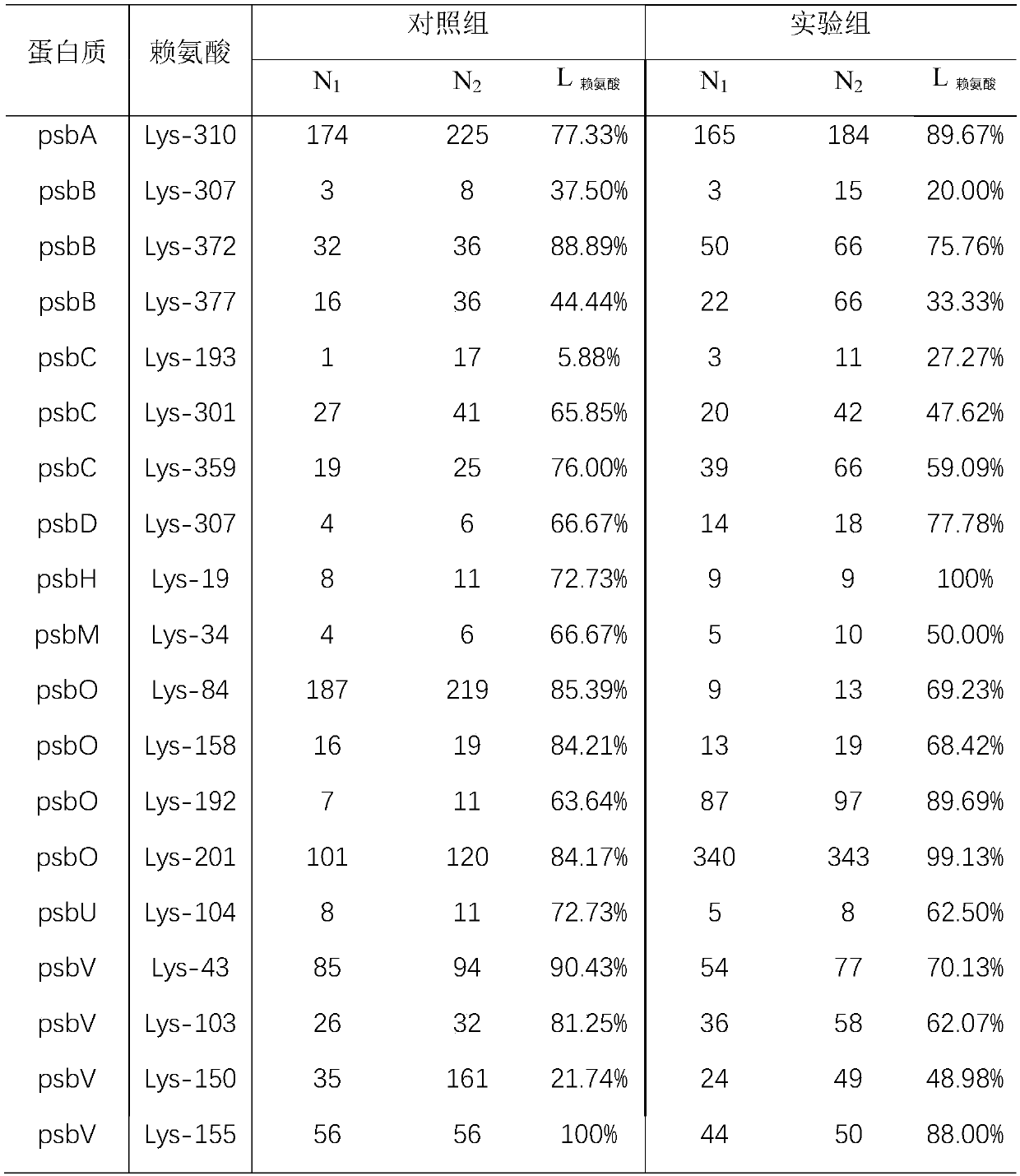
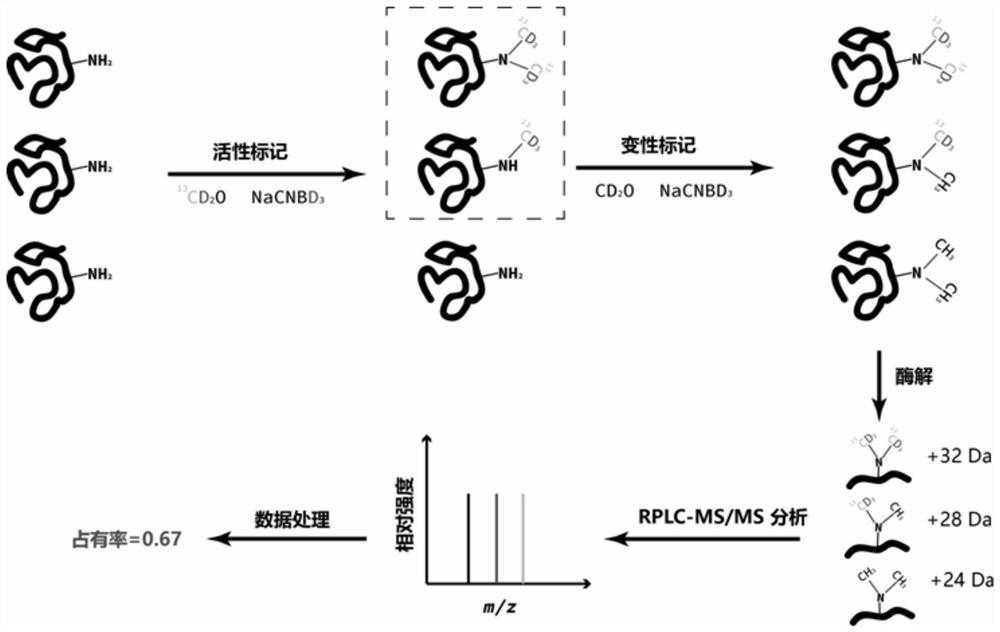
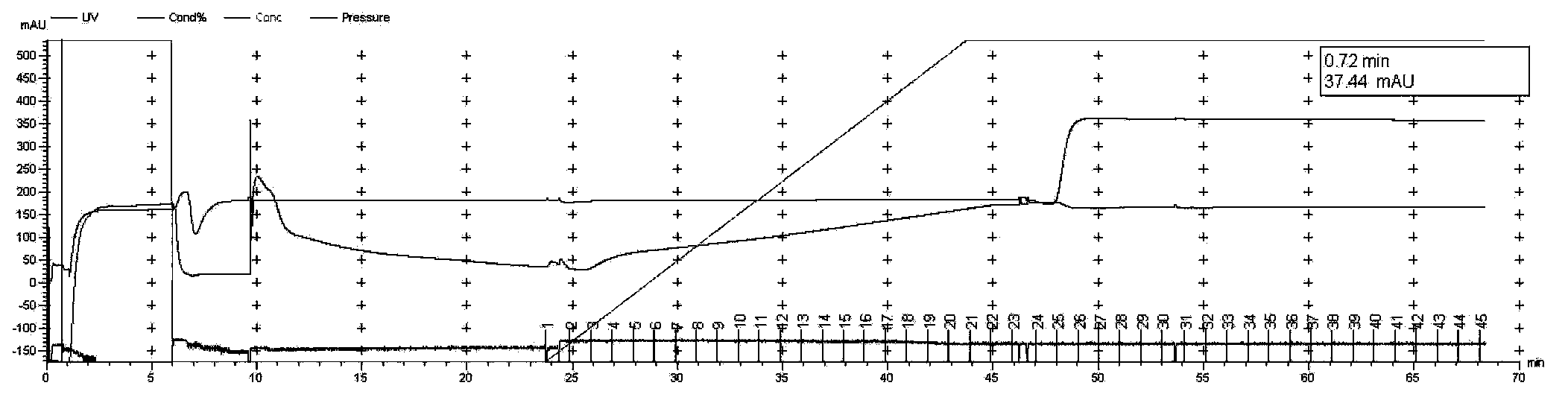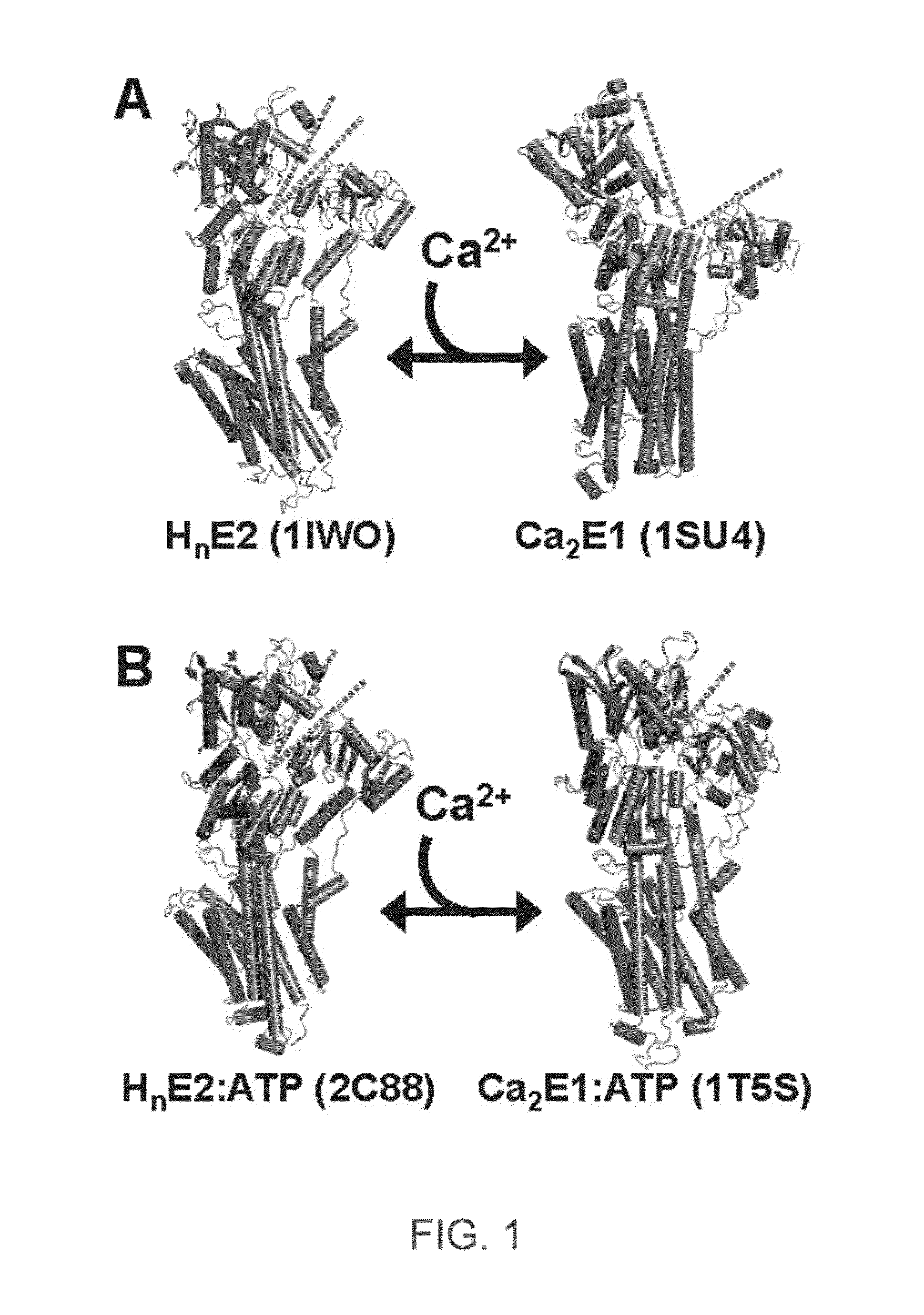Patents
Literature
42 results about "Chemical labeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
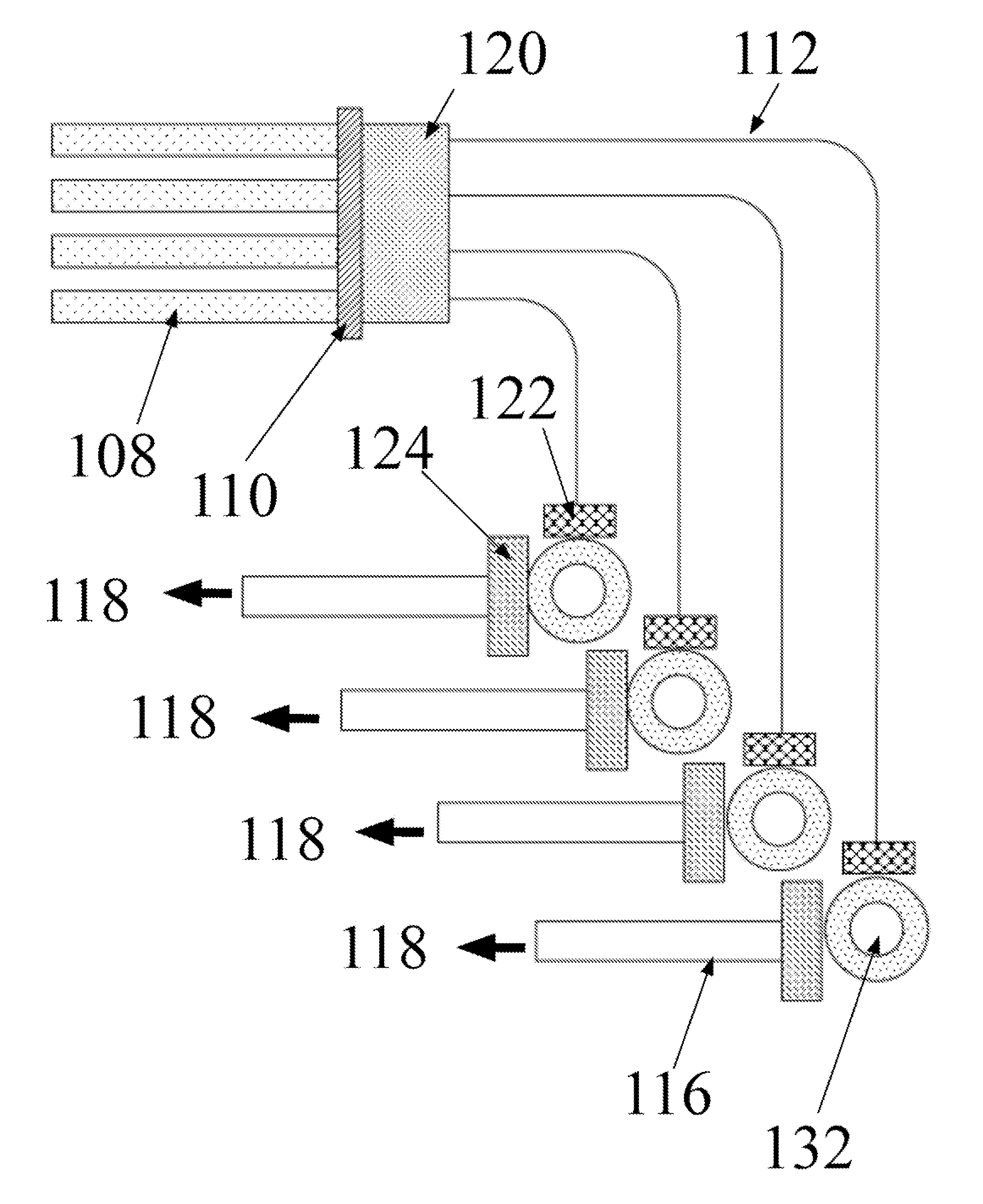
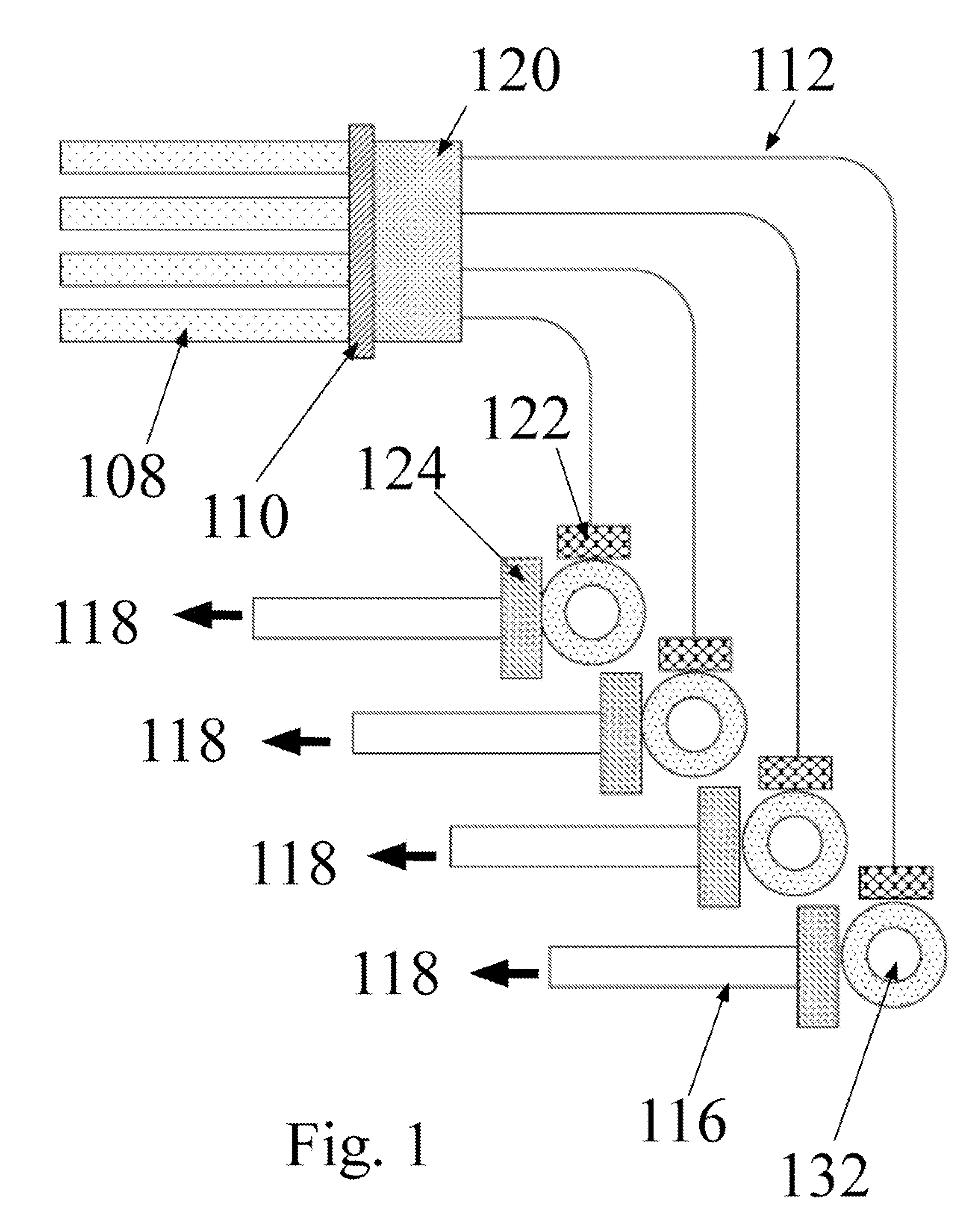
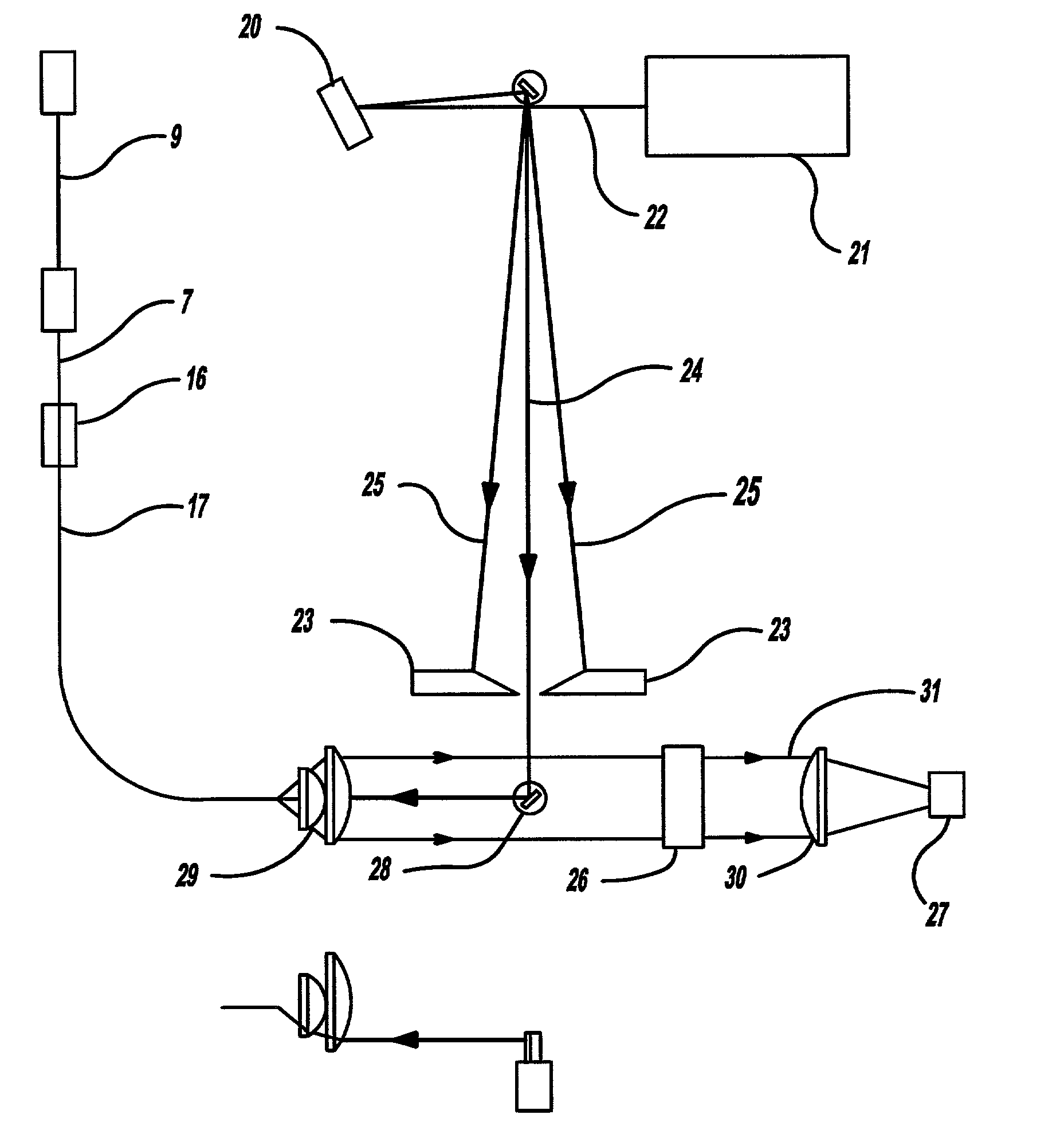
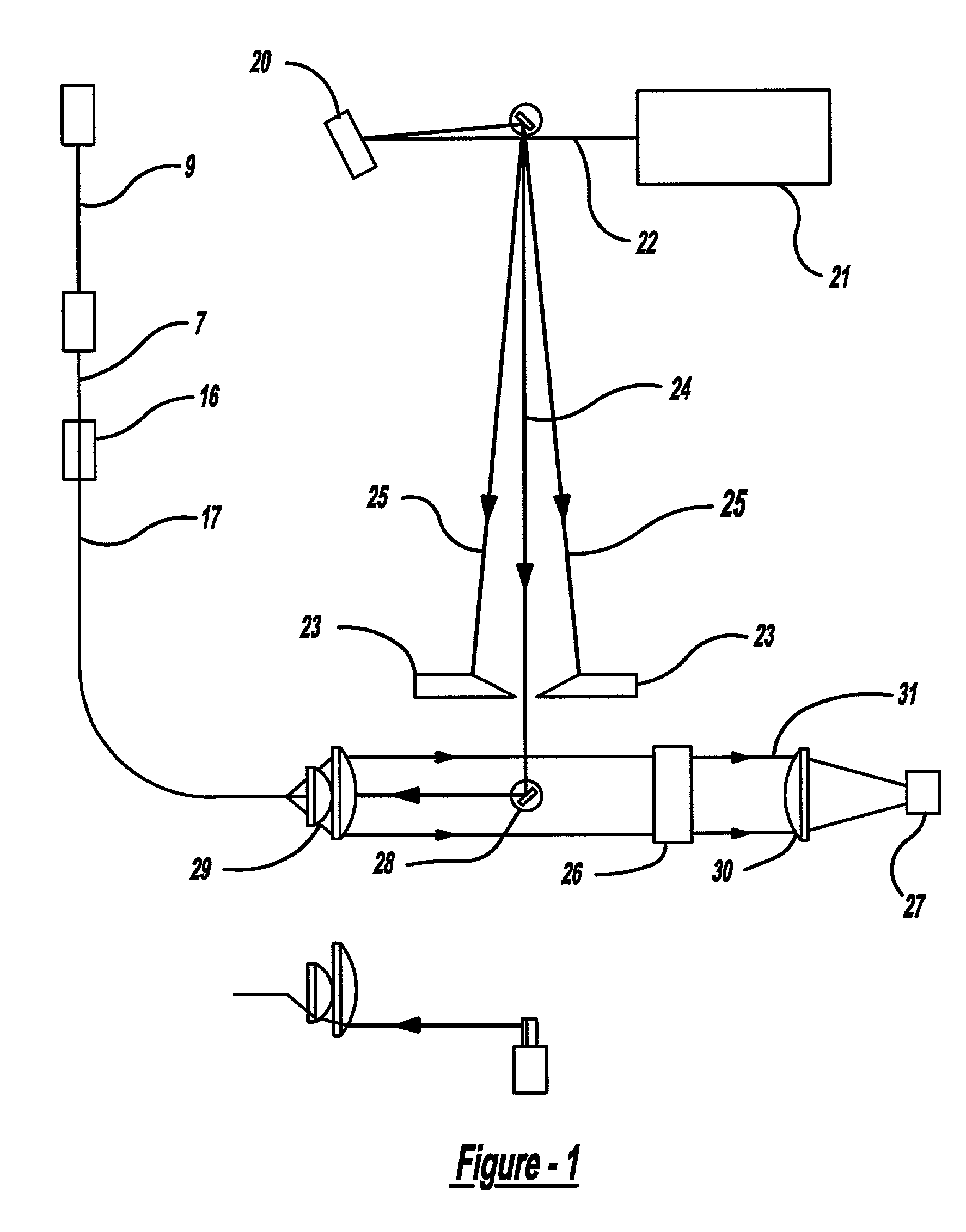
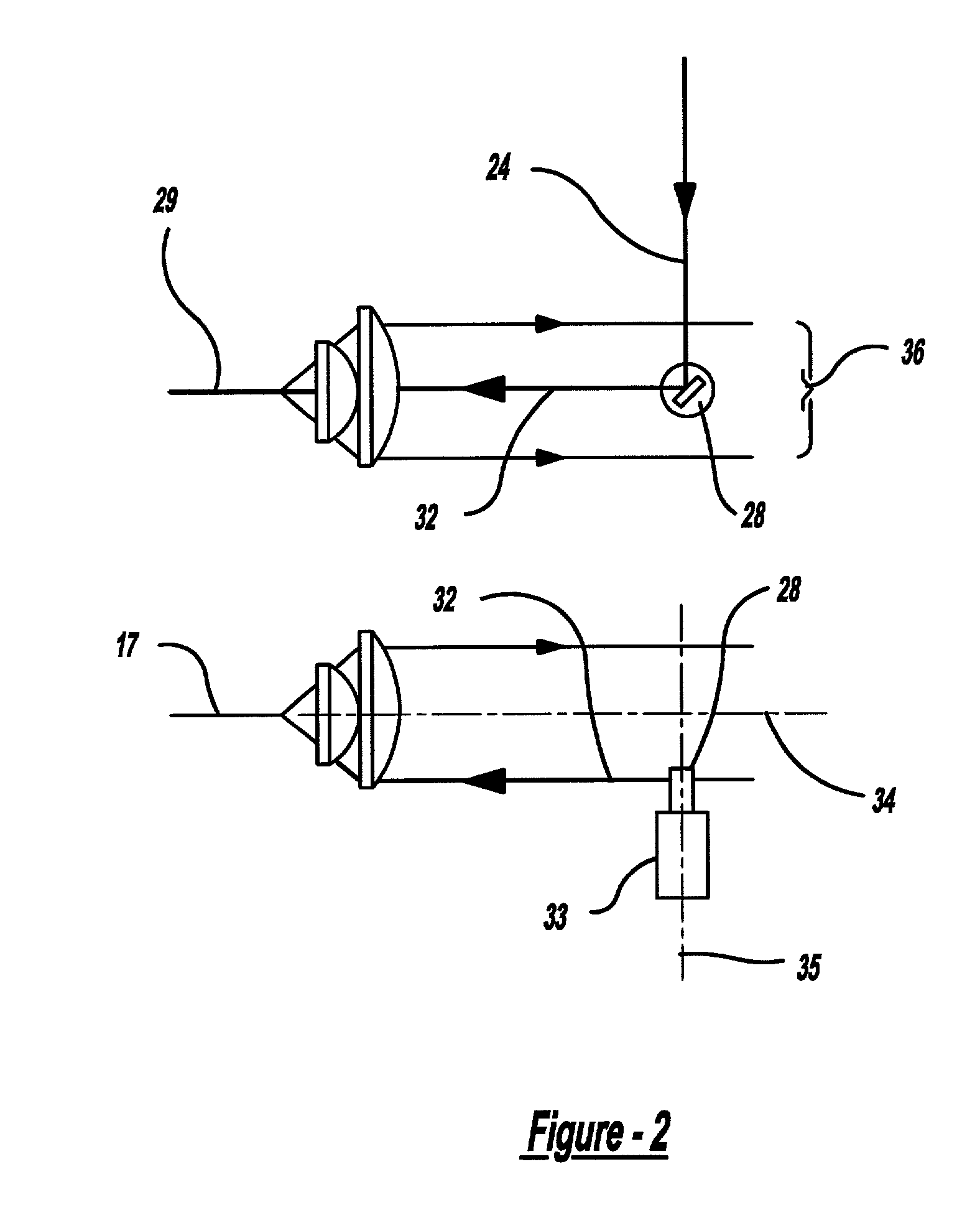
Bioanalytical instrumentation using a light source subsystem
ActiveUS20070281322A1Low heat generationStrong specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryChemical MoietyFluorescence
The invention relates to a light source for irradiating molecules present in a detection volume with one or more selected wavelengths of light and directing the fluorescence, absorbance, transmittance, scattering onto one or more detectors. Molecular interactions with the light allow for the identification and quantitation of participating chemical moieties in reactions utilizing physical or chemical tags, most typically fluorescent and chromophore labels. The invention can also use the light source to separately and simultaneously irradiate a plurality of capillaries or other flow confining structures with one or more selected wavelengths of light and separately and simultaneously detect fluorescence produced within the capillaries or other flow confining structures. In various embodiments, the flow confining structures can allow separation or transportation of molecules and include capillary, micro bore and milli bore flow systems. The capillaries are used to separate molecules that are chemically tagged with appropriate fluorescent or chromophore groups.
Owner:LUMENCOR
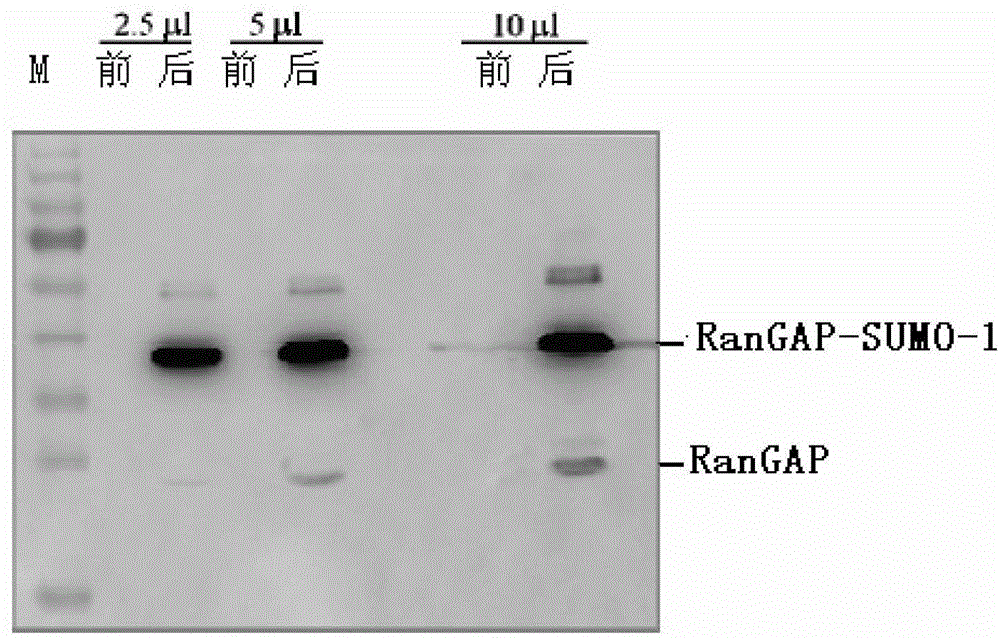
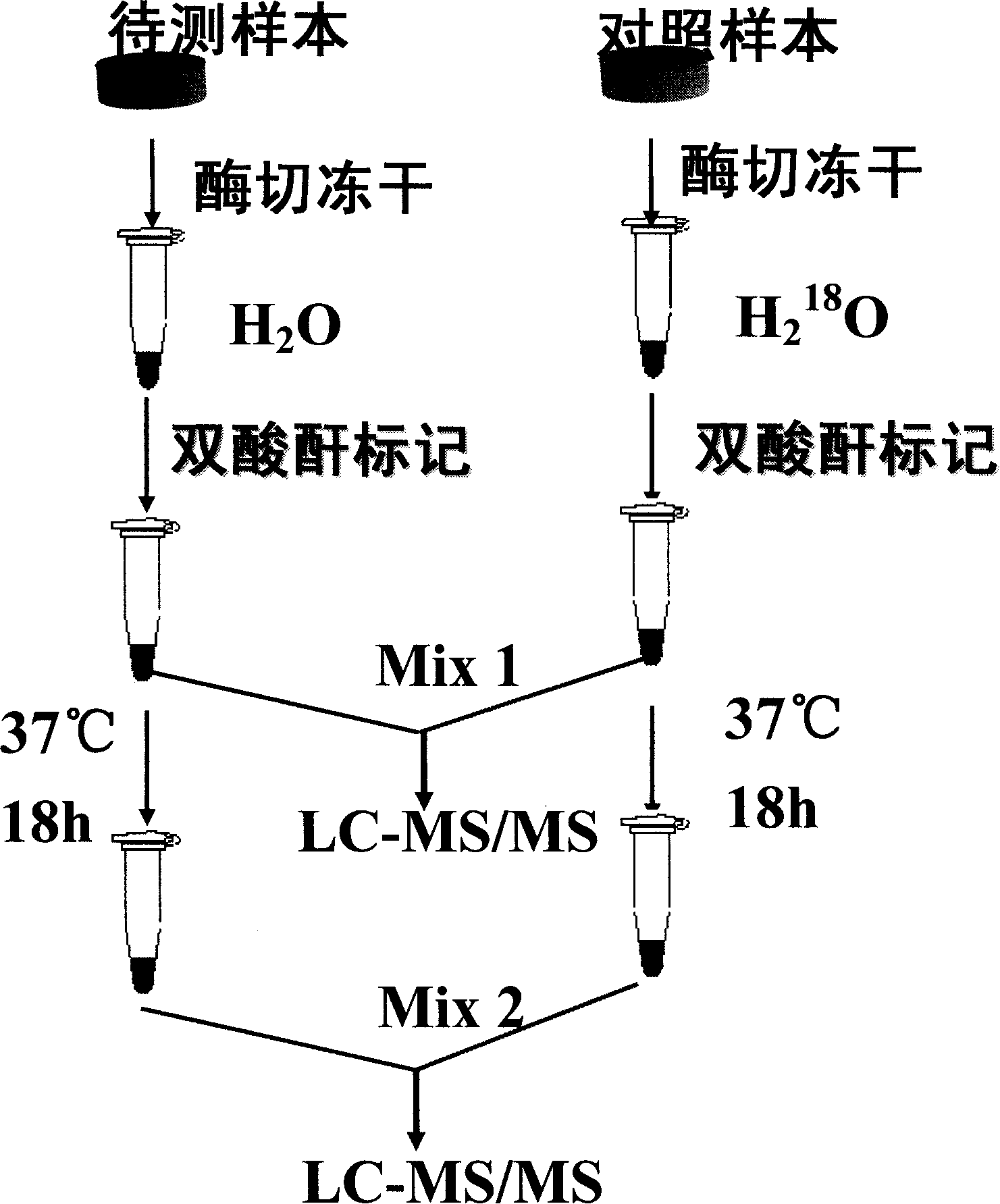
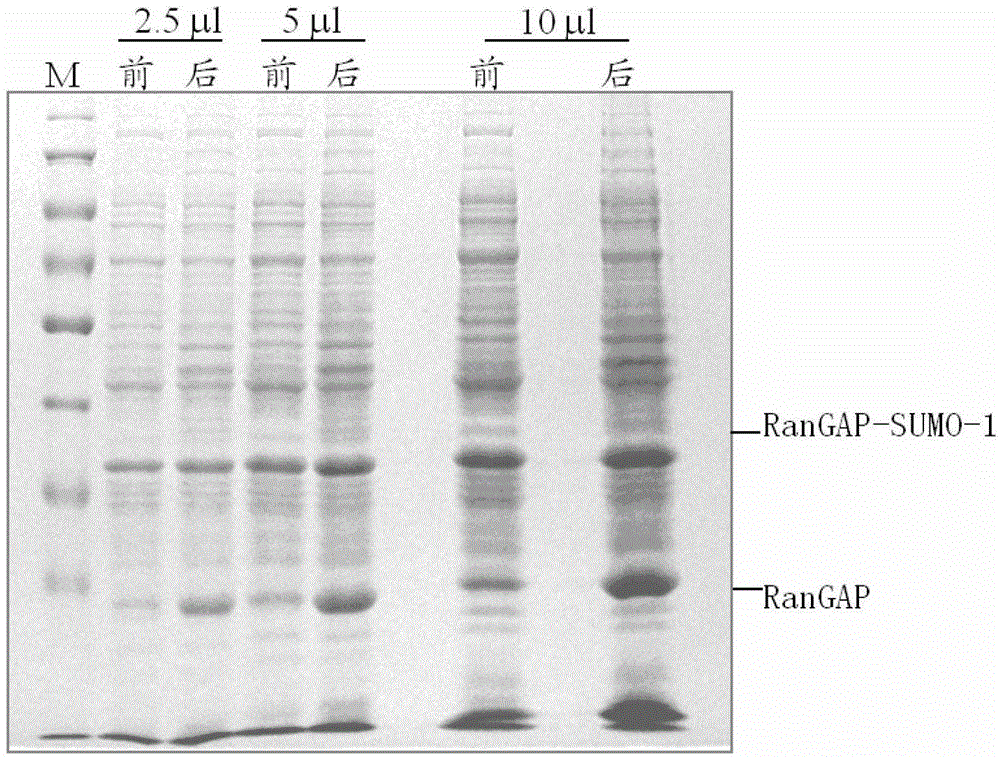
Dual quantification method and reagent kit for stable isotope 18 O marked proteome
InactiveCN101173926AFast wayEasy to useComponent separationBiological testingChemical labelingEnzyme digestion
The invention provides a new method for double quantifying the protein group marked on the basis of stable oxygen isotope <18>O, which is characterized in that: based on the fact that the N end peptide section and the C end peptide section are generally labeled, and by means of combining the <18>O chemical labeling and enzyme digestion, the quantifying strategy for two <18>O markings of the same sample can be accomplished. The method relates to the reductive alkylation and enzyme digestion of protein, dual-functional reagent modifying and <18>O marking of peptides, multi-dimensional liquid phase chromatogram separation and multistage Tandem Mass Spectrometry quantification and identification. A first mass spectrum peak area is used to quantify; and the identification of the protein is conducted through a second stage mass spectrum and by searching the database. The invention also provides a reagent box for facilitating the implementation of the method.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
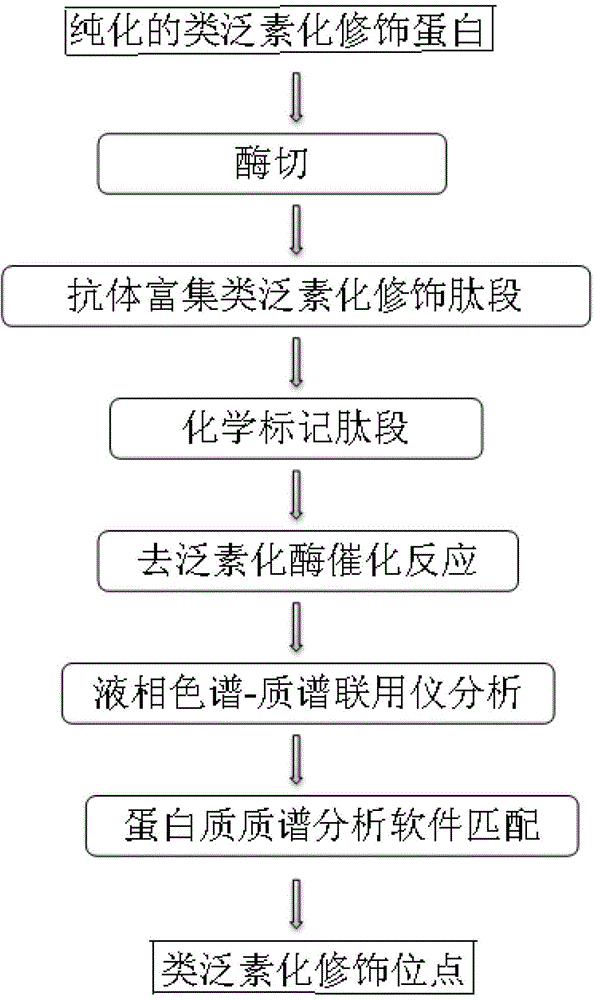
Method for identifying ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins
The invention relates to a method for identifying the ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins. The above specific enrichment labeling identification method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis of purified ubiquitin-like modification proteins, enriching the ubiquitin-like modification enzyme digestion peptide fragments through a specific ubiquitin-like antibody, protecting the non-modification lysine amino residues in the enriched peptide fragments through utilizing chemical labeling, carrying out a deubiquinaning enzyme catalysis reaction to expose modified lysine on a substrate peptide fragment sequence, analyzing the peptide segment sequences through a liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer, and matching through protein mass spectrum data analysis software to obtain the chemically modified peptide fragment sequence, wherein lysine sites containing free amino groups in the finally obtained sequence are the ubiquitin-like modification sites. Compared with common gene mutation methods for obtaining the sites at present, the method provided by the invention has an advantage that information about the ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins can be rapidly, efficiently and accurately obtained without a tedious gene mutation technology.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
