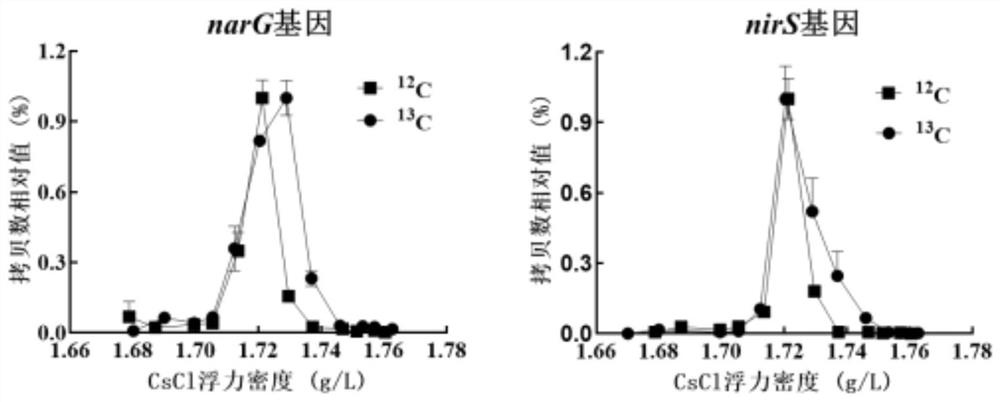
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Microbial ecology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial ecology (or environmental microbiology) is the ecology of microorganisms: their relationship with one another and with their environment. It concerns the three major domains of life—Eukaryota, Archaea, and Bacteria—as well as viruses.
Compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102229900APromote growthImprove firmnessBio-organic fraction processingFungiAureobasidium sp.Streptomyces variabilis
The invention discloses a compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing activated culture of 14 kinds of probiotics, including Pseudomona putida, Streptomyces violovariabilis, Rhizobium sp., Azotobacter chroococcum, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus weihenstephanensis, Bacillus mucilaginosus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Saccharomyces rouxii, Streptomyces griseus var. ferrugineus, and Streptomyces microflavus; performing mixed inoculation at a proportion of 1% to 5% to a 500 mL liquid seed culture medium; then performing amplification culture; and finally delivering the strains to a 500 mL fermentor and fermenting for 3 to 5 days under such conditions that the temperature ranges from 28 DEG C to 30 DEG C and the rotational speed is 200 rpm, to obtain a liquid-state compound probiotics preparation. The compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers, provided by the invention, plays important roles of taking advantage of microbial ecology, improving soil, promoting plant growth, improving the yield and disease resistance of crops and reducing the consumption of fertilizers.
Owner:周剑平 +1
Microbial agent for repairing petroleum-polluted saline alkali soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102994431AEasy to makeImprove stabilityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentAlkali soil
The invention relates to a microbial agent for repairing petroleum-polluted saline alkali soil and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of resource environment. According to a principle of microbial ecology, microbial community is extracted and screened from soils with high salt and alkali and high petroleum pollution to prepare the microbial agent, wherein obligate petroleum degrading bacteria can be sphingolipid bacteria, comamonas, chitin autophagy bacteria and bacillus. According to culture medium and soil environment experiments, the microbial agent can guarantee that the extracted microorganism can be survived in the soils with the salt content of 5,000mg / kg, and meanwhile, the degradation capability to the polluted soils with the petroleum content of 10-50g / kg can reach 80%. The microbial agent has the advantages of simple process, rich microorganisms, obvious dominant bacteria, good stability and capability of facilitating obligate petroleum degrading bacteria to adapt to a new pollution environment, increasing and improving the micro-ecological environment quality of the soils and avoiding secondary pollution to the environment, and can obviously improve the degradation efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon in the saline alkali soil.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for constructing oil reservoir oil displacement microbial community to improve crude oil recovery ratio
ActiveCN101988380AEasy to operateImprove targetingFluid removalMicrobial enhanced oil recoveryOperability
The invention relates to a microbial enhanced oil recovery technique, in particular to a method which is suitable for constructing an oil reservoir oil displacement microbial community to improve crude oil recovery ratio in the middle and later periods of a water-drive reservoir. The technical scheme is that the method for constructing the oil reservoir oil displacement microbial community comprises but is not limited to the following steps of: a, performing field sampling analysis on a target oil reservoir; b, determining a preliminary construction scheme according to field sampling test results; and c, optimizing the construction scheme by using a mixed culture experiment. The method has the following advantages that: (1) aiming at a specific oil reservoir, a targeted assessment is performed on oil reservoir microbial ecology to find out missed parts of a metabolic link, and the oil reservoir has high adaptability; and (2) the operability is strong. The method is used for adjusting the microbial community to evolve towards a target structure in a targeted mode, thereby improving the pertinence and the effectiveness of the field implementation of the oil recovery ratio by using microbes.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for studying structural diversity of daqu bacterial community
InactiveCN102382877AAvoid the downside of losingReveal and recognize diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementCommunity structureMicrobial ecology
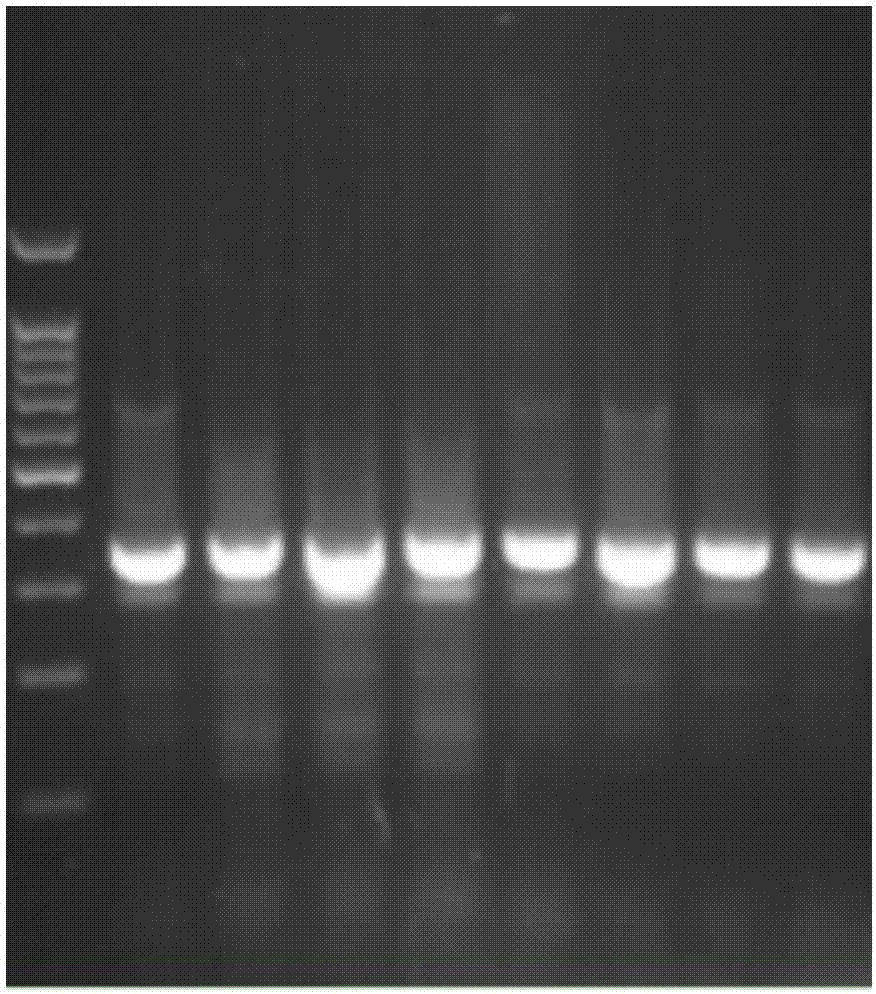
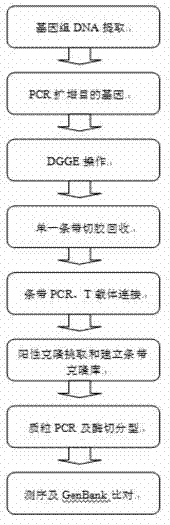
The invention relates to a method for studying the structural diversity of a daqu bacterial community, i.e. the denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) technology, which belongs to the technical field of microbial ecology and mainly comprises the following steps that: 1), daqu genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is directly extracted; 2), bacterial universal primers are selected, and specific DNA fragments in the bacterial ribosome DNA are amplified; 3), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products are separated through DGGE; 4), corresponding strips of microbes in the DGGE fingerprint map are recovered in a gel cutting way; 5), PCR is carried out again, products are connected to a T carrier, the blue and white spot screening is carried out, and positive clone verification is carried out; and 6), the species information of the corresponding microbes of the DGGE strips is obtained through the sequence test. The method does not rely on the molecular biology technology of the traditional culture method, has the characteristics of sensitivity, convenience and accuracy and solves the difficult problems to study some microbes incapable of being cultured or difficult to culture, and the method provides the technical basis for the verification of the daqu bacterial community structure and the discovery of new wine brewing microbes or functional microbes.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Method for remedying salmonella-polluted soil by utilizing antagonistic microbe agent
InactiveCN101628296AProtect ecological functionsReduce in quantityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesMicrobial ecology
The invention discloses a method for remedying salmonella-polluted soil by utilizing antagonistic microbe agent, comprising the following steps: separating the salmonella-polluted soil by utilizing an aseptic filter paper plate method to obtain antagonistic bacterium suitable for the soil environment and having the function of inhibiting or killing the salmonella; fermenting antagonistic microbe strains through the following processes: inoculum inoculation, first-stage culture, second-stage culture and inoculation and second-stage extensive culture to obtain antagonistic bacteria liquid; spraying the antagonistic bacteria liquid to the salmonella-polluted soil, and then uniformly raking the soil. In the method, the microbial ecology principle is applied, and the function of inhibiting or killing the antagonistic bacterium of the salmonella which is obtained from the soil separated and screened from the soil is utilized to remedy the in-situ microbes for the salmonella-polluted soil, not only the damage of the physical remediation to the soil structure and the soil organism is avoided, but also the secondary pollution caused by the chemical remediation is avoided, therefore, the method is a low-cost and environmentally friendly remediation way.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Litopenaeus vannamei relay breeding mode
InactiveCN105766708ARealization of relay farmingIncrease profitClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffWater qualityMicrobial ecology
The invention relates to a litopenaeus vannamei relay type breeding mode. For the litopenaeus vannamei relay type breeding mode, phased breeding management of specific pond desalination and standard size breeding, high-density fine breeding and timely accurate sparse breeding is conducted in a greenhouse pond, a transition pond and a breeding bond respectively, beneficial microorganisms are used for conducting directional adjustment and control on pond microbial ecology in the whole breeding process, a technology of catching and stocking in rotation is combined, and litopenaeus vannamei relay breeding in different spaces is achieved. The litopenaeus vannamei relay type breeding mode has the advantages that the pond utilization rate is high, two-batch litopenaeus vannamei larvae can be bred in one year, the time of juvenile litopenaeus vannamei staying in the breeding pond is short, the water quality and substrate are not prone to deterioration, after the juvenile litopenaeus vannamei is put into the breeding pond, the survival rate is high, precision of breeding management measures of feeding and the like is easy, the breeding water quality and microbial ecology are easy to control, the breeding yield is high, and the breeding benefit is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for analyzing Bacillus community structure in white spirit fermentation system
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the Bacillus community structure in a white spirit fermentation system, belonging to the technical field of microbial ecology. According to the invention, the diversity of a Bacillus community structure in the white spirit fermentation system is semi-quantitatively analyzed by a nested PCR-DGGE (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis) method. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting the total genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in a yeast or fermented grains sample by a bead milling method; performing two steps of amplification of the Bacillus specific segment through the nested PCR; performing DGGE electrophoretic analysis; determining the microorganism species corresponding to the DNA stripe by use of a standard strain; performing glue cutting of the unknown stripe and recycling and then performing PCR again; connecting the T vector and cloning; performing DGGE electrophoresis again; performing positive cloning sequencing and performing blast comparison in the GenBank databae to obtain the microorganism information; digitally processing DGGE map by use of quantityone software; and calculating the proportion of different Bacillus strains in the total Bacillus flora according to the brightness of the stripe. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, strong specificity and good repeatability, and lays foundation for further studying the importance of Bacillus in white spirit production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane and using method thereof
ActiveCN104150606ASimple structureReduce processing costsBiological water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention provides an aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane and a using method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of aquaculture and environmental protection. A functional element of the composite microbial membrane is a membrane component in which paenibacillus polymyxa, lactobacillus plantarum, rhodobacter sphaeroides, rhodococcus pyridinovorans, bacillus amyloliquefaciens and other beneficial microorganisms are immobilized. A preparation process of the aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane comprises selecting of a soft packing microorganism carrier, composite bacteria liquid preparation, microorganism immobilization and other steps; the composite microbial membrane is mounted in aquaculture water, beneficial microbes begin activation reproduction, long-term regulation of microbial ecology of the aquaculture water can be realized, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite and hydrogen sulfide and other toxic and harmful substances in pond can be controlled, metabolites can be licked by farmed fish, shrimp, and other aquatic organisms, so that the immunity is improved, the growth speed of the farmed species is increased, and the aquaculture water in-situ purification composite microbial membrane is especially adapt to ponds for high density aquaculture of shrimp, crab, fish and the like.
