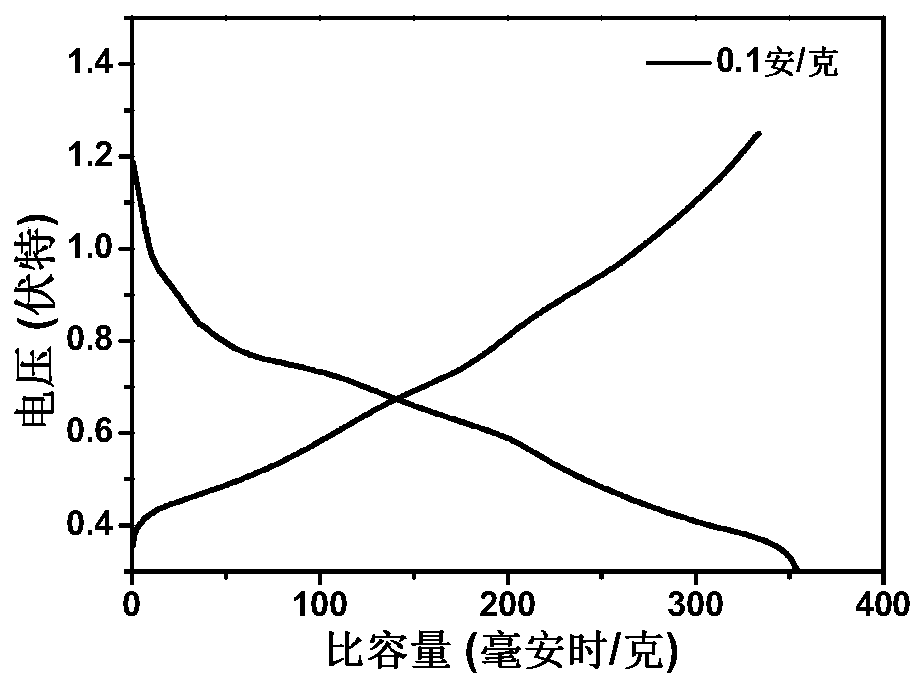
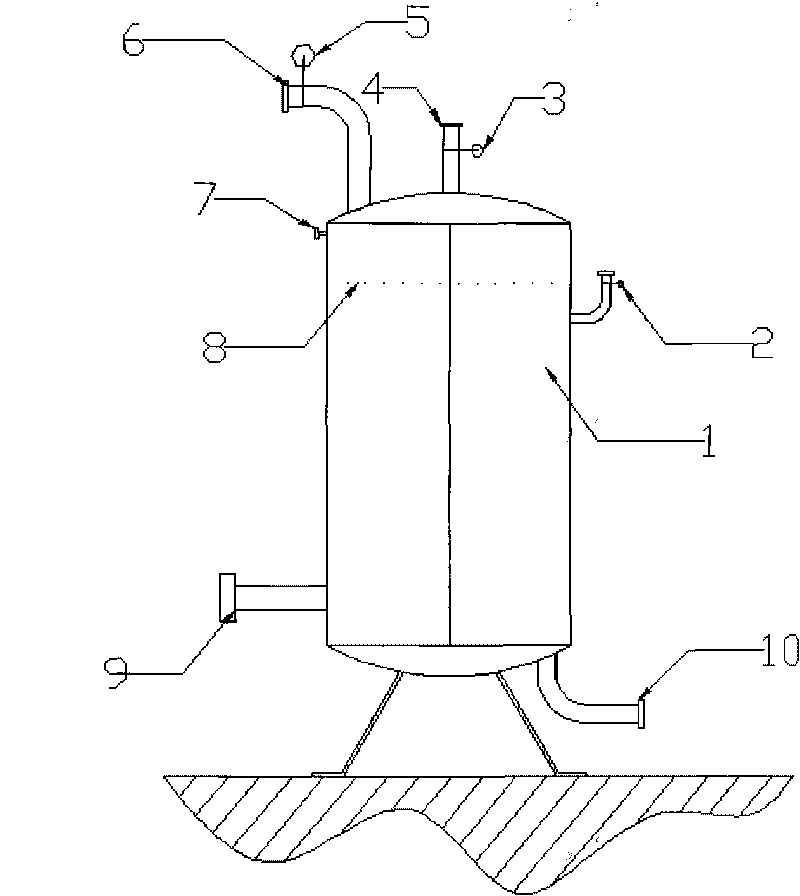
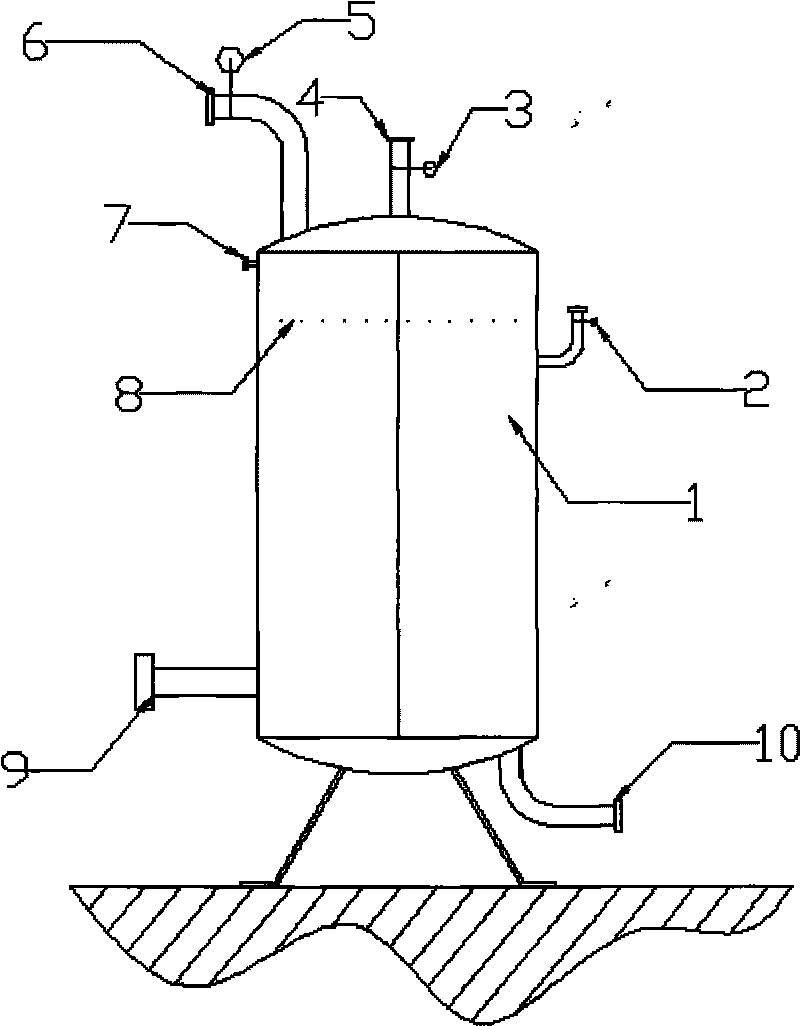
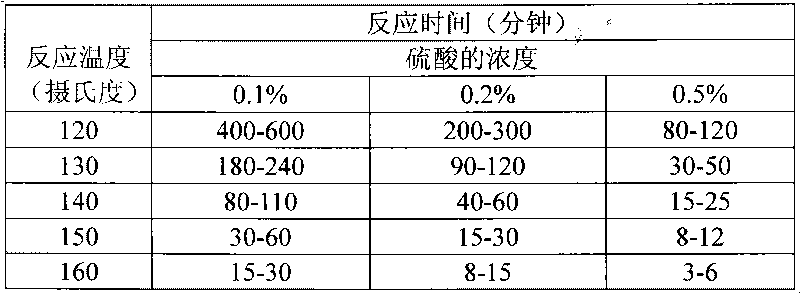
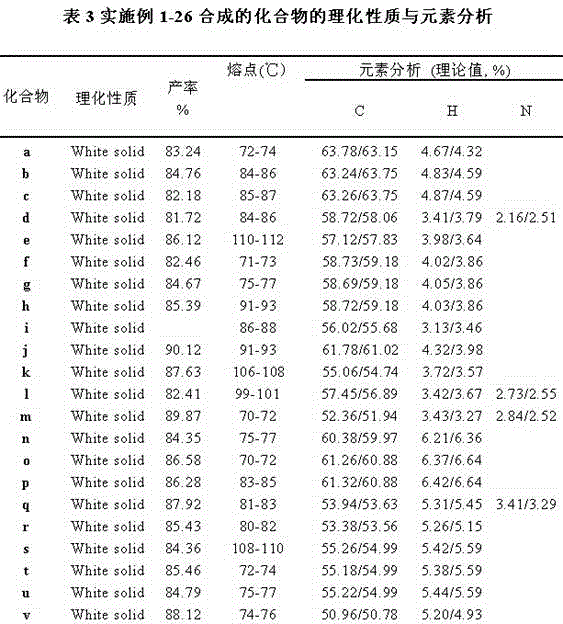
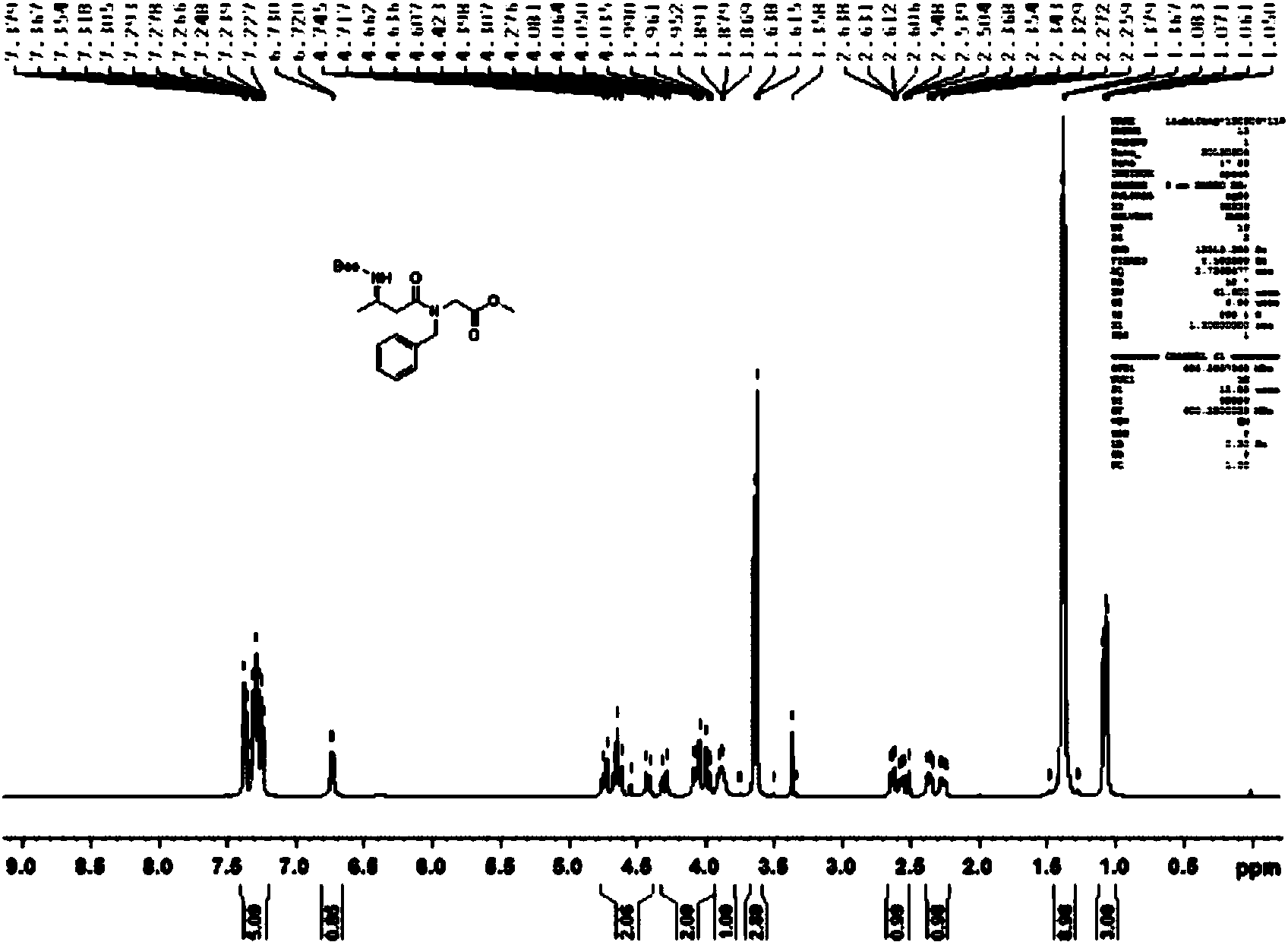
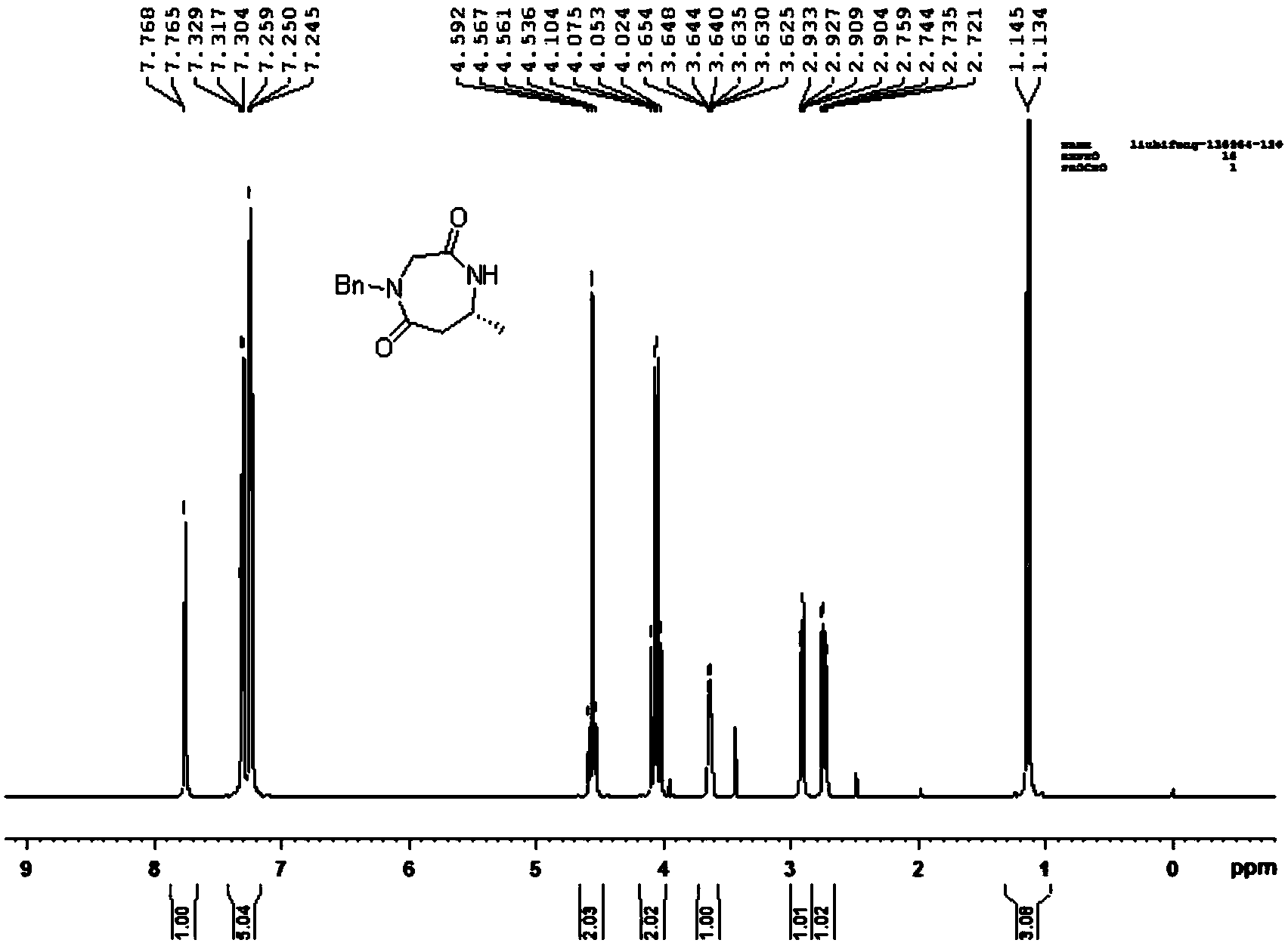
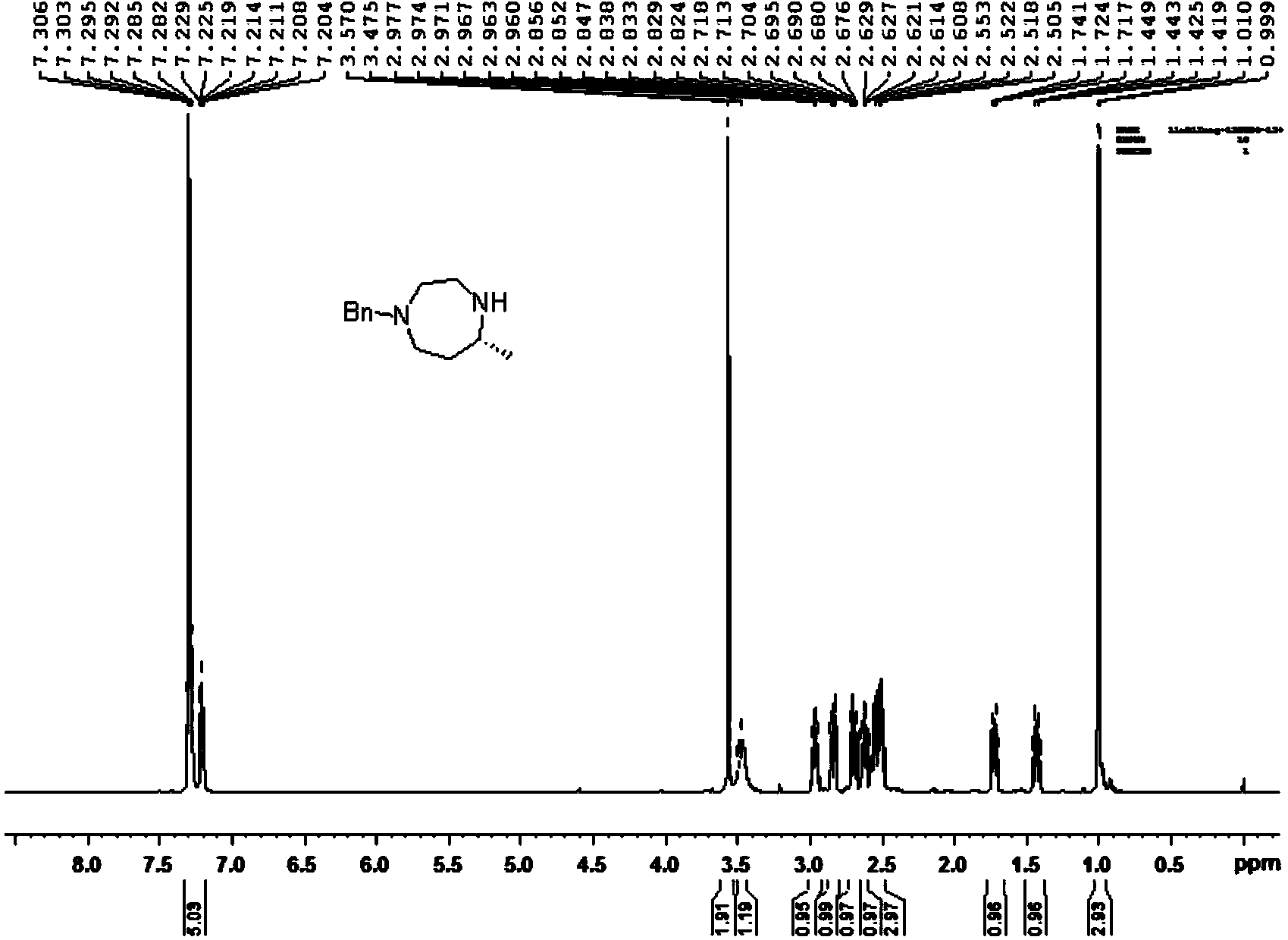
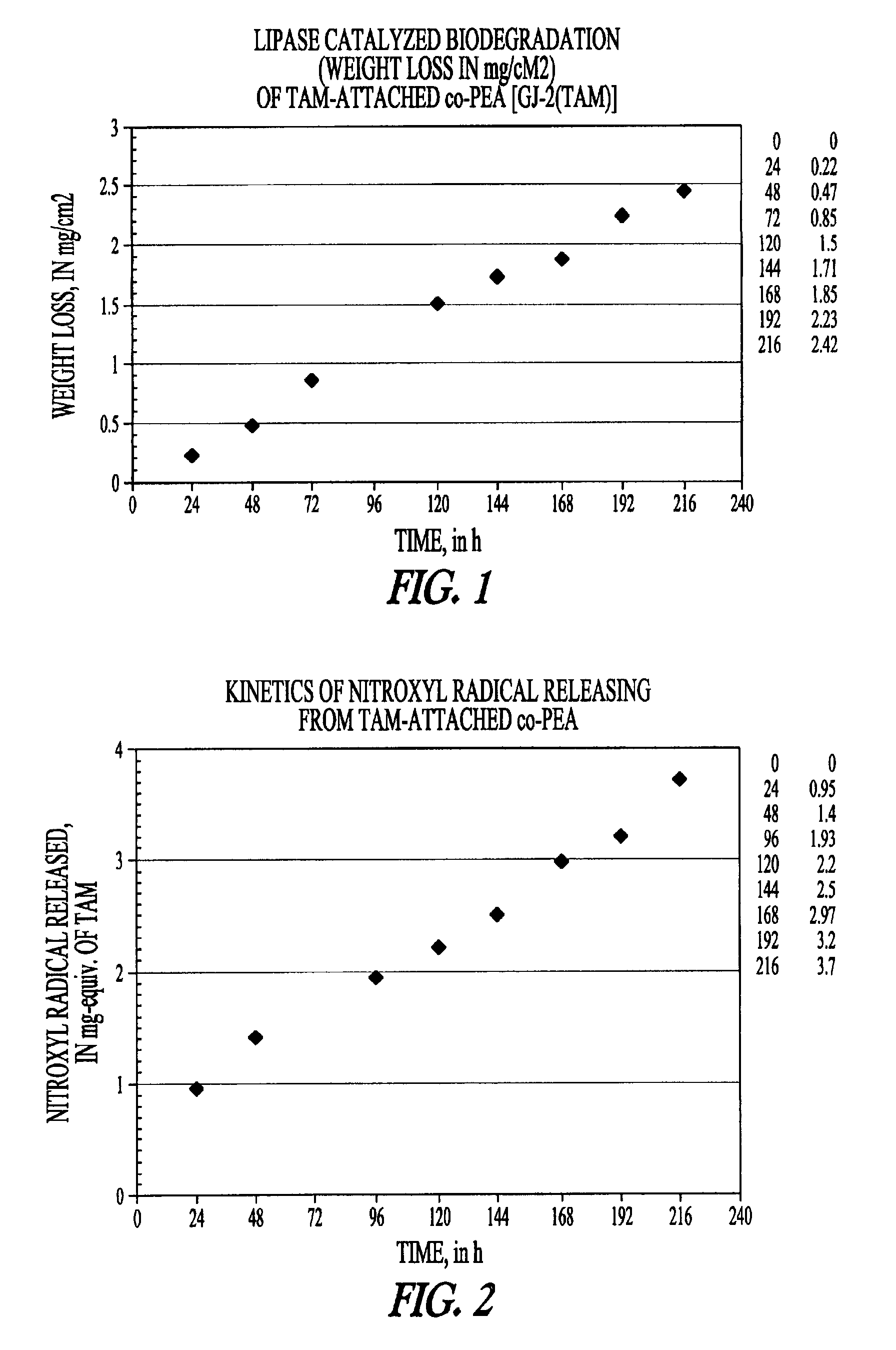
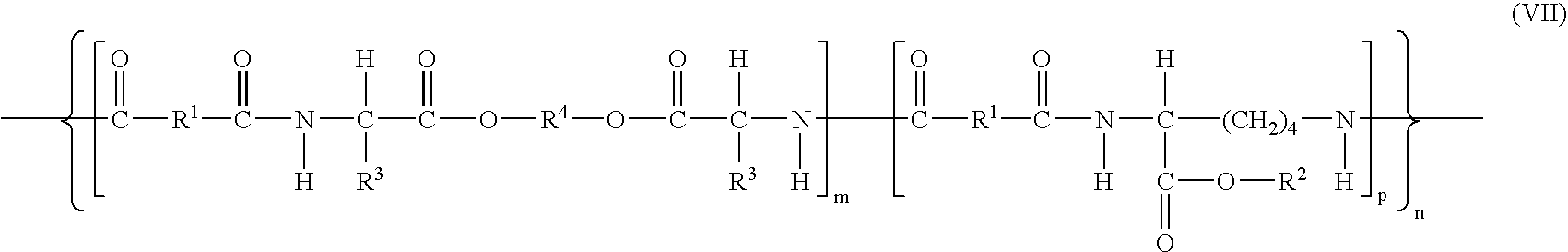
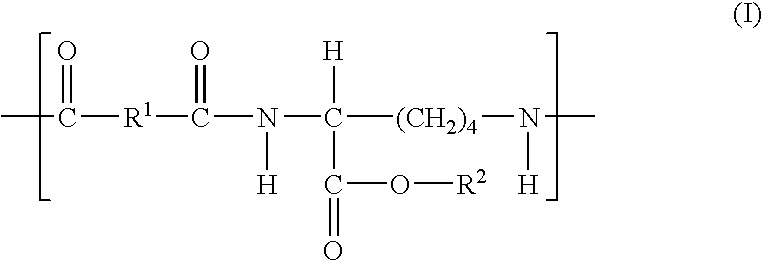
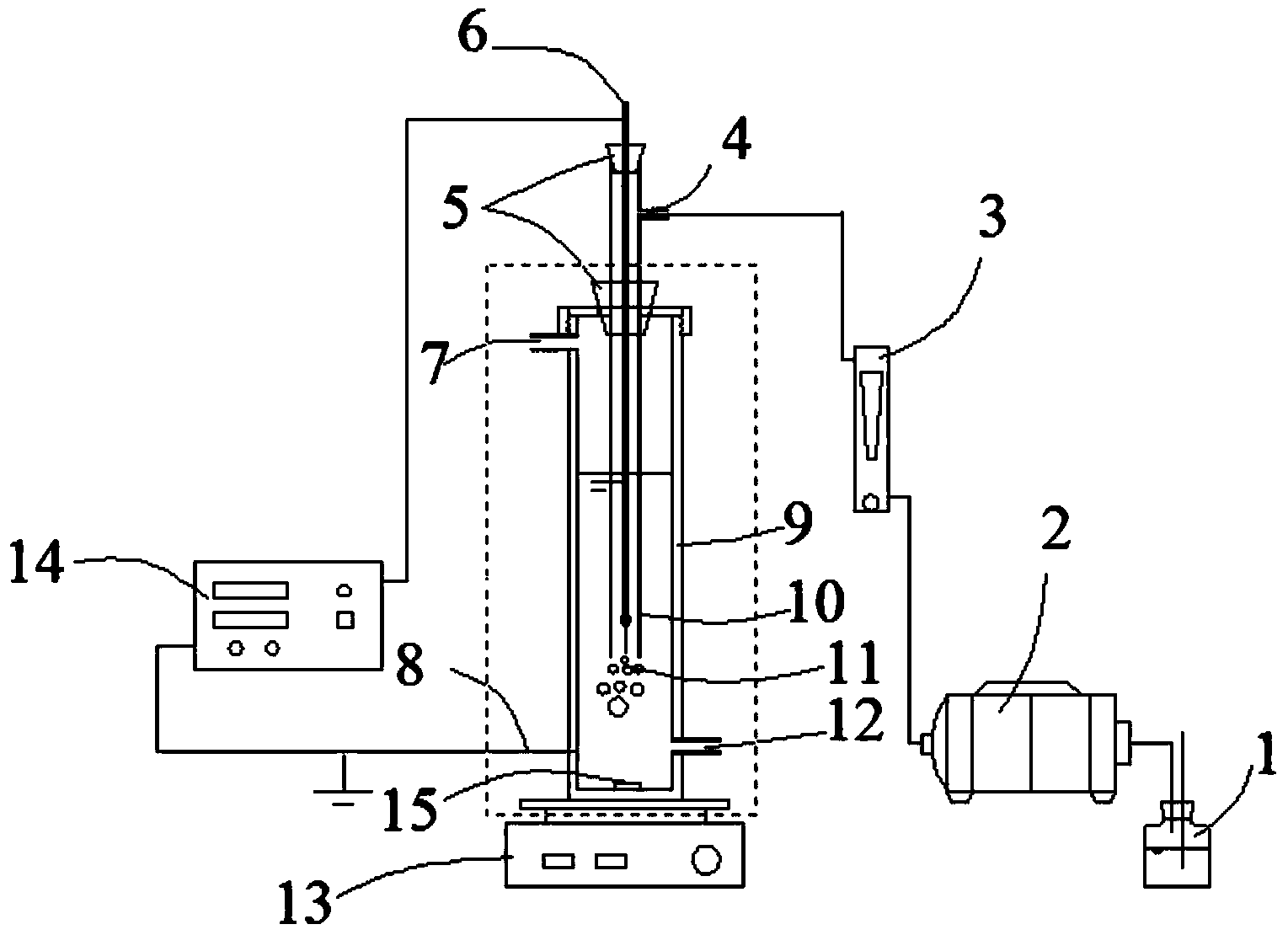
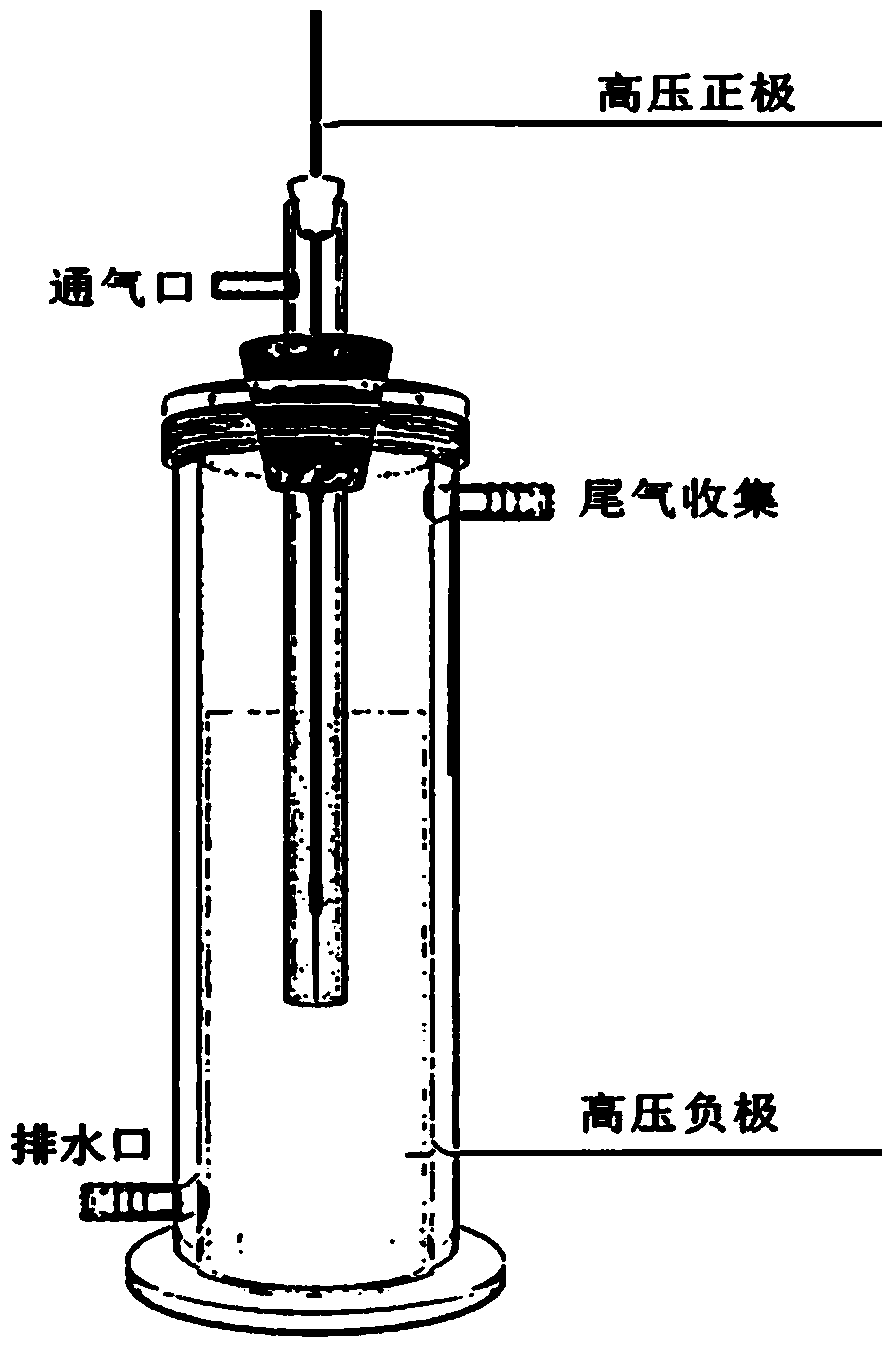
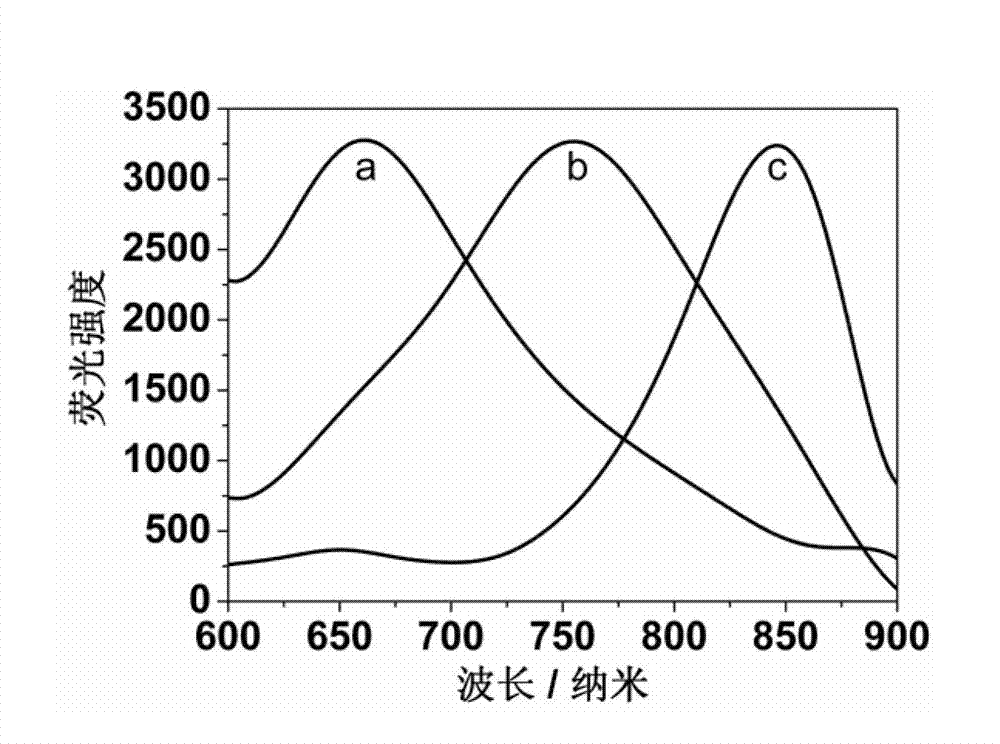
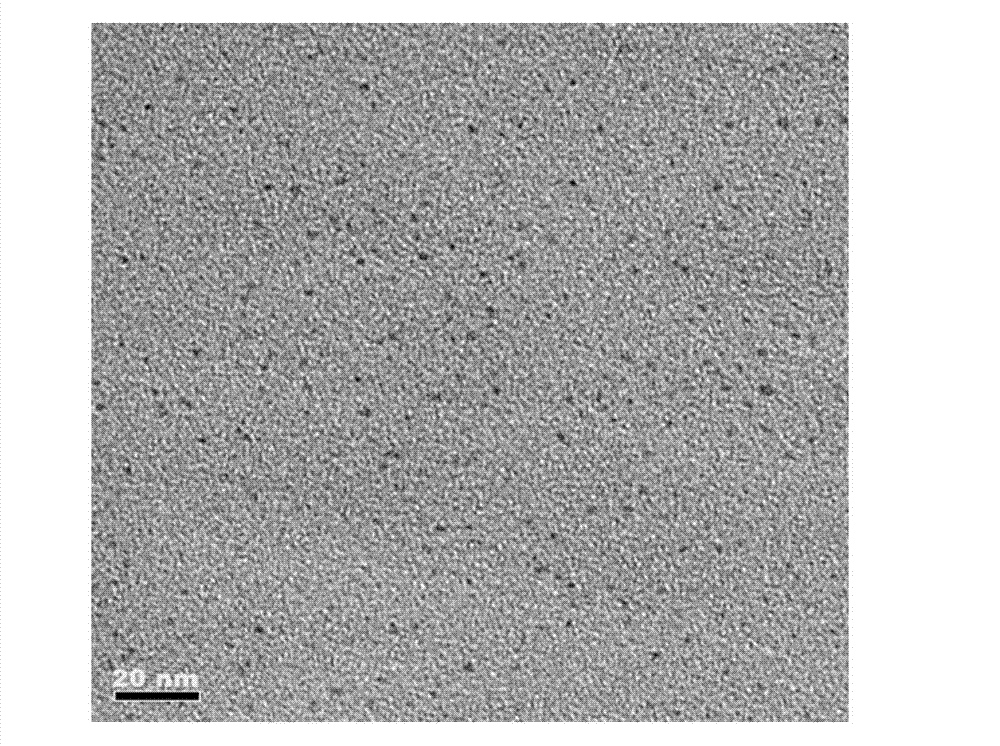
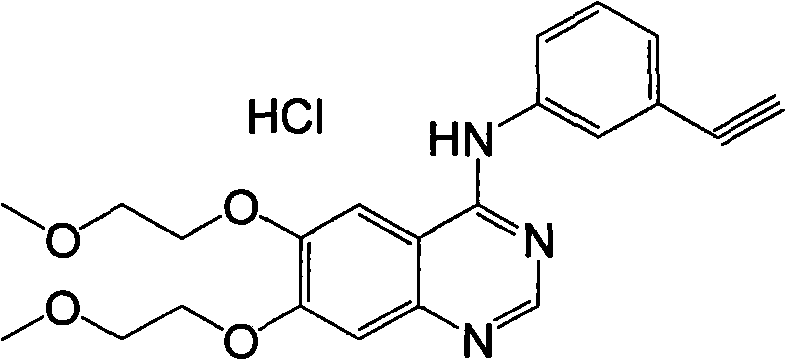
Patents
Literature
2369results about How to "Simple reaction conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
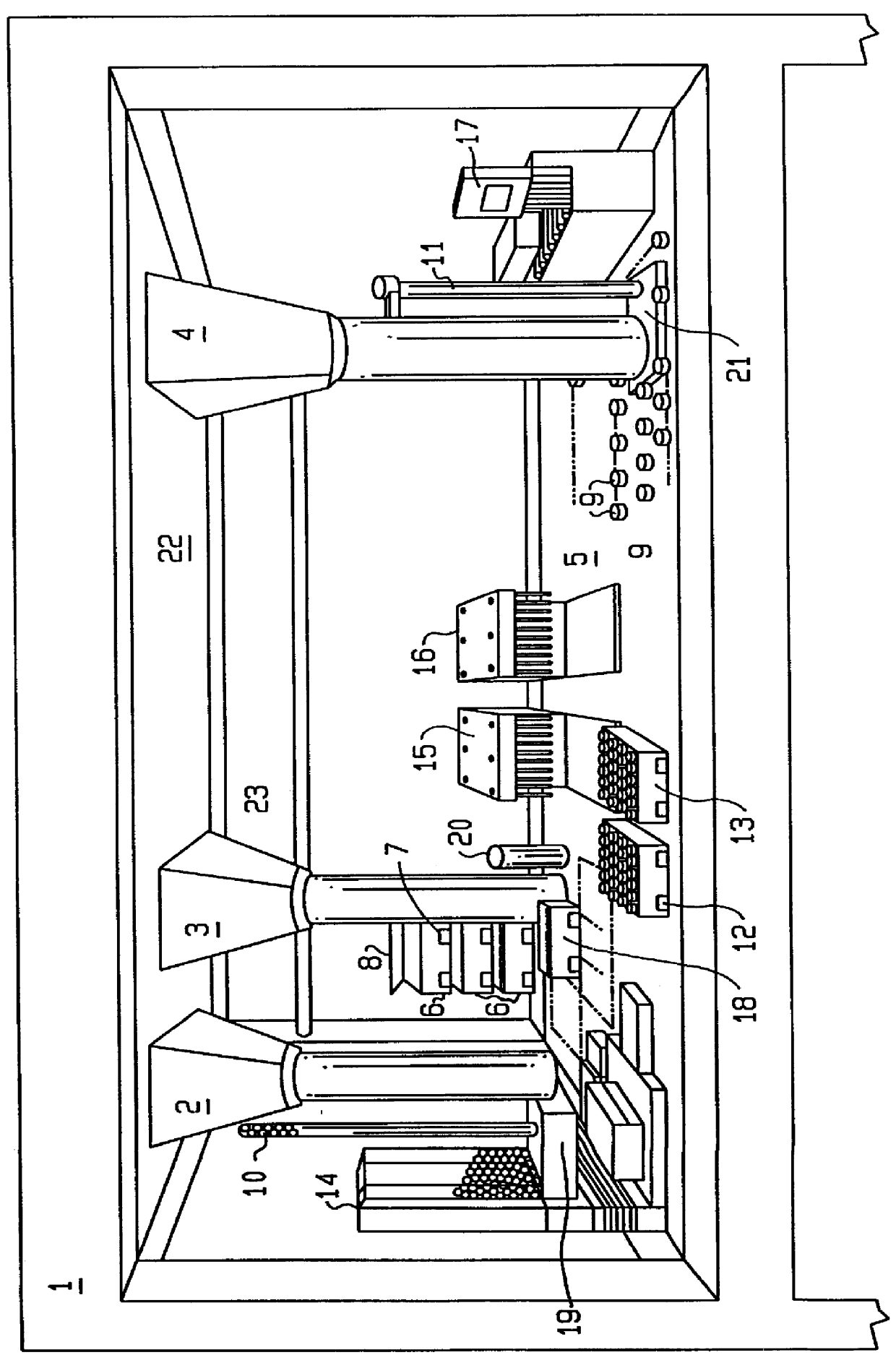
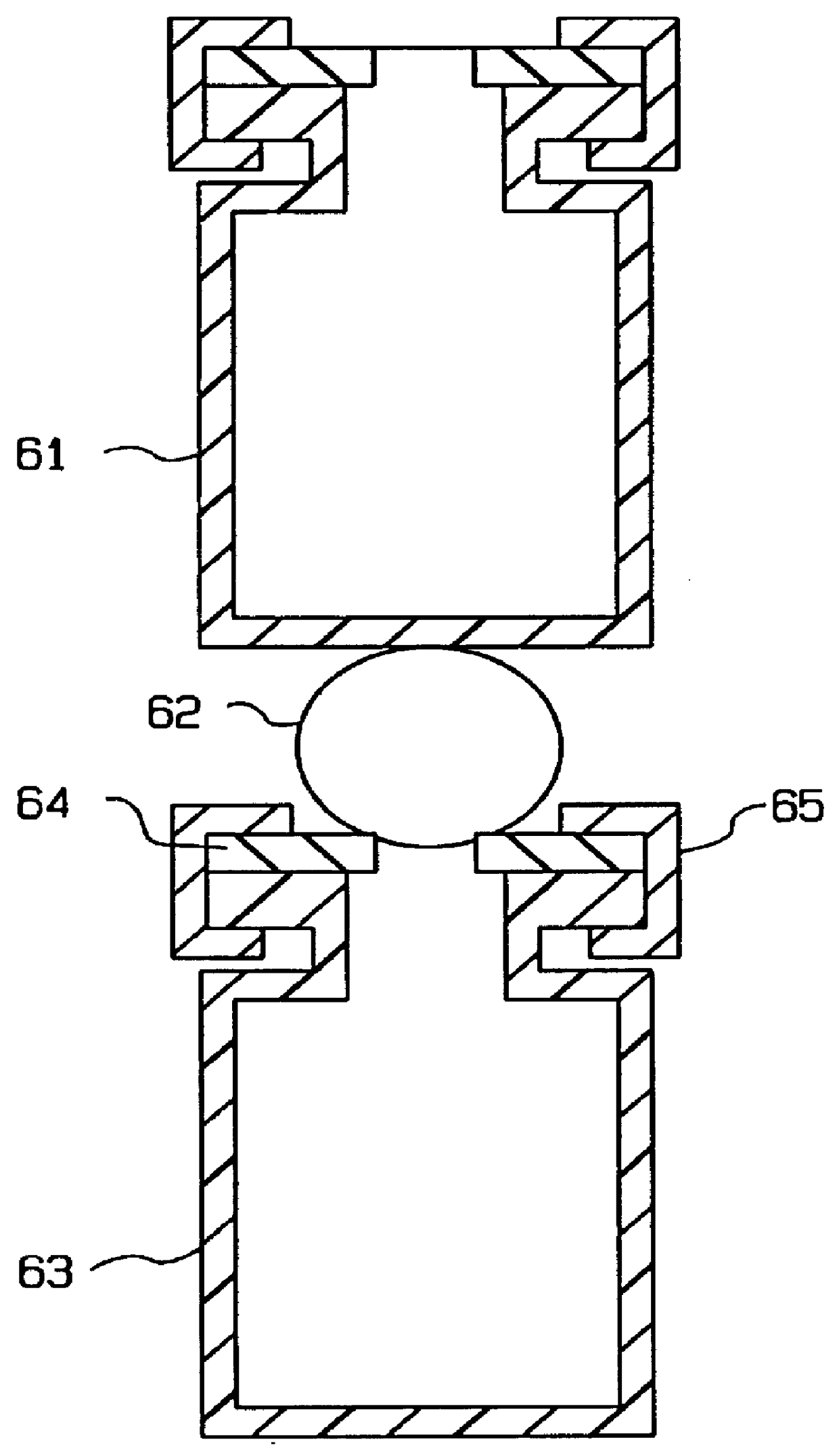
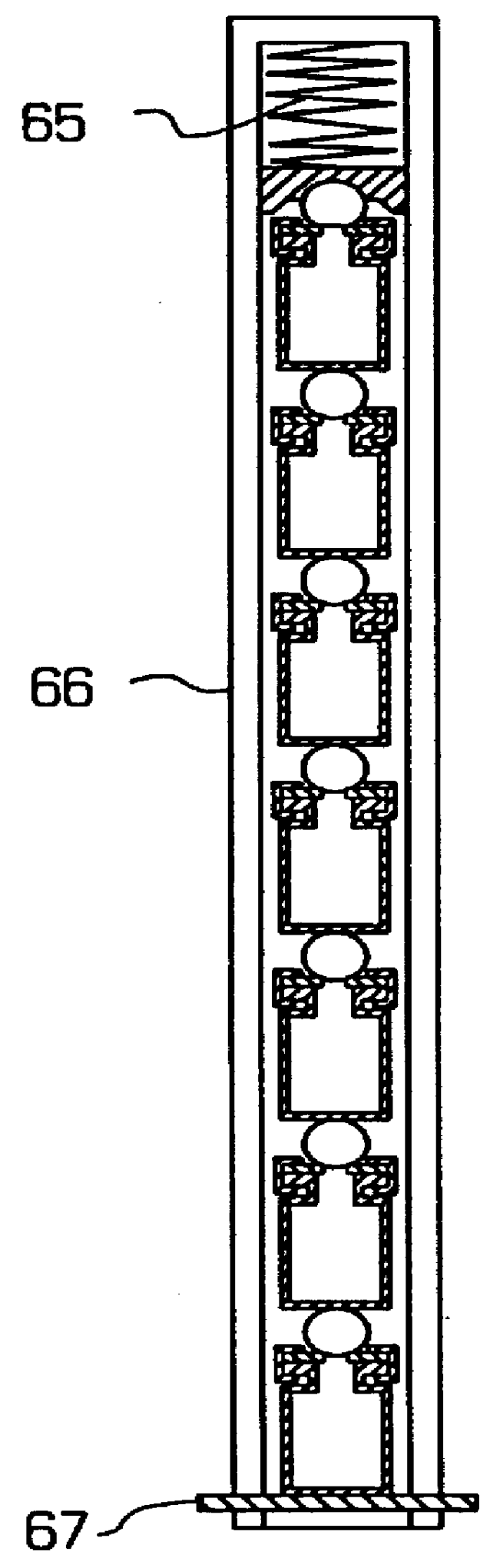
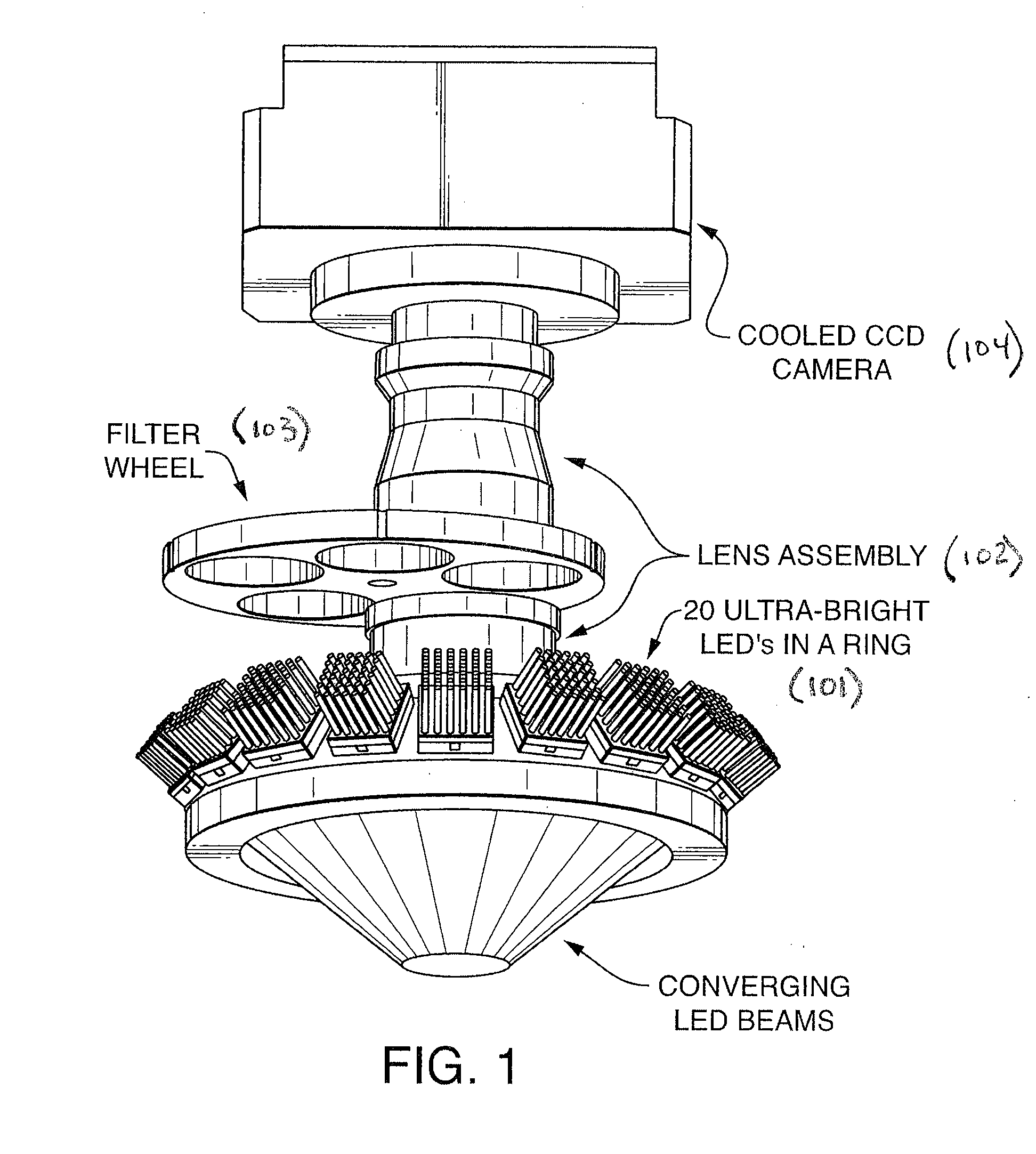
