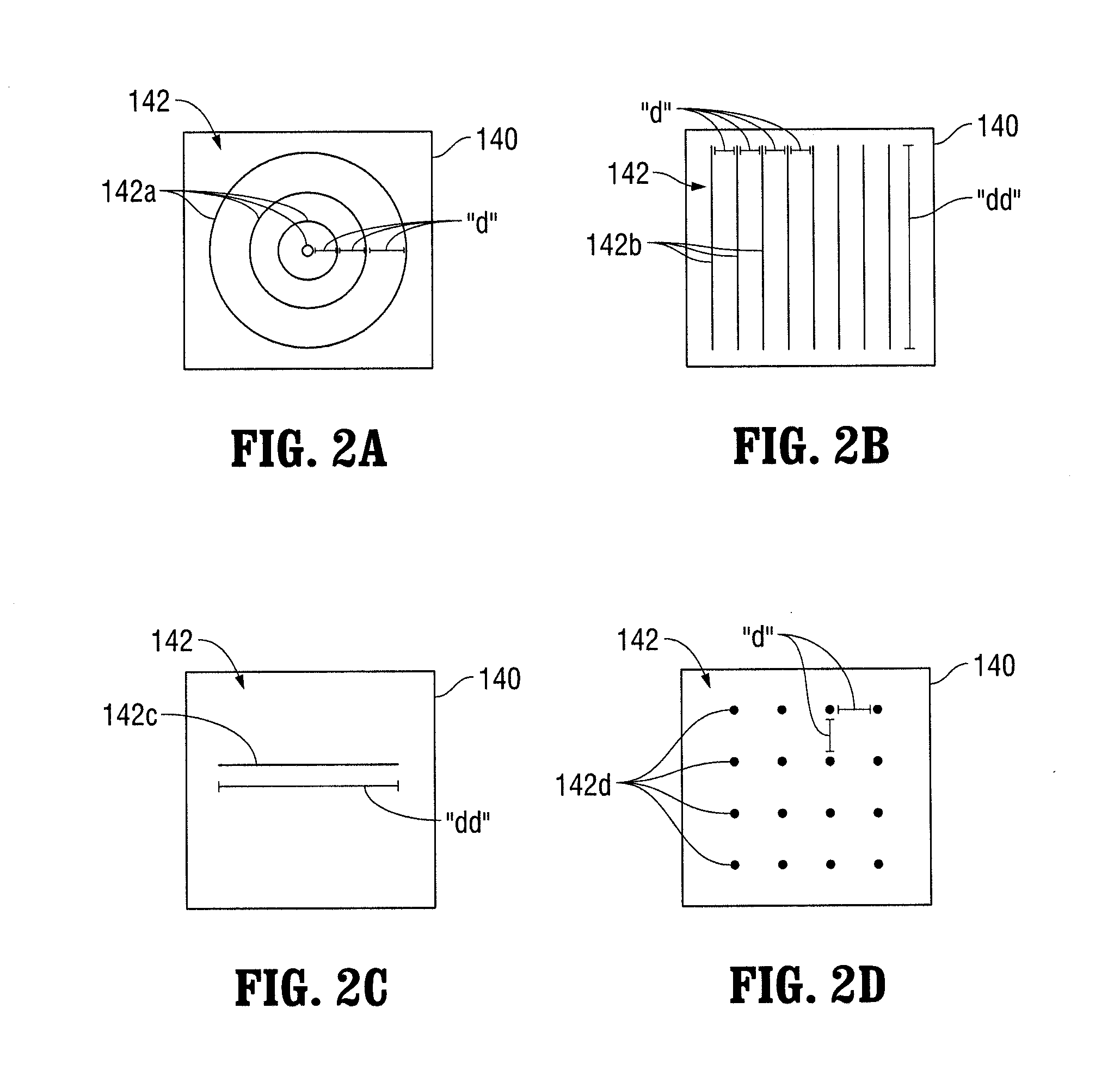
Patents
Literature
1524 results about "Projection plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A projection plane, or plane of projection, is a type of view in which graphical projections from an object intersect. Projection planes are used often in descriptive geometry and graphical representation. A picture plane in perspective drawing is a type of projection plane.
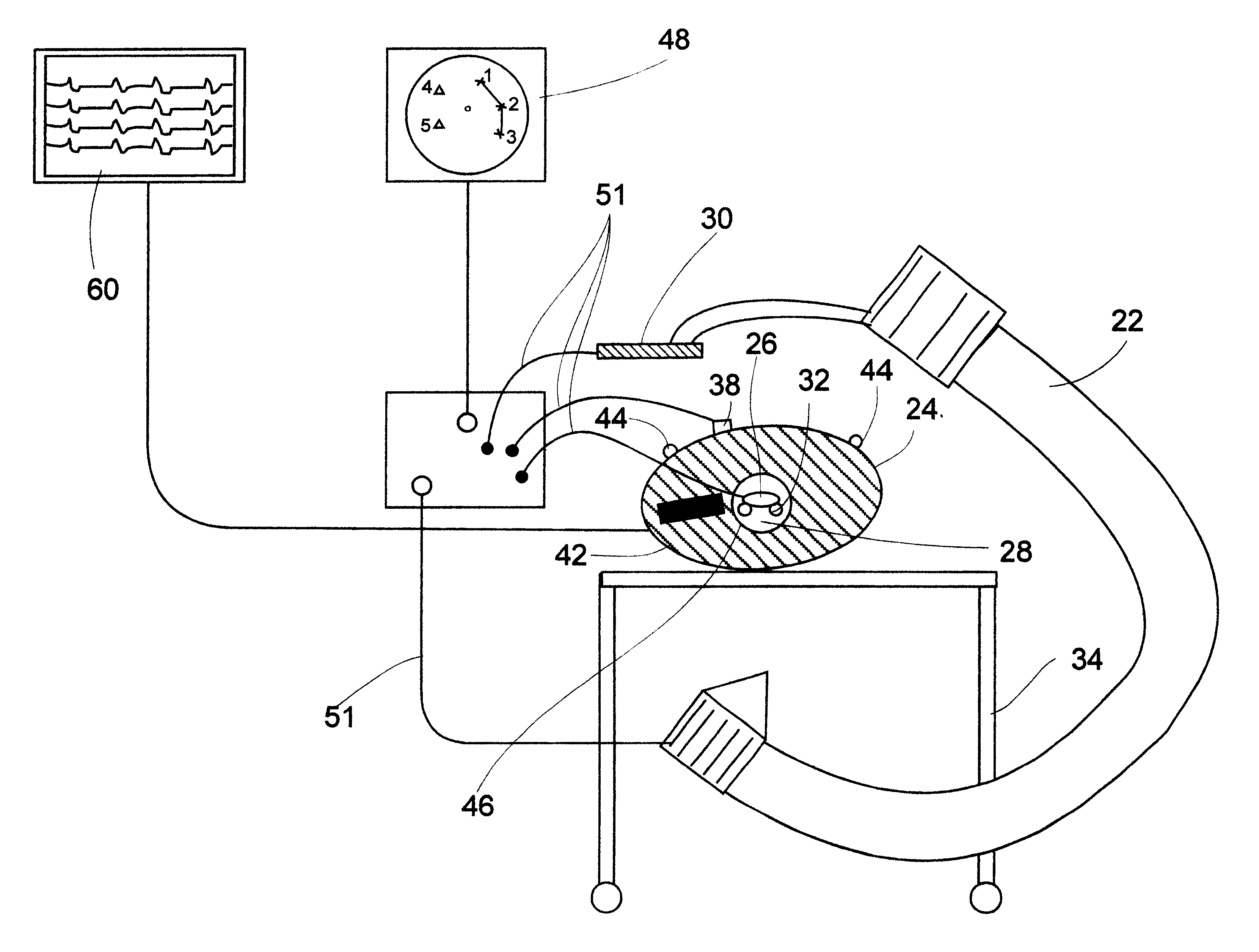
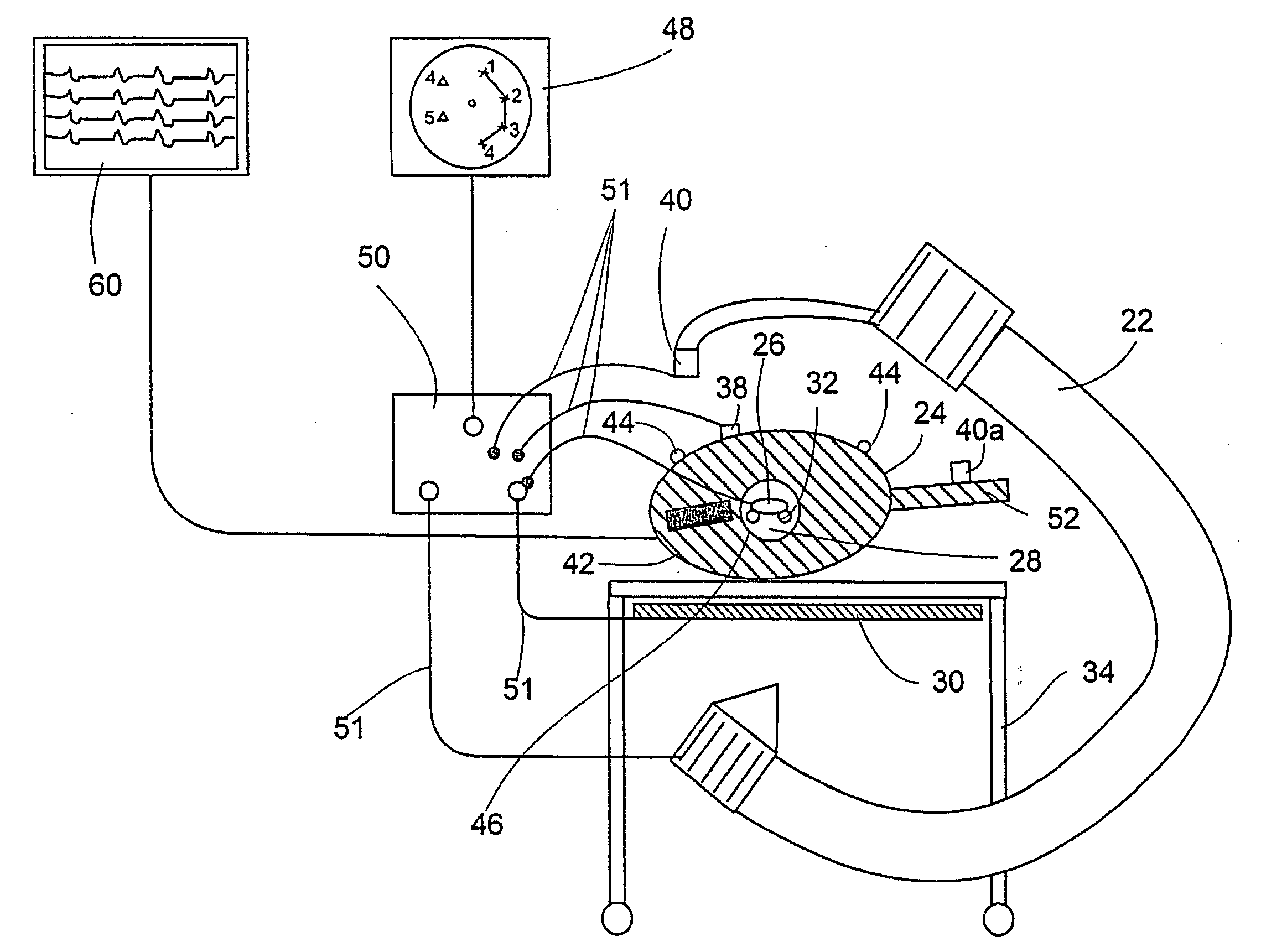
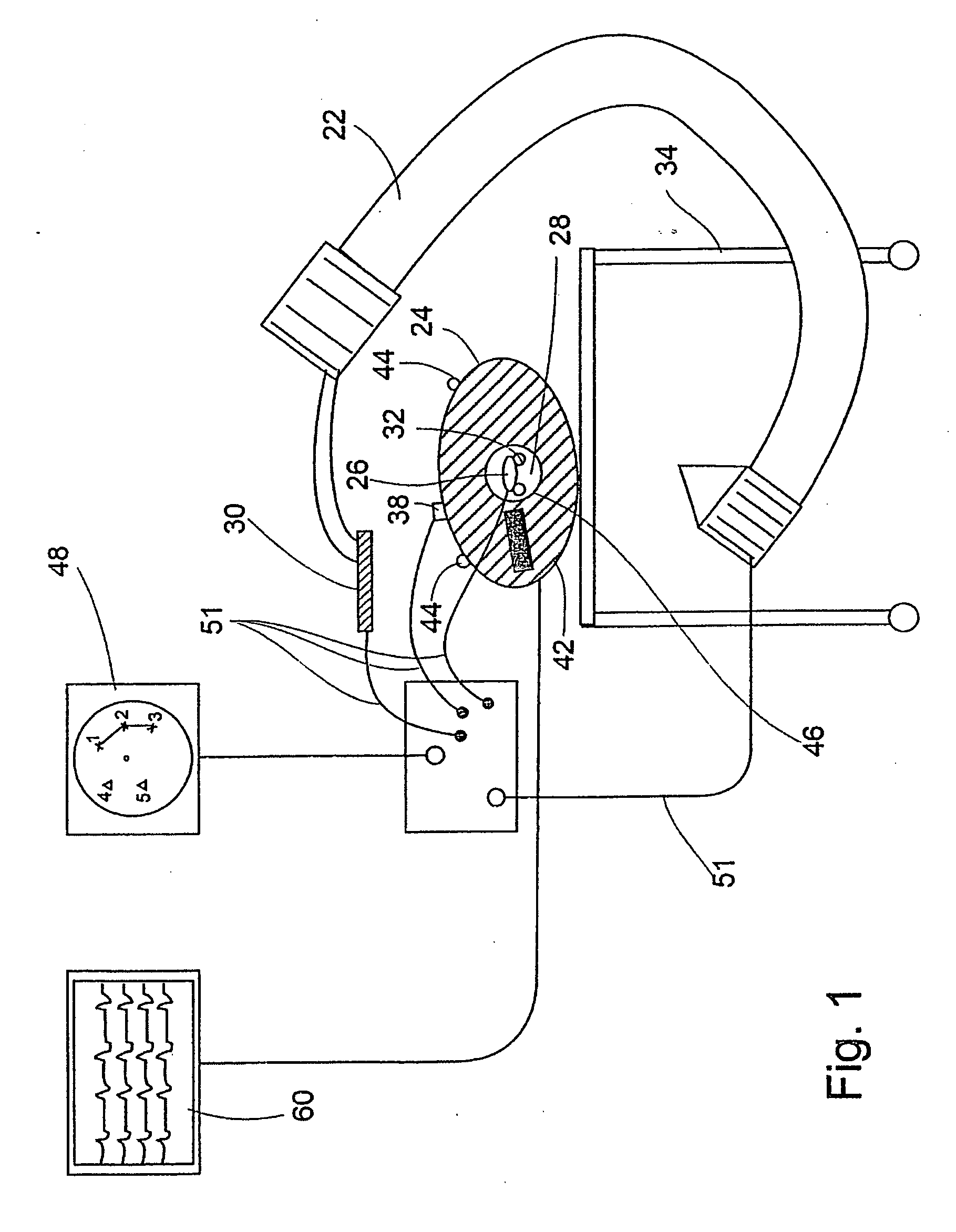
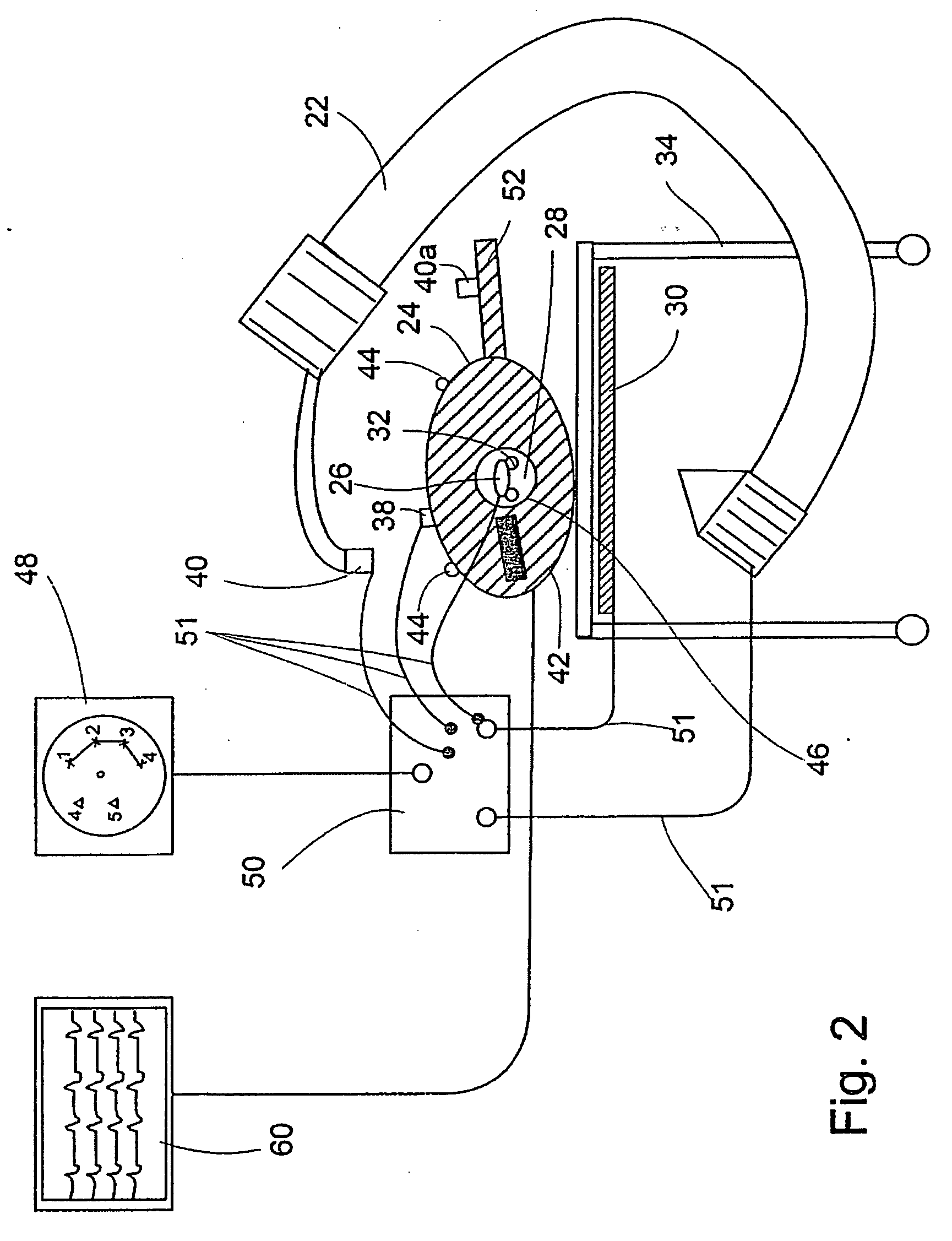
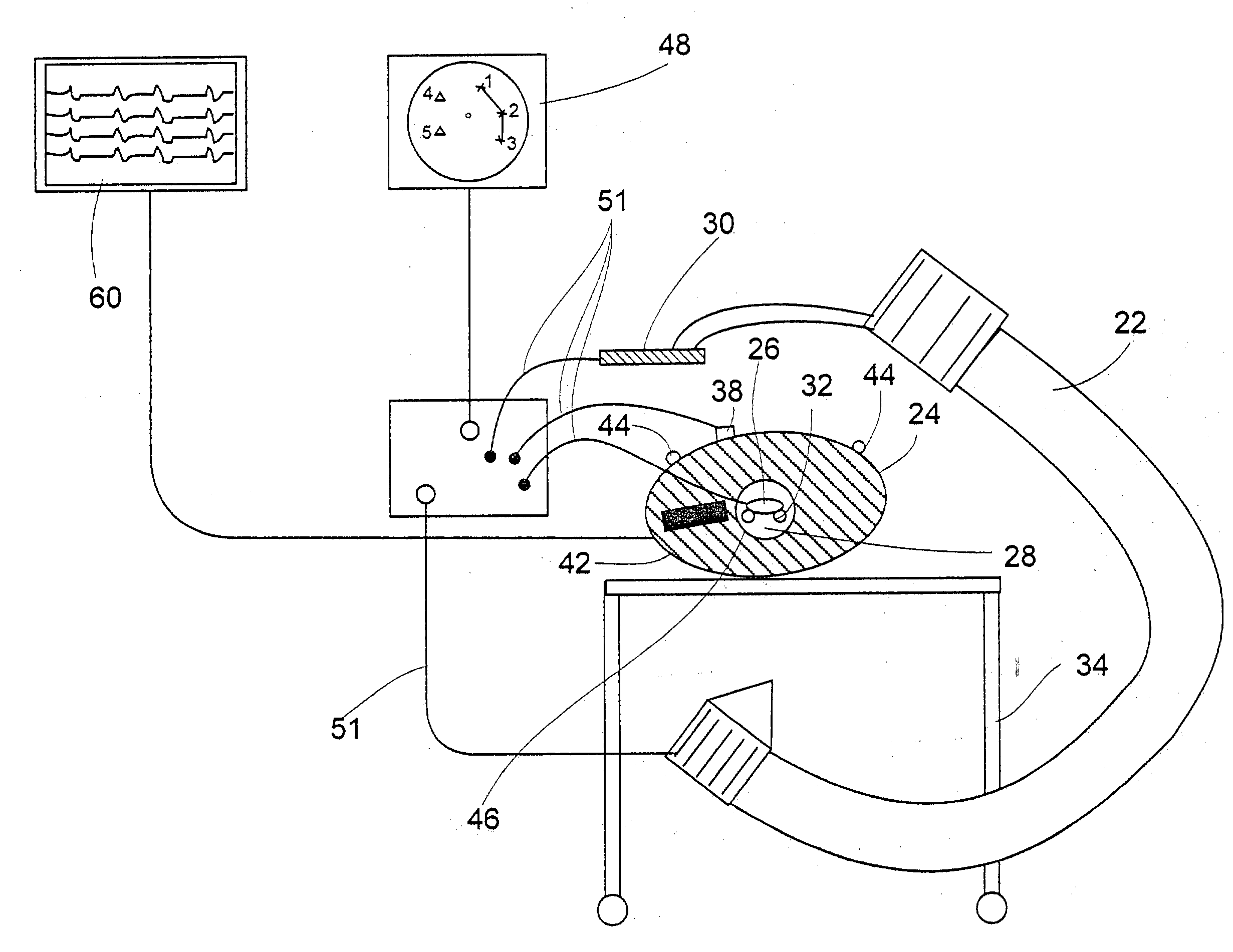
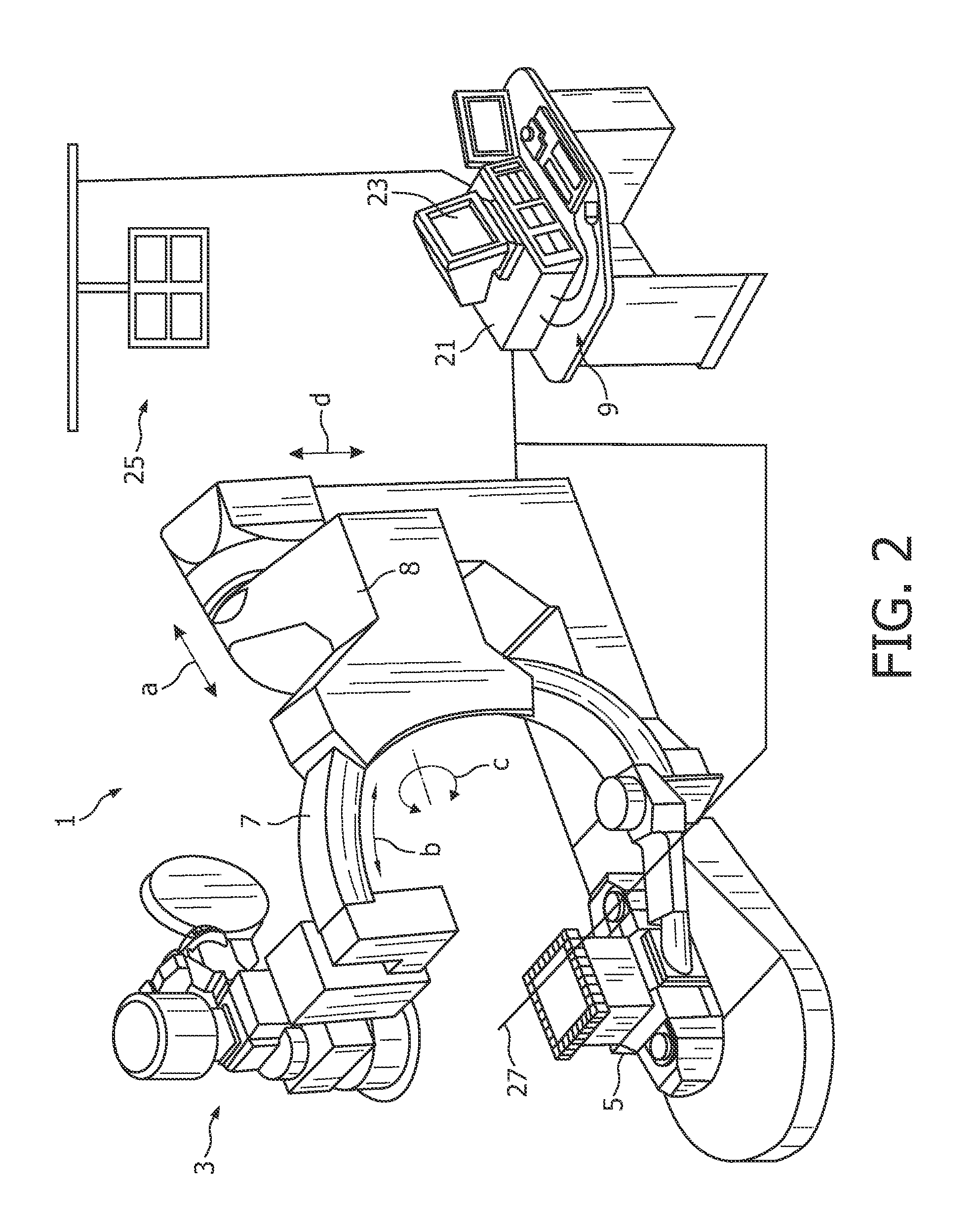
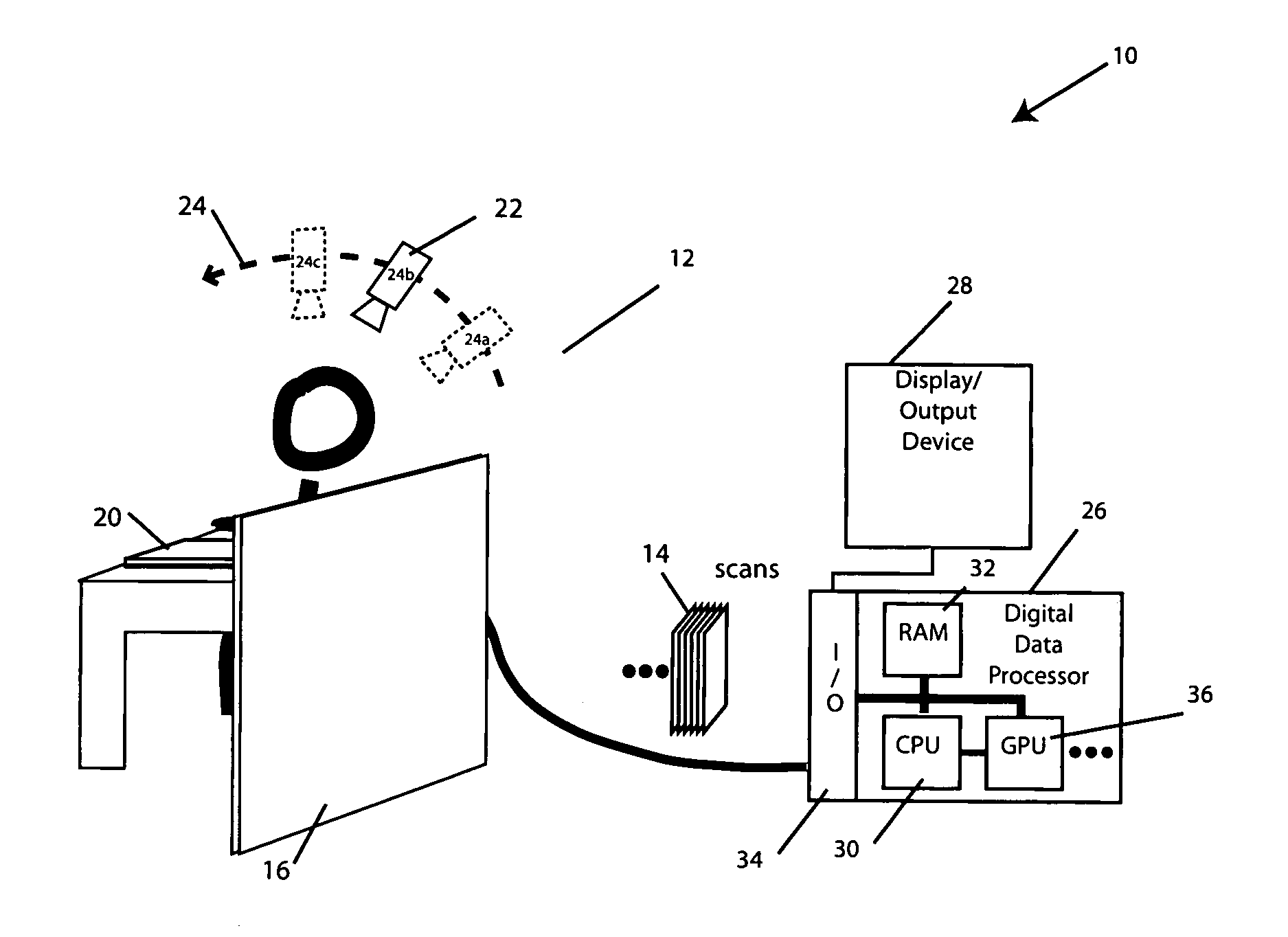
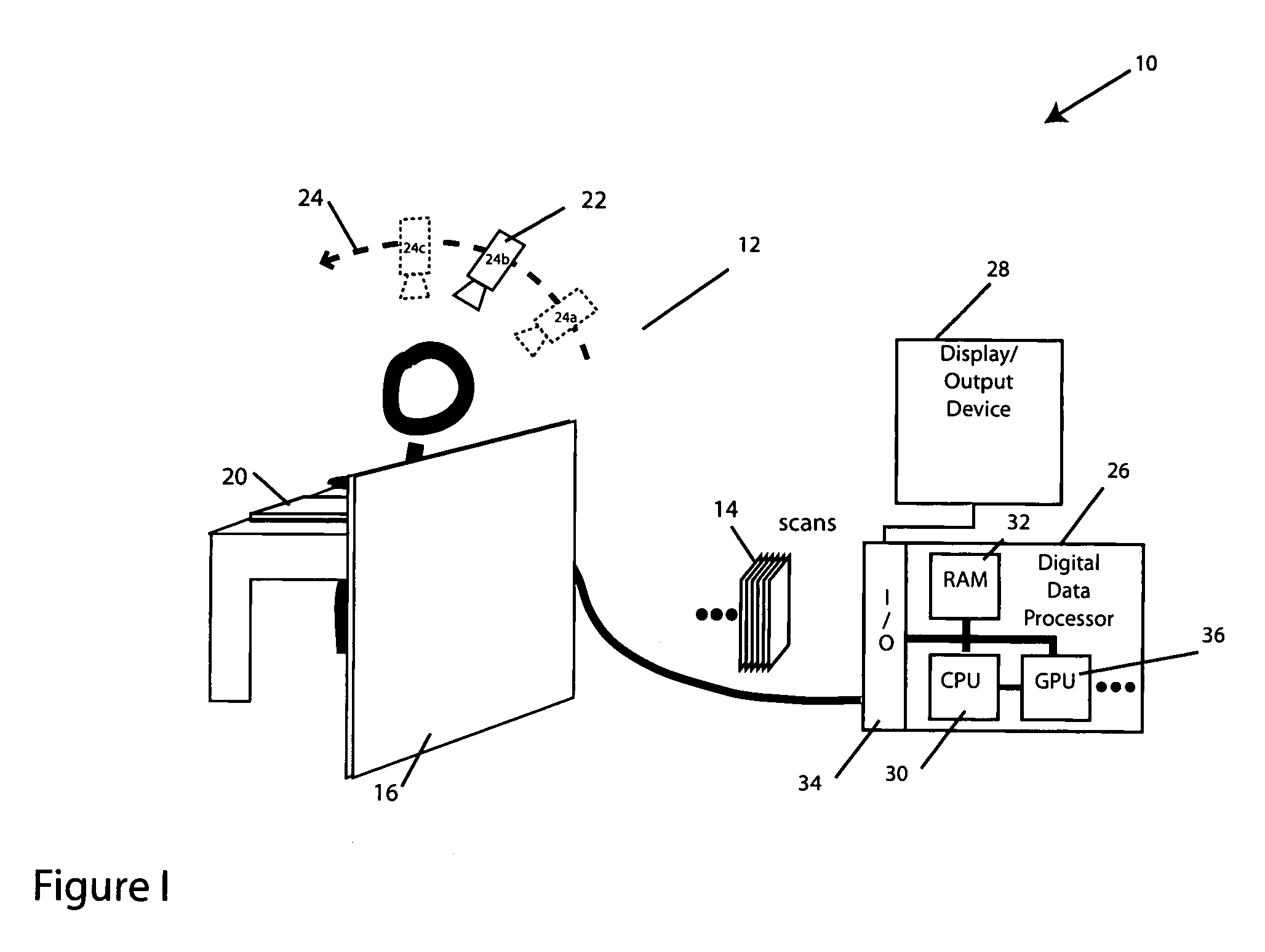
System and method for determining the location of a catheter during an intra-body medical procedure
A system and method of displaying at least one point-of-interest of a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) establishing a location of an imaging instrument being for imaging at least a portion of the body; (c) defining at least one projection plane being in relation to a projection plane of the imaging instrument; (d) acquiring at least one point-of-interest of the body; and (c) projection said at least one point-of-interest on said at least one projection plane; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable on the at least one projection plane even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
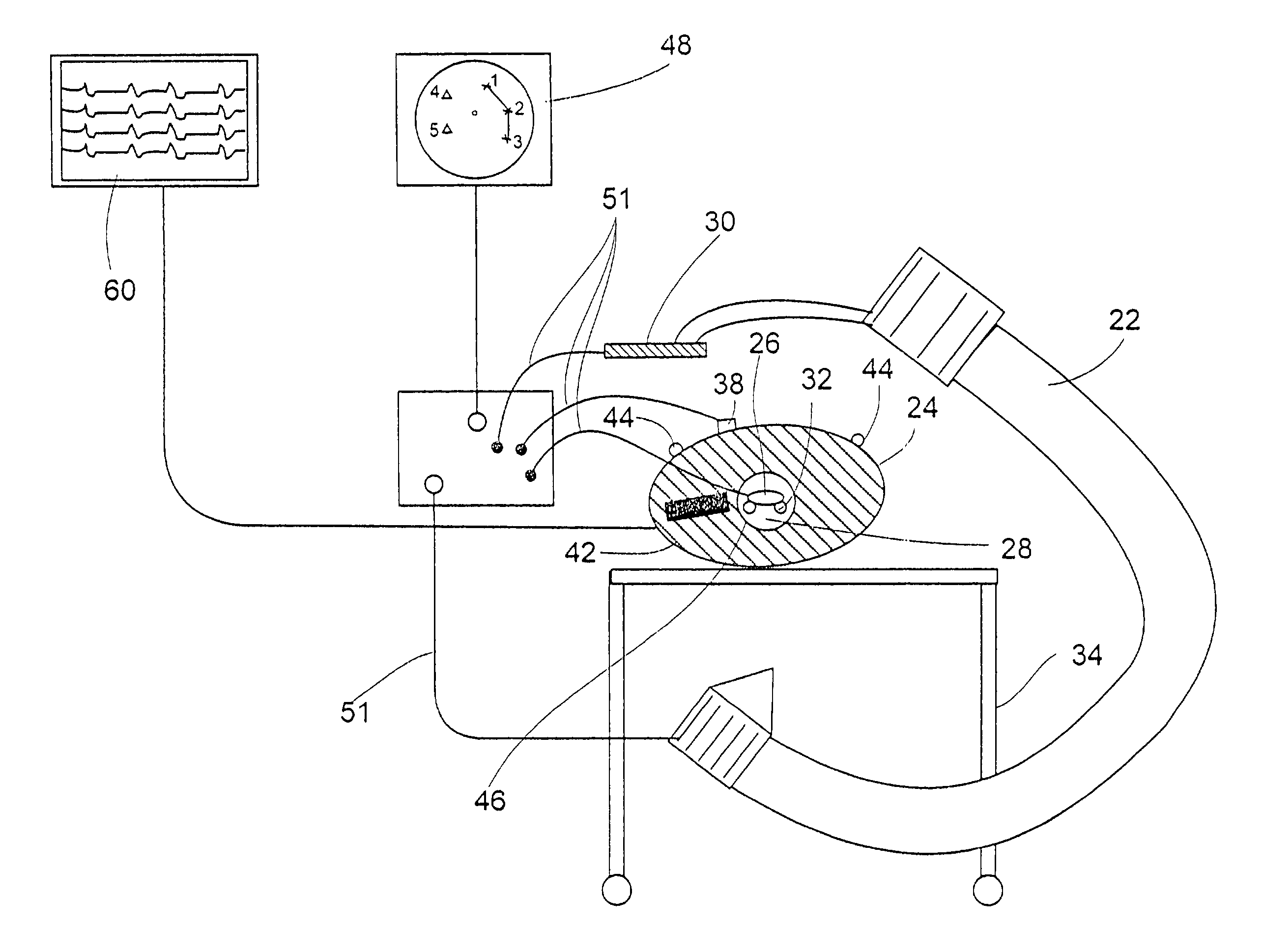
System and method of recording and displaying in context of an image a location of at least one point-of-interest in a body during an intra-body medical procedure
InactiveUS20030074011A1Accurate returnSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer graphics (images)Projection plane
A method of displaying at least one point-of-interest of a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) establishing a location of an imaging instrument being for imaging at least a portion of the body; (c) defining at least one projection plane being in relation to a projection plane of the imaging instrument; (d) acquiring at least one point-of-interest of the body; and (e) projecting said at least one point-of-interest on said at least one projection plane; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable on the at least one projection plane even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:SUPER DIMENSION
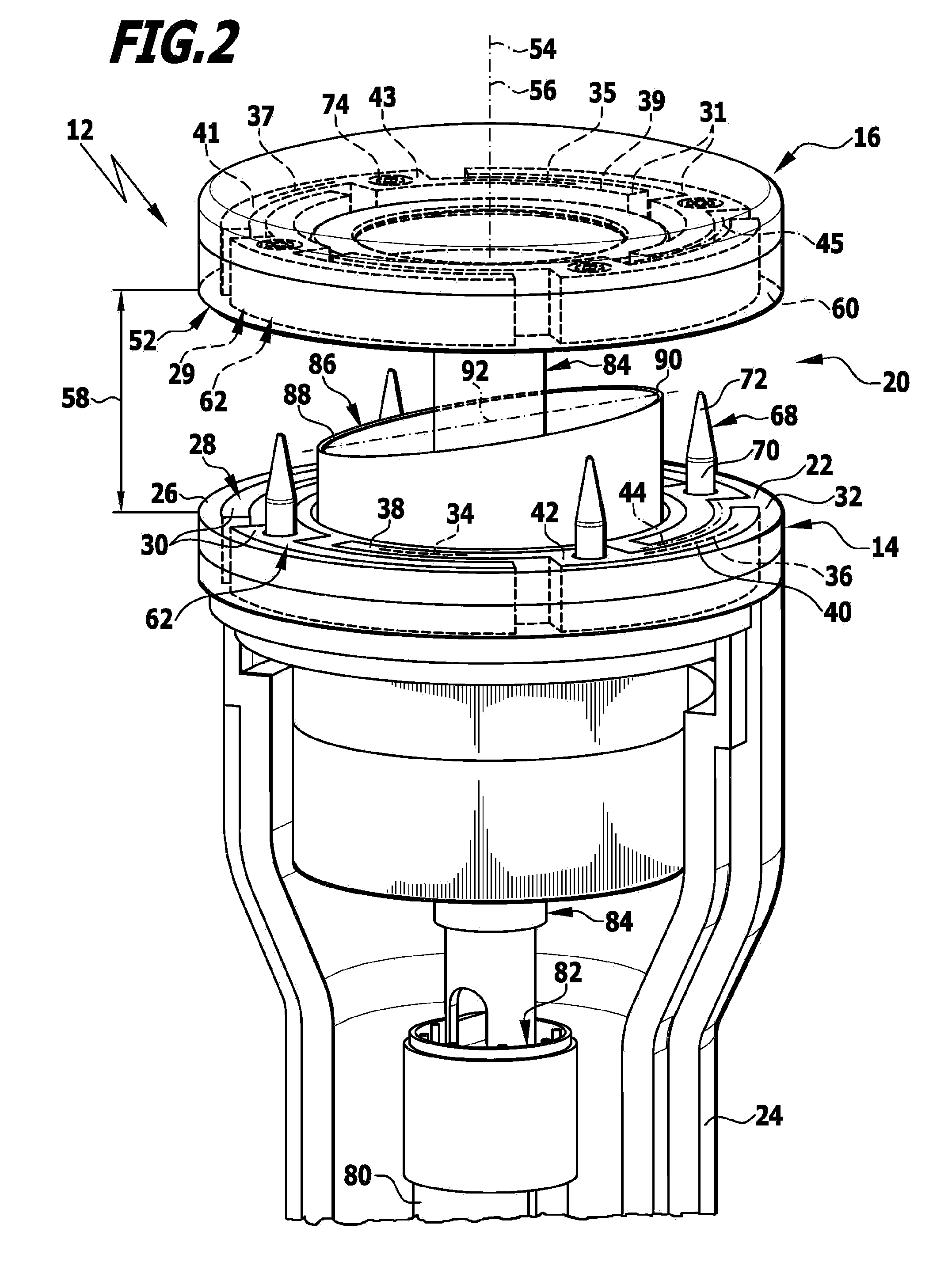
Surgical system for connecting body tissue
In order to so improve a surgical system for connecting body tissue, comprising a surgical instrument having two tool elements movable relative to each other, each of which comprises a high-frequency electrode, the high-frequency electrodes, in an approach position of the tool elements, defining a minimum distance from each other, lying opposite each other and facing each other, that an overstretching of connections of parts of body tissue, in particular, made by a flow of current, is avoided when removing the surgical instrument, it is proposed that the instrument comprise a shaft at the distal end of which at least a first one of the tool elements is arranged or formed, and that a second tool element be adapted to be moved from an operating position, in which it is adapted for movement into the approach position, into a removal position and / or vice versa, a surface area of a perpendicular projection of the second tool element onto a projection plane extending perpendicularly to the shaft direction in the region of the second tool element being smaller in the removal position than in the operating position.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
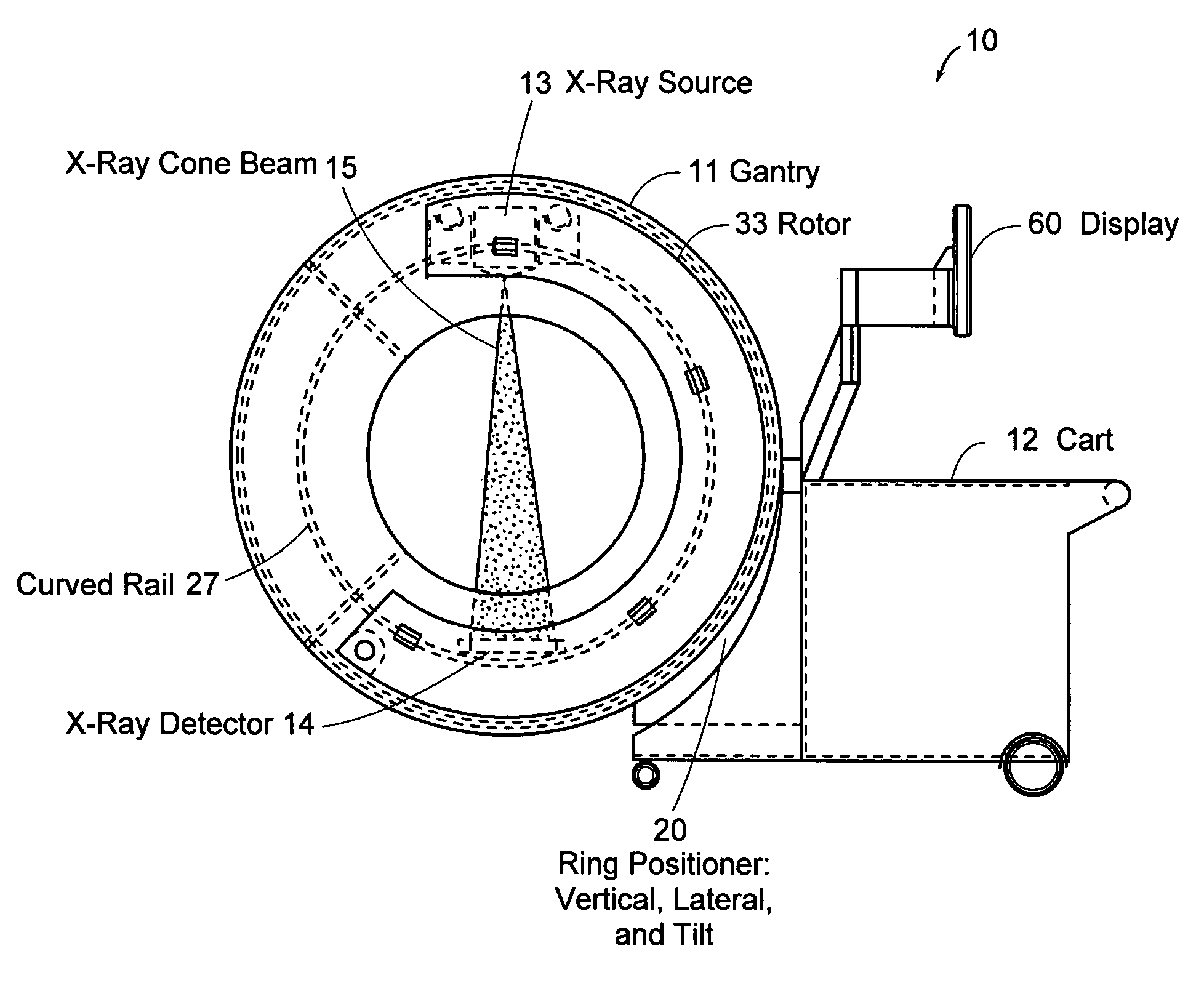
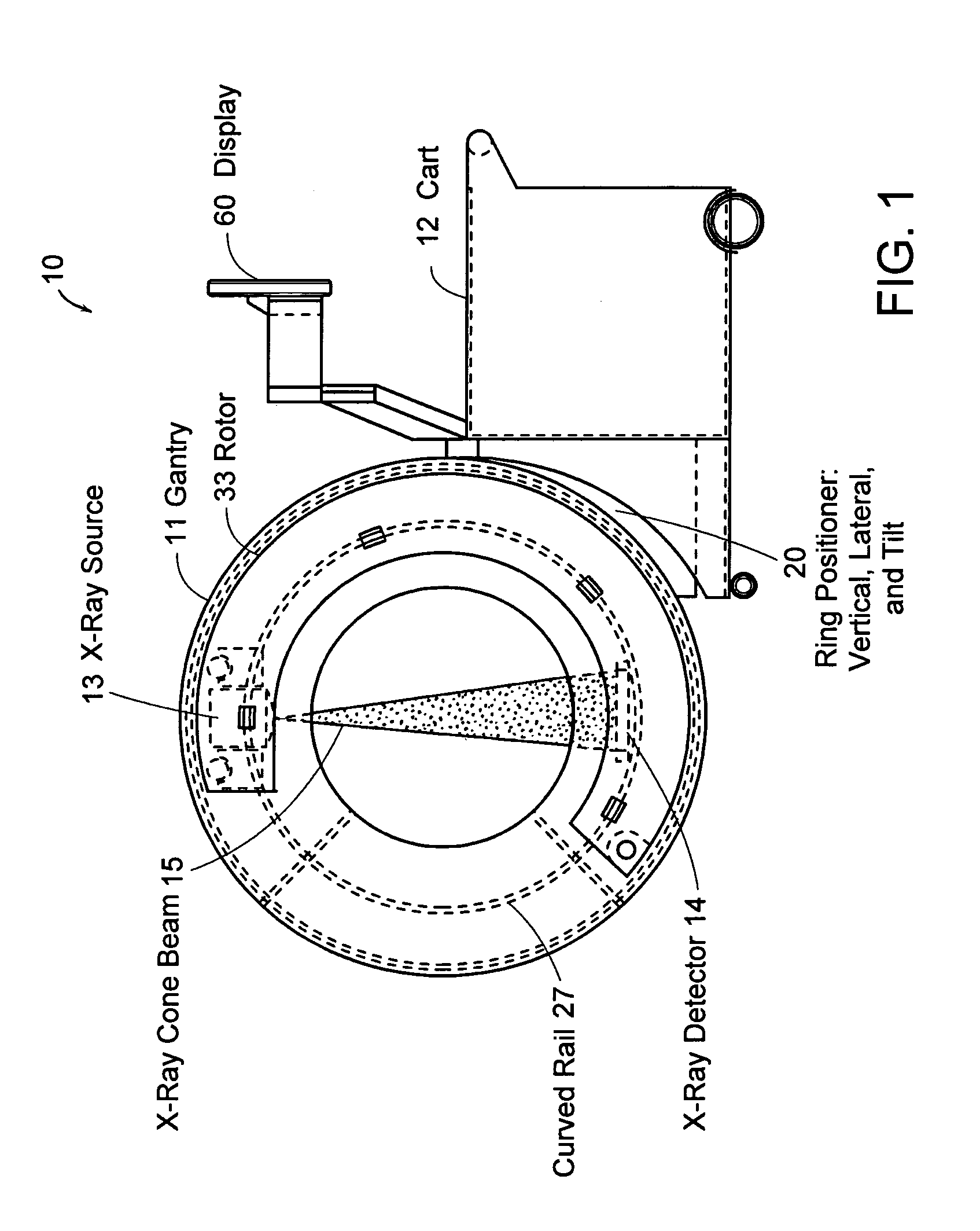
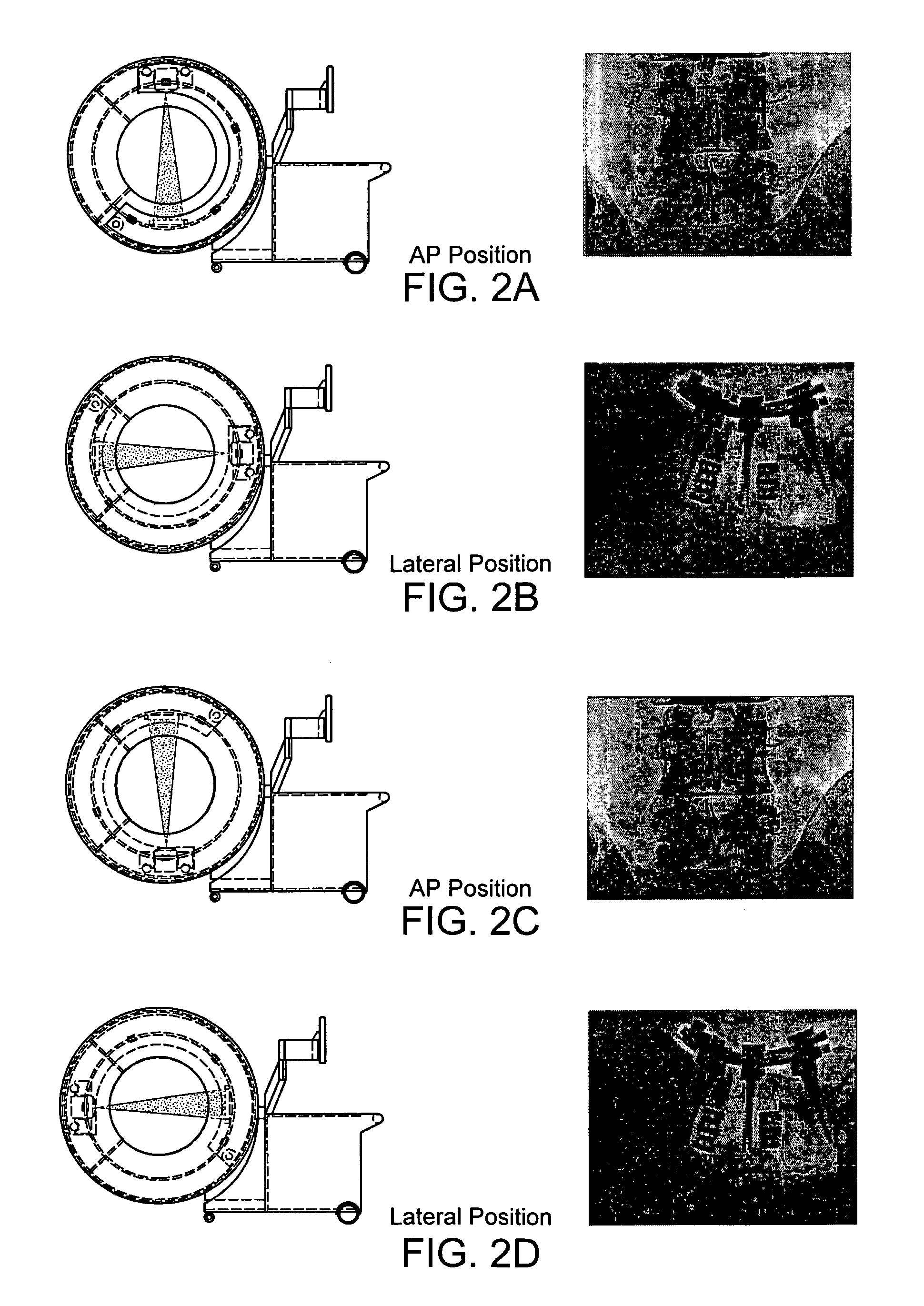
Systems and methods for quasi-simultaneous multi-planar x-ray imaging
InactiveUS7188998B2Radiation diagnosis data transmissionTomographySoft x rayTwo dimensional detector
