Patents
Literature
193 results about "Second quantization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Second quantization, also referred to as occupation number representation, is a formalism used to describe and analyze quantum many-body systems. In quantum field theory, it is known as canonical quantization, in which the fields (typically as the wave functions of matter) are thought of as field operators, in a manner similar to how the physical quantities (position, momentum, etc.) are thought of as operators in first quantization. The key ideas of this method were introduced in 1927 by Paul Dirac, and were developed, most notably, by Vladimir Fock and Pascual Jordan later.
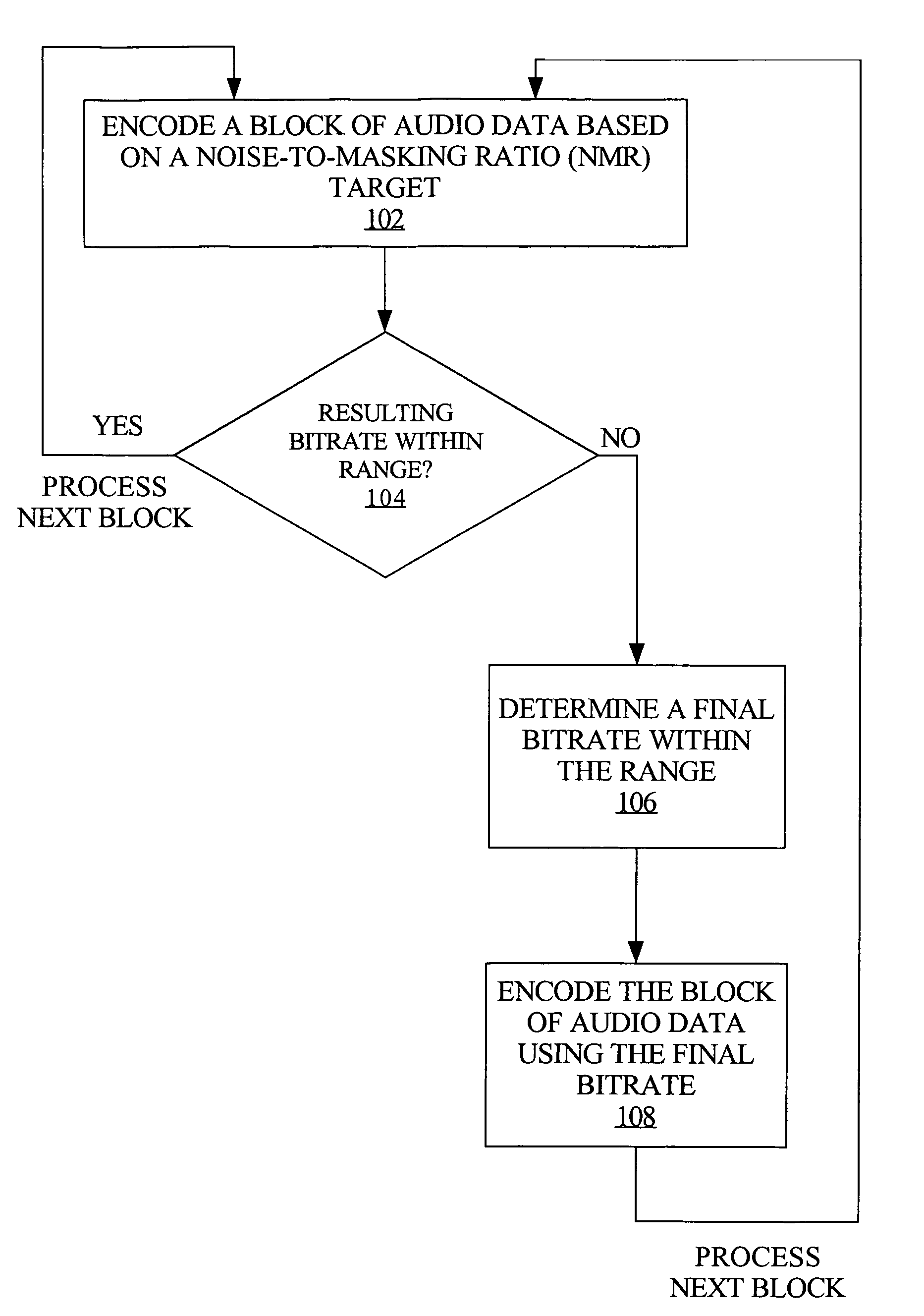
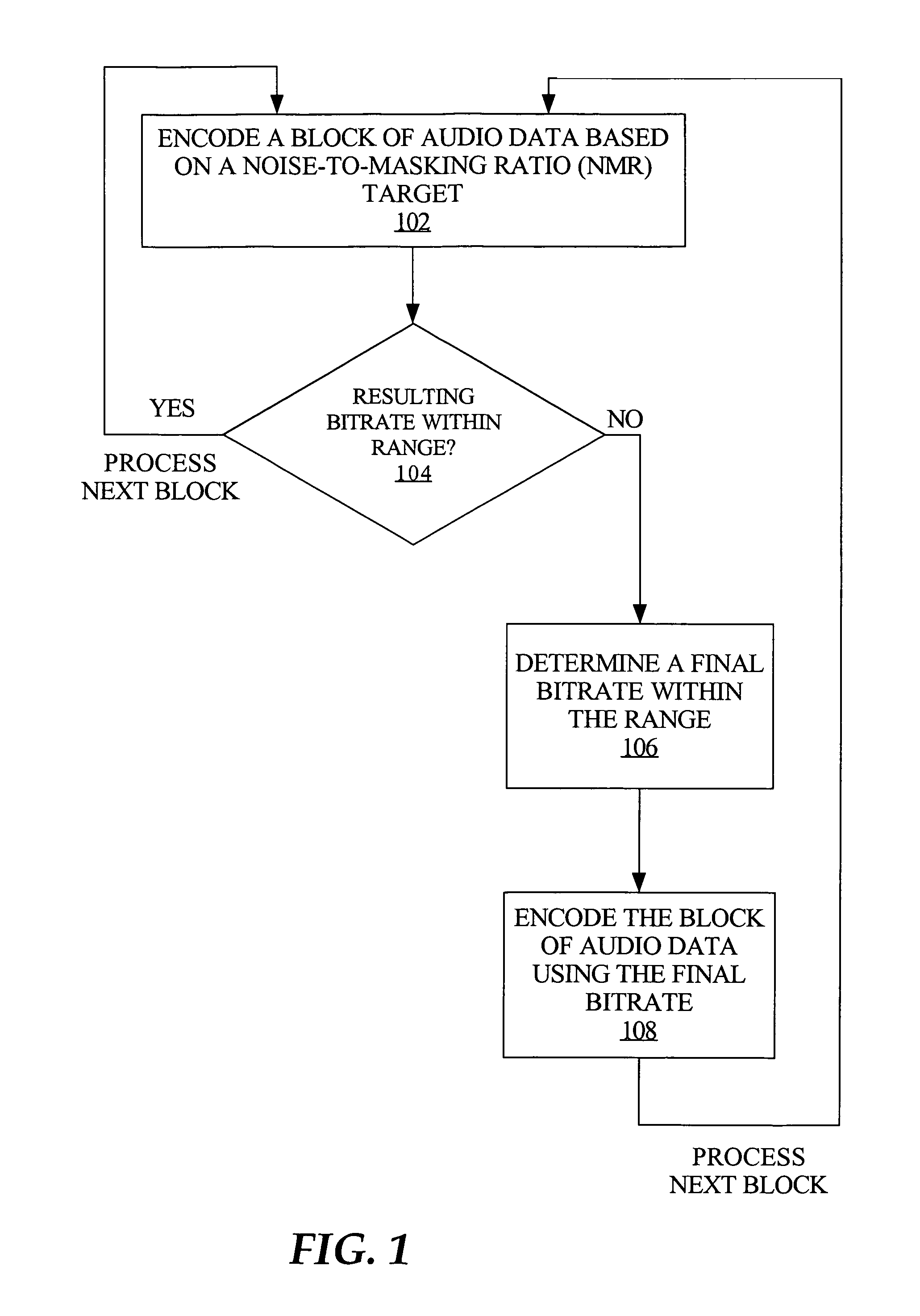
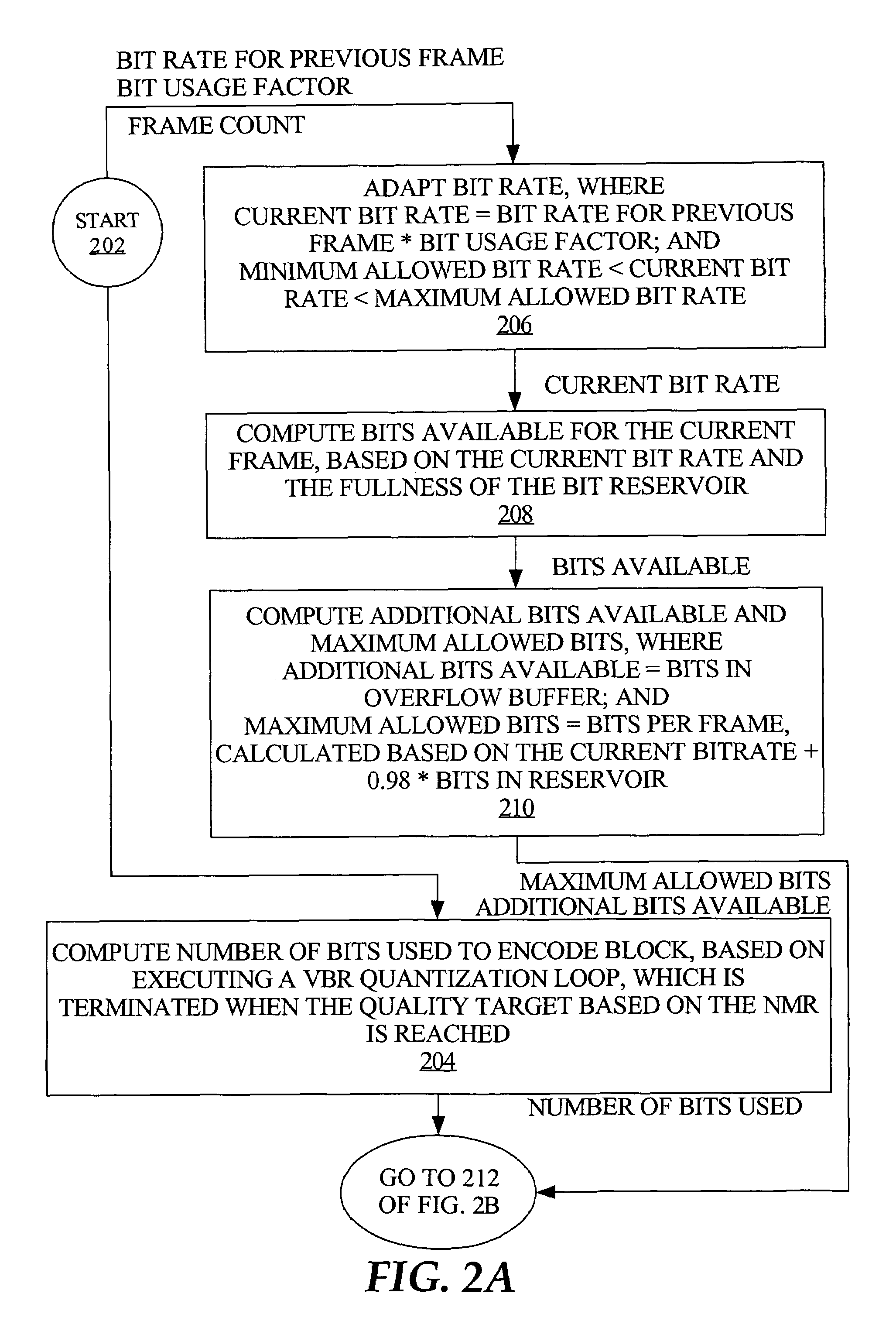
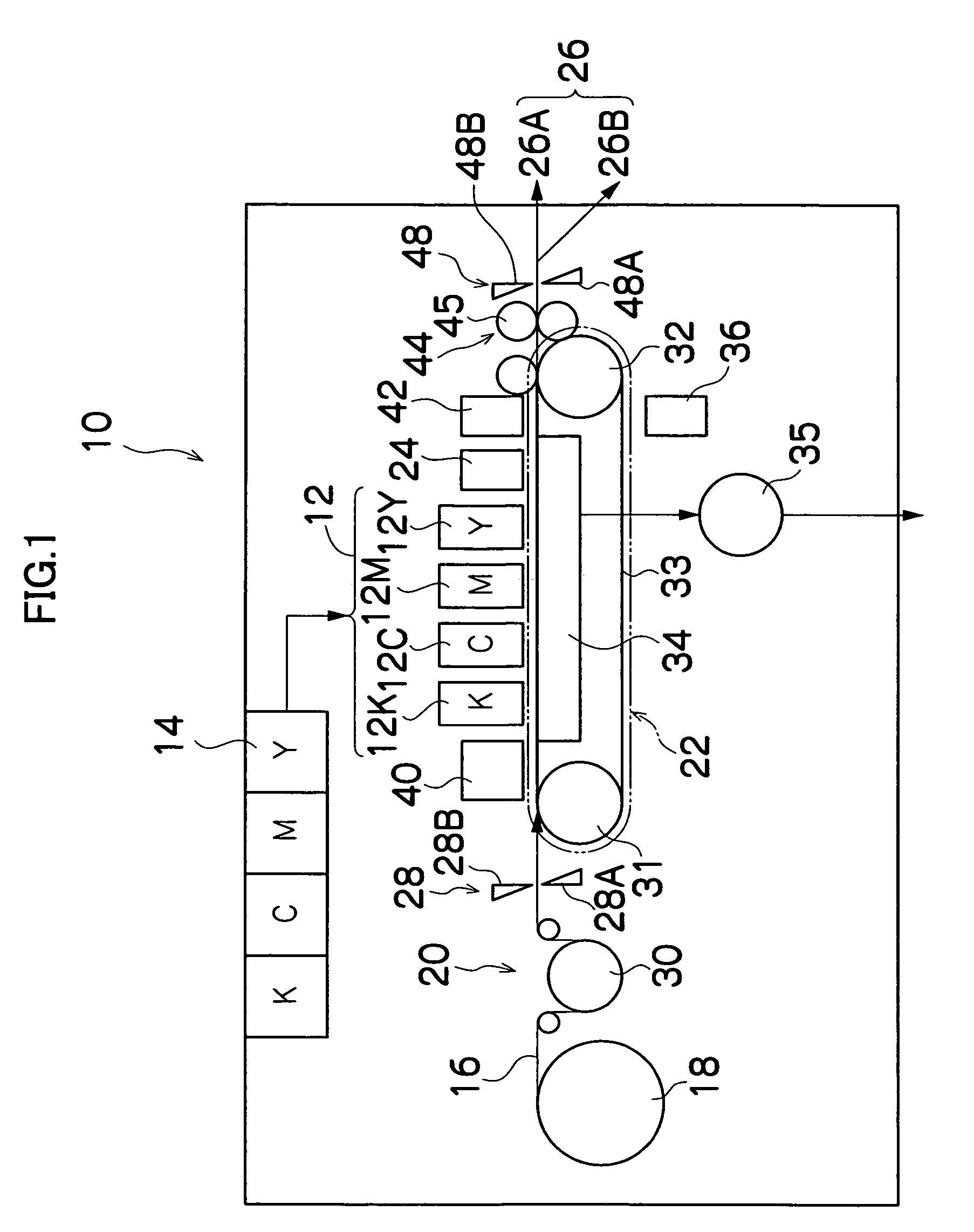
Bitrate constrained variable bitrate audio encoding
ActiveUS7634413B1Excessively high bitratesImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisCoding blockSound quality
A hybrid audio encoding technique incorporates both ABR, or CBR, and VBR encoding modes. For each audio coding block, after a VBR quantization loop meets the NMR target, a second quantization loop might be called to adaptively control the final bitrate. That is, if the NMR-based quantization loop results in a bitrate that is not within a specified range, then a bitrate-based CBR or ABR quantization loop determines a final bitrate that is within the range and is adaptively determined based on the encoding difficulty of the audio data. Excessive bitrates from use of conventional VBR mode are eliminated, while still providing much more constant perceptual sound quality than use of conventional CBR mode can achieve.
Owner:APPLE INC
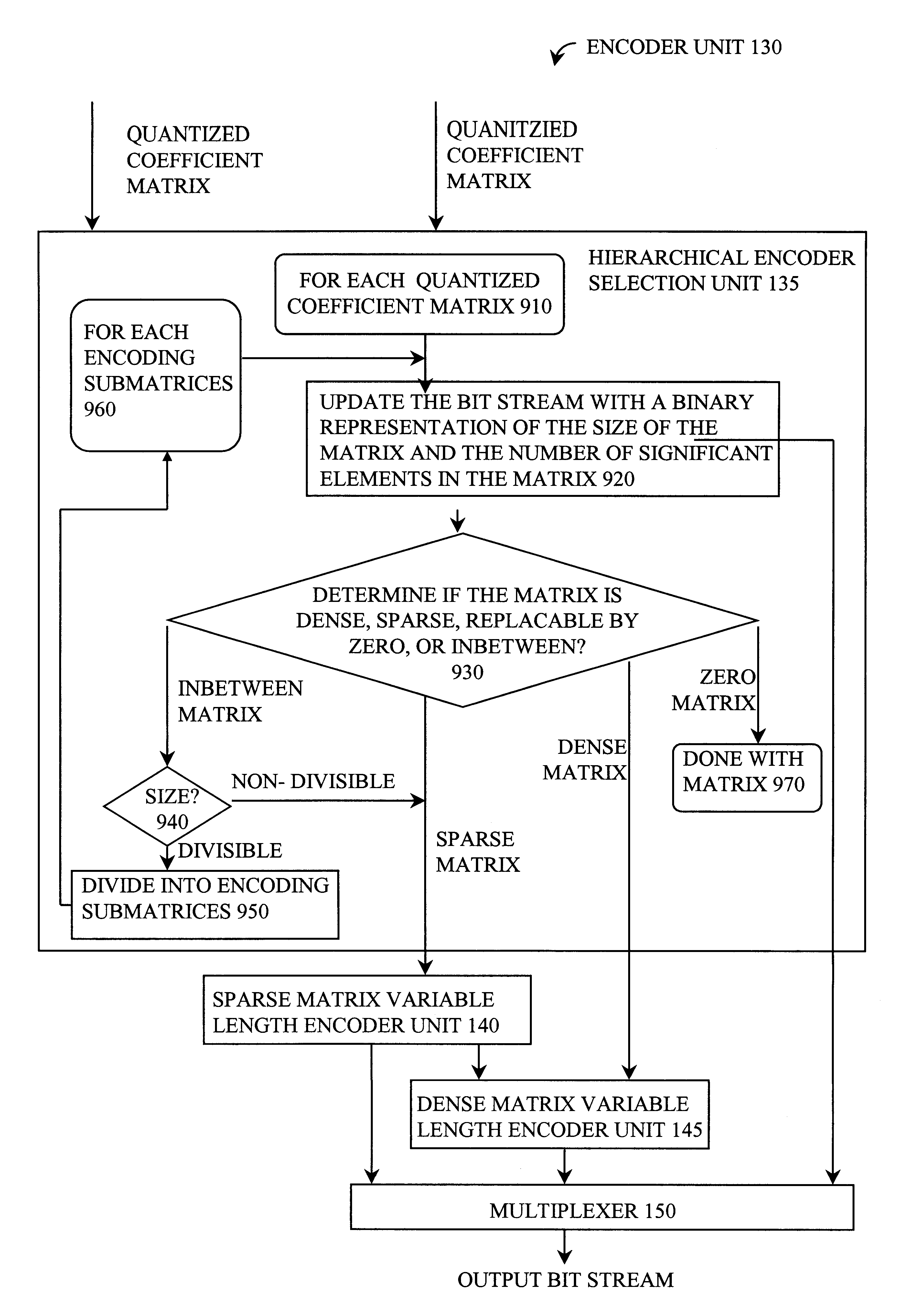
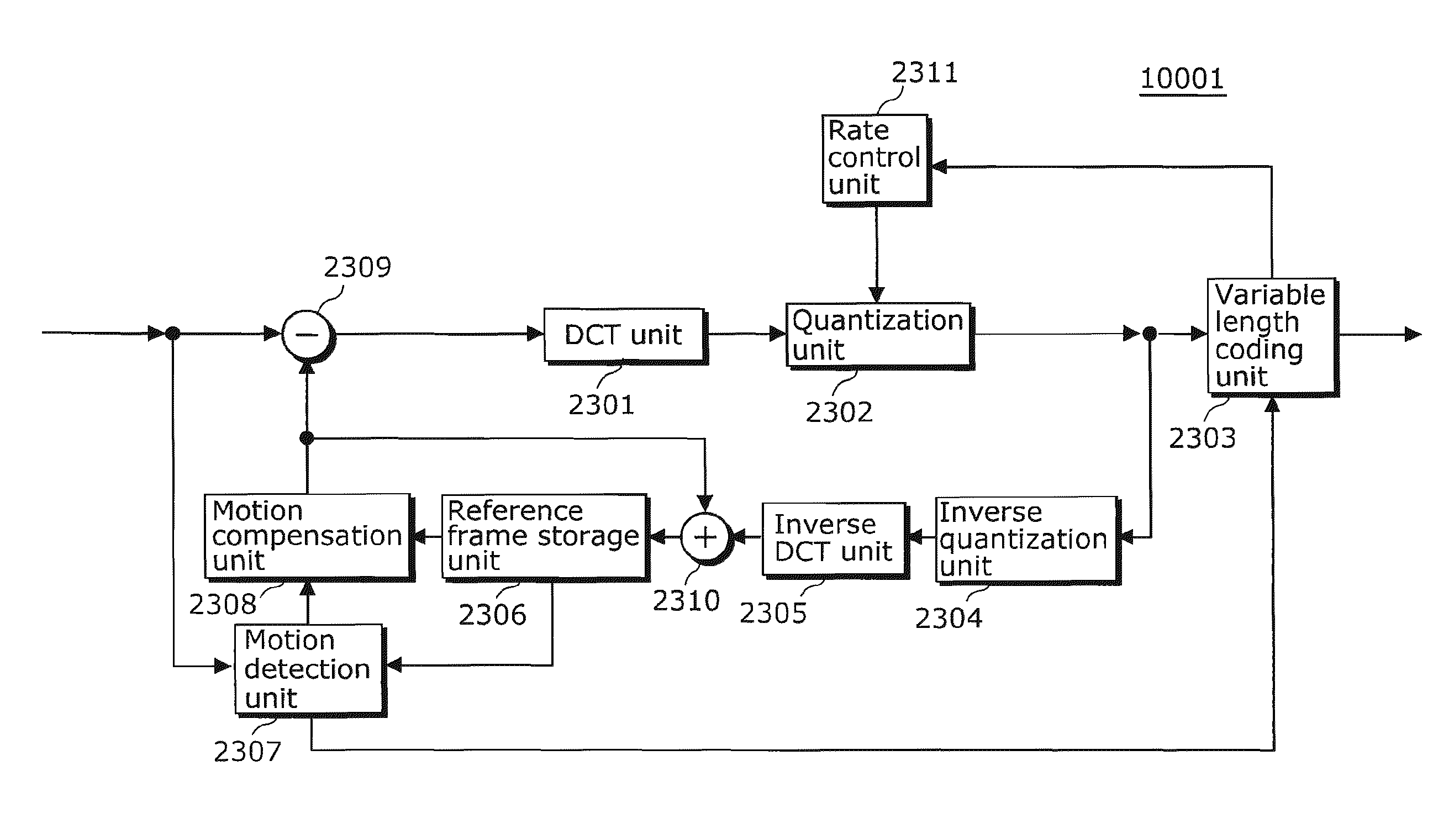
Video compression and decompression using dynamic quantization and/or encoding
InactiveUS6249614B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionQuantization matrix
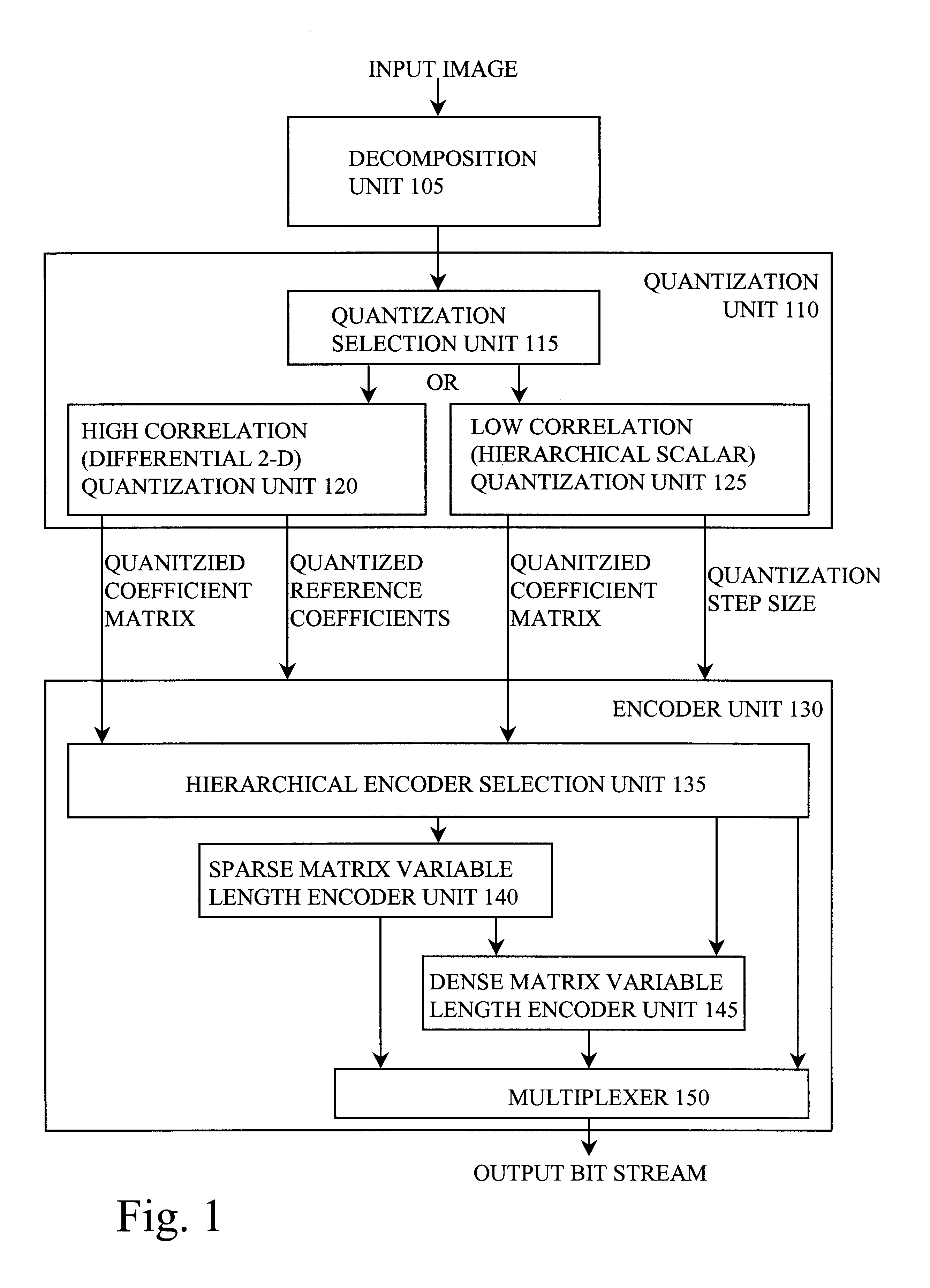
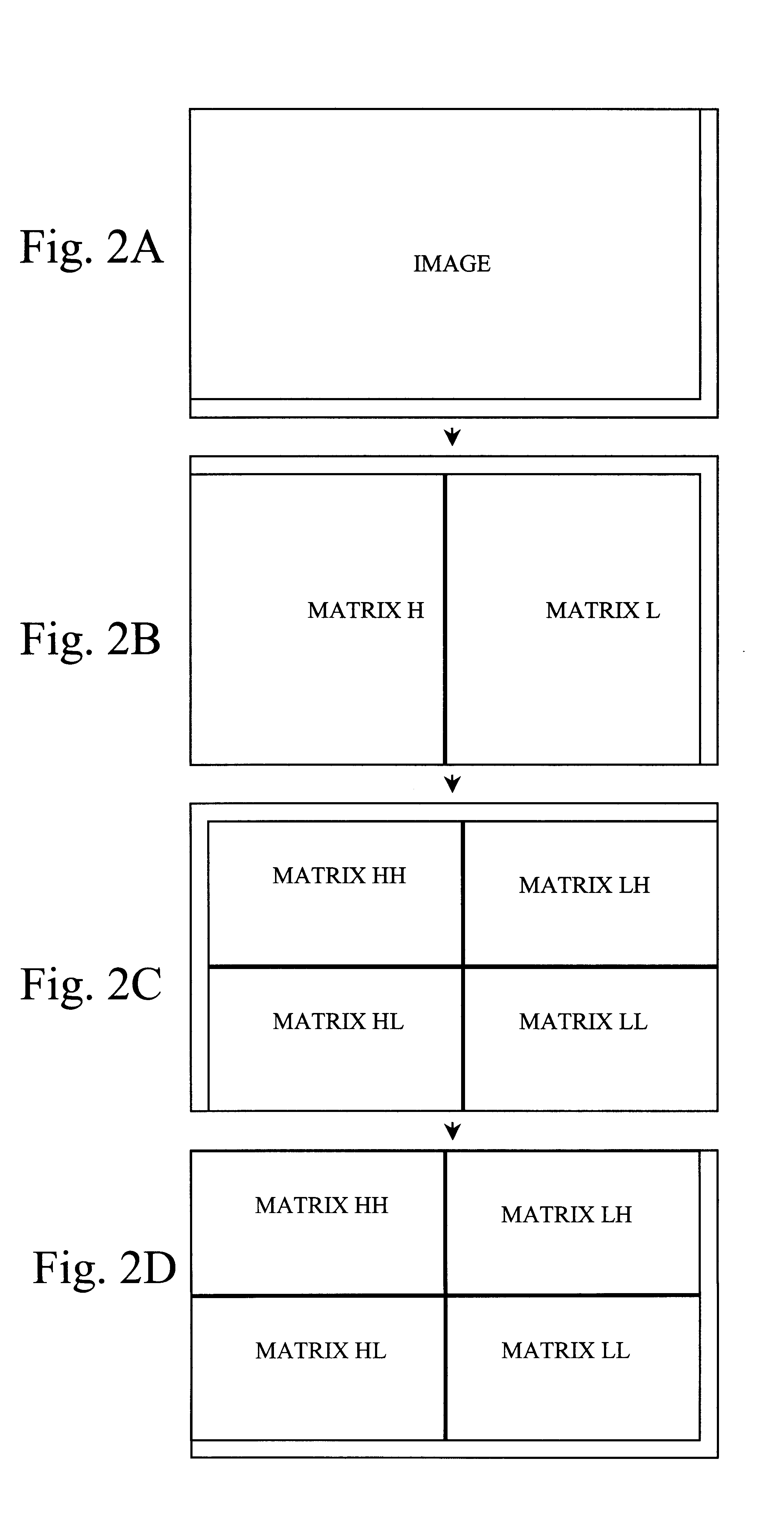
A method and apparatus for performing video compression and decompression using dynamic quantization and / or encoding. According to one aspect of the compression method, an image is recursively filtered into its constituent components each represented by a matrix of coefficients. Next, the level of correlation of a first of the matrices of coefficients is determined. Based on the level of correlation of this first coefficient matrix, one of a first quantization technique and a second quantization technique is selected. The first coefficient matrix is then quantized using the selected quantization technique.According to another aspect of the compression method, an image is digitally filtered into its constituent components, each represented by a matrix of coefficients. At least certain matrices are quantized to generated a first quantized matrix. The first quantized matrix is then recursively divided until the first quantized matrix or each of the resulting submatrices is sufficiently dense or sufficiently sparse. Each of the sufficiently dense matrices are encoded using a first technique, while each of the sufficiently sparse matrices are encoded a second technique.
