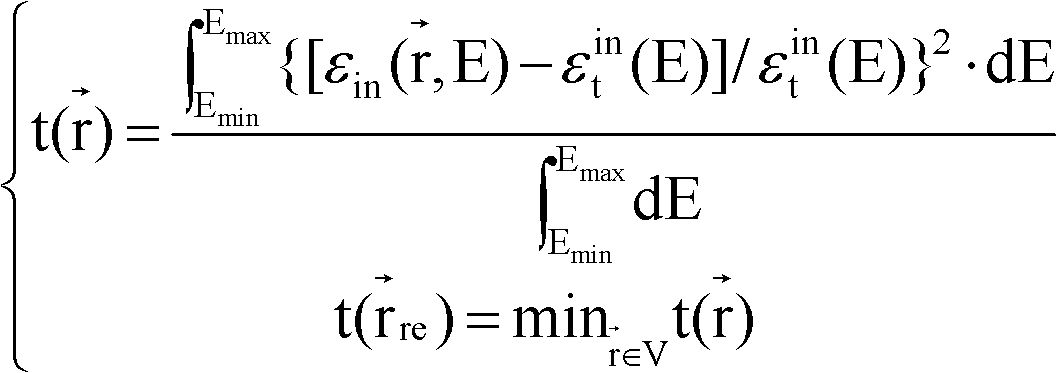Patents
Literature
1086 results about "Nuclide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
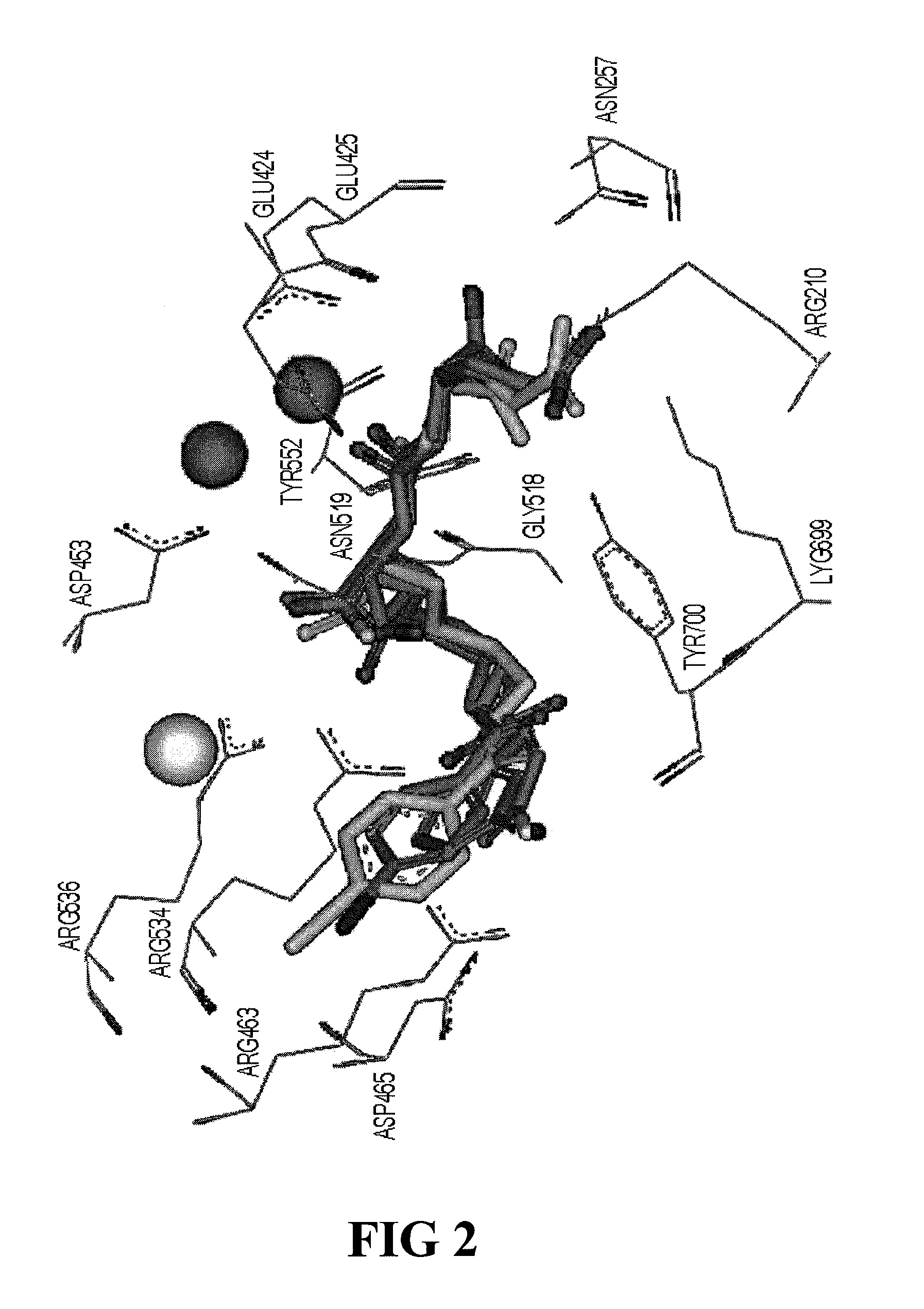
A nuclide (or nucleide, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) is an atomic species characterized by the specific constitution of its nucleus, i.e., by its number of protons Z, its number of neutrons N, and its nuclear energy state.
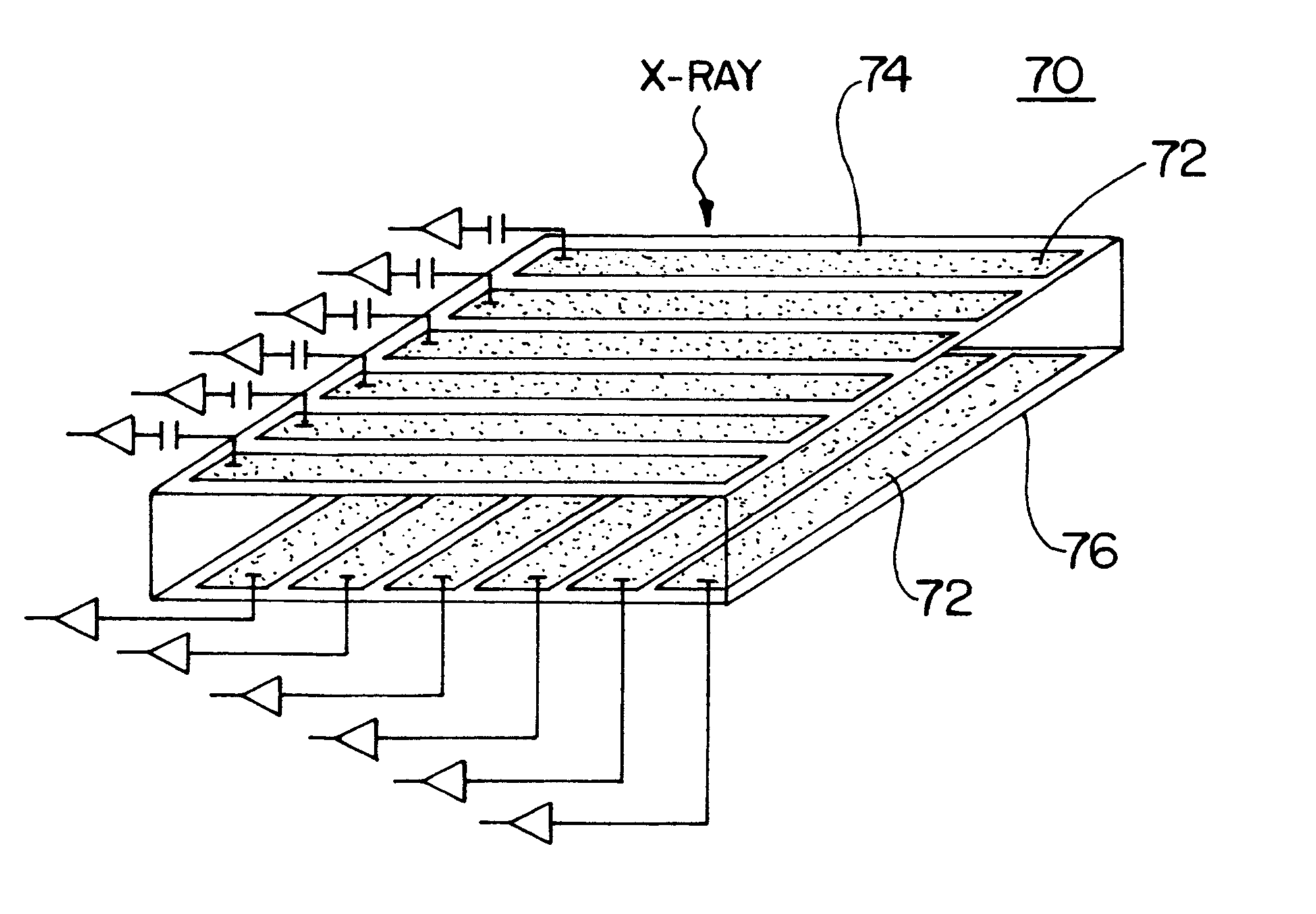
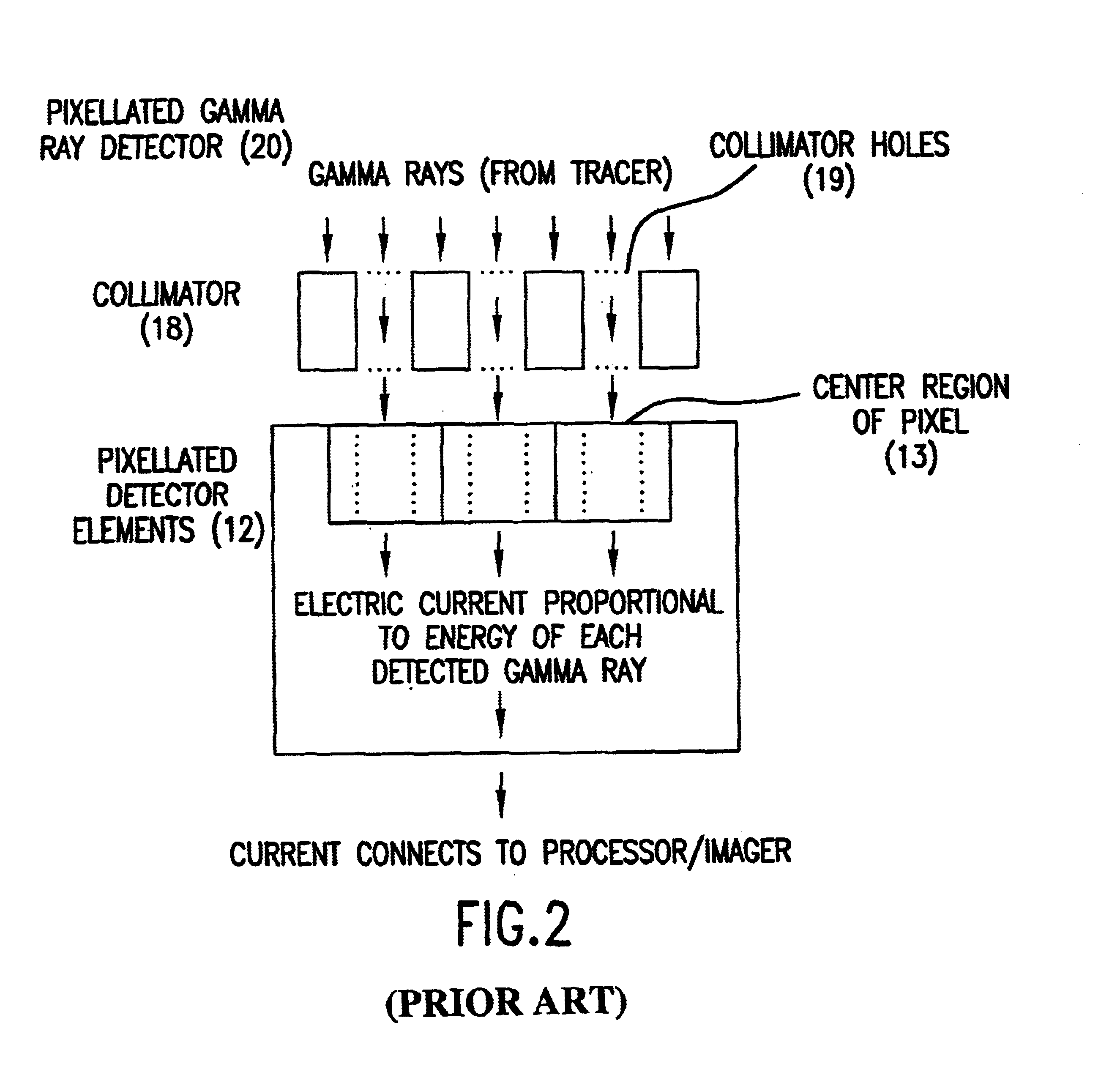
Simultaneous CT and SPECT tomography using CZT detectors
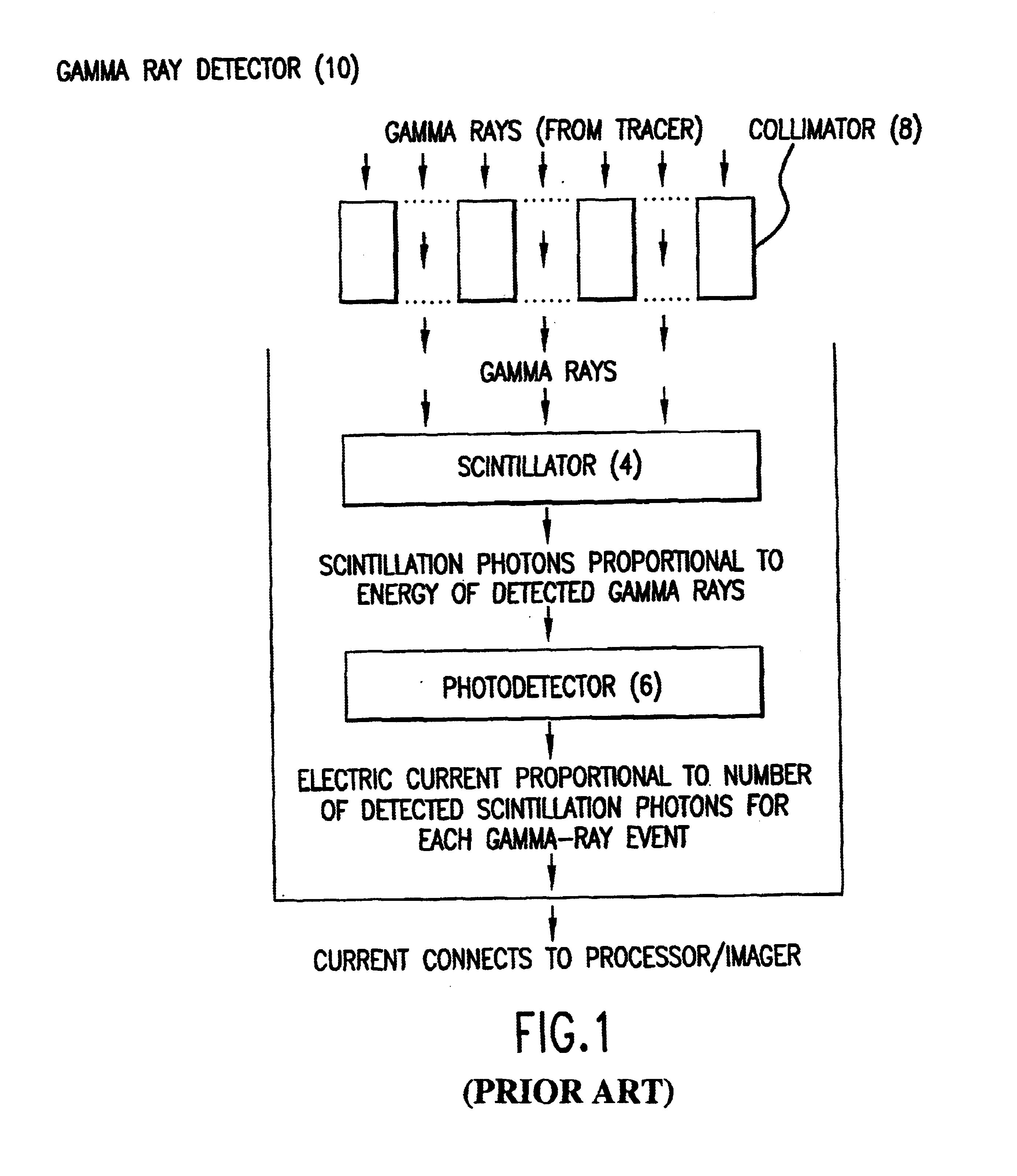
A method for simultaneous transmission x-ray computed tomography (CT) and single photon emission tomography (SPECT) comprises the steps of: injecting a subject with a tracer compound tagged with a gamma-ray emitting nuclide; directing an x-ray source toward the subject; rotating the x-ray source around the subject; emitting x-rays during the rotating step; rotating a cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) two-sided detector on an opposite side of the subject from the source; simultaneously detecting the position and energy of each pulsed x-ray and each emitted gamma-ray captured by the CZT detector; recording data for each position and each energy of each the captured x-ray and gamma-ray; and, creating CT and SPECT images from the recorded data. The transmitted energy levels of the x-rays lower are biased lower than energy levels of the gamma-rays. The x-ray source is operated in a continuous mode. The method can be implemented at ambient temperatures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
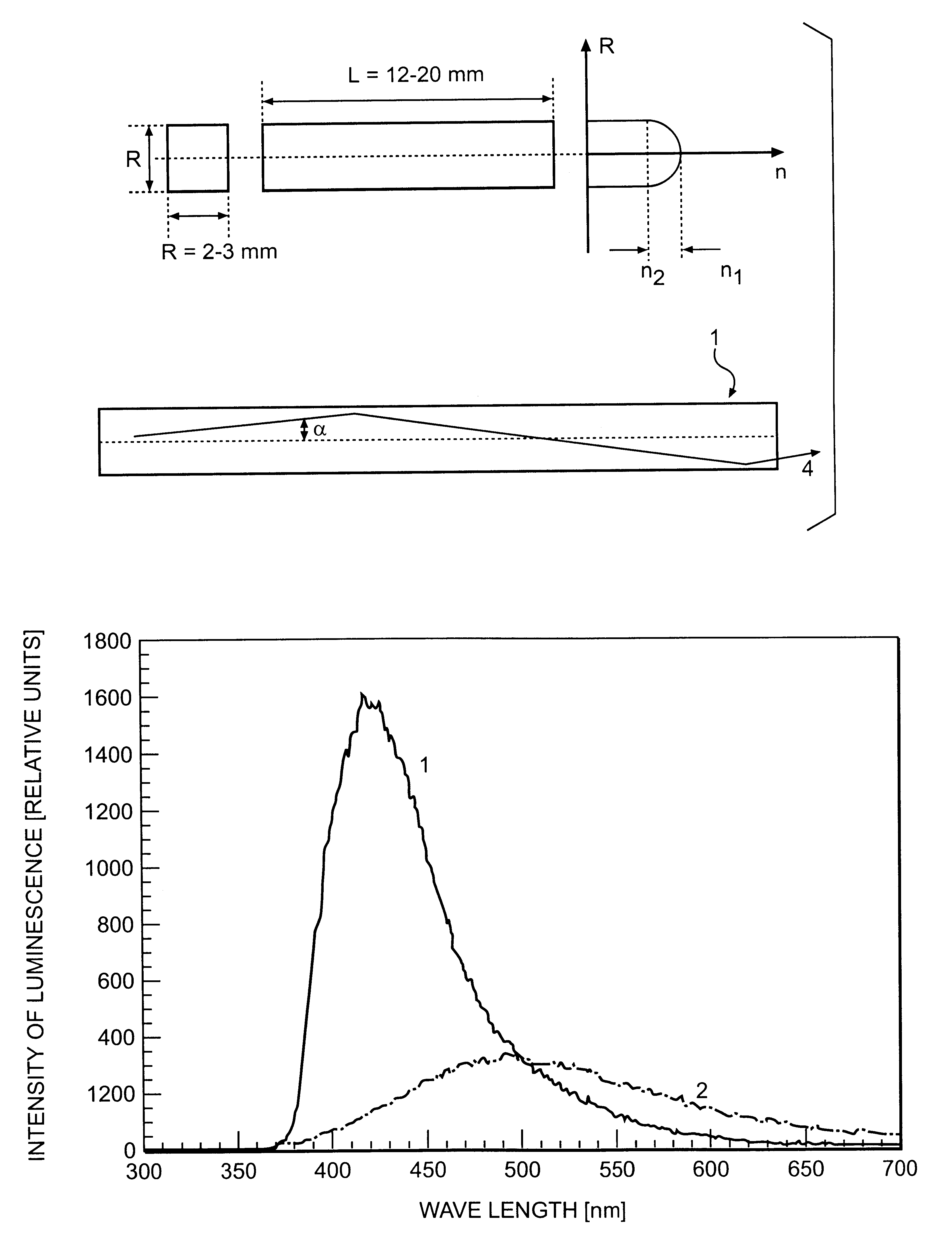
Scintillating substance and scintillating wave-guide element
InactiveUS6278832B1Improve light outputShorten the timePolycrystalline material growthOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberAdditive ingredient
The invention is related to nuclear physics, medicine and oil industry, namely to the measurement of x-ray, gamma and alpha radiation; control for trans uranium nuclides in the habitat of a man; non destructive control for the structure of heavy bodies; three dimensional positron-electron computer tomography, etc.The essence of the invention is in additional ingredients in a chemical composition of a scintillating material based on crystals of oxyorthosilicates, including cerium Ce and crystallized in a structural type Lu2SiO5.The result of the invention is the increase of the light output of the luminescence, decrease of the time of luminescence of the ions Ce3+, increase of the reproducibility of grown crystals properties, decrease of the cost of the source melting stock for growing scintillator crystals, containing a large amount of Lu2O3, the raise of the effectiveness of the introduction of SCintillating crystal luminescent radiation into a glass waveguide fibre, prevention of cracking of crystals during the production of elements, creation of waveguide properties in scintillating elements, exclusion of expensive mechanical polishing of their lateral surface.
Owner:SOUTHBOURNE INVESTMENTS
Membrane-permeant peptide complexes for medical imaging, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical therapy
InactiveUS7306784B2Accelerate the accumulation processImprove clearance rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHydrolasesCell membranePharmacologic therapy
Methods and compositions for medical imaging, evaluating intracellular processes and components, radiotherapy of intracellular targets, and drug delivery by the use of novel cell membrane-permeant peptide conjugate coordination and covalent complexes having target cell specificity are provided. Kits for conjugating radionuclides and other metals to peptide coordination complexes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Assembly for transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material
InactiveUS6233299B1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationRadioactive agentTechnetium-99
A new transmutation assembly permits an efficient transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material (long-lived FP nuclides such as technetium-99 or iodine-129) which was produced in the nuclear reactor. Wire-type members of a long-lived radioactive material comprised of metals, alloys or compounds including long-lived FP nuclides are surrounded by a moderator material and installed in cladding tubes to form FP pins. The FP pins, and nothing else, are housed in a wrapper tube to form a transmutation assembly. The wire-type members can be replaced by thin ring-type members. The transmutation assemblies can be selectively and at least partly loaded into a core region, a blanket region or a shield region of a reactor core in a fast reactor. From a viewpoint of reducing the influence on the reactor core characteristics, it is optimal to load the transmutation assemblies into the blanket region.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
