Patents
Literature
482 results about "X ray computed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
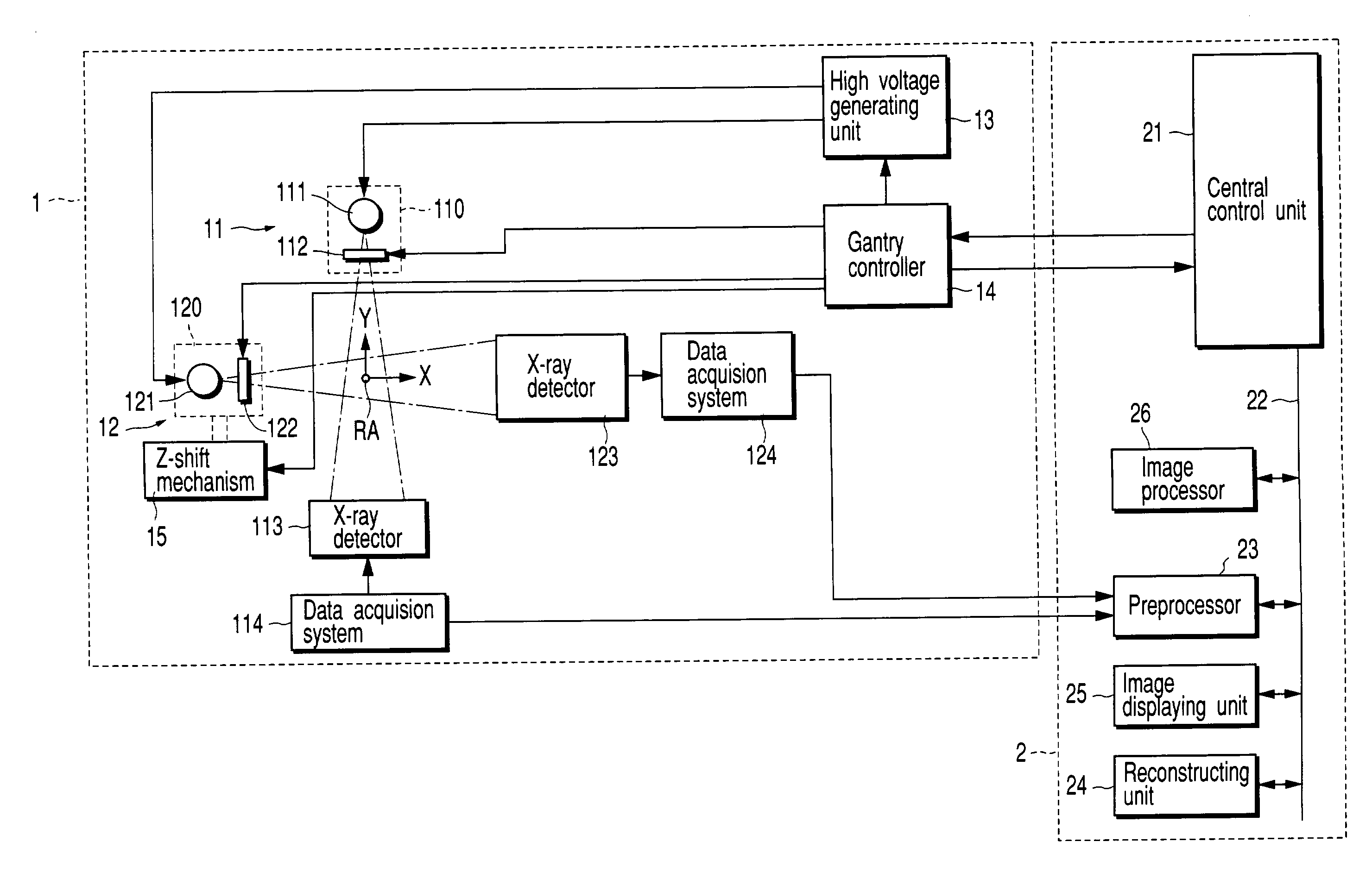
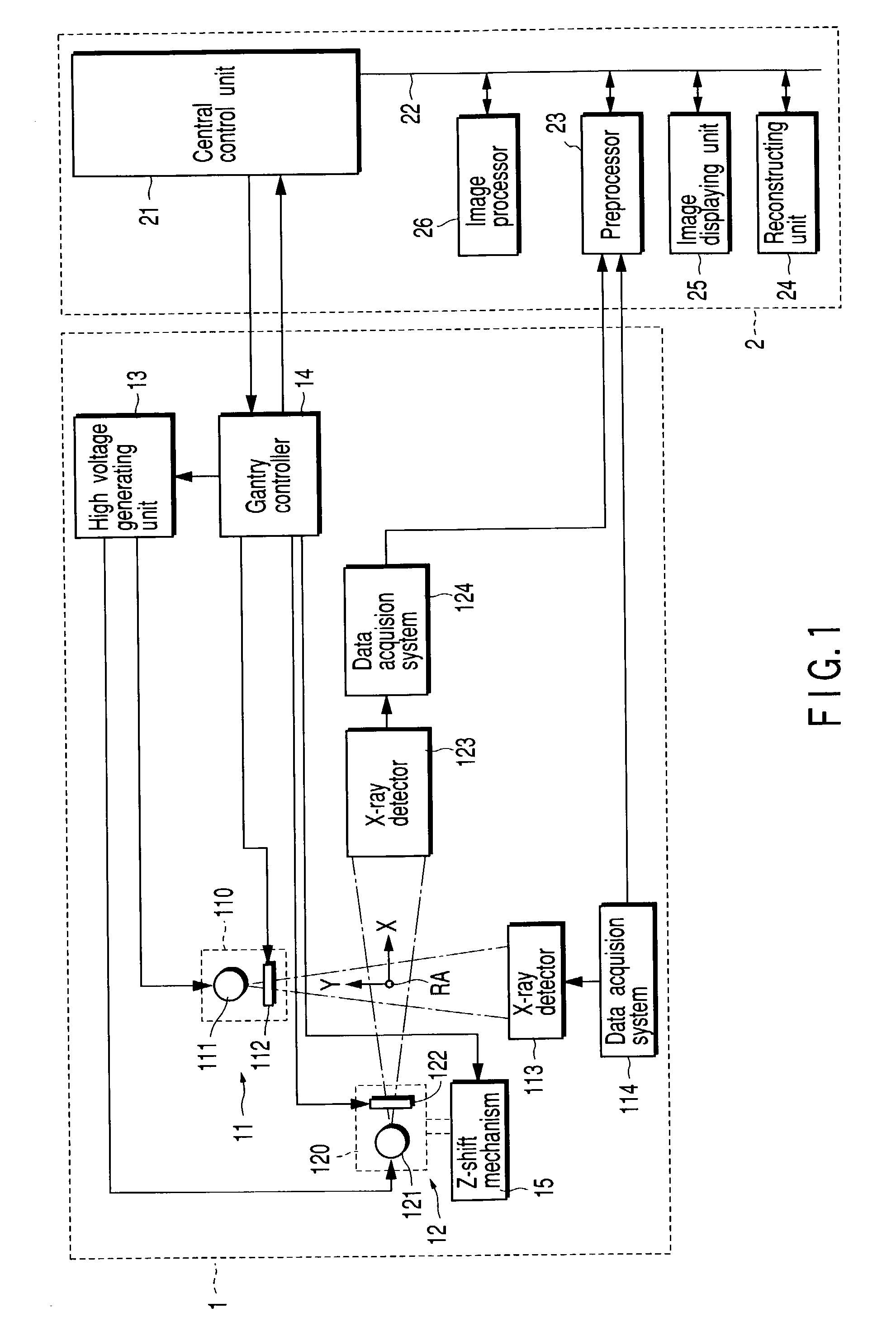
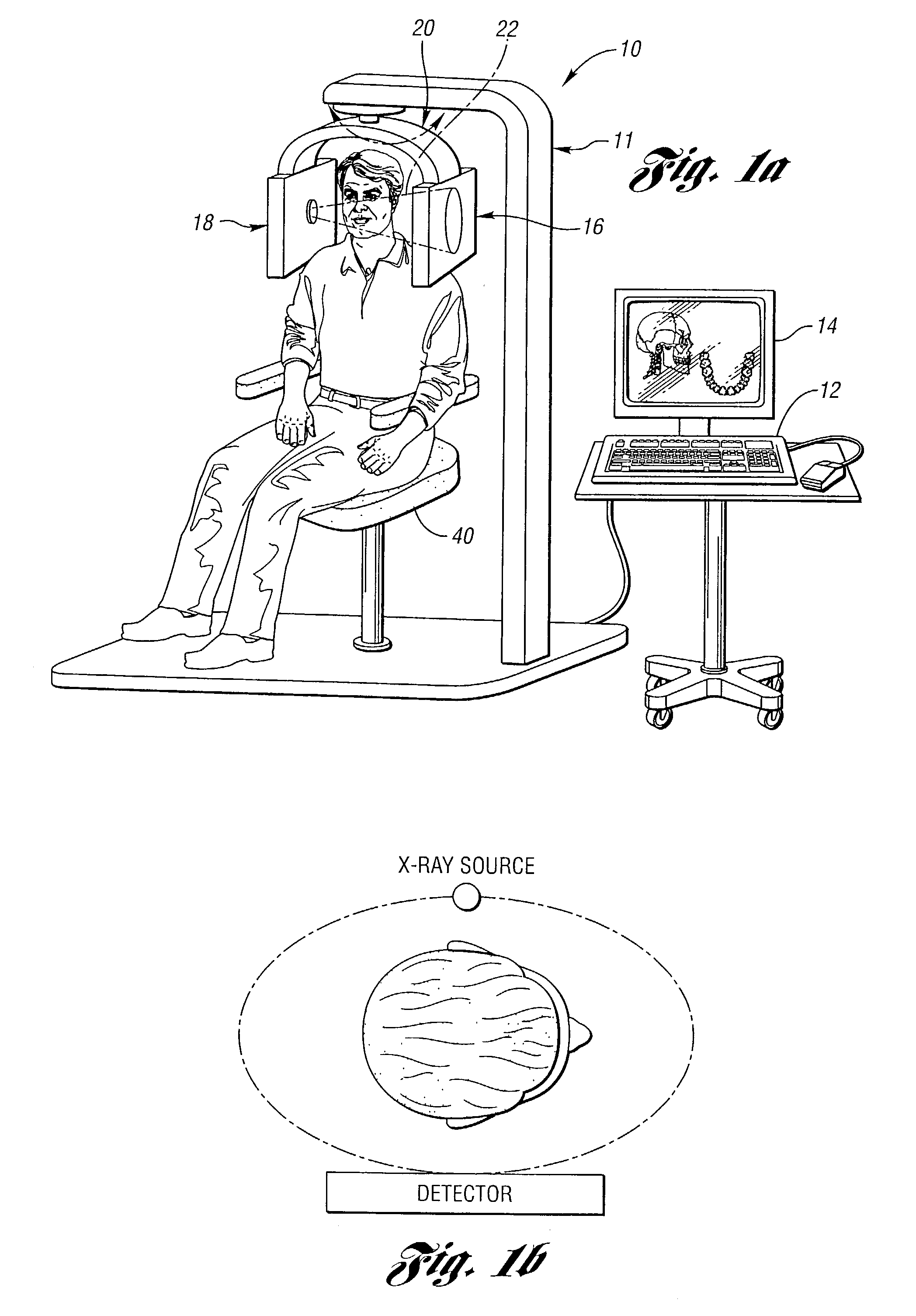
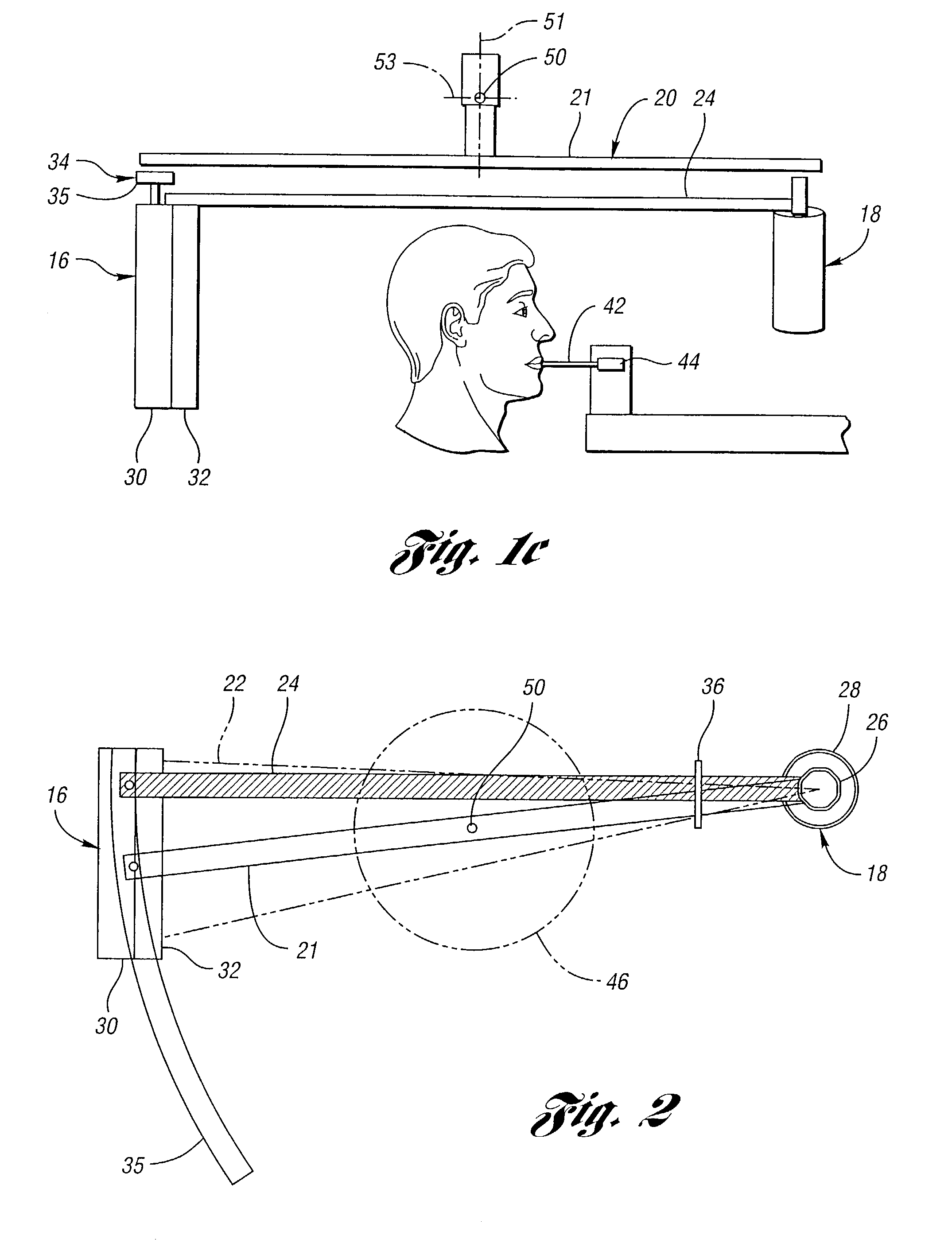
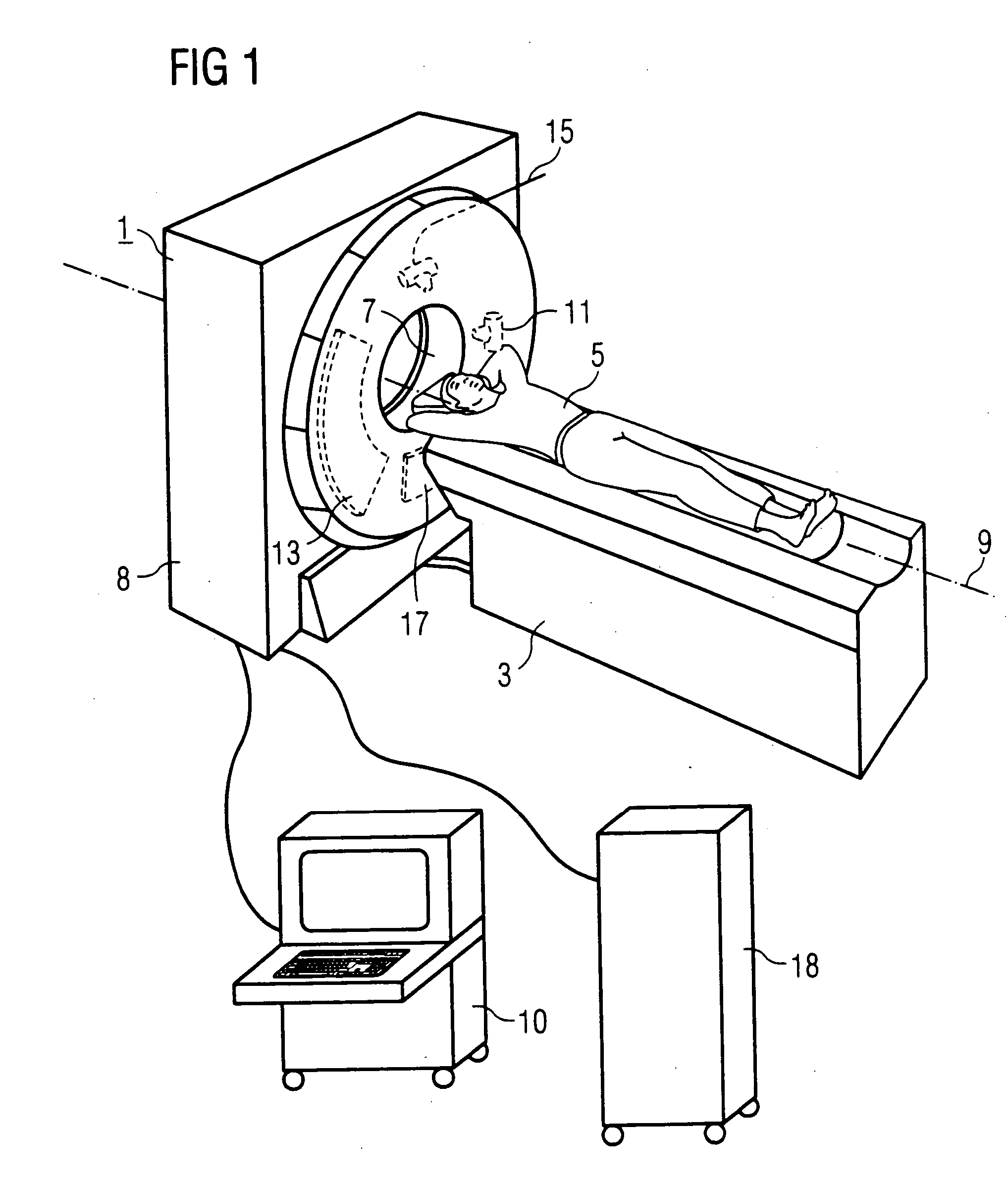
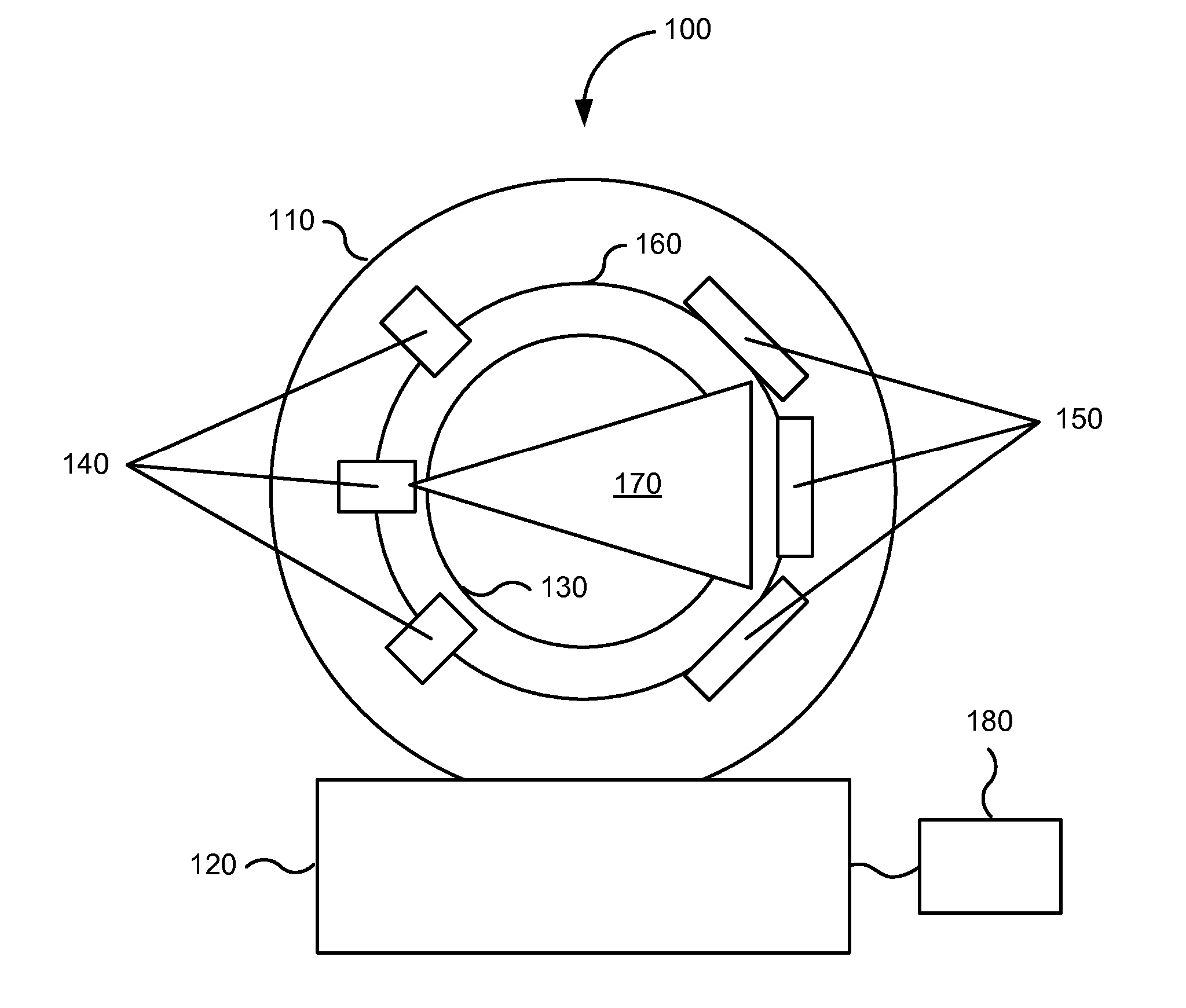
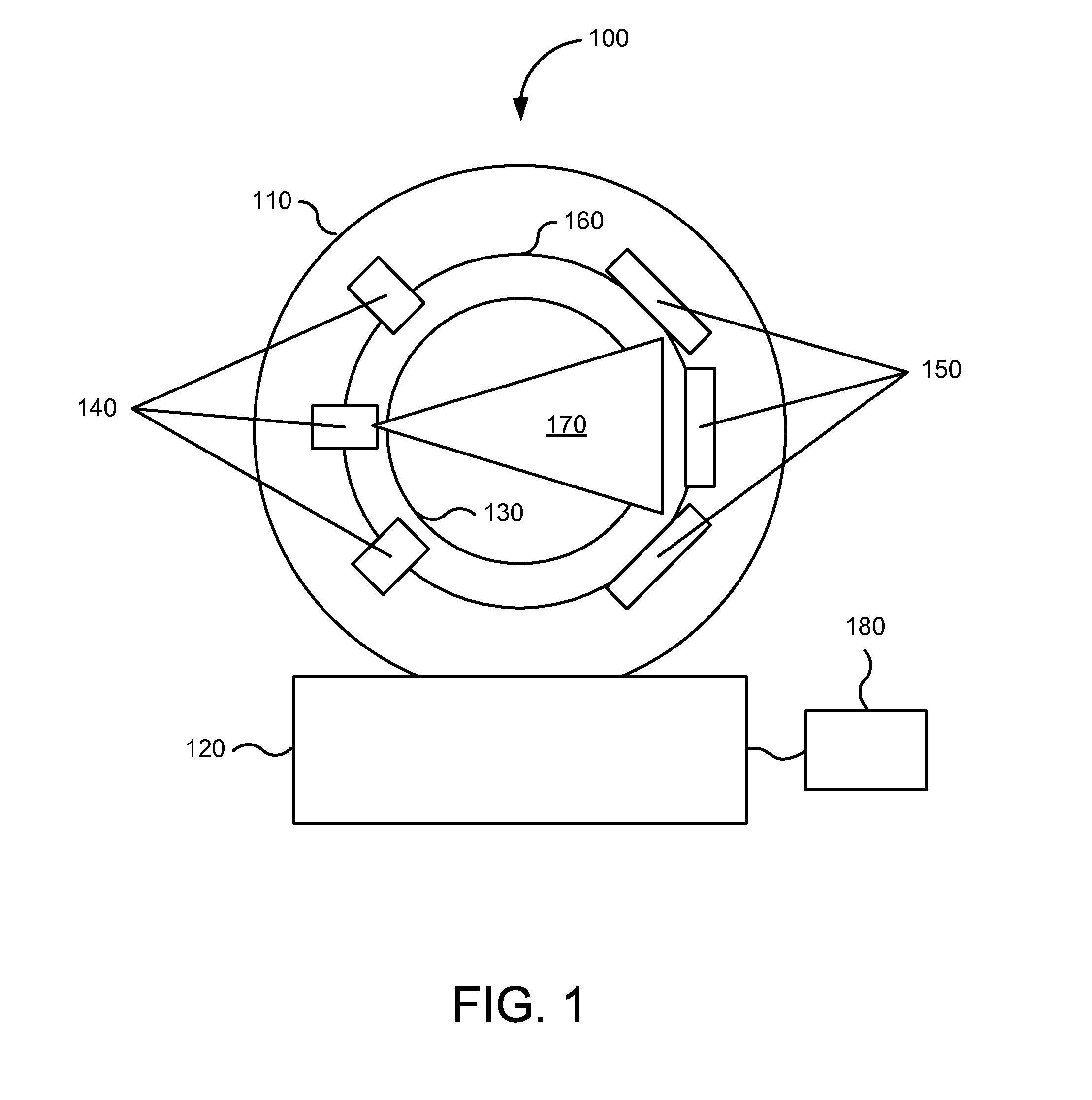
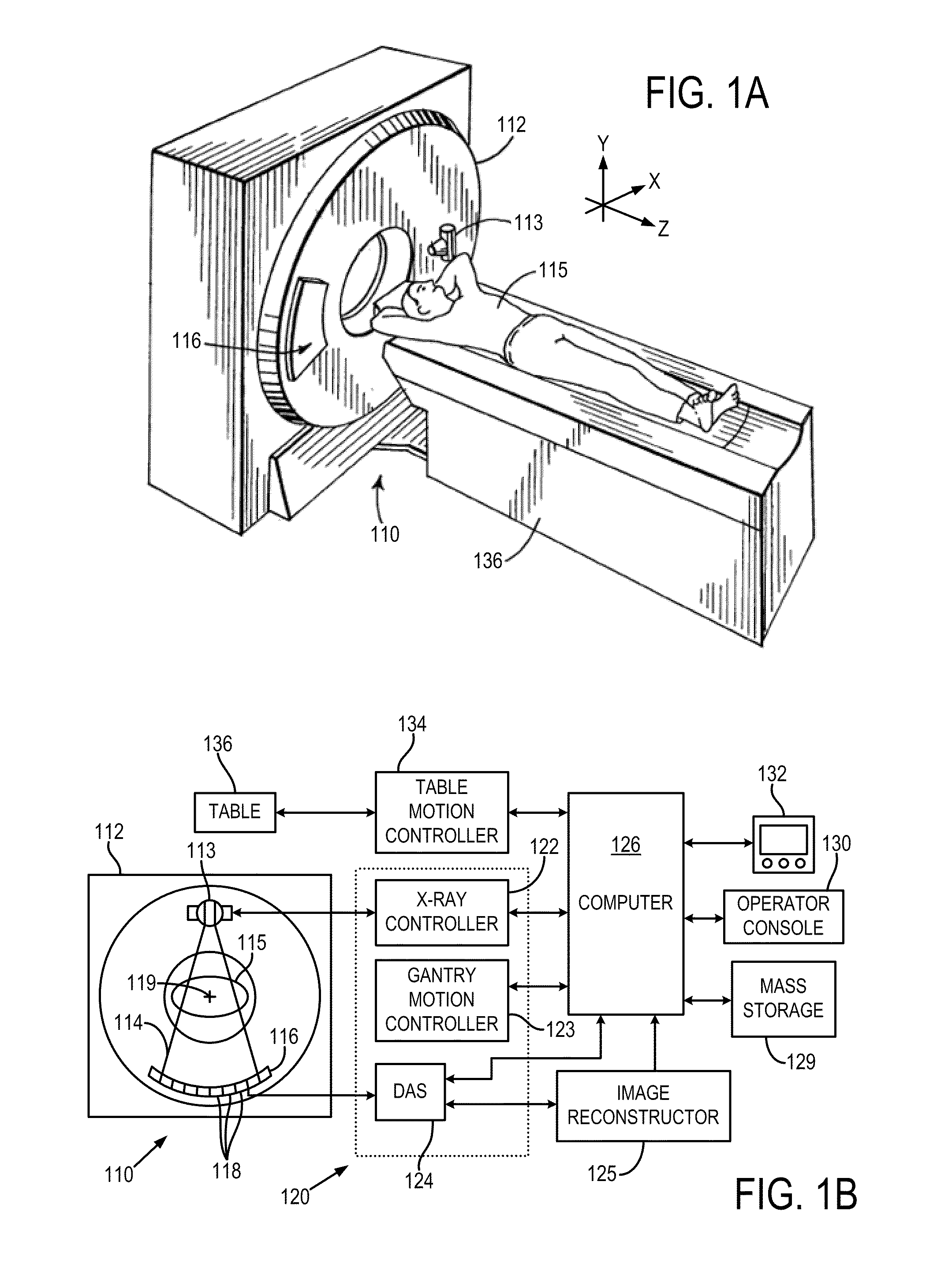
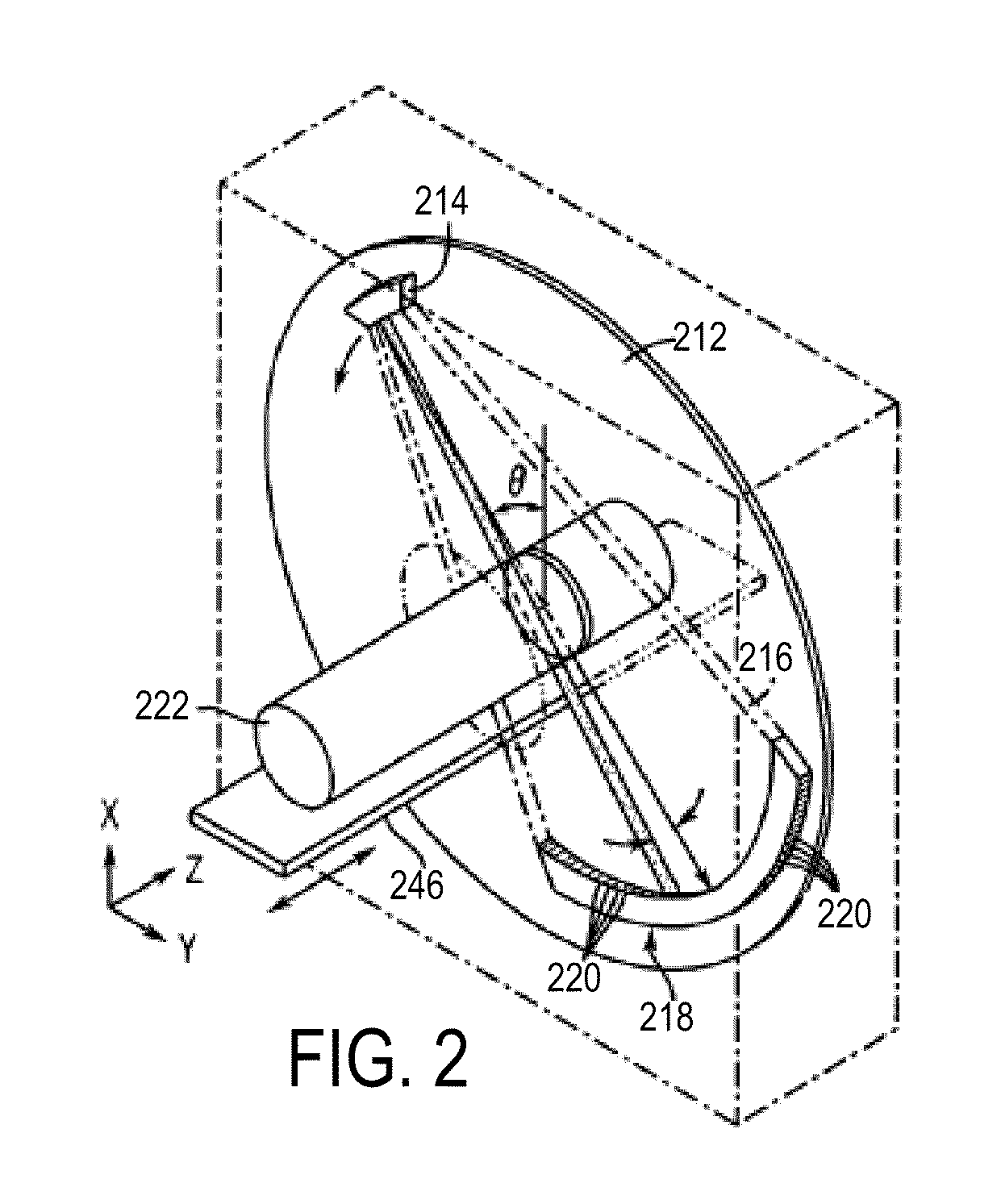
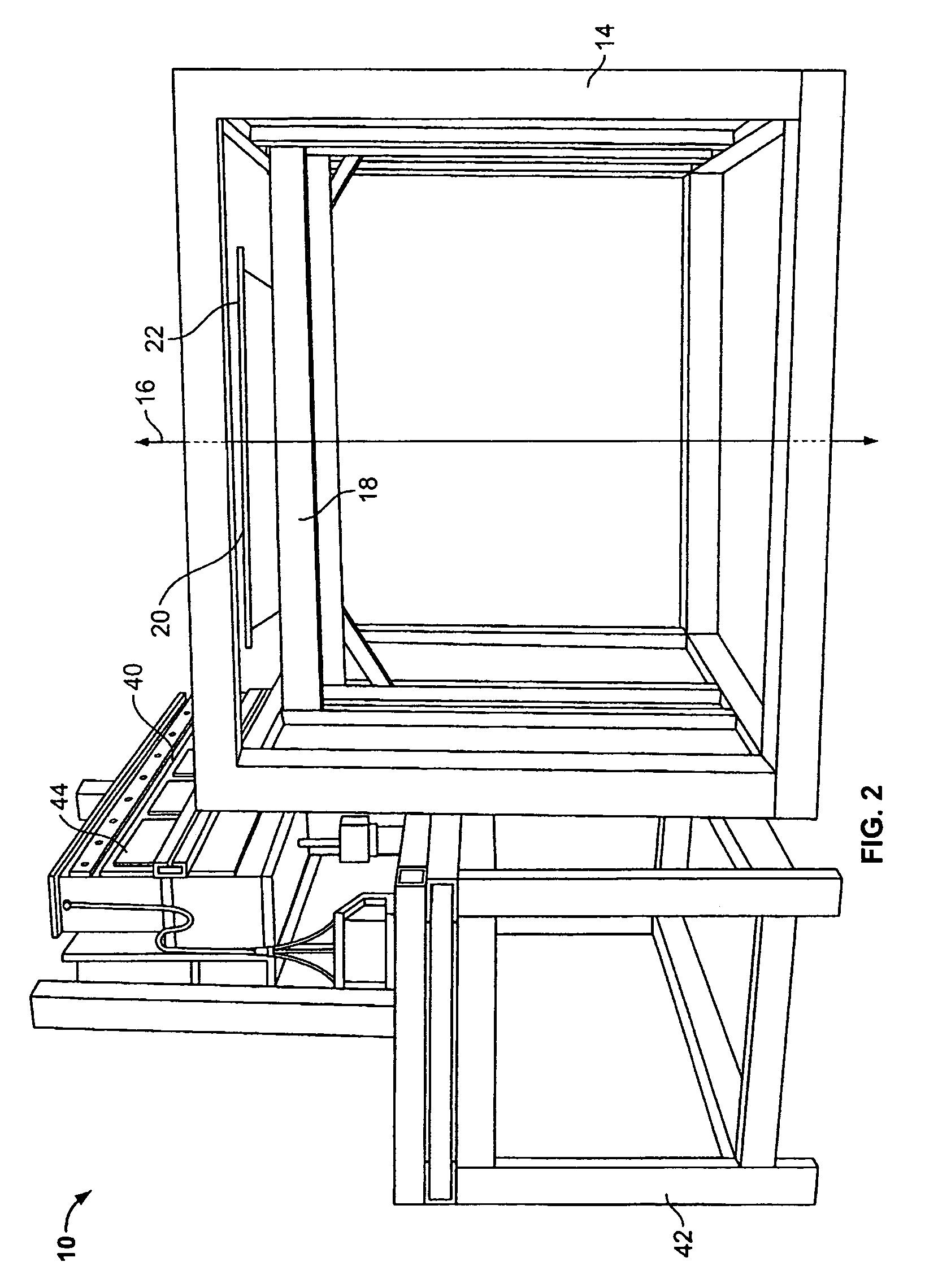
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
InactiveUS6990175B2High positioning accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayBody axis
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes a first X-ray tube configured to generate X-rays with which a subject to be examined is irradiated, a first X-ray detector configured to detect X-rays transmitted through the subject, a second X-ray tube which generates X-rays with which a treatment target of the subject is irradiated, a rotating mechanism which rotates the first X-ray tube, the first X-ray detector, and the second X-ray tube around the subject, a reconstructing unit configured to reconstruct an image on the basis of data detected by the first X-ray detector, and a support mechanism which supports the second X-ray tube. The central axis of X-rays from the second X-ray tube tilts with respect to a body axis of the subject. This makes it possible to reduce the dose on a portion other than a treatment target.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
High spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system
InactiveUS7099428B2Reduce dispersionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyHigh spatial resolution
A high spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system is provided. The system includes a support structure including a gantry mounted to rotate about a vertical axis of rotation. The system further includes a first assembly including an X-ray source mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith for generating a cone X-ray beam and a second assembly including a planar X-ray detector mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith. The detector is spaced from the source on the gantry for enabling a human or other animal body part to be interposed therebetween so as to be scanned by the X-ray beam to obtain a complete CT scan and generating output data representative thereof. The output data is a two-dimensional electronic representation of an area of the detector on which an X-ray beam impinges. A data processor processes the output data to obtain an image of the body part.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Multi-parameter X-ray computed tomography
ActiveUS8121249B2Eliminate crosstalkIncrease sampling rateRadiation/particle handlingTomographyData setX-ray
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Simultaneous CT and SPECT tomography using CZT detectors
A method for simultaneous transmission x-ray computed tomography (CT) and single photon emission tomography (SPECT) comprises the steps of: injecting a subject with a tracer compound tagged with a gamma-ray emitting nuclide; directing an x-ray source toward the subject; rotating the x-ray source around the subject; emitting x-rays during the rotating step; rotating a cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) two-sided detector on an opposite side of the subject from the source; simultaneously detecting the position and energy of each pulsed x-ray and each emitted gamma-ray captured by the CZT detector; recording data for each position and each energy of each the captured x-ray and gamma-ray; and, creating CT and SPECT images from the recorded data. The transmitted energy levels of the x-rays lower are biased lower than energy levels of the gamma-rays. The x-ray source is operated in a continuous mode. The method can be implemented at ambient temperatures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