Owner:XVD TECH HLDG LTD IRELAND
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative converter accoding to the correlation of residual signal
InactiveUS20090238271A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareRate distortion
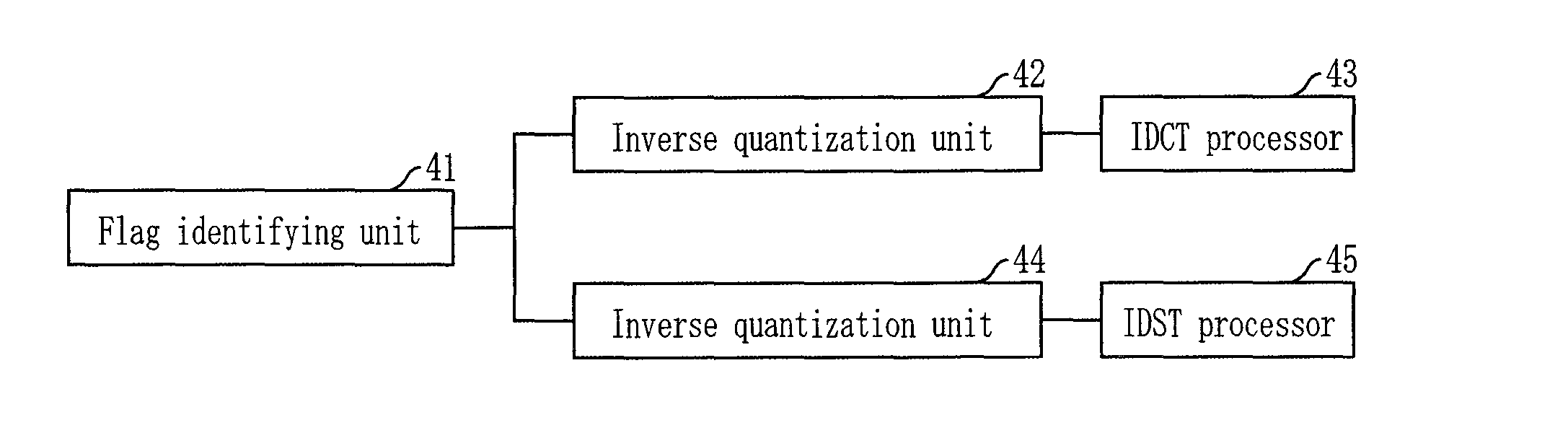
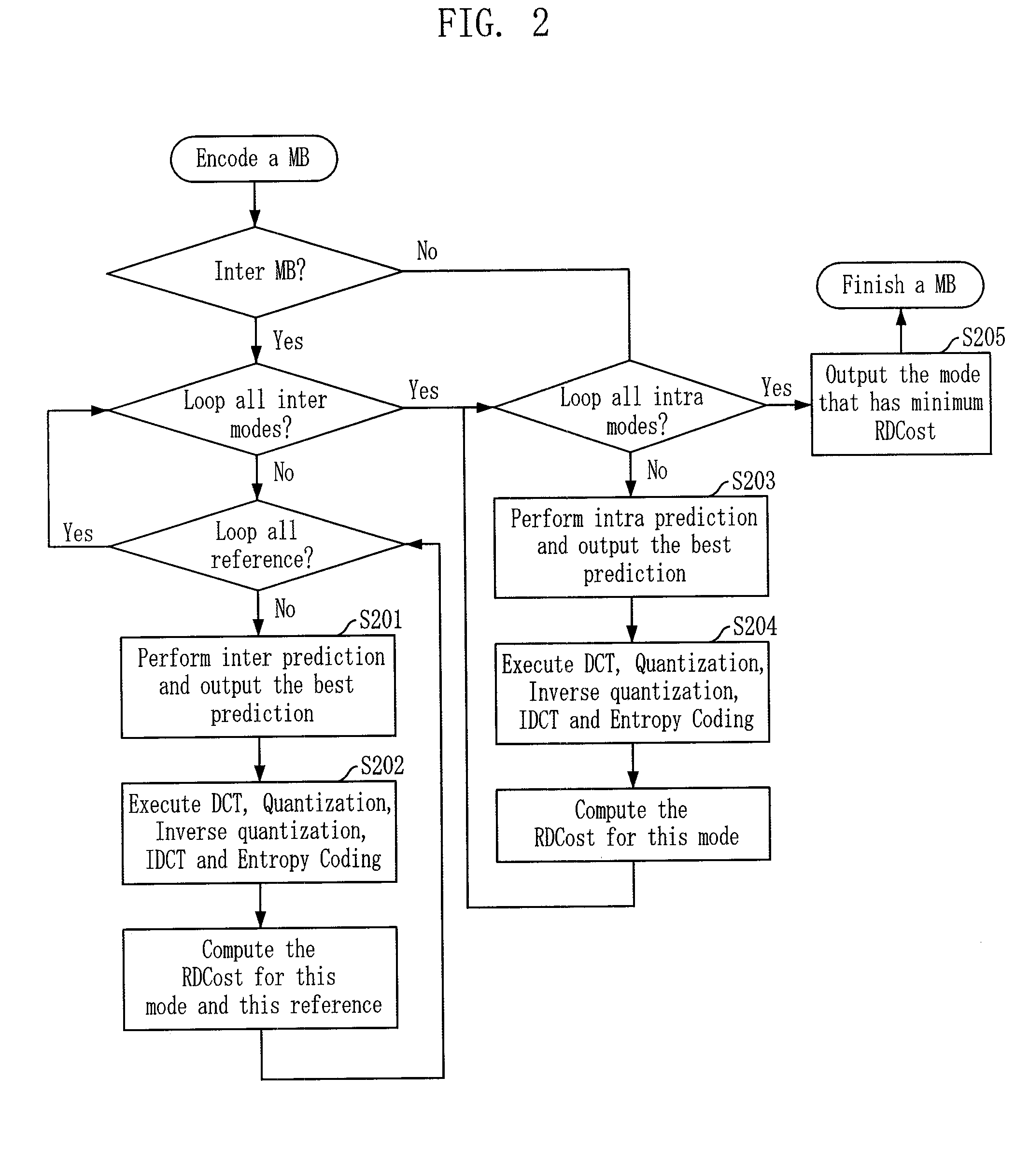
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative transform units according to the correlation of residual signals. The video encoding apparatus includes a first transforming unit for performing discrete cosine transform (DCT), first quantization, first inverse quantization, and inverse DCT on a block basis onto residual coefficients generated after intra frame prediction or inter frame prediction; a second transforming unit for performing discrete sine transform (DST), second quantization, second inverse quantization, and inverse DST on a block basis onto the residual coefficients; a selecting unit for selecting one having a high compression rate between the first and second transforming units for each block through performing rate-distortion optimization; and a flag marking unit for recording information about the selected transforming unit at a flag bit provided on a macroblock basis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
Apparatus and methods for recompression of digital images
ActiveUS20120201476A1Substantial size reductionSmall sizeCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationCoding blockReduced size
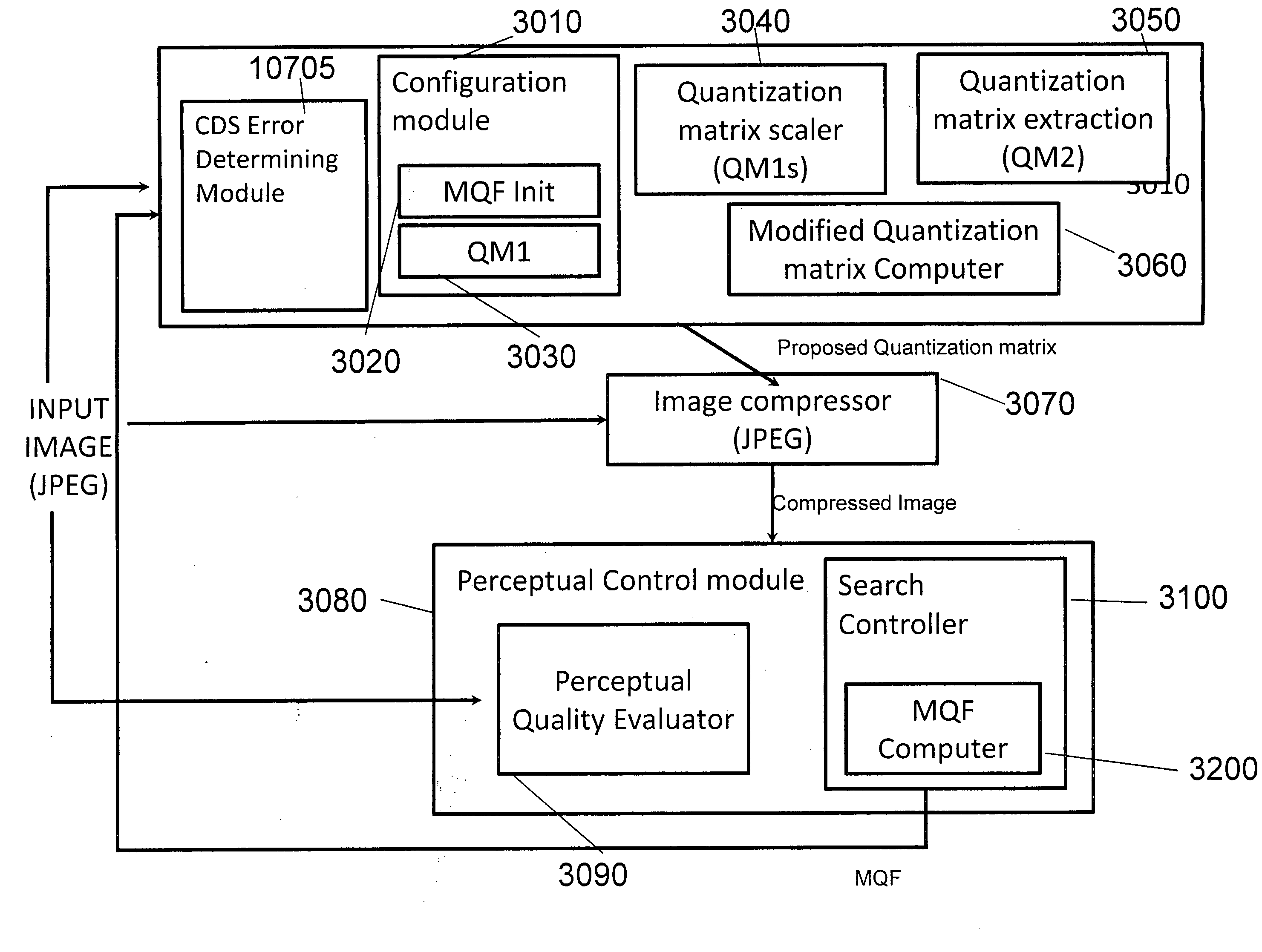
A system and method for generating a second reduced size digital image from a first digital image, the method including iteratively compressing the first digital image to an extent determined by a quality measure comprising at least a blockiness measure quantifying added artifactual edges along coding block boundaries of the second image and / or use of a quantization matrix generated by computing a weighted average of the quantization matrix of the first digital image and a scaled second quantization matrix.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Video encoding method, apparatus, and program
InactiveUS20070071094A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmVideo encoding
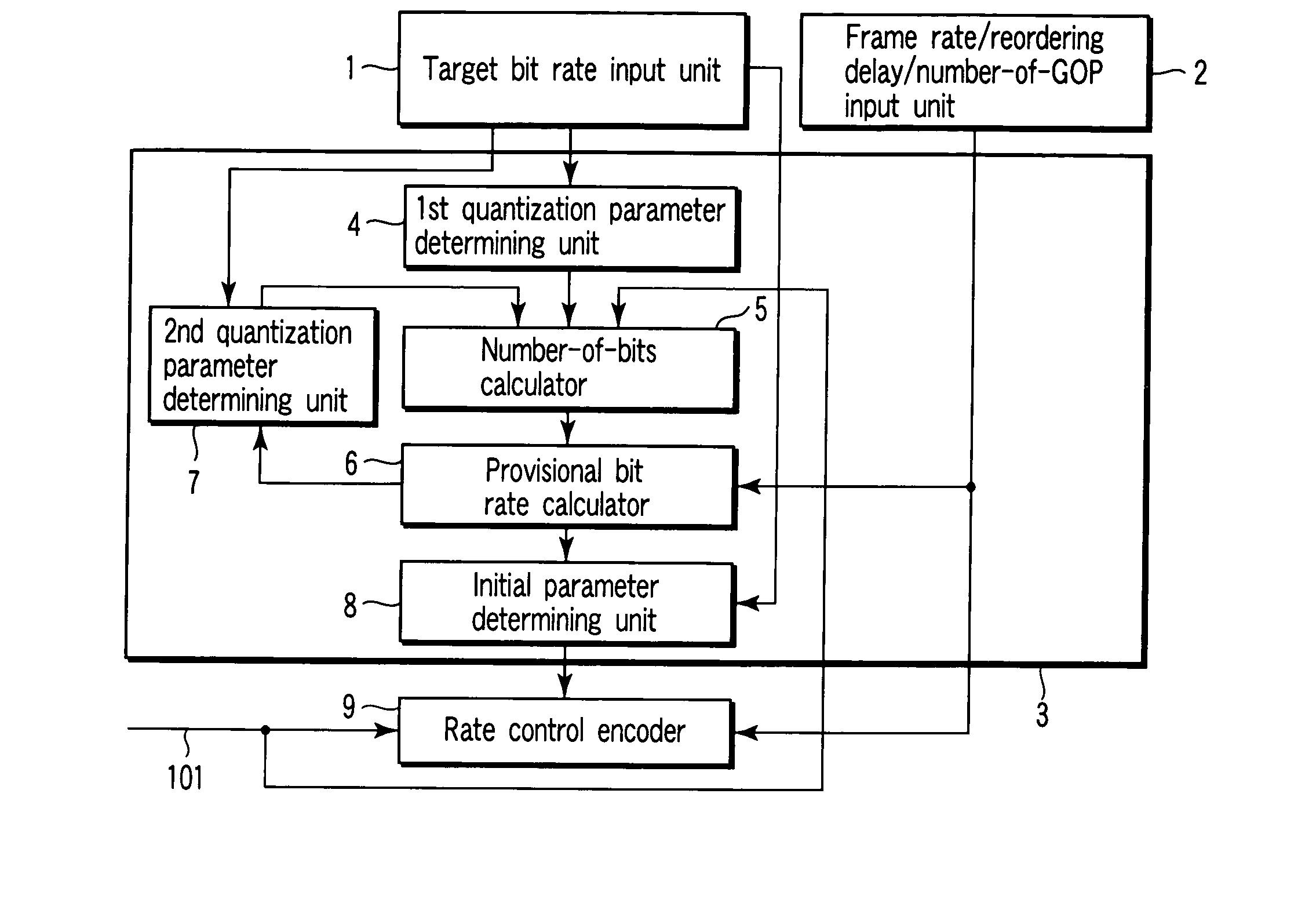
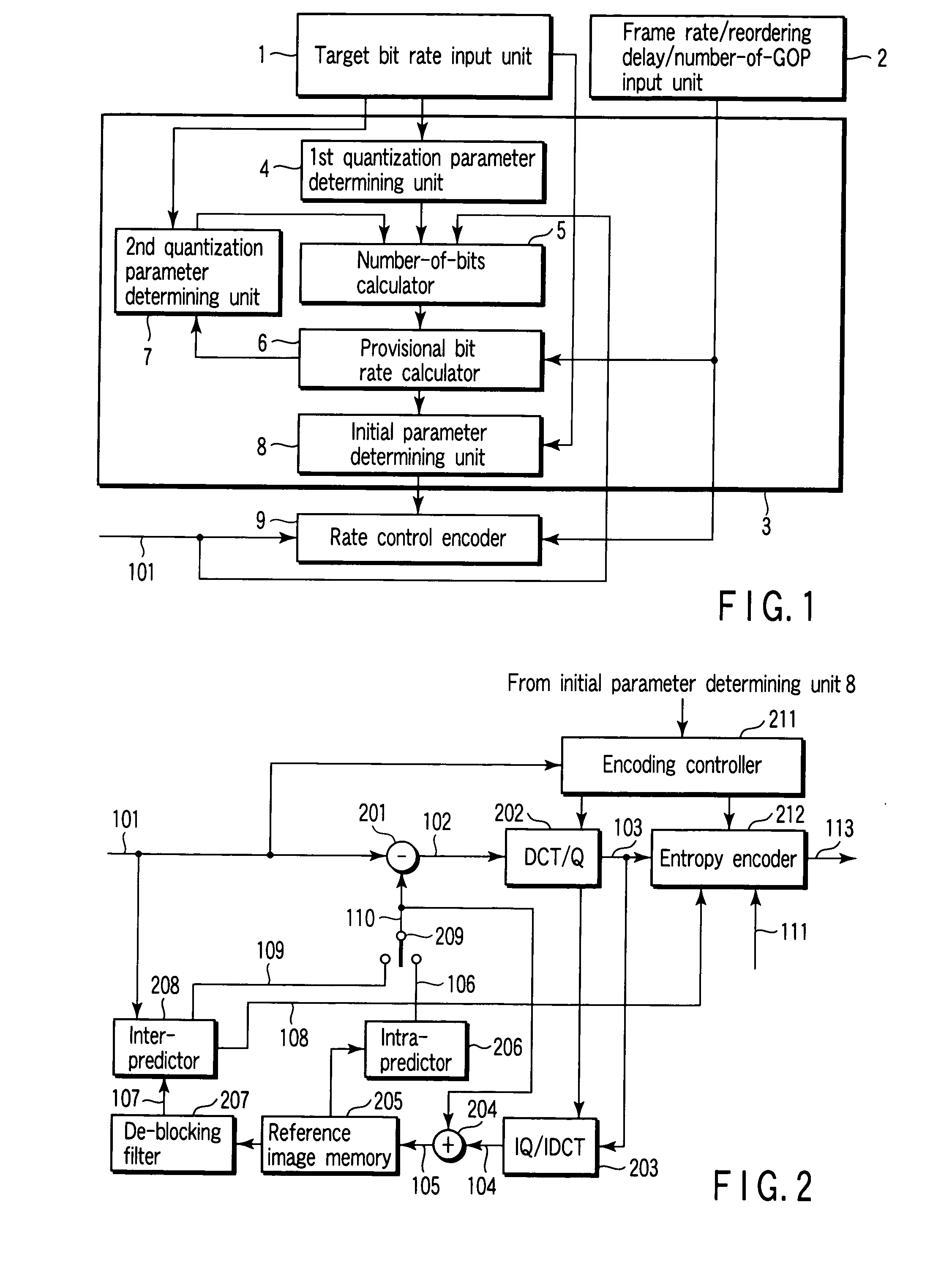
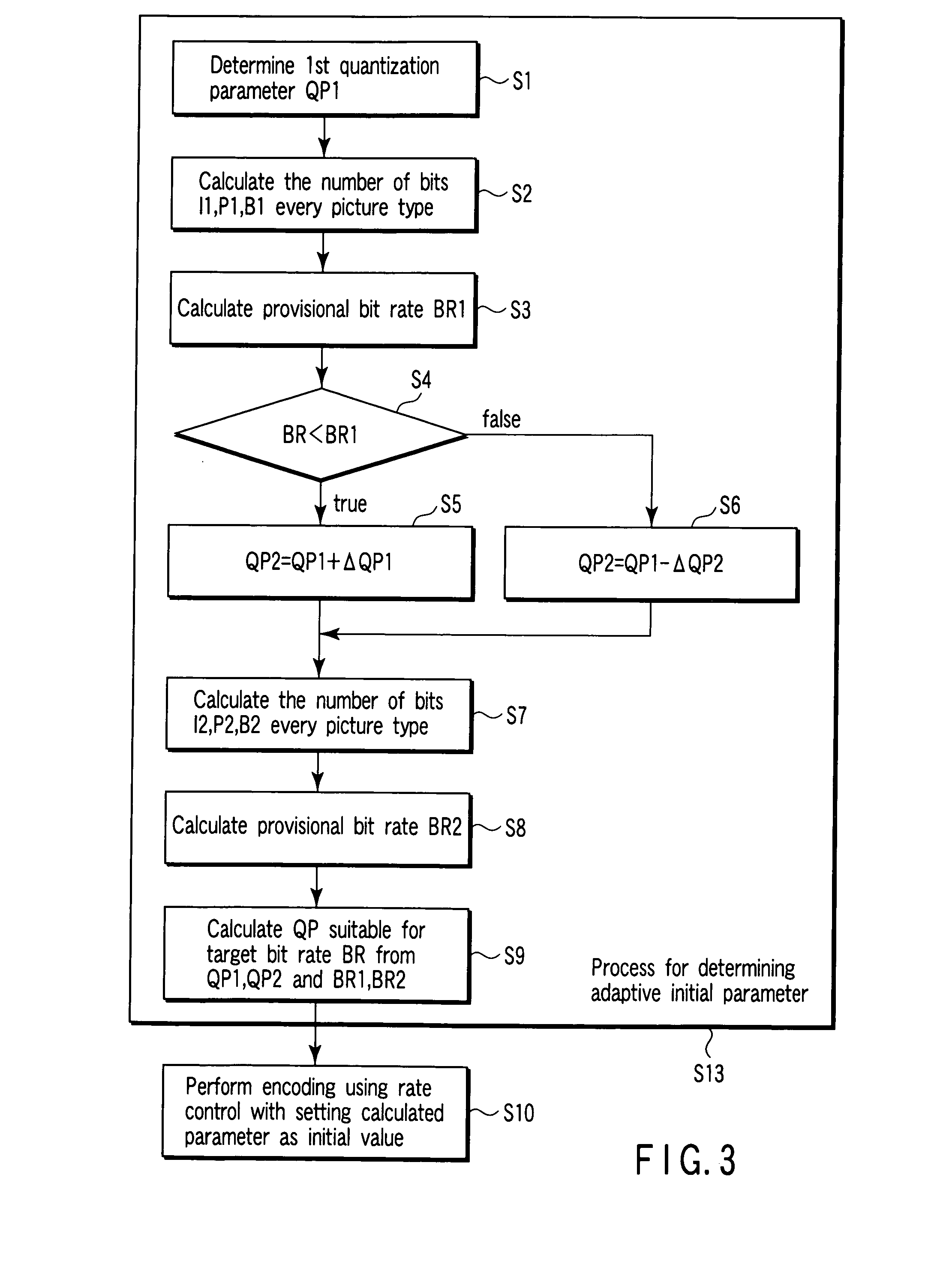
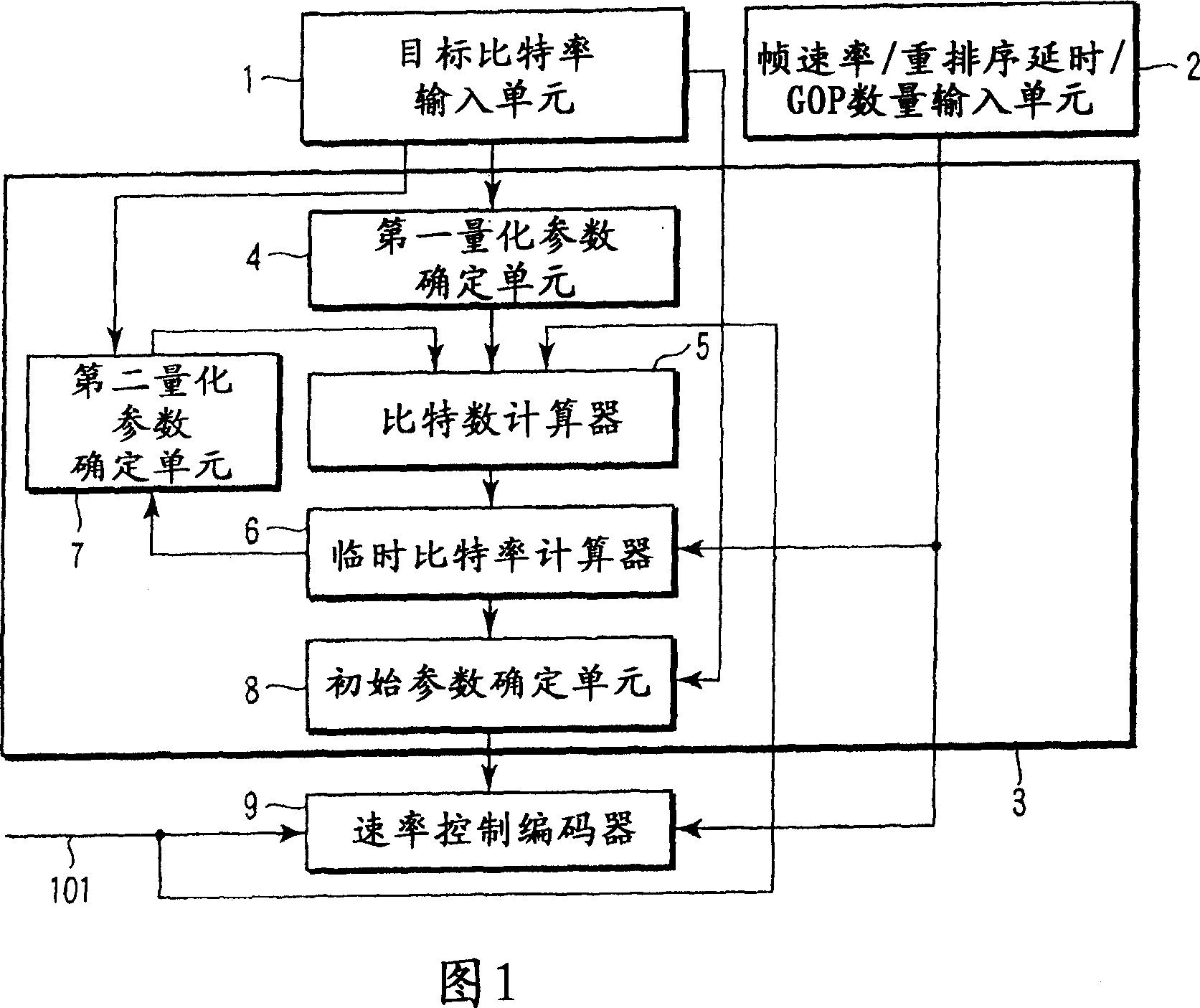
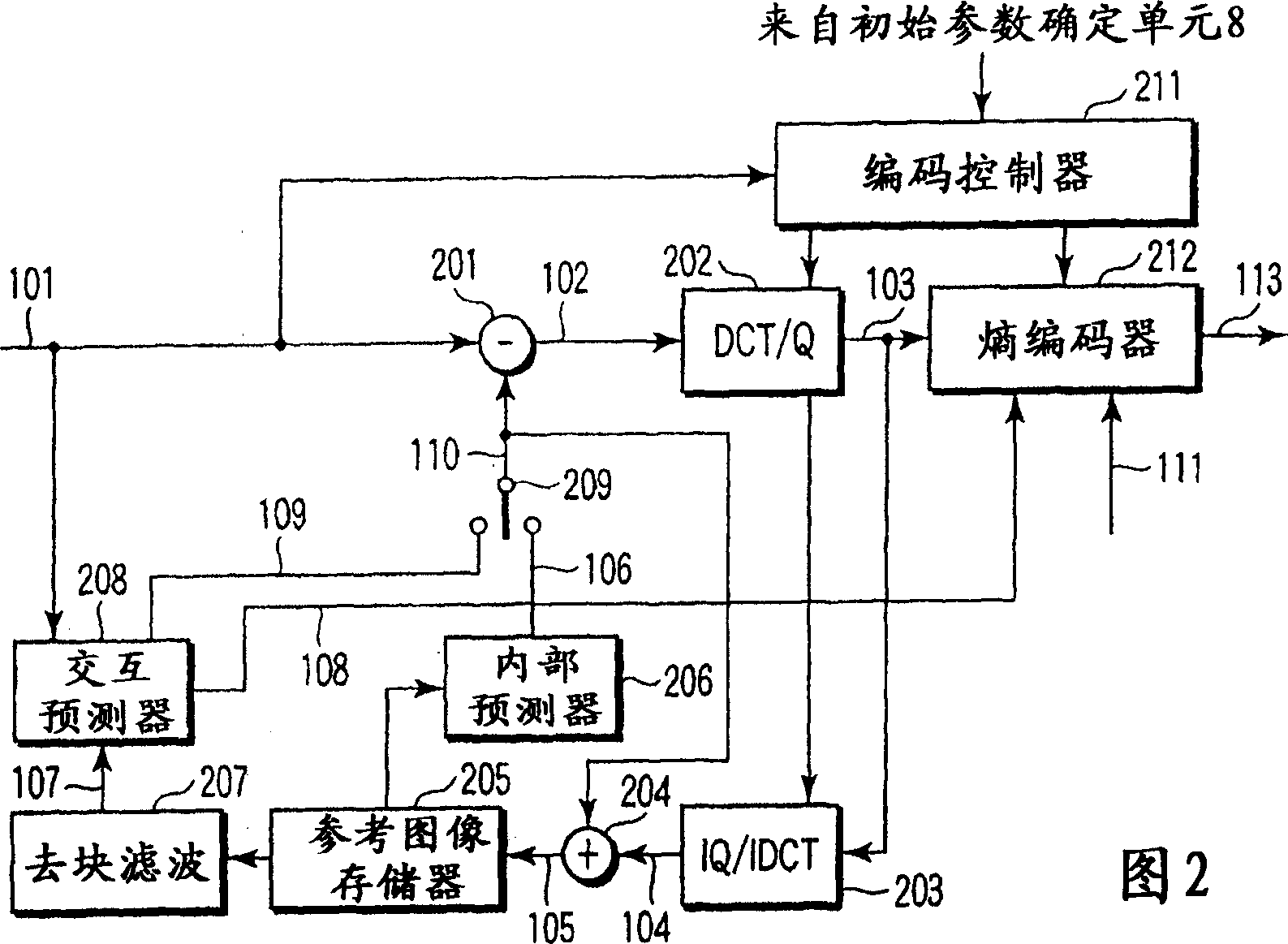
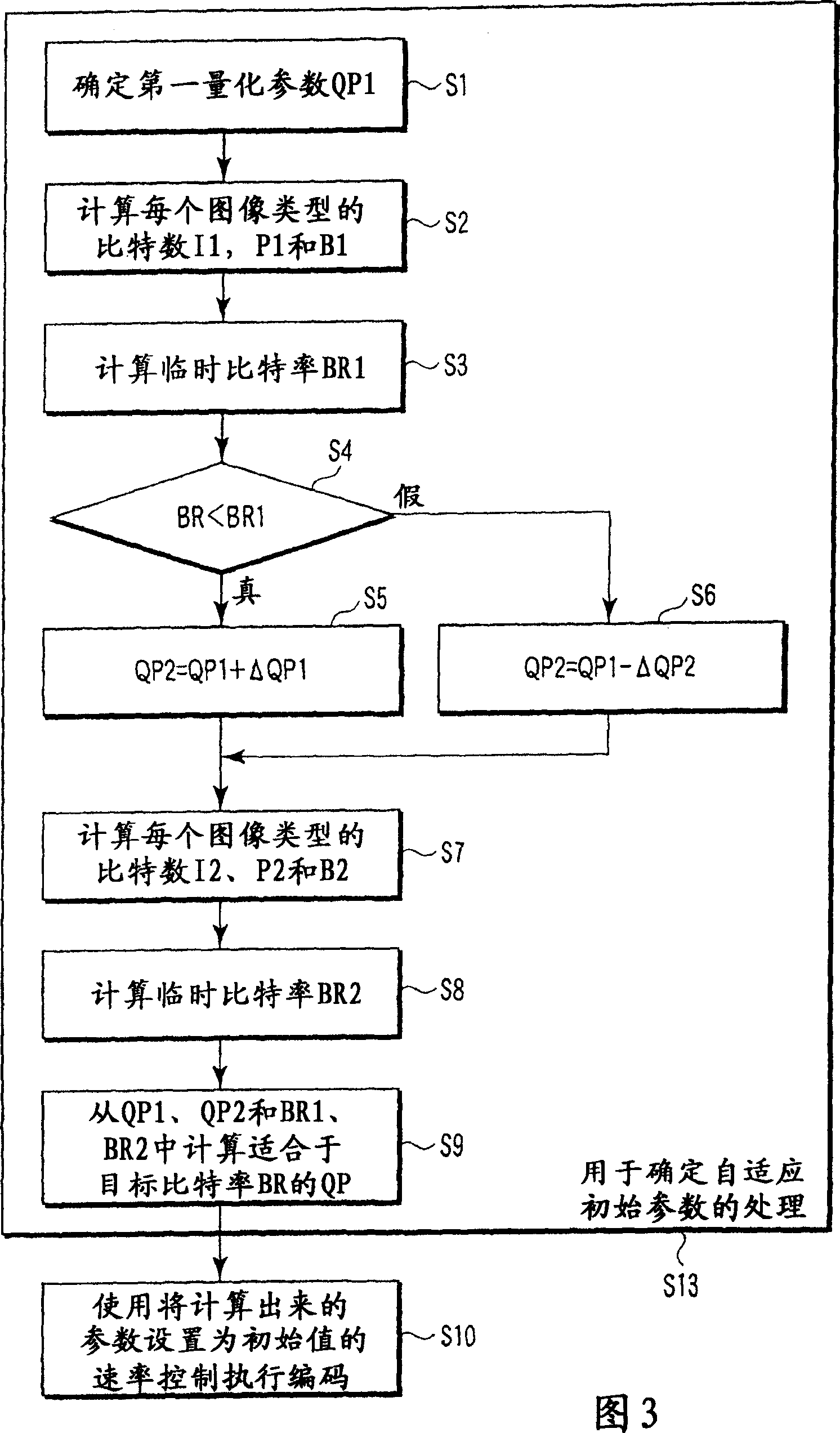
A video encoding method includes encoding n pictures included in a video image using a first quantization parameter, calculating first number-of-encoded-bits information indicating number of encoded bits of every picture type, multiplexing a set frame rate by an average first-number-of-encoded-bits per picture calculated from the first-number-of-encoded-bits information to obtain a first bit rate, encoding the n pictures using a second quantization parameter, calculating second number-of-encoded-bits information indicating number of encoded bits of every picture type, multiplexing the set frame rate by an average second number-of-encoded-bits per picture calculated from the first-number-of-encoded-bits information to obtain a second bit rate, calculating a third quantization parameter, using the first bit rate, first quantization parameter, second bit rate, second quantization parameter and target bit rate, and performing the rate control using the third quantization parameter as an initial value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Rate control method with frame-layer bit allocation and video encoder
ActiveUS20080063051A1Improve video qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareBit allocation
A video encoder controlling rate of each frame in a current frame set (Group of Picture, GOP), and method thereof. The video encoder comprises a frame grouping device, a GOP initialization device, and a GOP encoding device. The frame grouping device allocates a target bit budget RGOP to the current frame set. The GOP initialization device is coupled to the frame grouping device, and estimates a first quantization parameter QP1 based on the target bit budget RGOP and complexity of the current frame set. The GOP encoding device is coupled to the GOP initialization device, and encoding a frame in the current frame set with the second quantization parameter QP2 to generate output data.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Apparatus and methods for recompression of digital images