Capsule seed
InactiveUS6716156B2Radioactive sourcesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMetallic materialsAlloy
Owner:AEA TECH QSA
Non-Rotating Transaxial Radionuclide Imaging
ActiveUS20090001273A1Low costEfficient preparationAdditive manufacturing apparatusRadiation/particle handlingRadionuclide imagingNuclide
Transaxial radionuclide imaging is implemented without relative rotation between detectors and a patient by employing a collimator comprising segments sharing a common central axis, each segment having a plurality of apertures extending therethrough, wherein the segments are angularly displaced from one another about the common central axis. Embodiments include SPECT systems comprising a polygonal detector having a collimator on at least two sides thereof. Embodiments further include collimators comprising six segments, each offset by an angle of 7 to 9°.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
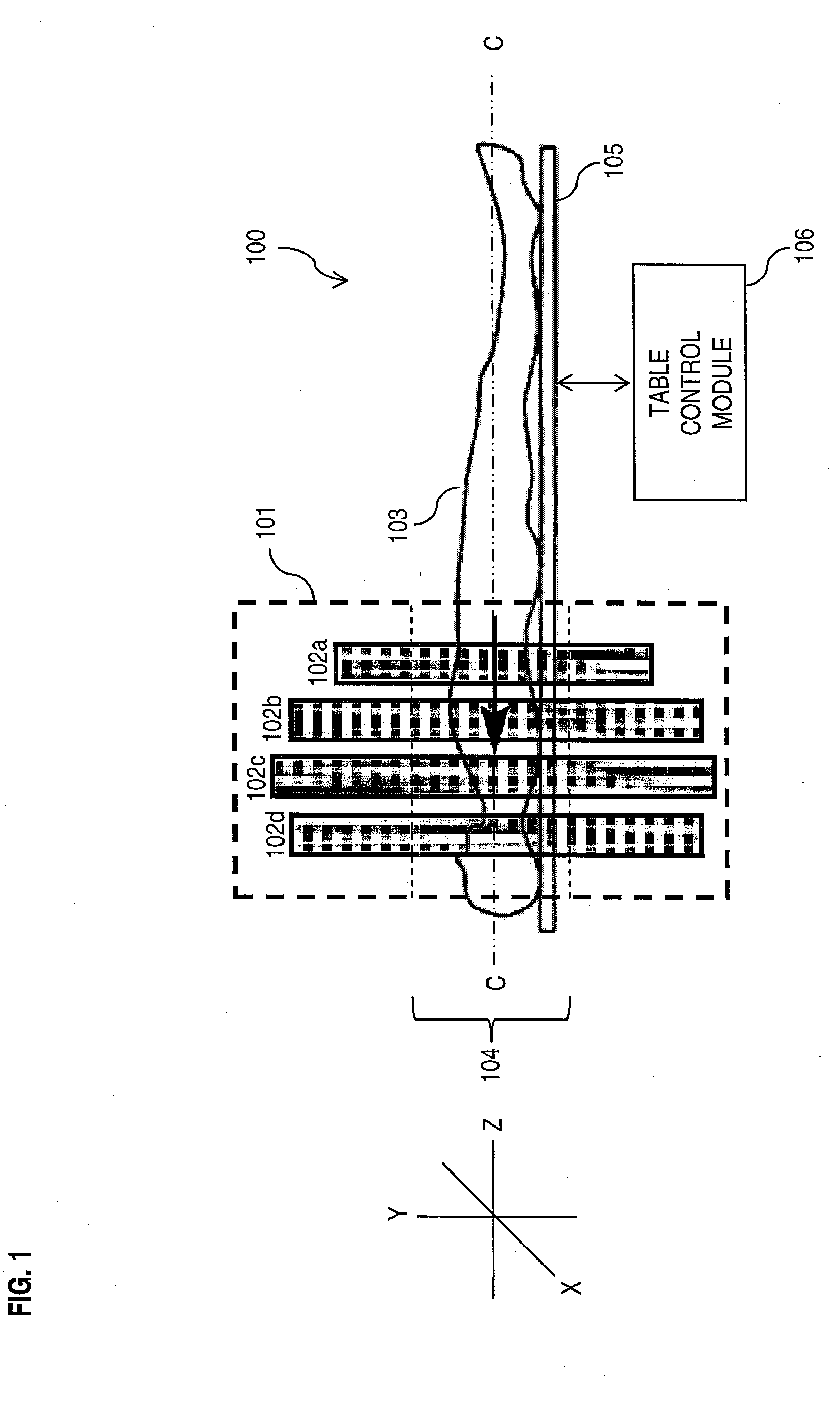
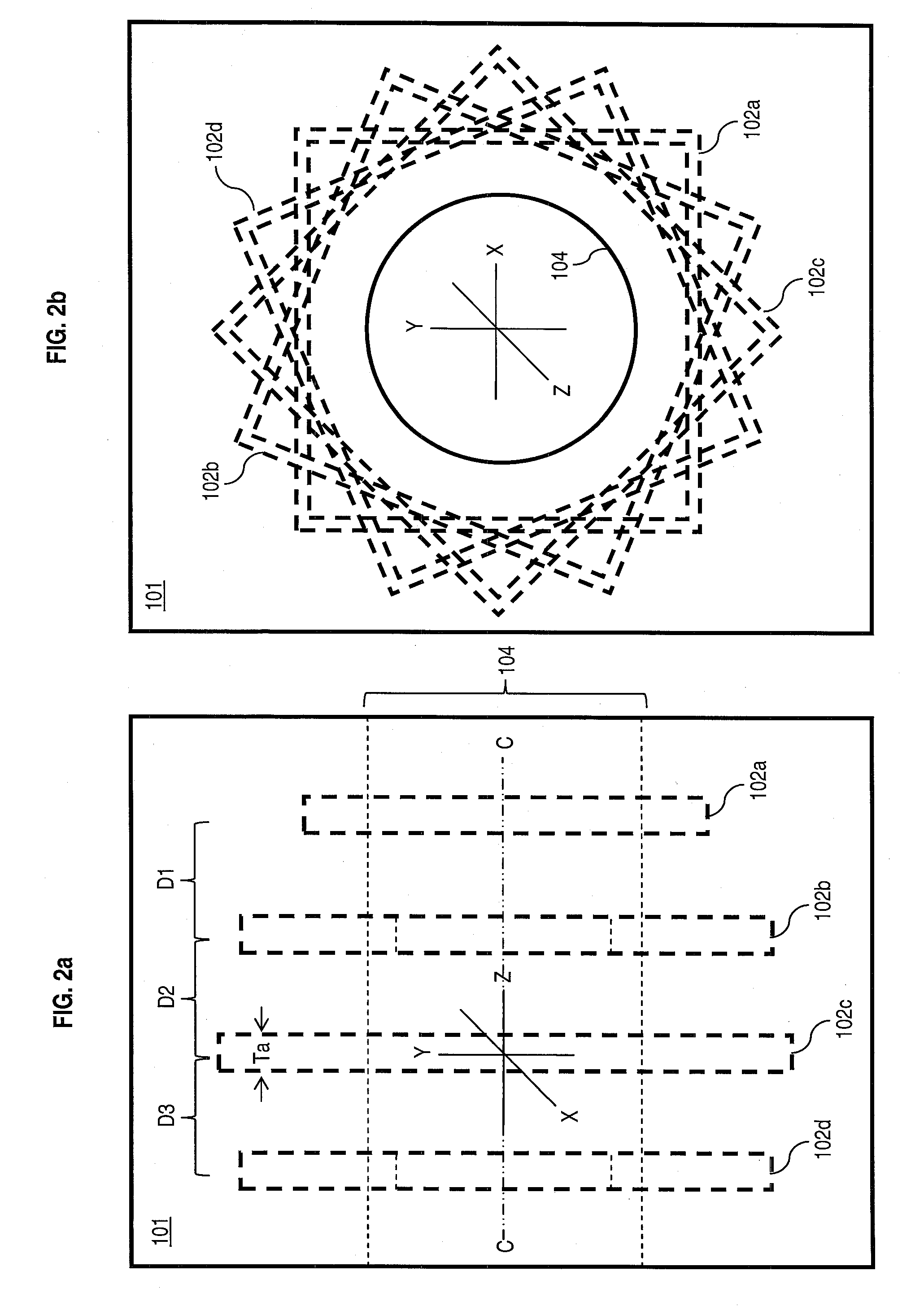
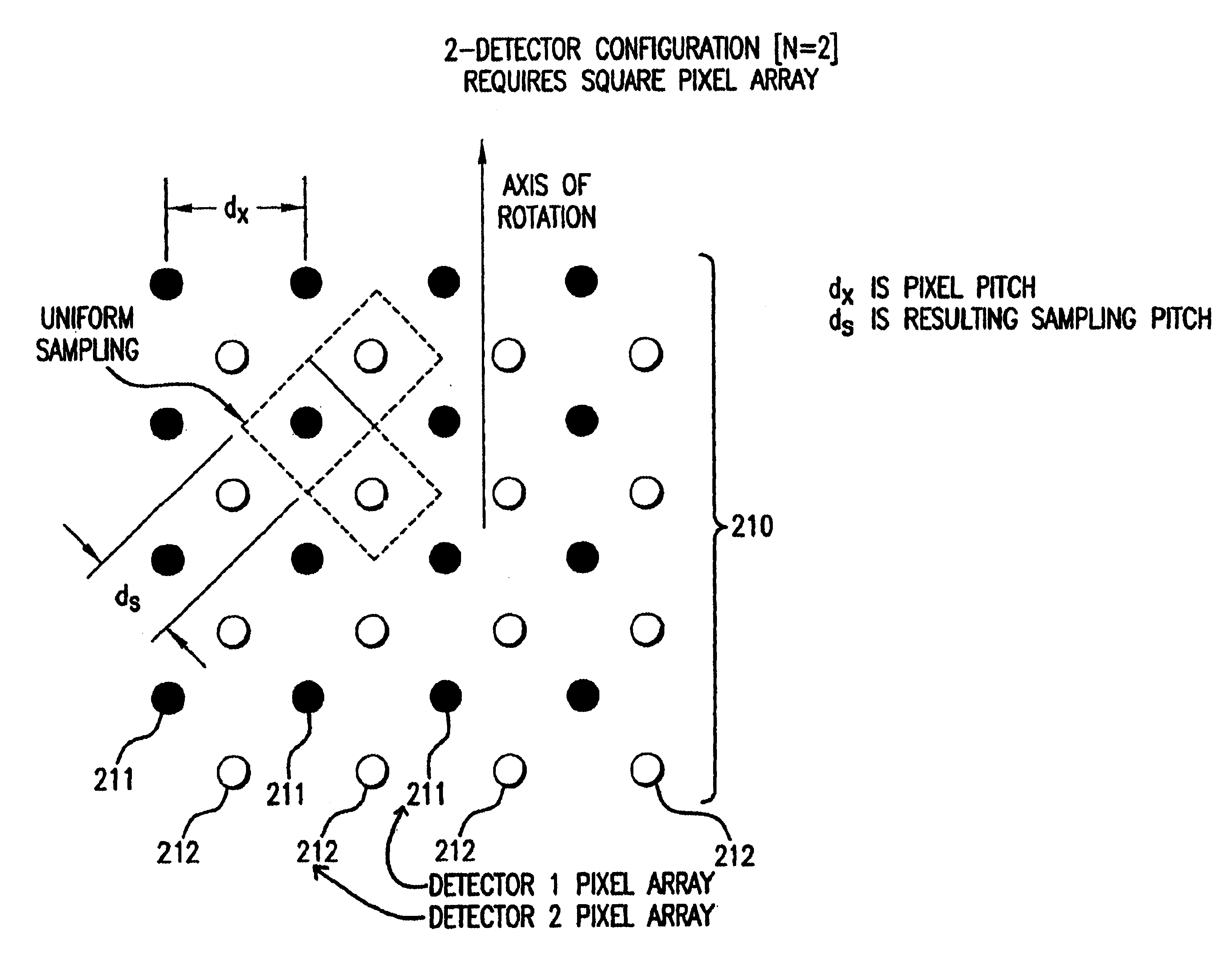
High resolution, multiple detector tomographic radionuclide imaging based upon separated radiation detection elements
InactiveUS6838672B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansRadionuclide imagingMulti detector
A radionuclide scanner in which multiple detectors are equipped with collimators such that a circular rotation of the detector around a target provides the movement needed for collimator sampling. This collimator sampling is accomplished through strategic placement of the detector heads relative to each other such that for any given projection, a complete imaging of the projection is acquired by summing the complementary contributions of the multiple detector heads at the projection under consideration.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method for preparing radioactive nuclide magnetic microsphere used in vivo
InactiveCN1593665ASolve the problem of large damagePowder deliveryRadioactive preparation carriersMicrosphereNormal tissue
The invention provides a method for preparing radioactive nuclide magnetic microsphere used in vivo for the treatment of vessel embolism and tumor, wherein the process by the invention comprises the steps of, preparing magnetic ferrosic oxide particles, preparing magnetic microballoons, marking protein #+[131] and preparing radioactive nuclide. The invention solves the problems of rejection reaction of heterology antibody and damage of normal tissues.
Owner:北京倍爱康生物技术有限公司
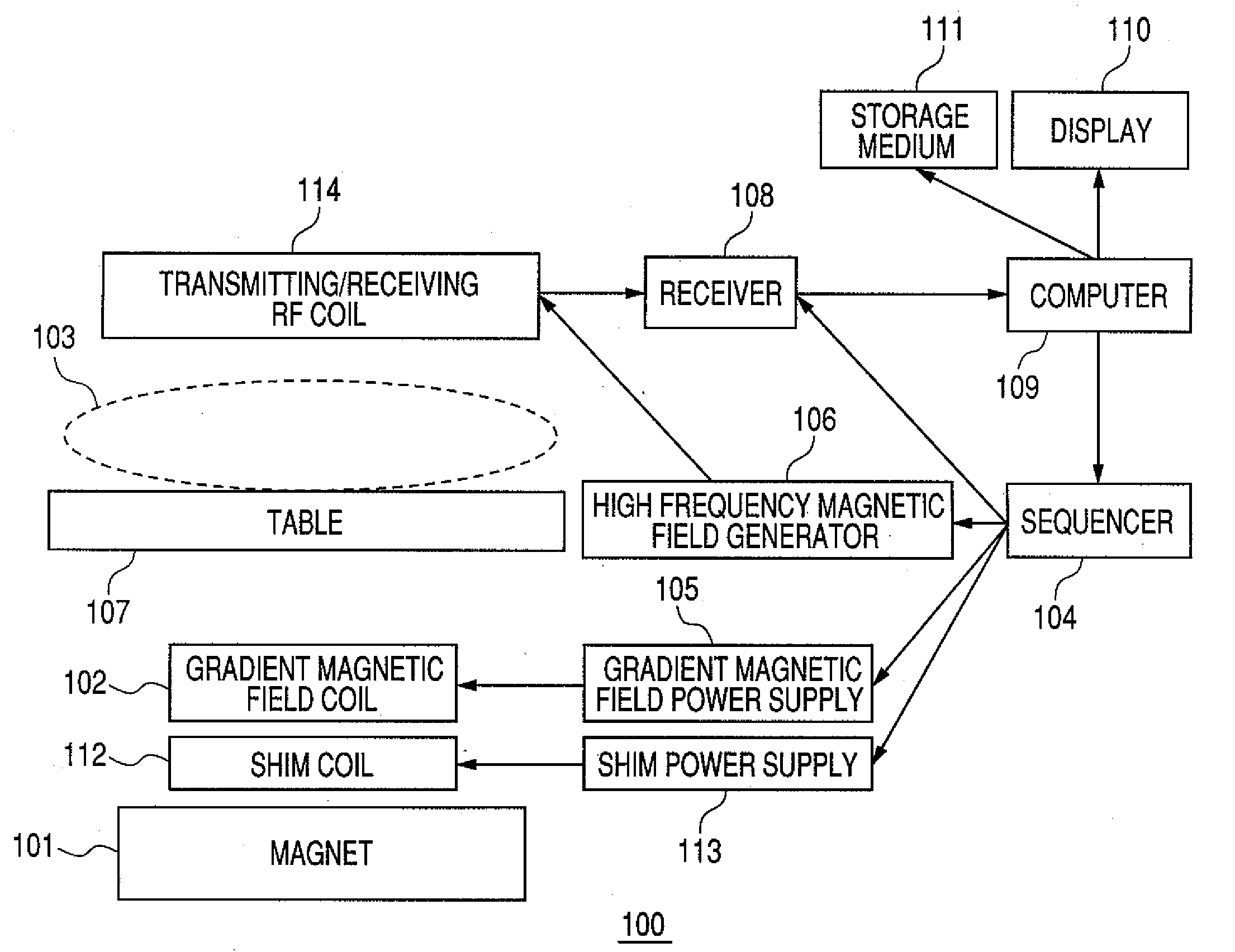
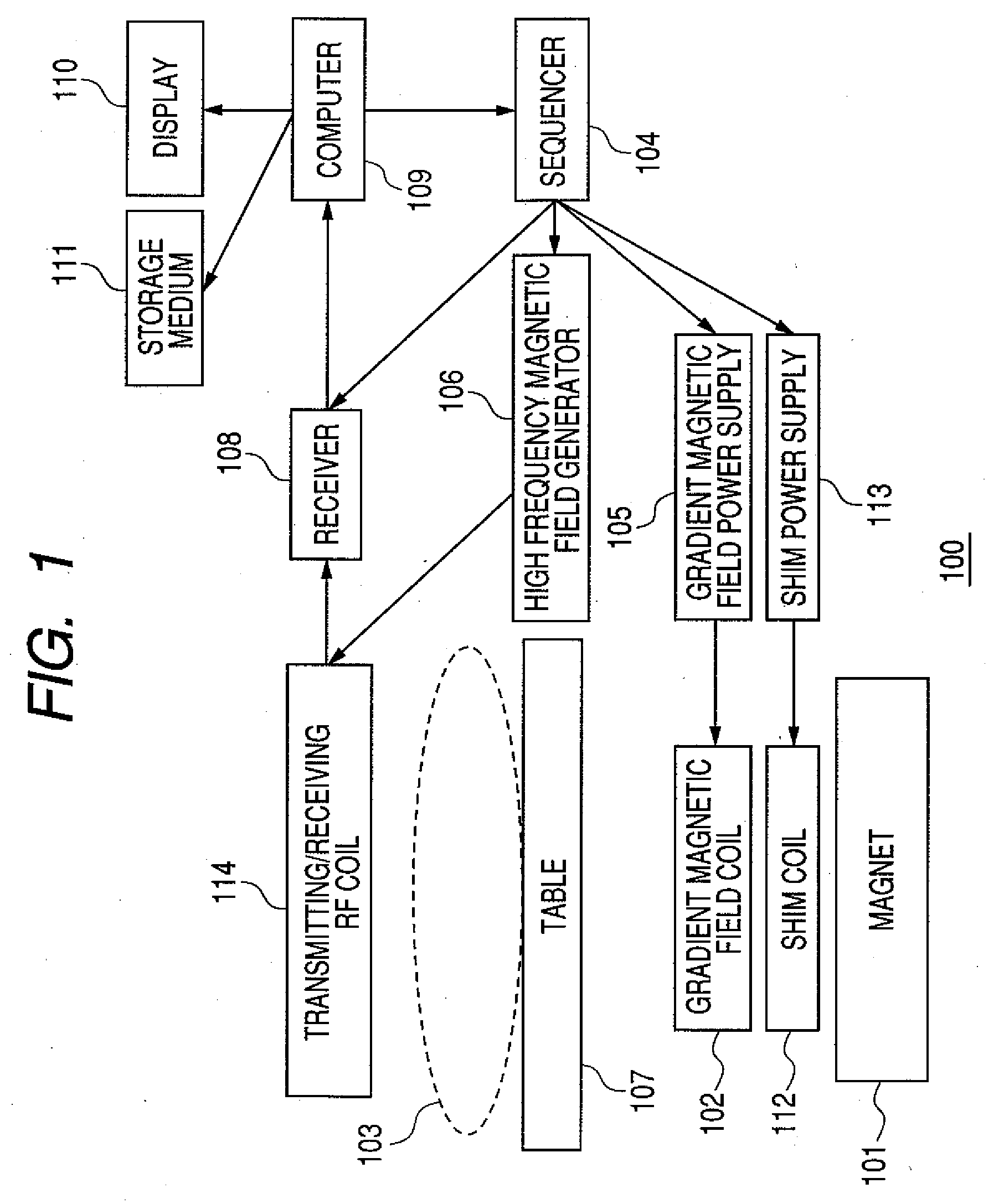
High frequency magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus with the same
InactiveUS20090251145A1Slight lowering in sensitivityMagnetic measurementsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceCouplingResonance
An RF coil for MR Imaging that can change a resonance frequency easily and instantaneously in response to a nuclide to be imaged without exchange and adjustment and that also causes only small lowering of sensitivity. The RF coil has a sub coil for changing a resonance frequency of the transmitting / receiving RF coil for transmitting and receiving an MR signal between itself and a nuclide that is an object to be imaged. The sub coil is equipped with a switch, and at the time of switching-on, shifts the resonance frequency of the RF coil by changing an inductance value of the RF coil in a noncontact manner using inductance coupling.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
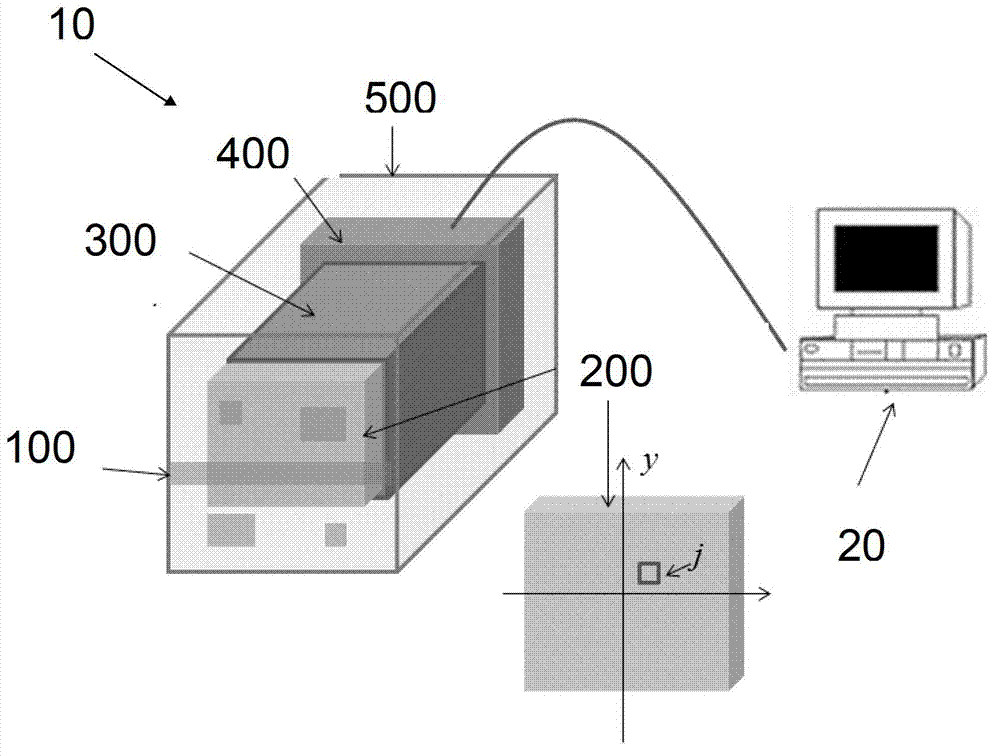
Radioactive substance detection method, device and system based on gamma camera
ActiveCN103163548AImprove spatial resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioX-ray spectral distribution measurementPhotographic dosimetersRadioactive agentNuclide
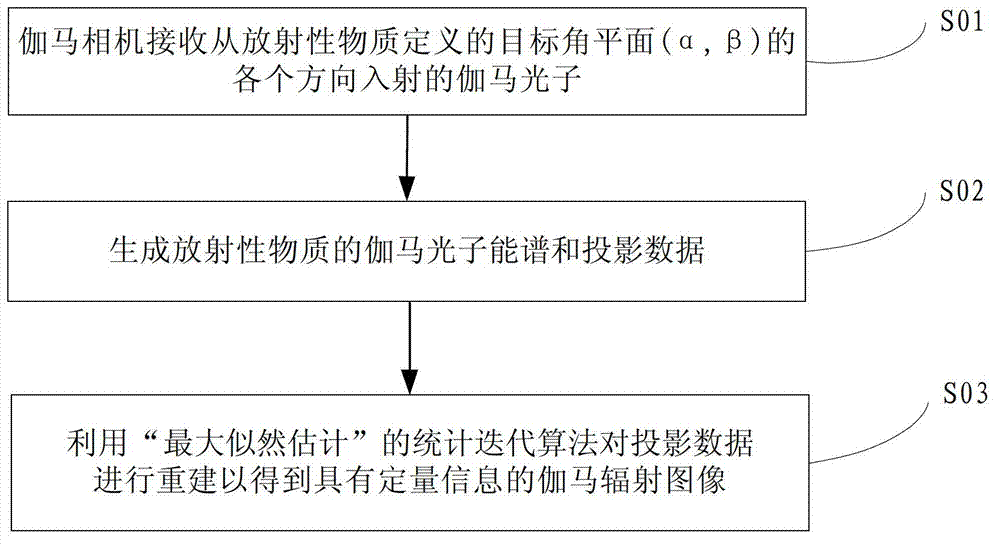
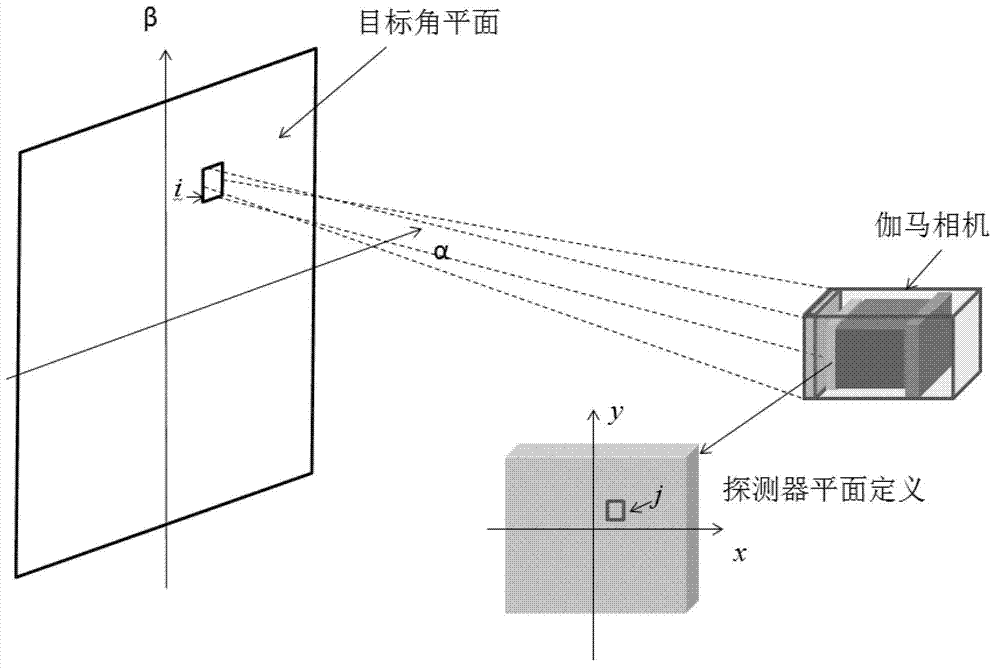
