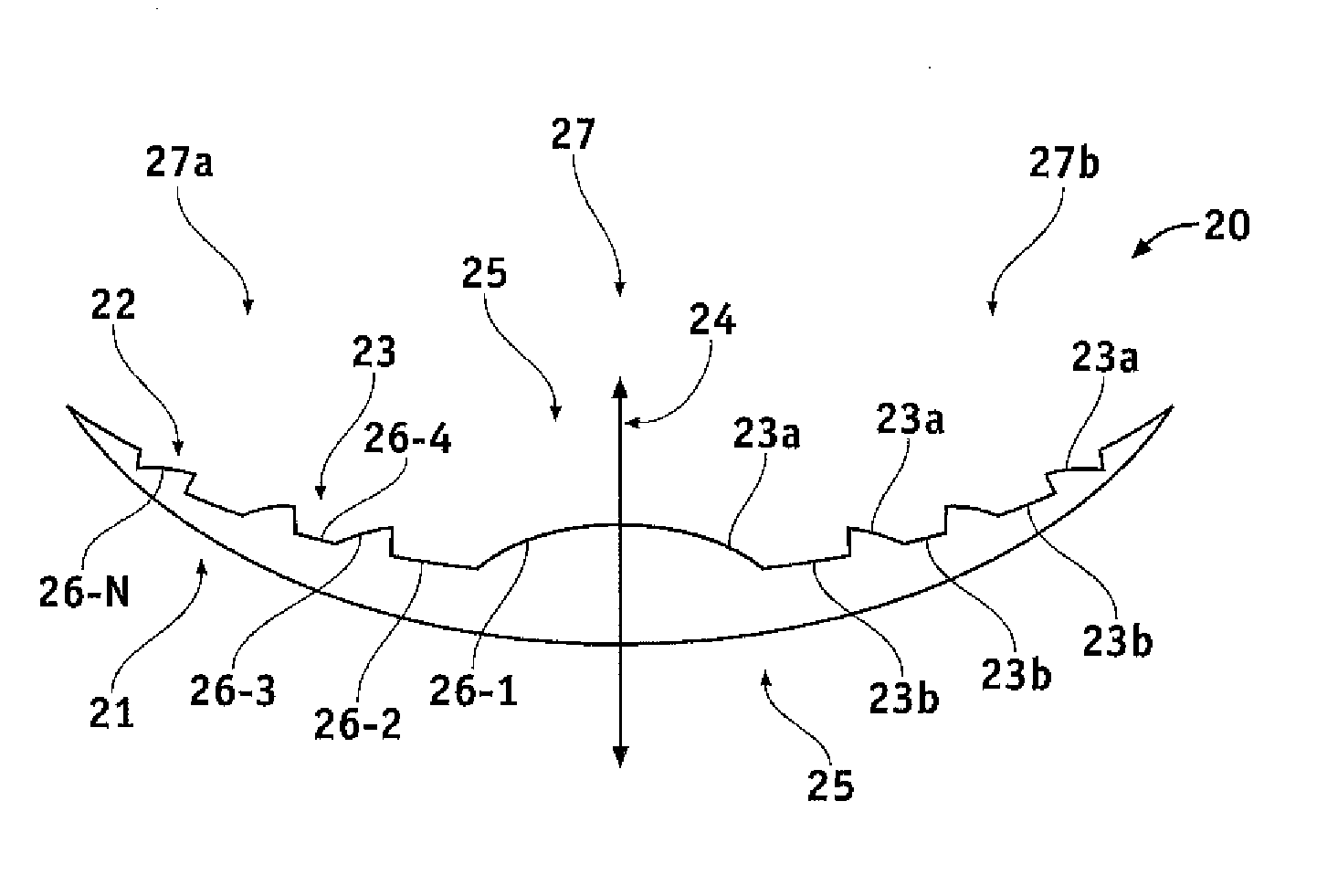