ActiveUS8908984B2Small sizeQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCoding blockReduced size
A system and method for generating a second reduced size digital image from a first digital image, the method including iteratively compressing the first digital image to an extent determined by a quality measure comprising at least a blockiness measure quantifying added artifactual edges along coding block boundaries of the second image and / or use of a quantization matrix generated by computing a weighted average of the quantization matrix of the first digital image and a scaled second quantization matrix.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Decoding device and decoding method
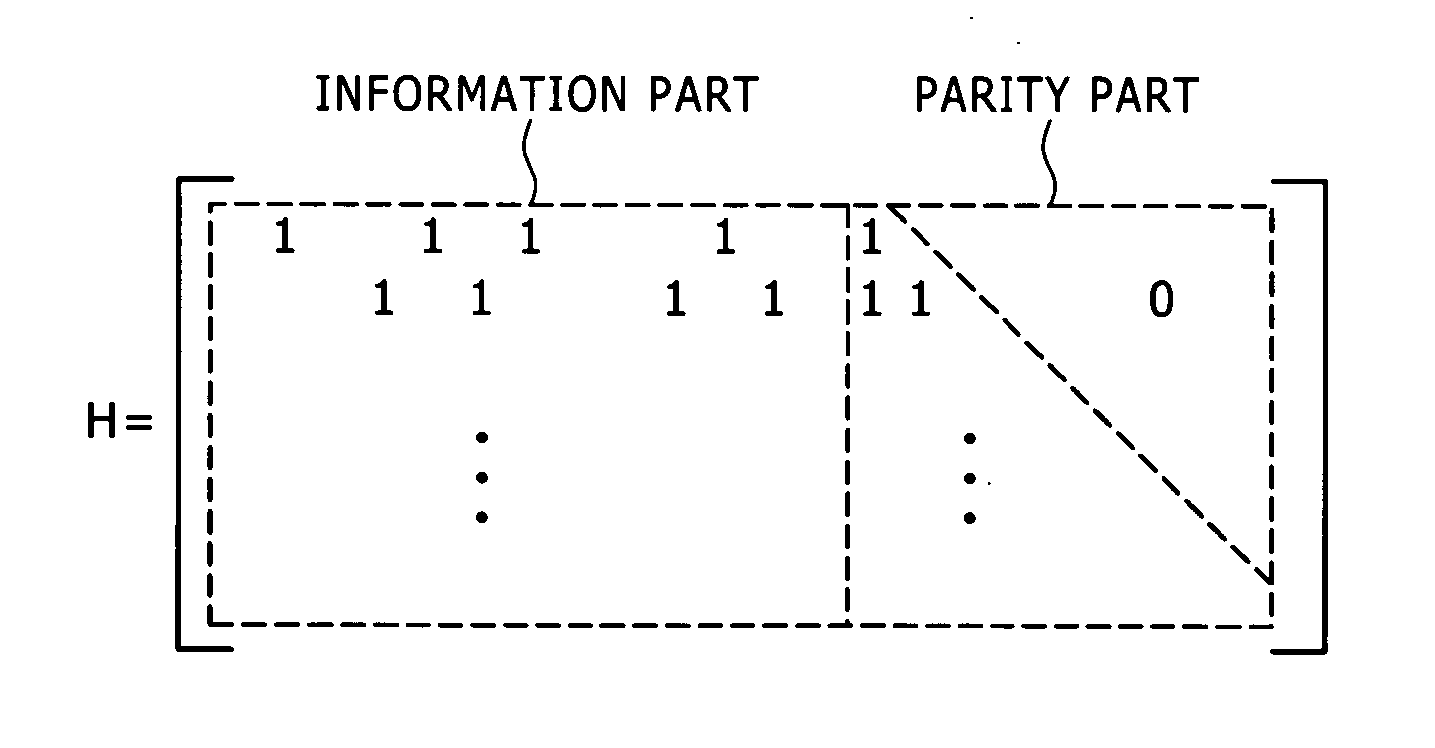
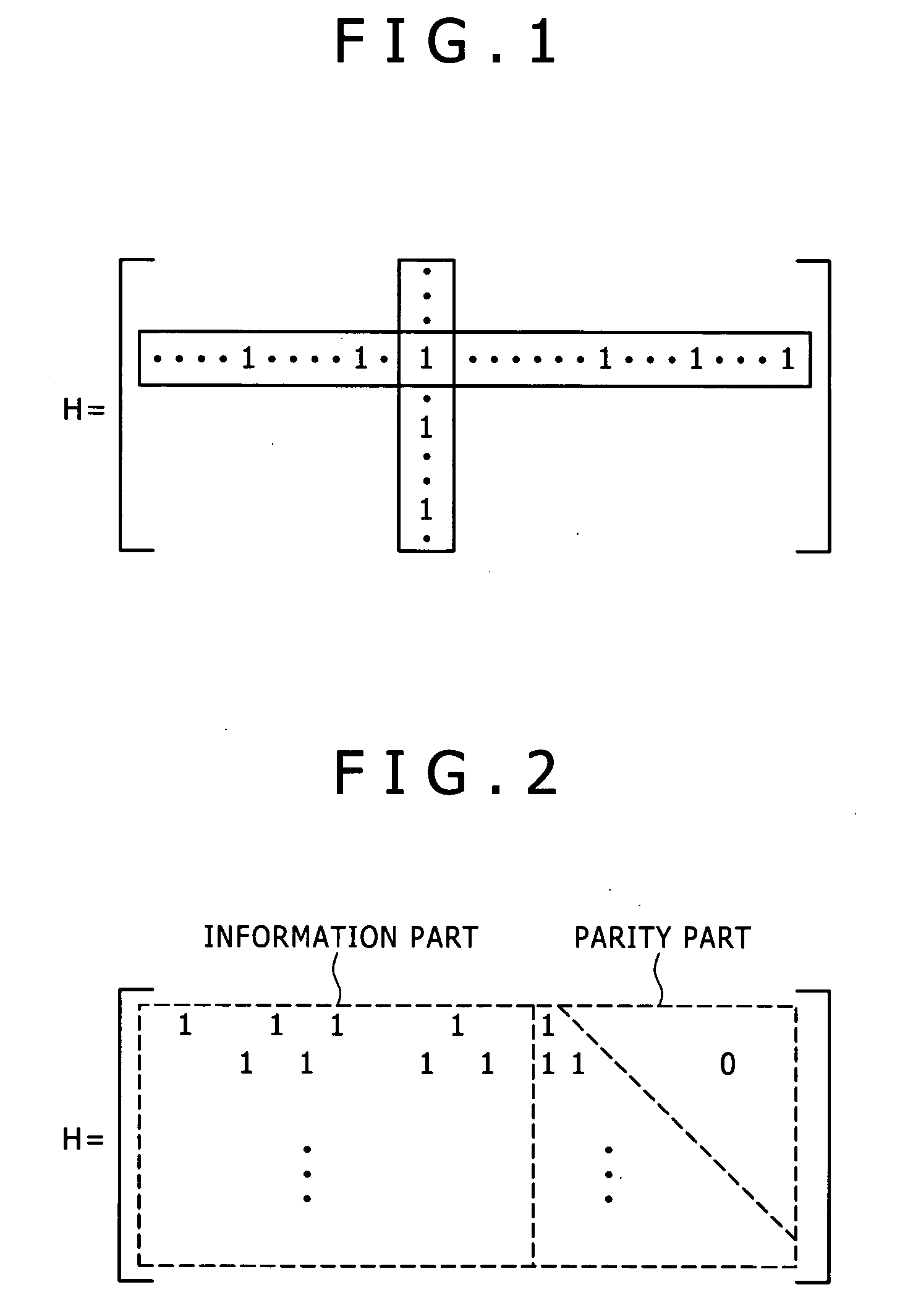
InactiveUS20060242536A1Improve accuracyImprove scaleData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer architectureLow-density parity-check code
The present invention provides a decoding device for decoding an LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code. The decoding device include: a first operation unit for performing a check node operation for decoding the LDPC code, the operation including an operation of a nonlinear function and an operation of an inverse function of the nonlinear function; and a second operation unit for performing a variable node operation for decoding the LDPC code. The first operation unit includes a first converting unit for converting a first quantization value assigned to a numerical value into a second quantization value representing a numerical value with a higher precision than the first quantization value, and a second converting unit for converting the second quantization value into the first quantization value. In processing performed as the check node operation and the variable node operation, the first operation unit and the second operation unit use the second quantization value in processing from after the operation of the nonlinear function to the operation of the inverse function, and use the first quantization value in the other processing.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Coding rate conversion apparatus, coding rate conversion method, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20100091842A1Suppresses image quality degradationSuppress errorColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmQuantization matrix
A plurality of macroblocks constituting coded data are inverse quantized using a first quantization matrix that is used when coding a picture, to obtain a plurality of sets of coefficient data. The first quantization matrix is converted to a second quantization matrix using a first conversion value and a second conversion value, where the first conversion value is for converting a low frequency coefficient corresponding to a frequency lower than a predetermined frequency among a plurality of coefficients shown by the first quantization matrix, and the second conversion value is for converting a high frequency coefficient among the plurality of coefficients and is larger than the first conversion value (Step S408). When the second quantization matrix is a matrix for increasing a coding rate of the coded data, a converted scale is calculated by multiplying a quantization scale corresponding to at least one macroblock by β1 (≧1). At least one part of the plurality of sets of coefficient data is quantized using the second quantization matrix and a calculated converted scale that corresponds to a macroblock corresponding to the at least one part of the plurality of sets of coefficient data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Transducer amplification circuit
ActiveUS20150281836A1Accurate representationImprove responseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSemiconductor electrostatic transducersSonificationTransducer
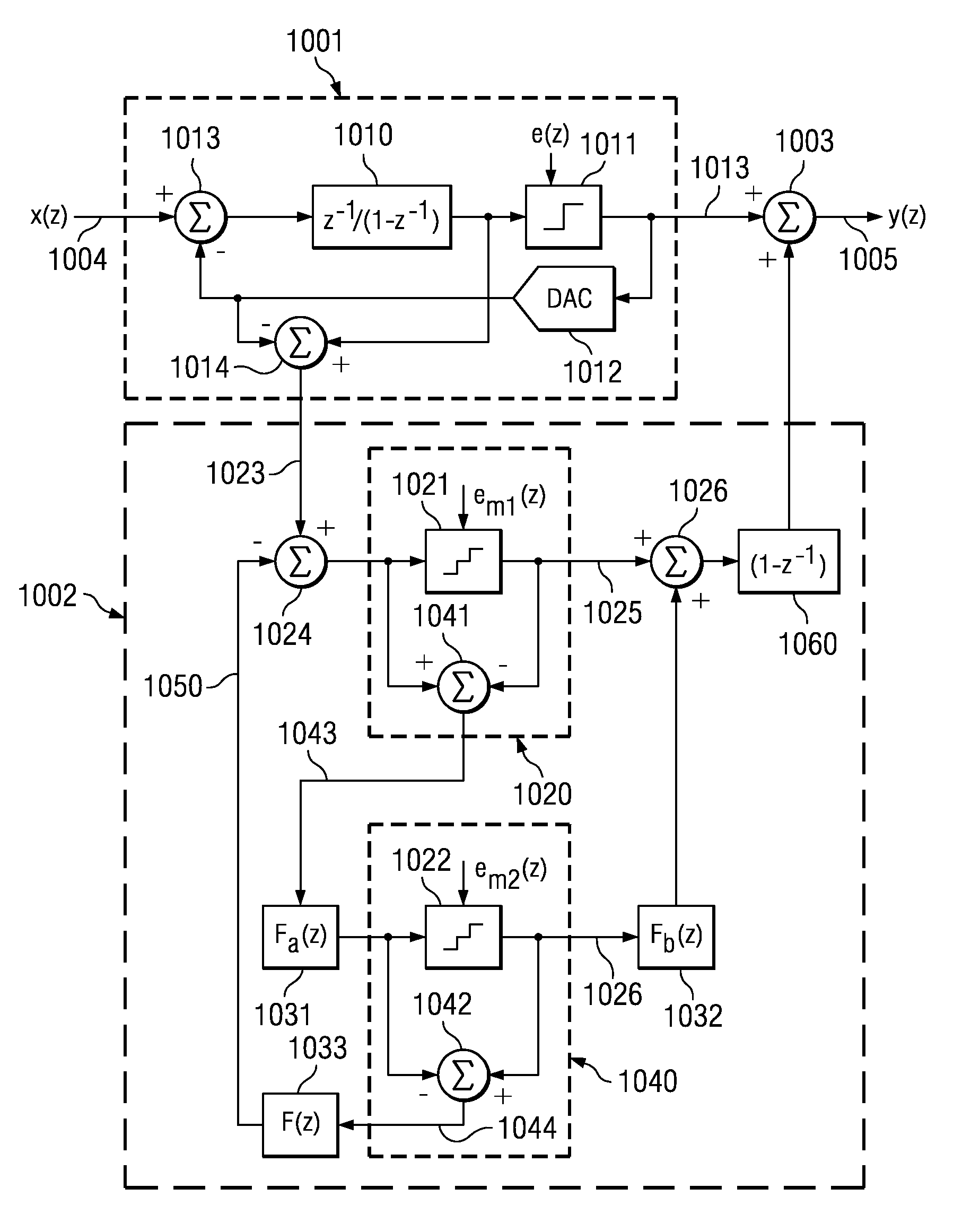