Owner:无锡中科活力生物技术有限公司 +1
Marsh gas engineering inoculum and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104805125AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaGas production bioreactorsMicroorganismMixed culture
The invention discloses a marsh gas engineering inoculum and a preparation method thereof, and aims to solve the problems of low anaerobic fermentation speed, long fermentation period and poor marsh gas engineering gas productivity and engineering running efficiency in the conventional marsh gas engineering. Organic waste sludge or biogas slurry is taken as a raw material, and a special marsh gas engineering inoculum is prepared through mixed culture and a fixed anaerobic fermentation microbial flora according to an anaerobic fermentation principle and a microbial ecology principle. Compared with the prior art in which an inoculum is prepared by culturing single strains respectively and mixing proportionally, the preparation method has the advantages that the inoculum is prepared through mixed culture of sludge or biogas slurry is stable in micro-ecology; moreover, the marsh gas engineering fermentation period can be remarkably shortened, the marsh gas yield is increased, and the marsh gas engineering economical benefit is increased.
Owner:马力通
Method for producing bio-organic fertilizer by using sheep manure
InactiveCN103145457AEfficient use ofIncrease profitBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilizerMicrobial ecology
The invention discloses a method for producing a bio-organic fertilizer by using sheep manure, which relates to a method for producing a bio-organic fertilizer through comprehensive utilization of sheep manure and belongs to the technical fields of agricultural science and environmental biology. According to the invention, based on microbiological and microbial ecological principles, diluted manure water of sheep manure is treated and is then cyclically utilized, so high efficiency utilization of sheep manure is realized and no waste is caused. The invention has the following beneficial effects: process flow design for treatment of sheep manure is more reasonable; a converted product has substantially improved quality; particularly, raw materials for the fertilizer are rich in nutrients needed by crops; a utilization rate of sheep manure is high; compared with utilization of a chemical fertilizer, utilization of manure in the invention exerts small adverse influence on the crops; based on microbiological and microbial ecological principles, diluted manure water of sheep manure is treated and is then cyclically utilized, so high efficiency utilization of sheep manure is realized and no waste is caused.
Owner:何诚慧
Biocontrol synergistic nutrient package fertilizer special for solanaceous vegetables and application method thereof
ActiveCN105330486AMeet nutrient needsIncrease annual outputFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesMicroorganismGreenhouse
The invention relates to biocontrol synergistic nutrient package fertilizer special for solanaceous vegetables and an application method thereof. The nutrient package fertilizer is prepared from, by mass, 12%-31% of synergistic compost tea, 58%-70% of major element compound fertilizer, 9%-20% of soil conditioner and 0.1%-0.2% of medium trace element leaf fertilizer. The nutrient package fertilizer can meet the requirement of the solanaceous vegetables for nutrients at different growth and development stages, a large quantity of organic matter and microbial florae contained in the synergistic compost tea of the nutrient package fertilizer can balance the microbial ecology of soil, and soil-borne disease antagonistic bacteria are introduced for efficiently preventing soil-borne diseases of the solanaceous greenhouse vegetables.
Owner:KINGENTA ECOLOGICAL ENG GRP +1
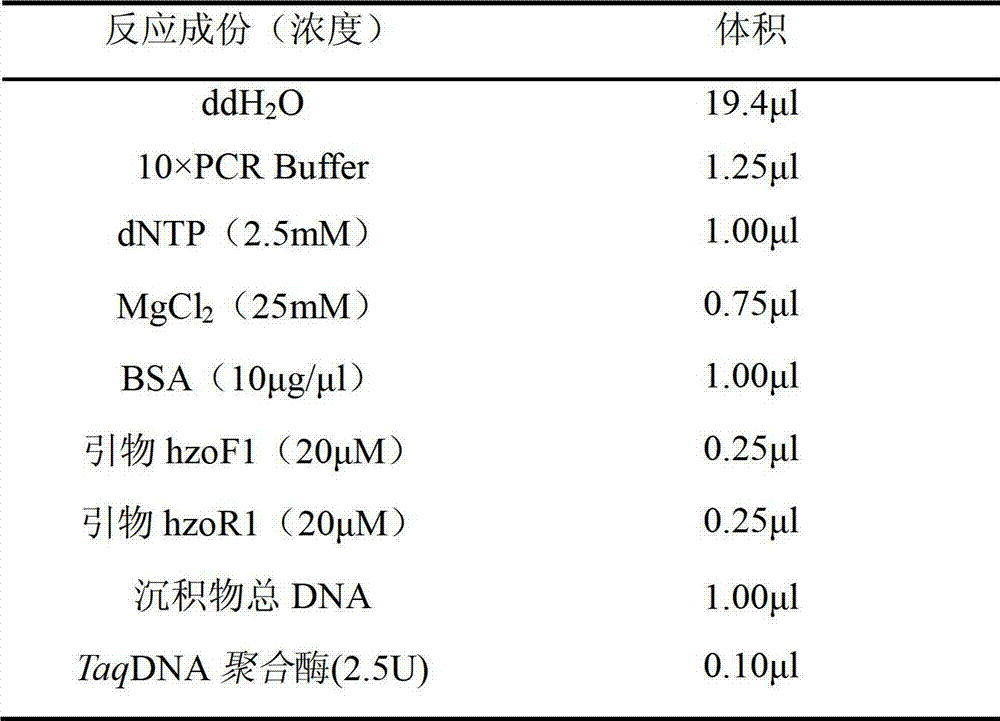
Method for quantitating anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria in sediment of aquiculture environment
