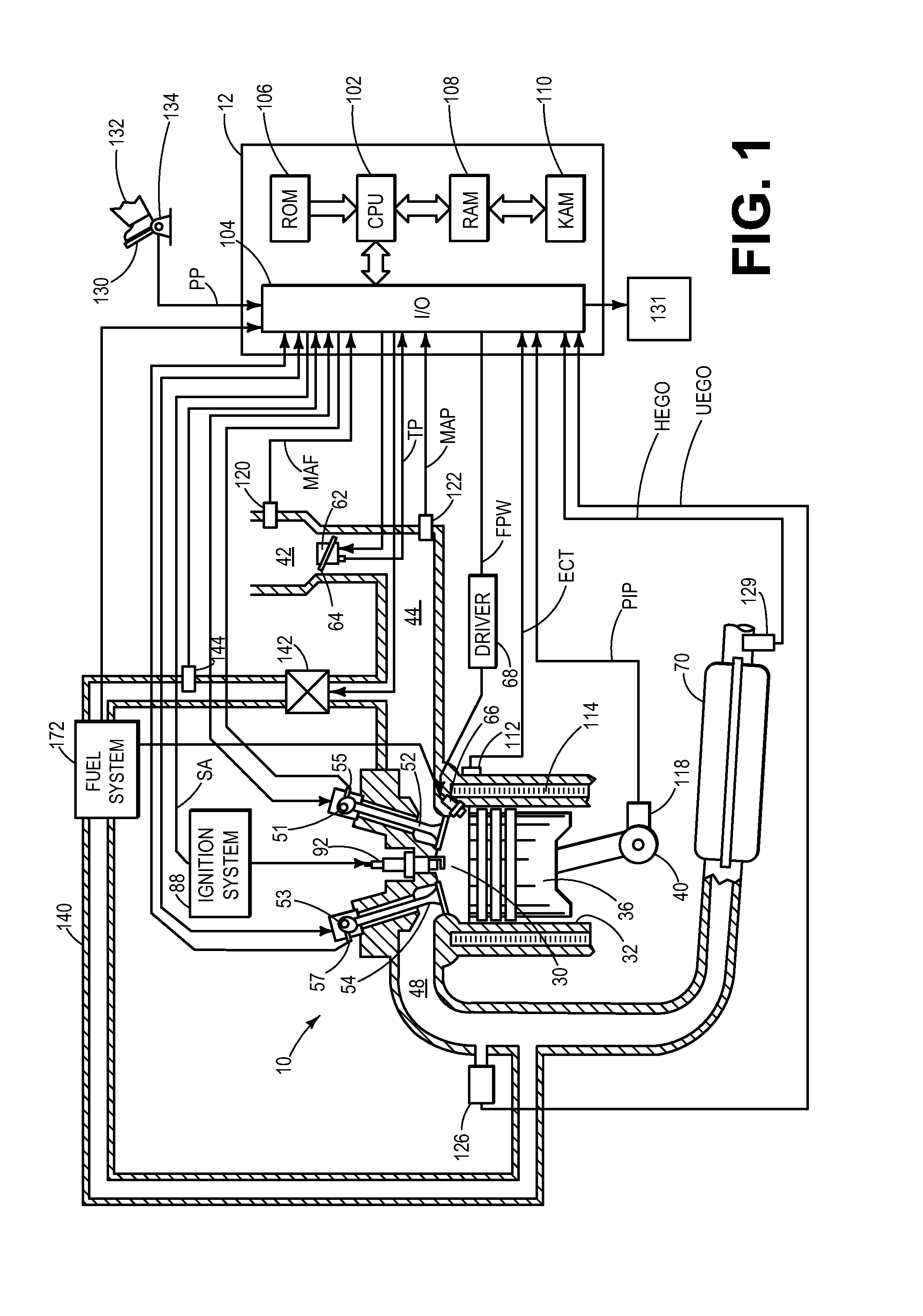
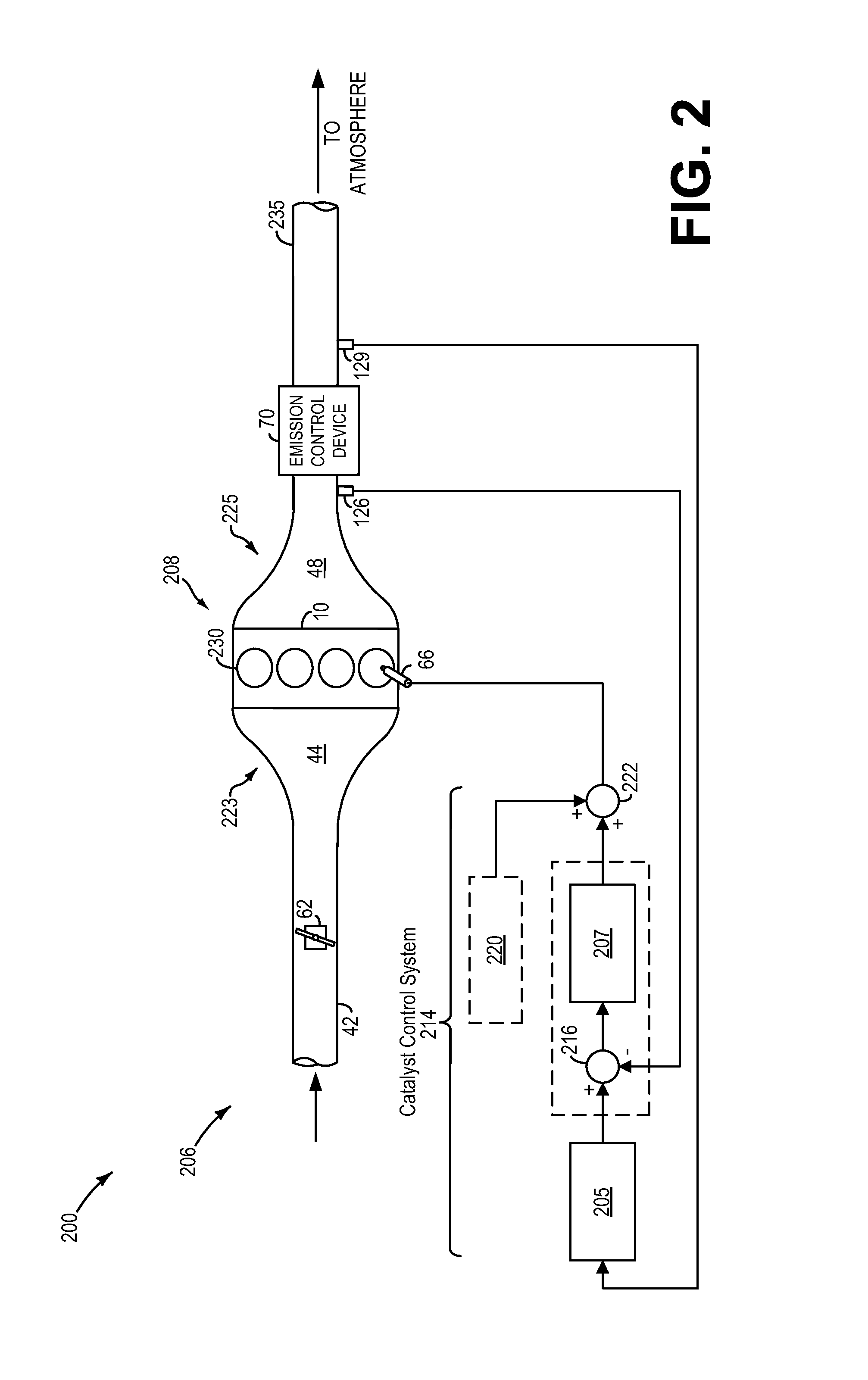
Patents
Literature
224 results about "Catalyst degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
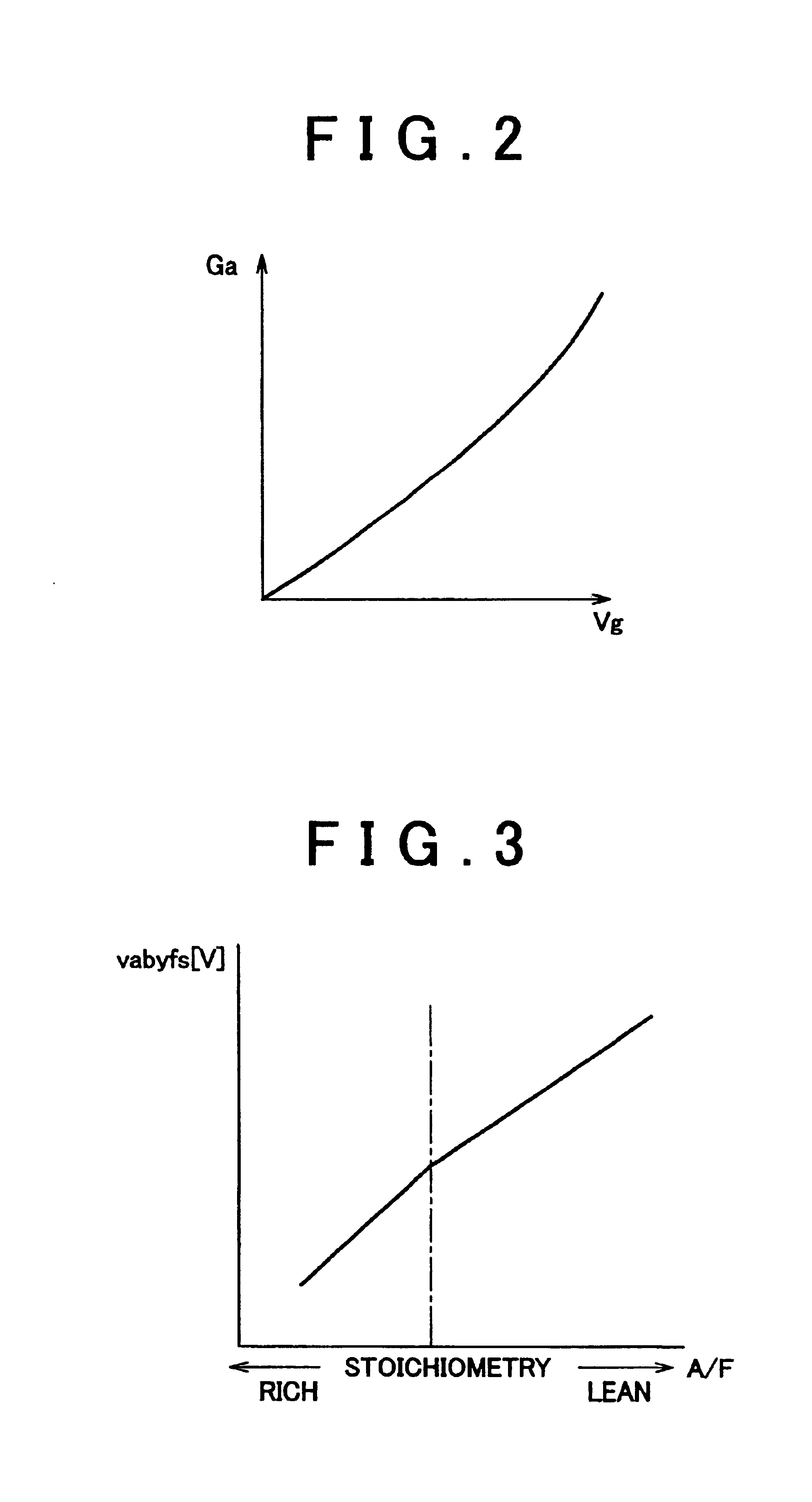
Thermal degradation of a Three-Way Catalyst begins at temperatures between 800° - 900° C, or in some cases, at lower temperatures depending upon the catalytic material. Thermal degradation is a physical process which leads to catalytic deactivation at high temperatures.
Method for preparing high activity non-metallic ion co-doped titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst
InactiveCN101444724ASimple processLow equipment requirementsPhysical/chemical process catalystsCatalyst degradationUltraviolet lights
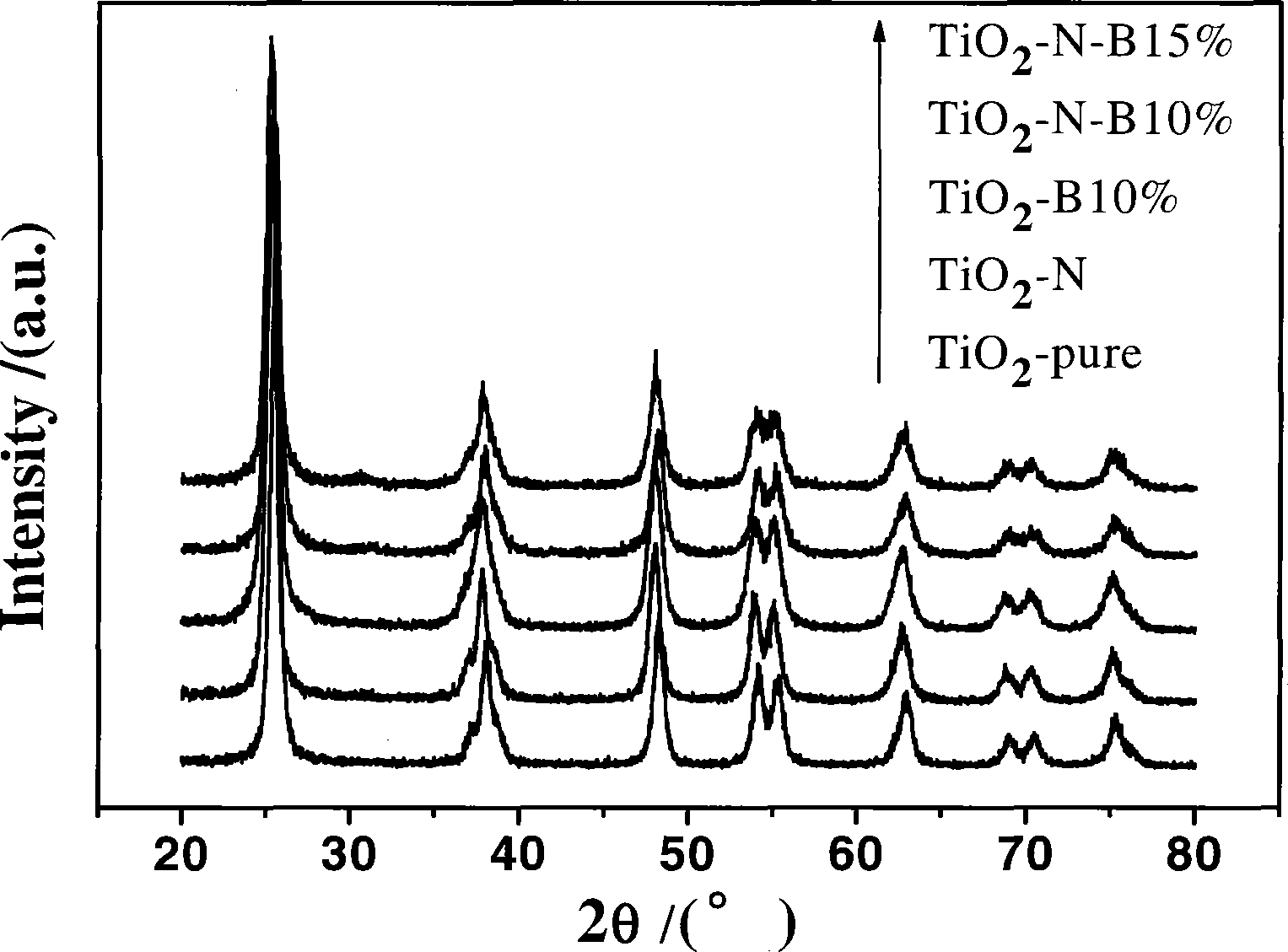
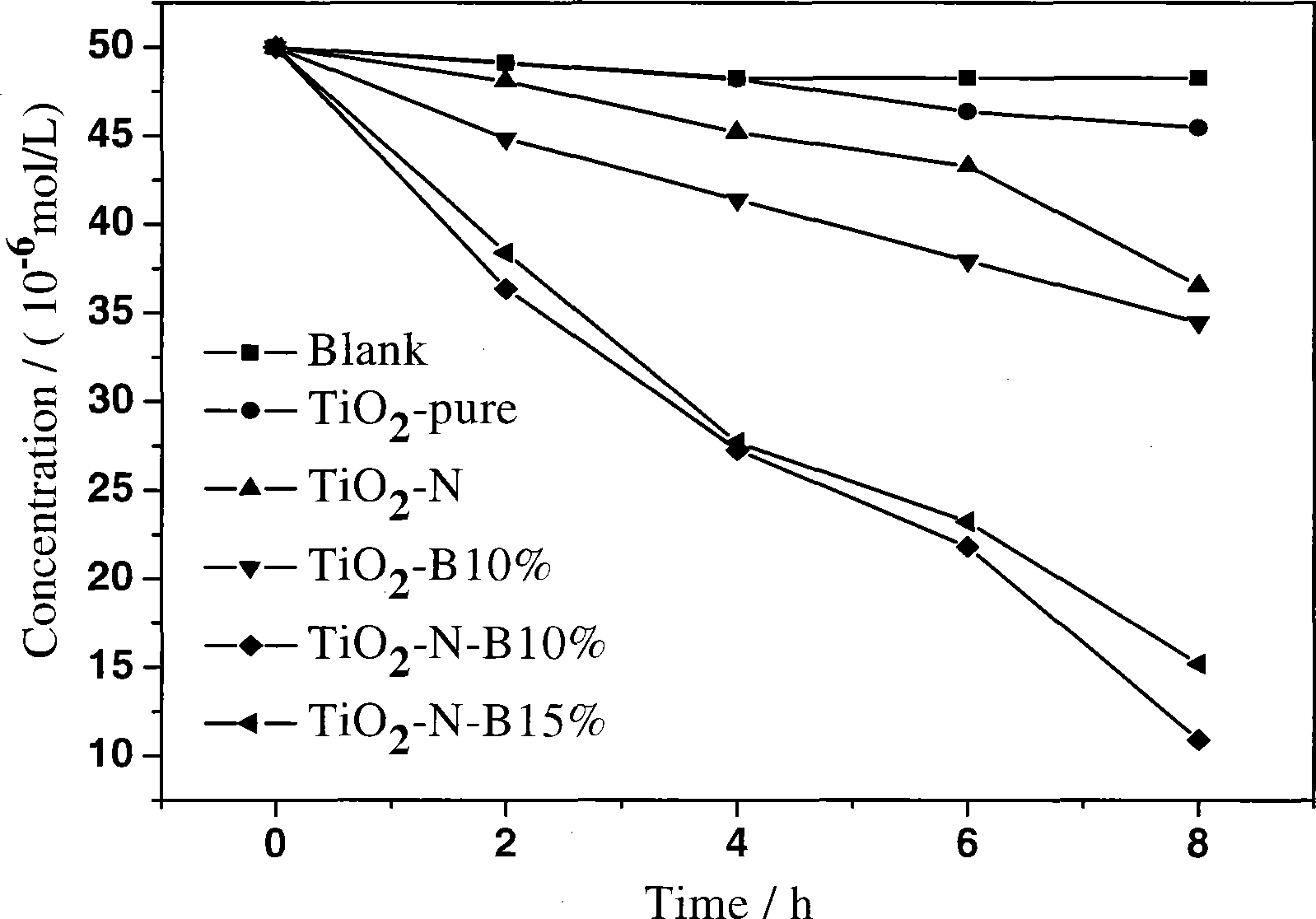
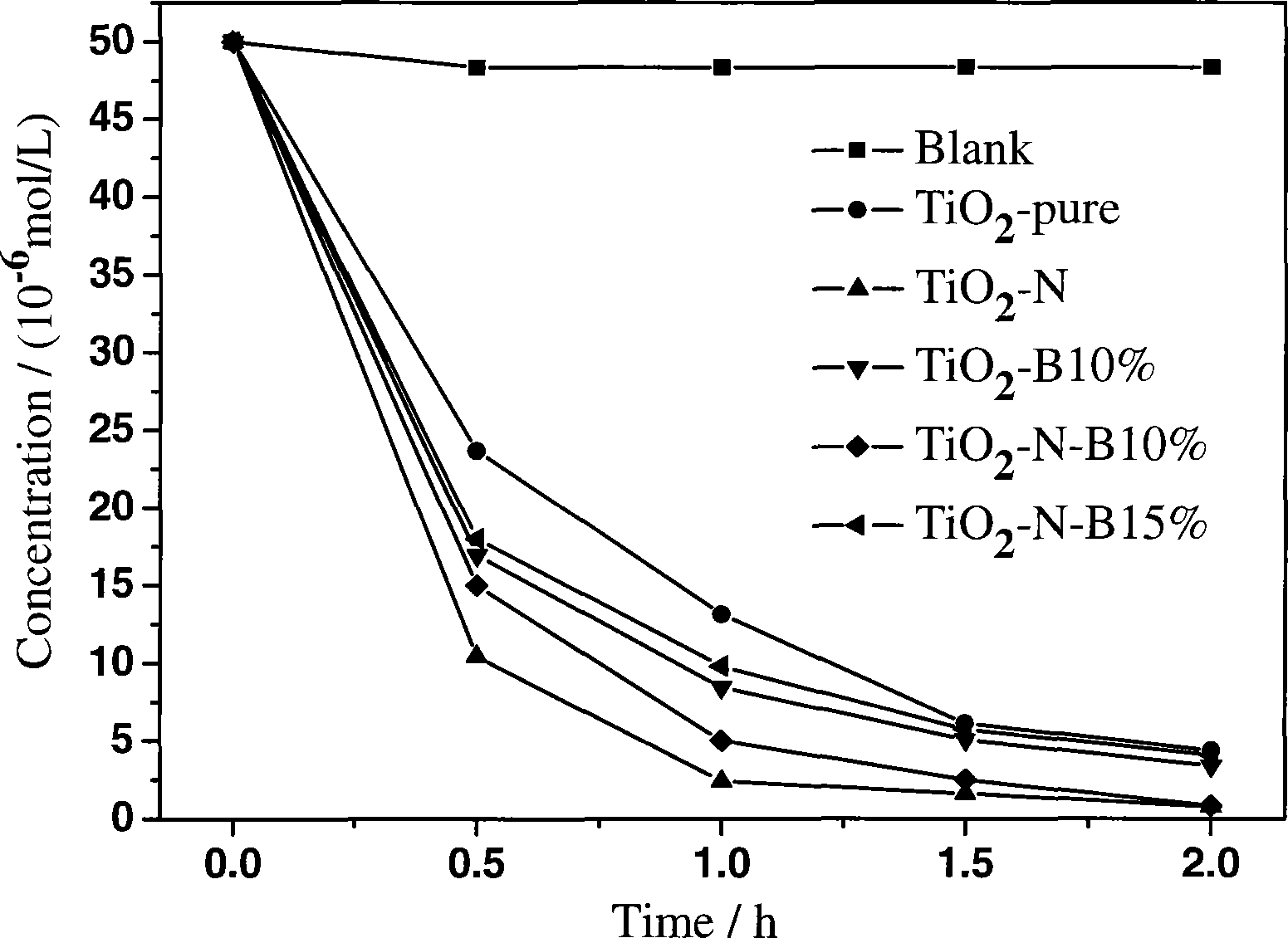
In order to degrade the pollutants in water and atmosphere by the photocatalysis technology, the invention discloses a method for preparing a high activity non-metallic ion co-doped titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst. In the photochemical catalyst, titanium ester or titanate is used as a precursor, non-metallic compound comprising boron, carbon, nitrogen, fluorin, silicon, phosphor, sulfur, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and the like, are used as doping agents, the high activity non-metallic ion co-doped titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst is prepared by adopting the sol gel method. Compared with a titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst single-doped with pure titanium dioxide and the non-metallic irons, the visible light catalytic activity of the titanium dioxide photochemical catalyst on the degradation of parachlorophenol is greatly improved, and the ultraviolet light catalytic activity can also exceed the catalytic activity of the pure titanium dioxide catalyst. The method also has the advantages that the preparation technique is simple, the equipment requirement is low; the particle diameter of the product is small, the specific surface is relatively high, the dispersivity is good, thus having a wide application prospect in the environmental cleaning scientific field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
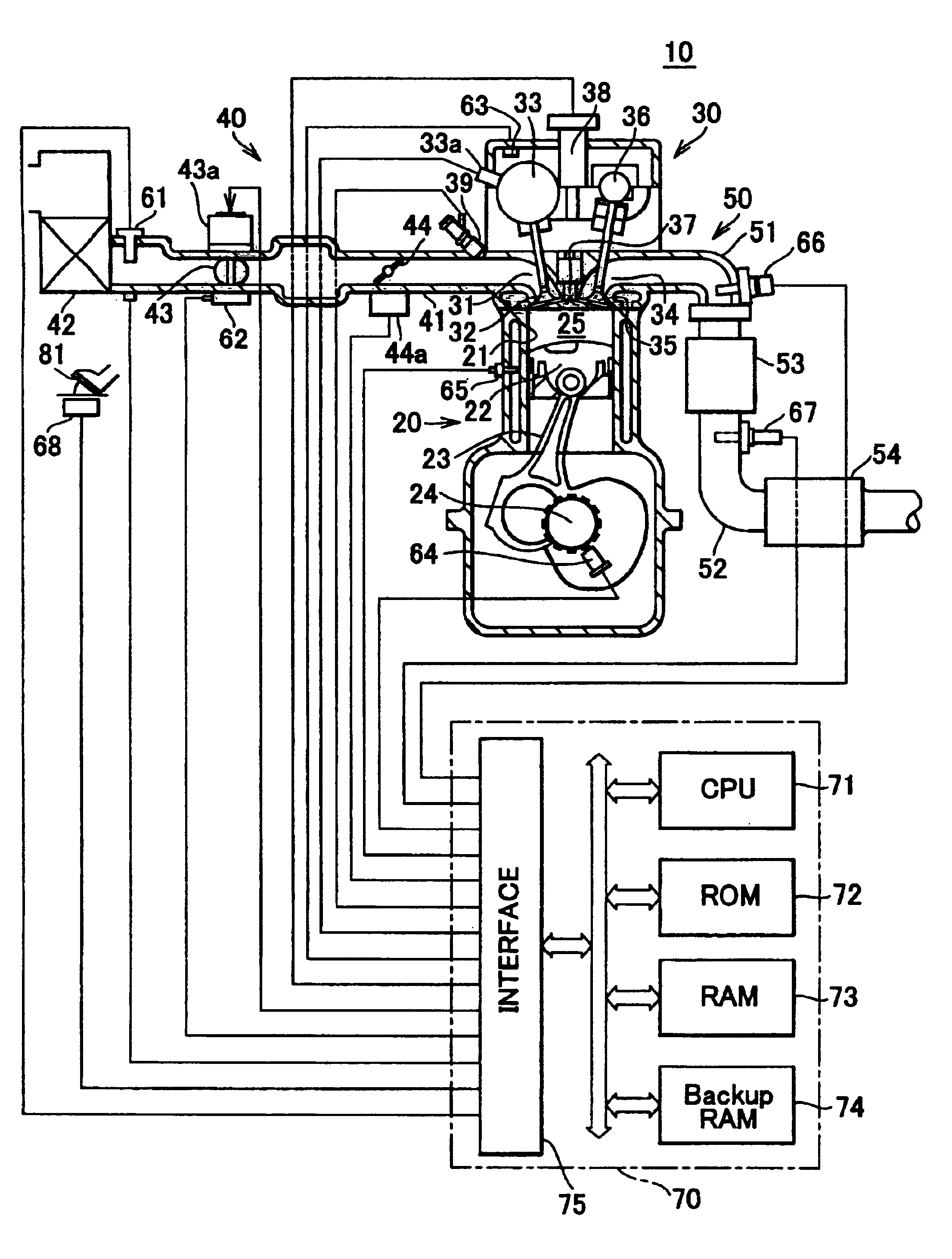
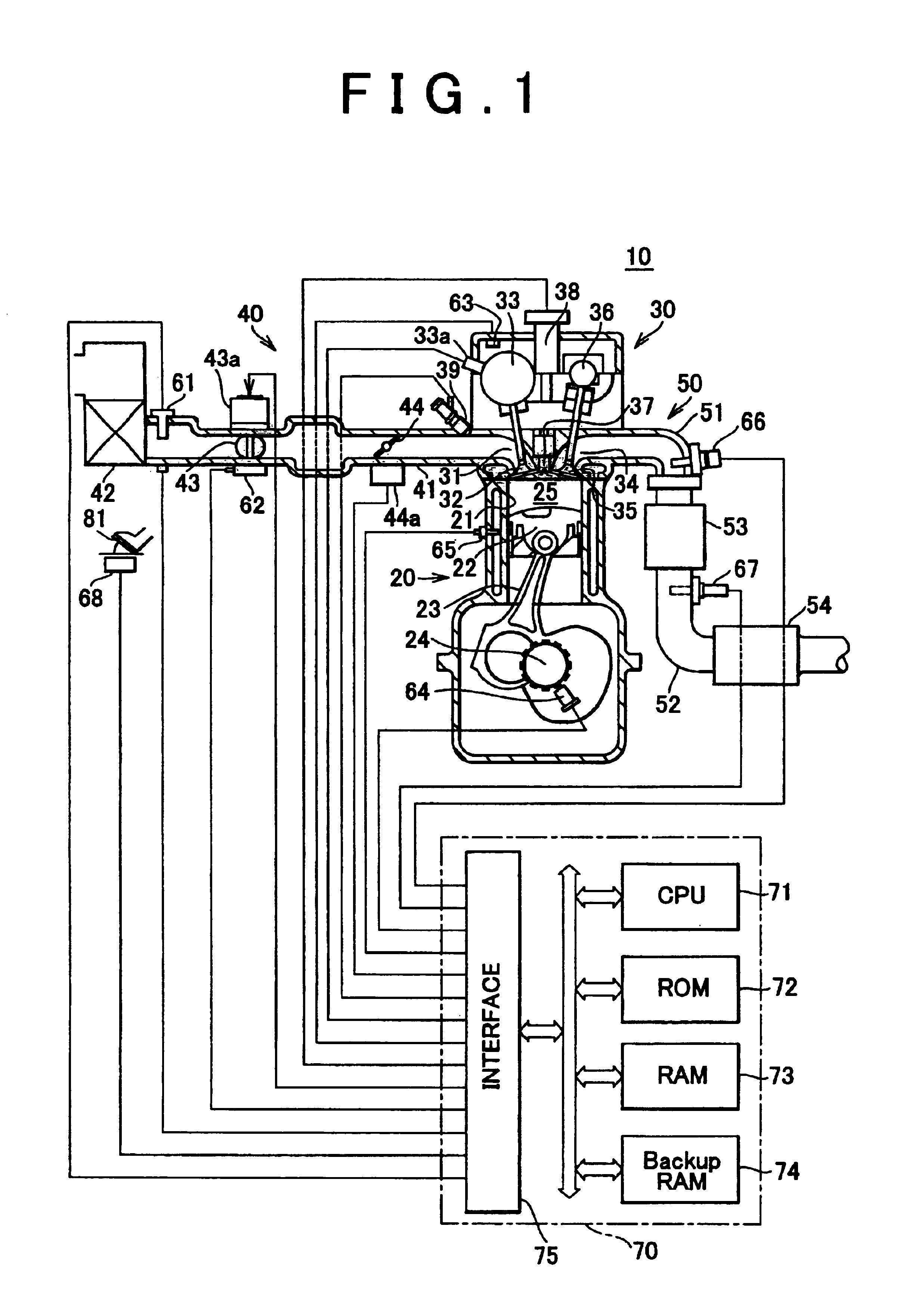
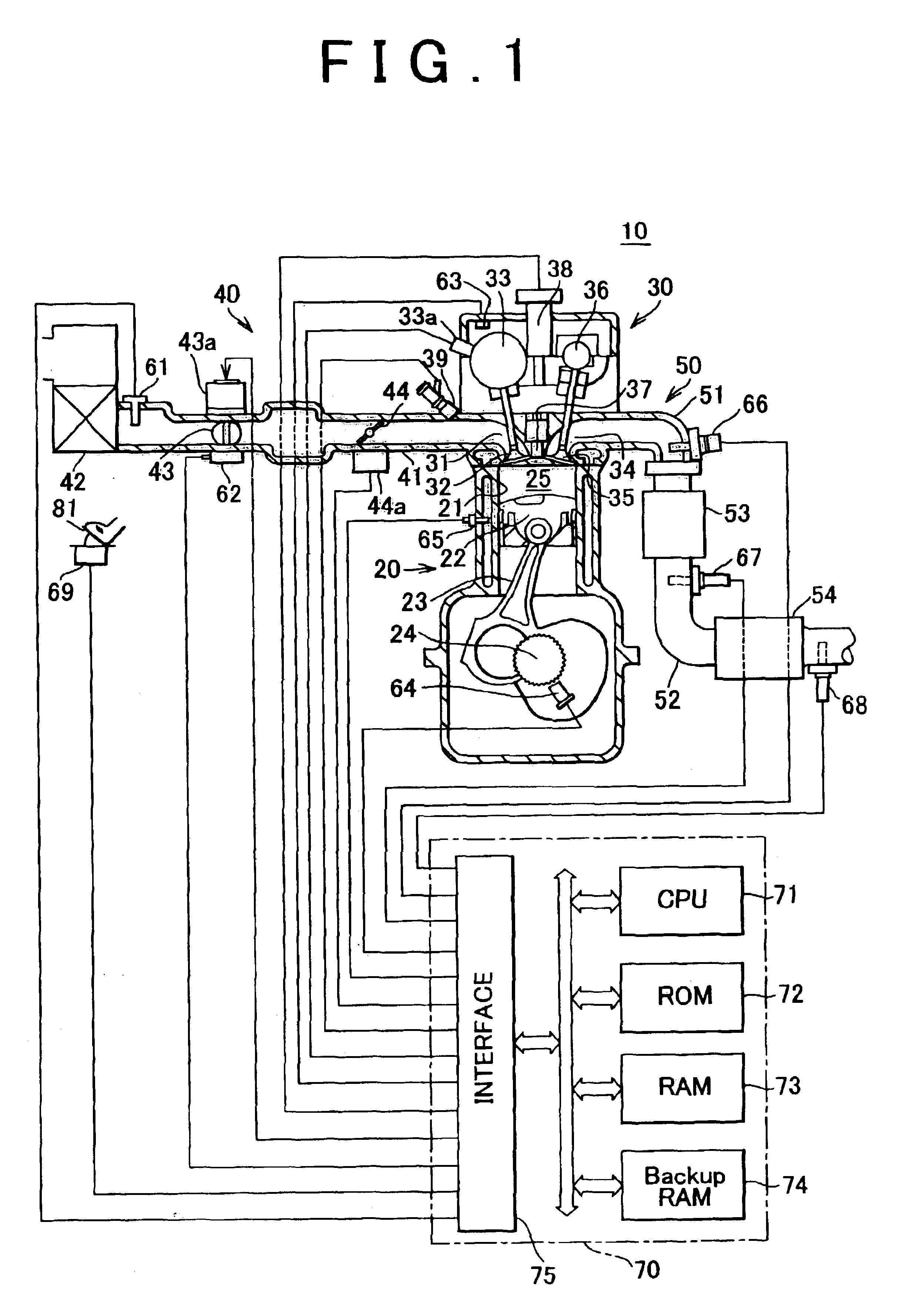
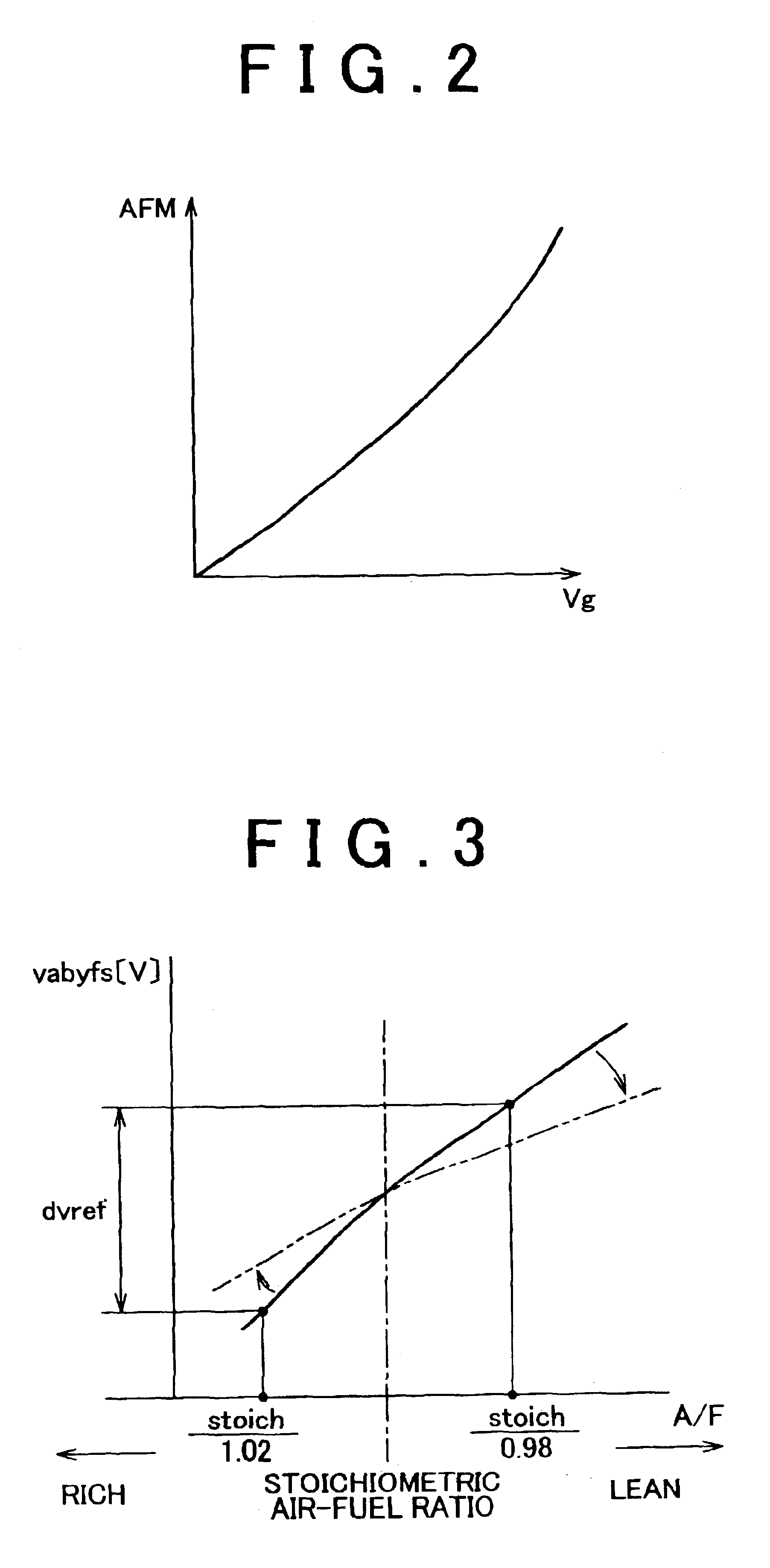
Catalyst degradation determining apparatus and method
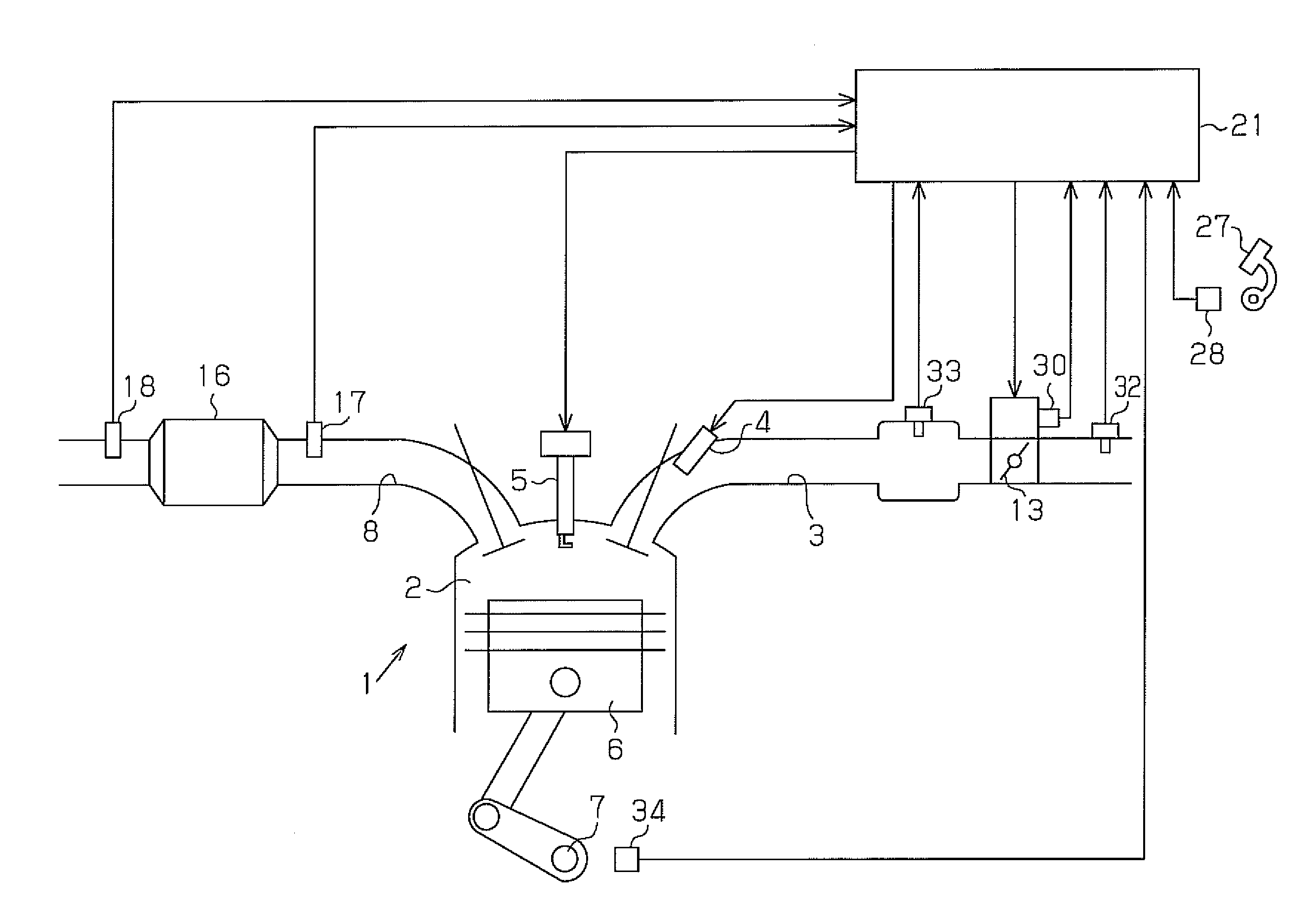
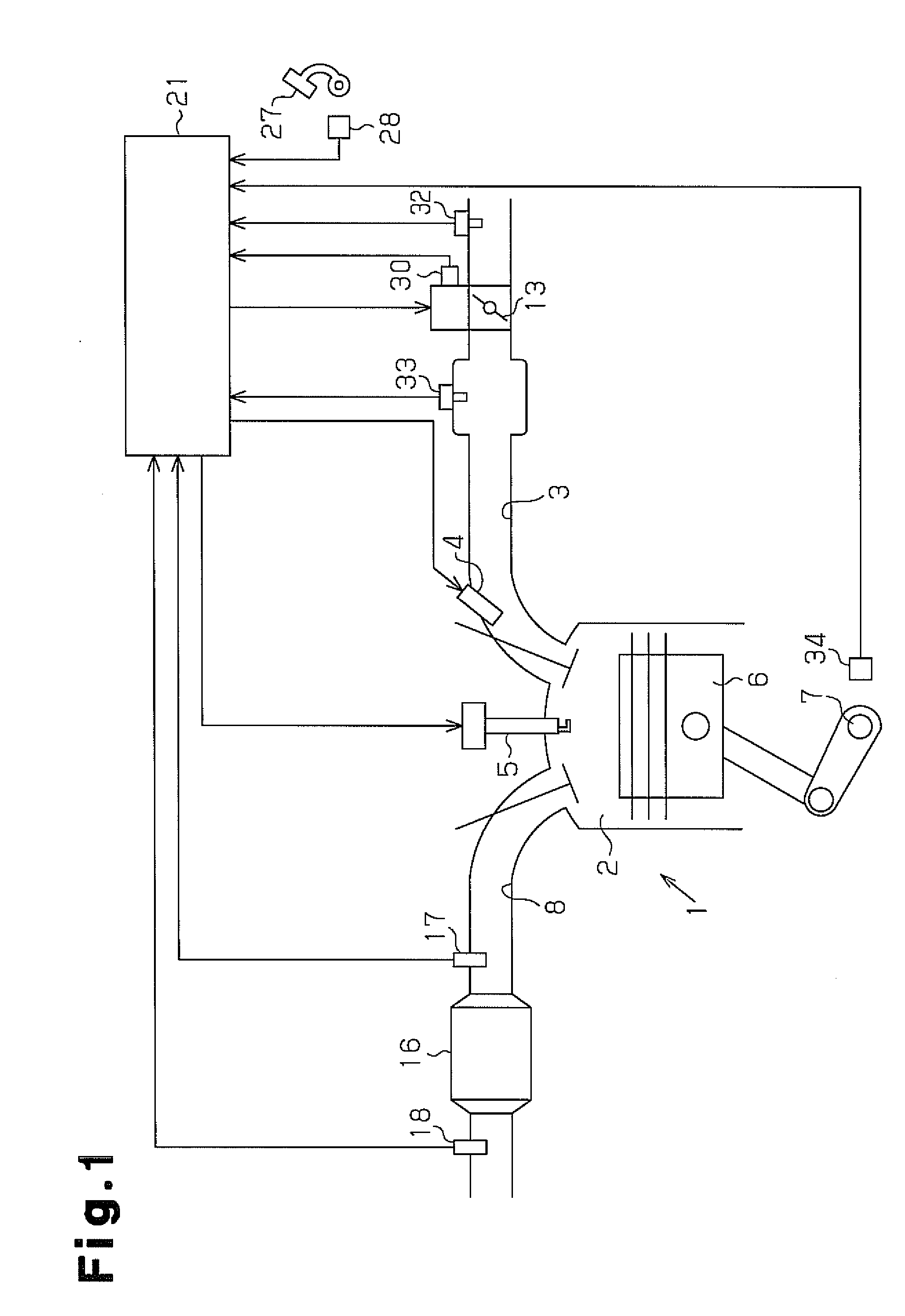
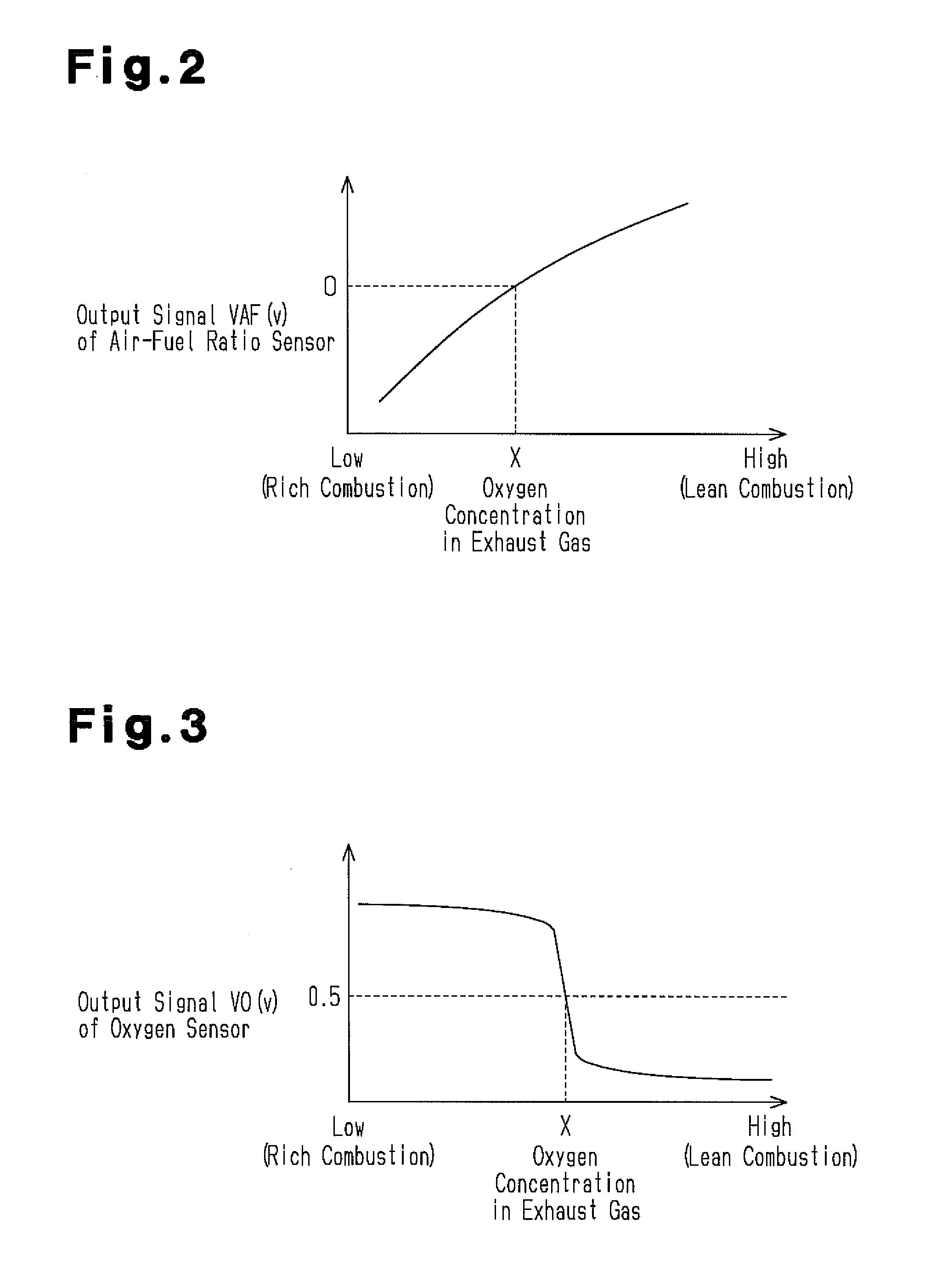
InactiveUS6877311B2Easily determine whether correction is appropriateHigh frequencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCatalyst degradationEngineering
A catalyst degradation determining apparatus determines whether a catalyst provided in an exhaust passage of an internal combustion engine has degraded. The apparatus includes a controller. The controller acquires a degradation index value that changes in accordance with a degree of degradation of the catalyst. The controller corrects the degradation index value acquired, based on a factor that affects the degradation index value, so that the degradation index value becomes equal to a post-normalization index value that is a degradation index value acquired when the factor is a predetermined value. The controller also determines whether the catalyst has degraded, based on a result of comparison regarding whether the post-normalization index value is greater than a catalyst degradation criterion value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Membrane Separation Of A Metathesis Reaction Mixture
