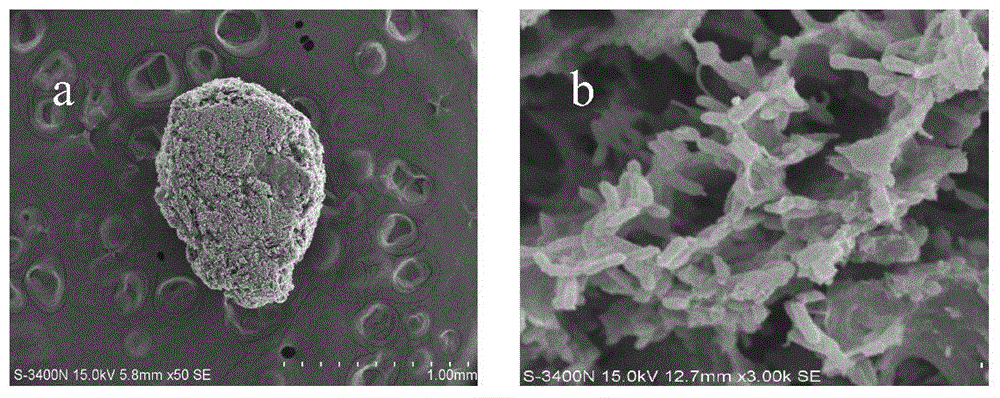
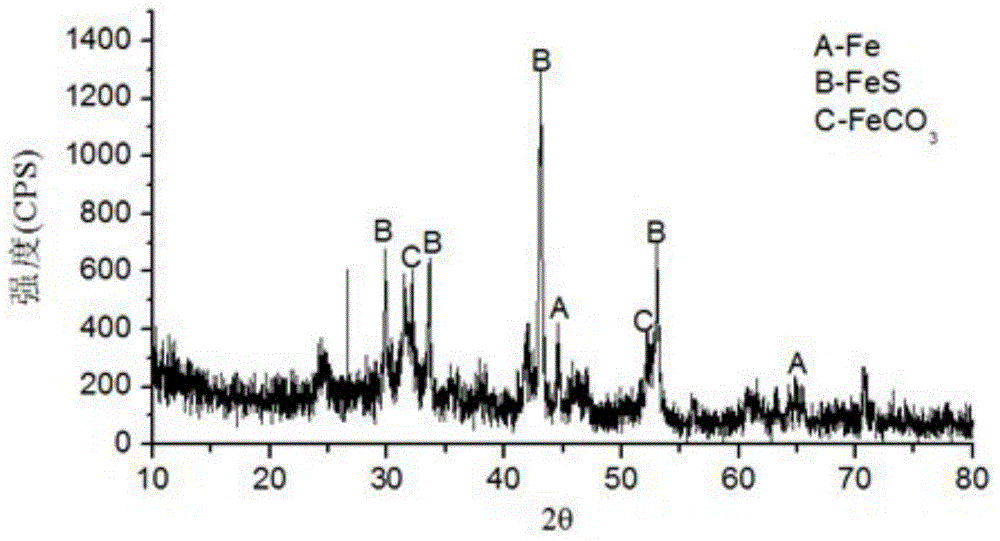
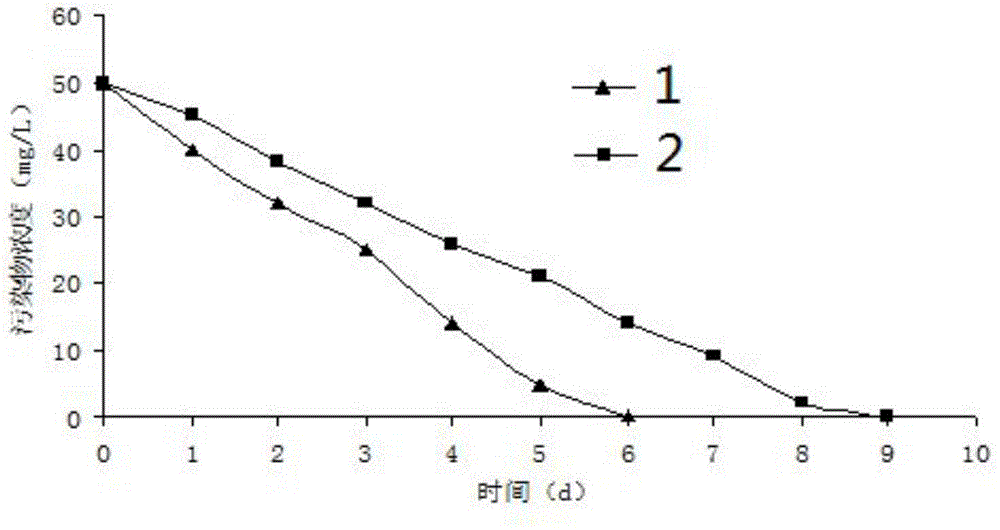
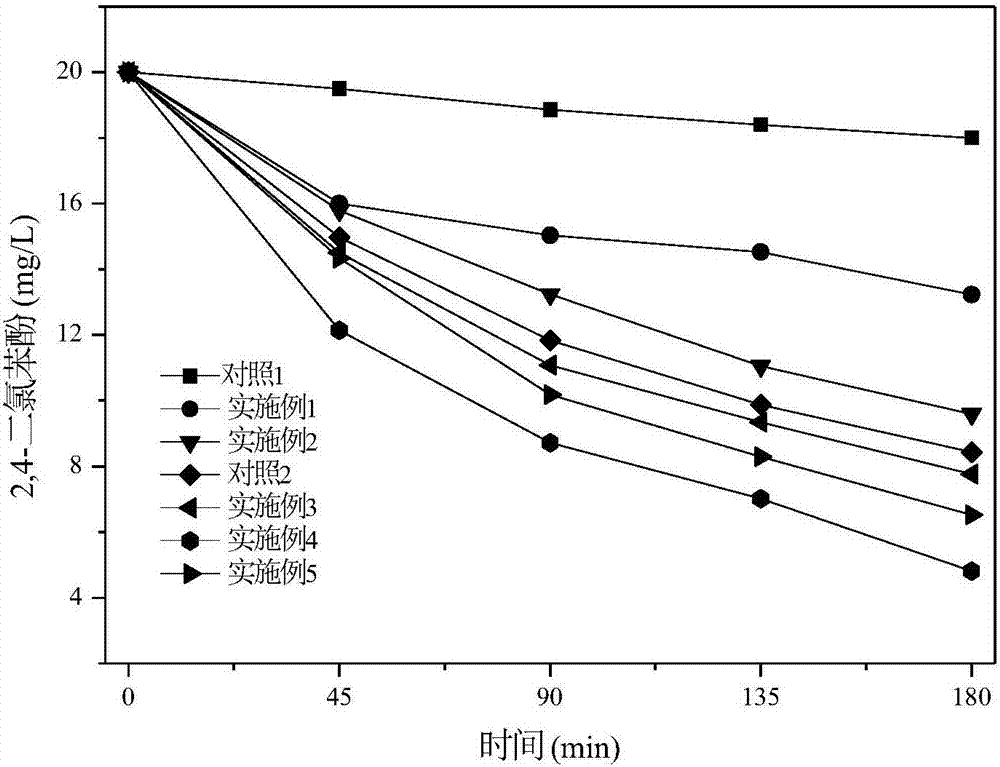
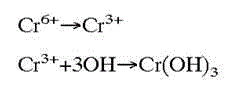Patents
Literature
84 results about "Reductive dechlorination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
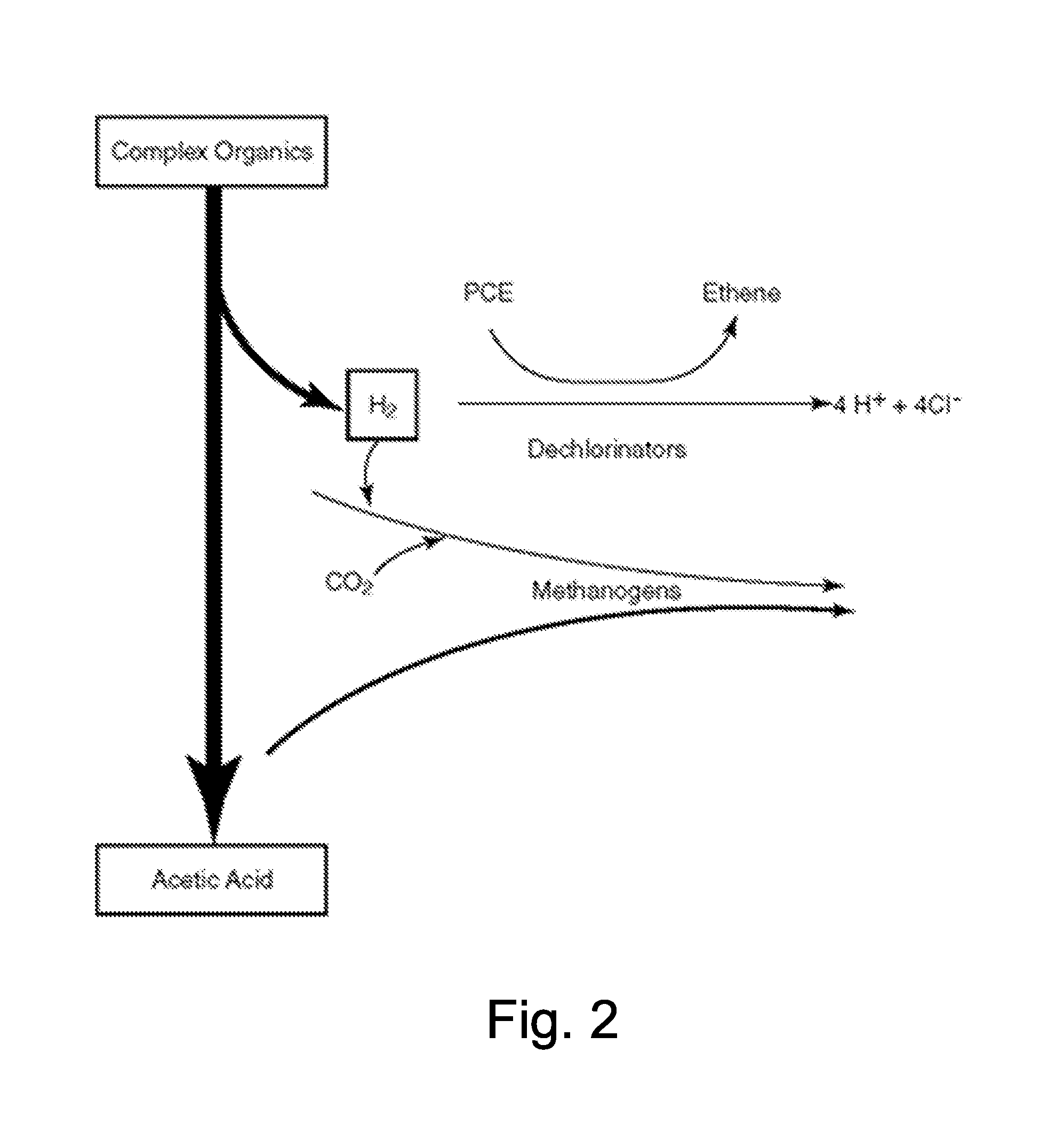
Reductive dechlorination is degradation of chlorinated organic compounds by chemical reduction with release of inorganic chloride ions by reductive dehalogenases.
Method for in-situ bioremediation of pollution caused by chlorohydrocarbon of underwater
InactiveCN102976490AReliable in situ repairMaintain securityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectron donorIn situ bioremediation
The invention discloses a method for in-situ bioremediation of pollution caused by chlorohydrocarbon of underwater, which specifically comprises a coupling process of anaerobic reductive dechlorination and aerobiotic oxydative degradation. An anaerobic reaction area and an aerobiotic reaction area are established in the front and back of a chlorohydrocarbon pollution area along the flowing direction of underwater in a zone of saturation. Poly-chlorohydrocarbon (trichloro or tetrachloro) in the anaerobic reaction area is quickly reduced and dechlorinated to low chlorohydrocarbon (monochloro or bichloro), the low chlorohydrocarbon is transferred to the aerobiotic reaction area and oxidized and degraded to products such as carbon dioxide. The anaerobic reaction area is realized by providing electron donor materials, a deoxidant and a reducer through the injection of an injection well, while the aerobiotic area is realized by aeration toward underground water.
