Patents
Literature
2105 results about "Light flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
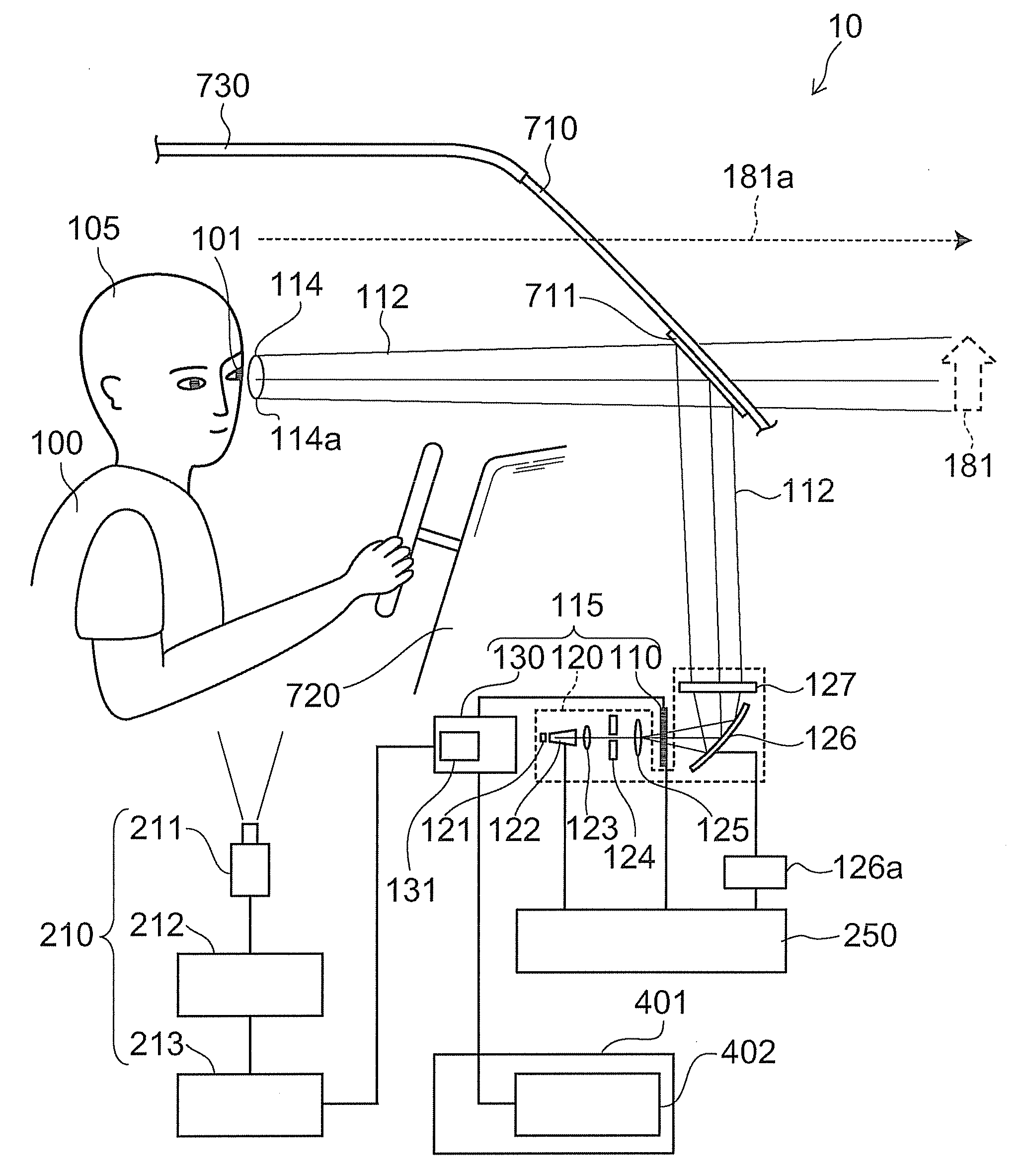
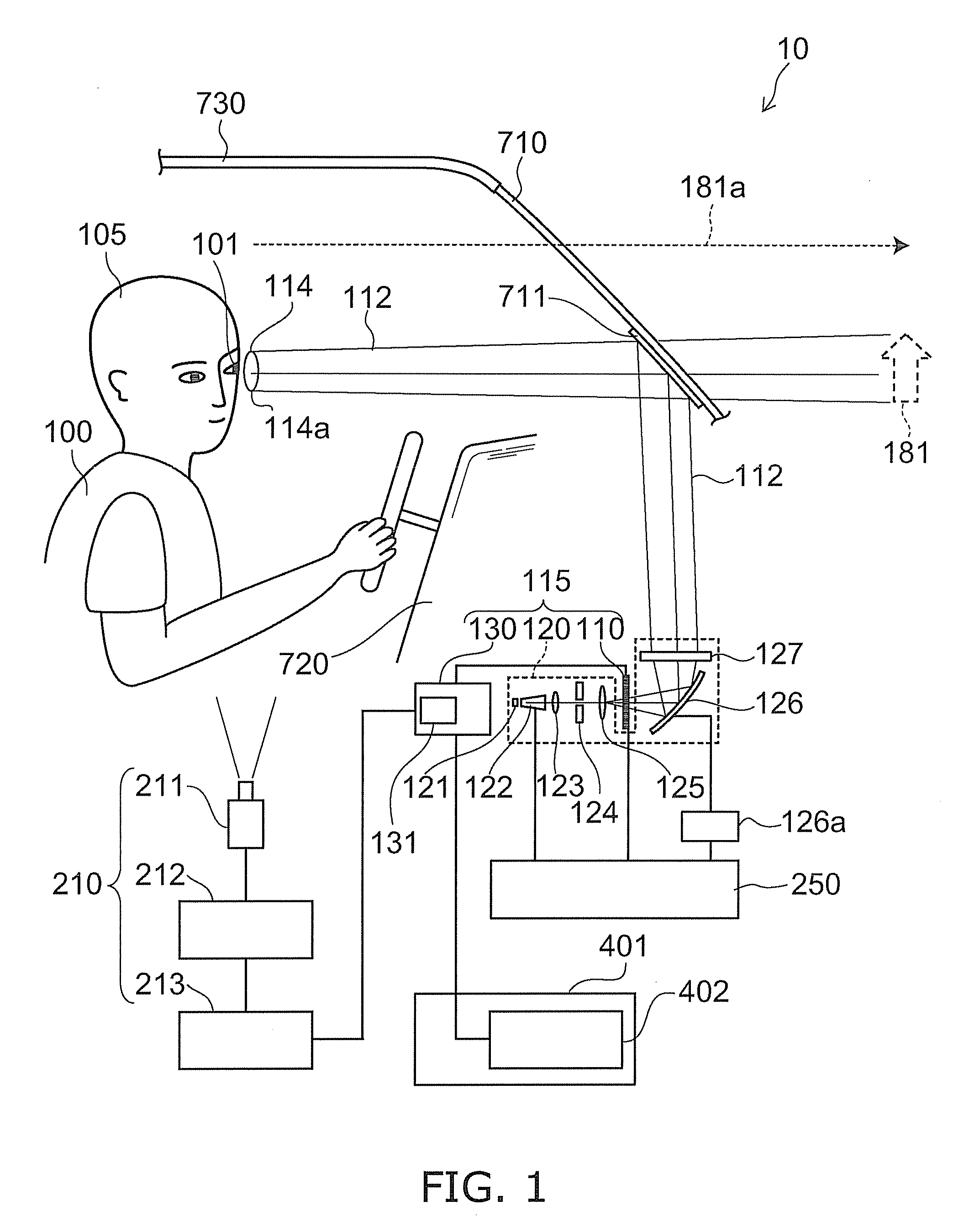
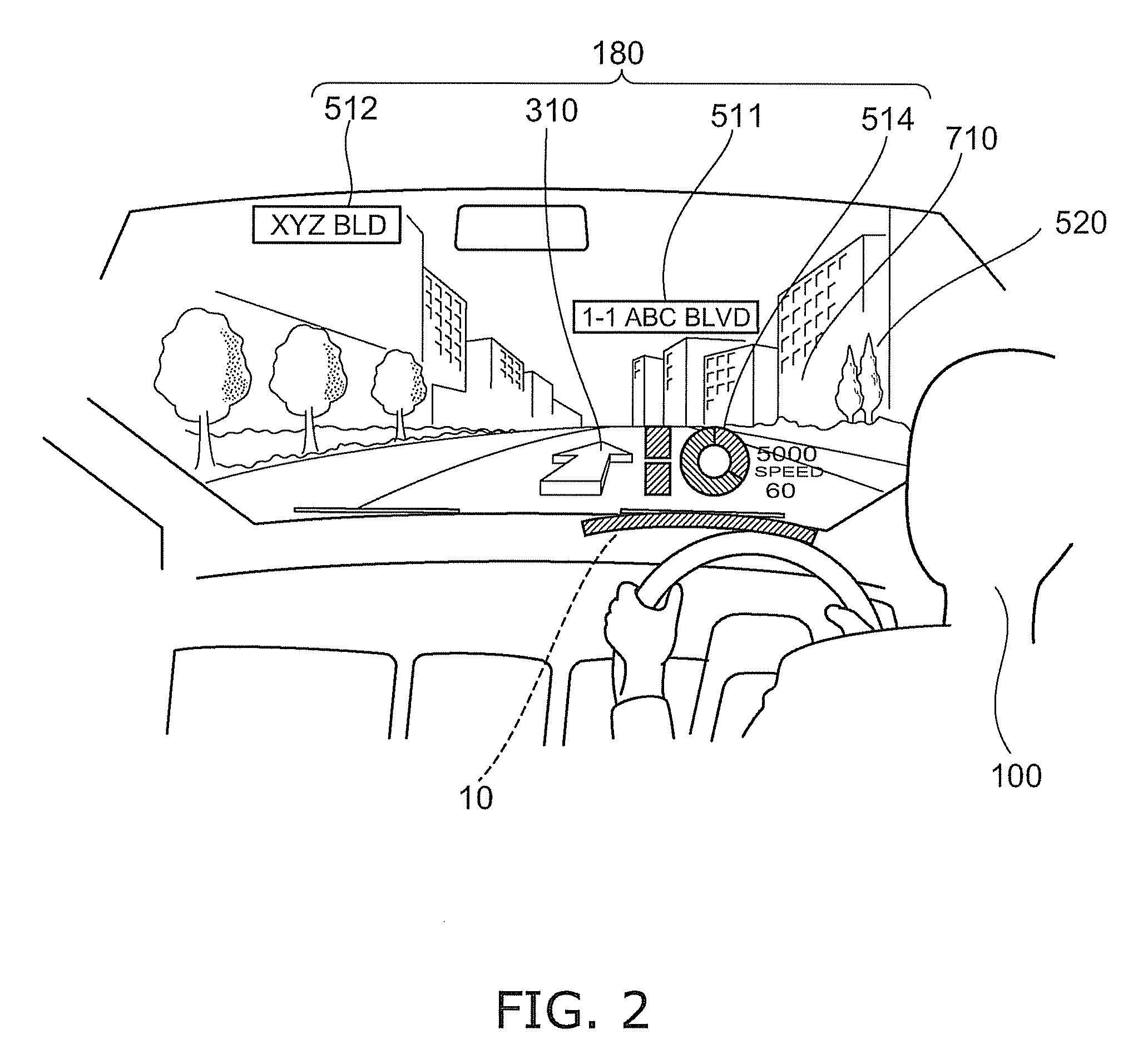
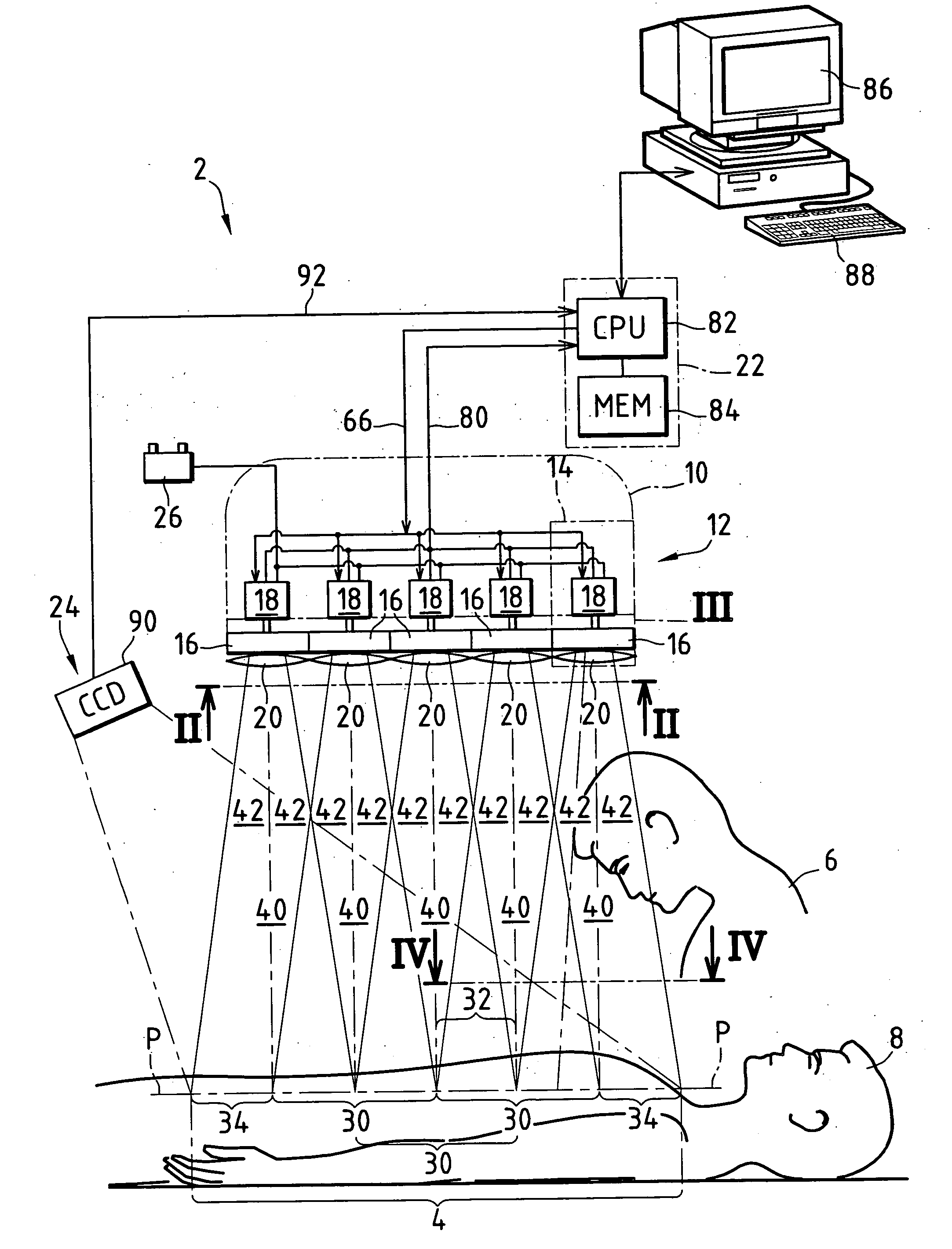
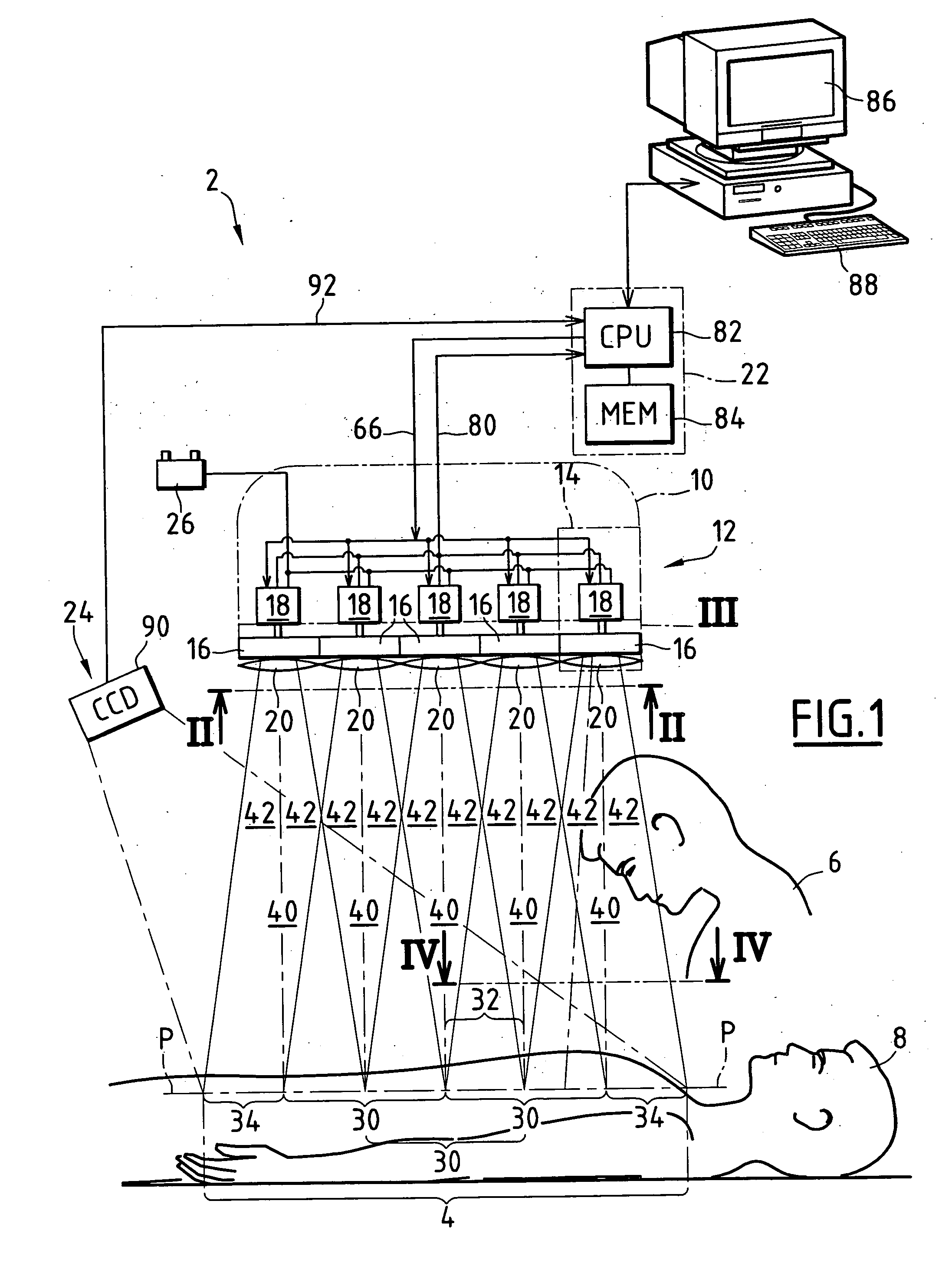
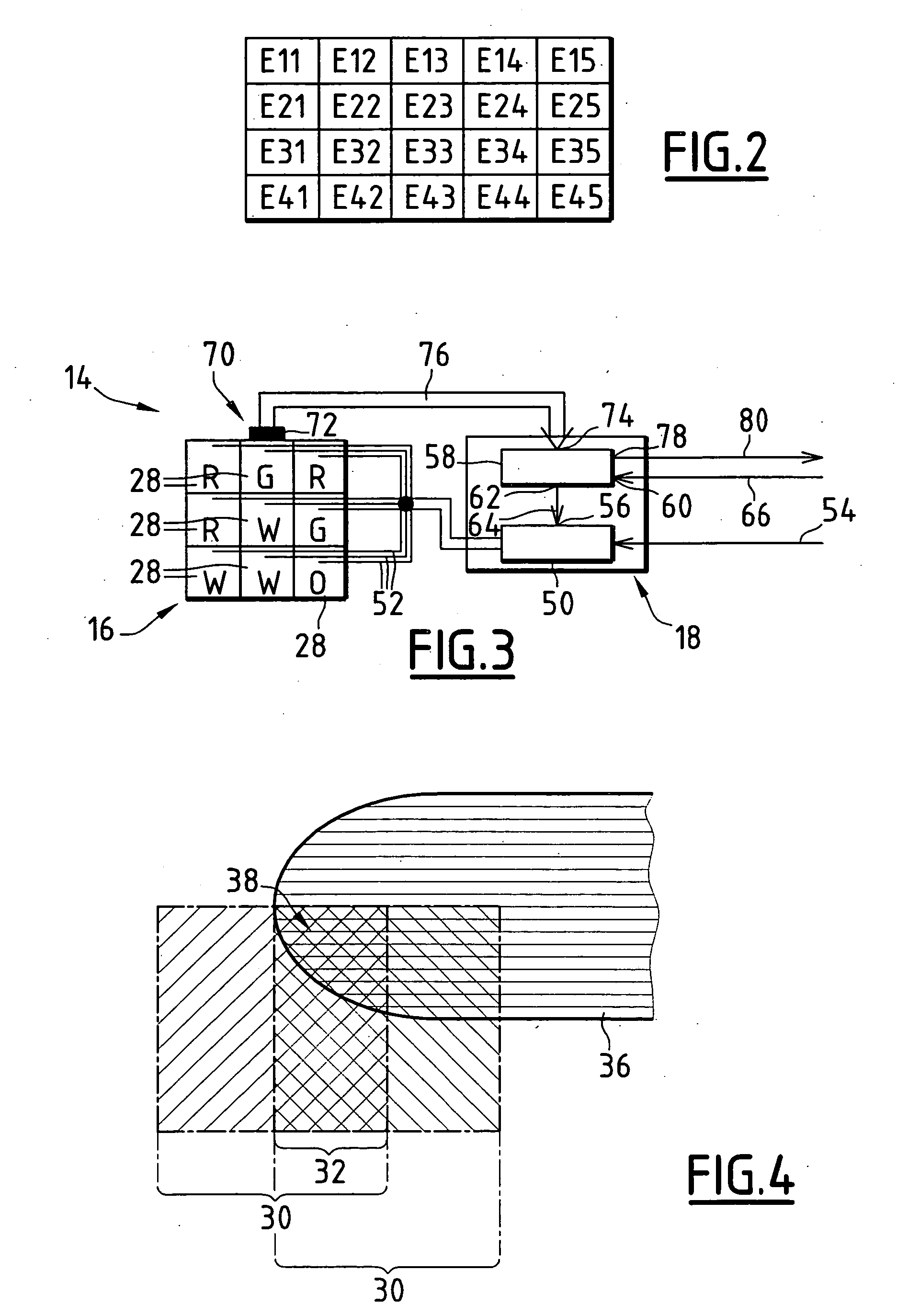
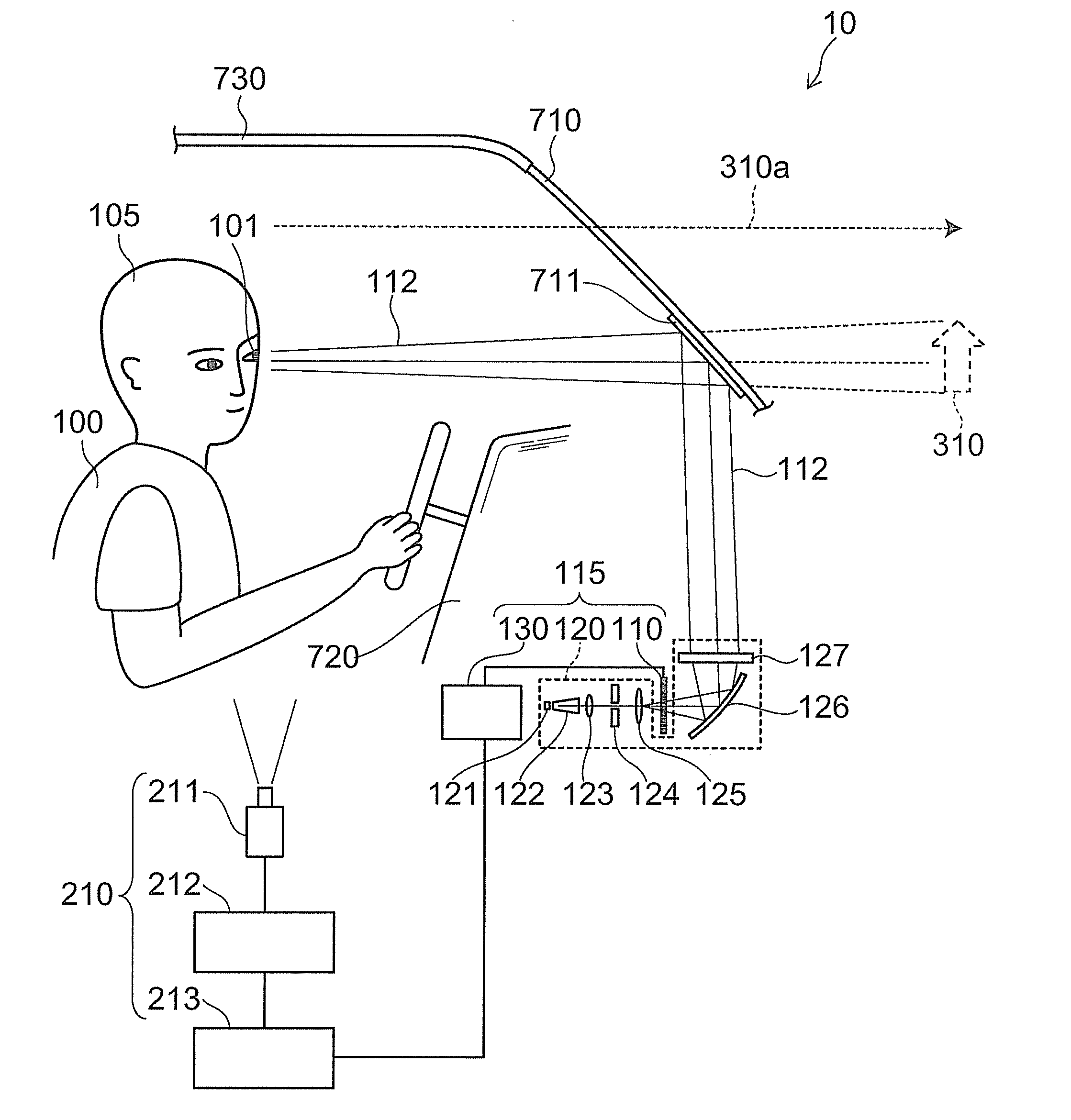
Automotive display system and display method
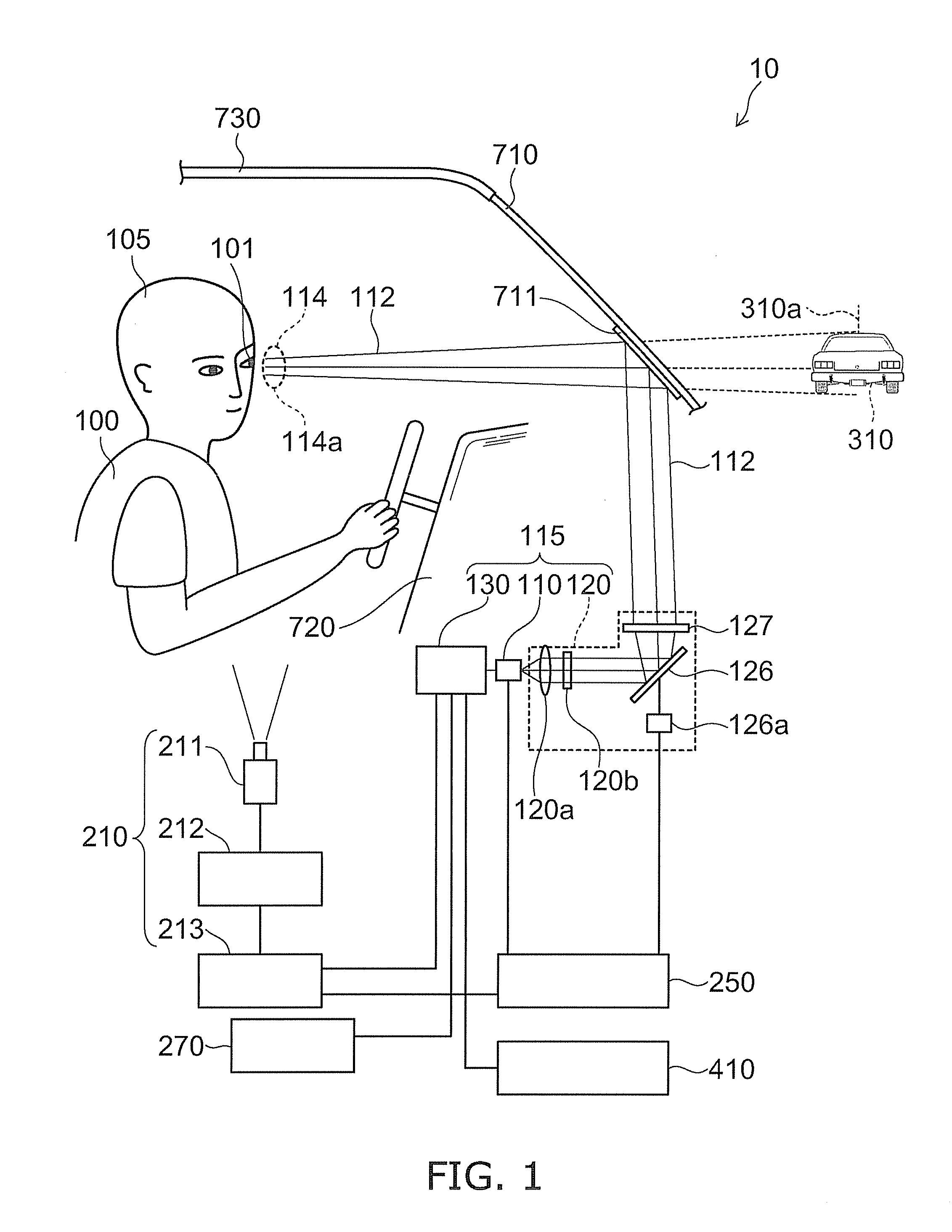
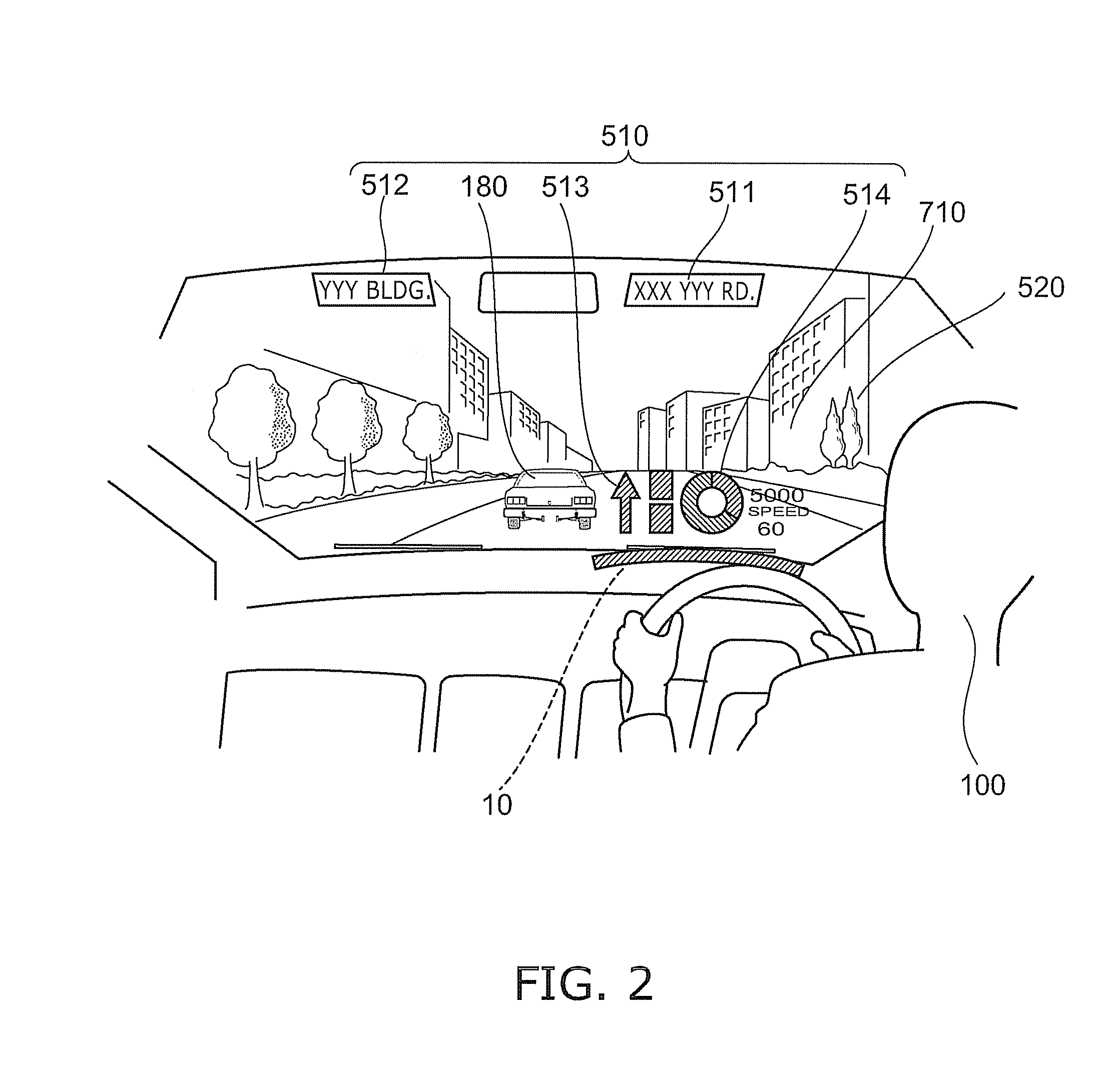
An automotive display system includes an image projection unit and an angle information acquisition unit. The image projection unit projects a light flux including an image including a display object toward one eye of an image viewer. The angle information acquisition unit acquires at least one of vehicle angle information and external environment angle information. The vehicle angle information relates to an angle of at least one of an attitude and a heading of a vehicle carrying the image viewer. The external environment angle information relates to an angle of a background object at a target position of the display object in a background of an external environment of the vehicle. The image projection unit changes an angle of the display object in the image based on at least one of the vehicle angle information and the external environment angle information acquired by the angle information acquisition unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
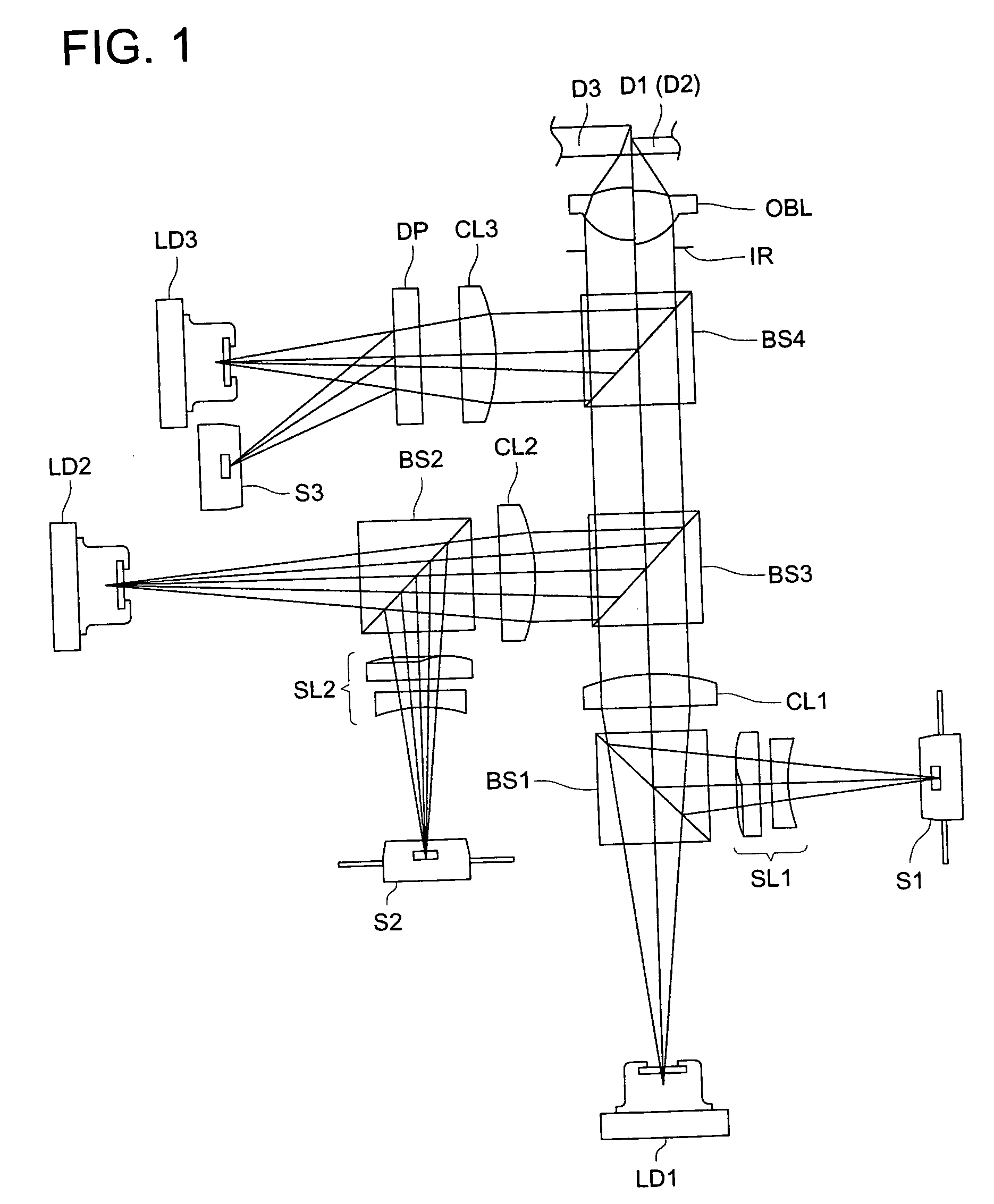
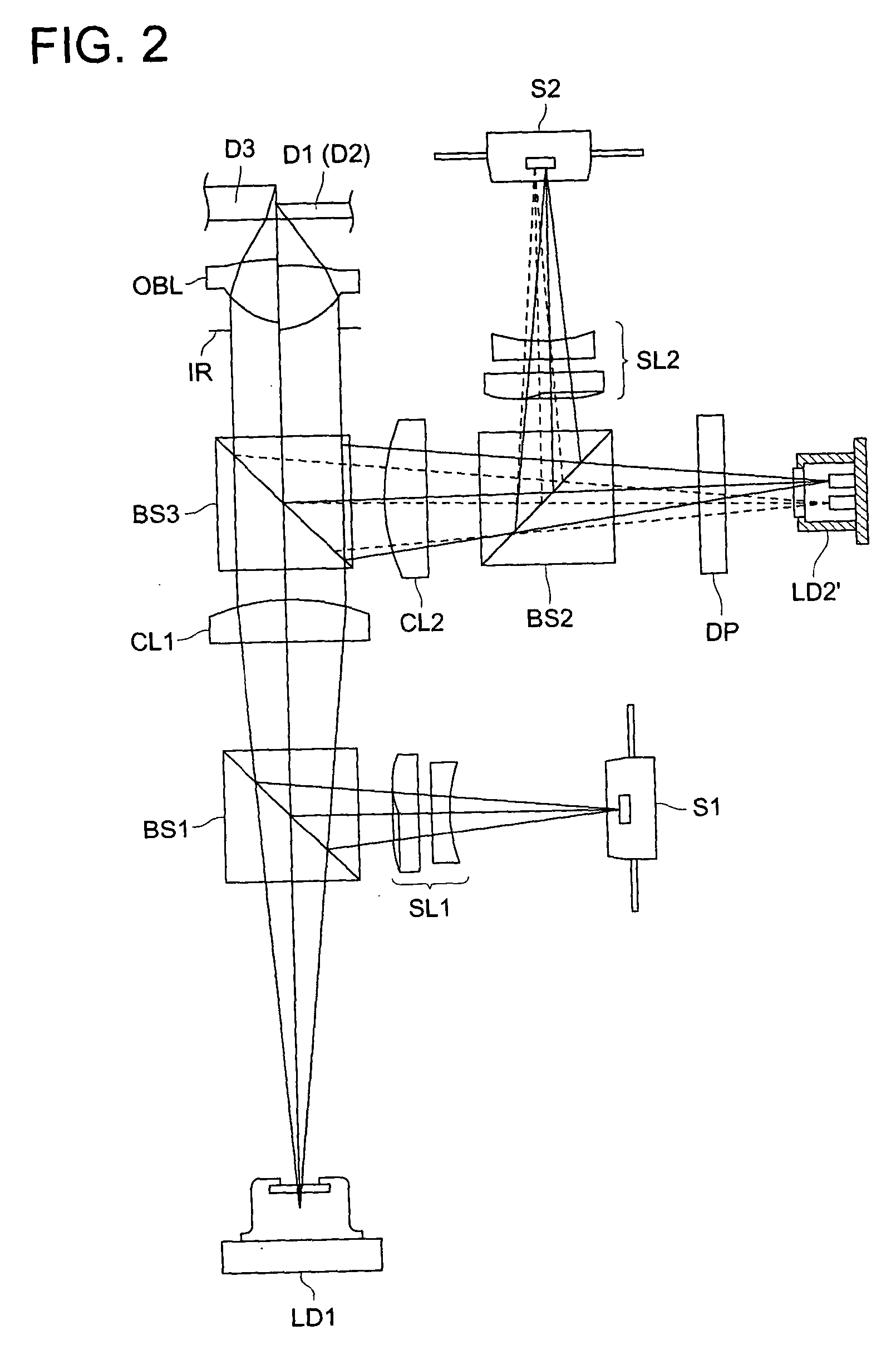
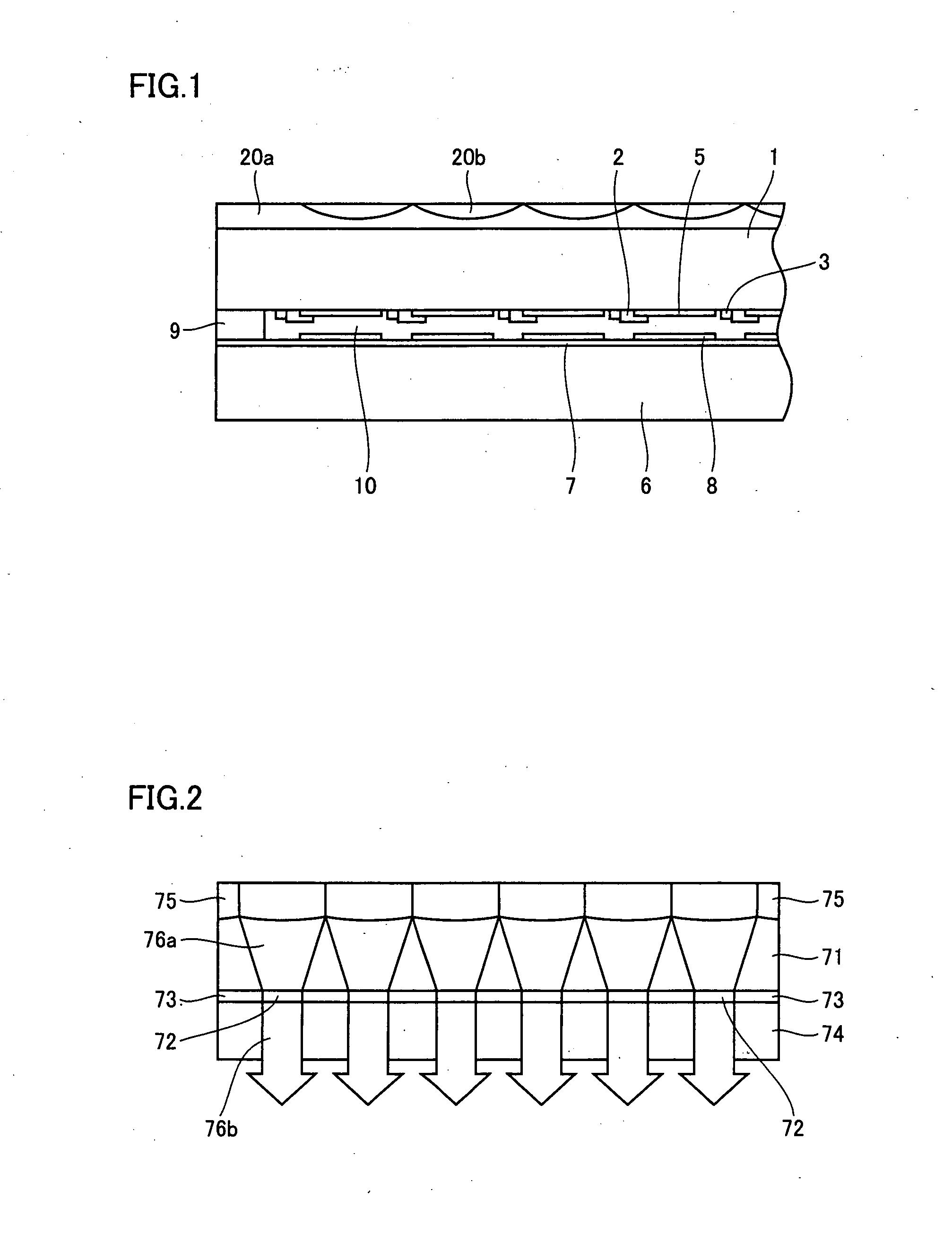
Optical pickup apparatus and optical element
InactiveUS20040047269A1Reduce the number of partsReduce in quantityOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupLight flux
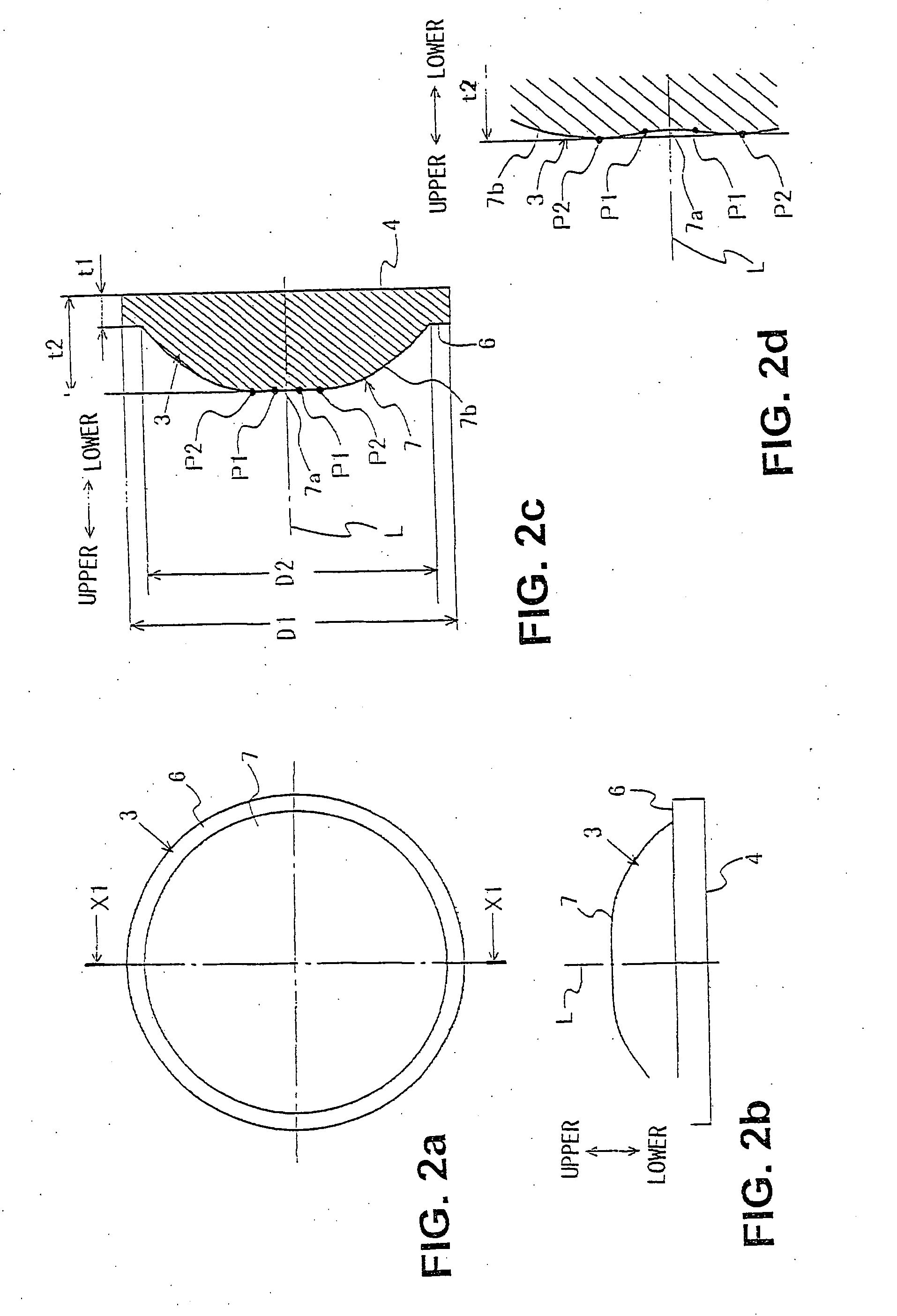
An optical pickup apparatus comprises first, second and third light sources to emit light fluxes of wavelength lambda1, lambda2 and lambda3 for conducting recording and / or reproducing information for first, second and third optical information recording mediums having respective protective substrates of thickness t1, t2 and t3 and a diffractive optical element located on a common optical path for the first, second and third light sources. A converged-light spot is formed on the first optical information recording medium with m-th order diffracted-light ray of the wavelength lambda1, on the second optical information recording medium with n-th order diffracted-light ray of the wavelength lambda2, and on the third optical information recording medium with k-th order diffracted-light ray of the wavelength lambda3 generated by the diffractive optical element respectively, wherein one of m, n and k is different from one of other two numbers.