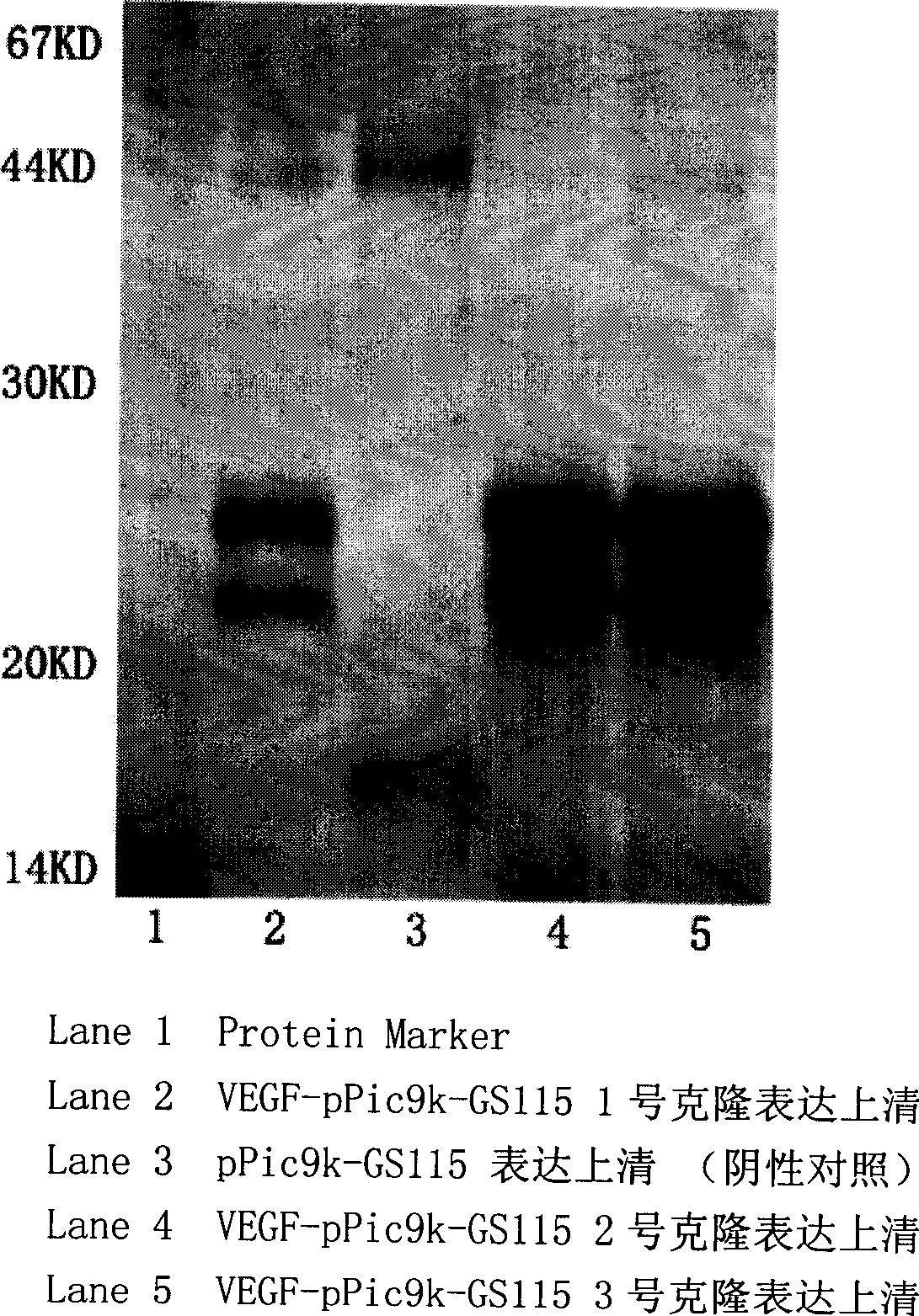
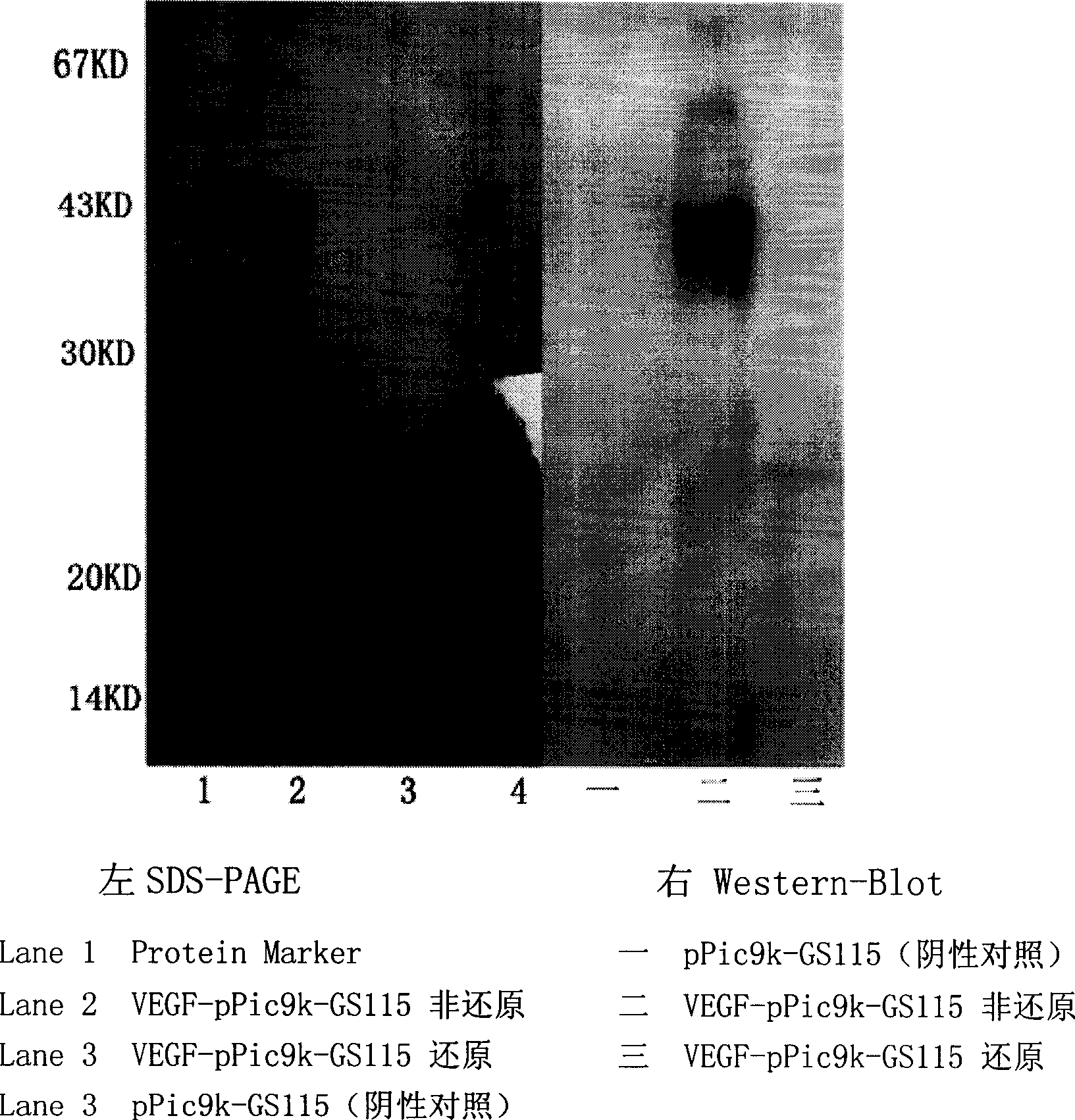
Separation and purification of recombinant human blood vessel endothelia cell growth factor, chemical labeling in vitro and use thereof
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology. A vascular endothelial cell grow factor (VEGF) plays an important function in the regeneration and hyperplasia of blood vessels; but the VEGF in the body has low content and a short half life; therefore, sufficient endogenous VEGF protein is hardly extracted to meet the ever growing experimental study and clinical requirements. The invention discloses a method for economically and conveniently preparing, extracting, purifying and recombining the VEGF protein of a human body through a recombination gene engineering and immunity affinity column method. The invention also discloses a method for carrying out the in-vitro non-radioactive chemical coupling label processing of the purified VEGF protein. The VEGF protein (including the protein having no label or having the chemical coupling label) can be widely applied to experimental study and clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:SUZHOU STAINWEI BIOTECH INC
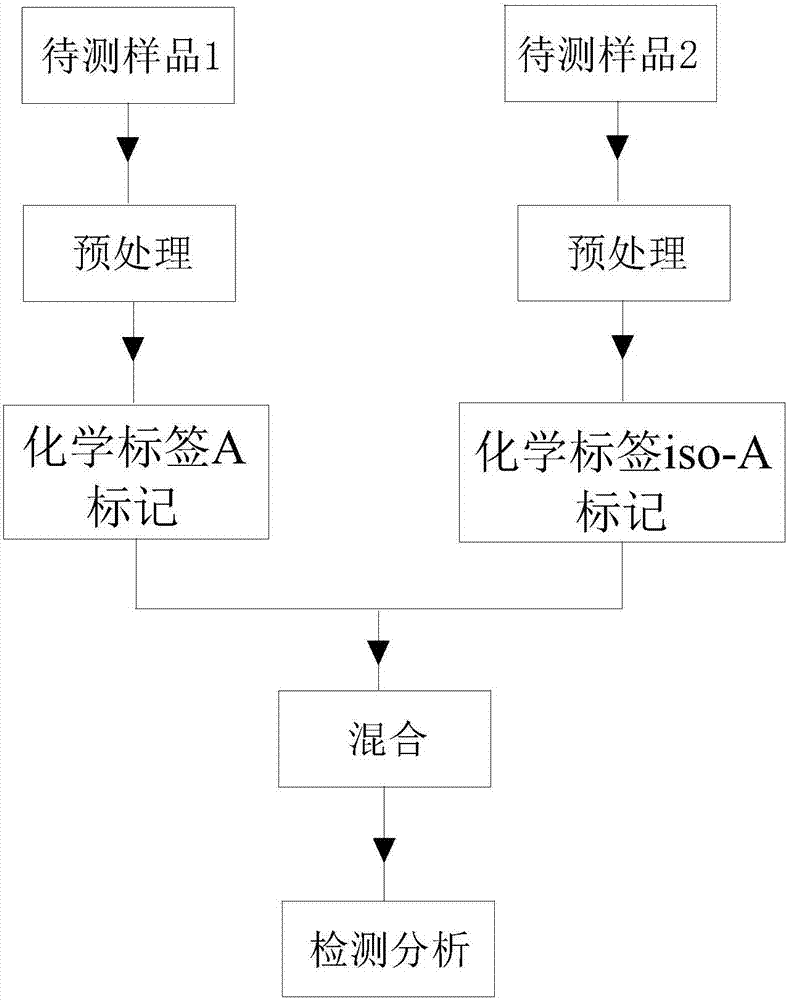
Protein isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry method based on chemical labeling technology
InactiveCN106855543ASame matrix effectSame operating errorComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical labelingInternal standard
The invention discloses a protein isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry method based on a chemical labeling technology. The method comprises (1) labeling a sample to be detected by a chemical label A to obtain a labeled sample, (2) labeling an internal standard substance with a chemical label iso-A with an isotope label to obtain a labeled internal standard substance, (3) uniformly mixing the labeled sample and the labeled internal standard substance according to a preset ratio to obtain an initial sample, (4) pretreating the initial sample to obtain a fed sample, and (5) carrying out mass spectrometry on the fed sample. The sample and internal standard substance are respectively labeled, then are mixed, then added into a reaction system and then are treated so that the sample and internal standard substance are subjected to the same matrix effect and have the same operation error in the same system and thus the error can be corrected.
Owner:GREENTOWN AGRI TESTING TECH CO LTD
Mass spectrum detection method for interaction between active protein and small molecule
ActiveCN108508125ARealize detectionAchieve confirmationComponent separationBiological testingChemical labelingProtein target
The invention provides a mass spectrum detection method for interaction between an active protein and a small molecule. According to the method, in-vivo covalent chemical labeling is performed on a protein while the active state is maintained; and the site and the intensity of the interaction between a small molecule and the protein are judged through the difference in the labeling efficiency before and after the interaction between the specific amino acid position on the protein and the small molecule. According to the present invention, with the mass spectrum detection method, the protein inhibitor candidate small molecule can be subjected to high-throughput screening, and the potential protein target of the specific small molecule can be subjected to large-scale identification analysis;and through the large-scale identification analysis of the Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)-small molecule interaction and the ATP-binding protein in the complex system biological system, the method has accuracy and high efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chemical vapor deposition during additive manufacturing