Owner:TIANJIN ECOLOGY CITY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
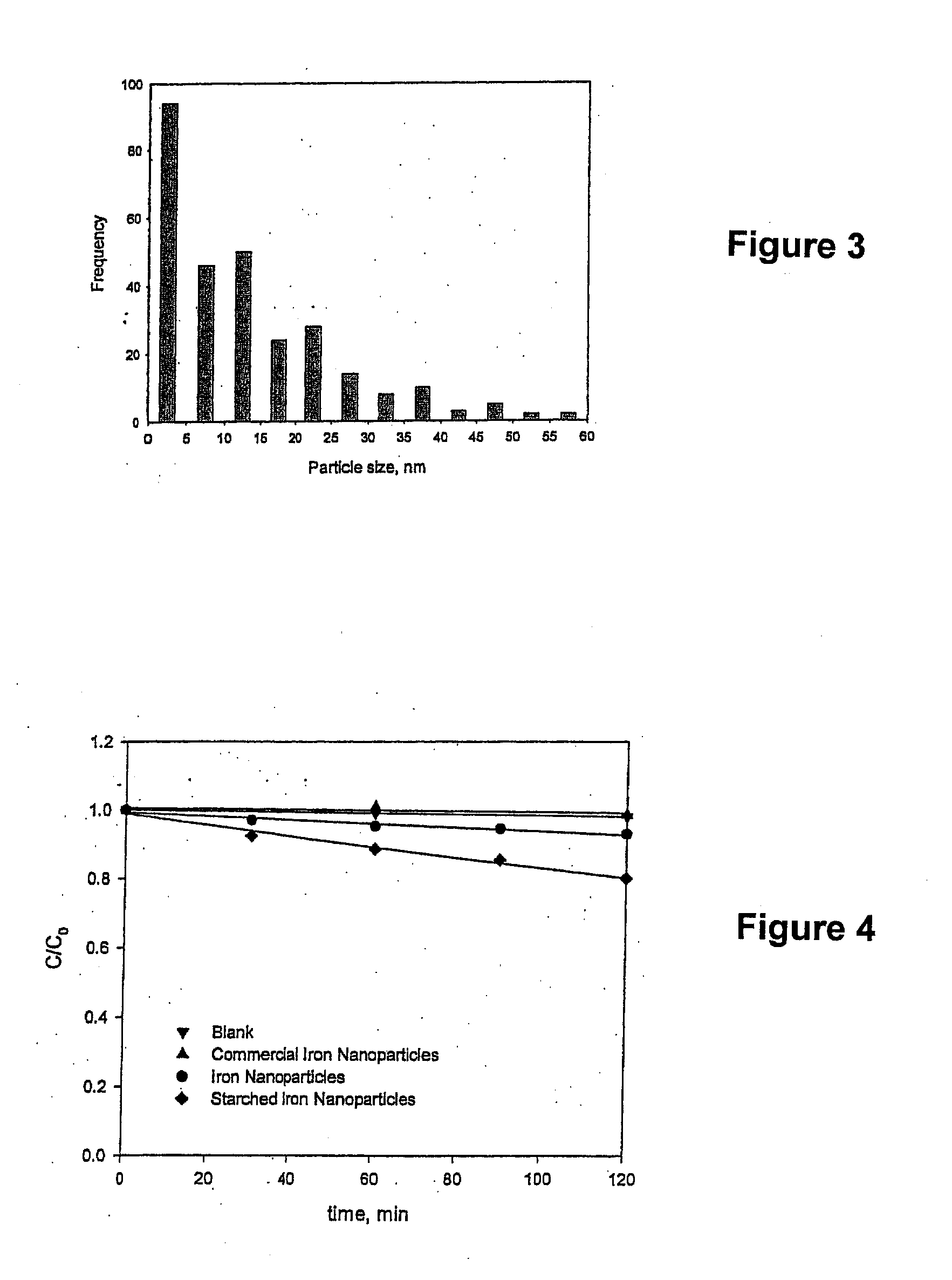
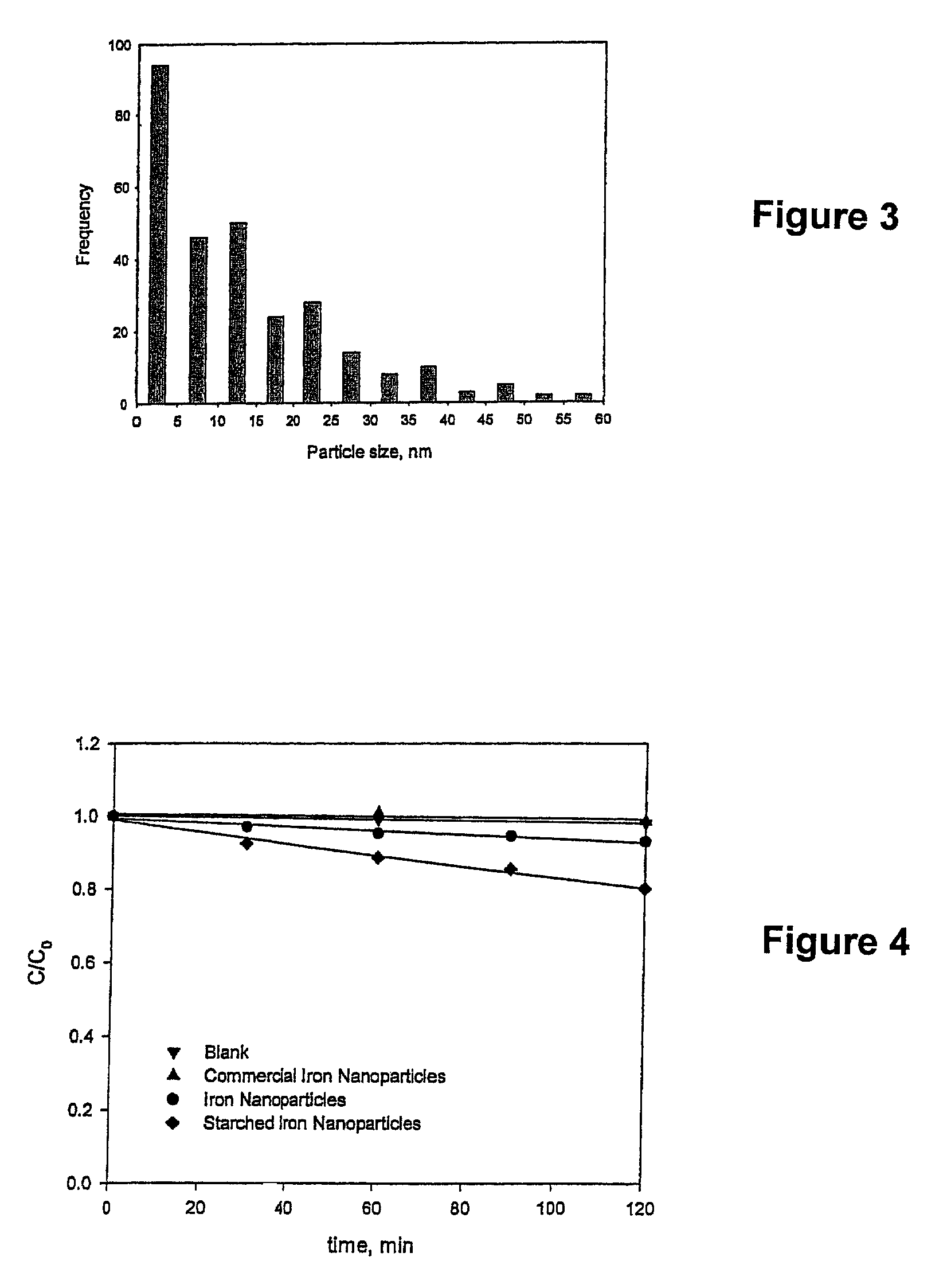
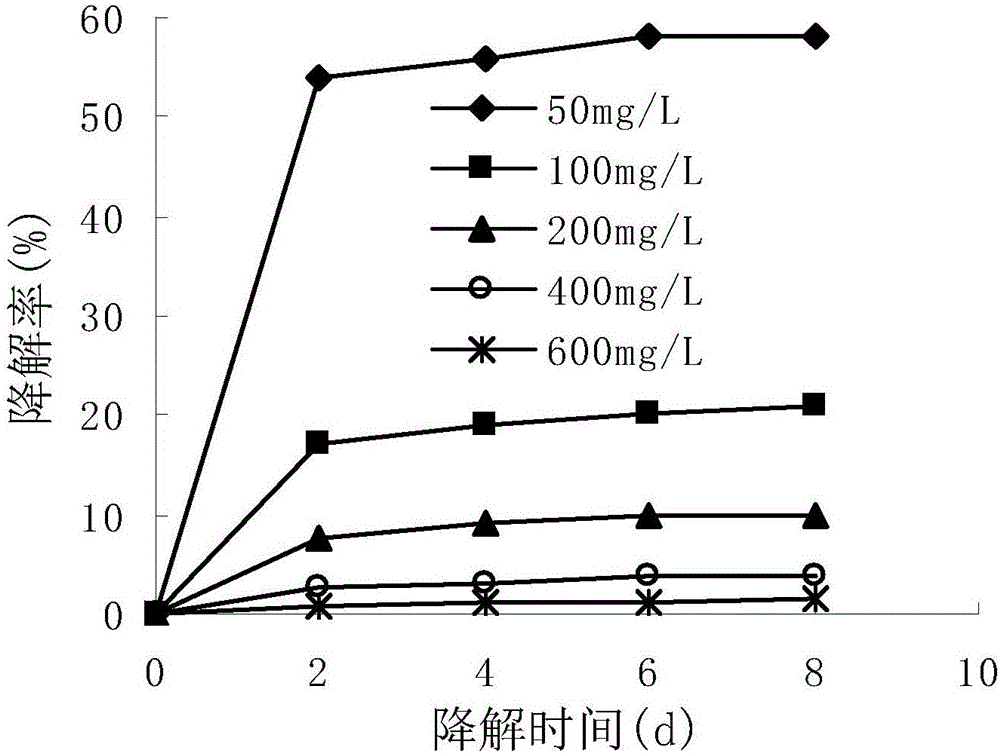
Preparation and Applications of Stabilized Metal Nanoparticles for Dechlorination of Chlorinated Hydrocarbons in Soils, Sediments, and Ground Water
InactiveUS20080190865A1Low costIncrease ratingsWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationCelluloseChemical reaction
A stabilized, chemically reactive, metallic nano-material effective for degradation of chlorinated organic compounds in soils, sediments and groundwater. The nano-material is composed of a magnetic metal nanoparticle and a carbohydrate stabilizer bound to the nanoparticle. The preferred metal nanoparticle is iron and the preferred carbohydrate stabilizer is either a starch or a water soluble cellulose such as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. The nanoparticle may be either mono-metallic, bi-metallic or multi-metallic in nature, but is preferably bi-metallic wherein it is coated with a secondary catalytic metal coating, preferably palladium. A method of making the metallic nano-material is further disclosed wherein a solution of the metal nanoparticle and carbohydrate stabilizer is prepared, and the nanoparticle is then reduced under inert conditions. A process for reductive dechlorination of chlorinated organic compounds is also disclosed wherein the reduced magnetic metal nanoparticle is prepared, and then contacted with a chlorinated organic compound to dechlorinate the compound. Preferably, the nano-material is injected into a site such as soil subsurface or groundwater contaminated with a chlorinated organic compound to provide in-situ dechlorination.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Systems and methods for microbial reductive dechlorination of environmental contaminants