Systems and methods for obtaining two-dimensional images of an object, such as a patient, in multiple projection planes. In one aspect, the invention advantageously permits quasi-simultaneous image acquisition from multiple projection planes using a single radiation source.An imaging apparatus comprises a gantry having a central opening for positioning an object to be imaged, a source of radiation that is rotatable around the interior of the gantry ring and which is adapted to project radiation onto said object from a plurality of different projection angles; and a detector system adapted to detect the radiation at each projection angle to acquire object images from multiple projection planes in a quasi-simultaneous manner. The gantry can be a substantially “O-shaped” ring, with the source rotatable 360 degrees around the interior of the ring. The source can be an x-ray source, and the imaging apparatus can be used for medical x-ray imaging. The detector array can be a two-dimensional detector, preferably a digital detector.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
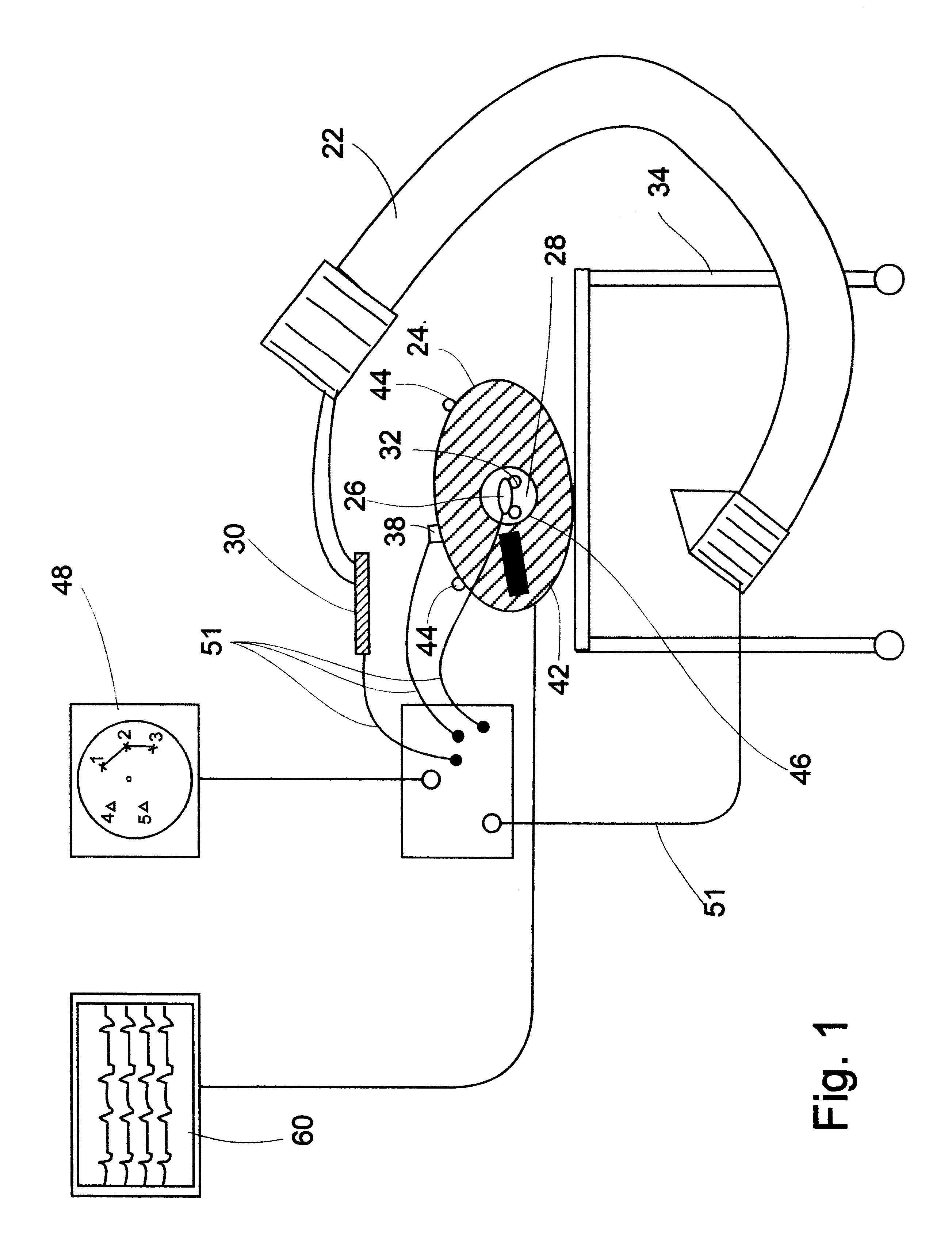
System and method of recording and displaying in context of an image a location of at least one point-of-interest in a body during an intra-body medical procedure
A method of displaying at least one point-of-interest of a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) establishing a location of an imaging instrument being for imaging at least a portion of the body; (c) defining at least one projection plane being in relation to a projection plane of the imaging instrument; (d) acquiring at least one point-of-interest of the body; and (e) projecting said at least one point-of-interest on said at least one projection plane; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable on the at least one projection plane even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:SUPERDIMENSION LTD
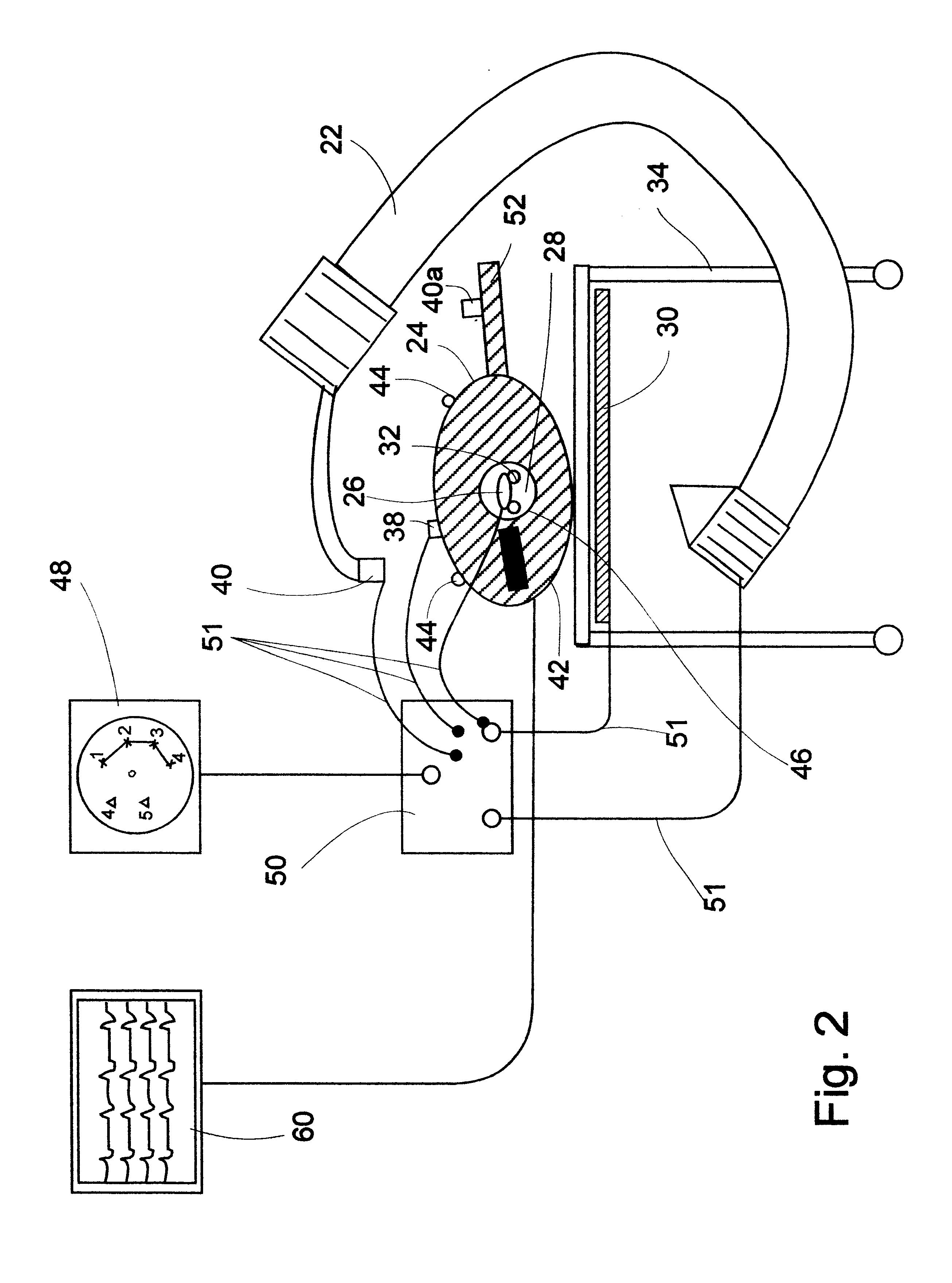
System and method of recording and displaying in context of an image a location of at least one point-of-interest in a body during an intra-body medical procedure
InactiveUS20040006268A1Accurate returnSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringProjection planeComputer science
A method of displaying at least one point-of-interest of a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) establishing a location of an imaging instrument being for imaging at least a portion of the body; (c) defining at least one projection plane being in relation to a projection plane of the imaging instrument; (d) acquiring at least one point-of-interest of the body; and (e) projecting said at least one point-of-interest on said at least one projection plane; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable on the at least one projection plane even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:SUPER DIMENSION WAS FILED & PARENT CASE
Projection system and method
InactiveUS20060279662A1Large and clear imageReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsProjectorsSpatial light modulatorMagnification
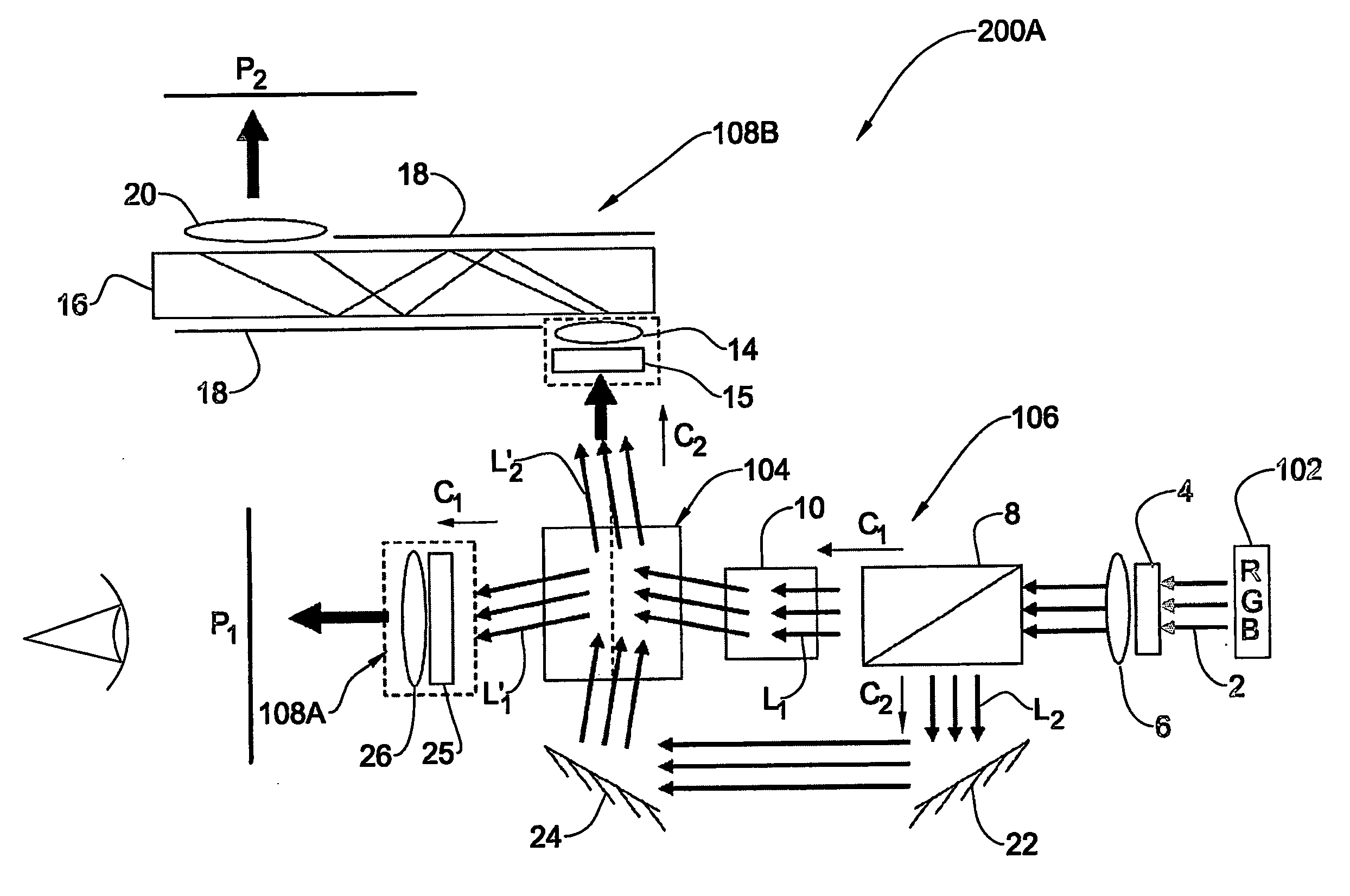
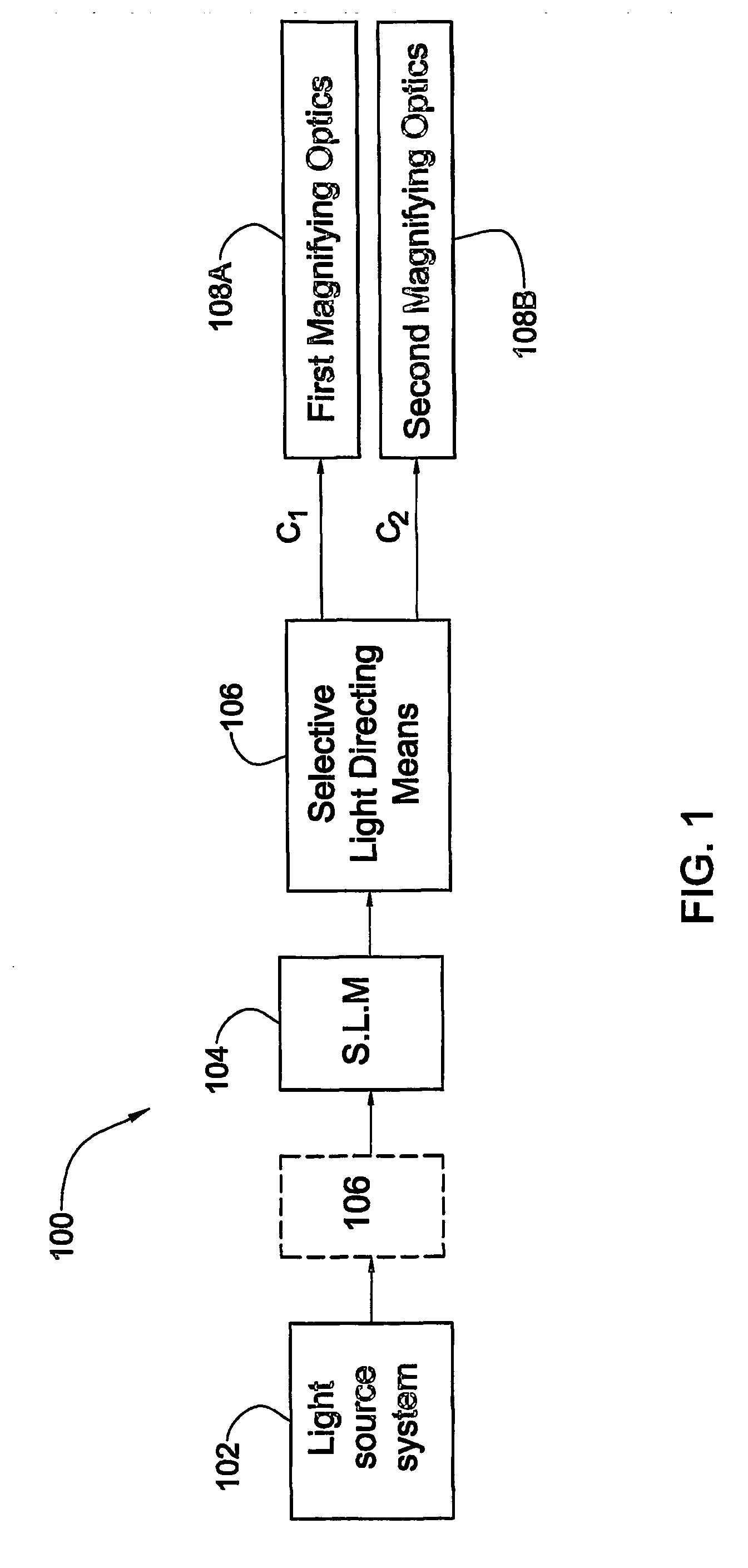
An image projection system and method are presented to project an image on at least one of first and second projection planes. The system comprises a light source system including one or more light source assemblies operable to generate light of one or more predetermined wavelength range; a spatial light modulator (SLM) system including one or more SLM units operable to spatially modulate input light in accordance with an image to be directly projected or viewed; and two optical assemblies associated with two spatially separated light propagation channels, respectively, to direct light to, respectively, the first and second projection planes with desired image magnification. The system is configured to selectively direct the input light propagating towards the SLM system or light modulated by the SLM system to propagate along at least one of the two channels associated with the first and second projection planes, respectively.
