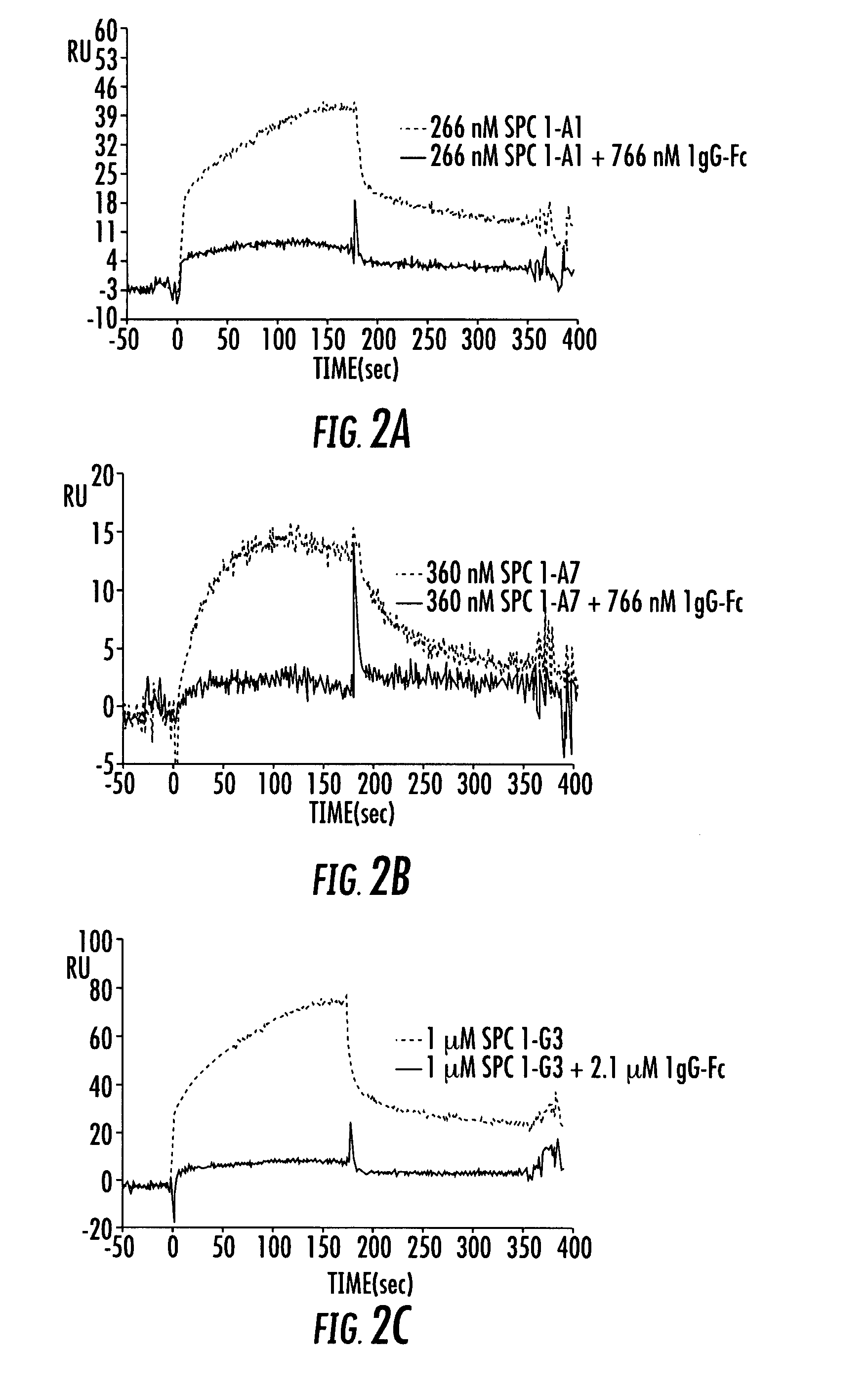
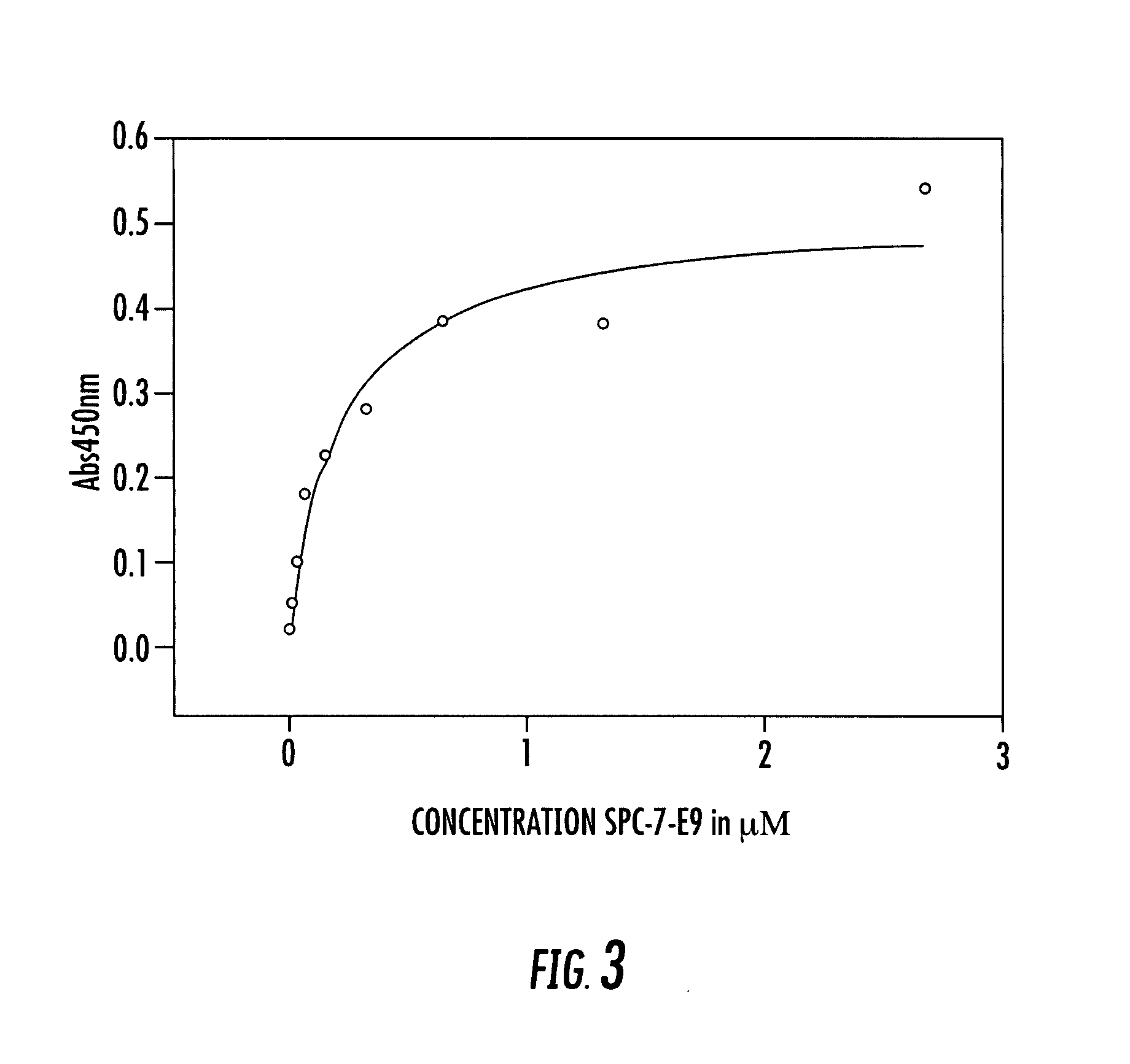
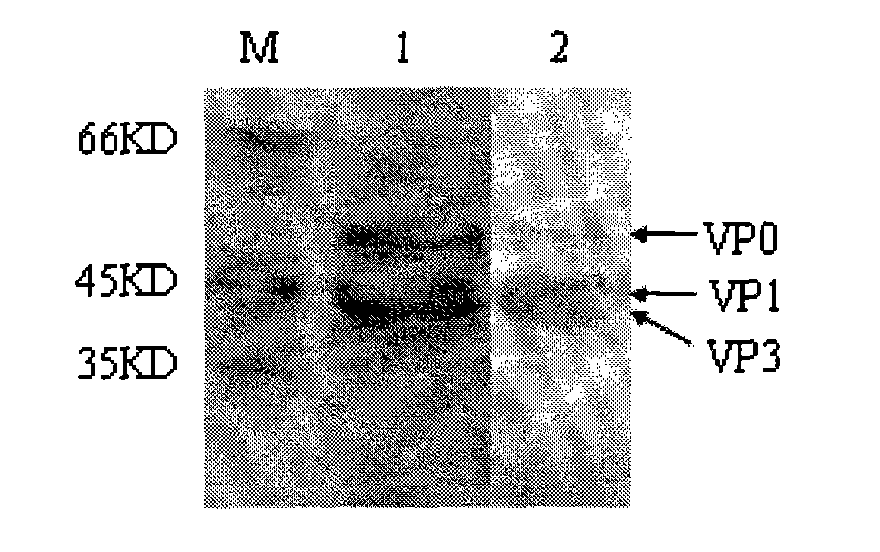
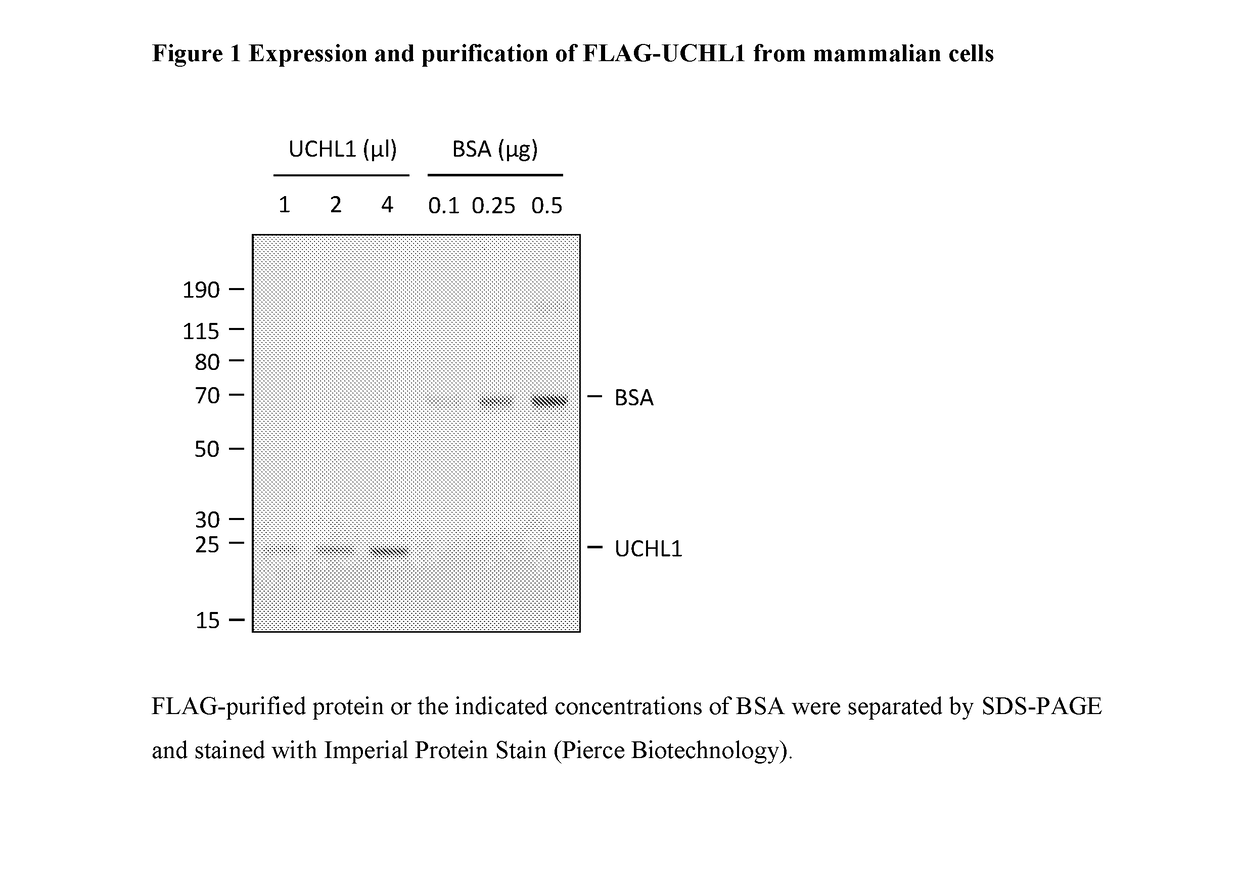
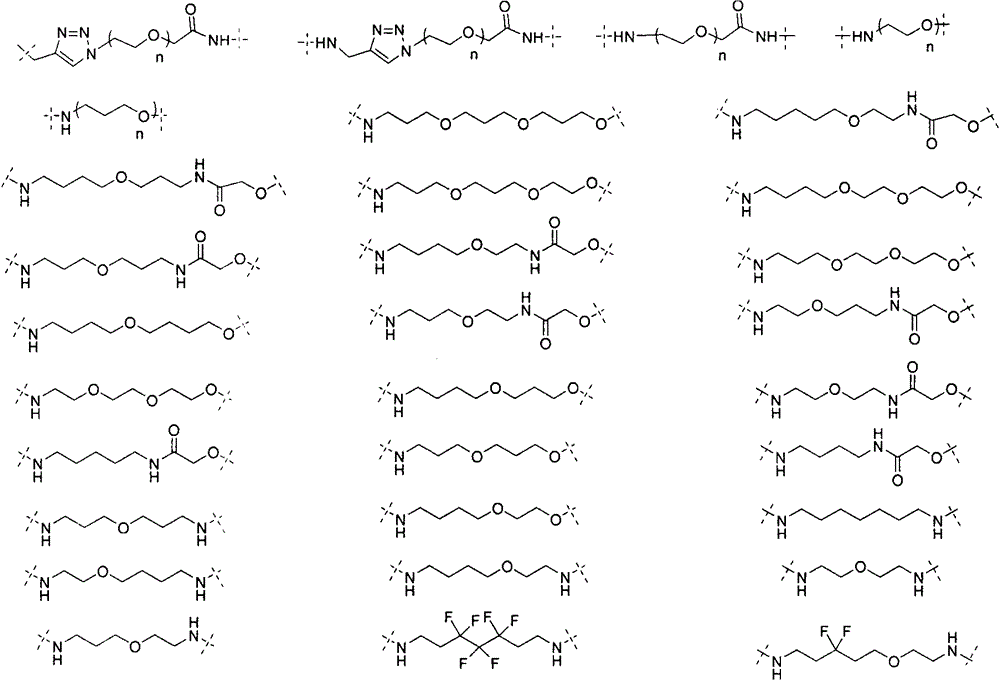
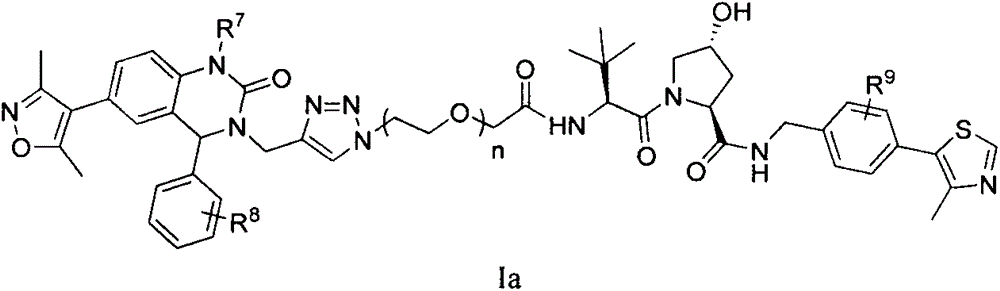
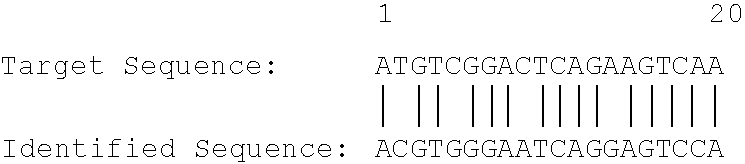Patents
Literature
484 results about "Ubiquitin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e. it occurs ubiquitously. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A.
Immobilizing mediator molecules via anchor molecules on metallic implant materials containing oxide layer
A mediator molecule is immobilized on the surface of a metallic or ceramic implant material. An anchor molecule such as a dialdehyde having a functional group that covalently binds the mediator molecule is covalently bound to the surface, and the mediator molecule is coupled to the functional group of the anchor molecule. The implant material may be composed of titanium, titanium alloy, aluminum, stainless steel or hydroxylapatite. Oxide units on the surface of the implant material can be increased preferably by treating with hot chromic-sulphuric acid for 0.5 to 3 hours at a temperature between 100 to 250° C. prior to binding the anchor molecule. Also, prior to binding the anchor molecule, the surface of the implant material can be activated by reacting with a silane derivative. Mediator molecules include BMP protein, ubiquitin and antibiotics, and the implant material may be an artificial joint or coronary vessel support such as a stent.