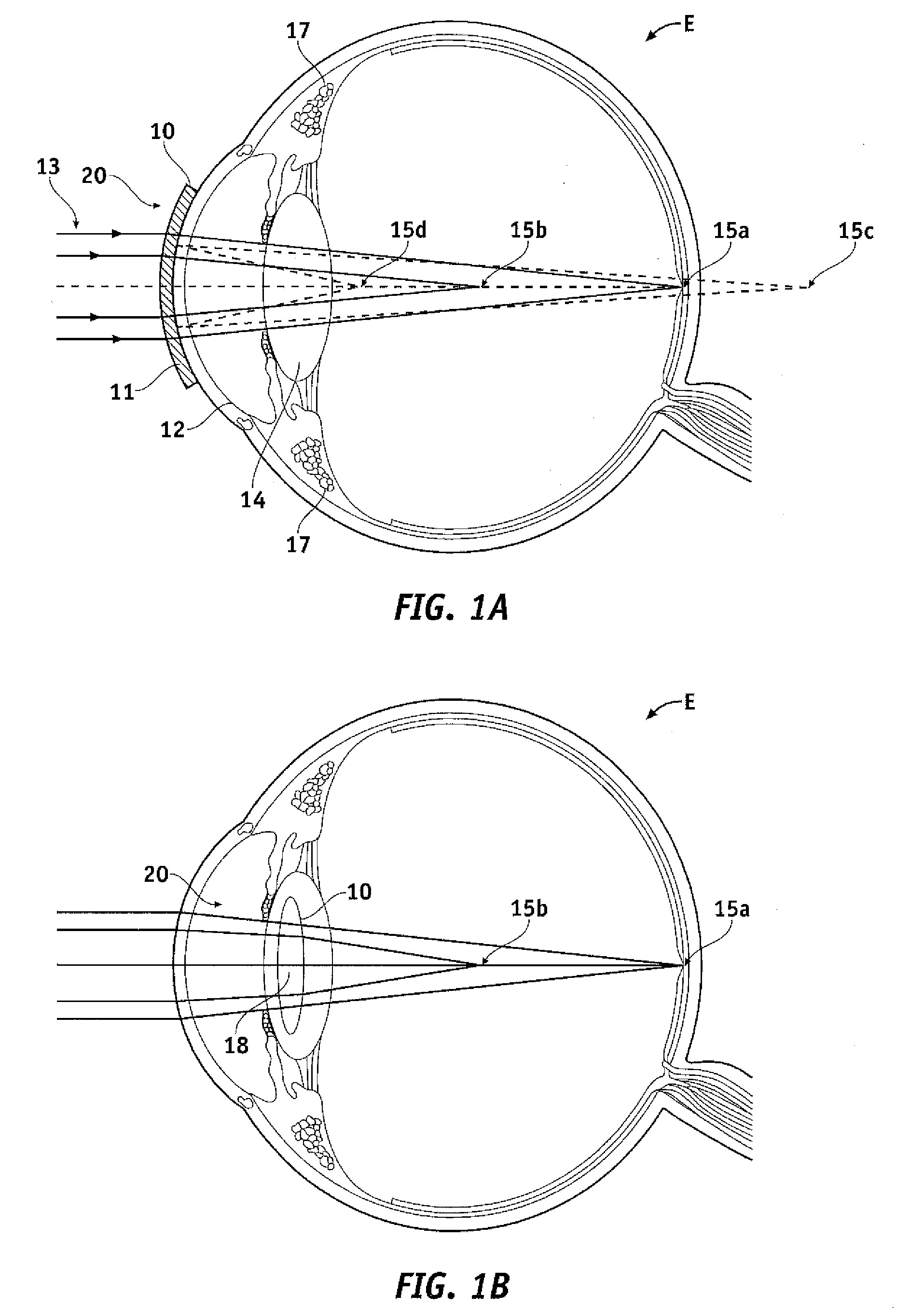
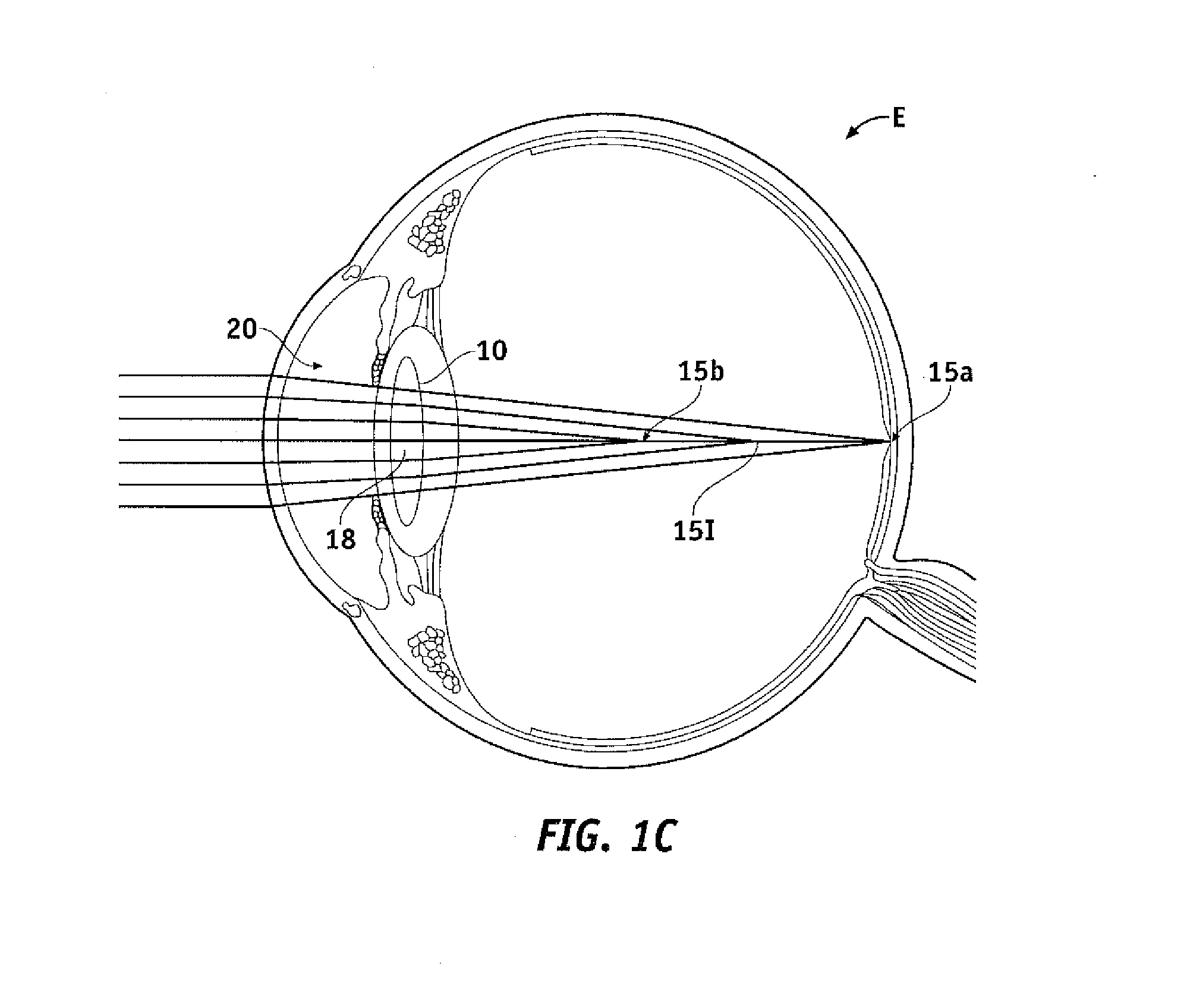