Owner:EXPLAY
Projection display device
InactiveUS6945652B2Less expensiveAccurate color reproductionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageProjection plane
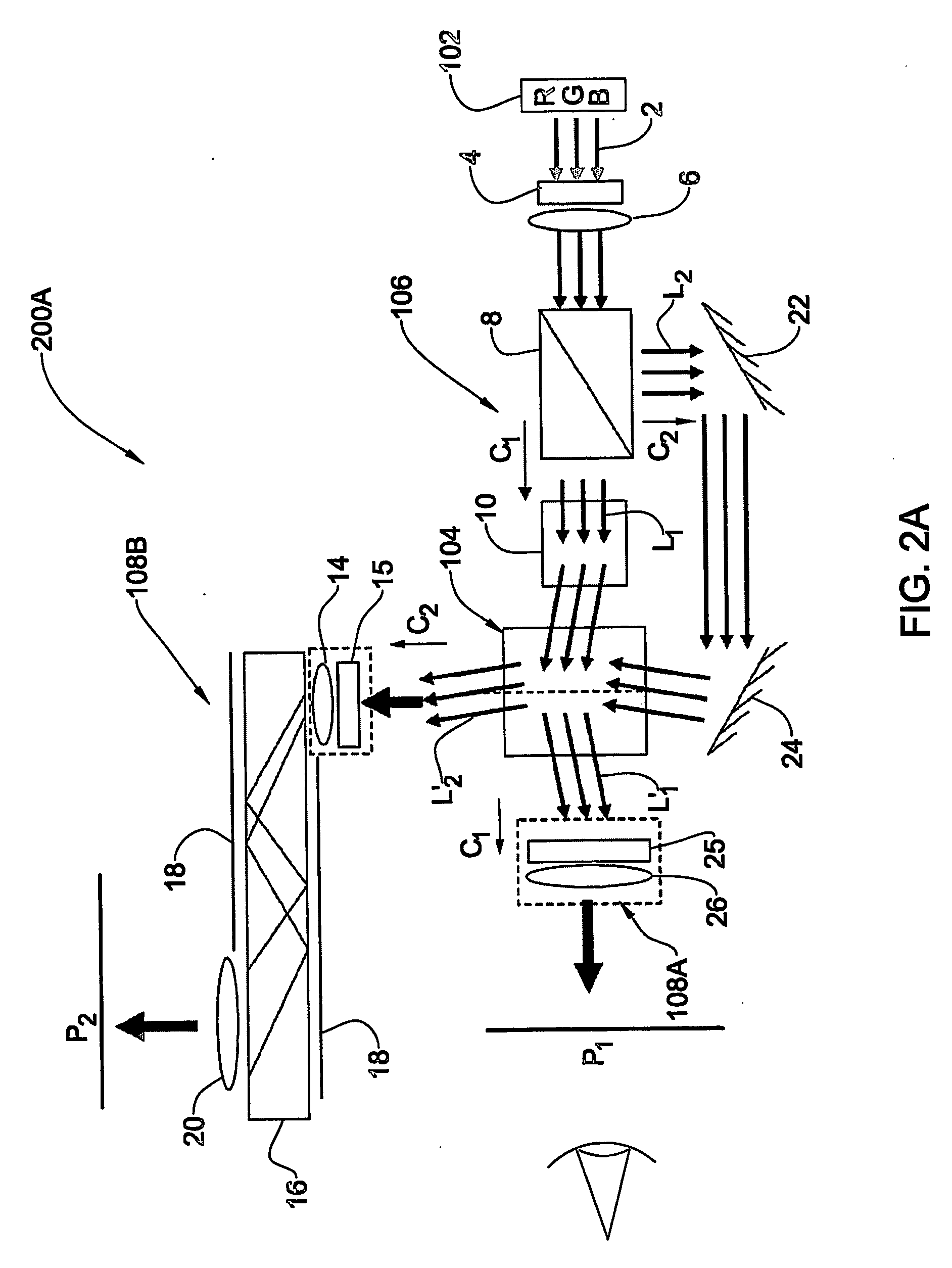
Light beams having different wavelengths emitted from red and blue semiconductor lasers and a laser diode pumped green solid-state laser are incident on respectively different surfaces of a color combining element and are overlaid on a single light path. Multiple beam interference films of the color combining element allow only the light beams having the oscillating wavelengths corresponding to the respective light sources to pass therethrough or reflect thereon so as to combine the light beams. A collimator collimates the light beams so that the beam waist of the light beams lies around a projection plane. When two-dimensional scanning is performed by radiating the light beams onto a micromechanical mirror and then onto a galvanometer mirror for scanning light in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, a color image is displayed on the projection plane by arranging pixels in array, each pixel consisting of overlapping pulses of light of three colors.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection type image display device
InactiveUS20030090597A1Improve optical efficiencyHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesProjection planeMultiple image
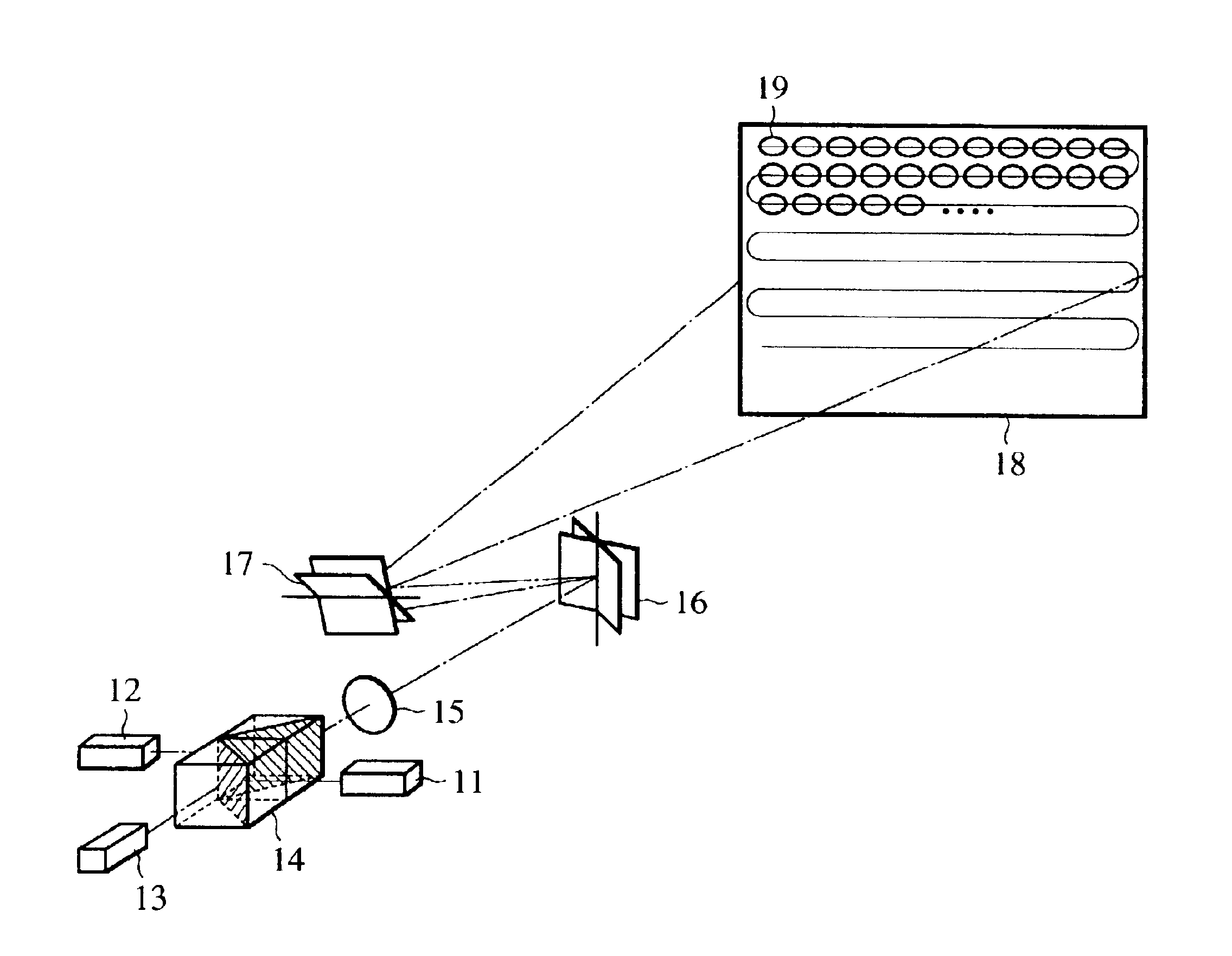
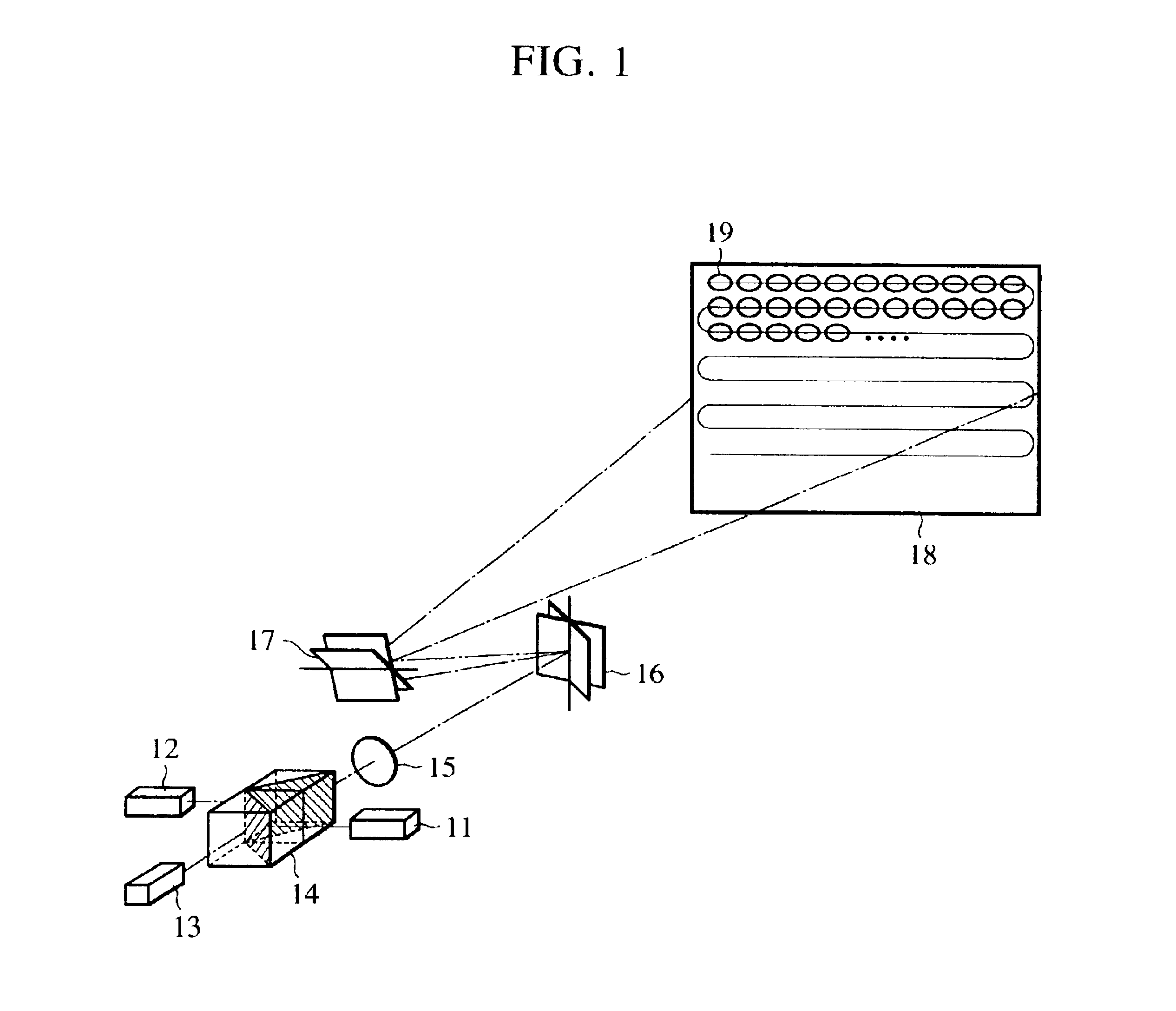
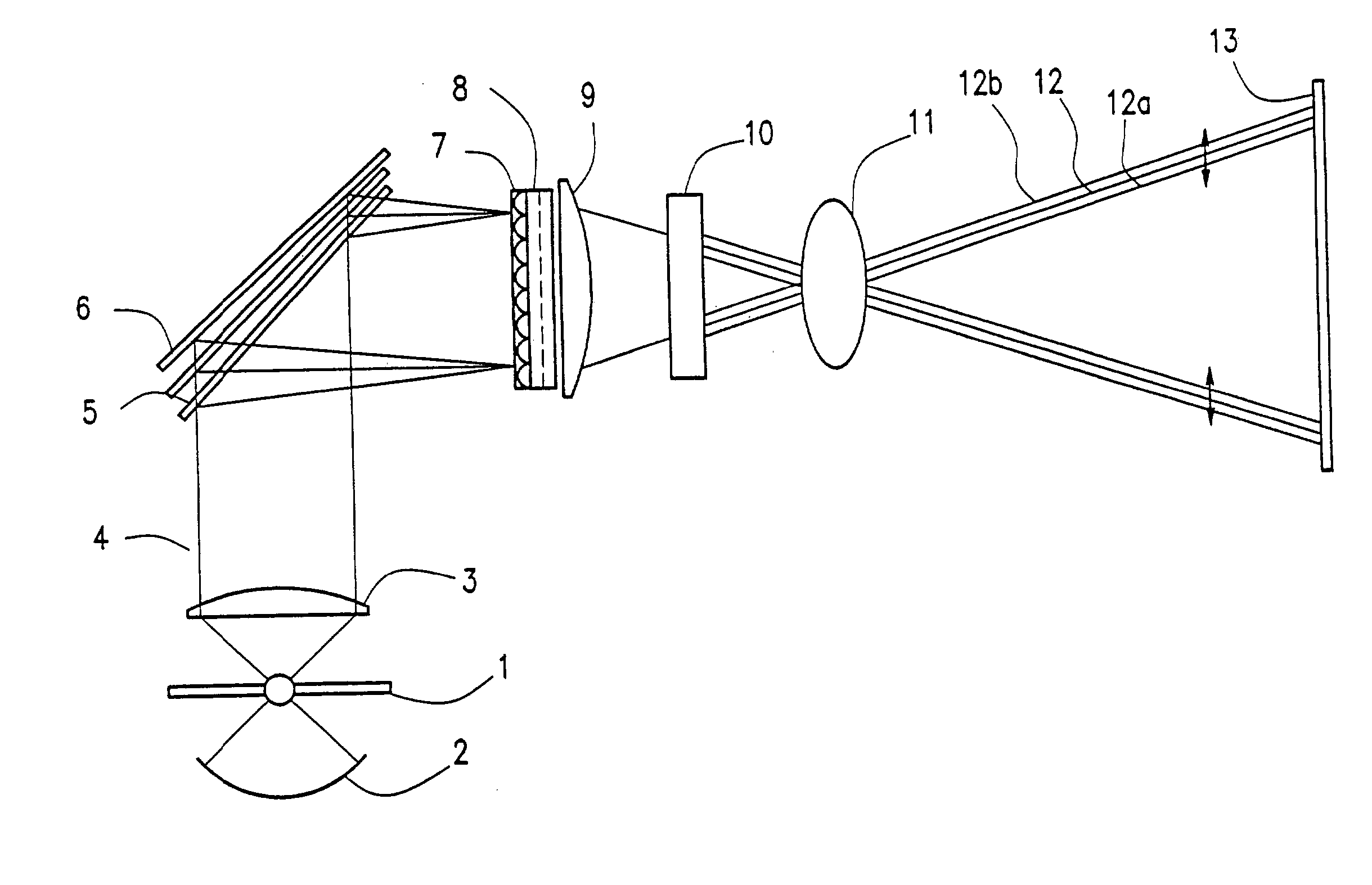
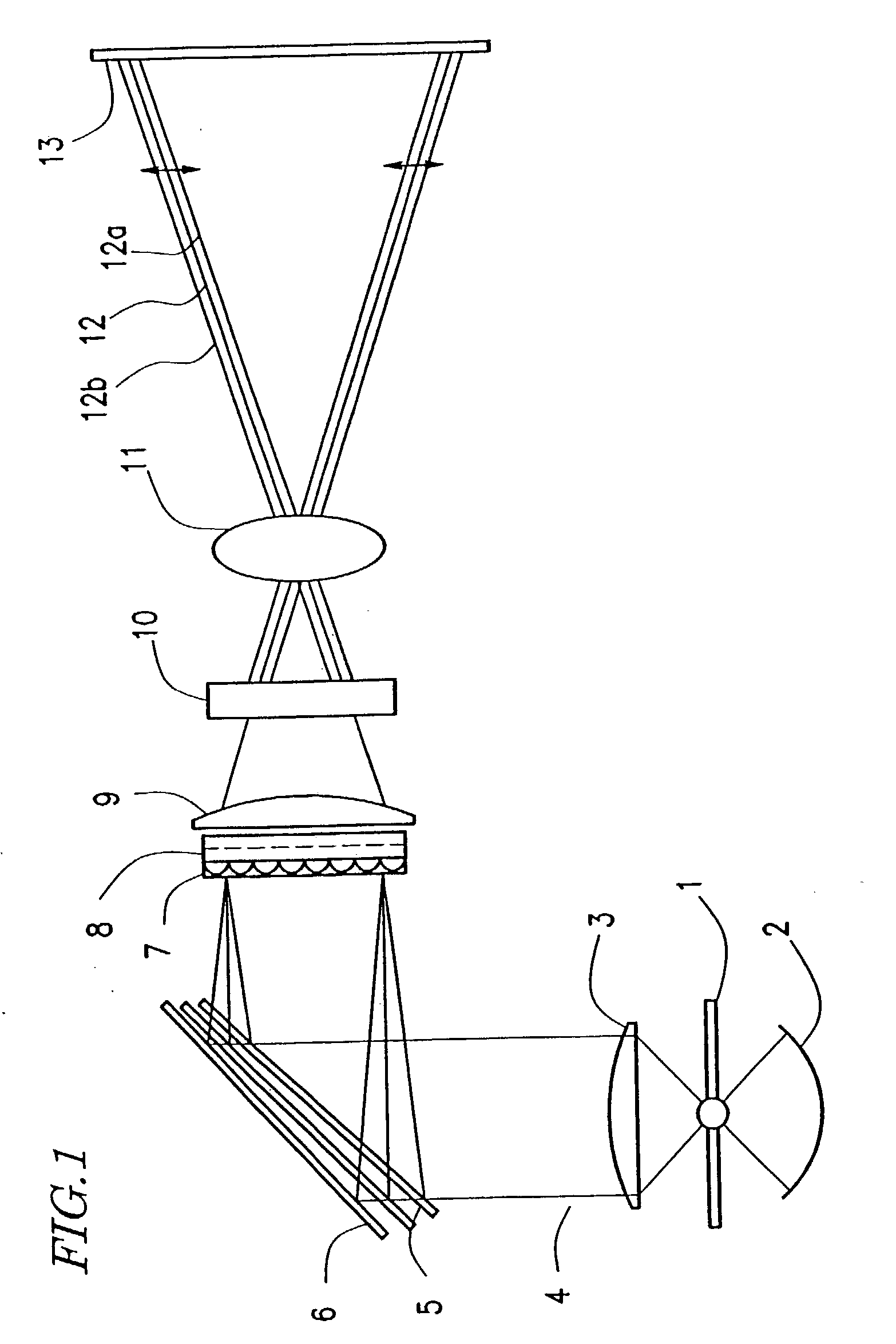
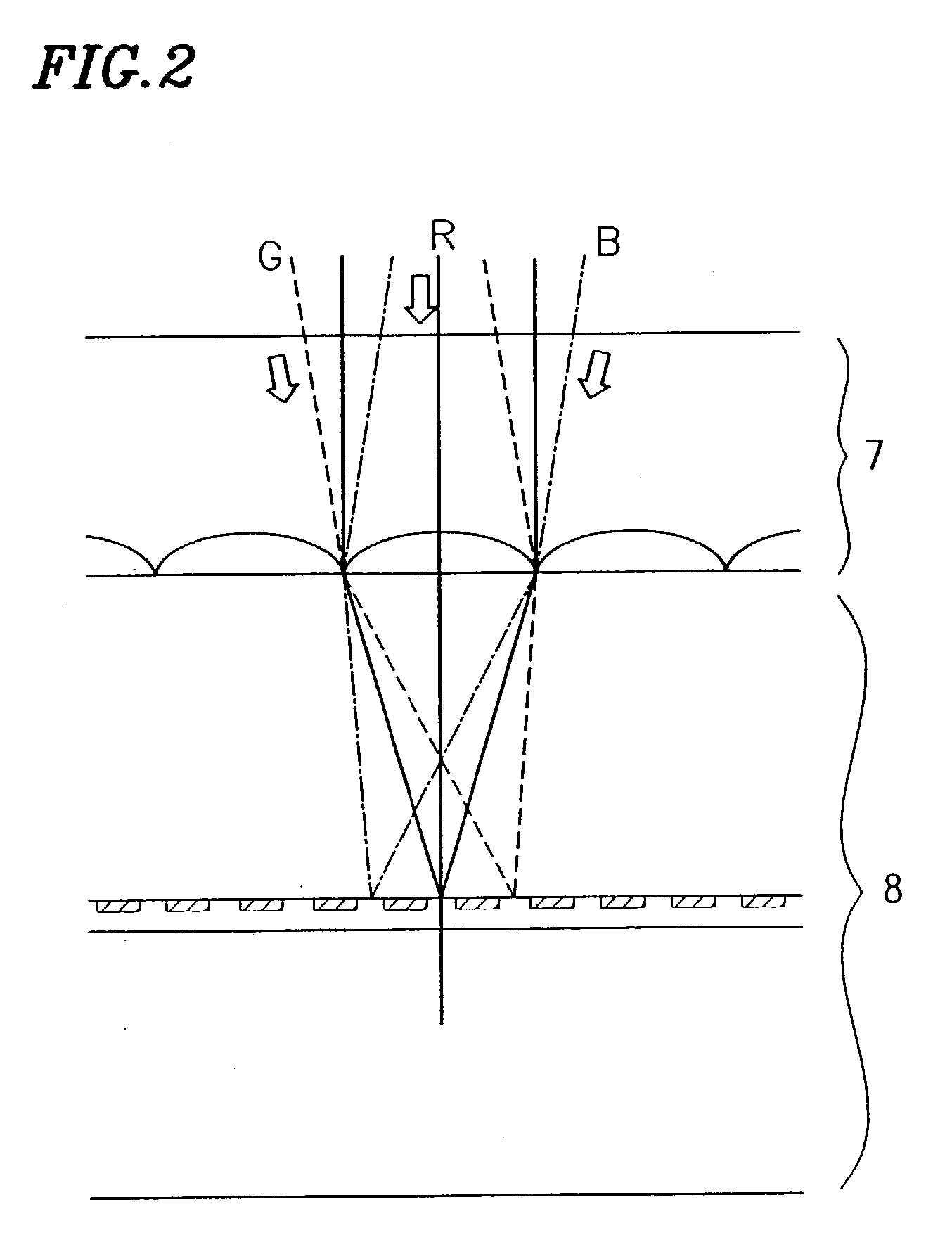
A light source 1, an image display panel 8 including multiple pixel regions, each of which can modulate light, light control means 4 to 6 for focusing light from the light source 1 onto associated pixel regions according to their wavelength ranges, and optical systems 9 and 11 that form an image on a projection plane 13 by the light that has been modulated by the panel 8 are provided. A circuit for generating data representing multiple image subframes from data representing each image frame as a component of the image and getting the subframes displayed by the panel time-sequentially, and an image shifter 11 for shifting a selected one of the subframes on the projection plane are further provided. The same area on the projection plane 13 is sequentially irradiated with light rays that have been modulated by different pixel regions of the panel 8 and that fall within respectively different wavelength ranges. Thus, a projection type image display device, realizing a bright, high-resolution and uniform display and contributing to downsizing and cost reduction, is provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
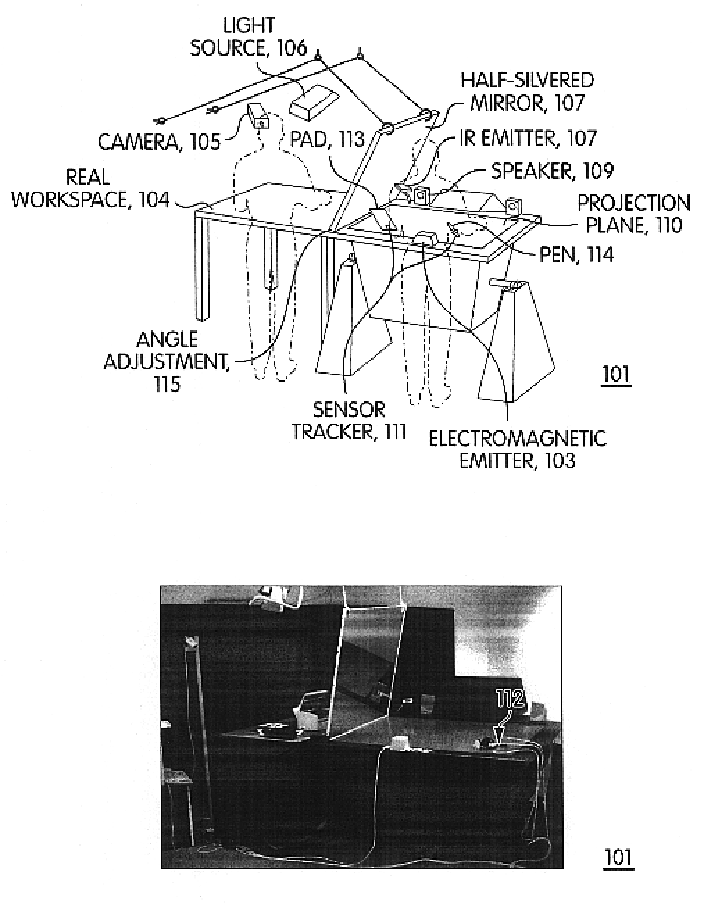
Extended virtual table: an optical extension for table-like projection systems
InactiveUS6803928B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Projection system
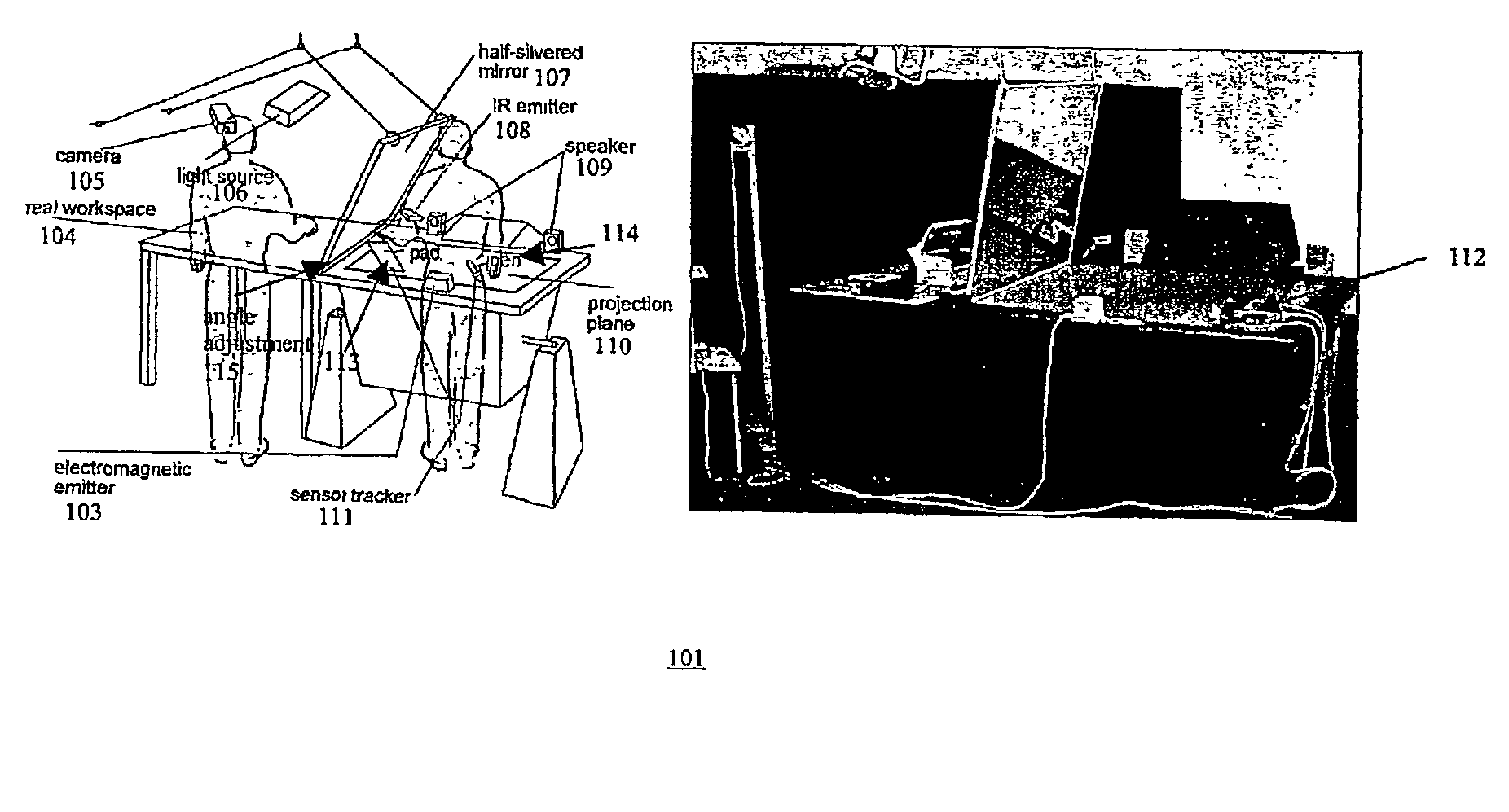
Apparatus that uses a large transflective mirror to extend a virtual reality system such as a virtual table that employs a projection plane to produce the virtual reality. The transflexive mirror is positioned relative to the projection plane such that the plane of the mirror intersects the projection plane and the angle of the mirror relative to the projection plane is such that the user of the system who looks at the mirror sees the projection plane reflected in the mirror. The virtual reality system is responsive to the position of the mirror and the direction in which a user is looking and produces separate virtual realities on the projection plane: one when the user is looking at the mirror and another when the user is looking at the projection plane. The virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the mirror may or may not be coherent with the virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the projection plane. The two virtual realities may share a global coordinate system that is divided into two parts by the plane of the mirror, and what the user sees when looking into the mirror may be what the user would see looking through a window into the part of the global coordinate system behind the mirror. Because the mirror is transflective, real objects whose locations are known to the virtual reality system can he placed behind the mirror and the virtual reality reflected in the mirror may be used to augment the real objects. One use of such augmentation is virtual trial assembly of a virtual mockup with a physical mockup.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
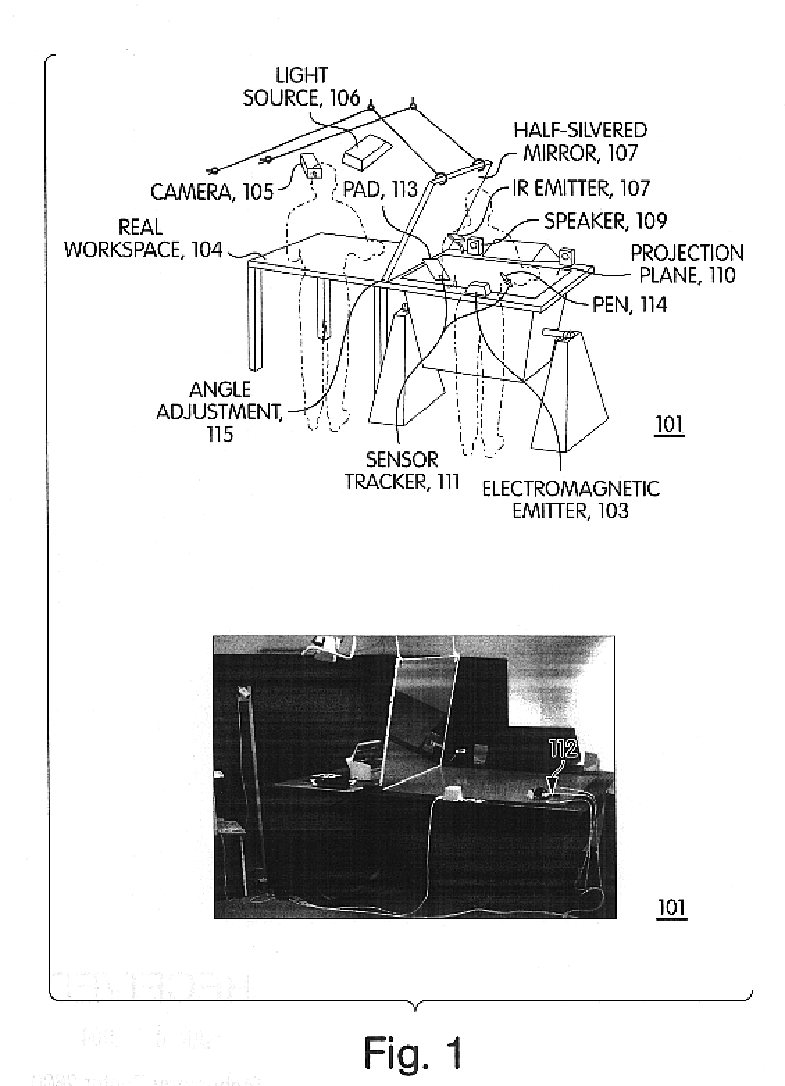
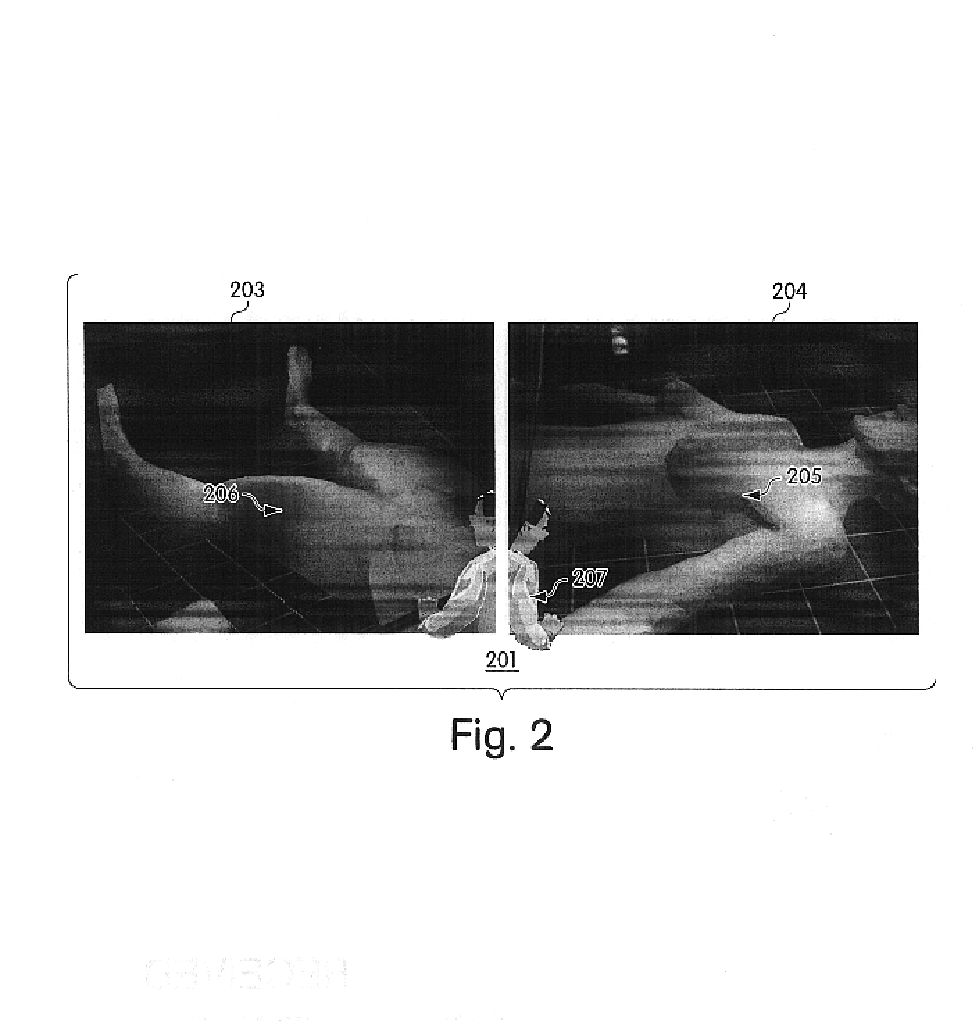
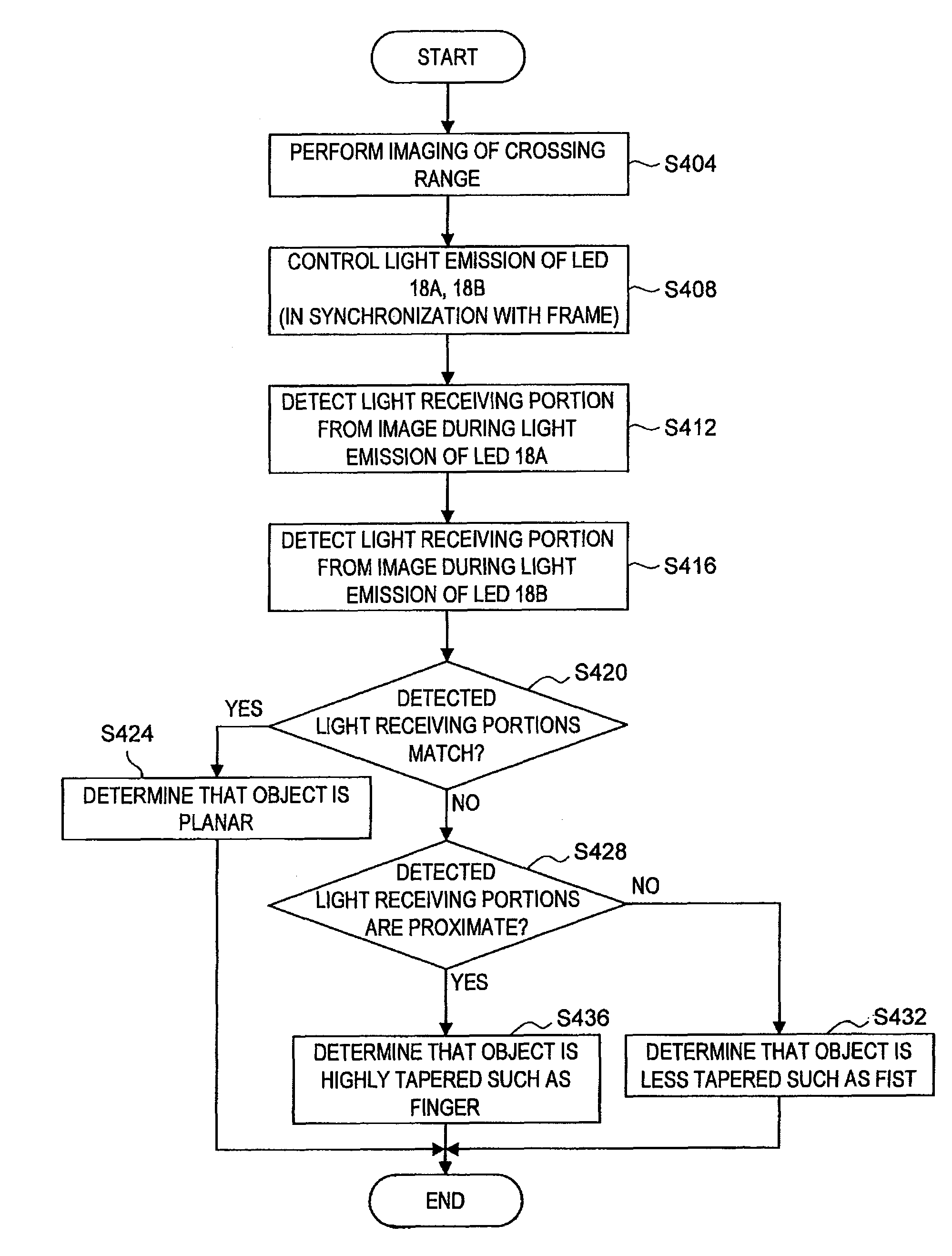
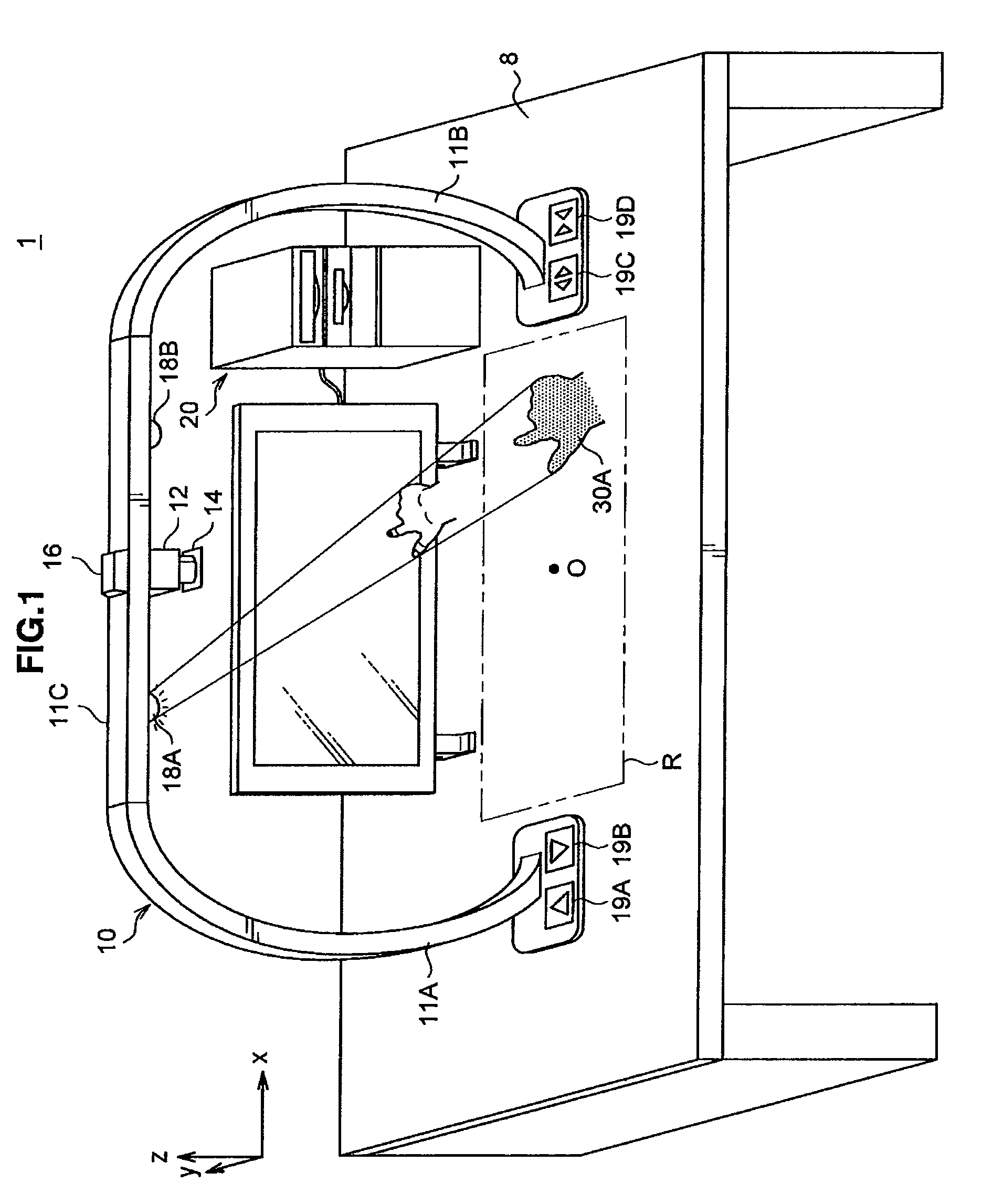
Position detection system, position detection method, program, object determination system and object determination method
ActiveUS8897499B2Accurate detectionInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementLocation detectionObject based
There is provided a position detection system including an imaging unit to capture an image of a projection plane of an electromagnetic wave, an electromagnetic wave emission unit to emit the electromagnetic wave to the projection plane, a control unit to control emission of the electromagnetic wave by the electromagnetic wave emission unit, and a position detection unit including a projected image detection section to detect a projected image of an object existing between the electromagnetic wave emission unit and the projection plane based on a difference between an image of the projection plane captured during emission of the electromagnetic wave by the electromagnetic wave emission unit and an image of the projection plane captured during no emission of the electromagnetic wave, and a position detection section to detect a position of the object based on a position of the projected image of the object.