ActiveUS20100059436A1Improve solubilityHigh activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesMicroorganismIn situ bioremediation
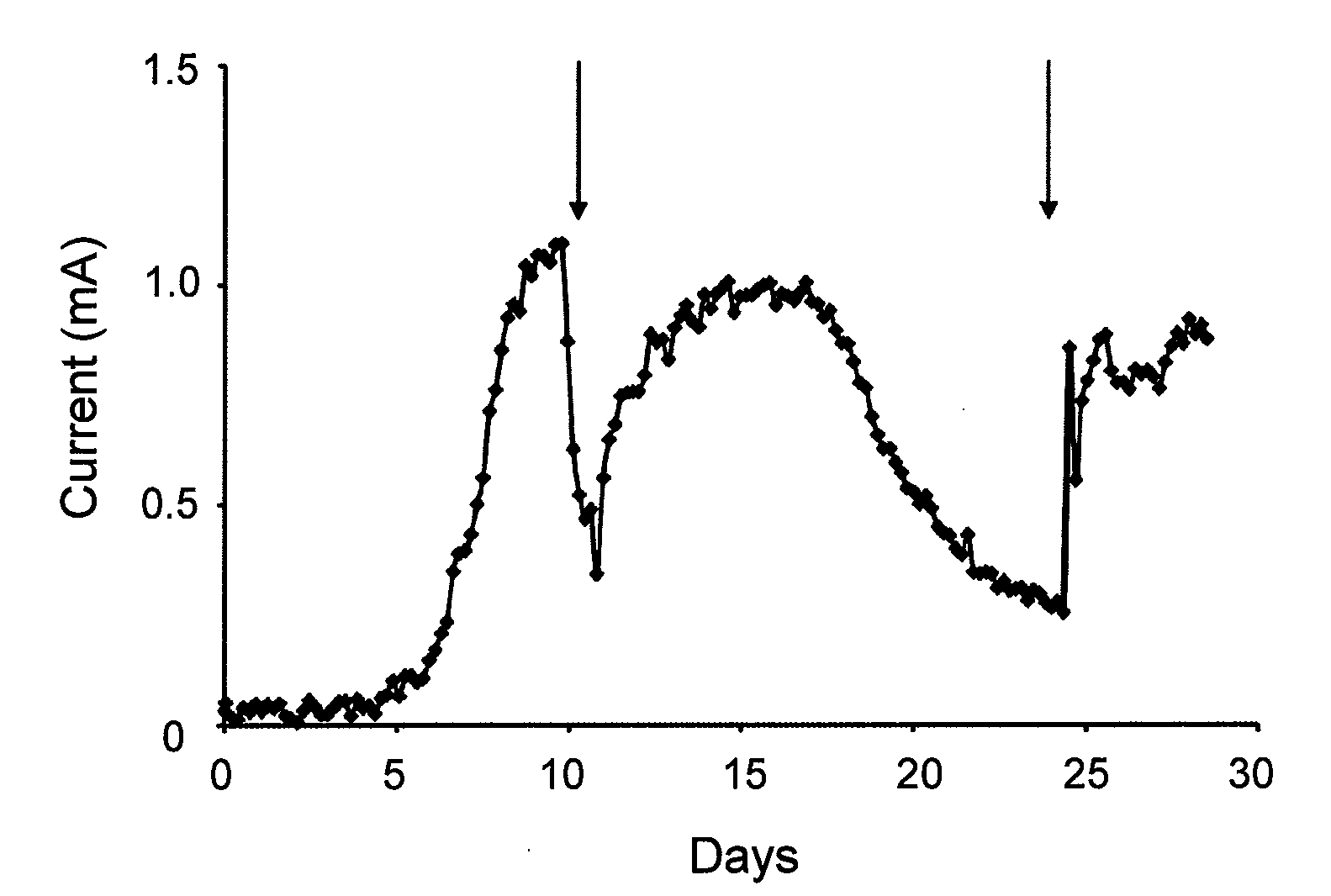
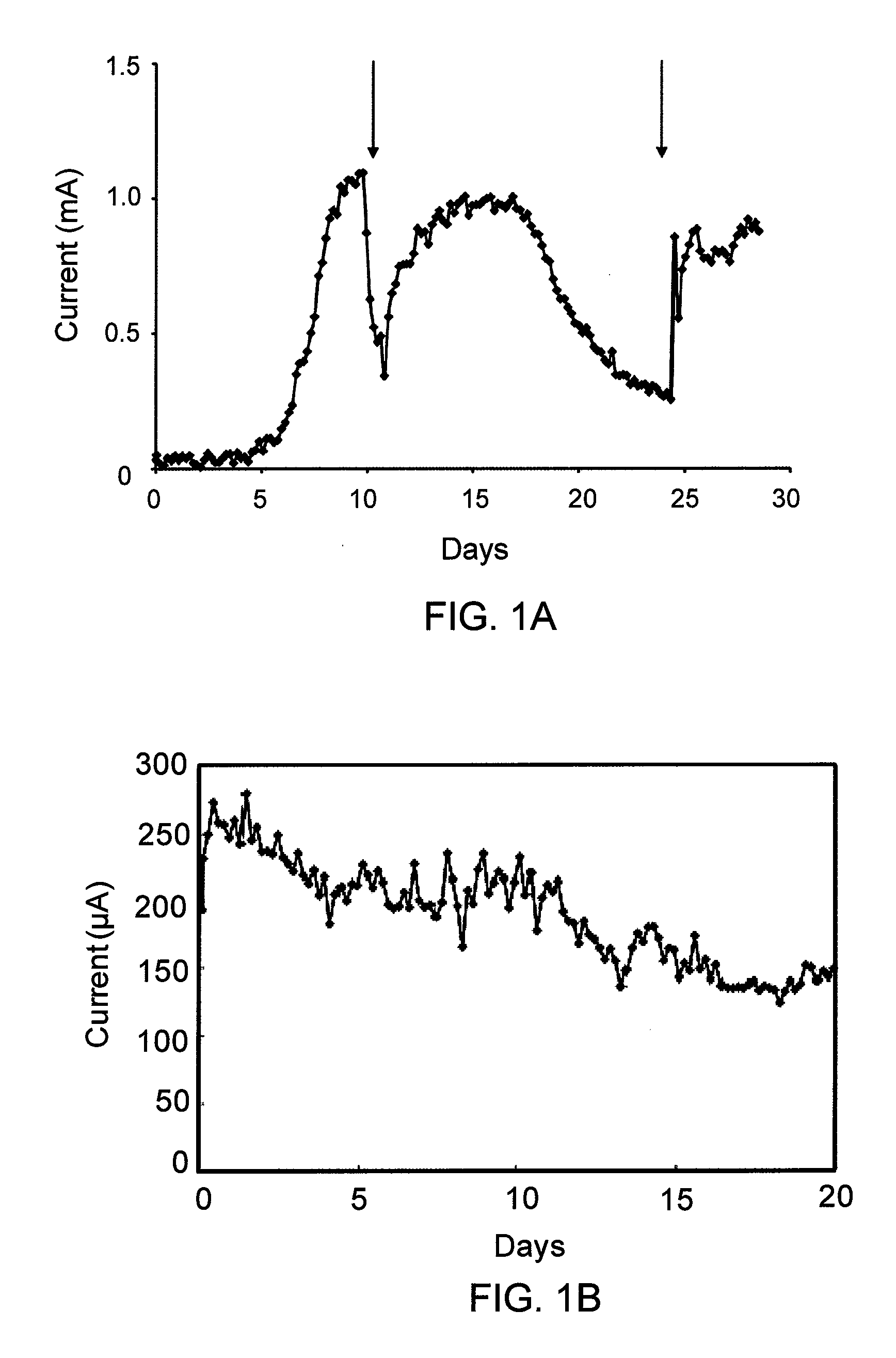
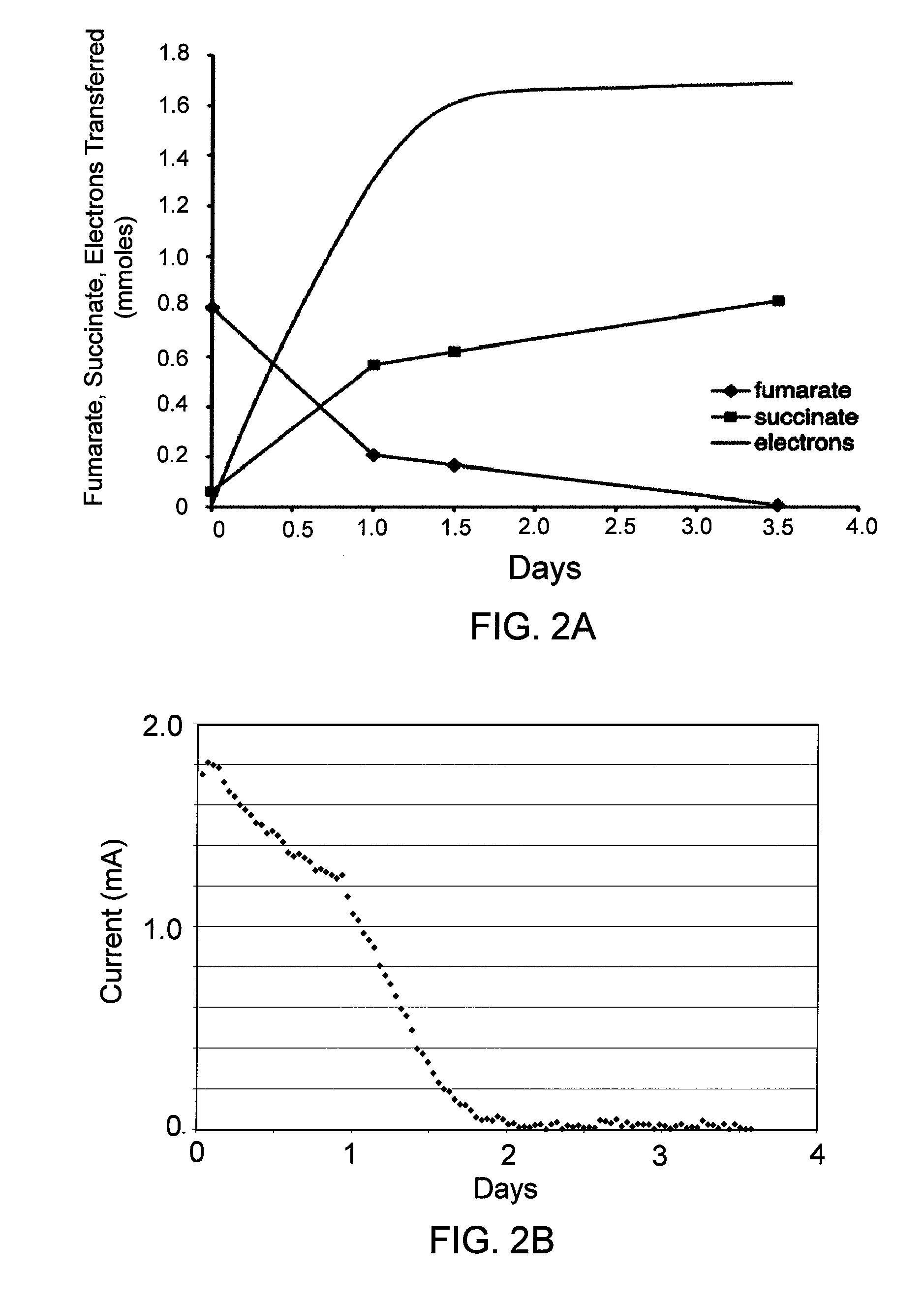
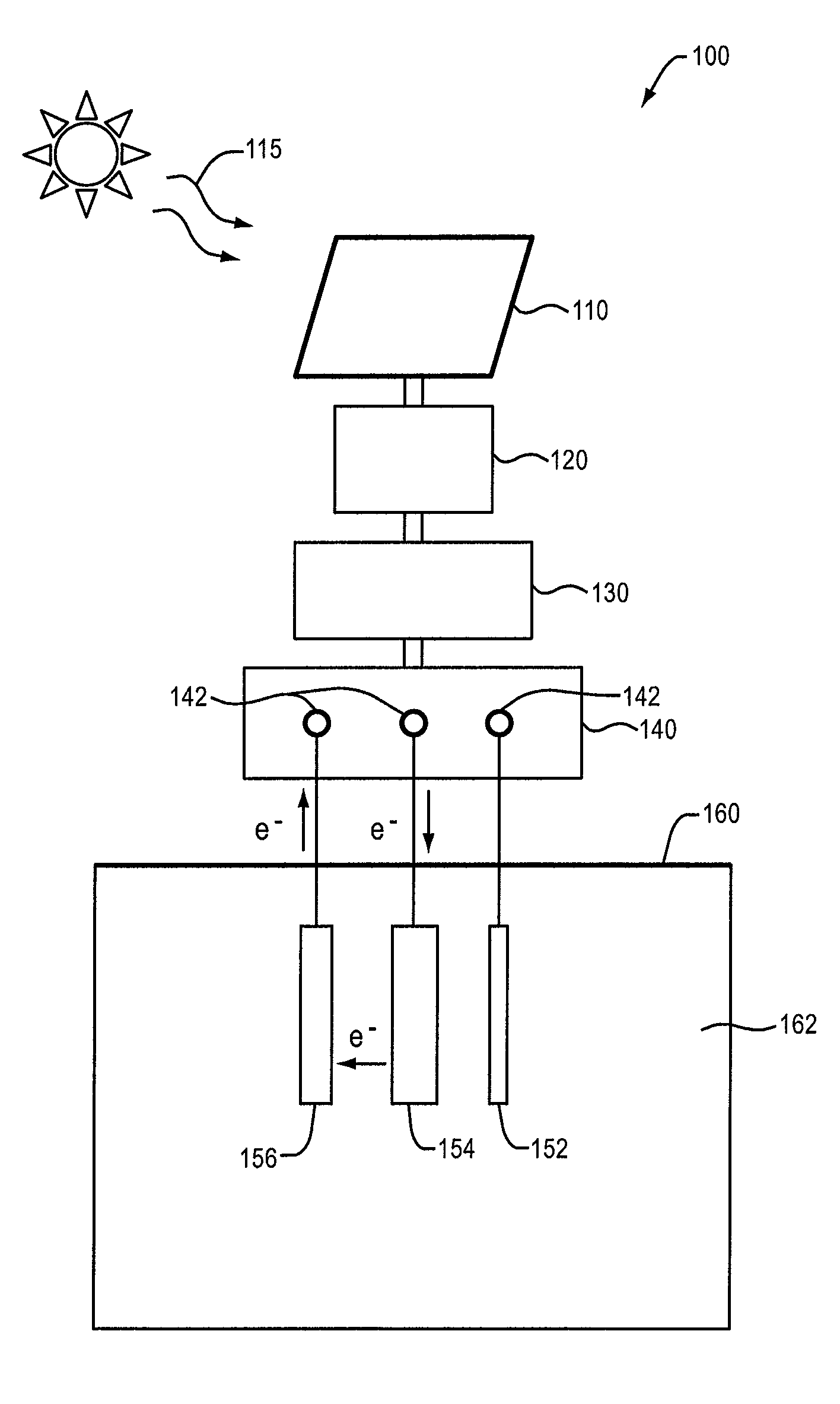
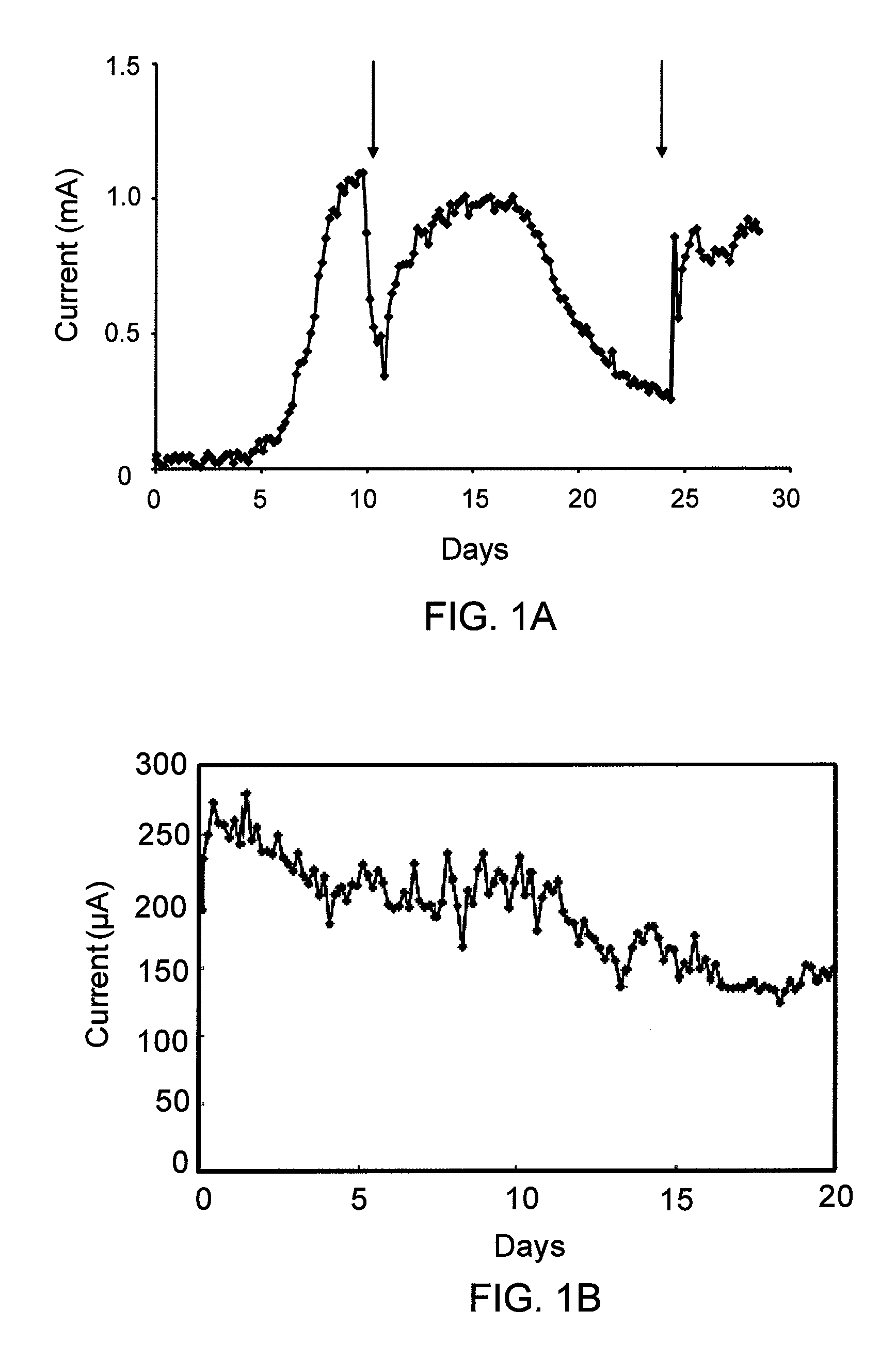
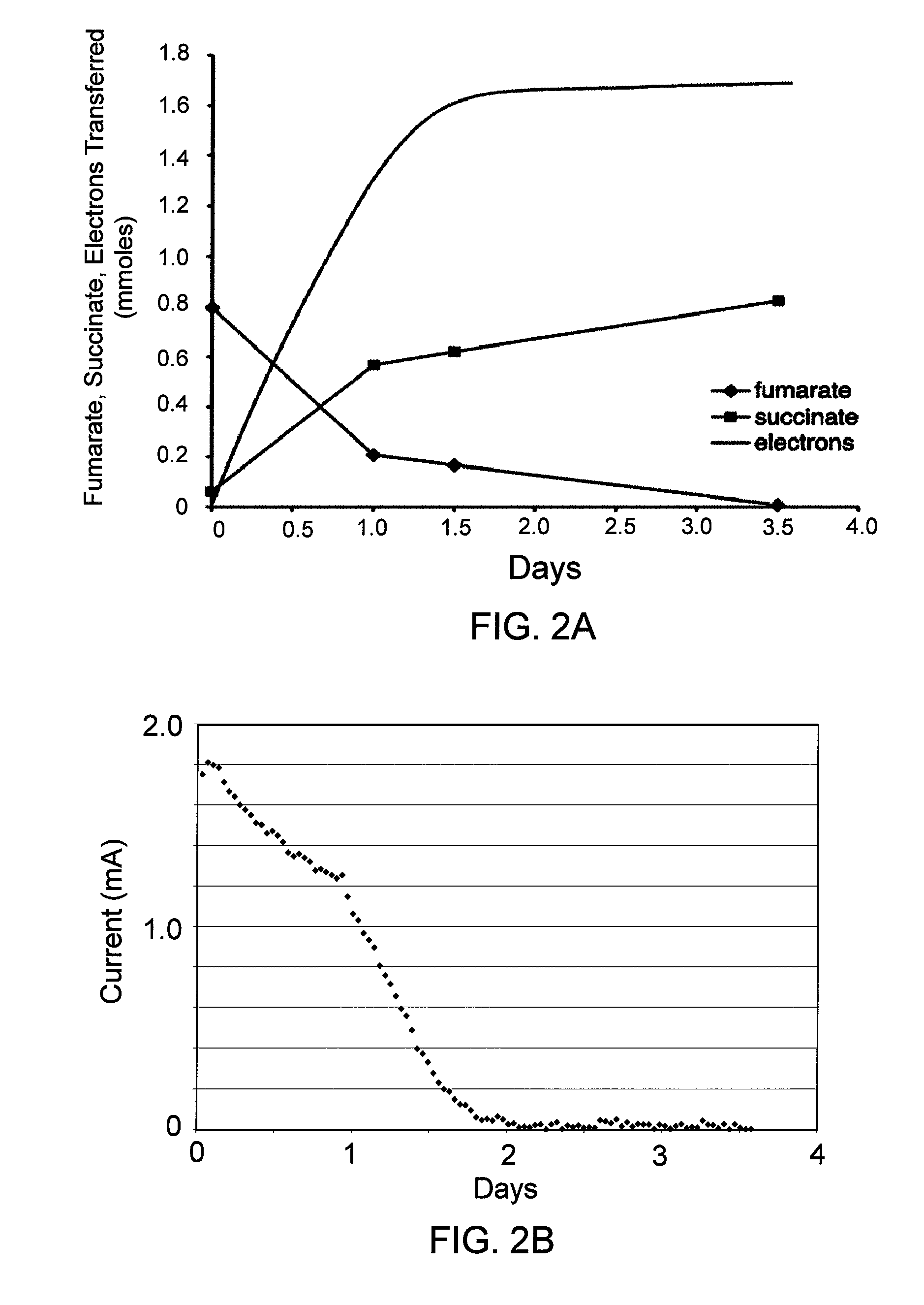
In preferred embodiments, bioremediation systems are provided that comprise electricigenic microbes that use electrons provided directly from the anode of an electrical bioremediation system to carry out reductive dehalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants, including chlorinated solvents. The present invention also provides methods of performing in situ bioremediation of halogenated solvents in groundwater or soil through the use of the provided systems.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Method for remedying OCPs contaminated soil by combining zero-valent iron composite material with microorganisms
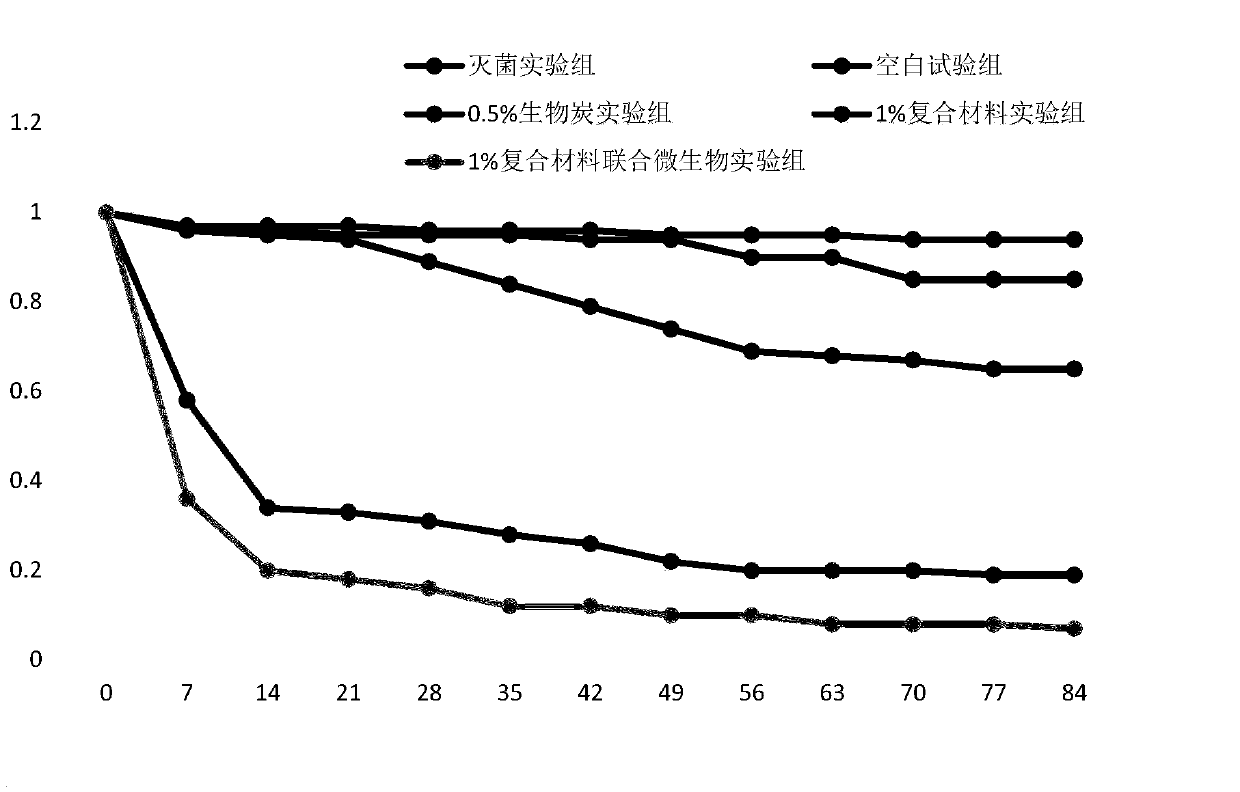
The invention discloses a method for remedying organo-chlorine pesticide (OCPs) contaminated soil by combining a zero-valent iron composite material with microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a biomass material is taken, and biochar is prepared by means of the biomass material and serves as a nanometer zero-valent iron loaded material; by means of a liquid phase reduction method, a biochar loaded nanometer zero-valent iron material (BC / nZVI) is prepared; 