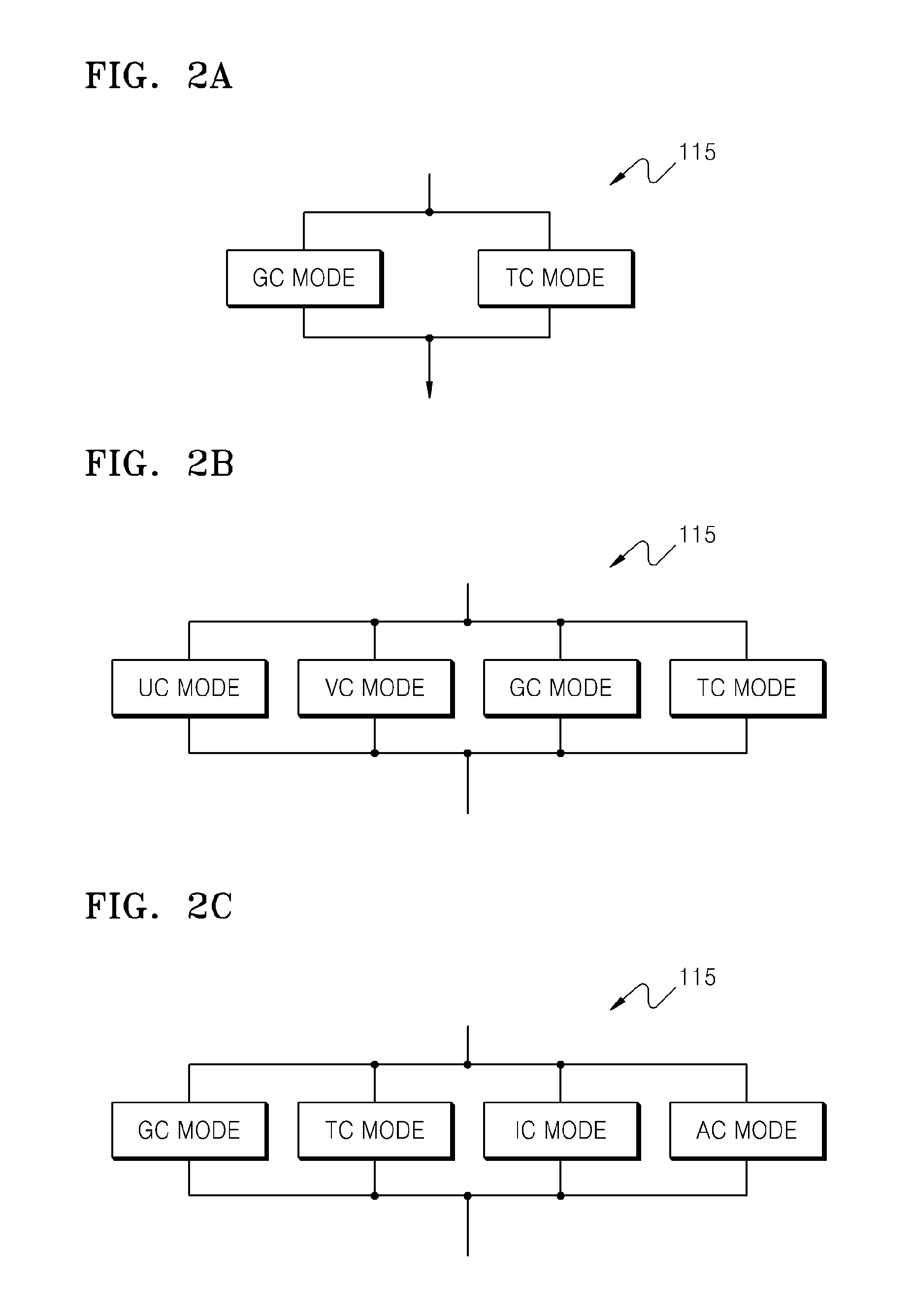
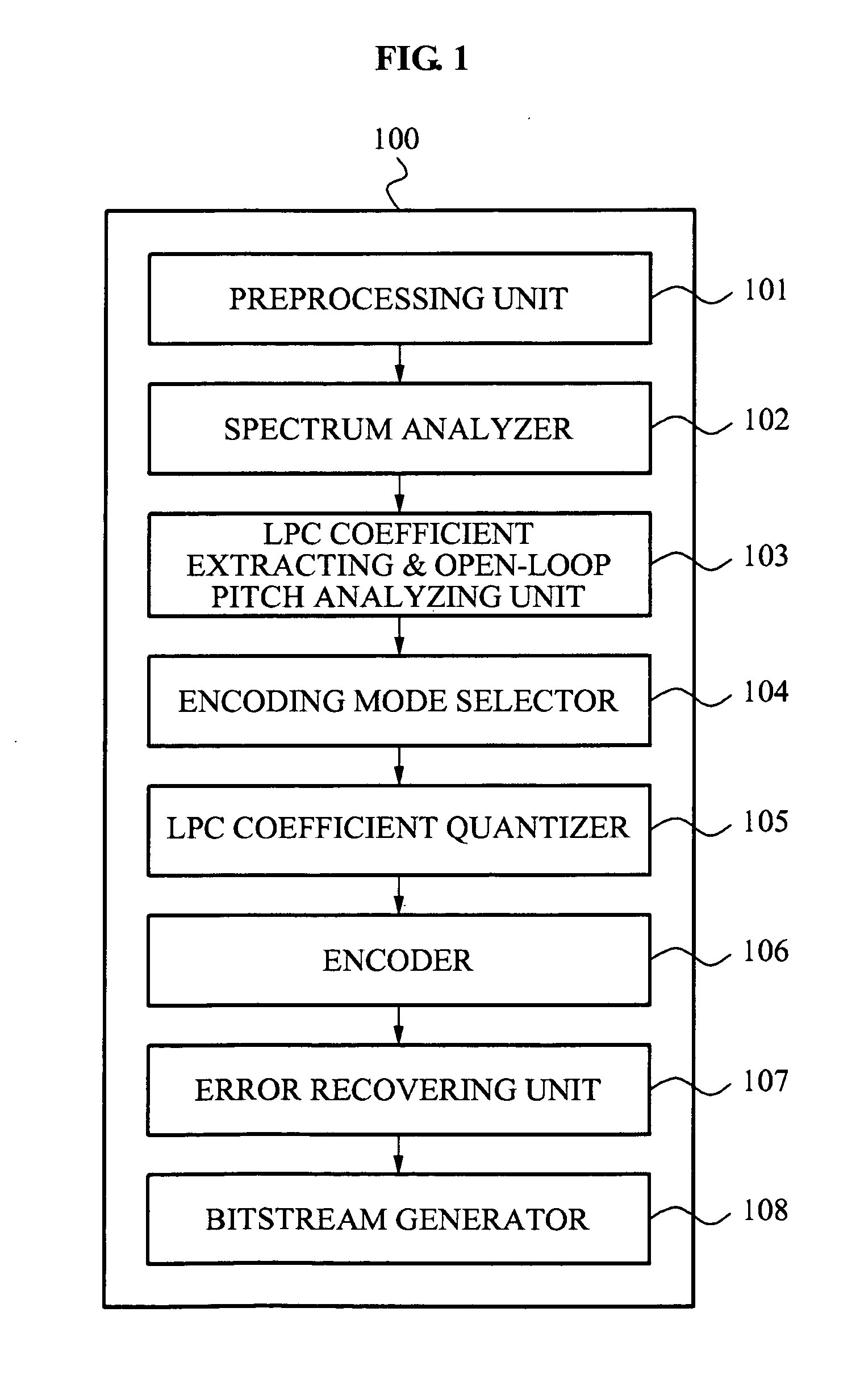
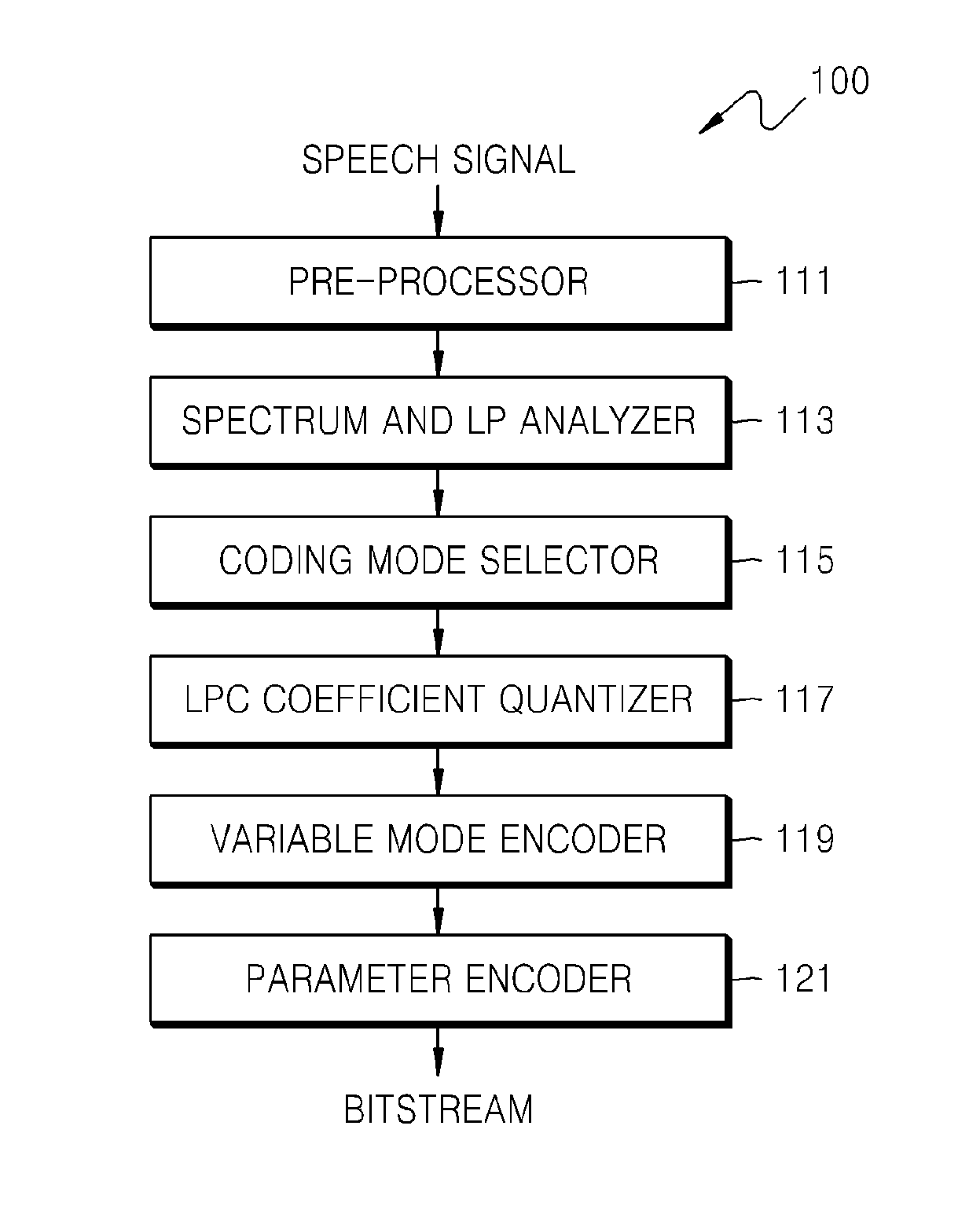
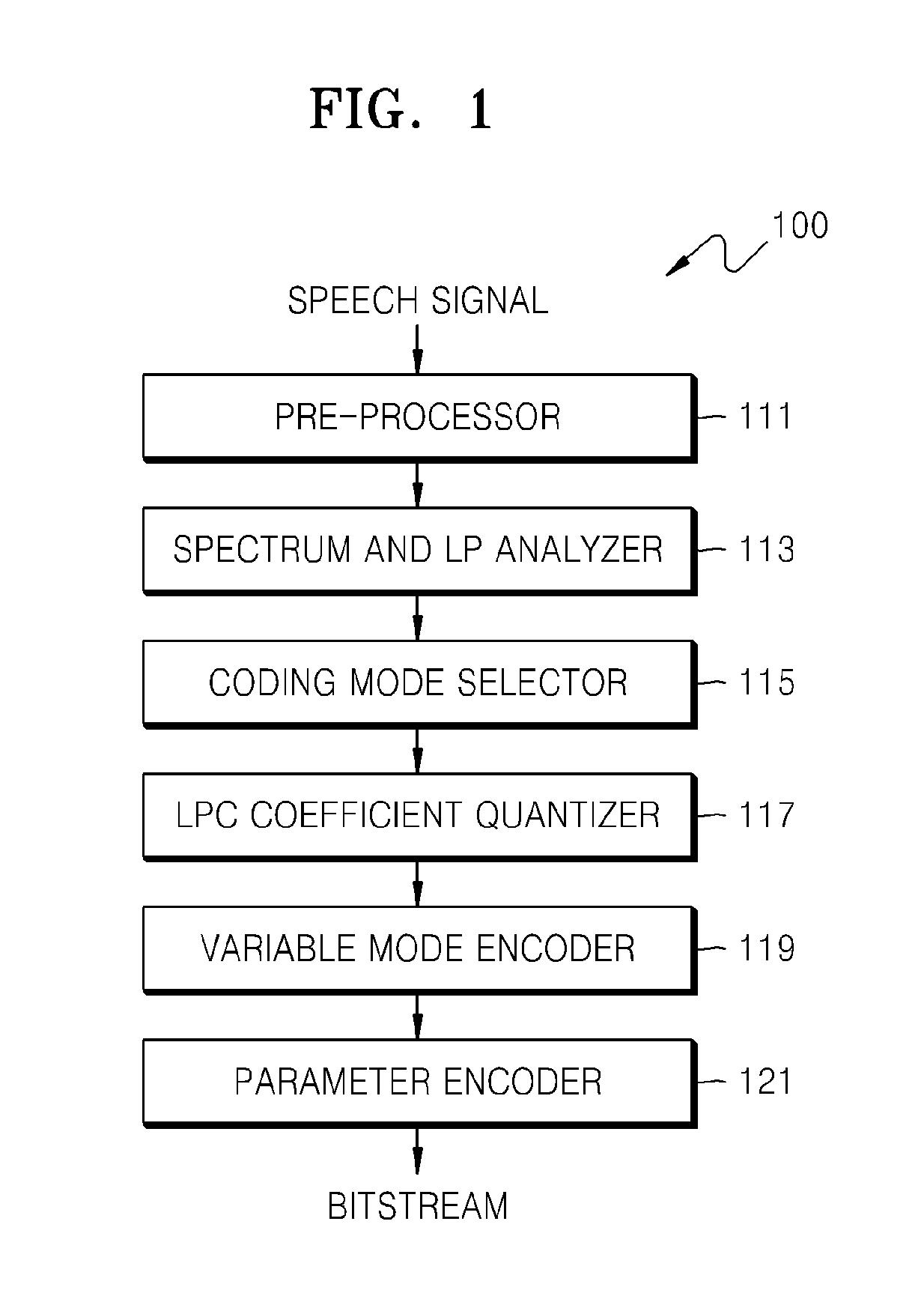
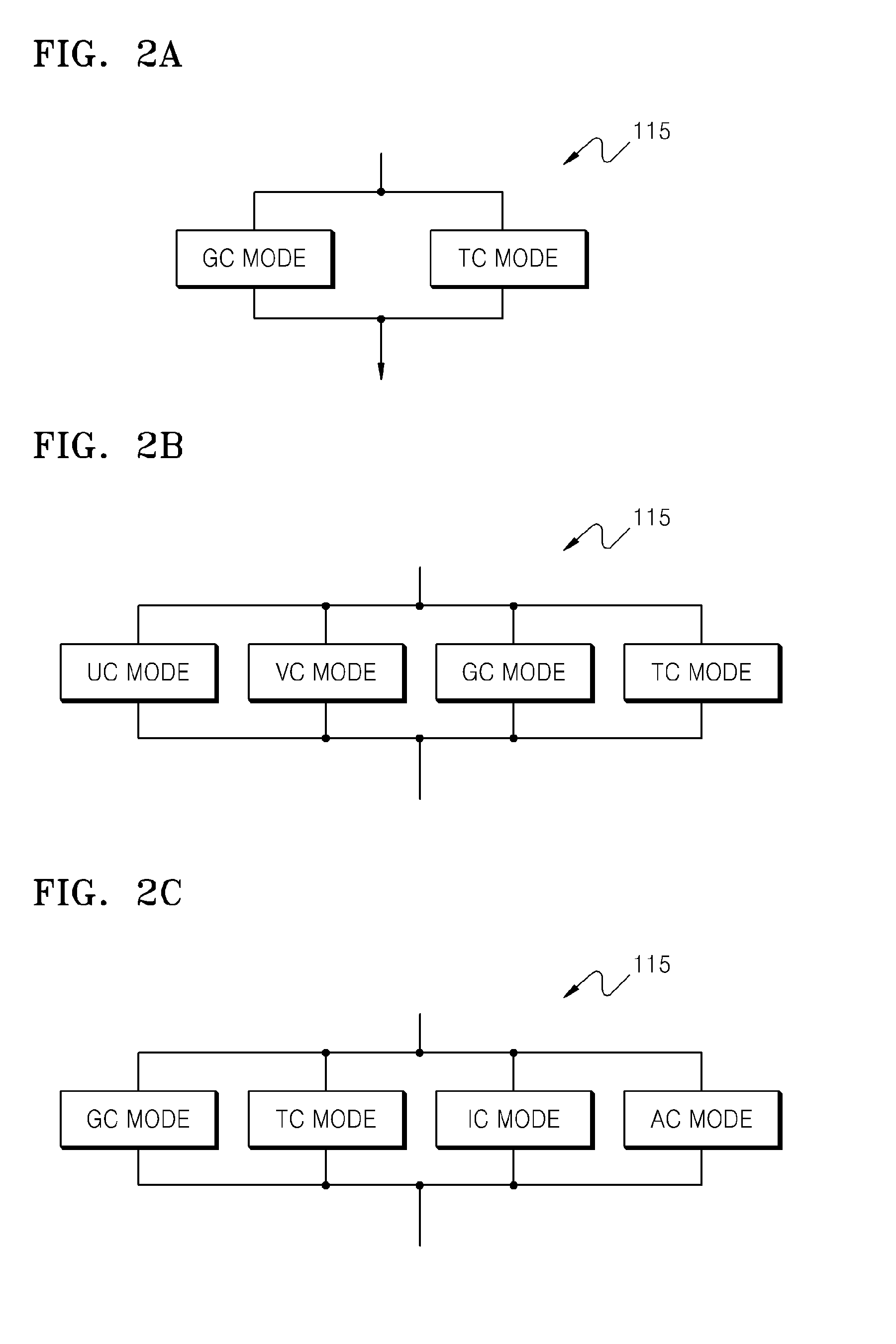
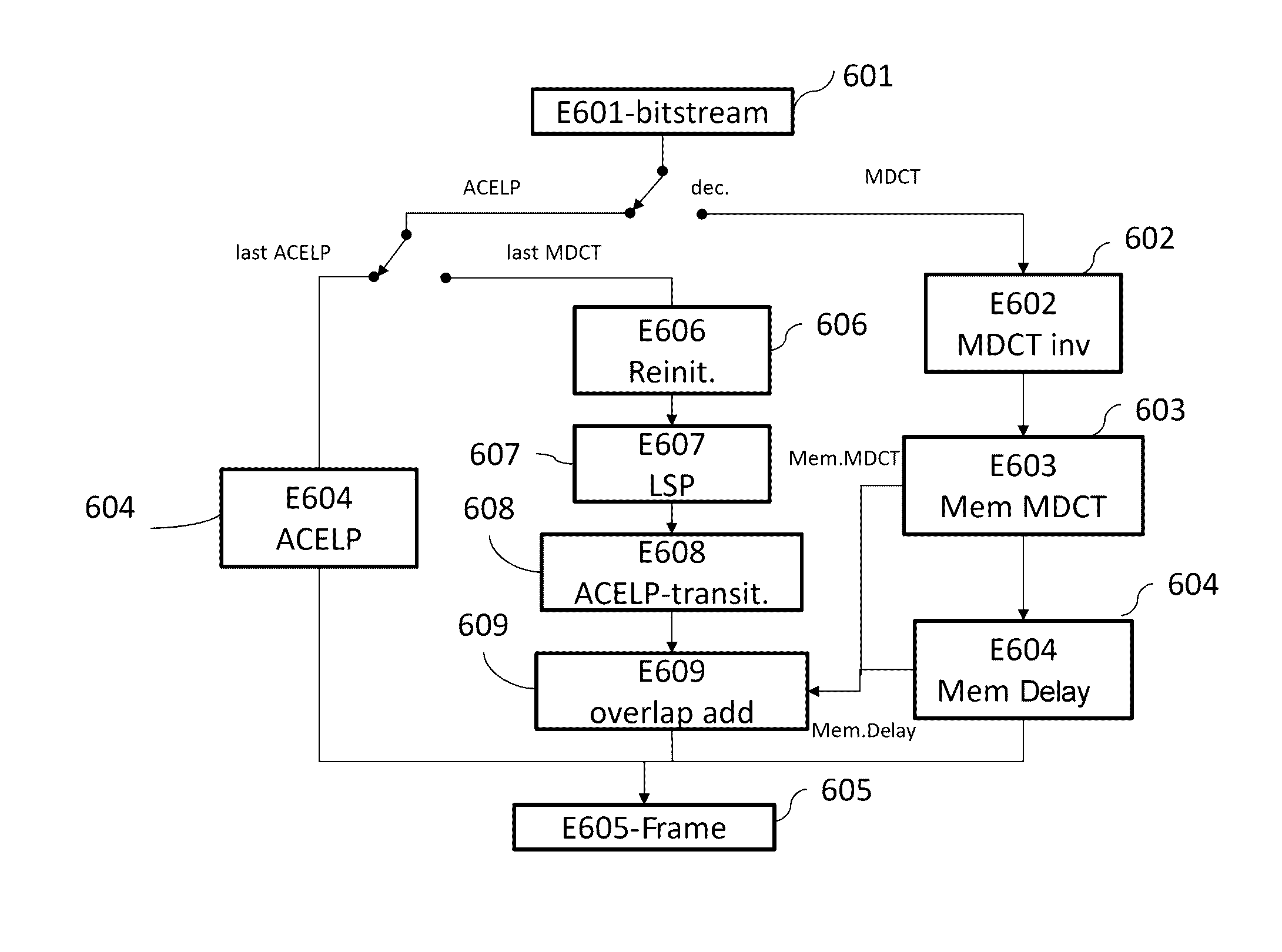
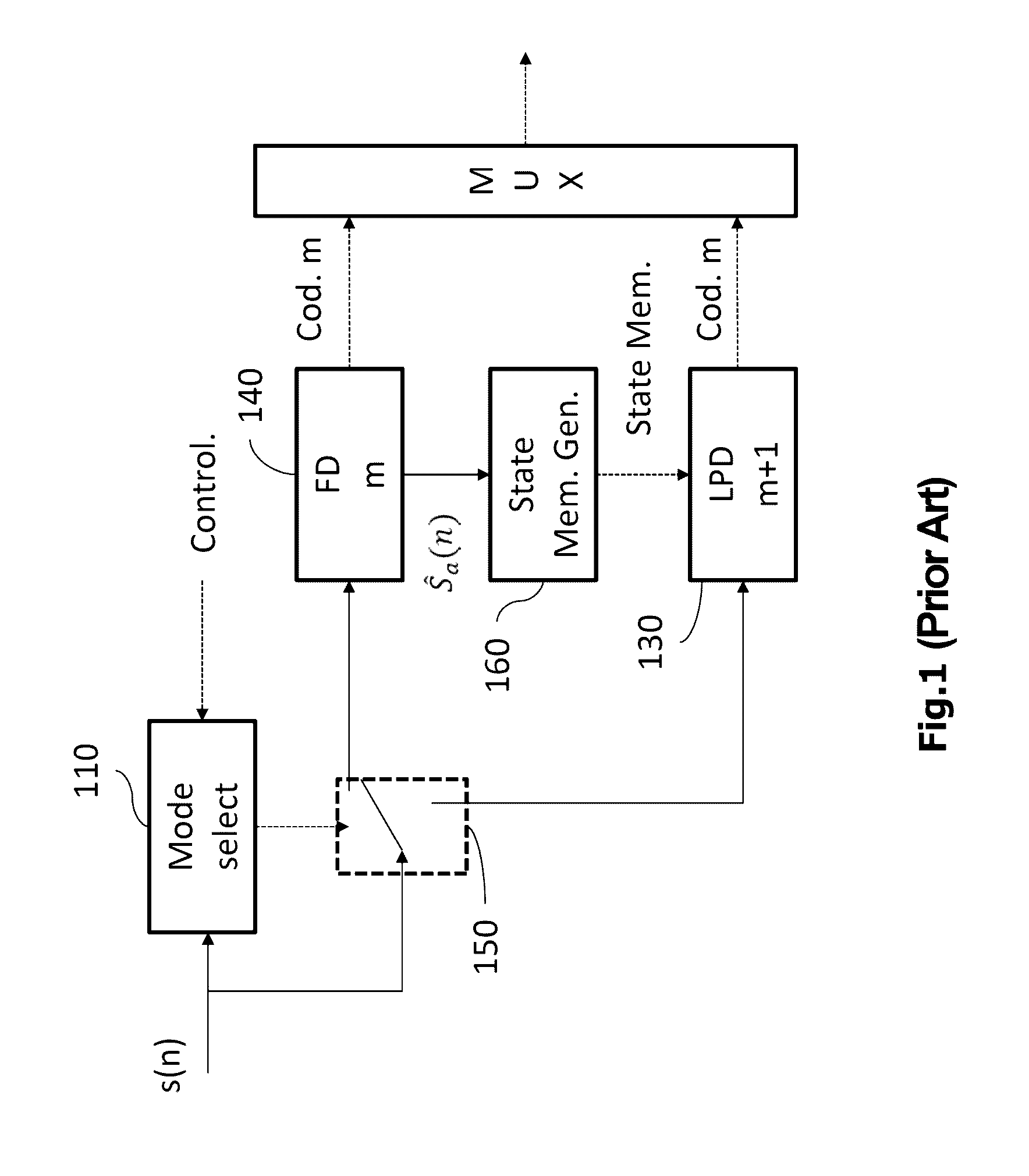
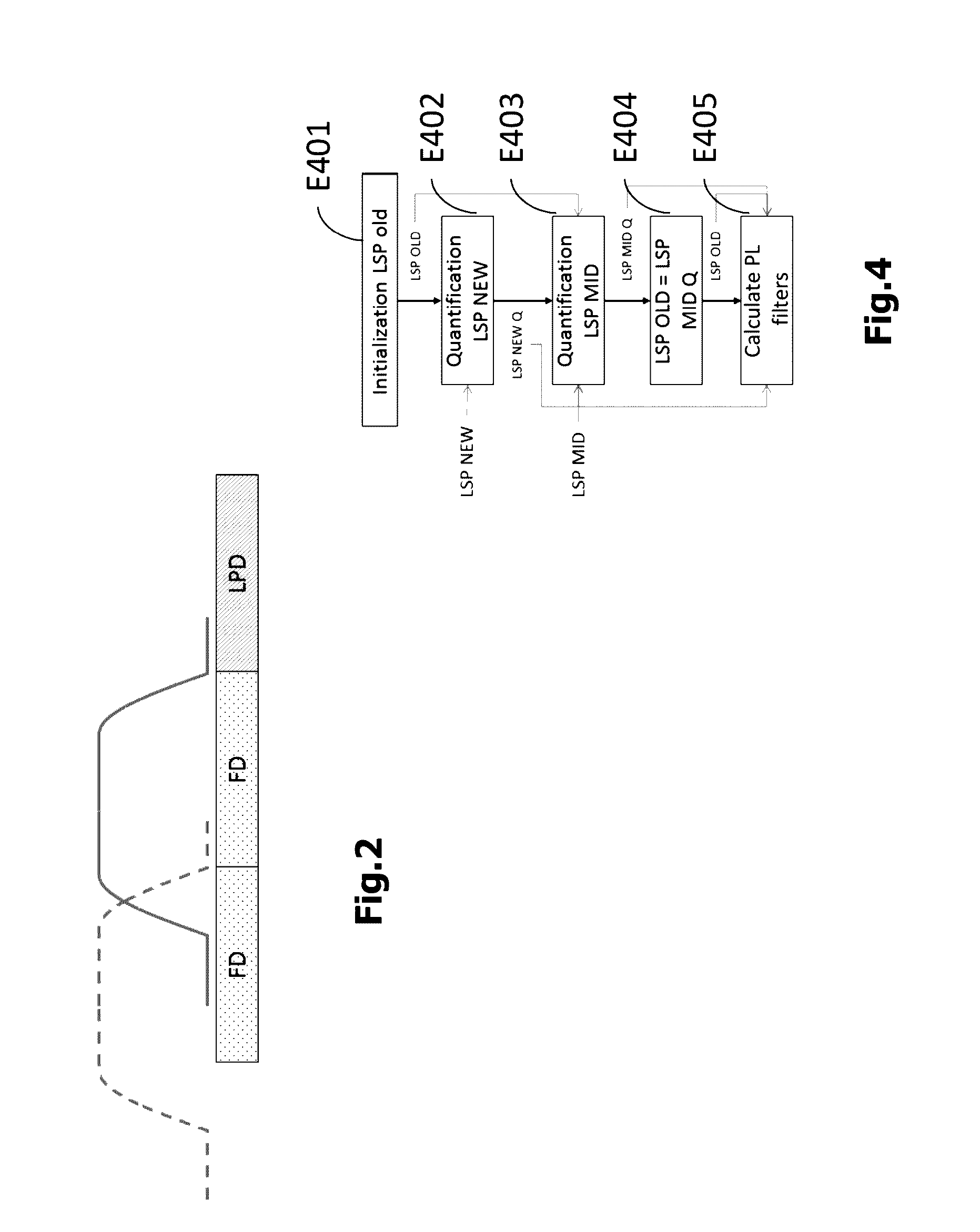
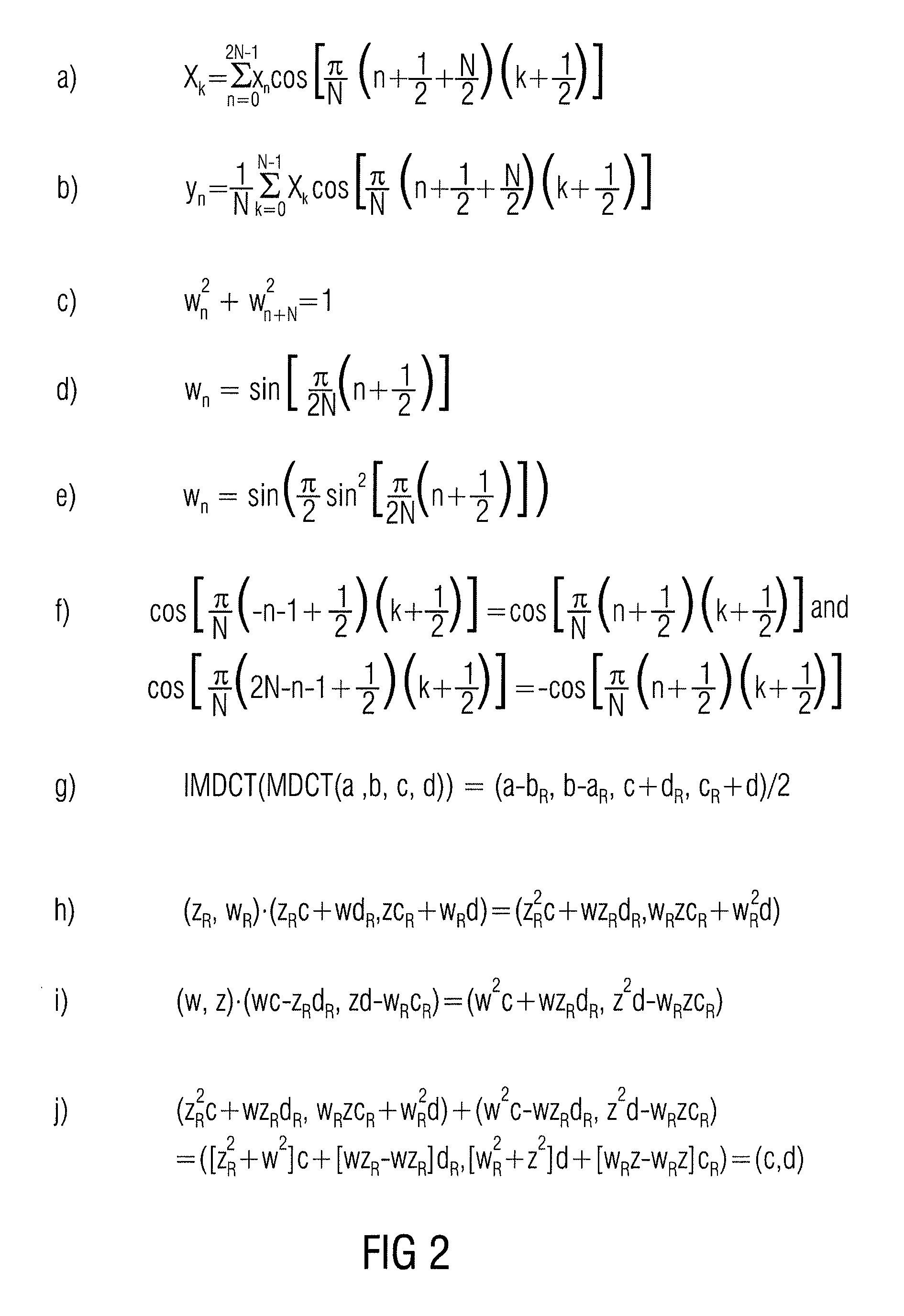Patents
Literature
129 results about "Linear predictive coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear predictive coding (LPC) is a tool used mostly in audio signal processing and speech processing for representing the spectral envelope of a digital signal of speech in compressed form, using the information of a linear predictive model. It is one of the most powerful speech analysis techniques, and one of the most useful methods for encoding good quality speech at a low bit rate and provides extremely accurate estimates of speech parameters.