Owner:SONY CORP
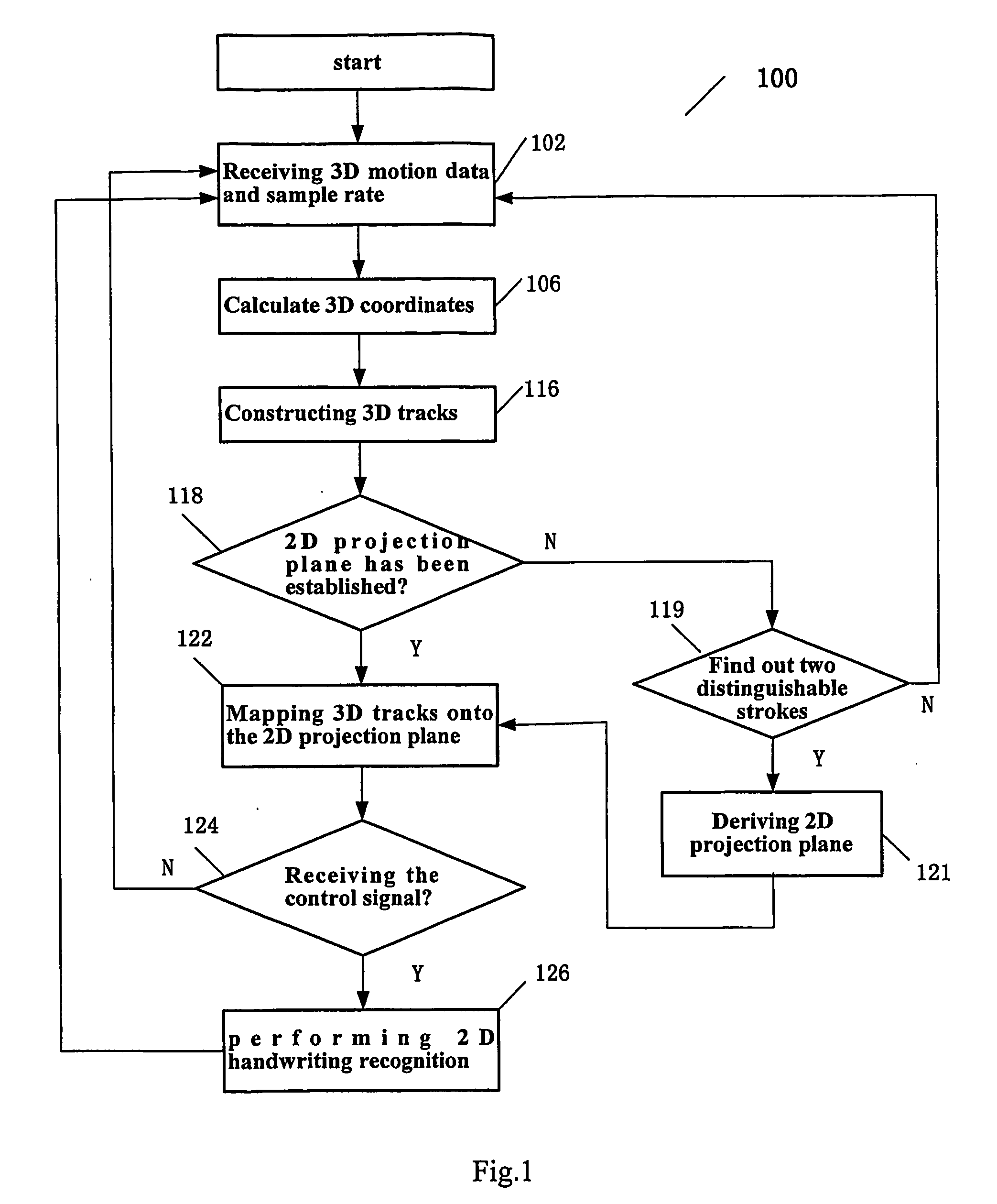
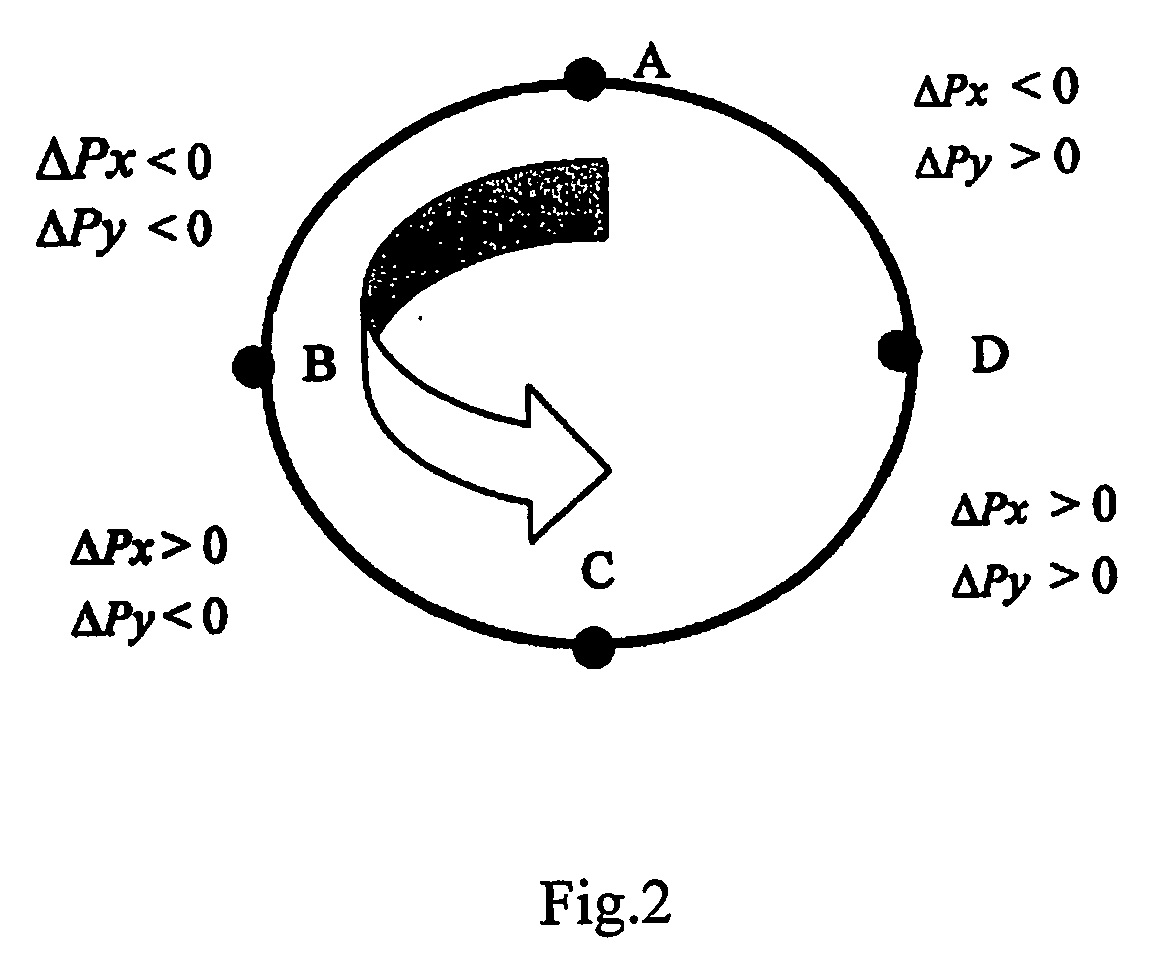
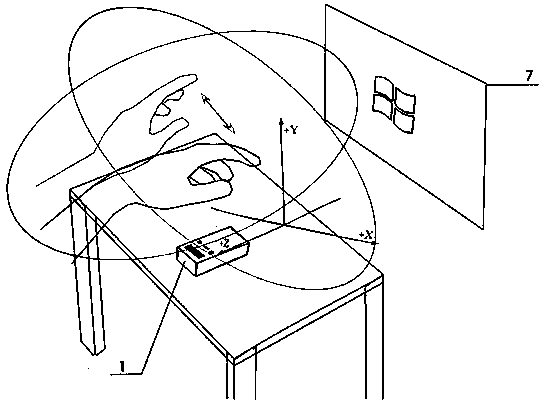
Method and system for three-dimensional handwriting recognition
InactiveUS20060159344A1Processing ability of efficiencyShort timeCharacter and pattern recognitionInput/output processes for data processingProjection planeHandwriting recognition
The present invention relates to three-dimensional (3D) handwriting recognition methods and systems. The present invention provides a 3D handwriting recognition method and corresponding system which allows to generate 3D motion data by tracking corresponding 3D motion, calculate corresponding 3D coordinates, construct corresponding 3D tracks, derive 2D projection plane based on some strokes 3D tracks of on character, and generate 2D image for handwriting recognition by mapping the 3D tracks onto the said 2D projection plane. The 3D handwriting recognition method according to the present invention can use the processing power of system more efficiently and highly improve the system performance. So that the system can get the final input result in a much shorter time after the user finishes writing a character without a long time waiting between two characters input, thus the user has more pleased and natural input experience.
Owner:SHAO XIAOLING +2
Extended virtual table: an optical extension for table-like projection systems
InactiveUS20030085866A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Projection plane
Apparatus that uses a large transflective mirror to extend a virtual reality system such as a virtual table that employs a projection plane to produce the virtual reality. The transflexive mirror is positioned relative to the projection plane such that the plane of the mirror intersects the projection plane and the angle of the mirror relative to the projection plane is such that the user of the system who looks at the mirror sees the projection plane reflected in the mirror. The virtual reality system is responsive to the position of the mirror and the direction in which a user is looking and produces separate virtual realities on the projection plane: one when the user is looking at the mirror and another when the user is looking at the projection plane The virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the mirror may or may not be coherent with the virtual reality that the user sees when looking at the projection plane. The two virtual realities may share a global coordinate system that is divided into two parts by the plane of the mirror, and what tile user sees when looking into the mirror may be what the user would see looking through a window Into the part of the global coordinate system behind the mirror. Because the mirror is transflective, real objects whose locations are known to the virtual reality system can he placed behind the mirror and the virtual reality reflected in the mirror may be used to augment the real objects. One use of such augmentation is virtual trial assembly of a virtual mockup with a physical mockup.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
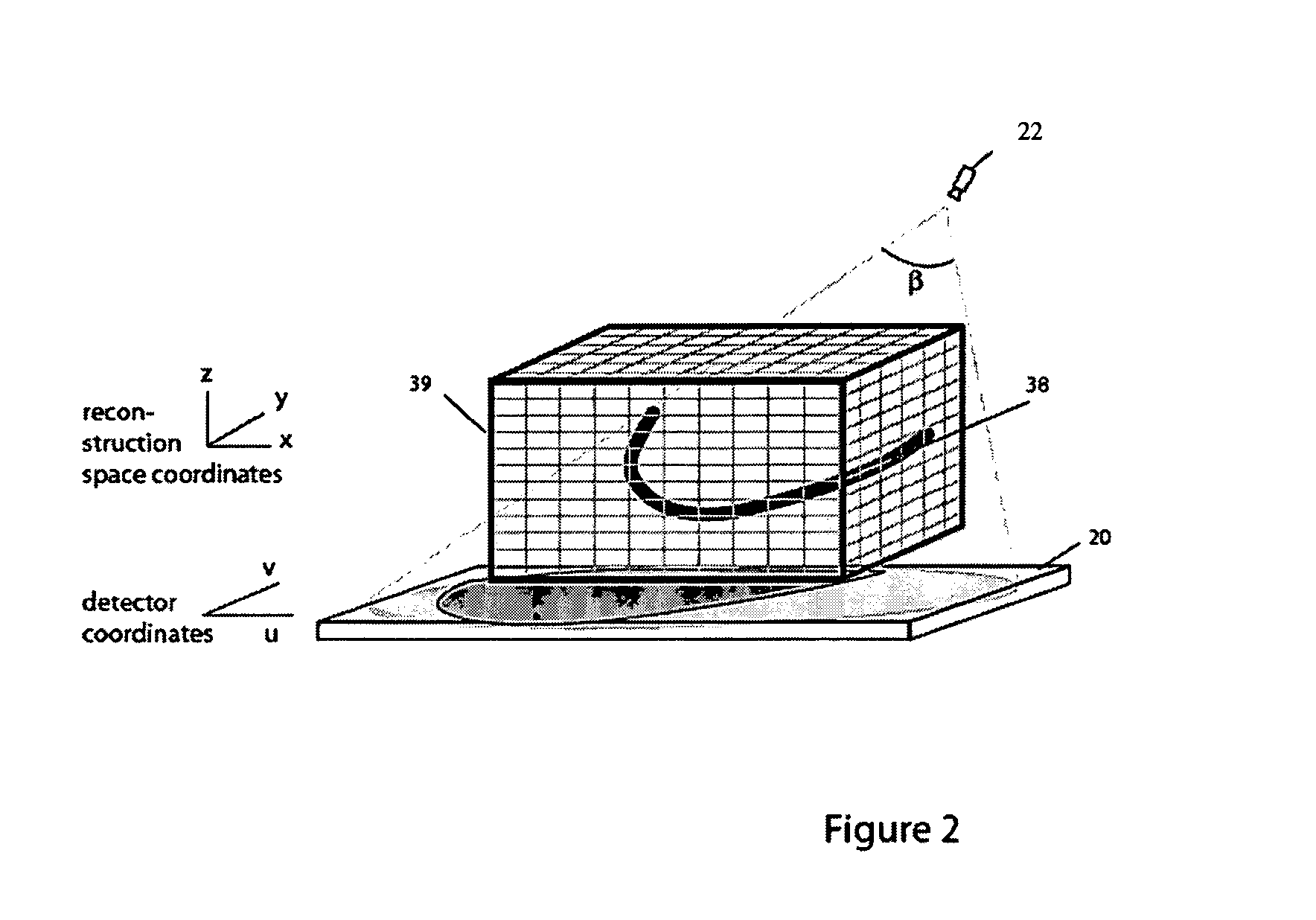
Methods and apparatus for back-projection and forward-projection
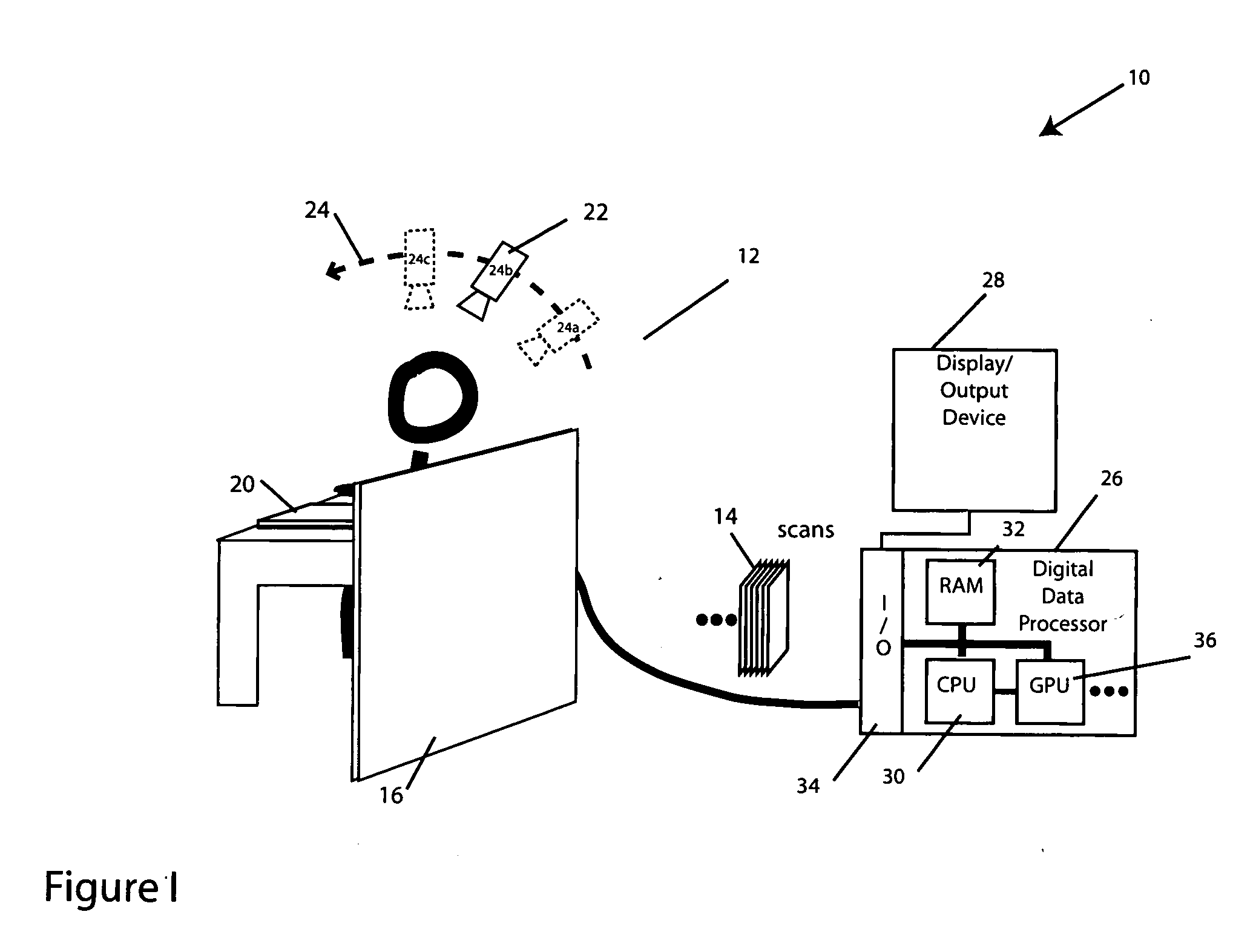
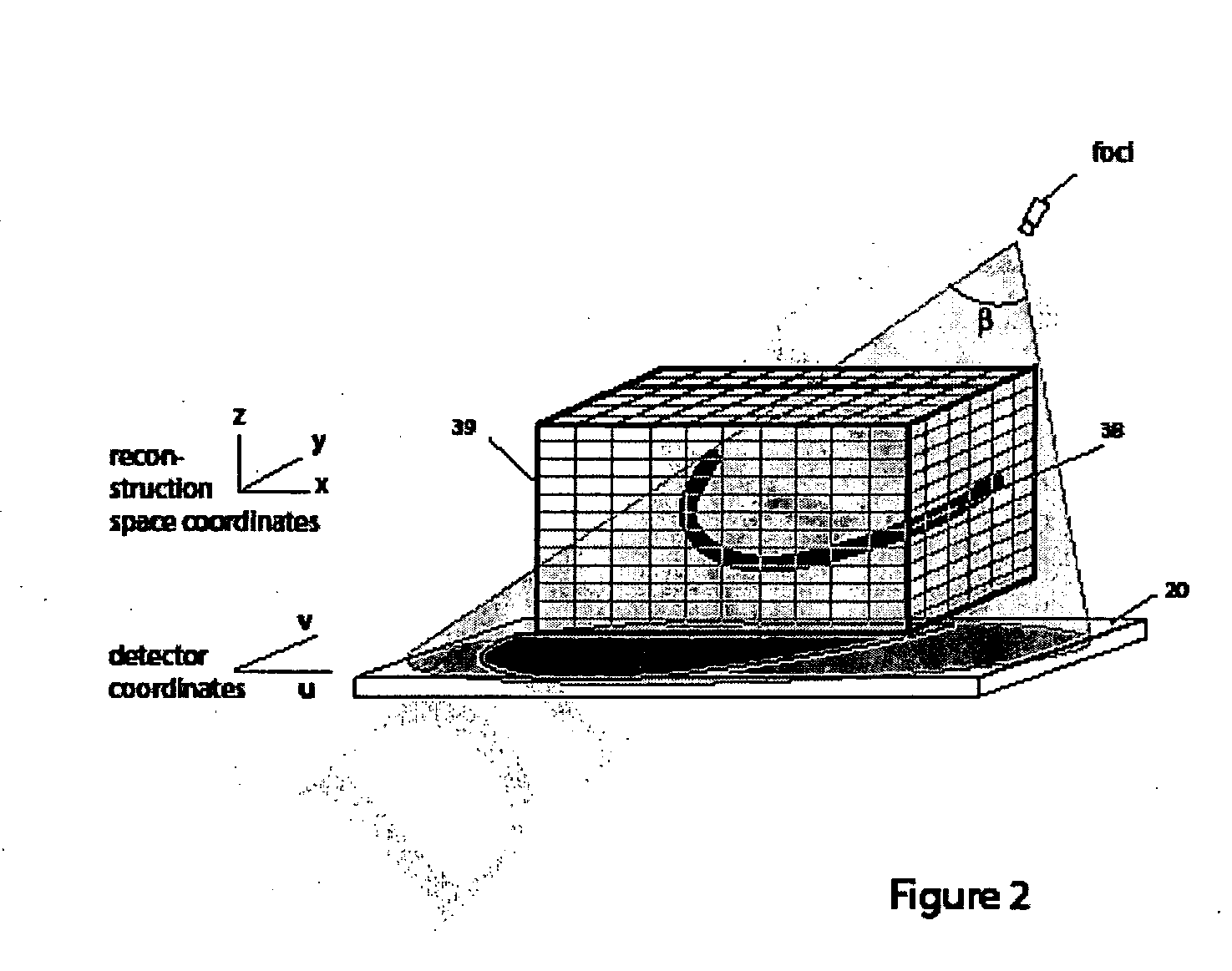
ActiveUS20050152590A1Few computational resourceAddressing slow performanceReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelProjection image
The invention provides improvements in reconstructive imaging of the type in which a volume is reconstructed from a series of measured projection images (or other two-dimensional representations) generated by projection of a point x-ray source (or other radiation source), positioned at a distinct focus, through the volume to a plane at which the respective projection image is acquired (“detector plane”). In one aspect, the improvements are with respect to back-projecting a two-dimensional representation lying in the detector plane (representing, for example, a difference between an originally-acquired measured projection image and a subsequently-generated estimate thereof) to generate three-dimensional representation (which can be used, for example, to update an estimate of the volume). According to this aspect, for each of one or more slices of the 3D representation parallel to the projection plane and for each distinct focus at which a projection is generated, the following steps are performed in connection with the back-projection: (i) warping the first 2D representation to generate a second 2D representation by applying to the first 2D representation a selected linear mapping, where that selected linear mapping would map, in order to match dimensions of the respective slice within the 3D representation, a region defined by projection, at the respective focus, of comers of that slice onto the detector plane, and (ii) incrementing values of each of one or more voxels of the respective slice by an amount that is a function of a value of a correspondingly indexed pixel of the second 2D representation. A related aspect provides improvements with respect to forward-projecting, as well as in iterative (and non-iterative) methodologies that incorporate both back-projection and forward-projection.