Owner:MORPHOPLANT
Ubiquitin or gamma-crystalline conjugates for use in therapy, diagnosis and chromatography
The present invention relates to conjugates containing a covalent linkage between one or more polypeptide molecules based on gamma-crystallin or ubiquitin and one or more functional components. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a method for the preparation of such a conjugate as well as to the use of the conjugate in diagnostics, therapy and chromatography.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
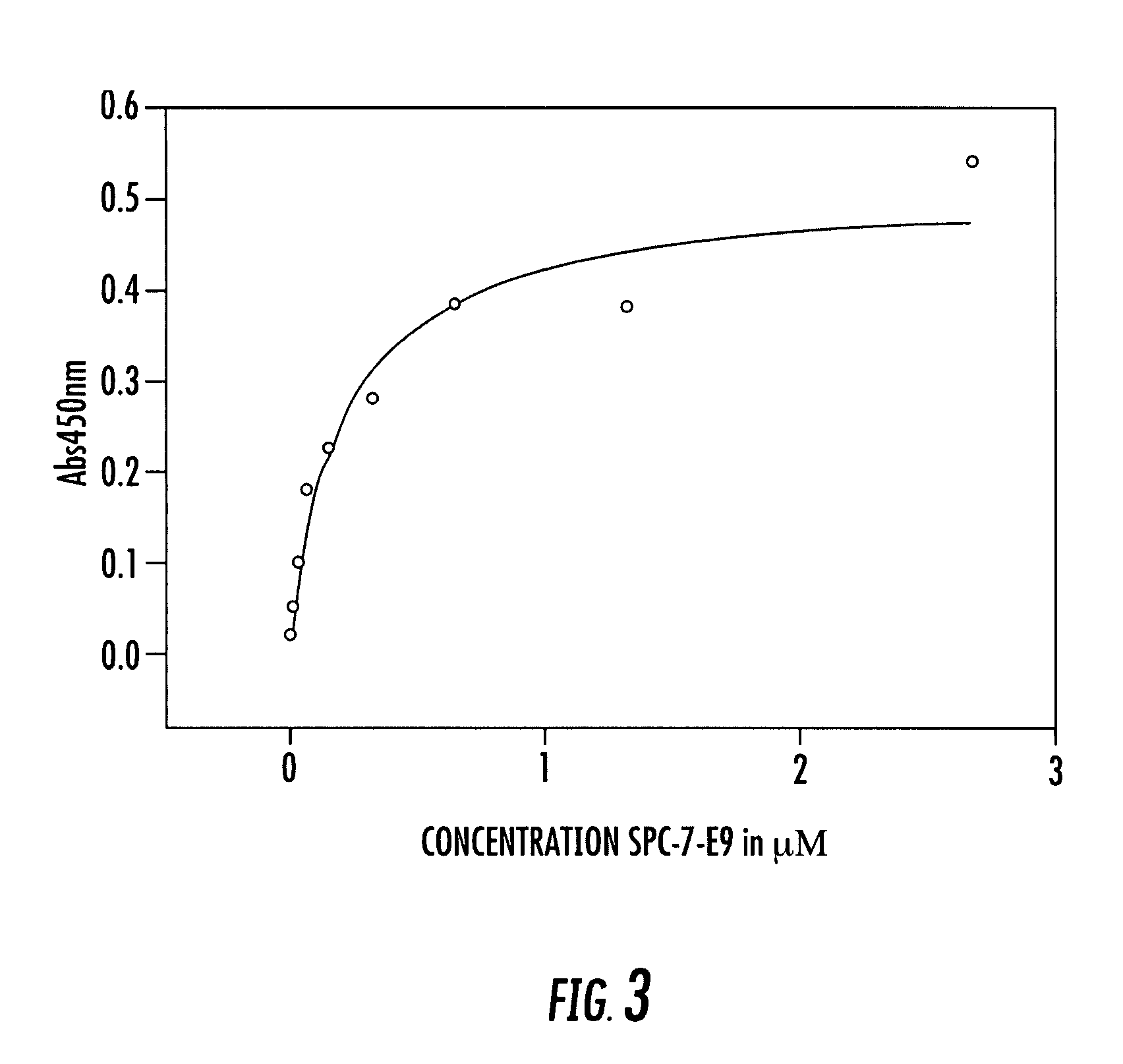
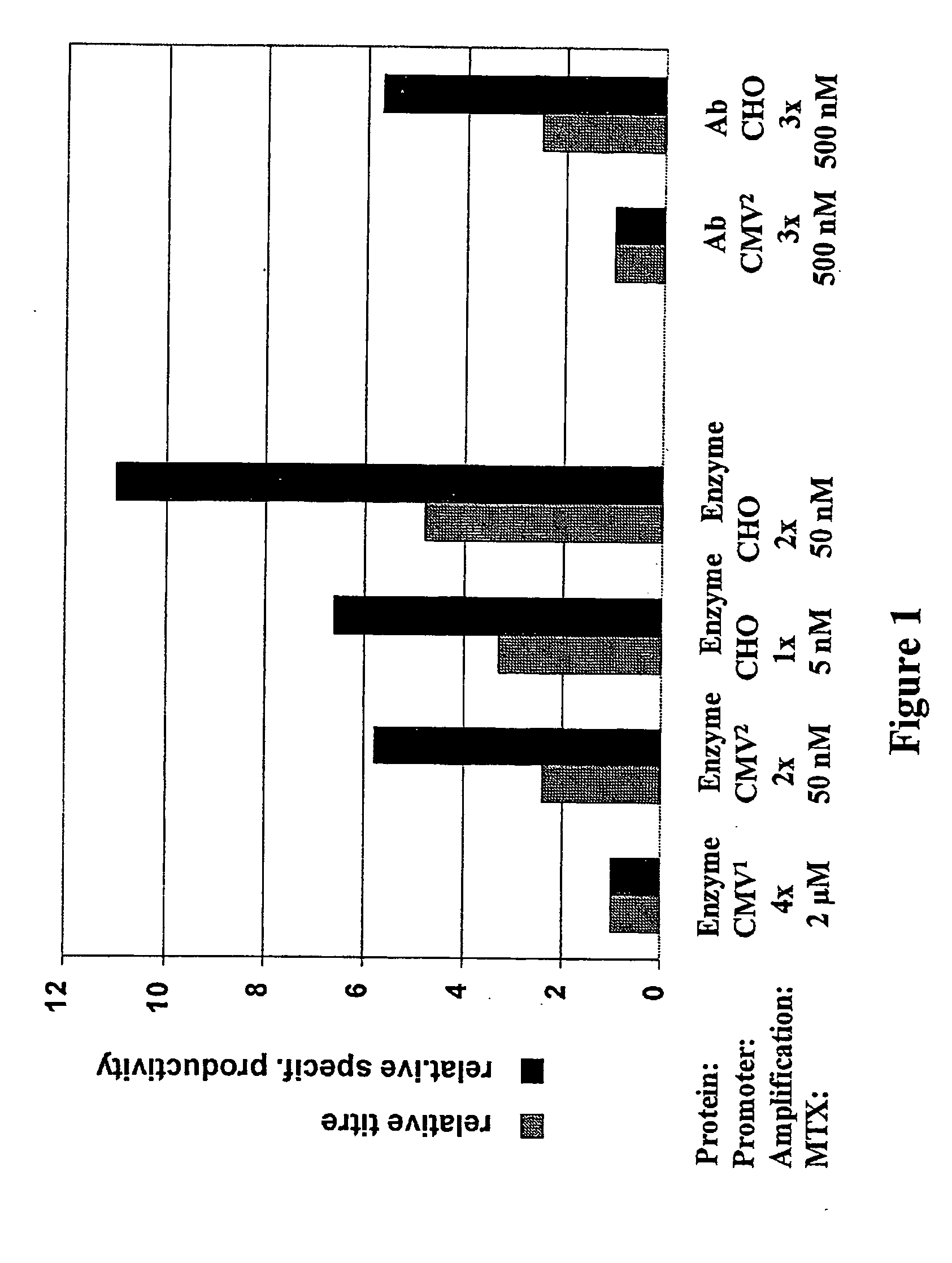
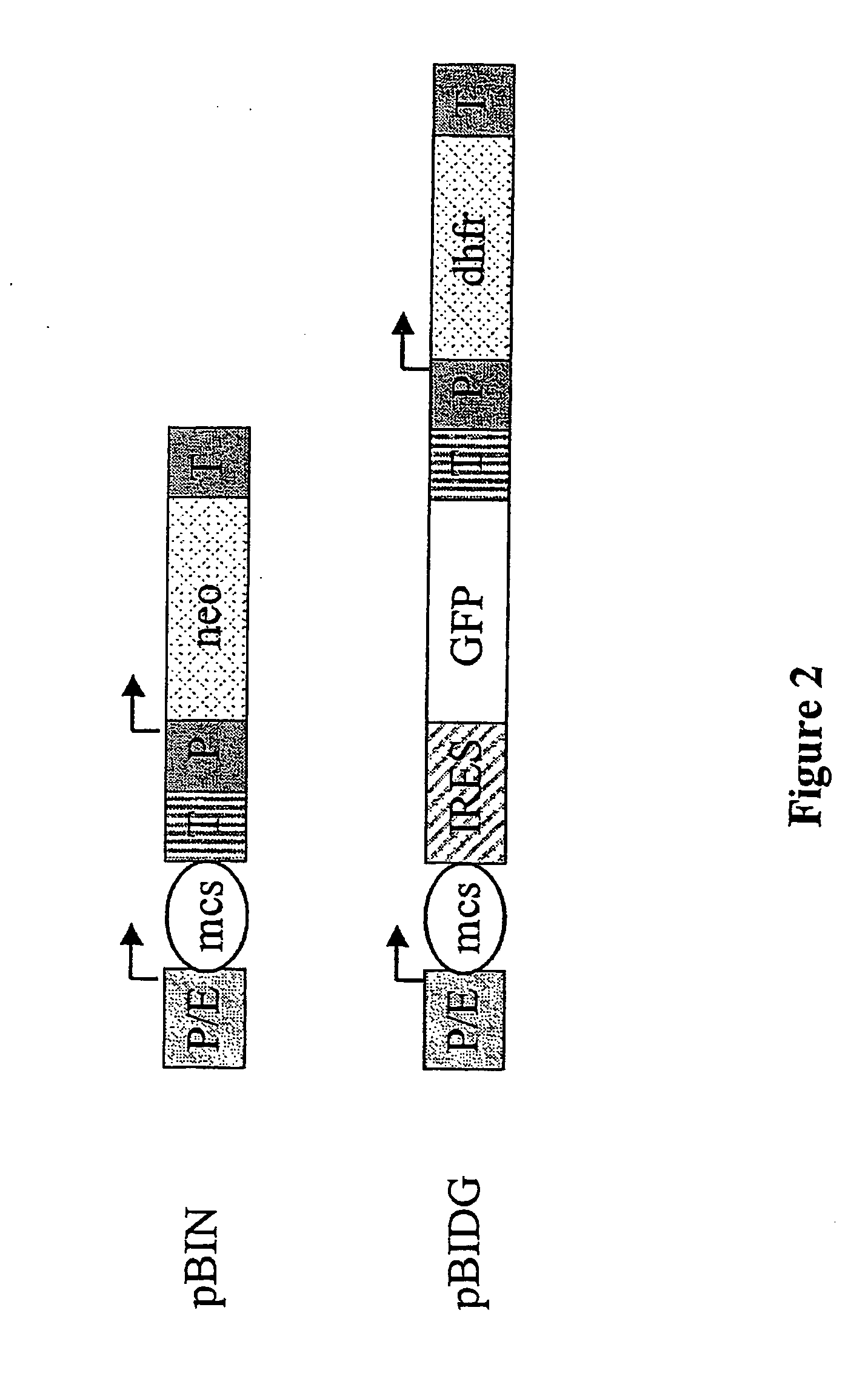
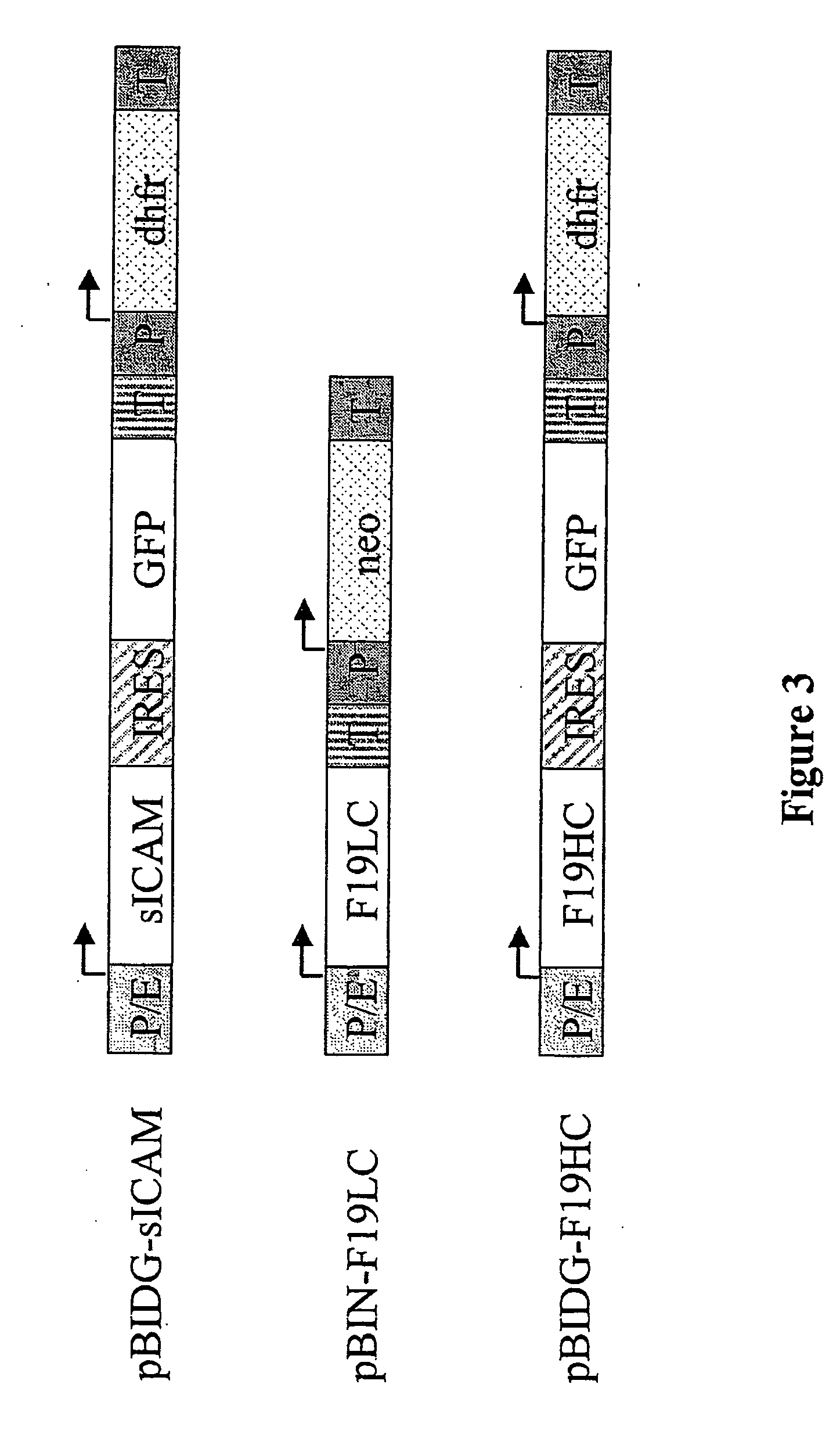
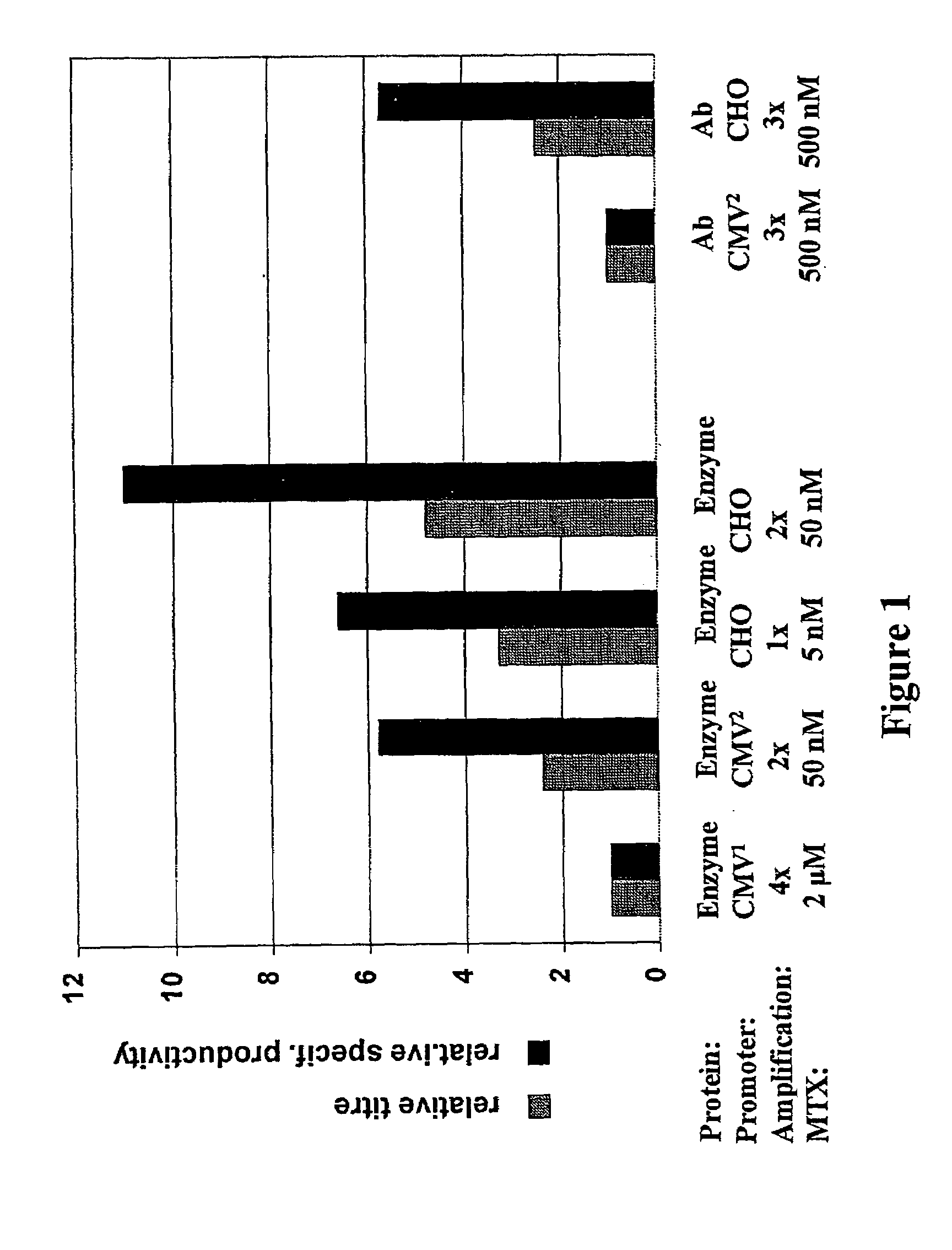
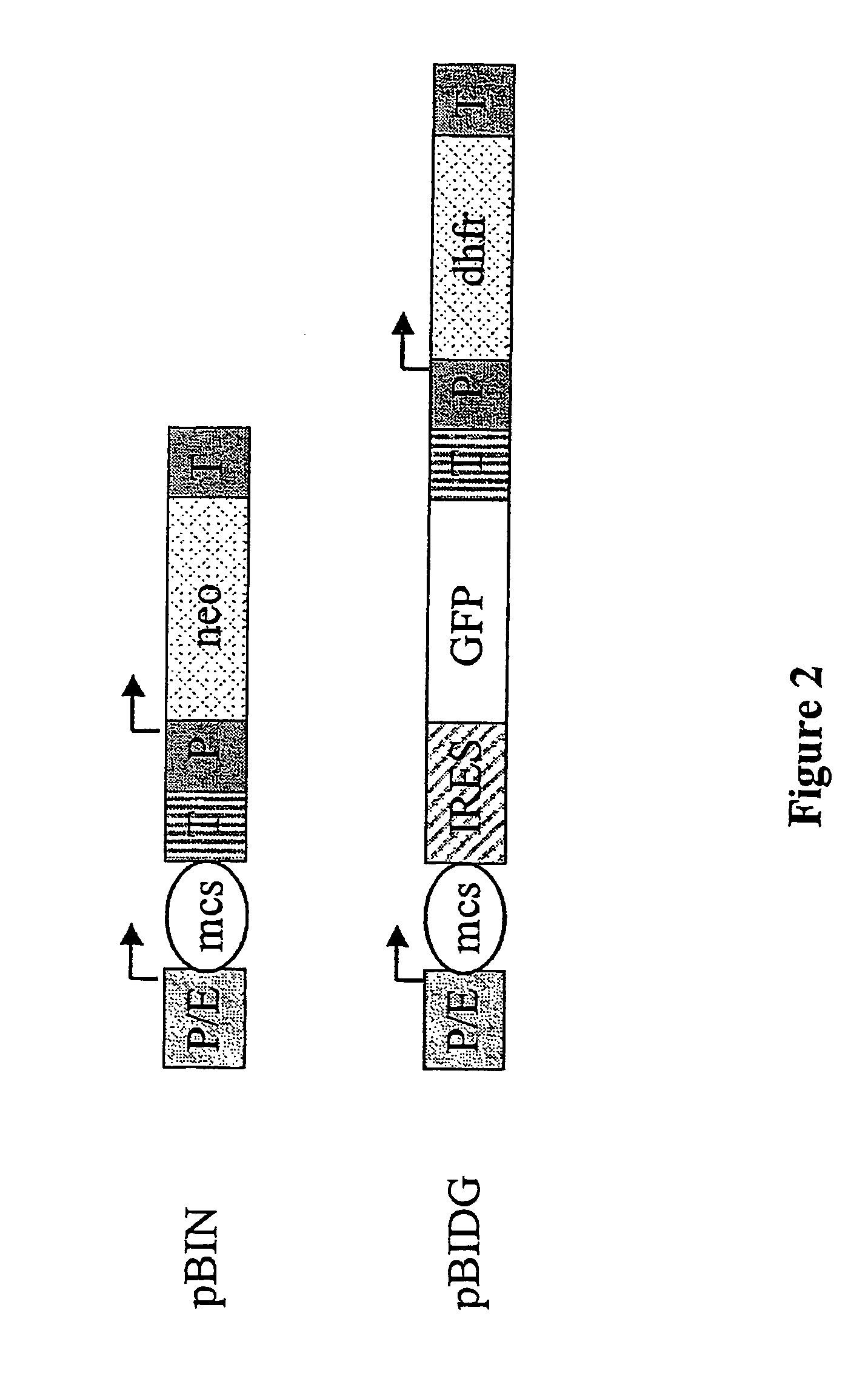
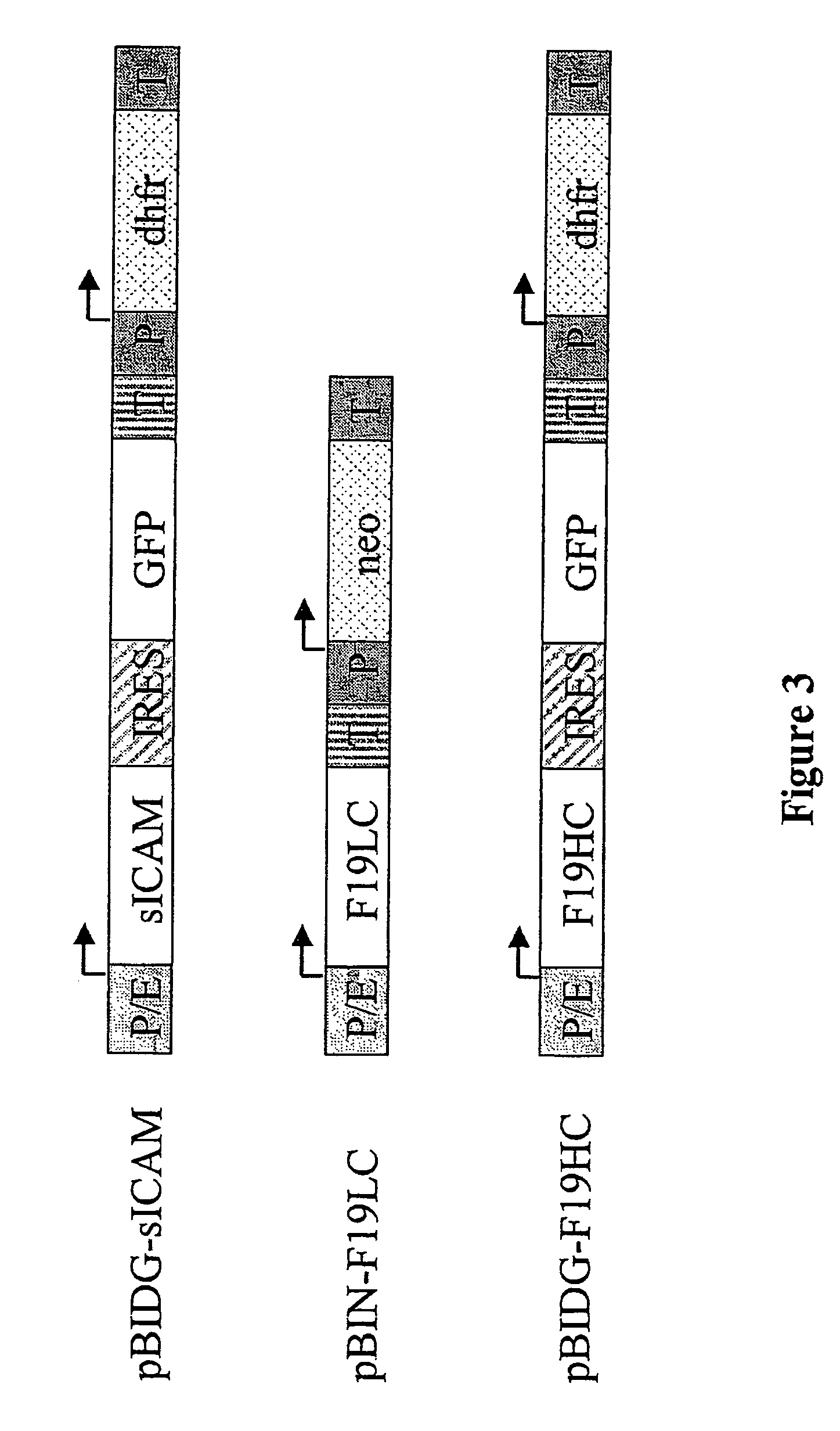
Expression vector, methods for the production of heterologous gene products and for the selection of recombinant cells producing high levels of such products
ActiveUS20040148647A1Shorten the timeReduce development costsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHamster
An expression vector for eukaryotic cells comprising a gene which codes for a protein of interest, functionally linked to a hamster-ubiquitin / S27a-promoter and a gene which codes for a fluorescent protein. Preferably the expression vector also contains an amplifiable selectable marker gene. The invention also describes host cells, preferably mammalian cells, which have been transfected with the expression vector, processes for producing heterologous gene products and a method of selecting high-producing cells.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Diagnostic and screening methods and kits associated with proteolytic activity
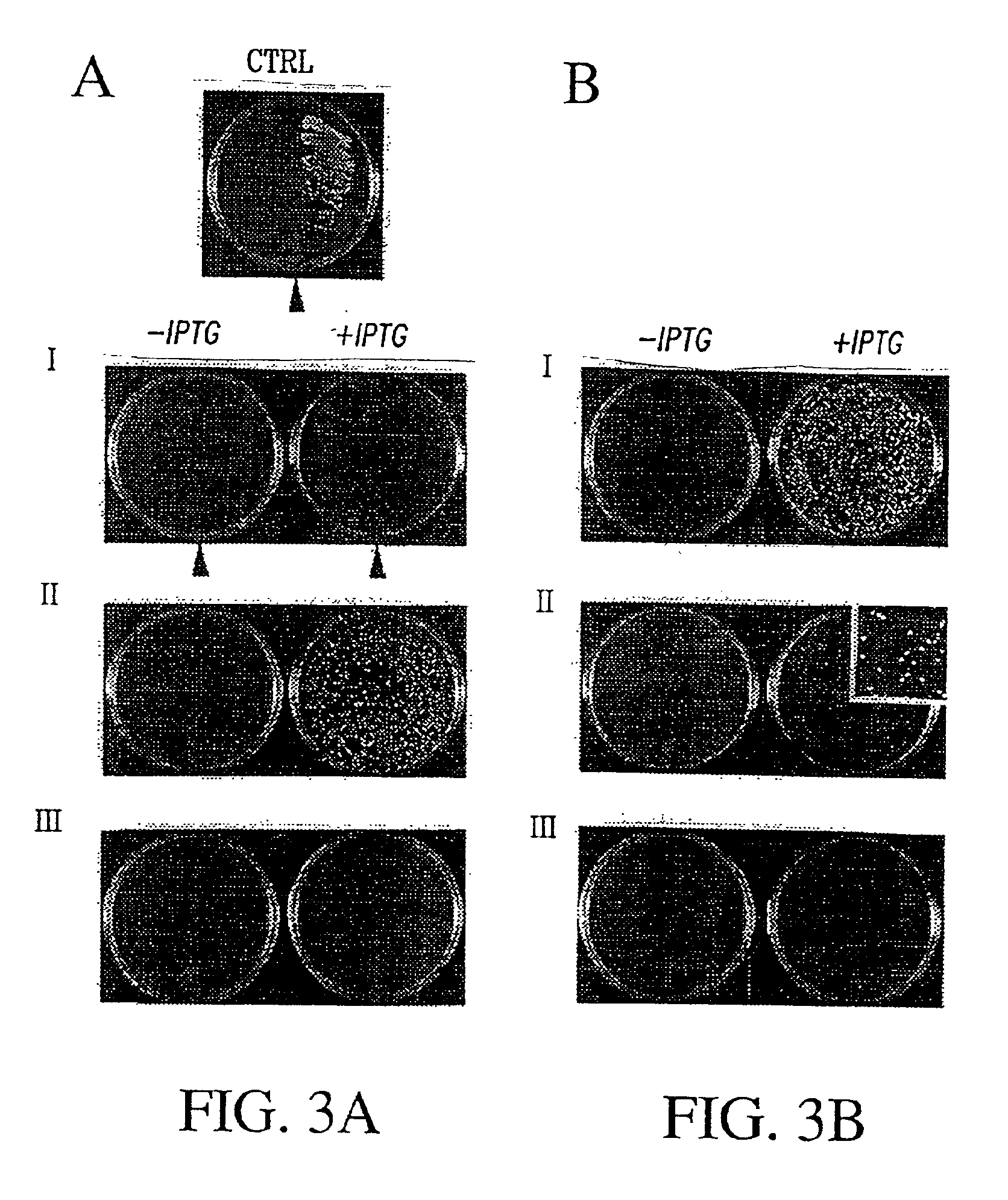
Methods and kits for assessing proteolytic enzyme activity and a modulator's effect thereof employ a Ubiquitin or Ubiquitin-like Protein and a signal producing structure. The corresponding fusion polynucleotide is employed for production of transgenic cells, plants and animals that may be produced by stably transfection, optionally transforming the cell, plant or animal with a Ubiquitin-, UBL- or their C-terminal binding functional fragment-Reporter fusion polynucleotide. A method of diagnosing a disease or condition, comprises contacting or administering a sample obtained from a subject suspected of being afflicted with the disease or condition with the cell, plant or animal, detecting any signal produced by the reporter in the presence of the sample and comparing the signal to controls for 0% and 100% signals.
Owner:PROGENRA INC
Biochemical method for specific protein labeling
InactiveUS20080305519A1Easy to operatePeptide sourcesTripeptide ingredientsProtein targetProtein insertion
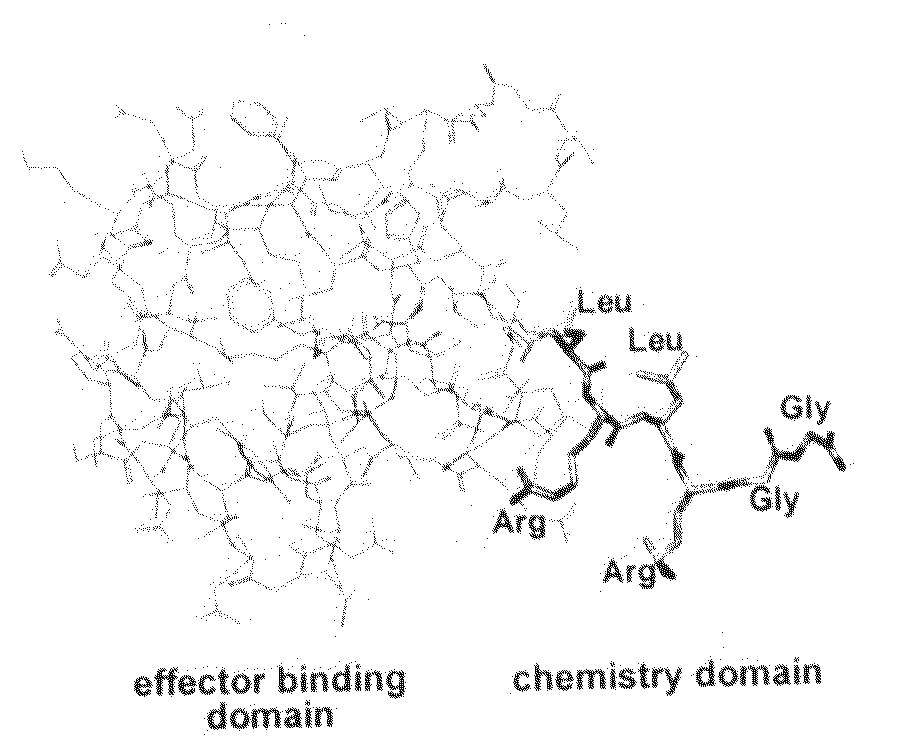
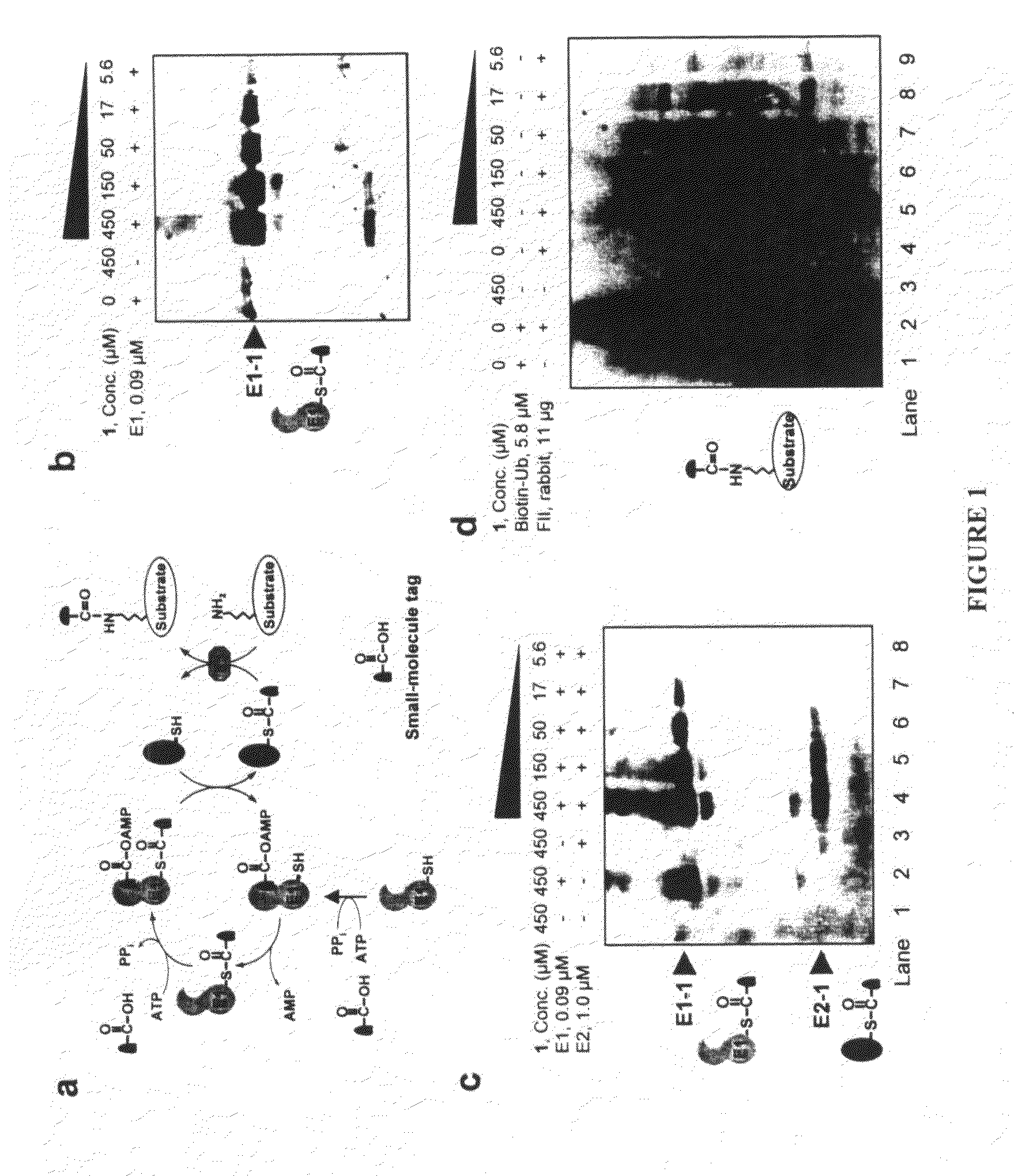
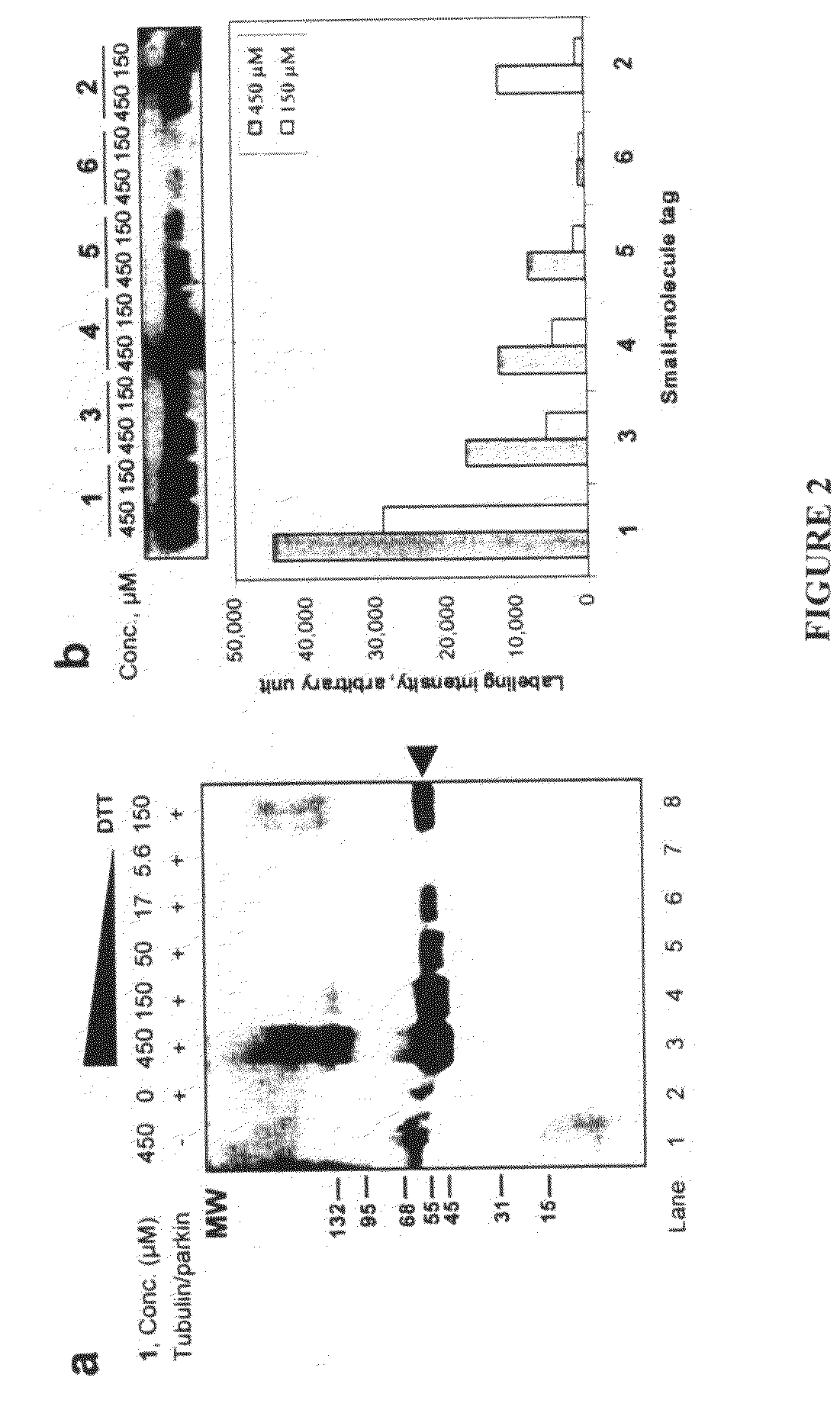