A transducer amplification circuit may include a preamplifier circuit with a signal input receiving a transducer signal to provide an amplified transducer signal comprising audible frequency components and ultrasonic frequency components. The transducer amplification circuit may include a first sigma-delta modulator configured to sample and quantize the amplified transducer signal to generate a first digital transducer signal comprising a first quantization noise signal. The first sigma-delta modulator may include a first noise transfer function having a high pass response in at least a portion of an audible frequency range to push the quantization noise signal to ultrasonic frequencies. A second sigma-delta modulator is configured to sample and quantize the amplified transducer signal to generate a second digital transducer signal comprising a second quantization noise signal. The second sigma-delta modulator may include a second noise transfer function with a magnitude minimum placed at the ultrasonic frequencies.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Video signal coding apparatus and video signal coding method
ActiveUS20100202513A1Improve image qualityAmount of codeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel computingQuantization matrix
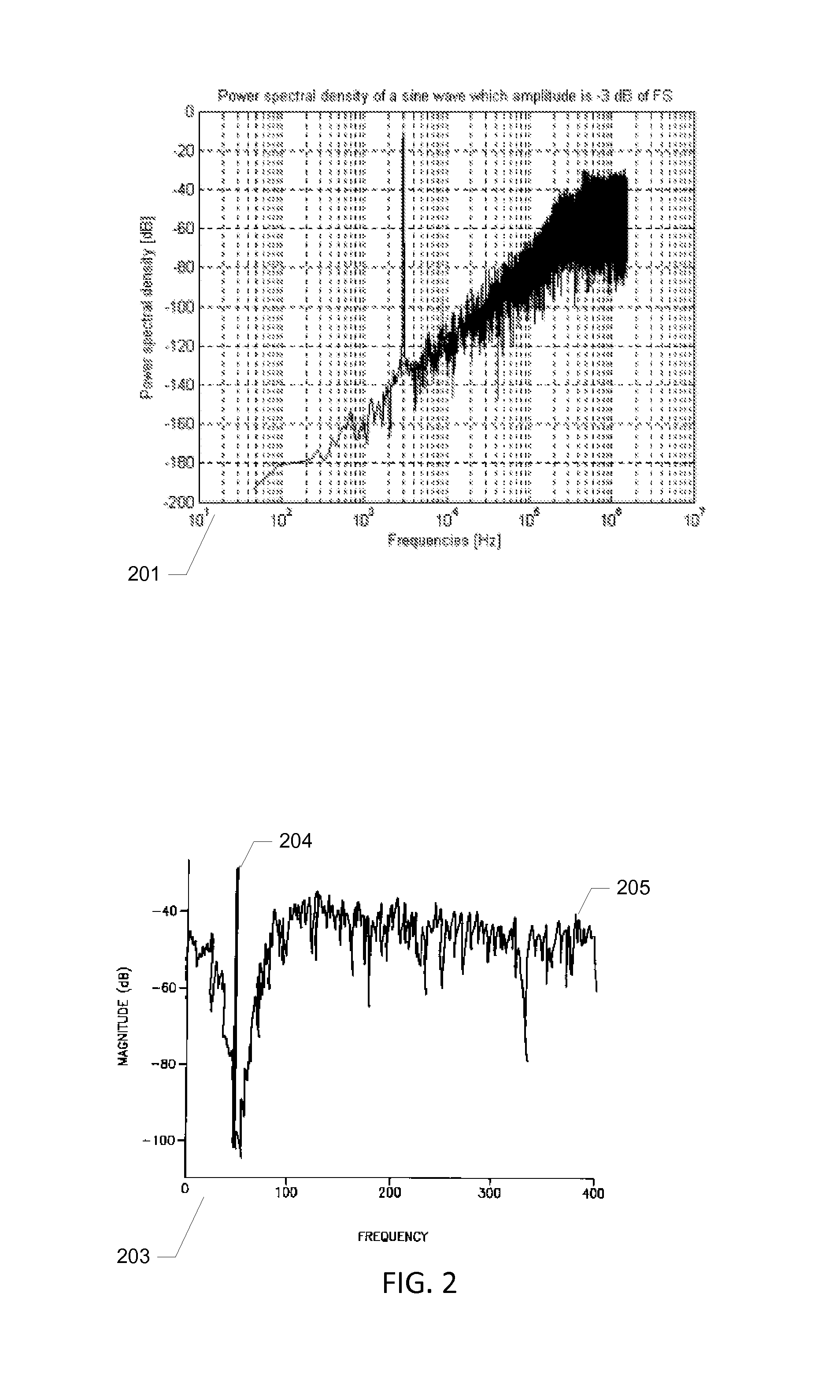
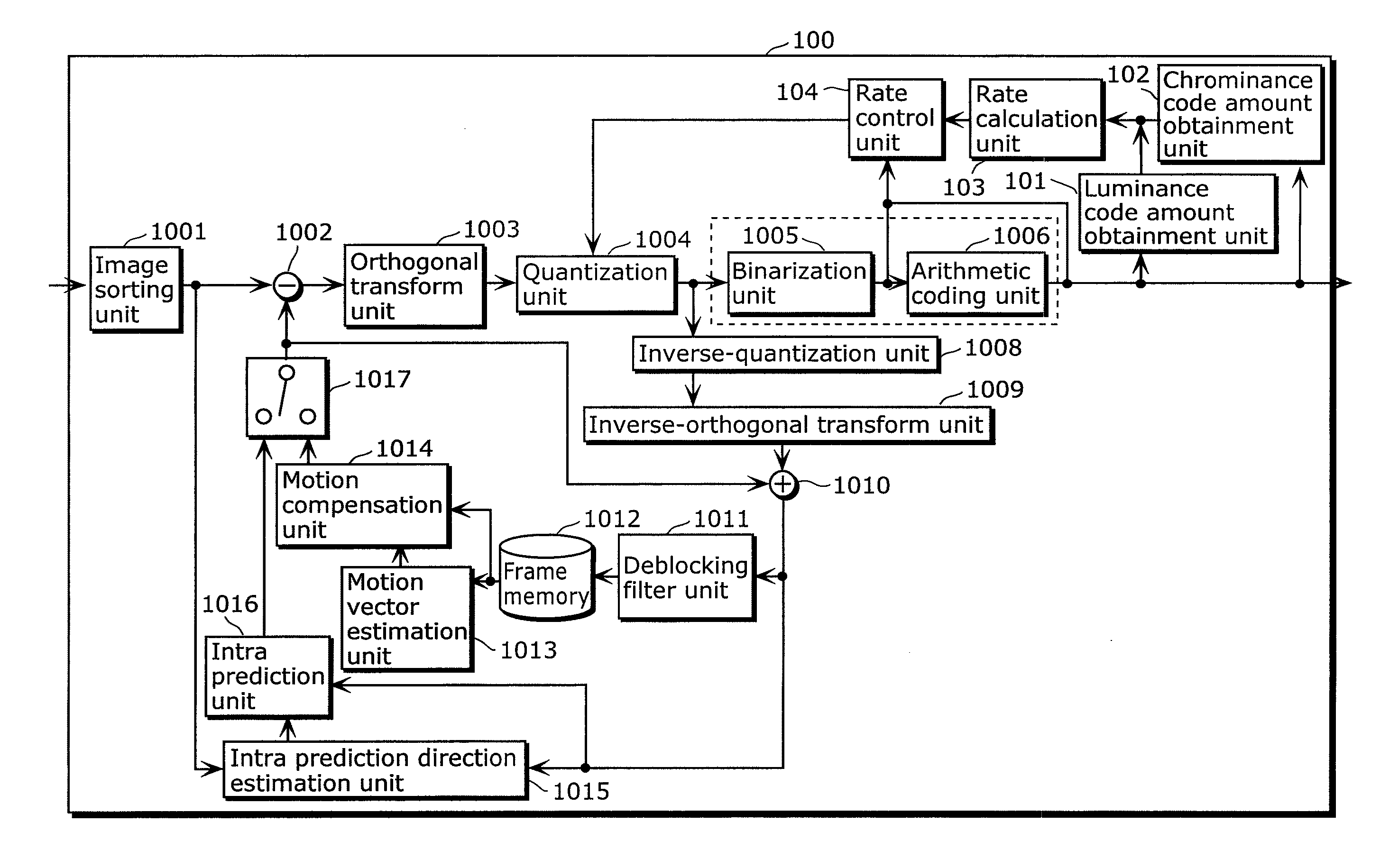
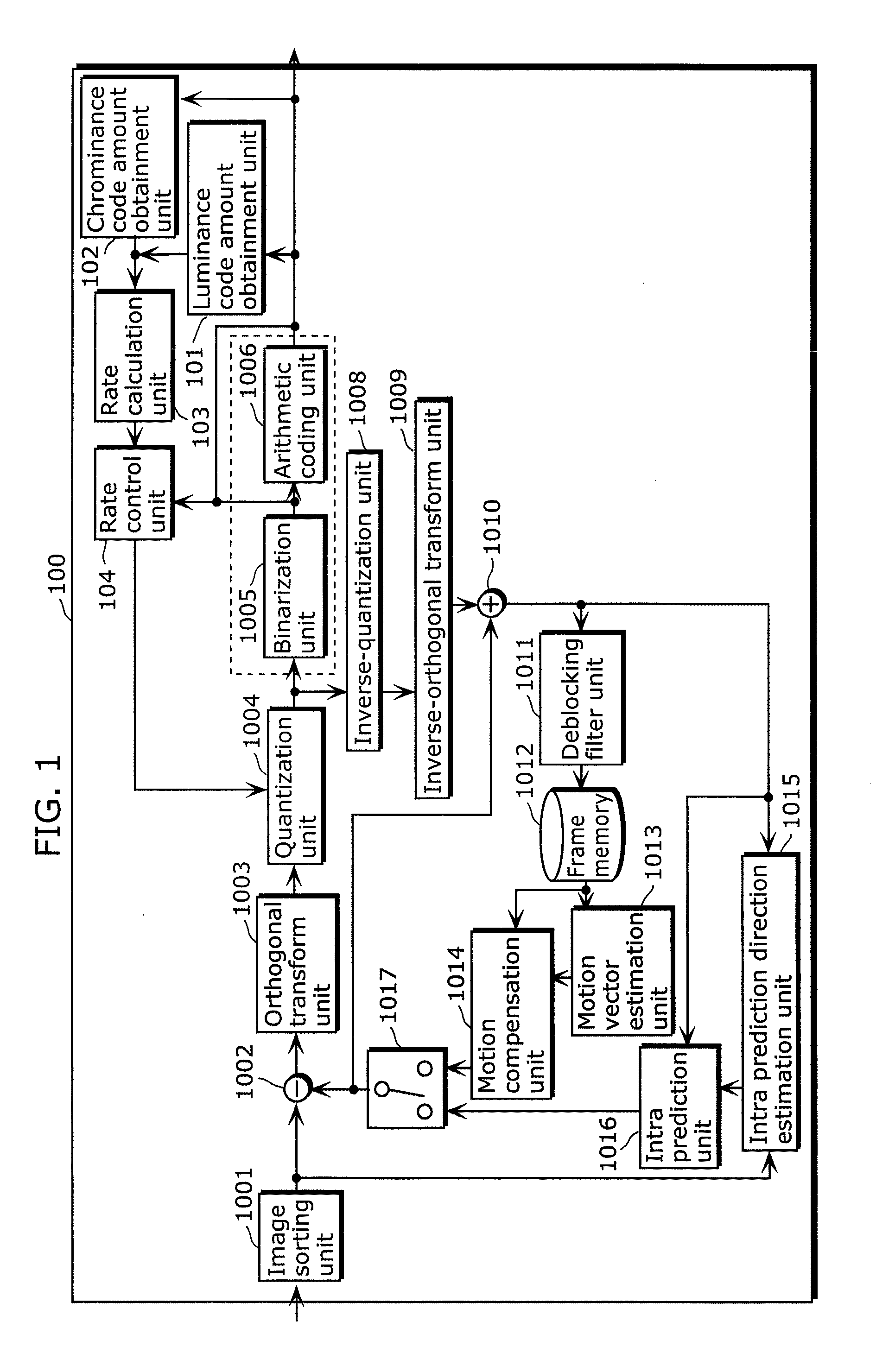
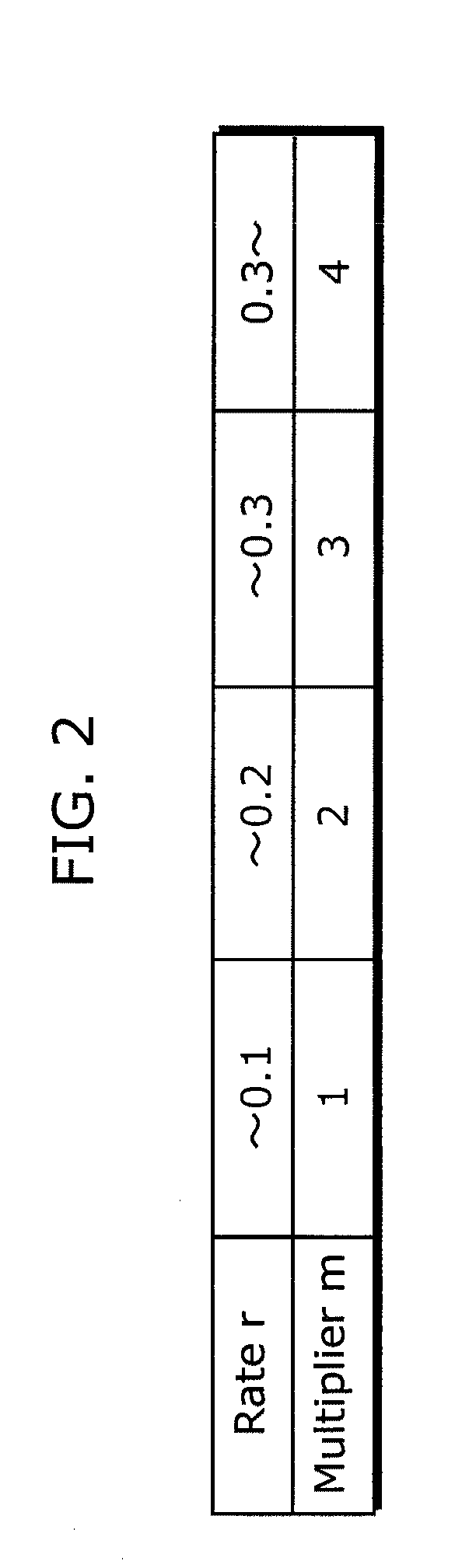
Video signal coding apparatus includes: a quantization unit which quantizes, using coefficient values in a first quantization matrix, a luminance signal of each of a first picture and a second picture coded after the first picture, and quantizes, using coefficient values in a second quantization matrix, a chrominance signal of each of the first picture and the second picture; a code amount obtainment unit which obtains a luminance code amount and a chrominance code amount of each of the first picture and the second picture; a rate calculation unit which calculates a rate of the chrominance code amount with respect to the luminance code amount for each of the first picture and the second picture, obtained by the code amount obtainment unit; and a rate control unit which changes a coefficient value of at least one of the first matrix and the second matrix used in quantizing the second picture, before the quantization unit quantizes the second picture, so that the rate for the second picture becomes smaller than the rate for the first picture.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Encoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS6928113B1Quality improvementHigh frequencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVariable-length codeAlgorithm
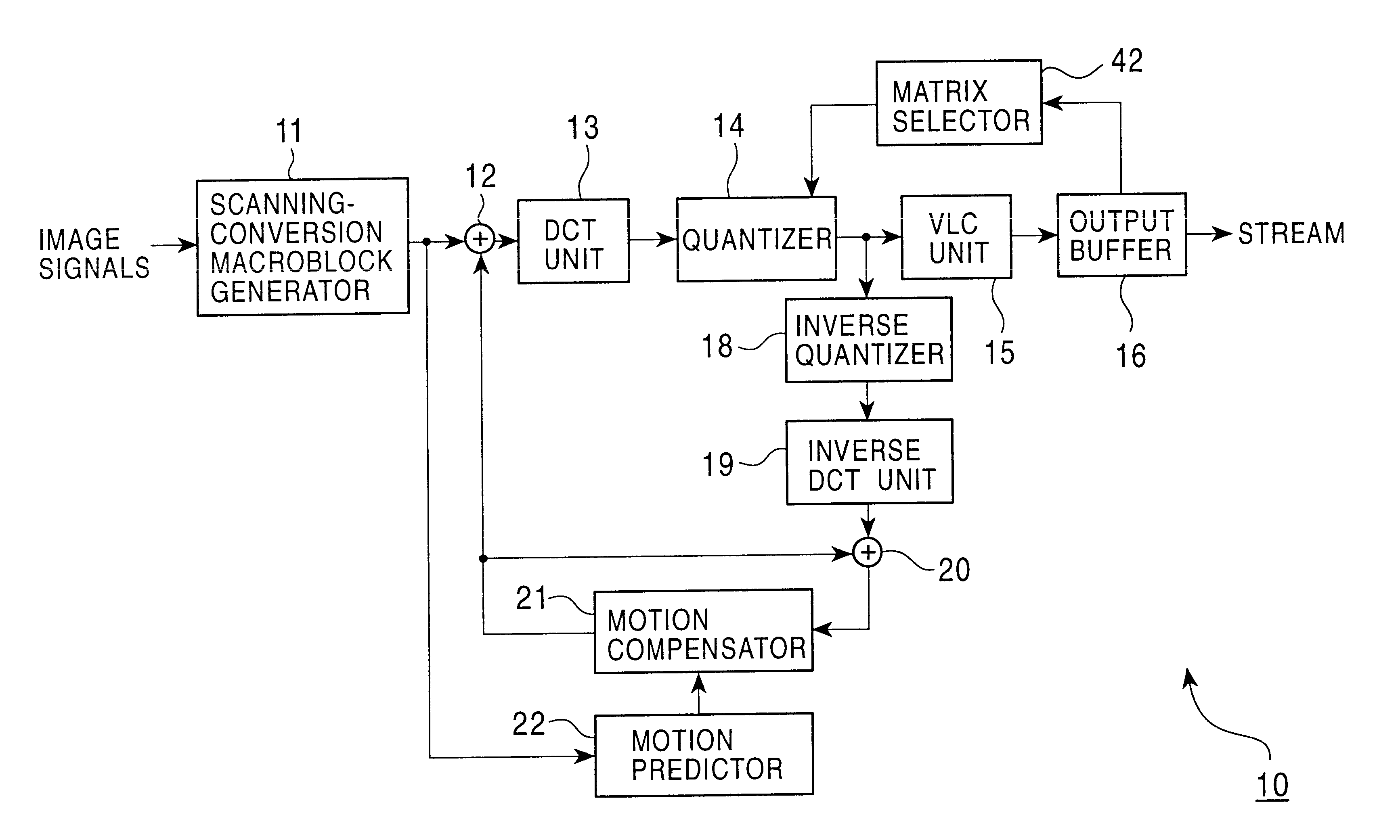
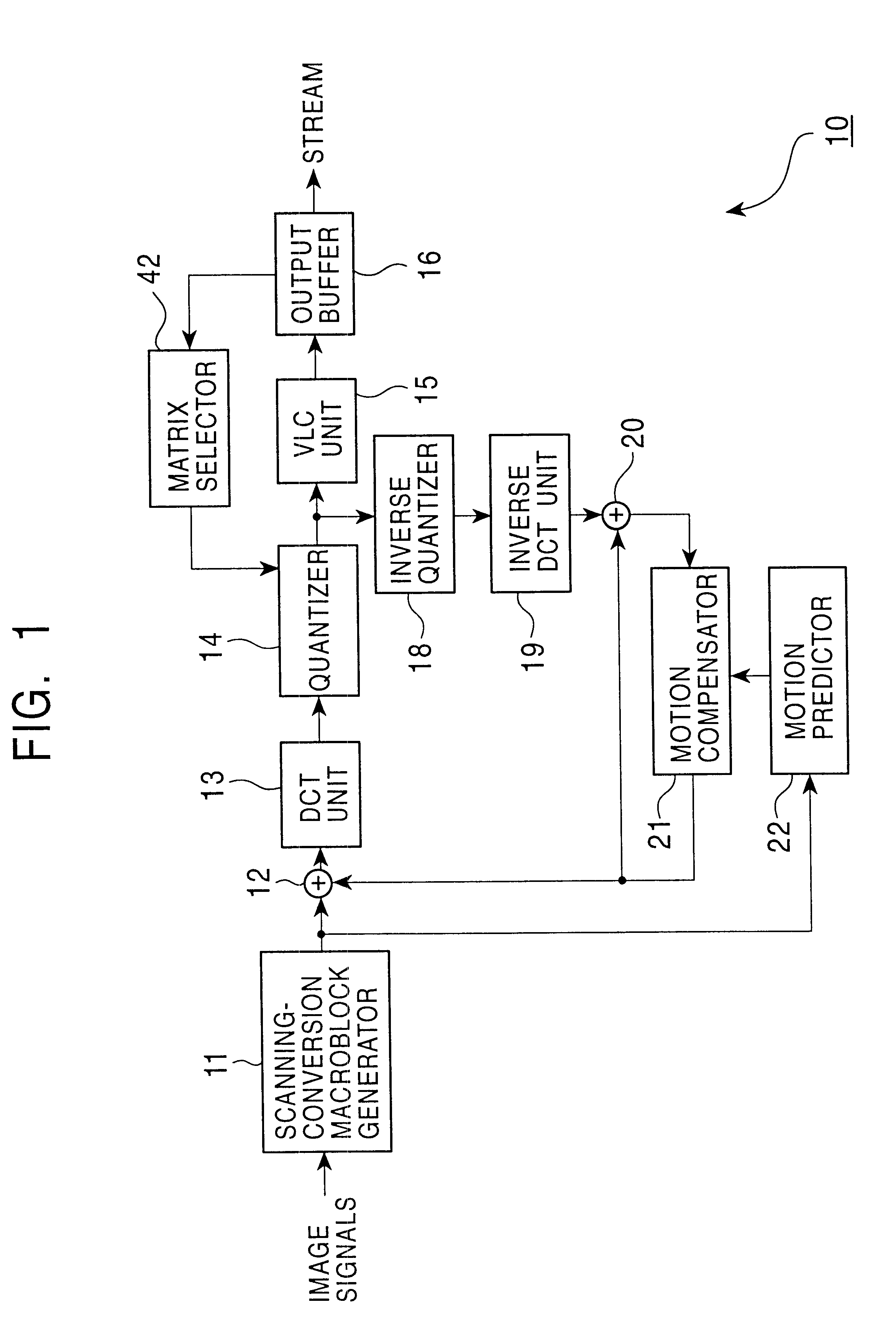
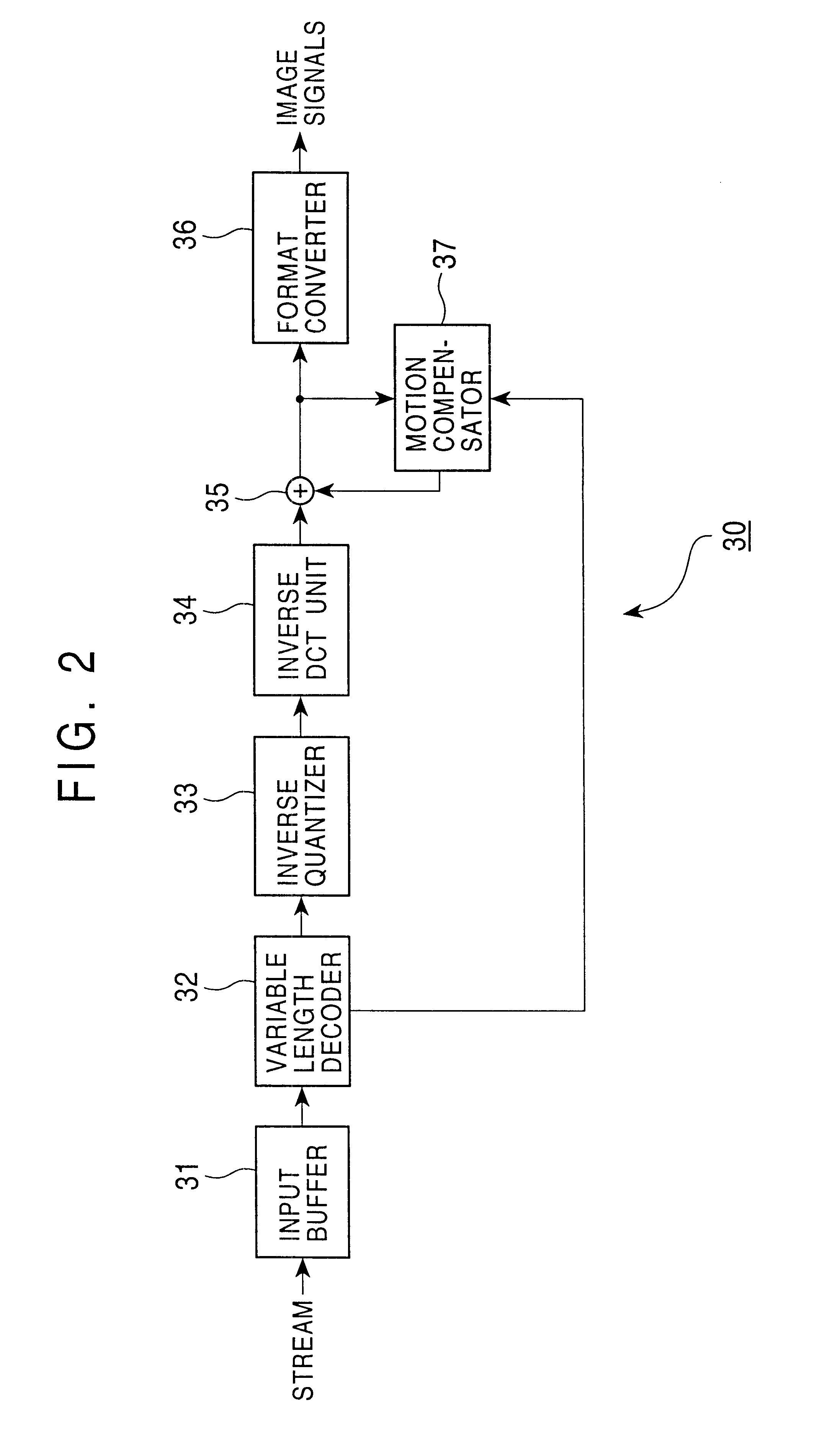
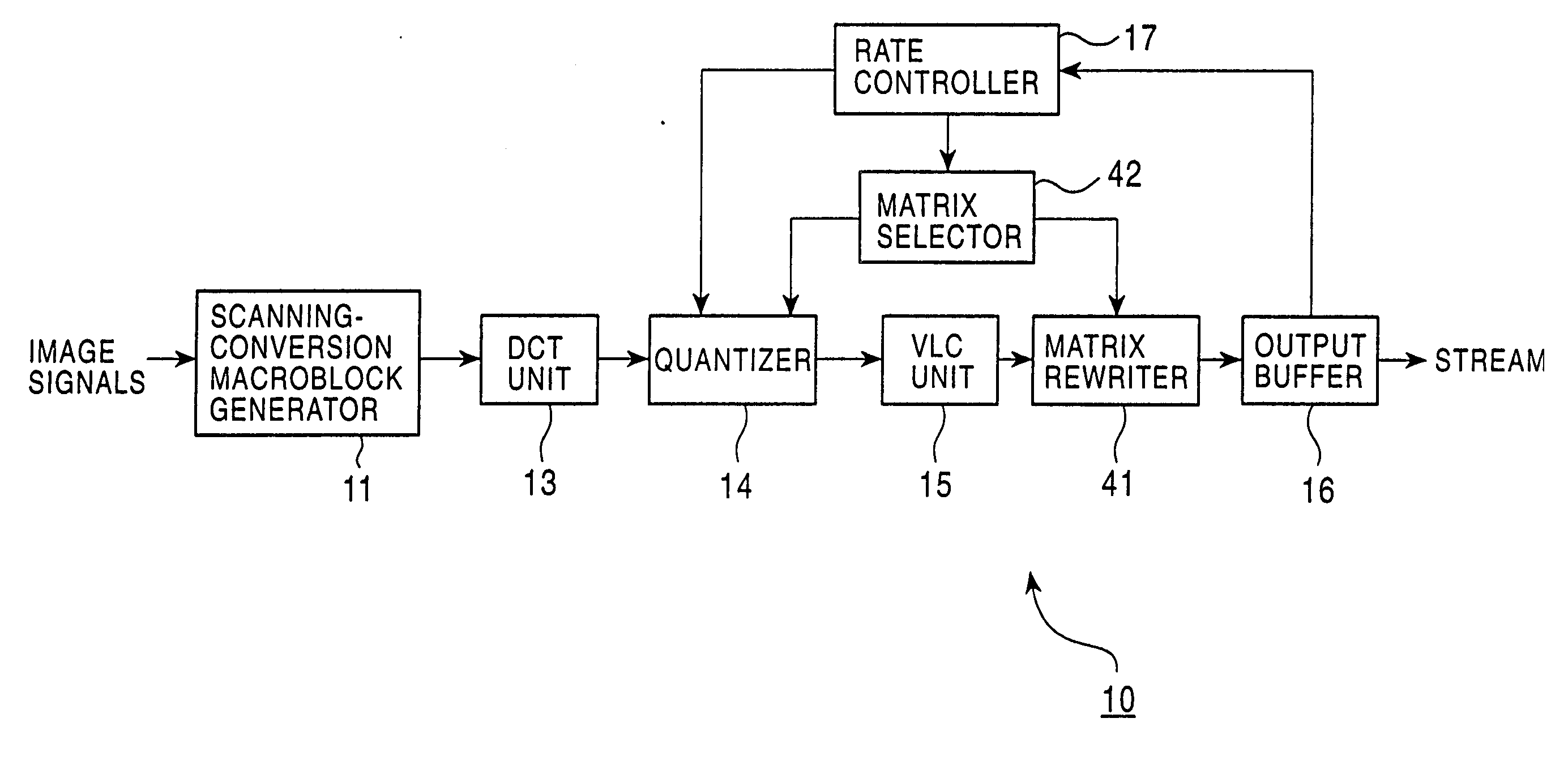
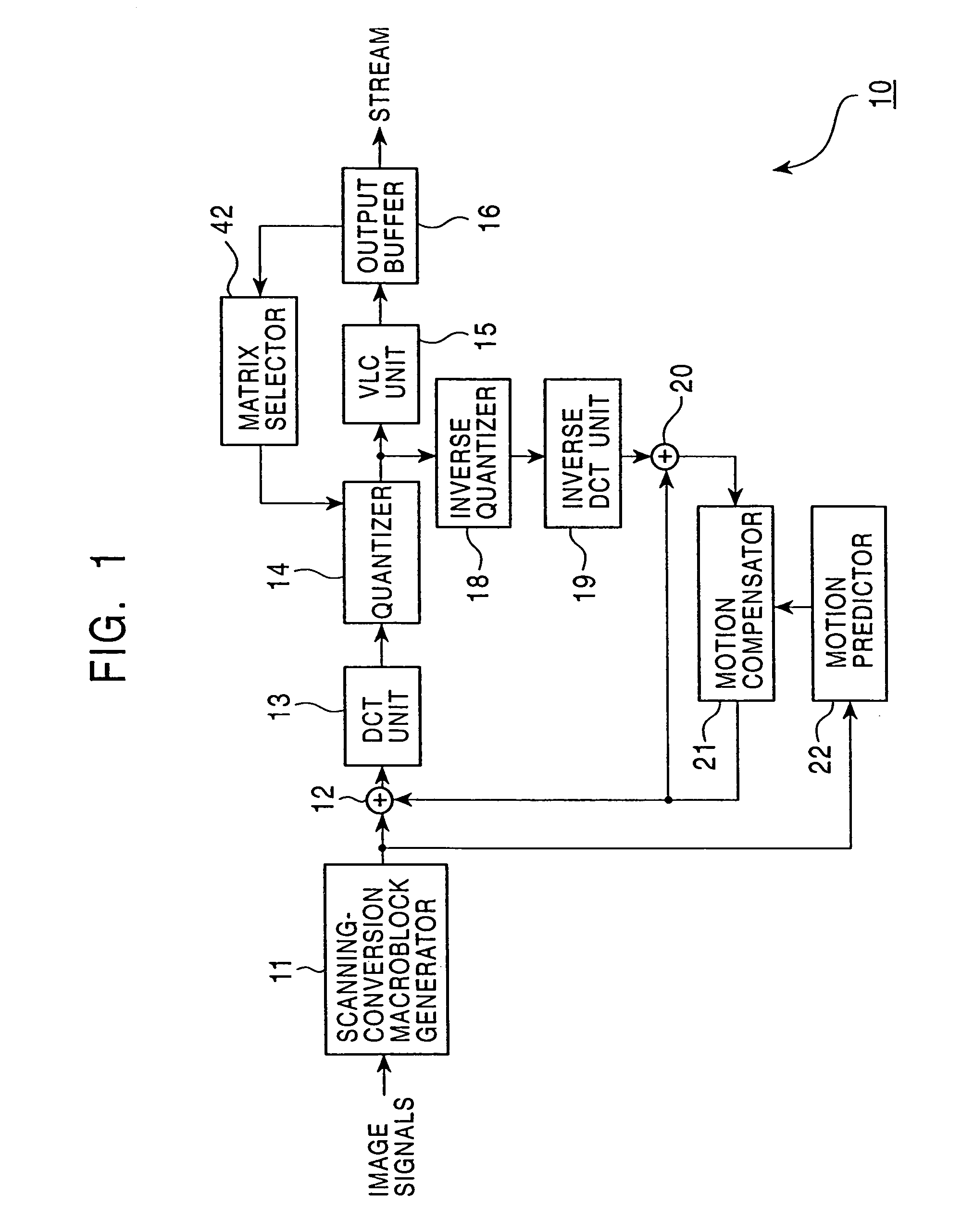
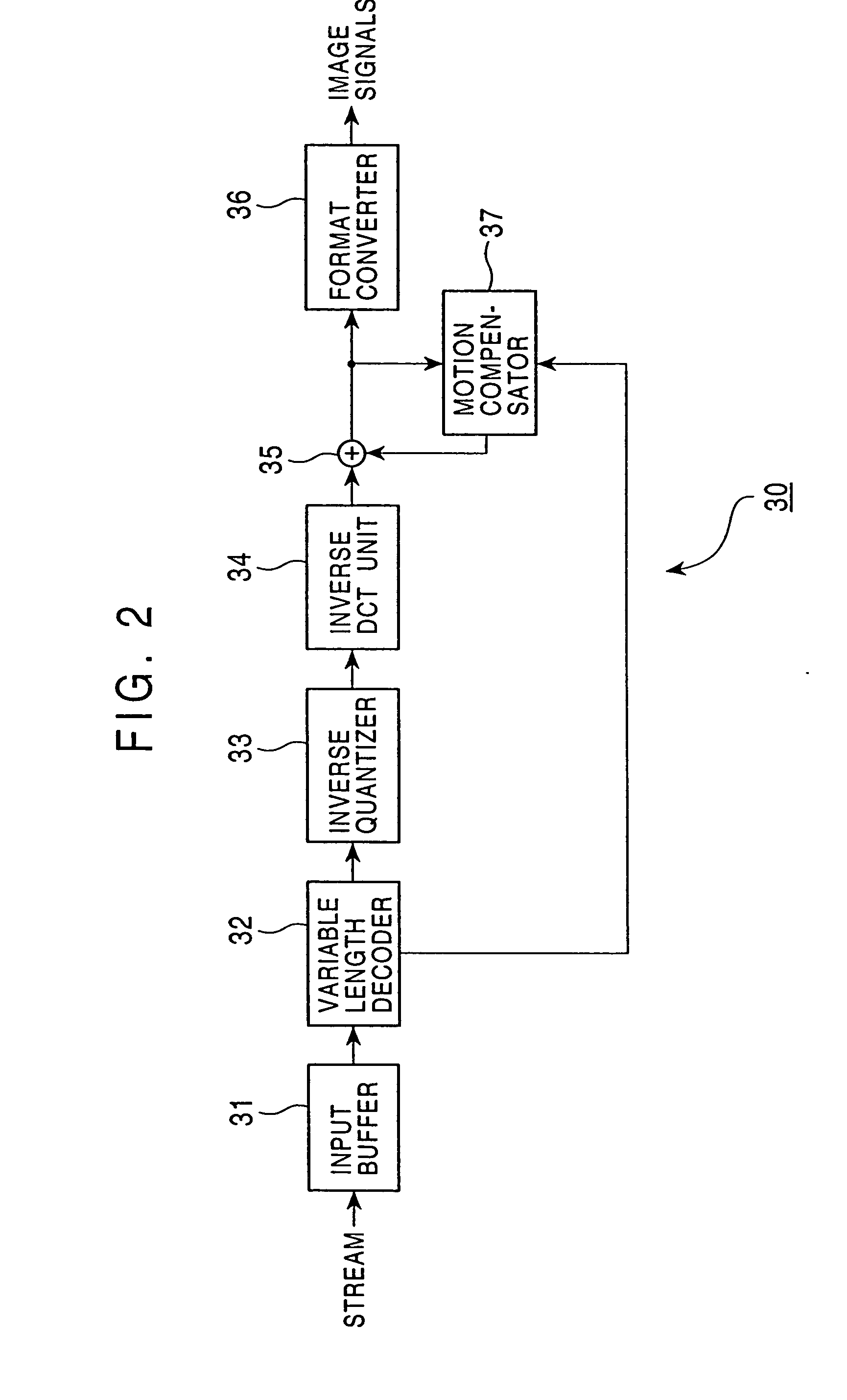
An encoding apparatus and method prevents image deterioration generated by repeatedly performing encoding and decoding by using a quantization matrix for quantization which is different from a quantization matrix for inverse quantization. In the encoding apparatus, a matrix selector selects a first quantization matrix in accordance with the complexity of an encoded picture pattern, and supplies a quantizer with information on the selected first quantization matrix. A matrix unit rewrites, by information on a second quantization matrix, the information described in an encoded stream output from a variable length code unit so that a quantization matrix to be used for inverse quantization is a second quantization matrix different from the first quantization matrix.
Owner:SONY CORP
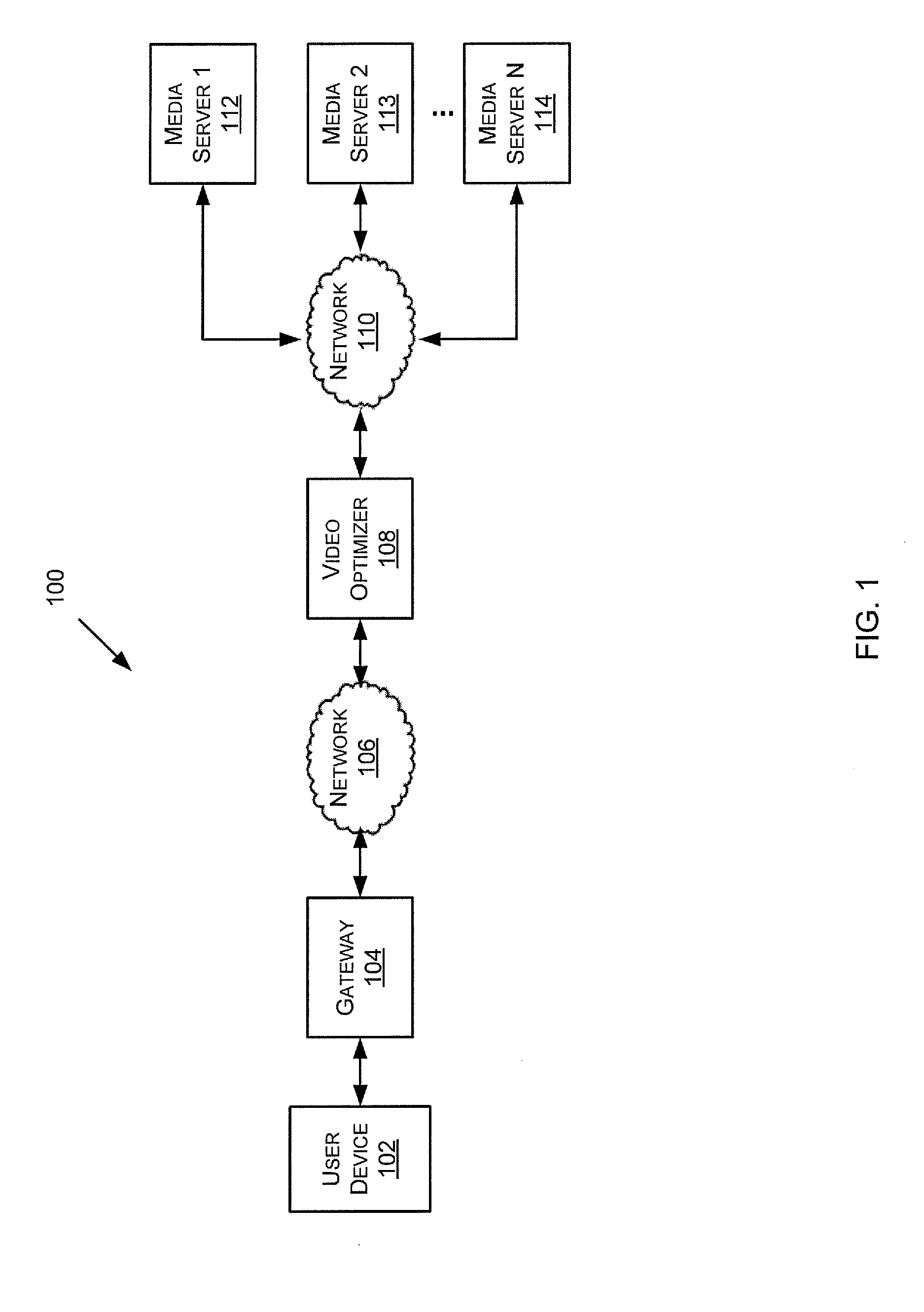
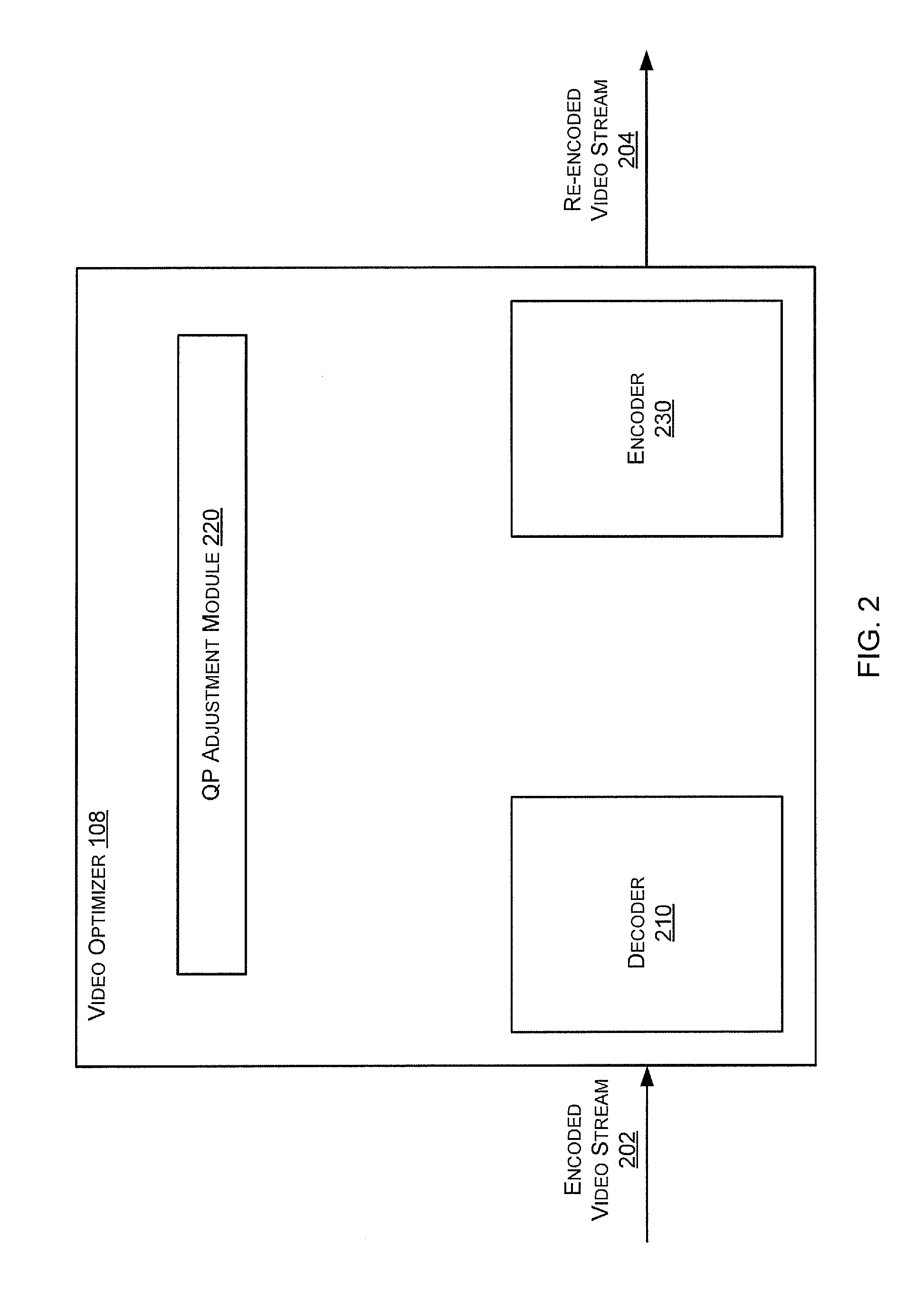
Macroblock-Level Adaptive Quantization in Quality-Aware Video Optimization
ActiveUS20120314764A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo optimizationPattern recognition
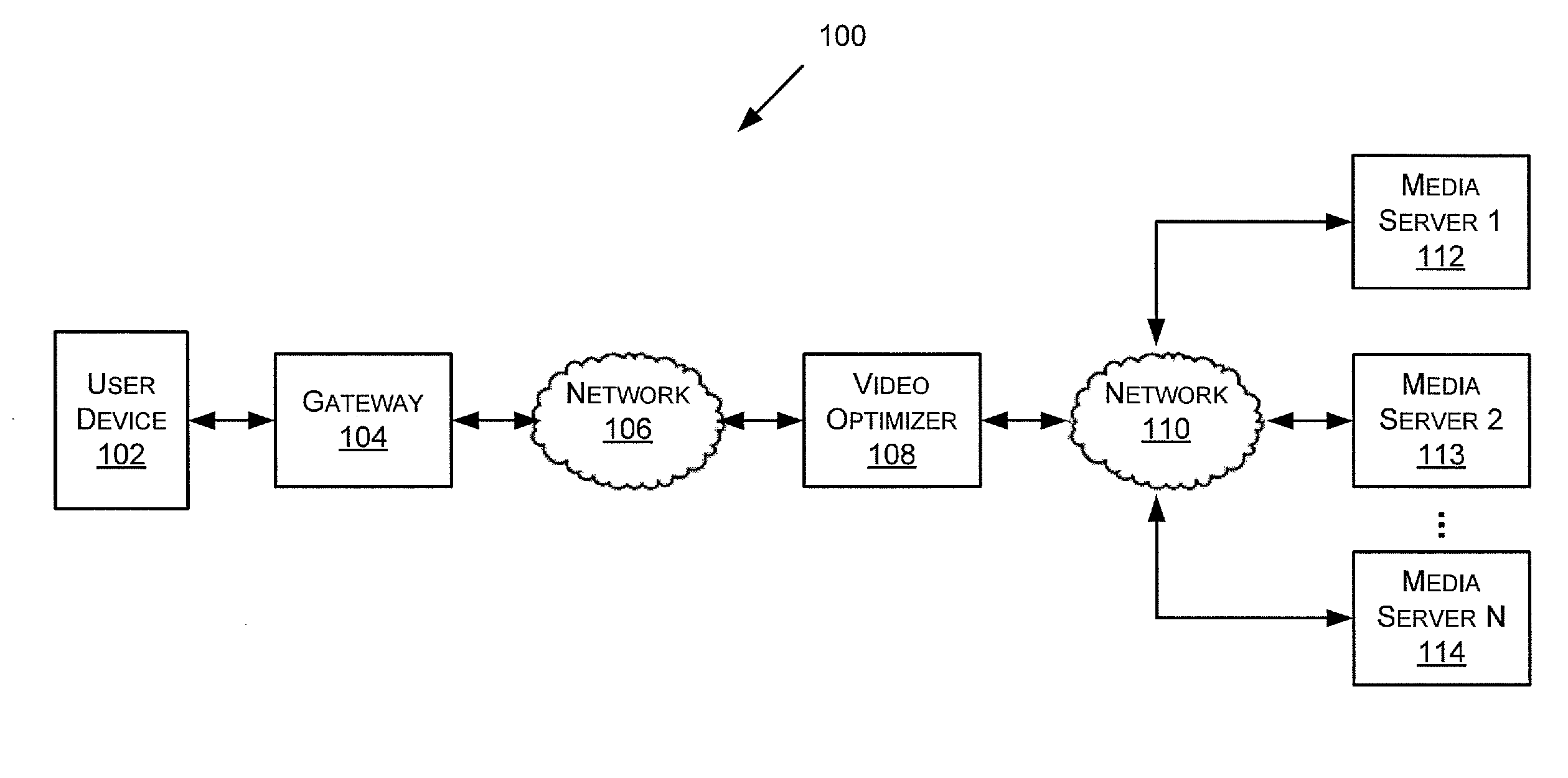
A method of optimizing an encoded video stream comprising one or more video frames, each video frame comprising a plurality of macroblocks, each macroblock comprising a plurality of pixels. The method includes receiving an encoded macroblock, decoding the encoded macroblock, and extracting a first quantization parameter. The first quantization parameter corresponds to quantization settings originally used for compressing the encoded macroblock. The method also includes computing a second quantization parameter based at least in part on the first quantization parameter, re-encoding the decoded macroblock based on the second quantization parameter, and providing the re-encoded macroblock.