Owner:PME IP
Beam focusing and scanning system using micromirror array lens
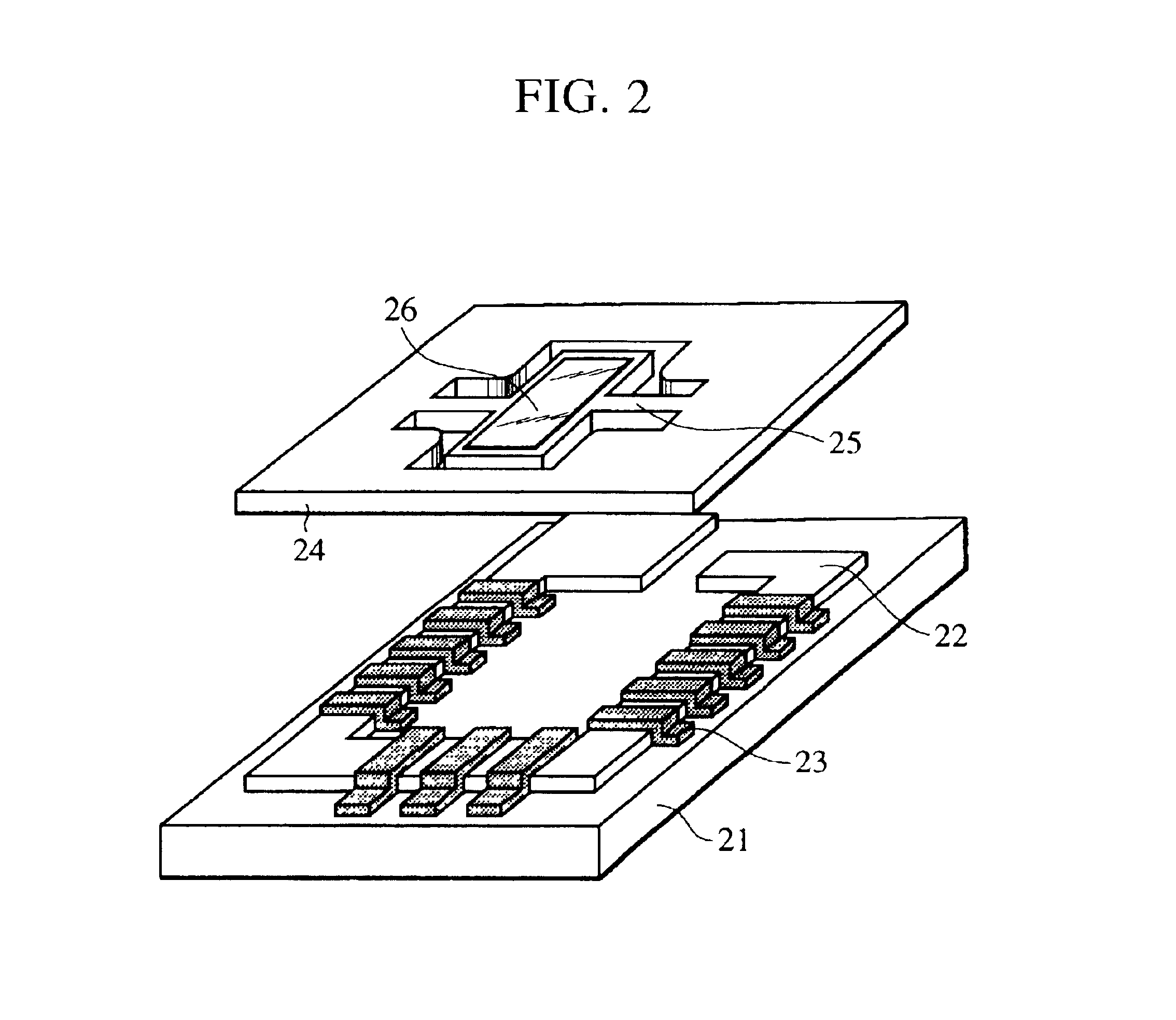
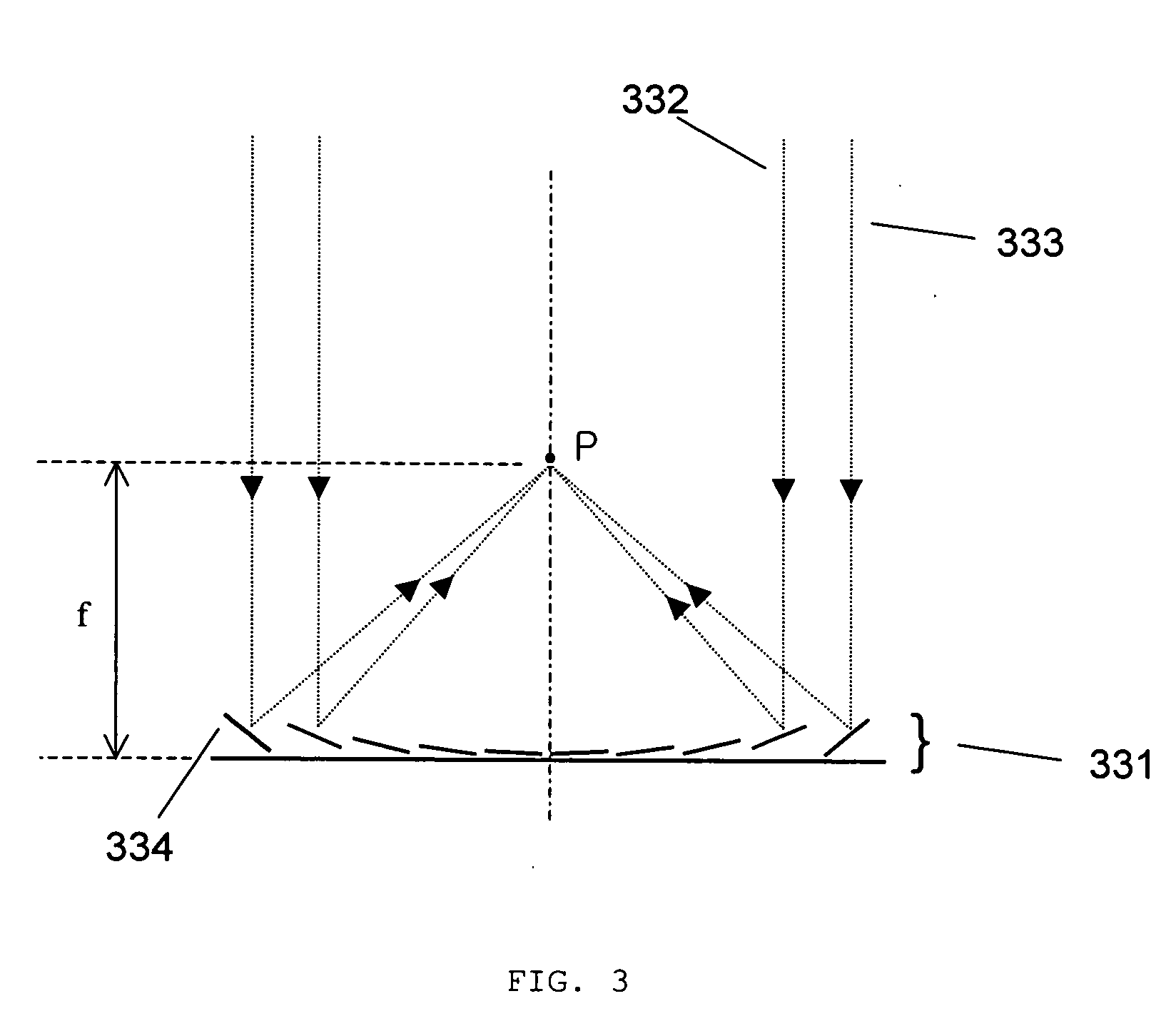
ActiveUS20050264867A1Increase speedLarge focal length variationMirrorsMountingsLight beamProjection plane
A beam focusing and scanning system using a micromirror array lens (optical system) includes a light source configured to emit light and a micromirror array lens, including at least one micromirror, optically coupled to the light source, configured to reflect the light onto a projection medium (projection plane). The optical system also includes at least one actuating component coupled to the at least one micromirror, configured to move the at least one micromirror to enable the at least one micromirror to focus the light on the projection medium. The advantages of the present invention include high speed variable focusing and scanning, large focal length variation, phase compensation, high reliability and optical efficiency, low power consumption and low cost.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Virtual visual point image generating method and 3-d image display method and device
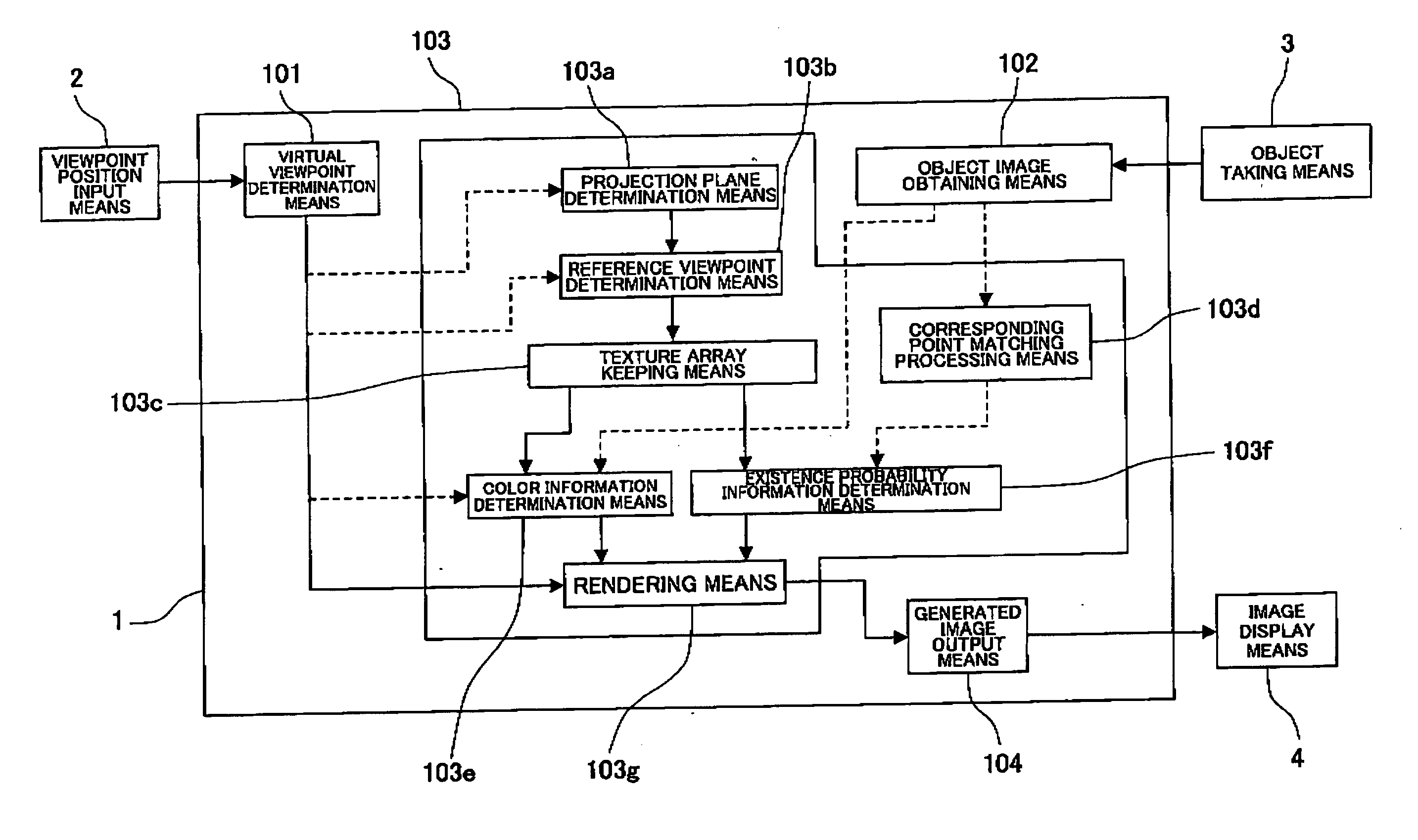
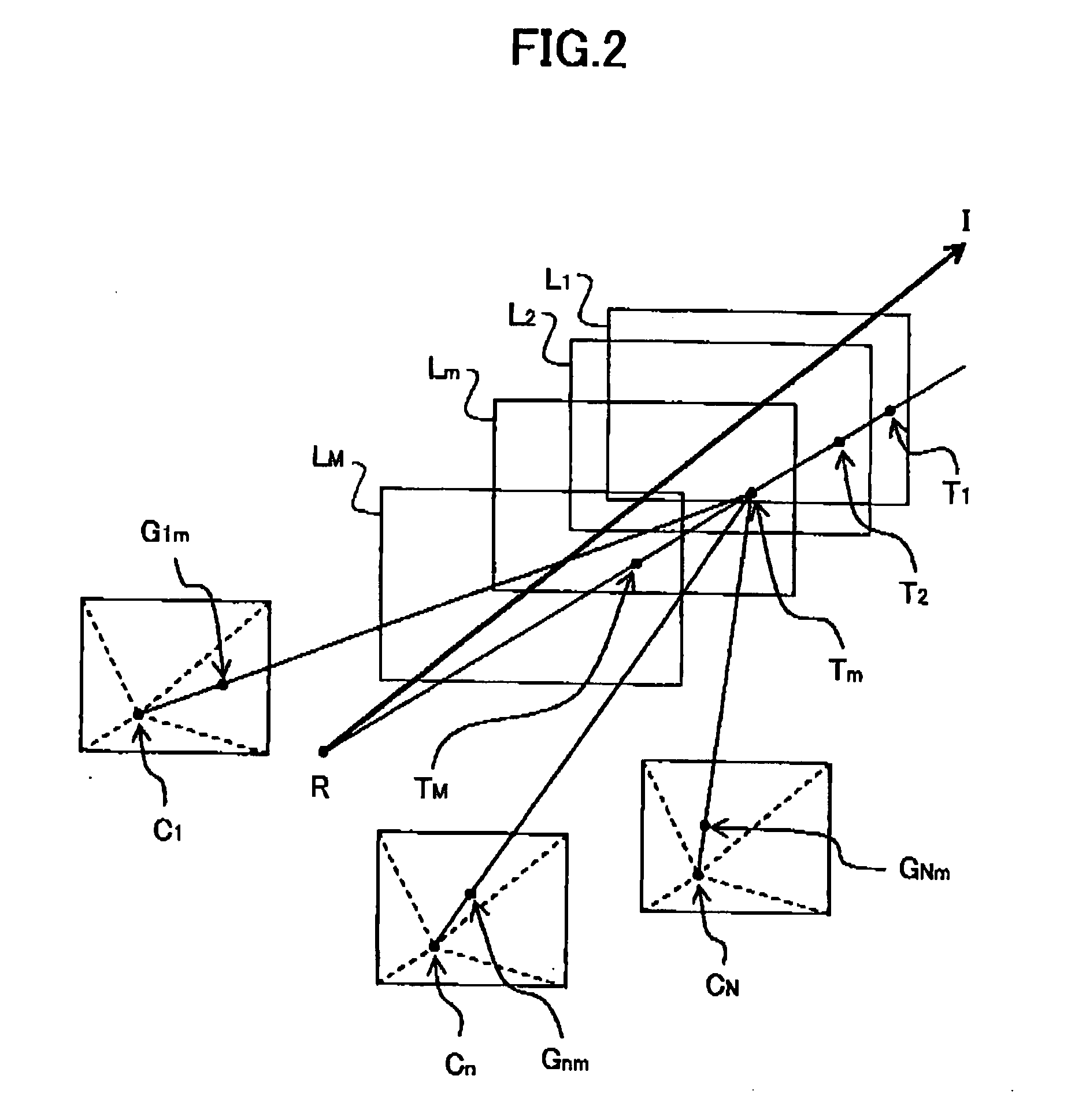
ActiveUS20070122027A1Reduce remarkable deterioration of image qualitySmall partial deterioration of image qualityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
A virtual viewpoint image generation method for generating a virtual viewpoint image that is an image of an object viewed from a virtual viewpoint based on plural images of the object taken by plural cameras is provided. In the virtual viewpoint image generation method, projection planes having a multi-layered structure are set, each corresponding point, on the images of the object, corresponding to a projection point of a projection plane is obtained, color information of each projection point is determined based on color information of corresponding points, for each of the projection points overlapping when viewed from a reference viewpoint in a space, a degree of probability that the object exists at a distance corresponding to a position of the projection point is determined based on a degree of correlation of the corresponding points, mixing processing is performed on color information of reference points overlapping when viewed from the virtual viewpoint according to the degree of probability of existence of the object so as to determine color information of each pixel of the virtual viewpoint image.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method for acquiring 3-dimensional images of coronary vessels, particularly of coronary veins
InactiveUS20100189337A1Quality improvementImprove representationImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsVeinX-ray
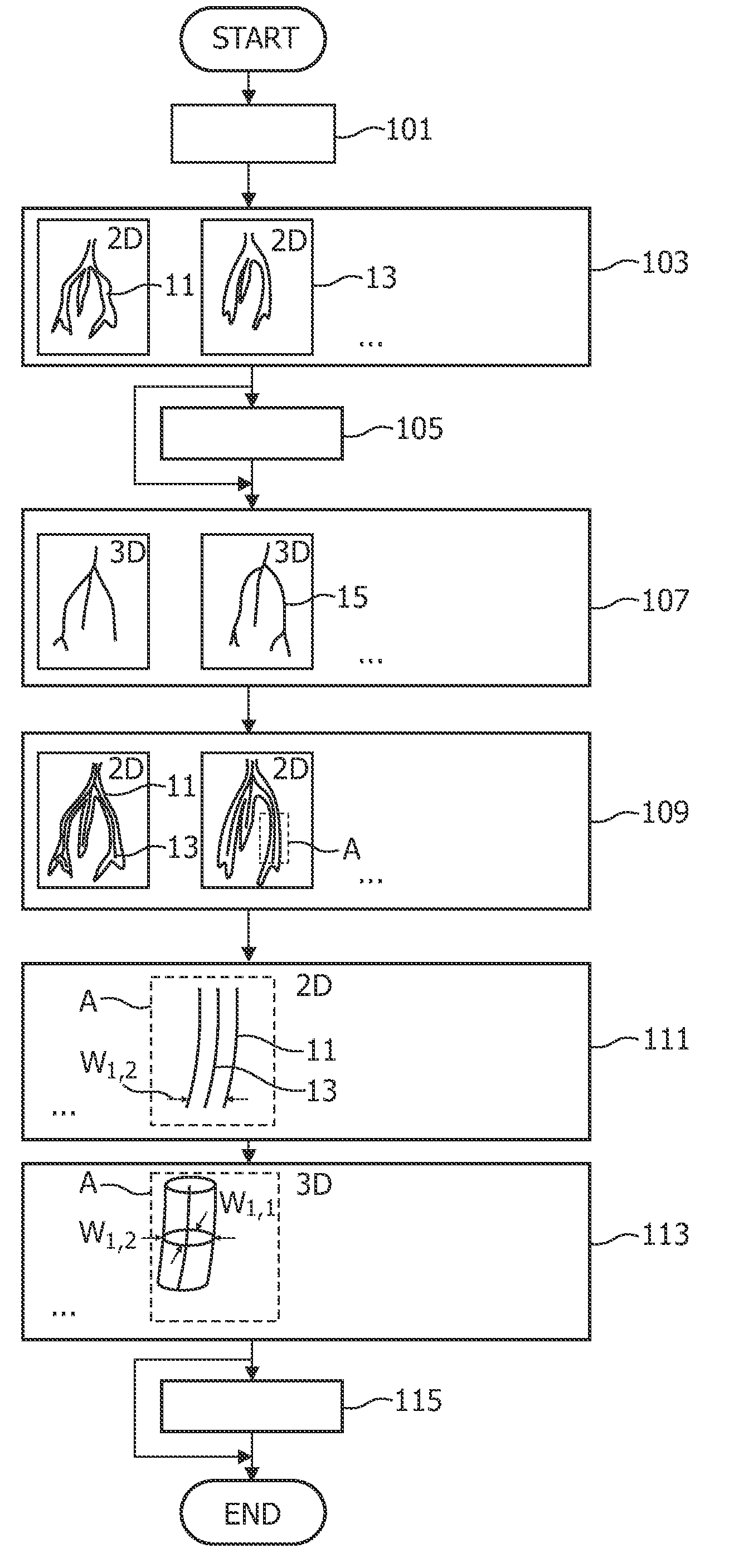
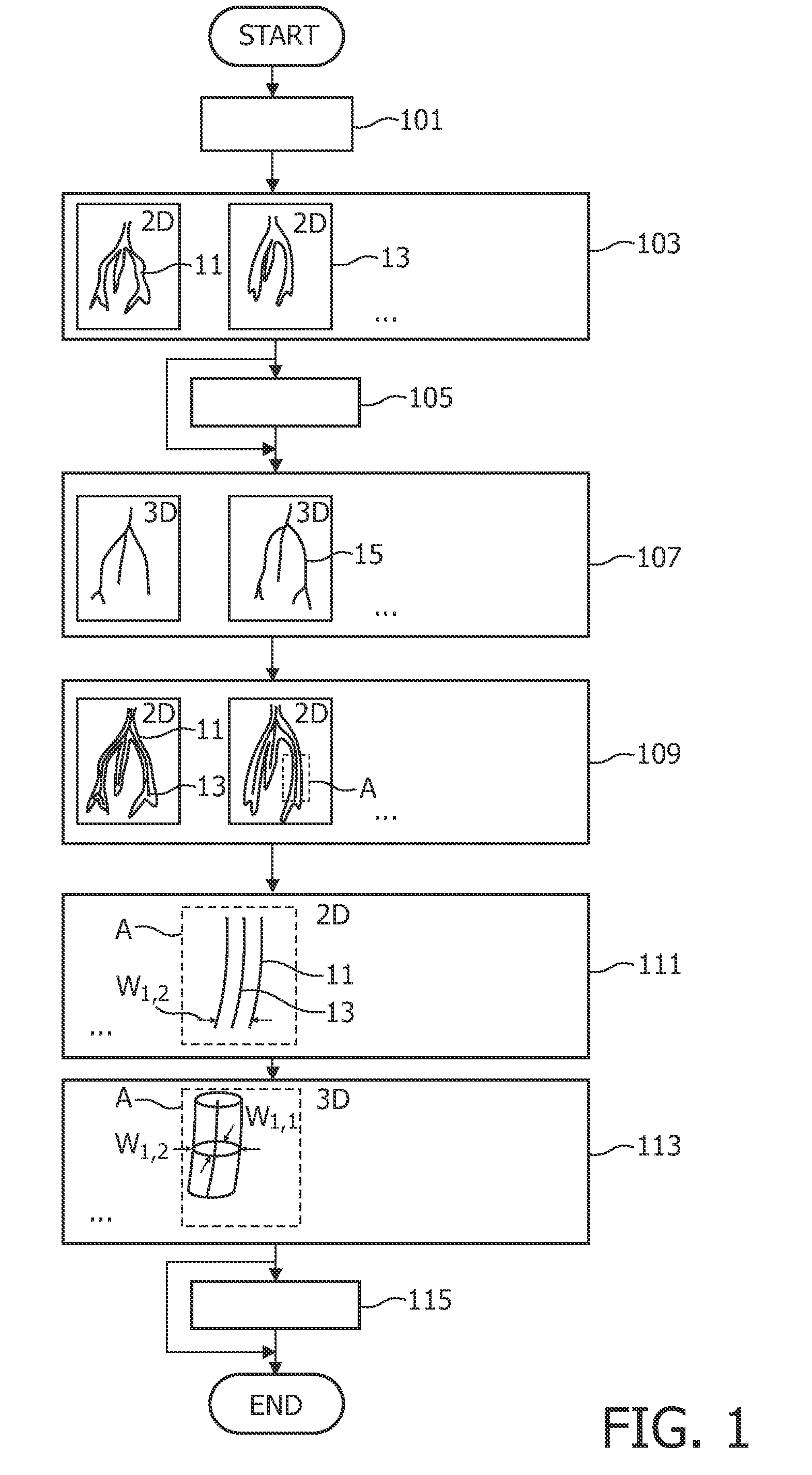
A method and an apparatus for acquiring 3-dimensional images of coronary vessels (11), particularly of coronary veins, is proposed. 2-dimensional X-ray images (13) are acquired within a same phase of a cardiac motion. Then, a 3-dimensional centerline model (15) is generated based on these 2-dimensional images. From 2-dimensional projections of the centerline model into respective projection planes, the local diameters (w) of the vessels in the projection plane can be derived. Having the diameters, a 3-dimensional hull model of the vessel system can be generated and, optionally, 4-dimensional information about the vessel movement can be derived.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for processing three-dimensional images
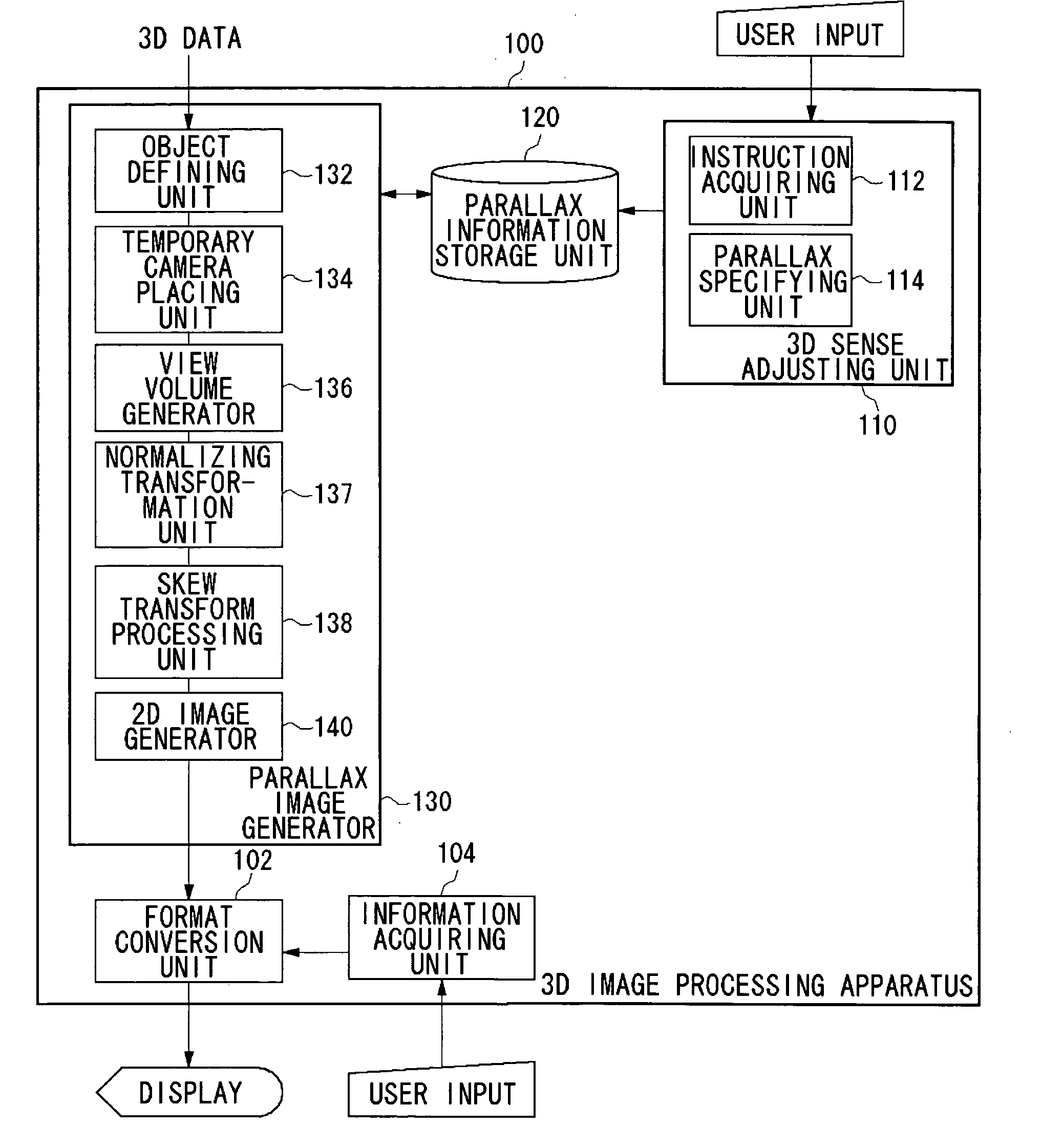
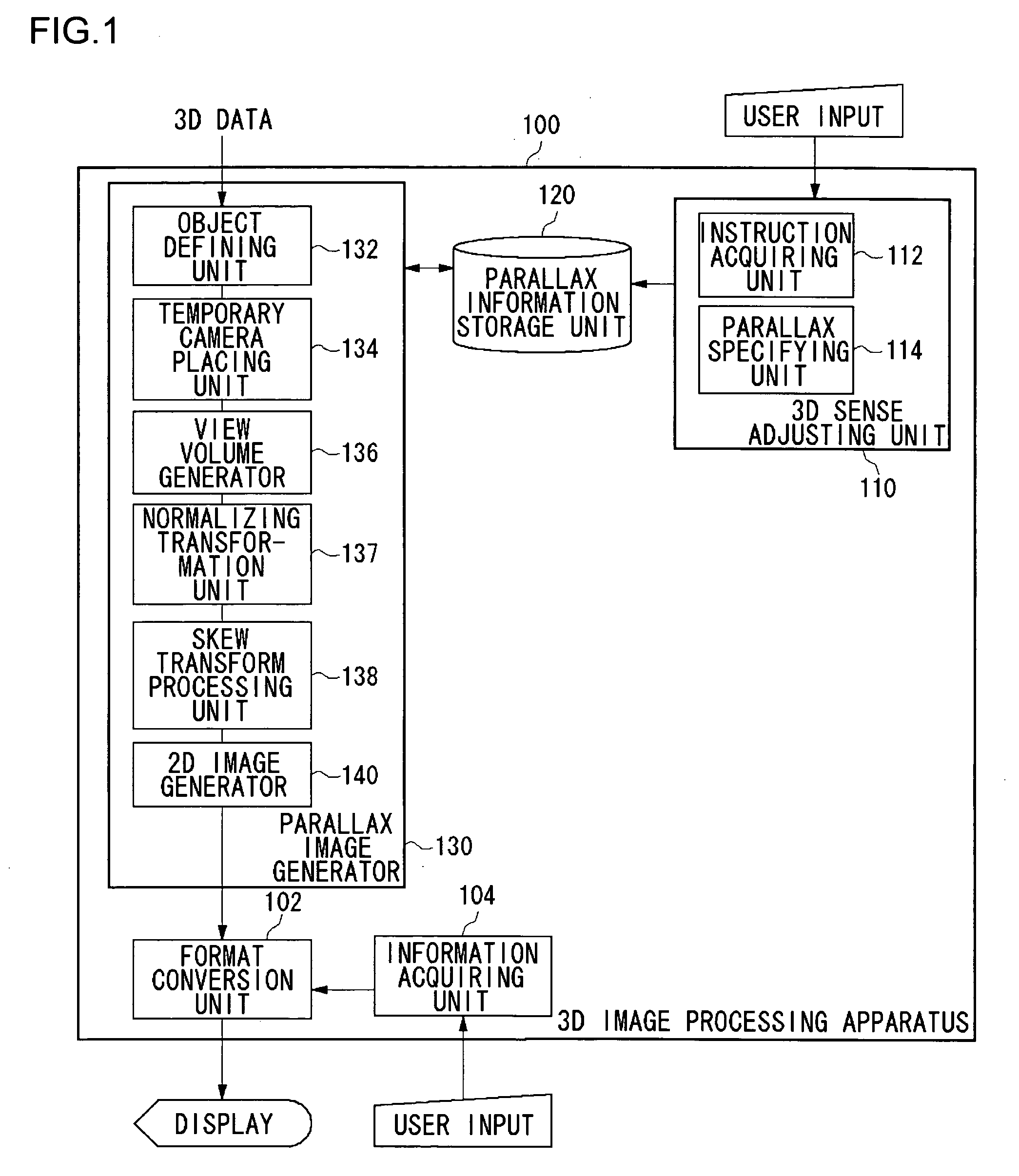
InactiveUS20050253924A1Easy to handleIncrease the compression ratioSteroscopic systemsParallaxComputer graphics (images)
A 3D image processing apparatus first generates a combined view volume that contains view volumes set respectively by a plurality of real cameras, based on a single temporary camera placed in a virtual 3D space. Then, this apparatus performs skewing transformation on the combined view volume so as to acquire view volumes for each of the plurality of real cameras. Finally, two view volumes acquired for the each of the plurality of real cameras are projected on a projection plane so as to produce 2D images having parallax. Using the temporary camera alone, the 2D images serving as base points for a parallax image can be produced by acquiring the view volumes for the each of the plurality of real cameras. As a result, a processing for actually placing the real cameras can be skipped, so that a high-speed processing as a whole can be realized.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
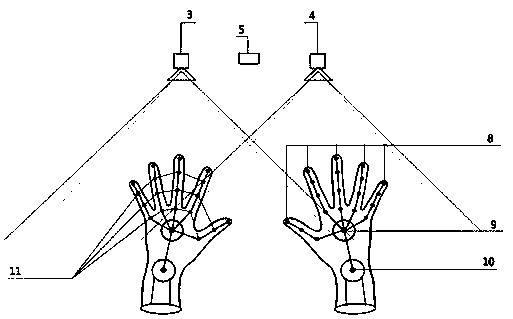