An improved method for protein labeling comprising the steps of providing a synthetic small molecule tag, providing a target protein to be tagged, providing at least two enzymes for catalyzing a conjugation reaction between the tag and the target protein, incubating the tag, the protein and the enzyme, and allowing the tag to conjugate to the target protein. The tag may embody at least one structural feature of an ubiquitin C-terminus, and the structural feature may comprise a recognition sequence that is recognizable by an ubiquitin activating enzyme.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Ubiquitin or gamma-crystalline conjugates for use in therapy, diagnosis and chromatography
ActiveUS20070248536A1Lower capability requirementsIncrease dissociationImmunoglobulins against bacteriaFermentationUbiquitinsDiagnosis treatment
The present invention relates to conjugates containing a covalent linkage between one or more polypeptide molecules based on gamma-crystallin or ubiquitin and one or more functional components. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a method for the preparation of such a conjugate as well as to the use of the conjugate in diagnostics, therapy and chromatography.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Foot and mouth disease virus-like particle, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101914501AImproving immunogenicityImprove biological activityInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsEnzyme digestionStructural protein
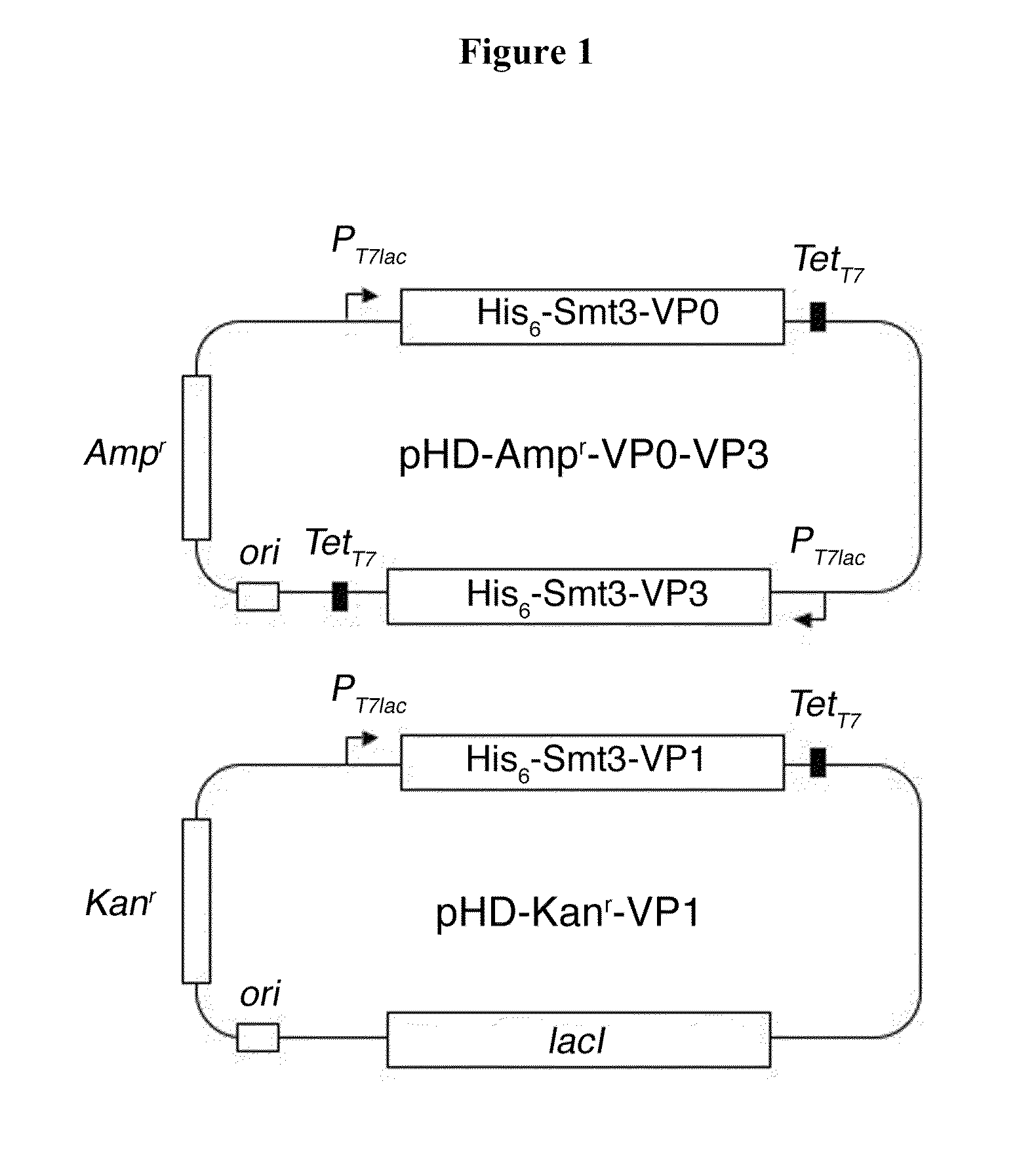
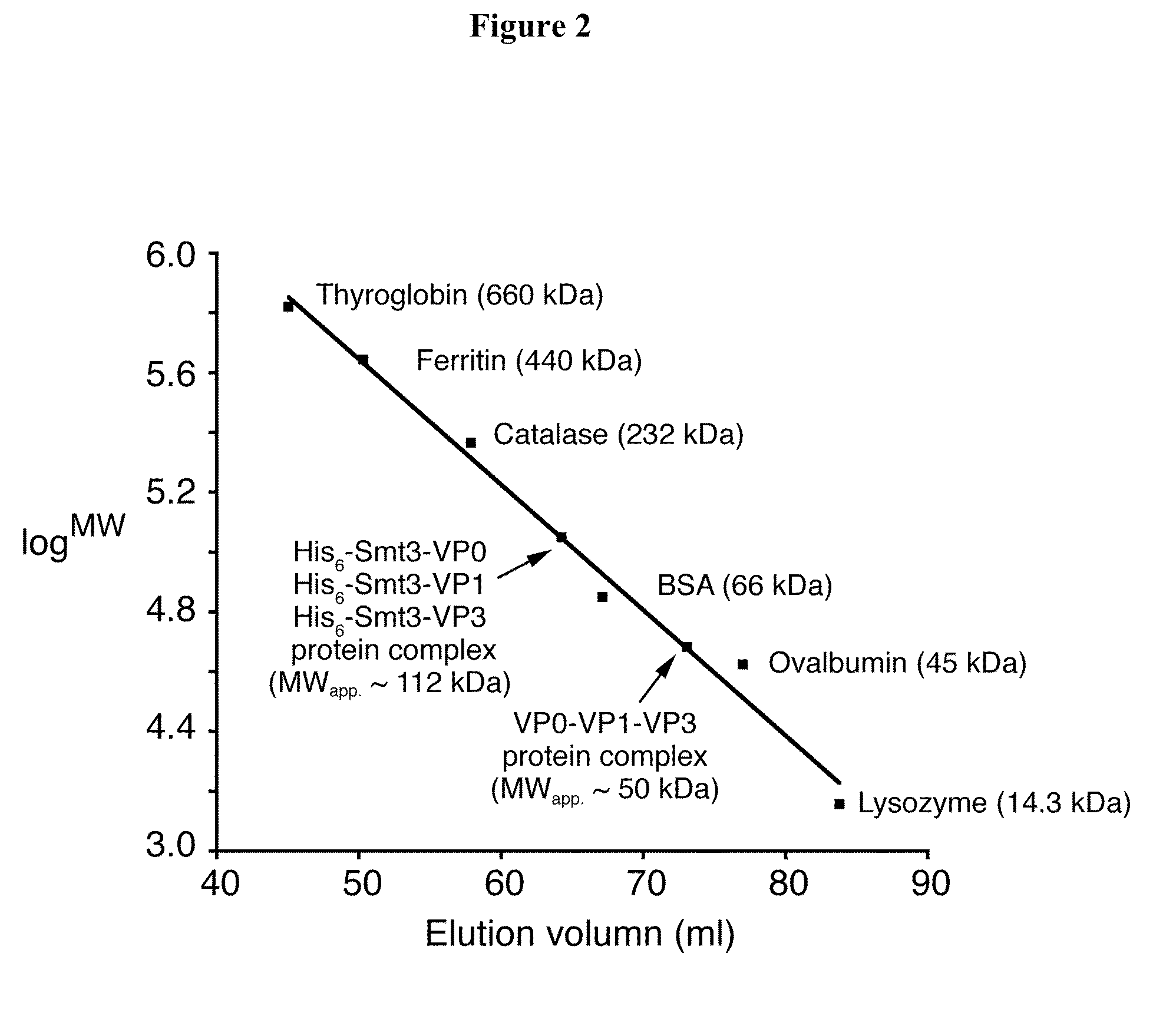
The invention discloses an Asia I type foot and mouth disease virus-like particle, a preparation method and an application thereof. The Asian I type foot and mouth disease virus-like particle comprises structural proteins of VP0, VP3 and VP1 of Asia I type foot and mouth disease virus, wherein the gene sequence of VP0 is shown in SEQ 1, the gene sequence of VP3 is shown in SEQ 3, and the gene sequence of VP1 is shown in SEQ 2. The preparation method of the Asian I type foot and mouth disease virus-like particle has the following steps: performing amplification to obtain the VP0, VP3 and VP1, performing enzyme digestion to obtain a recombinant expression vector, performing enzyme digestion on fusion protein by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO), and carrying out in-vitro assembling to obtain the foot and mouth disease virus-like particle.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel compounds
ActiveUS20170247365A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicinal chemistryUbiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase
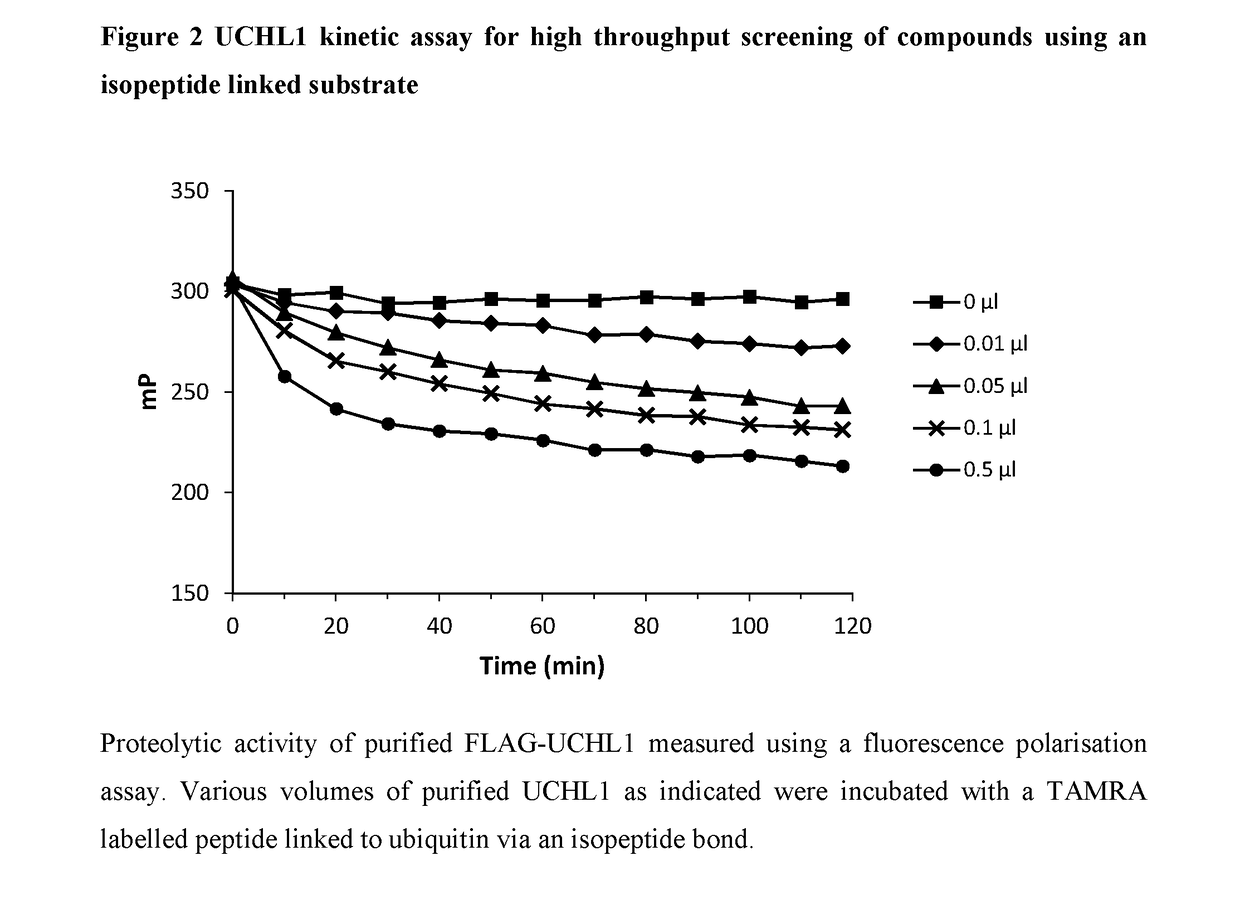
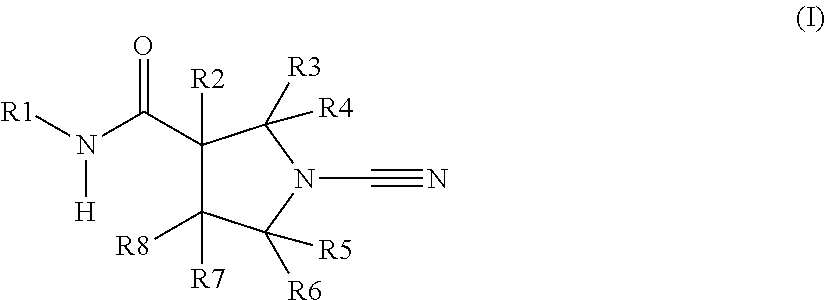
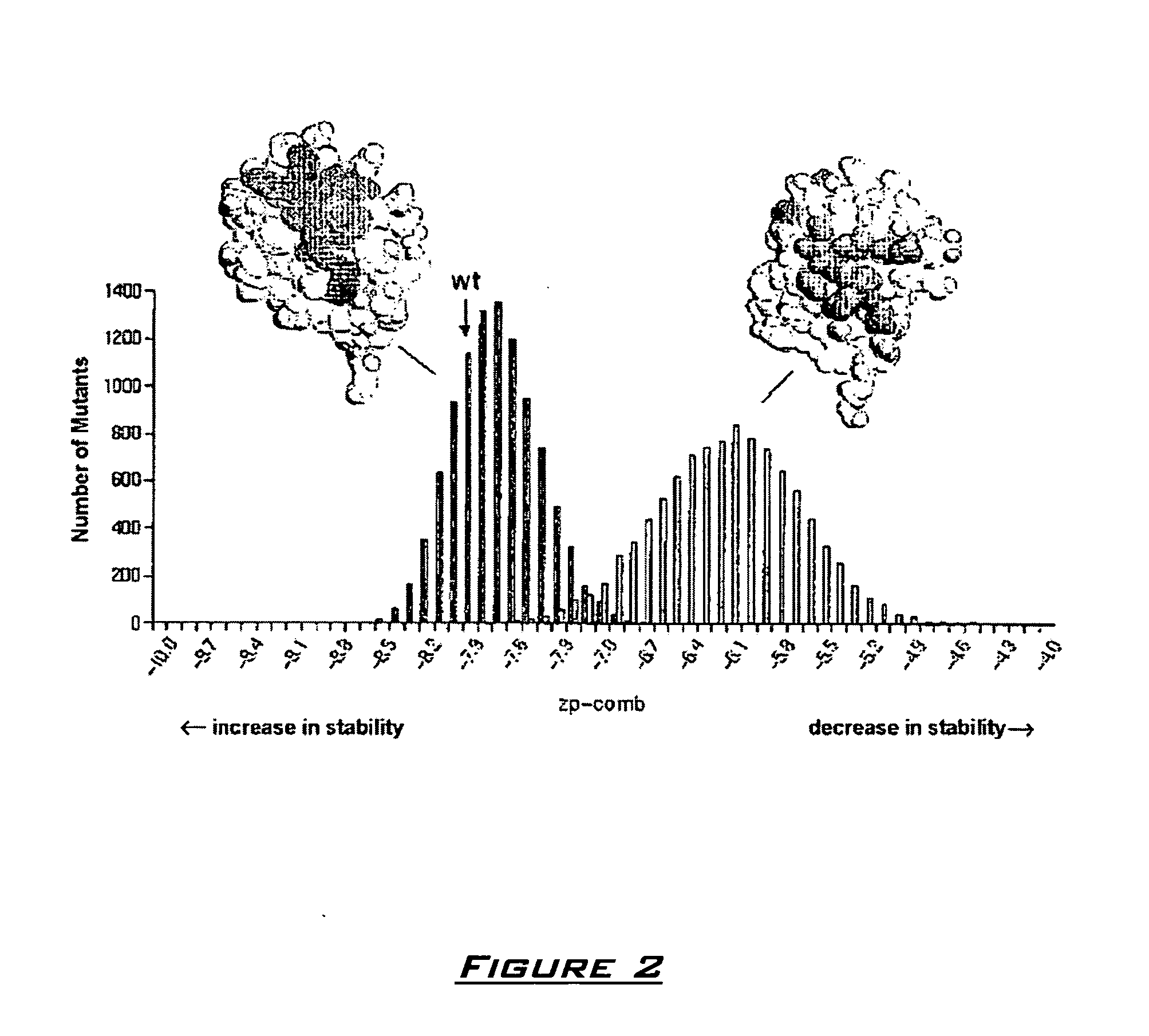
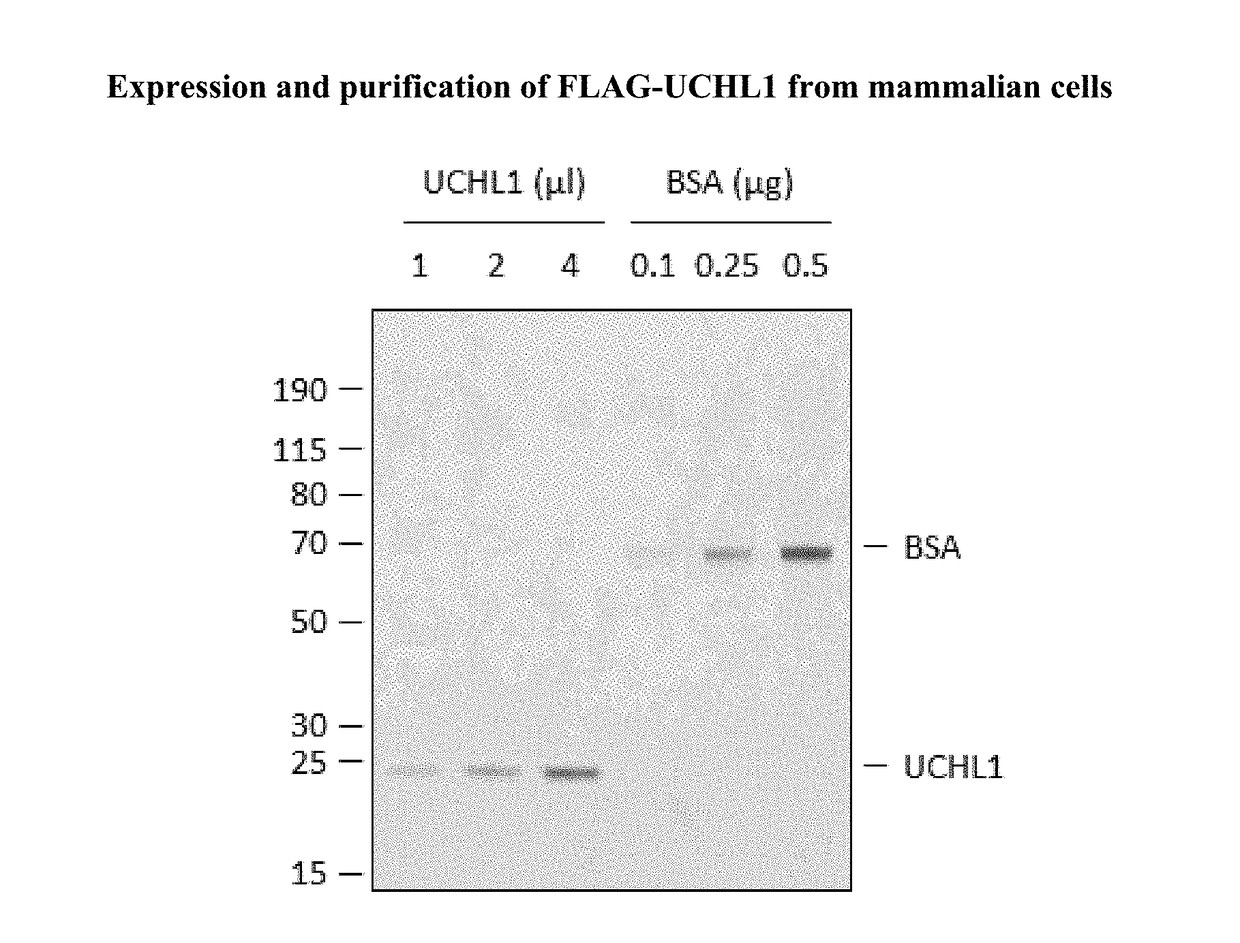
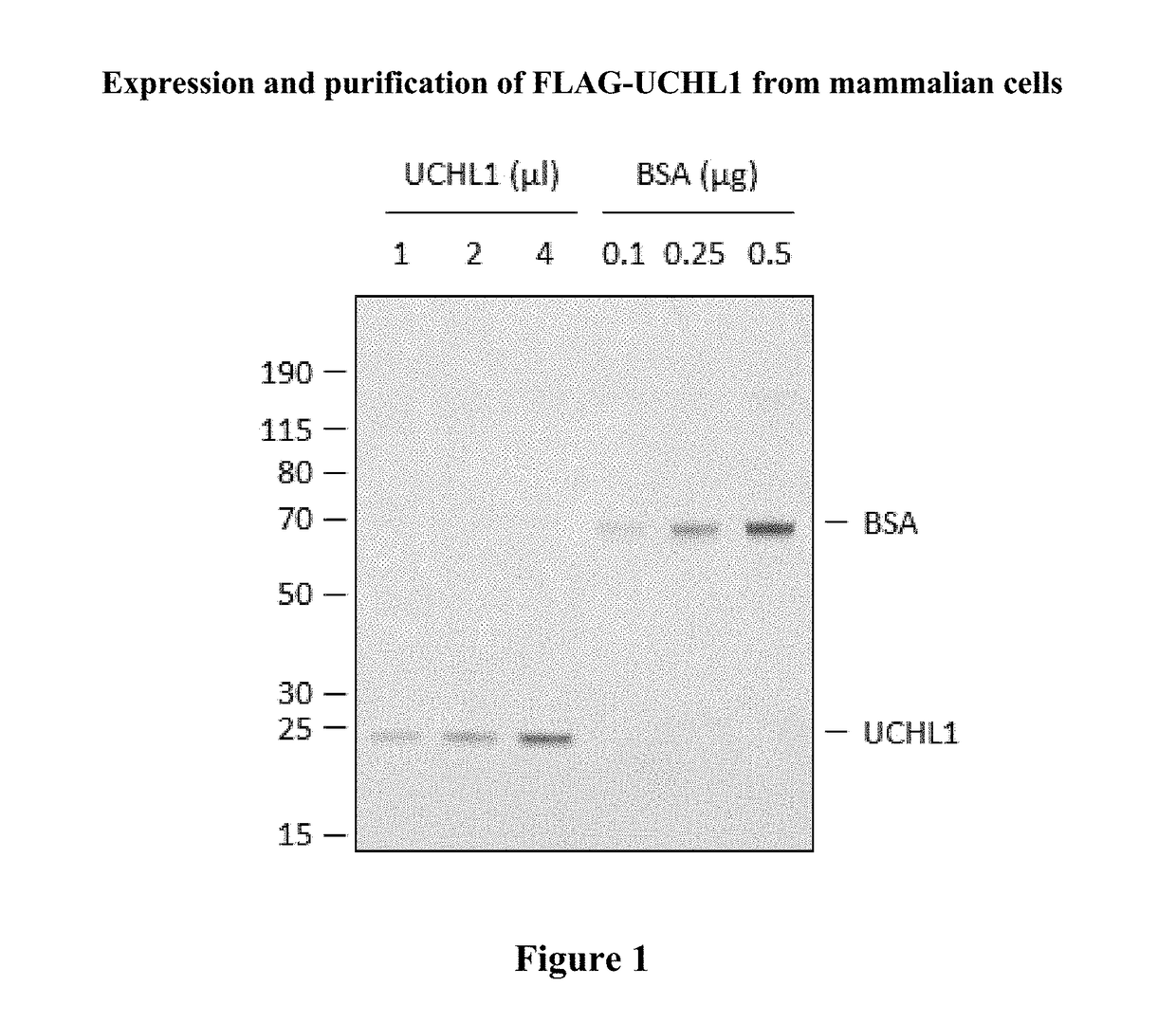
The present invention relates to novel compounds and methods for the manufacture of inhibitors of deubiquitylating enzymes (DUBs). In particular, the invention relates to the inhibition of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1). The invention further relates to the use of DUB inhibitors in the treatment of cancer and other indications. Compounds of the invention include compounds having the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1 to R8 are as defined herein.
Owner:MISSION THERAPEUTICS
Protein fragment complementation assays for the detection of biological or drug interactions
