Patents
Literature
195results about How to "Effective approach" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
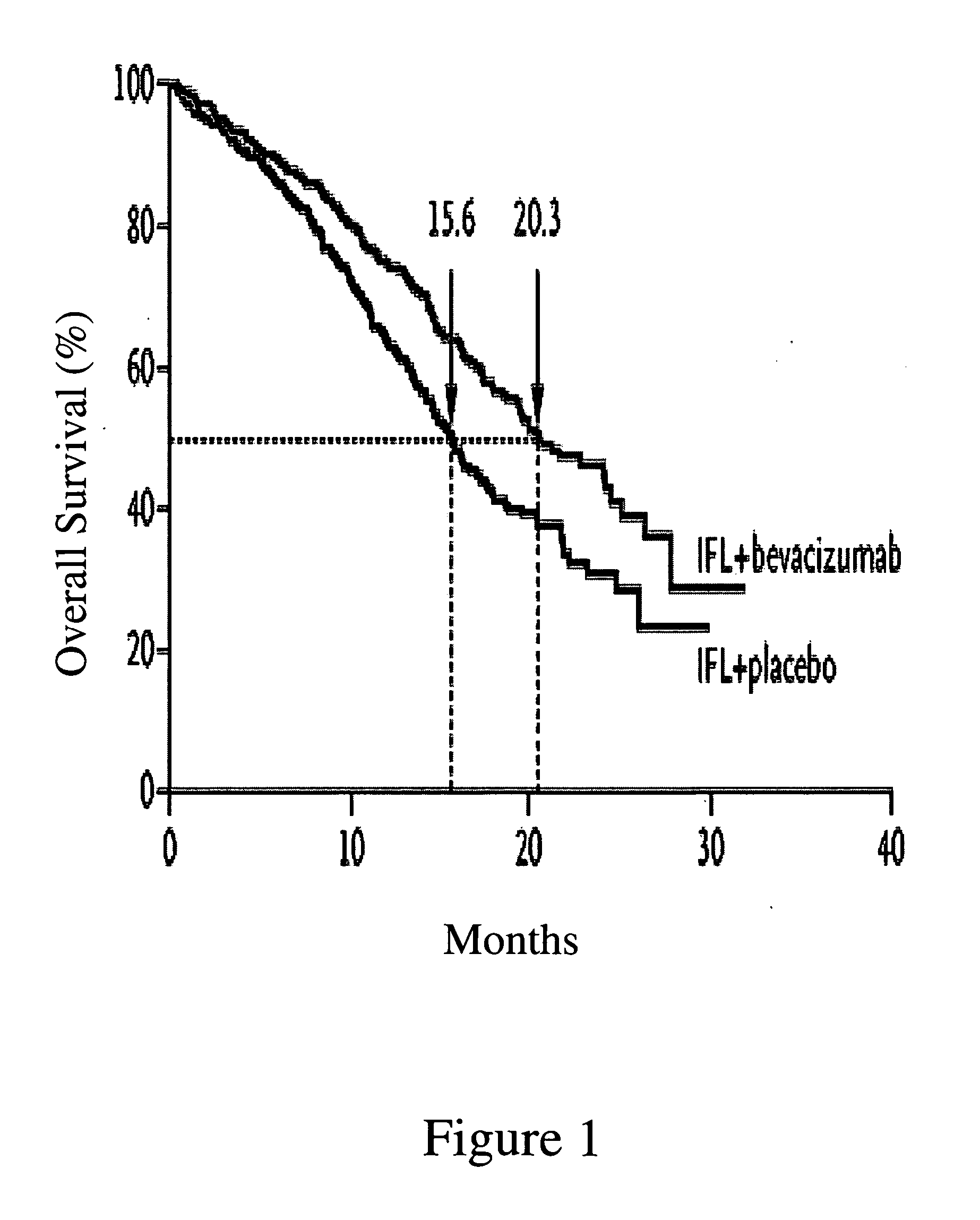
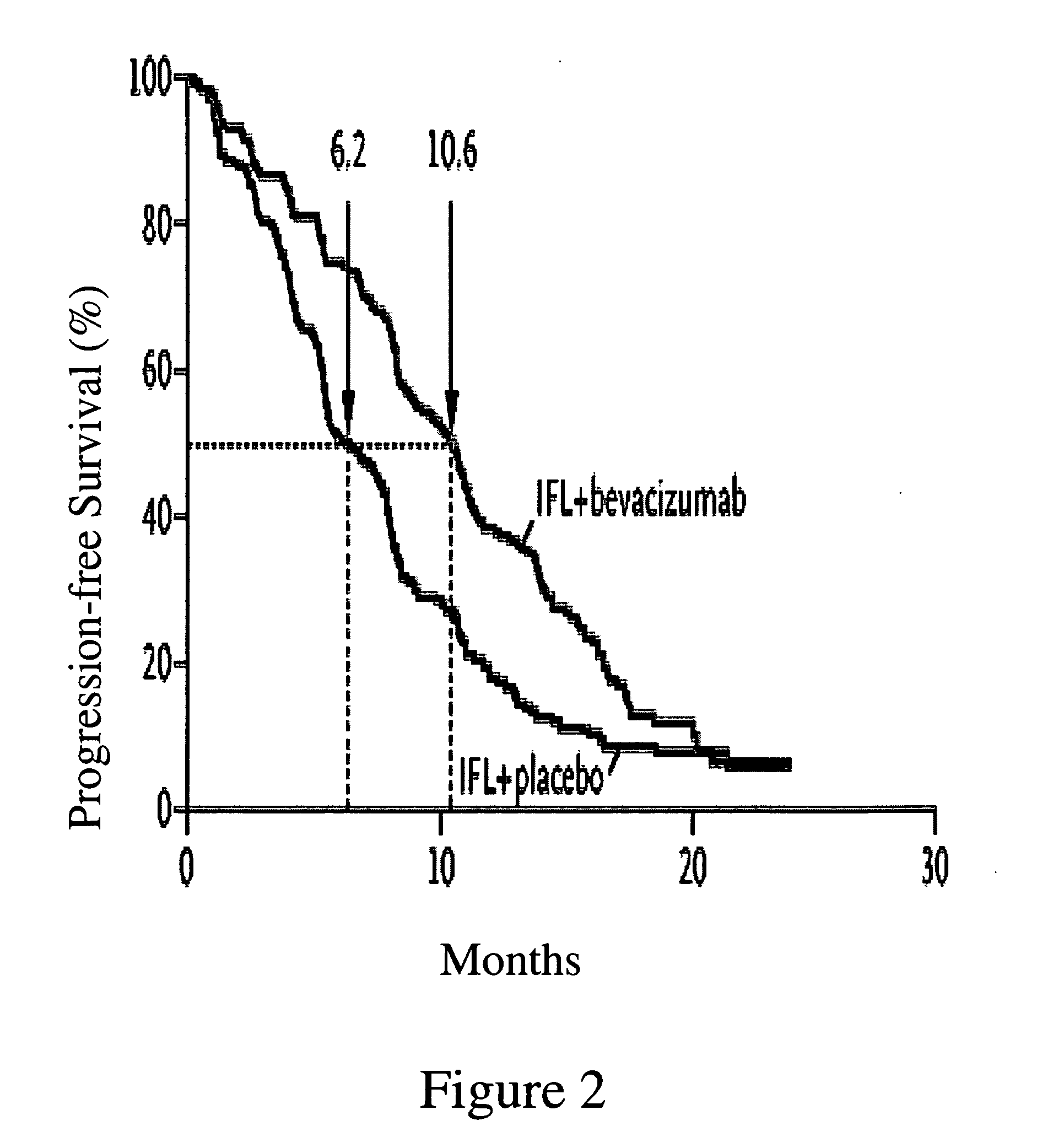
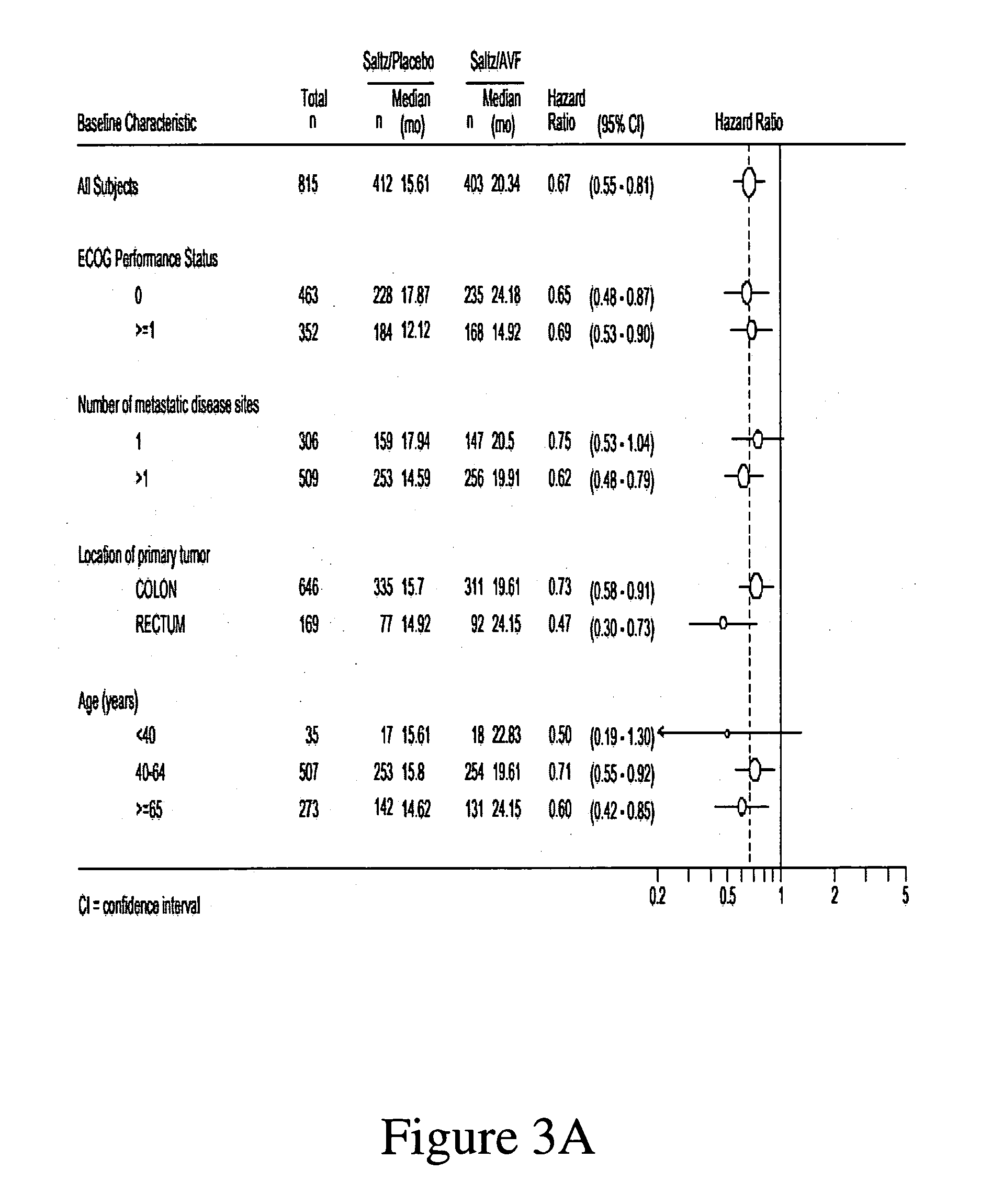
Treatment with anti-VEGF antibodies
InactiveUS20050186208A1Effective approachExtended durationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAnti vegf antibody
This invention concerns in general treatment of diseases and pathological conditions with anti-VEGF antibodies. More specifically, the invention concerns the treatment of human patients susceptible to or diagnosed with cancer using an anti-VEGF antibody, preferably in combination with one or more additional anti-tumor therapeutic agents.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Breed-specific canine food formulations
InactiveUS6156355AUnique shapeManaged fat levelMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffFood formulationAdditive ingredient
Breed-specific dog food formulations that comprise chicken meat as the major ingredient, rice as the predominant (or sole) grain source, fruit and / or vegetable fiber as the primary or sole fiber source, unique fat and antioxidant blend, vitamins, herbs and spices, carotenoids, and no corn or artificial colors, preservatives, flavors or sugars are provided.
Owner:BIG HEART PET INC
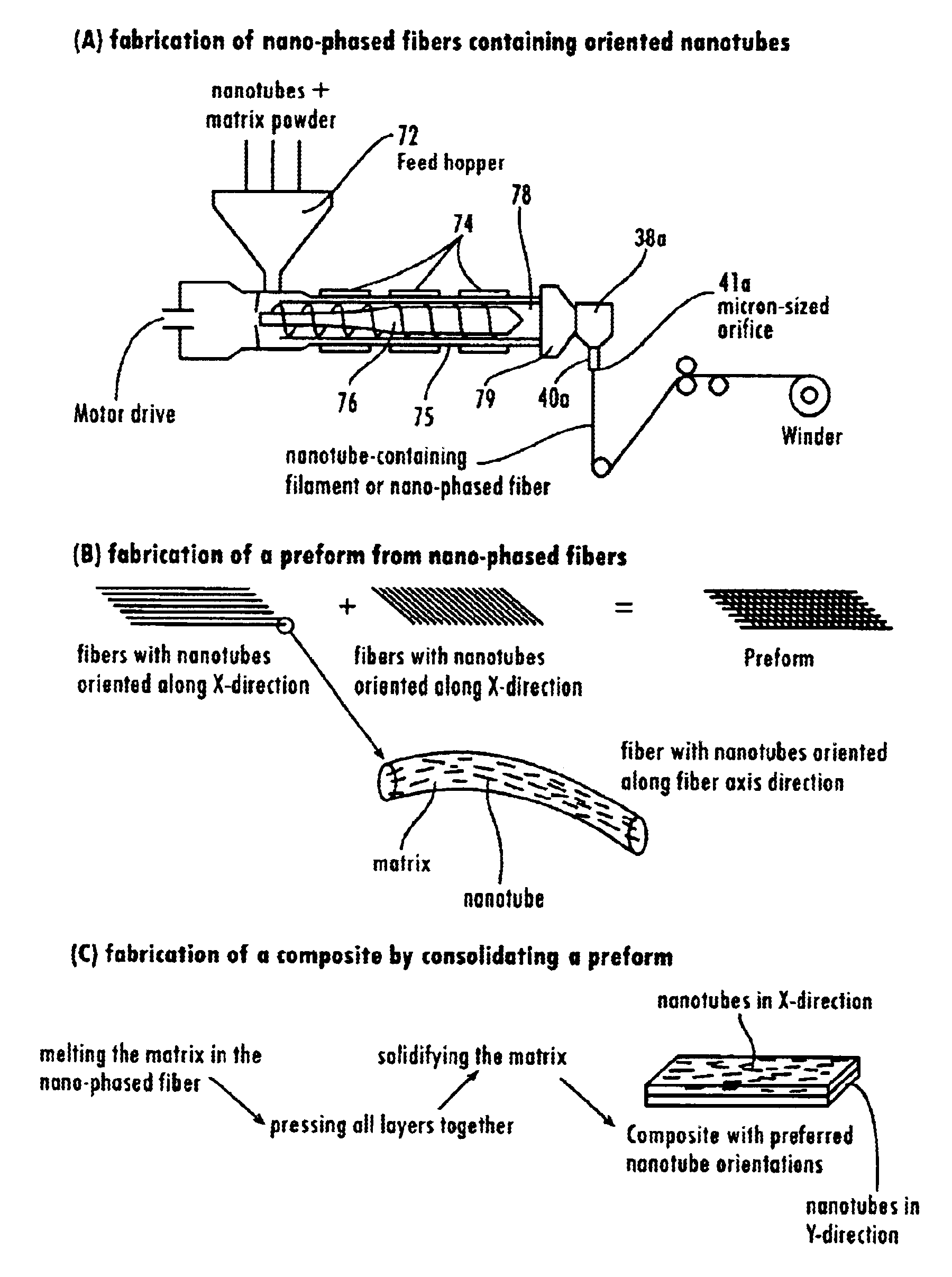
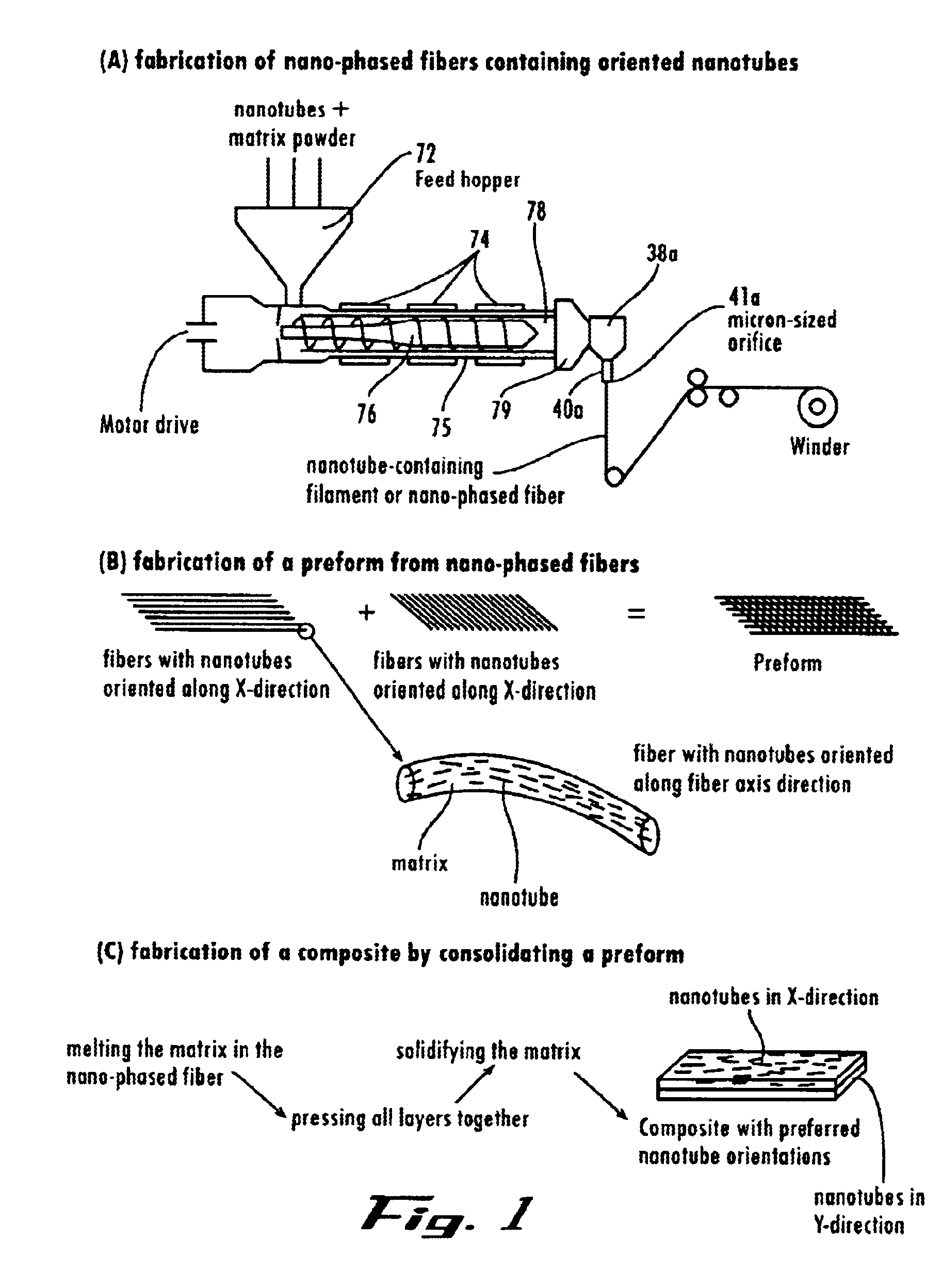
Nanotube fiber reinforced composite materials and method of producing fiber reinforced composites
InactiveUS6934600B2Requires minimizationGenerate efficientlyMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiber-reinforced compositeMotion controller
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
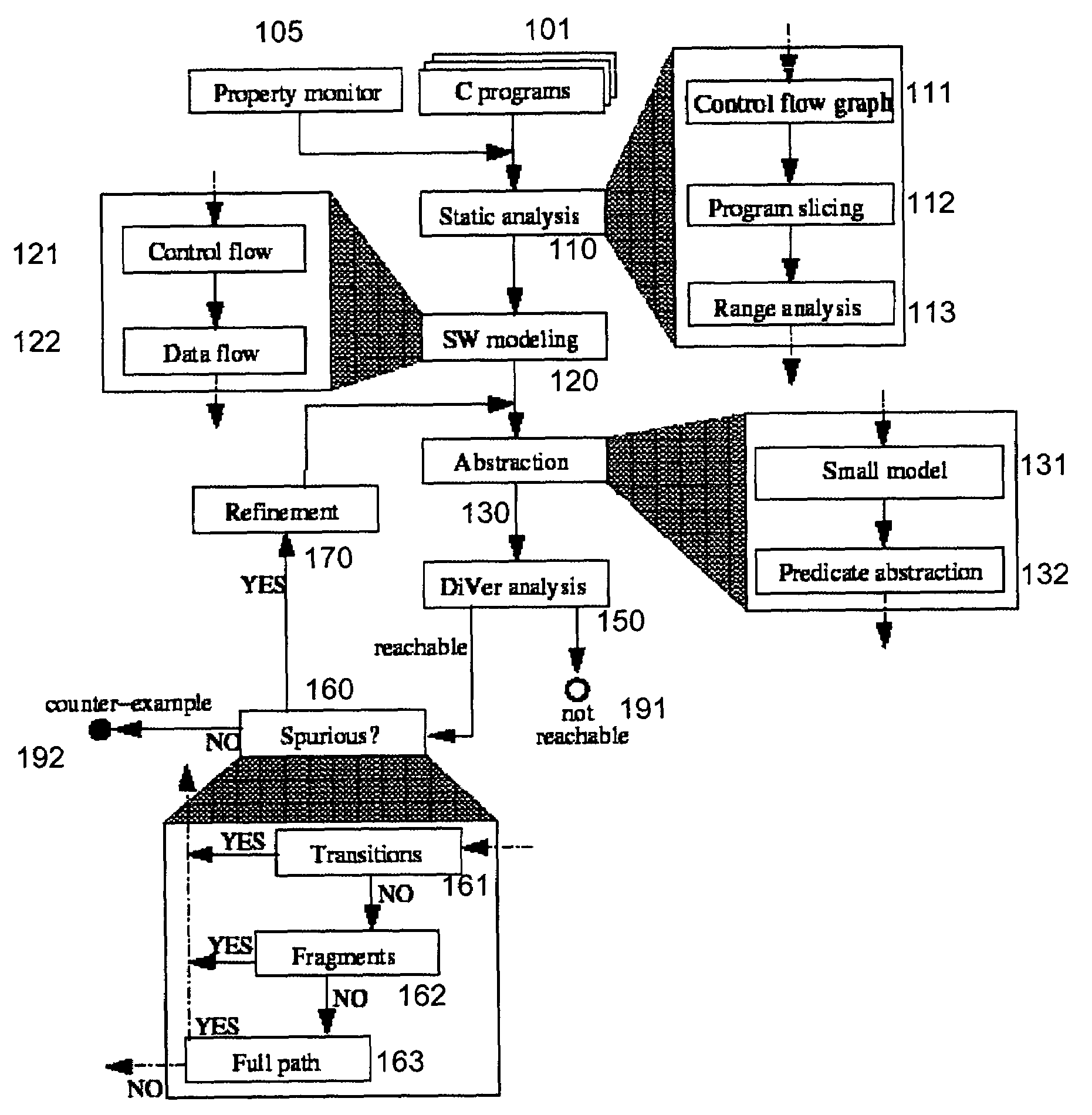
System and method for modeling, abstraction, and analysis of software
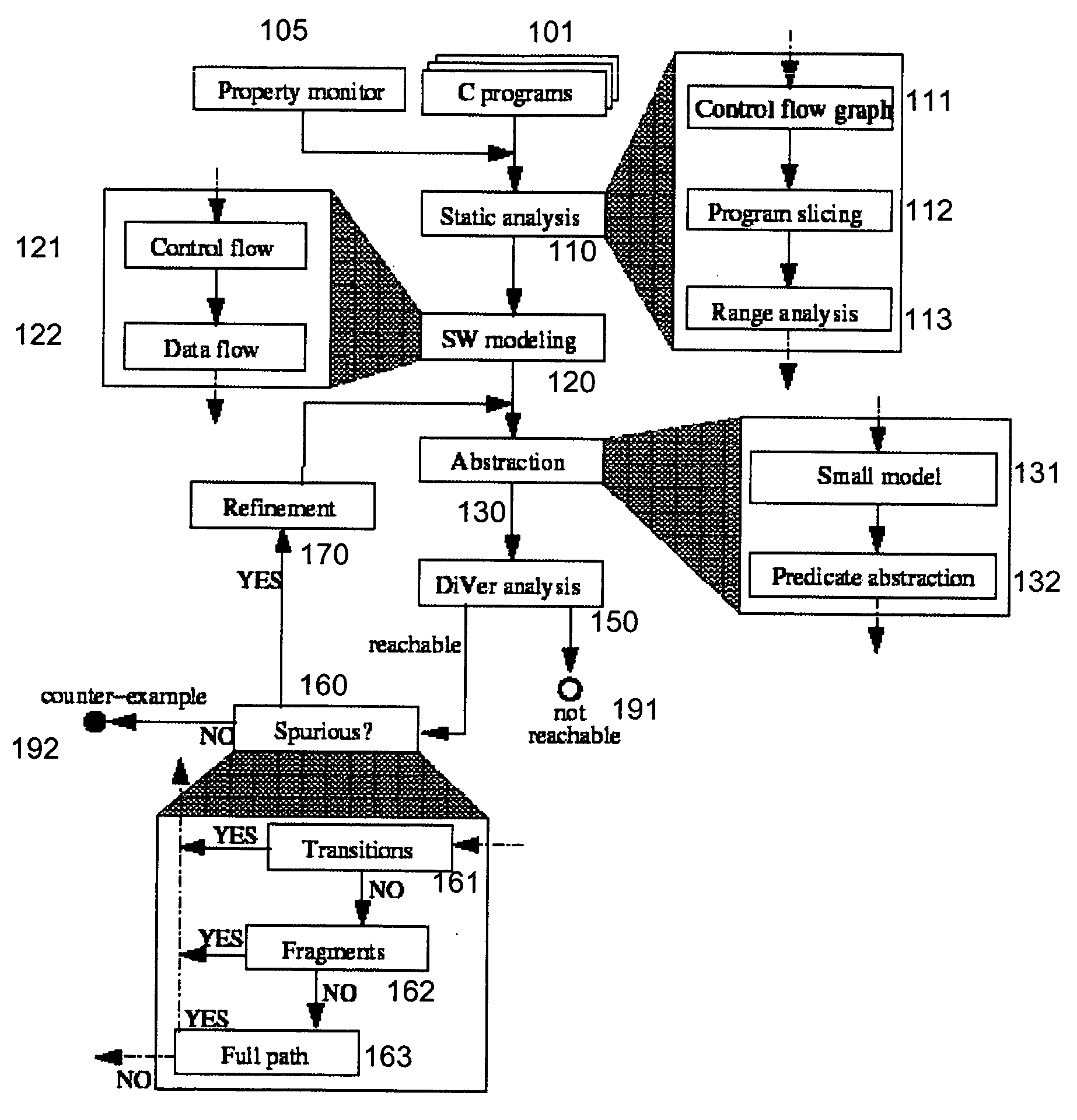
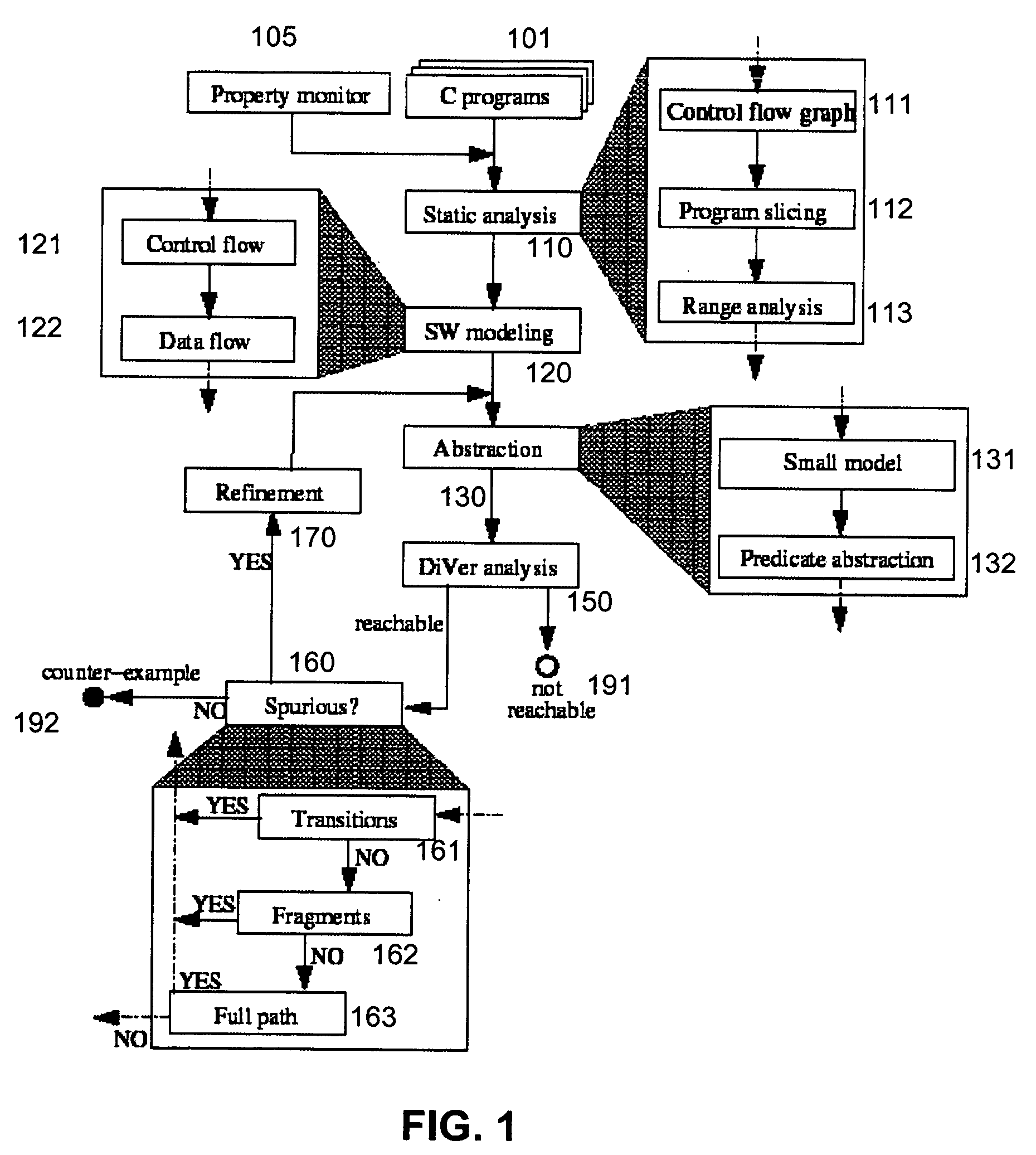
ActiveUS7346486B2Improve verification efficiencyImprove translationError detection/correctionComputation using non-denominational number representationBasic blockSoftware
A system and method is disclosed for formal verification of software programs that advantageously translates the software, which can have bounded recursion, into a Boolean representation comprised of basic blocks and which applies SAT-based model checking to the Boolean representation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Refuelable battery-powered electric vehicle
ActiveUS20080053716A1Enabling useEffectivelyMobile unit charging stationsElectric/hybrid propulsionElectrical batteryGasoline
The electrical vehicle energy storage system permits the electric refueling of the electric vehicle just like an automobile would be refueled with gasoline at a gas station. Circuitry on board the vehicle accessible by the electric refueling station enables the determination of the energy content of the battery module or modules returned to the electric refueling station and the owner of the vehicle is given credit for the energy remaining in the battery module or modules which have been exchanged. Selective refueling may take place for given battery modules by removing them from the battery system and charging them at home, office or factory. A process for operating an electric vehicle is also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:SCHEUCHER KARL FREDERICK
System and method for detecting proximity between mobile device users
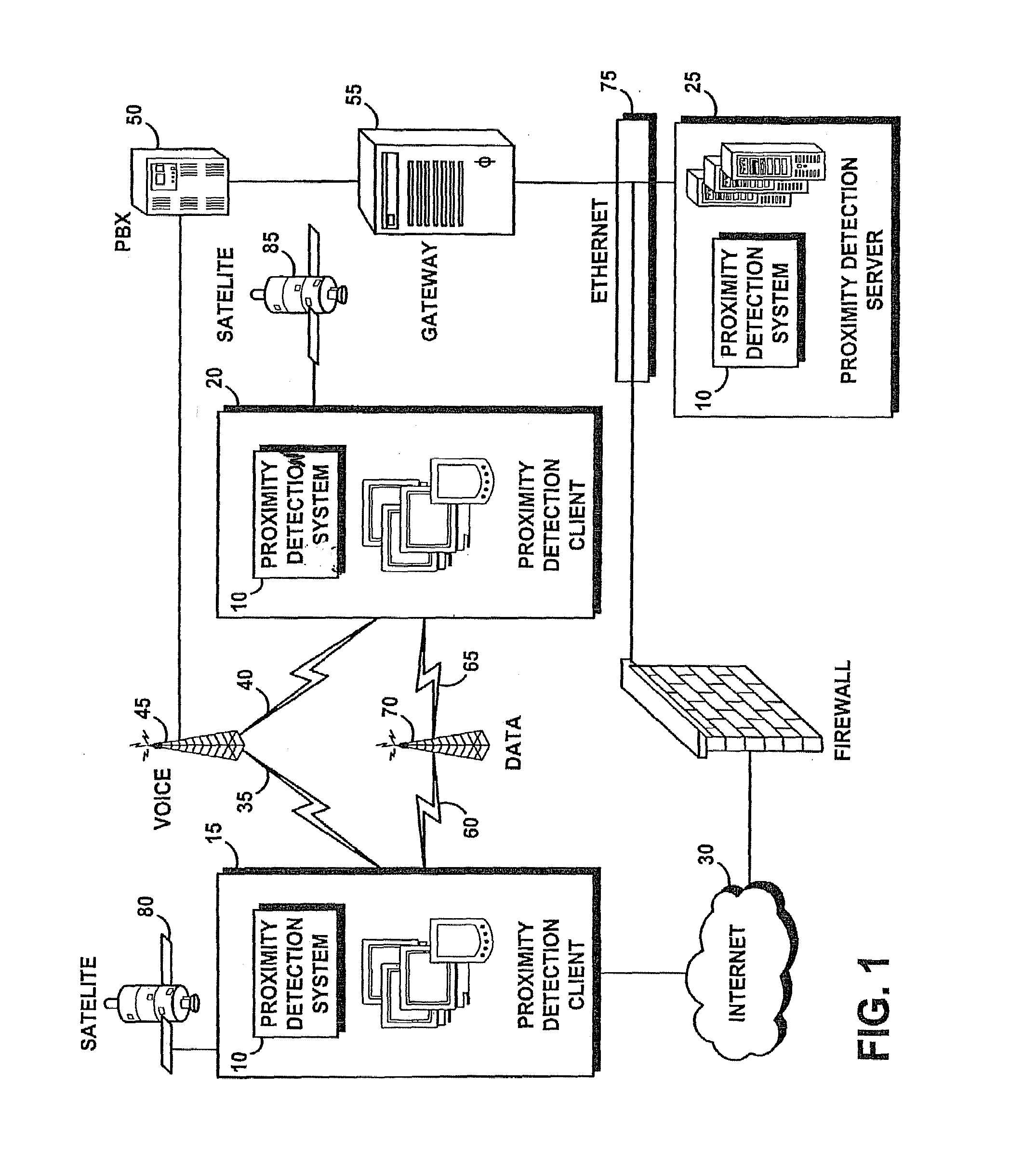
ActiveUS7289814B2Maximizes expected timeLong distanceNetwork topologiesSpecial service for subscribersProximity measureSystem usage
A system and method are provided to alert two mobile communications users in the event they come in close proximity to one another. The present system uses a distributed algorithm denoted as the Strips algorithm, in which a pair of moving friends with mobile telecommunications devices makes an agreement about a static buffering region between them. After the agreement is made, the users do not need to follow each other's location until one of them enters the buffering region for the first time. By doing so, they invalidate the agreement. Consequently, they replace a location update message between them, determine if they got within the vicinity of each other, and otherwise make a new agreement on a new buffering region. When one of them enters the buffering region for the first time, a message is sent to both friends alerting them of the proximity of the other.
