Patents
Literature
1244 results about "Intra-frame" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
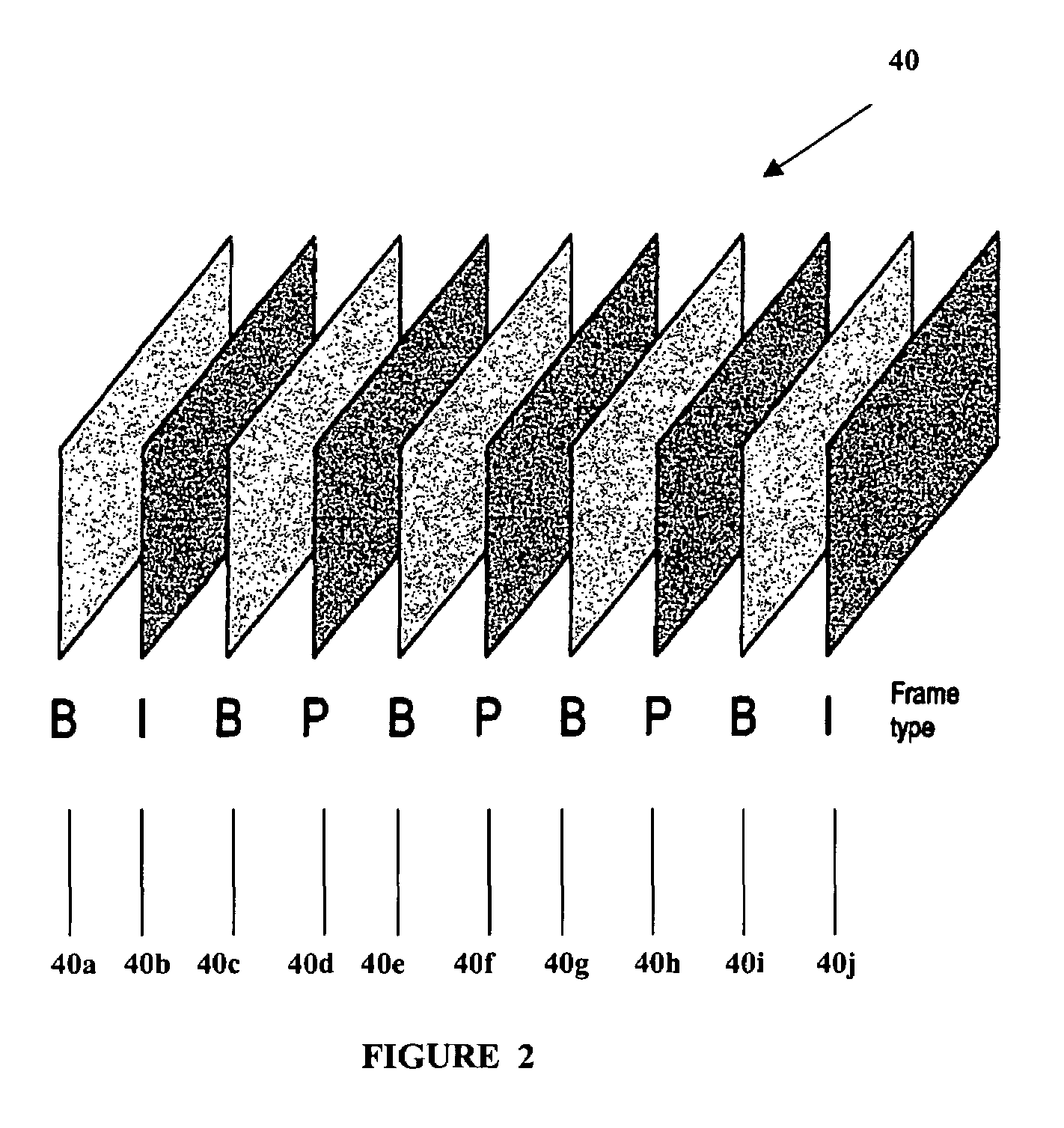
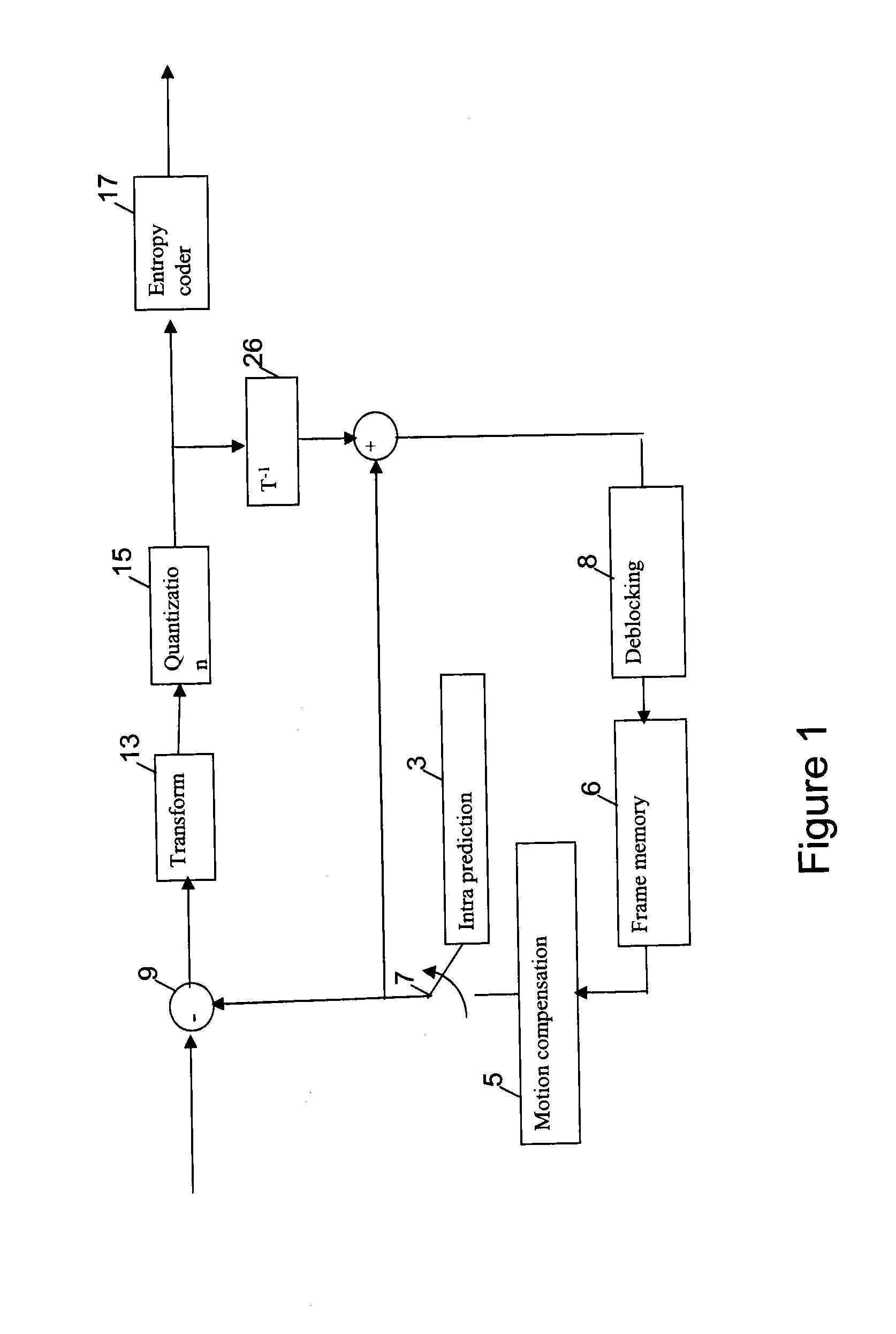
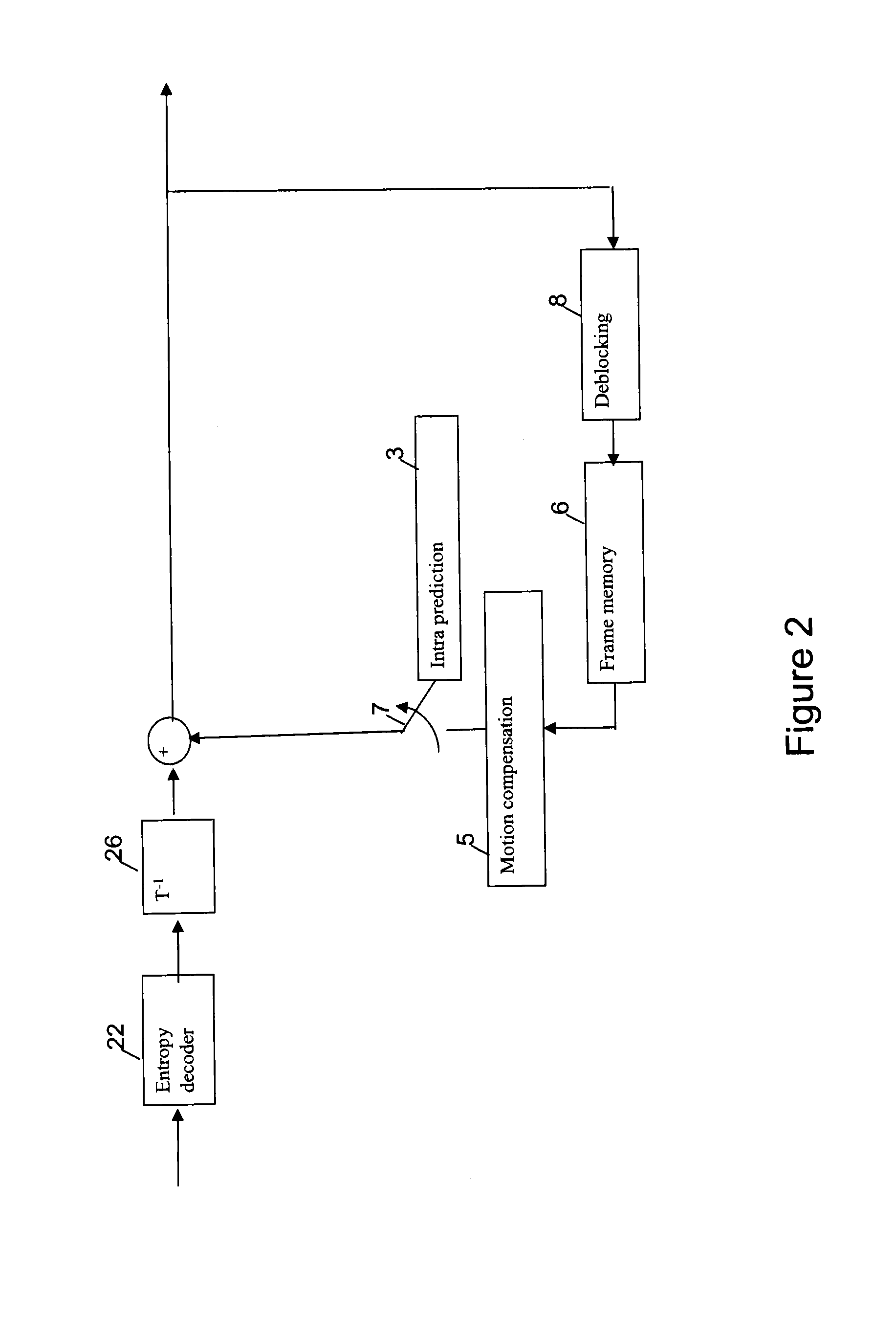
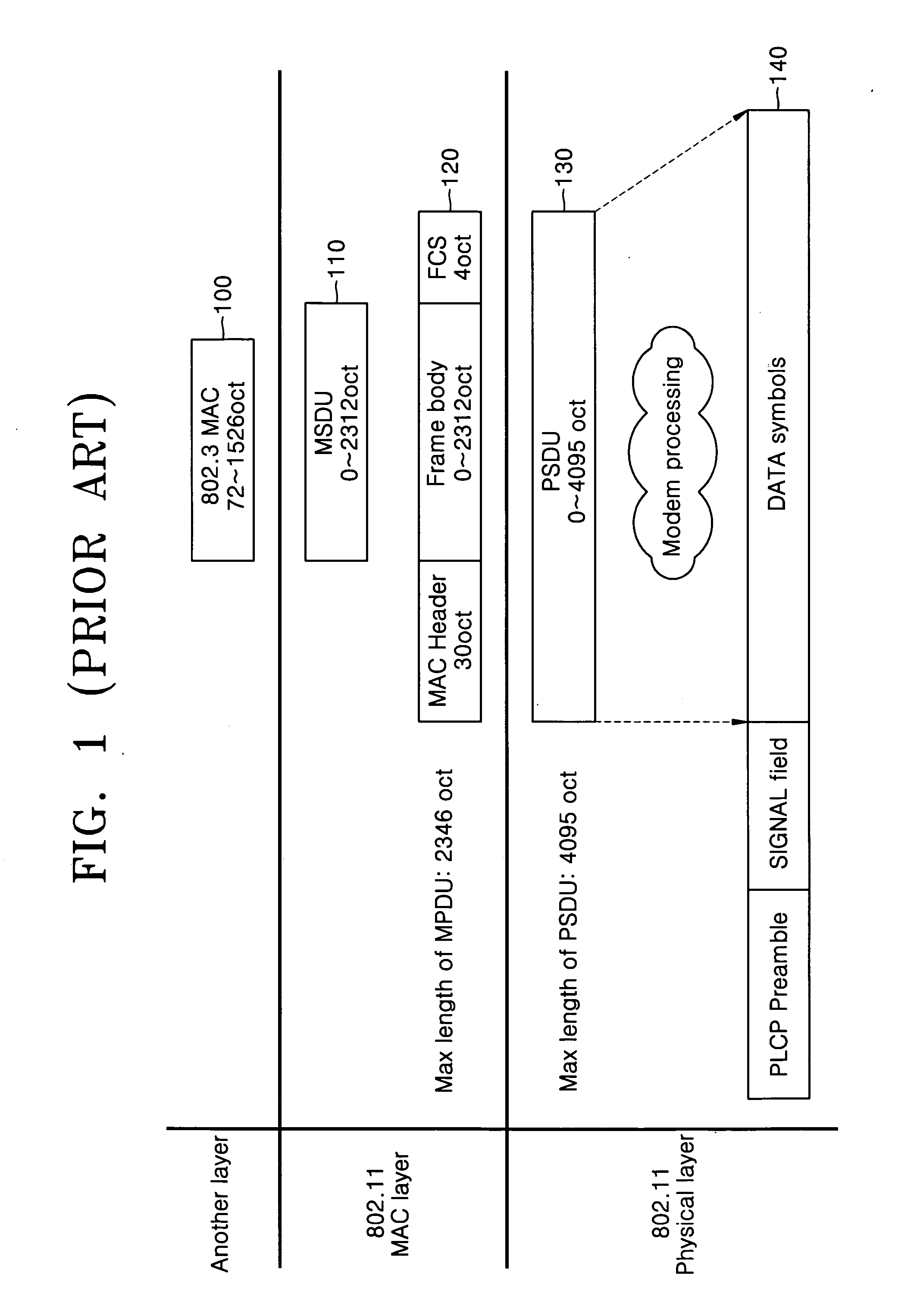
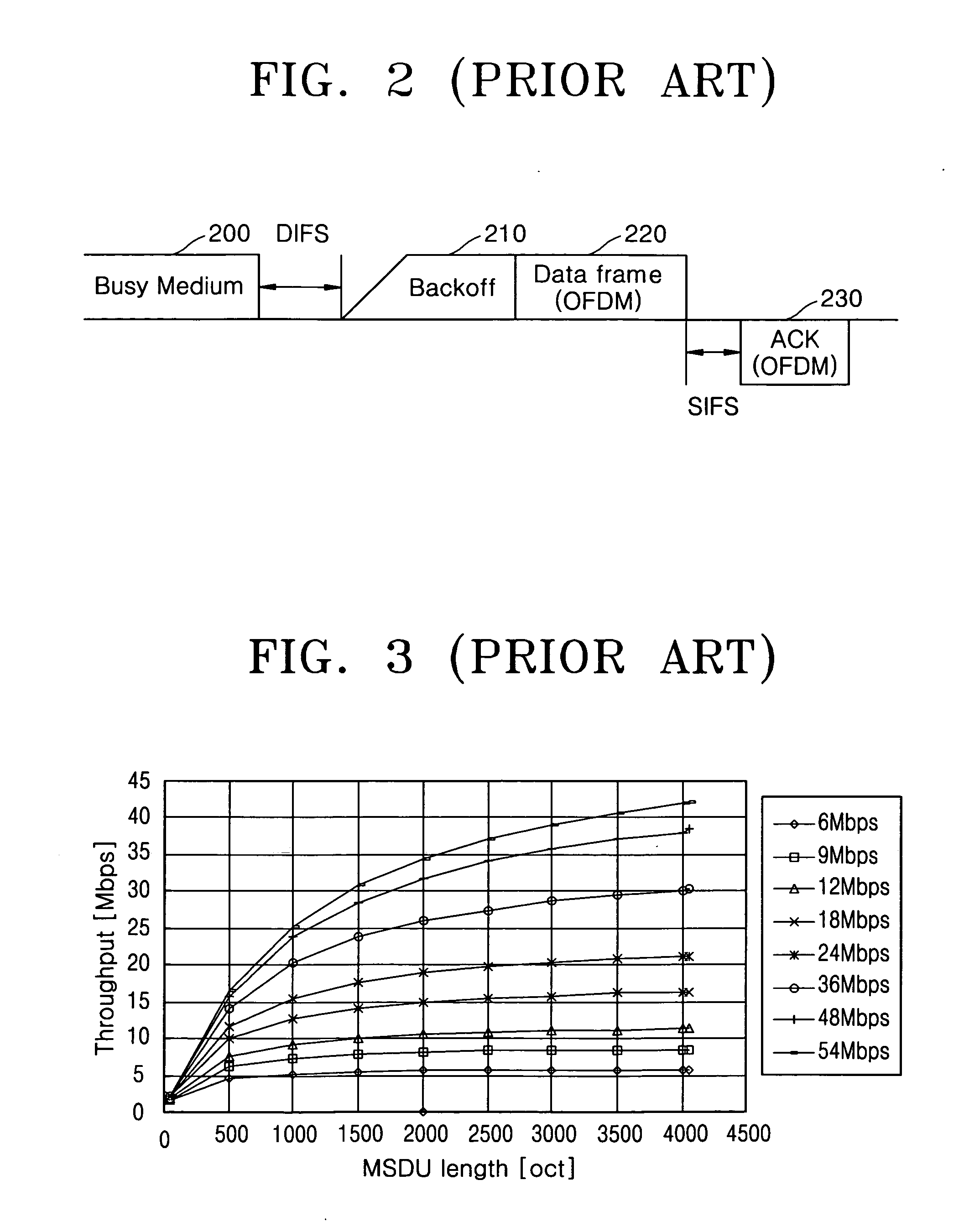
Intra-frame coding is used in video coding (compression). It is part of an intra-frame codec like ProRes: a group of pictures codec without inter frames. Intra-frame prediction exploits spatial redundancy, i.e. correlation among pixels within one frame, by calculating prediction values through extrapolation from already coded pixels for effective delta coding. It is one of the two classes of predictive coding methods in video coding. Its counterpart is inter-frame prediction which exploits temporal redundancy. Temporally independently coded so-called intra frames use only intra coding. The temporally coded predicted frames (e.g. MPEG's P- and B-frames) may use intra- as well as inter-frame prediction.
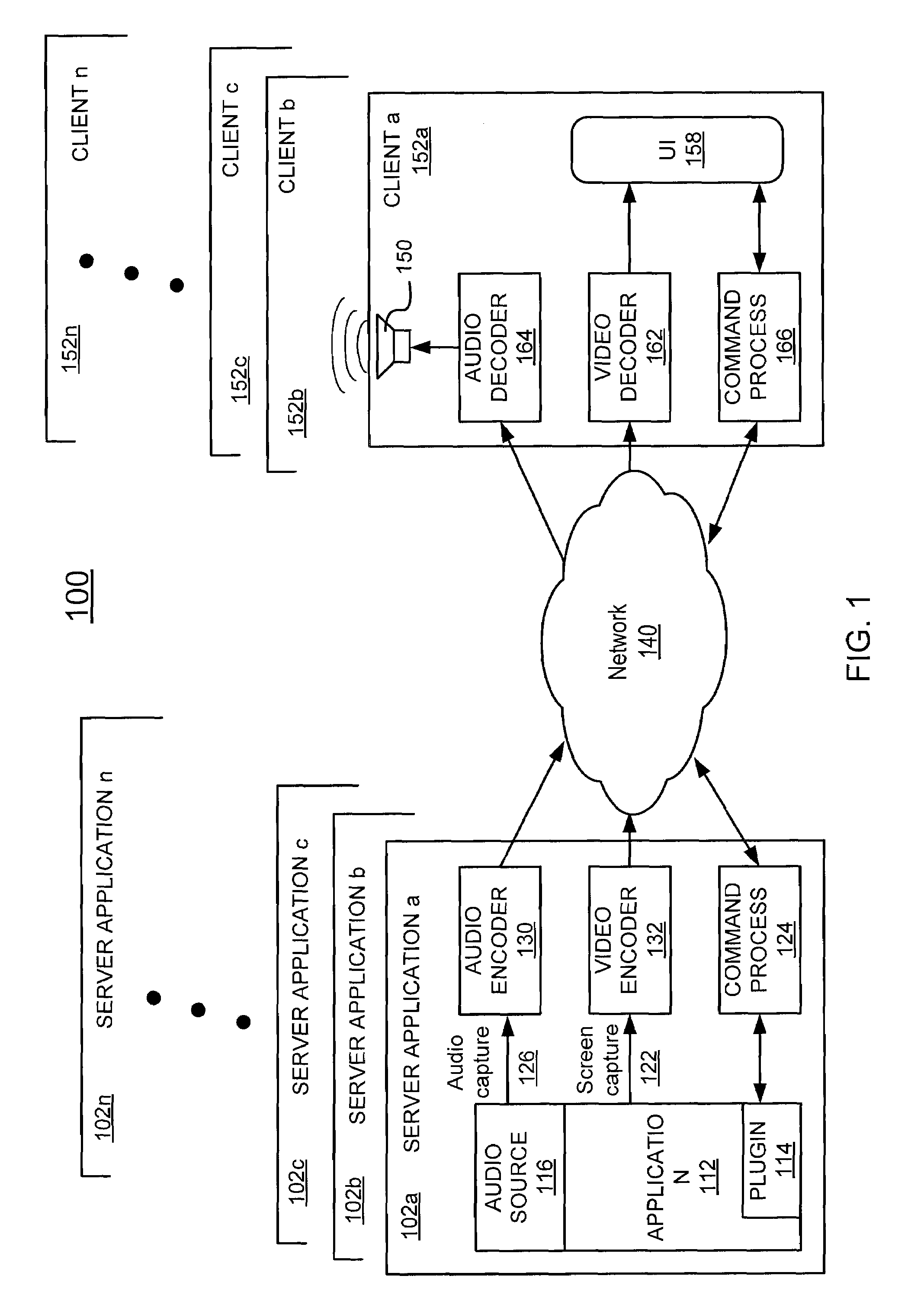
Method of band multiplexing to improve system capacity for a multi-band communication system
ActiveUS20070054680A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMulti bandCommunications system
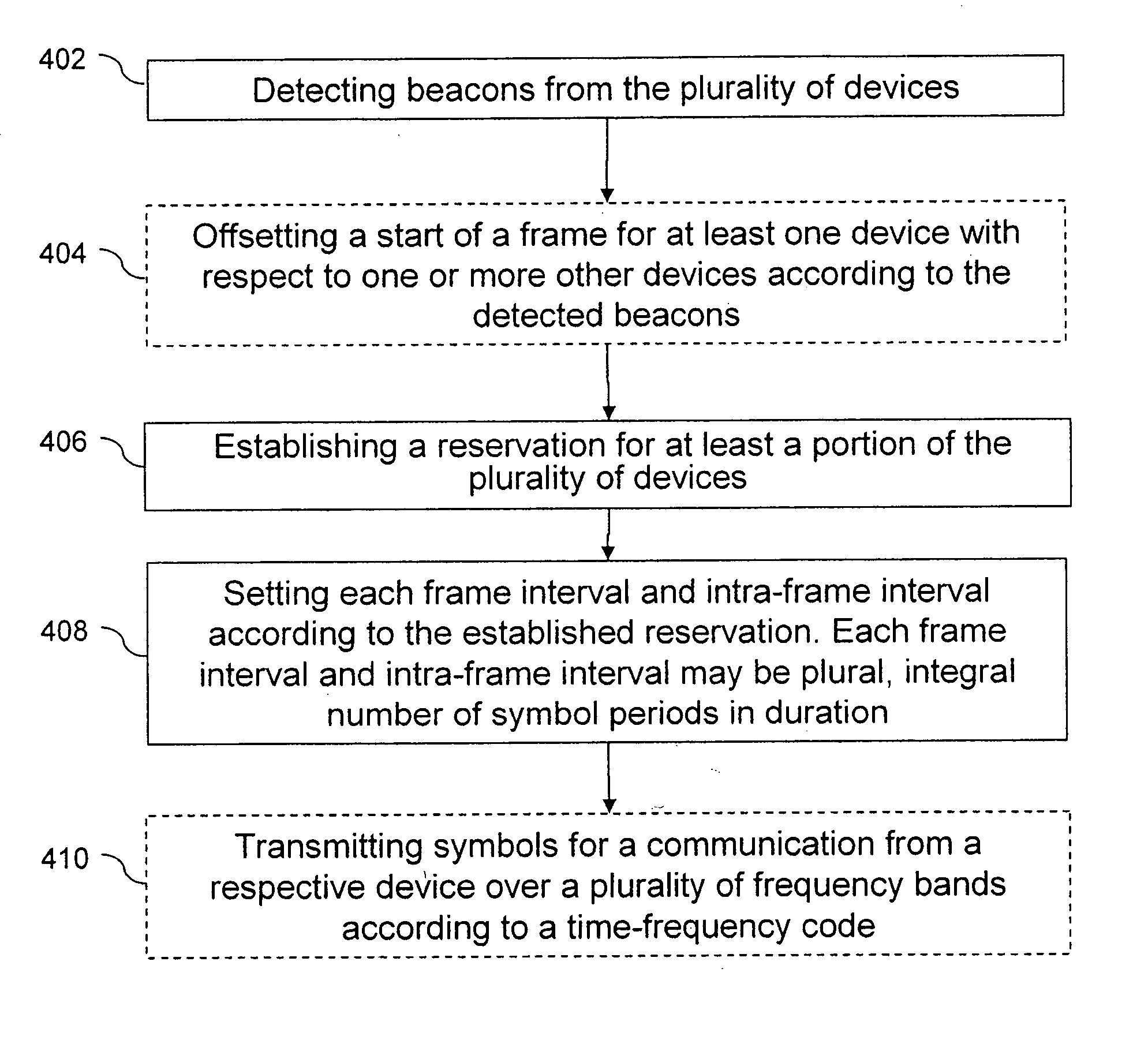
A control method of synchronizing communications between or among a plurality of devices in a communication system includes detecting beacons from the plurality of devices in the communication system, and establishing a reservation for at least a portion of the plurality of devices in the communication system. Each reservation is a frame interval in which to transmit symbols from one device to one or more of the other devices in the communications system. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is set according to the established reservation. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is a plural, integral number of symbol periods in duration.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Network-Based Dynamic Encoding
ActiveUS20080101466A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo encodingIntra-frame
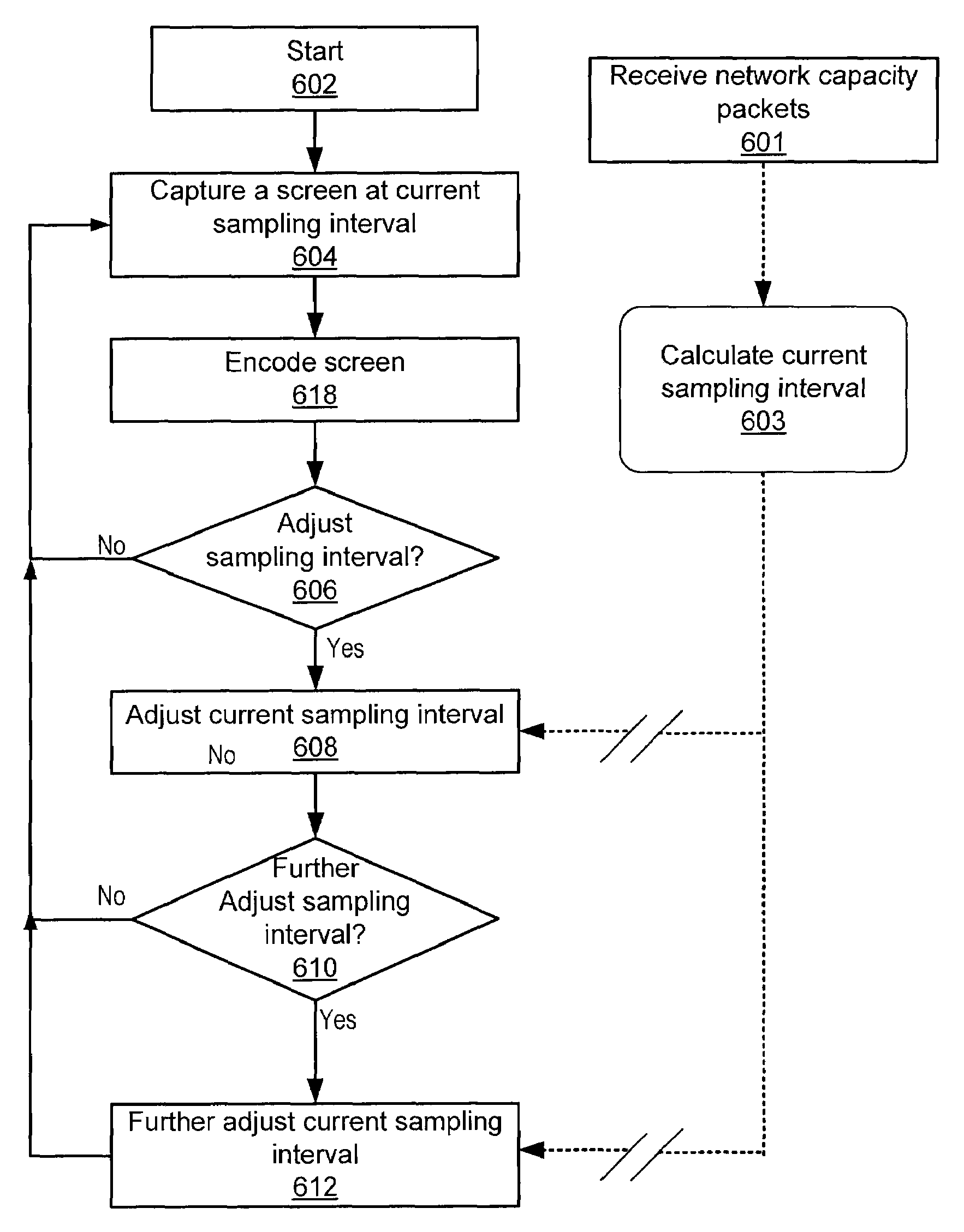
A network-based video encoding and decoding system encodes and decodes remotely displayed user application data on a centralized desktop computer. Remotely displayed user application data are screen captures of a browsing application run by the centralized desktop computer on user's behalf. The encoding system optimizes its encoding performance using back channel information which includes real time network capacity information and decoder feedback. The encoding system consults a back channel information manager to dynamically adjust encoding parameters. Based on the real time network capacity information received, the encoding system adjusts its capturing sampling rate. Based on encoding errors identified by the decoding system, the encoding system selectively re-send previously encoded frames / blocks, or send intra frames on demand to allow the decoding system to correct encoding errors. In response to encoding customization requests from the decoding system, the encoding system adjusts its encoding parameters to meet such requests.