InactiveUS6929916B2Level of simplicitySimple versatilityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDrug interactionProtein Fragment
The present invention describes a method for detecting biomolecular interactions said method comprising: (a) selecting an appropriate reporter molecule selected from the group consisting of a protein, a fluorescent protein, a luminescent protein and a phosphorescent protein; (b) effecting fragmentation of said reporter molecule such that said fragmentation results in reversible loss of reporter function; (c) fusing or attaching fragments of said reporter molecule separately to other molecules; followed by (d) reassociation of said reporter fragments through interactions of the molecules that are fused to said fragments; and (e) detecting said biomolecular interactions by reconstitution of activity of the reporter molecule with the proviso that said protein is not ubiquitin.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Fusion protein comprising ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like protein, membrane translocation sequence and biologically active molecule and use thereof
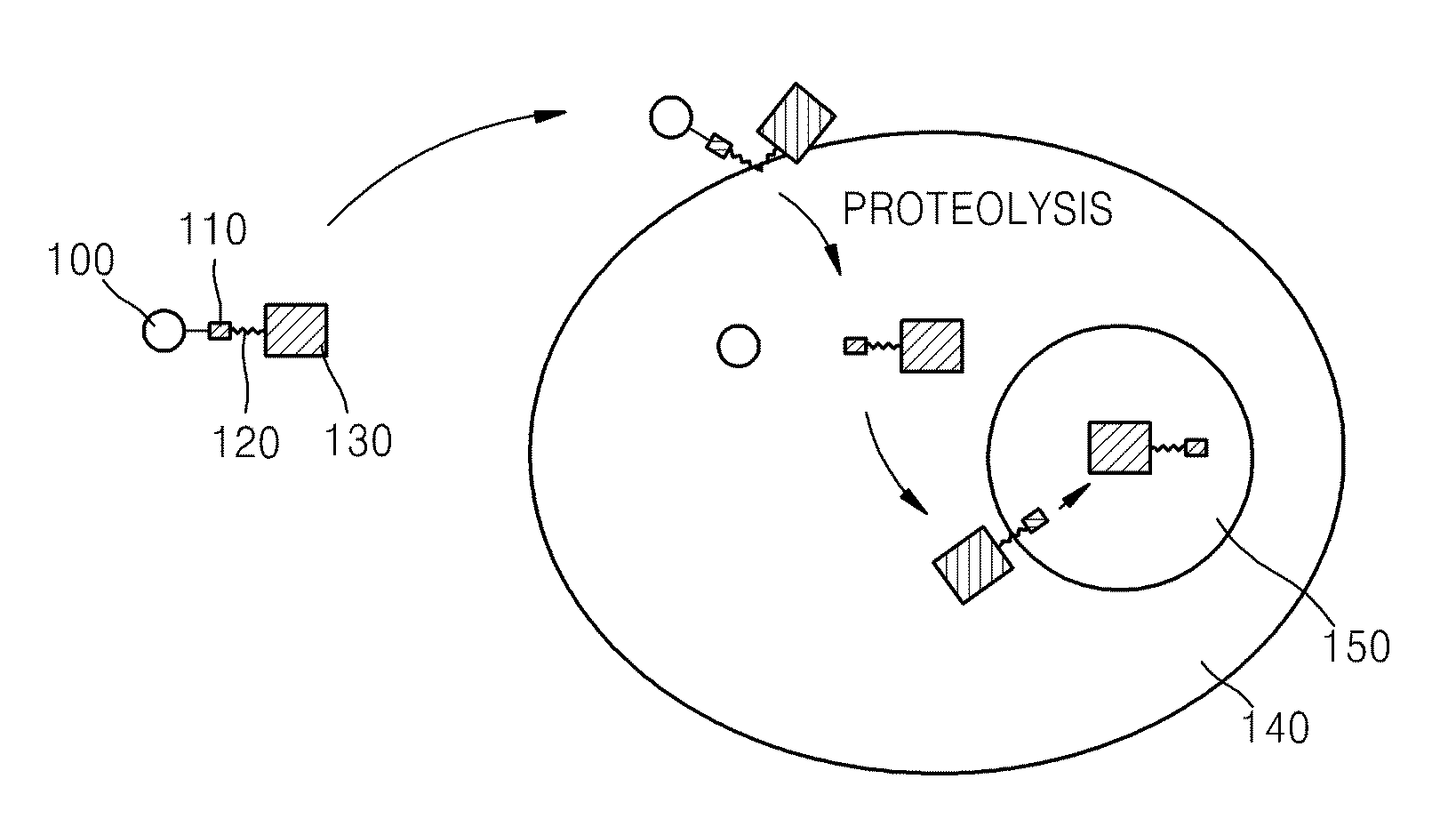
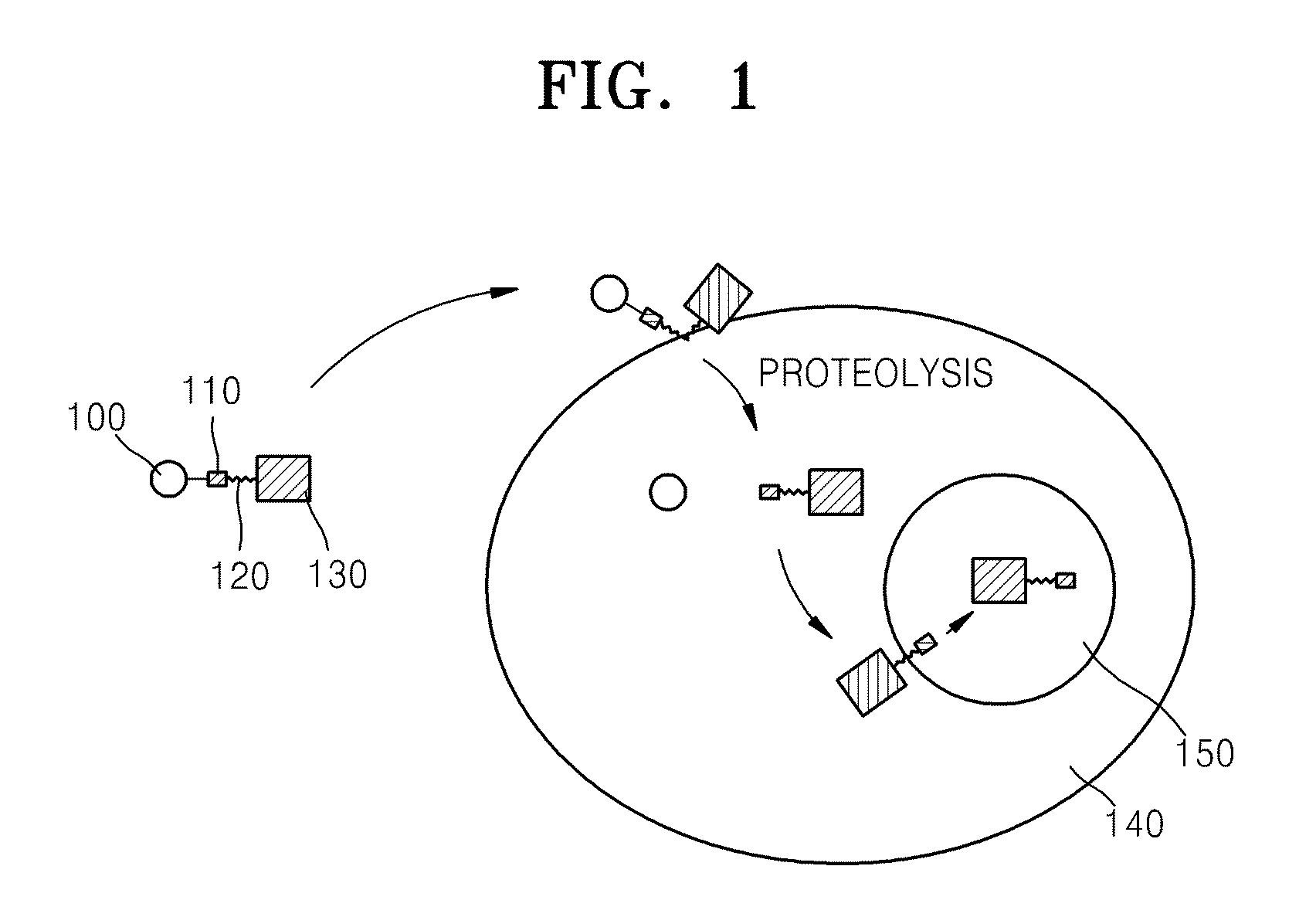
A transmembrane fusion protein including ubiquitin or a ubiquitin-like protein, a membrane translocation sequence linked to the C-terminus of the ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like protein, and a biologically active molecule linked to the C-terminus of the membrane translocation sequence is disclosed herein. A polynucleotide encoding the transmembrane fusion protein, a recombinant expression vector including the polynucleotide sequence, a cell transformed by the recombinant expression vector, and a method of delivering the biologically active molecule into a cell using the transmembrane fusion protein are also disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
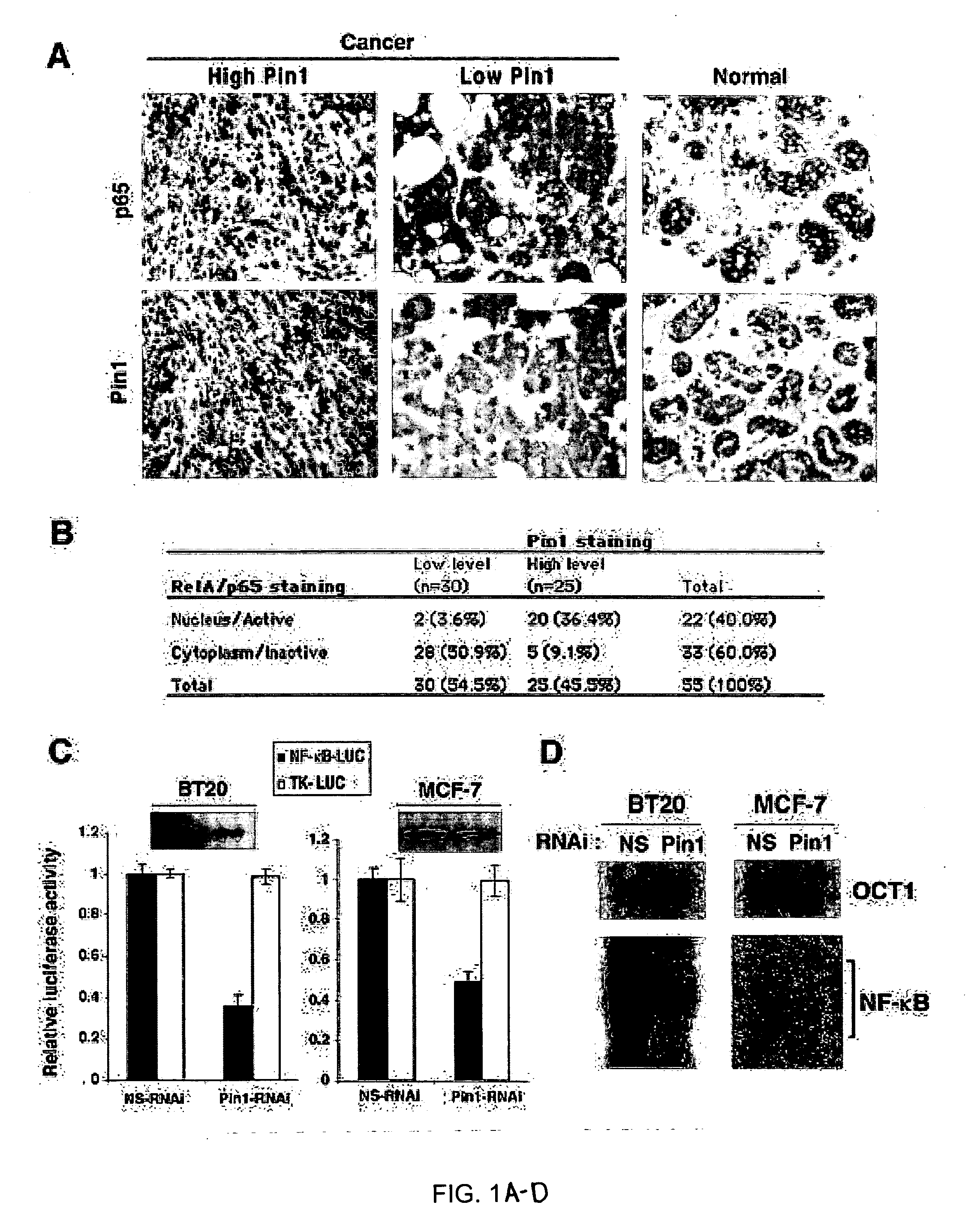
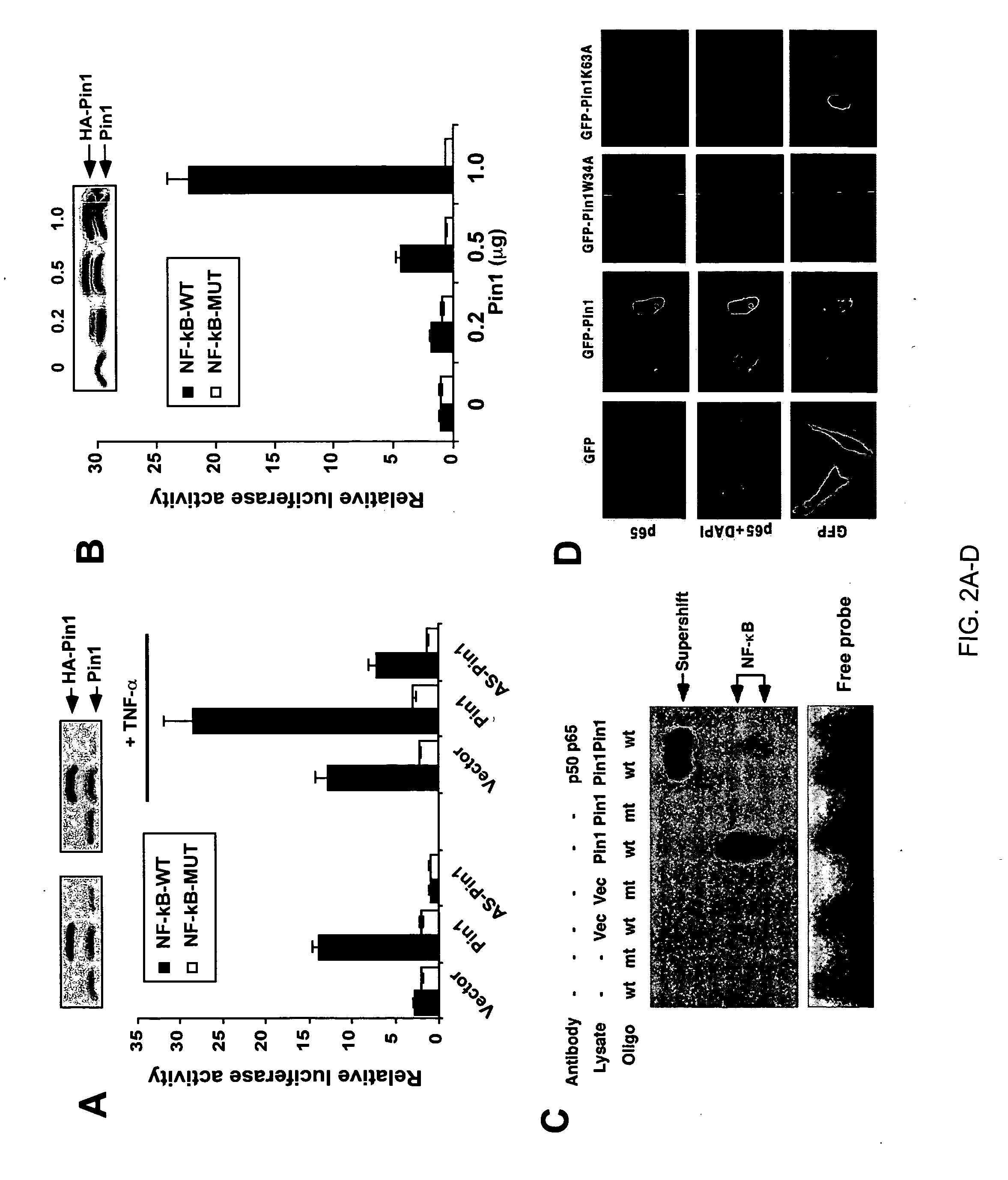
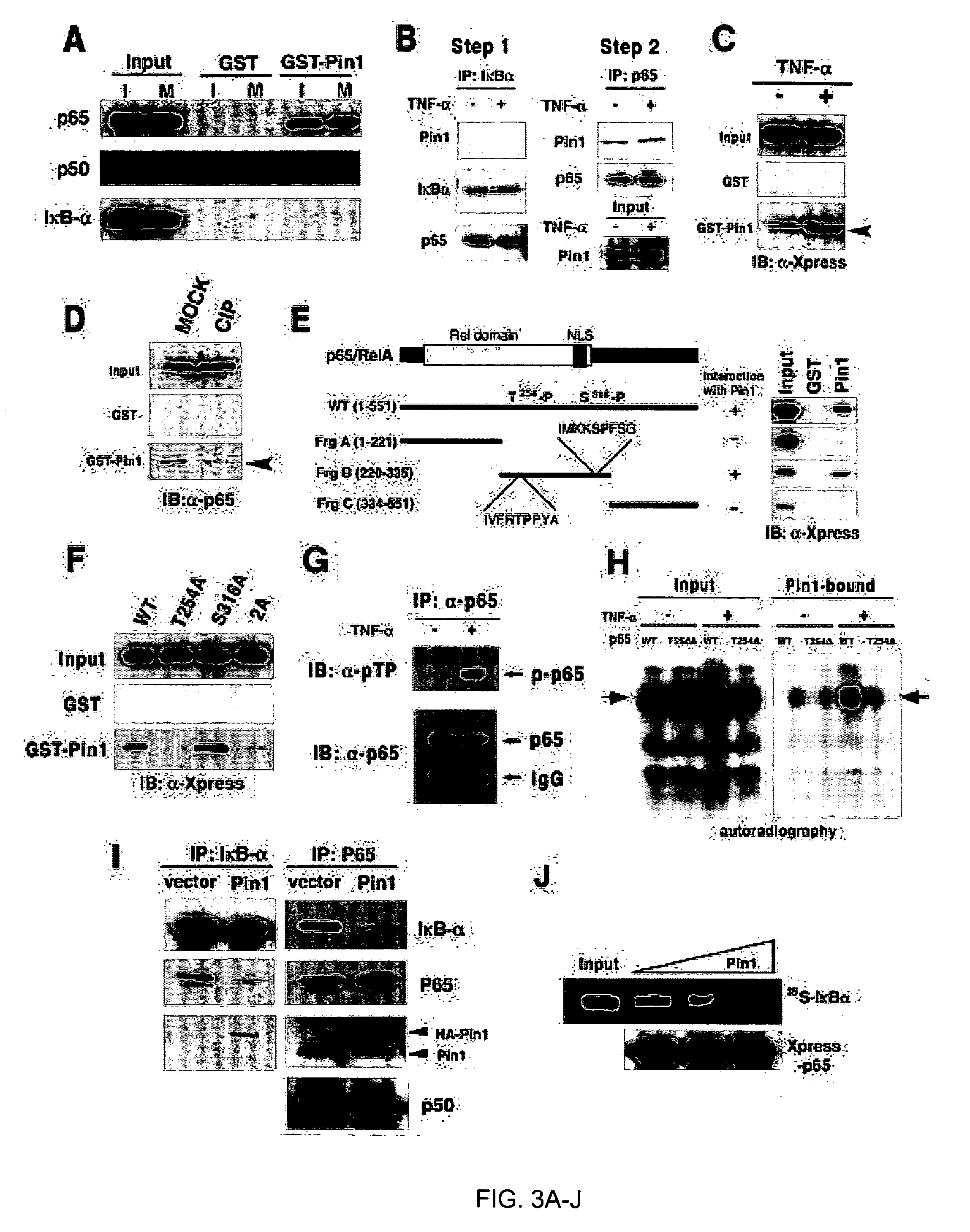
Novel regulatory mechanisms of NF-kappaB
InactiveUS20050147608A1Inhibiting degredation of NF-kBIncreasing nuclear accumulation and protein stabilityHydrolasesAntipyreticIsomerizationProteolysis
The instant invention pertains to the discovery of two novel regulatory mechanisms of NF-kB. The instant invention demonstrates that NF-kB is regulated by Pin1-catalyzed prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65. Accordingly, the instant invention provides methods for regulating NF-kB, and diseases and disorders associated with NF-kB. Further, the invention provides compositions capable of modulating the activity or expression of NF-kB, Pin1, and / or the proteolysis of p65.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
DNA sequence with multi-tag series connection and application of DNA sequence to protein expression and purification system
