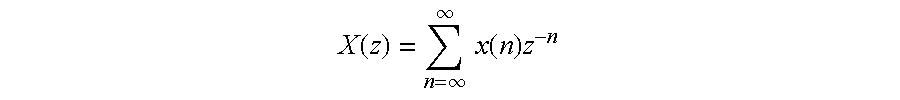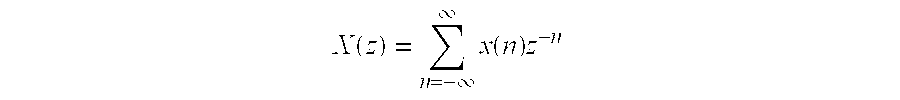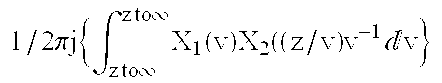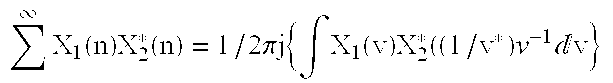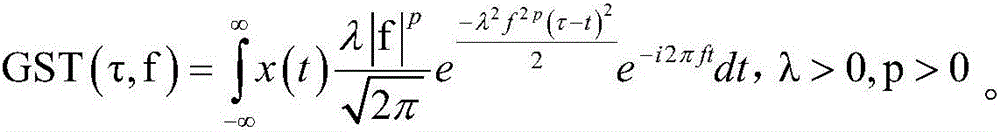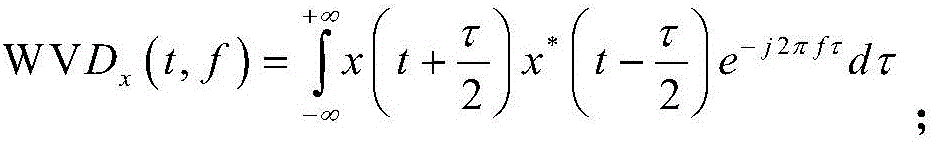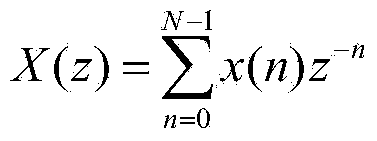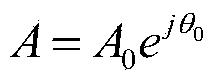Patents
Literature
65 results about "Z-transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics and signal processing, the Z-transform converts a discrete-time signal, which is a sequence of real or complex numbers, into a complex frequency-domain representation. It can be considered as a discrete-time equivalent of the Laplace transform. This similarity is explored in the theory of time-scale calculus.
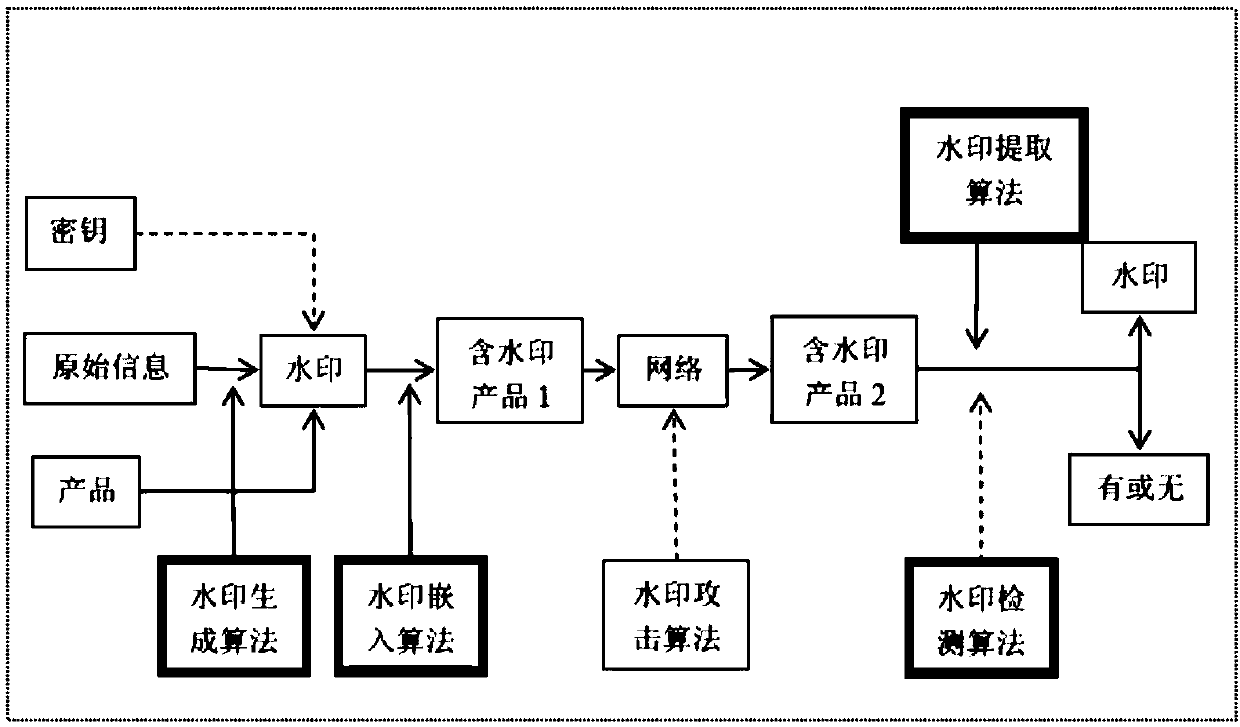
Z-transform implementation of digital watermarks
InactiveUS6853726B1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCarrier signalData encoding
Z-transform calculations may be used to encode (and / or decode) carrier signal independent data (e.g., digital watermarks) to a digital sample stream. Deterministic and non-deterministic components of a digital sample stream signal may be analyzed for the purposes of encoding carrier signal independent data to the digital sample stream. The carrier signal independent data may be encoded in a manner such that it is restricted or concentrated primarily in the non-deterministic signal components of the carrier signal. The signal components can include a discrete series of digital samples and / or a discreet series of carrier frequency sub-bands of the carrier signal. Z-transform calculations may be used to measure a desirability of particular locations and a sample stream in which to encode the carrier signal independent data.
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
Linear predictive coding implementation of digital watermarks
InactiveUS20070079131A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsCarrier signalData encoding
Z-transform calculations may be used to encode (and / or decode) carrier signal independent data (e.g., digital watermarks) to a digital sample stream. Deterministic and non-deterministic components of a digital sample stream signal may be analyzed for the purposes of encoding carrier signal independent data to the digital sample stream. The carrier signal independent data may be encoded in a manner such that it is restricted or concentrated primarily in the non-deterministic signal components of the carrier signal. The signal components can include a discrete series of digital samples and / or a discreet series of carrier frequency sub-bands of the carrier signal. Z-transform calculations may be used to measure a desirability of particular locations and a sample stream in which to encode the carrier signal independent data.
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
Z-transform implementation of digital watermarks
InactiveUS20050135615A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsCarrier signalData encoding
Z-transform calculations may be used to encode (and / or decode) carrier signal independent data (e.g., digital watermarks) to a digital sample stream. Deterministic and non-deterministic components of a digital sample stream signal may be analyzed for the purposes of encoding carrier signal independent data to the digital sample stream. The carrier signal independent data may be encoded in a manner such that it is restricted or concentrated primarily in the non-deterministic signal components of the carrier signal. The signal components can include a discrete series of digital samples and / or a discreet series of carrier frequency sub-bands of the carrier signal. Z-transform calculations may be used to measure a desirability of-particular locations and a sample stream in which to encode the carrier signal independent data.
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
Residue division multiplexing system and apparatus for discrete-time signals
InactiveUS6317409B1Easy to useSimple structureFrequency-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiscrete-time signalEngineering
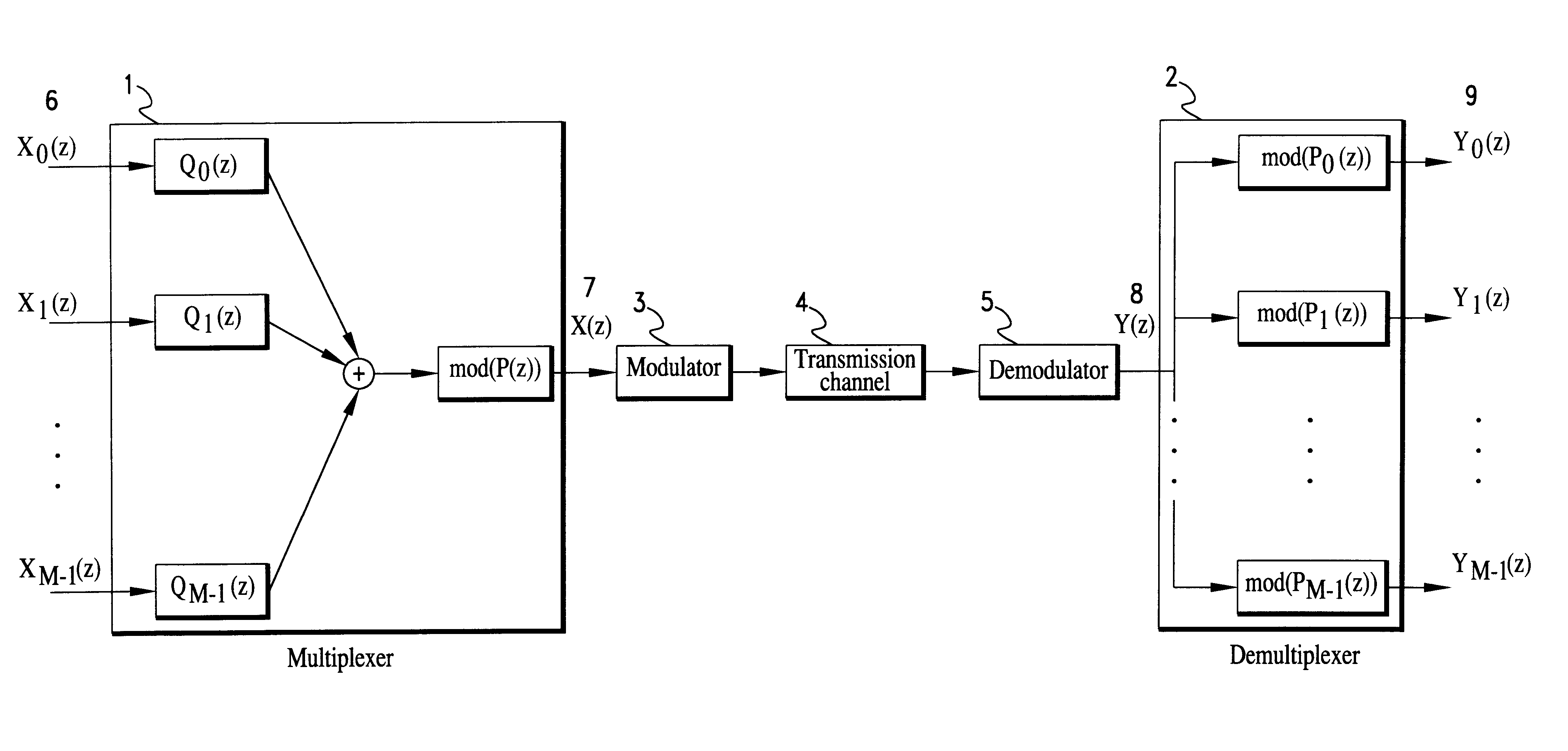
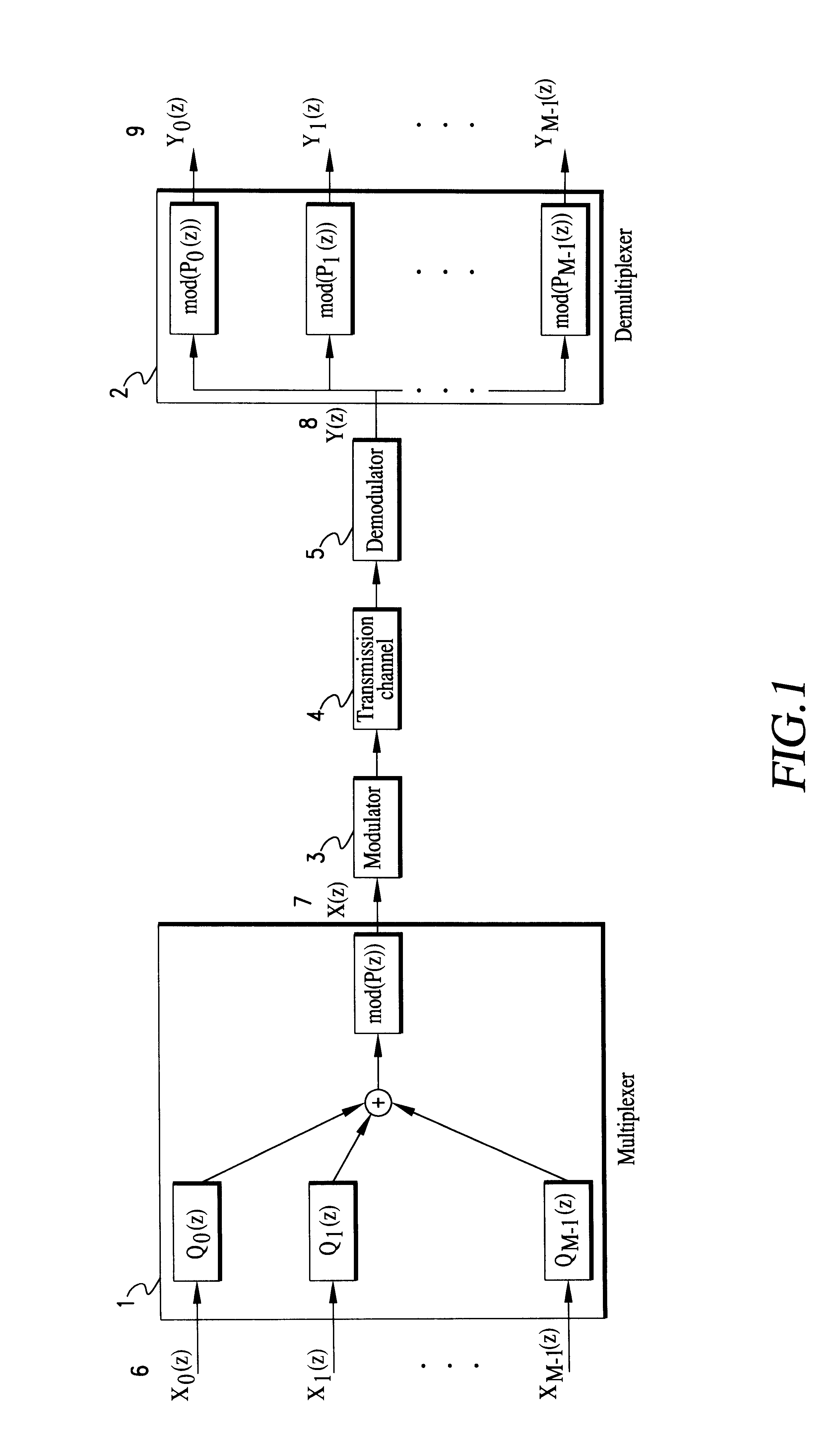
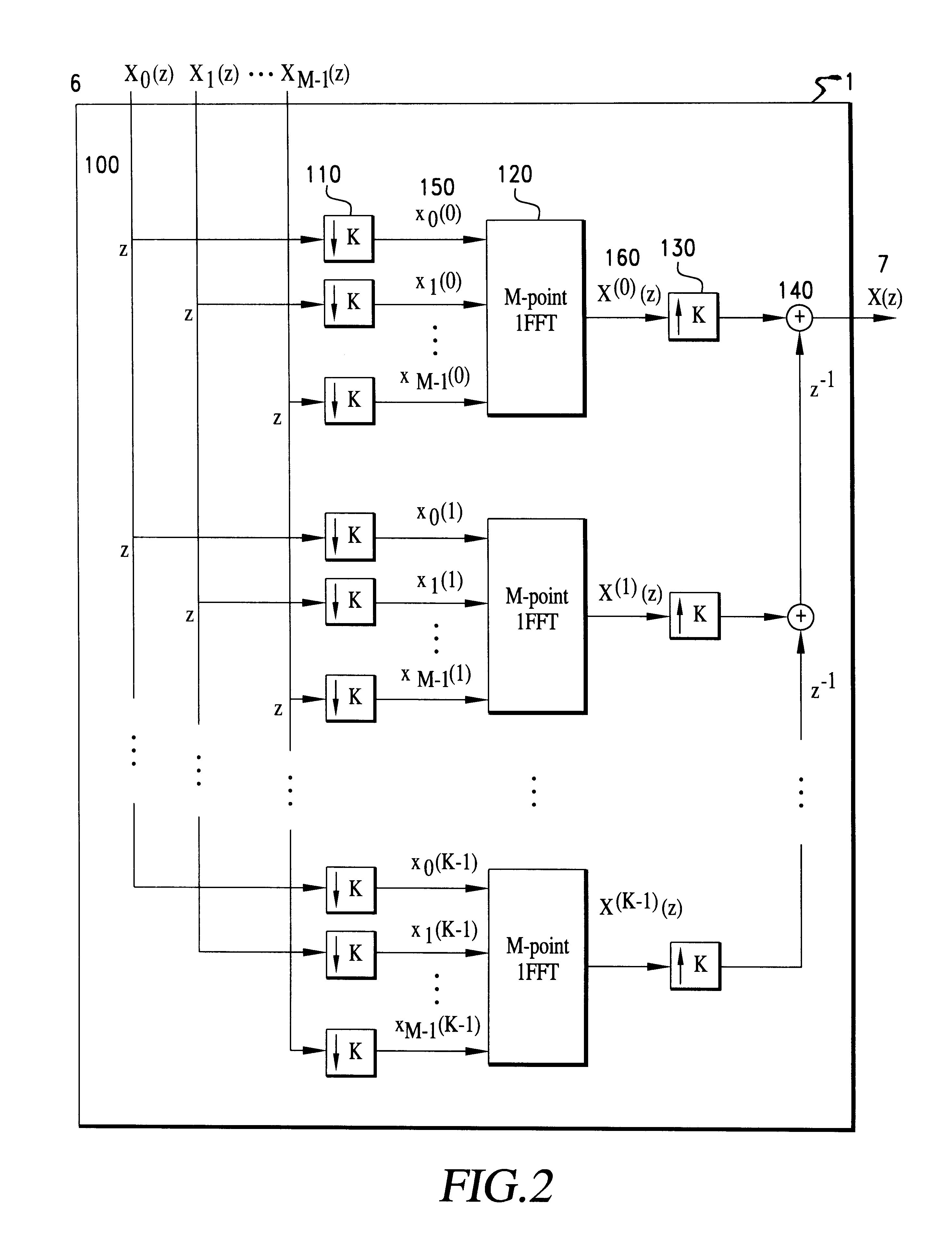
A multiplexing system utilizes the whole transmission bandwidth without inducing interchannel interference for a linear channel with additive noise. Using the multiplexing system, the linear distortion channel is decomposed into independent linear distortion subchannels. Treating z-transforms as polynomials, a multiplexer at a receiver utilizes the Chinese remainder procedure to combine subchannel signals into a multiplexed signal to be transmitted through a single transmission channel. A demultiplexer at a receiver recovers the transmitted subchannel signals by taking residue polynomials on the factor polynomials used in the Chinese remainder procedure. The multiplexer that combines M subchannel signals of length K may be implemented by K M-point IFFT processors using 1-ej2pim / Mz-K (m=0 to M-1) as relatively prime polynomials required in the Chinese remainder procedure. Samples from the subchannel signals are arranged in K groups of M samples such that each group contains samples at the same position in the subchannel signals, M-point inverse DFTs of the arranged samples are computed for all of the groups, and finally the multiplexed signal is obtained by performing polyphase composition of the inverse DFT outputs. Reversing the process of multiplexing, the demultiplexer is implemented by K M-point FFT processors. Another class of the system is a multiplexing system using (1-ej2pim / Mr0z-1) (1-ej2pim / Mr1z-1) . . . (1-ej2pim / MrK-1z-1) (m=0 to M-1) as relatively prime polynomials, wherein ri is a non-zero complex number (i=0 to K-1). The multiplexer obtains the multiplexed signal by applying the Chinese remainder procedure recursively, starting with the subchannel signals Xm(z) regarding them as residue polynomials on mod((1-ej2pim / Mr0z-1) (1-ej2pim / Mr1z-1) . . . (1-ej2pim / MrK-1z-1)) (m=0 to M-1).