Owner:THE TORONTO DOMINION BANK
Apparati, methods, and compositions for universal microbial diagnosis, detection, quantification, and specimen-targeted therapy
InactiveUS20120129794A1Increase productivityAccurate and rapid and sensitive microbial diagnosis and detection and quantificationAntibacterial agentsBiocidePopulationMolecular Targeted Therapies
Microbial ecology of a specimen is evaluated using an approach (Level I) that utilizes nucleic acid amplification with specific gene primers that will identify panels of microorganisms and antibiotic-resistance factors generating a diagnostic report (optionally with quantification of each microorganism or antibiotic-resistance factor) and an approach (Level II) that utilizes universal or semi-universal primers to amplify conserved genes at a general or specific taxonomic level that are tagged specimen specifically using a genetic or chemical marker that is specific to the specimen from which it was derived, then sequencing the amplified products with highly-parallel, high-throughput technology to provide comprehensive sequences of the microbial population in the specimen followed by analysis of this sequence information and specific targeted information from Level I and / or Level II to generate a comprehensive analysis, interpretation, and / or diagnostic report.
Owner:DOWD SCOT E +2
Dimeric IAP inhibitors
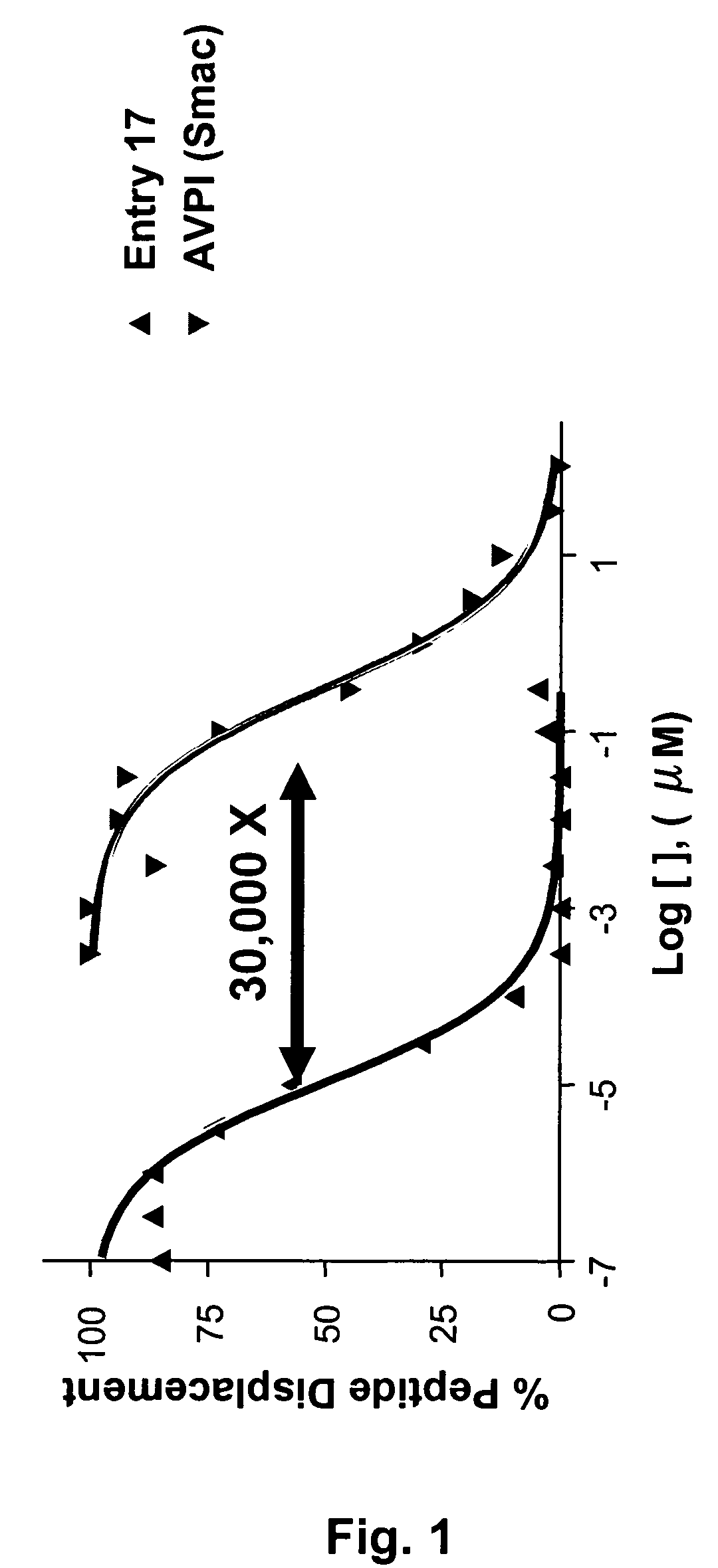
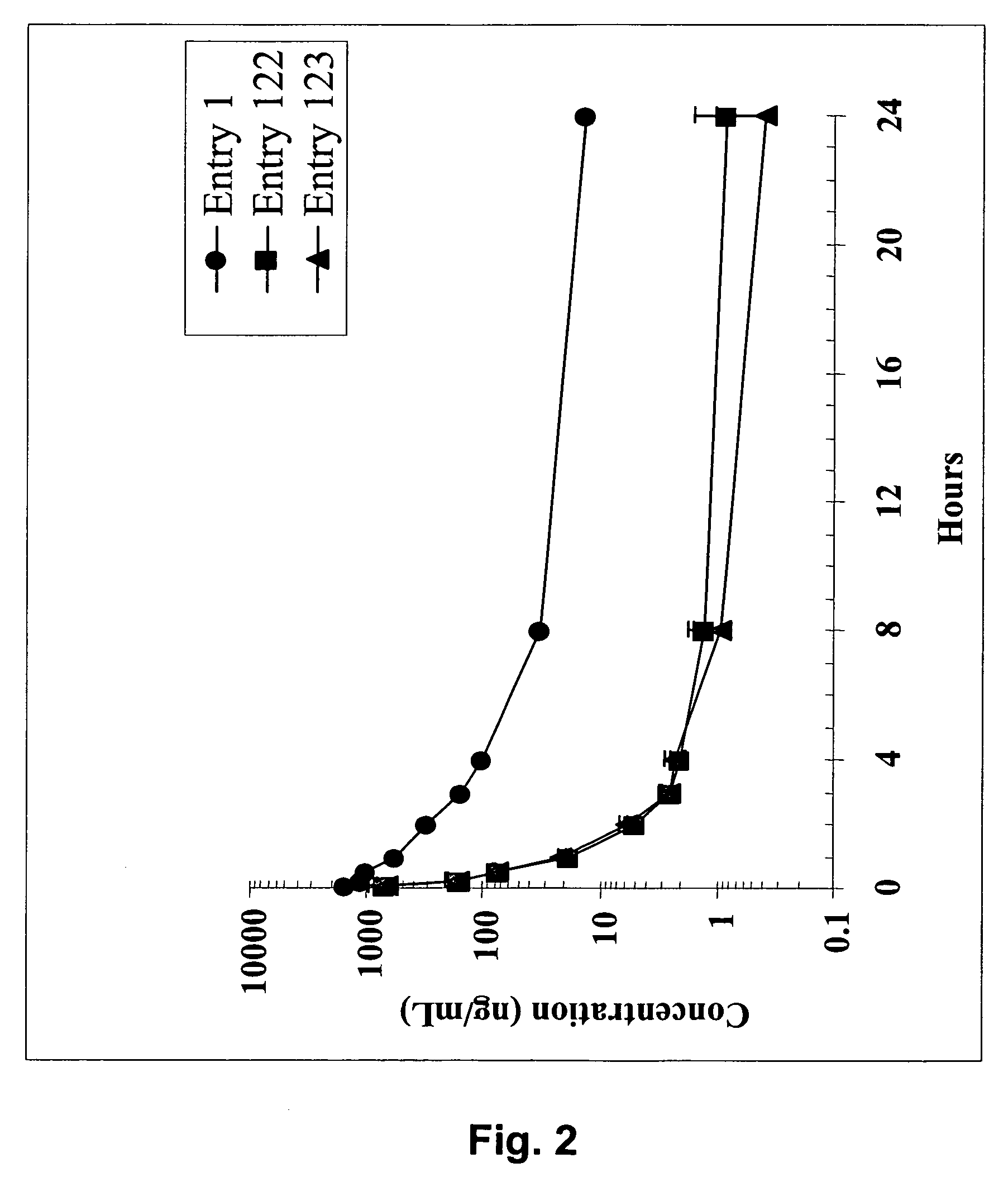
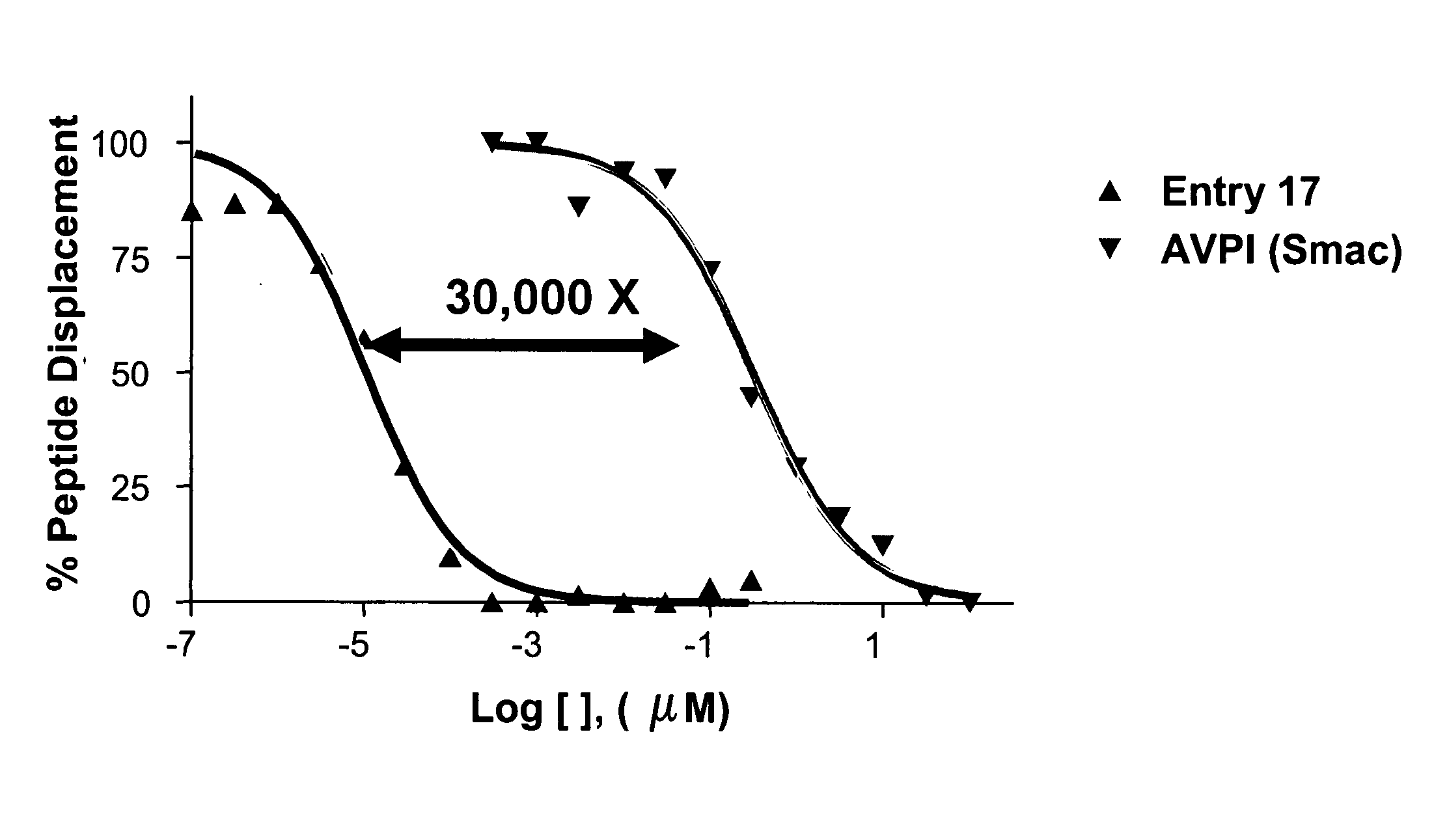
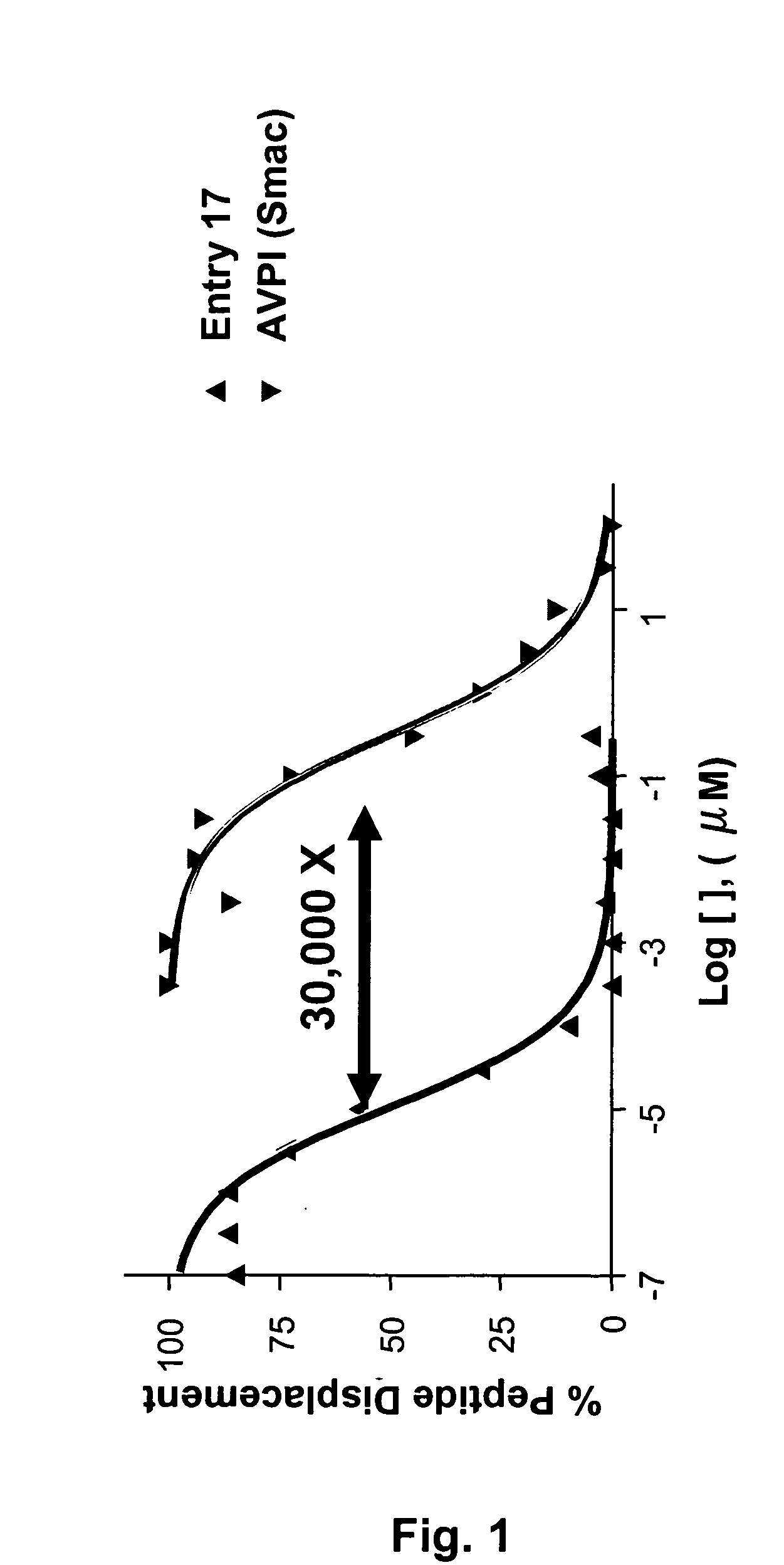
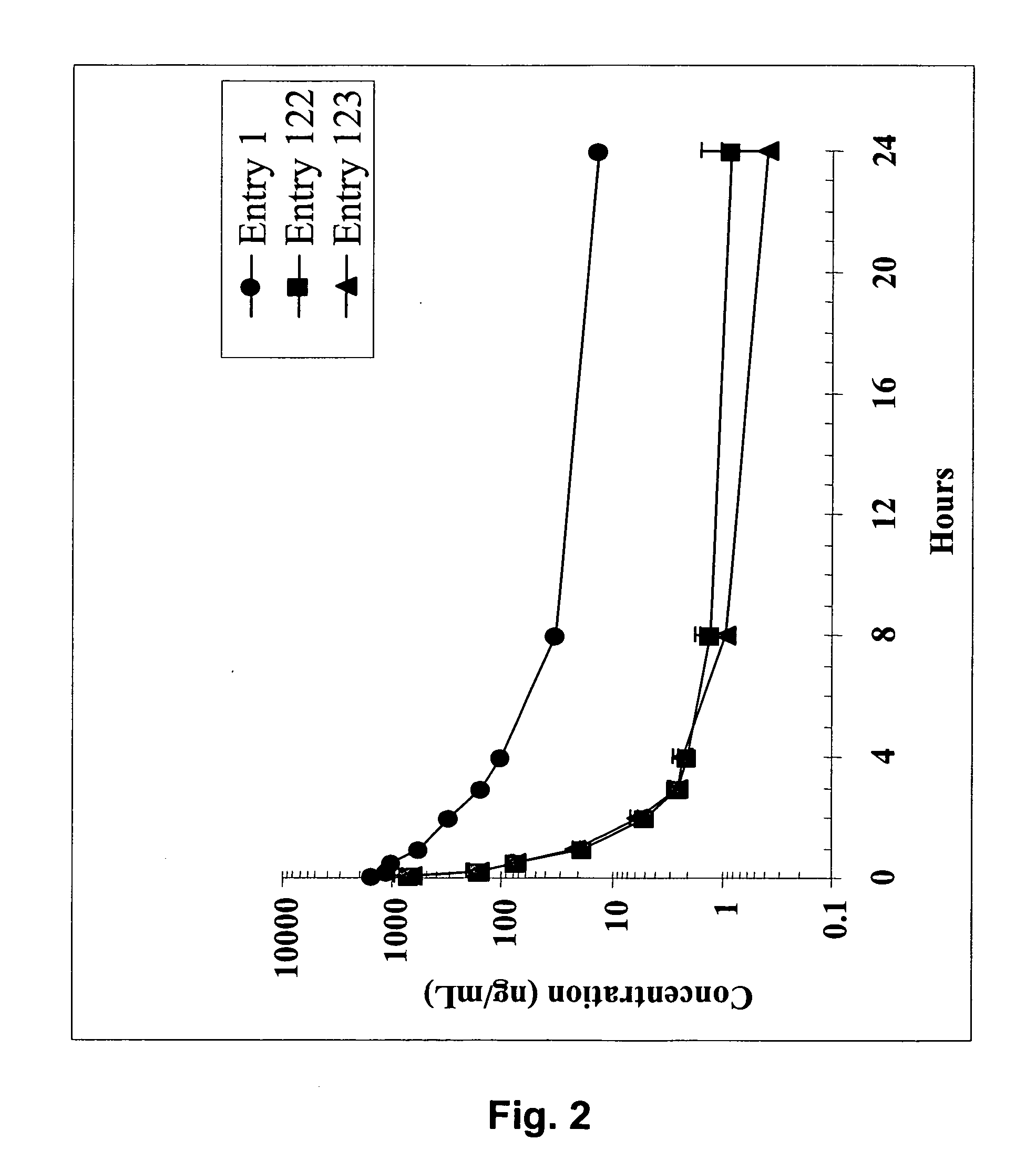
ActiveUS7517906B2High sensitivityAccelerated deathOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSmac mimeticsTopoisomerase inhibitor
Molecular mimics of Smac are capable of modulating apoptosis through their interaction with cellular IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins). The mimetics are based on a monomer or dimer of the N-terminal tetrapeptide of IAP-binding proteins, such as Smac / DIABLO, Hid, Grim and Reaper, which interact with a specific surface groove of IAP. Also disclosed are methods of using these peptidomimetics for therapeutic purposes. In various embodiments of the invention the Smac mimetics of the invention are combined with chemotherapeutic agents, including, but not limited to topoisomerase inhibitors, kinase inhibitors, NSAIDs, taxanes and platinum containing compounds use broader language
Owner:MEDIVIR AB
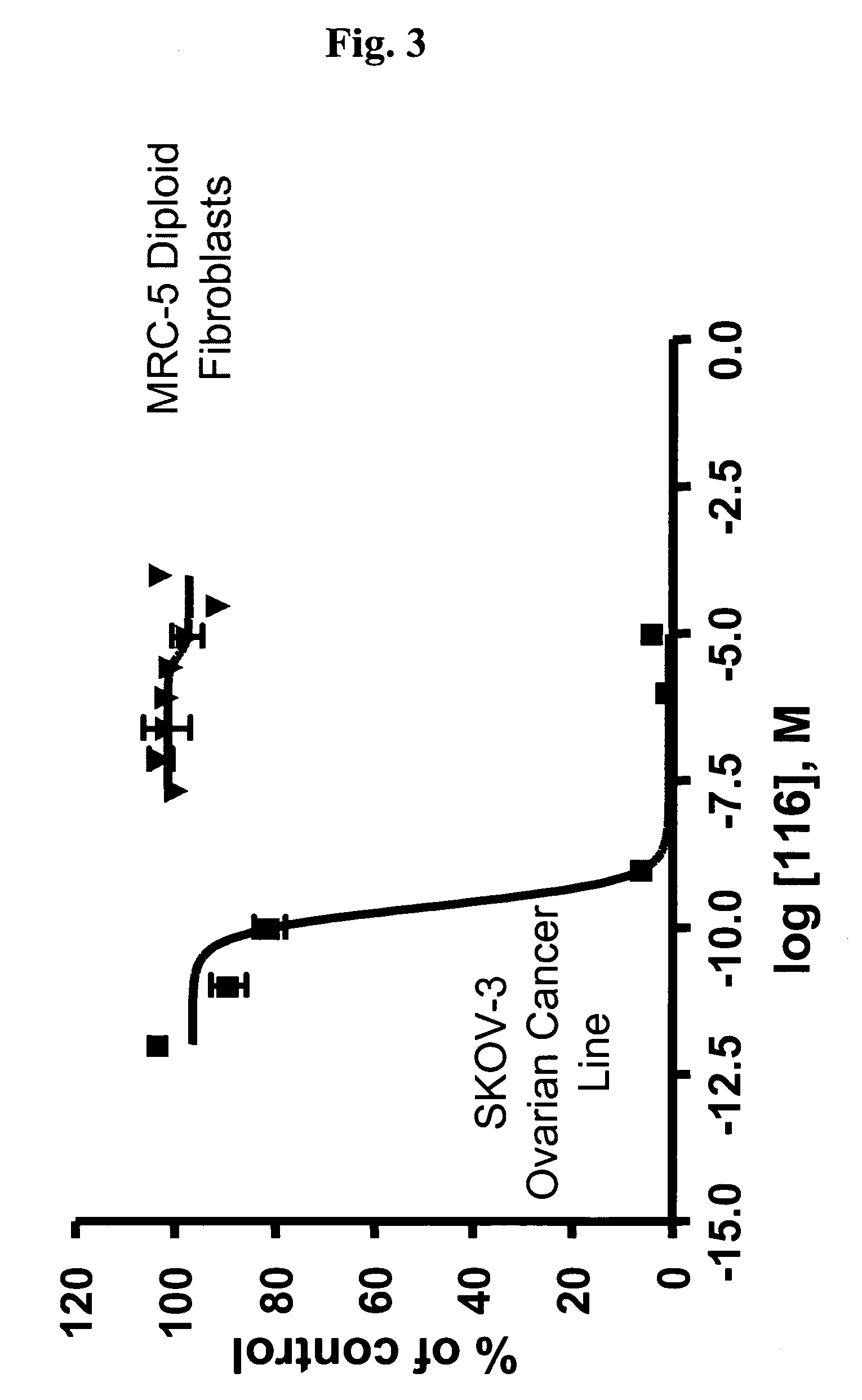
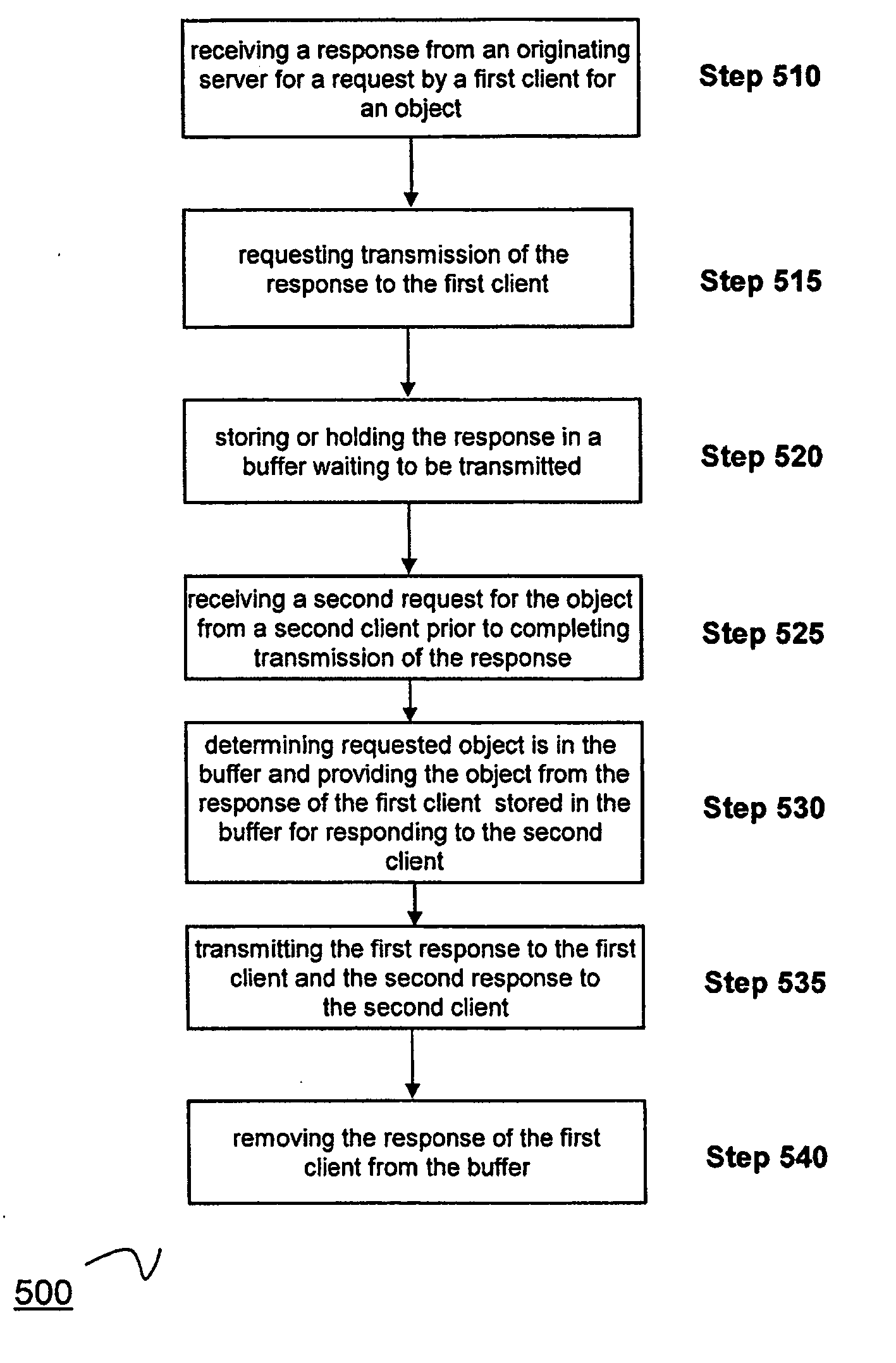
Method and device for performing caching of dynamically generated objects in a data communication network
ActiveUS20070156965A1Improve abilitiesEasy to handleDigital data information retrievalTransmissionObject storeClient-side