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Insertion detector for medical probe
ActiveUS20110257521A1Reduce fluxUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsThermometer detailsProximity sensorLight flux
An insertion detector for monitoring a position of a medical probe relative to a body cavity of a patient, the probe incorporates a proximity sensor that is responsive to a predetermined property of the patient's body. The proximity sensor may include a light emitter and a light detector. When the medical probe is inserted into the body cavity, a light flux between the light emitter and light detector is changed due to either obstruction by the cavity walls or reflection by the patient's skin. A response from the proximity sensor may be used to adjust a temperature measured from the body cavity to correct for errors due to non-insertion or partial insertion of the probe into the body cavity.
Owner:HELEN OF TROY LIMITED
Indicator lamp having a converging lens
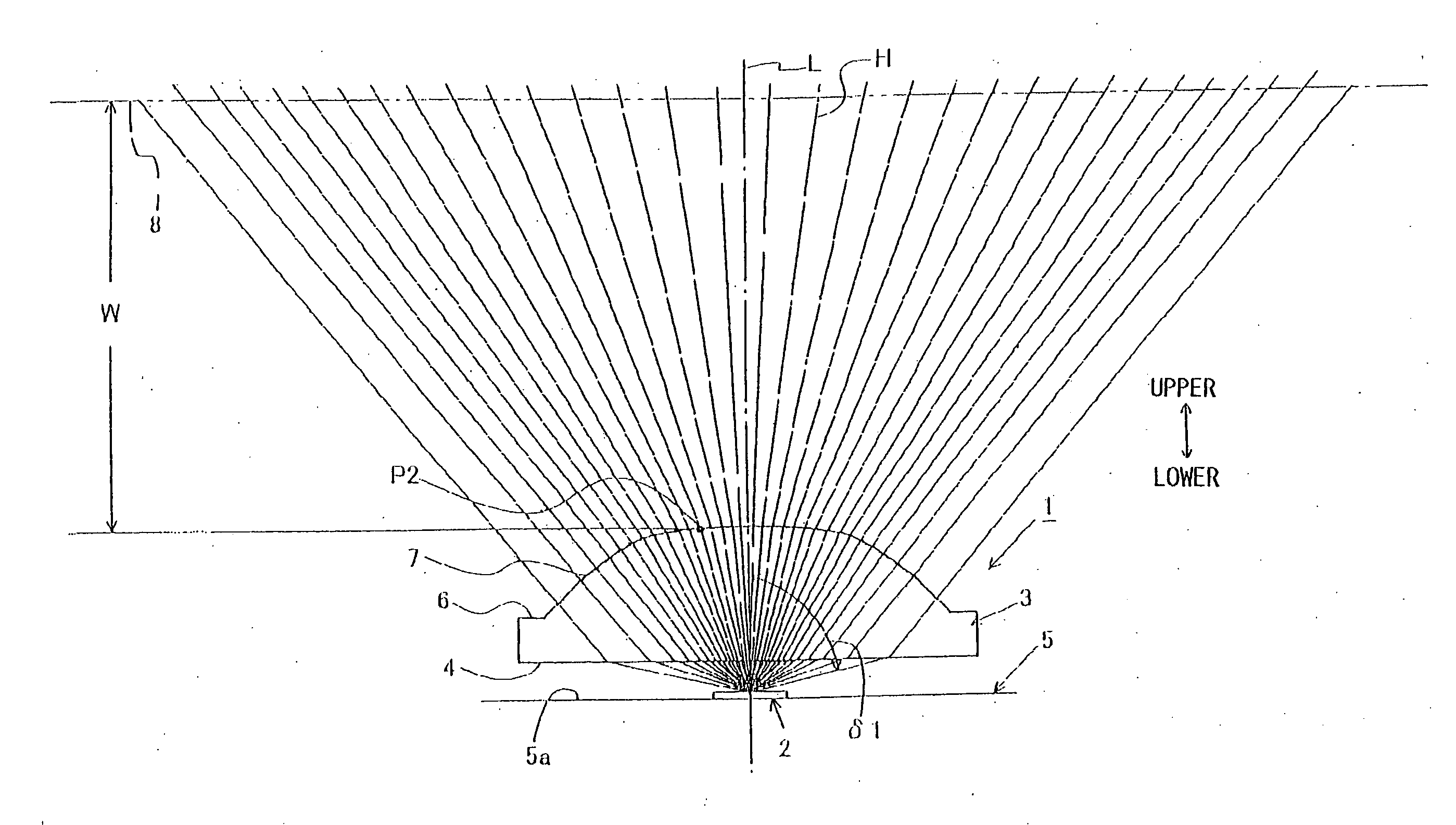
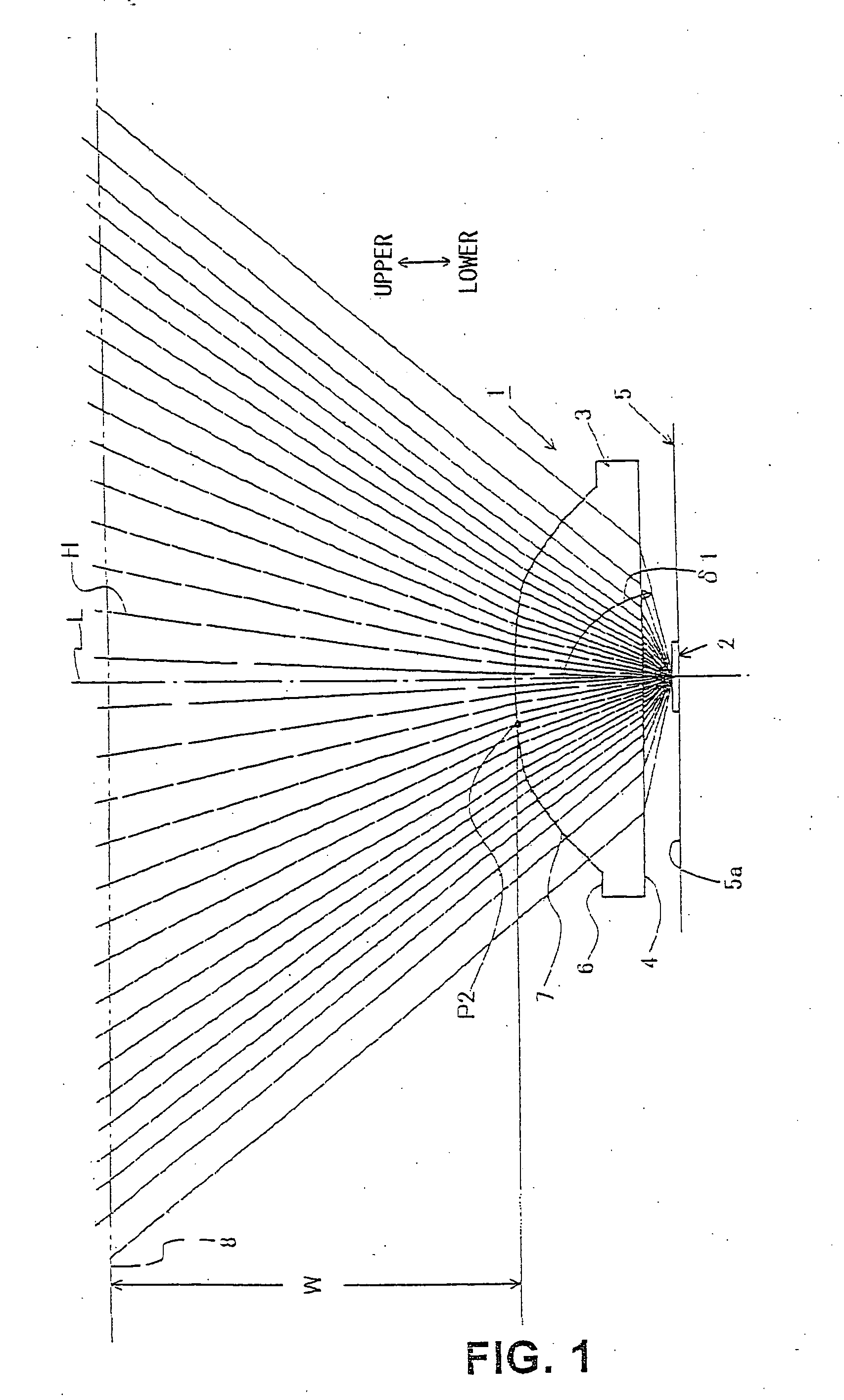
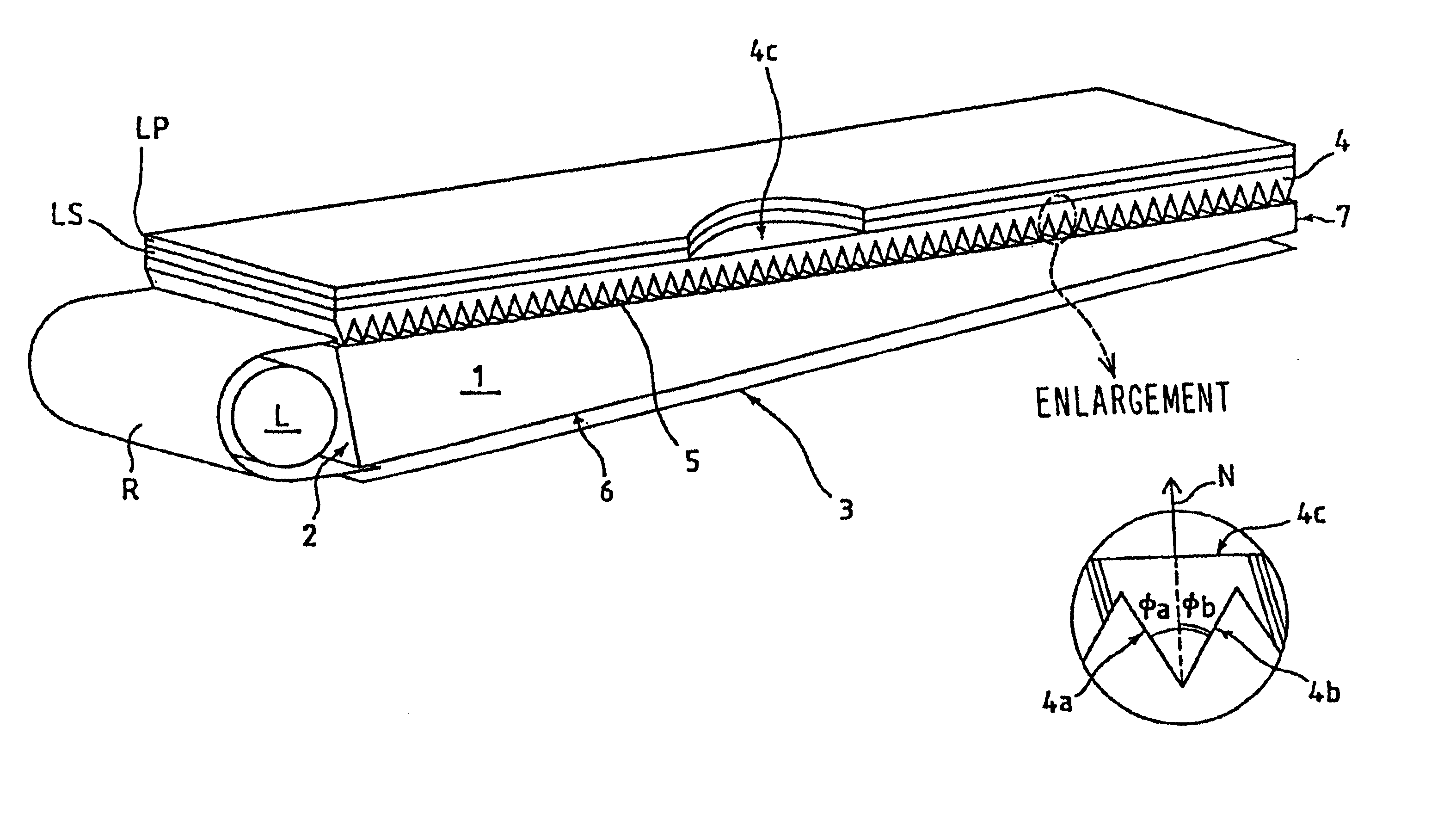
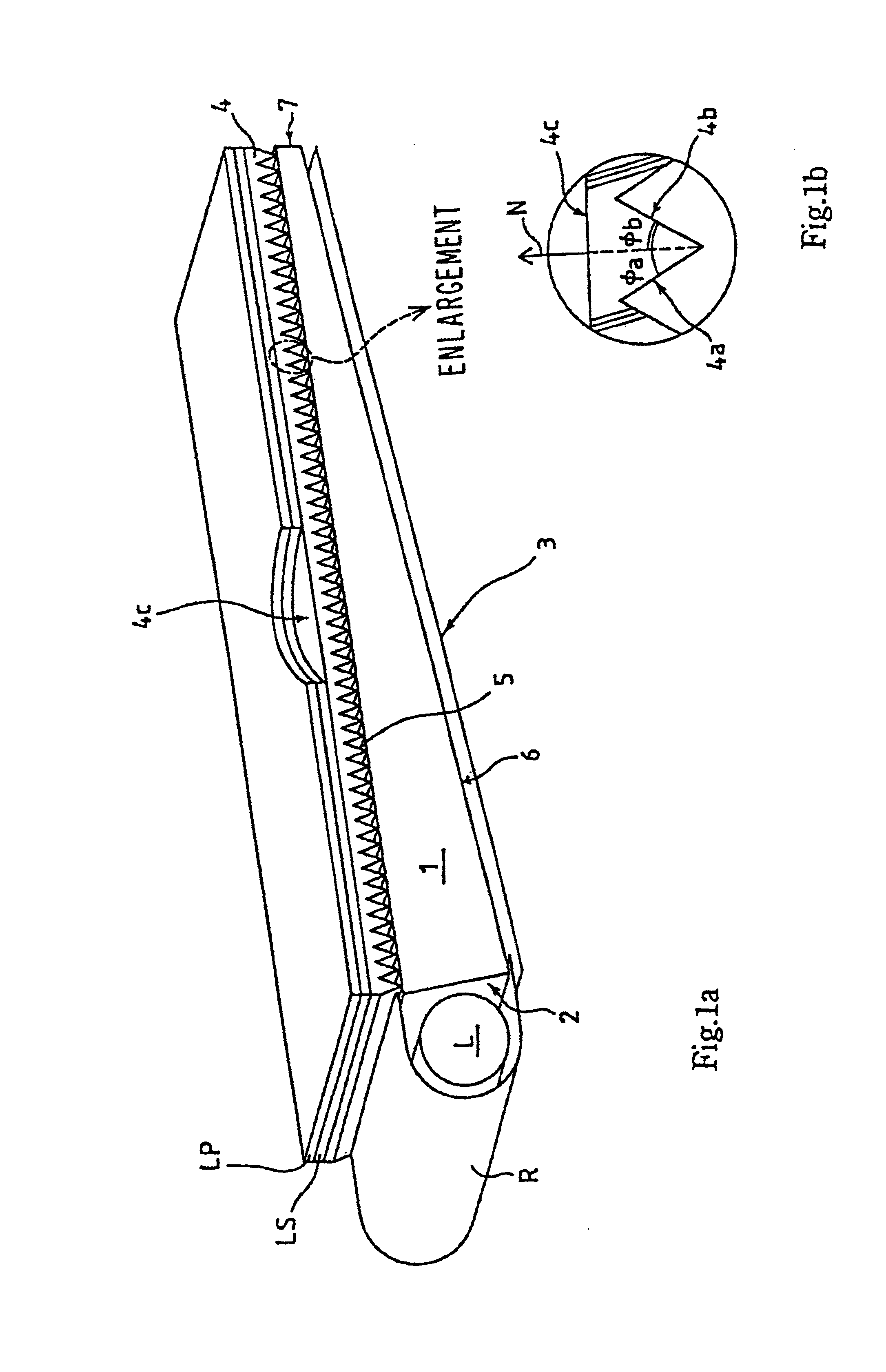
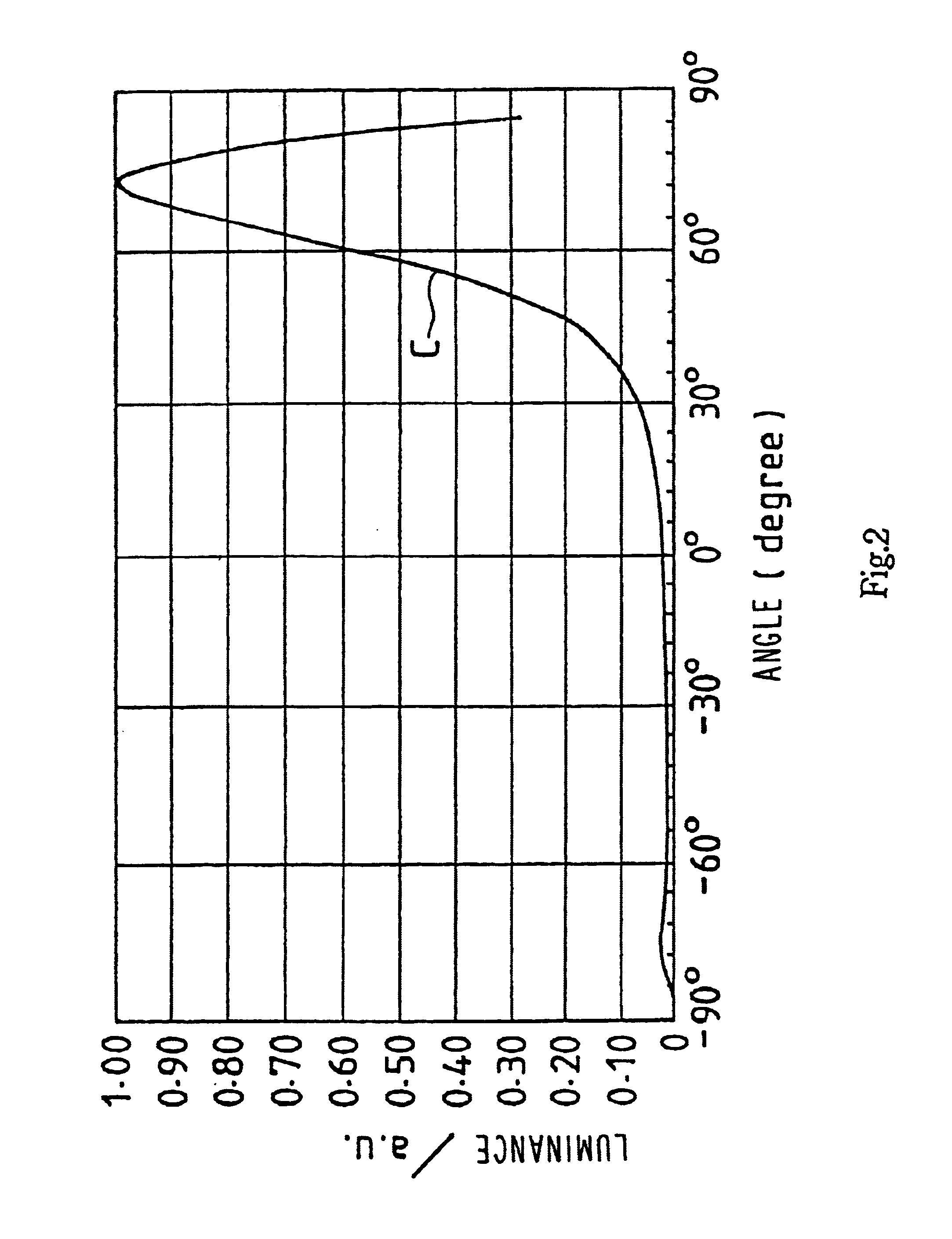
It is sought to provide an indicator lamp, which is excellent not only in short distance visual recognition property but also in long distance one, as well as being further excellent in sight field angle property.An indicator lamp includes a light-emitting element 1 and a light-emitting element lens 2 having a light-emitting element mounting cavity 3 formed at the bottom, in which the light-emitting element disposed in the cavity 3 emits light to be fully reflected by the peripheral surface of the lens 1 and proceeds as emission light flux forwardly of the lens 1. The slope angle of the peripheral surface with respect to the lens axis is reduced progressively from the bottom toward the lens front surface 5 in three stages, thus forming circumferential corners 7 and 8 as boundaries between adjacent ones of the three stages. The circumferential corners scatter light emitted from the light emitting element 2 to provide concentric emission light fluxes as viewed from the side of the lens front.