Owner:MURAKAMI HIDEO
Digital equalizing method and radio communication receiver implementing said method
InactiveUS6850562B1Increase valueSolution value is not highMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationChannel impulse responsePartition of unity
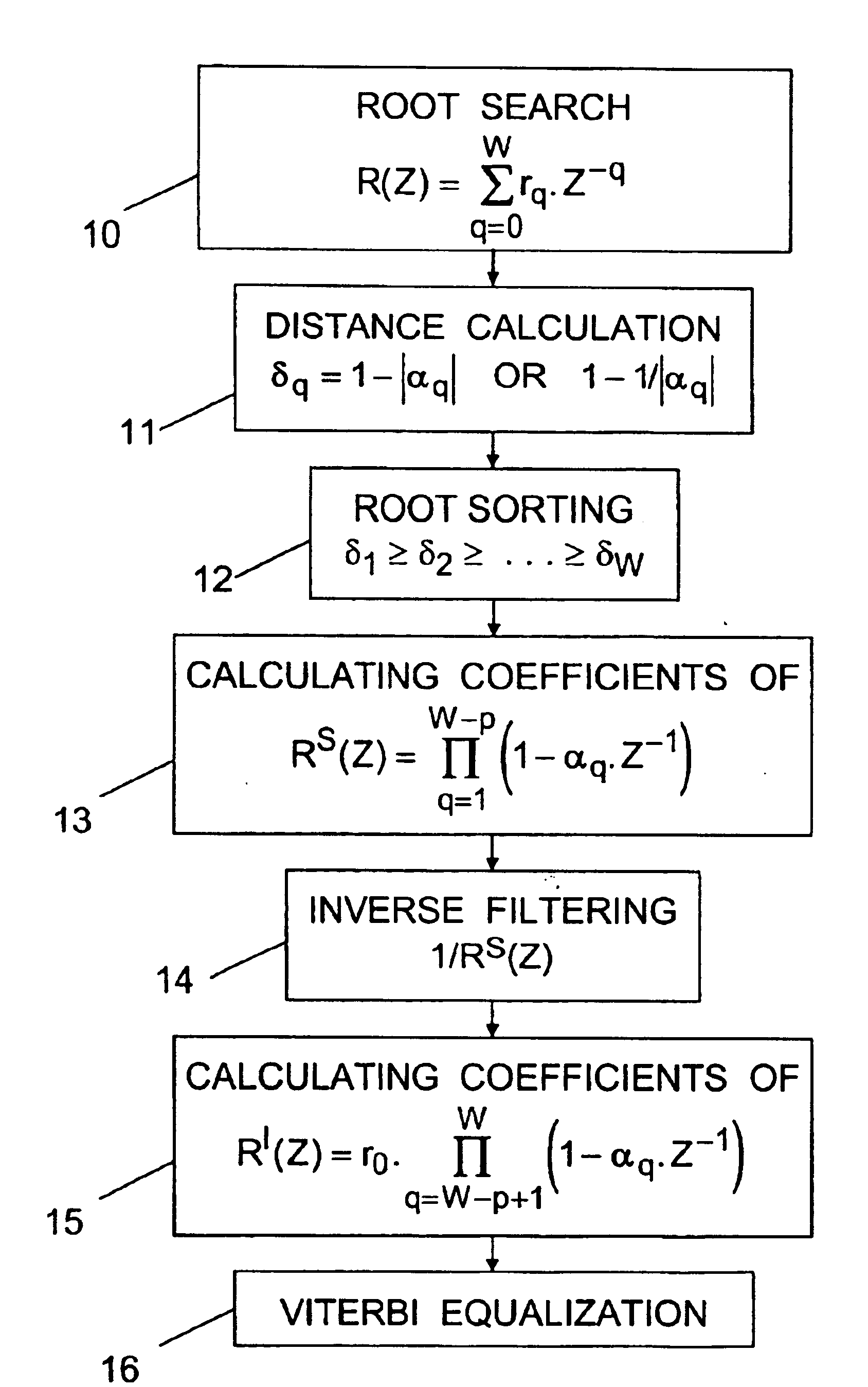
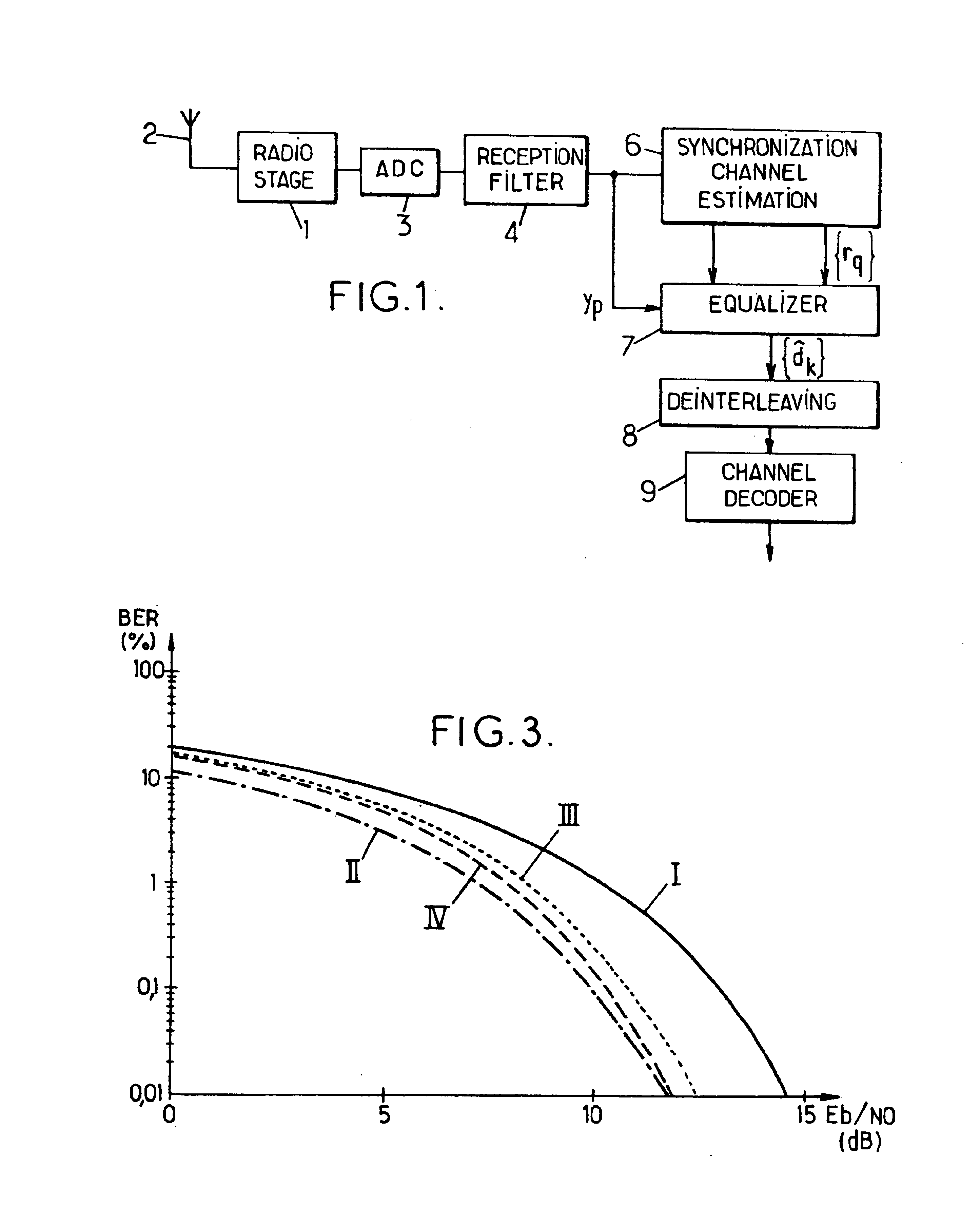
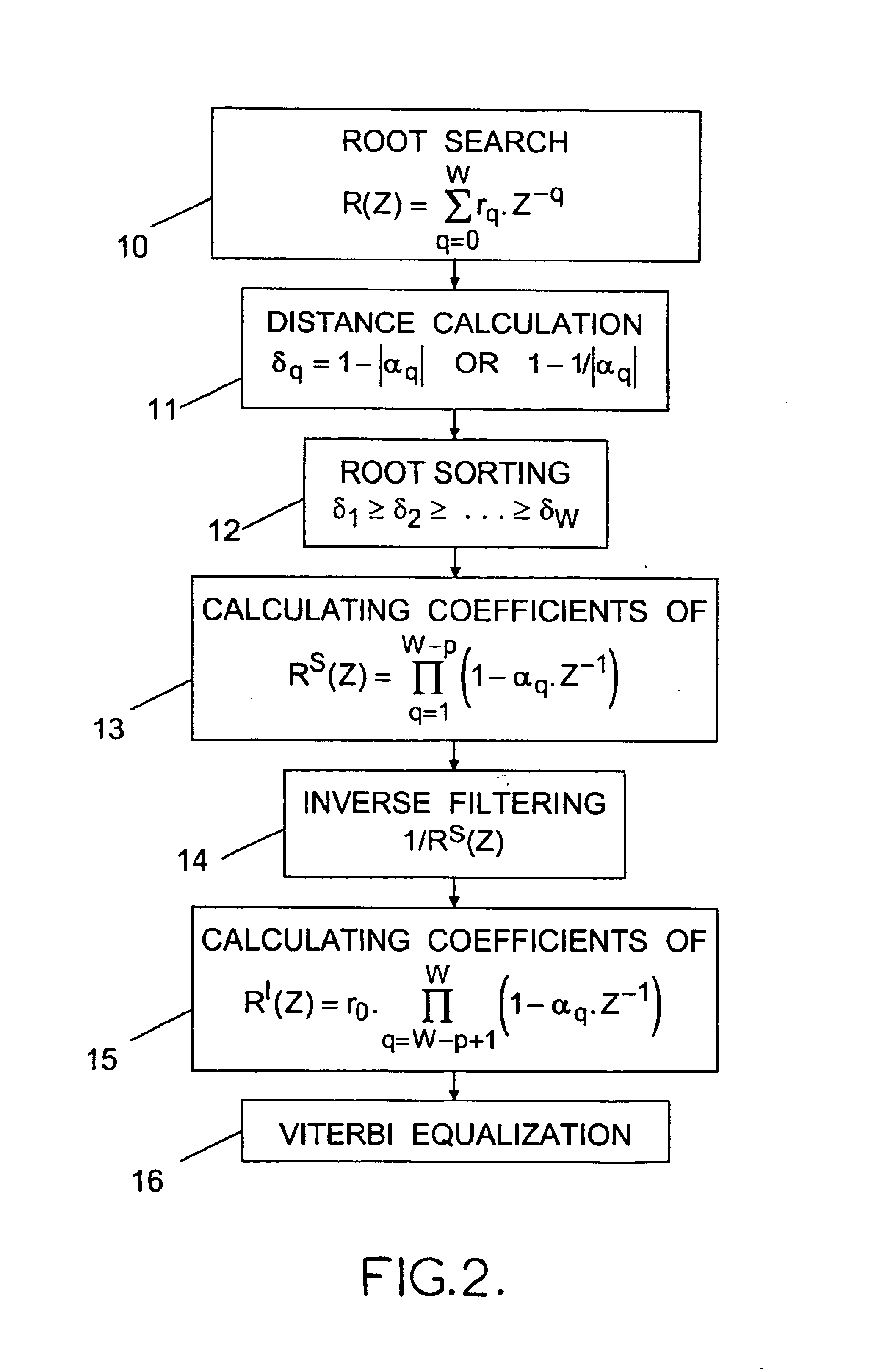
For processing samples of a signal received via a channel represented by an impulse response of W−1 coefficients, the method comprises: determining the W roots of the Z-transform of the channel impulse response; producing an intermediate signal by equalizing the received signal by a zero-forcing method or the like based on an impulse response whose Z-transform is a Z−1 polynomial of degree W-p having as roots those of the W roots which are furthest from the unit circle of the complex plane; and then obtaining estimations of the transmitted signal symbols by applying a Viterbi-type equalization method or the like based on an impulse response whose Z-transform is a Z−1 polynomial of degree p having as roots those of the W roots which are nearest to the unit circle.
Owner:APPLE INC
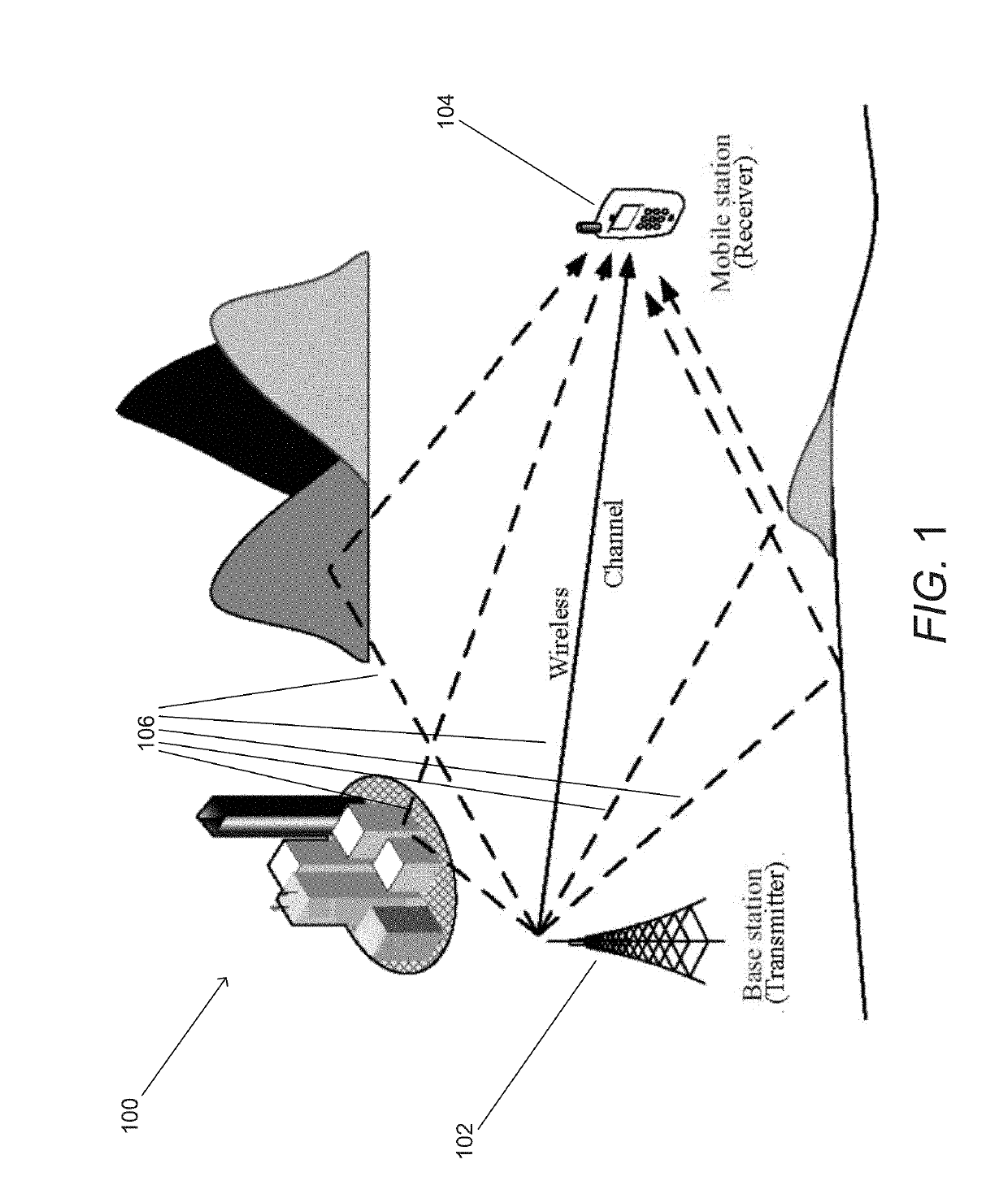
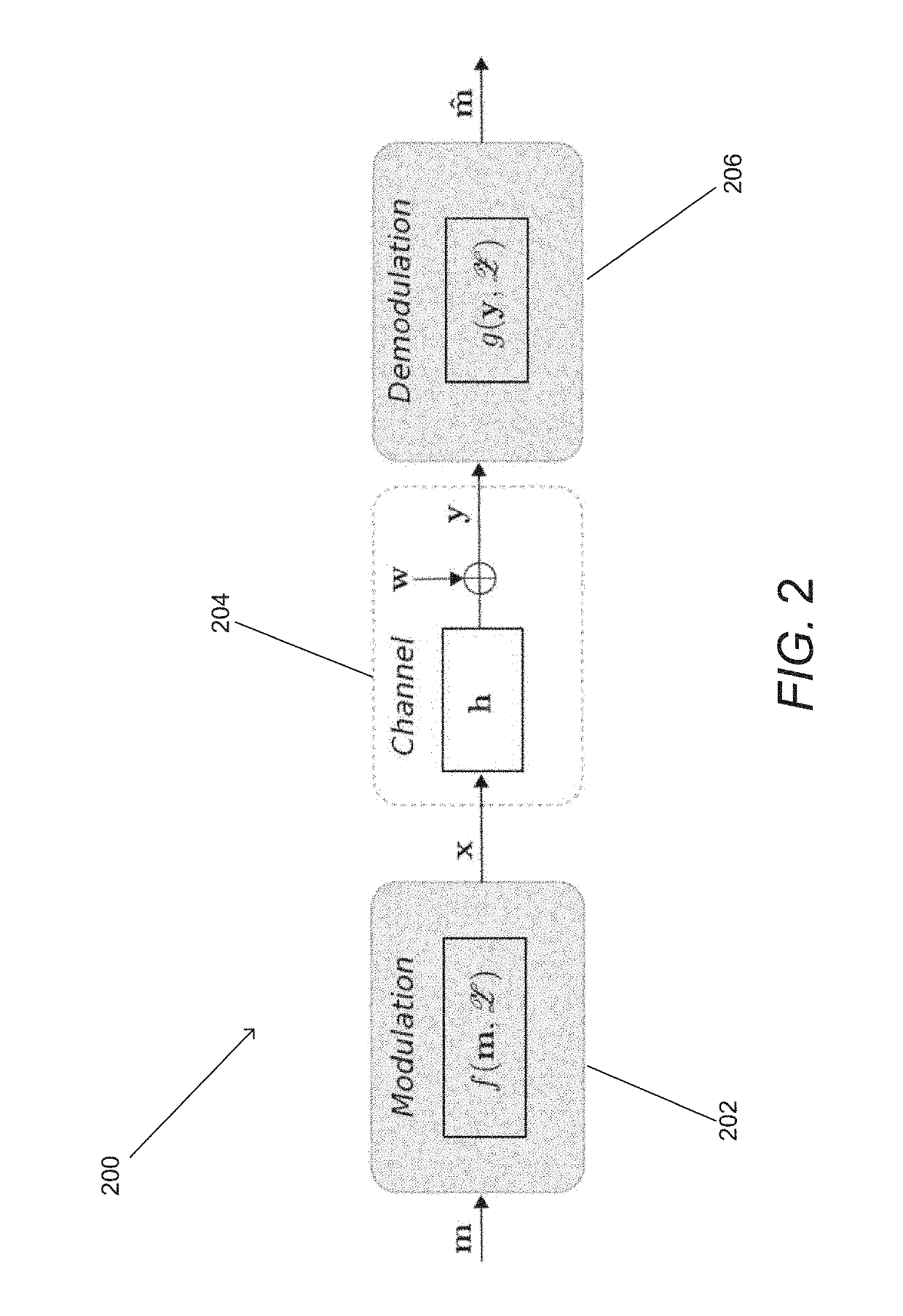
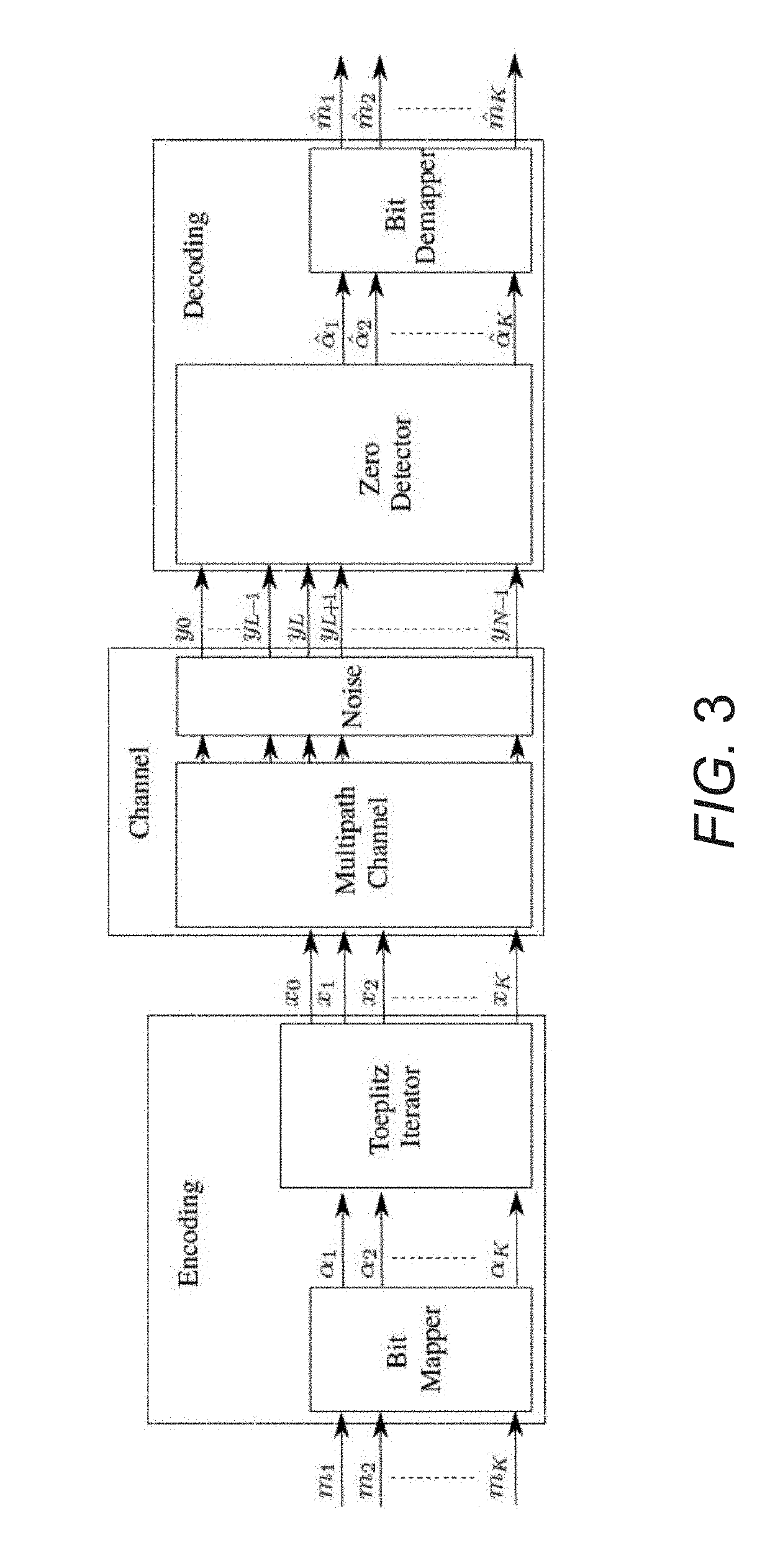
Systems and Methods for Communicating by Modulating Data on Zeros
ActiveUS20190238379A1Improve performanceChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsVIT signalsZ-transform
Systems and methods for transmitting data using various Modulation on Zeros schemes are described. In many embodiments, a communication system is utilized that includes a transmitter having a modulator that modulates a plurality of information bits to encode the bits in the zeros of the z-transform of a discrete-time baseband signal. In addition, the communication system includes a receiver having a decoder configured to decode a plurality of bits of information from the samples of a received signal by: determining a plurality of zeros of a z-transform of a received discrete-time baseband signal based upon samples from a received continuous-time signal, identifying zeros that encode the plurality of information bits, and outputting a plurality of decoded information bits based upon the identified zeros.