ActiveCN109109314AAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusChemical labelingEnvironmental engineering
The present disclosure generally relates to methods and apparatuses for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) during additive manufacturing (AM) processes. Such methods and apparatuses can be used to embedchemical signatures into manufactured objects, and such embedded chemical signatures may find use in anti-counterfeiting operations and in manufacture of objects with multiple materials.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
5-formylcytosine specific chemical labeling method and related applications
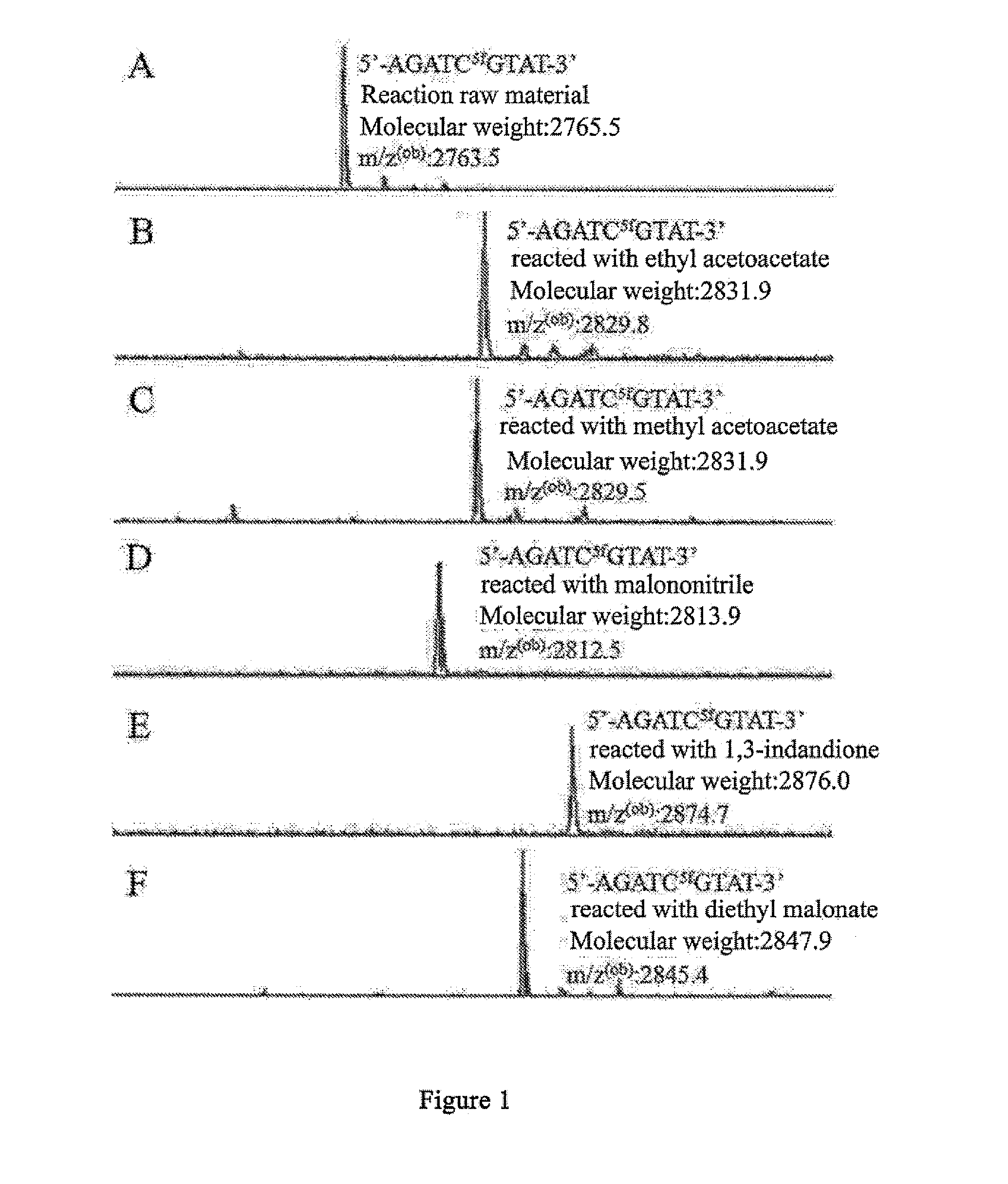
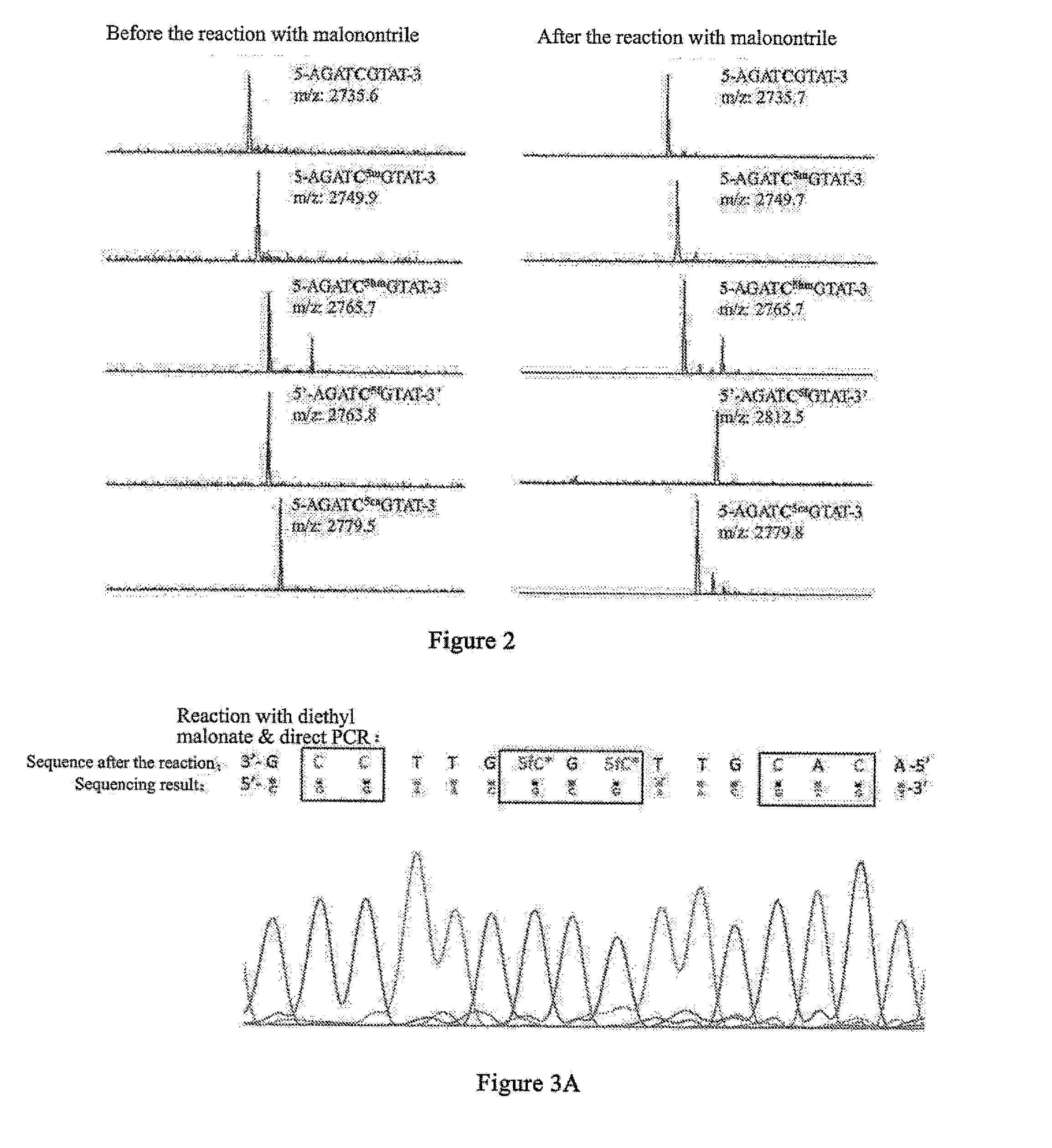
ActiveUS20160362438A1Achieve conversionHigh selectivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical labelingCytosine
The present invention relates to a 5-formylcytosine specific chemical labeling method and related applications in aspects such as sequencing, detection, imaging, and diagnosis. In the method, a condensation reaction occurs between an active methylene group in an active methylene compound containing a side-chain reactive group and an aldehyde group in 5-formylcytosine or a 1-substituted derivative of 5-formylcytosine, and at the same time an intramolecular reaction occurs between the side-chain reactive group of the active methylene compound and a 4-amino group of cytosine to implement ring closing. By means of the 5-formylcytosine specific chemical labeling method and related compounds of the present invention, detection of the content of 5-formylcytosine in nucleic acid molecules, and specific concentration of 5-formylcytosine-containing nucleic acid samples, and analysis of sequence distribution information of 5-formylcytosine and / or single-base resolution sequence information in nucleic acid molecules and the like may be implemented. The present invention provides various effective research methods in the research fields of epigenetics and nucleic acid biochemistry.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
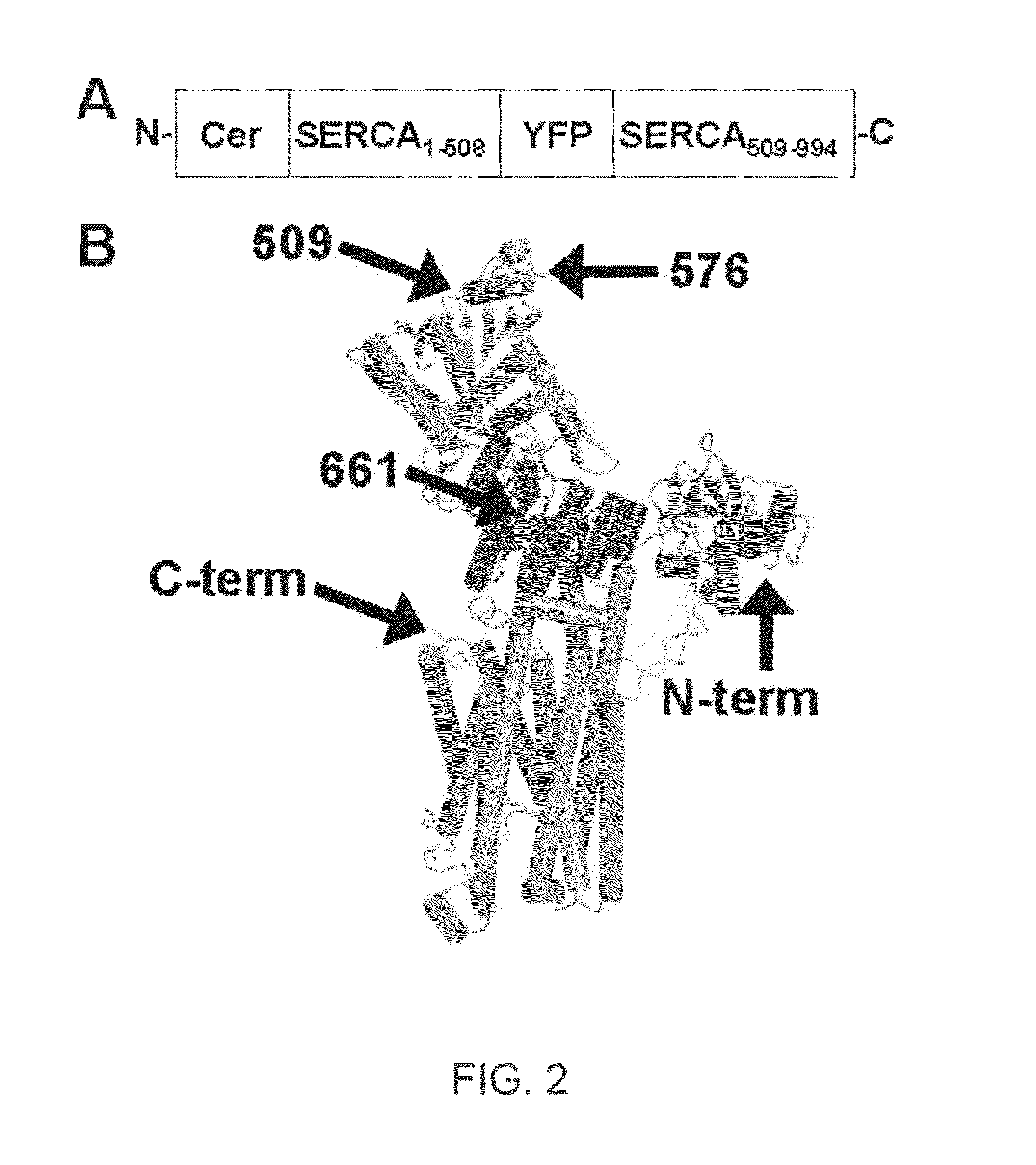
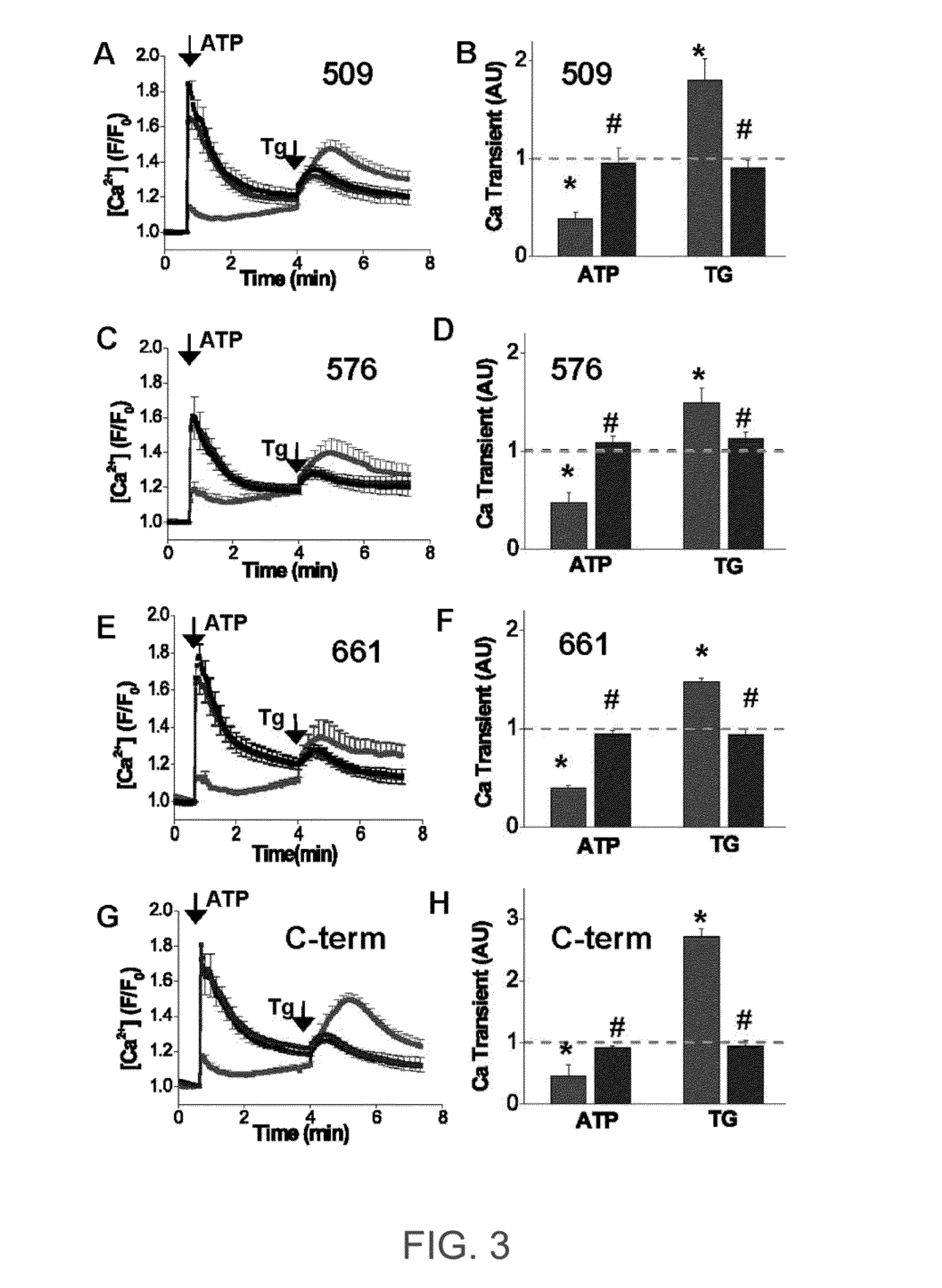
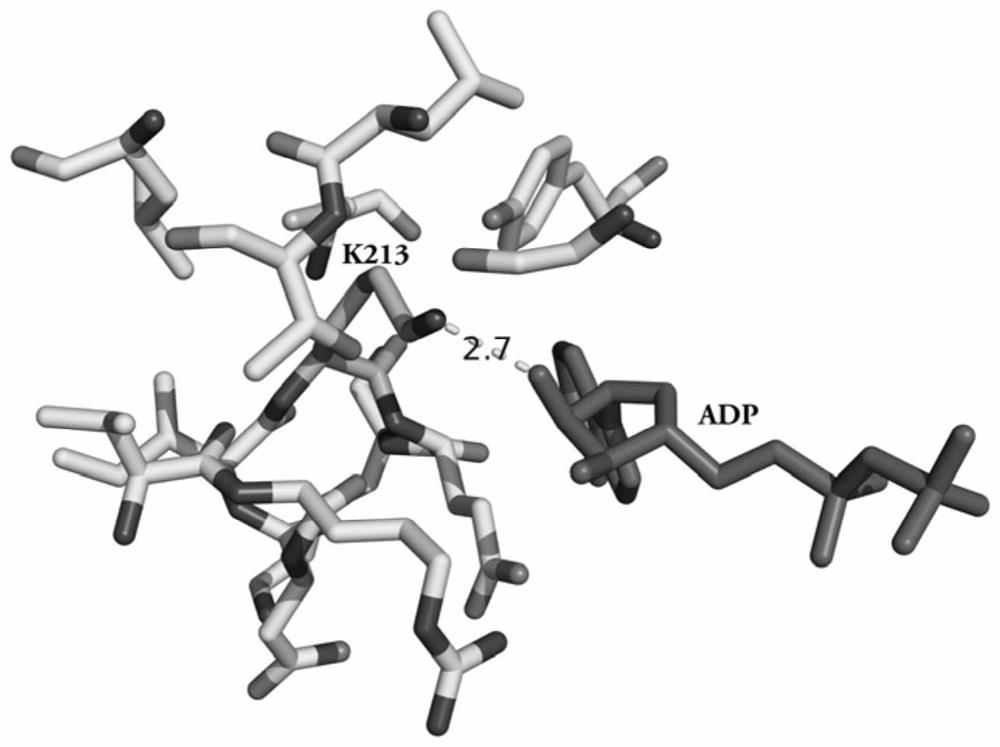
ENGINEERED PROTEIN: "2-COLOR SERCA", AN ION-MOTIVE ATPase FUSED TO CERULEAN AND YELLOW FLUORESCENT PROTEIN
A method and engineered proteins for use therewith suitable for studying SERCA that are capable of being used in vivo and do not require protein purification or chemical labeling of SERCA, or reconstitution into artificial membranes. The engineered protein for calcium handling within human cells includes a two-color SERCA construct having three component proteins fused together. The three component proteins include a blue fluorescent protein (cerulean), SERCA2a and a yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), or a red fluorescent protein (tagRFP acceptor), SERCA and a green fluorescent protein (GFP). The method of determining SERCA activity for optimization of cardiac function includes resolving structure changes of the two-color SERCA construct. The two-color SERCA constructs are catalytically active and able to pump calcium following the step of resolving structure changes.
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO
Application of general fluorescence labeling probe on PCR-LDR gene mononucleotide polymorphism chip
InactiveCN101358231ALow costShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical labelingFluorescence