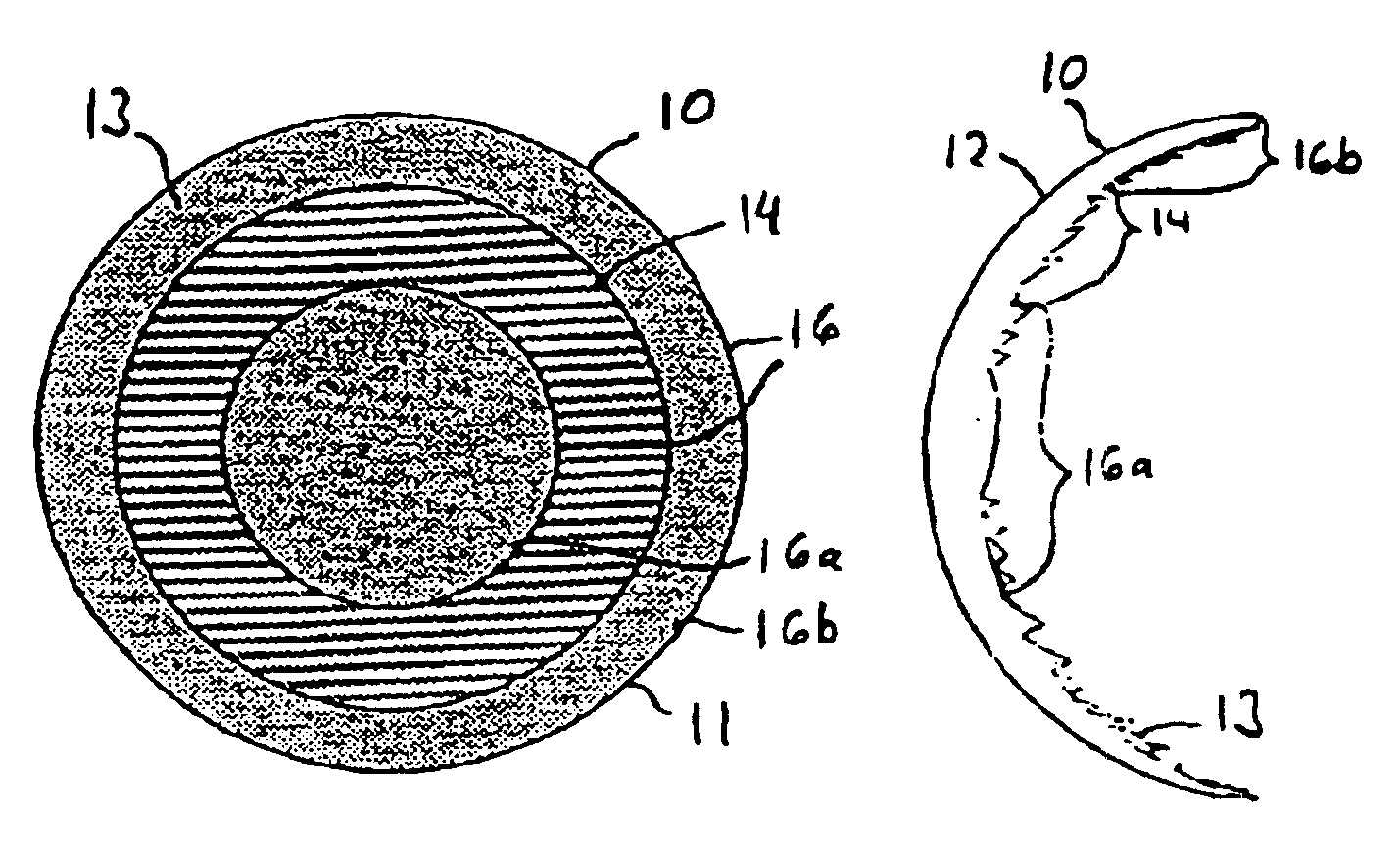