InactiveUS20080103346A1Reduces possibility of undesirableImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesCatalystsPolymer scienceCatalyst degradation
A process for separating a homogeneous metathesis catalyst and, optionally, one or more homogeneous metathesis catalyst degradation products from a metathesis reaction mixture containing in addition to said metathesis catalyst and said metathesis catalyst degradation product(s), one or more olefin metathesis products, one or more unconverted reactant olefins, and optionally, a solvent. The process involves contacting the metathesis reaction mixture with a nanofiltration membrane, such as a polyimide nanofiltration membrane, so as to recover a permeate containing a substantial portion of the olefin reaction products, the unconverted reactant olefins, and optional solvent, and a retentate containing the metathesis catalyst, and optionally, metathesis catalyst degradation product(s). In another aspect, this invention pertains to a continuous metathesis reaction-catalyst separation process, preferably, conducted in a nanofiltration membrane reactor.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for aromatic alkylation
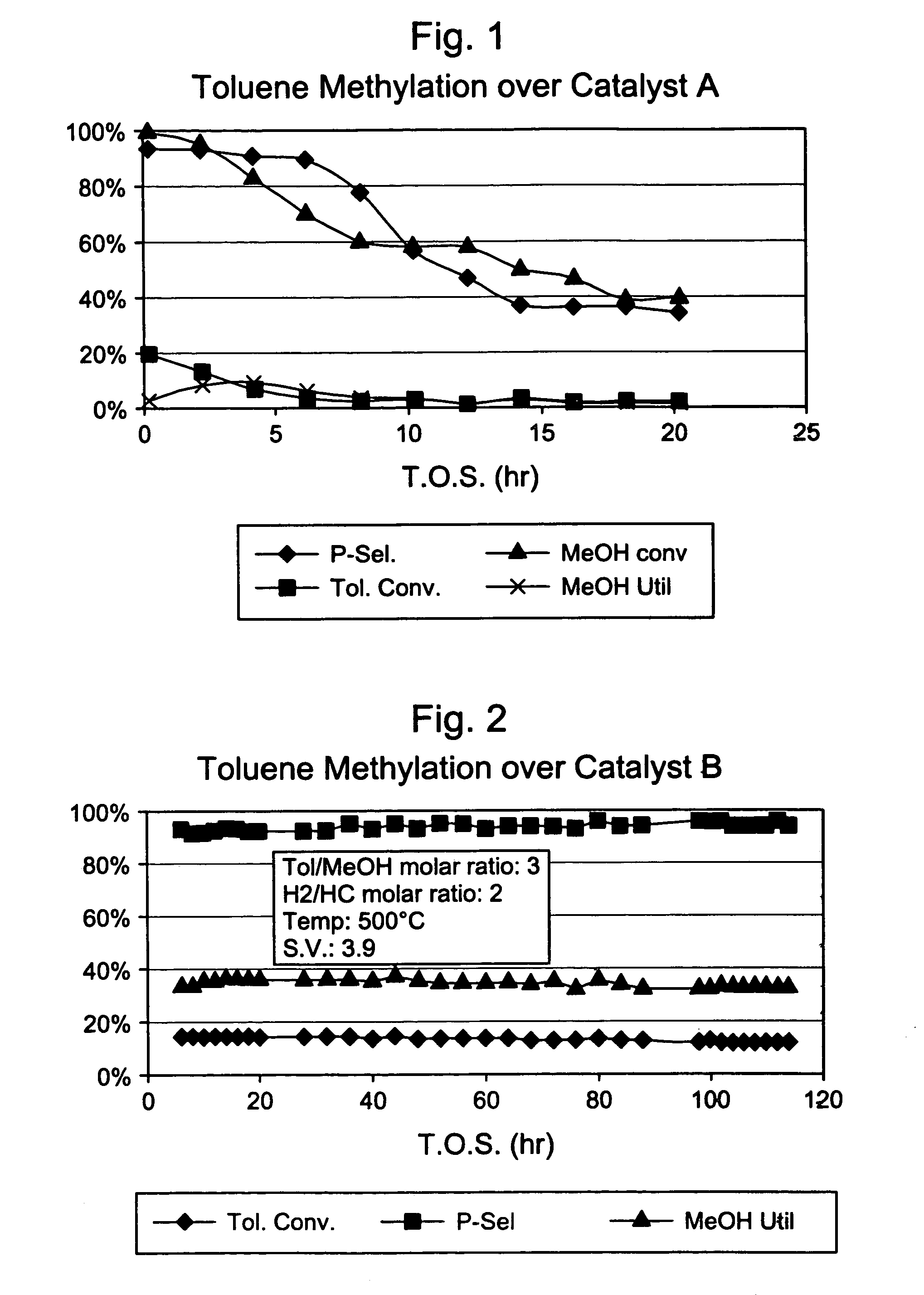
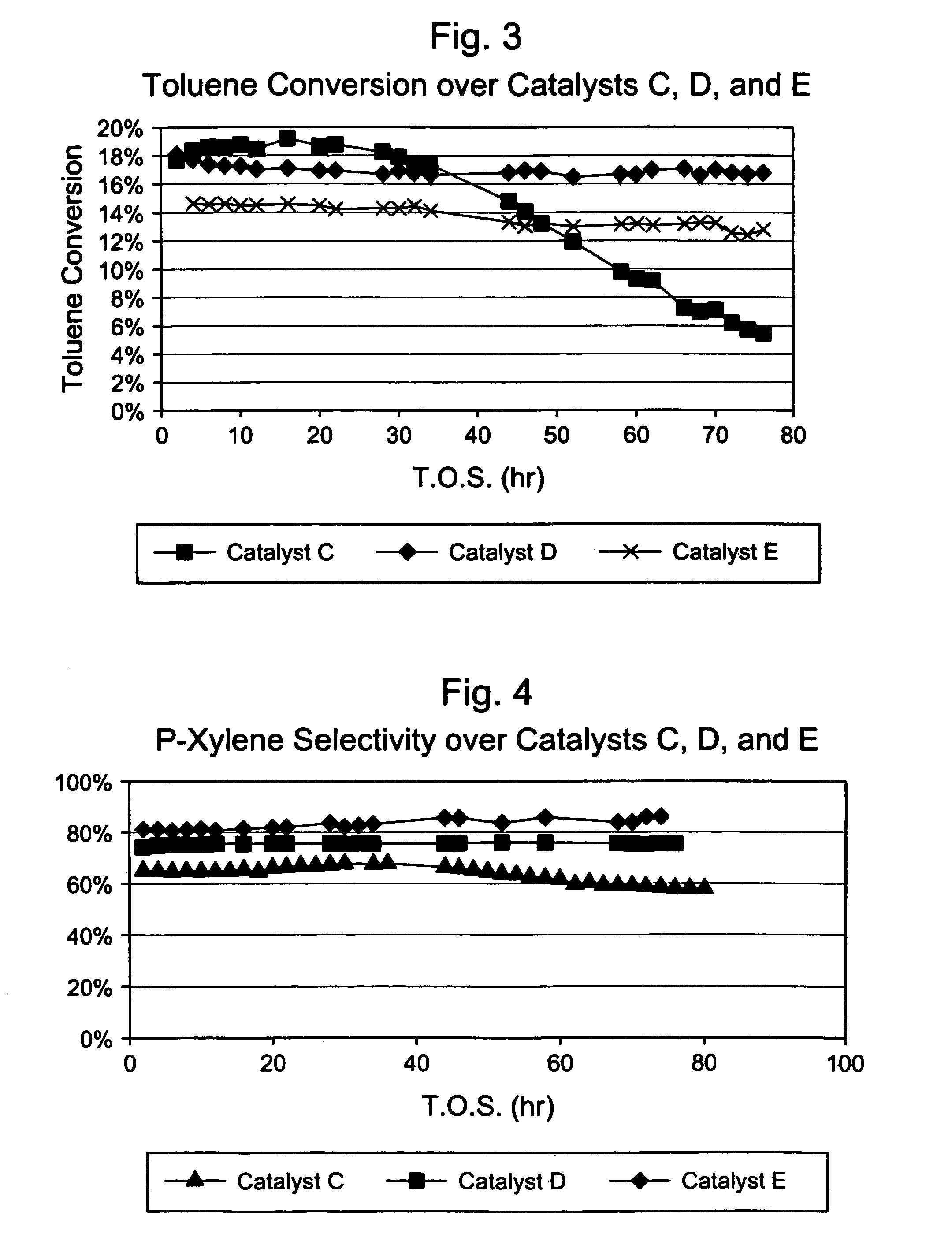
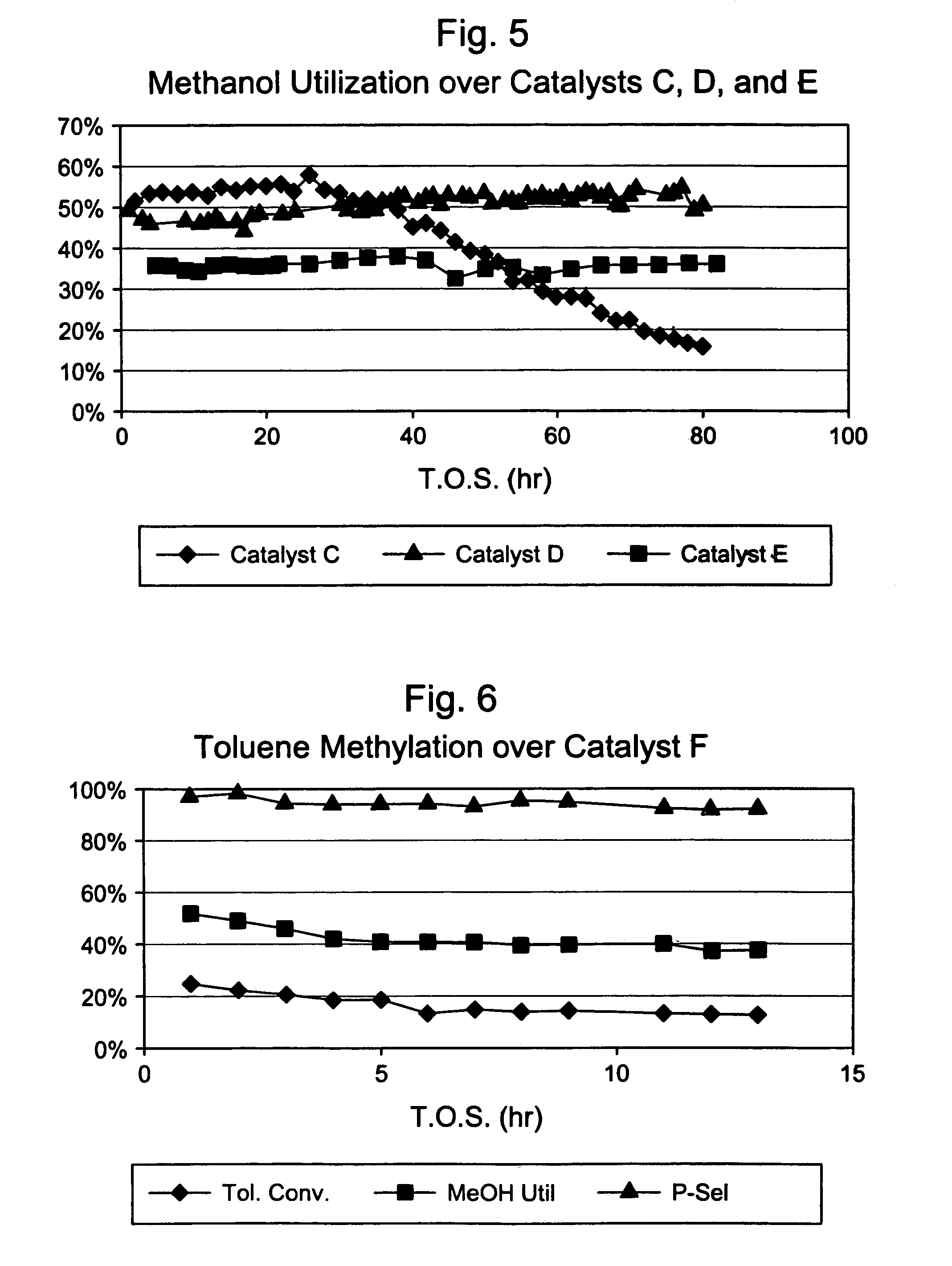
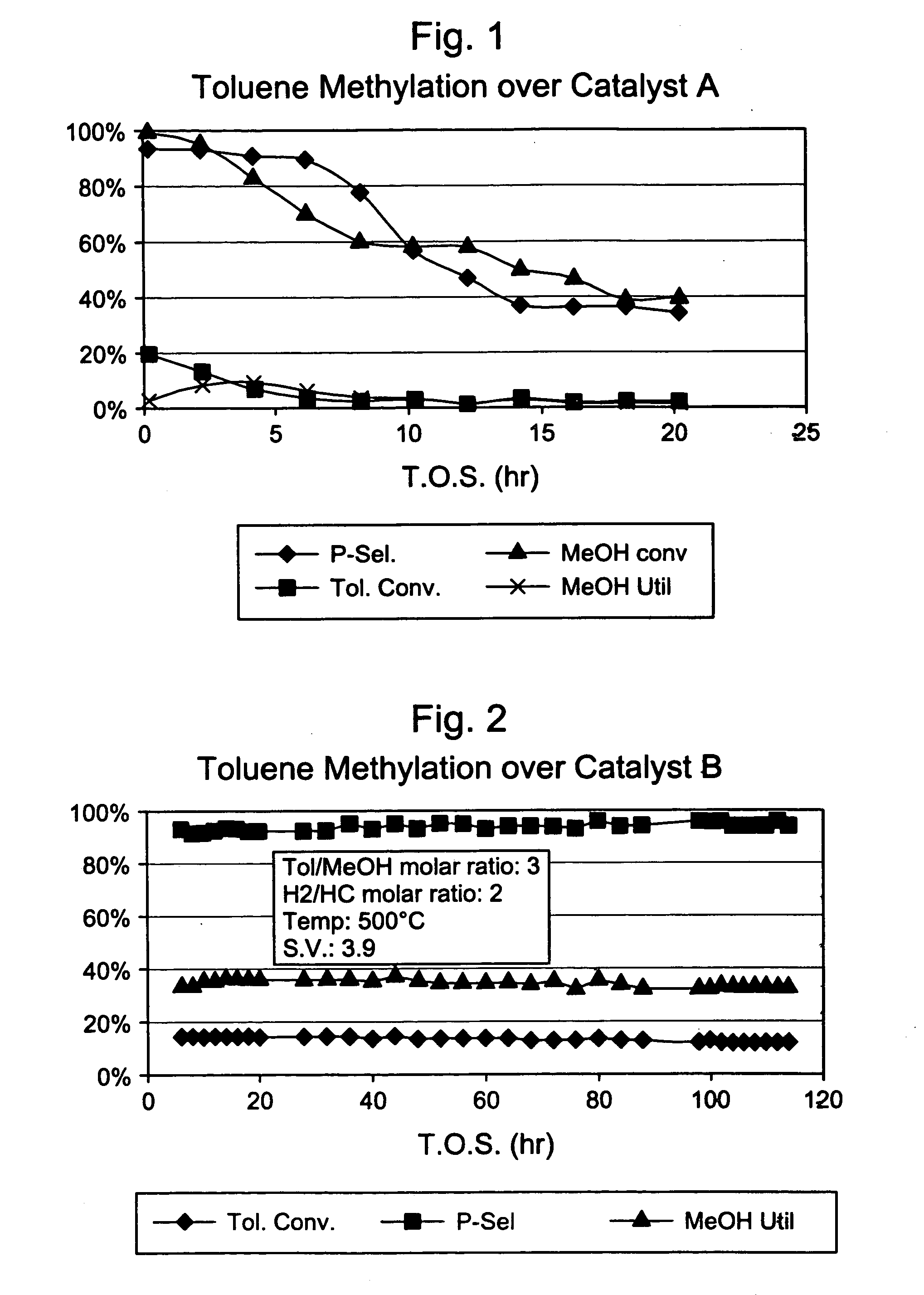
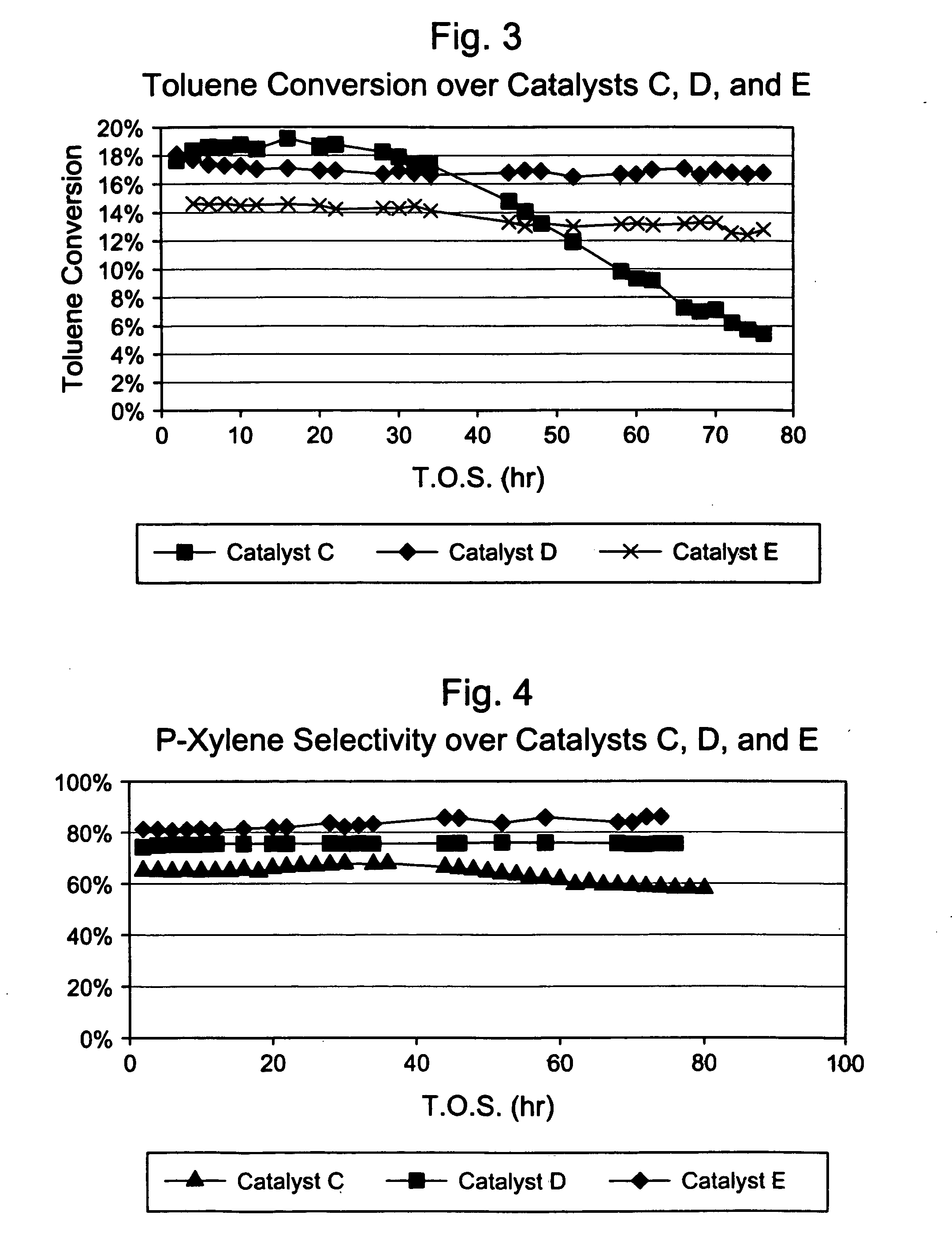
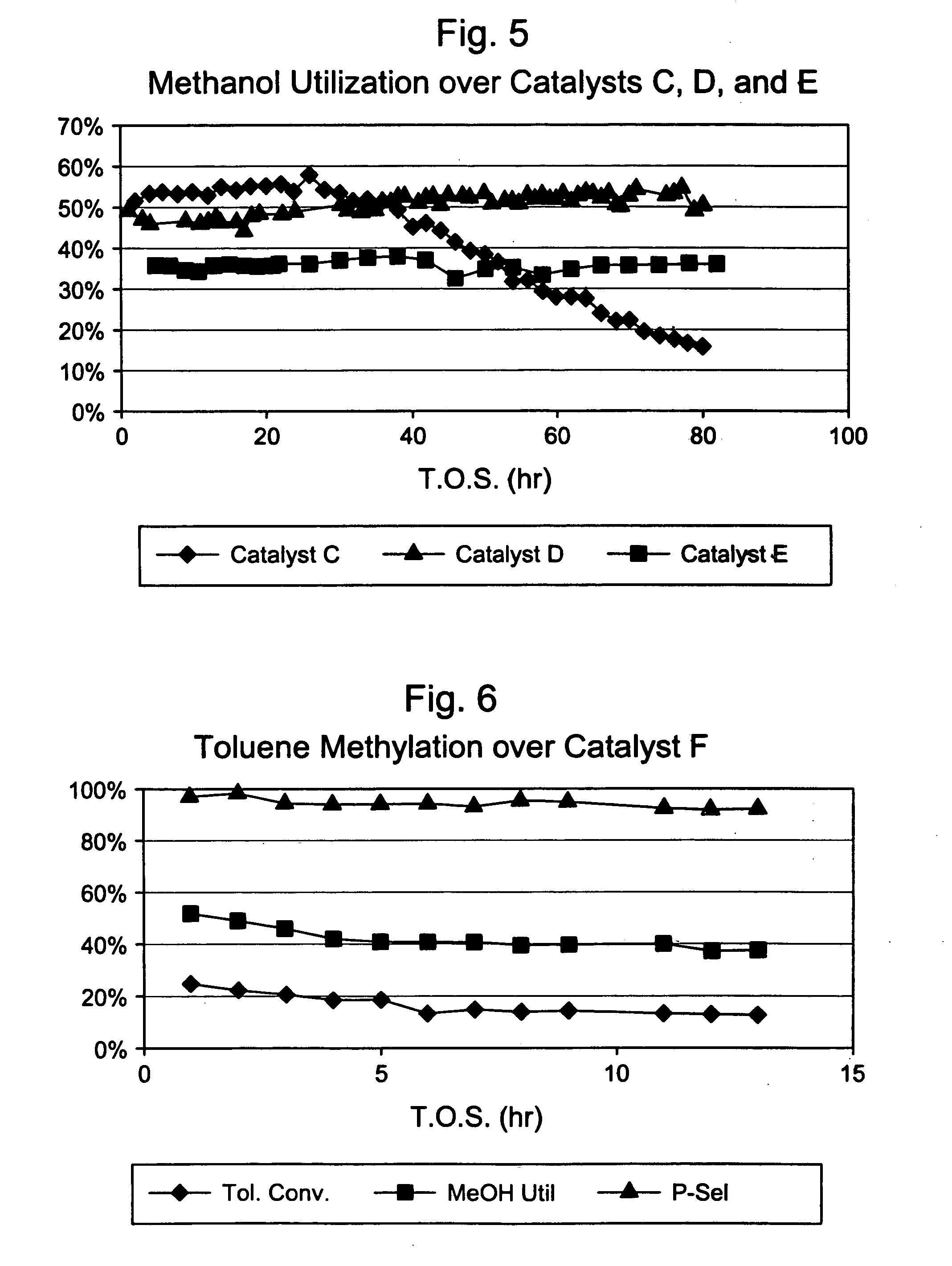
This invention relates to a process for the selective alkylation of toluene and / or benzene with an oxygen-containing alkylation agent. In particular, the process uses a selectivated molecular sieve which has been modified by the addition of a hydrogenation component, wherein at least one of the following conditions is met: (a) the selectivated molecular sieve has an alpha value of less than 100 prior to the addition of the hydrogenation component, or (b) the selectivated and hydrogenated catalyst has an alpha value of less than 100. The process of this invention provides high selectivity for the alkylated product while reducing catalyst degradation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for aromatic alkylation
This invention relates to a process for the selective alkylation of toluene and / or benzene with an oxygen-containing alkylation agent. In particular, the process uses a selectivated molecular sieve which has been modified by the addition of a hydrogenation component, wherein at least one of the following conditions is met: (a) the selectivated molecular sieve has an alpha value of less than 100 prior to the addition of the hydrogenation component, or (b) the selectivated and hydrogenated catalyst has an alpha value of less than 100. The process of this invention provides high selectivity for the alkylated product while reducing catalyst degradation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
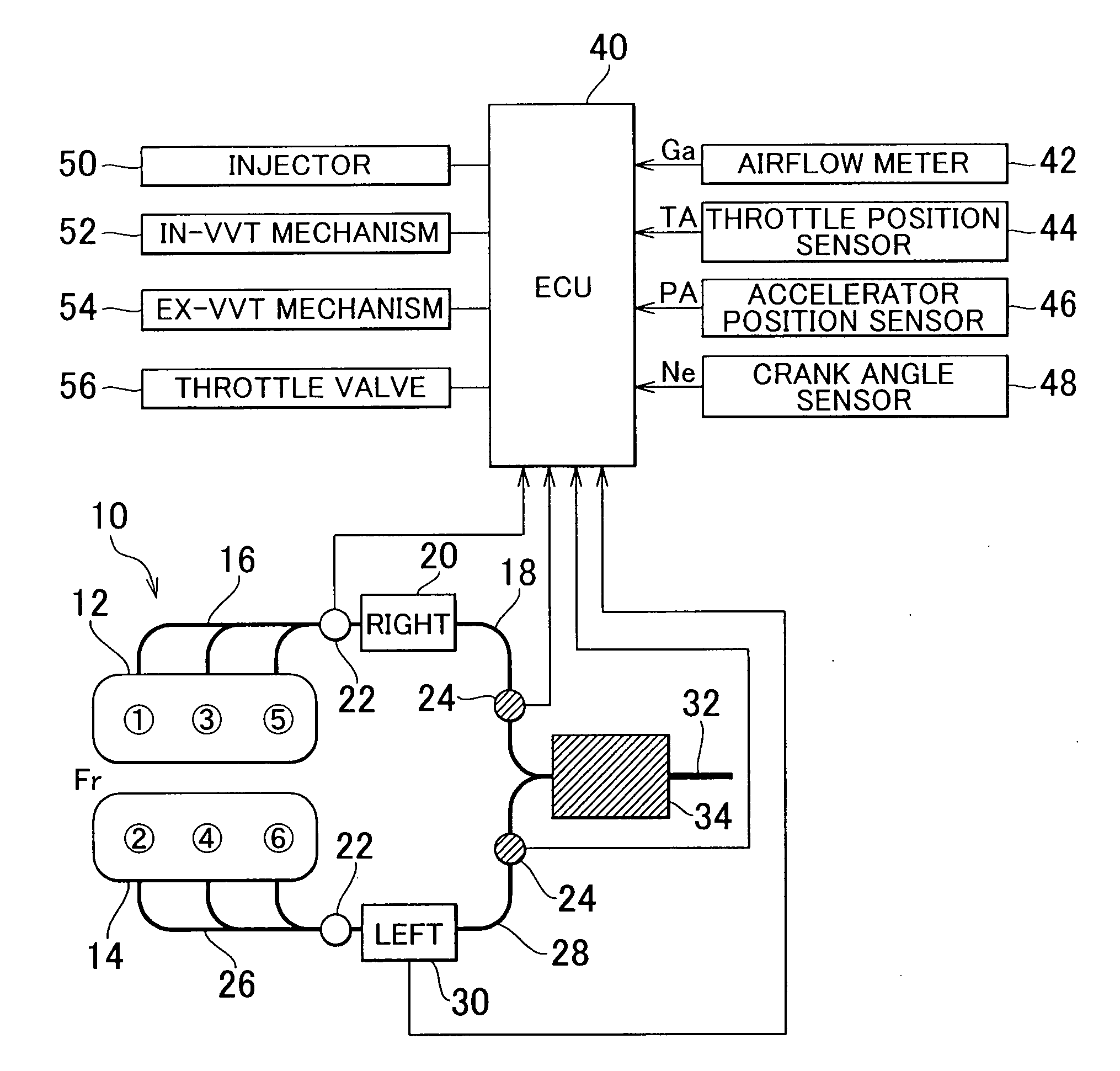
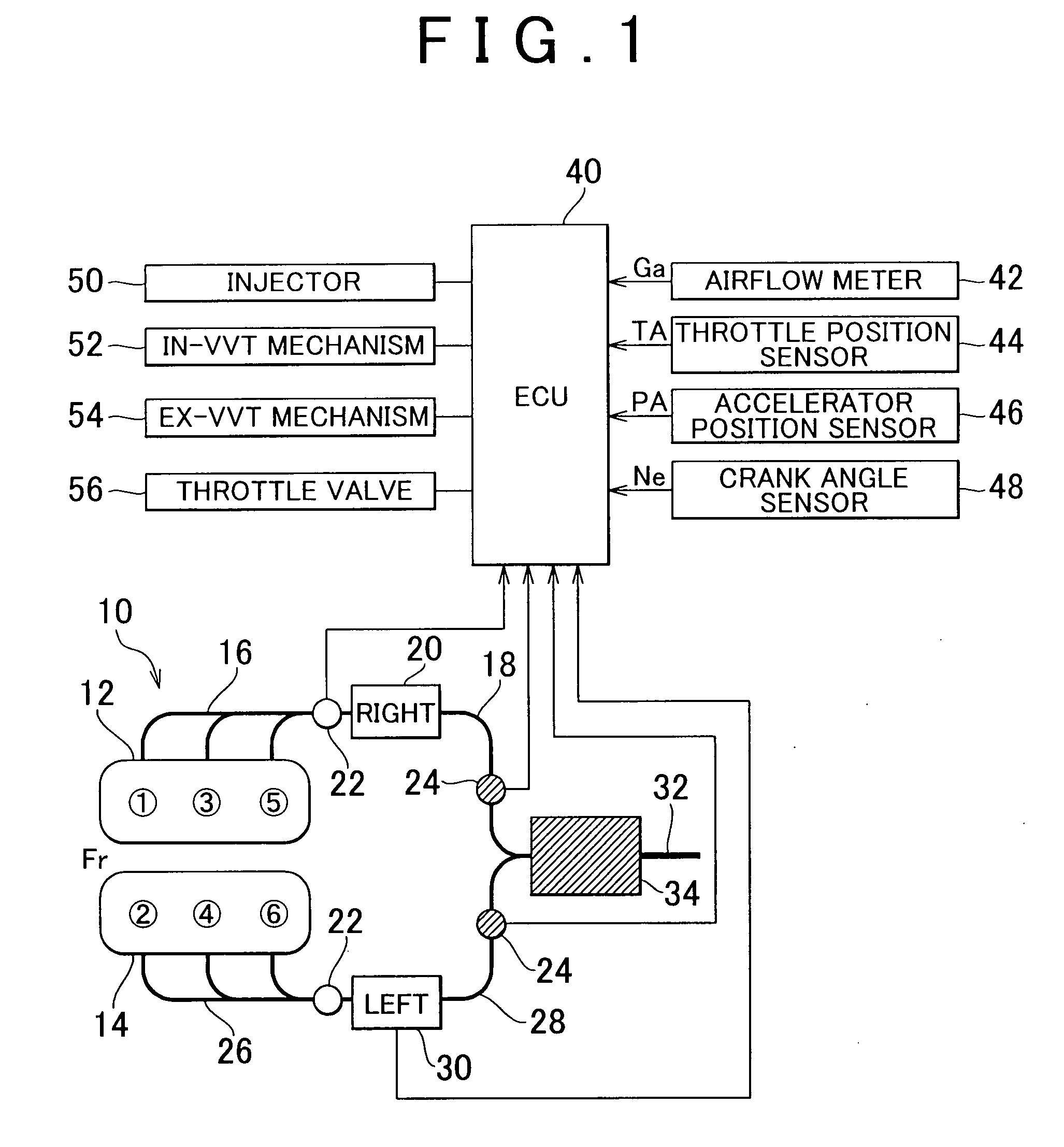
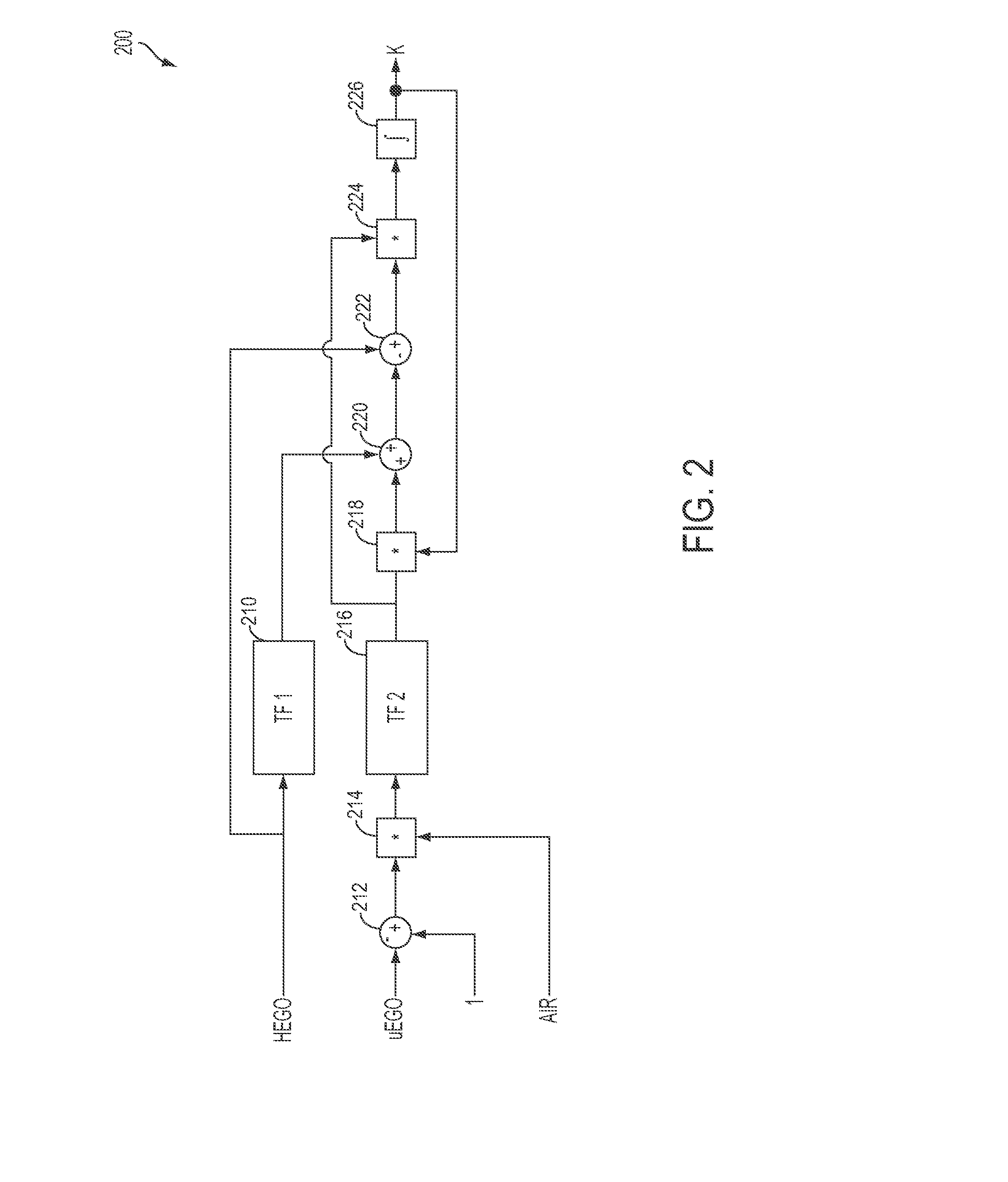
Air fuel ratio control apparatus for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20080154476A1Improve diagnostic accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCatalyst degradationExternal combustion engine