Owner:TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF BERLIN +1
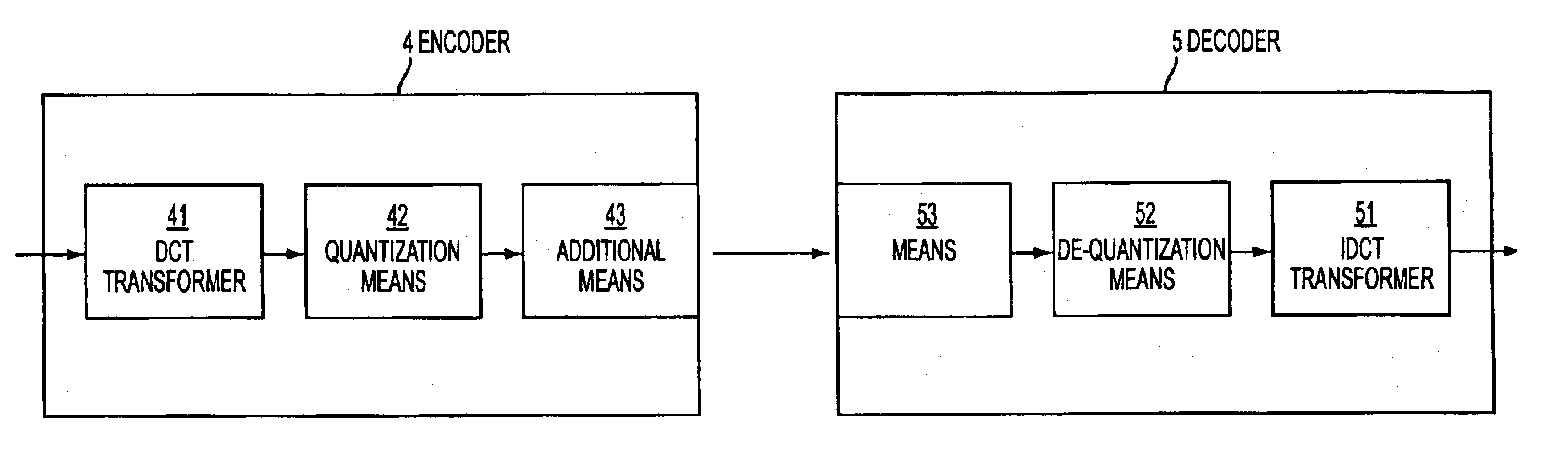
Implementation of a transform and of a subsequent quantization
InactiveUS7082450B2Fast computerReduce in quantityCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital dataComputer science
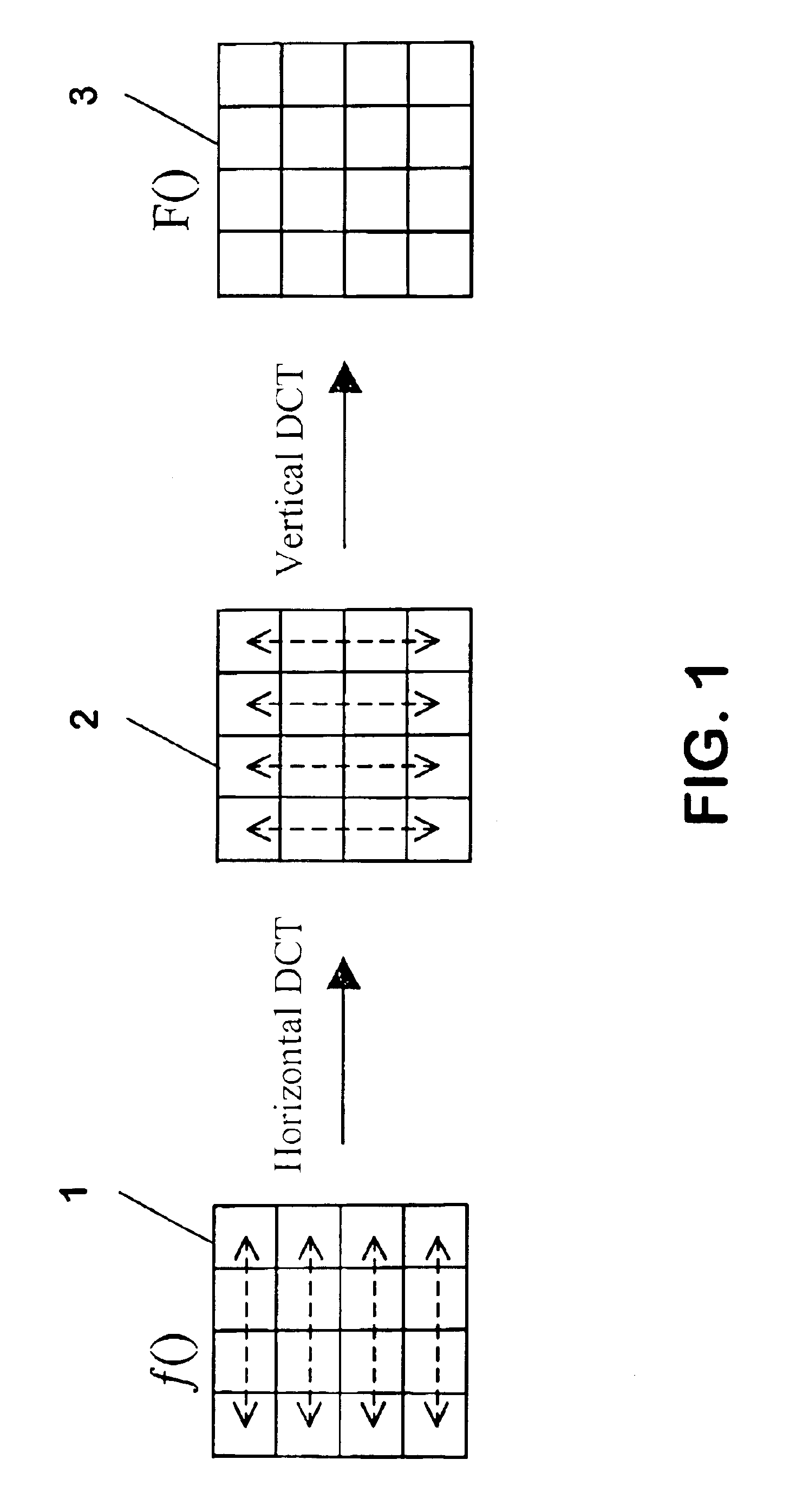
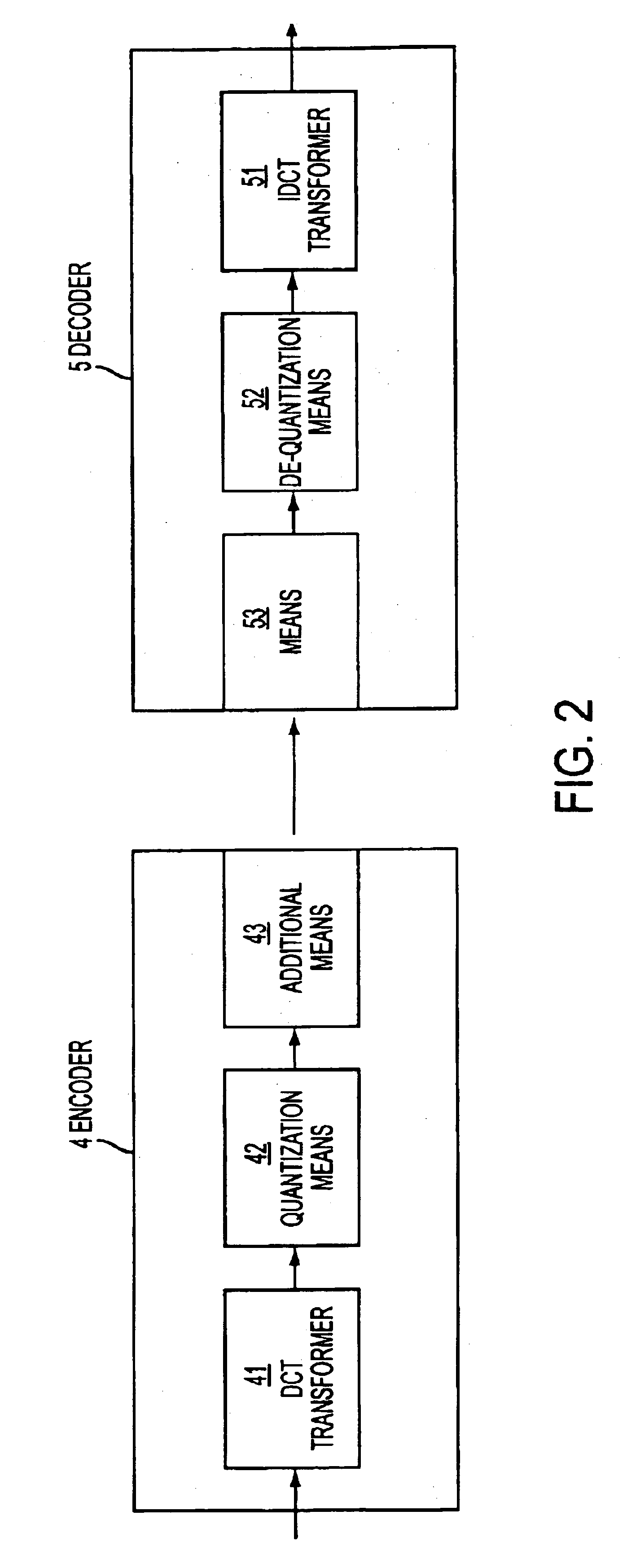
The invention relates to an approximation of a DCT and a quantization which are to be applied subsequently to digital data for compression of this digital data. In order to improve the transform, it is proposed to simplify a predetermined transform matrix to require less operations when applied to digital data. In addition, elements of the simplified transform matrix constituting irrational numbers are approximated by rational numbers. These measures are compensated by extending a predetermined quantization to include the operations which were removed in the simplification of the predetermined transform matrix. The included operations are further adjusted to compensate for the approximation of elements of the simplified transform matrix by rational numbers. If the simplified transform matrix and the extended quantization are used as basis for implementation, a fast transform with a good resulting quality can be achieved. An approximation of an IDCT employed in decompression of compressed digital data can be simplified correspondingly.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
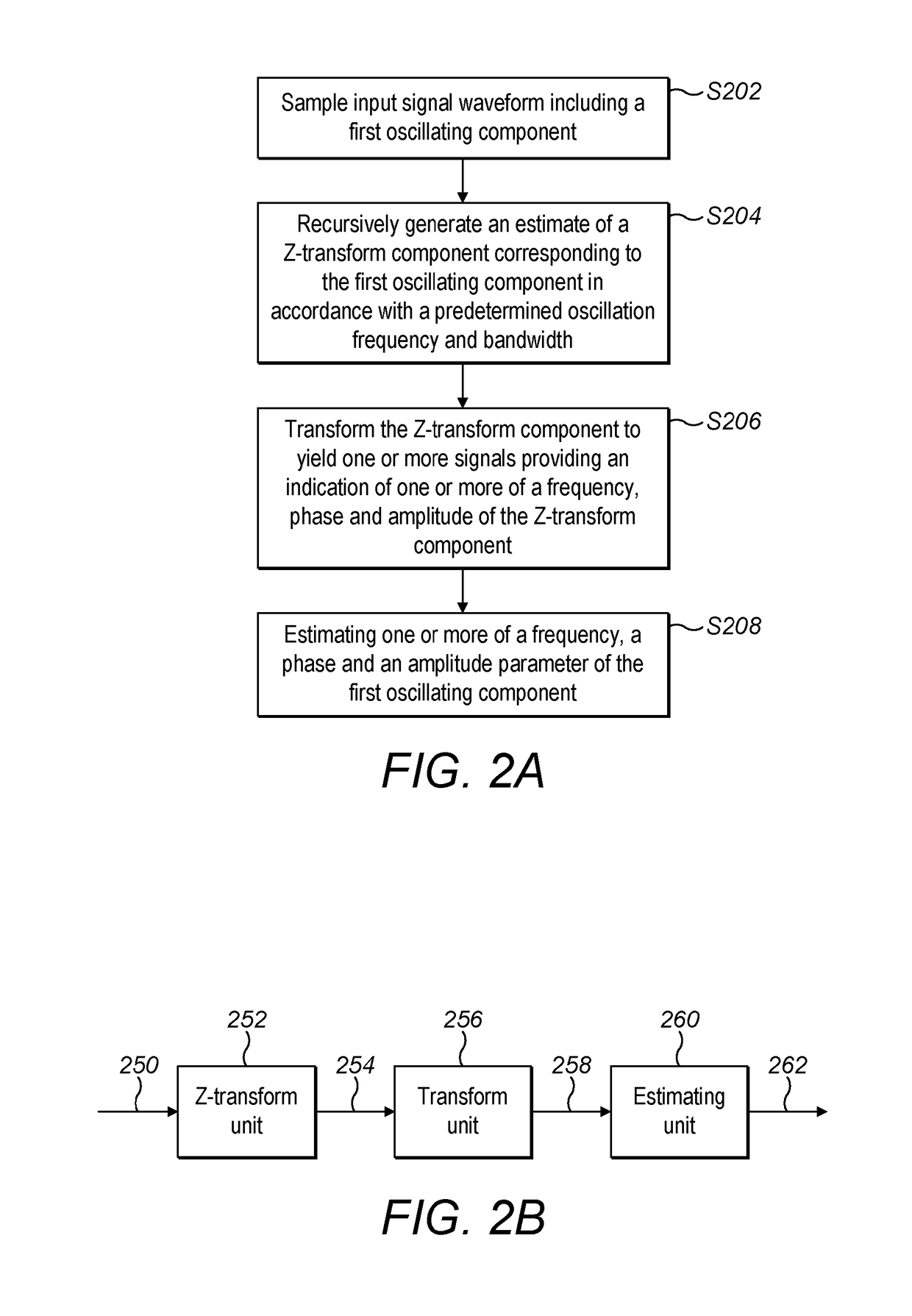
Parameter estimation and control method and apparatus
InactiveUS20180017604A1Effective approachAccurate parameterAC motor controlFrequency measurement arrangementRelative phaseComputer science
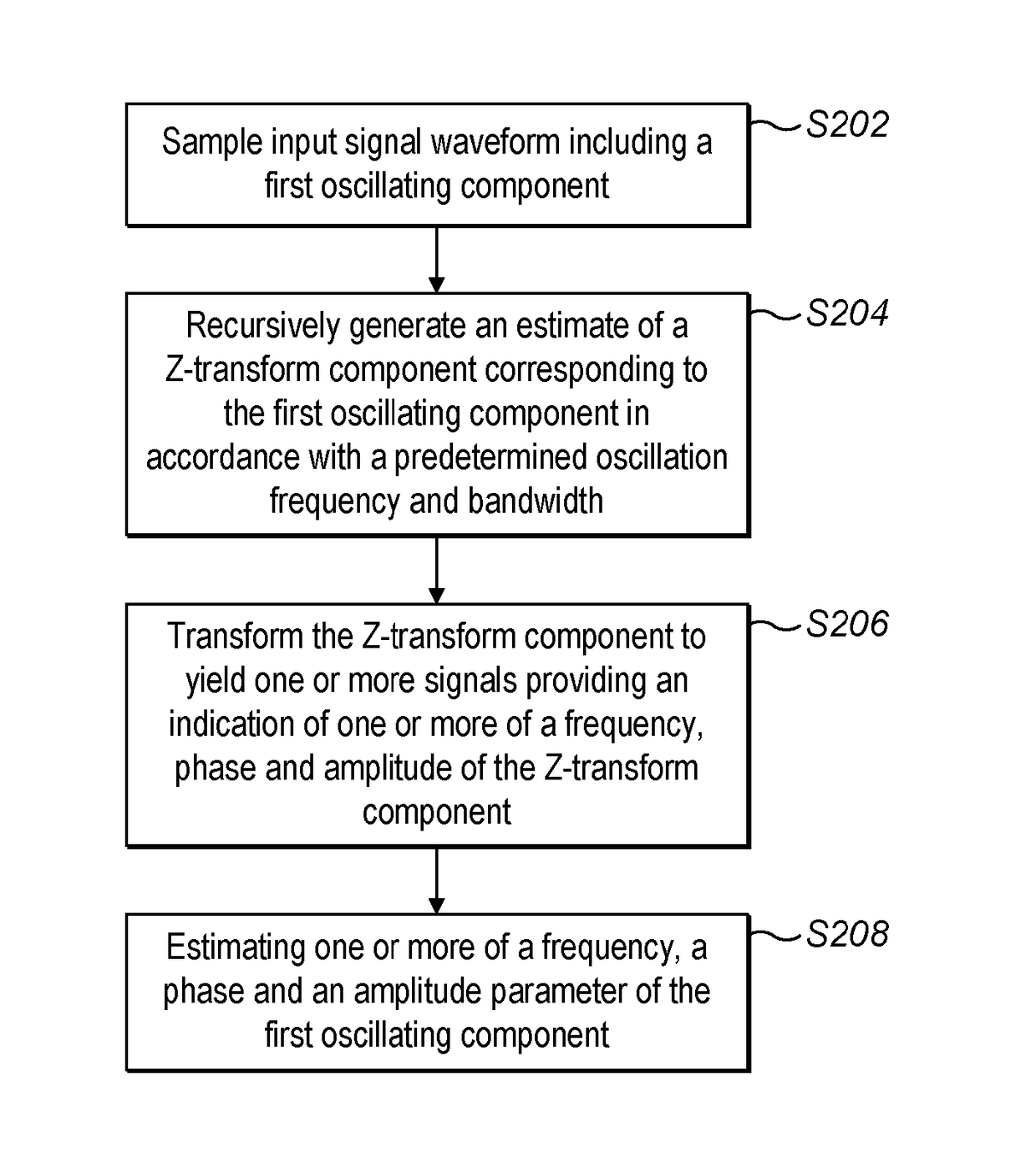
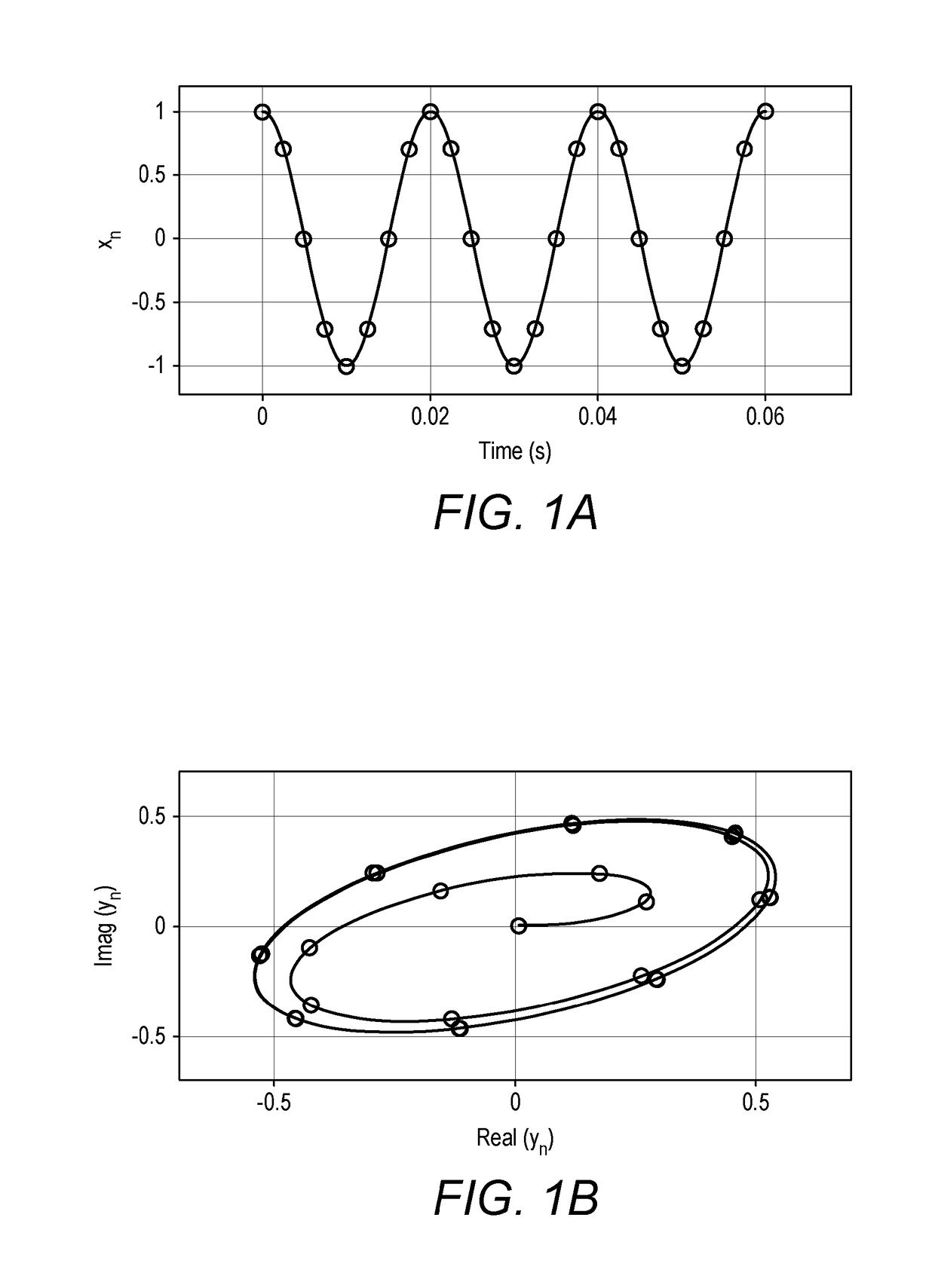
A method for recursively estimating at least one parameter of a first oscillating component represented by one or more sampled noisy input signal waveforms, the method comprising, recursively generating from the one or more sampled noisy input signals an estimate of a Z-transform component corresponding to the first oscillating component, forming, from the estimated Z-transform component, one or more signals providing an indication of one or more of a frequency and an amplitude of the Z-transform component; and estimating, from the one or more signals, one or more of a frequency, a relative phase and an amplitude parameter of the first oscillating component.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD
Seismic spectrum imaging method based on deconvolution generalized S transform
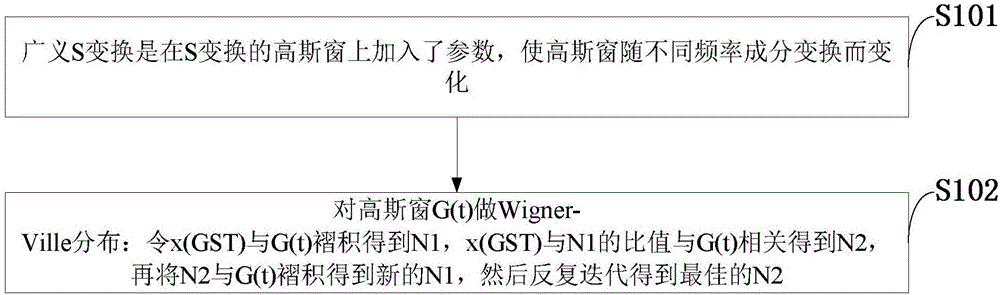
InactiveCN106405654AImprove forecast accuracyAdaptableSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingFrequency spectrumGeneralized s transform
The invention discloses a seismic spectrum imaging method based on deconvolution generalized S transform, which comprises the steps that a generalized S transform spectrum is acquired by performing two-dimensional convolution on Wigner distribution of original signals and a Gaussian window, a transform spectrum is acquired by performing generalized S transform on seismic data, and time-frequency distribution of the original signal can be acquired through deconvolution when the generalized S transform spectrum and the Wigner distribution of a window function are known. The seismic spectrum imaging method combines advantages of generalized S transform and Wigner-Ville distribution, generation of a cross term of the Wigner-Ville distribution is effectively suppressed through a generalized S transform window, and the generalized S transform spectrum is enabled to acquire high time-frequency aggregation at the same time; and deconvolution generalized S transform can adaptively adjust an analysis window along with variations of a frequency component, is applicable to time-frequency analysis for unstable seismic data, and can acquire high time-frequency resolution; and the seismic spectrum imaging method is applied to detecting the oil-gas possibility of a reservoir, thereby being conducive to improving the reservoir prediction accuracy.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