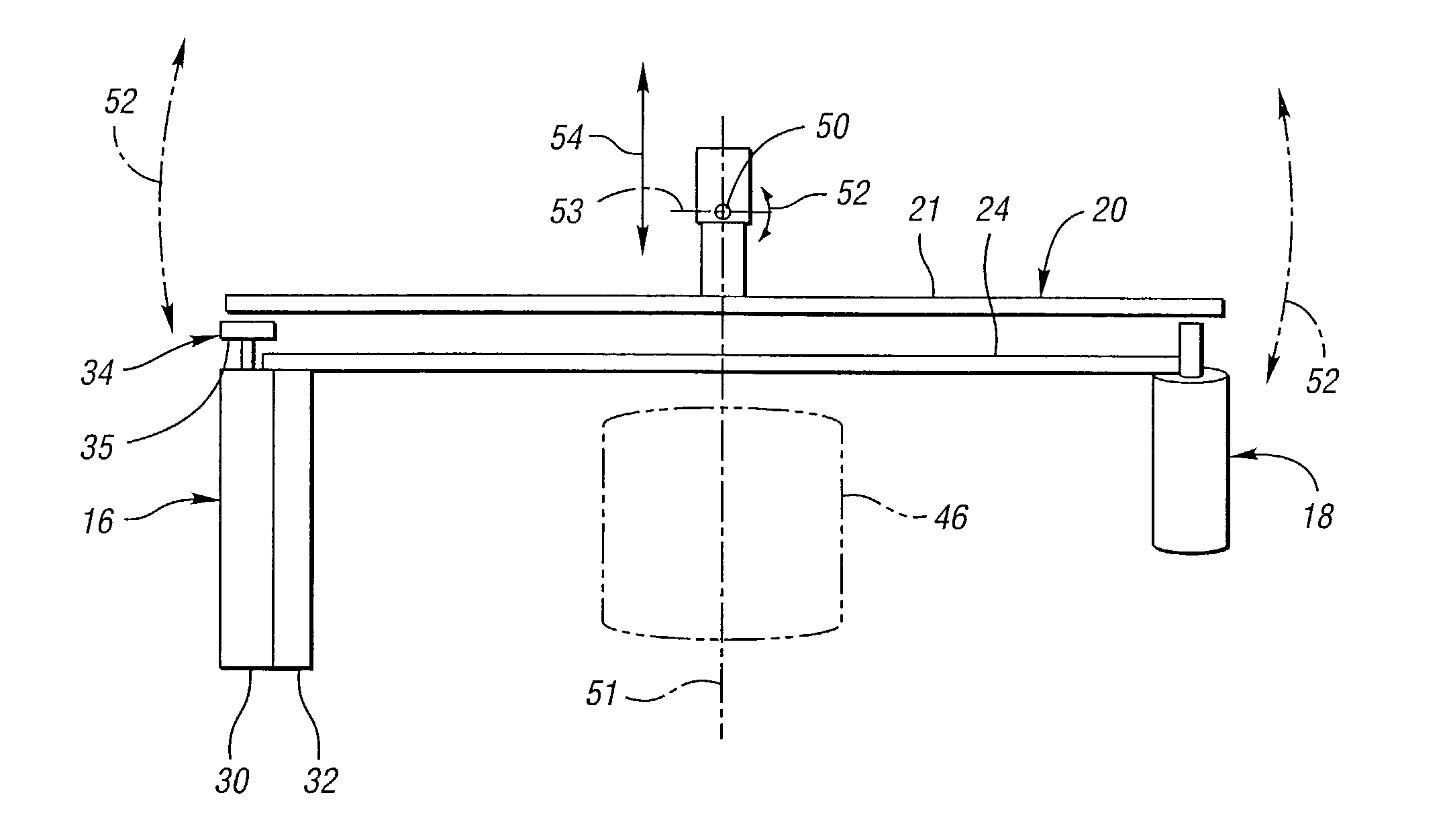
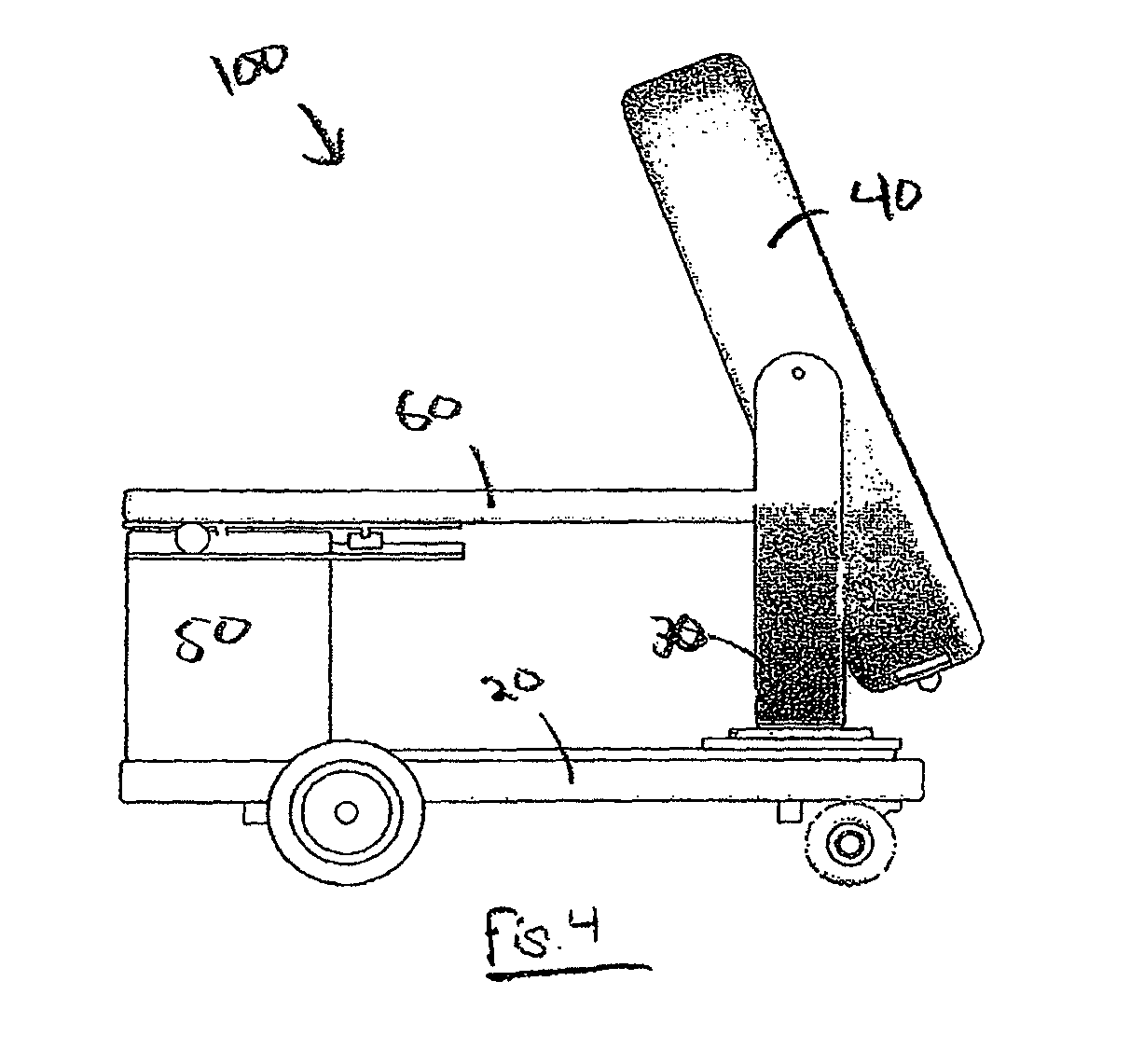
Mobile medical imaging system and methods
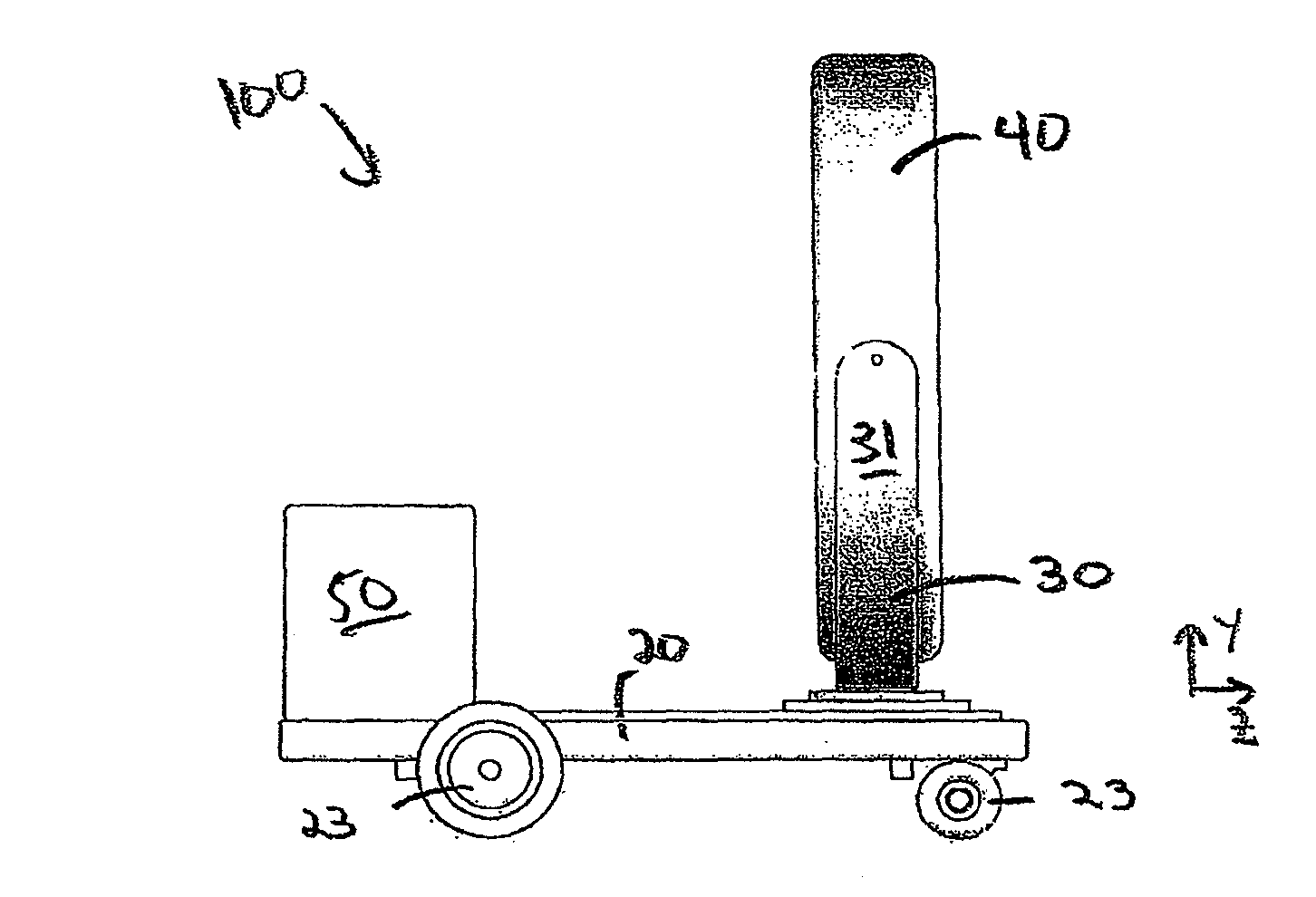
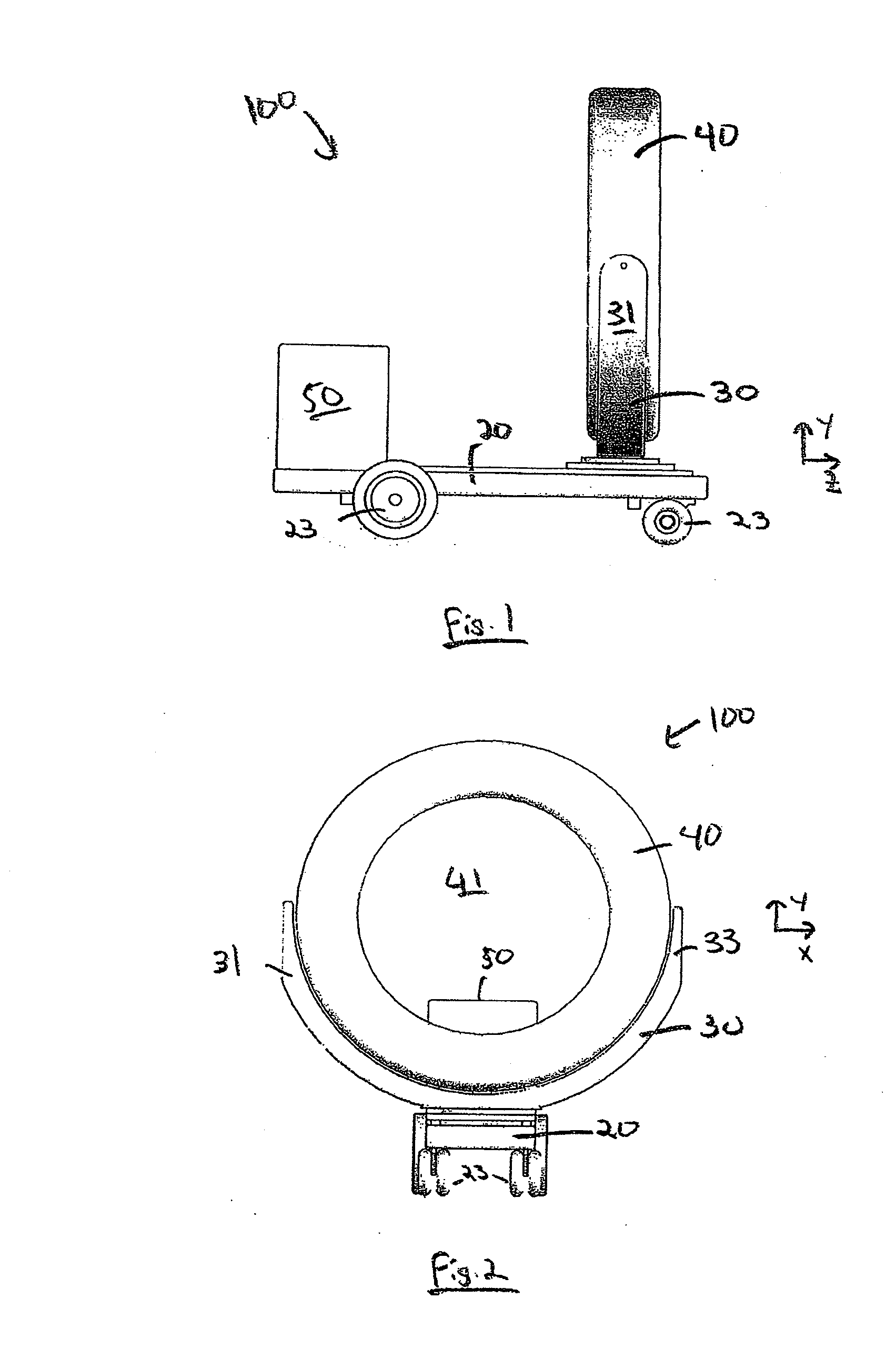
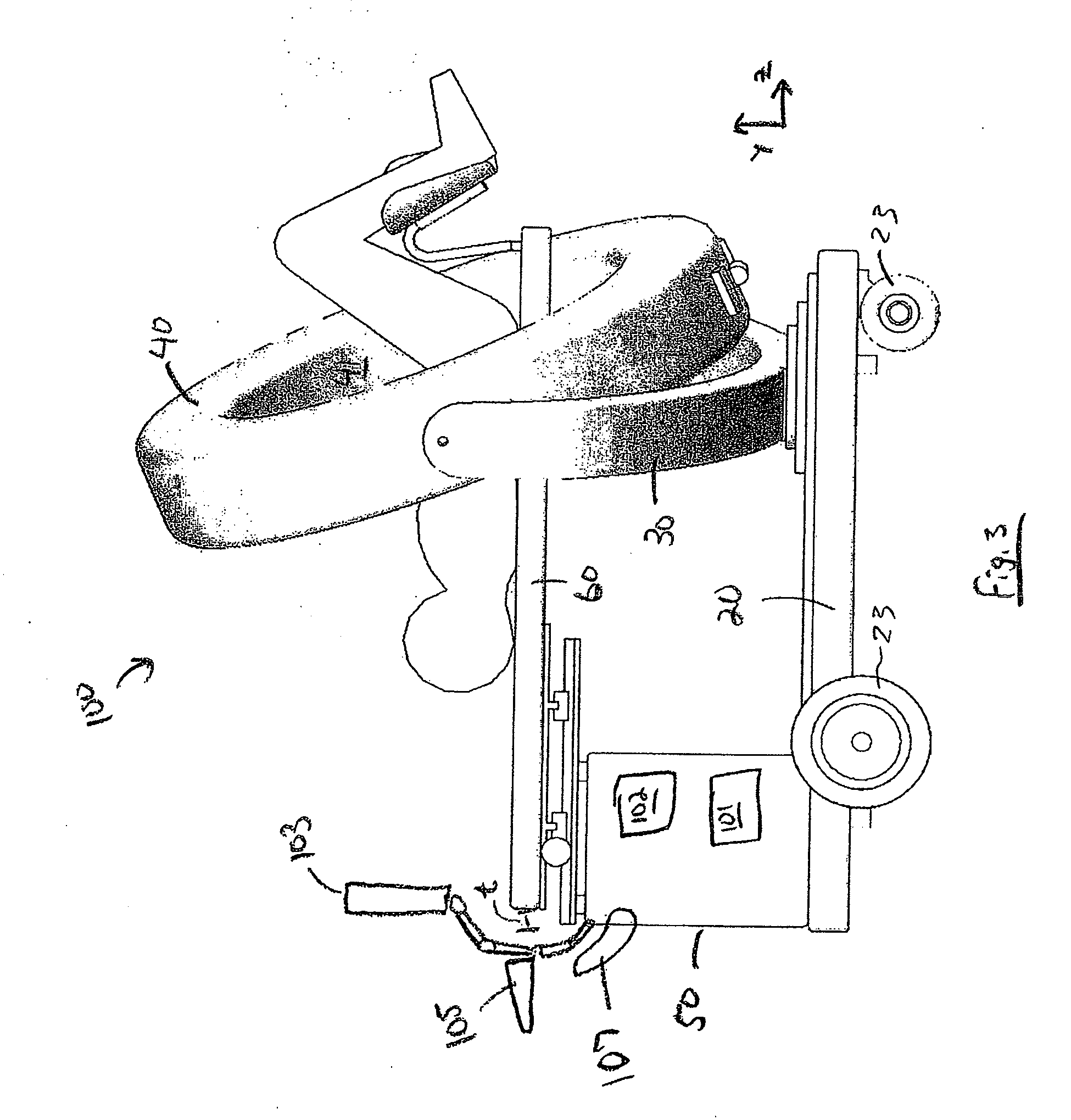
ActiveUS20100172468A1Easy to transportFacilitate easy transportRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsMedical imagingEngineering
A mobile medical imaging device that allows for multiple support structures, such as a tabletop or a seat, to be attached, and in which the imaging gantry is indexed to the patient by translating up and down the patient axis. In one embodiment, the imaging gantry can translate, rotate and / or tilt with respect to a support base, enabling imaging in multiple orientations, and can also rotate in-line with the support base to facilitate easy transport and / or storage of the device. The imaging device can be used in, for example, x-ray computed tomography (CT) and / or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications.
Owner:MOBIUS IMAGING
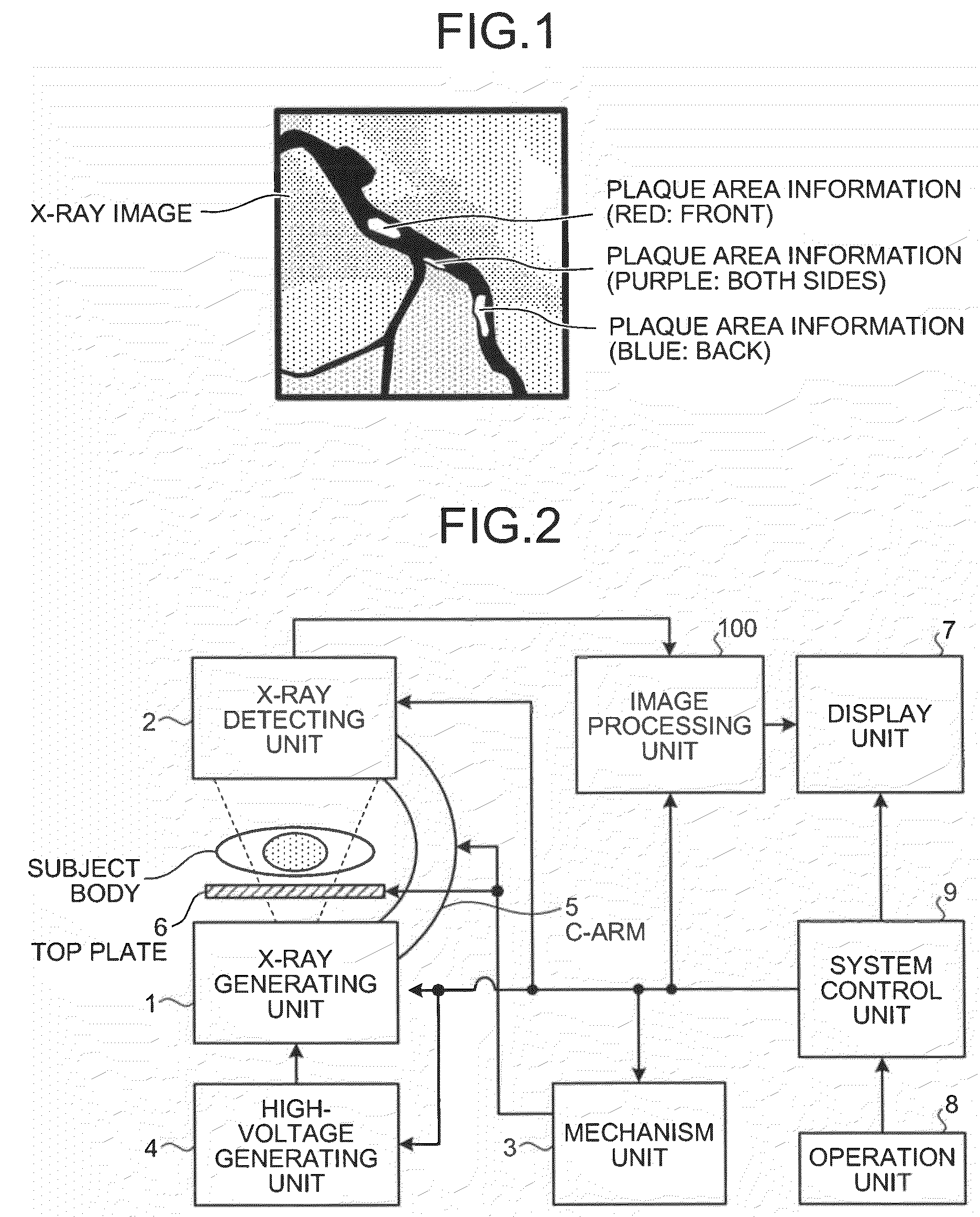
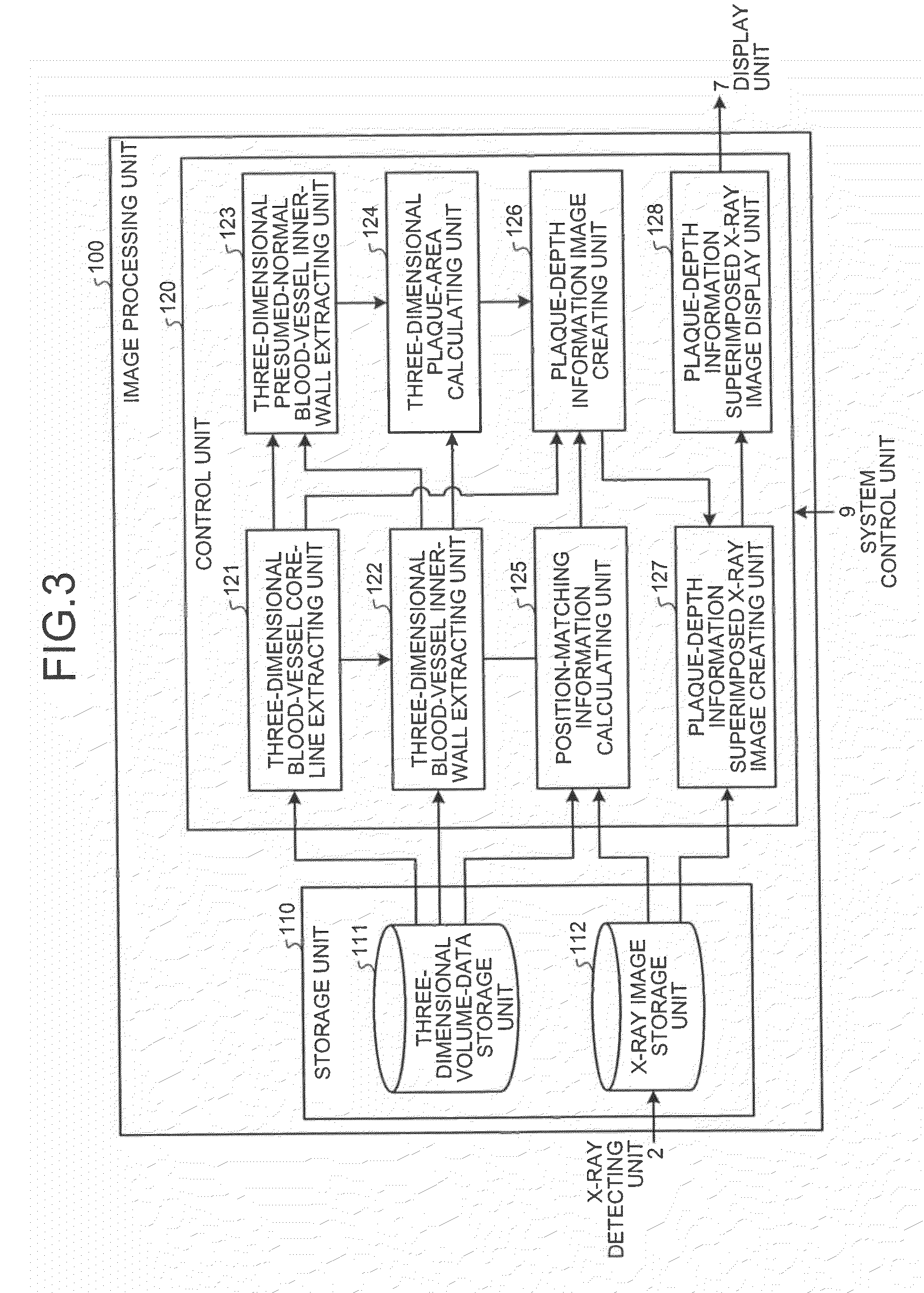
X-ray apparatus, image processing display apparatus and computer program product
ActiveUS20090016483A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging processingX-ray
An X-ray imaging machine is configured such that a three-dimensional blood-vessel information creating unit creates information concerning a three-dimensional blood-vessel core line and a position of a plaque in a subject blood vessel based on three-dimensional volume data obtained from an image taken by an X-ray computed tomography apparatus. A plaque-depth information image creating unit creates a plaque-depth information image on which the plaque is differently displayed in accordance with whether the plaque is present in front of or in the back of the three-dimensional blood-vessel core line with respect to a projection direction, based on the created information concerning the three-dimensional blood-vessel core line and the position of the plaque. An X-ray image display unit displays the created plaque-depth information image over an X-ray image in a superimposed manner.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Mobile medical imaging system and methods
ActiveUS8118488B2Easy to transportFacilitate easy transport and storagePatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical imagingEngineering
A mobile medical imaging device that allows for multiple support structures, such as a tabletop or a seat, to be attached, and in which the imaging gantry is indexed to the patient by translating up and down the patient axis. In one embodiment, the imaging gantry can translate, rotate and / or tilt with respect to a support base, enabling imaging in multiple orientations, and can also rotate in-line with the support base to facilitate easy transport and / or storage of the device. The imaging device can be used in, for example, x-ray computed tomography (CT) and / or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications.