The invention discloses an application of a general fluorescence labeling probe on a PCR-LDR gene SNP single nucleotide polymorphism chip. The application of the invention comprises the steps which are probe design, PCR product preparation, LDR product preparation and result detection, etc. The probe of the invention comprises a labeling probe and a testing probe, because the labeling probe is modified and the chemical labeling does not need to be directly carried out, the technical cost of the PCR-LDR combined chips can be reduced and the synthesis time of the probes can be saved, and the testing results reach the accuracy and the precision tested by the direct labeling technology.
Owner:上海翼和应用生物技术有限公司
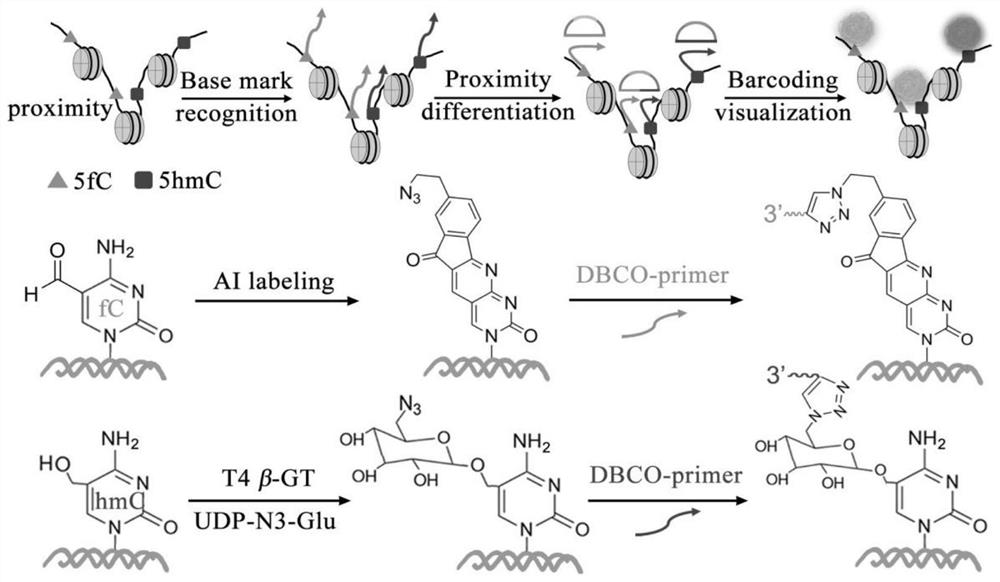
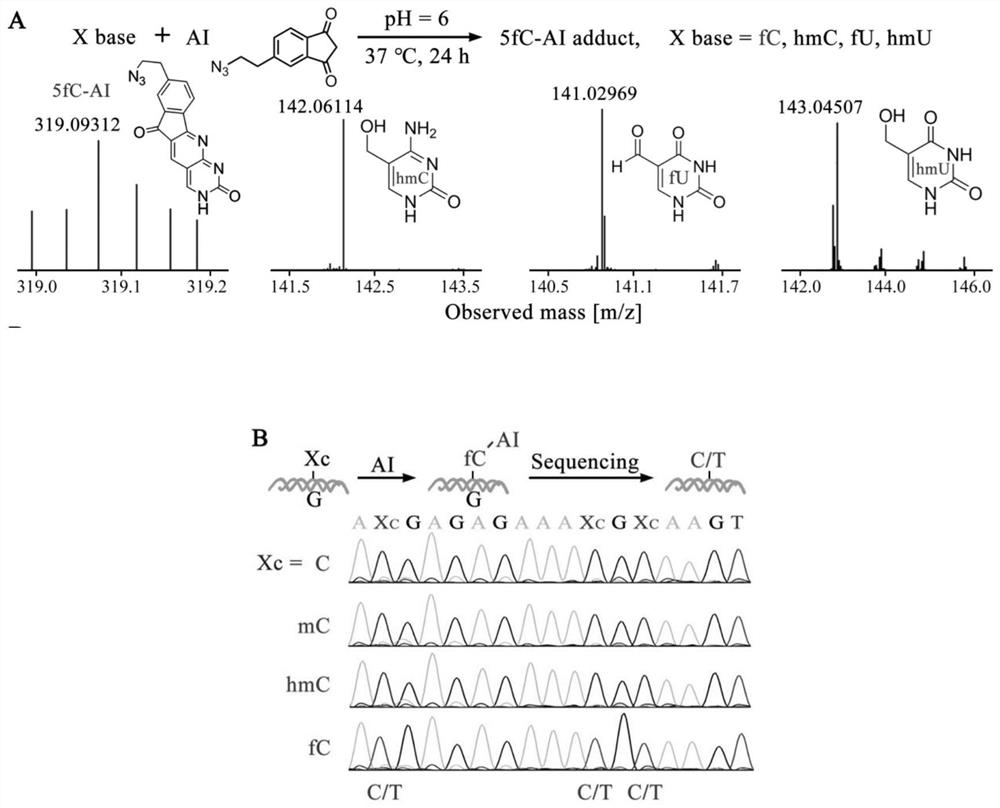
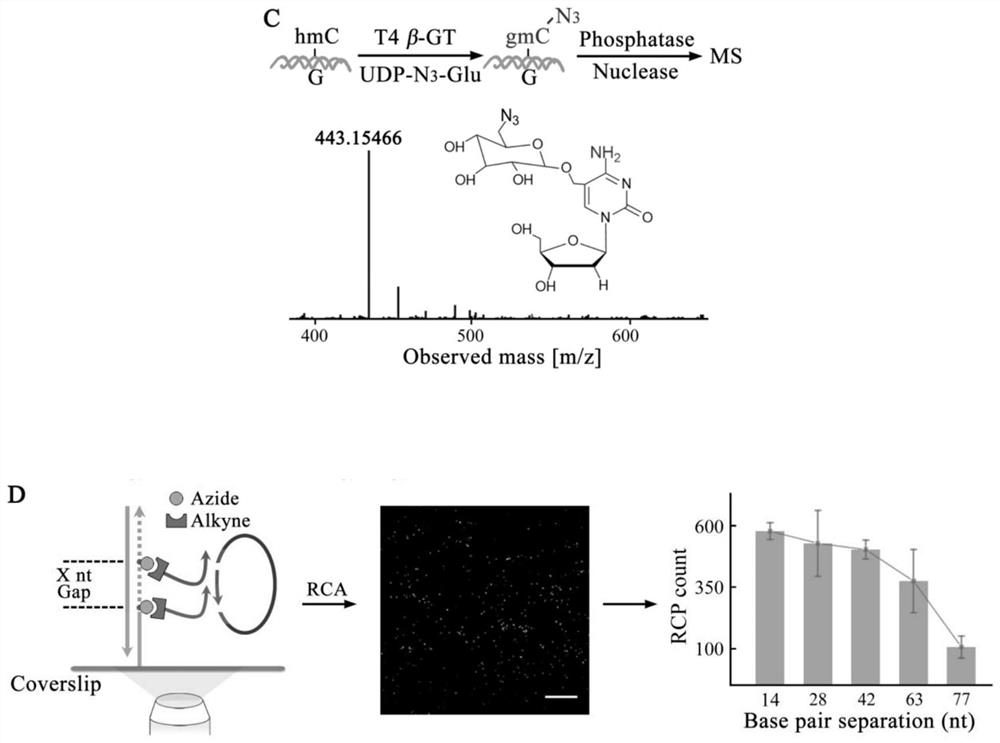
Visual distinguishing method for single-cell DNA epigenetic modification space positioning and adjacent distribution
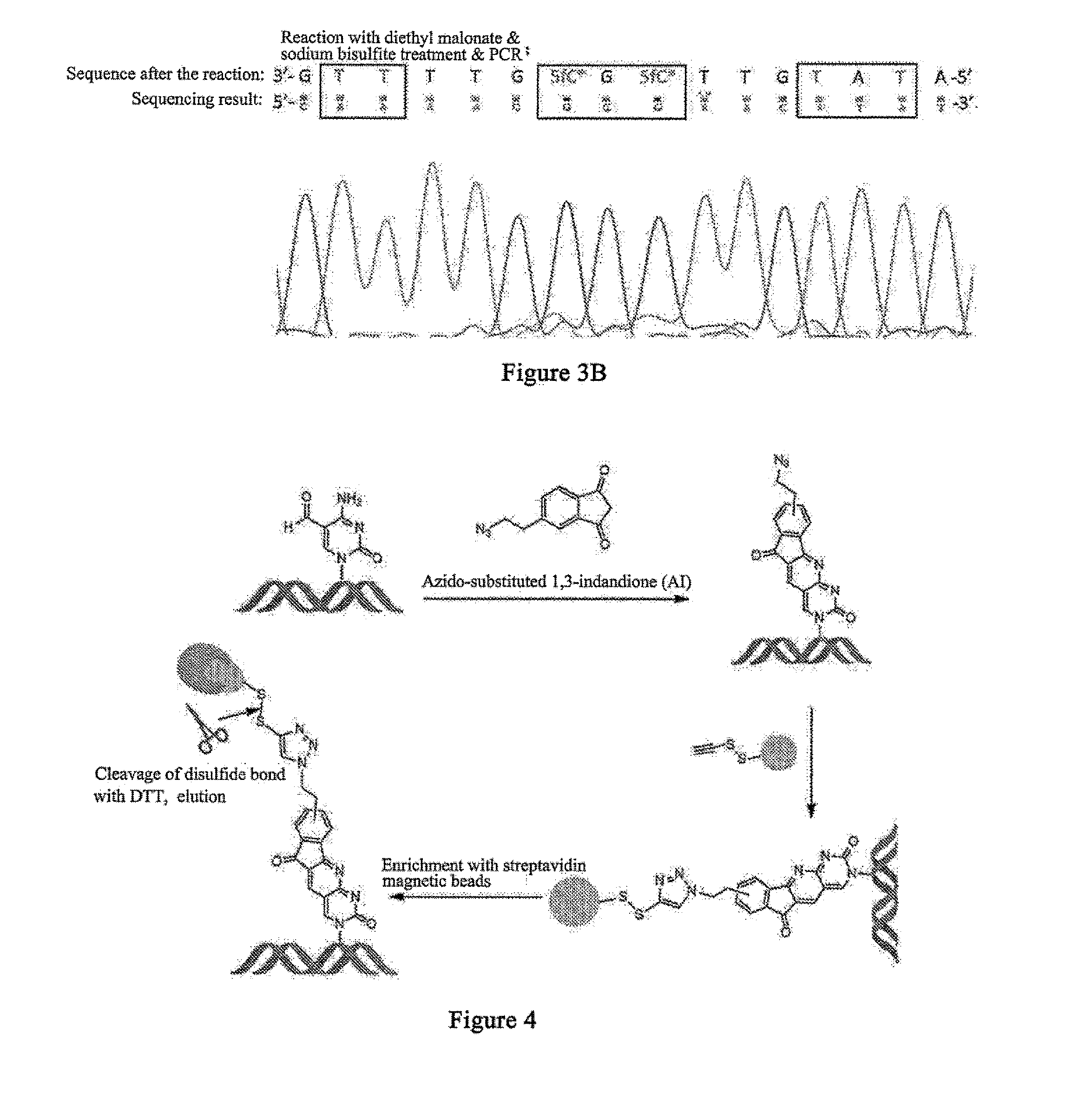
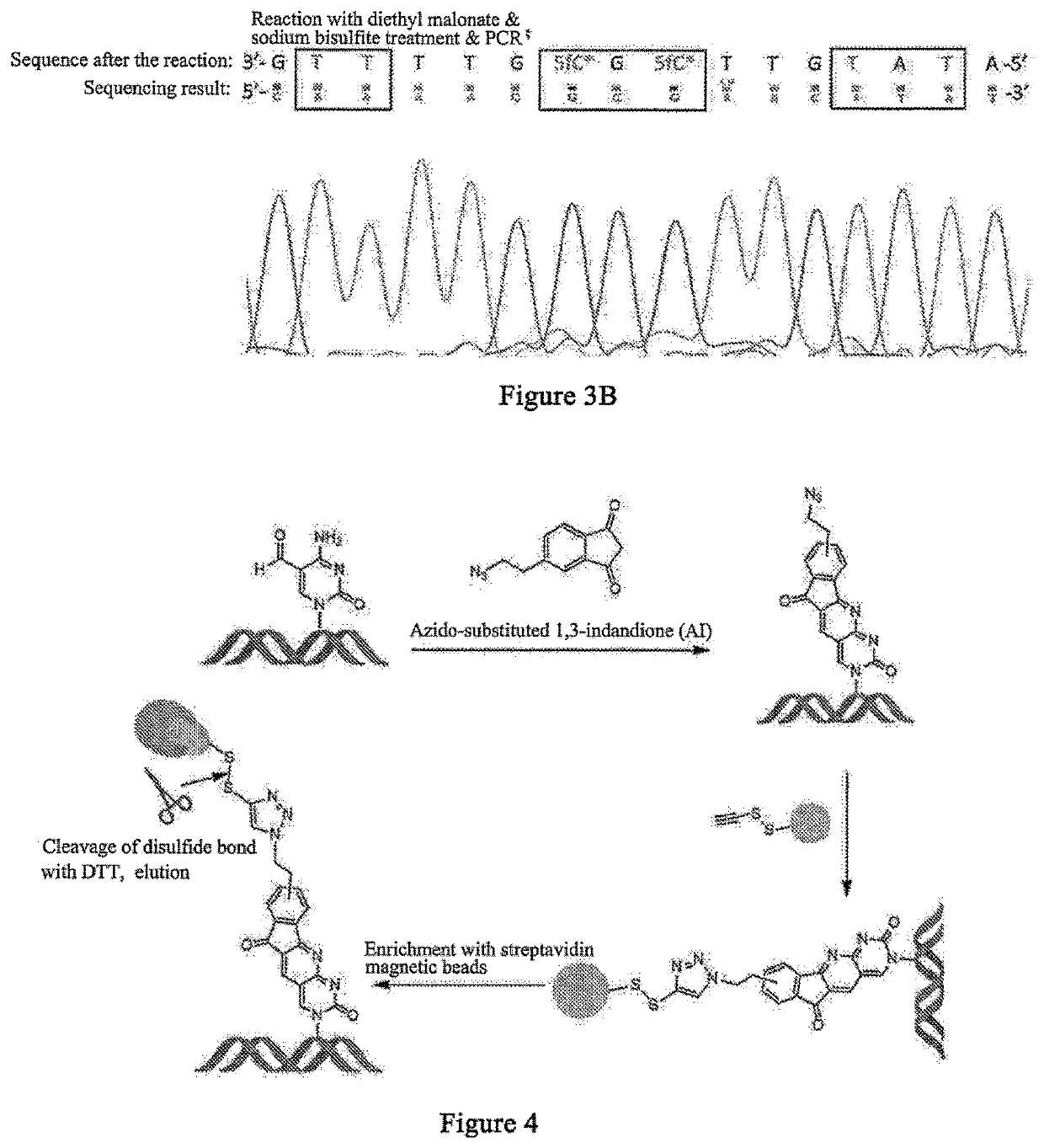
ActiveCN111850101APromote in-depth researchStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical labelingCytosine
The invention discloses a visual distinguishing method for single-cell DNA epigenetic modification space positioning and adjacent distribution, belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and particularly relates to chemical labeling of an azide (N3) functional group on 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) through an azide derivative probe 1, 3-indadione (AI), and enzyme-mediated labeling of the azide (N3) functional group on 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) through T4 phage beta-glucosyltransferase (beta-GT). The paired primers close to the sites jointly achieve in-situ close connection on a ring template with a notch, the unpaired 5-fC and 5-hmC modification sites are left, the primers are released through strand displacement reaction, and then the corresponding specific ring template is hybridized;nucleic acid amplification and fluorescence probe hybridization are combined to realize single-cell DNA epigenetic modification space positioning and adjacently distributed single-molecule visual distinguishing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Bioluminescent detection probe based on transcriptional activator like effector factor and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN108796040AAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical labelingMagnetic bead
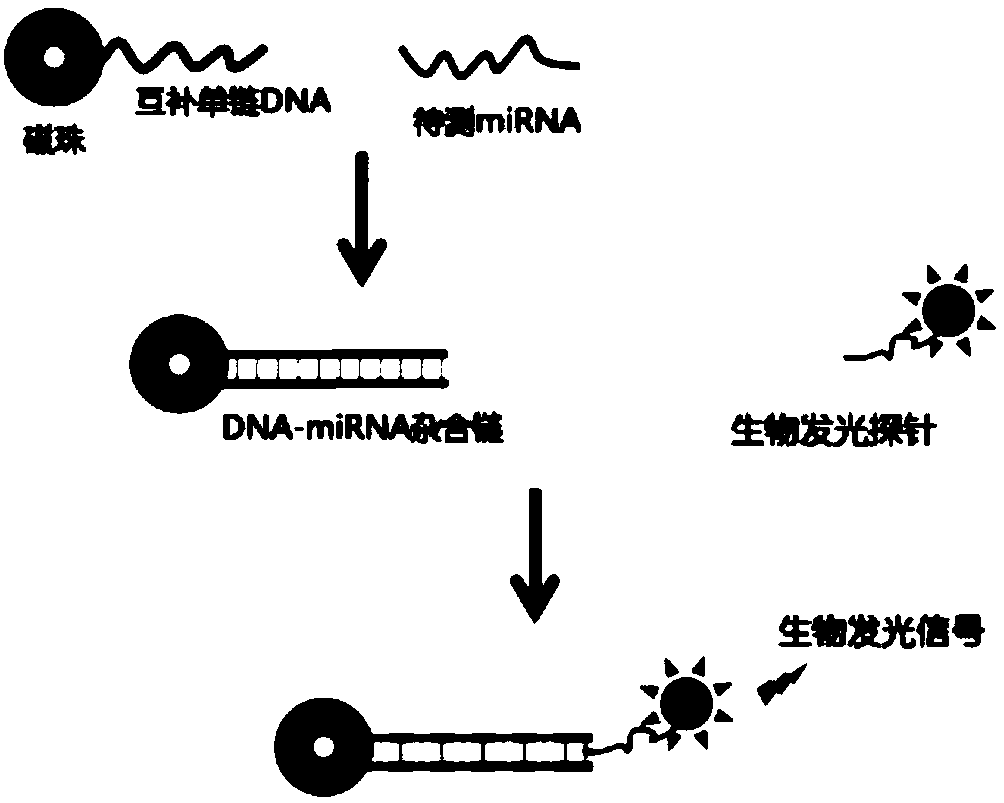
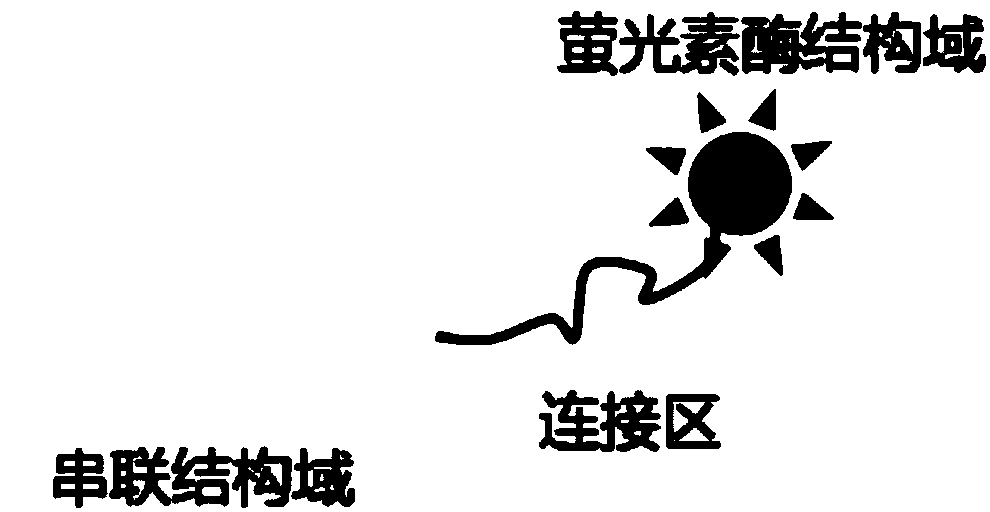
The invention provides a bioluminescent detection probe based on a transcriptional activator like effector. The probe can achieve bioluminescence detection of microRNA (miRNA) without chemical labeling. The probe is a monomeric protein, and includes the following three parts: 1) a transcriptional activator like effector domain capable of specifically recognizing a DNA-miRNA hybrid chain; 2) a luciferase domain with bioluminescence; 3) a connecting region of the above two domains. The probe uses a single-stranded DNA coupled to the surface of a magnetic bead to hybridize with the miRNA to be tested, and a DNA-miRNA hybrid chain produced by hybridization is specifically recognized by the bioluminescent probe formed by the transcriptional activator like effector and the luciferase domain to achieve high sensitivity detection of the miRNA. The probe has the advantages of being low in cost, intuitive in result and convenient to use.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
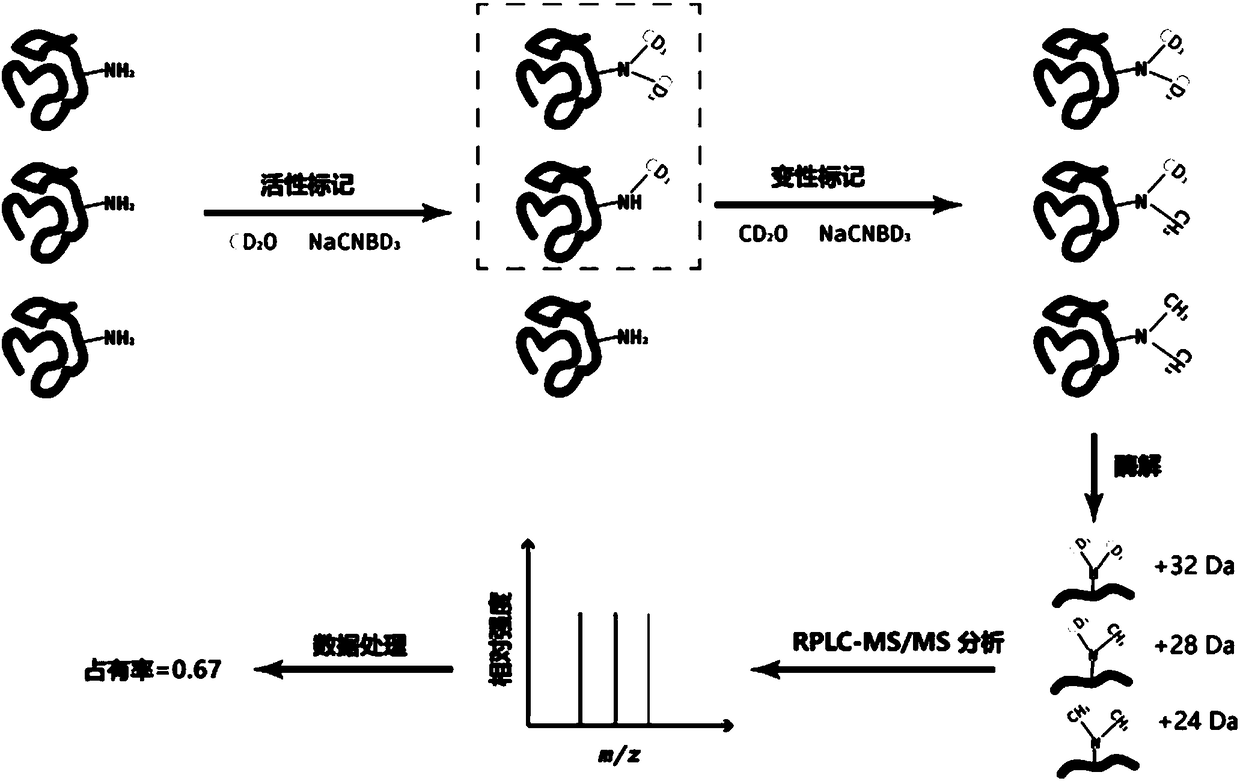
Method for detecting conformational changes of proteins by mass spectrometry technology
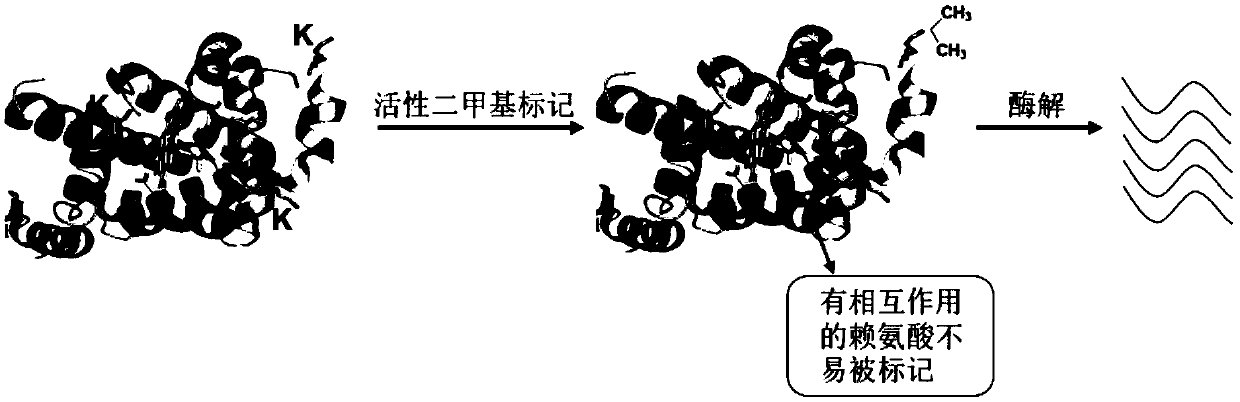
ActiveCN107219292AConformation realSimple methodMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSolubilityChemical labeling
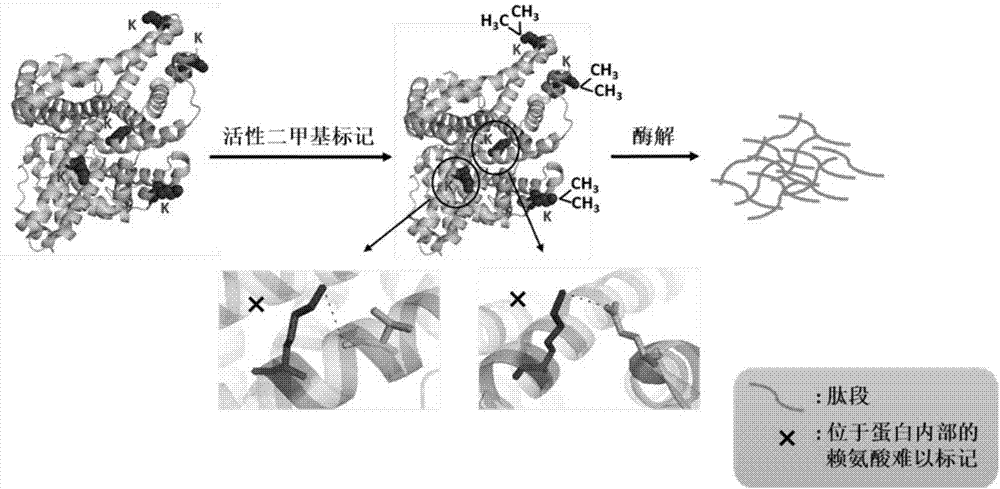