The invention provides a DNA sequence with multi-tag series connection and application of the DNA sequence to a protein expression and purification system and particularly relates to a nucleic acid structure. The nucleic acid structure is provided with a structure from 5' to 3' in the formula I, wherein the structure is Z1-Z2-Z3-Z4-Z5 (I); in the formula, Z1 to Z5 are elements used for constituting the nucleic acid structure; all '-' parts are bond or nucleotide connecting sequences; Z1 is the coding sequence of leading peptide; Z2 is the coding sequence without ubiquitin or with ubiquitin; Z3is the coding sequence of tab proteins; Z4 is the connecting sequence; and Z5 is the coding sequence without foreign proteins or with the foreign proteins. According to the nucleic acid structure, the efficiency of the foreign protein synthesis can be significantly improved, and the expression and purification processes of the target foreign proteins are simplified.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
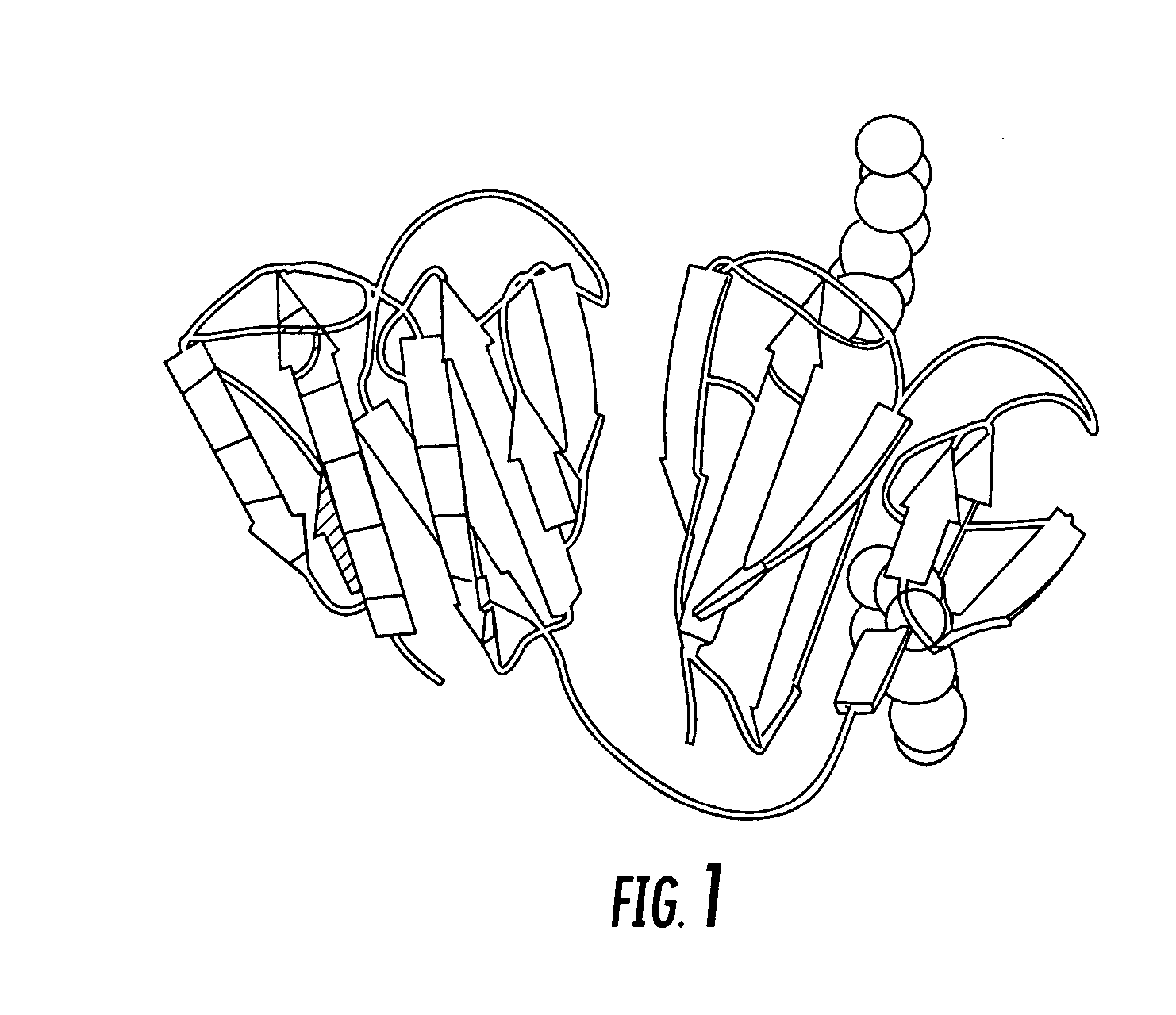
Generation of artificial binding proteins on the basis of ubiquitin proteins
ActiveUS20080171851A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsUbiquitin-Protein LigasesADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to modified proteins of the superfamily of “ubiquitin-like proteins”, proteins that have a ubiquitin-like fold and fragments or fusion proteins thereof. As a result of said modification, the proteins have a binding affinity with respect to a predetermined binding partner that did not exist previously. The invention also relates to a method for the production and utilization of said proteins.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
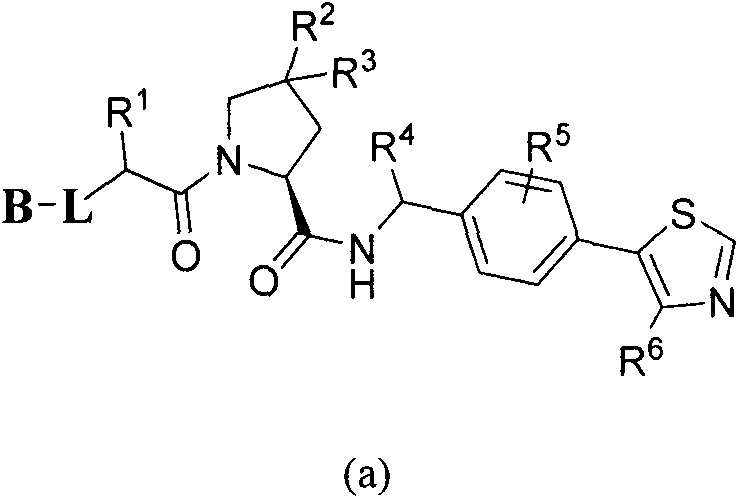
Cyanopyrrolidines as dub inhibitors for the treatment of cancer
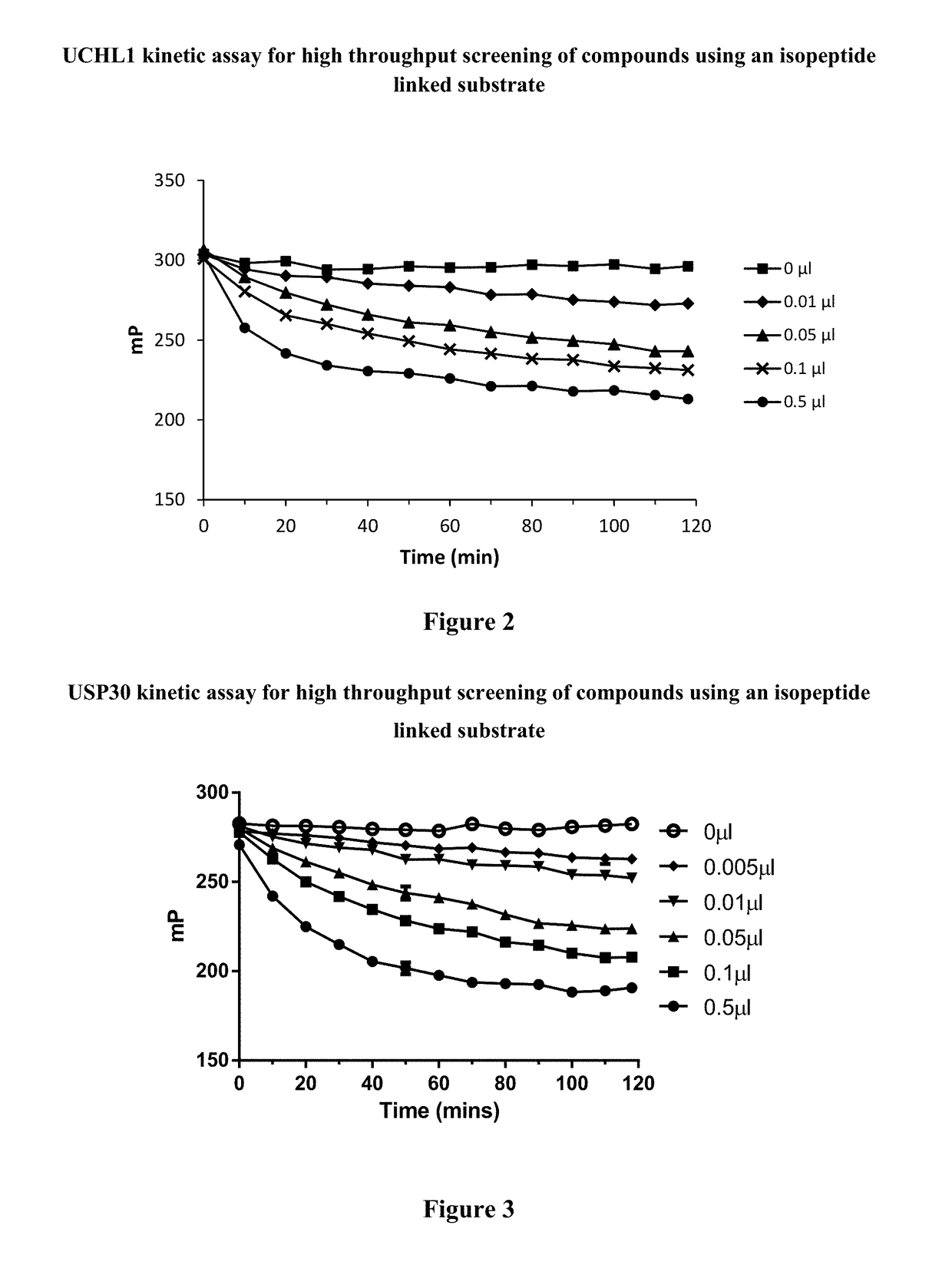
The present invention relates to novel compounds and method for the manufacture of inhibitors of deubiquitylating enzymes (DUBs). In particular, the invention relates to the inhibition of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 30 or ubiquitin specific peptidase 30 (USP30). The invention further relates to the use of DUB inhibitors in the treatment of cancer and conditions involving mitochondrial dysfunction. Compounds of the invention include compounds having the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1,R2,R3,R4,R5,R6,R7,R8 and R9 are as defined herein.
Owner:MISSION THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and methods for producing bioactive fusion proteins
Disclosed is a composition of matter involving a recombinant fusion protein comprising a a pharmacologically active protein partner, and a small pharmacologically inactive protein domain partner of human origin, such as but not limited to, a 10th fibronectin III domain, a SH3 domain, a SH2 domain, a CH2 domain of IgG1, a PDZ domain, a thrombospondin repeat domain, an ubiquitin domain, a leucine-rich repeat domain, a villin headpiece HP35 domain, a villin headpiece HP76 domain, or a fragment or modification of any of these. Also disclosed are nucleic acids (e.g., DNA constructs) encoding the fusion protein, expression vectors and recombinant host cells for expression of the fusion protein, and pharmaceutical compositions containing the recombinant fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and method of producing a pharmacologically active recombinant fusion protein.
Owner:AMGEN INC
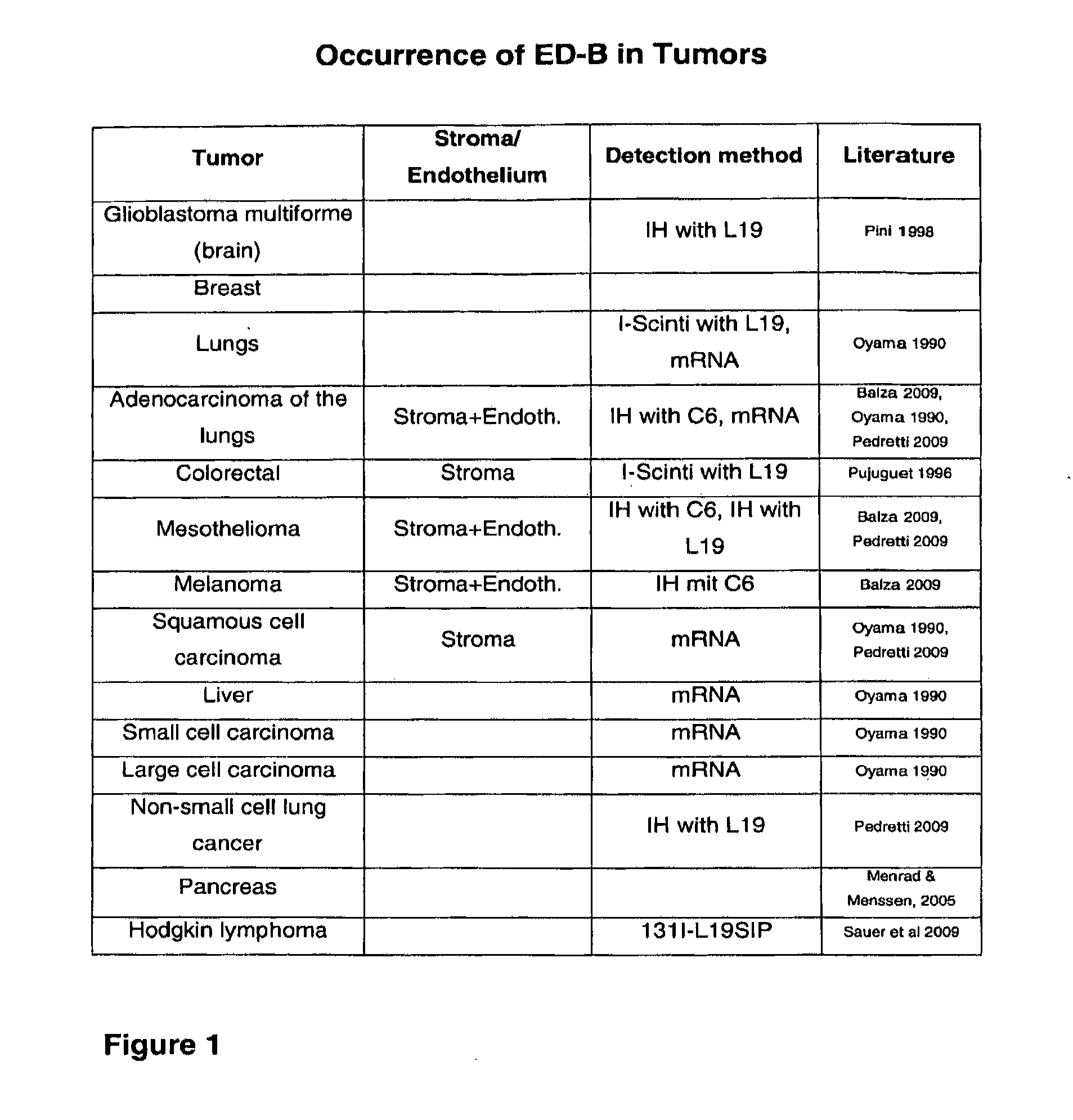
Modified ubiquitin proteins having a specific binding activity for the extradomain b of fibronectin