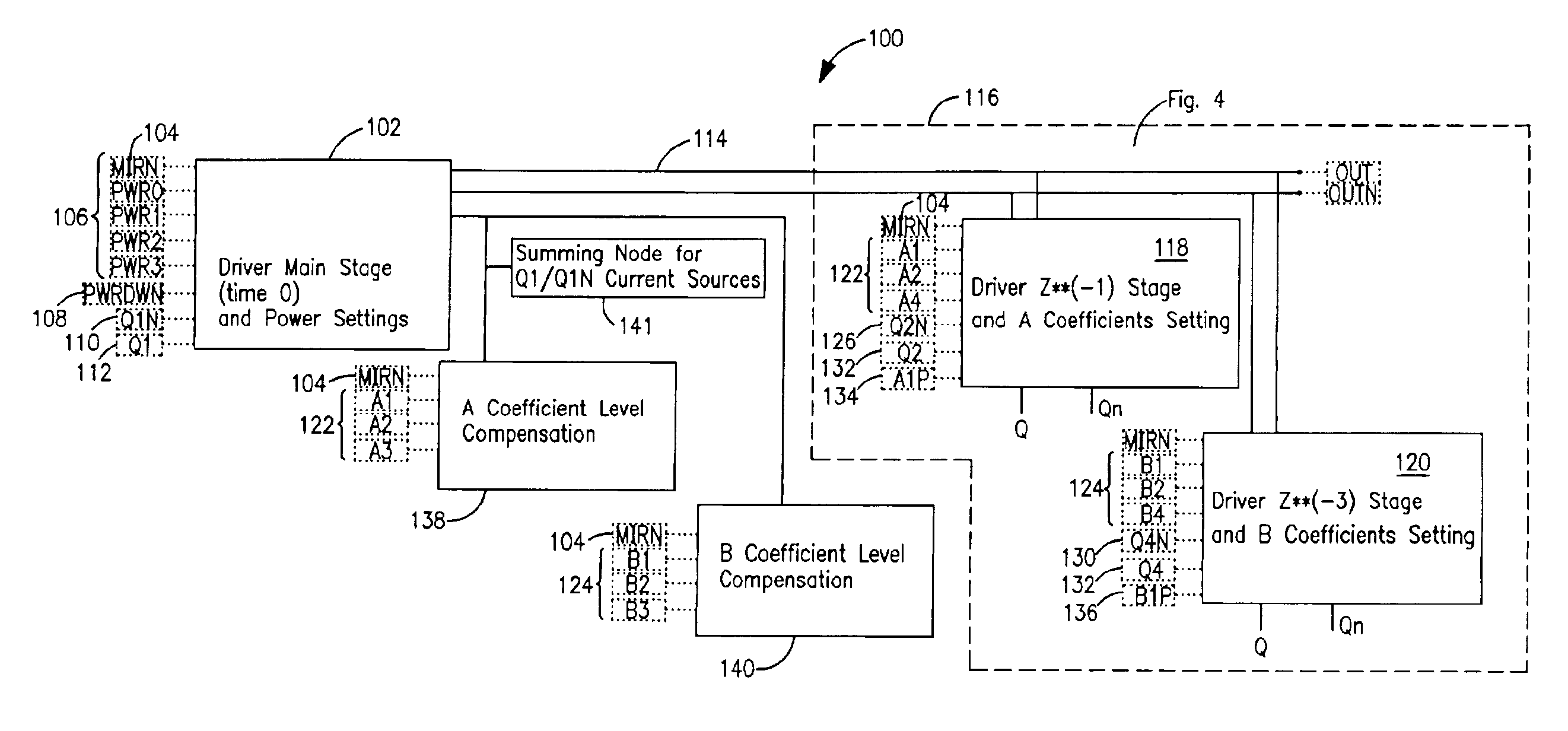
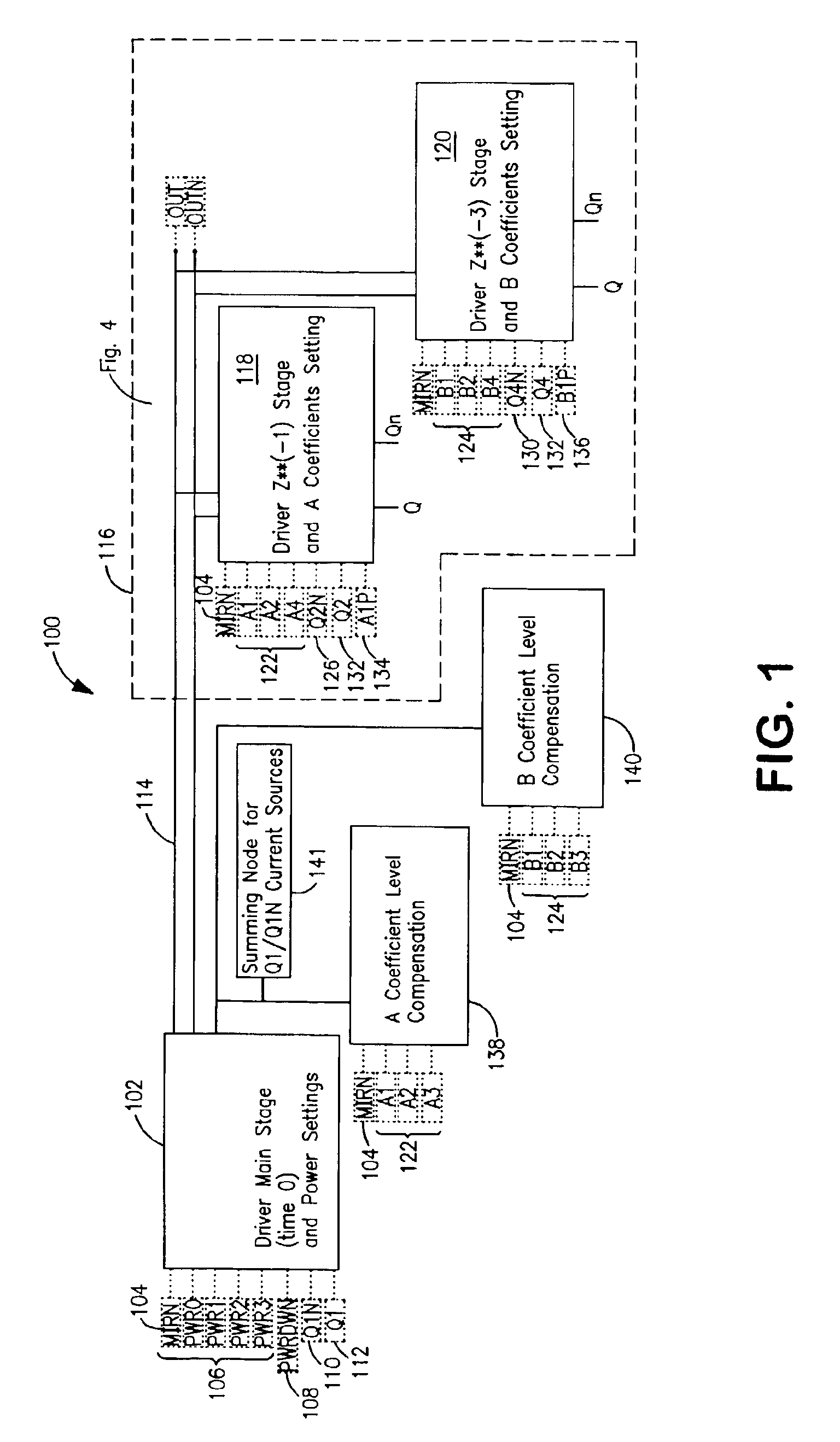
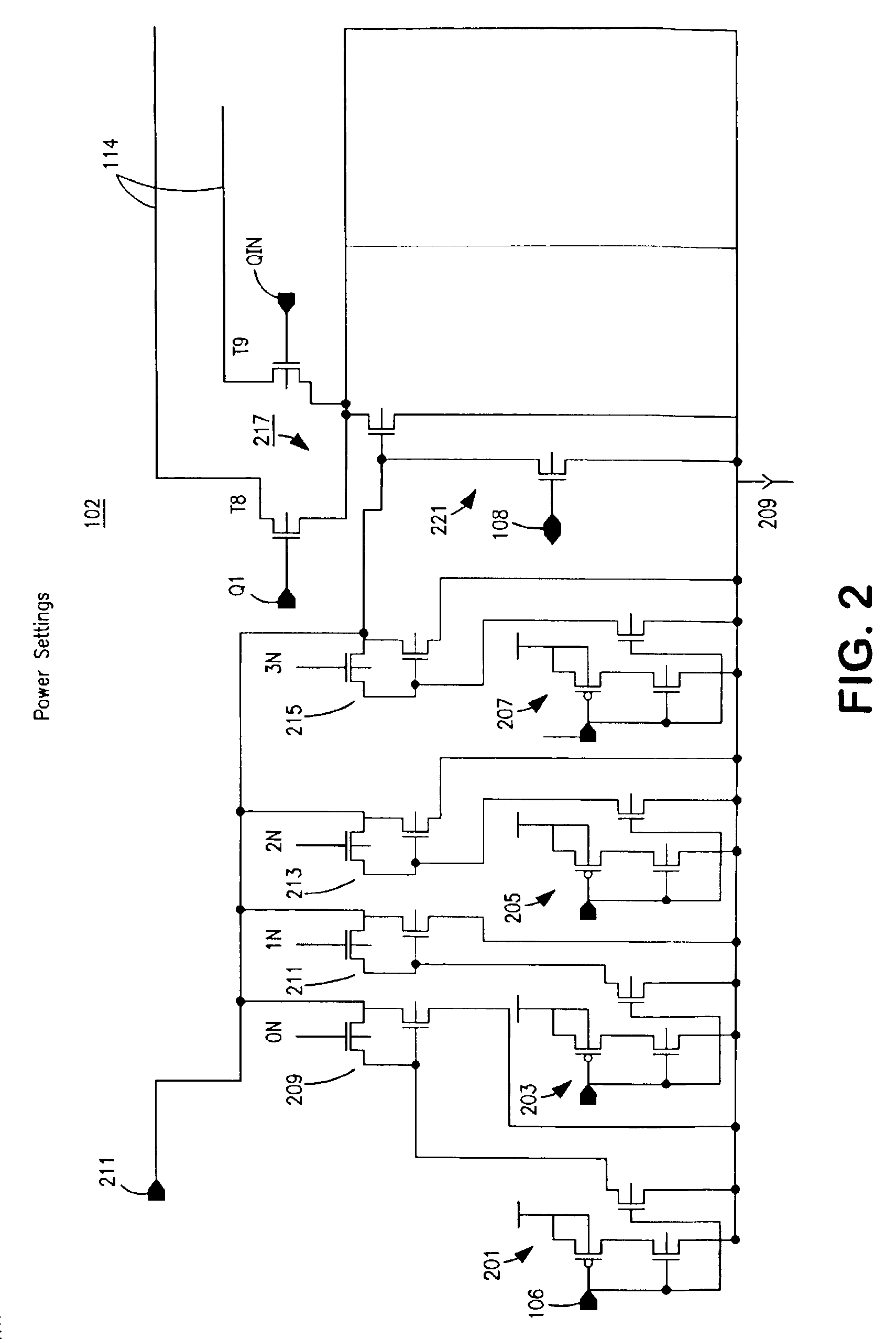
Programmable driver/equalizer with alterable analog finite impulse response (FIR) filter having low intersymbol interference and constant peak amplitude independent of coefficient settings
InactiveUS6999540B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceConstant peak amplitudeMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseDriver circuit
Owner:TWITTER INC
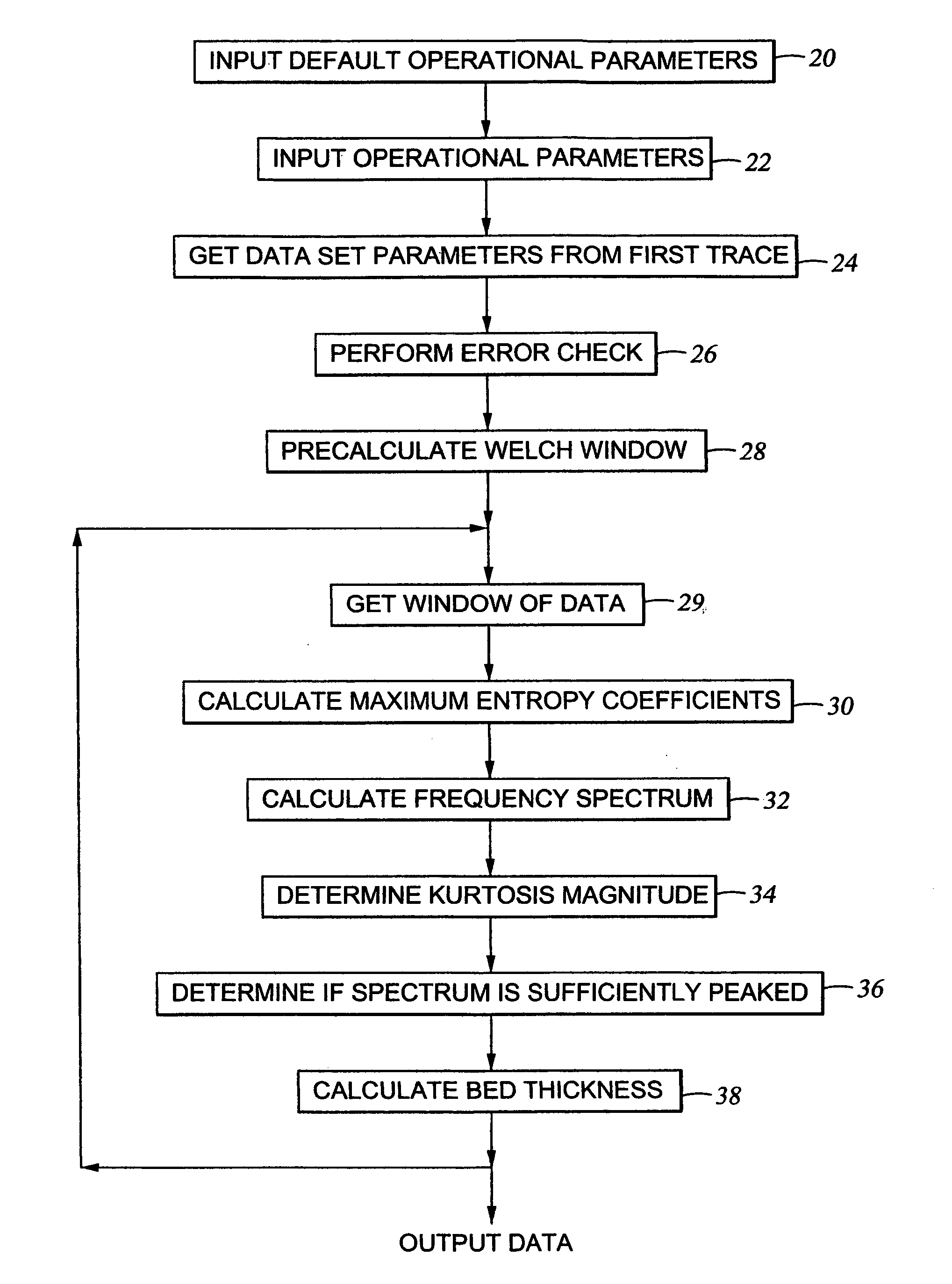
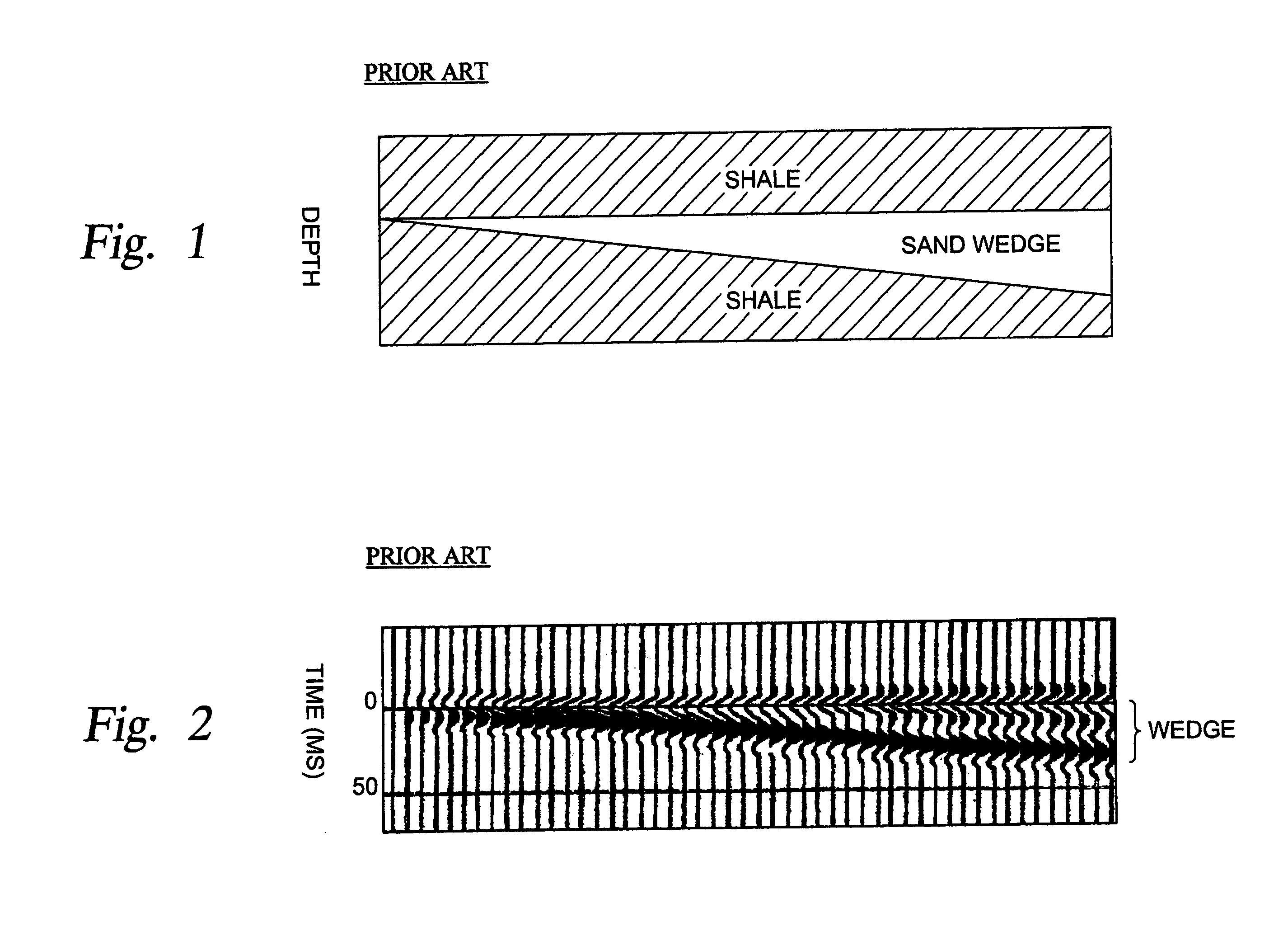
System for estimating thickness of thin subsurface strata
InactiveUS6985838B1Computation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingSpatial correlationFrequency spectrum
The invention comprises a method for processing seismic data to generate data related to the location of thin beds in the earth's subsurface. Seismic data windows are defined extending over selected portions of a group of spatially related seismic data traces. Frequency spectra of successively selected windows of the seismic data are generated by applying a transform having poles on the unit z-circle, where z is the z-transform, to the data windows; and the frequency spectra are utilized to generate data related to the location of thin beds in the earth's subsurface.
Owner:APACHE CORPORATION
Time frequency decomposition and reconstruction method of generalized S transform signals for synchronous extrusion
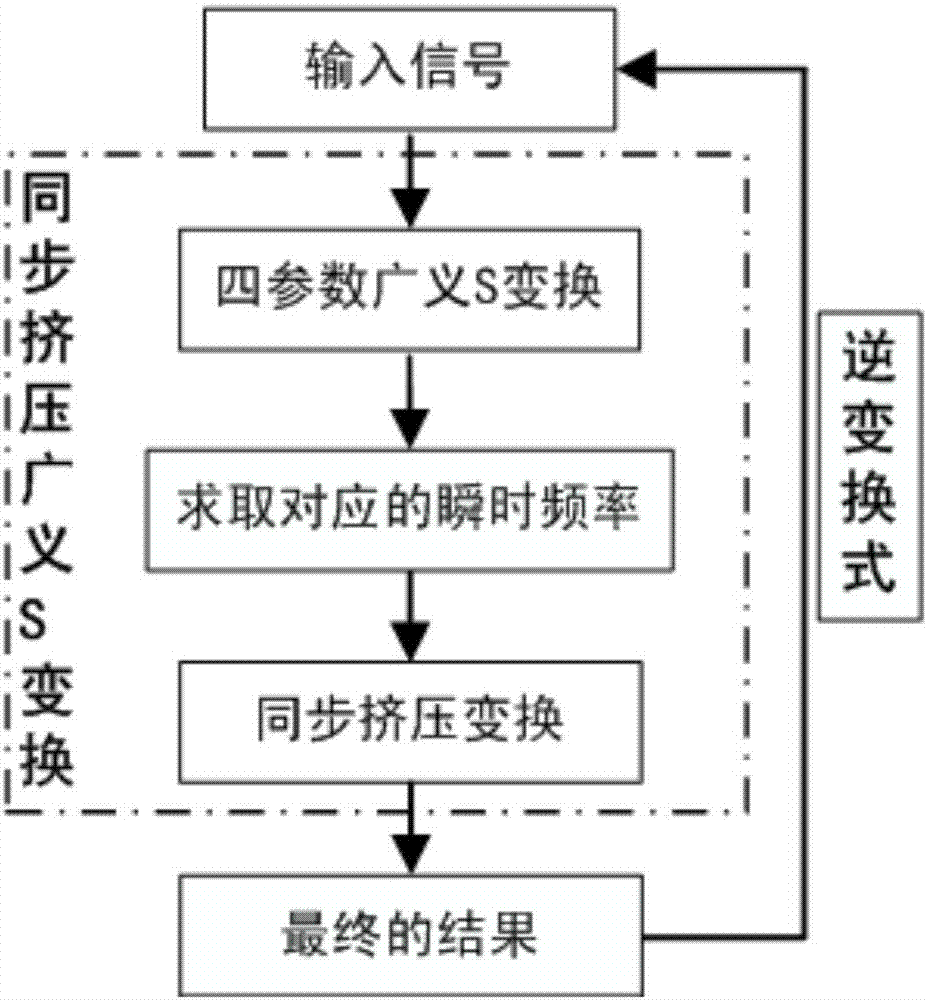
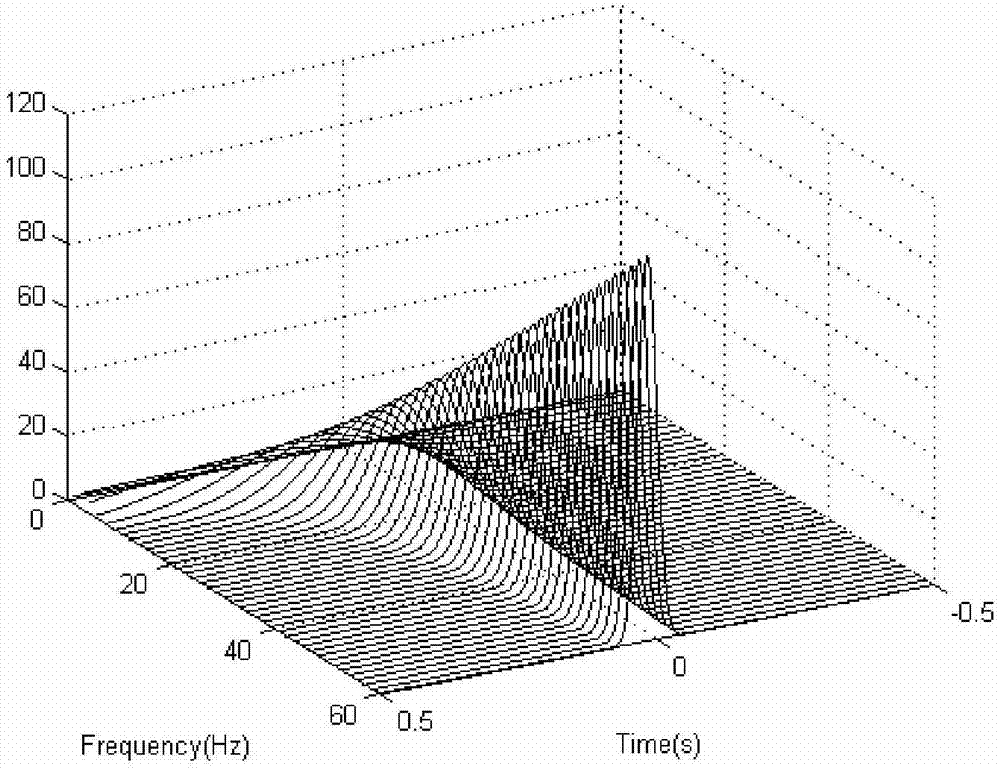
PendingCN107229597AHigh precisionImprove reconstruction accuracyComplex mathematical operationsFrequency spectrumDelayed time
The invention discloses a time frequency decomposition and reconstruction method of generalized S transform signals for synchronous extrusion. Firstly, the four parameter generalized S transform is conducted on a signal, the variation trend of a basic wavelet function is adjusted by the adjustment of the basic wavelet amplitude, energy attenuation rate, energy delay time and basic wavelet video rate; secondly, the modulus of the result of the four parameter generalized S transform is obtained, and the energy of each time-frequency point is obtained, thus the time-frequency spectrum is obtained; thirdly, the instantaneous frequency is obtained by the four parameter generalized S transform of the signal; fourthly, the frequency set after the generalized S transform is set as the central frequency set, each time frequency point corresponding to the instantaneous frequency close to the interval of the central frequency is extruded to the central frequency point, and the generalized S transform of synchronous extrusion is obtained; finally, the inverse transformation formula of generalized S transform for synchronous extrusion is deduced. The generalized S transform of synchronous extrusion has the advantages of synchronous extrusion transform and generalized S transform, and is a time-frequency decomposition and reconstruction method for high precision signals.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Discrete digital signal hopping sliding discrete Fourier transform method
InactiveCN104268123AEfficient removalGuaranteed smooth progressComplex mathematical operationsSliding discrete fourier transformS transform
The invention provides a digital discrete signal hopping sliding discrete Fourier transform method, namely an SDFT (Modulated Hopping DFT, mHDFT) transform method for solving the problem of potential instability and accumulated errors of HDFT transform of an HDFT (hexagon discrete Fourier transform) transform method in practical engineering application. The method utilizes DFT circulating frequency domain shifting characteristics and modified UVT transform for effectively removing twiddle factors in a feedback loop of an HDFT resonator, accurately fixing HDFT poles on a unit circle and obtaining a DFT transform result of a frequency point k at n time, thereby effectively reducing the cumulative errors as well as ensuring the constant stability of the HDFT.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Linear predictive coding implementation of digital watermarks