InactiveCN102925581ACreate Quantitative ResearchOvercome the disadvantages of difficult isolation and cultureMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBacteroidesCoverage ratio
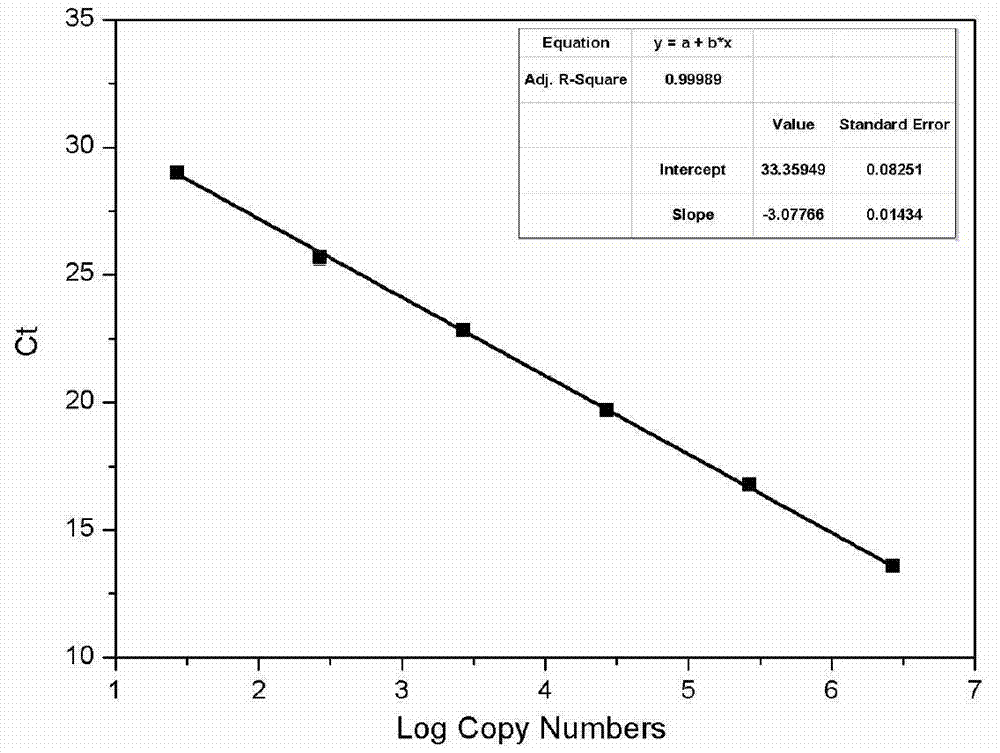
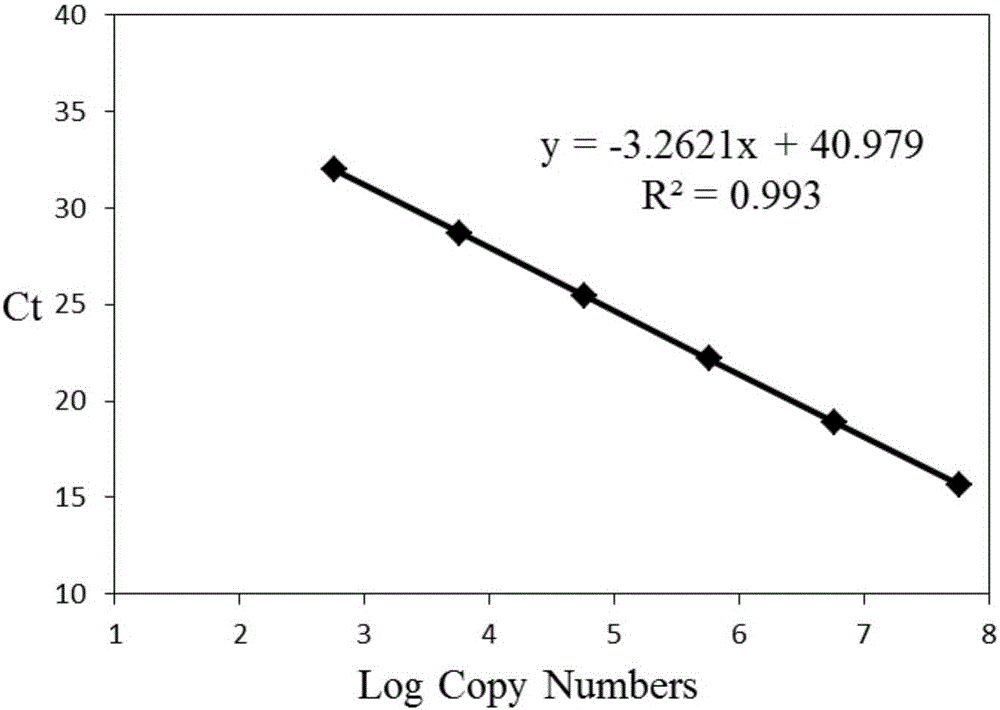
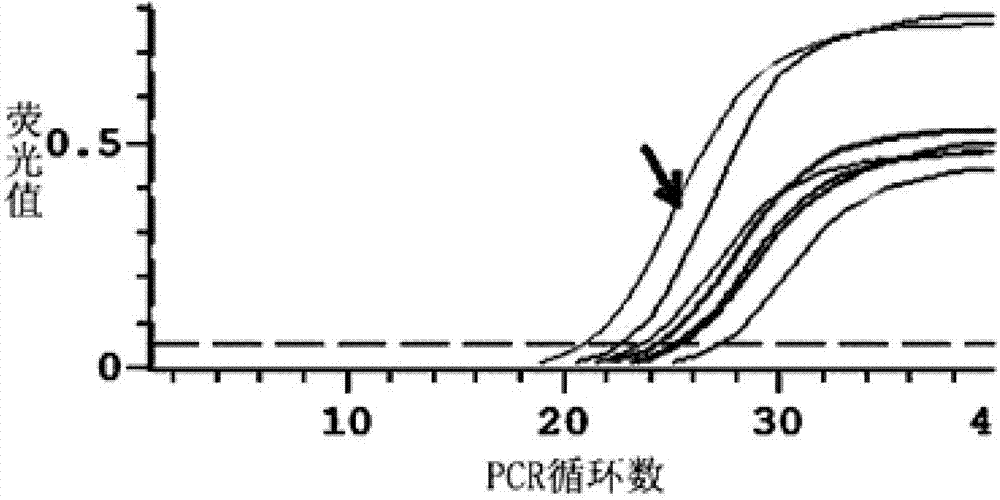
The invention relates to a method for quantitating ammonia oxidizing bacteria in a sediment of an aquiculture environment by a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology, which belongs to the field of environmental microbial ecology. The method comprises the steps that DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample sediment is extracted and quantitated; an HZO (hydrazine oxidordeuctase) gene specific primer is subjected to PCR amplification; standard plasmids are constructed; and a fluorescent quantitation PCR amplification curve and a standard curve are made. The quantity of the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria in a sample is calculated by comparing a detected sample Ct value with the standard curve; an obtained log value of the initial template gene copy number has a better linear relationship with the Ct value; and a regression coefficient is greater than 0.99. According to the method, an HZO gene is used for conducting quantitative analysis on the ammonia oxidizing bacteria under an anaerobic condition; the deficiencies that the specificity is not high, the coverage ratio is low and the method is inaccurate due to the fact that the a 16S rRNA (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) gene is used for quantitating in the existing method are overcome; and the method for quantitating the ammonia oxidizing bacteria in the sediment of the aquiculture environment is high in specificity, quick and accurate.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Sinapic Acid Supplementation
InactiveUS20080113003A1Increase productionImprove efficiencyAntibacterial agentsBiocideHuman animalIntestinal microorganisms
An animal feed composition for monogastric non-human animals is disclosed comprising supplemental sinapic acid or derivatives thereof. Sinapic acid may be supplemented at a level of from 0.0005% to 3% of the feed composition by weight. The feed composition has the beneficial effect of promoting favourable intestinal microbial ecology by reducing pathogenic microbial populations, increasing favourable microbial populations, and increasing performance and growth characteristics in livestock animals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
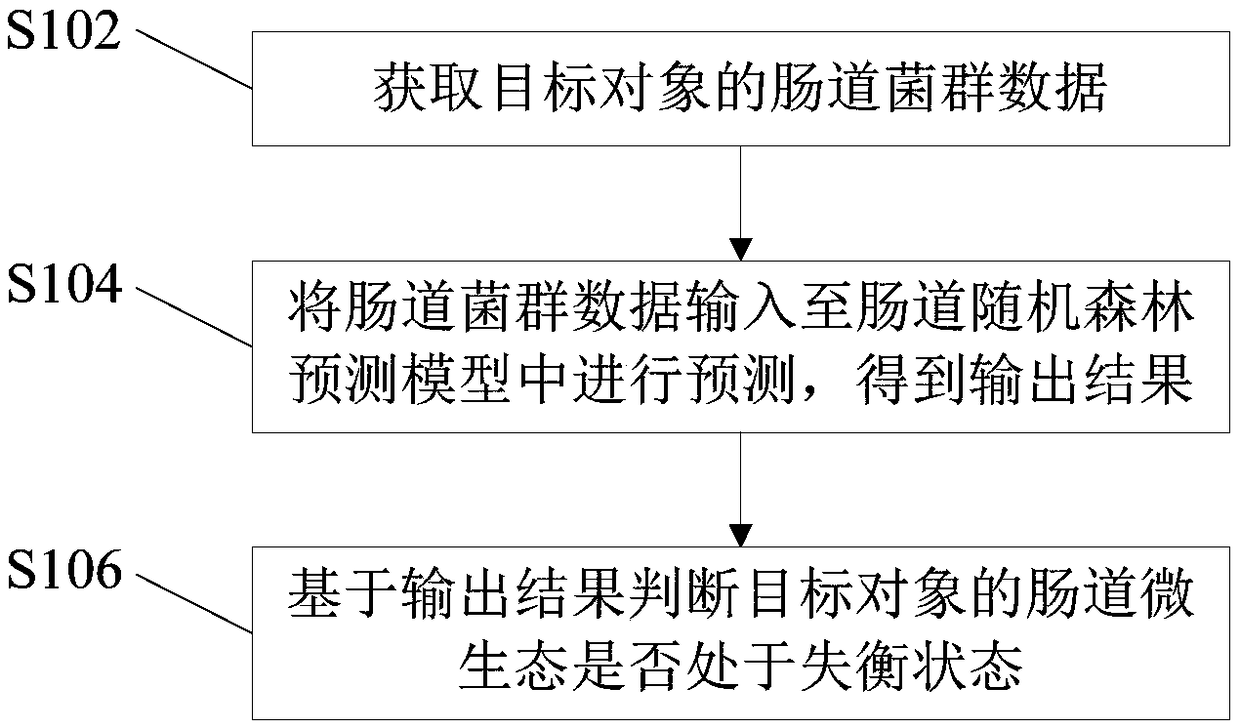
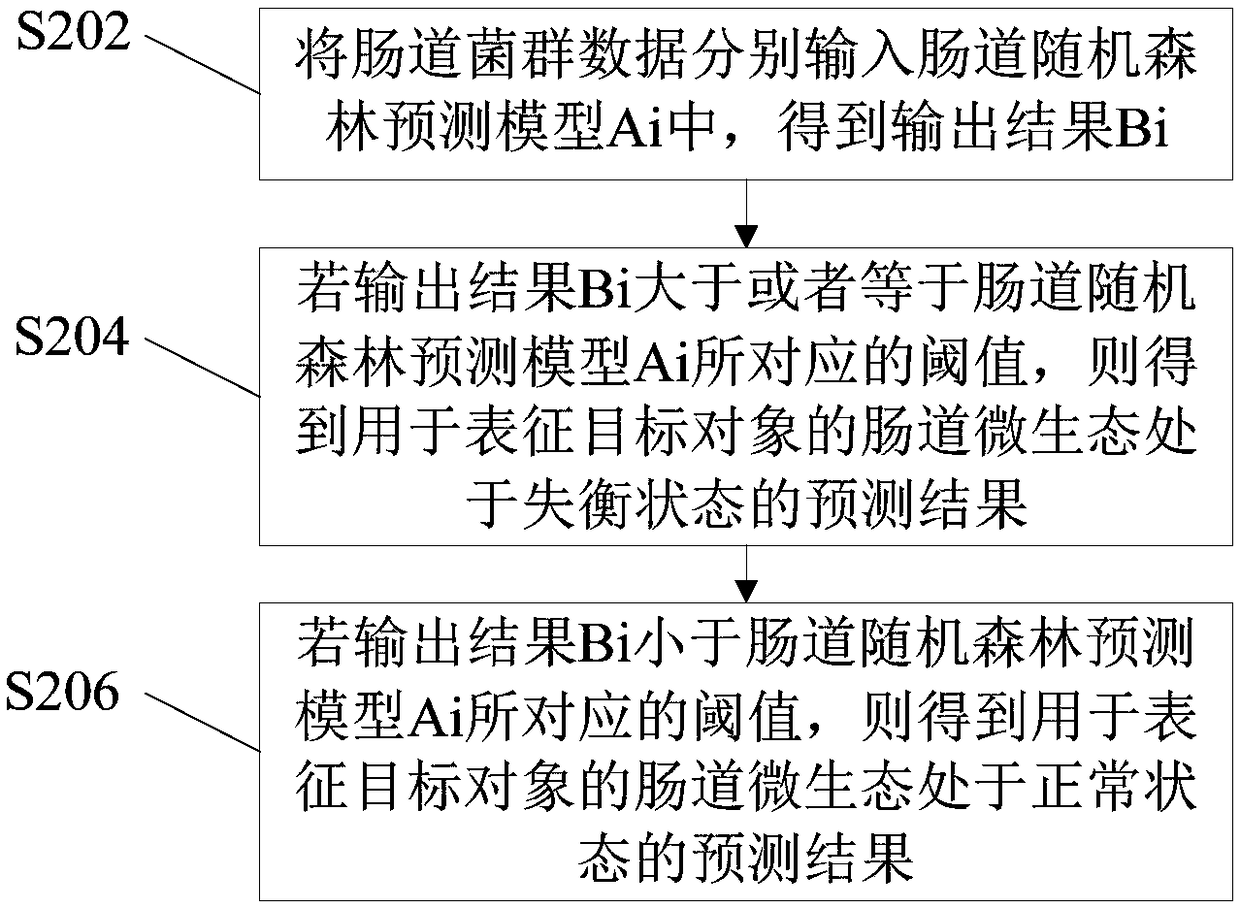
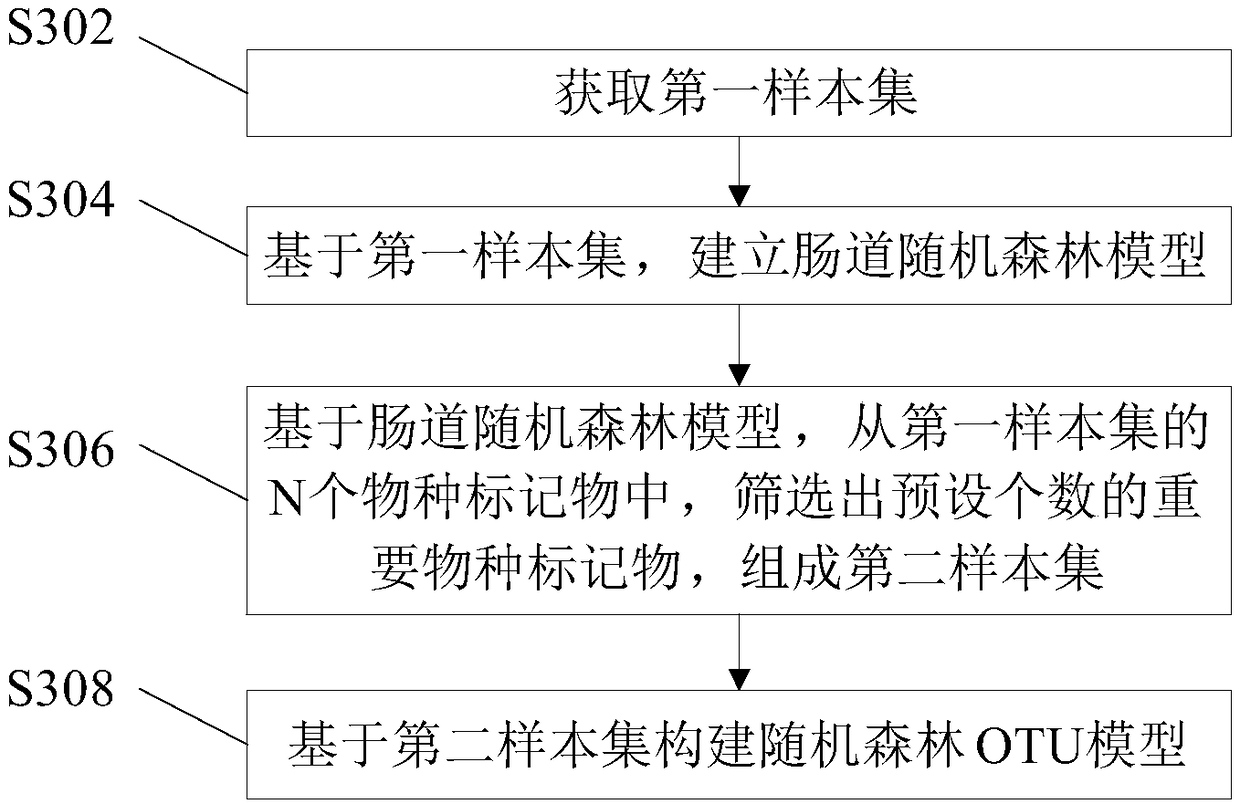
Method and device for determining micro-ecological imbalance of human intestinal tract and electronic equipment
The invention provides a method and device for determining micro-ecological imbalance of the human intestinal tract and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of microbial ecology. The method for determining the micro-ecological imbalance of the human intestinal tract comprises the steps that intestinal flora data of the target human body is obtained, wherein the intestinal floradata is sample data containing markers of multiple species; the intestinal flora data is input into an intestinal random forest prediction model for prediction, and an output result is obtained; theintestinal random forest prediction model is correspondingly provided with a threshold used for judging the phenotypes of samples, the intestinal random forest prediction model comprises a random forest OTU model or a Shannon exponential random forest model; based on the output result, whether or not the micro-ecology of the intestinal tract of the target human body is in an unbalanced state is judged. The method and device for determining the micro-ecological imbalance of the human intestinal tract and the electronic equipment can judge whether or not the target human body is in an intestinalmicro-ecological imbalance state through the prediction model.