Owner:OKAYA ELECTRIC INDS
LED lighting system
ActiveUS8436556B2Reduce impactElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentEffect light
A system and method involving lighting fixtures, a control network, a controller and other devices such as light sensors, input devices and network adapters for coordinating precise brightness and color schedules among the lighting fixtures while maintaining a high color reliability including provisions for managing a plurality of lighting fixtures. The lighting fixtures contain lighting elements selected such that when controlled properly, operating along a daytime locus, the resultant light output closely resembles sunlight on a cloudless day in spectral characteristics, and wherein the total flux of blue light can be adjusted from a relative level of 1-100% the maximum blue flux of the lighting fixture by controlling individual lighting elements.
Owner:DELOS LIVING LLC
Automotive display system and display method
An automotive display system includes a frontward information acquisition unit, a position detection unit and an image projection unit. The frontward information acquisition unit acquires frontward information. The frontward information includes information relating to a frontward path of a vehicle. The position detection unit detects a position of one eye of an image viewer riding in the vehicle. The image projection unit generates a first virtual image at a corresponding position in scenery of the frontward path based on the frontward information acquired by the frontward information acquisition unit and projects a light flux including an image including the generated first virtual image toward the one eye of the image viewer based on the detected position of the one eye. The first virtual image has a size corresponding to at least one of a vehicle width and a vehicle height.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Illumination device and lens of illumination device
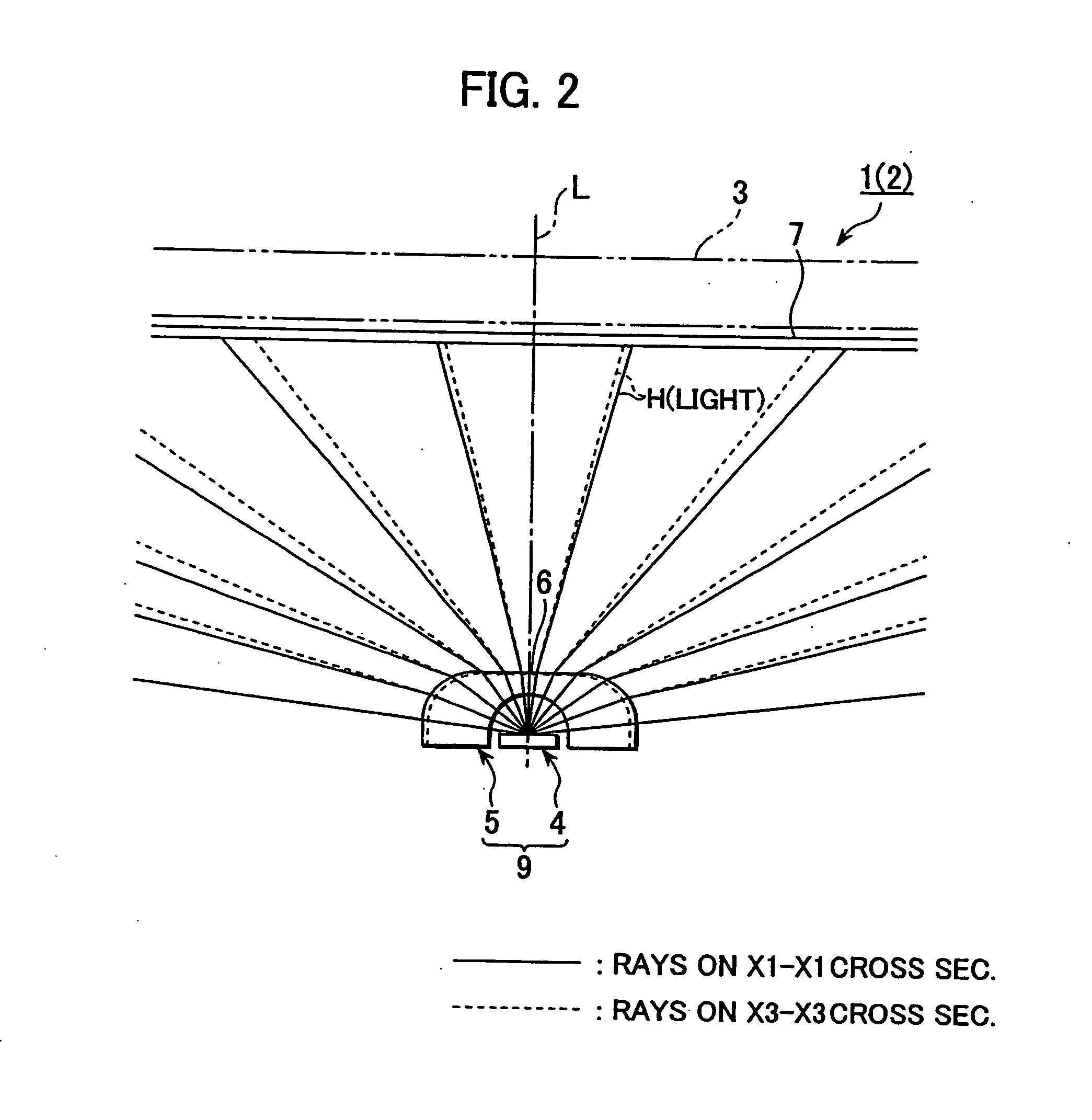
Provided are an illumination device and a lens employed in the device for controlling light travelling direction, the device being capable of illuminating brightly and uniformly a certain limited region (region-to-be-illuminated) corresponding to an object such as subject for photography. The illumination device emits light H coming from a light emitting element (point-like light source) employing a LED as a light emitting source via the lens. A light control emission face of the lens emits light (rays), which is included in light H introduced into the lens through an incidence face thereof and travelling within the lens to the light control emission face without undergoing inner-reflection at any surface of the light control emission face, as illumination light. The light control emission face is configured so that no set of rays included in the illumination light make any crossover at least before reaching a region-to-be-illuminated and rays within a direction range near to a direction of optical axis L have lower light flux density as compared with that in the outside of the direction range.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Light control sheet, surface light source device and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6746130B2Well-controlled emission directivityPrismsDiffusing elementsLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
A light control sheet suitable for direction-controlling an angularly extending oblique input light, surface light source device and LCD using the light control sheet. A light control sheet is disposed along an emission face of a light guide plate direction-controls main and subsidiary light fluxes to cause them to be emitted toward a desired direction. Main beam S1 emitted from the emission face transmits (with a small refraction) through a first face, being inner-reflected (total reflection) by a first slope region and then outputted from a light output face (SS1). First subsidiary beam T1 transmits (with a small refraction) through the first face, being inner-reflected (total reflection) by a second slope region and then outputted from the light output face (TT1).