Owner:OTELLO CORP ASA
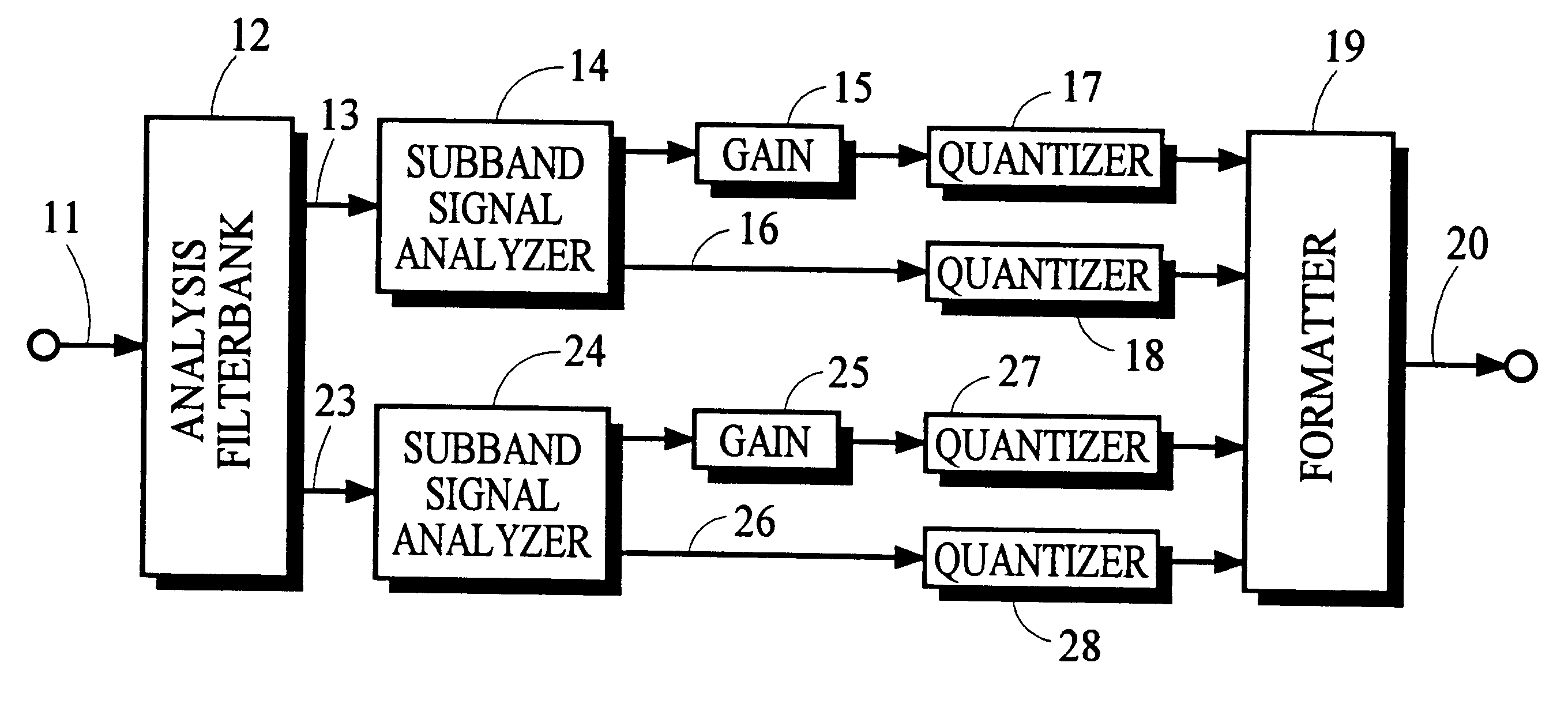
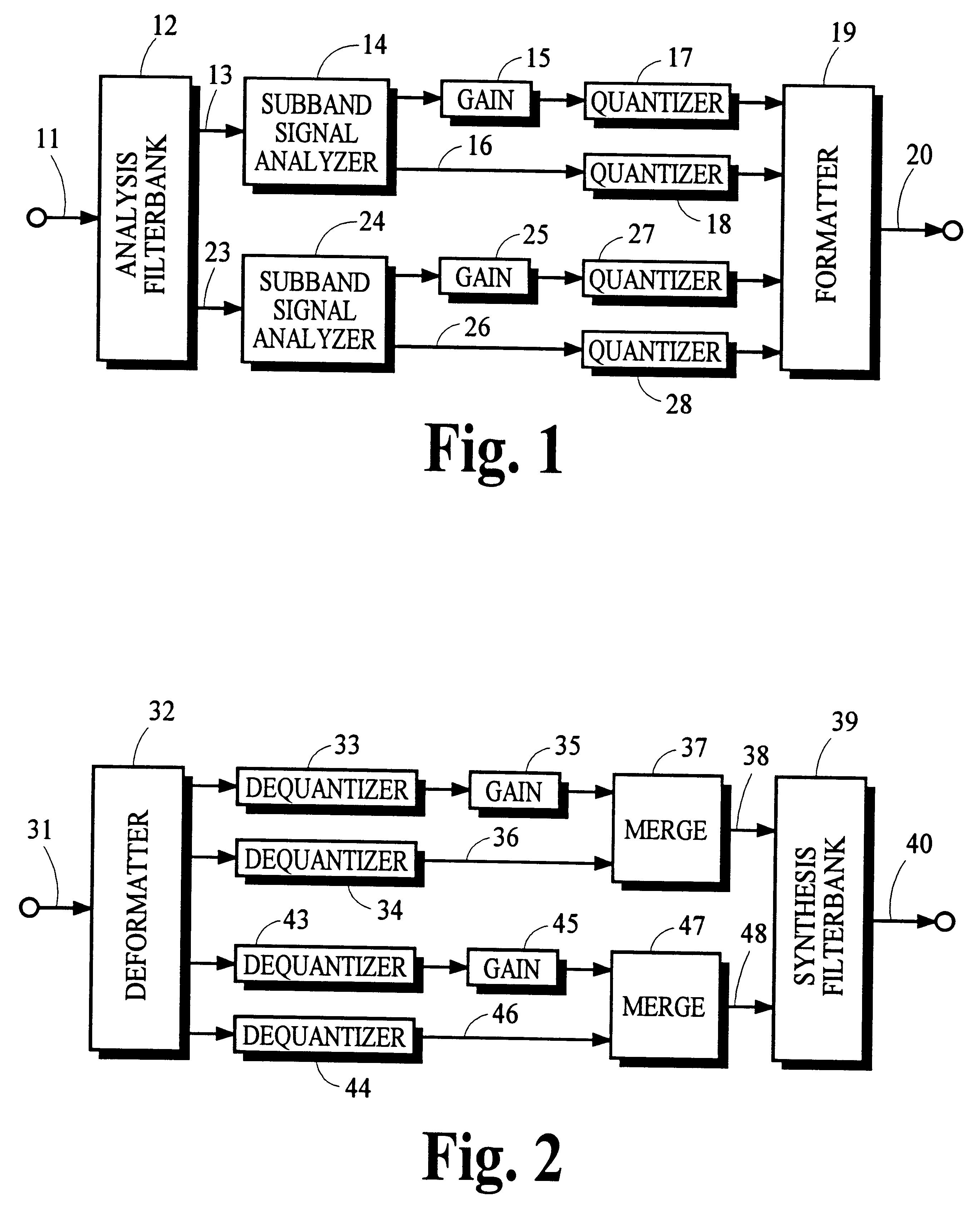
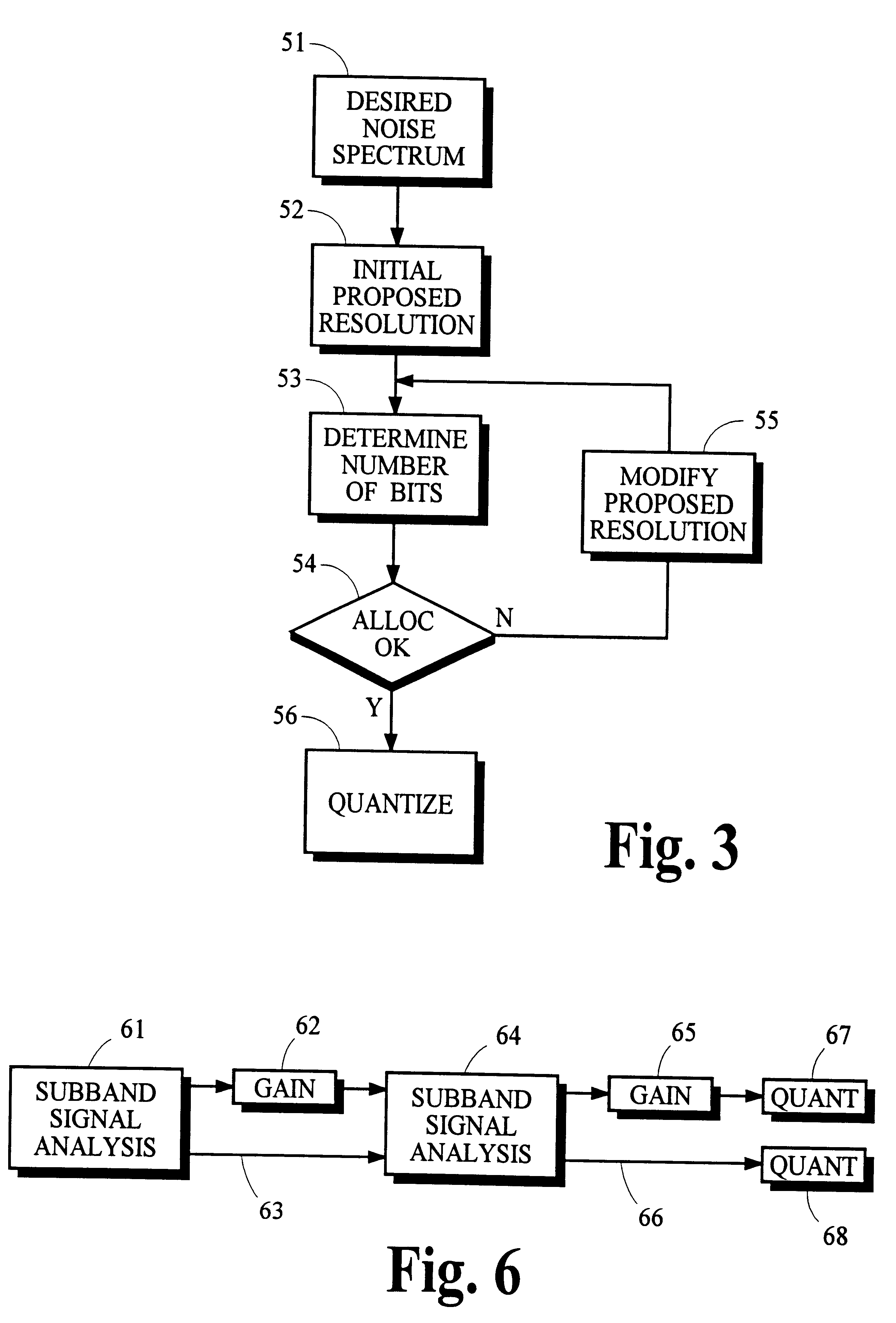
Using gain-adaptive quantization and non-uniform symbol lengths for improved audio coding
InactiveUS6246345B1Good coding gainEfficient executionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNormal densityIntra-frame
Techniques like Huffman coding can be used to represent digital audio signal components more efficiently using non-uniform length symbols than can be represented by other coding techniques using uniform length symbols Unfortunately, the coding efficiency that can be achieved by Huffman coding depends on the probability density function of the information to be coded and the Huffman coding process itself requires considerable processing and memory resources. A coding process that uses gain-adaptive quantization according to the present invention can realize the advantage of using non-uniform length symbols while overcoming the shortcomings of Huffman coding. In gain-adaptive quantization, the magnitudes of signal components to be encoded are compared to one or more thresholds and placed into classes according to the results of the comparison. The magnitudes of the components placed into one of the classes are modified according to a gain factor that is related to the threshold used to classify the components. Preferably, the gain factor may be expressed as a function of only the threshold value. Gain-adaptive quantization may be used to encode frequency subband signals in split-band audio coding systems. Additional features including cascaded gain-adaptive quantization, intra-frame coding, split-interval and non-overloading quantizers are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
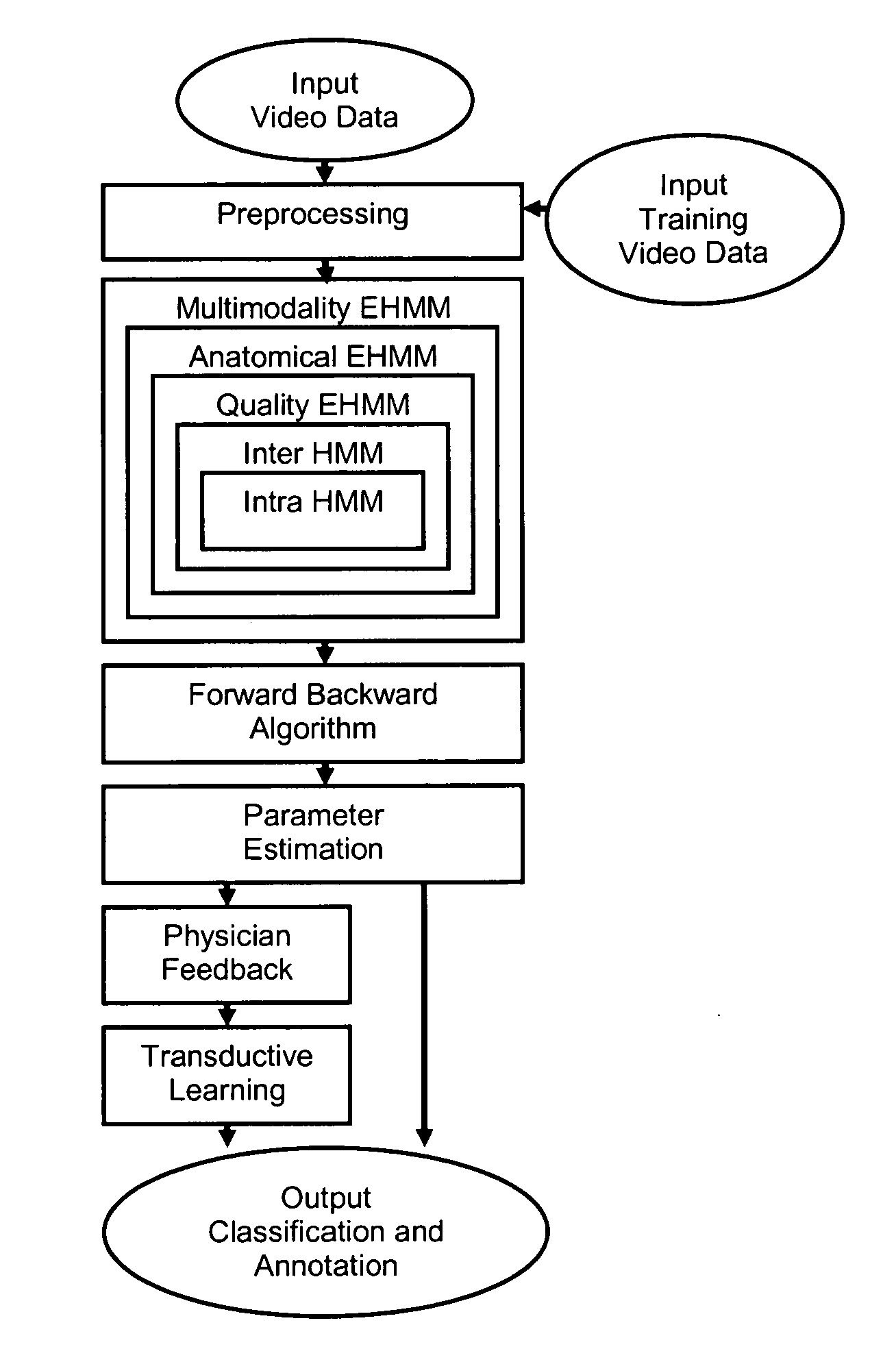
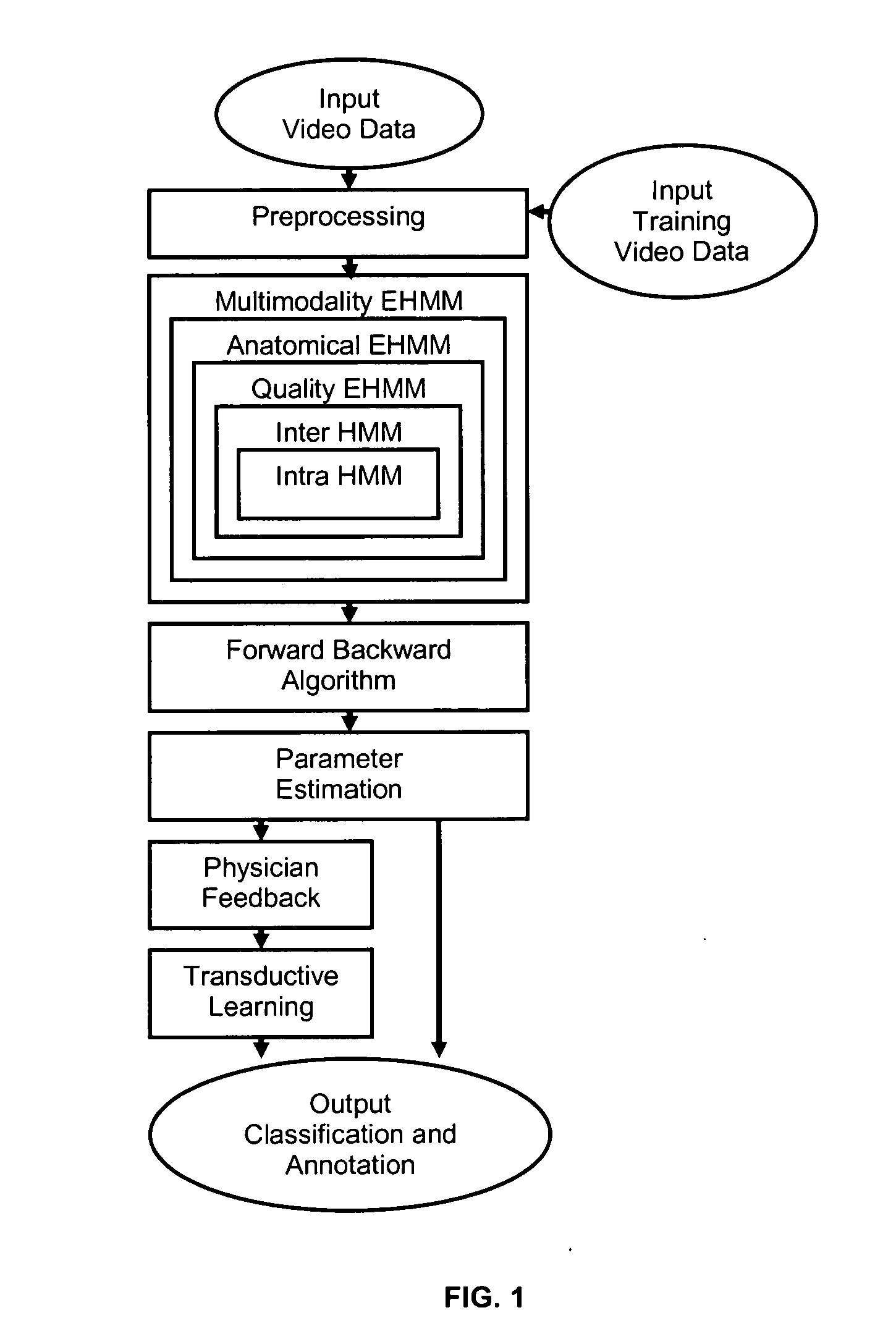
Versatile video interpretation, visualization, and management system
A process and device for detecting colon cancer by classifying and annotating clinical features in video data containing colonoscopic features by applying a probabilistic analysis to intra-frame and inter-frame relationships between colonoscopic features in spatially and temporally neighboring portions of video frames, and classifying and annotating as clinical features any of the colonoscopic features that satisfy the probabilistic analysis as clinical features. Preferably the probabilistic analysis is Hidden Markove Model analysis, and the process is carried out by a computer trained using semi supervised learning from labeled and unlabeled examples of clinical features in video containing colonoscopic features.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
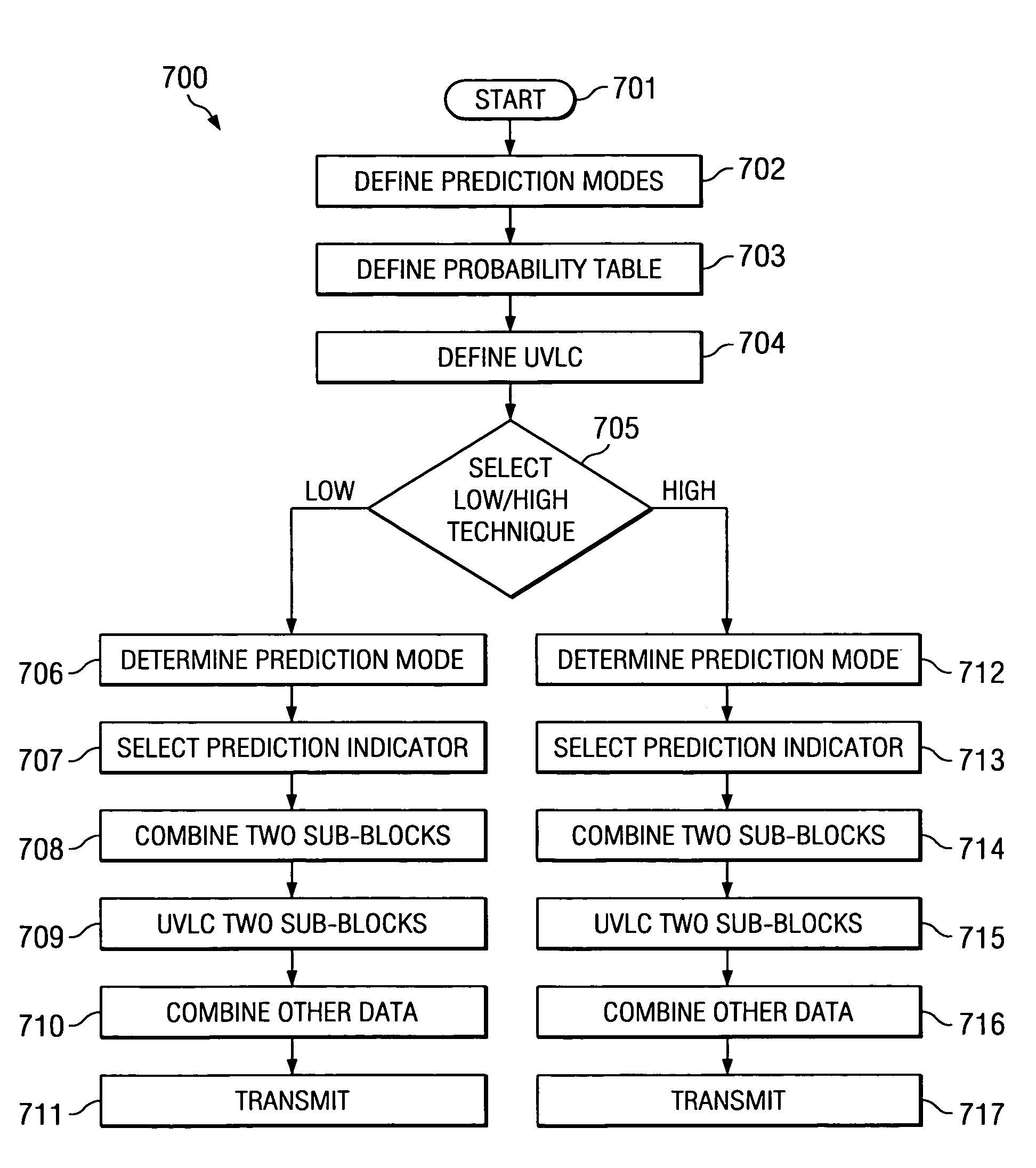
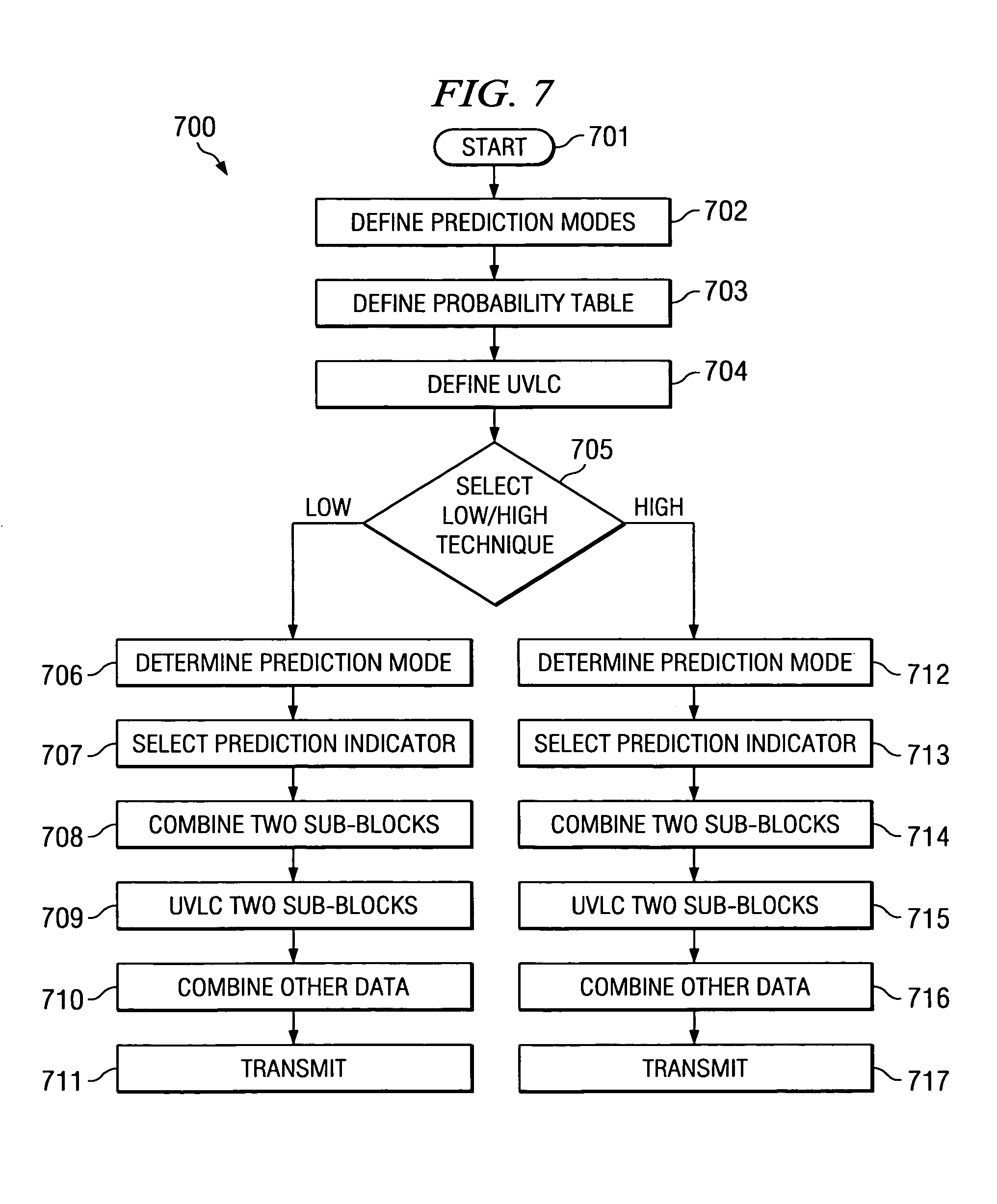
Complexity-scalable intra-frame prediction technique
ActiveUS7170937B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceIntra-frame
This invention is a method of encoding intra frames when encoding a motion picture. A set of intra frame prediction modes includes a low-complexity subset. A probability table relates the prediction mode of adjacent sub-blocks to the prediction mode of the current sub-block. For each combination of adjacent sub-blocks, the probability table includes a list of prediction modes in order of expected occurrence. The probability table is adjusted so that each list for prediction modes within the low-complexity subset include initial prediction modes of the low-complexity subset. Individual sub-blocks of intra frames are predictively coded in a low-complexity encoding the using the low-complexity subset or in a high-complexity encoding using any prediction mode. This permits a low-complexity decoder responsive to only the low-complexity subset.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative converter accoding to the correlation of residual signal
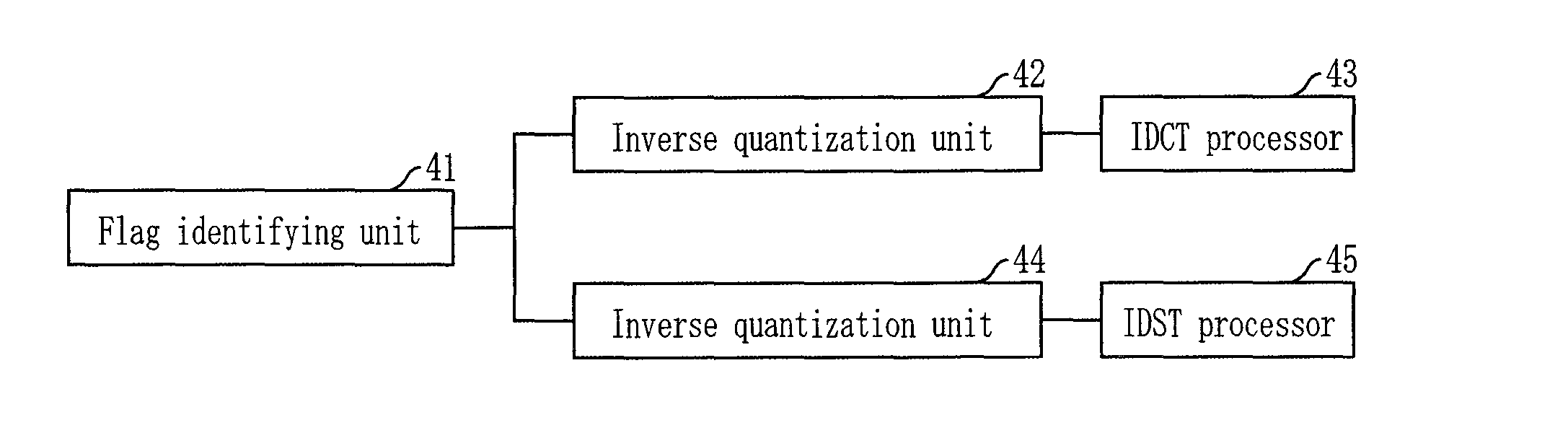
InactiveUS20090238271A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareRate distortion