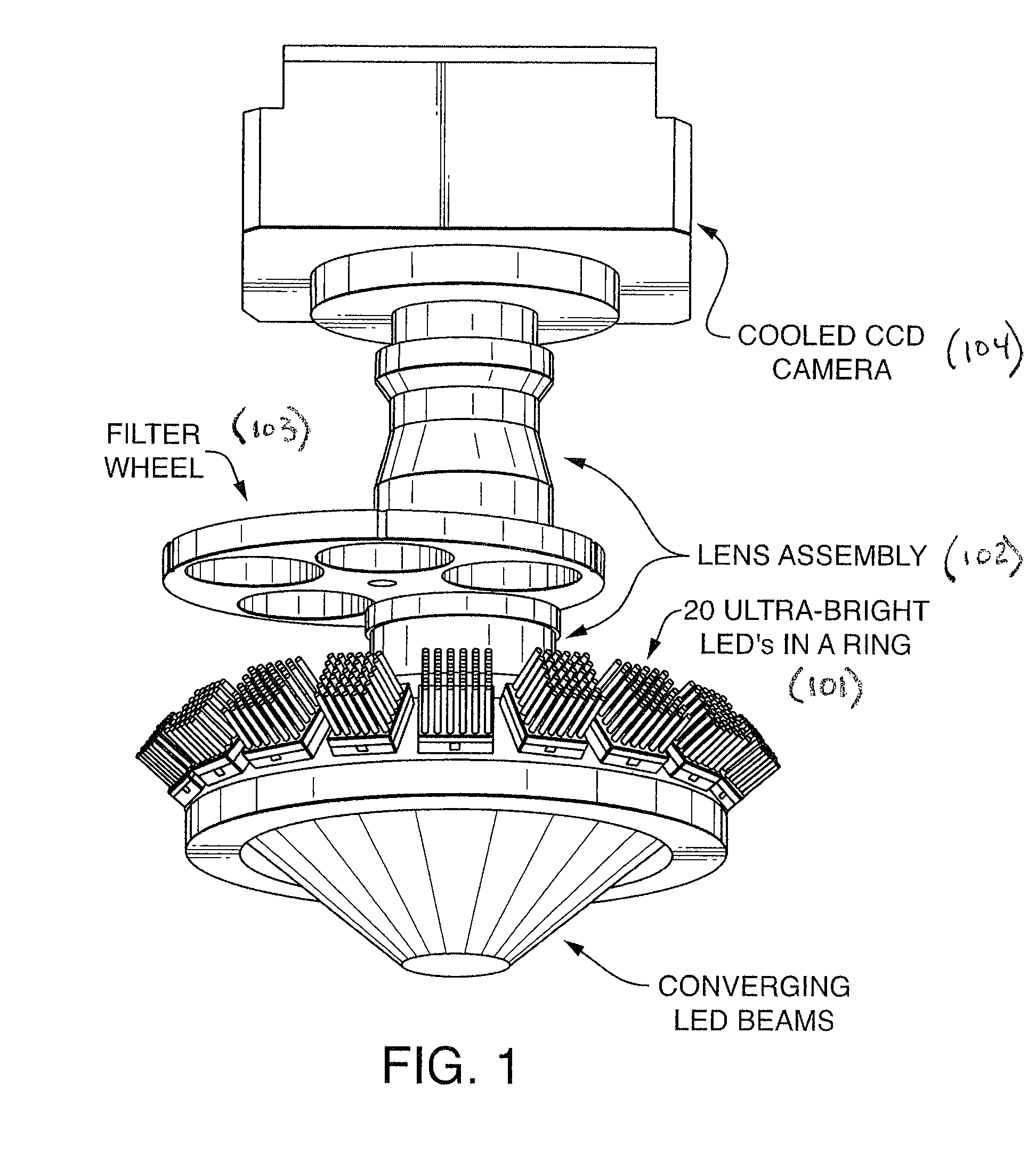
Apparatus and method for combinatorial chemistry synthesis
InactiveUS6045755AOvercome problemsImprove throughputEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisProcess engineering
In a first embodiment, this invention includes an integrated robot apparatus for performing combinatorial chemistry synthesis protocols and having interchangeable work-stations, robot arm tools, and reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays. The work-stations and tools are specialized to perform tasks necessary for the synthesis in a plurality of the reaction vessels grouped in a plurality of the reaction vessel arrays. Preferably, these elements function interchangeably because they have standardized sizes and conformation. The work-stations and tools include those for fluid dispensing or aspirating from individual reaction vessels or from all the reaction vessels in an array simultaneously. The reaction vessels can