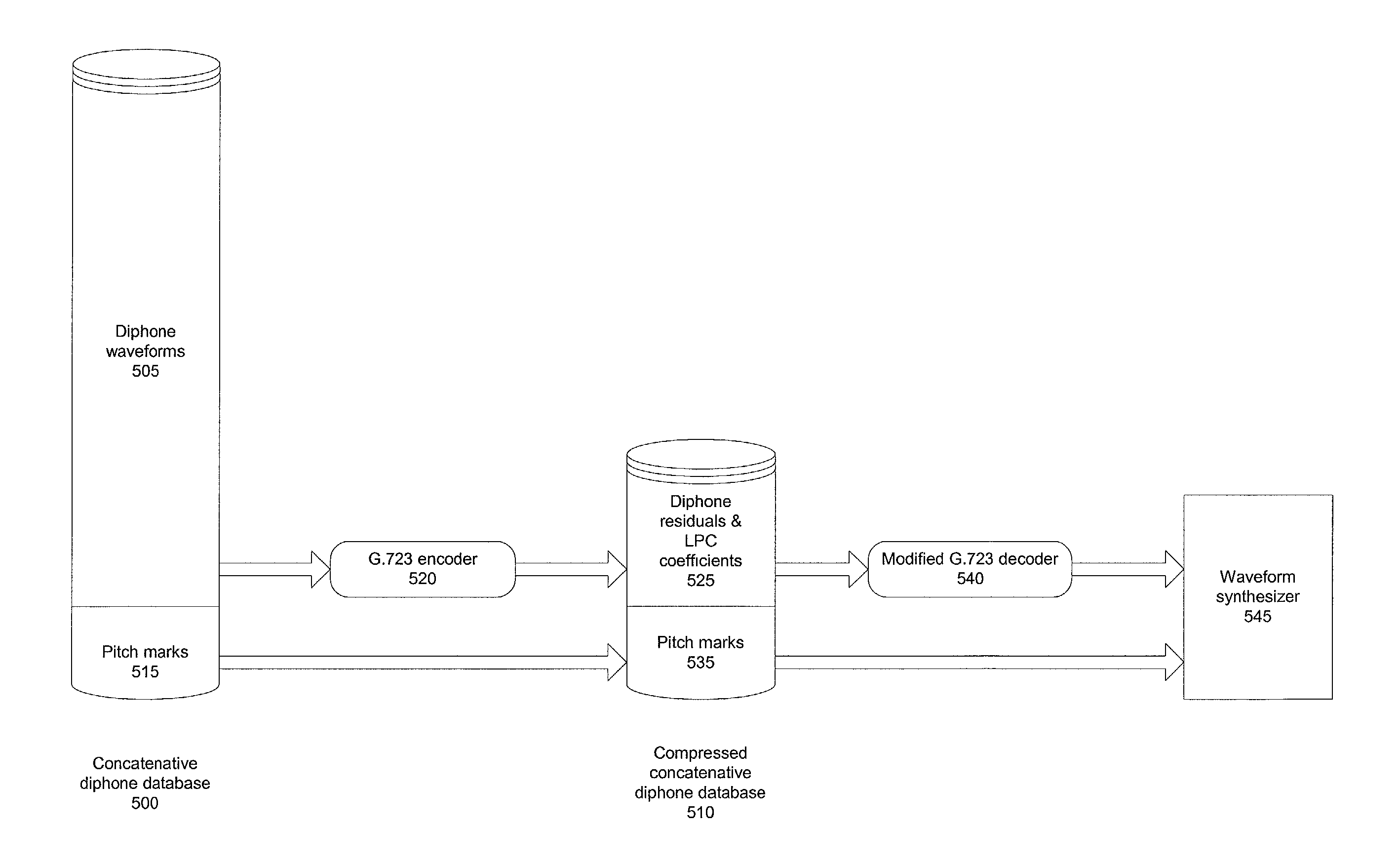
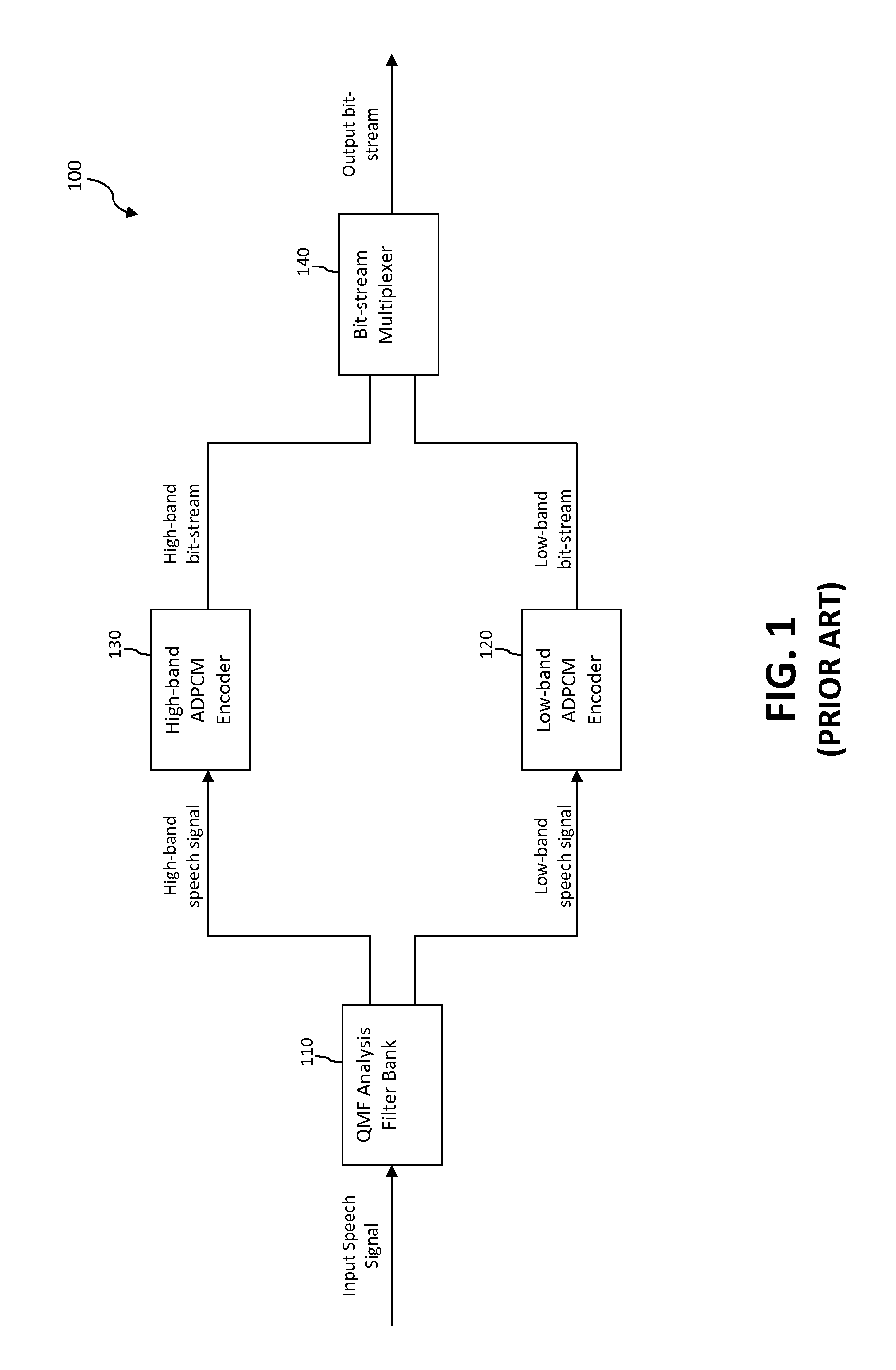
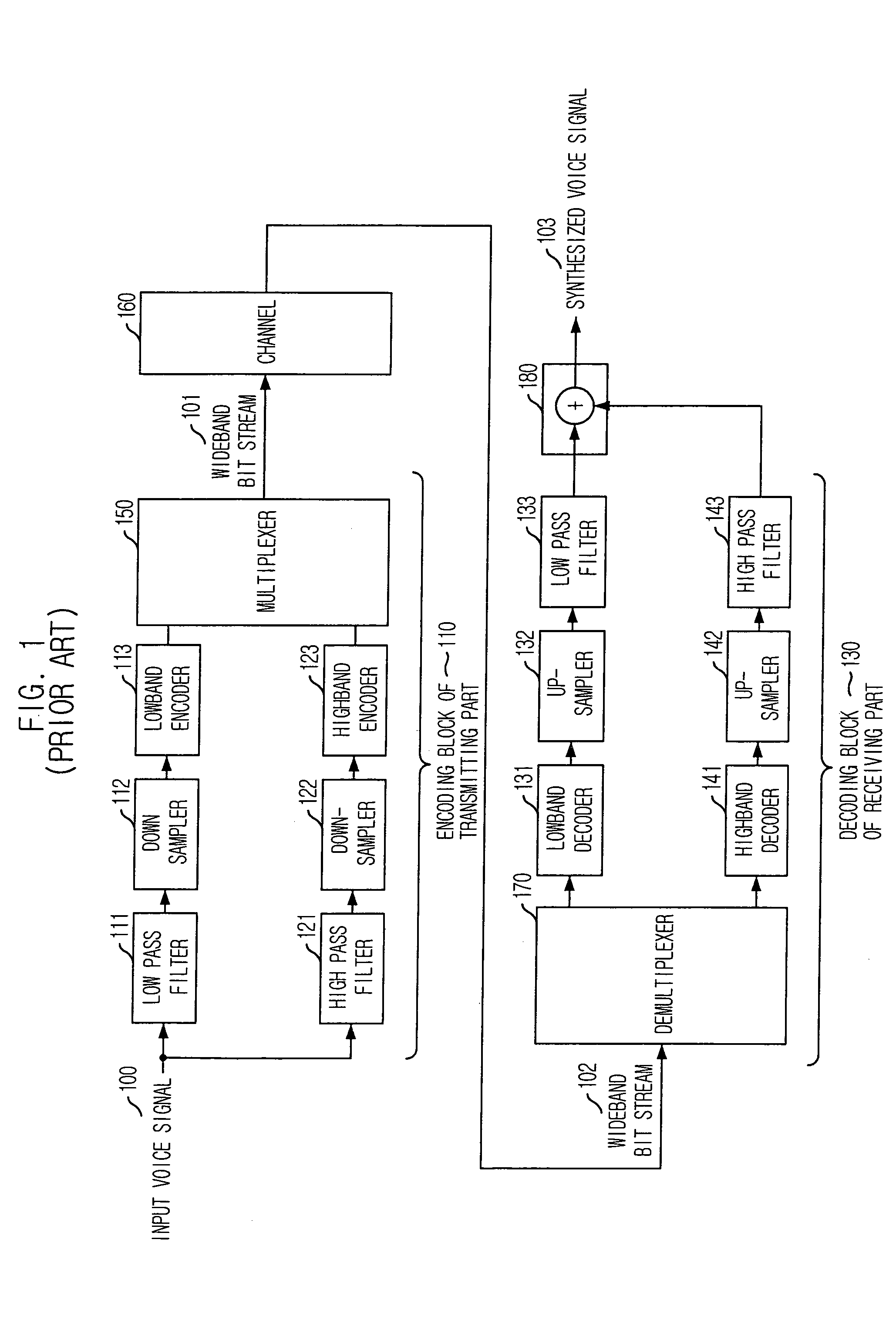
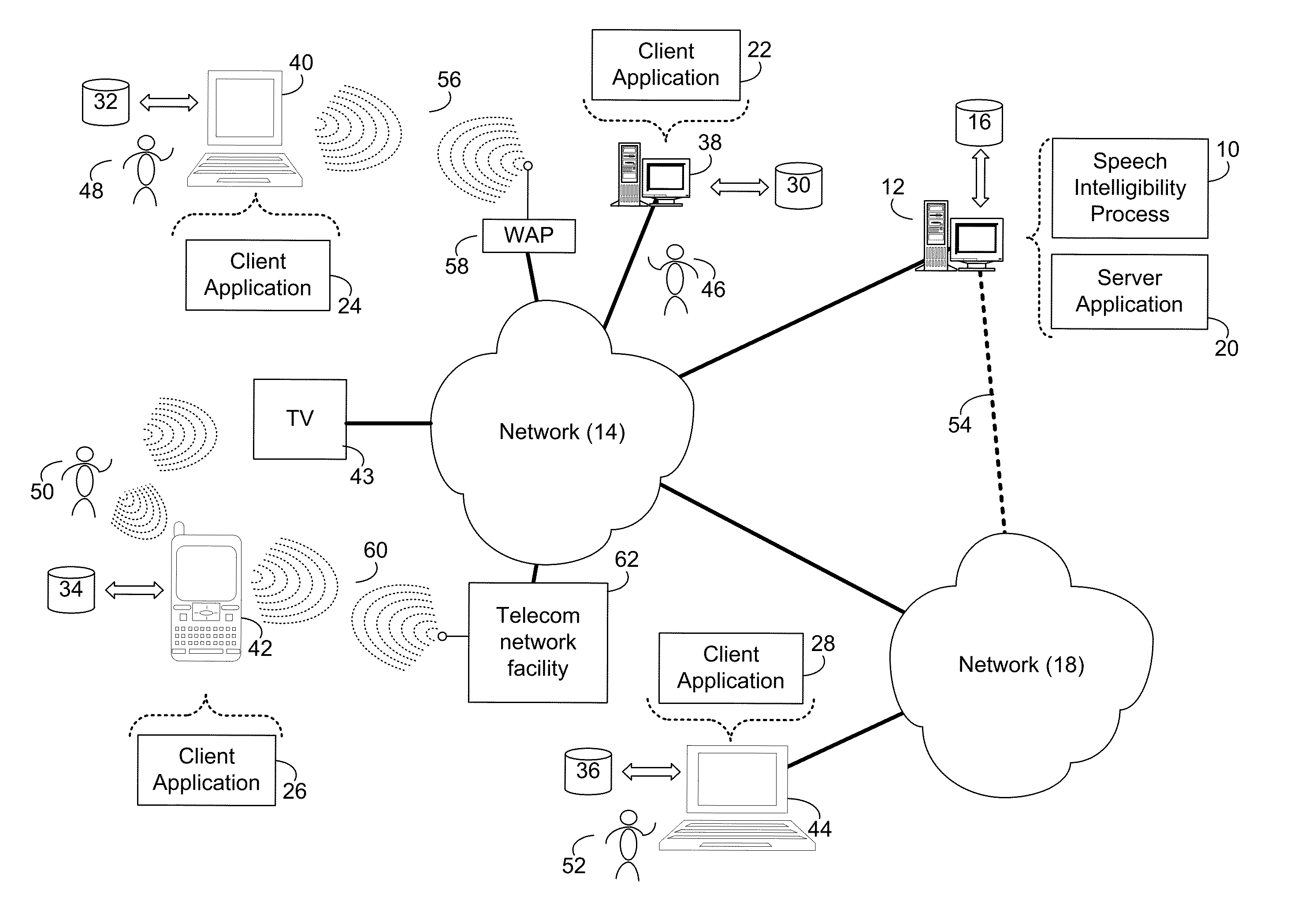
Compressing and using a concatenative speech database in text-to-speech systems
A method and apparatus are provided for compressing and using a concatenative speech database in TTS systems to improve the quality of speech output generated by handheld TTS systems by allowing synthesis to occur on the client. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a G.723 encoder receives diphone waveforms, and compresses them into diphone residuals. While compressing the diphone waveforms, the encoder generates Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) coefficients. The diphone residuals, and the encoder-generated LPC coefficients are then stored in encoder-generated compressed packet.
Owner:INTEL CORP
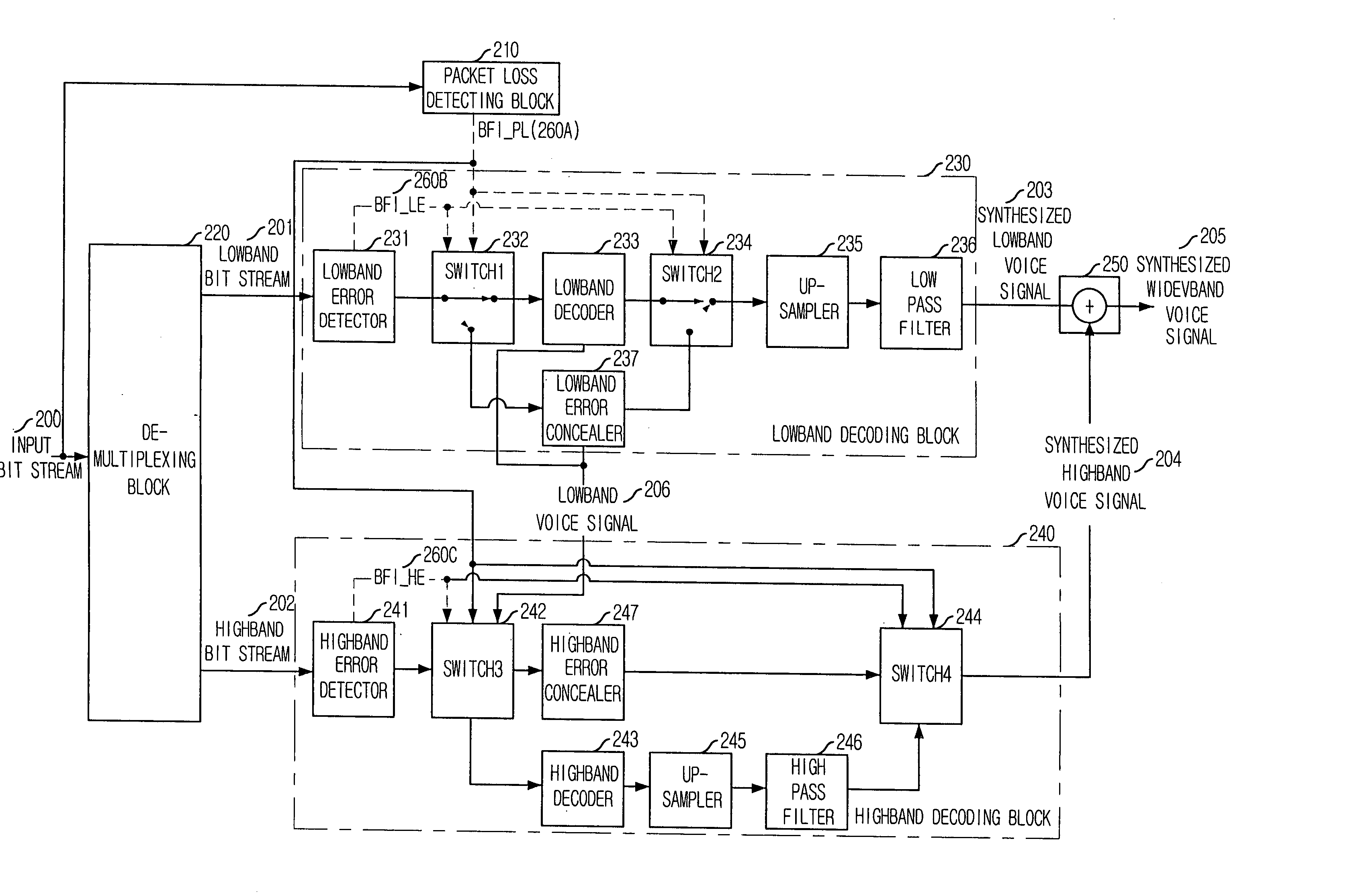
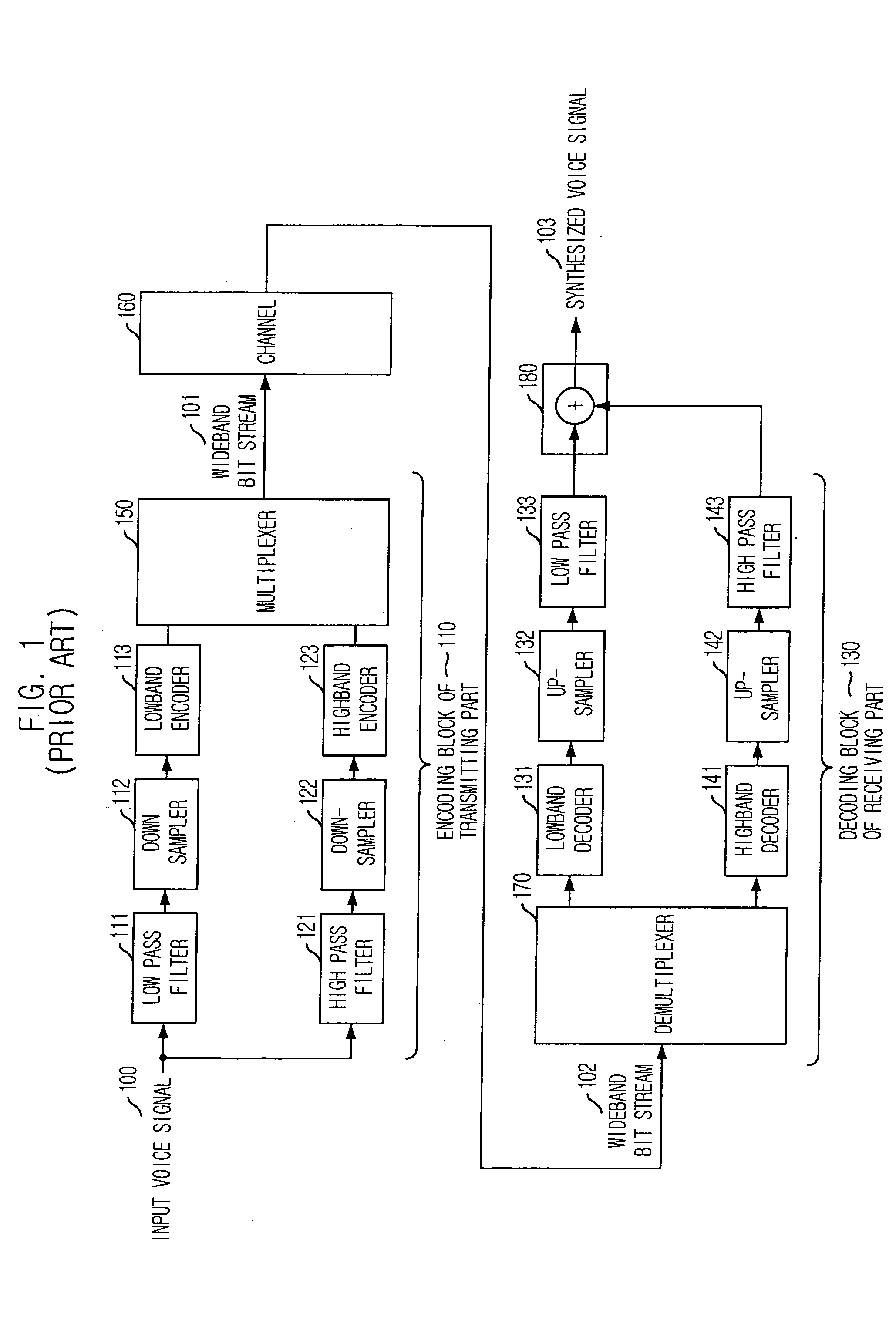
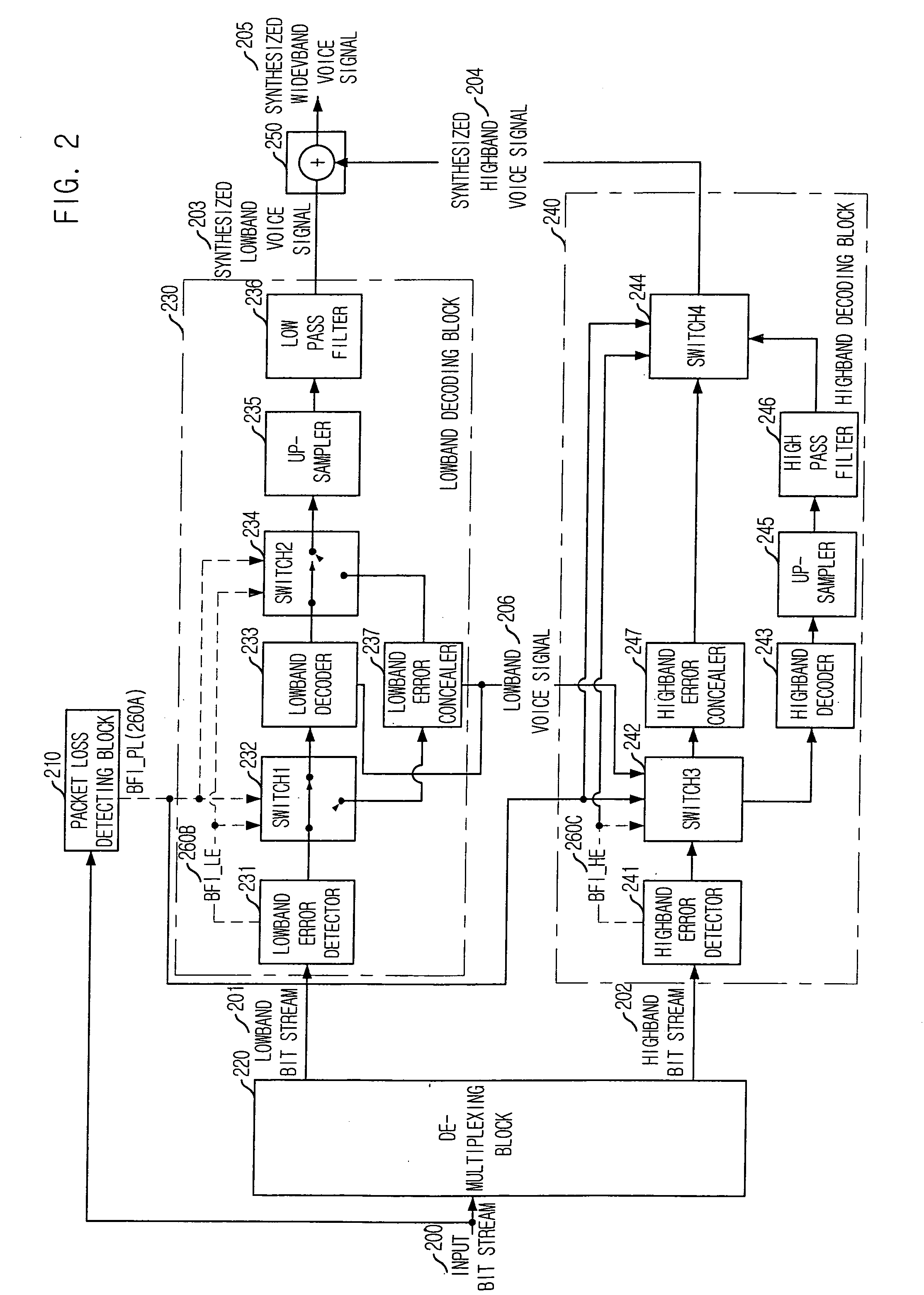
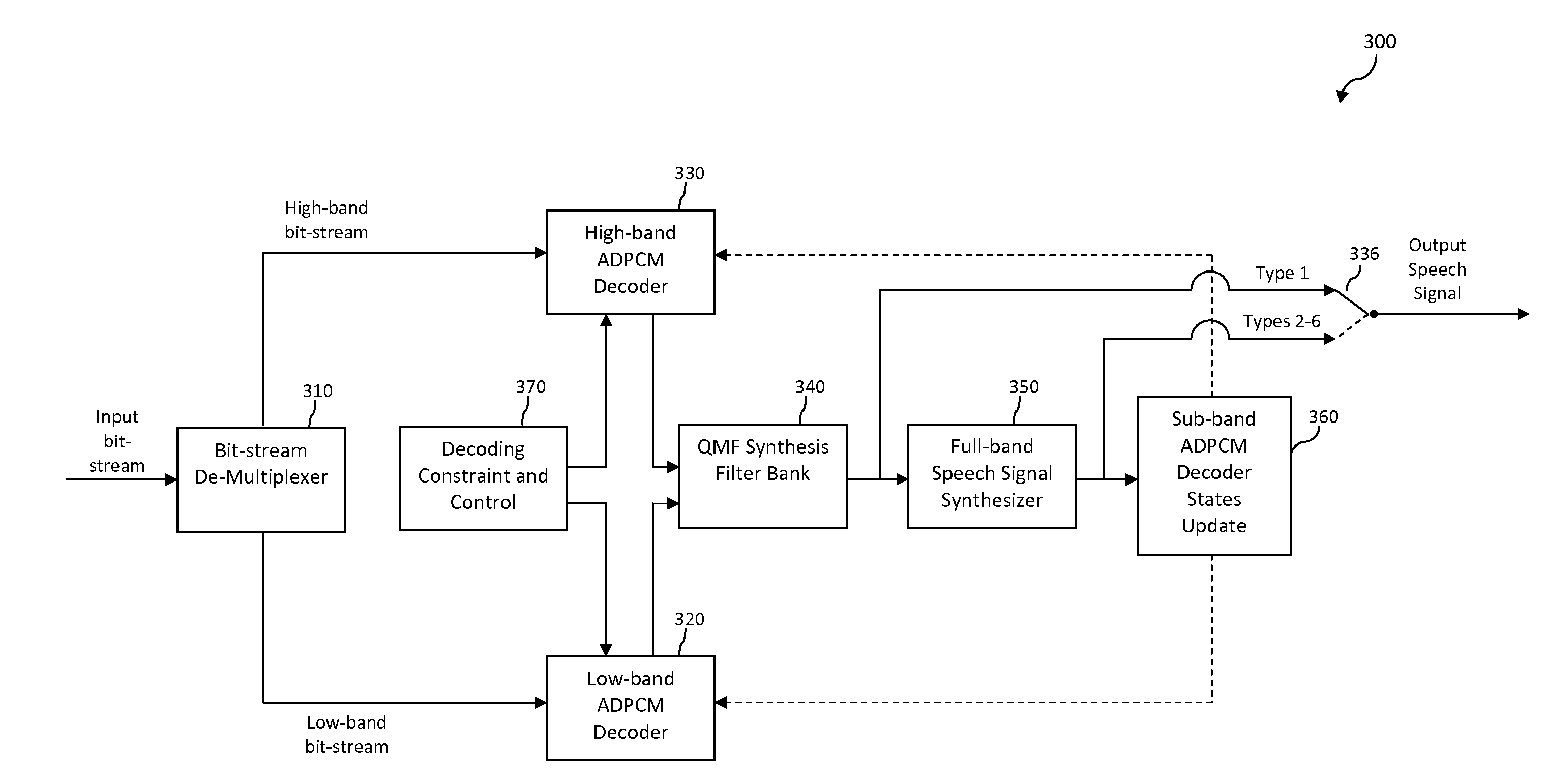
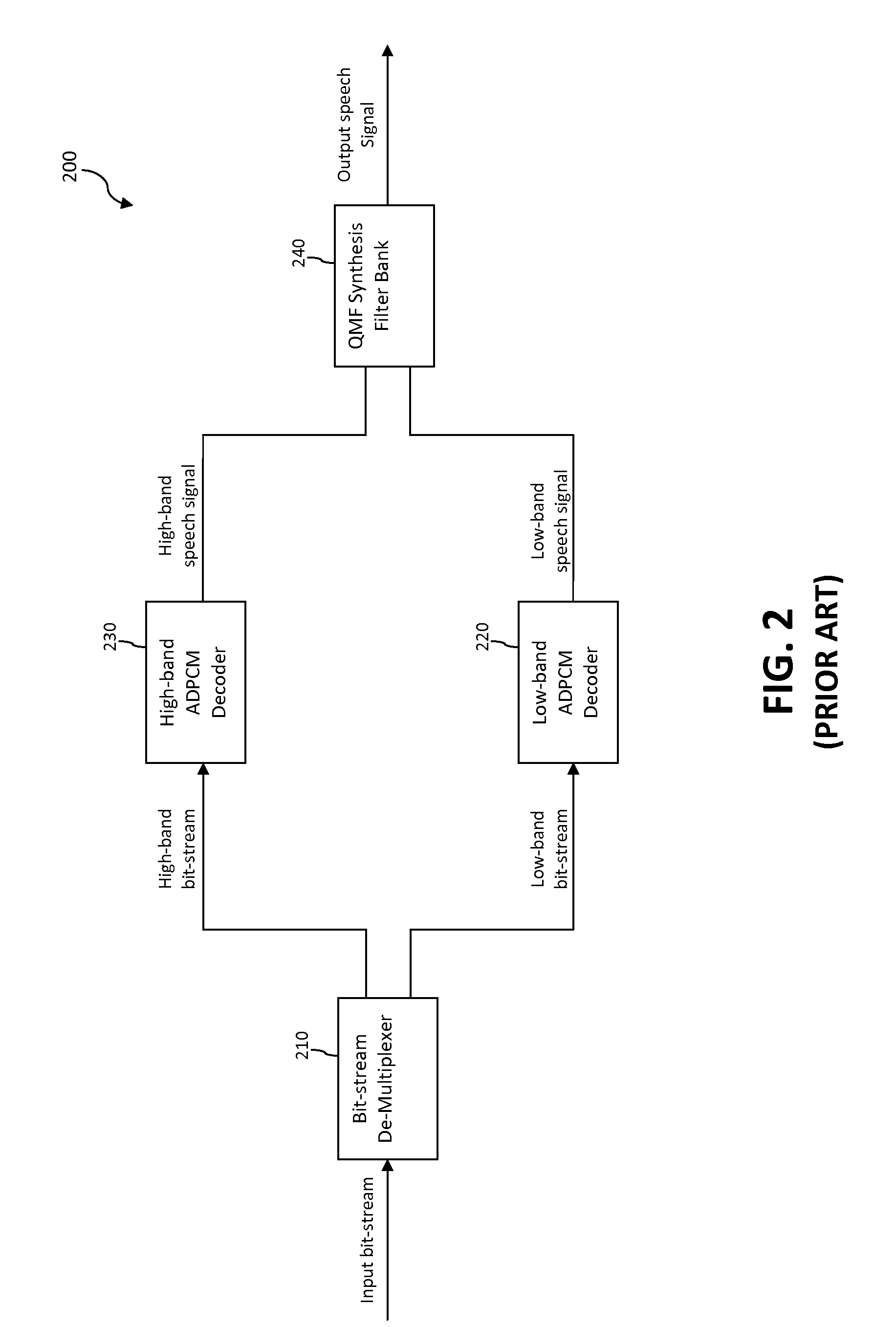
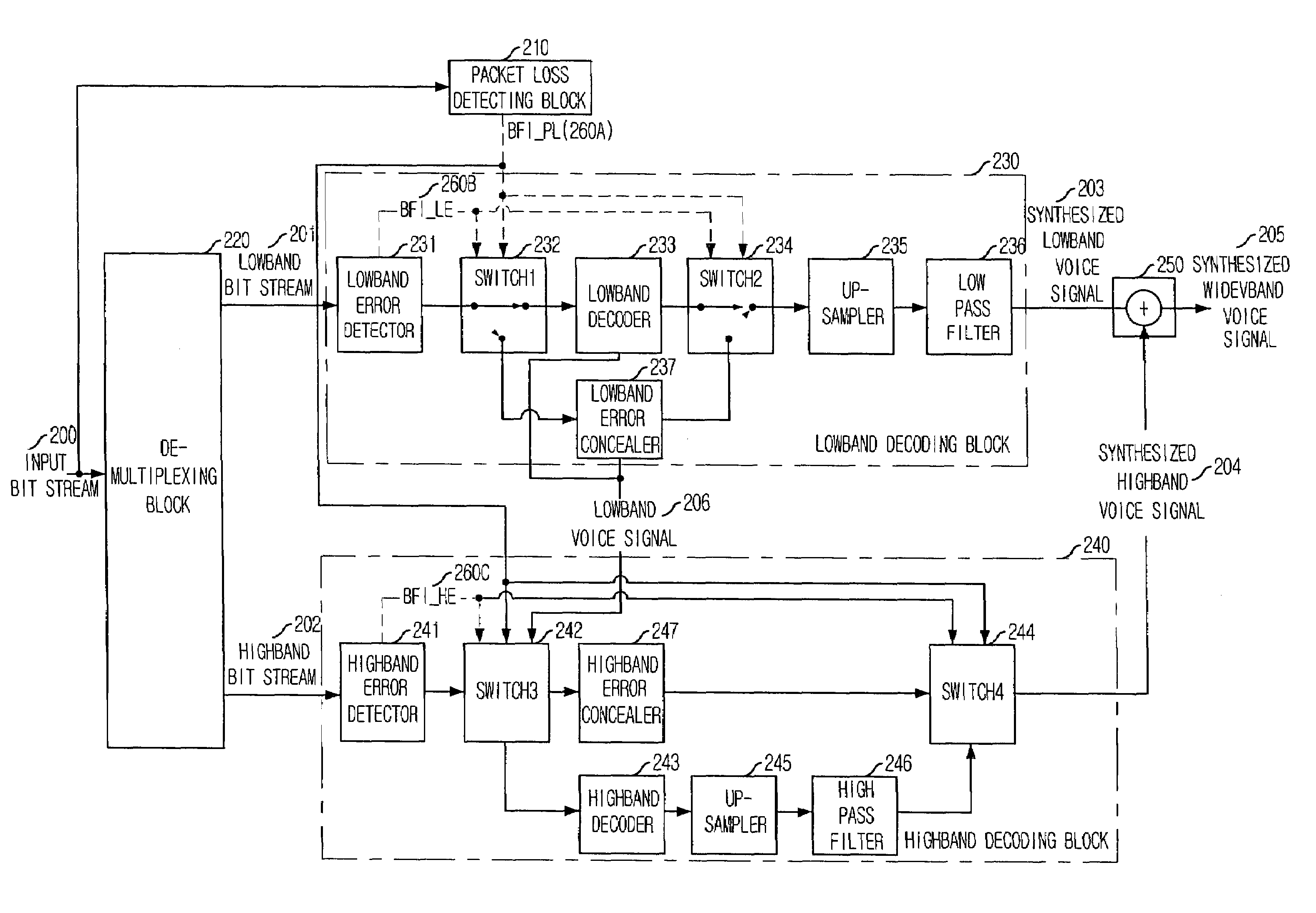
Apparatus and method for concealing highband error in spilt-band wideband voice codec and decoding system using the same
InactiveUS20050143985A1Quality improvementSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBroadbandExcitation signal
An apparatus for concealing a highband error in a spilt-band wideband voice codec in accordance with the present invention is disclosed. The apparatus includes: a lowband LPC coefficient extracting unit for extracting a lowband linear predictive coding (LPC) coefficient from a lowband voice signal passed by a lowband decoding unit; a highband excitation signal generating unit for generating a highband excitation signal based on the lowband voice signal and the lowband LPC coefficient; a highband LPC coefficient generating unit for generating a highband LPC coefficient based on the lowband LPC coefficient; a highband voice synthesizing unit for synthesizing a highband voice signal based on the highband excitation signal and the highband LPC coefficient; and a high pass filtering unit for removing a lowband component of the synthesized highband voice signal by the highband voice synthesis unit and generating the synthesized highband voice signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Linear predictive coding implementation of digital watermarks
InactiveUS20070079131A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsCarrier signalData encoding
Z-transform calculations may be used to encode (and / or decode) carrier signal independent data (e.g., digital watermarks) to a digital sample stream. Deterministic and non-deterministic components of a digital sample stream signal may be analyzed for the purposes of encoding carrier signal independent data to the digital sample stream. The carrier signal independent data may be encoded in a manner such that it is restricted or concentrated primarily in the non-deterministic signal components of the carrier signal. The signal components can include a discrete series of digital samples and / or a discreet series of carrier frequency sub-bands of the carrier signal. Z-transform calculations may be used to measure a desirability of particular locations and a sample stream in which to encode the carrier signal independent data.
