Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Efficiently quantized" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
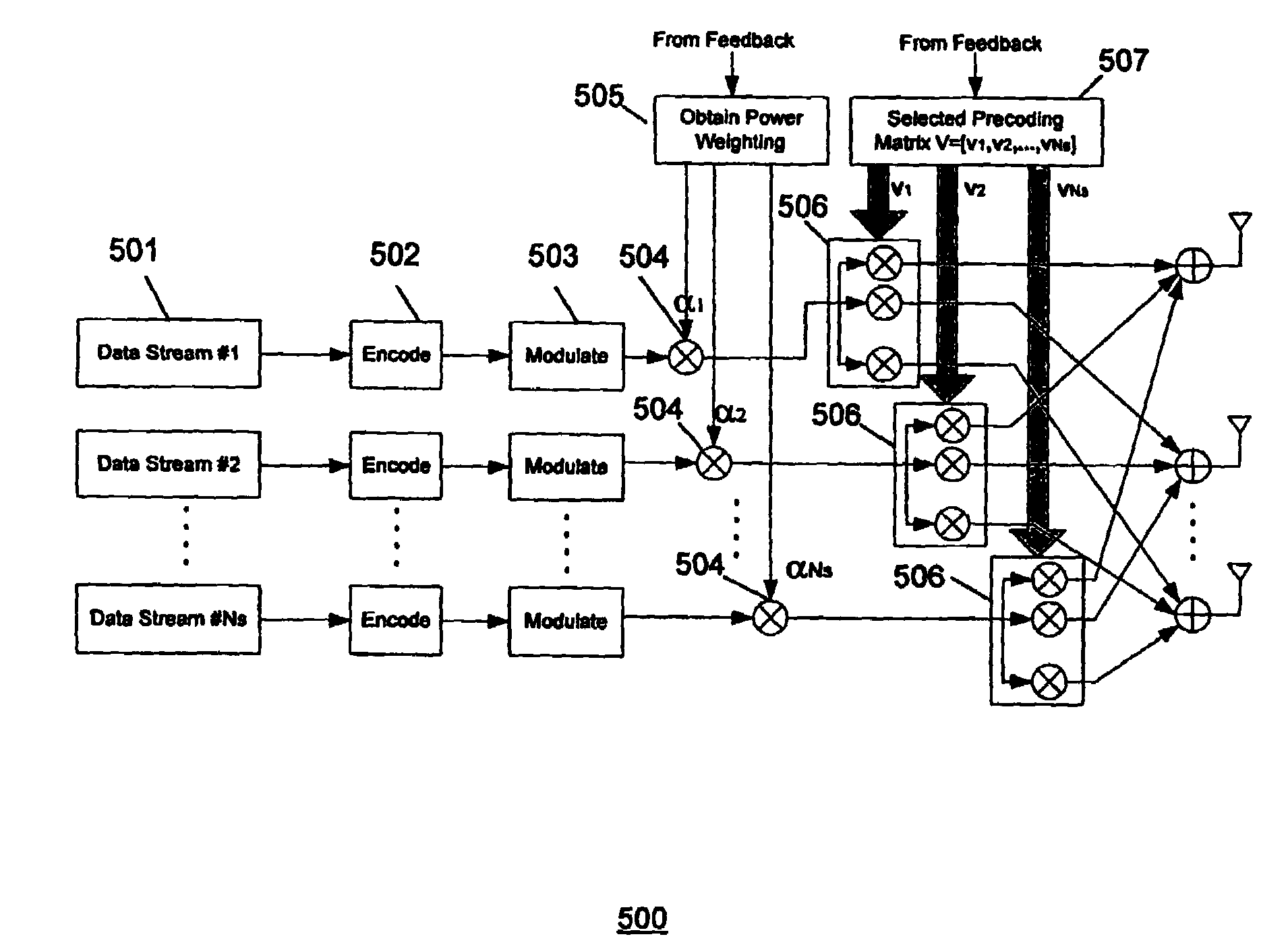
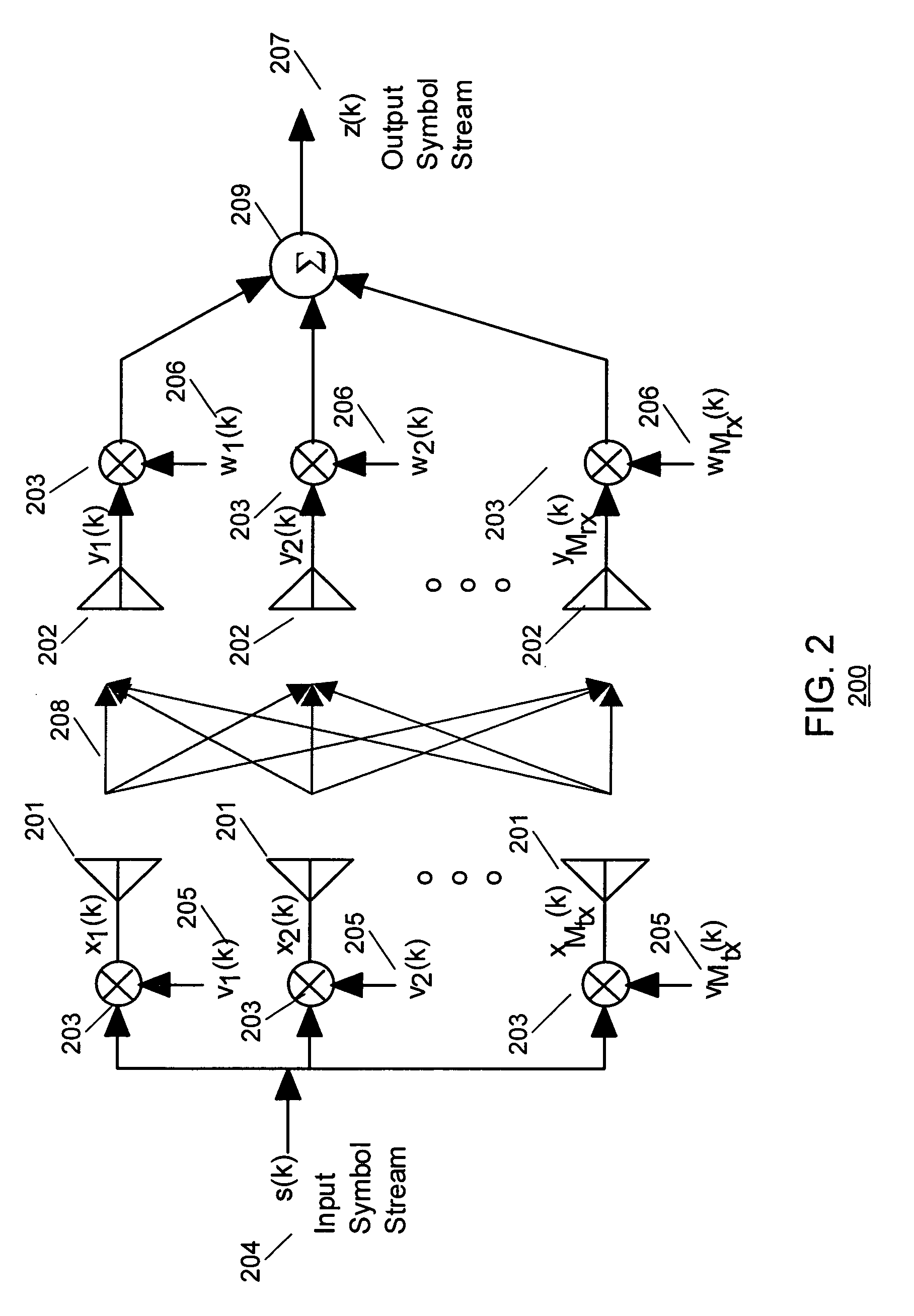
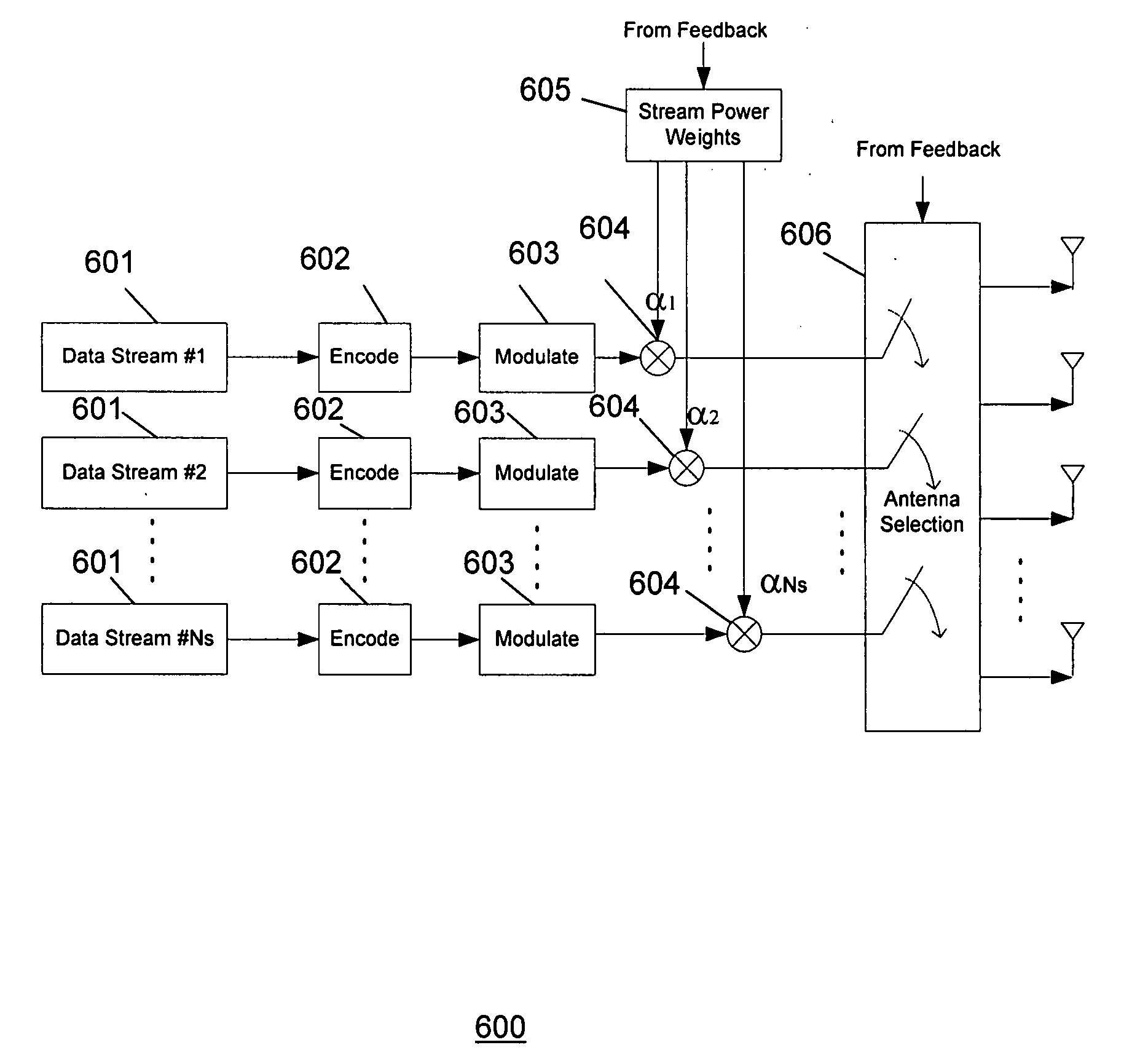
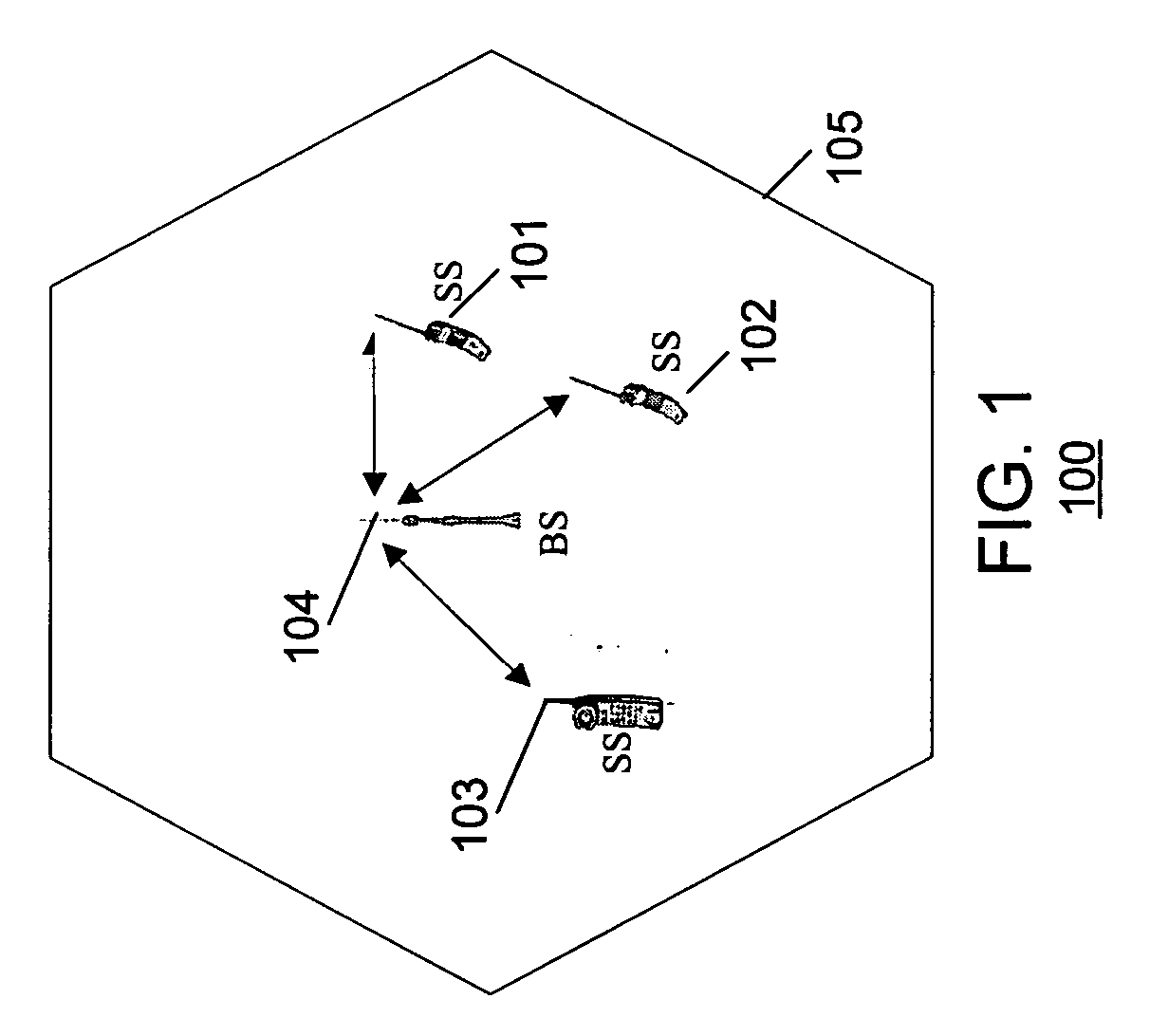
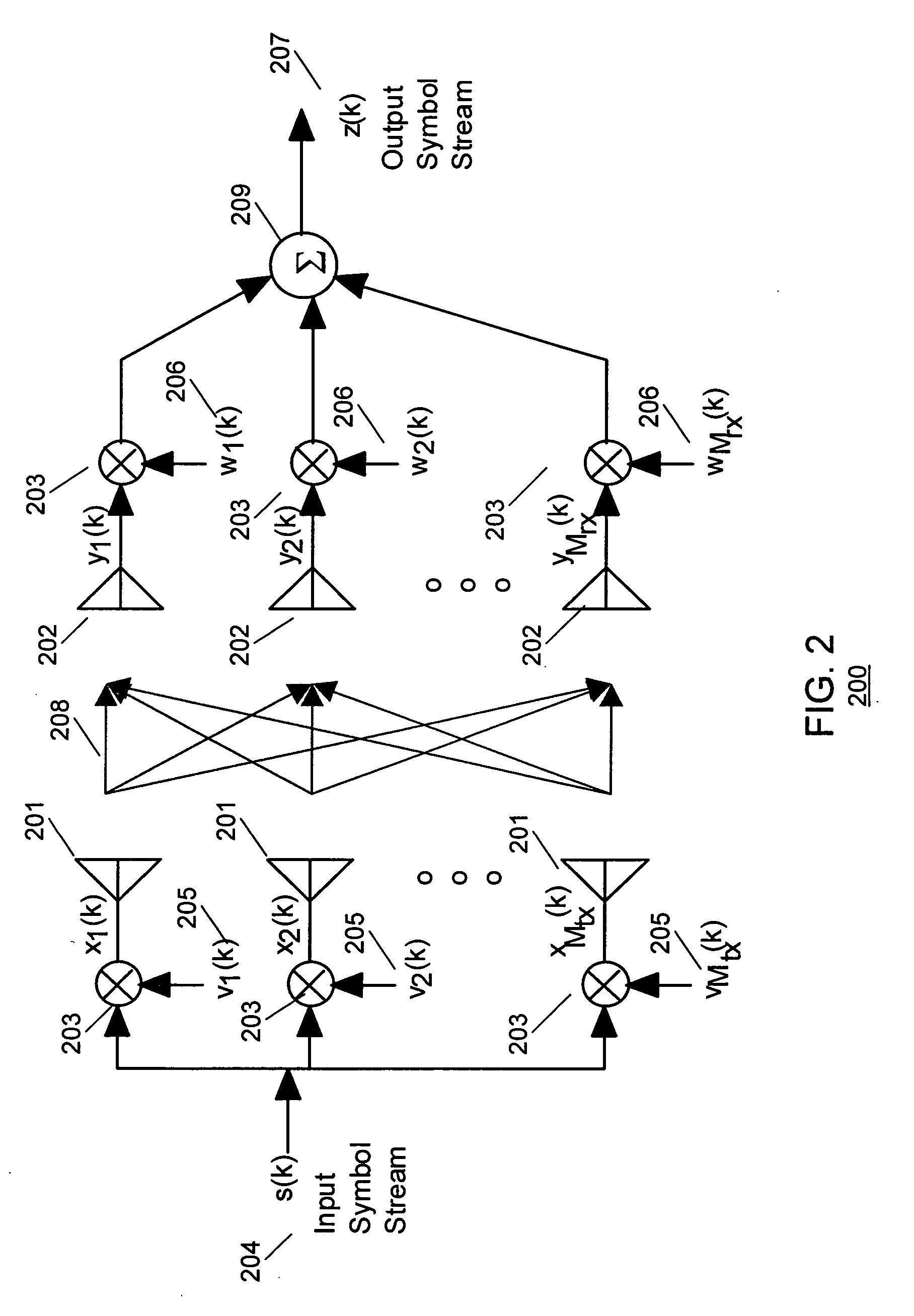
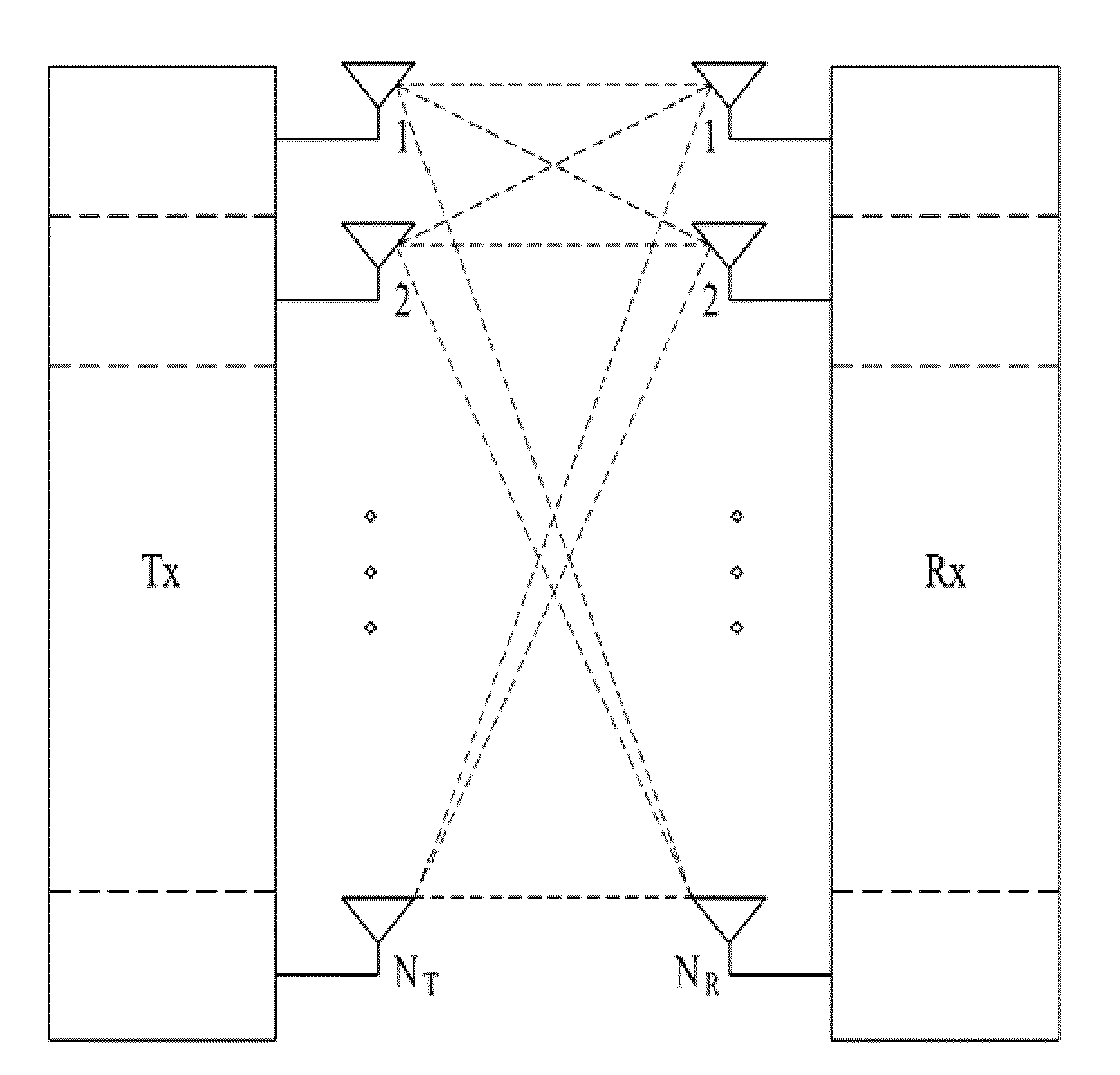
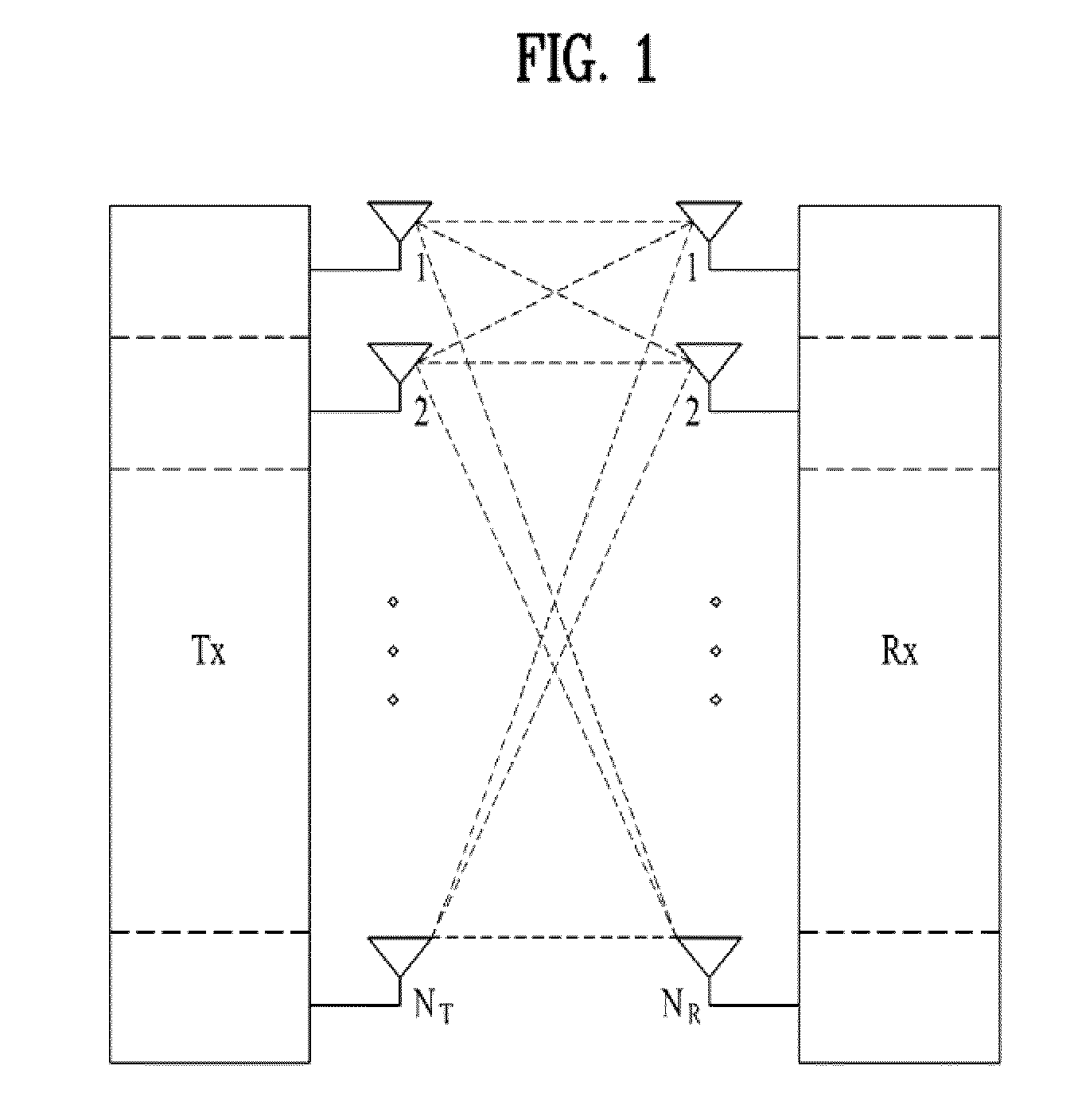
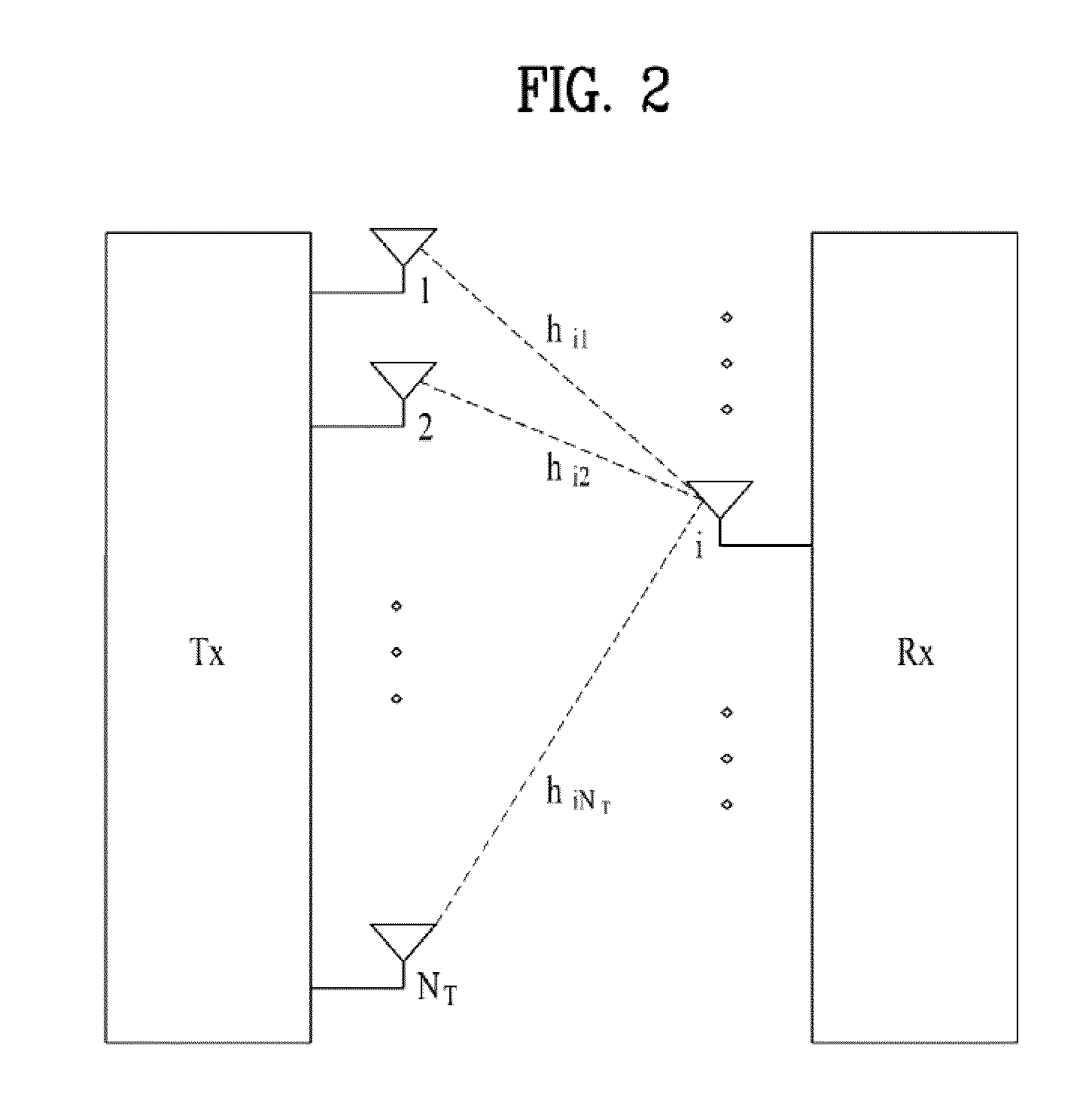
Method and apparatus for closed loop data transmission
ActiveUS7139328B2Improve performanceReduce the amount requiredPower managementMultiplex communicationData streamClosed loop
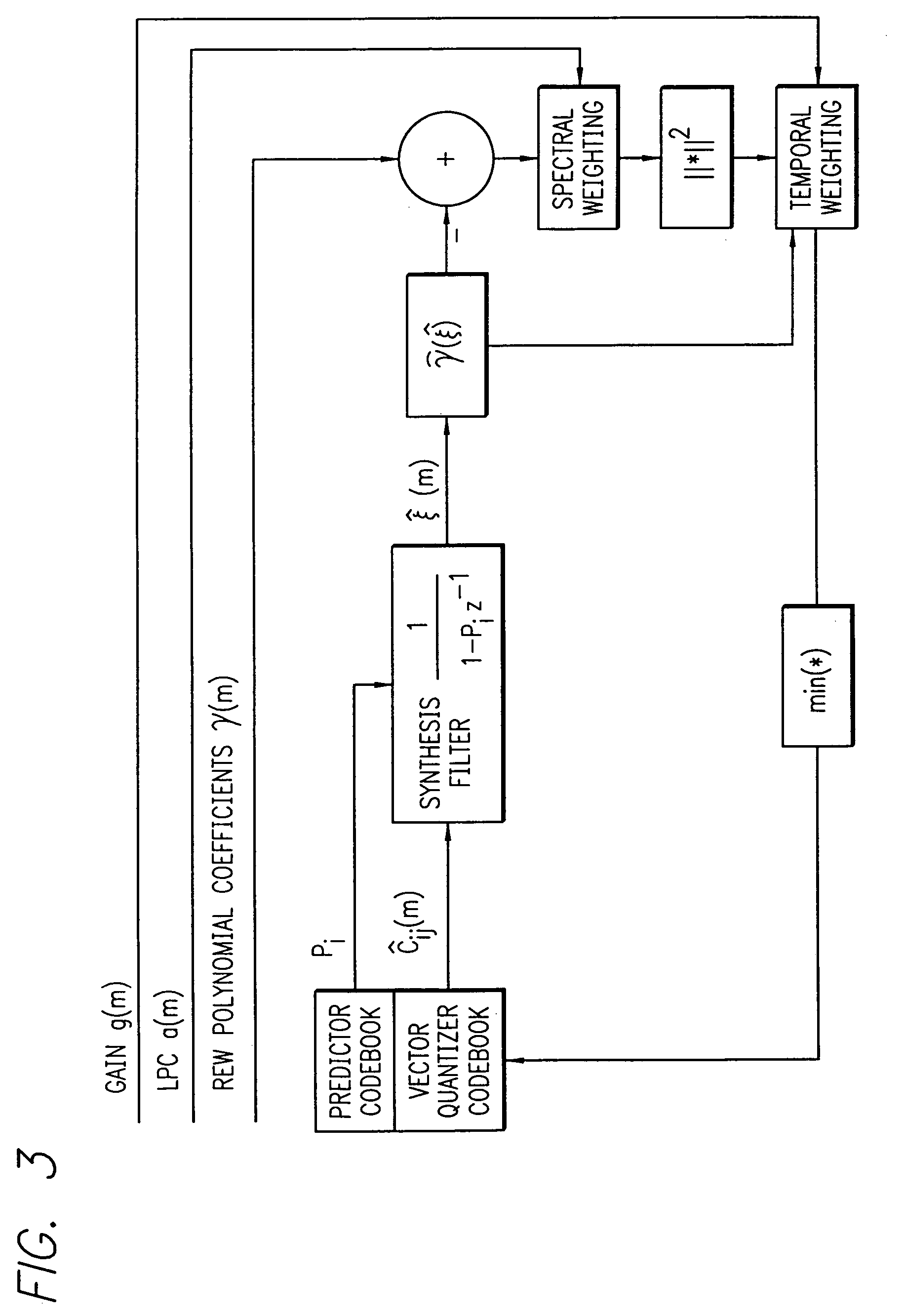
A method for communicating a plurality of data streams between a transmitting device with multiple transmit antennas and a receiving device, is disclosed. The method comprises determining a set of power weightings, efficiently quantizing the power weightings, and providing the set of power weightings the transmitting device. Another aspect of the invention comprises the transmitter implicitly signaling the number of data streams which the receiver should feedback information for through the amount of feedback requested. An additional aspect of the invention is a means of determining the best codebook weights by combining the maximum power and maximum capacity criteria.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Method and apparatus for closed loop data transmission
ActiveUS20060093065A1Improve performanceReduce the amount requiredPower managementMultiplex communicationData streamClosed loop
A method for communicating a plurality of data streams between a transmitting device with multiple transmit antennas and a receiving device, is disclosed. The method comprises determining a set of power weightings, efficiently quantizing the power weightings, and providing the set of power weightings the transmitting device. Another aspect of the invention comprises the transmitter implicitly signaling the number of data streams which the receiver should feedback information for through the amount of feedback requested. An additional aspect of the invention is a means of determining the best codebook weights by combining the maximum power and maximum capacity criteria.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
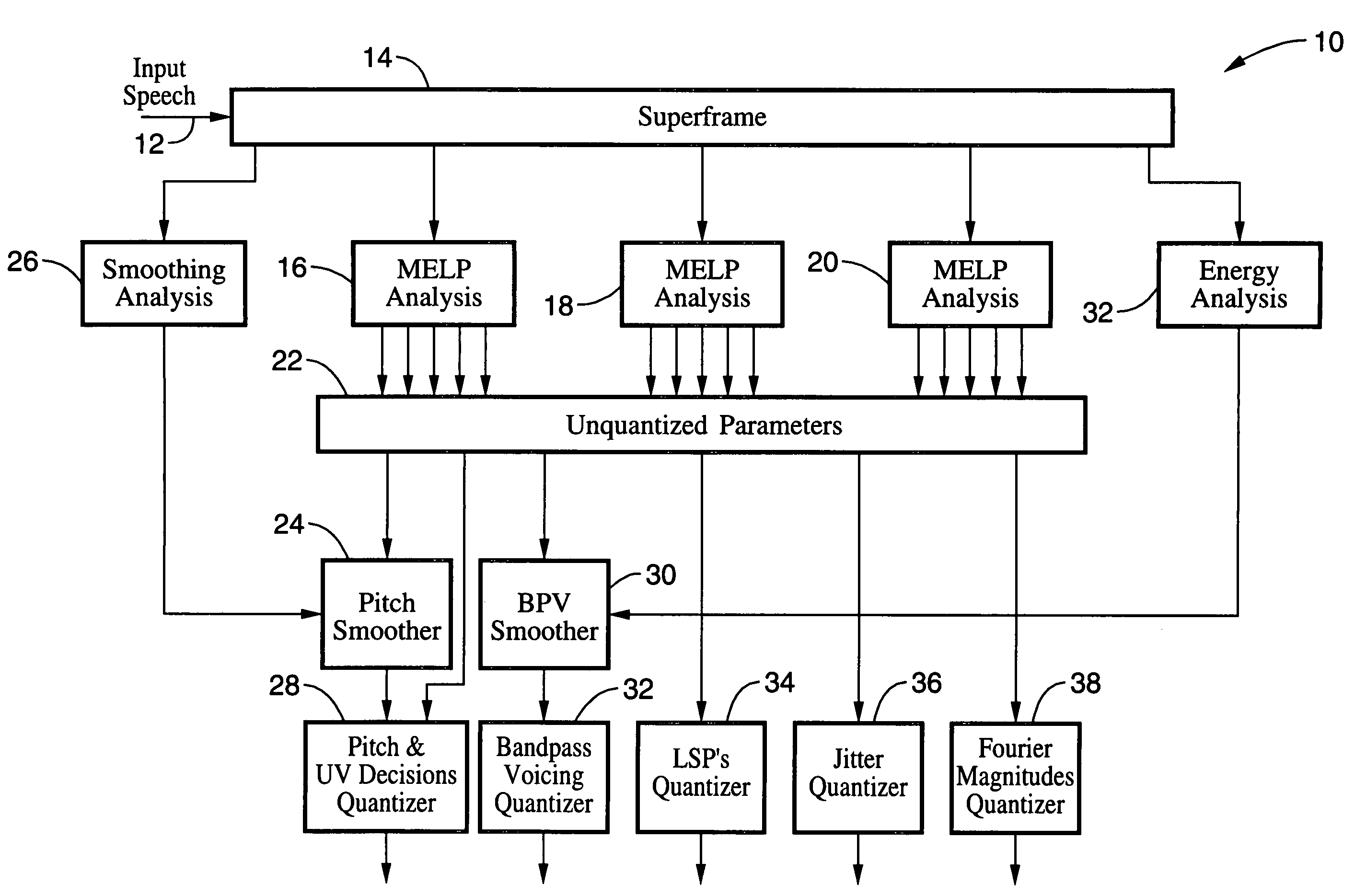
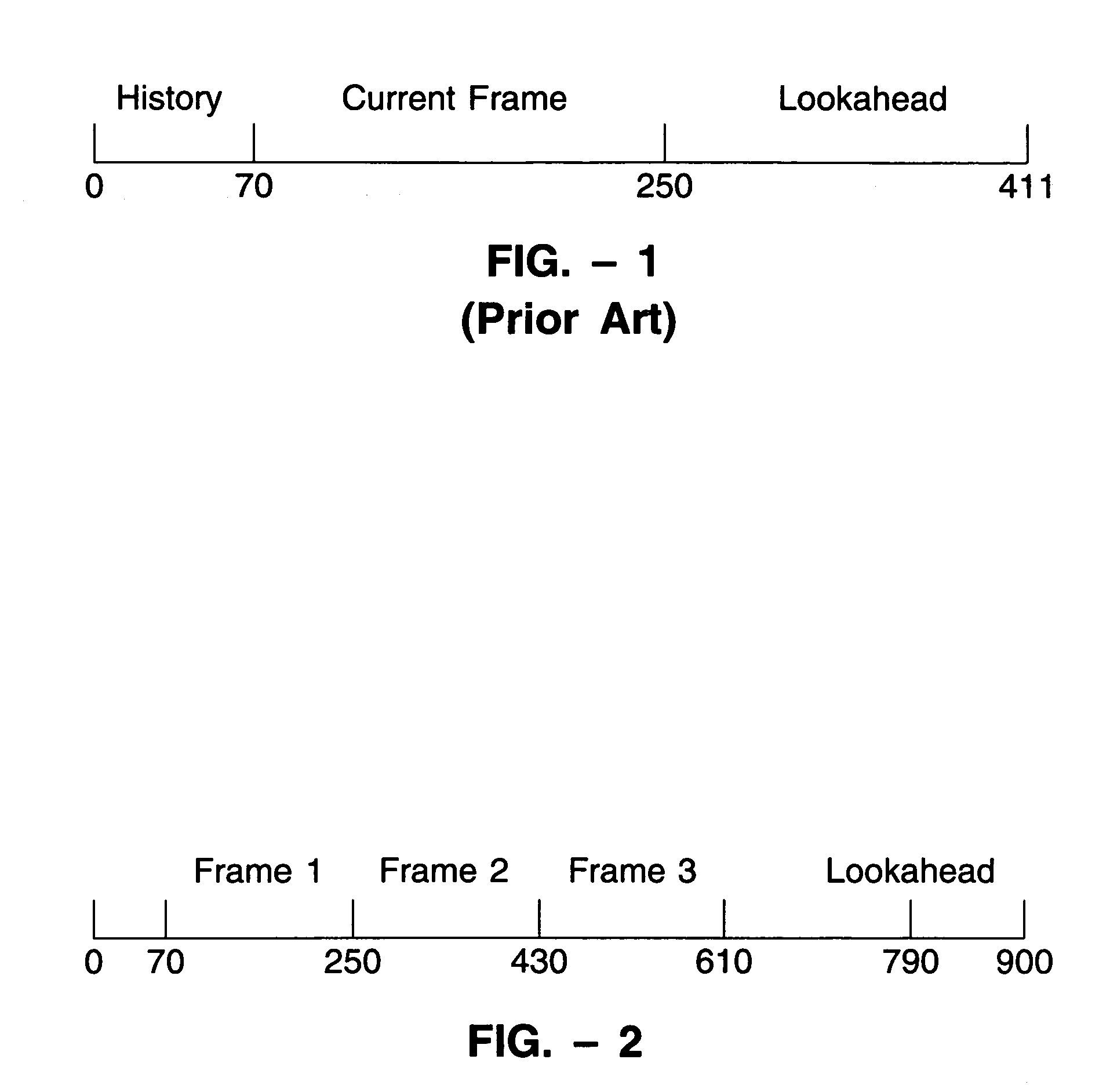
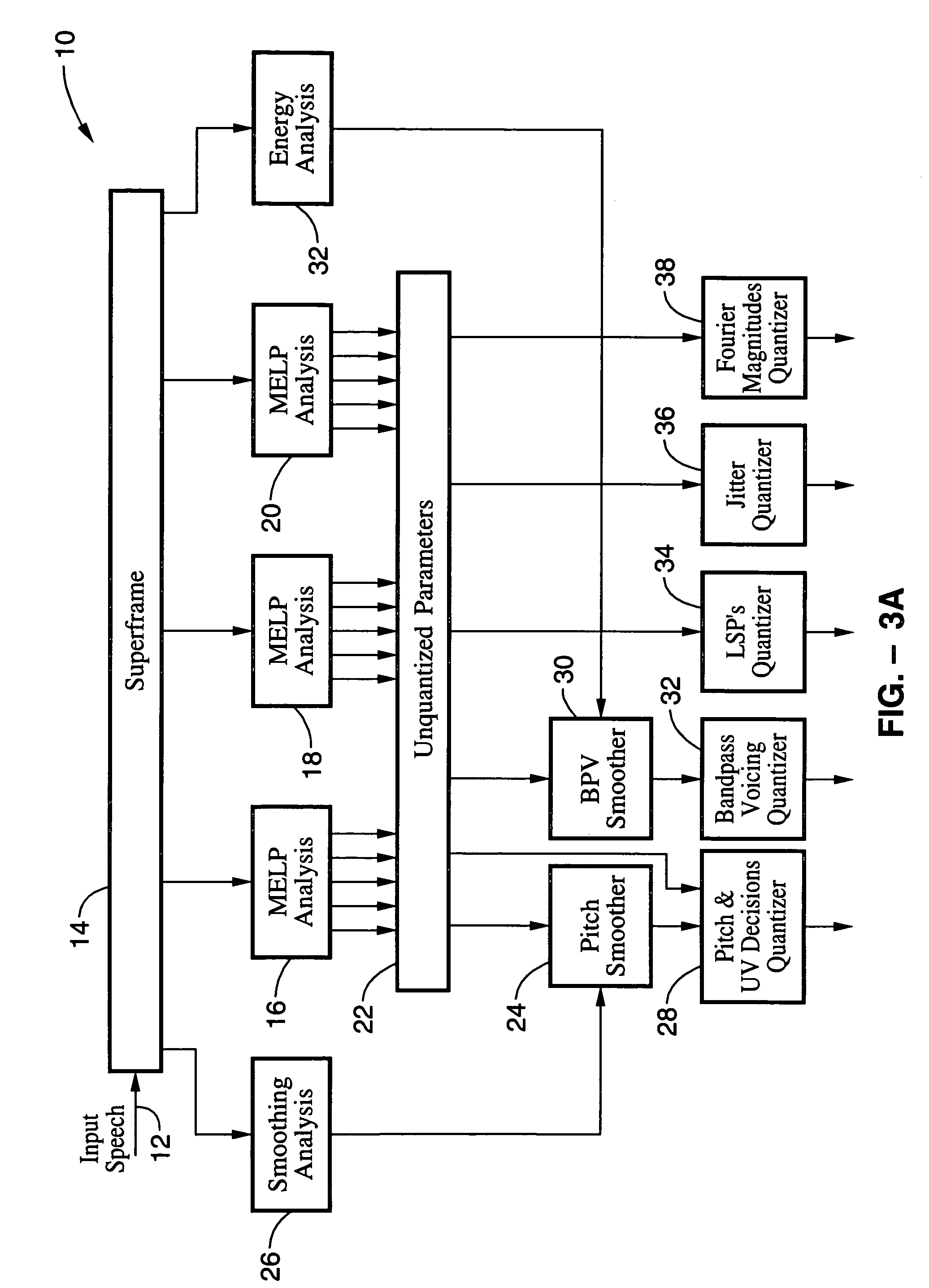
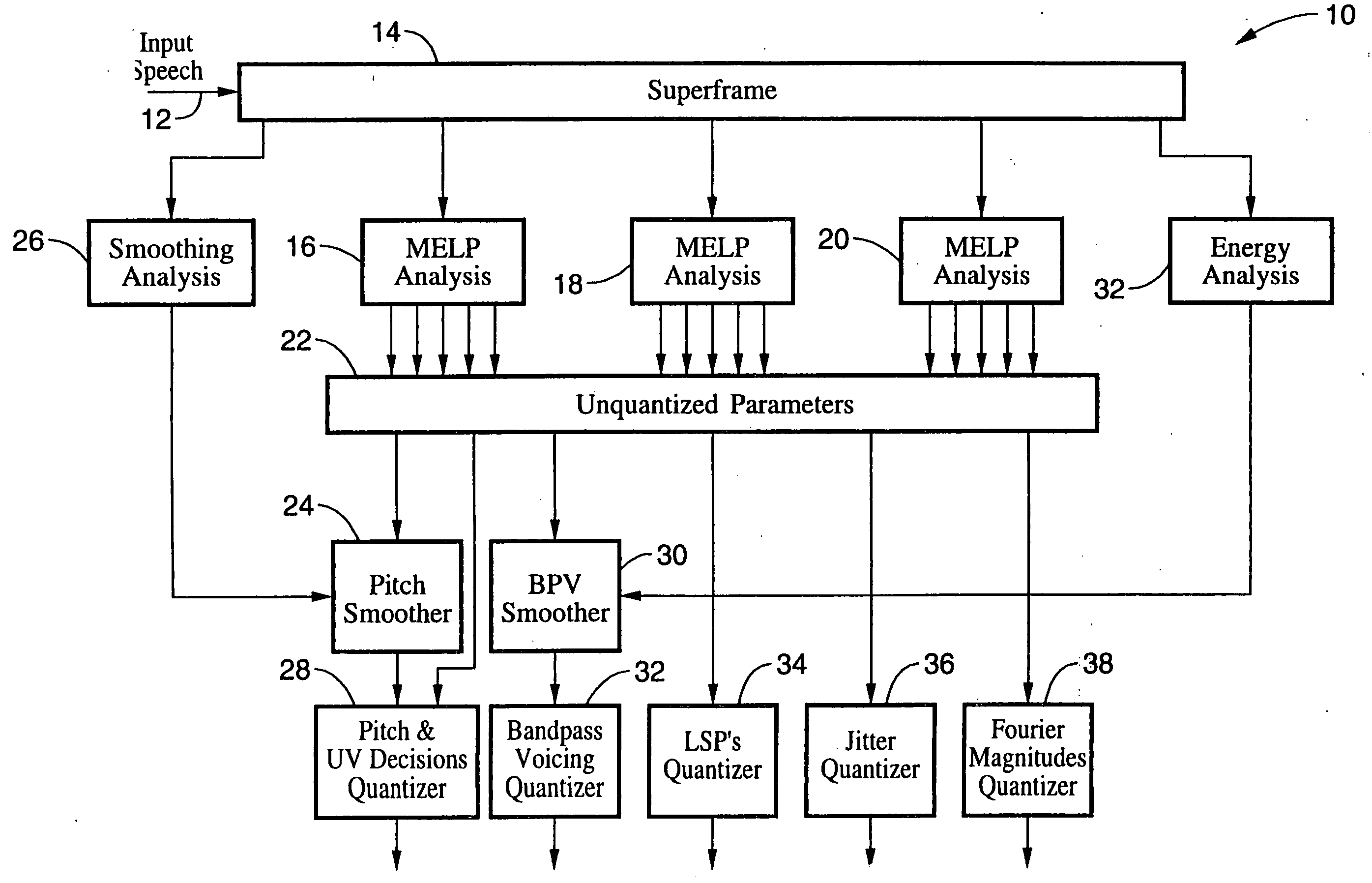
