Patents
Literature
611 results about "Diffraction order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diffraction order can refer to a couple concepts. In dispersive optical systems (e.g. a spectrometer), light diffracting off a grating is split into multiple orders (or rainbows) because if sin(x) is a solution to the scattering problem, so is sin(2x) and sin(3x), etc.
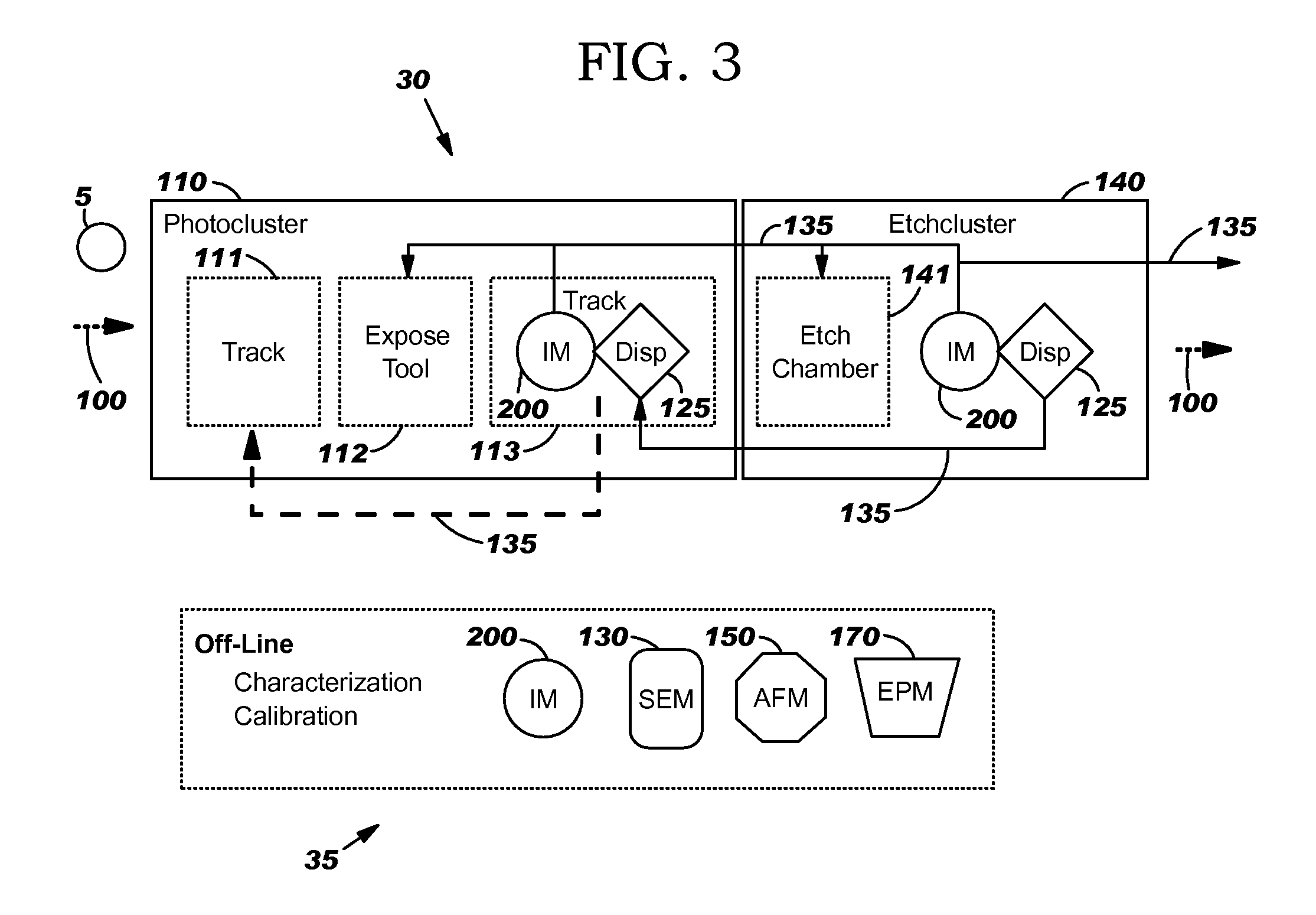
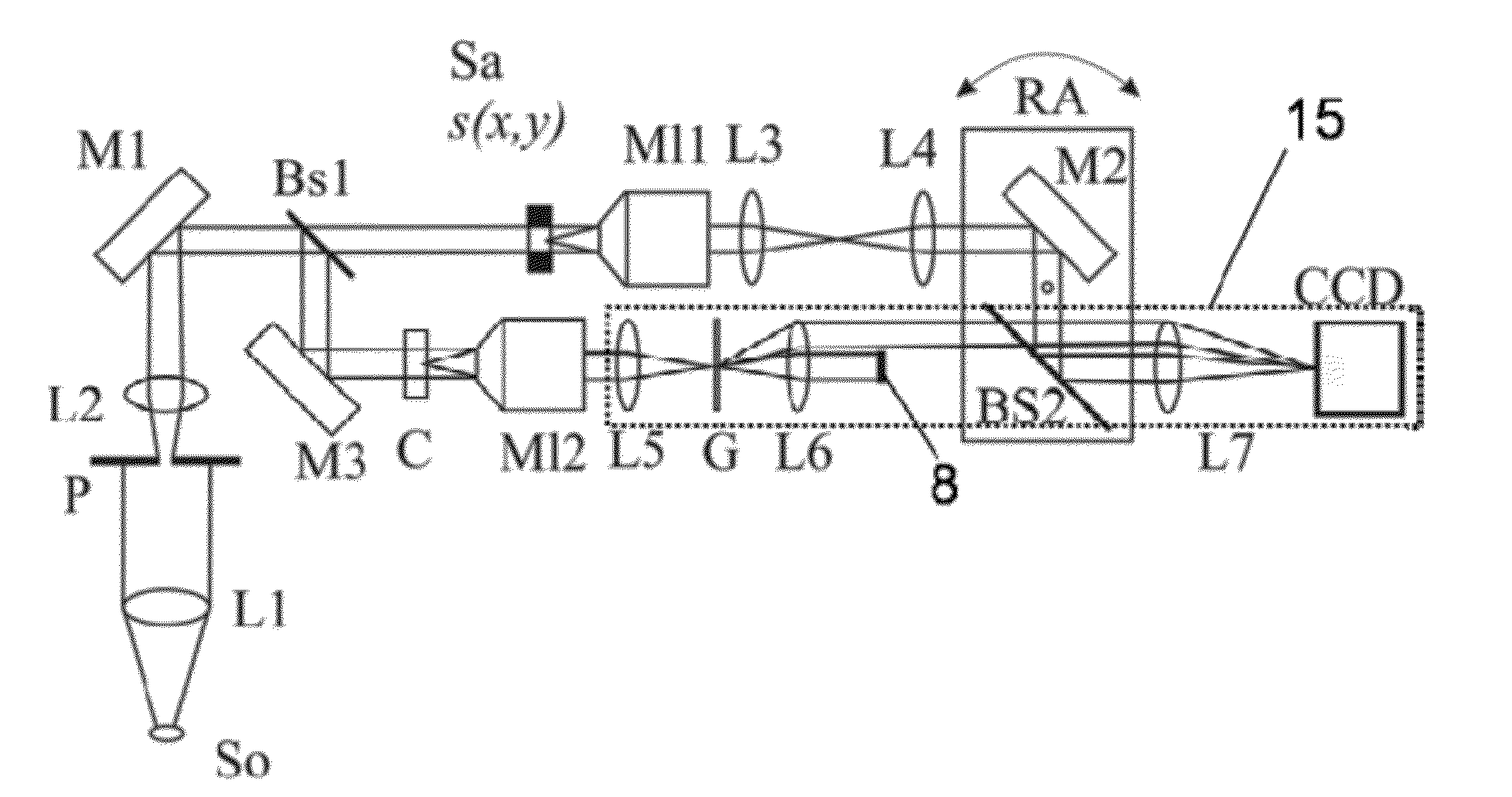
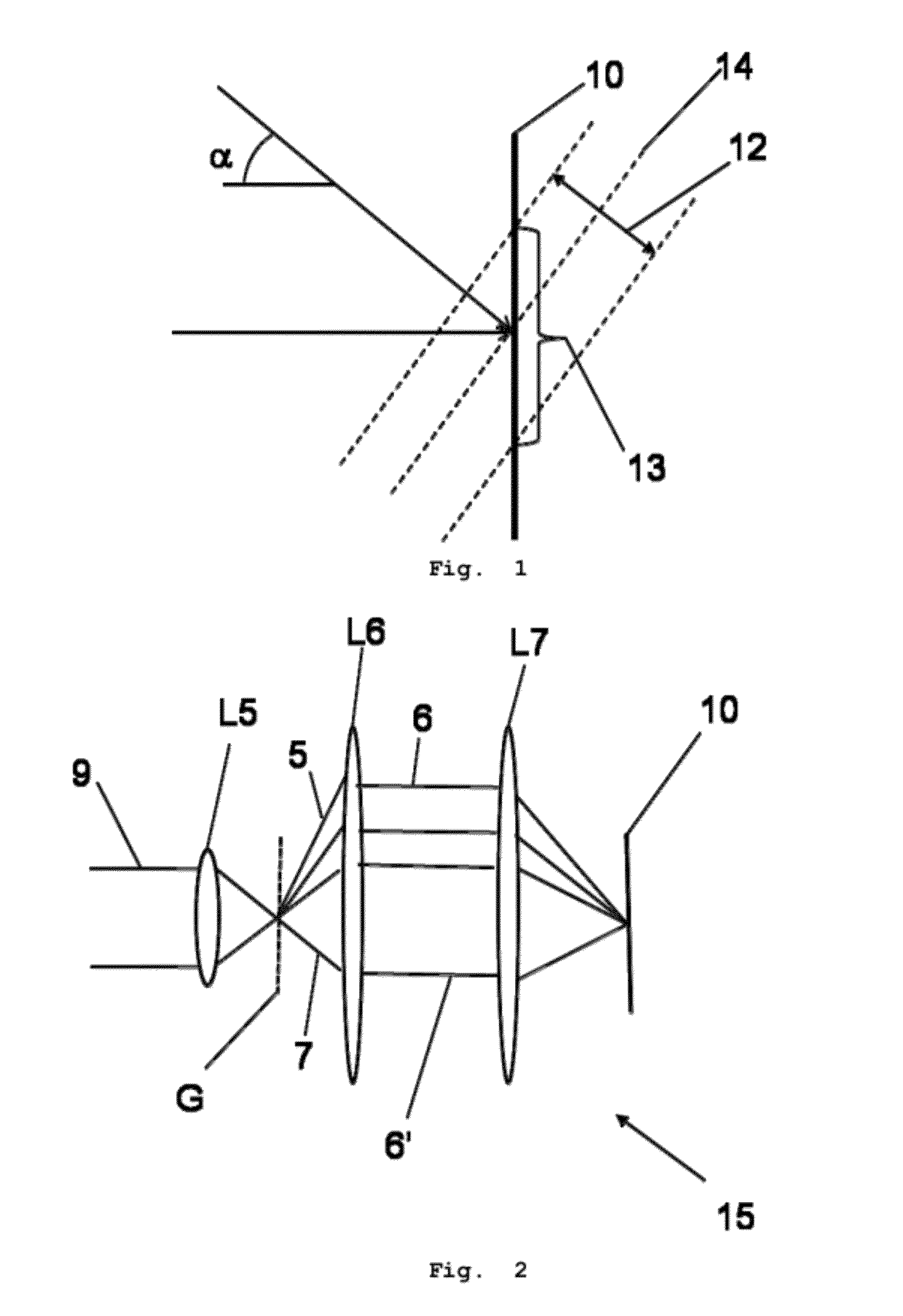
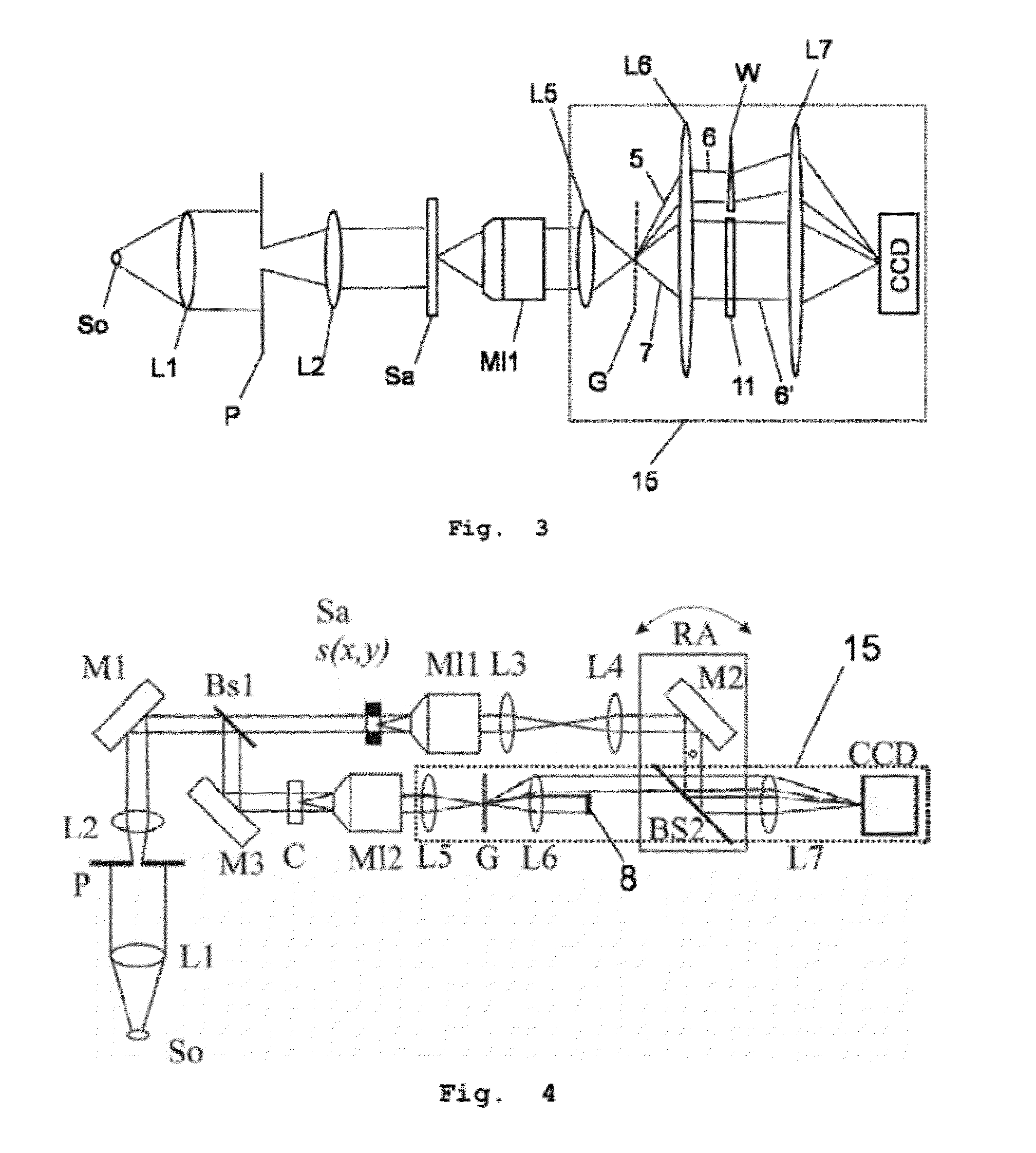
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
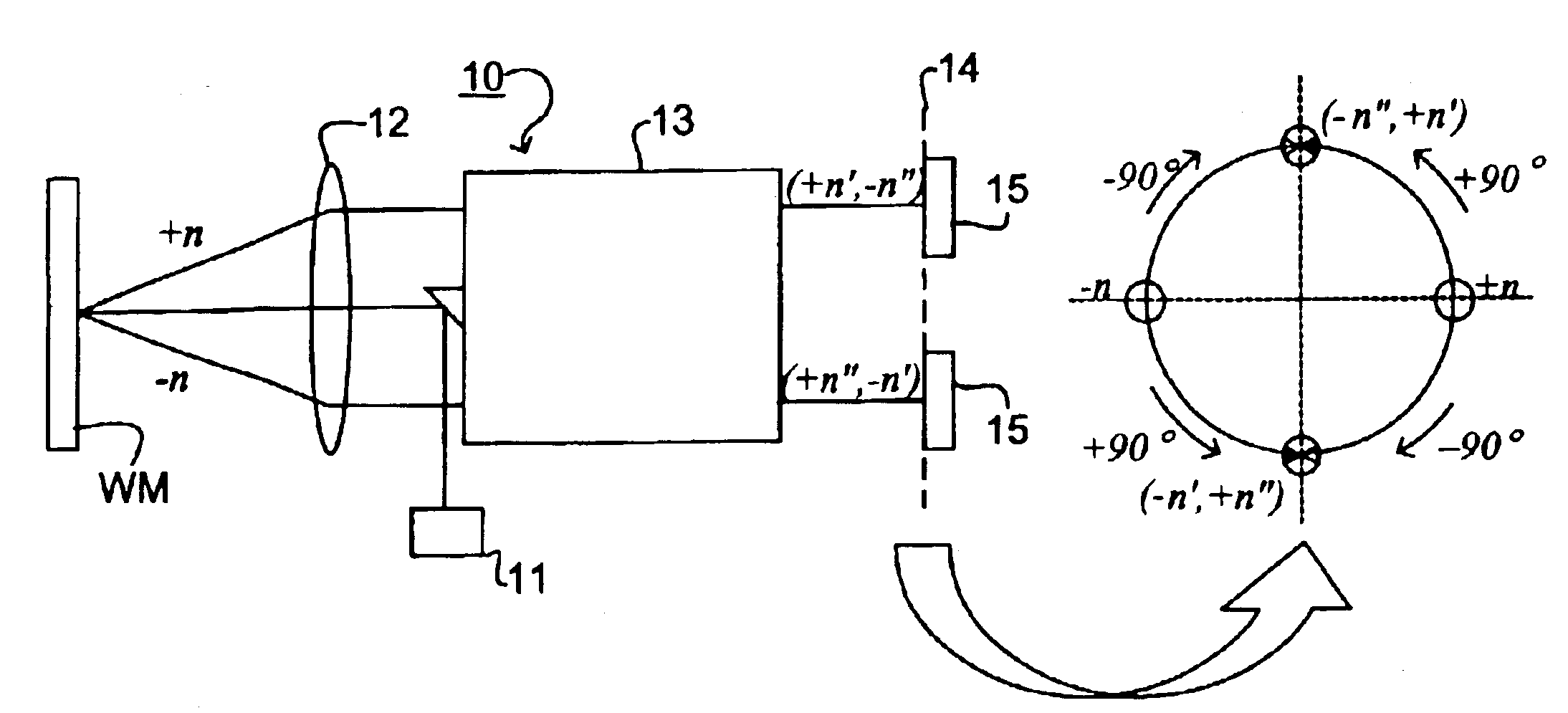
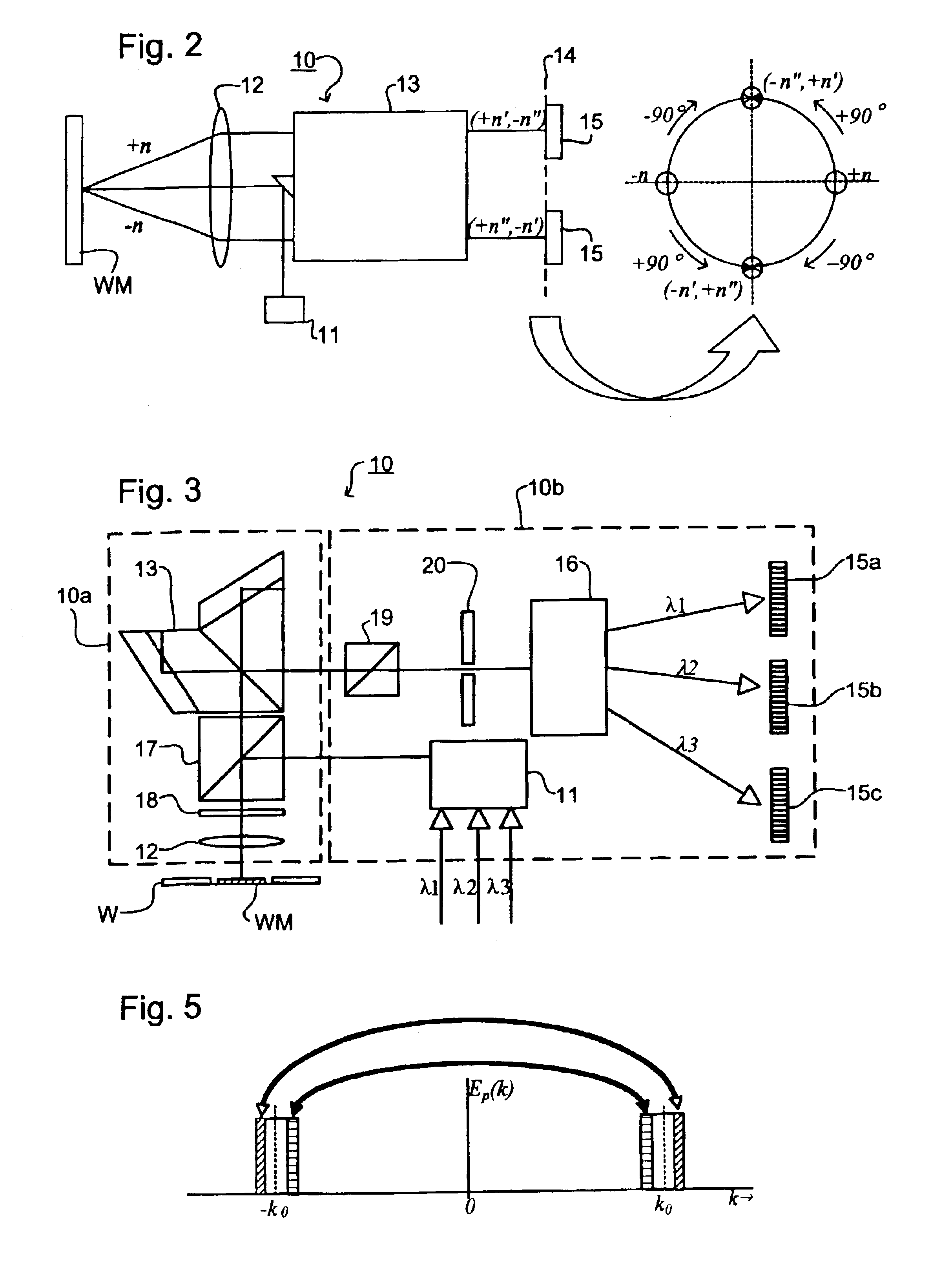
InactiveUS6961116B2Fine positioning informationLarge capture rangeDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsDiffraction orderPhase difference
An alignment system uses a self-referencing interferometer that produces two overlapping and relatively rotated images of an alignment markers. Detectors detect intensities in a pupil plane where Fourier transforms of the images are caused to interfere. The positional information is derived from the phase difference between diffraction orders of the two images which manifests as intensity variations in the interfered orders. Asymmetry can also be measured by measuring intensities at two positions either side of a diffraction order.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Scatterometry-Based Imaging and Critical Dimension Metrology
ActiveUS20150300965A1Improve the measurement effectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDiffraction orderMetrology
Methods and systems for performing measurements of semiconductor structures and materials based on scatterometry measurement data are presented. Scatterometry measurement data is used to generate an image of a material property of a measured structure based on the measured intensities of the detected diffraction orders. In some examples, a value of a parameter of interest is determined directly from the map of the material property of the measurement target. In some other examples, the image is compared to structural characteristics estimated by a geometric, model-based parametric inversion of the same measurement data. Discrepancies are used to update the geometric model of the measured structure and improve measurement performance. This enables a metrology system to converge on an accurate parametric measurement model when there are significant deviations between the actual shape of a manufactured structure subject to model-based measurement and the modeled shape of the structure.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Differential critical dimension and overlay metrology apparatus and measurement method
InactiveUS20070105029A1Using optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMetrologyCritical dimension
A method is described for measuring a dimension on a substrate, wherein a target pattern is provided with a nominal characteristic dimension that repeats at a primary pitch of period P, and has a pre-determined variation orthogonal to the primary direction. The target pattern formed on the substrate is then illuminated so that at least one non-zero diffracted order is detected. The response of the non-zero diffracted order to variation in the printed characteristic dimension relative to nominal is used to determine the dimension of interest, such as critical dimension or overlay, on the substrate. An apparatus for performing the method of the present invention includes an illumination source, a detector for detecting a non-zero diffracted order, and means for positioning the source relative to the target so that one or more non-zero diffracted orders from the target are detected at the detector.