The invention belongs to the field of researches of microcosmic conformation of proteins by utilizing a proteomic analysis technology, relates to a method for detecting conformational changes of the proteins by a mass spectrometry technology and in particular relates to a method for detecting the conformational changes of the proteins by combining active covalent chemical labeling and the mass-spectrometry technology. Lysine residues are subjected to the active chemical labeling from the whole level of the proteins; then protein denaturation and enzymolysis are carried out and then a mass spectrometry is used for detecting; the labeling efficiency of the lysine residues is calculated through an identification result of the mass spectrometry. The method is rapid and simple, is stable and efficient and can be used for inspecting the fine conformational changes of protein structures; in a labeling process, the activity of the protein keeps unchanged and the labeling process is not limited by the size, solubility and purity of the proteins and the like; the conformation of the proteins under a physiological activity state can be reflected more really.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
5-formylcytosine specific chemical labeling method and related applications
ActiveUS10519184B2High selectivityGood fluorescence propertiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical labelingSide chain
The present invention relates to a 5-formylcytosine specific chemical labeling method and related applications in aspects such as sequencing, detection, imaging, and diagnosis. In the method, a condensation reaction occurs between an active methylene group in an active methylene compound containing a side-chain reactive group and an aldehyde group in 5-formylcytosine or a 1-substituted derivative of 5-formylcytosine, and at the same time an intramolecular reaction occurs between the side-chain reactive group of the active methylene compound and a 4-amino group of cytosine to implement ring closing. By means of the 5-formylcytosine specific chemical labeling method and related compounds of the present invention, detection of the content of 5-formylcytosine in nucleic acid molecules, and specific concentration of 5-formylcytosine-containing nucleic acid samples, and analysis of sequence distribution information of 5-formylcytosine and / or single-base resolution sequence information in nucleic acid molecules and the like may be implemented. The present invention provides various effective research methods in the research fields of epigenetics and nucleic acid biochemistry.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Fluorescence labeling biological material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111138682AAvoid the disadvantage of easy diffusion out of the systemLuminescent compositionsChemical labelingCarboxyl radical
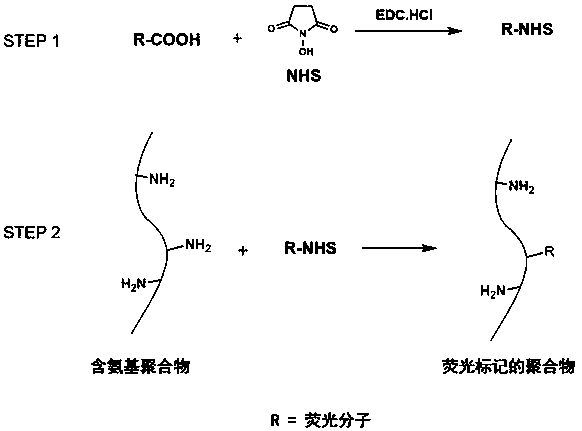
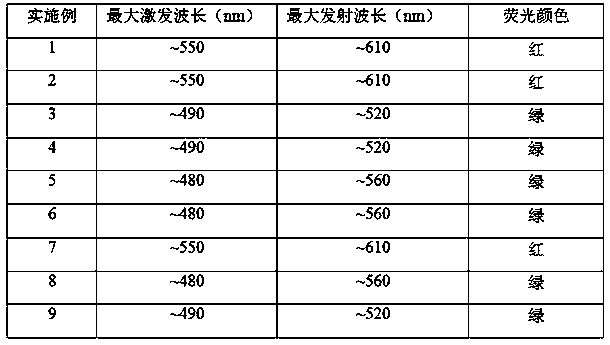
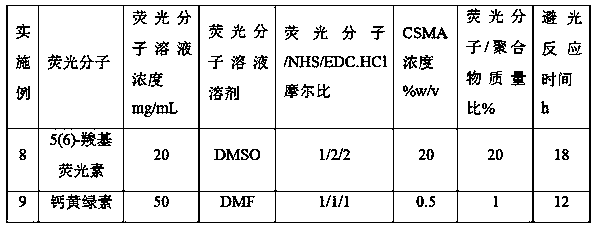
The invention discloses a fluorescence labeling biological material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) activating fluorescent molecules; (2) carrying out areaction on a polymer and activated fluorescent molecules; (3) dialyzing the solution after the reaction in the step (2) with deionized water, and freeze-drying to obtain a fluorescence labeling biological material, wherein the polymer is a polyamino acid-based polymer or a chitosan-based polymer. According to the invention, the carboxyl on a fluorescent molecule is activated into active ester, then the active ester and the amino on a biopolymer are subjected to an amidation reaction, and the fluorescent molecule is chemically coupled to the biopolymer, so that the fluorescence labeling material has different fluorescence colors due to different labeled fluorescence molecules, and the chemical labeling method avoids the defect that fluorescent molecules or particles thereof are easy to diffuse out of a system in physical mixing or electrostatic adsorption and other methods; and the fluorescence labeling biological material has a wide application prospect in the research fields of in-vitro and in-vivo imaging, tracing, material degradation, biosensing, 3D printing and the like.