Human-machine interaction method and system based on binocular stereoscopic vision
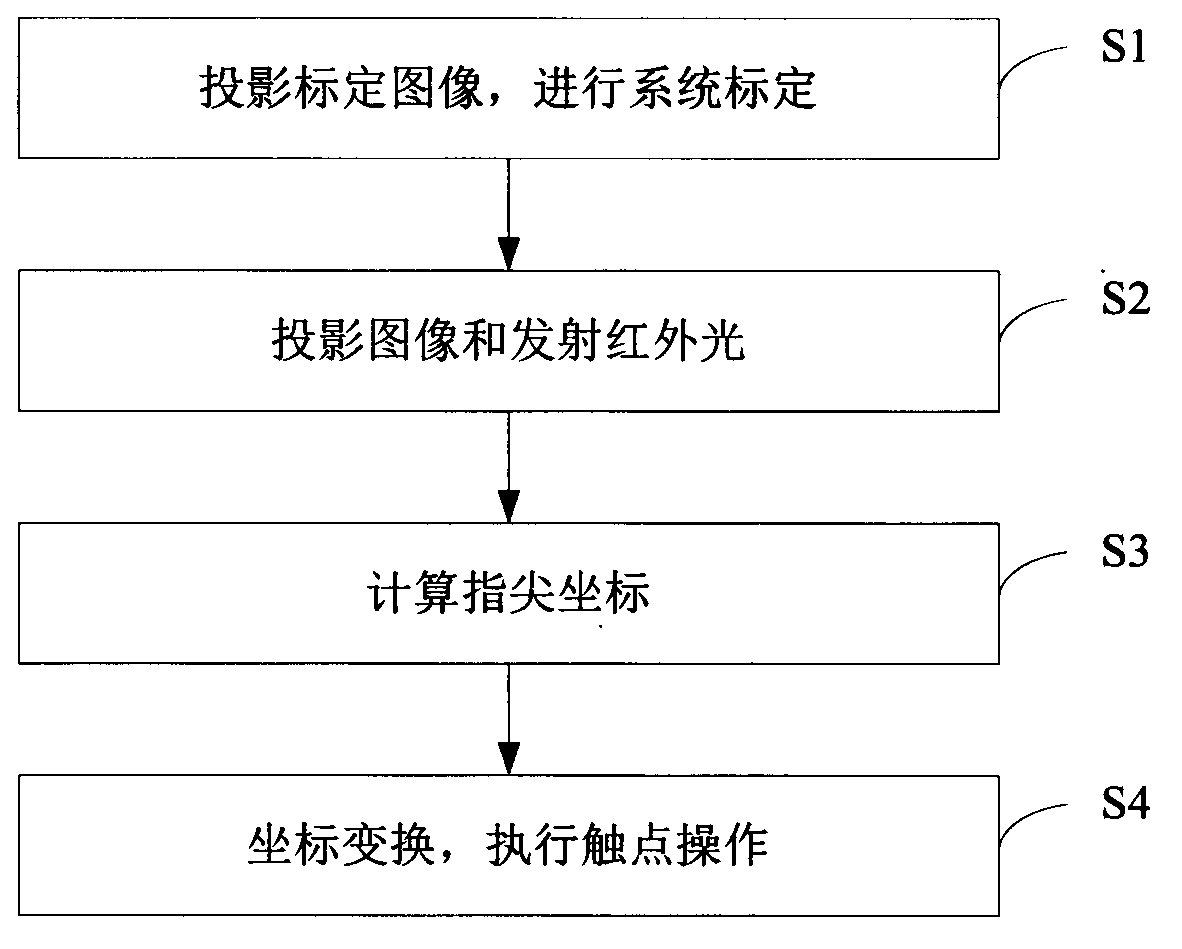
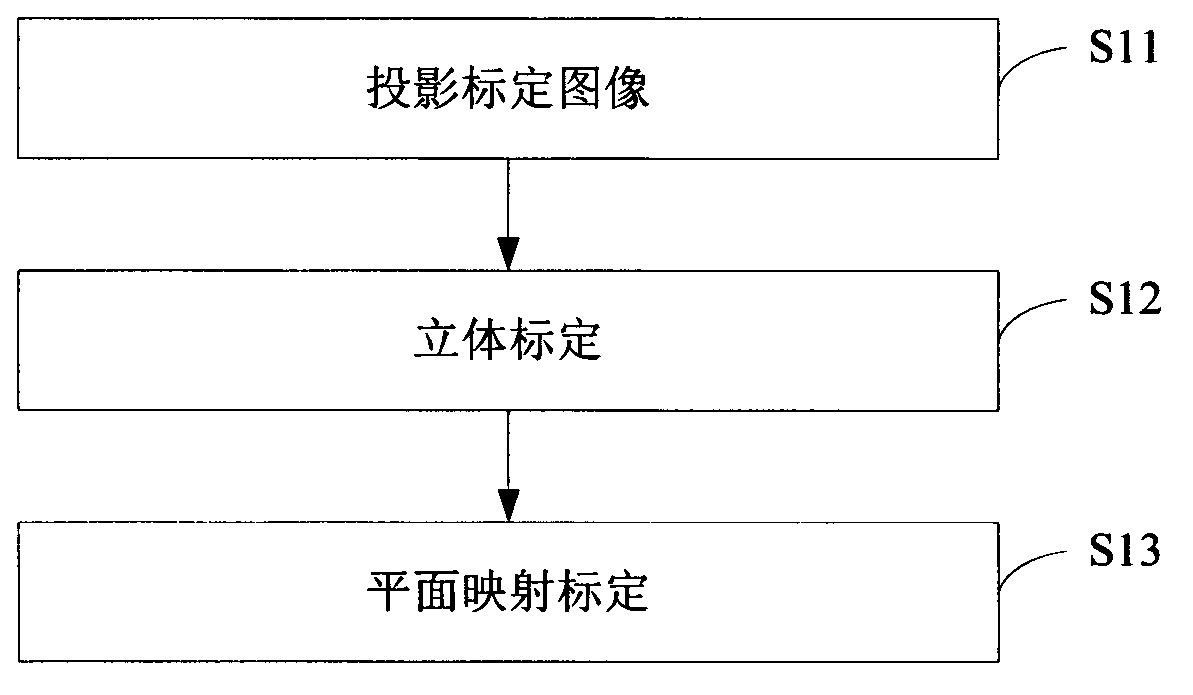
ActiveCN102799318AImprove human-computer interactionEnhanced interactionInput/output processes for data processingHuman–robot interactionProjection plane
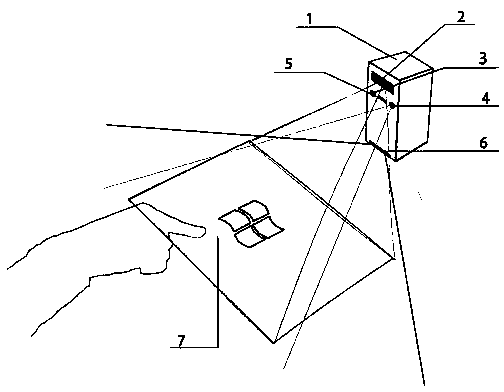
The invention relates to the technical field of human-machine interaction and provides a human-machine interaction method and a human-machine interaction system based on binocular stereoscopic vision. The human-machine interaction method comprises the following steps: projecting a screen calibration image to a projection plane and acquiring the calibration image on the projection surface for system calibration; projecting an image and transmitting infrared light to the projection plane, wherein the infrared light forms a human hand outline infrared spot after meeting a human hand; acquiring an image with the human hand outline infrared spot on the projection plane and calculating a fingertip coordinate of the human hand according to the system calibration; and converting the fingertip coordinate into a screen coordinate according to the system calibration and executing the operation of a contact corresponding to the screen coordinate. According to the invention, the position and the coordinate of the fingertip are obtained by the system calibration and infrared detection; a user can carry out human-machine interaction more conveniently and quickly on the basis of touch operation of the finger on a general projection plane; no special panels and auxiliary positioning devices are needed on the projection plane; and the human-machine interaction device is simple in and convenient for mounting and using and lower in cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
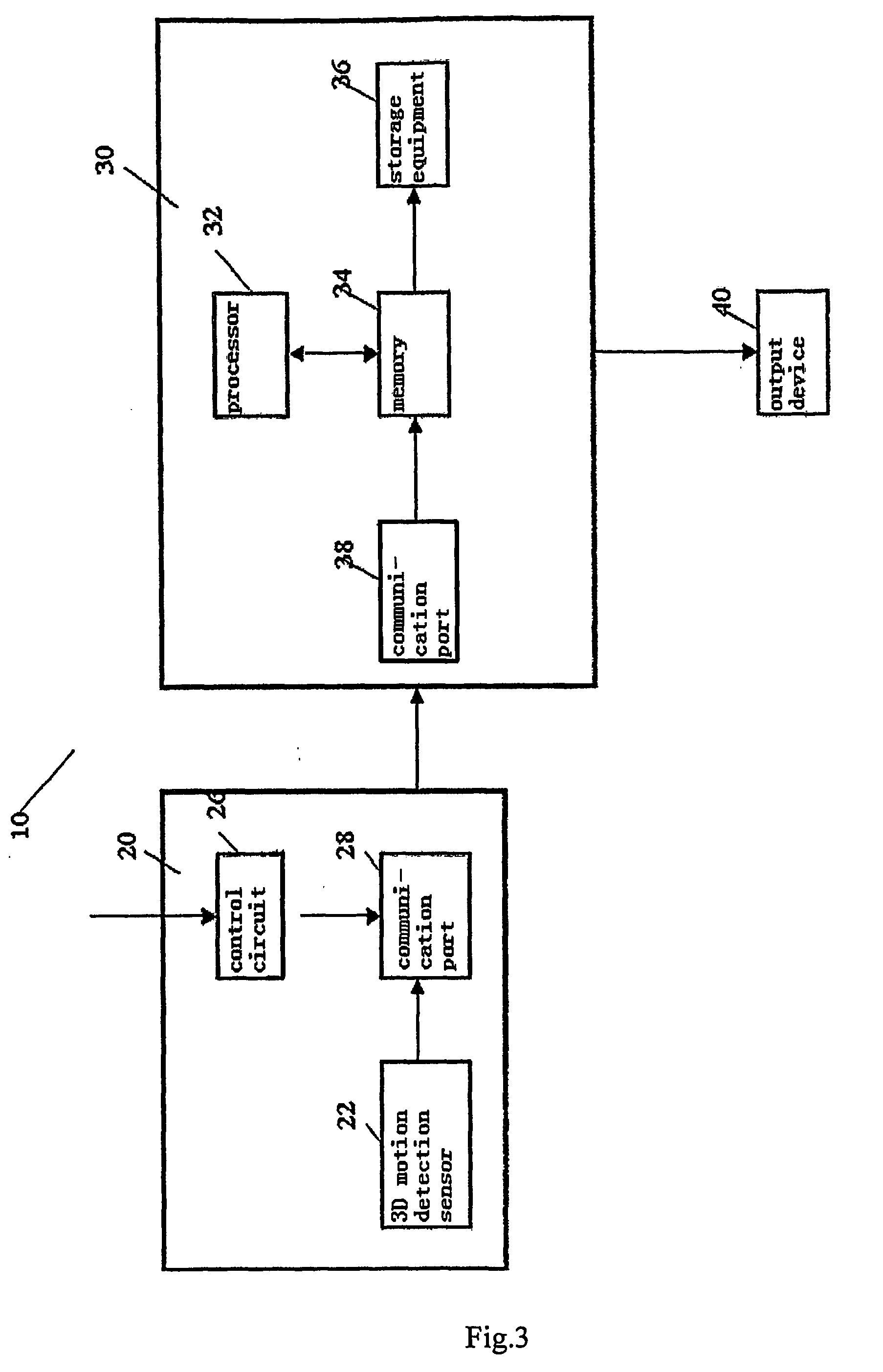
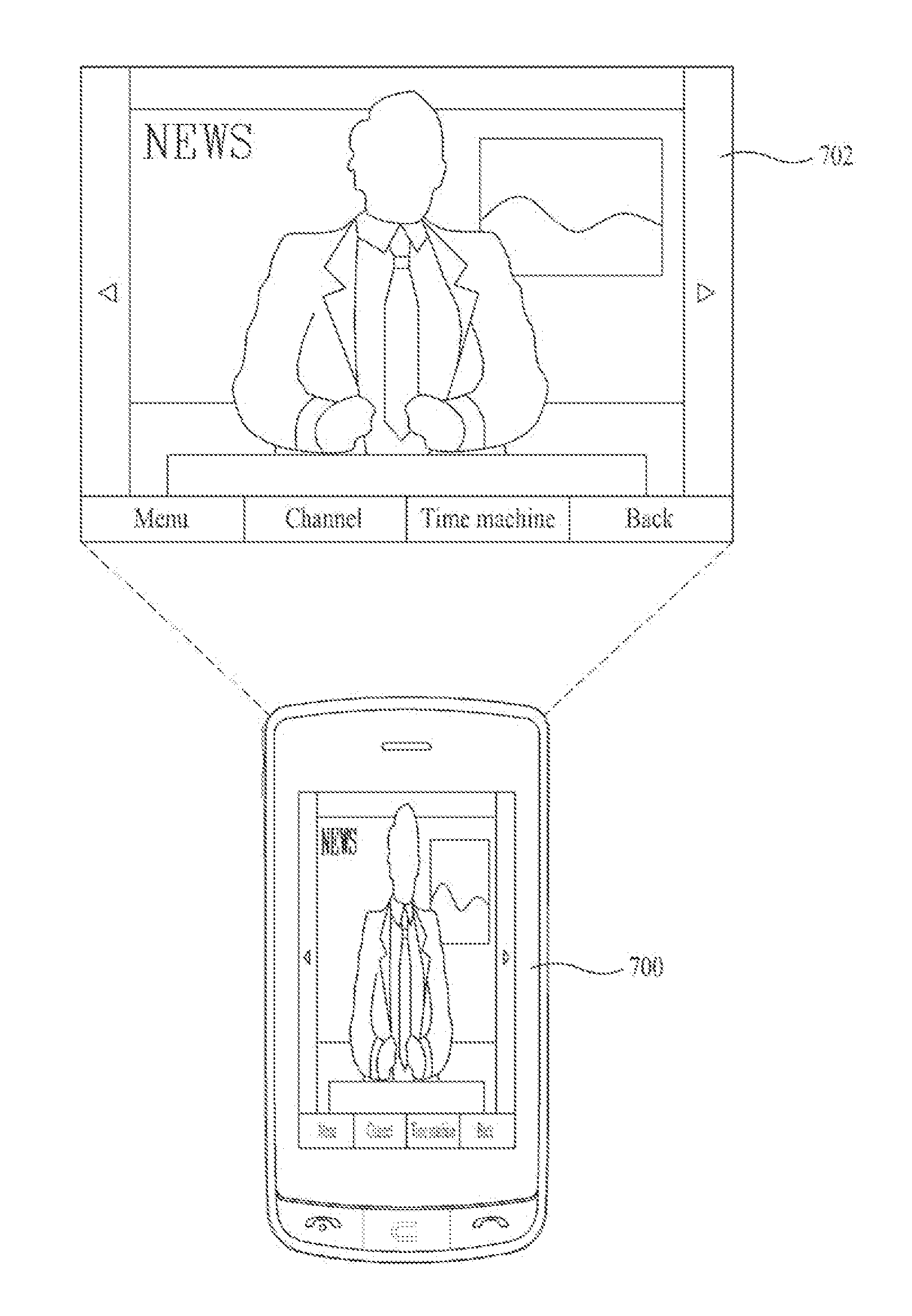
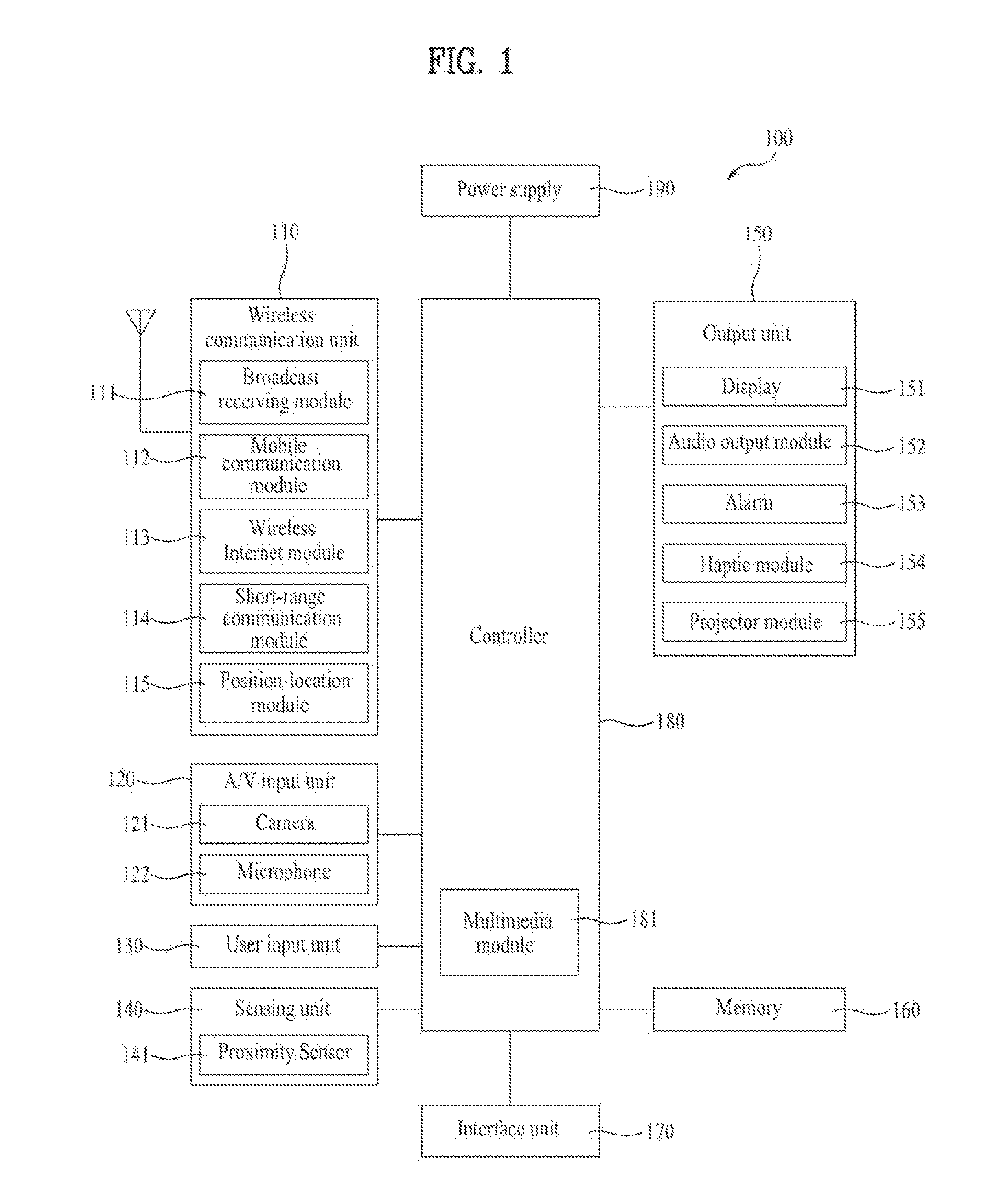
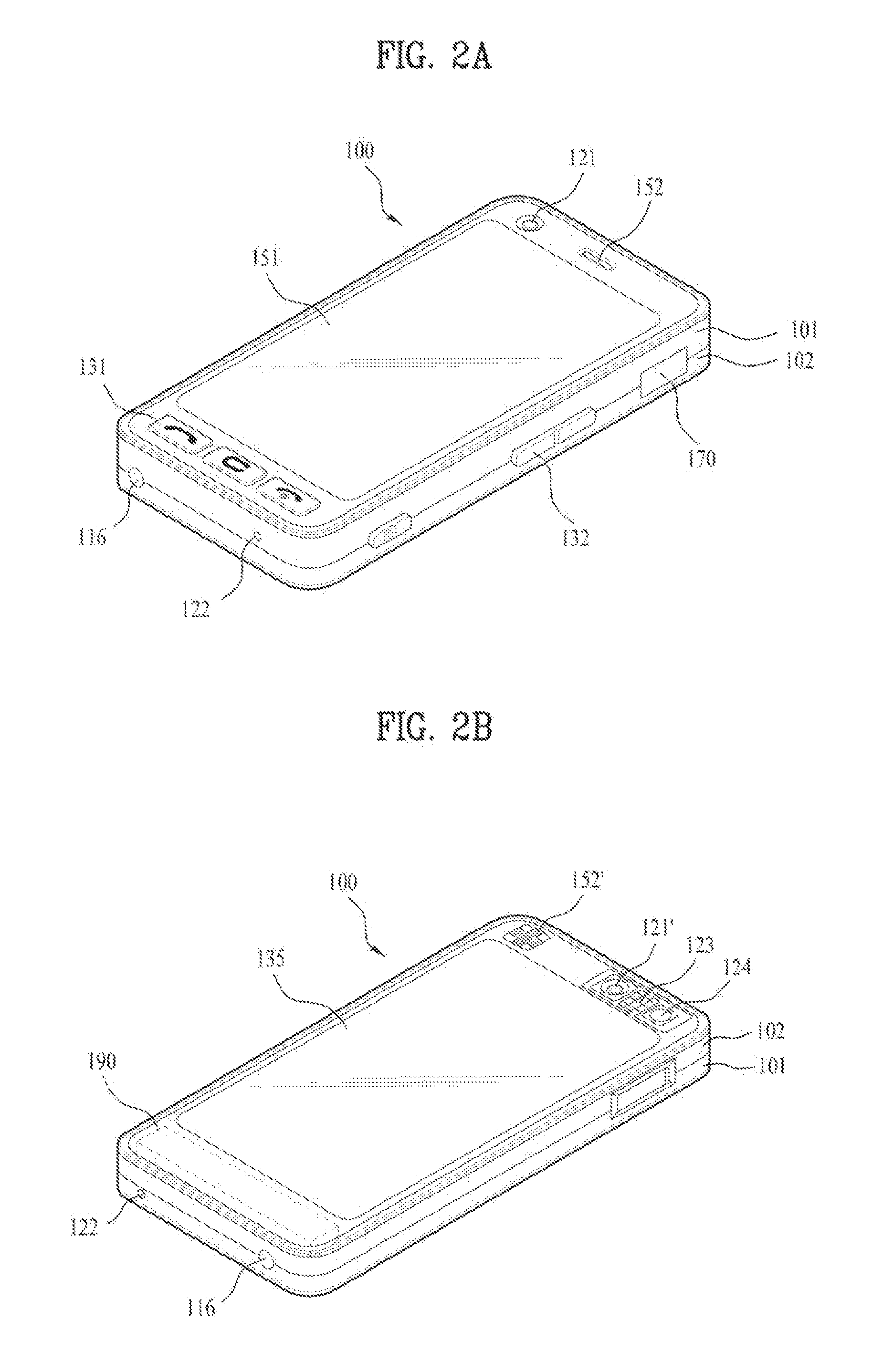
Mobile communication terminal and power saving method thereof
A mobile communication terminal and power saving method thereof are disclosed, by which display information can be outputted to an external projection plane using a projector module. Accordingly, if an event by a system or user occurs, power saving can be performed by controlling an operation of the projector module. A mobile terminal may include a terminal body, a motion sensor configured to detect a motion of the terminal body, a projector module configured to project an image onto an external surface, a power supply configured to supply power to the projector module, and a controller configured to control an operation of the projector module and to discontinue the supply of power to the projector module in response to detecting the motion by the motion sensor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Methods and apparatus for back-projection and forward-projection
ActiveUS7120283B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelProjection image
The invention provides improvements in reconstructive imaging of the type in which a volume is reconstructed from a series of measured projection images (or other two-dimensional representations) generated by projection of a point x-ray source (or other radiation source), positioned at a distinct focus, through the volume to a plane at which the respective projection image is acquired (“detector plane”). In one aspect, the improvements are with respect to back-projecting a two-dimensional representation lying in the detector plane (representing, for example, a difference between an originally-acquired measured projection image and a subsequently-generated estimate thereof) to generate three-dimensional representation (which can be used, for example, to update an estimate of the volume). According to this aspect, for each of one or more slices of the 3D representation parallel to the projection plane and for each distinct focus at which a projection is generated, the following steps are performed in connection with the back-projection: (i) warping the first 2D representation to generate a second 2D representation by applying to the first 2D representation a selected linear mapping, where that selected linear mapping would map, in order to match dimensions of the respective slice within the 3D representation, a region defined by projection, at the respective focus, of corners of that slice onto the detector plane, and (ii) incrementing values of each of one or more voxels of the respective slice by an amount that is a function of a value of a correspondingly indexed pixel of the second 2D representation. A related aspect provides improvements with respect to forward-projecting, as well as in iterative (and non-iterative) methodologies that incorporate both back-projection and forward-projection.