Owner:IBM CORP
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
ActiveUS7156516B2Smooth edgesEasy to manufactureSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensSquare waveformDiffraction order
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. The first diffractive structure may have blazed (i.e., sawtooth), sinusoidal, sinusoidal harmonic, square wave, or other shape profile. A sinusoidal harmonic diffractive structure is particularly useful in applications where smooth rather than sharp edges are desirable.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
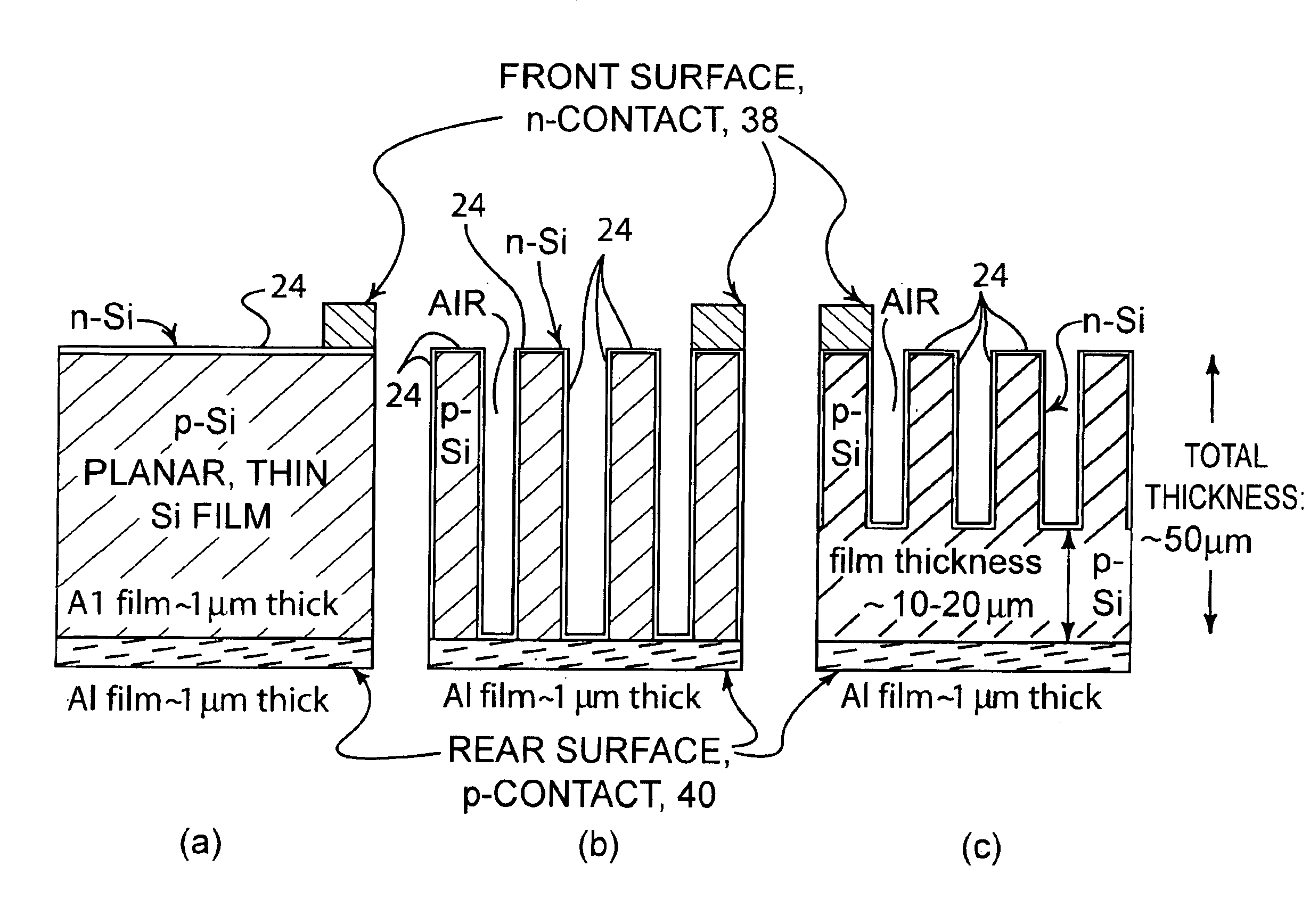
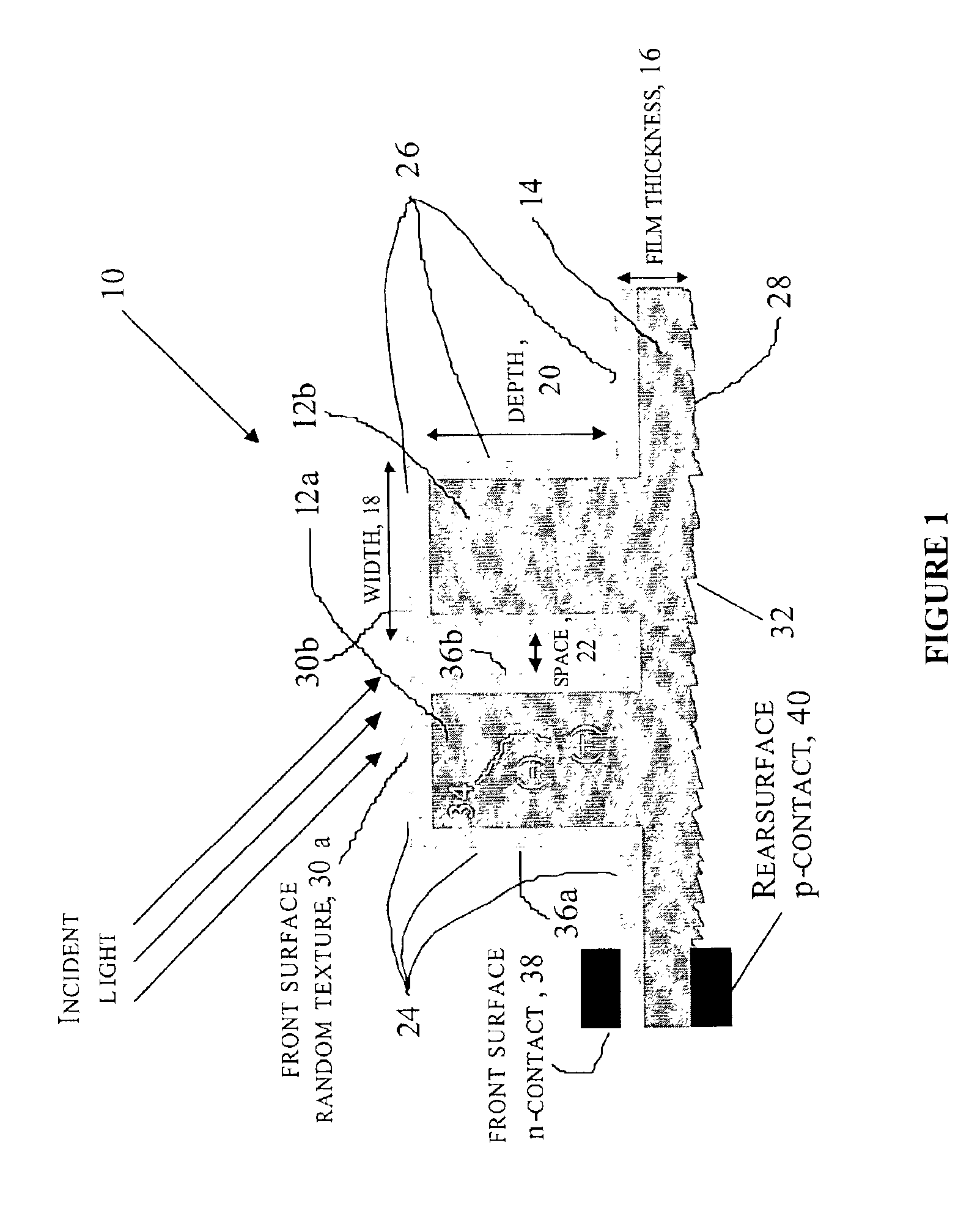
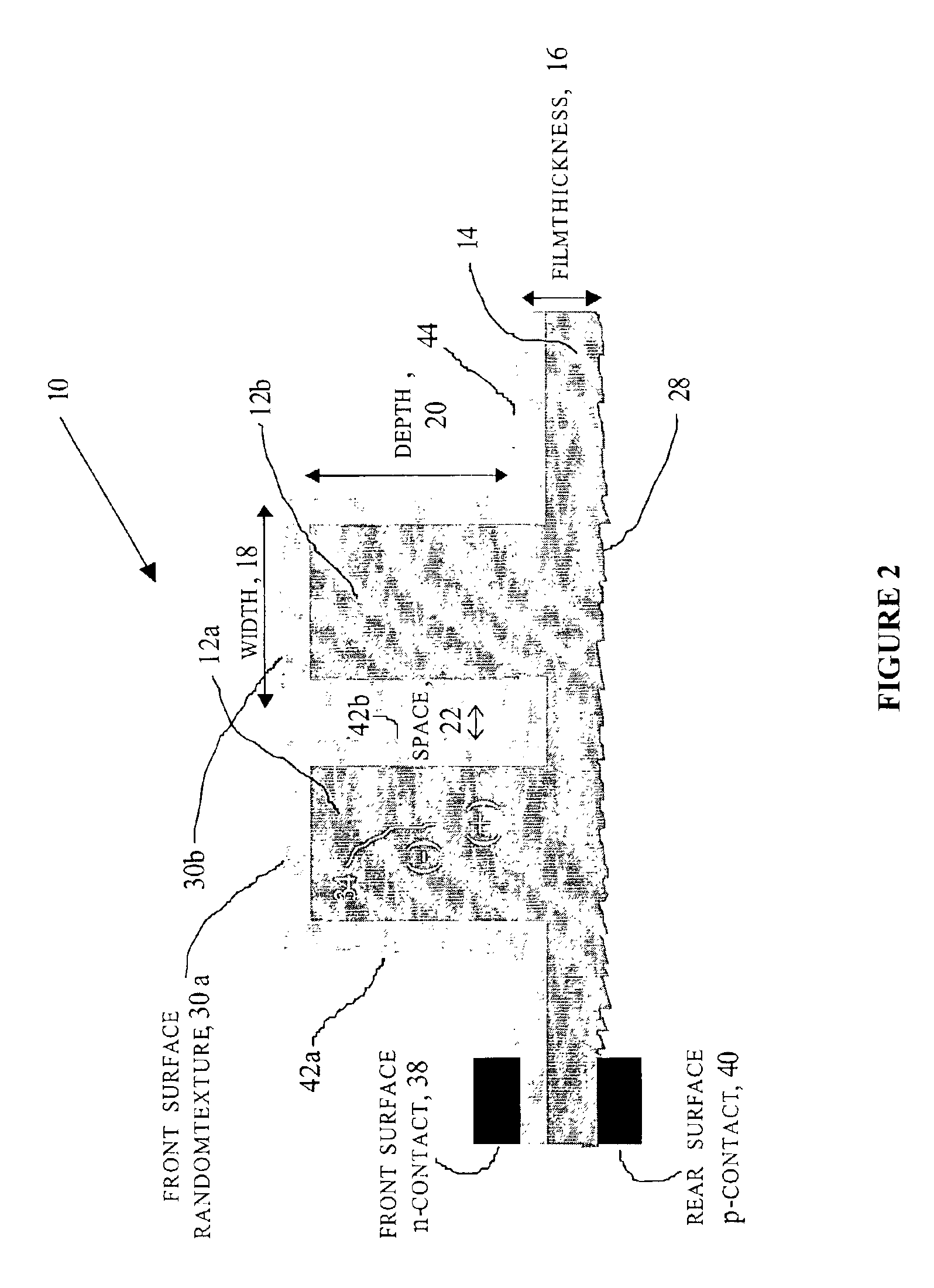
Method of making an enhanced optical absorption and radiation tolerance in thin-film solar cells and photodetectors
InactiveUS7109517B2Promote absorptionImprove toleranceFinal product manufacturePhotoelectric discharge tubesDiffraction orderPhotodetector
Subwavelength random and periodic microscopic structures are used to enhance light absorption and tolerance for ionizing radiation damage of thin film and photodetectors. Diffractive front surface microscopic structures scatter light into oblique propagating higher diffraction orders that are effectively trapped within the volume of the photovoltaic material. For subwavelength periodic microscopic structures etched through the majority of the material, enhanced absorption is due to waveguide effect perpendicular to the surface thereof. Enhanced radiation tolerance of the structures of the present invention is due to closely spaced, vertical sidewall junctions that capture a majority of deeply generated electron-hole pairs before they are lost to recombination. The separation of these vertical sidewall junctions is much smaller than the minority carrier diffusion lengths even after radiation-induced degradation. The effective light trapping of the structures of the invention compensates for the significant removal of photovoltaic material and substantially reduces the weight thereof for space applications.
Owner:ZAIDI SALEEM H
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
ActiveUS20060055883A1Smooth edgesEasy to manufactureSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensSquare waveformDiffraction order
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. The first diffractive structure may have blazed (i.e., sawtooth), sinusoidal, sinusoidal harmonic, square wave, or other shape profile. A sinusoidal harmonic diffractive structure is particularly useful in applications where smooth rather than sharp edges are desirable.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Resonant Leaky-Mode Photonic Elements and Methods for Spectral and Polarization Control
ActiveUS20100092124A1Increase varietyImprove performanceCoupling light guidesSpecial surfacesDiffraction orderFtir spectra
Optical devices with versatile spectral attributes are provided that are implemented with one or more modulated and homogeneous layers to realize leaky-mode resonance operation and corresponding versatile spectral-band design. The first and / or higher multiple evanescent diffraction orders are applied to excite one or more leaky modes. The one- or two-dimensional periodic structure, fashioned by proper distribution of materials within each period, can have a resulting symmetric or asymmetric profile to permit a broadened variety of resonant leaky-mode devices to be realized. Thus, the attributes of the optical device permit, among other things, adjacent, distinct resonance frequencies or wavelengths to be produced, convenient shaping of the reflection and transmission spectra for such optical device to be accomplished, and the wavelength resonance locations to be precisely controlled so as to affect the extent to which the leaky modes interact with each other. Further, the profile asymmetry allows for the precise spectral spacing of interactive leaky modes so as to provide greater flexibility in optical device design.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Illumination optimization for specific mask patterns
InactiveUS6871337B2Reduce in quantityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsDiffraction order
A method and apparatus for microlithography. The method and apparatus include optimizing illumination modes based on characteristics of a specific mask pattern. The illumination is optimized by determining an appropriate illumination mode based on diffraction orders of the reticle, and the autocorrelation of the projection optic. By elimination of parts of the illumination pattern which have no influence on modulation, excess DC light can be reduced, thereby improving depth of focus. Optimization of mask patterns includes addition of sub-resolution features to reduce pitches and discretize the probability density function of the space width.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
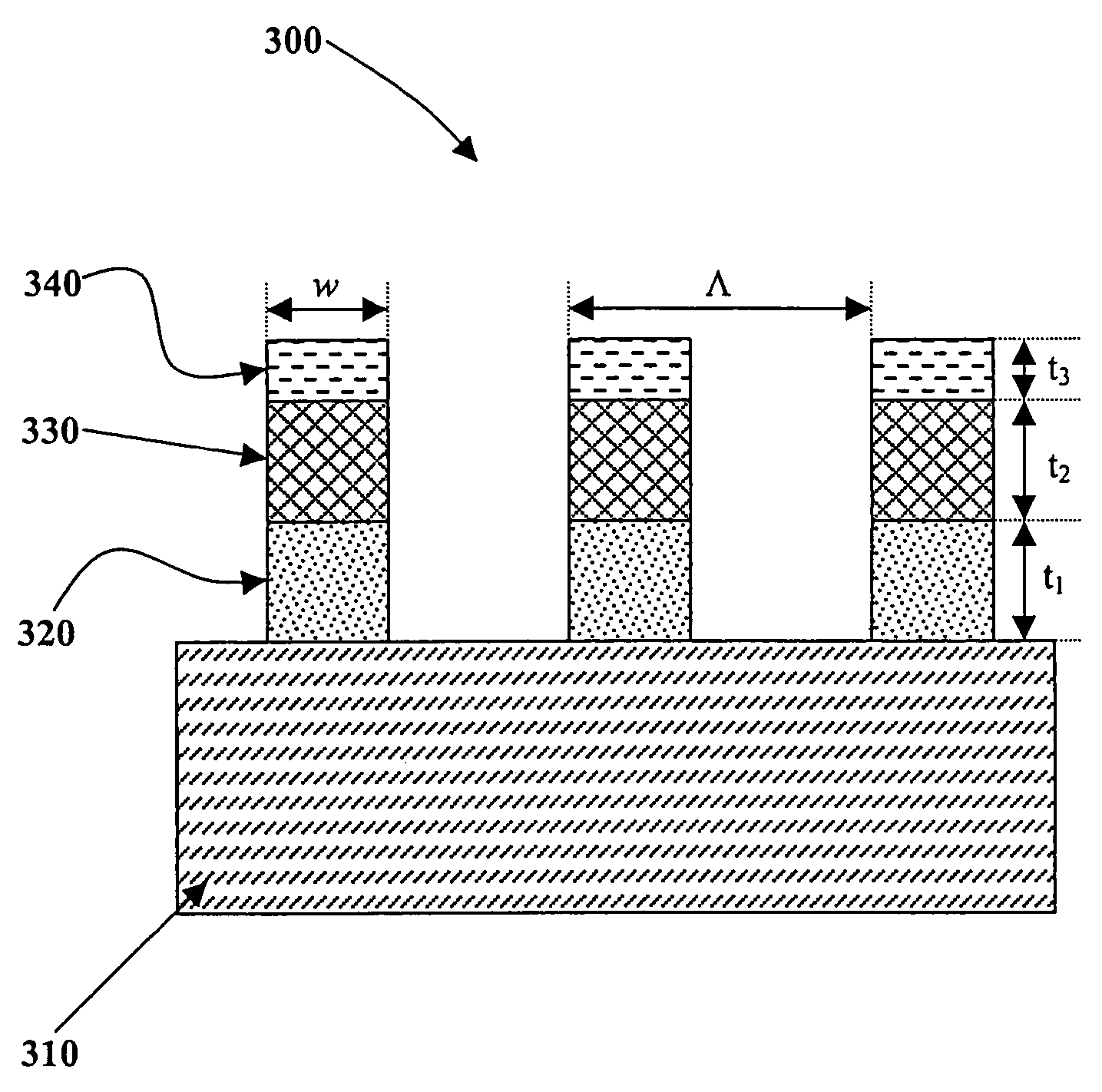
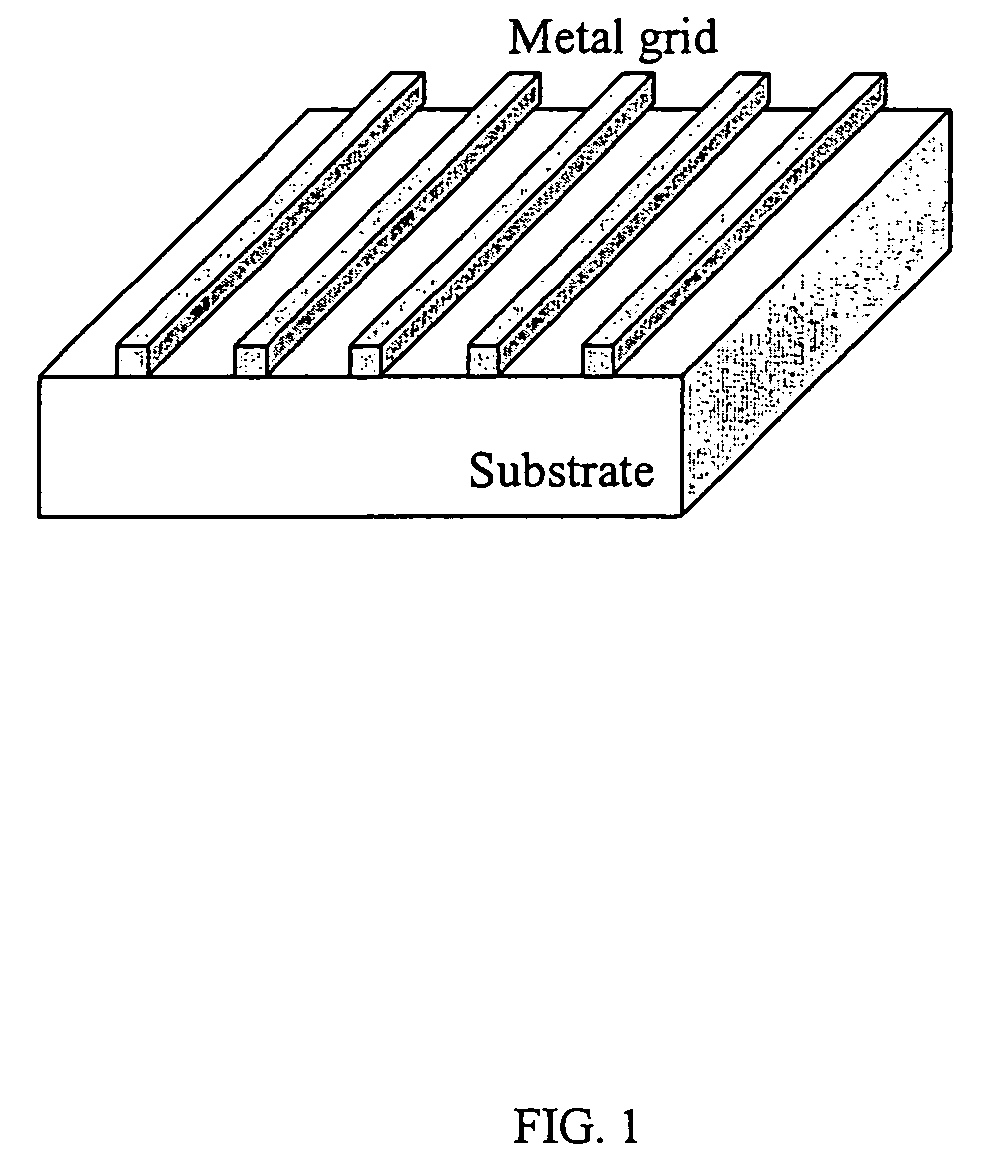
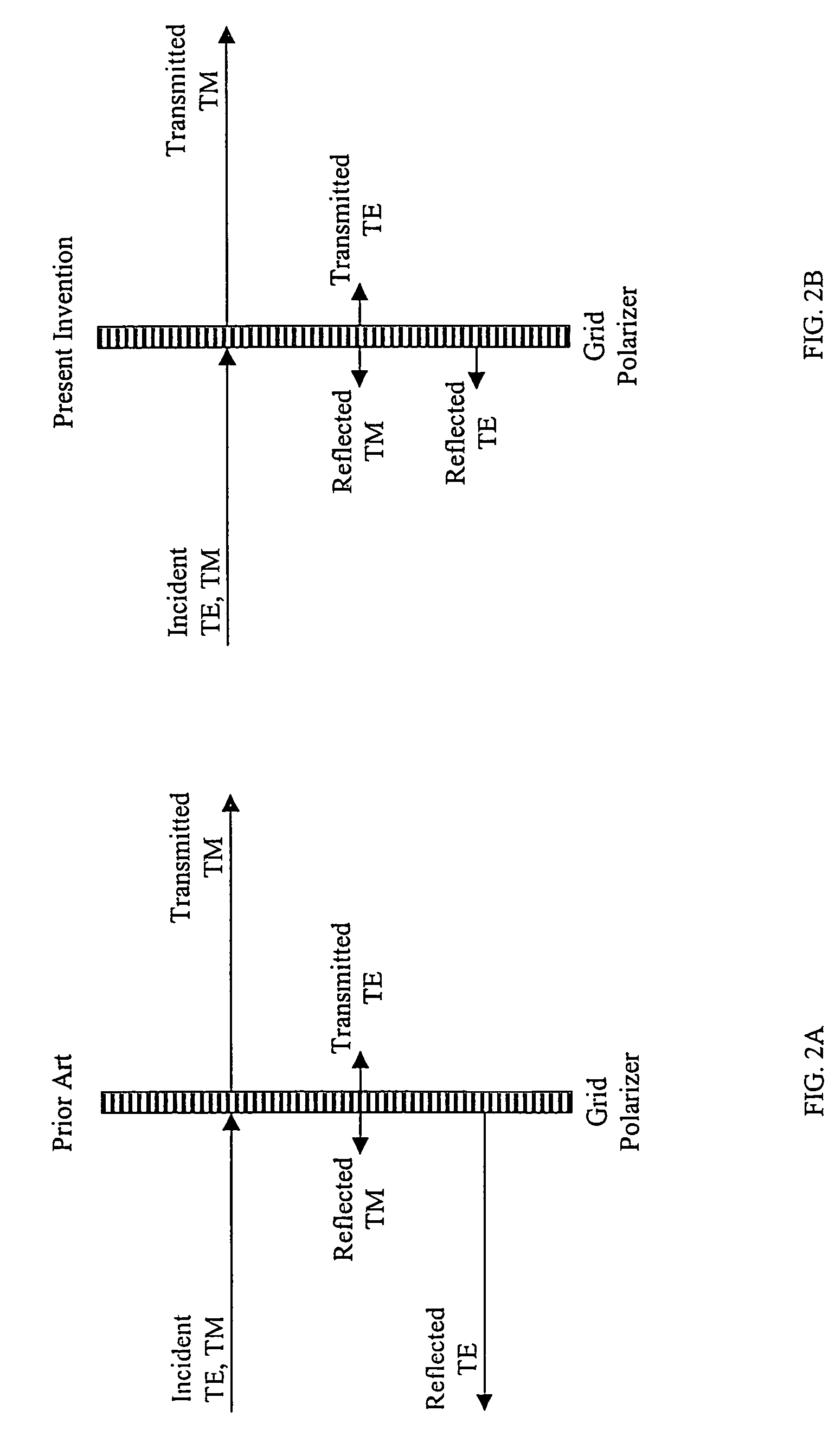
Grid polarizer with suppressed reflectivity
Disclosed is a grid polarizer comprising a substrate; and a plurality of stacked metal and dielectric layers, having a width w, disposed on the substrate and forming a parallel grid of stacked layers. The stacked layers are spaced apart to form a repetition space between the stacked layers, such that no diffraction orders are allowed to propagate except the zero order. The grid polarizer that is capable of transmitting substantially all illumination of a given polarization while suppressing at least of portion of the illumination reflected due to an orthogonal polarization component.