Owner:MOBIUS IMAGING
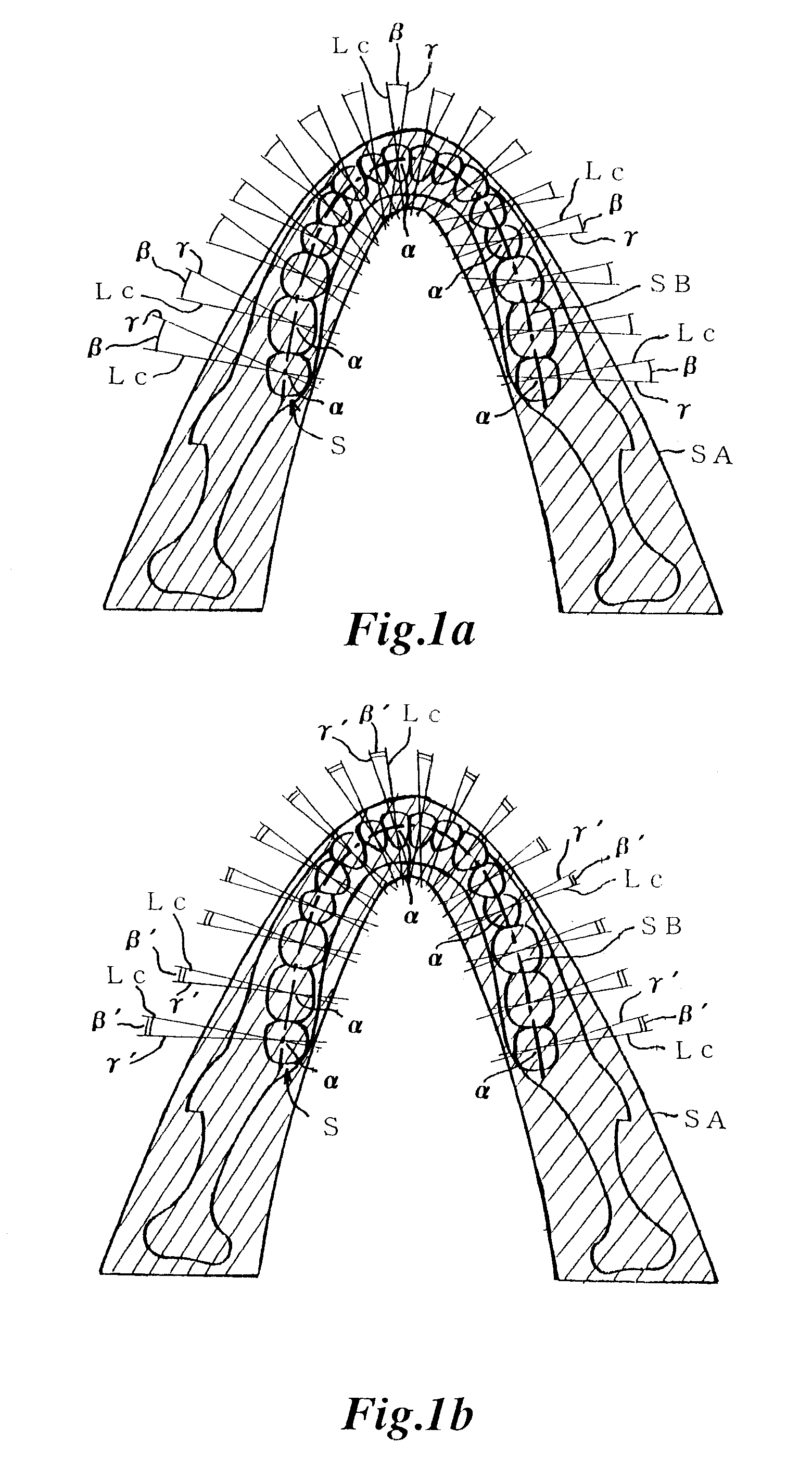
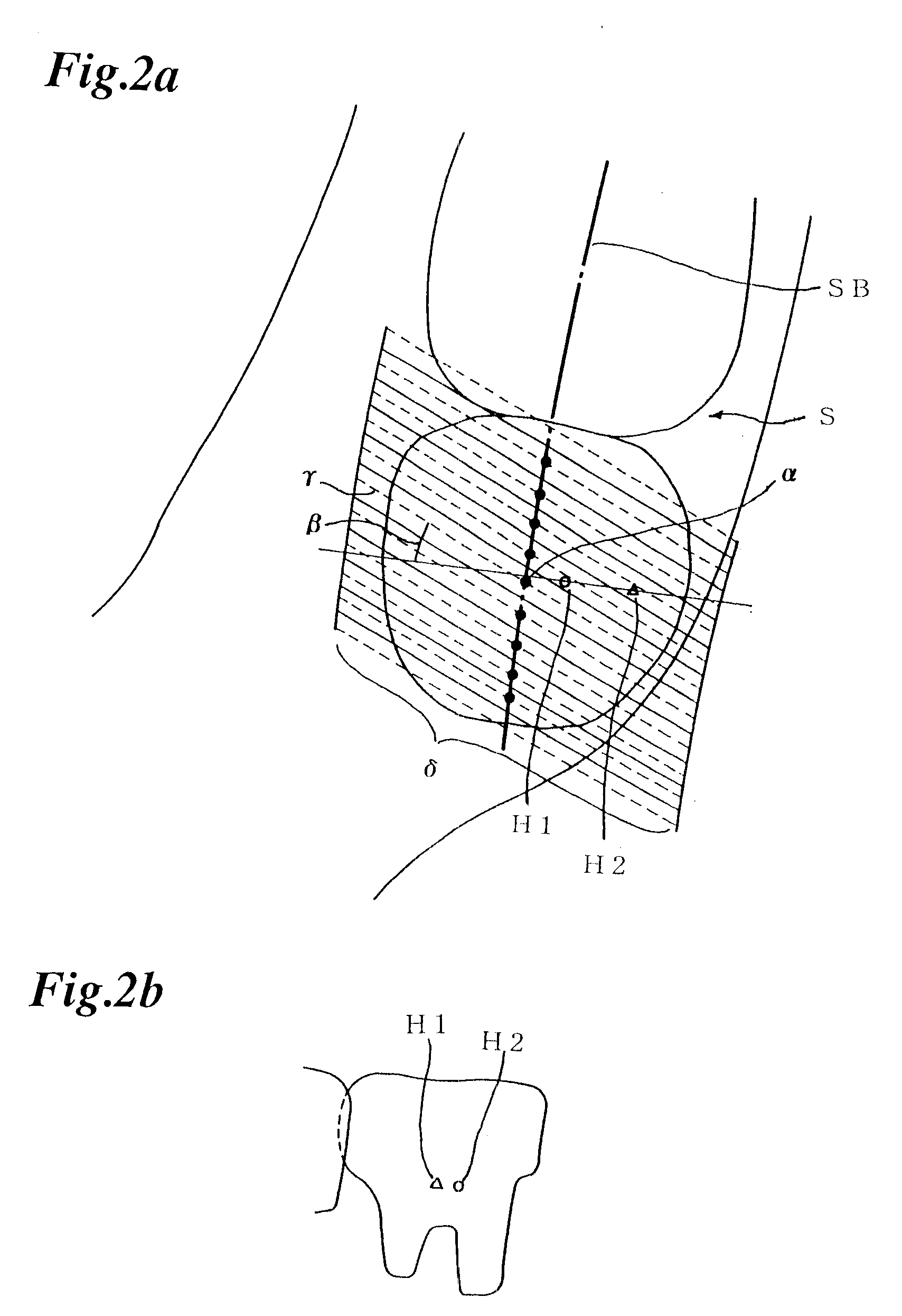
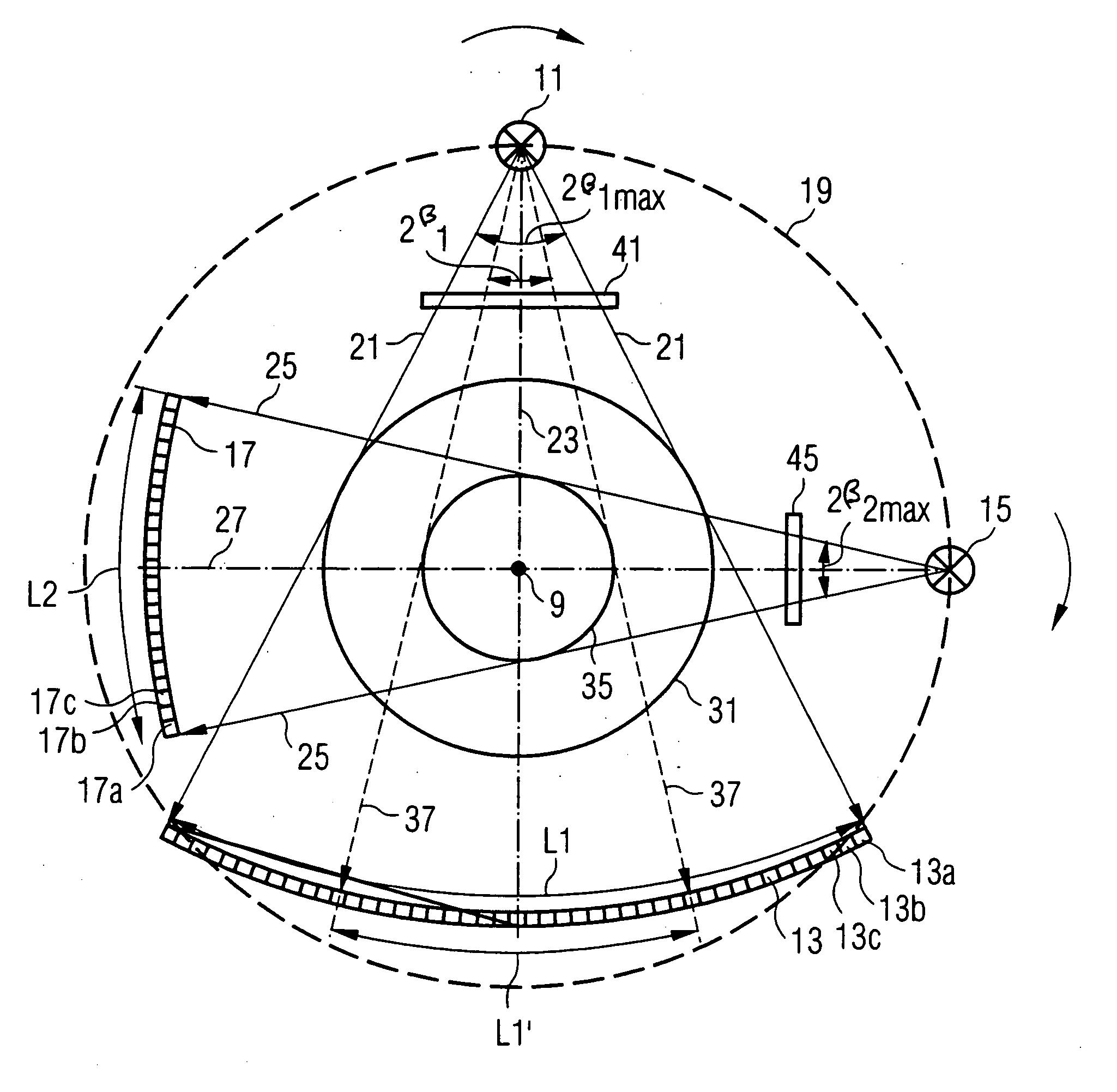
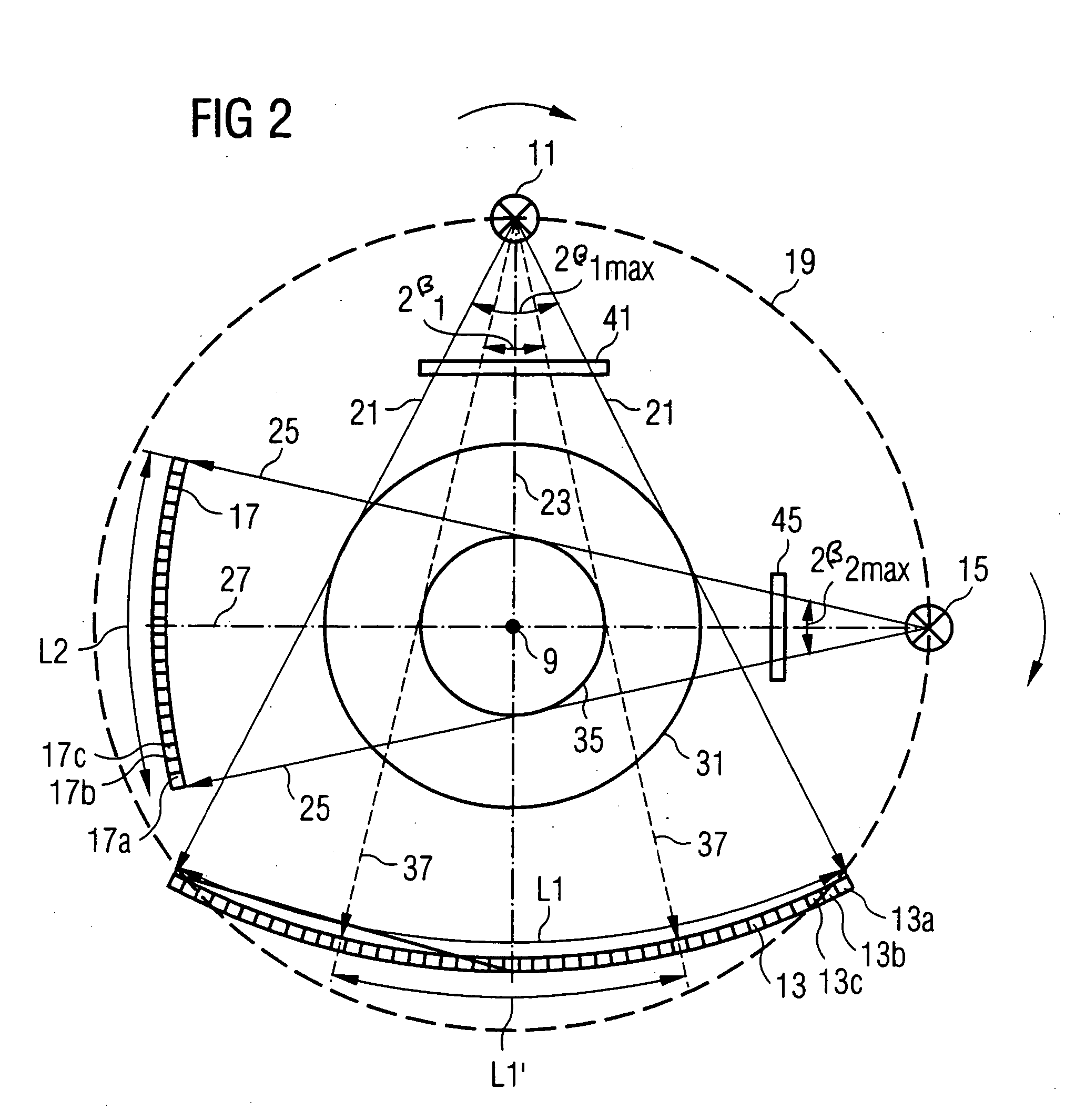
X-ray computed tomography method and apparatus
InactiveUS6493415B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
An X-ray computed tomography method and apparatus for obtaining a panoramic X-ray image seen from a direction of a projection line gamma (gamma') of a curved sectional area SA by expanding calculation results of three-dimensional distribution information of X-ray absorption coefficient on the projection line gamma (gamma') intersecting at a specified angle beta (beta') for any regions alpha of the panoramic sectional image layer SB on a two-dimensional plane based on the three dimensional distribution information of X-ray absorption coefficient of the curved sectional area SA obtained by a X-ray CT.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY +1
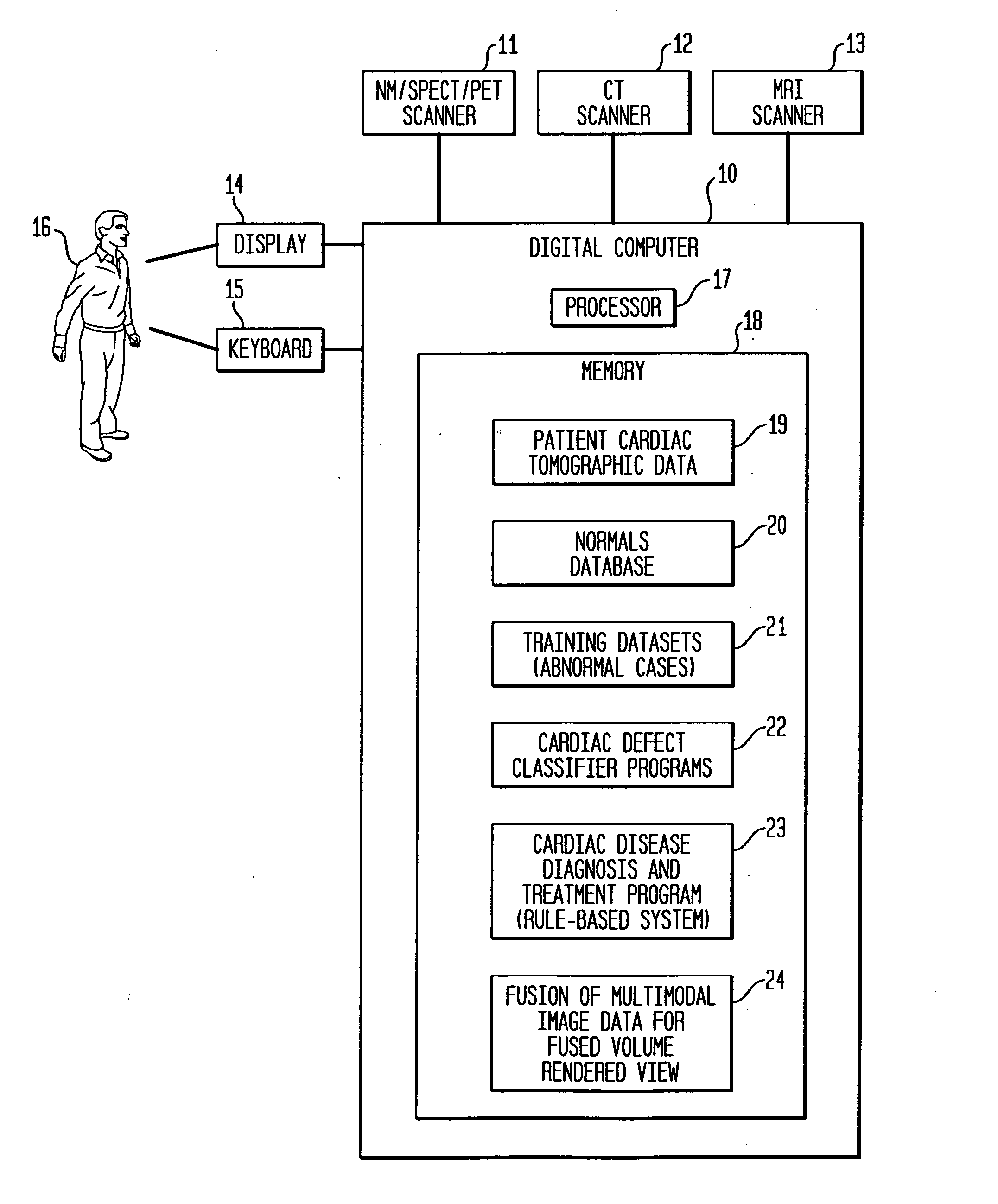
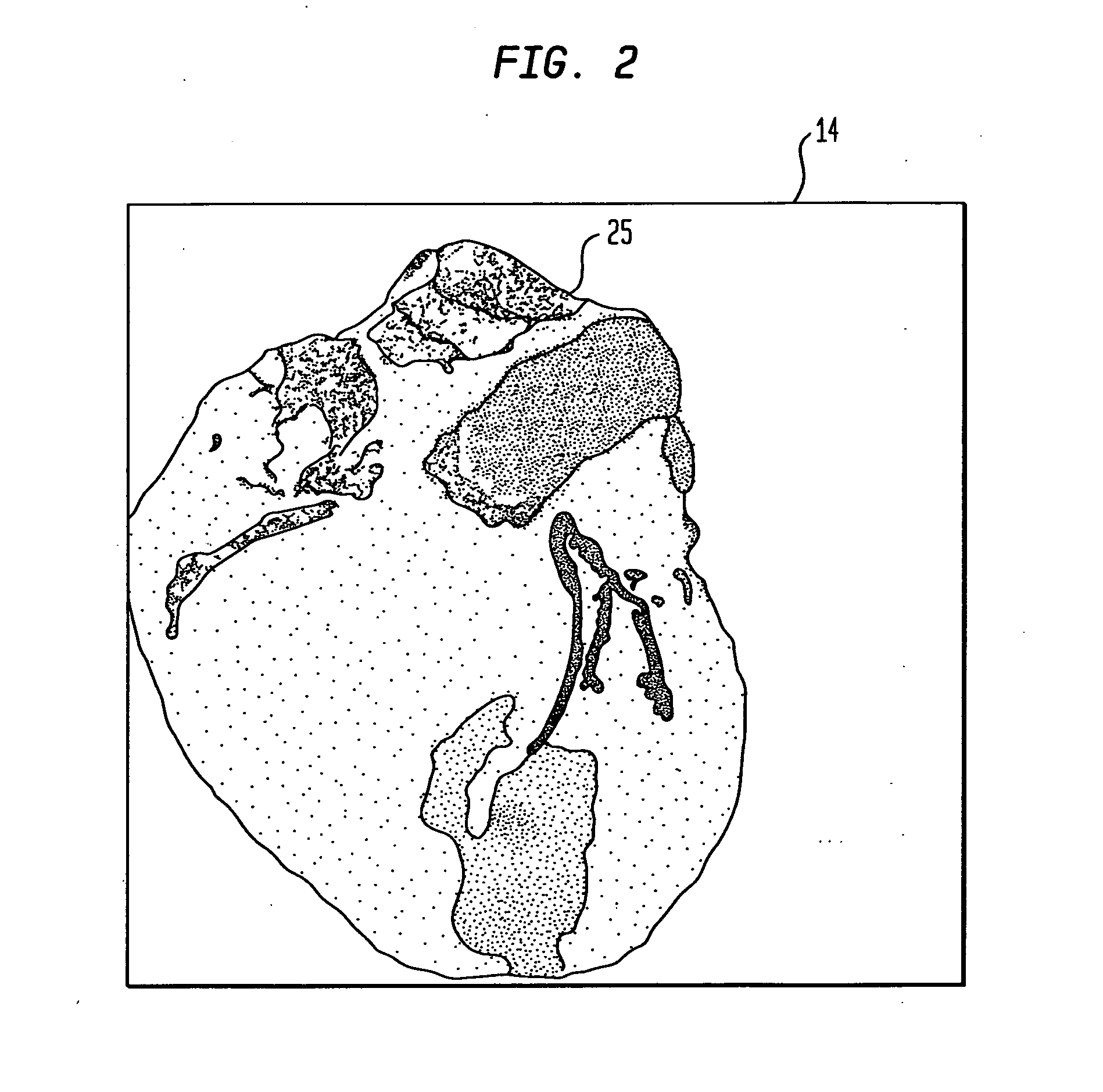
Dedicated display for processing and analyzing multi-modality cardiac data
For diagnosis and treatment of cardiac disease, images of the heart muscle and coronary vessels are captured using different medical imaging modalities; e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), electron-beam X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (US). For visualizing the multi-modal image data, the data is presented using a technique of volume rendering, which allows users to visually analyze both functional and anatomical cardiac data simultaneously. The display is also capable of showing additional information related to the heart muscle, such as coronary vessels. Users can interactively control the viewing angle based on the spatial distribution of the quantified cardiac phenomena or atherosclerotic lesions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
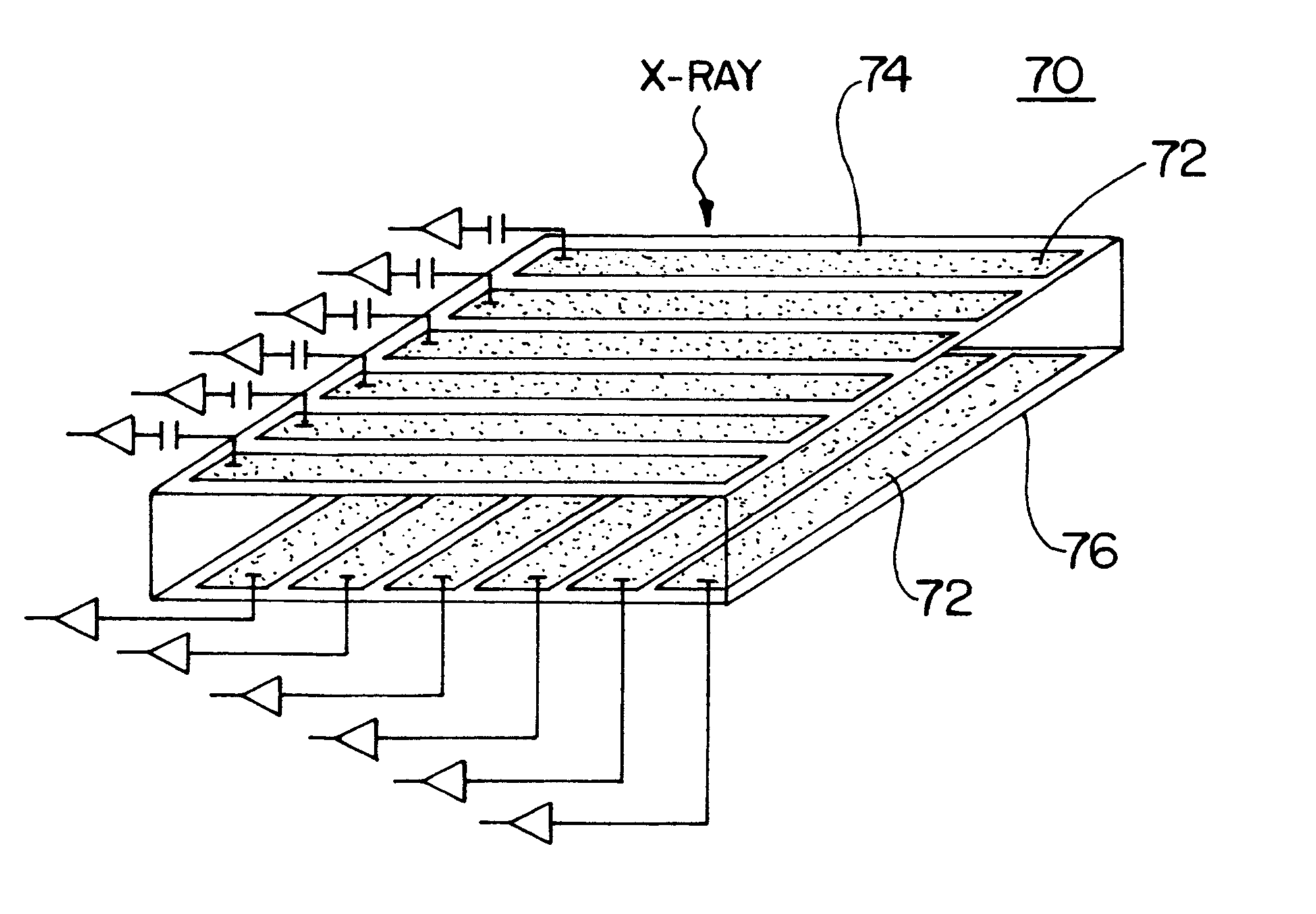
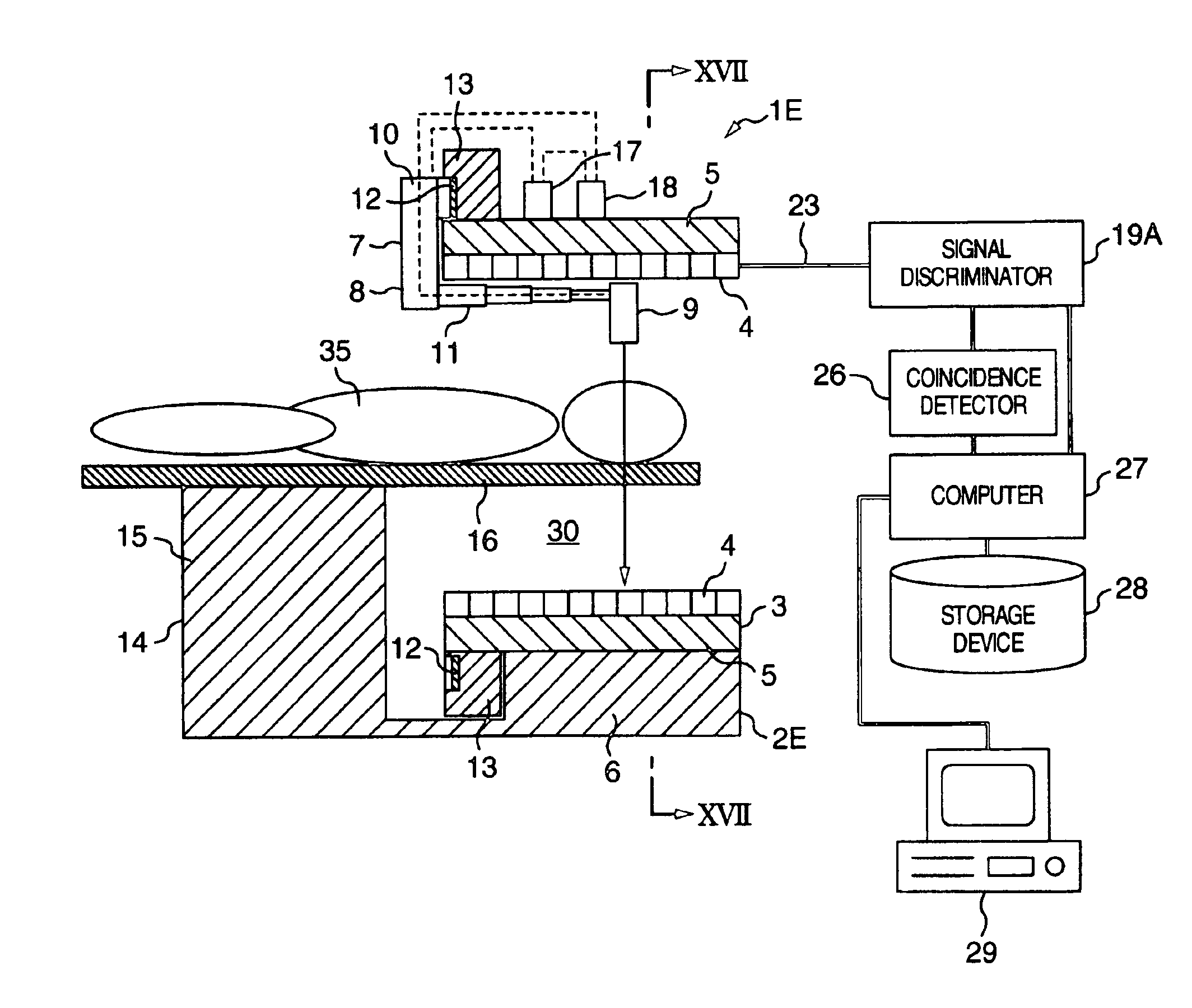
Radiological imaging apparatus and radiological imaging method
InactiveUS6965661B2Simple configurationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
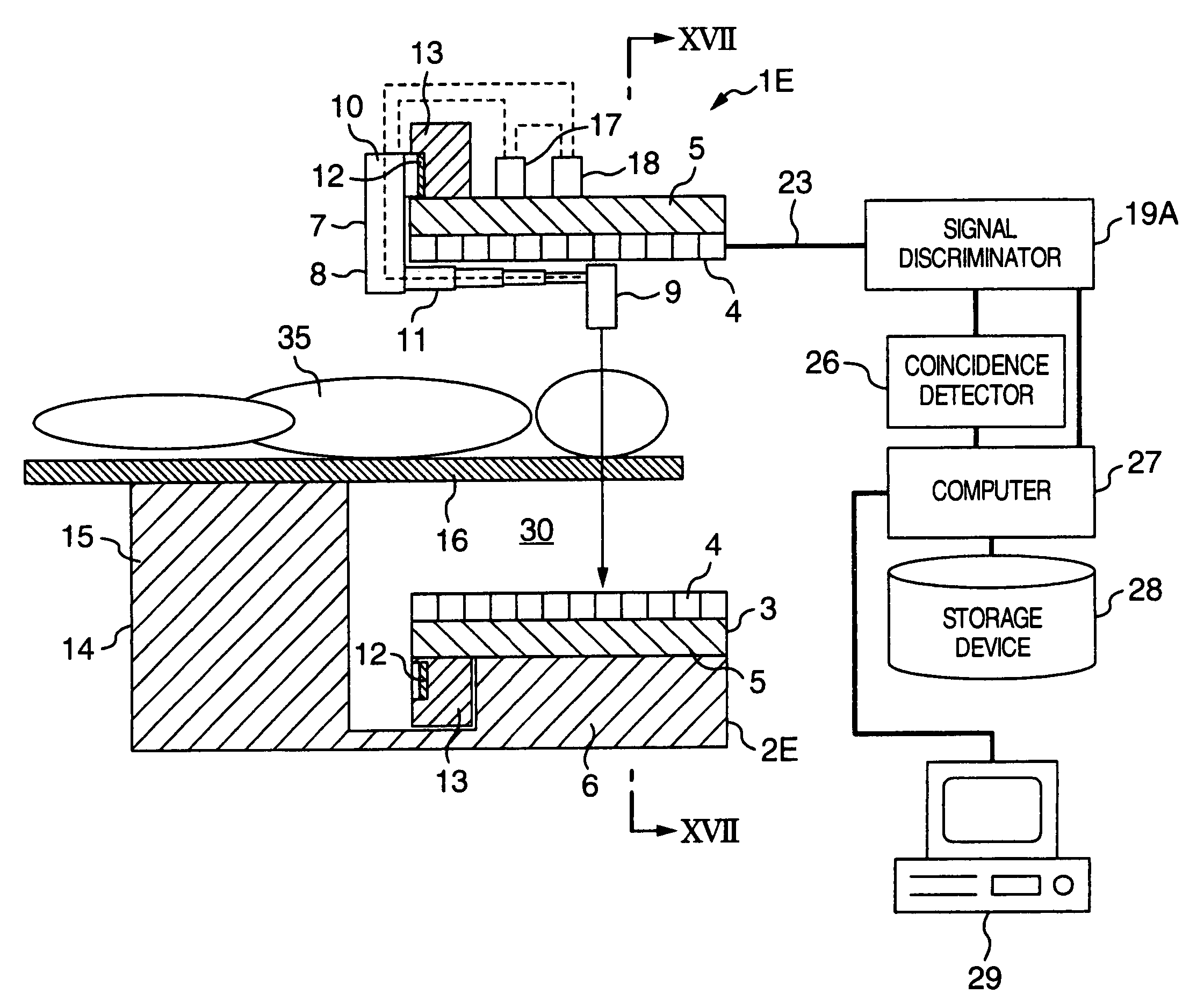
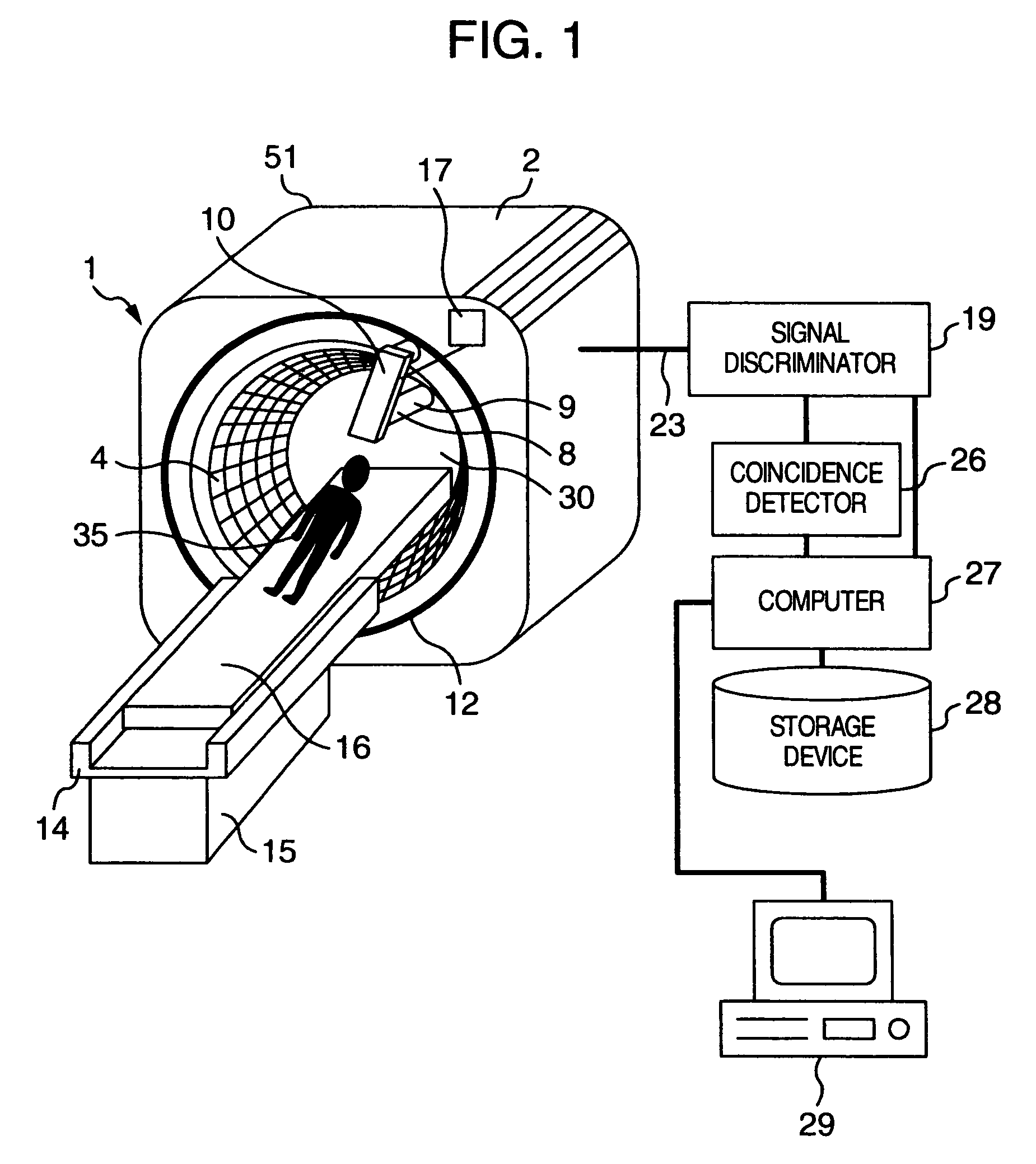
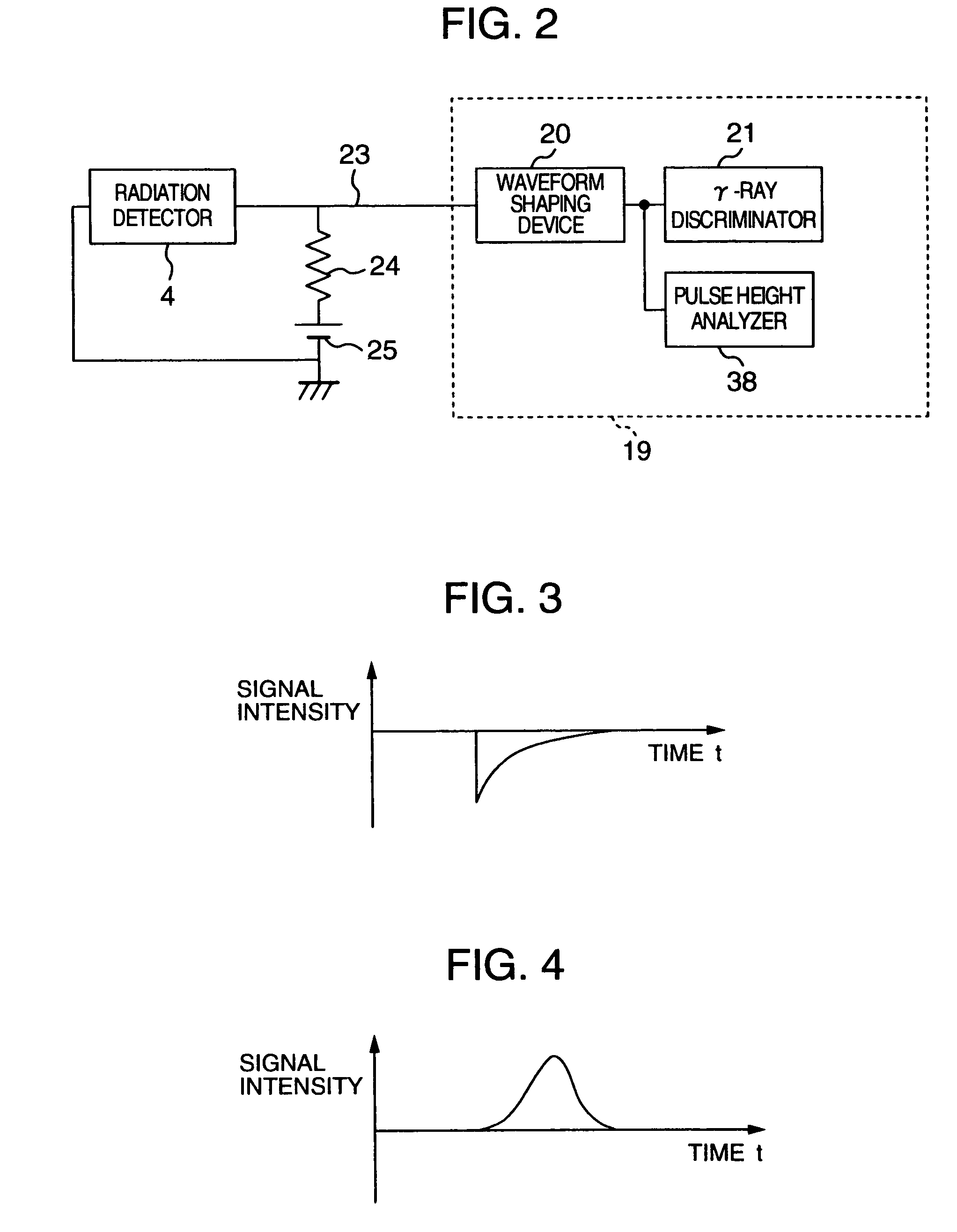
An image pickup apparatus of a radiological imaging apparatus includes a plurality of radiation detectors arranged in a ring form around a through hole section formed on a casing into which an examinee is inserted. An X-ray source unit having an X-ray source moves in a circumferential direction of the through hole section along a ring-shaped guide rail provided on the casing. Each radiation detector outputs both an X-ray detection signal which is a detection signal of X-rays that have passed through the examinee and a γ-ray detection signal which is a detection signal of γ-rays radiated from the examinee caused by radiopharmaceutical. A computer creates an X-ray computed tomographic image data based on the X-ray detection signal and a PET image data based on the γ-ray detection signal and creates fused tomographic image data using the X-ray computed tomographic image data and the PET image data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
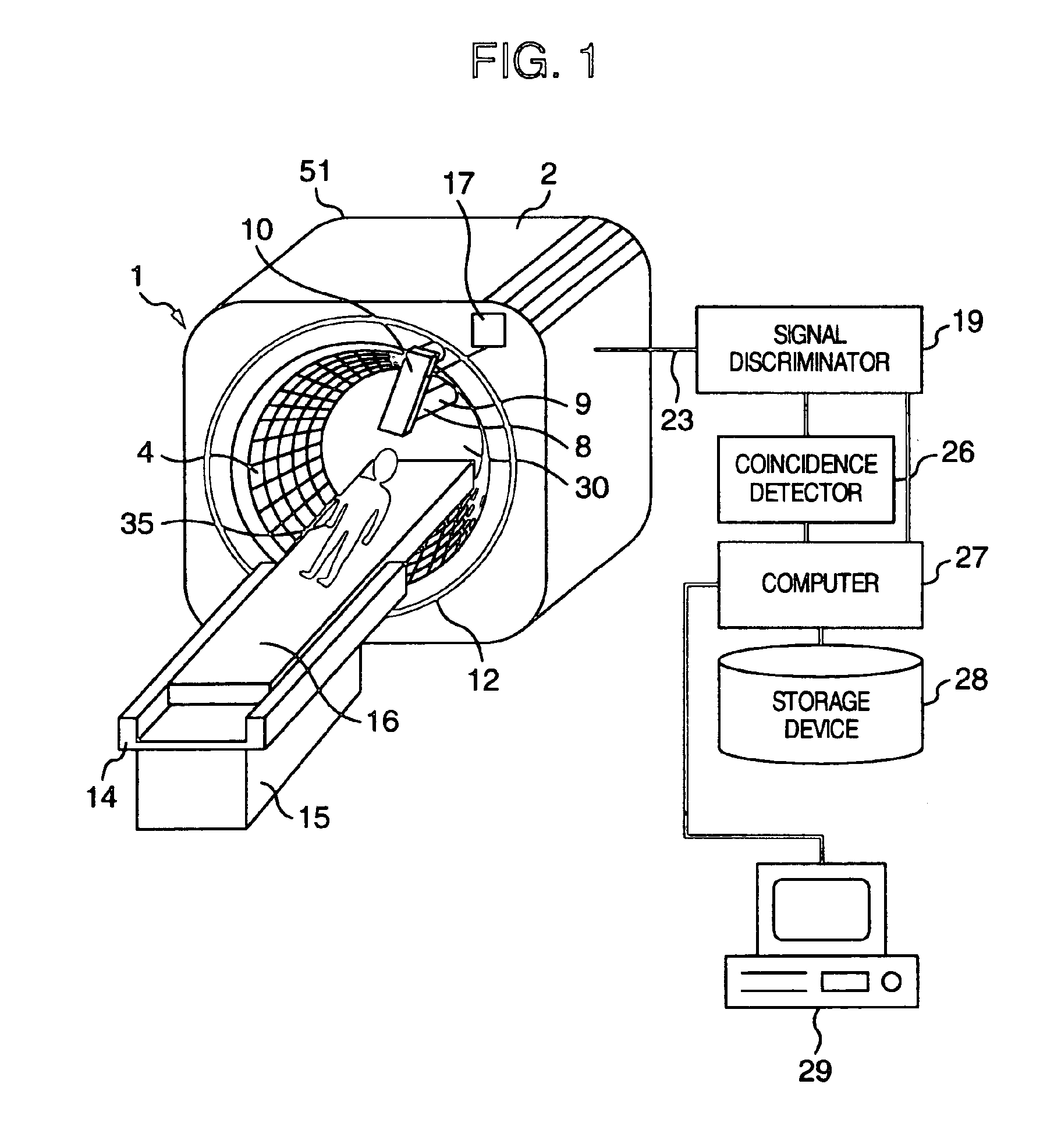
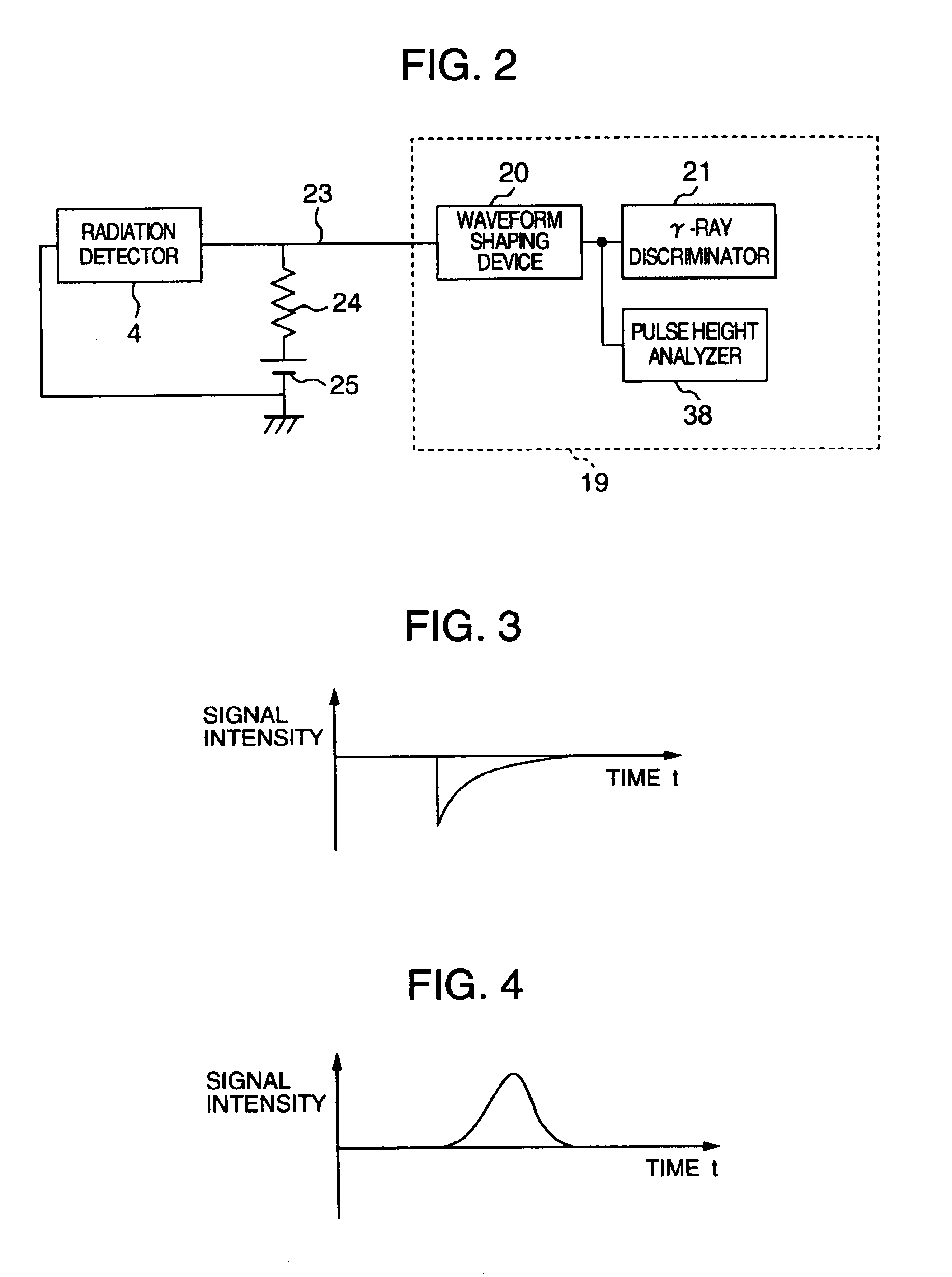
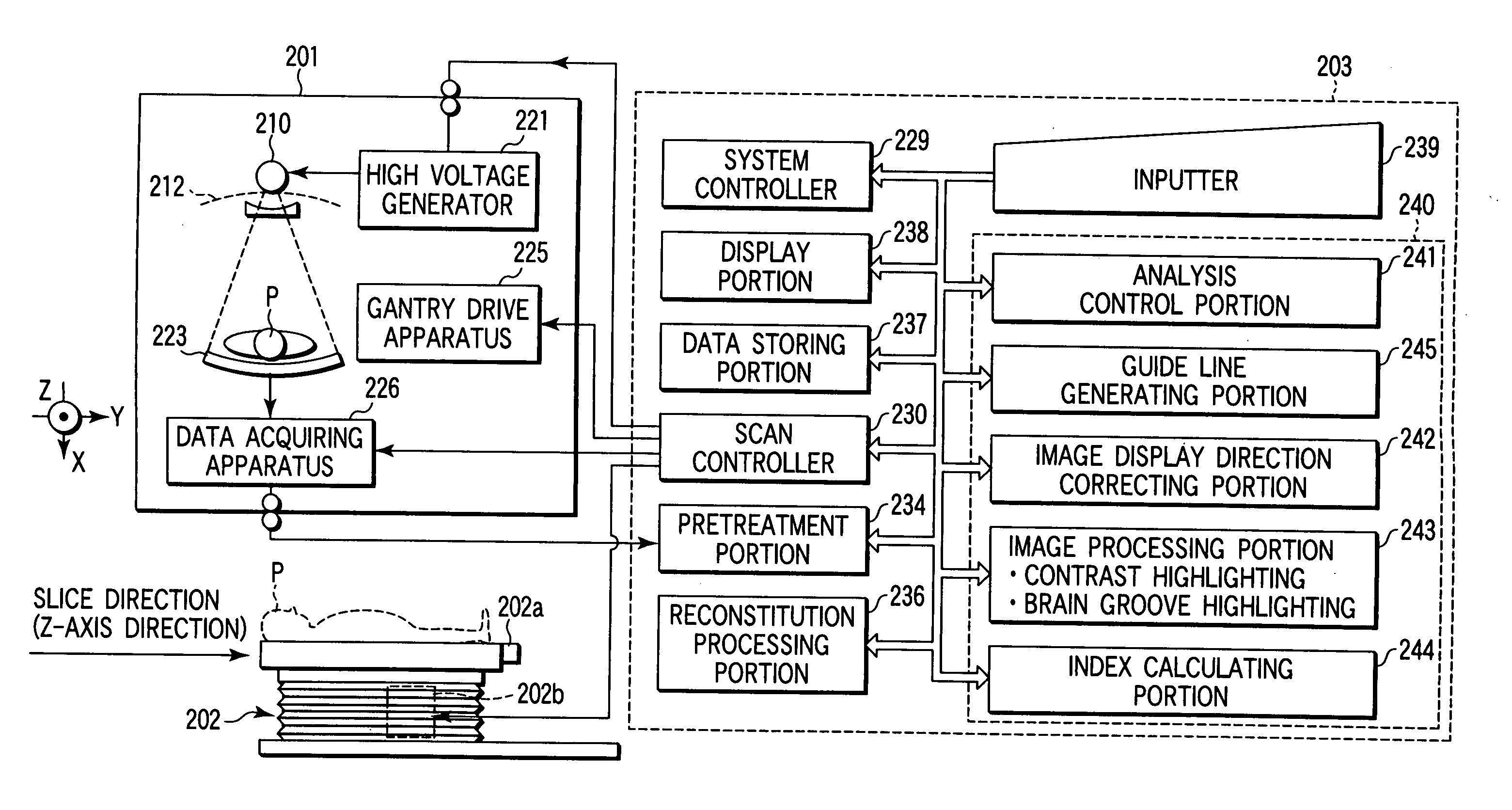
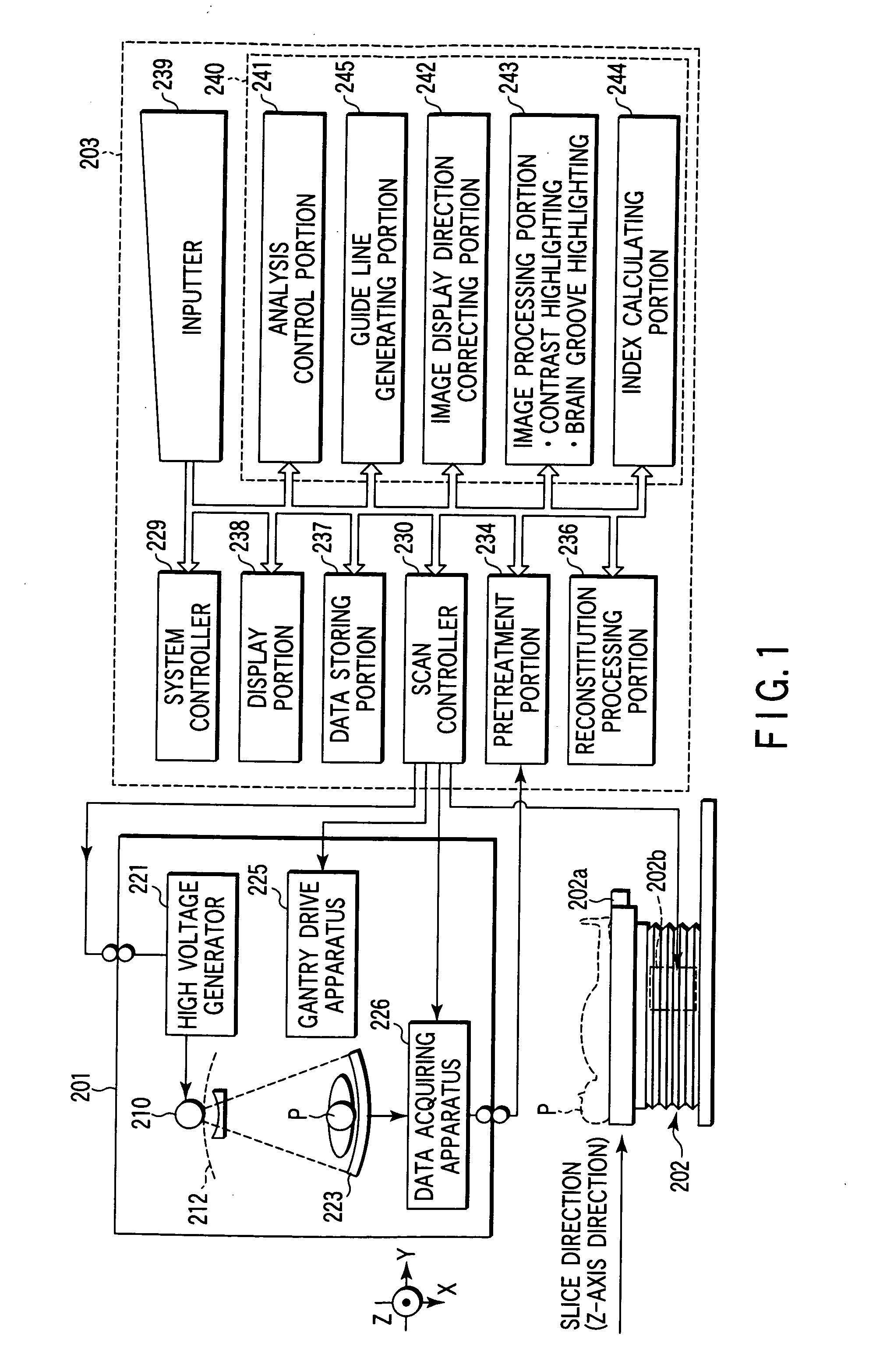
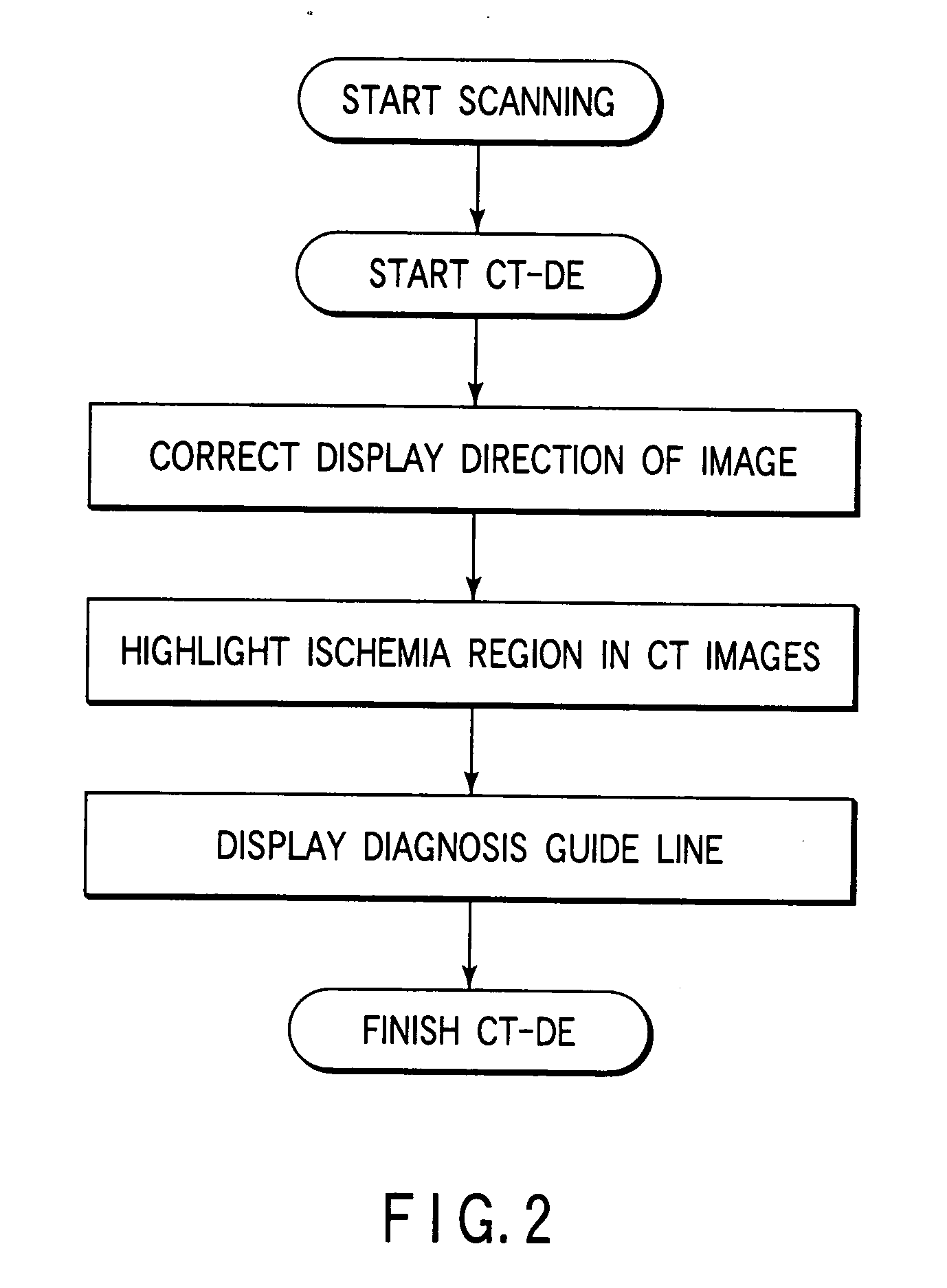
Cerebral ischemia diagnosis assisting apparatus, X-ray computer tomography apparatus, and apparatus for aiding diagnosis and treatment of acute cerebral infarct
A cerebral ischemia diagnosis assisting apparatus comprises a storing portion for storing multi-slices or volume data with regard to the head portion of a subject, an image generating portion for generating a tomography image of a brain from the multi-slices or the volume data, an image processing portion for processing the tomography image for generating a contrast highlighting image and a brain sulci highlighting image or either thereof, and a display portion for displaying the tomography image along with the contrast highlighting image and the brain sulci highlighting image.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +2