Owner:PME IP
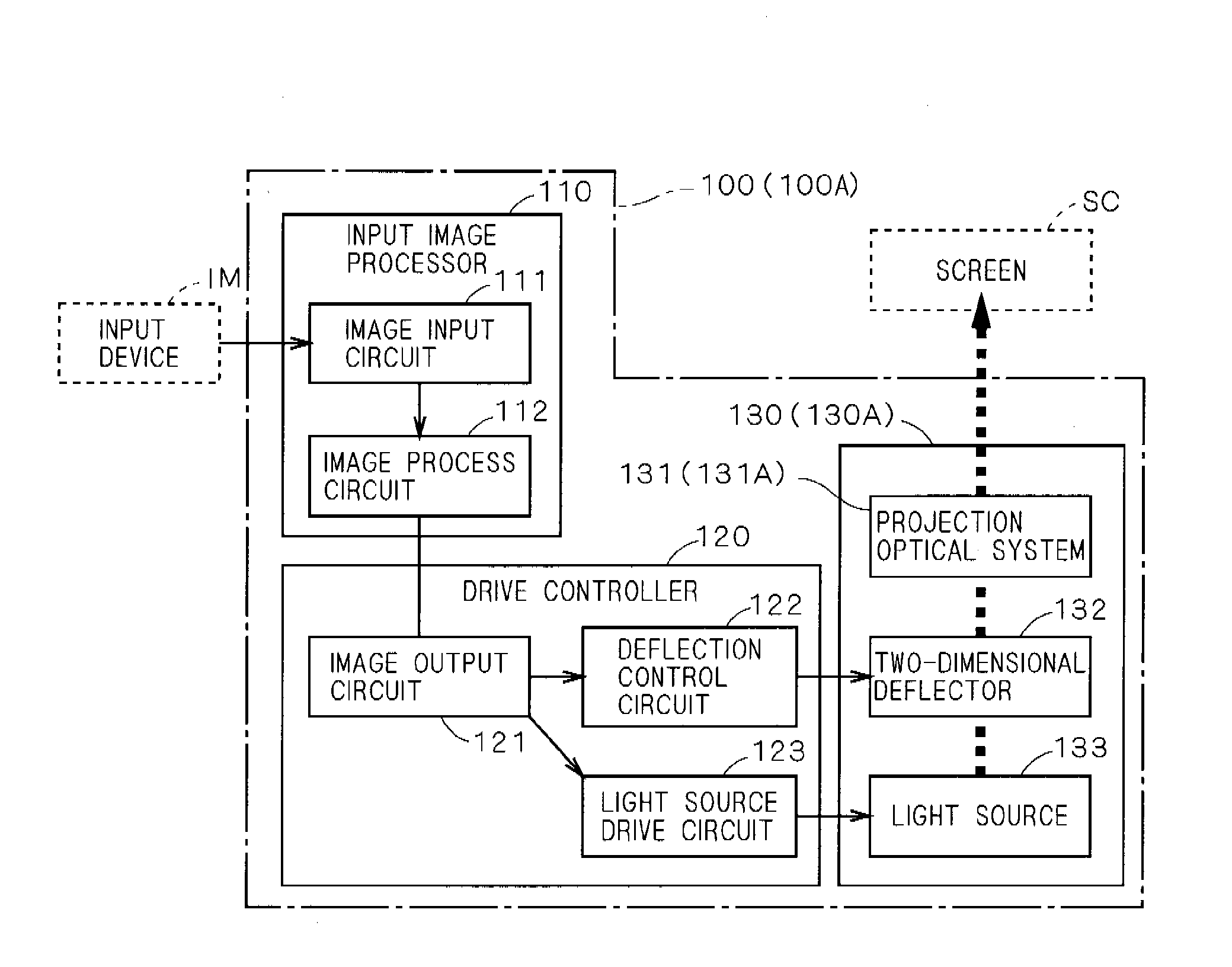
Projection apparatus, projection method and recording medium recording the projection method
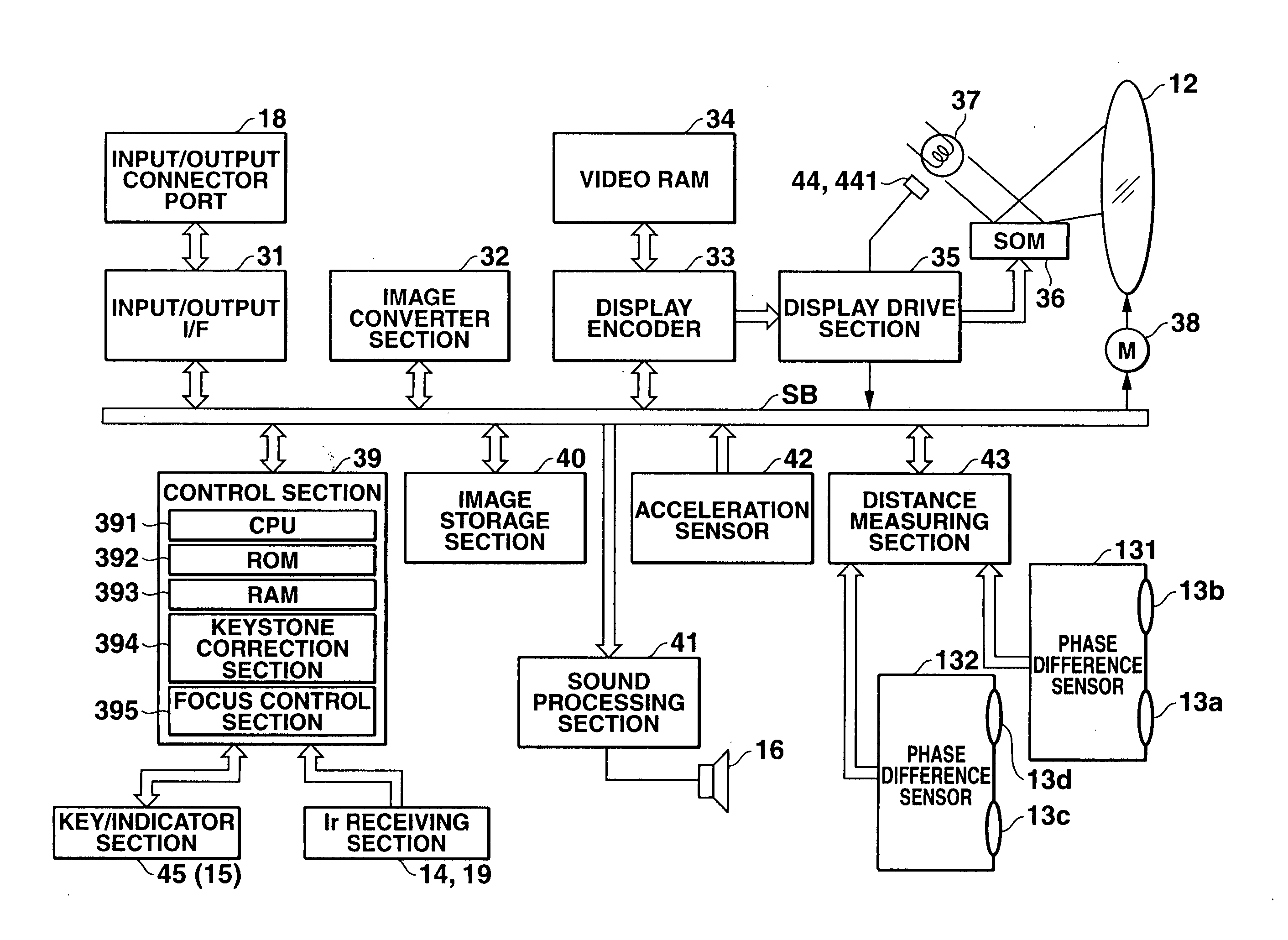
ActiveUS20050046803A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProjection imageImage formation
A projection apparatus comprising a projection section for projecting an image corresponding to an input image signal, a distance measuring section for measuring each distance of several positions on an image projection plane made by the projection section, a focus control section for making keystone correction on an image projected by the projection section so that a projection image is formed into a rectangular shape having a proper aspect ratio based on each distance obtained by the distance measuring section while controlling a focus position of the image projected by the projection section, and a control section for instructing to carry out processing by the focus control section.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Telecentric Scale Projection System for Real-Time In-Situ Surgical Metrology
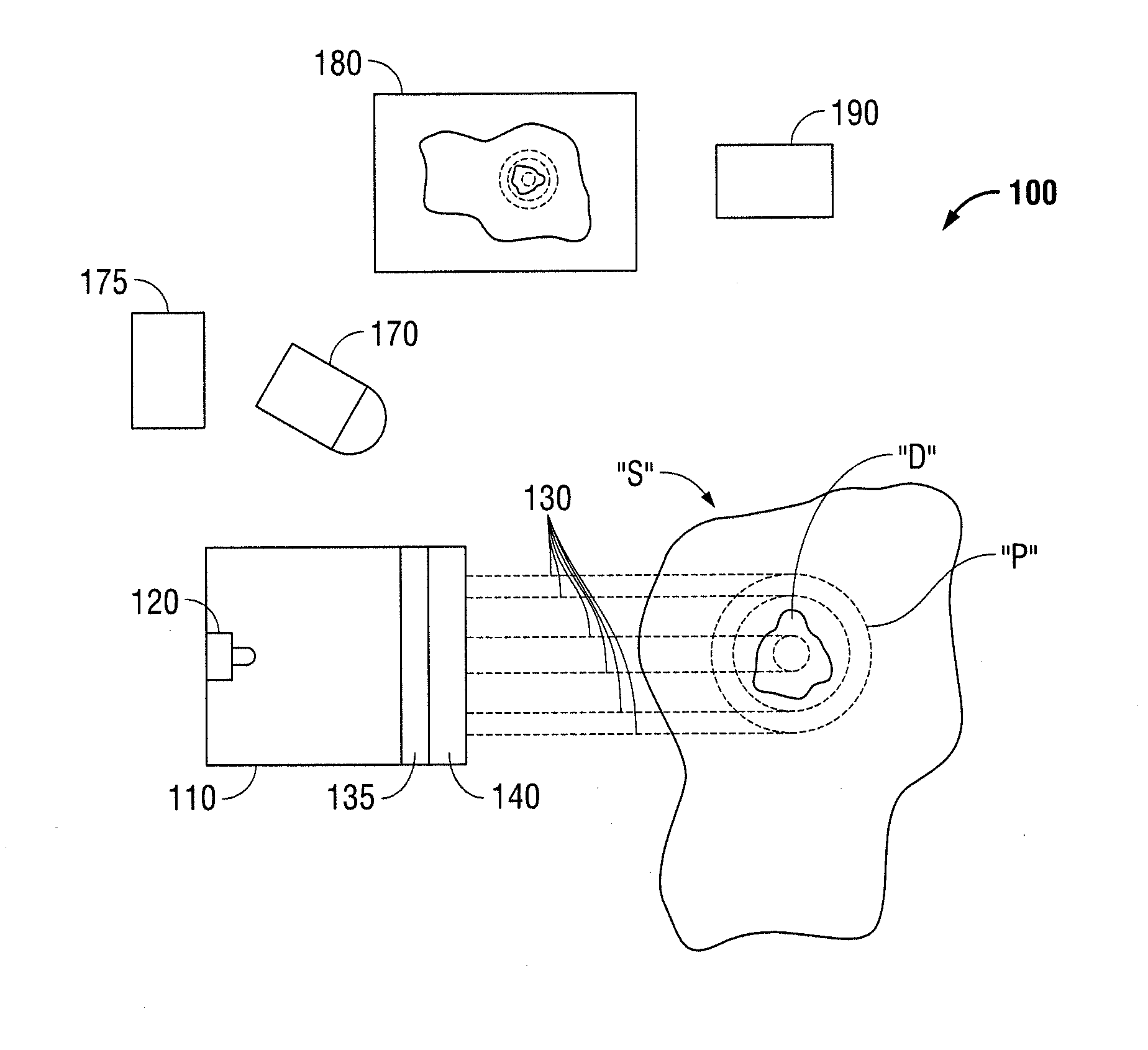
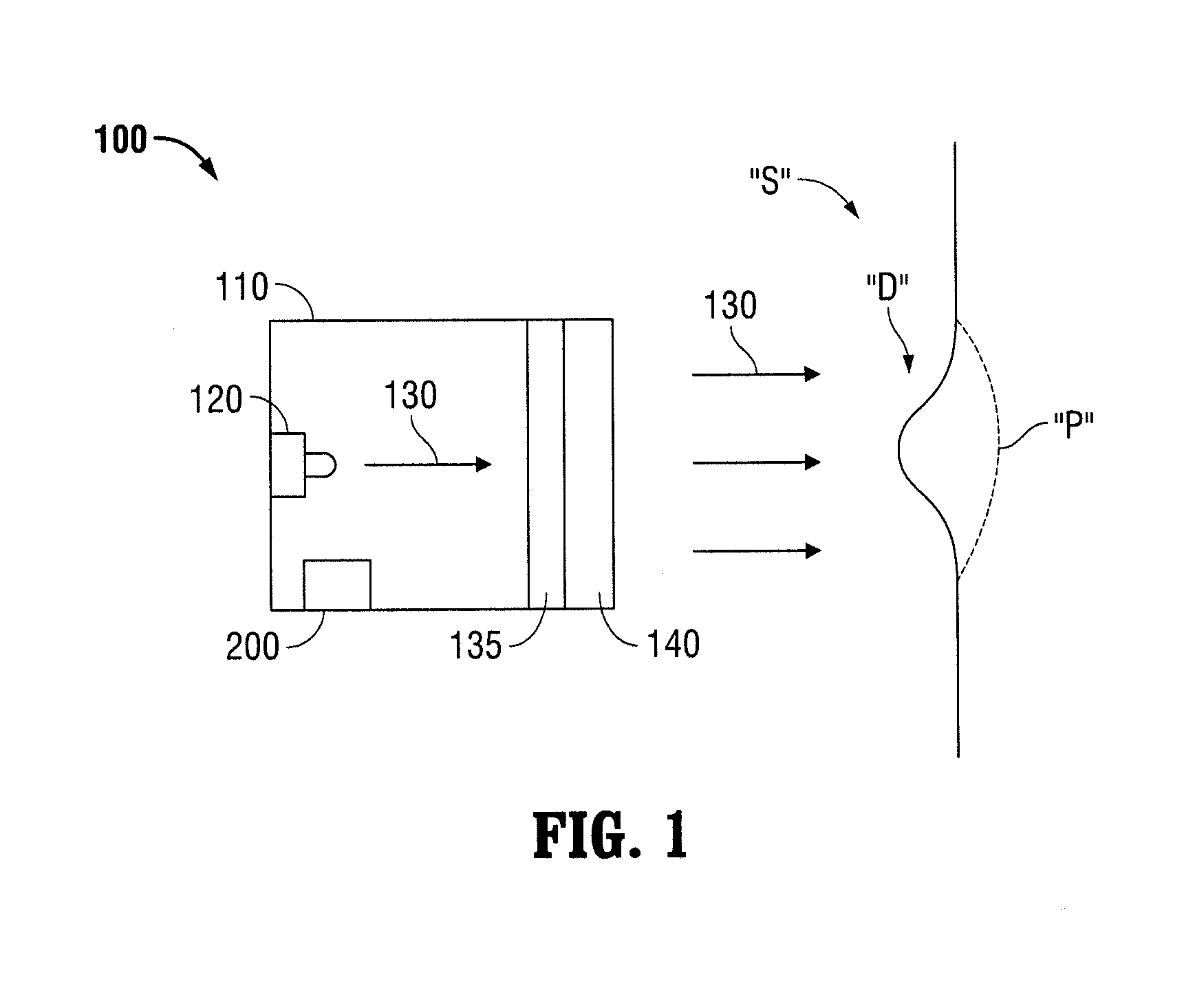
InactiveUS20140031665A1Superior in pointAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryMetrologySurgical site
A system and method for determining endoscopic dimensional measurements including a projector assembly comprising a light source for projecting light through a telecentric lens and into a surgical site, and a mask coupled to the projector assembly. Light projected from the light source projects through the mask. The projected light through the mask may be a collimated pattern which does not significantly change in size as a function of the distance to a projected plane. The projected light patterns may include multiple wavelengths of light for measurements of different features of tissue and may be produced using a laser in conjunction with a light shaping optical diffuser, or using a light emitting diode in conjunction with a light shaping optical diffuser, or using a spatial filter. The projected light patterns may take the form of concentric rings with each ring representing a radius of a given dimension.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Optical scan unit, image projector including the same, vehicle head-up display device, and mobile phone
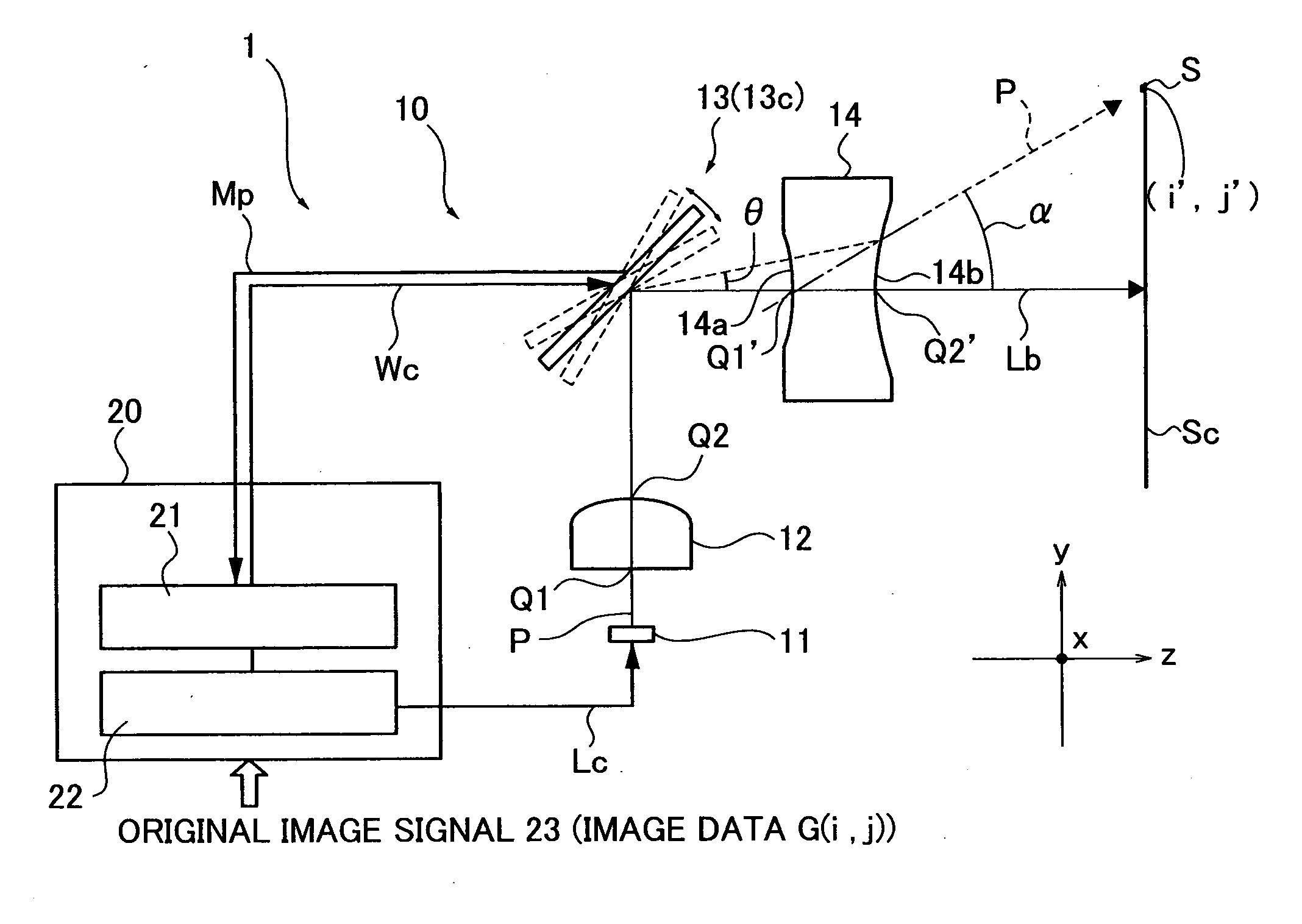
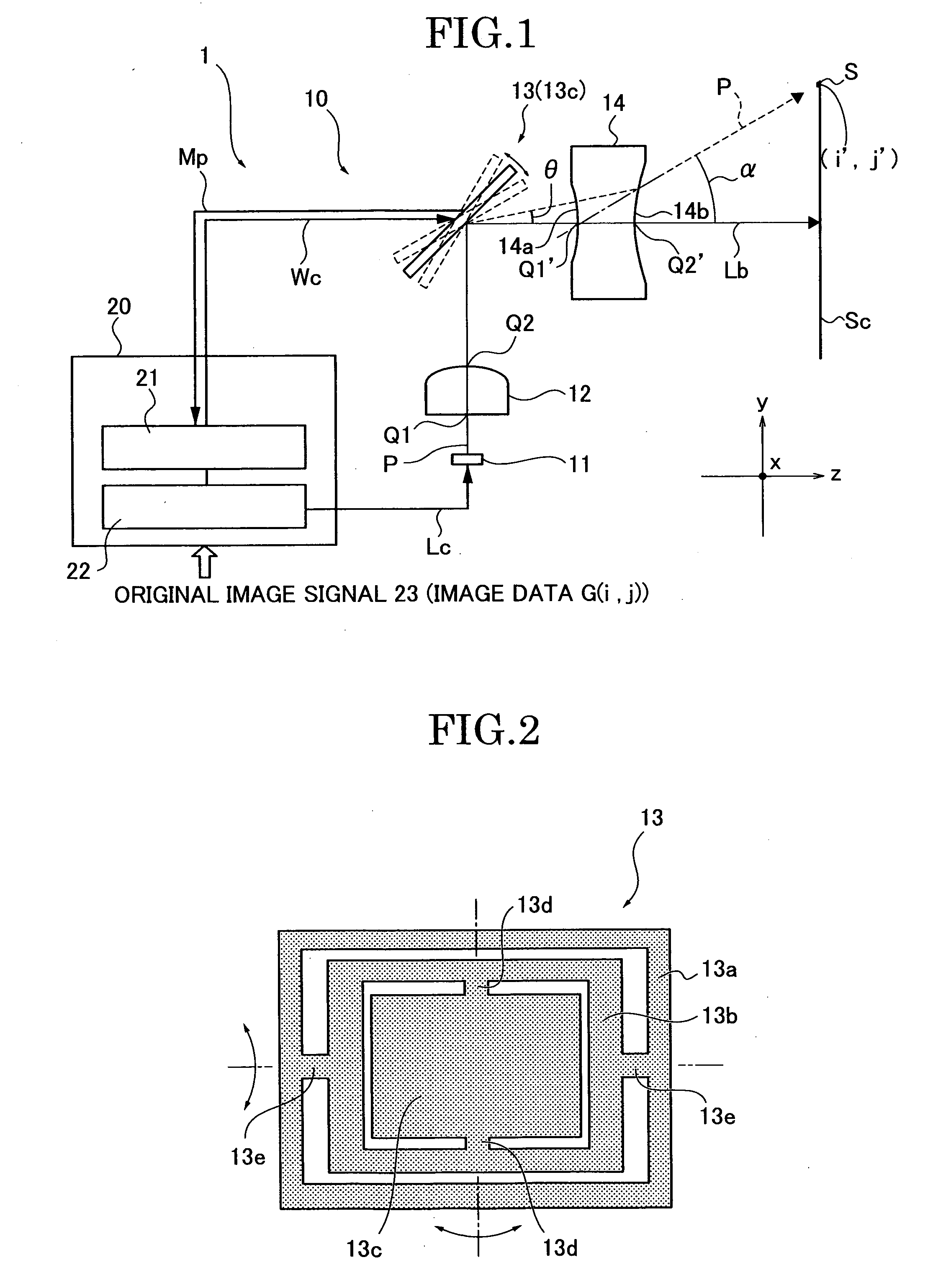
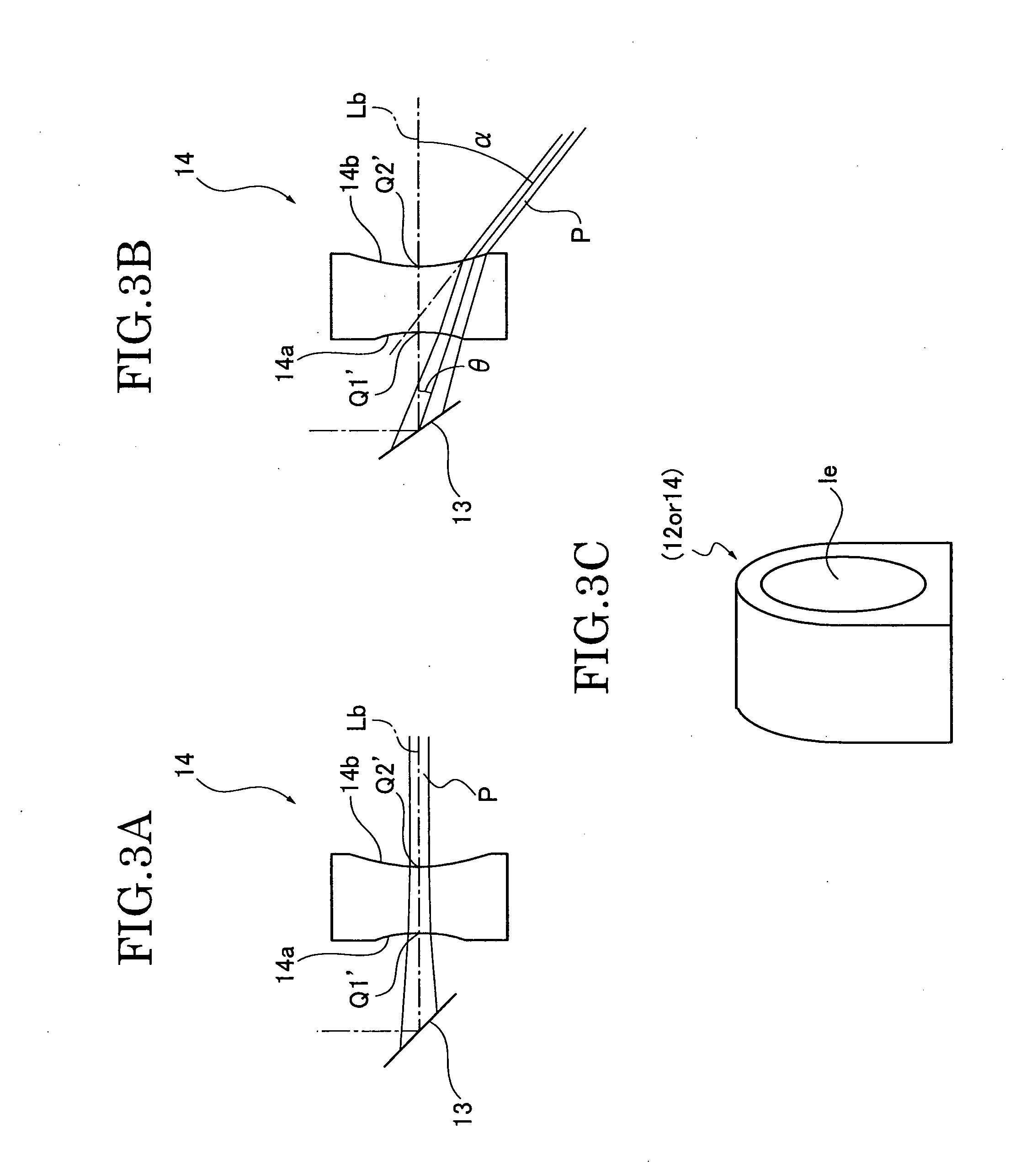
An optical scan unit (10) is configured to include a light source (11), a divergent light conversion element (12) having such positive power as to convert divergent light from the light source (11) into convergent light to form a spot on a projection plane, an optical deflector (13) deflecting a light beam from the divergent light conversion element (12) to a first scan direction and a second scan direction which is orthogonal to the first scan direction, and a deflection angle conversion element 14 (14) having such negative power as to convert a deflection angle of the light deflected by the optical deflector (13).
Owner:RICOH KK
Image processing method and apparatus, digital camera, image processing system and computer readable medium
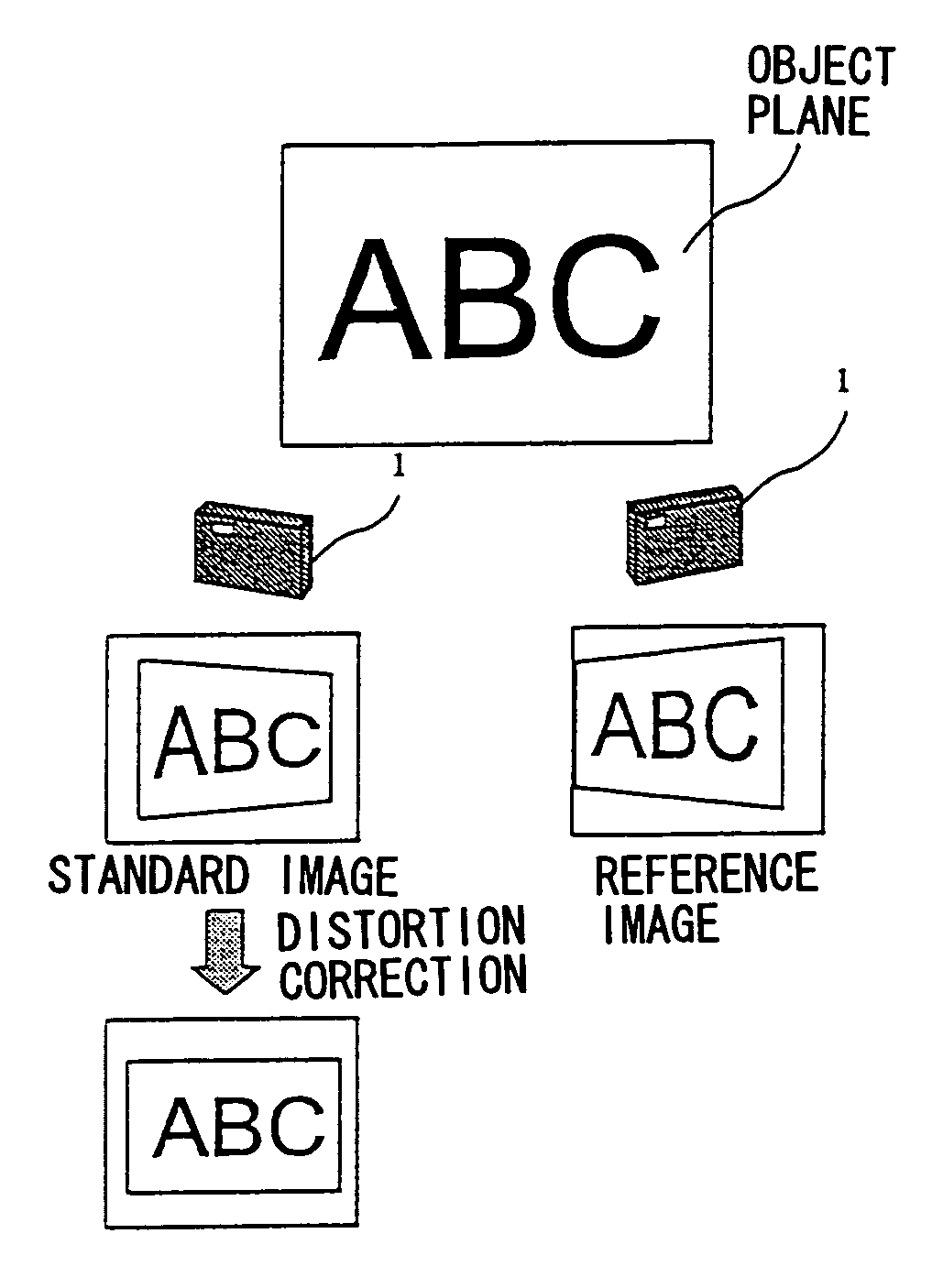
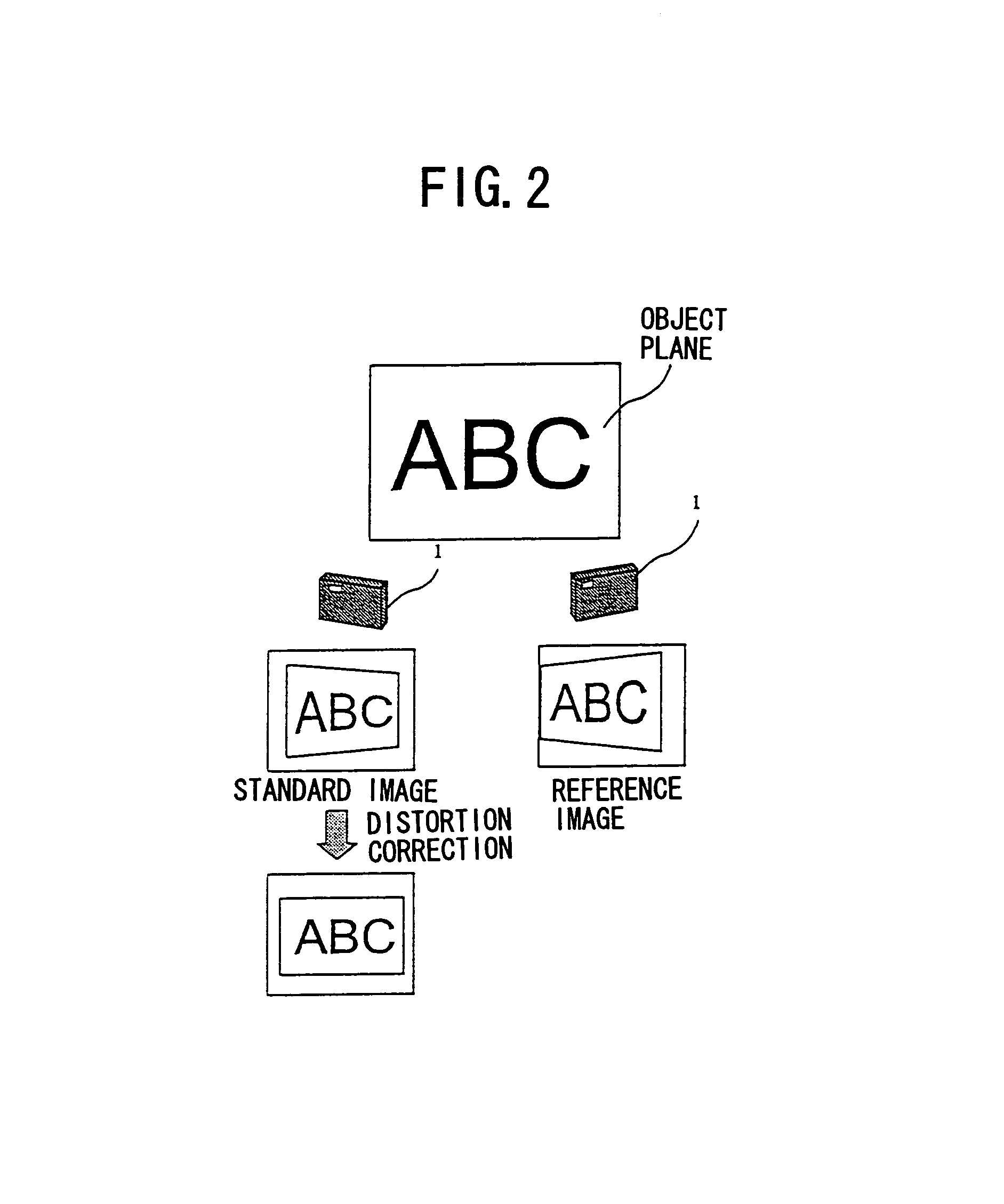
InactiveUS7268803B1Correct image distortionEasily and accurately correcting image distortionTelevision system detailsImage analysisViewpointsImaging processing
In image processing method and apparatus of the present invention, an image distortion caused by an oblique image pickup is corrected. A plurality of images of an object on an object plane are input, the plurality of images including at least a pair of partially overlapping first and second images that are taken at two viewpoints, the first and second images sharing a common location on the object plane. A feature point of the first image corresponding to the common location and a matched point of the second image corresponding to the feature point of the first image are determined. A direction of the object plane is calculated based on the feature point and the matched point. A distortion-corrected image on a projection plane, which is parallel to the object plane, is generated by projecting one of the first and second images onto the projection plane based on the direction of the object plane through a perspective projection.
Owner:RICOH KK
Recognition method and system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in three-dimensional space
InactiveCN103914152AHigh precisionIncreased image capture capabilitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingLaser transmitterThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a recognition system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in three-dimensional space, and belongs to the technical field of intelligent recognition. The recognition system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in the three-dimensional space comprises a miniature computer host, a laser projector, a first infrared camera, a second infrared camera, an LED (light emitting diode) lamp, a linear laser transmitter and a projection plane, wherein the laser projector projects contents processed by the miniature computer host, so that the projection plane is generated; the illumination plane of the linear laser transmitter is parallel to the projection plane; and the view field of the first infrared camera and the view field of the second infrared camera cover the projection plane and an aerial gesture recognition area. By using the recognition system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in the three-dimensional space, the shortcoming that the present gesture recognition is based on a computer display is overcome. The recognition system for aerial gestures can be conveniently applied to the fields such as speech presentation by projectors, and is high in recognition precision.