The invention provides a radioactive substance detection method, a radioactive substance detection device and a radioactive substance detection system based on a gamma camera. The detection method comprises the following steps of: receiving gamma photons incident from all directions of a target angle plane (alpha, beta) defined by radioactive substances by using the gamma camera; generating gamma photon energy spectrums and projection data of the radioactive substances; and reconstructing the projection data by using a 'maximum likelihood estimation' statistical iterative algorithm to obtain a gamma radiation image with quantitative information. By the method, the spatial resolution and the signal to noise ratio of the gamma radiation image are increased, spaces of the radioactive substances are positioned, the radiation dose is measured, nuclide types of the radioactive substances are identified, and the radioactive activity is measured.
Owner:BEIJING NOVEL MEDICAL EQUIP LTD +1
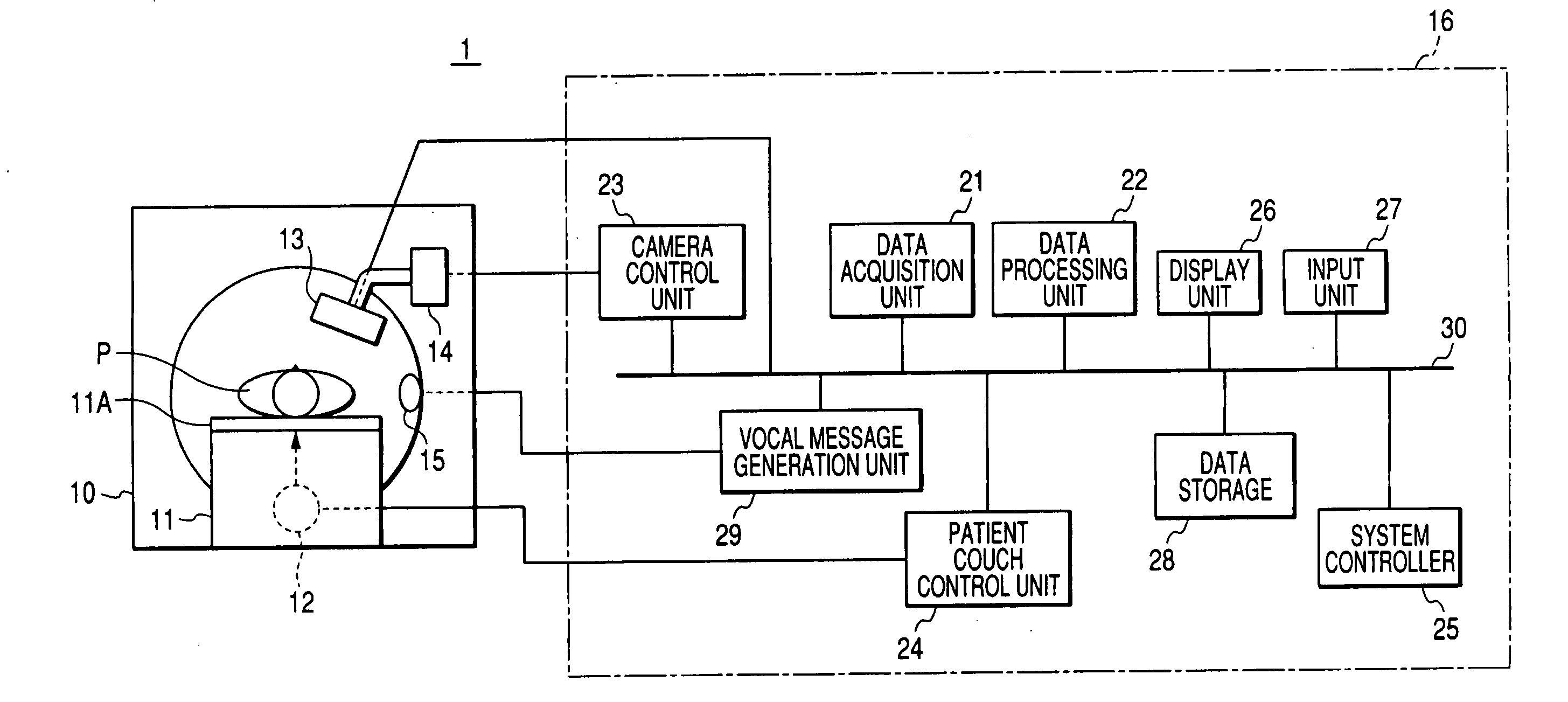
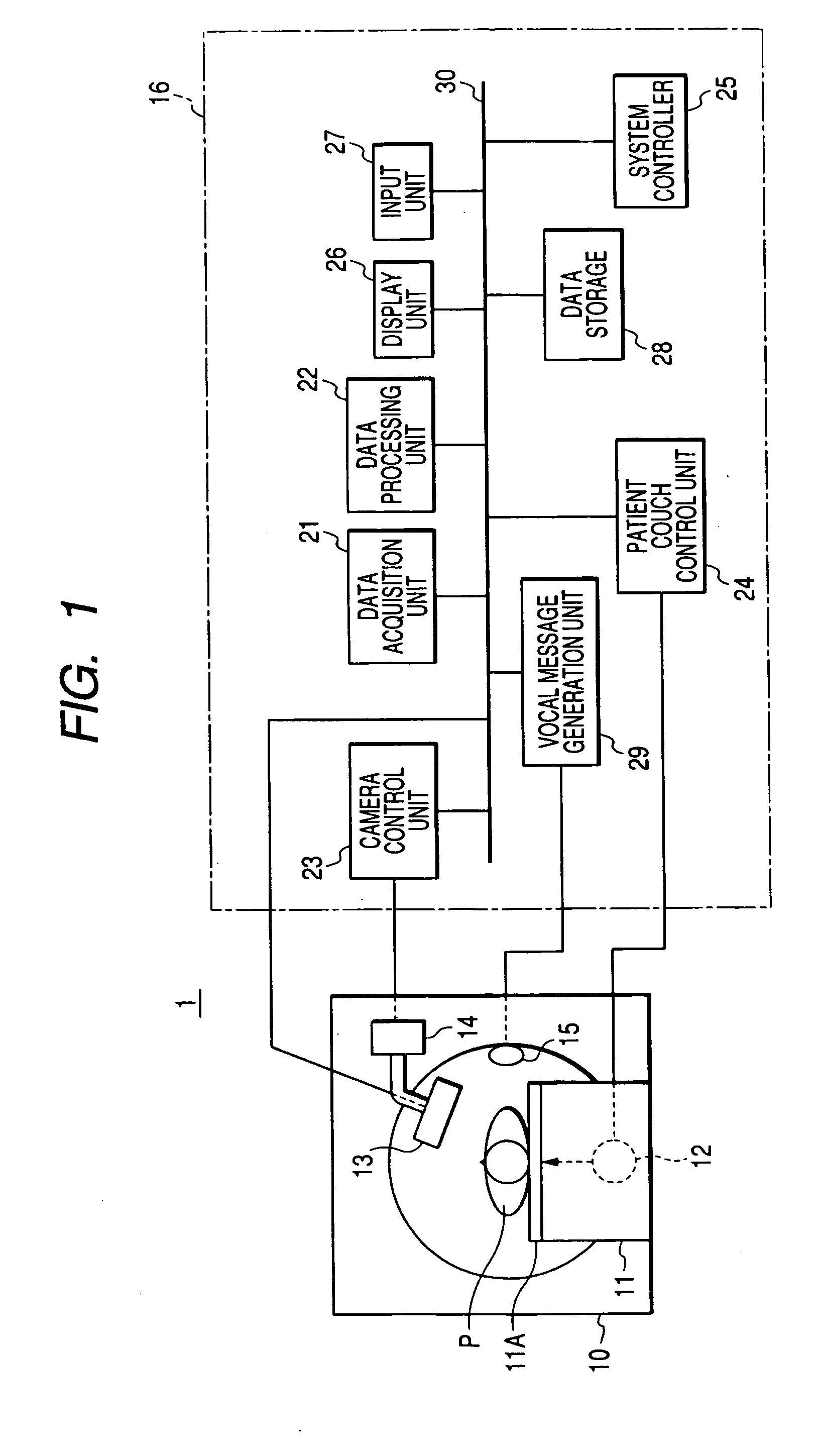
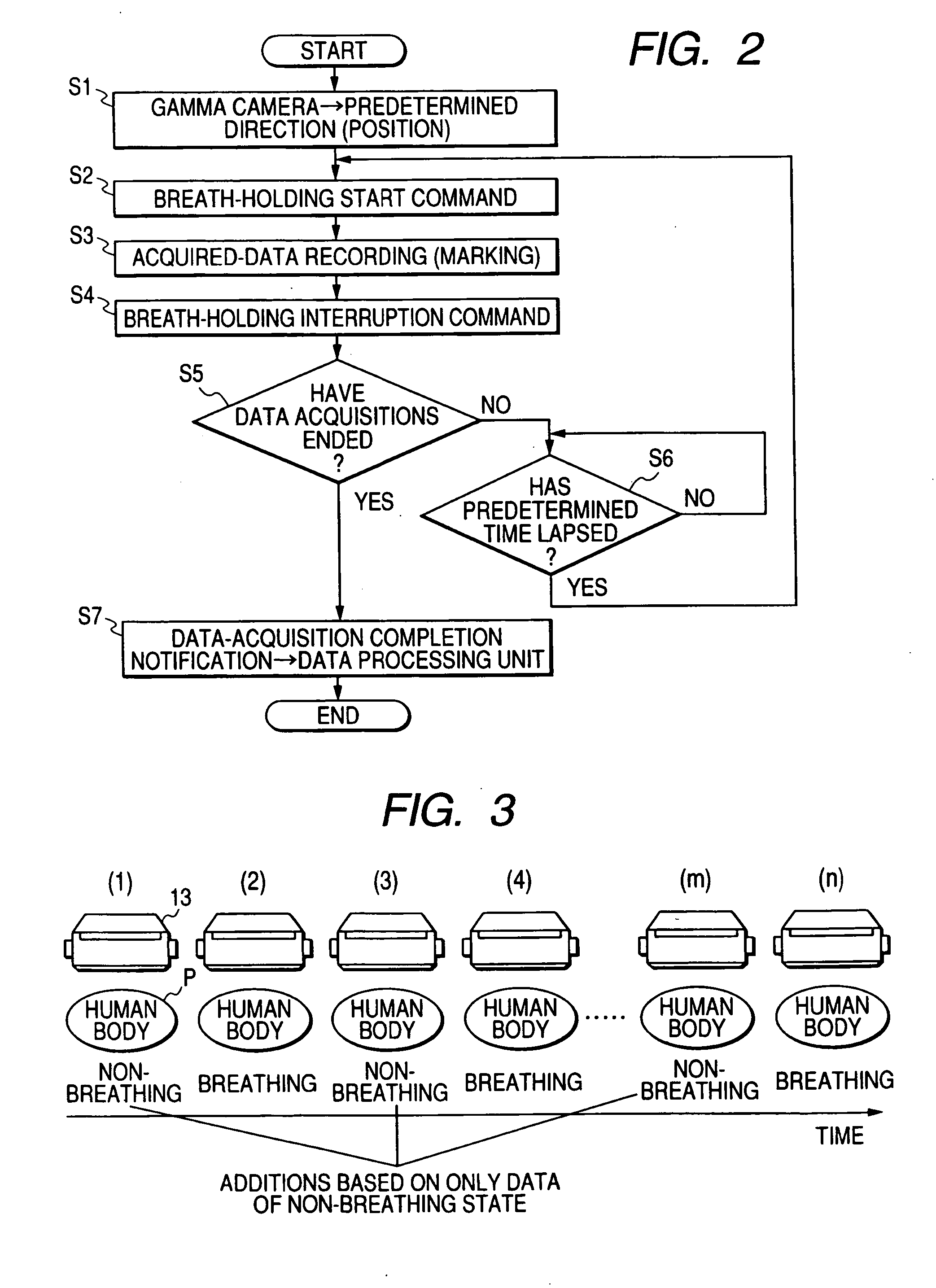
Nuclear medical diagnostic equipment and data acquisition method for nuclear medical diagnosis
ActiveUS20050187465A1High position resolutionHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyData acquisitionMedical diagnosis
A nuclear medical diagnostic equipment wherein radiation which is emitted by a nuclide administered into the body of a patient is detected as projection data by a gamma camera, and an image which indicates the distribution of the nuclide within the body of the patient is obtained on the basis of the projection data. The equipment comprises a rotation unit which rotates the radiation detector round the patient, a respiration identification unit which identifies breathing of the patient and non-breathing thereof based on breath holding, a data storage unit in which the radiation detection data acquired by the radiation detector are stored in an identifiable manner on the basis of a result of the identification by the respiration identification unit, and an image generation unit which generates the image from the radiation detection data stored in the data storage unit on the basis of the result of the identification by the respiration identification unit.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Psma-binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110142760A1Satisfies long standingSharp contrastUrea derivatives preparationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsAntigenProstate cancer cell
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding compounds having radioisotope substituents are described, as well as chemical precursors thereof. Compounds include pyridine containing compounds, compounds having phenylhydrazine structures, and acylated lysine compounds. The compounds allow ready incorporation of radionuclides for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging, for example, prostate cancer cells and angiogenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Fast reactor type coupling nuclear reaction implementation method and nuclear reactor for same
InactiveCN105023621AInherently safeReduce engineering difficultyFuel elementsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreInherent safety
The present invention relates to a fast reactor type coupling nuclear reaction implementation method and a nuclear reactor for same. The main contents comprise: a fast reactor type coupling nuclear reaction implementation method, a reactor modular design approach, a fast reactor type coupling nuclear reactor, a reactor core, a fuel element, a nuclear control system, and a proliferation fuel system. The fast reactor type coupling nuclear reactor mainly combusts thorium and nuclear waste, and has inherent security. The reactor main container is composed of a fission pool and a moderating pool that are completely isolated from each other but coupling to each other. A primary coolant is separated from a moderator. A thermal insulation layer is disposed between the fission pool and the moderating pool so that both can perform neutron exchange but heat exchange is blocked. Fast neutrons produced by the fission pool and moderated neutrons reflected by the moderating pool may enable the reactor core to simultaneously perform coupling nuclear reaction of the two types of neutrons. The moderating pool may be provided with the nuclear control system, and ex-core coupling core control may be implemented. The moderating pool is provided with a thorium purification fuel system, and on-line extraction of the purification fuel can be performed, and separation of nuclide is safe and simple, thereby providing a solution to the technical bottleneck of "thorium reactor".
Owner:陈安海
Method and device for treating radioactive wastes