X-ray computed tomographic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6990170B2Prevent irradiationAvoid omissionsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanData reconstruction
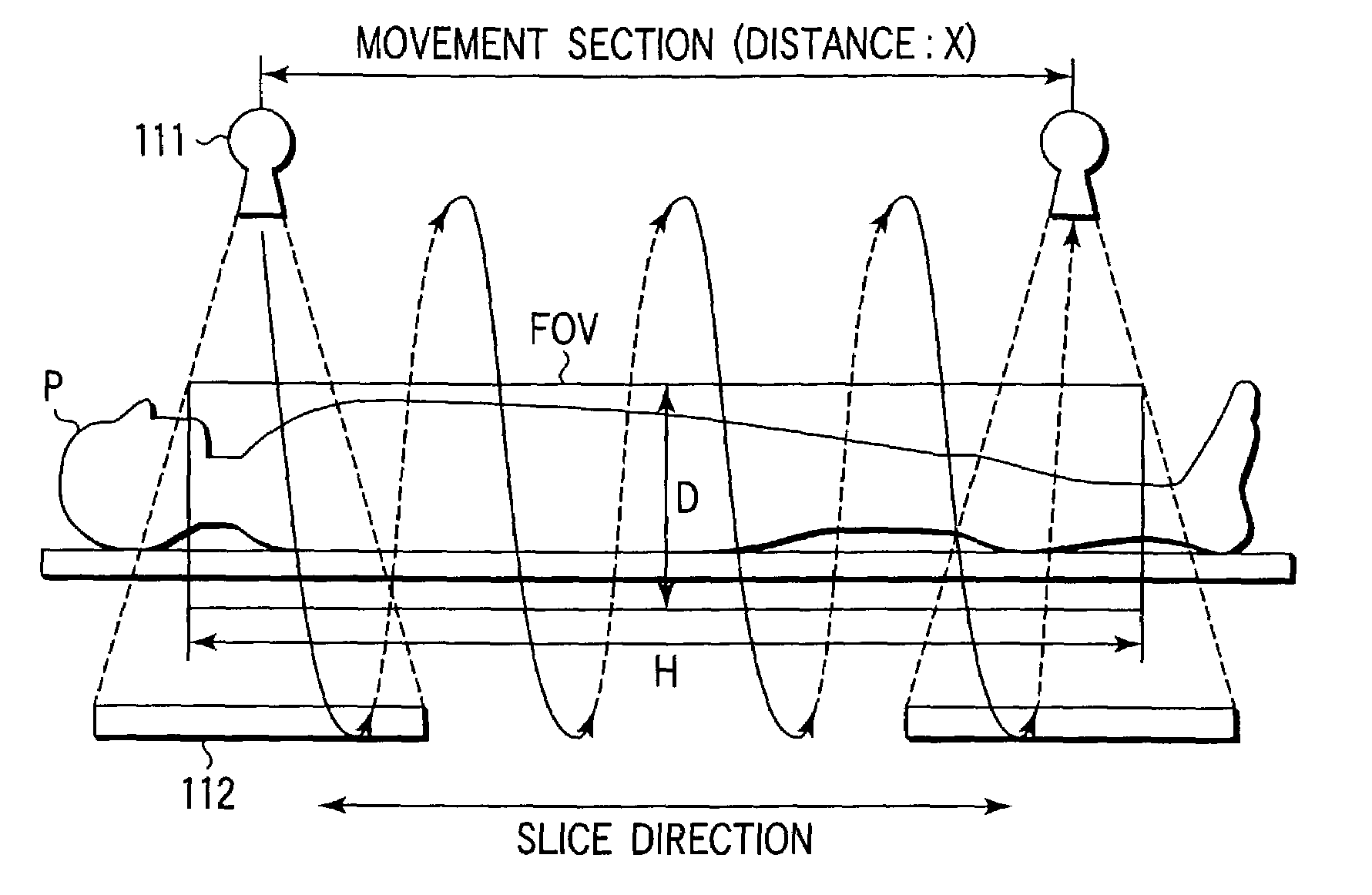
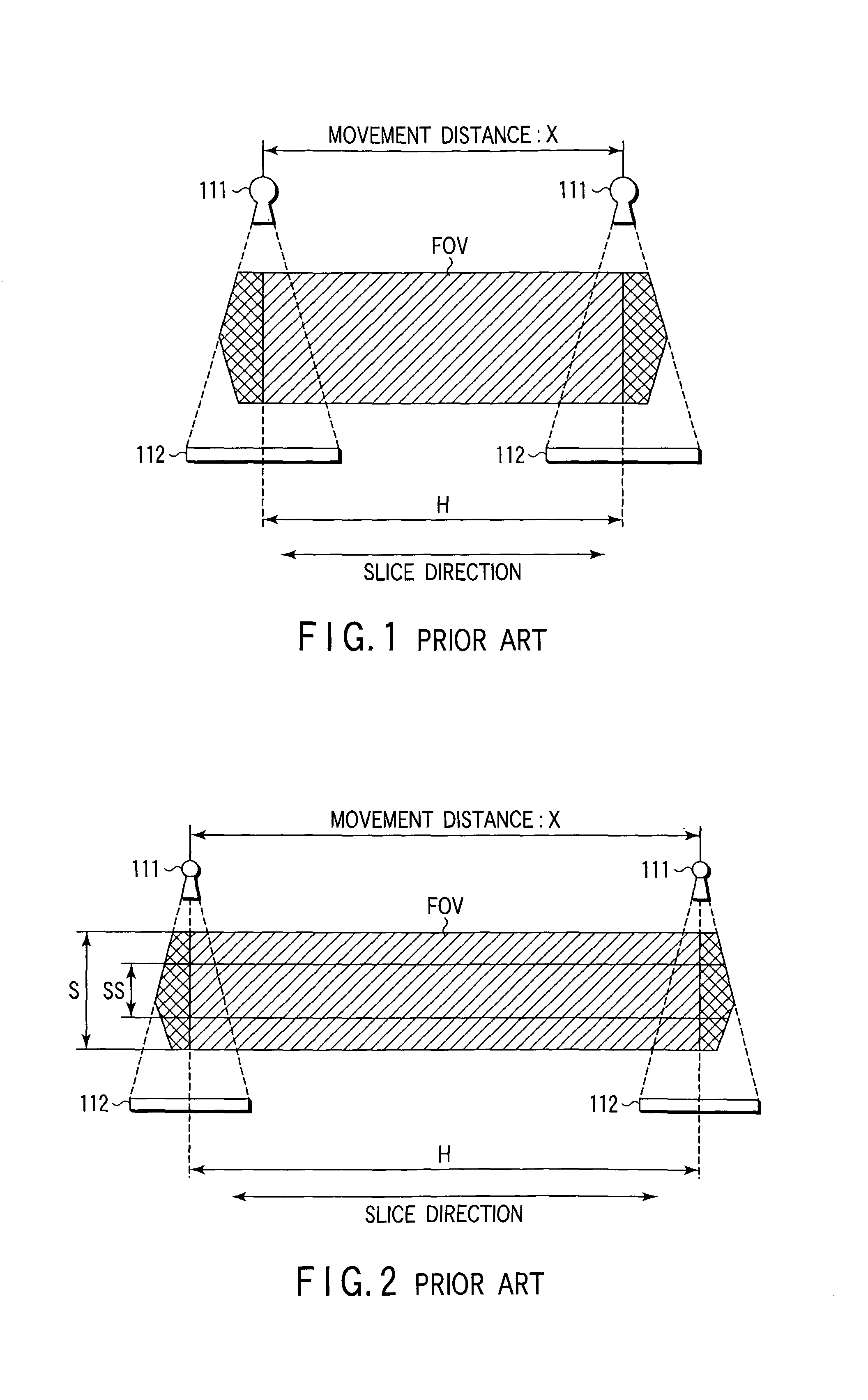
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes a cone beam X-ray tube, an X-ray detector, a rotating mechanism for supporting the X-ray tube and X-ray detector, a moving mechanism for moving the object in the slice direction, a control unit for controlling the rotating mechanism and moving mechanism to execute helical scan operation and move relative to the object, an input device for setting a substantially cylindrical reconstruction area, and an image reconstructing unit for reconstructing image data within the set reconstruction area based on the output of the detector. The apparatus also includes a movement distance determining unit for determining the movement distance of the X-ray tube and X-ray detector relative to the object on the basis of the radius of the set reconstruction area as well as its height.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
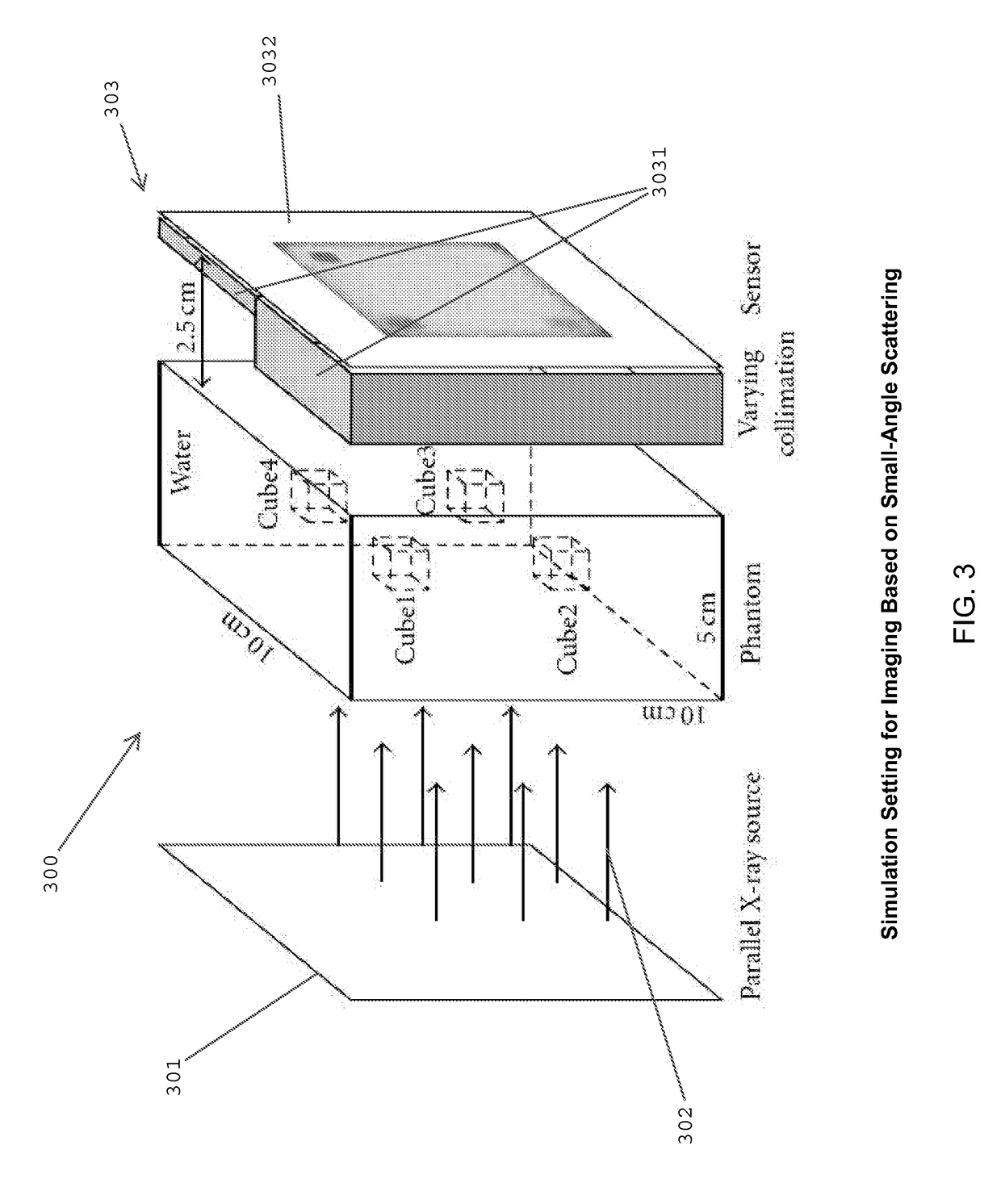
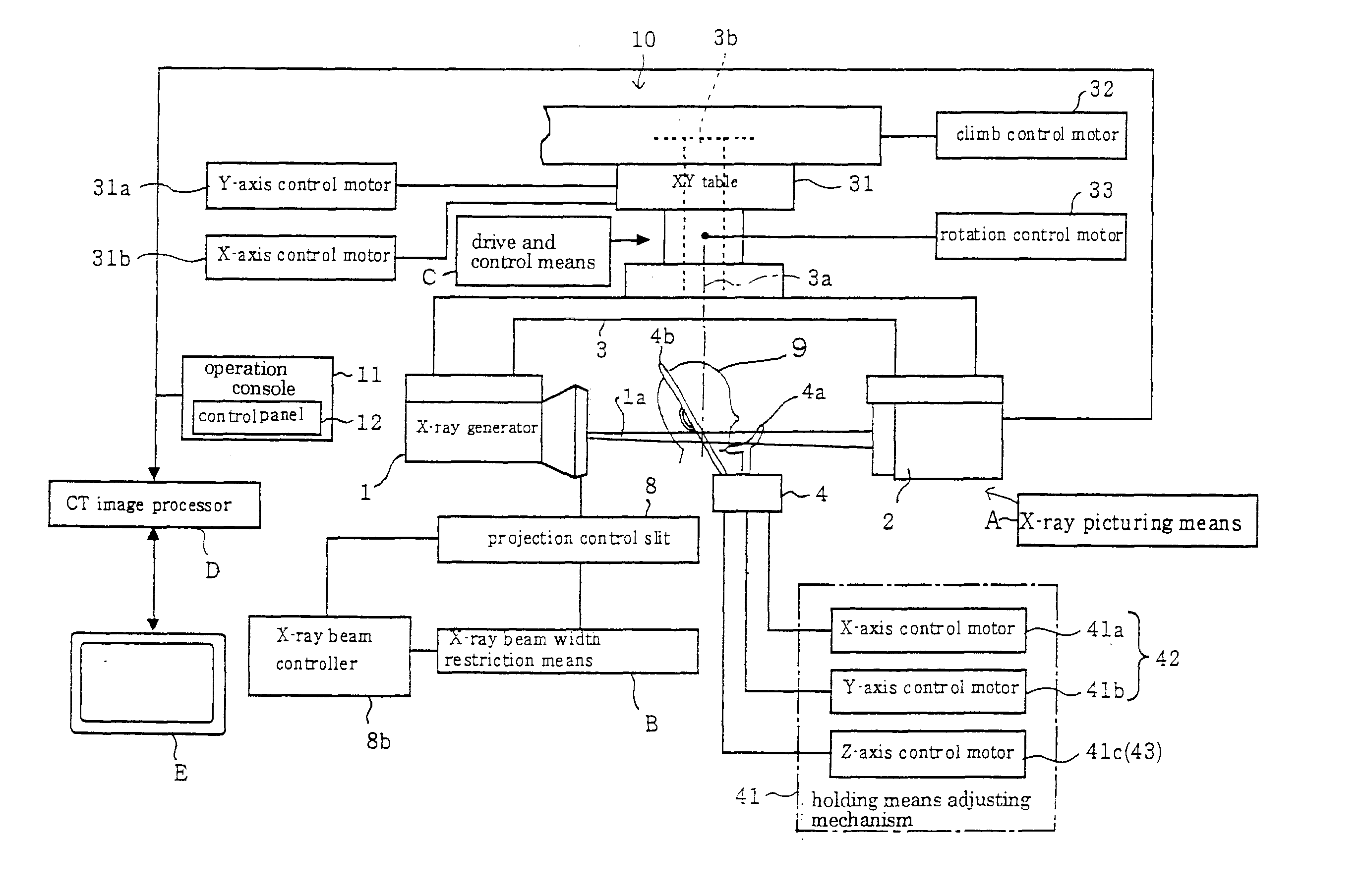
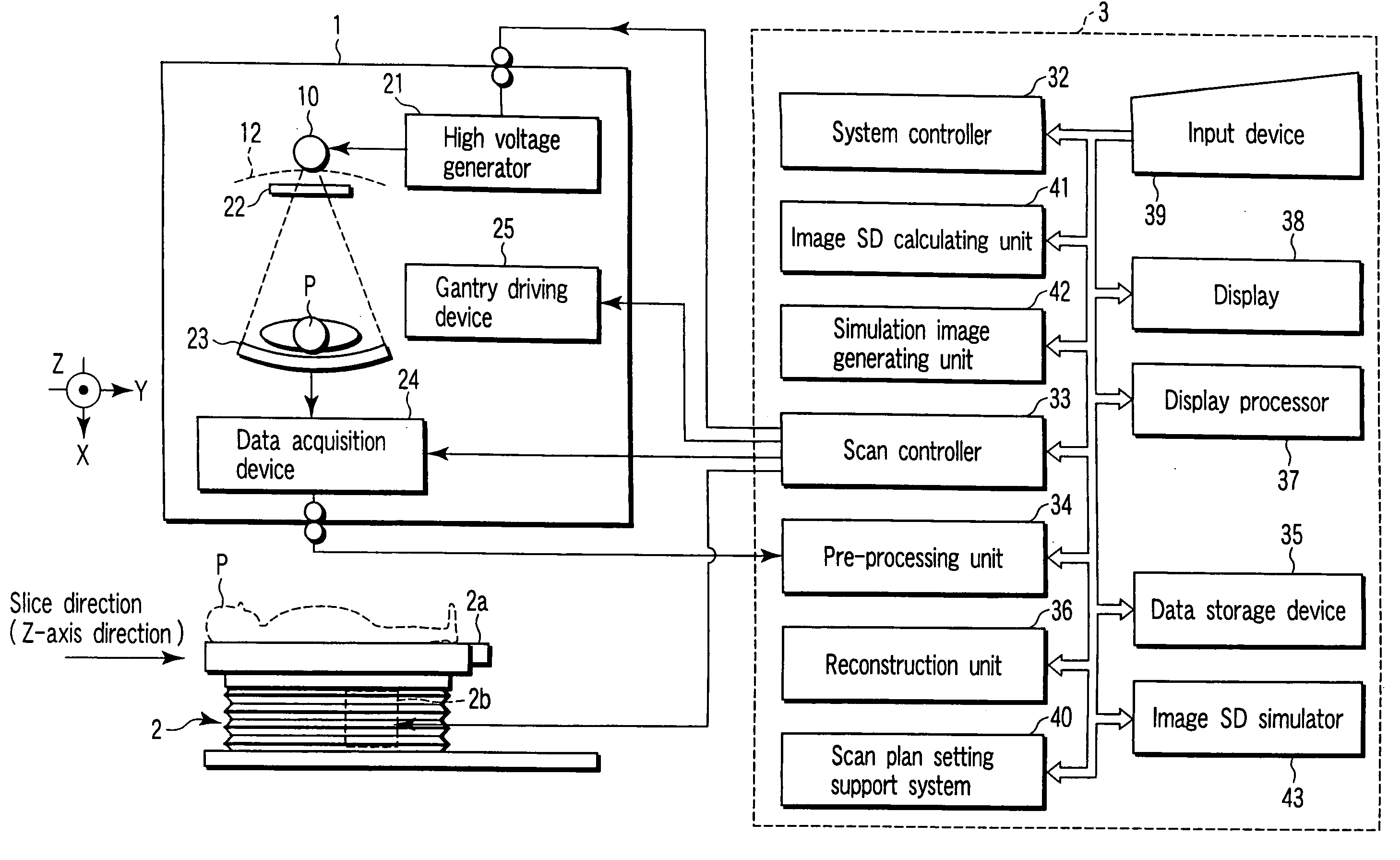
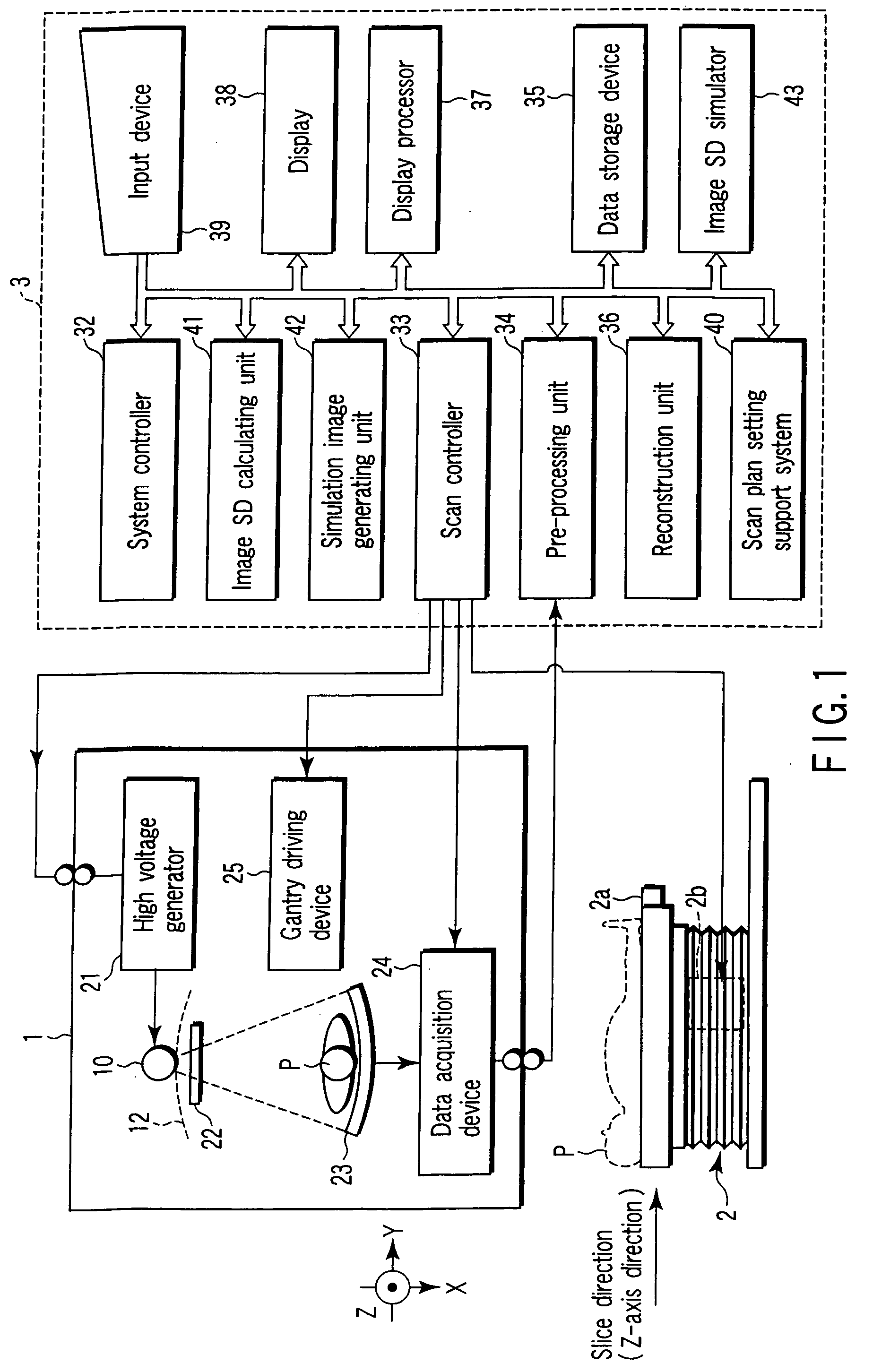
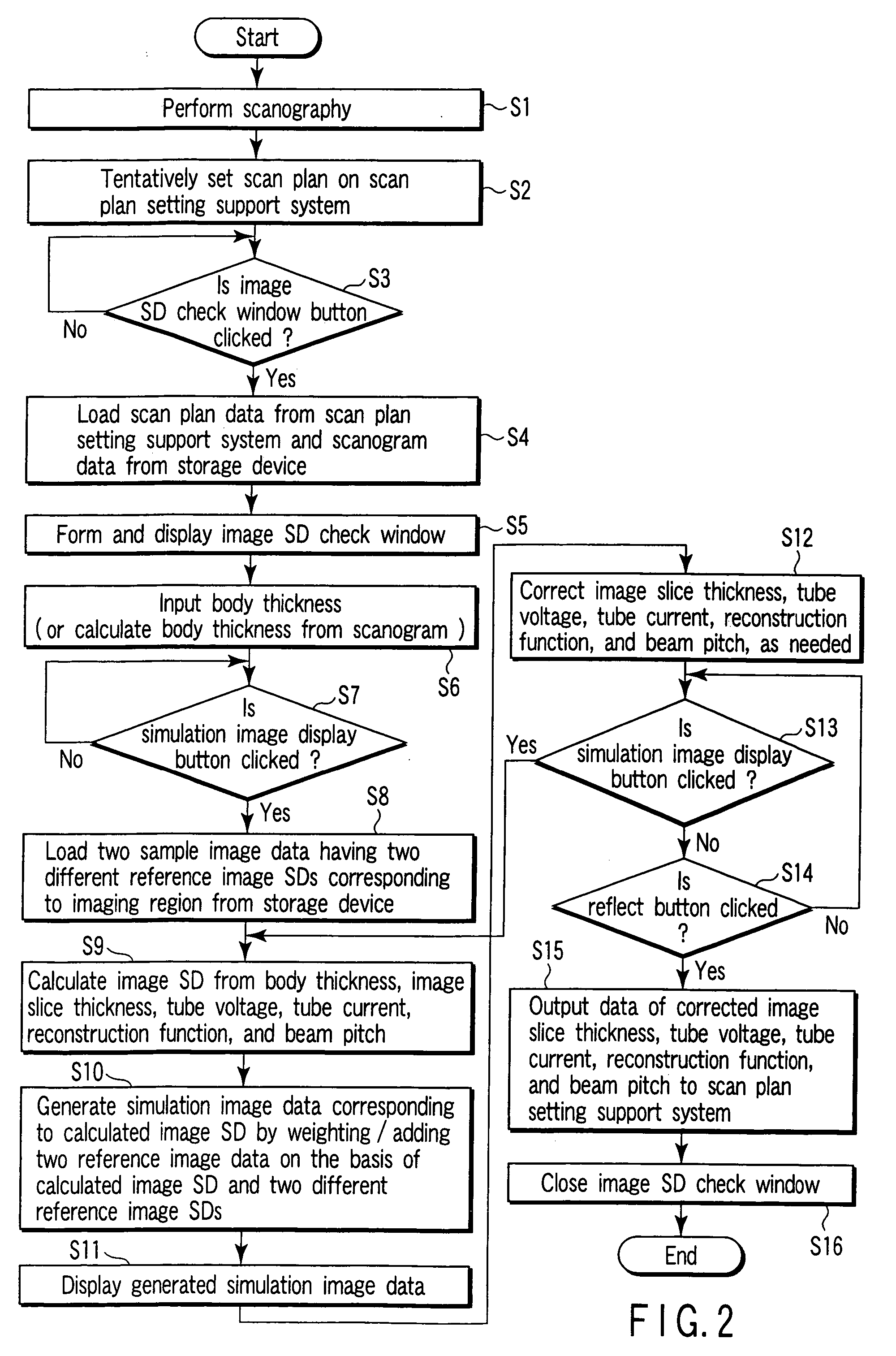
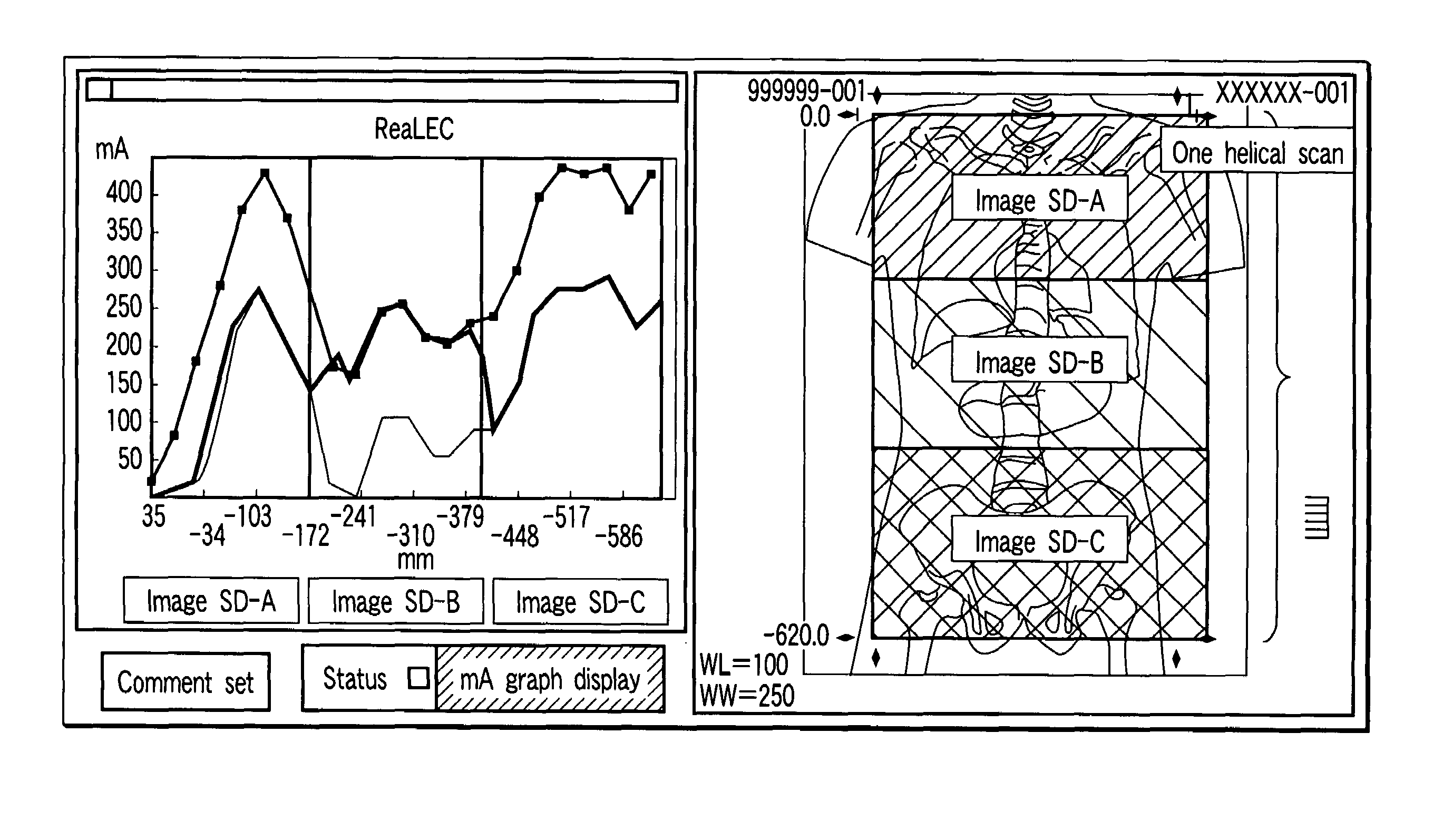
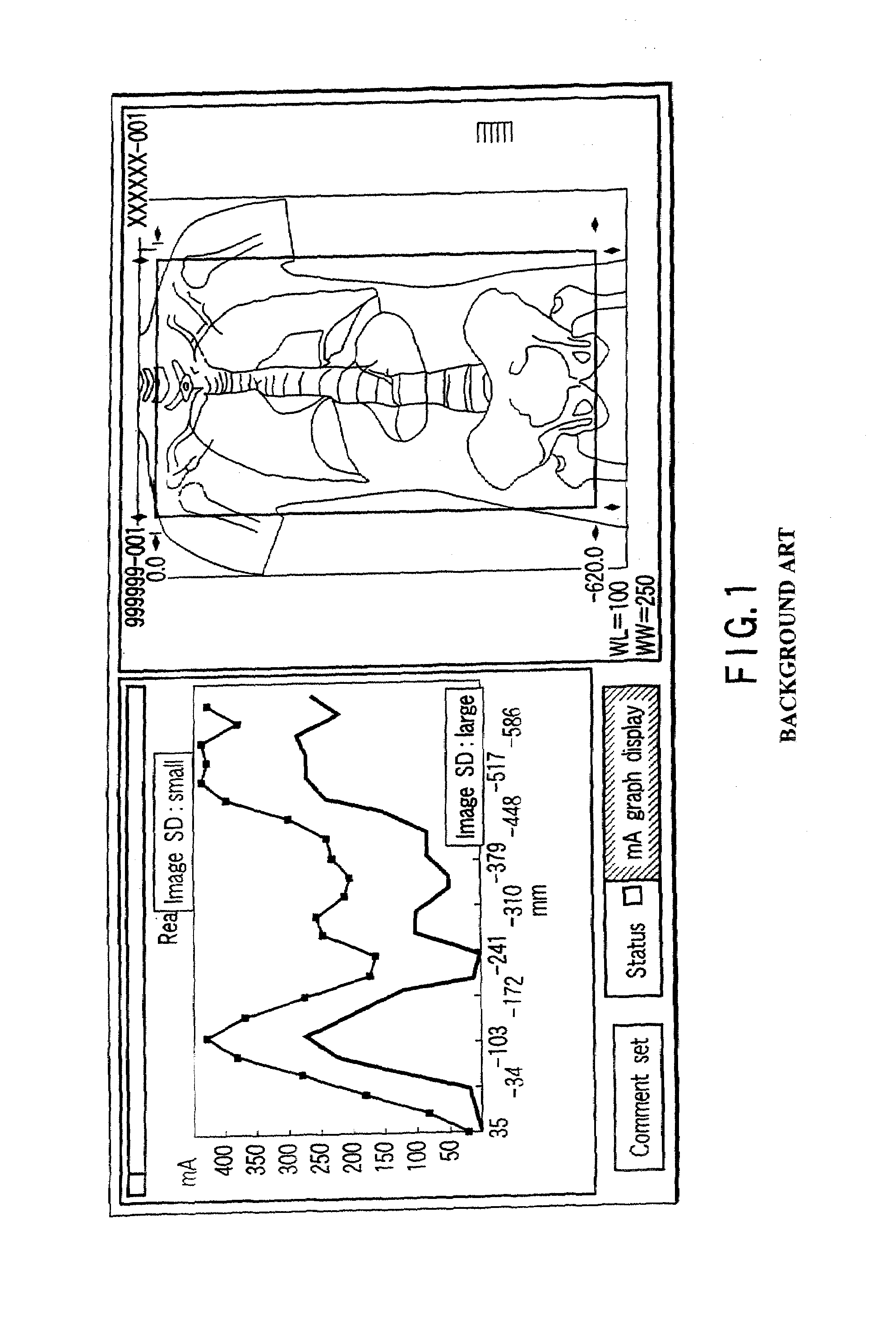
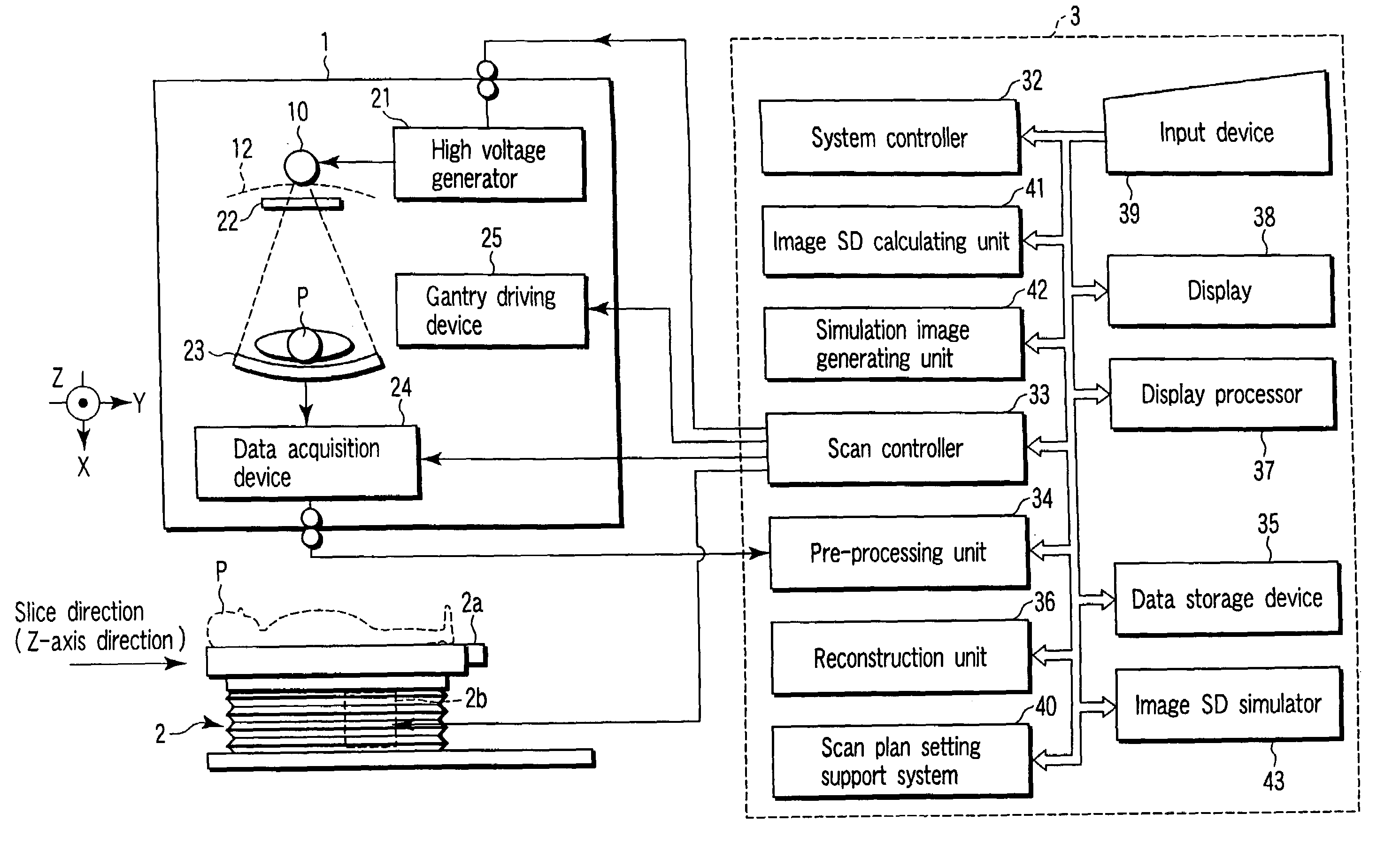
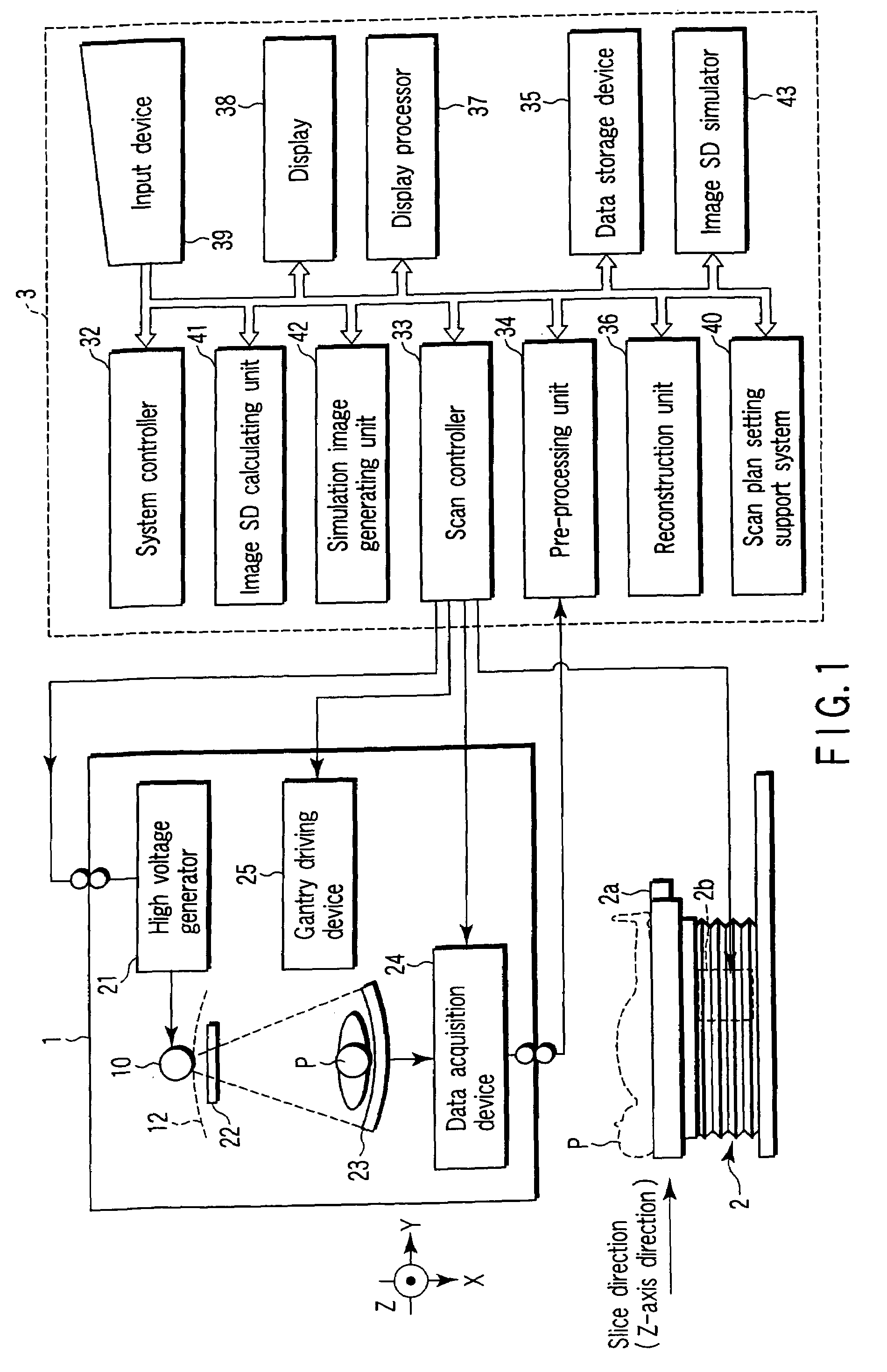
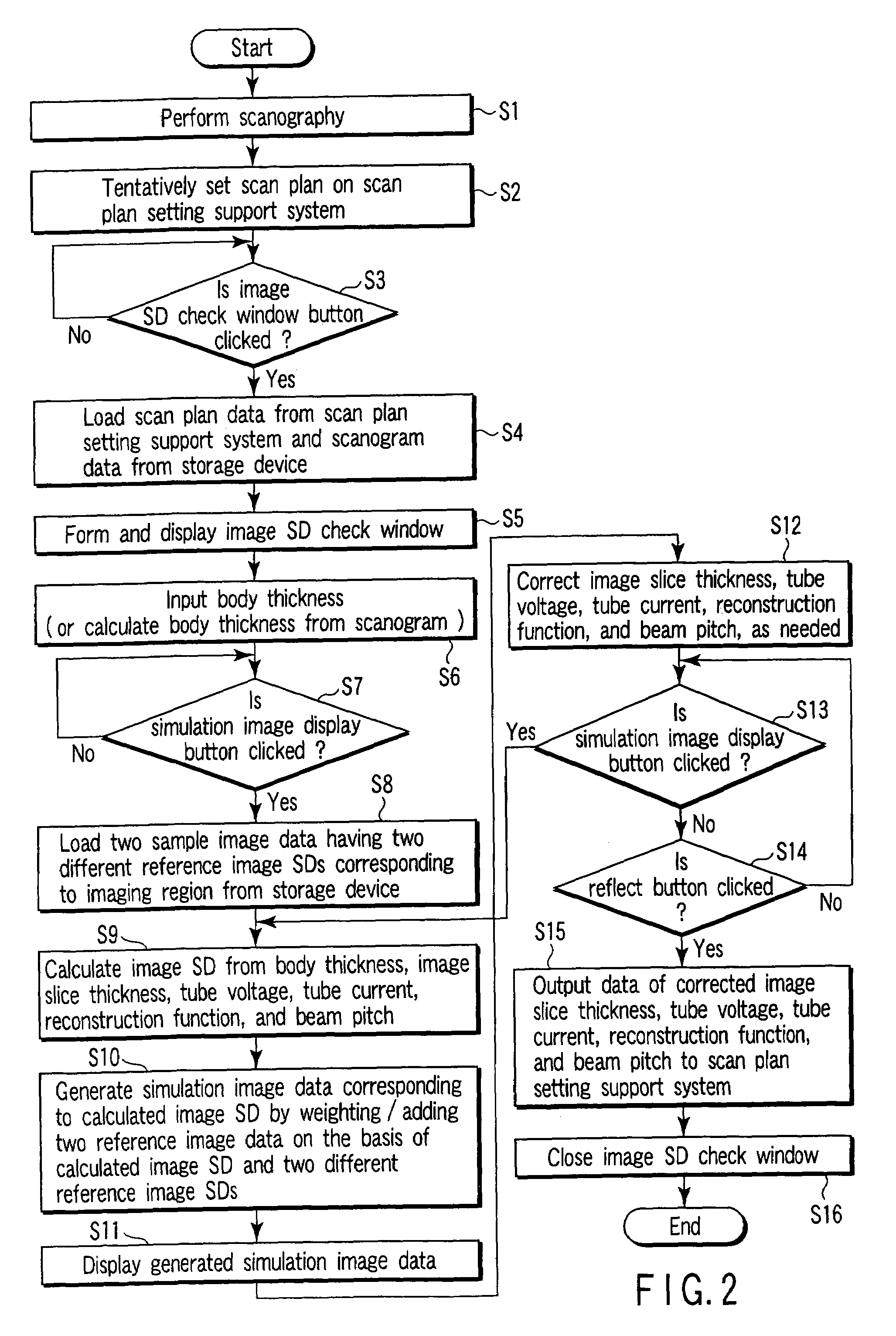
X-ray computed tomography apparatus and picture quality simulation apparatus
ActiveUS20050008115A1Set scan conditions more suitablyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSupporting systemData simulation
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus according to this invention includes a gantry (1) which scans an imaging target region of a subject to be examined in accordance with scan conditions, a reconstruction unit (36) which reconstructs image data from projection data, a scan plan setting support system (40) which sets scan conditions, an image SD calculating unit (41) which calculates an image SD associated with an index of picture quality on the basis of the set scan conditions, a data storage device (35) which stores sample image data having a reference value of an image SD, a simulation image generating unit (42) which generates simulation image data corresponding to the calculated image SD from the sample image data on the basis of the calculated image SD and the reference value of the image SD, and a display (38) which displays the generated simulation image data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Virtual spherical anode computed tomography
InactiveUS7333588B2Improved volumetric acquisitionIncrease flexibilityRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsIn planeHelical scan
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
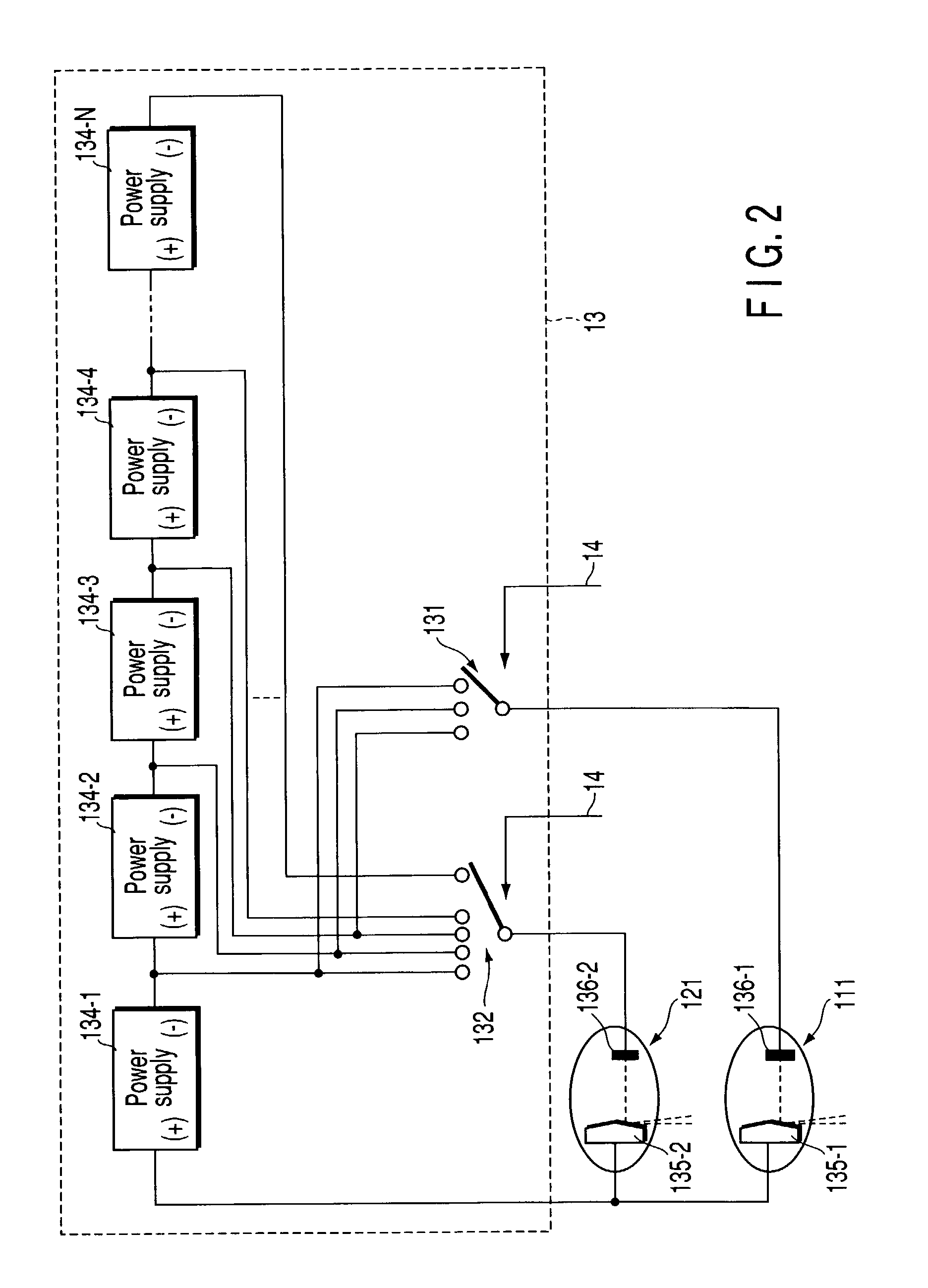
Method of and system for stabilizing high voltage power supply voltages in multi-energy computed tomography
InactiveUS7136451B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingNonlinear modelLeast squares minimization
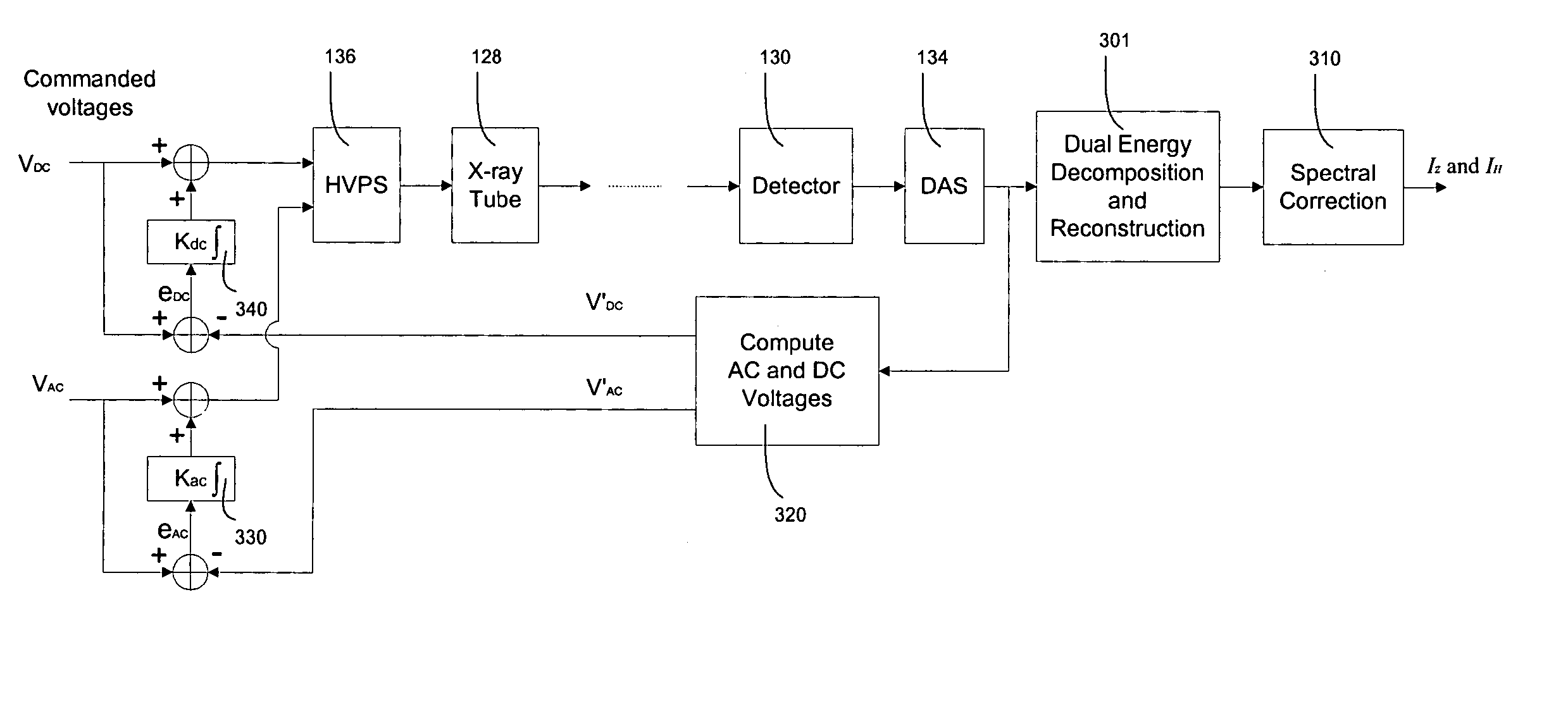
A method of and a system for stabilizing High Voltage Power Supply (HVPS) DC and AC voltages in multi-energy X-ray computed tomography scanners are provided. The method comprises generating filter ratios, computing DC and AC voltages, and feeding back the computed DC and AC voltages to the commanded voltages. The filtered ratios including an air ratio and a copper ratio are modeled as nonlinear functions of the DC and AC voltages. Computing DC and AC voltages include computing an m-ratio and an n-ratio. The parameters of the nonlinear model comprise an exponent parameter and a set of polynomial coefficients. The parameters are determined by a calibration procedure, which performs scanning at different combination of DC and AC voltages. The optimal parameters are obtained through a nonlinear least square minimization, which is solved through a brute force search over the exponent parameter and a closed form solution of the polynomial coefficients. Feeding back the computed DC and AC voltages include comparing the computed voltages with commanded voltages, integrating the difference between the computed voltages and commanded voltages, and adding the integrated voltage differences to the commanded voltages.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