ActiveUS20130011334A1Without decreasing overall stabilityIncrease the number ofBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsUbiquitin-Protein LigasesActive component
The present invention refers to novel hetero-multimeric proteins obtained from modified ubiquitin capable of binding the extradomain B of fibronectin (ED-B) with high affinity. Furthermore, the invention refers to fusion proteins comprising said recombinant protein fused to a pharmaceutically and / or diagnostically active component. The invention is further directed to the use of said proteins in medical treatment methods.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Cis-acting regulatory elements from tripsacum dactyloides
InactiveUS20060218662A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousMicroorganism
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of heterologous nucleotide sequences in a plant. Compositions include a novel promoter nucleotide sequence for the gene encoding ubiquitin in Tripsacum dactyloides, as well as vectors, microorganisms, plants and plant cells comprising the promoter nucleotide sequence, or variants and fragments thereof. Methods for expressing a heterologous nucleotide sequence in a plant using the promoter sequences disclosed herein are also provided. The methods comprise stably incorporating into the genome of a plant cell a nucleotide sequence operably linked to the promoter of the present invention and regenerating a stably transformed plant that expresses the nucleotide sequence.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Expression vector, methods for the production of heterologous gene products and for the selection of recombinant cells producing high levels of such products
ActiveUS7384744B2Shorten the timeReduce development costsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousFluorescence
An expression vector for eukaryotic cells comprising a gene which codes for a protein of interest, functionally linked to a hamster-ubiquitin / S27a-promoter and a gene which codes for a fluorescent protein. Preferably the expression vector also contains an amplifiable selectable marker gene. The invention also describes host cells, preferably mammalian cells, which have been transfected with the expression vector, processes for producing heterologous gene products and a method of selecting high-producing cells.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Bifunctional molecule based on VHL ligand induced BET degradation as well as preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a new bifunctional small molecule, a preparation method of pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, hydrate or prodrug and application of the compounds and medicinal compositions in treating diseases such as tumor, inflammation and immune diseases. The bifunctional small molecule provided by the invention is a protein degradation targeted combo (PROTACs) which can selectively induce BET protein degradation. According to the invention, a BET protein small molecular inhibitor is connected with a von Rippel-Lindau (VHL) protein ligand in E3 ubiquitin ligase complex by a connecting arm to obtain the bifunctional small molecule.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
