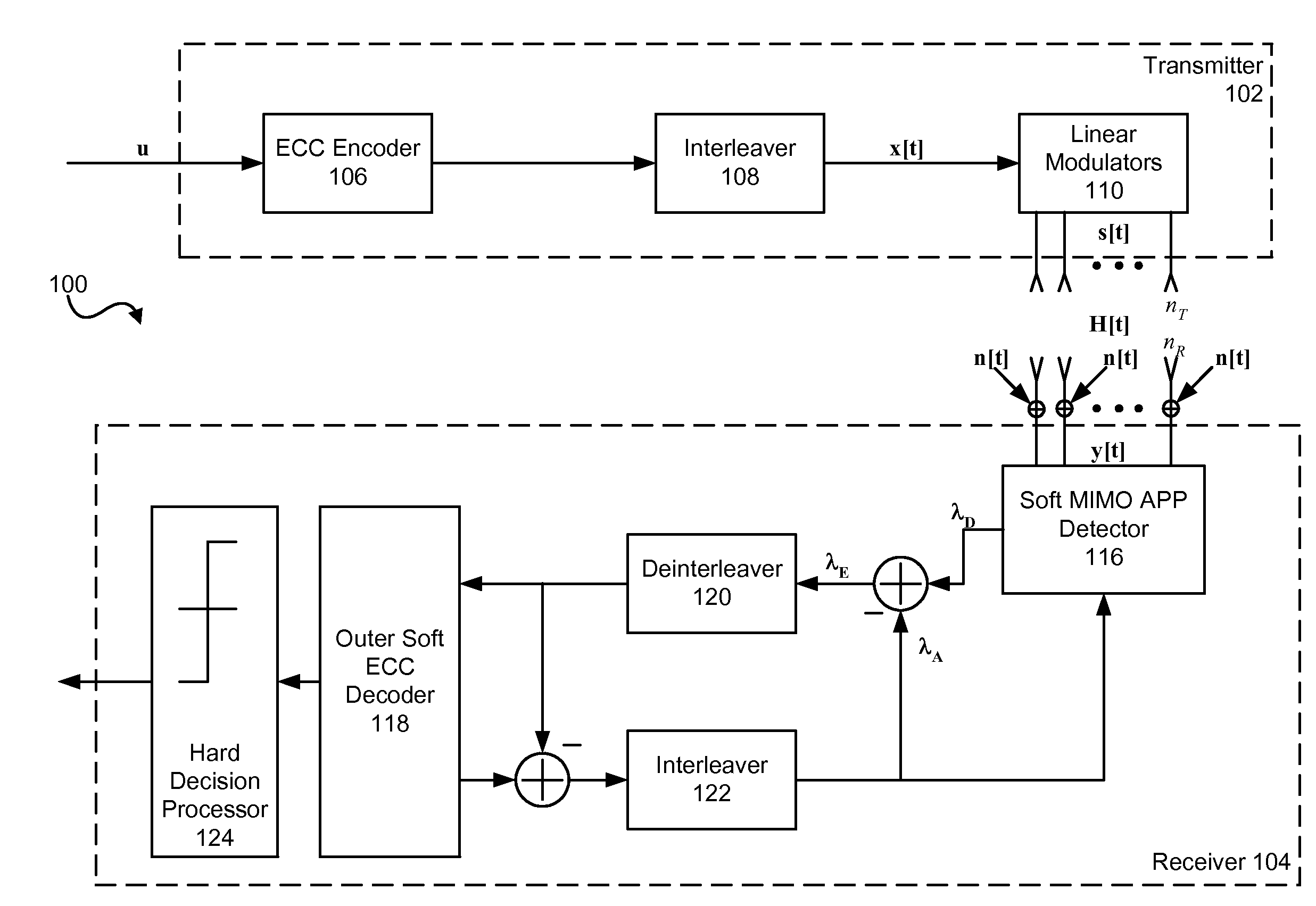
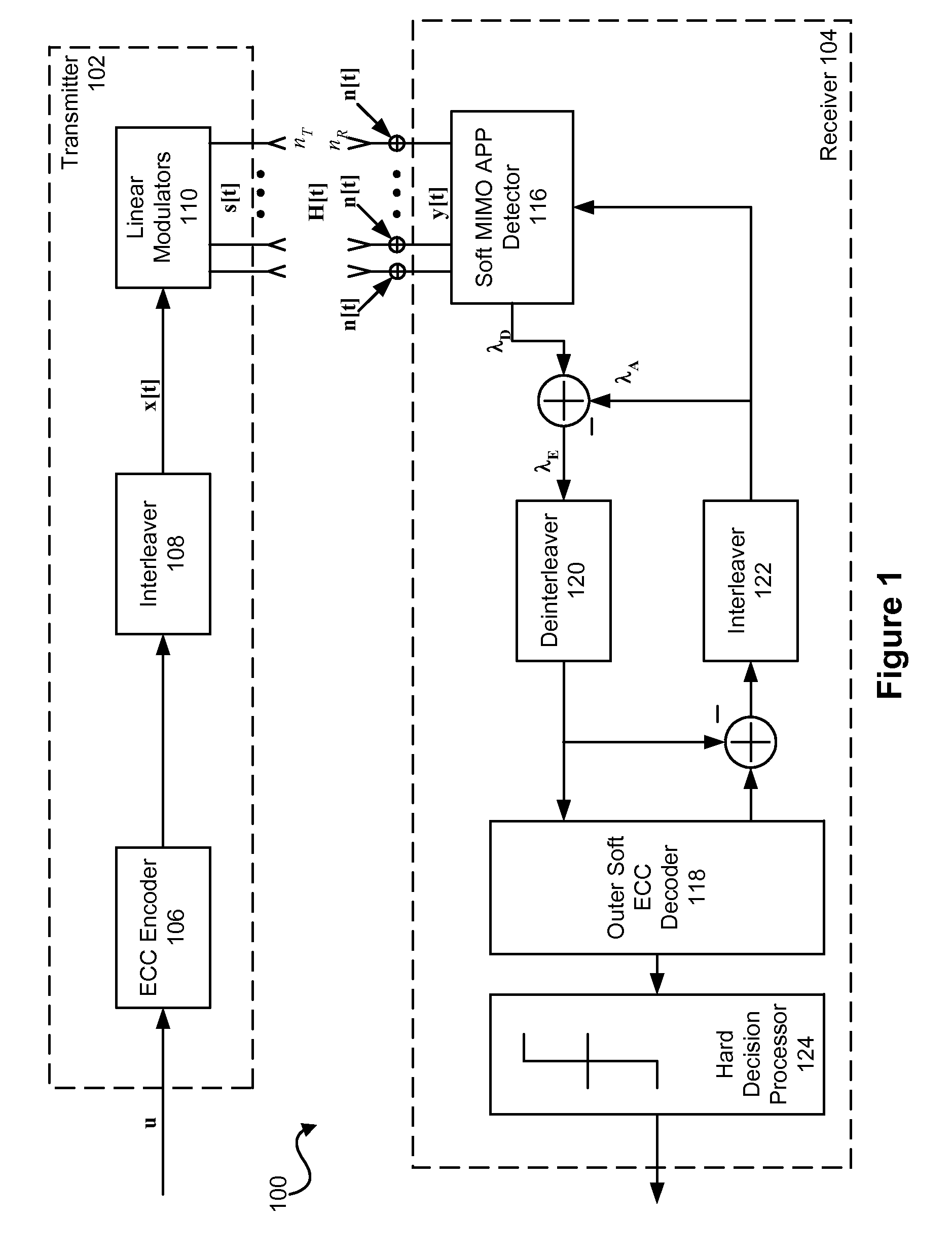
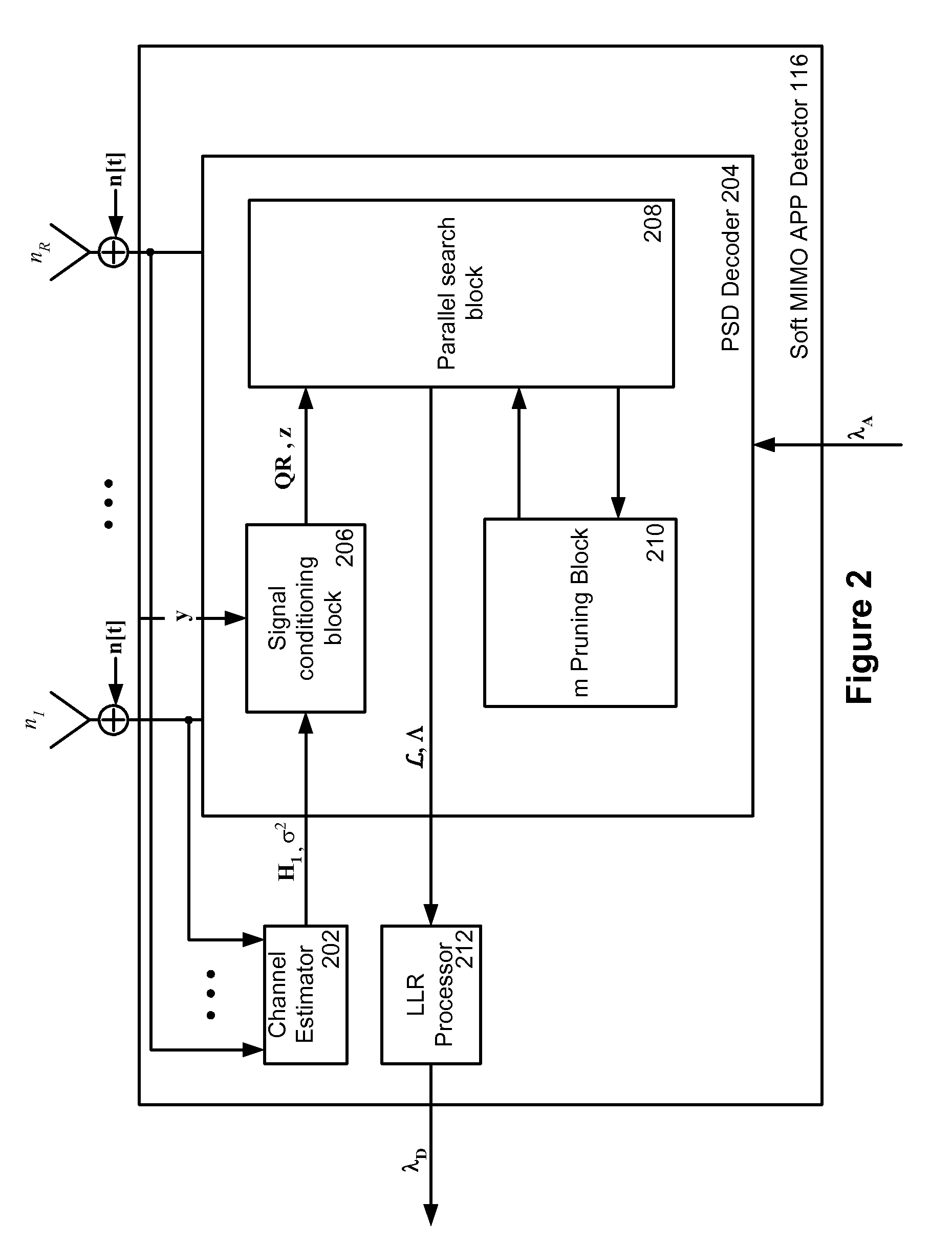
Parallel soft spherical MIMO receiver and decoding method
ActiveUS20070286313A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionDecoding methodsSelf adaptive
A method and system for detecting and decoding multiple signals. A low-complexity MIMO detector that combines sphere decoding and m-algorithm approaches, while accounting for the effect of channel condition on the decoding operation, is provided. Taking into account the channel condition effectively controls the size of the search tree, and consequently the search complexity, in an adaptive manner. The channel condition is exploited in the construction of the tree to manage the number of branches in the tree and to avoid undesirable growth.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com