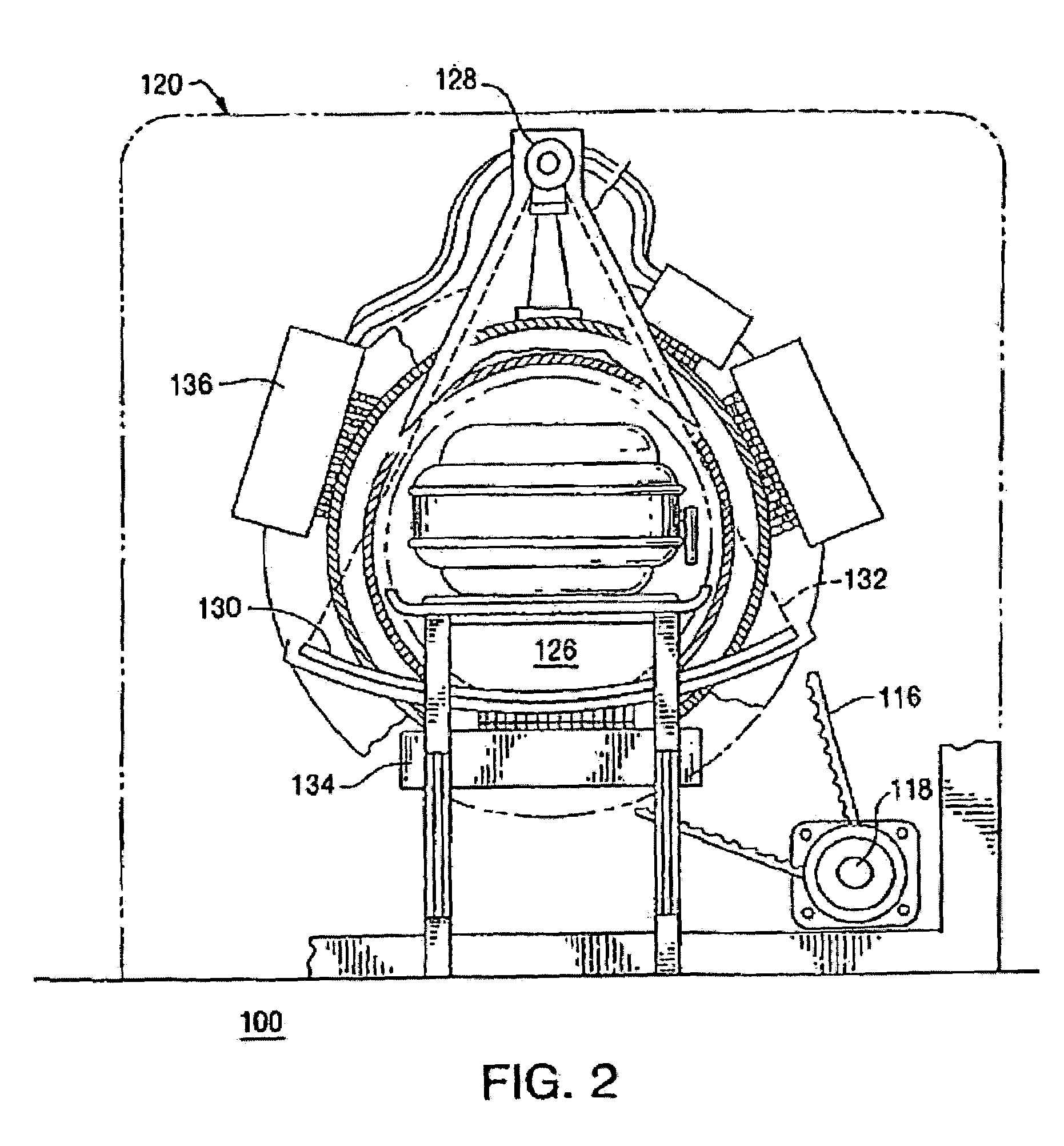
Imaging tomography apparatus with at least two radiator-detector combinations
ActiveUS20050089134A1High resolutionLarge regionRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsSoft x rayTemporal resolution
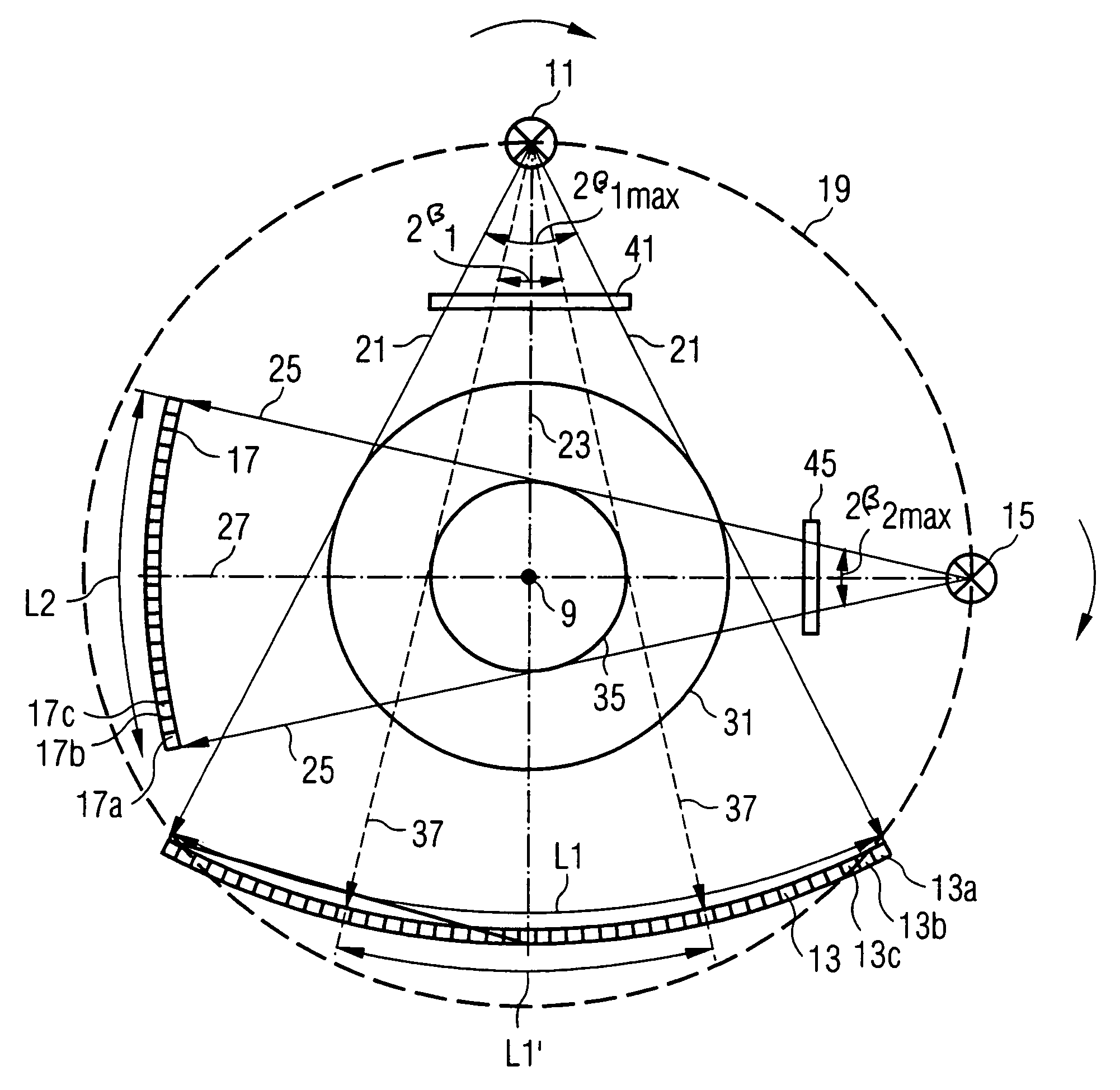
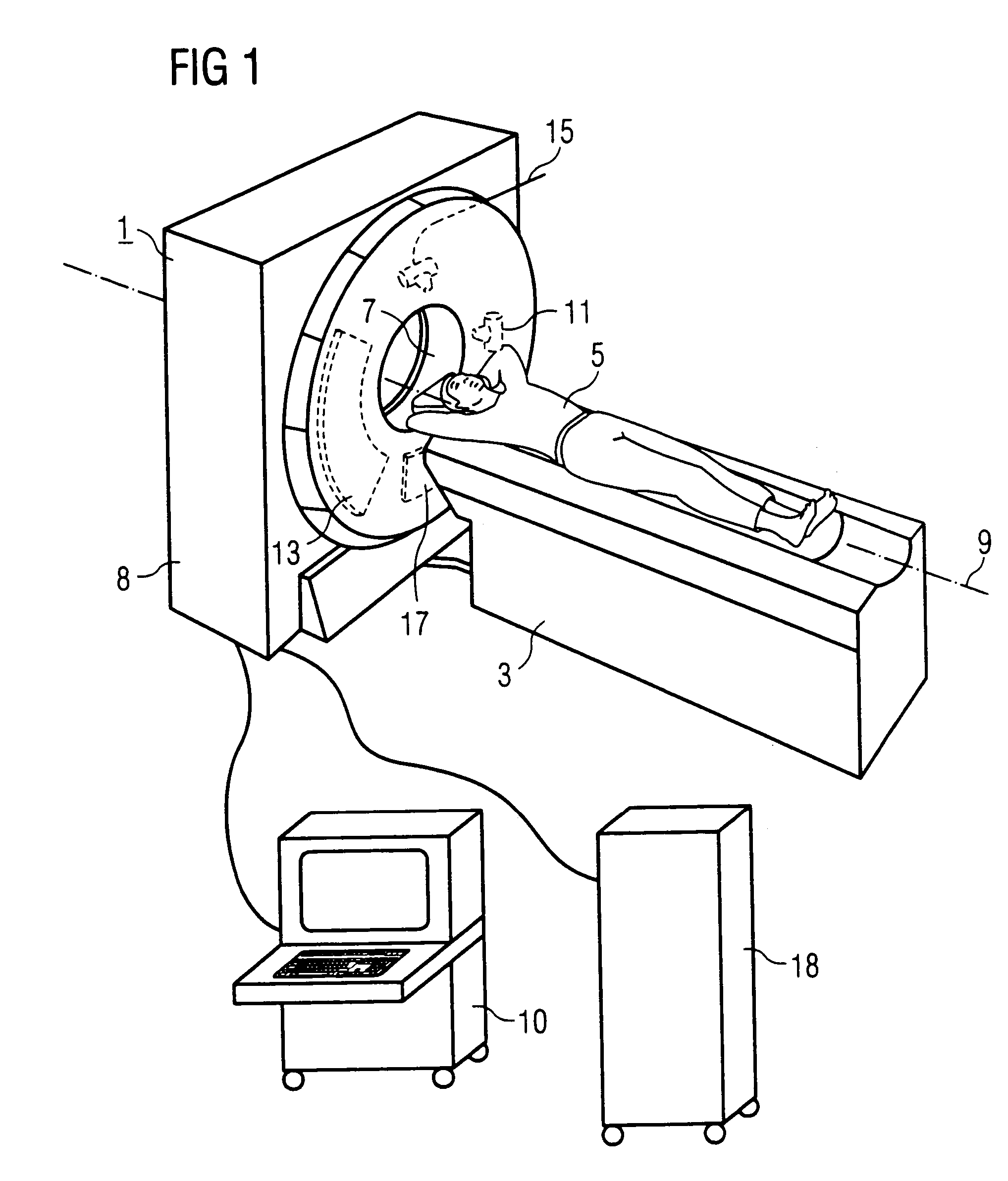
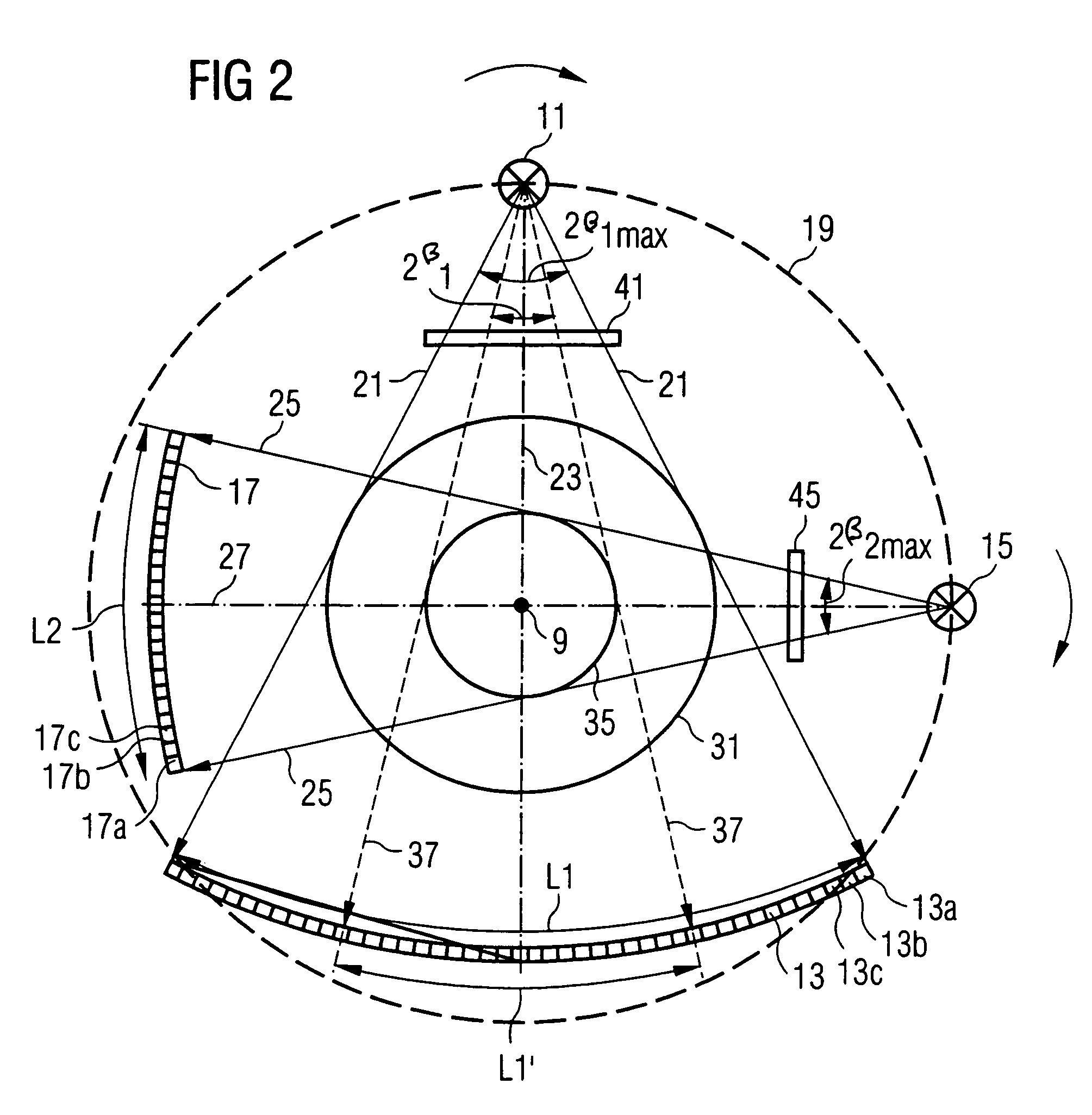
An imaging tomography apparatus, in particular an x-ray computed tomography apparatus, has two acquisition systems capable of rotating around a common rotation axis. Each of the acquisition systems has a radiator as well as a detector. The maximum measurement fields scanned by the two acquisition systems given rotation around the rotation axis are of different sizes, or can be adjusted to different sizes. In particular, the lengths of both detectors measured in the azimuthal direction—are of different sizes. The tomography apparatus can be fashioned to scan the entire body cross-section of an examination subject or of a patient with conventional temporal resolution, and to scan detail region, such as a heart region, with an increased temporal resolution or accelerated data acquisition rate in comparison to a device with only one acquisition system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for convection enhanced delivery of therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20060073101A1Improve securityFast imagingNervous disorderMagnetic measurementsTherapeutic effectConvection-Enhanced Delivery
A method for monitoring and controlling convection enhanced delivery of a therapeutic agent to a target tissue is disclosed. A tracer that is detectable, for example, by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or by X-ray computed tomography (CT) is co-infulsed with the therapeutic agent and used to monitor the distribution of the therapeutic agent as it moves through the target tissue. The images obtained during delivery are used to confirm delivery of the therapeutic agent to the target tissue and to avoid exposure of tissue outside of the targeted area to the therapeutic agent. In addition, the signal intensity of the images may be used to confirm that the therapeutic agent has been delivered to the target tissue at a desired concentration.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Registration of thoracic and abdominal imaging modalities
InactiveUS7397934B2Precise positioningMinimal computationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImaging modalitiesX-ray
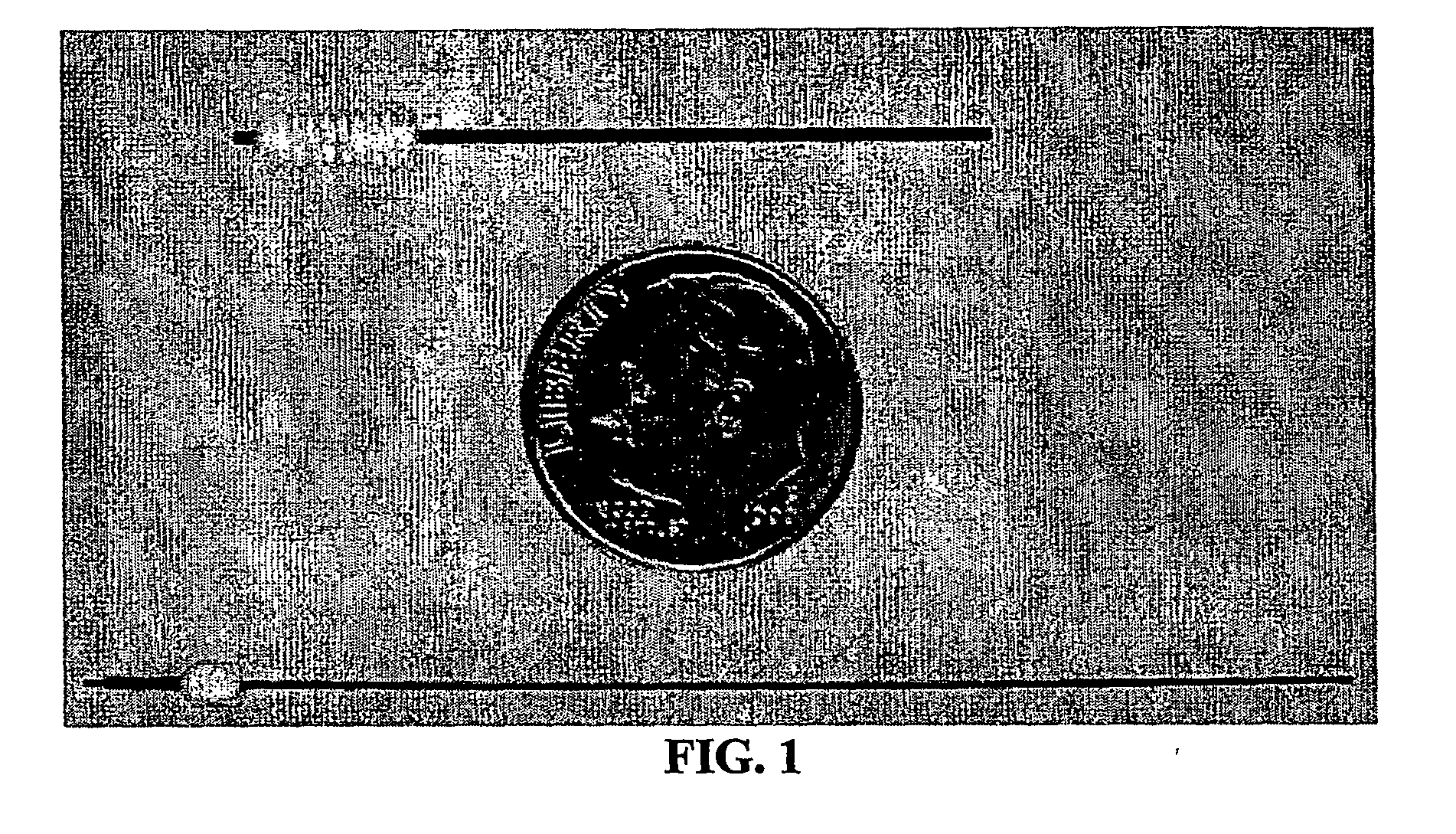
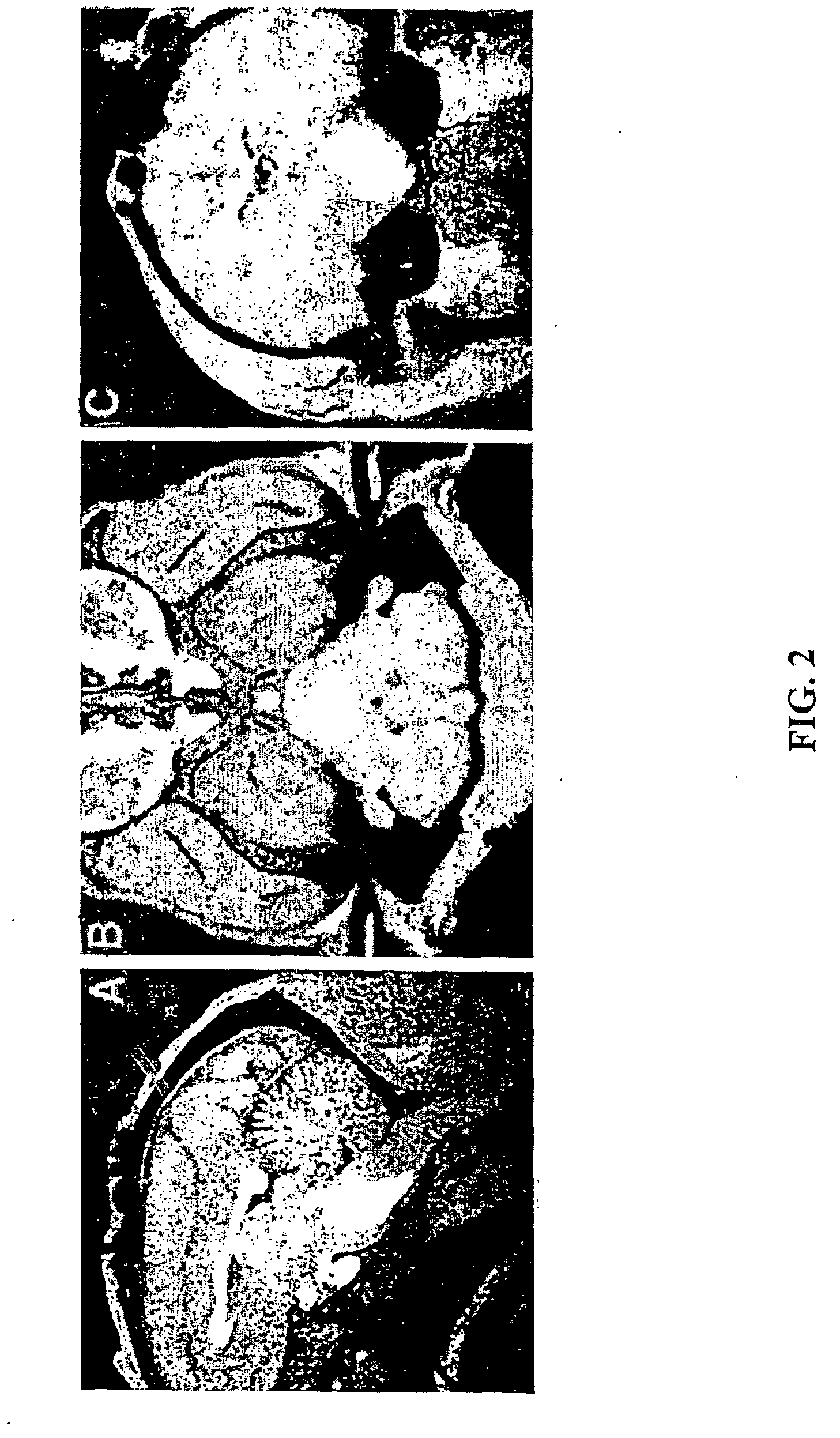
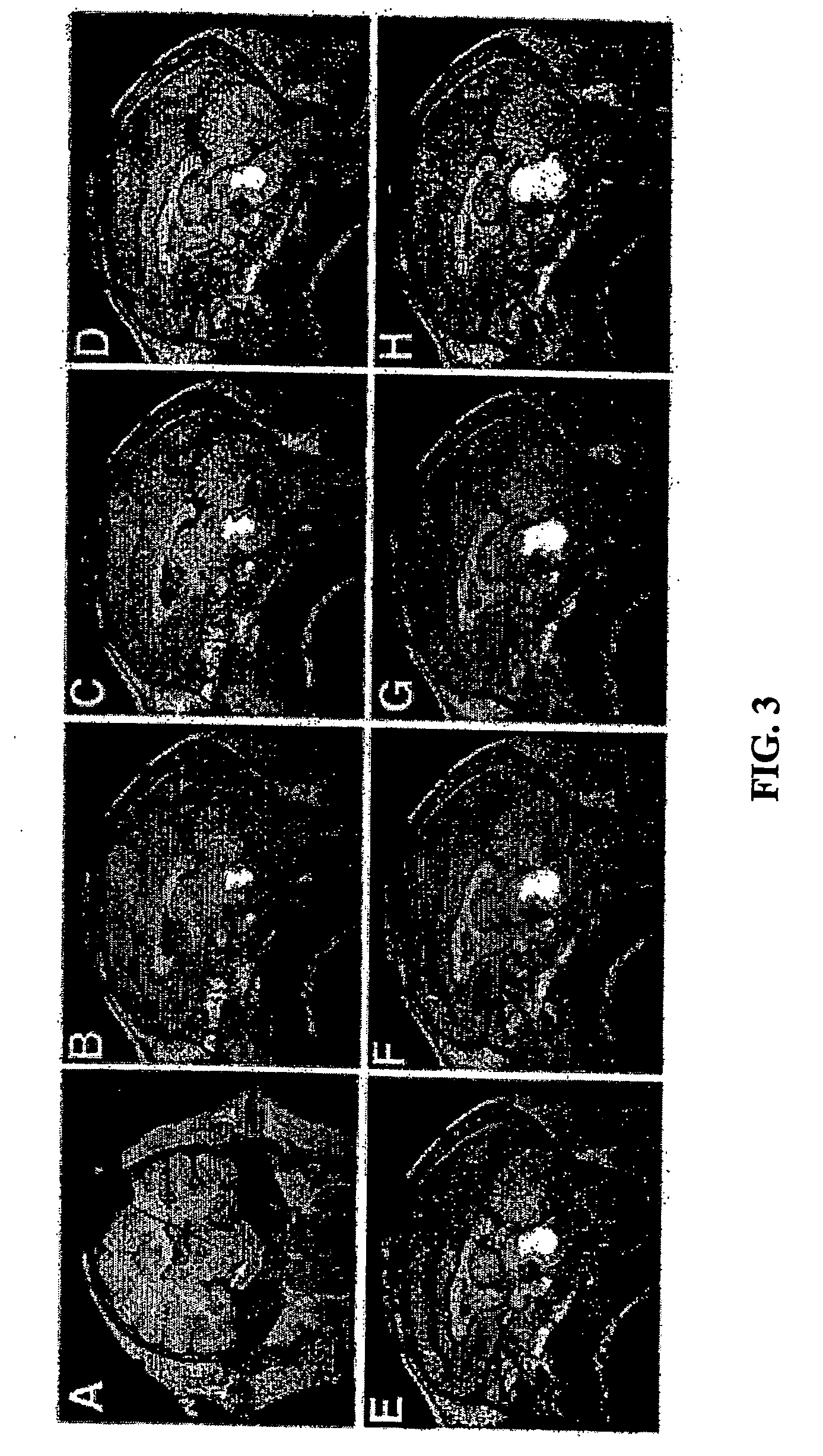
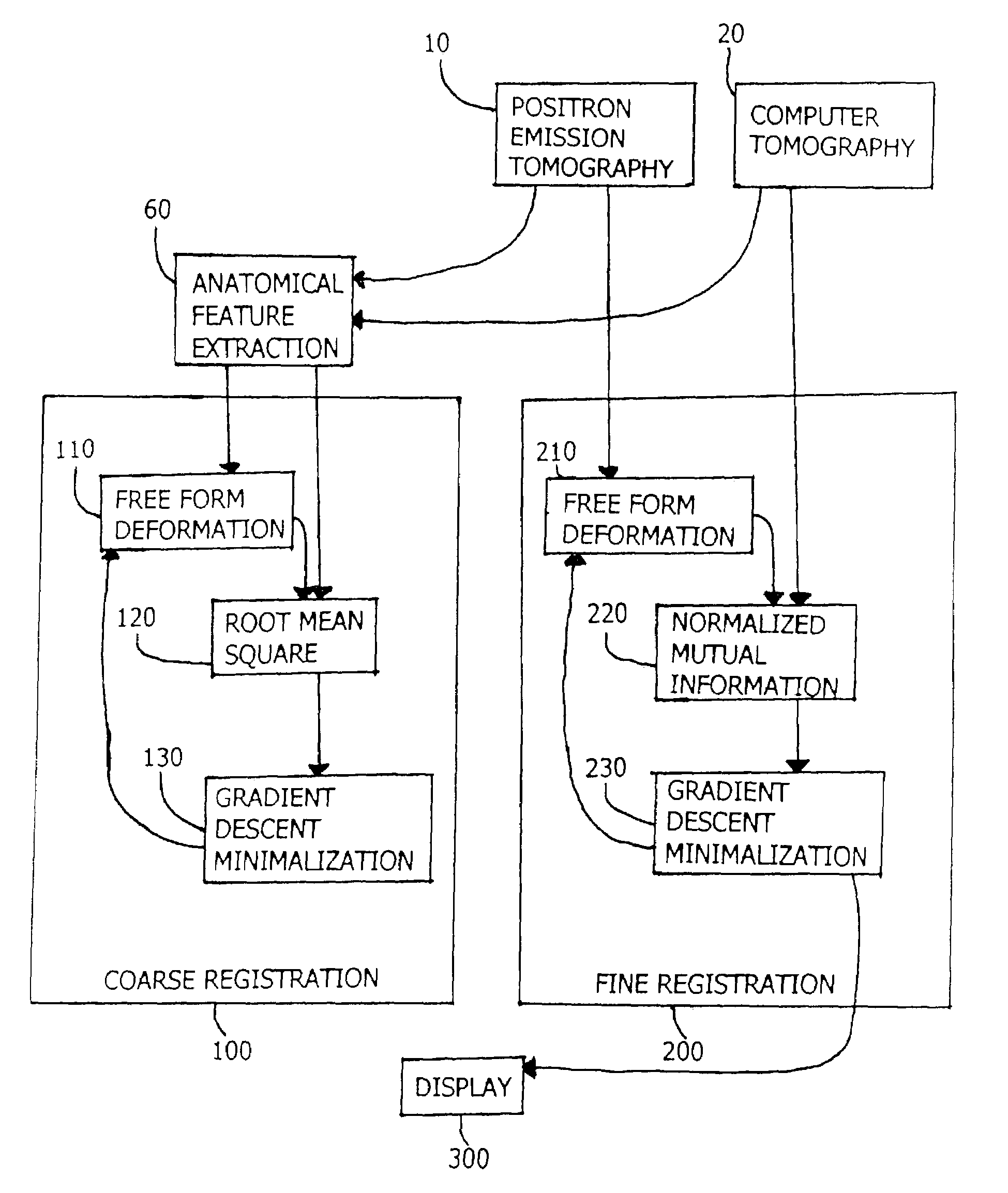
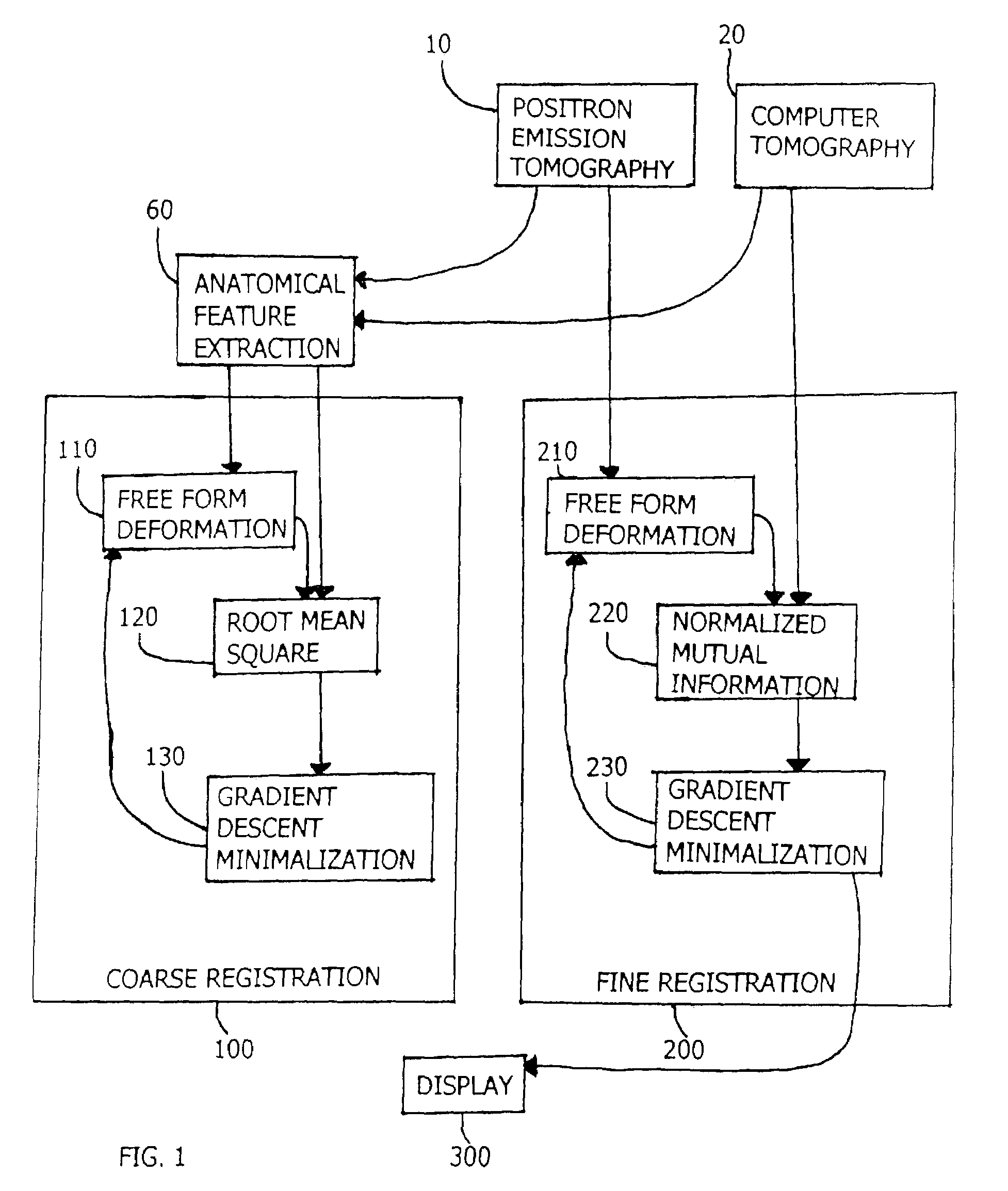
This disclosure presents an improved method for registering anatomical medical images and functional medical images. The example deals with the registration of x-ray computer tomography images with positron emission tomography images. The process is characterized by clinically useful registration with minimal computer calculations and minimal delay for computation. A nonrigid B-Spline free form deformation is used in both a preliminary coarse registration and the finished fine registration. Additional steps are used to insure accurate and complete registrations.
Owner:SEGAMI R L
Imaging tomography apparatus with at least two radiator-detector combinations
ActiveUS7016455B2High resolutionLarge regionRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsSoft x rayTemporal resolution