Owner:CORNING INC
Coherent fiber diffractive optical element beam combiner
ActiveUS20070201795A1Improve cooling effectDiffraction gratingsUsing optical meansFiberDiffraction order
An optical beam combiner and a related method for its operation, in which multiple coherent input beams are directed onto a diffractive optical element (DOE) along directions corresponding to diffraction orders of the DOE, such that the DOE generates a single output beam in a direction corresponding to a desired diffraction order, and suppresses outputs in directions corresponding to unwanted diffraction orders. The phases of the input beams are actively controlled to ensure and maintain the condition that only a single diffraction mode is present in the output of the DOE.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Apparatus with enhanced resolution for measuring structures on a substrate for semiconductor manufacture and use of apertures in a measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20080278790A1High resolutionDiffraction gratingsMicroscopesDiffraction orderMeasurement device
A measuring system is disclosed with enhanced resolution for periodic structures on a substrate for semiconductor manufacture. Aperture structures of varying geometries are provided in the illumination beam path. The aperture structures differ regarding the transmission characteristics of light, and which adjust the intensity distribution of the diffraction orders in the imaging pupil of the optical system.
Owner:VISTEC SEMICON SYST
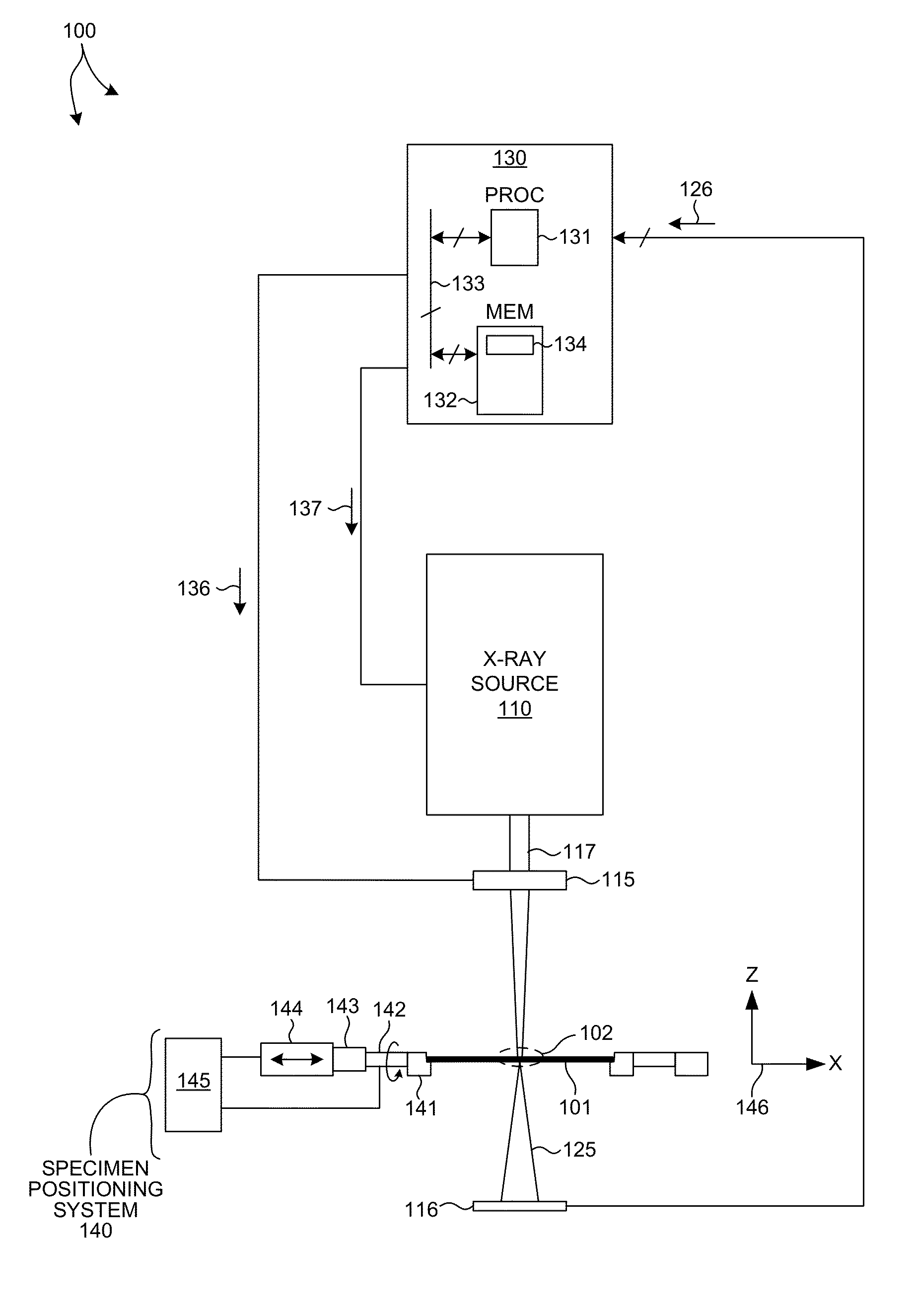
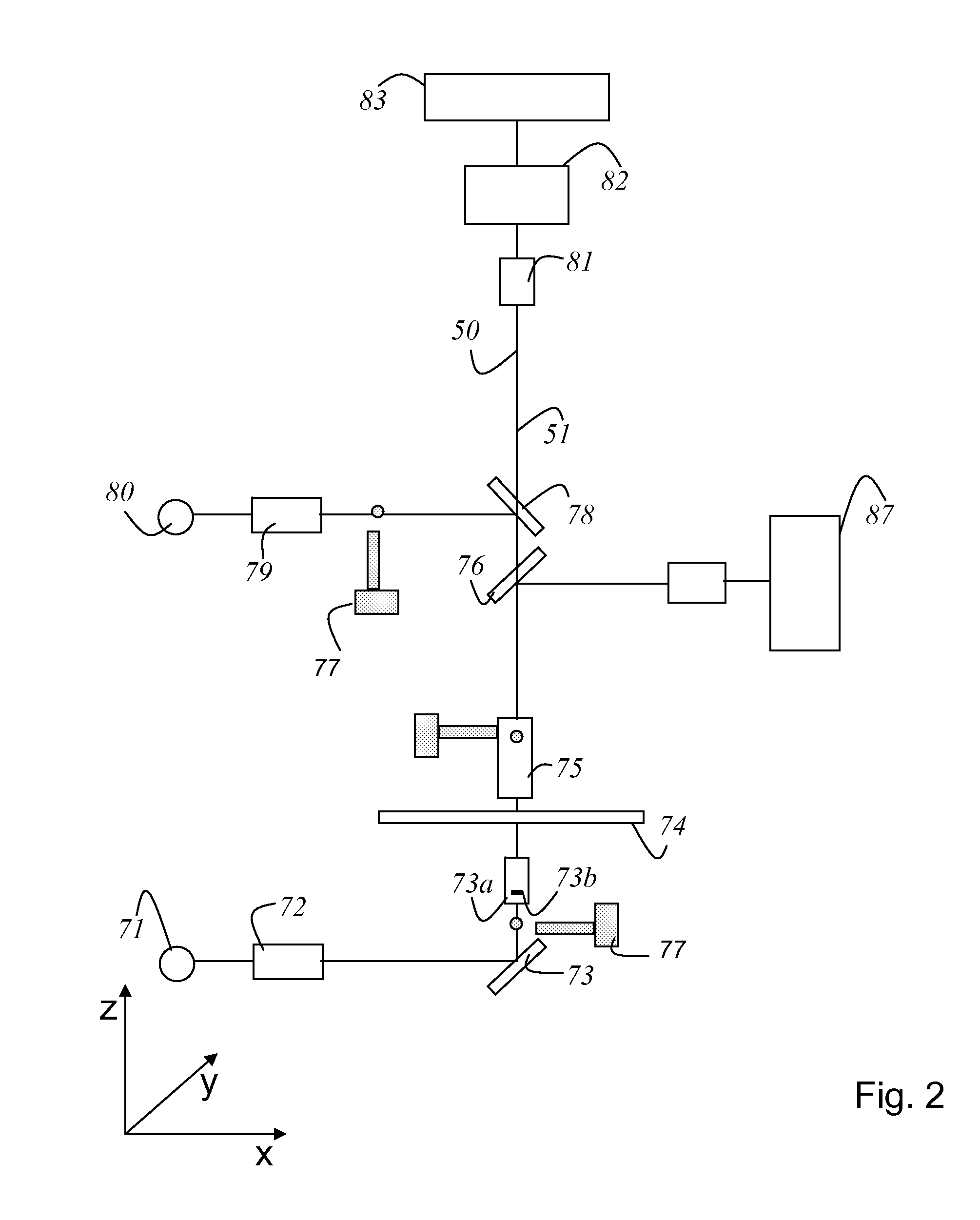
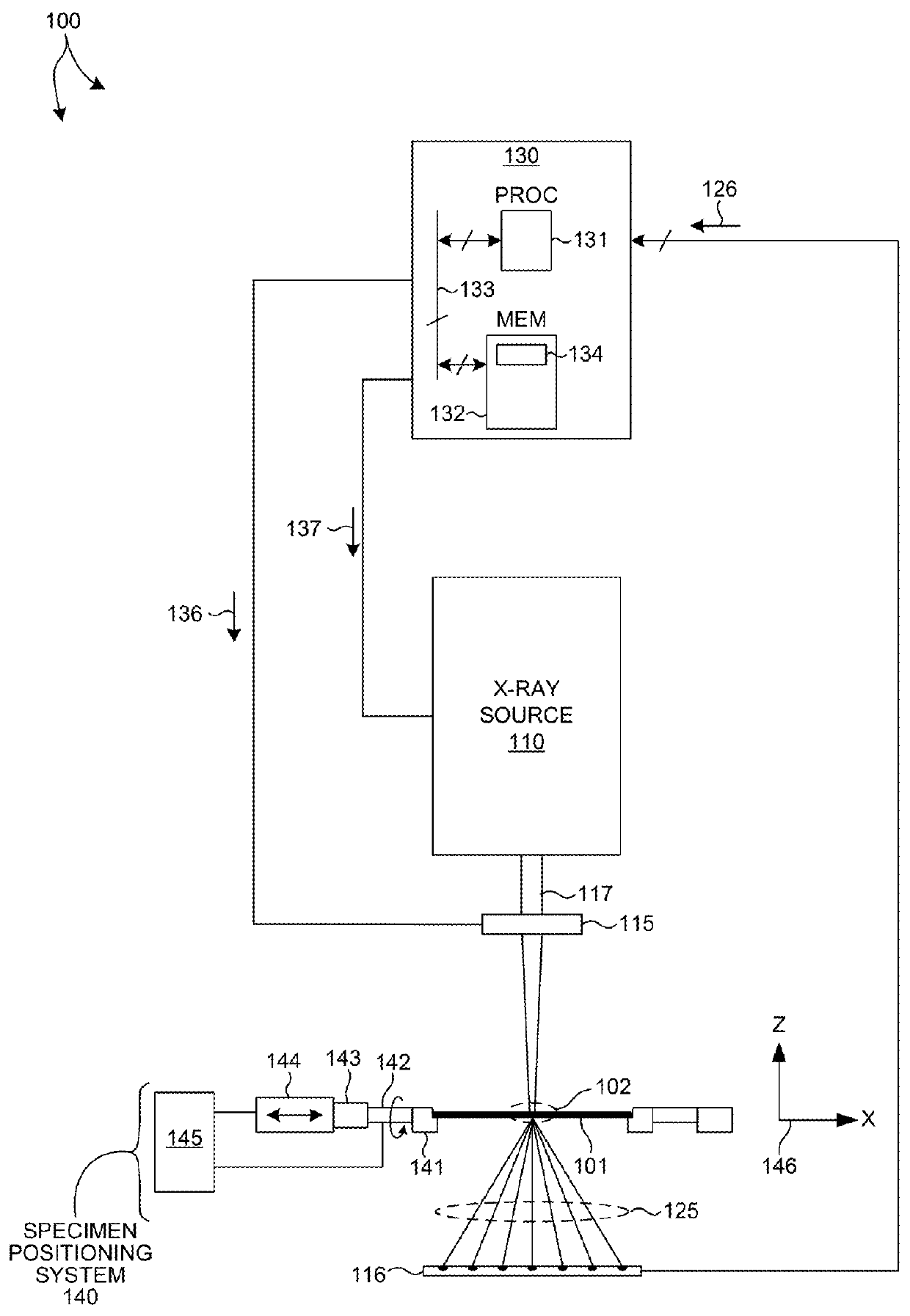
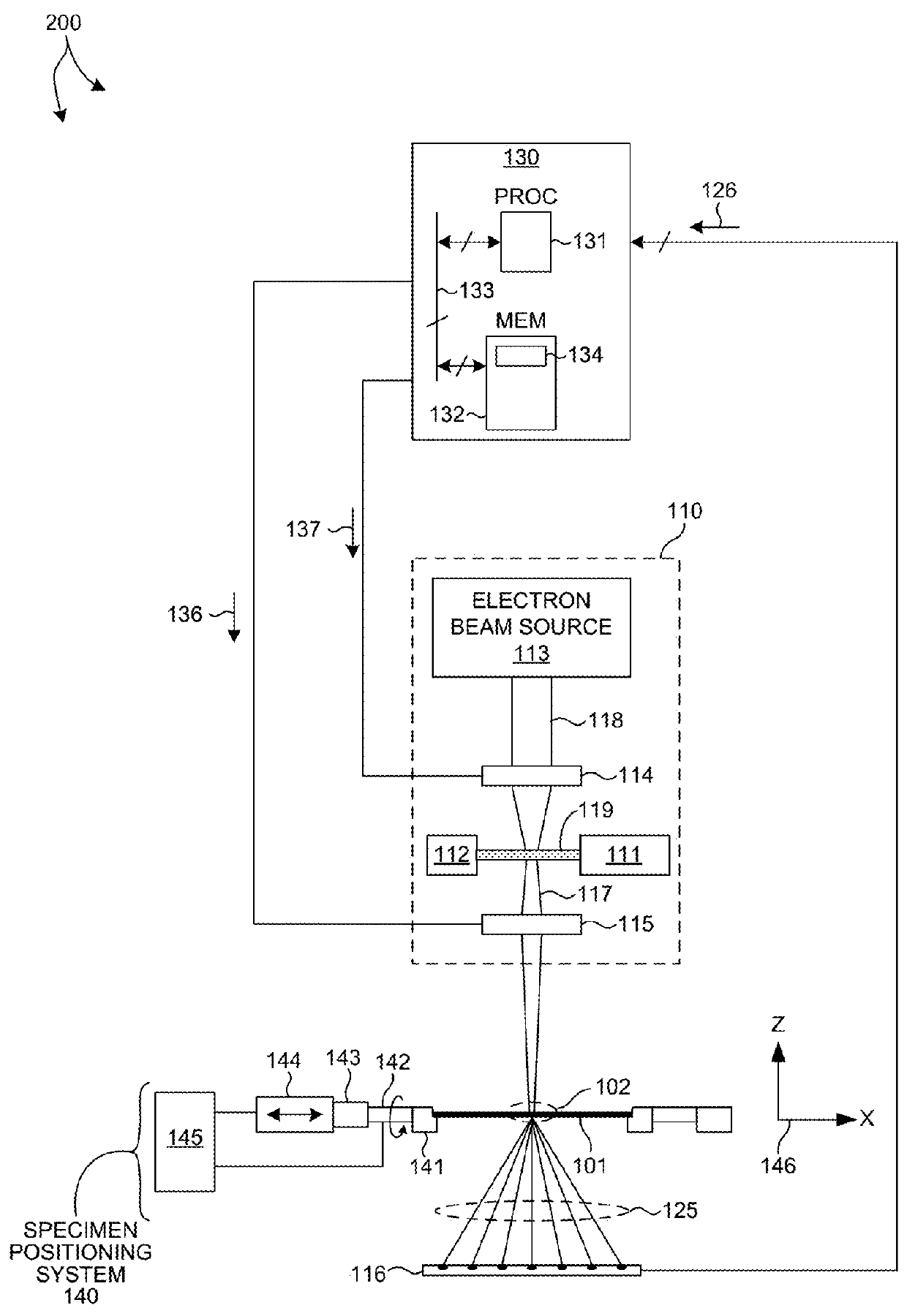
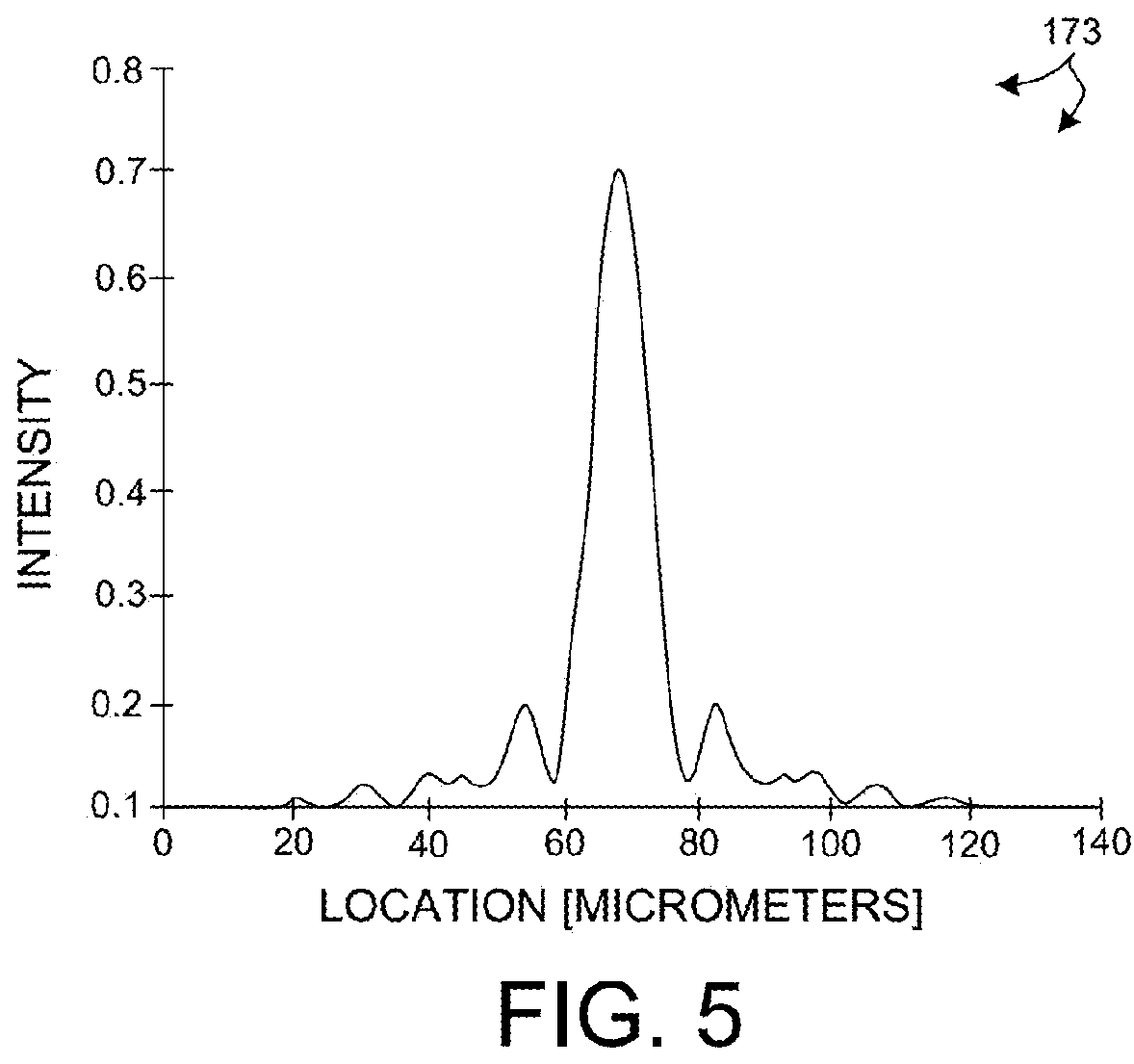
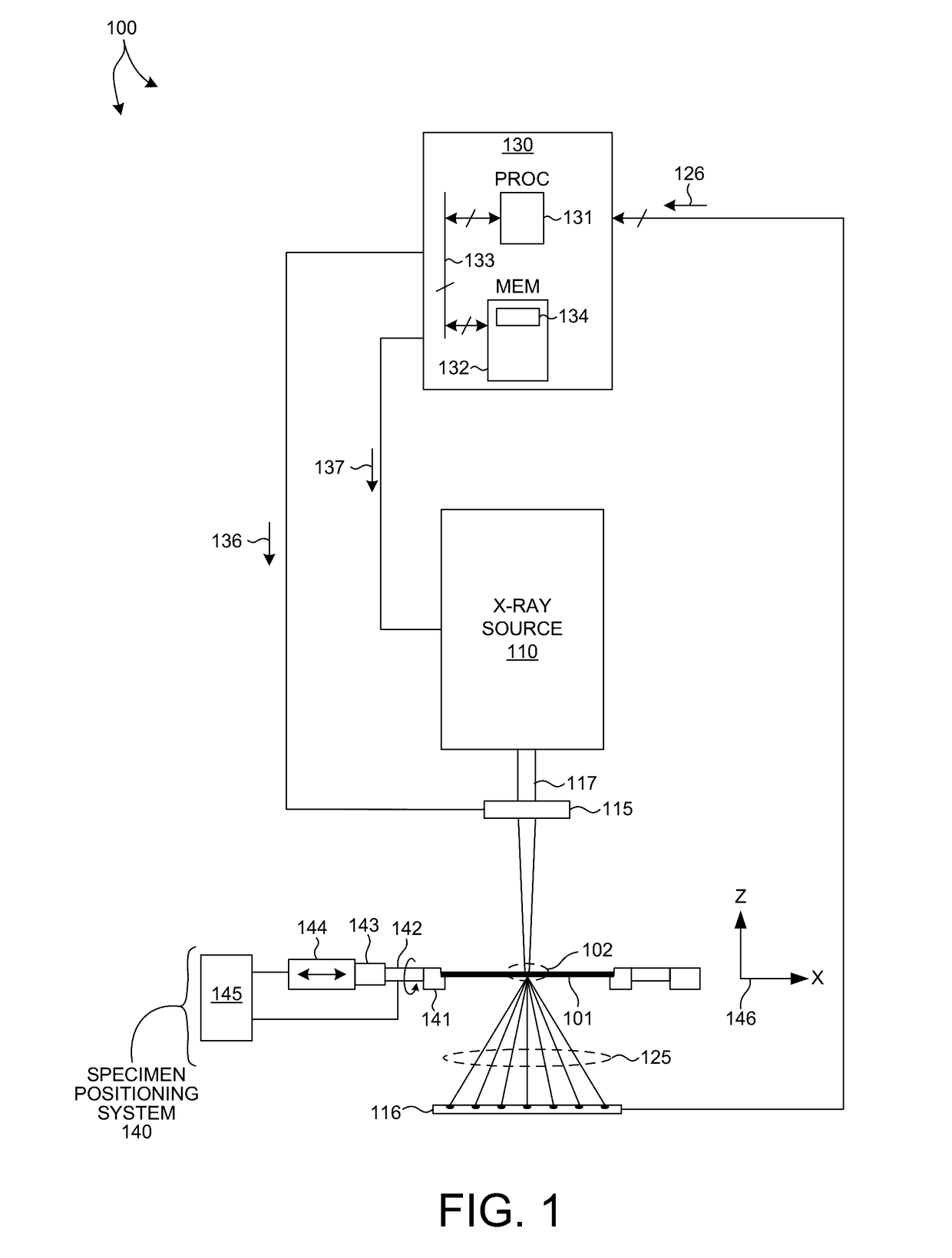
Full Beam Metrology For X-Ray Scatterometry Systems
ActiveUS20180106735A1Improve throughputImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisAngle of incidenceMetrology
Methods and systems for characterizing dimensions and material properties of semiconductor devices by full beam x-ray scatterometry are described herein. A full beam x-ray scatterometry measurement involves illuminating a sample with an X-ray beam and detecting the intensities of the resulting zero diffraction order and higher diffraction orders simultaneously for one or more angles of incidence relative to the sample. The simultaneous measurement of the direct beam and the scattered orders enables high throughput measurements with improved accuracy. The full beam x-ray scatterometry system includes one or more photon counting detectors with high dynamic range and thick, highly absorptive crystal substrates that absorb the direct beam with minimal parasitic backscattering. In other aspects, model based measurements are performed based on the zero diffraction order beam, and measurement performance of the full beam x-ray scatterometry system is estimated and controlled based on properties of the measured zero order beam.