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative transform units according to the correlation of residual signals. The video encoding apparatus includes a first transforming unit for performing discrete cosine transform (DCT), first quantization, first inverse quantization, and inverse DCT on a block basis onto residual coefficients generated after intra frame prediction or inter frame prediction; a second transforming unit for performing discrete sine transform (DST), second quantization, second inverse quantization, and inverse DST on a block basis onto the residual coefficients; a selecting unit for selecting one having a high compression rate between the first and second transforming units for each block through performing rate-distortion optimization; and a flag marking unit for recording information about the selected transforming unit at a flag bit provided on a macroblock basis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
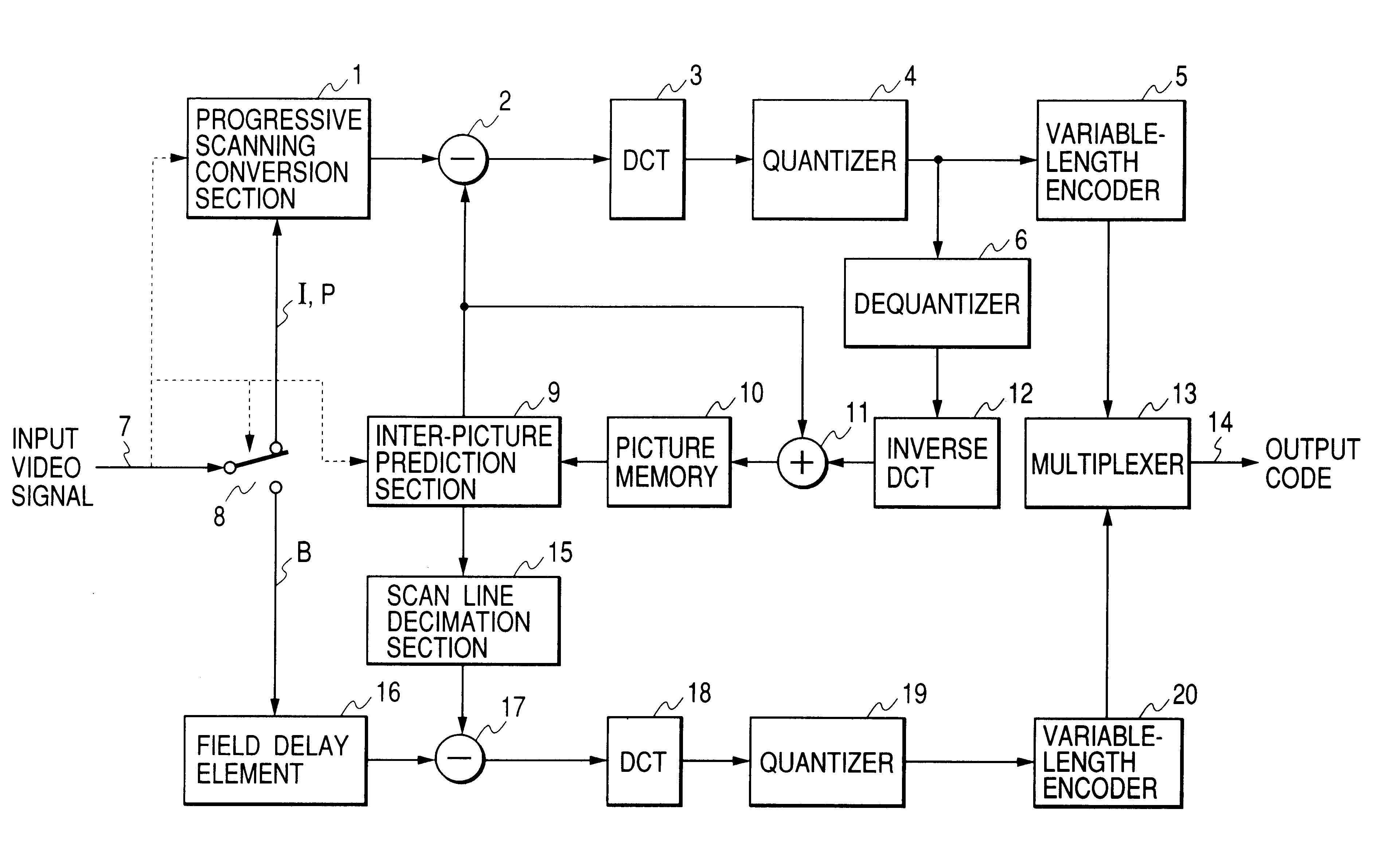
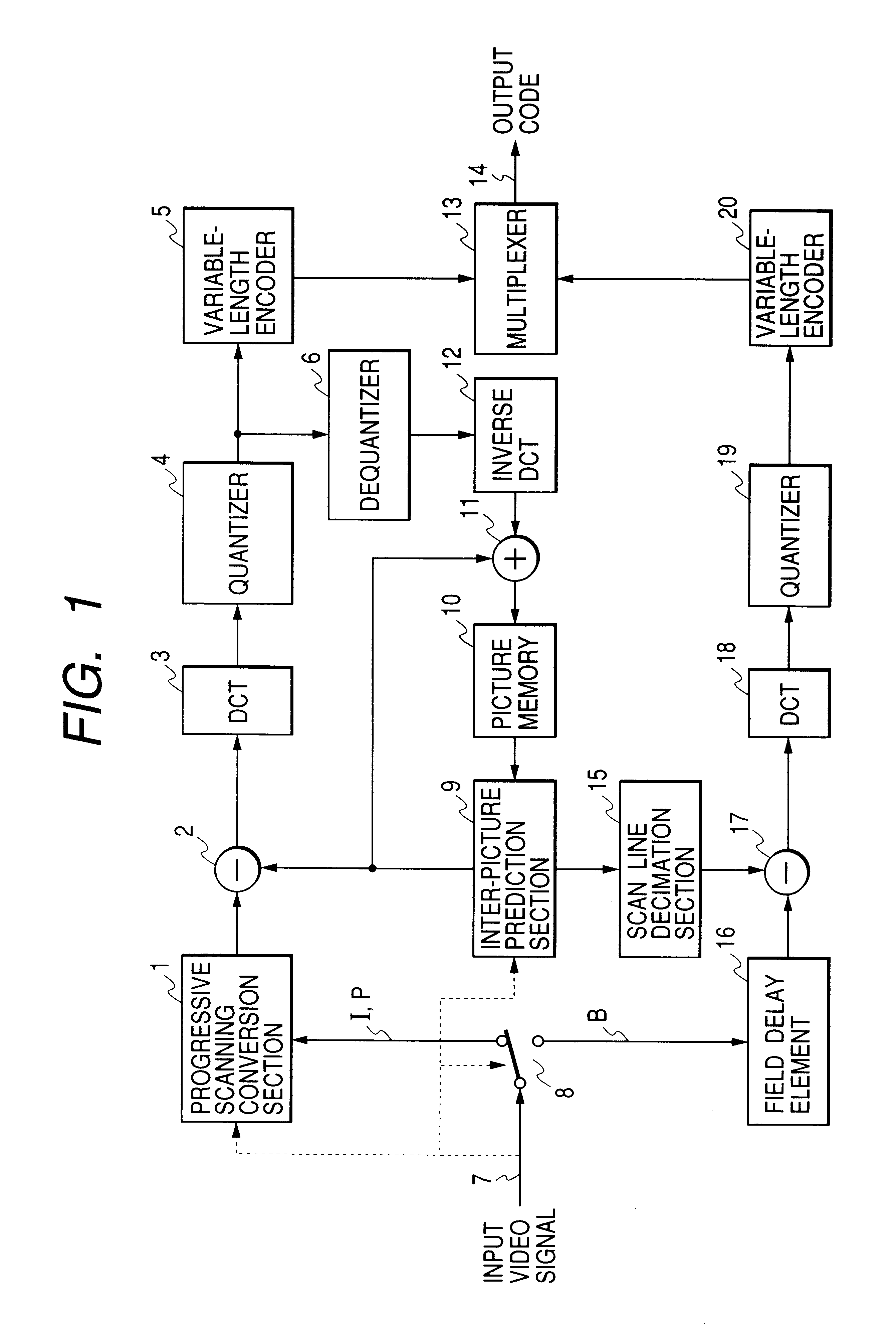
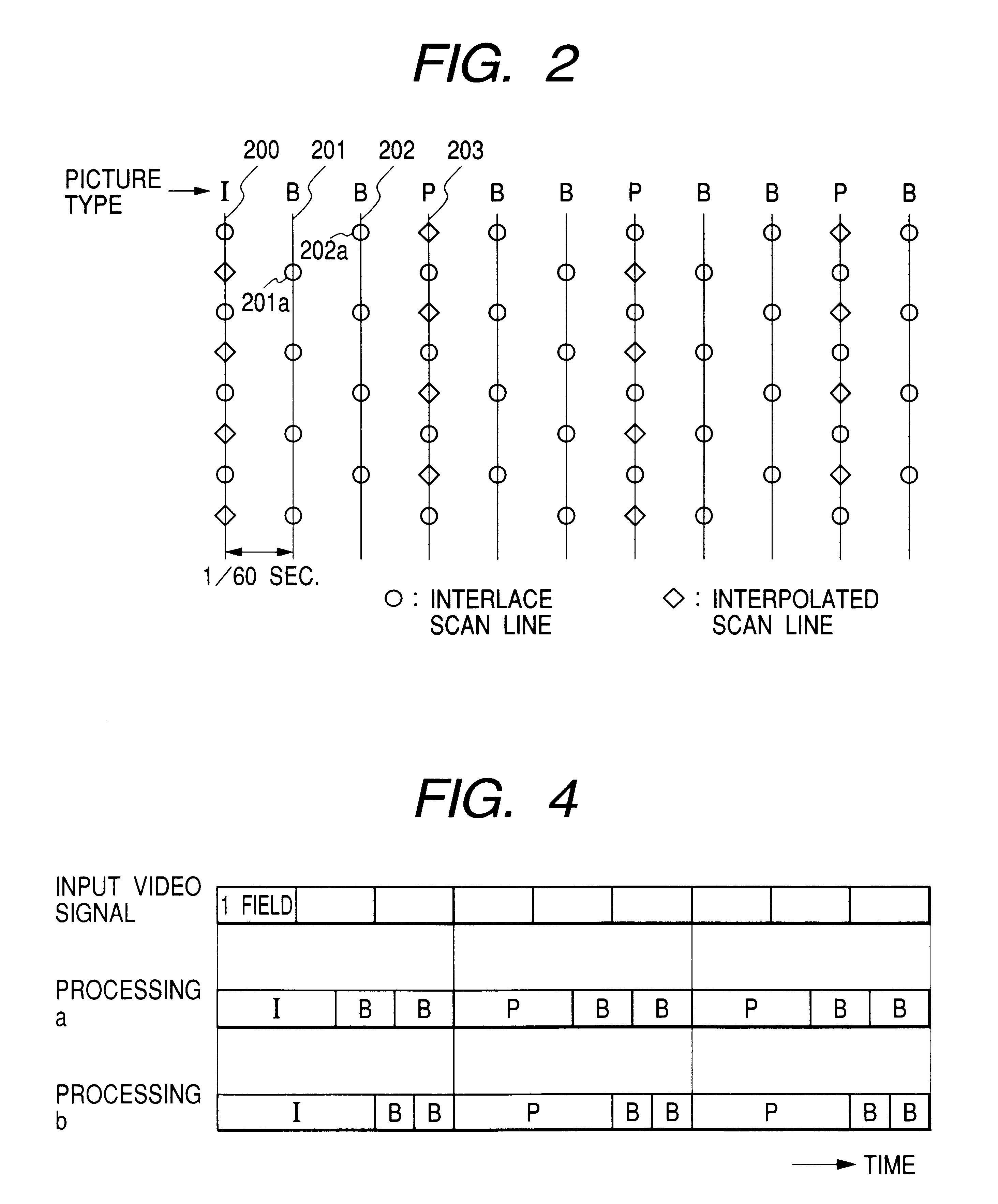
Interplaced video signal encoding and decoding method, and encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus utilizing the method, providing high efficiency of encoding by conversion of periodically selected fields to progressive scan frames which function as reference frames for predictive encoding
InactiveUS6188725B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesScan conversionInterlaced video
An encoding apparatus includes a selector for periodically selecting fields of an interlaced video signal to be converted to respective progressive scanning frames, by a scanning converter which doubles the number of scanning lines per field. The apparatus encodes these frames by intra-frame encoding or unidirectional predictive encoding using preceding ones of the frames, and encodes the remaining fields of the video signal by bidirectional prediction using preceding and succeeding ones of the progressive scanning frames for reference. The resultant code can be decoded by an inverse process to recover the interlaced video signal, or each decoded field can be converted to a progressive scanning frame to thereby enable output of a progressive scanning video signal. Enhanced accuracy of motion prediction for inter-frame encoding can thereby be achieved, and generation of encoded aliasing components suppressed, since all reference pictures are progressive scanning frames rather than pairs of fields constituting interlaced scanning frames.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
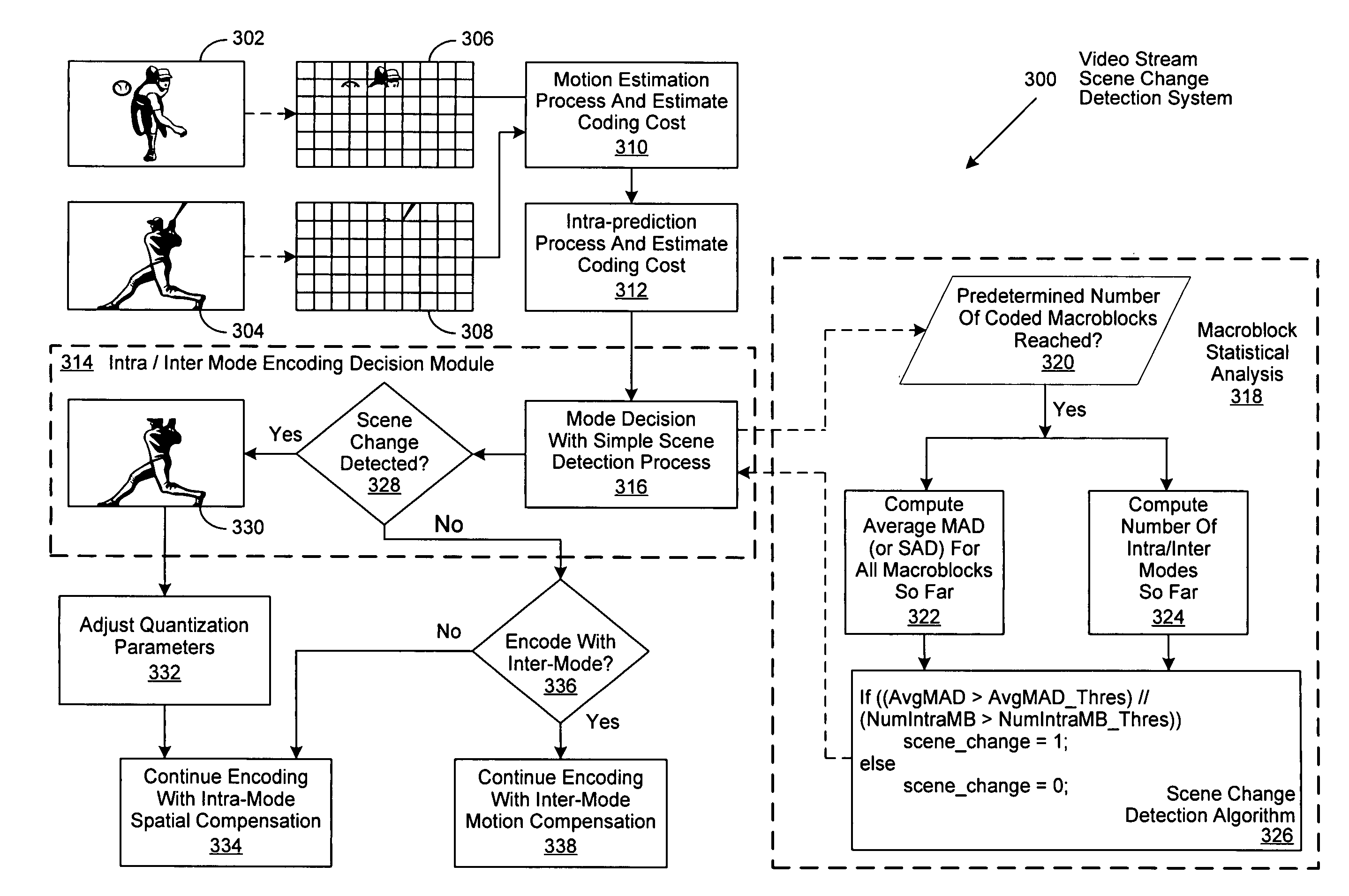
Method of increasing coding efficiency and reducing power consumption by on-line scene change detection while encoding inter-frame
InactiveUS20070274385A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionComputation complexity
A system and method for on-the-fly detection of scene changes within a video stream through statistical analysis of a portion of the macroblocks comprising each video frame as they are processed using inter-frame coding. If the statistical analysis of the selected macroblocks of the current frame differs from the previous frame by exceeding predetermined thresholds, the current video frame is assumed to be a scene change. Once a scene change is detected, the remainder of the video frame is encoded as an intra-frame, intra-macroblocks, or intra slices, through implementation of one or more predetermined or adaptively adjusted quantization parameters to reduce computational complexity, decrease power consumption, and increase the resulting video image quality. As decoding is the inverse of encoding, these improvements are similarly recognized by a decoder as it decodes a resulting encoded video stream.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Video encoding methods and devices
ActiveUS20060098738A1Quality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCoding blockVideo encoding
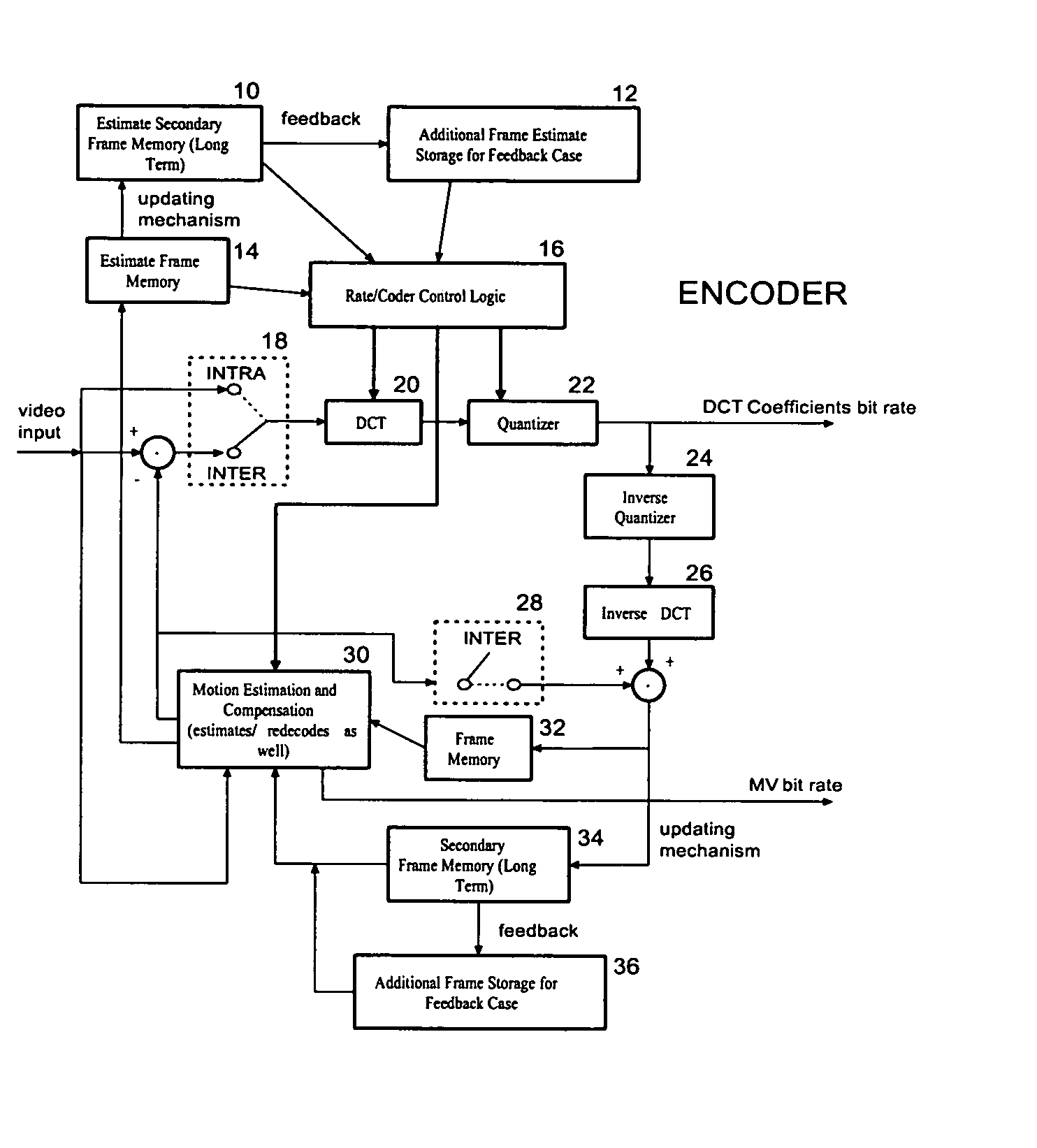
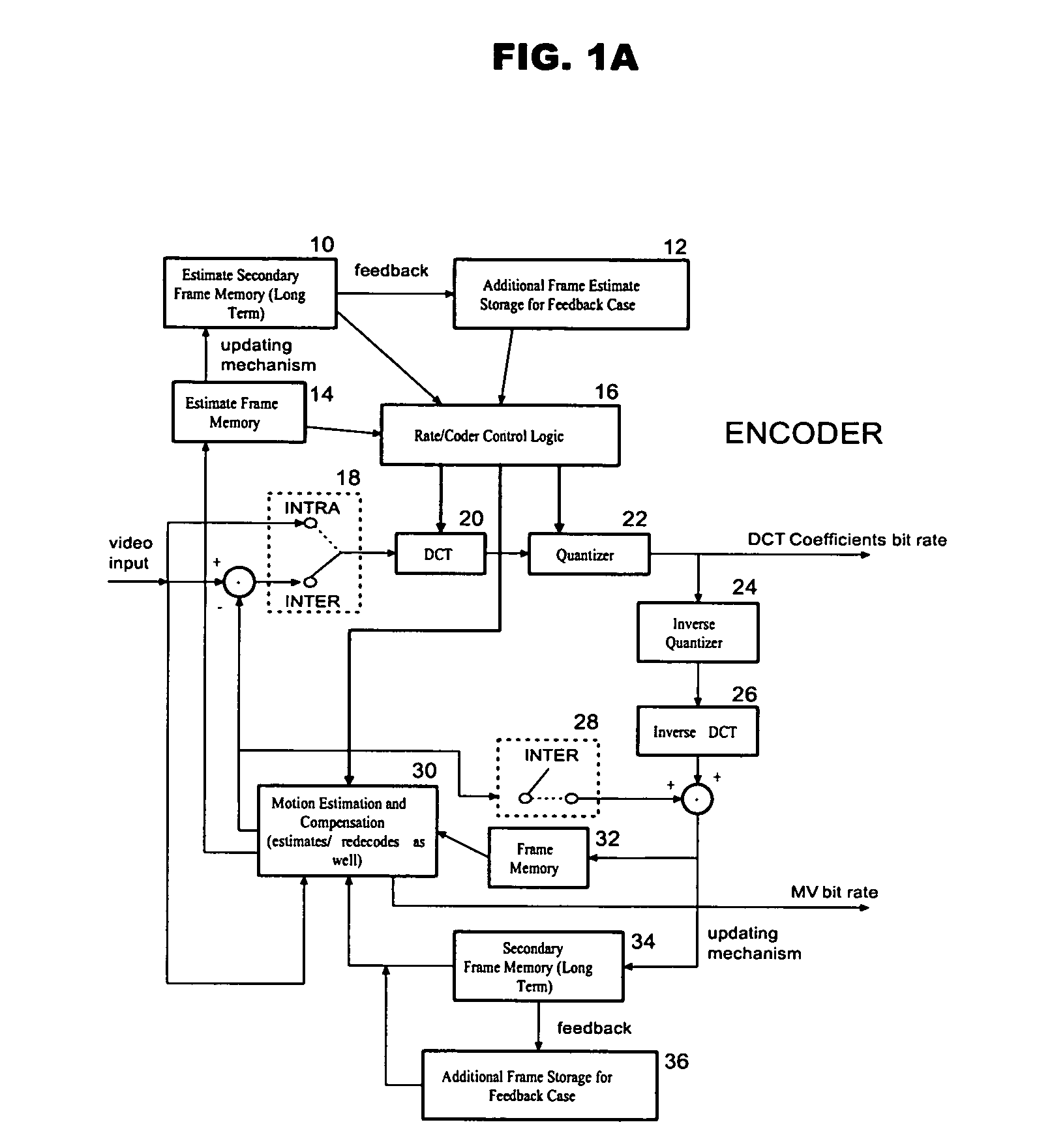
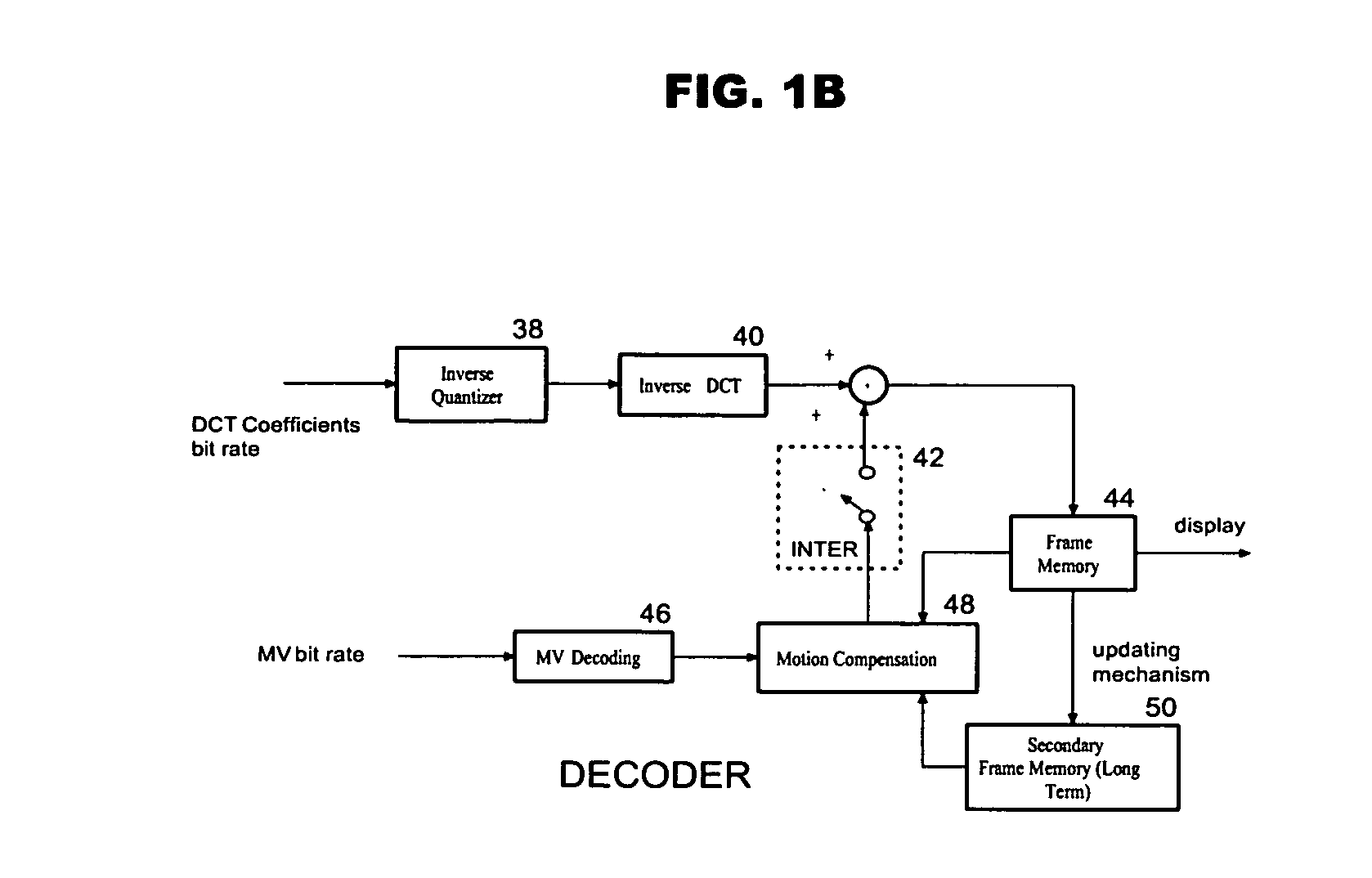
A dual, and possibly multiple, frame approach is used by the invention. Embodiments of the invention include making a decision to use a long term reference frame, which is a frame other than an immediate past reference frame, to conduct INTER coding, or to conduct INTRA frame coding. Other embodiments include use of long and short term reference blocks, and make a decision between two types of INTER coding blocks and INTRA coding. In accordance with embodiments of the invention, a long term frame is a high quality frame. The high quality frame may be used as a reference frame under particular conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Image encoding device and encoding method, and image decoding device and decoding method