African swine fever virus vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112876570AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesAntiendomysial antibodiesAfrican swine fever
The invention discloses an African swine fever vaccine and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, the structural proteins P72, P30, P54 or CD2v-AC of the African swine fever virus are respectively displayed on the surface of the cage-shaped structure of the self-assembled ferritin, so that the humoral immune efficacy and width of the vaccine are improved, and the immunogenicity of the structural proteins of the African swine fever virus is improved. Structural proteins P30, P54 and CD2v are recombined to obtain recombinant proteins, and the recombinant proteins are connected with ubiquitin to obtain two recombinant proteins, so that the cellular immune effect of the structural proteins of the African swine fever virus is further improved, and better immune protection is provided for animals. The invention also provides a method for preparing the recombinant protein or the African swine fever vaccine. The African swine fever vaccine provided by the invention can initiate a wide neutralizing anti-African swine fever antibody, not only improves the immune efficacy, but also expands the immune range, provides effective immune protection for virulent infection, and has the potential of becoming a universal safe vaccine with multiple protection effects.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cereblon ligand-induced BET degradation-based bifunctional molecule and preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel preparation method of a bifunctional molecule and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate or prodrug thereof and application of these compounds and a medicinal composition thereof in treatment of diseases such as tumors, inflammation and immunity. The bifunctional molecule is a protein degradation-targeted complex (PROTACs), and is capable of selectively inducing BET protein degradation. A BET protein small-molecule inhibitor is connected with a cereblon protein ligand in an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to obtain the bifunctional molecule.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
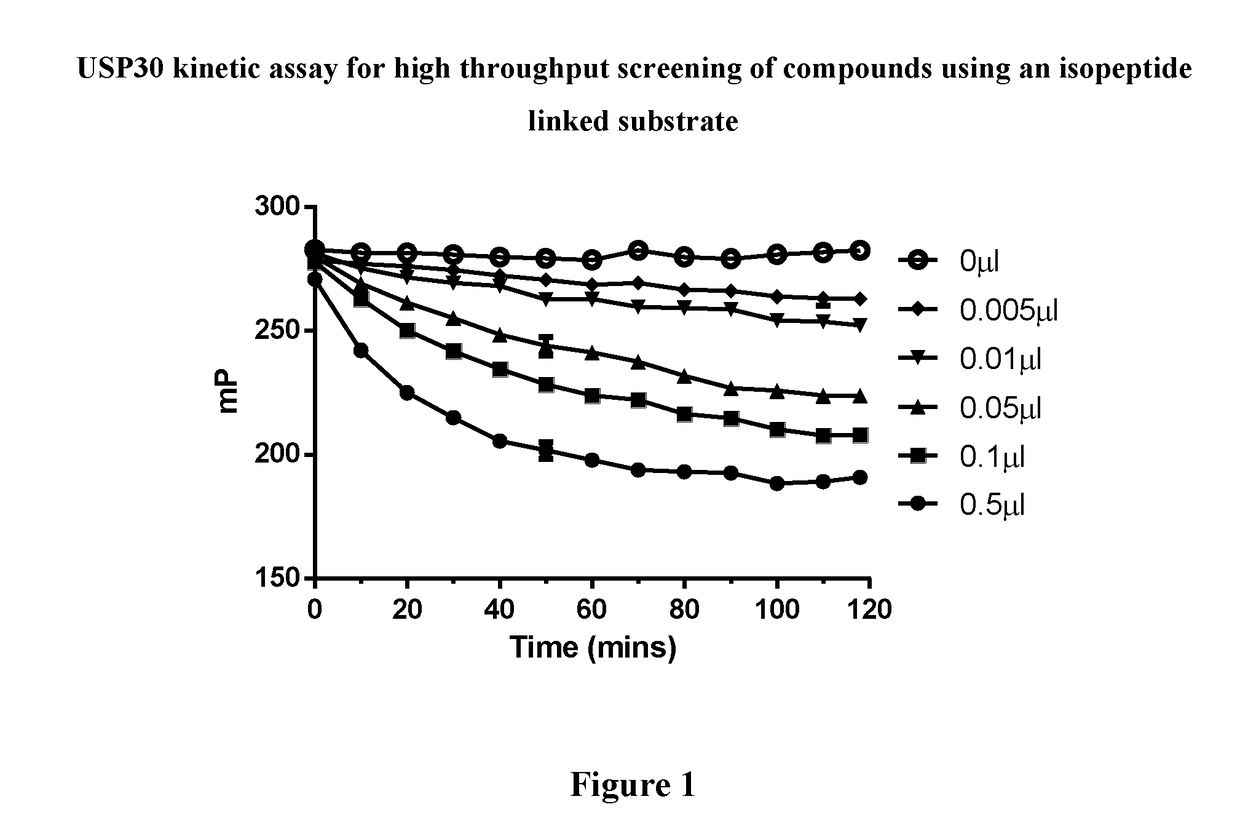
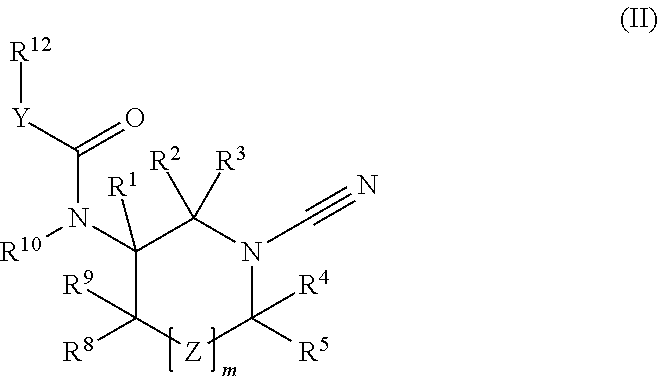
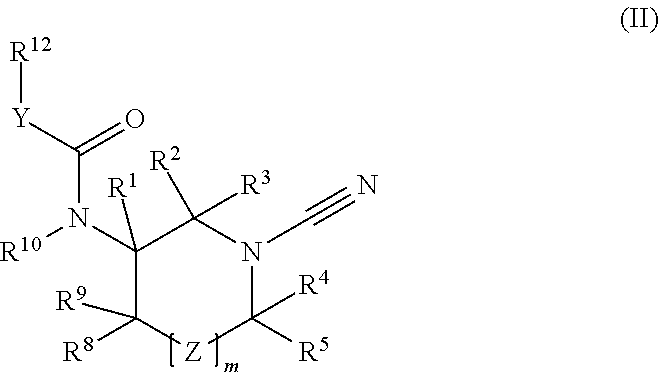
1-cyano-pyrrolidine compounds as usp30 inhibitors
ActiveUS20180086708A1Organic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsPyrrolidineUbiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase
The present invention relates to novel compounds and method for the manufacture of inhibitors of deubiquitylating enzymes (DUBs). In particular, the invention relates to the inhibition of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 30 (USP30). The invention further relates to the use of DUB inhibitors in the treatment of conditions involving mitochondrial dysfunction and cancer. Compounds of the invention include compounds having the formula (II) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R8, R9, R10, R12, Z, Y and m are as defined herein.