include, alternatively, stackable, ball-sealed reaction vessels, microtitre-like reaction vessel arrays, arrays of independent reaction vessels, valve-sealed reaction vessels, septum-sealed reaction vessels, and syringe reaction vessels. In alternative embodiments, this invention includes these work-stations, tools, reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays in various combinations or sub-combinations either for use in partially integrated robots or for manual or standalone use.
Owner:LION BIOSCIENCE AG
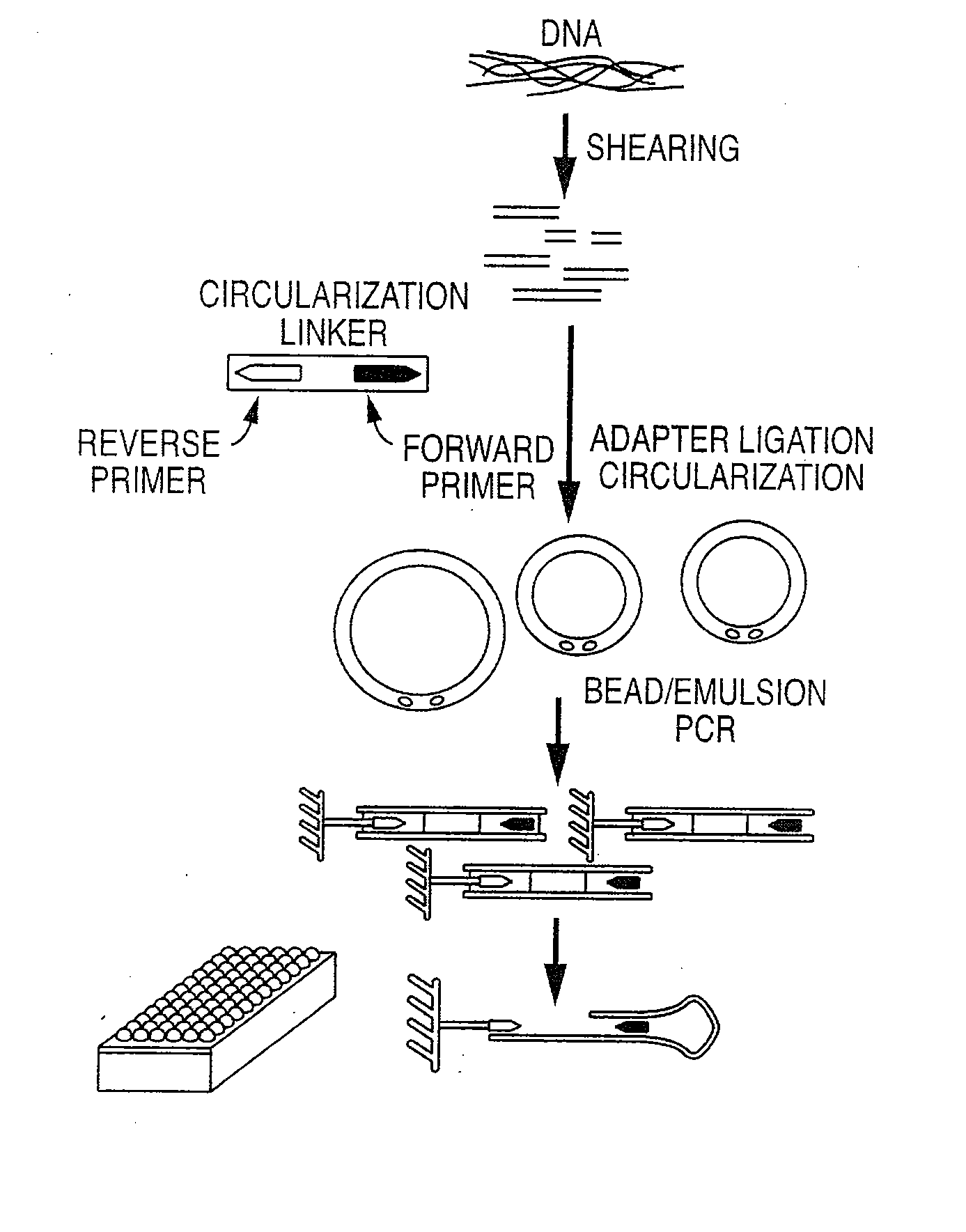
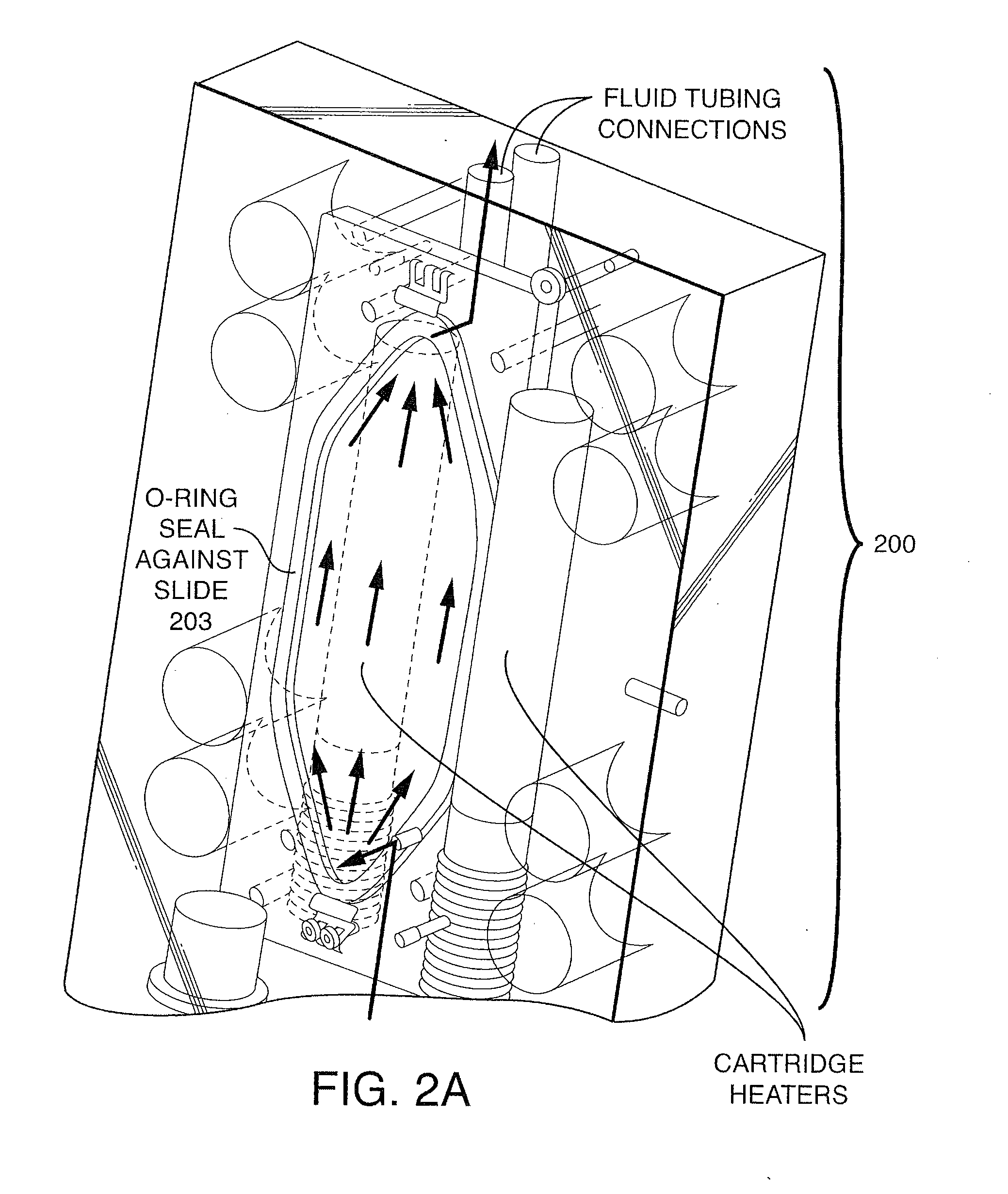
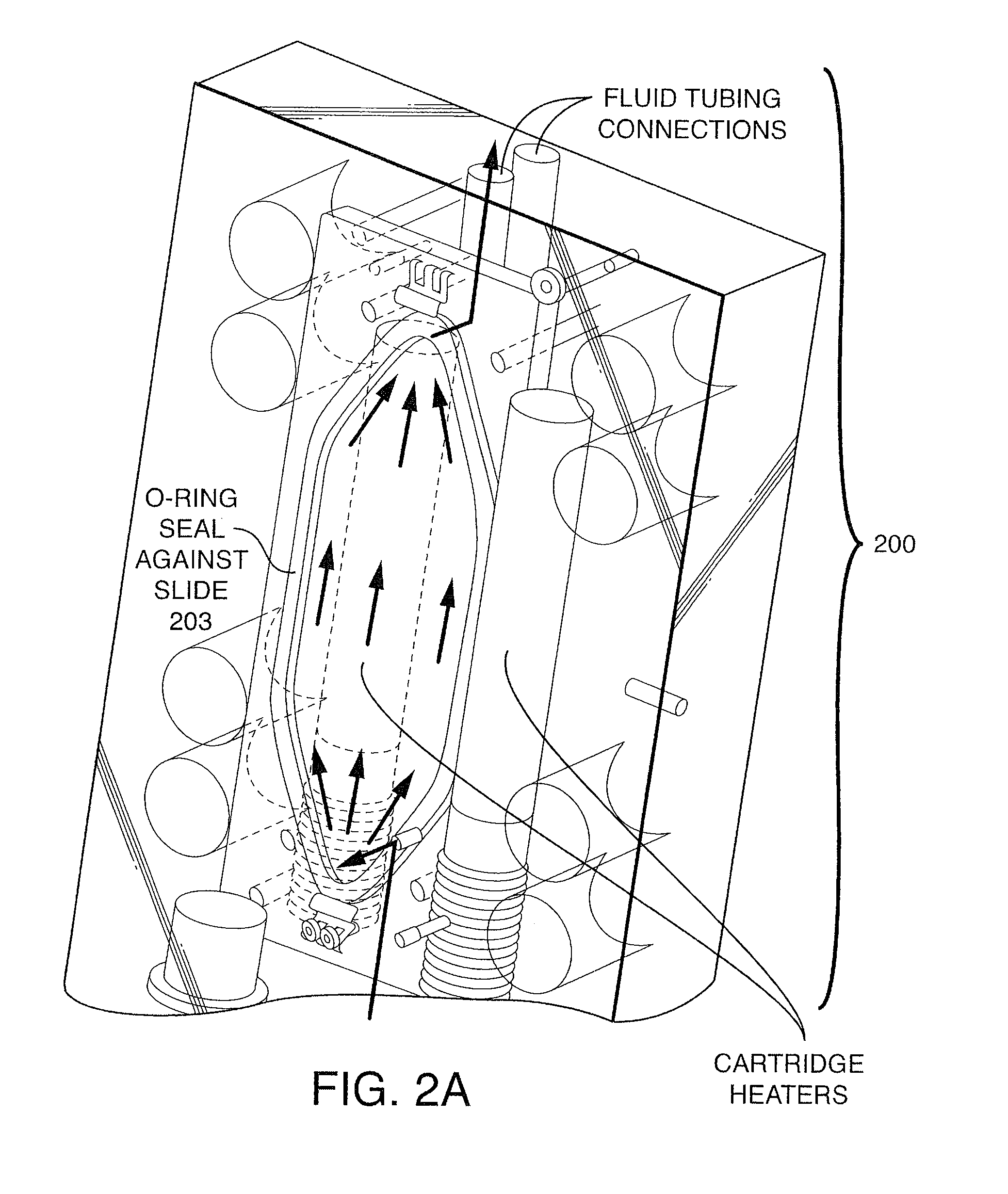
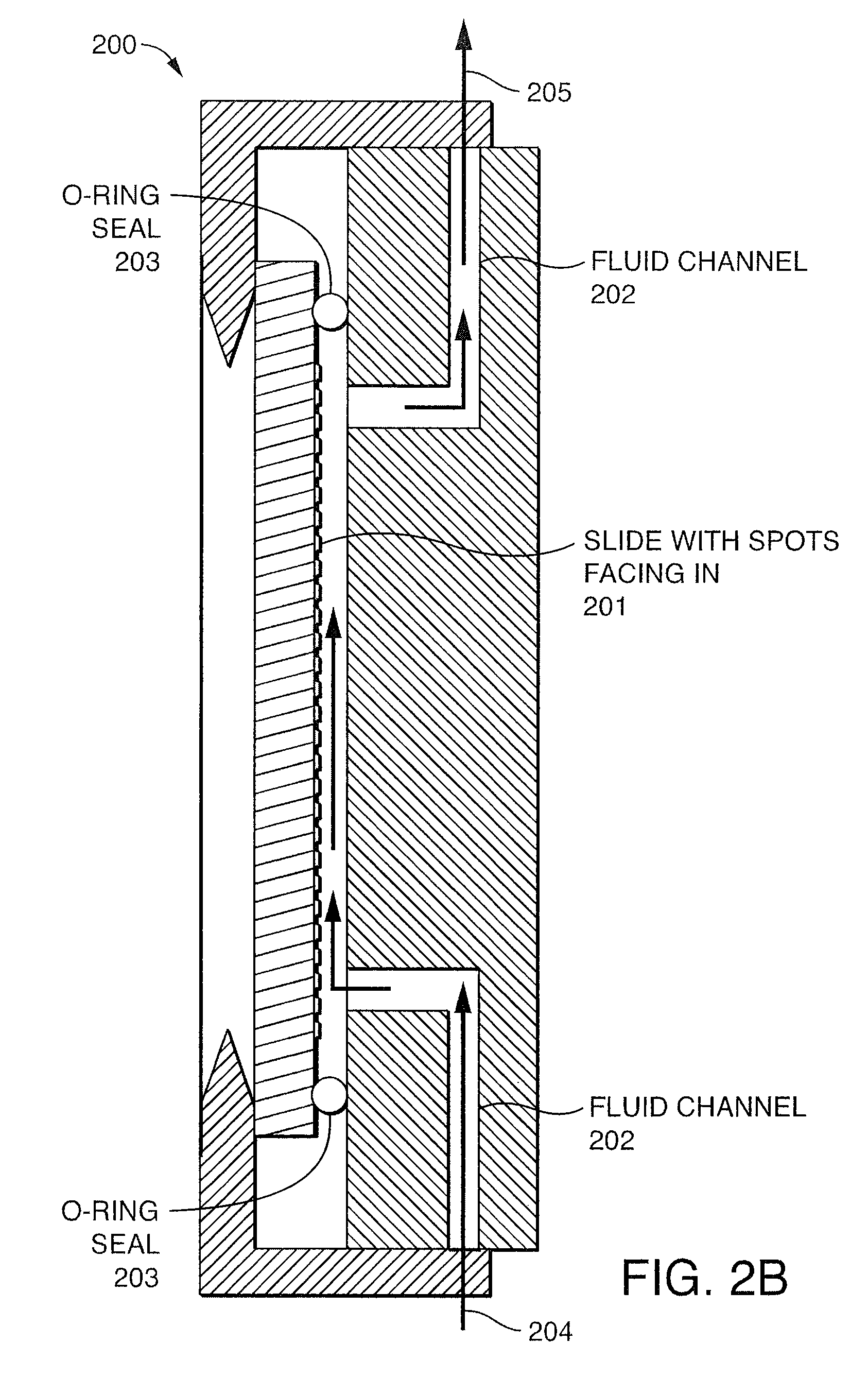
Methods And Devices For Sequencing Nucleic Acids In Smaller Batches
ActiveUS20100323350A1Reducing spectral crosstalkHigh strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotide sequencingComputational biology