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
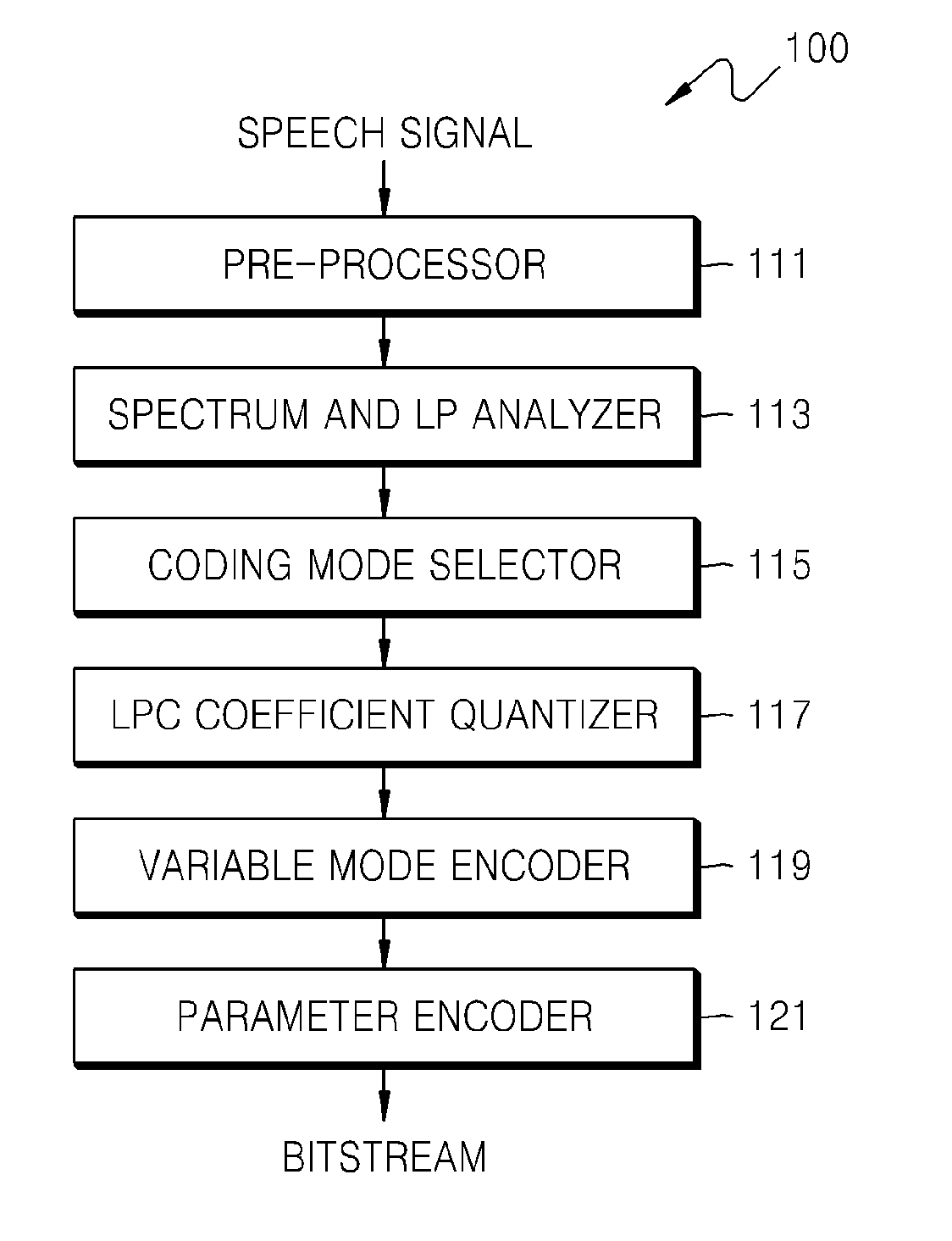
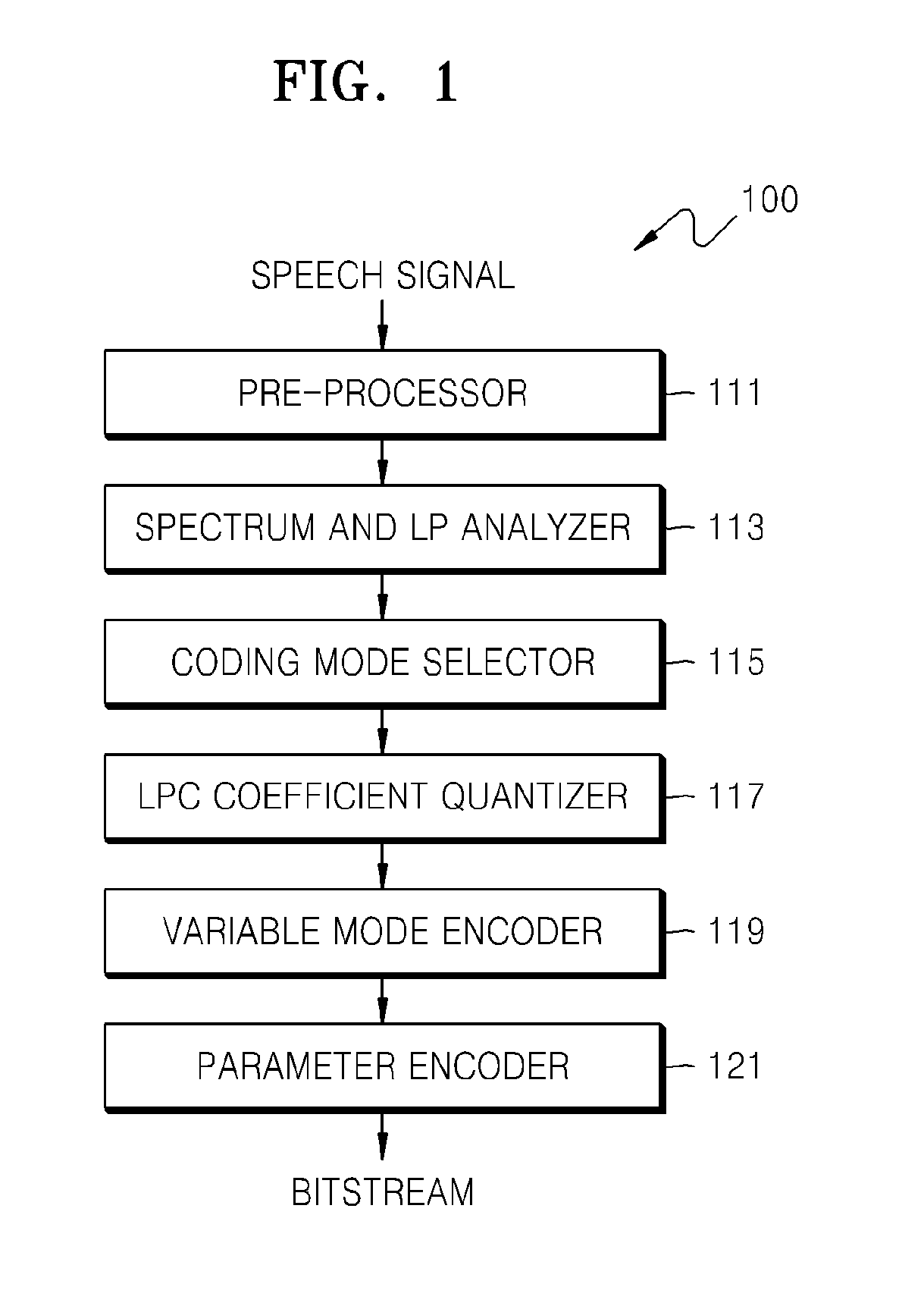
Apparatus for quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound encoding apparatus, apparatus for de-quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound decoding apparatus, and electronic device therefore
ActiveUS20120271629A1Efficiently quantizedReduce complexitySpeech analysisInter frameLinear predictive coding
A quantizing apparatus is provided that includes a quantization path determiner that determines a path from a first path not using inter-frame prediction and a second path using the inter-frame prediction, as a quantization path of an input signal, based on a criterion before quantization of the input signal; a first quantizer that quantizes the input signal, if the first path is determined as the quantization path of the input signal; and a second quantizer that quantizes the input signal, if the second path is determined as the quantization path of the input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
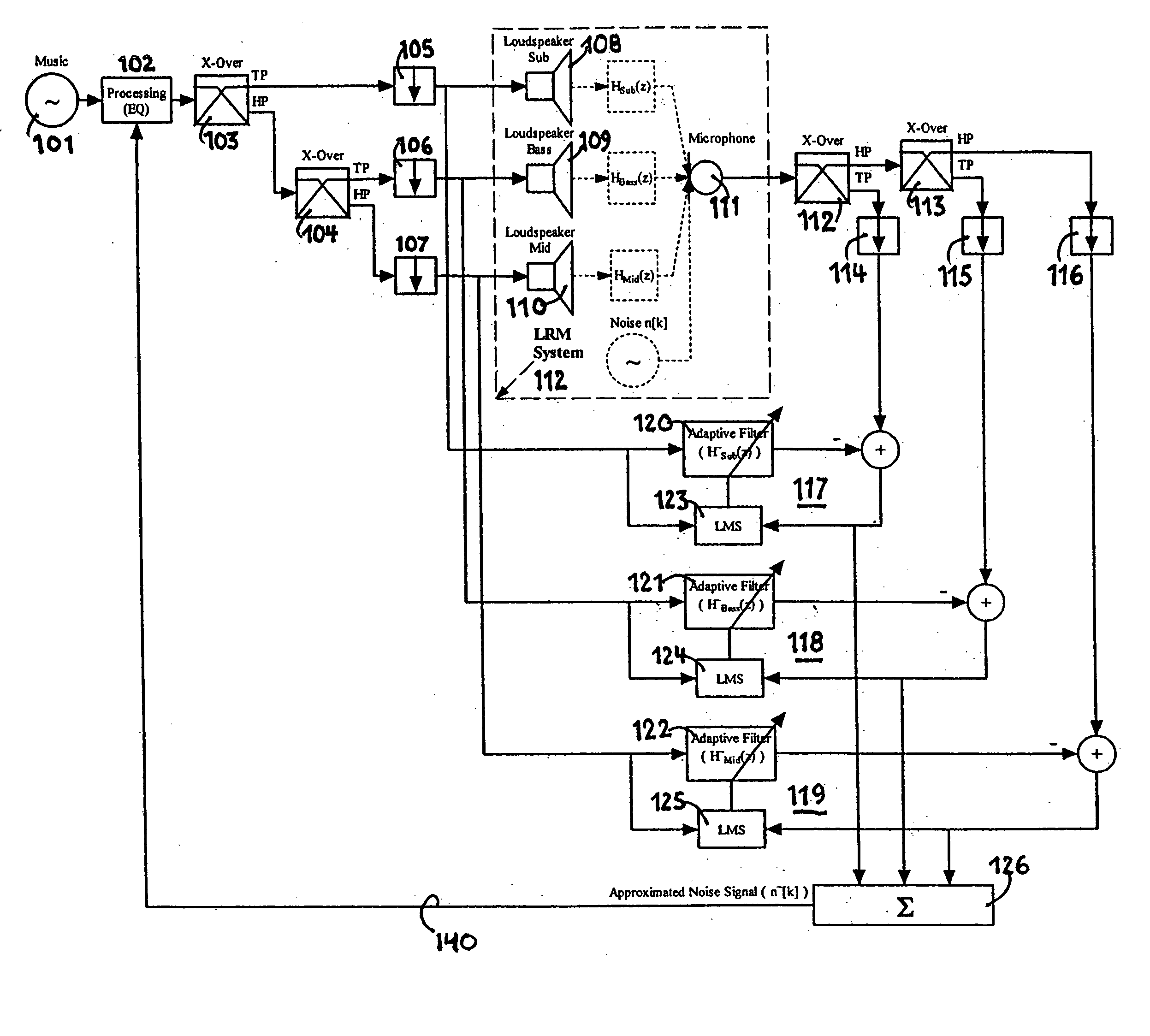
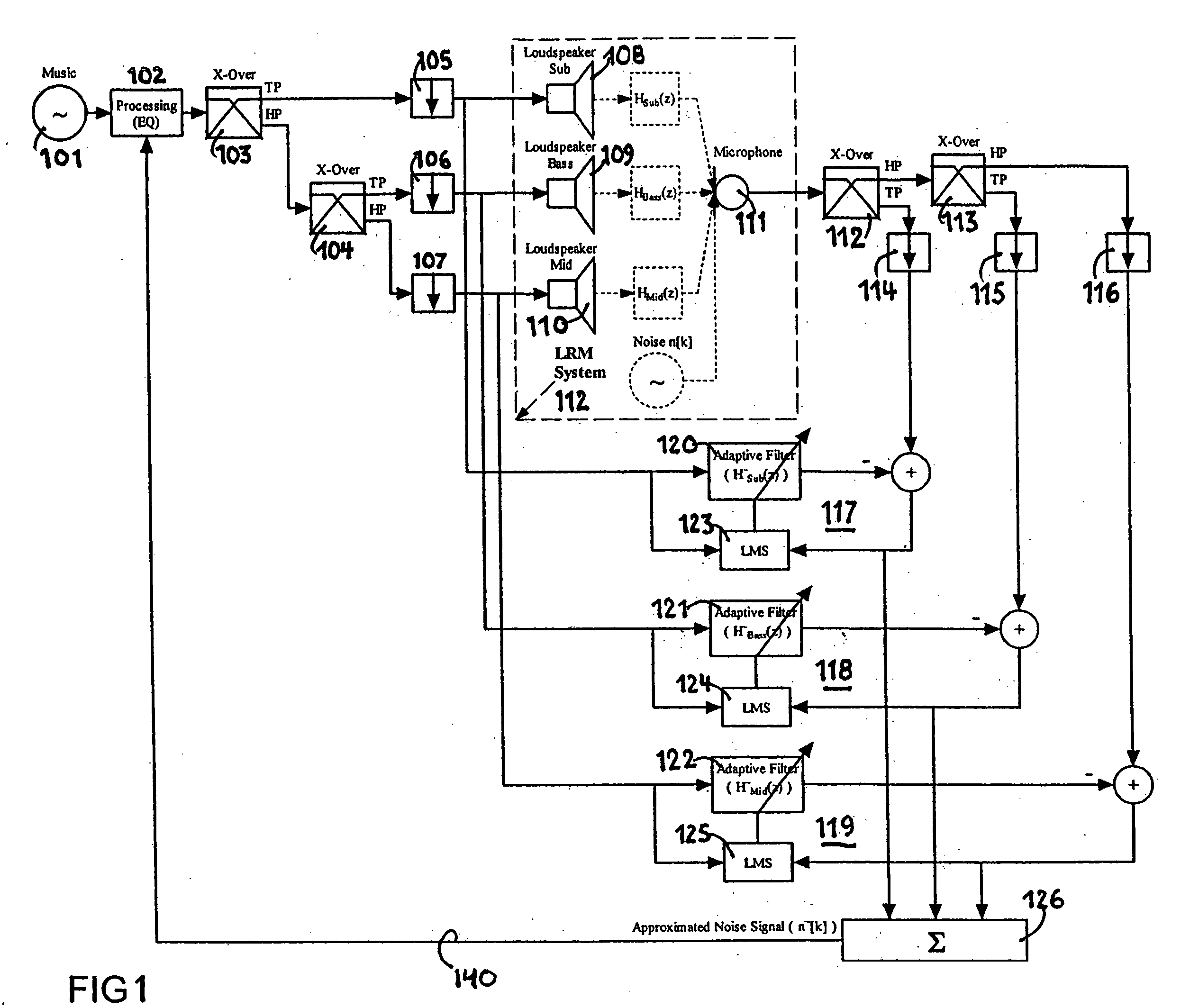
Audio enhancement system
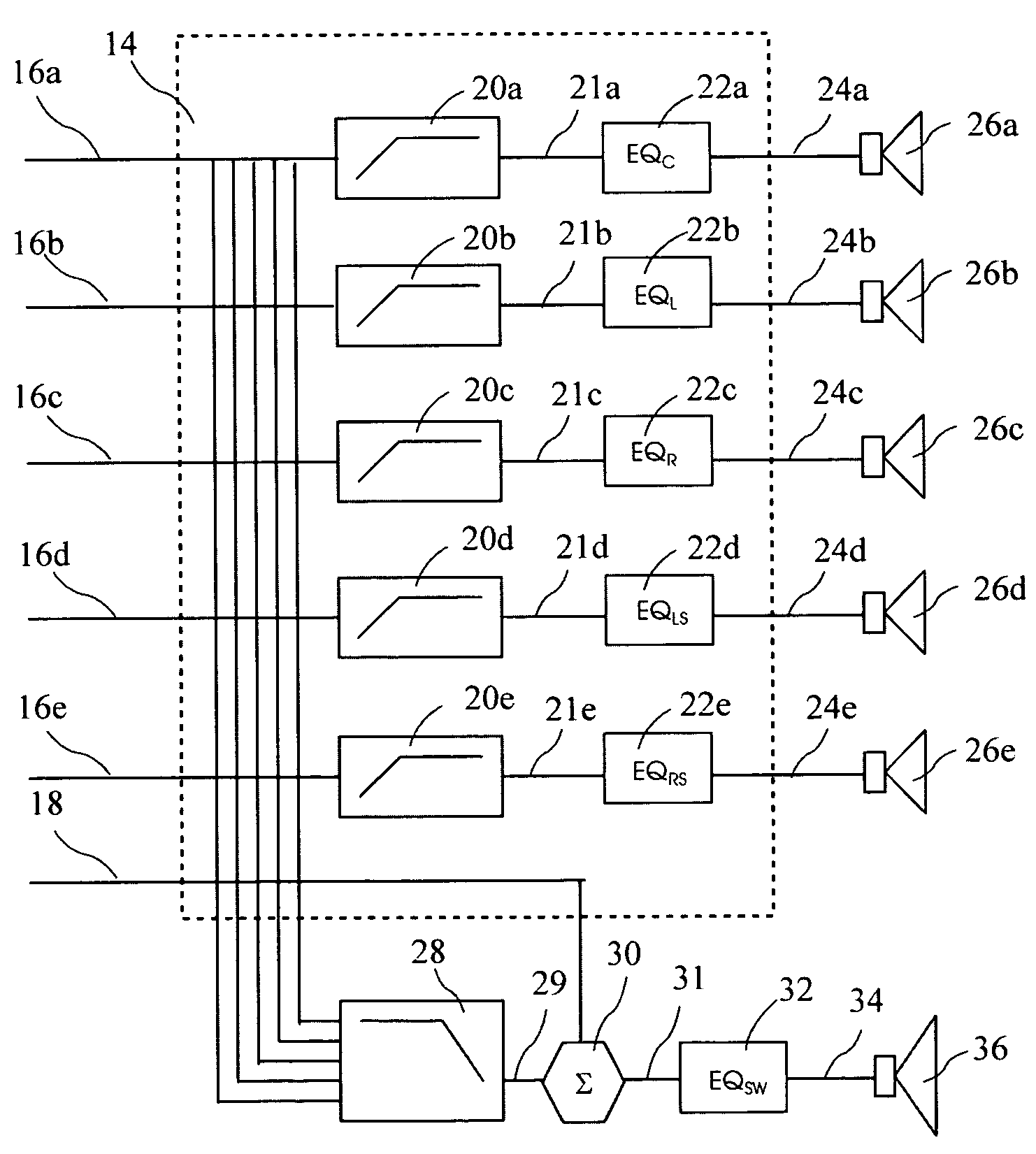
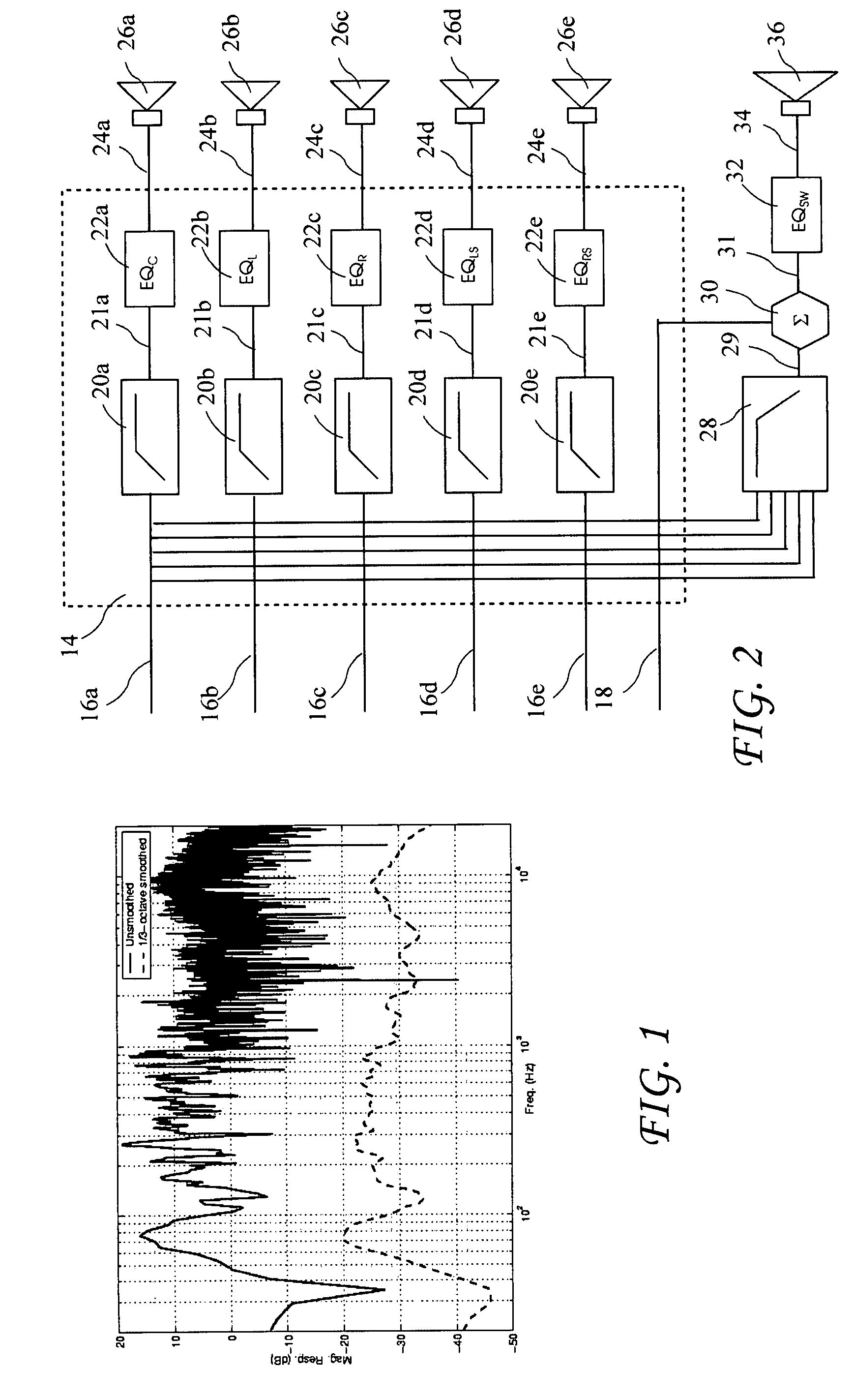
An audio enhancement system for compensating for ambient noise in a listening environment, comprises an audio system that produces an electrical sound signal and generates a sound output from the electrical sound signal. A sensor (e.g., a microphone) senses a total sound signal representative of the total sound level in the listening environment, including the sound output from the audio system and the ambient noise within the listening environment. A processing unit responsive to the total sound signal and the electrical sound signal extracts from the total sound signal an ambient noise signal representative of the ambient noise in the listening environment. A controller responsive to the ambient noise signal performs a linear predictive coding (LPC) analysis and generates a control signal, which is input to an equalizer to adjust the sound output of the audio system in order to compensate for the ambient noise level.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
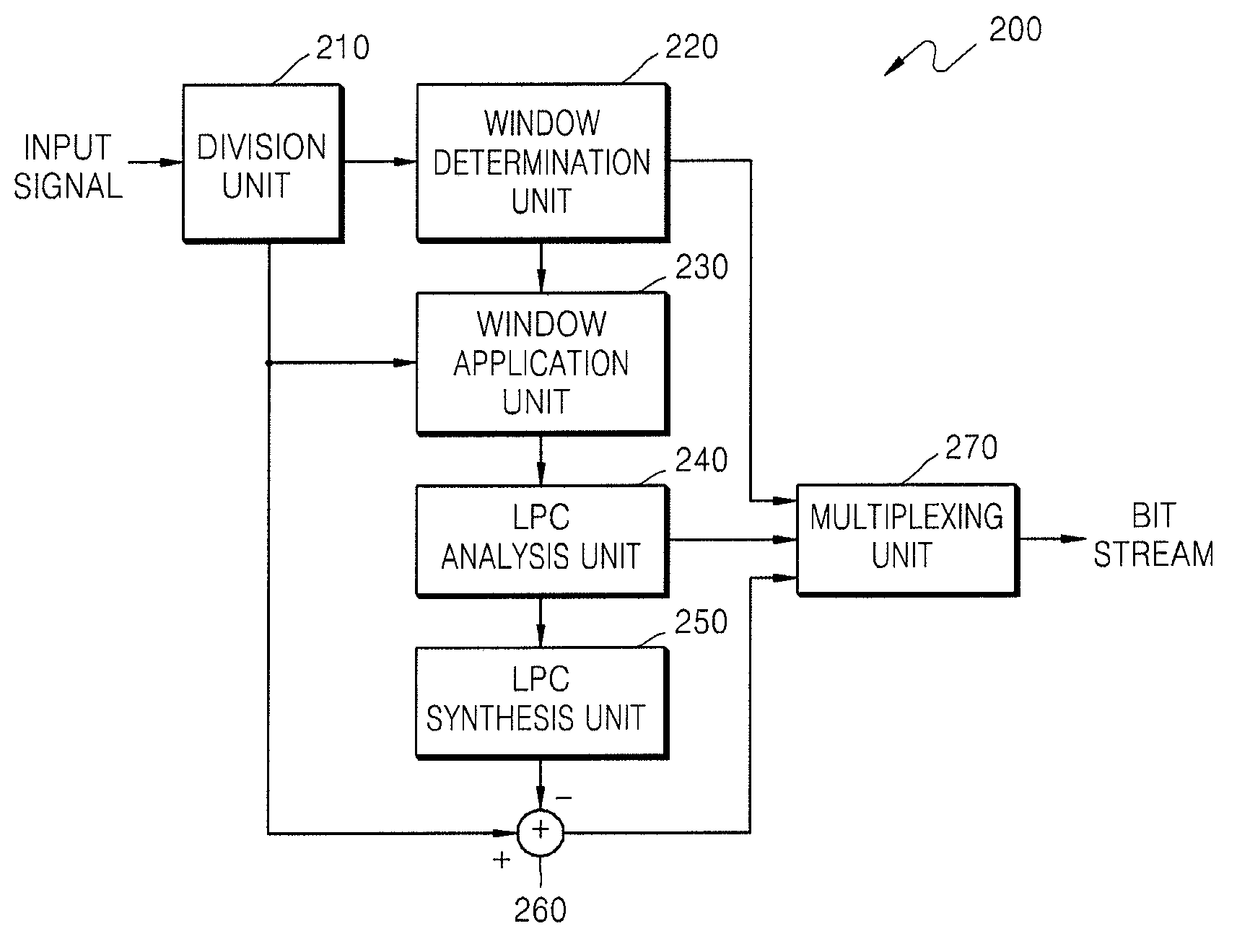
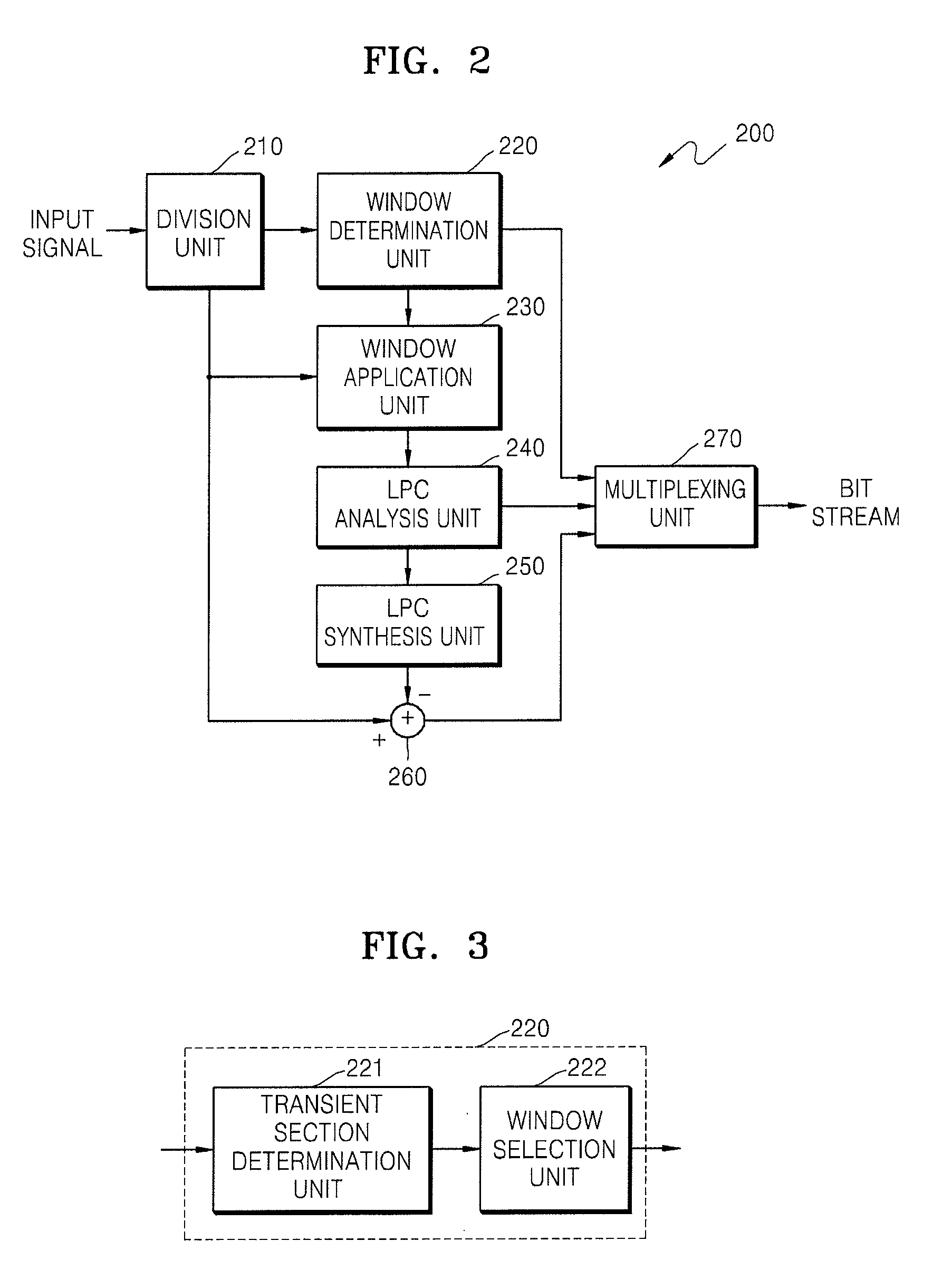
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding audio signal using adaptive lpc coefficient interpolation
InactiveUS20090198501A1Improve efficiencySpeech synthesisSpeech analysisLinearityLinear predictive coding
Provided are a method and apparatus for encoding or decoding an audio signal by adaptively interpolating a linear predictive coding (LPC) coefficient. In the method and apparatus of encoding or decoding an audio signal, LPC coefficient interpolation is selectively performed depending on whether a transient section is present in a current frame, thereby preventing noise from occurring when interpolating LPC coefficients in the transient section.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
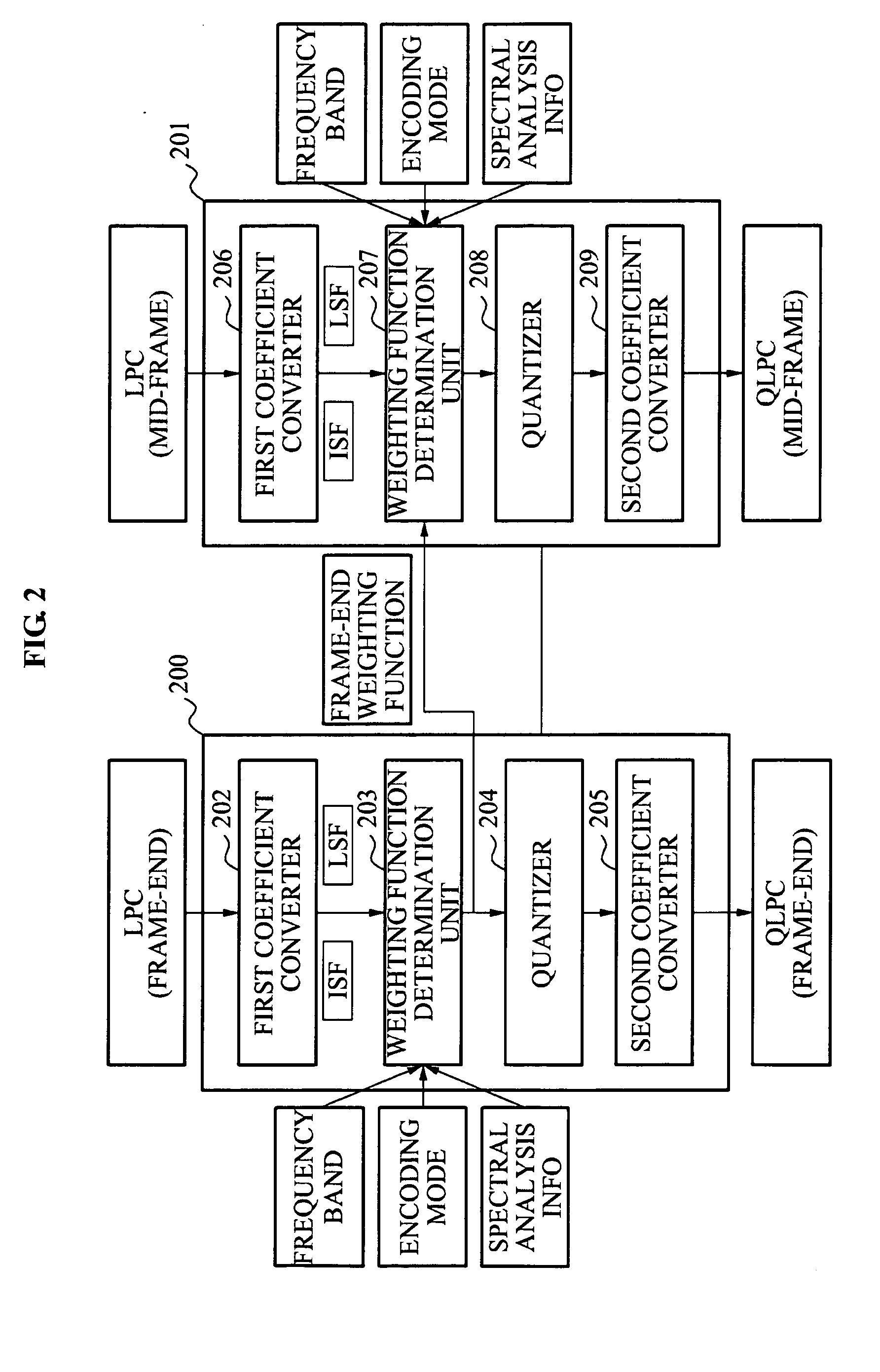
Apparatus and method for determining weighting function having low complexity for linear predictive coding (LPC) coefficients quantization
ActiveUS20120095756A1Improve Quantization EfficiencySpeech analysisLinear predictive codingLow complexity
Proposed is a method and apparatus for determining a weighting function for quantizing a linear predictive coding (LPC) coefficient and having a low complexity. The weighting function determination apparatus may convert an LPC coefficient of a mid-subframe of an input signal to one of a immitance spectral frequency (ISF) coefficient and a line spectral frequency (LSF) coefficient, and may determine a weighting function associated with an importance of the ISF coefficient or the LSF coefficient based on the converted ISF coefficient or LSF coefficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
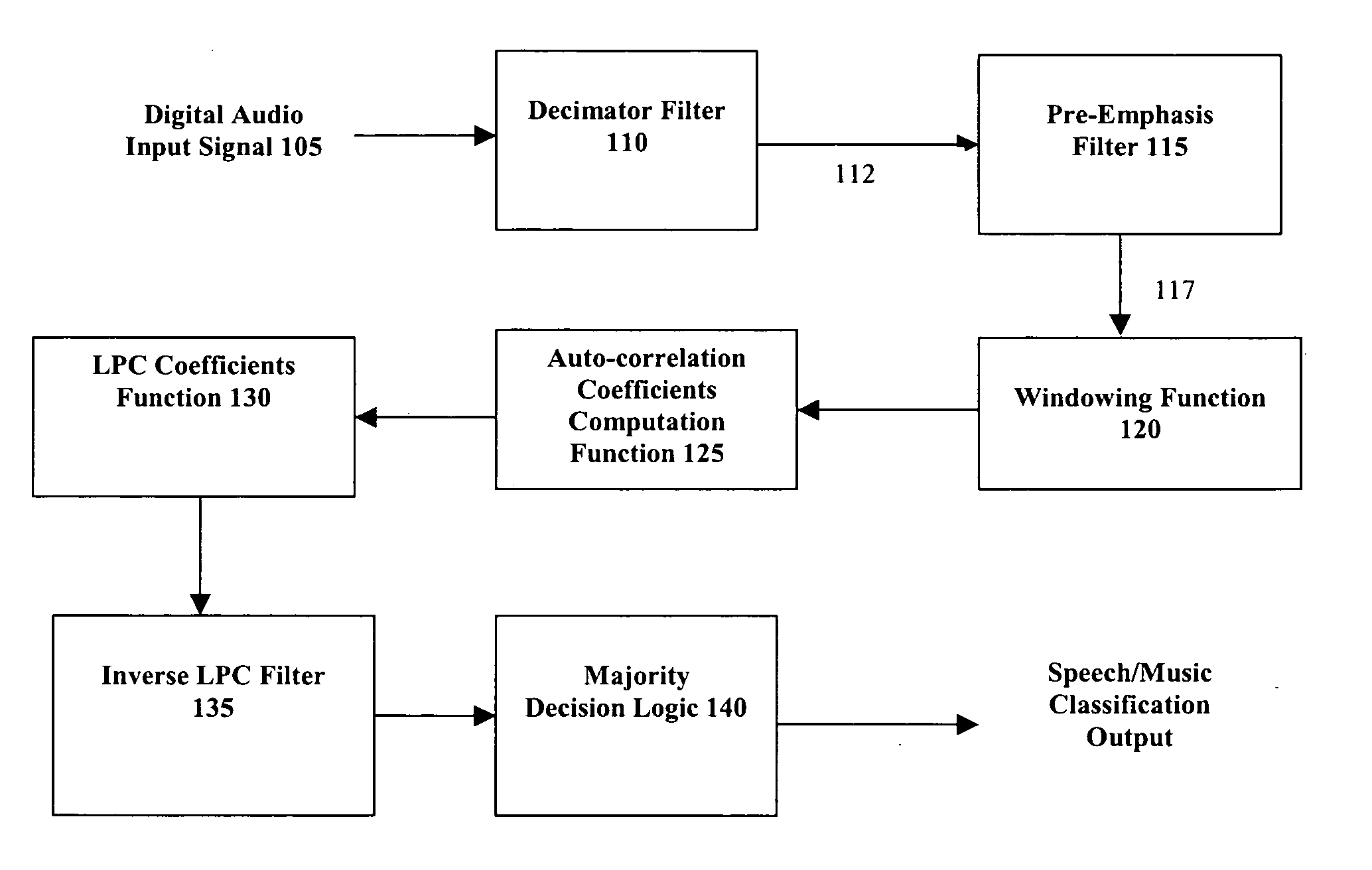
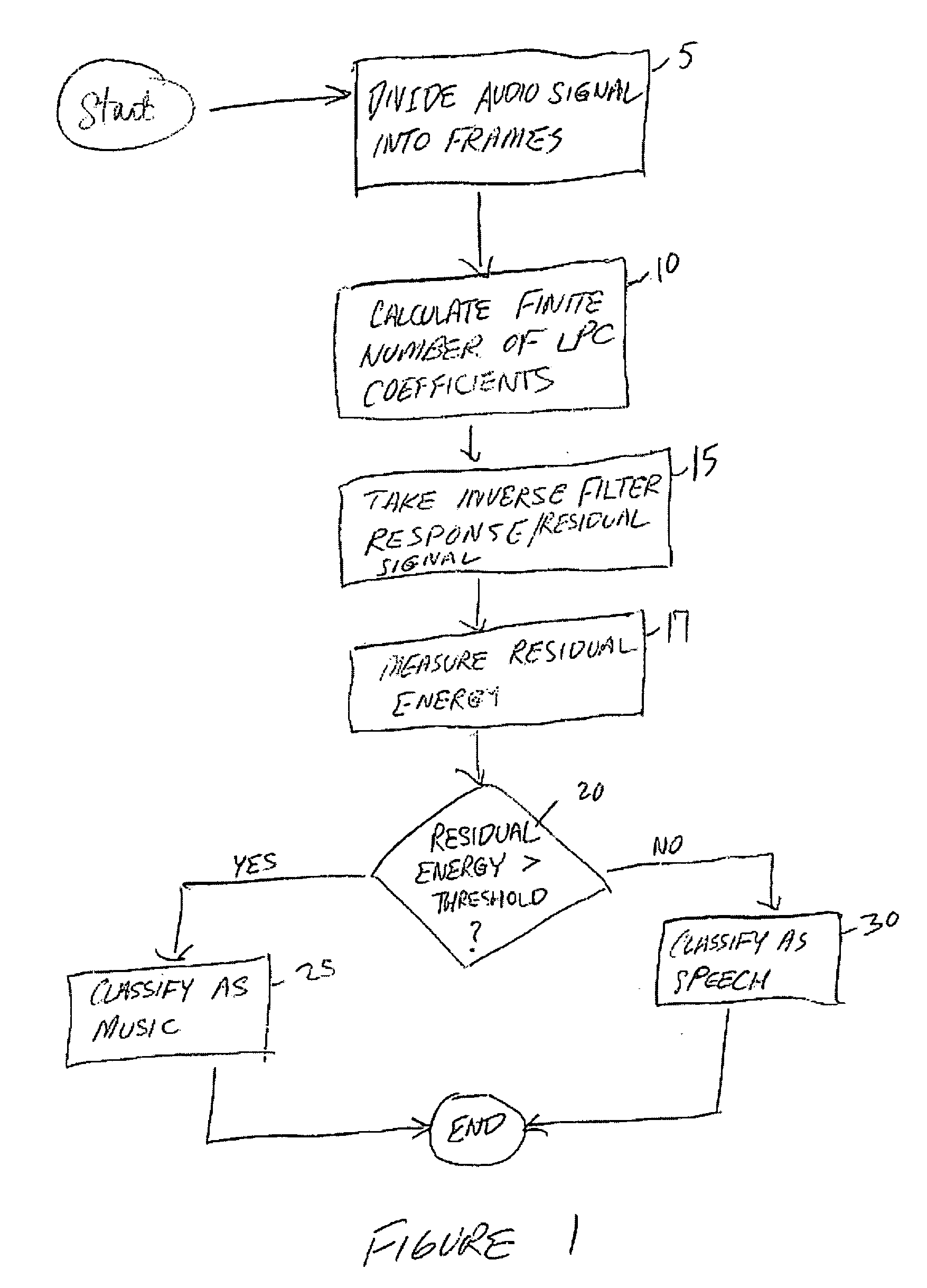
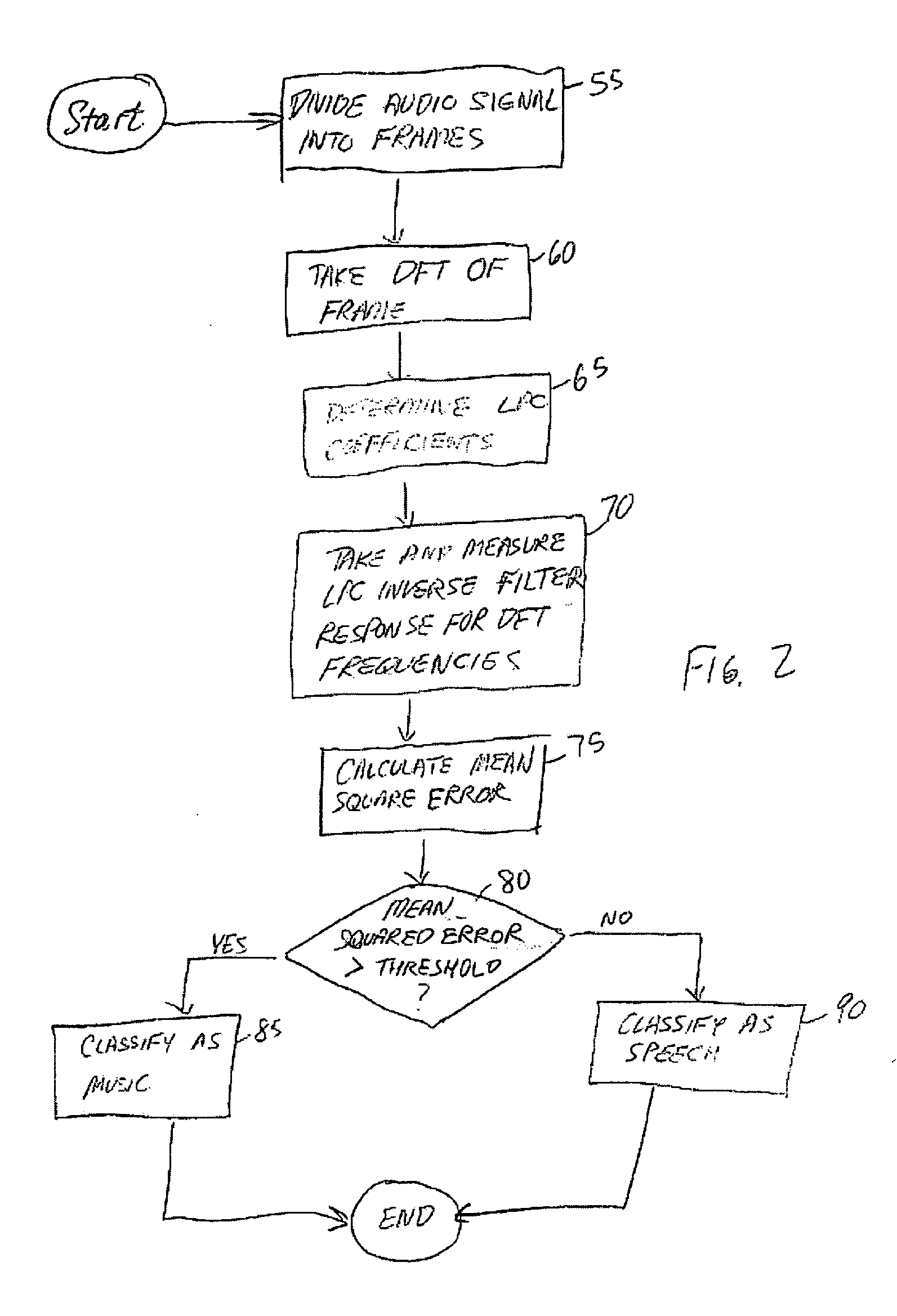
Classification of speech and music using linear predictive coding coefficients
InactiveUS20050159942A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisLinear predictive codingLinearity
Presented herein are systems and methods for classifying an audio signal. The audio signal is classified by calculating a plurality of linear prediction coefficients (LPC) for a portion of the audio signal; inverse filtering the portion of the audio signal with the plurality of linear prediction coefficients (LPC), thereby resulting in a residual signal; measuring the residual energy of the residual signal; and comparing the residual energy to a threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
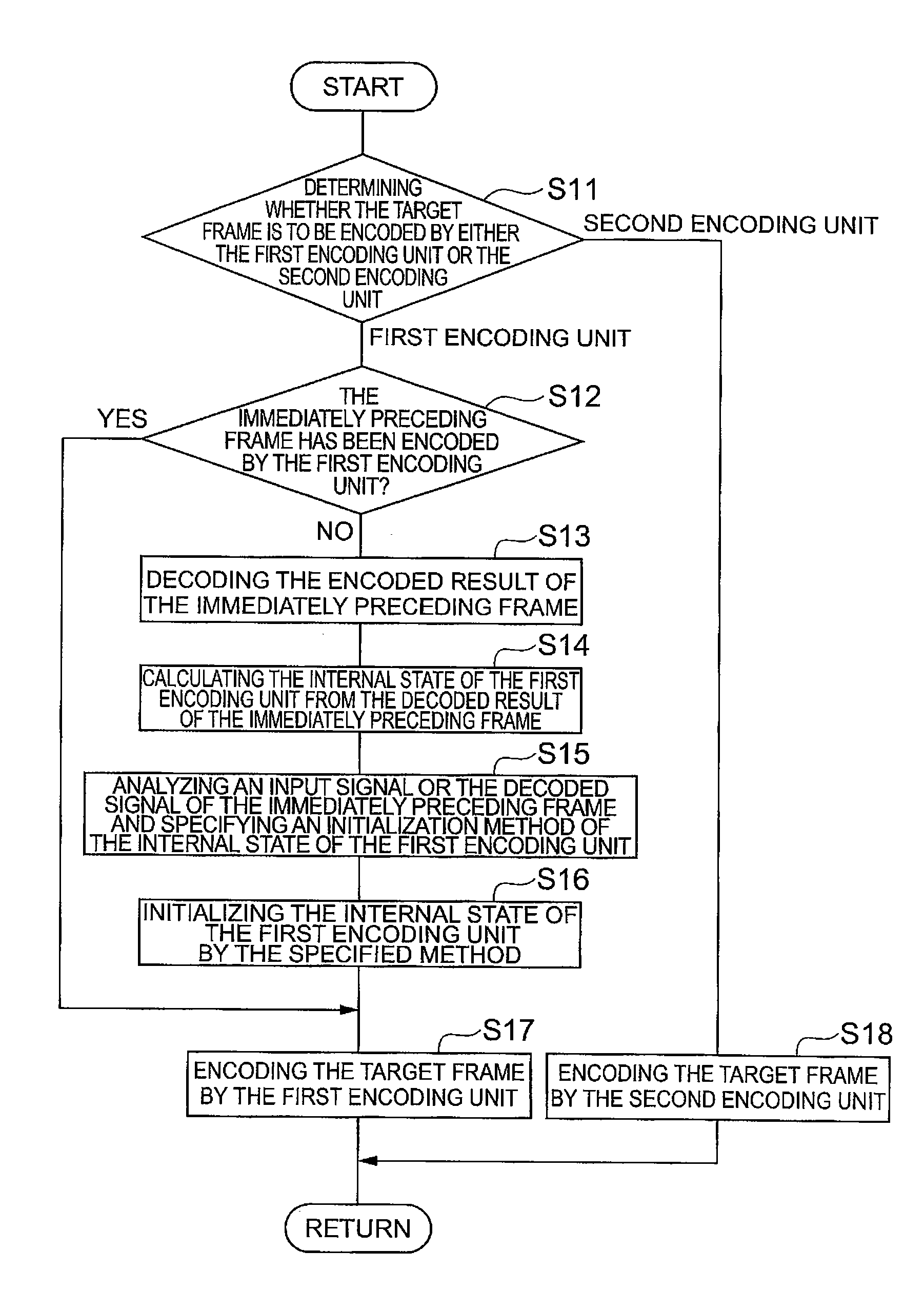
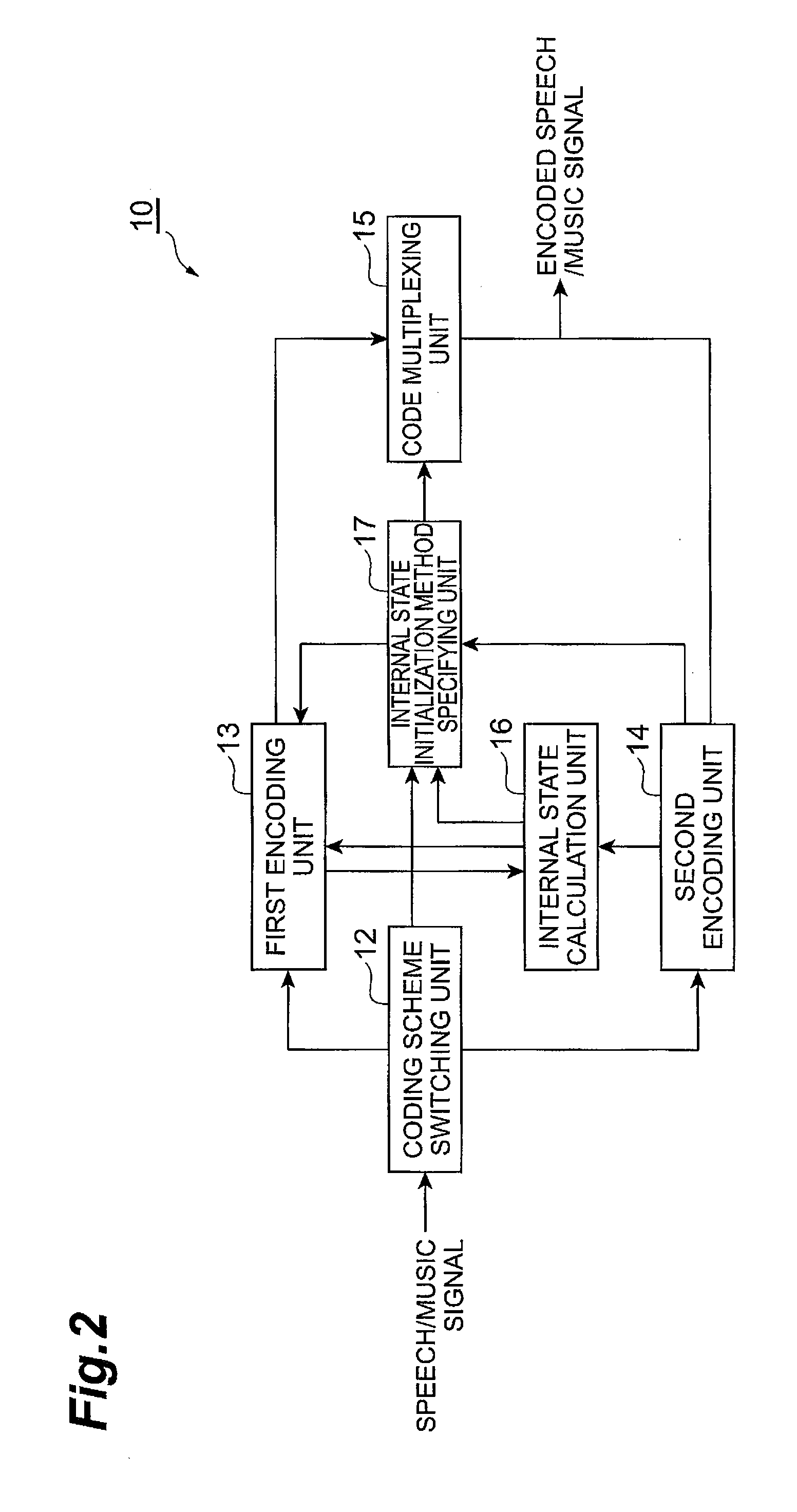
Audio signal encoding method, audio signal decoding method, encoding device, decoding device, audio signal processing system, audio signal encoding program, and audio signal decoding program