Owner:MISSION THERAPEUTICS
Cereblon ligand mediated novel BET protein degradation bifunctional molecules, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of new bifunctional small molecules and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates or prodrugs thereof, and application of the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof in treatment of tumors, inflammation, immunity and other diseases. The bifunctional small molecules involved in the invention are protein degradation targeting chimeras (PROTACs), and can selectively induce BET protein degradation. According to the invention, a connecting arm is employed to connect a BET protein small molecule inhibitor and a cereblon protein ligand in theE3 ubiquitin ligase complex so as to obtain the bifunctional small molecules.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Production of Anti-microbial peptides
InactiveUS20100048480A1Decrease native antimicrobial activityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismAnti microbial peptide
The present application provides methods of producing antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in a cell, for example by expression a fusion protein that includes small ubiquitin related modifier (SUMO) and an AMP in the cell. Also provided are nucleic acid and protein sequences of SUMO-AMP fusion proteins, and kits that include such molecules.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for producing bioactive fusion proteins
InactiveUS20090118181A1Low immunogenic riskReduce riskBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA constructActive protein
Disclosed is a composition of matter involving a recombinant fusion protein comprising a a pharmacologically active protein partner, and a small pharmacologically inactive protein domain partner of human origin, such as but not limited to, a 10th fibronectin III domain, a SH3 domain, a SH2 domain, a CH2 domain of IgG1, a PDZ domain, a thrombospondin repeat domain, an ubiquitin domain, a leucine-rich repeat domain, a villin headpiece HP35 domain, a villin headpiece HP76 domain, or a fragment or modification of any of these. Also disclosed are nucleic acids (e.g., DNA constructs) encoding the fusion protein, expression vectors and recombinant host cells for expression of the fusion protein, and pharmaceutical compositions containing the recombinant fusion protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and method of producing a pharmacologically active recombinant fusion protein.
Owner:AMGEN INC
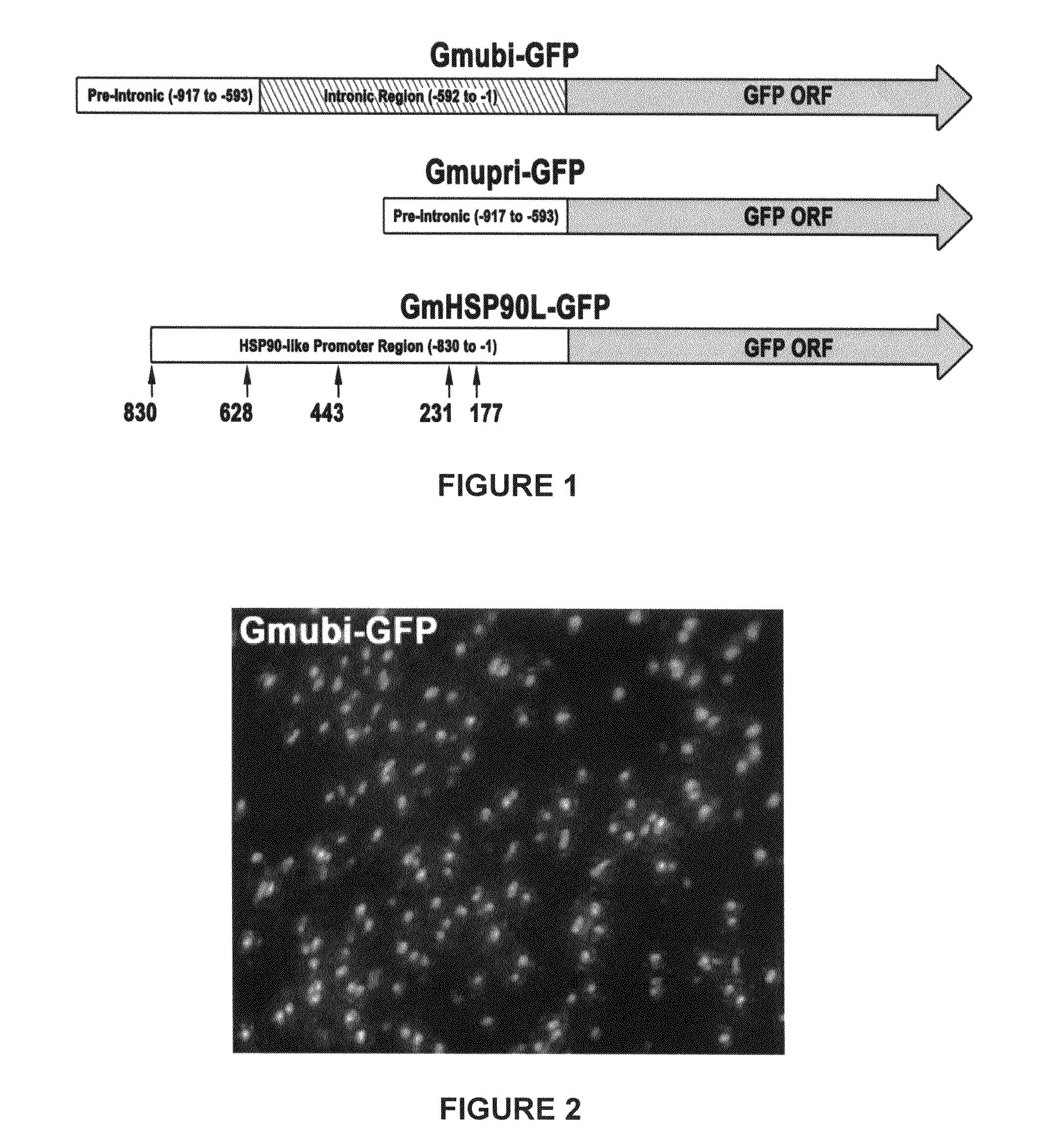
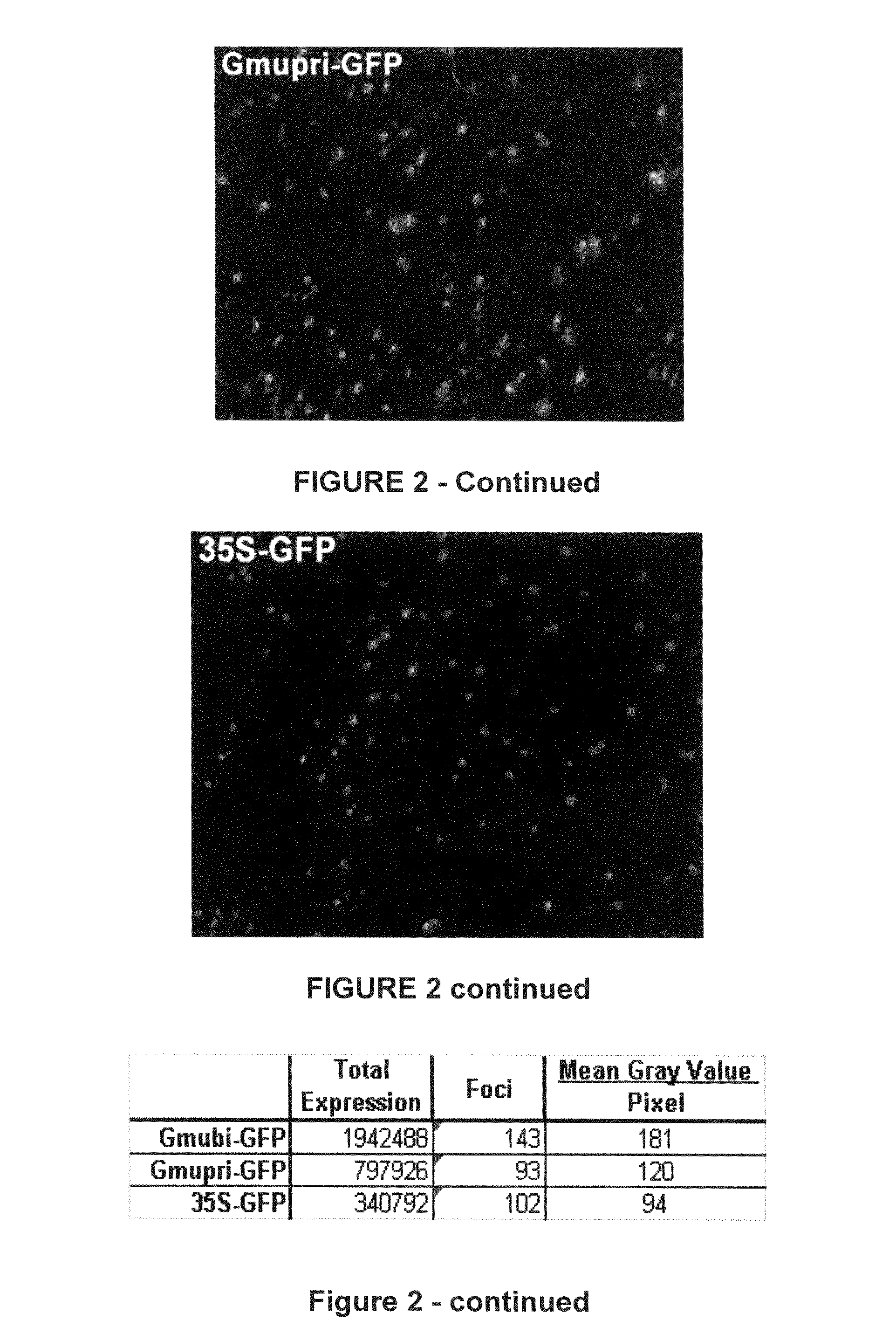
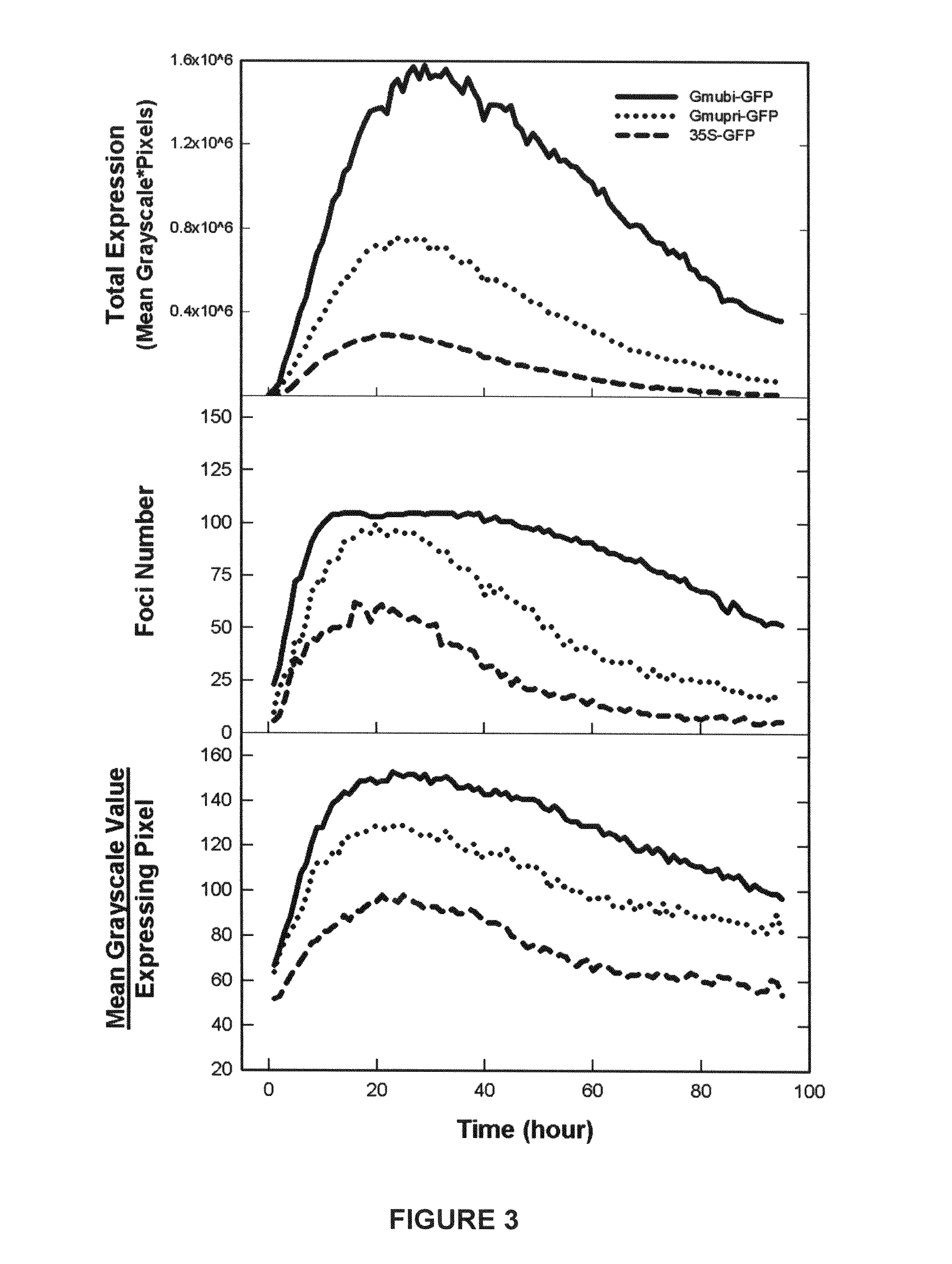
Highly active soybean promoter from the SUBI-3 polyubiquitin gene and uses thereof
Soybean ubiquitin promoters is from the soybean SUBI-3 polyubiquitin gene and processes for expressing nucleic acids of interest in transgenic plants under the control of the soybean ubiquitin promoter pare described. Higher expression levels of the nucleic acids are achieved when the promoter is included.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method of producing virus-like particles of picornavirus using a small-ubiquitin-related fusion protein expression system
A method for producing picornaviral capsid protein complexes (e.g., picornavirus like particles) in E. coli using a small-ubiquitin-related fusion protein expression system and an E. coli strain used in practicing this method. Also disclosed is use of the picornaviral capsid protein complexes like thus prepared for eliciting immune responses.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method for identifying ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins
The invention relates to a method for identifying the ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins. The above specific enrichment labeling identification method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis of purified ubiquitin-like modification proteins, enriching the ubiquitin-like modification enzyme digestion peptide fragments through a specific ubiquitin-like antibody, protecting the non-modification lysine amino residues in the enriched peptide fragments through utilizing chemical labeling, carrying out a deubiquinaning enzyme catalysis reaction to expose modified lysine on a substrate peptide fragment sequence, analyzing the peptide segment sequences through a liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer, and matching through protein mass spectrum data analysis software to obtain the chemically modified peptide fragment sequence, wherein lysine sites containing free amino groups in the finally obtained sequence are the ubiquitin-like modification sites. Compared with common gene mutation methods for obtaining the sites at present, the method provided by the invention has an advantage that information about the ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins can be rapidly, efficiently and accurately obtained without a tedious gene mutation technology.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis urine protein marker, and application of same to diagnosis and prognosis
The invention relates to an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis urine protein marker, and application of the same to diagnosis and prognosis. Specifically, the invention relates to application of a urine protein marker obtained by using an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis model and mass spectrometry to early-stage diagnosis, pathogenesis monitoring and curative effect assessment of human pulmonary fibrosis. The urine protein marker comprises collagen alpha-1(I) chain, vimentin, protein RUFY3, keratin type-II skeleton 8, a sodium-hydrogen exchange regulation factor NHE-RF2, a threonine synthase sample 2, zinc-actin binding repeat protein 2, low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein 4, alpha-11 of a guanine nucleotide binding protein subunit, an alpha-1 chain of tropomyosin, mitochondrial stress-70 protein, NSFL1 cofactor P47, ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1, etc.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Modified ubiquitin proteins having a specific binding activity for the extradomain b of fibronectin
InactiveUS20120301393A1Without decreasing overall stabilityIncrease the number ofBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsUbiquitinProtein L
The present invention refers to novel recombinant proteins obtained from modified ubiquitin capable of binding the extradomain B of fibronectin (ED-B). Furthermore, the invention refers to fusion proteins comprising said recombinant protein fused to a pharmaceutically and / or diagnostically active component.
Owner:SCIL PROTEINS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com