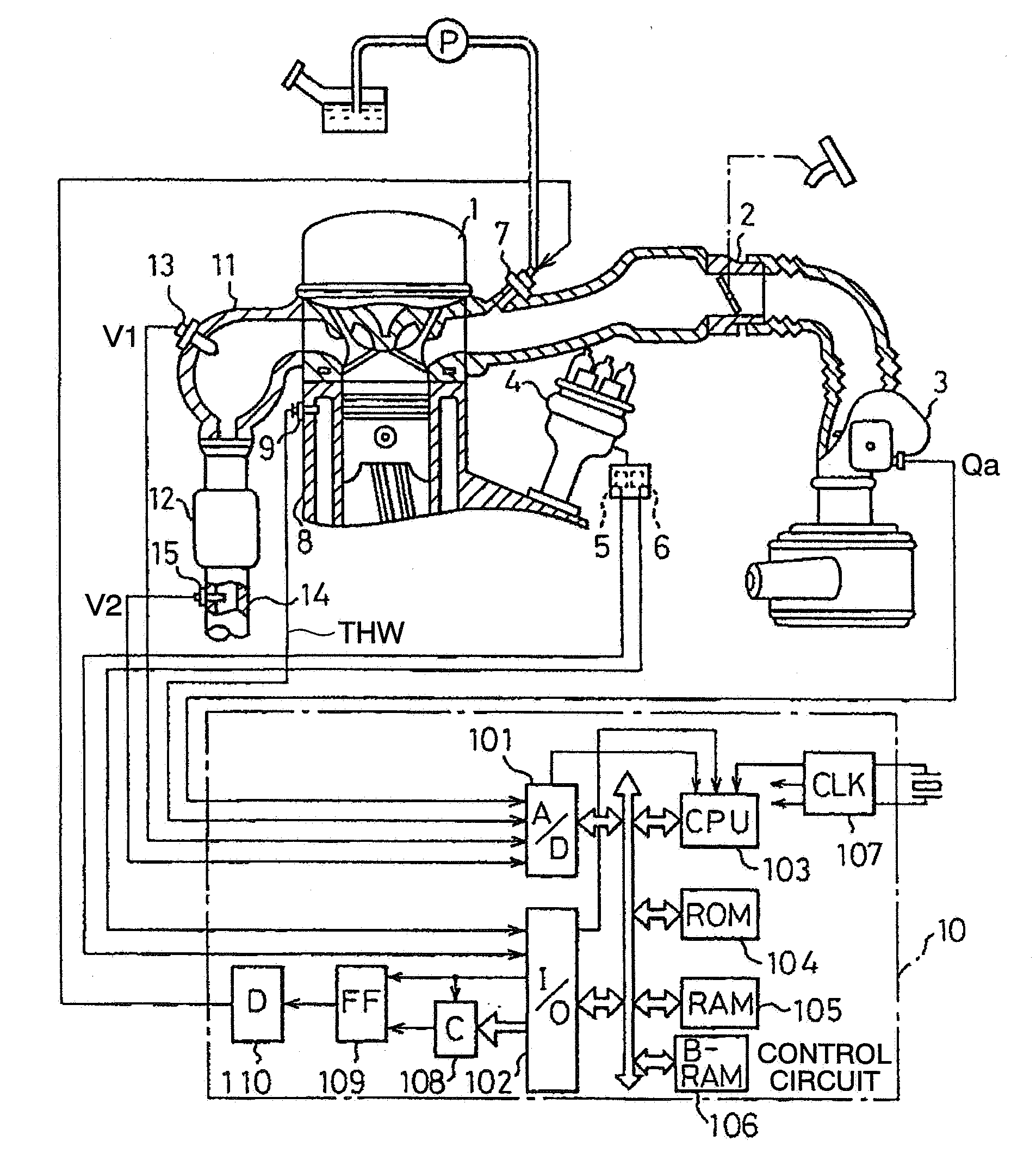
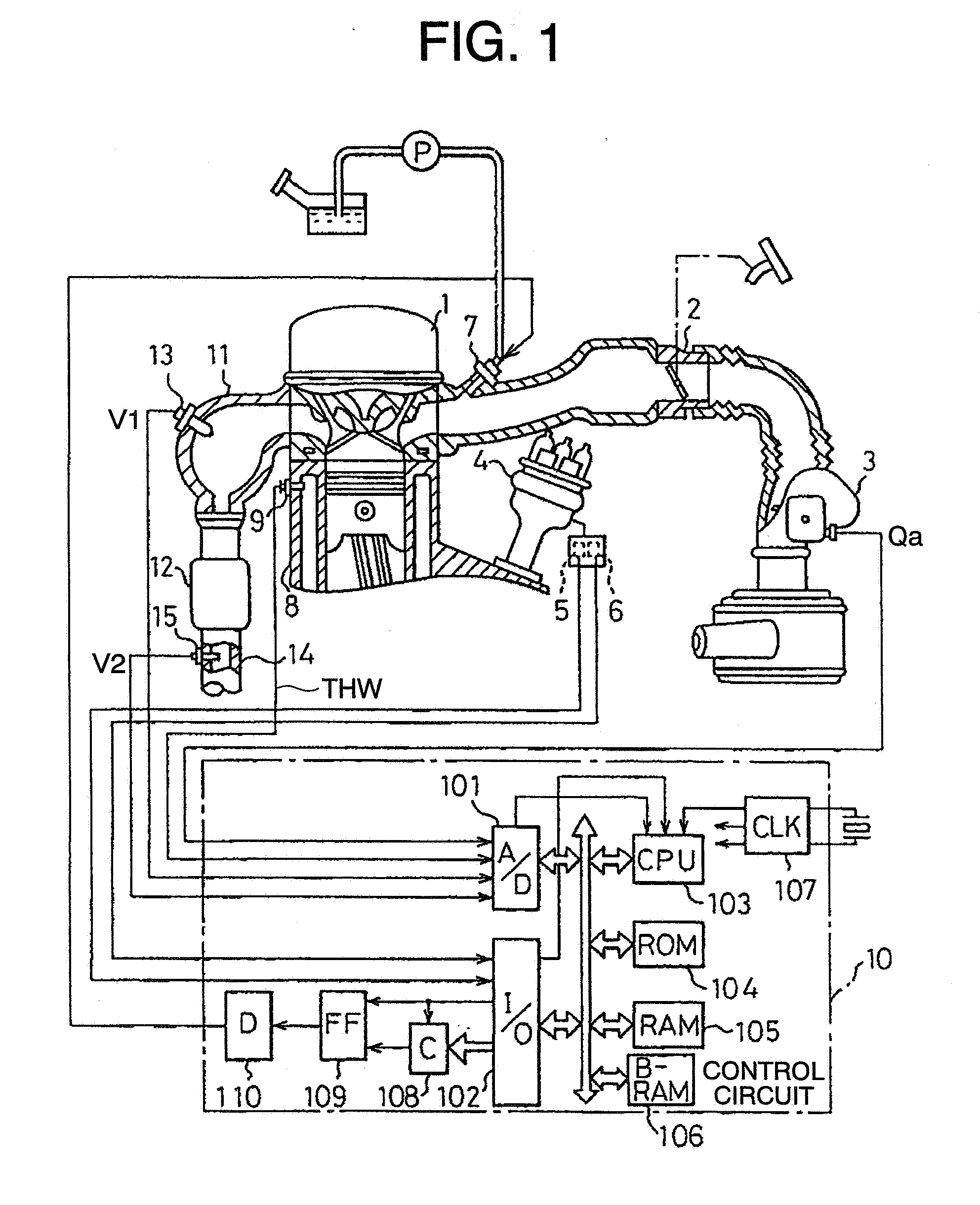
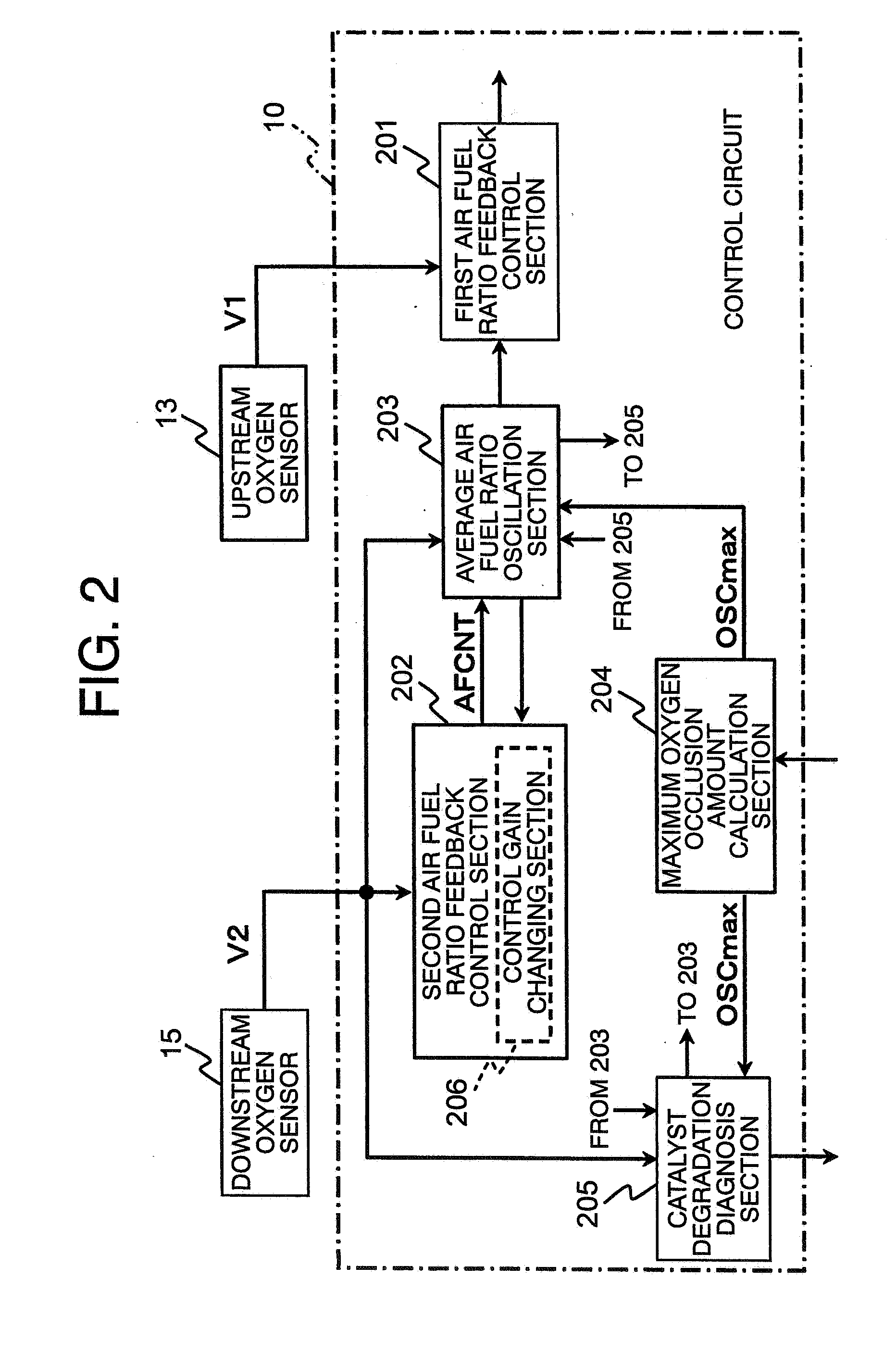
An air fuel ratio control apparatus for an internal combustion engine can improve accuracy in catalyst degradation diagnosis. The apparatus includes a first air fuel ratio feedback control section that adjusts the air fuel ratio of a mixture supplied to an engine in accordance with an output of an upstream air fuel ratio sensor and a predetermined control constant thereby to make the air fuel ratio periodically oscillate in rich and lean directions, an average air fuel ratio oscillation section that operates the control constant based on an amount of oxygen occlusion of a catalyst so that an average air fuel ratio obtained by averaging the periodically oscillating air fuel ratio is caused to oscillate in the rich and lean directions, and a catalyst degradation diagnosis section that diagnoses catalyst degradation based on correlation between the oscillation of the average air fuel ratio and an output of the downstream oxygen sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
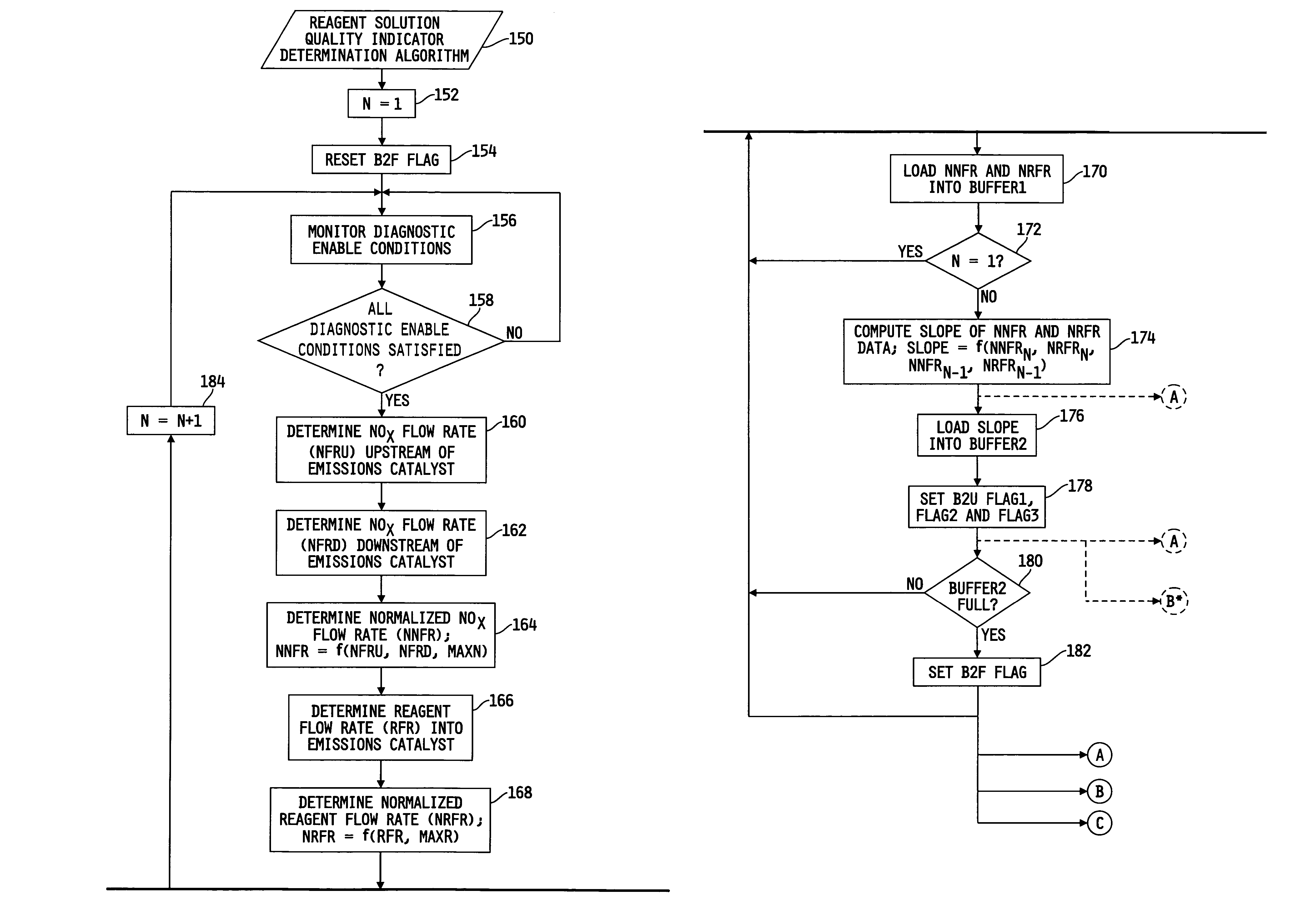
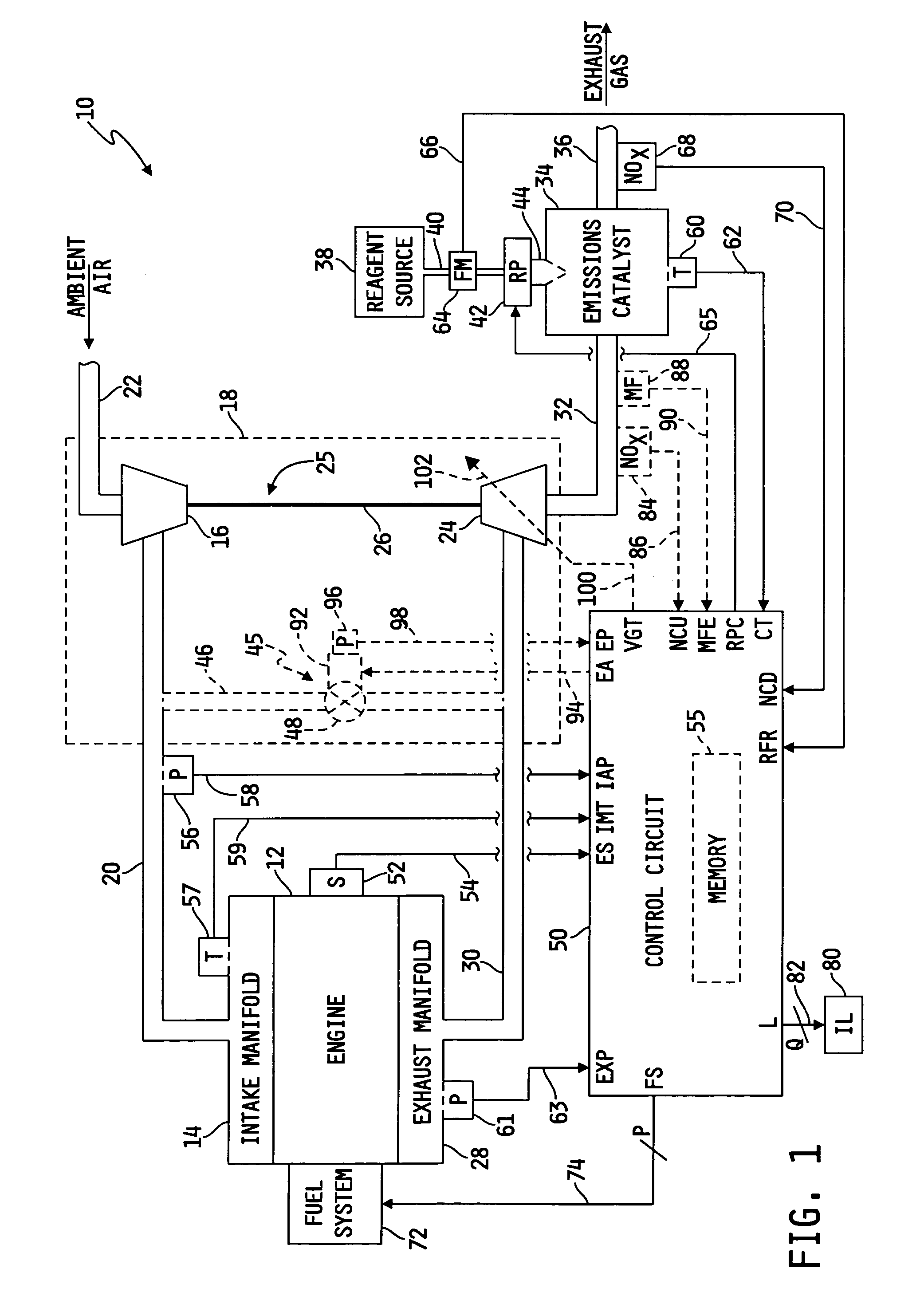
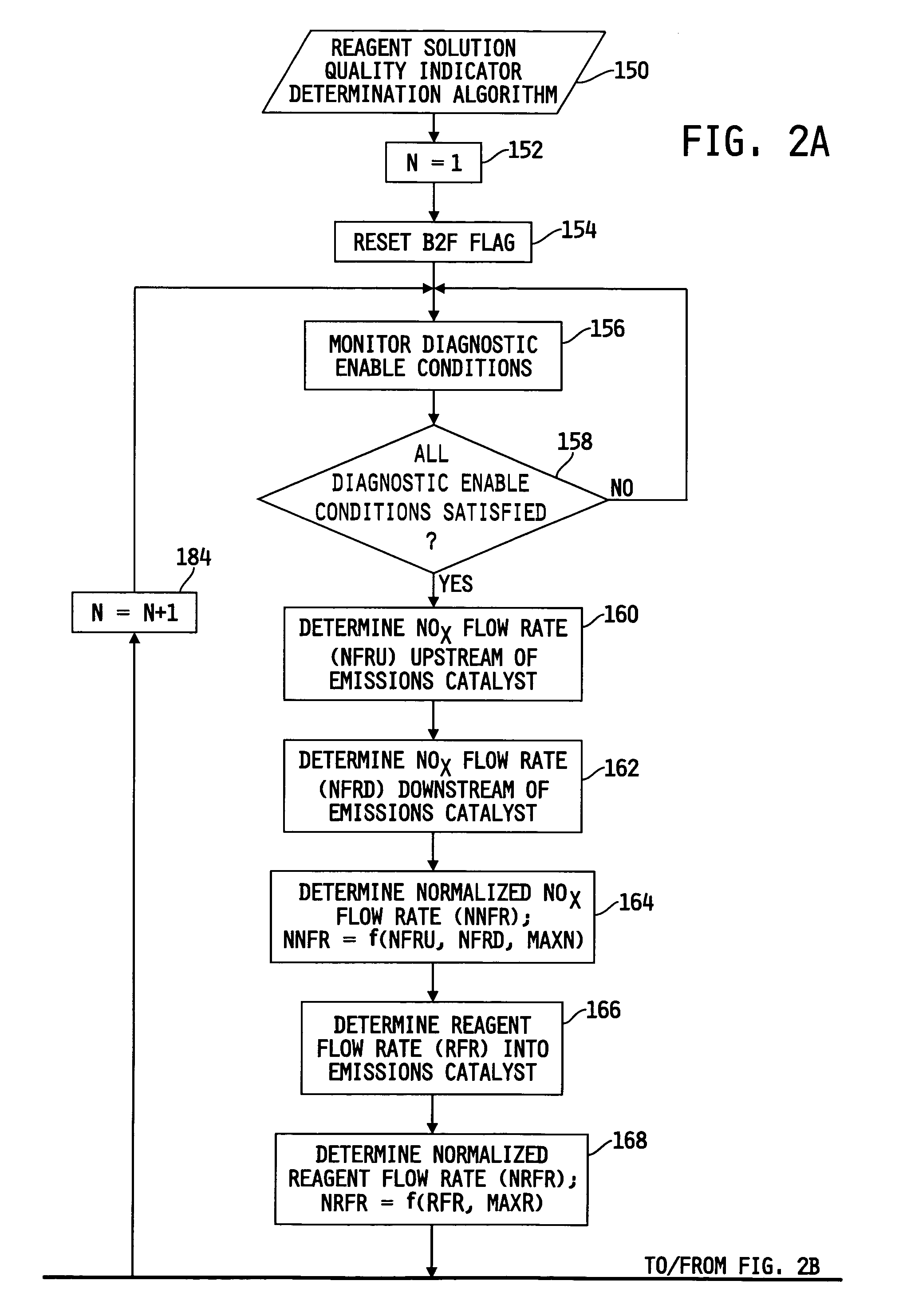
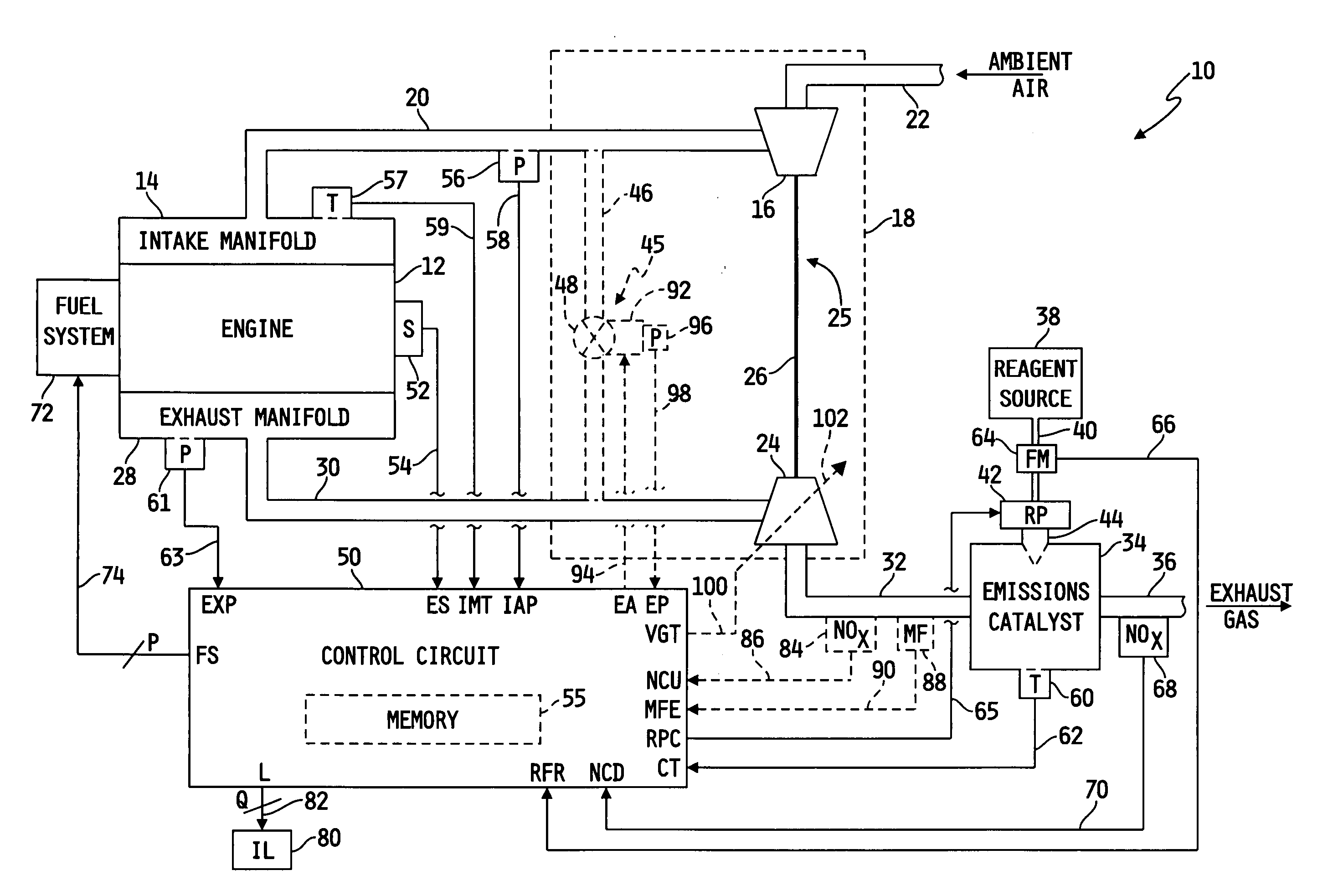
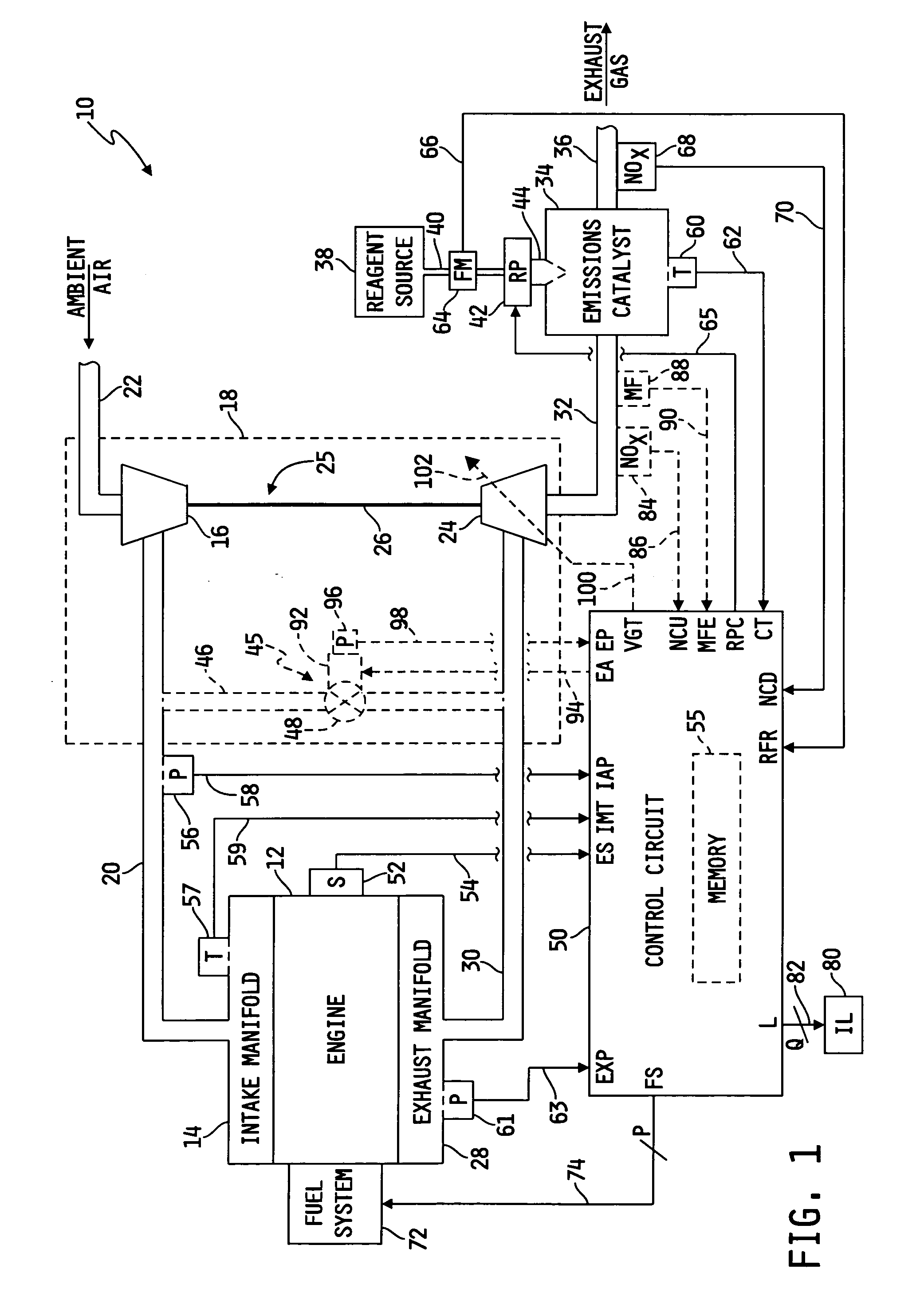
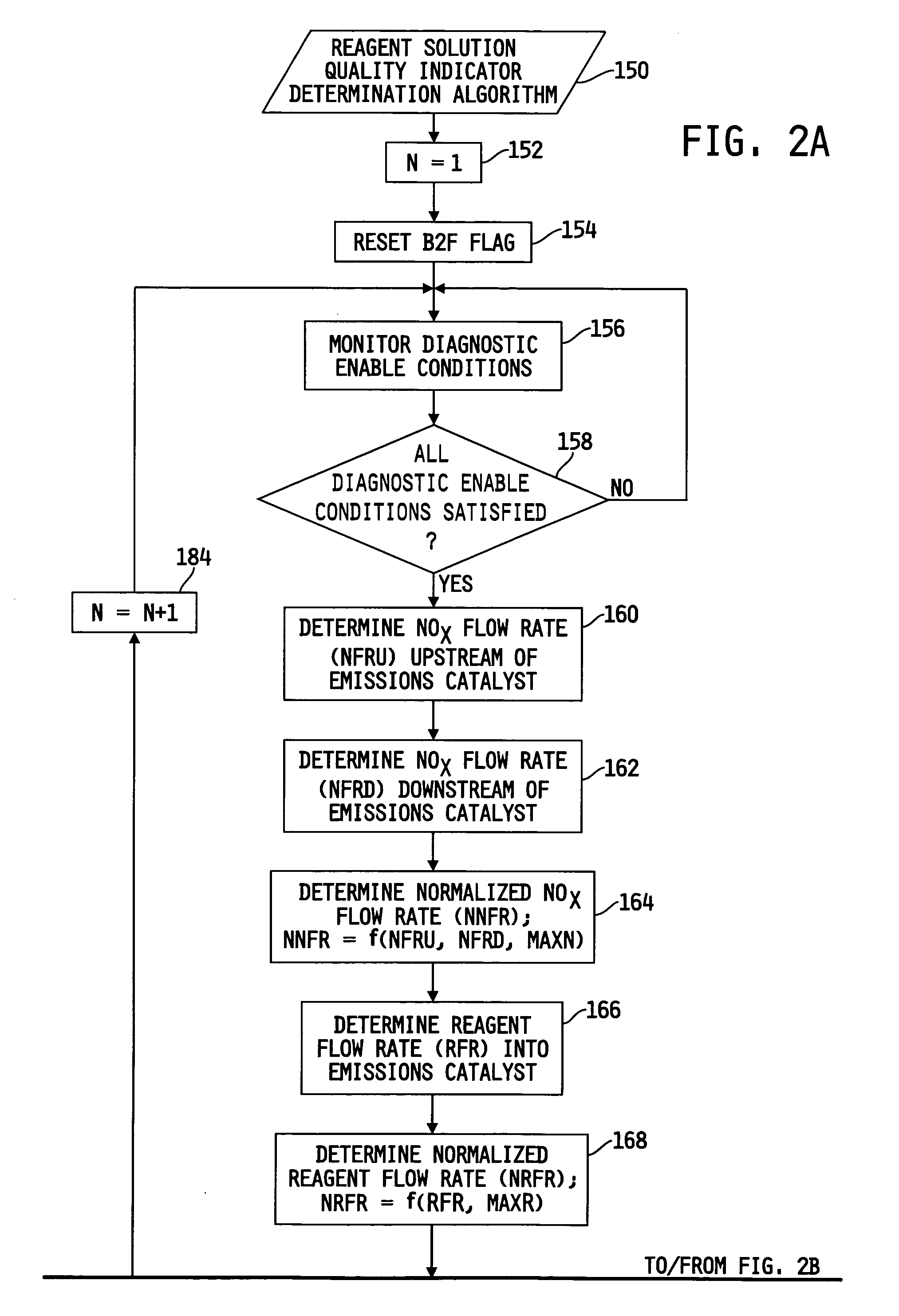
System for diagnosing reagent solution quality and emissions catalyst degradation
A system for determining a reagent solution quality indicator includes a reagent solution source for supplying the reagent solution to an emissions catalyst configured to receive a NOx-containing gas therethrough, means for determining a flow rate of NOx reduced from the gas by the catalyst, means for determining a flow rate of the reagent solution into the catalyst, and a control circuit determining the reagent solution quality indicator as a function of the NOx flow rate and the reagent solution flow rate. The system may additionally be configured to diagnose reagent solution quality by configuring the control circuit to monitor the reagent solution quality indicator over time and produce a fault value if the reagent solution quality indicator crosses a reagent quality indicator threshold, and to diagnose the catalyst by producing another fault value if the catalyst capacity point falls outside of a catalyst capacity point threshold.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
Catalyst degradation determining method
InactiveUS6915628B2Emission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCatalyst degradationOxygen
A catalyst degradation determining method includes the steps of: controlling an upstream-of-catalyst air-fuel ratio occurring upstream of a first catalyst to an air-fuel ratio that is rich of a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio so that first and second catalysts store oxygen up to a maximum storage amount of oxygen. The method then includes the steps of controlling the upstream-of-catalyst air-fuel ratio to a first lean air-fuel ratio until an output of a downstream-of-first-catalyst sensor indicates a lean air-fuel ratio, and then to a second lean air-fuel ratio and that has a value that is determined in accordance with an oxidizing-reducing capability index value, until a time point when an output of a downstream-of-second-catalyst air-fuel ratio sensor indicates an air-fuel ratio that is lean.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