InactiveUS20090110070A1Improve compression efficiencyReduce the amount of codeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVariable-length codeIntra-frame
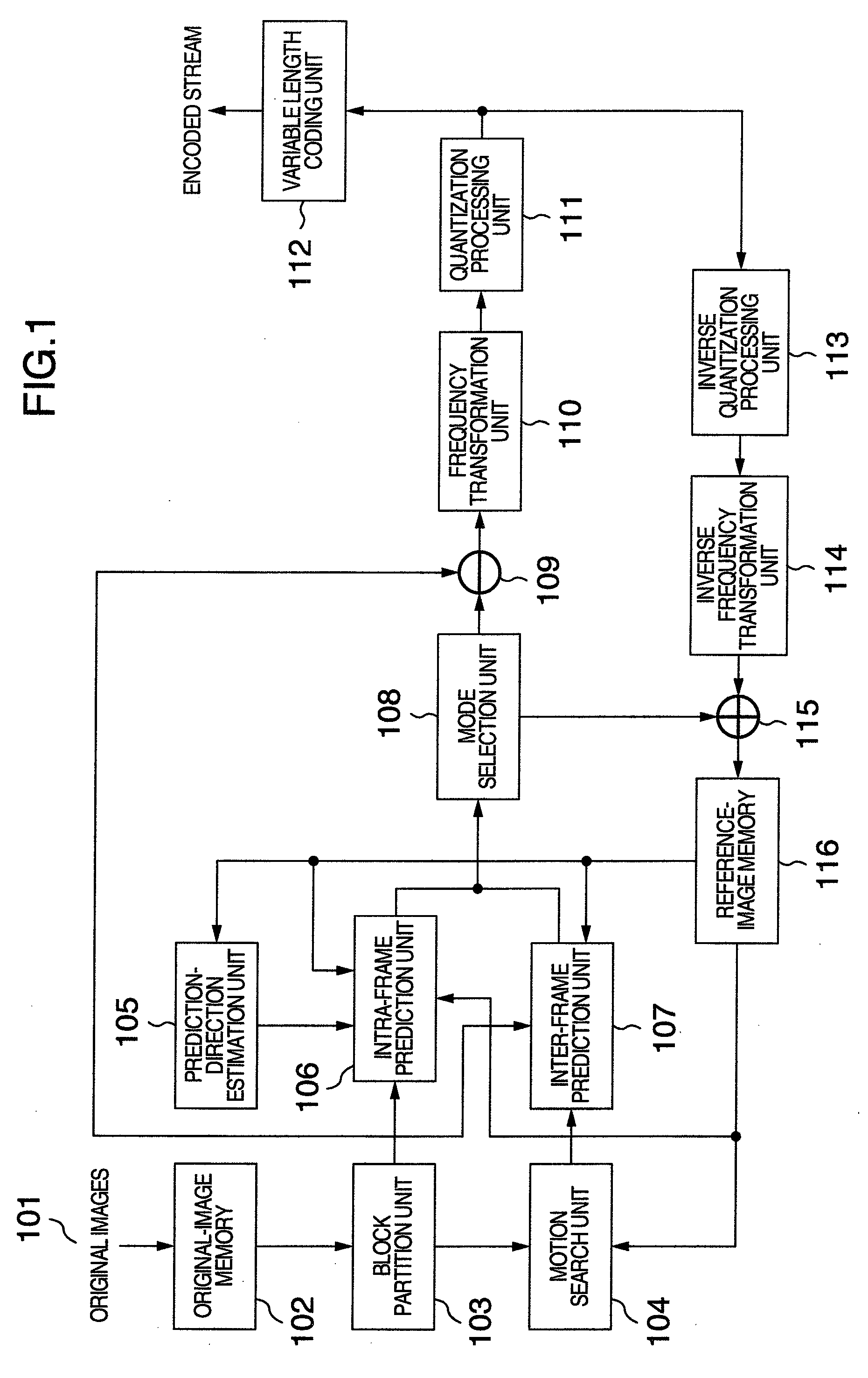
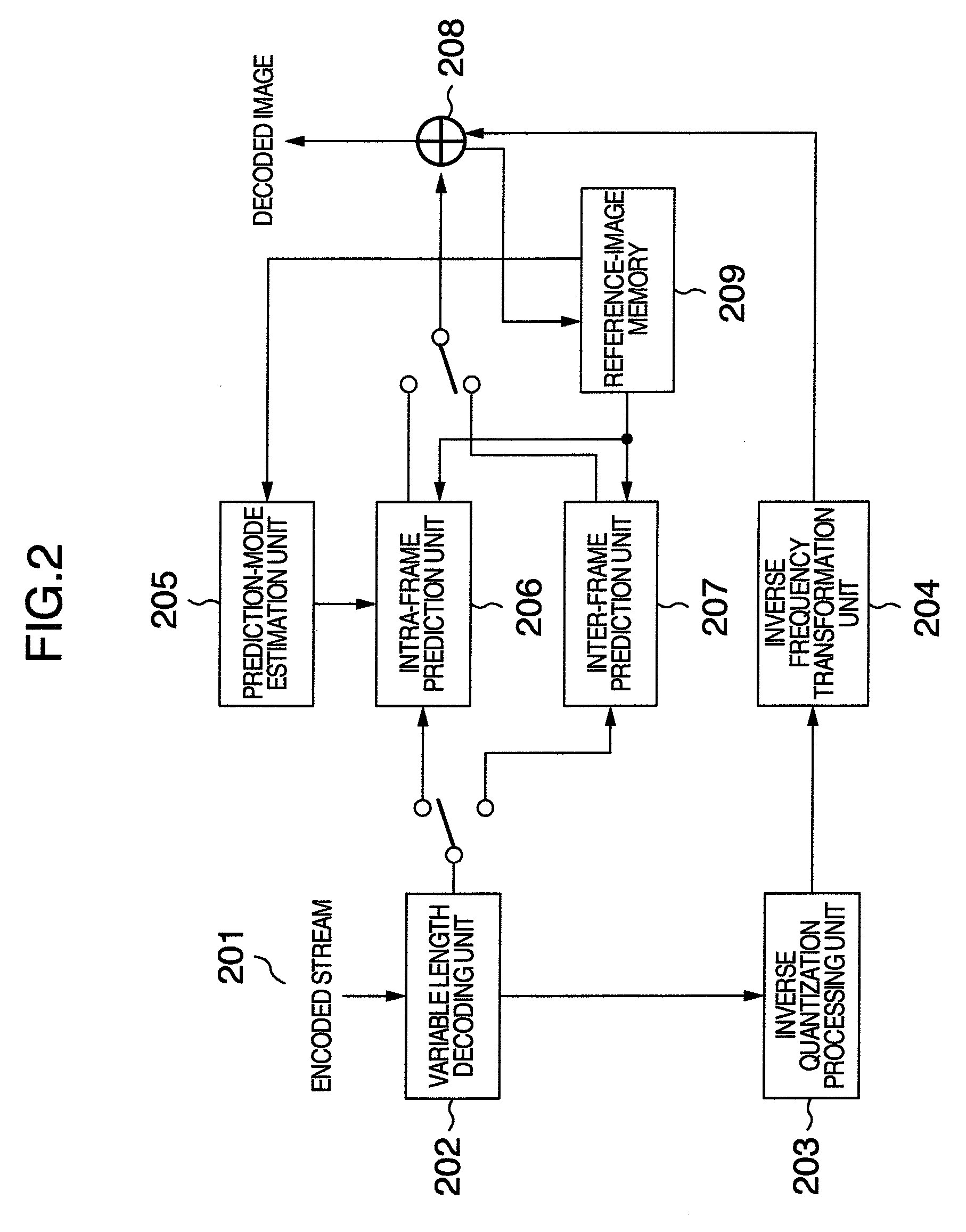
In an image encoding / decoding device of the present invention, the prediction direction in a target block, i.e., a block which becomes the target of the intra-frame prediction processing, is estimated by taking advantage of pre-encoded blocks which are adjacent to the target block. First, as edge information on decoded images on the adjacent blocks, intensities and angles of the edges are calculated. Next, of the degrees of likelihood calculated with respect to each prediction direction by taking advantage of this edge information and, e.g., a neural network, the prediction direction whose degree of likelihood is the highest is employed as the prediction direction in the target block. Also, a variable-length code table is dynamically created based on the estimated result, which allows a significant reduction in the prediction-direction representing code amount.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Imagine information describing method, video retrieval method, video reproducing method, and video reproducing apparatus
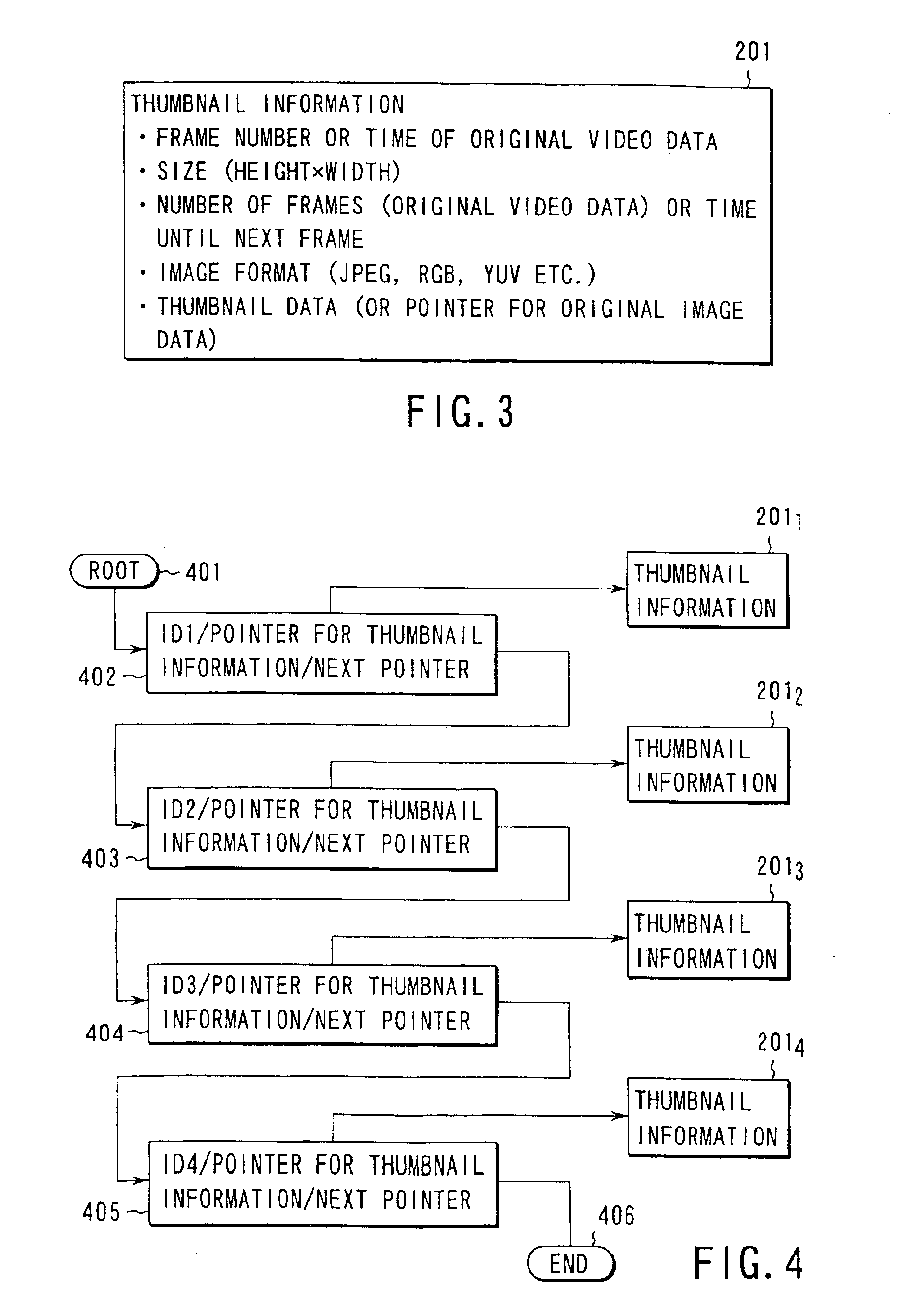
InactiveUS6912327B1Easy to manufactureData processing applicationsMetadata video data retrievalVideo retrievalThumbnail
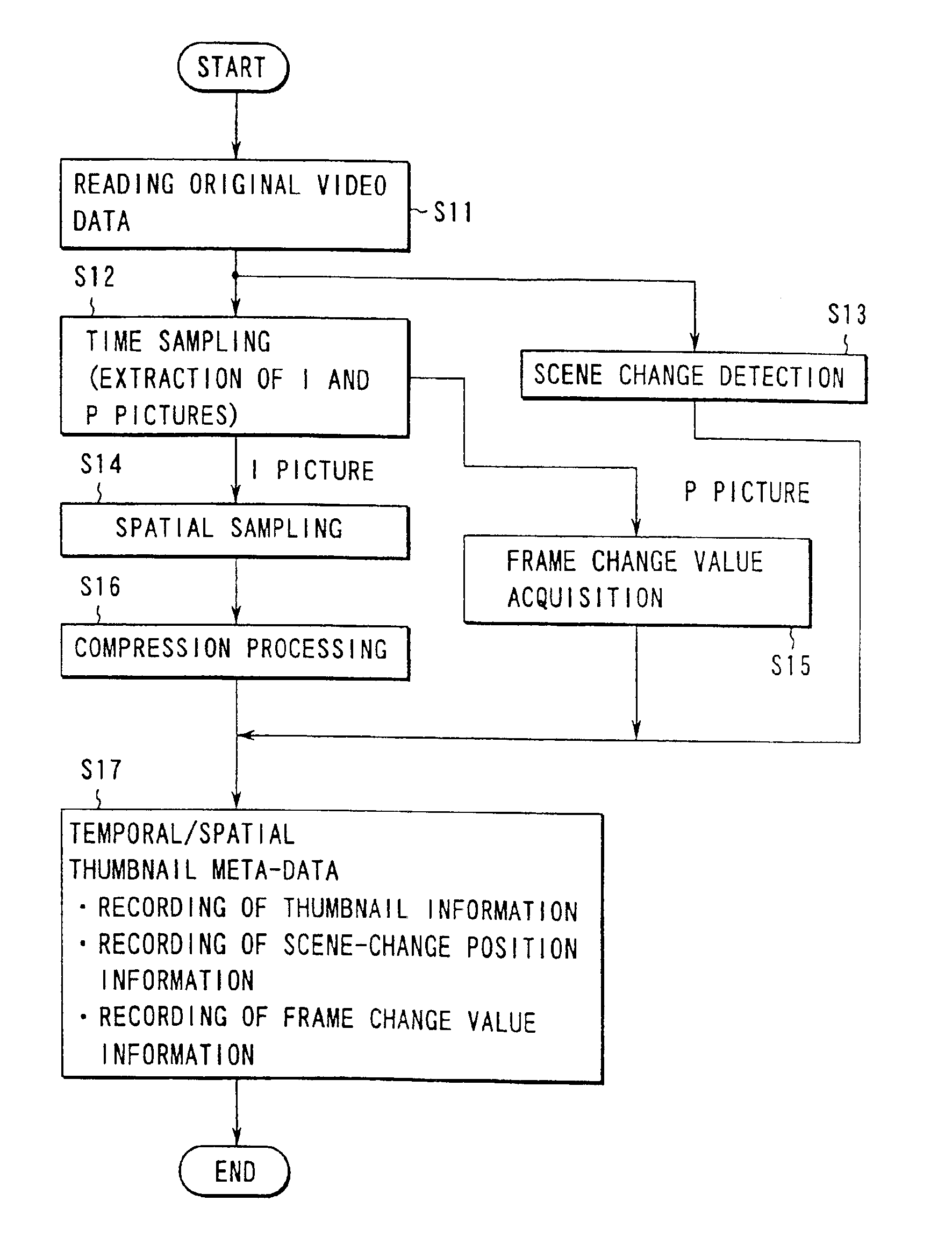
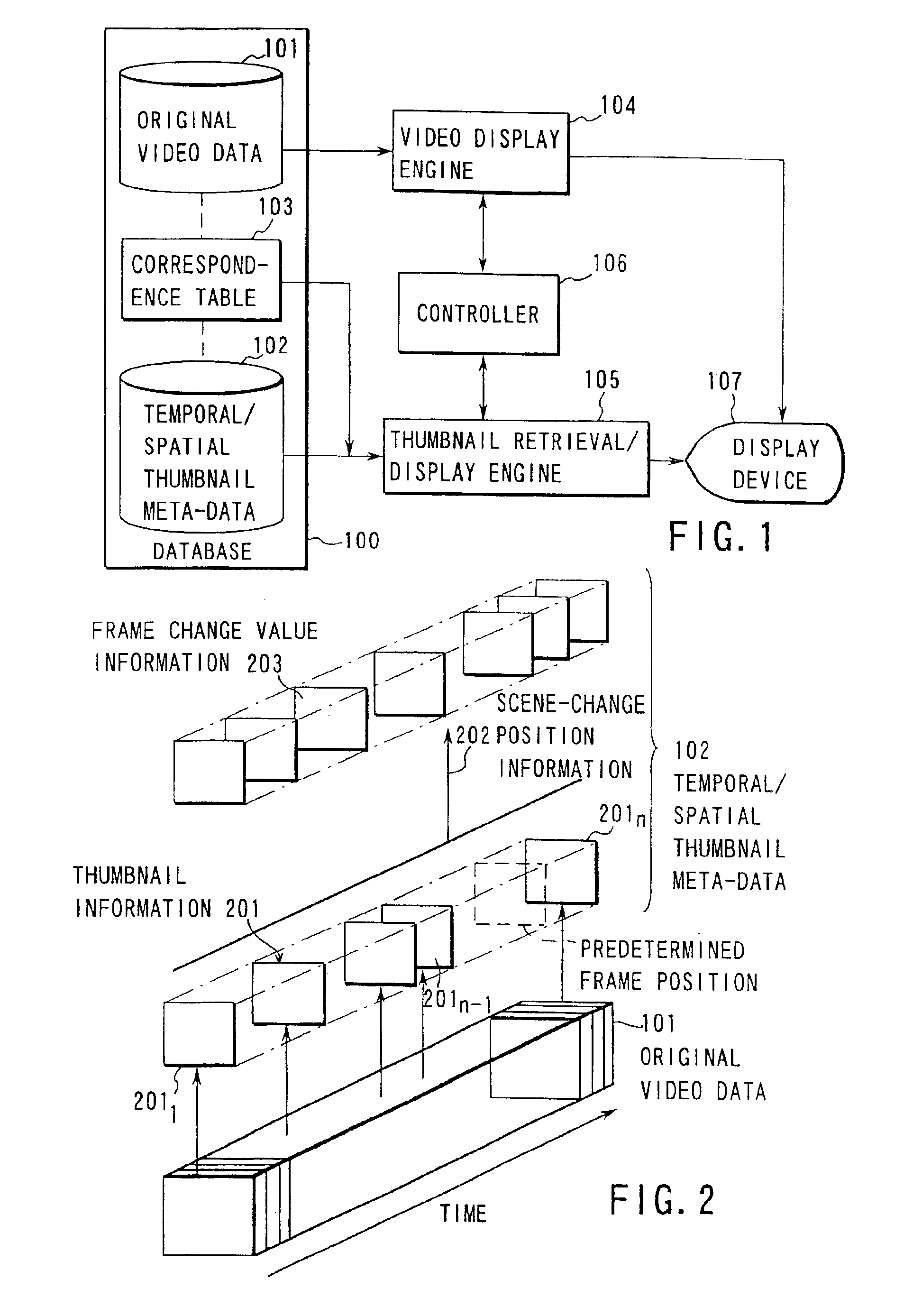
Video frames of original video data are sampled with arbitrary time interval and size, and thumbnail frames are obtained. As thumbnail information concerning these frames, information on frame number of the original video frame corresponding each of the thumbnail frames and size of each thumbnail frame are described. Further, scene change information on the original video frames or intra-frame frame change value information are described altogether as additional information, and temporal / spatial thumbnail meta-data is obtained. The meta-data is associated with original video data, and a database is constructed. Then, the meta-data is employed, thereby performing typical frame display of original video data or variable speed reproduction. In this manner, even with a device with its low CPU capability, typical frame display or variable speed reproduction is performed for compressed and encoded video data such as MPEG-2, and the contents of video is checked, and retrieval is easily performed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Moving picture encoding/transmission system, moving picture encoding/transmission method, and encoding apparatus, decoding apparatus, encoding method decoding method and program usable for the same
ActiveUS20040233989A1Inhibit deteriorationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSignal correlationIntra-frame
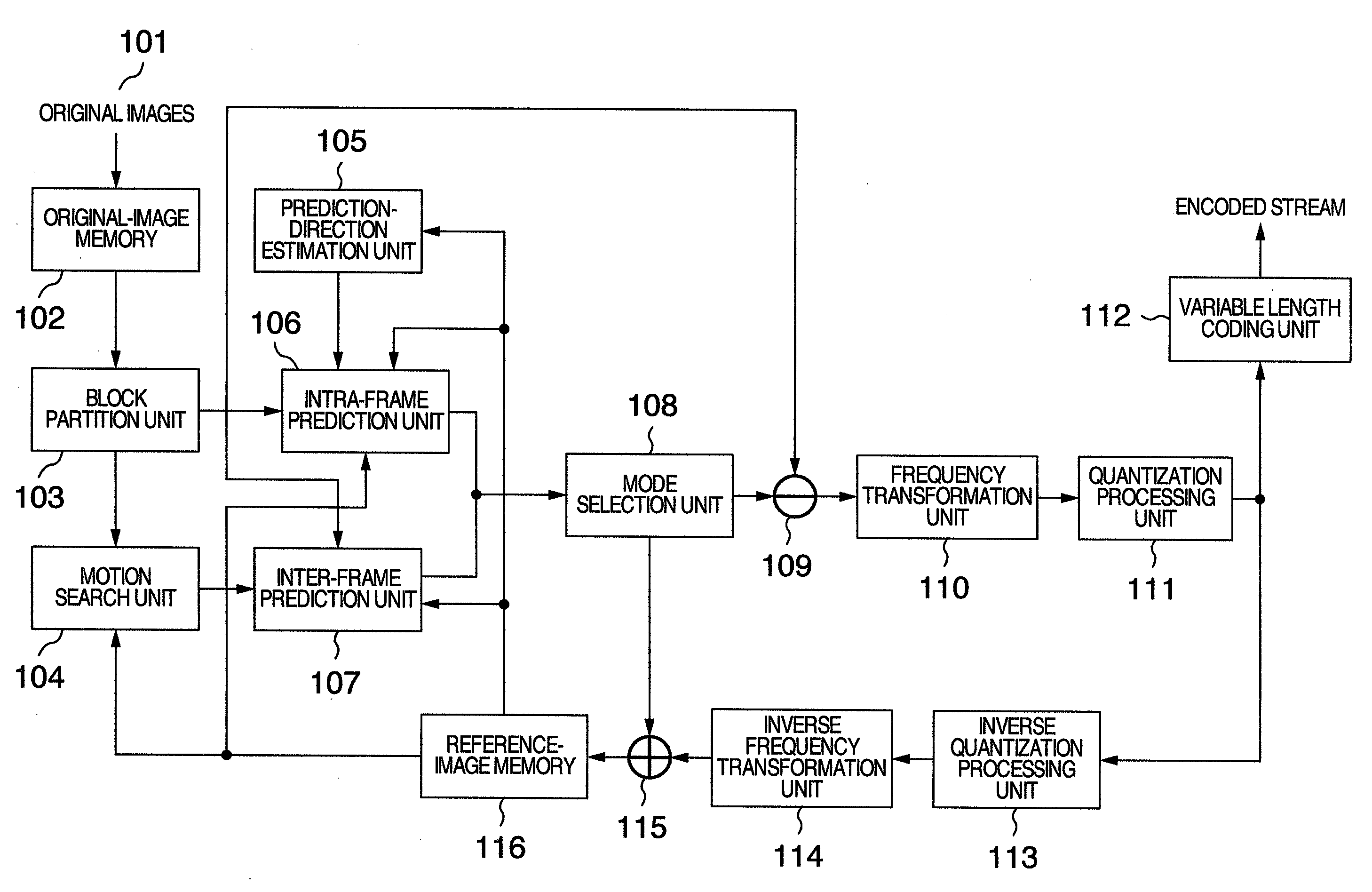
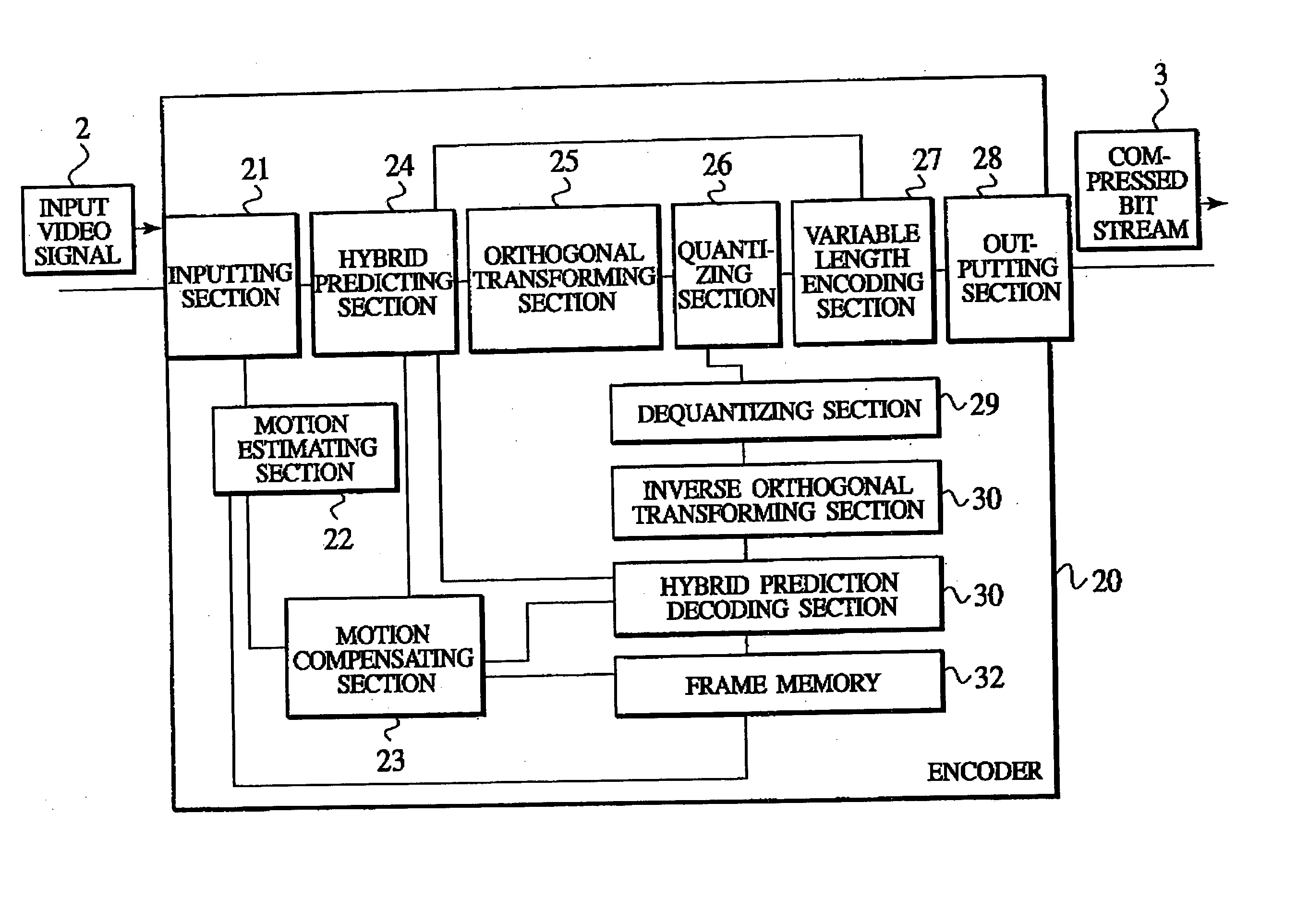
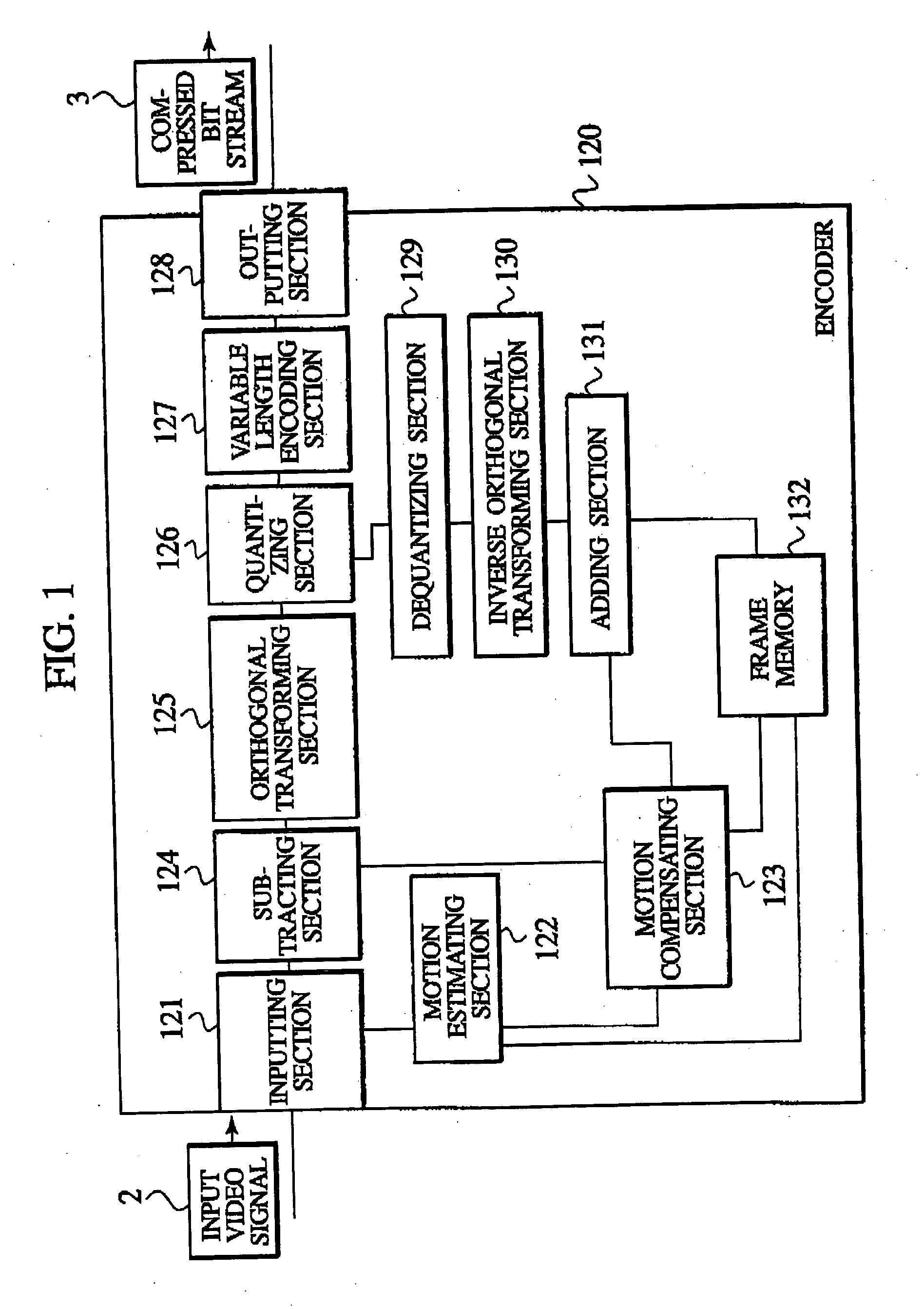
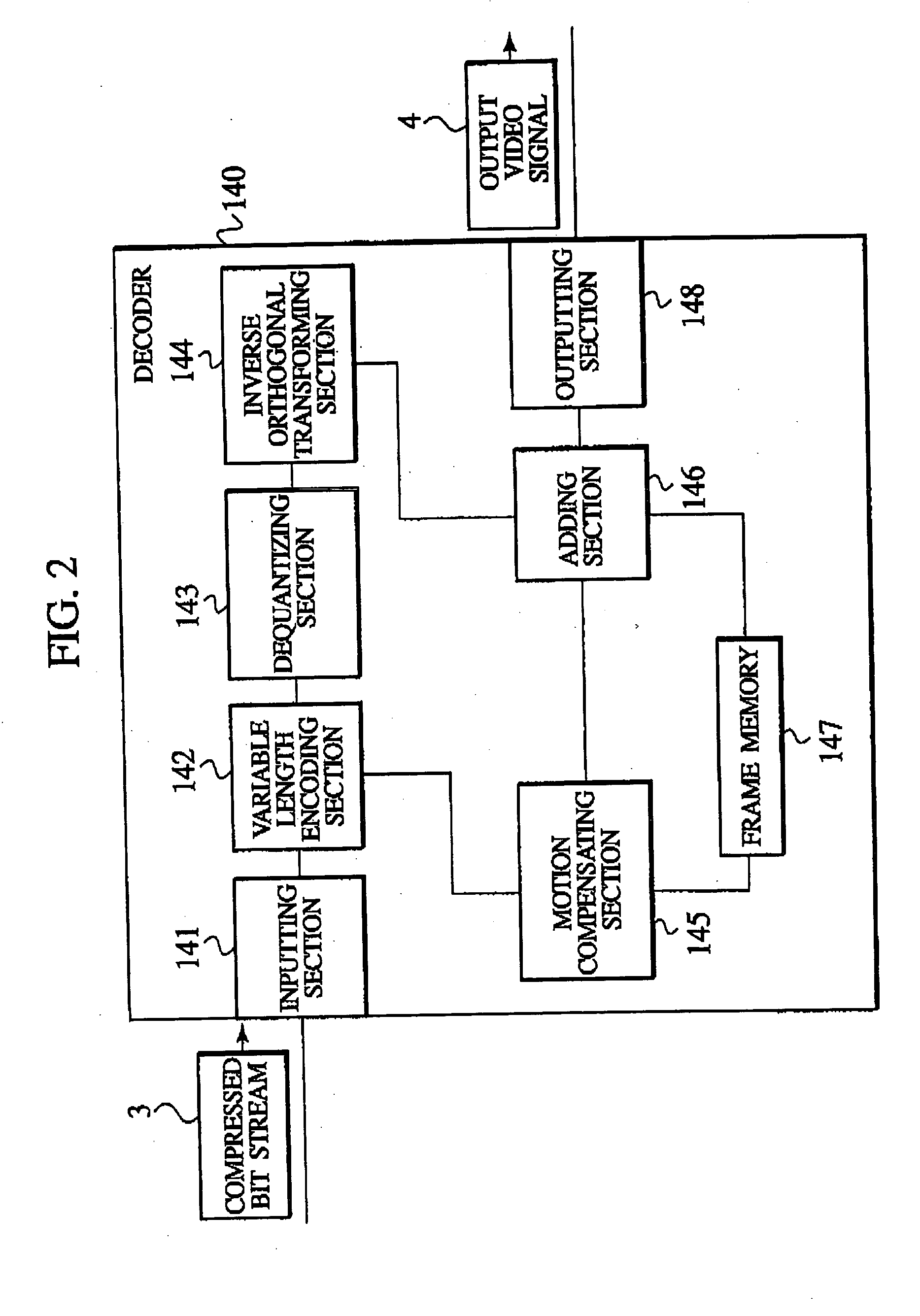
An object of the present invention is to allow portions which are subjected to a coding in inter-frame prediction mode and portions which are subjected to coding in intra-frame prediction mode to be mixed in one macro block without changing the framework of macro blocks. The present invention provides an encoder which encodes each of first image blocks of a video. The encoder includes prediction mode selection information generating means for generating prediction mode selection information which indicates that a first prediction mode for reducing temporal redundancy is applied to each of second image blocks or that a second prediction mode for reducing spatial redundancy is applied to each of the second image blocks. The second image blocks are obtained by dividing the first image blocks. The encoder includes predictive residual signal generating means for generating a predictive residual signal by applying the selected first or second prediction mode to each of the second image blocks. The encoder includes transmitting means for transmitting the prediction mode selection information in association with the predictive residual signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