Owner:异象科技(北京)有限公司
Image projector
InactiveUS20080239252A1Deteriorating brightness of imageConstant speedVehicle headlampsLighting and heating apparatusLight fluxLight beam
An object of the present invention is to provide an image projector capable of projecting a high-quality image while realizing small size. In the image projector, a light flux is deflected two-dimensionally by turning a reflector for reflecting a light flux emitted from a light source around a second axis almost orthogonal to a first axis as a center by resonant drive while turning the reflector around the first axis as a center by non-resonant drive. Shape of one or more optical surfaces of a projection optical system for projecting an image onto a projection plane by guiding light onto the projection plane includes a shape for performing a correction for maintaining scanning speed of the light flux along one scan direction on the projection plane almost constant and a shape for performing a correction for suppressing a distortion in an image along the other scan direction almost orthogonal to the one scan direction on the projection plane. By controlling turn of the reflector, at least one of a correction for maintaining scanning speed of the light flux along the other scan direction on the projection plane almost constant and a correction for suppressing a distortion in an image along the one scan direction on the projection plane is performed.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
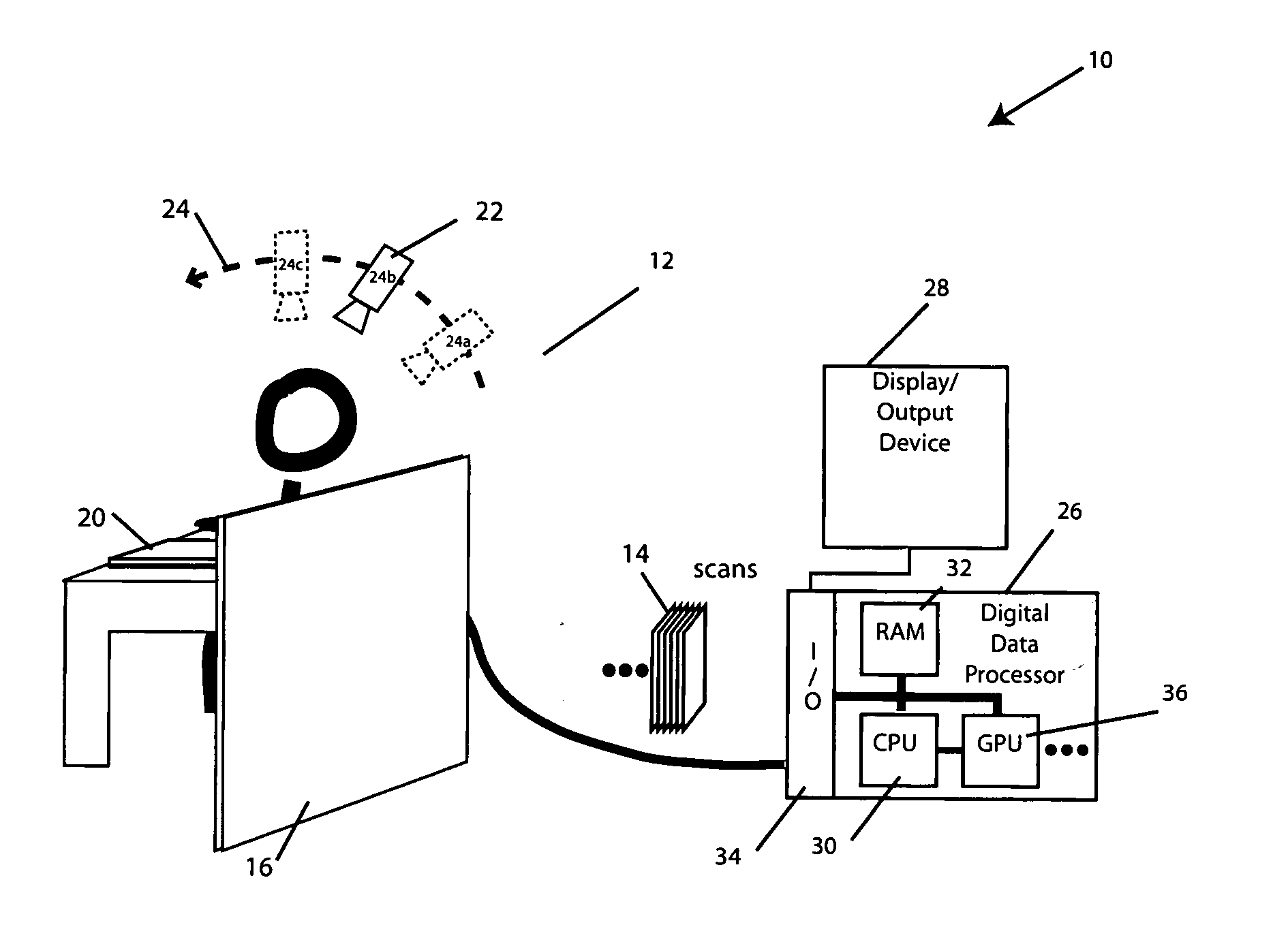
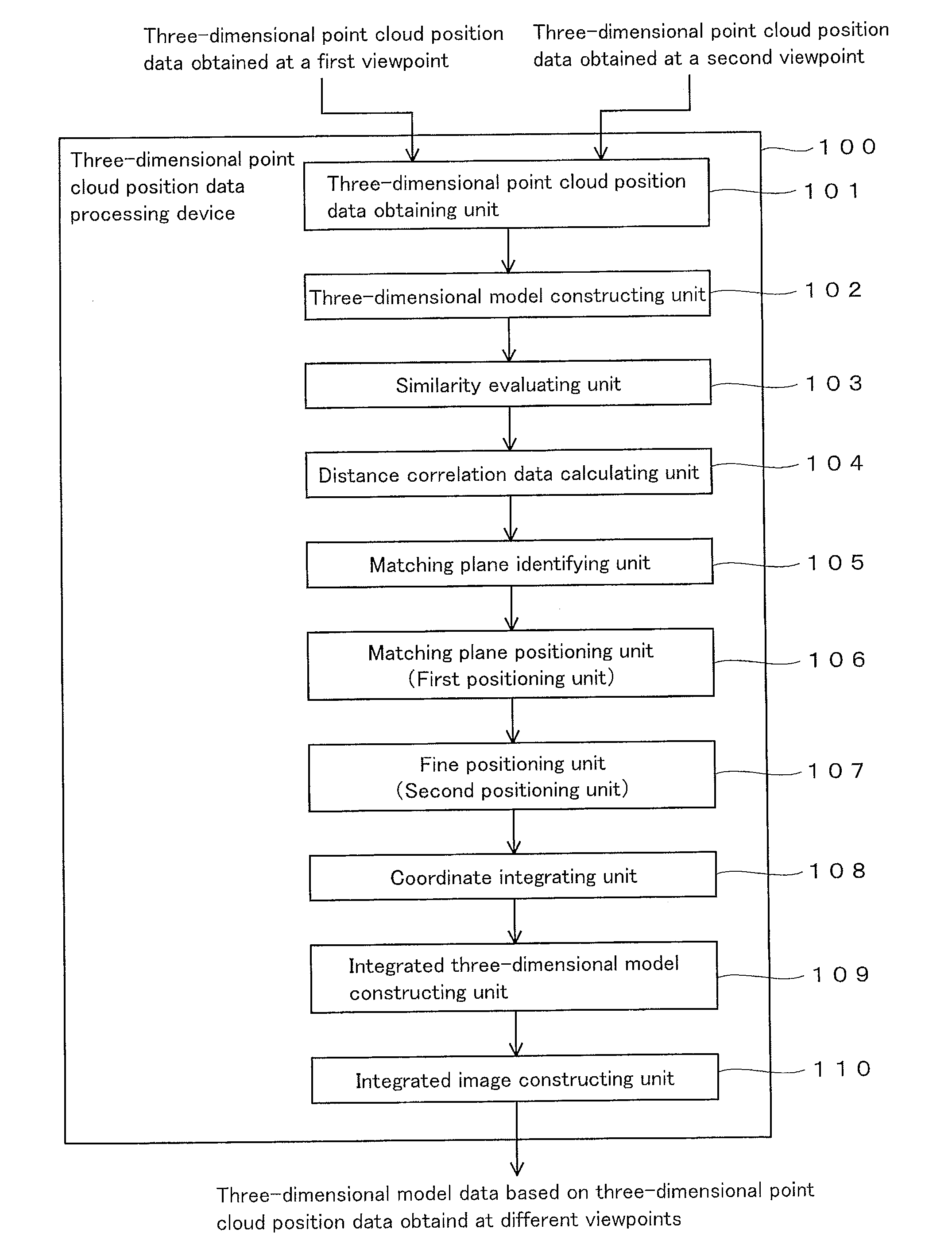
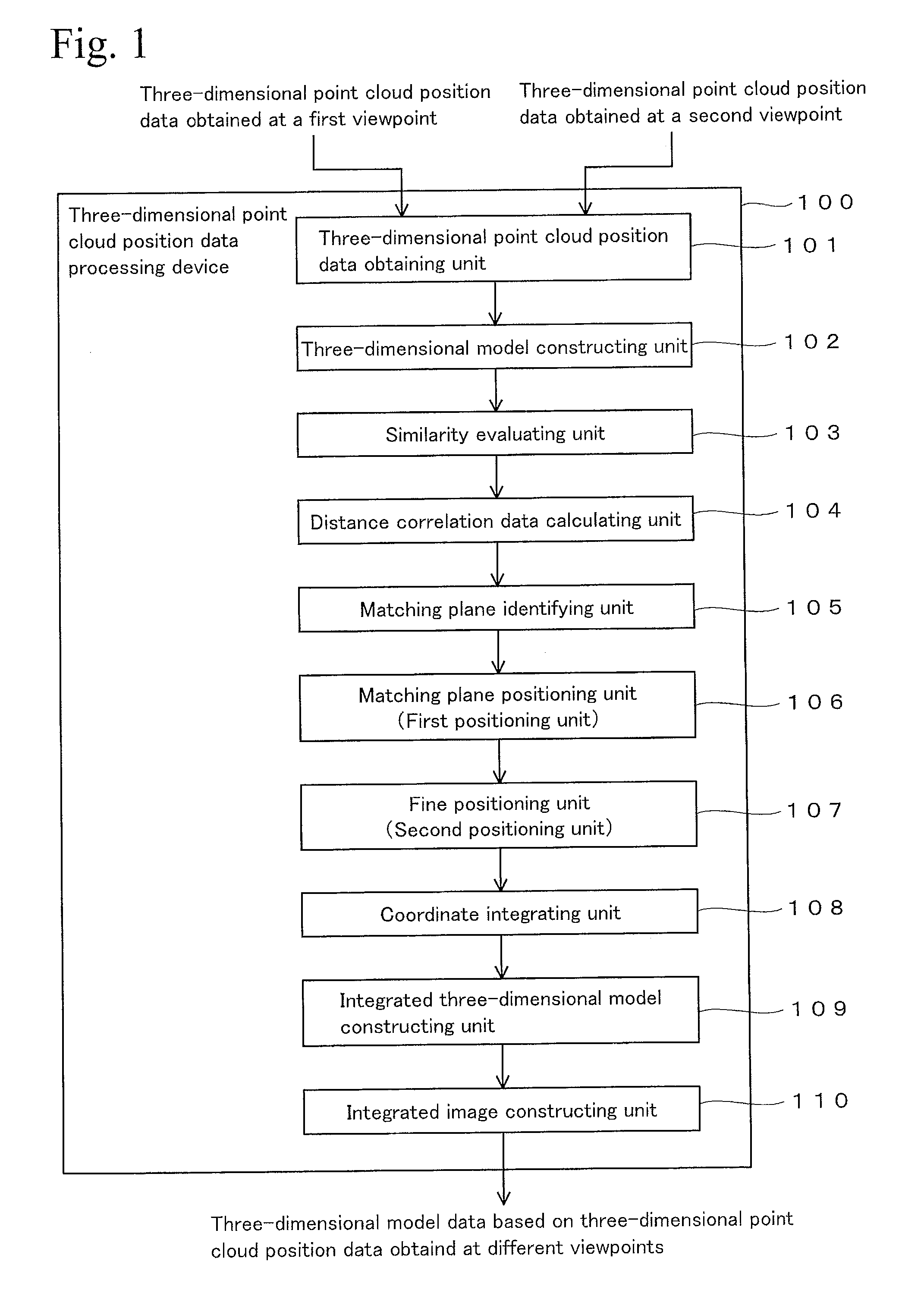
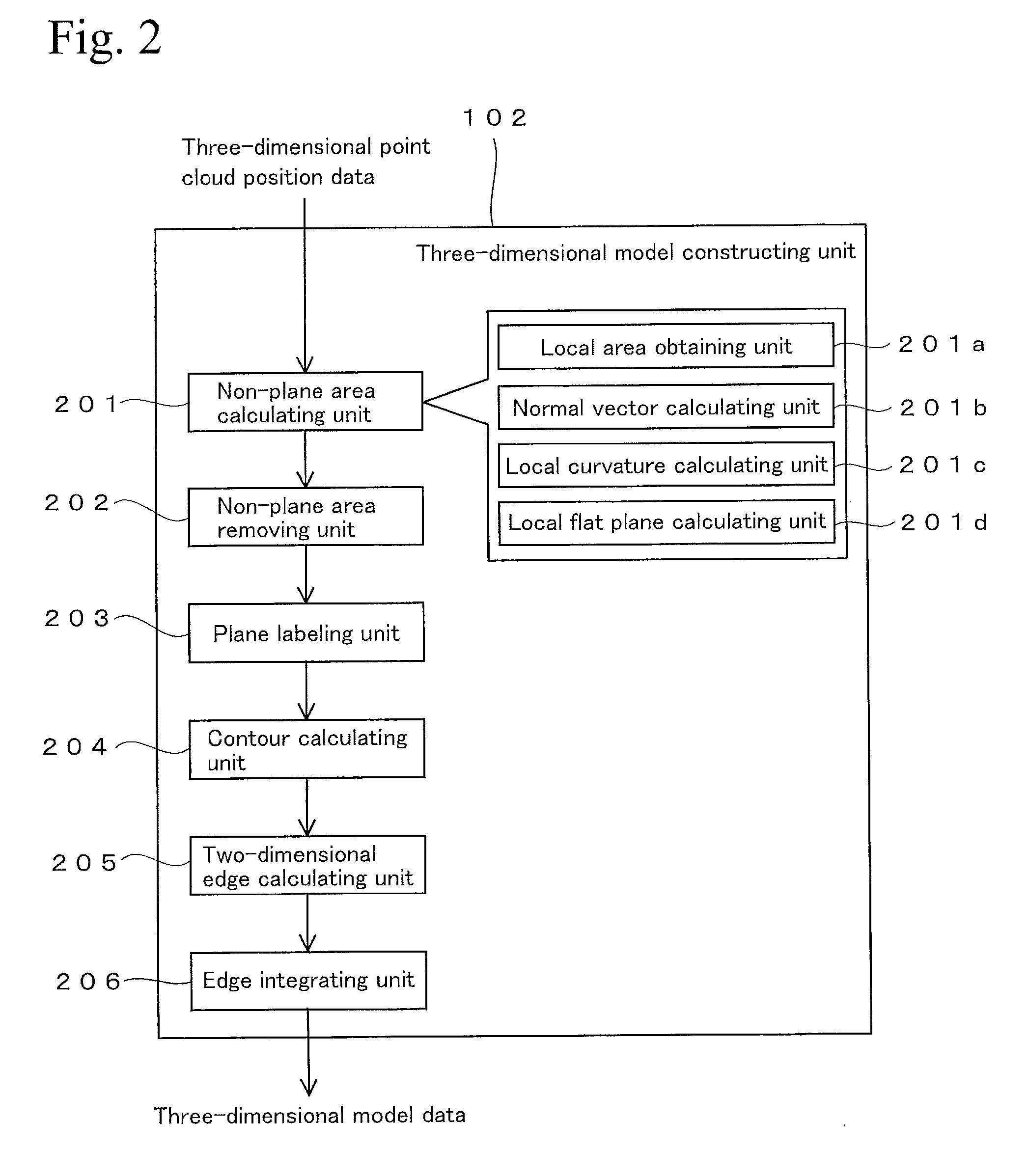
Three-dimensional point cloud position data processing device, three-dimensional point cloud position data processing system, and three-dimensional point cloud position data processing method and program
ActiveUS20140037194A1Efficient executionImage enhancementImage analysisData processing systemViewpoints
A technique is provided for efficiently process three-dimensional point cloud position data that are obtained at different viewpoints. A projecting plane is set in a measurement space as a parameter for characterizing a target plane contained in plural planes that form an object. The target plane and other planes are projected on the projecting plane. Then, a distance between each plane and the projecting plane is calculated at each grid point on the projecting plane, and the calculated matrix data is used as a range image that characterizes the target plane. The range image is also formed with respect to the other planes and with respect to planes that are viewed from another viewpoint. The range images of the two viewpoints are compared, and a pair of the planes having the smallest difference between the range images thereof is identified as matching planes between the two viewpoints.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Process for the acquisition of information intended for the insertion of a locking screw into an orifice of an endomedullary device
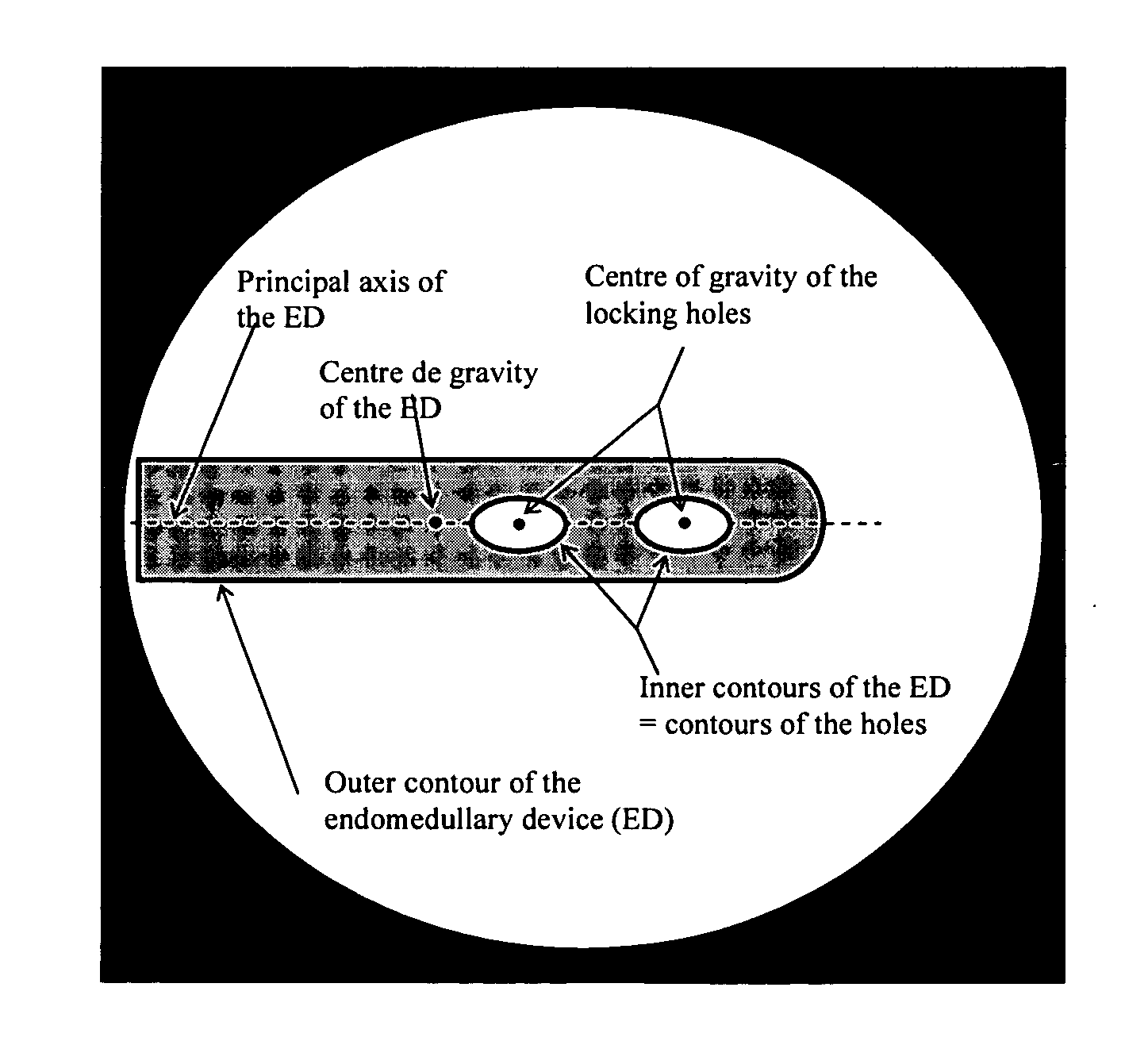
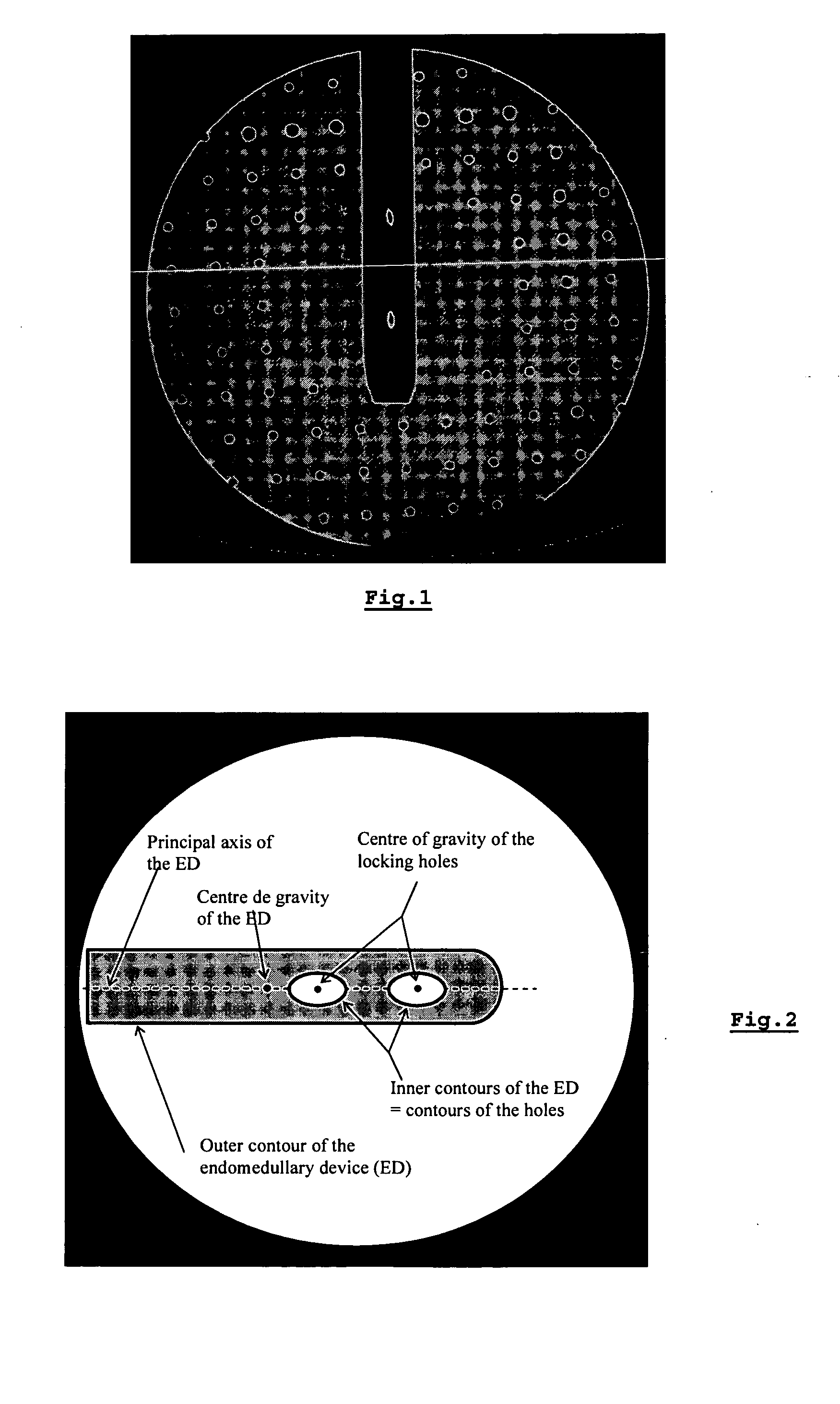
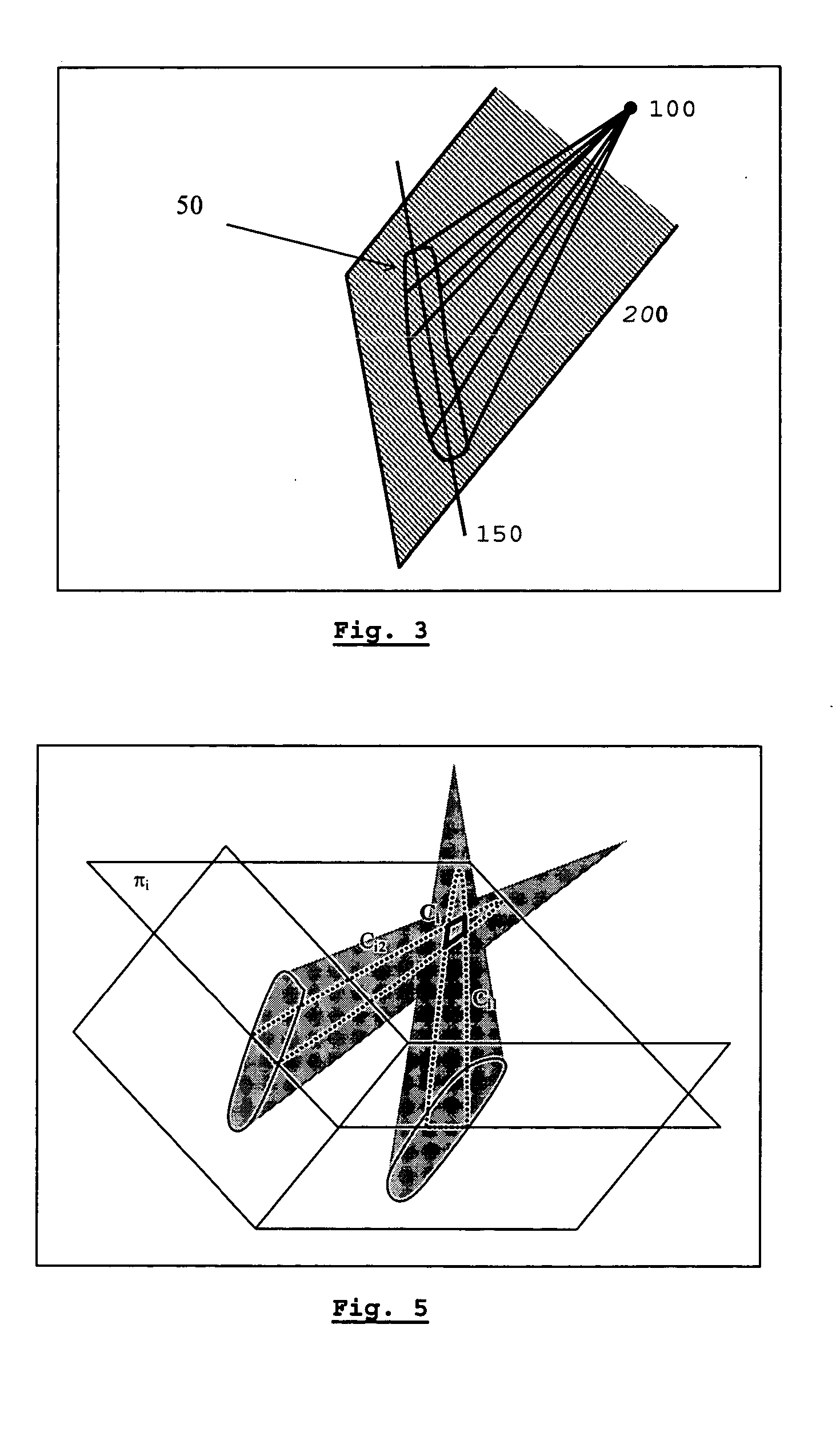
The present invention is related to a process for the acquisition of information intended for the insertion of a locking screw into a distal locking hole of an endomedullary device, comprising the following steps: taking of two images of different orientations of the distal part of the said endomedullary device using a radioscopic unit; acquisition of the projection parameters especially the position of the X-ray source and of the projection plane, of each image by locating a fixed reference frame on the said endomedullary device and another fixed reference frame on said radioscopic unit; correction of any distortion of the images; segmentation of the distal part of the said endomedullary device in each image and calculation of the attributes relating to the position of the said device and to that of the holes, said attributes comprising at least the contours of the said device, its centre of gravity and its principal axis; construction of the projection cone of the distal part of the device for each image; determination of the intersection of the two projection cones; modelling of the said endomedullary device on the basis of the said intersection obtained in the preceding step; determination of the centre of the locking hole with the aid of the modelling obtained in the preceding step and of the centres of gravity of the holes determined on the images; and determination of the orientation of the locking orifice in an iterative manner.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Method and apparatus for generating a bird's-eye view image
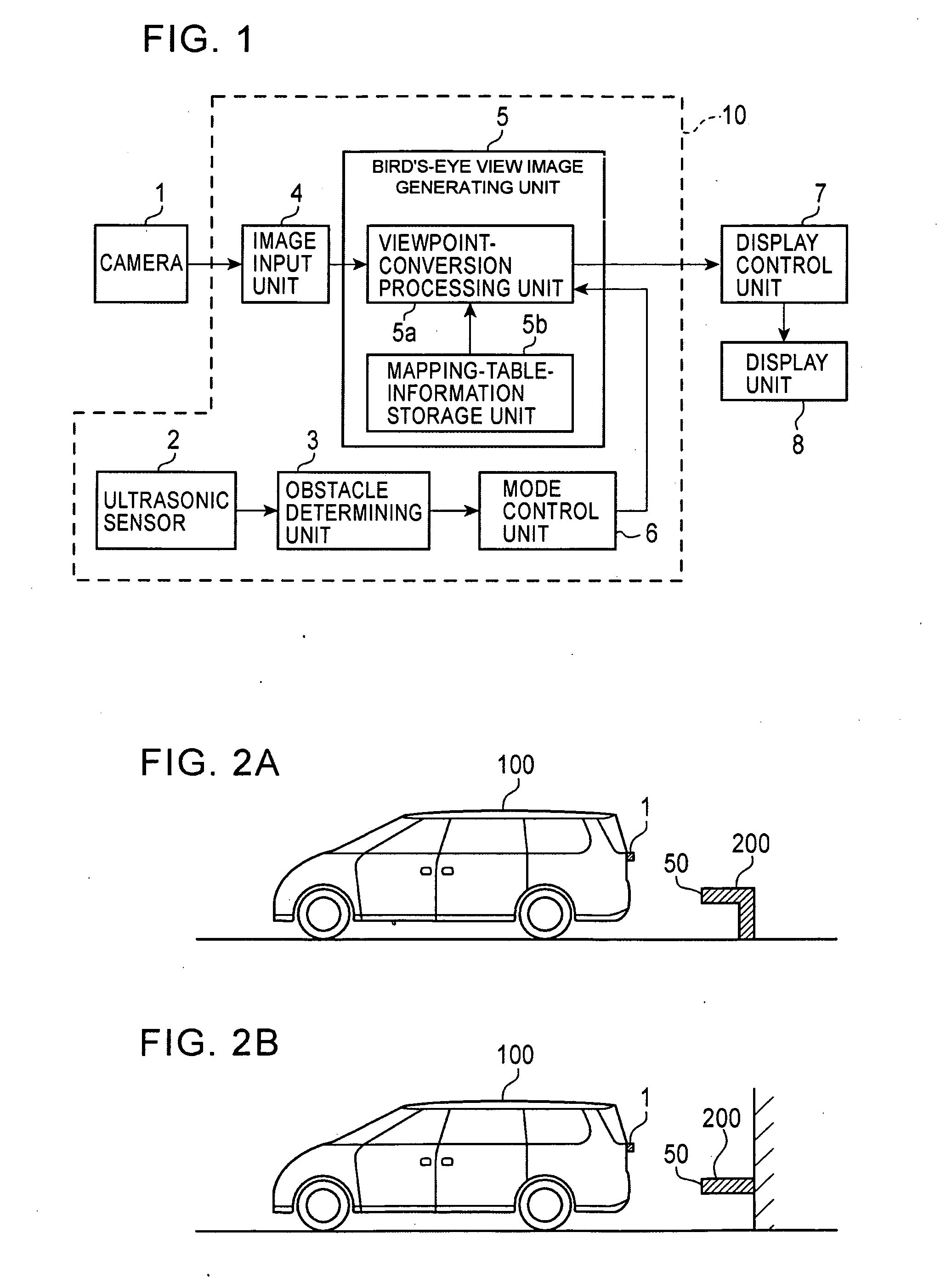
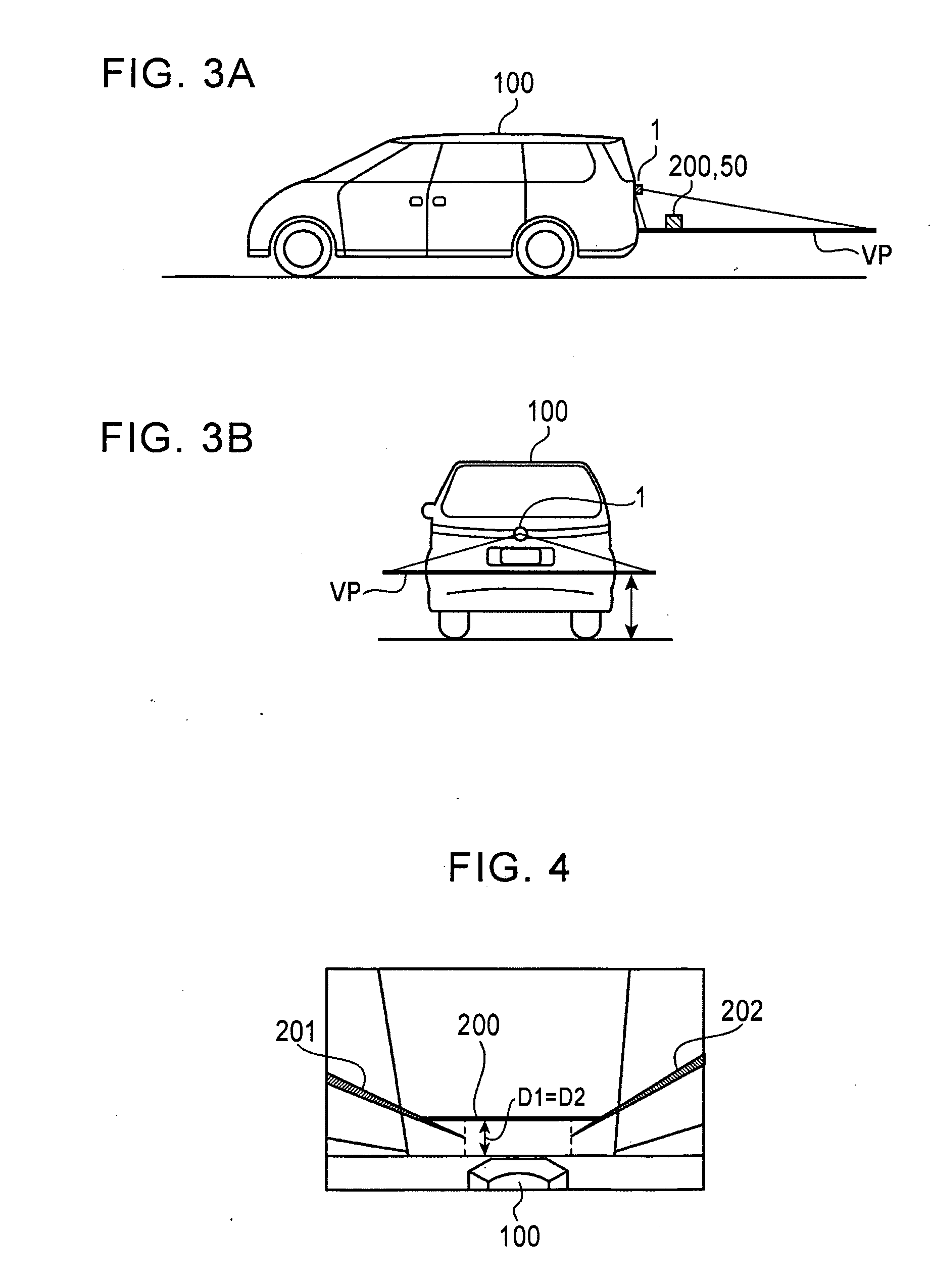
ActiveUS20090122140A1Shorten the timeAccurate expressionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsRoad surface
An obstacle detecting unit detects whether an obstacle exists in an area surrounding a vehicle in the direction a camera installed on the vehicle is pointed. If the obstacle is determined to have a portion at a predetermined height above a road surface with which the vehicle may make initial contact when the vehicle moves toward the obstacle, a virtual projection surface is set to the height of the predicted contact portion and viewpoint conversion processing is performed so as to project pixels of an image captured by the camera onto the virtual projection plane. In this way, the height of the projection plane and the height of the predicted contact portion match each other and the distance between the predicted contact portion and the vehicle is accurately expressed on a bird's-eye view image resulting from the viewpoint conversion.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com