A method for maintaining a cache of dynamically generated objects. The method includes storing in the cache dynamically generated objects previously served from an originating server to a client. A communication between the client and server is intercepted by the cache. The cache parses the communication to identify an object determinant and to determine whether the object determinant indicates whether a change has occurred or will occur in an object at the originating server. The cache marks the object stored in the cache as invalid if the object determinant so indicates. If the object has been marked as invalid, the cache retrieves the object from the originating server.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Dimeric IAP inhibitors
ActiveUS20060194741A1Increased cell deathIncreased apoptotic activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSmac mimeticsApoptosis
Molecular mimics of Smac are capable of modulating apoptosis through their interaction with cellular IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins). The mimetics are based on a monomer or dimer of the N-terminal tetrapeptide of IAP-binding proteins, such as Smac / DIABLO, Hid, Grim and Reaper, which interact with a specific surface groove of LAP. Also disclosed are methods of using these peptidomimetics for therapeutic purposes. In various embodiments of the invention the Smac mimetics of the invention are combined with chemotherapeutic agents, including, but not limited to topoisomerase inhibitors, kinase inbhibitors, NSAIDs, taxanes and platinum containing compounds use broader language
Owner:MEDIVIR AB
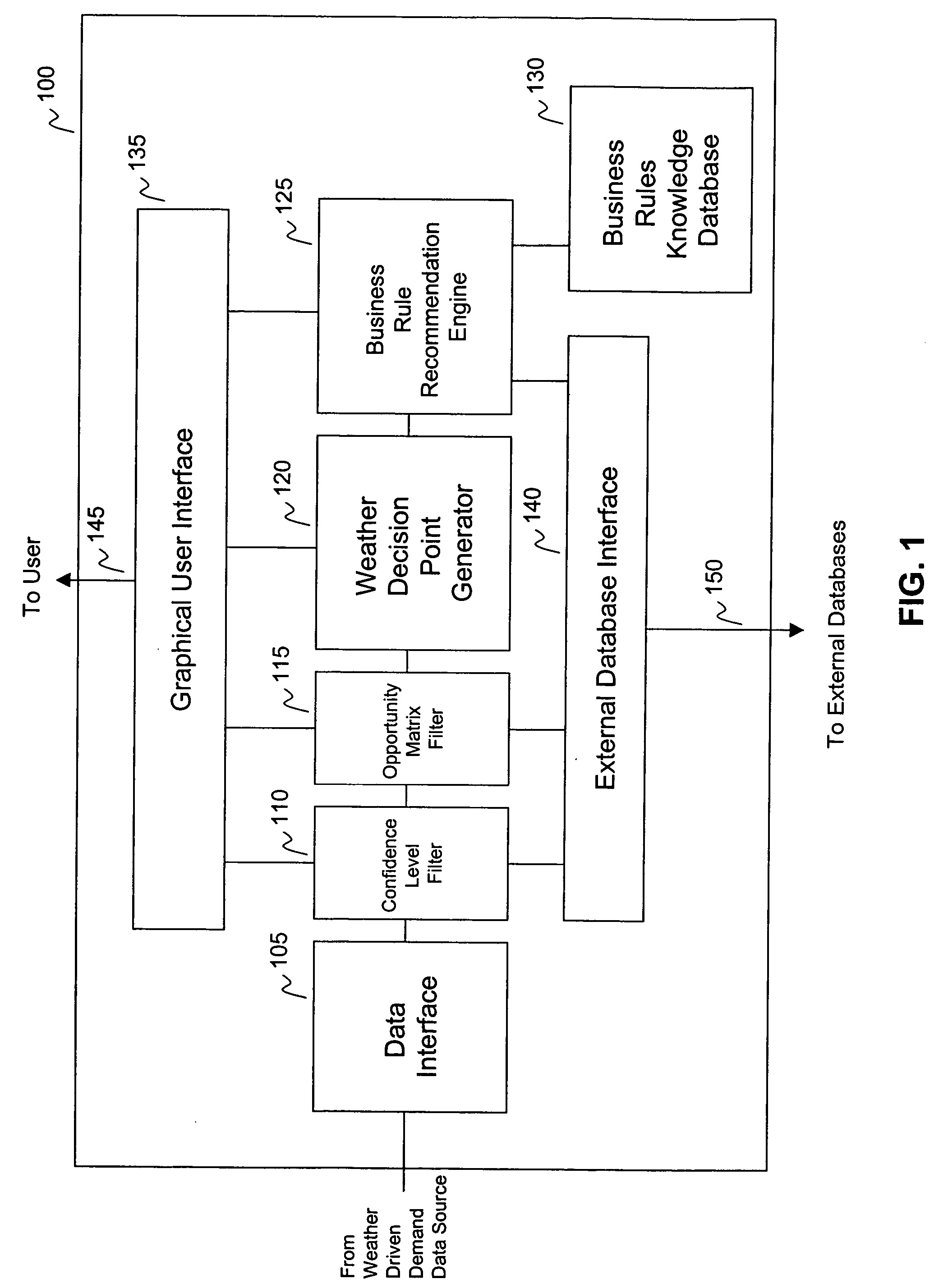
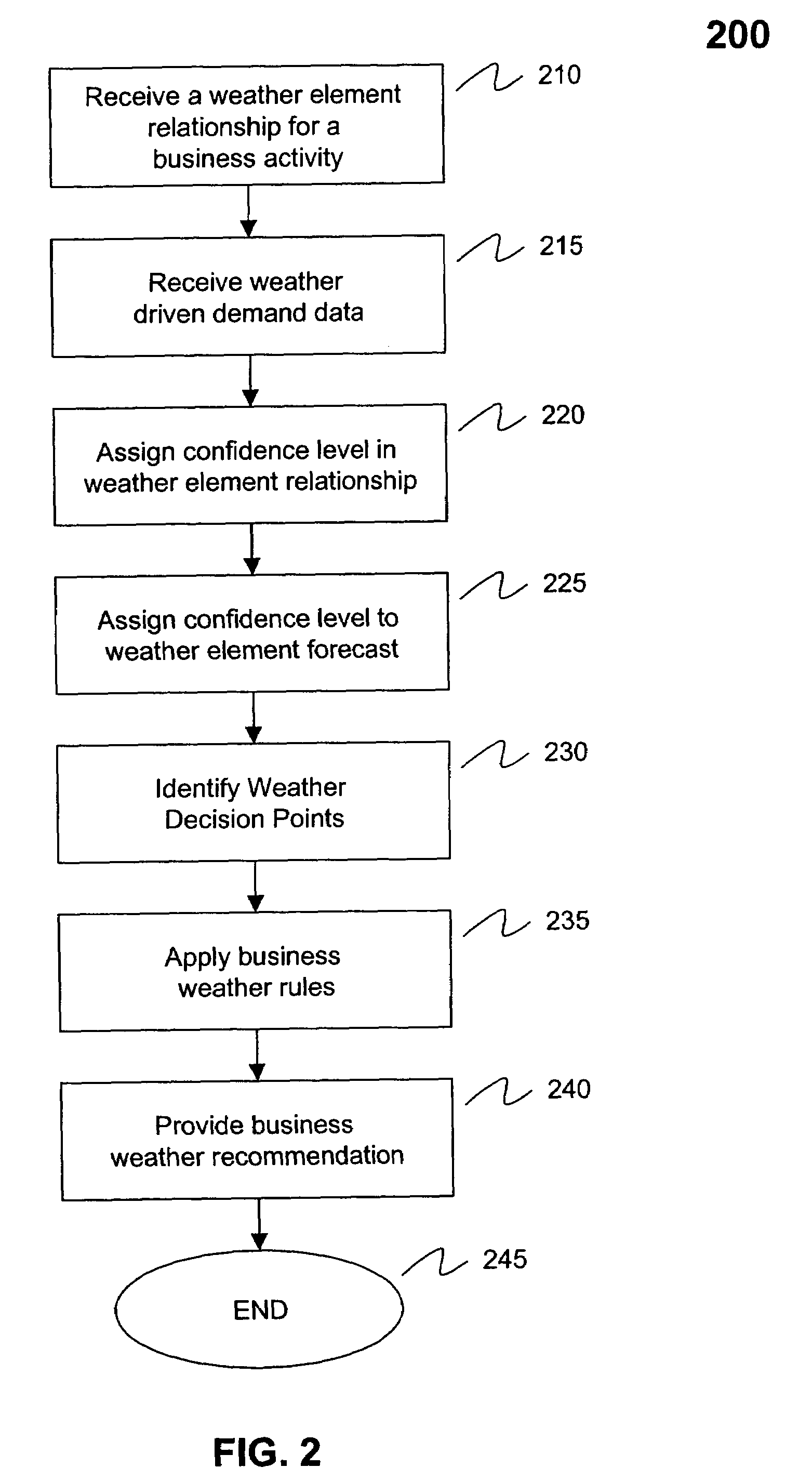
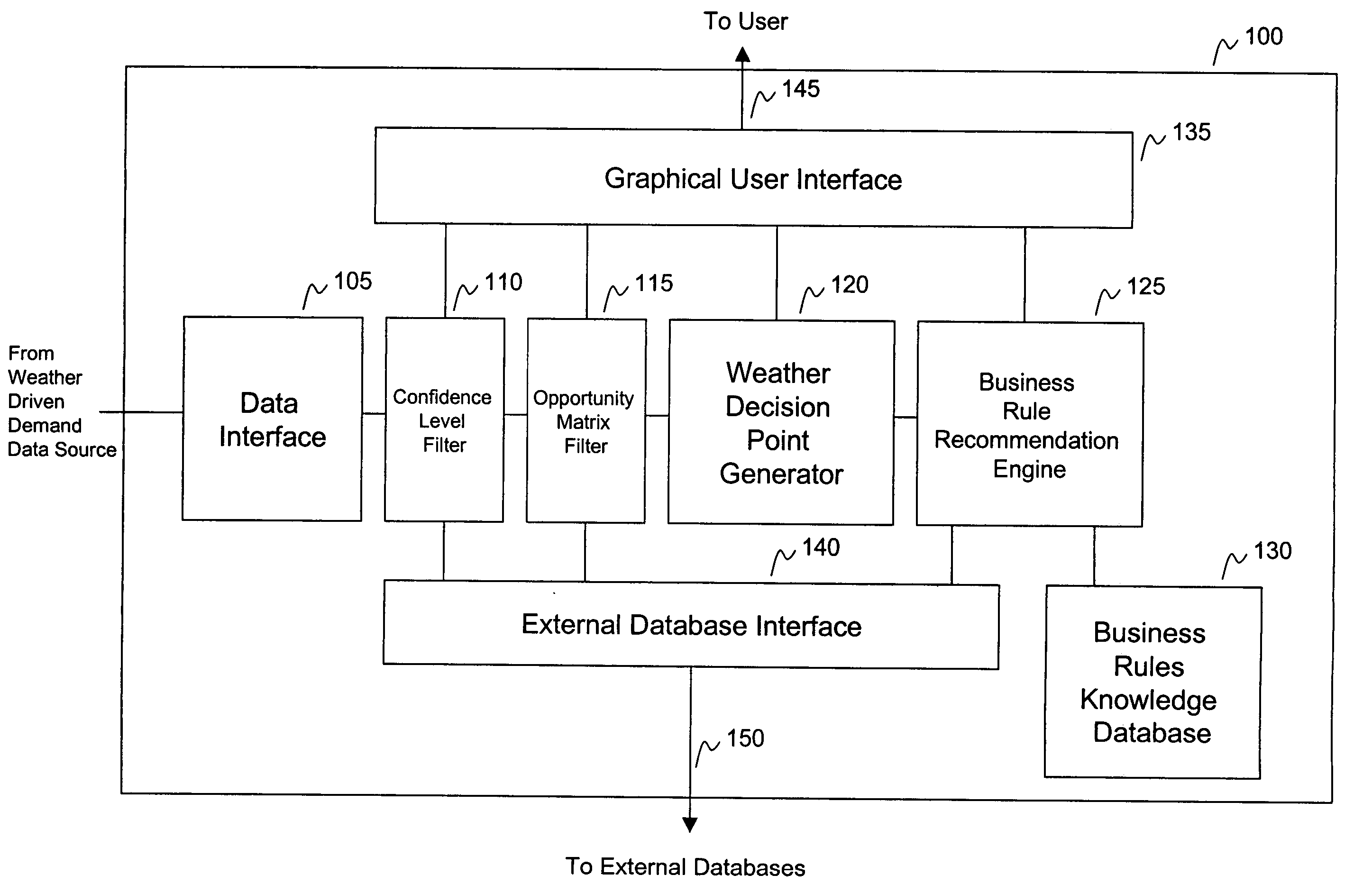
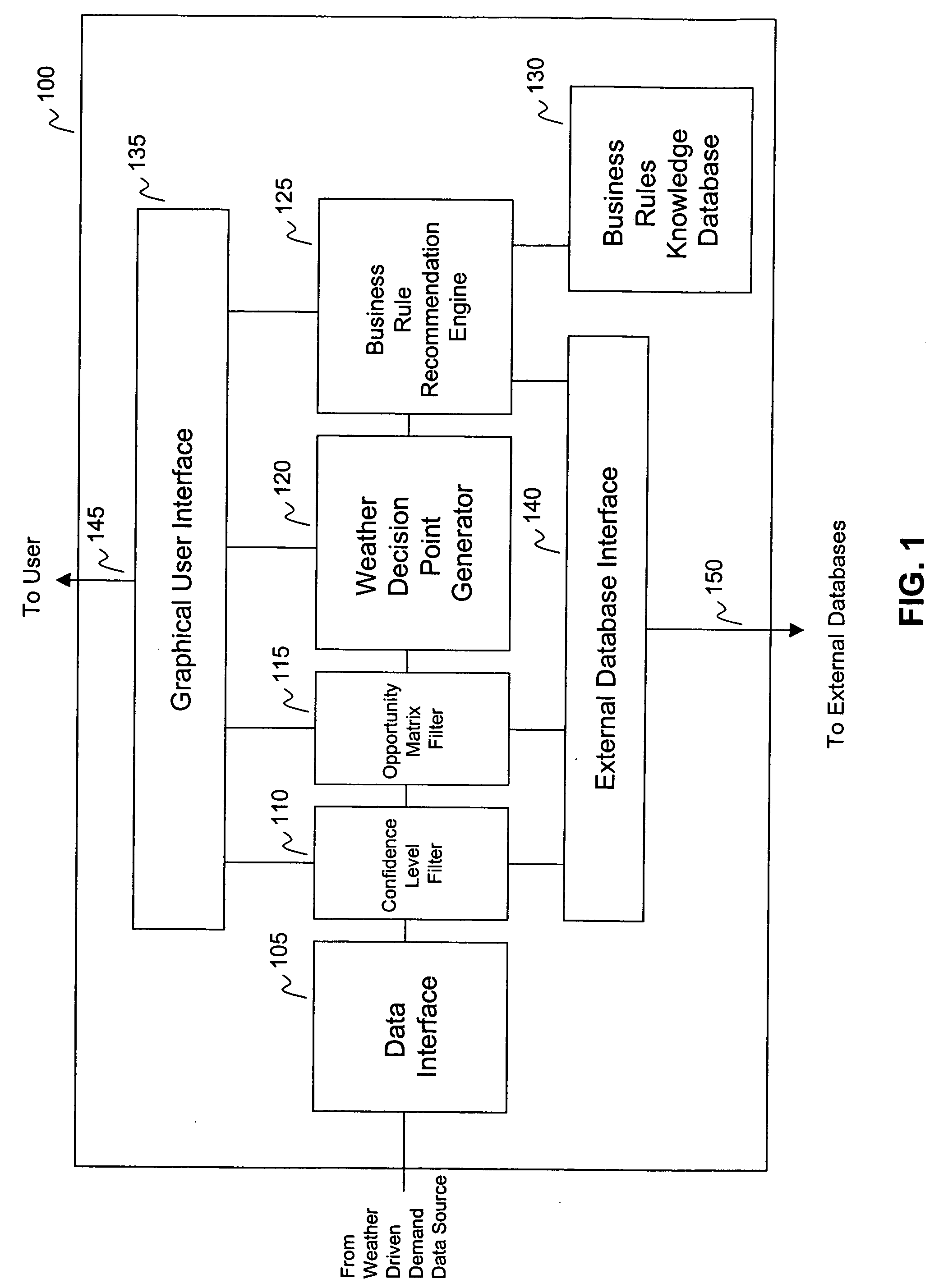
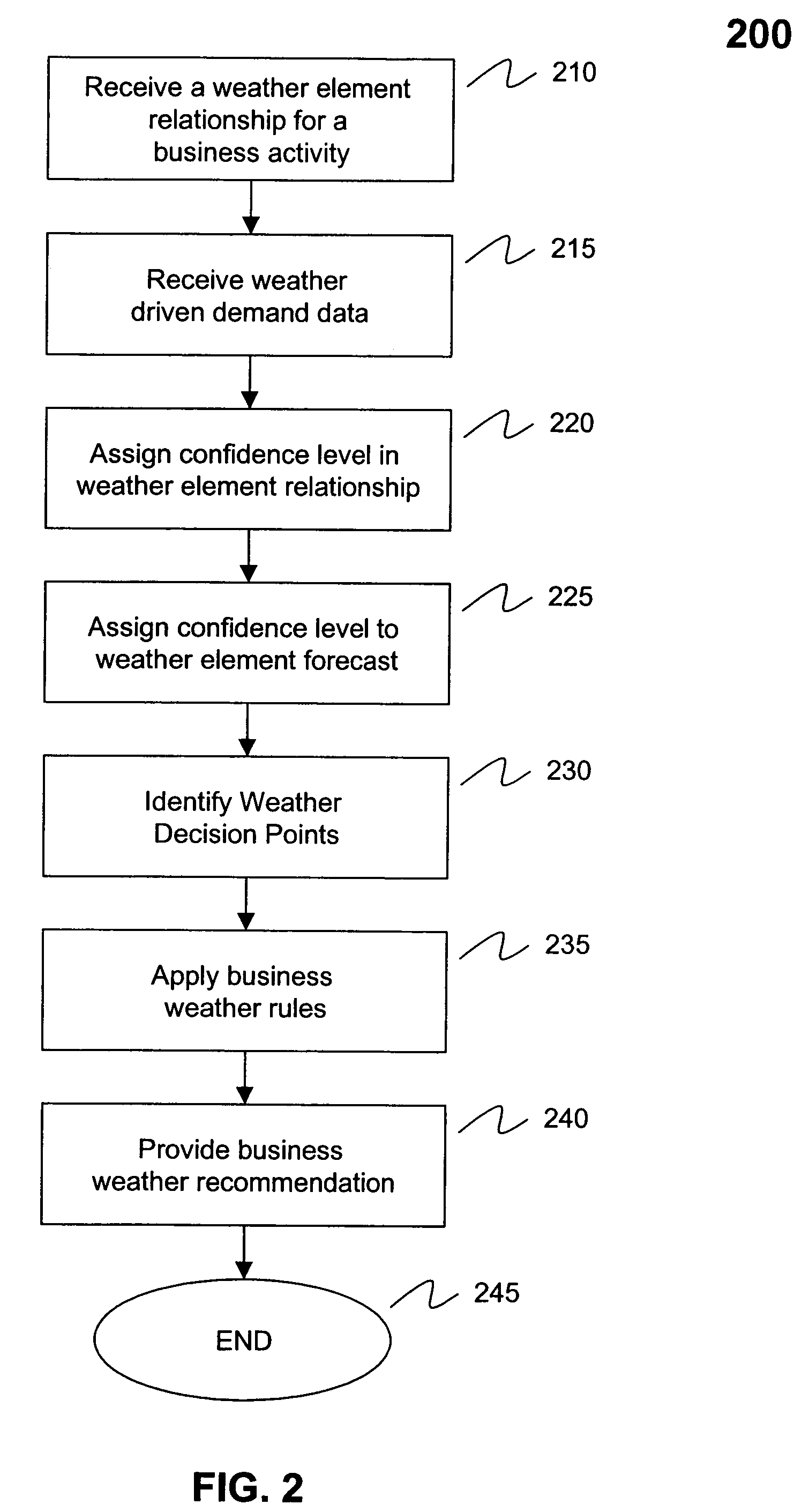
Systems and methods for recommending business decisions utilizing weather driven demand data and opportunity and confidence measures
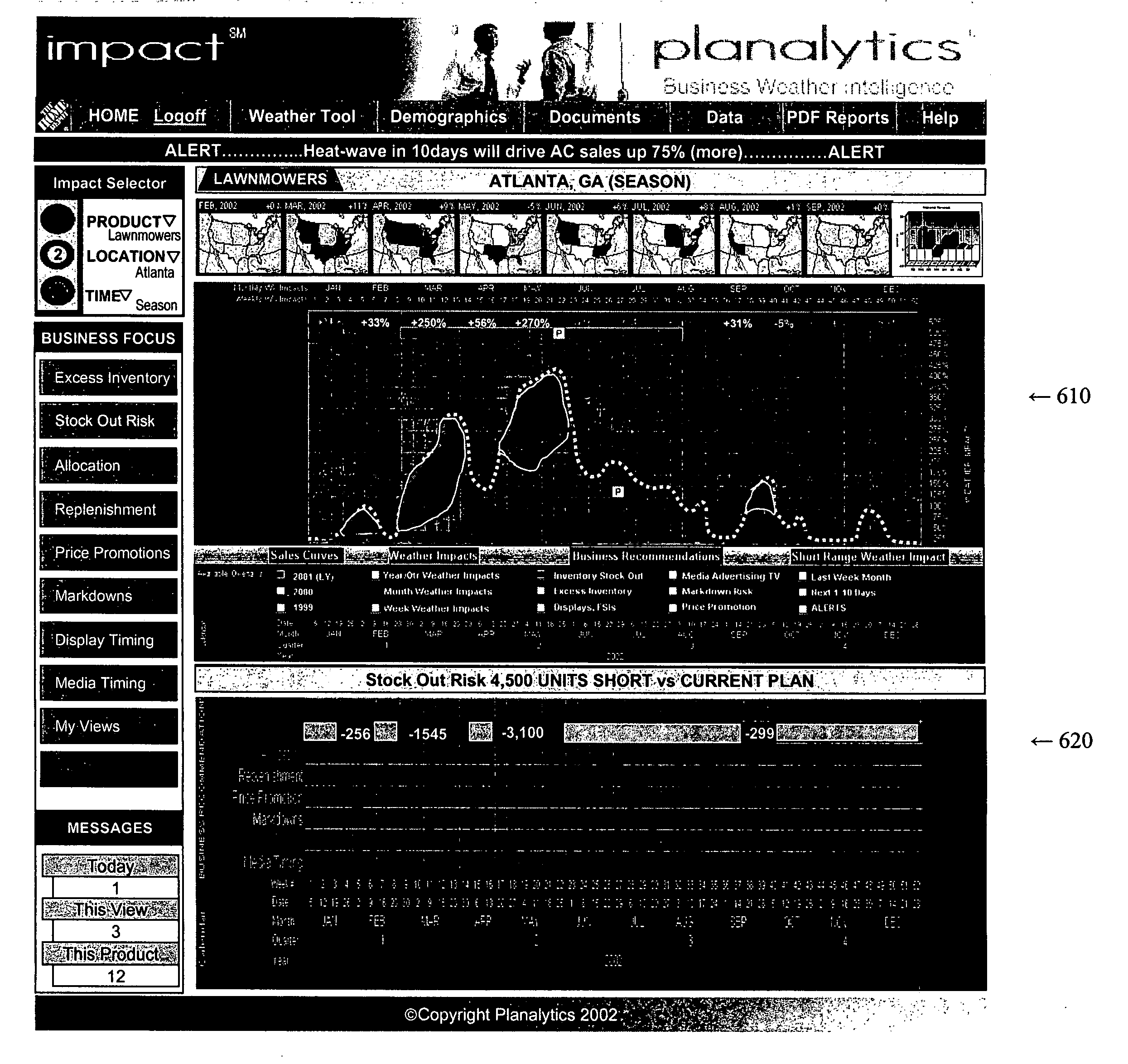
InactiveUS7184965B2Cost effectiveEffective approachResourcesSpecific program execution arrangementsBusiness activitiesConfidence factor
Systems and methods to generate business recommendations for specific business actions based on weather element forecasts and known relationships between a business activity and weather elements are provided. The system includes a confidence level filter, an opportunity matrix filter, a weather decision point generator, a business rule recommendation engine and a business rule knowledge database. Methods to generate a business recommendation for a business activity are also provided. The methods include receiving weather driven demand data, assigning opportunity measures to each of the data points, identifying weather decision points based on opportunity measures, and applying business weather rules to the weather decision points to generate business recommendations. In a further feature, a weather element relationship and / or a weather element forecast confidence level is assigned to each data point within the weather driven demand data. These confidence levels are then factored in to determine weather decision points.