Owner:苏州永沁泉智能设备有限公司
Chemical labeling and LC-MS combined method, and applications thereof in nucleotide analysis
InactiveCN106950326AReduce matrix interferenceAvoid pollutionComponent separationChemical labelingReversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography
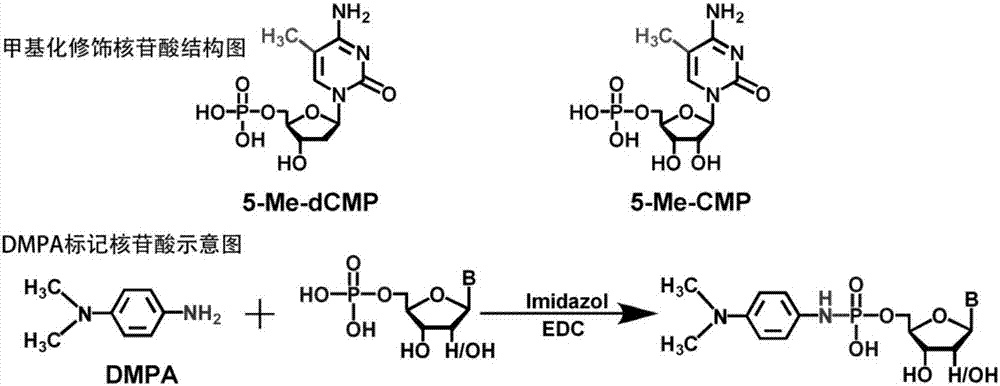
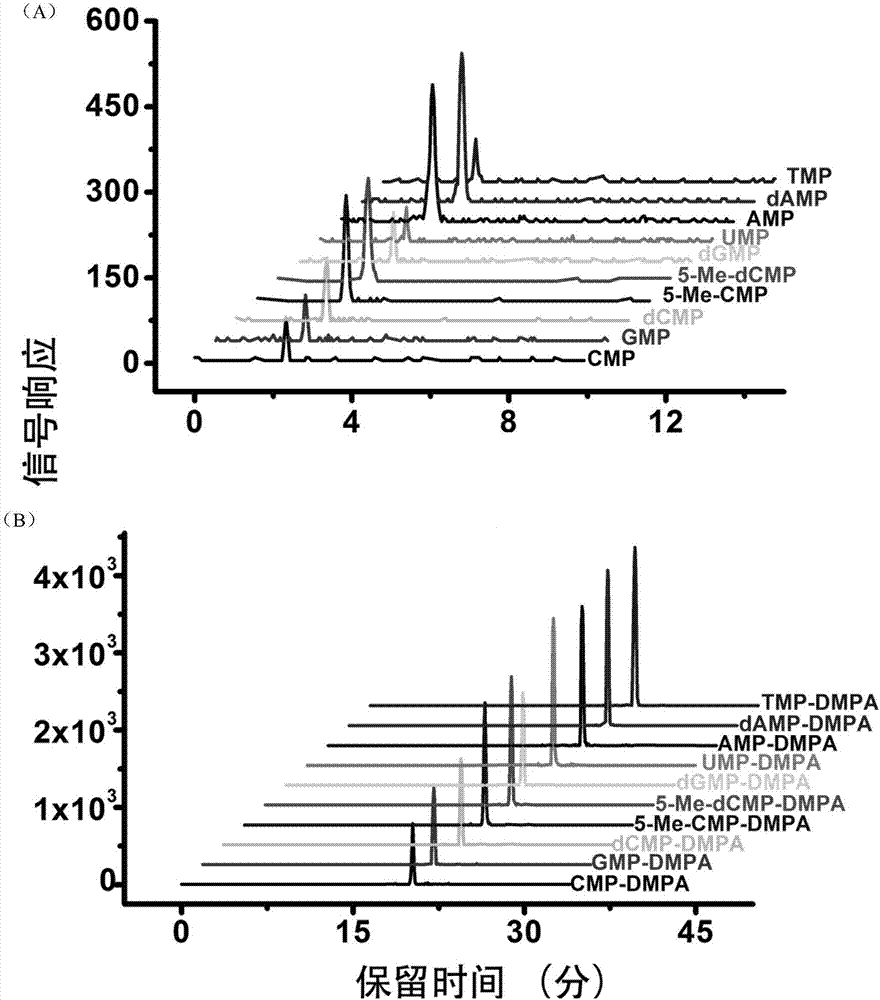
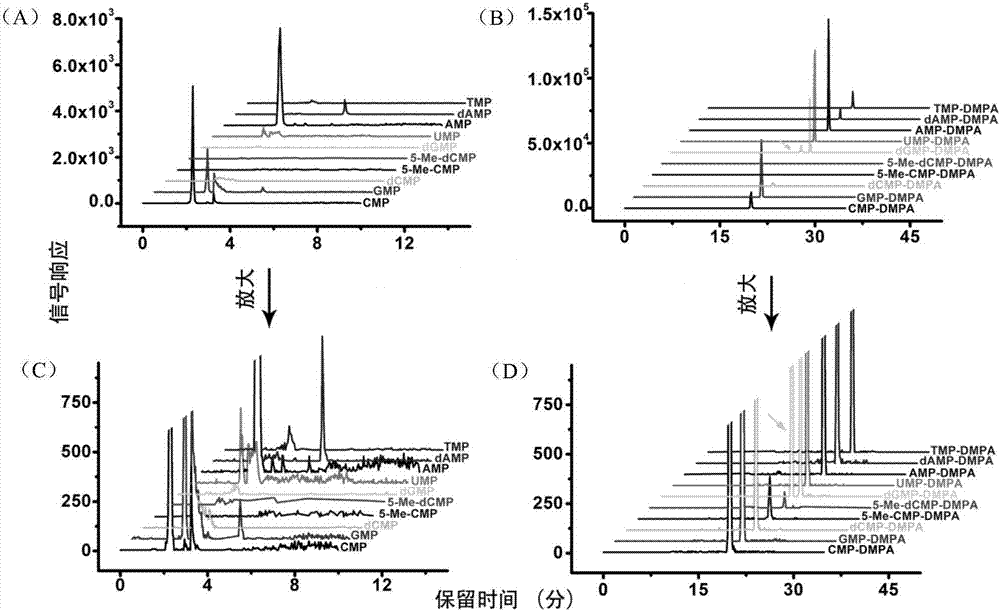
The invention discloses a chemical labeling and LC-MS combined method, and applications thereof in nucleotide analysis. According to the chemical labeling and LC-MS combined method, N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine is used for chemical labeling of 10 monophosphate nucleotides containing two methylation modified nucleotides, so that the retention behavior of the modified nucleotides in reversed phase liquid chromatography is improved obviously, and detection sensitivity of the modified nucleotides in mass spectrometric detection is increased. The chemical labeling and LC-MS combined method is high in sensitivity and selectivity; liquid-liquid extraction can be adopted to remove excess labeling reagent DMPA effectively, Strata X solid phase extraction columns can be used for removing excess activator EDC, quantitative determination of extremely-low-abundance methylation modified cytidylate in living bodies can be realized, LC separation sensitivity and ESI-MS detection sensitivity of nucleotides can be improved obviously, and signal responsiveness is increased by 1 to 2 magnitude orders.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
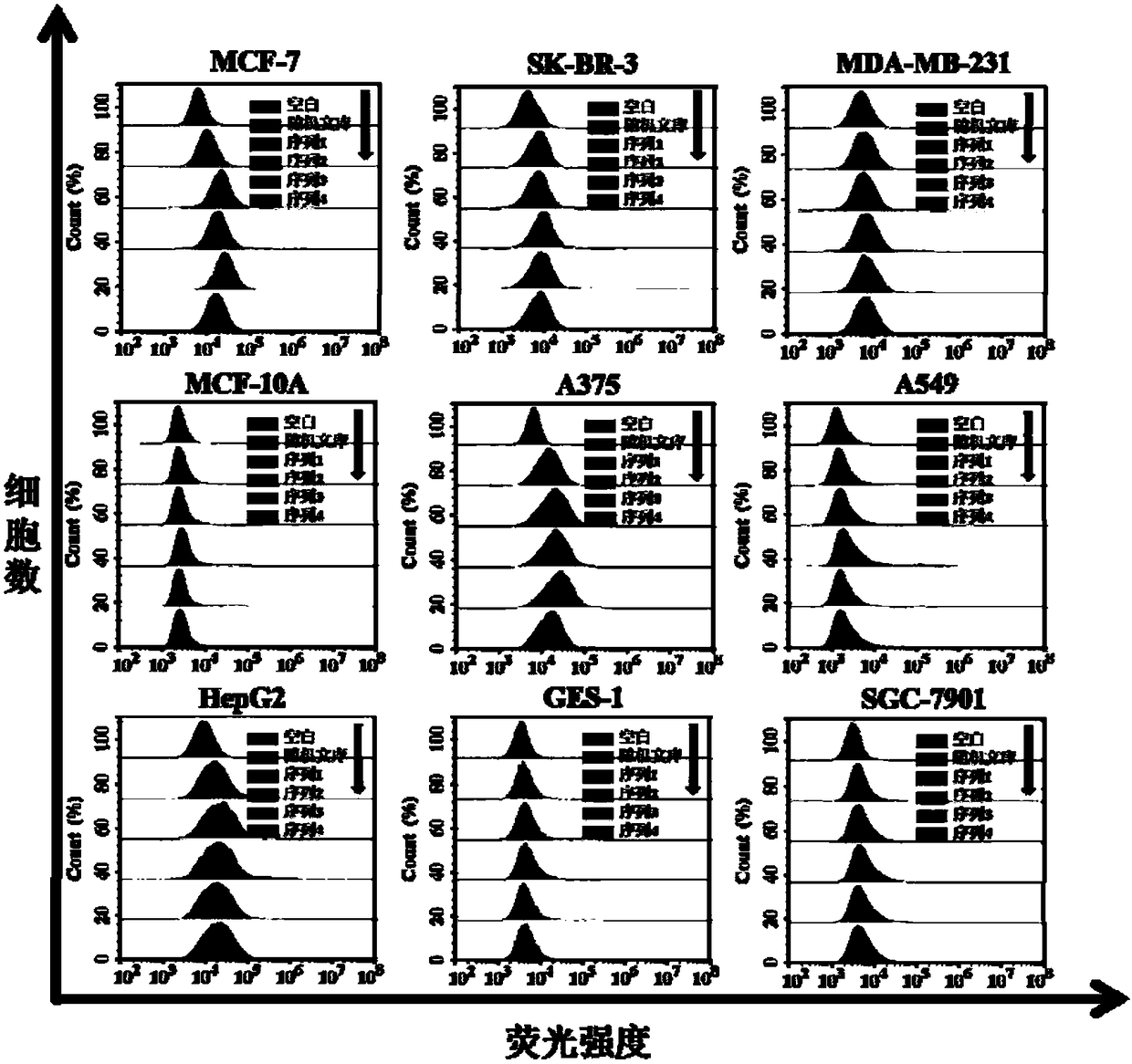
DNA aptamer specifically combined with human breast cancer cells MCF-7 and application thereof
ActiveCN108265055AWith the requirement of rapid diagnosisHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical labelingA-DNA
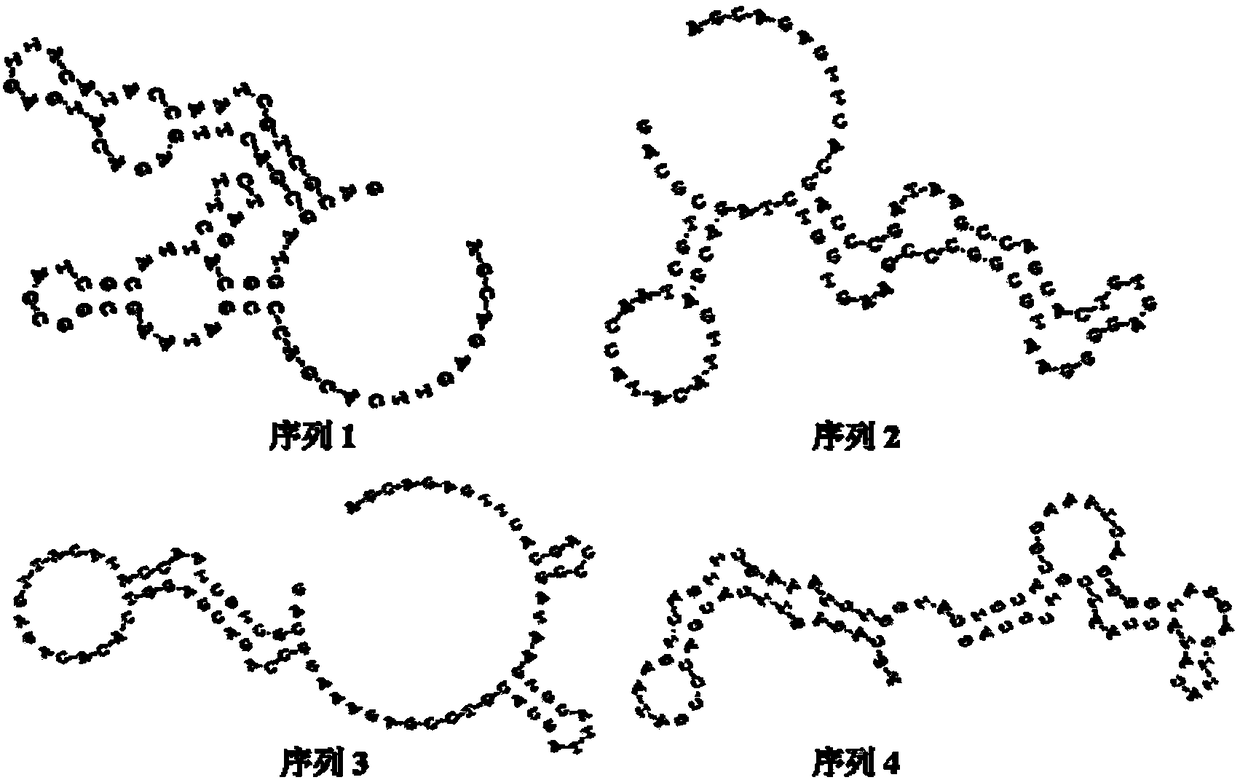
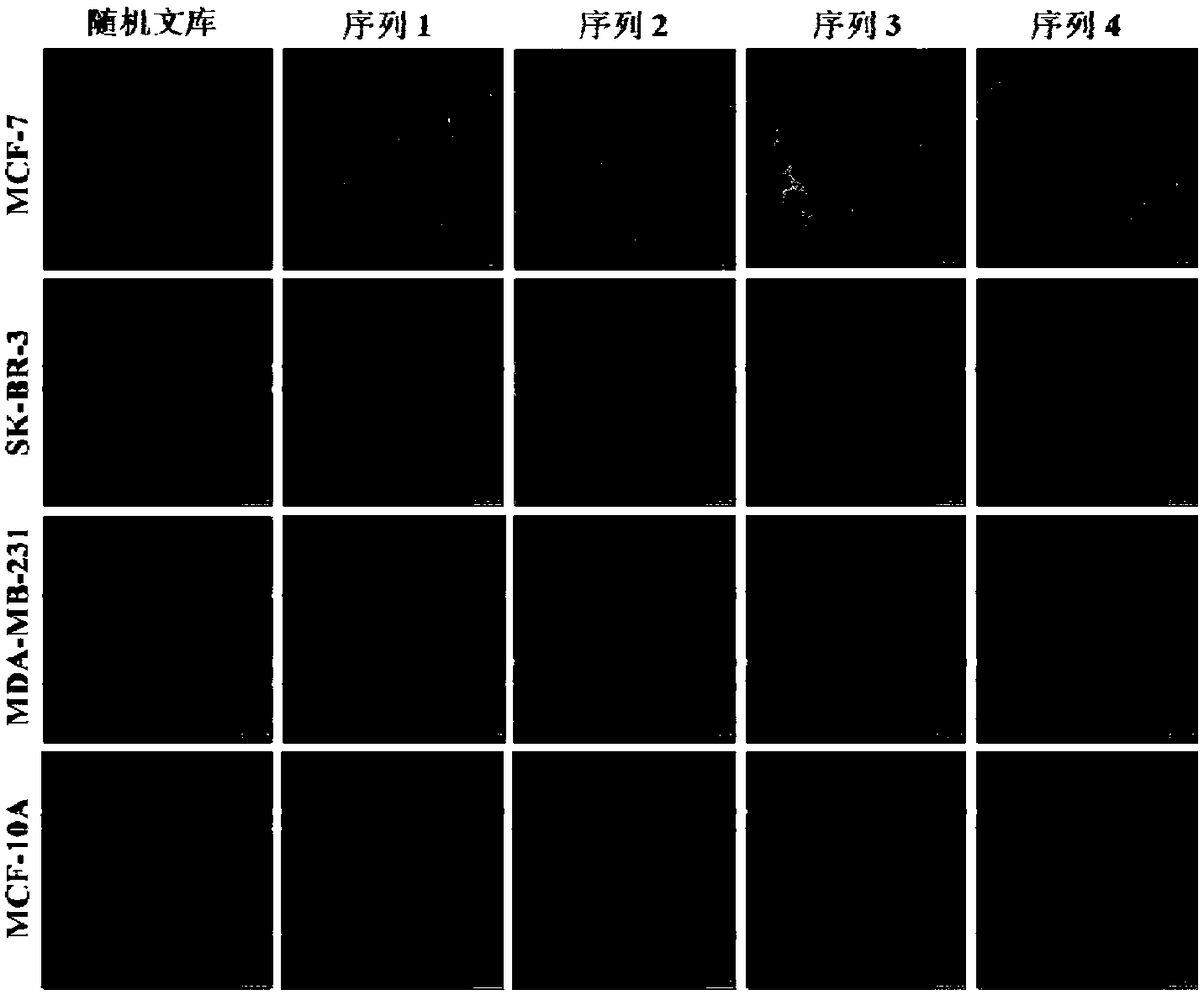
The invention discloses a DNA aptamer specifically combined with human breast cancer cells MCF-7. The nucleotide sequence of the DNA aptamer is shown by any one or several sequences in SEQ ID NO:1 toSEQ ID NO:4, or is obtained through chemical modification, chemical labeling or basic group change on any one sequence in SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:4. The invention also discloses application of the DNA aptamer or the nucleotide sequence to diagnosis reagents, molecular imaging probes or target media. The invention also relates to a human breast cancer detection and diagnosis kit, which has wide application prospects in breast cancer detection, diagnosis and treatment. The DNA aptamer related by the invention has the advantages of high affinity, high specificity, small molecular weight, high stability, synthesis simplicity, low cost, simplicity in modification, no immunogenicity and the like, and can meet the requirement of human breast cancer fast diagnosis at present.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus for measurement of the effect of test compounds on signal transduction at the level of biological receptors
InactiveUS20020137055A1The process is simple and fastQuick and easy determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWaveguideHormonal activity
A method and apparatus for measuring binding between a plurality of molecules of a biological receptor protein and a plurality of molecules of a type which binds to said biological receptor is presented. Apparatus utilizes a sensor possessing a waveguide to which have been attached in close proximity to its surface, features resembling molecules having binding affinity for said biological receptor. Light is injected into said waveguide so as to produce an evanescent field at its surface. Molecules of receptor protein are tagged with a tag belonging to that class of chemicals which alters a characteristic of light, when said light passes through said chemical tag. Apparatus utilizes a rapid means of monitoring the change in optical signal coming from the waveguide as binding proceeds between tagged receptor protein and the binding molecular feature of the waveguide. This allows direct measurement of binding and dissociation rates between the receptor and the binding feature of the waveguide. By using a waveguide having a feature resembling a ligand for the receptor, the potential hormonal activity of a test substance may be evaluated from its ability to compete with the waveguide for binding with the receptor. The effect of a test compound on binding of receptor protein to a subsequent element in a hormonal signal transduction mechanism is evaluated by measuring the impact of the test compound on binding between receptor protein and a feature resembling said next element of the signal transduction mechanism. Methods are provided whereby such data may be used to compute affinity constants, binding activity, complex affinity constants resulting from cooperativity, and kinetic parameters for the receptor and test ligand and for the receptor and the next element of the signal transduction mechanism. Preferred embodiments of the invention illustrate application of the method and apparatus to measuring binding between biological receptors and their nuclear response elements, and the use of this type of measurement for assessment of the activity of estrogen mimics present in a test sample, and for evaluation of pharmaceuticals intended to treat hormone dependent cancers.