An imaging tomography apparatus, in particular an x-ray computed tomography apparatus, has two acquisition systems capable of rotating around a common rotation axis. Each of the acquisition systems has a radiator as well as a detector. The maximum measurement fields scanned by the two acquisition systems given rotation around the rotation axis are of different sizes, or can be adjusted to different sizes. In particular, the lengths of both detectors measured in the azimuthal direction—are of different sizes. The tomography apparatus can be fashioned to scan the entire body cross-section of an examination subject or of a patient with conventional temporal resolution, and to scan detail region, such as a heart region, with an increased temporal resolution or accelerated data acquisition rate in comparison to a device with only one acquisition system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Measurement of blood flow dynamics with x-ray computed tomography: dynamic ct angiography
ActiveUS20110274333A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNuclear medicineDynamic ct
In various embodiments, systems and methods can provide accurate measurements of blood flow dynamics in a subject. Projection data acquired during a computed tomography (CT) scan of the subject can be used to determine information representing inflow of a contrast material. Accordingly, a measurement of flow velocity, in addition to other aspects of flow, may be obtained from the projection data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
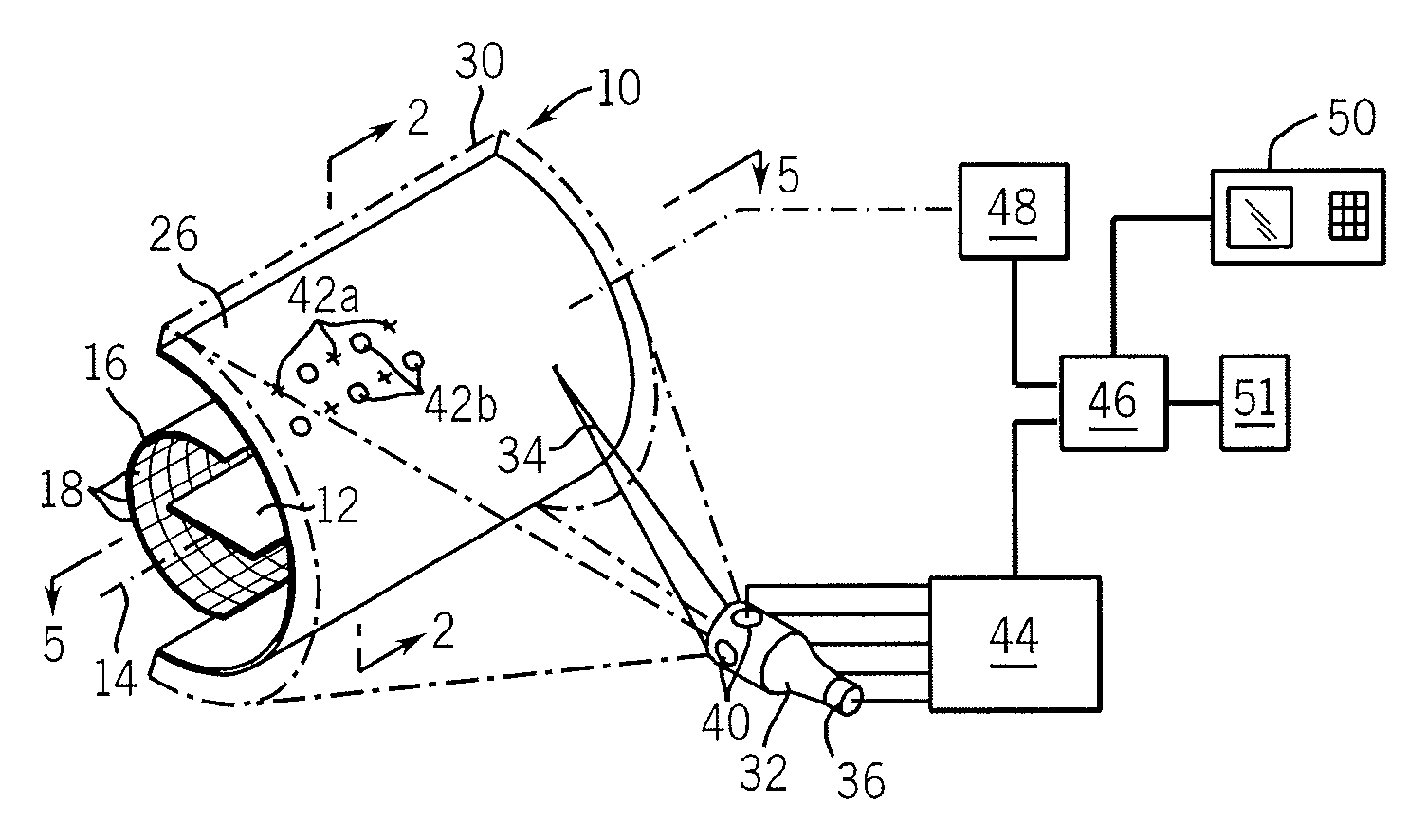
Source grating for X-rays, imaging apparatus for X-ray phase contrast image and X-ray computed tomography system
InactiveUS8243879B2Reduce spatial coherenceImprove coherenceImaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayGrating
A source grating for X-rays and the like which can enhance spatial coherence and is used for X-ray phase contrast imaging is provided. The source grating for X-rays is disposed between an X-ray source and a test object and is used for X-ray phase contrast imaging. The source grating for X-rays includes a plurality of sub-gratings formed by periodically arranging projection parts each having a thickness shielding an X-ray at constant intervals. The plurality of sub-gratings are stacked in layers by being shifted.
Owner:CANON KK
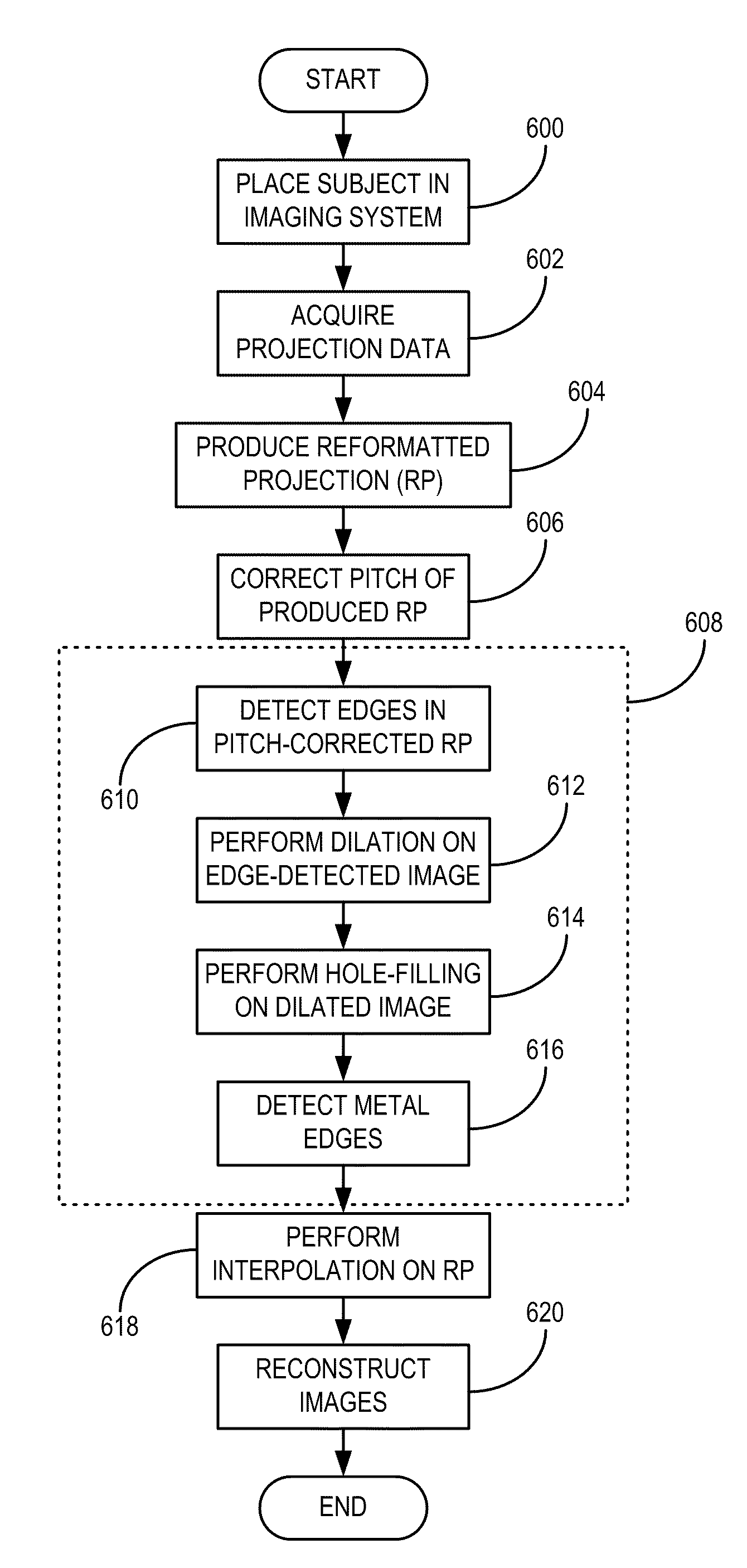
System and Method for Highly Attenuating Material Artifact Reduction in X-Ray Computed Tomography
The present invention is a method for reducing artifacts caused by highly attenuating materials in x-ray computed tomography (“CT”) images. The method includes combining projection views acquired at equivalent view angles to generate a projection plane data set, from which a reformatted projection is produced. The reformatted projection is then processed to detect and segment regions corresponding to objects composed of metals, metal alloys, or other highly attenuating materials. These segmented regions are then removed from the reformatted projection and the removed portions replaced by attenuation information interpolated from portions of the reformatted projection adjacent the removed portions. The interpolated reformatted projection is then mapped back to a projection plane data set, and an image of the subject is reconstructed from the projection views contained in that data set. The reconstructed image, therefore, is one in which artifacts caused by highly attenuating materials are substantially suppressed.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
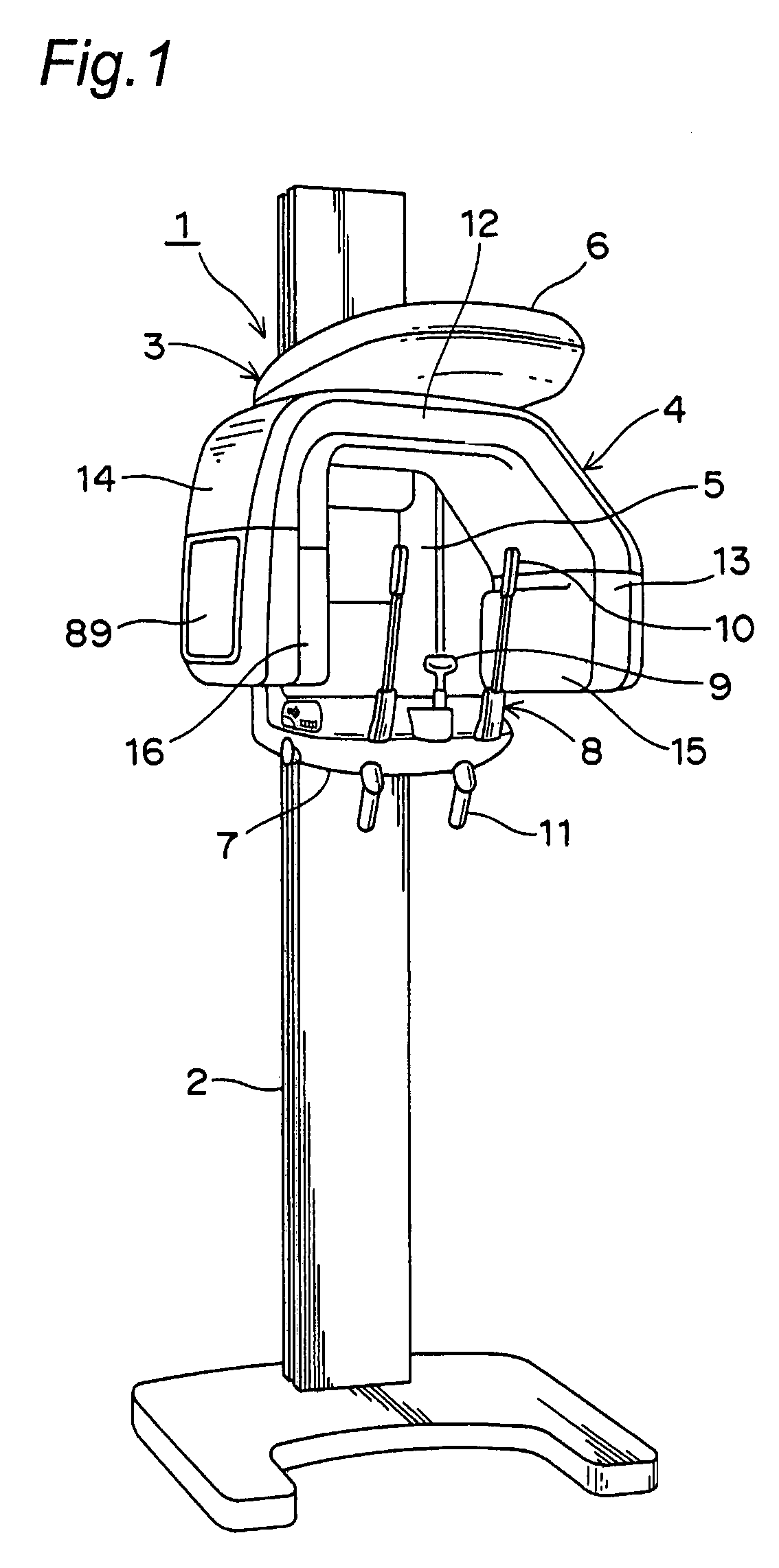
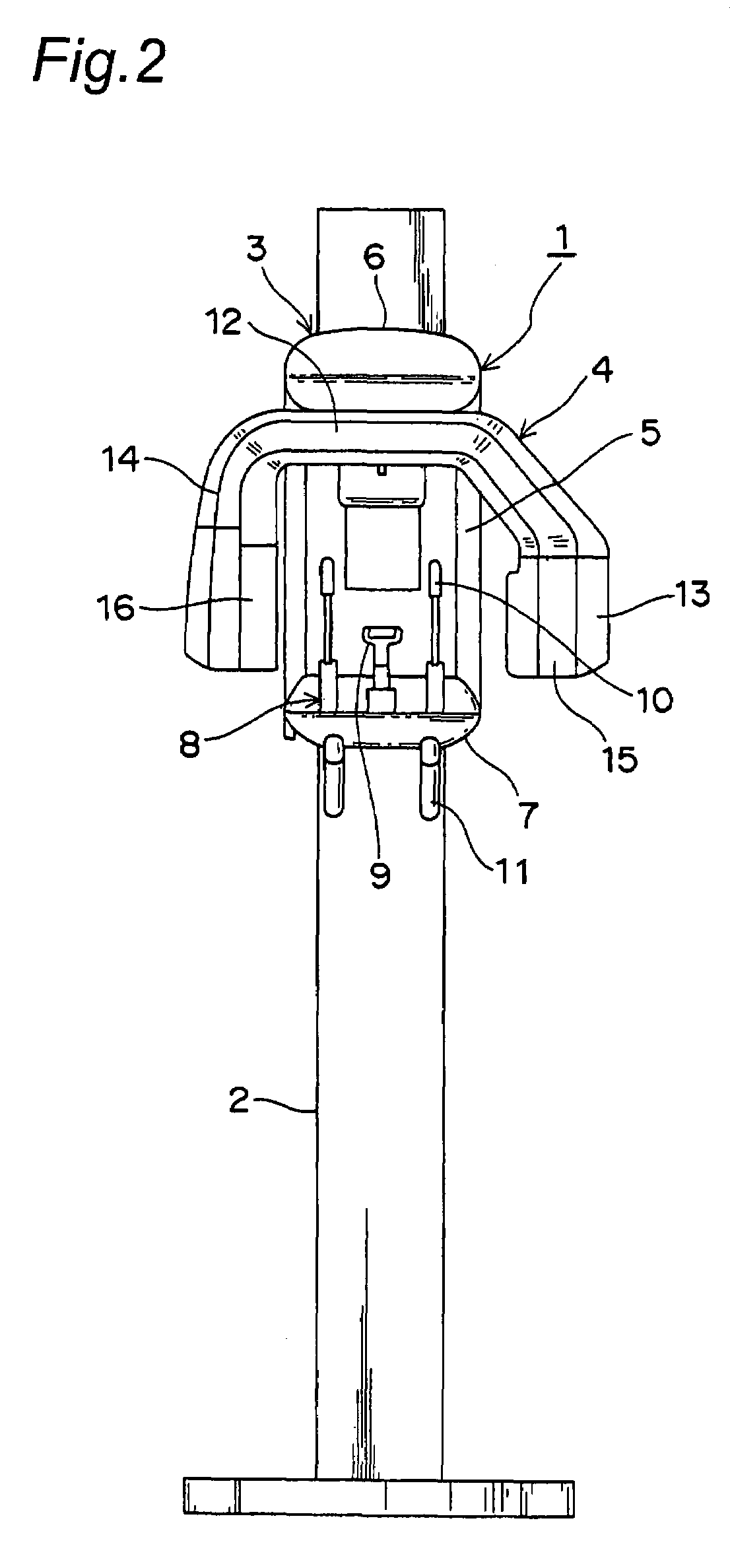
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
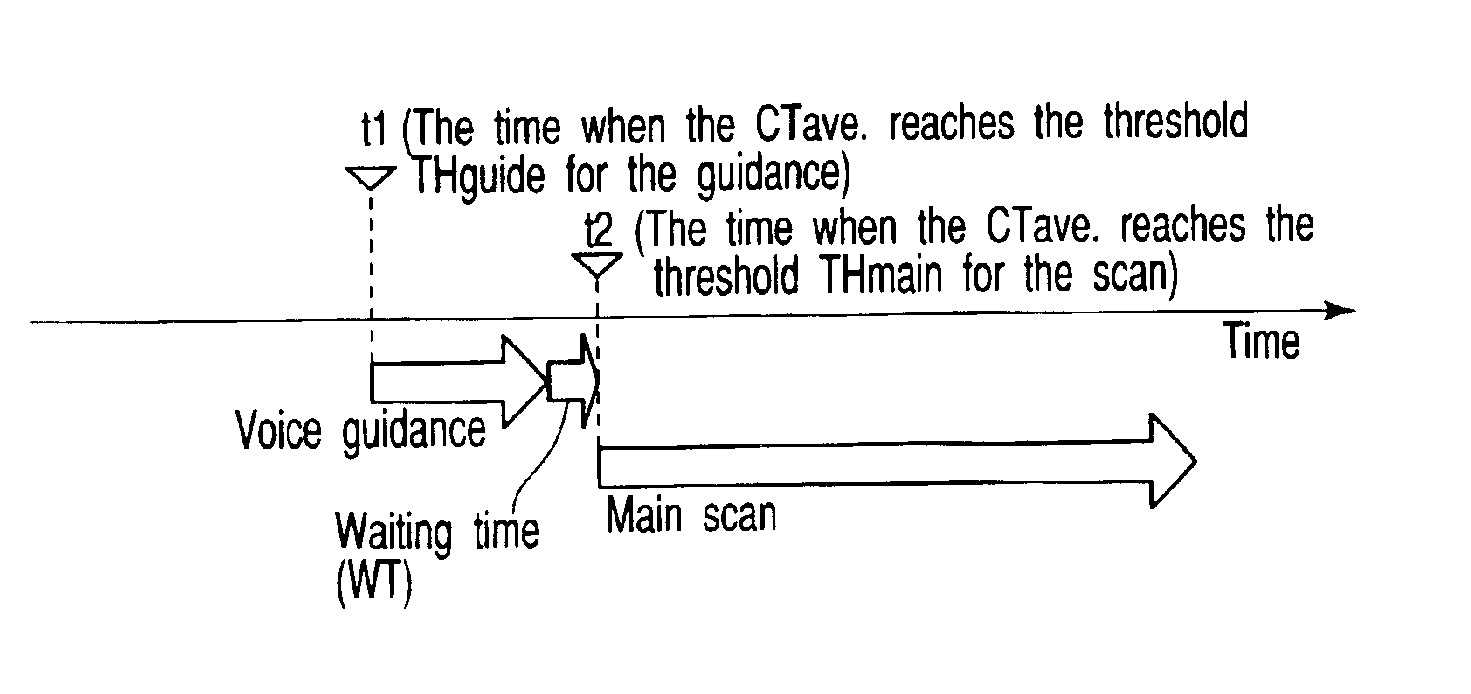
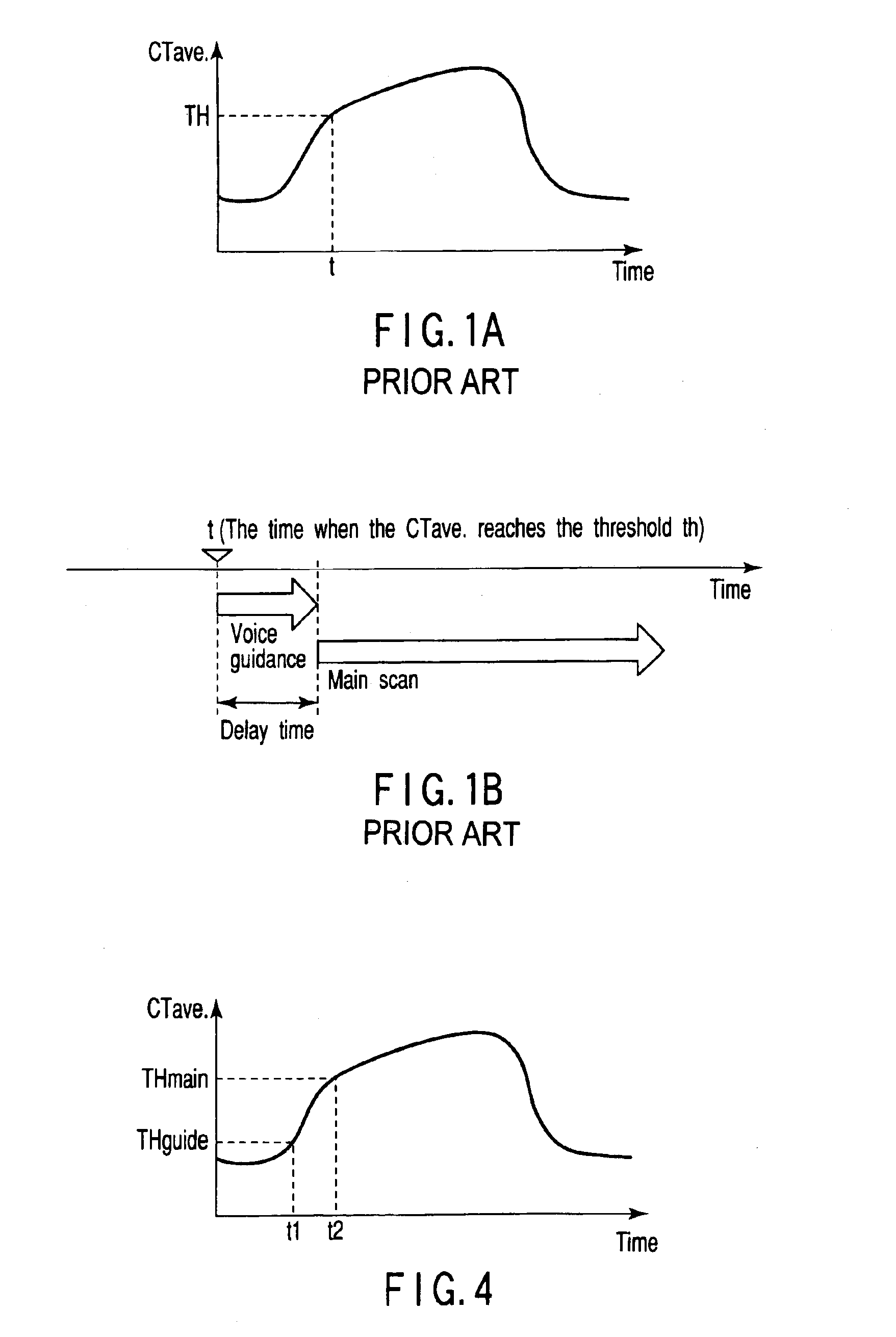
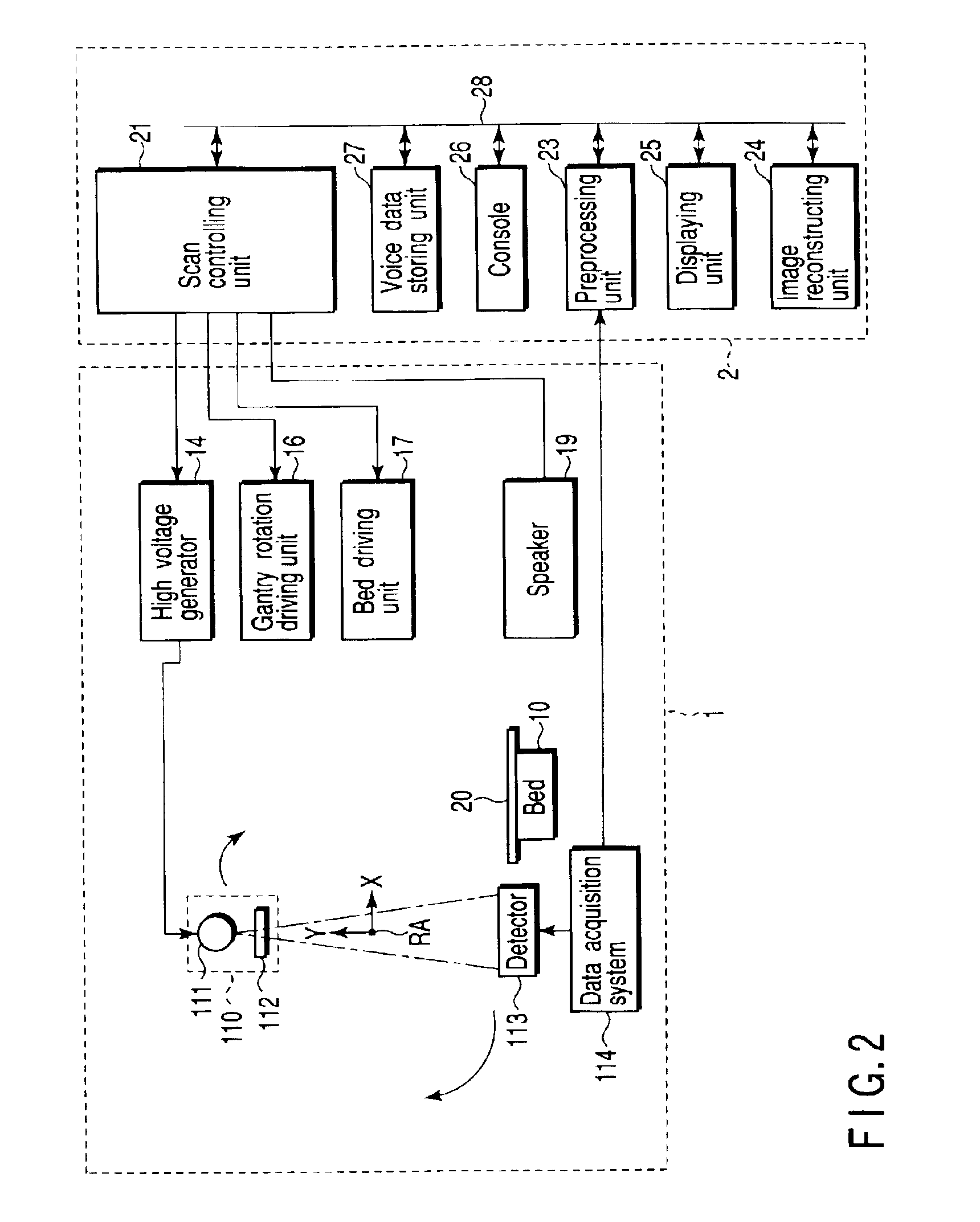
InactiveUS6876720B2Reduce delaysRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsTomographic imageNuclear medicine