Owner:PANALEC
Refuelable battery-powered electric vehicle
ActiveUS20100250043A1EffectivelyRecharge time is considerableDigital data processing detailsMobile unit charging stationsOn boardElectrical battery
The electrical vehicle energy storage system permits the electric refueling of the electric vehicle just like an automobile would be refueled with gasoline at a gas station. Circuitry on board the vehicle accessible by the electric refueling station enables the determination of the energy content of the battery module or modules returned to the electric refueling station and the owner of the vehicle is given credit for the energy remaining in the battery module or modules which have been exchanged. Selective refueling may take place for given battery modules by removing them from the battery system and charging them at home, office or factory. A process for operating an electric vehicle is also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:SCHEUCHER KARL F
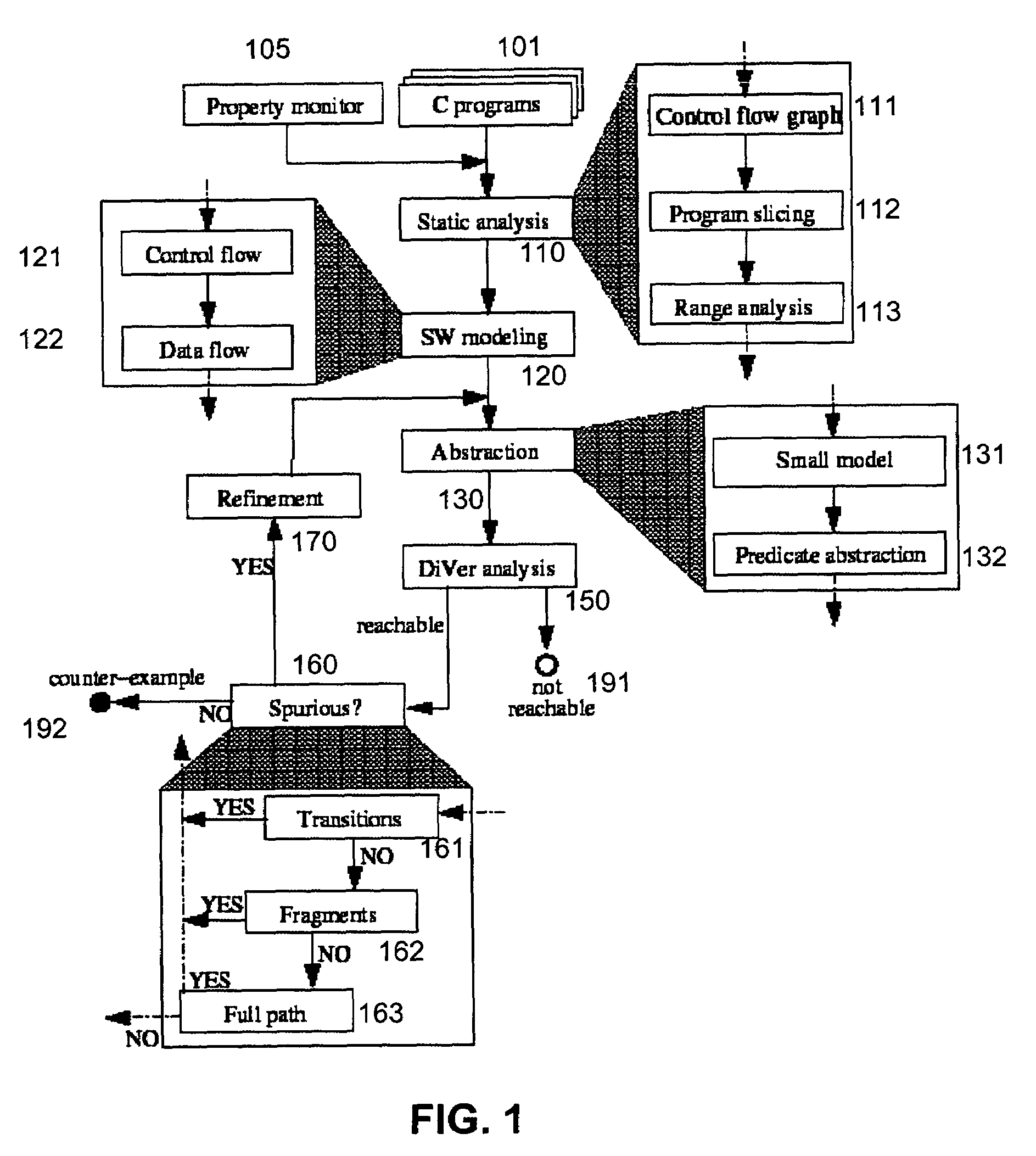
System and method for modeling, abstraction, and analysis of software
ActiveUS20050166167A1Improve verification efficiencyImprove translationError detection/correctionComputation using non-denominational number representationBasic blockSoftware
A system and method is disclosed for formal verification of software programs that advantageously translates the software, which can have bounded recursion, into a Boolean representation comprised of basic blocks and which applies SAT-based model checking to the Boolean representation.
Owner:NEC CORP
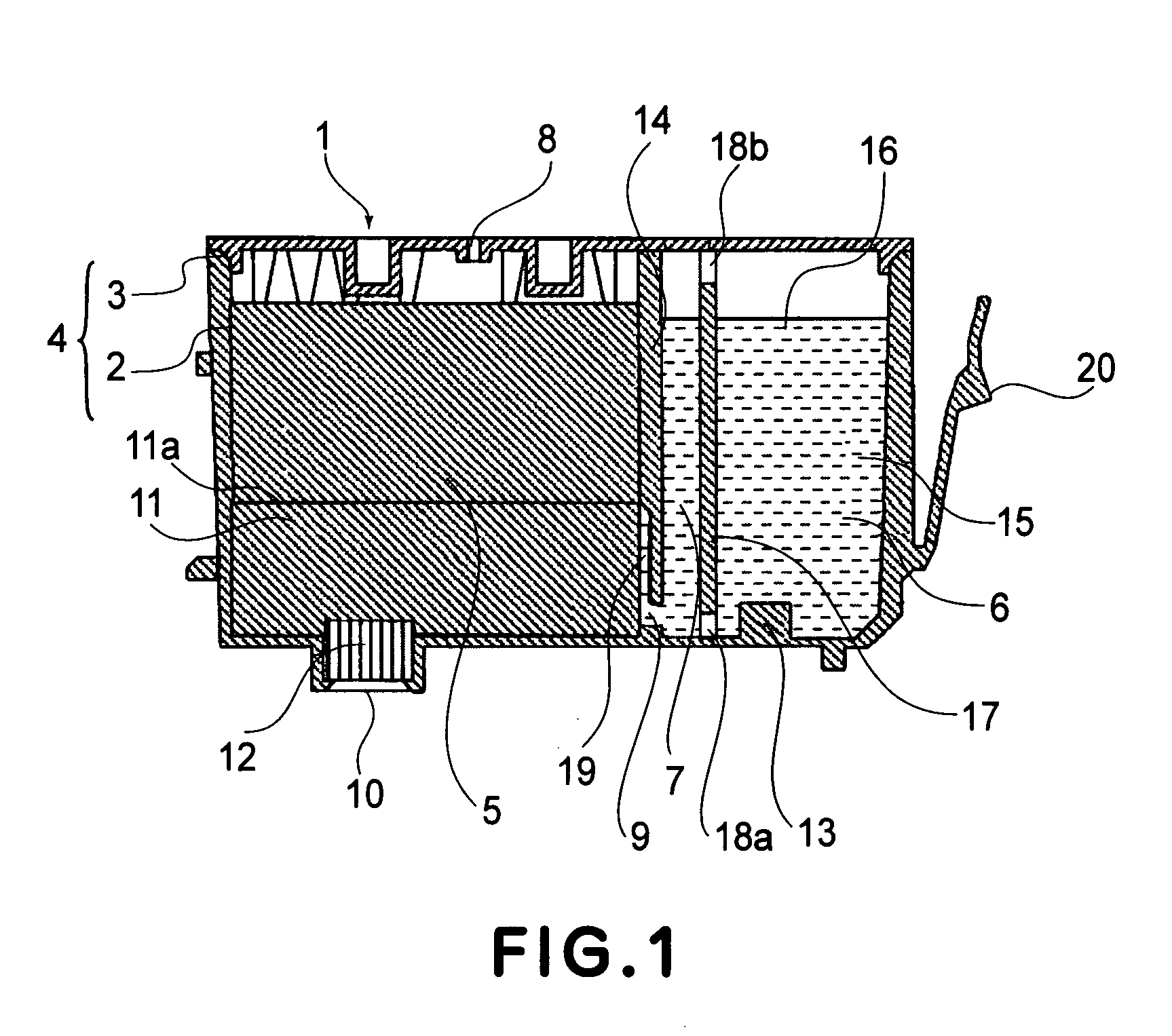
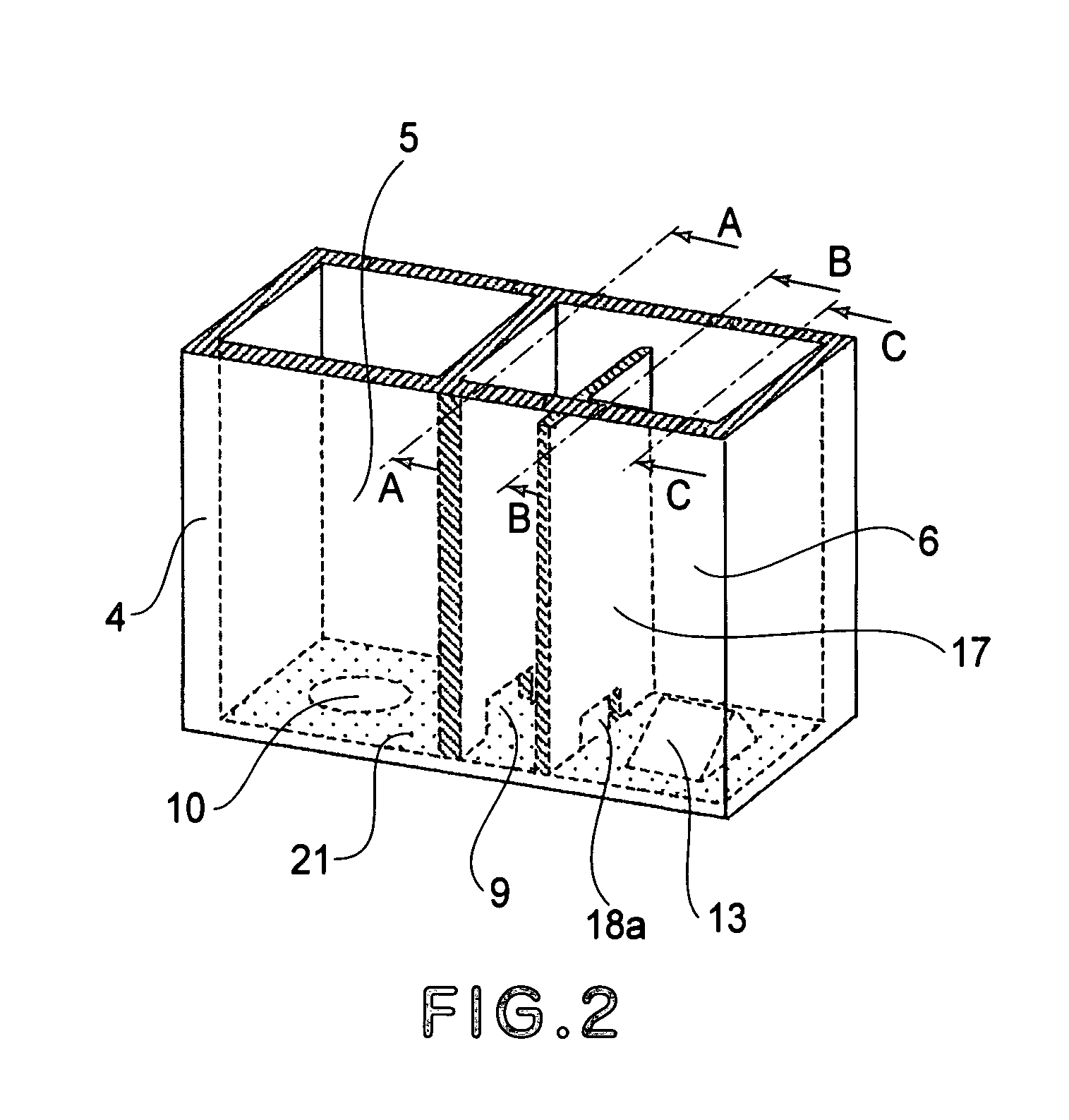
Ink container
An ink container includes an ink accommodation chamber for directly accommodating ink; a sensor portion for detecting a remaining amount of the ink in said ink accommodation chamber, wherein ambient air is introduced from an outside of said ink accommodation chamber into the ink in accordance with supplying the ink into an ink jet recording head; a division wall extended from an inner bottom portion of said ink accommodation chamber substantially upwardly, said division wall divides a space between an ambient air introducing portion which introduces the air into the ink in said ink accommodation chamber and said sensor portion to permit passage of the ink therethrough and to prevent passage, therethrough, of bubbles which are produced with introduction of the air.
Owner:CANON KK
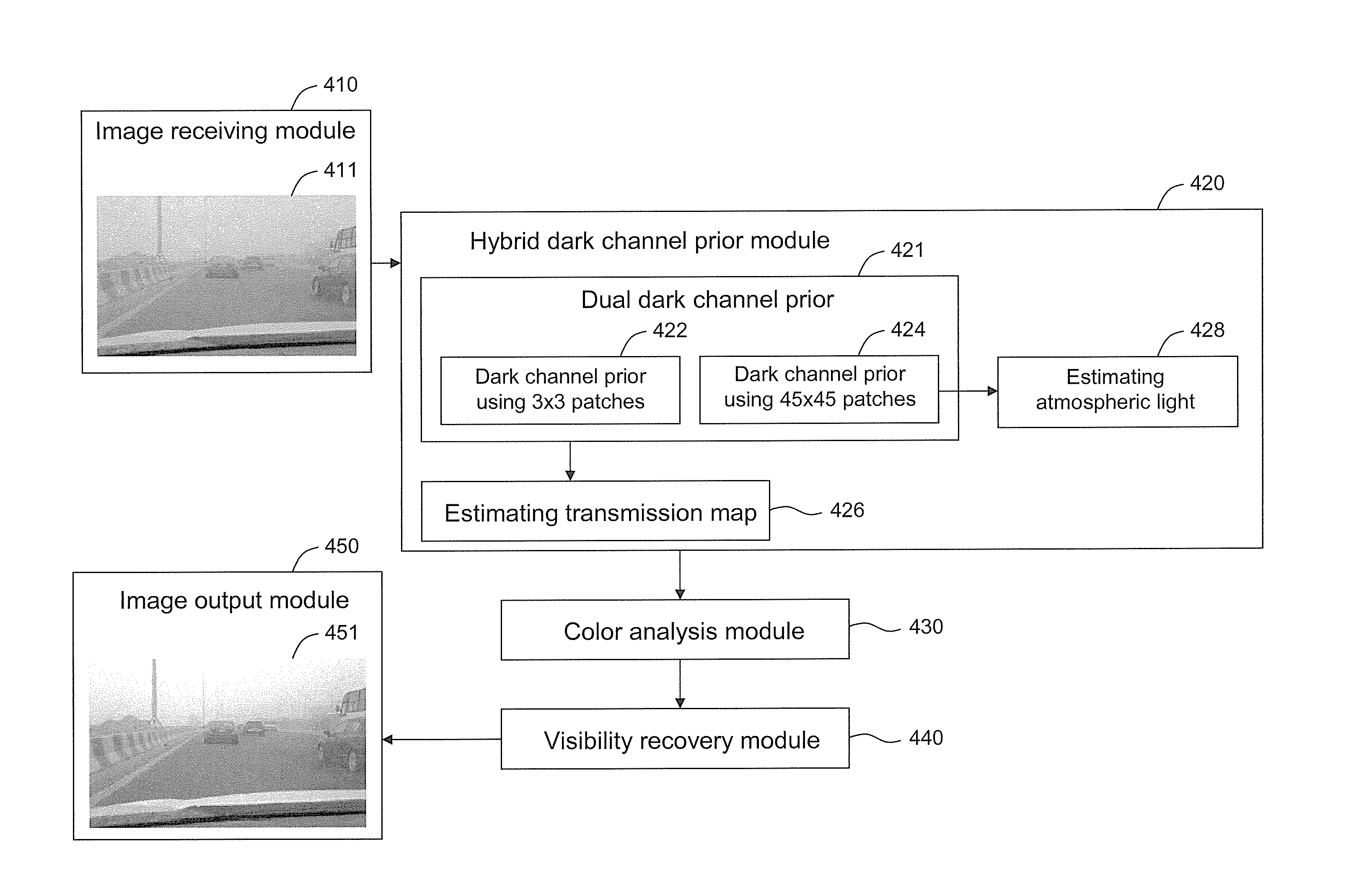
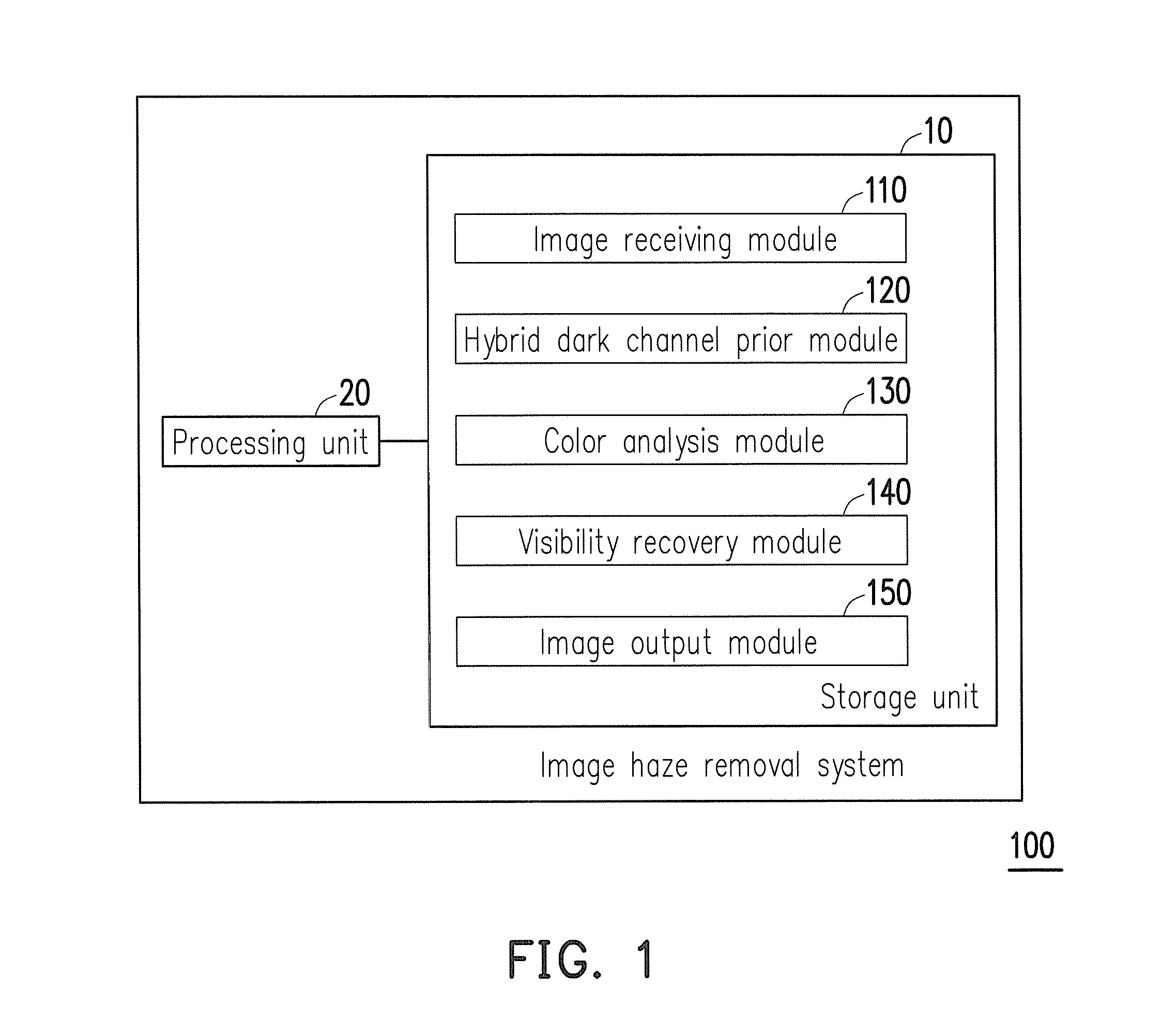
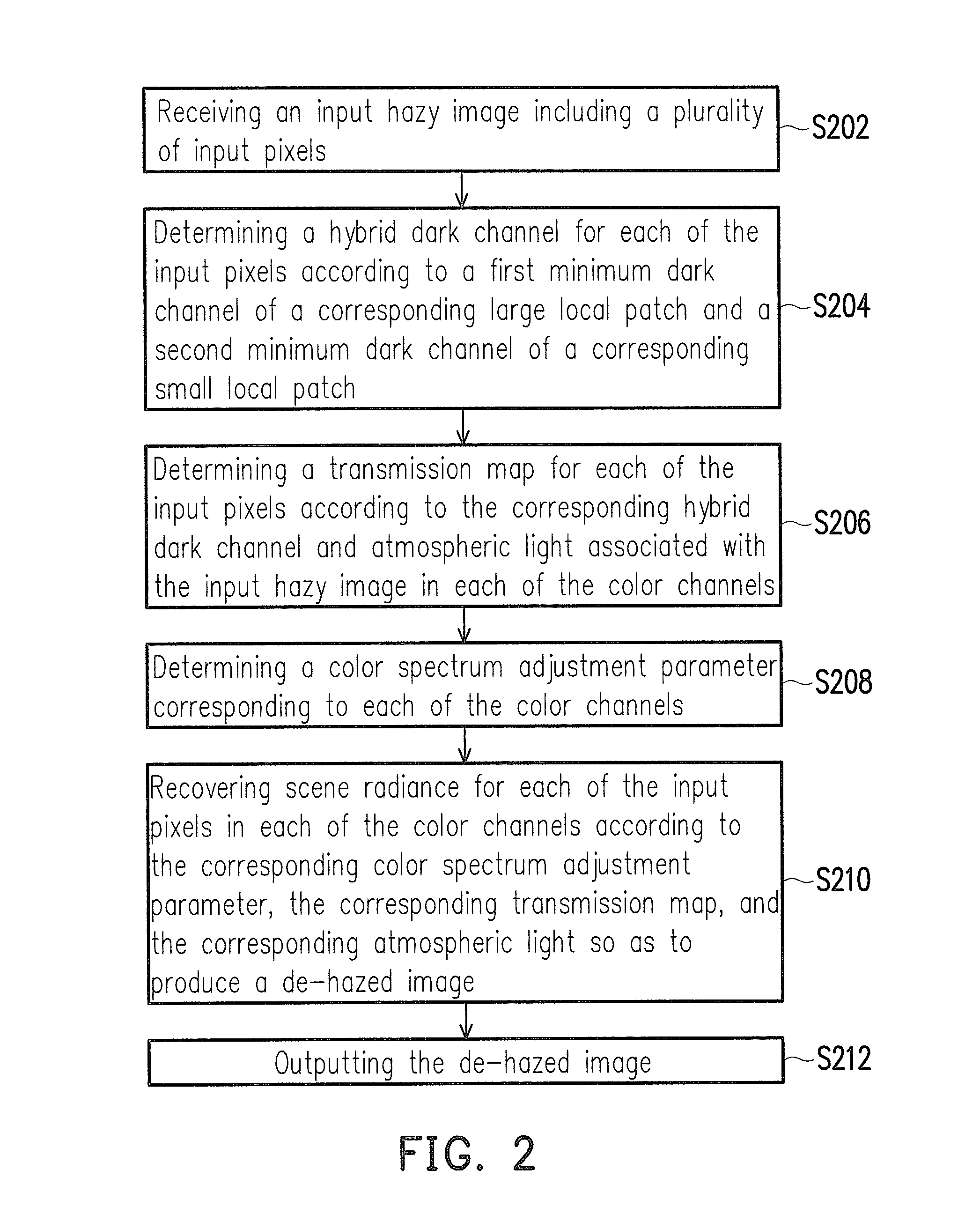
Method and system for image haze removal based on hybrid dark channel prior
ActiveUS20160071244A1Efficient removalEfficiently concealedImage enhancementImage analysisRadianceLightness
A method and a system for image haze removal are provided. The method includes the following steps: receiving an input hazy image including input pixels; determining a hybrid dark channel for each of the input pixels according to a first minimum dark channel of a corresponding large local patch and a second minimum dark channel of a corresponding small local patch; determining a transmission map for each of the input pixels according to the hybrid dark channel prior, the corresponding hybrid dark channel, and atmospheric light associated with the input hazy image in each color channel; determining a color spectrum adjustment parameter corresponding to each of the color channels; recovering scene radiance for each of the input pixels in each of the color channels according to the corresponding color spectrum adjustment parameter, the transmission map, and the corresponding atmospheric light to produce and output a de-hazed image.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
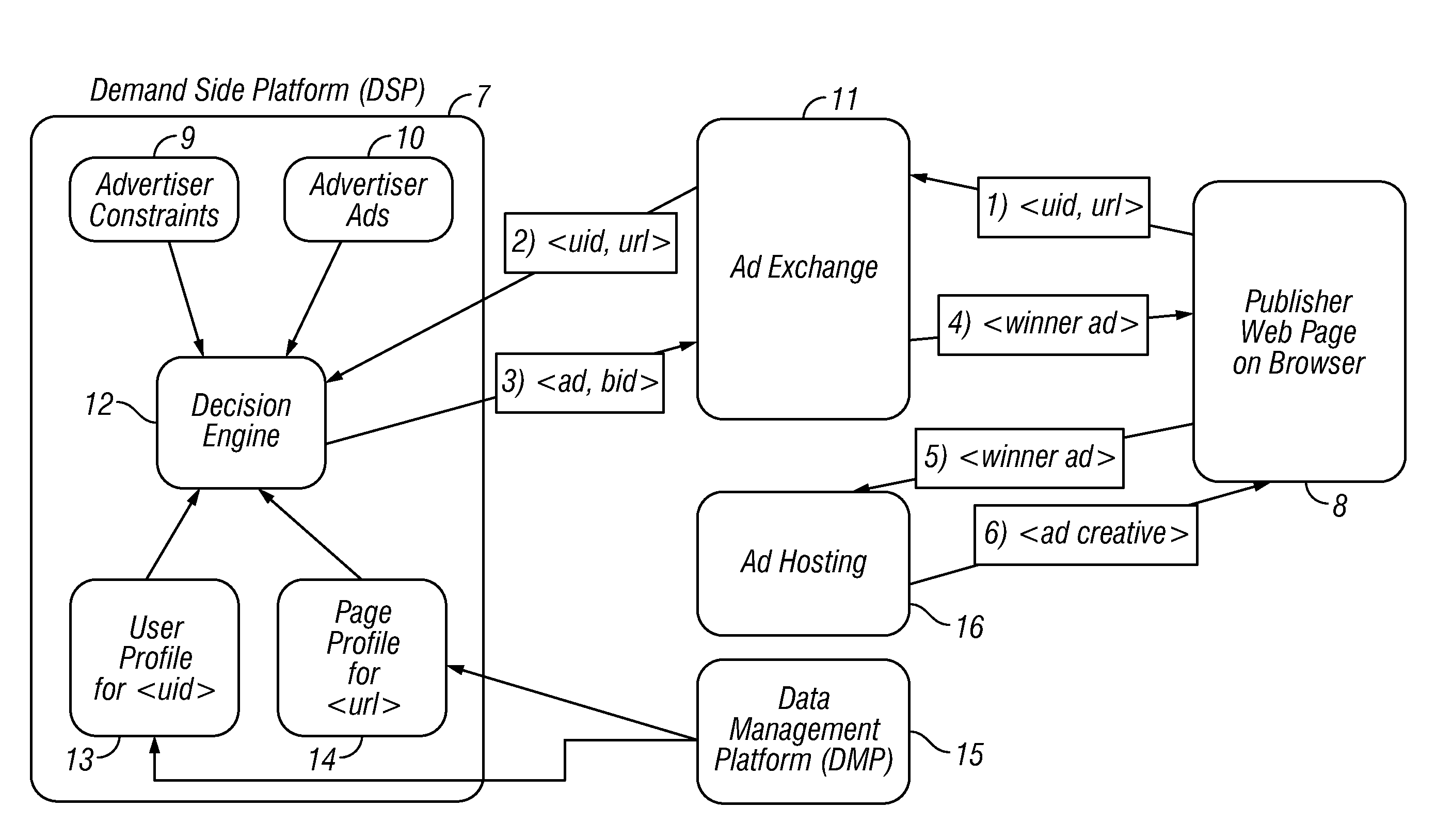
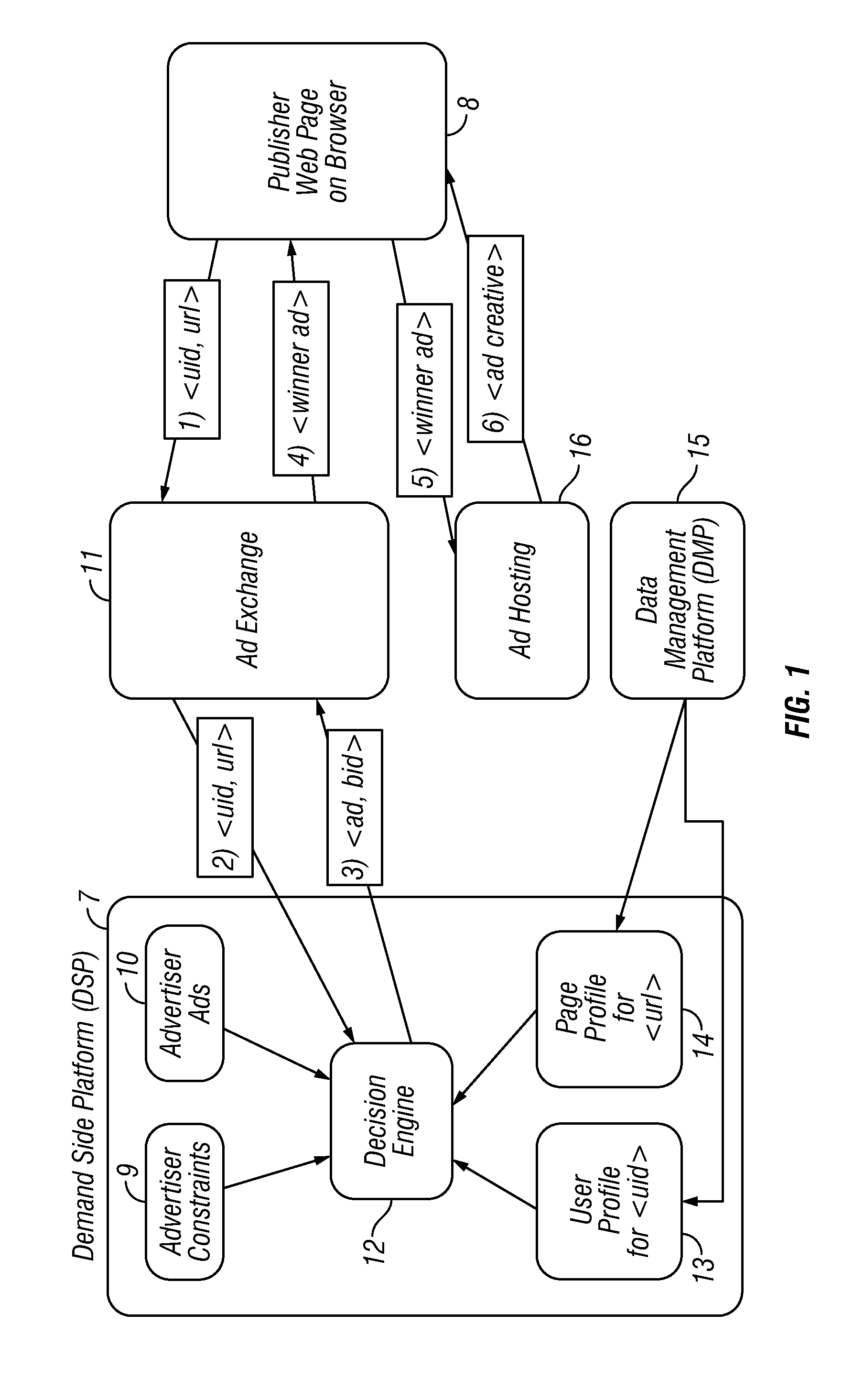
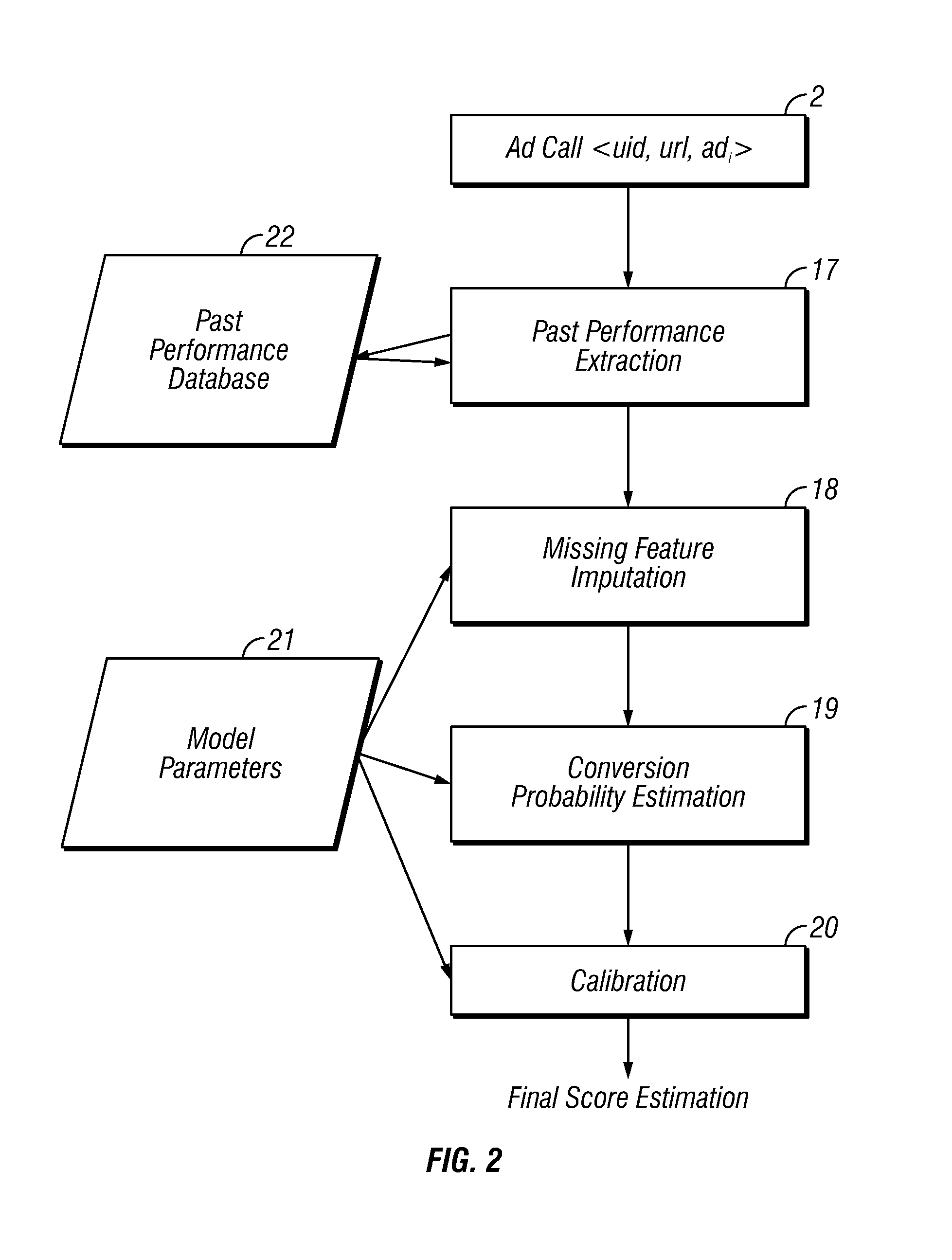
Estimating conversion rate in display advertising from past performance data
Embodiments of the invention present an approach to conversion rate estimation which relies on using past performance observations along user, publisher, and advertiser data hierarchies. More specifically, embodiments of the invention model the conversion event at different select hierarchical levels with separate binomial distributions and estimate the distribution parameters individually. It is shown how to combine these individual estimators using logistic regression to identify conversion events accurately. Embodiments of the invention can also handle many practical issues, such as data imbalance, missing data, and output probability calibration, which render this estimation problem more difficult for a real-world implementation of the approach.