Owner:JIANGXI PRECISION GENE CO LTD
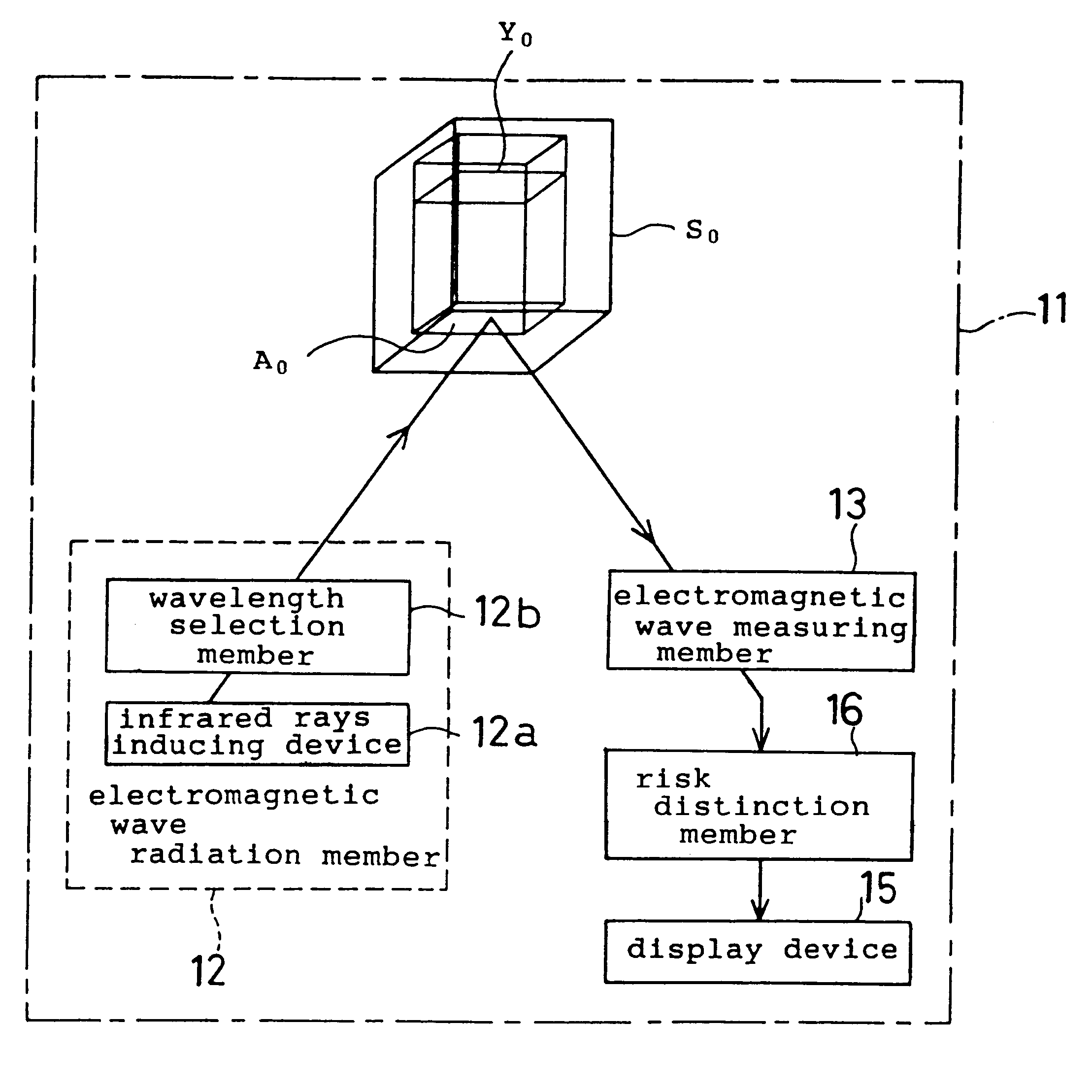
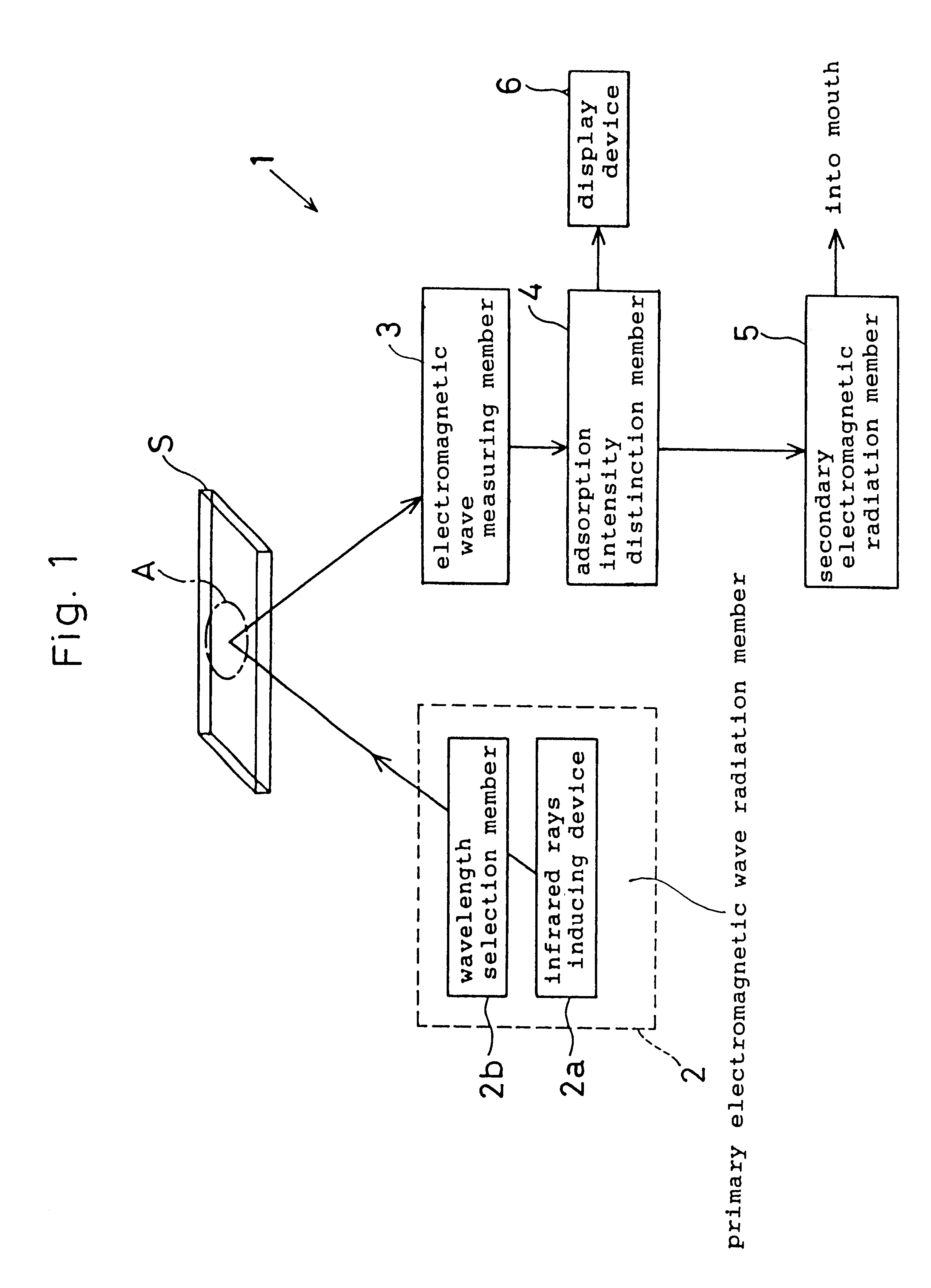
Microbe and cell function control device, a microbial ecology detector device, and a method of controlling a microbe and cell function control device
InactiveUS6373972B1Limited functionEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWave measureComputational physics
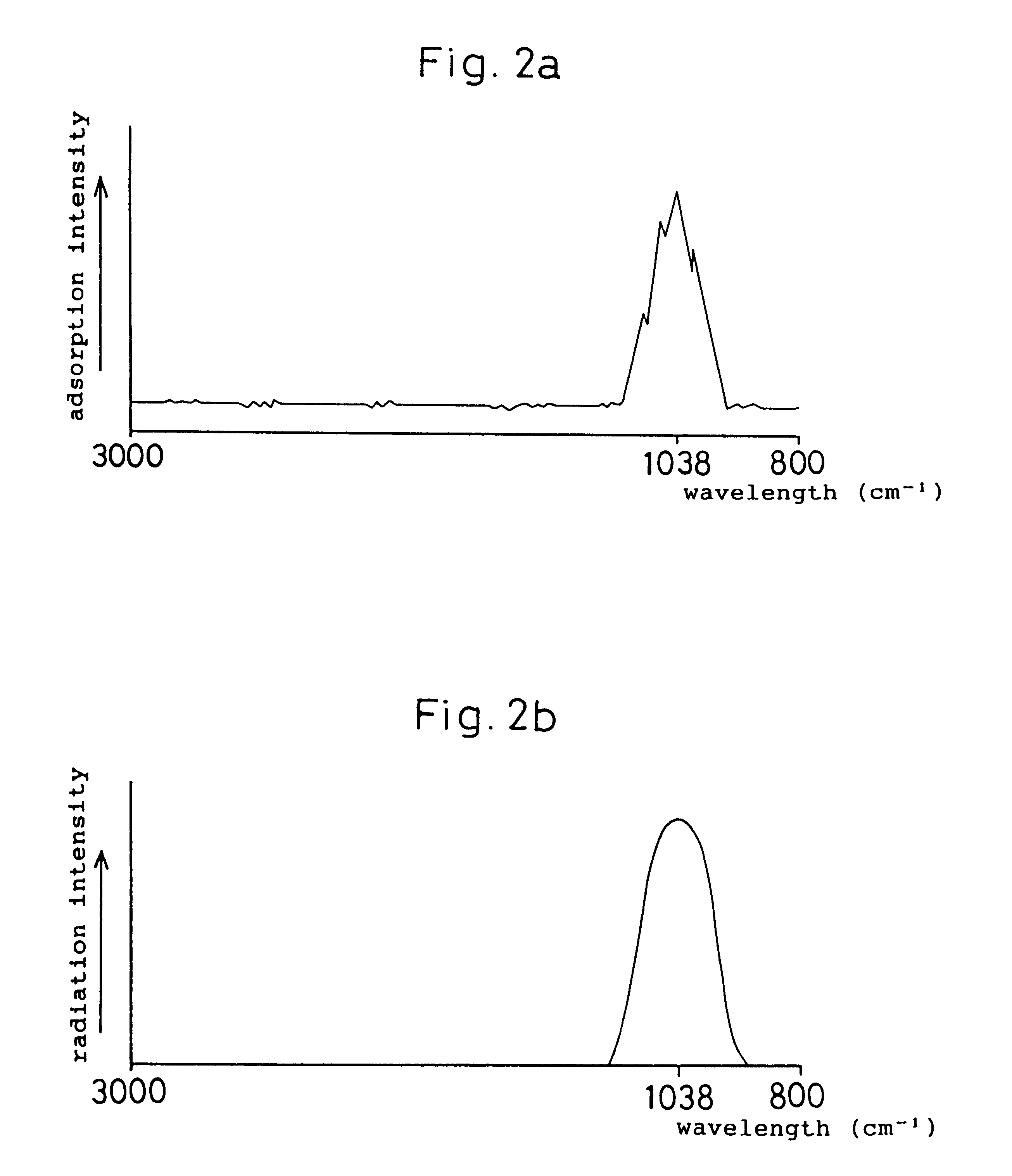
In a microbe and cell function control device, a primary electromagnetic wave radiation member is provided to radiate electromagnetic wave on microbes and cells within a predetermined wave length range thereof. An electromagnetic wave measuring member measures an intensity of a predetermined range of the electromagnetic wave permeated or reflected from the microbes and cells. An absorption intensity distinction member determines wavelength the microbes and cells absorb based on the intensity of the electromagnetic wave measured by the electromagnetic wave measuring member. A secondary electromagnetic wave radiation member radiates the electromagnetic wave absorbed by the absorption intensity distinction member on the microbes and cells.