Owner:KLA CORP
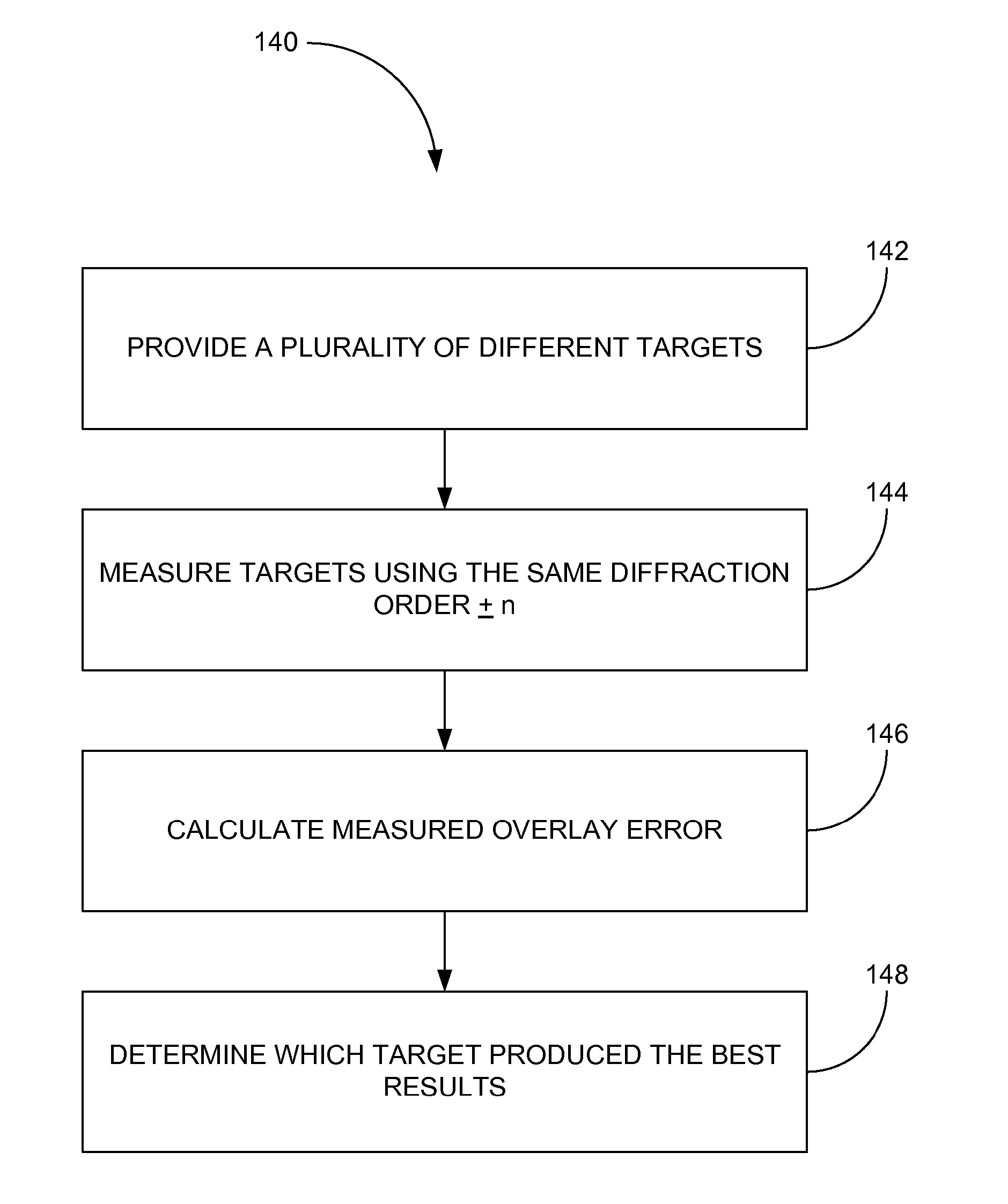
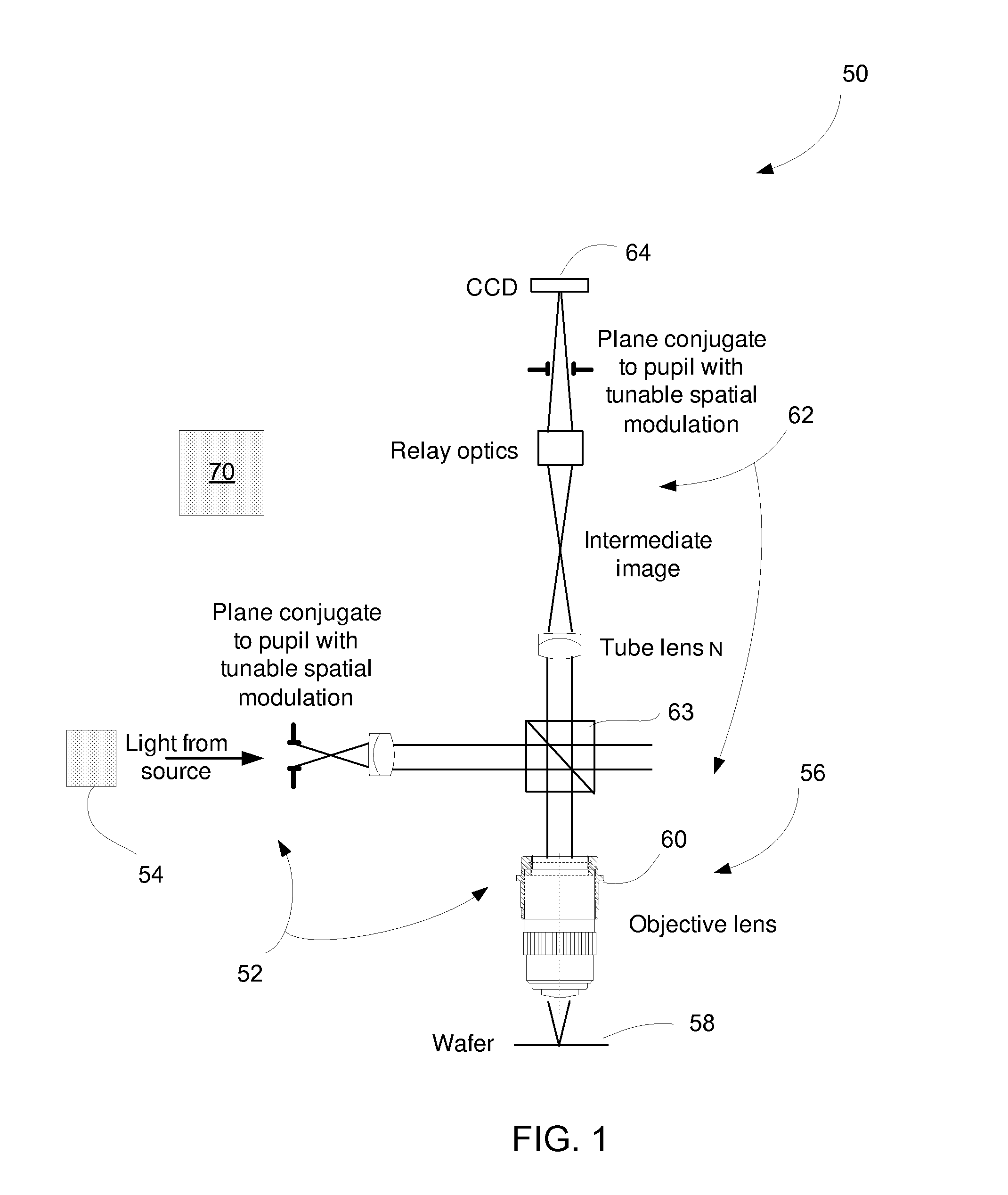
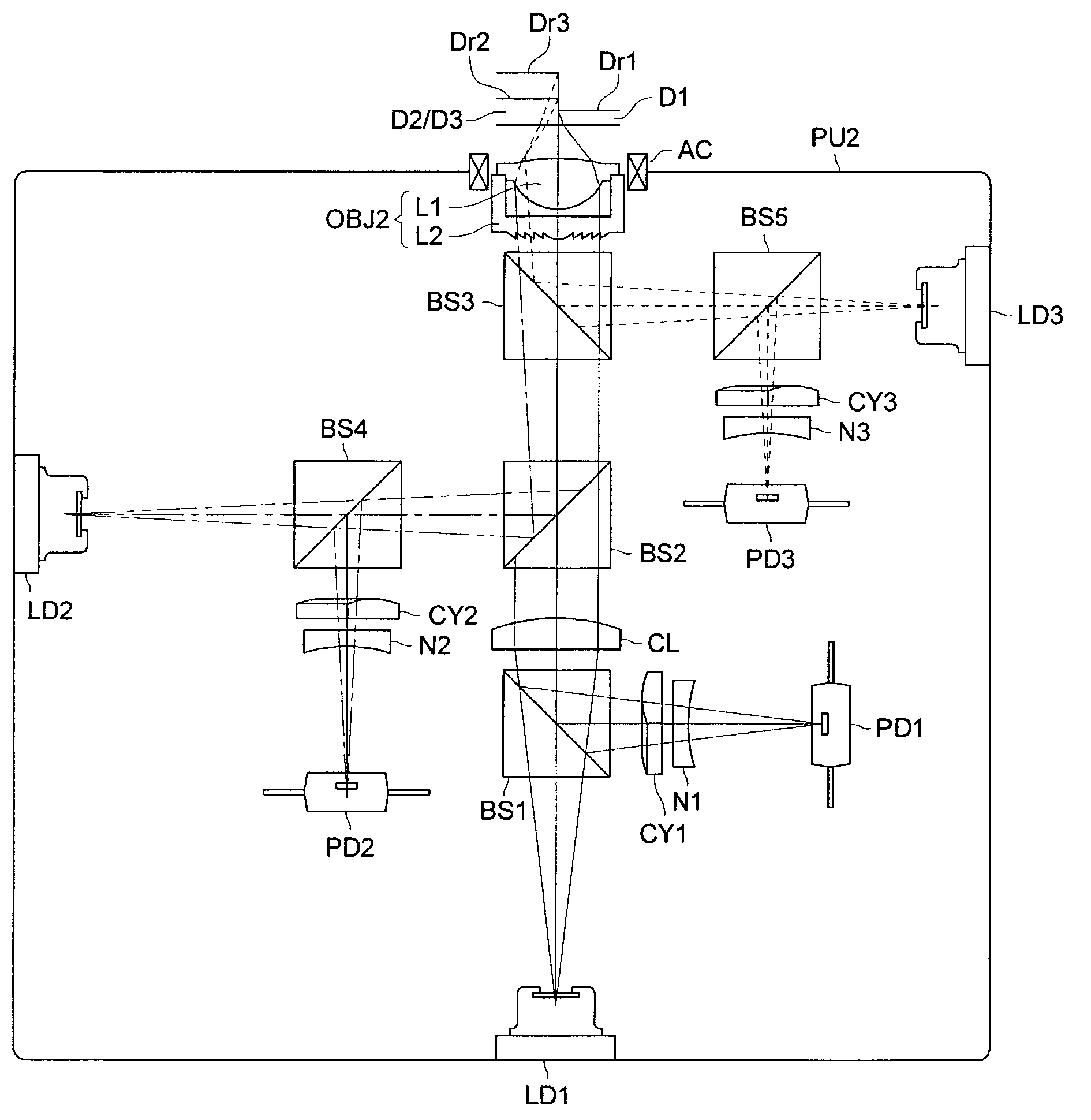
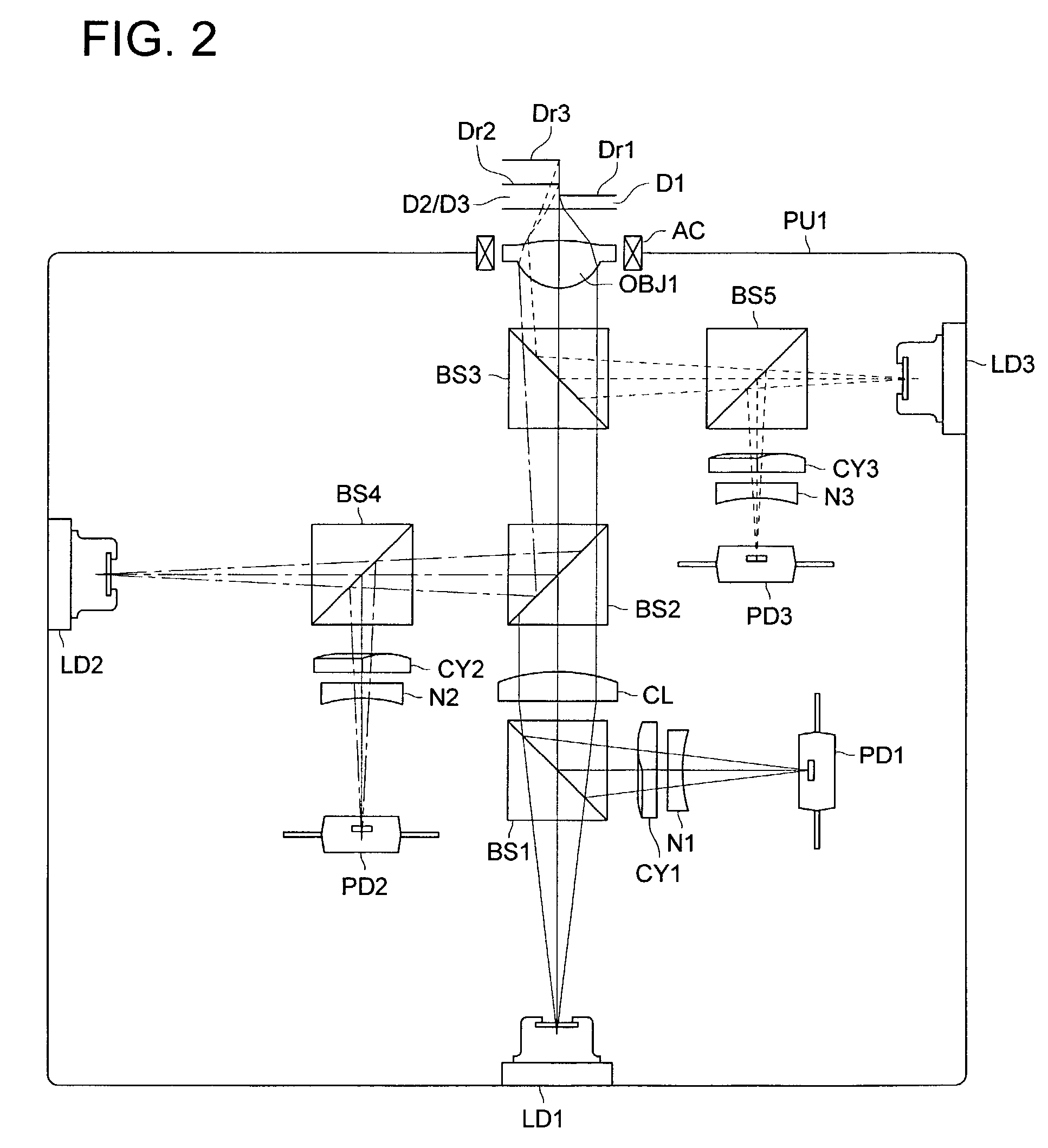
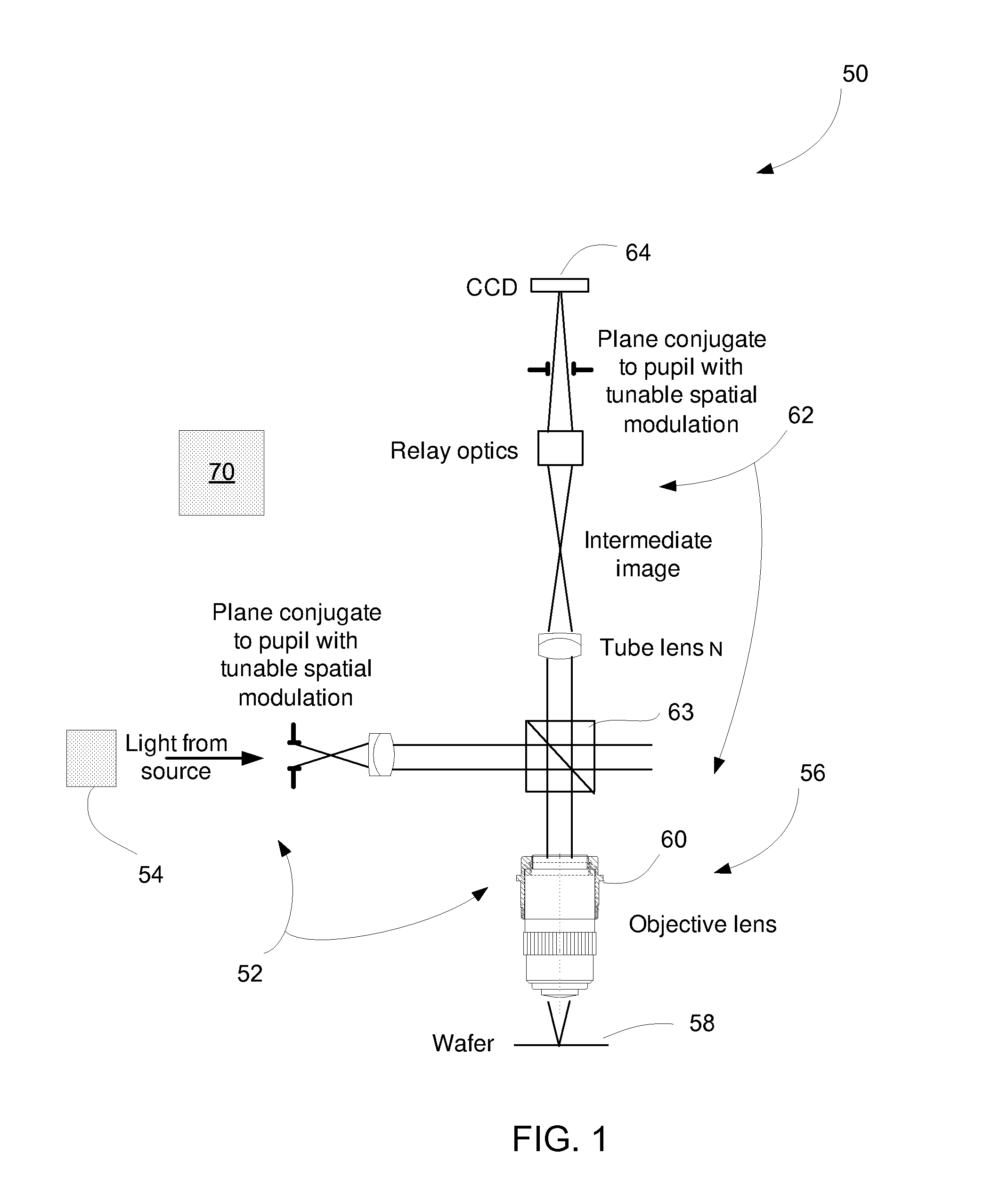
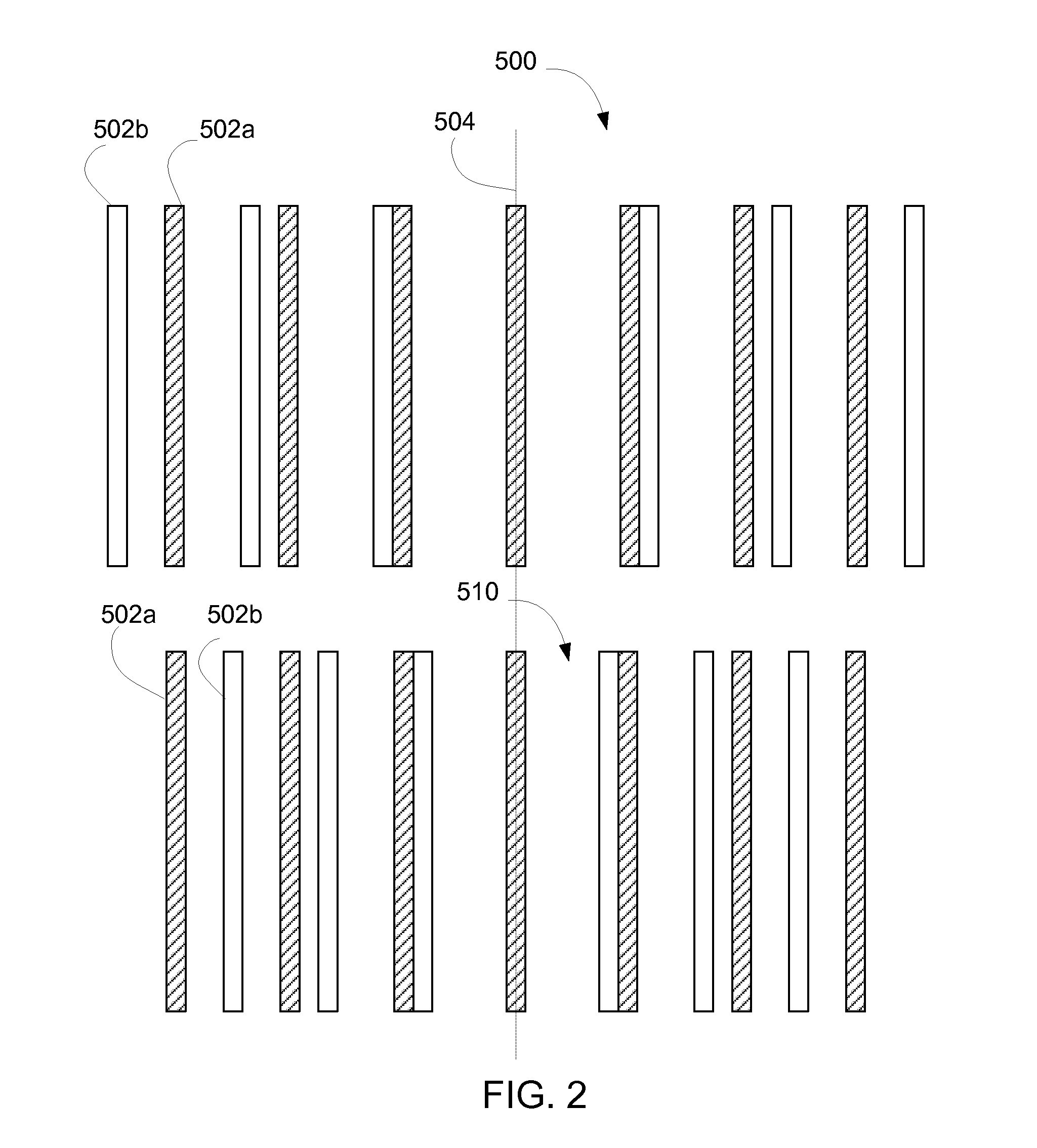
Order selected overlay metrology
ActiveUS20070279630A1Maximize contrastPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansDiffraction orderMetrology
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for measuring a characteristic, such as overlay, of a semiconductor target. In general, order-selected imaging and / or illumination is performed while collecting an image from a target using a metrology system. In one implementation, tunable spatial modulation is provided only in the imaging path of the system. In other implementations, tunable spatial modulation is provided in both the illumination and imaging paths of the system. In a specific implementation, tunable spatial modulation is used to image side-by-side gratings with diffraction orders ±n. The side-by-side gratings may be in different layers or the same layer of a semiconductor wafer. The overlay between the structures is typically found by measuring the distance between centers symmetry of the gratings. In this embodiment, only orders ±n for a given choice of n (where n is an integer and not equal to zero) are selected, and the gratings are only imaged with these diffraction orders.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
X-Ray Scatterometry Metrology For High Aspect Ratio Structures
ActiveUS20170167862A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyStatic random-access memory
Methods and systems for characterizing dimensions and material properties of high aspect ratio, vertically manufactured devices using transmission, small-angle x-ray scattering (T-SAXS) techniques are described herein. Exemplary structures include spin transfer torque random access memory (STT-RAM), vertical NAND memory (V-NAND), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), three dimensional FLASH memory (3D-FLASH), resistive random access memory (Re-RAM), and PC-RAM. In one aspect, T-SAXS measurements are performed at a number of different orientations that are more densely concentrated near the normal incidence angle and less densely concentrated at orientations that are further from the normal incidence angle. In a further aspect, T-SAXS measurement data is used to generate an image of a measured structure based on the measured intensities of the detected diffraction orders. In another further aspect, a metrology system is configured to generate models for combined x-ray and optical measurement analysis.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Resonant leaky-mode optical devices and associated methods
ActiveUS20060024013A1Increase varietyImprove utilizationSemiconductor lasersOptical waveguide light guideSpectral bandsDiffraction order
Optical devices with versatile spectral attributes are provided that are implemented with one or more modulated and homogeneous layers to realize leaky-mode resonance operation and corresponding versatile spectral-band design. The first and / or higher multiple evanescent diffraction orders are applied to excite one or more leaky modes. The one- or two-dimensional periodic structure, fashioned by proper distribution of materials within each period, can have a resulting symmetric or asymmetric profile to permit a broadened variety of resonant leaky-mode devices to be realized. Thus, the attributes of the optical device permit, among other things, adjacent, distinct resonance frequencies or wavelengths to be produced, convenient shaping of the reflection and transmission spectra for such optical device to be accomplished, and the wavelength resonance locations to be precisely controlled so as to affect the extent to which the leaky modes interact with each other. Further, the profile asymmetry allows for the precise spectral spacing of interactive leaky modes so as to provide greater flexibility in optical device design.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