Owner:AMOBEE
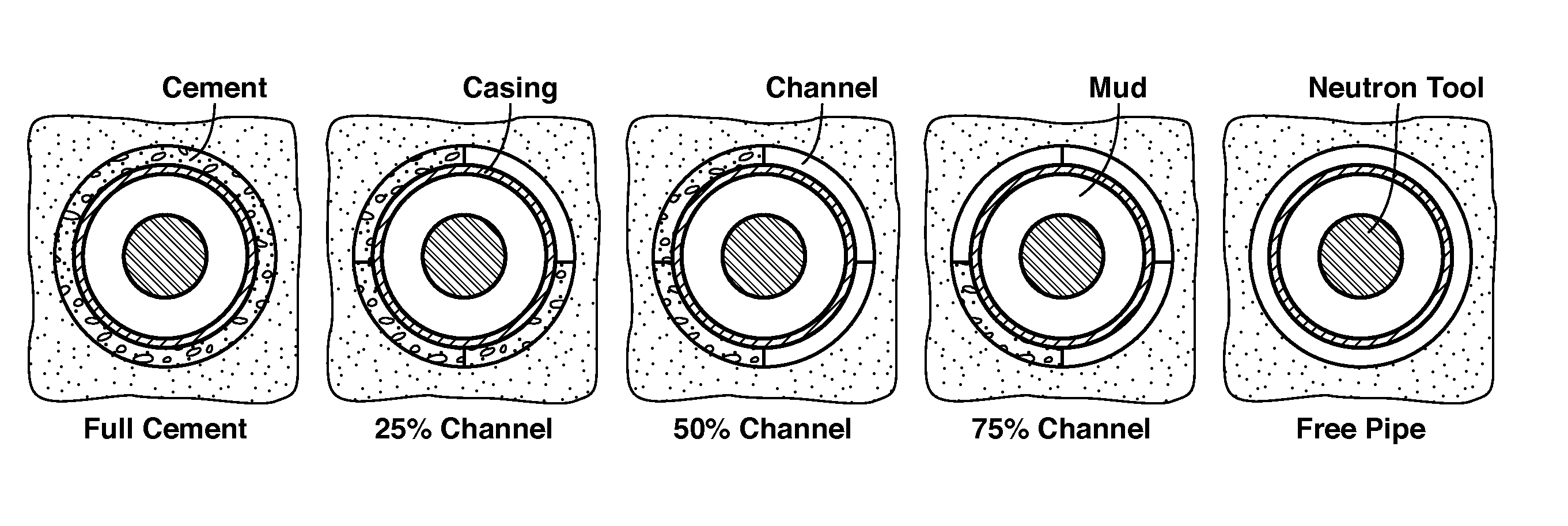
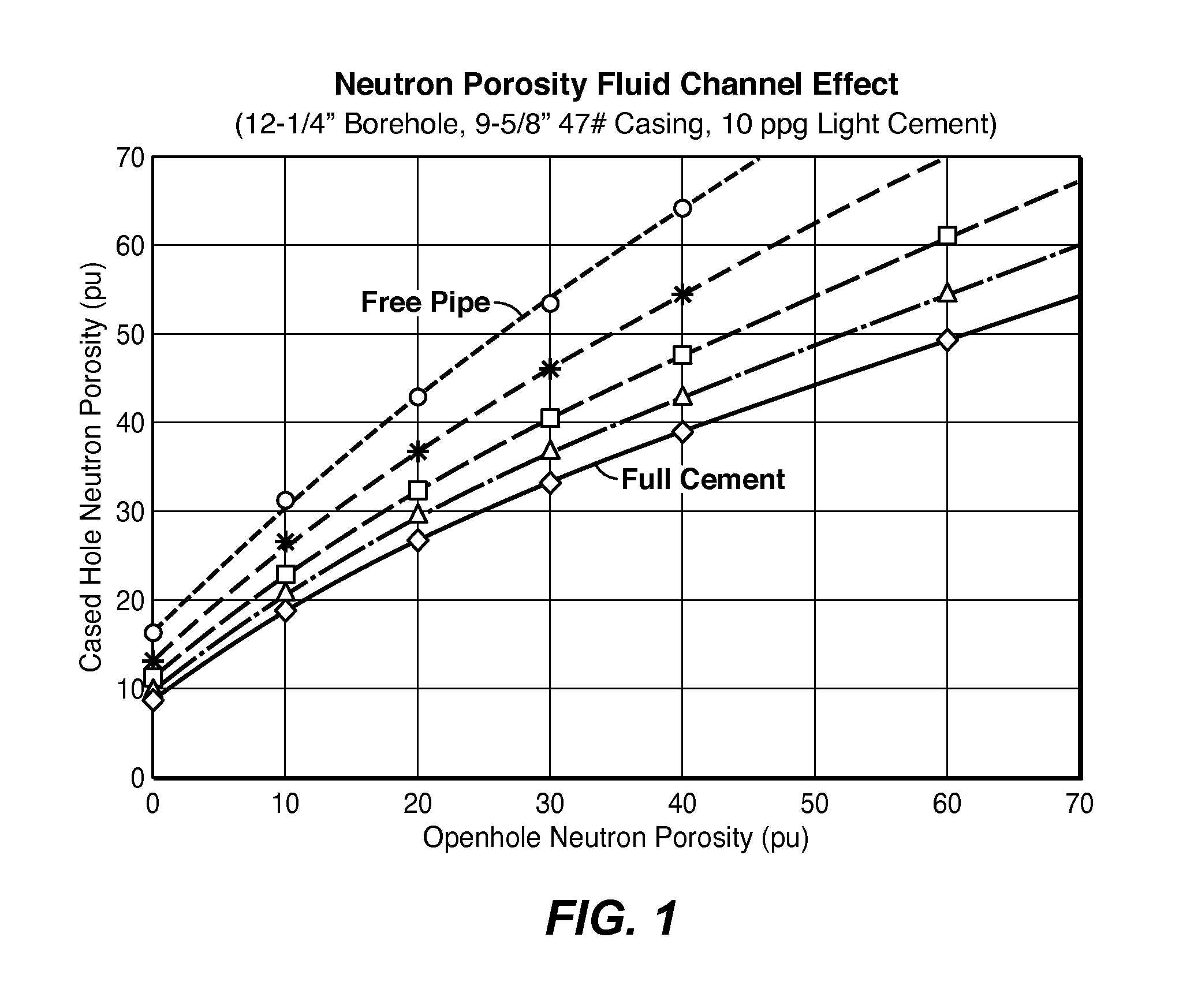
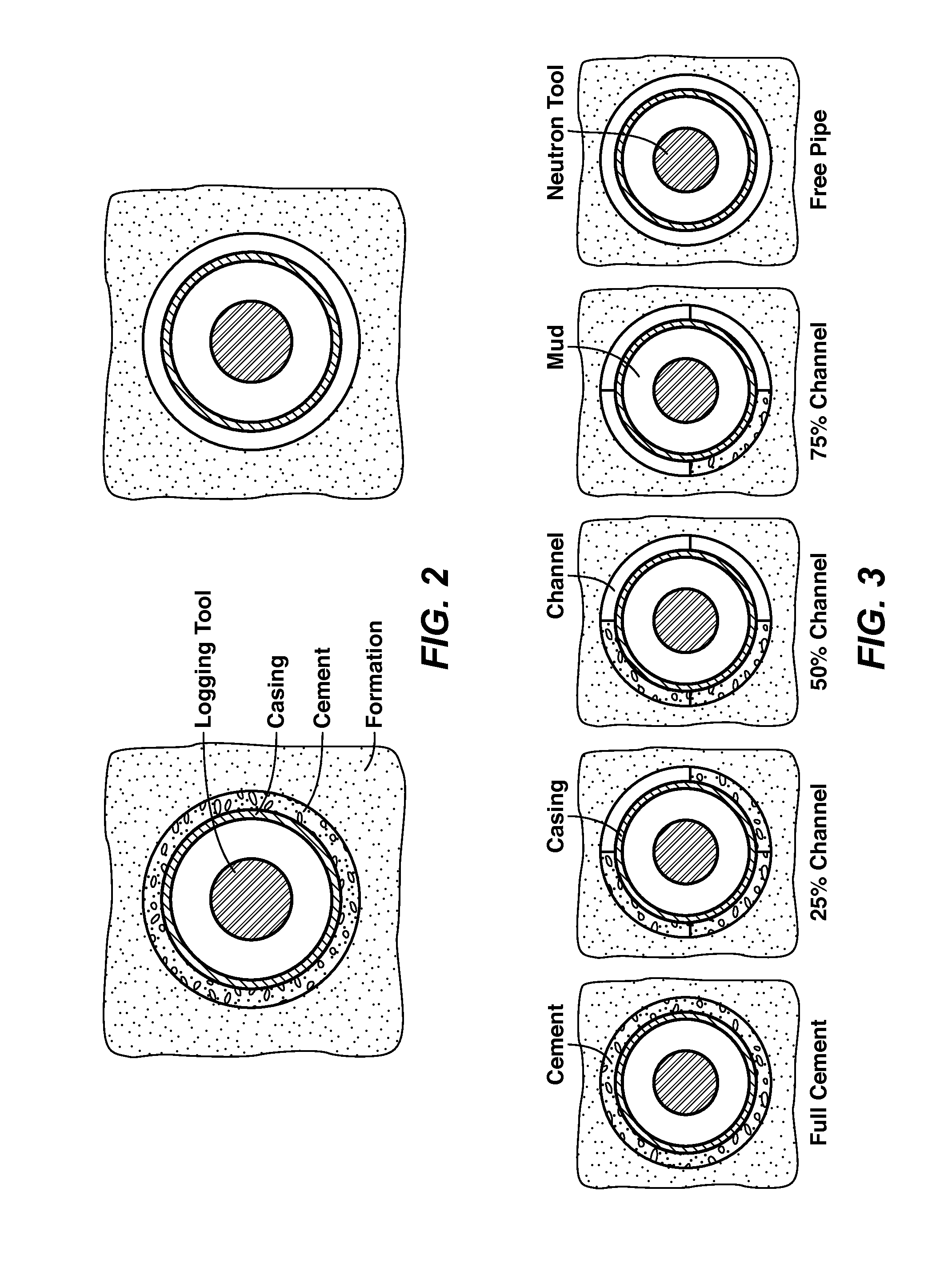
Method For Cement Evaluation With Neutron Logs
ActiveUS20130345983A1Effective approachEasy to explainElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsNeutron porosityMulti parameter
Method for evaluating cement integrity in a cased well environment using a logging tool that has a neutron source and one or more neutron or gamma ray detectors. Neutron porosity logs are obtained from the well before (42) and after (41) casing. This log data along with well dimensions and material composition parameters are the input quantities to a multi-parameter database (43) that is constructed by computer modeling or laboratory experiments to relate volume fraction for fluid filled channels in the cement sheath to the input quantities. The channel volume fraction (45) corresponding to the input quantities is identified or interpolated (44) from the multi-parameter database.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
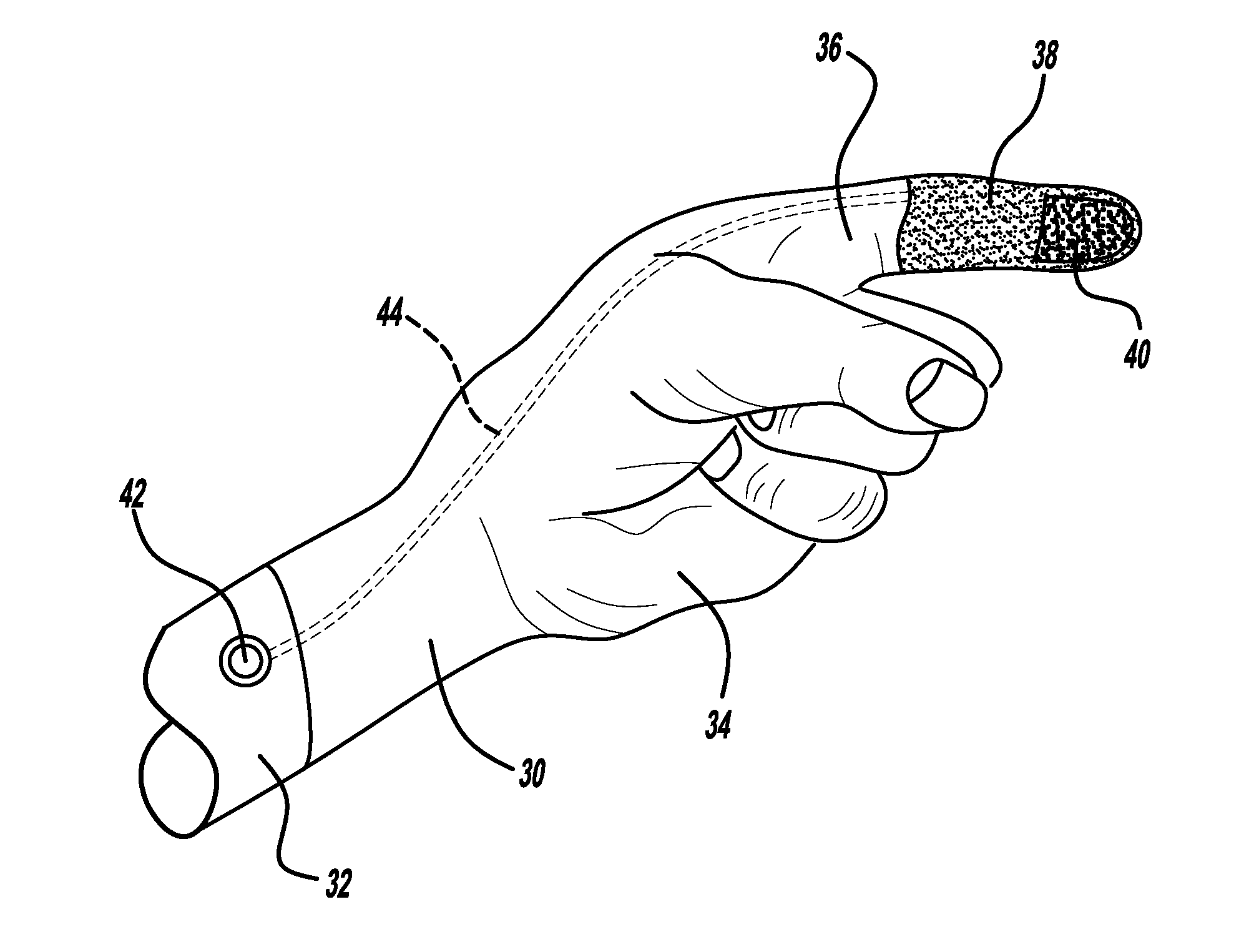
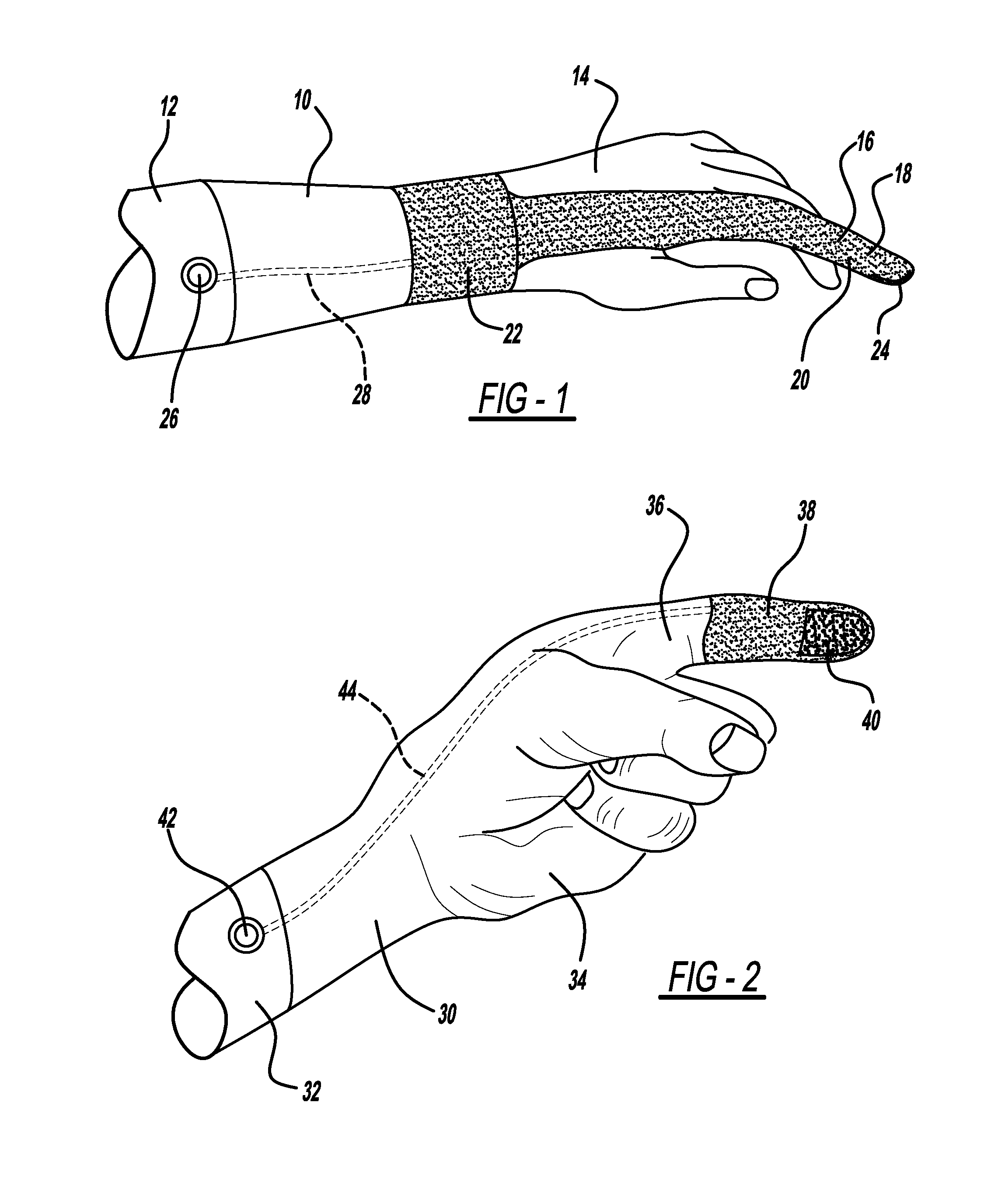
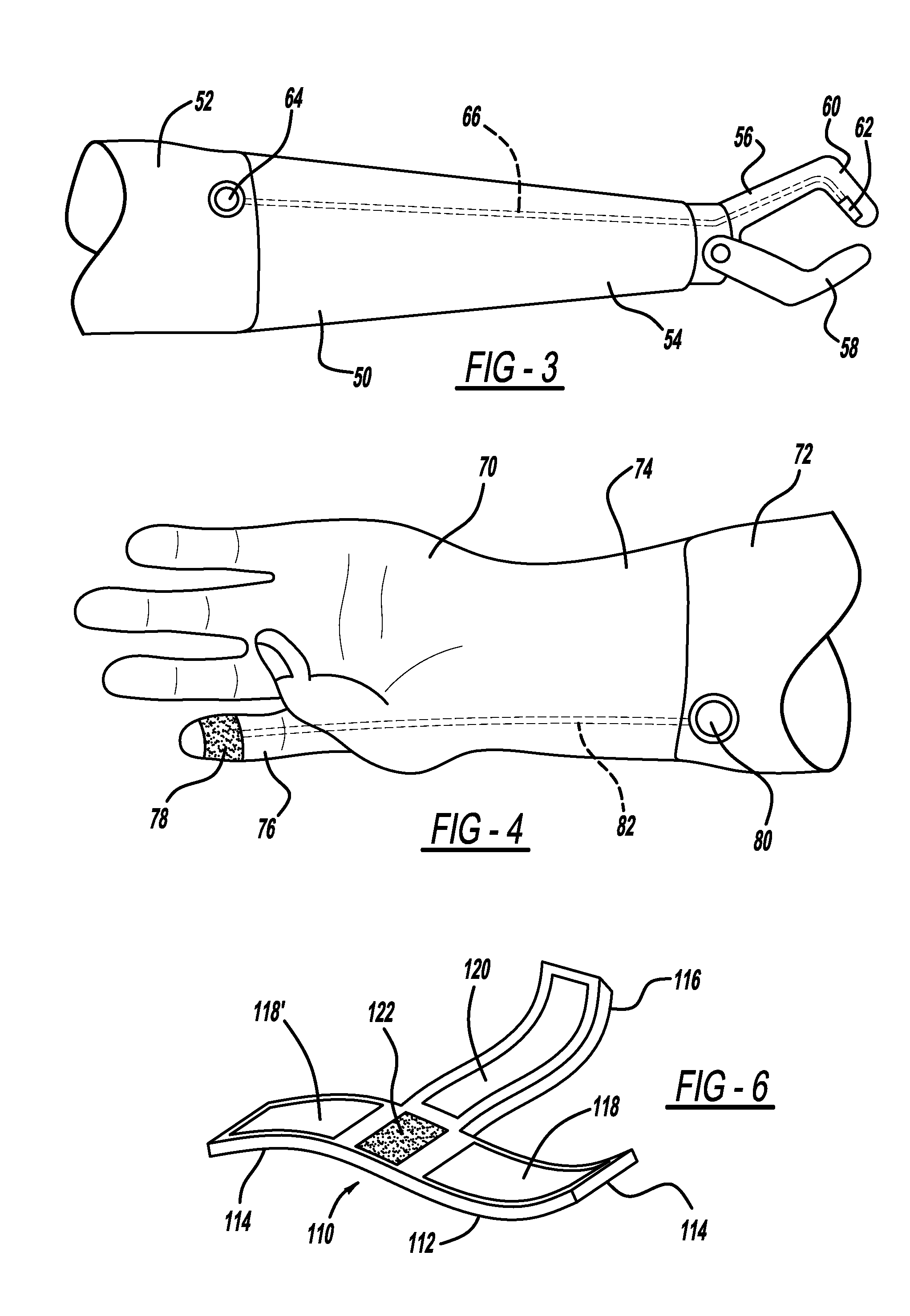
Add-on capacitive touchscreen aid
InactiveUS20130268094A1Effective approachInvalid friendly devicesArtificial legsBandageBiomedical engineering
An apparatus that allows a glove wearer or the wearer of a prosthetic limb to operate a device having a capacitive touchscreen is disclosed. The first embodiment of the disclosed invention is a conductive finger sock that can be applied to the tip or all of a digit of a non-conductive artificial limb. The second embodiment is an adhesive element having a conductive material such as conductive thread or a conductive sponge material. The adhesive element can be attached to a glove or to a prosthetic limb or may be used as an actual bandage. The third embodiment is directed to a factory integrated conductive tip that is part of a digit of a non-conductive artificial limb. The conductive element may be attached to the wearer's skin by a conductive line or may be used without the conductive line and thus may function in isolation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
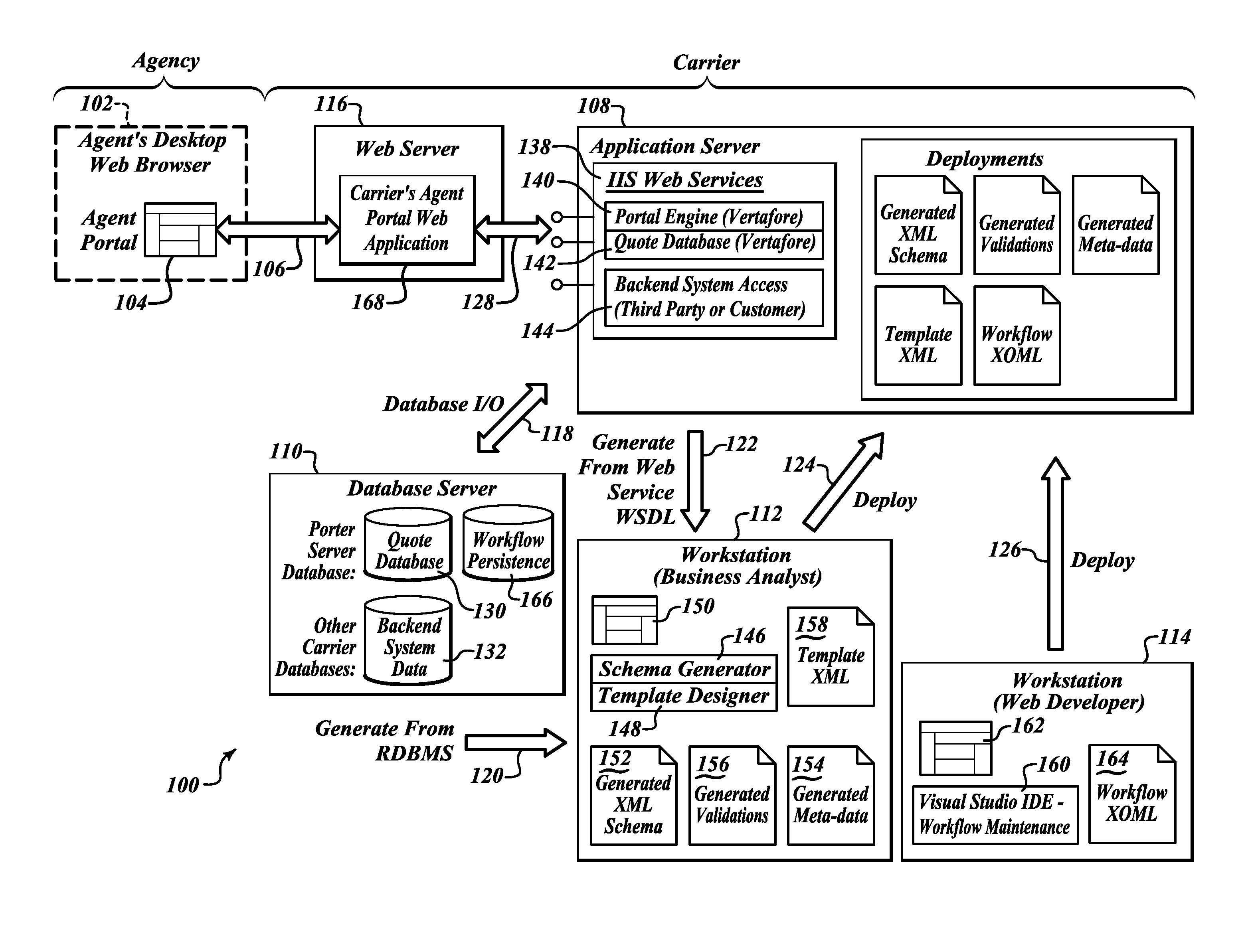
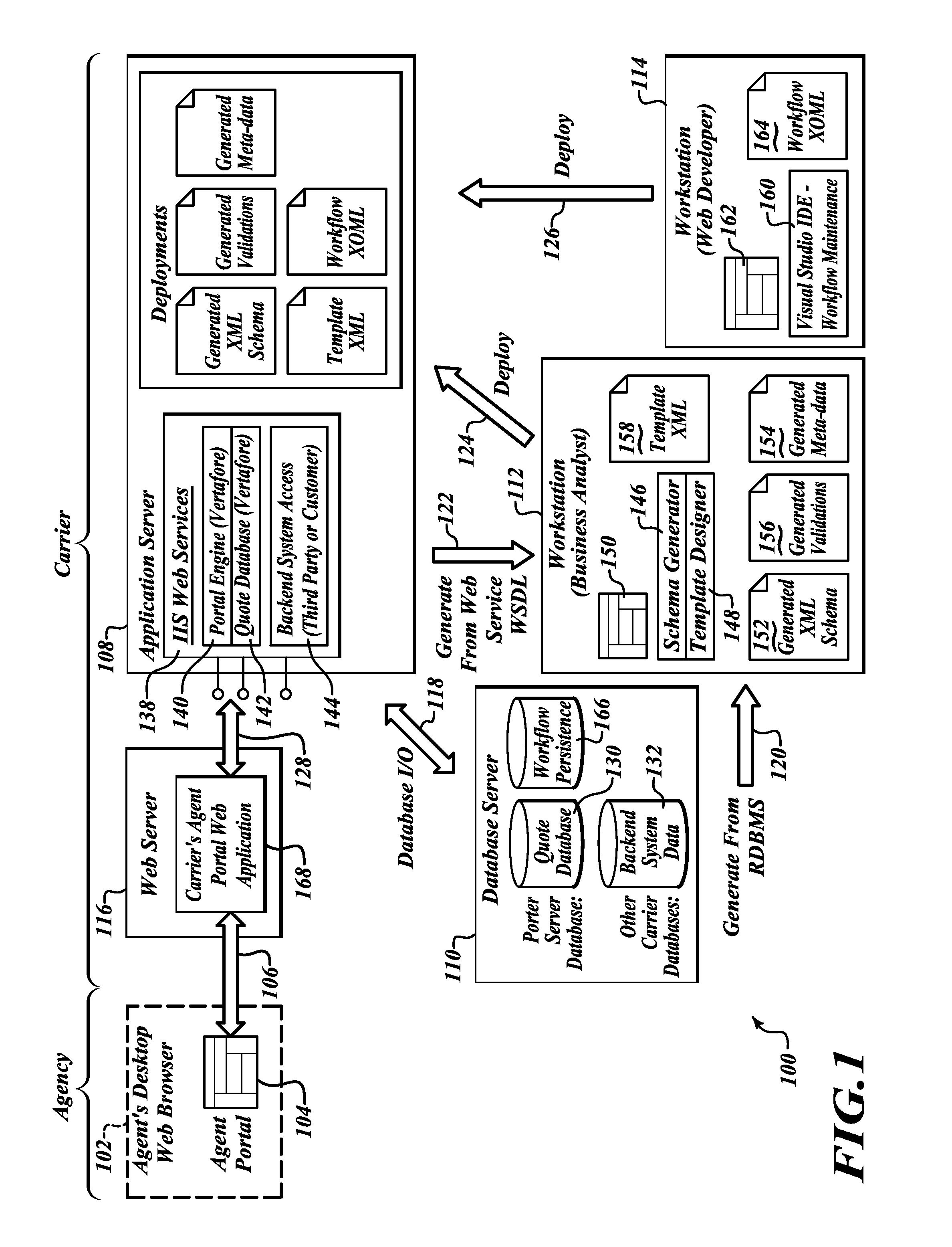
Systems, methods and articles for template based generation of markup documents to access back office systems
ActiveUS20110161375A1Quick implementationEffective approachDigital data processing detailsWebsite content managementAbstraction layerTemplate based
An abstraction layer is provided between databases of back office systems and a markup language based interface, which may allow Web access to data in the databases of the back office systems. Schemas, metadata and validation files are generated from an intermediary representation of the database, which may be flat, non-hierarchical files. Markup language based templates may be generated based on the schemas, metadata and validation files. Markup documents or “markup” may be generated using the templates and the schemas, metadata and validation files. Workflow may be defined and imposed on the generation of the markup.