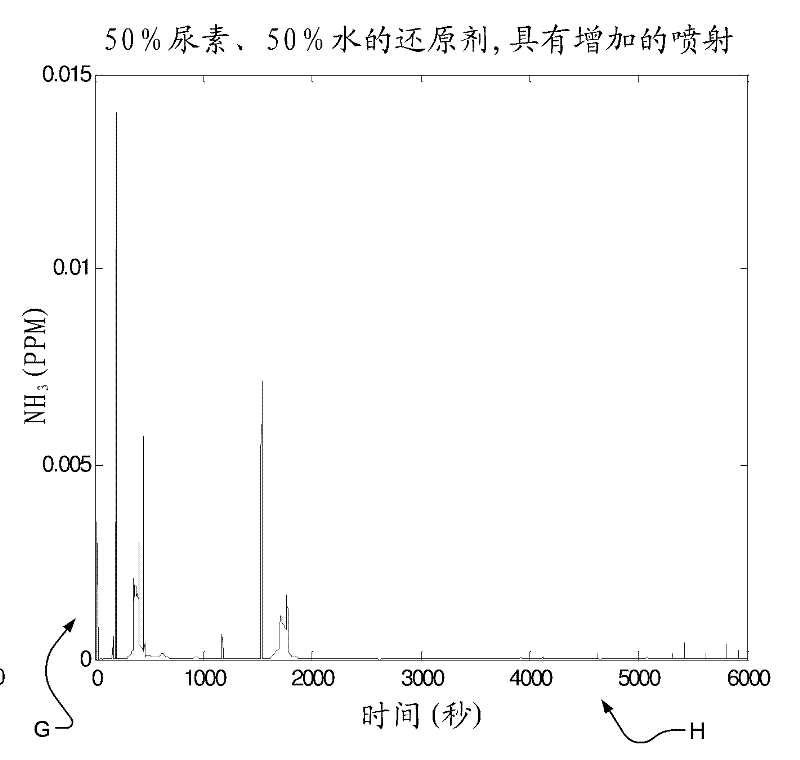
System and method for detecting low quality reductant and catalyst degradation in selective catalytic reduction systems
InactiveCN102444458AInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCatalyst degradationControl system
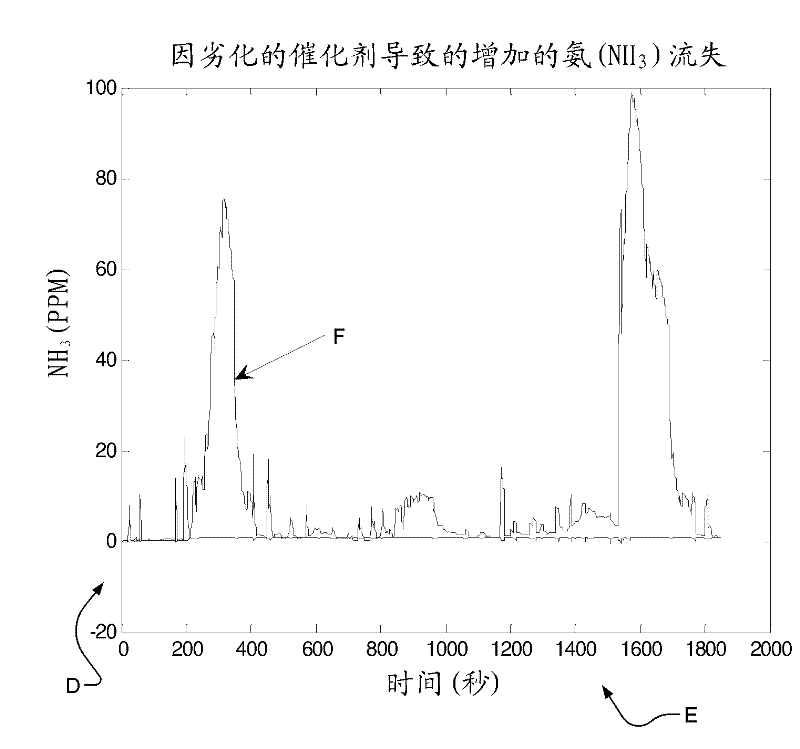
The invention relates to a system and method for detecting low quality reductant and catalyst degradation in selective catalytic reduction systems, in particular, a control system for a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system includes a conversion efficiency determination module, an ammonia slip determination module, and a diagnostic module. The conversion efficiency determination module determines a conversion efficiency of an SCR catalyst. The ammonia slip determination module determines an amount of ammonia slip across the SCR catalyst when the conversion efficiency is less than a predetermined threshold. The diagnostic module determines pass / fail statuses of a reductant supply and the SCR catalyst based on the amount of ammonia slip and at least one ammonia slip threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Stabilization of olefin metathesis product mixtures
InactiveUS20060167326A1Losses in target product olefins and raw material olefins are reducedInexpensive and readily materialOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPolymer scienceCatalyst degradation
A process of stabilizing an olefin metathesis product mixture, preferably, against double bond isomerization and thermal and chemical degradation. The process involves (a) contacting an olefin metathesis product mixture comprising one or more olefins produced in a metathesis process, a metathesis catalyst comprising a catalytic metal and one or more ligands, optionally, one or more metathesis catalyst degradation products, and optionally, one or more metals derived from sources other than the catalyst or catalyst degradation product(s), with an adsorbent, more preferably carbon; or alternatively, (b) subjecting the olefin metathesis product mixture to a two-step distillation, preferably, including short path wiped-film evaporation. A stabilized olefin metathesis product mixture is disclosed containing one or more olefins obtained in a metathesis process and having a total concentration of metal(s) of less than about 30 parts per million by weight.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fuel Cell Flow Channels and Flow Fields
ActiveUS20150180052A1Uniform current densityReduce the cross-sectional areaFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesCarbon corrosionCatalyst degradation
A fuel cell anode flow field includes at least one flow channel with a cross-sectional area that varies along at least a portion of its length. In some embodiments, the channel width decreases along at least a portion of the channel length according to a natural exponential function. This type of anode flow field can improve performance, reduce fuel consumption and / or reduce detrimental effects such as carbon corrosion and catalyst degradation, thereby improving fuel cell longevity and durability. When operating the fuel cell on either a substantially pure or a dilute fuel stream, this type of anode flow field can provide more uniform current density. These flow channels can be incorporated into reactant flow field plates, fuel cells and fuel cell stacks.