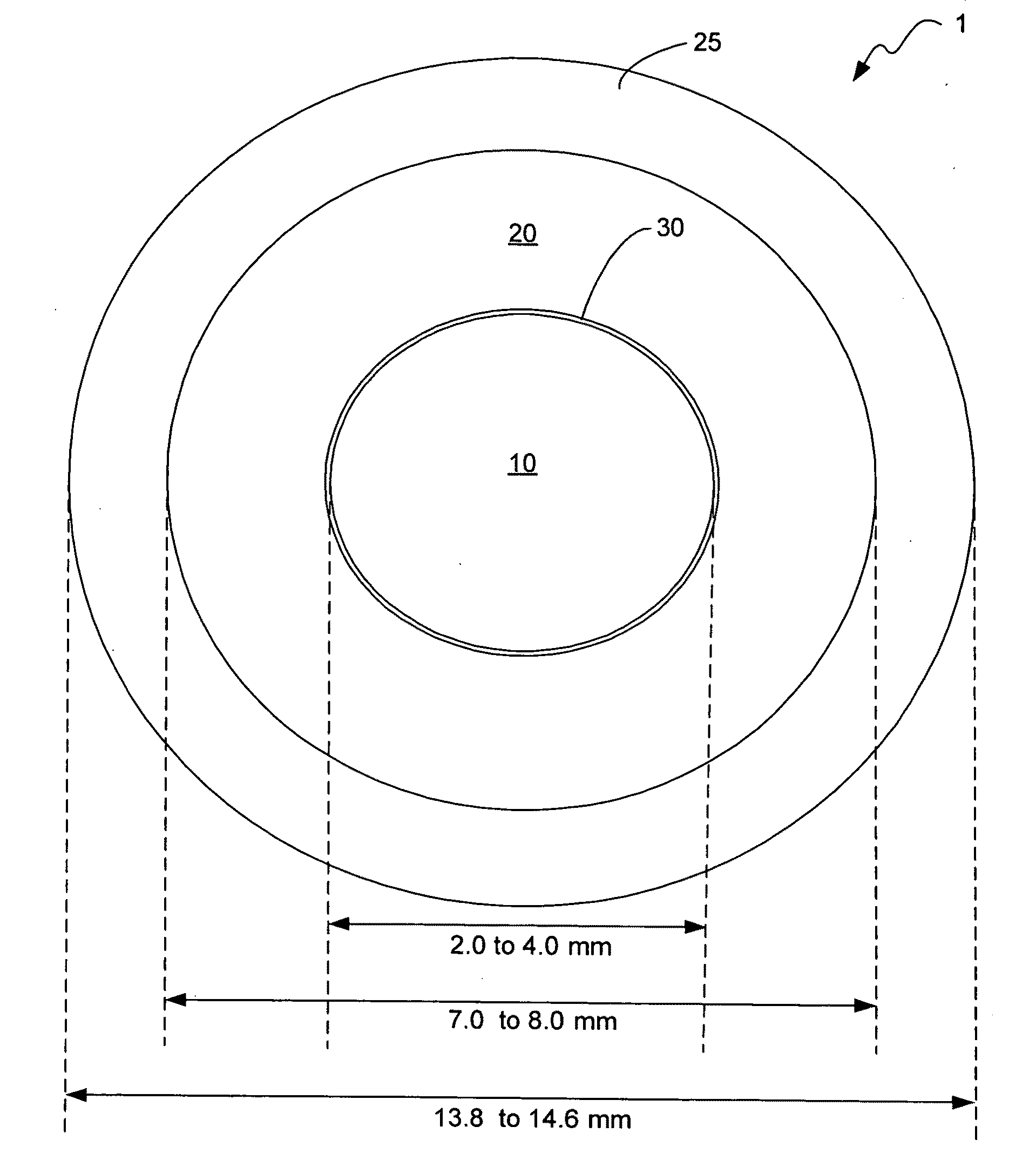
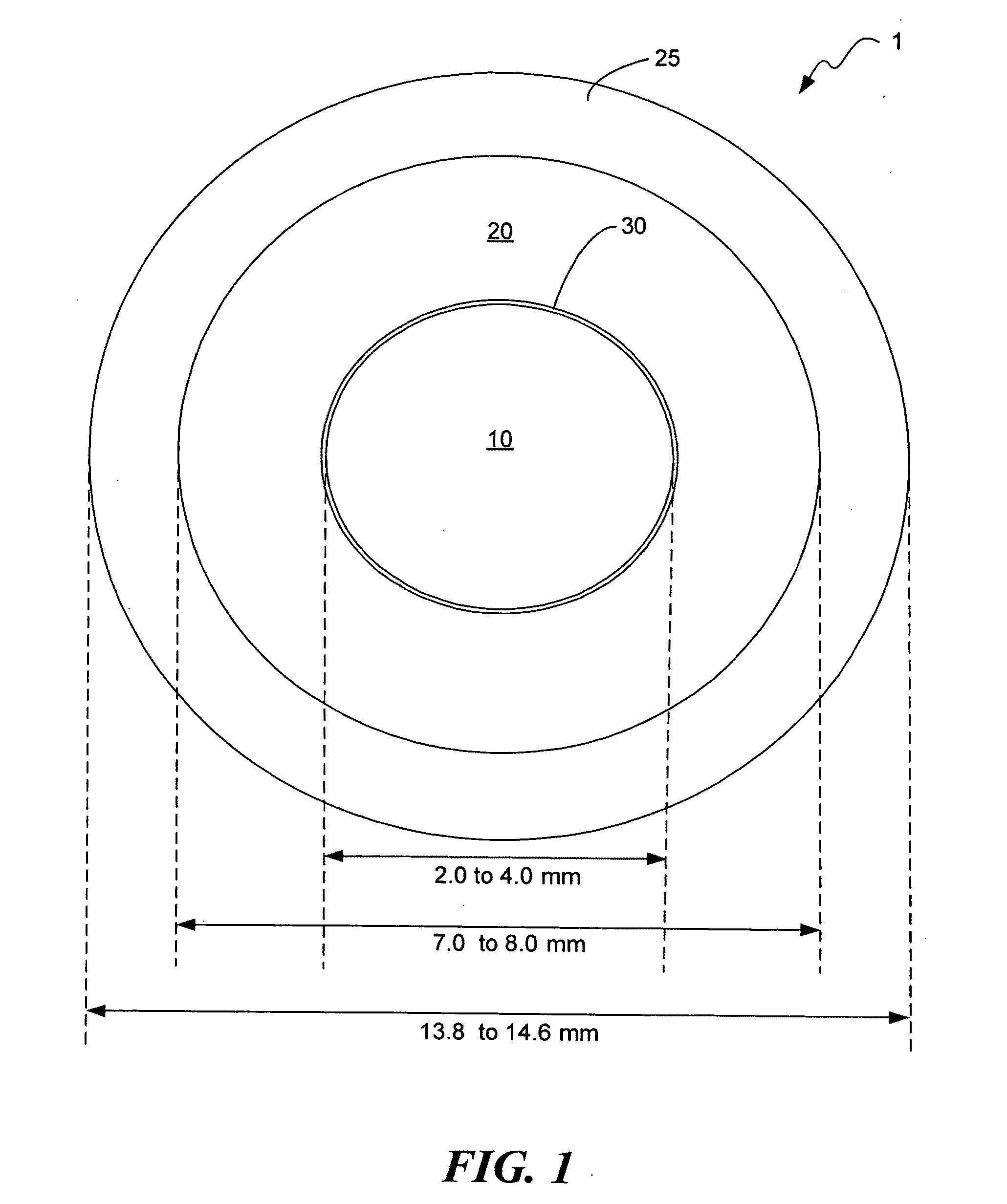