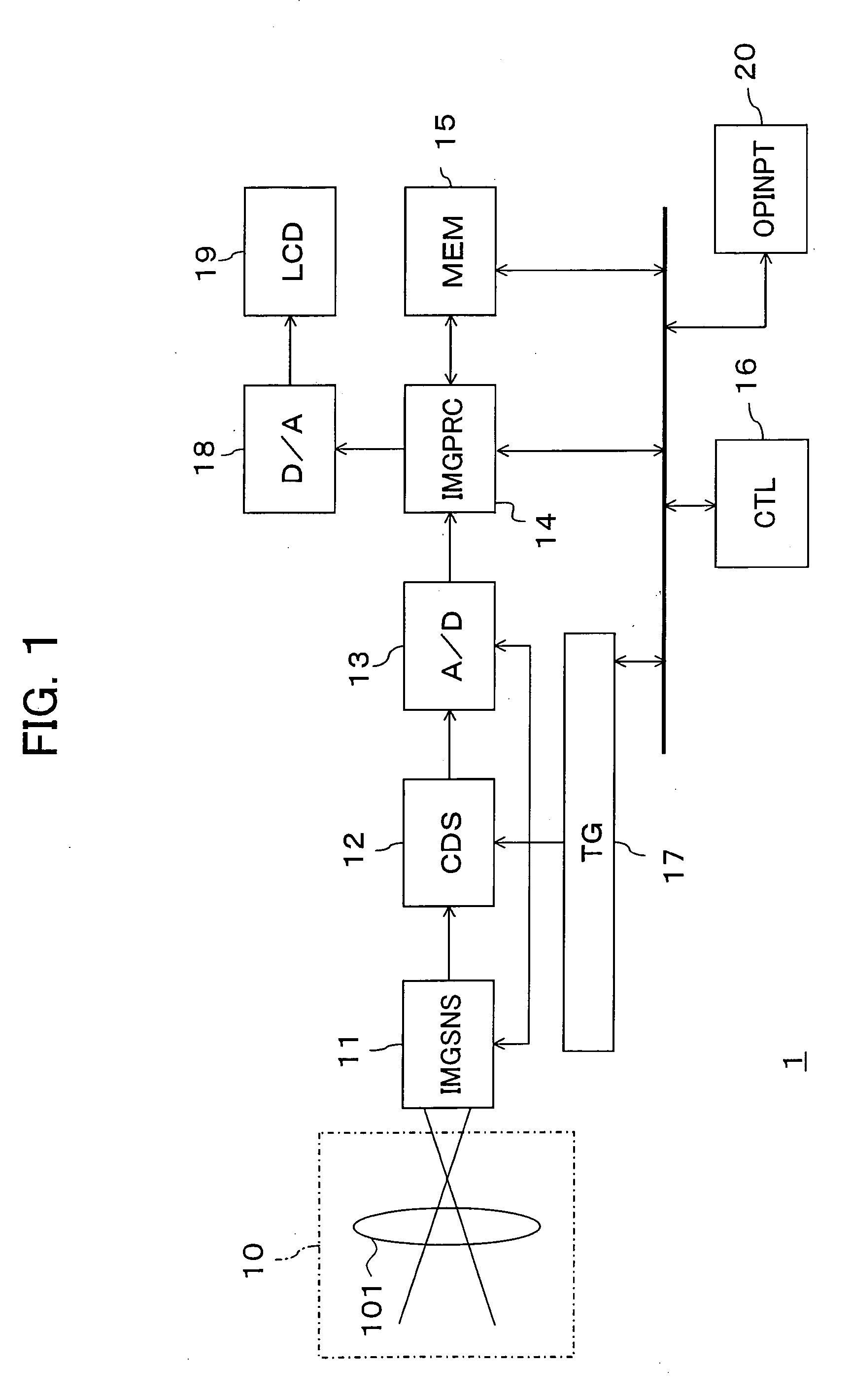
Imaging device and image generation method of imaging device
InactiveUS20050190274A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingMethod of images
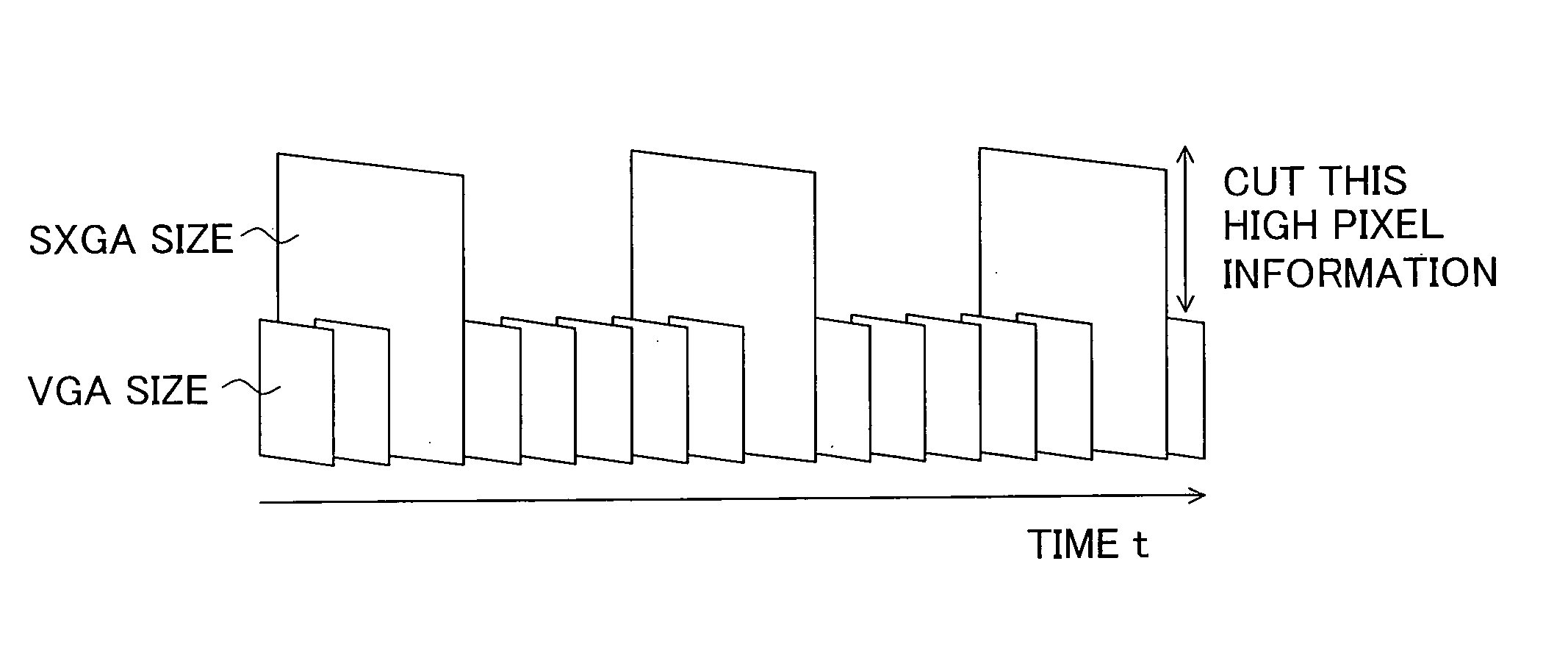
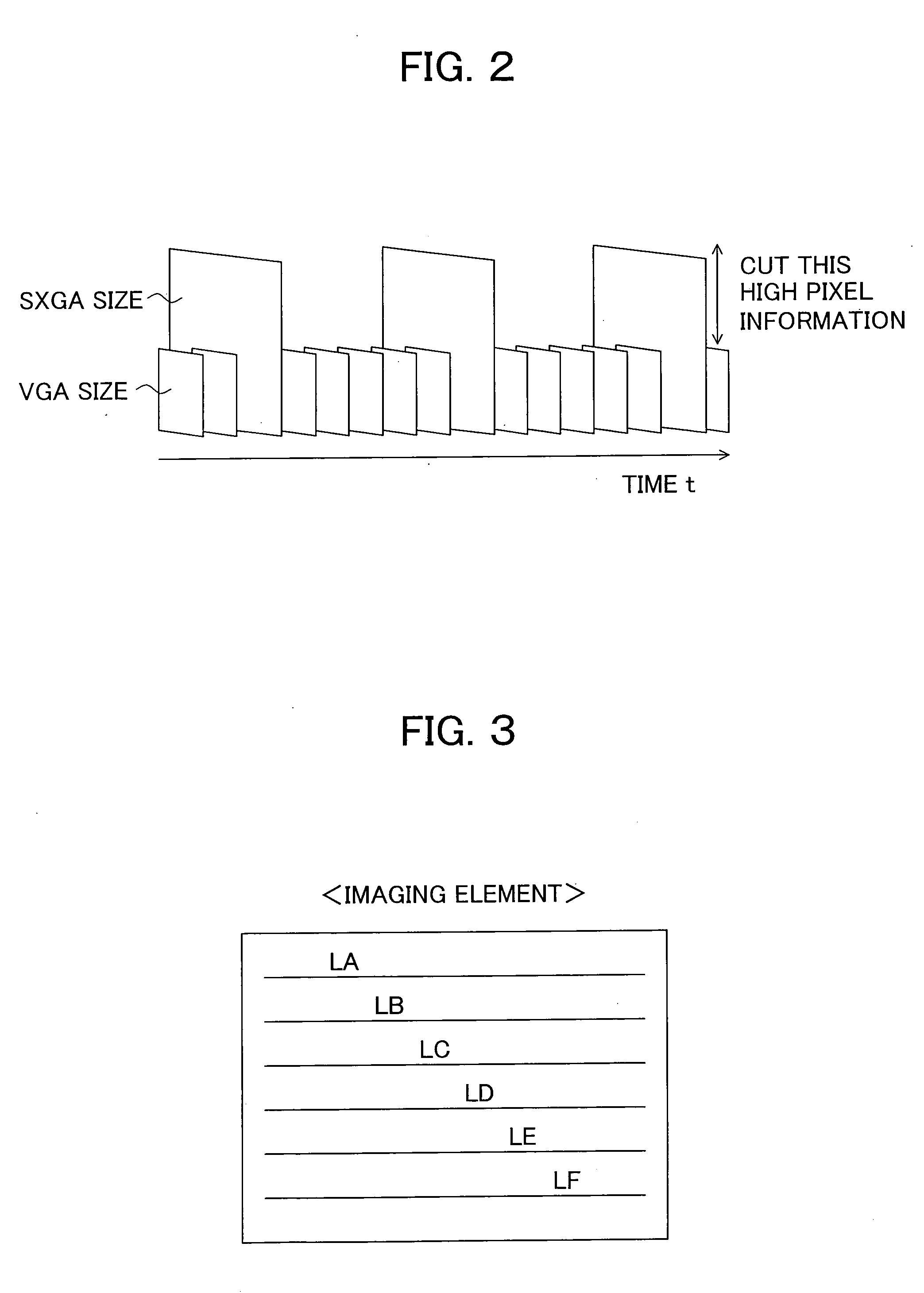
An imaging device having nonconventional and a completely new imaging method and an image generation method of the imaging device, wherein the imaging device has an image processing section generating a first compressed image compressed high image data with intra-frame compression in capturing single moving image data and a second compressed image compressed low image data with inter-frame compression in a front period and / or in a rear period of a period generating the first compressed image as one stream, where the imaging device generates still image data having high-resolution indicating one screen designated by decompression and decoding by the second compressed image and the other compressed image including the first compressed image when one screen of a second compressed image is designated.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Method and device for encoding and decoding video
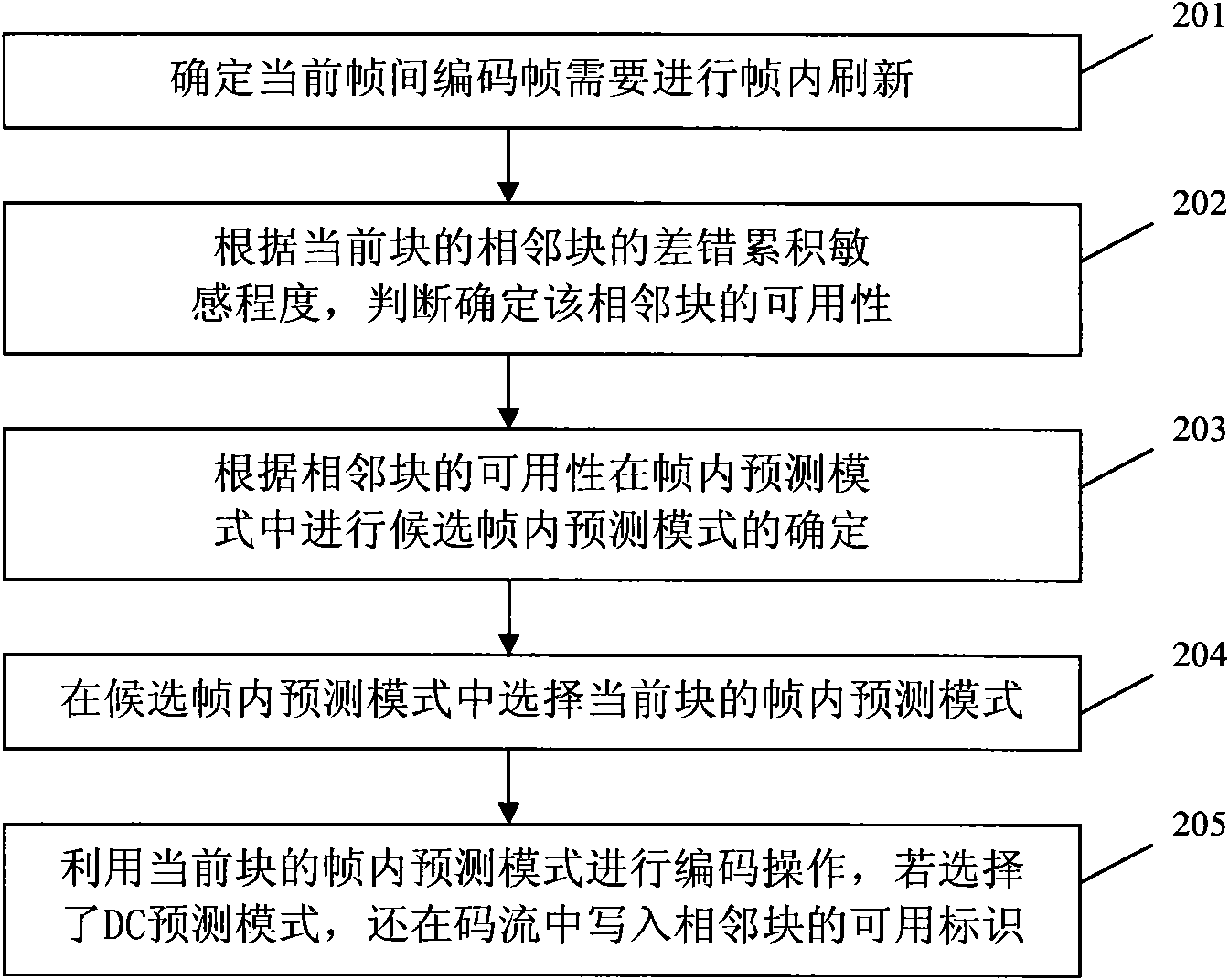
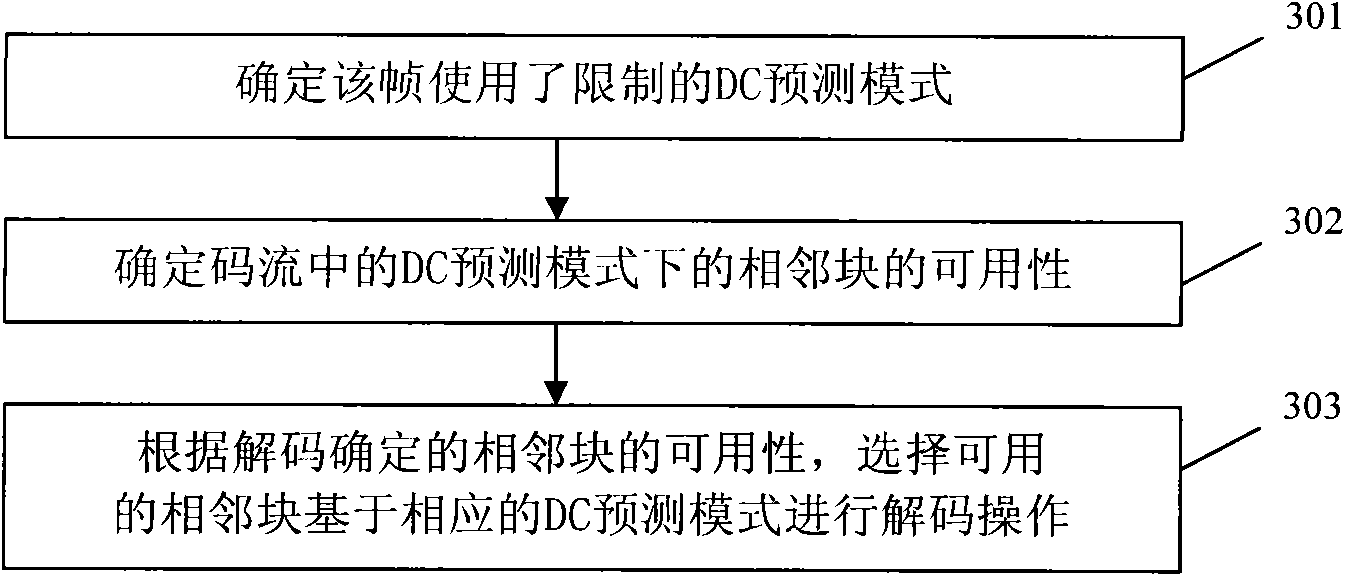
ActiveCN101605255AImprove coding efficiencyGuaranteed error recovery performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCommunications systemRecovery performance
The invention discloses a method and a device for encoding and decoding a video. The method comprises the following steps: executing a selection of an intra frame predictive mode according to available adjacent blocks, writing in the available marks of each adjacent block in a code stream when the selected intra frame encoding mode is a limited DC predictive mode; thus, determining that the limited DC predictive mode is adopted for encoding by a current block at an decoding end, and then analyzing the available marks for indicating whether adjacent blocks are available, and determining available adjacent blocks according to the available marks of the adjacent blocks so as to perform decoding operation according to available adjacent blocks based on the DC predictive mode. The embodiment of the invention can set availability of left adjacent blocks and upper adjacent blocks of the DC mode when the intra frame encoding mode is the DC predictive mode, thereby ensuring the error recovery performance to improve the performance of encoding and decoding in a video communication system.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
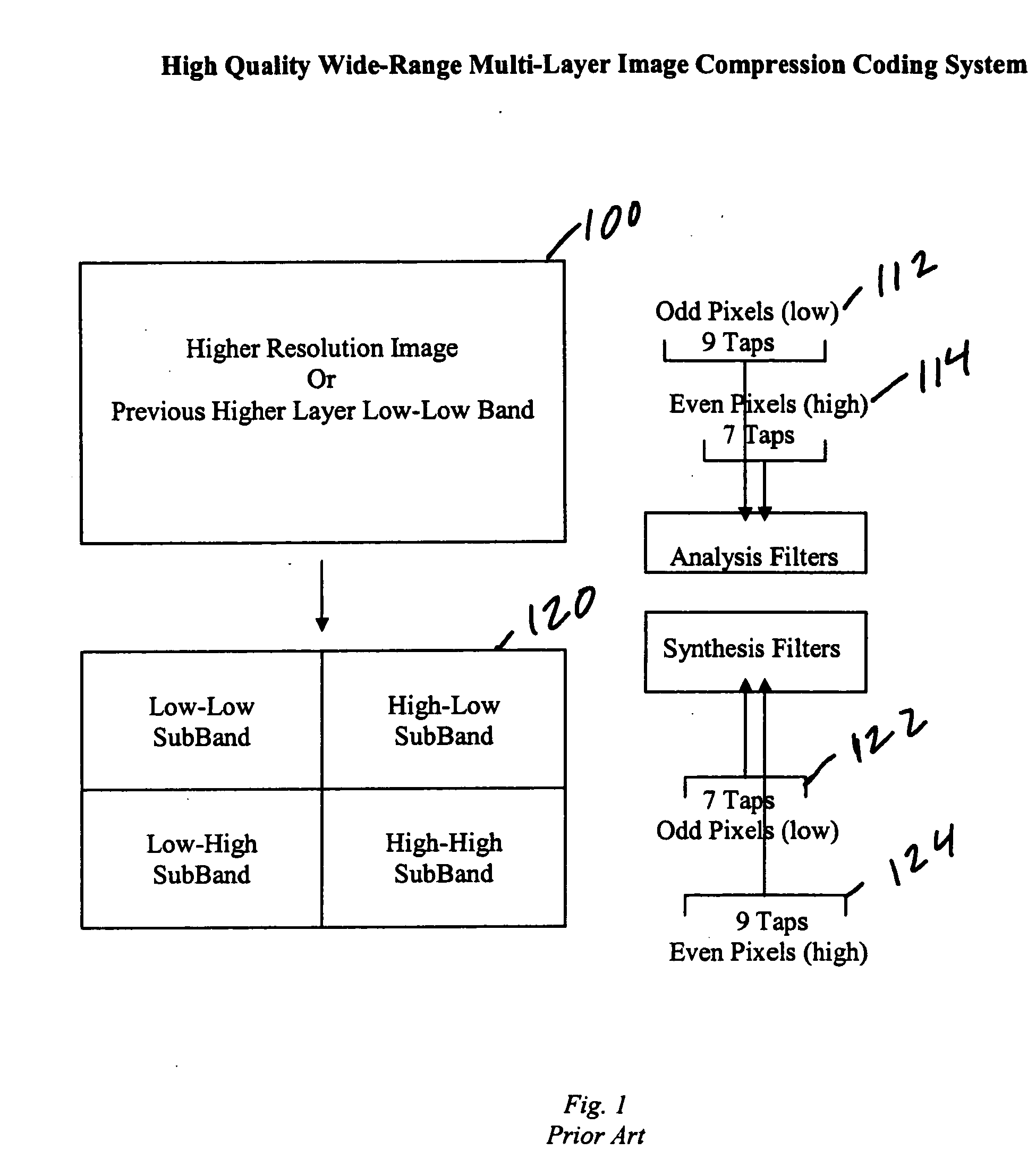
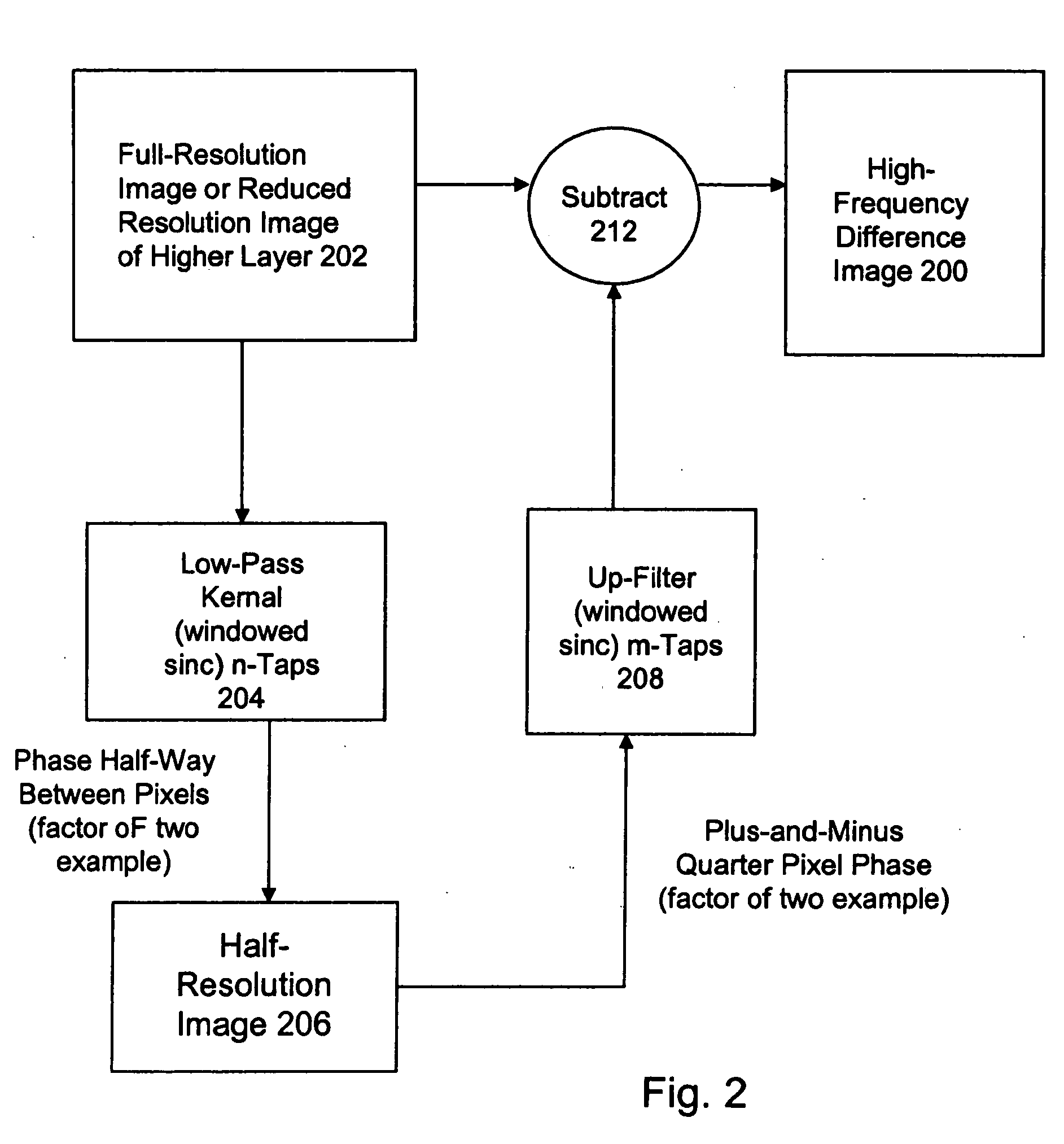
High quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding system
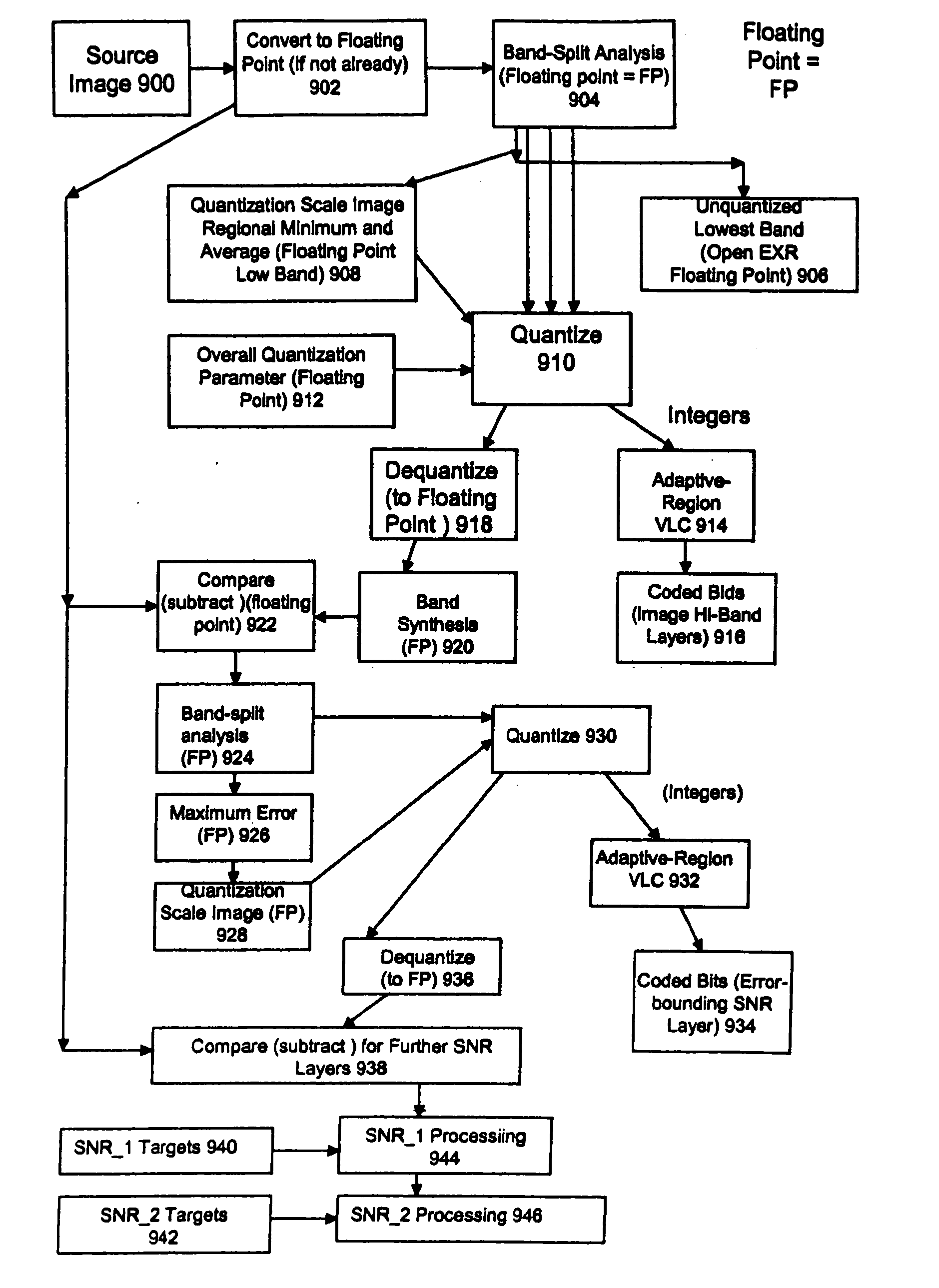
ActiveUS20060071825A1Reduce sharpnessReduce detailsCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionFloating pointImage compression
Systems, methods, and computer programs for high quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding, including consistent ubiquitous use of floating point values in essentially all computations; an adjustable floating-point deadband; use of an optimal band-split filter; use of entire SNR layers at lower resolution levels; targeting of specific SNR layers to specific quality improvements; concentration of coding bits in regions of interest in targeted band-split and SNR layers; use of statically-assigned targets for high-pass and / or for SNR layers; improved SNR by using a lower quantization value for regions of an image showing a higher compression coding error; application of non-linear functions of color when computing difference values when creating an SNR layer; use of finer overall quantization at lower resolution levels with regional quantization scaling; removal of source image noise before motion-compensated compression or film steadying; use of one or more full-range low bands; use of alternate quantization control images for SNR bands and other high resolution enhancing bands; application of lossless variable-length coding using adaptive regions; use of a folder and file structure for layers of bits; and a method of inserting new intra frames by counting the number of bits needed for a motion compensated frame.