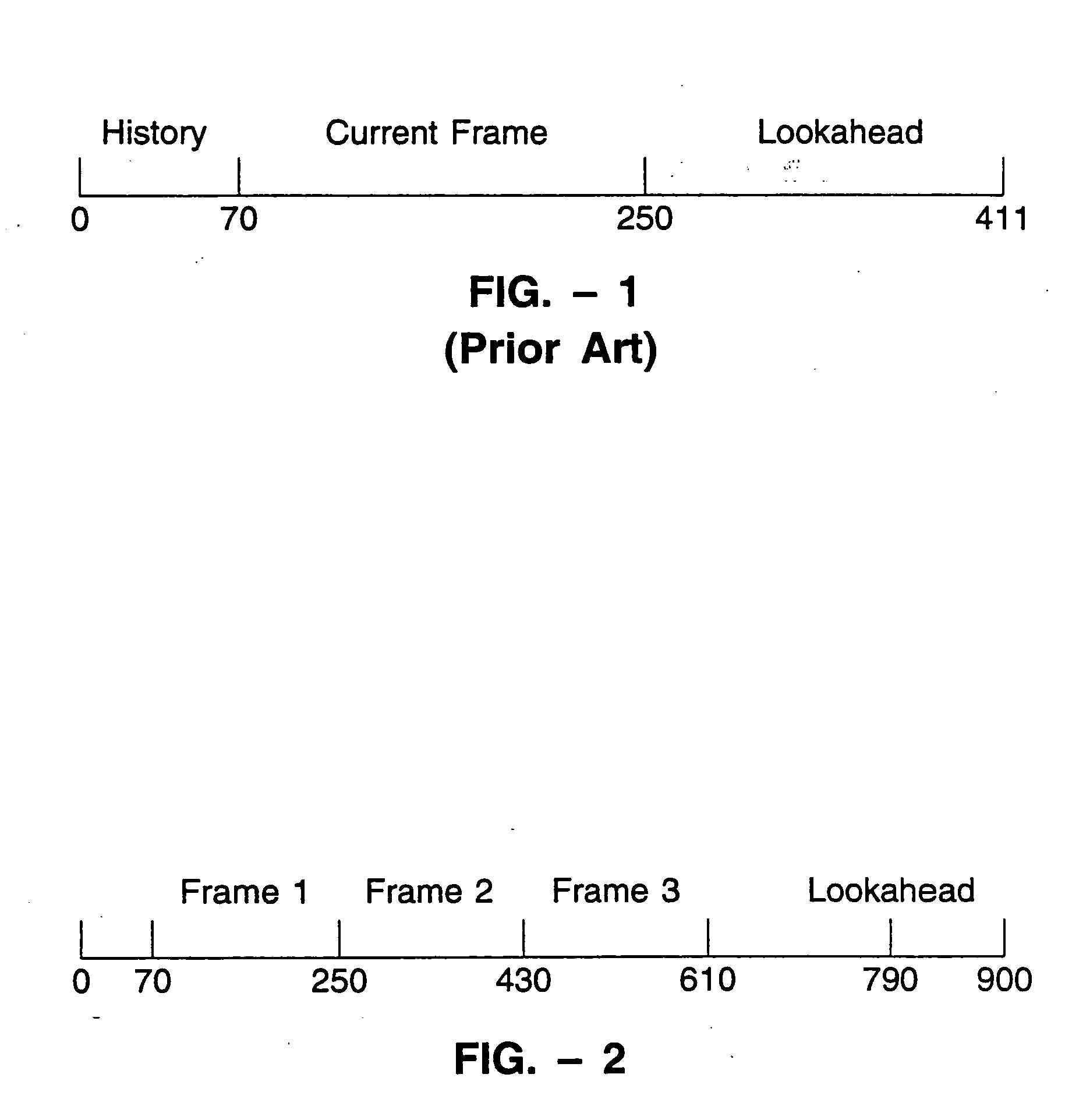
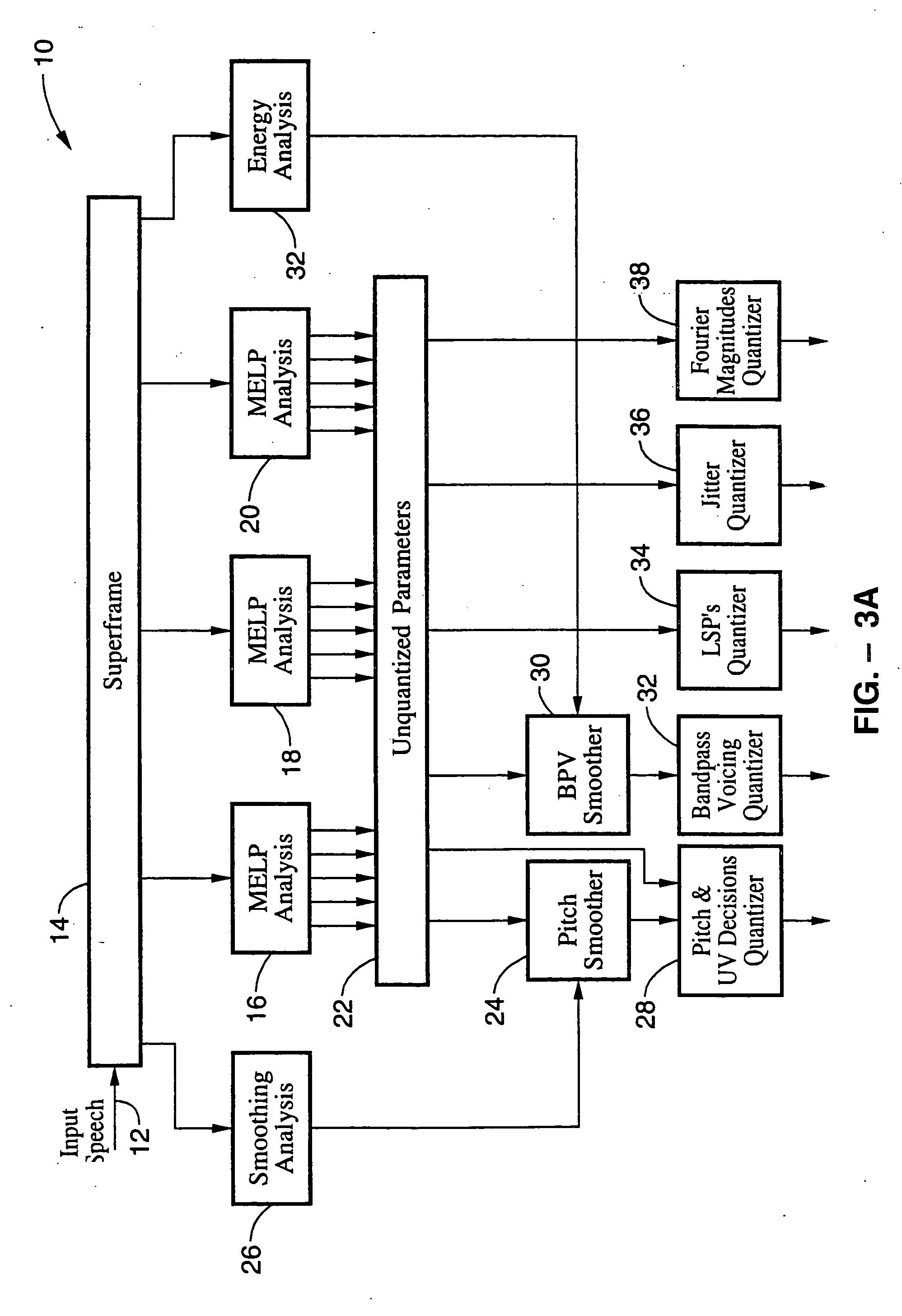
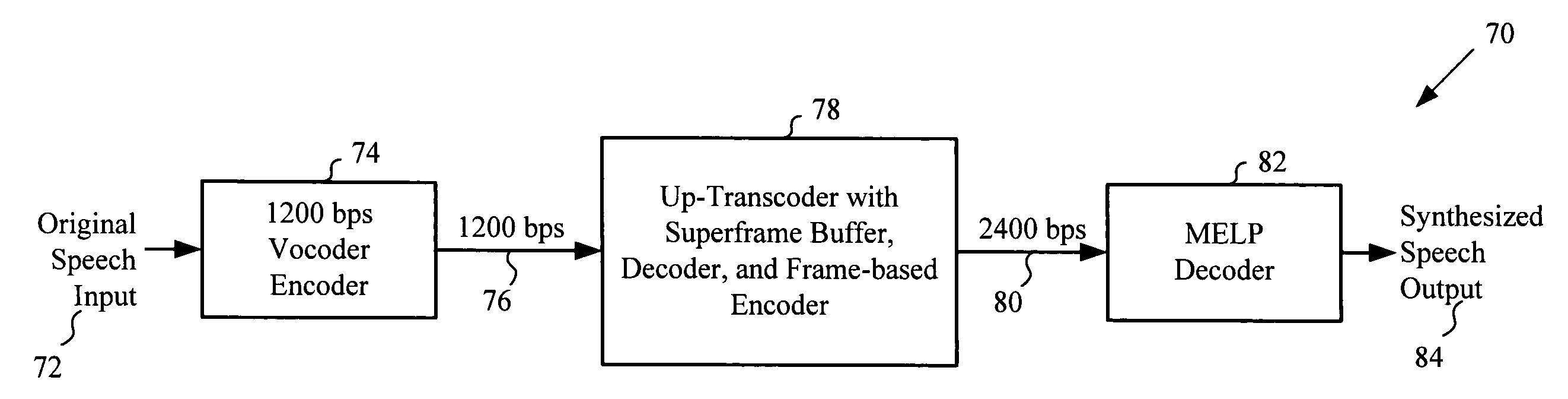
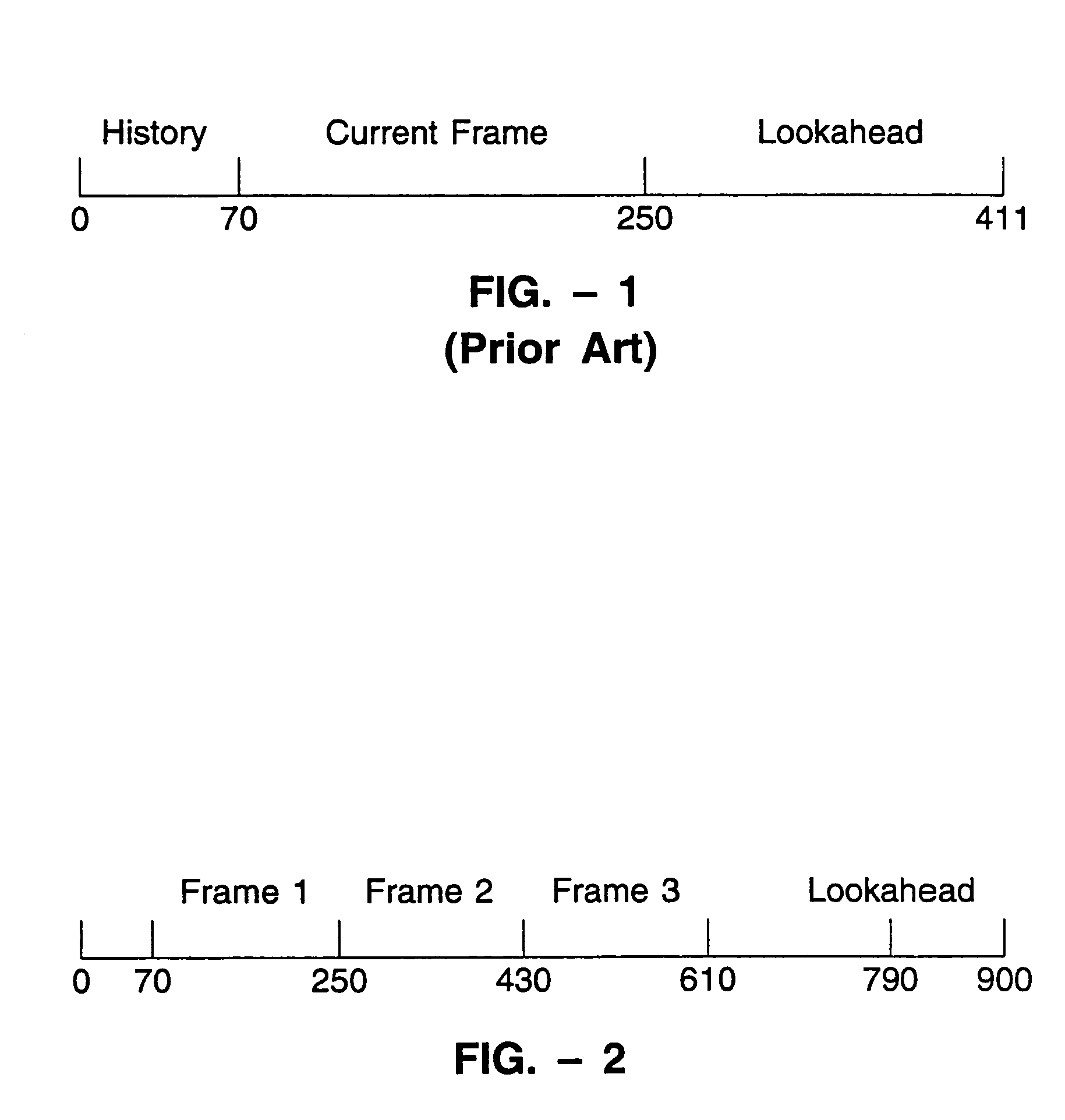
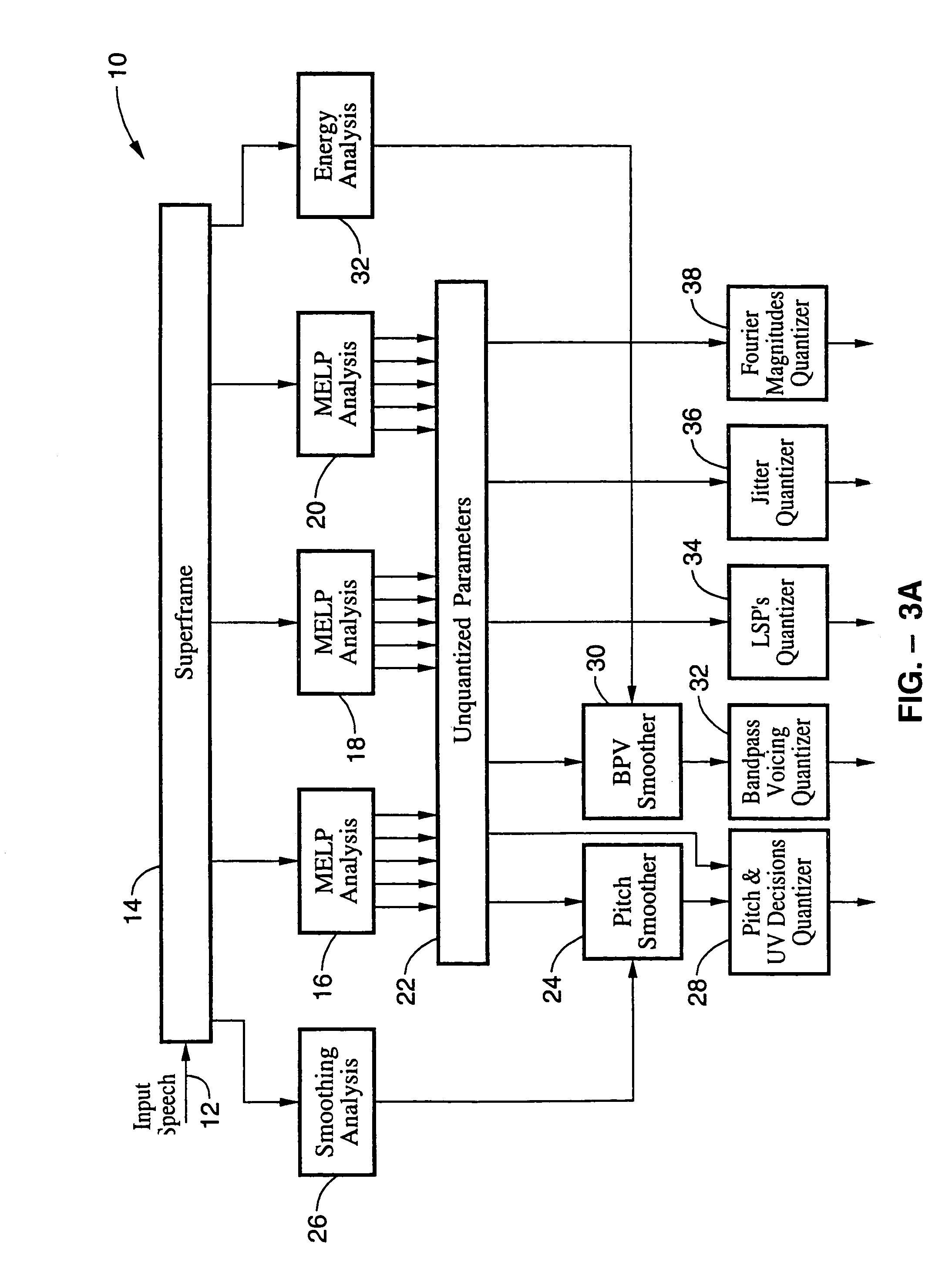
LPC-harmonic vocoder with superframe structure
An enhanced low-bit rate parametric voice coder that groups a number of frames from an underlying frame-based vocoder, such as MELP, into a superframe structure. Parameters are extracted from the group of underlying frames and quantized into the superframe which allows the bit rate of the underlying coding to be reduced without increasing the distortion. The speech data coded in the superframe structure can then be directly synthesized to speech or may be transcoded to a format so that an underlying frame-based vocoder performs the synthesis. The superframe structure includes additional error detection and correction data to reduce the distortion caused by the communication of bit errors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
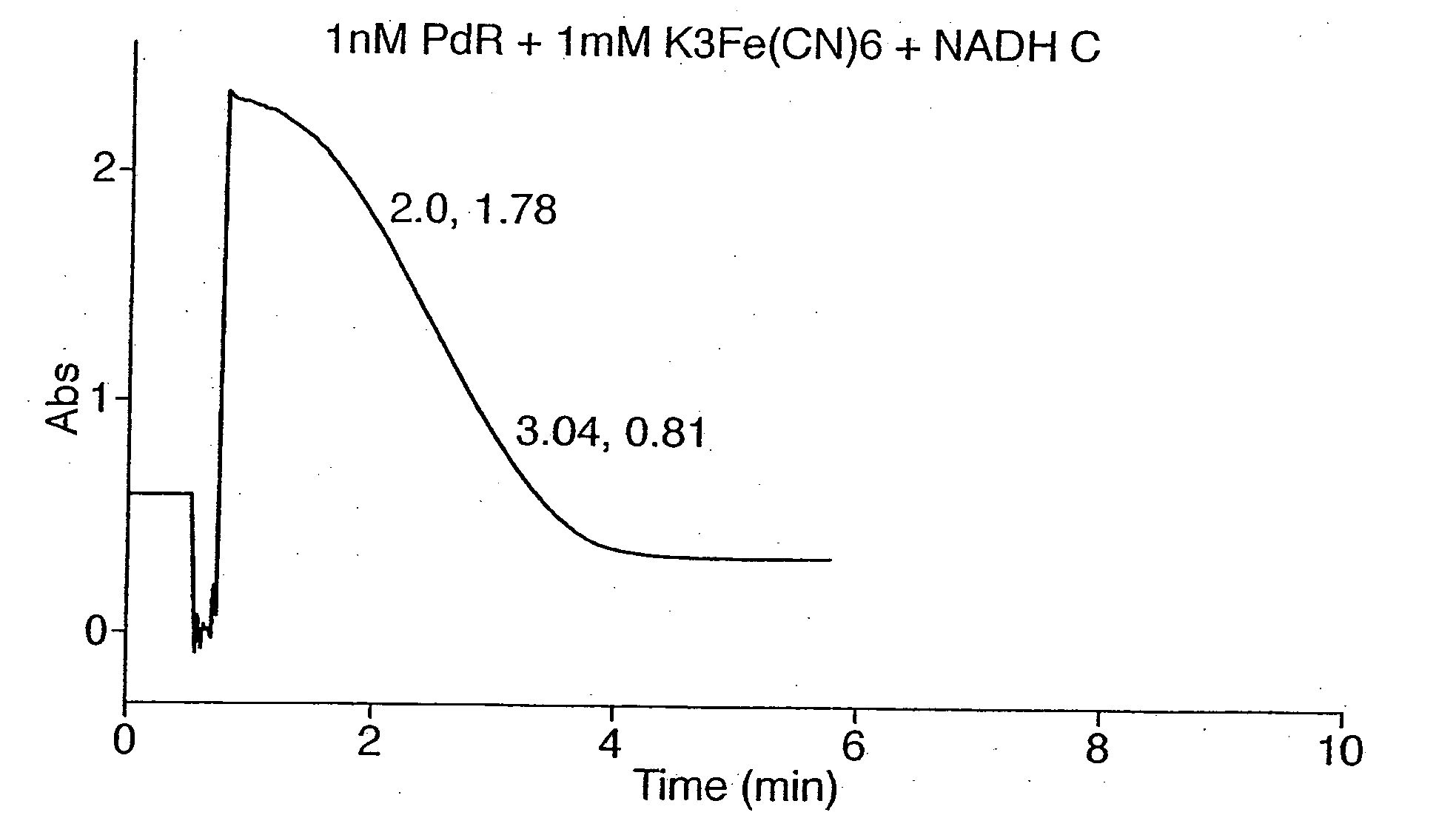
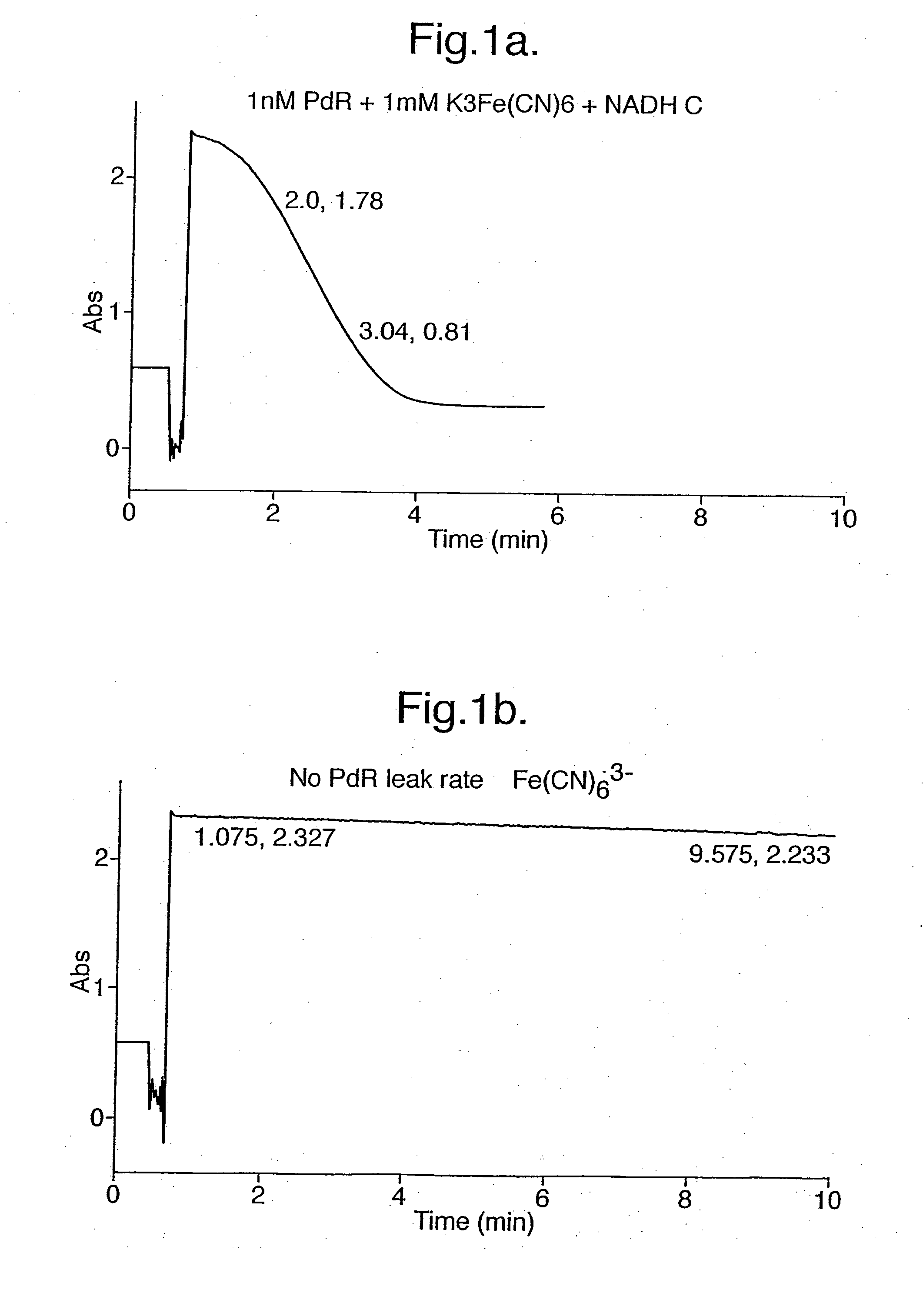
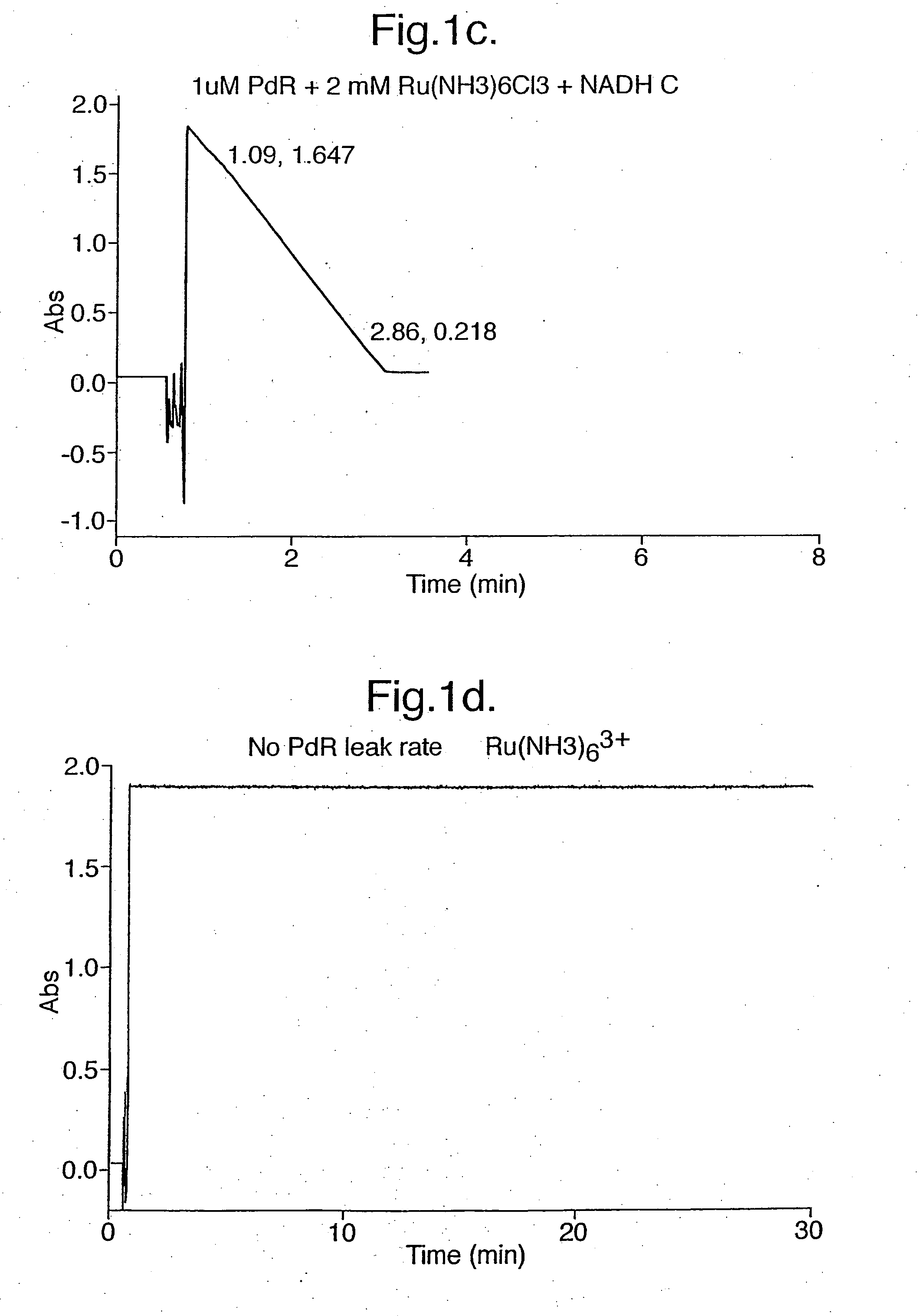
Electrochemical detection of nadh or naph
InactiveUS20050067303A1Easy to carryFast electron transfer rateImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductaseReductase
A method for detecting the presence or absence of, or for determining the concentration of, NADH or NADPH in a sample is provided, wherein the method comprises contacting a reductase and a redox active agent to said sample; and measuring the quantity of reduced redox active agent produced by the reductase, by electrochemical means. The method may be used to quantify the amount or activity of a redox enzyme or its substrate, wherein the redox enzyme uses NAD+, NADP+, NADPH or NADP as a cofactor.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
LPC-harmonic vocoder with superframe structure
InactiveUS20050075869A1Efficiently quantizedSimplified descriptionSpeech analysisFrame basedHarmonic
An enhanced_low-bit rate parametric voice coder that groups a number of frames from an underlying frame-based vocoder, such as MELP, into a superframe structure. Parameters are extracted from the group of underlying frames and quantized into the superframe which allows the bit rate of the underlying coding to be reduced without increasing the distortion. The speech data coded in the superframe structure can then be directly synthesized to speech or may be transcoded to a format so that an underlying frame-based vocoder performs the synthesis. The superframe structure includes additional error detection and correction data to reduce the distortion caused by the communication of bit errors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