Owner:IA +1
P16 immune cell chemical labeling color-developing kit
PendingCN110501497APrecise positioningGood colorColor/spectral properties measurementsCytochemistryChemical labeling
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology, and specifically relates to a p16 immune cell chemical labeling color-developing kit. The detection kit comprises the following reagents:0.5-1.0 ml of a p16 immune cell standard substance with the concentration of 81 pg / mL, 1.5 to 2.0 ml of a standard substance diluent, 2-4 ml of horseradish peroxidase, 2-4 ml of a sample diluent, 2-4ml of a color-developing agent solution A, 2-4 ml of a color-developing agent solution B, 2-4 ml of a stop solution, and 20ml of 20 times of concentrated washing solution. The method comprises the steps of coating a microporous plate with a purified human p16 antibody to prepare a solid-phase antibody, adding p16 into micropores coated with a monoclonal antibody, combining with a horseradish peroxidase-labeled p16 antibody to form an antibody-antigen-enzyme-labeled antibody compound, thoroughly washing, and then adding a color-developing agent A substrate for color development. The color-developing agents A and B are converted into blue under the catalysis of horseradish peroxidase and converted into final yellow under the action of acid, the positioning effect and the color-developing effect are good, the labeling is more obvious, the color depth is in positive correlation with p16 in a sample, and the absorbance is measured by using a microplate reader at the wavelength of 450 nm.
Owner:深圳市森盈生物科技有限公司
Method for identifying ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins
The invention relates to a method for identifying the ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins. The above specific enrichment labeling identification method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis of purified ubiquitin-like modification proteins, enriching the ubiquitin-like modification enzyme digestion peptide fragments through a specific ubiquitin-like antibody, protecting the non-modification lysine amino residues in the enriched peptide fragments through utilizing chemical labeling, carrying out a deubiquinaning enzyme catalysis reaction to expose modified lysine on a substrate peptide fragment sequence, analyzing the peptide segment sequences through a liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer, and matching through protein mass spectrum data analysis software to obtain the chemically modified peptide fragment sequence, wherein lysine sites containing free amino groups in the finally obtained sequence are the ubiquitin-like modification sites. Compared with common gene mutation methods for obtaining the sites at present, the method provided by the invention has an advantage that information about the ubiquitin-like modification sites of proteins can be rapidly, efficiently and accurately obtained without a tedious gene mutation technology.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
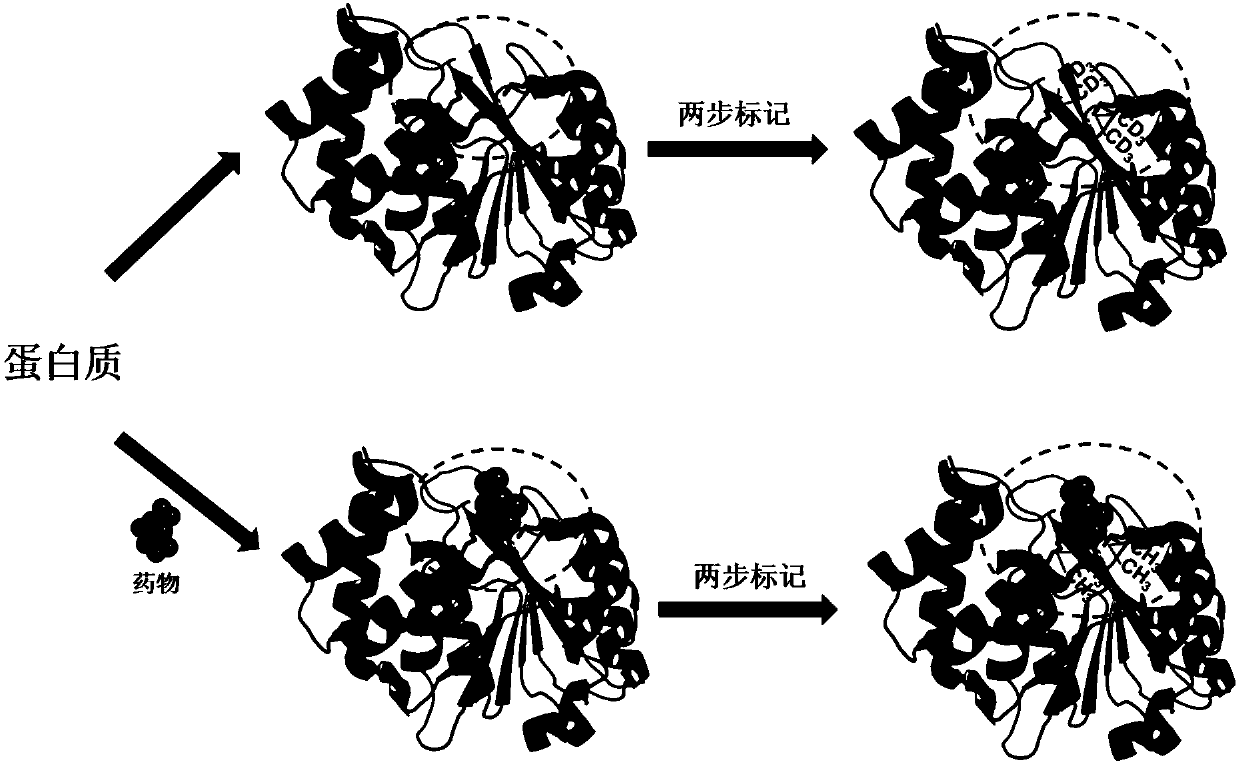
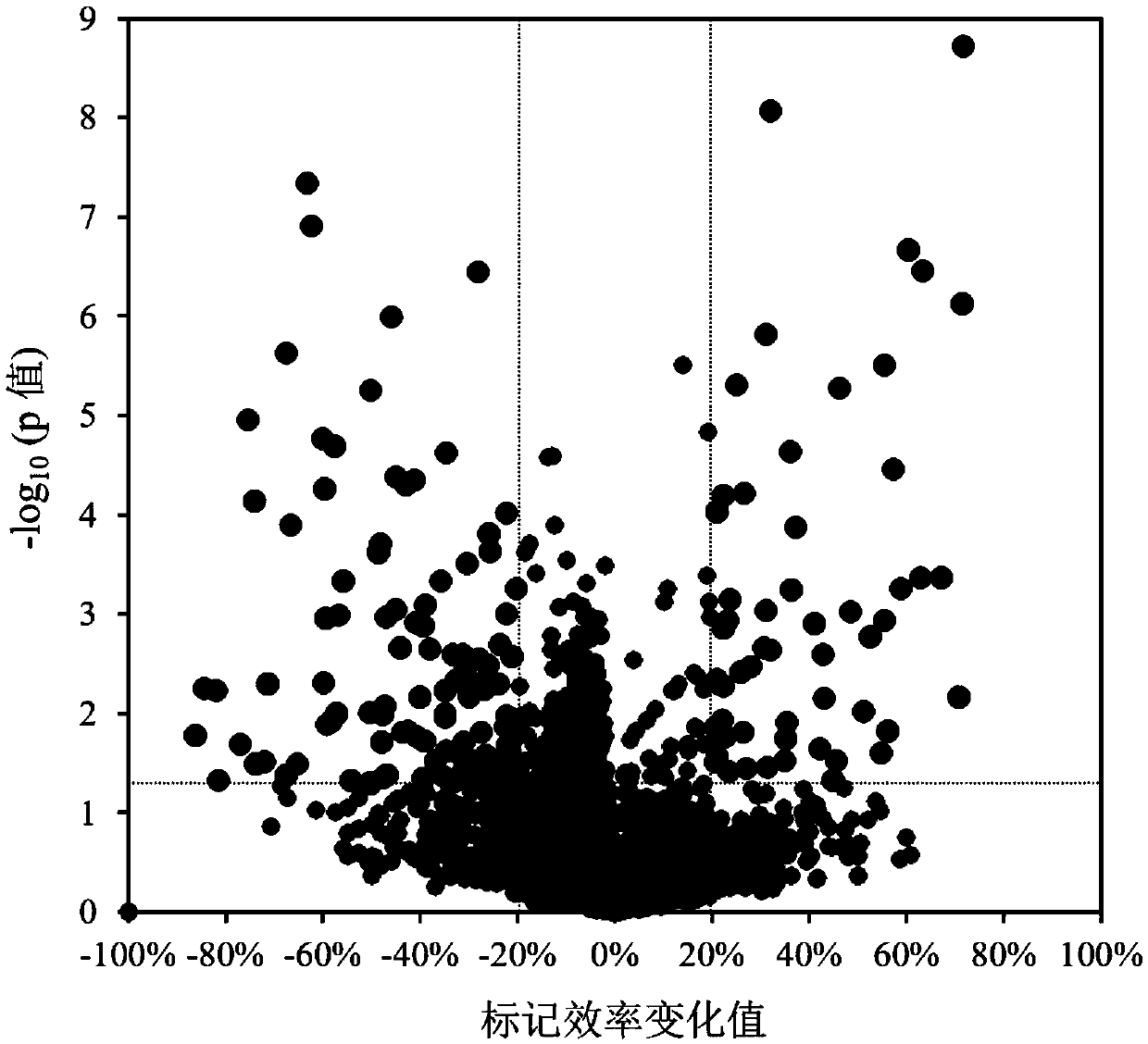
Mass spectrometry method for screening protein with structure and interaction changes caused by drug
ActiveCN110873766AReduce the difficulty of analysisEnable high-throughput detectionComponent separationBiological testingChemical labelingProtein target
The invention relates to a mass spectrometry method for rapidly screening a specific protein with structure and interaction changes caused by drug molecules from a complex cell or tissue lysed proteinsample. The mass spectrometry analysis method is specifically an activity-denaturation two-step stable isotope covalent chemical labeling method. In the two-step labeling, an isotope mass differencelabeling reagent is used, and the protein with the structure and interaction being changed by the drug molecules causes changes of the labeling efficiency of a change region in the first step of activity labeling process, so that the difference of isotope peaks is shown in a final mass spectrum quantitative result. The method provides a brand-new high-throughput mass spectrometry method for rapidly screening a target protein with structure and interaction changes caused by drug molecule binding in a complex system.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Immune cell chemical labeling chromogenic kit for auxiliary diagnosis of cervical cancer
PendingCN112881691AUse low concentrationReduce dosageMaterial analysisChemical labelingTissue staining
The invention relates to the technical field of cell chromogenic reagents, in particular to an immune cell chemical labeling chromogenic kit for auxiliary diagnosis of cervical cancer. The kit comprises a ready-to-use antibody working solution, a reagent solution C, a reagent solution D, a reagent solution E, a reagent solution F and a reagent solution G; the ready-to-use antibody working solution comprises an antibody reagent, bovine serum albumin, non-reducing sugar, fish skin gelatin, a preservative proclin-950, tender leaf green pigment, polyethylene glycol, casein, a surfactant, 4-aminoantipyrine and sodium chloride, and the antibody reagent comprises a reagent solution A and a reagent solution B. The kit can be used for cervical decellularization and can also be used for tissue staining. The blue returning mode is newly created, the blue returning effect is better than that of kits of other manufacturers in the market, the sheet sealing mode is simpler, and the experiment time is greatly shortened.
Owner:杭州百殷生物科技有限公司
Chemical labeling and mass spectrometry-based structure analysis method for protein and material interaction
PendingCN110609103AMaintain normal physiologyMaintain physiological activityComponent separationChemical labelingStructure analysis
The invention relates to a new structure analysis method for researching protein and material interaction based on chemical labeling and mass spectrometry technologies. The method is characterized inthat firstly proteins and protein-material complexes are chemically labeled, then denaturation, enzymatic hydrolysis, chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and database retrieval of the proteins are carried out, and the change conditions of the chemical labeling efficiency of specific amino acid sites on the proteins before and after materials are added are compared, so that a region with theobviously reduced labeling efficiency is namely a protein-material interaction region and a region with the obviously improved labeling efficiency is namely a protein conformation change region afterthe materials are combined. The protein-material interaction analysis method has the advantages of being rapid and simple, stable and efficient, high in sensitivity and capable of realizing high-throughput dynamic analysis, the physiological structures and activities of the proteins are still kept in the labeling process, and an analysis result is not limited by conditions such as the molecular weight, the purity and the like of the proteins.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Mass Spectrometry Method for the Interaction of Active Proteins and Small Molecules
ActiveCN108508125BAccurate identificationHigh sensitivityComponent separationBiological testingChemical labelingProtein target
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
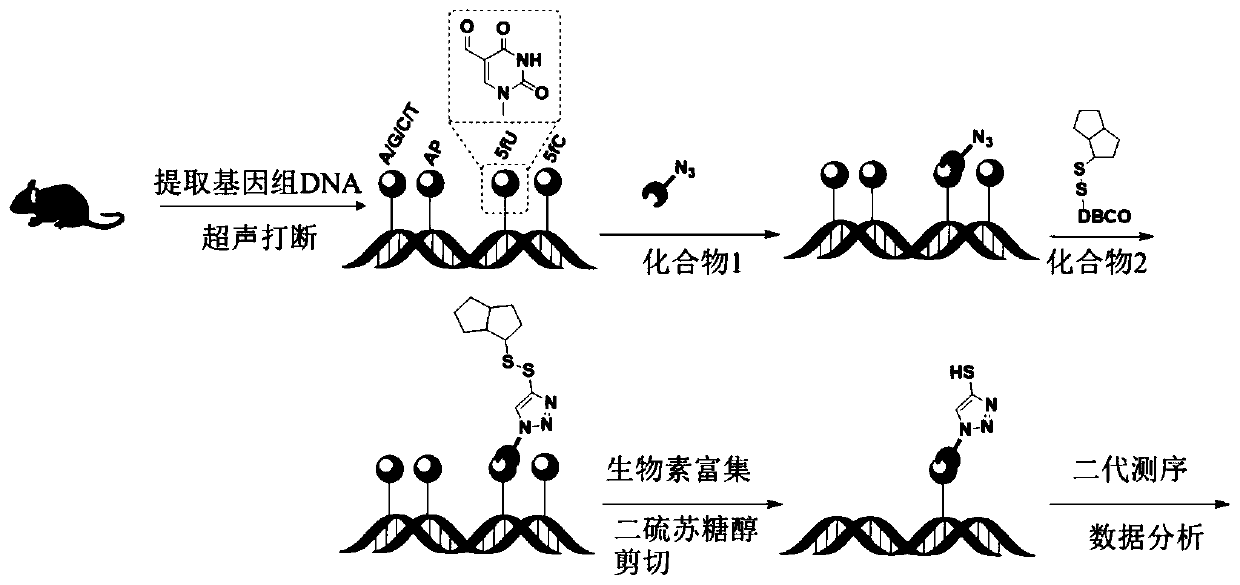
A kind of specific chemical labeling compound of 5-formyl uracil, labeling method and application