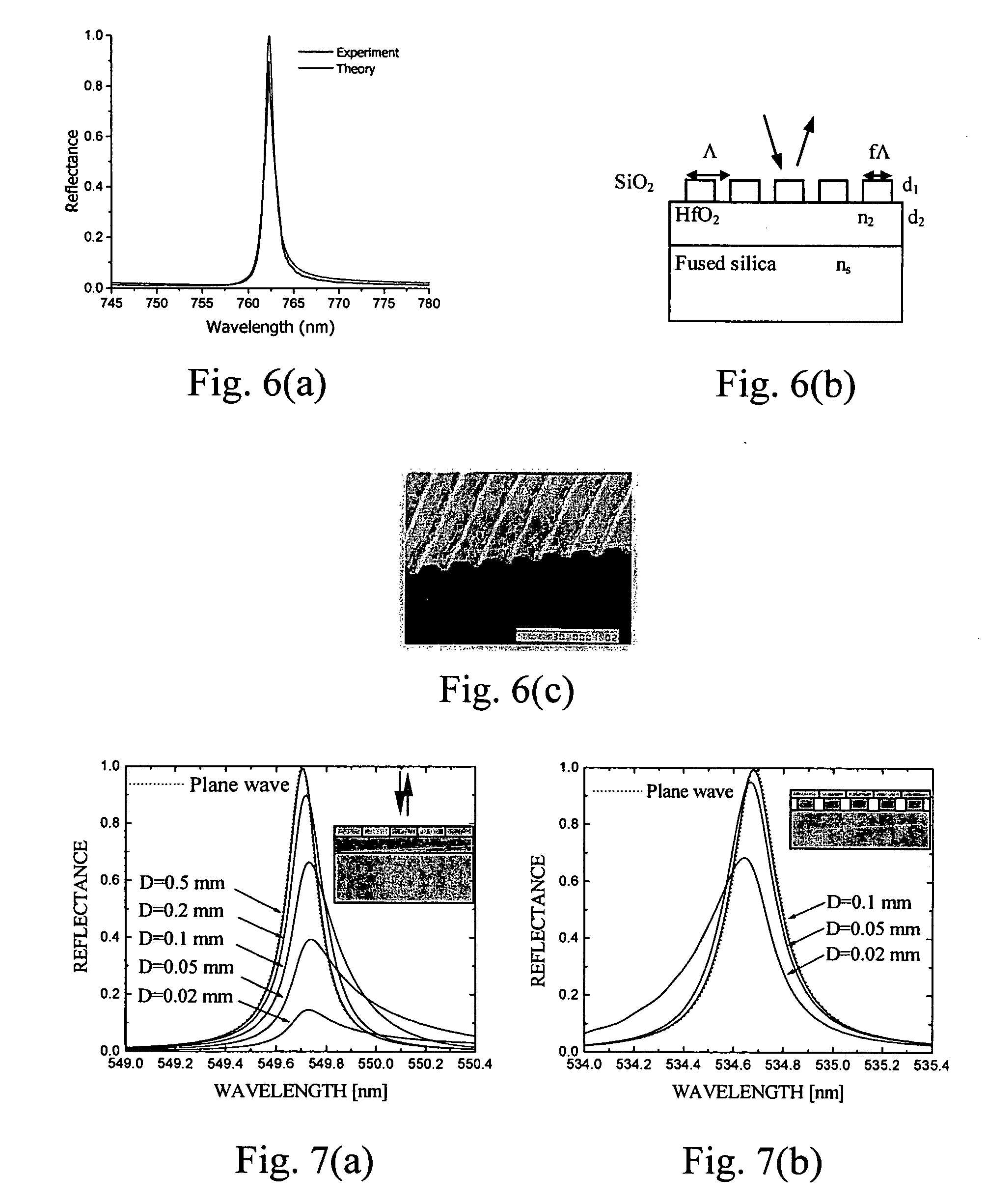
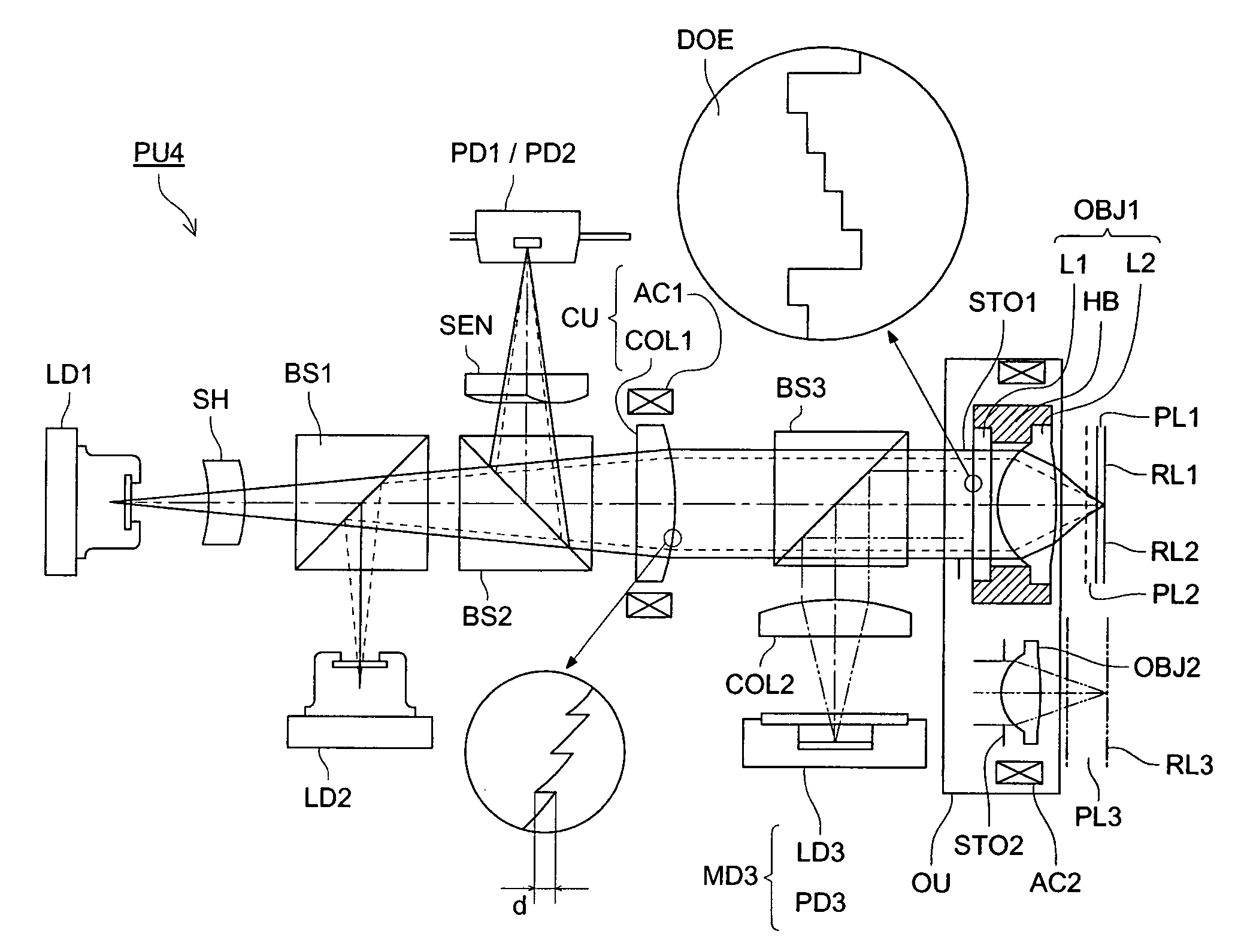
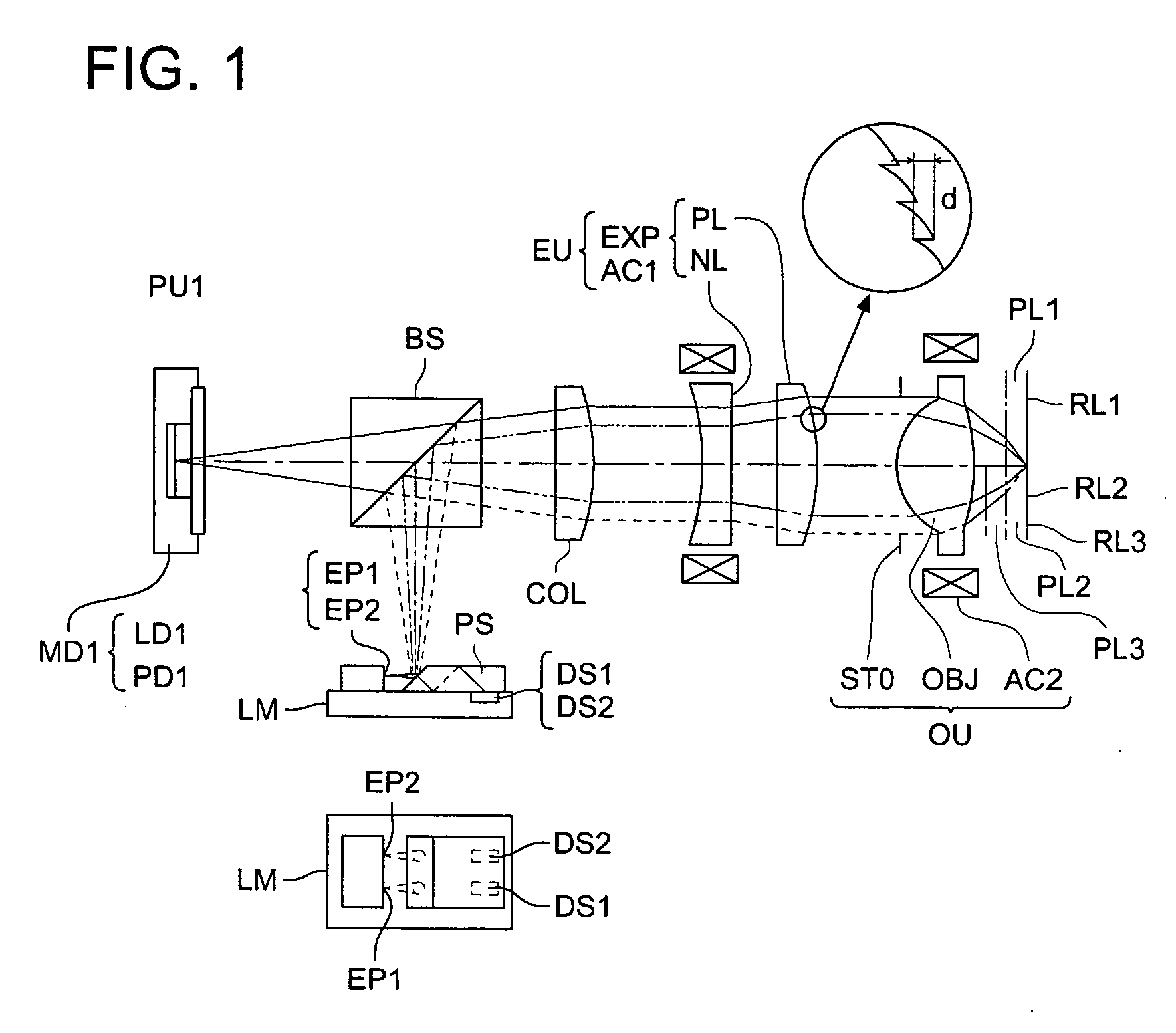
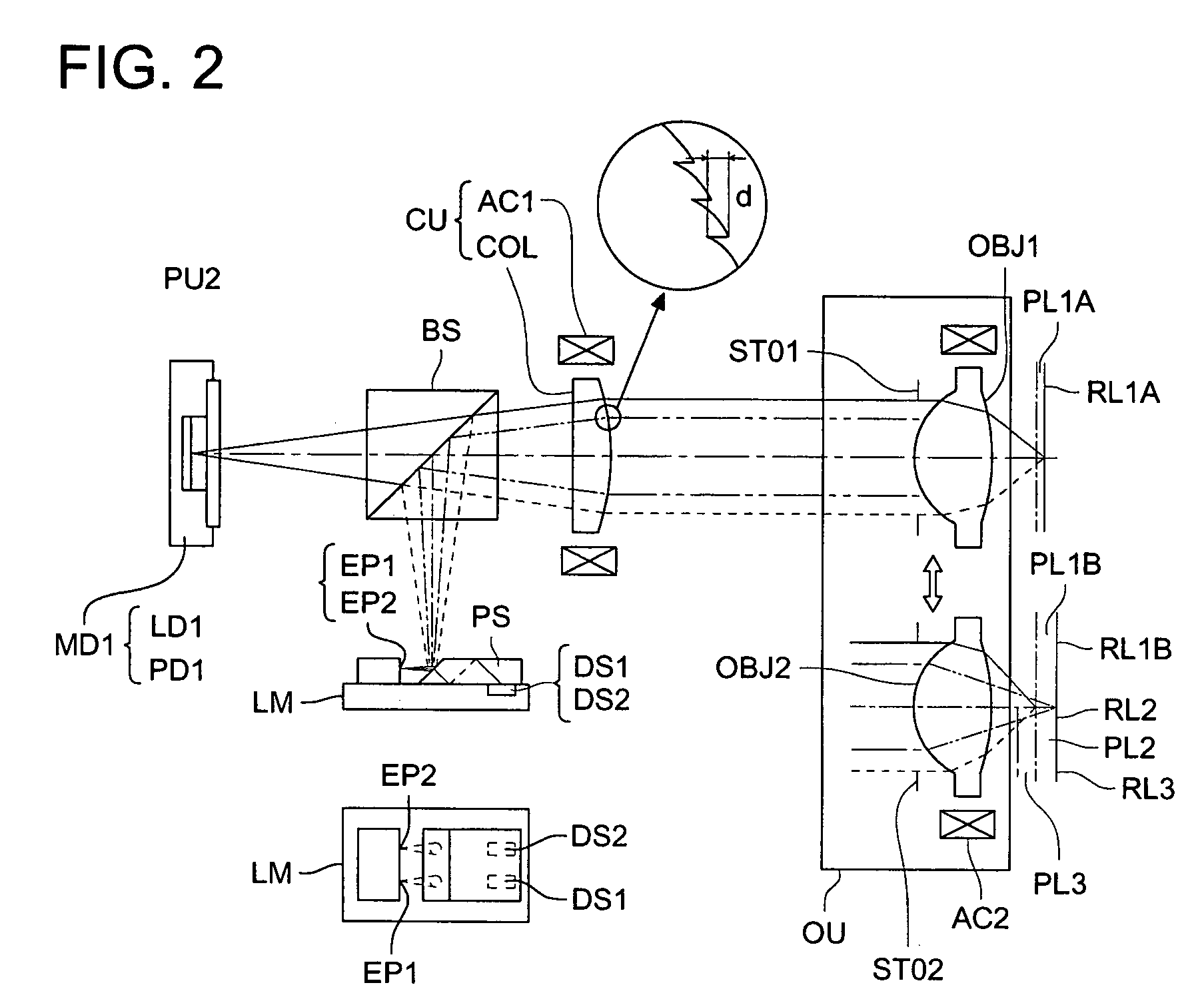
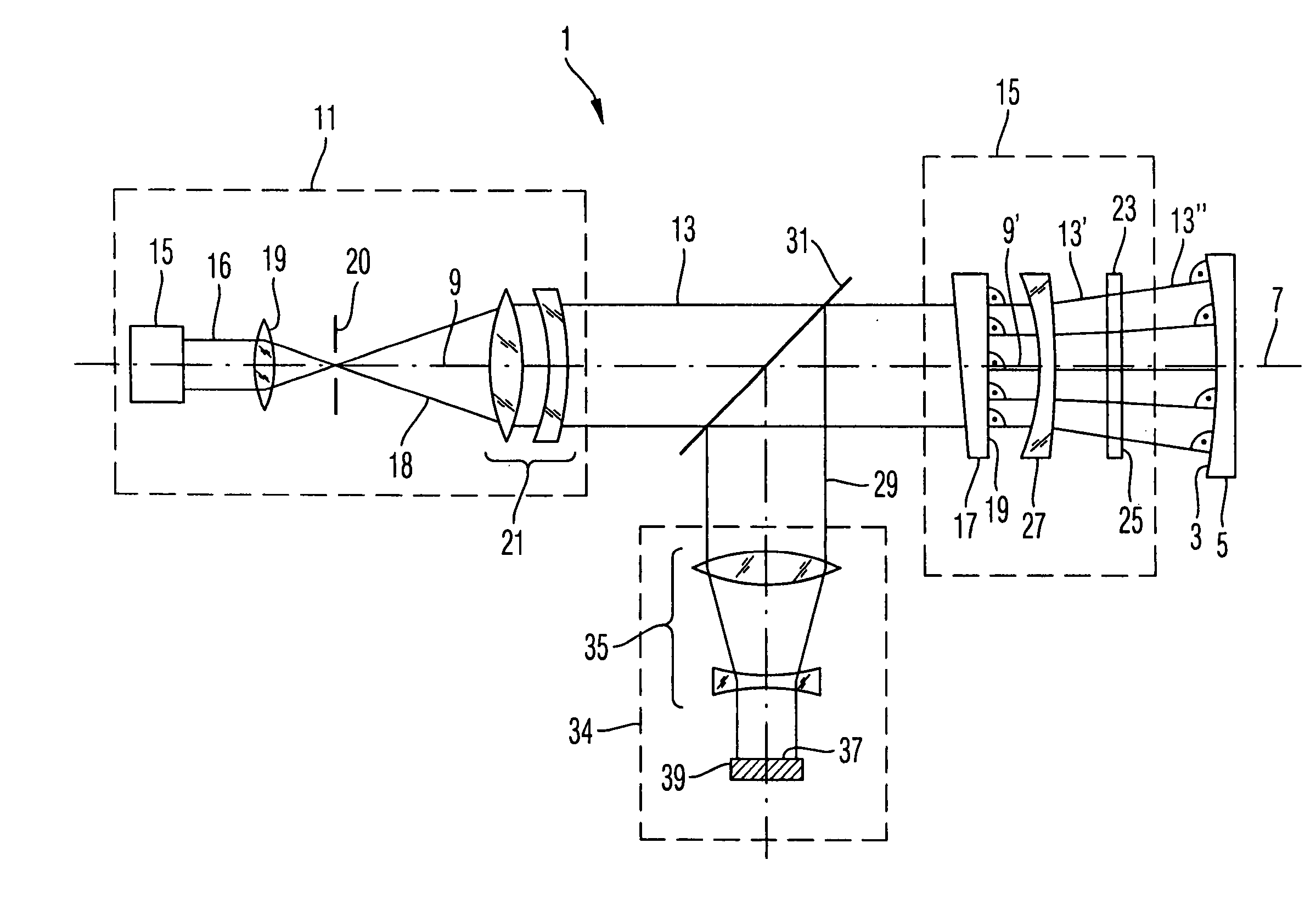
Optical pickup device, optical information recording and reproducing apparatus, expander lens, coupling lens and chromatic aberration correcting optical element
An optical pickup apparatus includes first and light sources; an objective lens; a spherical aberration correcting optical unit; and a chromatic aberration correcting optical element which includes a diffractive surface on at least one of optical surfaces of the chromatic aberration correcting optical element such that a diffractive structure which is constructed by a plurality of ring-shaped zones separated by fine steps is formed on the diffractive surface, wherein the depth of steps along an optical axis is designed so that n2 which is a diffraction order of a diffracted ray having a largest diffraction efficiency among diffracted rays caused when the second light flux enters into the diffractive structure, is lower order than n1 which is a diffraction order of a diffracted ray having a largest diffraction efficiency among diffracted light rays caused when the second light flux enters into the diffractive structure.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Objective lens, optical element, optical pick-up apparatus and optical information recording and/or reproducing apparatus equipped therewith
ActiveUS7206276B2Compact structureReduce the number of partsOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageDiffraction orderWavefront
A hybrid objective lens has a refractive lens and a diffractive optical element constructed by plural coaxial ring-shaped zones on at least one optical surface thereof. When n1, n2 and n3 each is a diffraction order of a diffracted ray having a maximum light amount among diffracted rays of each of first, second and third light flux having wavelength λ1, λ2 and λ3 when respective light flux comes to be incident into the diffractive structure respectively, the following formulas are satisfied:|n1|>|n2|, and |n1|>|n3|, andthe hybrid objective lens converges a n1-th, n2-th and n3-th order diffracted ray of the first, second and third light flux onto an information recording plane of each of the first, second ant third optical information recording medium respectively so as to form an appropriate wavefront within respective prescribed necessary image side numerical apertures.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Order selected overlay metrology
ActiveUS7528941B2Maximize contrastPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansDiffraction orderMetrology
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for measuring a characteristic, such as overlay, of a semiconductor target. In general, order-selected imaging and / or illumination is performed while collecting an image from a target using a metrology system. In one implementation, tunable spatial modulation is provided only in the imaging path of the system. In other implementations, tunable spatial modulation is provided in both the illumination and imaging paths of the system. In a specific implementation, tunable spatial modulation is used to image side-by-side gratings with diffraction orders ±n. The side-by-side gratings may be in different layers or the same layer of a semiconductor wafer. The overlay between the structures is typically found by measuring the distance between centers symmetry of the gratings. In this embodiment, only orders ±n for a given choice of n (where n is an integer and not equal to zero) are selected, and the gratings are only imaged with these diffraction orders.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