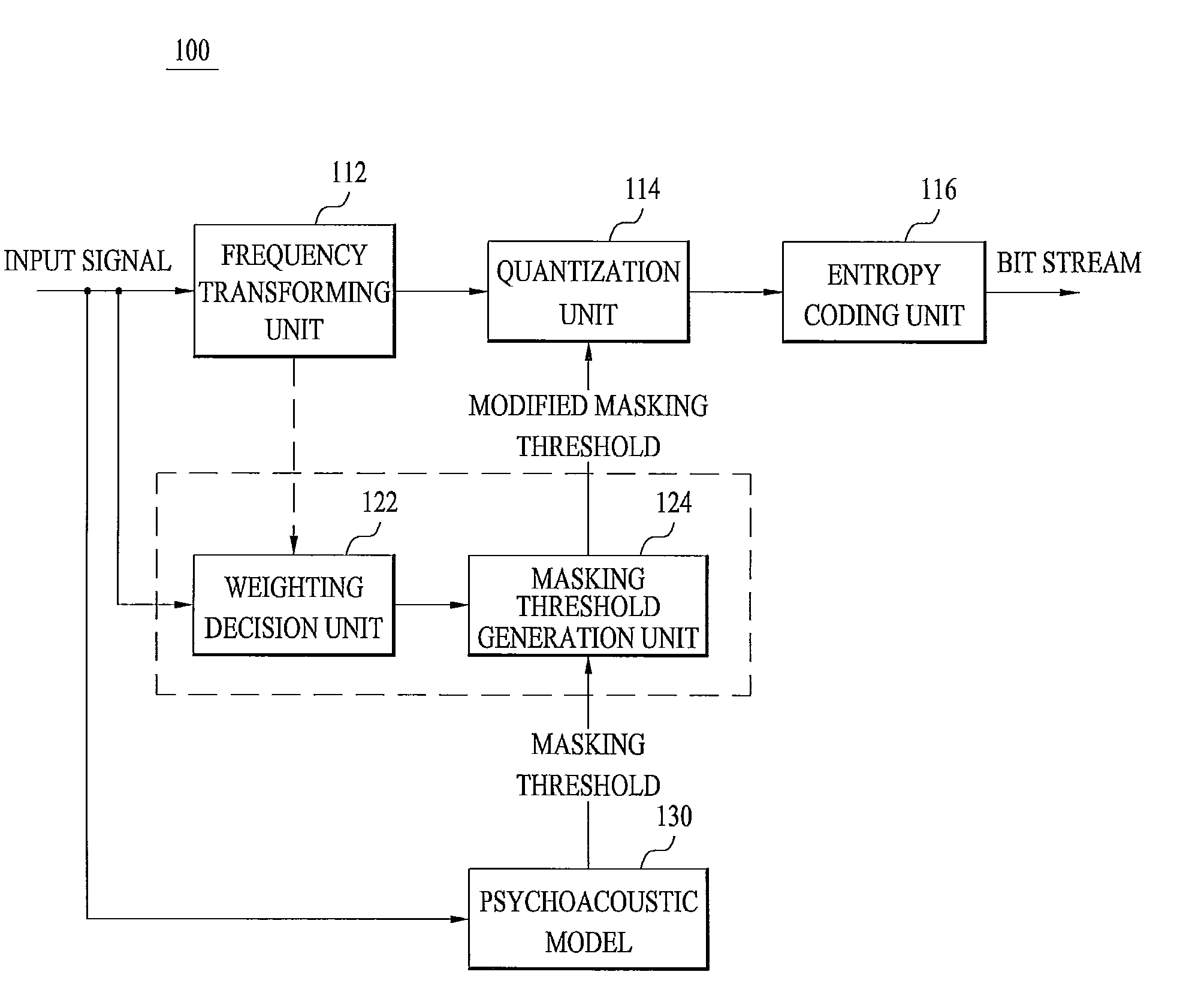
Method and apparatus for processing audio signals
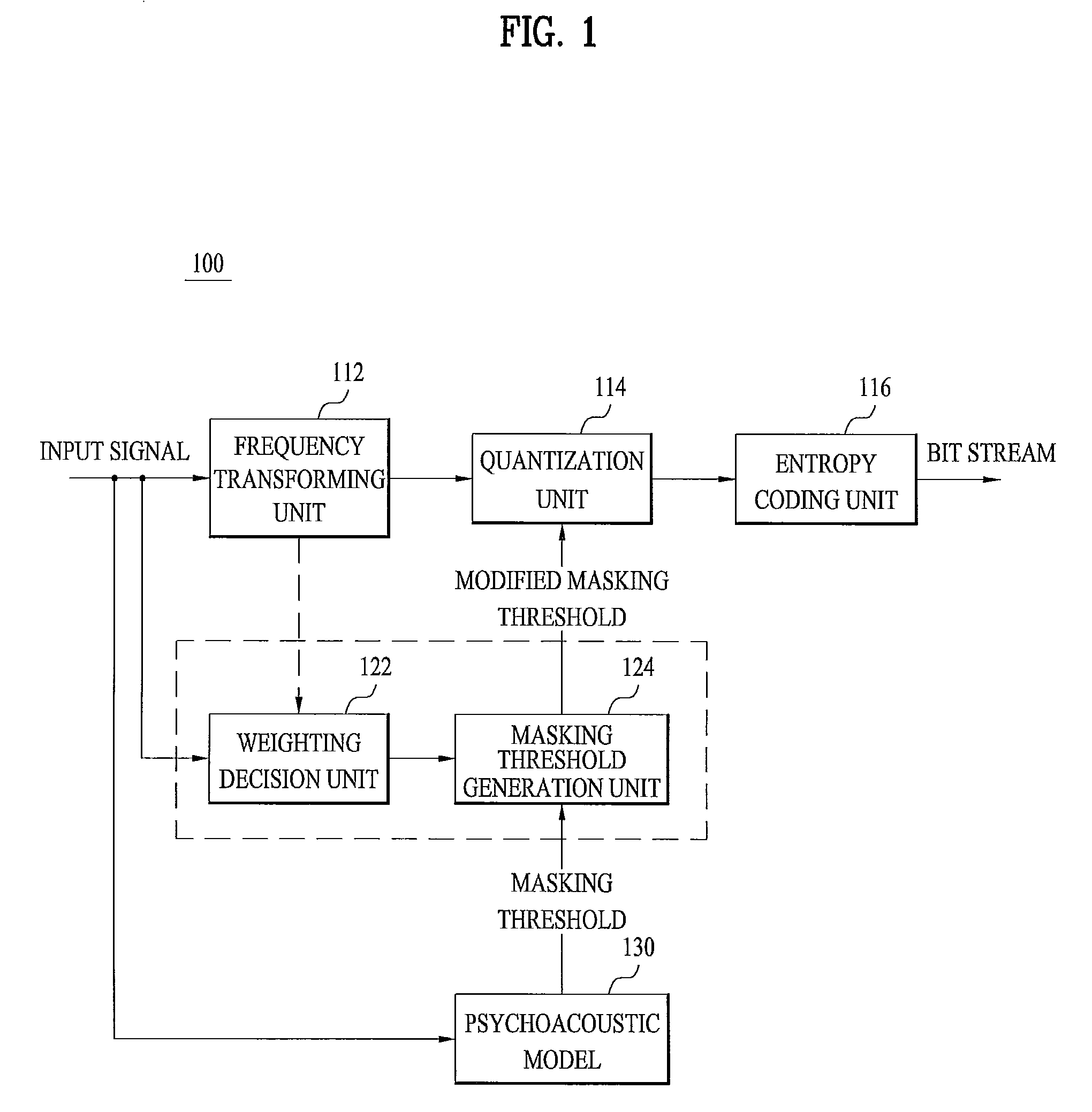
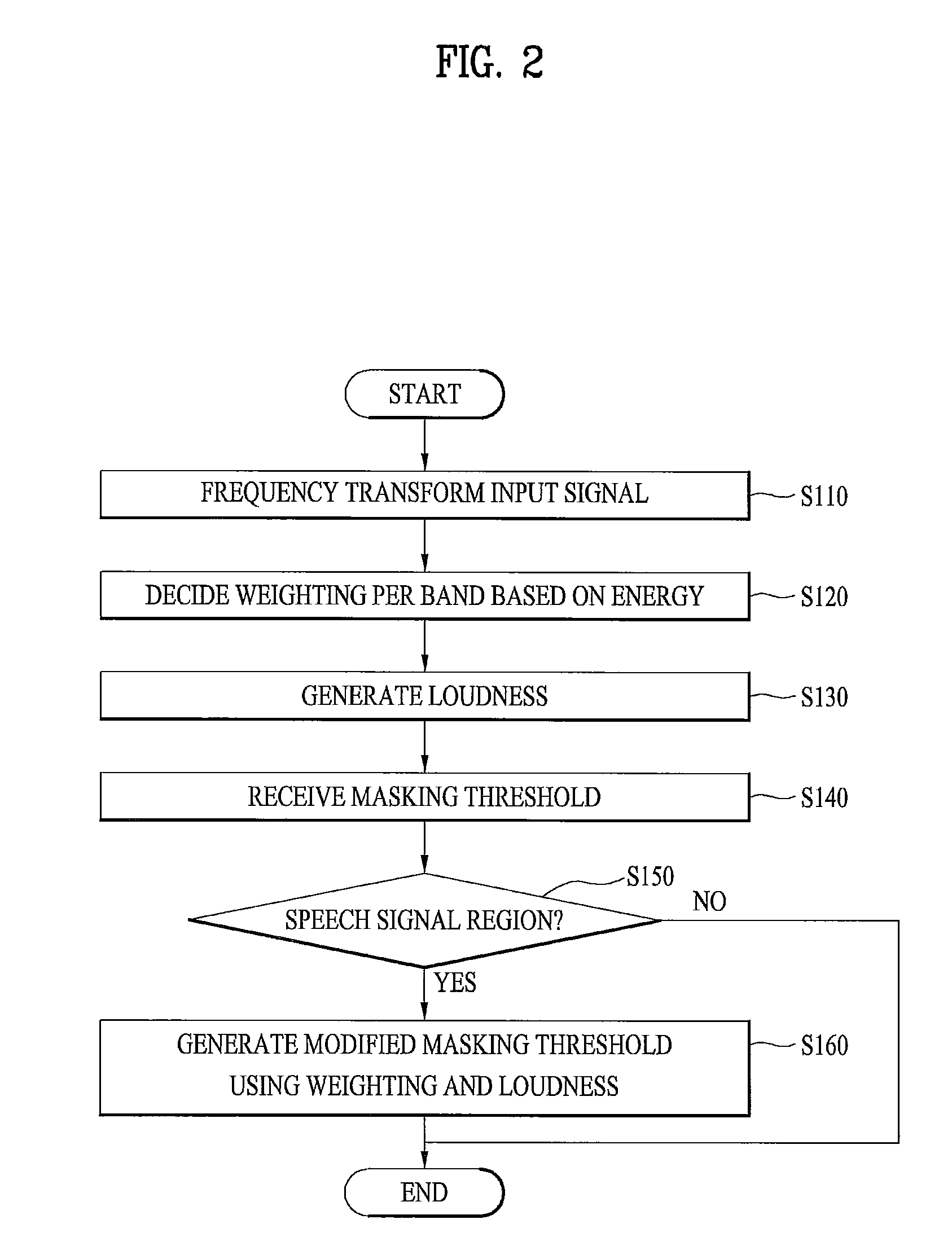
ActiveUS20110075855A1Minimizing perceived distortionMaintain sound qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumMasking threshold
A method for processing an audio signal is disclosed. The method for processing an audio signal includes frequency-transforming an audio signal to generate a frequency-spectrum, deciding a weighting per band corresponding to energy per band using the frequency spectrum, receiving a masking threshold based on a psychoacoustic model, applying the weighting to the masking threshold to generate a modified masking threshold, and quantizing the audio signal using the modified masking threshold.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
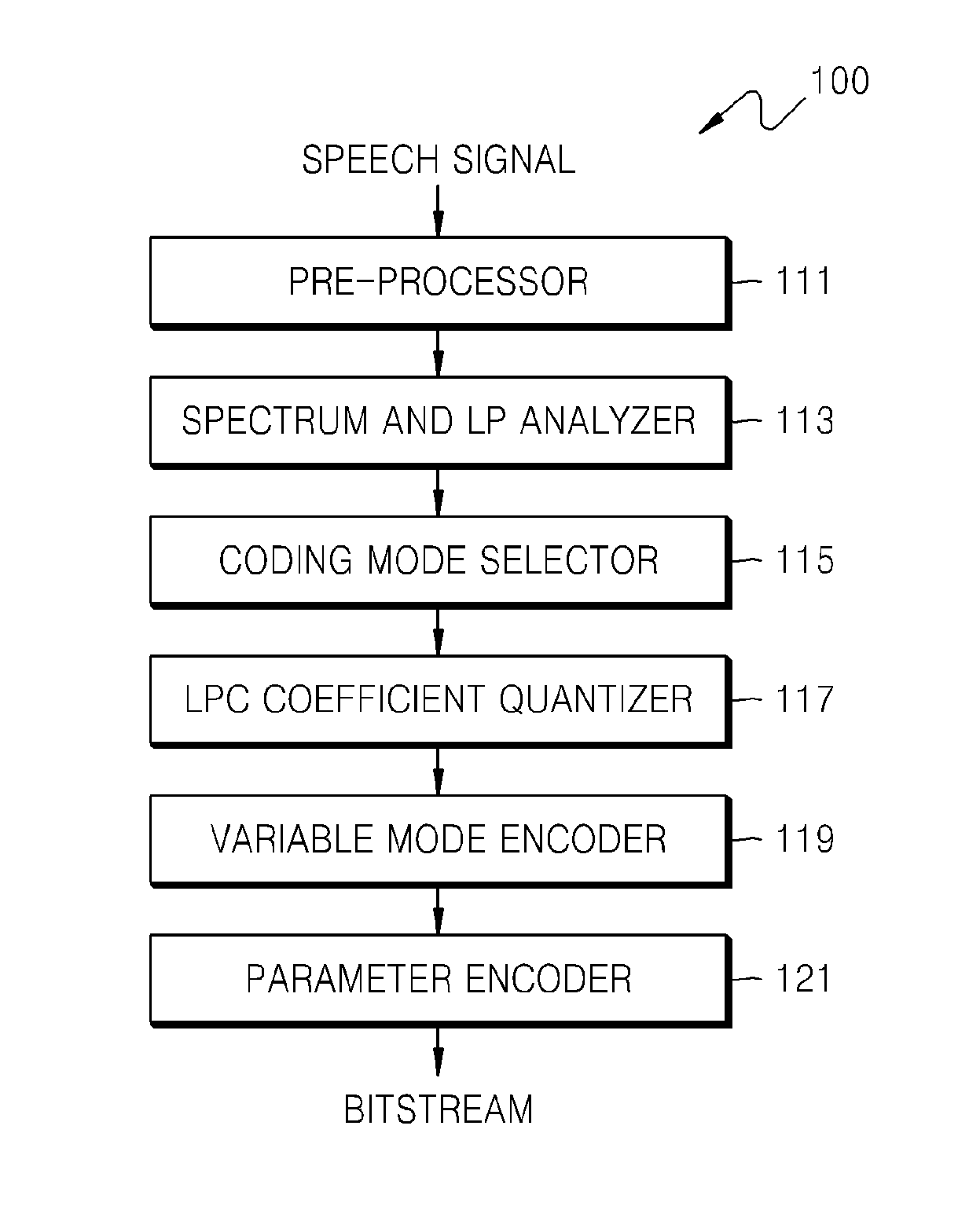
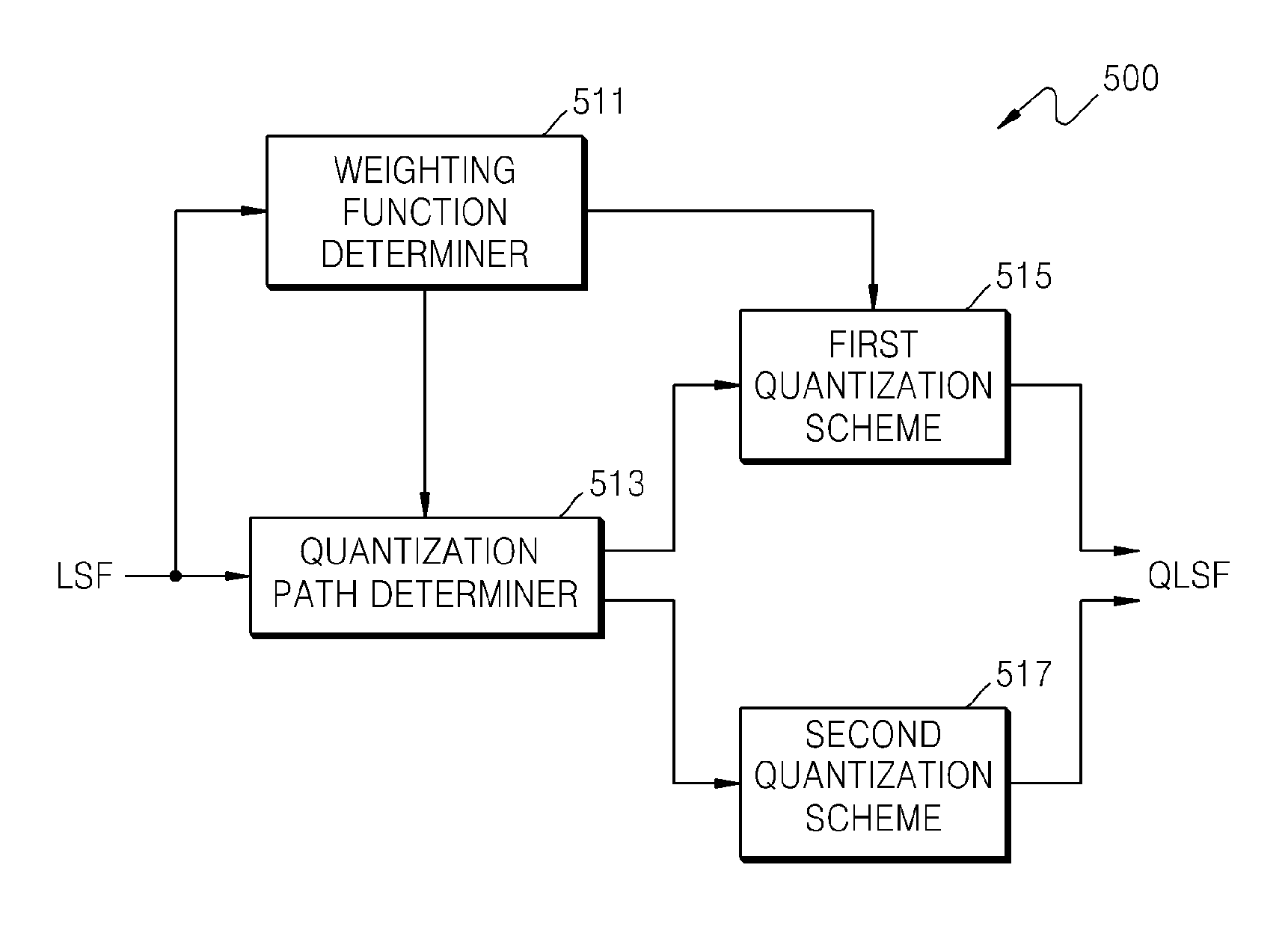
Apparatus for quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound encoding apparatus, apparatus for de-quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound decoding apparatus, and electronic device therefore
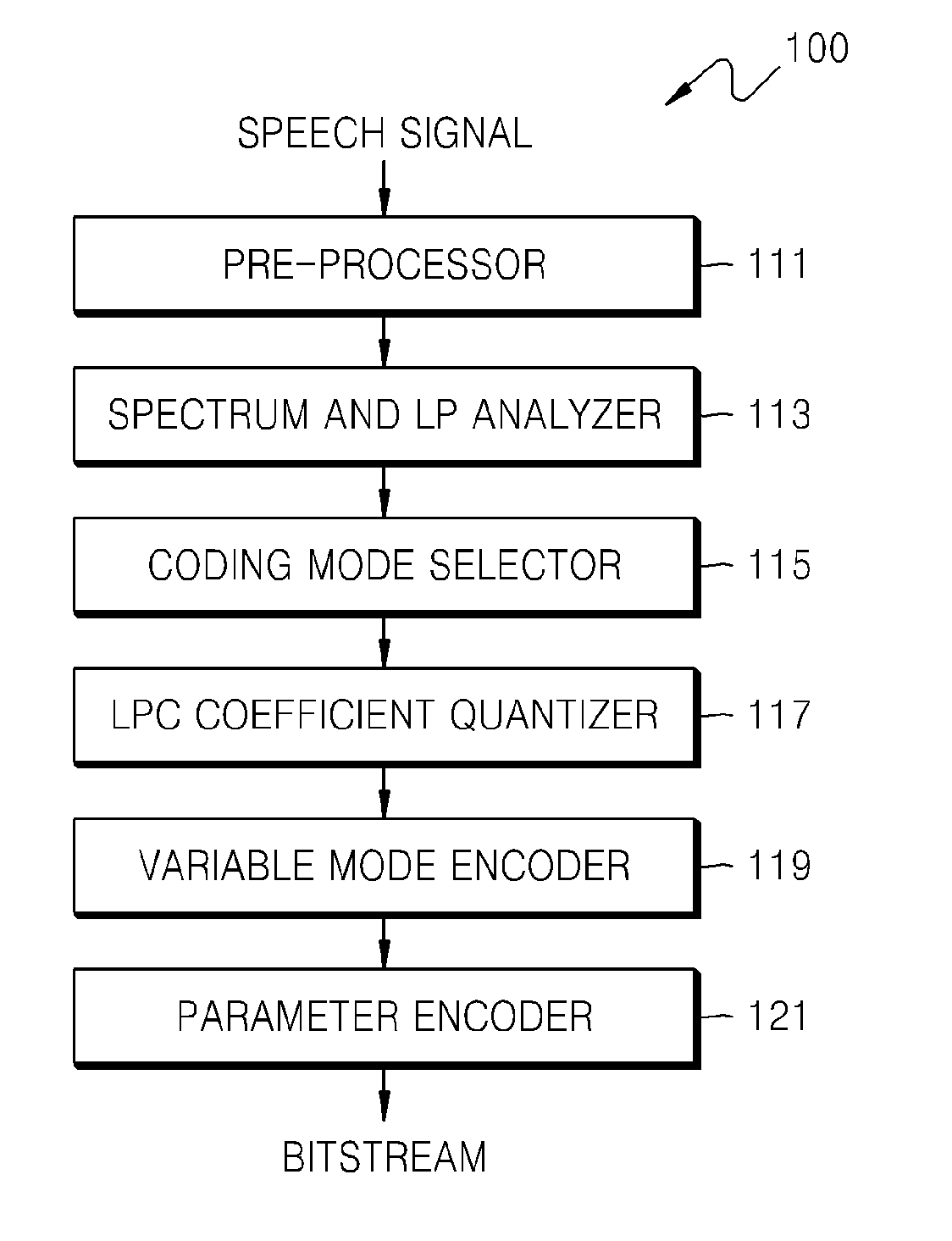
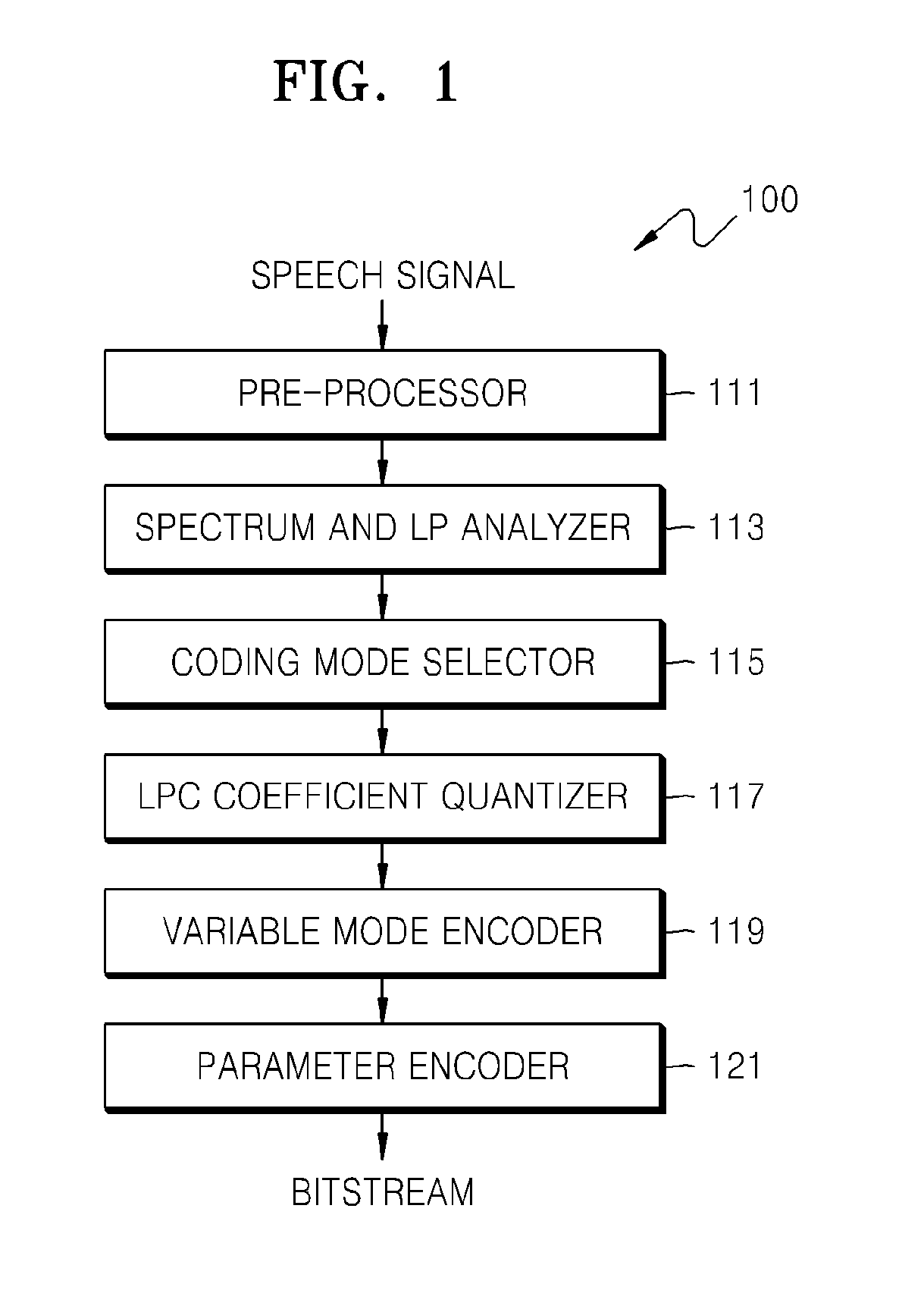
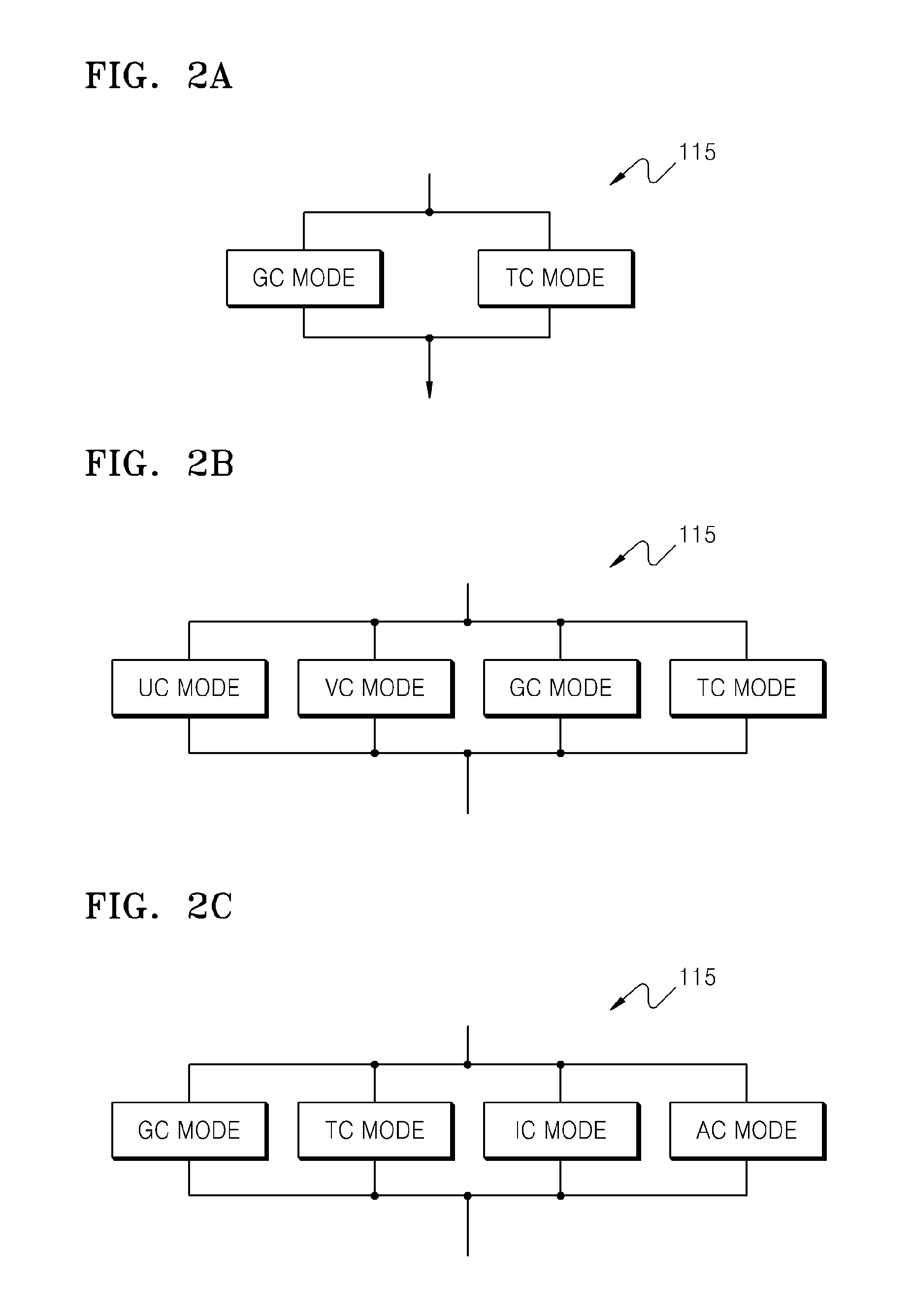
ActiveUS20120271629A1Efficiently quantizedReduce complexitySpeech analysisInter frameLinear predictive coding
A quantizing apparatus is provided that includes a quantization path determiner that determines a path from a first path not using inter-frame prediction and a second path using the inter-frame prediction, as a quantization path of an input signal, based on a criterion before quantization of the input signal; a first quantizer that quantizes the input signal, if the first path is determined as the quantization path of the input signal; and a second quantizer that quantizes the input signal, if the second path is determined as the quantization path of the input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
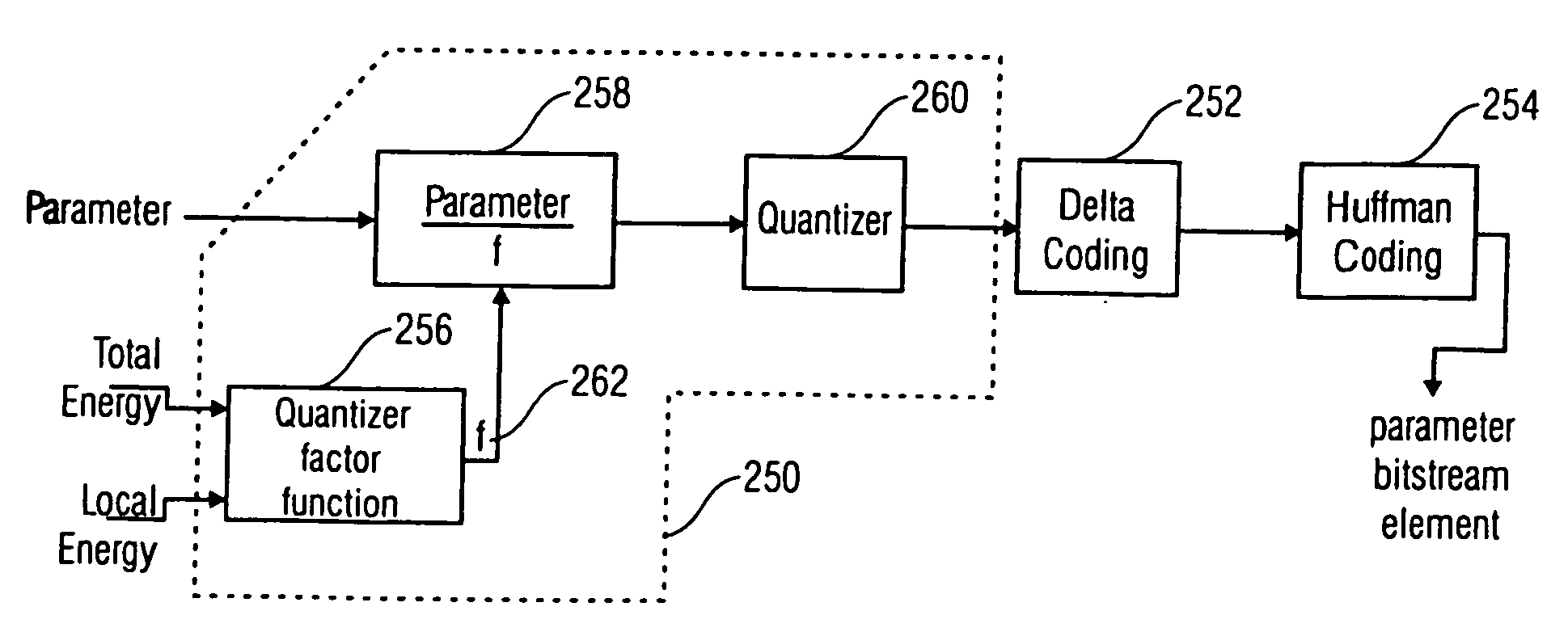
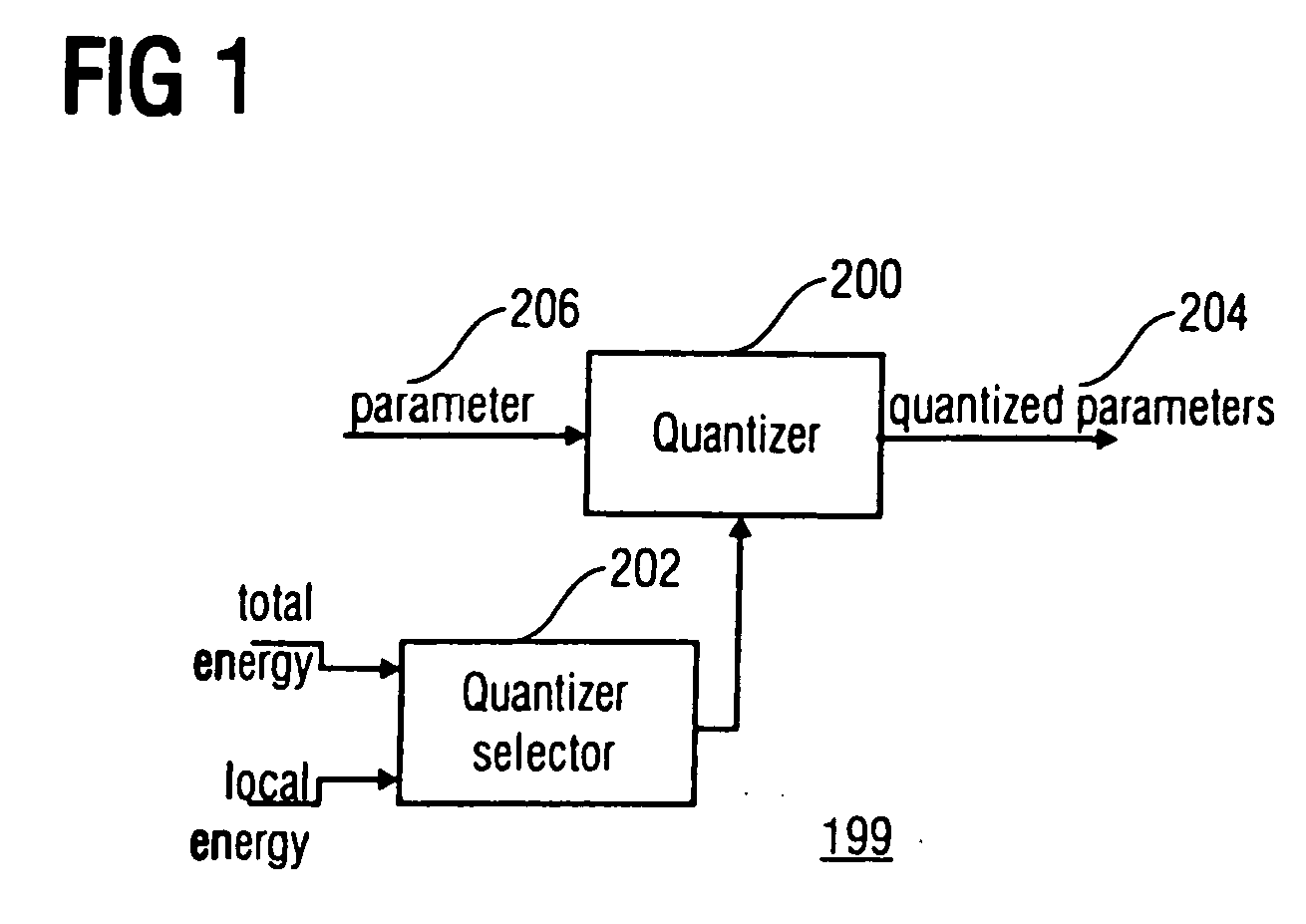
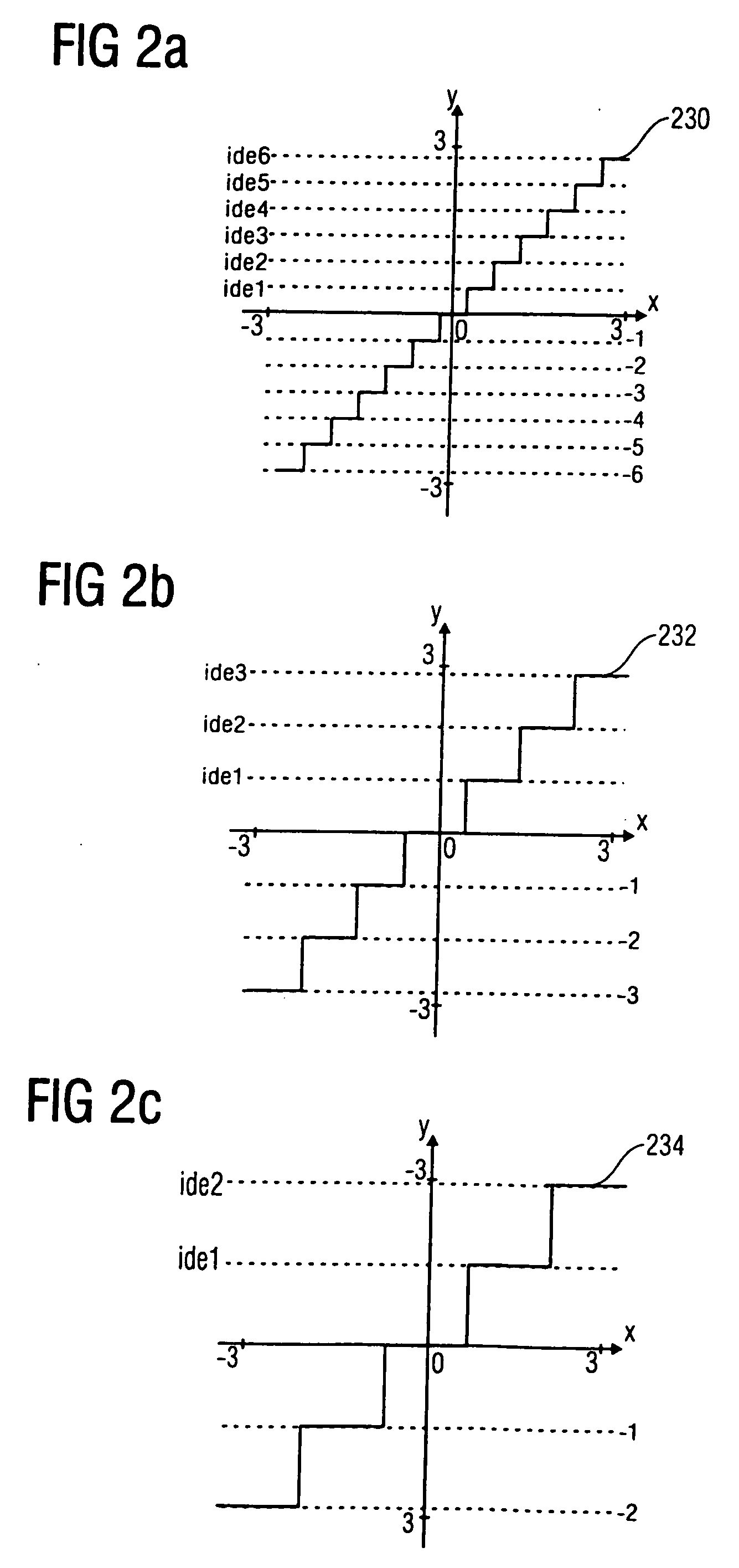
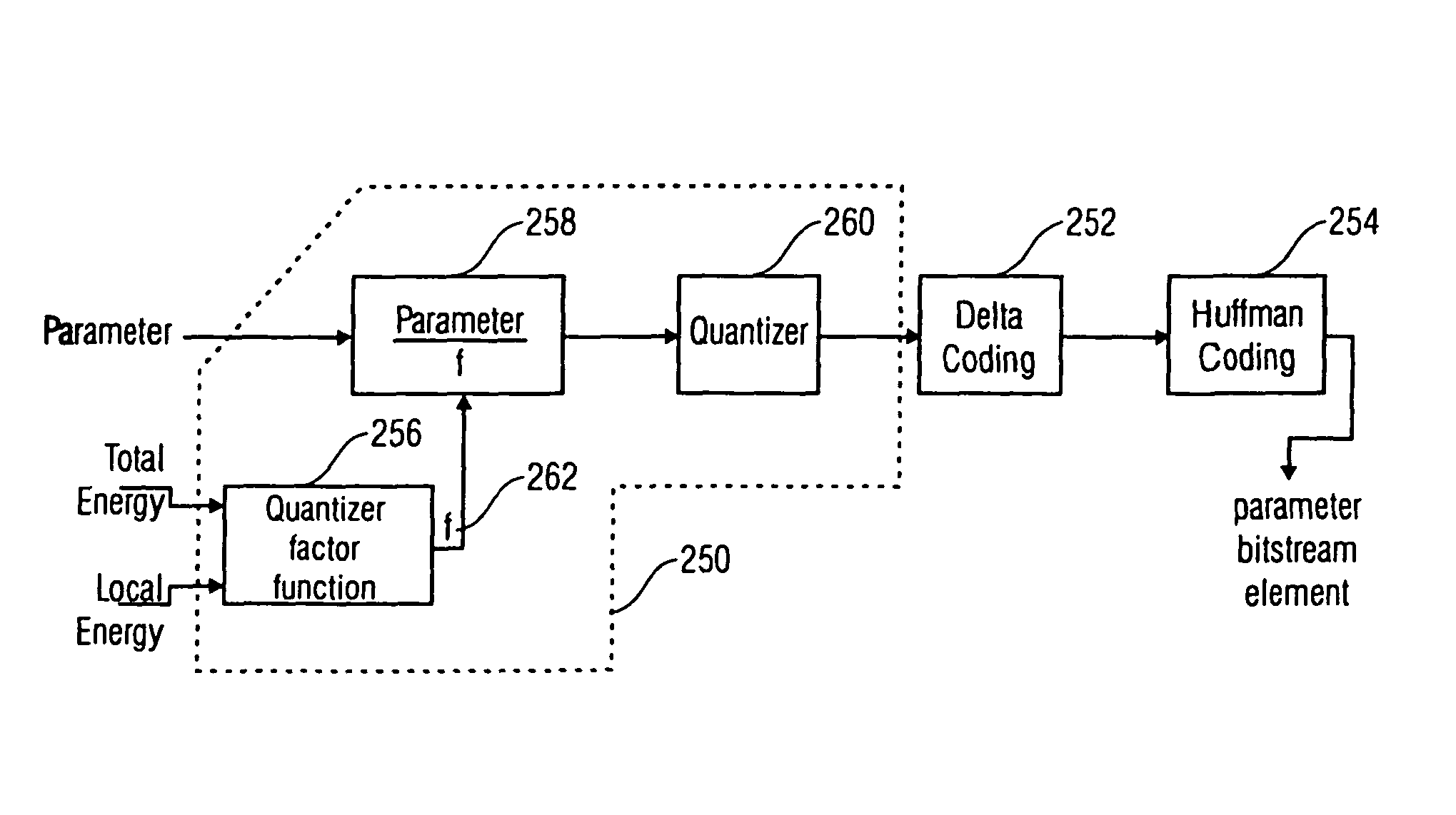
Energy dependent quantization for efficient coding of spatial audio parameters