Owner:DEMOS GARY
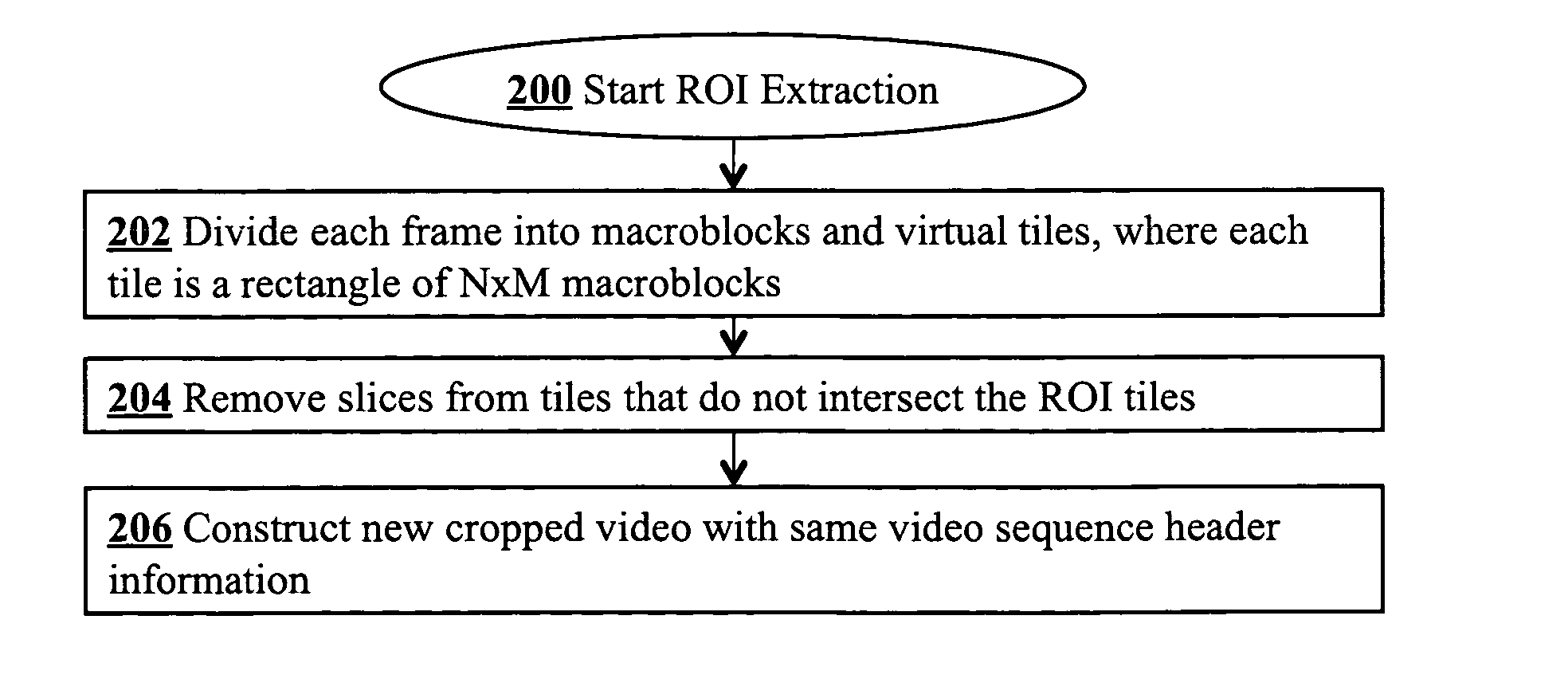
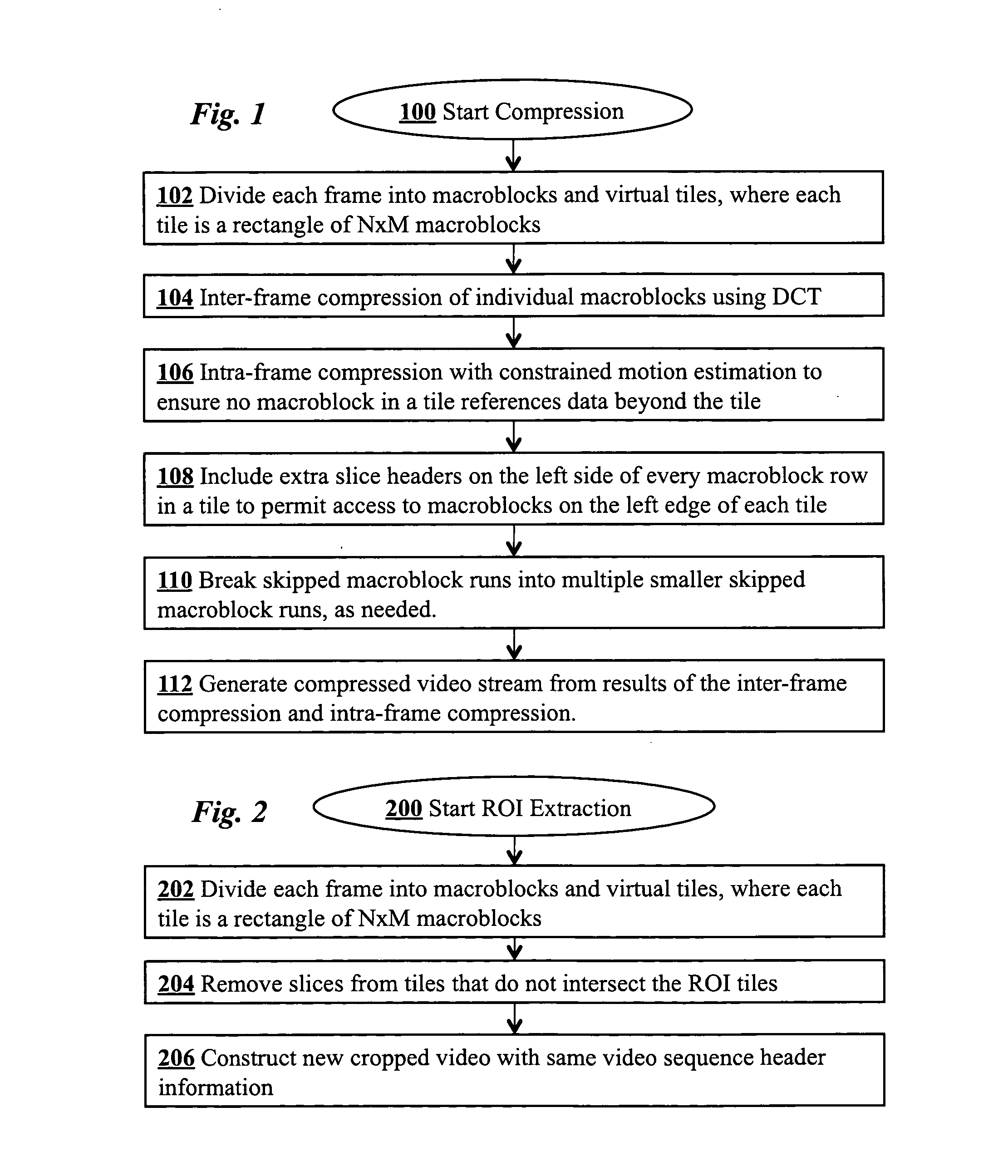
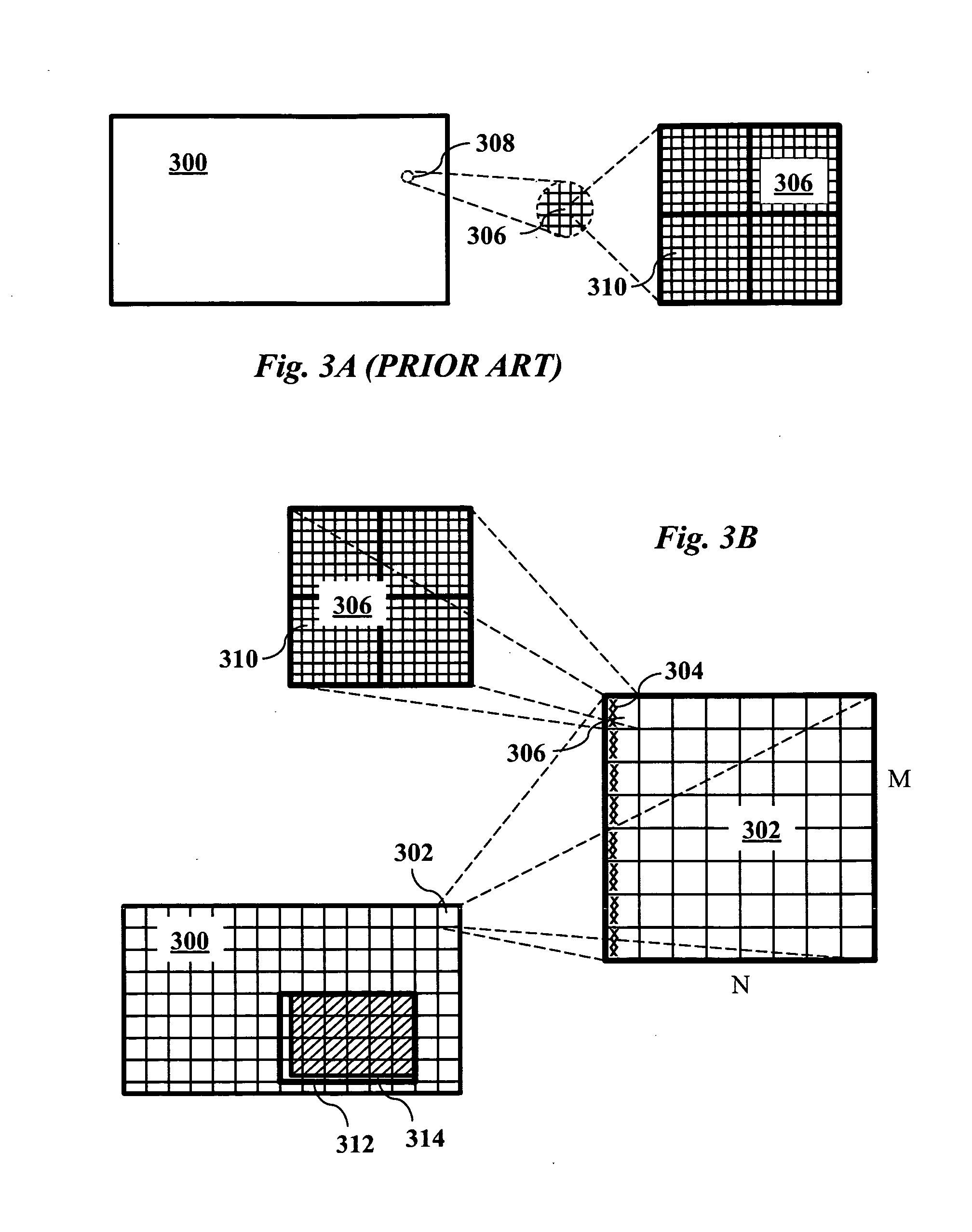
Supporting region-of-interest cropping through constrained compression
InactiveUS20100232504A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
Region-of-interest cropping of high-resolution video is supported video compression and extraction methods. The compression method divides each frame into virtual tiles, each containing a rectangular array of macroblocks. Intra-frame compression uses constrained motion estimation to ensure that no macroblock references data beyond the edge of a tile. Extra slice headers are included on the left side of every macroblock row in the tiles to permit access to macroblocks on the left edge of each tile during extraction. The compression method may also include breaking skipped macroblock runs into multiple smaller skipped macroblock runs. The extraction method removes slices from virtual tiles that intersect the region-of-interest to produce cropped frames. The cropped digital video stream and the compressed digital video stream have the same video sequence header information.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV
Dynamic GOP system and method for digital video encoding
InactiveUS6959044B1Improve performanceTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoVideo quality
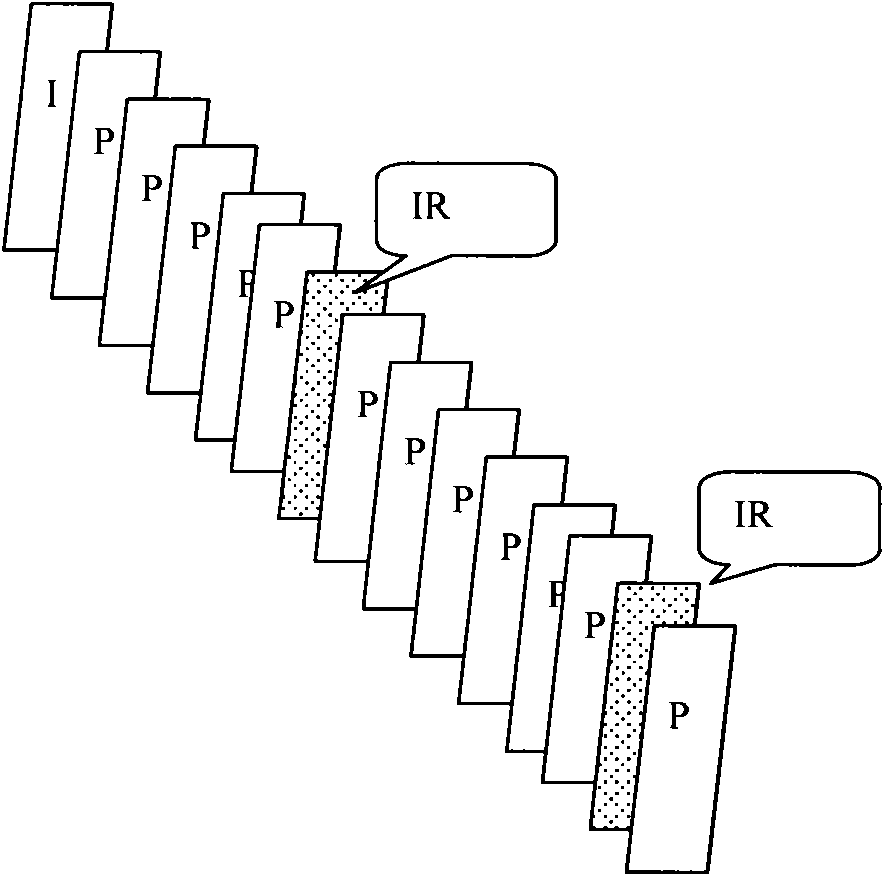
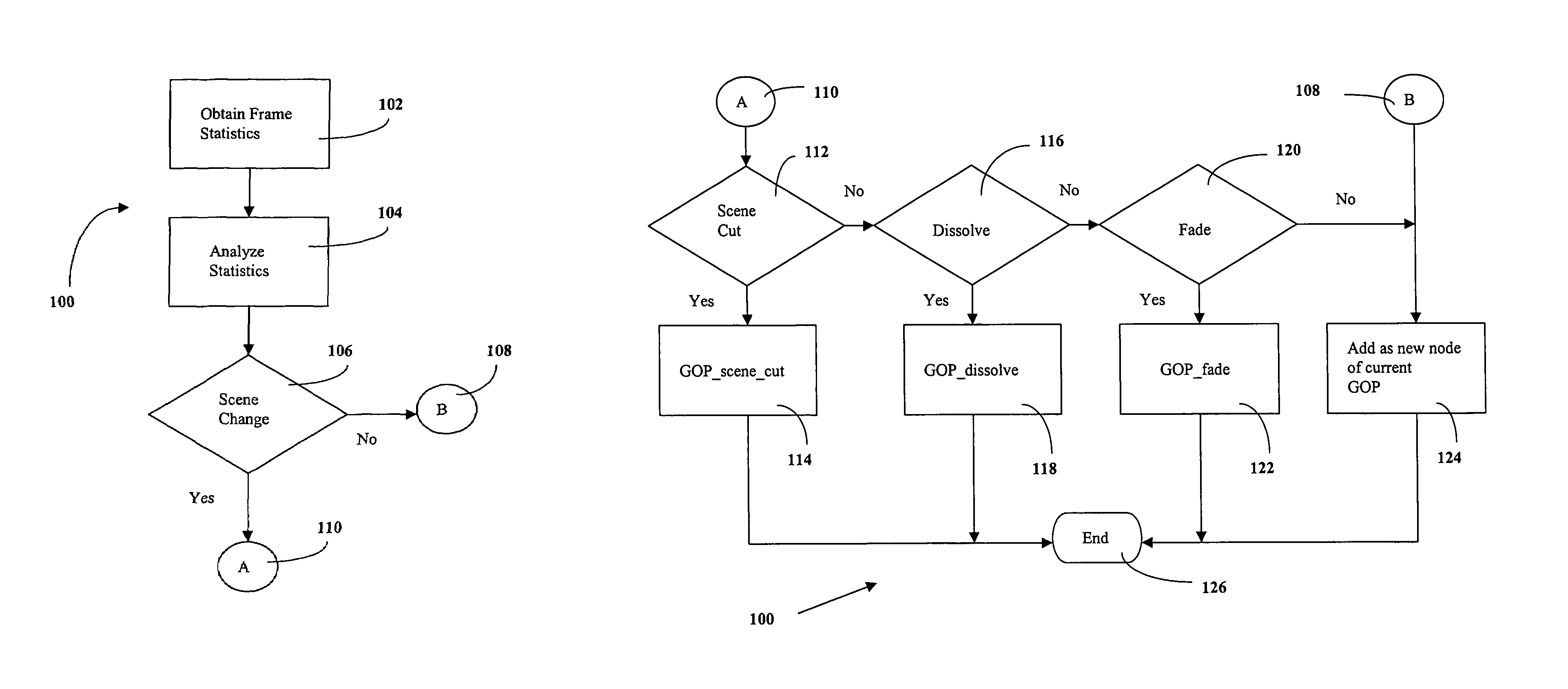
This invention discloses an intra-frame complexity based dynamic GOP system and method for the encoding of MPEG-2 video streams. The present invention may be used as a rate control tool to improve video quality. The selective insertion of low complexity I frames in scene changes such as fades is disclosed. It is disclosed that the selective use of I frames in certain scene change situations can improve encoder performance, particularly when encoding at a low bit rate.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
Using numbers of non-zero quantized transform signals and signal differences to determine when to encode video signals using inter-frame or intra-frame encoding
InactiveUS6222881B1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionInterframe coding
A transform is applied to a region of a current video frame to generate transform signals corresponding to the region. An activity measure is generated using the transform signals. The activity measure is then used to determine whether to encode the region as a skipped region. The region is encoded in accordance with that determination to generate an encoded bit stream for the region. In a preferred embodiment, the transform signals are DCT coefficients and the activity measure is a weighted sum of the DCT coefficients, where the weighting of the low-frequency DCT coefficients is greater than the weighting of the high-frequency DCT coefficients. The region is encoded as a skipped region if the activity measure is less than a threshold value; otherwise, the region is encoded as either an inter encoded region or an intra encoded region.
Owner:INTEL CORP
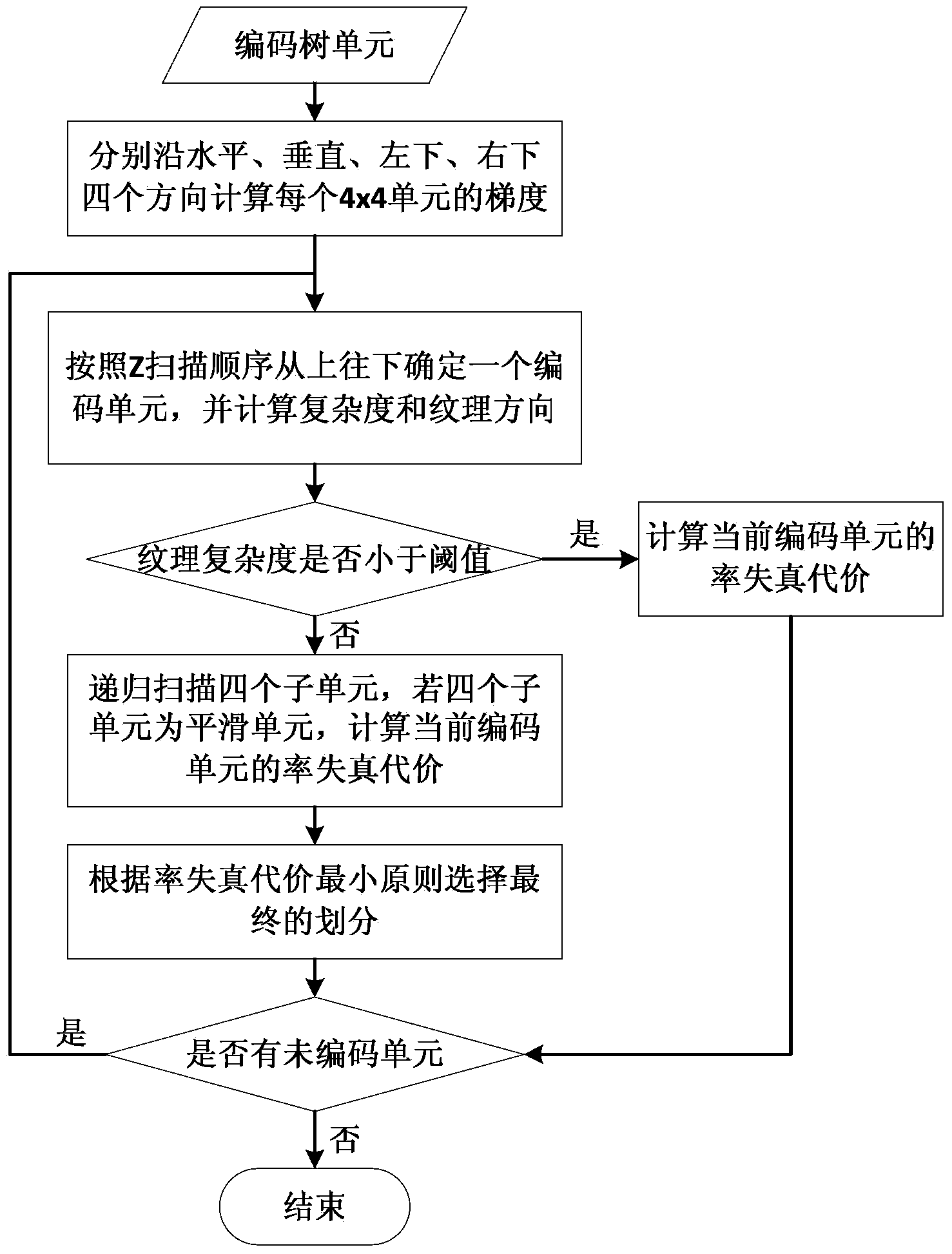
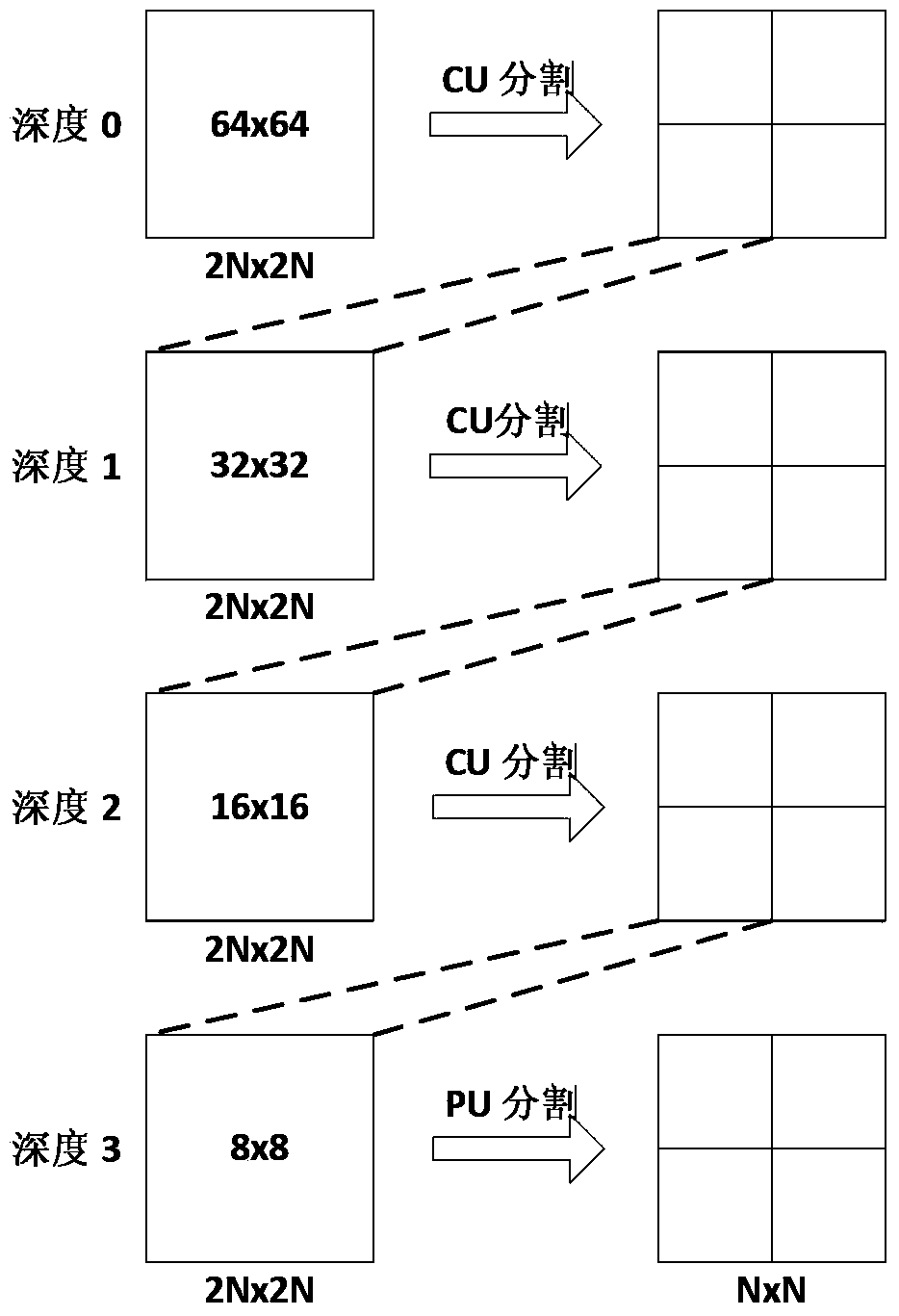
HEVC intra-frame prediction quick mode selection method based on texture analysis
ActiveCN103517069AGuaranteed coding qualityReduce coding timeDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionLeft direction
The invention discloses an HEVC intra-frame prediction quick mode selection method based on texture analysis. According to the method, before intra-frame prediction is carried out on an encoding tree unit, the main texture direction and the texture complexity of each 4*4 unit in the encoding tree unit are determined according to the sum of absolute values of gradients in the horizontal direction, the vertical direction, the lower left direction and the lower right direction, and division of the current encoding tree unit is determined according to the principle that a larger encoding unit is adopted in a texture smooth area and a smaller encoding unit is adopted in a texture complex area. During prediction, according to the main texture direction of the prediction unit, a plurality of prediction modes with least probability are eliminated, and rough mode selection and rate-distortion optimization mode selection are carried out according to an HEVC encoding standard. According to the HEVC intra-frame prediction quick mode selection method based on texture analysis, on the premise that encoding quality is guaranteed, the encoding speed can be obviously improved.