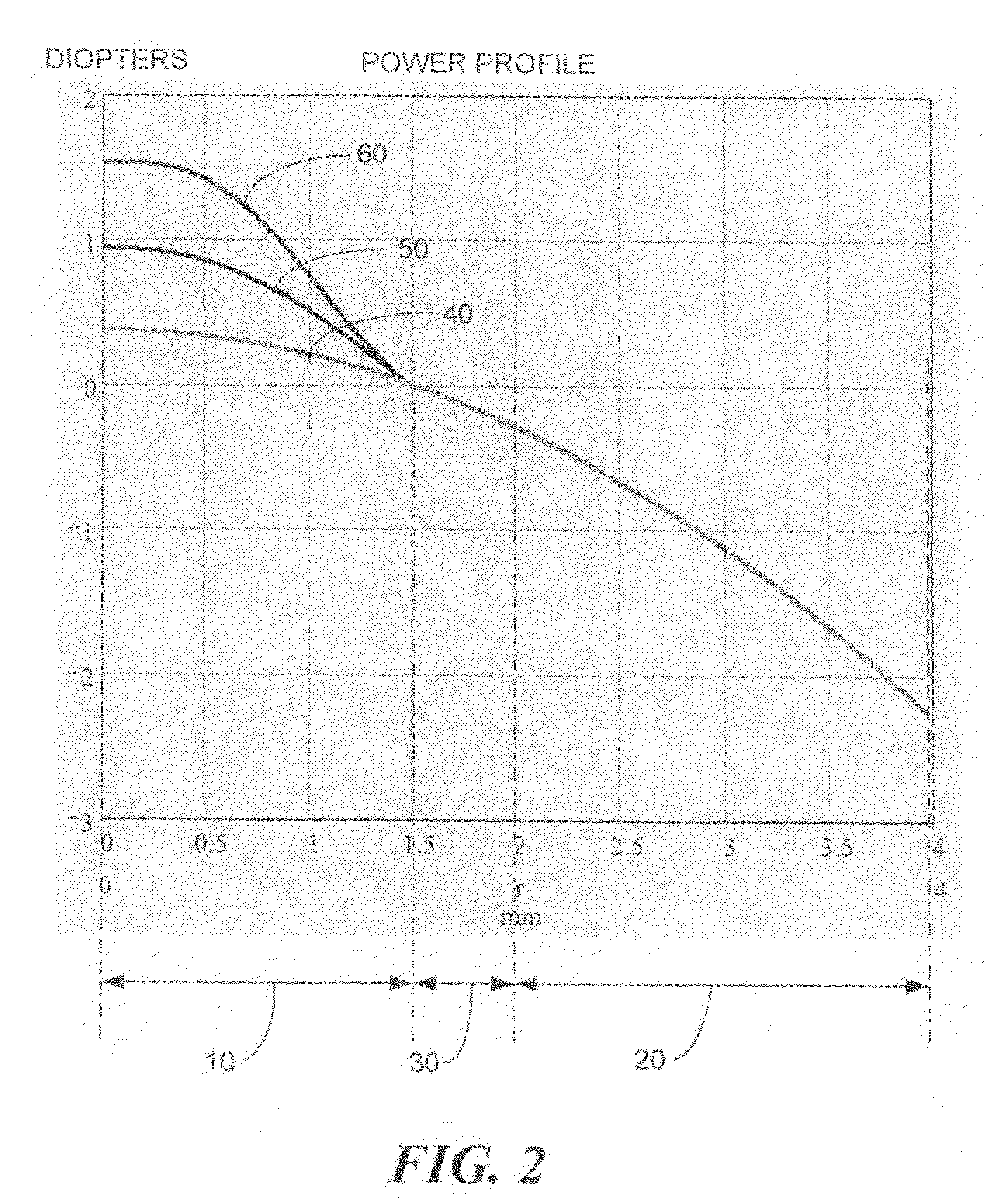