The invention provides methods and compositions, including, without limitation, algorithms, computer readable media, computer programs, apparatus, and systems for determining the identity of nucleic acids in nucleotide sequences using, for example, data obtained from sequencing by synthesis methods. A plurality of smaller flow cells is employed, each with a relatively small area to be imaged, in order to provide greater flexibility and efficiency.
Owner:ISOPLEXIS
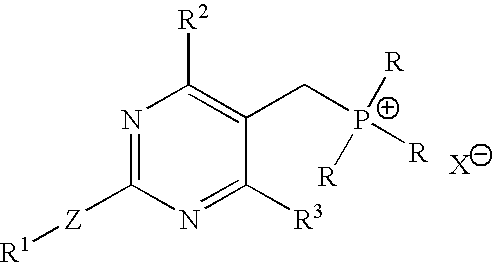
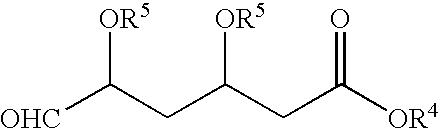
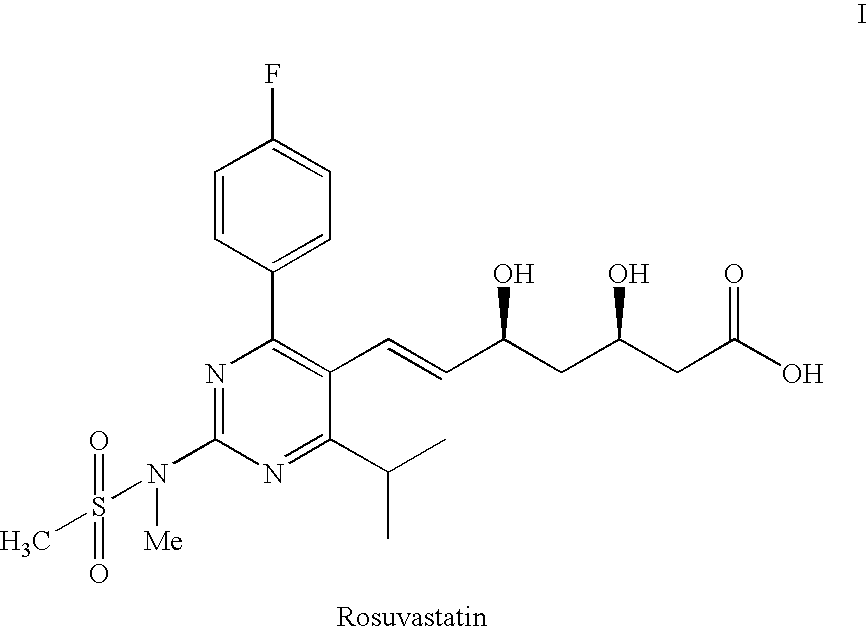
Process for the preparation of pyrimidine derivatives
ActiveUS20050124639A1Easier and economical productionSimple reaction conditionsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsOxygenAldehyde
An improved process for the preparation of pyrimidine derivatives is provided comprising reacting a Wittig reagent of the general formula wherein R is an alkyl of from 1 to 10 carbon atoms, aryl or arylalkyl, R1 is a substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon group, R2 and R3 are the same or different and are hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon group; Z is sulfur, oxygen, sulfonyl, or imino which may be substituted by formyl, acetyl, propionyl, butyryl, isobutyryl, valeryl, isovaleryl, amino substituted by sulfonyl or alkylsulfonyl, and sulfonyl substituted by alkyl, amino or alkylamino and X is a halogen; with an aldehyde of the general formula wherein R4 is hydrogen, a lower alkyl or a cation capable of forming a non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable salt and each R5 are the same or different and are hydrogen or a hydrolyzable protecting group, or each R5, together with the oxygen atom to which each is bonded, form a hydrolyzable cyclic protecting group, or each R5 is bonded to the same substituent which is bonded to each oxygen atom to form a hydrolyzable protecting group; in the presence of a base.