Owner:北京畅景立达软件技术有限公司
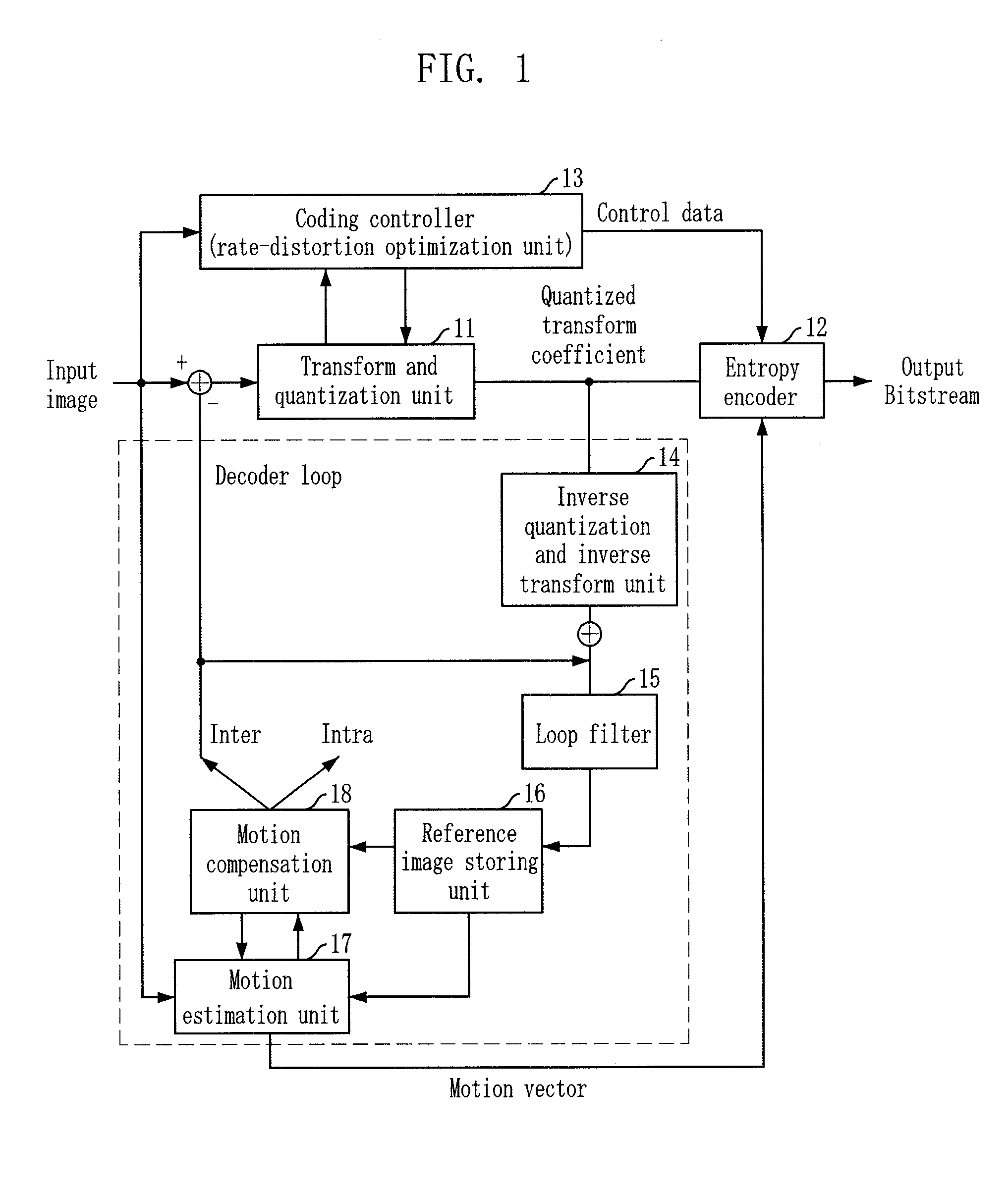
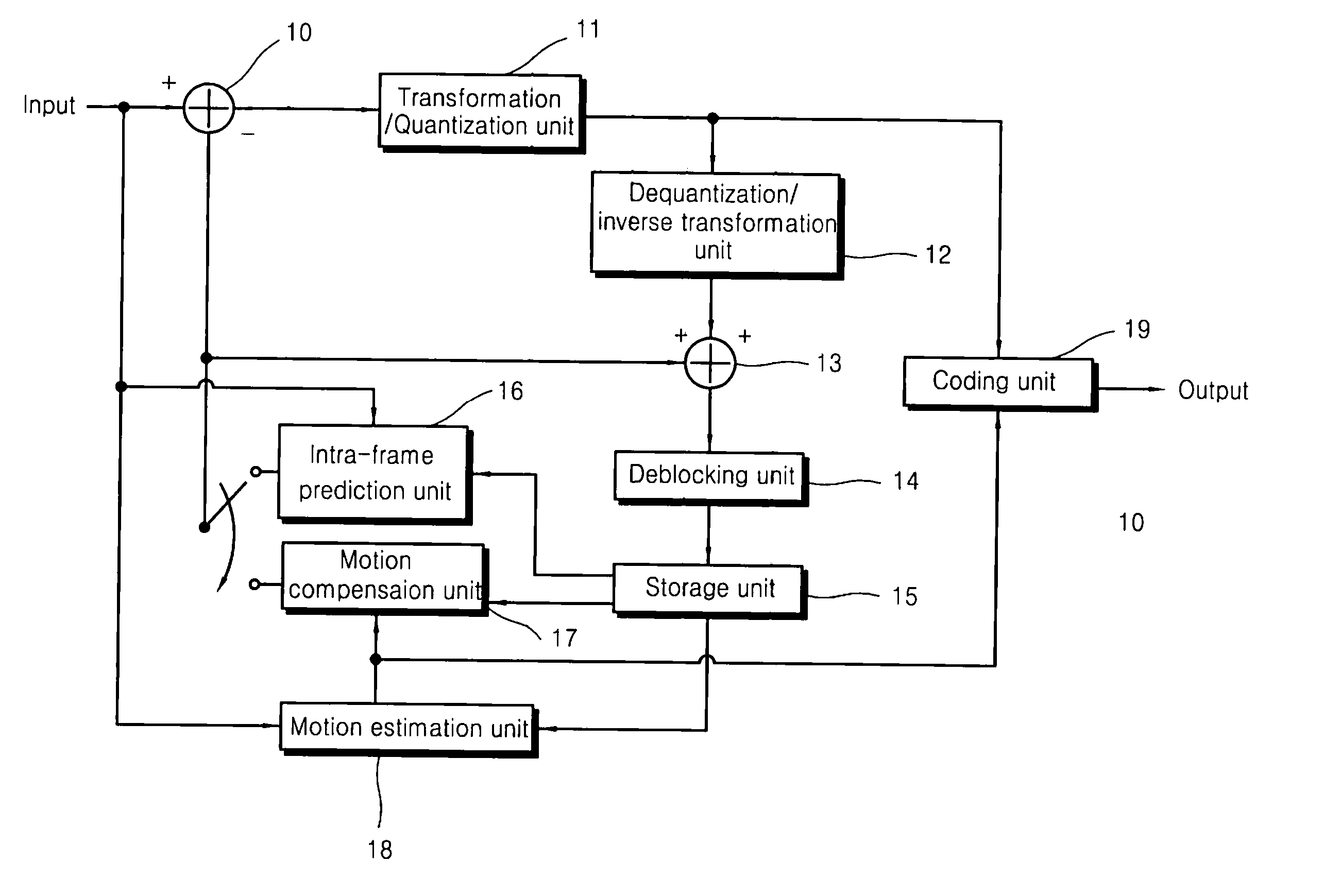
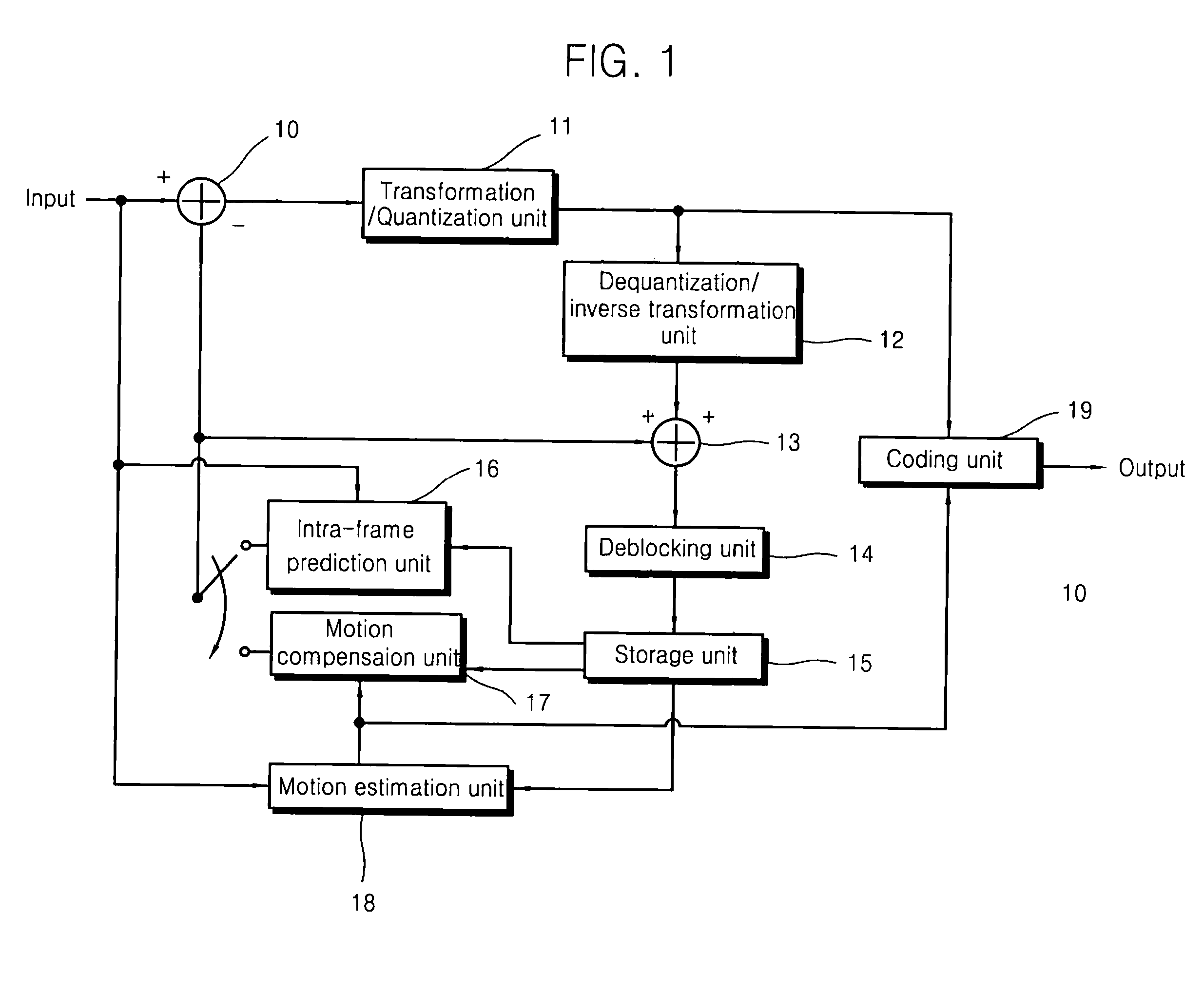
Intra-coding apparatus and method
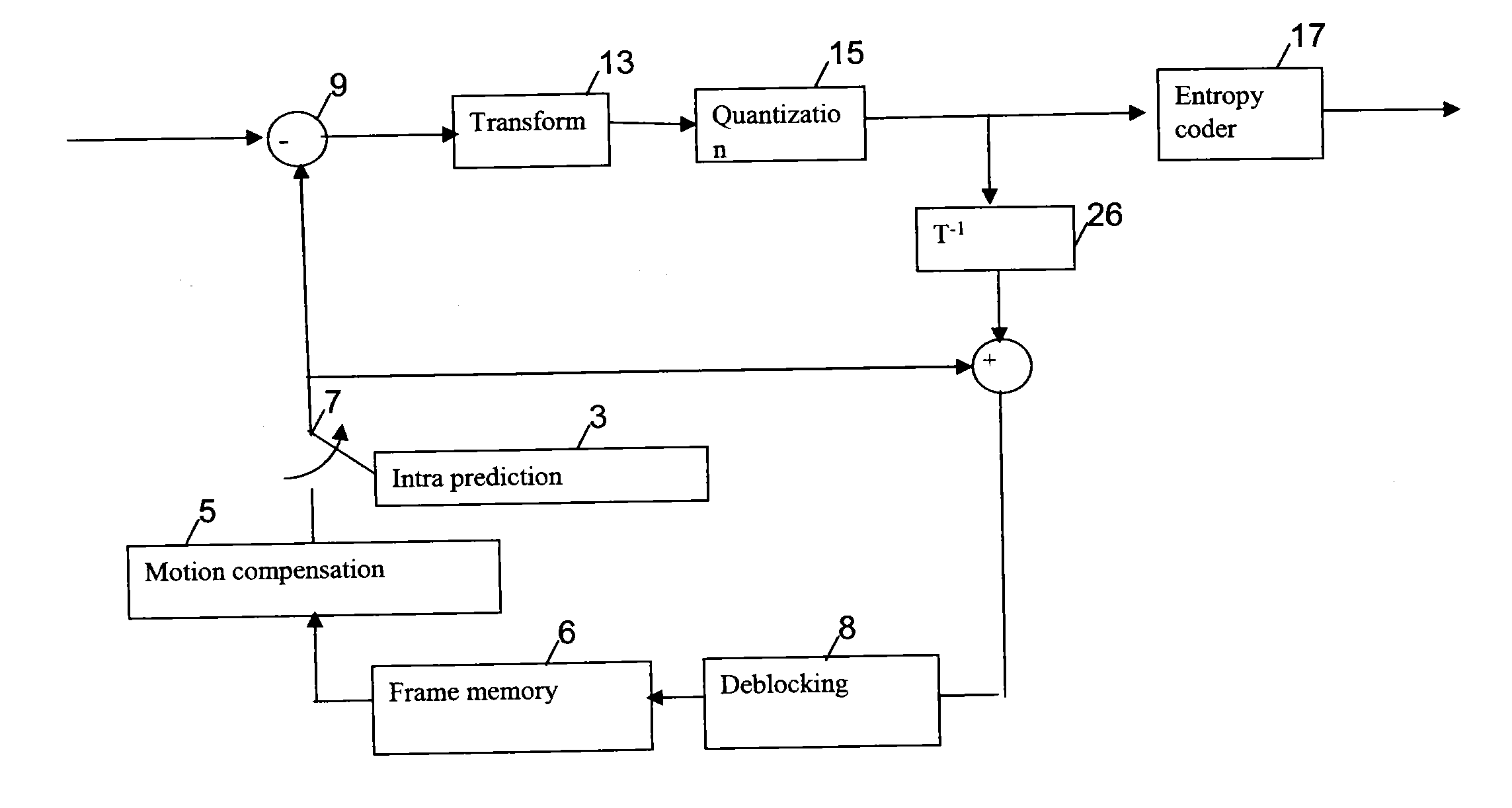
An intra-coding apparatus and method for coding an image including a plurality of macroblocks are provided. The intra-coding apparatus includes an intra-frame prediction unit determining an intra prediction mode using border pixels on borders between a current macroblock to be coded and adjacent macroblocks and generating a predicted macroblock corresponding to the current macroblock in the determined intra prediction mode; a subtractor outputting a difference between the current macroblock and the predicted macroblock; a transformation / quantization unit transforming the difference into a frequency band signal and quantizing the frequency band signal; and a coding unit coding a quantization result.
Owner:KOREA POLYTECHNIC UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Server-side support for seamless rewind and playback of video streaming
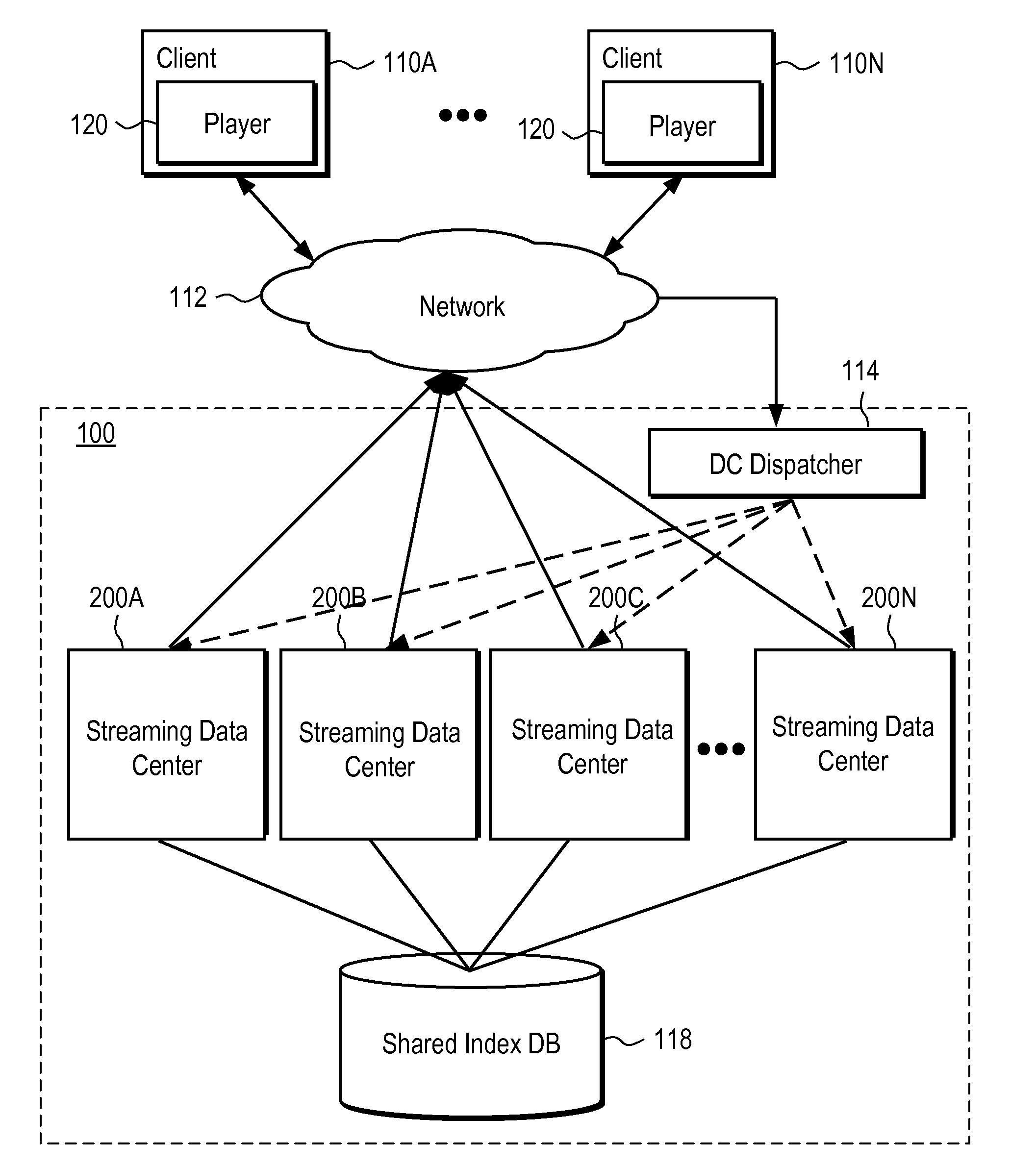
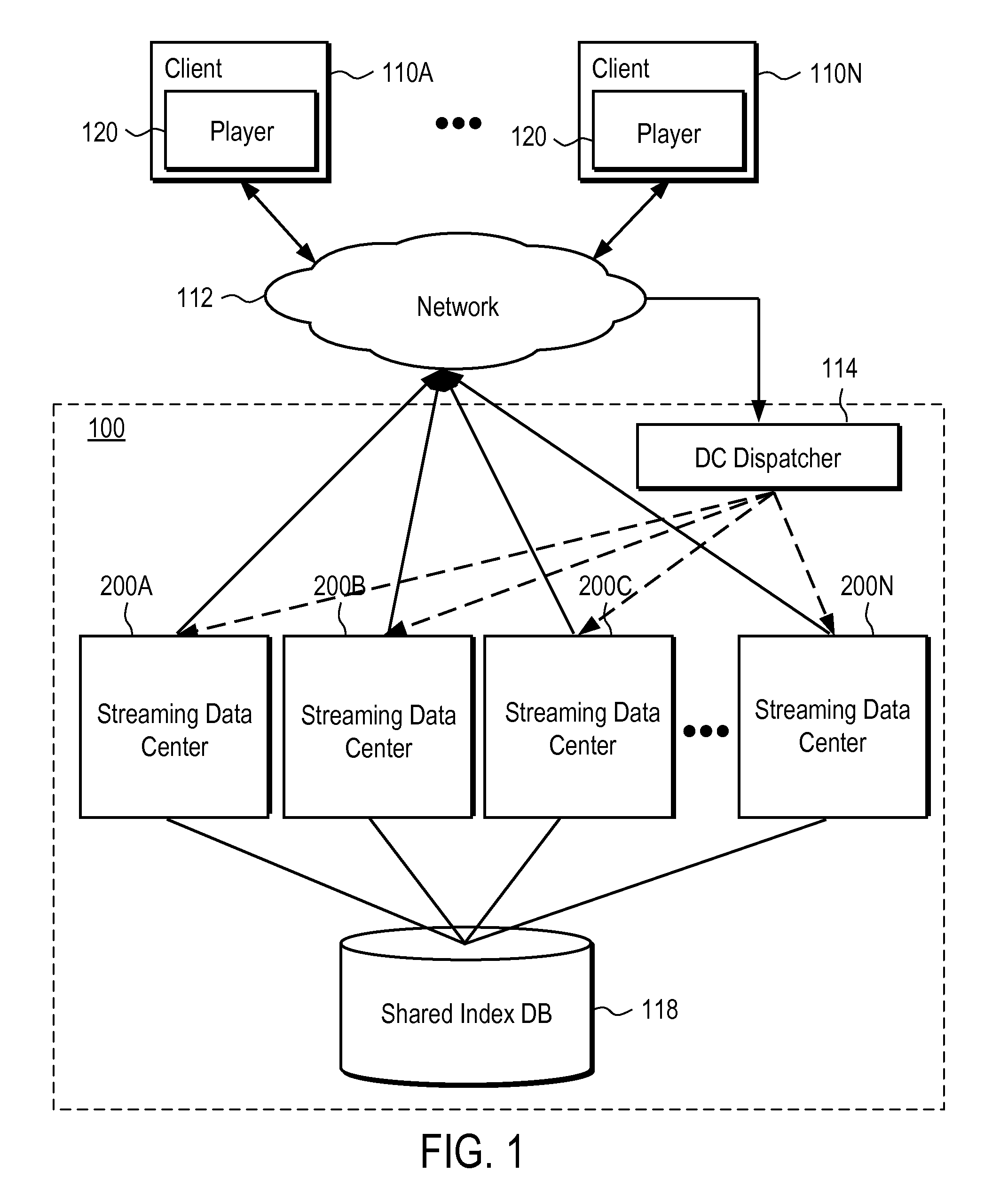
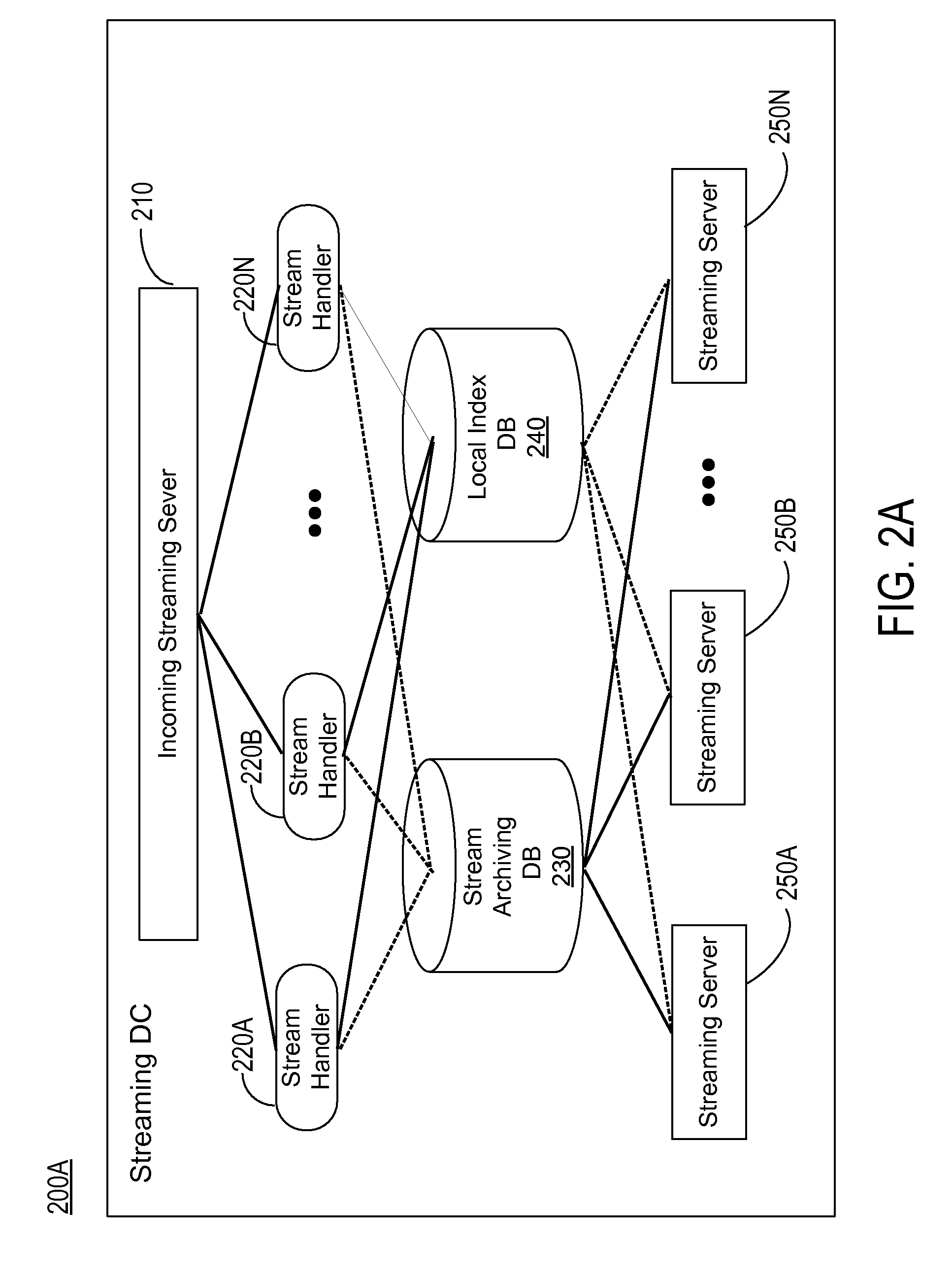
A system and method provide server side support for seamless, scalable rewind and playback of a video stream. A video stream is stored and indexed in a network storage place. A video stream can be indexed at frame level where each intra frame of the video stream has an index indicating the file offset and the time stamp of the intra frame in the video stream. A user request for rewinding of a video stream while the video stream is being broadcast is processed by extracting the rewinding time requirement from the user request. The extracted rewinding time value is used to calculate the requested file offset. The video stream starting at the requested time is retrieved and played back according to the user request. The system also provides server side support for seamless rewinding of a video stream and scalable system performance across multiple streaming data centers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Video encoder/decoder, method and computer program product that process tiles of video data
ActiveUS20120183074A1Maximum efficiencyMaximizing degreeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionGratingVideo encoding
In video encoding it is common to encode the image data to remove redundancies in the information to be transmitted. While the pixel data is usually arranged in pixel blocks, the blocks can be arranged in one or more groups of N×M blocks called tiles. The tiles avoid the need to send header information on a tile-by-tile or block-by-block basis, and simplifies parallel processing of the tiles. Bits from respective tiles may then be reformatted to recreate bits according to a raster-scan direction. This enables the decoder to receive the bits in a regular raster-scan format, but also have the ability to decode the tiles once the bits are reformatted. By partitioning an image into tiles of size N×M, it is possible to further exploit the intra-frame correspondence of images in a vertical direction as well as horizontal direction since the tiles need not destroy as many dependencies between blocks in a tile as if the blocks where organized in slices or slice groups.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
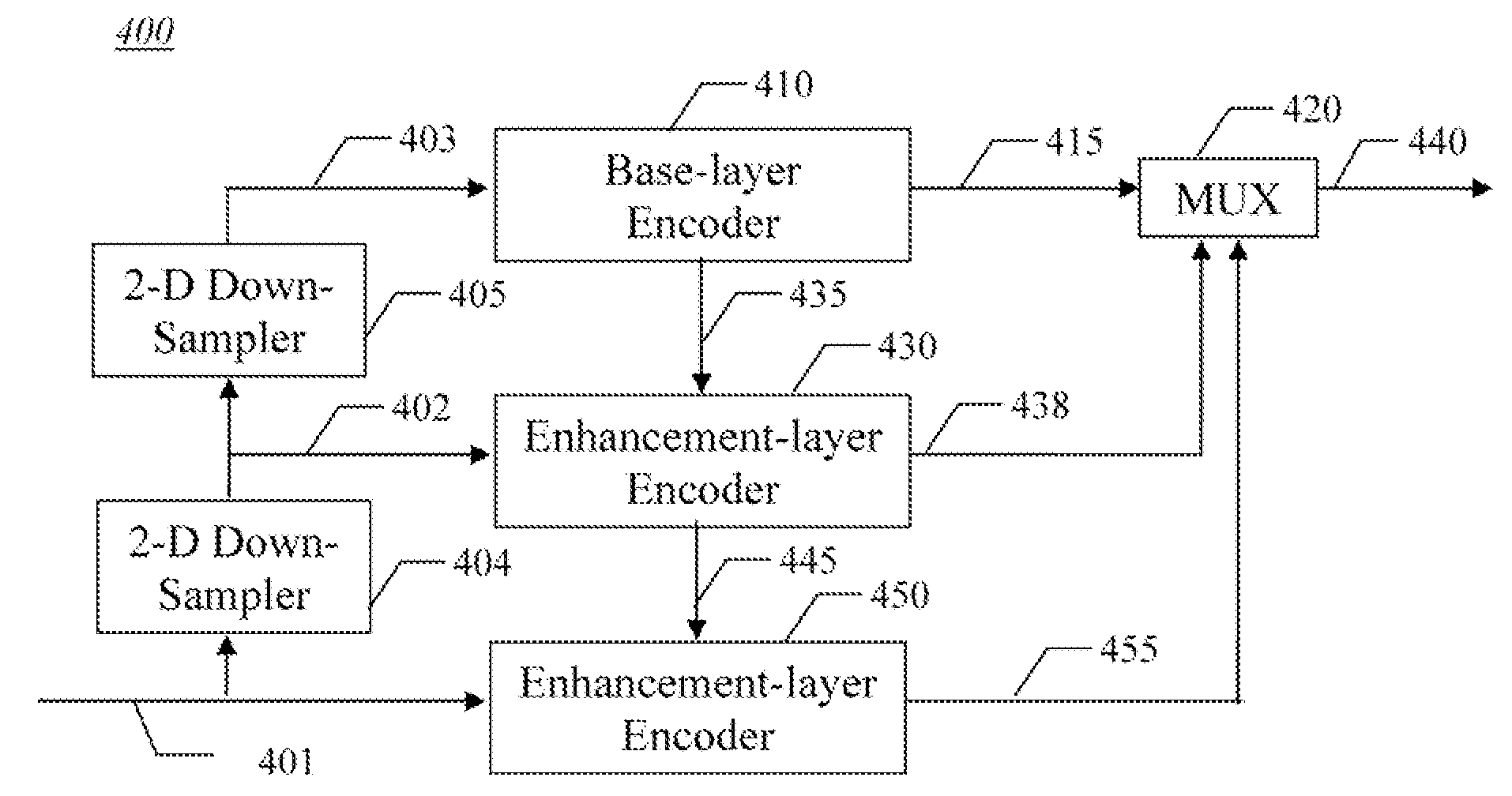
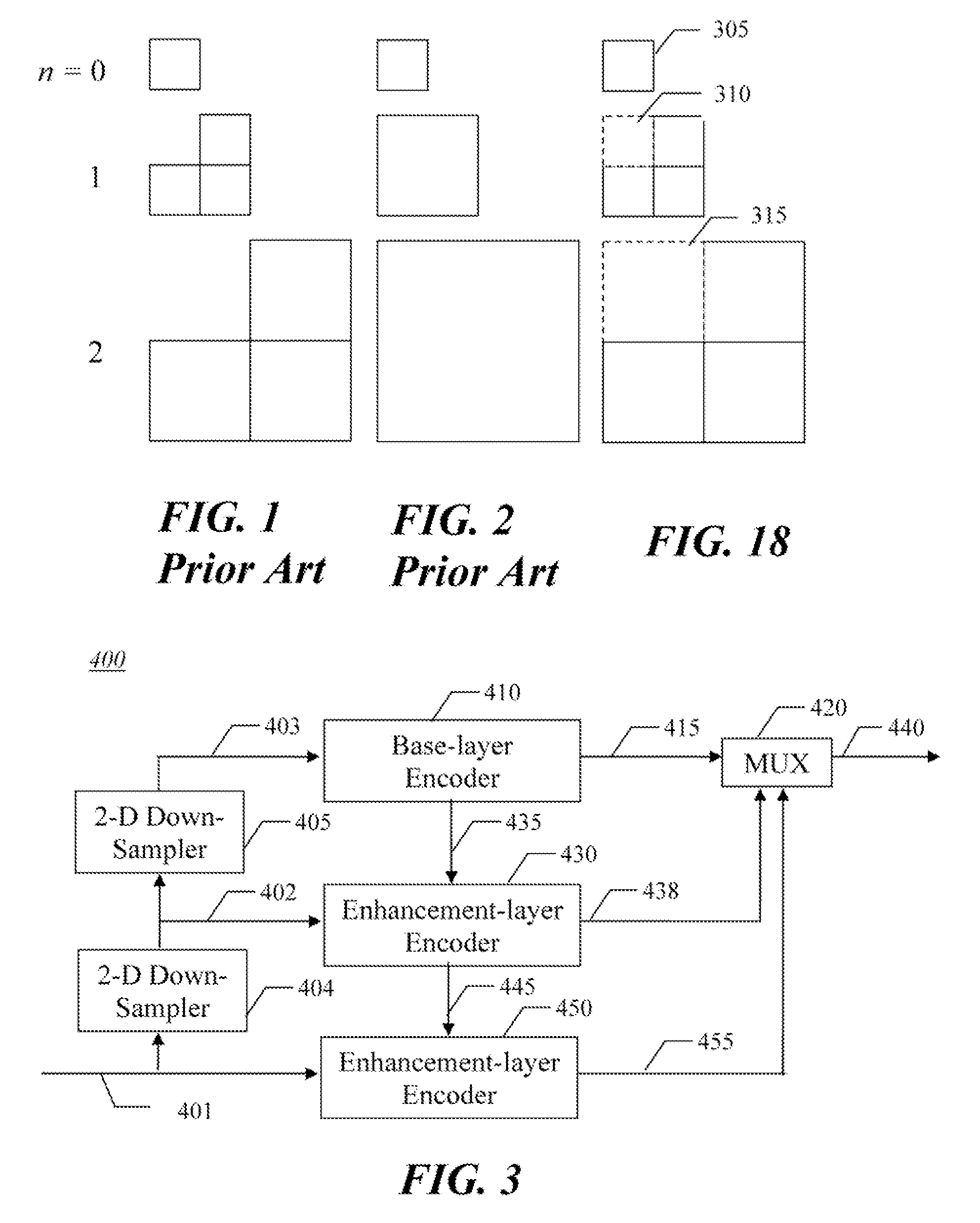
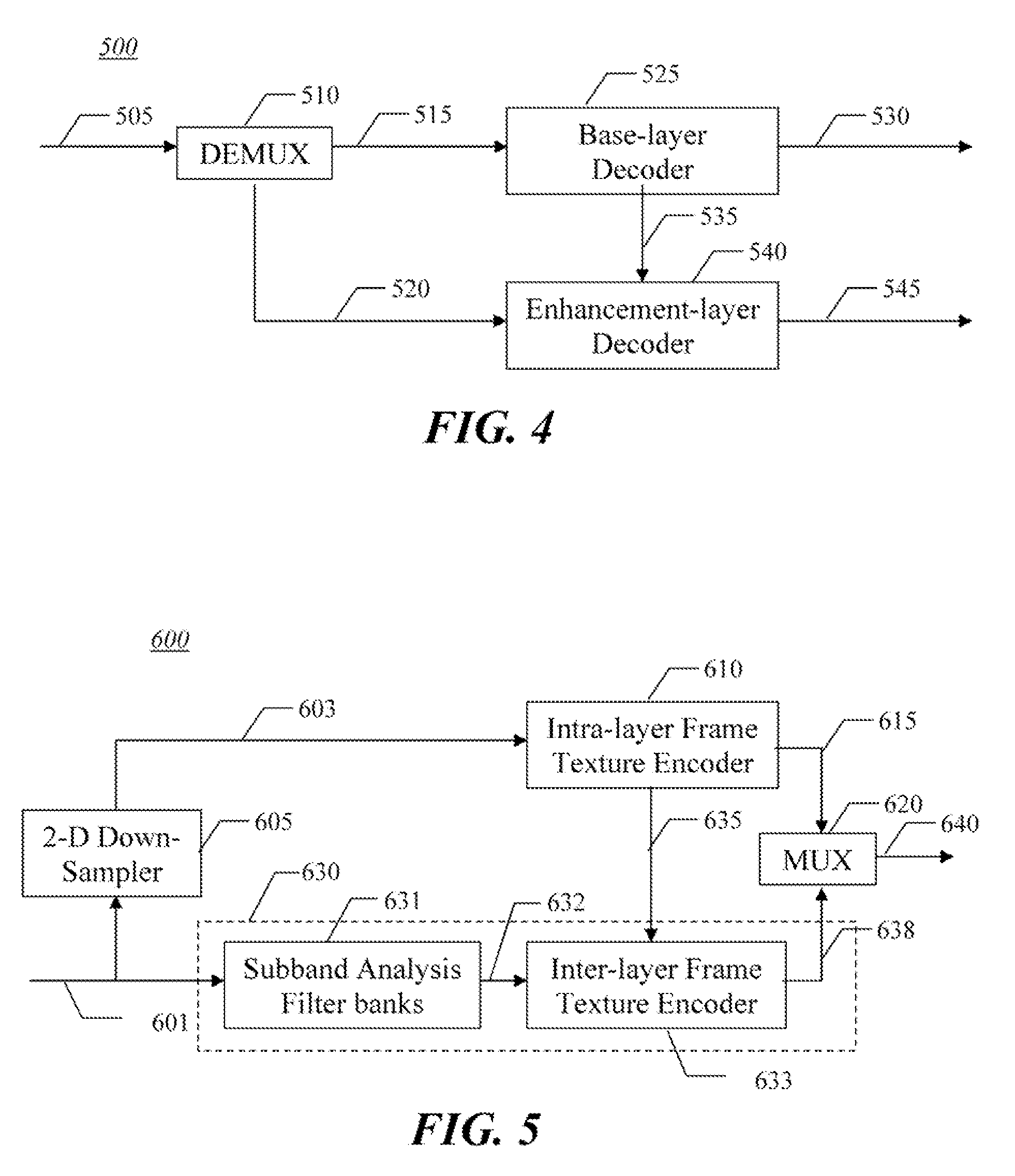
Method and apparatus for intra-frame spatial scalable video coding
InactiveUS20080095235A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamVideo encoding
An apparatus and method are for intra-frame spatial scalable video encoding. The method codes a low resolution base layer video bitstream from low resolution base layer video using a single layer encoder, and codes an enhancement layer in which individual videos frames are represented by wavelet coefficients for an LL residual sub-band, an HL sub-band, an LH sub-band; and an HH sub-band. The LL residual sub-band is generated as a difference of an LL sub-band and a recovered version of the base layer video bitstream.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
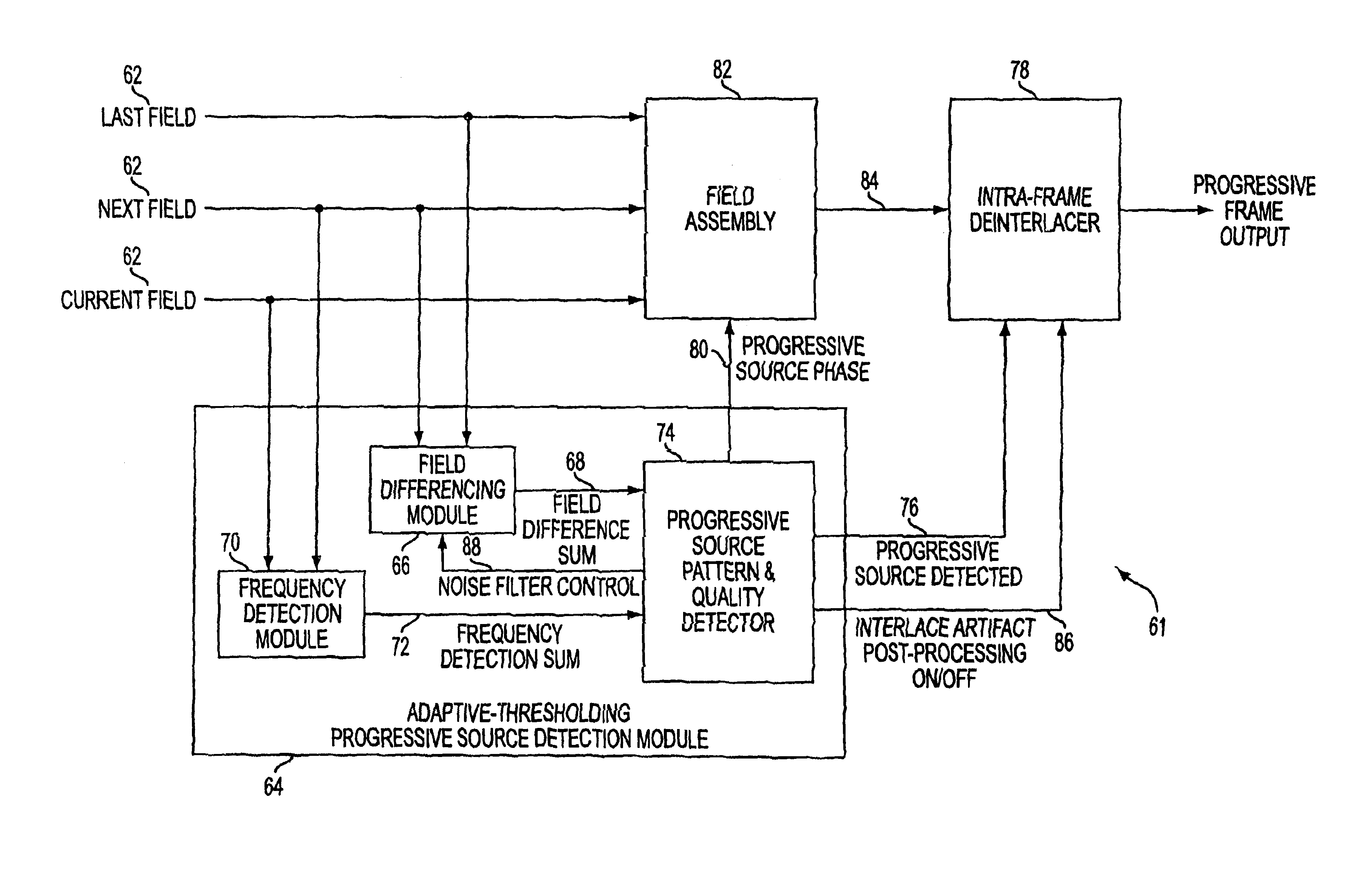
Method, system and article of manufacture for identifying the source type and quality level of a video sequence
InactiveUS6867814B2Reduce Motion ArtifactsAccurately determineTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsQuality levelInterlaced video
A deinterlacing system which converts an interlaced video stream into a progressive video stream is disclosed. The deinterlacing system includes a field assembly responsive to a last field, a next field, a current field and progressive source phase and operative to develop a progressive output frame, a source detection module responsive to last, next and current fields and operative to develop a progressive source phase and a progressive source detected and an intra-frame deinterlacer responsive to the progressive output frame and the progressive source detected and operative to develop a progressive frame output.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
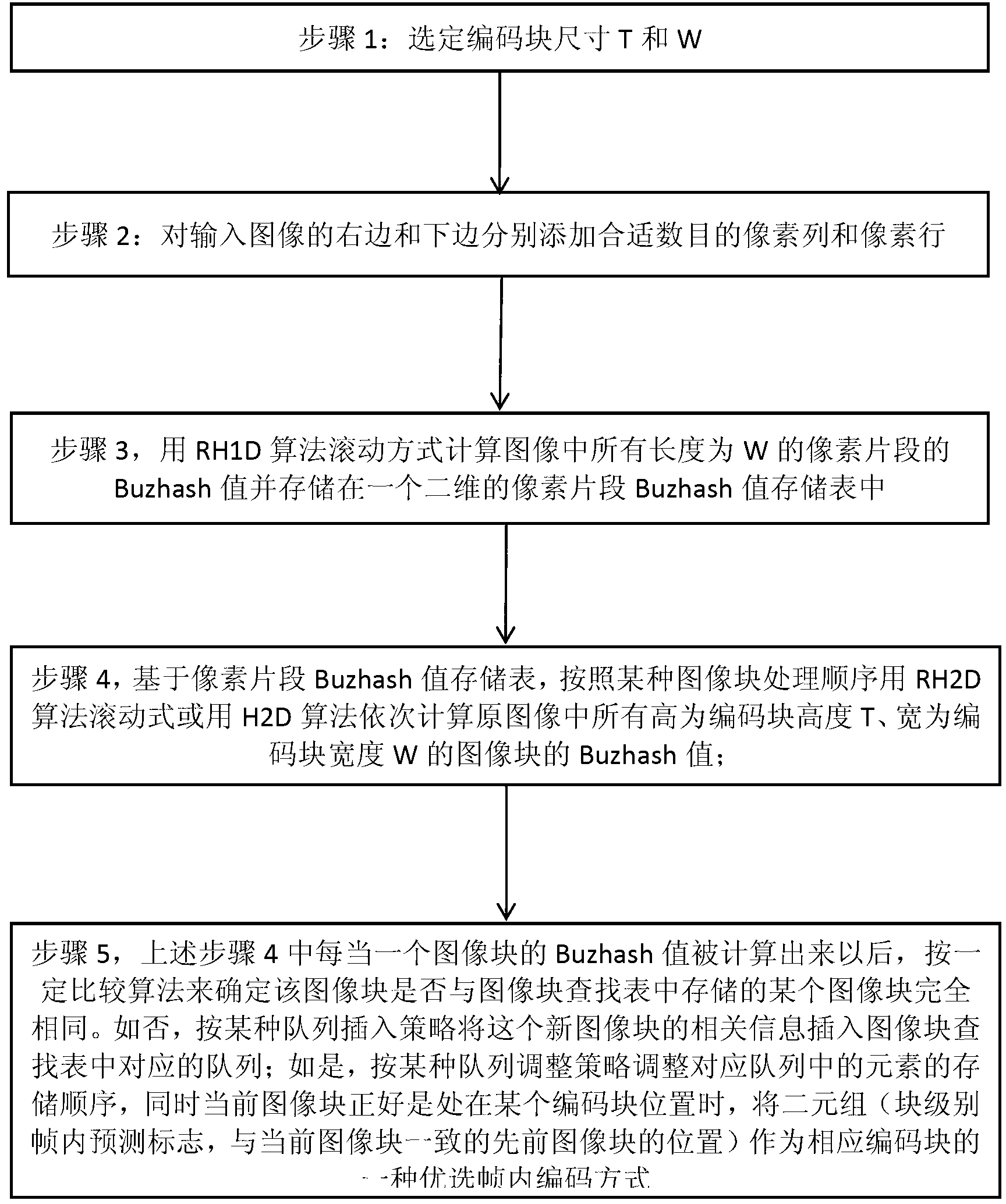
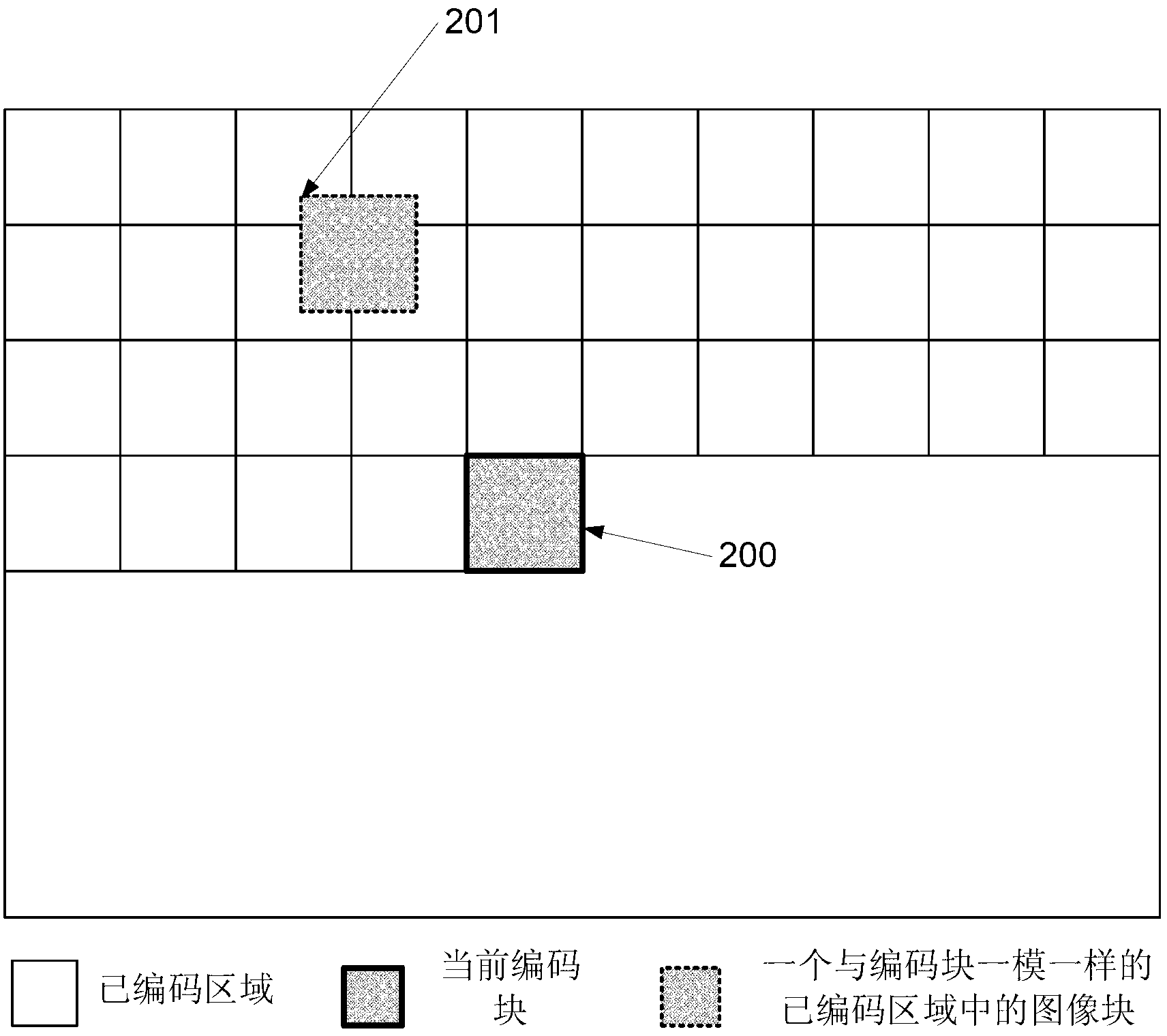
Intra-frame coding method based on rolling hush and block-level intra-frame prediction
InactiveCN103281538AExplicit Computational ComplexityTelevision systemsPattern recognitionCoding block
The invention provides an intra-frame coding method based on a rolling hush and block-level intra-frame prediction of the technical field of image processing. A hash function with a rolling type calculation characteristic and a corresponding rolling type algorithm are selected and utilized to set up an image block lookup table about positional information contained in an image coded area of various image blocks with different pixel contents and hash values of the pixel contents of the image blocks, the image block lookup table is used for judging whether a current image block to be coded is a stored image block in the image block lookup table or not, and two-tuples further serve as coding information of the current image block to be coded or adding is carried out on the image block lookup table. According to the intra-frame coding method, a number of repeated image blocks existing in screen images are fully utilized to further improve intra-frame compressibility, on the premise that calculation expenditures at worst are guaranteed, little calculation expenditures are used for determining whether a prediction block the same as the current image block to be coded exists in the image coded area or not, and when a number of repeated image blocks exist in the screen images, the intra-frame coding method can obtain higher compressibility compared with an existing method.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