Owner:BYTEMOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
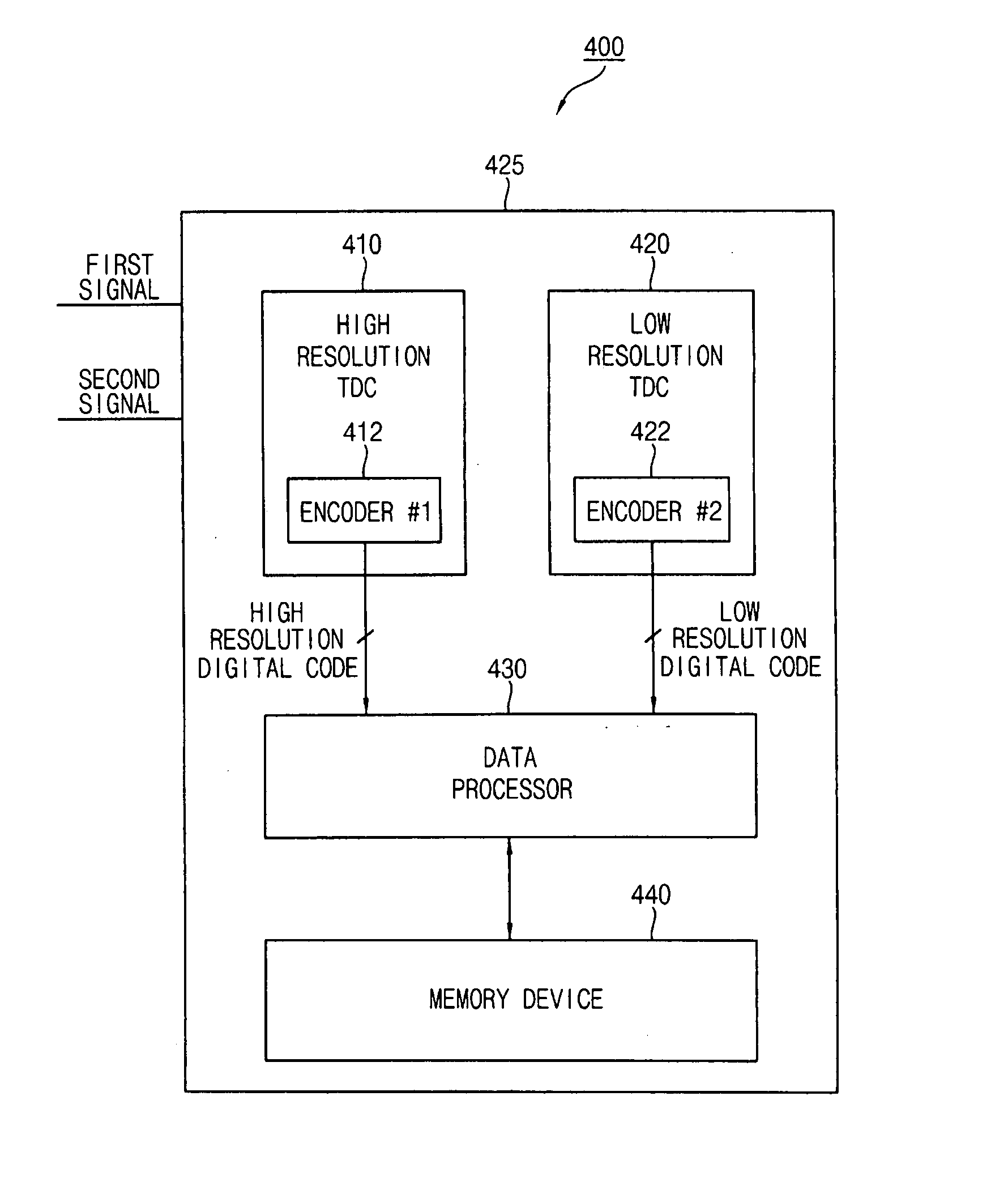
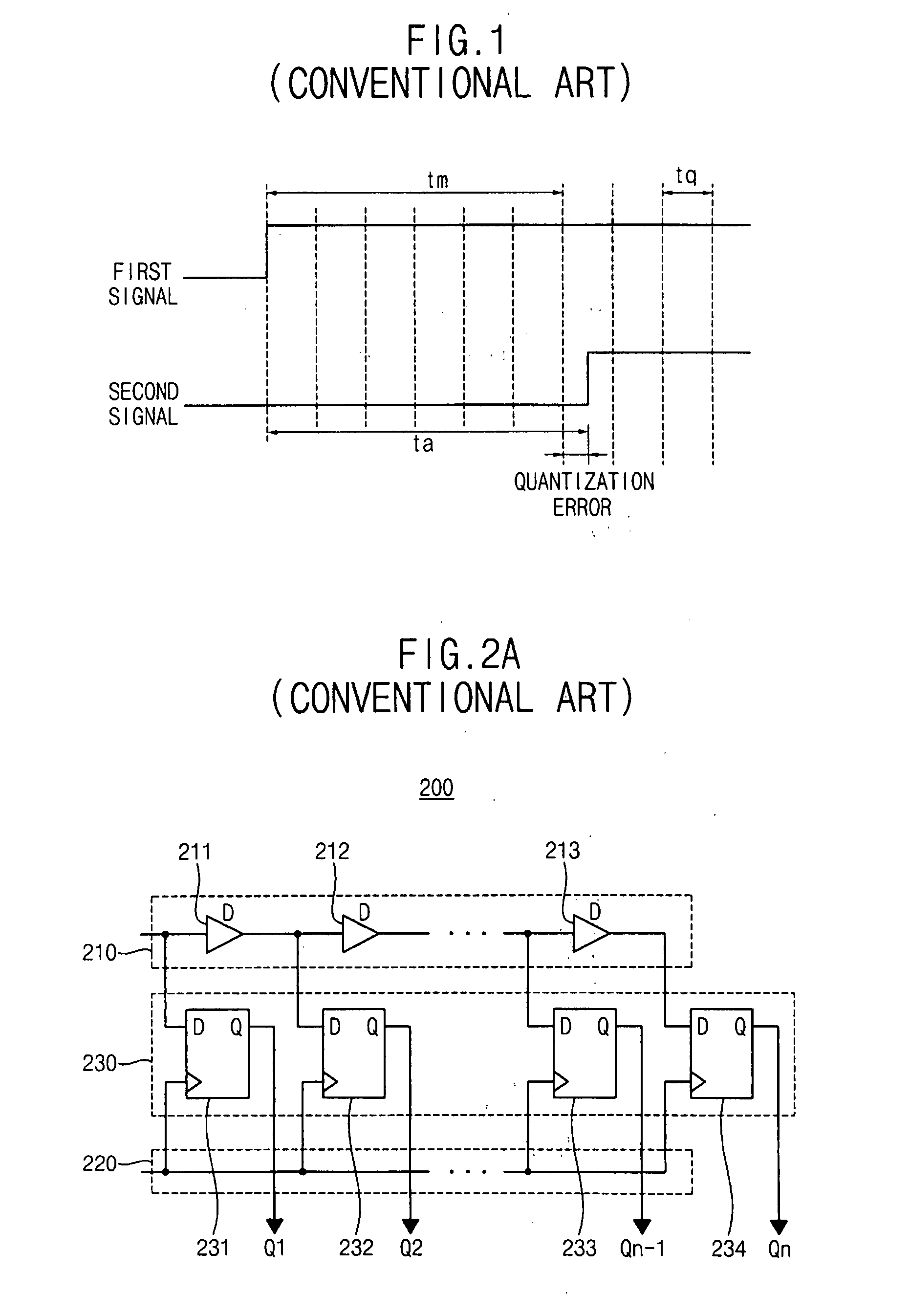
Time-to-digital converter with high resolution and wide measurement range
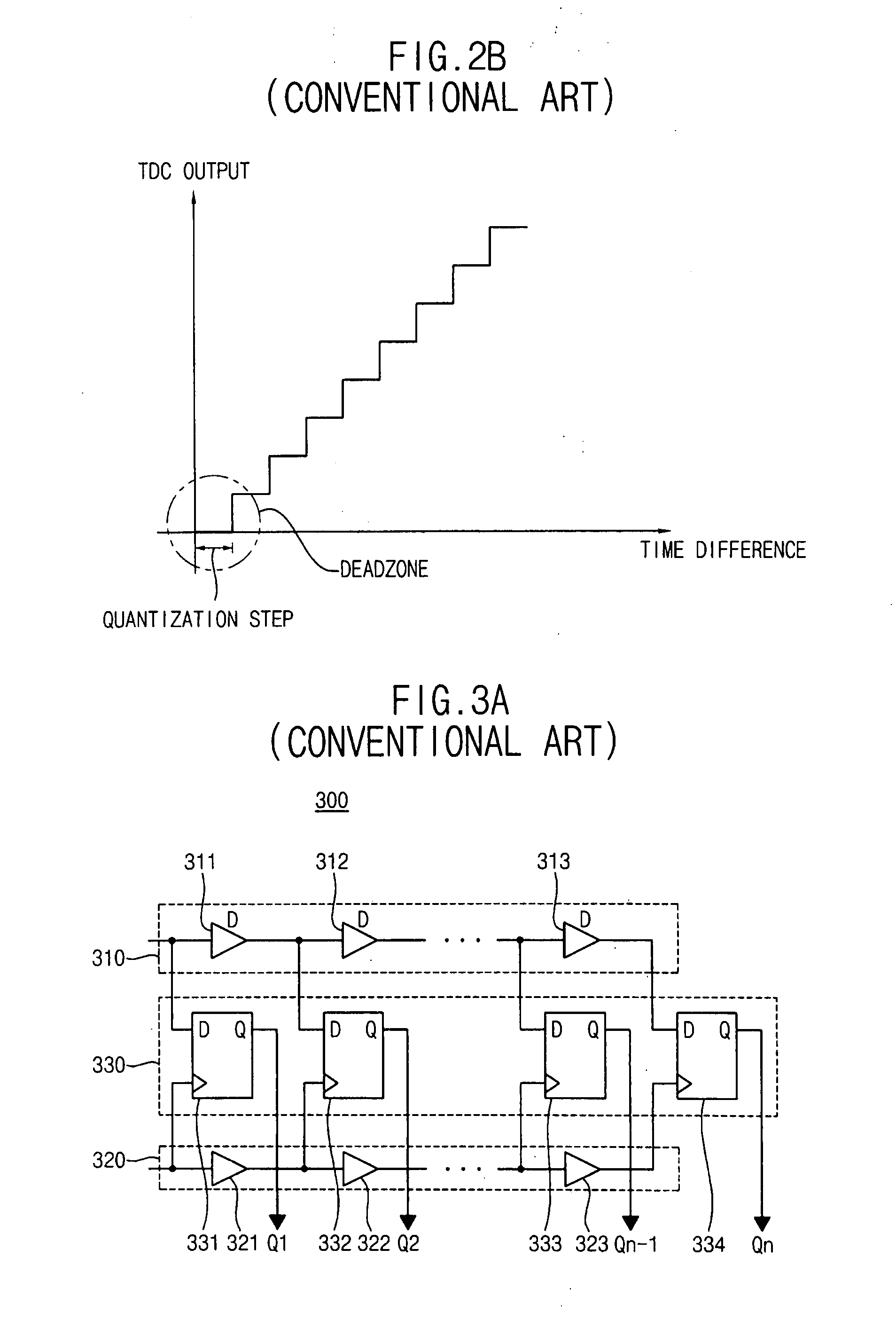
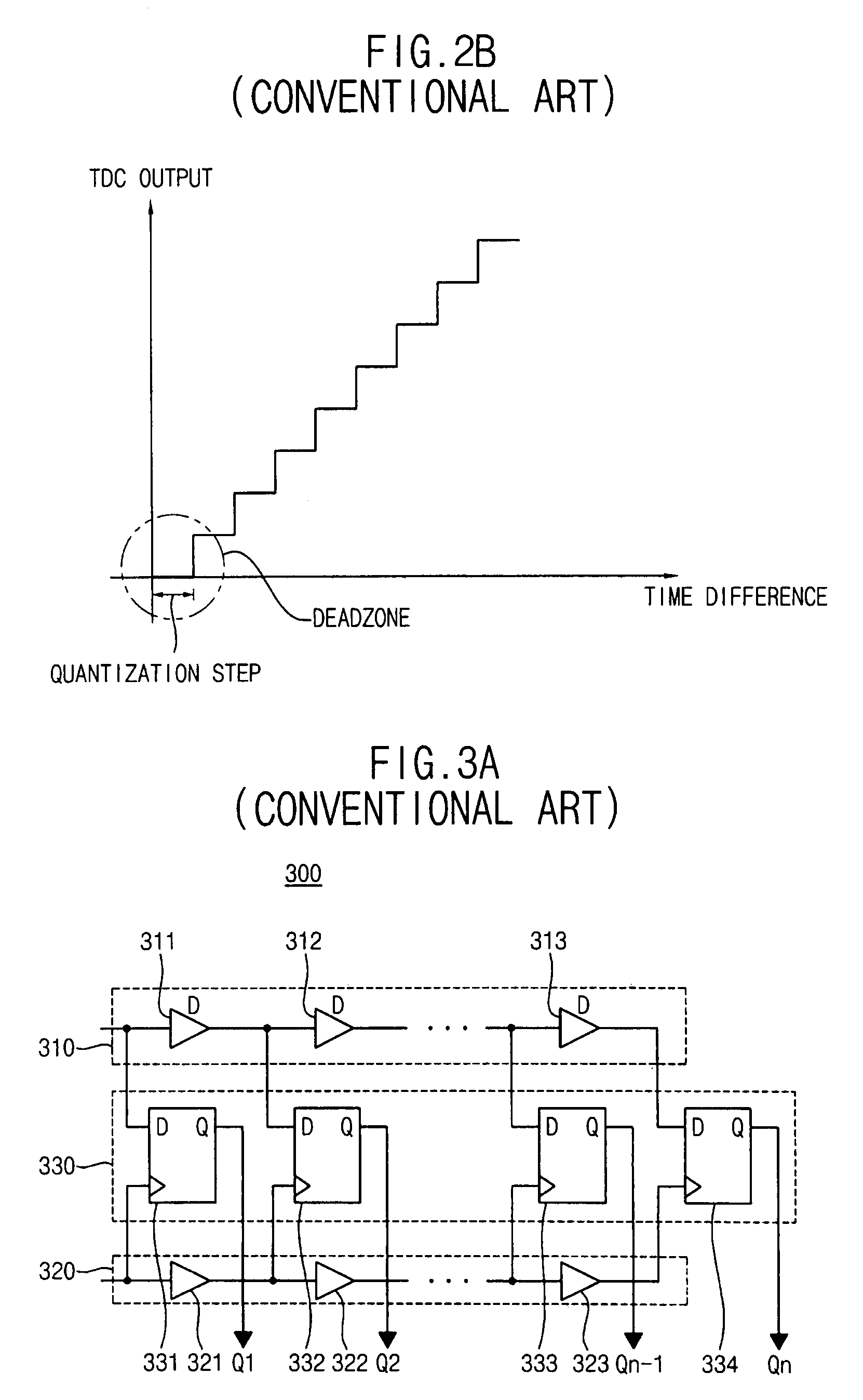
ActiveUS20080129574A1High resolutionWide measurement rangeElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlImage resolutionDigital converter
A time-to-digital converter includes low and high resolution time-to-digital converters for providing both high resolution and wide measurement range. The low resolution time-to-digital converter measures a time difference between first and second signals with a first quantization step. The high resolution time-to-digital converter measures the time difference between the first and second signals with a second quantization step that is smaller than the first quantization step. The low resolution time-to-digital converter has a wider measurement range than the high resolution time-to-digital converter
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
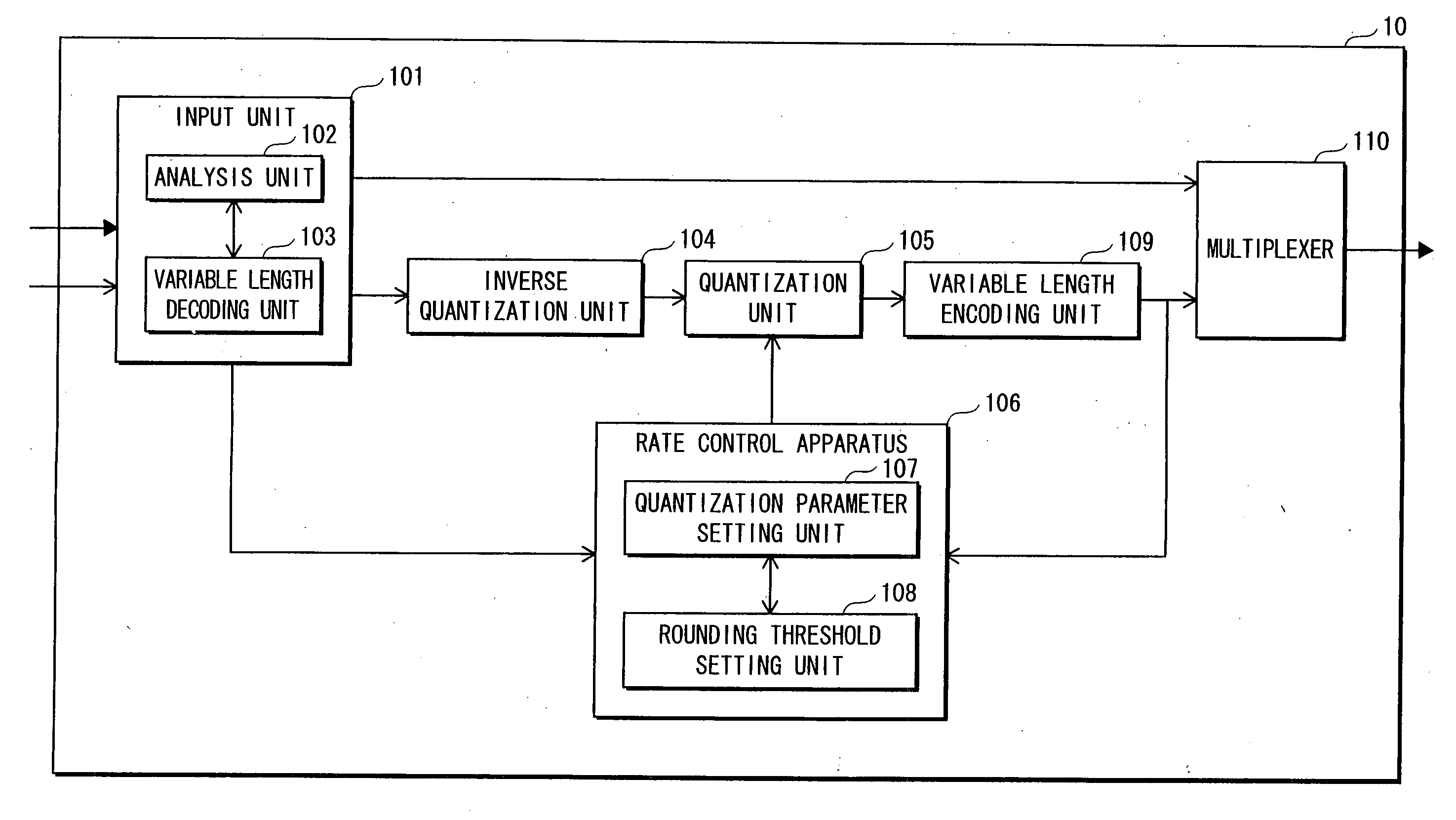
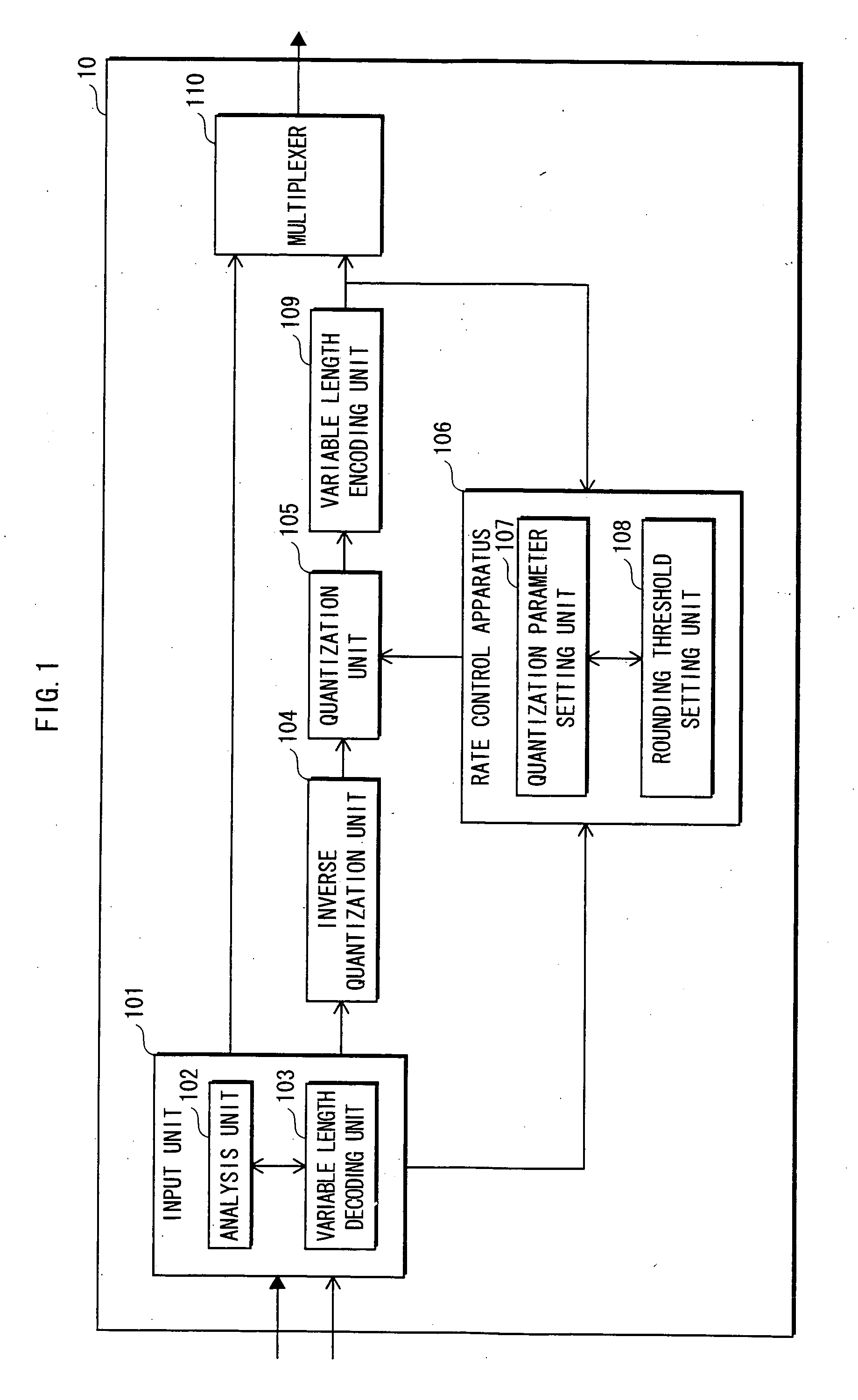
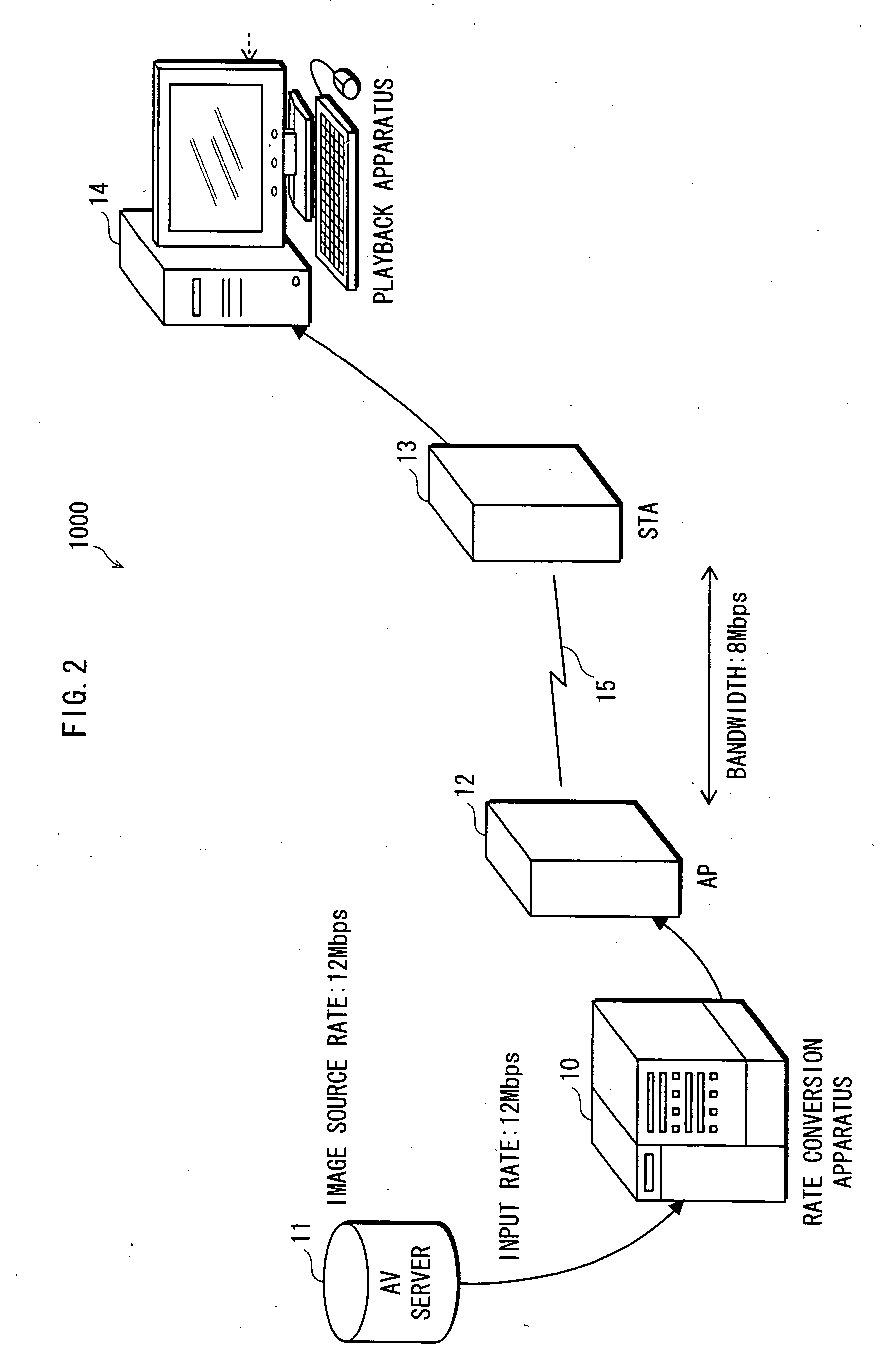
Image conversion apparatus
InactiveUS20060171460A1Reduce deteriorationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage conversionVariable length
A rate conversion apparatus 10 includes a quantization parameter setting unit 107 and a rounding threshold value setting unit 108. The quantization parameter setting unit 107 determines a quantization parameter change amount according to a code amount of encoded data output from a variable length encoding unit 109 and a target code amount. The quantization parameter setting unit 107 adds a first quantization amount used in an image before conversion to the quantization parameter change amount, to generate a second quantization parameter to be used in re-quantization processing in a quantization unit 105. The rounding threshold value setting unit 108 sets the rounding threshold value according to the quantization parameter change amount. The quantization unit 105 performs re-quantization using the second quantization parameter and the rounding threshold value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Encoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050169547A1Reduce image qualityHigh spatial frequencyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingVariable-length codeAlgorithm
An encoding apparatus and method prevents image deterioration generated by repeatedly performing encoding and decoding by using a quantization matrix for quantization which is different from a quantization matrix for inverse quantization. In the encoding apparatus, a matrix selector selects a first quantization matrix in accordance with the complexity of an encoded picture pattern, and supplies a quantizer with information on the selected first quantization matrix. A matrix unit rewrites, by information on a second quantization matrix, the information described in an encoded stream output from a variable length code unit so that a quantization matrix to be used for inverse quantization is a second quantization matrix different from the first quantization matrix.