InactiveUS7730317B2User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsCarrier signalData encoding
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
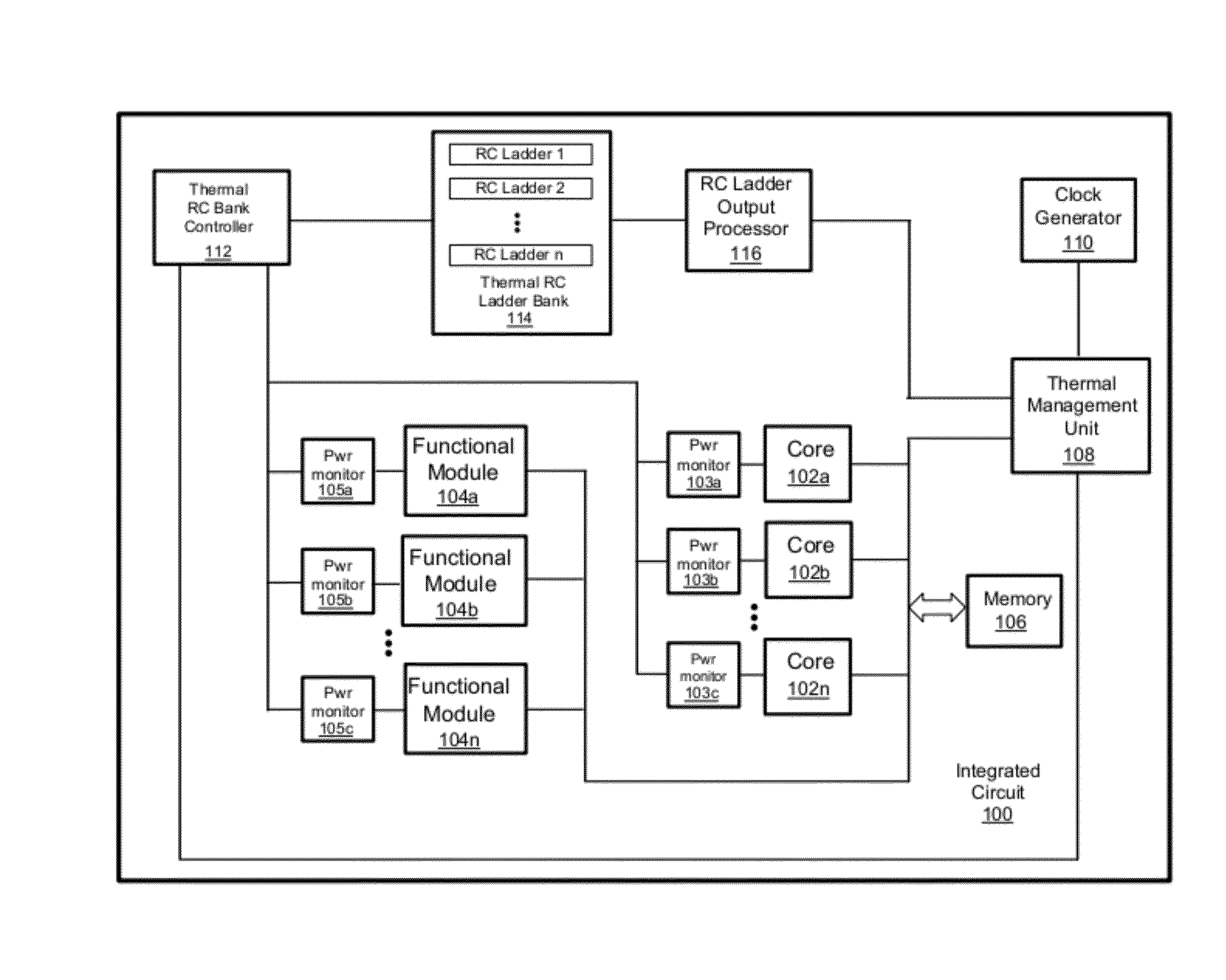
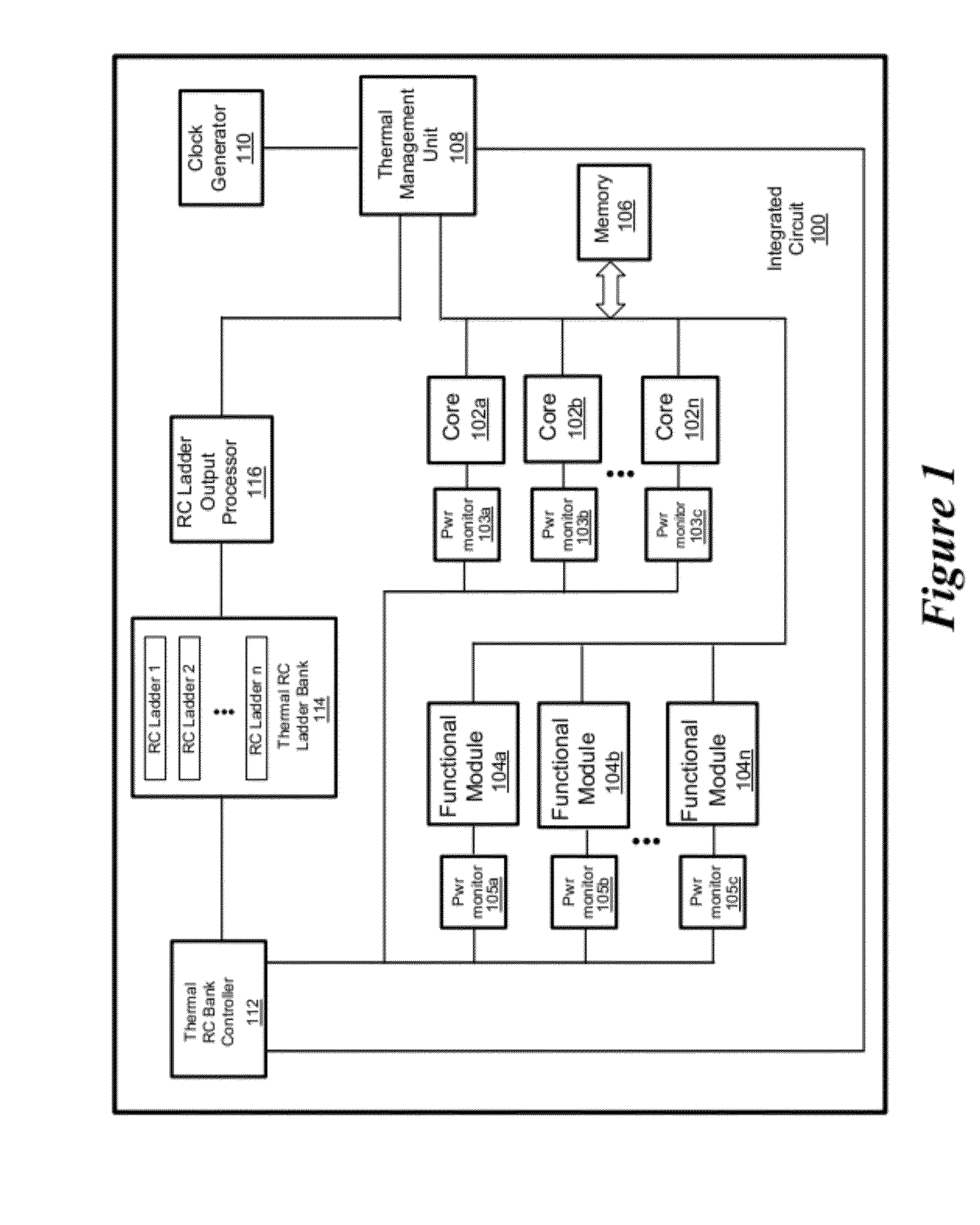
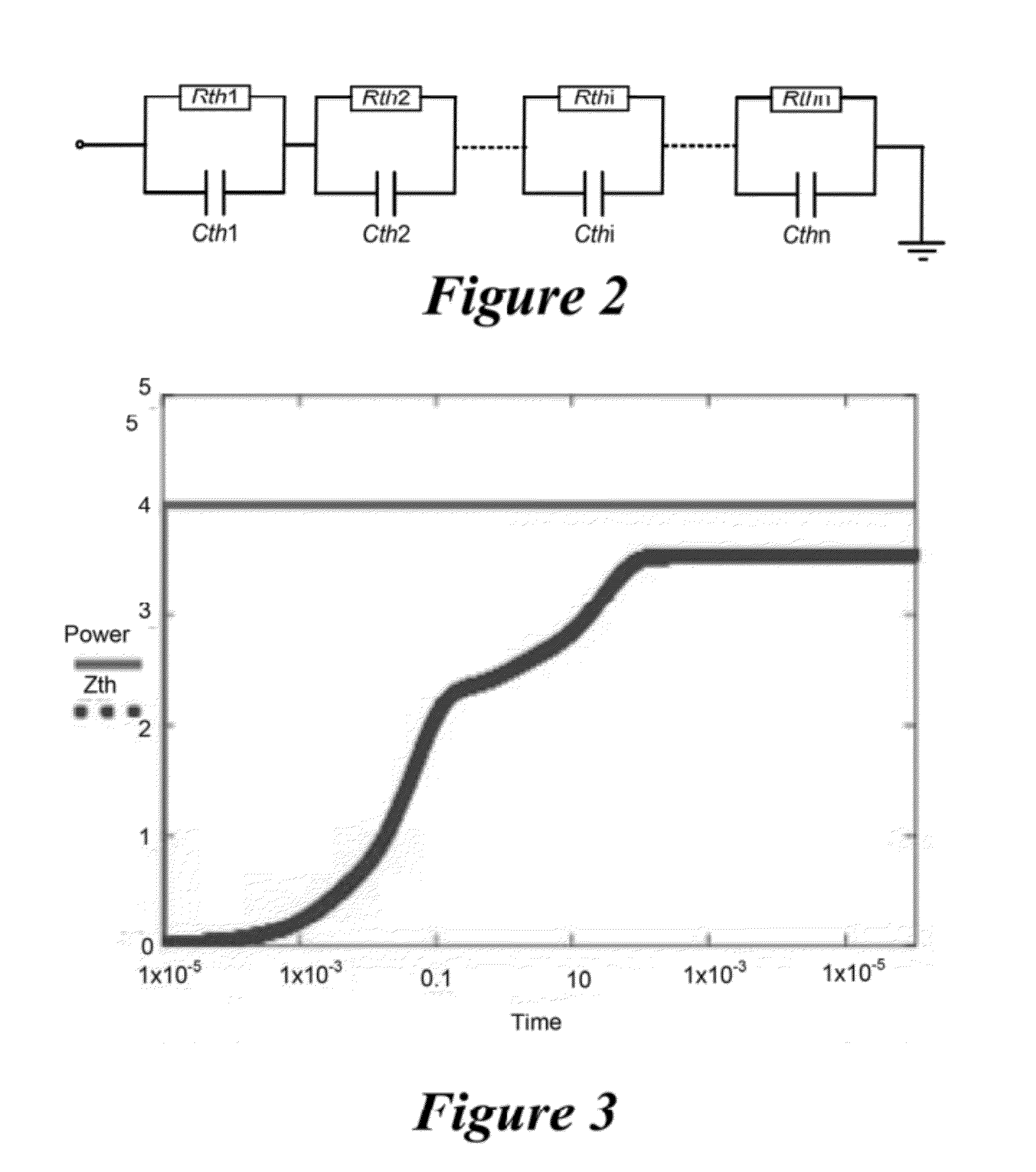
Transient Thermal Modeling of Multisource Power Devices
ActiveUS20120278029A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionTemperature responseEngineering
Embodiments of systems and methods for improved measurement of transient thermal responses in electronic systems are described herein. Embodiments of the disclosure use the known thermal transfer function of an electronic system to generate an equivalent resistor-capacitor (RC) network having a dynamic response that is identical to a given power excitation as the actual electronic system would have to that power excitation. Using the analogy between thermal and electrical systems, a Foster RC network is constructed, comprising a plurality of RC stages in which resistors and capacitors are connected in parallel. Subsequently, the analog thermal RC network is converted into an infinite impulse response (IIR) digital filter, whose coefficients can be obtained the Z-transform of the analog thermal RC network. This IIR digital filter establishes the recursive relationship between temperature output at the current time step and measured power input at the previous time step. Using this IIR digital filter, temperature response subject to arbitrary time-dependent power can be calculated in very small amount of time compared with prior art methods.
Owner:ATI TECH INC +1
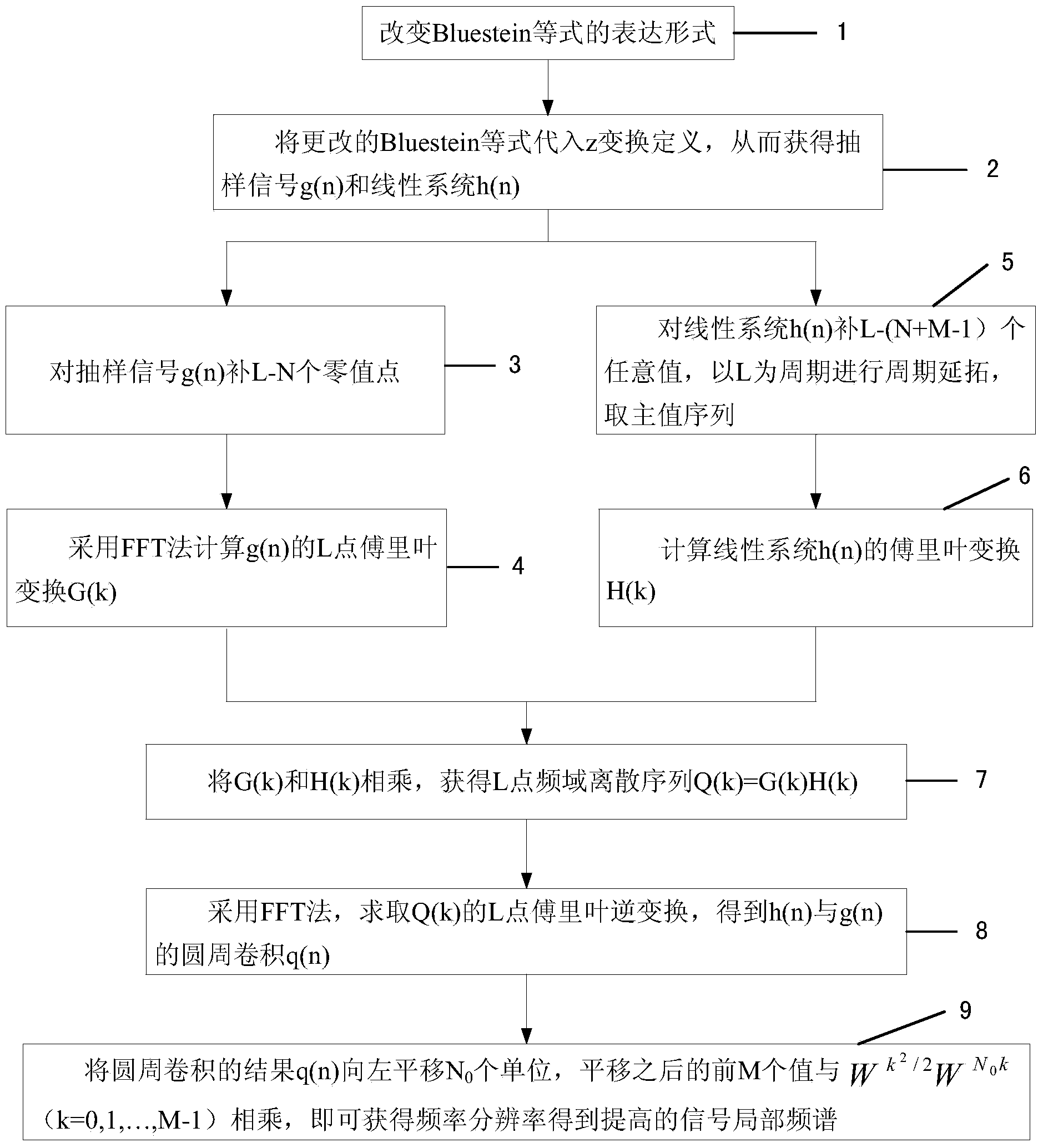
Signal spectrum zooming method based on linear frequency modulation z transform
InactiveCN103646011AReduce storageSmall amount of calculationComplex mathematical operationsFrequency spectrumPartition of unity
The invention provides a signal spectrum zooming method based on linear frequency modulation z transform. A symmetrical linear system h(n) is obtained by changing the expression form of a Bluestein equation and carrying out zero filling and periodic extending on the linear system h(n); the method for calculating the Fourier transform of an L point linear system sequence h(n) through a stored L / 2+1 point linear system sequence is put forward; the result q(n) of the circular convolution is horizontally moved leftwards by N0 units, the front M values obtained after horizontal movement are multiplied with k (k=0,1,..., M-1), and then the signal partial spectrum with the improved frequency resolution can be obtained. By means of the scheme, the storage data size of the linear system sequence and the Fourier transform of the linear system sequence can be reduced, the storage space is saved, the Fourier transform of an L point linear system can be calculated through the stored L / 2+1 point linear system data, the calculated quantity of an FFT is reduced, and the calculating efficiency is improved.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
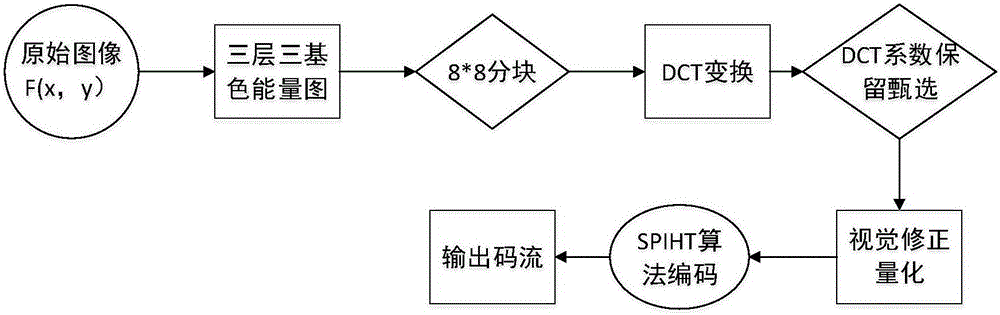
Visual perception correction image compression method based on DCT transform
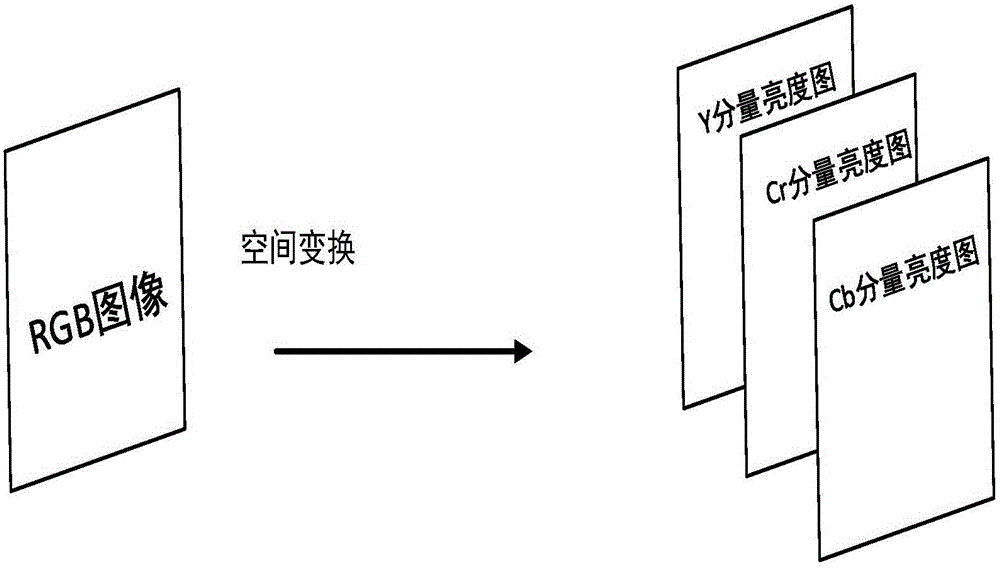
InactiveCN106612436AIncrease the compression ratioReduced compression efficiencyDigital video signal modificationImage compressionSpatial transformation