ActiveCN107573289BAchieve enrichmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical labelingNucleic acid chemistry
The invention discloses compounds for specifically and chemically marking 5-aldehyde uracil and a marking method and application. A compound 1 with an azide group can be selectively reacted with an aldehyde group of 5-aldehyde uracil, and then alkynyl-carrying biotin DBCO-S-S-PEG3-biotin is added to generate an click reaction with azide without a catalyst. By using the 5-ldehyde uracil specific chemical marking method disclosed by the invention, specific enriching of nucleic acid samples containing 5-aldehyde uracil can be realized, and the sequence distribution information of the 5-aldehyde uracil in nucleic acid molecules can be analyzed. The invention provides an effective research method for the field of epigenetics and nucleic acid chemicobiology.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A fluorescent sensor, its preparation method and use
ActiveCN104730055BIncreased sensitivityEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical labelingProtein secondary structure
The present invention relates to a kind of fluorescence sensor, and its preparation method and application, specifically relate to the biological fluorescence sensor of manganese dioxide nano-sheet and super-sandwich base, use manganese dioxide nano-sheet to quench fluorescence, and single-stranded DNA can be adsorbed on the carbon dioxide The properties of manganese nanosheets and dsDNA and other secondary structures of DNA can be used in the detection of heparin away from the manganese dioxide nanosheets. It includes the following steps: (1) dissolving the DNA sequence (HP1, HP2, helperDNA) in a buffer solution, and saving it for later use; (2) configuring the substances used to a corresponding concentration; (3) dissolving the HP1, HP2, helperDNA and the used Substances are added to the solution for incubation. The preparation method of the bioluminescent sensor uses unlabeled DNA, which is simple to operate and low in cost, and avoids any chemical labeling and modification. The results show that the sensor has a satisfactory detection result for heparin, and has simple operation, high sensitivity, Features low detection limit.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
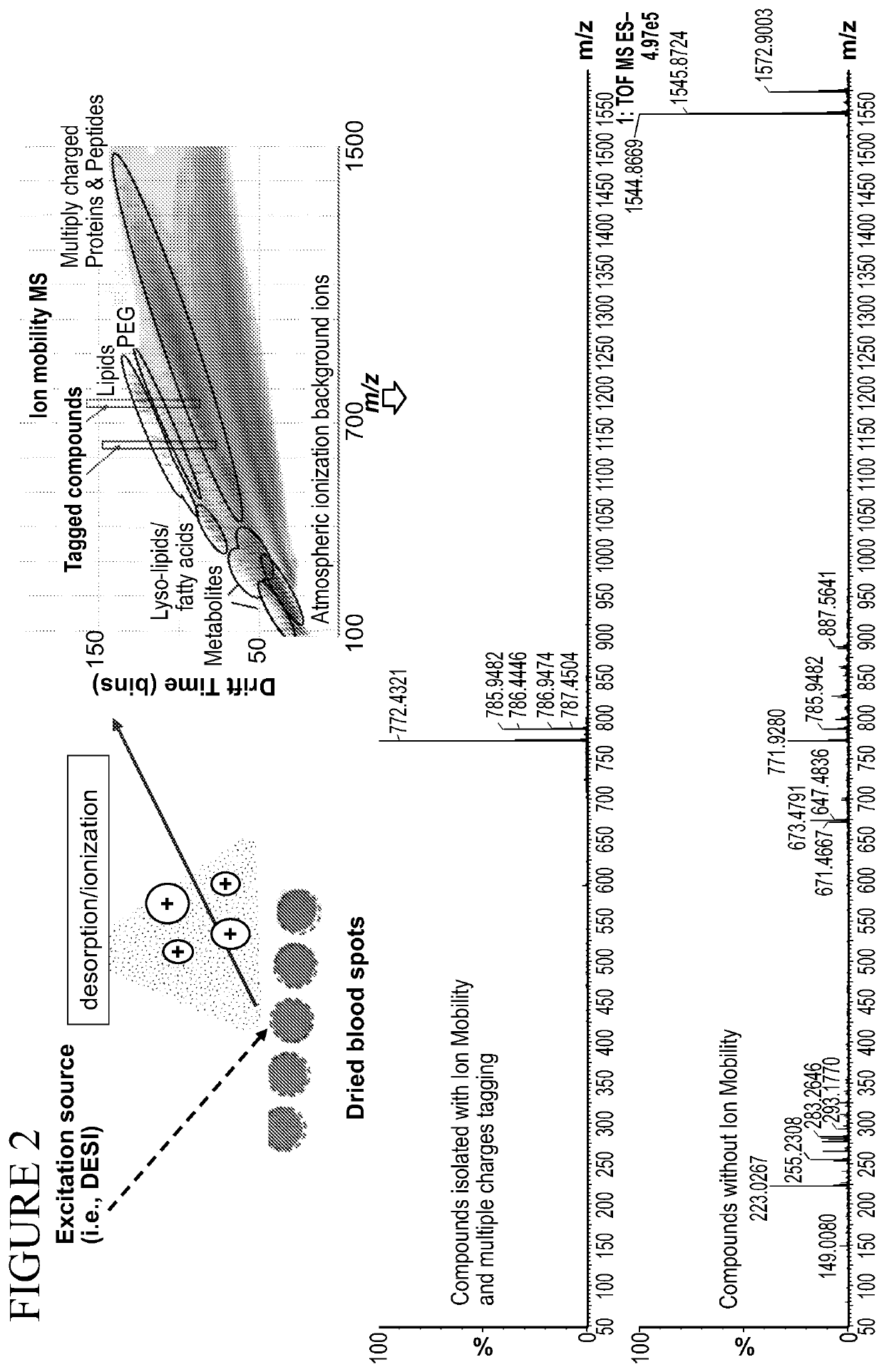
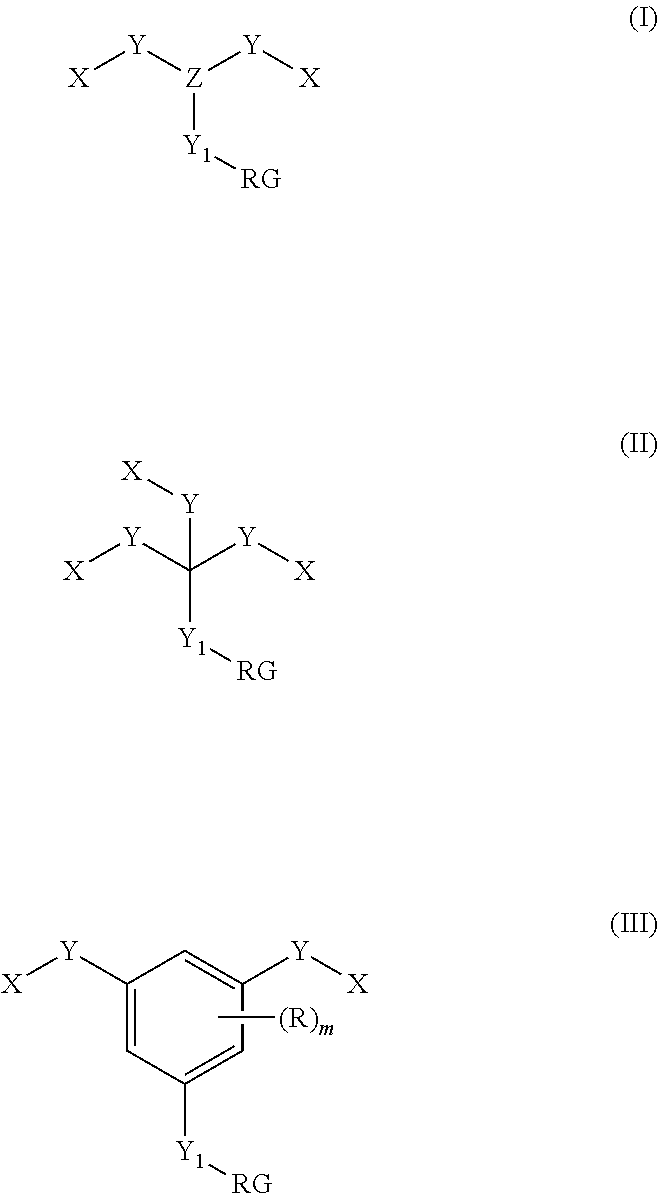
Method of using chemical tags to improve the identification, quantification and spatial localization of components in a sample
ActiveUS20200217855A1High selectivityHigh sensitivityComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical labelingChemical compound
The present disclosure relates to a method for using chemical tags which have two or more sites for ionization to improve quantification and identification of components of interest from a complex mixture. This method relies on first selectively reacting one or more component in a sample with a chemical tag having two or more sites for ionization, followed by separation of components based on charge status, and finally characterization of each component to identify the same. Additionally disclosed are compounds useful as chemical tags in the disclosed methods.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
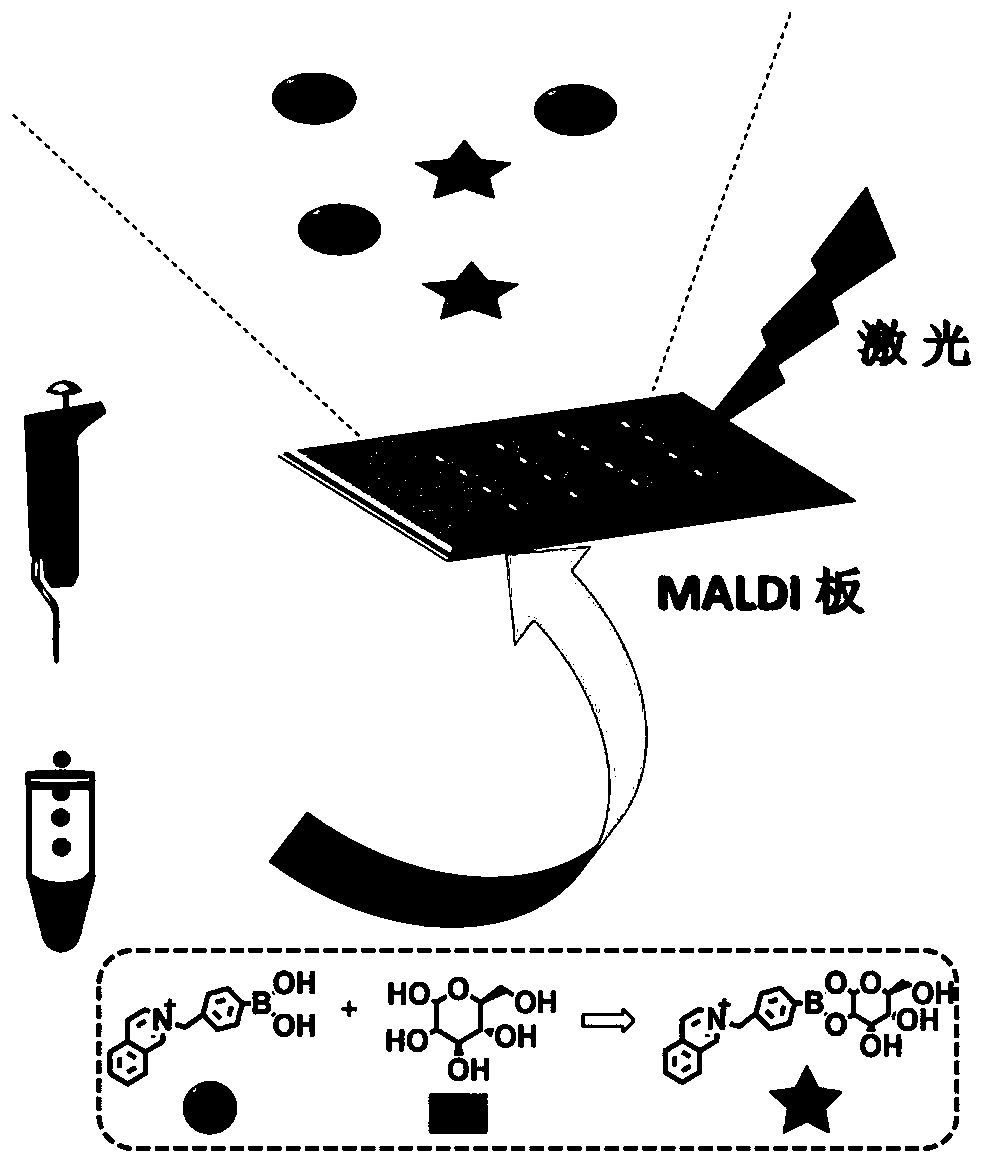
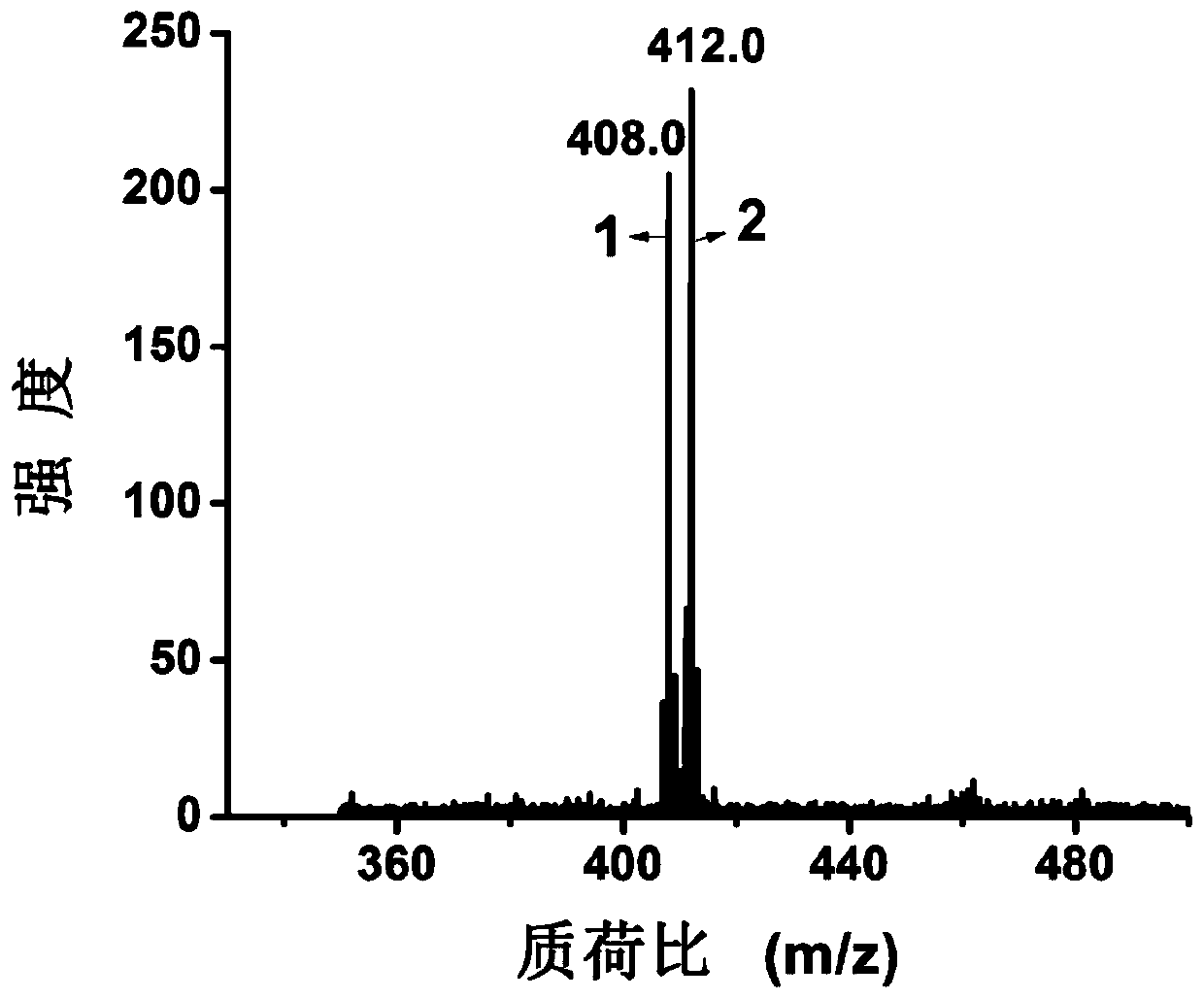
A method for quantitatively detecting glucose in serum
InactiveCN107085031BGood reproducibilitySolve signal interferenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical labelingSerum ige
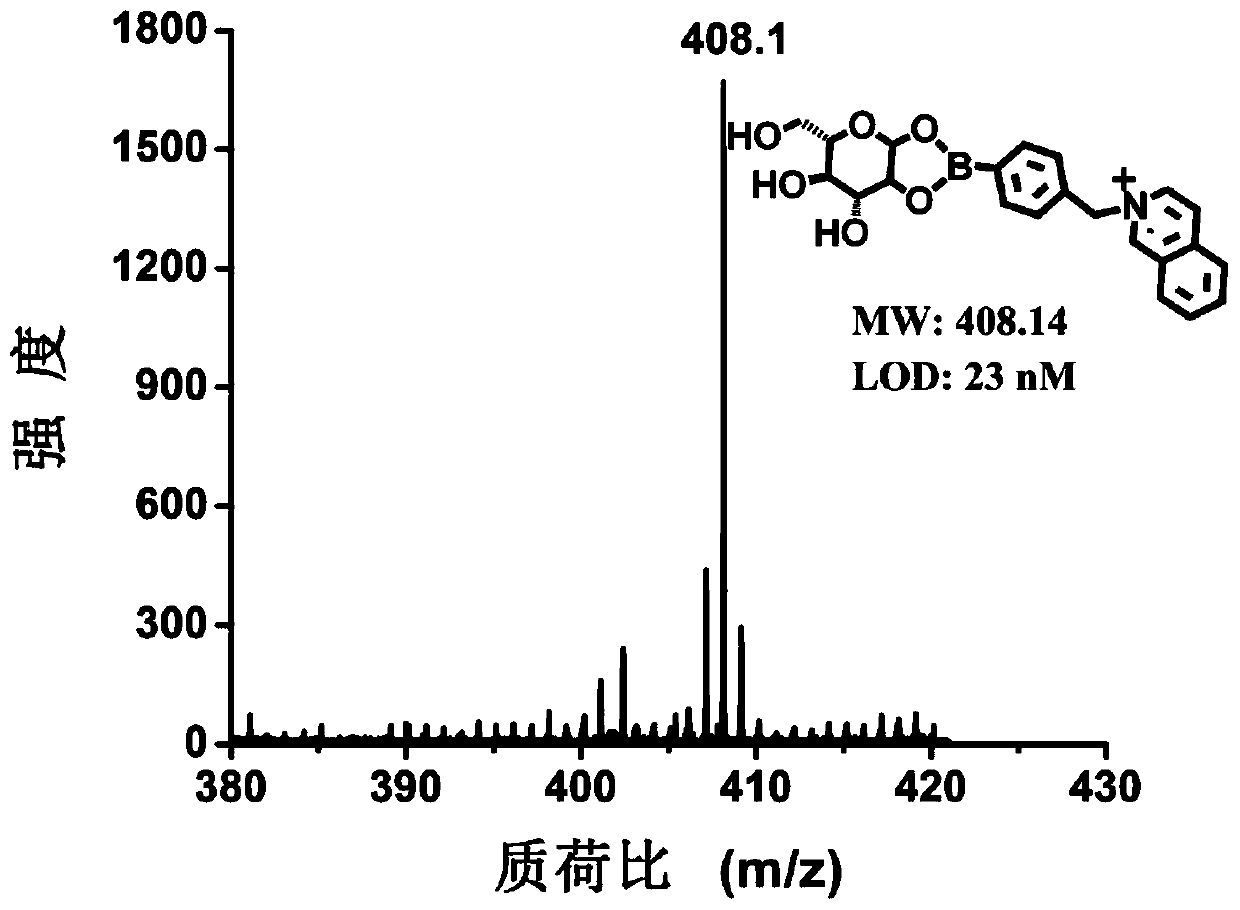
The invention discloses a method for rapidly, sensitively and quantitatively detecting glucose in serum and belongs to the field of biochemical reagent detection. The method comprises the following steps: firstly removing protein in the serum by adopting an organic solvent, carrying out chemical labeling by virtue of a boric acid group and a quaternary ammonium group which are contained in a structure, then adopting black phosphorus-assisted laser desorption ionization-flight time mass spectrometry, and then realizing quantitative detection on the glucose in the serum. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and rapid in operation, and the whole experimental procedure can be completed within 5 minutes; sample consumption amount is low, and endogenous glucose detection can be realized in 0.5 microliter of the serum only; and result is accurate, and large-scale sample determination requirement is met.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Nucleic acid aptamers for detecting extracellular vesicles of human lung cancer cell strain A549 and application of nucleic acid aptamers
PendingCN113528531ASmall molecular weightImprove stabilityMaterial analysisDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerChemical labeling
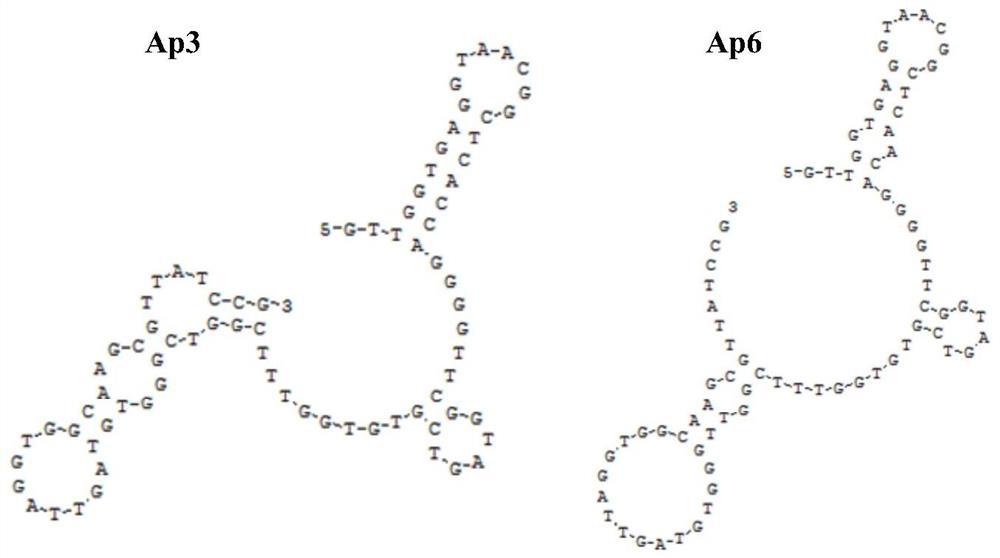
The invention discloses nucleic acid aptamers for detecting extracellular vesicles of a human lung cancer cell strain A549. Nucleotide sequences of the nucleic acid aptamers are shown as SEQ ID NO: 4 (Ap3) and SEQ ID NO: 5 (Ap6). Or the nucleic acid aptamers are a series of derivatives which are obtained through chemical modification, chemical labeling or basic group change on the basis of SEQ ID NO: 4 (Ap3) and SEQ ID NO: 5 (Ap6) sequences. The nucleic acid aptamers disclosed by the invention can be applied to the recognition of extracellular vesicles of the human lung cancer cell strain or the preparation of a kit for detecting the extracellular vesicles of the human lung cancer cell strain or a combination of extracellular vesicle drug delivery and specific recognition of targets. The nucleic acid aptamers can be applied to identification of human lung cancer or preparation of the kit for detecting human lung cancer. The nucleic acid aptamers have very wide application prospects in detection, diagnosis and treatment of human lung cancer.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
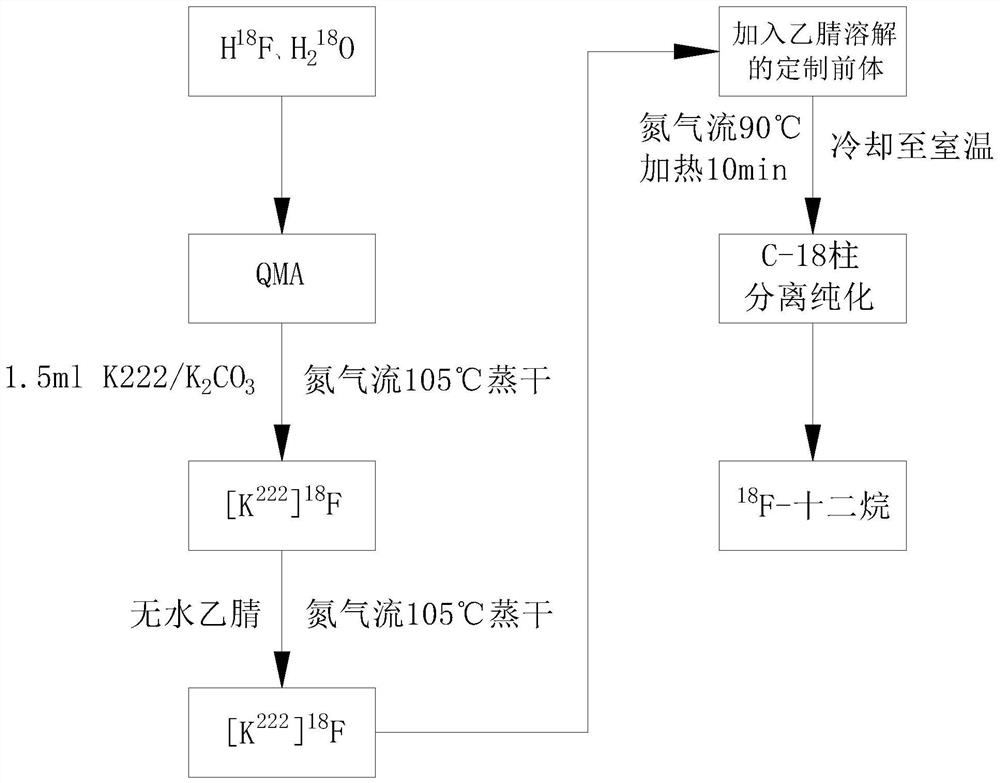
18F-dodecane positron imaging agent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114656329AHigh precisionDetection speedComponent separationOrganic chemistry methodsChemical labelingGamma photon
The invention discloses an < 18 > F-dodecane positron imaging agent and a preparation method thereof, is based on a positron nuclide chemical labeling method, and belongs to the field of industrial nondestructive testing. The invention discloses an < 18 > F-dodecane positron imaging agent and a preparation method thereof in order to overcome the defects of an existing marking scheme in accuracy and application range, so that the < 18 > F-dodecane positron imaging agent can determine that gamma photons are generated by burning kerosene instead of volatilized kerosene, the marking accuracy is realized, and the reliability is improved; secondly, the application range of the 18F-dodecane positron imaging agent is not only kerosene, but also can be used for detecting gasoline and aerospace kerosene, so that the application range of the 18F-dodecane positron imaging agent is expanded, and the applicability is improved; meanwhile, the finished product is subjected to structure confirmation and quality control experiment in the preparation process, so that the quality and accuracy of the < 18 > F-dodecane positron imaging agent are ensured.
Owner:南京航空航天大学深圳研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com