ActiveCN102157215AAvoid pollutionImprove corrosion resistanceRadioactive decontaminationPlasma techniqueRefractoryRadioactive waste
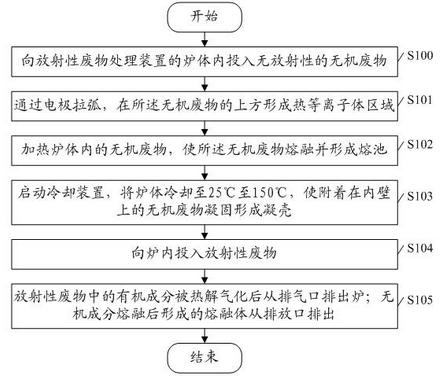
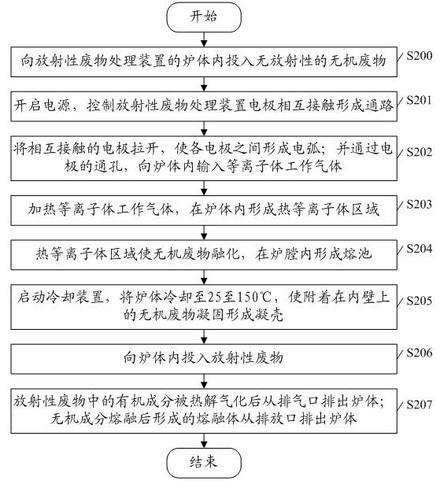
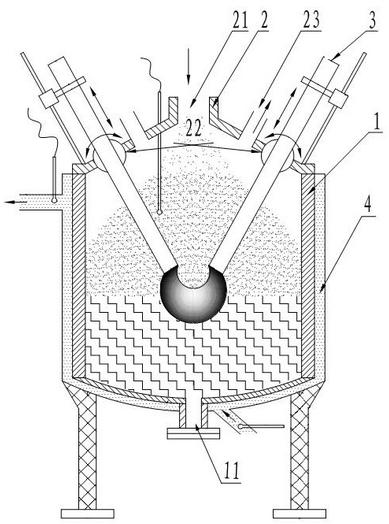
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for treating radioactive wastes. The method comprises the following steps of: putting nonradioactive inorganic wastes into a furnace body of a radioactive waste treatment device to form a thermal plasma area above the inorganic wastes by electrode arcing, and heating the putted inorganic wastes to form a molten pool; starting a coolingdevice to cool down the furnace body to a temperature of 25-150 DEG C so as to make the inorganic wastes attached to the inner wall of the furnace body be solidified to form a shell; putting radioactive wastes into the furnace body to pyrolyze organic elements of the radioactive wastes, and then exhausting the generated gas from the furnace body; and charging inorganic elements of the radioactivewastes into the molten pool to be molten, and discharging the molten inorganic elements out of the furnace body. During the implementation of the method and device disclosed by the invention, the furnace body does not need refractory materials, and the molten body is solidified in an area near the inner wall of the furnace to form the shell, thus the inner wall of the furnace does not directly contact with the molten body, radioactive nuclides are prevented from polluting the inner wall of the furnace, the device can be used for treating various wastes, the service life of the device is long and the amount of residual wastes is small.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD
Semi-chromatography gamma scanning method for low-medium radioactive waste barrel measurement
ActiveCN104714245AHigh measurement accuracyTomoscanX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateLow-level waste
The invention provides a semi-chromatography gamma scanning method for low-medium radioactive waste barrel measurement. A rotary platform, a detector platform, a detector with a collimator, a transmission source platform, a transmission source, a shielding part of the transmission source and an analysis module are adopted in the method. A waste barrel is divided into multiple section layers in the height direction, the waste barrel is rotated, surface distribution of radioactive point sources on the section layers is changed into linear distribution of ring sources in the radius direction, the detector conducts measurement at different section layer heights and different eccentric positions in the section layers, an equation set reflecting the mutual relation between the detector counting rate and the activity of nuclide in annular grids is established, the equation set is solved, distribution of the activity of the radioactive nuclide in the waste barrel in the diameter direction and the height direction of the barrel is acquired, and the total activity of the radioactive nuclide in the waste barrel is acquired through summation. The method is high in measurement accuracy, short in measurement time and high in practical value and application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
SSTR1-selective analogs
InactiveUS7019109B2High affinityEasy to markPeptide sourcesRadioactive preparation carriersNervous systemScreening method
Analogs of SRIF which are selective for SSTR1 in contrast to the other cloned SRIF receptors. These analogs are useful in determining the tissue and cellular expression of the receptor SSTR1 and its biological role in the endocrine, exocrine and nervous system, as well as in regulating tumor growth. SRIF analog peptides, such as des-AA1,2,5[D-Trp8, NαMeIAmp9, Tyr11]-SRIF and counterparts incorporating Cbm at the N-terminus and / or NαSer13, inhibit the binding of a universal SRIF radioligand to the cloned human receptor SSTR1, but they do not bind with significant affinity to human SSTR2, SSTR3, SSTR4 or SSTR5. By incorporating an iodinated tyrosine in position-2 or in position-11 in these SSTR1-selective SRIF analogs, a labeled compound useful in drug-screening methods is provided. The N-terminus accommodates bulky moieties without loss of selectivity, and a carbamoyl moiety or a conjugating agent that will accept a radioactive nuclide or will link to a cytotoxin may be present at the N-terminus.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Gamma nuclide identification method
ActiveCN105607111AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementX-ray spectral distribution measurementGamma energyRadiation field