2, specific degrading bacteria are screened and separated; 3, to-be-remedied soil is pretreated; 4, the to-be-remedied soil is treated. Accordingly, aiming at the damage of ZVI to the soil structure and soil environment and the defect of the microorganisms to OCPs degrading capability, the novel BC / ZVI compositematerial is combined with the microorganisms for remedying, the ZVI reductive dechlorination effect, the biochar adsorption and soil improvement effect and the microorganism degradation effect are fully utilized, and remedying on OCPs contaminated soil is achieved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Synthetic method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene
ActiveCN103193586BSimple processShort stepsPreparation by dehalogenationHexachlorobutadieneTetrachloroethylene
Owner:JUHUA GROUP TECH CENT
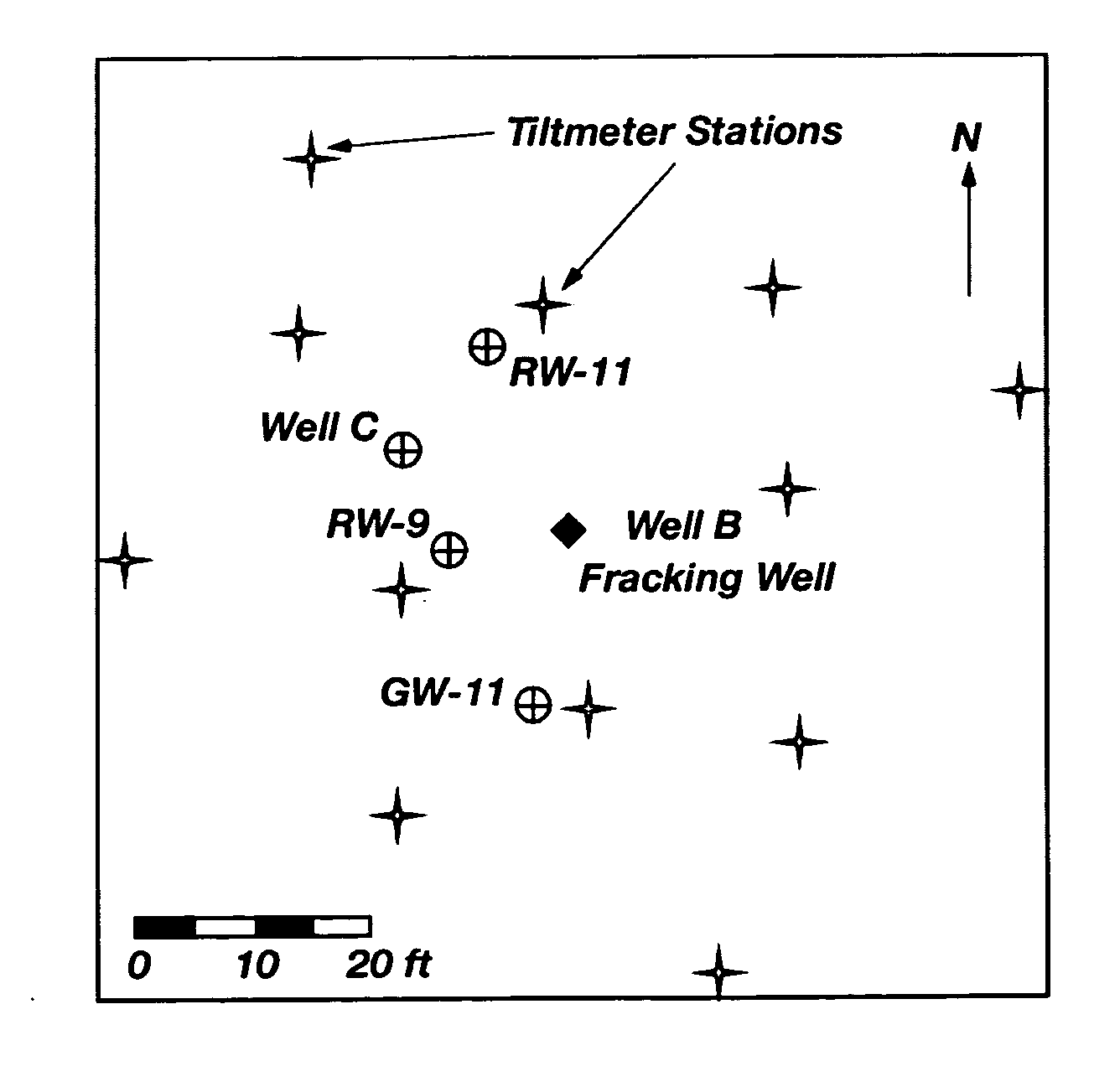
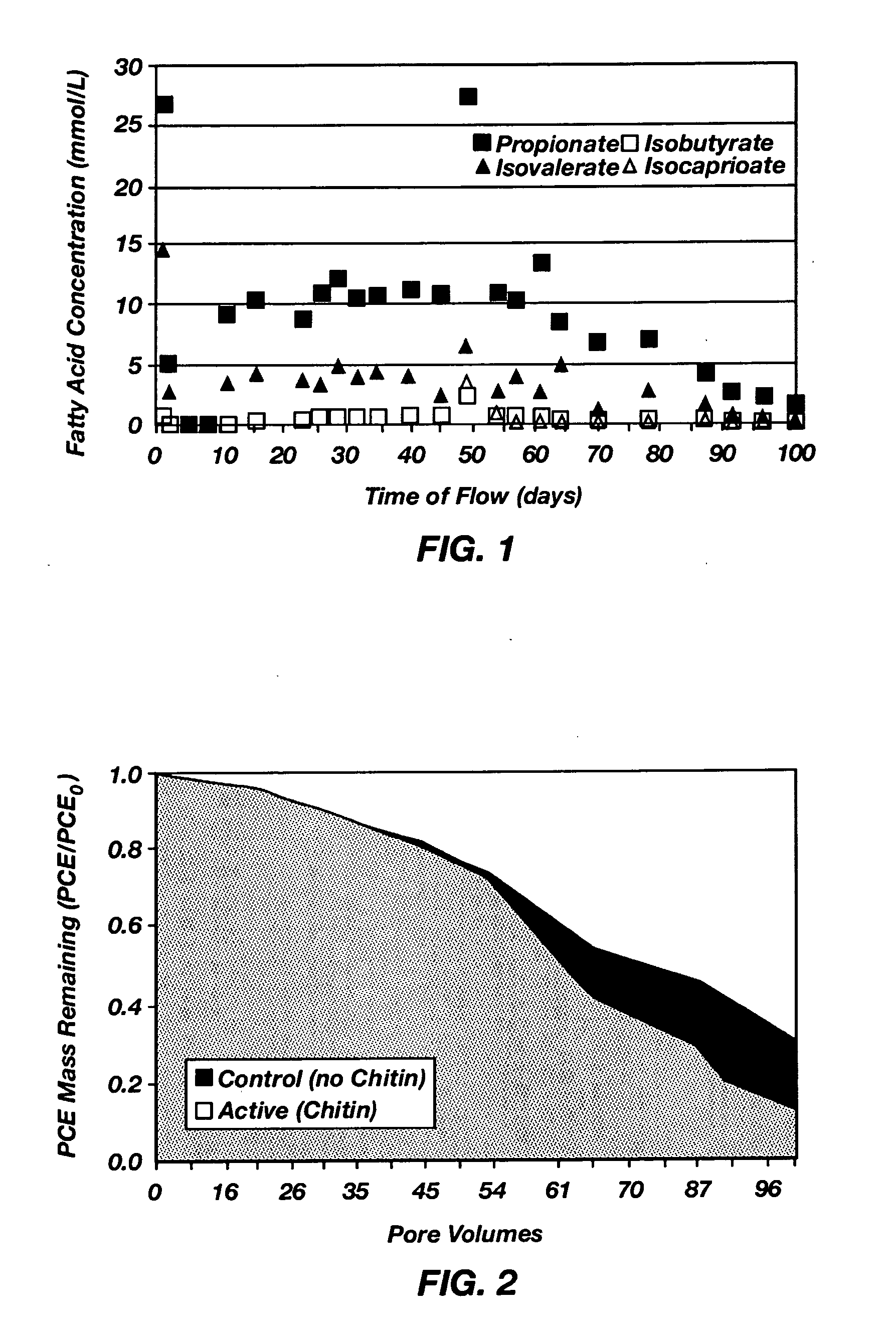
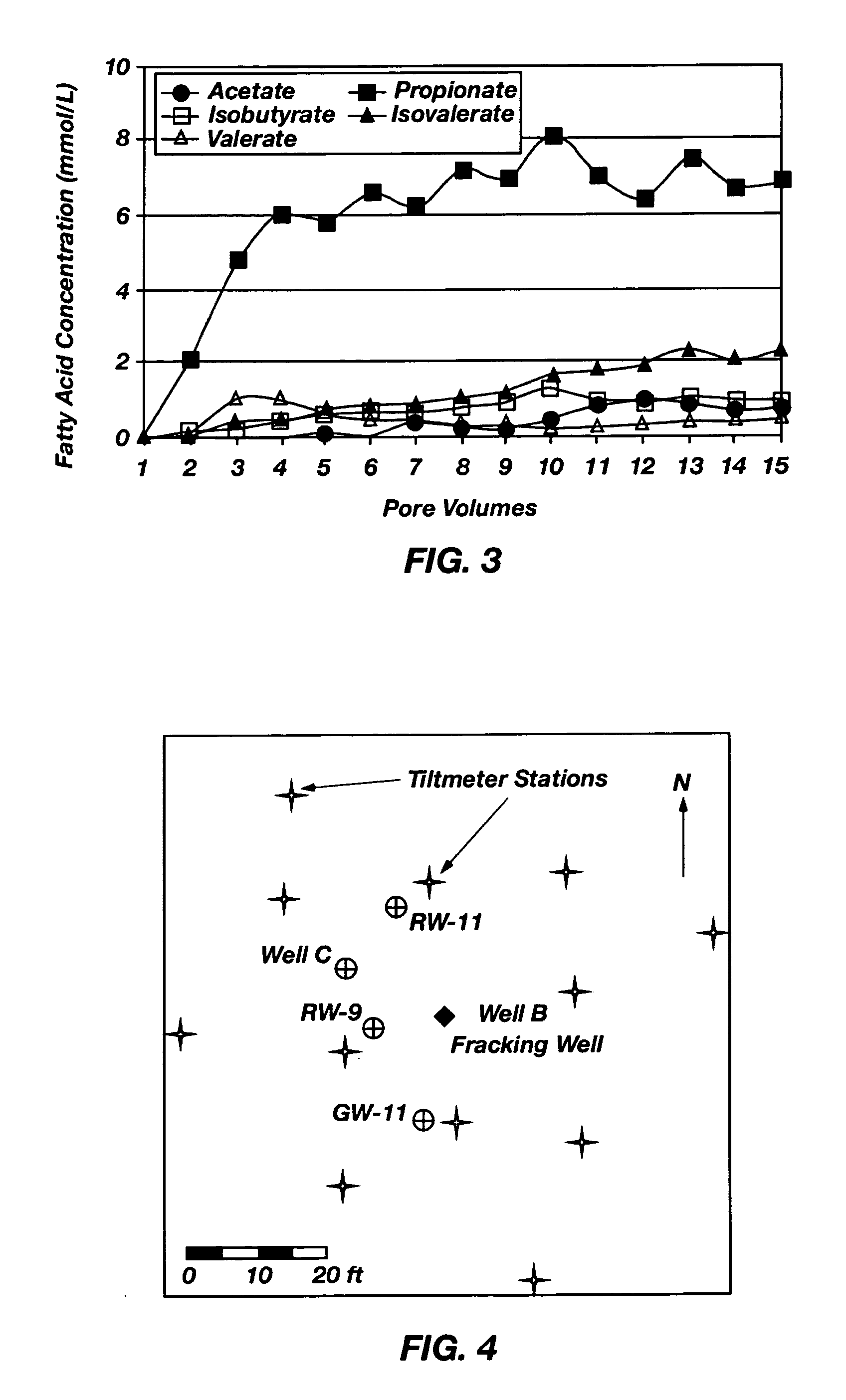
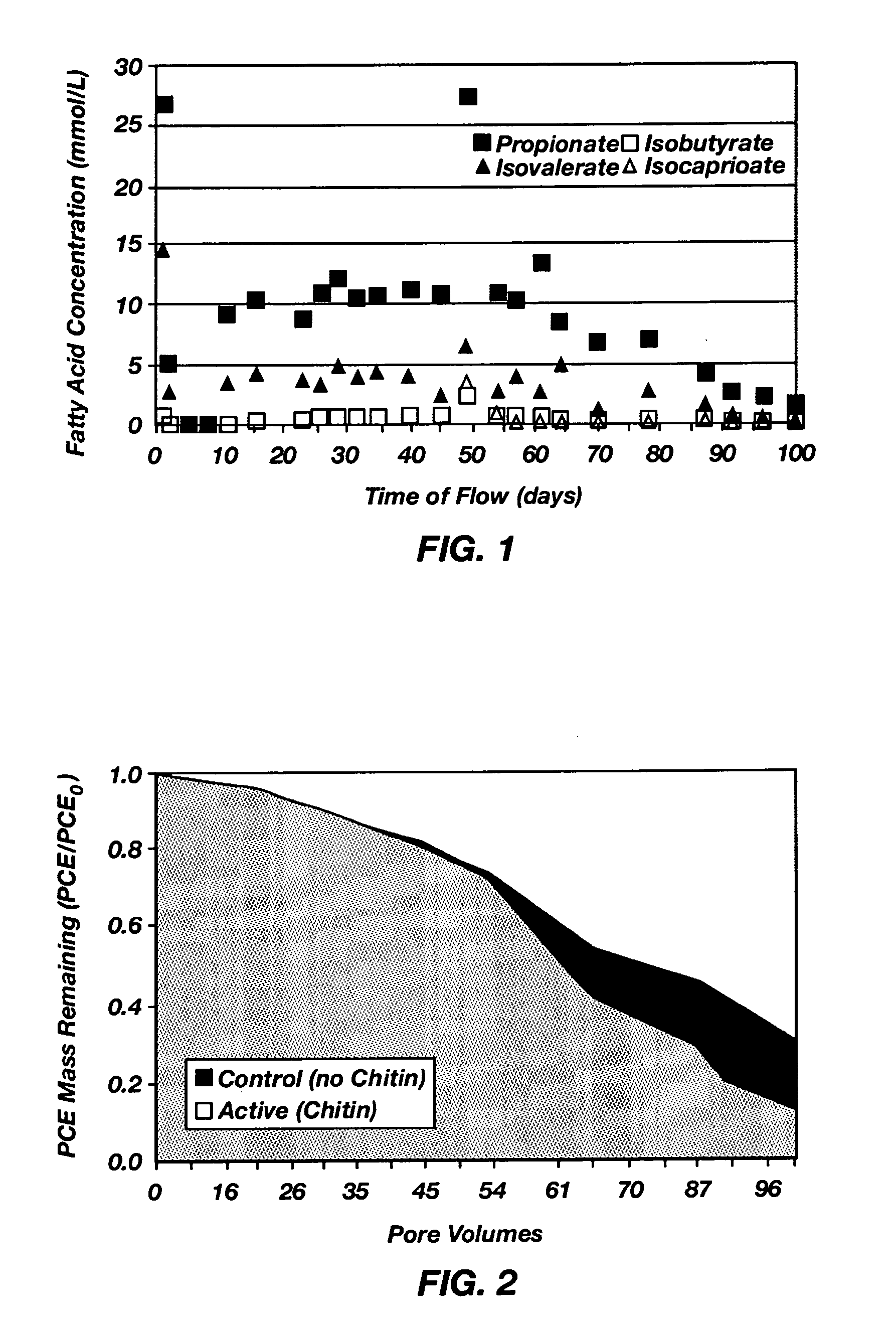
Emplacement of treatment agents using soil fracturing for remediation of subsurface environmental contamination
A method for treating contamination in subsurface formations includes fracturing the soil to produce a network of fractures in the formation and simultaneously injecting a slurry containing an optional proppant and a solid-phase or nonaqueous-phase treatment agent into the network of fractures. The proppant is for keeping the fractures open, and the treatment agent accelerates conversion of the contaminants into immobile or less toxic forms. Chitin is an illustrative solid-phase treatment agent, which functions as an electron donor for anaerobic reductive dechlorination mediated by dechlorinating bacteria.