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Light emitting device and lighting device having the same
ActiveUS7798679B2Improve the scattering effectMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLiquid-crystal displayLight flux
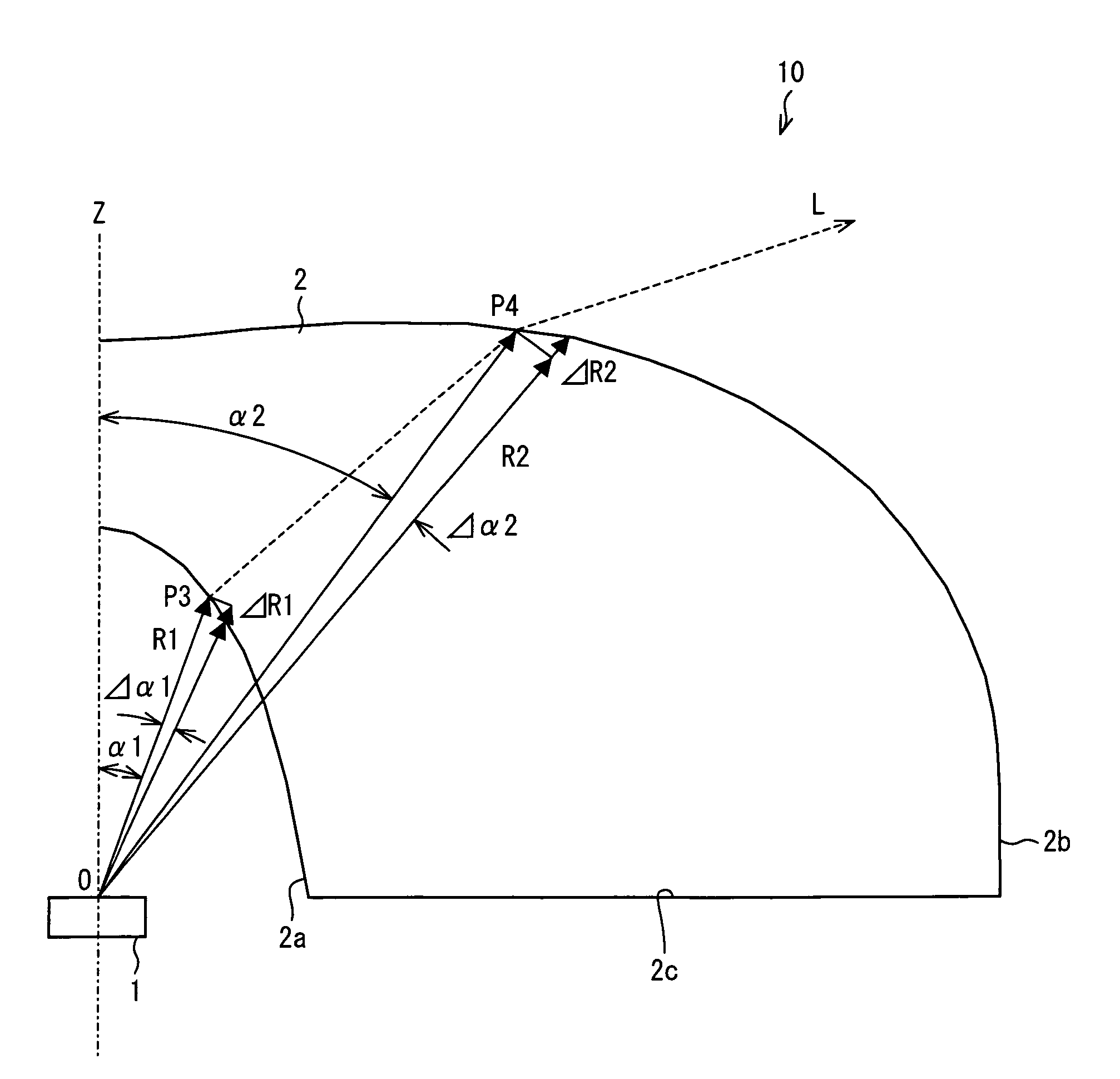
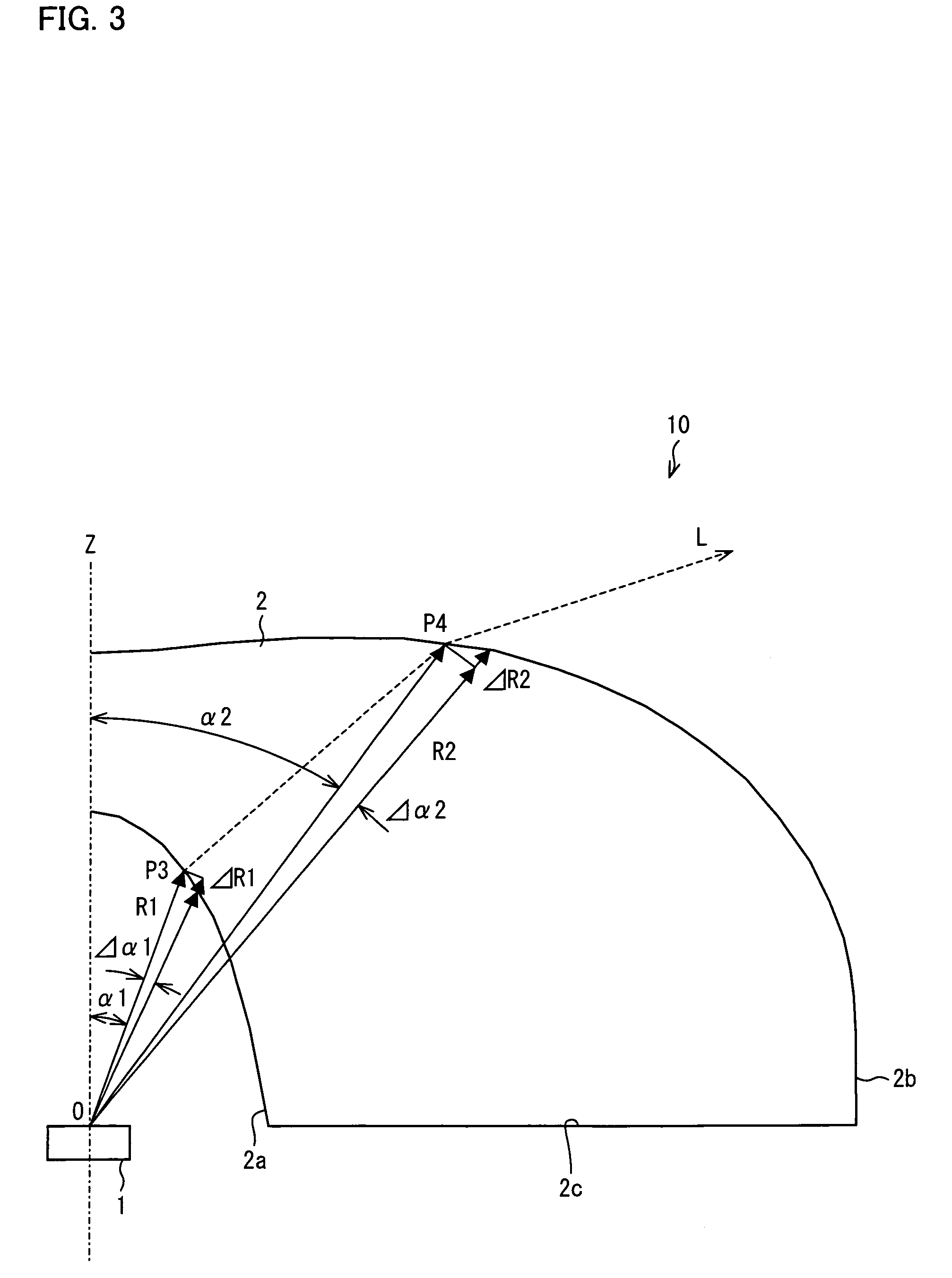
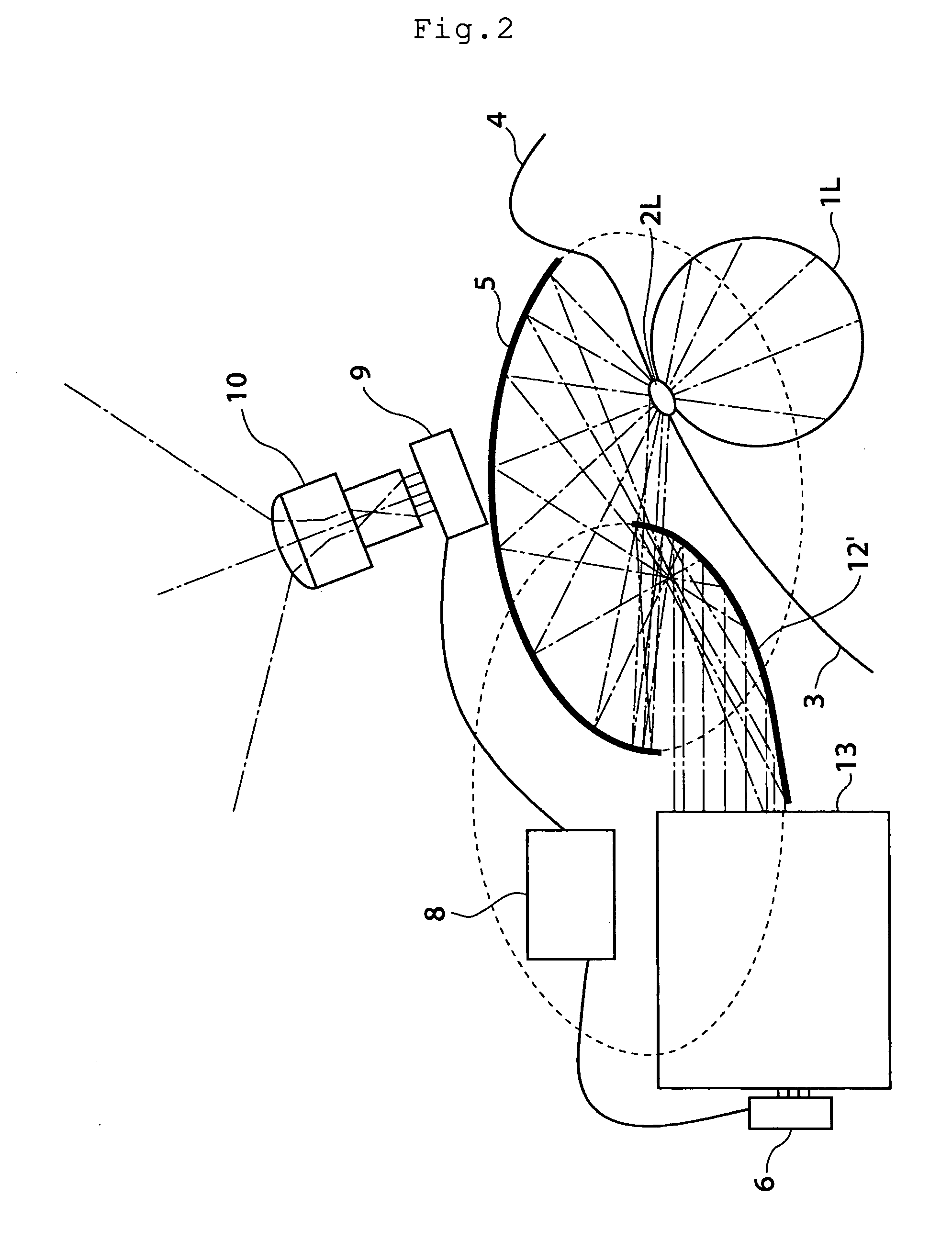
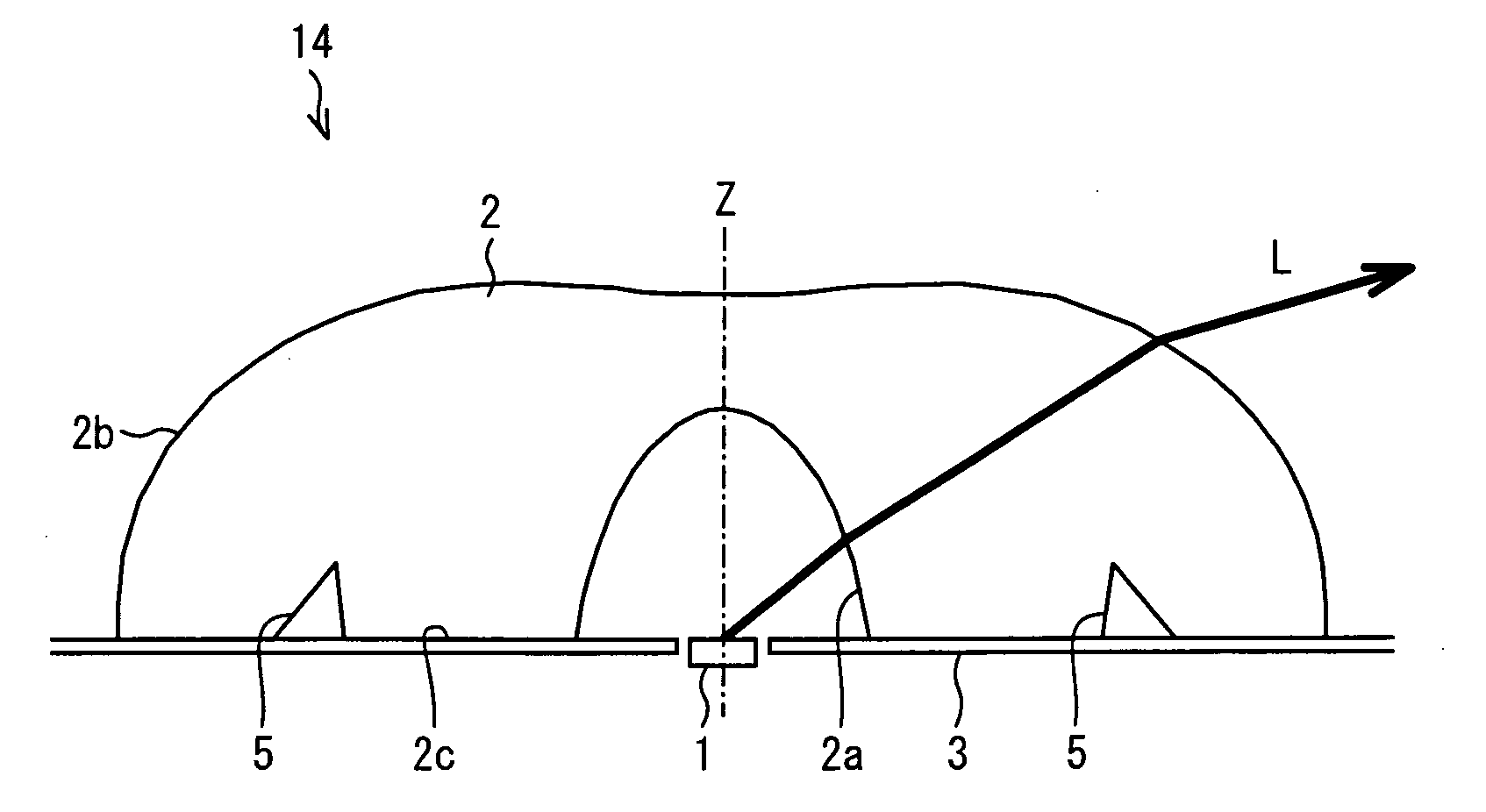
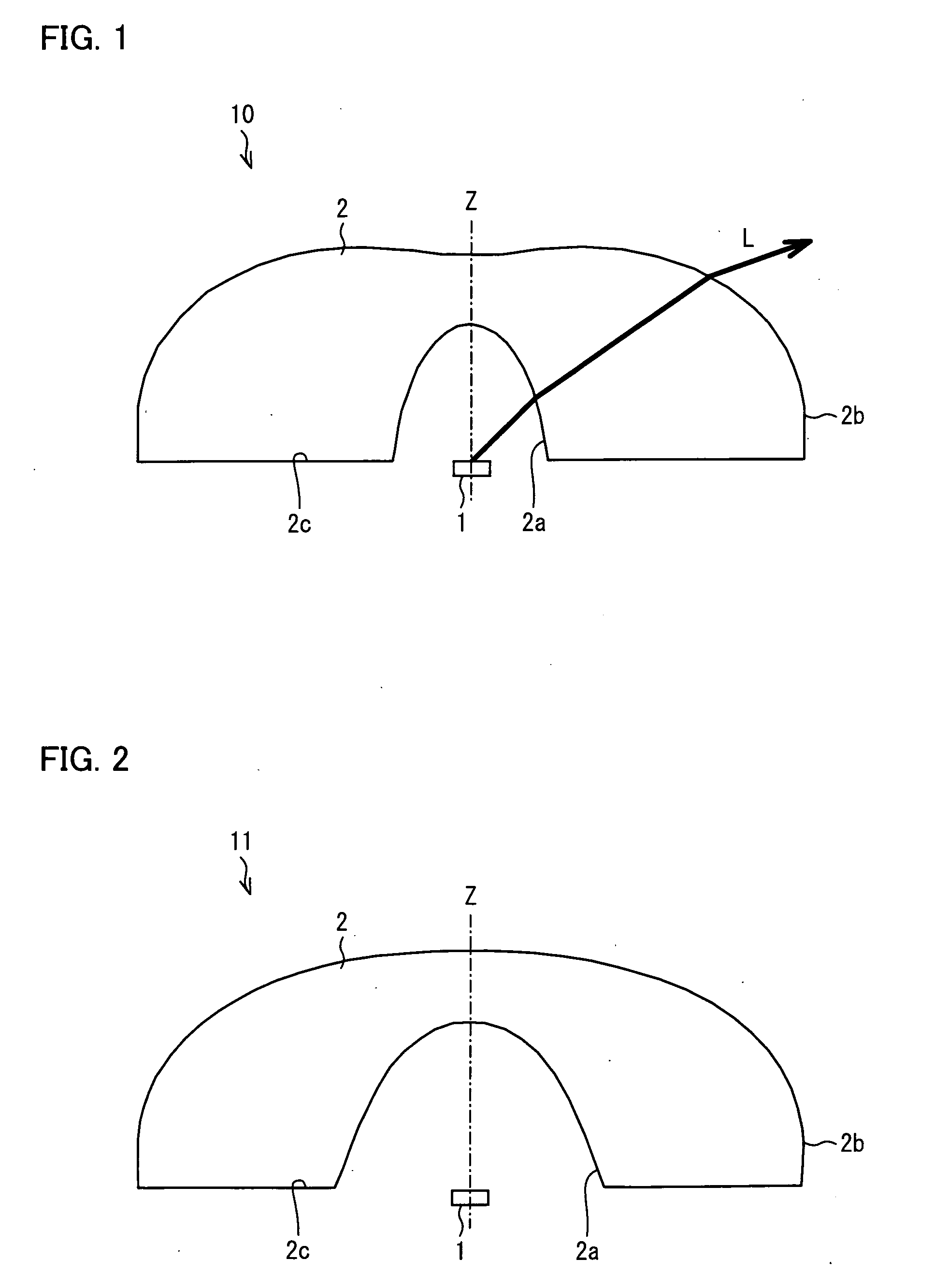
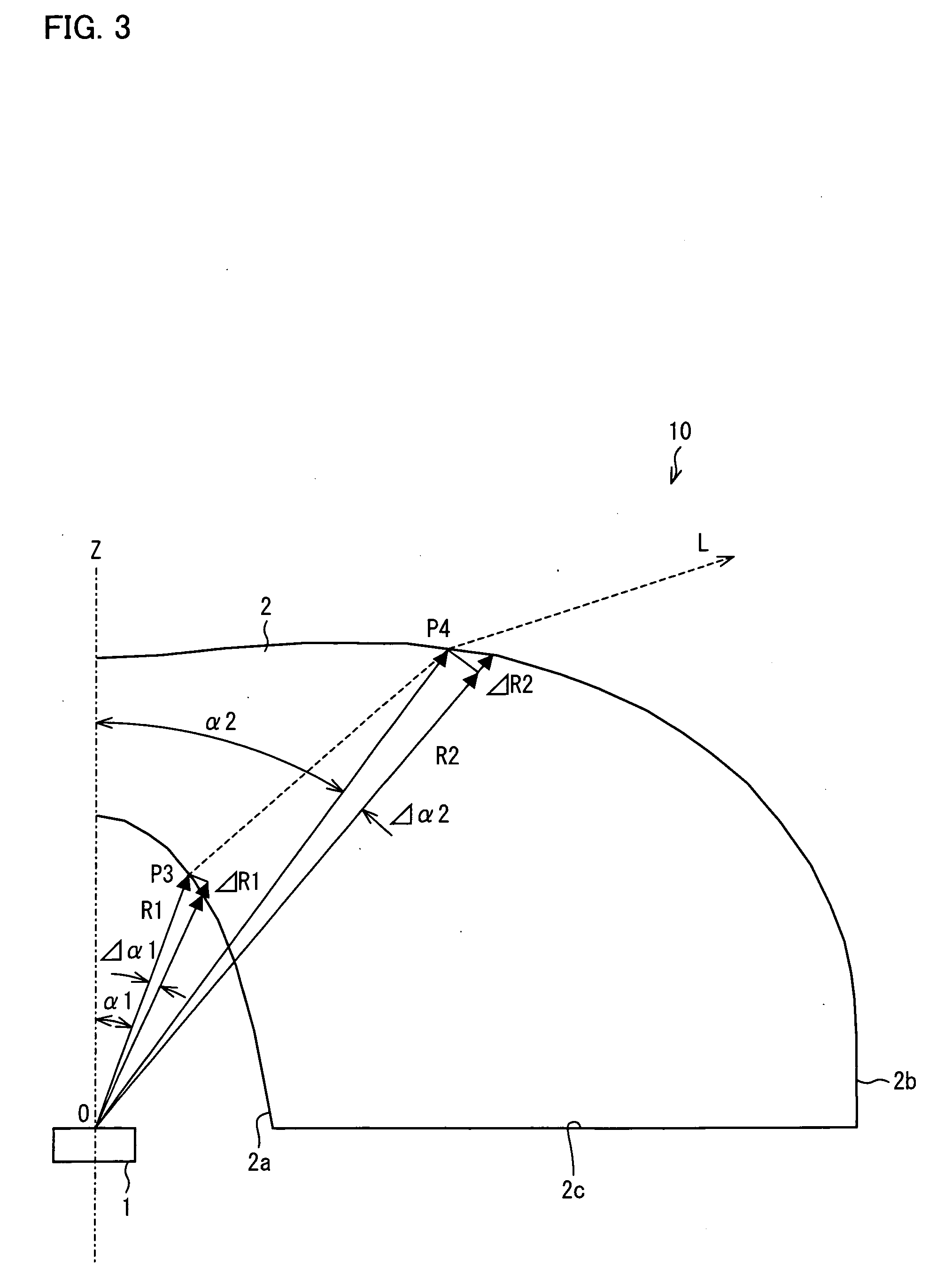
A light-emitting device (10) is arranged such that (x) R1 monotonically decreasing as α1 increases, at least in a range of α1<π / 3, where an intersection of a light axis Z and an emission surface of a light-emitting element (1) is a reference point; α1 is an angle between the light axis Z and a straight line that passes through the reference point and an arbitrary point on a light-incoming surface (2a), and R1 is a distance between the reference point and the arbitrary point on the light-incoming surface (2a); (y) R2 monotonically increasing as α2 increases, at least in a range of α2<π / 3, where α2 is an angle between the light axis Z and a straight line that passes through the reference point and an arbitrary point on a light-outgoing surface (2b), and R2 is a distance between the reference point and the arbitrary point on the light-outgoing surface (2b); and (z) A2 scatters light without generating uneven brightness on a liquid crystal display panel and has higher scattering ability that is obtained by decreasing a reflectance caused by the Fresnel reflection, where n is a refraction index of a material forming a light flux controlling member (2), and A2=ΔR2 / (R2Δα2), where ΔR2 is an increment of R2 and Δα2 is an increment of α2.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Light emitting device, surface light source device, display and light flux control member
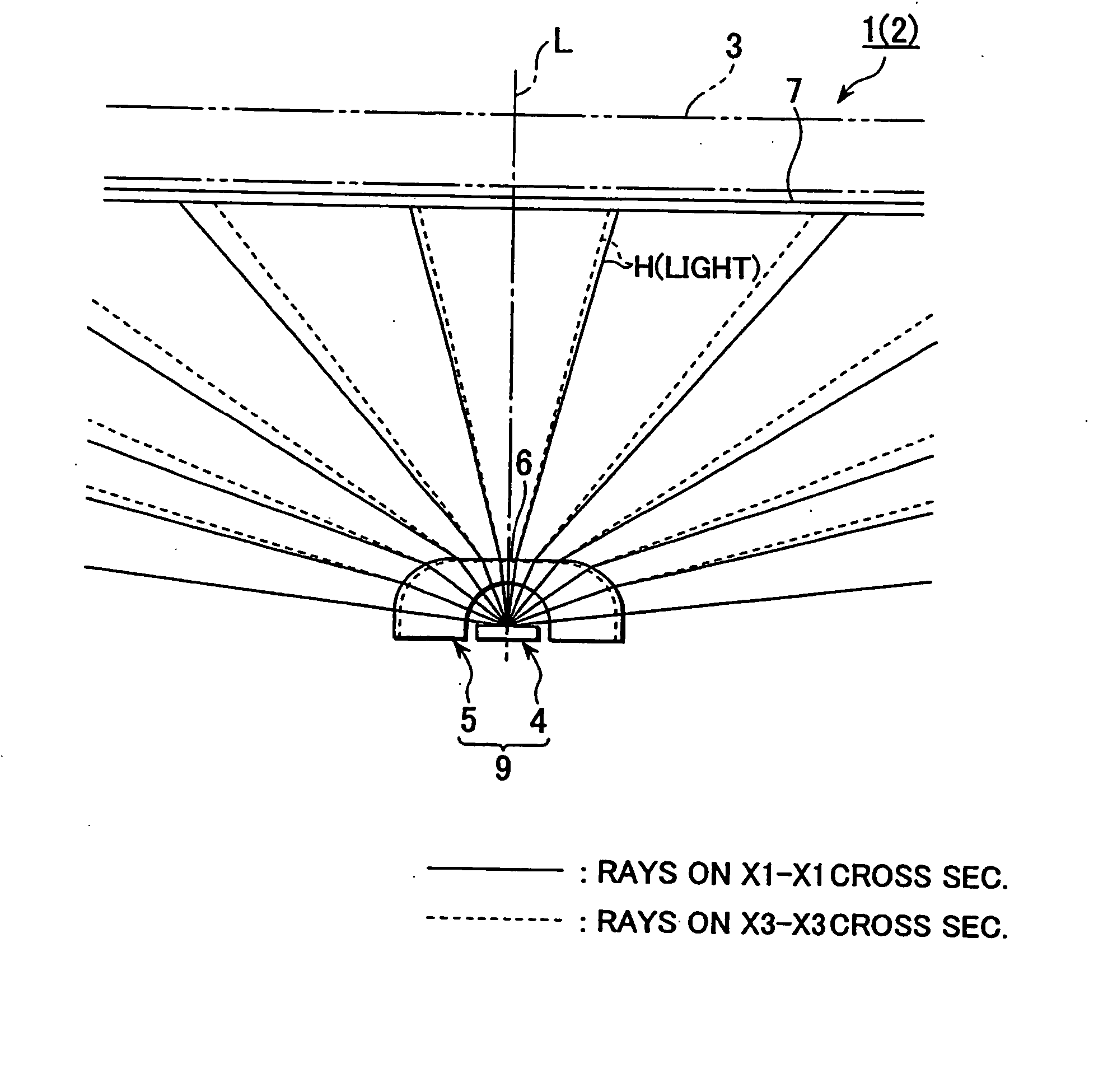
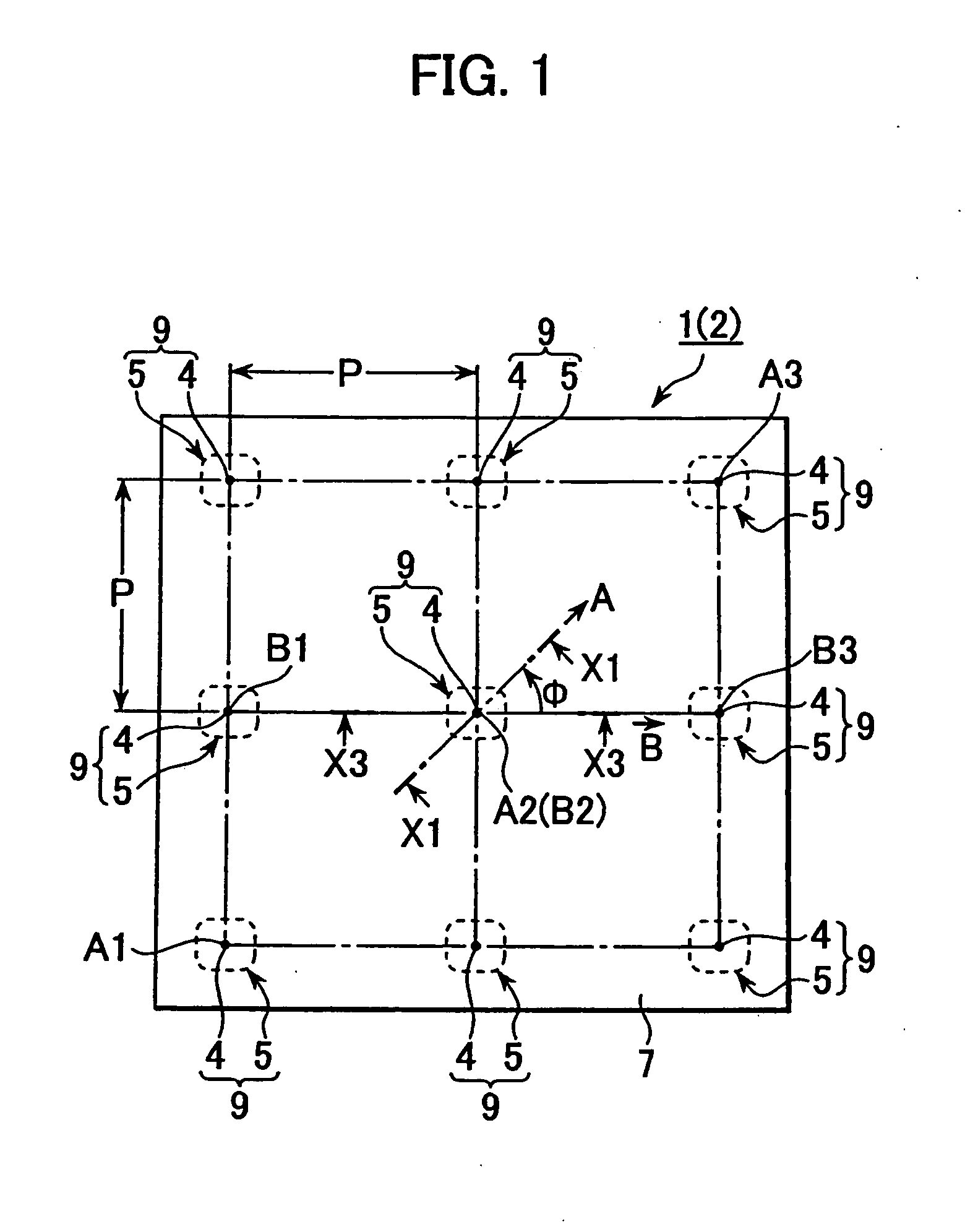
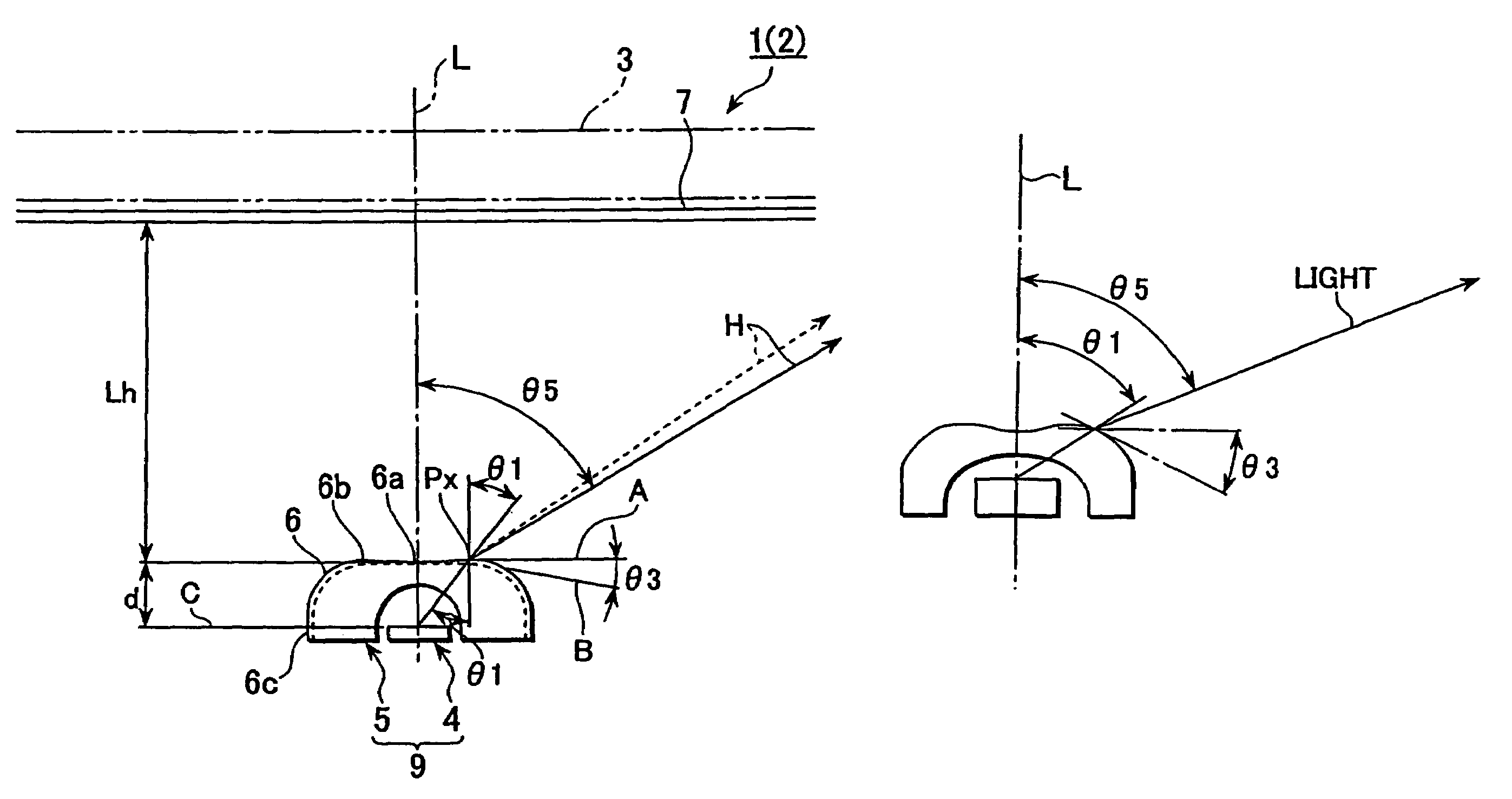
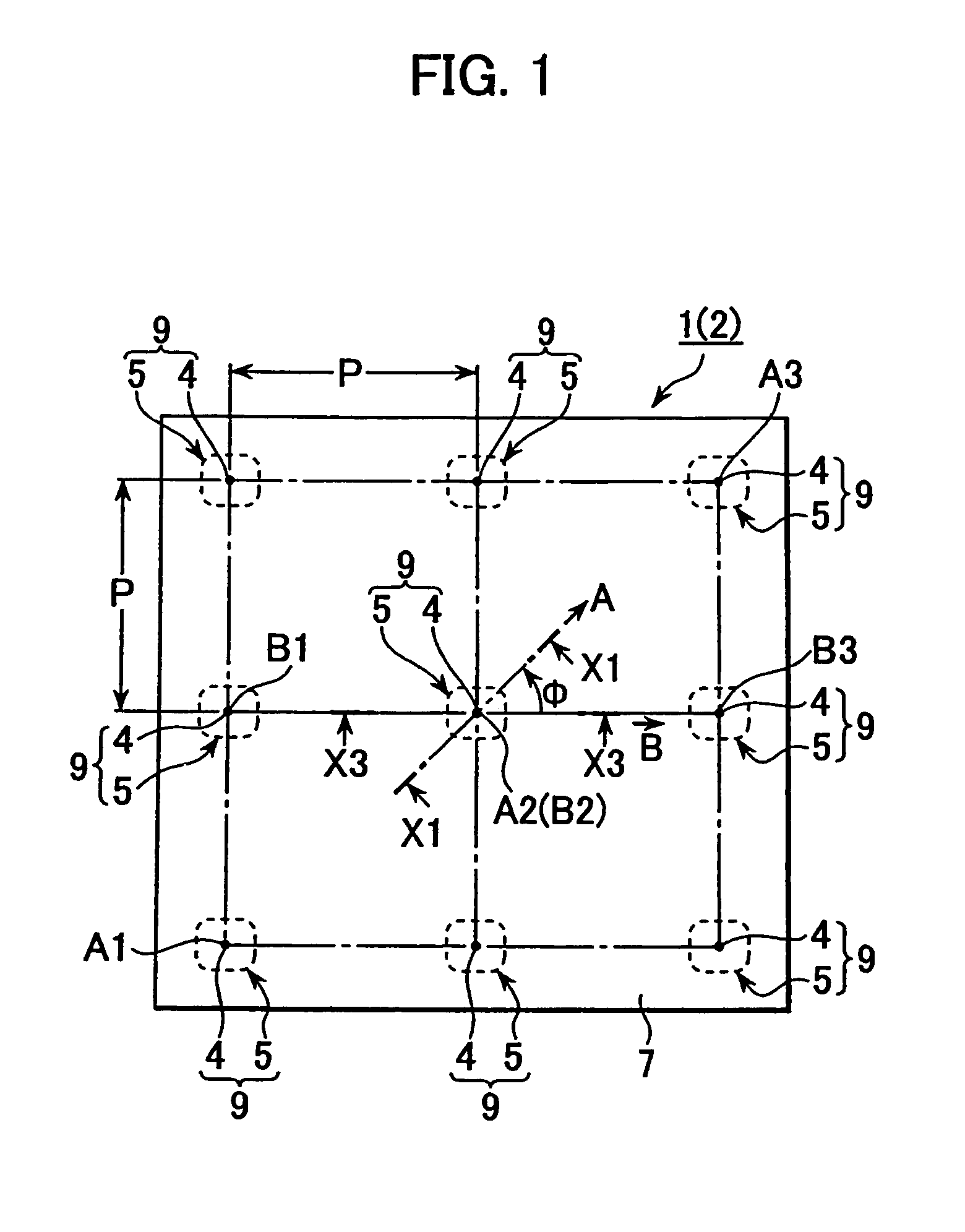
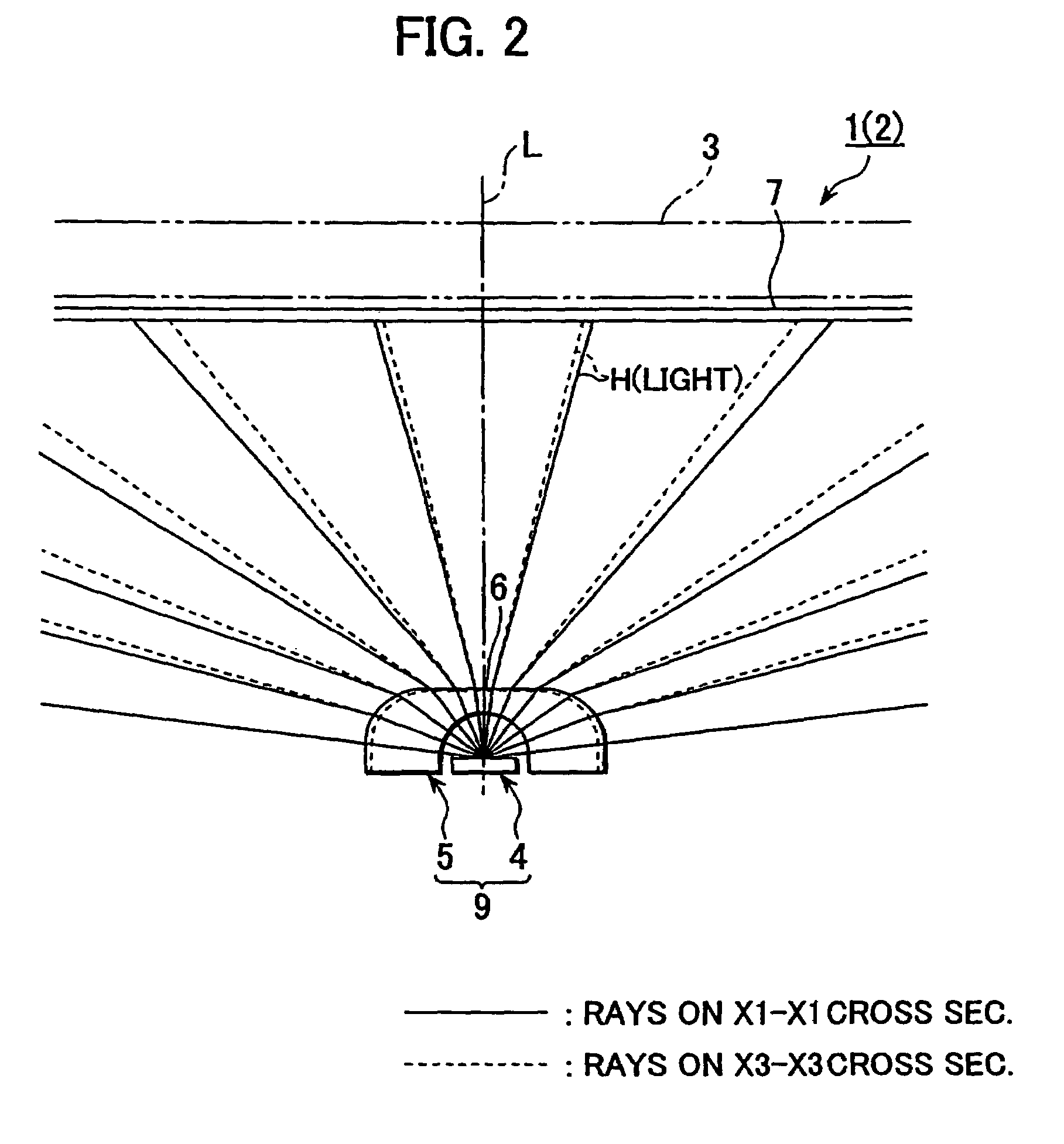
Light from light emitting element enters into a flux control member through a recess on an inner face of the light flux control member, being emitted from an emission control face (outer face). At least so far as light falls within a half-intensity-angular-range, the light satisfies Condition 1 (θ5 / θ1)>1 except for light in the vicinity of a normal direction of the emission control face) and Condition 2 (Value of θ5 / θ1>1 gets smaller gradually with increasing of θ1). It is noted that θ1, θ5 are angles made at being inner-incident to the emission control face and at being emitting from the same, respectively. The emission control face has a planar outline shape which is anisotropic around optical axis L, thereby causing value of θ5 / θ1 to have a change depending on direction angle φ around optical axis L, with the result that highly uniform light is supplied to a required anisotropic irradiation range.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
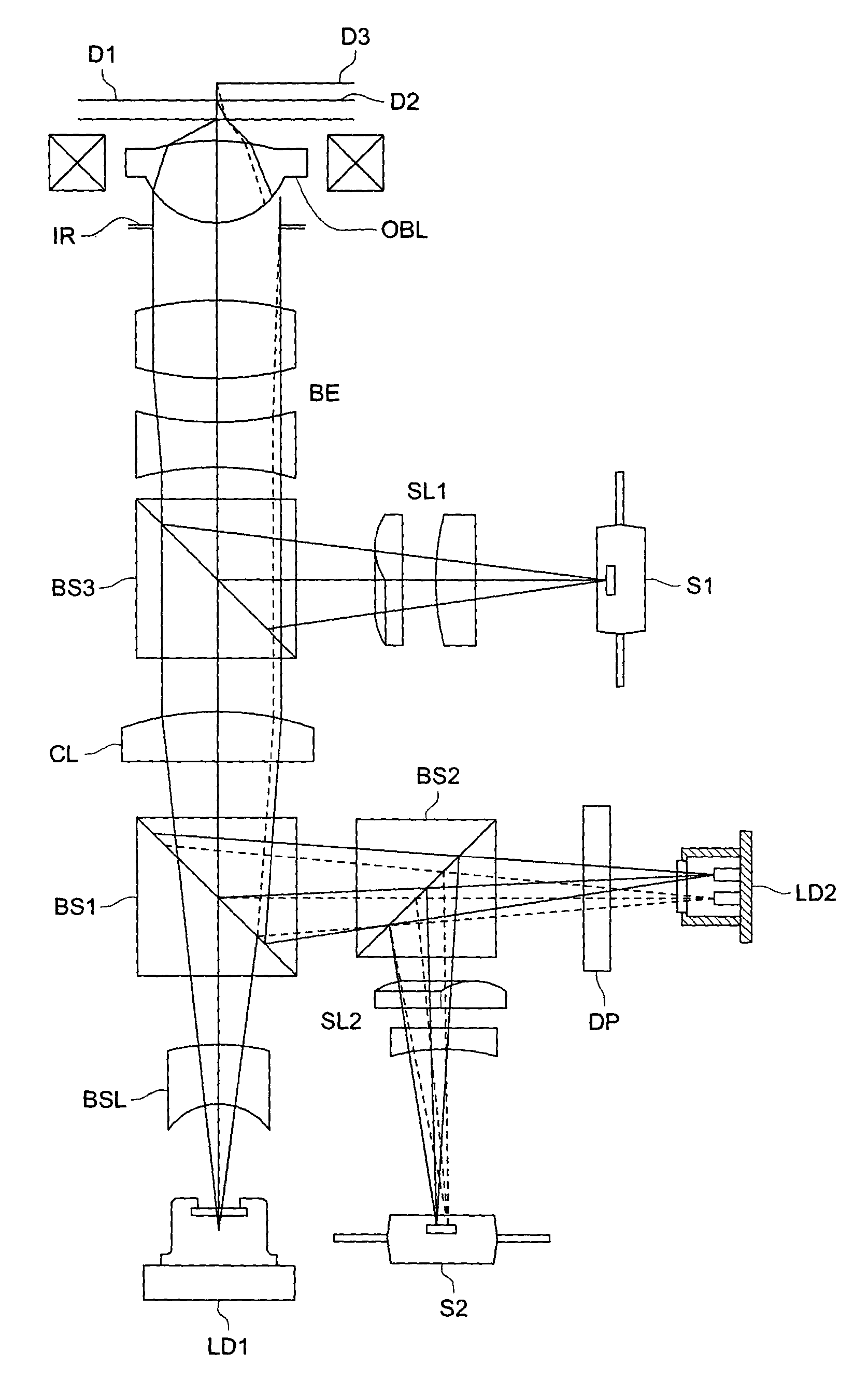
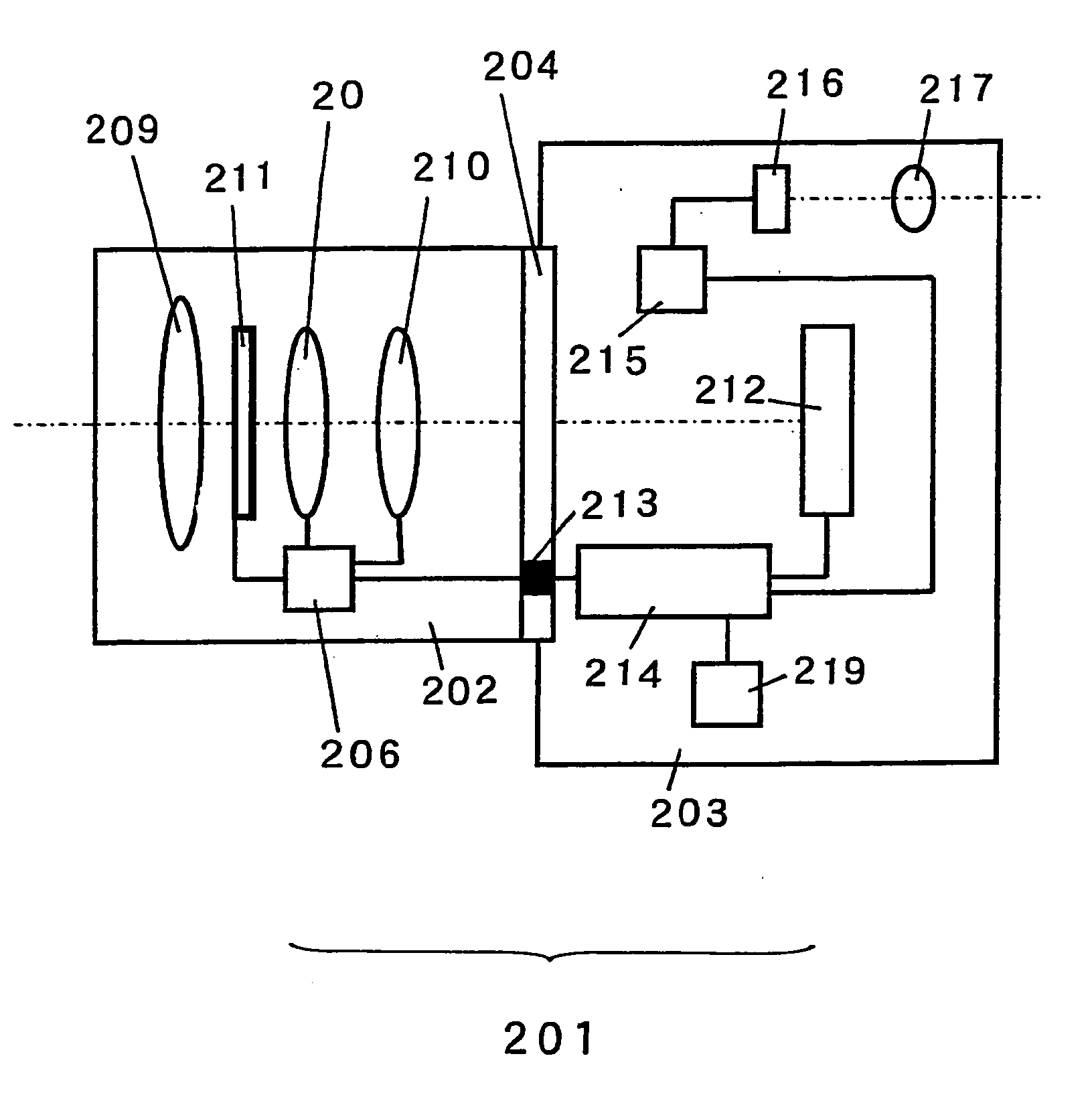
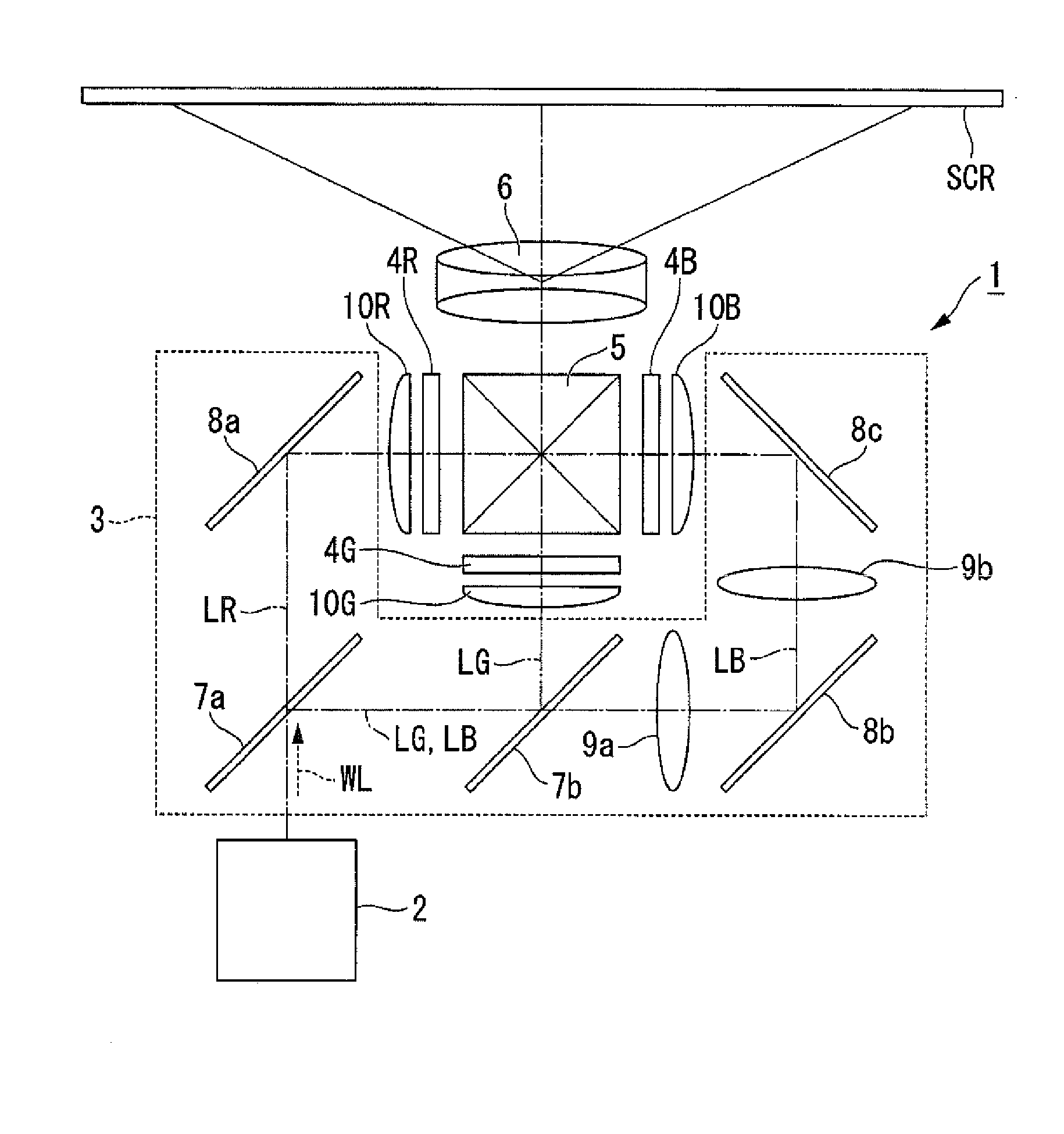
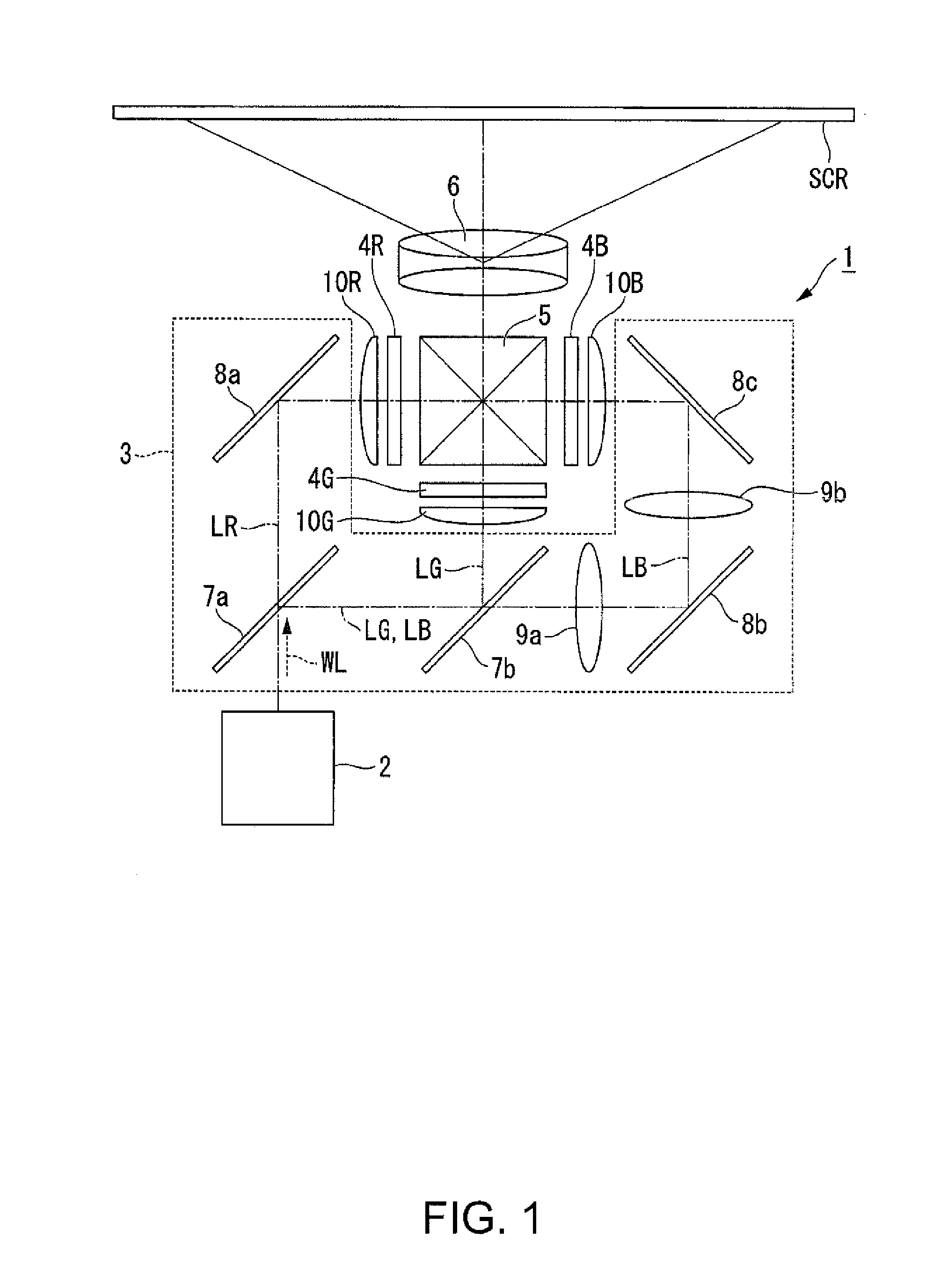
Image display unit and projection optical system
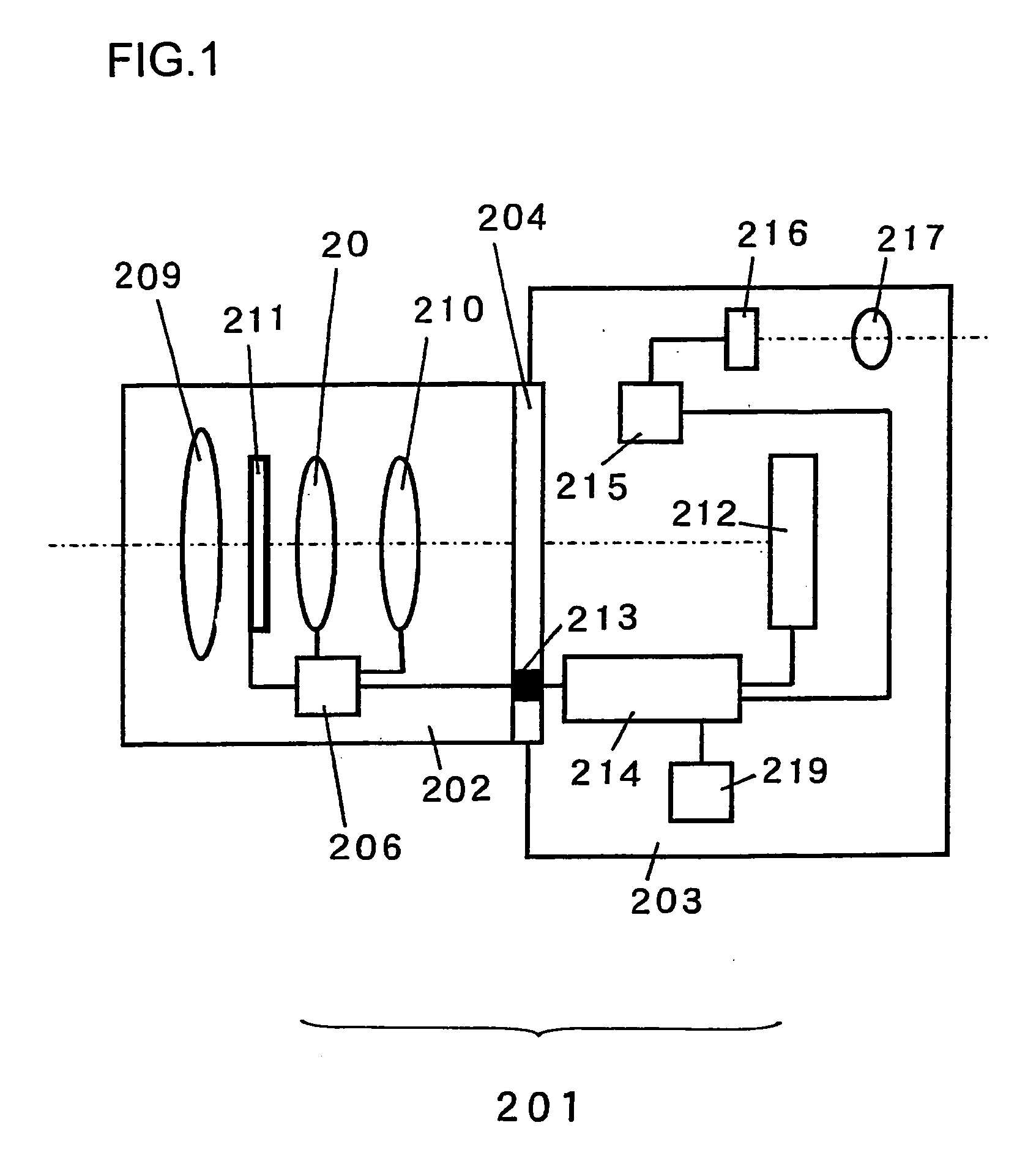
InactiveUS20060072215A1Telecentricity is deterioratedCathode-ray tube indicatorsTelescopesIntermediate imageEyepiece
An intermediate image of an image from the LCD module 142 is deflected by reflection mirrors M1 and M2 via zoom automatic focus control system (g) and then is formed on diffusion glass 131 via relay lens (b) and reflection mirrors M3 and M4. The LCD image is projected on the retina of eyeballs via eyepiece lens 132 by the light flux diffused at an order of ±20 degrees by diffusion glass 131. One side of the eyepiece lens 132 close to the crystal balls 2 has an aspherical shape of a Conic surface and a Conic coefficient of the Conic surface is −1 and less. Thereby the optical system that has a viewing angle of 60 degrees and over and has a small aberration can be obtained.