The invention provides a gamma nuclide fast identification method in a complex radiation field, comprising the following steps: measuring a radiation field to get a gamma energy spectrum; deducting a comprehensive background from the gamma energy spectrum and reducing the noise of the gamma energy spectrum to get a net energy spectrum; determining potential nuclides according to the peak positions in the net energy spectrum; calculating the total net peak area of each potential nuclide; standardizing the total net peak area of each potential nuclide to get the standardized total net peak area of the potential nuclide; deducting a Compton scattering background from the standardized total net peak area of each potential nuclide to get the pure peak area value of each potential nuclide; calculating the total probability value and the probability standard threshold of each potential nuclide in the radiation field; and calculating the existence probability of each potential nuclide. According to the invention, multiple times of background deduction calculation and standardization are performed on the measured energy spectrum data, and a nuclide can be identified and the existence probability of the nuclide can be calculated quickly based on the total probability value calculated based on the probability statistics principle and the standard threshold calculated by a standard source.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Nuclide rapid identification method based on pattern recognition
ActiveCN103424766ALong measurement timeMeet the statistical error requirementsX-ray spectral distribution measurementCharacteristic energyRapid identification
The present invention relates to a method of applying a pattern recognition method to a digital spectrometer to carry out nuclide rapid identification. The method comprises the steps of using the digital spectrometer to carry out real-time acquisition and data pre-processing on a nuclear radiation pulse signal, and selecting the characteristic energy ray and the area increase ratio of the characteristic energy peak of a correlated nuclide as the needed characteristic information, wherein the characteristic energy ray can be used as the main characteristic to identify the existence of the nuclide, and the area increase ratio of the characteristic energy peak is used as the auxiliary characteristic to be used as the criterion of the parallel analysis of a multi-ray nuclide. The advantages of the present invention are that: the area increase ratio of the characteristic energy peak of the nuclide substitutes the operation in the conventional method of selecting the full-energy peak area of the characteristic ray of the nuclide as the basis of identifying the existence of the nuclide, so that the identification of the nuclide is not interfered by the full-energy peak counting area of the characteristic ray of the nuclide accumulated in the early stage, and the identification reliability of the nuclide is improved; the characteristic extraction process maps an input pattern from the object space to the characteristic space, so that the quantity of information is compressed, the identification and judgement are easy, and the identification speed and efficiency of the nuclide are improved.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
Simulated dose calibrator source standard for positron emission tomography radionuclides
ActiveUS7825372B2Accurate activityCalibration apparatusPortable shielded containersEpoxyPositron emitters
A method for calibration and a calibrator source standard calibrated by the method are provided. The calibration method includes providing mock syringes, or other simulated dose container. A first of the mock syringes is filled with a short half life positron emitter. A second of the mock syringes is filled with a longer half life radionuclide set in a matrix material such as an epoxy. The activities of the two syringes can be determined, ideally in the same ion chamber, for example, against a radioactive source standard having a half life greater than the first and second radionuclides. This allows a conversion factor to be determined which can be used for a calibrator source standard formed as for the second mock syringe (i.e., with the same type of container containing the longer half life radionuclide set in a matrix material), when the calibrator source standard is used as a proxy for calibrating a calibrator for use in determining the activity of a dose container of the same configuration containing a dose of the short lived radionuclide.