The invention proposes a visual perception correction image compression method based on DCT transform. The method is used for lossy compression of an image, and comprises the following steps: firstly, converting the image into a Ycrcb format via domain space transformation; secondly, decomposing the image into 8x8 image subblocks, and performing DCT transform on each image subblock; thirdly, in a DCT coefficient of each subblock, processing the coefficient through a judgment method and then decomposing the coefficient into a high frequency coefficient and a low frequency coefficient, wherein an error compensation mechanism is adopted for the high efficiency coefficient and visual perception correction transformation is performed on the low frequency coefficient, and then encoding; and finally, the process of reconstructing the image is an inverse operation of the compression process. Through the method of the invention, the image can not only get a higher compression ratio, but also the compression efficiency of the image is not reduced due to the increase of the amount of calculation; and meanwhile, the reconstructed image is analyzed, the image restoration degree is increased, the signal to noise ratio is enhanced, and the image restoration quality is obviously improved, therefore, the visual perception correction image compression method based on the DCT transform provided by the invention has strong practicability.
Owner:SICHUAN YONGLIAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
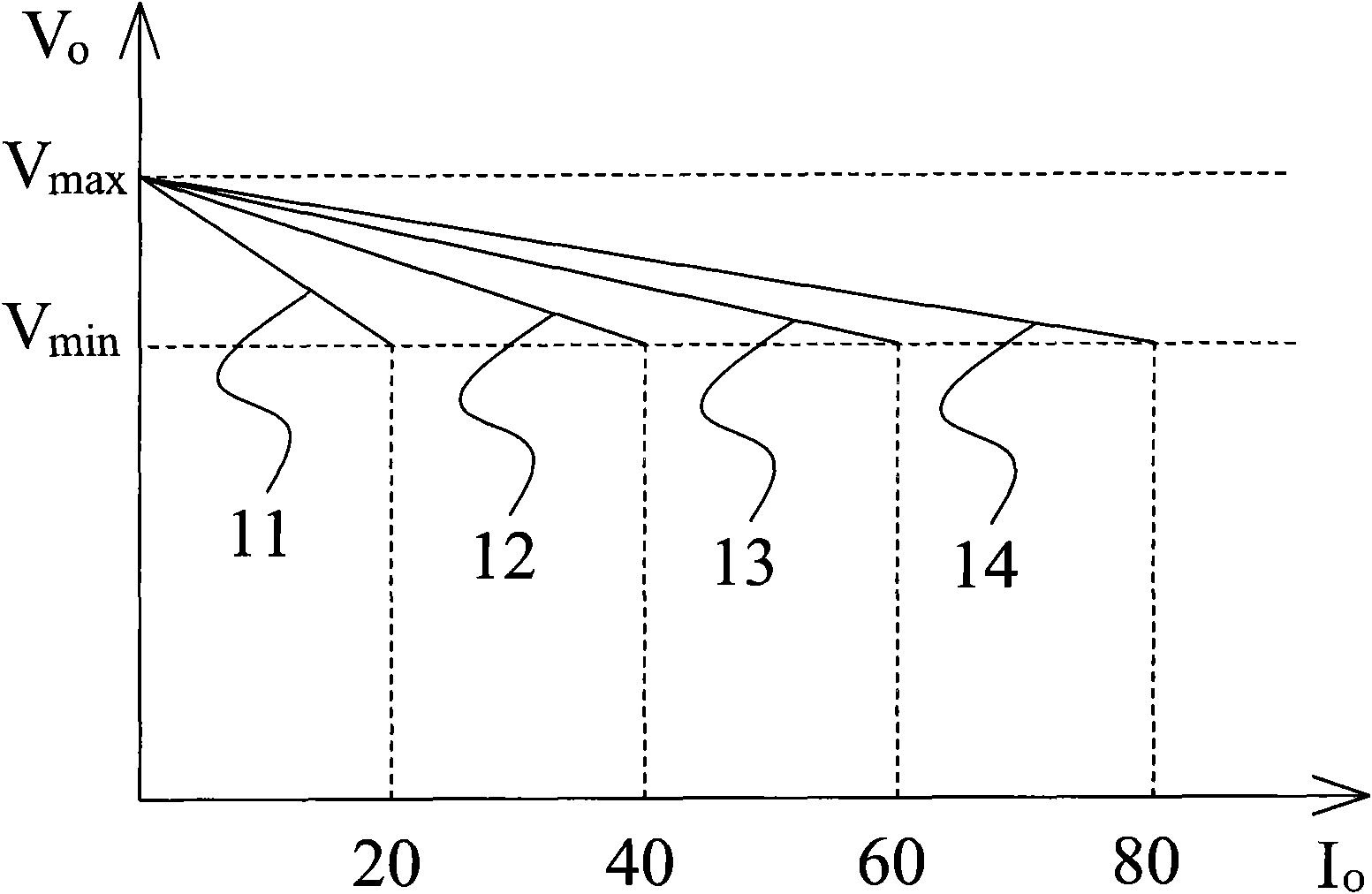
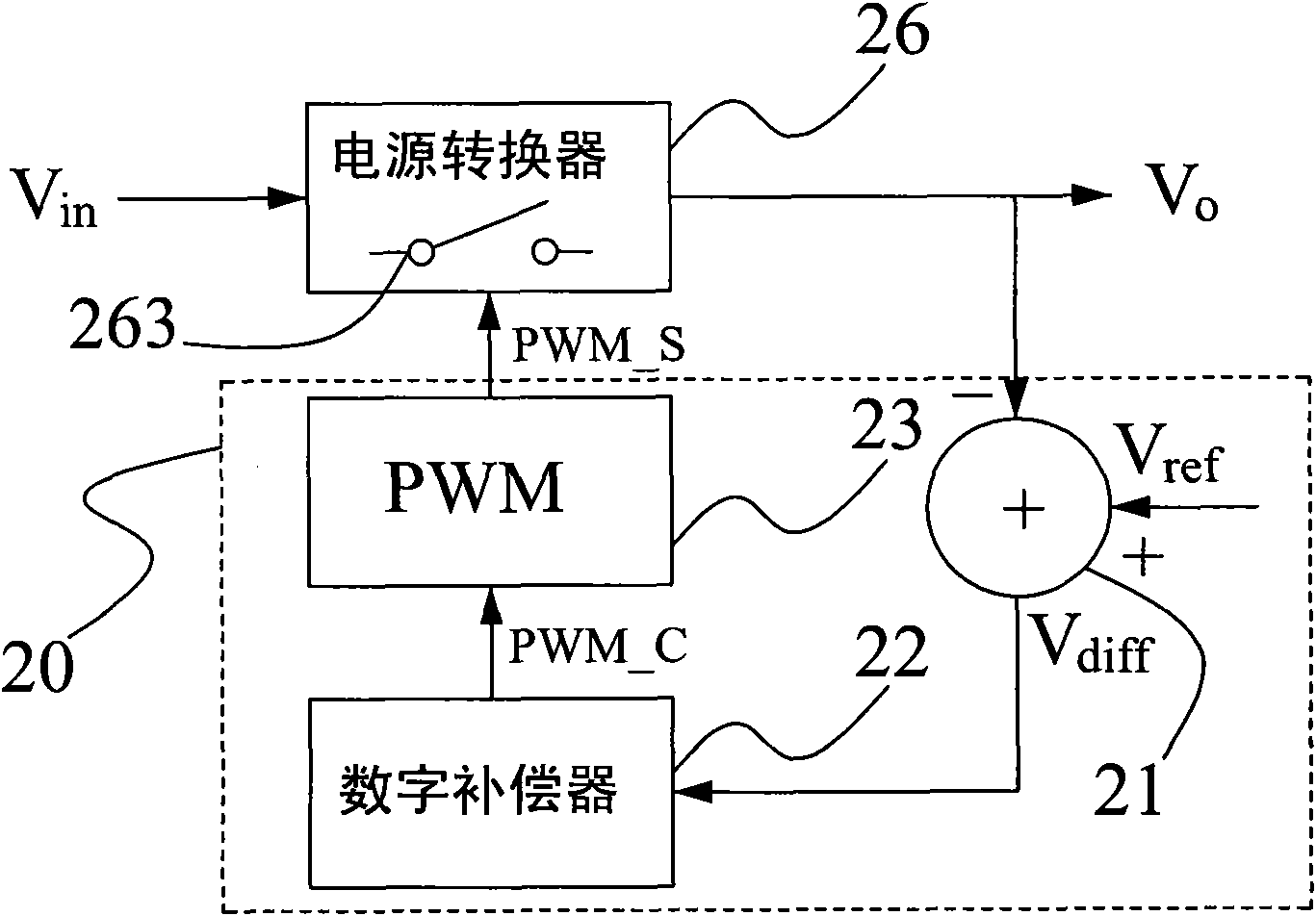
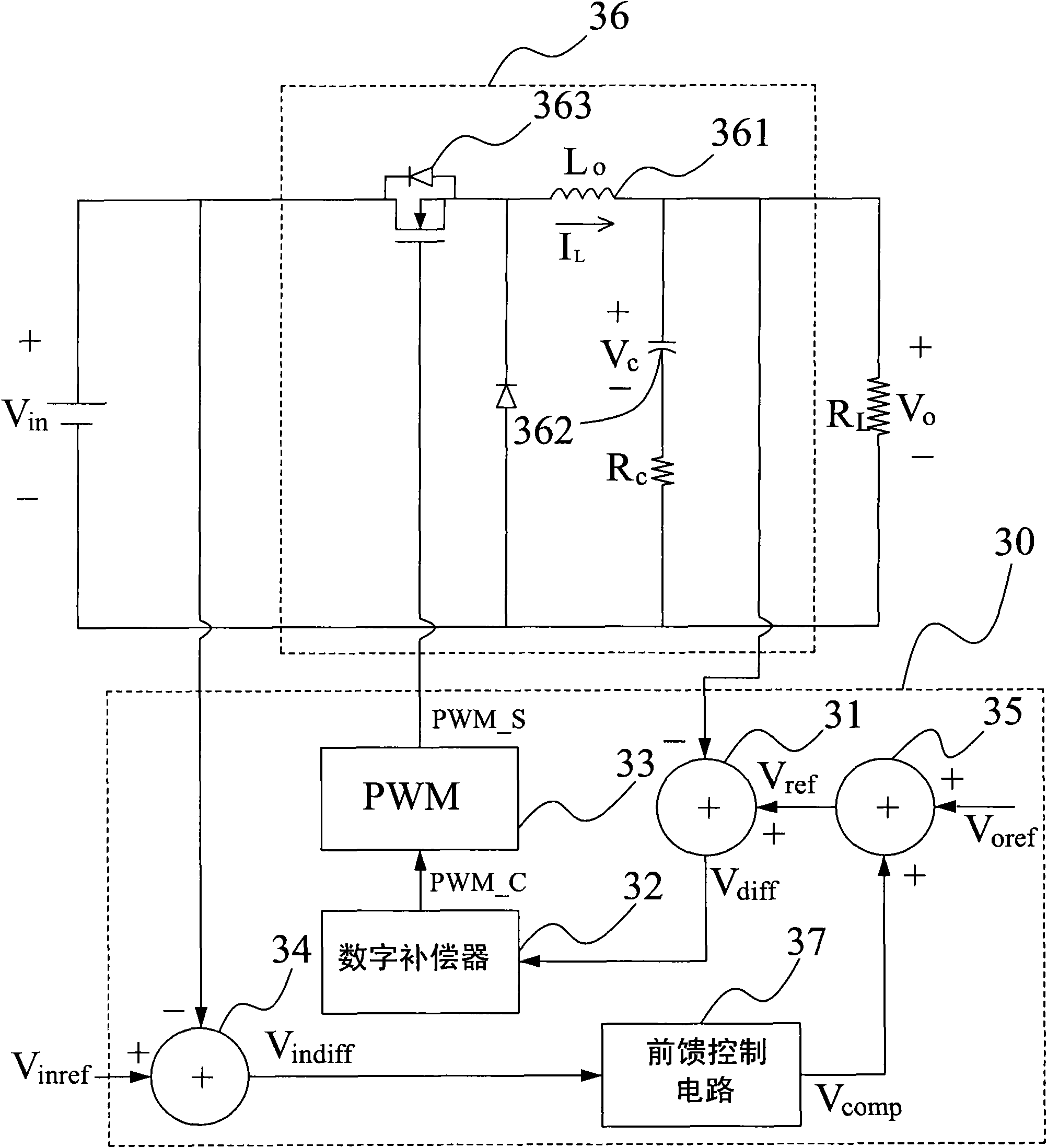
Control circuit and control method for power converter with adaptive voltage position control
InactiveCN102044966AAchieve load line functionRealize the control functionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalVoltage reference
The invention provides a control circuit and control method for a power converter with adaptive voltage position control. The control method comprises the following steps: acquiring an output voltage difference between an output voltage and an output reference voltage by using a summator; referring to the output voltage difference by using a digital compensator with a Z-transform transfer function so as to generate a pulse width control signal, adjusting least significant bit (LSB) of the denominator coefficient of the Z-transform transfer function to realize the load line controlling function of the power converter; and controlling the pulse width modulation circuit by using the pulse width control signal to generate a pulse width modulation signal for controlling power-on / off of the power of the power converter. Therefore, the control function of a negative load line or a positive load line, and a variable load line controlling function required by a multi-phase converter can be easily realized without complicated operation.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Method for estimating resonance frequencies
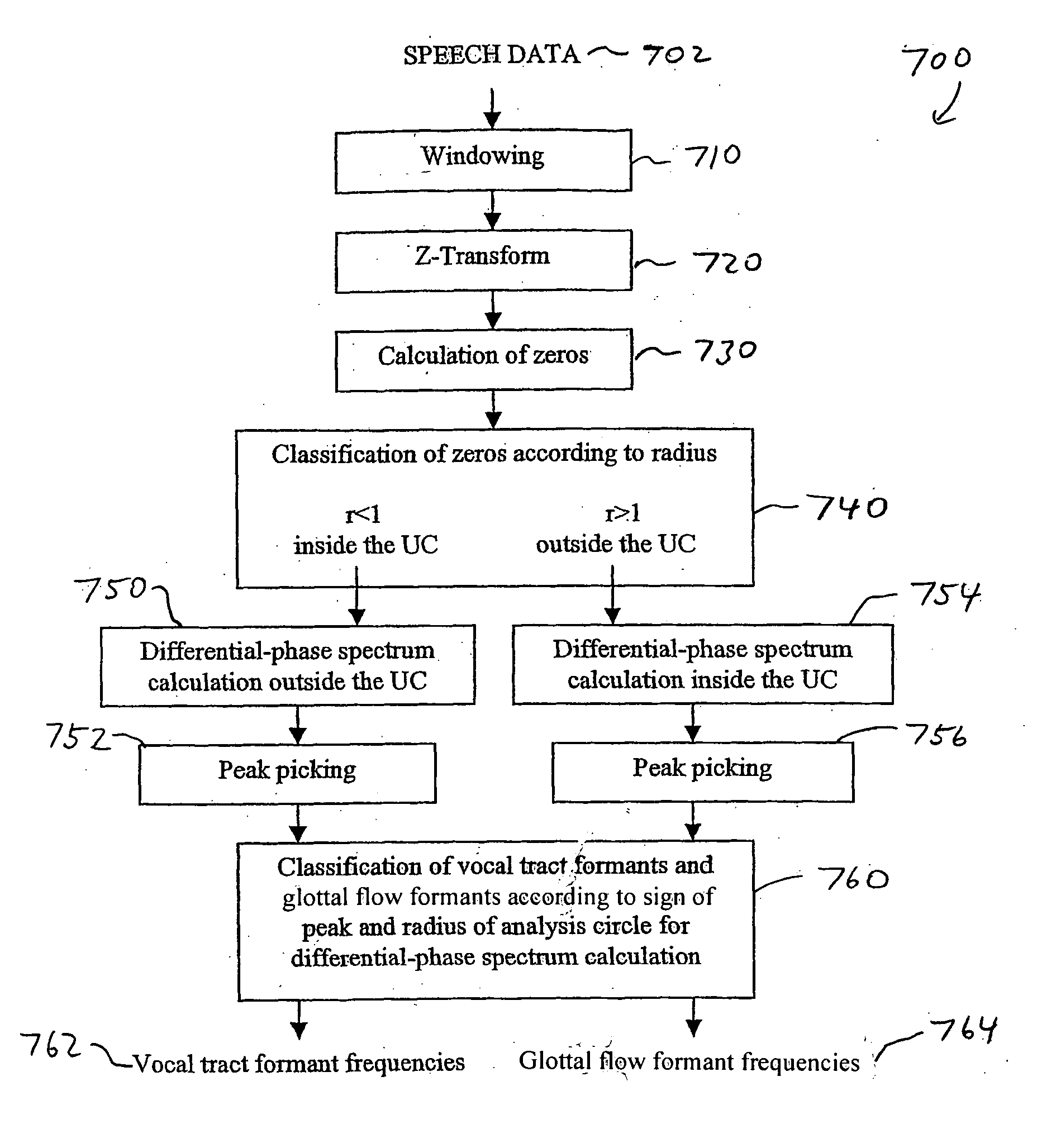
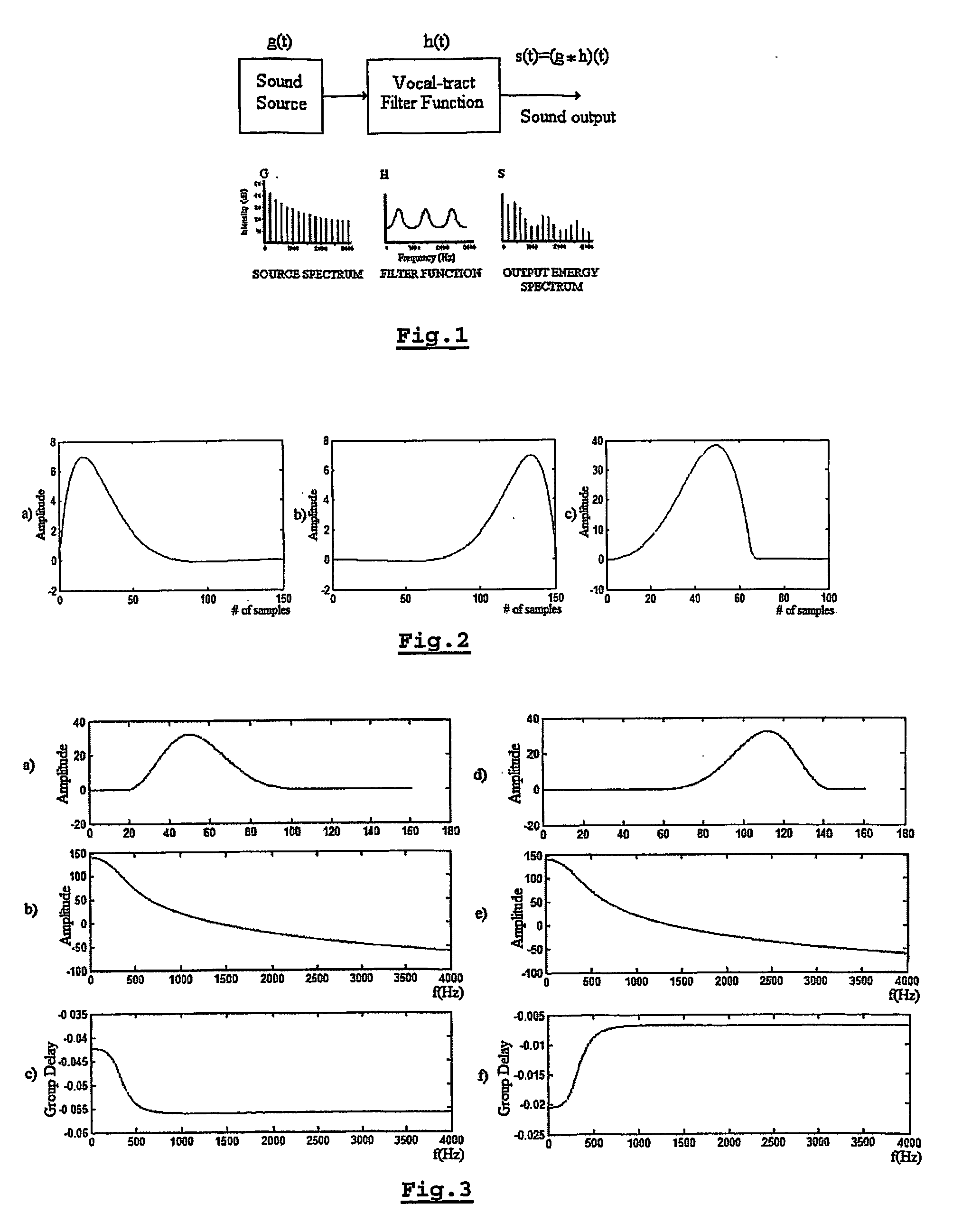
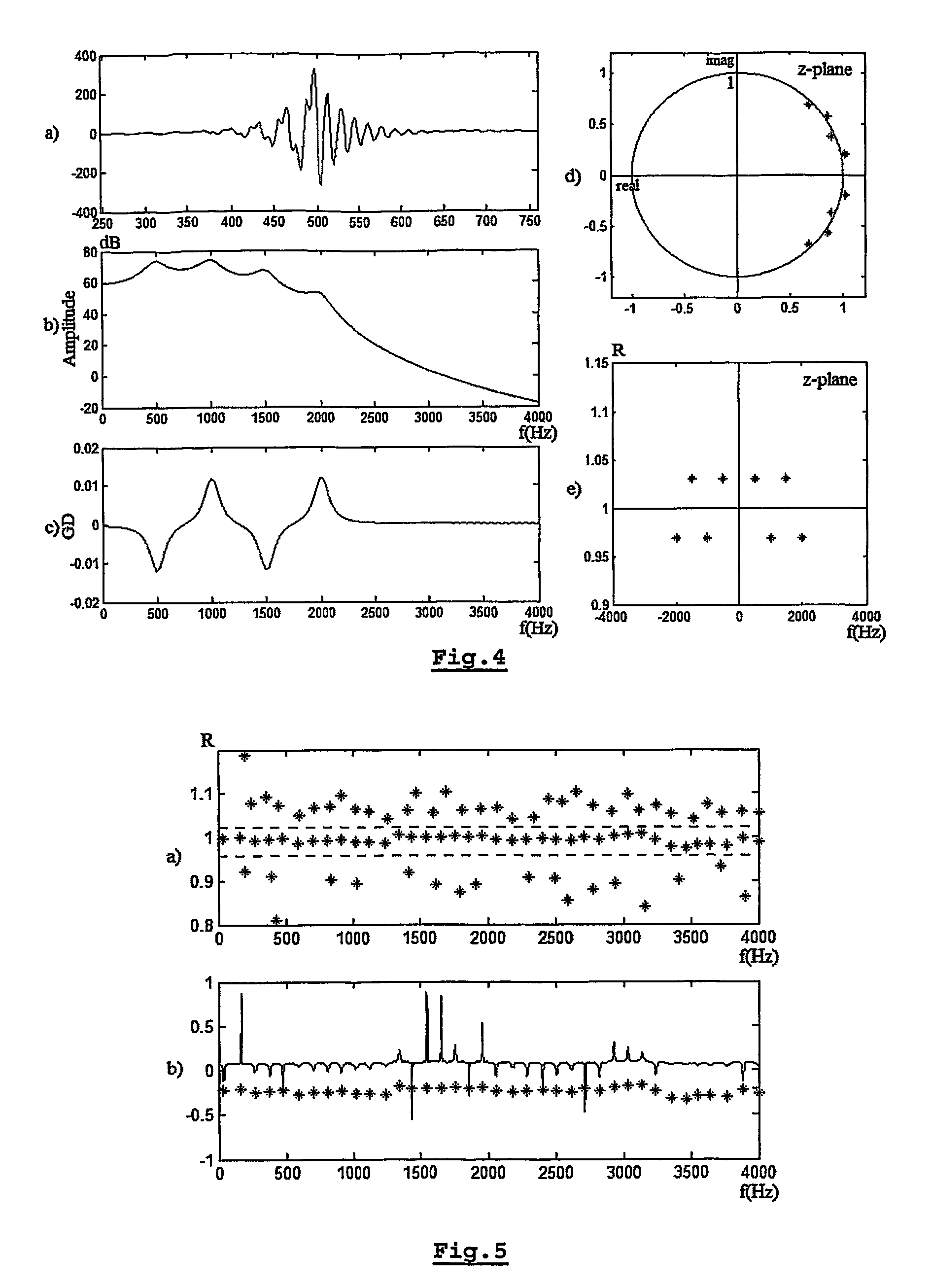
The present invention is related to a method for estimating from an input signal the resonance frequencies of a system modelled as a source and a filter, comprising the steps of—determining the Z-transform of the input signal,—calculating the differential-phase spectrum of the Z-transformed input signal, whereby the Z-transform is evaluated on a circle centered around the origin of the Z-plane,—detecting the peaks on said differential-phase spectrum,—attributing the peaks to either the source or the filter,—estimating the resonance frequencies from the peaks.
Owner:FACULTE POLYTECNIQUE DE MONS
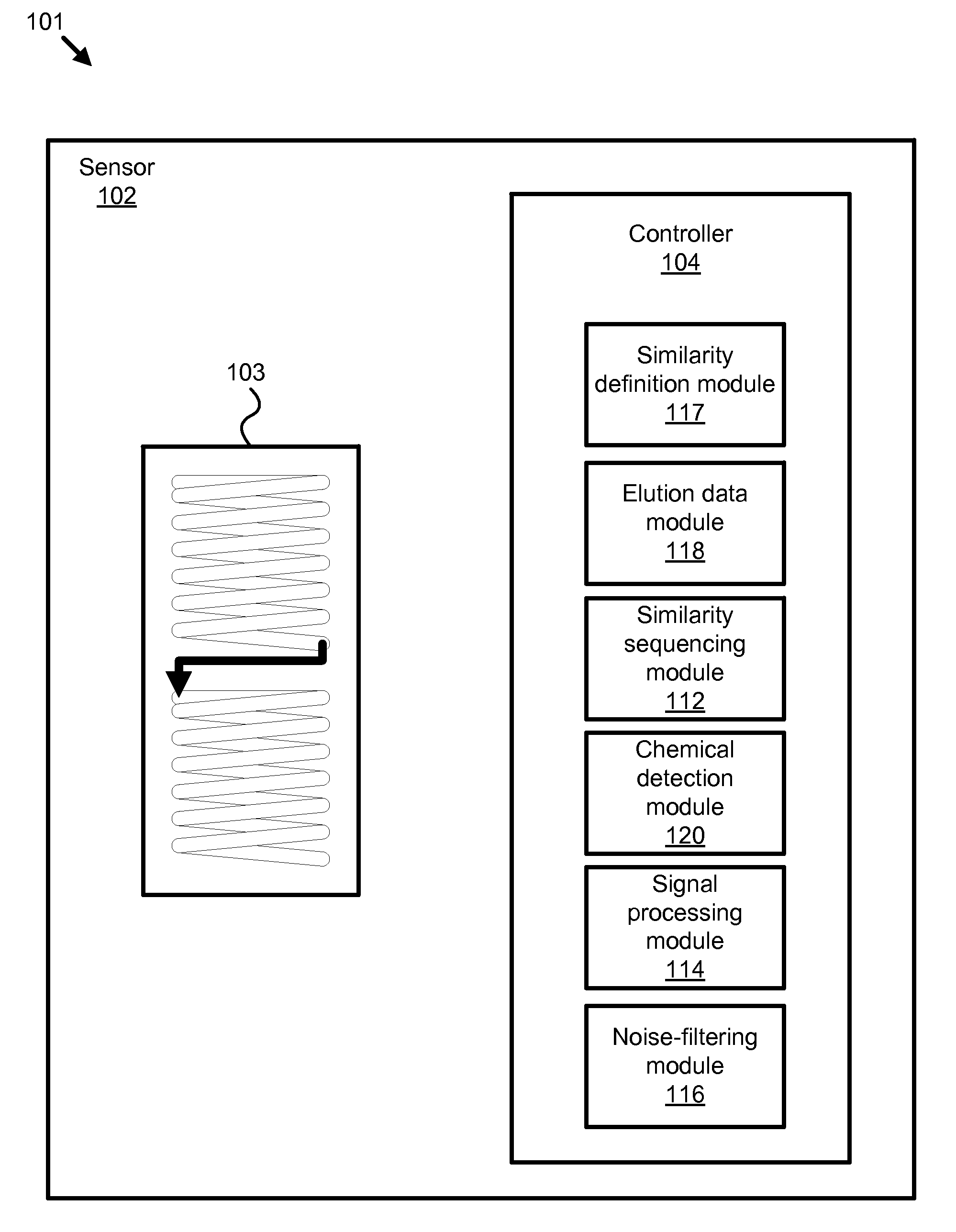
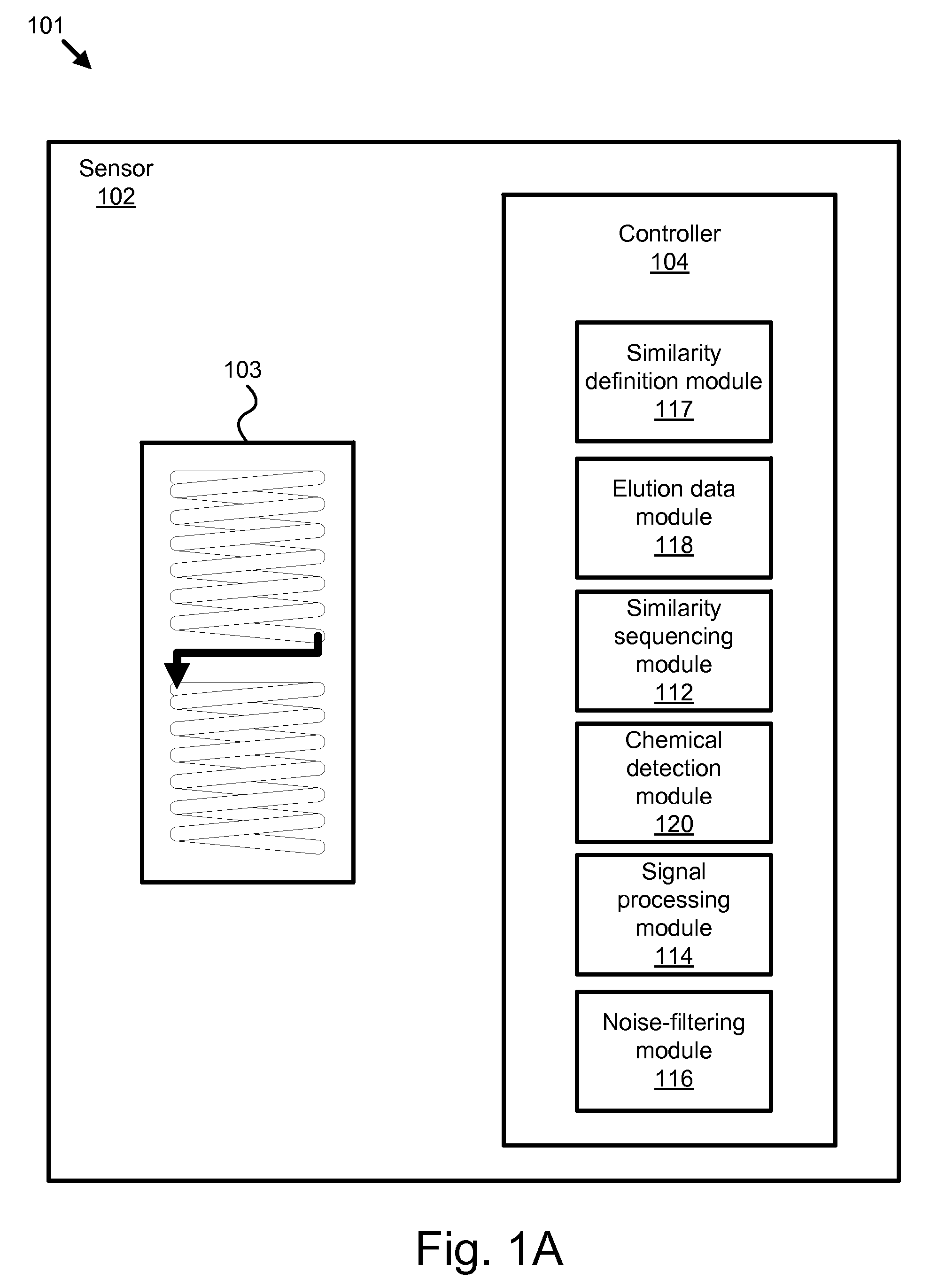
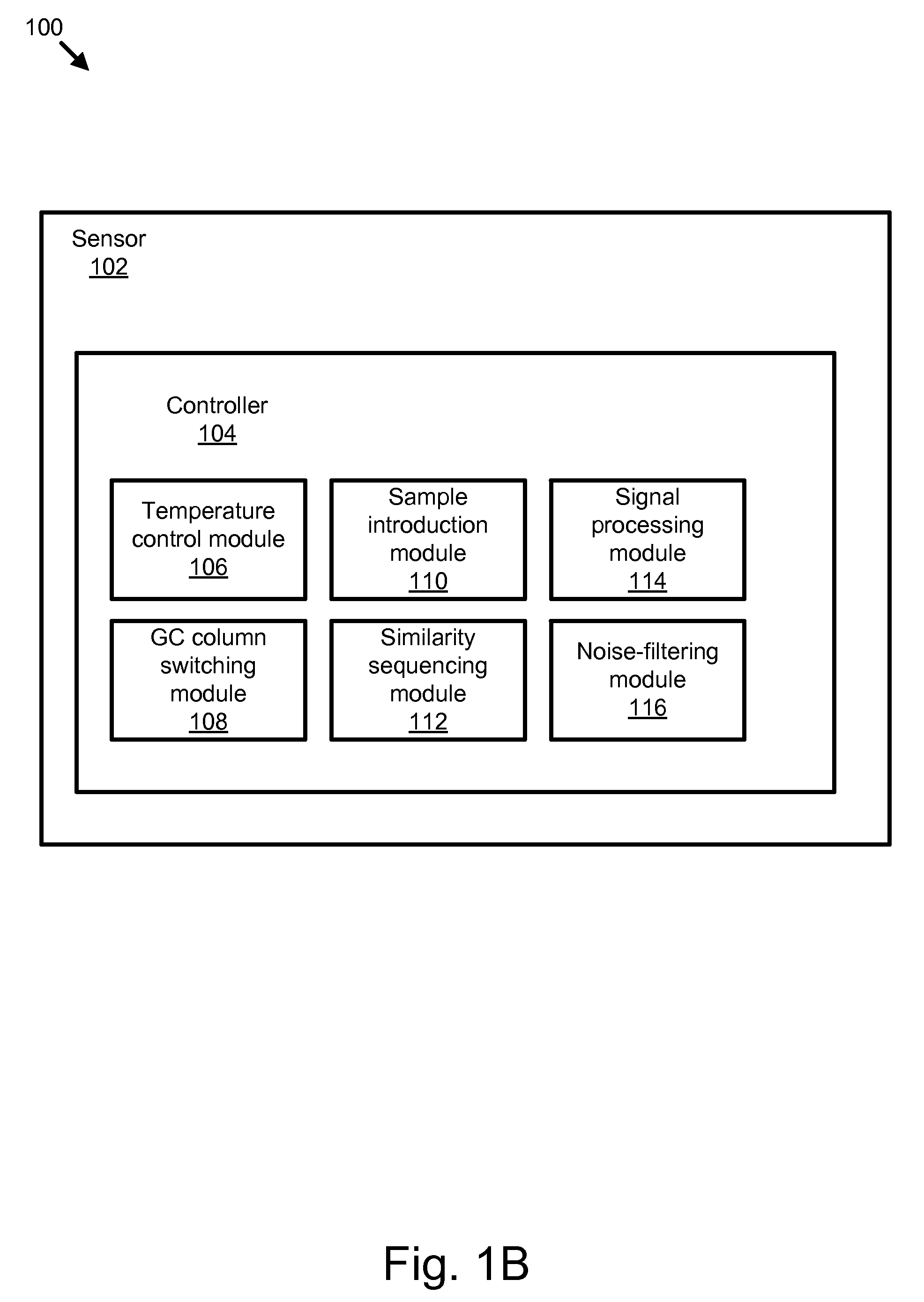
Apparatus, system, and method for broad spectrum chemical detection
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for broad spectrum chemical detection. The method includes determining a similarity sequencing scheme. The method includes receiving an ambient air sample and concentrating the ambient air sample. The method further includes providing the concentrated sample to a gas chromatography (GC) column, and detecting chemical elution from the GC column in a series of similarity sequenced samples based on the similarity sequencing scheme. The method includes de-convoluting the elution data to derive arrival peaks, and determining a concentration of a chemical in the ambient air based on the series of constant log-time data samples. In one embodiment, the method utilizes a modified Z-transform to de-convolute the elution data.