Owner:NISHI KENJI
Light emitting device and lighting device having the same
ActiveUS20090052192A1Improve the scattering effectMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLiquid-crystal displayLight flux
A light-emitting device (10) is arranged such that (x) R1 monotonically decreasing as α1 increases, at least in a range of α1<π / 3, where an intersection of a light axis Z and an emission surface of a light-emitting element (1) is a reference point; α1 is an angle between the light axis Z and a straight line that passes through the reference point and an arbitrary point on a light-incoming surface (2a), and R1 is a distance between the reference point and the arbitrary point on the light-incoming surface (2a); (y) R2 monotonically increasing as α2 increases, at least in a range of α2<π / 3, where α2 is an angle between the light axis Z and a straight line that passes through the reference point and an arbitrary point on a light-outgoing surface (2b), and R2 is a distance between the reference point and the arbitrary point on the light-outgoing surface (2b); and (z) A2 scatters light without generating uneven brightness on a liquid crystal display panel and has higher scattering ability that is obtained by decreasing a reflectance caused by the Fresnel reflection, where n is a refraction index of a material forming a light flux controlling member (2), and A2=ΔR2 / (R2Δα2), where ΔR2 is an increment of R2 and Δα2 is an increment of α2.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
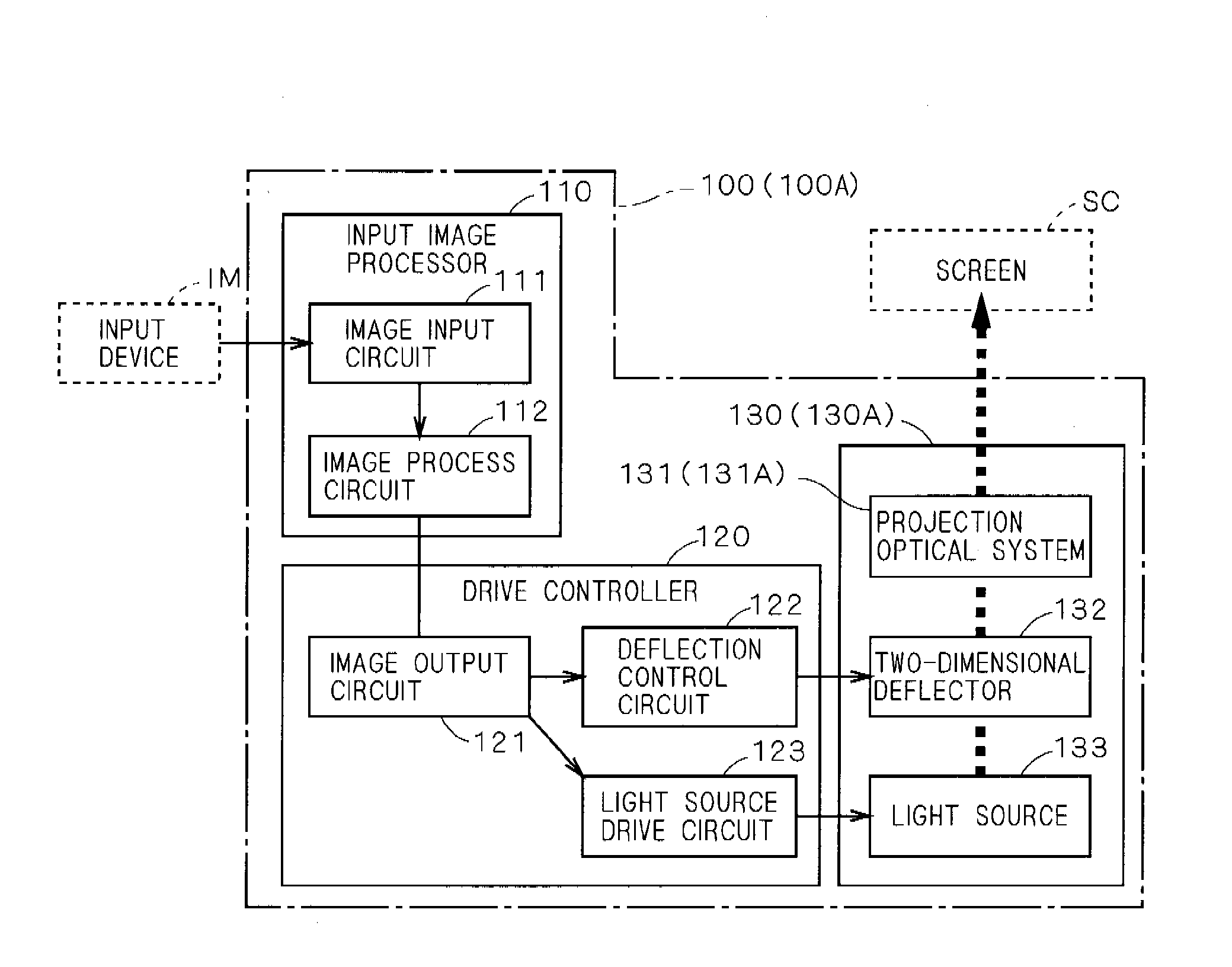
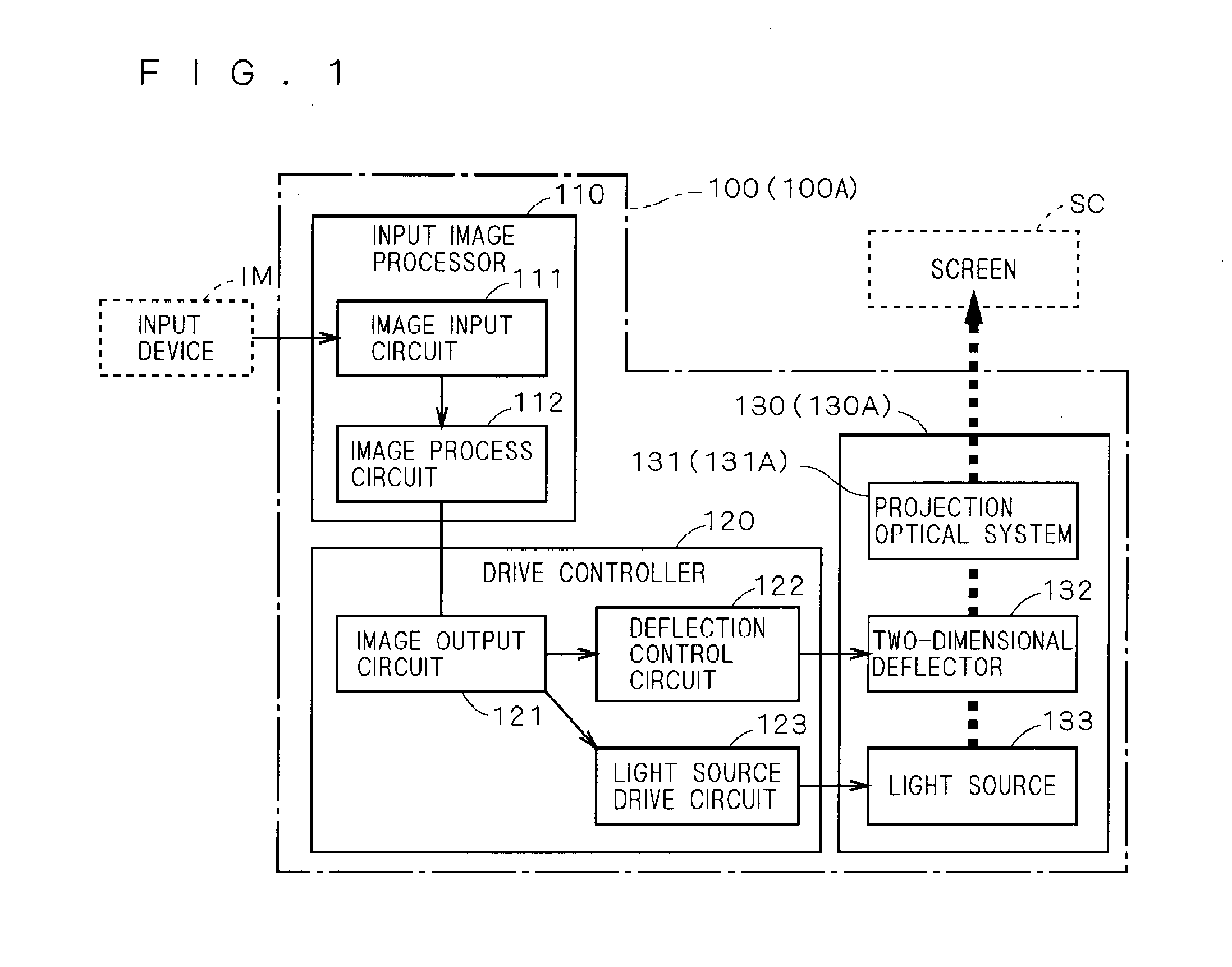
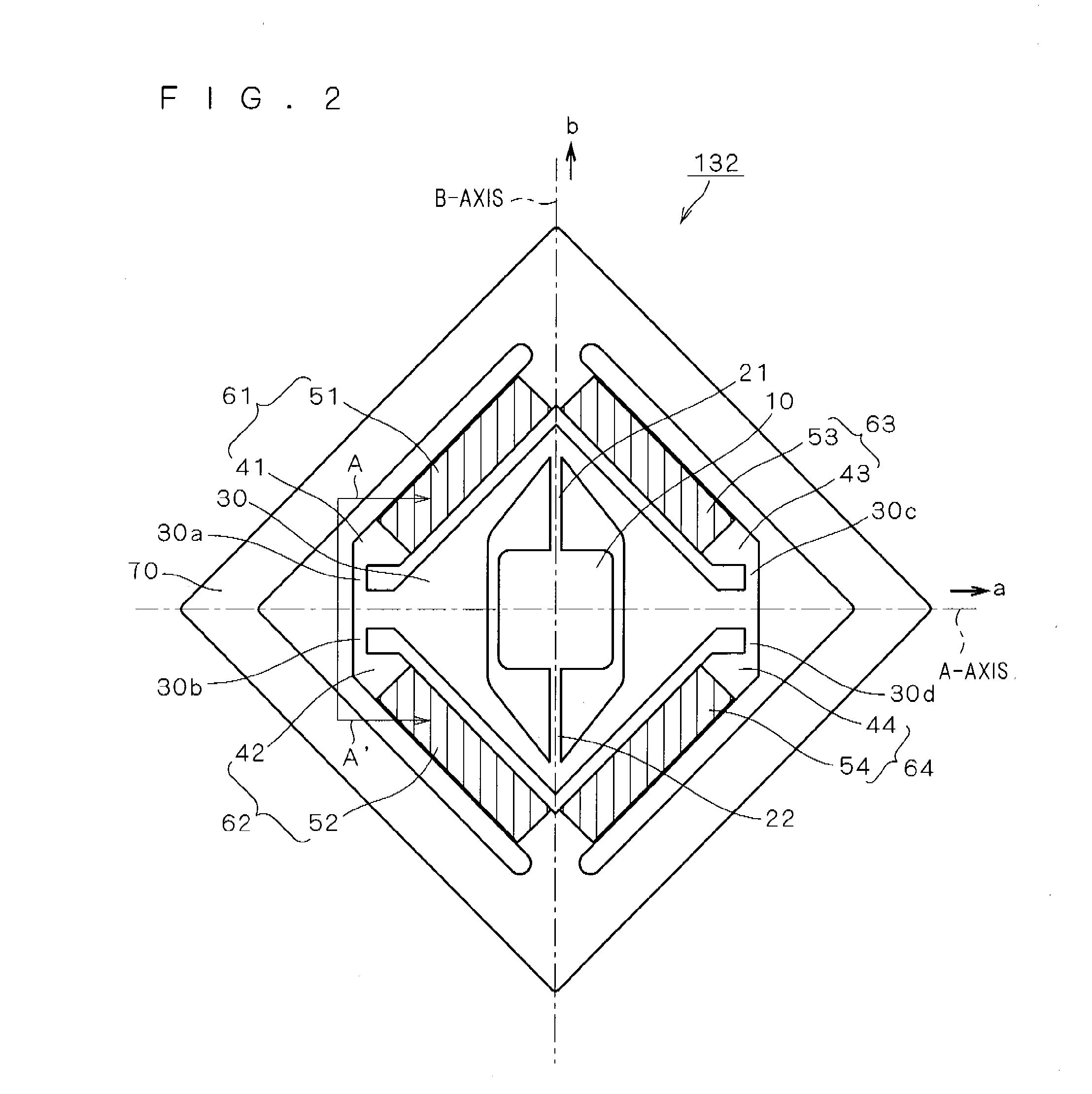
Image projector
InactiveUS20080239252A1Deteriorating brightness of imageConstant speedVehicle headlampsLighting and heating apparatusLight fluxLight beam
An object of the present invention is to provide an image projector capable of projecting a high-quality image while realizing small size. In the image projector, a light flux is deflected two-dimensionally by turning a reflector for reflecting a light flux emitted from a light source around a second axis almost orthogonal to a first axis as a center by resonant drive while turning the reflector around the first axis as a center by non-resonant drive. Shape of one or more optical surfaces of a projection optical system for projecting an image onto a projection plane by guiding light onto the projection plane includes a shape for performing a correction for maintaining scanning speed of the light flux along one scan direction on the projection plane almost constant and a shape for performing a correction for suppressing a distortion in an image along the other scan direction almost orthogonal to the one scan direction on the projection plane. By controlling turn of the reflector, at least one of a correction for maintaining scanning speed of the light flux along the other scan direction on the projection plane almost constant and a correction for suppressing a distortion in an image along the one scan direction on the projection plane is performed.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Image-capturing device
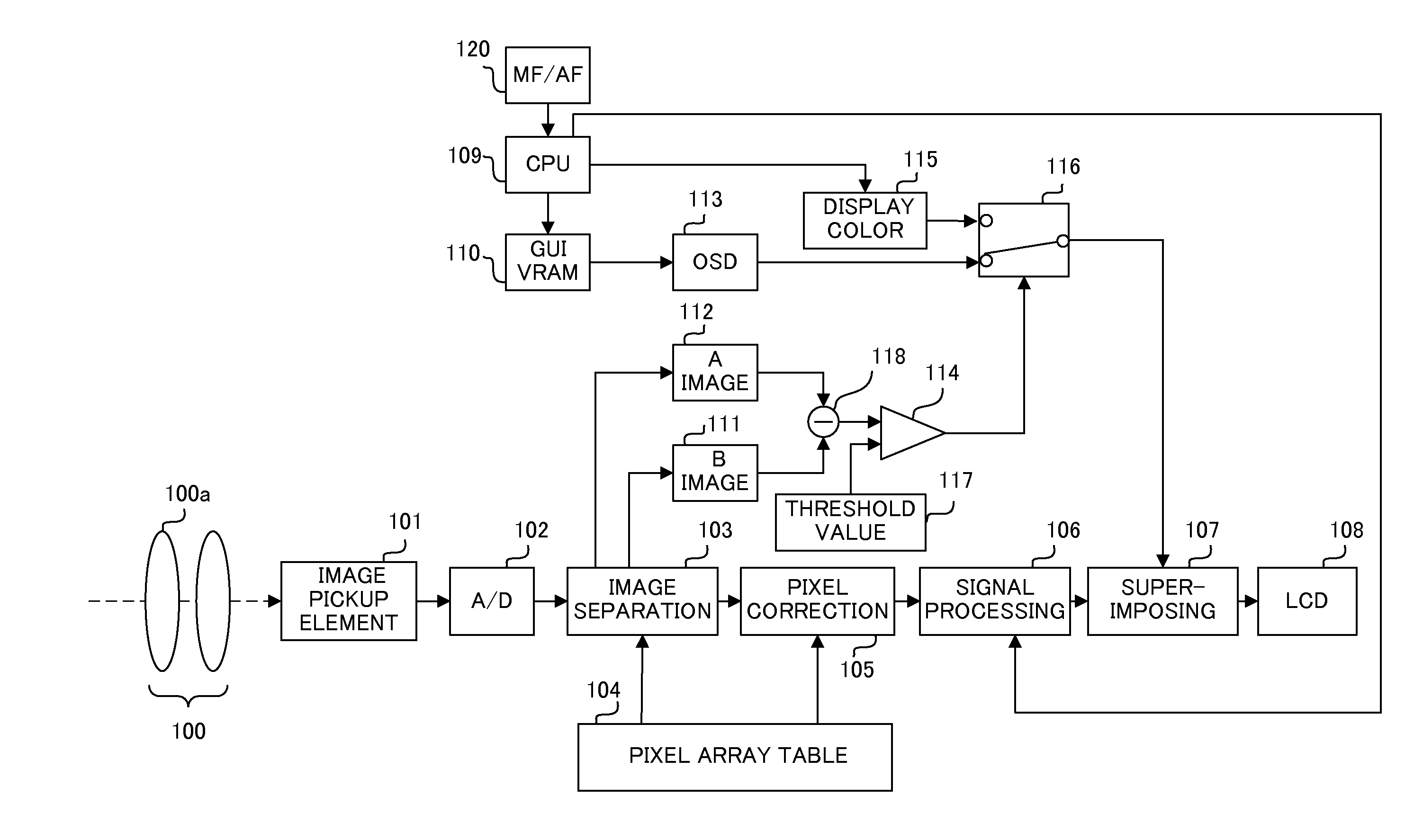
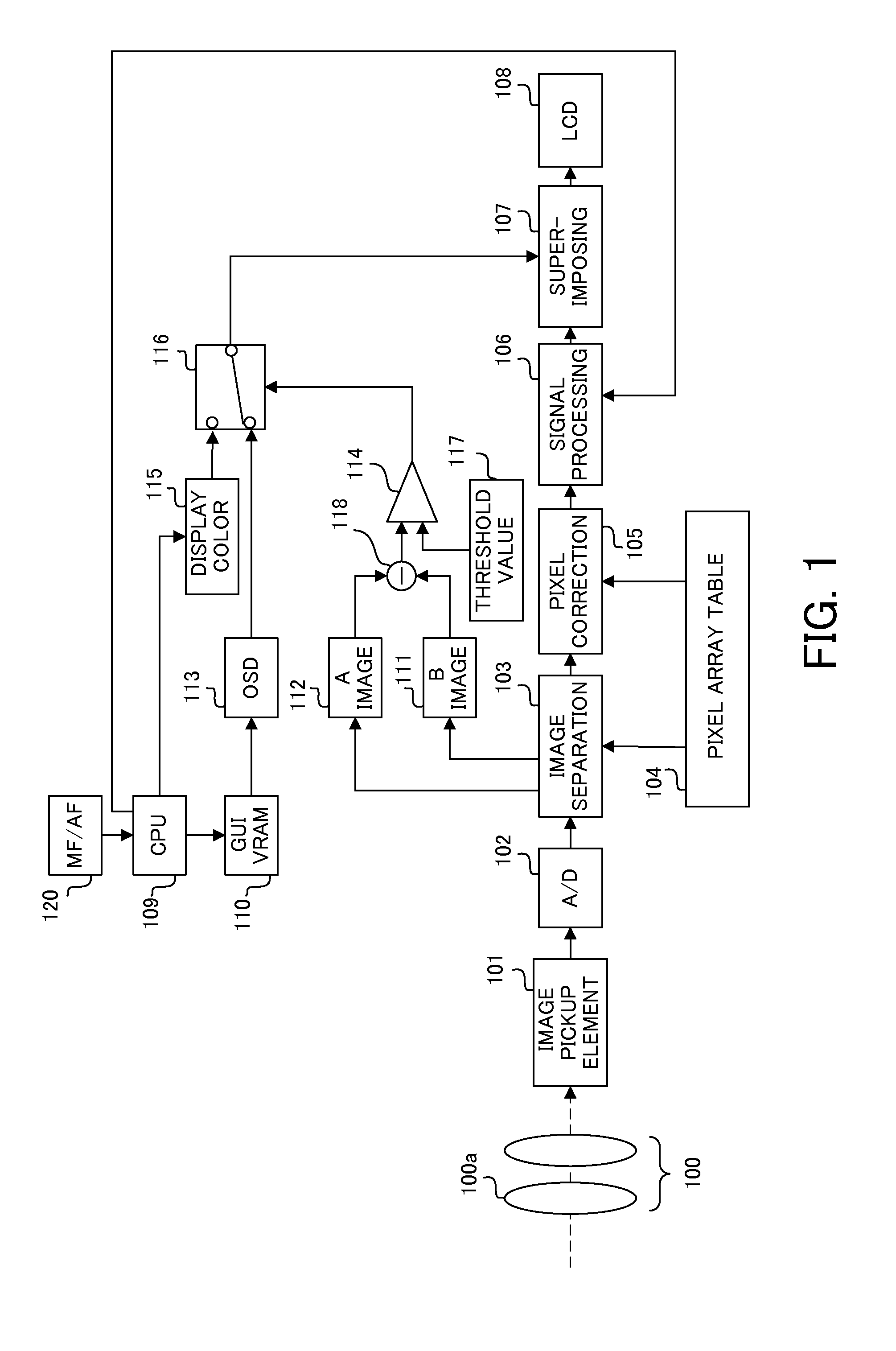
ActiveUS20080084483A1Television system detailsColor television detailsLight fluxPhotoelectric conversion
An image-capturing device includes: a destructive read-type image sensor that executes photoelectric conversion of a light flux from an optical system at a plurality of pixels, stores electrical charges resulting from the photoelectric conversion at the plurality of pixels, and outputs a signal corresponding to each of the stored electrical charges; a read unit that reads out the signal from the image sensor over a specific cycle; a display unit at which display is brought up based upon the signal read out by the read unit each time the read unit reads out the signal; a storage unit that individually stores signals read out by the read unit, each in correspondence to a read operation; an adding unit that adds up a plurality of signals obtained sequentially over time among the signals stored in the storage unit; and a focus detection unit that detects a focus adjustment state of the optical system based upon adding results provided by the adding unit.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Image sensor and image-capturing device
ActiveUS20090295964A1Poorer focus detection accuracyLess precisionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight fluxLight beam
An image sensor includes: a plurality of imaging pixels; and a plurality of focus detection pixels constituted with a micro-lens and a photoelectric conversion element that receives a focus detection light flux transmitted through a photographic optical system and executes photoelectric conversion. The photoelectric conversion element in each of the focus detection pixels includes a light-receiving area where the focus detection light flux is received; light-receiving area images corresponding to each of the focus detection pixels are each formed as the light-receiving area is projected via the micro-lens onto a pupil plane of the photographic optical system; and a positional relationship of the micro-lens and the light-receiving area is determined in correspondence to an image height so that the light-receiving area images corresponding to all the focus detection pixels are superimposed on one another on the pupil plane.