Owner:SRP TECH
Systems and methods for microbial reductive dechlorination of environmental contaminants
ActiveUS8277657B2High activityFacilitating in situ bioremediationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesIn situ bioremediationSolvent
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Method for synthetizing 3,5-dichloroaniline
InactiveCN103508901AReduce pollutionWith sustainable developmentOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationO-nitrochlorobenzeneChlorobenzene
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing 3,5-dichloroaniline by using industrial production residues, namely meta-position oil, of p-nitrchlorobenzene and ortho-nitrochlorobenzene by two steps of chlorination and reductive dechlorination. The method adopts the following technical scheme: adding an organic solvent to nitrochlorobenzene meta-position oil as a raw material, directly producing a quintozene mixture by one-step chlorination under the effect of a catalyst, reacting for 0.5-10 hours under the condition of 10-180 DEG C, and then cooling to 30 DEG C; filtering out quintozene, and putting into an autoclave after washing into a neutral state by hot water; carrying out dechlorination reduction reaction under the effects of an organic solvent and the catalyst, wherein the reaction temperature is 60-200 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 1-20 MPa, and the reaction time is 1-20 hours; cooling to room temperature after the reaction is ended; leading in oxygen or air to stir after blowing off; filtering and distilling under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, so as to obtain the product 3,5-dichloroaniline, wherein the yield is 80-90%. Waste materials are changed into precious materials by a synthetic route adopted by the technology disclosed by the invention; the target of zero emission is achieved; the method has the advantages of sustainable development, energy conservation and consumption reduction, and small environmental pollution.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
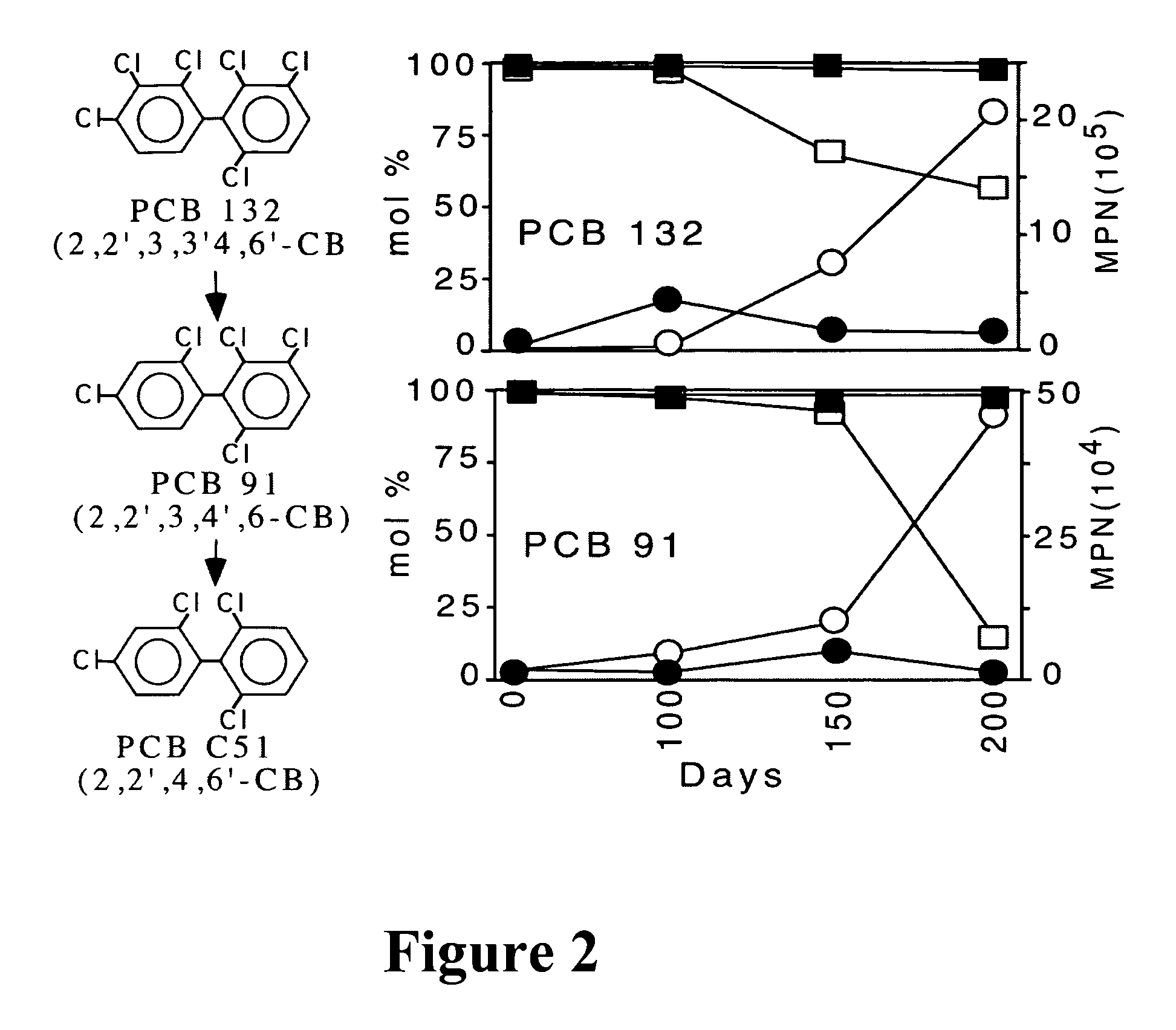
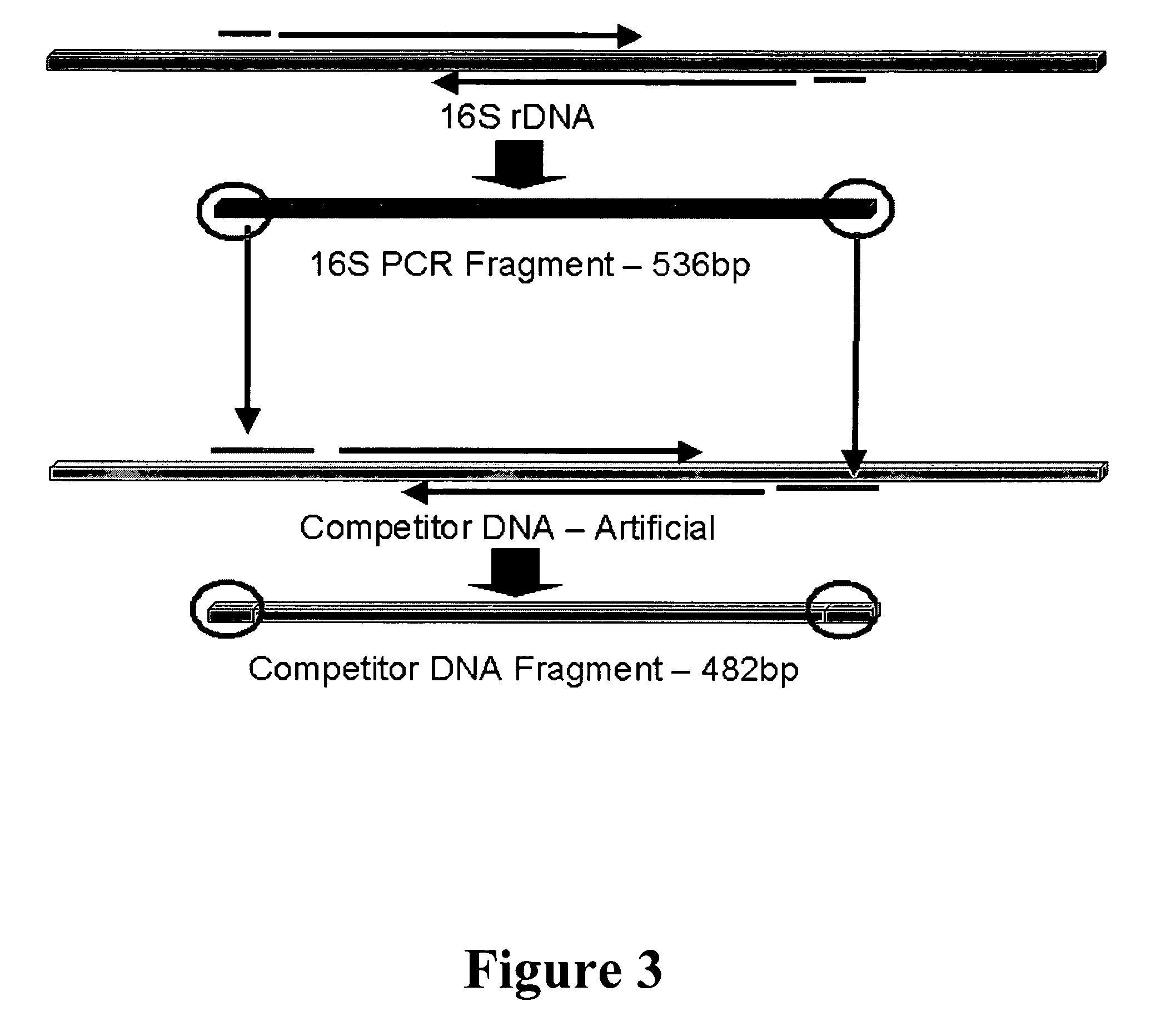
Gene probes for the selective detection of microorganisms that reductively dechlorinate polychlorinated biphenyl compounds
InactiveUS20060141492A1Maximize overall degradationFacilitates bioremediation treatmentBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismPolychlorinated biphenyl
The present invention relates to an assay for identification of PCB dechlorinating organisms that are capable of biologically removing PCBs from contaminated materials. Specifically, the invention provides a set of primers for detecting PCB dechlorinating organisms in a sample. These individual primers of the primer set have a sequence of at least 12 nucleotides that is unique to 16S rDNA of PCB dechlorinating organisms.
Owner:UNIV OF MARLYLAND BIOTECH INST +1
Emplacement of treatment agents using soil fracturing for remediation of subsurface environmental contamination
A method for treating contamination in subsurface formations includes fracturing the soil to produce a network of fractures in the formation and simultaneously injecting a slurry containing an optional proppant and a solid-phase or nonaqueous-phase treatment agent into the network of fractures. The proppant is for keeping the fractures open, and the treatment agent accelerates conversion of the contaminants into immobile or less toxic forms. Chitin is an illustrative solid-phase treatment agent, which functions as an electron donor for anaerobic reductive dechlorination mediated by dechlorinating bacteria.