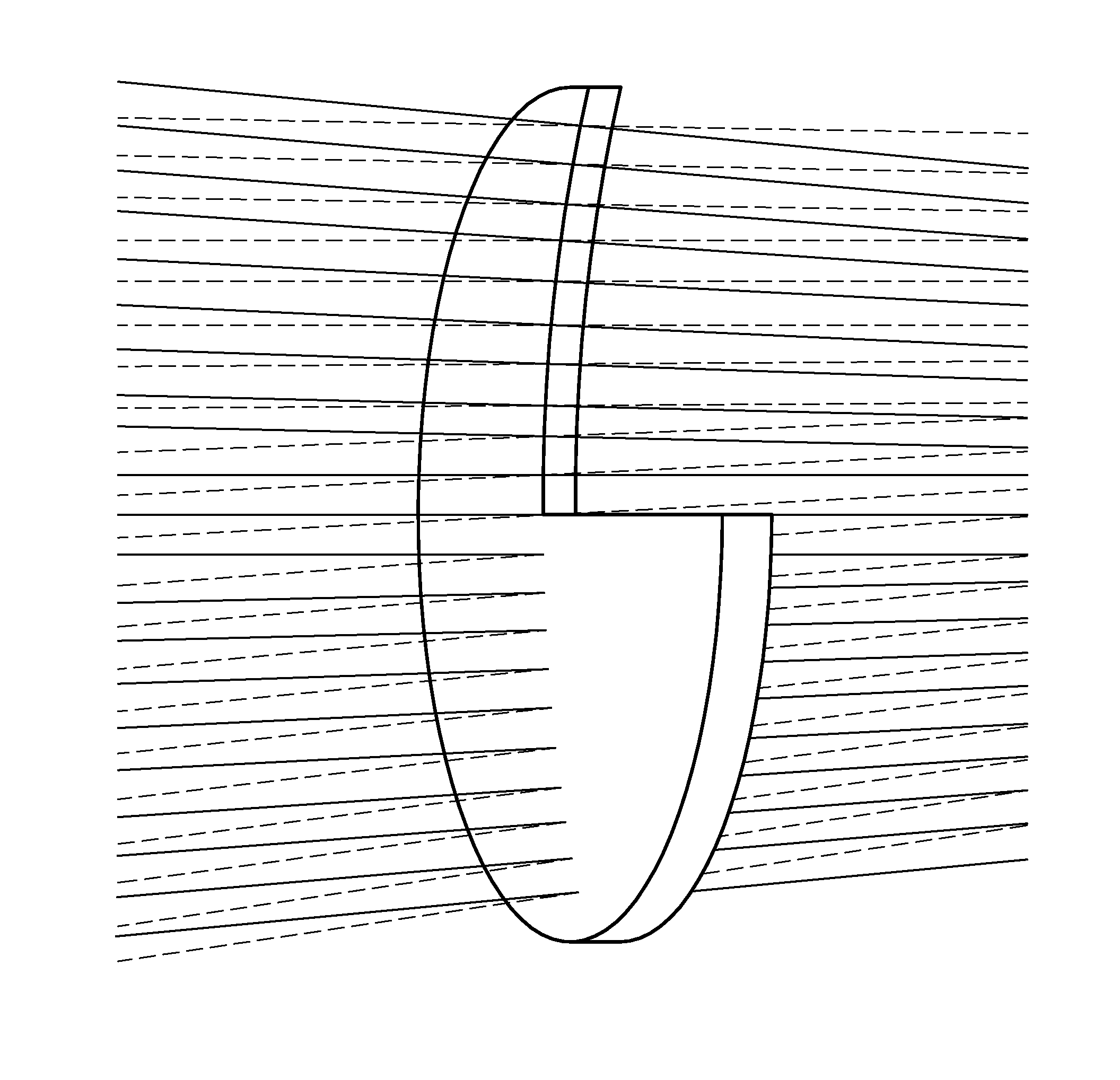
Patents
Literature