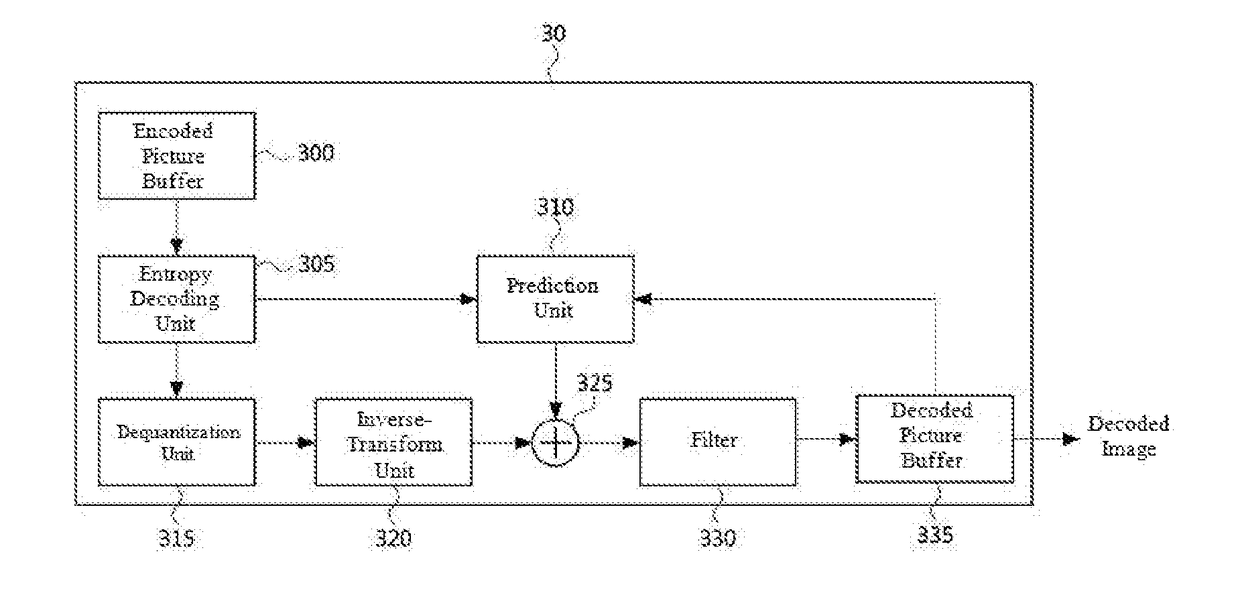
Method and device for encoding and decoding intra-frame prediction
InactiveUS20180160113A1Improve forecast accuracyImprove referenceDigital video signal modificationParallel computingIntra-frame
A method and a device for encoding and decoding intra prediction are disclosed. An image decoding method for performing intra prediction comprises the steps of: receiving a bitstream including data on prediction modes of a current block and a block adjacent to the current block; extracting the data from the received bitstream so as to confirm the prediction mode of the adjacent block; determining whether a boundary pixel within the adjacent block can be used as a reference pixel for the current block in consideration of the prediction mode of the adjacent block; obtaining the reference pixel of the current block according to the determined result; generating a prediction block predicted in the frame on the basis of the obtained reference pixel; and decoding the current block by using the generated prediction block.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Image encoding apparatus, method of controlling the same and computer program
InactiveUS20090310678A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionIntra-frameComputer science
An image encoding apparatus that performs intra-frame predictive encoding is provided. The apparatus includes a partitioning unit configured to partition an inputted macroblock into blocks as processing units, an encoding unit configured to encode each of blocks to be processed using a prediction value for each pixel contained in the block to be processed, the prediction value being calculated by referring to pixels contained in other blocks, and a sorting unit configured to sort the encoded blocks in a predetermined encoding order. The encoding unit starts encoding in an order in which the first block for which all the pixels to be referred to are available for calculation of the prediction value is the first to be encoded, and the encoding is performed by pipeline processing.
Owner:CANON KK
Adaptive Joint Source and Channel Coding Scheme for H.264 Video Multicasting Over Wireless Networks
InactiveUS20100226262A1Improve system performanceImprove performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTopology informationJoint source and channel coding
A method and apparatus for estimating packet loss rate are described including calculating a real packet loss rate in a time slot at the end of the time slot, estimating average packet loss rate for a subsequent time slot, estimating variance of packet loss rate for the subsequent time slot and estimating the packet loss rate for the subsequent time slot. A method and apparatus and also described for dynamically allocating available bandwidth for video multicast including selecting an intra-frame rate, determining a packet loss rate threshold, receiving user topology information, receiving channel conditions for each user, determining an optimal operation point for encoding and transmitting video frames in a subsequent time slot, adapting dynamically quantization parameters and a forward error correction code rate, encoding the video frames using the quantization parameters and applying forward error correction code with the forward error correction code rate to data packets of the video frames to generate forward error correction packets.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
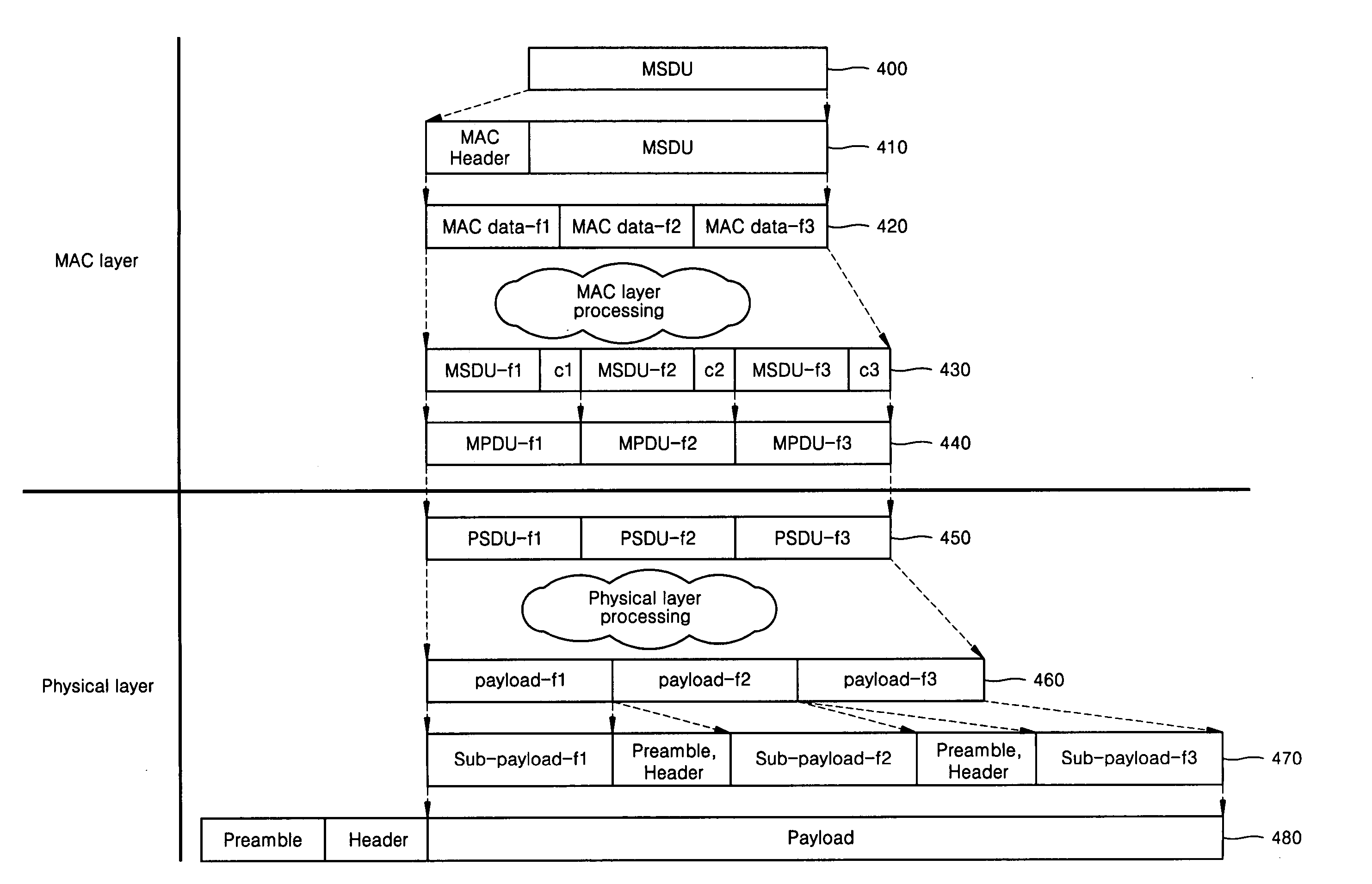
Method of dividing a payload intra-frame
InactiveUS20050111451A1Improve network throughputMinimizing deteriorationError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementPhysical layerCarrier signal
Provided is a method of dividing a payload intra-frame for improving throughput of a carrier sensing multiple access / collision avoidance (CSMA / CA) wireless communication network. The payload intra-frame dividing method includes a data frame dividing step and a physical layer frame generating step in which a physical layer receives a plurality of data frames from an upper layer within a range of the maximum data frame length the physical layer can transmit and transmits the data frames as a single physical layer data frame. Furthermore, an acknowledge (ACK) frame is provided, which can minimize the deterioration of throughput even when a data frame, which has been divided into a plurality of data frames and transmitted as a single data frame, is required to be re-transmitted because an error is generated in the data frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Undamaged encoding and decoding method and system based on interweave forecast
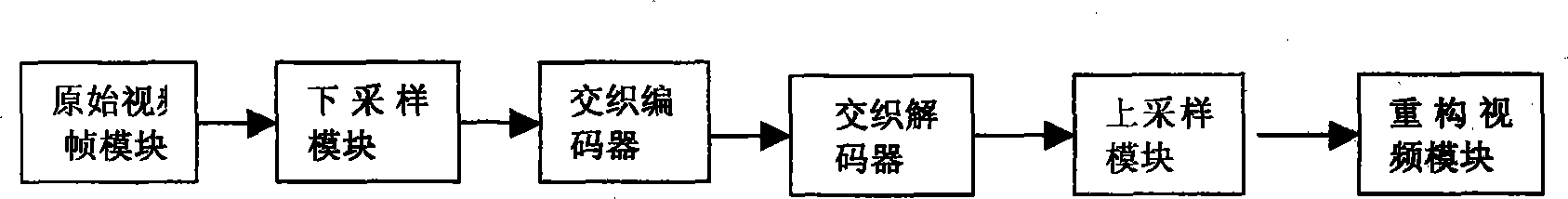
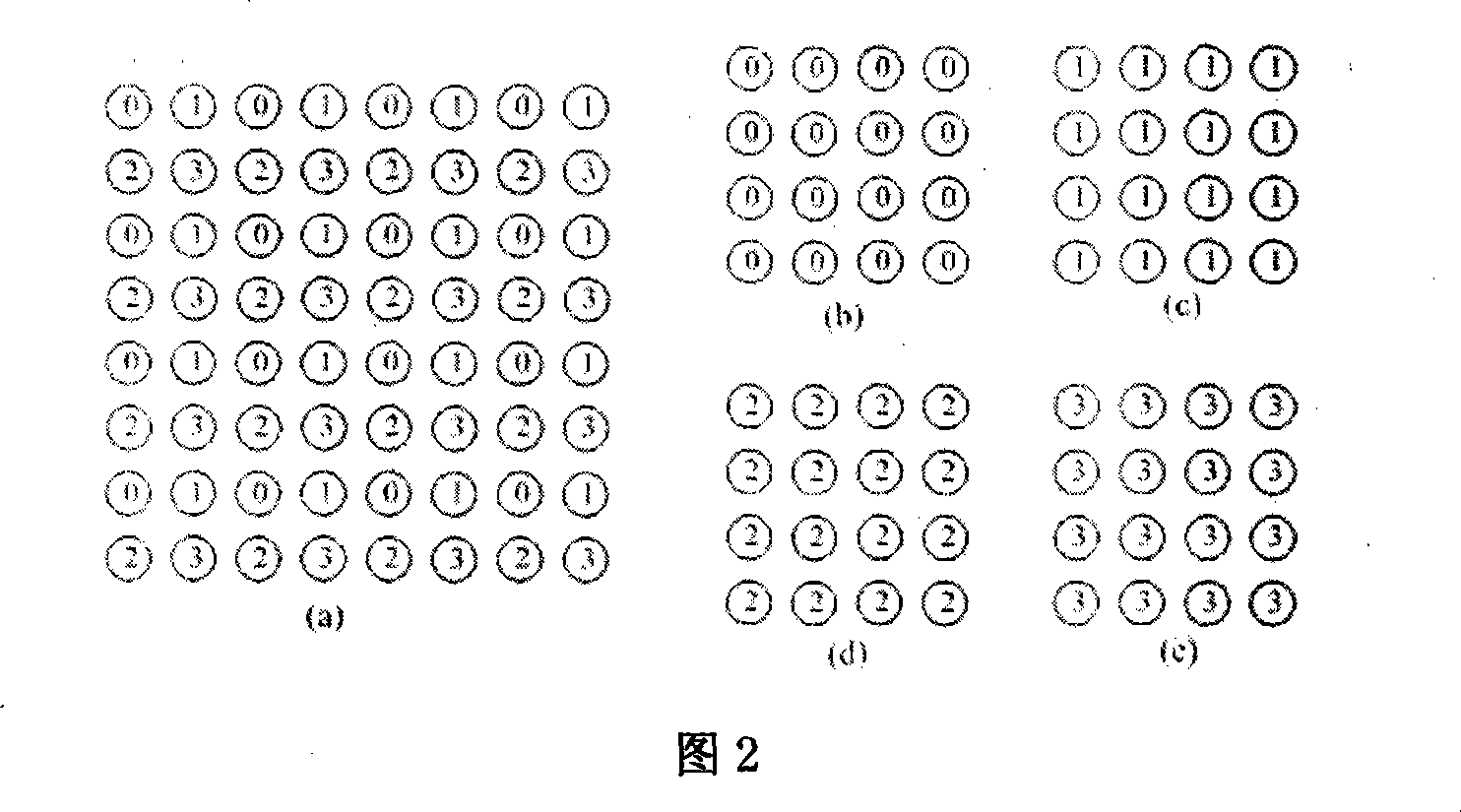
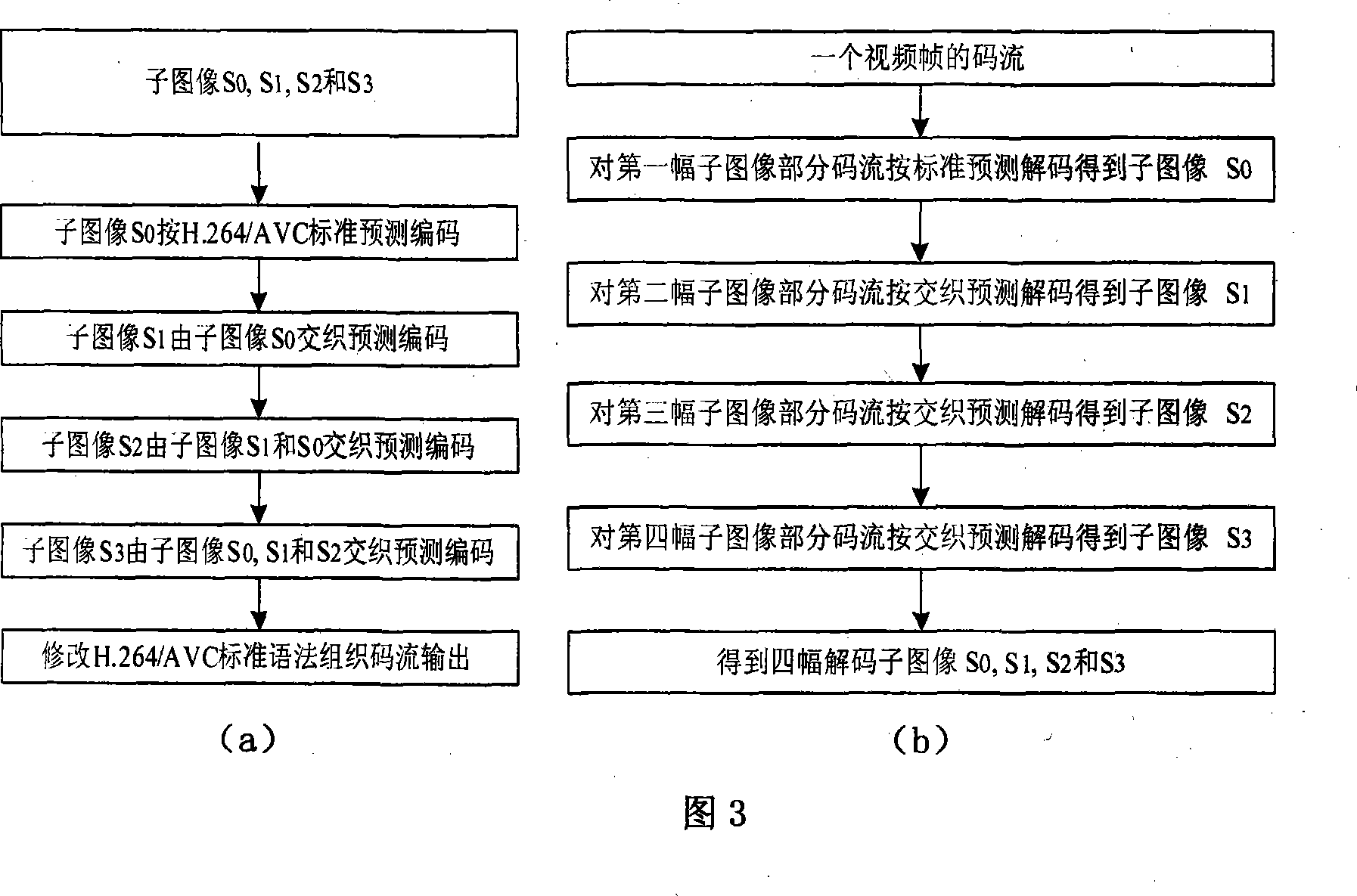
ActiveCN101252686ASignificant improvementFine forecastColor television with pulse code modulationTelevision systemsVideo encodingLossless compression
The invention relates to a video intraframe lossless encoding and decoding method based on interleaving prediction and the system thereof, and belongs to the technical field of the video encoding and decoding for signal processing. In the encoder end, each intra-frame coding frame (I frame) is down-sampled to form four subimages in certain sequence, encoding based on standard prediction is adopted for the first subimage, and decoding based on the interleaving prediction is adopted for the three subsequent subimages in sequence; in the decoder, each received I frame code stream is used for decoding the code stream of the first subimage section according to the standard prediction, and decoding the code stream of the three subsequent subimages on the basis of the pixel level interleaving prediction, and finally up-sampling combination is performed to the four decoded subimages to obtain I frame decoding image. Compared with the standard prediction method, the interleaving prediction method of the invention is provided with better prediction performance, thereby improving the video intraframe lossless compression performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com