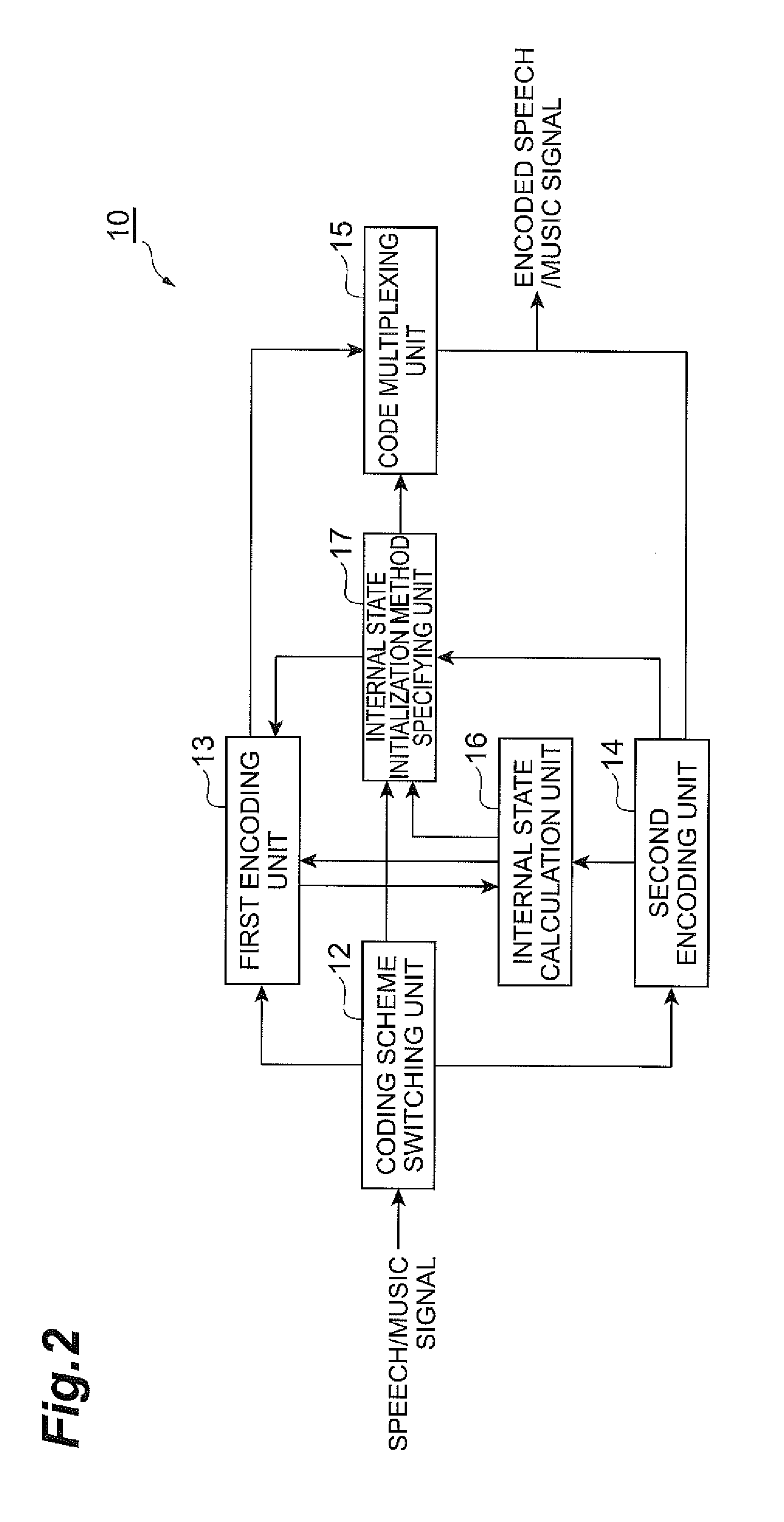
When a frame immediately preceding an encoding target frame to be encoded by a first encoding unit operating under a linear predictive coding scheme is encoded by a second encoding unit operating under a coding scheme different from the linear predictive coding scheme, the encoding target frame can be encoded under the linear predictive coding scheme by initializing the internal state of the first encoding unit. Therefore, encoding processing performed under a plurality of coding schemes including the linear predictive coding scheme and a coding scheme different from the linear predictive coding scheme can be realized.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
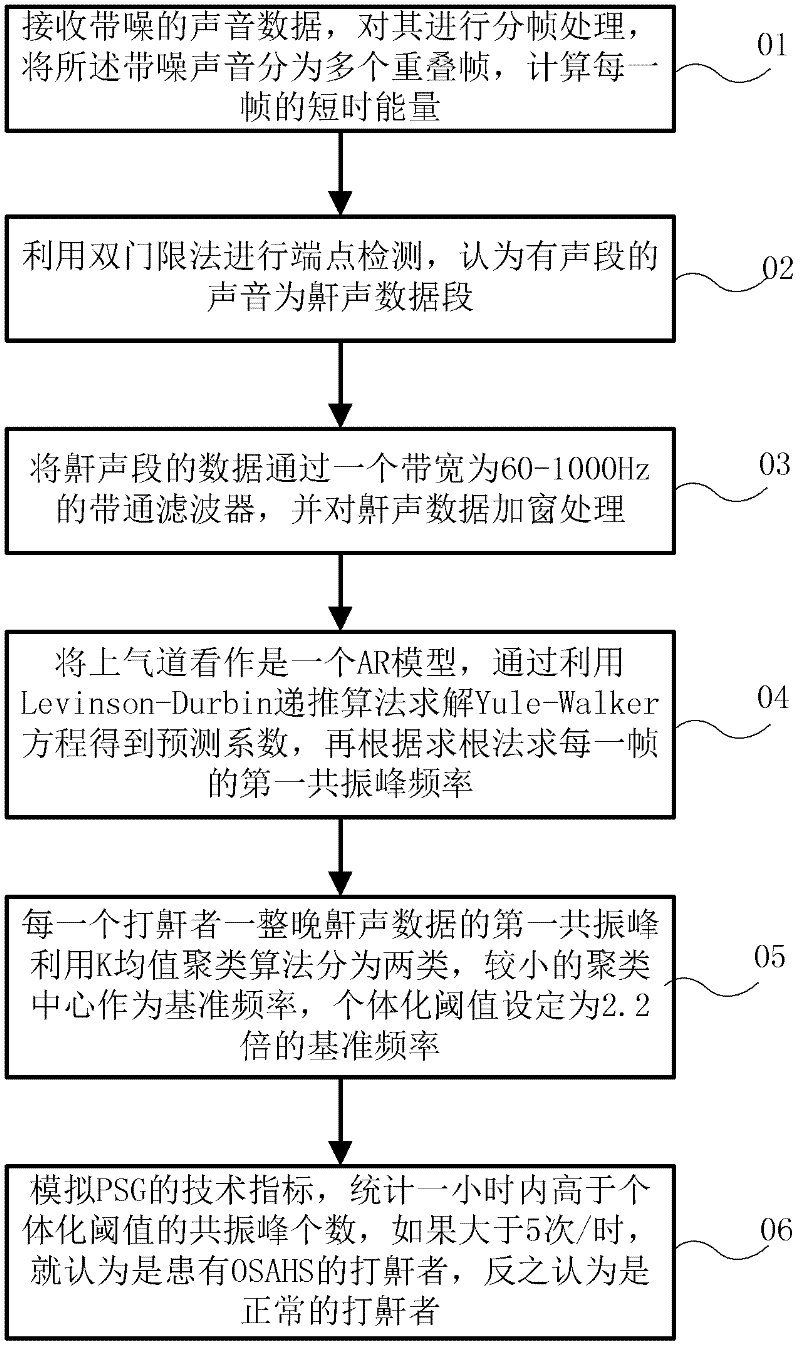
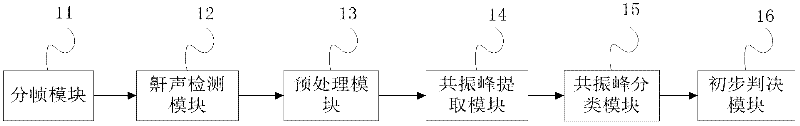
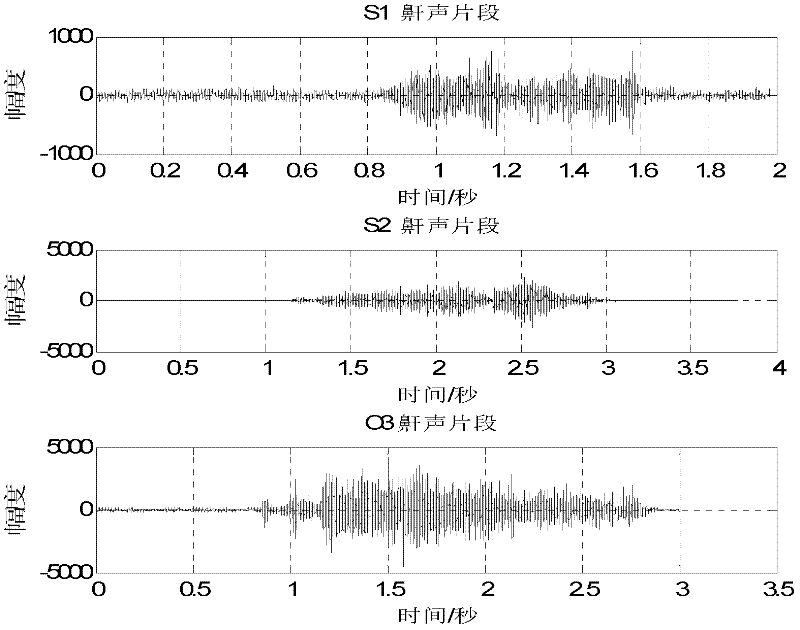
Obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome screening method and device thereof
ActiveCN102499637AImprove misjudgmentImprove missed detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPolysomnogramMedicine
The invention relates to an obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) screening method and a device. Formant characteristics of snore are adopted as technical indexes for screening OSAHS; Snore sections are extracted by a short-time energy method at first, then LPC (linear predictive coding) is used for modeling, after predicting factors of the LPC are obtained, a first formant frequency of each snore section is obtained by a root extraction method, as ranges of formant frequencies of different modes are different, the different snore sections can be distinguished, all first formant frequencies of all snorers are classified, by the aid of K mean values, and thresholds for distinguishing normal snore and abnormal snore of individuals are determined according to classified results; and then AHI (apnea-hypopnea indexes) in a PSG (polysomnogram) are simulated so that average times of apnea and hypopnea of the snorers within an hour are obtained. According to the OSAHS judgment standard, whether the data section has snore of a normal person or snore of a patient with the OSAHS is judged. The obstruction sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome screening method and the device are low in cost, high in applicability and simple in operation and are non-contacting.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Packet loss concealment for sub-band predictive coding based on extrapolation of sub-band audio waveforms
ActiveUS20090240492A1Analogue conversionSpeech analysisPacket loss concealmentLinear predictive coding
A technique is described for concealing the effect of a lost frame in a series of frames representing an encoded audio signal in a sub-band predictive coding system. In accordance with the technique, a first synthesized sub-band audio signal is synthesized, wherein synthesizing the first synthesized sub-band audio signal comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on a stored first sub-band decoded audio signal. A second synthesized sub-band audio signal is also synthesized, wherein synthesizing the second synthesized sub-band audio signal comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on the stored second sub-band decoded audio signal. The first synthesized sub-band audio signal and the second synthesized sub-band audio signal are combined to generate a synthesized full-band output audio signal corresponding to a lost frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Audio enhancement system and method
ActiveUS20050207583A1Enhance audio listening experienceEar treatmentGain controlEnvironmental noiseControl signal
An audio enhancement system for compensating for ambient noise in a listening environment, comprises an audio system that produces an electrical sound signal and generates a sound output from the electrical sound signal. A sensor (e.g., a microphone) senses a total sound signal representative of the total sound level in the listening environment, including the sound output from the audio system and the ambient noise within the listening environment. A processing unit responsive to the total sound signal and the electrical sound signal extracts from the total sound signal an ambient noise signal representative of the ambient noise in the listening environment. A controller responsive to the ambient noise signal performs a linear predictive coding (LPC) analysis and generates a control signal, which is input to an equalizer to adjust the sound output of the audio system in order to compensate for the ambient noise level.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
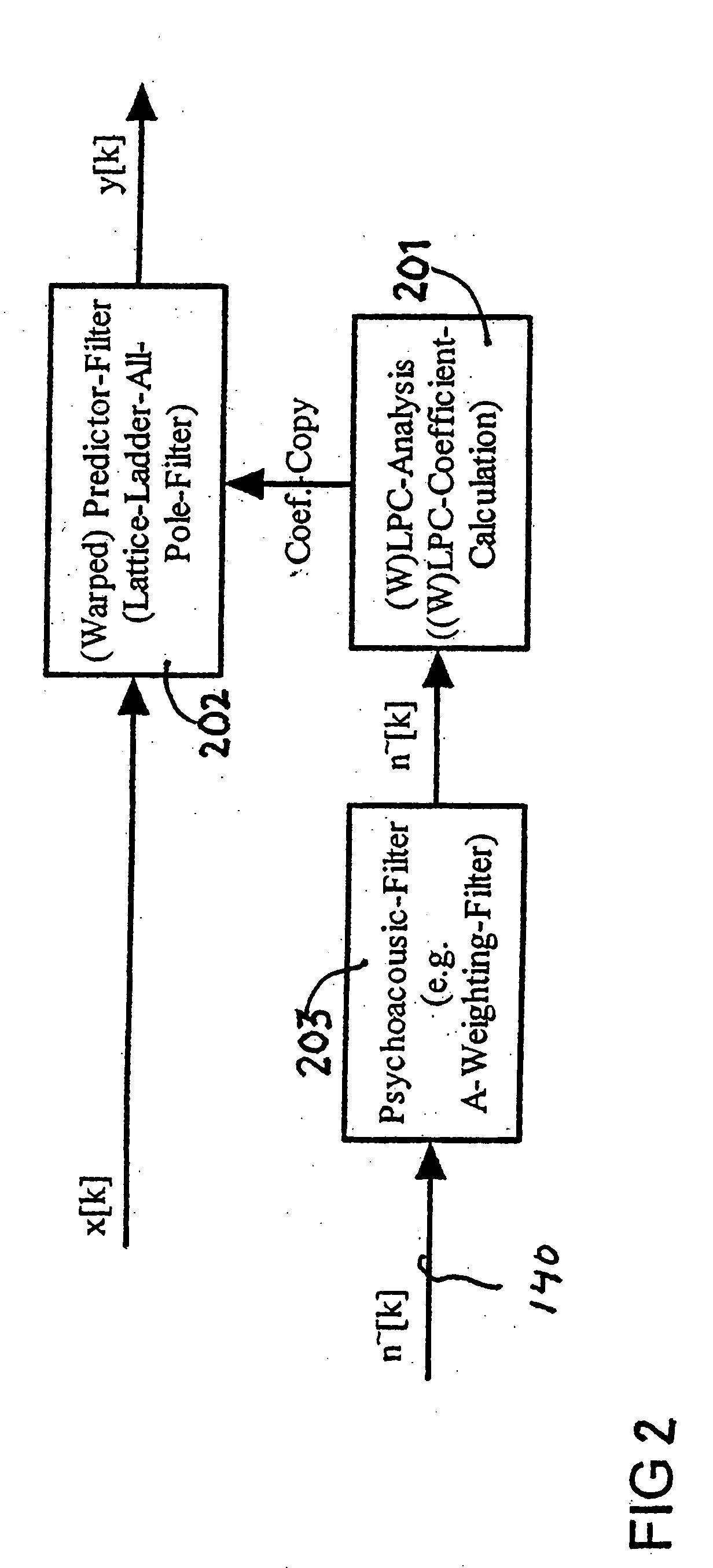
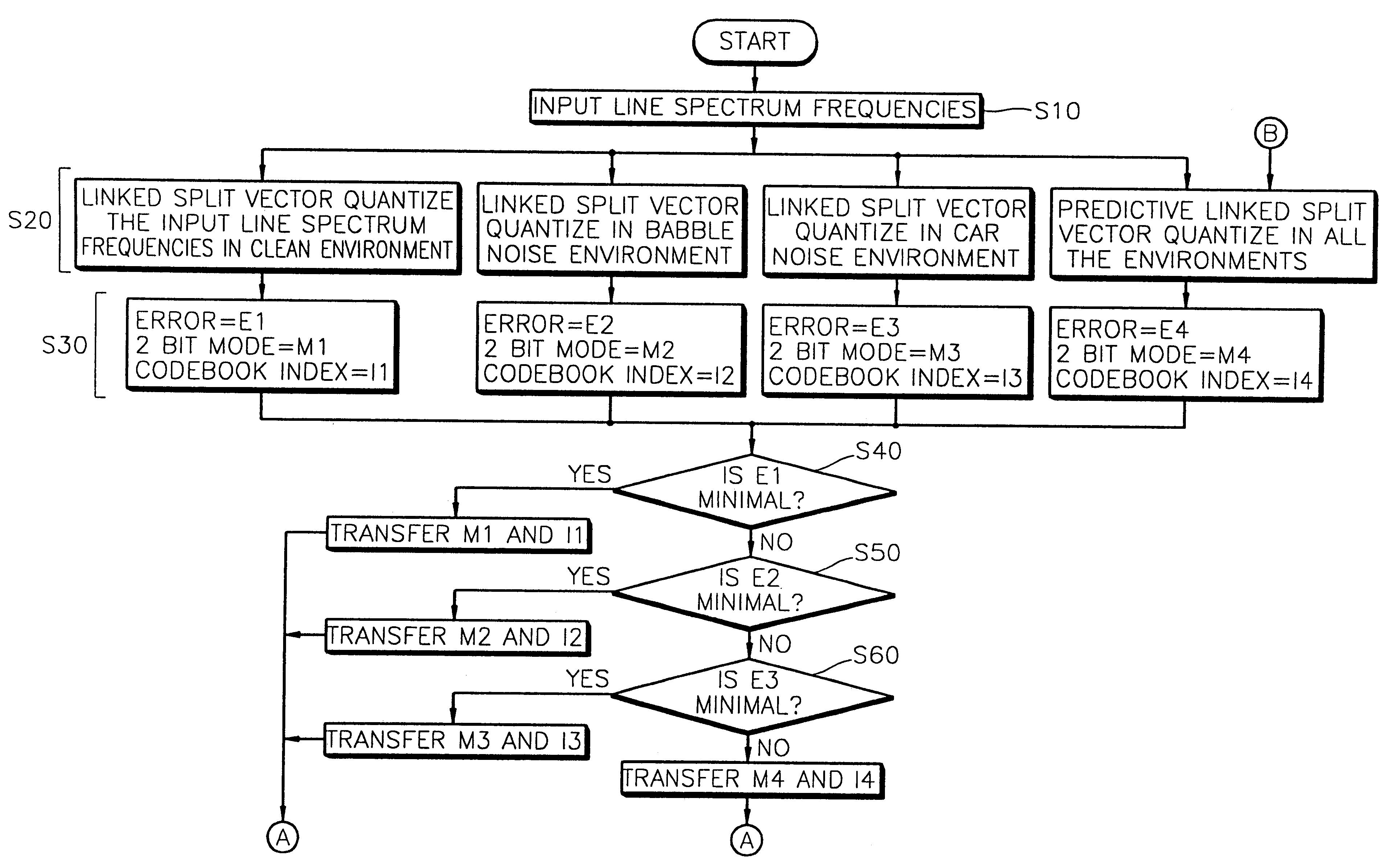
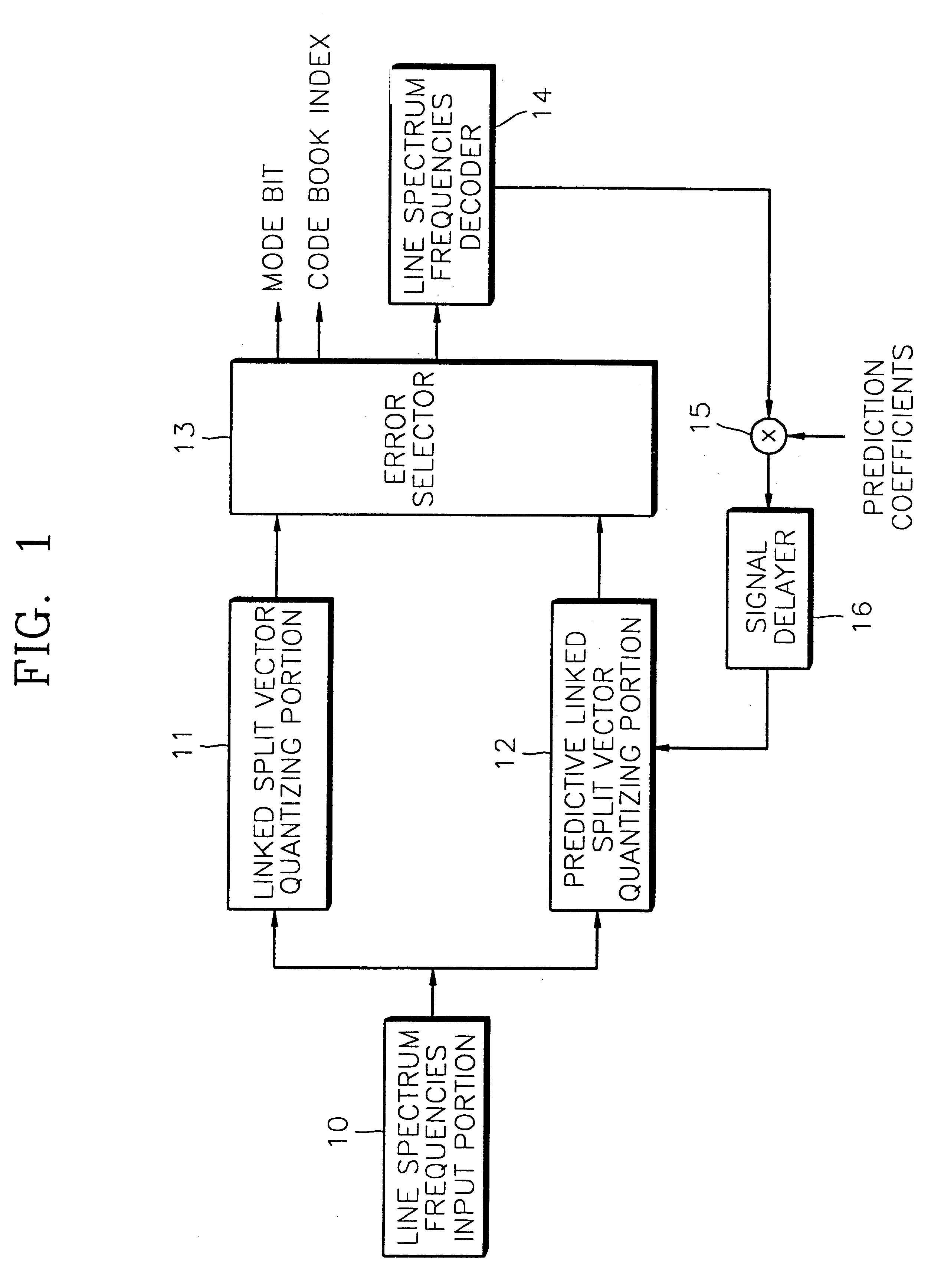
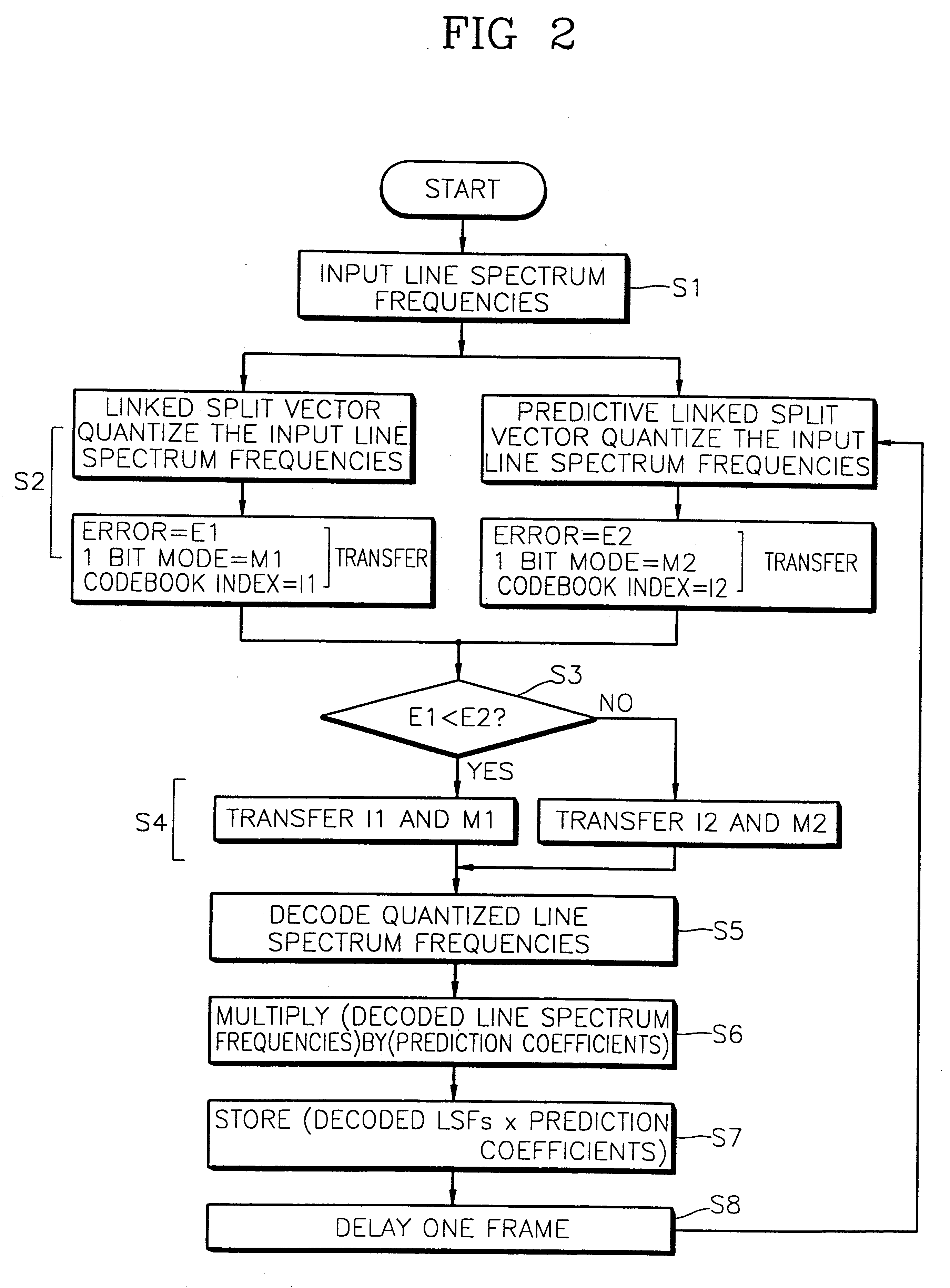