Owner:SRP TECH
Anaerobic granular sludge capable of reinforcing dechlorination performance and preparation method and application of anaerobic granular sludge
InactiveCN104876332AEliminate spatial barriersEnhanced reductive dechlorination performanceWater contaminantsWaste based fuelElectron donorFerric
The invention discloses anaerobic granular sludge capable of reinforcing dechlorination performance and a preparation method and an application of the anaerobic granular sludge. The anaerobic granular sludge capable of reinforcing the dechlorination performance comprises zero-valent iron and anaerobic sludge, wherein the anaerobic sludge is attached to the outer surface of the zero-valent iron and contains microbial thallus; and the anaerobic granular sludge capable of reinforcing the dechlorination performance can be applied to degradation of wastewater containing chlorinated hydrocarbon. The anaerobic granular sludge has the advantages of good settling property, stable granules, compact structure and efficient and stable reductive dechlorination activity; according to the granular sludge, functional flora such as reductive dechlorinating bacteria are effectively enriched; space obstacles in transferring of metabolic fluxes such as electron donors [H] and intermediate products are removed; and the reductive dechlorination performance of a UASB (upflow anaerobic sludge blanket) reactor is reinforced.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of Cu/Pd alloy modified TiO2 catalyst for reductive dechlorination materials
ActiveCN107224982AAchieving Visible Light ResponseExcellent catalytic dechlorination effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsAlloyLight response
The invention relates to the technology of preparation of catalytic materials, and aims to provide a preparation method of a Cu / Pd alloy modified TiO2 catalyst for reductive dechlorination materials. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a nano-sheet-like TiO2 catalyst by using tetrabutyl titanate as a titanium precursor and utilizing corrosion performance of HF(hydrogen fluoride) through hydrothermal reaction; preparing a Cu / Pd alloy co-modified TiO2 catalyst through an immersion-reducing atmosphere calcination method. Complex Cu and Pd salt solutions and the catalyst are mixed and immersed, and after vacuum drying, calcination under a hydrogen reducing atmosphere is carried out. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, visible light response of the catalyst is realized, and high-efficient reductive hydrogenation dechlorination in aqueous solutions under visible light can be carried out by utilizing a synergistic effect of Cu / Pd alloys, and a catalytic dechlorination effect of the catalyst is superior to that of a commercialized P25 / Pd individually-loaded TiO2 catalyst. By the formation of the Cu / Pd alloys, the catalyst has the advantages that the using amount of precious metals is reduced while the good dechlorination effect is achieved, and practical application of reductive dechlorination under visible light is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU ANQIER WASTE GAS PURIFICATION
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride)/Fe-Pd bi-metal nanoparticle hybrid membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103611436ASemi-permeable membranesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMicrosphereNitrobenzene
The invention relates to a PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) / Fe-Pd bi-metal nanoparticle hybrid membrane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of blending polymer microspheres and PVDF to prepare a membrane, and then, loading ferrum-palladium bi-metal nanoparticles to prepare the hybrid membrane with favorable catalytic reaction activity and separation performance. By using the PVDF / Fe-Pd bi-metal nanoparticle hybrid membrane, chlorine-contained organisms such as trichloro ethylene, monochloroacetic acid, dichlorinated biphenyl, dichlorphenoxyacetic acid and the like can be subjected to reductive dechlorination reaction, and chlorine atoms in the chlorine-contained organisms are converted into hydrogen atoms. In addition, the membrane can also be used for the catalytic reduction reaction of nitro in nitrobenzene molecules such as aminonitrobenzene, nitrobenzene, methylnitrobenzene and the like so as to convert the nitro into an amino group.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Synthetic method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene
ActiveCN103193586AShort stepsMild reaction conditionsPreparation by dehalogenationHexachlorobutadieneTetrachloroethylene
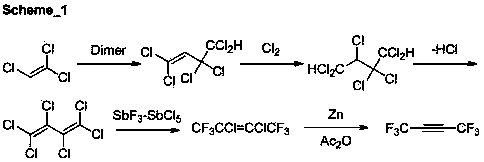
The invention discloses a synthetic method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene, and the synthetic method comprises the steps of carrying out a reaction between hexachlorobutadiene and hydrogen fluoride in the presence of a catalyst to generate 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2,3-dichlorobutane, and carrying out a reductive dechlorination reaction on the 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2,3-dichlorobutane in a solvent by using zinc powder to generate the 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene. According to the synthetic method, the process is simple, the steps are short, the reaction conditions are mild and the product can be obtained through two steps of reaction; and the raw materials are easy to get, the cost is low, and the byproduct hexachlorobutadiene obtained by reducing tetrachloroethylene by carbon tetrachloride at high temperature can be used as a raw material, so that the cost is further reduced.
Owner:JUHUA GROUP TECH CENT
Preparation method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butyne
ActiveCN103420783ALow purity requirementHigh yieldZinc halidesPreparation by dehalogenationButeneOrganosolv
The invention discloses a preparation method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butyne. In the present of an organic solvent and under the action of a reaction auxiliary agent, 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2,3-dichloro-2-butene and zinc powder are subjected to carry out a reductive dechlorination reaction so as to obtain 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butyne. The preparation method has the advantages of low raw material cost, simple operation, mild reactions, quick reaction speed, high yield, low cost, and high selectivity.
Owner:SINOCHEM LANTIAN +1
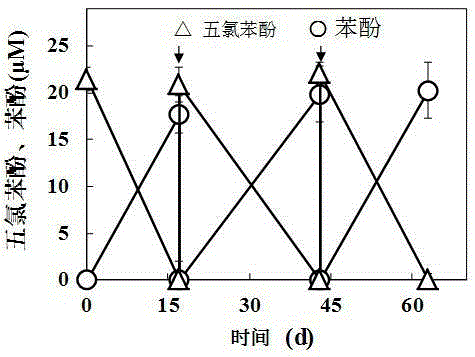
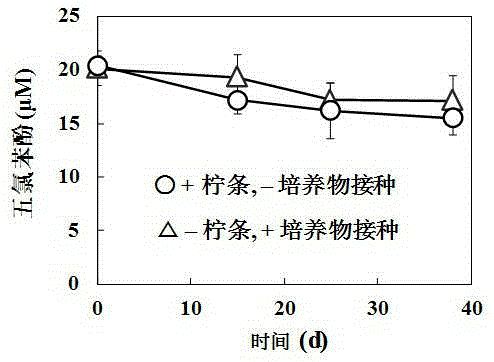
New application of caragana microphylla charcoal and mediate chlorophenasic acid anaerobic reductive dechlorination process thereof
ActiveCN105344057APromote biological anaerobic reduction dechlorinationMediated anaerobic reductive dechlorinationReductive dechlorinationNatural environment
The invention discloses a new application of caragana microphylla charcoal and a mediate chlorophenasic acid anaerobic reductive dechlorination process thereof. The caragana microphylla charcoal serves as a solid electronic medium for mediate chlorophenasic acid anaerobic reductive dechlorination. The caragana microphylla charcoal serves as the solid electronic medium, so that biological anaerobic reductive dechlorination of chlorophenasic acid is promoted; and the caragana microphylla charcoal is naturally made, is environment-friendly and widely exists in the natural environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Biochar preparation capable of mediating in anaerobic reductive dechlorination of chlorophenasic acid
ActiveCN105413094AConvenient sourceEffective mediation of anaerobic reductive dechlorinationInorganic saltsMicroorganism