Owner:LOOP ENERGY INC
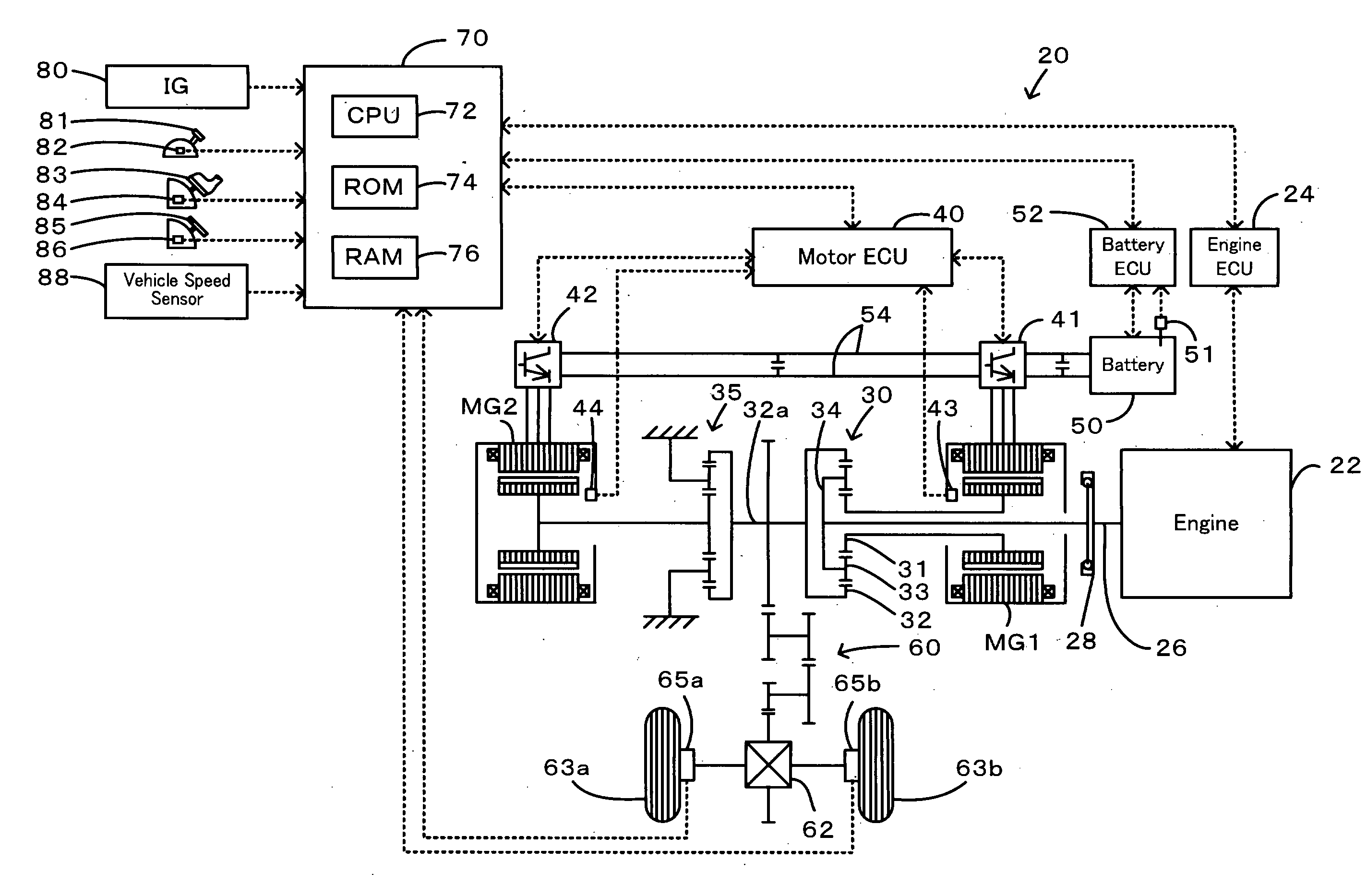
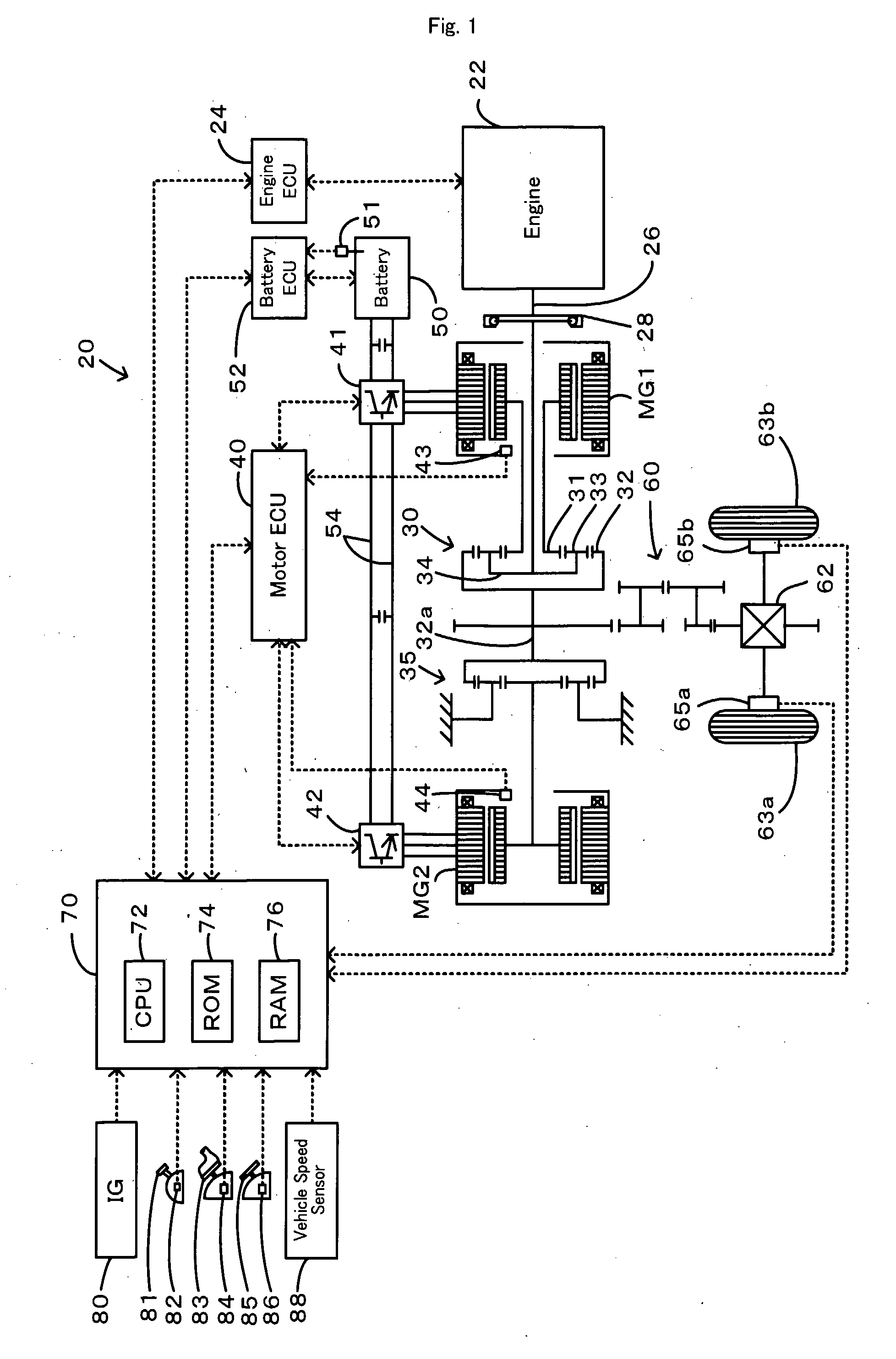
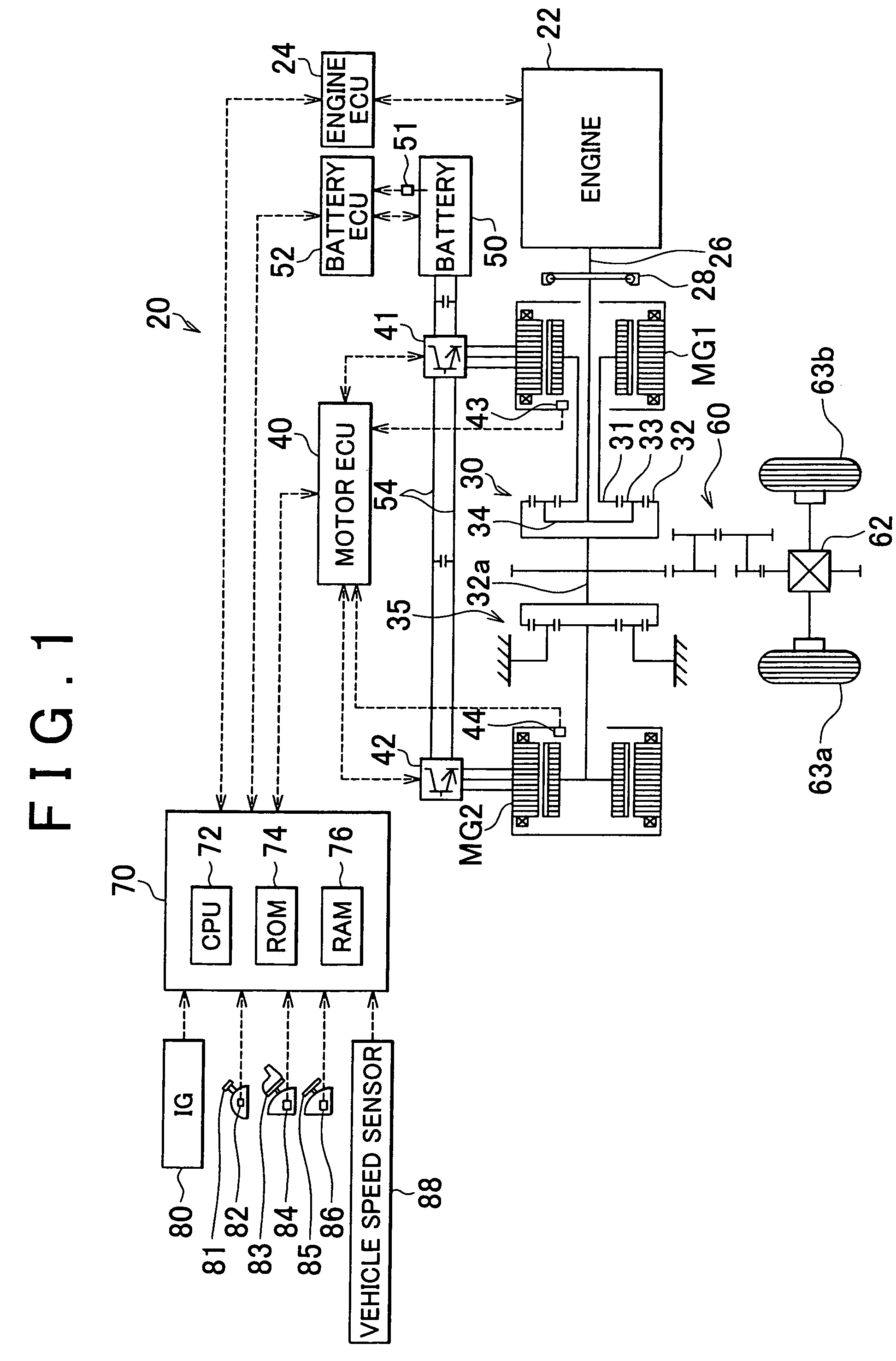
Power Output Apparatus, Motor Vehicle Equipped With Power Output Apparatus, And Control Method Of Power Output Apparatus
InactiveUS20080110684A1Method stableReduce speedAuxillary drivesInternal combustion piston enginesBrake torqueCatalyst degradation
In requirement of catalyst degradation control with setting of a catalyst degradation control flag Fc to 1, the braking control of the invention sets torque commands Tm1* and Tm2* of two motors and controls the operations of an engine and the two motors to shift a drive point of the engine on an optimum fuel consumption operation curve by a preset rotation speed variation Nrt1 in a specific range of rotation speed that ensures no occurrence of a misfire in the engine within an input limit Win of a battery and to ensure output of a braking torque demand Tr* to a ring gear shaft or driveshaft (steps S200 to S250). Such braking control stably lowers a rotation speed Ne of the engine to a target rotation speed Ne* and desirably enhances the fuel consumption under the catalyst degradation control.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
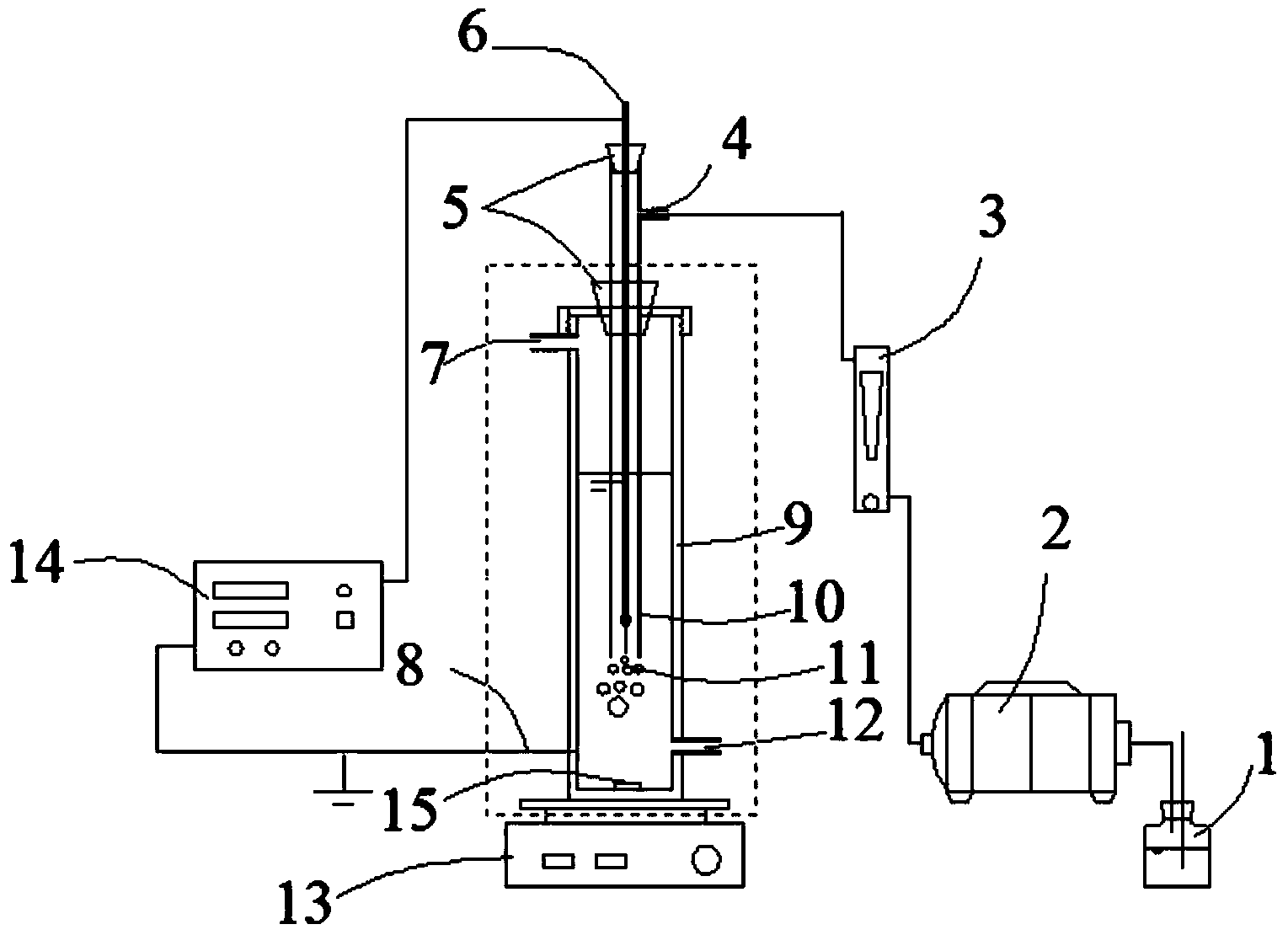
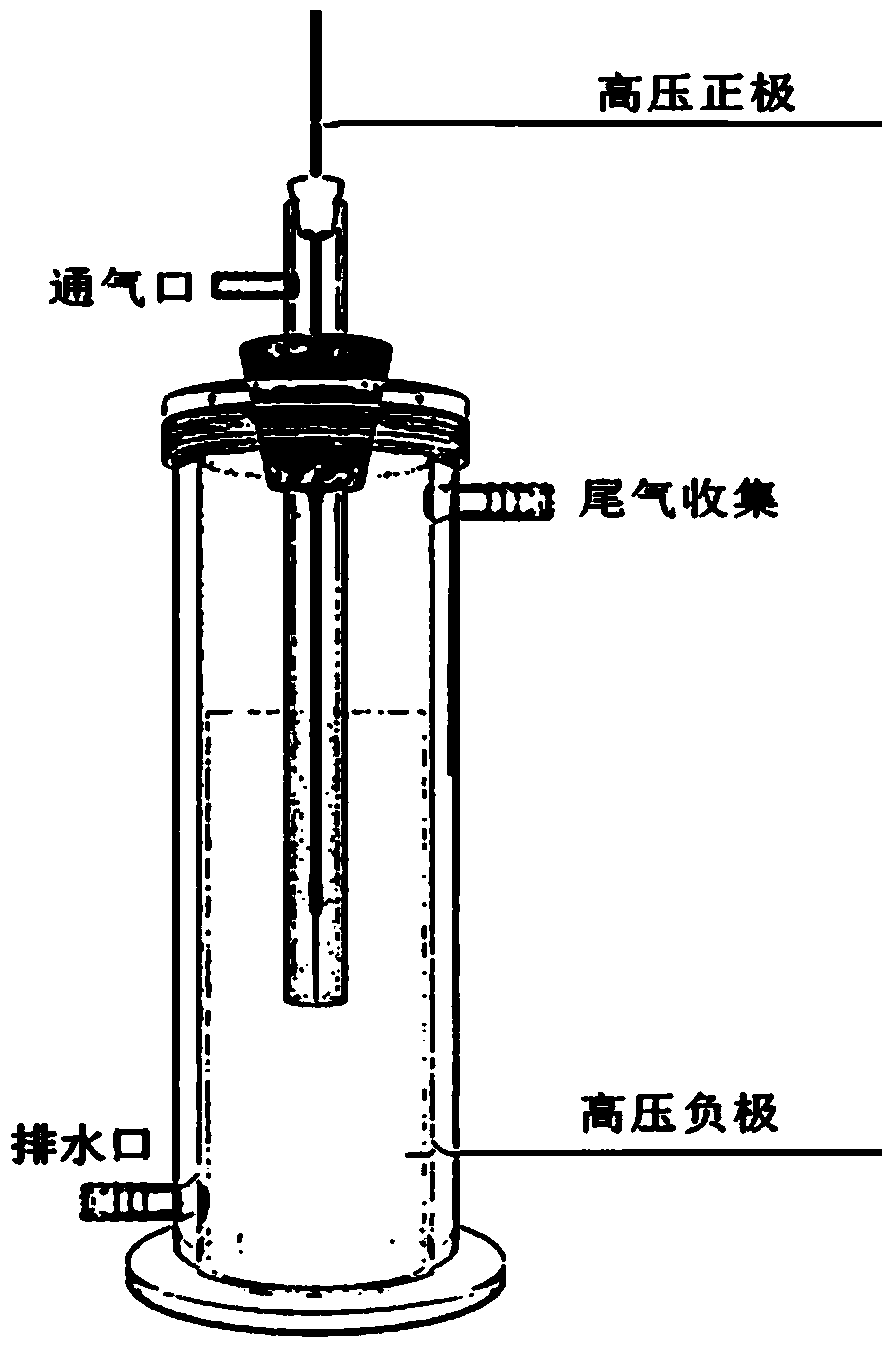
Device and method for degrading antibiotic wastewater by utilizing low temperature plasma in coordination with bismuth molybdate catalyst
InactiveCN103848484AImprove degradation rateHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCatalyst degradationBreather
The invention discloses a device and a method for treating antibiotic wastewater by utilizing low temperature plasma in coordination with a bismuth molybdate catalyst. The device for treating the antibiotic wastewater by utilizing the low temperature plasma in coordination with the bismuth molybdate catalyst comprises a barrel-shaped reactor, a breather pipe, a high voltage electrode, an alternating current high voltage power supply, an air pump and a stirrer, wherein the breather pipe is arranged inside the barrel-shaped reactor and is coaxial with the barrel-shaped reactor, the high voltage electrode is suspended inside the breather pipe, the lower port of the breather pipe is arranged at the lower bottom part inside the barrel-shaped reactor, the upper part of the breather pipe is arranged outside the barrel-shaped reactor, an air inlet is formed in the side wall of the upper part of the breather pipe, the air inlet is communicated with the outlet of the air pump by virtue of a pipeline; the alternating current high voltage power supply is respectively connected to the high voltage electrode and grounded, and the stirrer is arranged at the lower part of the barrel-shaped reactor. The device for treating the antibiotic wastewater by utilizing the low temperature plasma in coordination with the bismuth molybdate catalyst has the characteristics of simple design, low equipment investment and no secondary pollution and can be applied to the filed of treatment on antibiotic wastewater and organic wastewater difficult to be biochemically degraded, wherein a degradation reaction temperature can be increased by fully utilizing heat produced in a discharge process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Catalyst degradation determination device for exhaust purification system
InactiveUS20110131956A1Suppress temporary declineReliable purificationInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCatalyst degradationAmmonia
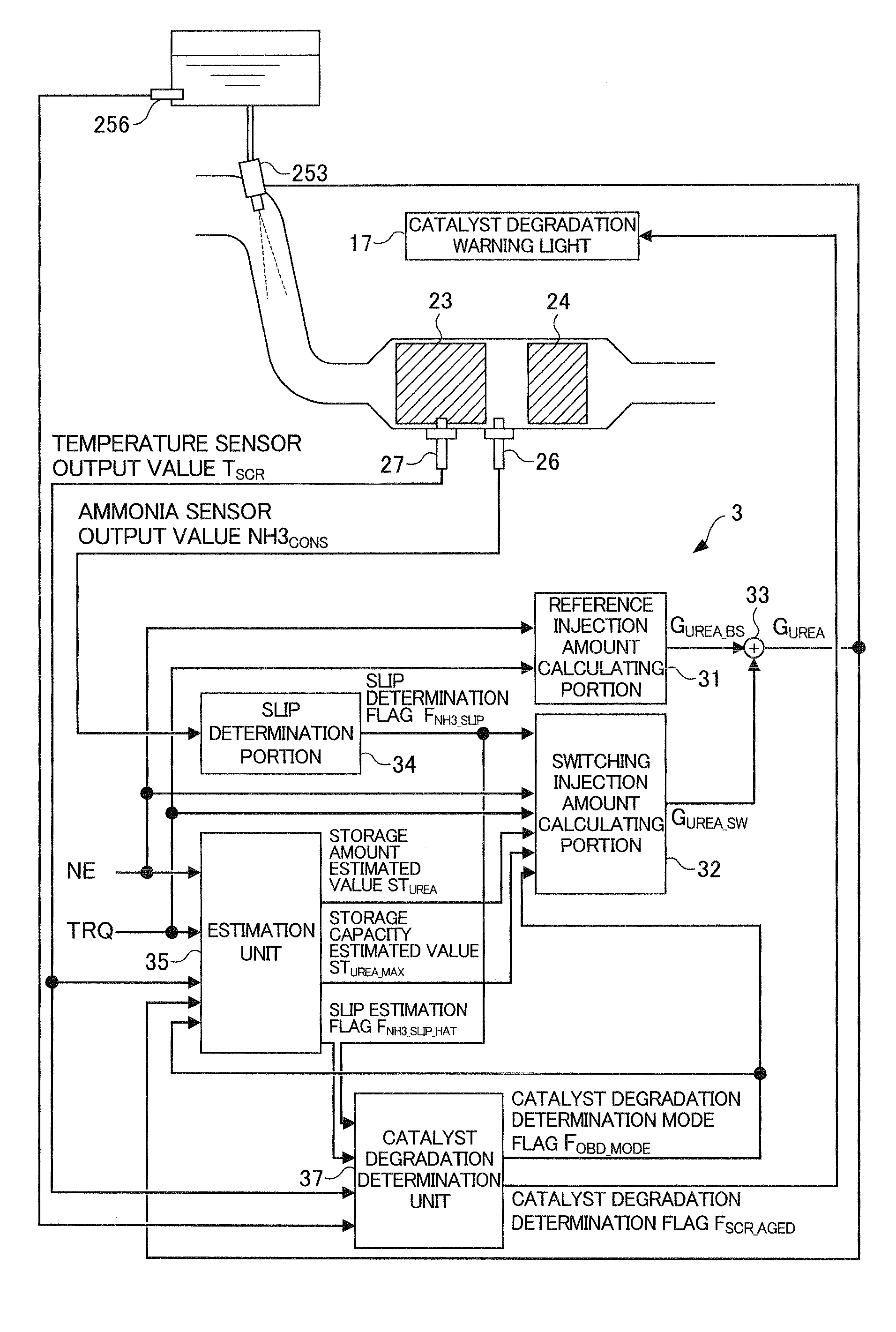
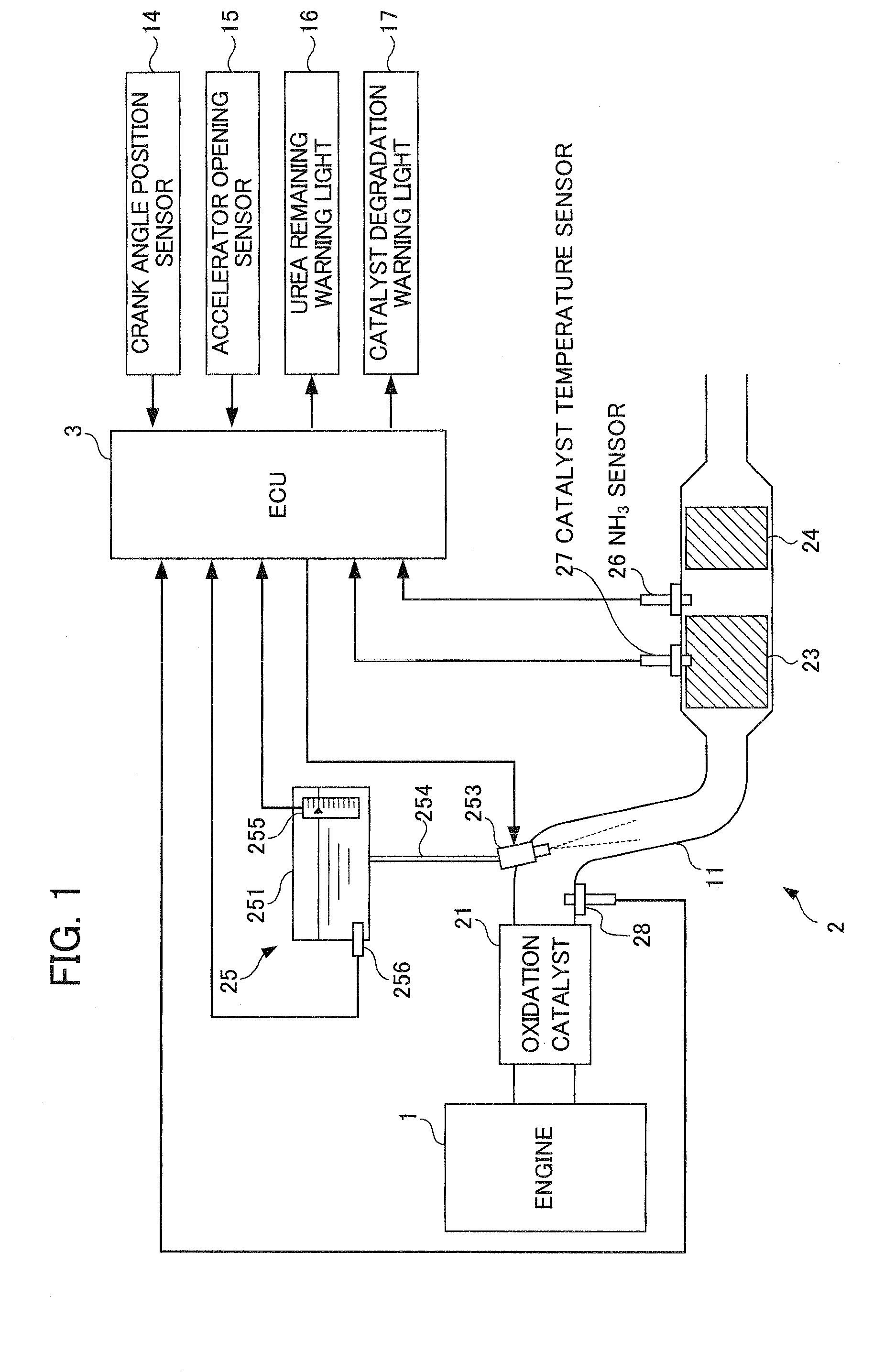
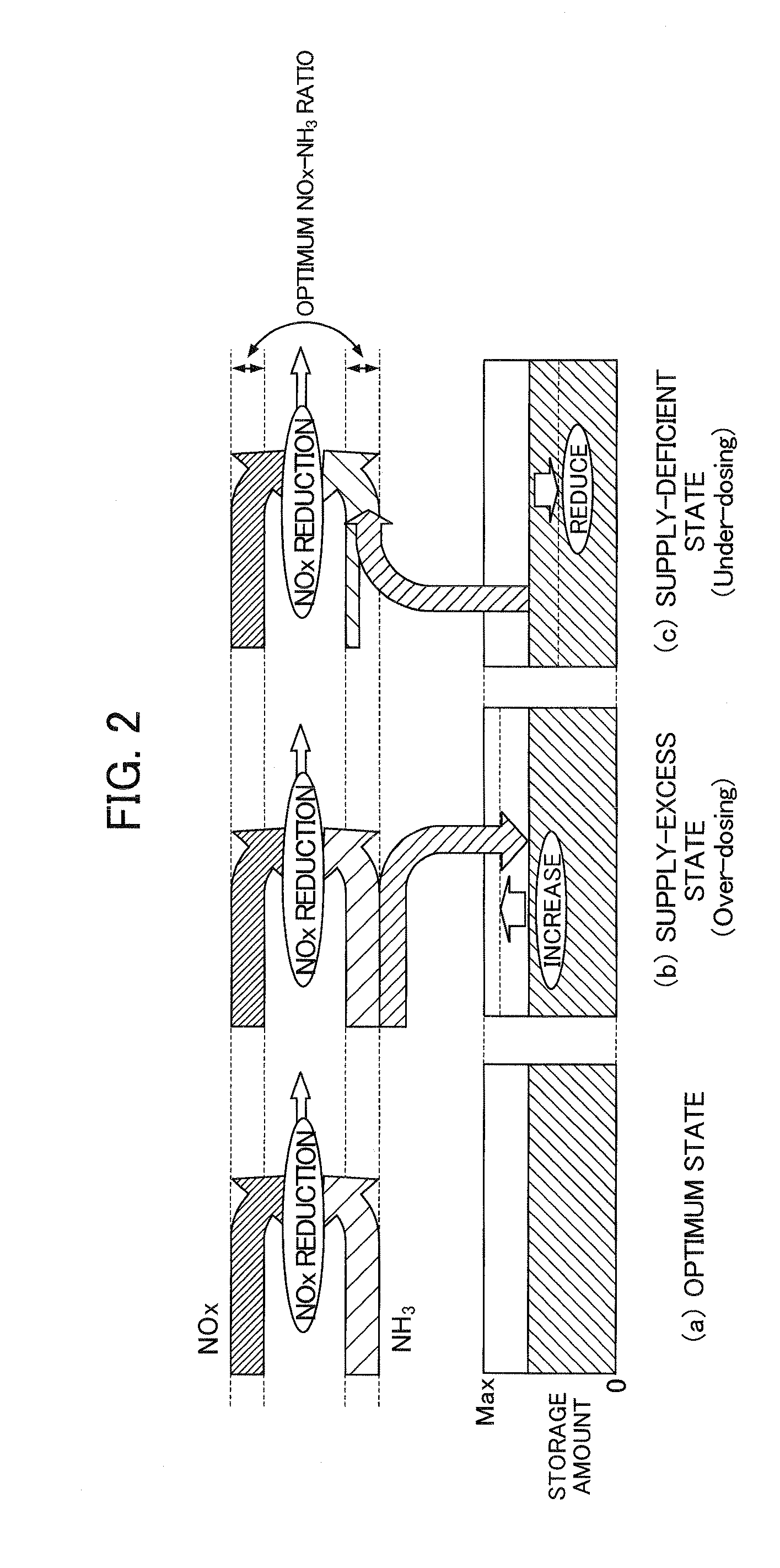
A catalyst degradation determination device is provided that can determine the degradation of a selective reduction catalyst with high precision while also suppressing a temporary decline in purification performance. By way of controlling a urea injection device, the catalyst degradation determination device increases, in a selective reduction catalyst in a state in which the storage amount is a maximum, the storage amount thereof by a detection reduced-amount portion DSTNH3<sub2>—< / sub2>JD and then decreases the amount until it is determined that ammonia slip has occurred. Then, degradation is determined based on the time at which the slip determination flag FNH3<sub2>—< / sub2>SLIP was set to “1” when fluctuating the storage amount. The detection reduced-amount portion DSTNH3<sub2>—< / sub2>JD is set to a value that is larger than the storage capacity of the selective reduction catalyst in a degraded state and smaller than the storage capacity of the selective reduction catalyst in a normal state.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Double-effect optical Fenton denitrification method of manganese ferrite or carbon composite material of manganese ferrite
ActiveCN104445508AQuick releaseEfficient releaseWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsCarbon compositesCatalyst degradation
The invention discloses a double-effect optical Fenton denitrification method of manganese ferrite or a carbon composite material of the manganese ferrite. The method comprises the following steps: at least under irradiation of ultraviolet light or visible light, preferably under the irradiation of the sunshine, degrading ammonia nitrogen in water by taking manganese ferrite and / or a manganese ferrite-carbon composite material as an optical Fenton catalyst, wherein the manganese ferrite-carbon composite material mainly comprises manganese ferrite, graphene and / or active carbon; and the manganese ferrite is distributed on a graphene interface or coated by the active carbon. By utilizing catalytic circulation of Mn (III) and Mn (II) and the catalytic circulation of Fe (III) and Fe (II), the method disclosed by the invention can be used for oxidizing the ammonia nitrogen into nitrogen gas by one step under the irradiation of various wavelengths so as to realize rapid and high-efficiency degradation of the ammonia nitrogen in water; and moreover, the adopted optical Fenton catalytic material can be separated from water by an externally applied magnetic field and is recyclable, low in cost and beneficial for environmental protection.