Apparatus for quantizing spectral envelope including error selector for selecting a codebook index of a quantized LSF having a smaller error value and method therefor
InactiveUS6275796B1Satisfactory performanceSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumLinearity
An apparatus for quantizing a spectral envelope with noise robustness showing high performance even under a background noise environment and a channel noise environment, and a method therefor, are provided. The spectral envelope quantizing apparatus includes a spectral envelope quantizing apparatus with noise robustness for representing a spectral envelope of speech by a minimum number of bits for the optimal coding of a speech signal. The apparatus includes a line spectrum frequencies (LSFs) input portion for converting linear predictive coding coefficients extracted from the speech into Nth order line spectrum frequencies coefficients and inputting the coefficients as the LSFs of a current frame. It also includes a linked split-vector quantizing portion for dividing the LSFs into a predetermined number of linked sub-vectors and quantizing the sub-vectors, and a predictive linked split-vector quantizing portion for obtaining the difference between the LSFs and the LSFs of a previous frame and vector-quantizing the difference. The apparatus further includes an error selector for comparing the error values of the LSFs quantized in the linked split-vector quantizing portion and the predictive linked split-vector quantizing portion, selecting the codebook index of the quantized LSFs having the smaller error value, and outputting the selected codebook index together with a mode bit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound encoding method, method of de-quantizing linear predictive coding coefficients, sound decoding method, and recording medium and electronic device therefor
ActiveUS20120278069A1Efficiently quantizedReduce complexitySpeech analysisDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsTransmission channel
A quantizing method is provided that includes quantizing an input signal by selecting one of a first quantization scheme not using an inter-frame prediction and a second quantization scheme using the inter-frame prediction, in consideration of one or more of a prediction mode, a predictive error and a transmission channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transition from a transform coding/decoding to a predictive coding/decoding
ActiveUS20160293173A1Reduce complexityEasy to implementSpeech analysisCode conversionLinear predictive codingDigital audio signals
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Audio Signal Encoding Method, Audio Signal Decoding Method, Encoding Device, Decoding Device, Audio Signal Processing System, Audio Signal Encoding Program, and Audio Signal Decoding Program
When a frame immediately preceding an encoding target frame to be encoded by a first encoding unit operating under a linear predictive coding scheme is encoded by a second encoding unit operating under a coding scheme different from the linear predictive coding scheme, the encoding target frame can be encoded under the linear predictive coding scheme by initializing the internal state of the first encoding unit. Therefore, encoding processing performed under a plurality of coding schemes including the linear predictive coding scheme and a coding scheme different from the linear predictive coding scheme can be realized.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method for converting emotional speech by combining rhythm parameters with tone parameters
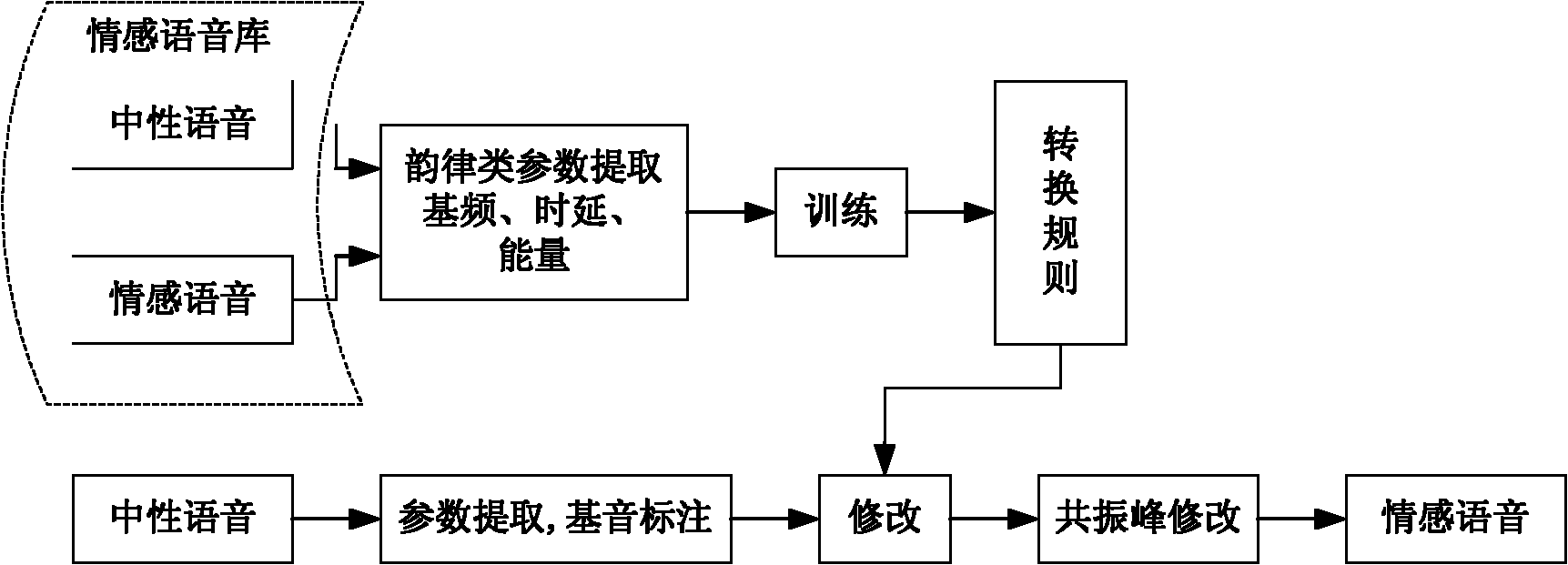
InactiveCN102184731AThe modification effect is goodEmotional Voice NaturalSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisFundamental frequencyFormant
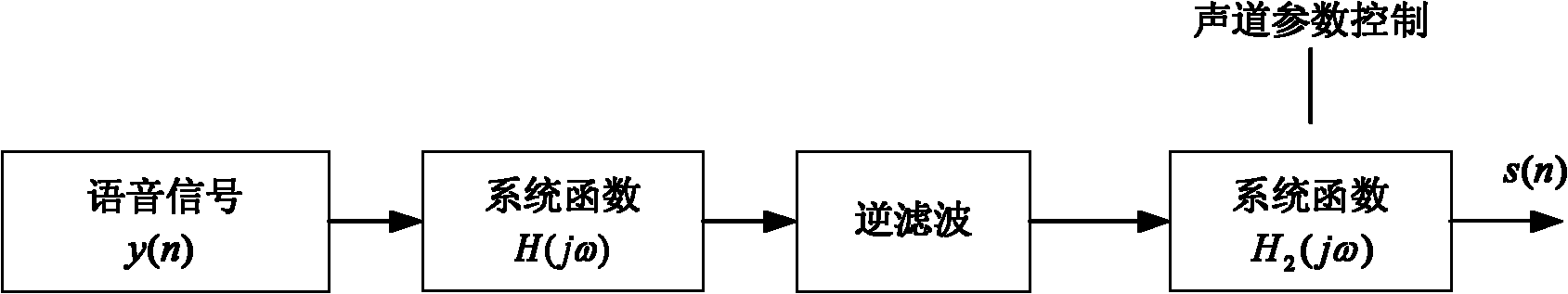
The invention discloses a method for converting emotional speech by combining rhythm parameters (fundamental frequency, time length and energy) with a tone parameter (a formant), which mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out extraction and analysis of feature parameters on a Beihang University emotional speech database (BHUDES) emotional speech sample (containing neutral speech and four types of emotional speech of sadness, anger, happiness and surprise); 2, making an emotional speech conversion rule and defining each conversion constant according to the extracted feature parameters; 3, carrying out extraction of the feature parameters and fundamental tone synchronous tagging on the neutral speech to be converted; 4, setting each conversion constant according to the emotional speech conversion rule in the step 2, modifying a fundamental frequency curve, the time length and the energy and synchronously overlaying fundamental tones to synthesize a speech signal; and 5, carrying out linear predictive coding (LPC) analysis on the speech signal in the step 4 and modifying the formant by a pole of a transfer function so as to finally obtain the emotional speech rich in expressive force.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