ActiveUS20070016416A1Quantized more efficientlyEfficiently quantizedSpeech analysisCode conversionEnergy measurePsychoacoustics
Parameters being a measure for a characteristic of a channel or of a pair of channels, wherein the parameter is a measure for a characteristic of the channel or of the pair of channels with respect to another channel of a multi-channel signal can be quantized more efficiently using a quantization rule that is generated based on a relation of an energy measure of the channel or the pair of channels and an energy measure of the multi-channel signal. With generation of the quantization rule taking into account a psycho acoustic approach, the size of an encoded representation of the multi-channel signal can be decreased by coarser quantization without significantly disturbing the perceptual quality of the multi-channel signal when reconstructed from the encoded representation.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +2
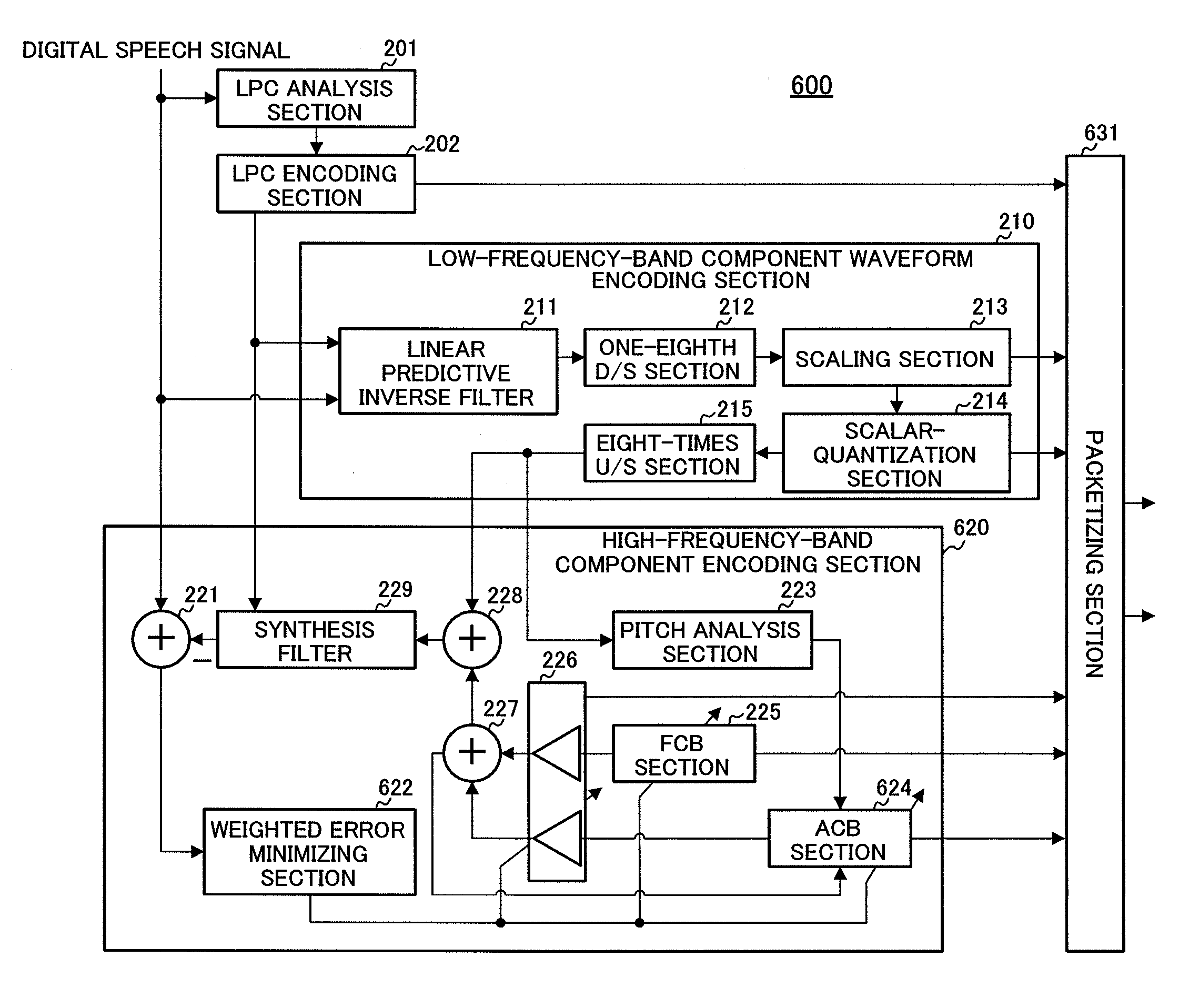
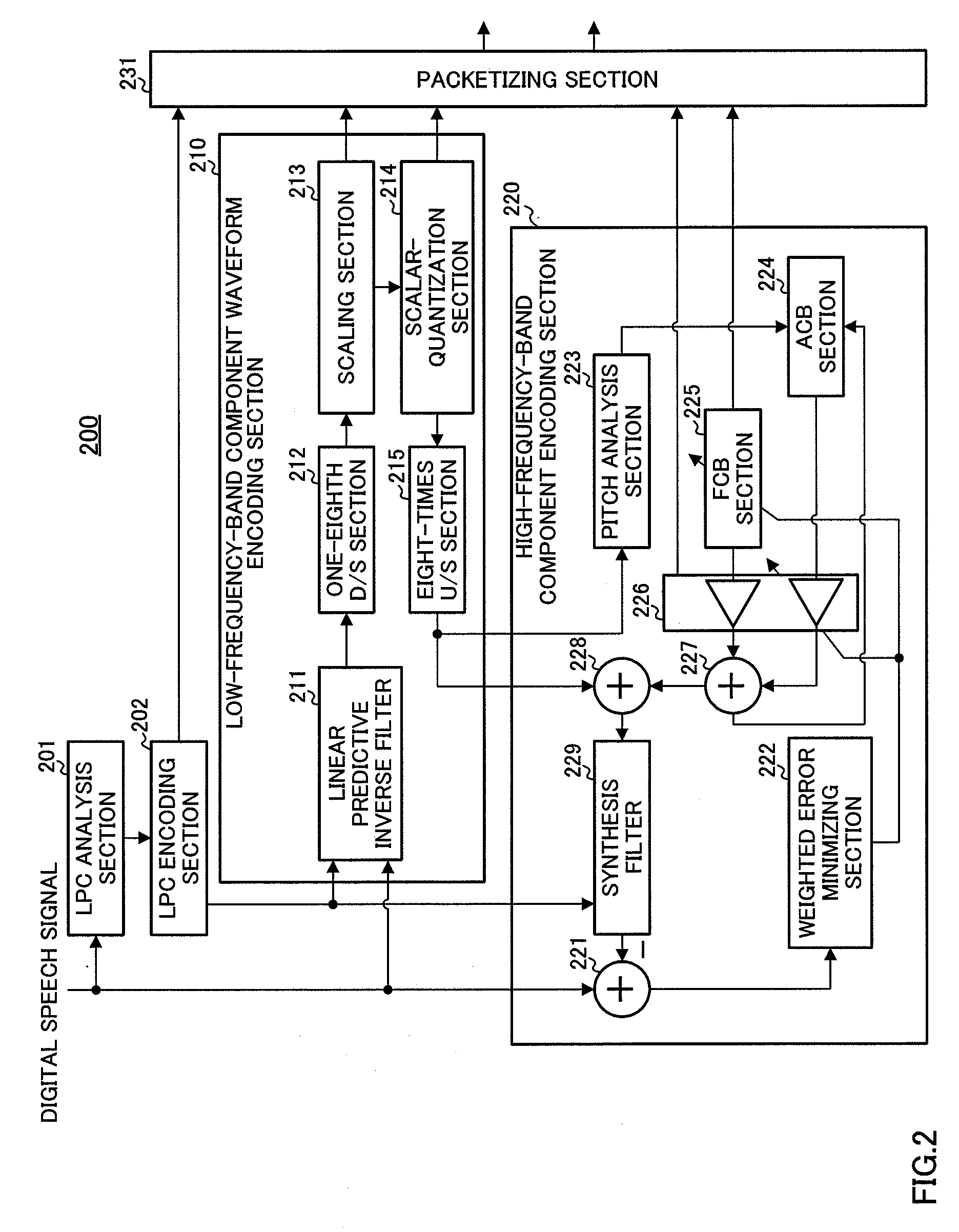
Low-frequency-band component and high-frequency-band audio encoding/decoding apparatus, and communication apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7848921B2Improve voice qualityError propagationSpeech analysisLow frequency bandCommunication device
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
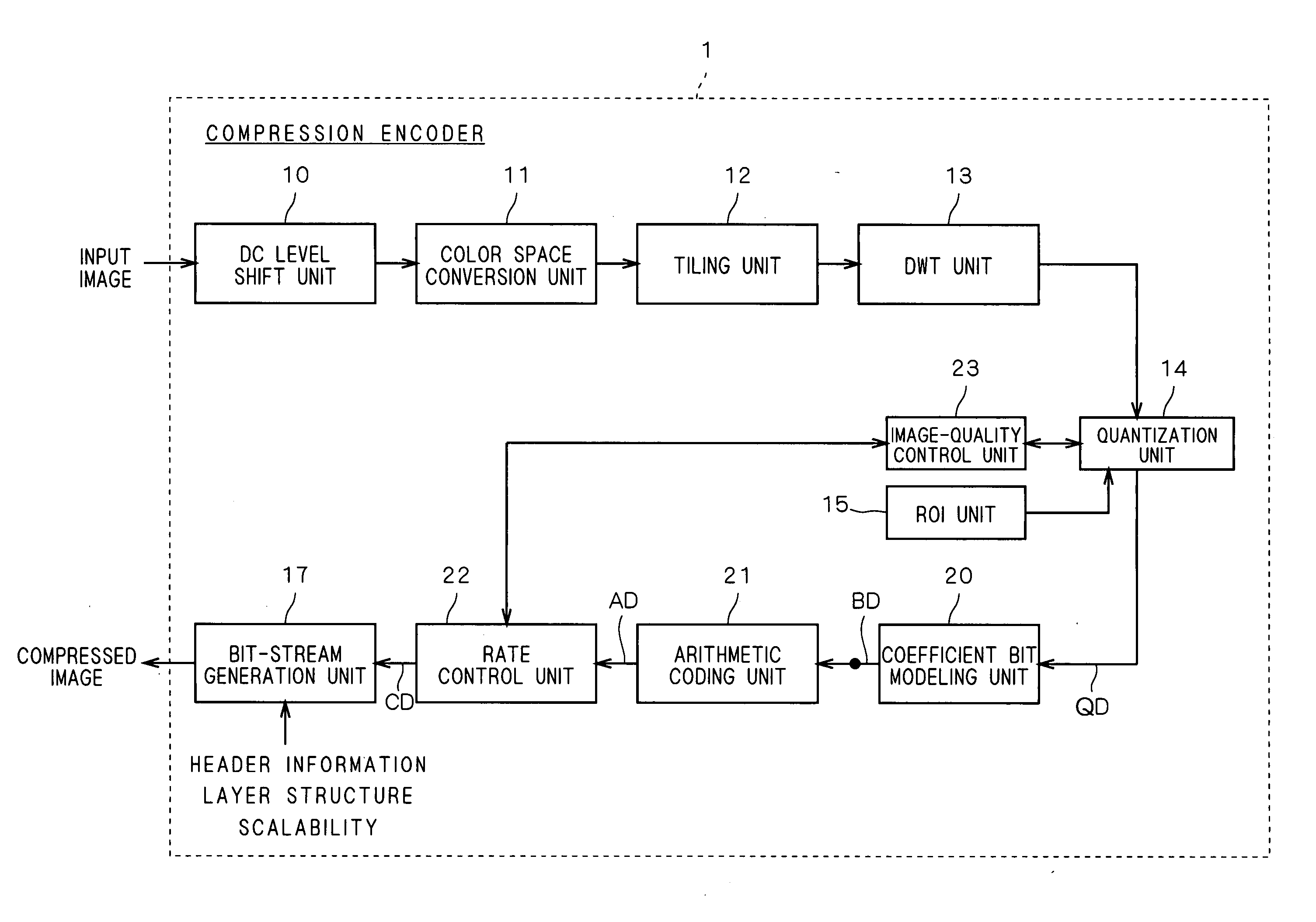
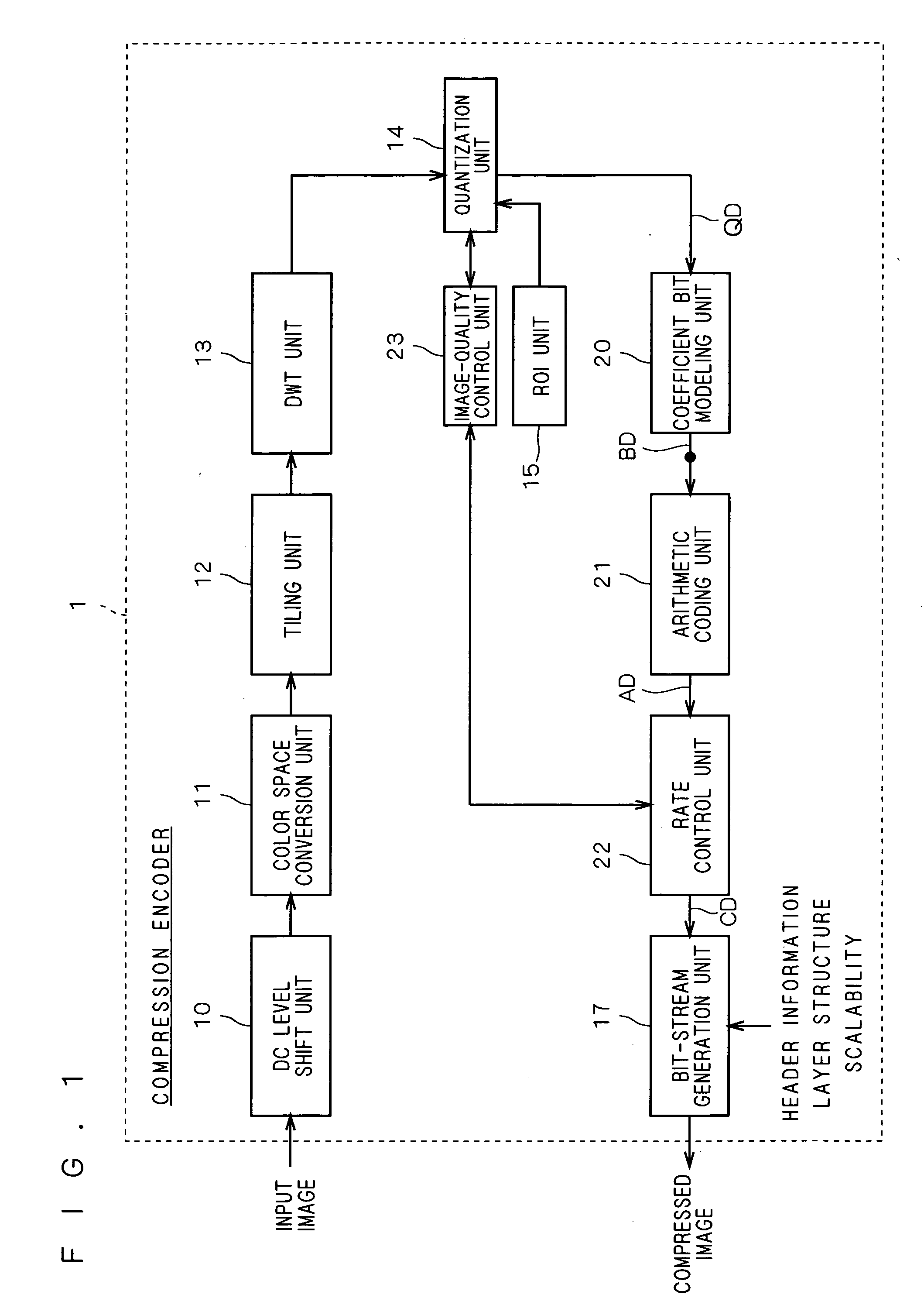
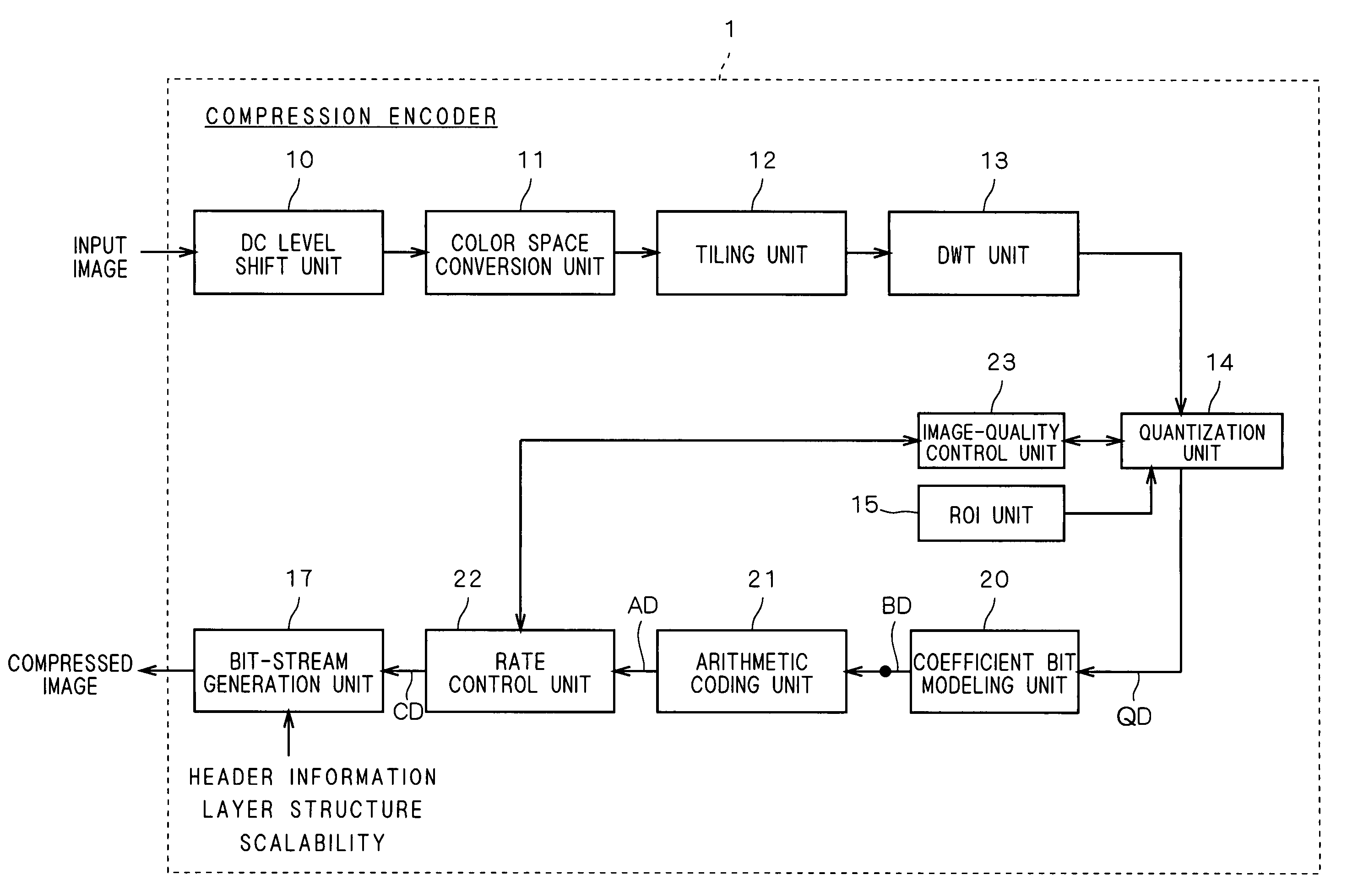
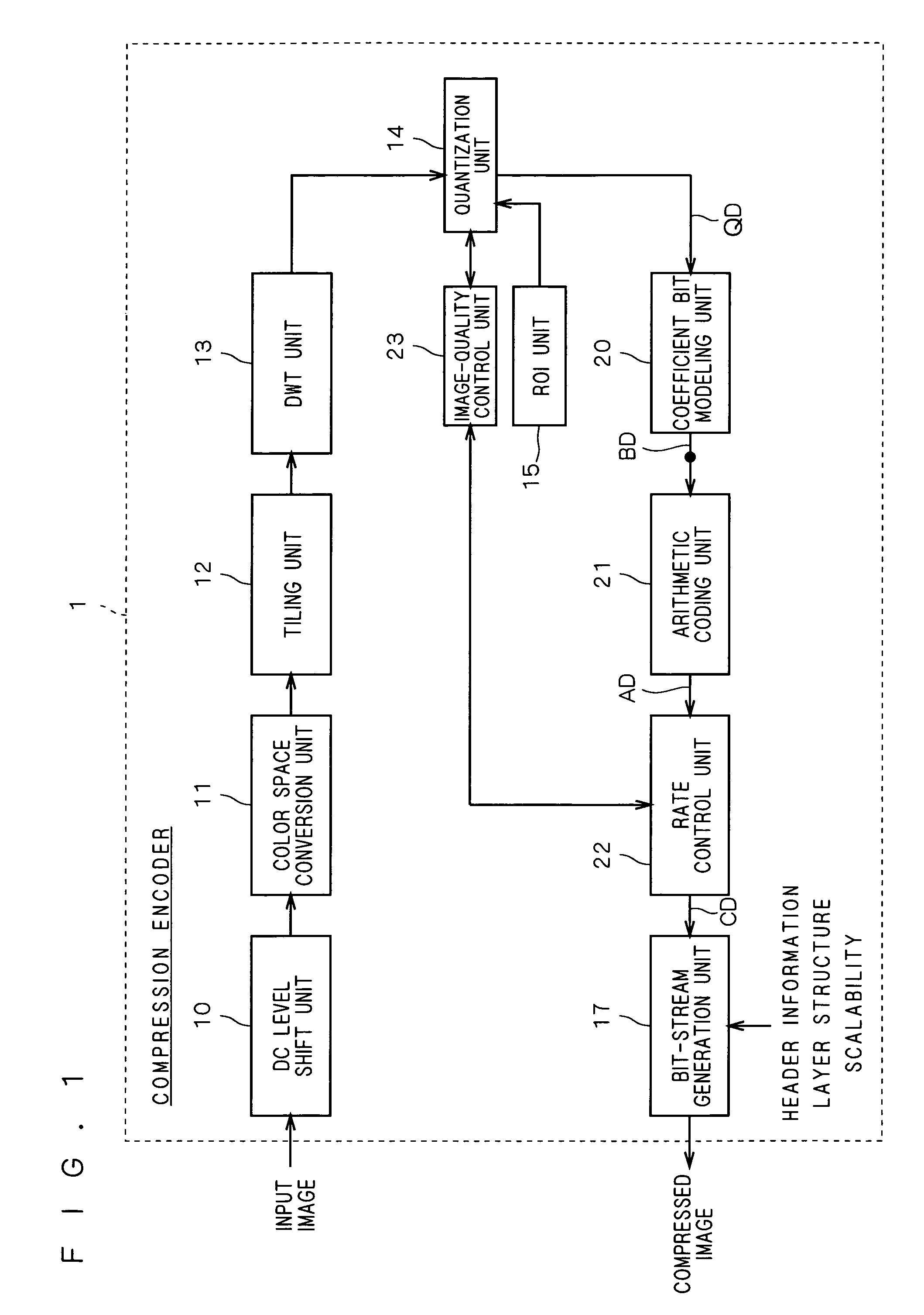
Compression encoder, compression encoding method and program
InactiveUS20060159357A1Generate efficientlyMaintain image qualityCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityBit plane
A DWT unit applies wavelet transform to an input image signal to output transform coefficients, and on those transform coefficients, a quantization unit performs quantization, sorting and bit shifting with a quantization step size determined by target image quality in an image-quality control unit as well as sorting and bit shifting based on information on a region of interest specified by a ROI unit. A coefficient bit modeling unit applies bit modeling on transform coefficients outputted from the quantization unit on a bit-plane-by-bit-plane basis, and an arithmetic coding unit applies arithmetic coding on coded data inputted from the coefficient bit modeling unit. Then, a rate control unit controls the rate of coded data inputted from the arithmetic coding unit.