Owner:NIKON CORP
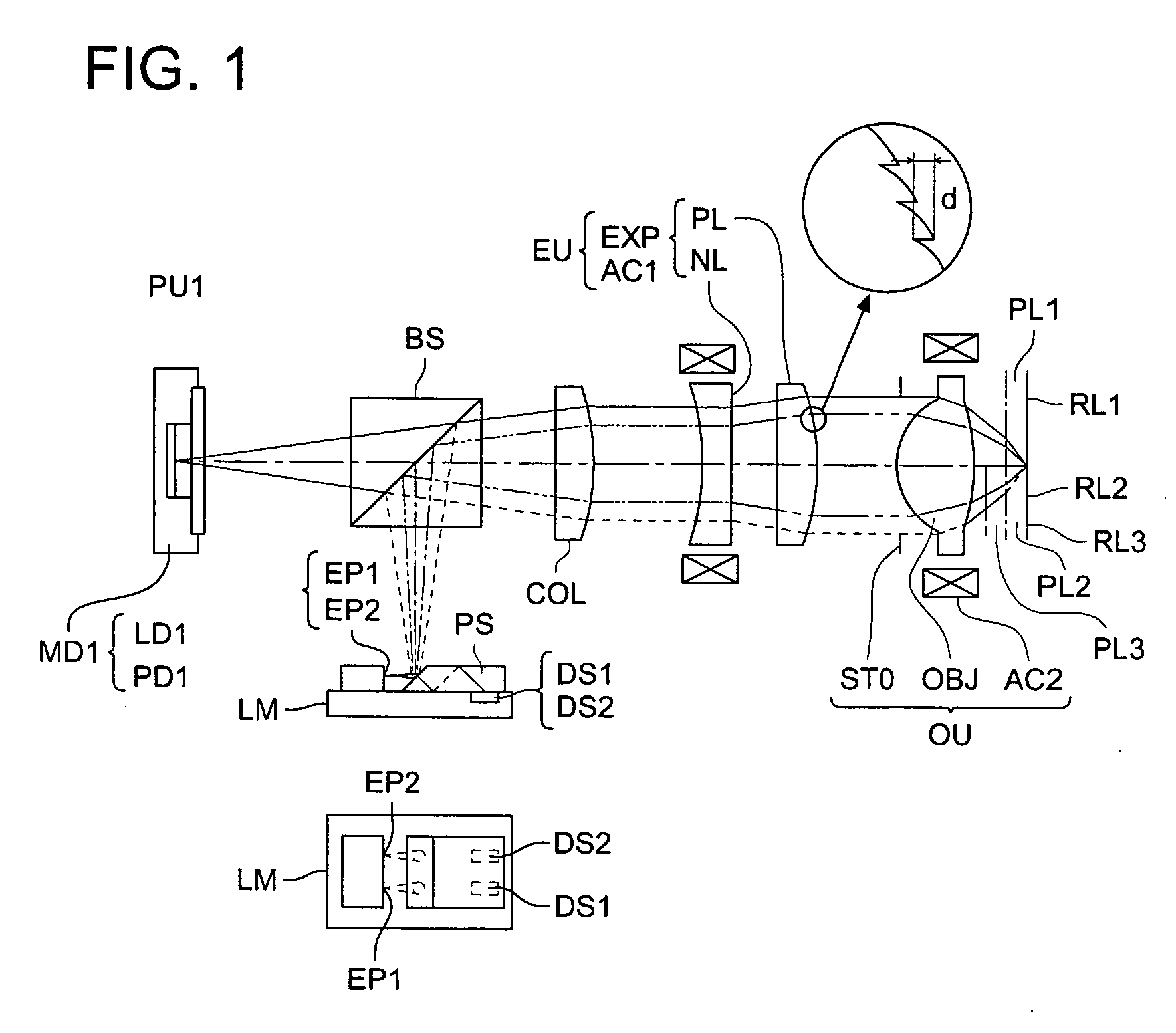
Lens, optical head, optical information writing/reading apparatus and optical information recording medium writing/reading method
InactiveUS6995909B1Increase rangeReduce variationOptical detectorsRecord information storageCamera lensPhase shifted
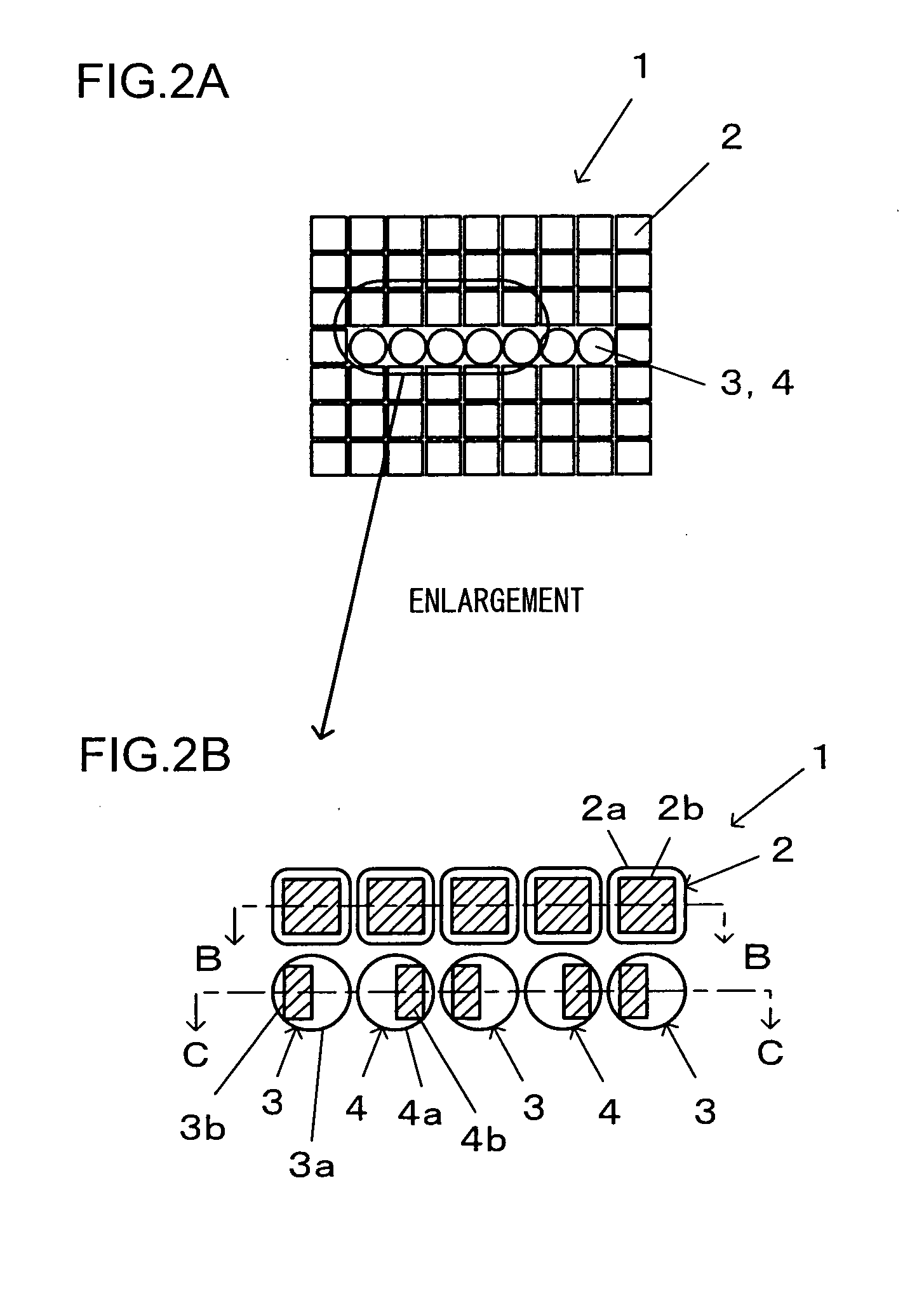
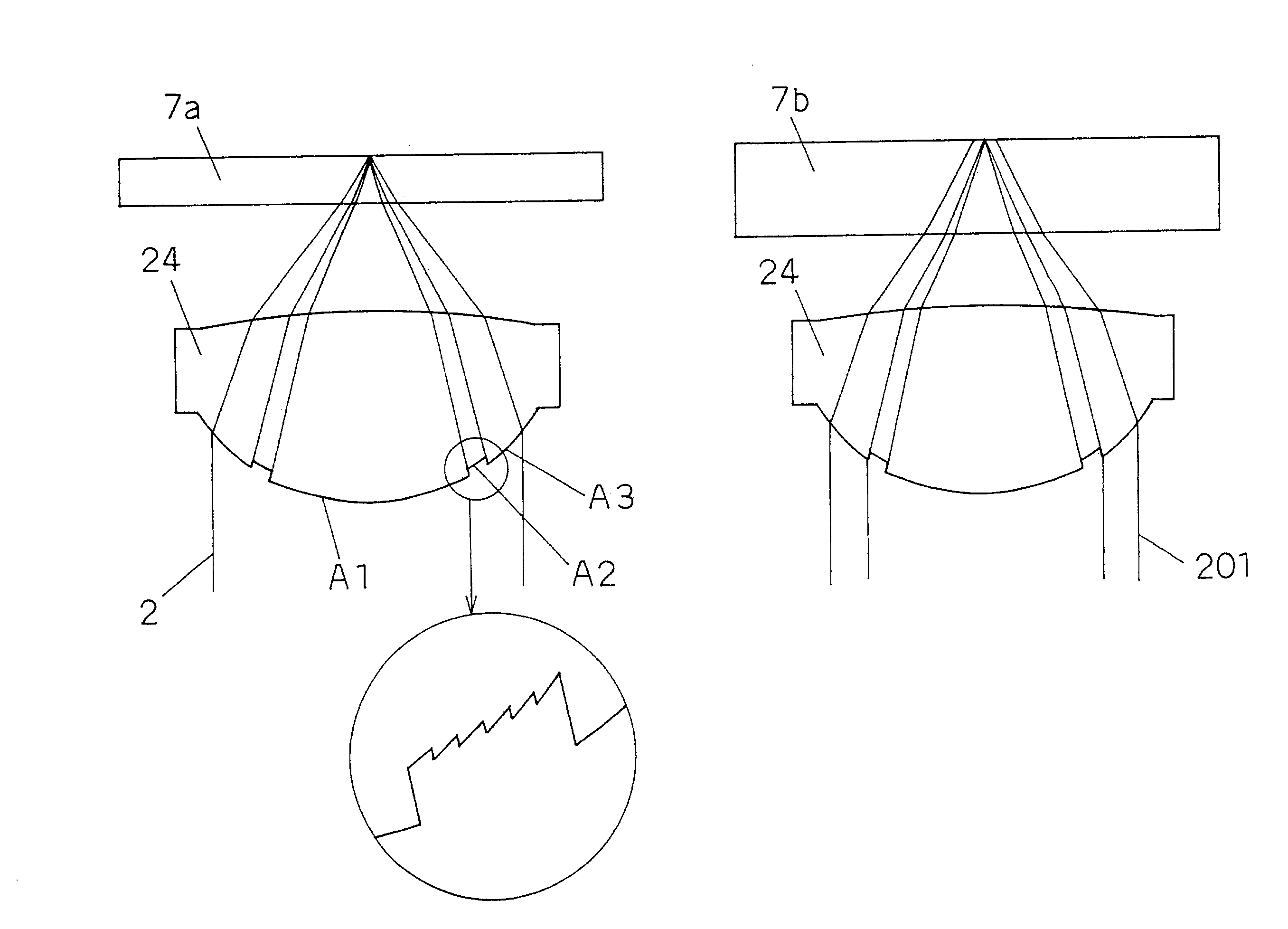
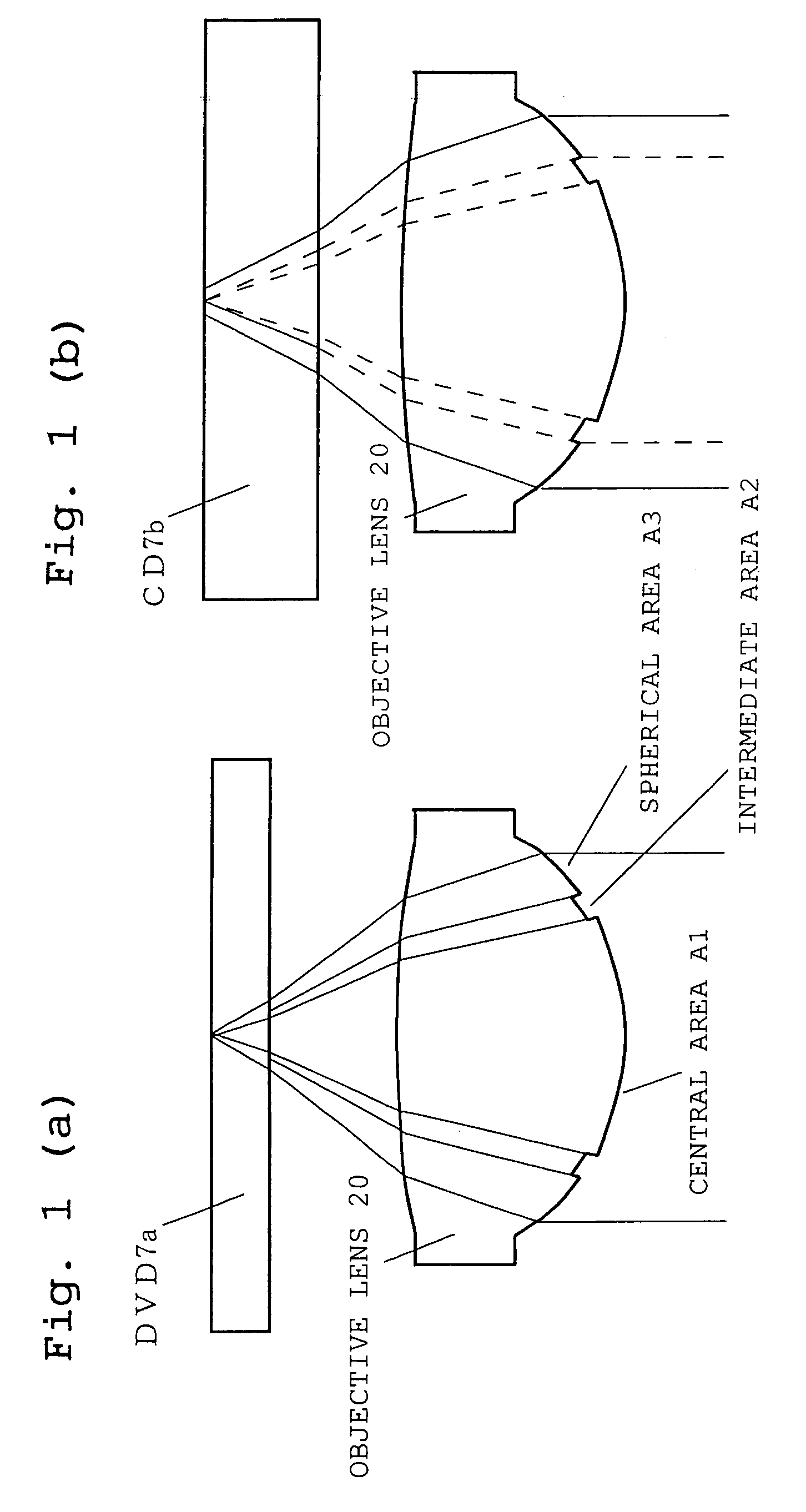
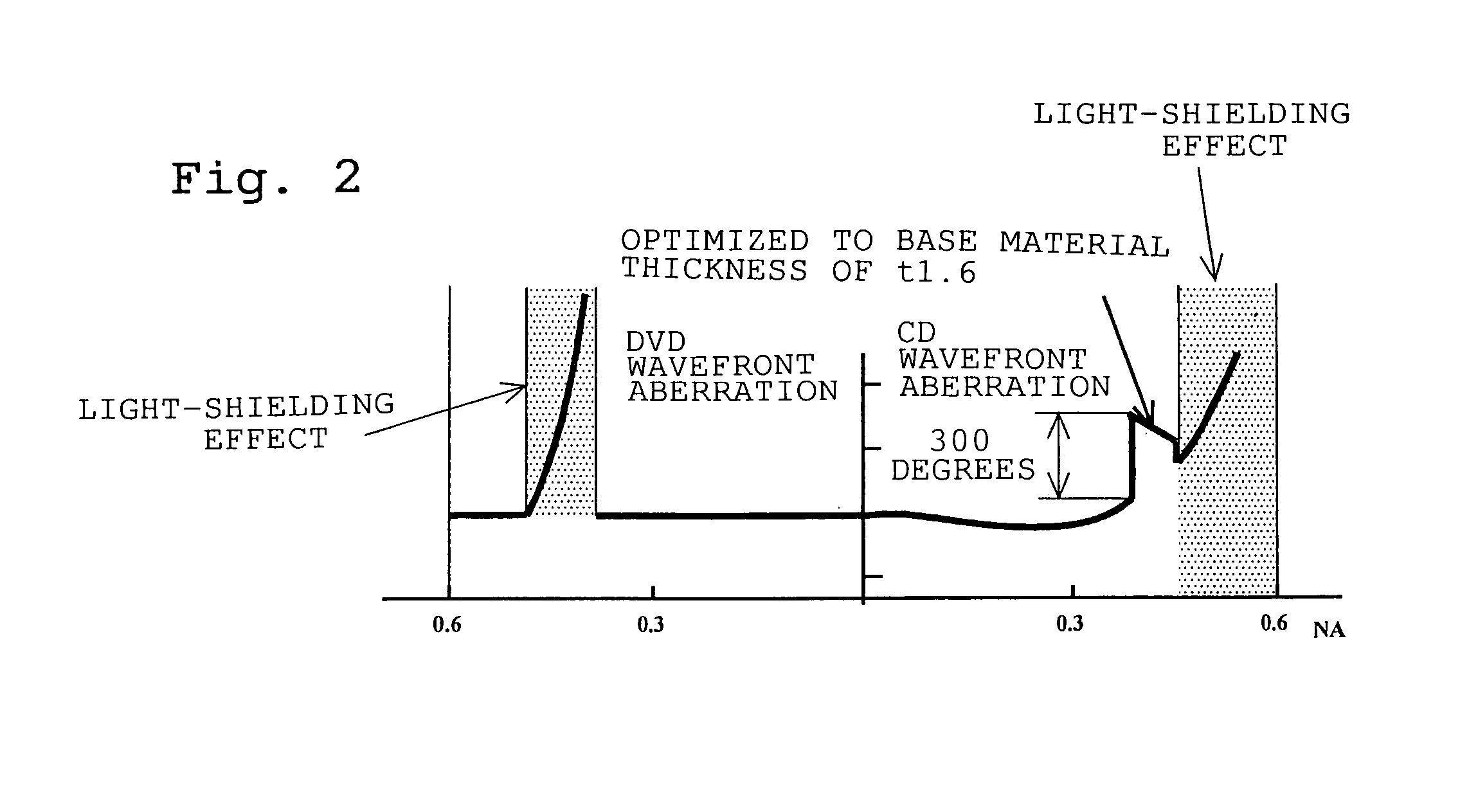
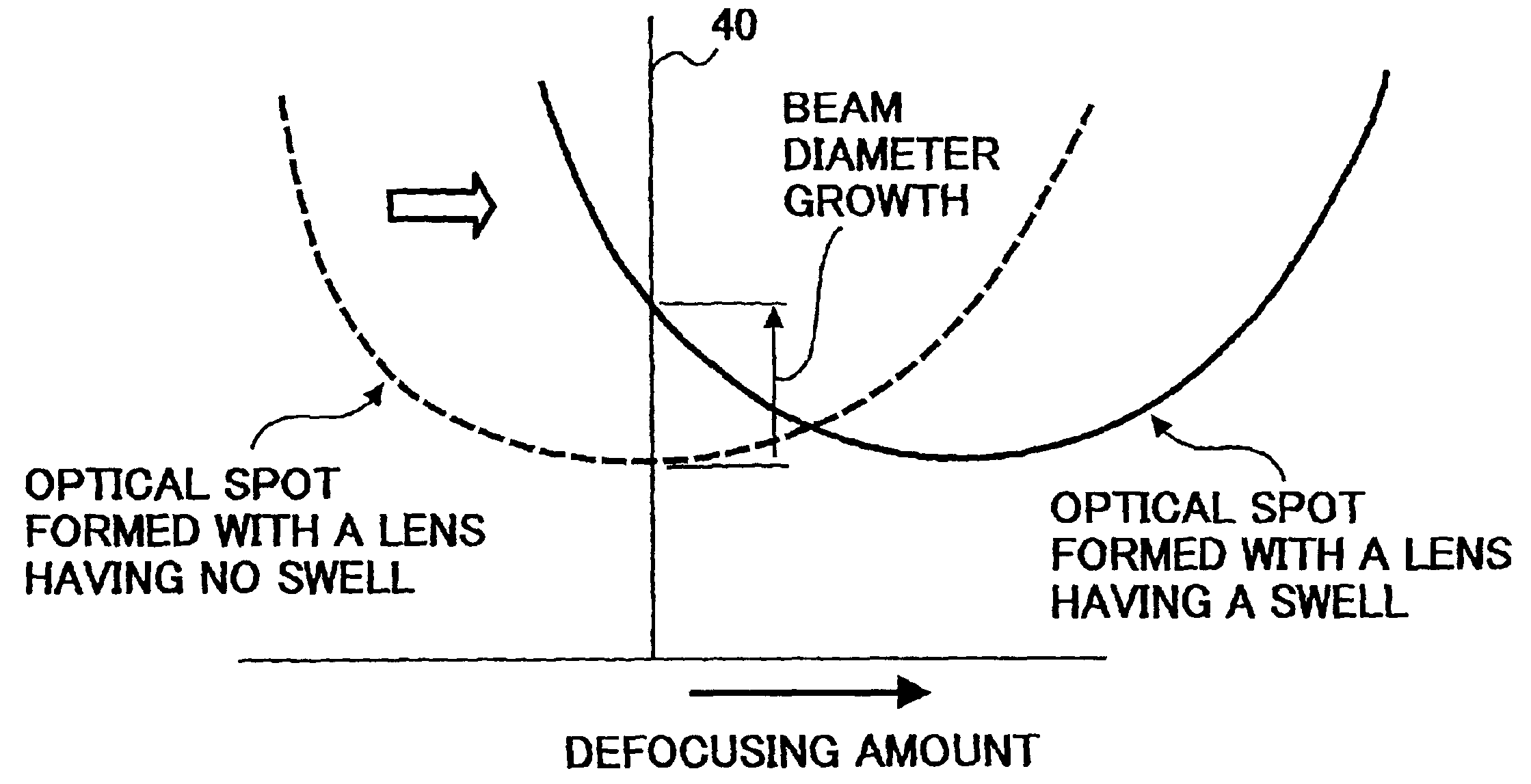
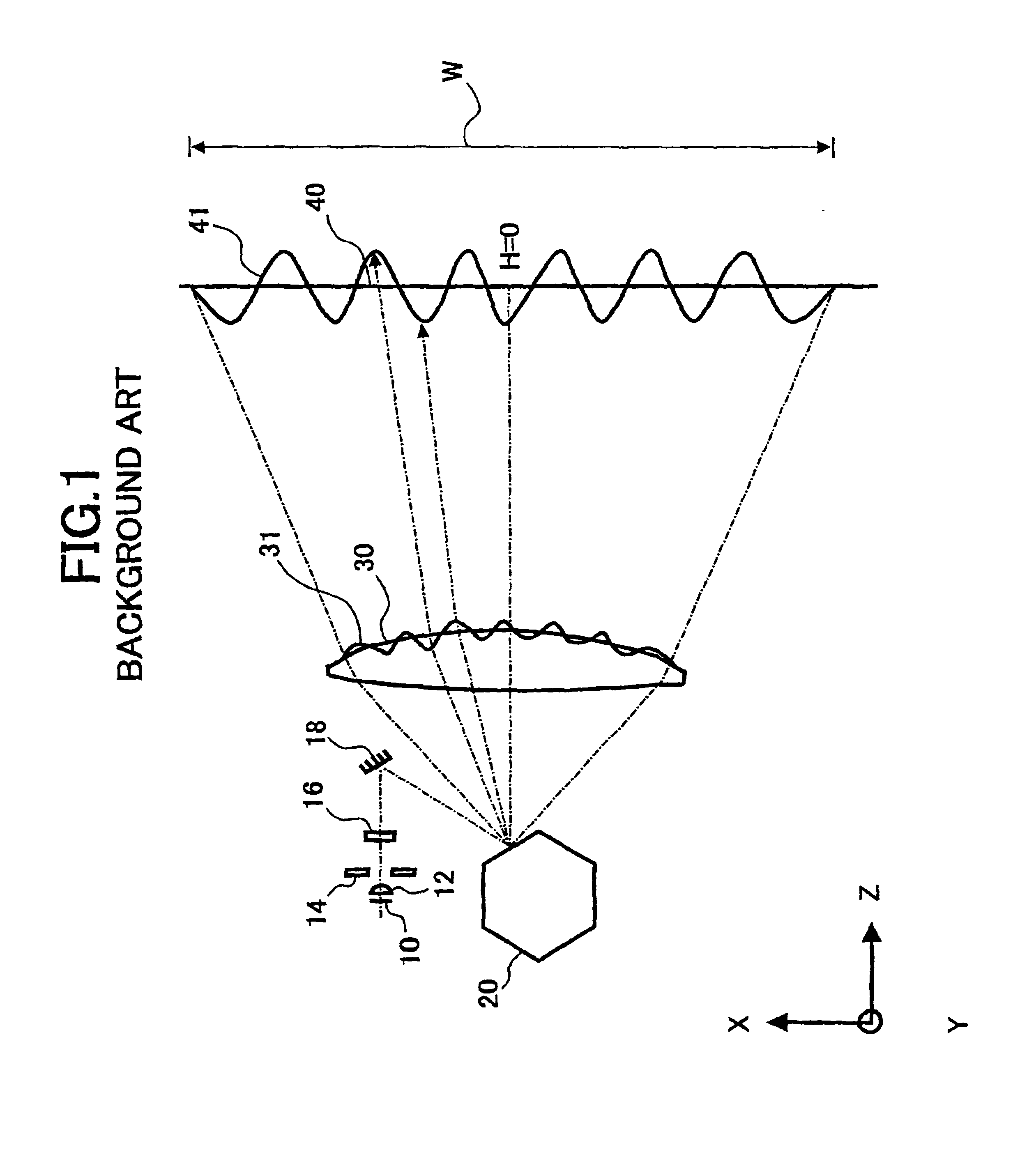
Conventional lenses for DVD / CD compatible writing / reading are liable to CD jitter deterioration due to phase shifts in a central area.Setting a corresponding base material thickness of an intermediate area of the circumference A2 to greater than 1.2 mm which is the base material thickness of the CD, that is, converging luminous flux that has passed through the intermediate area of the circumference A2 onto a farther place than the information recording surface of the base material thickness of the CD makes it possible to reduce jitter deterioration due to phase shifts. Further, it makes possible to provide a system with higher precision and higher reliability.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Lighting device and use thereof
InactiveUS20040129860A1Mitigate such drawbackPhotometry using reference valueMechanical apparatusOverlap zoneEffect light
The lighting device for lighting a lighted field comprises a light source having first and second lighting modules. The lighting modules are adapted to light lighted domains of the lighted field. The lighted domains form an overlap zone, and each lighting module defines an overlap volume. The device includes detector means adapted to detect a zone of reduced lighting in the overlap zone, and control means adapted to increase the light flux from said second lighting module when the detector means detect a zone of reduced lighting. The invention is applicable to lighting devices used in operating theaters.
Owner:ALM
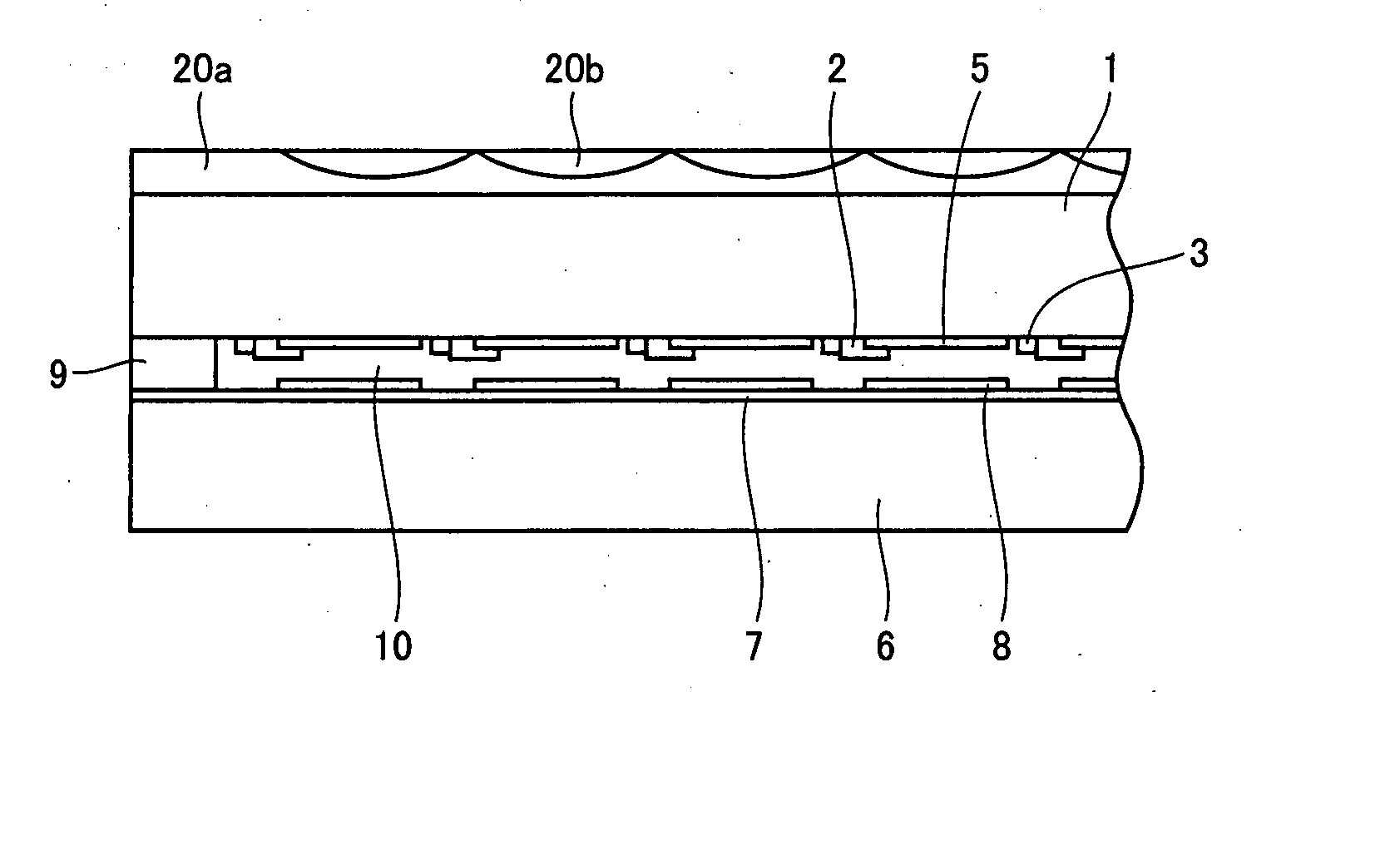
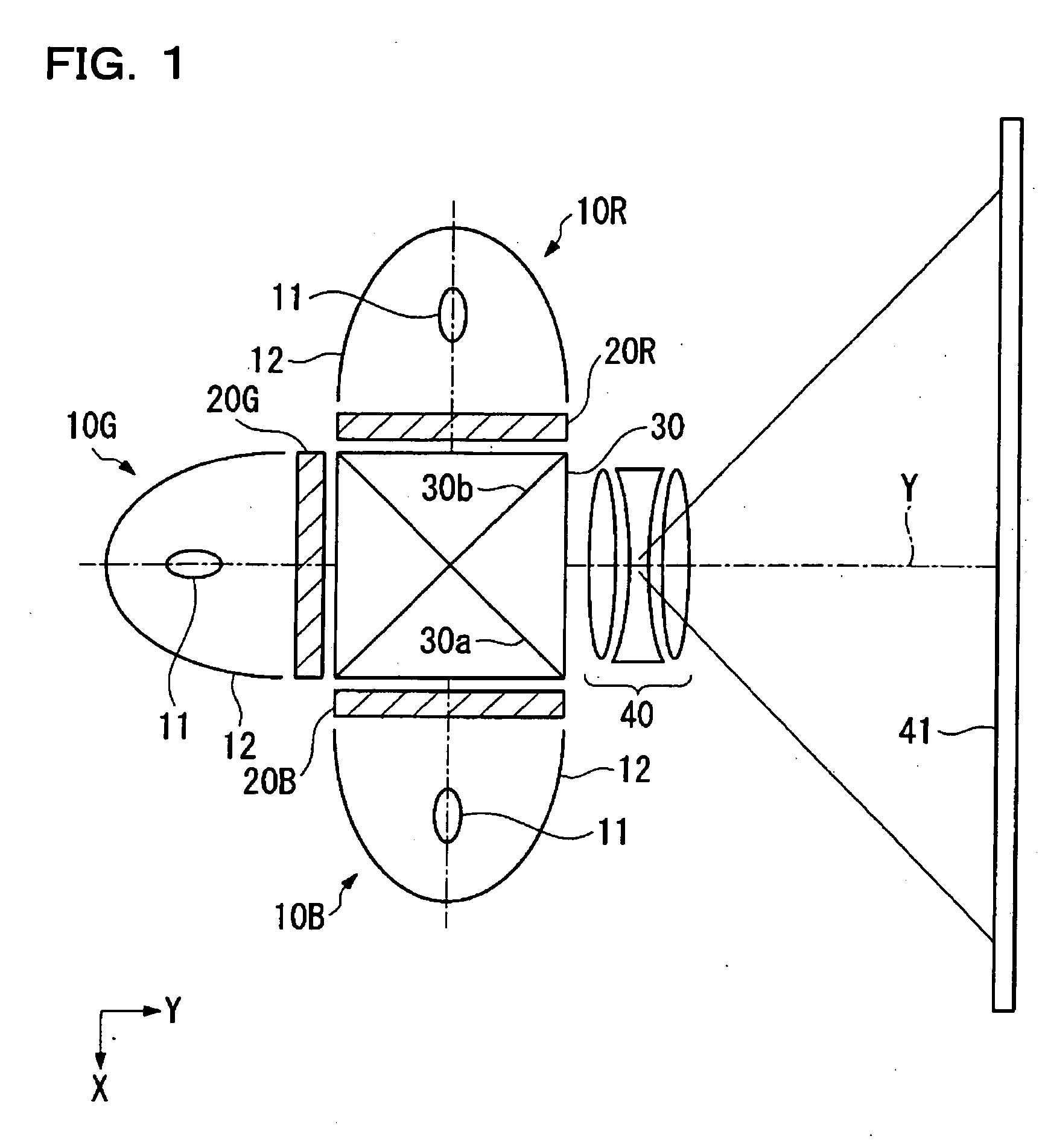
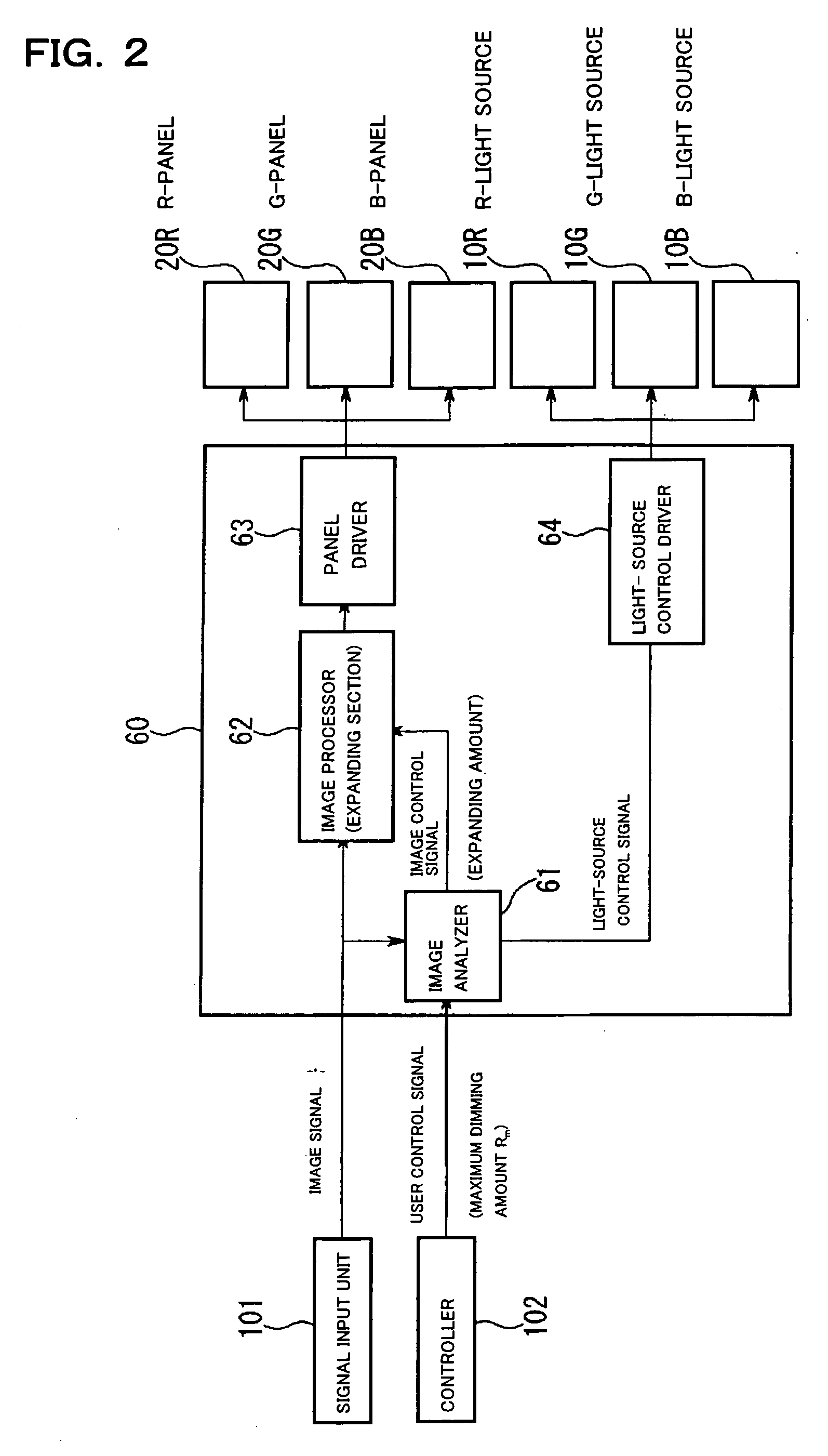
Transmission-Type Display Panel and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20080094716A1Low costIncrease display brightnessGlass making apparatusProjectorsLiquid-crystal displayDiamond-like carbon
A transmission-type display panel according to the present invention includes a plurality of transparency control regions arranged in an array, a non-transparent border region existing around each of the transparency control regions, and a microlens array including a plurality of microlenses arranged in an array so as to correspond to the plurality of transparency control regions. Each of the microlenses serves to converge incident light, which is about to advance straight to the non-transparent border region, into corresponding one of the transparency control regions. The microlens array is formed by use of a transparent diamond-like carbon (DLC) film. The DLC film includes a region having its refractive index modulated corresponding to each of the microlenses, and produces a light convergence effect when light flux passes through the region having its refractive index modulated. By applying the microlens array in the DLC film to a transmission-type display panel (e.g., a liquid crystal display panel), it is possible to provide a transmission-type display panel having improved display brightness, in a simple manner and at a low cost.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
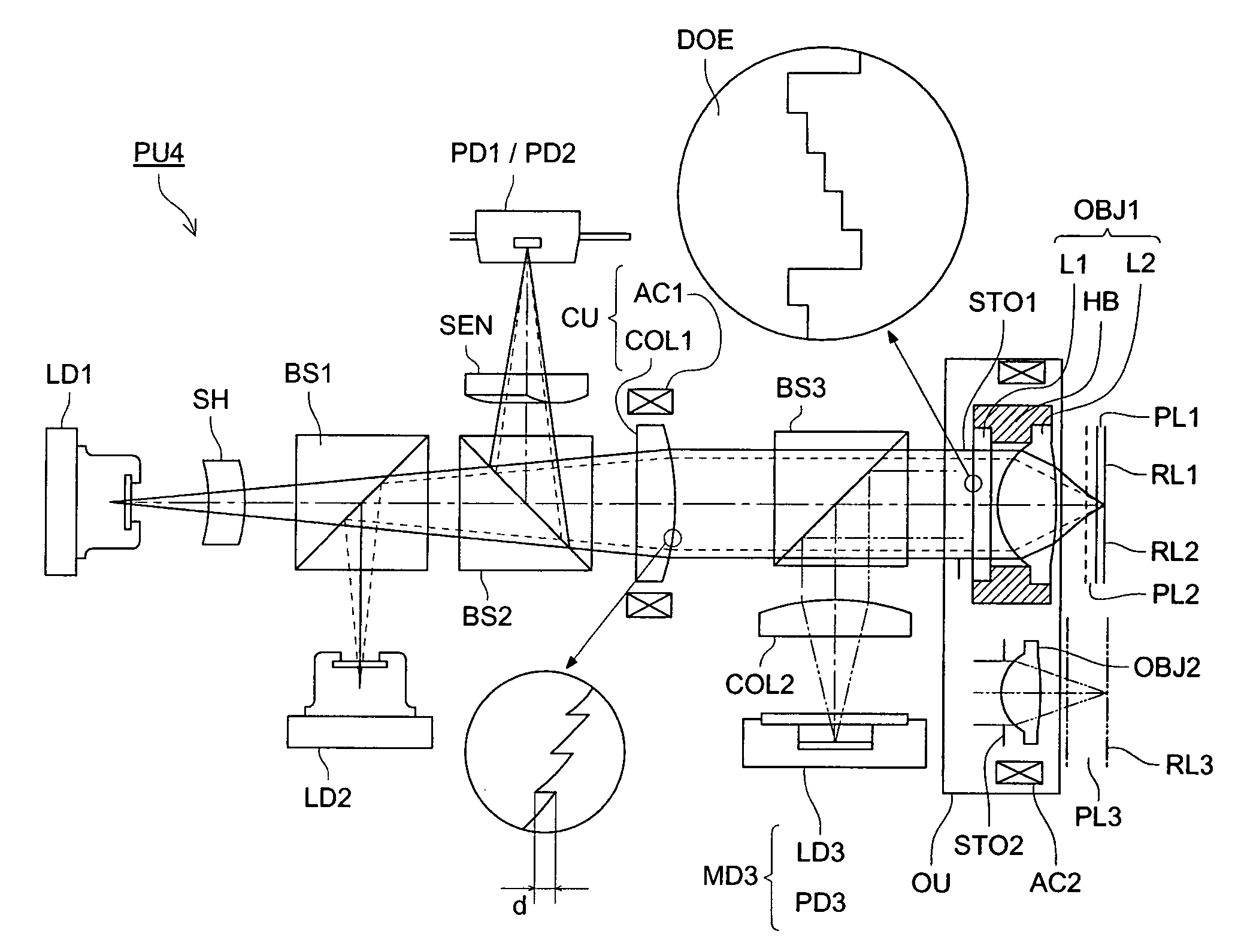
Optical pickup device, optical information recording and reproducing apparatus, expander lens, coupling lens and chromatic aberration correcting optical element
An optical pickup apparatus includes first and light sources; an objective lens; a spherical aberration correcting optical unit; and a chromatic aberration correcting optical element which includes a diffractive surface on at least one of optical surfaces of the chromatic aberration correcting optical element such that a diffractive structure which is constructed by a plurality of ring-shaped zones separated by fine steps is formed on the diffractive surface, wherein the depth of steps along an optical axis is designed so that n2 which is a diffraction order of a diffracted ray having a largest diffraction efficiency among diffracted rays caused when the second light flux enters into the diffractive structure, is lower order than n1 which is a diffraction order of a diffracted ray having a largest diffraction efficiency among diffracted light rays caused when the second light flux enters into the diffractive structure.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
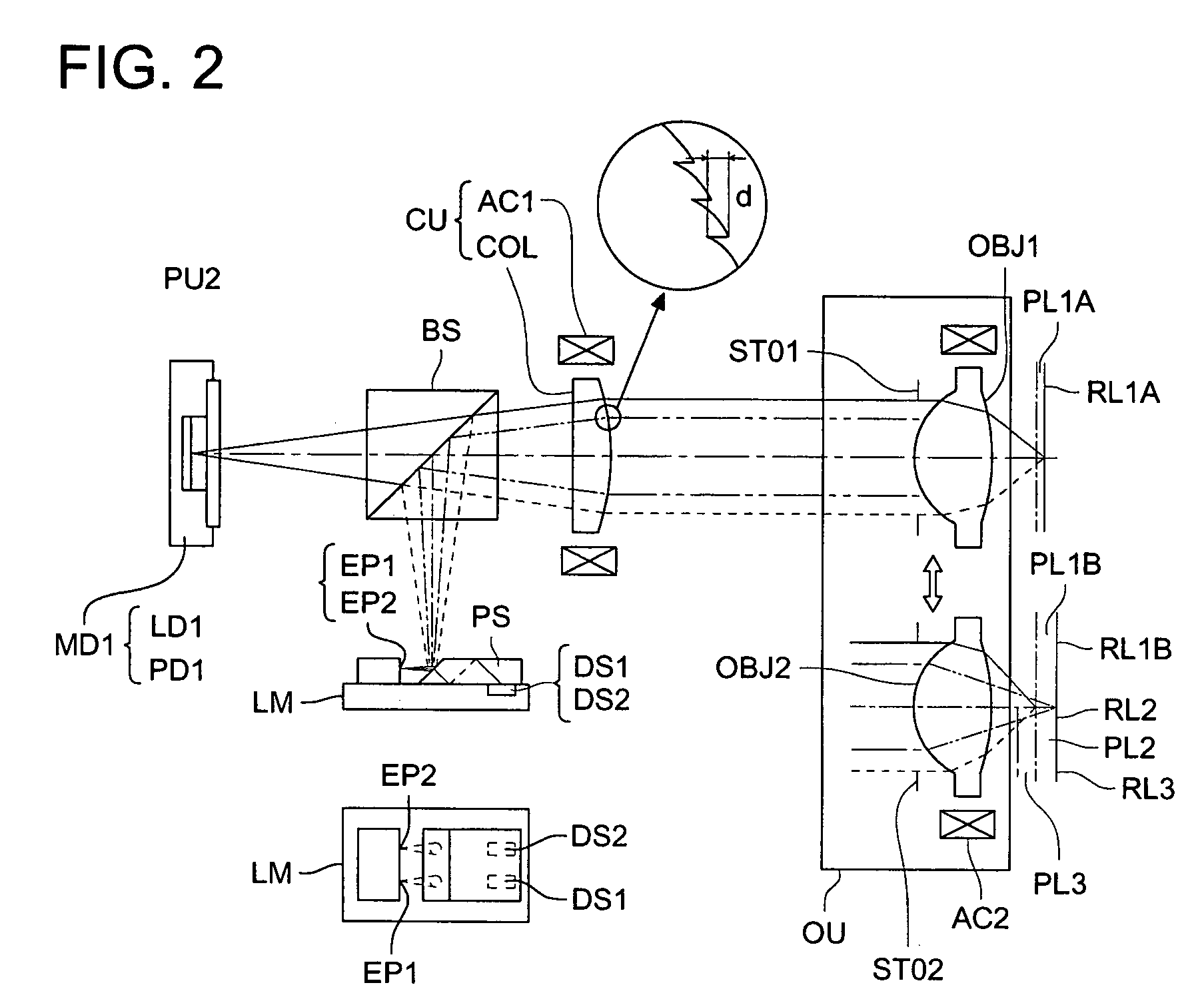
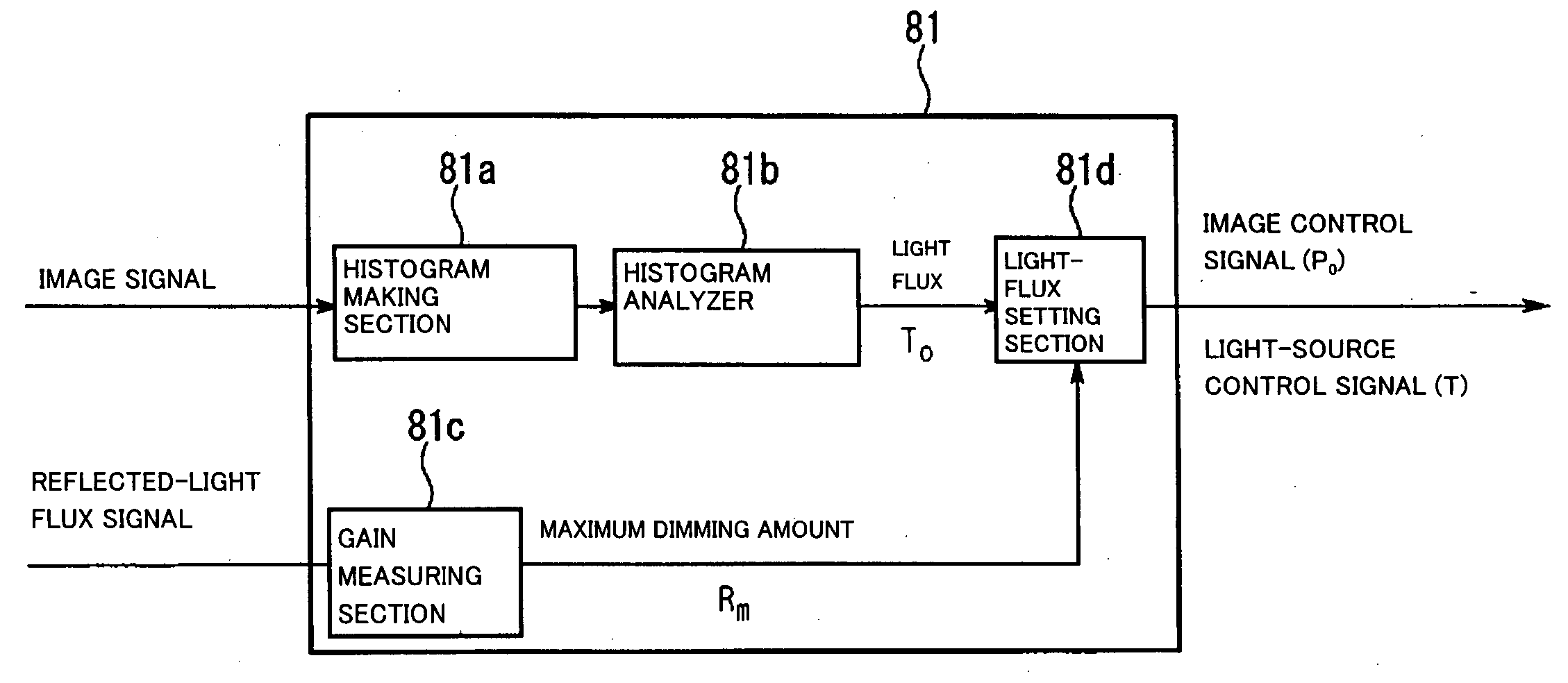
Illuminator, projection display device and method for driving the same
ActiveUS20050017990A1Sufficient tone reproductionDimming amount of the light source can be reducedTelevision system detailsProjectorsLuminous fluxBrightness perception
The invention provides a projection display device capable of appropriate light control depending on the kind of the image, the ambient brightness and so on, a method for driving the same, and an illuminator used in the same. The light flux of illumination can be adjusted on the basis of image information. The allowable light control range (dimming control) can be optimally set depending on the information (usage information) on the kind of viewed content, the brightness of viewing environment, the gain of a screen and the like.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Lighting device and projector