Owner:GLENMARK LIFE SCI LTD
Processes for the facile synthesis of diaryl amines and analogues thereof
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
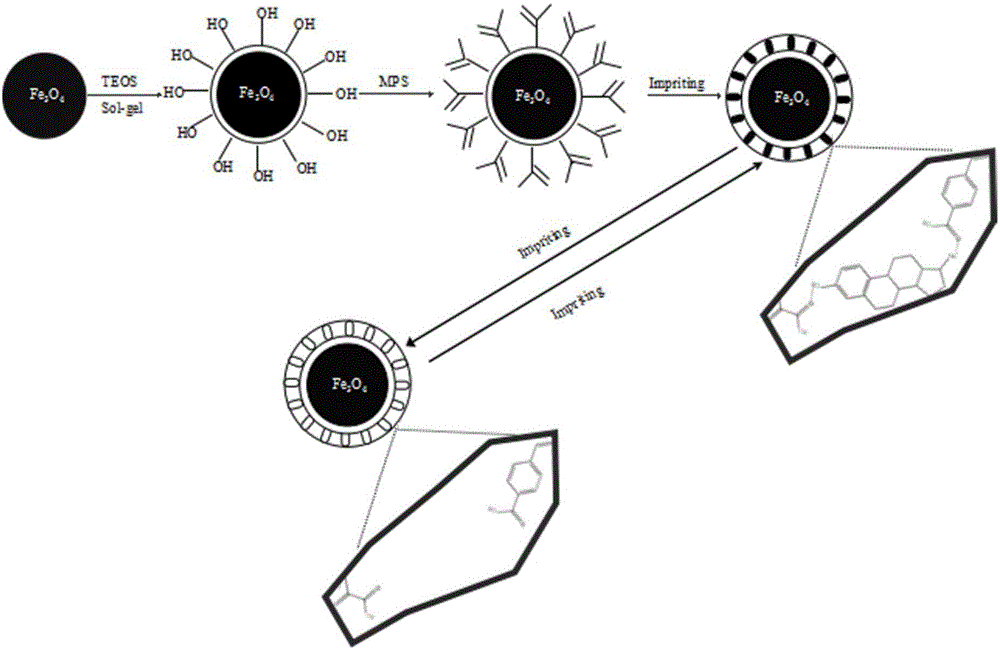
Preparation method for molecular imprinting material and molecular imprinting material prepared through preparation method
InactiveCN105107482AGood biocompatibilityImprove antioxidant capacityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSolubilityFunctional monomer
The invention provides a preparation method for a molecular imprinting material and the molecular imprinting material prepared through the preparation method. The preparation method comprises the steps that silicon oxide is coated on the surfaces of magnetic ferroferric oxide nanometer particles, the magnetic ferroferric oxide nanometer particles are modified with gamma-(methacryloyl chloride) amino propyl trimethoxy silane to obtain magnetic ferroferric oxide nanometer particles with propenyl on the surfaces, the magnetic ferroferric oxide nanometer particles with the propenyl on the surfaces serve as carriers, estrogen receptors are simulated, functional monomers are optimized, a surface imprinting technology is adopted, and then the molecular imprinting material which can simultaneously identify seven kinds of environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals is prepared. According to the preparation method, the easy separation of a magnetic nanometer material, the good water solubility of a silicon oxide nanometer material, the specific recognition ability of molecular imprinting polymers and the surface imprinting technology are mutually combined, the preparation technology is simple, the conditions are mild, the prepared molecular imprinting material is large in adsorption capacity, fast to respond, high in magnetism, good in chemical stability and high in repeating utilization rate, and the problems that at present, multiple trace, steroid and phenol environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals are difficult to simultaneously identify, separate and enrich are solved.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF CAAS
Novel reaction system for rapidly constructing plant gene site-directed knockout carrier
InactiveCN107254485AHigh speedImprove efficiencyHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyDouble chain
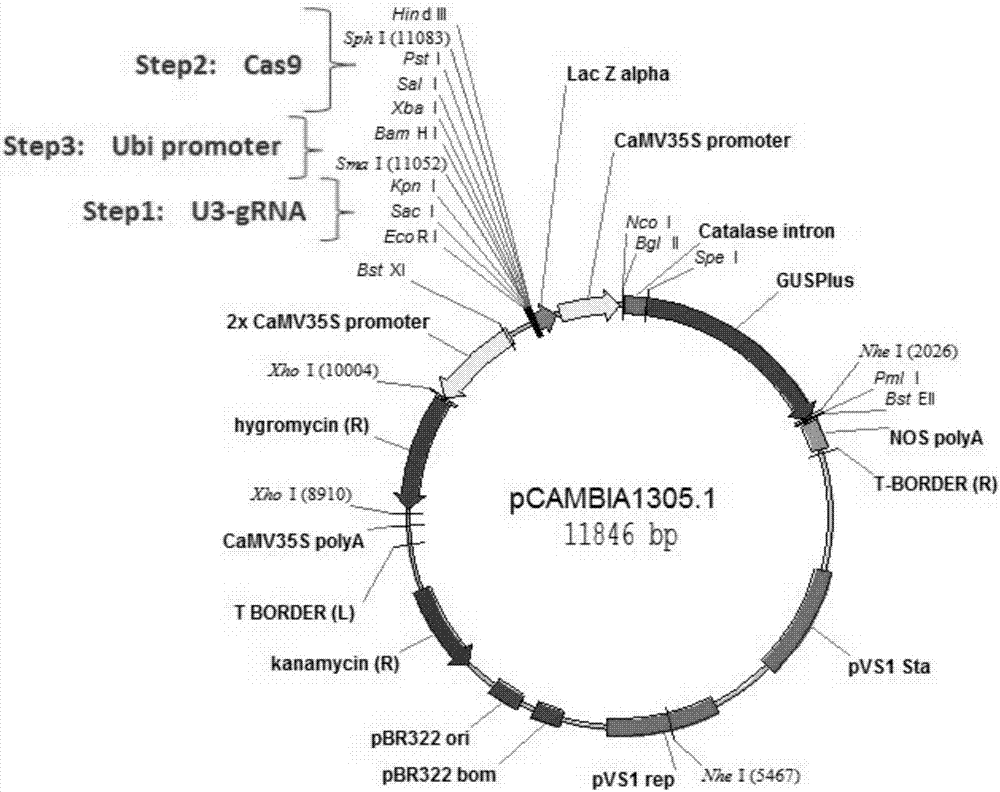
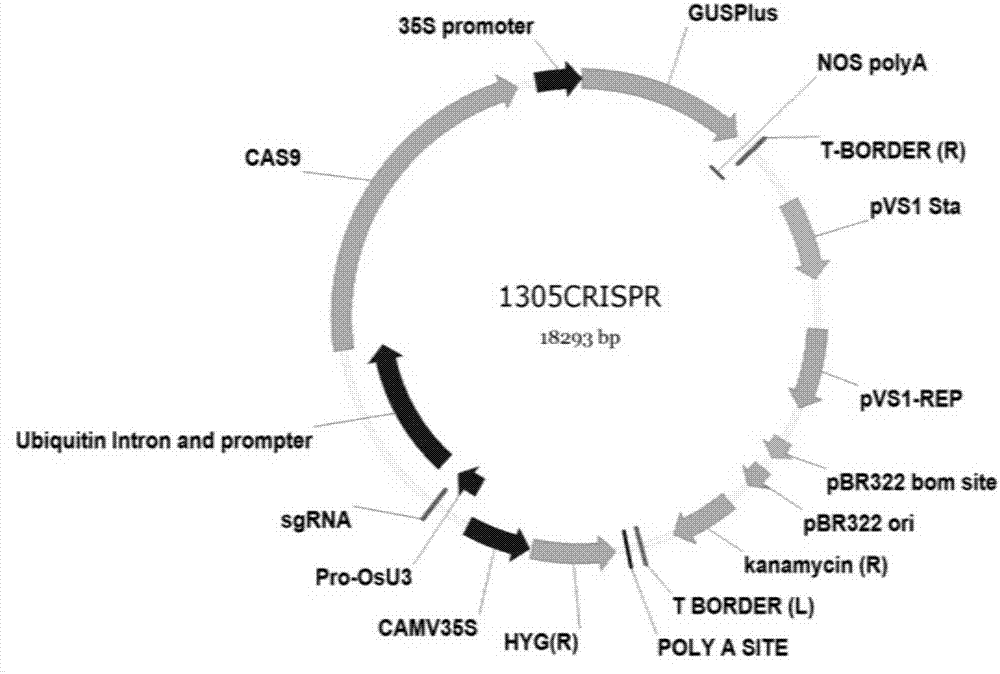
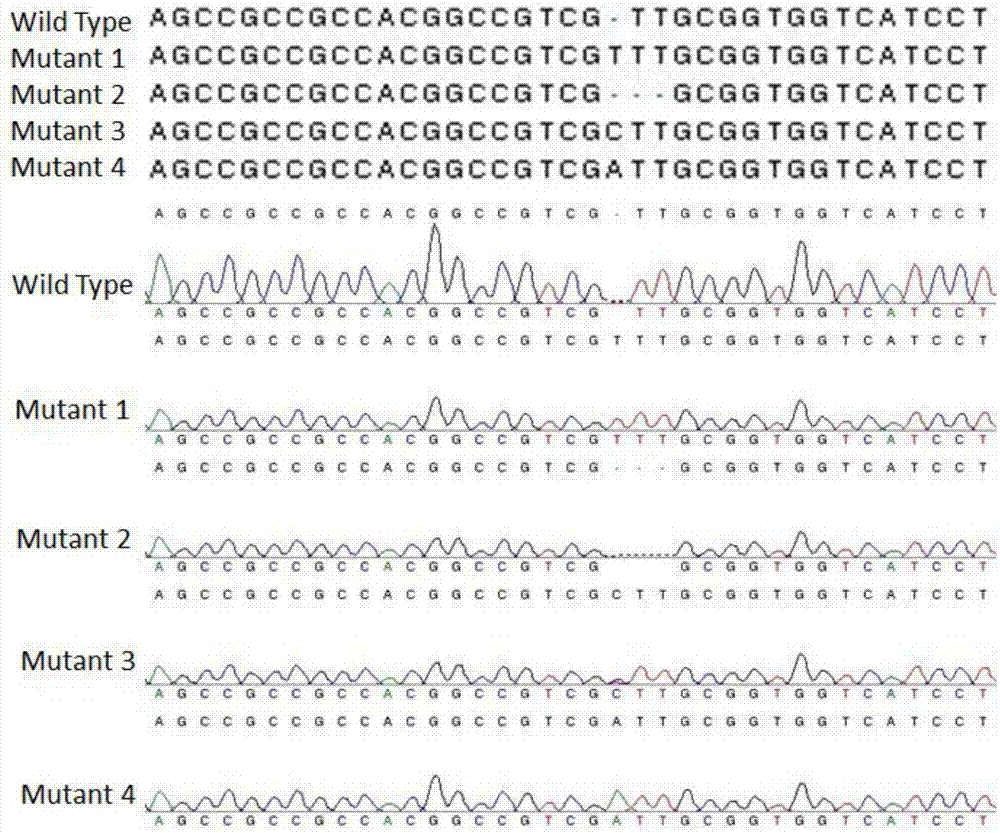
The invention discloses a novel reaction system for rapidly constructing a plant gene site-directed knockout carrier. The system comprises 1) based on a CRISPR-Cas system carrier, the carrier comprises the DNA molecules having the following characteristics: an agrobacterium infection method is used for carrier conversion to the plant, a carrier capable of simultaneously realizing driving of SgRNA by an OsU3 promoter for transcription and driving of Cas9 protein by an Ubiquitin promoter for expression; 2) restriction enzyme AarI; 3) buffer and Oligo required by a reaction of the restriction enzyme AarI; 4) target gene site specific DNA double chain; and 5) T4DNA ligase and ATP required by an enzyme reaction. The system only requires 5-10 reaction cycles for rapidly and efficiently completing a construction process of plasmid, greatly simplify the operation flow, and satisfies the requirement of rapid construction with high flux for plant gene site-directed knockout plasmid.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and devices for sequencing nucleic acids in smaller batches
ActiveUS8481259B2Good flexibilityCost-effective smaller runsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlow cellNucleotide sequencing
Owner:ISOPLEXIS
Method for preparing magnetic powder heavy metal ion blotting chitosan compound adsorbing agent
InactiveCN101301604AThe synthesis process is simpleEasy to separate and recycleOther chemical processesIonMagnetic powder
The present invention provides a preparation of a chitosan compound adsorbent for absorbing magnetic powder heavy metal ion imprint. The chitosan is employed as a imprinting matrix material, the nanometer magnetic powder Fe3O4 is employed as a magnetic component, the epichlorohydrin is employed as a crosslinking agent, the sodium tripolyphosphate is employed as a curing agent, after steps of ion imprinting, magnetic powder embedding and curing and template ion eliminating, the magnetic metal ion imprinting chitosan compound adsorbent is obtained. The compound absorbent prepared by the present invention can be separated from the solution after absorption efficiently and rapidly under the external magnetic field to realize the rapid efficient reclaim of the adsorbent. The compound absorbent has high mechanical strength and selective absorbability of imprint Cr(VI) or Zn (II), avoids the swelling loss of the chitosan in acidity solution and improves the absorption capacity of Cr(VI) or Zn (II). The preparation of the present invention has simple reaction conditions and has no rigorous limit of the experiment conditions. The preparation of the present invention can be used to process the heavy metal waste water containing Cr(VI) or Zn (II), also reclaim Cr(VI) or Zn (II).
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
High-performance water system zinc ion battery anode material, manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN110474044AEasy to prepareLow equipment requirementsFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsSpecific dischargeNanotechnology
The invention provides a high-performance water system zinc ion battery anode material, a manufacturing method and an application thereof. The anode material has the following general formula: (N,M) sigma=1V8O20 nH2O, wherein the N is one of Li, Na, K, Zn, Cu, Mg or Ca, the M is one of Mn, Fe, Co or Ni, and the n is 0.01-4. The anode material can be manufactured through one-step hydrothermal method, a reaction condition is mild, a manufacturing process is simple, and a requirement to equipment is low. A microscopic morphology of the obtained anode material is a nanobelt. The obtained anode material is firstly applied to a water system zinc ion battery, and has electrochemical performance such as a higher specific discharge capacity, a higher cycle stability and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Process for efficiently preprocessing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101736631ALess side effectsReduce usageFermentationPaper material treatmentDecompositionReaction temperature
The invention relates to a process for efficiently preprocessing lignocellulose. The process adopts the following procedures of stepwise optimizing and hydrolyzing: firstly, boiling the lignocellulose in overheated water to ensure that most hemicellulose is dissolved into oligosaccharide; continuously reacting the boiled mixture in a special flash evaporation reactor; and gradually changing reaction temperatures in the process of reaction to slow down xylose decomposition as far as possible and ensure that the hemicellulose is more completely transformed into xylose. The process has the advantages of simpleness, low cost, reasonable energy utilization, no solid-liquid separation in stepwise process, direct hydrolysis on the hot mixture, energy saving and high hydrolysis efficiency of processed cellulose on enzyme.
Owner:熊鹏
Preparation method of metformin hydrochloride
ActiveCN103435518AHigh recovery rateImprove securityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMetformin hclPharmacology
The invention discloses a preparation method of metformin hydrochloride. The preparation method is characterized by using dicyandiamide and dimethylamine hydrochloride as raw materials, feeding the materials in a mole ratio of (1:1)-(1:1.2), using N,N-dimethylacetamide or dimethyl sulfoxide 2-4 times dicyandiamide by weight as a solvent, and reacting for 4-8 hours at 140+ / -5 DEG C to prepare a crude metformin hydrochloride product; recrystallizing the crude product with ethanol, regulating the pH value to be 5-6, decoloring the crystal, cooling the crystal to minus 10-0 DEG C while stirring, precipitating the crystal, obtaining a refined metformin hydrochloride product through filtering and drying, and recovering the solvent from filtrate. The qualified product has yield of 80-85% and high purity. The preparation method has the advantages that as the selected reaction solvent has a relatively high boiling point, the recovery rate of the solvent is high; the phenomenon of material surging can be effectively avoided, so that the preparation method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simplicity in operation and high safety.
Owner:QINGDAO HUANGHAI PHARM CO LTD
Method for reducing content of reducing sugar in reconstituted tobacco
ActiveCN103948163ASimple reaction conditionsReduced reducing sugar contentTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentEthylene diamineCooking & baking
The invention relates to the field of reconstituted tobacco preparation, in particular to a method for reducing the content of reducing sugar in reconstituted tobacco, and an application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: adding a mixture material of tobacco stems, tobacco waste and tobacco pieces into hot water of 60-70 DEG C, keeping the temperature, performing solid-liquid separation, and preparing to obtain a tobacco extract liquid; respectively adding EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), proline, lysine, diammonium hydrogen phosphate and a catalyst into the obtained extract liquid, adjusting the pH value of the reaction liquid till the reaction liquid is faintly acid, stirring for more than 2 hours at the constant temperature of 70-80 DEG C, subsequently performing vacuum concentration, and uniformly applying the concentrated extract liquid onto the front and back sides of a paper substrate; putting the obtained product into a baking oven for baking under the condition of ventilation till the moisture content is 11.5-13.5%, and obtaining a finished reconstituted tobacco product. Compared with that of a thin piece which is not treated by using the technical method, the content of the reducing sugar is reduced by 10-20% on premise that the sensory quality of the product is not affected.