Owner:SONY CORP
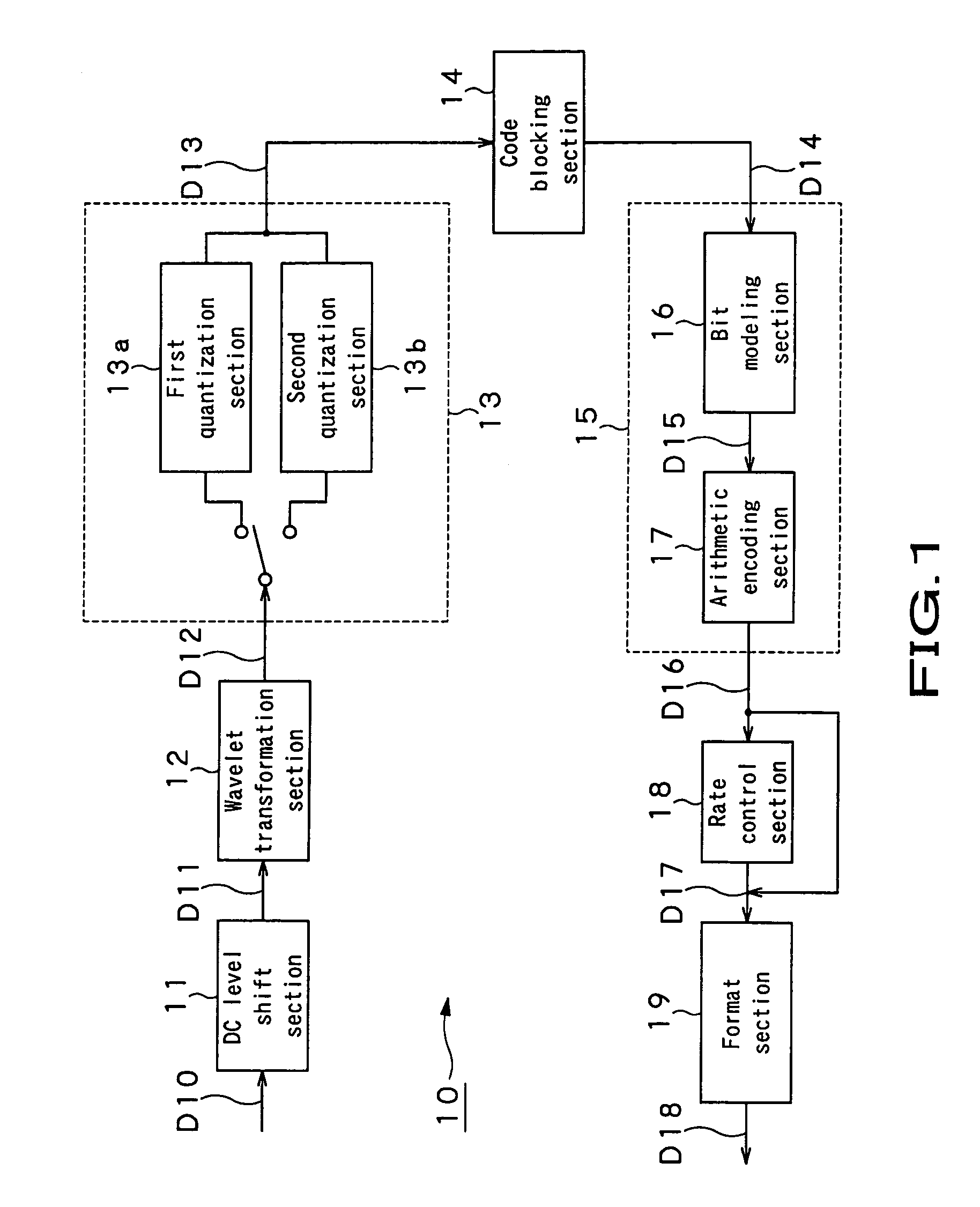
Image encoder, image encoding method, image decoder, and image decoding method
InactiveUS7463780B2Image quality variesEliminate loss of detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionImaging qualityDeadband
In an image encoder, a first quantization section which is selected when normal image quality is required performs quantization by dividing a wavelet transformation coefficient by a quantization step size and by thereafter rounding down a fraction thereof. On the other side, a second quantization section which is selected when high image quality is required performs quantization by dividing a wavelet transformation coeffient by a quantization step size, by adding 0.5 to the dividing result, and by thereafter rounding down a fraction thereof. Therefore, the width of a dead zone where coefficients are quantized to a value of 0 is narrower than that in the first quantization section, and higher image quality is obtained accordingly.
Owner:SONY CORP
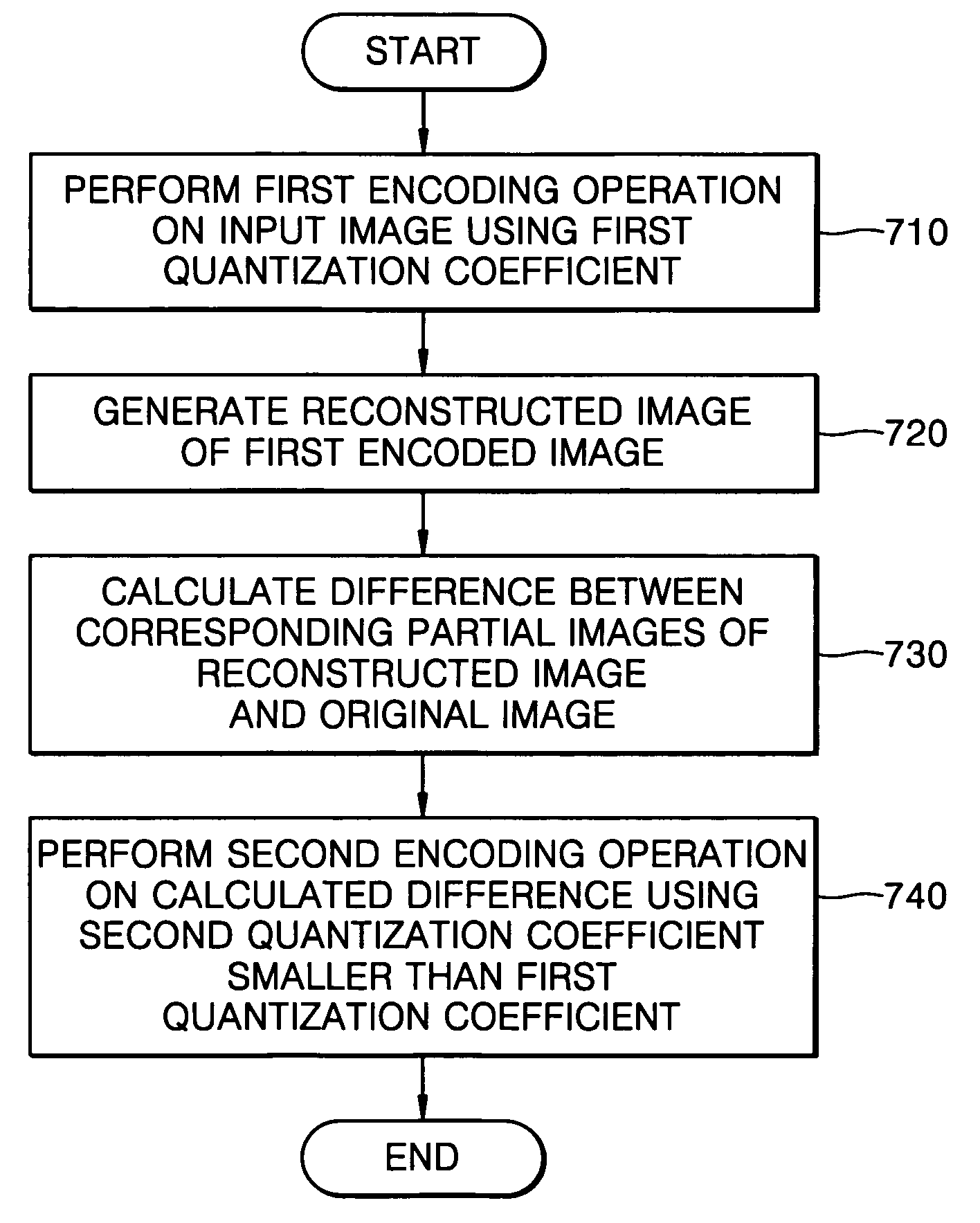
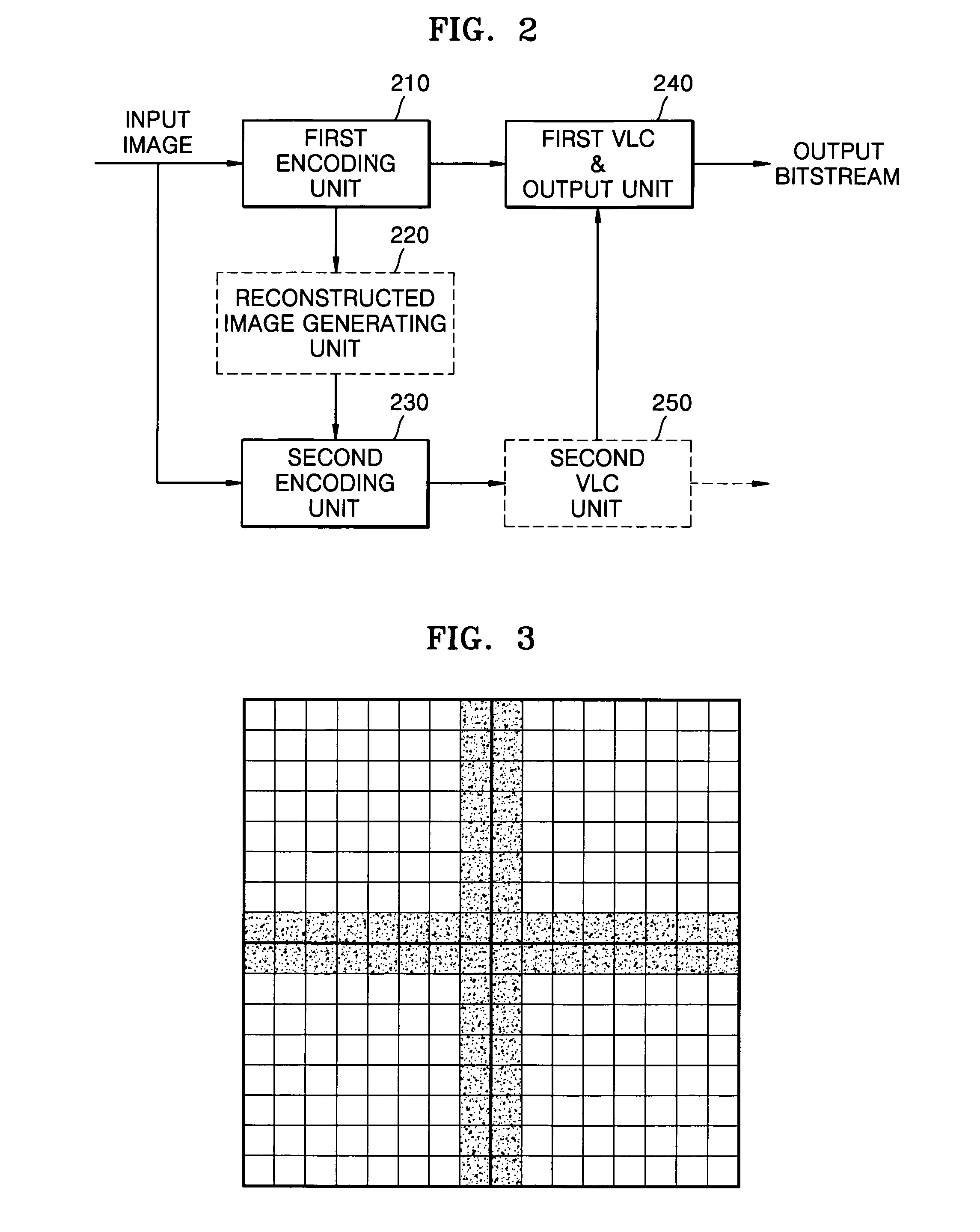
Encoding and decoding apparatus and method for reducing blocking phenomenon and computer-readable recording medium storing program for executing the method
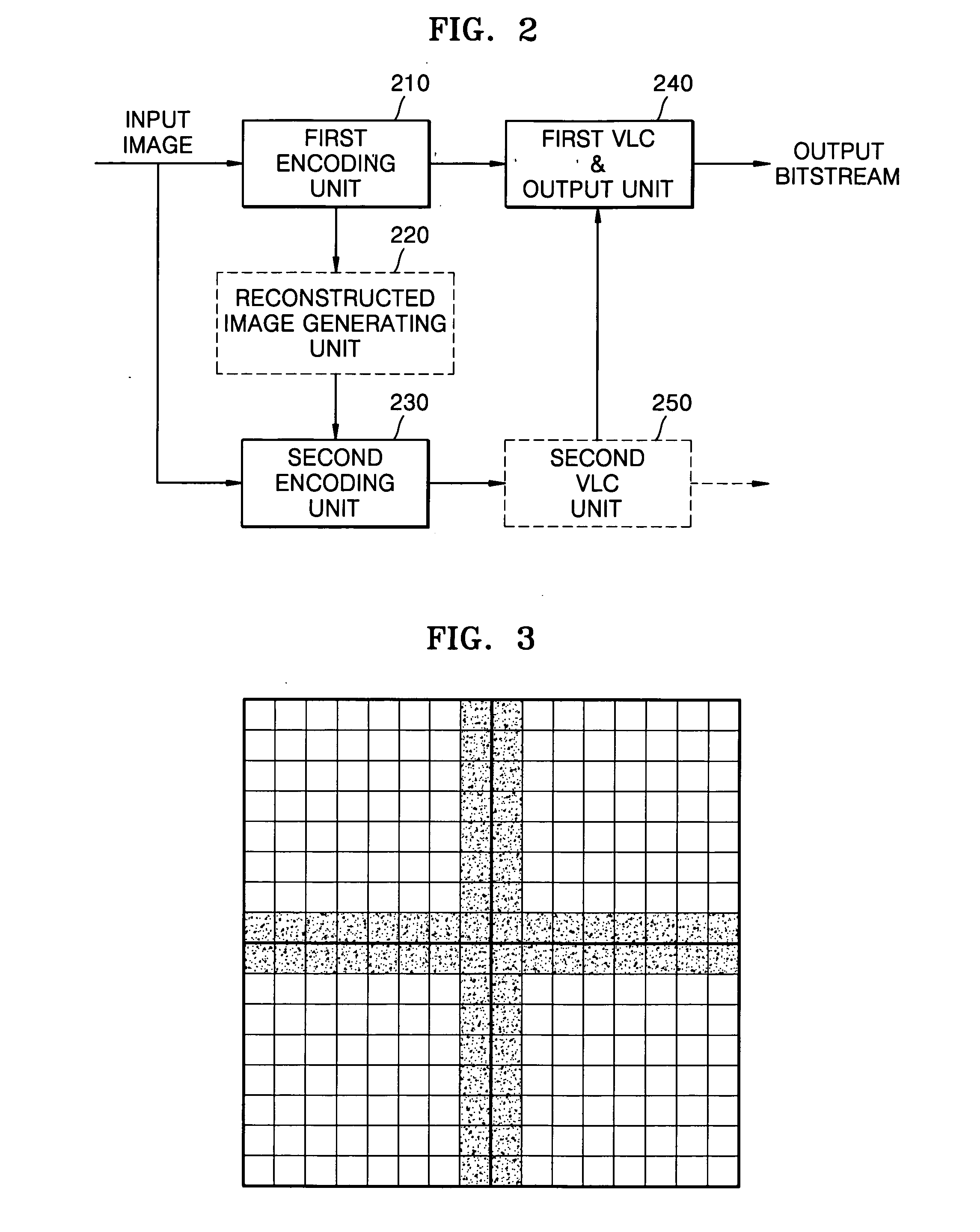
InactiveUS7738716B2Increase the number ofReduce cloggingCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareFirst quantization
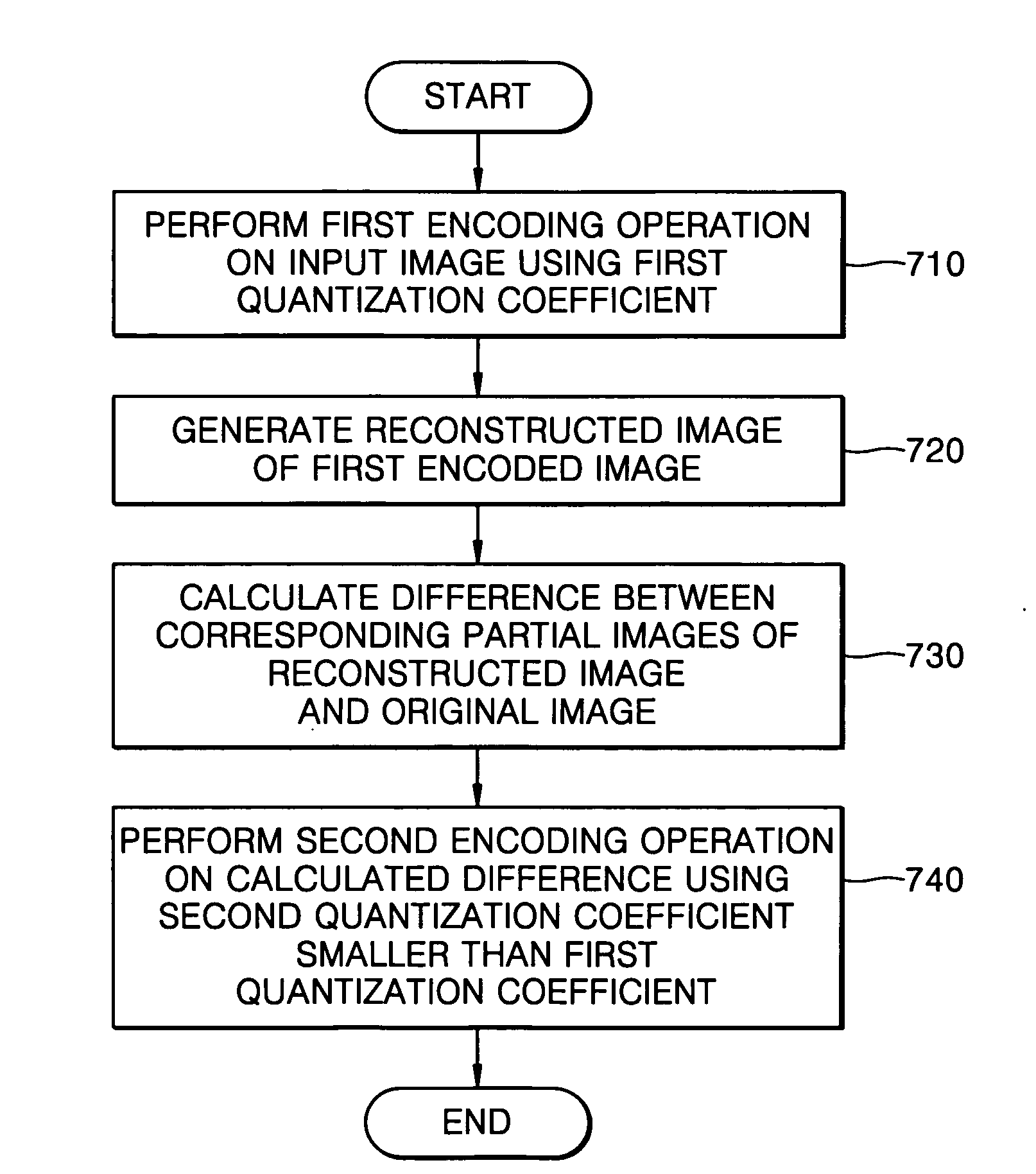
Provided is an encoding method capable of reducing a blocking phenomenon that occurs when moving-images are encoded and decoded. The method includes: performing a first encoding operation on an input image using a first quantization coefficient; generating a reconstructed image of the encoded image; calculating a difference between corresponding partial images of the reconstructed image and the input image; and performing a second encoding operation on the calculated difference using a second quantization coefficient smaller than the first quantization coefficient. Using the second encoded difference, a decoding unit can reconstruct an image of a block boundary portion more elaborately with a small number of bits, thereby significantly reducing the blocking phenomenon in the decoding operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
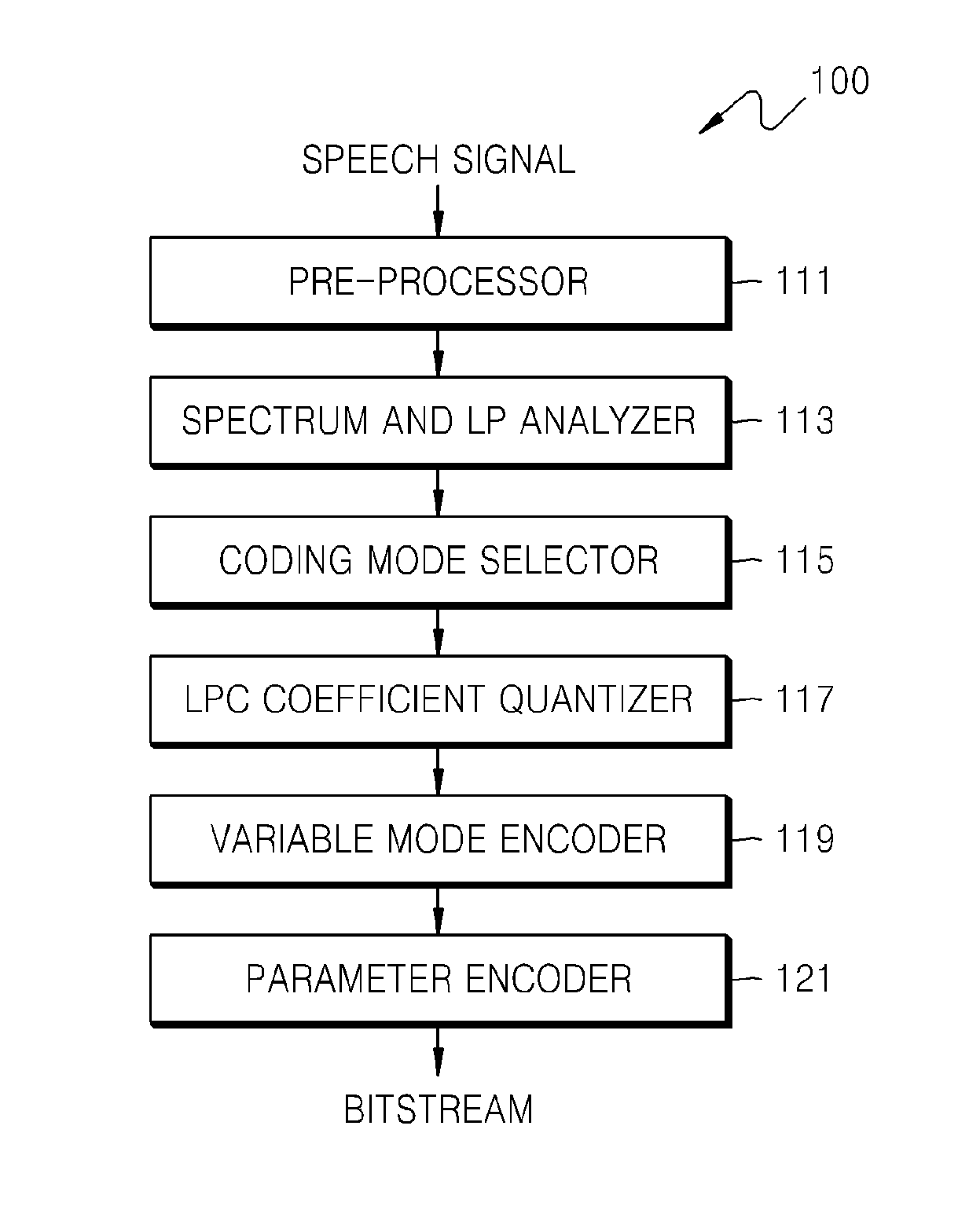
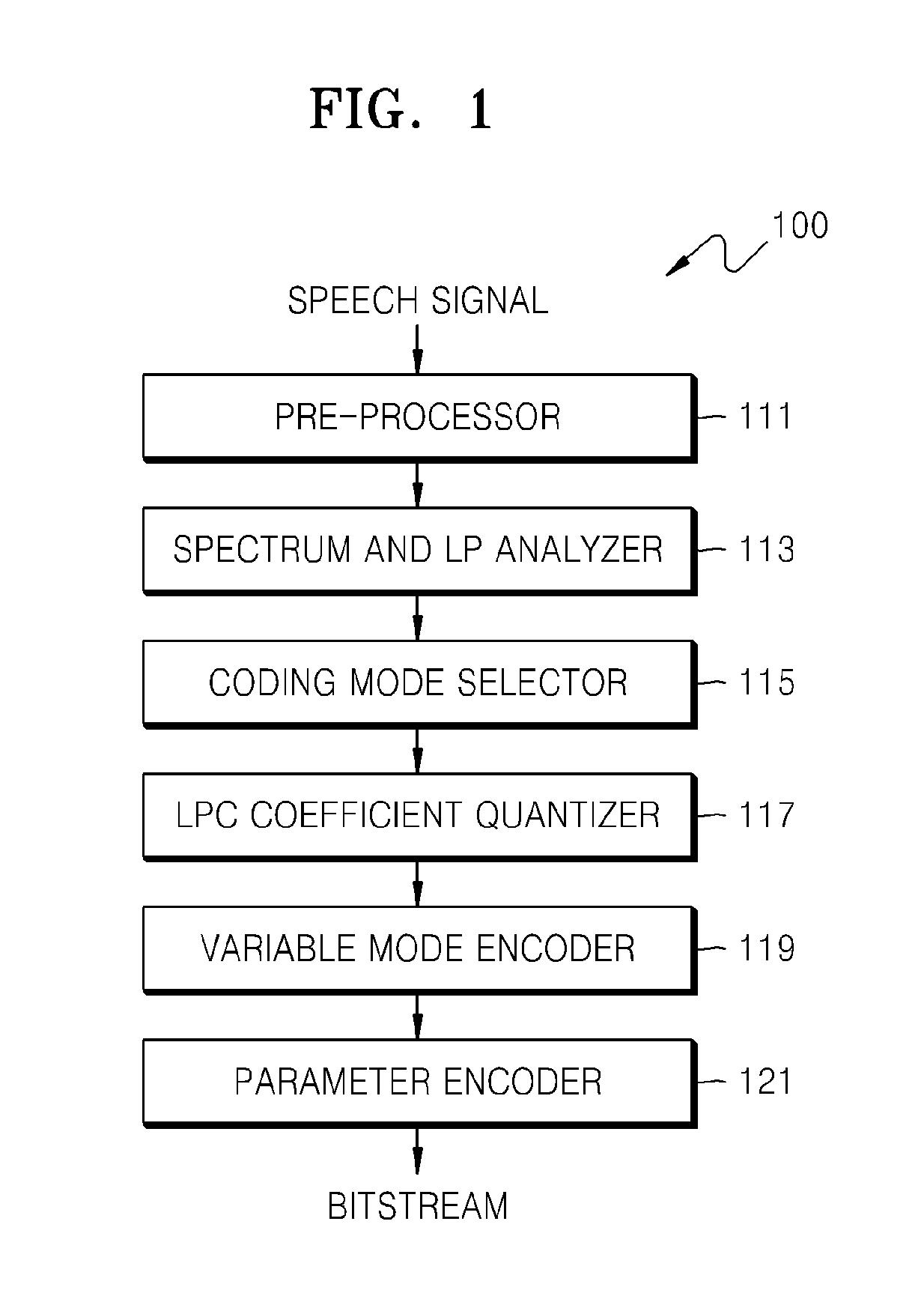
Method of quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound encoding method, method of de-quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound decoding method, and recording medium and electronic device therefor
ActiveUS20120278069A1Efficiently quantizedReduce complexitySpeech analysisDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsTransmission channel
A quantizing method is provided that includes quantizing an input signal by selecting one of a first quantization scheme not using an inter-frame prediction and a second quantization scheme using the inter-frame prediction, in consideration of one or more of a prediction mode, a predictive error and a transmission channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter with pipelined multi-bit quantization
ActiveUS7432841B1High accuracy conversionImprove performanceElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionLeast significant bitNoise shaping
A cascaded analog-to-digital converter includes a first stage delta-sigma modulator to quantize an input signal and produce a first quantization error signal. A second, coupled multi-stage delta-sigma modulator quantizes less significant bits of the input signal, wherein a first quantization stage is coupled to the first quantization error signal to quantize the next most significant bits of the input signal and produce a second quantization error signal. A second quantization stage is coupled to the second quantization error signal to quantize the least significant bits of the input signal and produce a third quantization error signal. A noise-shaping filter is coupled to the third quantization error signal, the output of which is subtracted from the first quantization error signal to produce said input of the first quantization stage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
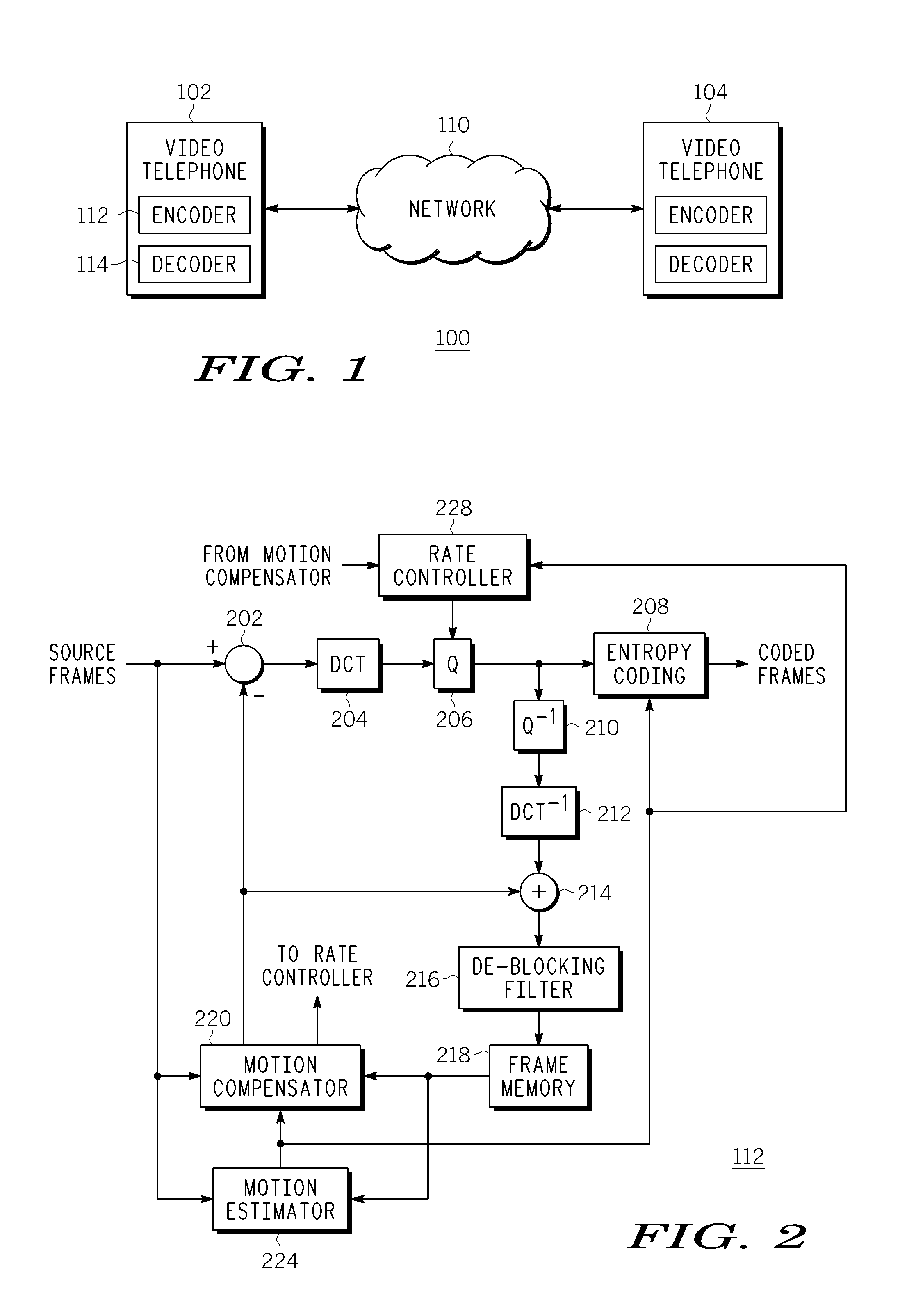
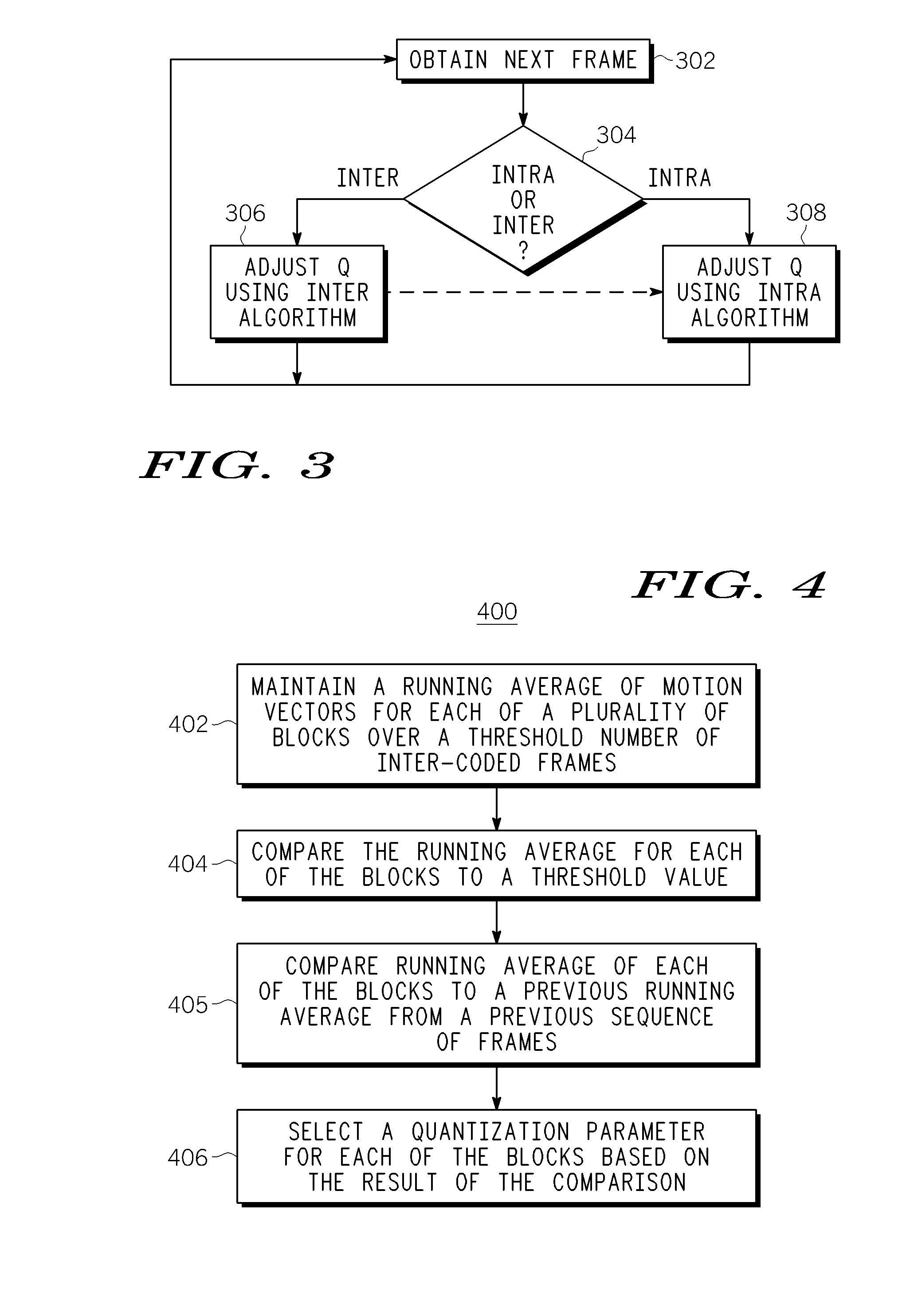
Method and Apparatus for Bit Rate Reduction in Video Telephony
Method and apparatus for encoding video is described. In one example, average of motion vectors for each of a plurality of blocks is maintained over a threshold number of inter-coded frames in the video. The running average of motion vectors for each of the plurality of blocks is compared to a threshold value. Each of the plurality of blocks the running average of which does not satisfy the threshold value is encoded using a first quantization parameter. Each of the plurality of blocks the running average of which satisfies the threshold value is encoded using a second quantization parameter. The second quantization parameter results in a coarser quantization of transformed coefficients than the first quantization parameter.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Time-to-digital converter with high resolution and wide measurement range
ActiveUS7667633B2Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlImage resolutionDigital converter