The invention discloses a biochar preparation capable of mediating in anaerobic reductive dechlorination of chlorophenasic acid. The biochar preparation is formed by mixing 1 L of inorganic salt culture media, 0.5-1 mg of anaerobes, 0.6-0.8 g of sodium formate, 1-2 mL of a vitamin solution and 4-6 g of caragana korshinskii biochar. Sources of the raw materials of the biochar preparation are easy to obtain, and the biochar preparation is environmentally friendly, non-toxic and capable of effectively mediating in anaerobic reductive dechlorination of the chlorophenasic acid, and therefore a new way is provided for degrading the chlorophenasic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Preparation and application of stabilized iron nanoparticles for dechlorination of chlorinated hydrocarbons in soils, sediments, and ground water
InactiveUS7887880B2Improve the effect of chemical reactionsReduce magnetically induced aggregationWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationCelluloseChemical reaction
A stabilized, chemically reactive, metallic nano-material effective for degradation of chlorinated organic compounds in soils, sediments and groundwater. The nano-material is composed of a magnetic metal nanoparticle and a carbohydrate stabilizer bound to the nanoparticle. The preferred metal nanoparticle is iron and the preferred carbohydrate stabilizer is either a starch or a water soluble cellulose such as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. The nanoparticle may be either mono-metallic, bi-metallic or multi-metallic in nature, but is preferably bi-metallic wherein it is coated with a secondary catalytic metal coating, preferably palladium. A method of making the metallic nano-material is further disclosed wherein a solution of the metal nanoparticle and carbohydrate stabilizer is prepared, and the nanoparticle is then reduced under inert conditions. A process for reductive dechlorination of chlorinated organic compounds is also disclosed wherein the reduced magnetic metal nanoparticle is prepared, and then contacted with a chlorinated organic compound to dechlorinate the compound. Preferably, the nano-material is injected into a site such as soil subsurface or groundwater contaminated with a chlorinated organic compound to provide in-situ dechlorination.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Bacterial strain for degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol and screening separation method thereof
PendingCN106119151AImprove degradation efficiencyHigh purityBacteriaWater contaminantsActivated sludgeAnaerobic reactor
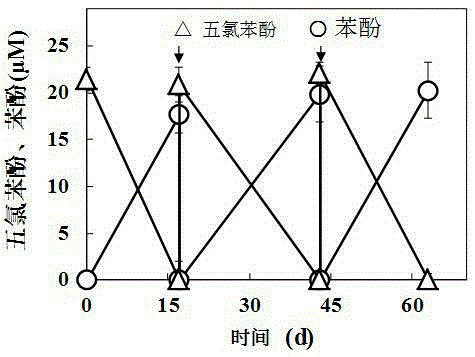
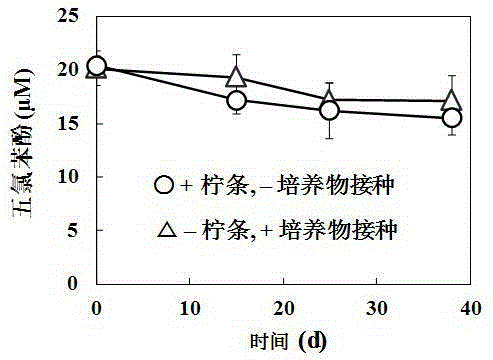
The invention discloses a screening separation method of a bacterial strain for degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and relates to the technical field of treatment of organic pollutants. The method comprises the steps: collecting activated sludge in a papermaking wastewater inner circulation anaerobic reactor, carrying out enrichment acclimation in a strictly anaerobic environment, then inoculating solid screening culture mediums having addition of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol respectively with the acclimated sludge according to the dilution gradient, and separating to obtain various purified bacterial strains having the ability to degrade 2,4,6-trichlorophenol; and finally, respectively inoculating degradation culture mediums having addition of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol with the various purified bacterial strains, and screening to obtain the bacterial strain having the highest degradation efficiency on 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. The method is simple, and the obtained spindle-shaped lysine bacillus has relatively high purity and high yield. The invention also provides the bacterial strain for degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol; the bacterial strain can degrade chlorophenol organic matters through reductive dechlorination under anaerobic conditions, and has good degradation effect.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for removing chlorinated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20200038926A1Avoid adverse reactionsHigh activityWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSimple Organic CompoundsSoil science
Compositions and methods for soil and groundwater remediation are contemplated as comprising a zero valent metal having a metal sulfide surface layer and an organic compound operative to degrade to produce molecular hydrogen. Such compositions may also include particulate activate carbon and anaerobic bacteria operative to perform reductive dechlorination. These compositions synergistically operate to remove chlorinated hydrocarbons from contaminated soil and groundwater.
Owner:REGENESIS BIOREMEDIATION PRODS
Process for combination degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls
ActiveCN102989101ARapid and efficient hydrodechlorinationLow toxicityChemical protectionHydrogenPolychlorinated biphenyl
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inhibition of methane production during anaerobic reductive dechlorination
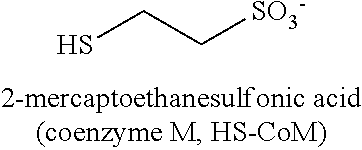
This method of restricting methane production in methanogenic bacteria, by the use of the enzyme and coenzyme inhibitors, works during anaerobic reductive dechlorination. Various compounds such as, but not limited to, red yeast rice, vitamin B10 derivatives, and ethanesulfonates are utilized to disrupt these different enzyme and coenzyme systems responsible for the production of methane. This method affects the competition of the methanogen and halo bacteria for the organic hydrogen donors that are injected in the soil and groundwater system during the remediation process.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
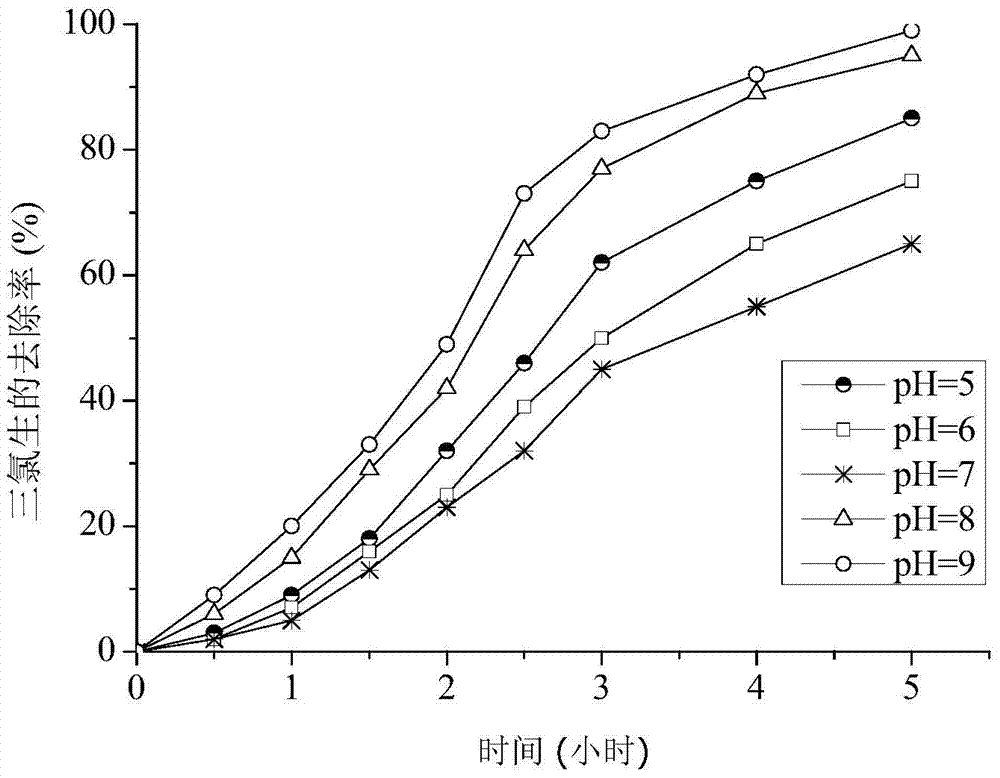
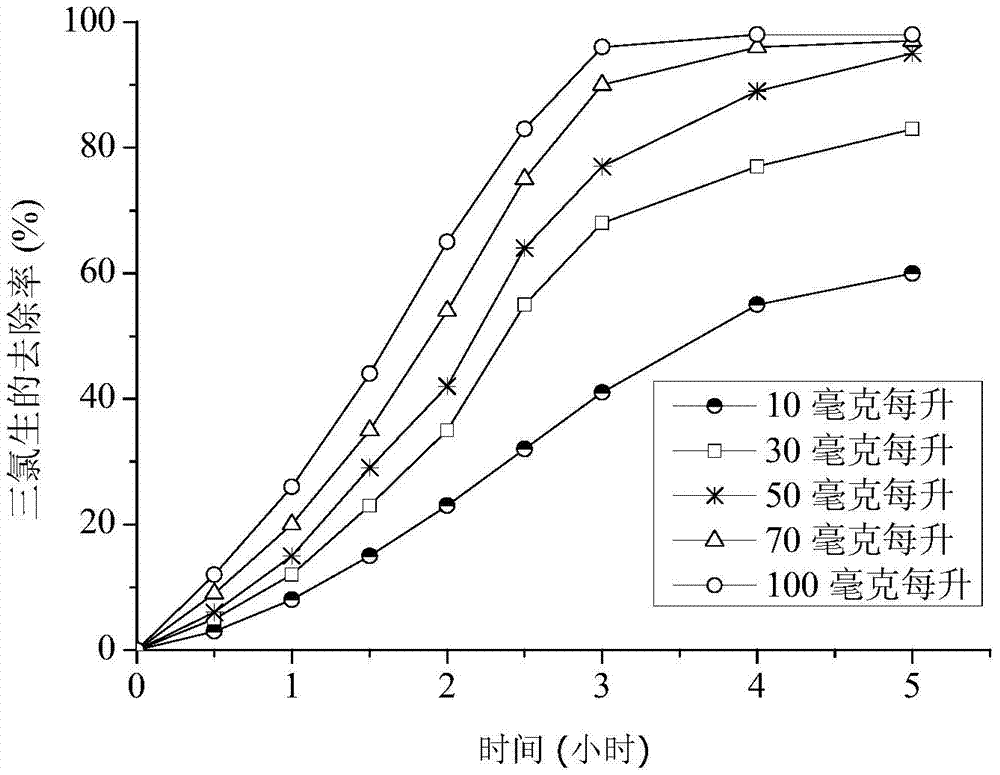
Method for carrying out intensified reductive dechlorination on triclosan in sewage by using vitamin B12
InactiveCN104229969ASimple reaction conditionsGood removal effectWater/sewage treatment by reductionTriclosanResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for carrying out intensified reductive dechlorination on triclosan in sewage by using vitamin B12. According to the method, nano zero-valent iron and vitamin B12 are added to sewage containing triclosan under the condition that the pH value is 5-9, the reaction time is 5-10 hours, so that sewage is subjected to intensified reductive dechlorination, wherein the mass concentration of triclosan in sewage is 1-20mg / L; 0.1-1g of nano zero-valent iron is added to each liter of sewage; and 10-100mg of vitamin B12 is added to each liter of sewage. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is simple in reaction condition, mild in reaction, short in treatment time, high in triclosan removal rate, free of secondary pollution, suitable for treatment of sewage containing triclosan and other pharmaceutical wastewaters, and beneficial to resource utilization of the sewage.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
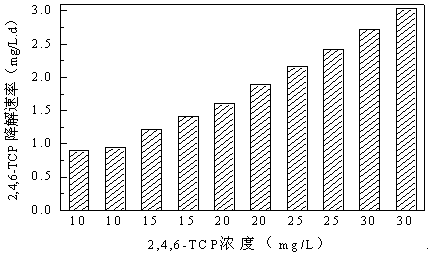
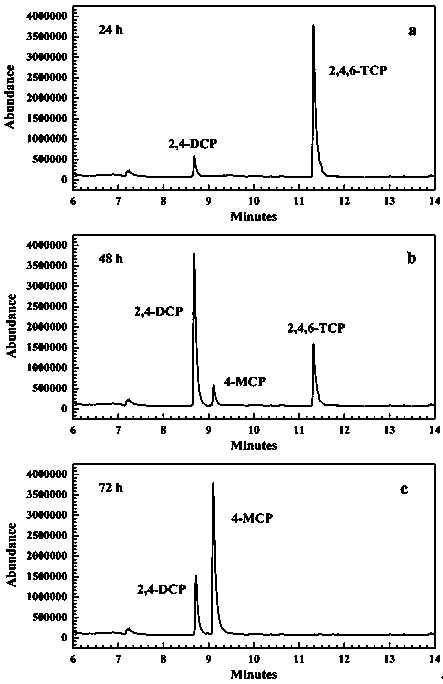
Efficient 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol degrading bacterial strain and separation method thereof