Owner:苏州尼普环境科技有限公司
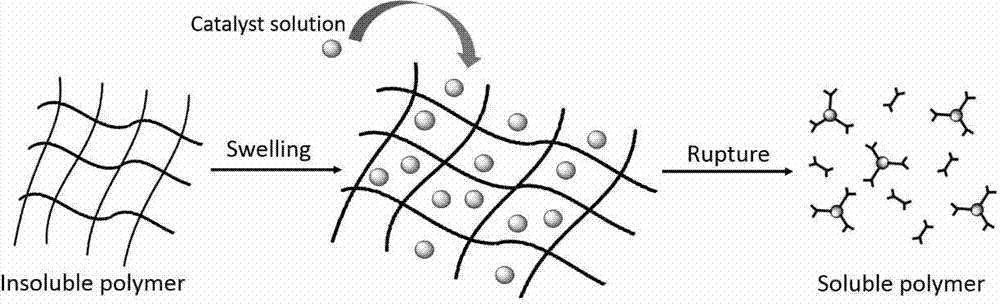
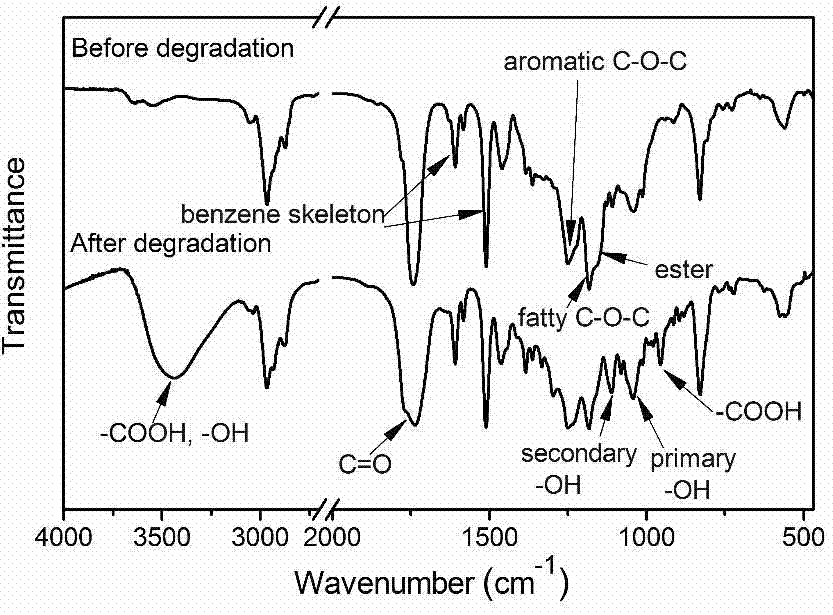
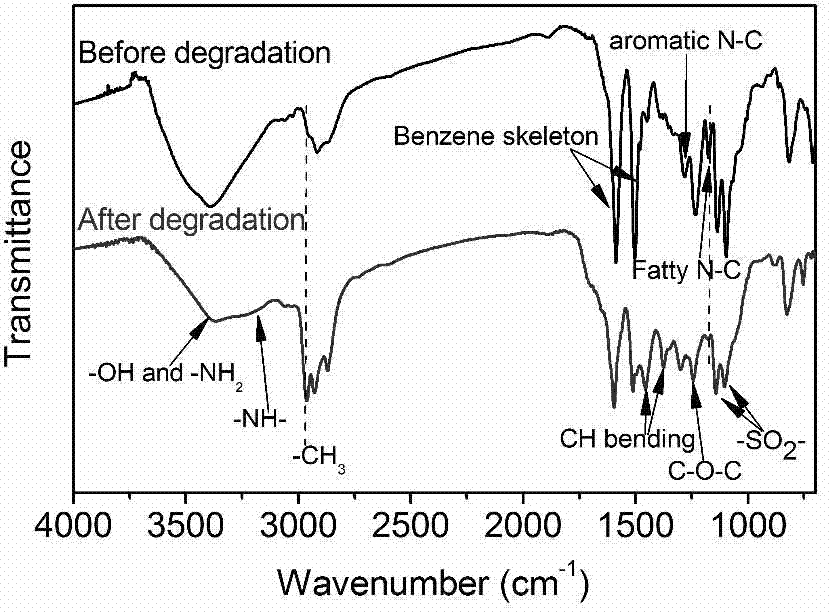
Application of heteropoly acid and lewis acid as catalyst to degradation of thermosetting resin
ActiveCN107365429AImprove mechanical propertiesEffective swellingPlastic recyclingBulk chemical productionCatalyst degradationHeteropoly acid
The invention discloses application of heteropoly acid and lewis acid as a catalyst to degradation of thermosetting resin. Compared with a supercritical and high-temperature pyrolysis method, a chemical catalyst degradation method can be used for selectively breaking a specific chemical bond (an ester or ether bond) of the thermosetting resin under a moderate reaction condition (less than 200 DEG C), so that soluble and machinable degradable resin is obtained. When the degradable resin is used as a reactive curing agent and is added into a novel resin system, an obtained curing material still keeps excellent mechanical properties.
Owner:江苏中信世纪新材料有限公司
Preparation of magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst and method for degrading organic pollutants
ActiveCN102125848AIncrease profitGood effectMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCatalyst degradationPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention provides preparation of a magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst. The preparation comprises the following steps of: preparing mixed solution by using ferric trichloride and nickel sulfate as raw materials, and performing heating, separation, washing and drying on the mixed solution to obtain the magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst NiFe2O4. The invention also provides a method for degrading organic pollutants by using the magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst. The method for degrading the organic pollutants comprises the following steps of: placing organic pollutant solution into a reaction container; adding a proper amount of oxalic acid into the reaction container; adding a proper amount of magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst into the reactioncontainer; and performing photocatalysis reaction under the irradiation of visible ultraviolet light. The magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst NiFe2O4 improves the utilization rate of sunlight; and the magnetic heterogeneous light Fenton catalyst has good effect on nickel ferrite photocatalysis of the organic pollutants and high degradation rate.
Owner:苏州尼普环境科技有限公司
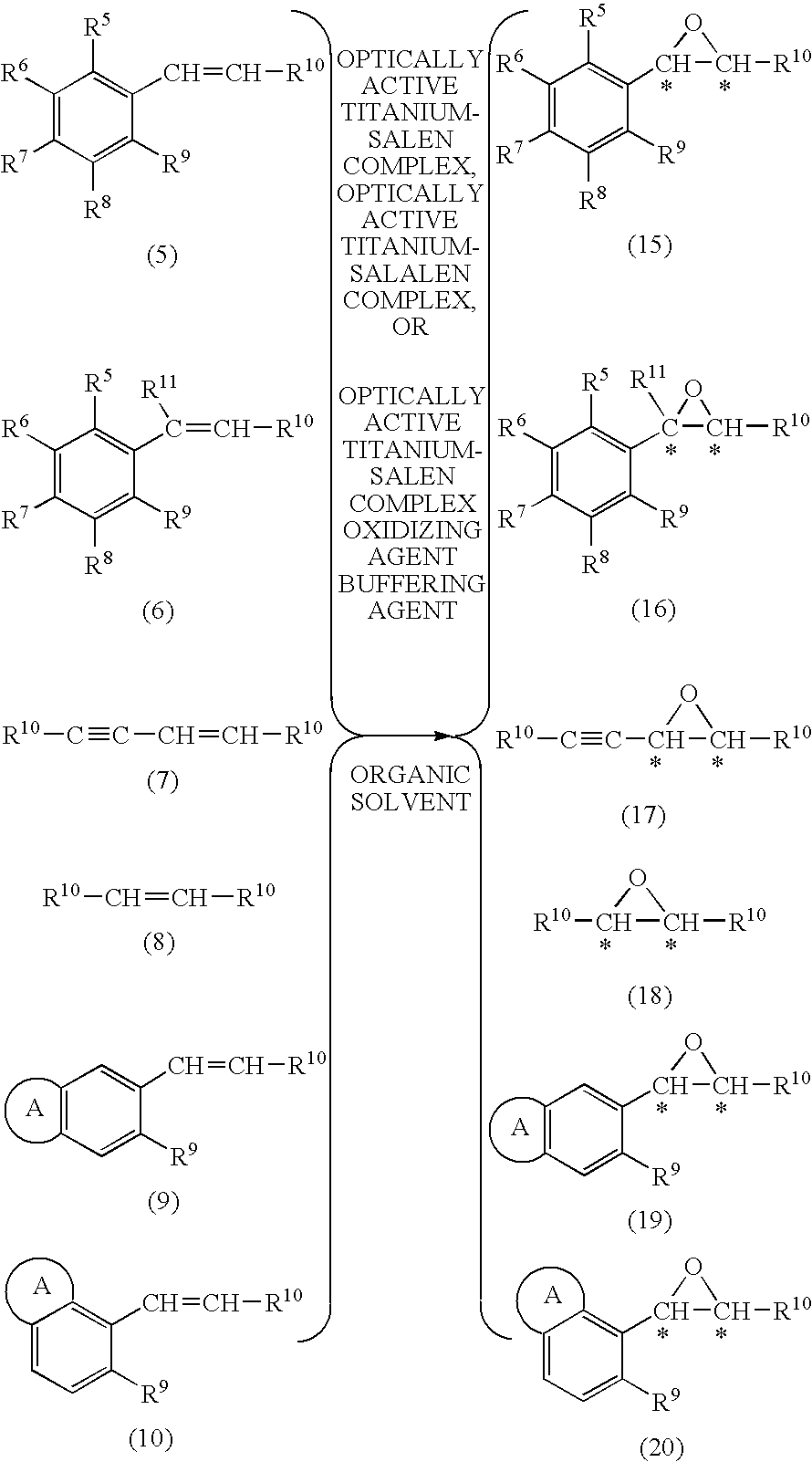
Process for production of optically active epoxy compound
InactiveUS20100081808A1Reduce the amount requiredHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsState of artCatalyst degradation
[Problems] To provide an efficient process for producing an optically active epoxy compound.[Means For Solving Problems] The process for producing an optically active epoxy compound comprises asymmetrically epoxidizing an unsaturated compound with an oxidizing agent in the presence of an optically active titanium-salen complex, an optically active titanium-salalen complex or an optically active titanium-salan complex, with addition of a buffering agent or a buffer solution. The process can inhibit catalyst degradation, reduce the amount of the catalyst used in the reaction, and inhibit a by-product, compared with the prior art, and can provide an optically active epoxy compound in high chemical yield and optical yield and with high quality, and therefore is an industrially useful process.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Preparation of Prussian blue photo-Fenton catalyst and method for degrading organic pollutant
InactiveCN102962063AReusableThe method is simpleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst degradationPotassium ferricyanide
The invention provides preparation of a Prussian blue photo-Fenton catalyst; ferric trichloride, ferric nitrate, ferric sulfate or ammonium ferrous sulfate, potassium ferricyanide, and potassium ferrocyanide are used as raw materials, and are dissolved in ultrapure water respectively to prepare a solution containing iron ions and ferricyanide ions; molecular sieve, kaolin or construction waste are used as carriers, and Prussian blue is fixed on the carriers to obtain fixed Prussian blue photo-Fenton catalyst. The invention also provides a method for degrading organic pollutants by the Prussian blue photo-Fenton catalyst, which comprises mixing of the prepared photo-Fenton catalyst with hydrogen peroxide under a light condition to degrade organic simulated pollutants. The method of the invention is simple and practical; the catalyst is suitable for recycle, can both effectively remove chroma of polluted water, and reduce COD of the polluted water.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
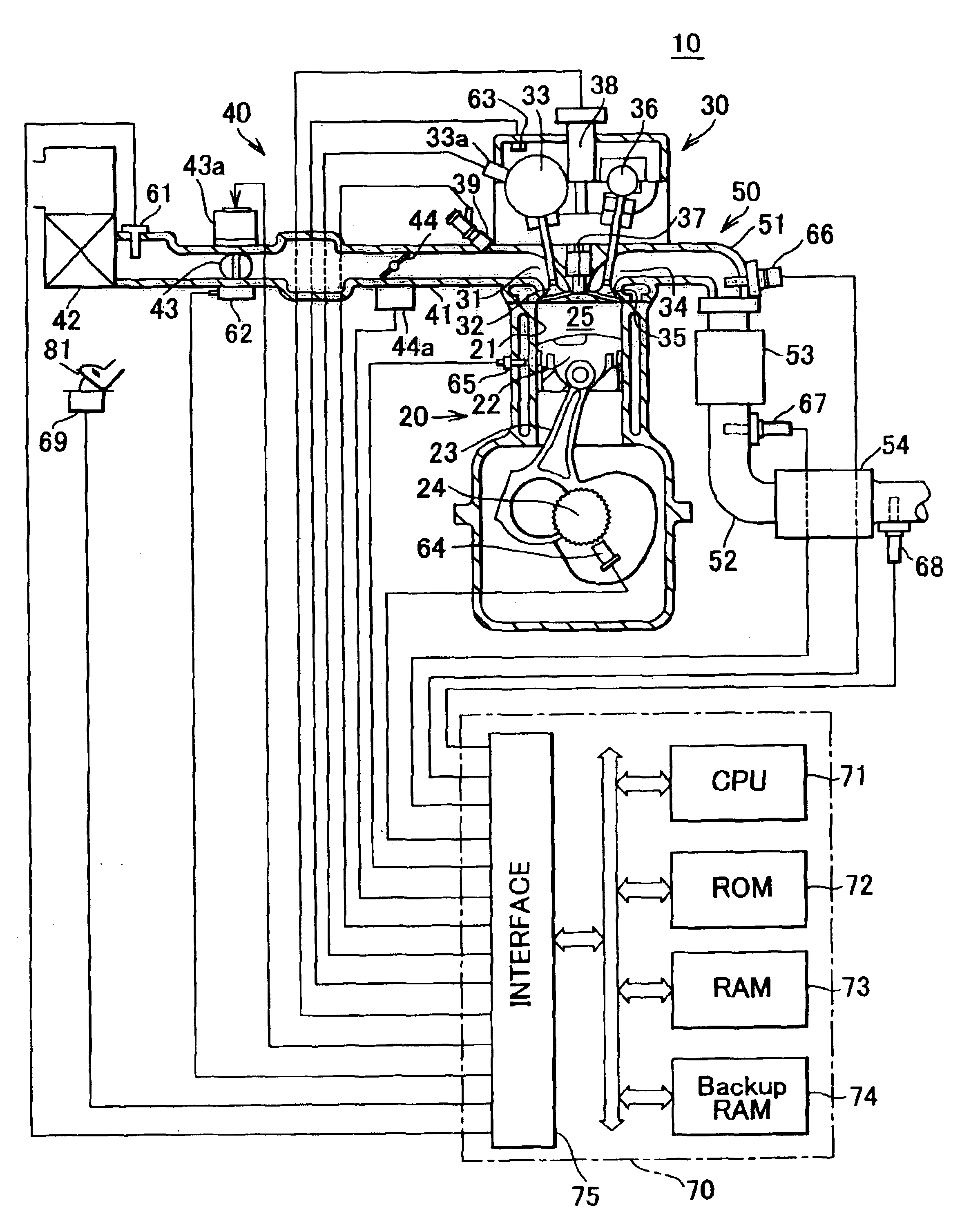
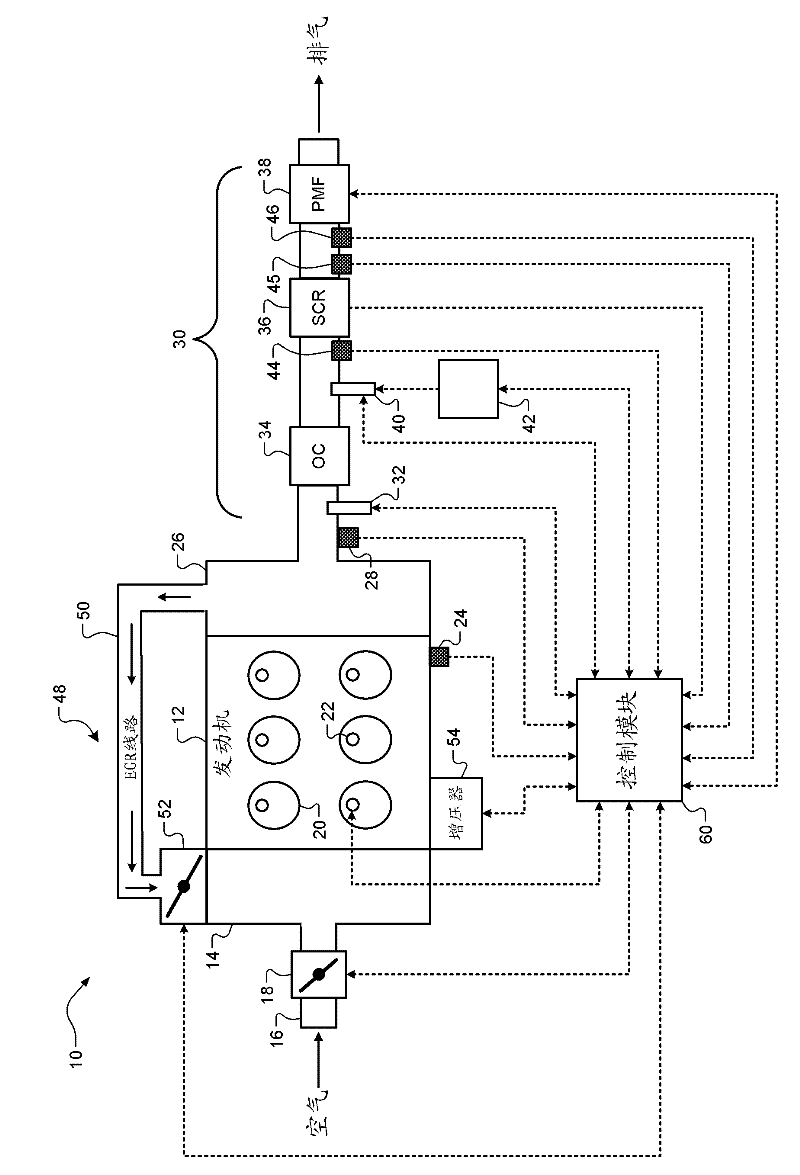
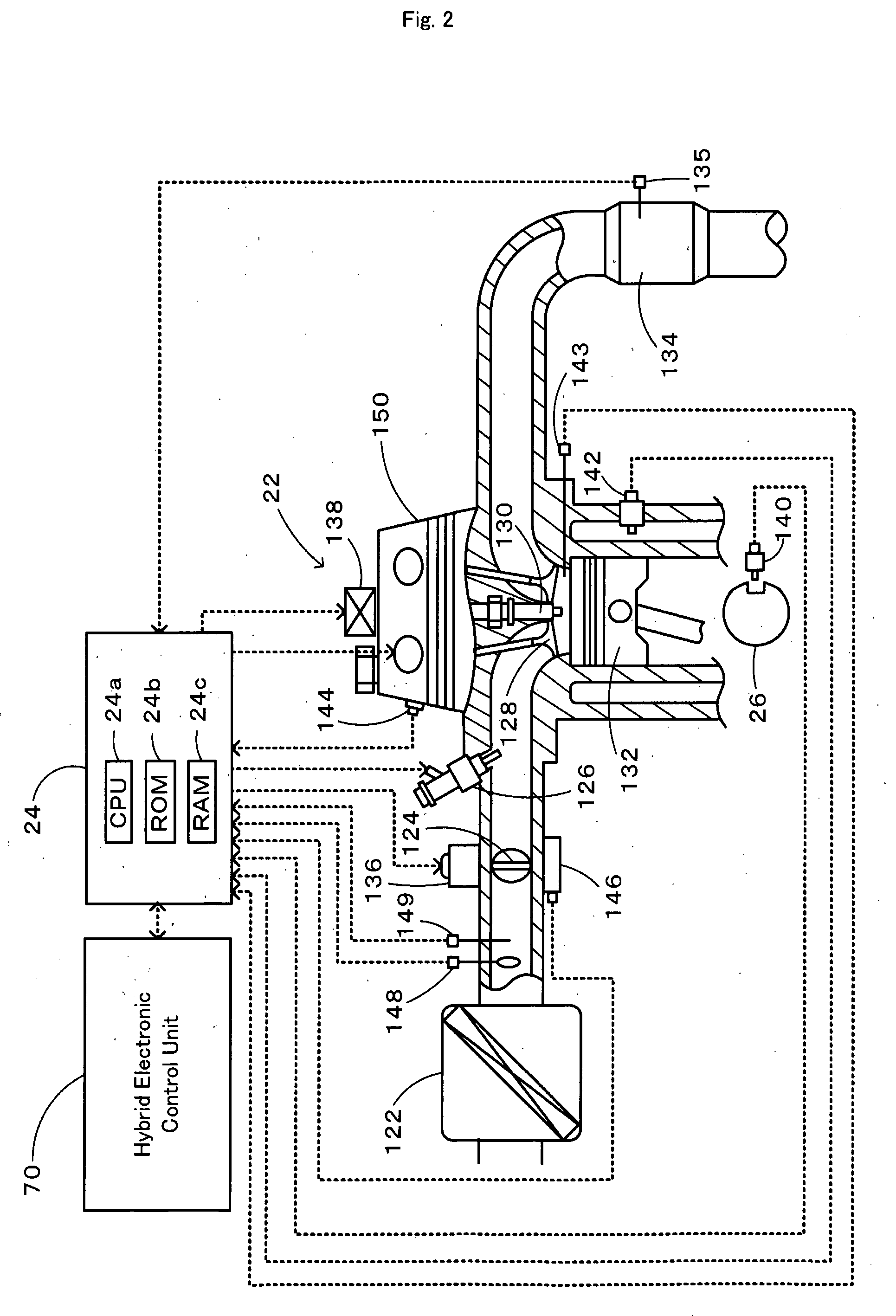
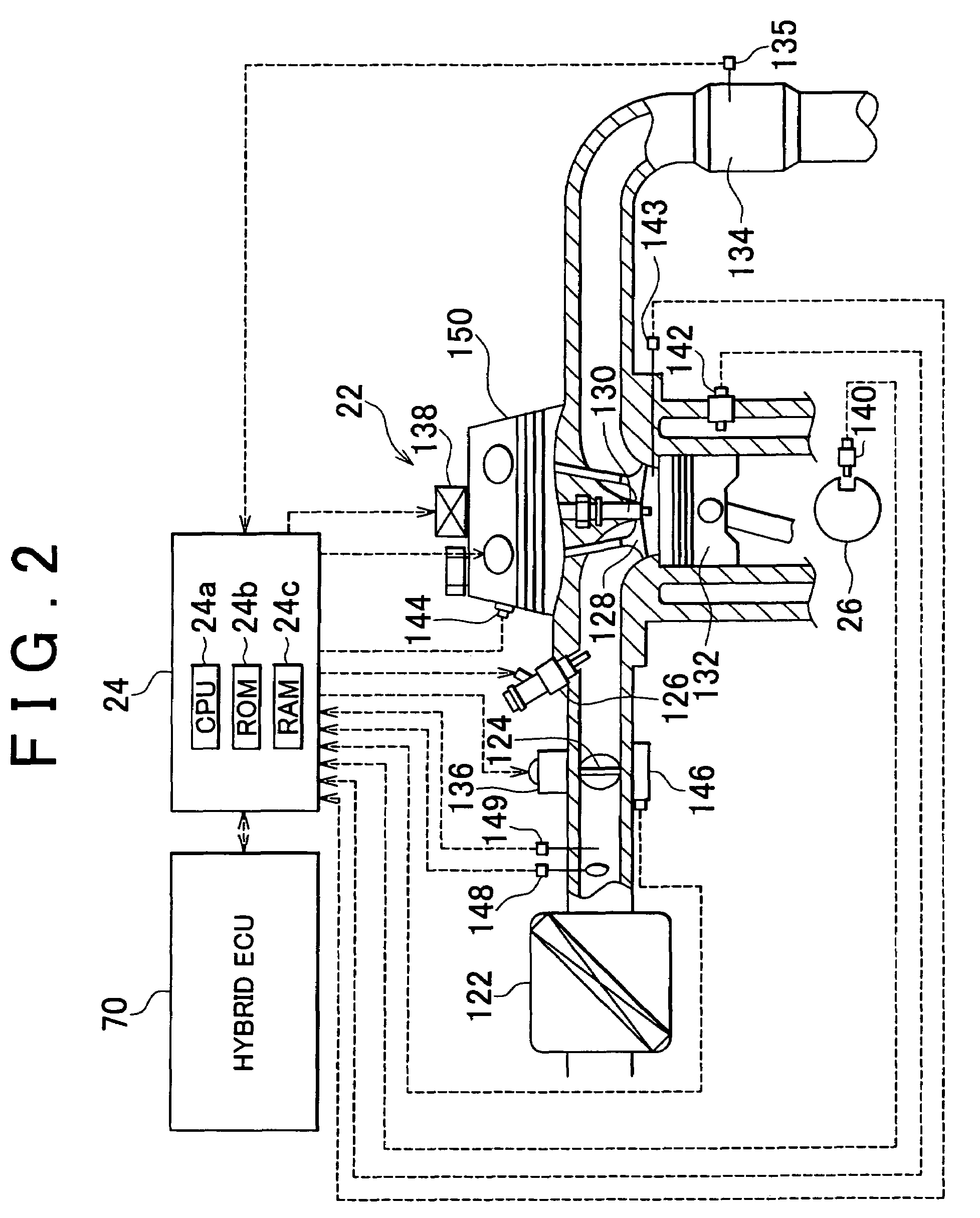
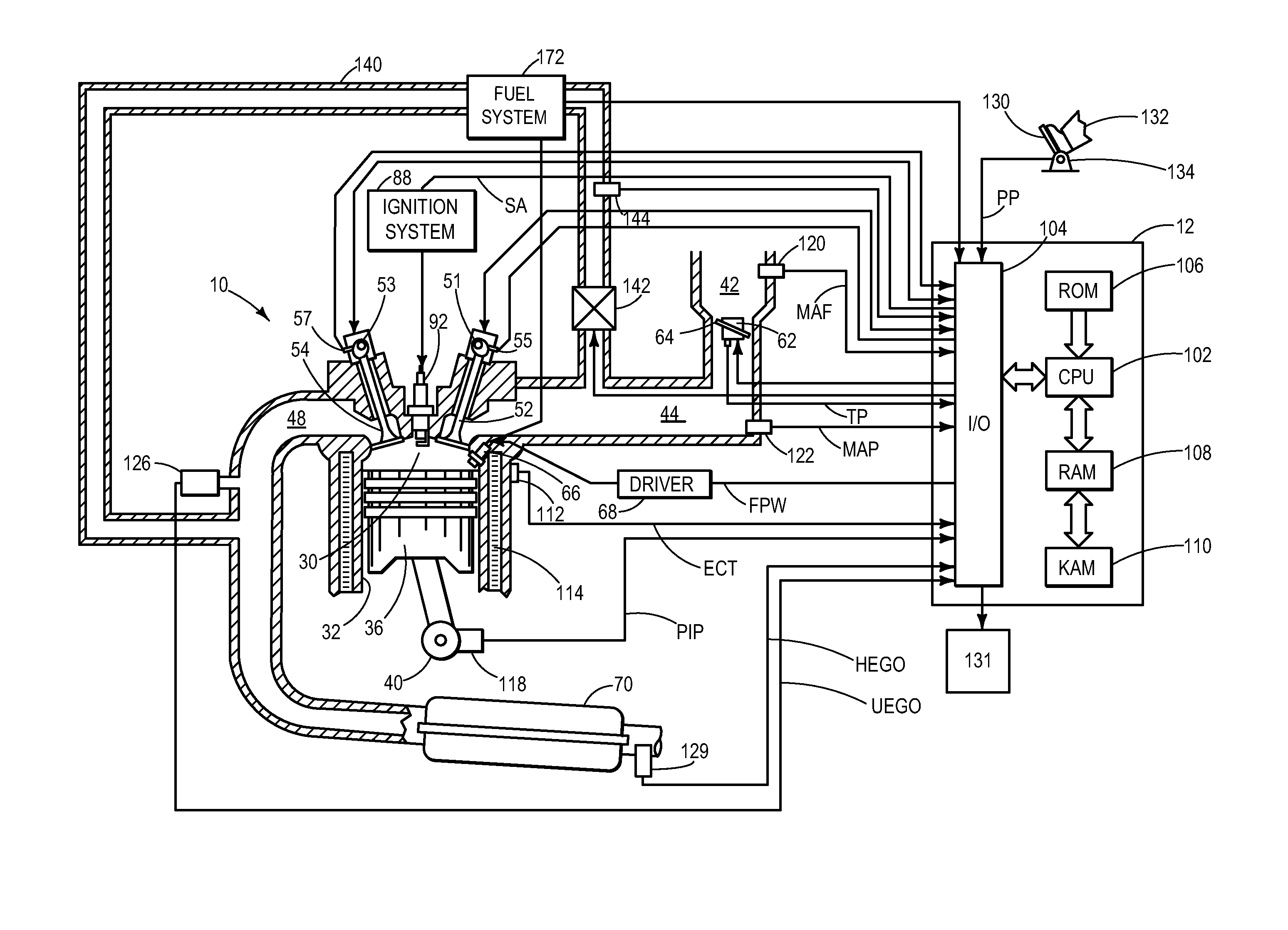