Owner:WELCH EDWARD K II
Method of data interpolation with bi-switch slope control scaling
InactiveUS20030187893A1Geometric image transformationComplex mathematical operationsDown scalingScale down
The present invention provides a method of down scaling a source data to generate a destination data. By using 2 source points on a discontinued curve as reference, each piece of destination data can be generated. A midpoint of these 2 neighbor pixels is generated with a slope defined at the midpoint points. It is easy to control the sharpness of the interpolation result by adjusting the gain factor of the slope. The final interpolation curve passes the midpoint point of the 2 neighbor source points with a slope S define at the midpoint point but does not pass the 2 original neighbor pixels. Although the curve is not continuous at the source reference points but it is seen as a smooth curve by the human eyes during scaling down. The curve is a linear equation which makes the computing storage and cost very low. The BSSC method is excellent in scaling down even compared to other high order equation interpolation curve. Furthermore, a Z transform is induced to minimize the computing complexity.
Owner:MSTAR SEMICON INC
A digital watermarking method based on neural network and DCT transform
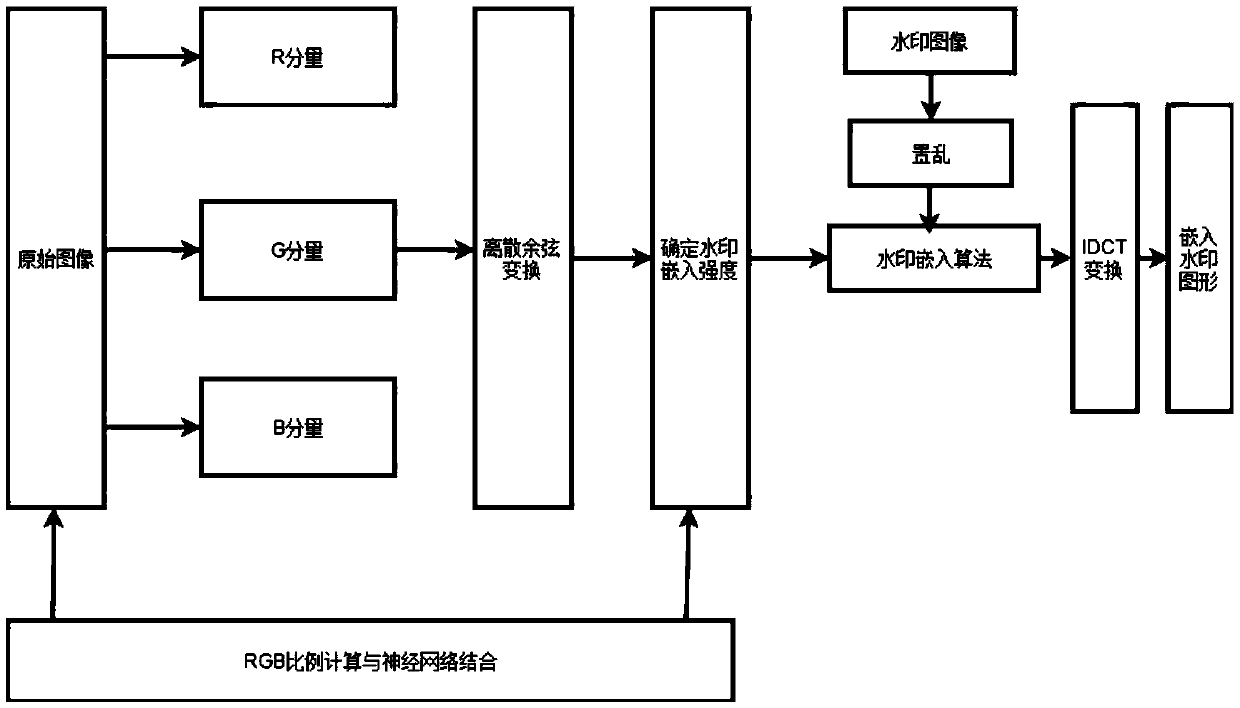
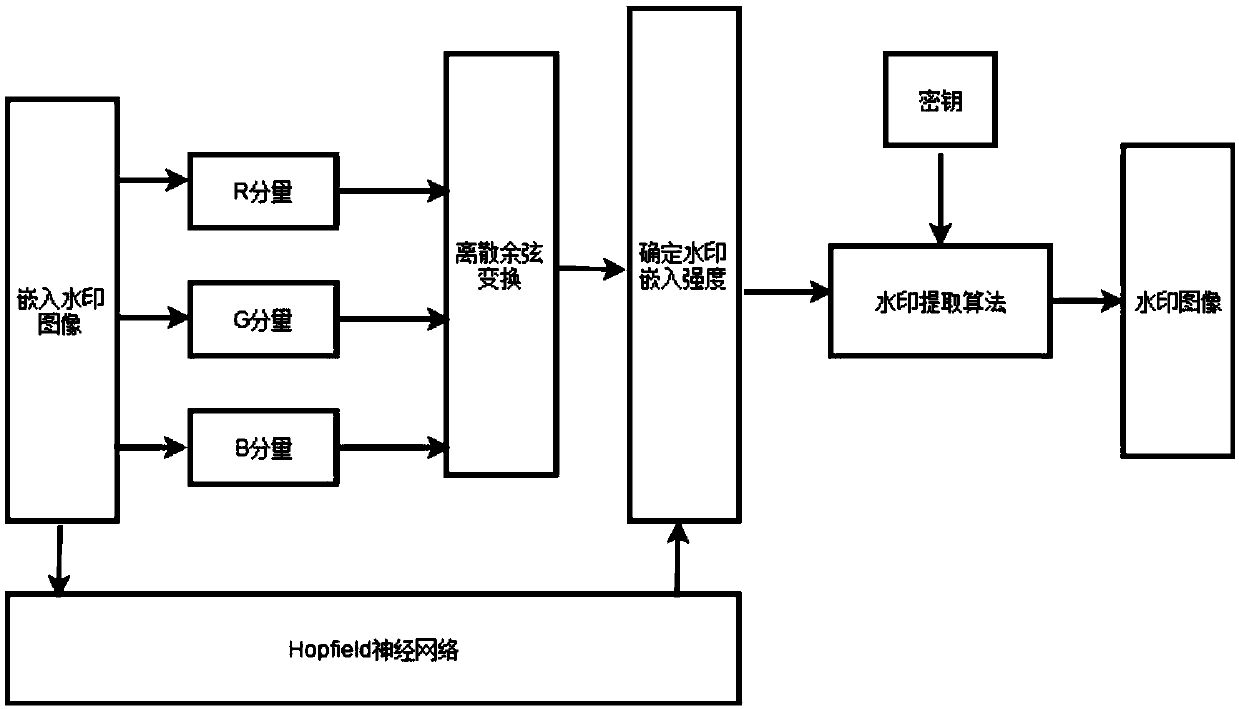
PendingCN109544438AHigh transparencyImprove robustnessImage data processing detailsNeural architecturesHopfield networkPattern recognition
The invention relates to a digital watermarking method based on neural network and DCT transformation, which relates to the technical field of digital watermarking and is a robust invisible digital watermarking method. According to the human visual characteristic and the proportion of the RGB component of the original image, the invention adaptively embeds the watermark to improve the transparency, and the digital watermark is insufficient in resisting the geometrical attack. By utilizing the advantages of the Hopfield neural network, the watermark image is corrected in the watermark detectionprocess, so as to improve the robustness. The new digital watermarking method can better balance the relationship between transparency and robustness of watermarking.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Transform-based methods to transmit the high-definition video
ActiveCN106688229AColor television with pulse code modulationTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsTime domainVideo transmission
The present invention presents the HD video transmission methods in a transform domain. In an aspect of the present invention, at the HD video transmitter the HD video is transformed into the transform domain by a multi-dimensional transform. Through the discrete-time continuous-valued or quasi-continuous-valued modulation, the obtained coefficients in transform domain are preferably carried in parallel in a multiple-access channel in time-domain to the HD video receiver.
Owner:重庆赛真达智能科技有限公司
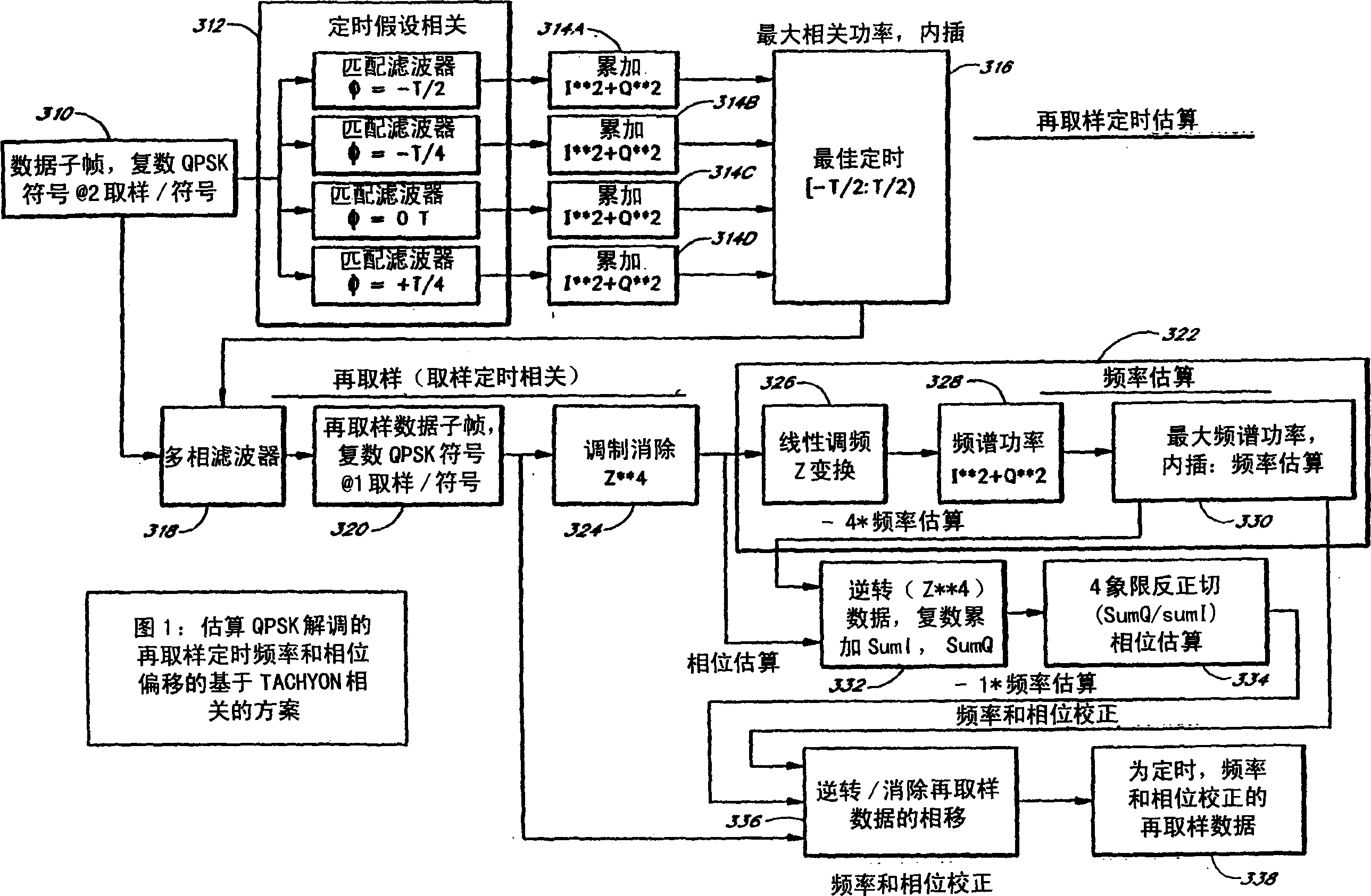
Timing synchronizaation and phase/frequency correction of QPSK signals
InactiveCN1385019AWireless network protocolsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase shiftedFrequency spectrum
A method and apparatus for digitally demodulating a QPSK signal includes resampling a first portion of a digitally sampled data subframe using a plurality of predetermined timing hypotheses. The timing offset is determined from analysis of the resampled data. The digitally sampled data subframes are then resampled based on the timing estimates. The modulation of the resampled data subframe is then removed by squaring the complex I / Q pair twice. A chirp-Z transform is performed on the data from which the modulation has been removed to shift the data into the frequency domain. Use the highest spectral power to determine the frequency offset. A phase offset is determined and the resampled data bursts are derotated and phase-shifted based on the phase offset and the frequency offset.
Owner:TECH INC
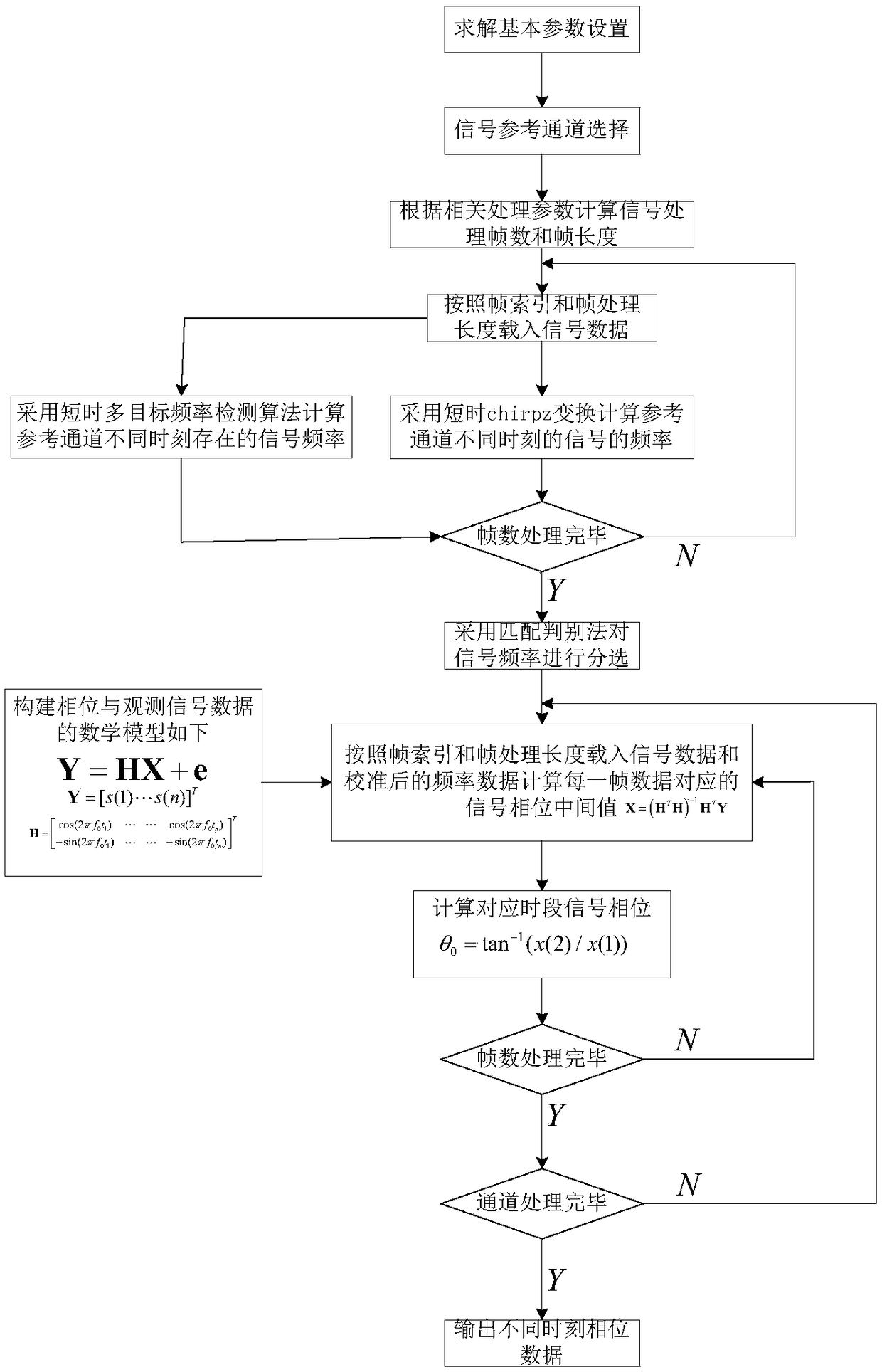
LS (Least Square) based phase information calculating method in complex environment
The invention discloses an LS (Least Square) based phase information calculating method in a complex environment. The method comprises the following steps of simultaneously calculating by adopting short-time chirp-z transform, obtaining signal frequencies, at different moments, of a reference channel through a selected amplitude maximum method and calculating and extracting multiple signal frequencies, exceeding a detection threshold, at the different moments, of the reference channel by adopting a short-time multi-target frequency detection algorithm; and calibrating actual signal frequencies, at the different moments, of the reference channel by adopting a matching discrimination method, which particularly comprises: calculating phase values, corresponding to frequency values of the reference channel at the different moments, of different receiving channels by adopting an LS method. By using the method provided by the invention, the frequency of a useful signal is extracted from a disorderly signal frequency spectrum; a disorderly frequency spectrum brought by random noise and clutter is abandoned; by utilizing the signal frequencies obtained by discriminatory analysis, a mathematic model between an observed signal and a signal initial phase is constructed; and next, the information of the signal initial phase of the corresponding receiving channel is calculated and obtainedby adopting an LS algorithm, so as to be called by other application of target location and the like.