Owner:RADQUAL
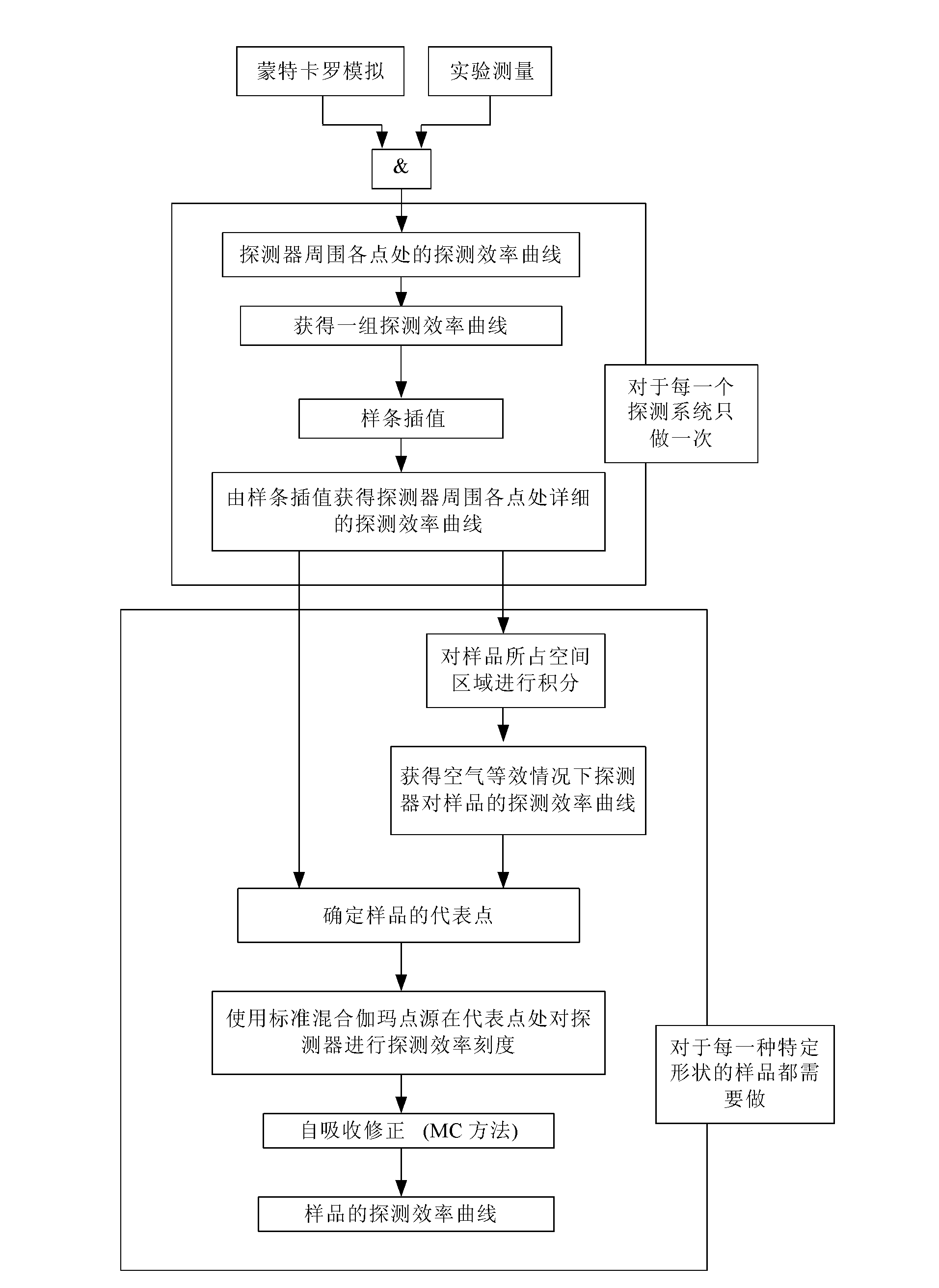
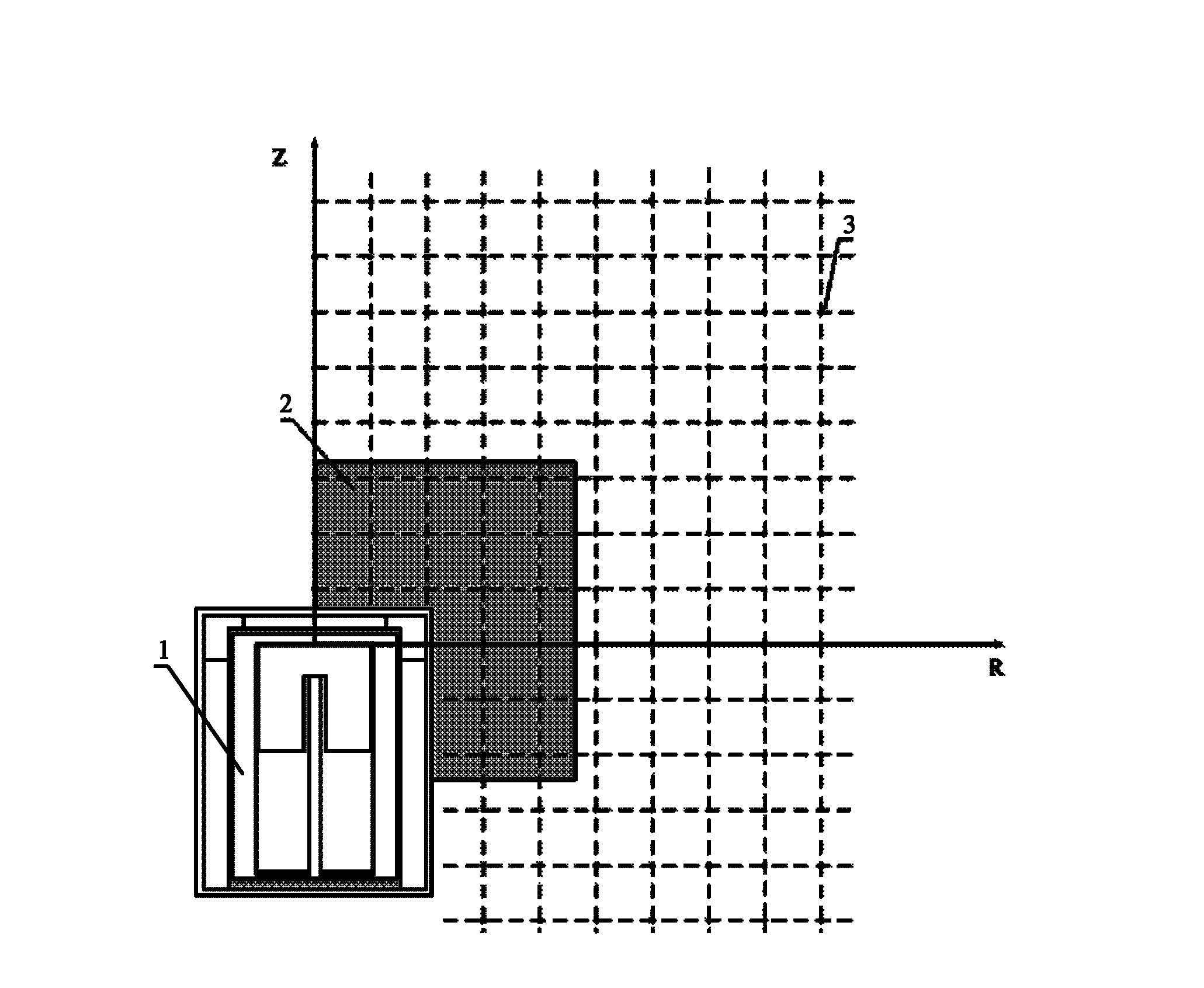
Mixed nuclide gamma point source volume sample efficiency calibration method
InactiveCN103135122AGuarantee the traceability of the quantity valueAvoid complexityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCalibration resultRadioactive waste
The invention belongs to the ionizing radiation measurement technology, in particular to a mixed nuclide gamma point source volume sample efficiency calibration method. Measurement results of solid mixed nuclide gamma point source around a detector are adopted and the monte carlo simulation calculation is combined to determine the detection efficiency of the detector to arbitrary axisymmetric shape volume samples. Through the measurement results of solid mixed nuclide gamma point source around the detector, a volume sample detection efficiency curve can be determined. Under the premise that the traceability of calibration result values is guaranteed, the problems that complex manufacturing process and occurrence of radioactive wastes which are brought by other calibration methods ( such as standard volume sample calibration) are avoided.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Biodegradable and absorbable polymer superfine fibre film with radioactive nuclide marker and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101301496AImprove effectivenessRadioactiveSurgeryRadioactive preparation carriersFiberAbsorbable polymers
The invention relates to a bio-degradable and bio-absorbable macromolecule superfine fiber film with a radioactive nuclide mark and a method for making the same as well as medical use. The invention comprises the bio-degradable and bio-absorbable macromolecule superfine fiber film material or a composite superfine fiber film material with physically embedding radioactive nuclide mark, or the bio-degradable and bio-absorbable macromolecule superfine fiber film material or the composite superfine fiber film material with chelate radioactive nuclide mark having a bi-functional group coupling agent with surface chemical modification. The film material is a non-woven material consisting of fibers with diameters ranging from scores of nanometers to thousands of nanometers which is made through an electrostatic spinning process, and the radioactive nuclide is compounded inside the fibers or on the surfaces of the fibers by means of physics and chemic. The fiber film material with the radioactive nuclide mark is covered at a tumour part or a lesion tissue part after resection, thereby effectively killing the residual tumour cells, and playing roles in stanching, healing wound and preventing adhesion and so on.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic particle extractive agent and method for isolating radionuclide
InactiveCN101231899AEasy to desorbEasy to operateOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismLiquid solutions solvent extractionLiquid wasteAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses finished magnetic-particle extractant combined with magnetic nanometer microspheres, a preparation method thereof and application thereof in separation of radioactive species. The extractant consists of magnetic fine particles carrying separated functional groups of radioactive species. Nanometer particles of magnetism Fe3O4 are dispersed inside a polymer. A layer of ingredients selected from crown ether and ramification thereof or neutral phosphorus (TBP, TOPO) ramification and tertiary amine (TOA) ramification connected with chemical bonds is arranged on the surface of the polymer. The magnetic particle extractant can be directly added to solution containing radioactive species, and is stirred at a room temperature. The magnetic extractant is separated out with the applied magnetic field to separate radioactive species. The invention is integrated with the advantages of simple operation of magnetic separation and high selectivity of extraction separation, and can separate target radioactive species out from complicated radioactive liquid waste containing one or a plurality of kinds of <90>Sr and actinide elements. The magnetic-particles can be desorbed easily, and can be used repeatedly without producing secondary waste. In addition, by adopting the invention, continuous large-scale separation can be completed.