Owner:KUBUSHIKI KAISHA MARUTOMO
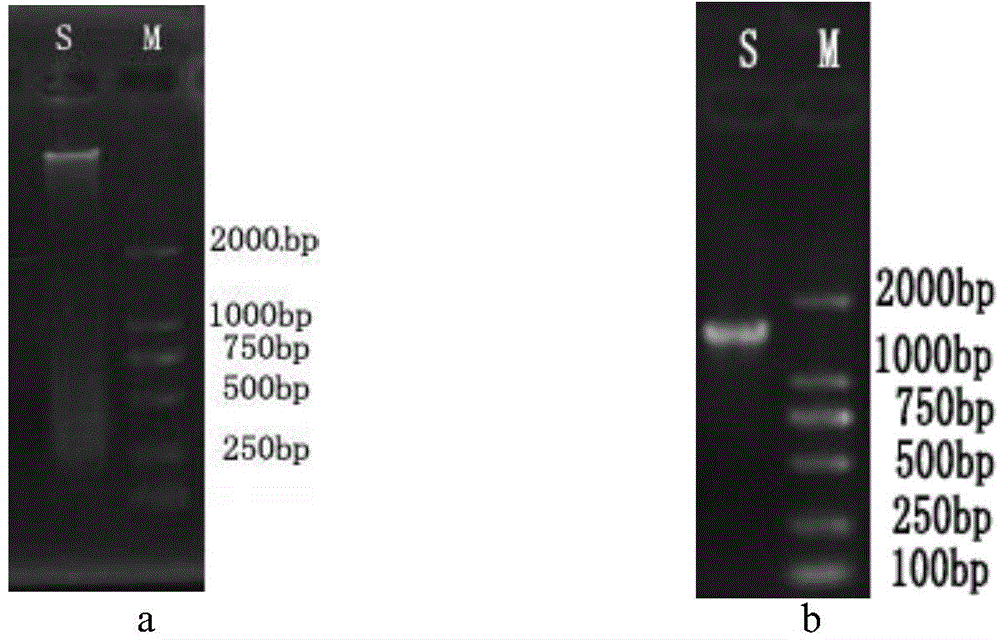
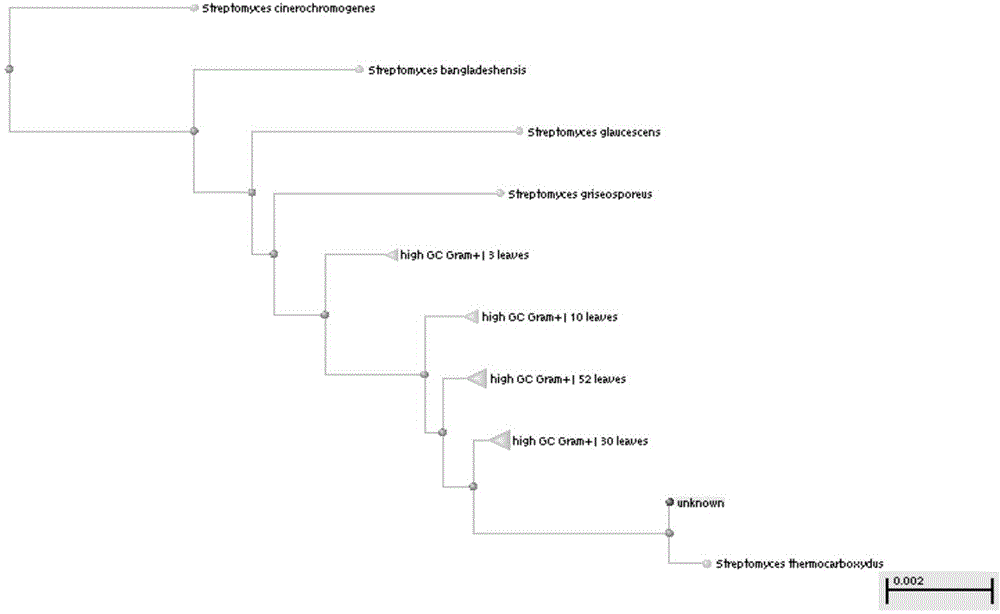
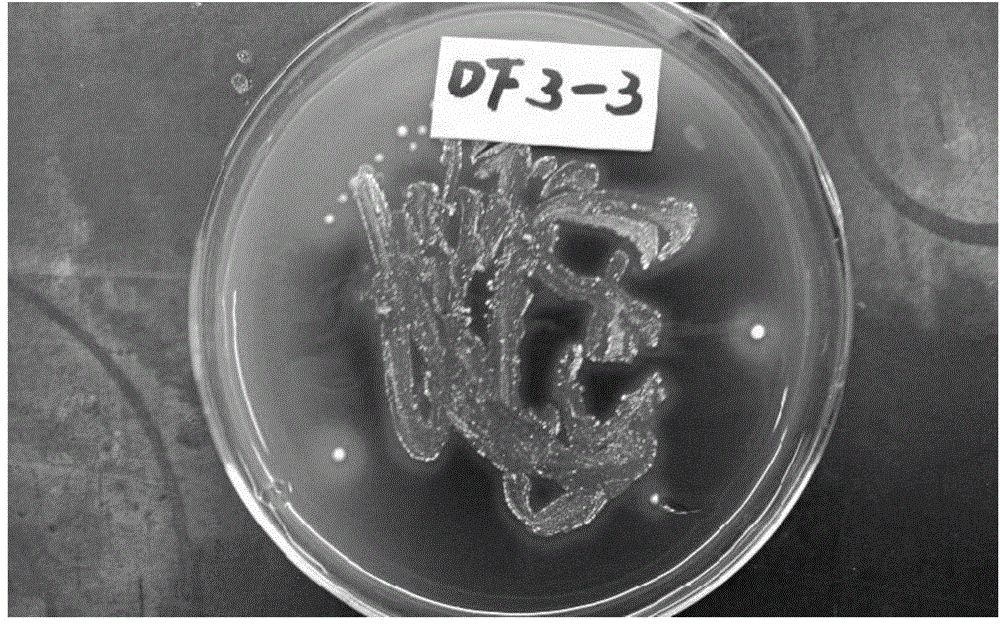
Thermophilic carbon monoxide streptomycete low-temperature subspecies Dstr3-3 and application thereof
The invention discloses a thermophilic carbon monoxide streptomycete low-temperature subspecies Dstr3-3 and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial ecology. The preservation number of thermophilic carbon monoxide streptomycete strains is CGMCC No.10774. The invention further provides a product which uses the thermophilic carbon monoxide streptomycete strains as active ingredients and is used for degrading lignin and a product, an additive and a microbial inoculum used for garden waste compost. In addition, the invention further provides a compost method for garden waste based on the thermophilic carbon monoxide streptomycete strains. The compost time can be effectively shortened by adopting the thermophilic carbon monoxide streptomycete strains for garden waste compost, compost maturity is promoted substantially, and a compost product large in nutrient content and high in quality is obtained.
Owner:北京大地聚龙生物科技有限公司
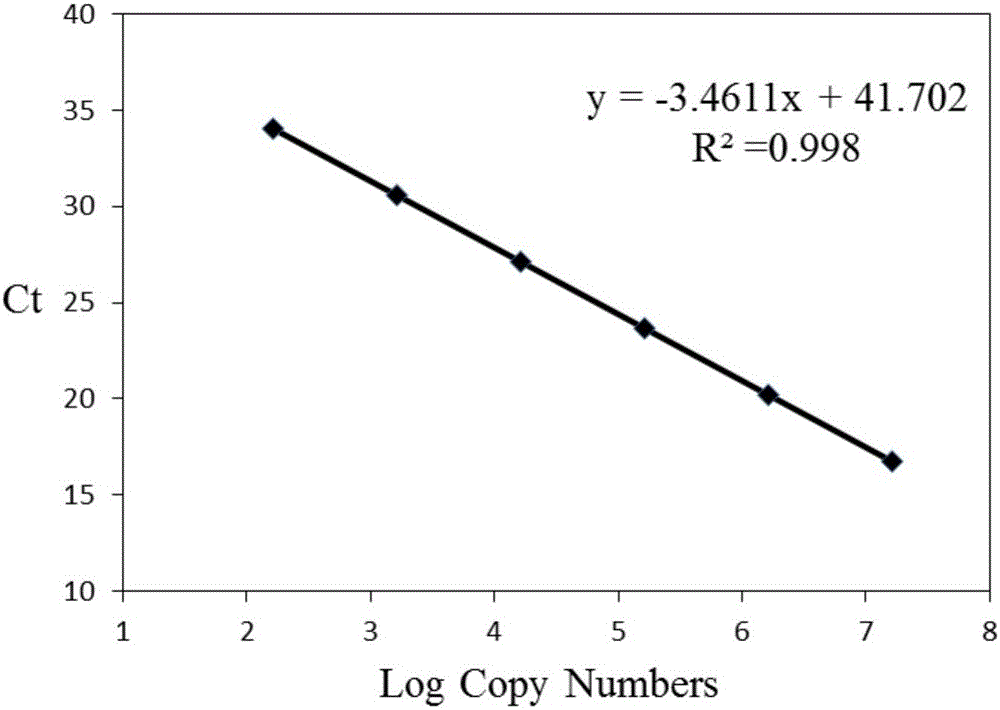
Quantification method for denitrifying microorganisms in aquaculture environment sediments
InactiveCN105132553AShorten the timeGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceEcological study
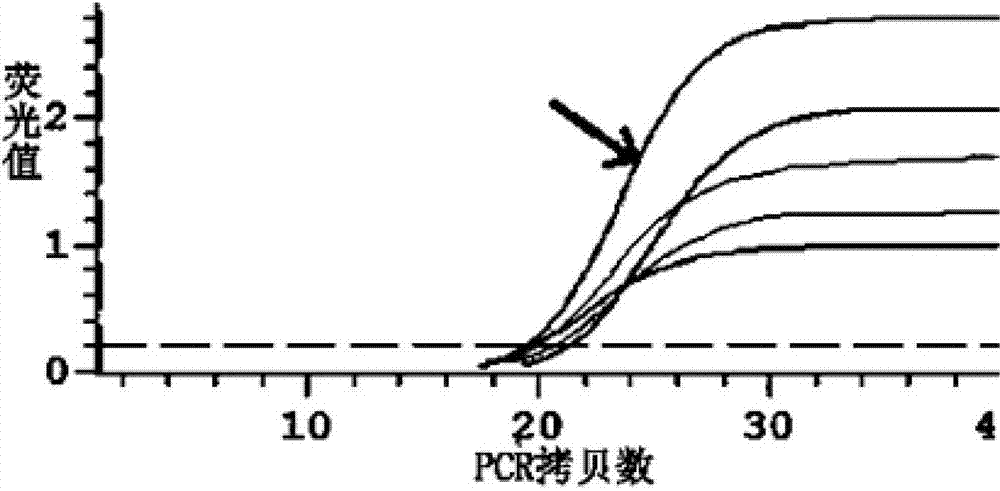
The invention discloses a method for real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (qPCR) detection of denitrifying microorganisms in aquaculture environment sediments, and belongs to the technical field of environmental microbial ecology. The method comprises the following contents: metagenome DNA extraction and concentration determination of sediment samples in various stations, PCR amplification of nirK and nirS genes, construction of a standard plasmid, preparation of a standard curve, qPCR amplification and calculation of the number of denitrifying microorganisms in the samples according to a qPCR result in accordance with the standard curve. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for determining the number of the denitrifying microorganisms in an aquaculture environment through quantitative analysis on two genes, namely nirK and nirS, so as to overcome the shortcoming that 16S rRNA gene cannot be used in the quantification of the denitrifying microorganisms as well as the shortcoming that the prior art, which focuses on some functional gene only, is incomplete in quantification; and the provided method for detecting the number of the denitrifying microorganisms in the aquaculture environment is good in specificity, high in repeatability and high in accuracy. According to the method disclosed by the invention, logarithm values of nirK and nirS gene copy numbers keep a good linear relation with Ct value of a luminescence threshold, and the regression coefficient of the standard curve is above 0.99.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102229900BPromote growthImprove firmnessFungiBio-organic fraction processingAureobasidium sp.Streptomyces variabilis
The invention discloses a compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing activated culture of 14 kinds of probiotics, including Pseudomona putida, Streptomyces violovariabilis, Rhizobium sp., Azotobacter chroococcum, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus cereus,Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus weihenstephanensis, Bacillus mucilaginosus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Saccharomyces rouxii, Streptomyces griseus var. ferrugineus, and Streptomyces microflavus; performing mixed inoculation at a proportion of 1% to 5% to a 500 mL liquid seed culture medium; then performing amplification culture; and finally delivering the strains to a 500 mL fermentor and fermenting for 3 to 5 days under such conditions that the temperature ranges from 28 DEG C to 30 DEG C and the rotational speed is 200 rpm, to obtain a liquid-state compound probiotics preparation. The compound probiotics preparation for biological organic fertilizers, provided by the invention, plays important roles of taking advantage of microbial ecology, improving soil, promoting plant growth, improving the yield and disease resistance of crops and reducing the consumption of fertilizers.