Control apparatus and method for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20070199305A1Electrical controlExhaust apparatusCatalyst degradationExternal combustion engine
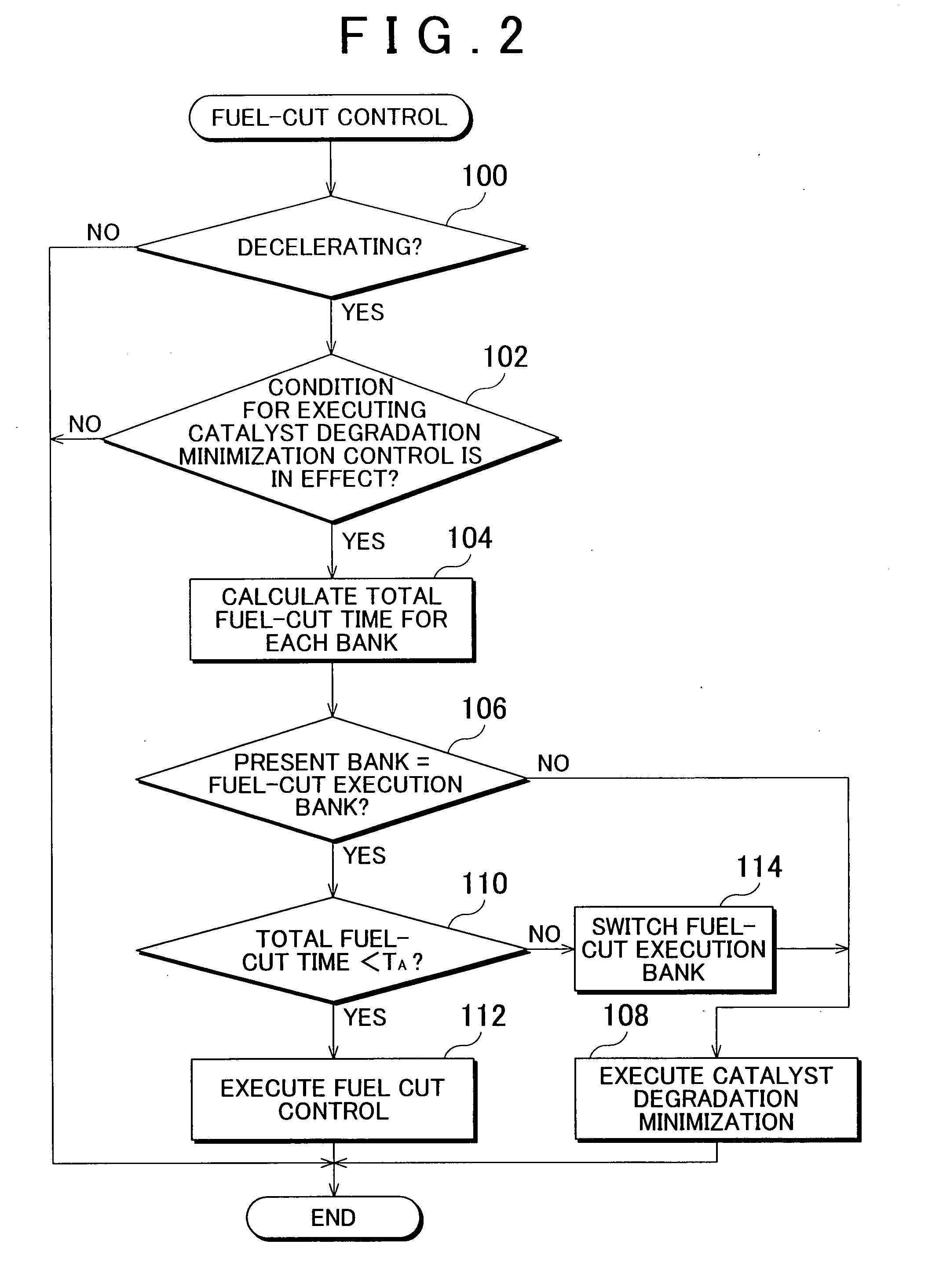
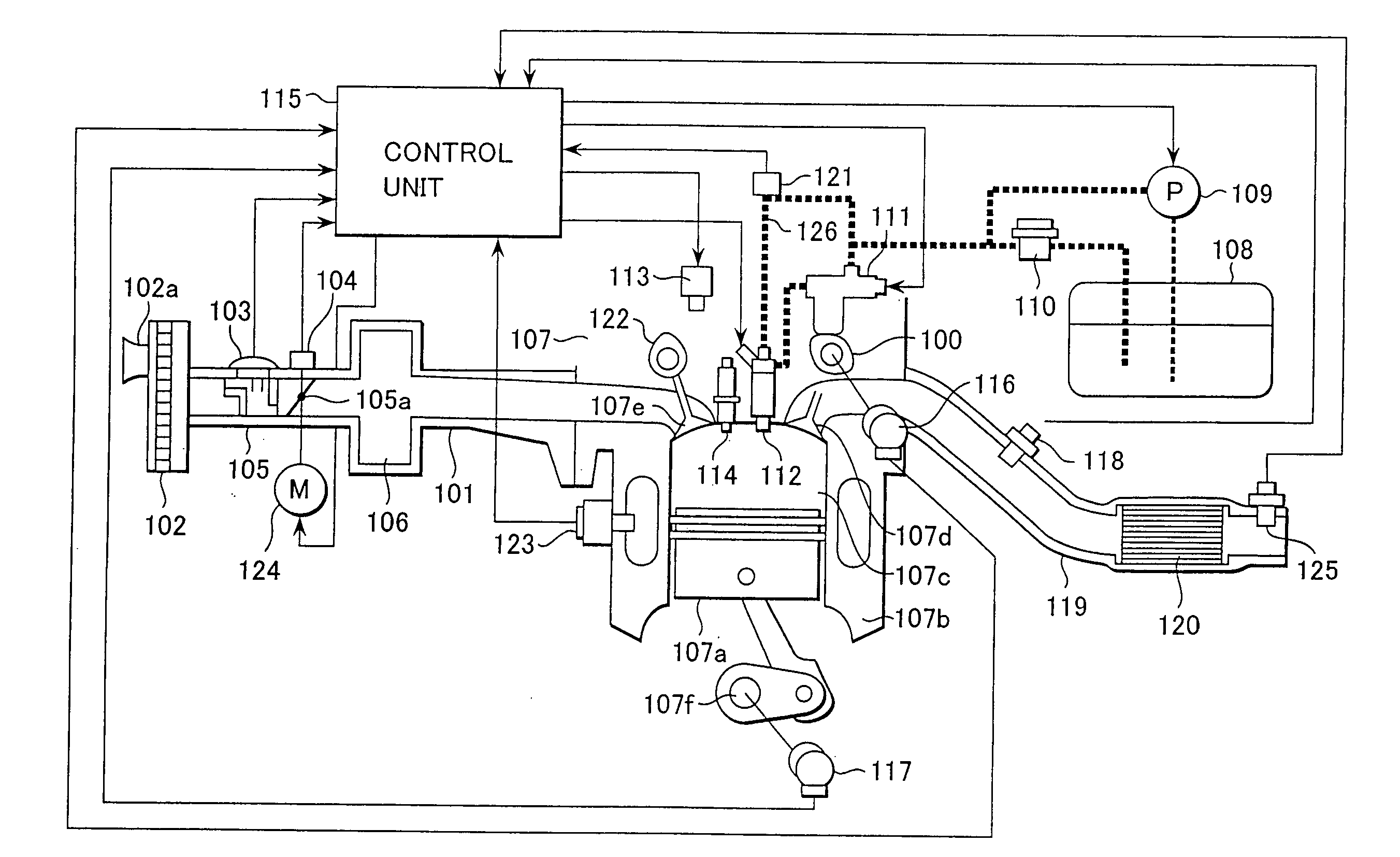
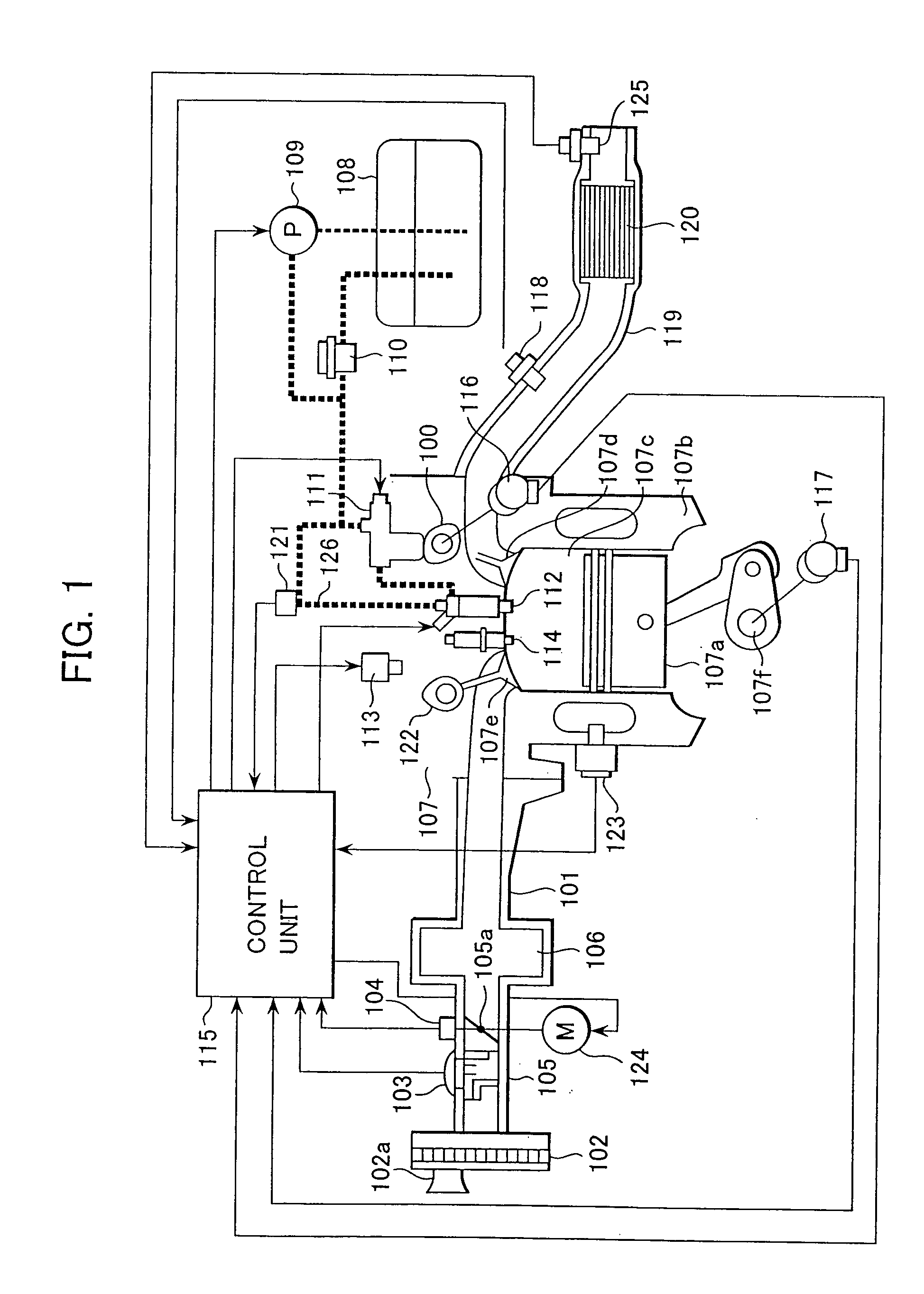
A control apparatus for an internal combustion engine that includes right and left banks, first and second catalysts provided in the right and left exhaust pipes, respectively, and a downstream catalyst provided in a common exhaust pipe downstream of the upstream catalysts is adapted to alternately switch execution of catalyst degradation minimization and execution of fuel cut between the two banks if at least one of the temperature of the first catalyst and temperature of the second catalyst is higher than a predetermined value during deceleration of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Catalyst diagnosis apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20070017212A1Improve accuracyImprove catalytic performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCatalyst degradationChemical reaction
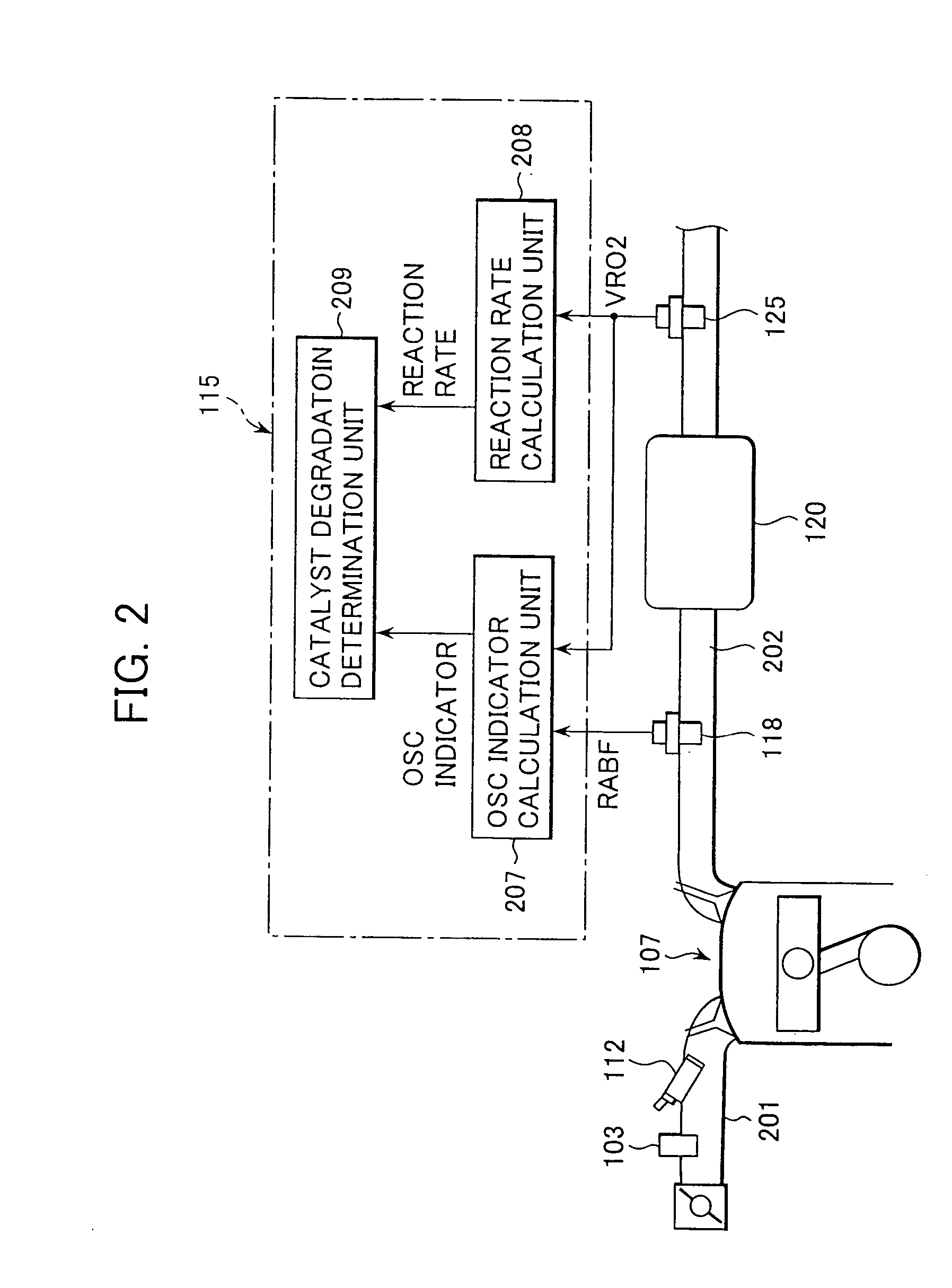
A catalyst diagnosis apparatus comprises a reaction rate calculation unit for calculating a reaction rate of chemical reaction in a three-way catalyst based on an output of an oxygen sensor, and an OSC indicator calculation unit for calculating an OSC indicator indicating an oxygen storage capacity (OSC) of the three-way catalyst based on outputs of a linear air-fuel ratio sensor and the oxygen sensor, and a catalyst degradation determination unit for determining degradation of the three-way catalyst based on the reaction rate and the OSC indicator. The determination of the catalyst degradation can be performed with high accuracy in a manner adapted for influences of external environments, etc.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and method for determining reforming catalyst degradation
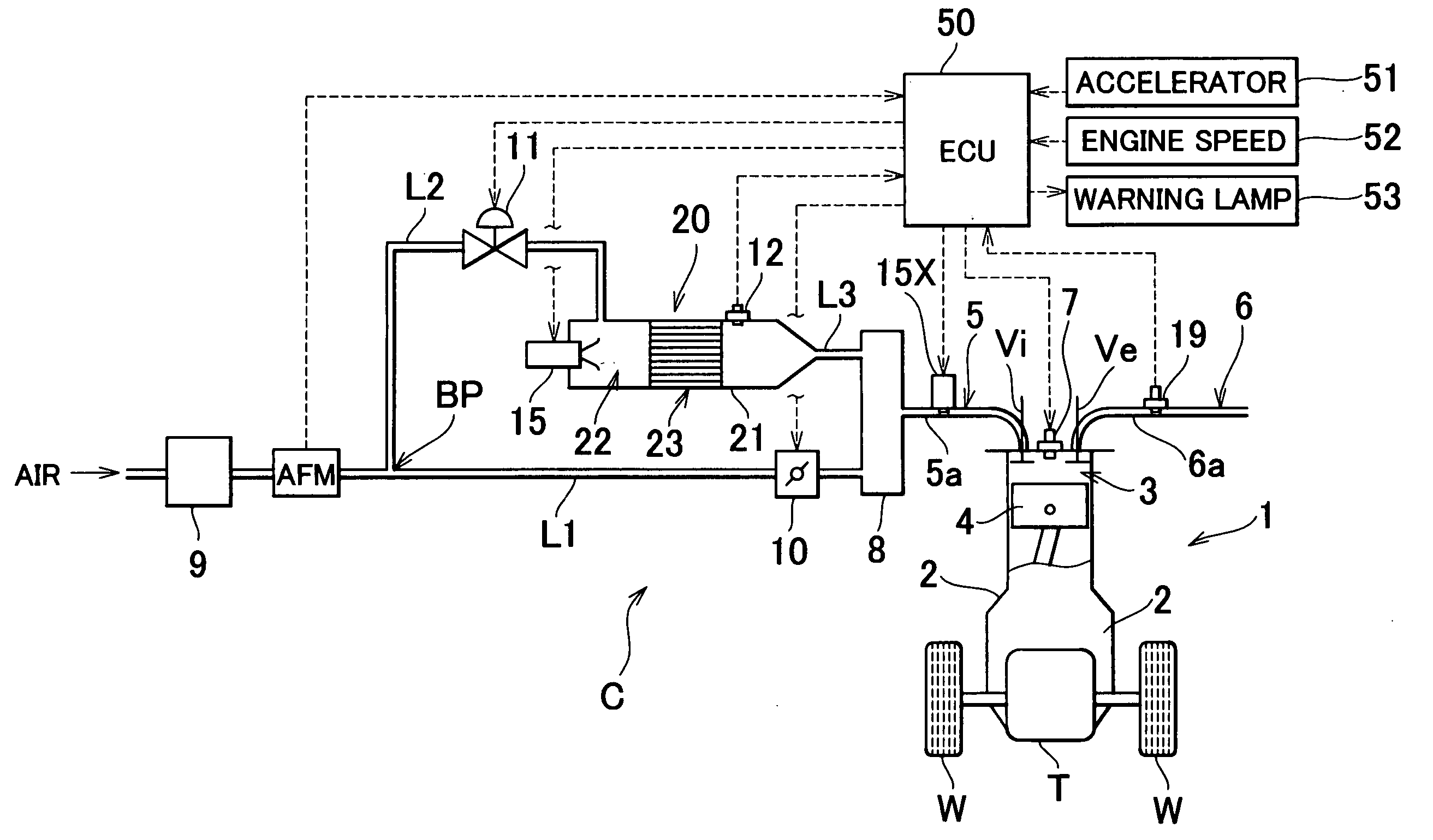
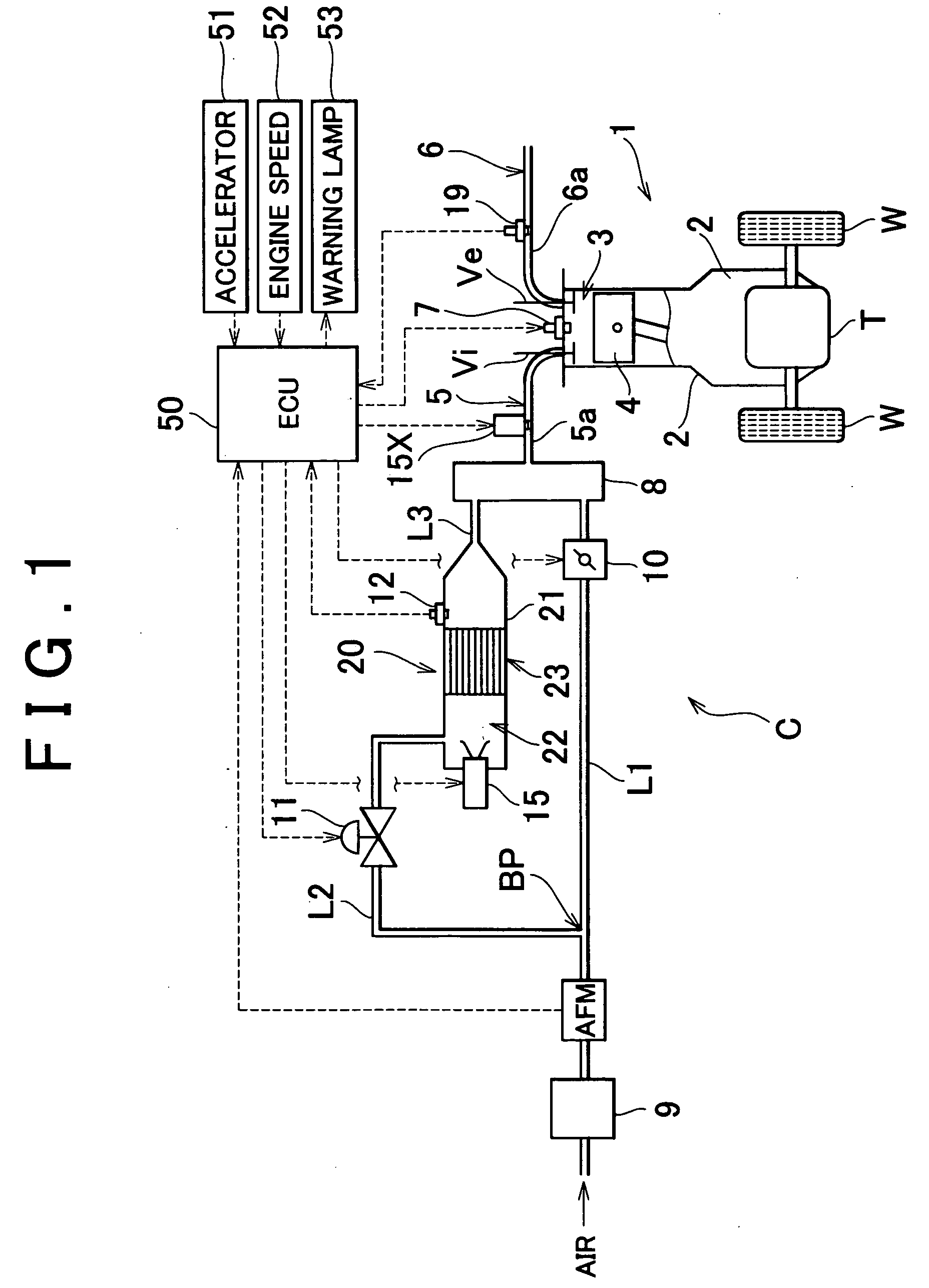
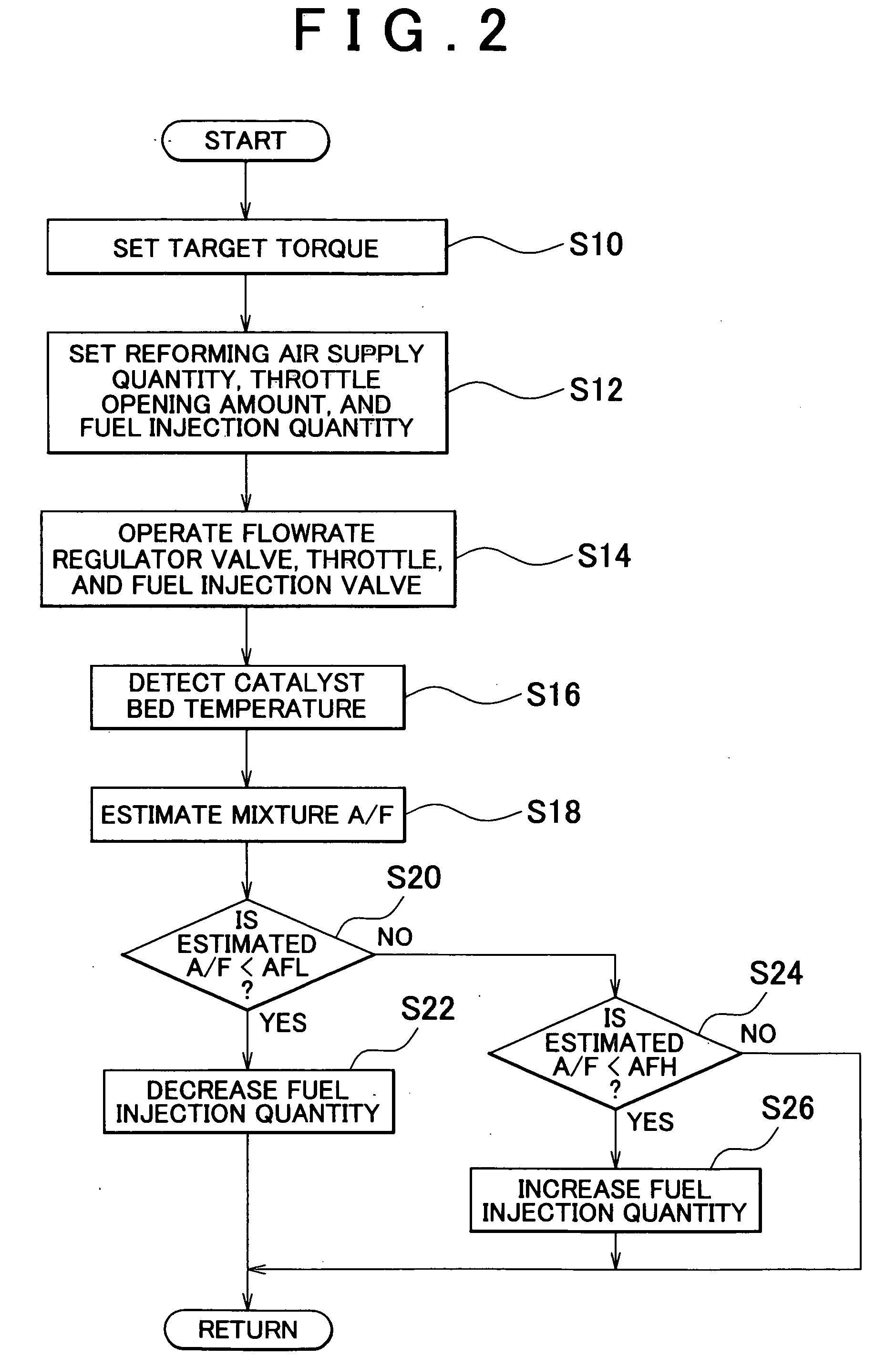
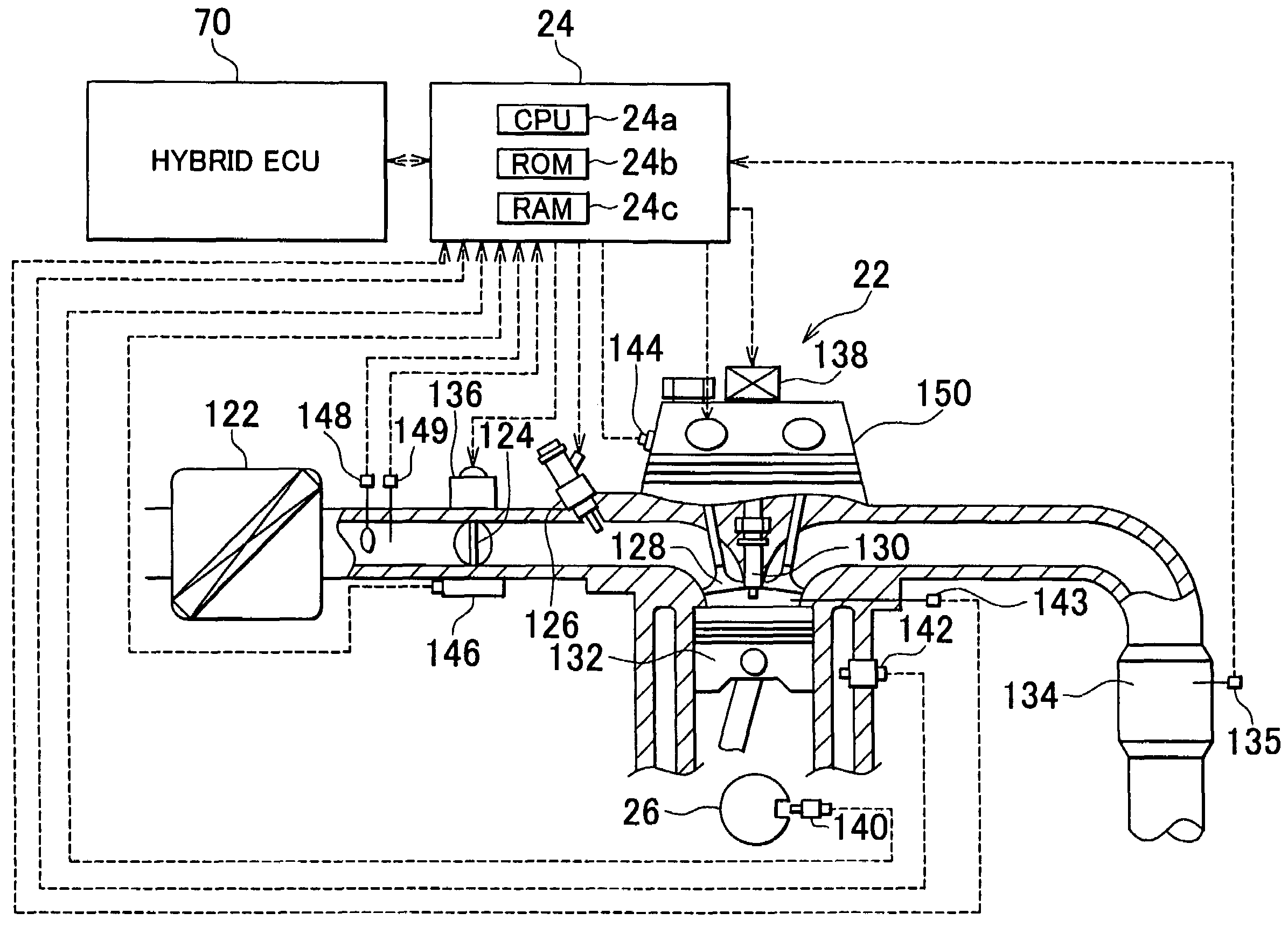
InactiveUS20040205998A1Reliable detectionIncrease temperatureChemical analysis using catalysisHydrogenCatalyst degradationProcess engineering
According to an apparatus and method for determining degradation of a reforming catalyst degradation which reforms a mixture of air and fuel, in a reformer that supplies a reformate gas to an engine of a vehicle, a temperature sensor detects a temperature of a reforming reaction portion in which is provided a reforming catalyst. An ECU then determines the extent of degradation of the reforming catalyst based on the temperature detected by the temperature sensor.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Vehicle and control method thereof
ActiveUS7624568B2Reduce controlSmooth shiftingHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlCatalyst degradationEngineering
When both catalyst degradation and catalyst odor need to be suppressed when a fuel cut condition is satisfied, a fuel cut control is executed giving priority to control for suppressing catalyst odor, though a required air amount G* for idling is drawn in at that time. Therefore, when shifting the engine into an idle state to suppress catalyst degradation after the catalyst odor has been eliminated, the required air amount G* for idling is already being drawn in so there is no need to adjust the air amount. As a result, there is no time delay for air amount adjustment. Therefore, after the control to suppress catalyst odor has ended, a smooth shift can be made into control to suppress degradation of the exhaust gas control catalyst.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for degrading lignocellulose to generate reducing sugar
InactiveCN103409566ALow costIncrease reaction rateFructose productionGlucose productionCelluloseCatalyst degradation
The invention discloses a method for degrading lignocellulose to generate reducing sugar, and in particular relates to the method for degrading lignocellulose to generate reducing sugar by using H2O2 as a catalyst and using metal ion as a catalyst promoter. The method comprises the following steps: adopting an ionic liquid as a solvent, commercially available hydrogen peroxide with the mass fraction of 30% as a catalyst and metal ion as a catalyst promoter; and dissolving and degrading lignocellulose materials to generate water-soluble reducing sugar, wherein the ionic liquid can be recycled. The method for degrading lignocellulose to generate reducing sugar has the characteristics of being simple and convenient to operate, gentle in condition, environment-friendly, low in cost, less in byproducts, high in reducing sugar yield and the like. The method for degrading lignocellulose to generate reducing sugar can be used for treating various lignocellulose materials; and when the lignocellulose materials are treated by adopting the method, the conversion rate of the lignocellulose materials is bigger than 80%, the reducing sugar yield is bigger than 65%, and the recovery rate of the ionic liquid is bigger than 95%.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