Owner:VERTAFORE
Dielectrophoretic separation and immunoassay methods on active electronic matrix devices
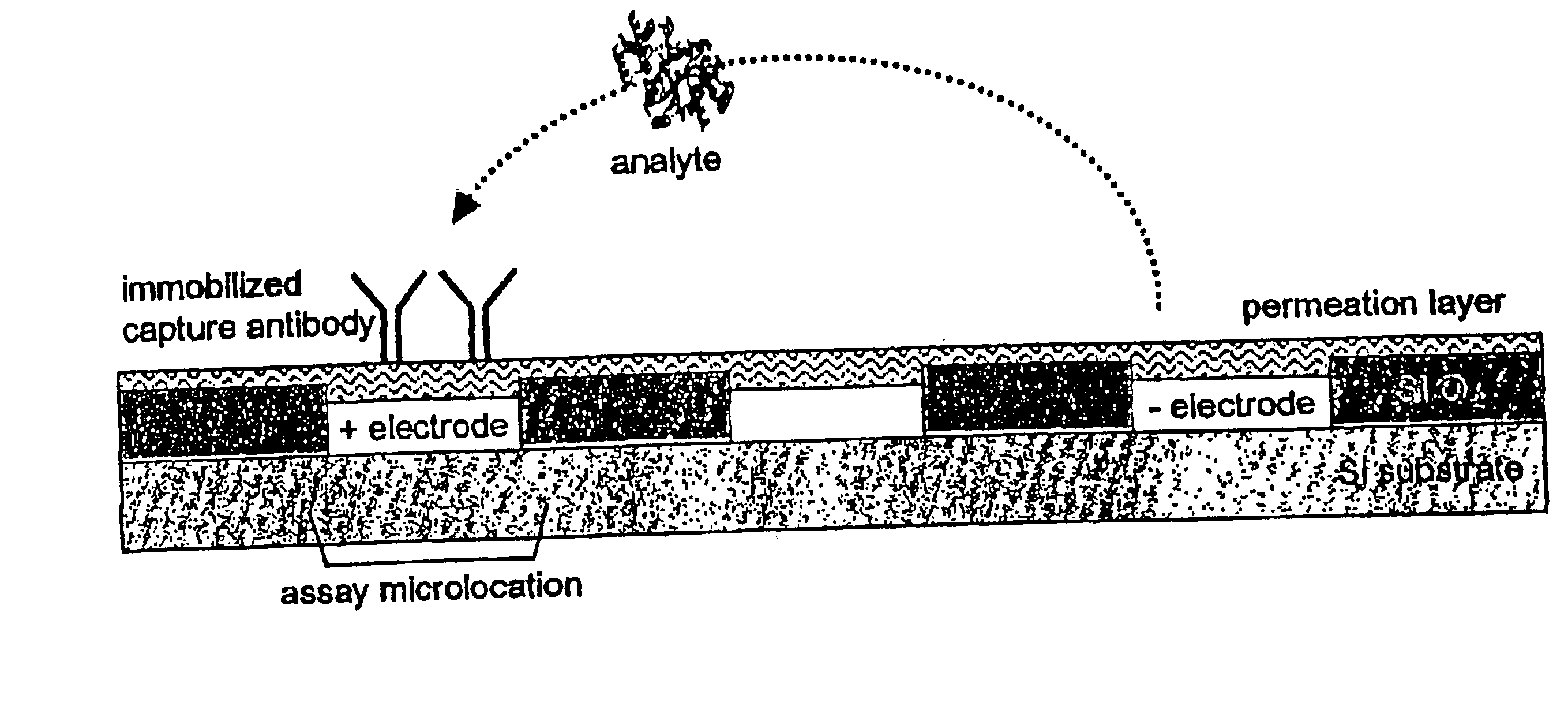
InactiveUS6887362B2Reduce the amount requiredDone quickly and efficientlyDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsAssayMedical product
This invention relates to devices and methods for performing active, multi-step molecular and biological sample preparation and diagnostic analyses employing immunochemical techniques. It relates generally to bioparticle separation, bioparticle enrichment, and electric field-mediated immunochemical detection on active electronic matrix devices utilizing AC and DC electric fields. More specifically, the invention relates to devices and methods for sample preparation / manipulation, immunoimmobilization, and immunoassays, all of which can be conducted on one or more active electronic chip devices within a single system. These manipulations are useful in a variety of applications, including, for example, detection of pathogenic bacteria and biological warfare agents, point-of-care diagnostics, food or medical product quality control assays, and other biological assays.
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE +1
Stable solid state raman laser and method of operating same
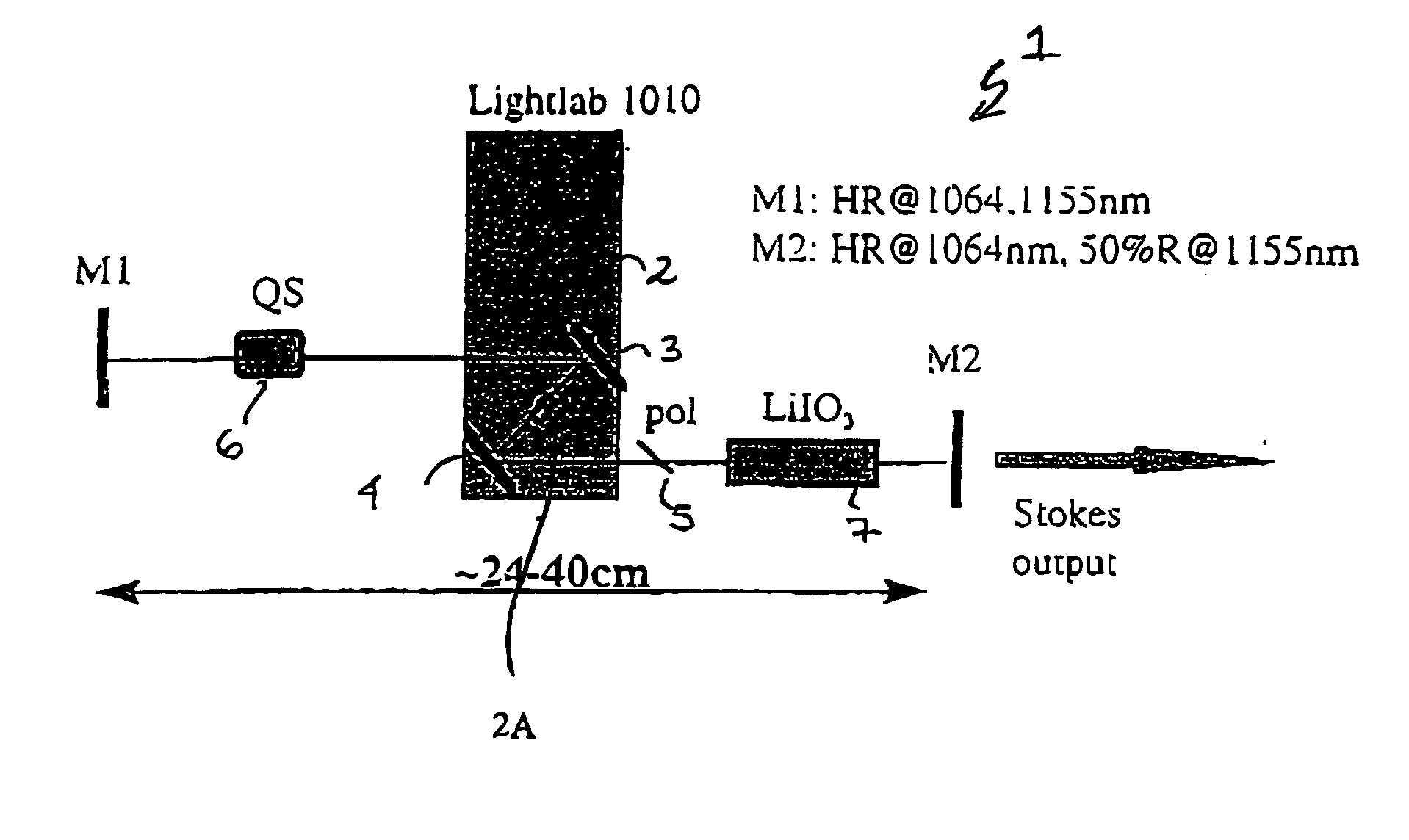
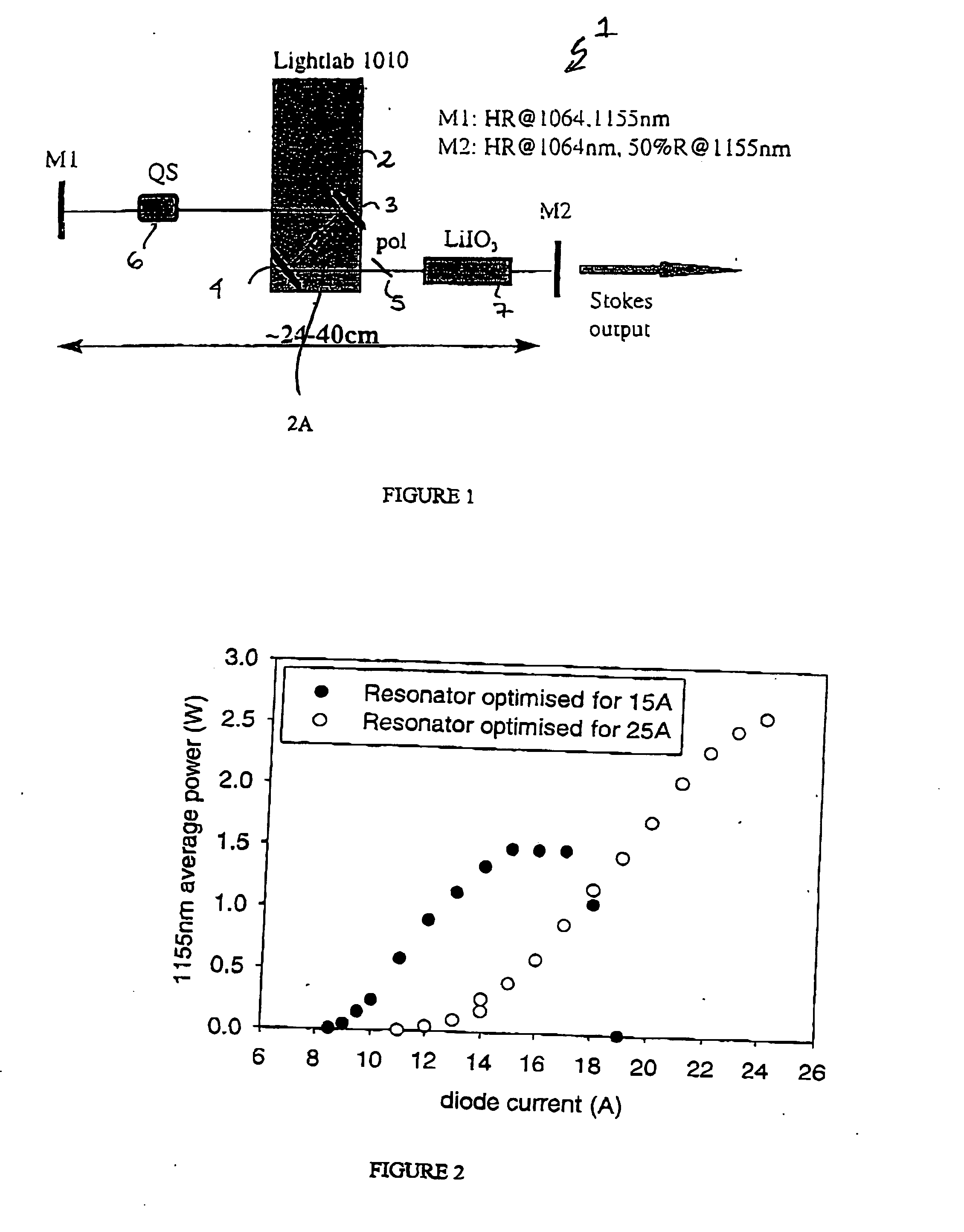
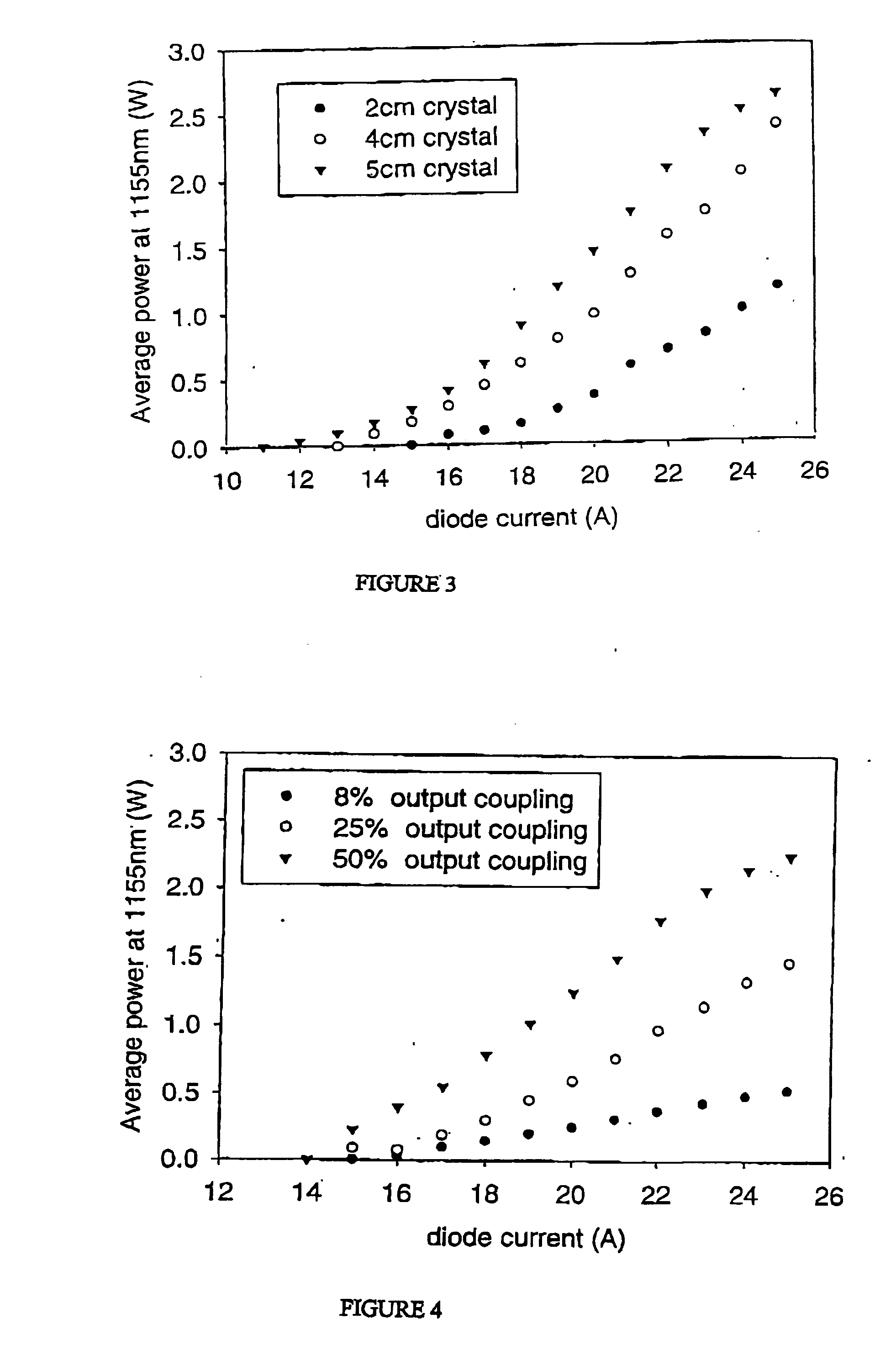
InactiveUS20040028090A1Effective approachLimited scalabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSolid massInstability
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser (1), the solid-state Raman laser including: (a) a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors (M1 and M2), (b) a laser material (2A) located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, (c) a solid Raman medium (7) located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and (d) an output coupler (M2) for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of (i) the position of the laser material (2A) relative to the position of the Raman medium (7) in the cavity, (ii) the length of the cavity and (iii) the curvature of at least one of the reflectors (M1 or M2), is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) as a result of thermal effects in the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Direction-recognizing apparatus, direction-recognizing method, direction-recognizing system, and robot apparatus
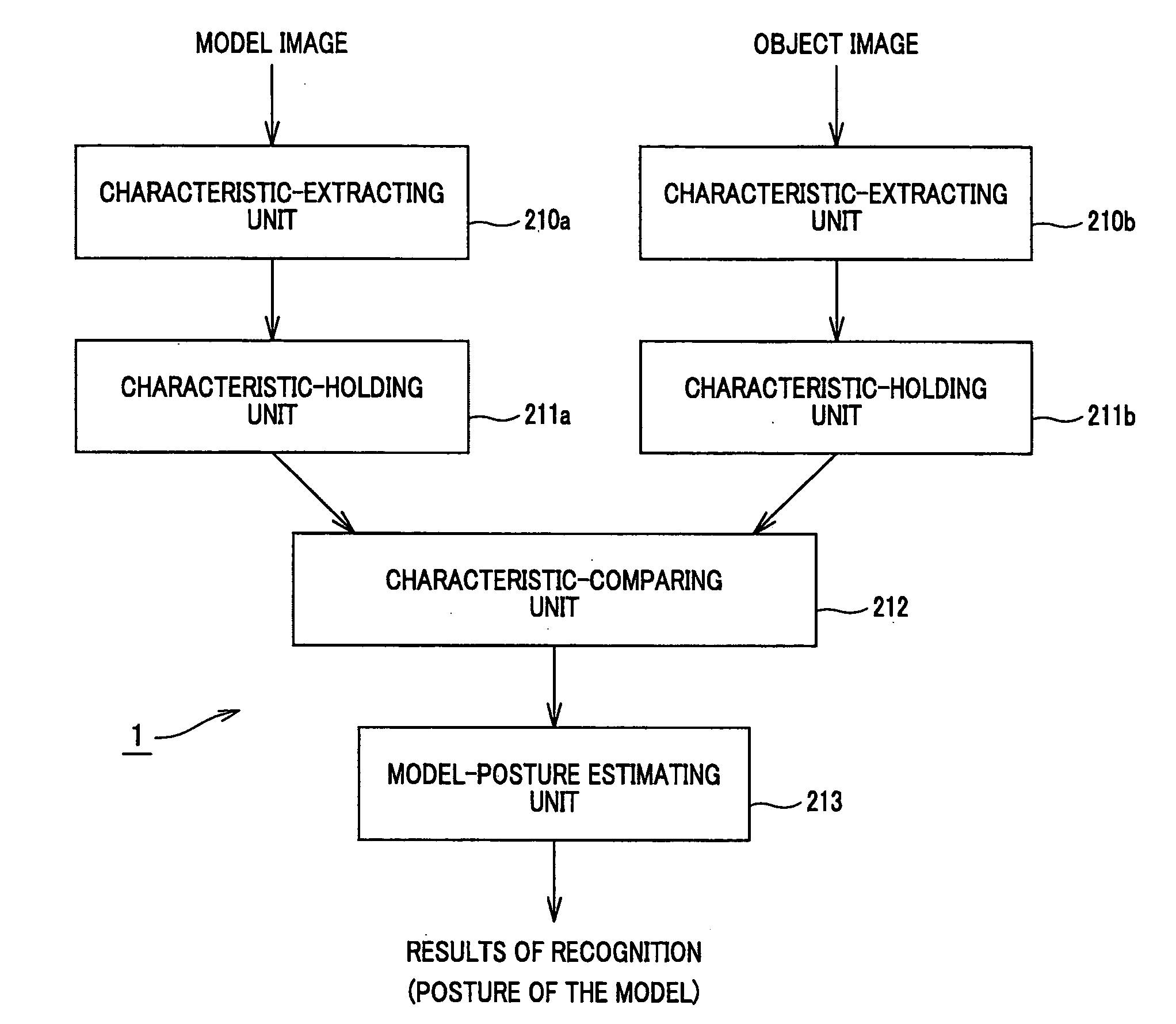
InactiveUS20050069173A1Effective approachImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Image database
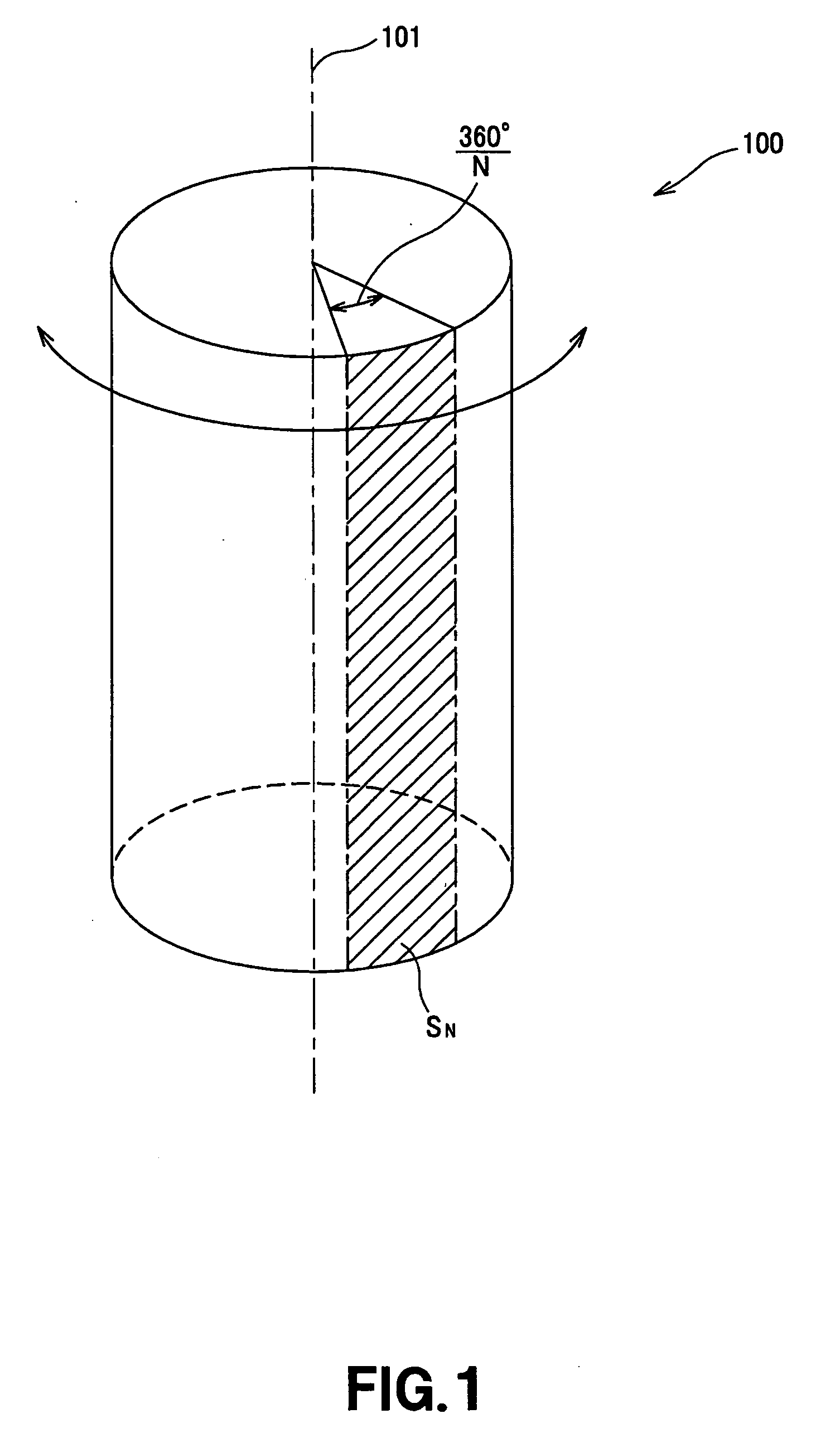
A direction-recognizing apparatus has a photographing unit, an image database, an image-recognizing unit, and a direction-recognizing unit. The database stores registered images and direction-data items associated with the registered images. The image-recognizing unit receives an input image and compares the input image with the registered images stored in the database. The image-recognizing unit selects one registered image that is identical or similar to the input image. The direction-recognizing unit recognizes a direction from the direction data associated with the registered image selected by the image-recognizing unit. The database may store N direction-data items associated with N surface segments SN of the circumferential surface of a pole 100. If so, the images registered in the database represent direction-recognition regions ASN that are larger than the N surface segments SN.