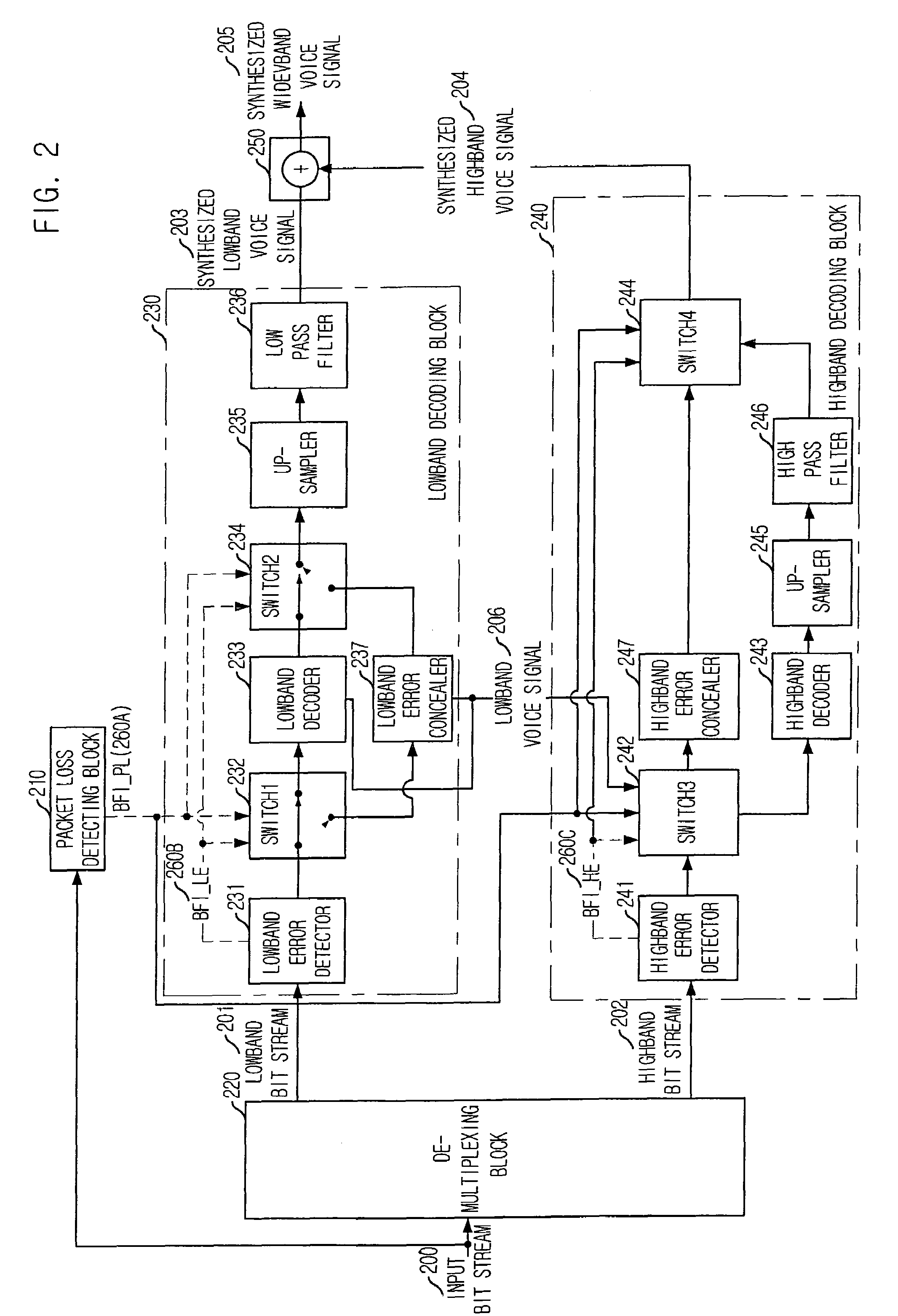
Apparatus and method for concealing highband error in split-band wideband voice codec and decoding
InactiveUS7596492B2Quality improvementSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsLinear predictive codingSpeech synthesis
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
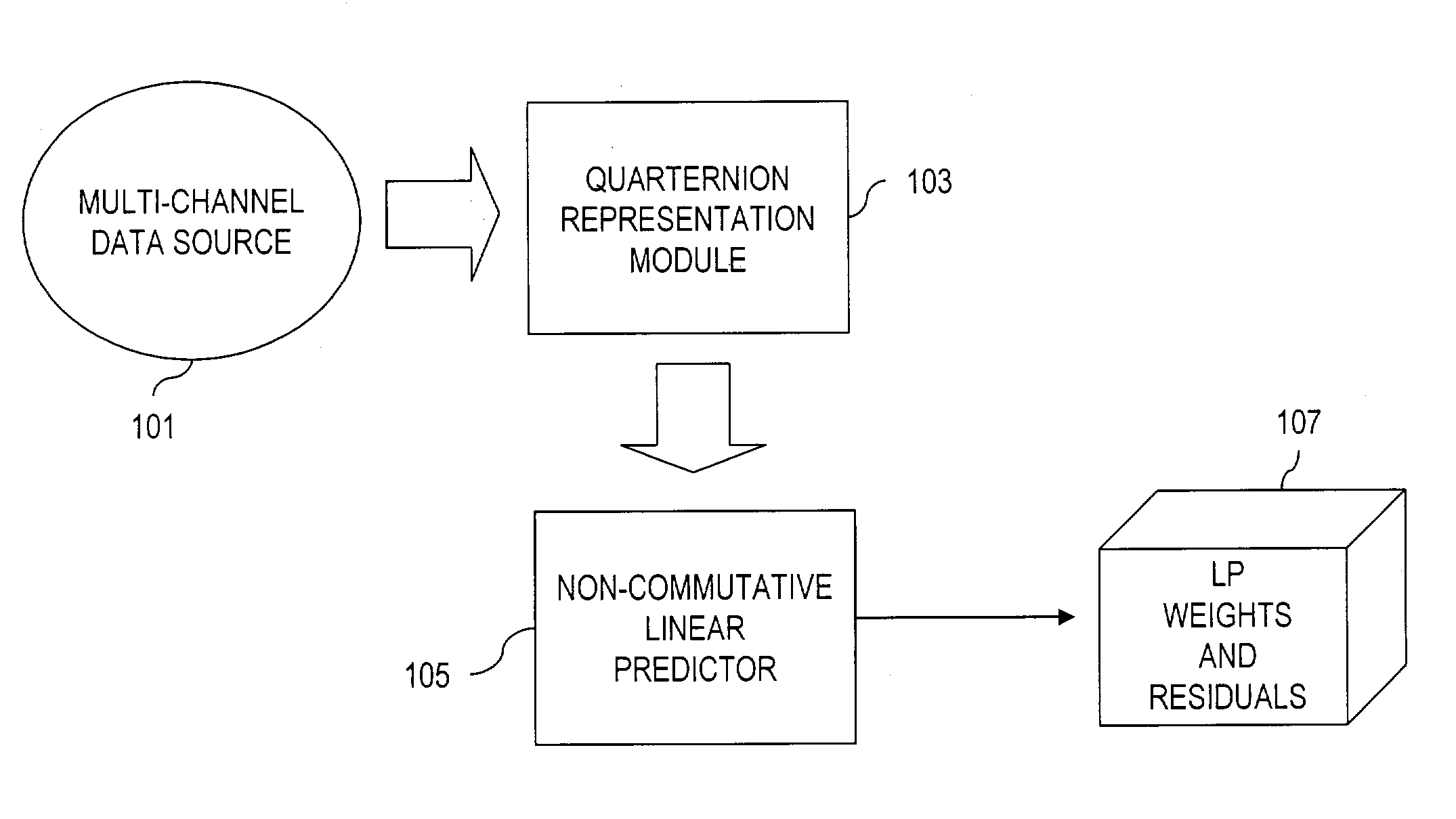
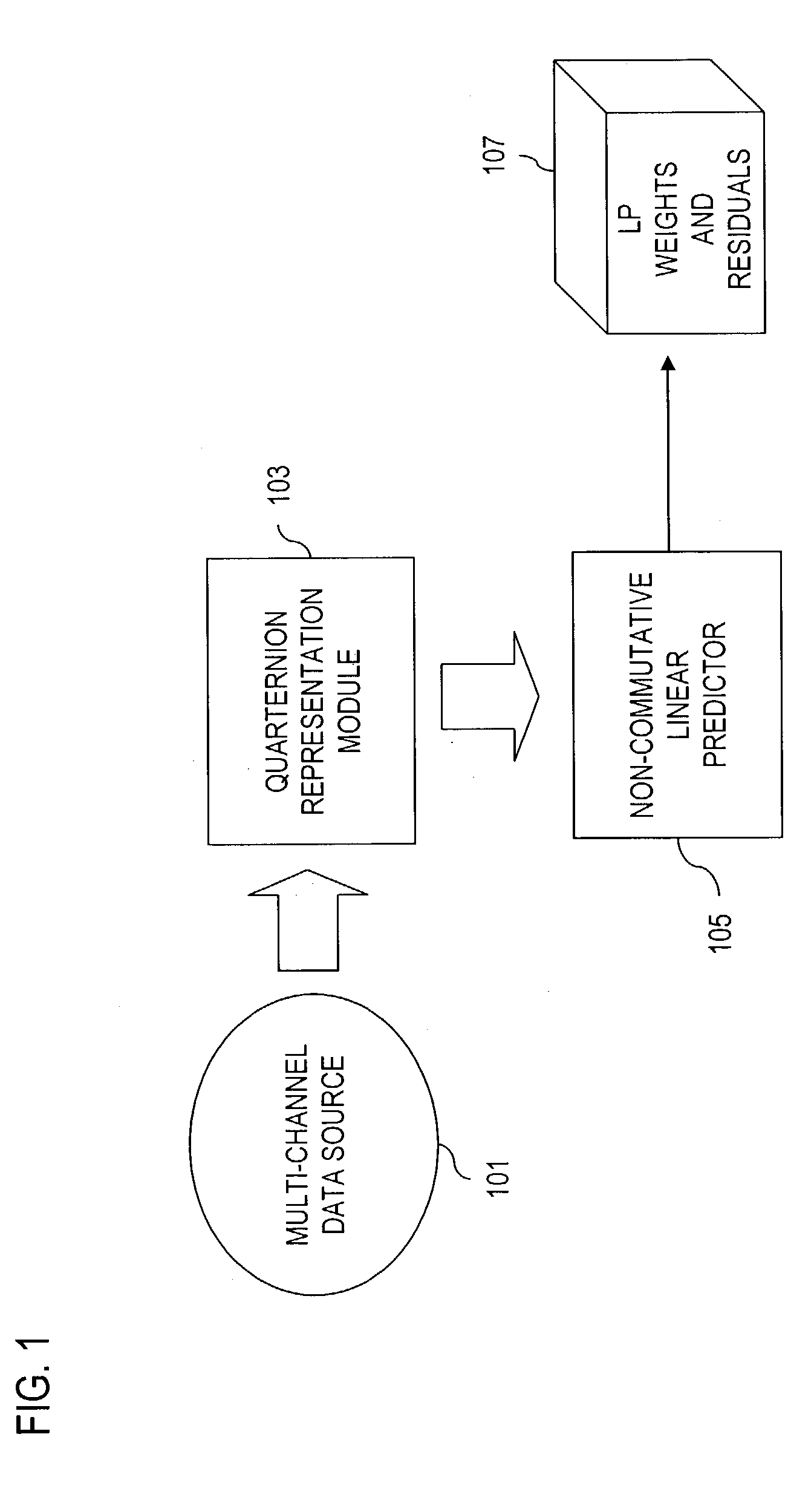
Signal processing of multi-channel data
InactiveUS7243064B2High correlationEffective approachColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuaternionMulti dimensional data
An approach for providing non-commutative approaches to signal processing. Quaternions are used to represent multi-dimensional data (e.g., three- and four-dimensional data). Additionally, a linear predictive coding scheme (e.g., based on the Levinson algorithm) that can be applied to wide class of signals in which the autocorrelation matrices are not invertible and in which the underlying arithmetic is not commutative. That is, the linear predictive coding scheme multi-channel can handle singular autocorrelations, both in the commutative and non-commutative cases. This approach also utilizes random path modules to replace the statistical basis of linear prediction.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
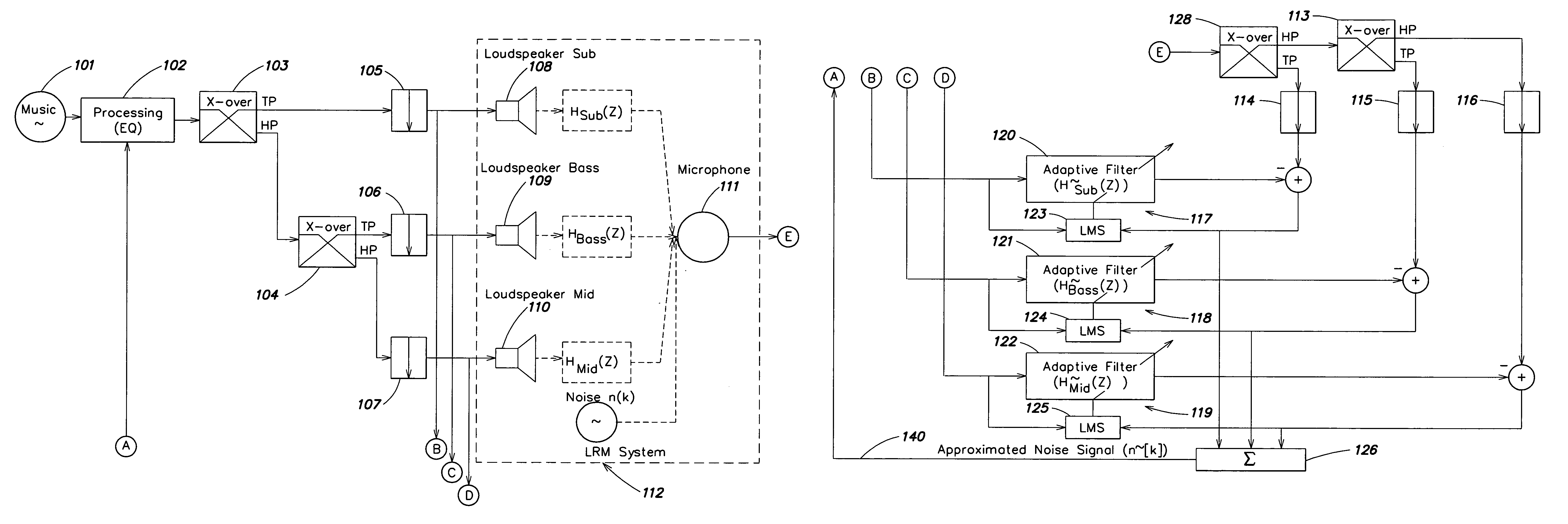
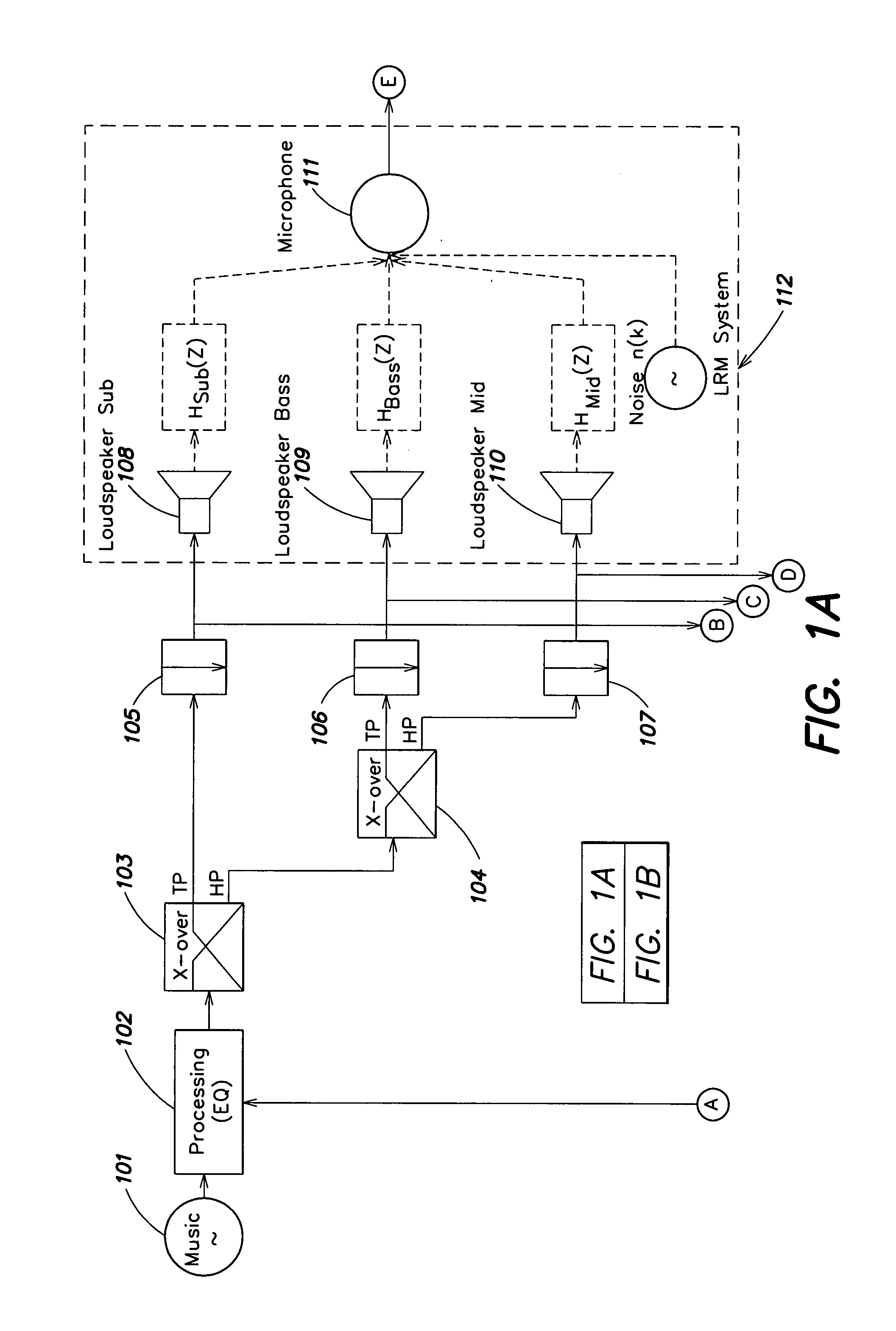
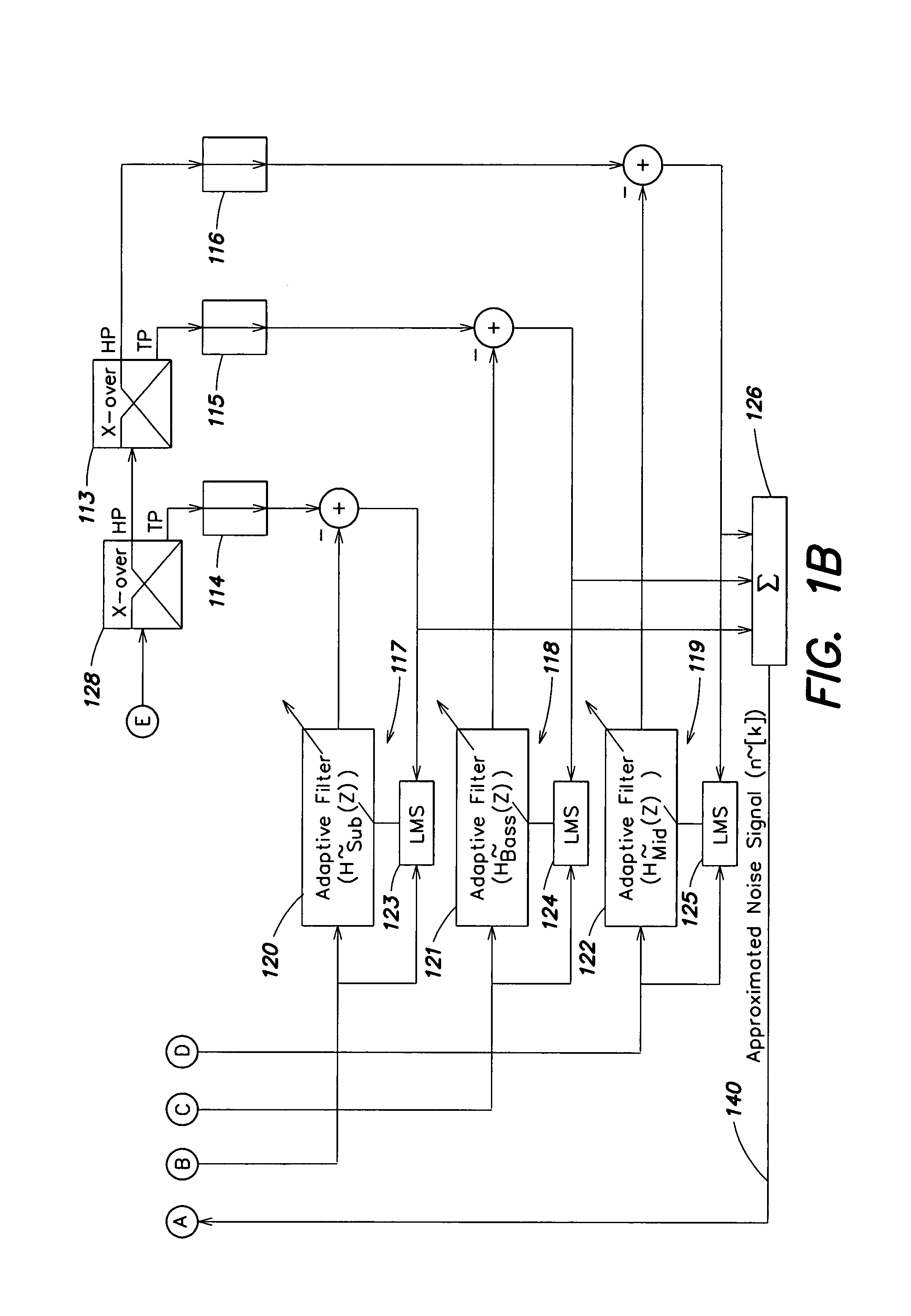
Room acoustic response modeling and equalization with linear predictive coding and parametric filters
A method for determining coefficients of a family of cascaded second order Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) parametric filters used for equalizing a room response. The method includes determining parameters of each IIR parametric filter from poles or roots of a reasonably high-order Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) model. The LPC model is able to accurately model the low-frequency room response modes providing better equalization of loudspeaker and room acoustics, particularly at the low frequencies. Advantages of the method include fast and efficient computation of the LPC model using a Levinson-Durbin recursion to solve the normal equations that arise from the least squares formulation. Due to possible band interactions between the cascaded IIR parametric filters, the method further includes optimizing the Q value of each filter to better equalize the room response.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
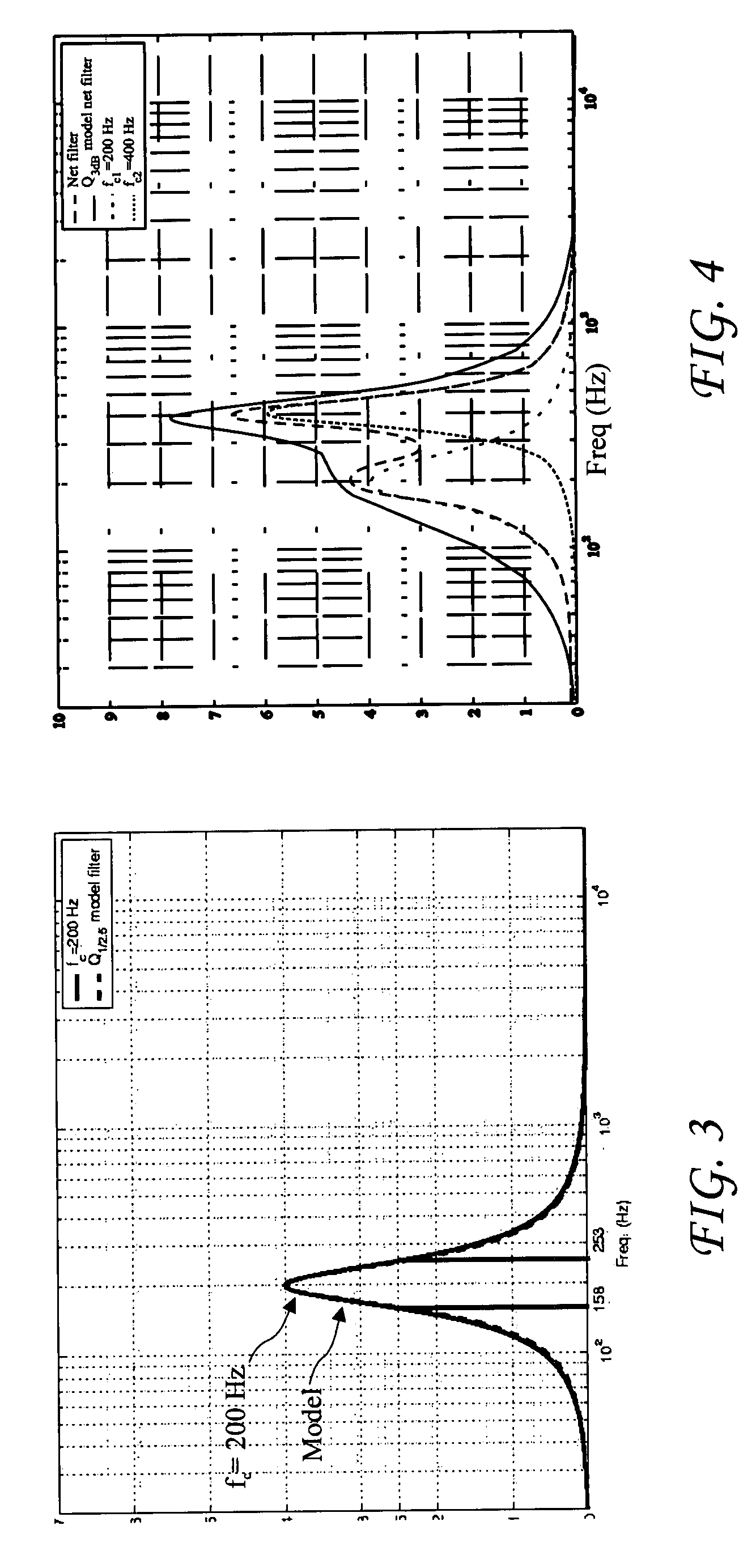
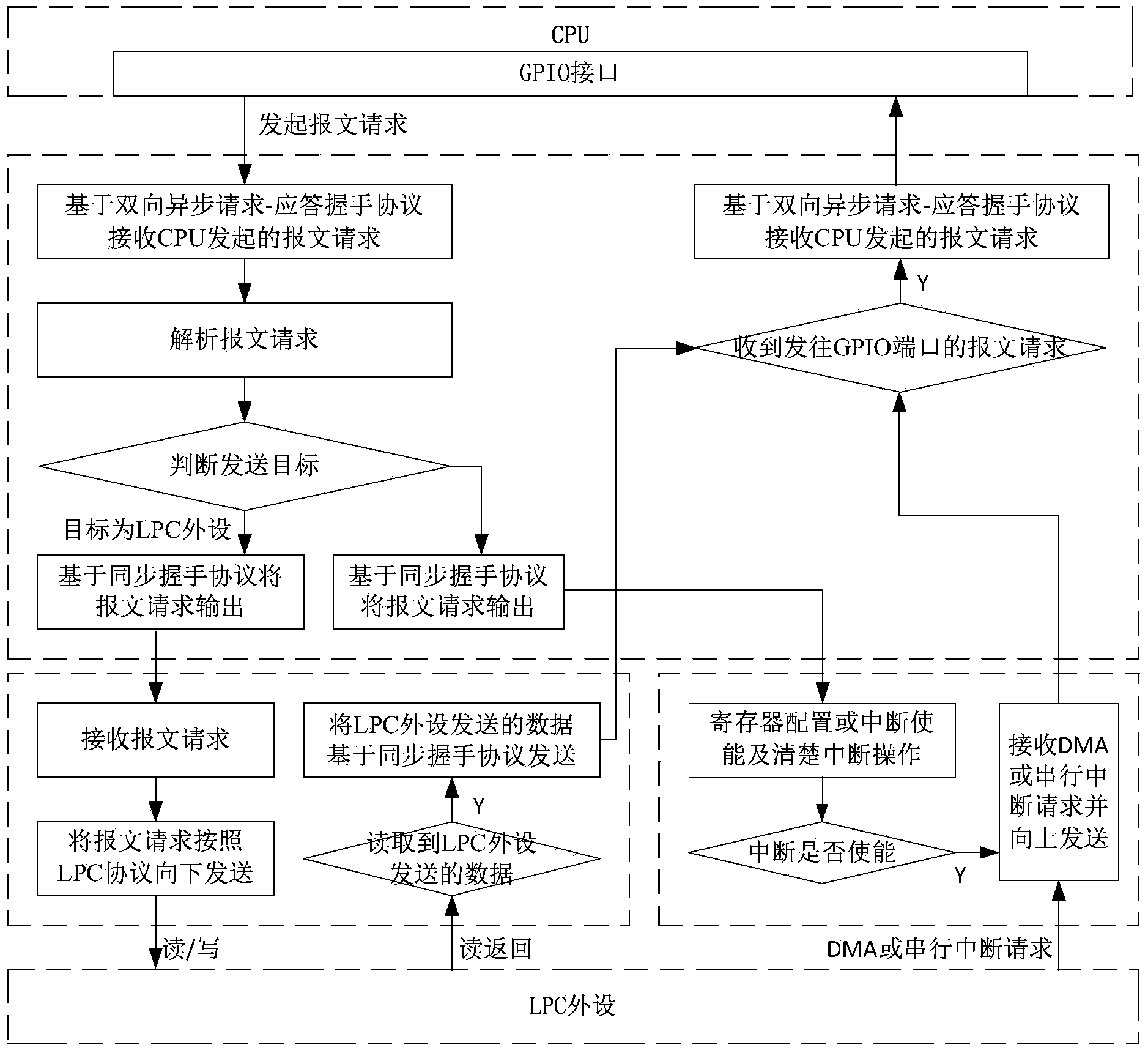
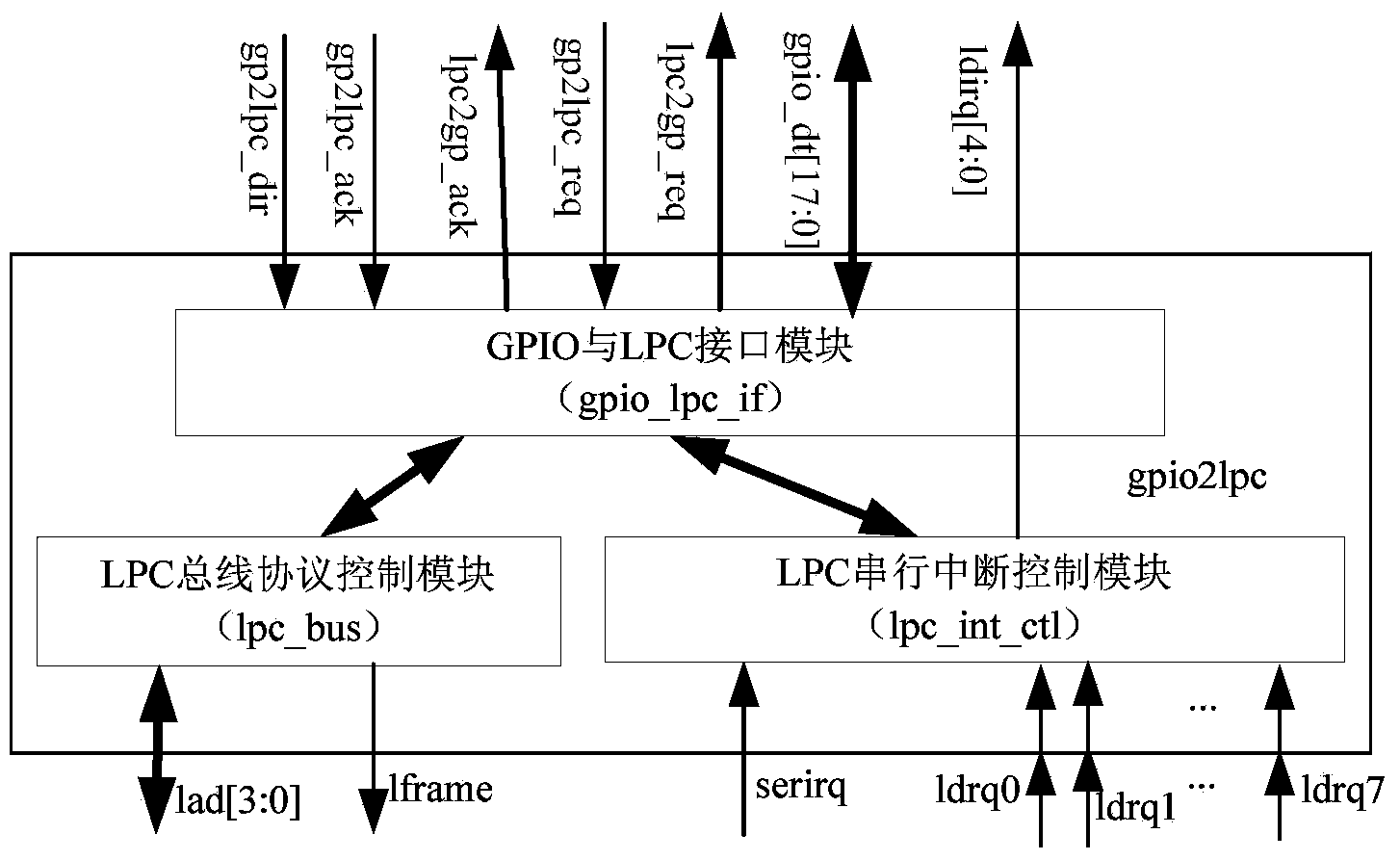
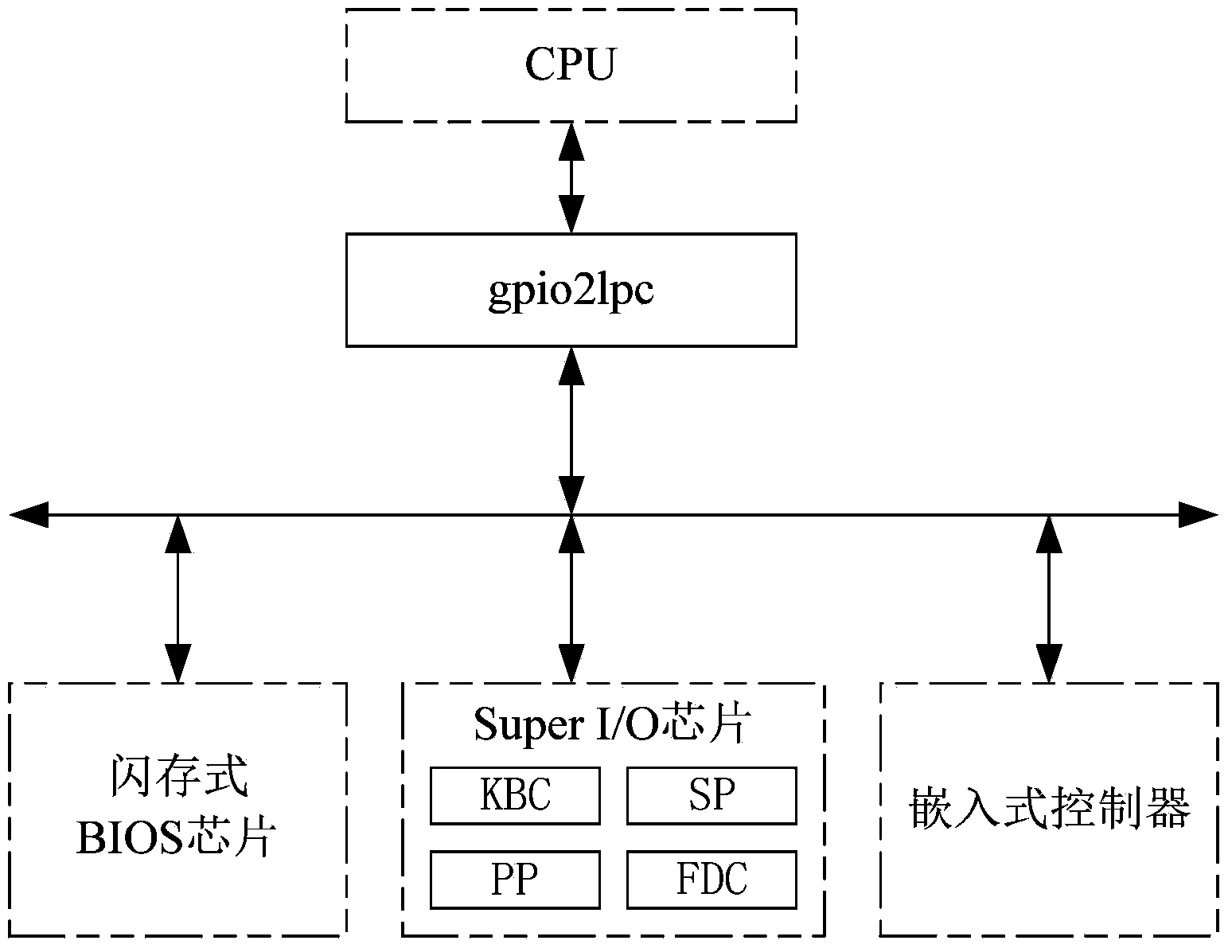
Method and device for expanding LPC (linear predictive coding) peripheral on basis of GPIO (general purpose input/output) interface
ActiveCN103914424ASolve the problem of communication infeasibilityMeet flexibilityElectric digital data processingProcessor registerComputer module
The invention discloses a method and a device for expanding an LPC (linear predictive coding) peripheral on the basis of a GPIO (general purpose input / output) interface. The method includes primarily communicating the LPC peripheral with the GPIO interface of a CPU (central processing unit) on the basis of a two-way asynchronous request-acknowledge handshake protocol; forwarding received messages to the lower-level LPC peripheral by the aid of a secondary synchronous handshake protocol or interrupting operation on an internal register; reversely initiating interrupt requests to the GPIO interface of the CPU if serial interrupt requests or internal interrupt requests of the LPC peripheral are received. The device comprises a GPIO and LPC interface module, an LPC bus protocol control module and an LPC serial interrupt control module. The GPIO and LPC interface module is connected with the CPU. The method and the device have the advantages that the LPC peripheral can be expanded easily and flexibly, a system can be expanded conveniently, communication is irrelevant to particular clocks, special requirements on a clock of the GPIO interface can be omitted, communication data are reliable, hardware resources can be saved, and the method and the device are transparent for upper-layer users.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
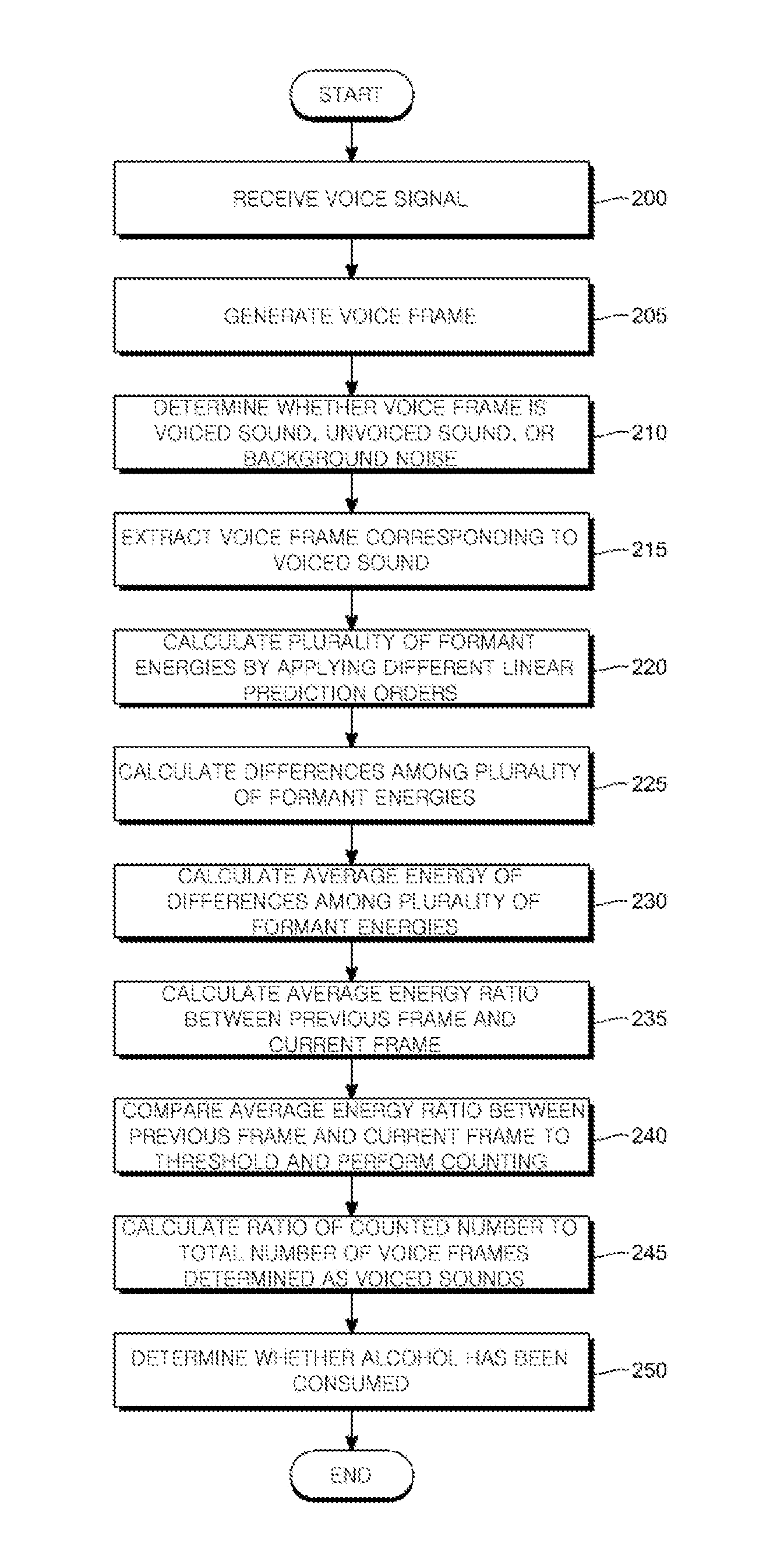
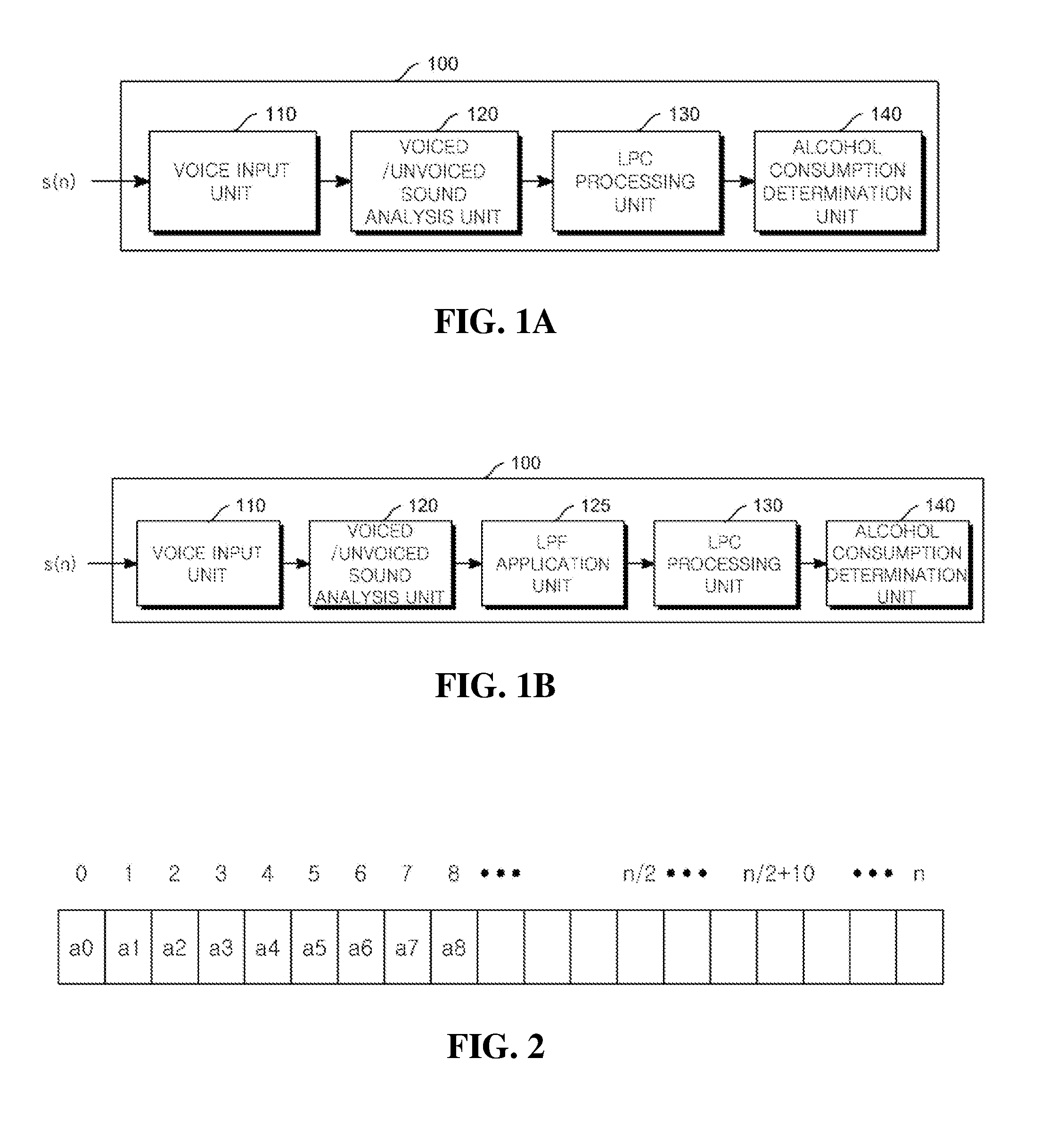
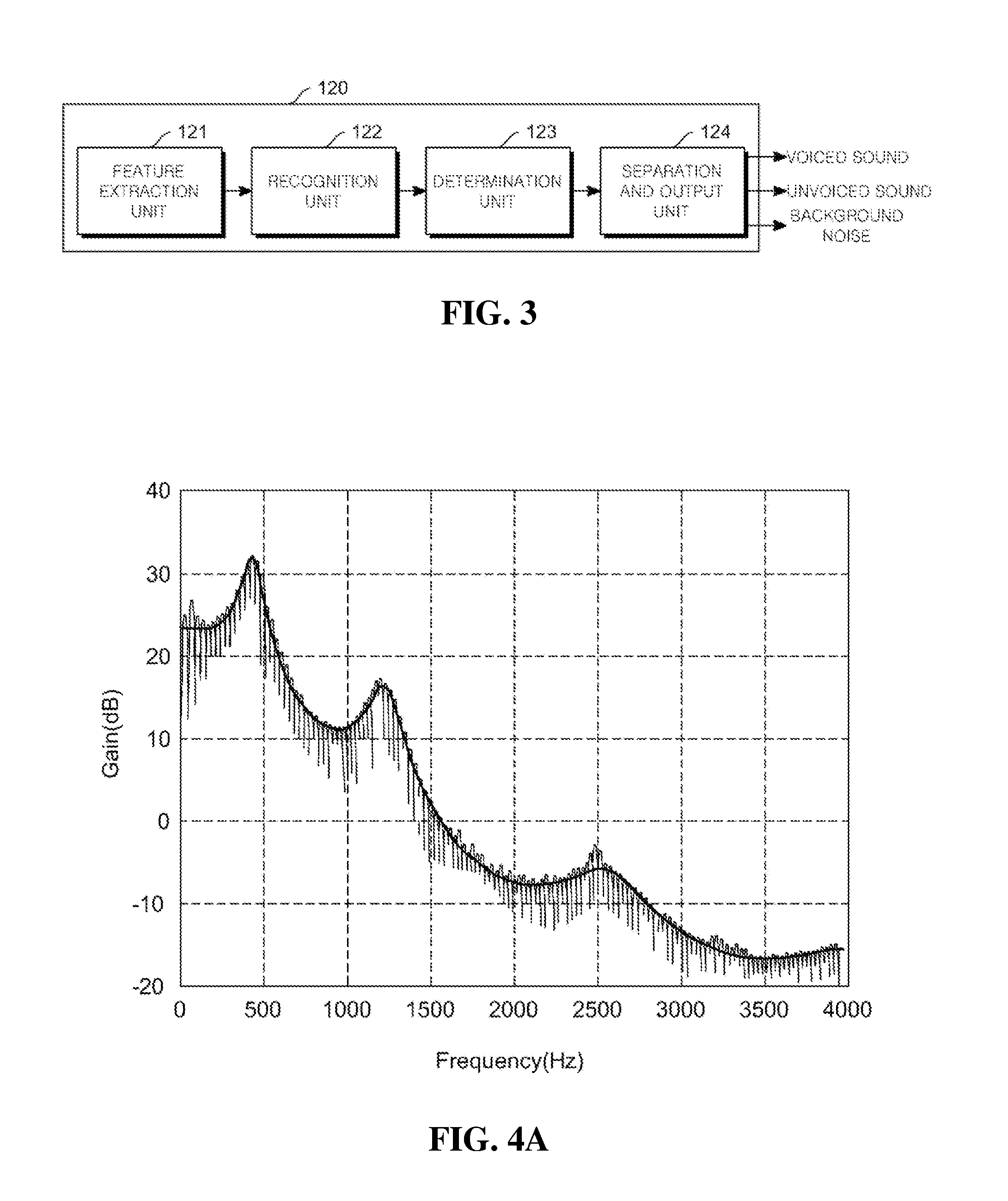
Method for determining alcohol consumption, and recording medium and terminal for carrying out same