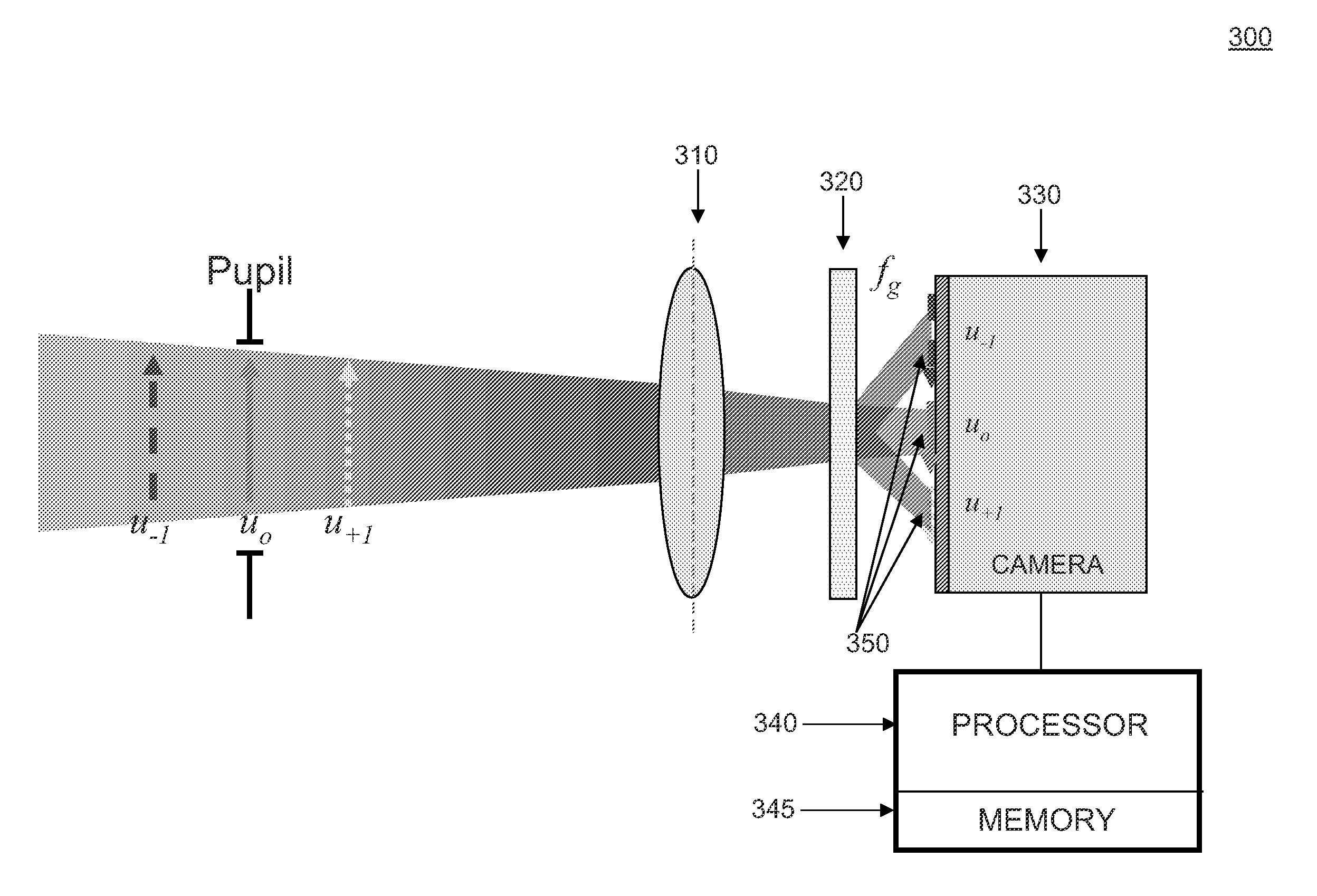
Systems and methods of phase diversity wavefront sensing
A phase diversity wavefront sensor includes an optical system including at least one optical element for receiving a light beam; a diffractive optical element having a diffractive pattern defining a filter function, the diffractive optical element being arranged to produce, in conjunction with the optical system, images from the light beam associated with at least two diffraction orders; and a detector for detecting the images and outputting image data corresponding to the detected images. In one embodiment, the optical system, diffractive optical element, and detector are arranged to provide telecentric, pupil plane images of the light beam. A processor receives the image data from the detector, and executes a Gerchberg-Saxton phase retrieval algorithm to measure the wavefront of the light beam.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method for designing a diffraction grating structure and a diffraction grating structure
InactiveUS20110038049A1Broaden applicationAccurately final performanceDiffraction gratingsComputation using non-denominational number representationDiffraction orderPhase shifted
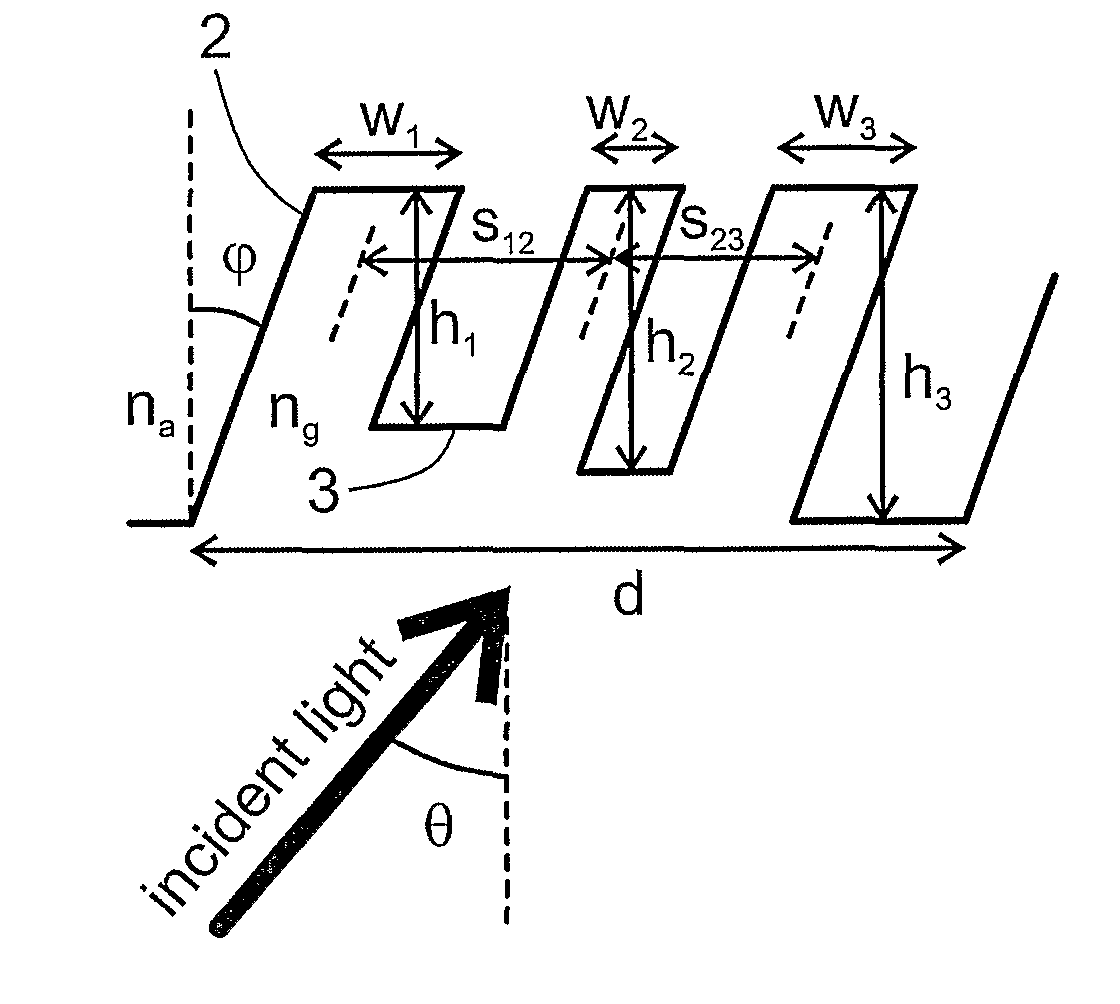
According to the present invention, the method for designing a diffraction grating structure (1), the grating period (d) of the structure comprising at least two grating lines each consisting of a pair of adjacent pillars (2) and grooves (3), comprises the steps of—determining desired diffraction efficiencies ηd of the diffraction orders, and—dimensioning the pillars (2) and grooves (3) so that when calculating for each pillar, on the basis of the effective refractive index neff for the fundamental wave mode propagating along that pillar, the phase shift Φ experienced by light propagated through the grating structure, the differences in the calculated phase shifts between adjacent pillars corresponds to the phase profile Φr required by the desired diffraction efficiencies.
Owner:NANOCOMP
Three-dimensional image display apparatus
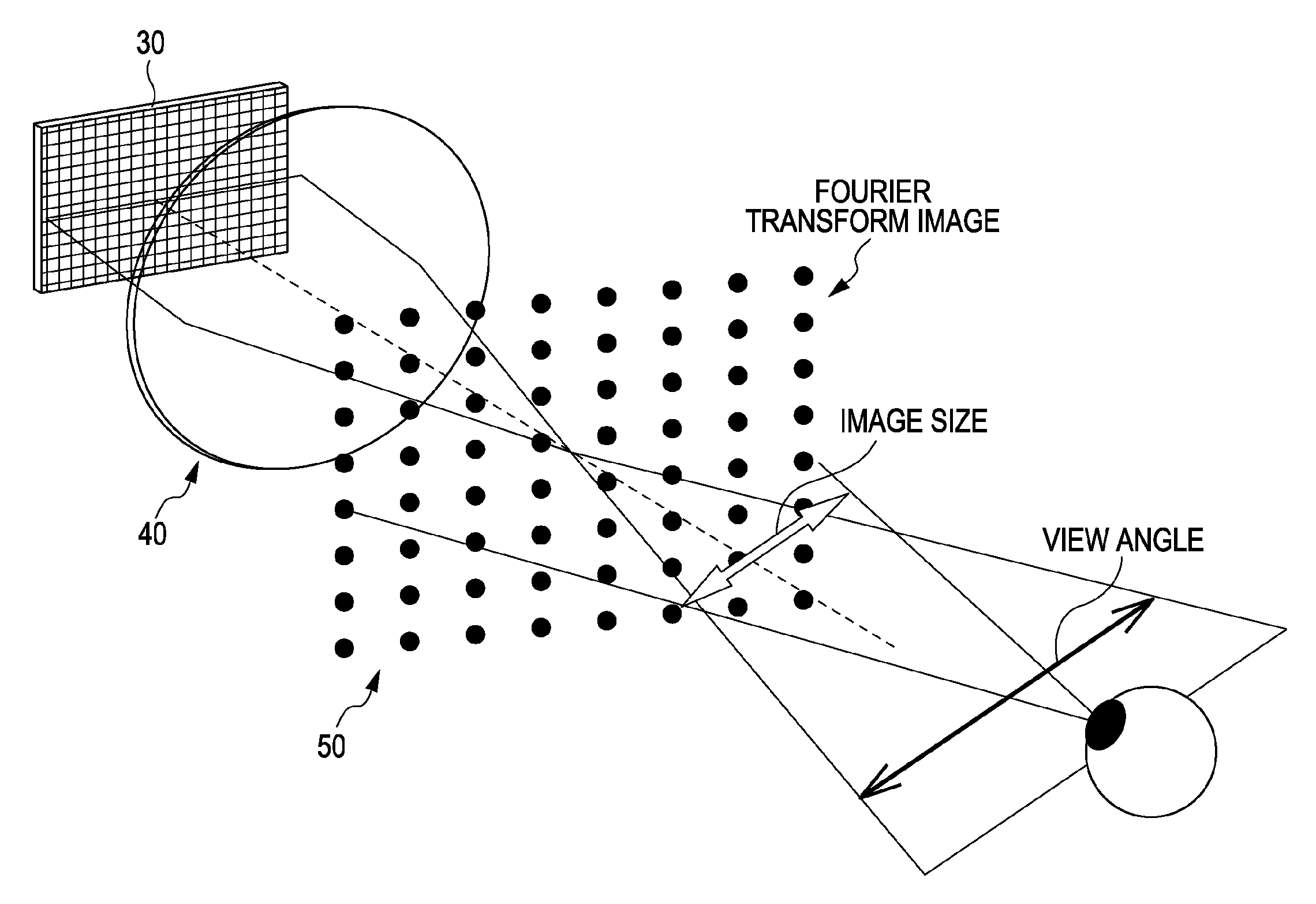
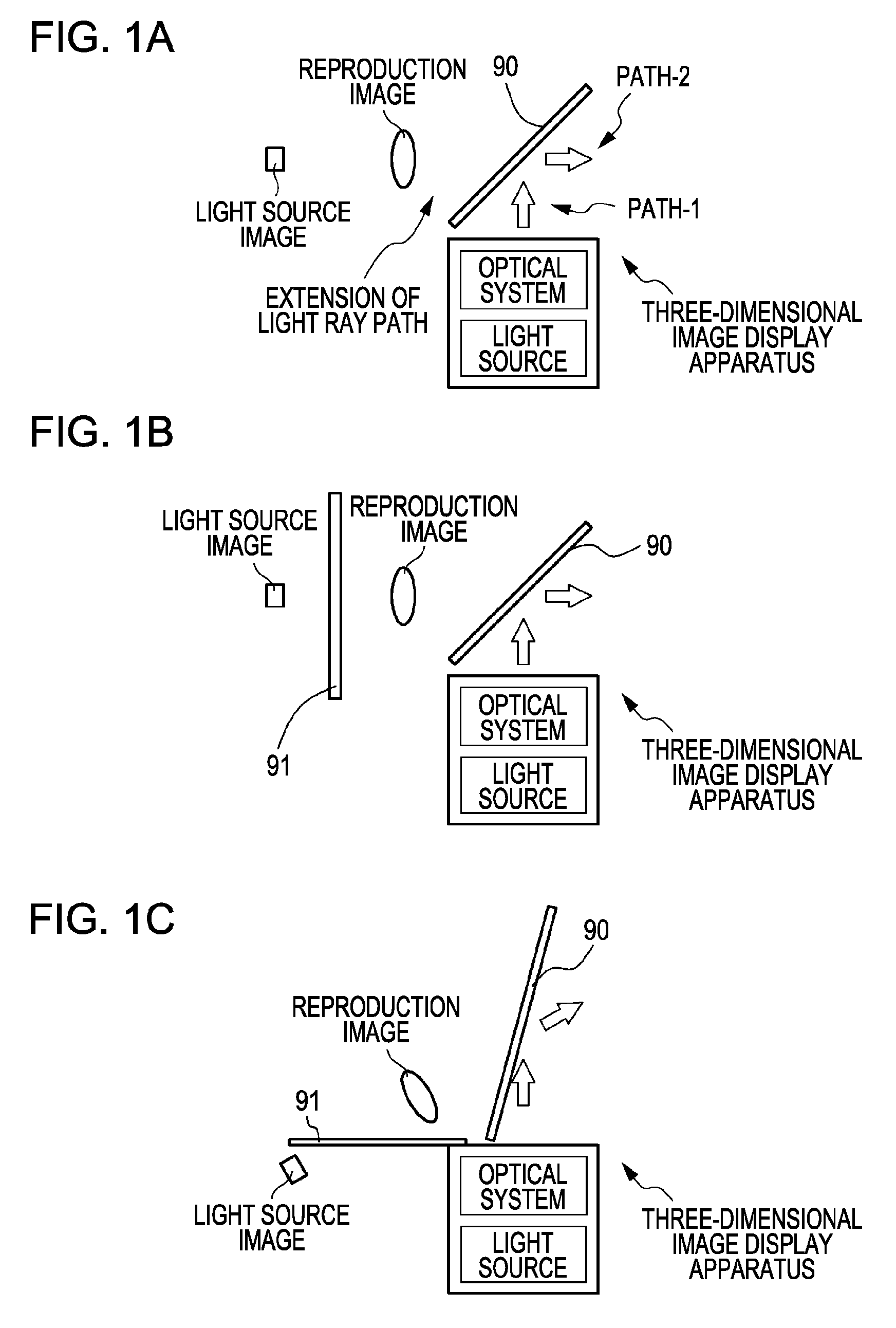
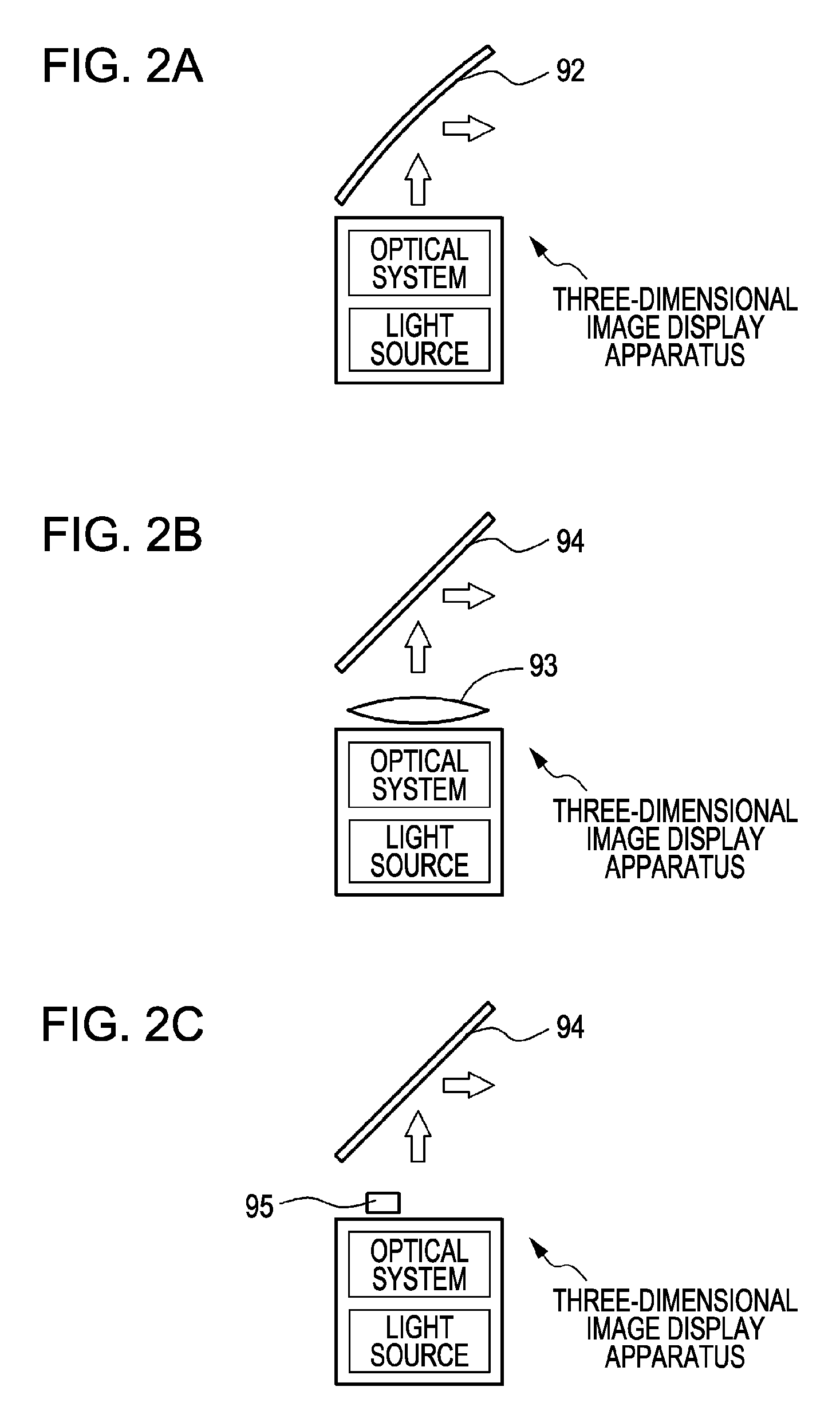
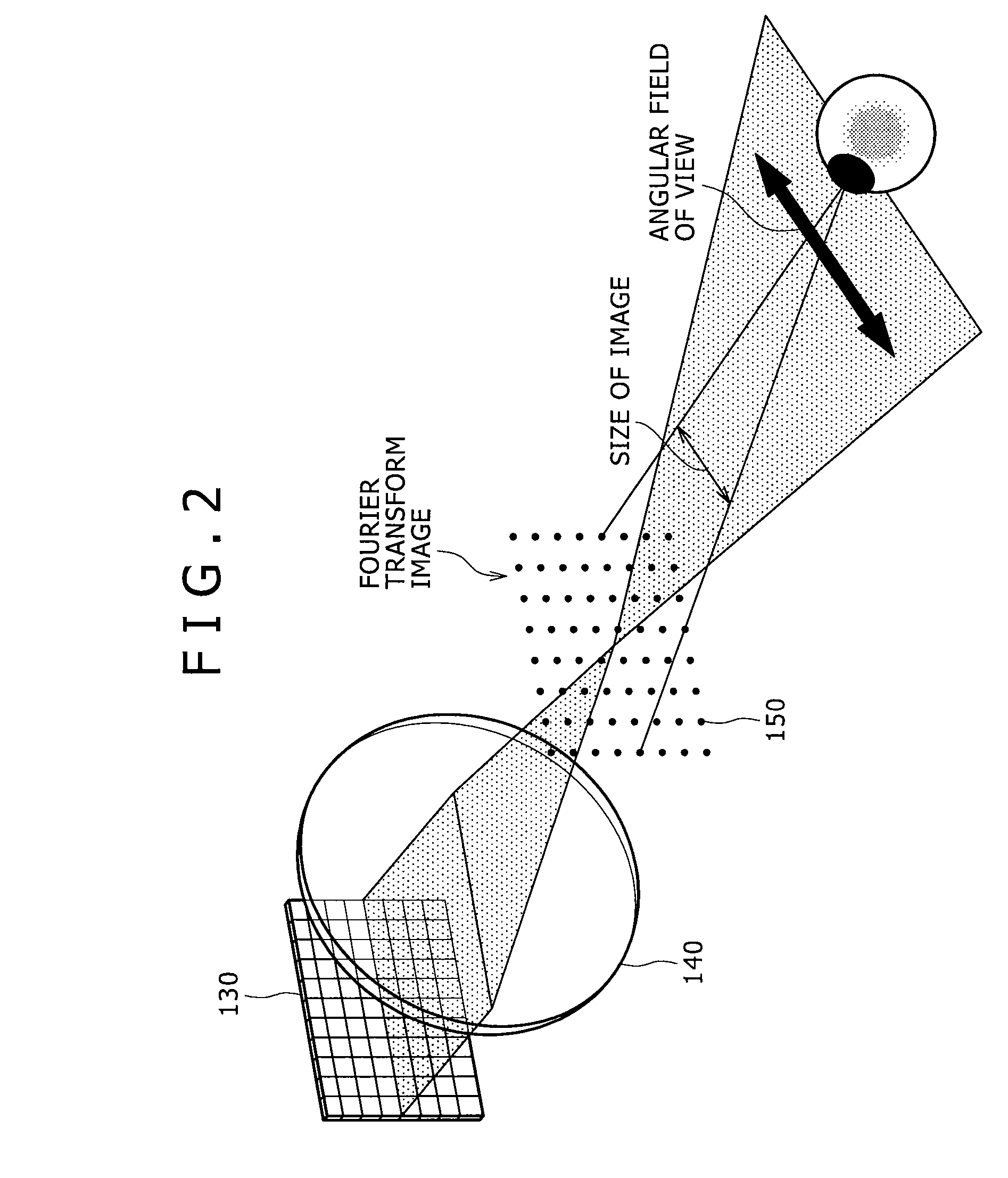
InactiveUS20090303597A1Strong demandReduce loadOptical computing devicesOptical elementsFast Fourier transformDiffraction order
A three-dimensional image display apparatus includes a light source and an optical system including a light modulation unit having pixels for generating a two-dimensional image by modulating light from the light source by the respective pixels and emitting a spatial frequency in the generated two-dimensional image along a diffraction angle corresponding to diffraction orders generated from the respective pixels, a Fourier transform image formation unit for performing Fourier transform on the spatial frequency in the two-dimensional image to generate Fourier transform images corresponding to the diffraction orders, a Fourier transform image selection unit for selecting a Fourier transform image corresponding to a desired diffraction order among the Fourier transform images, and a conjugate image formation unit for forming a conjugate image of the selected Fourier transform image, and further includes a semi-transmissive mirror for changing a light ray travelling direction emitted from the optical system.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of qualifying a diffraction grating and method of manufacturing an optical element