The invention discloses a separation method of an efficient chlorophenol degrading bacterial strain, and the efficient chlorophenol degrading bacterial strain Pseudomonassp.TB-1, with the collection number of CGMCCNo.9686. obtained through the separation method. The separation method comprises the following steps: obtaining anaerobic activated sludge from an internal-circulating anaerobic papermaking wastewater treatment reactor, domesticating and screening for a long time, and separating to obtain a bacterial strain for efficiently degrading 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol through reductive dechlorination. The bacterial strain can completely degrade the 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol with a concentration of 30mg / L within 72 hours, and still has a degrading rate of 72% when the concentration of the 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol (2, 4, 6-TCP) is as high as 150mg / L.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
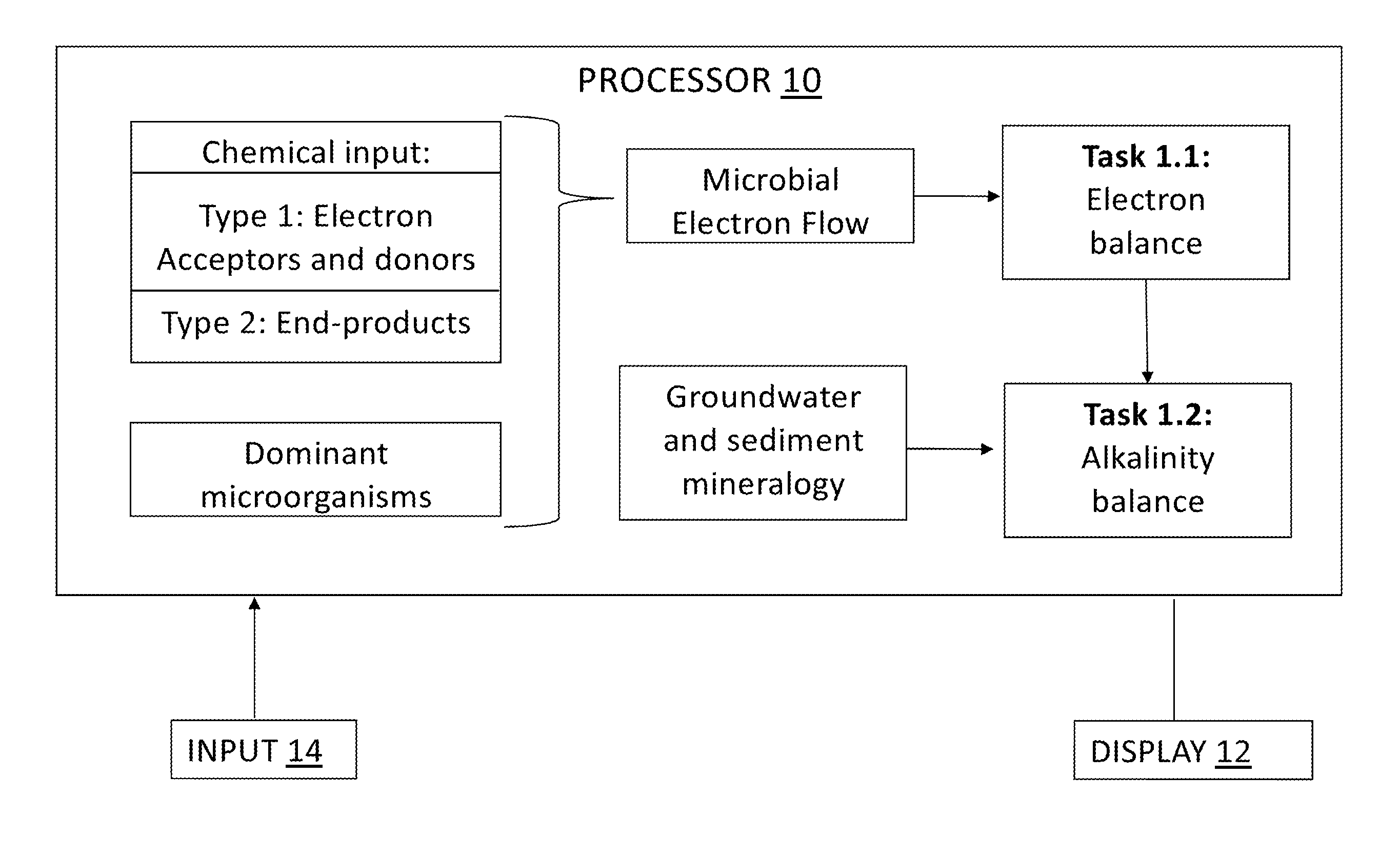
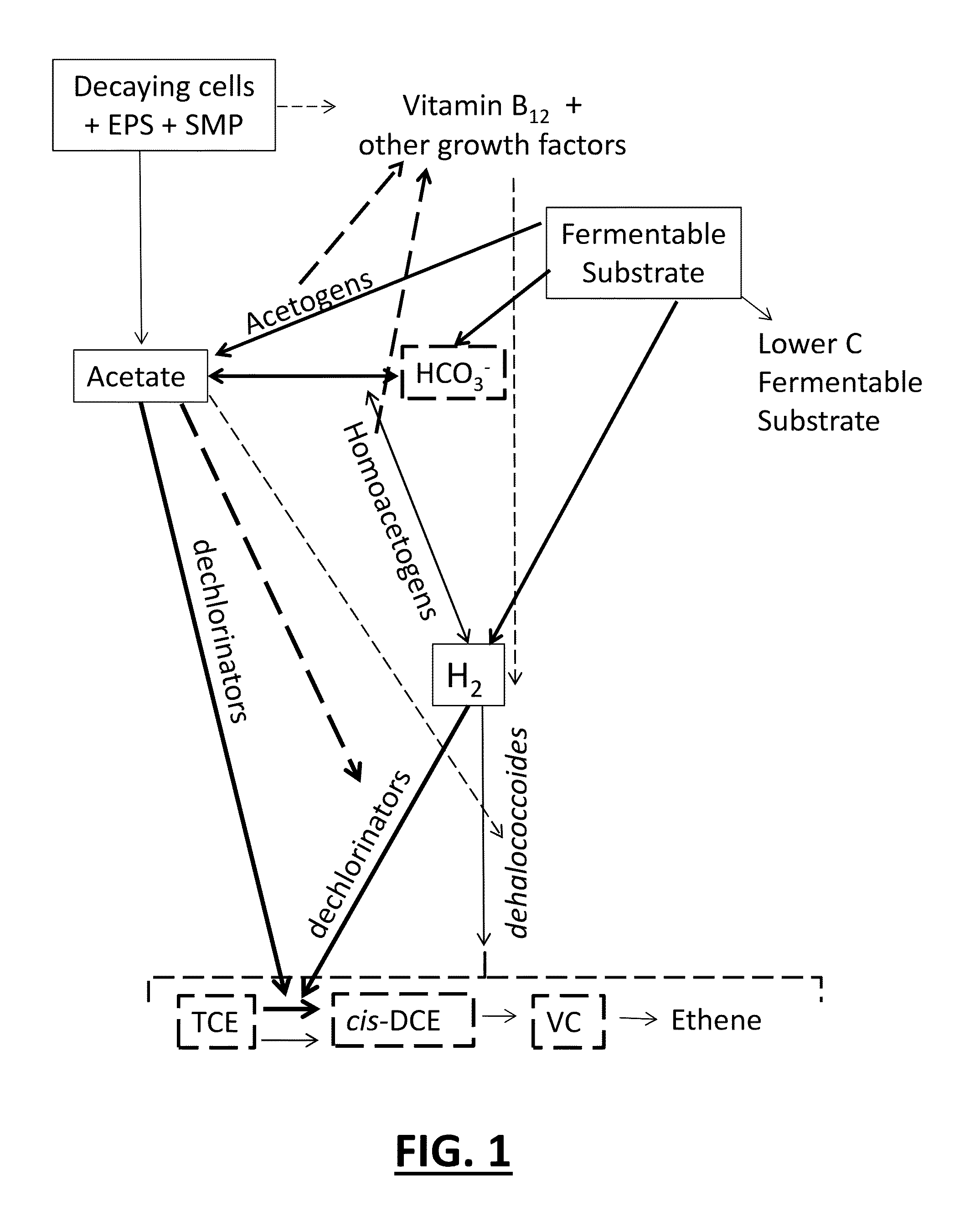
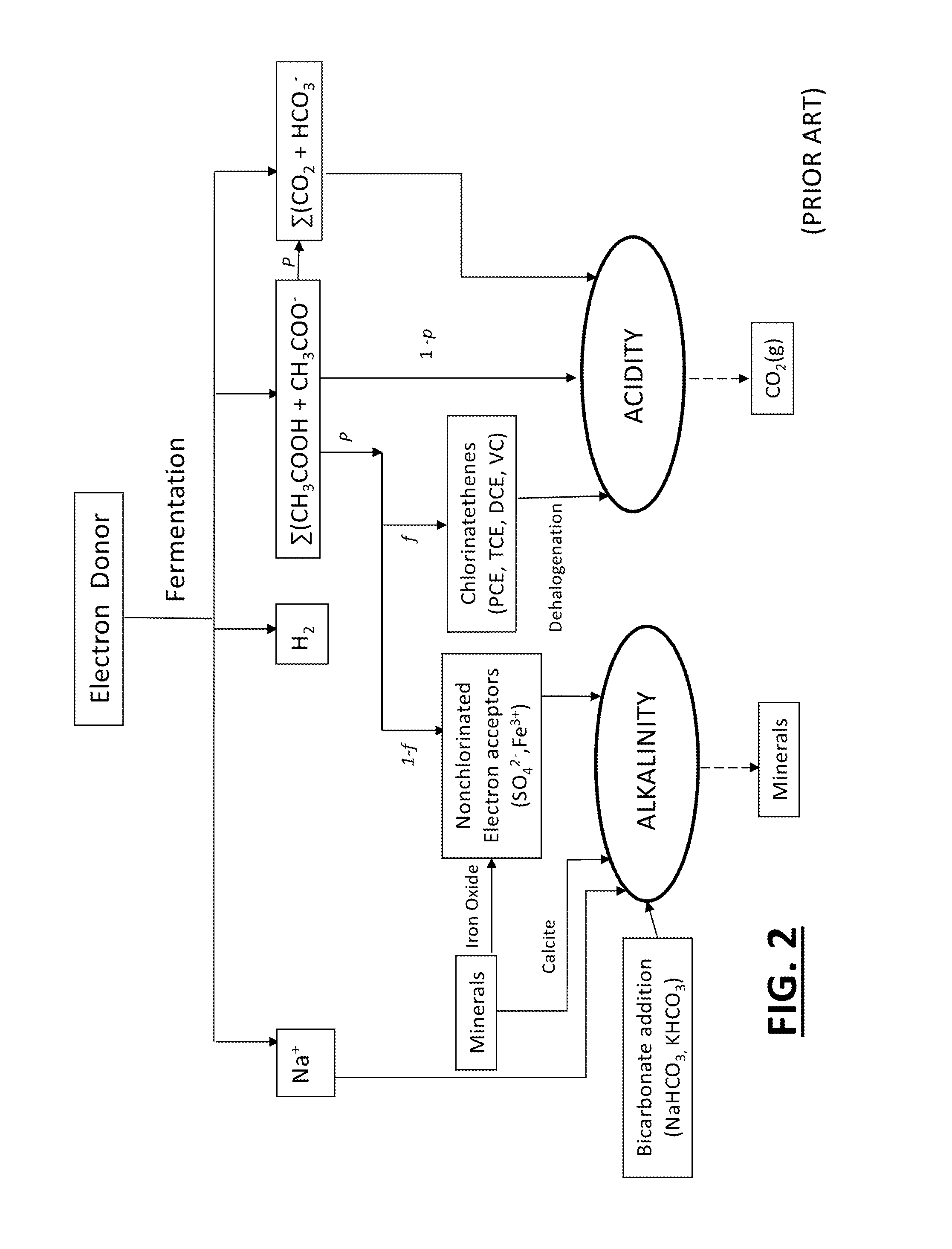
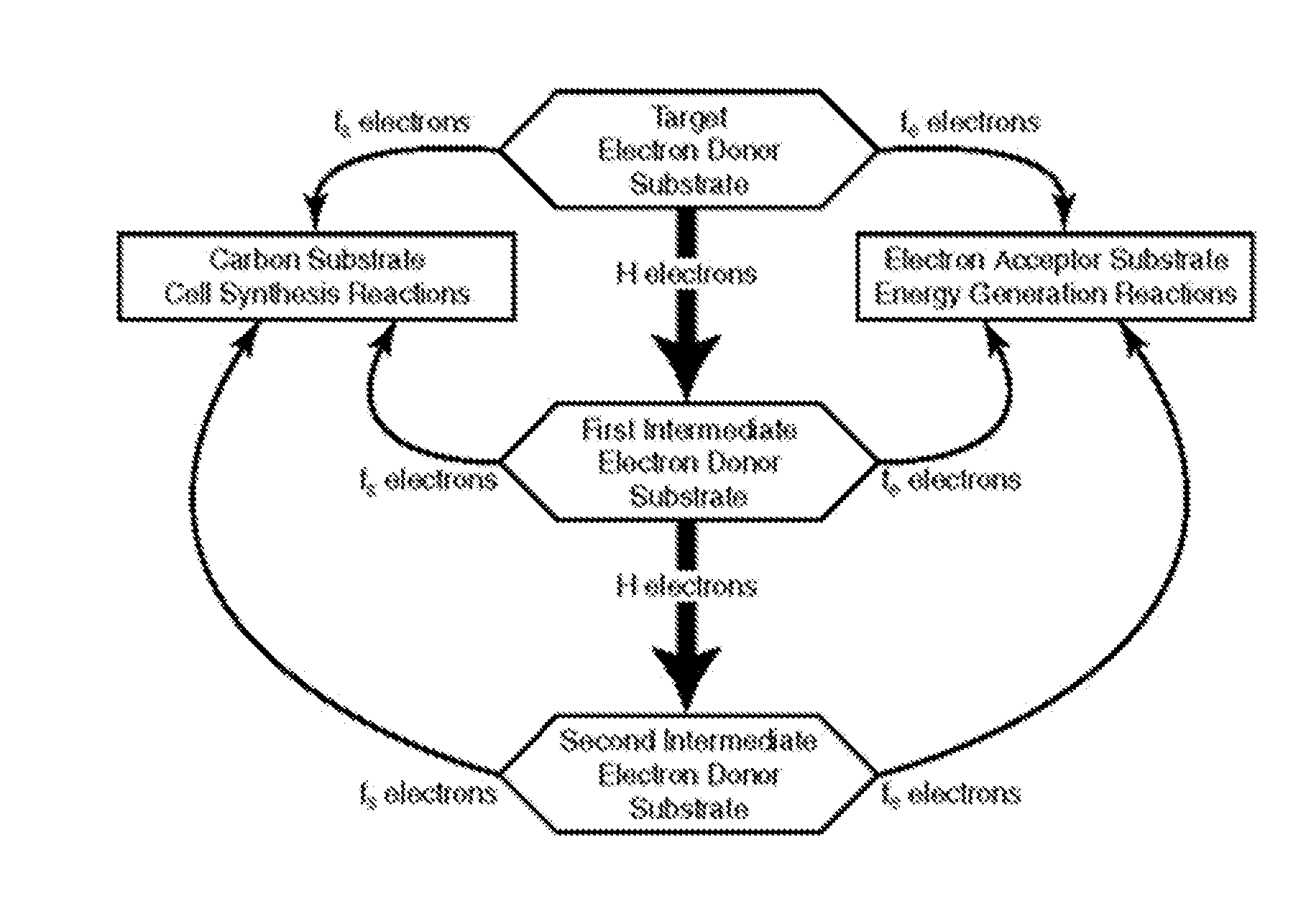
Tool for optimizing chlorinated-solvent bioremediation through integration of chemical and molecular data with electron and alkalinity balances
InactiveUS20130345990A1Maximize accuracyMitigate incomplete reductive dechlorinationContaminated soil reclamationSpecial data processing applicationsAlkalinityOrganismal Process
A prediction and assessment tool for bioremediation performance based on a comprehensive understanding of the link between chemical flow and microbial community interactions includes linking molecular microbial ecology data with electron and alkalinity balances to make it possible to understand dechlorinating microbial communities and their metabolic processes. The interactions of biological processes and site mineralogy result in changes to alkalinity and pH that can lead to incomplete reductive dechlorination resulting from suboptimal pH. Understanding these interactions allows for strategies to predict expected bioremediation outcomes and / or to mitigate incomplete reductive dechlorination.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Use of encapsulated substrates that controlthe release rates of organic hydrogen donors
ActiveUS20140311971A1Control releaseContaminated soil reclamationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesOrganismal ProcessHydrogen
Anaerobic reductive dechlorination processes remove chlorinated solvents from contaminated subsurface soil and ground water. The presence of organic hydrogen donors enables anaerobic microorganisms present in the subsurface soil and groundwater to accelerate the reductive dechlorination process. The present invention provides an alternative method to control the release rate of organic hydrogen donors during dechlorination. The invention utilizes encapsulated substrates to control the release rate of organic hydrogen donors, therefore accelerating the biotic process of anaerobic reductive dechlorination.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
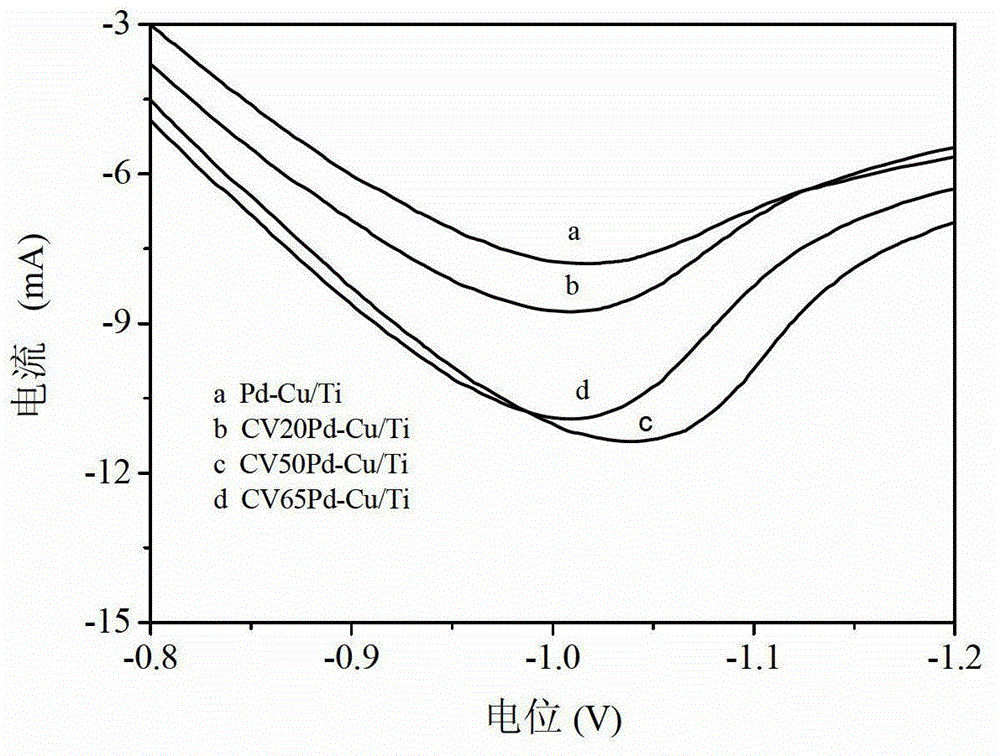
CA scanning assisted preparation method and applications of Pd-Cu/Ti electrode
ActiveCN103334121ALong electrode lifeThere will be no secondary pollution problemsWater/sewage treatmentElectrodesPlatinumElectrochemistry
The invention discloses a CA scanning assisted preparation method and applications of a Pd-Cu / Ti electrode, and belongs to the field of electrochemical water treatment technologies. The CA scanning assisted preparation method comprises following steps: firstly, preparing a PdCl2 solution containing CuSO4, and adjusting the pH value of the solution to 1.0; taking a titanium mesh as a cathode, and a platinum sheet as an anode, and performing deposition with a constant potential so as to obtain the Pd-Cu / Ti electrode, wherein the constant potential relative to the potential of a Hg / Hg2SO4 electrode is -0.9V; and then subjecting the Pd-Cu / Ti electrode to CV scanning in a H2SO4 solution of 0.5M, wherein the potential scanning range is -800mV to 700mV, the scanning speed is 50Mv / S, and the scanning circles are 1 to 65. The Pd-Cu / Ti electrode can be used for electrocatalytic reductive dechlorination of PCP, and the reaction solution is close to neutral after the reaction by controlling an initial pH value, so that it is convenient for subsequent processing.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
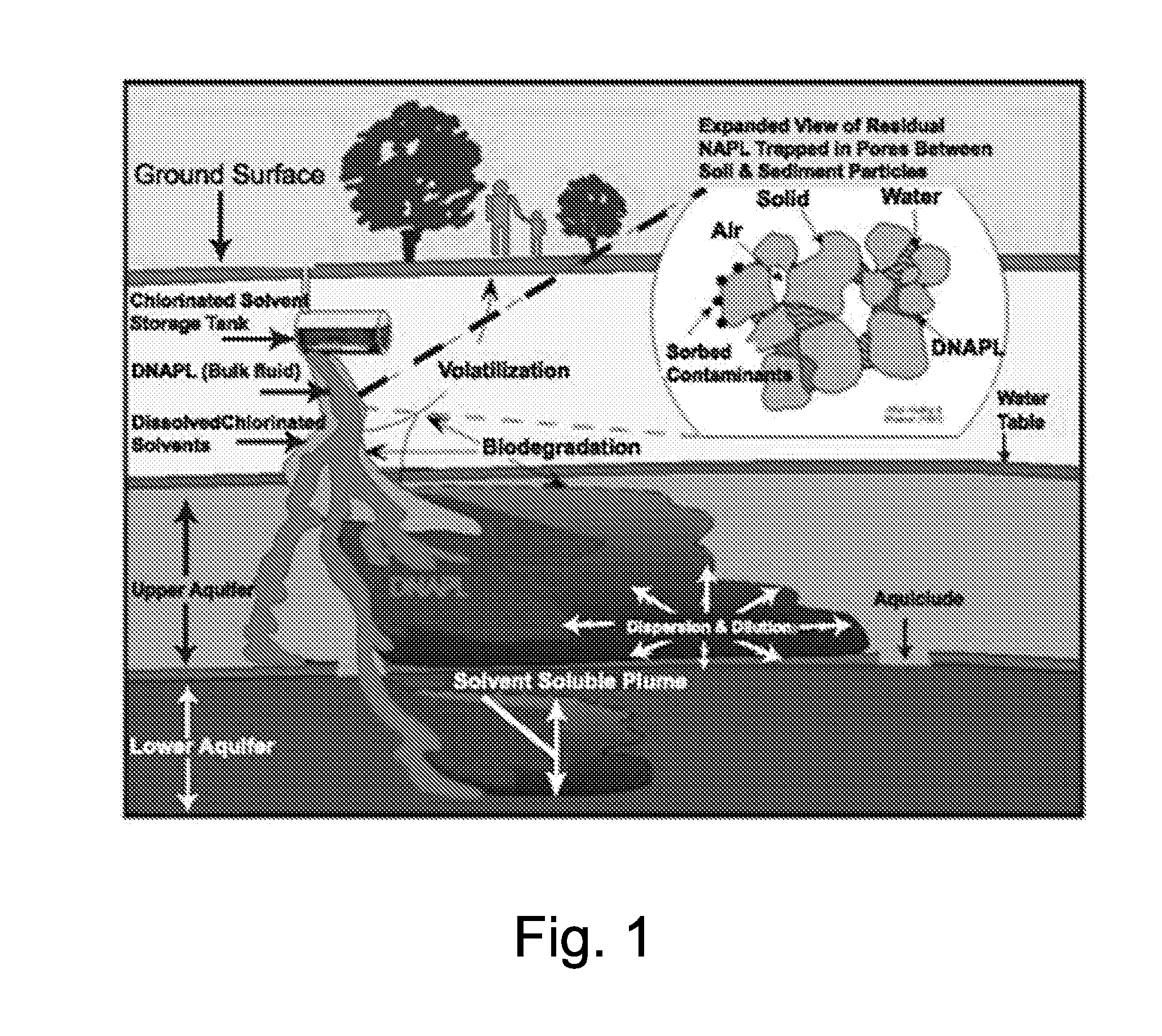
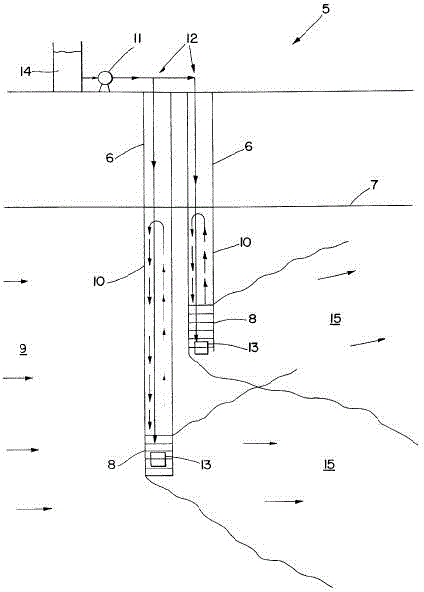
Polluted groundwater in-situ remediation technology
InactiveCN104556530AWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesProcess systemsBiogeochemistry
The invention relates to an in-situ purification technology which can be used for reductive dechlorination, heavy metal precipitation and microbial denitrification reaction. The in-situ purification technology requires an anaerobic reaction area used for precipitating and filtering soluble heavy metal, such as metal sulfide and nitrate which are converted to nitrogen, precipitates and filtered chromium. A pump process system is composed of one or more wells which extend to an underground pollution saturated zone. There are conduits in the wells, and the conduits are used for conveying carbohydrate and sulfate to the pollution saturated zone. In a reaction zone, dissolved state oxygen content is lower than 0.5mg / L, redox potential is lower than -250mv, and the ratio of soluble organic carbon compounds to pollutants is higher than 50:1. Meanwhile, microbes digest carbohydrate, sulfate can be reduced and methane can be generated. In this biogeochemical environment, PCE dechlorination can be caused for reduction to obtain TCE, TCE further undergoes dechlorination to generate DCE, dechlorination is carried out again to generate VE, and ethene is finally generated. Meanwhile, heavy metal precipitation and microbial denitrification reaction are also caused in the biogeochemical environment.
Owner:KESHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Inhibition of methane production during anaerobic reductive dechlorination
ActiveUS20140251900A1Affect competitionLower emission levelsWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsRed yeast riceHydrogen
This method of restricting methane production in methanogenic bacteria, by the use of the enzyme and coenzyme inhibitors, works during anaerobic reductive dechlorination. Various compounds such as, but not limited to, red yeast rice, vitamin B10 derivatives, and ethanesulfonates are utilized to disrupt these different enzyme and coenzyme systems responsible for the production of methane. This method affects the competition of the methanogen and halo bacteria for the organic hydrogen donors that are injected in the soil and groundwater system during the remediation process.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Biochar preparation for anaerobic reductive dechlorination of mediated polychlorinated biphenyls
ActiveCN107929998AEffective mediation of anaerobic reductive dechlorinationEnvironmentally friendlyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSodium lactateInorganic salts
The invention discloses a biochar preparation for anaerobic reductive dechlorination of mediated polychlorinated biphenyls. The biochar preparation is prepared from the following components of, by weight, 1 L of an inorganic salt culture medium, 1.5-2.5 Ml of sodium lactate, 1-2 mL of a vitamin solution, 1-2 mg of an anaerobic microorganism, and 4-6 g of rape stem biochar. The biological preparation has the characteristics of being environment-friendly, non-toxic and the like, anaerobic reductive dechlorination of the polychlorinated biphenyls can be effectively mediated, and the biological preparation provides a new way for degrading of the polychlorinated biphenyls.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com