Owner:MEGACHIPS
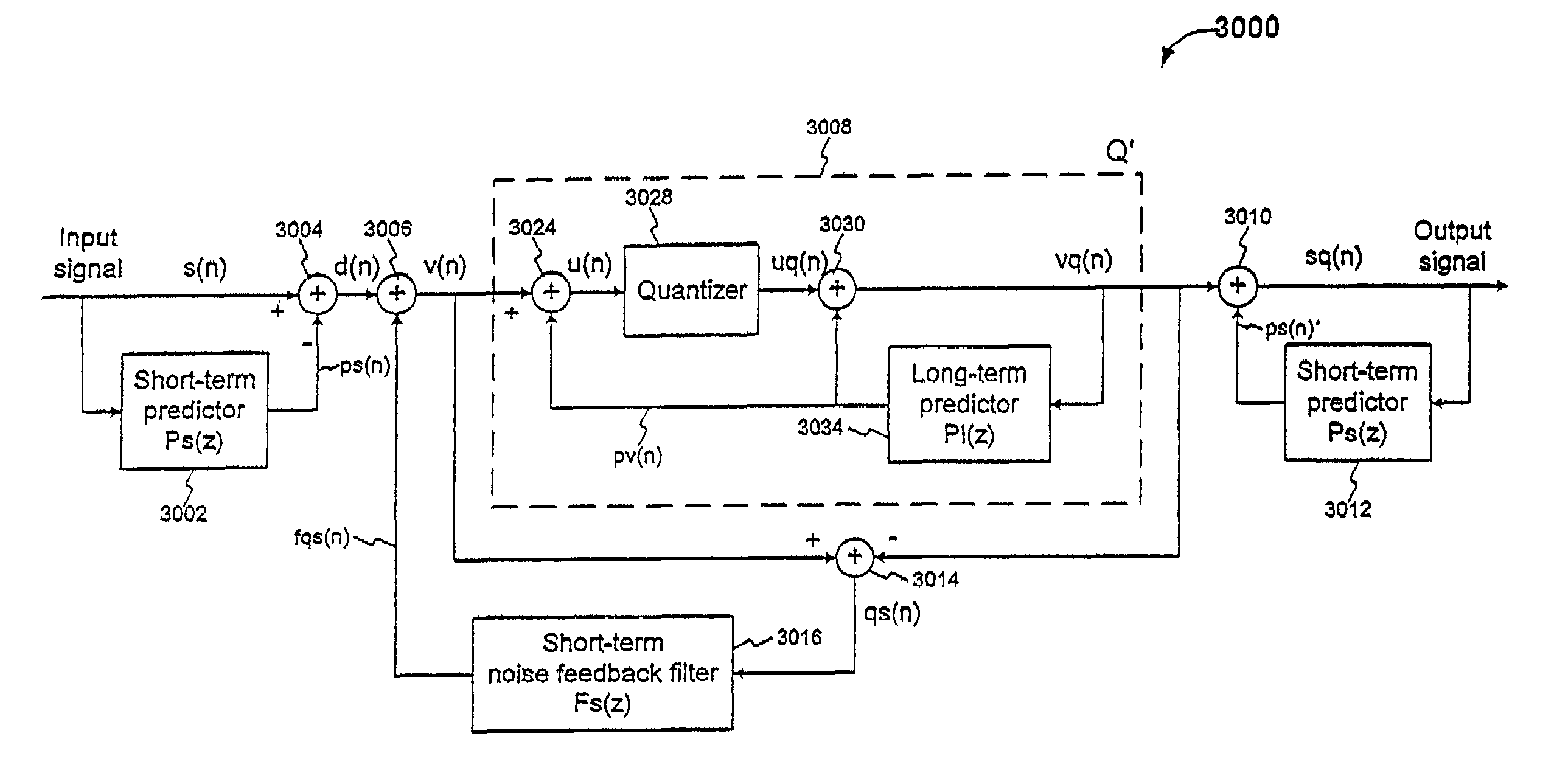
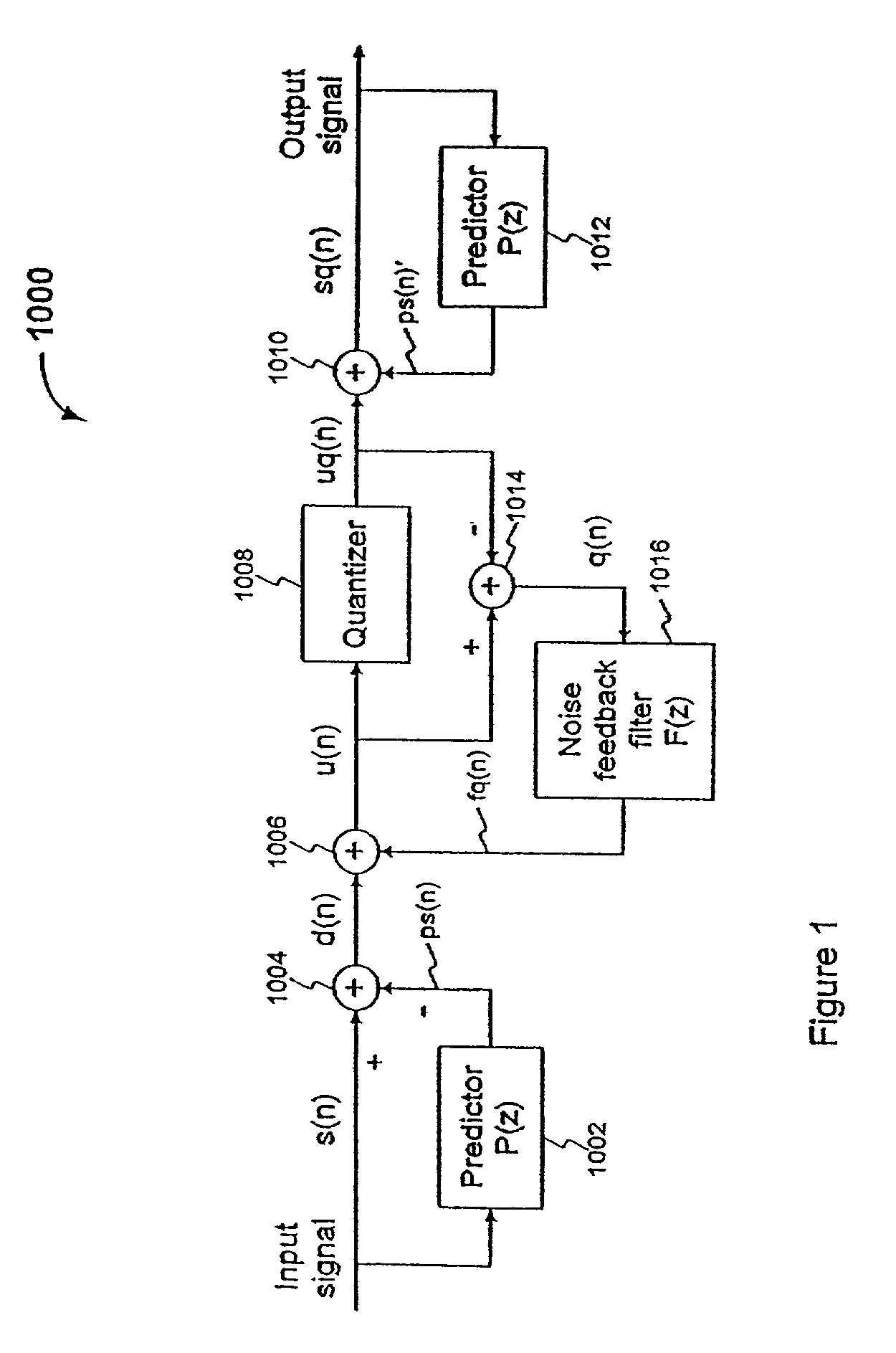
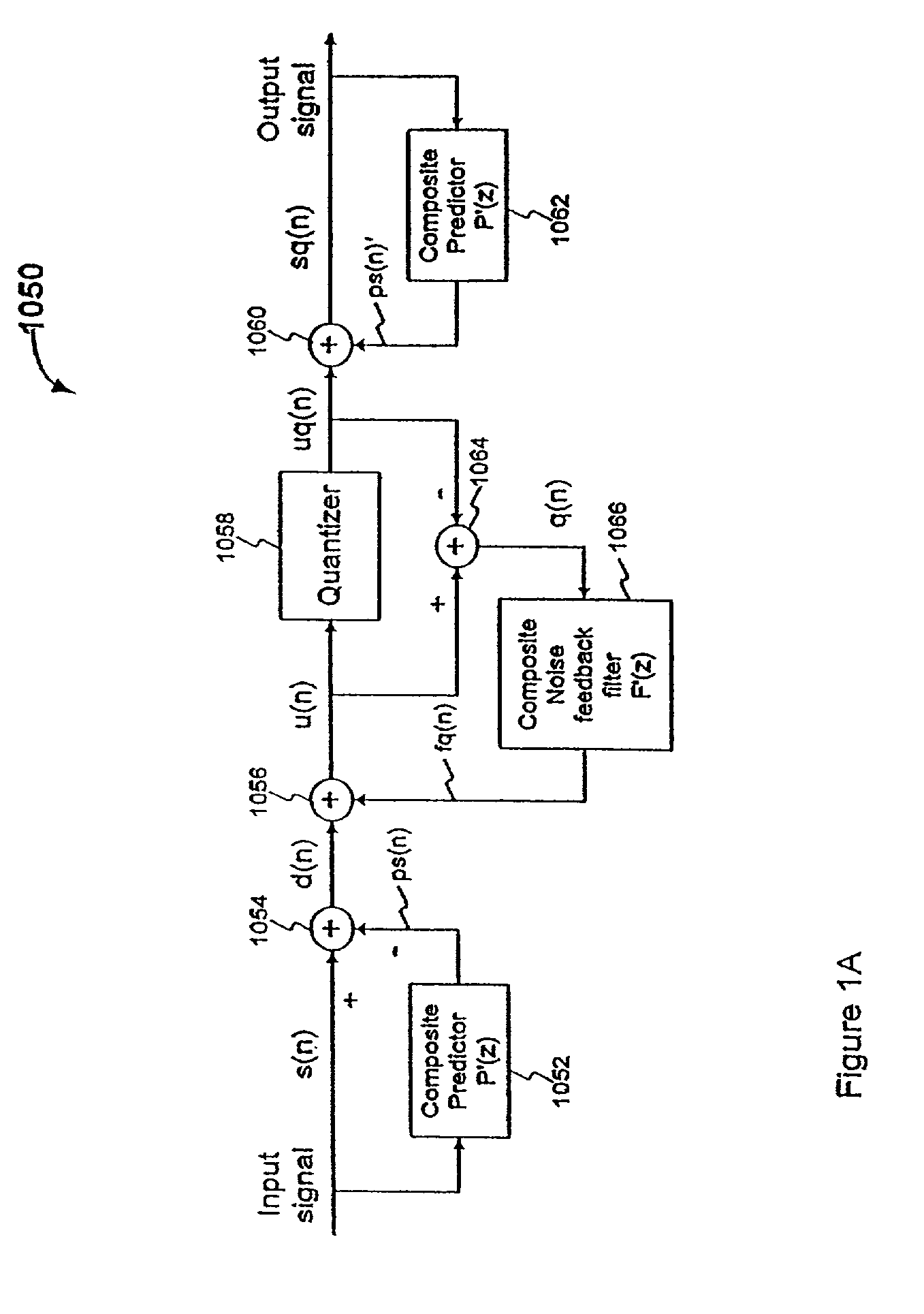
Efficient excitation quantization in noise feedback coding with general noise shaping
In a Noise Feedback Coding (NFC) system operable in a ZERO-STATE condition and a ZERO-INPUT condition, the NFC system including at least one filter having a filter memory, a method of updating the filter memory. The method comprises: (a) producing a ZERO-STATE contribution to the filter memory when the NFC system is in the ZERO-STATE condition; (b) producing a ZERO-INPUT contribution to the filter memory when the NFC system is in the ZERO-INPUT condition; and (c) updating the filter memory as a function of both the ZERO-STATE contribution and the ZERO-INPUT contribution.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
LPC-harmonic vocoder with superframe structure
An enhanced low-bit rate parametric voice coder that groups a number of frames from an underlying frame-based vocoder, such as MELP, into a superframe structure. Parameters are extracted from the group of underlying frames and quantized into the superframe which allows the bit rate of the underlying coding to be reduced without increasing the distortion. The speech data coded in the superframe structure can then be directly synthesized to speech or may be transcoded to a format so that an underlying frame-based vocoder performs the synthesis. The superframe structure includes additional error detection and correction data to reduce the distortion caused by the communication of bit errors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound encoding method, method of de-quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound decoding method, and recording medium and electronic device therefor
ActiveUS20120278069A1Efficiently quantizedReduce complexitySpeech analysisDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsTransmission channel
A quantizing method is provided that includes quantizing an input signal by selecting one of a first quantization scheme not using an inter-frame prediction and a second quantization scheme using the inter-frame prediction, in consideration of one or more of a prediction mode, a predictive error and a transmission channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
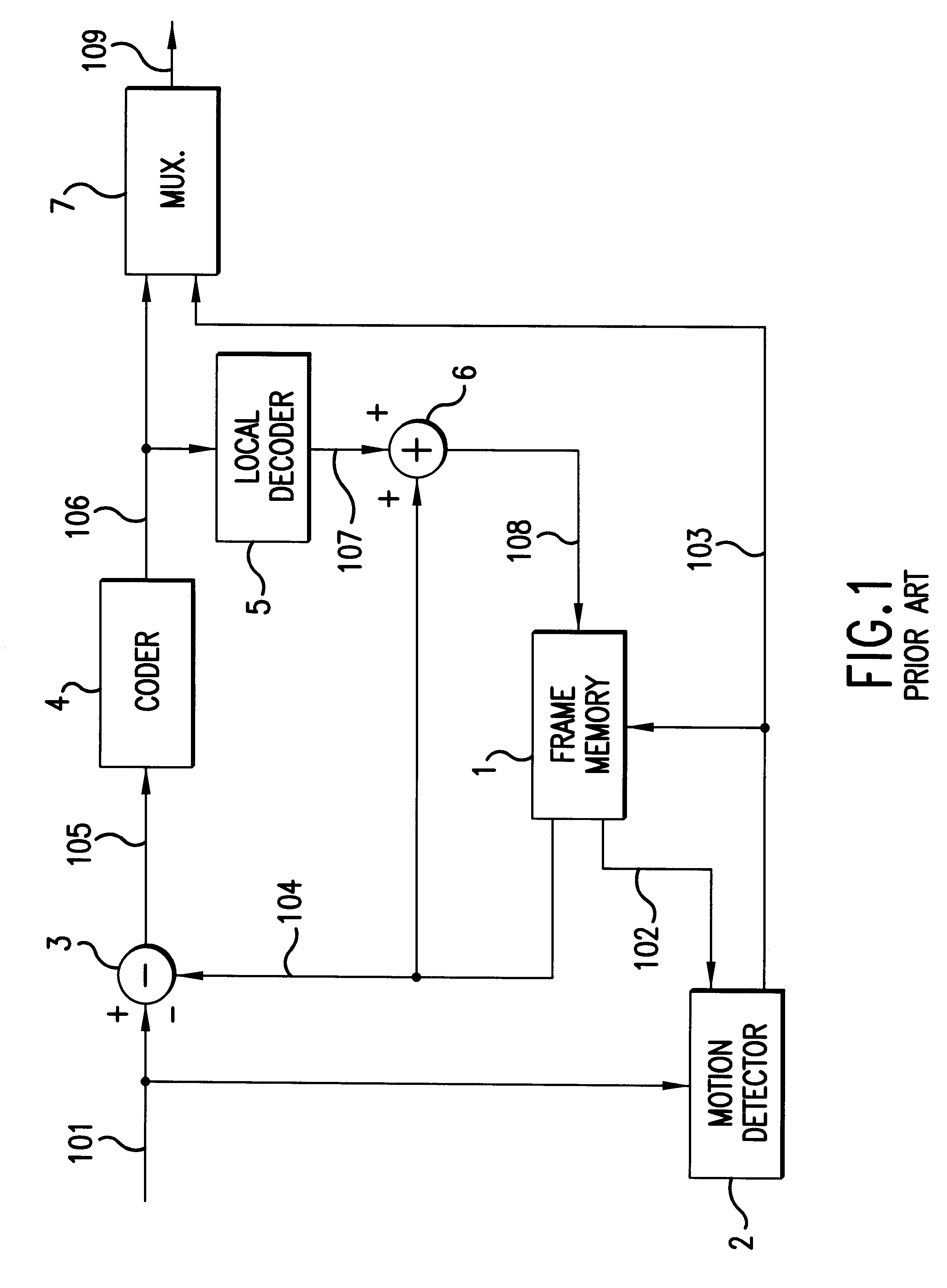
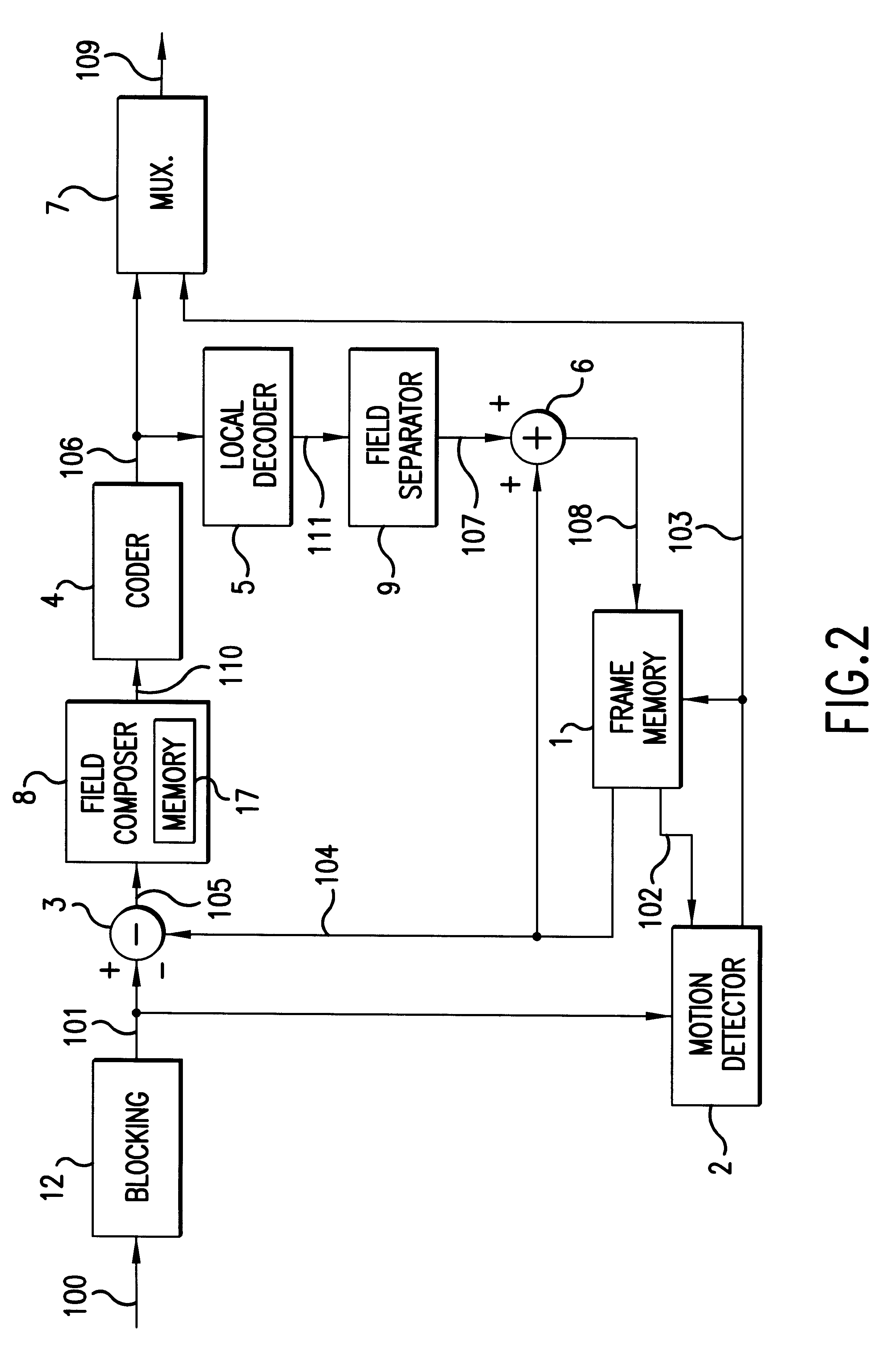
Motion compensation predicting encoding method and apparatus
InactiveUSRE37858E1Efficiently quantizedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionMotion detector
A motion compensation predicting coding apparatus includes a motion detector for comparing pixel data in an image signal with pixel data of the previous image signal to generate a motion vector. The motion vector is indicative of the displacement differences between the image signal and the previous image signal. The image signal may be organized into blocks of pixel data for a single field or for multiple fields when notion detection is performed on the image signal by the motion detector. A subtracter generates a prediction compensation error signal by subtracting the pixel data in the previous image signal from the pixel data of the image signal. A coder receives the prediction compensation error signal and generates an appropriate coded output. The apparatus may also include an adaptive blocking mechanism for receiving the prediction compensation error signal and organizing the data in the signal into blocks into one of several fashions as dictated by the motion vector.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Device and method for detection of analyte from a sample
InactiveUS20110192726A1Large dead volumeEnhancing impedance detection sensitivityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentAnalyteDielectrophoresis
There is presently provided a device for detecting an analyte particle in a sample. The device comprises a chamber having an interior surface upon which is located an electrode array. The electrode array comprises pairs of electrodes, each pair having an inner electrode and an outer electrode that substantially surrounds the inner electrode. Each pair of electrodes is coated with a capture molecule that recognises and binds the analyte particle that is to be identified and quantified. The device uses a combination of dielectrophoresis and impedance measurements to capture and measure analyte particles from a sample.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE +1
Energy dependent quantization for efficient coding of spatial audio parameters
ActiveUS8054981B2Quantized more efficientlyEfficiently quantizedSpeech analysisCode conversionPsychoacousticsEnergy measure
Parameters being a measure for a characteristic of a channel or of a pair of channels, wherein the parameter is a measure for a characteristic of the channel or of the pair of channels with respect to another channel of a multi-channel signal can be quantized more efficiently using a quantization rule that is generated based on a relation of an energy measure of the channel or the pair of channels and an energy measure of the multi-channel signal. With generation of the quantization rule taking into account a psycho acoustic approach, the size of an encoded representation of the multi-channel signal can be decreased by coarser quantization without significantly disturbing the perceptual quality of the multi-channel signal when reconstructed from the encoded representation.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +2
Image code estimation
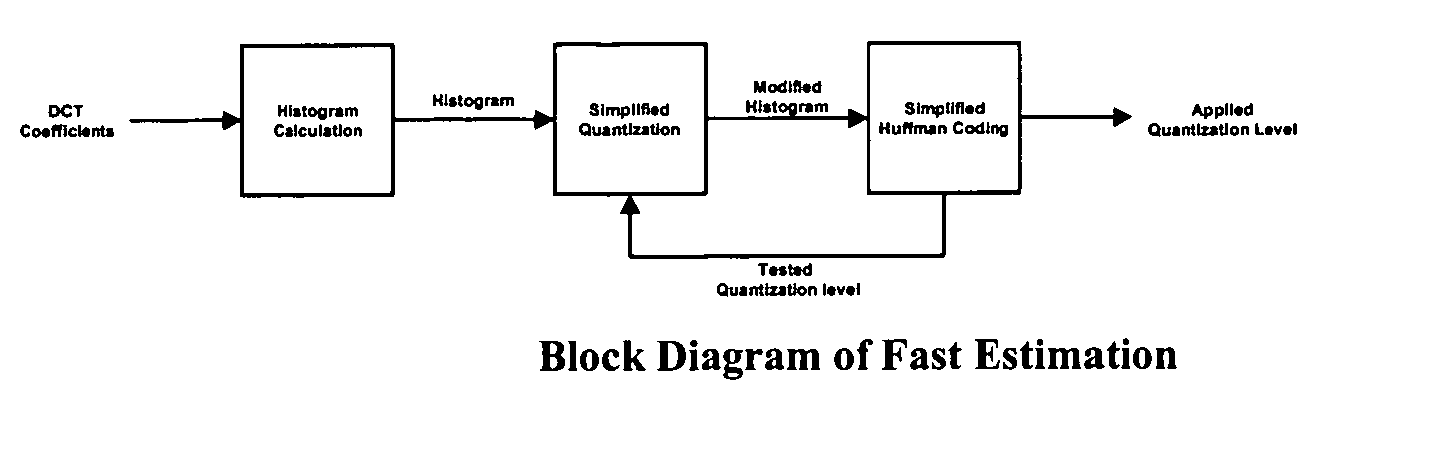
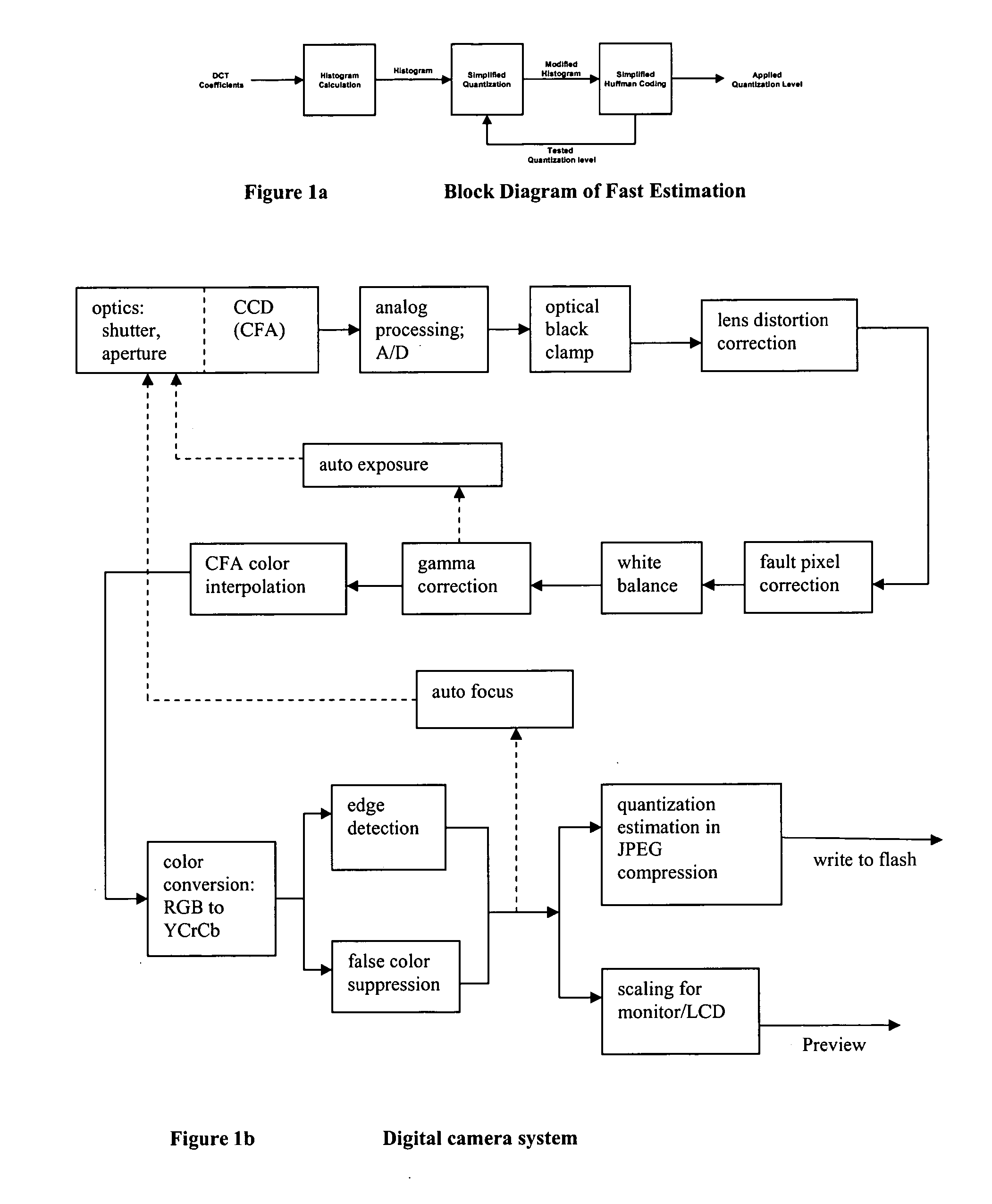
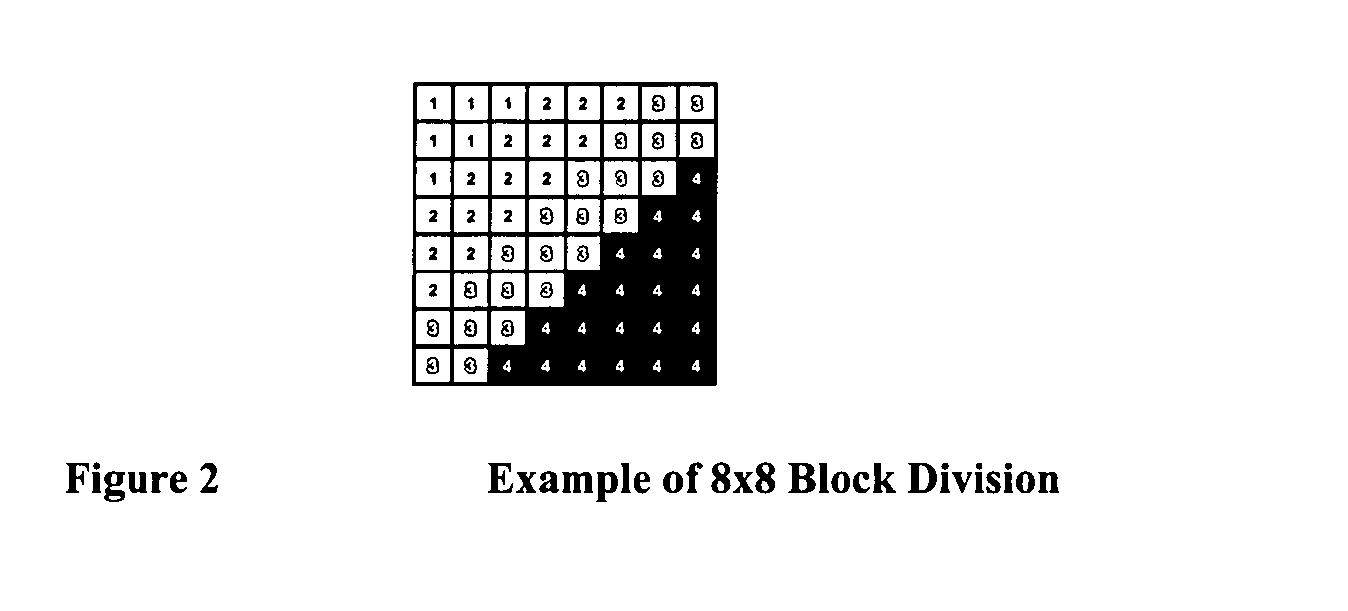
ActiveUS20050025370A1Simplifying feedback flowEfficiently quantizedCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVariable-length codeVariable length
Estimation of the code size of variable length encoding of quantized DCT coefficients by summation over histogram bins of products of number of bin members and a code size of an average run of zero coefficients coupled with a representative level from the bin. The estimation provides low-complexity feedback for quantization level adjustment to obtain variable length code size target without actual performance of a quantization level plus variable length encoding.