ActiveUS20150153020A1Improve display qualityProjectorsColor television detailsLight equipmentLight flux
In a lighting device, light in a first wavelength range which is output from a light emitting element passes through a first phase difference plate, and is separated into a first light flux and a second light flux by a polarization separation element. A wavelength conversion unit converts the first light flux to a third light flux. An optical element converts the second light flux into a fourth light flux. A first color combining element combines the third light flux with the fourth light flux. A first control unit changes a direction of an optical axis of the first phase difference plate according to an intensity of the third light flux and an intensity of the fourth light flux.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
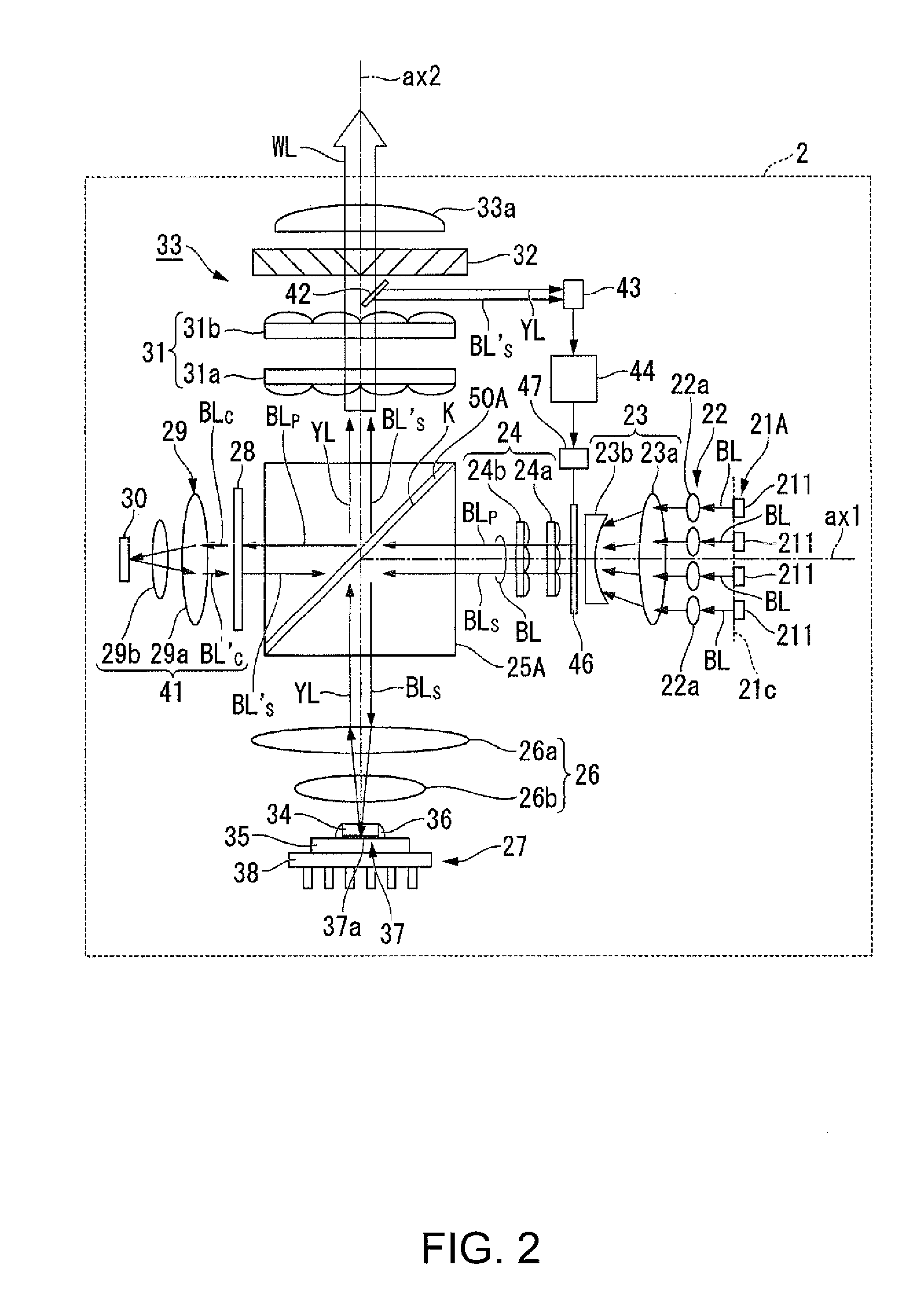
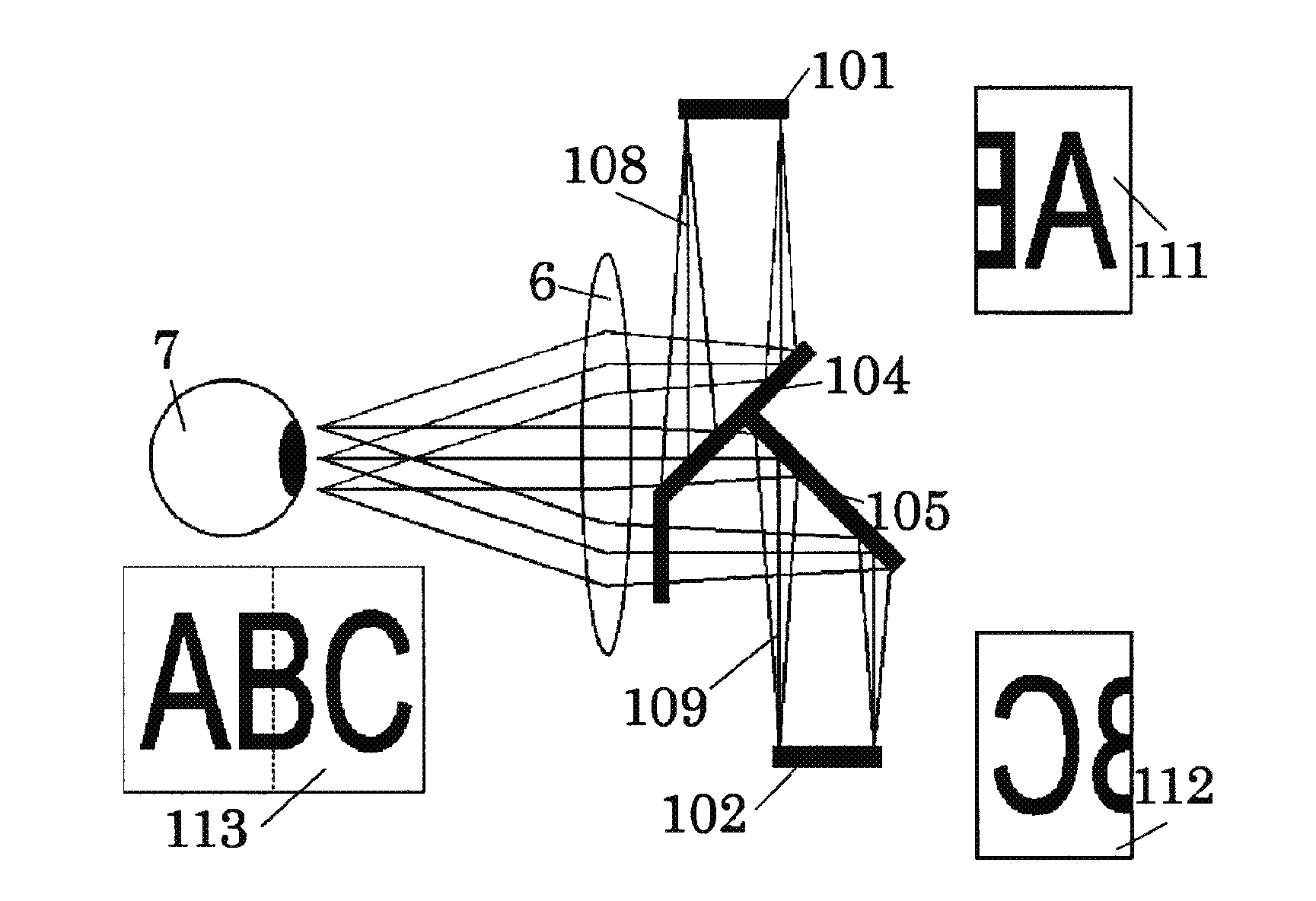
Image display apparatus
The image display apparatus includes first and second display elements respectively displaying first and second original images, and an optical system presenting an enlarged combined image of the first and second original images with first and second light fluxes from the first and second display elements. The optical system includes at least one reflective surface. When a cross-section of the optical system on which optical paths of the first and second light fluxes are turned by reflections at the reflective surface is defined as a decentering cross-section, the first and second original images correspond to different view angles in the decentering cross-section. Light flux components respectively included in the first and second light fluxes and introduced to a same image point in the enlarged combined image are overlapped with each other on an exit pupil plane.
Owner:CANON KK
Image pickup apparatus and display control method for the same
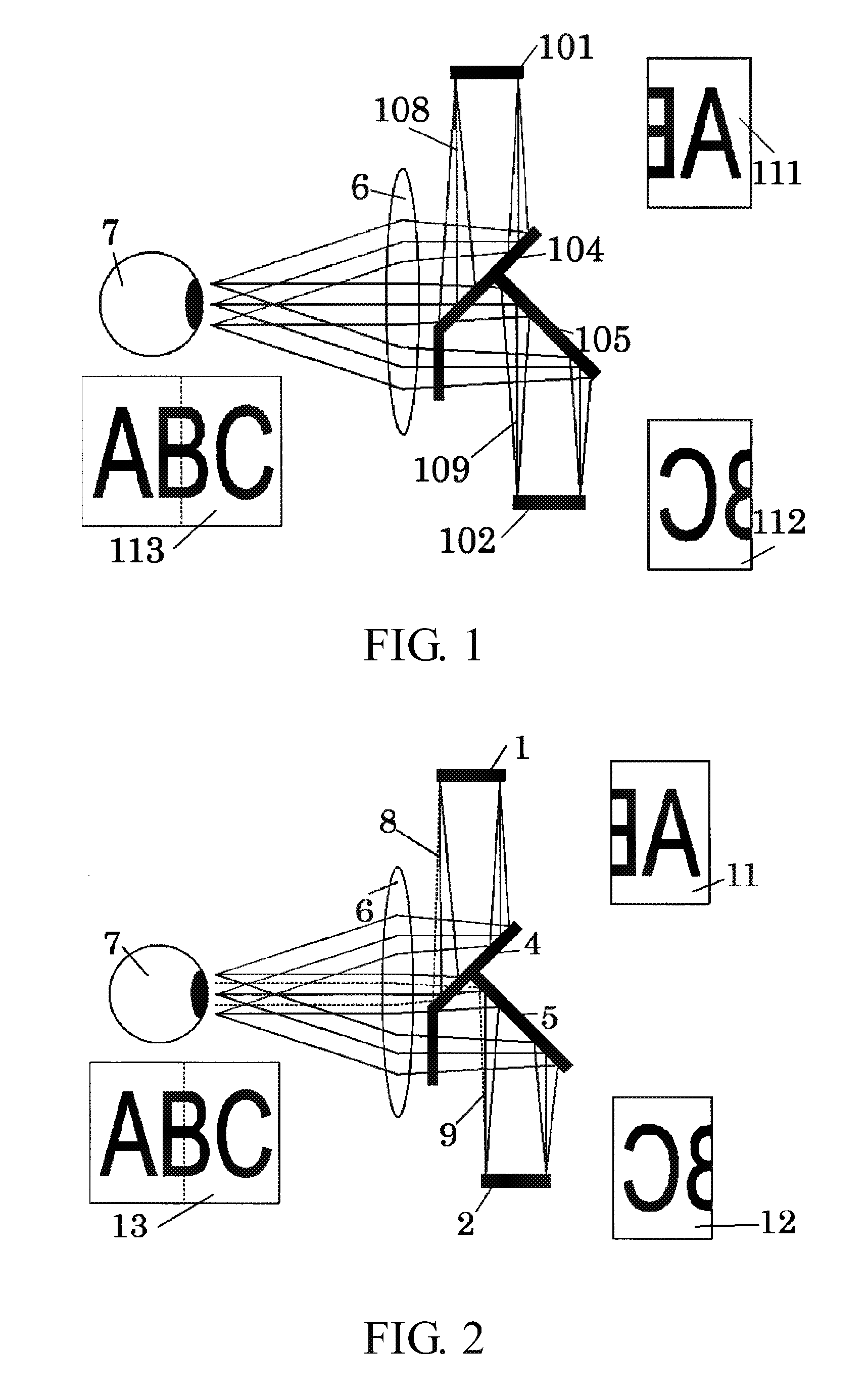
InactiveUS20090153720A1Easy to understandTelevision system details2D-image generationComputer graphics (images)Light flux
An image pickup apparatus of the present invention comprises an image obtaining part configured to photoelectrically convert a first object image and a second object image formed by light fluxes divided by a pupil divider among light fluxes from an image pickup optical system to generate a first image and a second image, a displaying part configured to display images, and a processing part configured to cause the displaying part to display a superimposed image formed by superimposing the first and second images on each other.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection optical system and image display apparatus
ActiveUS20100238416A1Reduce the overall heightBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsMicroscopesProjection opticsLight flux
A projection optical system for enlarging and projecting a light flux from an image display panel modulating an irradiation light, onto a screen in an oblique direction, the projection optical system includes: a lens system including a plurality of lenses, the lens system refracting the light flux from the image display panel; a single convex mirror reflecting the light flux from the lens system, the lens system and the convex mirror being arranged in an order from the image display panel; and a stop disposed in an optical path after an emission from the lens system to an incidence on the convex mirror.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7068406B2Non-uniformity in quantity of lightImprove wavelength dependent characteristic and angle characteristicMirrorsPrintingAngle dependenceLight flux
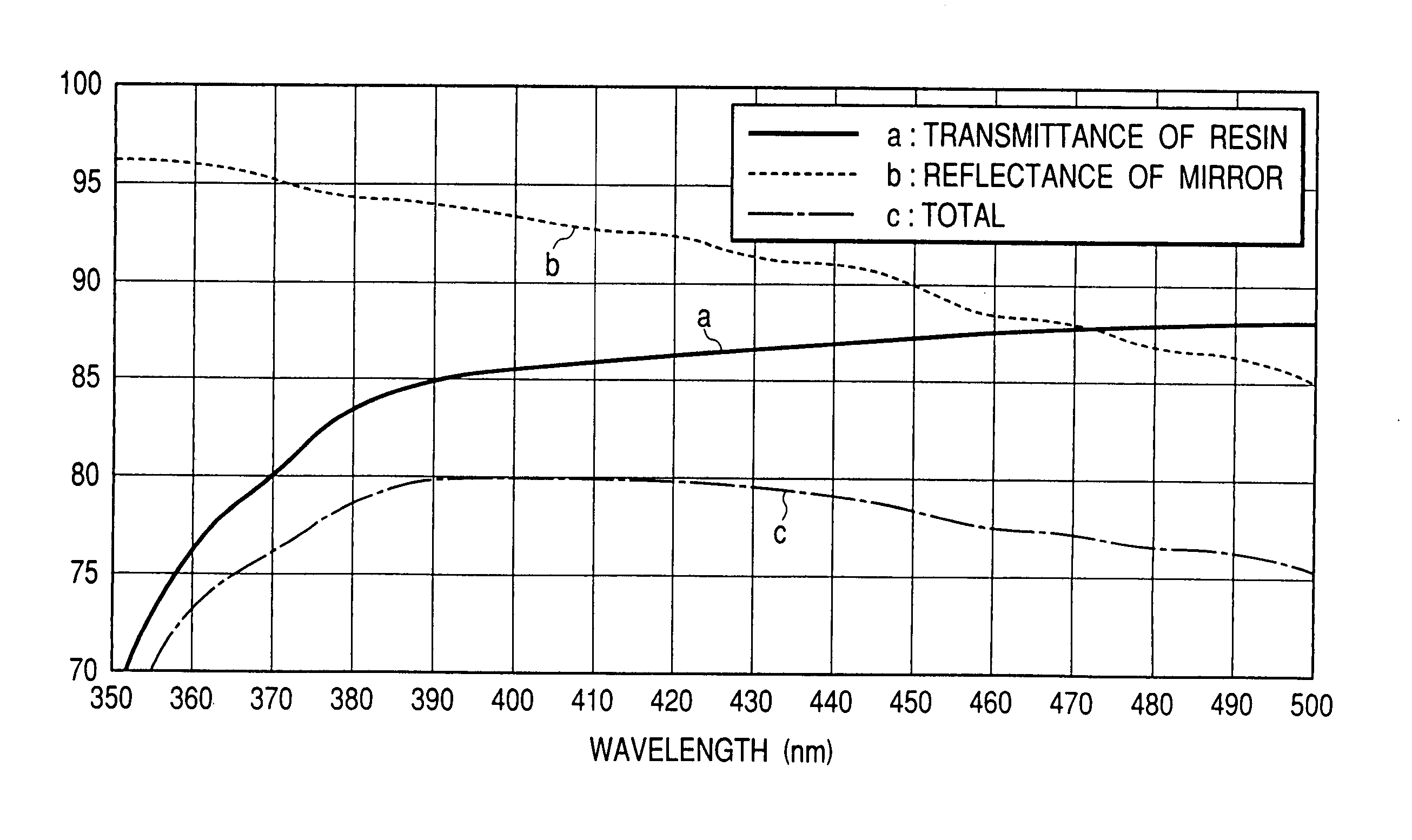
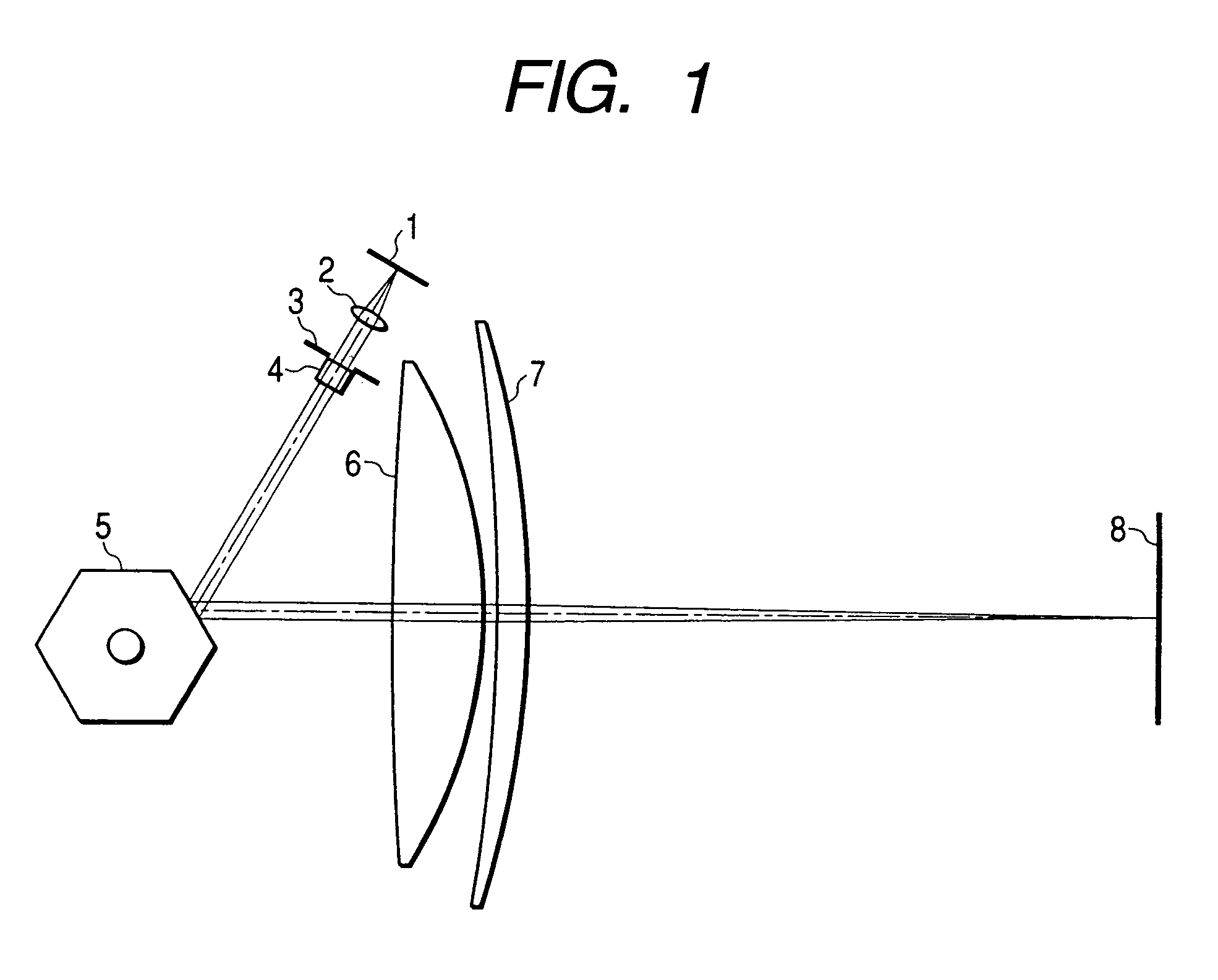
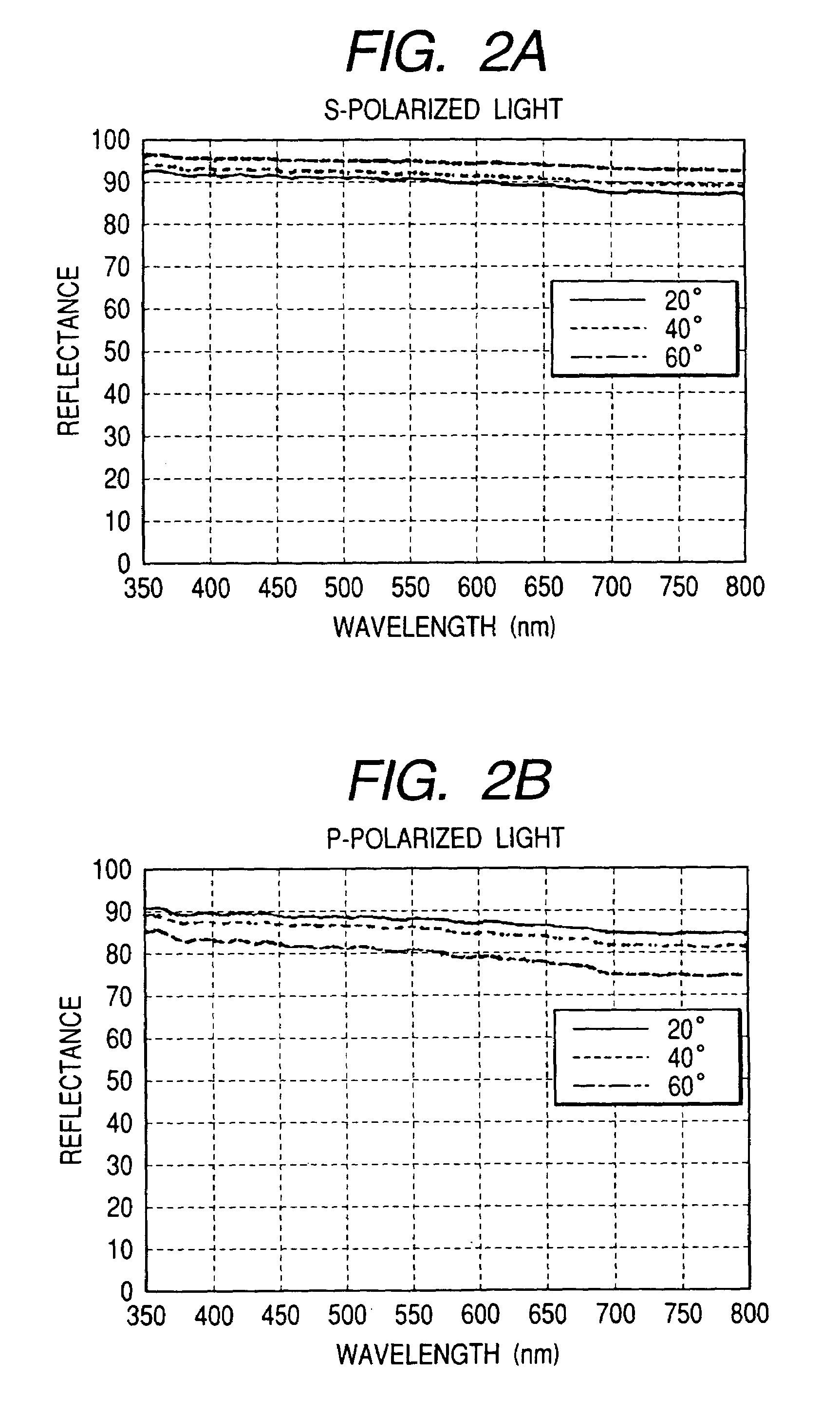
A scanning optical system using a short-wavelength light of 500 nm or less uses a reflecting mirror having a higher absolute reflectivity and having reduced wavelength and angle dependences. Divergent ray of light emitted from a semiconductor laser is converted into an approximately parallel light beam by a collimator lens and the diameter of the light flux is reduced by an aperture before travel to a polygon mirror. The light beam from the polygon mirror passes through scanning lenses to form a small spot at any point in the entire scanning area. The semiconductor laser is a gallium nitride semiconductor laser having an oscillation wavelength of 408 nm. The polygon mirror has such a characteristic that, if the complex refractive index N of a metallic film contributing to a reflection characteristic of the reflecting mirror is defined as N(λ)=n(λ)−ik(λ), then k(λ)>√{square root over ((−n(λ)2+18n(λ)−1))}{square root over ((−n(λ)2+18n(λ)−1))} is satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
Light emitting device, surface light source device, display and light flux control member