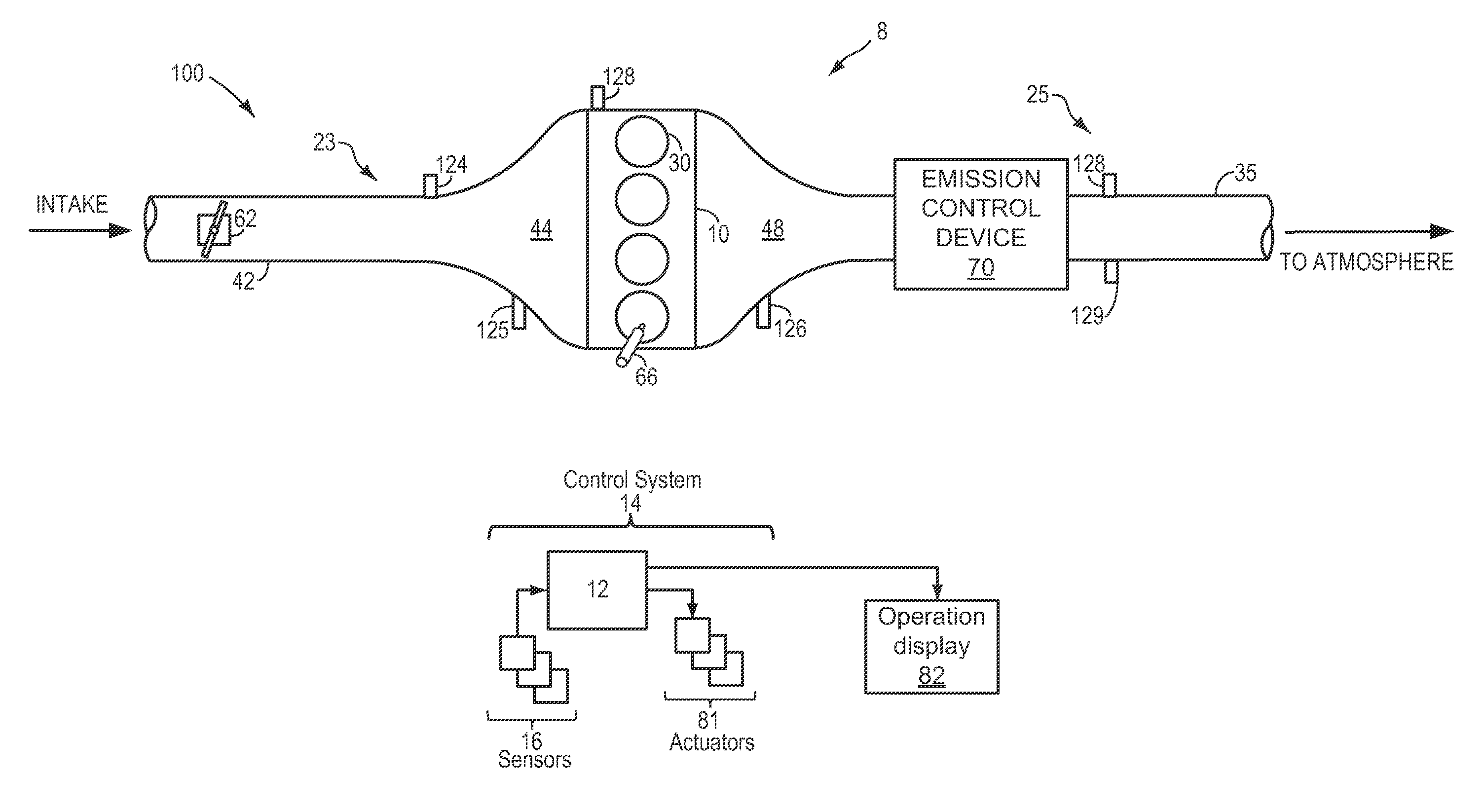
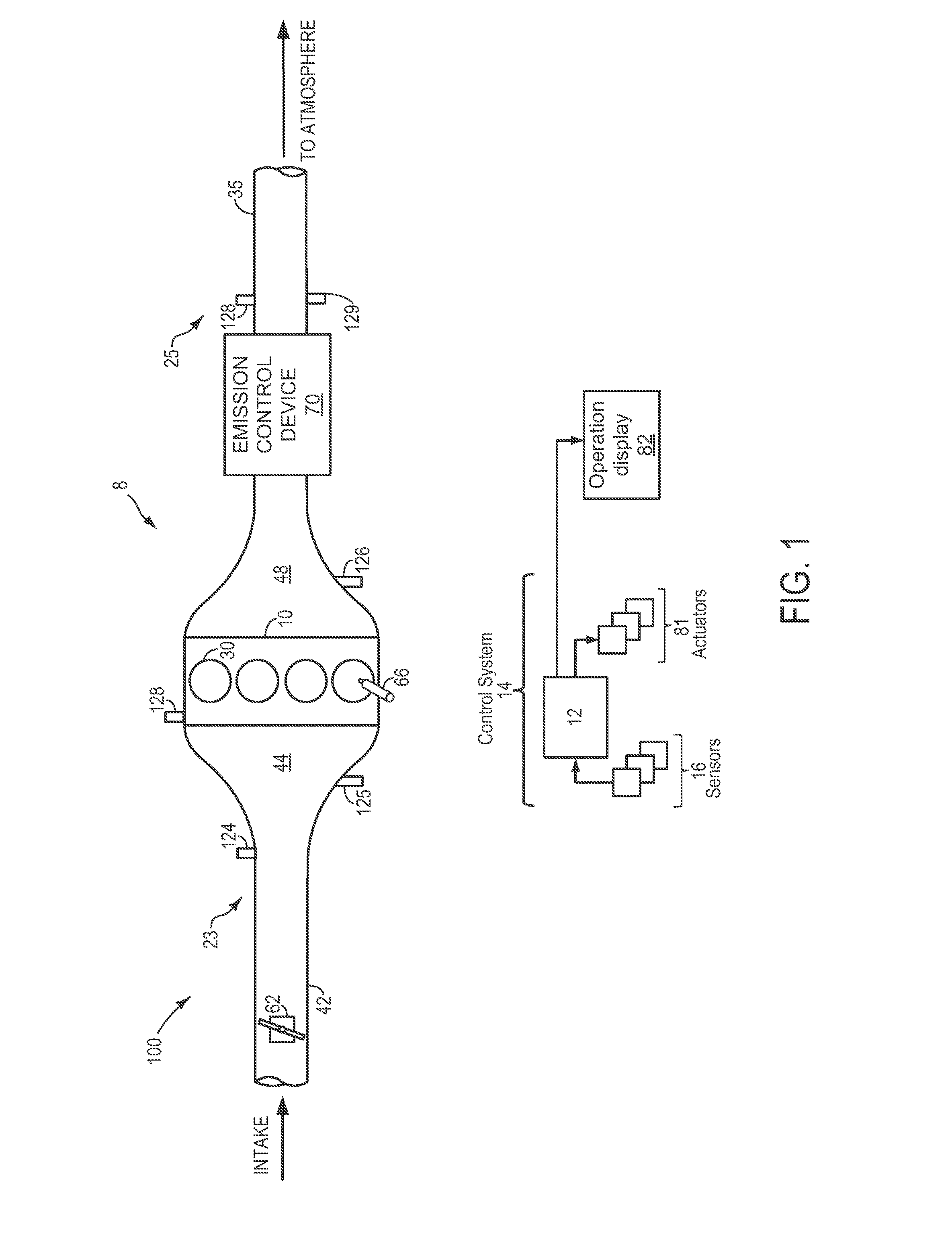
Engine catalyst diagnostics
ActiveUS20130078725A1Easy CalibrationImprove accuracyChemical analysis using catalysisInternal combustion piston enginesReduced modelSupport vector machine
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
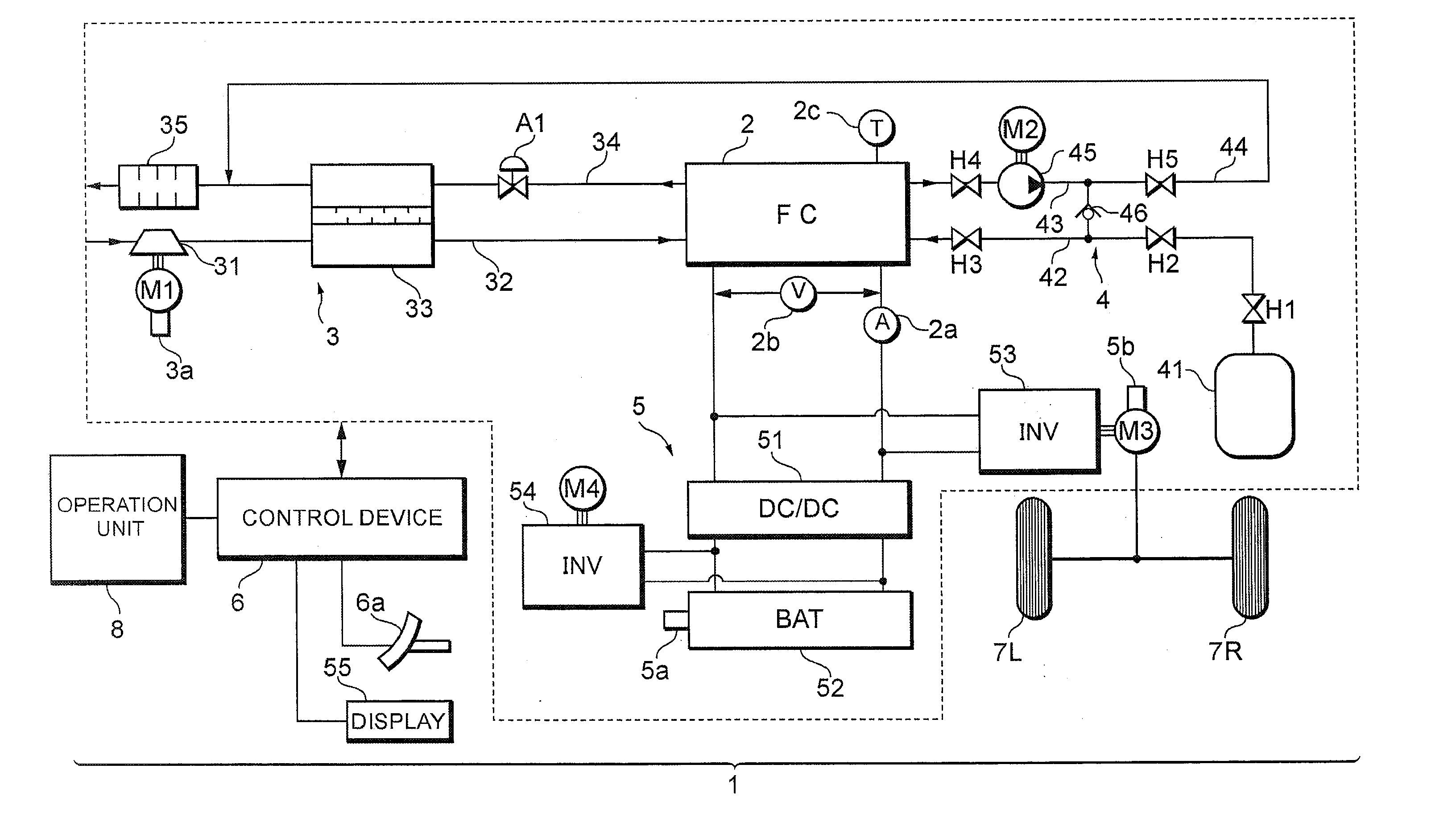
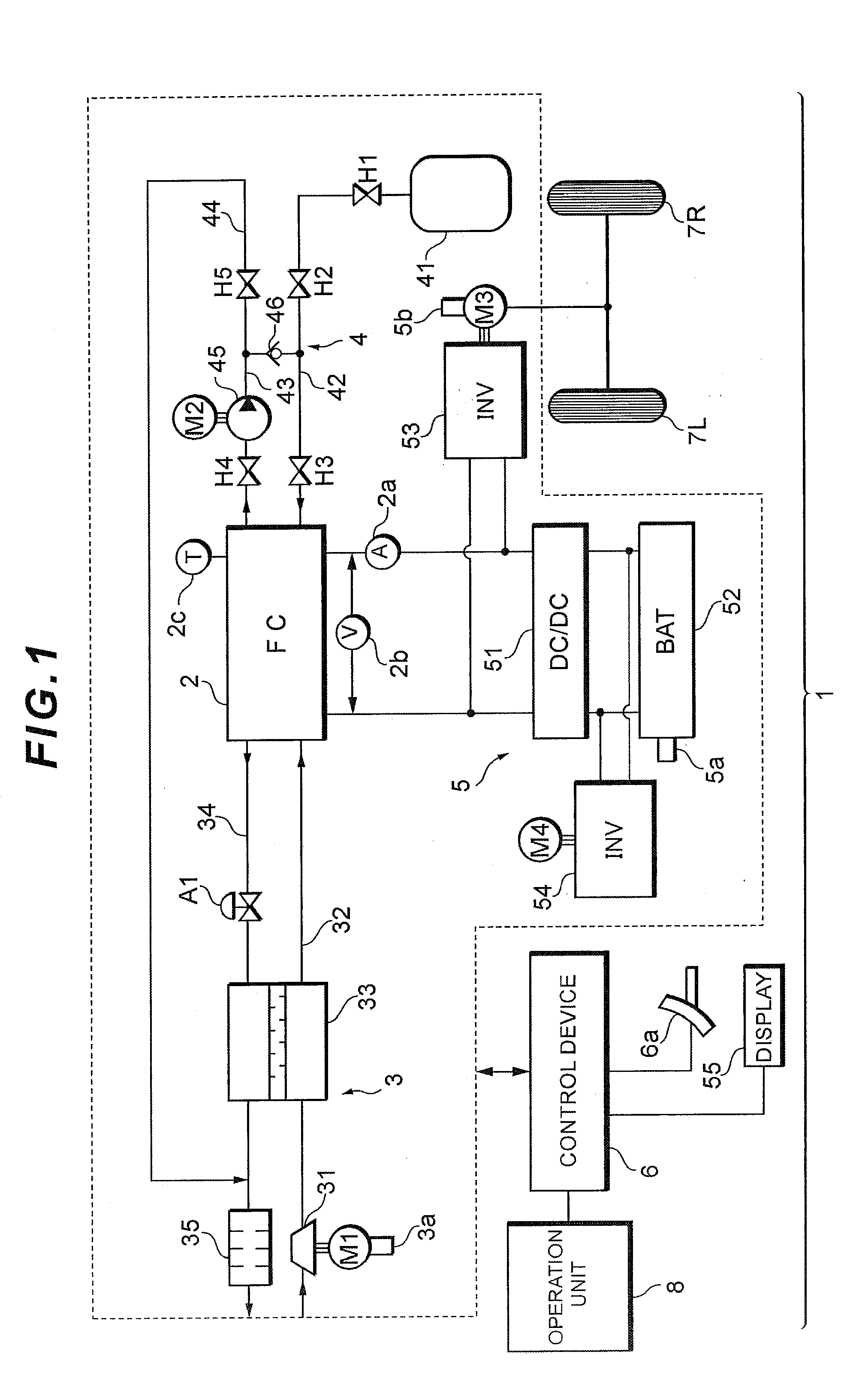
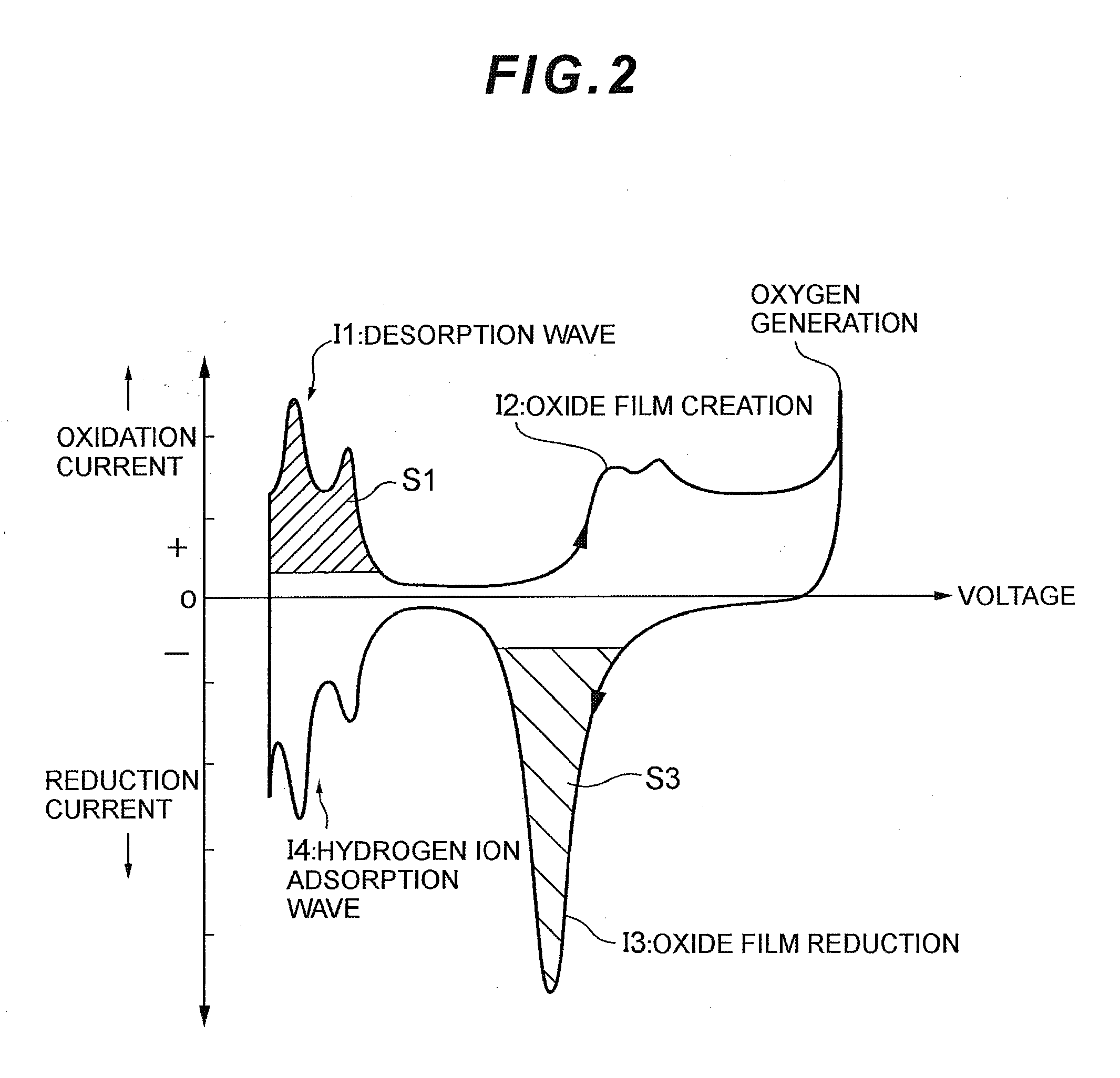
Fuel cell system, electrode catalyst degradation judgment method, and moving body
ActiveUS20100112401A1Accurate decisionCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesCatalyst degradationFuel cells
Output voltage of a fuel cell 2 is decreased by a converter 51 to conduct an activation treatment to catalyst of the fuel cell 2, while measuring reduction current by a current sensor 2a while scanning output voltage of the fuel cell 2 over a certain range by the converter 51 as measurement of cyclic voltammetry under the condition that supply of oxidation gas to the fuel cell 2 is stopped from a compressor 31, and this measurement value is integrated by a control device 6. The control device 6 finds a charge amount of electrode catalyst of the fuel cell 2 based on this integration value, decides whether this charge amount is smaller or not than a degradation decision value, and displays this decision result on a display 55. A decision can be made precisely as to whether the electrode catalyst of the fuel cell is degraded or not.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Catalyst degradation detection device
ActiveUS20120317960A1The measurement result is accuratePrevent deviationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCatalyst degradationOxygen sensor
A catalyst degradation detection device, determines whether a three-way catalyst has degraded on the basis of the maximum value of the amount of oxygen stored by the catalyst. When determining whether the three-way catalyst has degraded, the amount of stored oxygen is calculated, and the responsiveness of change in the output signal of an oxygen sensor to oxygen concentration change in catalyst-downstream exhaust is measured. Then, on the basis of the responsiveness of the oxygen sensor which measured the oxygen storage amount, the oxygen storage amount is corrected by reducing the same such that the worsened the measured responsiveness relative to a reference value, the greater the reduction in the oxygen storage amount used in determining whether the three-way catalyst has degraded. The corrected oxygen storage amount used is prevented from deviating from the correct value on the basis of a worsening of the responsiveness of the oxygen sensor.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for identification of a threshold-level catalyst
ActiveUS20160061131A1High catalytic efficiencyImprove vehicle catalyst diagnosticsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCatalyst degradationProcess engineering
Systems and methods for estimating catalyst transfer function gain are disclosed. In one example, an air-fuel ratio forcing function is applied to a catalyst. Air-fuel ratios upstream and downstream of the catalyst are manipulated to determine a transfer function gain of the catalyst. The transfer function gain may be a basis for indicating the presence or absence of catalyst degradation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for preparing flyash-supporting nanometer titanic oxide composite photochemical catalyst material
InactiveCN101584982AImprove adsorption capacitySolve storage problemsSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationTetramethylammonium hydroxideCatalyst degradation
The present invention discloses a method for preparing flyash-supporting nanometer titanic oxide composite photochemical catalyst material, including the following steps: (1) dissolving a formwork in a deionized water to form a homogeneous phase solution, then adding the tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide to obtain a homogeneous phase stable solution A; (2) mixing and agitating the titanoxy sulfate and the deionized water to form a stock white shape liquid, then adding the flyash powder to obtain a mixture B; (3) mixing the solution A and the mixture B, and aging; (4) finally laundering, drying and heat treating to obtain the flyash-supporting nanometer titanic oxide composite material. The dimension of the flyash-supporting nanometer titanic oxide composite photochemical catalyst material is from 10-20nm, and the nanometer particle is supported on the flyash particle surface uniformly. It is not only capable of reusing the solid wastes flyash, also resolving the storage and handling problem of the wastes, moreover the flyash has a strong adsorption capacity, which improves a photochemical catalyst degradation capability of a photocatalyst to an organic compound greatly.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com