Owner:MAGFUSION +1
Method for transmitting and identifying transmit power value in multi-user MIMO
ActiveUS20100074237A1Efficiently quantizedReduce overheadEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransmitted powerEngineering
A method for transmitting and identifying a transmit power value in a multi-user MIMO scheme is disclosed. The transmit power value transmission method includes calculating available transmit power ratios for respective layers, reducing a number of bits used to represent entire transmit power ratio values by allocating same bit value to a plurality of same transmit power ratio values among the calculated transmit power ratio values for the respective layers; quantizing a transmit power ratio values of symbols to be transmitted to the UE using the entire transmit power ratio values of the reduced number of bits; and transmitting the quantized transmit power ratio values to the UE.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
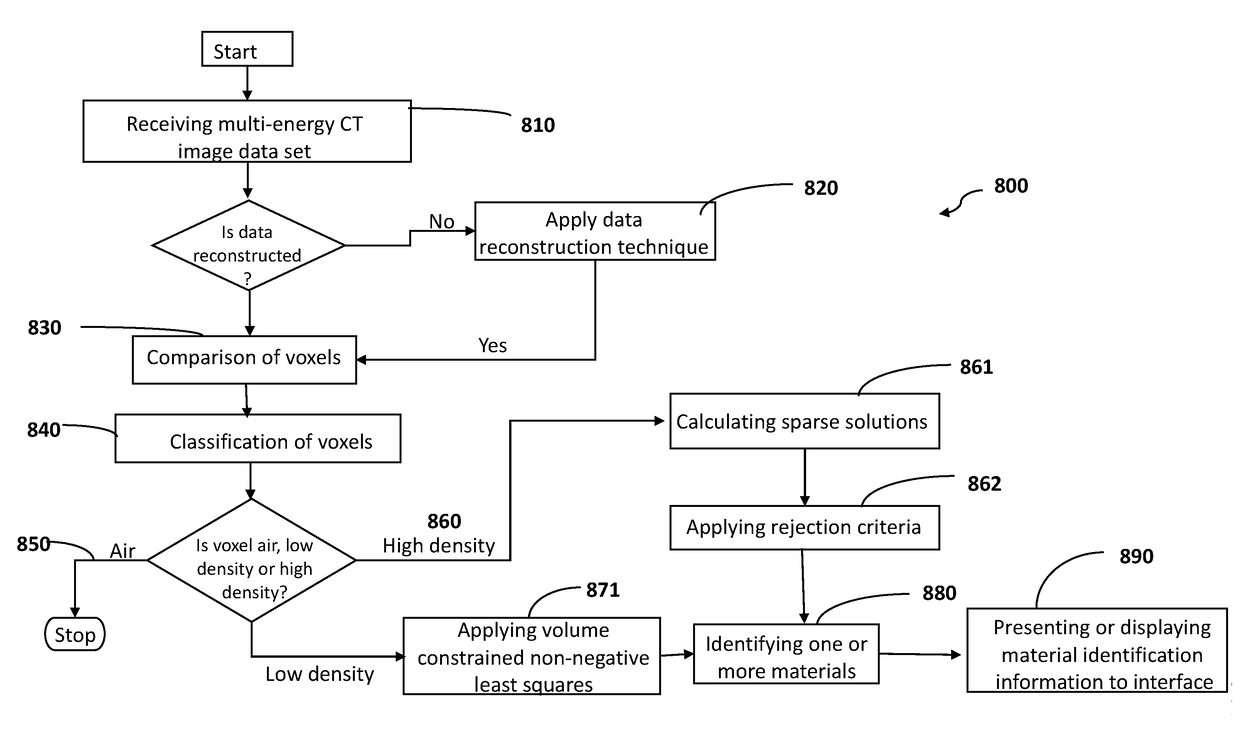
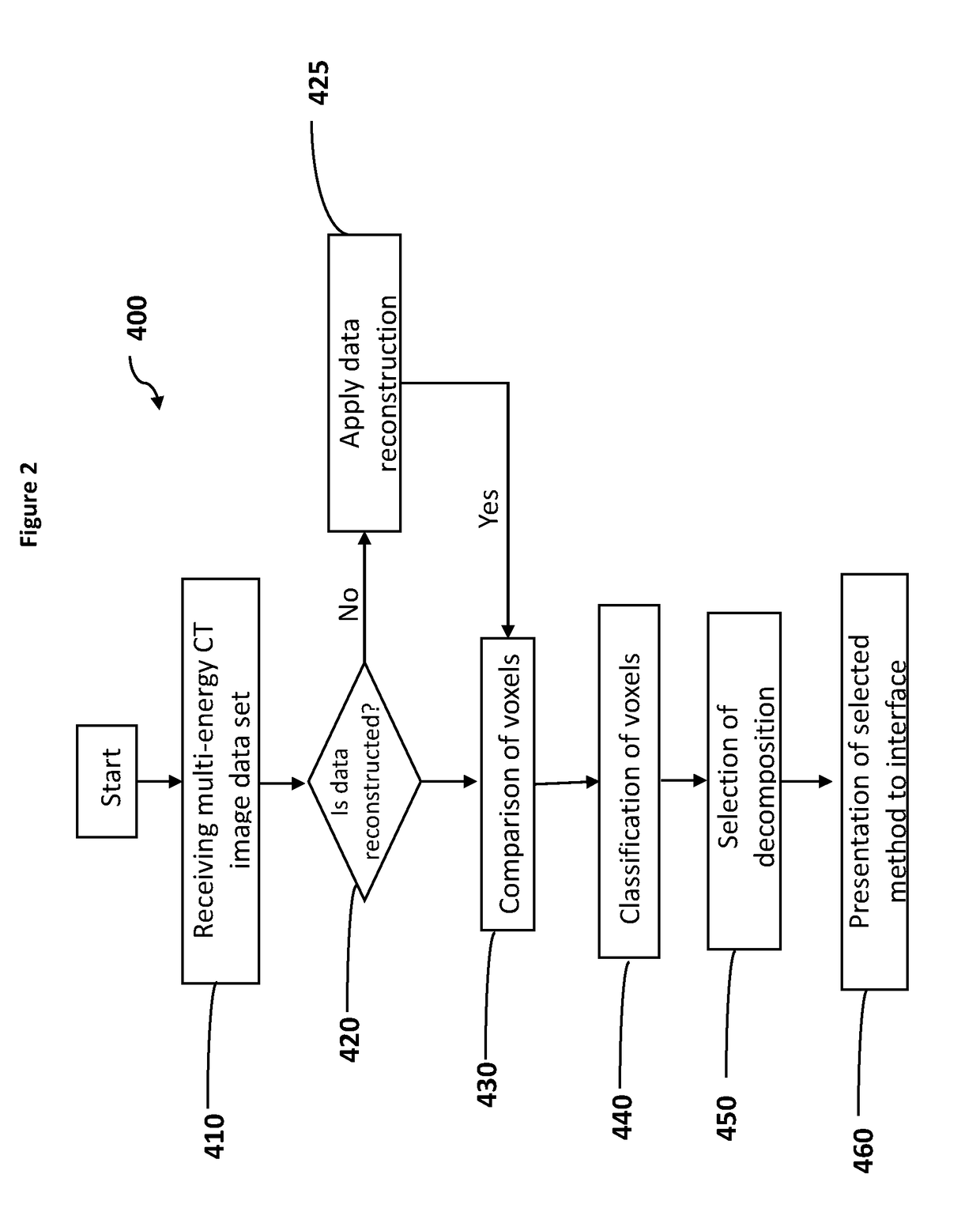
Improving material identification using multi-energy ct image data
ActiveUS20180114314A1Efficiently quantizedImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMulti materialComputer science
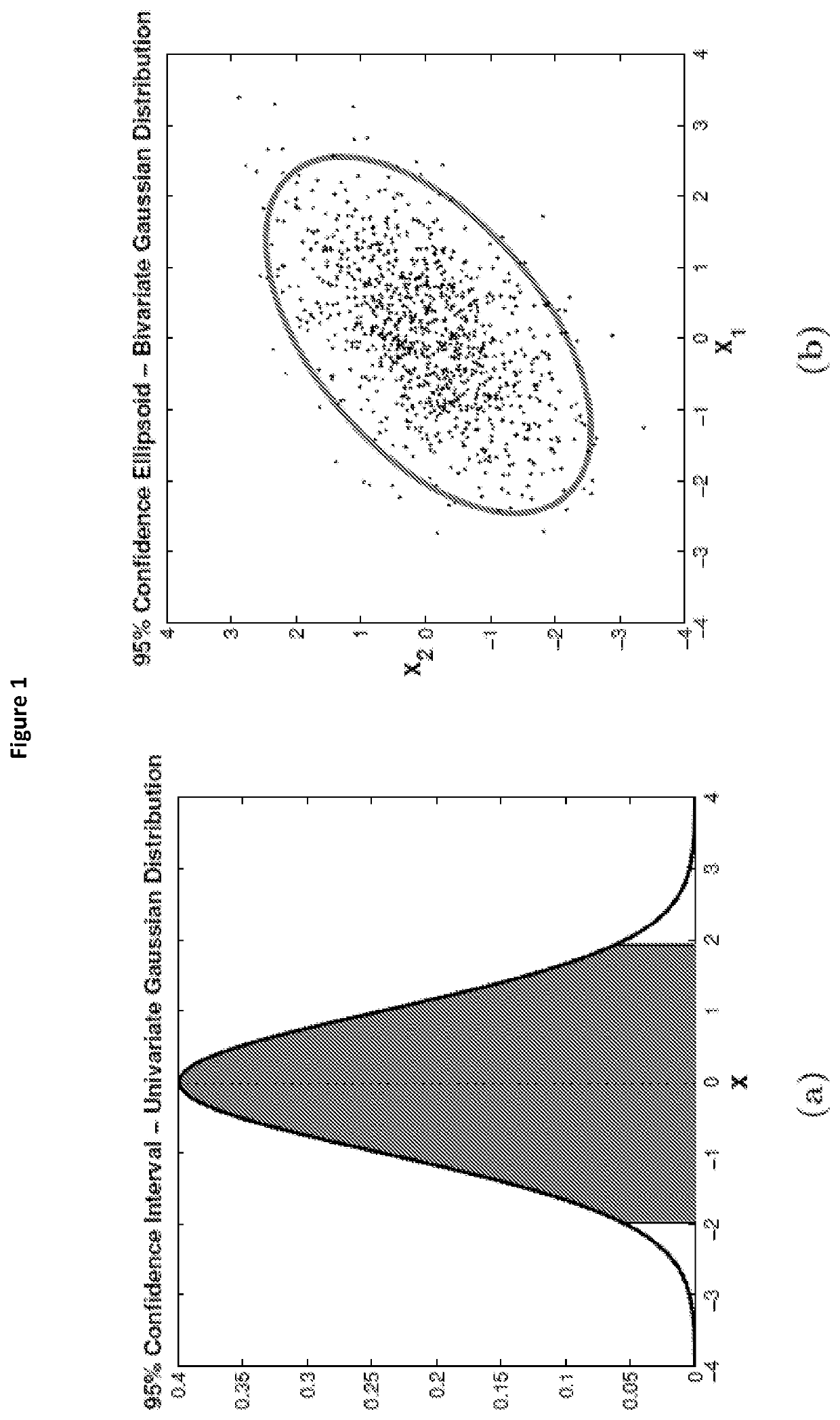
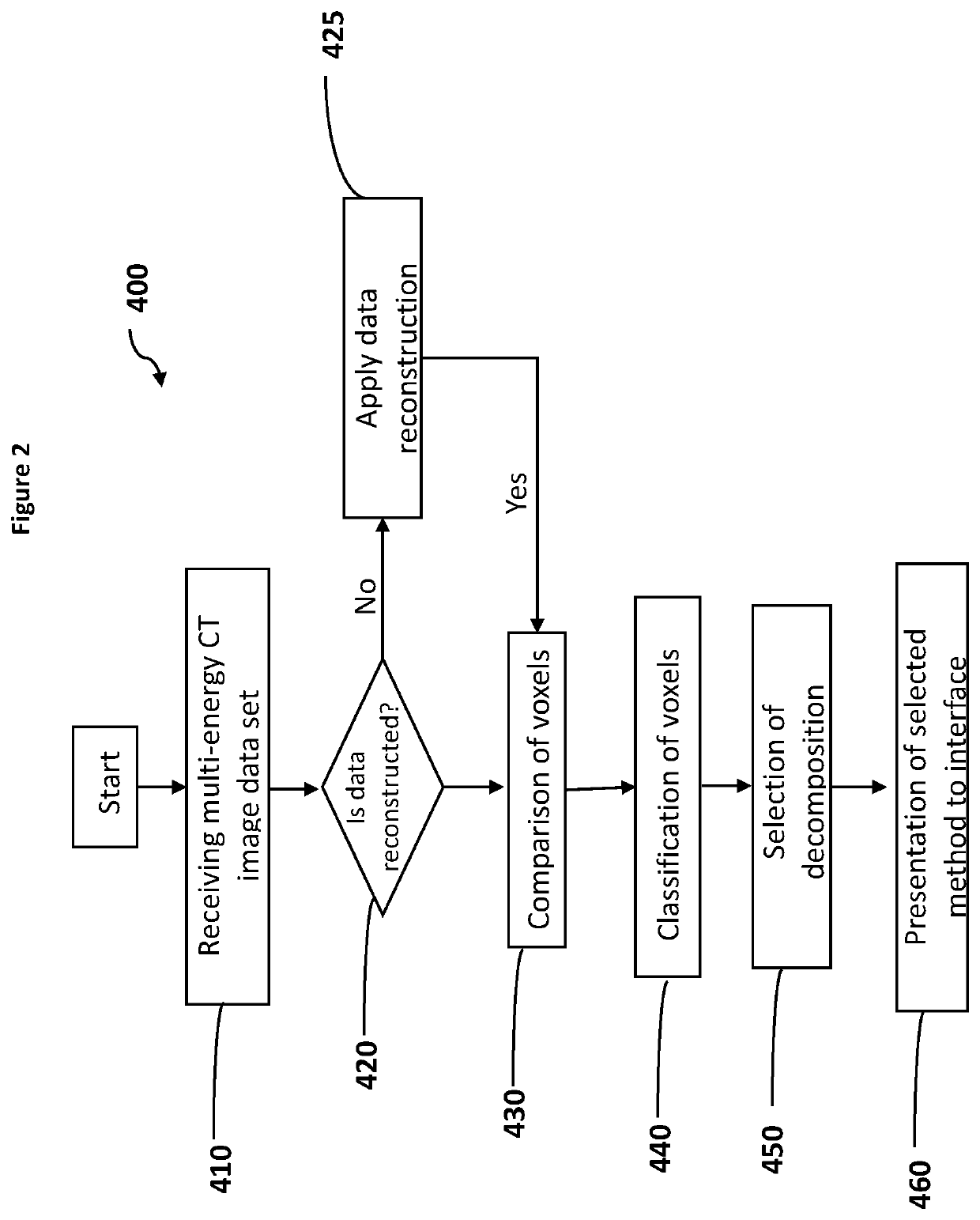
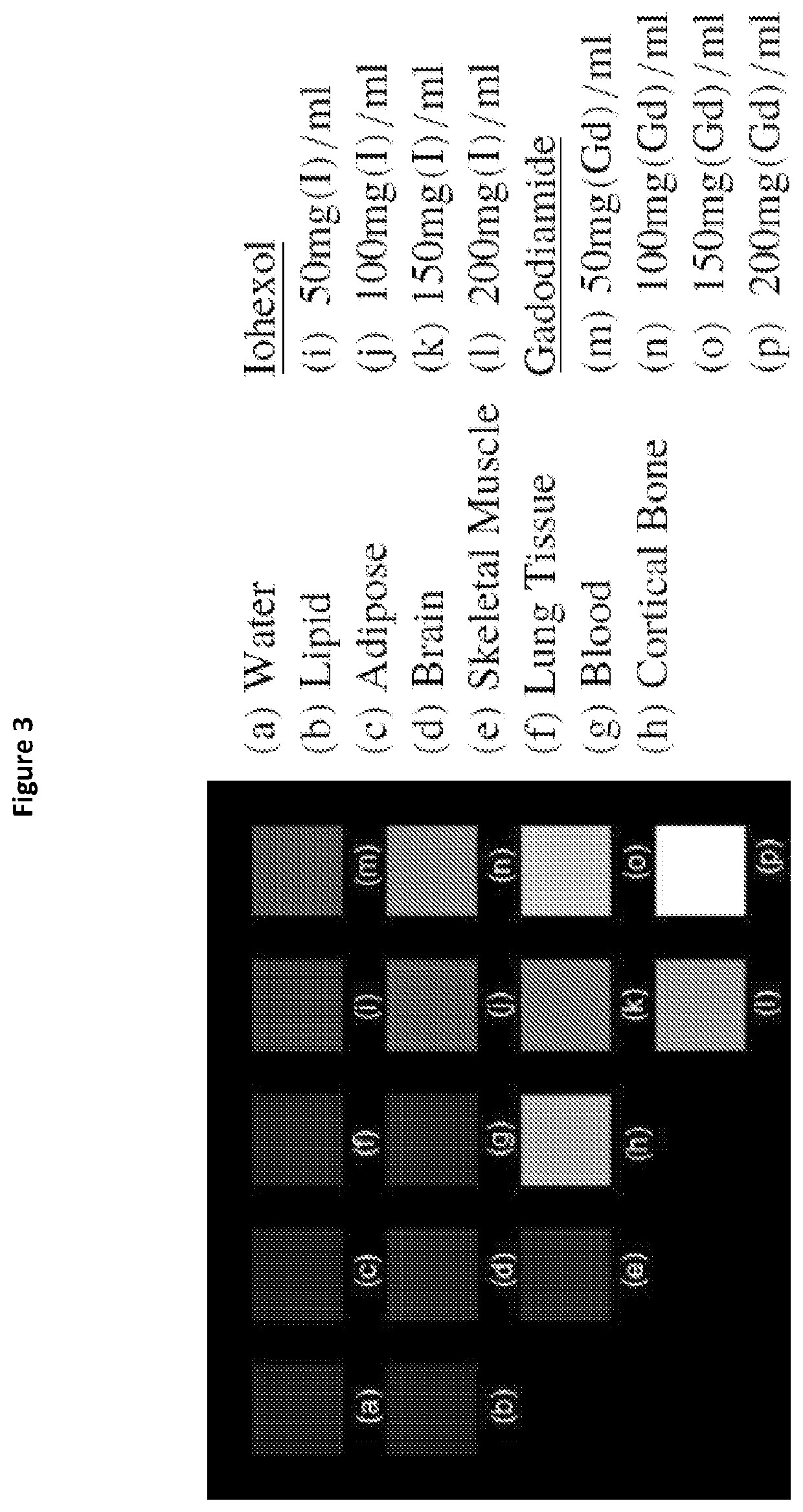
Disclosed are methods for identification and quantification of a number of different materials within an object using one or more multi-energy CT imaging devices and the image data sets produced therefrom. Identification and quantification of different materials is achieved by using the following three properties: solve only for sparse solutions; separate the soft tissue problem from the dense material problem; and use a combinatorial approach to allow for simple application of different constraints to different combinations of materials. Also disclosed are one or more computer program products, computer systems or computer implemented methods for the identification of multiple materials within an object.
Owner:MARS BIOIMAGING LTD
Compression encoder, compression encoding method and program
InactiveUS7792376B2Maintain image qualityPromote generationCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityArithmetic coding
A DWT unit applies wavelet transform to an input image signal to output transform coefficients, and on those transform coefficients, a quantization unit performs quantization, sorting and bit shifting with a quantization step size determined by target image quality in an image-quality control unit as well as sorting and bit shifting based on information on a region of interest specified by a ROI unit. A coefficient bit modeling unit applies bit modeling on transform coefficients outputted from the quantization unit on a bit-plane-by-bit-plane basis, and an arithmetic coding unit applies arithmetic coding on coded data inputted from the coefficient bit modeling unit. Then, a rate control unit controls the rate of coded data inputted from the arithmetic coding unit.