Light from light emitting element enters into a flux control member through a recess on an inner face of the light flux control member, being emitted from an emission control face (outer face). At least so far as light falls within a half-intensity-angular-range, the light satisfies Condition 1 ((θ5 / θ1)>1 except for light in the vicinity of a normal direction of the emission control face) and Condition 2 (Value of θ5 / θ1>1 gets smaller gradually with increasing of θ1). It is noted that θ1, θ5 are angles made at being inner-incident to the emission control face and at being emitting from the same, respectively. The emission control face has a planar outline shape which is anisotropic around optical axis L, thereby causing value of θ5 / θ1 to have a change depending on direction angle φ around optical axis L, with the result that highly uniform light is supplied to a required anisotropic irradiation range.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Optical scanner, optical scanning method, scanning image forming optical system, optical scanning lens and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS6999208B2Alleviate and eliminate occurrenceDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersOptical scannersLight flux
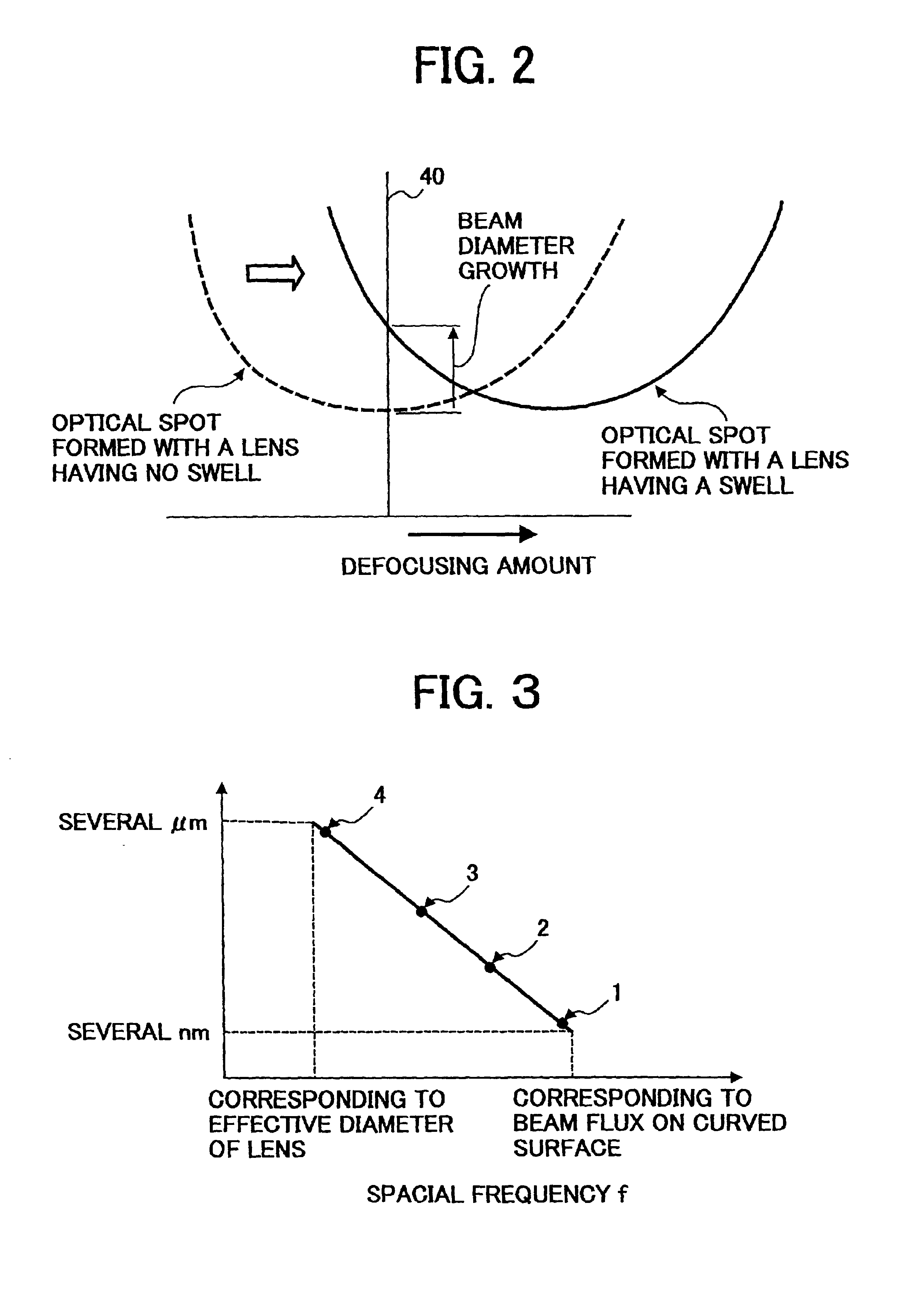
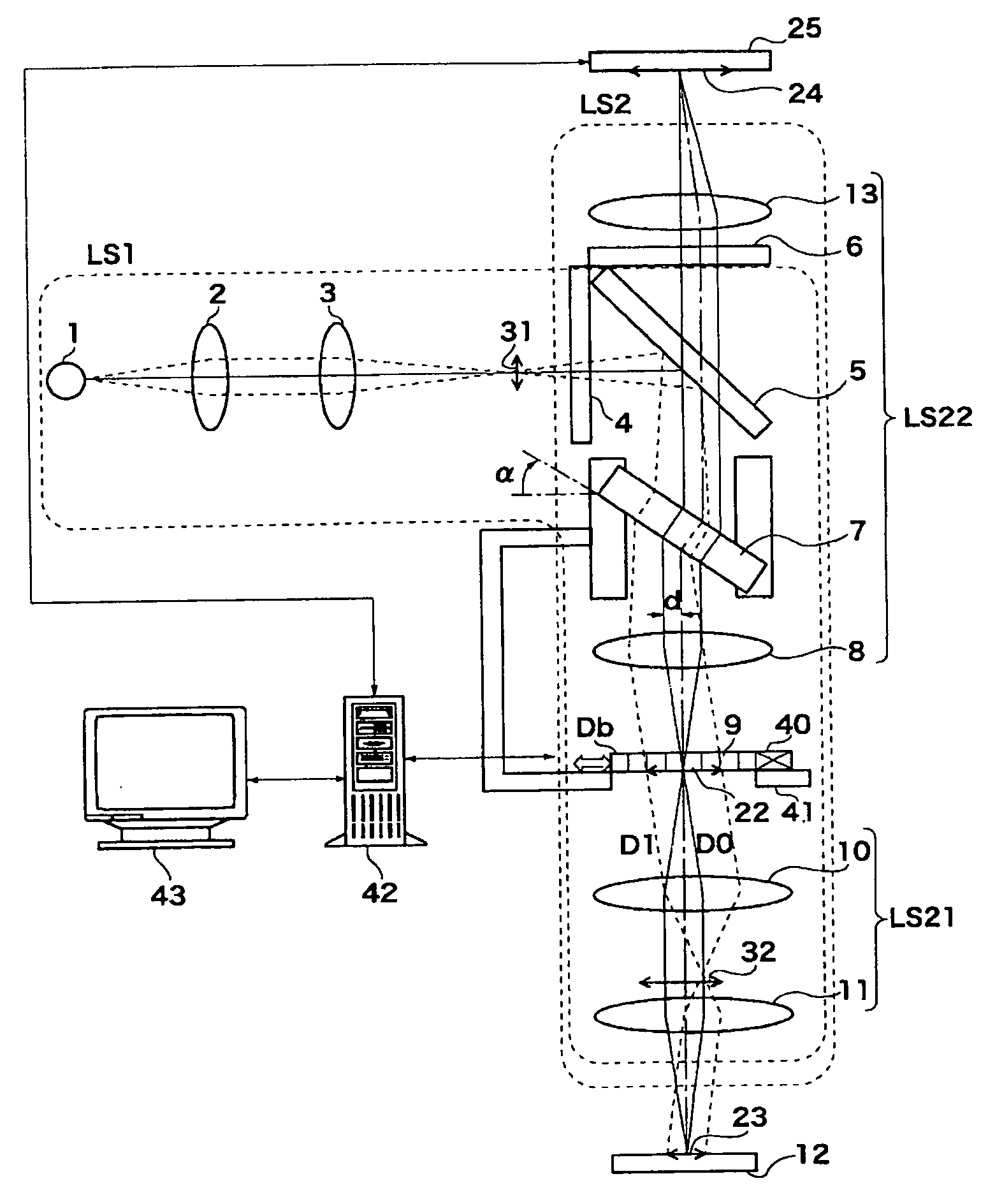
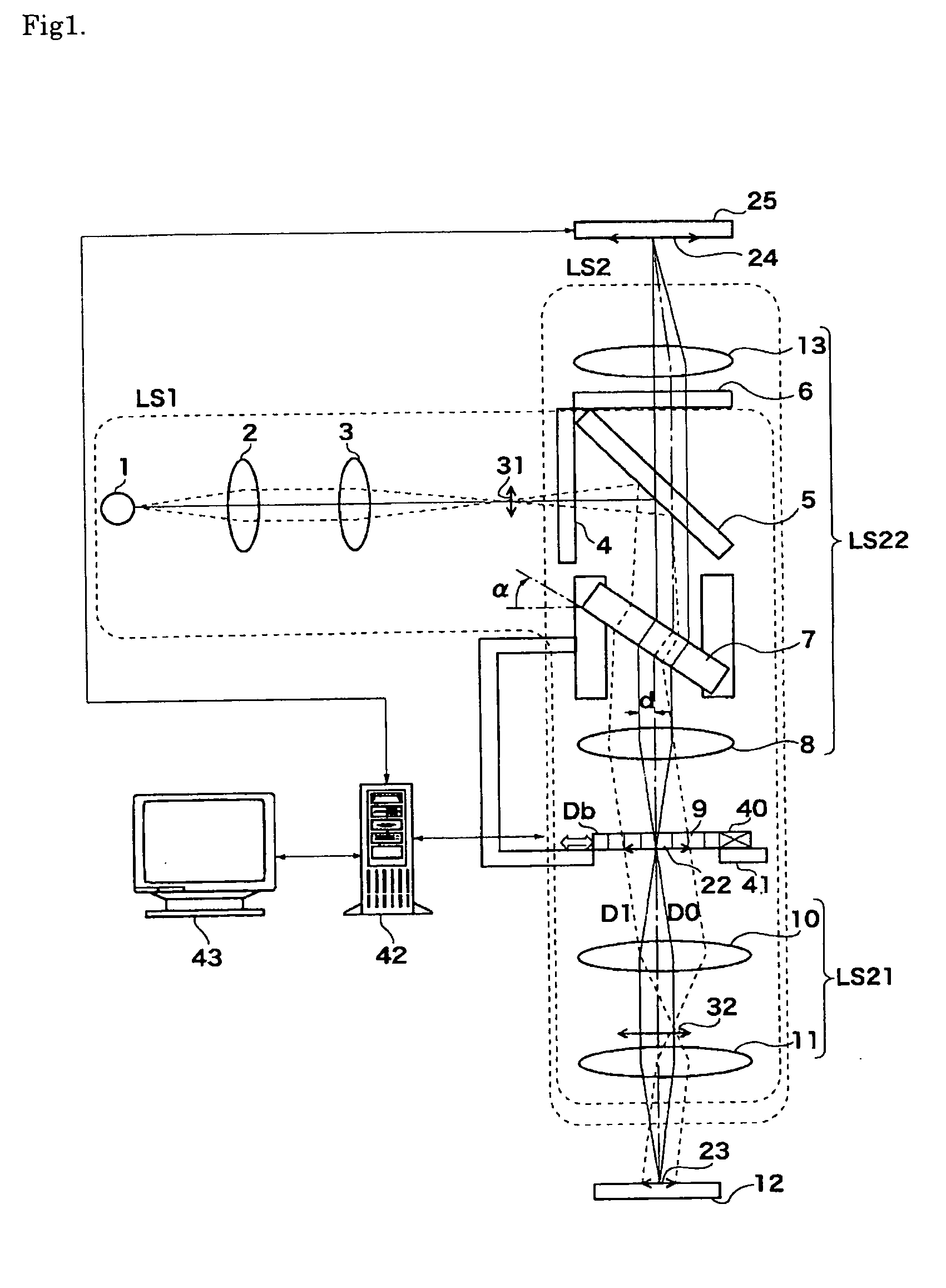
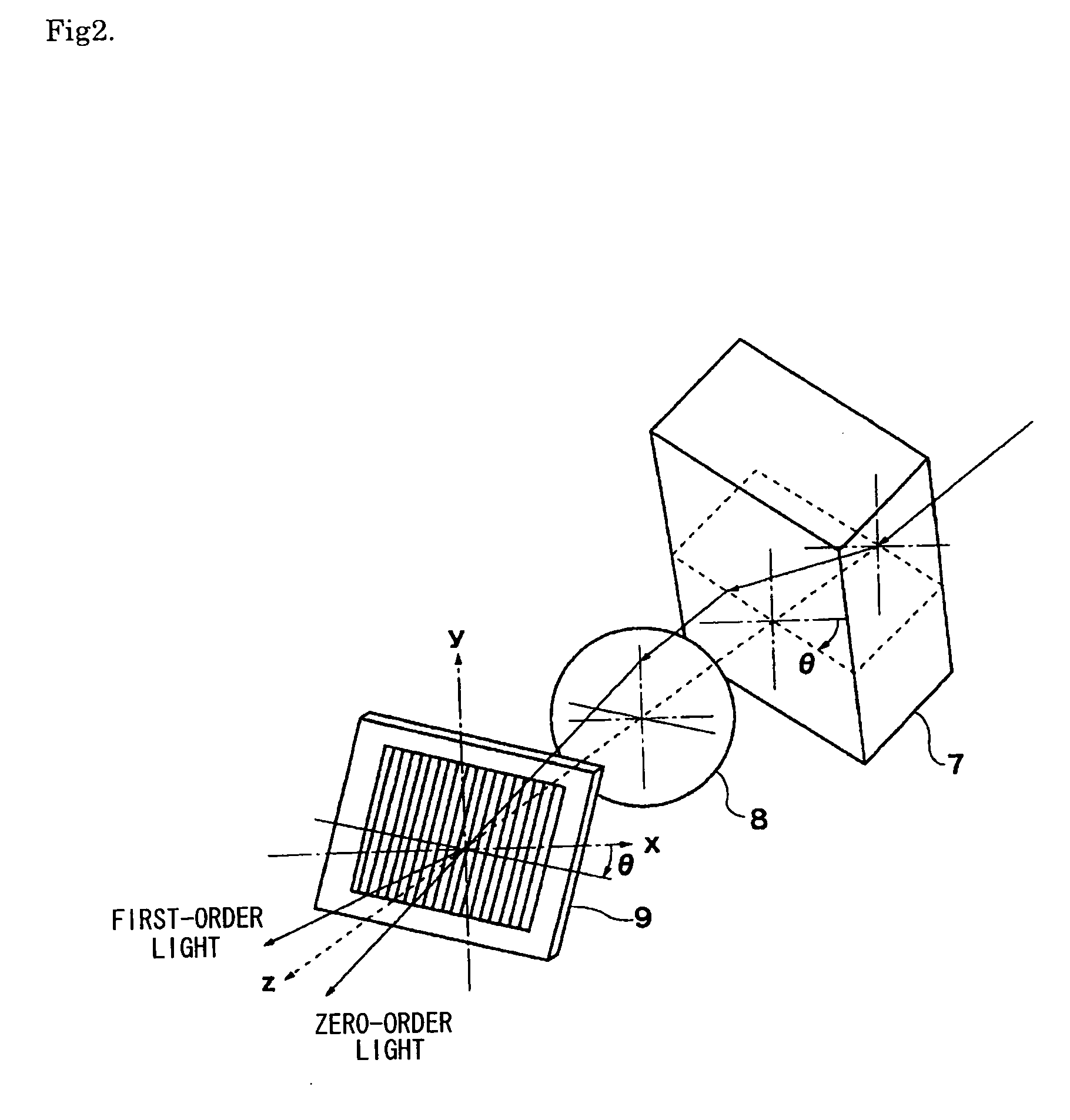
An optical scanner which performs optical scanning of a surface to be scanned by deflecting a luminous flux having a wavelength λ from a light source by means of an optical deflector, and condensing the deflected flux toward the surface to be scanned through a scanning image forming optical system, thereby forming an optical spot on the surface to be scanned. The scanning image forming optical system has at least one lens, and when the focal length fσ in the main scanning direction at a surface accuracy σi is defined as follows: fσ={2.6846 λ×√(k)×fm2 / ω2}−fm where, fm represents the focal length in the main scanning direction of the scanning image forming optical system; k represents the number of lens surfaces; ω represents the aimed spot diameter of the optical spot in the main scanning direction at an image height of 0; σI represents the surface accuracy of the i-th lens surface as counted from the optical deflector side; n represents the refractive index of material of the lens having the i-th lens surface; and 1 / l represents the spatial frequency in the main scanning direction on the lens surface; then, the surface accuracy σi, the focal length fσ, the refractive index n, and the spatial frequency 1 / L satisfy, for each lens surface, the following condition: 0<log σi<−2 log (1 / L)+log [1 / {32 fσ(n−1)}]. (1)
Owner:RICOH KK
Microscope device and image processing method
ActiveUS20090225407A1Increase speedCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopesImaging processingFluorescence
A diffraction grating produces the first diffraction light in a symmetrical direction with respect to the 0-th diffraction light and the optical axis. Each light flux forms two flux interference patterns on a sample surface through a second objective lens and a first objective lens, and a sample is illuminated by spatially modulated illumination light. Fluorescence is generated on the sample by structured illumination light as excitation light. The fluorescence caught by the first objective lens forms a modulated image of the sample on a sample conjugate surface through an objective optical system comprised of the first objective lens and the second objective lens. The modulated image is further modulated through the diffractive grating. Fluorescence from the further modulated image passes through a lens and a dichroic mirror, enters into a single light path of an observation optical system, passes through a fluorescent filter, and forms an enlarged image of the further modulated image through a lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Display apparatus for vehicle and display method
A display apparatus for vehicle includes: an image projector configured to project a light flux including an image having a display object toward a one eye of an image viewer; and a position detector configured to detect the one eye of the image viewer. The image projector changes at least one of a position, a shape and a size of the display object in the image on the basis of a position of the one eye detected by the position detector.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
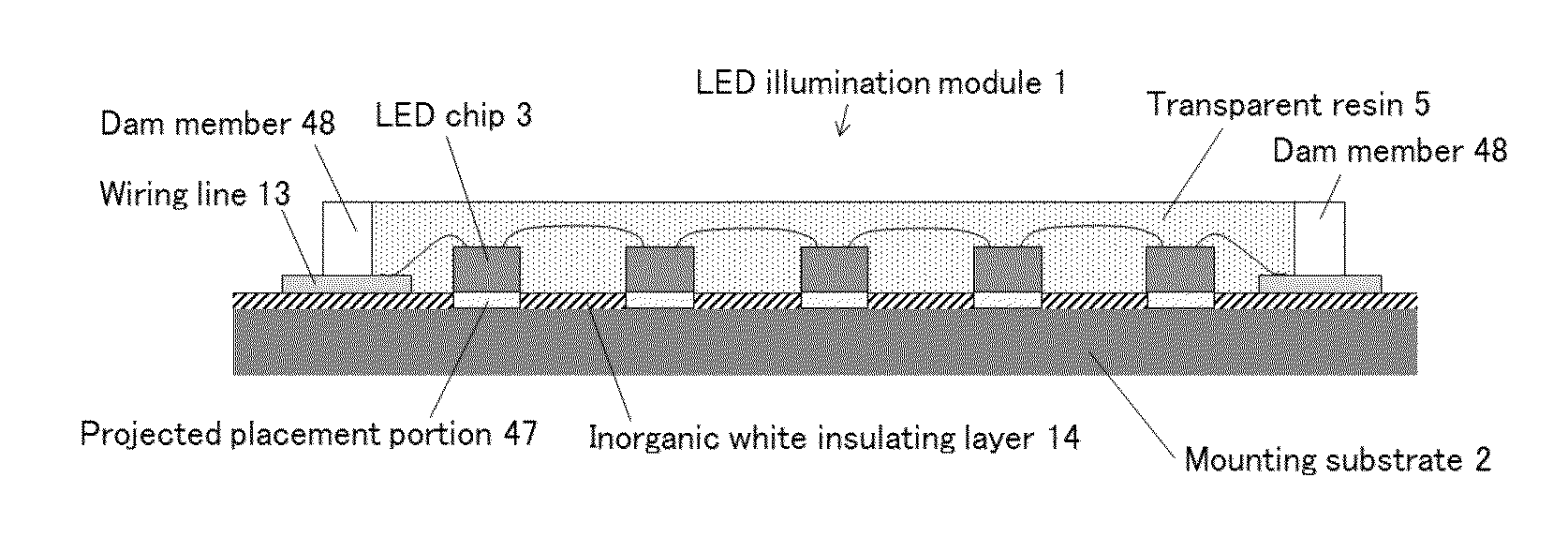
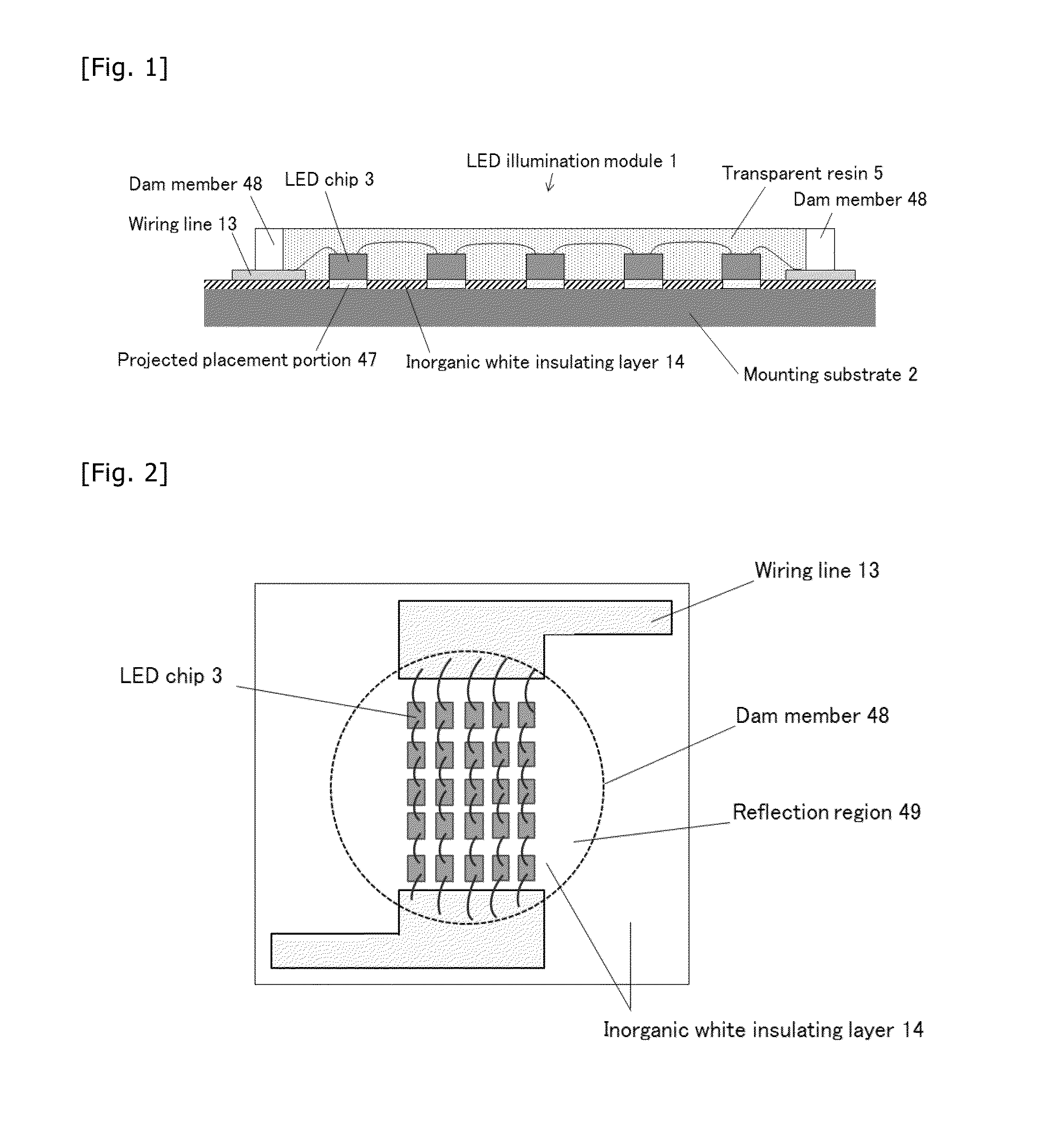
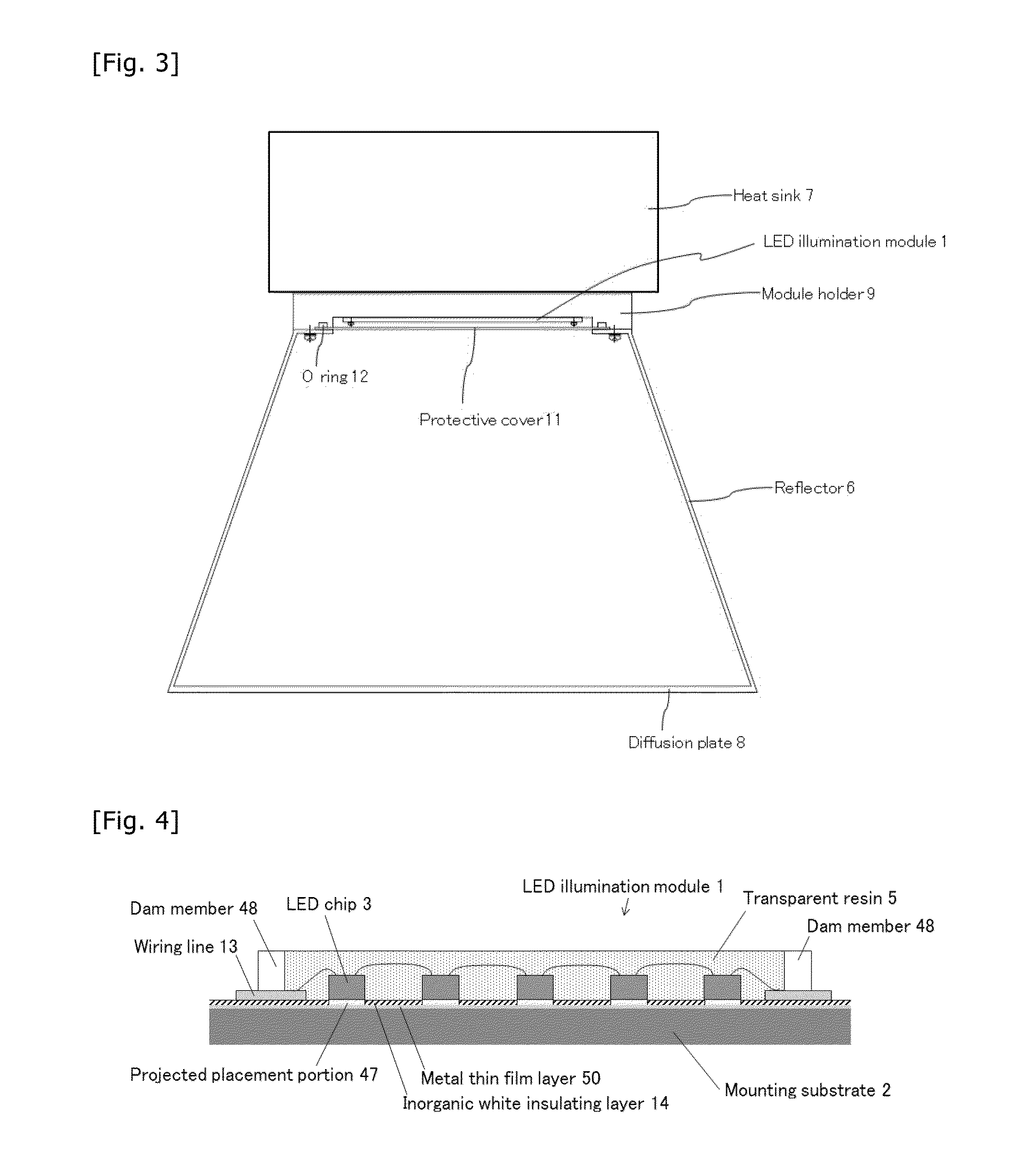
LED illumination module and LED illumination apparatus
ActiveUS20150155459A1Increase brightnessLess fluctuationCircuit optical detailsElectric circuit arrangementsHigh densityLight flux
An LED illumination module in which LED bare chips are mounted on a mounting substrate at a high density, the module comprising many LED bare chips having the same specifications, the mounting substrate at least a surface of which is metal, and a reflection region in which the LED bare chips are sealed off with resin, wherein a surface of the reflection region of the mounting substrate is covered with an inorganic white insulating layer that functions as a reflection member, a unit LED chip group including a plurality of LED bare chips connected in series is disposed plural, the plural unit LED chip groups being connected in parallel, overall light flux is 10,000 lumens or more, and a mounting area density of the LED bare chips in the reflection region is 15 mm2 / cm2 or more. An LED illumination apparatus including the LED illumination module is also provided.
Owner:SHIKOKU INSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com