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus monitors the density of a contrast medium injected into a subject with a CT value by a preparation scan so as to adjust the main scan start timing. A guidance output unit outputs guidance to the subject. A control unit compares the CT value of tomographic image data obtained by the preparation scan with the first threshold, supplies guidance data to the guidance output unit to output the guidance to the subject when the CT value has reached the first threshold. The control unit compares the CT value of the tomographic image obtained by the preparation scan with the second threshold different from the first threshold, and starts executing the main scan or preparing the execution of the main scan when the CT value has reached the second threshold.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Radiological imaging apparatus and radiological imaging method
An image pickup apparatus of a radiological imaging apparatus includes a plurality of radiation detectors arranged in a ring form around a through hole section formed on a casing into which an examinee is inserted. An X-ray source unit having an X-ray source moves in a circumferential direction of the through hole section along a ring-shaped guide rail provided on the casing. Each radiation detector outputs both an X-ray detection signal which is a detection signal of X-rays that have passed through the examinee and a γ-ray detection signal which is a detection signal of γ-rays radiated from the examinee caused by radiopharmaceutical. A computer creates an X-ray computed tomographic image data based on the X-ray detection signal and a PET image data based on the γ-ray detection signal and creates fused tomographic image data using the X-ray computed tomographic image data and the PET image data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
X-ray computer tomography apparatus
ActiveUS7486759B2Low costImprove convenienceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
There is provided a new X-ray imaging apparatus by the use of which X-ray CT and panoramic imaging can be effectively performed. In an X-ray imaging apparatus which rotates an X-ray generating section and an X-ray detecting section around an imaging object arranged between these X-ray generating section and the X-ray detecting section and also detects in the X-ray detecting section X-rays having been radiated from the X-ray generating section and transmitted through the imaging object to form an X-ray image, a panoramic imaging mode in which the X-ray generating section and the X-ray detecting section are driven to form a panoramic image of the imaging object and an offset scan / CT mode in which the X-ray generating section and the X-ray detecting section are driven to form a tomographic image of the imaging object are set, so as to selectively execute these two imaging modes. Consequently, the panoramic imaging mode and the offset scan / CT mode can be arbitrarily selected, thereby allowing formation of an X-ray imaged image that is optimum for treatment.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
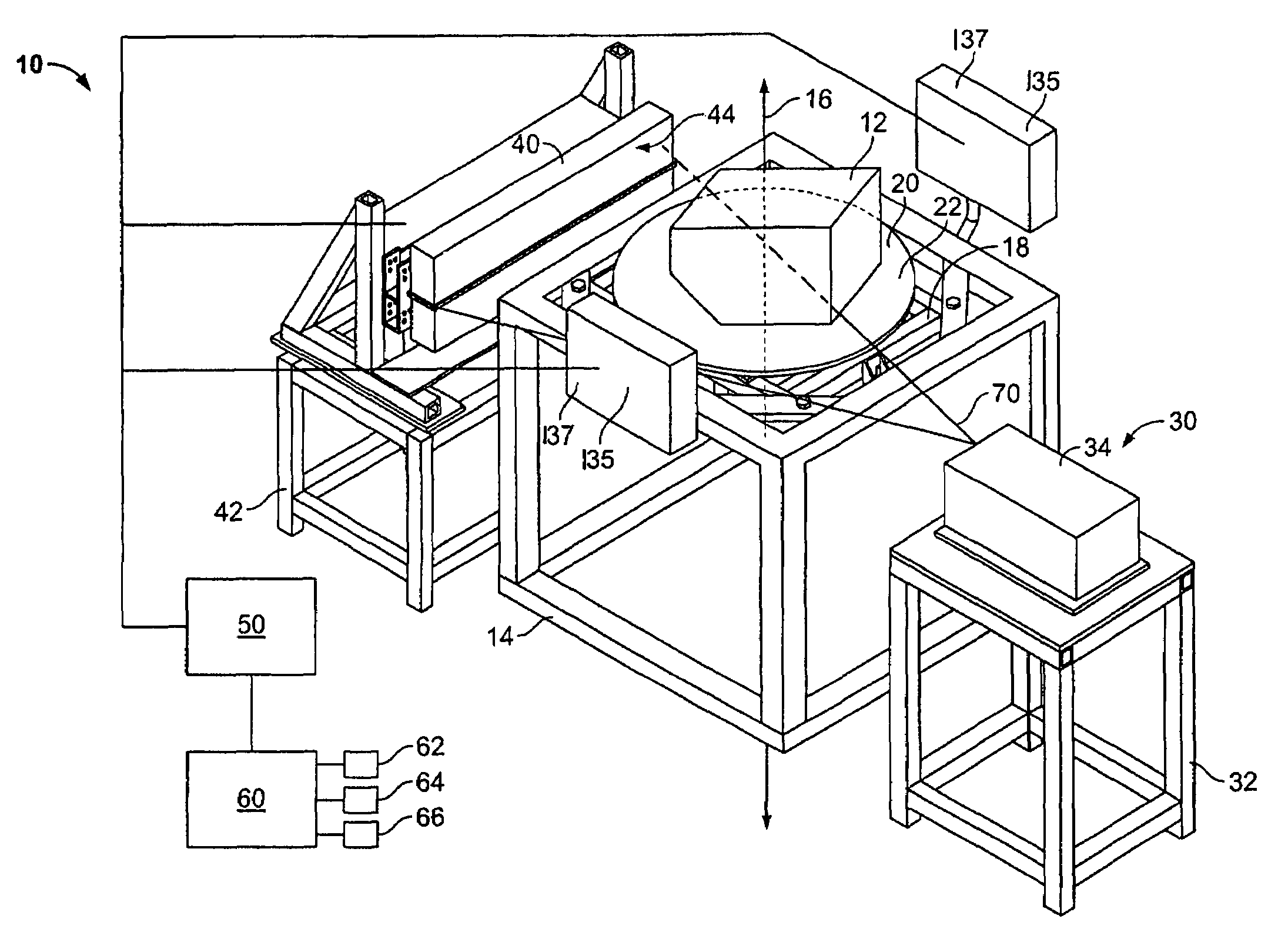
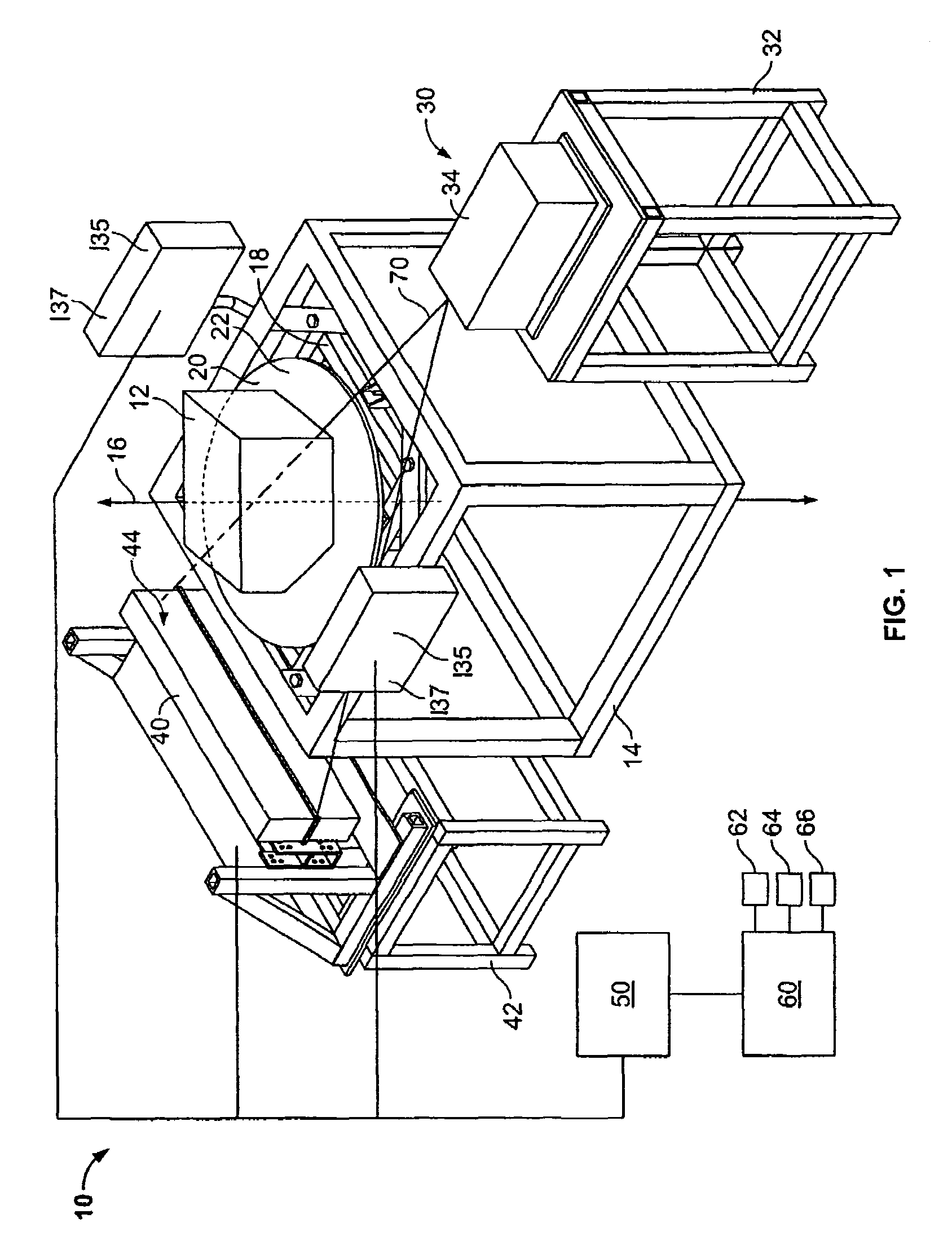
Computed tomography cargo inspection system and method
An X-ray computed tomography scanning system for inspecting an object includes a platform configured to support the object. The platform is rotatable about an axis and movable in a direction parallel to the axis. At least one X-ray source is fixedly positioned with respect to the platform and configured to transmit radiation through the object. At least one X-ray detector is fixedly positioned with respect to the platform. The at least one X-ray detector is configured to detect the radiation transmitted through the object and generate a signal representative of the detected radiation.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
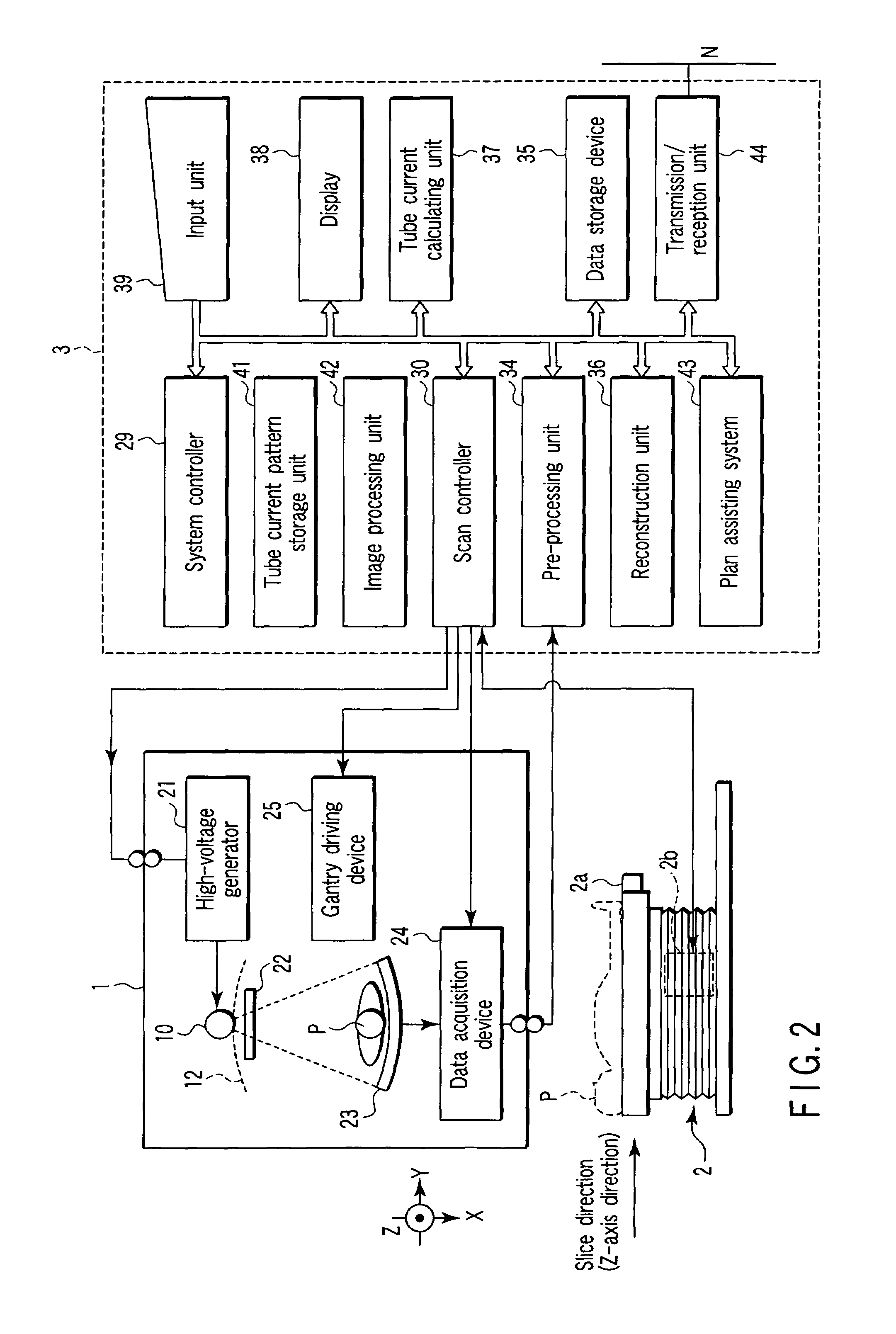
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
ActiveUS7215733B2Reduce operating loadReduce exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayEngineering
A plurality of region-specific areas are set on a scanogram, and an image SD value is set for each region-specific area. A tube current calculating unit calculates a tube current value at each position on the basis of a tube current pattern in a tube current pattern storage unit, an image SD value for each region-specific area, and a CT value at each position on the scanogram in each region-specific area. A scan controller controls X-ray emission in accordance with a calculated tube current value at each position.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