Owner:SHANGHAI TOBACCO GRP CO LTD +1
Rare-earth oxide modified high-selectivity catalyst for adiponitrile hydrogenation and hexylenediamine production, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109647419AHigh mechanical strengthReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationRare earthSolvent
The invention discloses a rare-earth oxide modified high-selectivity catalyst for adiponitrile hydrogenation and hexylenediamine production, a preparation method and application thereof. An alumina-supported nickel-based catalyst is used as an active component, and at 25-90 DEG C and through a parallel flow precipitation process, a low-content rare-earth oxide is used for the modification. A tankreactor is adopted at the low temperature and without an alkaline reagent to carry out a reaction at the pressure of 1-9 MPa for 1-6 h so as to achieve adiponitrile catalytic conversion for high-selectivity preparation of hexylenediamine. No alkaline reagent or NH3 is added during the reaction process to inhibit side reaction of cyclization. The environmental pollution is reduced; and the catalysthas high mechanical strength, the reaction post-treatment is simple and the reaction condition is relatively mild. According to the method and in part of the embodiments, the conversion rate of adiponitrile reaches up to 100% according to set reaction parameters, and selectivity of the product hexylenediamine can reach up to 90%. The invention has good economic benefit and industrial applicationprospects.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Carbon-silicon composite lithium ion battery cathode material and preparation method thereof
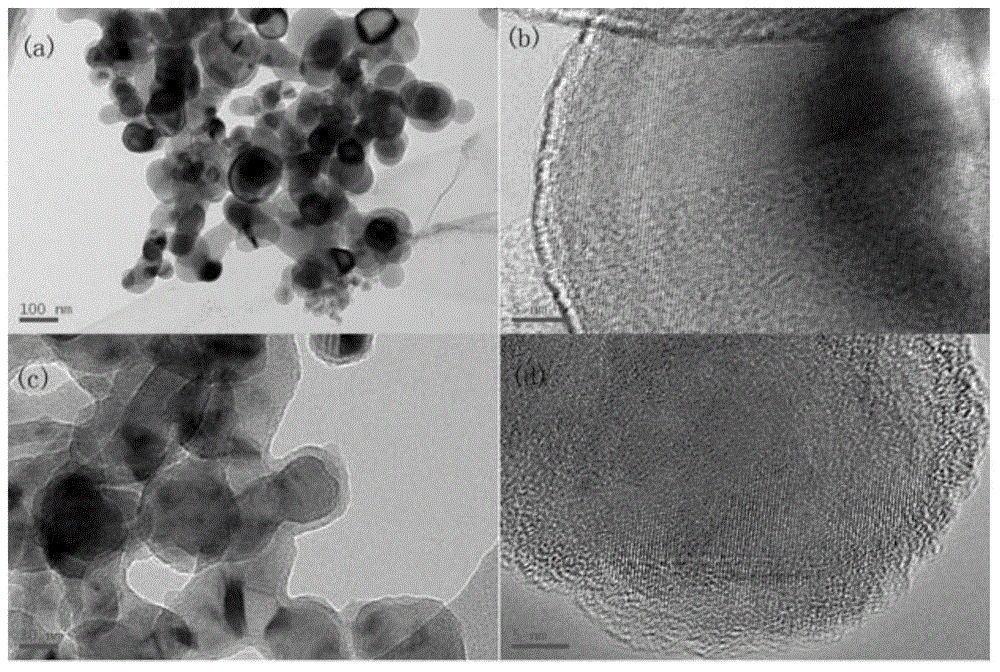
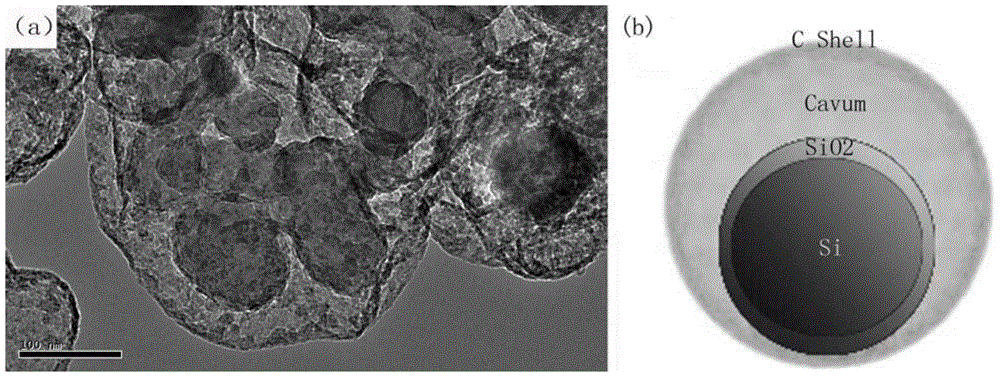
InactiveCN105006549AImprove discharge specific energyImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesSiliconLithium electrode
A carbon-silicon composite lithium ion battery cathode material and its preparation method are disclosed. Si which is used as an inner core is tightly coated with a SiO2 layer, and a hollow layer is arranged between the SiO2 layer and the outermost C coating layer. The inner core Si accounts for 30-70 wt% of mass of the composite material. The hollow layer is obtained by etching the SiO2 part of the middle layer on the synthesized Si / SiO2 / C composite material. When used as a lithium ion battery cathode material in the field of electrochemical application, the material provided by the invention has advantages of high cyclic stability and high coulombic efficiency. There is less environmental pollution during the experimental process. The technology is easy to control and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Cu-Cu2O-CuO ternary copper-based solid solution catalyst and its preparation method
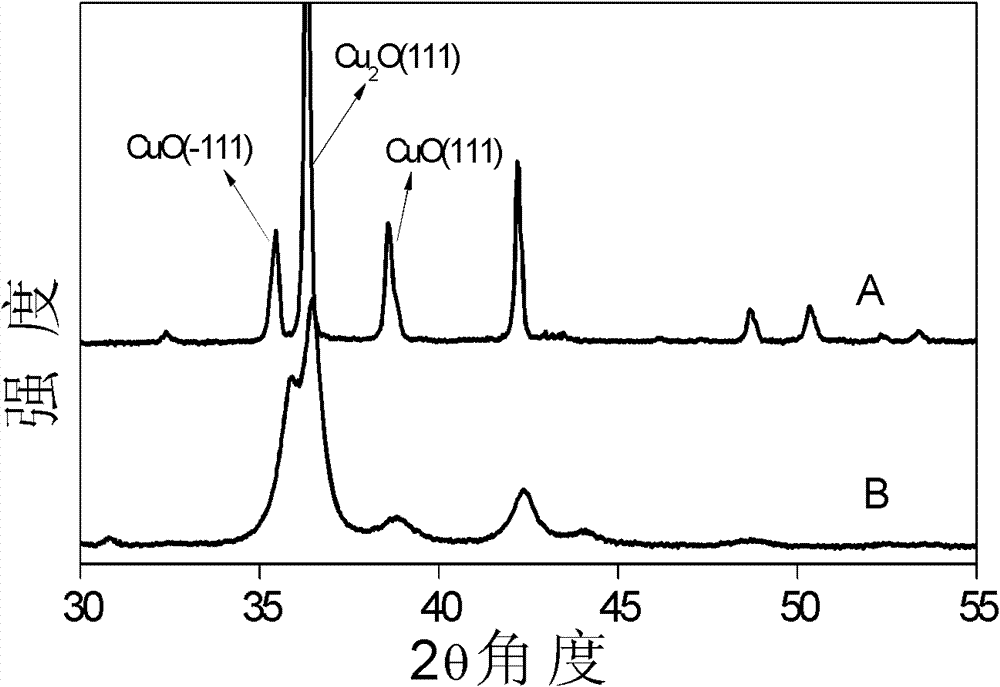
InactiveCN102773099AHigh selectivityHigh yieldGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationCopper oxideSolid solution
The invention relates to the organosilicon monomer synthesis field, and particularly relates to a Cu-Cu2O-CuO ternary copper-based solid solution catalyst and its preparation method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) taking a mixture composed of 0.5-40wt% of metal copper powder and 20-80wt% of copper oxide as a raw material, conducting heat treatment at a temperature of 600-1000DEG C for 0.5-12h under inert gas protection, and then carrying out ageing at a temperature of 300-600DEG C for 1-15h so as to obtain a ternary copper-based solid solution; and 2) subjecting the ternary copper-based solid solution from step 1) to shattering and milling to obtain the Cu-Cu2O-CuO ternary copper-based solid solution catalyst. The copper-based solid solution catalyst prepared in the invention shows high dimethyldichlorosilane selectivity and silicon power raw material conversion rate.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
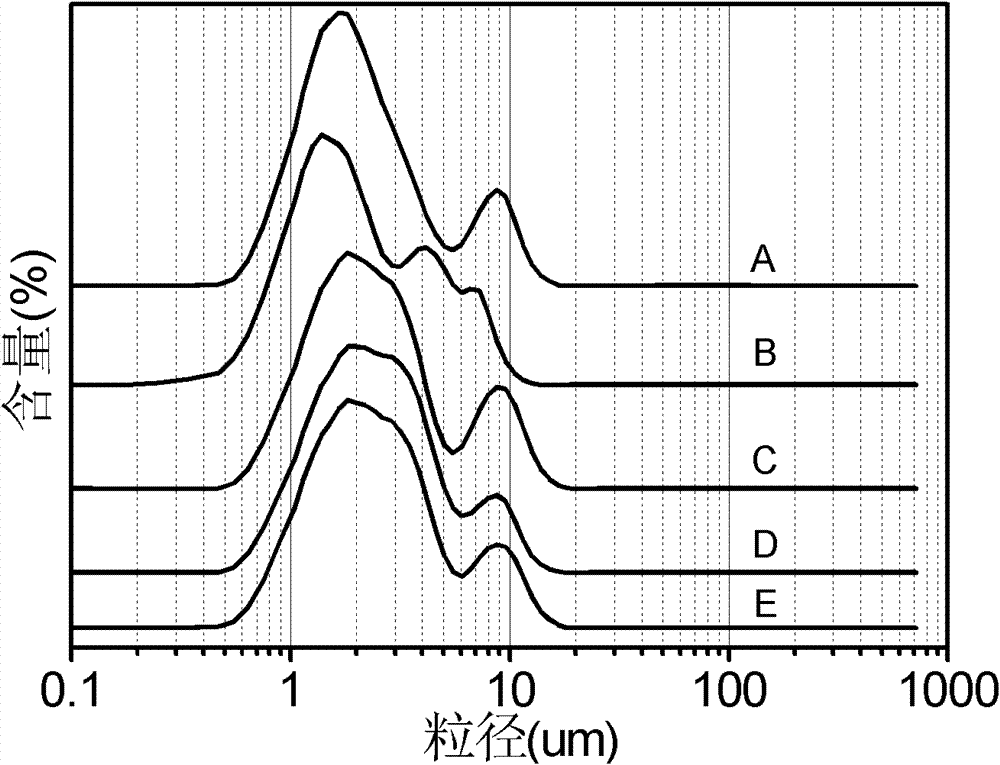
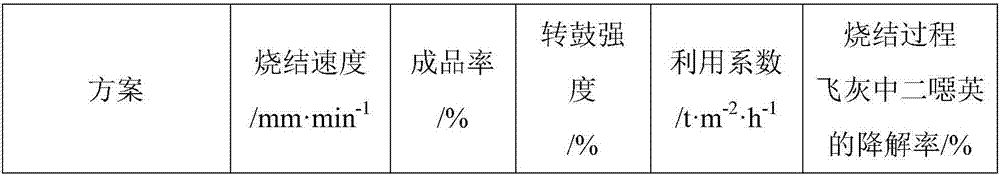
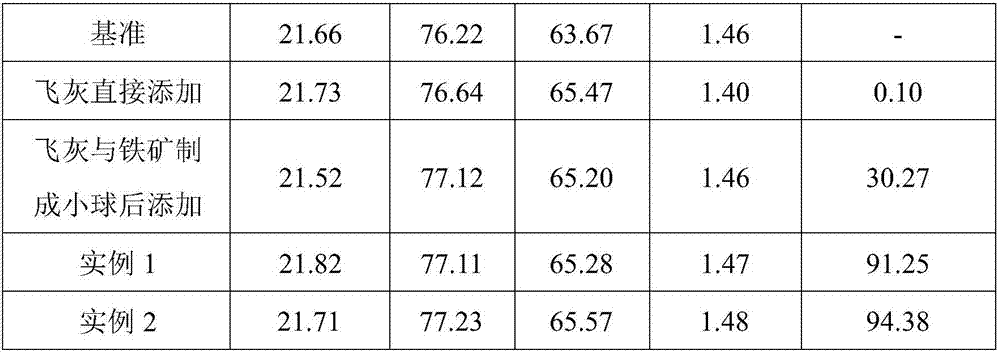
Dioxin control method for iron ore sintering garbage fly ash coprocessing process
ActiveCN107159678ARealize normal sinteringEffectively fixedTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalSludgeLitter
The invention discloses a dioxin control method for the iron ore sintering garbage fly ash coprocessing process. According to the method, garbage fly ash, lime milk, flammable solid fuel and sludge are subject to mixed granulation and drying, and small balls containing garbage fly ash are obtained; iron core sintering raw materials are granulated and then are mixed with the small balls of the garbage fly ash, and after distribution, ignition and sintering are carried out. According to the method, on the premise that the iron ore sintering is not affected, efficient decomposing of dioxin contained in the fly ash can be achieved, dioxin secondarily formed in the garbage fly ash sintering process is prevented, according to the method, the decomposing rate of the garbage fly ash dioxin reaches 90% or above, meanwhile, effective solidifying of the garbage fly ash can be ensured, and in the sintering process, the aim of cleaning the garbage fly ash is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Microorganism desulfurizing and sulfur recycling method
InactiveCN105498470AAvoid cloggingReduce energy consumptionChemical industryDispersed particle separationMicroorganismAbsorption column
A microorganism desulfurizing and sulfur recycling method. A gas material flow containing hydrogen sulfide is fed into an absorption column and then is subjected to chemical absorption with an alkali solution sprayed from the top of the column in a counter-contact manner, wherein treated purified gas is discharged out from the top of the absorption column. A back-washing apparatus is arranged in the absorption column to wash the sulfur attached to a filling material. A rich solution, in which the hydrogen sulfide is dissolved, is fed into a rich solution tank from the bottom of the absorption column and then is fed into a bio-reactor for aeration, so that a carrier, on which desulfurization bacteria is immobilized, is fluidized and the sulfide in the absorption solution is biologically oxidized to generate elementary sulfur. The regenerated solution containing the sulfur then is fed into a settling tank through an overflow weir of the bio-reactor and a supernatant liquid is fed into a barren solution tank. The supernatant liquid then is fed back to the absorption column for being recycled through a barren solution pump. Sulfur slurry in the bottom layer is discharged through the bottom of the settling tank and then is subjected to solid-liquid separation in a centrifugal machine to obtain biological sulfur. A separated filtrate is fed back to the bio-reactor for being recycled. The bio-desulfurization technology is green and environment-friendly, is energy-saving and emission-reducing and can recycle resources, and has social, economical and environmental benefits.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Vanillin derivative containing dithioacetals, preparation method and purpose thereof
The invention discloses a vanillin derivative containing dithioacetals, a preparation method and a purpose thereof. A structural general formula of the derivative is shown in a specification, wherein, R1 is a substituted aromatic ring, heterocycle or 1,1-dichloroethylene; a methyl atom, a nitro atom or a halogen atom is contained on an o-position, a meta-position and a para-position of the aromatic ring, the halogen atom can be fluorine, chlorine, or bromine; the heterocycle is five-membered or six-membered heterocycle, and one halogen atom is contained on the heterocycle. R2 is substituted aromatic ring, 1-propanol or heterocycle; fluorine or chlorine is contained on para-position of the aromatic ring, and the heterocycle is furan ring. The compound can inhibit plant virus such as tobacco mosaic virus, cucumber mosaic virus and potato y potyvirus.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Compound for preparing suvorexant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103923068AAvoid chiral separation and the use of chiral catalystsEasy to operateCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationStereochemistryStereoisomerism
The invention relates to three novel compound formulas I, II and III for preparing suvorexant, stereoisomers or salt thereof and a preparation method of the formulas I, II and III. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the suvorexant. The preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used for synthesizing to obtain the chiral compounds I, II and III through a chiral initiator and use the chiral compounds I, II and III for the synthesis of the suvorexant and has the advantages of easiness for operation, moderation in reaction condition, easiness for post processing, easiness for purification, high yield, high ee value and easiness for industrialization.