Owner:SONY CORP
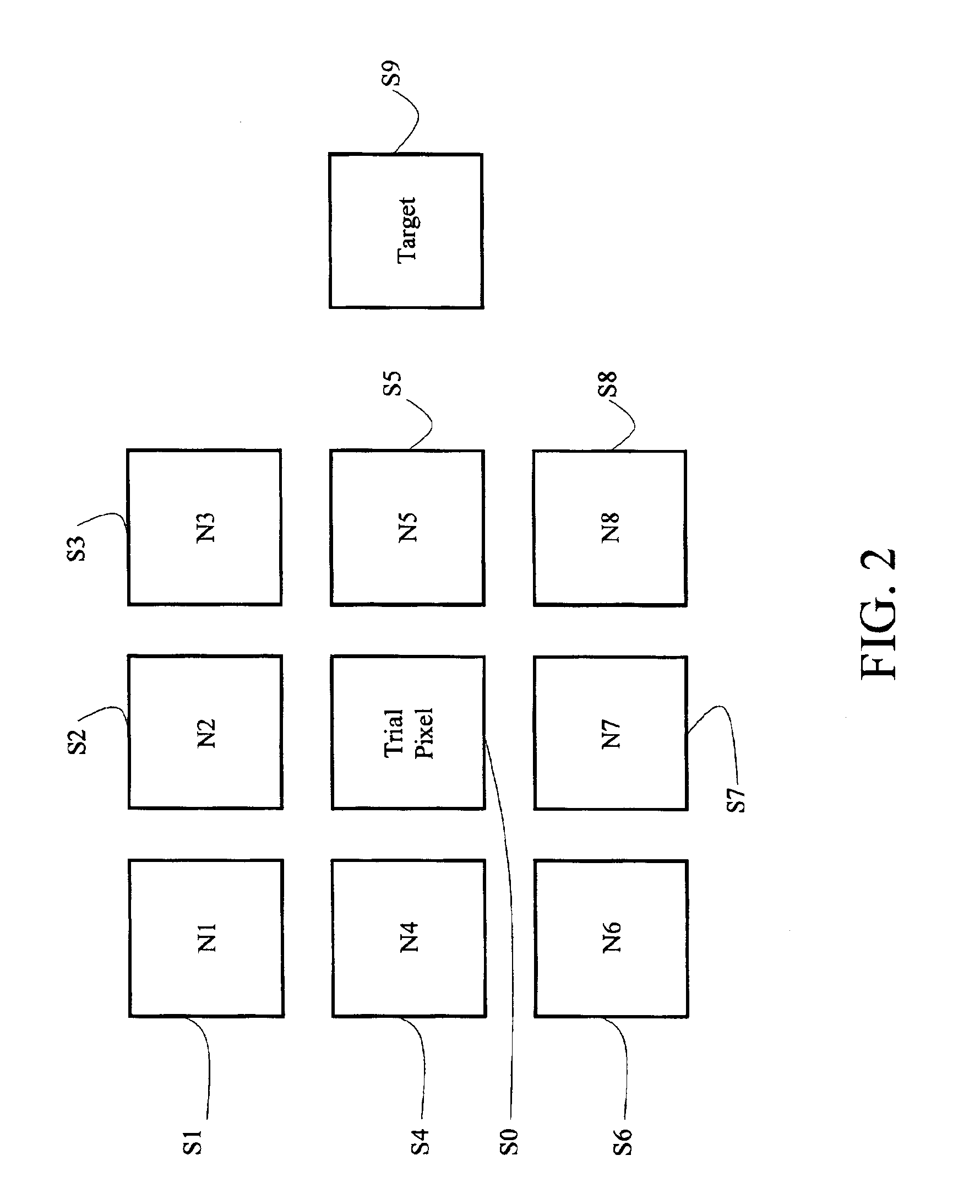
Method for target detection and identification by using proximity pixel information
ActiveUS6940999B2Effective approachHigh-precision detectionRadiation pyrometryColor signal processing circuitsTerrainSpectral image
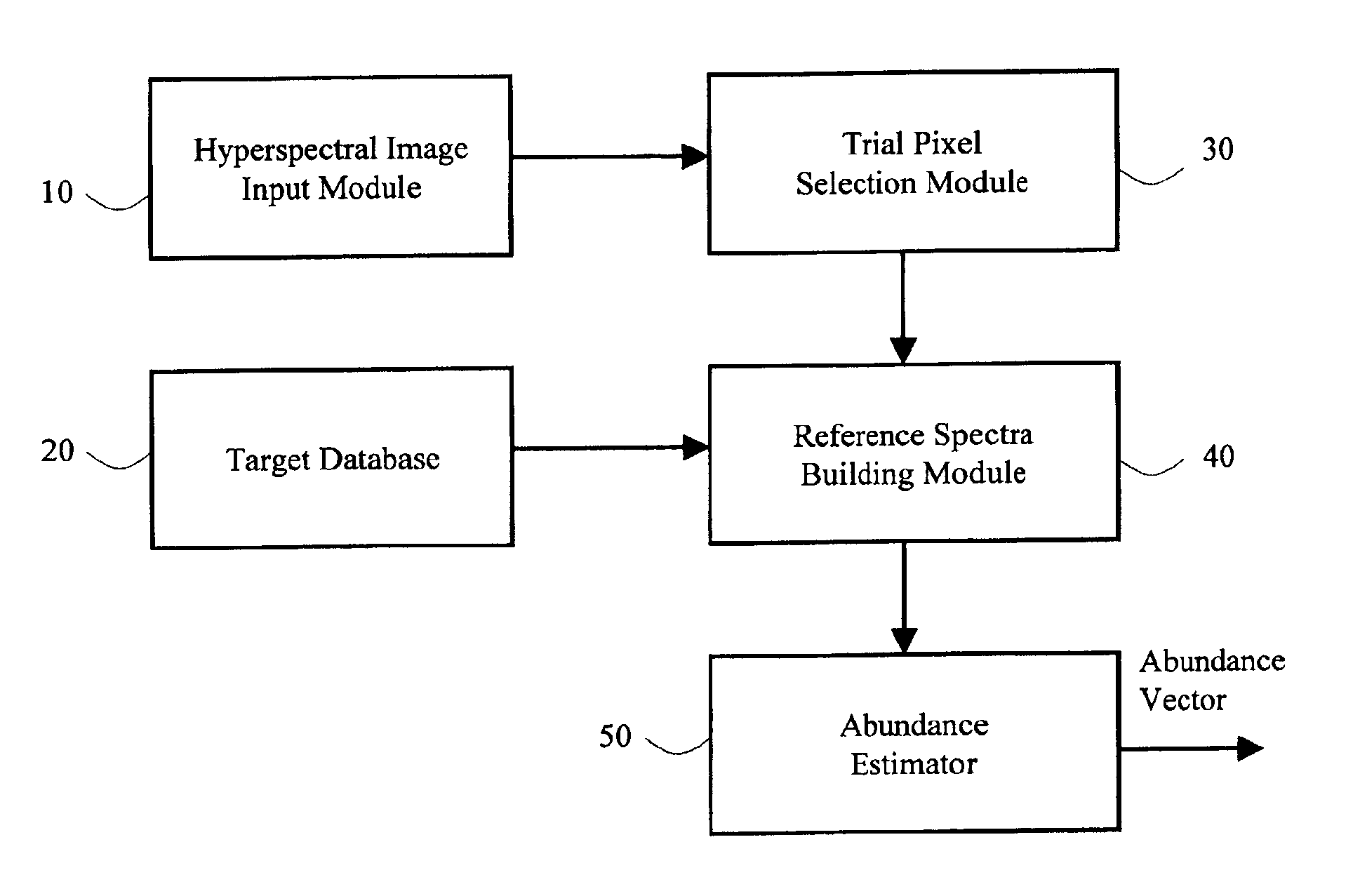
An efficient approach to exploit hyperspectral imagery and detect target of interest is disclosed. This approach uses proximity pixels as reference signatures to detect potential discontinuity that represents material of unknown existing on the terrain. By incorporating signature of a chosen material of interest, this approach provides an effective way for target detection and identification. An evolutionary algorithm is employed to estimate the abundance of material of interest.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
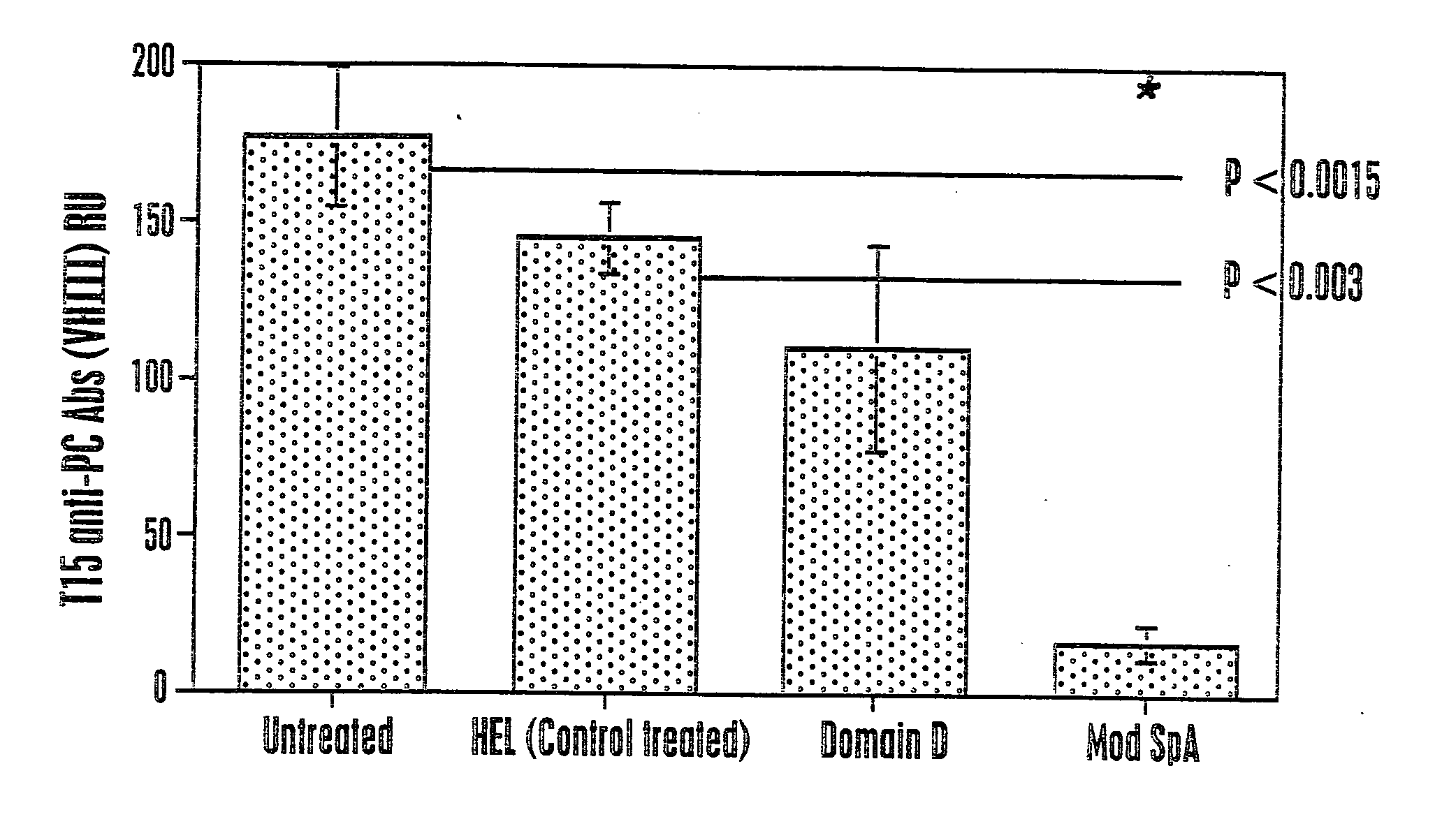
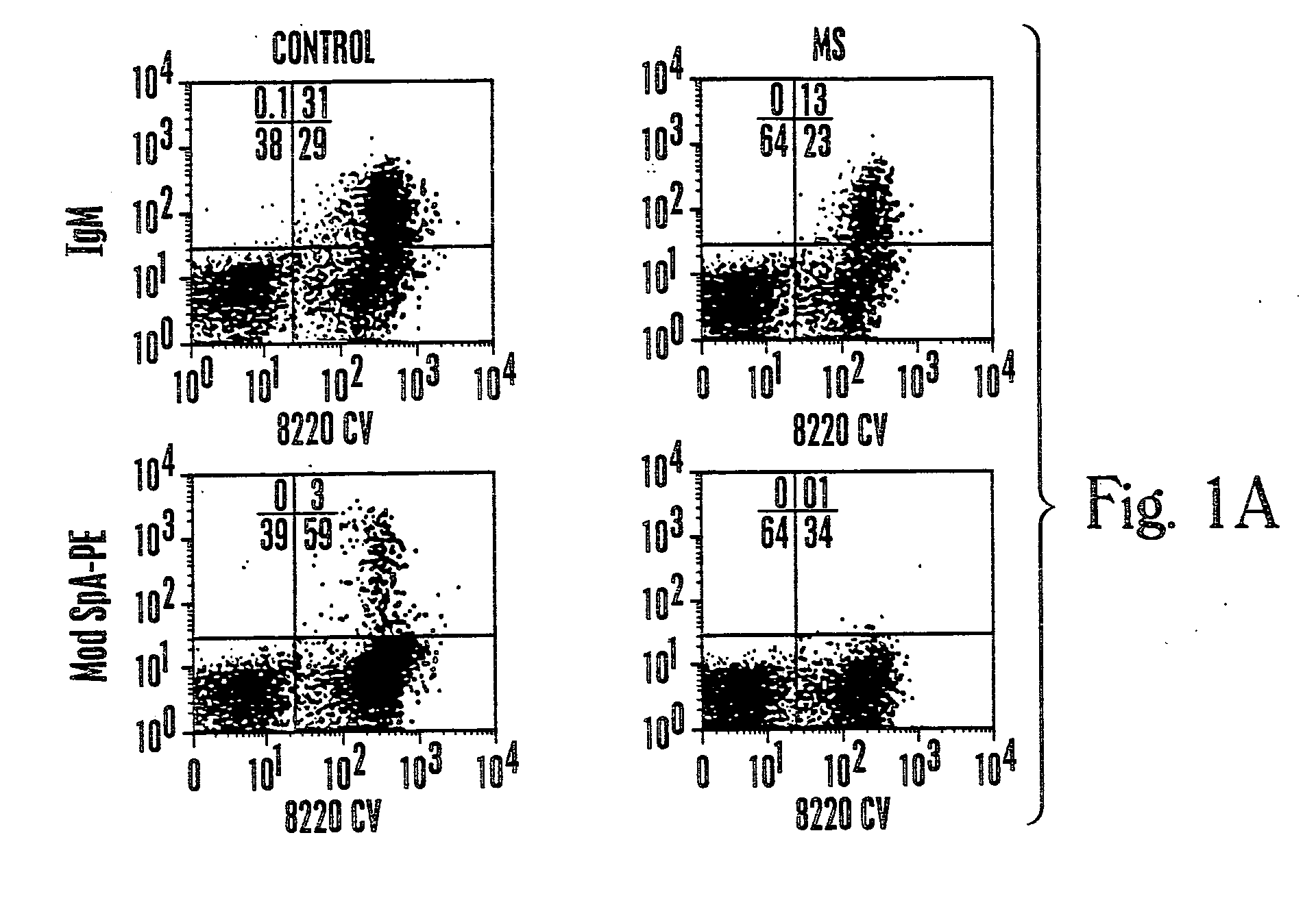
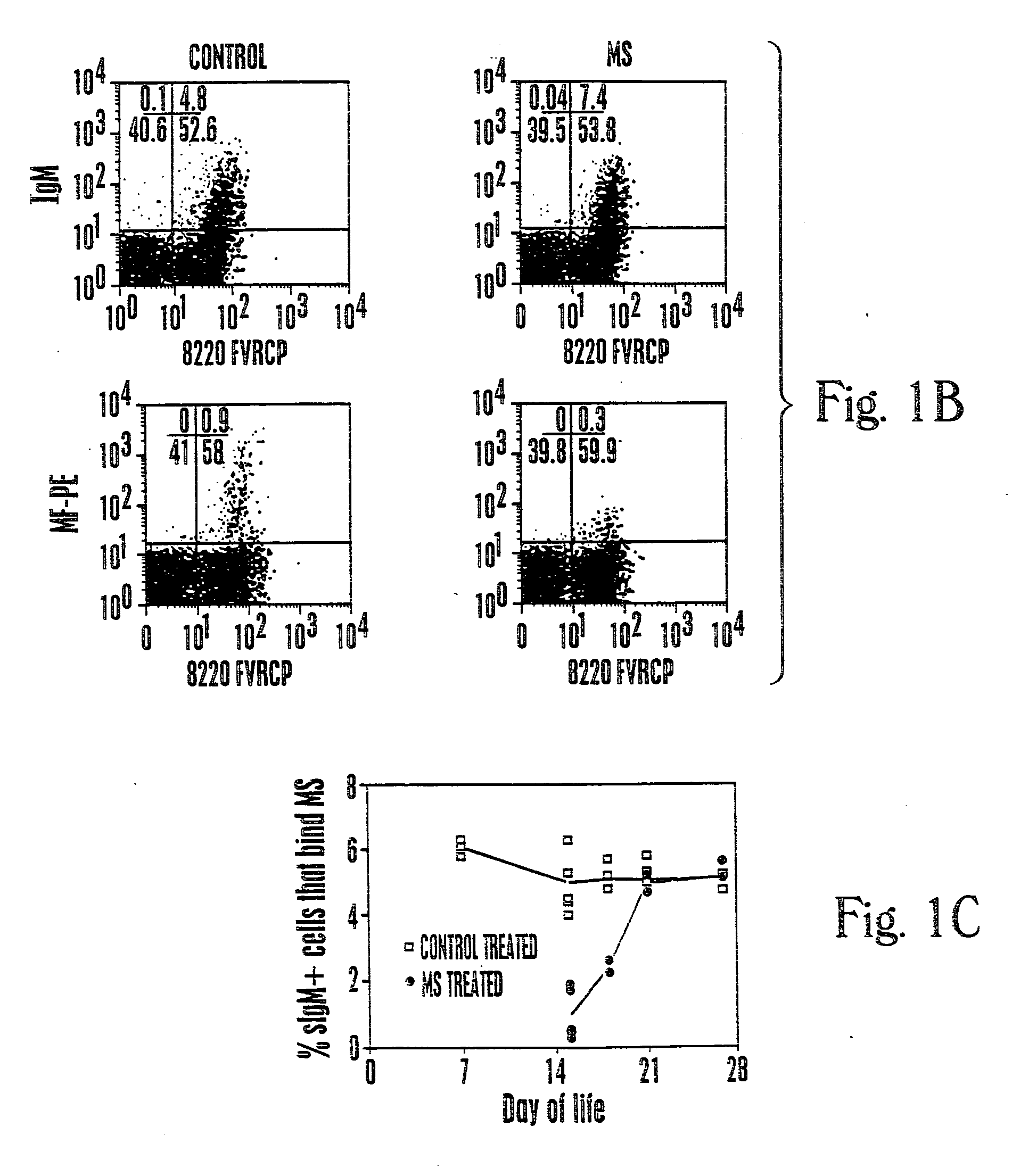
Protein a based binding domains with desirable activities
InactiveUS20060205016A1Effective approachNewBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsHeavy chainBinding domain
Provided are Staphylococcal protein A (SpA) variants for binding immunoglobulin (Ig), comprising a polypeptide which varies by one or more amino acids from the amino acid sequence of a natural variable heavy chain III (“VH3”) Ig-Fab binding region (“binding region”) of SpA, wherein the polypeptide exhibits a different binding specificity for Ig-Fab than does SpA or exhibits a different binding specificity for a non-Ig target molecule than does SpA. Further provided are methods of making the variants and methods of using the variants, as well as native SpA, for in purification of Ig as well as diagnostic and therapeutic intervention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Draw-in map for stamping die tryout
ActiveUS7130708B2Rapid productionMinimum effortShaping toolsSpecial data processing applicationsMetal formingSize determination
Sheet metal forming is a manufacturing process in which flat sheet metal is drawn into a die cavity to form a product shape. Draw-in amount is the single most important stamping index that controls all forming characteristics (strains and stresses), formability failures (splits, wrinkles) and surface quality (distortions) on a panel. Adaptation of a new die set for repetitively stamping sheet metal parts to a part design specification is simplified by using a math-based simulation of the stamping operation under specified engineering stamping conditions for the specified part. The stamping simulations are used to create an engineered draw-in map comparing selected locations on the peripheral edge of the stamped part with corresponding locations on the peripheral edge of its original sheet metal blank. The resulting map of sheet metal draw-in dimensions reflect suitable displacements of the metal sheet between the binder ring and binder surface of the female die member at all such locations as the punch member of the die set executes its stamping operation. The engineered draw-in dimensions for a simulated part identify specific locations for adjustment of the binder ring / binder surface system in adapting the die set for production of parts.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
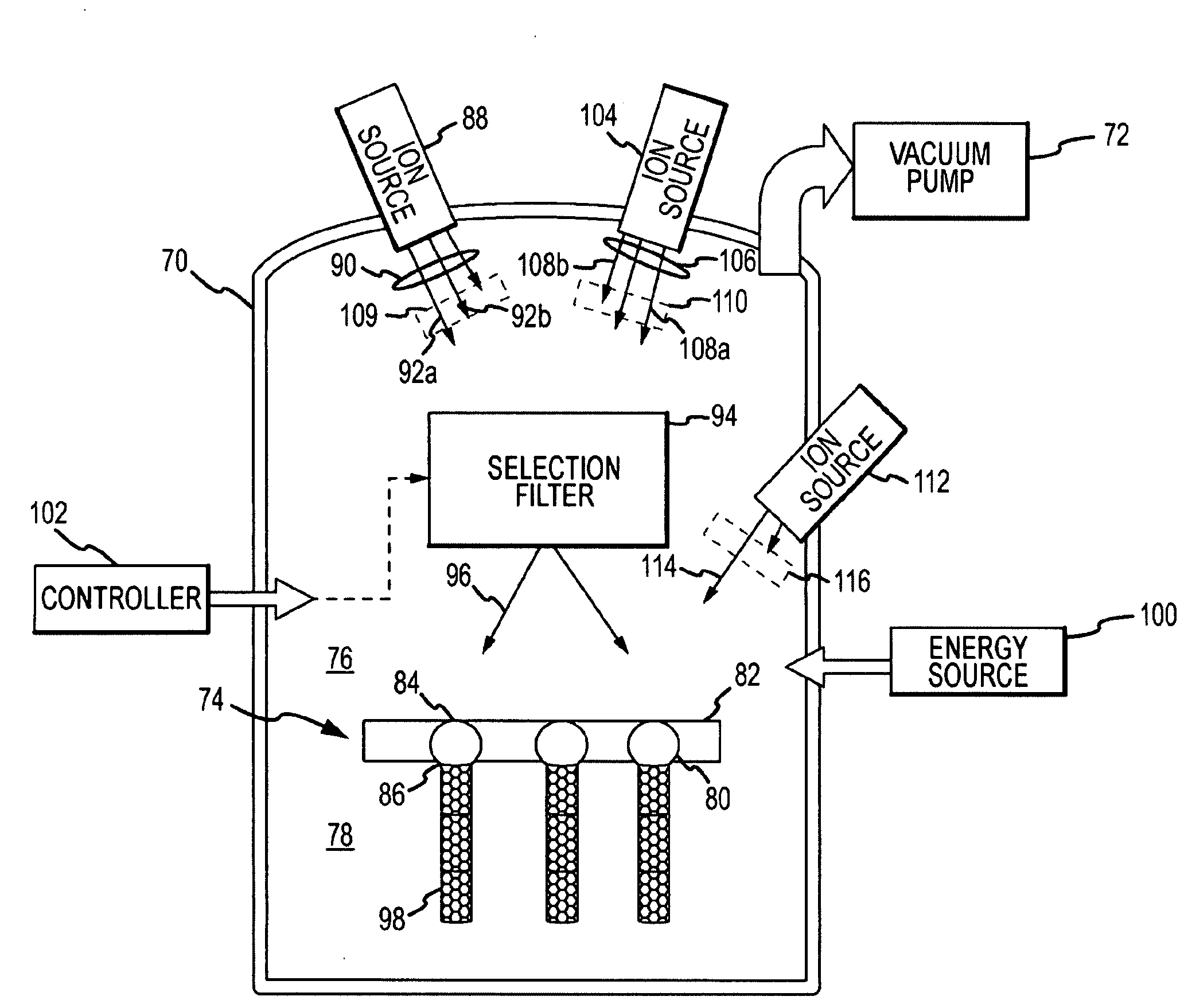
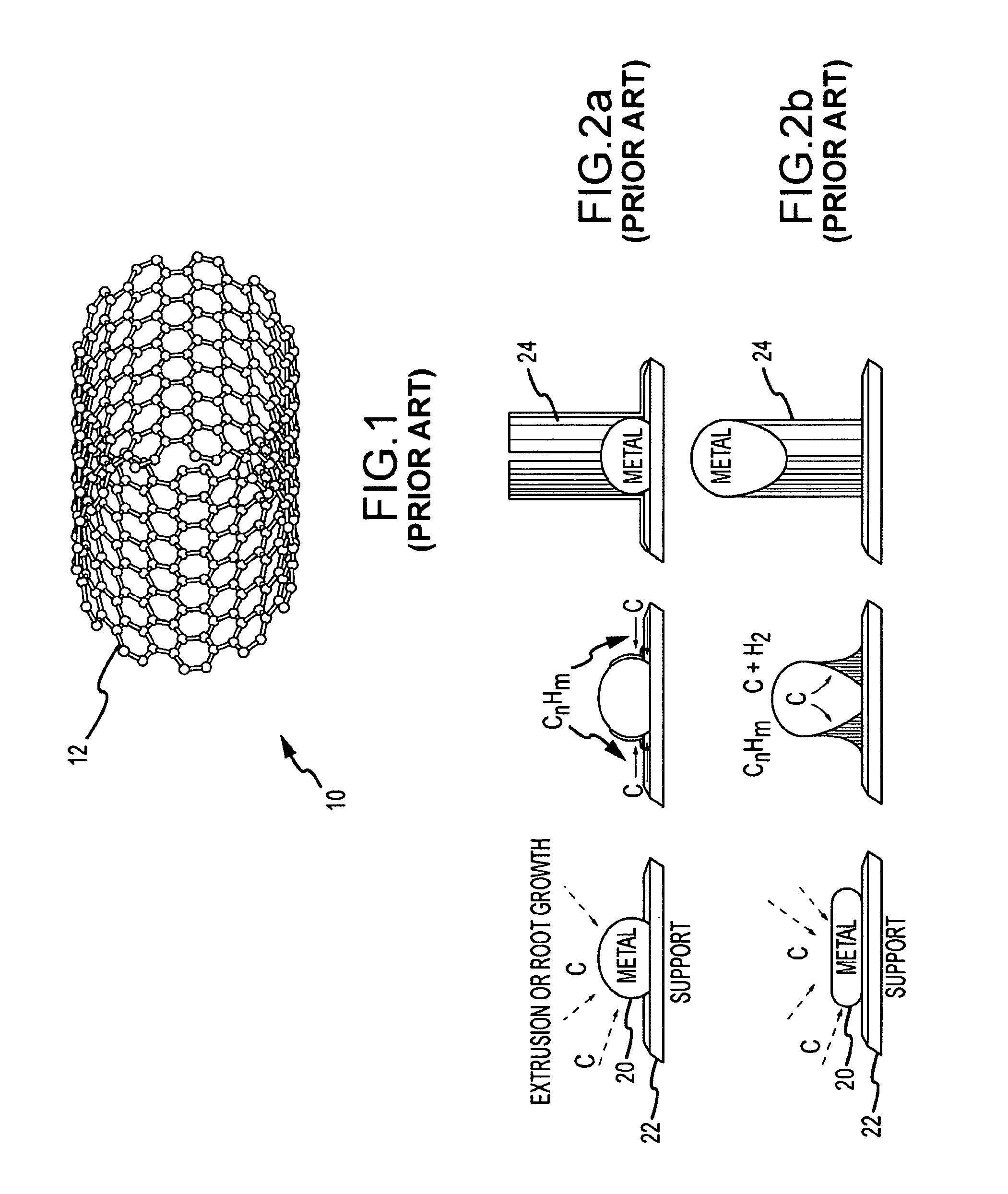
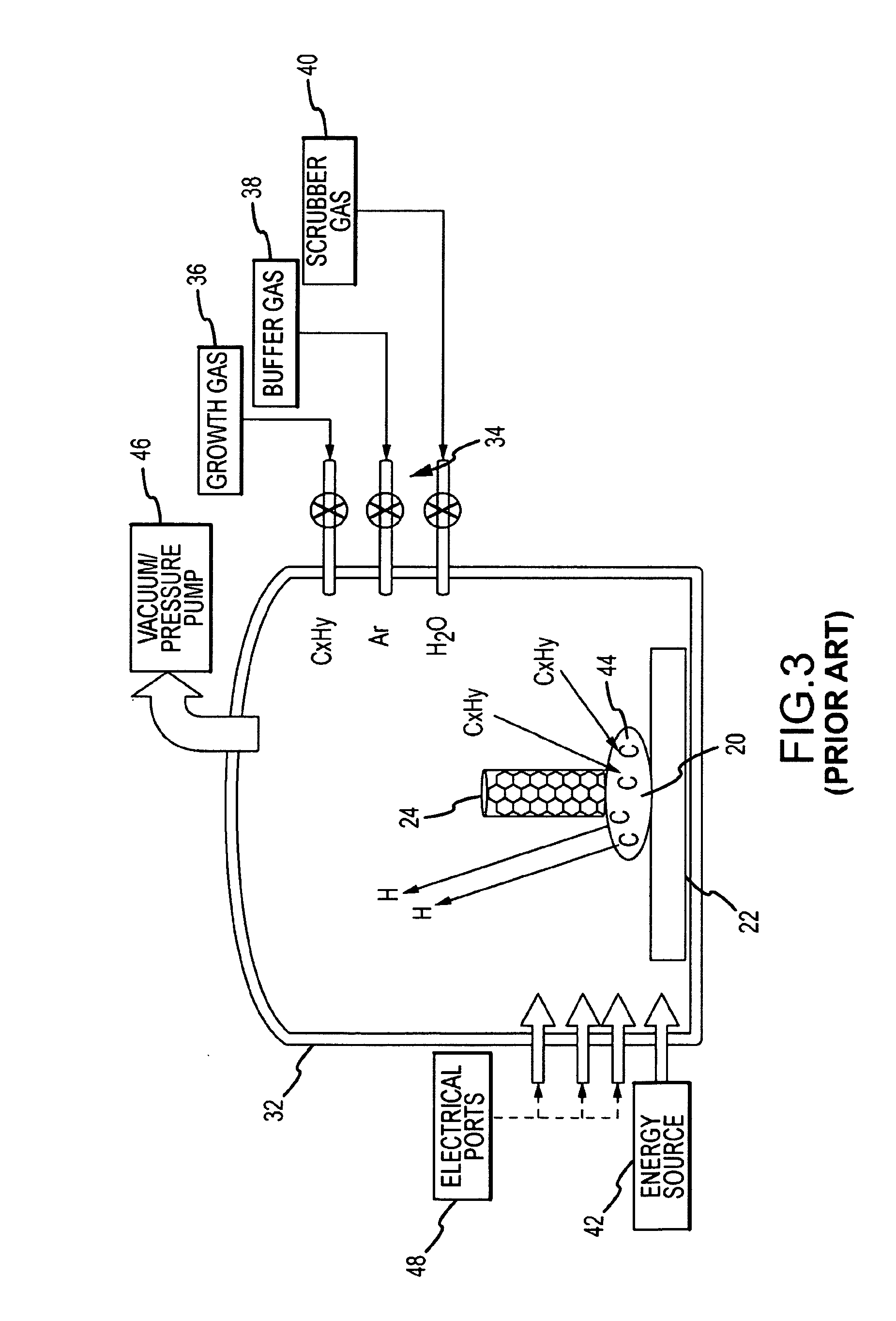
System and method for growing nanotubes with a specified isotope composition via ion implantation using a catalytic transmembrane
ActiveUS20090252887A1Avoid contaminationAvoid erosionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsDopantIsotopic composition
An ion source(s) is configured to generate ions from one or more elements including a plurality of different isotopes or unique molecular combinations of two or more different isotopes from at least one of the selected elements. A selection filter(s) directs a subset of the ions onto a catalytic transmembrane to grow nanotubes of a specific isotope composition on the opposite side of the transmembrane. The nanotubes may be uniformly or selectively doped with dopant atoms. A controller can configure the selection filter(s) to sequentially pass different subsets of ions to form isotope, molecular or element junctions in the growing nanotubes.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
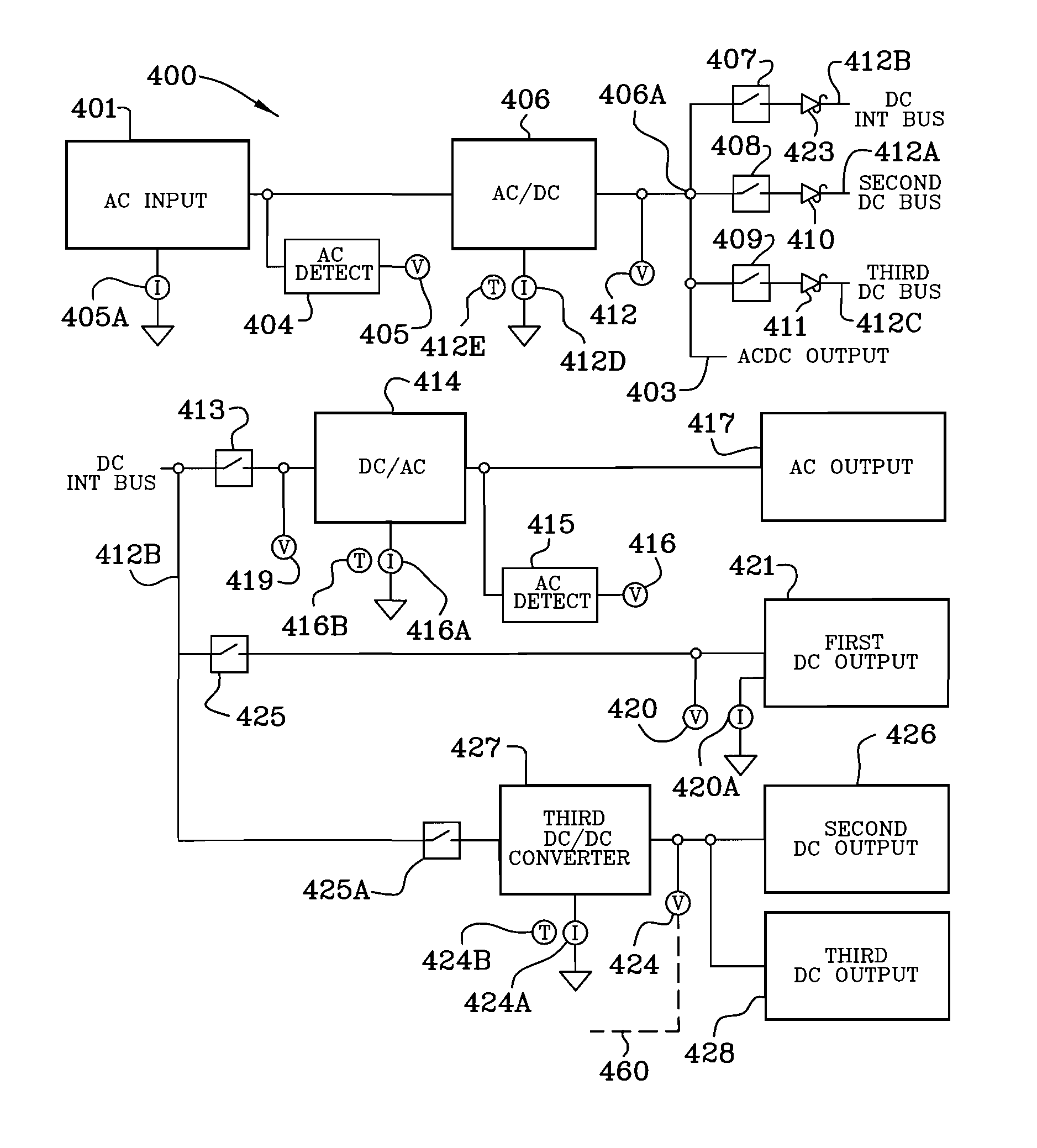
Systems for and methods of controlling operation of a UPS