Owner:NAT INST FOR RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION & NUCLEAR SAFETY CHINESE CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
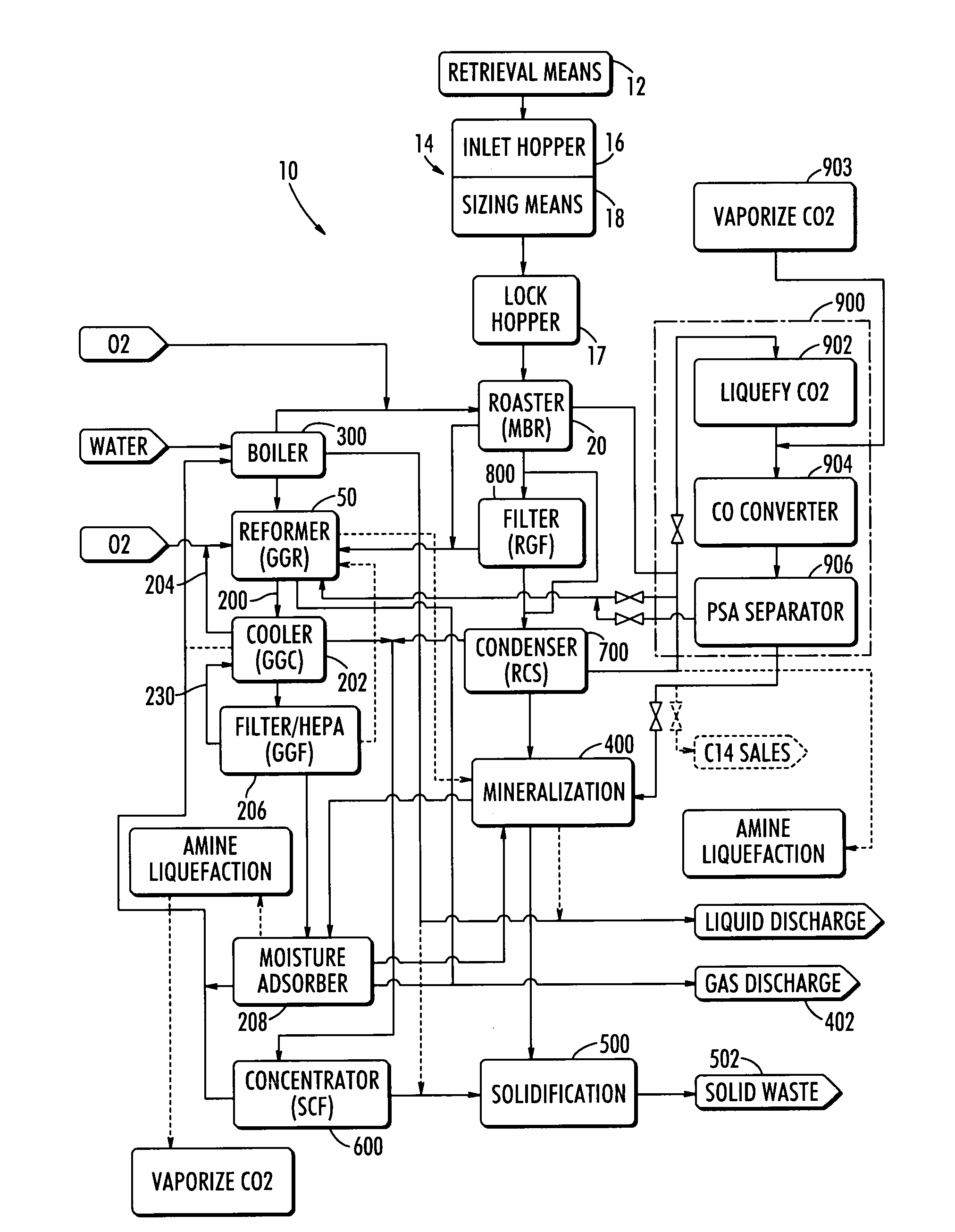
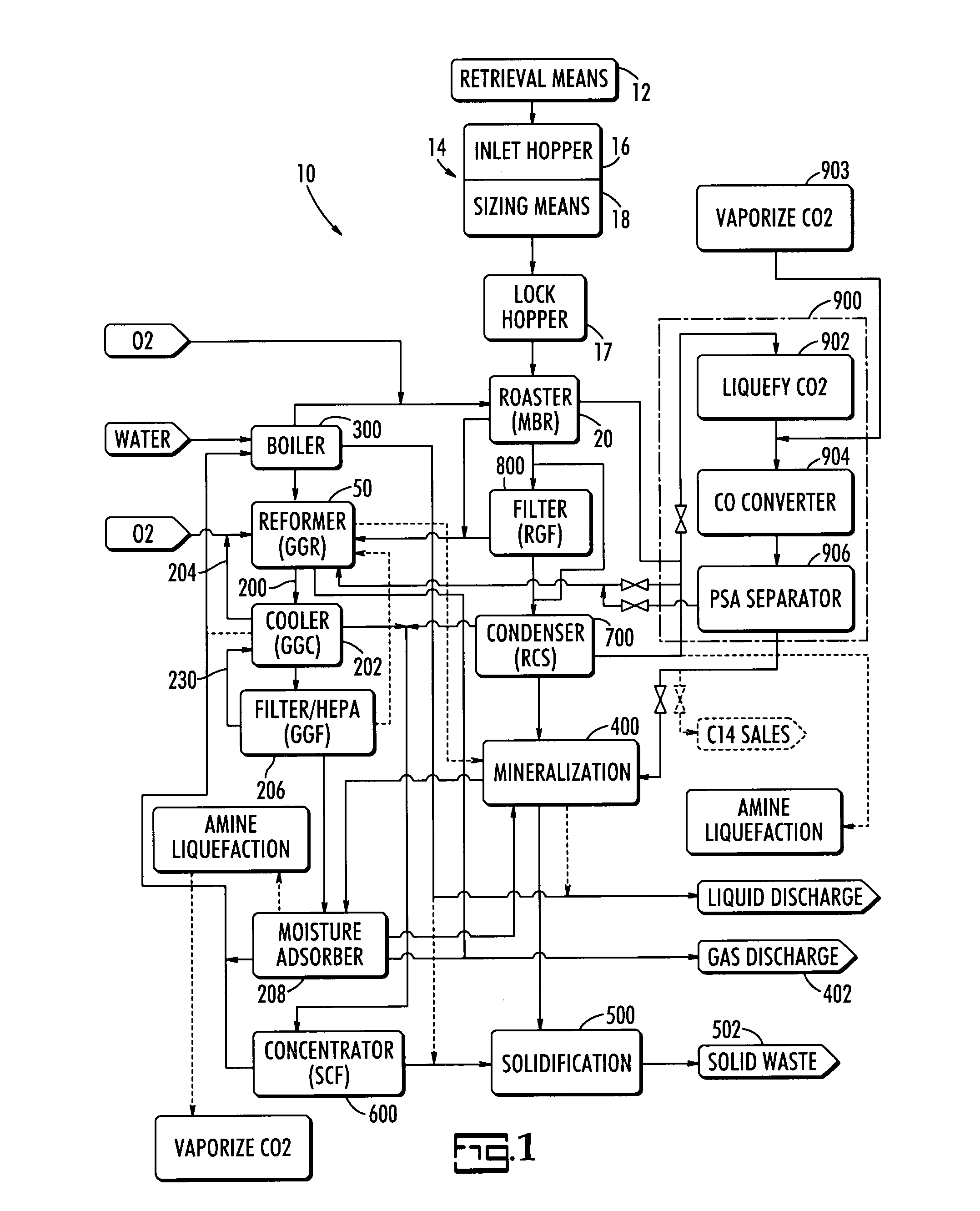
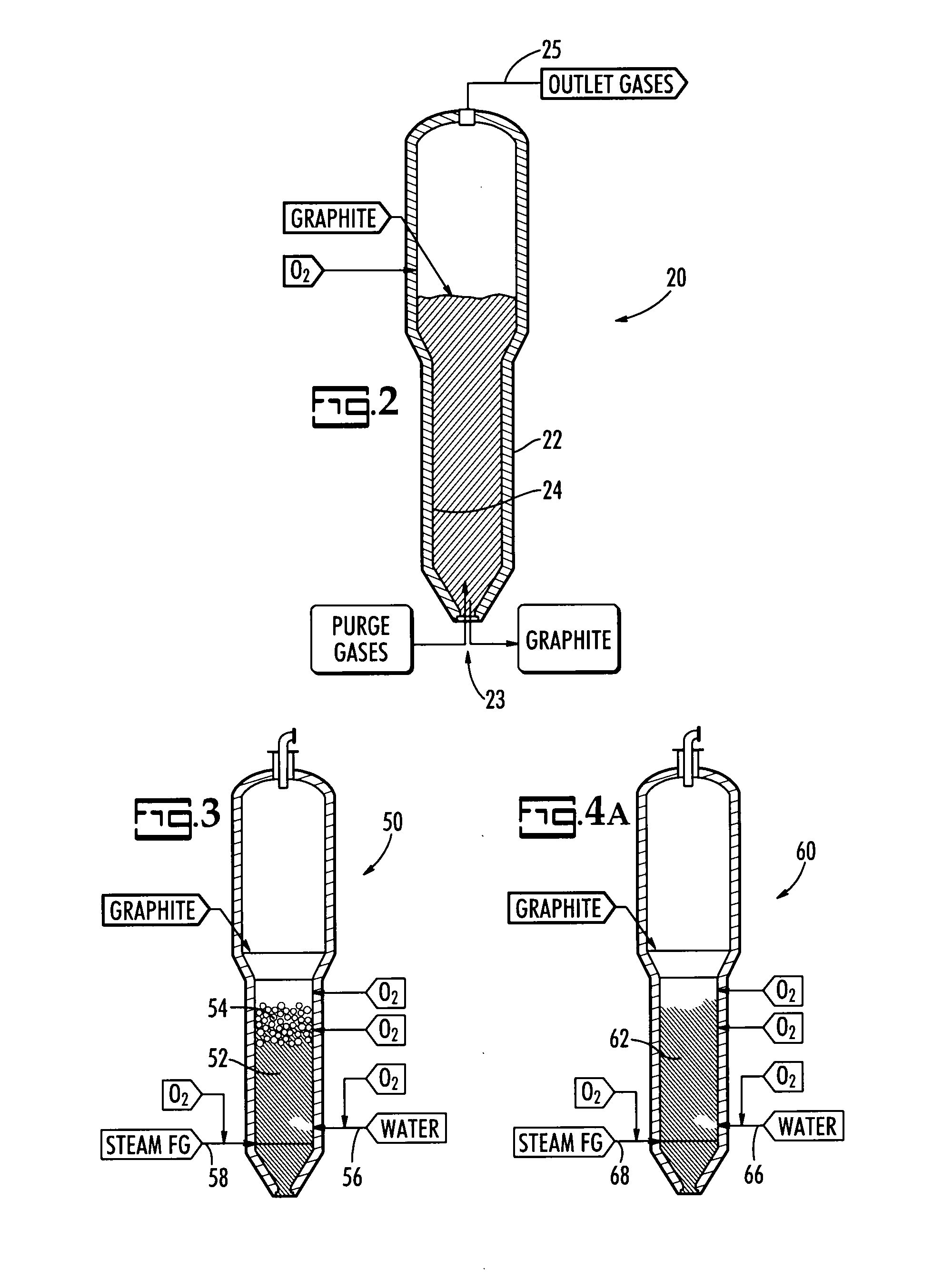
Steam reforming process system for graphite destruction and capture of radionuclides
InactiveUS20080181835A1Step is made and efficientAvoid excessive dischargeTransuranic element compoundsRadium compoundsProcess systemsSteam reforming
A system for the treatment and recycling of graphite containing radionuclides including a two stage method that employes a thermal roaster that is operatively connected to a steam reformer. In the first stage, radioactive graphite is roasted or heated to volatize a first amount of radionuclides contained in the graphite. In the second stage, the roasted graphite is reacted with steam or gases containing water vapor so that a second amount of radionuclides is removed. Optionally, the present system also processes the radionuclides to enable their disposal.
Owner:STUDSVIK INC
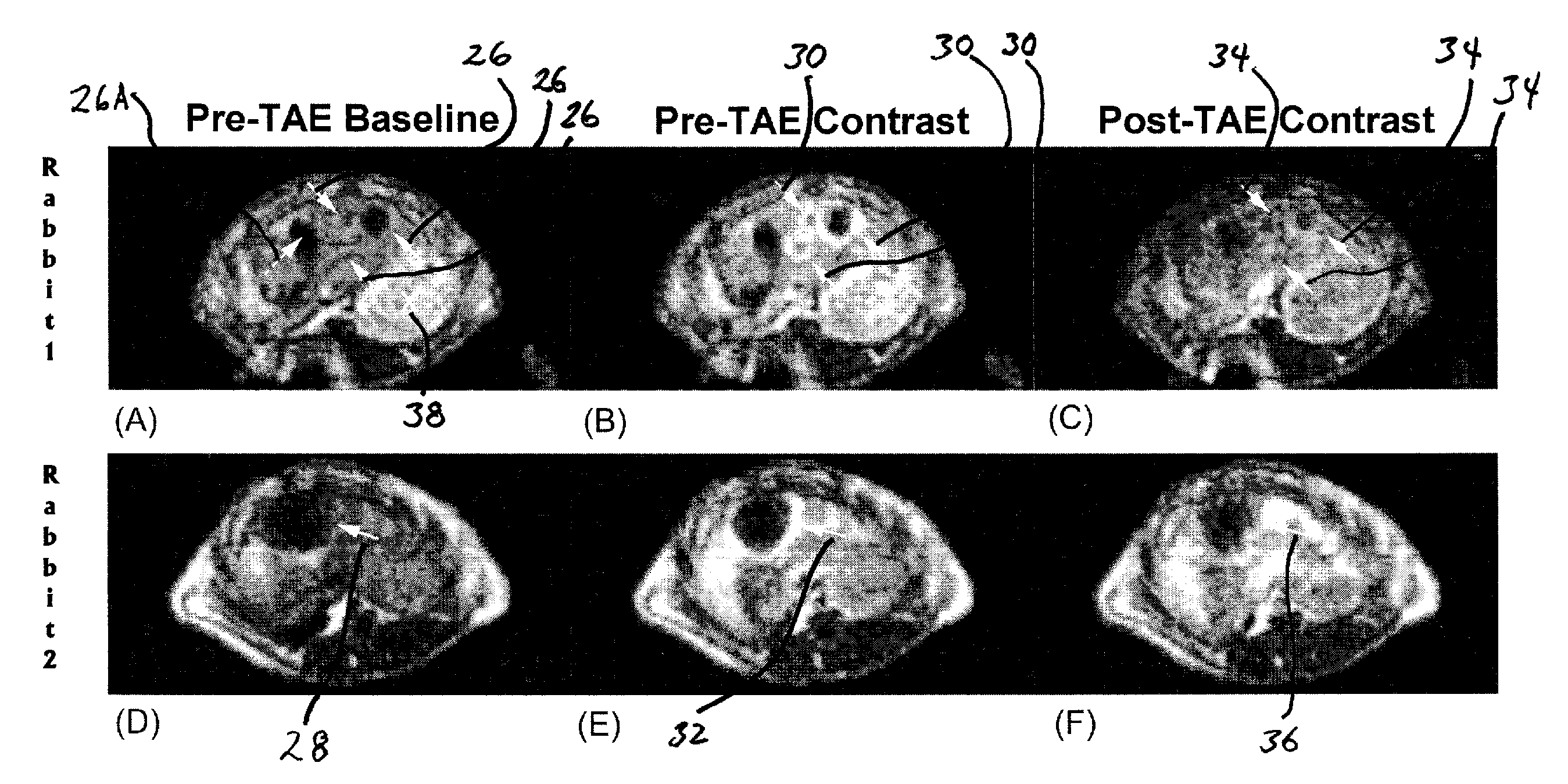
Method for transcatheter intra-arterial perfusion magnetic resonance imaging
A method to serially determine changes in perfusion to tissues is provided. This method involves injecting contrast material into a catheter that is positioned in the blood supply proximal to the targeted tissue of interest, acquiring a time series of images that depicts the uptake of this contrast material within the tissue, deriving semi-quantitative or quantitative perfusion metrics based upon the time series of perfusion images, altering perfusion to the targeted tissue by means of injecting pharmacologic agents or embolic agents into the blood vessels supplying the targeted tissue, repeating the acquisition of perfusion images to serially monitor changes in tissue perfusion after each alteration, and calculating changes in perfusion metrics after each series of perfusion images. This method is used to monitor changes in perfusion to various tissues, including a diverse array of tumors. The perfusion imaging method can be acquired using magnetic resonance, x-ray computed tomography, or radionuclide imaging. The perfusion metric is serially measured during an embolization procedure as a means of measuring changes in tissue perfusion or to target an endpoint based upon a specific alteration in the calculated perfusion metric.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
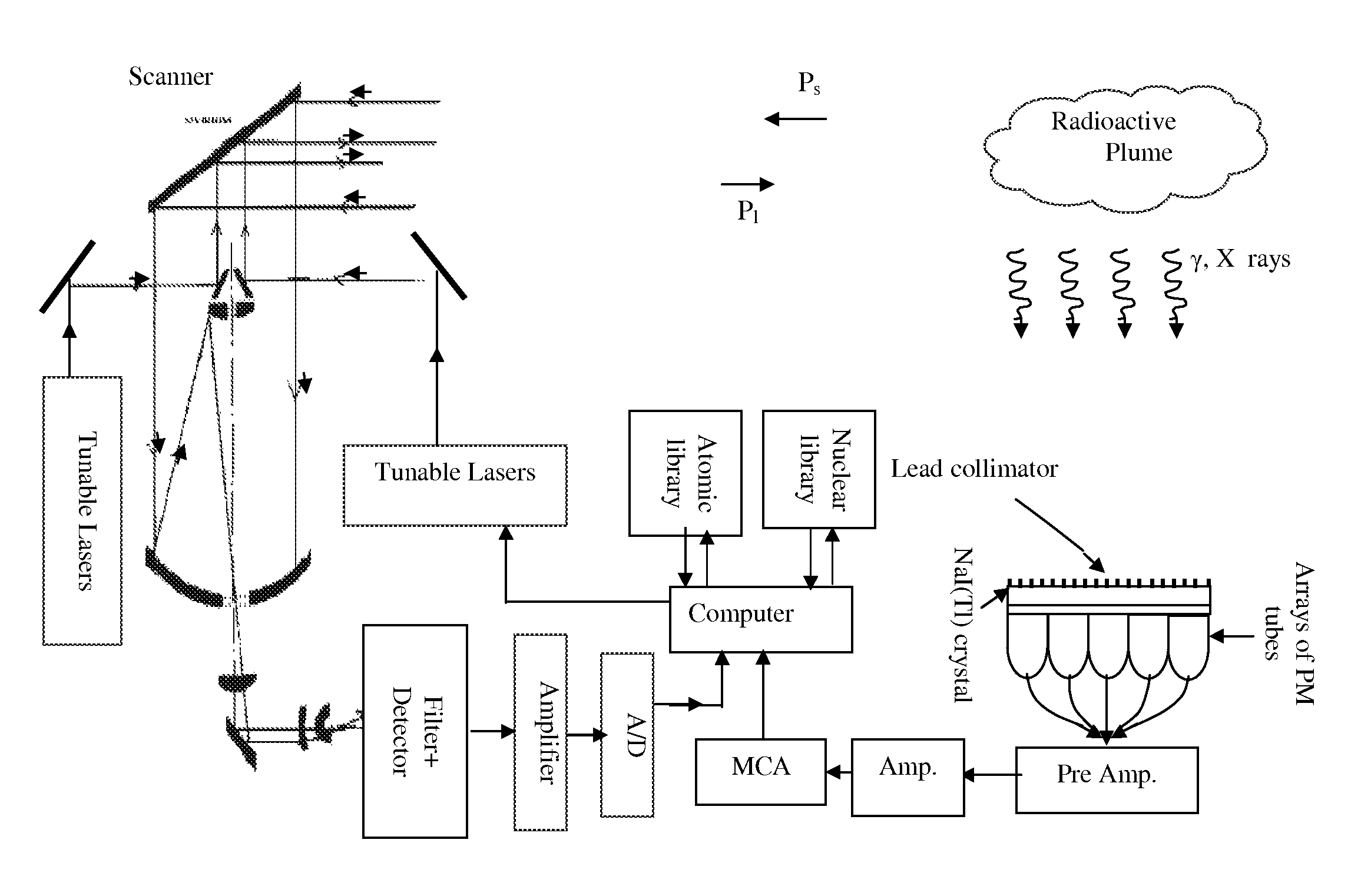
DIAL-Phoswich hybrid system for remote sensing of radioactive plumes in order to evaluate external dose rate
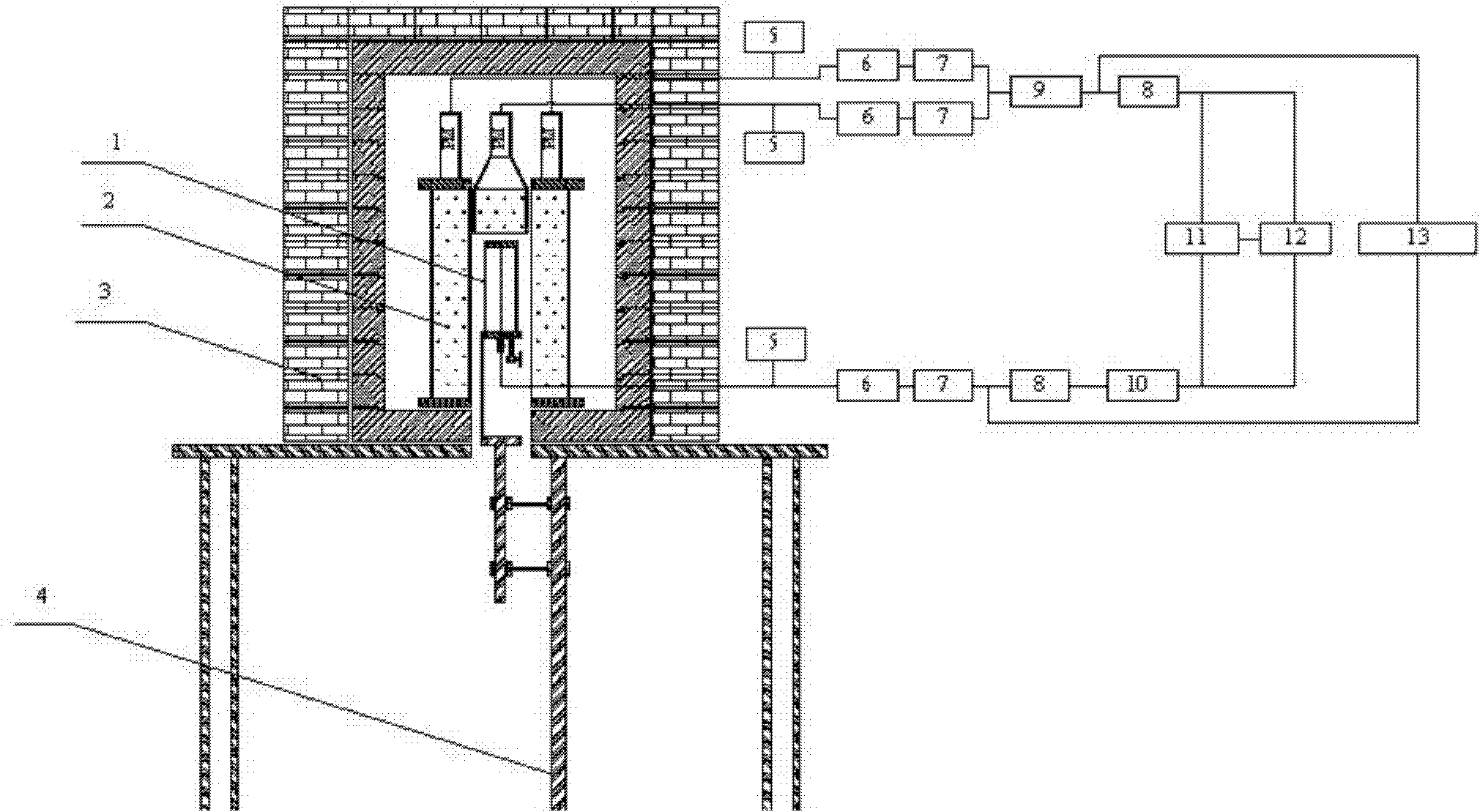
InactiveUS7566881B2Rapid responseHigh gainVolume/mass flow measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsDose rateNuclear power
An interactive combination of Phoswich detector array (PDA) and differential absorption lidar (DIAL) is proposed to trace the unknown radioactive plumes released into the atmosphere from a reactor stack, containment of the nuclear power plants, radioisotope separation laboratories, reprocessing plants or the uranium conversion facilities. The hybrid system represents a powerful technique for the prompt identification and quantification of the effluents with various radionuclide contents to determine the corresponding external dose rate accordingly.