Owner:MEGACHIPS
Method of quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound encoding method, method of de-quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound decoding method, and recording medium and electronic device therefor
ActiveUS8977544B2Efficiently quantizedReduce complexitySpeech analysisDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsTransmission channel
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
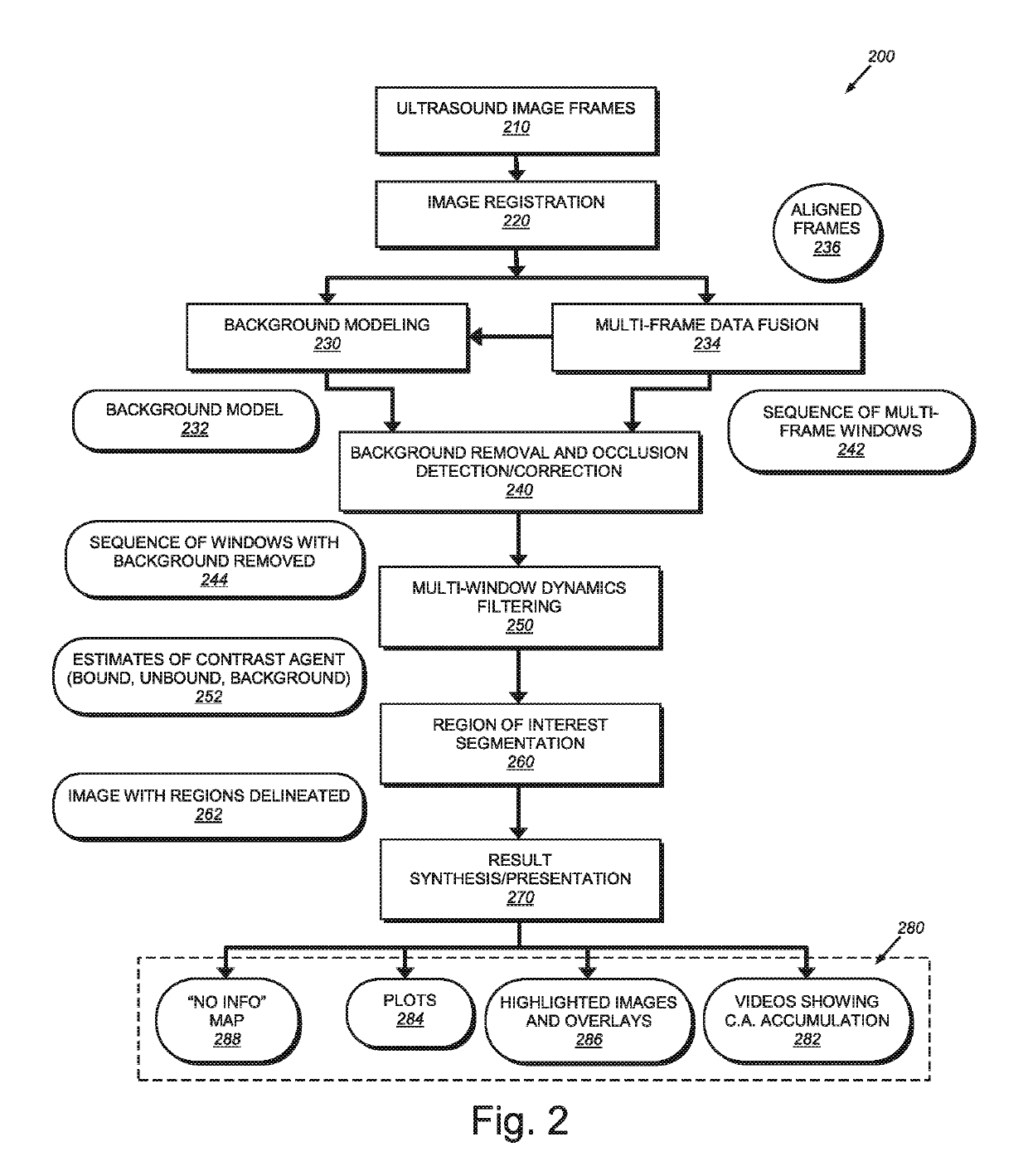
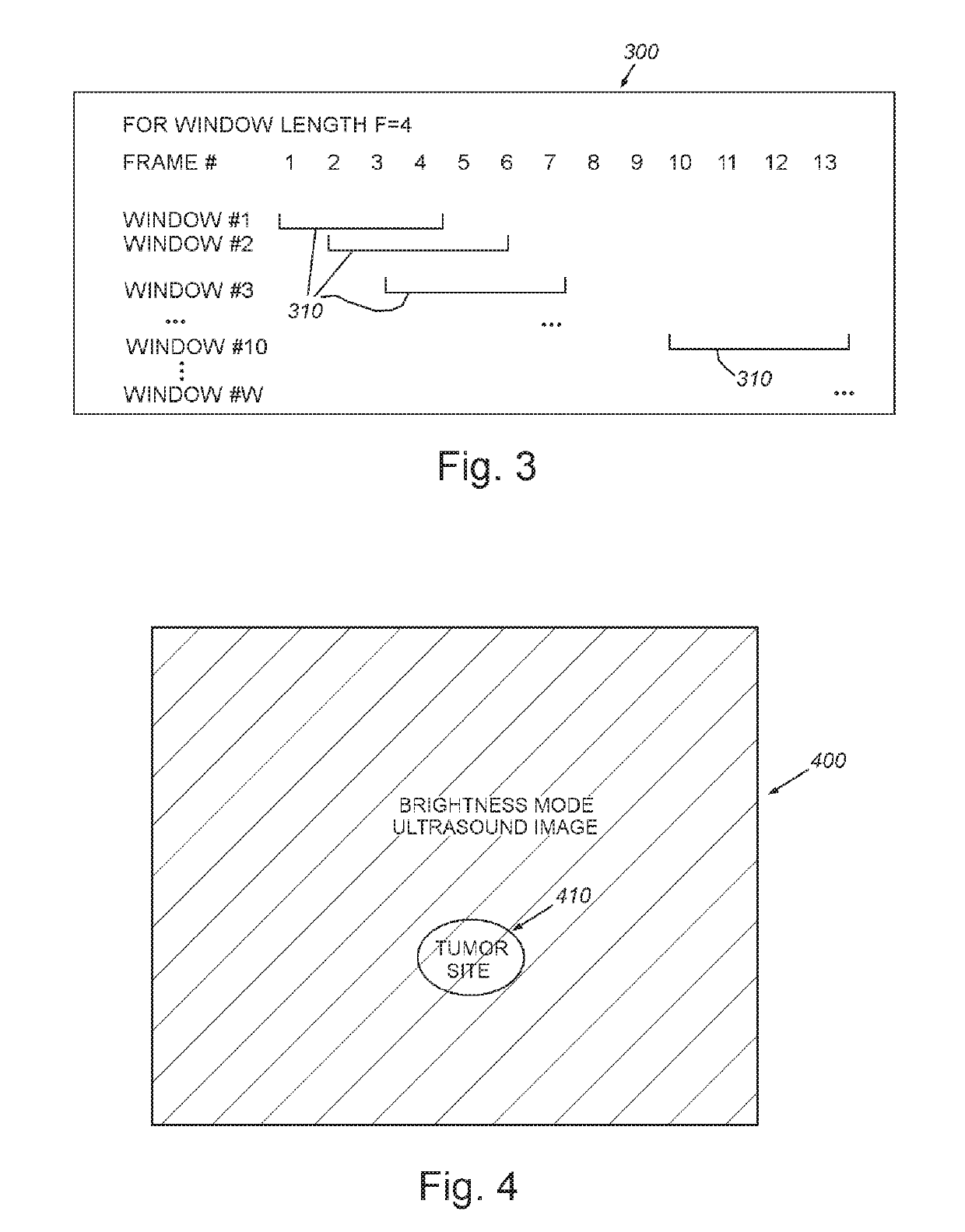
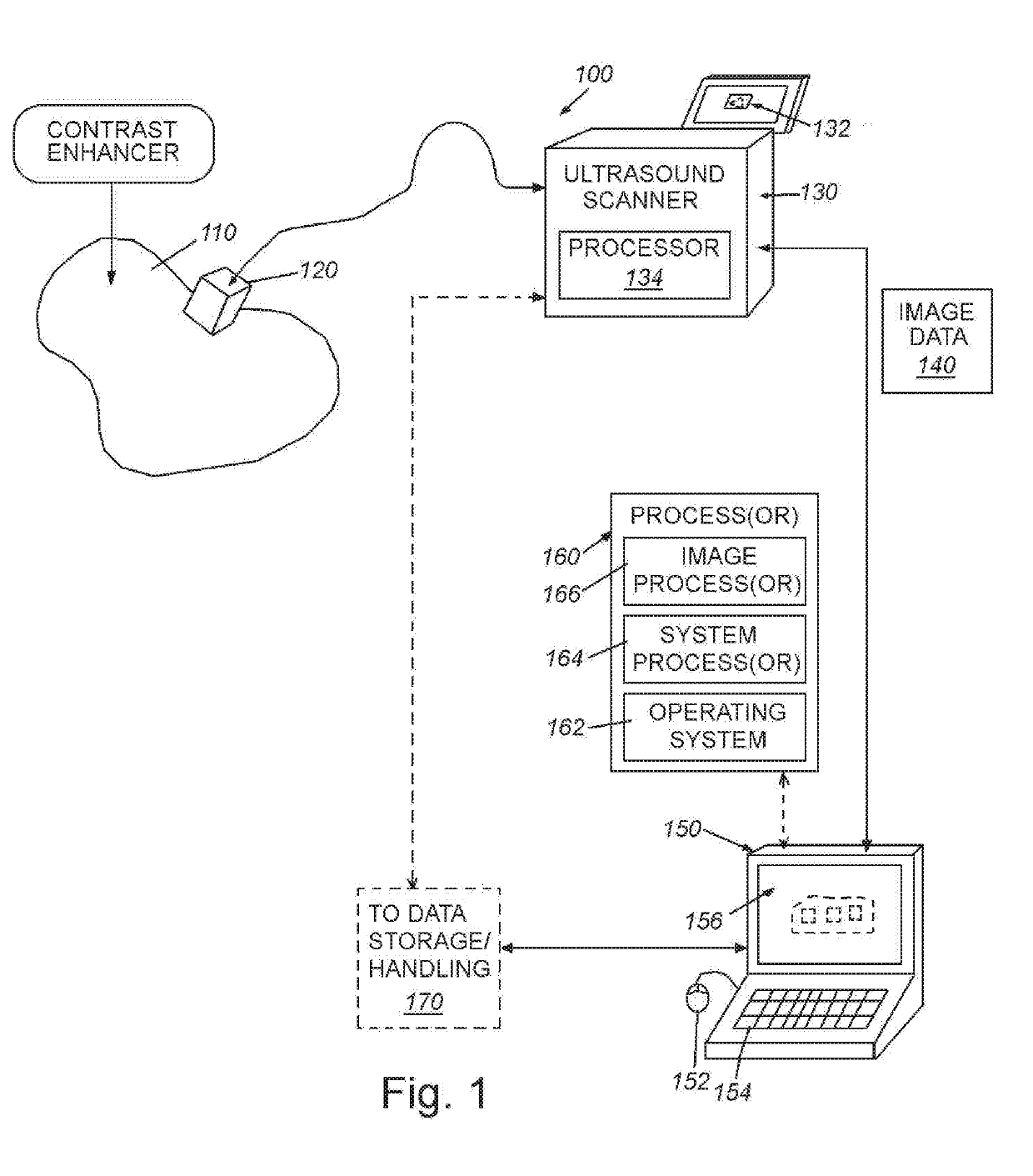
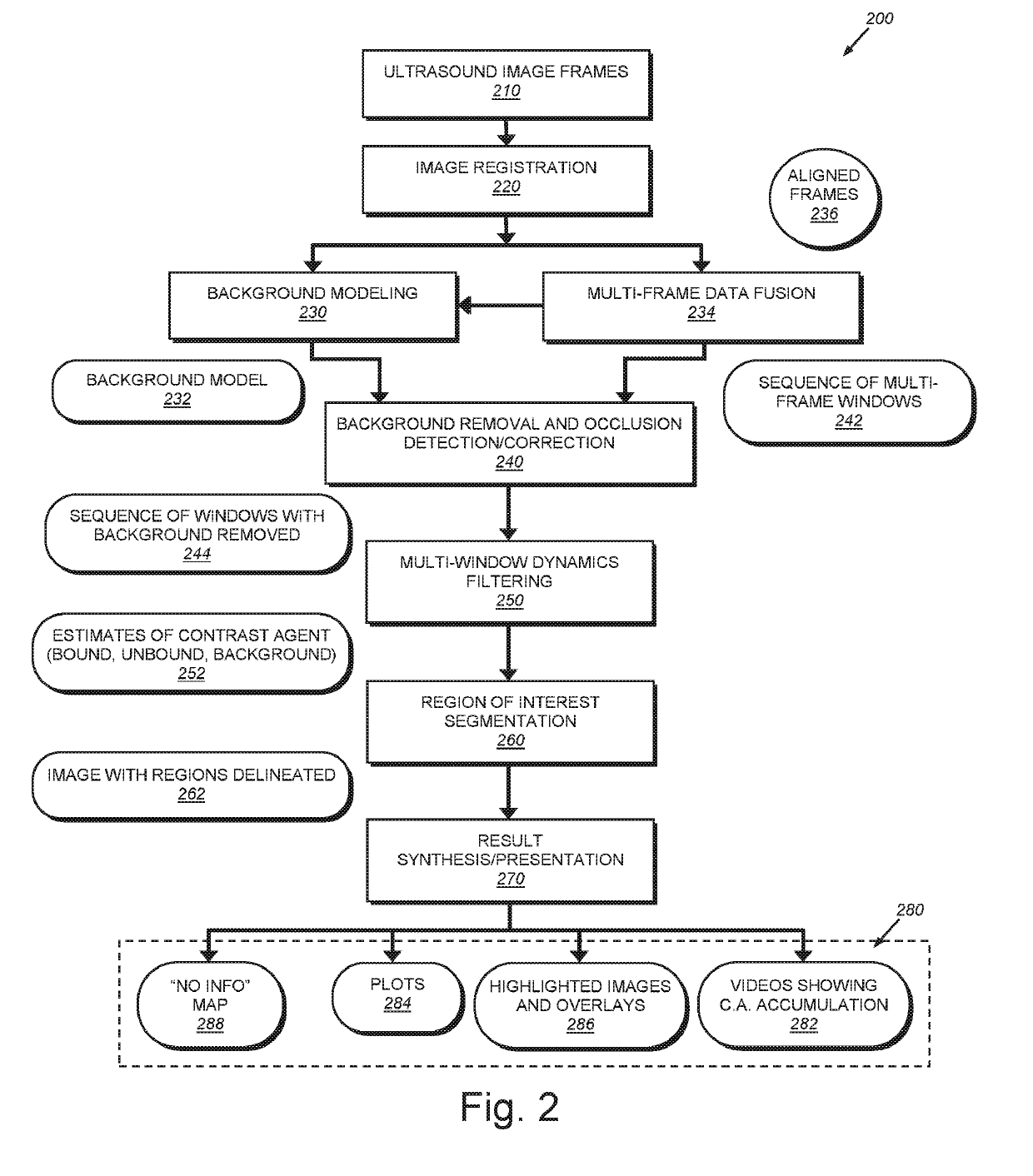
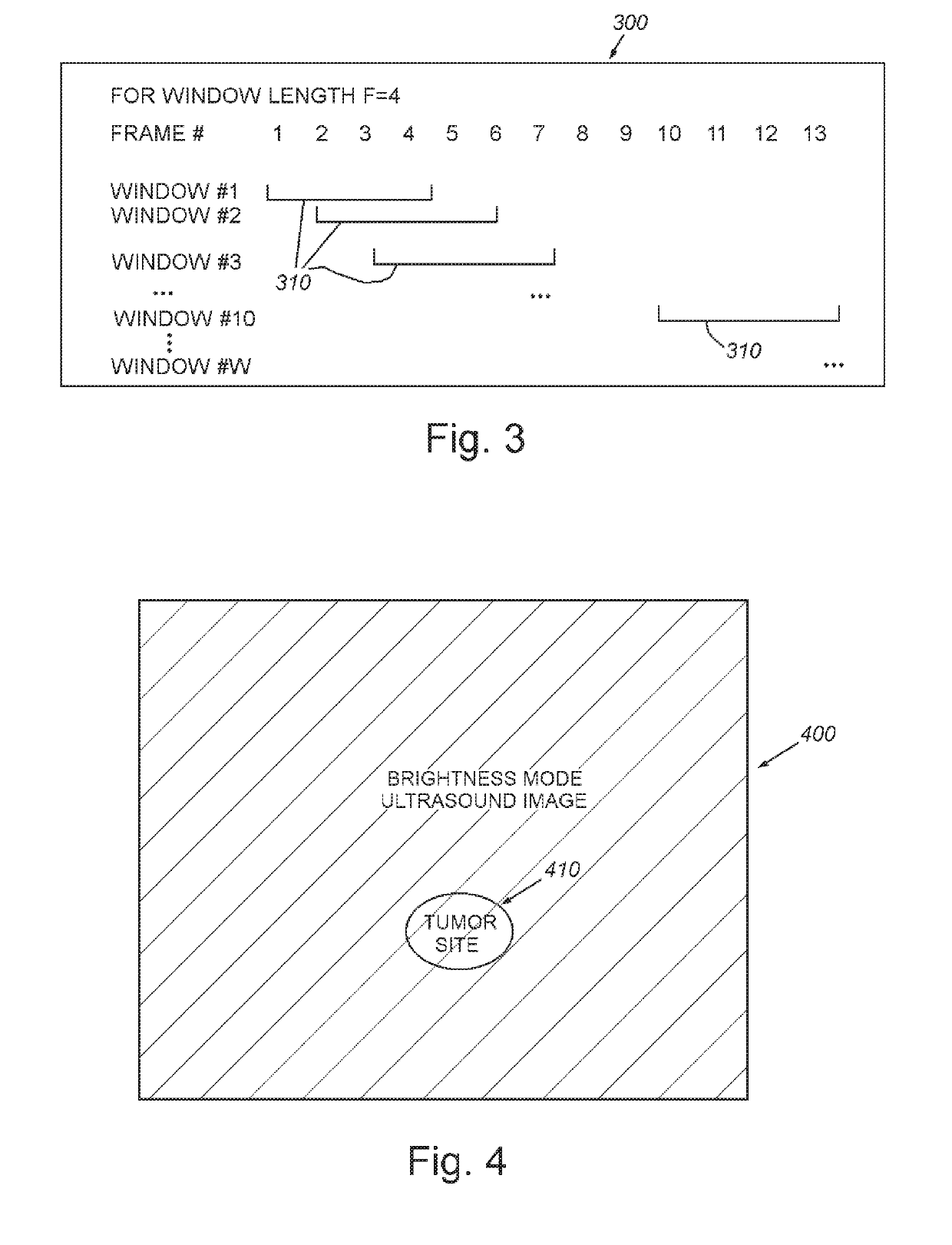
System and method for guiding invasive medical treatment procedures based upon enhanced contrast-mode ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS20190192229A1Improved signal clarityOvercome disadvantagesBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
This invention provides a system and method for guiding a surgical instrument based on information obtained using enhanced contrast-mode ultrasound. The enhanced information can be added to information or images obtained in one or more imaging modes. Various pieces of information can be combined and composited, including information regarding tumors, blood vessels, location information, confidence levels, and other information, and can be composited into operative imaging.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
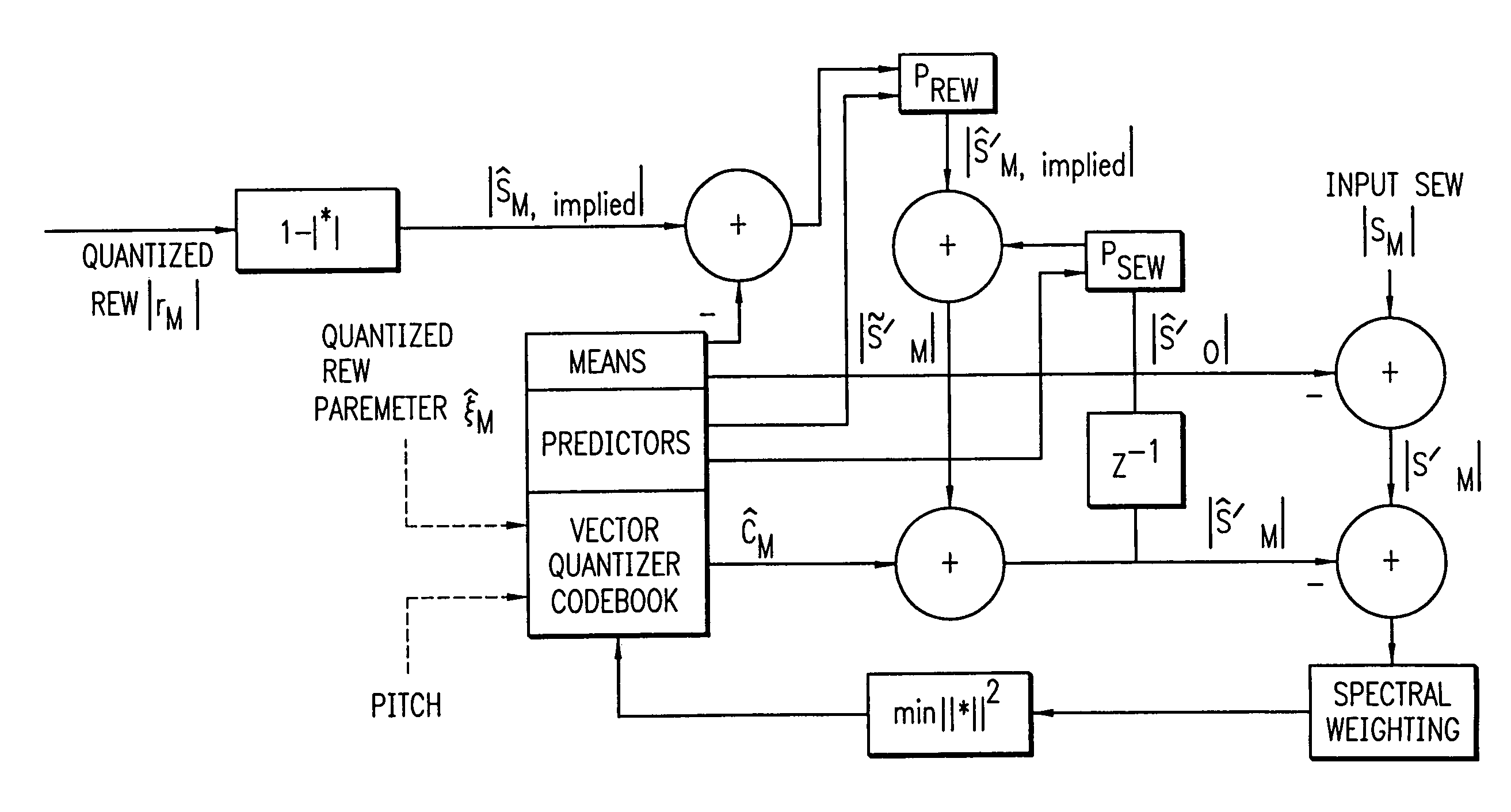
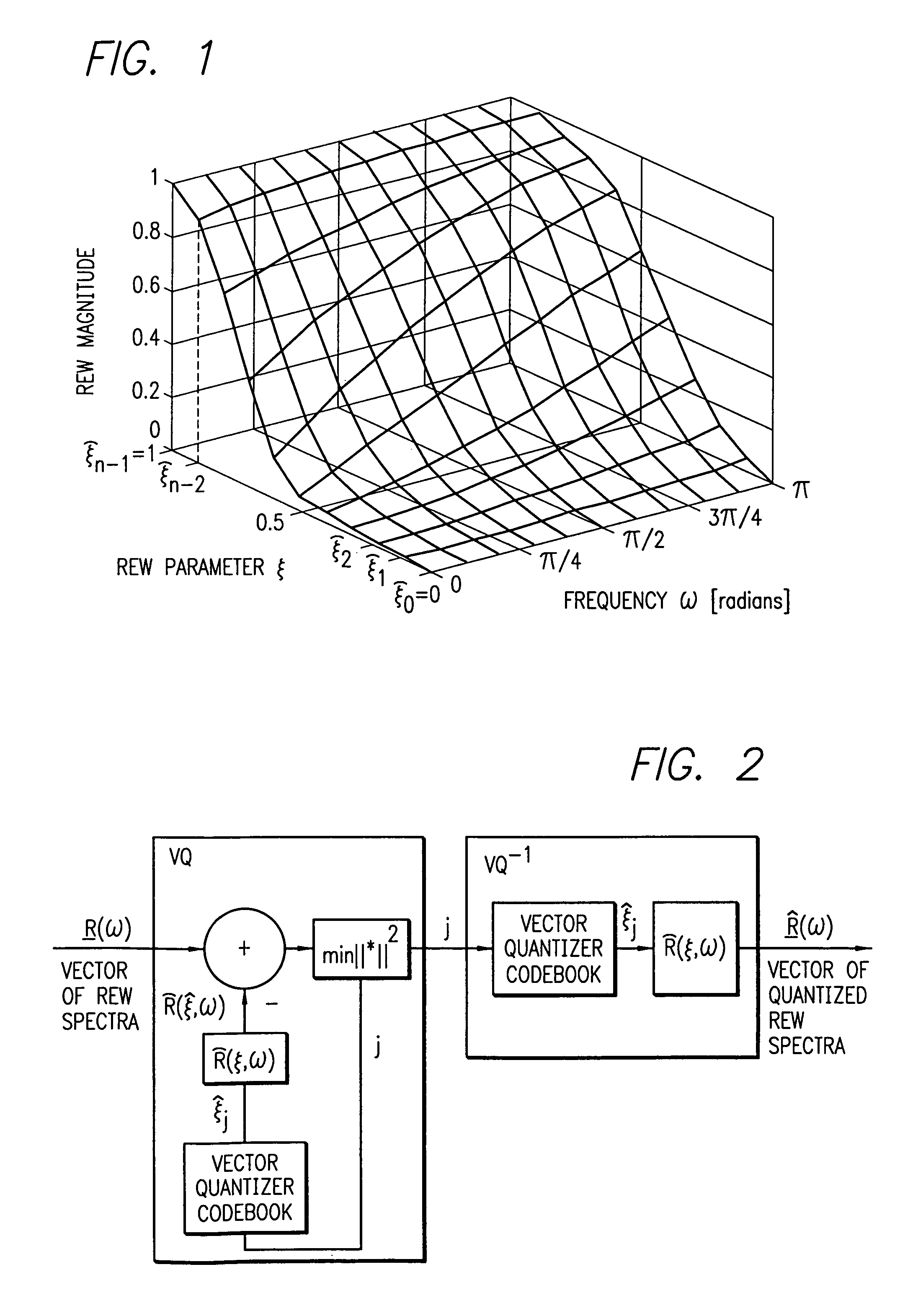
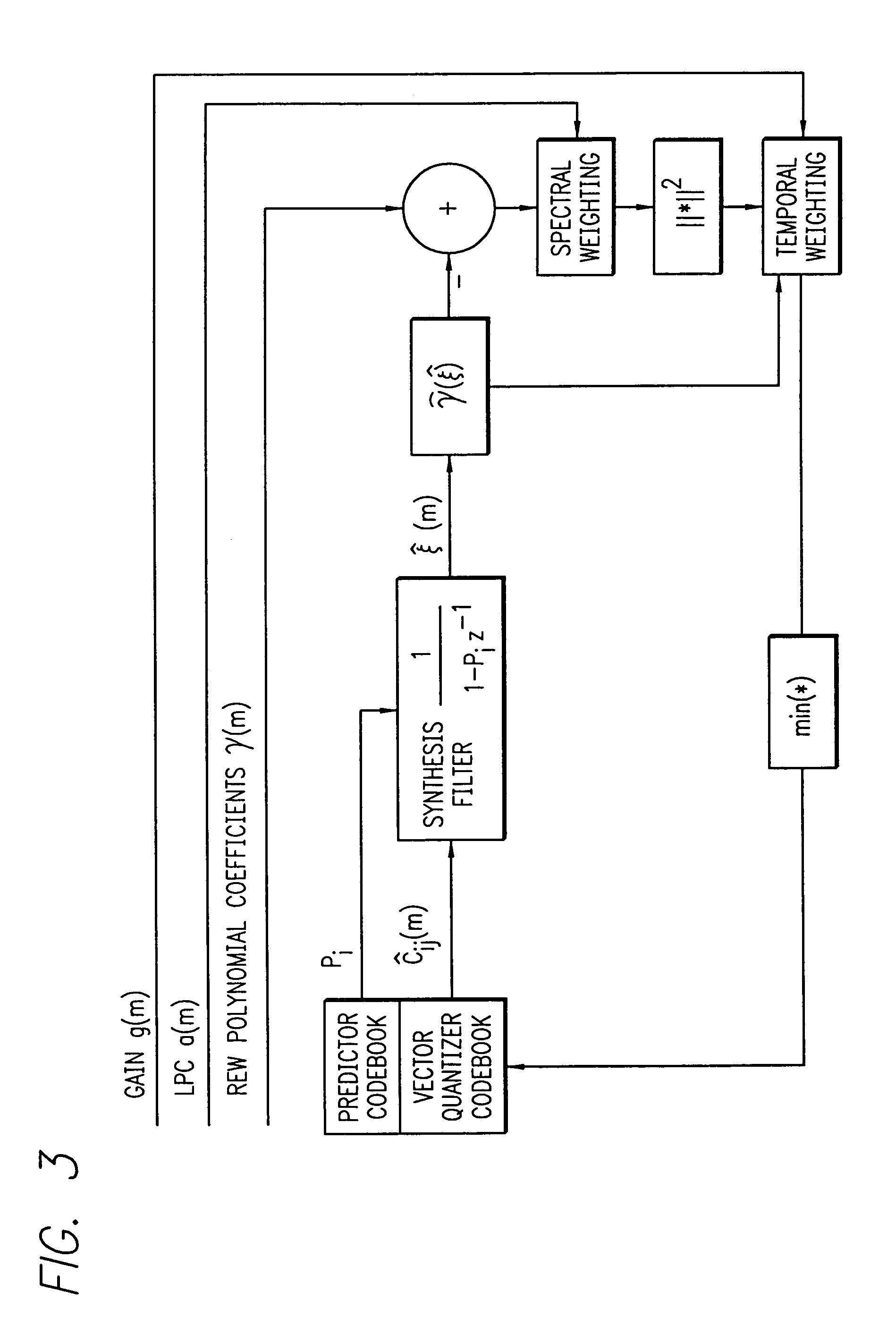
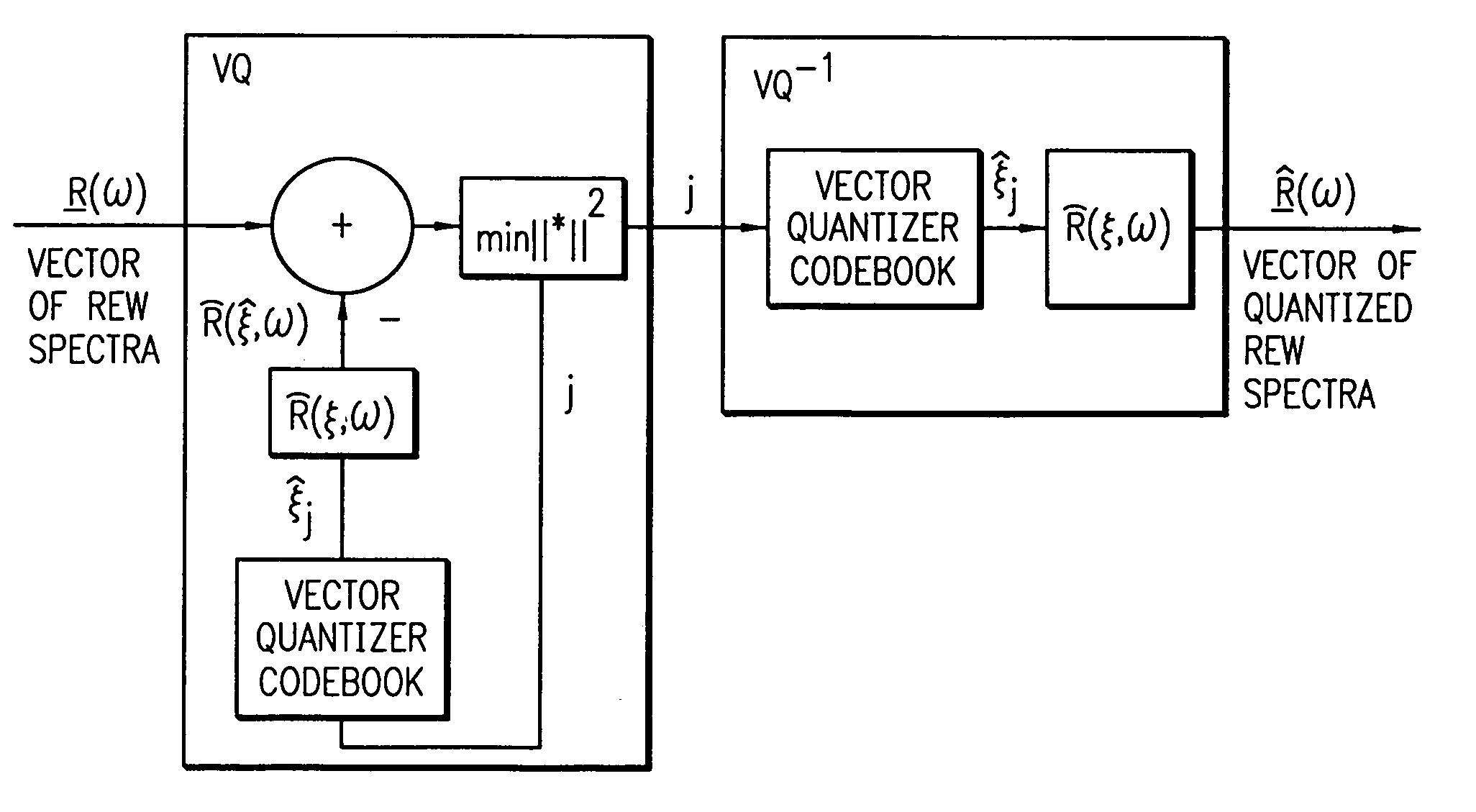
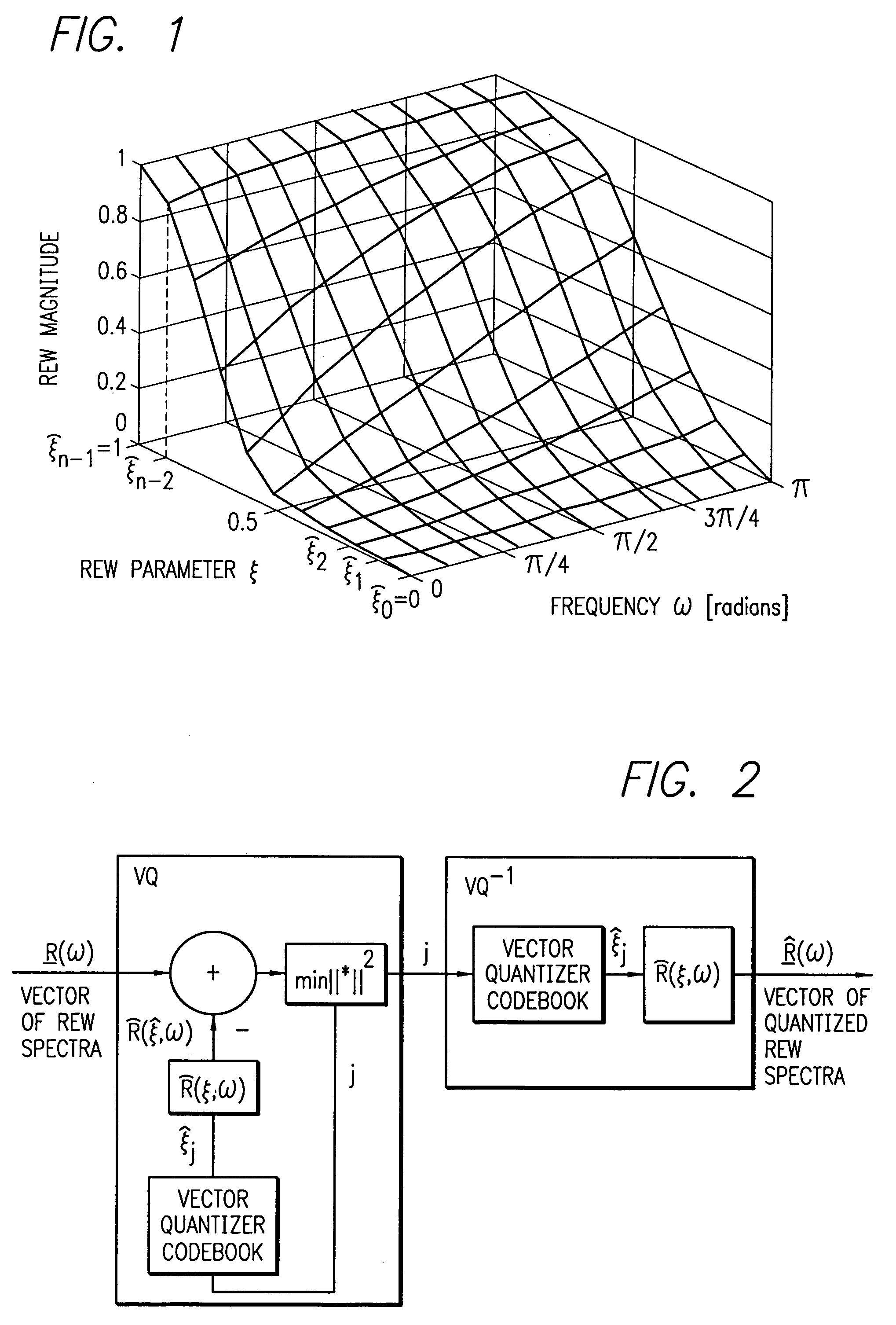
REW parametric vector quantization and dual-predictive SEW vector quantization for waveform interpolative coding
InactiveUS7010482B2High temporal and spectral resolutionEfficiently quantizeSpeech analysisSubjective qualityPredictive analytics
An enhanced analysis-by-synthesis waveform interpolative speech coder able to operate at 2.8 kbps. Novel features include dual-predictive analysis-by-synthesis quantization of the slowly-evolving waveform, efficient parametrization of the rapidly-evolving waveform magnitude, and analysis-by-synthesis vector quantization of the rapidly evolving waveform parameter. Subjective quality tests indicate that it exceeds G.723.1 at 5.3 kbps, and of G.723.1 at 6.3 kbps.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
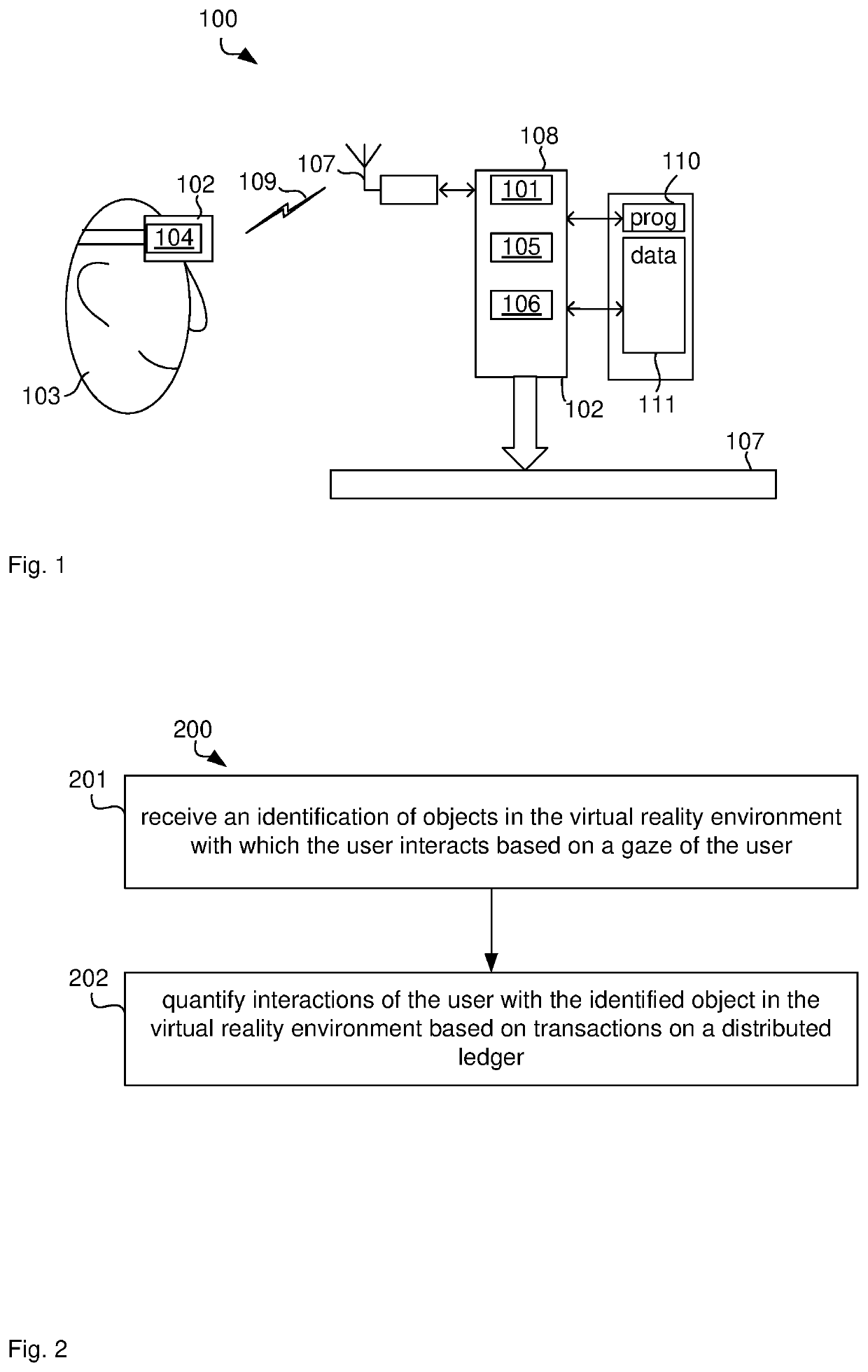
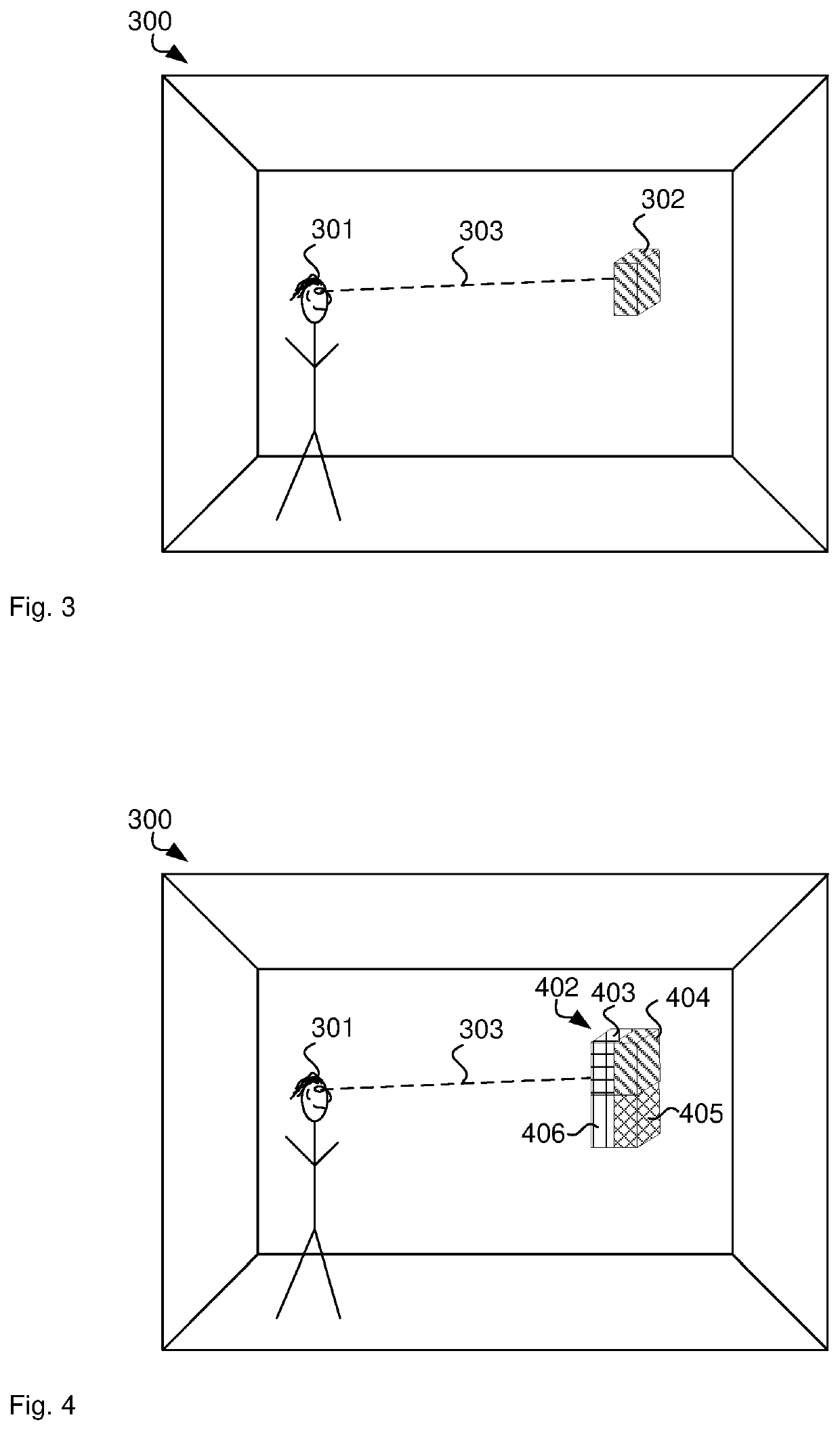
Virtual reality interaction monitoring
ActiveUS20200174563A1Efficiently quantizedInput/output for user-computer interactionDatabase updatingGraphicsEngineering
A computer system that monitors interactions with a virtual reality environment includes a graphics processor that generates images representing the virtual reality environment, a headset that displays the generated images to a user interacting with the virtual reality environment, a sensor that detects motion of the user as the user interacts with the virtual reality environment, a gaze controller that calculates a gaze of the user based on the detected motion of the user and identifies objects in the virtual reality environment with which the user interacts based on the calculated gaze of the user, and an interaction monitor that quantifies interactions of the user with an identified object in the virtual reality environment based on transactions on a distributed ledger. The transactions comprise logic expressions that define an automatic execution triggered by the interaction of the user with the object in the virtual reality environment.