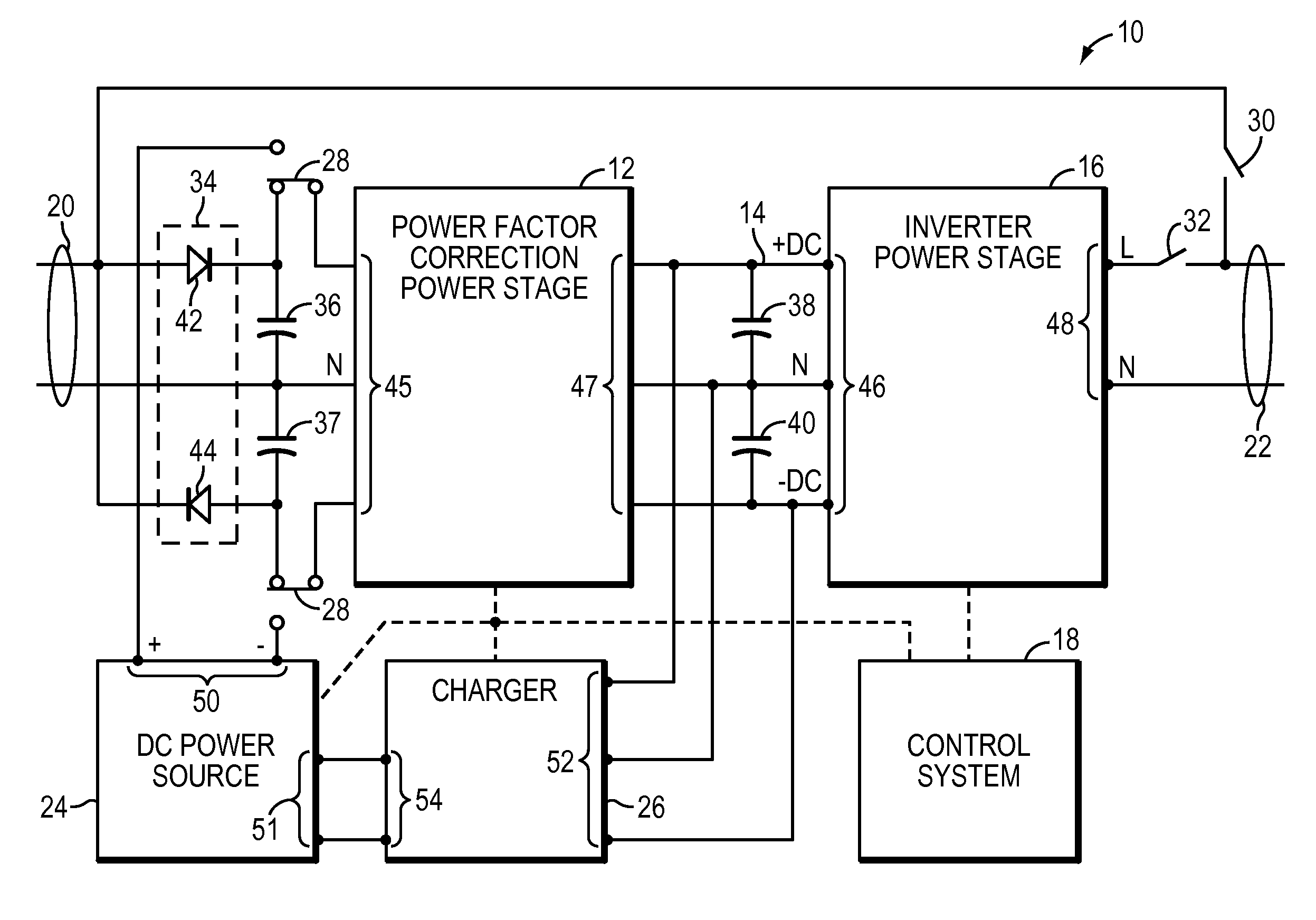
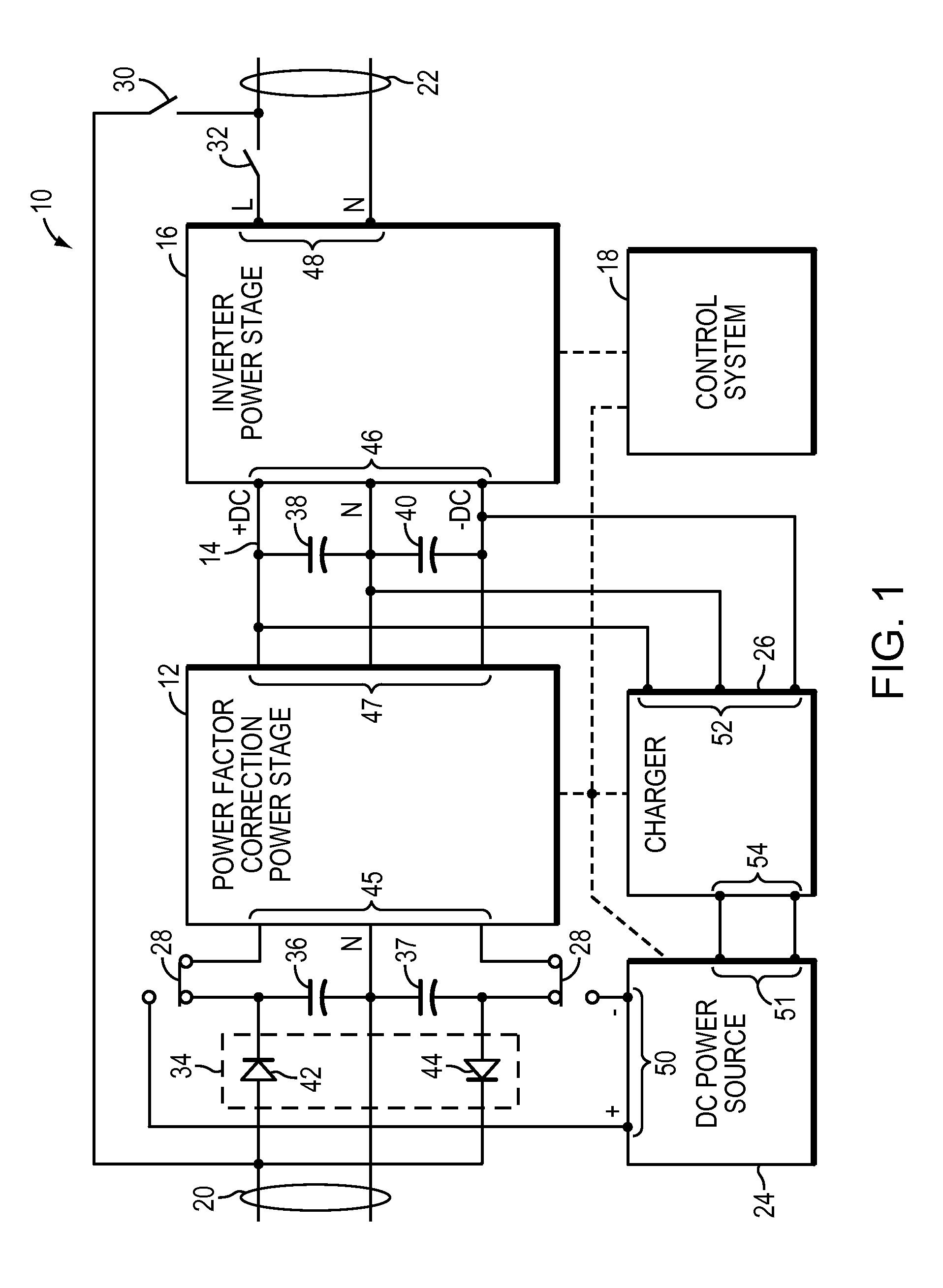
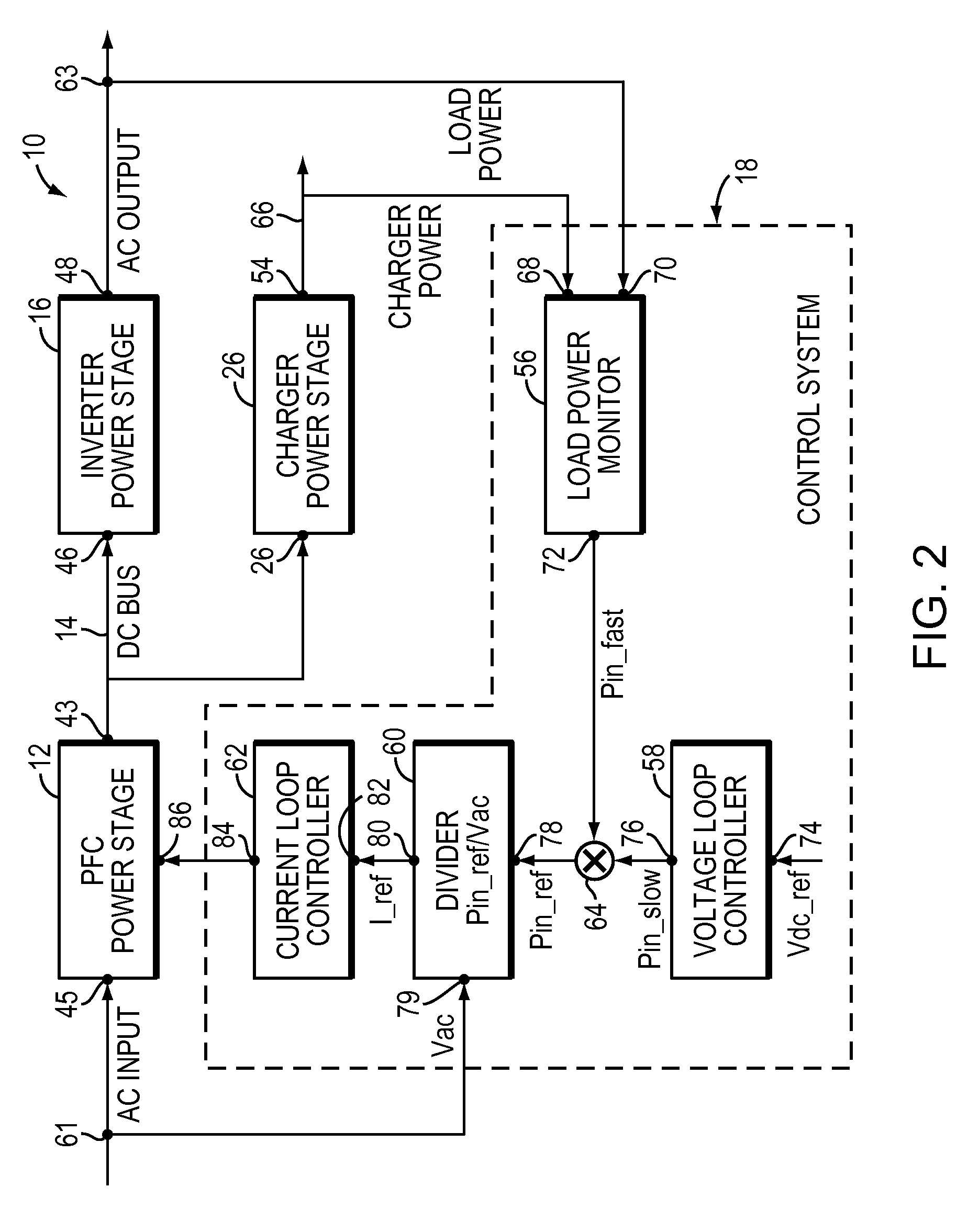
ActiveUS7615891B2Reduce offsetEffective approachBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionPower factor controlEngineering
A UPS includes an AC output, power factor control circuitry; and a DC bus coupled to the power factor control circuitry where the power factor control circuitry is configured to determine a difference in instantaneous power supplied to the AC output and to adjust a voltage of the DC bus based, at least partly, on the difference. In one embodiment, the UPS includes a single phase AC input. In another embodiment, the power factor control circuitry is configured to determine a cumulative difference in instantaneous power supplied to the AC output.
Owner:AMERICA POWER CONVERSION CORP
Active learning framework
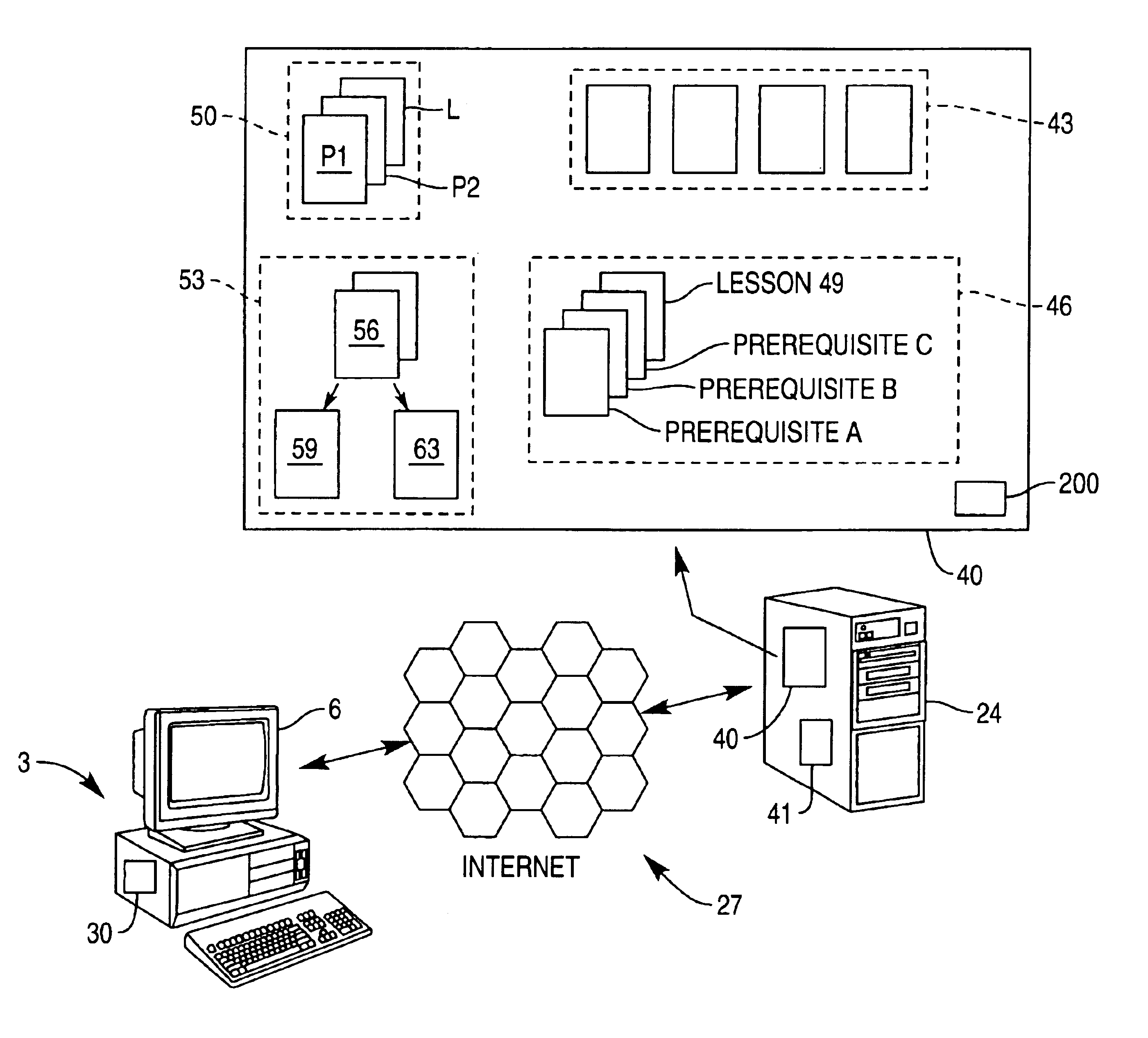
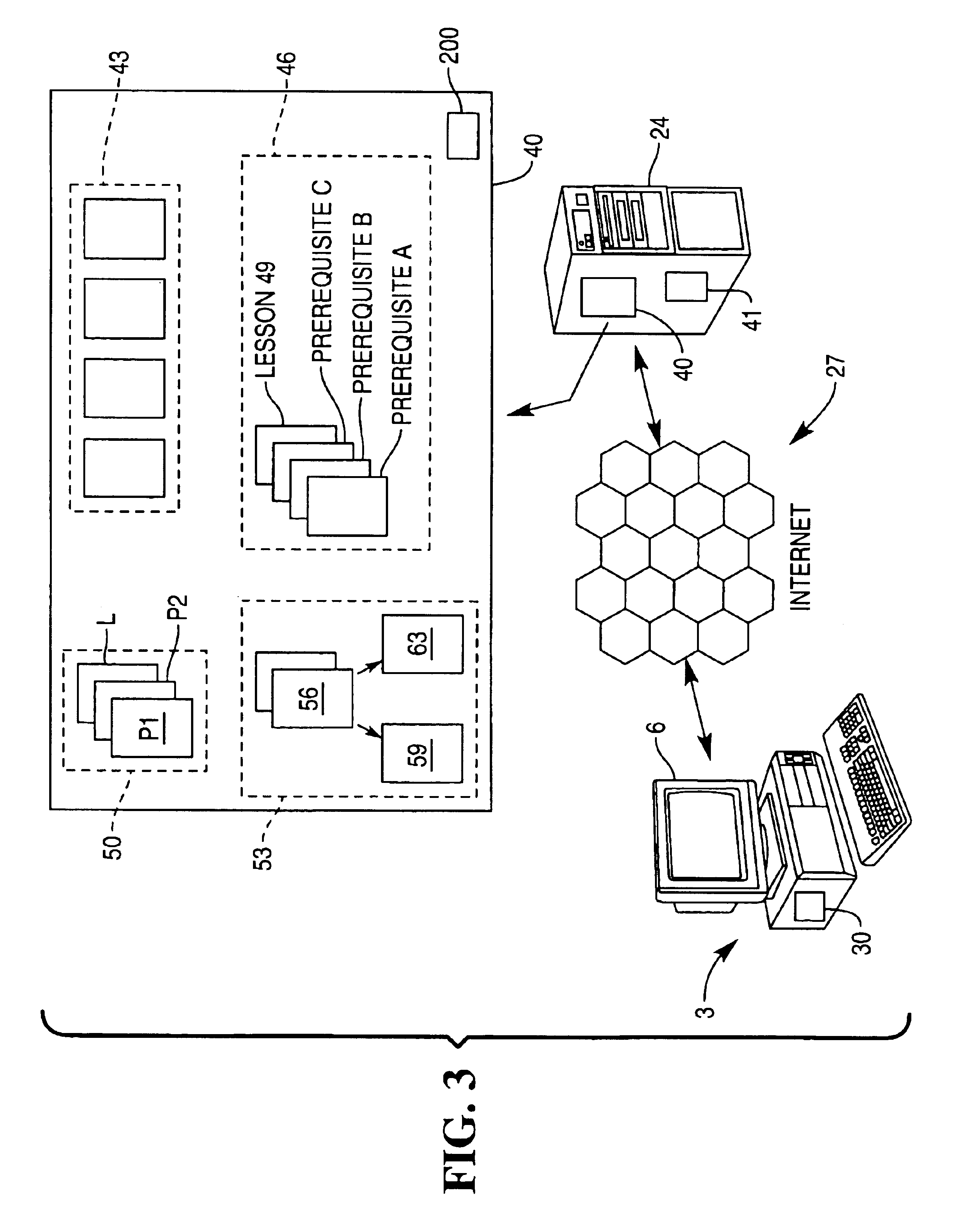
InactiveUS6905341B1Facilitates passing of messageEffective approachElectrical appliancesMechanical appliancesComputer aided educationThe Internet
A computer-assisted educational system. Educational courses are provided, comprising individual lessons. The lessons are stored at one, or more, servers, and are transmitted to remote computers over a network, such as an internet. Students utilize the remote computers to participate in the lessons. At any given time, the remote computer displays the lessons available to a student, so that, for a given course, the student is not held in lock-step with the other students, but may study the lesson's of the student's own choice. This freedom is subject to any requirements of certain lessons which require prerequisite lessons be completed. The prerequisites must be completed first.
Owner:NCR CORP
Systems and methods for recommending business decisions influenced by weather elements
ActiveUS20050096947A1Cost-effectiveEffective approachResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsConfidence metricBusiness activities
Systems and methods to generate business recommendations for specific business actions based on weather element forecasts and known relationships between a business activity and weather elements are provided. The system includes a confidence level filter, an opportunity matrix filter, a weather decision point generator, a business rule recommendation engine and a business rule knowledge database. Methods to generate a business recommendation for a business activity are also provided. The methods include receiving weather driven demand data, assigning opportunity measures to each of the data points, identifying weather decision points based on opportunity measures, and applying business weather rules to the weather decision points to generate business recommendations. In a further feature, a weather element relationship and / or a weather element forecast confidence level is assigned to each data point within the weather driven demand data. These confidence levels are then factored in to determine weather decision points.
Owner:PANALEC
Dynamic asset allocation using stochastic dynamic programming
InactiveUS20080010181A1Maximize utilizationAccurate solutionFinanceComplex mathematical operationsHorizonMulti dimensional
A system and method are disclosed for capturing the full dynamic and multi-dimensional nature of the asset allocation problem through applications of stochastic dynamic programming and stochastic programming techniques. The system and method provide a novel approach to asset allocation and based on stochastic dynamic programming and Monte Carlo sampling that permit one to consider many rebalancing periods, many asset classes, dynamic cash flows, and a general representation of investor risk preference. The system and method further provide a novel approach of representing utility by directly modeling risk aversion as a function of wealth, and thus provide a general framework for representing investor preference. The system and method demonstrate how the optimal asset allocation depends on the investment horizon, wealth, and the investors risk preference and how optimal asset allocation therefore changes over time depending on cash flow and the returns achieved and how dynamic asset allocation leads to superior results compared to static or myopic techniques. Examples of dynamic strategies for various typical risk preferences and multiple asset classes are described.
Owner:INFANGER GERD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com