Owner:武汉久安药业有限公司
Nano-iron powder prepn. method
InactiveCN1751829AImprove reducibilityImprove magnetic propertiesCoatingsIron saltsHydrazine compound
A process for preparing iron nanoparticles includes such steps as proportionally dissolving iron salt in alcohol, water, or their mixture, proportionally adding NaOH solution and hydrazine hydrate solution, stirring, and heating at 80-120 deg.C while refluxing until the mother liquid becomes colorless and transparent. Its advantages are high purity, adjustable granularity and high output rate (more than 99%).
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for synthesizing cyclic carbonate ester in presence of acidic ionic liquid catalyst
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing cyclic carbonate ester in presence of an acidic ionic liquid catalyst, which relates to a method for synthesizing the cyclic carbonate ester. The invention solves the problems of strict reaction conditions, low catalyst activity, environmental pollution and high cost of the traditional method for synthesizing the cyclic carbonate ester. In the method of the invention, the acidic ionic liquid catalyst is adopted, and carbon diode and an epoxy compound undergo cycloaddition to form the corresponding cyclic carbonate ester. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high catalyst activity, environmental protection and low cost.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
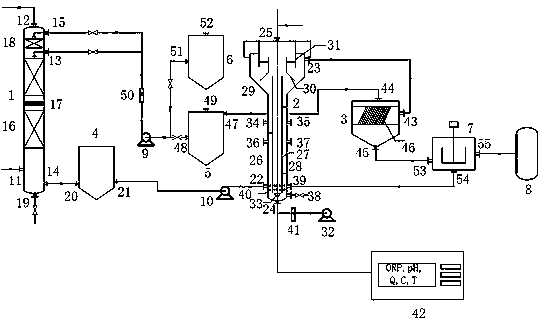
Organic waste water processing method
ActiveCN101139154ARelease influenceEfficient removalTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogenMembrane bioreactor
The present invention relates to an organic wastewater treatment method of membrane bioreactor, which has dephosphorization and denitriding functions. The method is provided with an oxygen-poor pool before the typical anaerobic-oxygen-poor-aerobic dephosphorization and denitriding method and provided with an aerobic pool adopting integrated membrane bioreactor behind the method. The method of the present invention not only has the advantages of the membrane bioreactor, but also can more completely remove organic contaminations, dephosphorize and denitride as well as eliminate the chroma of yielding water efficiently. The present invention is a method to reach the regenerated water standard of high quality by one time treatment of wastewater.
Owner:BEIJING ORIGINWATER TECH CO LTD
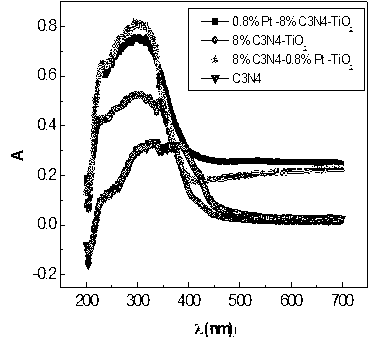
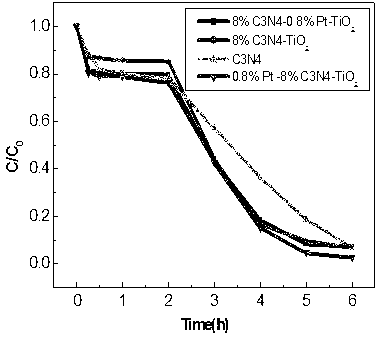
Method for preparing Pt-C3N4-TiO2 three-component visible light photocatalyst
InactiveCN103230808ASimple reaction conditionsMild and stable reactionPhysical/chemical process catalystsLight ActivityCarbide
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Pt-C3N4-TiO2 three-component visible light photocatalyst. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of: firstly heating melamine up to the temperature of 540 DEG C so as to be cracked into graphite-like nitrogen carbide (g-C3N4); then carrying out ultrasonic mixing so as to enable P25 to be loaded with g-C3N4; and finally synthesizing by using an immobilized sol process, thereby preparing the target product. The composite photocatalyst with the structure has high visible light activity, thus the photocatalyst becomes an important sewage treatment agent with a potential research value. The method has the advantages that the reaction conditions are simple, the reaction is mild and stable, and the production enlargement is facilitated.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
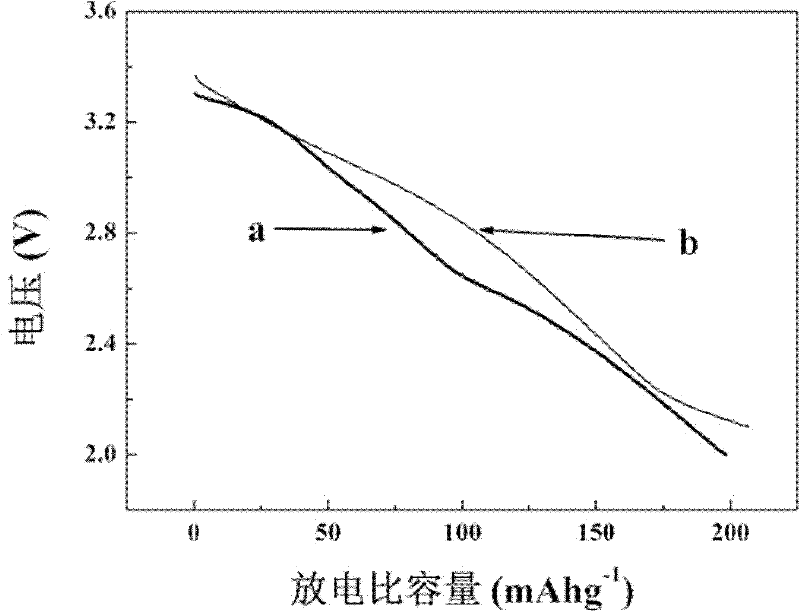
Lithium secondary battery with metal fluoride as positive electrode material
ActiveCN102315482AEasy to prepareSimple reaction conditionsCell electrodesSecondary cellsChemical compositionFluoride
The invention which discloses a lithium secondary battery with a metal fluoride as a cathode material belongs to the technical field of environmentally friendly secondary batteries. The lithium secondary battery is characterized in that: the lithium secondary battery comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a membrane, an electrolyte or a polymer dielectric, a current collector, a positive electrode shell, and a negative electrode shell; the membrane or the polymer dielectric immersed with the electrolyte separates the positive electrode and the negative electrode; the positive electrode material which is coated on the current collector is connected with the positive electrode shell of the battery; the negative electrode is connected with the negative electrode shell of the battery; the positive electrode shell and the negative electrode shell mutually insulate; the positive electrode comprises the metal fluoride, a conductive agent, a binder, and the current collector; and the positive electrode material is the metal fluoride, and the chemical composition of the positive electrode material is MFa(H2O)b, wherein a is equal to or less than 3 and equal to or more than 1, and b which is equal to or less than 4 and equal to or more than 0 is an integer. The lithium secondary battery of the present invention has the advantages of simple preparation method, easily realized reaction condition, easily available raw material, low energy consumption in the preparation process, good security, and good electrochemical performance.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Elastomeric functional biodegradable copolyester amides and copolyester urethanes
InactiveUS7304122B2Promote repairInhibit cell proliferationPowder deliveryBiocidePolymer scienceCarbamate
The present invention provides elastomeric copolyester amides, elastomeric copolyester urethanes, and methods for making the same. The polymers that are based on α-amino acids and possess suitable physical, chemical and biodegradation properties. The polymers are useful as carriers of drugs or other bioactive substances. The polymers can be linked, intermixed, or a combination thereof, to one or more drugs.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Device and method for degrading antibiotic wastewater by utilizing low temperature plasma in coordination with bismuth molybdate catalyst
InactiveCN103848484AImprove degradation rateHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCatalyst degradationBreather
The invention discloses a device and a method for treating antibiotic wastewater by utilizing low temperature plasma in coordination with a bismuth molybdate catalyst. The device for treating the antibiotic wastewater by utilizing the low temperature plasma in coordination with the bismuth molybdate catalyst comprises a barrel-shaped reactor, a breather pipe, a high voltage electrode, an alternating current high voltage power supply, an air pump and a stirrer, wherein the breather pipe is arranged inside the barrel-shaped reactor and is coaxial with the barrel-shaped reactor, the high voltage electrode is suspended inside the breather pipe, the lower port of the breather pipe is arranged at the lower bottom part inside the barrel-shaped reactor, the upper part of the breather pipe is arranged outside the barrel-shaped reactor, an air inlet is formed in the side wall of the upper part of the breather pipe, the air inlet is communicated with the outlet of the air pump by virtue of a pipeline; the alternating current high voltage power supply is respectively connected to the high voltage electrode and grounded, and the stirrer is arranged at the lower part of the barrel-shaped reactor. The device for treating the antibiotic wastewater by utilizing the low temperature plasma in coordination with the bismuth molybdate catalyst has the characteristics of simple design, low equipment investment and no secondary pollution and can be applied to the filed of treatment on antibiotic wastewater and organic wastewater difficult to be biochemically degraded, wherein a degradation reaction temperature can be increased by fully utilizing heat produced in a discharge process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for producing ultra-small water soluble near-infrared Ag2S quantum dots
ActiveCN102826585ASmall sizeGood water solubilityNanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsSolubilityFluorescence spectra
The invention relates to a method for producing ultra-small water soluble near-infrared Ag2S quantum dots, which adopts the one-pot method for production. The method for producing ultra-small water soluble near-infrared Ag2S quantum dots comprises the following steps of: 1) uniformly mixing a protein water solution with an AgNO3 water solution and carrying out reaction for 5 minutes at the normal temperature under the condition of magnetic stirring; 2) adjusting the pH value of the liquid with a NaOH water solution to 12.0; and 3) adding a chalcogenide water solution with the concentration of 10-100 millimole / l into the liquid and adjusting the mole ratio of the Ag element and the S element to (6-1):1, and reacting for 12 hours under the conditions of stirring and 37 DEG C to produce the ultra-small water soluble near-infrared Ag2S quantum dots of smaller than 2 nanometers. The method has the advantages that the quantum dots produced by the method have the excellent properties of no-toxic heavy metal elements, small size, good water solubility, high luminous efficiency, adjustability in fluorescence spectra within near-inferred areas and the like; and the production method is safe, easy and convenient to operate, has small toxicity and low cost, and is easy to popularize and use in a large scale.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for preparing isopentenol from 3-methyl-3-butenol
ActiveCN101544538ALow content of active ingredientsReduce manufacturing costPreparation by isomerisationIsomerizationHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for preparing isopentenol from 3-methyl-3-butenol, which performs isomerization reaction on a raw material of 3-methyl-3-butenol to generate the isopentenol in the presence of a catalyst in an atmosphere containing hydrogen, wherein the reaction pressure is normal pressure, the reaction temperature is between 50 and 90 DEG C, the reaction time is between 25 and 40 minutes, the catalyst uses Al2O3 as a carrier, a load active component is metal Pd, the content of the Pd in the catalyst in percentage by weight is between 0.1 and 2.0 percent, the particle size of the catalyst is between 80 and 200 meshes, and the weight ratio of the raw material to the catalyst is 30-100:1. Compared with the prior art, the method has obvious improvement, the catalyst is simpler, and the content of the active component is lower, thus the preparation is easier and the cost is lower; the reaction condition is mild; and on the premise of ensuring the selectivity and the product yield of a perfect product, the reaction time is greatly shortened. The reduction of the preparation cost of the catalyst and shortening of the reaction time finally reduce the overall production cost greatly.
Owner:SINOPEC SHANGHAI PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
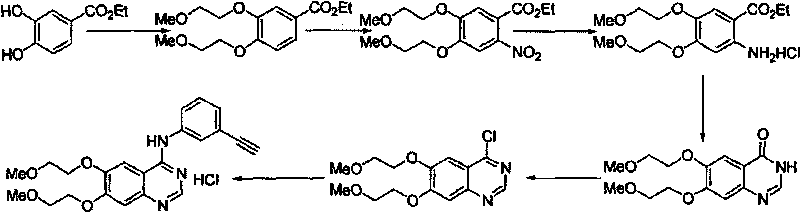
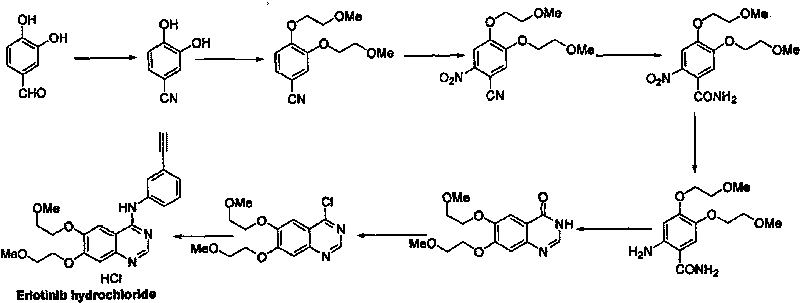
Preparation method of erlotinib hydrochloride
The invention provides a preparation method of erlotinib hydrochloride. The method comprises the following steps: taking 6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline as an initial raw material, chlorinating directly, then reacting with 3-aminophenylacetylene, afterwards removing methyl on the positions of 6 and 7 and finally introducing a methoxyethyl side chain to generate the erlotinib hydrochloride. The invention has the technological lines of mild reaction condition, no need of high temperature, deep cooling, energy saving and environment friendliness; the whole line has better yield and quality; and the reaction steps are little, the reaction is stable and controllable, the postprocessing is very simple and convenient, and the industrialized production is easy.
Owner:BIOCOMPOUNDS PHARMACEUTICAL INC +1
Method for preparing intermediate of Entecavir antiviral agent
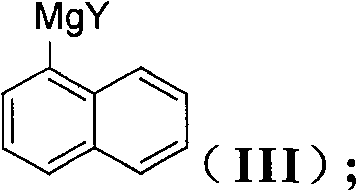
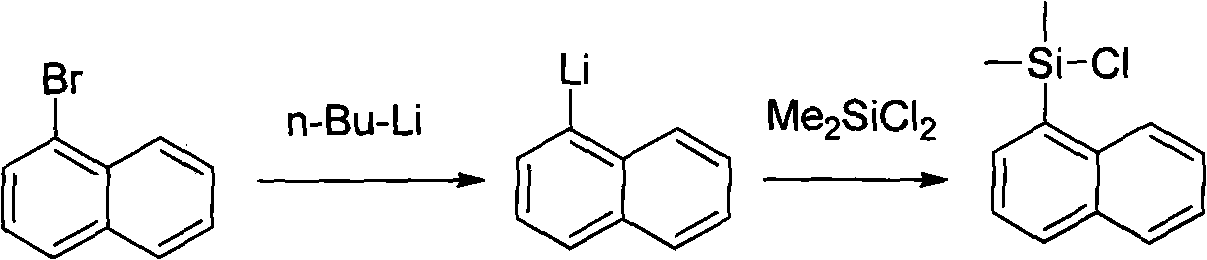
InactiveCN101906113ASimple reaction conditionsRaw materials are cheap and easy to getGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsEntecavirSolvent
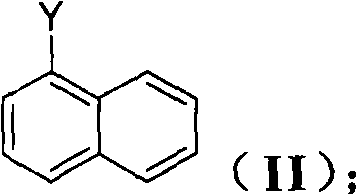
The invention discloses a method for preparing an intermediate (I) of an Entecavir antiviral agent, which comprises the following steps: (1) reacting a compound of a formula (II) with magnesium under a condition of a proper solvent to generate a compound of a formula (III); and performing the Grignard reaction of the compound of the formula (III) and a compound of a formula (IV). In the formulae, X and Y are identical or different and may be F, Cl and Br atoms. The method has the advantages of simple reaction conditions, cheap and readily available raw materials, simple and safe process, low cost and easy industrial production.
Owner:HANDE PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com