Owner:周剑平 +1
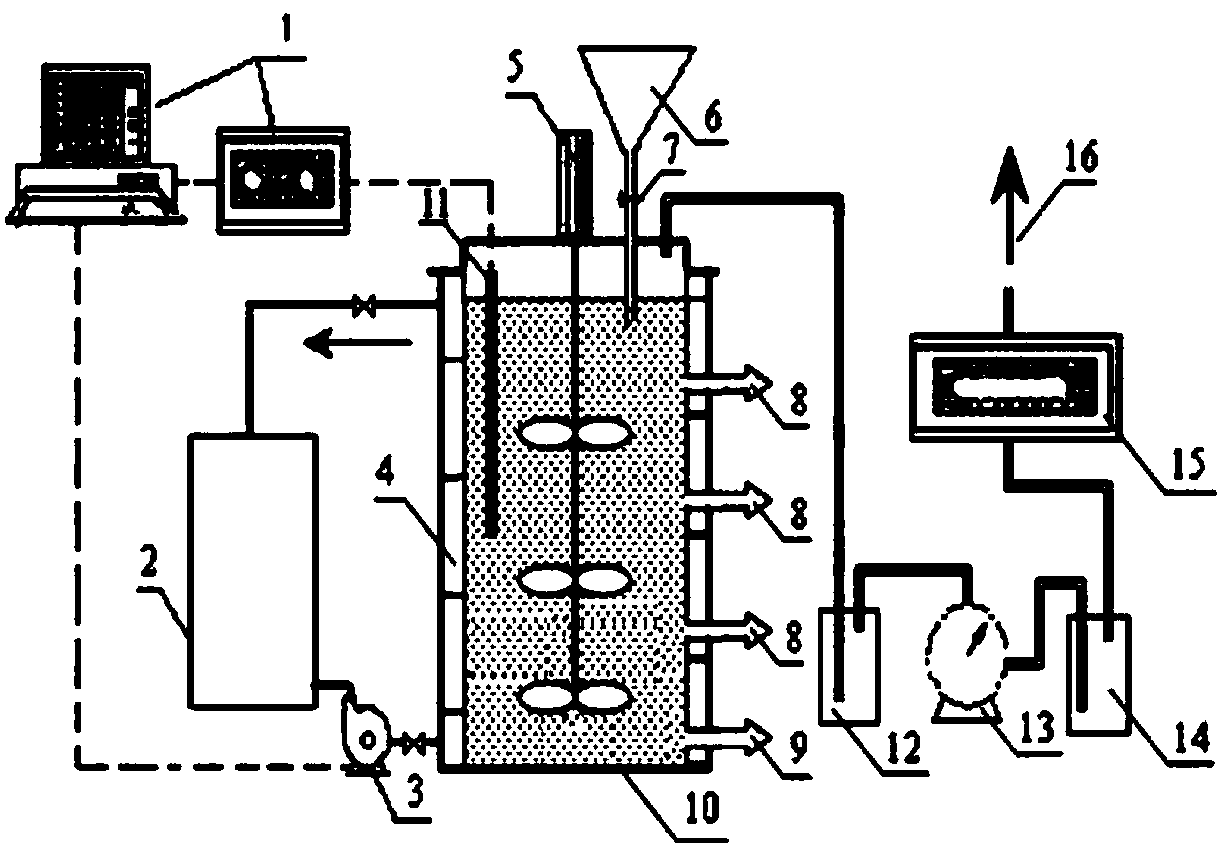
Landfill stink in-situ control reactor and operation method thereof
ActiveCN103071661AEasy to collectAchieve optimizationSolid waste disposalLandfill technologiesMonitoring systemProduct gas
The invention discloses a landfill stink in-situ control reactor and an operation method thereof. The landfill stink in-situ control reactor comprises a landfill system, a stink in-situ purification system, a gas sample on-line monitoring system, a liquid sample on-line monitoring system and an environmental condition simulation system. Aiming at actual garbage or simulated garbage, different types of earthing materials are selected, overlaid or combined so as to simulate the development of study for landfill stink pollution in-situ control under different environment conditions; the on-line monitoring for effects of stink pollution in-situ control can be realized; stink gas samples produced by the landfill can be collected, so that the study of stink production regularity can be possibly realized; and the collection of earthing biological samples is realized, so that the analysis for earthing microbial ecology is possibly realized, and further, the biological ecological regulation and control of landfill earthing stink gas in-situ control can be realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
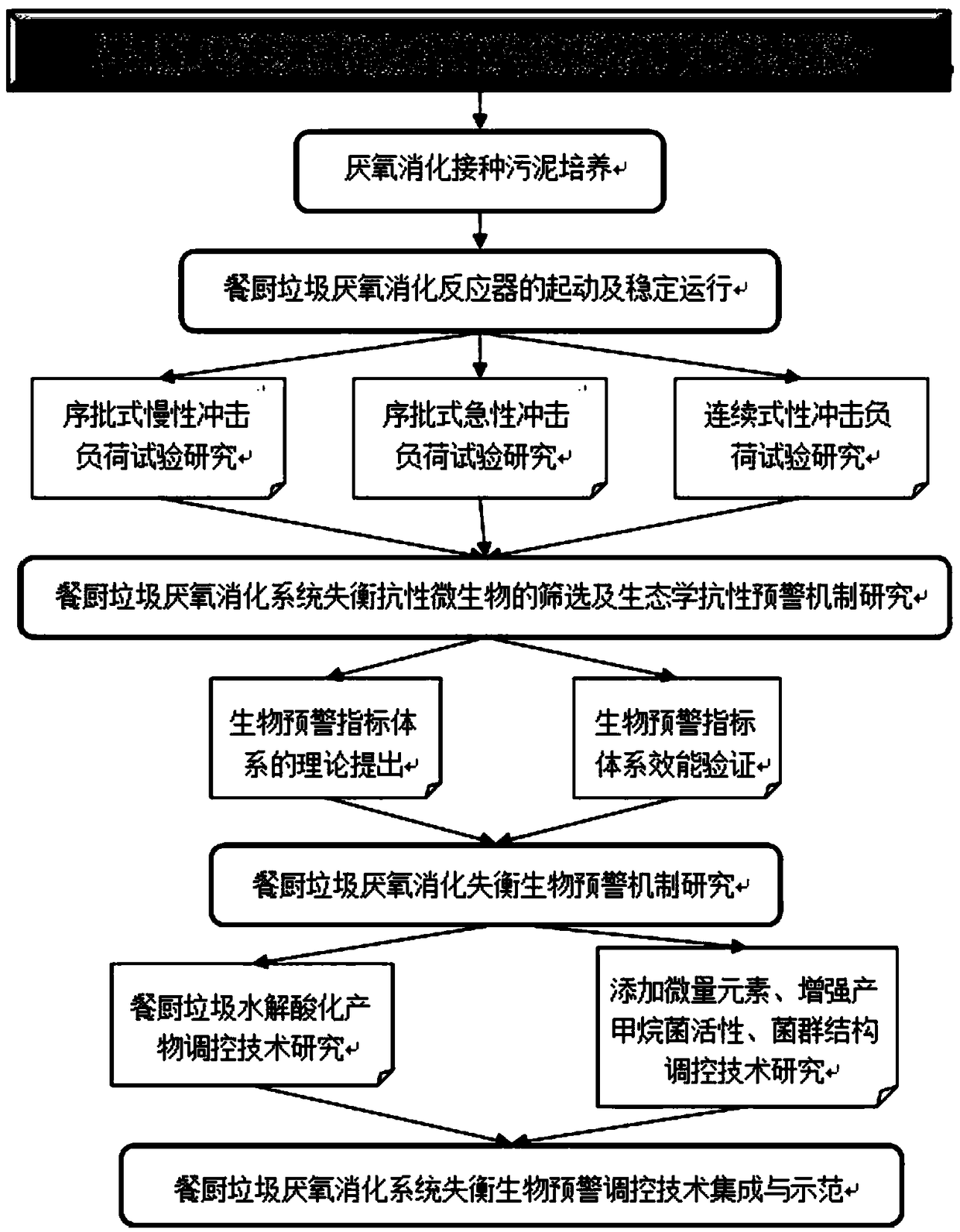
Early warning regulation and control method based on anaerobic digestion unbalance microorganism resistance enhancement
PendingCN109337809ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWater bathsRedox
The invention discloses an early warning regulation and control method based on anaerobic digestion unbalance microorganism resistance enhancement. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out researches through various impact load tests, and in a self-controlled continuous single-phase anaerobic digestion reactor, carrying out water bath heating, controlling the temperature within 35-38DEG C, carrying out online real-time monitoring on pH values and temperatures, at a redox potential, taking kitchen waste samples from different types of catering departments of school canteens and restaurants around, collecting, mixing according to a certain ratio, removing impurities, crushing into slurry, and preserving at 4 DEG C for later use, wherein an organic load of stable operation of asystem is set as 3.0kgVS*m<-3>d<-1>, the temperature inside the reactor is controlled as 35-38 DEG C, and a pH value change range is 7.40-7.80. The method has the beneficial effects that a resistantmicrobial ecological resistance early warning mechanism in a kitchen waste anaerobic digestion unbalance process is explored and analyzed, and a kitchen waste anaerobic digestion unbalance biologicalearly warning mechanism is established.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Soil conditioner and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104962294AAchieve governanceRealize the purpose of soil heavy metal passivation treatmentAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersMineral SourcesSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a soil conditioner and a preparation method thereof. The soil conditioner is prepared by mixing boiler ash, a carbon material, a plant vinegar liquid, waste molasses and water according to a mass ratio of 30-80:20-50:0.5-2:0.5-2:12-27. Water is used to adjust the total water content to 15-30% and assist reduction of flying of dusts. The soil conditioner saves energy and mineral product resources, realizes shell waste treatment and soil heavy metal passivation treatment, almost realizes zero discharge of ashes, effectively passivates soil metals and recovers the microbial ecology, has crop growth promotion and disease prevention effects, and realizes changing of wastes into valuables.
Owner:广东巴斯德环境科技有限公司
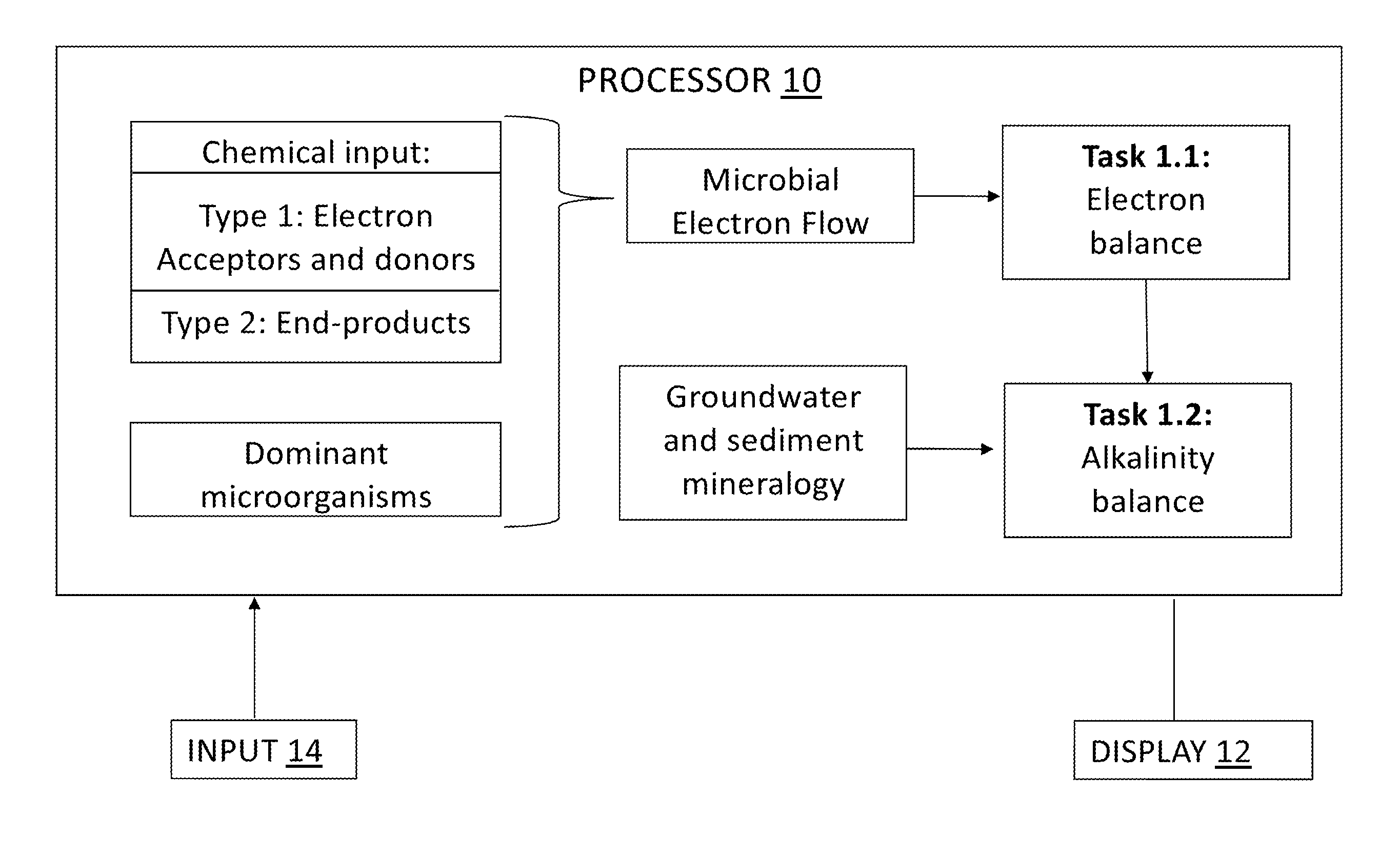
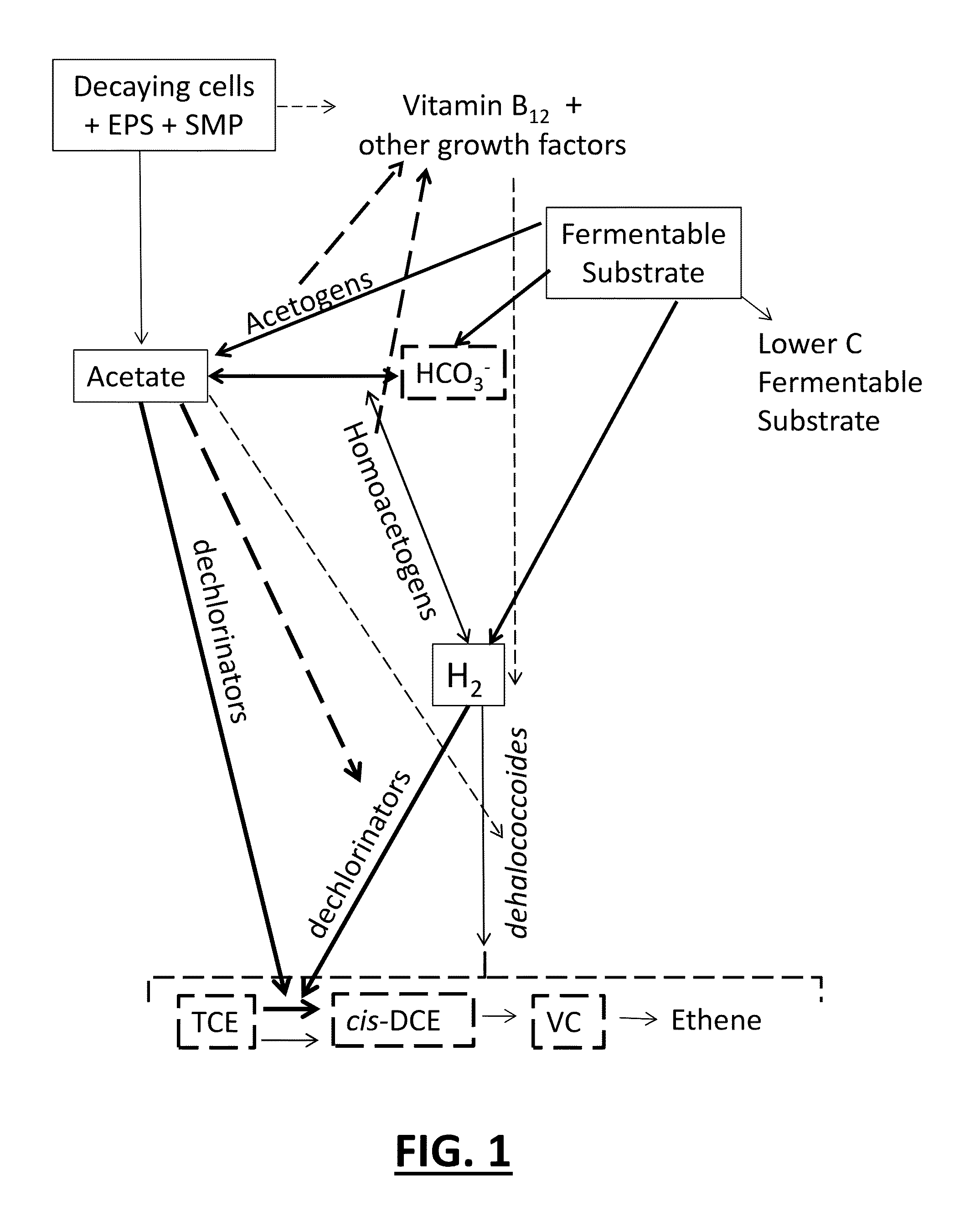
Tool for optimizing chlorinated-solvent bioremediation through integration of chemical and molecular data with electron and alkalinity balances
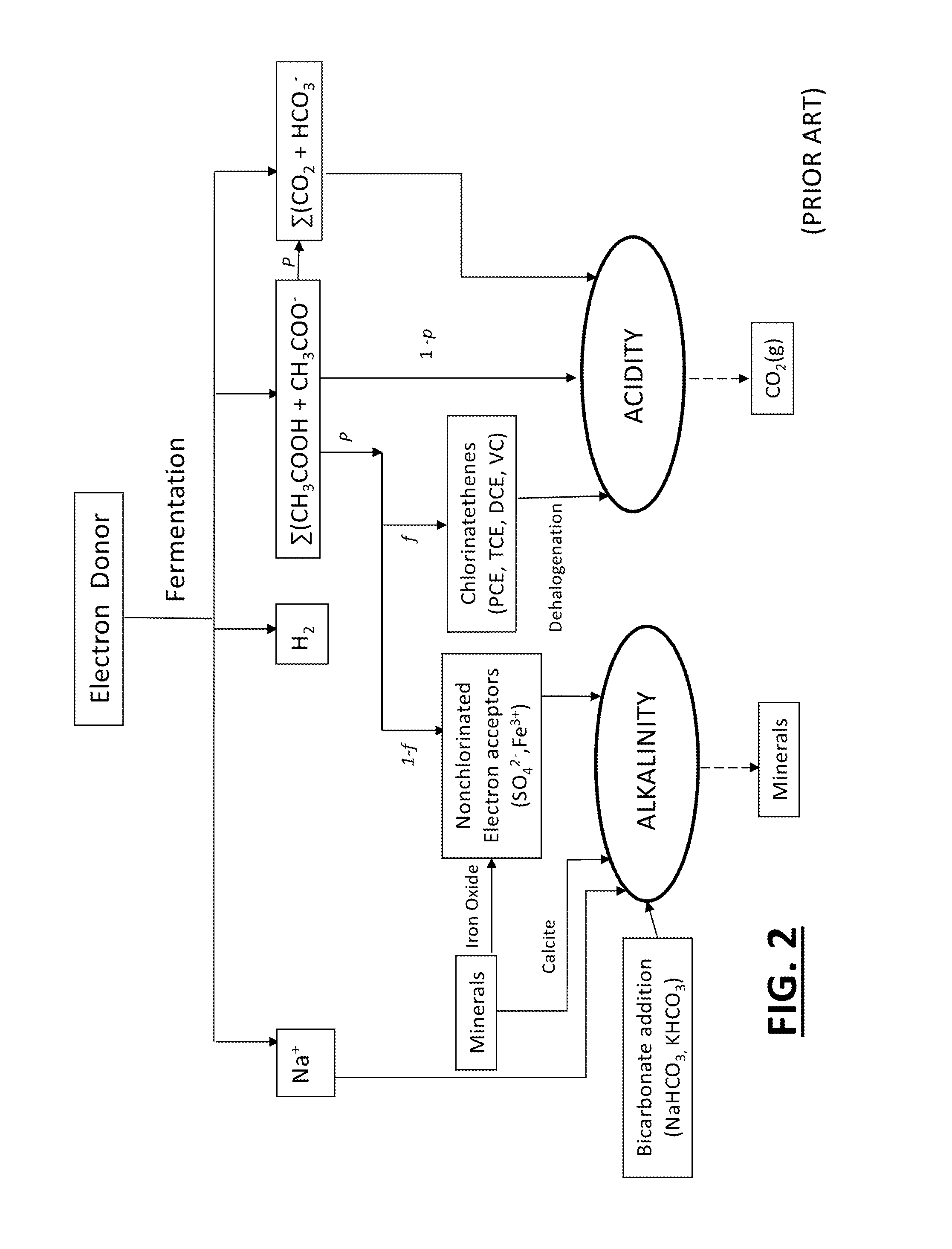
InactiveUS20130345990A1Maximize accuracyMitigate incomplete reductive dechlorinationContaminated soil reclamationSpecial data processing applicationsAlkalinityOrganismal Process
A prediction and assessment tool for bioremediation performance based on a comprehensive understanding of the link between chemical flow and microbial community interactions includes linking molecular microbial ecology data with electron and alkalinity balances to make it possible to understand dechlorinating microbial communities and their metabolic processes. The interactions of biological processes and site mineralogy result in changes to alkalinity and pH that can lead to incomplete reductive dechlorination resulting from suboptimal pH. Understanding these interactions allows for strategies to predict expected bioremediation outcomes and / or to mitigate incomplete reductive dechlorination.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Fermentation bacteria agent and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a fermentation bacteria agent and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing unsterilized cabbage stems, orange peels and wheat bran according to the weight ratio of (0.8-1.2):(1.5-1.9):(0.3-0.5), and adding water to wet the mixture, thereby obtaining a culturing substrate; (2) inoculating Aspergillus niger, Trichoderma koningii and wheat koji into the culturing substrate to be stirred evenly; and (3) carrying out a stationary culturing, thereby obtaining the fermentation bacteria agent. The invention further provides the fermentation bacteria agent obtained by utilizing the preparation method and the application thereof in the production of a cellulose compound enzyme system. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that microbes for producing enzyme are tamed by utilizing the natural bacteria strains on the unsterilized carriers, so that the obtained fermentation bacteria agent is stable in microbial ecology and is capable of performing a diastatic fermentation on a cellulose substrate to produce the cellulose compound enzyme system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microbe archaea species, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107130030AUniform brightnessSpecies-specificMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a special specie DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microbe archaea in the denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis (DGGE) molecule detection of coal geology environment microbe florae, and belongs to the field of molecular microbial ecology. The DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microbe archaea species is composed of a DNA fragment a with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.1, a DNA fragment b with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.2, a DNA fragment c with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.3, a DNA fragment d with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.4, a DNA fragment e with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.5, a DNA fragment f with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.6, a DNA fragment g with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.7, and a DNA fragment h with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.8.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Magnetization slow-release fertilizer capable of improving soil microbial ecology and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105461443APromote photosynthesisPromote growth and developmentCalcareous fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersEggshellPotassium
The invention discloses a magnetization slow-release fertilizer capable of improving soil microbial ecology and a preparation method thereof. The magnetization slow-release fertilizer capable of improving the soil microbial ecology is made from raw materials with parts by weight: egg shells 50-70, fulvic acid potassium 26-29, ammonium bicarbonate 23-26, furfural residues 260-270, grass carbon 190-210, sodium hydrogen sulfite 8-14, fly ash 100-110, pyrite ash 80-90, cassava starch 26-30, calcium acetate 4-8, composite bacterial strains 13-17 and moderate water. The magnetization slow-release fertilizer capable of improving the soil microbial ecology adds various magnetotactic microorganisms, various different kinds of beneficial magnetotactic microorganisms also exist in soils simultaneously, the magnetization slow-release fertilizer capable of improving the soil microbial ecology can affect activity of the beneficial magnetotactic microorganisms through magnetization of fertilizers by adopting organic humus in the fertilizers as a nutrient source, improves activity of proteins and enzymes, and enhances activity of microorganisms, thereby promoting organic matters in the soils to resolve, and improving the content of absorbable nutrients of crops.
Owner:ANHUI HUACHUANG MODERN AGRI TECH
Reagent kit and testing method for rapidly evaluating whether intestinal microecology of human body is unbalanced
InactiveCN103045748ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHuman bodyFluorescence
The invention relates to the field of microbial ecology, and aims at providing a reagent kit and a testing method for rapidly evaluating whether intestinal microecology of a human body is unbalanced. The reagent kit detects a level ratio of bifidobactirium to enteric bacilli in feces by a relative fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique, and then evaluates the unbalance degree of the intestinal microecology. The method comprises the steps that a bifidobactirium and enteric bacilli quantitative detection primer with best specificity and high amplification efficiency is selected; the DNA yield (deoxyribose nucleic acid) of bifidobactirium and enteric bacilli is calculated; microorganisms are subjected to total DNA extraction; relative quantitative detection of bifidobactirium DNA and enteric bacilli DNA in total DNA is conducted; an X value is calculated through a formula; and the unbalance degree of the intestinal microecology is evaluated according to the X value. The reagent kit optimizes bifidobactirium and enteric bacilli quantitative detection conditions, has the advantages of high speed, good accuracy and high sensitivity, can be used for clinically evaluating a therapeutic effect of a microecological modifier, and can also be used for guiding administration of drugs for clinical digestive system dysfunction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for analyzing microbial community structure of fermented grain
InactiveCN103031384AEasy to operateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementCommunity structureGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a method for analyzing a microbial community structure of a fermented grain, belongs to the technical field of microbial ecology and aims to provide the method for analyzing the microbial community structure of the fermented grain. The technical scheme of the invention is as follows: the method for analyzing the microbial community structure of the fermented grain comprises extracting genomic DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), expanding PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) of 16S rDNA, carrying out electrophoresis on DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis), recycling a single strip of the 16S rDNA which is subjected to electrophoresis, and analyzing the recycled strip, wherein the step of analyzing the recycled strip comprises the following steps: establishing a clone bank by using the recycled 16S rDNA which is subjected to electrophoresis, carrying out enzyme segmentation, testing the sequence and carrying out comparison and analysis on GenBank so as to obtain the community structure information of the microorganism in the fermented grain. The method provided by the invention is widely applied to microbial community structure analysis and change regulation research in the white wine brewing process.