A time-to-digital converter includes low and high resolution time-to-digital converters for providing both high resolution and wide measurement range. The low resolution time-to-digital converter measures a time difference between first and second signals with a first quantization step. The high resolution time-to-digital converter measures the time difference between the first and second signals with a second quantization step that is smaller than the first quantization step. The low resolution time-to-digital converter has a wider measurement range than the high resolution time-to-digital converter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
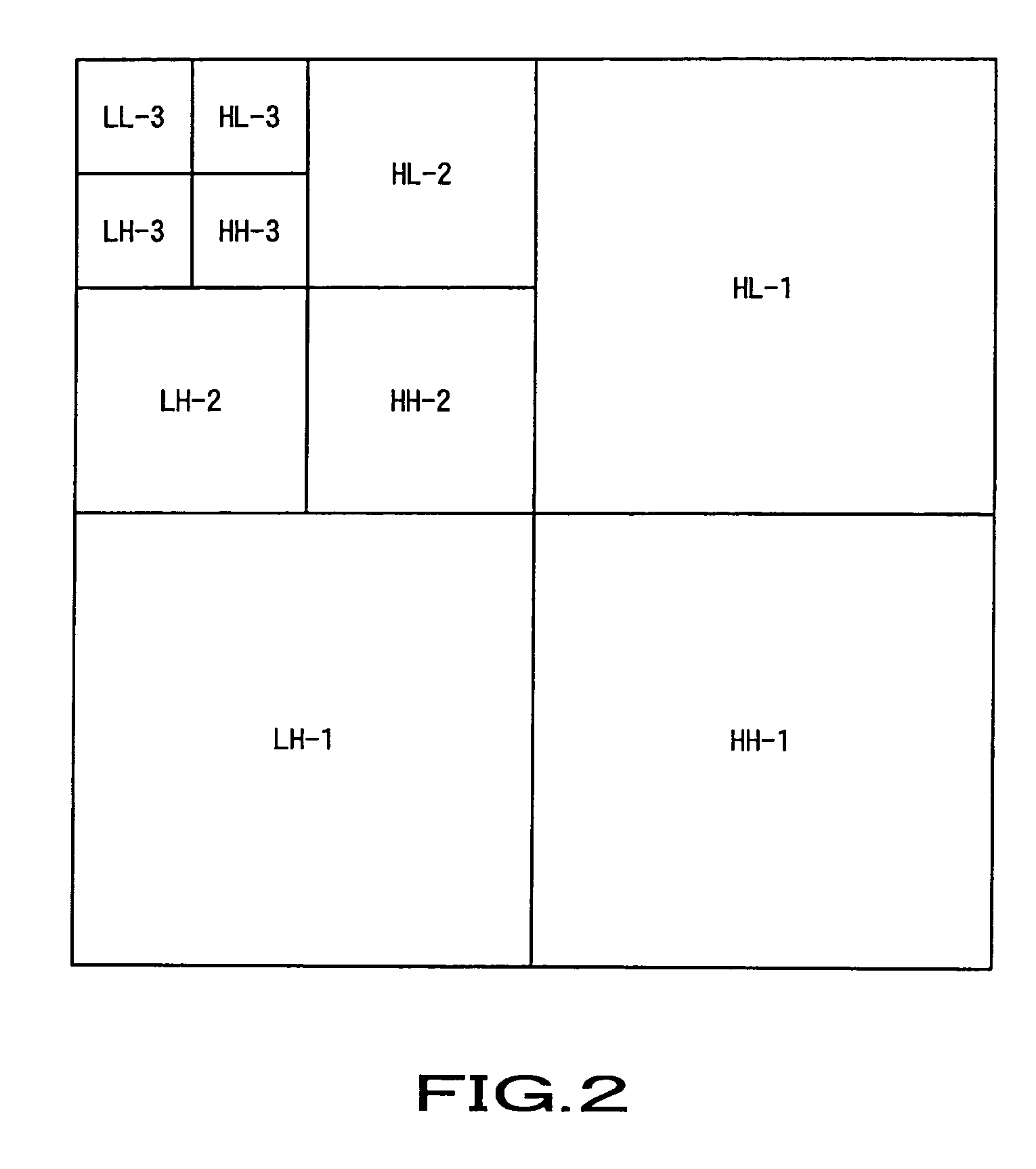
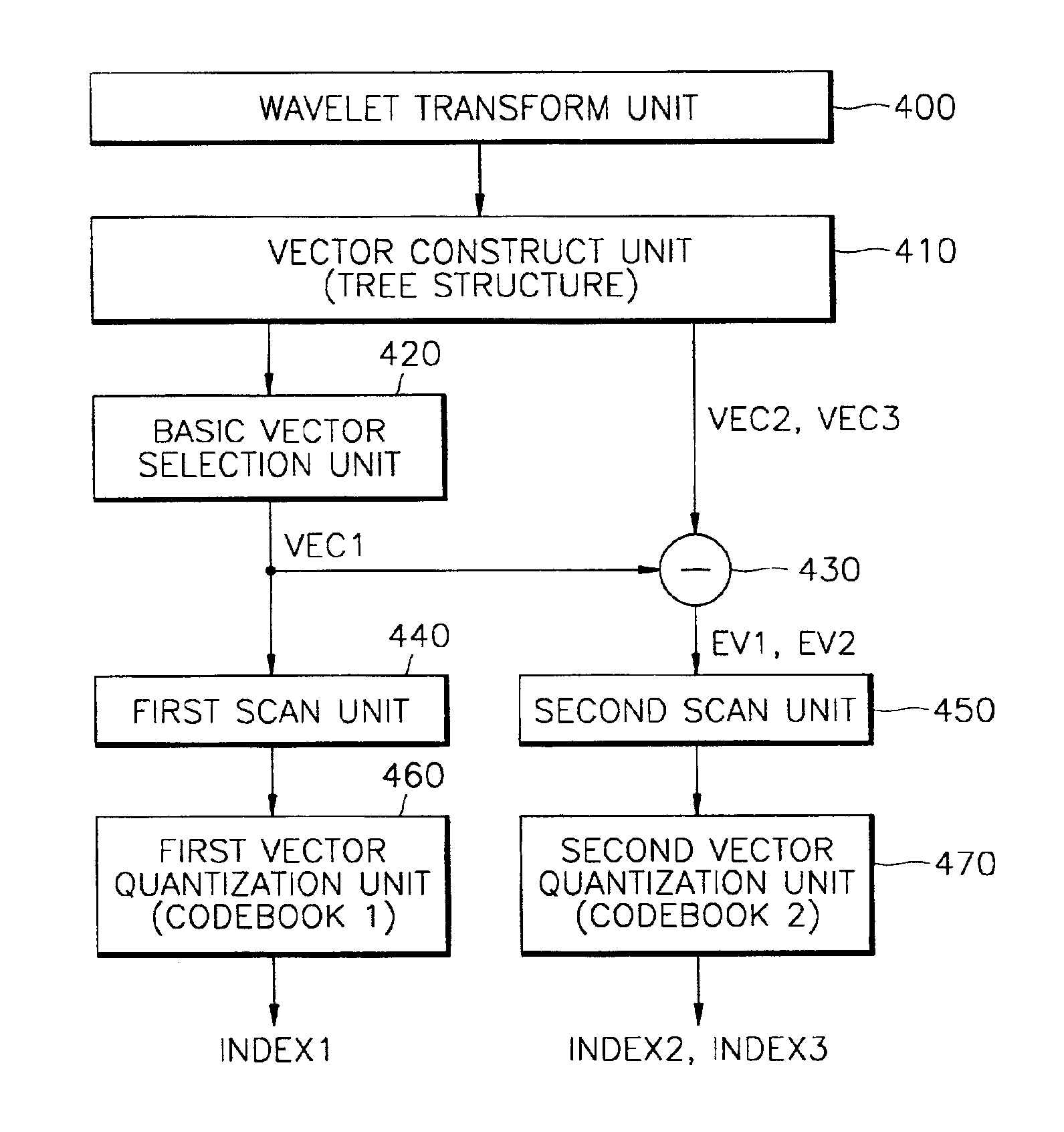
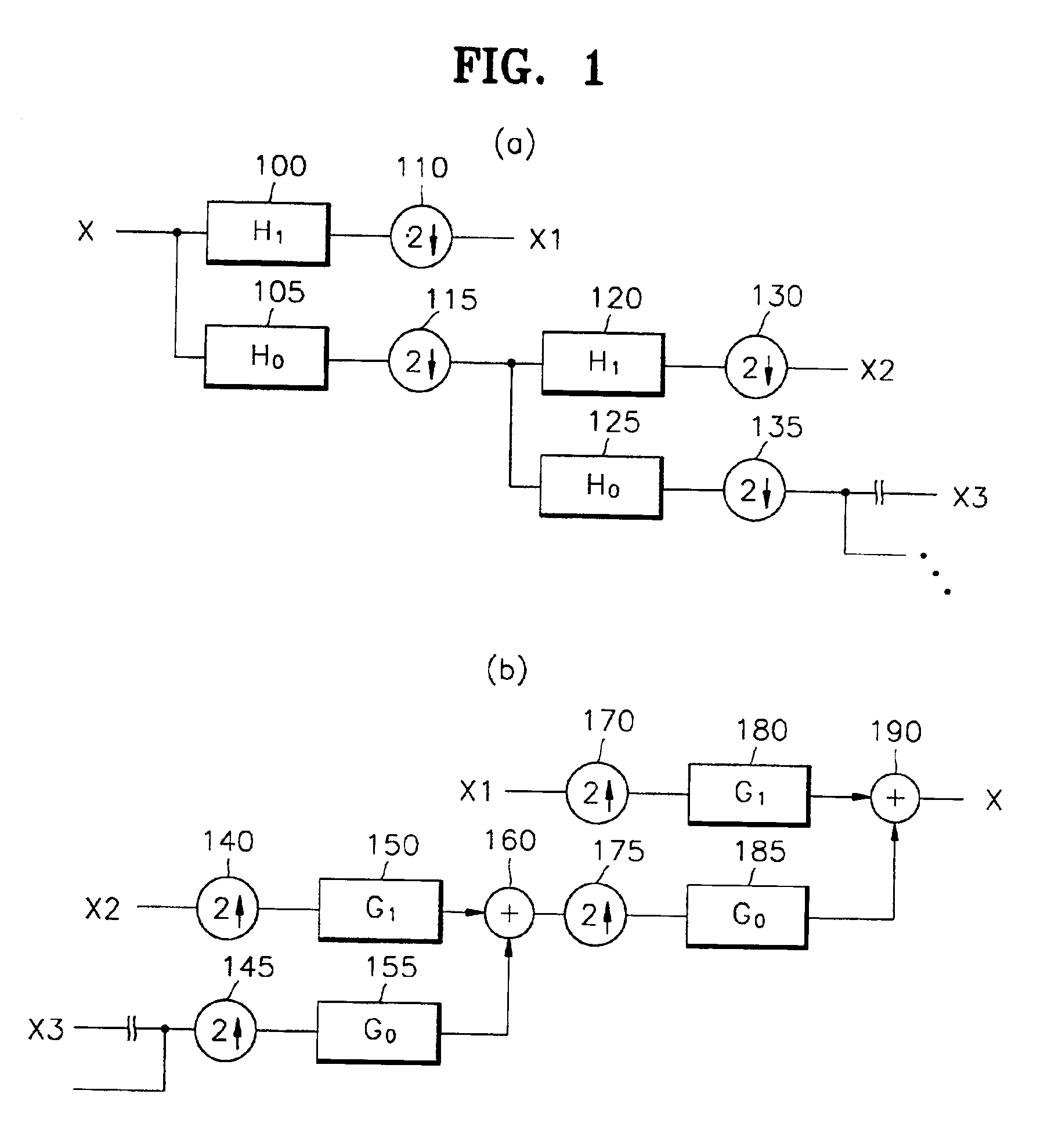
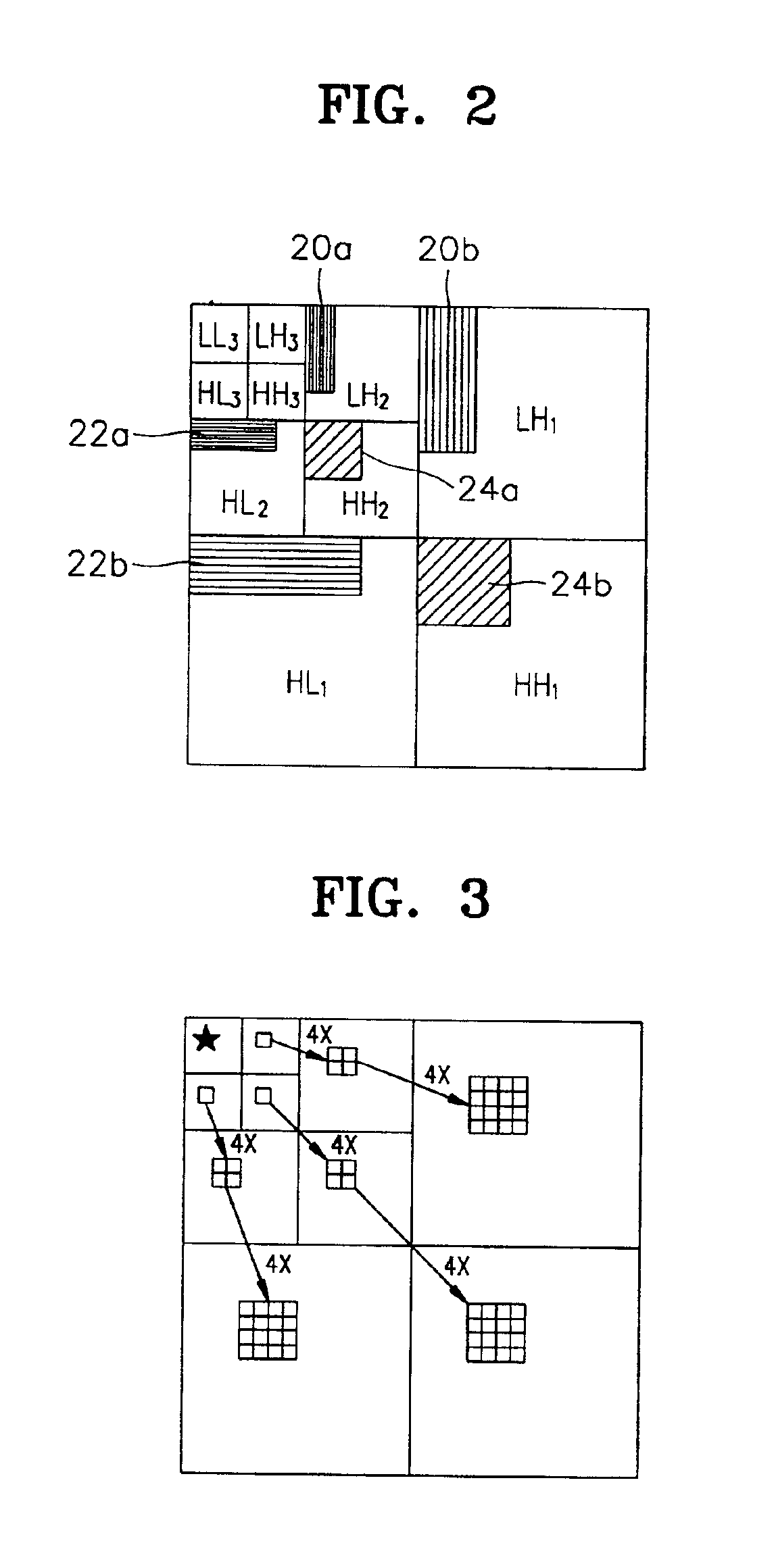
Apparatus and method for image coding using tree-structured quantization based on wavelet transform
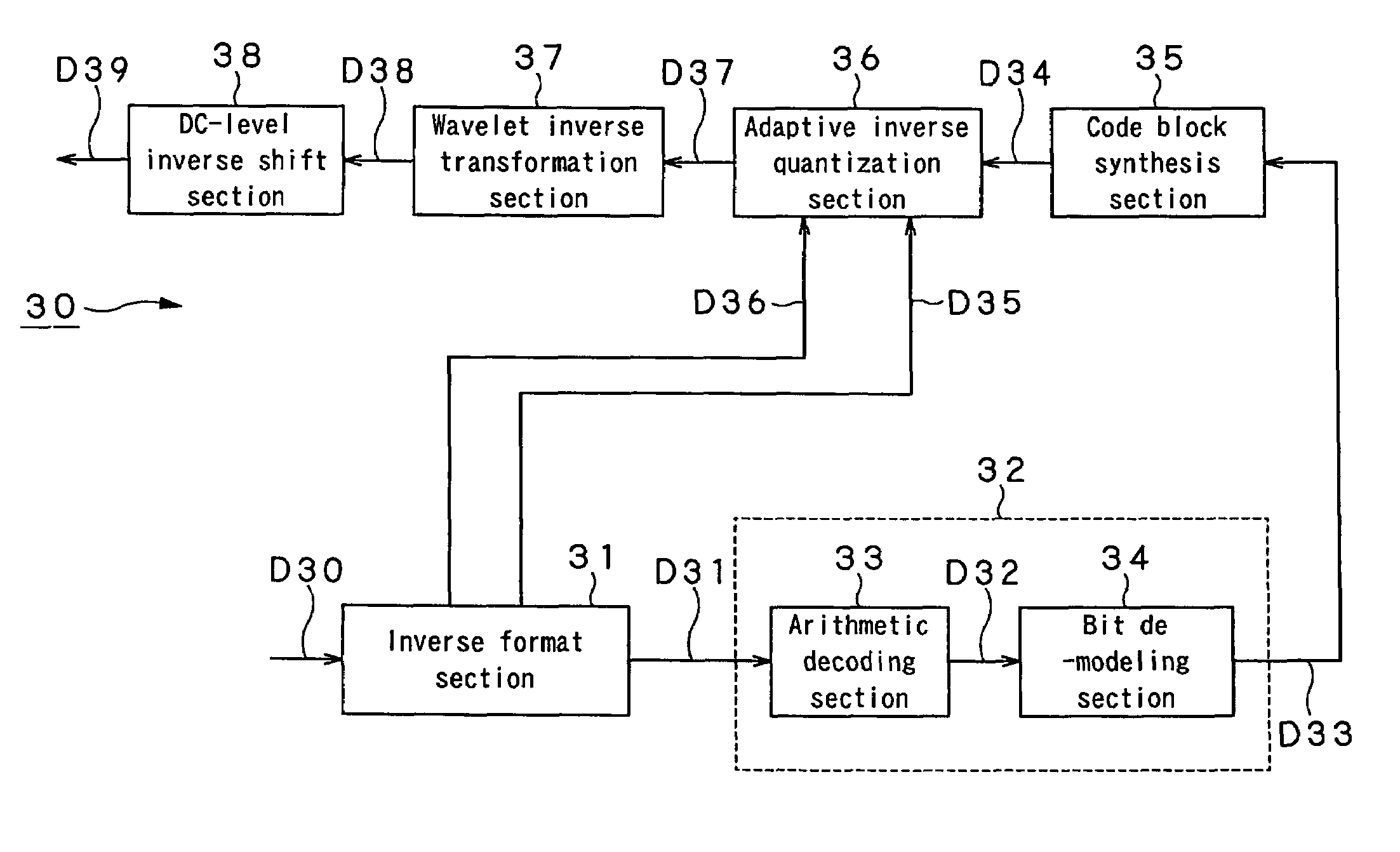
InactiveUS6931067B2Improve encoding performanceTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesWavelet transformImage signal
An apparatus for image coding using tree-structured vector quantization based on a wavelet transform and a method therefor are provided. The apparatus for image coding using a tree-structured vector quantization based on wavelet transform has a wavelet transform unit, a vector construct unit, an error vector unit, a scan unit, a first quantization unit and a second quantization unit. The wavelet transform unit wavelet transforms an input image signal. The vector construct unit constructs vectors, each having a tree structure in a different direction, using the wavelet transformed result. The error vector generation unit generates a plurality of error vectors by setting one of the vectors as a basic vector and performing a calculation on each of the vectors remaining with respect to the basic vector. The scan unit scans the coefficients of each of the basic vector and error vectors in a different direction. The first vector quantization unit generates a first codebook for the basic vector scanned in the scan unit, quantizes the scanned basic vector using the first codebook, and outputs the quantization result as the index of the first codebook. The second vector quantization unit generates a second codebook for the error vectors scanned in the scan unit, quantizes the scanned error vectors using the second codebook, and outputs the quantization results as the indices of the second codebook. According to the apparatus and method, the advantages of wavelet vector quantization and zerotree-coding are maximized so that the size of a codebook is reduced and the coding performance is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image processing method, apparatus, and program with selective error diffusion among a plurality of pixel groups within a digital image
InactiveUS7701614B2Reduce computing loadQuality improvementDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingError diffusion
The image processing method for performing halftoning of a digital image constituted by an array of pixels having grayscale values which correspond to a content of the digital image, the method comprises the steps of: grouping the pixels constituting the digital image into a first group comprising pixels in pixel positions from which a quantization error generated through quantization is diffused to a peripheral pixel, and a second group comprising pixels in pixel positions from which the quantization error generated through quantization is not diffused to a peripheral pixel; performing a first quantization process on the pixels belonging to the first group using a threshold matrix; determining the quantization error generated during the first quantization process; diffusing the quantization error obtained in the quantization error determining step to at least one non-quantized pixel belonging to the second group which is adjacent to the pixel subjected to the first quantization process; and performing a second quantization process, using a threshold matrix, on the non-quantized pixel to which an error value is diffused during the quantization error diffusing step.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Video encoding method and apparatus
A video encoding method includes encoding n pictures included in a video image using a first quantization parameter, calculating first number-of-encoded-bits information indicating number of encoded bits of every picture type, multiplexing a set frame rate by an average first-number-of-encoded-bits per picture calculated from the first-number-of-encoded-bits information to obtain a first bit rate, encoding the n pictures using a second quantization parameter, calculating second number-of-encoded-bits information indicating number of encoded bits of every picture type, multiplexing the set frame rate by an average second number-of-encoded-bits per picture calculated from the first-number-of-encoded-bits information to obtain a second bit rate, calculating a third quantization parameter, using the first bit rate, first quantization parameter, second bit rate, second quantization parameter and target bit rate, and performing the rate control using the third quantization parameter as an initial value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Encoding and decoding apparatus and method for reducing blocking phenomenon and computer-readable recording medium storing program for executing the method
InactiveUS20060269149A1Increase the number ofReduce cloggingCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareFirst quantization