Owner:DREAM CHANNEL PTY LTD
Method of measuring lipid in specific lipoprotein
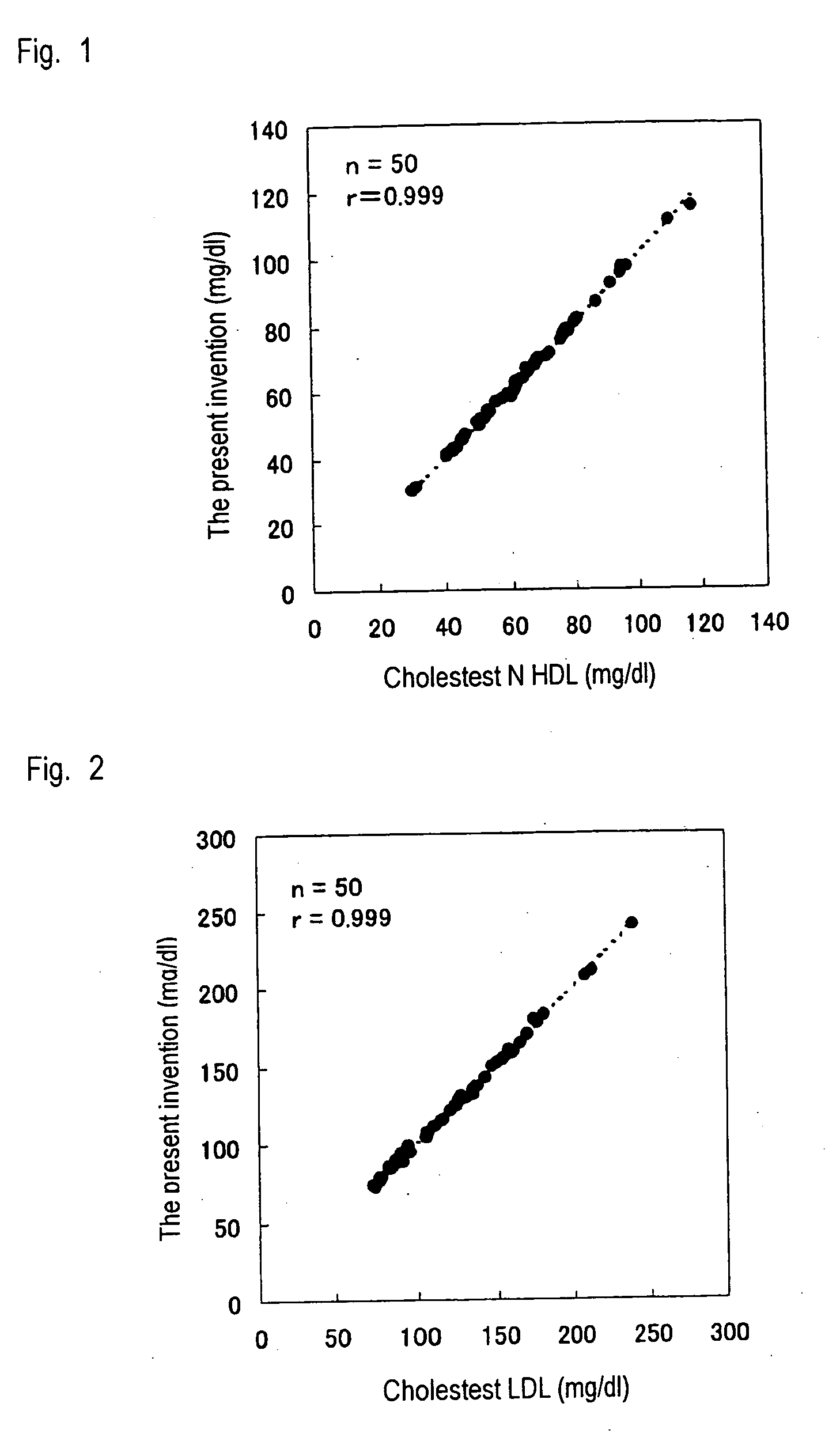
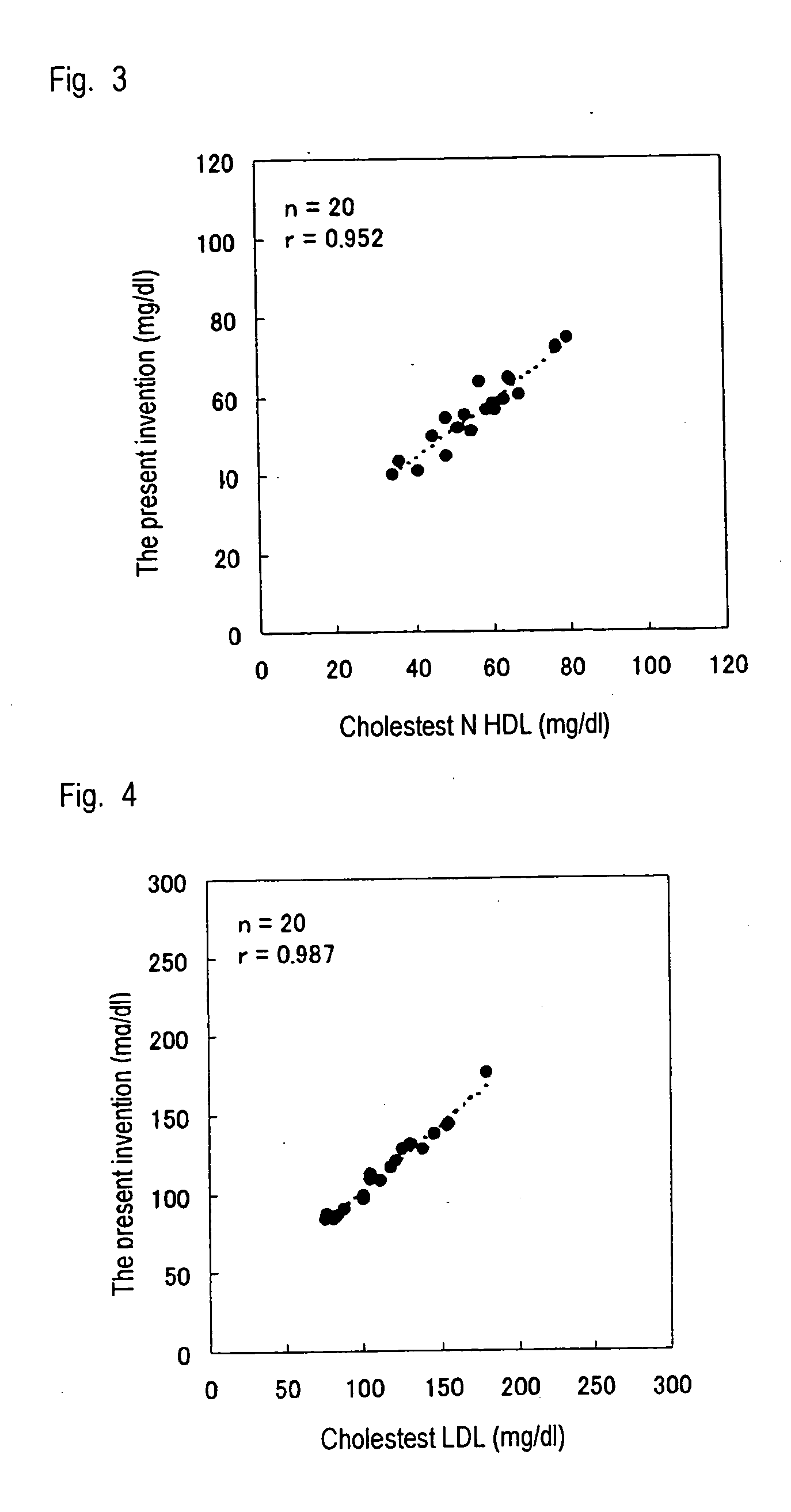
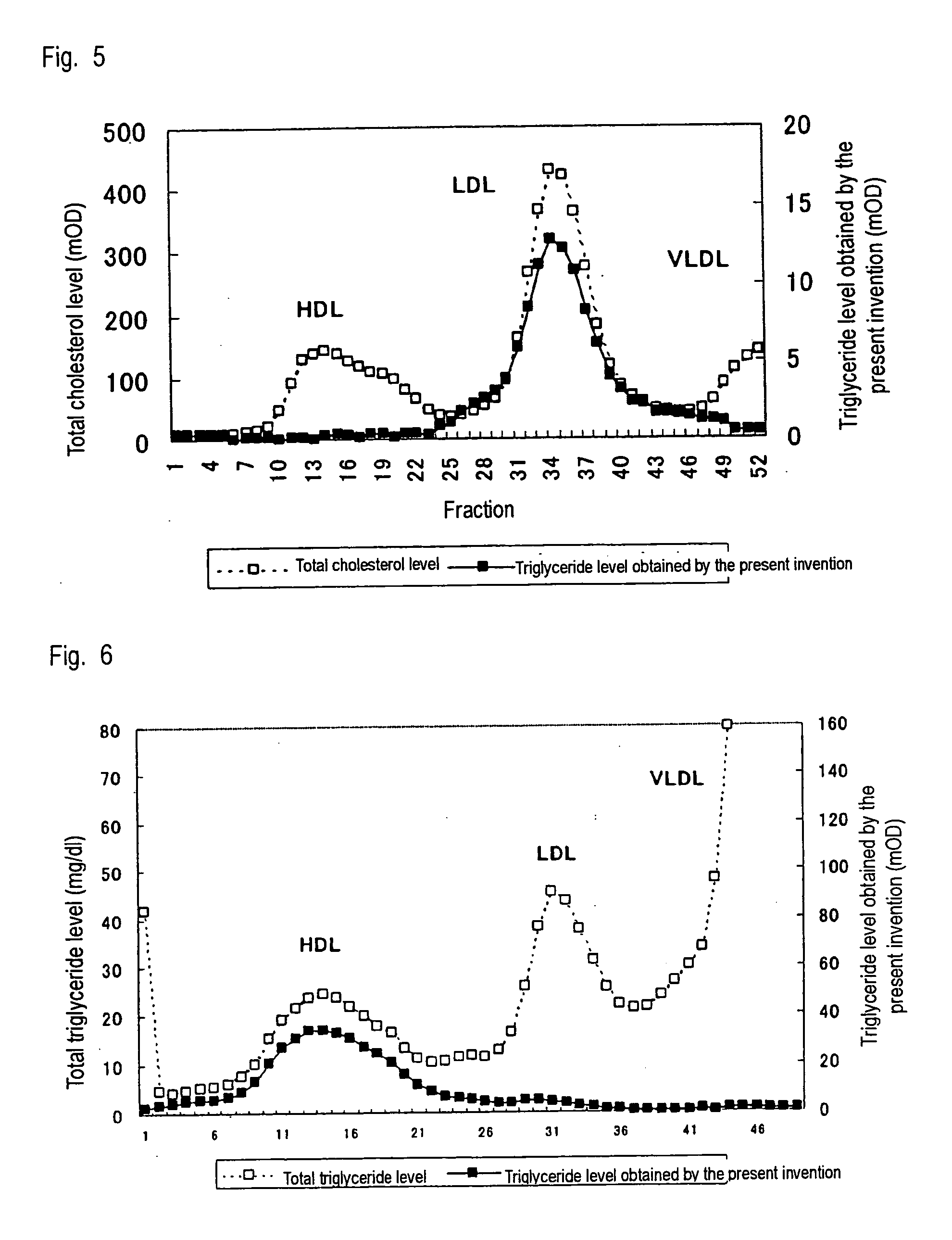
InactiveUS20060014207A1Efficiently quantizeEfficiently selectSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalytical chemistryLipoprotein
A method of measuring a lipid in a specific lipoprotein characterized by using a polycyclic polyoxyalkylene derivative at least in the step of determining the specificity of the measurement of the target lipid.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
System and method for imaging and localization of contrast-enhanced features in the presence of accumulating contrast agent in a body
InactiveUS20190154822A1Improved signal clarityOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisAbnormal tissue growthHuman body
This invention provides a system and method for background removal from images acquired by an ultrasound scanner in the presence of molecularly bound contrast agent. The system and method employs novel techniques that are compatible with the real-world constraints (i.e. energy levels, duration of exam, geometries involved, etc.) of imaging in mammalian tissue (e.g. tissues of human organs containing lesions / tumors), while providing the dramatically improved signal clarity required to reliably disambiguate contrast agent from other sources of signal intensity.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
REW parametric vector quantization and dual-predictive SEW vector quantization for waveform interpolative coding
InactiveUS20060069554A1Improve performanceHigh temporal and spectral resolutionSpeech analysisWaveform interpolationComputer science
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Quantifying curvature of biological structures from imaging data
ActiveUS20140064588A1Efficiently quantizedImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionBiological structure
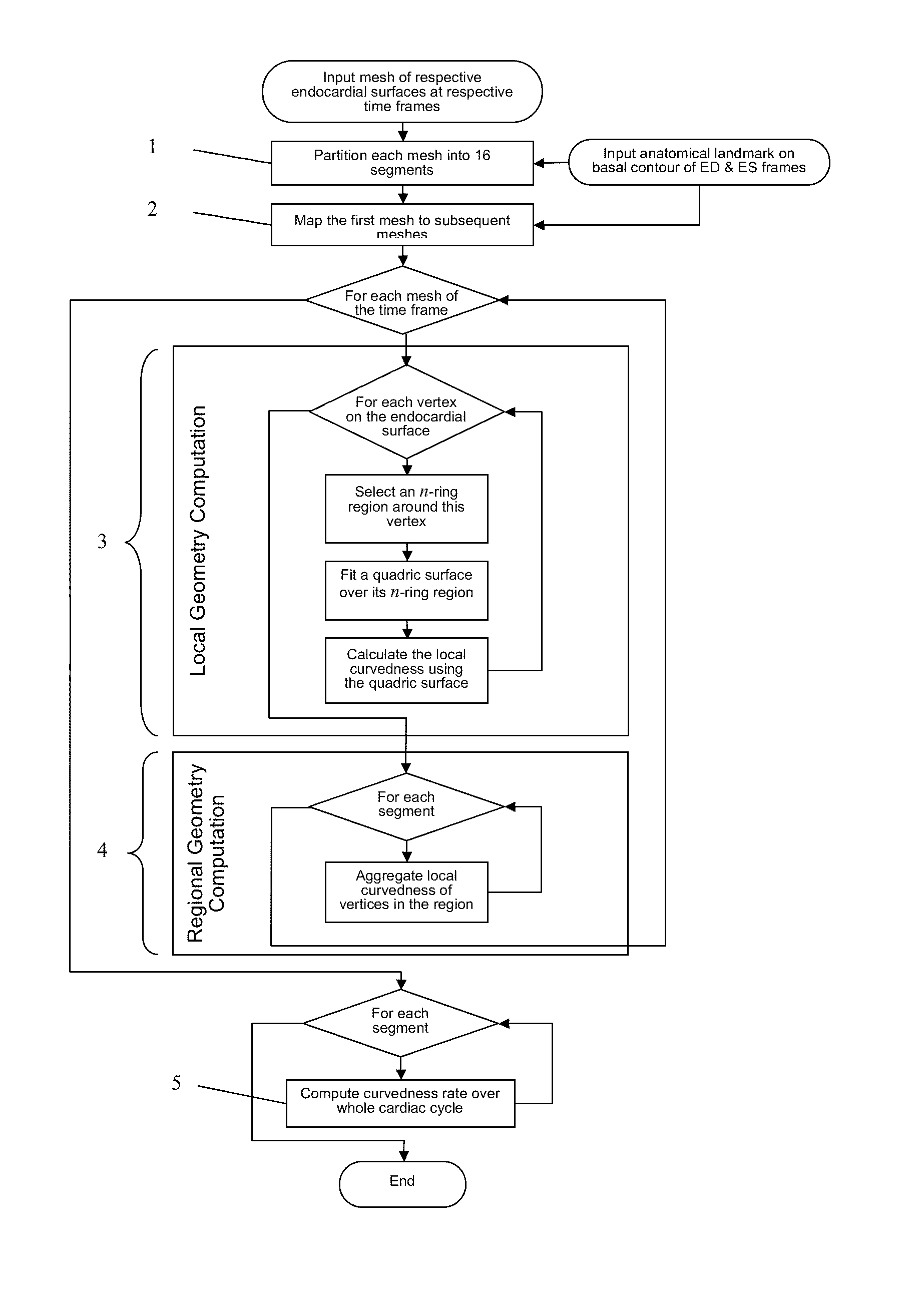
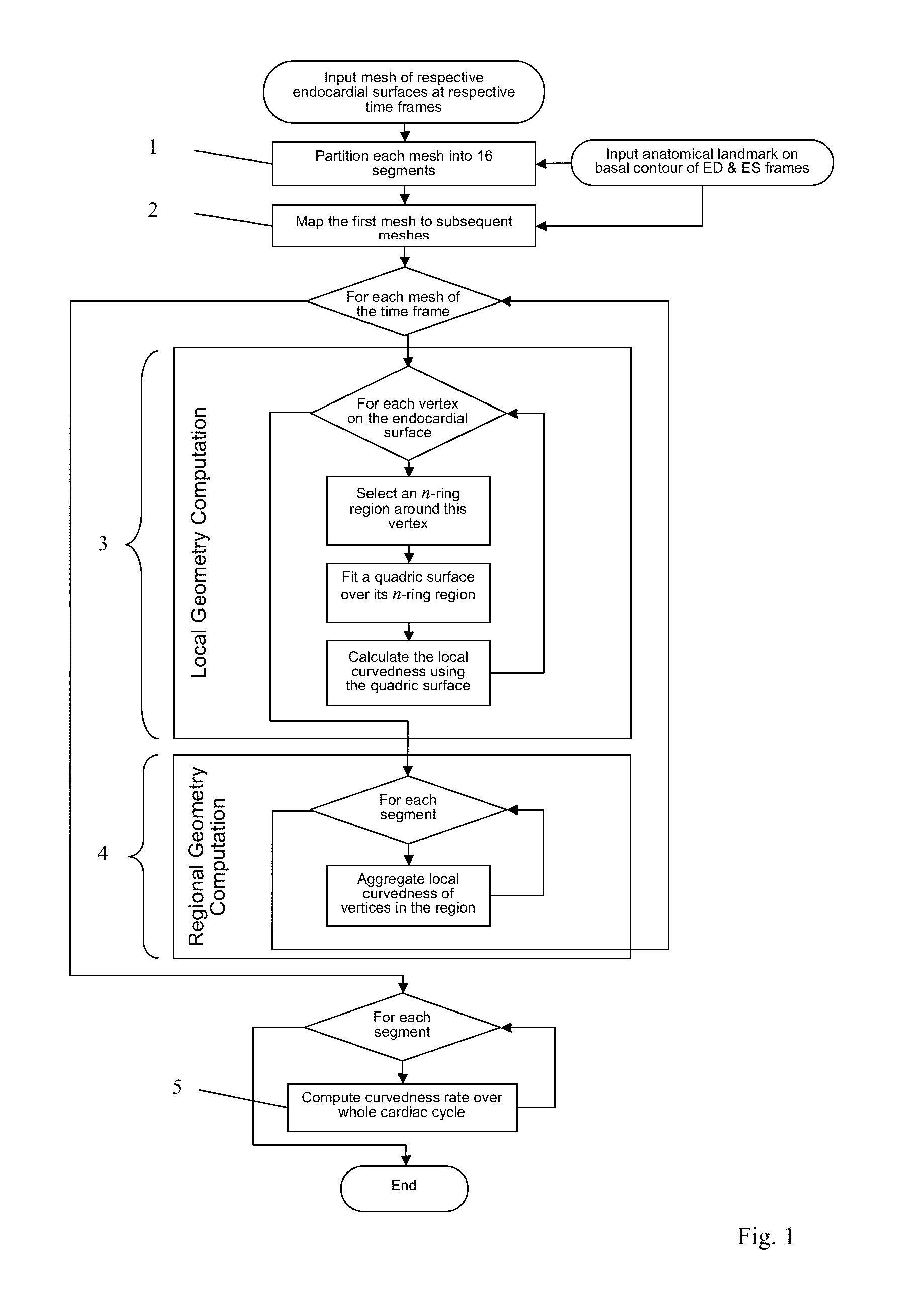
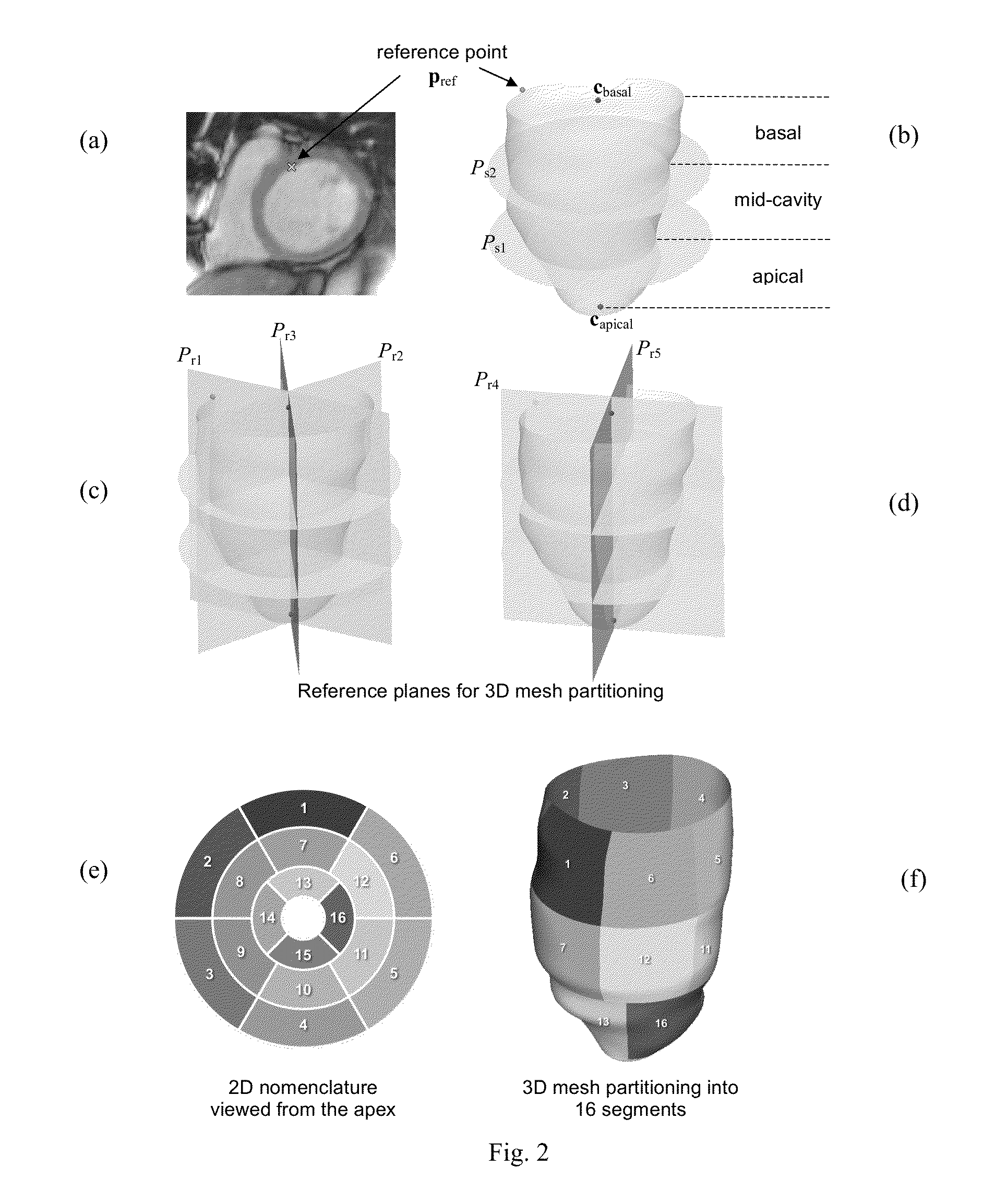
A method and system are proposed to obtain quantitative data about the shape of a biological structure, and especially a heart ventricle. A set of three-dimensional input meshes are generated from MRI data. They represent the shape of a ventricle at successive times. The input meshes are used to generate a set of three-dimensional morphed meshes which have the same number of vertices as each other, and have respective shapes which are the shapes of corresponding ones of the input meshes. Then, for each of the times, shape analysis is performed to obtain a curvedness value at each of a plurality of corresponding locations in the morphed meshes. The curvedness value may be used to obtain a curvedness rate at each of the locations, indicative of the rate of change of curvedness with time at each of the locations.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Material identification using multi-energy ct image data
ActiveUS20200242761A1Efficiently quantizedImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setEngineering
Disclosed are methods for identification and quantification of a number of different materials within an object using one or more multi-energy CT imaging devices and the image data sets produced therefrom. Identification and quantification of different materials is achieved by using the following three properties: solve only for sparse solutions; separate the soft tissue problem from the dense material problem; and use a combinatorial approach to allow for simple application of different constraints to different combinations of materials. Also disclosed are one or more computer program products, computer systems or computer implemented methods for the identification of multiple materials within an object.
Owner:MARS BIOIMAGING LTD
Method for the Quantification of Methylated DNA
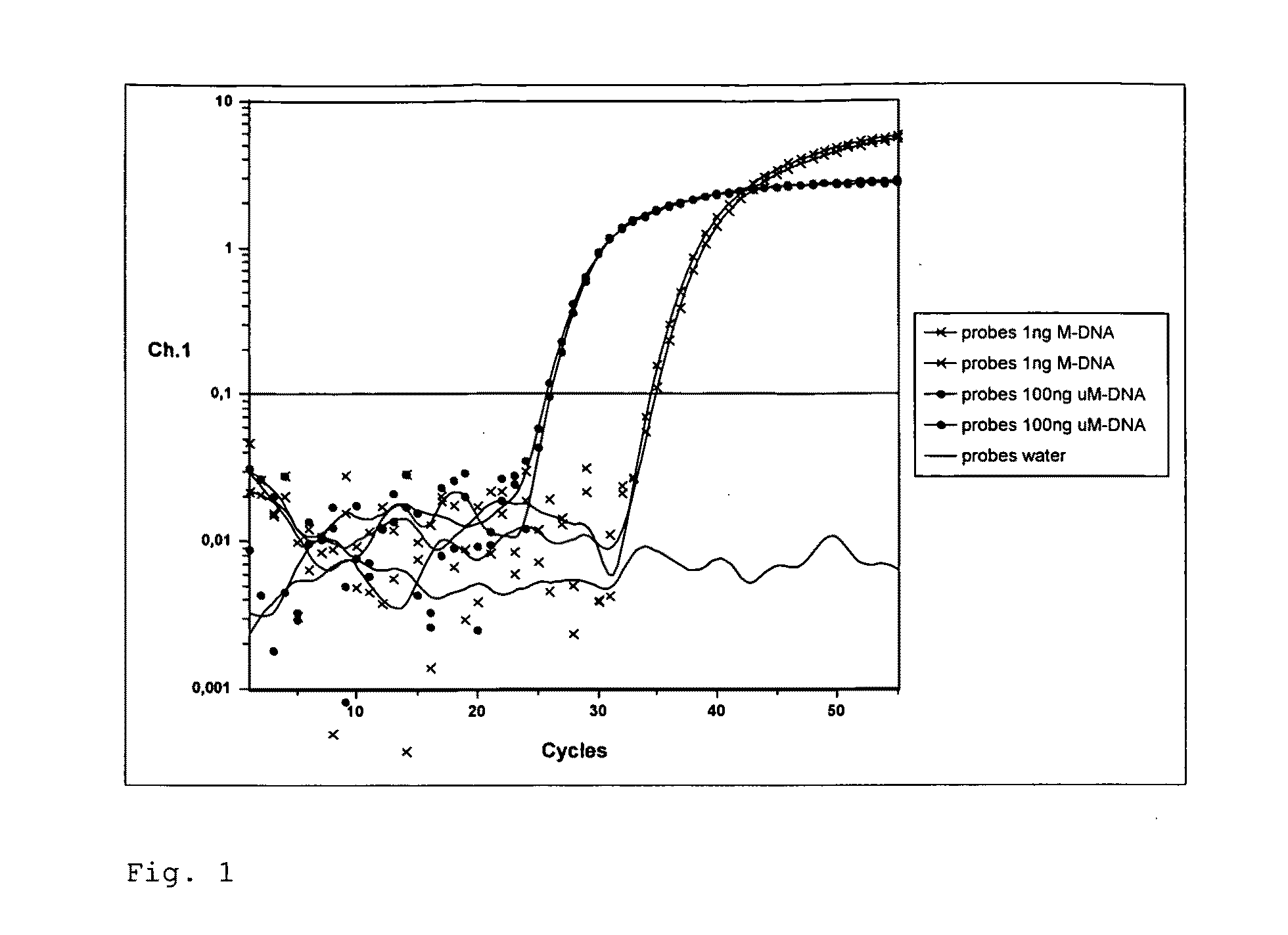
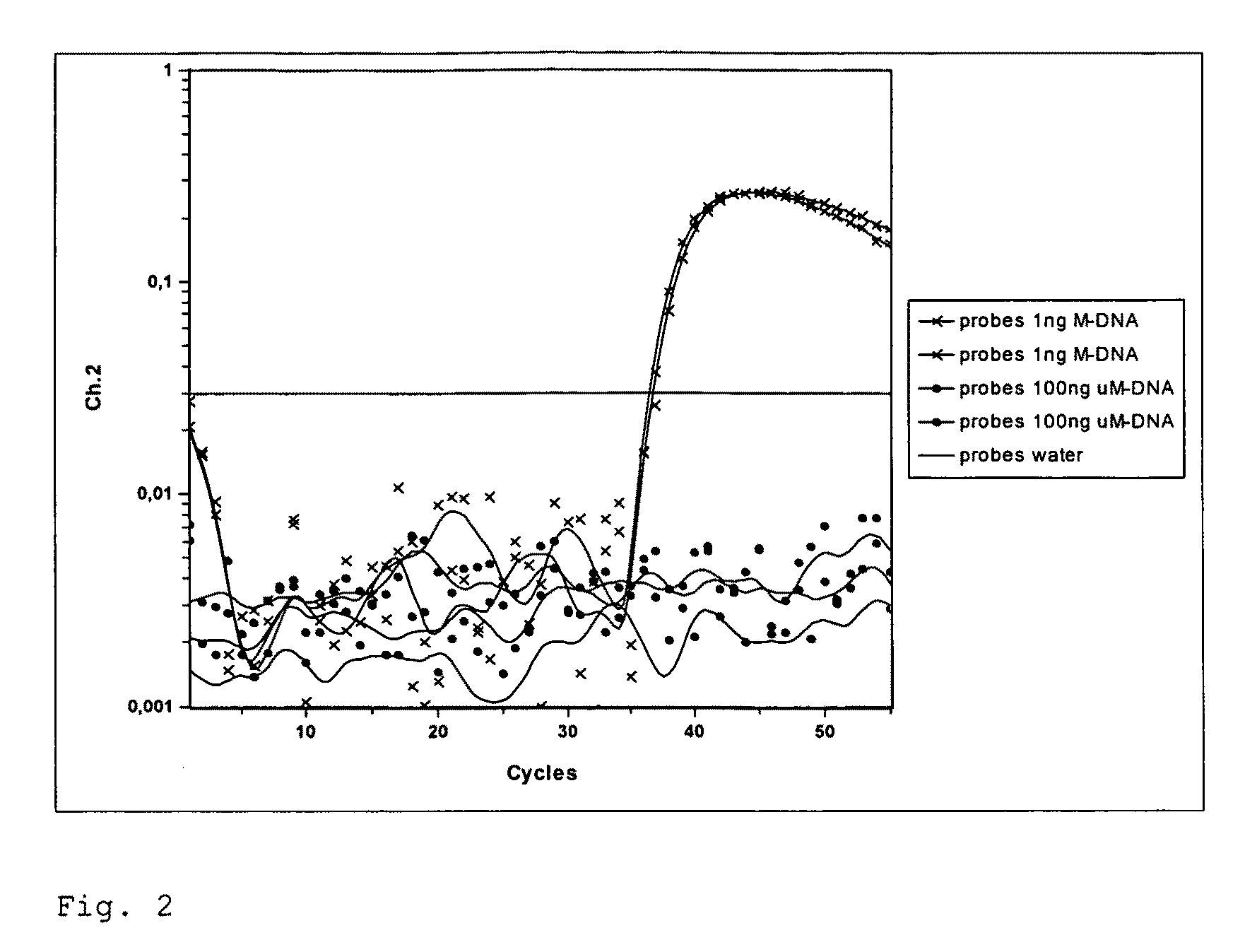
ActiveUS20110104663A1Efficiently quantizedAvoid interactionMicrobiological testing/measurementNon specificBiology
The method according to the invention concerns in particular a method for the quantification of methylated DNA. For this purpose, the DNA to be examined is first transformed such that unmethylated cytosine is converted to uracil while 5-methylcytosine remains unchanged. Subsequently, the transformed DNA is amplified in the presence of a pair of real-time probes. For this, a probe is constructed, which is specific for the methylated or for the unmethylated state of the DNA, and a probe, which binds methylation-unspecifically to the amplificate. The ratio of the signal intensities of the probes or the CT values allows for the calculation of the degree of methylation of the examined DNA. The method according to the invention is suited particularly for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and other diseases associated with a change in the methylation status, as well as, prediction of adverse for side-effects of pharmaceuticals.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com