X-ray computed tomography apparatus and picture quality simulation apparatus
ActiveUS7031423B2Set scan conditions more suitablyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSupporting systemDisplay device
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus according to this invention includes a gantry (1) which scans an imaging target region of a subject to be examined in accordance with scan conditions, a reconstruction unit (36) which reconstructs image data from projection data, a scan plan setting support system (40) which sets scan conditions, an image SD calculating unit (41) which calculates an image SD associated with an index of picture quality on the basis of the set scan conditions, a data storage device (35) which stores sample image data having a reference value of an image SD, a simulation image generating unit (42) which generates simulation image data corresponding to the calculated image SD from the sample image data on the basis of the calculated image SD and the reference value of the image SD, and a display (38) which displays the generated simulation image data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
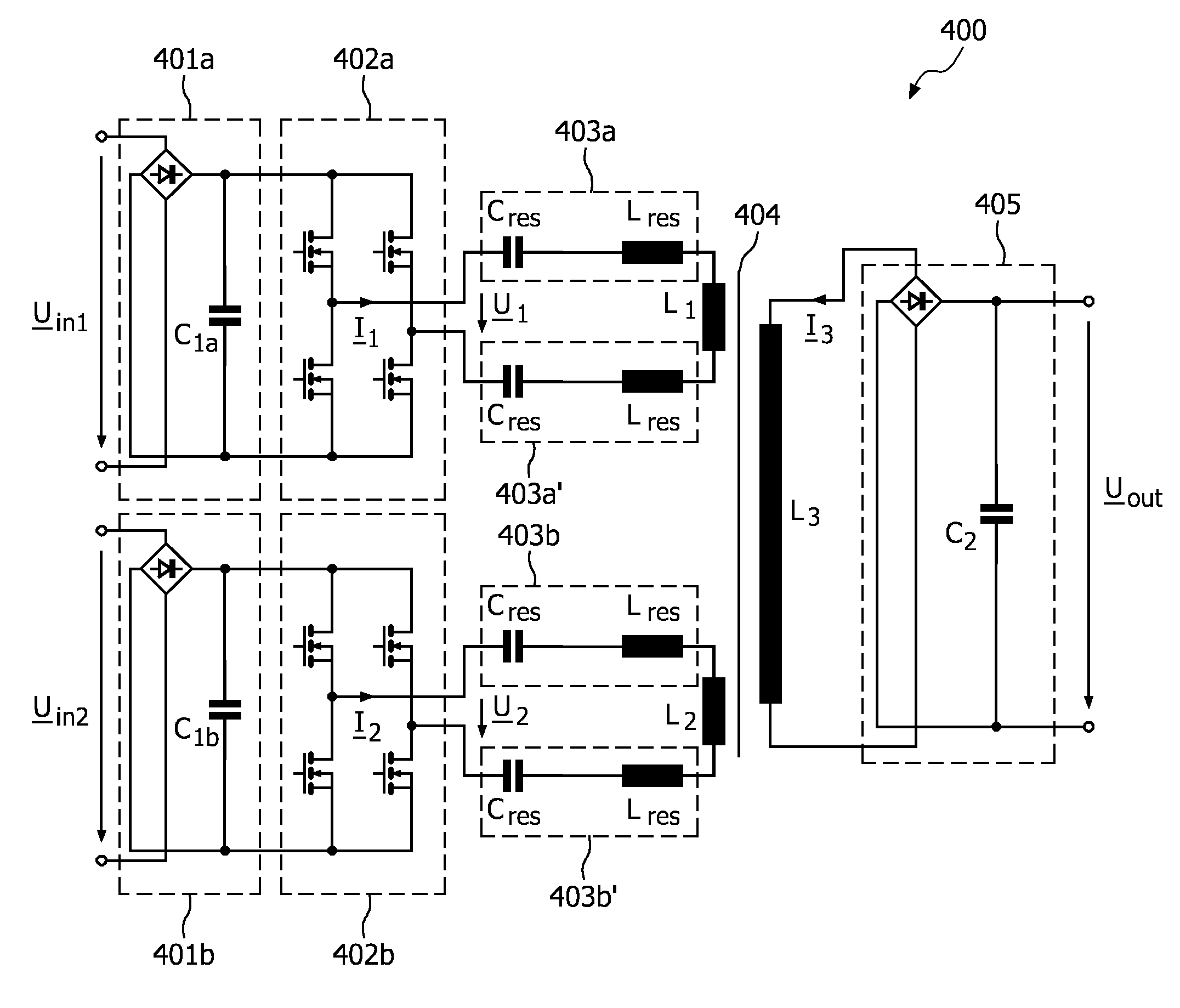
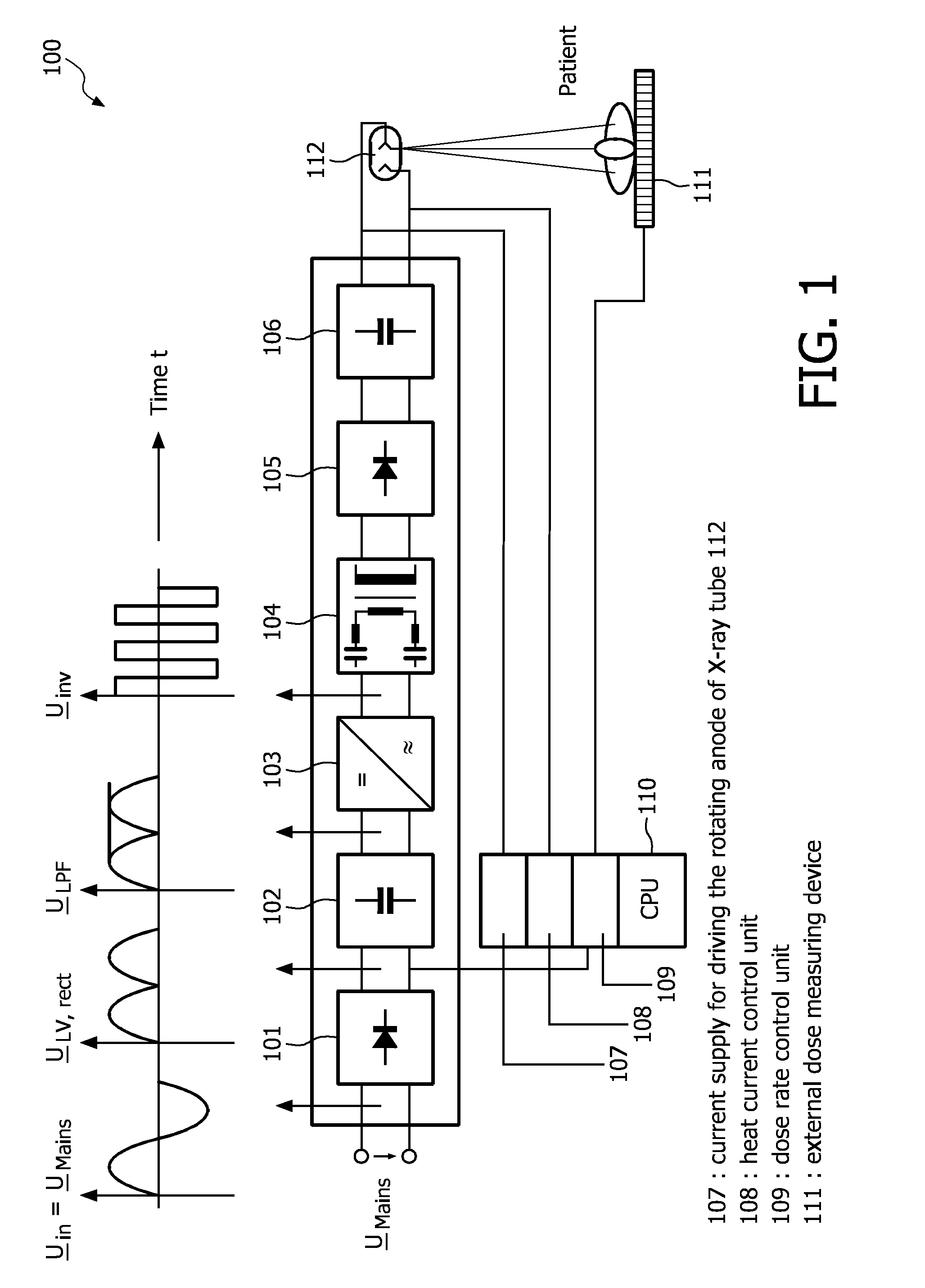
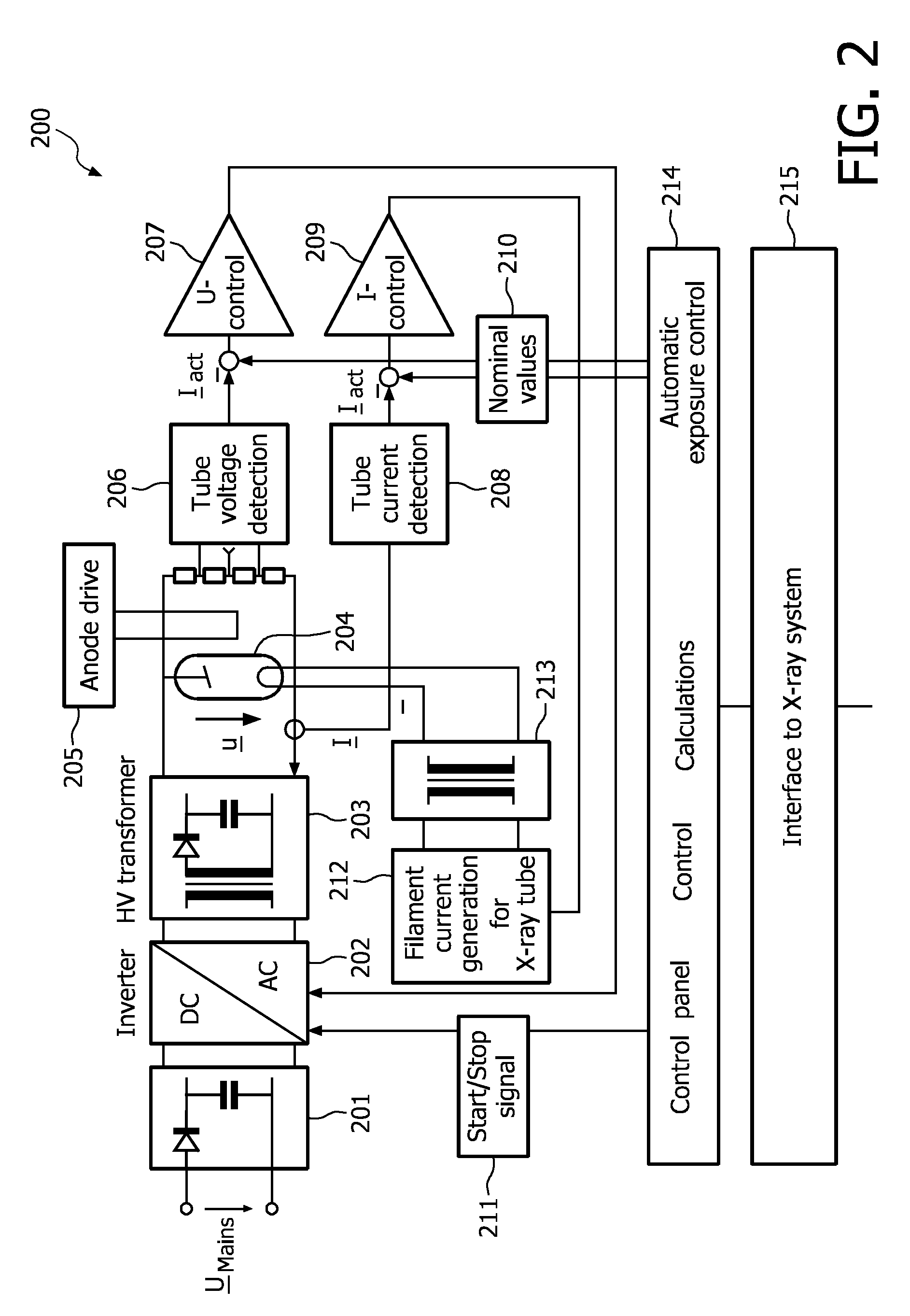
Dc/ac power inverter control unit of a resonant power converter circuit, in particular a dc/dc converter for use in a high-voltage generator circuitry of a modern computed tomography device or x-ray radiographic system
InactiveUS20110002445A1Zero current operationMagnitude is minimisedEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionResonant power convertersX-ray
The present invention refers to a DC / AC power inverter control unit of a resonant-type power converter circuit (400), in particular a DC / DC converter, for supplying an output power for use in, for example, a high-voltage generator circuitry of an X-ray radio-graphic imaging system, 3D rotational angiography device or X-ray computed tomography device of the fan-or cone-beam type. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a resonant-type power converter circuit out which comprises an interphase transformer (406) connected in series to at least one series resonant tank circuit (403a and 403a′ or 403b and 403b′) at the output of two DC / AC power inverter stages (402a+b) supplying a multi-primary winding high-voltage transformer (404), wherein said interphase transformer (406) serves for removing the difference (DI) in the resonant output currents (1 and 2) of the DC / AC power inverter stages (402a+b). Furthermore, the present invention is dedicated to a control method which assures that the interphase transformer (406) is not saturated. This control method ensures zero current operation and provides for that input power losses can be minimized.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) method and system
InactiveUS20060067464A1Smooth motionReduce dispersionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyHigh spatial resolution
A high spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system is provided. The system includes a support structure including a gantry mounted to rotate about a vertical axis of rotation. The system further includes a first assembly including an X-ray source mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith for generating a cone X-ray beam and a second assembly including a planar X-ray detector mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith. The detector is spaced from the source on the gantry for enabling a human or other animal body part to be interposed therebetween so as to be scanned by the X-ray beam to obtain a complete CT scan and generating output data representative thereof. The output data is a two-dimensional electronic representation of an area of the detector on which an X-ray beam impinges. A data processor processes the output data to obtain an image of the body part.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com