Provided is an encoding method capable of reducing a blocking phenomenon that occurs when moving-images are encoded and decoded. The method includes: performing a first encoding operation on an input image using a first quantization coefficient; generating a reconstructed image of the encoded image; calculating a difference between corresponding partial images of the reconstructed image and the input image; and performing a second encoding operation on the calculated difference using a second quantization coefficient smaller than the first quantization coefficient. Using the second encoded difference, a decoding unit can reconstruct an image of a block boundary portion more elaborately with a small number of bits, thereby significantly reducing the blocking phenomenon in the decoding operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
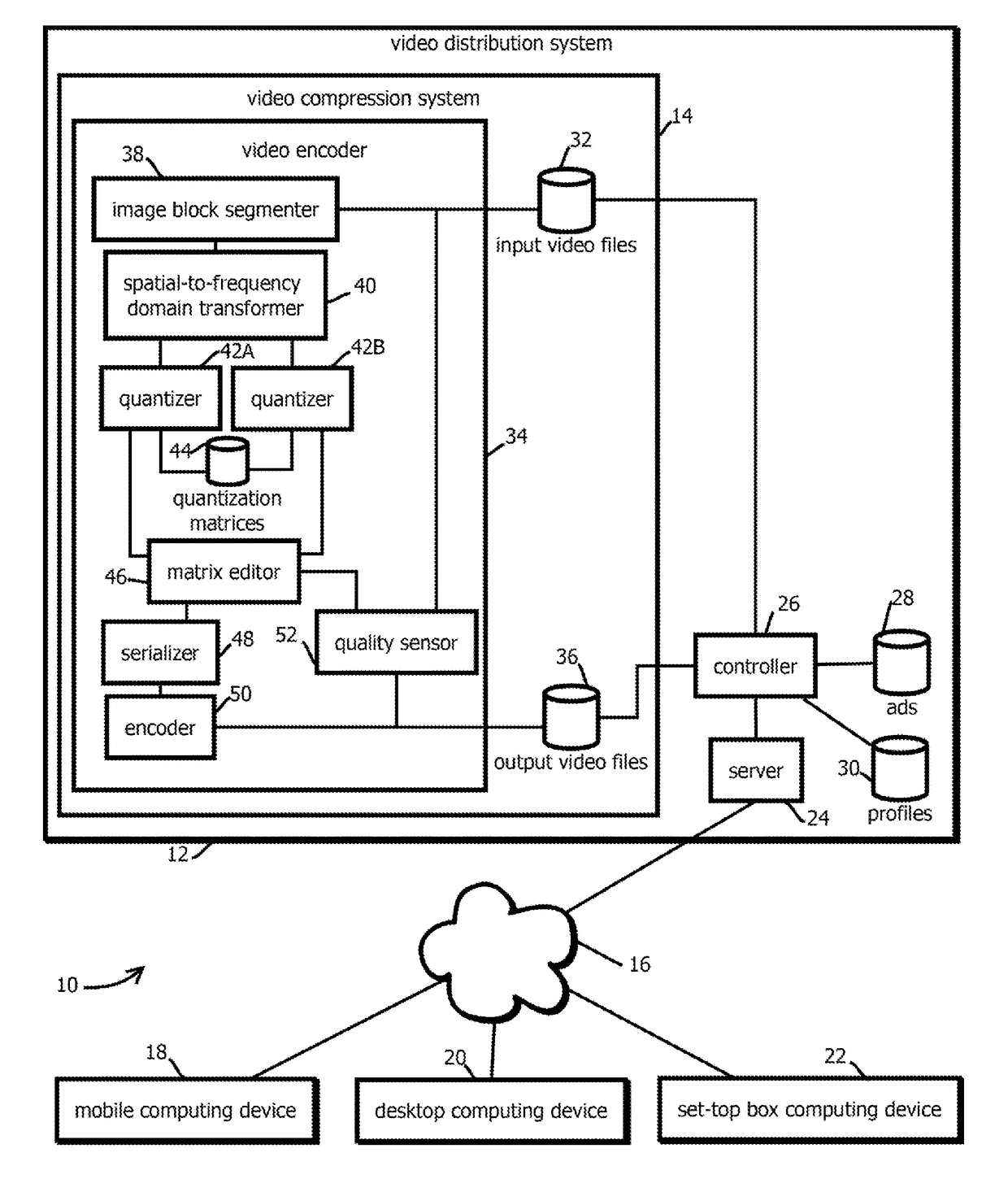
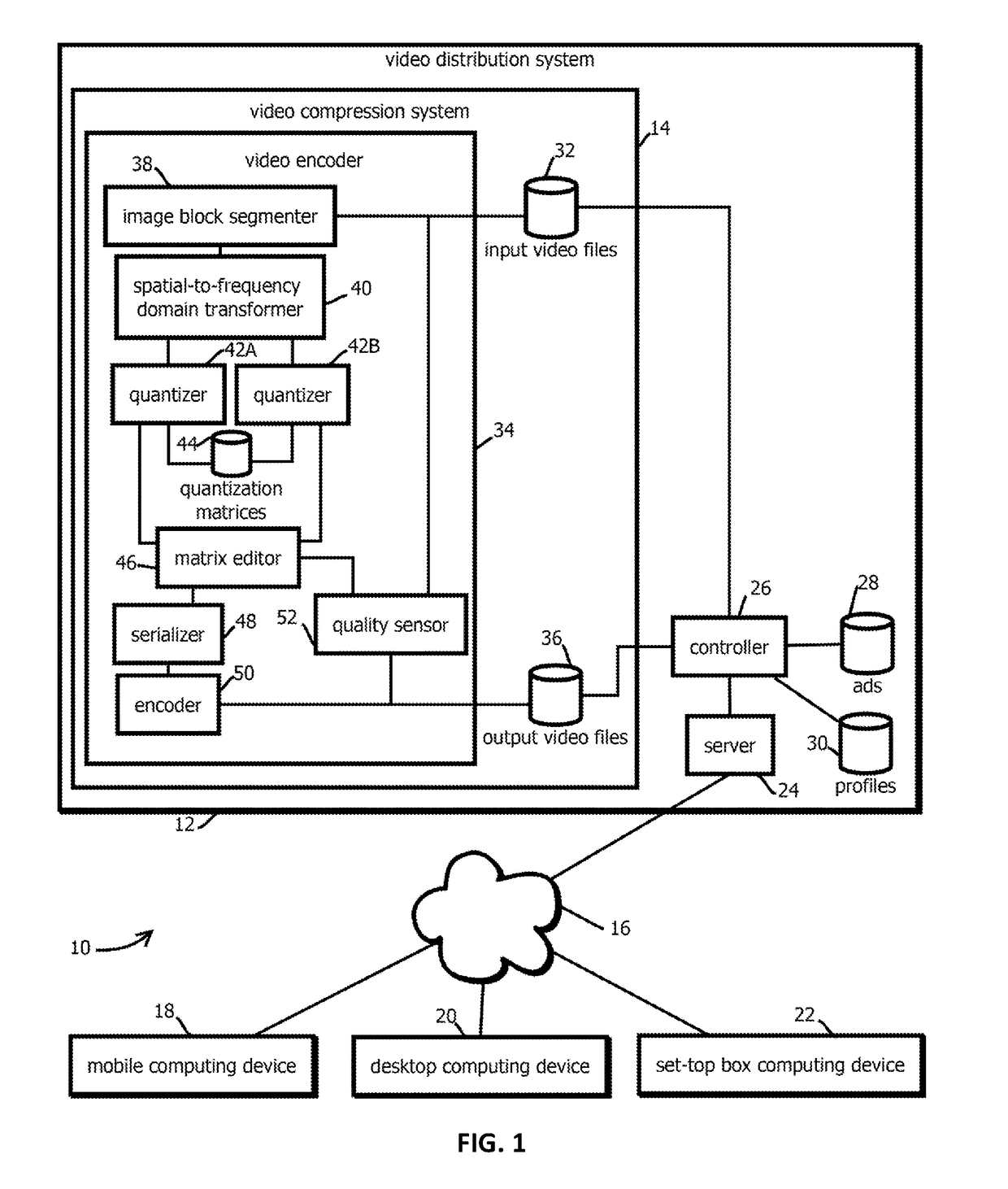
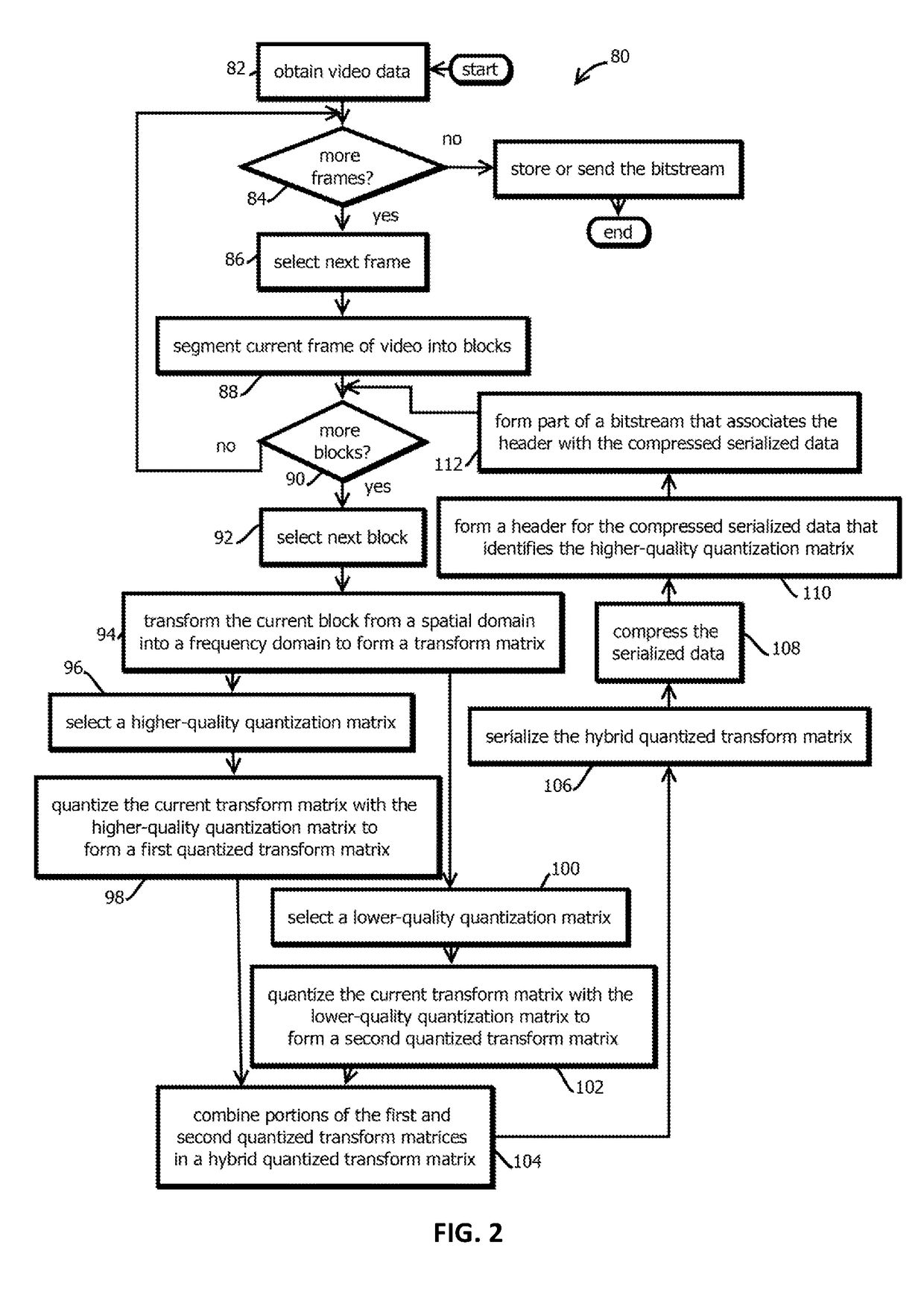
Video encoding with adaptive rate distortion control by skipping blocks of a lower quality video into a higher quality video
InactiveUS20180309991A1Speech analysisDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingRate distortion
Provided is a process including: segmenting a frame of video into a plurality of blocks; transforming each of the blocks to form respective transform matrices; for a given transform matrix, quantizing the given transform matrix with a first quantization matrix to form a first quantized transform matrix; quantizing the given transform matrix a second time with a second quantization matrix to form a second quantized transform matrix; and forming a sequence of hybrid quantized transform matrix values from part of the first quantized transform matrix and part of the second quantized transform matrix.
Owner:MATRIXVIEW
Apparatus and method for feedback of channel state information in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20180083683A1Small feedback overheadReliable feedbackSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesChannel state informationCommunications system
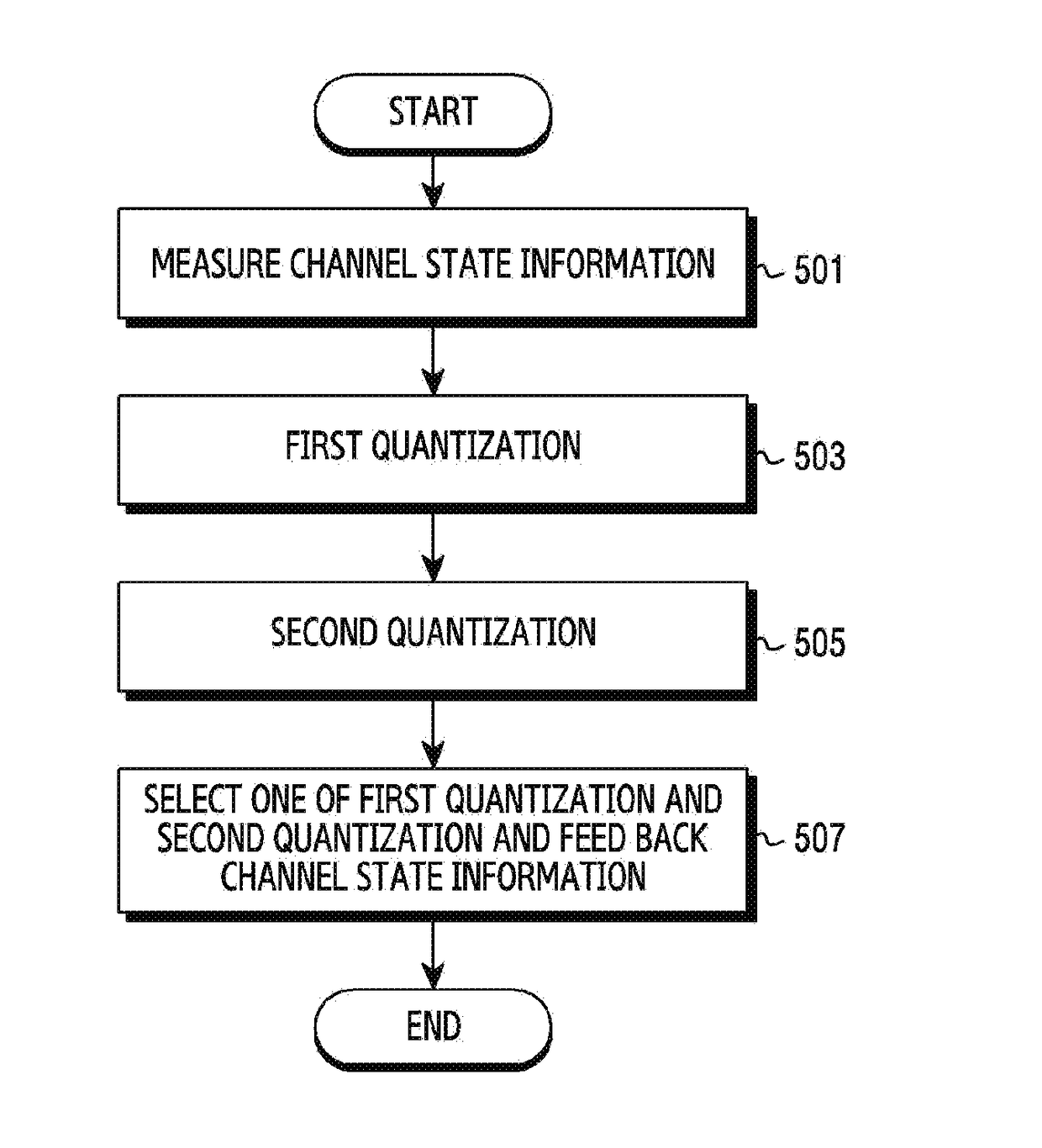
The present disclosure relates to a pre-5th-Generation (5G) or 5G communication system to be provided for supporting higher data rates Beyond 4th-Generation (4G) communication system such as Long Term Evolution (LTE). A feedback transmission method for a receiving device in a multiple input multiple output system according to one embodiment comprises: a step of measuring channel state information; a first quantization step of quantizing the channel state information using a first codebook; a second quantization step of quantizing the channel state information using second and third codebooks which are different from the first codebook; and a step of feeding back the channel state information on the basis of a selection result of one of the first and second quantization steps.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
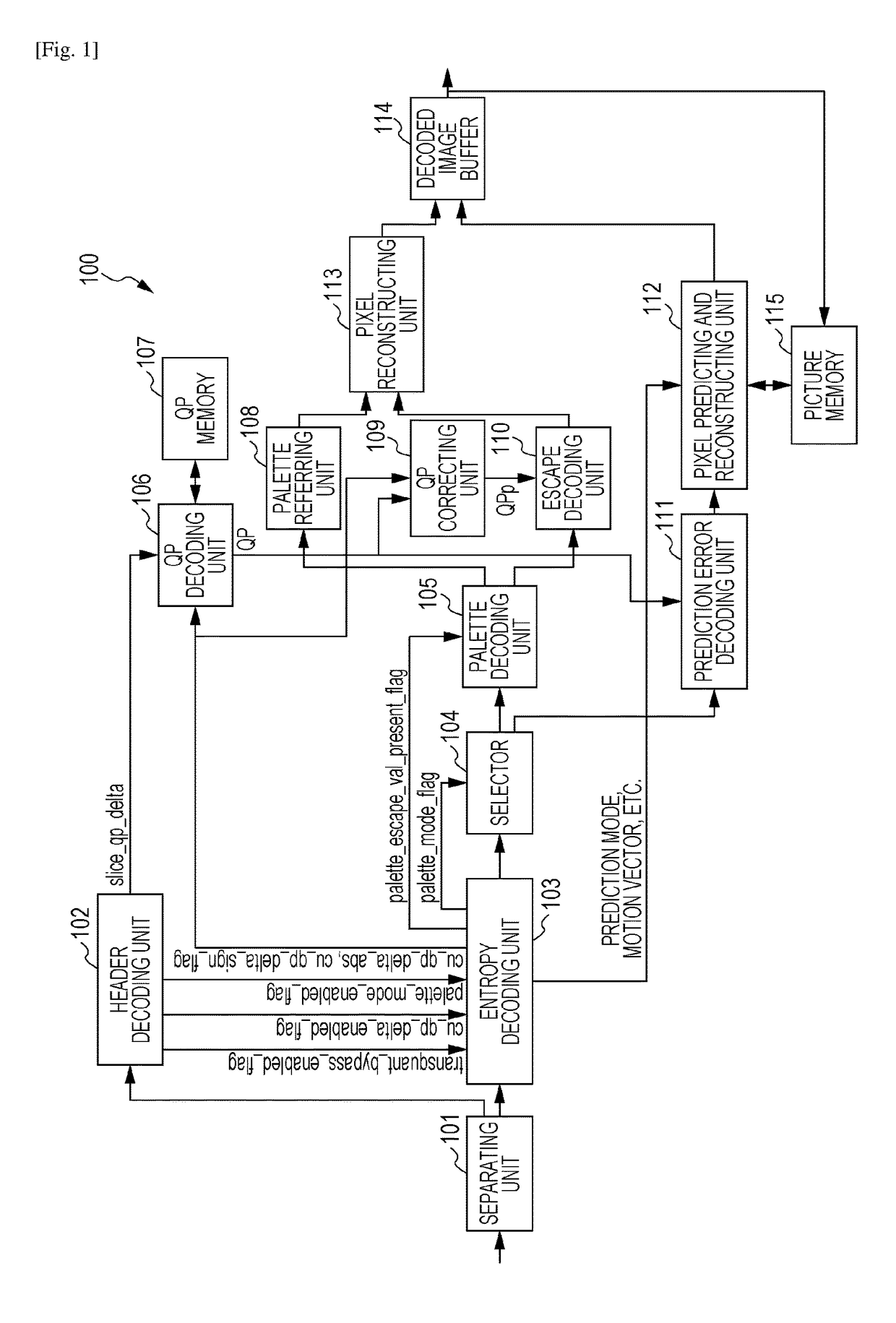
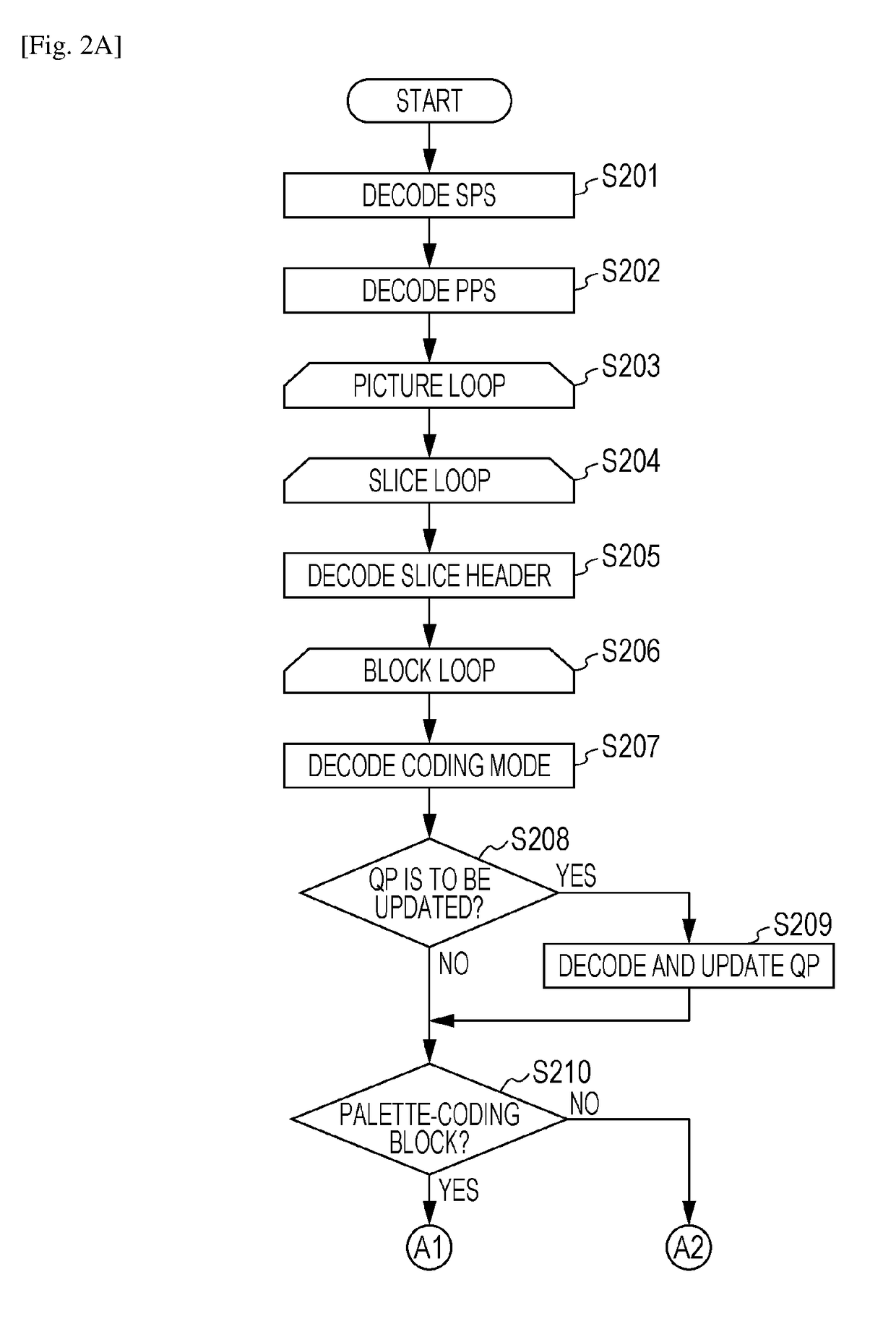
Image coding apparatus, image coding method, storage medium, image decoding apparatus, image decoding method, and storage medium
ActiveUS20170332091A1Improve coding efficiencyDigital video signal modificationImage codeFirst quantization
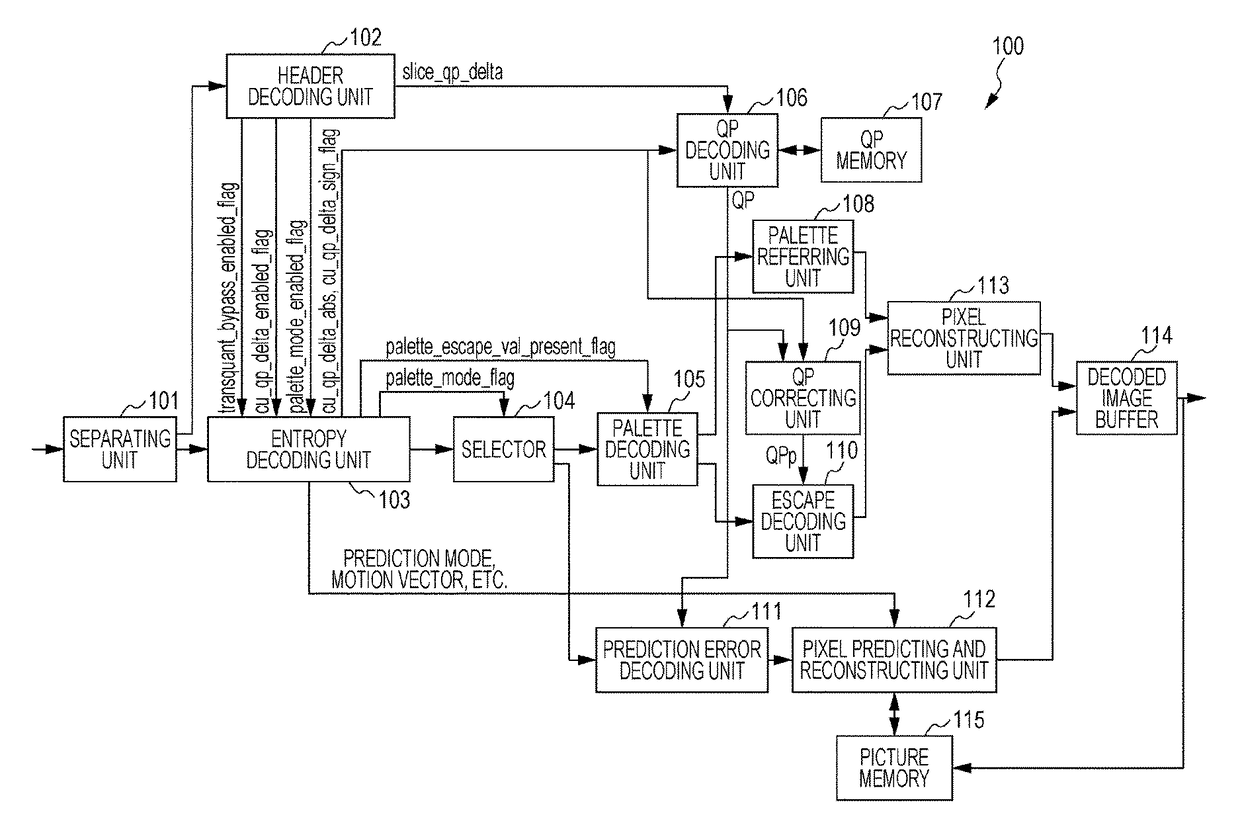
An image decoding apparatus decodes a bit stream generated by coding an image and decodes coded data included in the bit stream and corresponding to a target block to be decoded in the image. The apparatus includes a first determining unit configured to determine whether the target block is prediction-coded or palette-coded; a second determining unit configured to determine whether or not a pixel in the target block is escape-coded if the first determining unit determines that the target block is palette-coded; and a first decoding unit configured to decode the target block by using a second quantization parameter different from a first quantization parameter if the second determining unit determines that the pixel is escape-coded. The first quantization parameter is used to decode the coded data in a case where the first determining unit determines that the target block is prediction-coded.
Owner:CANON KK
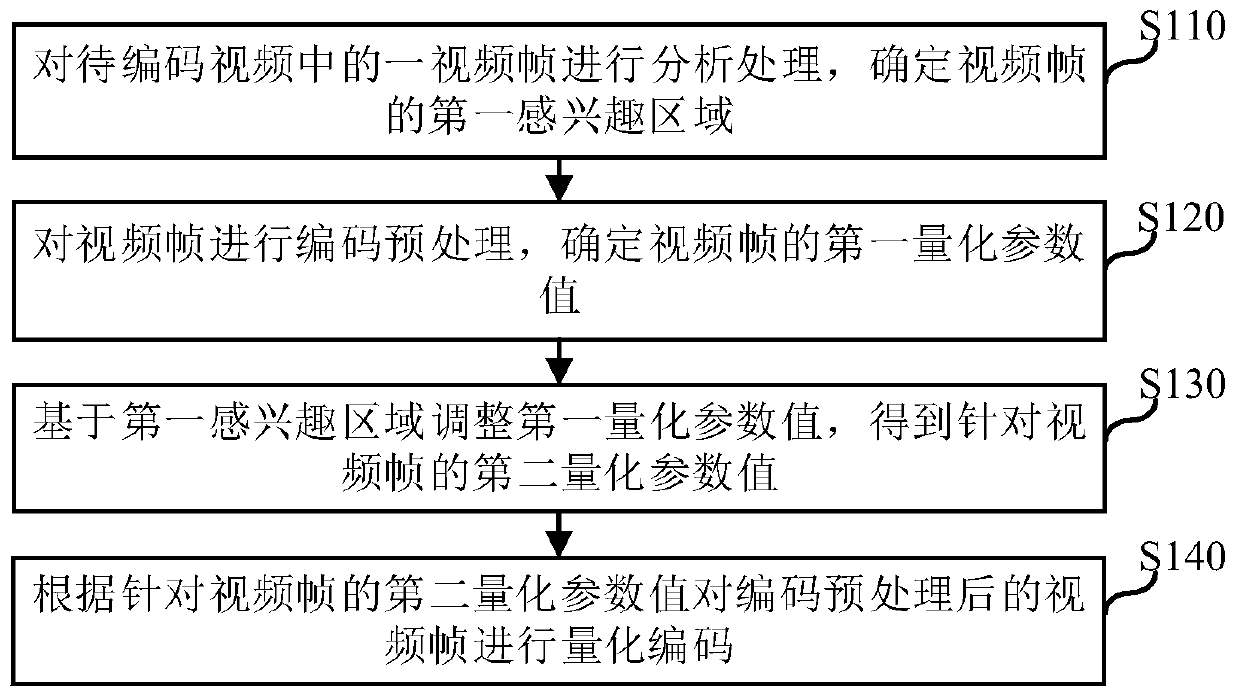
Video coding method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
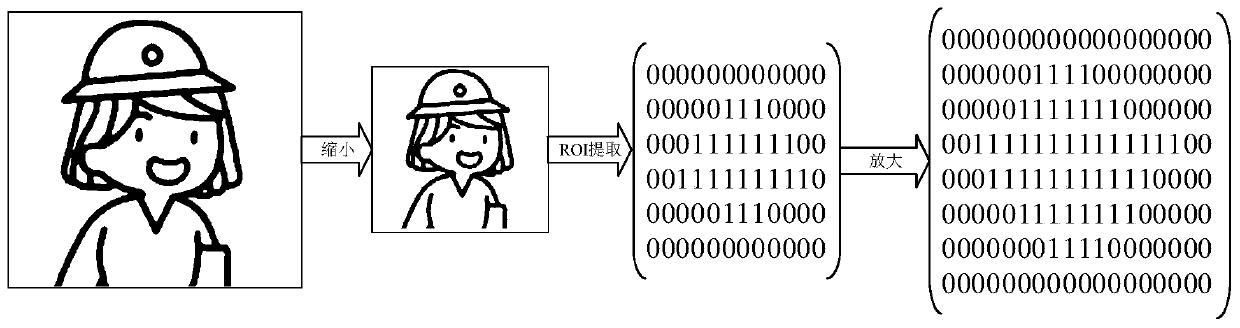
ActiveCN110267037AImprove viewing experienceEnhance sensory effectDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingVideo processing
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of video processing, and discloses a video coding method and device, electronic equipment and a computer readable storage medium, and the video coding method comprises the steps: analyzing and processing a video frame in a to-be-coded video, and determining a first region of interest of the video frame; performing coding preprocessing on the video frame, and determining a first quantization parameter value of the video frame; adjusting the first quantization parameter value based on the first region of interest to obtain a second quantization parameter value for the video frame; and then carrying out quantization coding on the video frame after coding preprocessing according to the second quantization parameter value for the video frame. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the code rate in any video frame can be dynamically adjusted according to the region of interest of any video frame, so that the video watching experience is greatly improved, and particularly, in a low-code-rate scene, the video watching effect of a watcher is effectively improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com