InactiveUS20060274325A1Accurate analysisAccurate determinationInterferometersUsing optical meansAngle of incidenceDiffraction order
A method of qualifying a diffraction grating comprises performing plural measurements by illuminating a region of the grating with a beam of measuring light and detecting an intensity of measuring light diffracted by the grating into a 0th diffraction order. A wavelength of the measuring light or a polarization of the measuring light or an angle of incidence of the measuring light onto the diffraction grating is varied between subsequent measurements. A shape parameter of diffracting elements forming the grating comprises a pitch, height or width of structural features of the diffracting elements. The shape parameter is advantageously used in analyzing interferometric measurements performed on optical surfaces during manufacture of optical elements of a high accuracy.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Three-dimensional image display apparatus
InactiveUS20060290777A1Increase space densityHolographic optical componentsSteroscopic systemsDiffraction order3d image
Disclosed herein is a three-dimensional image display apparatus includes a light source, a light modulation section modulates light from the light source by means of pixels to produce two-dimensional images and emits a spatial frequency of the produced two-dimensional images along diffraction angles corresponding to a plurality of diffraction orders produced from each pixel, a Fourier transform image formation section Fourier transforms the spatial frequency of the two-dimensional images emitted from the light modulation section to produce Fourier transform images whose number corresponds to the number of diffraction orders, a Fourier transform image selection section selects one of the Fourier transform images produced by the Fourier transform section which corresponds to a desired diffraction order, a conjugate image formation section forms a conjugate image of the Fourier transform image selected by the Fourier transform image selection section.
Owner:SONY CORP
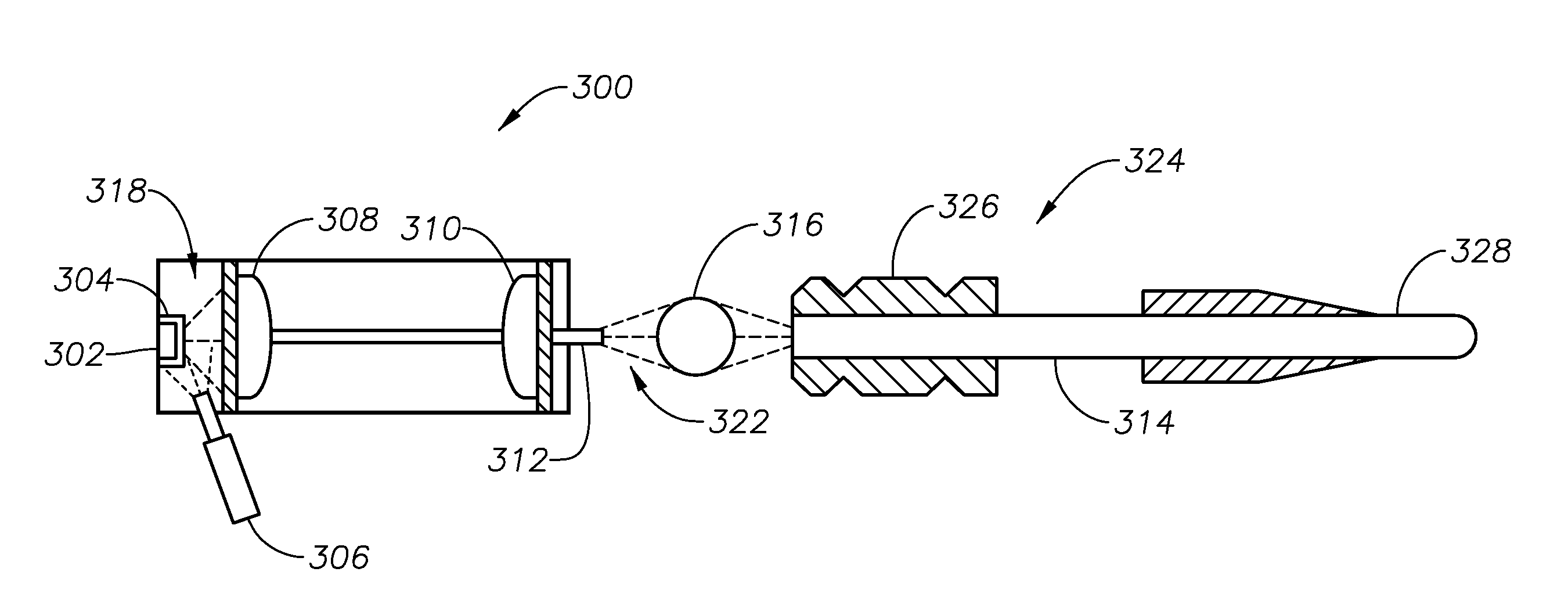
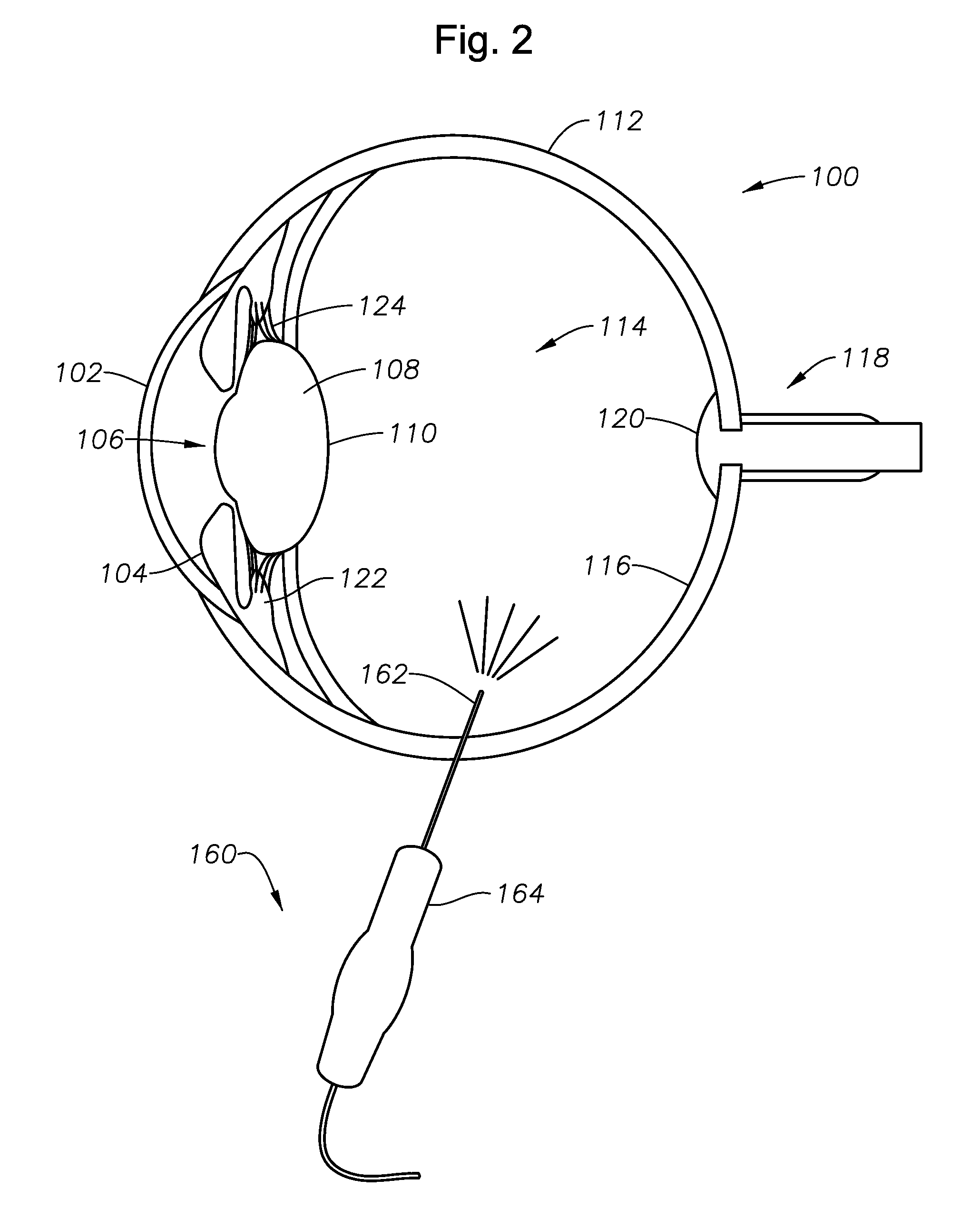
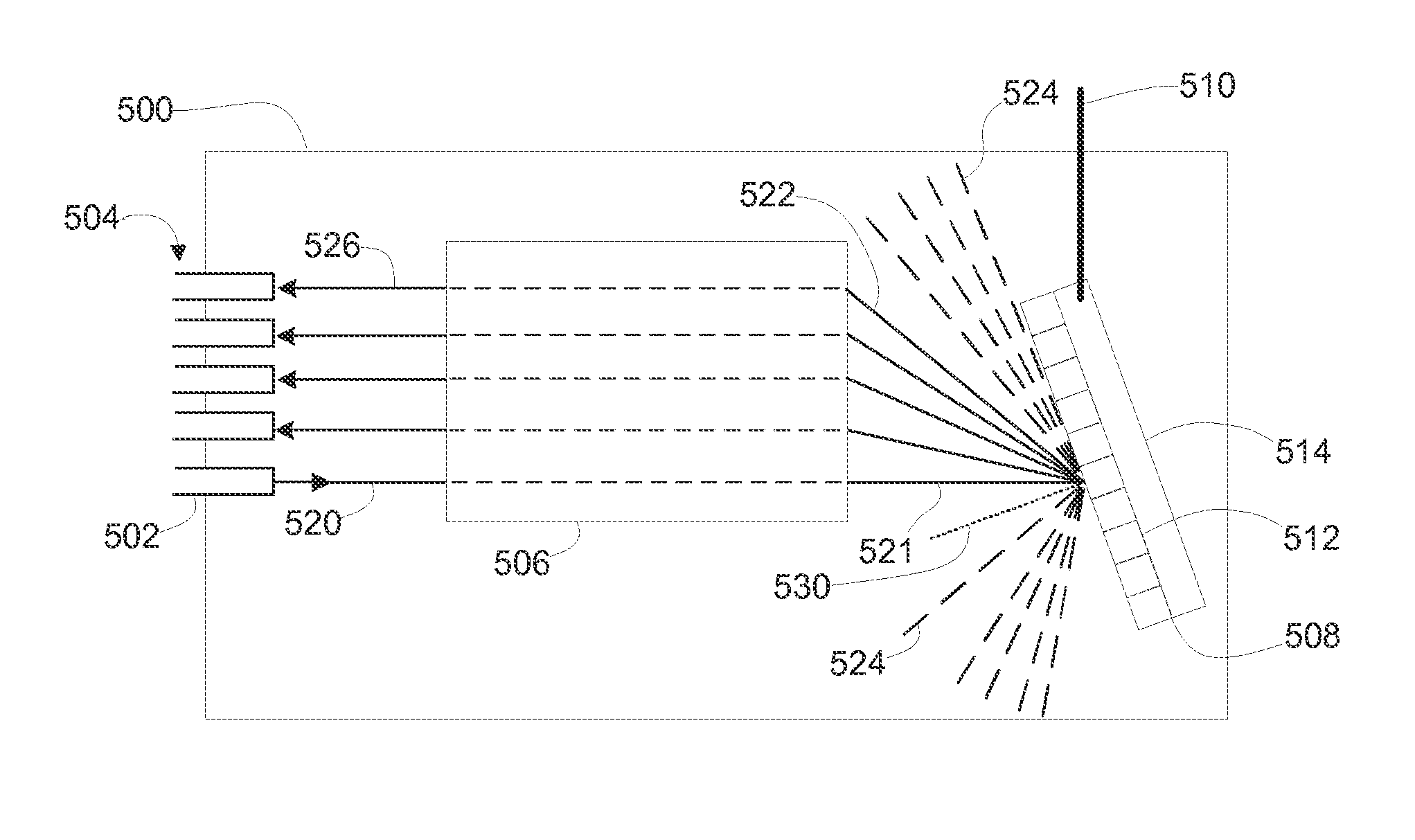
Single-fiber multi-spot laser probe for ophthalmic endoillumination
ActiveUS20110122366A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantageEliminates and reduces and problemLaser surgeryLaproscopesDiffraction orderGrating
An ophthalmic endoilluminator is provided. The ophthalmic endoilluminator includes a light source, a first optical assembly, an optical coupling element, and an optical fiber having an optical grating located distally on the optical fiber, the optical fiber optically coupled to the optical coupling element. The first optical assembly receives and substantially collimates the white light. The optical coupling element receives the substantially collimated white light from the first optical assembly and directs the light to an optical fiber. The optical grating couples to the distal end of the optical fiber, the optical grating having a surface relief grating, and an overlayer optically coupled to the surface relief grating. The optical grating is operable to substantially diffract incident light into N diffraction orders, the N diffraction orders having a substantially uniform intensity.