Disclosed are a method for determining whether a person is drunk after consuming alcohol on the basis of a difference among a plurality of formant energy energies, which are generated by applying linear predictive coding according to a plurality of linear prediction orders, and a recording medium and a terminal for carrying out the method. The alcohol consumption determining terminal comprises: a voice input unit for receiving voice signals and converting same into voice frames and outputting the voice frames; a voiced / unvoiced sound analysis unit for extracting voice frames corresponding to a voiced sound from among the voice frames; an LPC processing unit for calculating a plurality of formant energy energies by applying linear predictive cording according to the plurality of linear prediction orders to the voice frames corresponding to the voiced sound; and an alcohol consumption determining unit for determining whether a person is drunk after consuming alcohol on the basis of a difference among the plurality of formant energy energies which have been calculated by the LPC processing unit, thereby determining whether a person is drunk after consuming alcohol depending on a change in the formant energy energies generated by applying linear predictive coding according to the plurality of linear prediction orders to voice signals.
Owner:FOUND OF SOONGSIL UNIV IND COOP
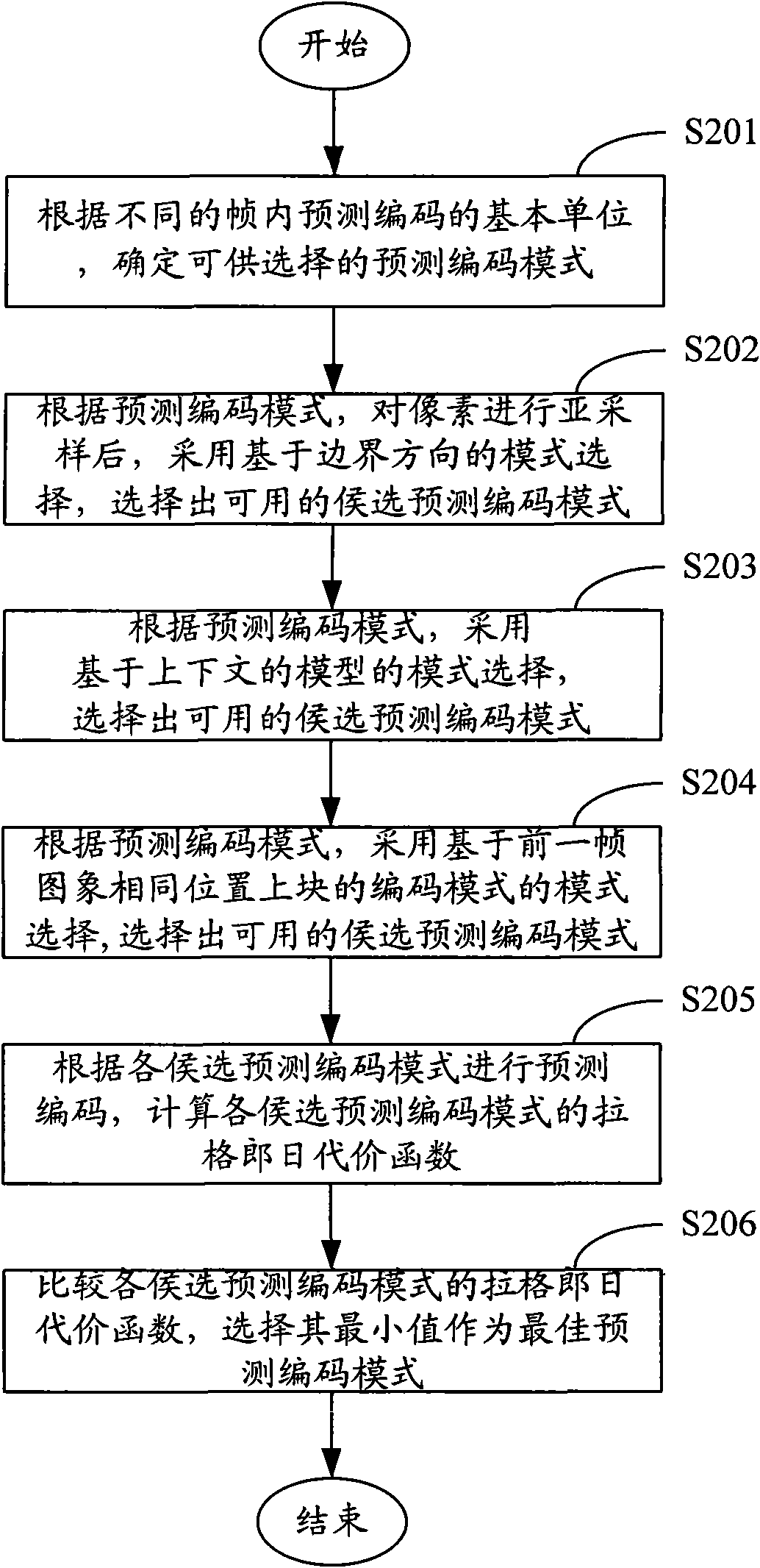
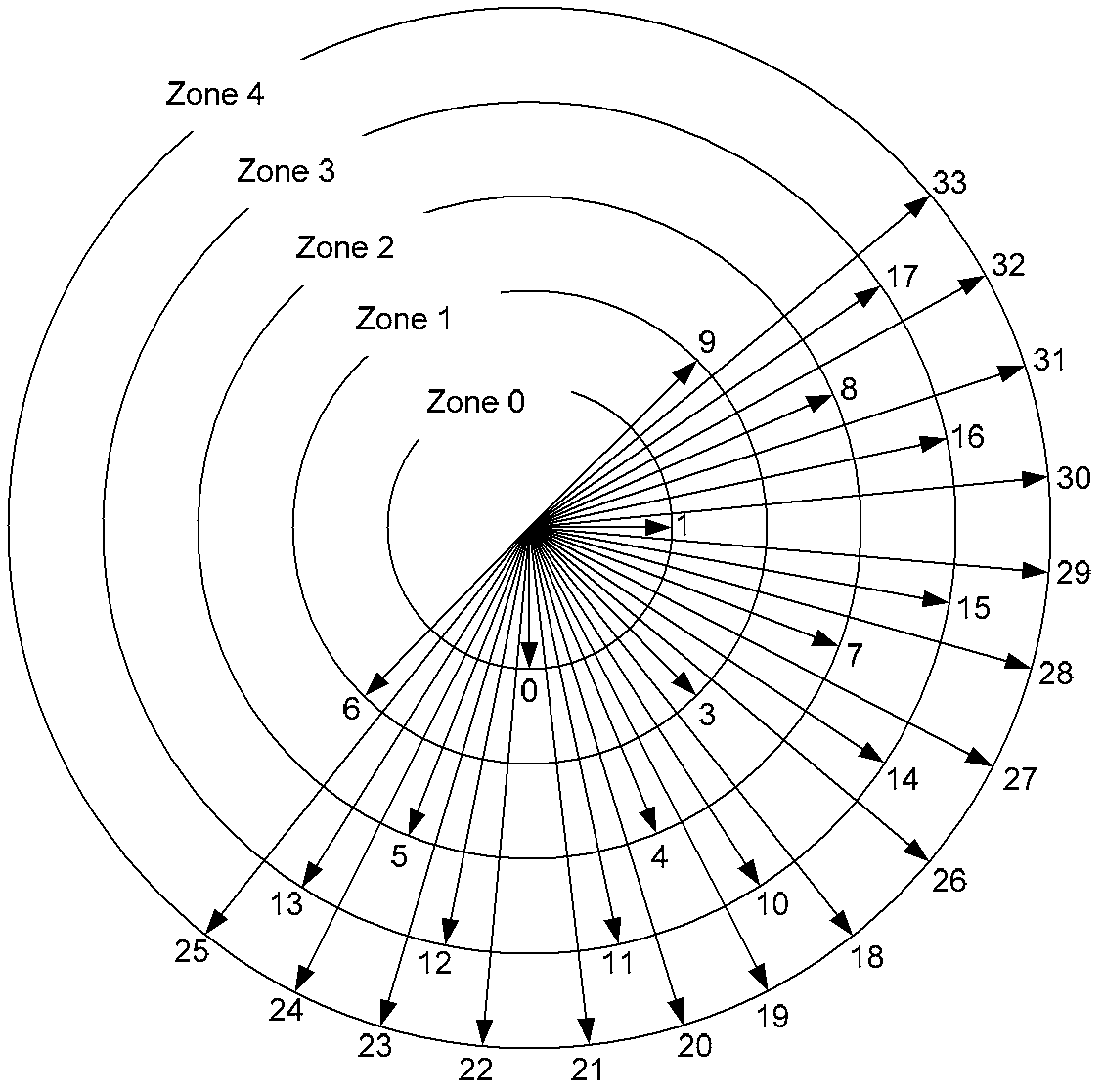
Spatial prediction method for video coding
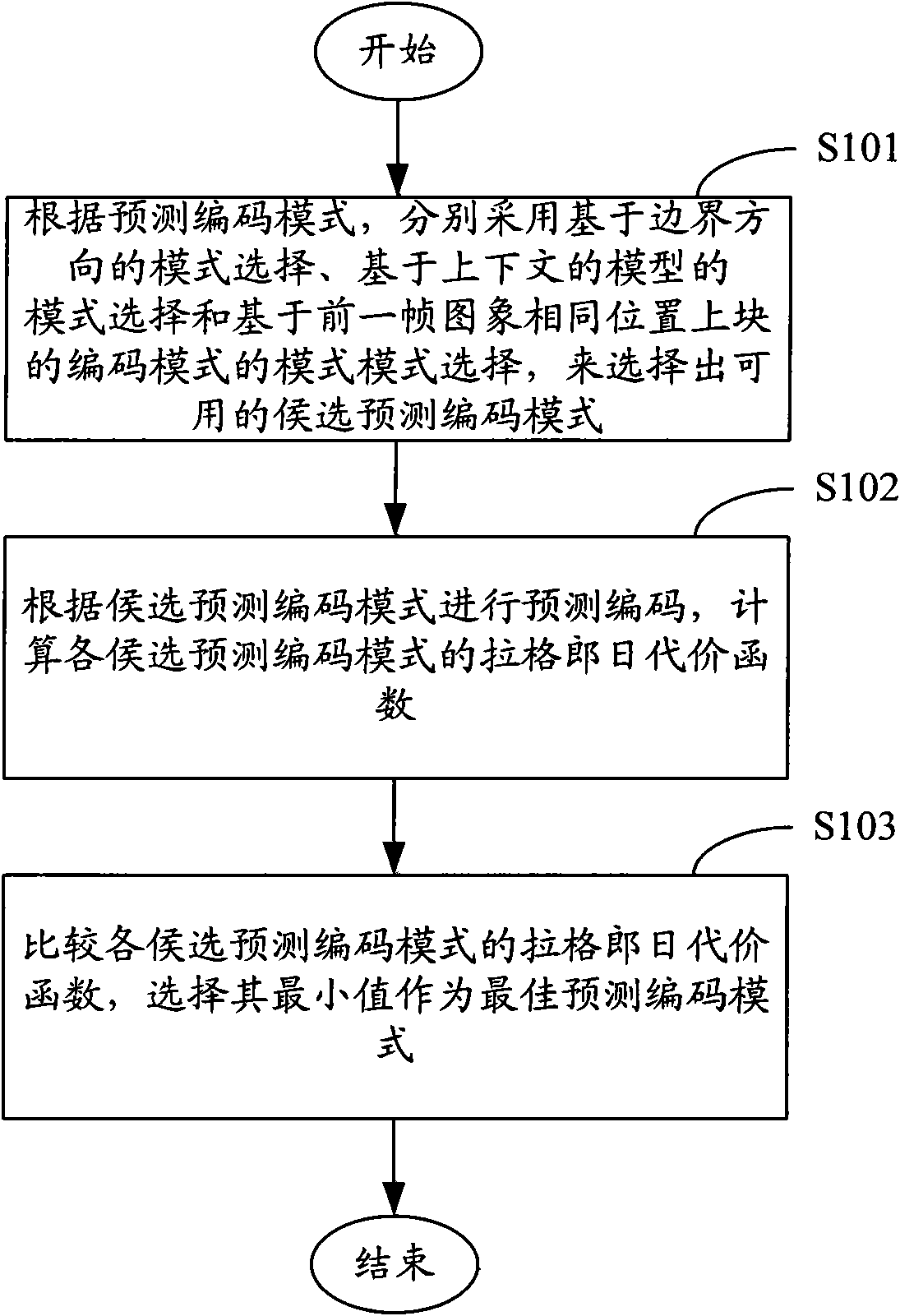
InactiveCN101552924AReduce computational complexitySmall amount of calculationPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationComputation complexitySpatial prediction
The invention relates to the field of video image processing and provides a spatial prediction method for video coding. The method comprises the following steps: A. a coder selects out usable candidate predictive coding modes by respectively adopting an edge-direction-based mode selection, a context-model-based mode selection and a mode selection which is based on the coding mode of image same position upper block of the last frame according to a predictive coding mode; B. predictive coding is carried out by the coder according to the candidate predictive coding modes, and the Lagrange cost functions of all the candidate predictive coding modes are calculated; and C. the coder compares the Lagrange cost functions of the candidate predictive coding modes and selects the minimum value as the optimal predictive coding mode. By adopting the method, high-accurate judgment is ensured, and the calculation complexity is reduced simultaneously, thereby the calculation amount is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN TEMOBI SCI &TECH
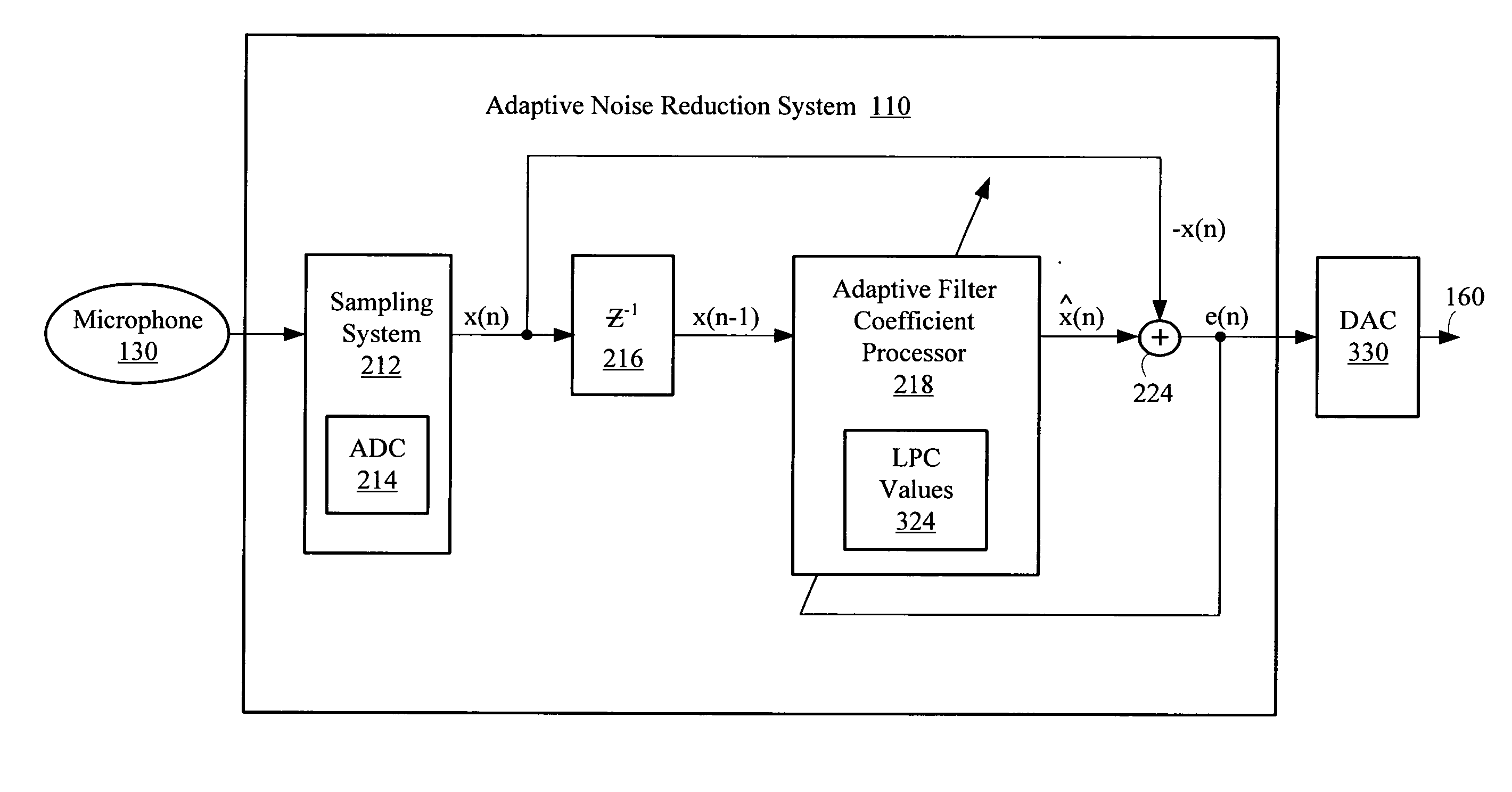
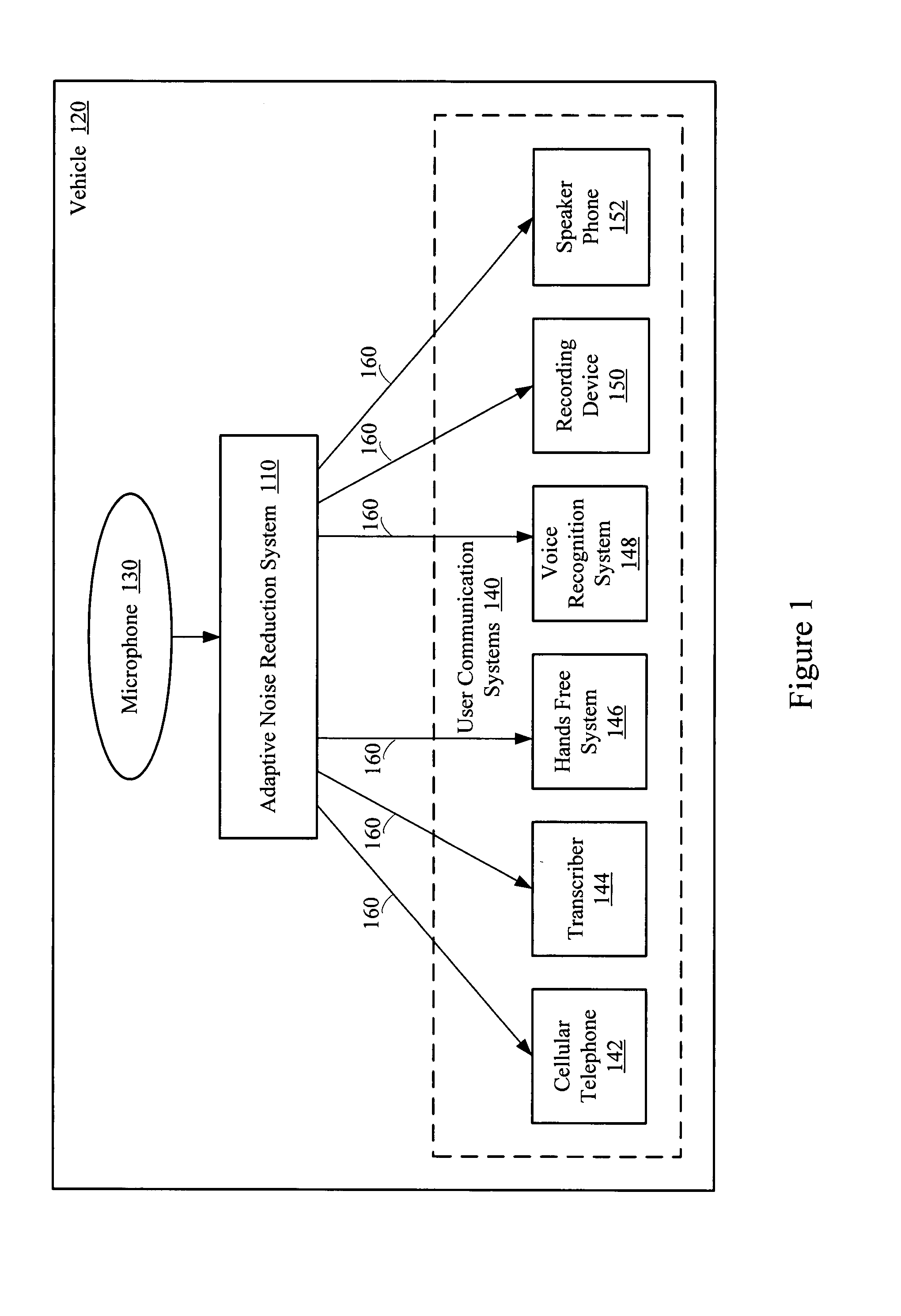
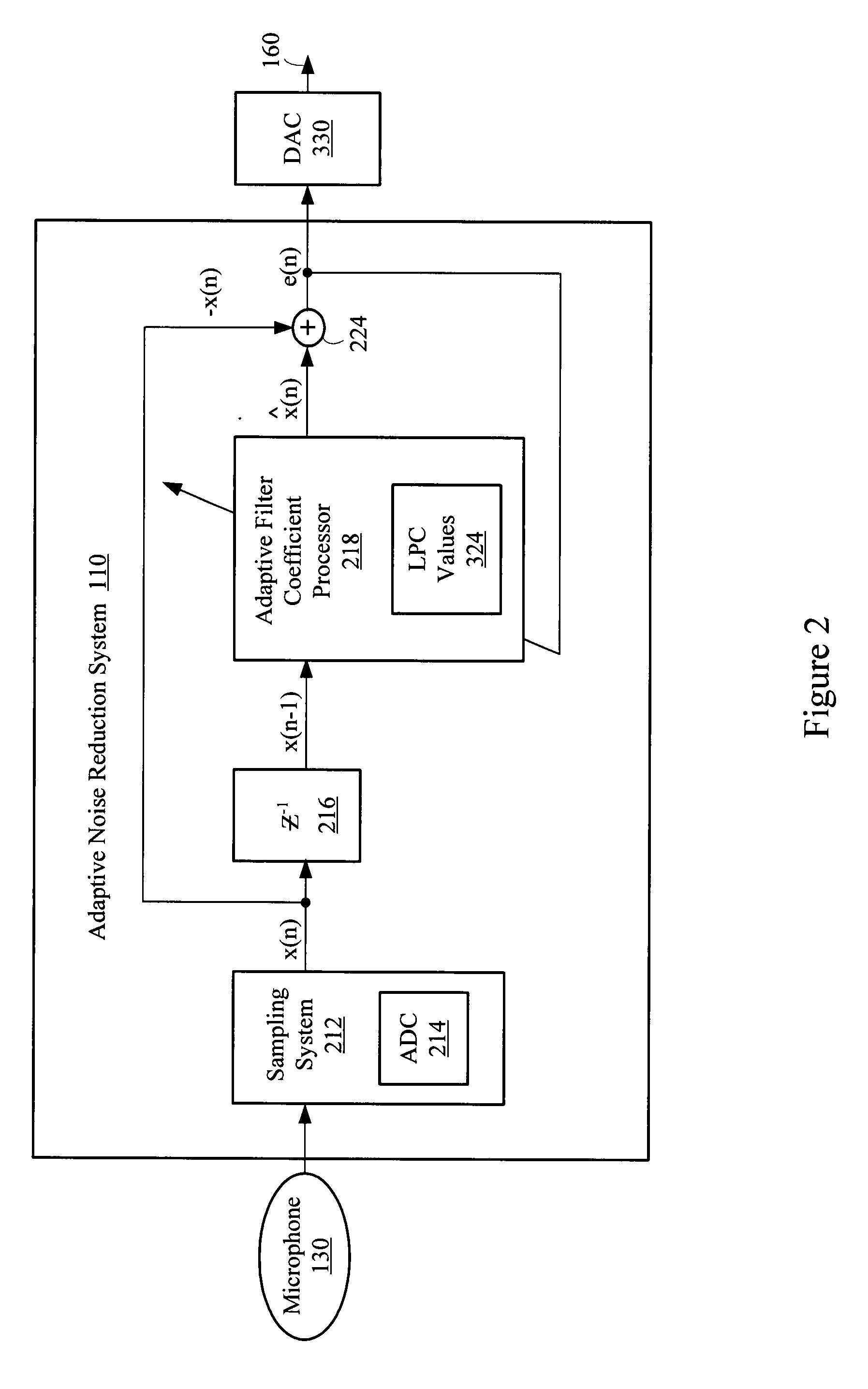
Adaptive LPC noise reduction system
ActiveUS20080285773A1Reduce low frequency noiseLimited setEar treatmentSpeech analysisNoise reductionNoise suppression
A noise suppression system reduces low-frequency noise in a speech signal using linear predictive coefficients in an adaptive filter. A digital filter may update or adapt a limited set of linear predictive coefficients on a sample-by-sample basis. The linear predictive coefficients may be used to provide an error signal based on a difference between the speech signal and a delayed speech signal. The error signal represents an enhanced speech signal having attenuated and normalized low-frequency noise components.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
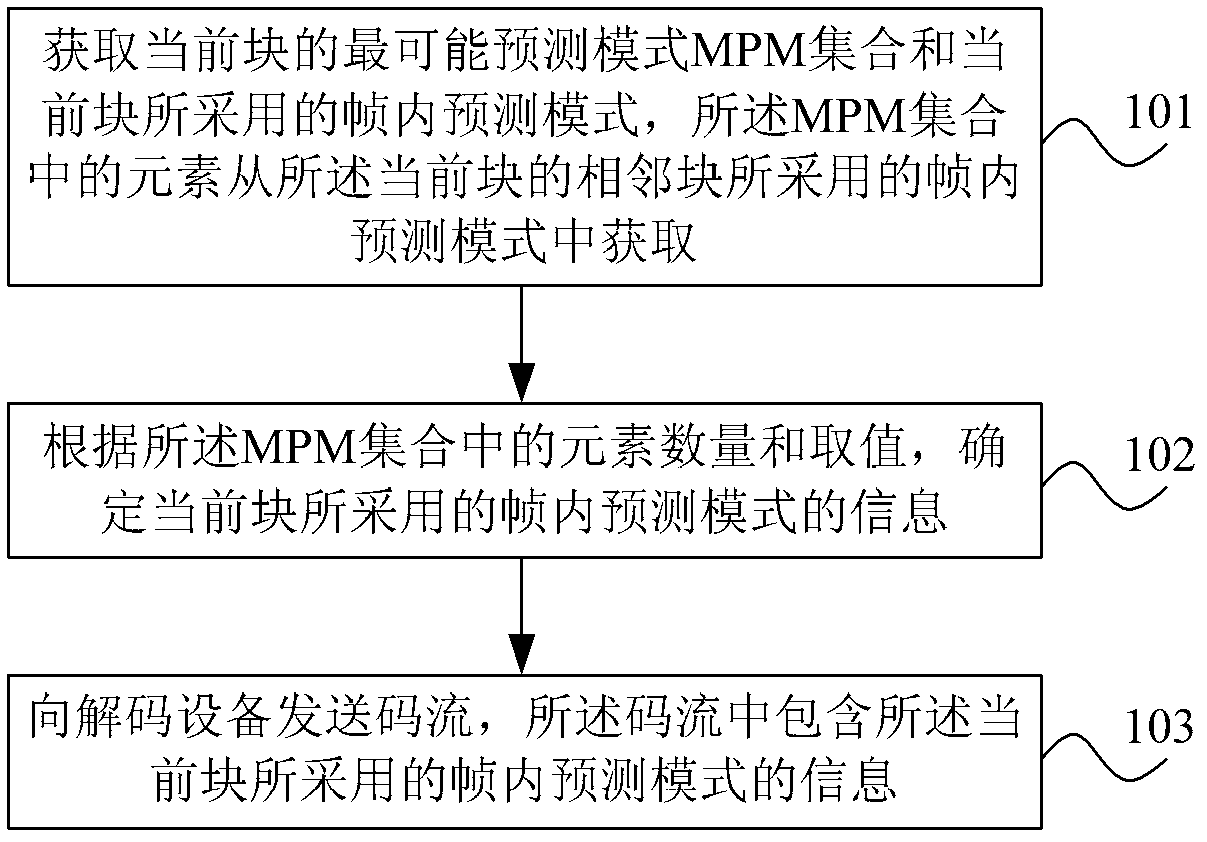
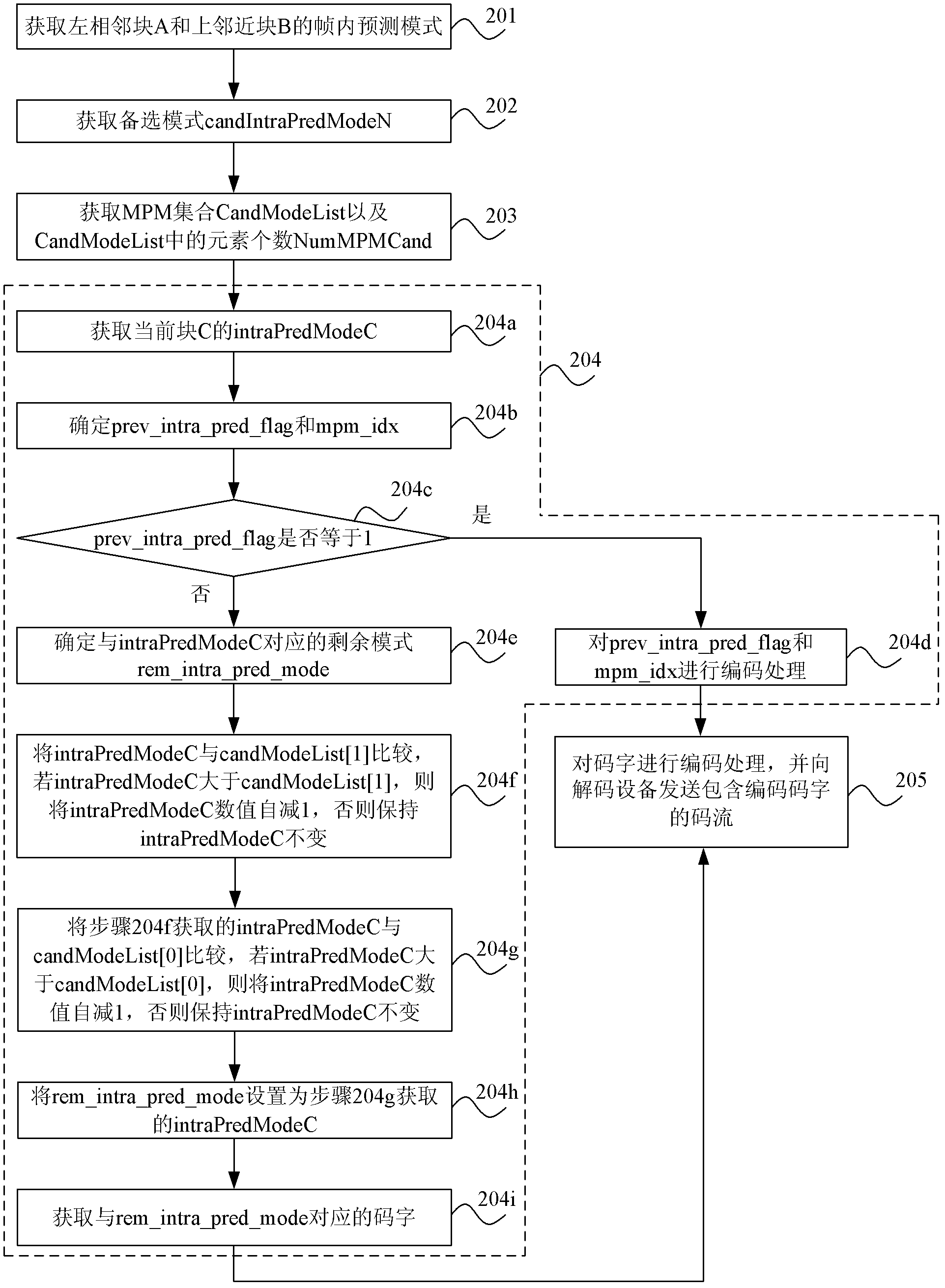
Method, device and system for in-frame predictive coding and encoding
ActiveCN102857750ATake advantage ofCoding is flexiblePulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationParallel computingLinear predictive coding
An embodiment of the invention provides a method, a device and a system in-frame predictive coding and encoding. The method includes the steps of acquiring the most probable mode (MPM) set of a current block and in-frame predicting mode utilized in the current block, wherein elements in the MPM set are acquired from an in-frame predicting mode of a block adjacent to the current block t; determining information of the in-frame predicting mode utilized by the current block according to the number of elements and the evaluation of the MPM set; and sending code stream including the information of the in-frame predicting mode of the current block to a decoding device. When in coding the in-frame predicting mode of the current block, the number of the elements and the evaluation of the MPM set can be fully considered, by aiming at different number of the elements and evaluations, a coding device is capable of selecting corresponding codes to code the in-frame predicting mode of the current block, so that the coding mode is more flexible.
Owner:MIGU CO LTD
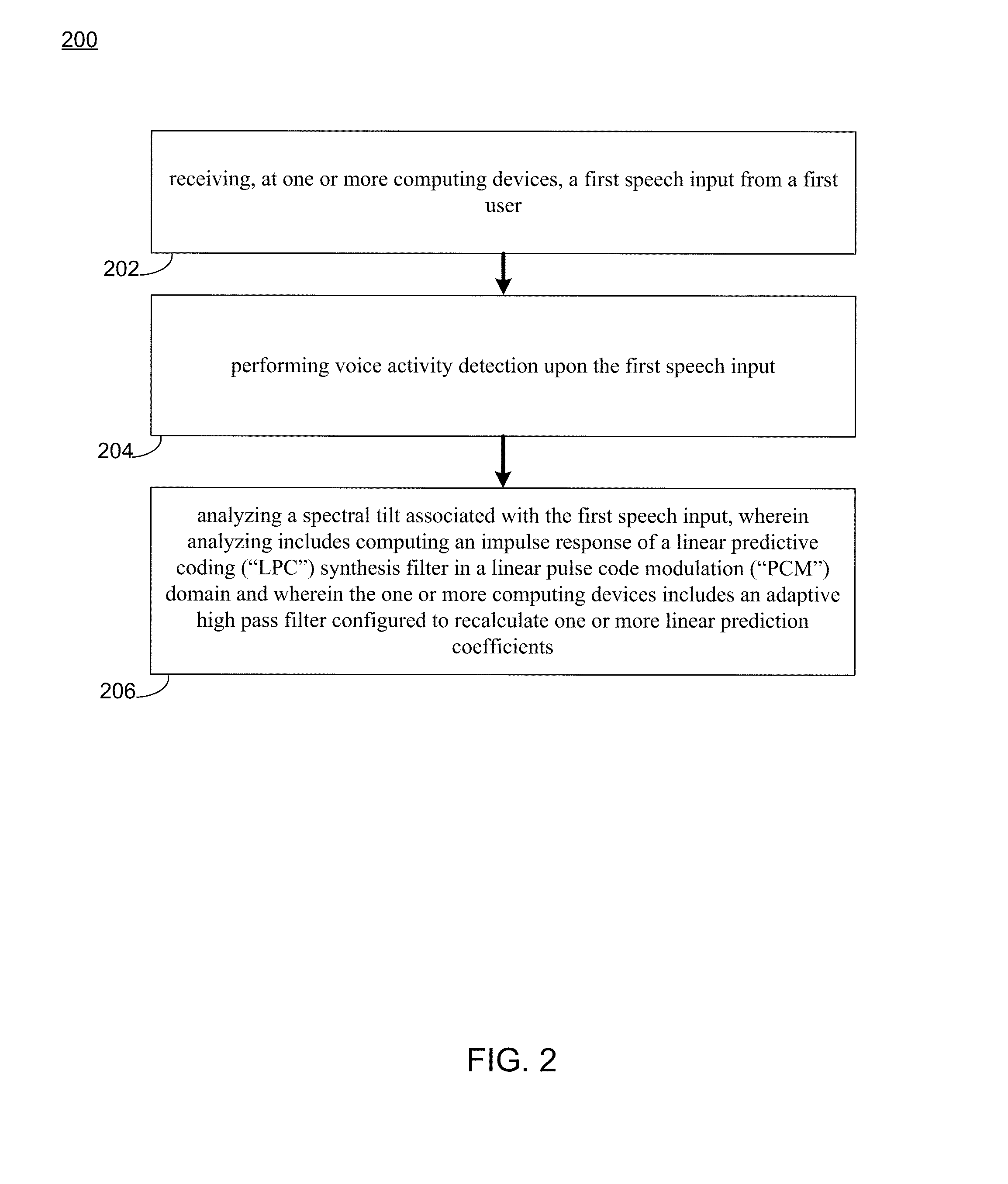
System and method for speech enhancement on compressed speech
ActiveUS20150371653A1Enhanced speech signalEnhanced signalSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumPulse-code modulation