Owner:SHAHI LAILA
Pyrochlore type high-entropy oxide solidified body and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111533557AHigh selectivityPromote solid solutionRare-earth elementDeep geological repository
The invention relates to a pyrochlore type high-entropy oxide solidified body and a preparation method thereof. The high-entropy oxide solidified body has a pyrochlore structure, and the chemical formula is RE2M2O7, wherein RE is a rare earth element, and M is a transition metal element. The pyrochlore-type high-entropy oxide solidified body of the invention has excellent chemical stability. Radioactive nuclides of different valence states and types can be solidified in crystal lattices of a high-entropy oxide base material, deep geological disposal is facilitated, , and the system of solidification treatment of base materials for radioactive nuclear waste is enriched. The method is low-cost, is simple and feasible and has a wide application range. The process is high in efficiency and good in safety, and is expected to be applied to the technical field of radioactive nuclear waste treatment.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Channel type radioactive detector with low detection limit
ActiveCN102455431ALow detection limitImprove signal-to-noise ratioX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioChannel types
The invention discloses a channel type radioactive detector with a low detection limit, which is used for a channel type radioactive monitoring system. The channel type radioactive detector comprises a shell, a shielding body arranged in the shell, a plastic scintillator, a first photomultiplier, a first preamplifier, a second photomultiplier, a second preamplifier, a signal processing and controlling unit. Two ends of the plastic scintillator are coupled with two photomultipliers through light guides to output two paths of pulse signals. The signal processing and controlling unit is internally provided with an adder circuit and an accordance circuit, which are used for adding two paths of the pulse signals to detect whether the pulse signals accord with requirements. In the invention, through a signal adding and accordance method and the shielding by using a lead shielding body, the cost can be effectively reduced, the noise is reduced, the signal to noise ratio is improved, the detection efficiency and the sensitivity are improved, and the energy detection lower limit is reduced, so that low-energy nuclides can be more effectively detected and measurement requirements are better met.
Owner:上海新漫传感科技有限公司
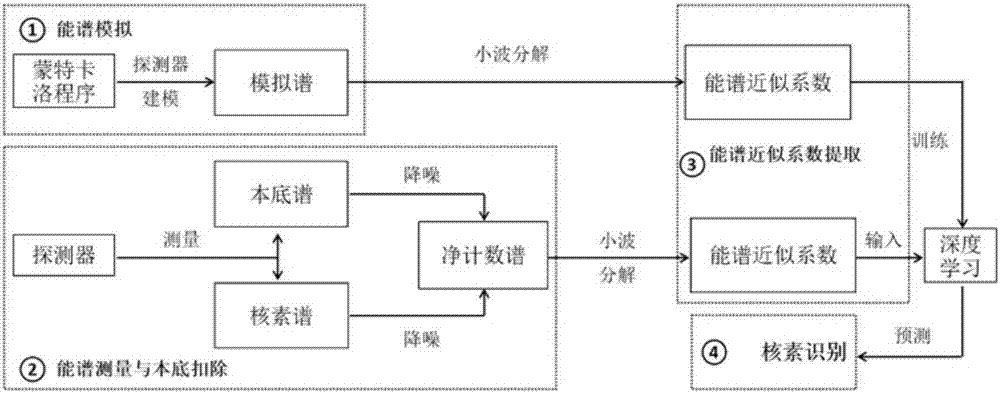
Gamma-ray energy spectrum analysis method based on approximation coefficient and deep learning
ActiveCN107229787AReduce distractionsReduced Signal DimensionalityX-ray spectral distribution measurementDesign optimisation/simulationWavelet decompositionTime ratio
The invention discloses a gamma-ray energy spectrum analysis method based on the approximation coefficient and deep learning. The gamma-ray energy spectrum analysis method comprises following steps of modeling a gamma-ray detector by means of a monte carlo method, and simulating an interested nuclide energy spectrum to obtain a simulated energy spectrum; measuring the energy spectrum by the gamma-ray detector, carrying out smoothing processing on the energy spectrum, carrying out background rejection according to the time scale, and obtaining a pure count spectrum; extracting the approximation coefficient of the simulated energy spectrum by means of a wavelet decomposition method, carrying out normalization processing on the approximation coefficient of the simulated energy spectrum, extracting the approximation coefficient of the pure count spectrum by means of the wavelet decomposition method, and carrying out normalization processing on the approximation coefficient of the pure count spectrum; and taking the approximation coefficient of the simulated energy spectrum as a training sample of a deep learning network in order to predict the nuclide composition in the power spectrum actually measured by the gamma-ray detector. According to the invention, by extracting the approximation coefficient of the simulated energy spectrum and training the deep learning network by means of the simulation sample, and employing the simulation sample to predict the nuclide composition of the actually measured energy spectrum, the energy spectrum nuclides can be identified quickly and stably.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
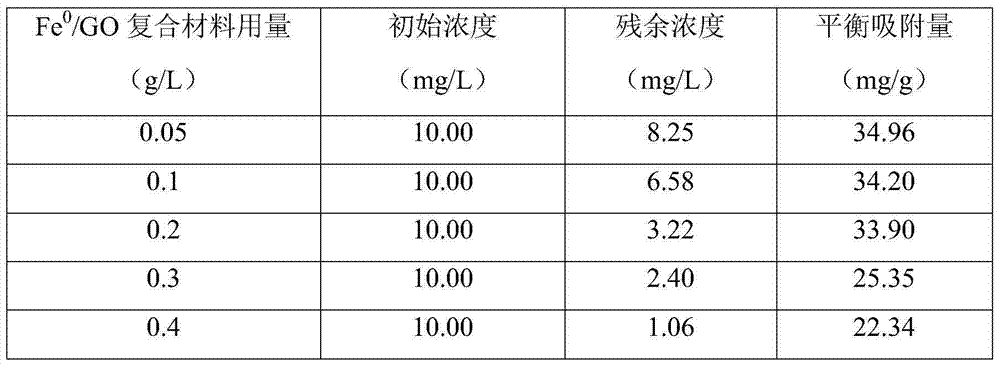
Method for removing radioactive cobalt by using graphene loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material
ActiveCN103578593AAvoid reunionWith adsorption selectivityRadioactive decontaminationDesorptionWastewater
The invention discloses a method for removing radioactive cobalt by using a graphene loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material, and belongs to the technical field of radioactive waste treatment. The method comprises the following steps: adding the graphene loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material into a water sample containing the radioactive nuclide Co, vibrating the mixture at constant temperature, and removing the radioactive nuclide Co after a certain time. The graphene loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material used in the method disclosed by the invention can absorb and select the nuclide, is large in adsorption capacity, and less susceptible to desorption; the absorbed particle has the magnetic property, easy to recycle, small in size, and convenient to store temporarily, the experiment condition is mild, and therefore the composite material has an advantage in the aspect of removing the nuclide Co in the radioactive wastewater. The maximal equilibrium adsorption capacity of the graphene loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material used in the method disclosed by the invention on Co is 114.08mg / g.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for absolutely measuring for radioactive gas nuclide activity
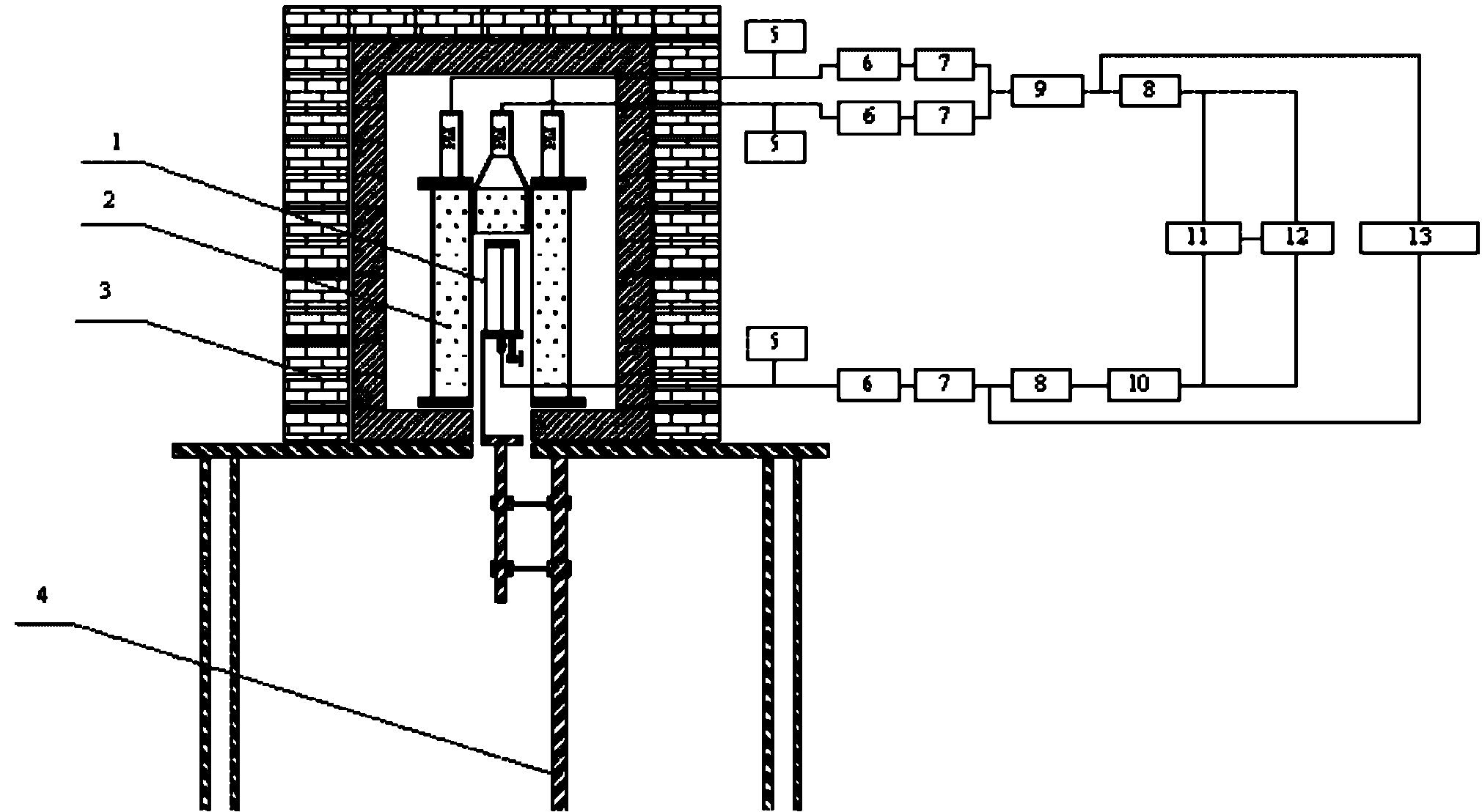
InactiveCN101806910AGuaranteed uniformityRadiation intensity measurementRadioactive gasMeasurement device
The invention relates to a method and a device for absolutely measuring for radioactive gap nuclide activity. The method comprises the following steps: 1) building a gas nuclide coincidence measurement device; 2) preparing a sample; 3) debugging the device; 4) measuring performance parameters of the device; and 5) measuring a gas radioactivity body source, and calculating specific activity. The invention solves the technical problem that the existing length compensation method has low absolute measurement specific activity to certain high-energy beta radial gas nuclide activity. The invention provides a new method for the absolute measurement of the gas nuclide activity.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com