Owner:ALCON INC
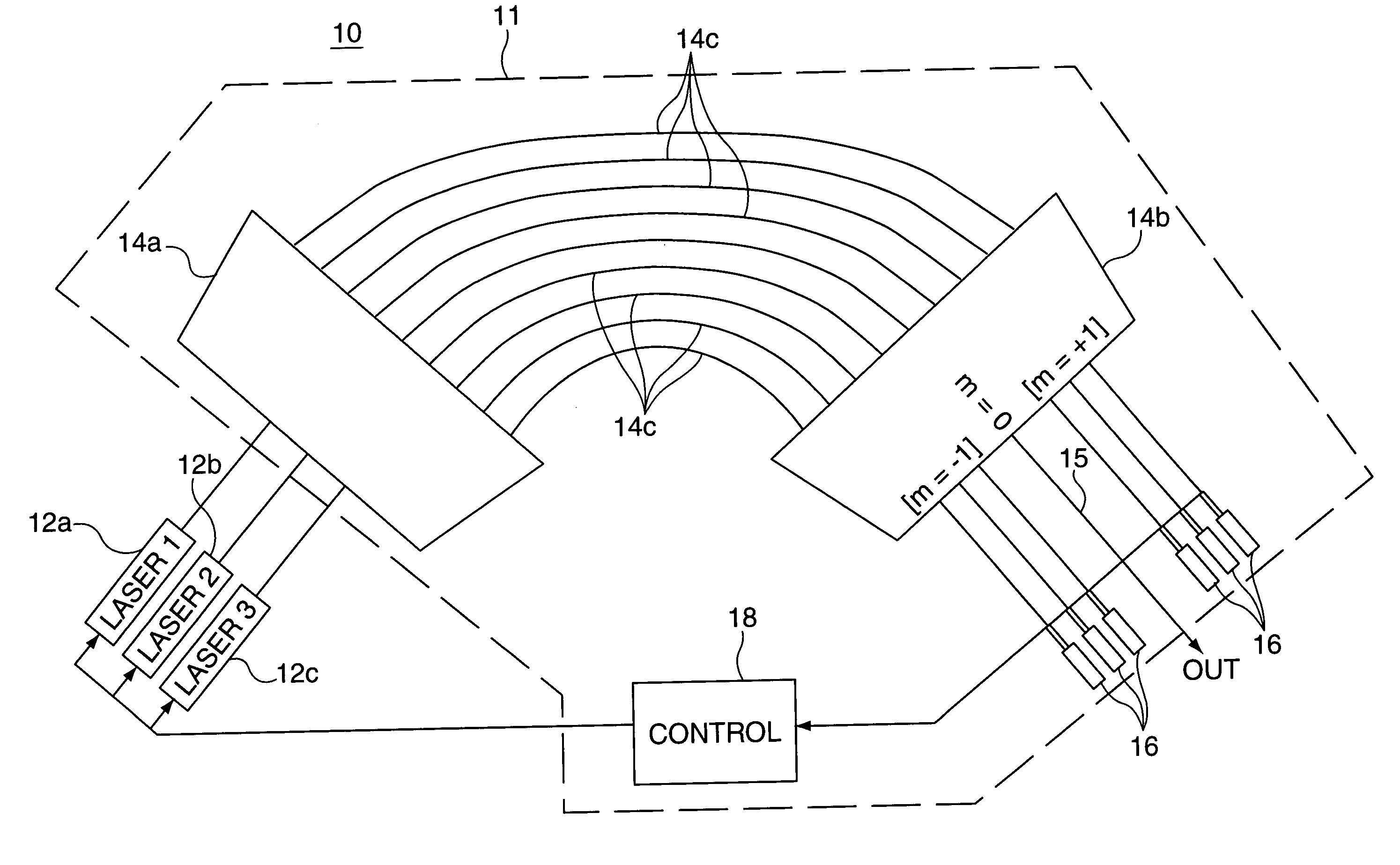
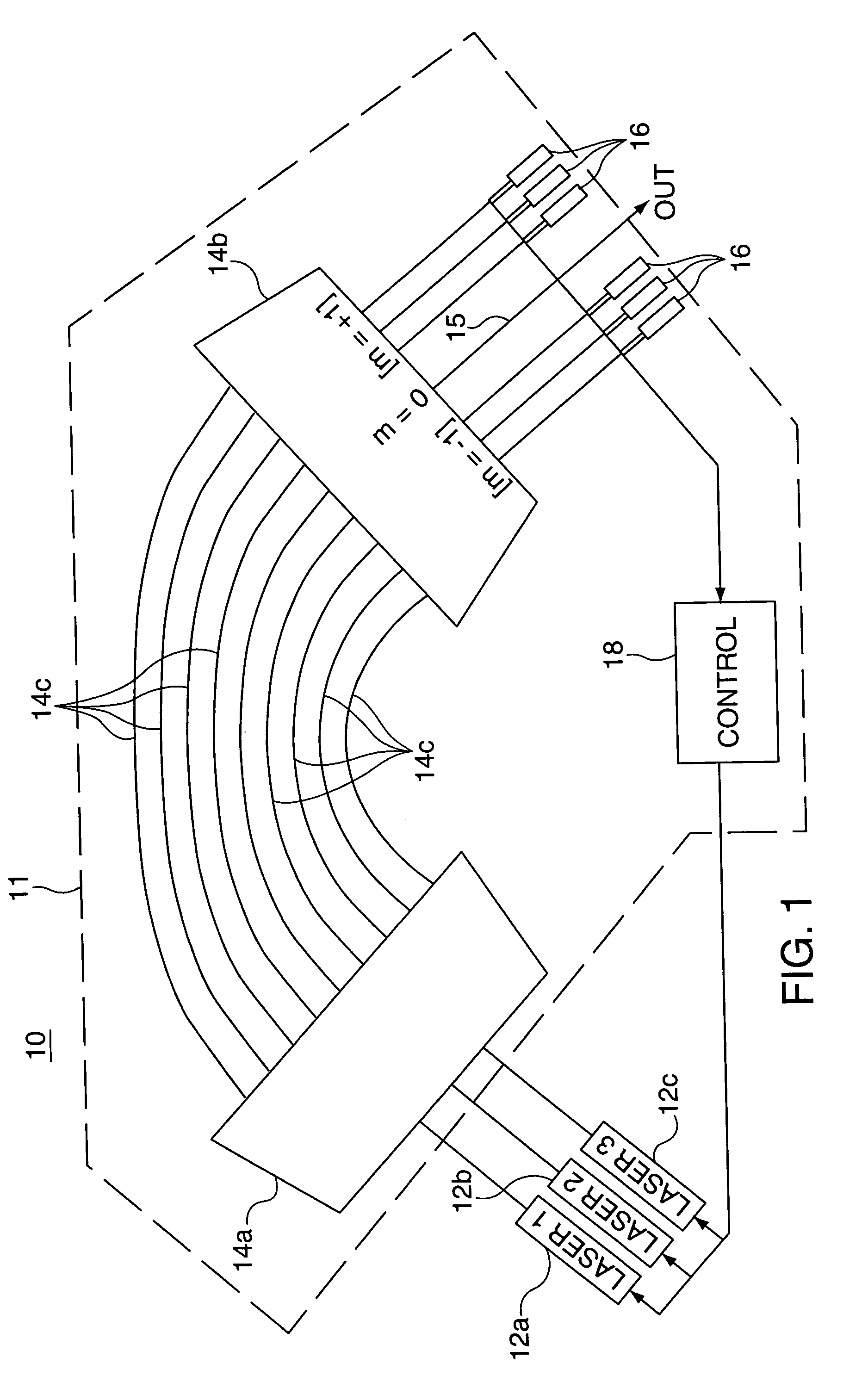
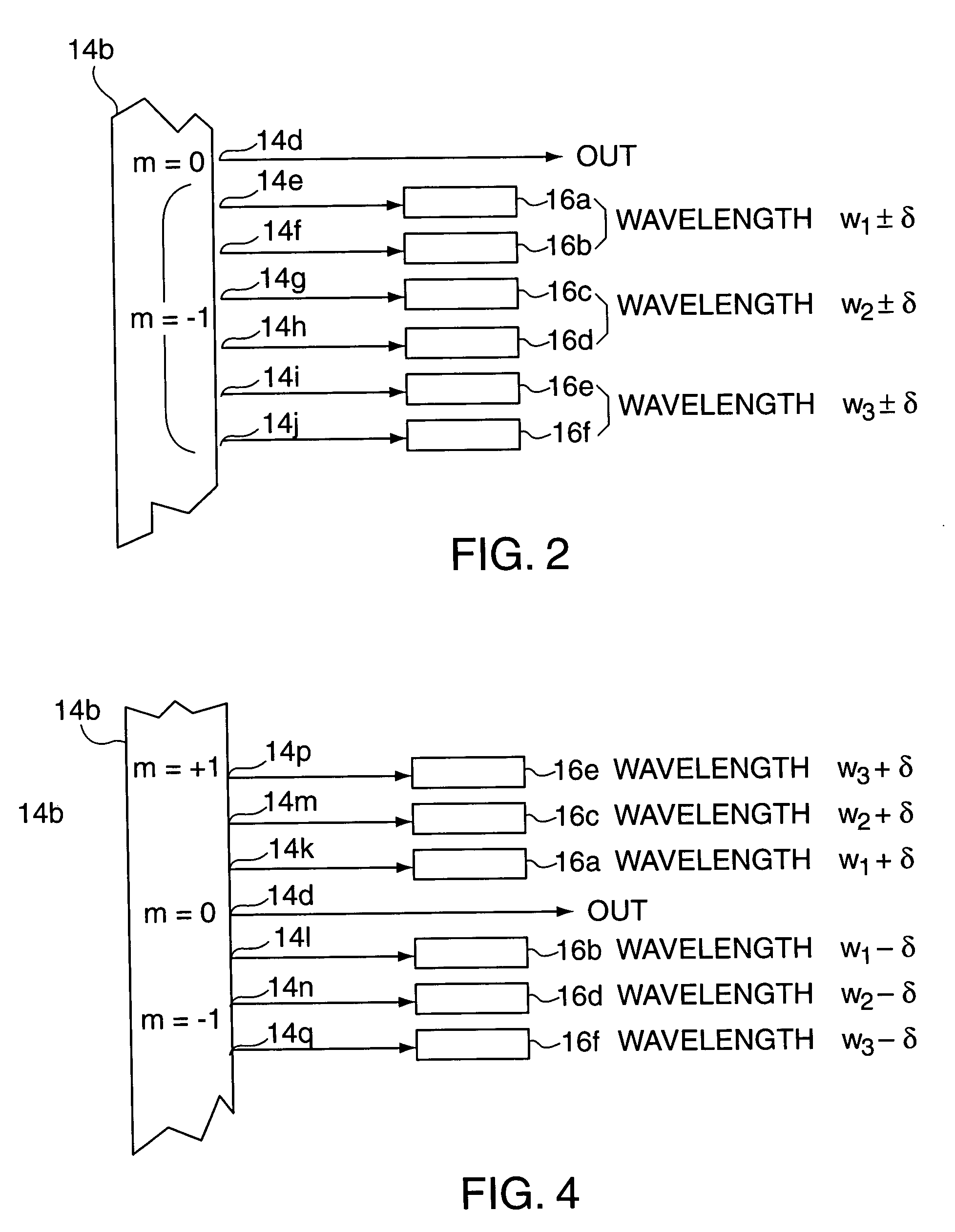
Combination wavelength multiplexer and wavelength stabilizer
InactiveUS6937795B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesDiffraction orderGrating
In an optical device, each of a plurality of radiation sources generates a separate different wavelength output signal to a wavelength locking device wherein a grating device receives the separate wavelength output signals from the plurality of radiation sources. The grating device generates a multiplexed wavelength output signal at a zero diffraction order output port thereof, and resolves separate symmetric wavelength−δ and wavelength−δ output signals at separate predetermined locations within at least one non-zero diffraction order thereof for each of the radiation sources. Each of a plurality of radiation detectors is coupled to receive a separate one of the symmetric wavelength−δ and wavelength−δ output signals and generate an output signal representing the magnitude of the received wavelength output signal. A control device is responsive to output signals from each pair of radiation detectors coupled to receive the separate symmetric wavelength+δ and wavelength−δ output signals from a specified predetermined radiation source for generating an output control signal appropriate to that radiation source for locking the wavelength thereof.
Owner:OPTOVIA +1
Energy dispersion device
ActiveUS8885161B2Increase the number of pixelsEasy to useRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryDiffraction orderEnergy dispersion
The invention provides an energy dispersion device, spectrograph and method that can be used to evaluate the composition of matter on site without the need for specialized training or expensive equipment. The energy dispersion device or spectrograph can be used with a digital camera or cell phone. A device of the invention includes a stack of single- or double-dispersion diffraction gratings that are rotated about their normal giving rise to a multiplicity of diffraction orders from which meaningful measurements and determinations can be made with respect to the qualitative or quantitative characteristics of matter.
Owner:SPECTROCLICK
Two-dimensional blazed MEMS grating
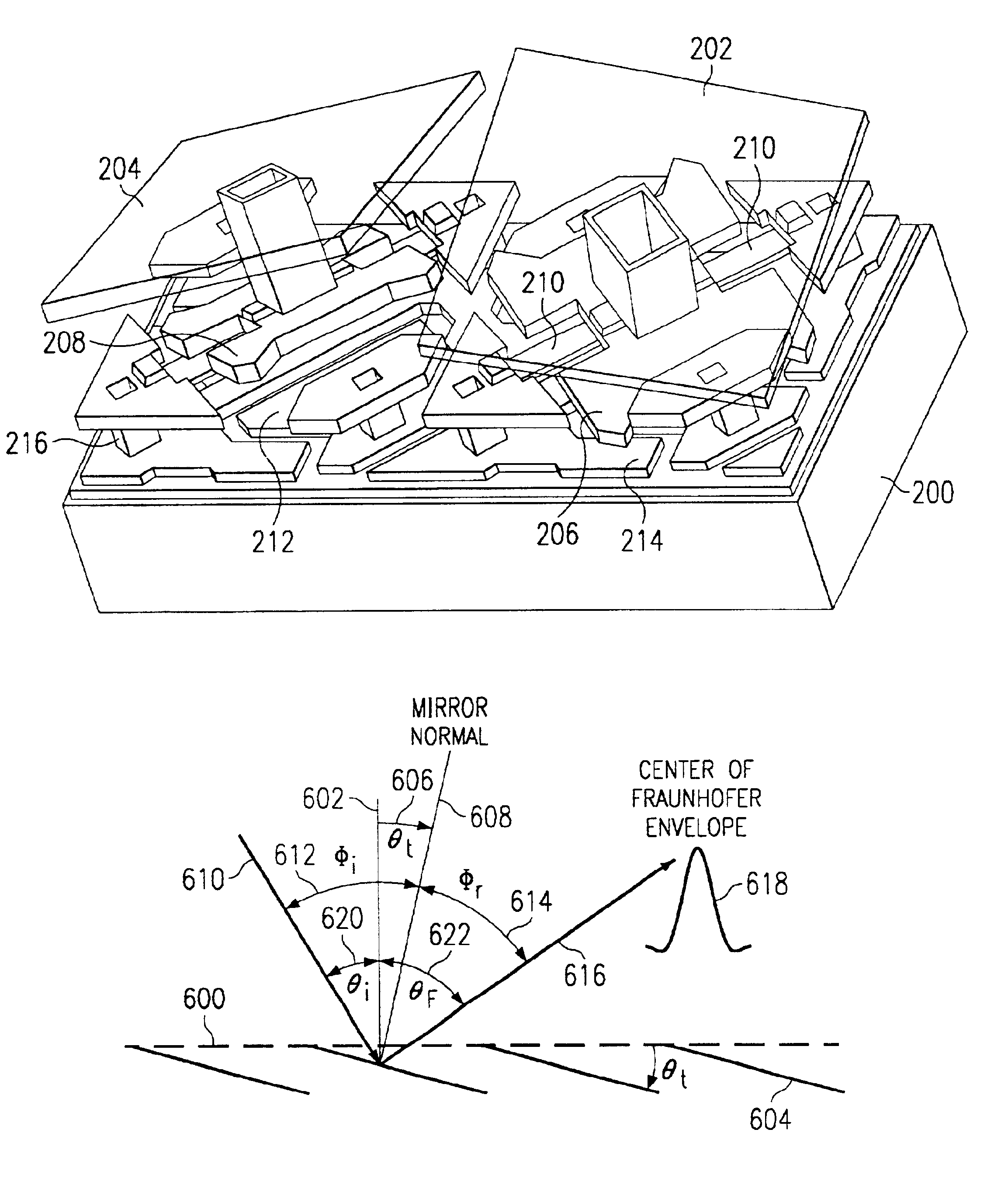
InactiveUS6943950B2Efficient switchingAccurately determineBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingDiffraction order
A method for assuring a blazed condition in a DMD device used in telecommunications applications. By meeting certain conditions in the fabrication and operation of the DMD, the device can achieve a blazed condition and be very effective in switching near monochromatic spatially coherent light, thereby opening up a whole new application field for such devices. This method determines the optimal pixel pitch and mirror tilt angle for a given incident angle and wavelength of near monochromatic spatially coherent light to assure blazed operating conditions. The Fraunhofer envelope is determined by convolving the Fourier transforms of the mirror aperture and the delta function at the center of each mirror and then aligning the center of this envelope with a diffraction order to provide a blazed condition. The method of the present invention presents a formula for precisely determining the mirror pitch and tilt angle to assure that a blazed condition exists for a given incident angle and wavelength of near monochromatic spatially coherent light. Considerations for the special case, know as Littrow conditions, where the incident and the reflected light transverse the same path, are also given. This case is particularly attractive for fiber optic / telecommunication applications since the same optics can be used for incoming and outgoing (reflected) light.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Geometrically-desensitized interferometer incorporating an optical assembly with high stray-beam management capability
InactiveUS6072581AReduce in quantityHigh measurement accuracyDiffraction gratingsUsing optical meansMetrologyDiffraction order
The optical assembly of a GDI instrument is configured to deviate or steer stray beams away from the pupil of the instrument's imaging device and / or to suppress stray beams. Stray beam deviation is optimized by selecting particular wedge and / or tilt configurations that achieve the desired stray beam deviation while avoiding or at least minimizing phase offset at the optimum metrology plane. Stray beam suppression can be achieved by providing the diffractive groove profile of the instrument's optical assembly with smooth edges. The resultant profile facilitates effective diffraction order management as well as a reduction in back reflection. The invention is particularly well-suited for use with a GDI instrument in which the optical assembly comprises first and second diffraction gratings. In this case, any average phase offset that remains after setting wedge and / or tilt can be eliminated by inserting a suitable compensating plate between the first and second diffraction gratings or between the second diffraction grating and the object.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Off-axis interferometer
ActiveUS20120200901A1Avoid spreadingHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesGratingDiffraction order
An Interferometer for off-axis digital holographic microscopy includes a recording plane, and a grating located in a plane optically conjugated with the recording plane. The grating defining a first and a second optical path, the optical path corresponding to different diffraction order.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Wss with high port isolation and close spaced ports
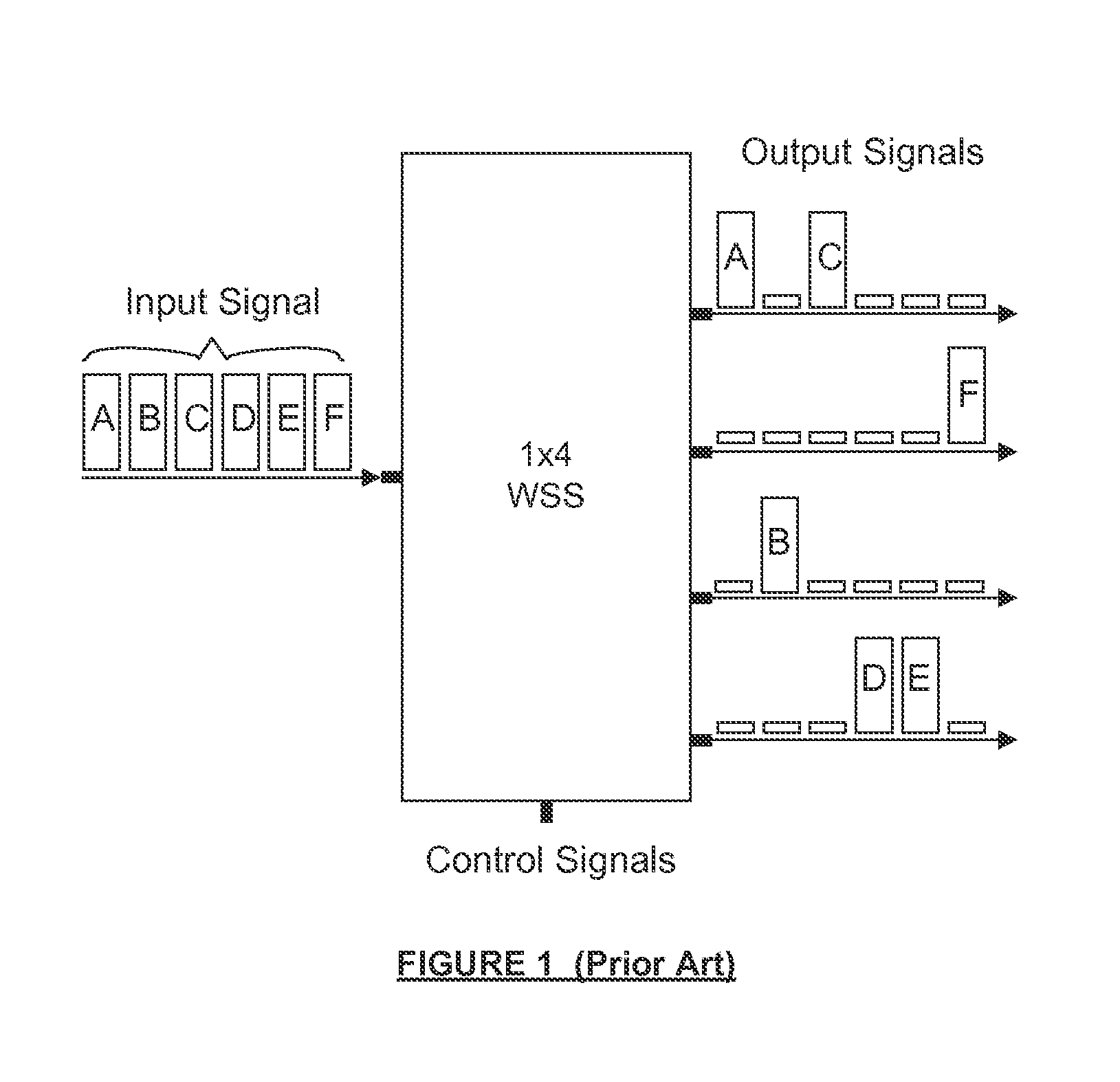
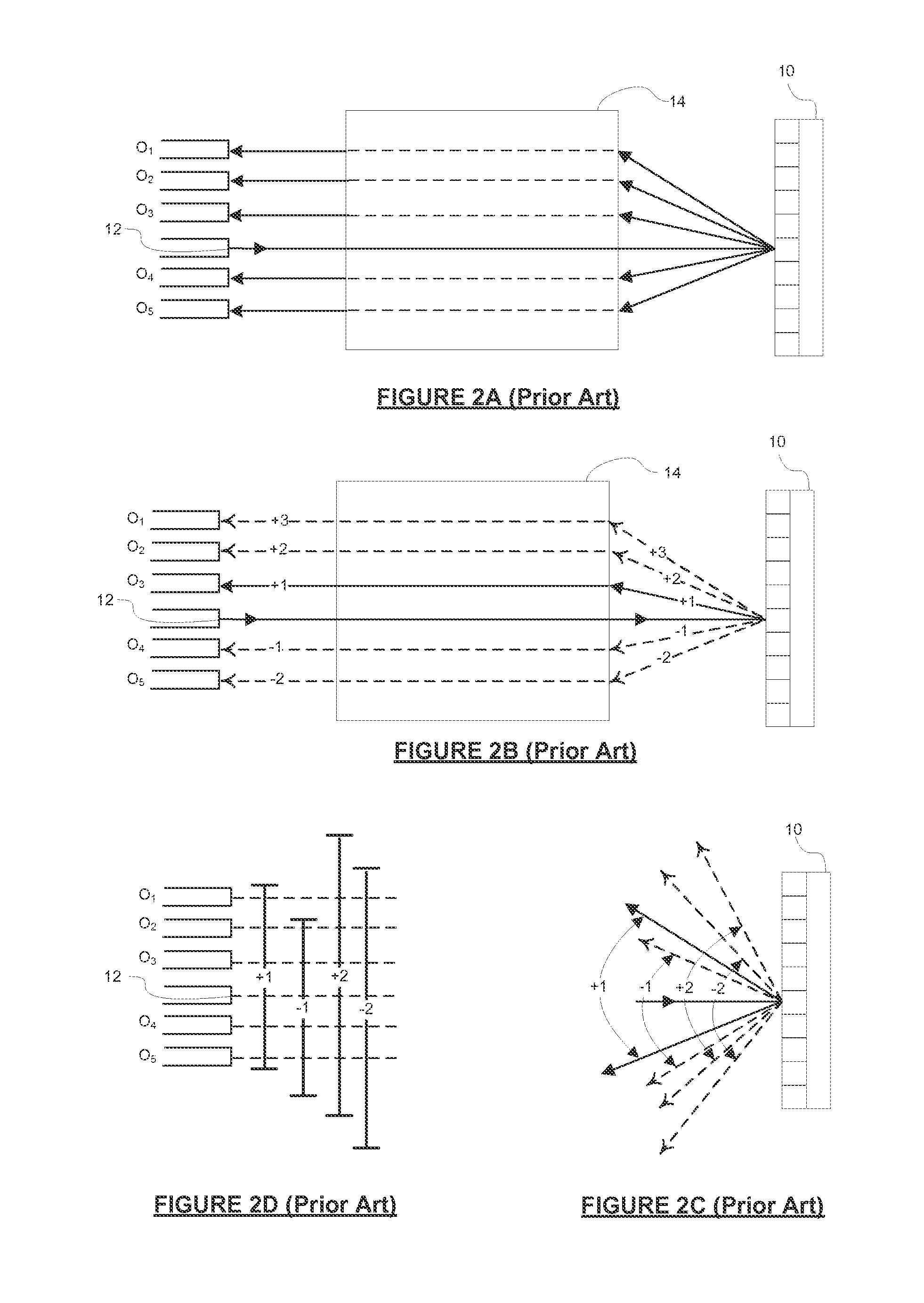
ActiveUS20140023316A1Improved isolation between portsComplex calibrationCoupling light guidesDiffraction orderSteering angle
By steering wanted diffraction orders within a concentrated angular region and steering all unwanted diffraction orders outside that region, a wavelength selective switch achieves high port isolation and densely spaced ports. N inputs receive an optical signal. Optics spatially separate and direct wavelength channels from the signal. A phased array switching engine comprising cells steers a wanted diffraction order of each spatially separated wavelength channel from each cell at an angle within a concentrated angular region relative to the PASE, and steers all unwanted diffraction orders of spatially separated wavelength channels from cells outside the concentrated angular region. Optics direct each wanted diffraction order to one of N outputs in accordance with the steering of the wanted diffraction orders by the PASE. The concentrated angular region is defined by a largest and smallest steering angle wherein the largest steering angle is a margin less than the smallest steering angle.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com