The present disclosure is directed towards a method for speech intelligibility. The method may include receiving, at one or more computing devices, a first speech input from a first user and performing voice activity detection upon the first speech input. The method may also include analyzing a spectral tilt associated with the first speech input, wherein analyzing includes computing an impulse response of a linear predictive coding (“LPC”) synthesis filter in a linear pulse code modulation (“PCM”) domain and wherein the one or more computing devices includes an adaptive high pass filter configured to recalculate one or more linear prediction coefficients.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
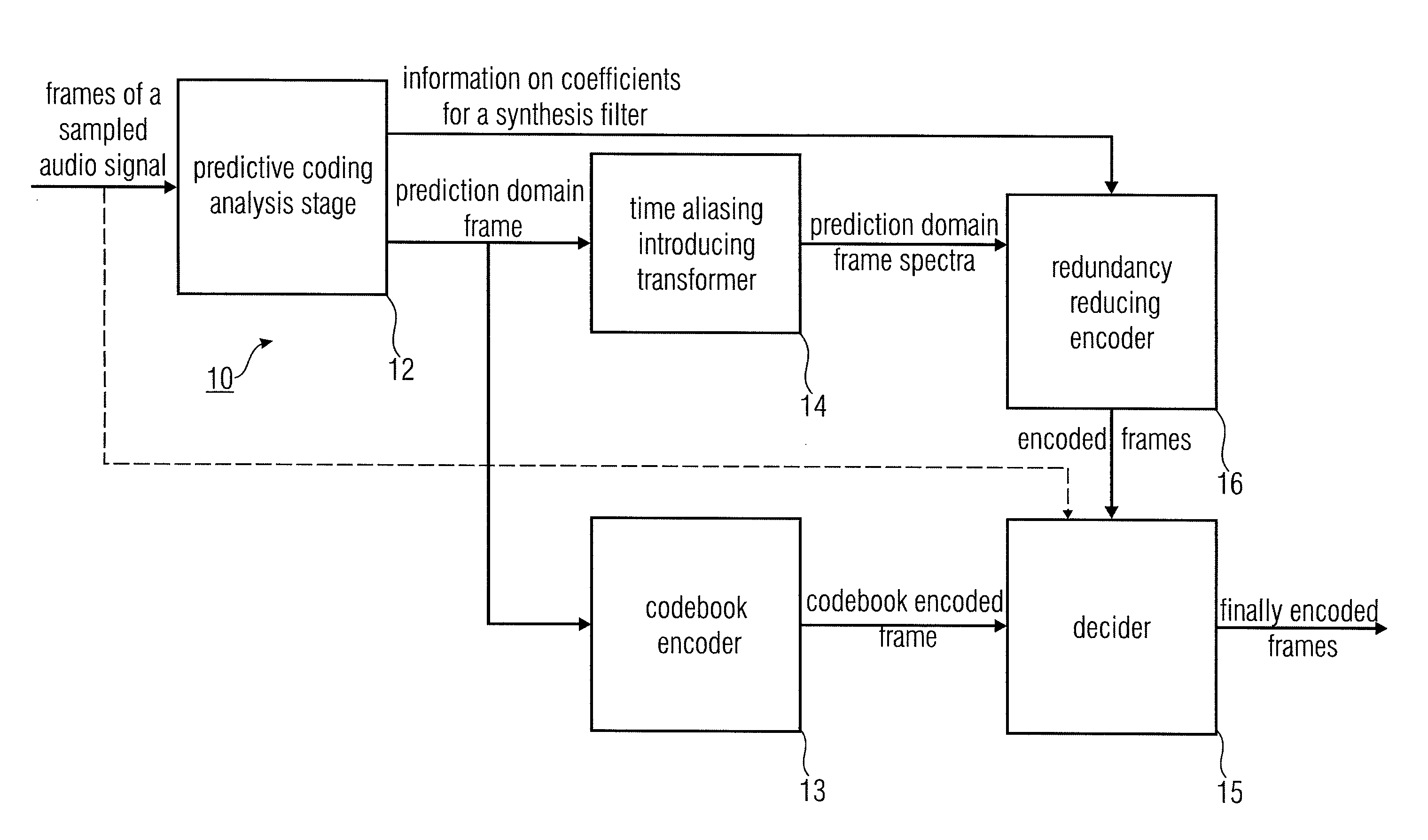
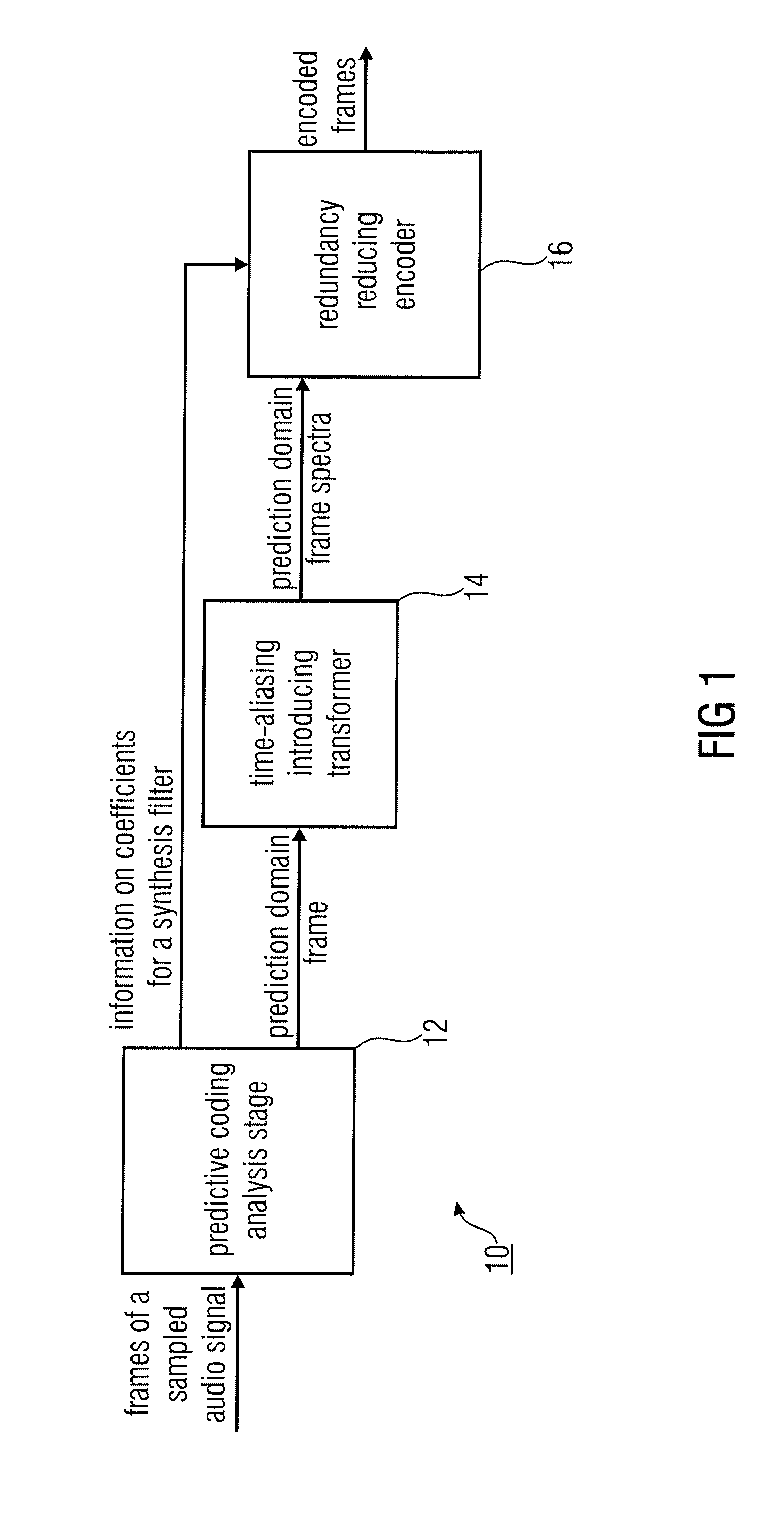
Audio coder/decoder with predictive coding of synthesis filter and critically-sampled time aliasing of prediction domain frames
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
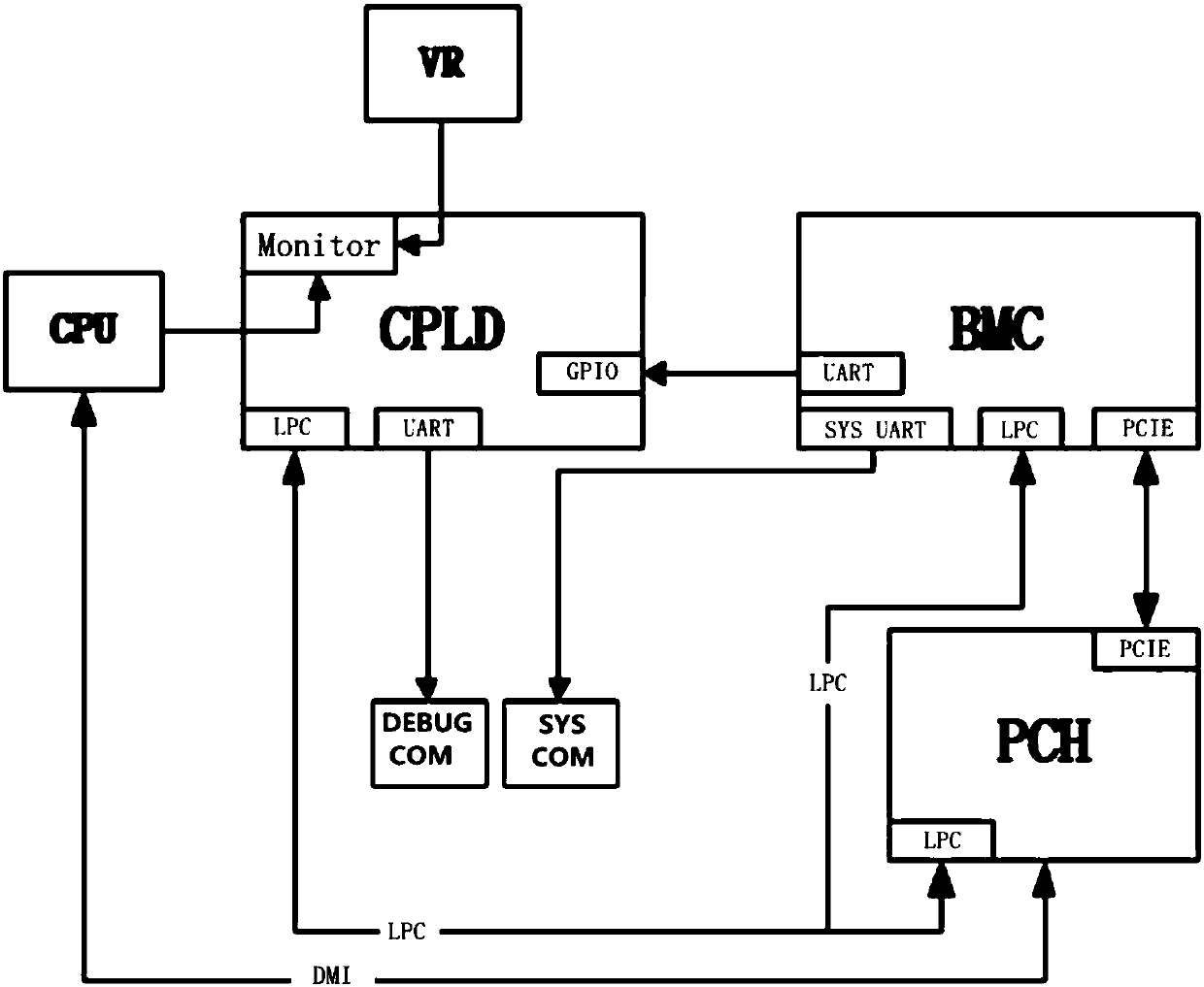
System state display method and device based on CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device)
ActiveCN107656856ASolve the problem that the fast signal cannot be capturedSolve resource problemsHardware monitoringBaseboardPlatform Controller Hub
The invention provides a system state display method and device based on a CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device). The method comprises the following steps that: through the CPLD, monitoring the activation state of a BMC (Baseboard Management Controller); when the BMC is not activated, sending system state information obtained by a PCH (Platform Controller Hub) to the CPLD, carrying out LPC (Linear Predictive Coding) decoding on the system state information by the CPLD, outputting the decoded system state information through a simulation UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver / Transmitter) interface, and displaying the decoded system state information; when the BMC is activated, sending the system state information obtained by the PCH to the BMC, carrying out LPC decoding on the system state information, and outputting and displaying the decoded system state information through an SYS UART interface. By use of the method, a CPLD chip is selected to assist the BMC in outputting the system UART interface, a GPIO (General Purpose Input / Output), the LPC and the UART is analyzed, the relevant signal of a peripheral chip is detected, the UART interface output is simulated, and therefore,state information can be more comprehensively collected.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Reconstruction excitation with LPC parameters and long term prediction lags
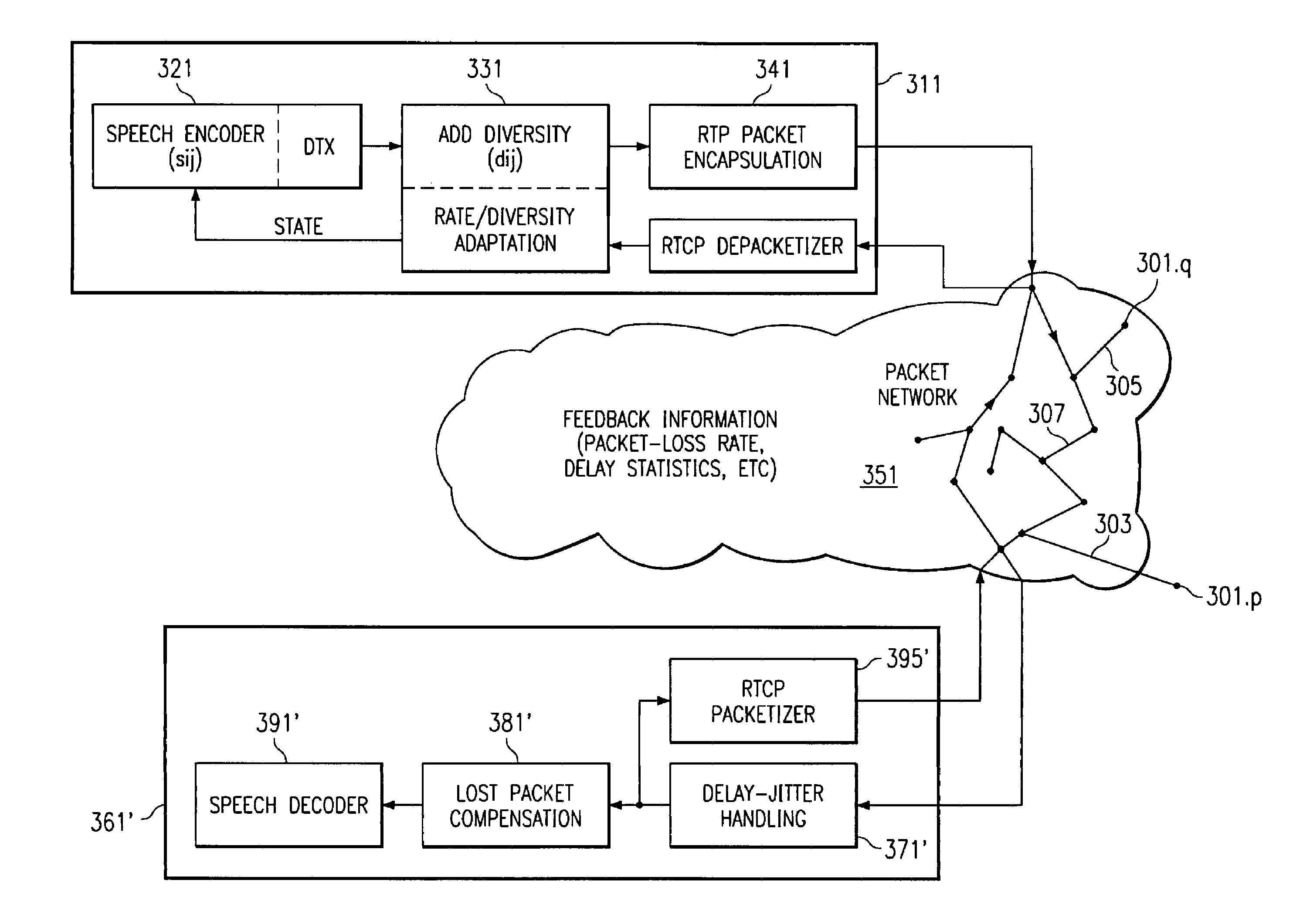
InactiveUS7653045B2Spatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket lossTransducer
A media over packet networking appliance provides a network interface, a voice transducer, and at least one integrated circuit assembly coupling the voice transducer to the network interface. The at least one integrated circuit assembly provides media over packet transmissions and holds bits defining reconstruction of a packet stream having a primary stage and a secondary stage. The secondary stage has one or more of linear predictive coding parameters, long term prediction lags, parity check, and adaptive and fixed codebook gains. The packet stream has an instance of single packet loss, and the reconstruction includes receiving a packet sequence represented by P(n)P(n−1)′, [Lost Packet], P(n+2)P(n+1)′, and P(n+3)P(n+2)′, obtaining as information from the secondary stage one or more of the linear predictive coding parameters, long term prediction lags, parity check, and adaptive and fixed codebook gains, and performing an excitation reconstruction utilizing said packet sequence thus received.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
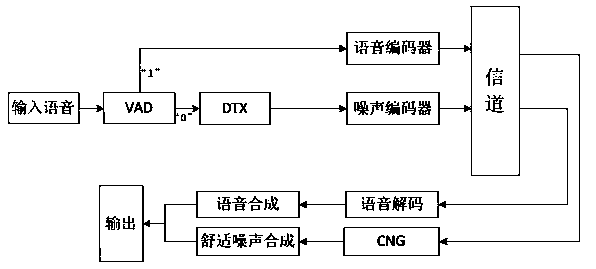
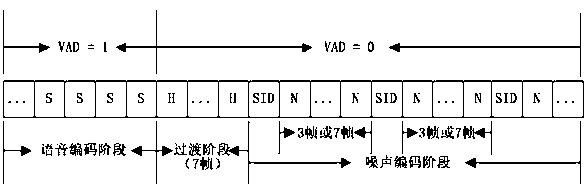
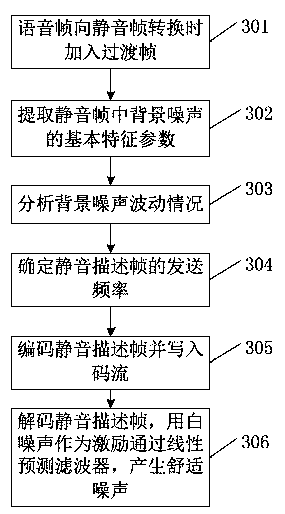
Method for discontinuous transmission of voice signals and generation of background noise
The invention relates to a method for discontinuous transmission of voice signals and generation of background noise. The method comprises the steps that a transition frame is added when a voice frame is converted into a mute frame, and the frequency for sending a mute description frame is determined according to the size of fluctuating values of the background noise in the mute frame; at a decoding end, white noise is used as stimulus signals, and after a linear predictive coding resulting filter is passed through, comfortable noise is obtained through gain adjustment. The method for the discontinuous transmission of the voice signals and the generation of the background noise has good adaptivity when used for transmitting noise signals, and composite background noise has good continuity and comfortableness in subjective auditory sense.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com