Owner:NANJING CHANGFENG AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH
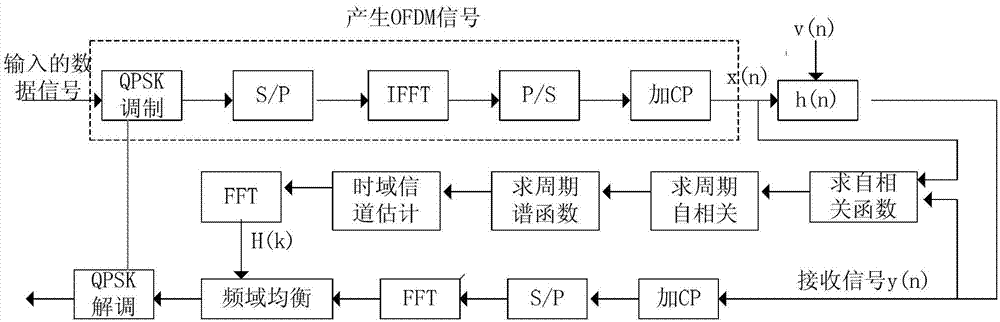
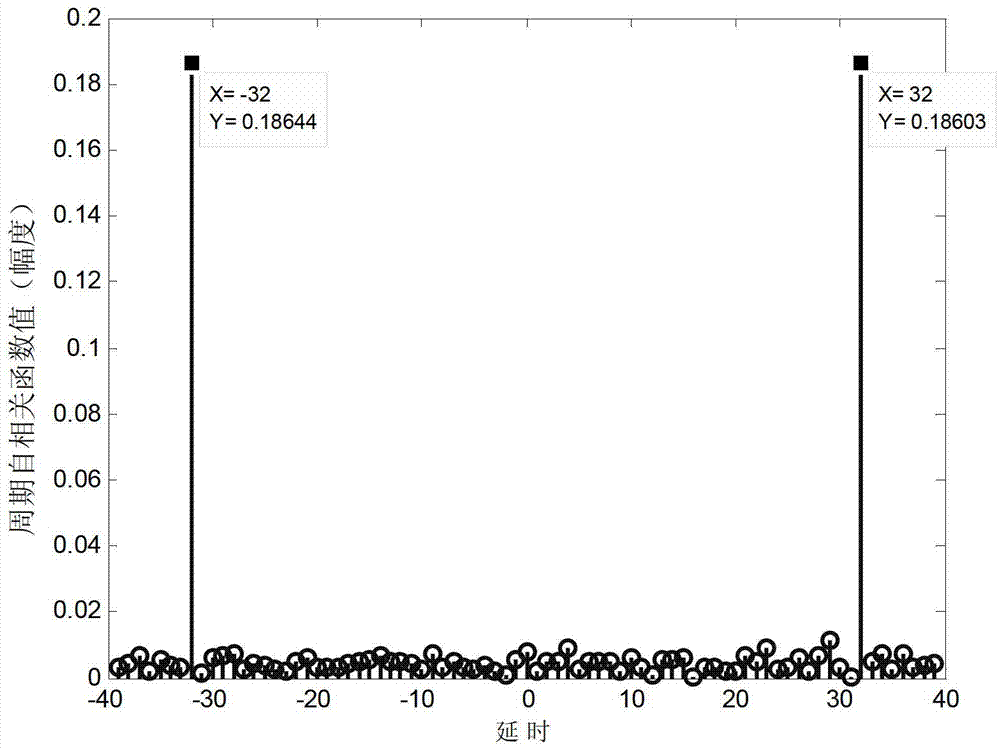
Blind channel estimation method based on OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) signal cyclostationary features
InactiveCN102821078AReduce the numberImprove spectrum resource utilizationBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumComputation complexity
The invention discloses a blind channel estimation method based on OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) signal cyclostationary features, and the method is characterized in that on a fixed cycle frequency, z-transform of a delay variable Tau in a period spectrum function of an OFDM received signal is analyzed, and the accurate estimation of channel information is realized by selecting two different correlation values of the z-transform of the delay variable Tau, finally utilizing H(z) containing channel amplitude and minimal phase information and utilizing the existing least square method. Only the frequency spectrum information of one cycle frequency is adopted by the method, the quantity of the cycle frequency is reduced, so that the utilization rate of the frequency resource is effectively improved, the accuracy of the channel estimation is improved, and the performance of the method is obviously better than that of the existing blind channel estimation method through simulation verification; and by analyzing the energy distribution regulation of the self-correlation function of the OFDM received signal, the frequency spectrum information centralizing partial energy is adopted, the rest frequency spectrum information is set as zero, and the quantity of matrixes to be constructed is reduced, so that the calculation complexity is reduced.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
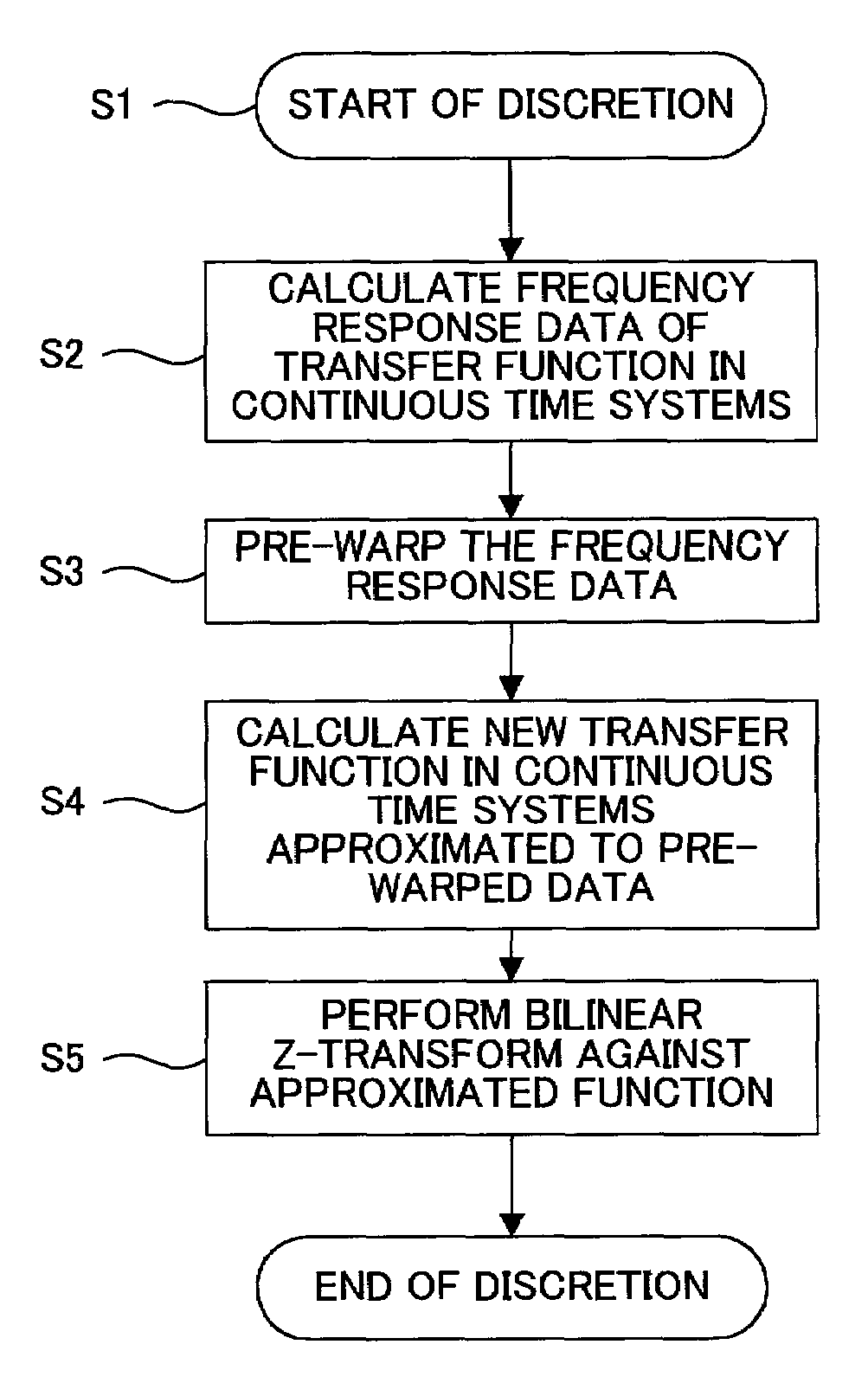
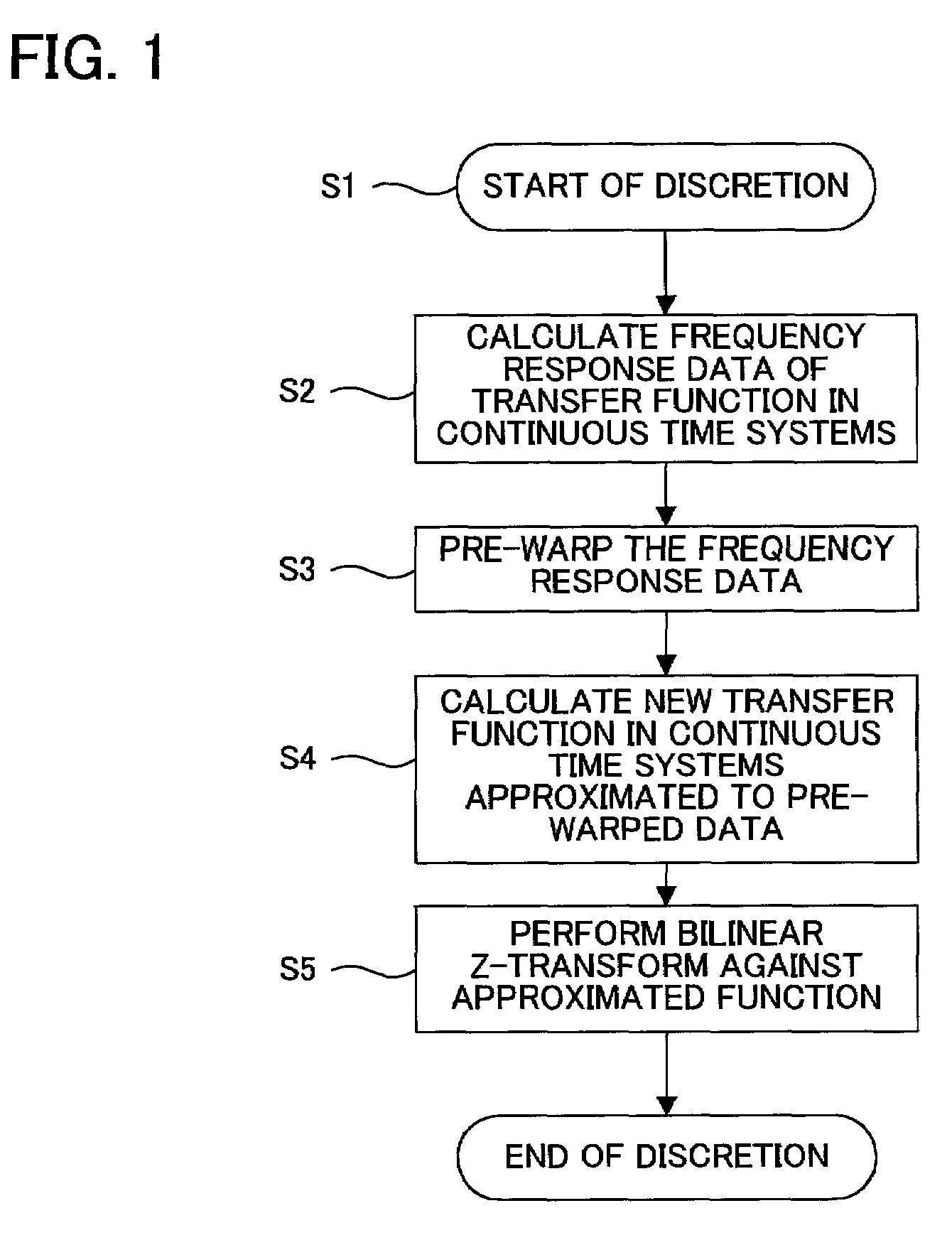
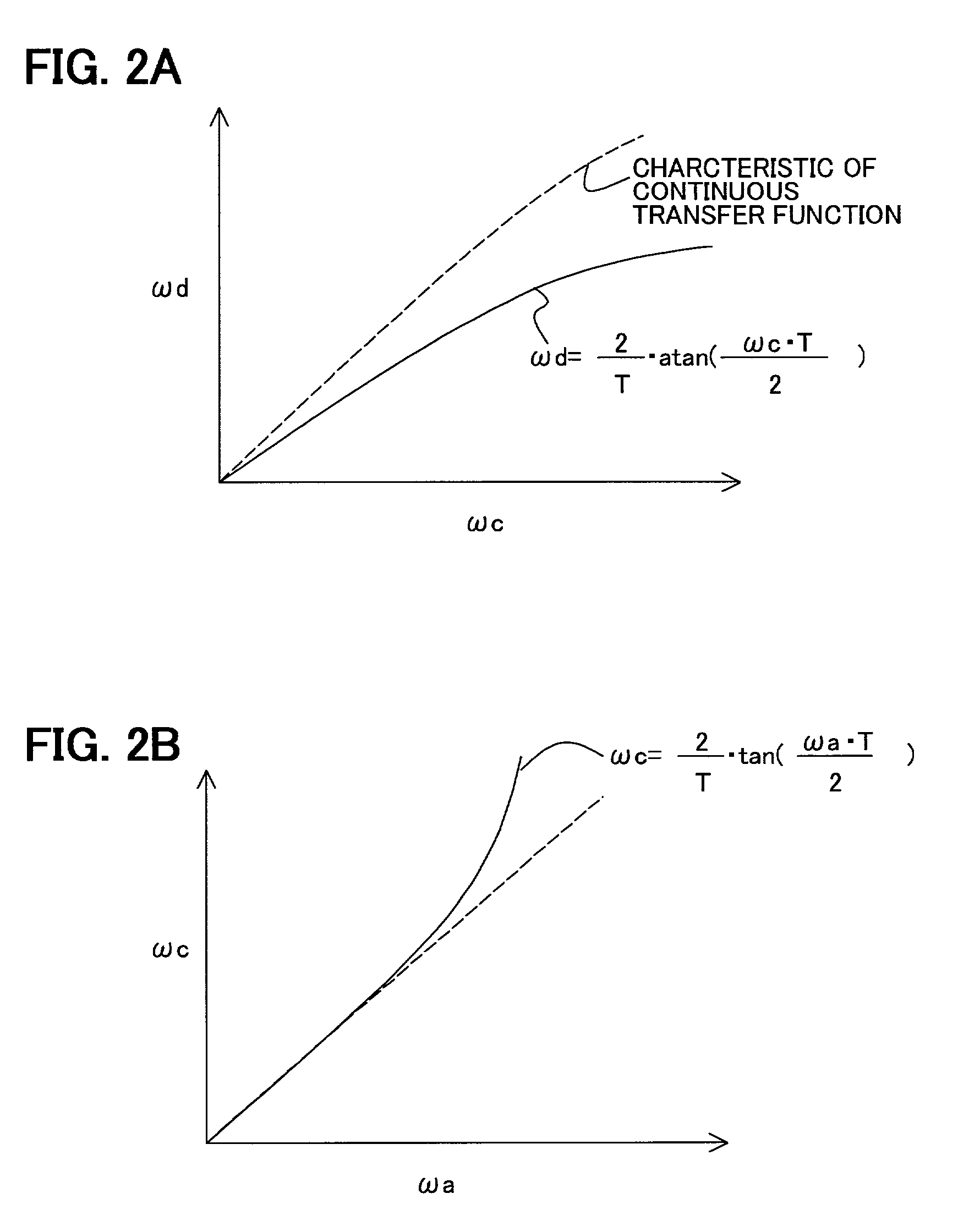
Discretization processing method of transfer function in continuous time systems, system and program therefor, and compensator and feedback control system using the same
InactiveUS6996592B2Easily approximatedReduce product manufacturing costsSampled-variable control systemsTrack finding/aligningControl systemSignal transfer function
A discretization processing method for transforming a transfer function in continuous time systems to a transfer function in discrete time systems is disclosed. To obtain the new transfer function, angular frequency ωa of the original transfer function in continuous time systems is transformed to angular frequency ωc using the bilinear z-transform of the inverse characteristic. In the discretion processing result, the equivalent characteristics of the original transfer function in continuous time systems can be obtained by performing the bilinear z-transform against the new transfer function in continuous time systems having been obtained by the angular frequency transformation of inverse characteristic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Spatial domain color image blind watermarking method fused with Haar transform
ActiveCN110415155AIncrease watermark capacityStrong Watermark RobustnessImage watermarkingHadamard transformColor image
The invention discloses a spatial domain color image blind watermarking method fused with Haar transform by combining the advantages of good concealment of an airspace digital watermarking algorithm and strong robustness of a frequency domain digital watermarking algorithm. According to the method, based on the characteristic that Haar transform has correlation between space-frequency domains, themaximum energy coefficient in a matrix of an image block after Haar transform is directly obtained in a space domain. The embedding and blind extraction of digital watermarks are completed by quantizing the maximum energy coefficient. According to the method, the color image digital watermark can be embedded into the color host image. The method has the advantages of being high in robustness, good in watermark concealment, high in safety, high in execution efficiency and high in embedding amount. The method is suitable for occasions of high-concealment high-capacity color digital image rapidcopyright protection.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
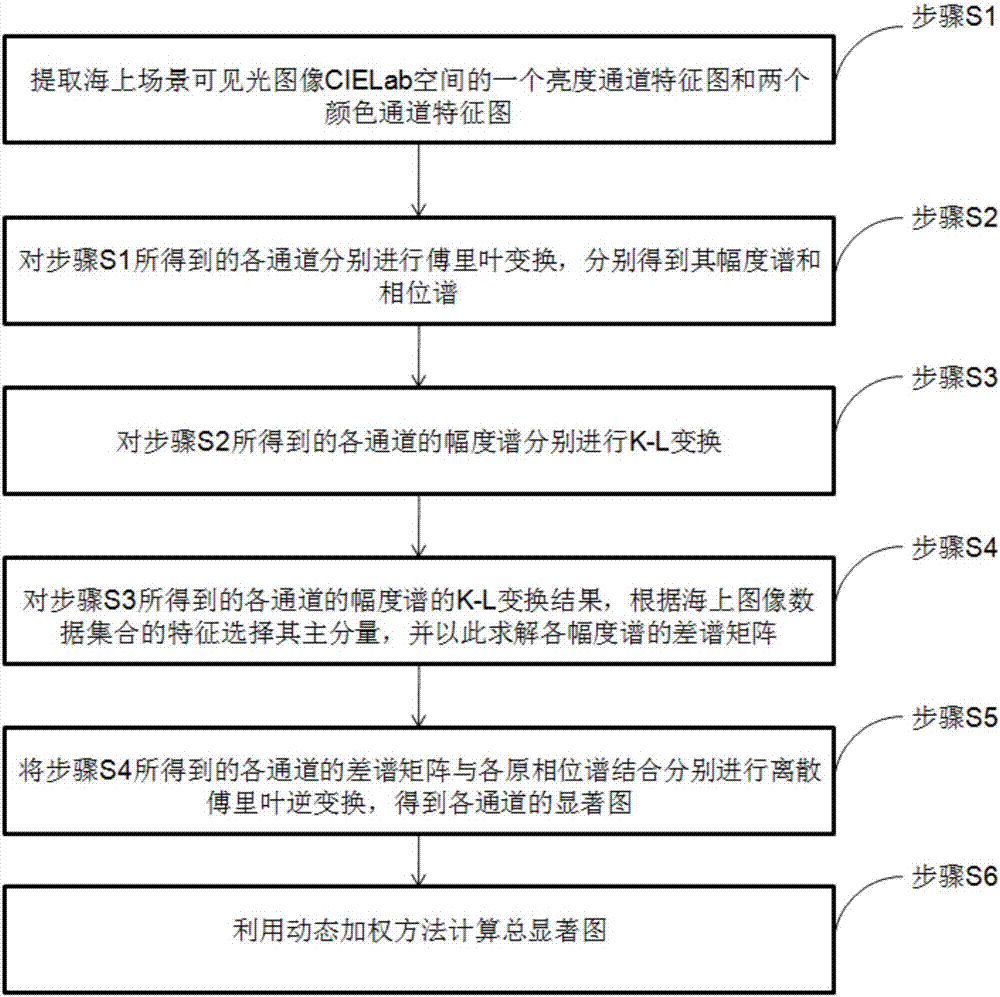
K-L transform-based method for detecting saliency of small object on sea
The invention discloses a K-L transform-based method for detecting saliency of a small object on the sea. The method comprises: S1, extracting a brightness channel feature graph and two color channel feature graphs in seaborne scene visible image CIELab space; S2, carrying out Fourier transform on all channels obtained by the S1 to obtain amplitude spectra and phase spectra; S3, carrying out K-L conversion on the amplitude spectra, obtained at the S2, of all channels; S4, selecting main components of K-L transform results, obtained at the S3, of the amplitude spectra of the respective channels according to features of a seaborne image data set, and calculating a differential spectrum matrix of all amplitude spectra; S5, combining the differential spectrum matrix, obtained at S4, of all channels with all original amplitude spectra to carry out inverse discrete Fourier transform, thereby obtaining saliency maps of all channels; and S6, calculating a total saliency map by using a dynamic weighting method. According to the invention, small targets are highlighted and a background is suppressed, so that small target detection and tracking on the sea are realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
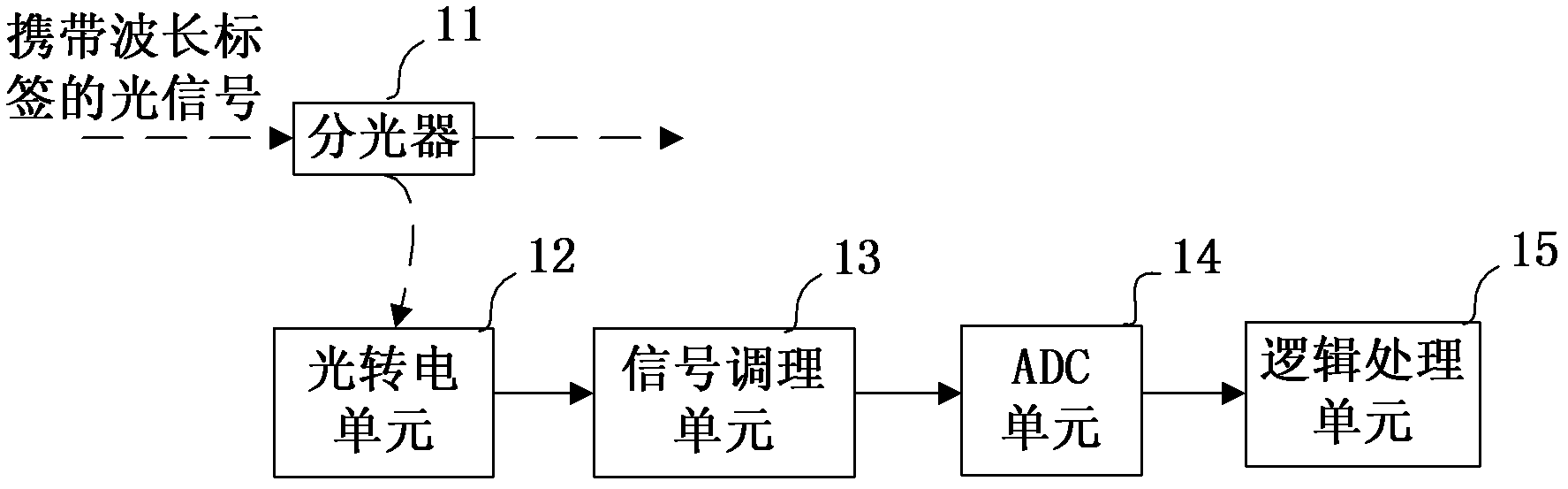
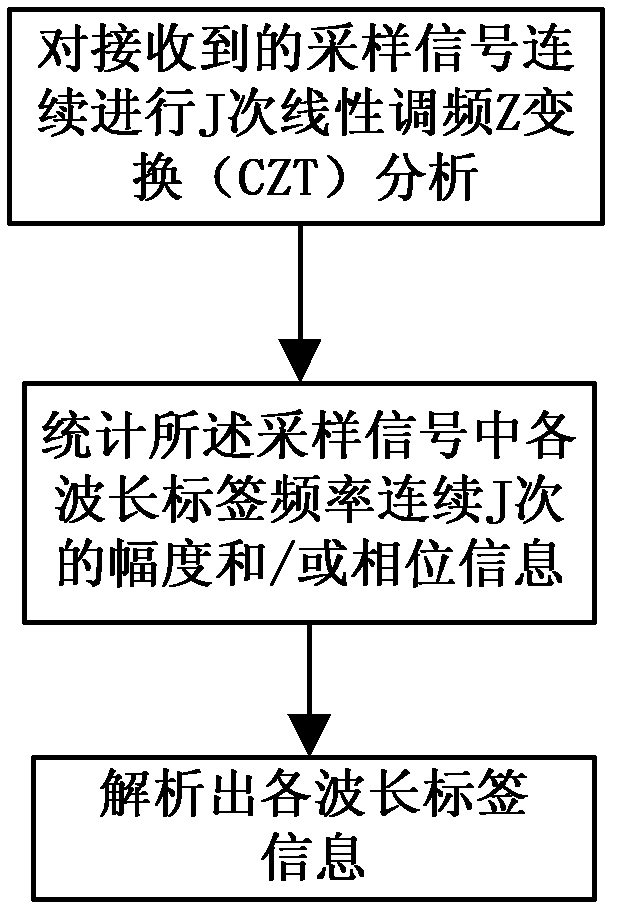
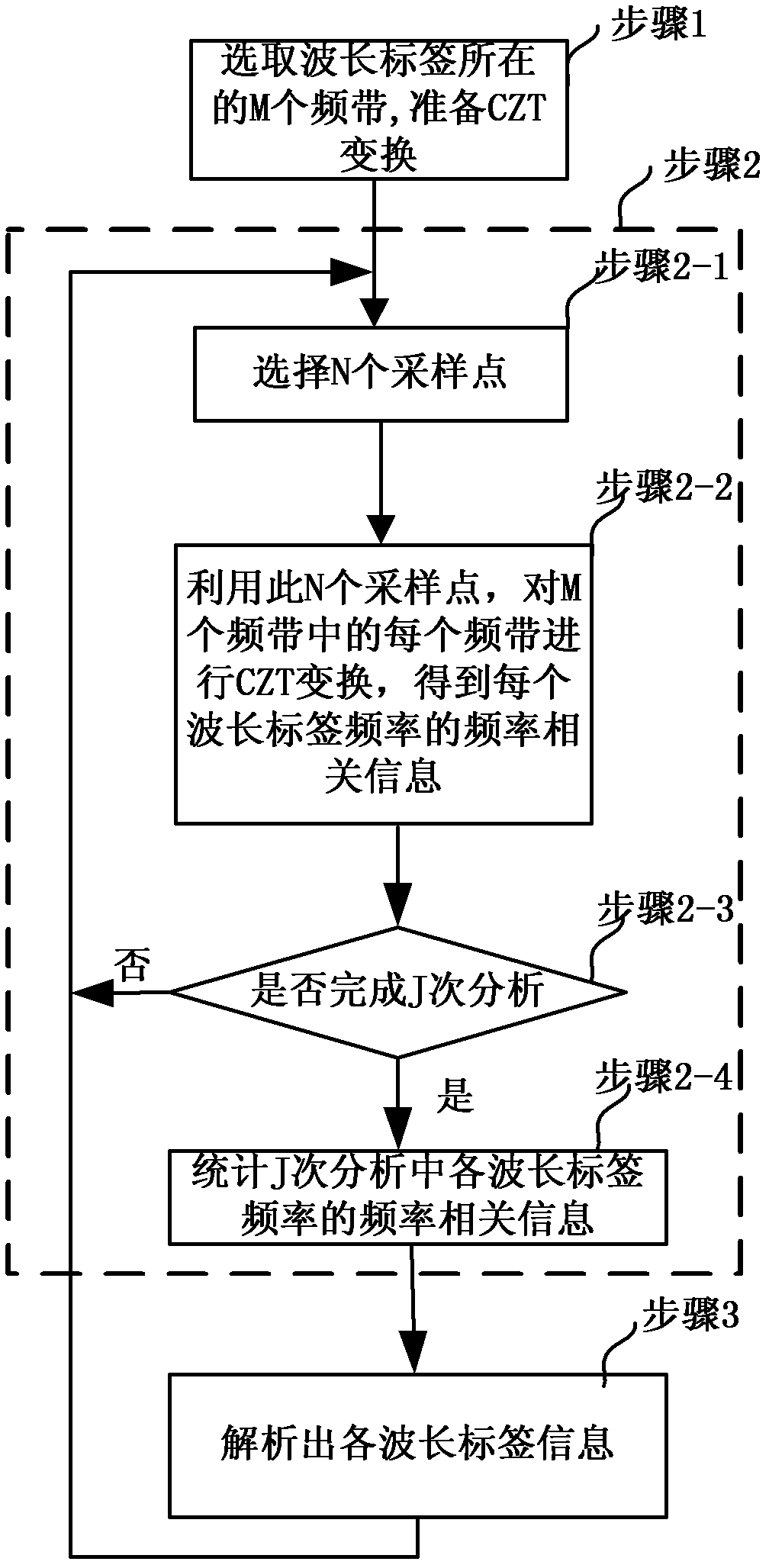
Wavelength tag information analysis device and analysis method
ActiveCN102611520AOvercome inaccuraciesWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionInformation analysisFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a wavelength tag information analysis device and an analysis method. The received sampling signals are subjected to chirp-Z transform (CZT) analysis continuously by J times by a logic processing unit, and the frequency-related information of the continuous J times of each wavelength tag frequency in the sampling signals is counted to resolve wavelength tag information, wherein J is an integer larger than zero. Based on the characteristic of CZT that can select an arbitrary start frequency and frequency resolution (or stop frequency), the device and method provided by the invention can realize spectral zooming during frequency analysis by subjecting the sample signal to Z transform, thereby obtaining higher start frequency resolution, and reducing frequency measurement error caused by picket fence effect.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com