Owner:LUZHOU PINCHUANG TECH CO LTD
Method for simultaneously identifying short-cut denitrifying bacteria and triclosan degrading bacteria based on DNA stable isotope nucleic acid probe technology
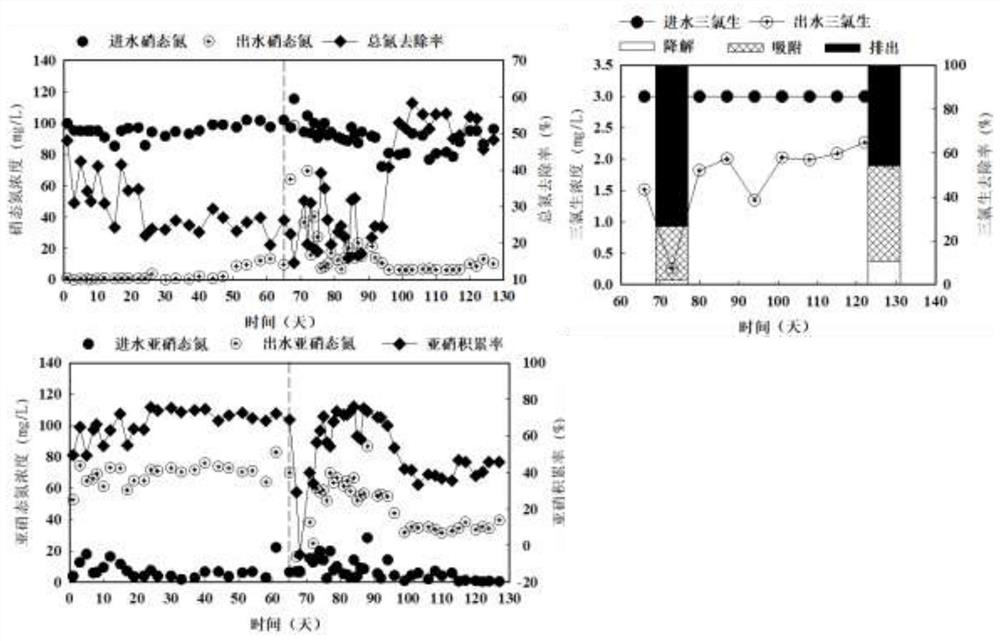
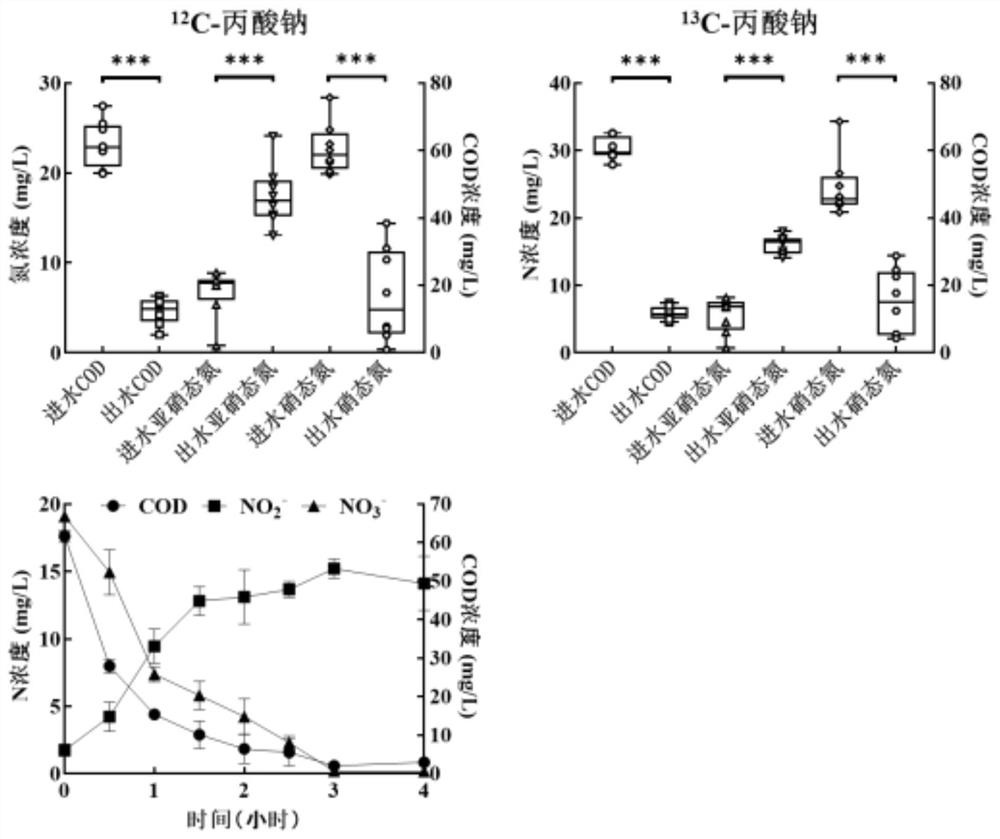
ActiveCN112608981AIncrease the distribution ratioImprove identification rateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTriclosanMicrocosm
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously identifying short-cut denitrifying bacteria and triclosan degrading bacteria based on a DNA stable isotope nucleic acid probe technology, and belongs to the technical field of sewage biological treatment technologies and microbial ecology. The method comprises the steps of (1) starting a short-cut denitrification system based on granular sludge and biologically removing triclosan in the system; (2) carrying out 13C-propionic acid sodium and 13C-triclosan isotope microcosm experiments; (3) separating heavy-layer DNA by adopting an ultra-high-speed centrifugation method based on a cesium chloride density gradient solution; and (4) carrying out DNA marking degree evaluation and flora structure analysis. According to the method for simultaneously identifying active short-cut denitrifying bacteria and triclosan degrading bacteria in the short-cut denitrification granular sludge system based on the DNA stable isotope nucleic acid probe technology, a microorganism capable of simultaneously realizing short-cut denitrification and triclosan removal can be explored and disclosed, and a theoretical support is provided for an actual process of removing triclosan by short-cut denitrification in a sewage treatment plant.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for extracting metagenome DNA of compost and application thereof in identifying denitrifying bacteria
InactiveCN102533736AEfficient extractionEfficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDecompositionNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a method for extracting metagenome DNA of compost and application thereof in identifying denitrifying bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: (1), a compost sample is subjected to physical splitting decomposition in DNA extraction solution; (2), lysozyme is added into the mixture; (3), protease K is added into the mixture; (4), SDS water solution is added into the mixture; (5), liquid supernatant is collected by centrifugation; (6), DNA extraction liquid and SDS water solution are added into sediment obtained in the step (5), then liquid supernatant is collected by centrifugation; (7), the liquid supernatant obtained in the step (5) and the liquid supernatant obtained in the step (7) are mixed; (8), phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol is extracted; and (9) the liquid supernatant obtained in the step (8) and isopropyl alcohol are blended, then sediment, which is metagenome DNA of compost, is collected. The method for extracting metagenome DNA of compost and the application thereof in identifying denitrifying bacteria are of great application value for the research on the varieties of bacteria (especially the variety of denitrifying bacteria) in the compost samples produced by different fermentation times. And effective technical support is provided for the research and the application of the compost as well as the research on molecular microbial ecology.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
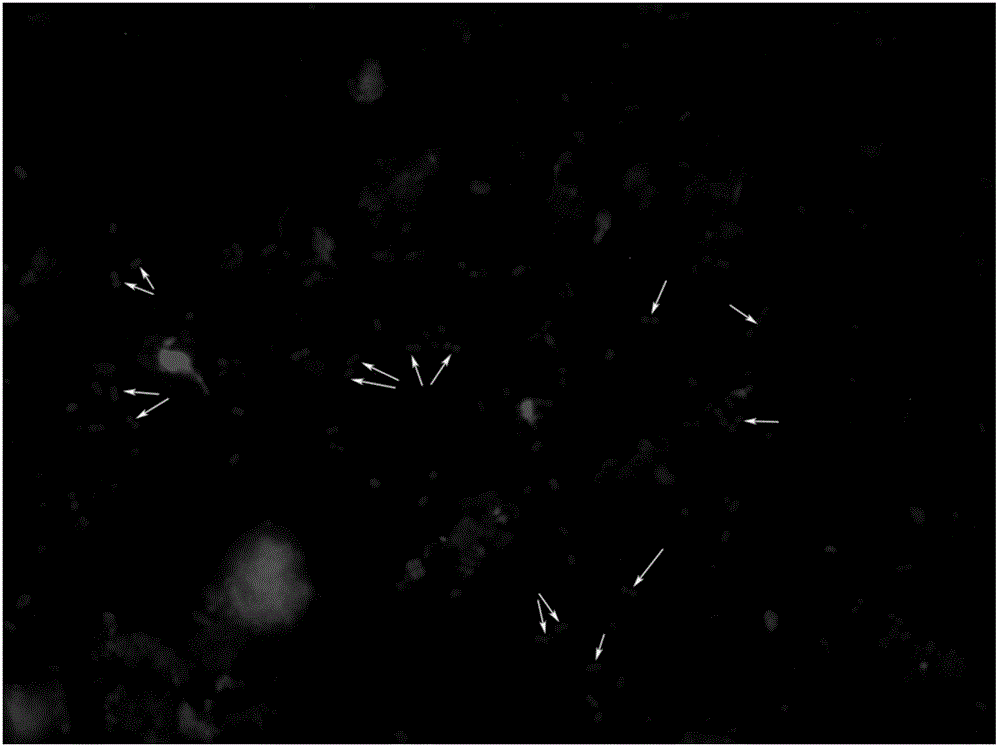
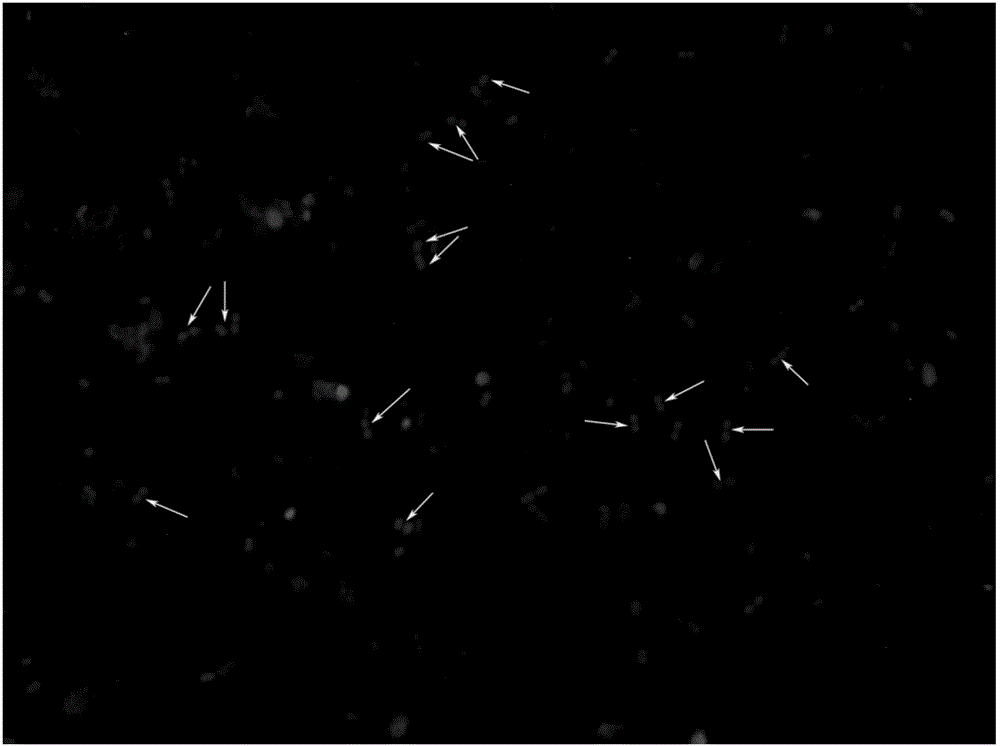
Method for rapidly detecting proteolysis bacteria in human excrement
InactiveCN105886595AReduce labor intensityThe operation process is simple and convenientMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesFeces
The invention relates to a method for rapidly detecting proteolysis bacteria in human excrement and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The method completely adopts a culture-free molecular microbial ecology without separating strains and can conduct calibration and tracking on proteolysis bacteria in the human intestinal tract in an in-situ state. The method uses the intestinal tract proteolysis bacteria as a target serving as a long-term directional human indicator for health intervention and provides a data support for definition and diagnosis of the stability of human intestinal tract microbial functional flora. In addition, by means of detecting and calibrating the intestinal tract proteolysis bacteria, the relation between the physiological differences of individuals and the response to host energy metabolism can be found. Compared with existing pure culture methods, the method has the advantages that the method is rapid, low in cost and simple and convenient to operate, does not require special personnel training, has no special requirement for detection places, experimental results are accurate, and related data can be quickly provided for a diagnosis worker.
Owner:夏云
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com