331 results about "Near vision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
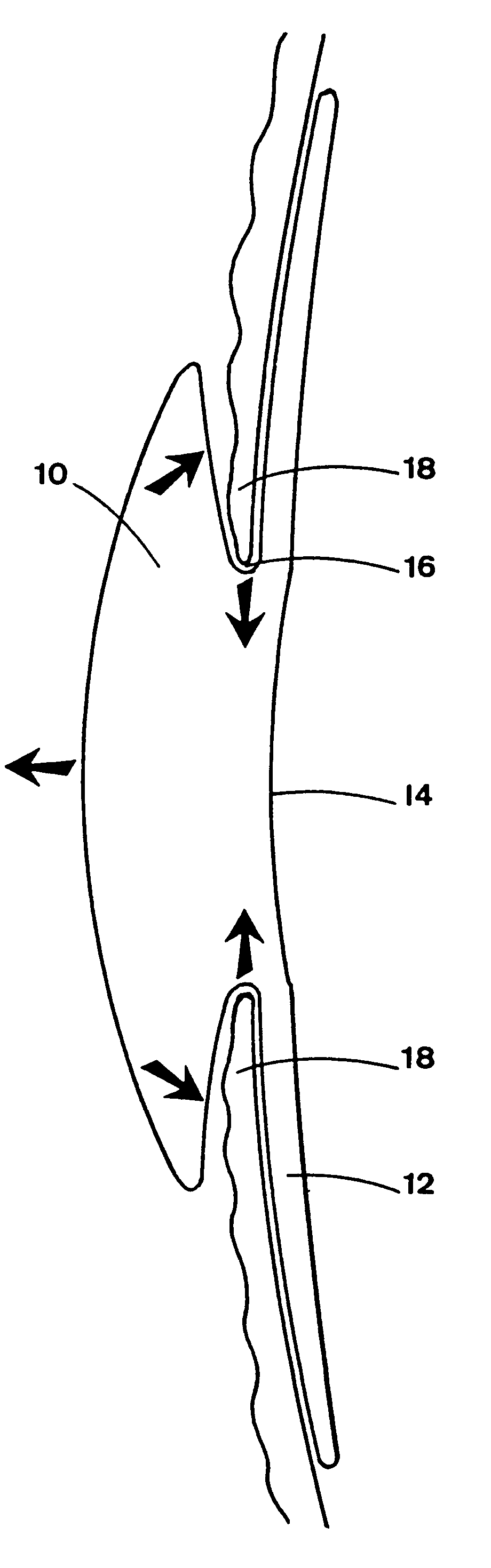
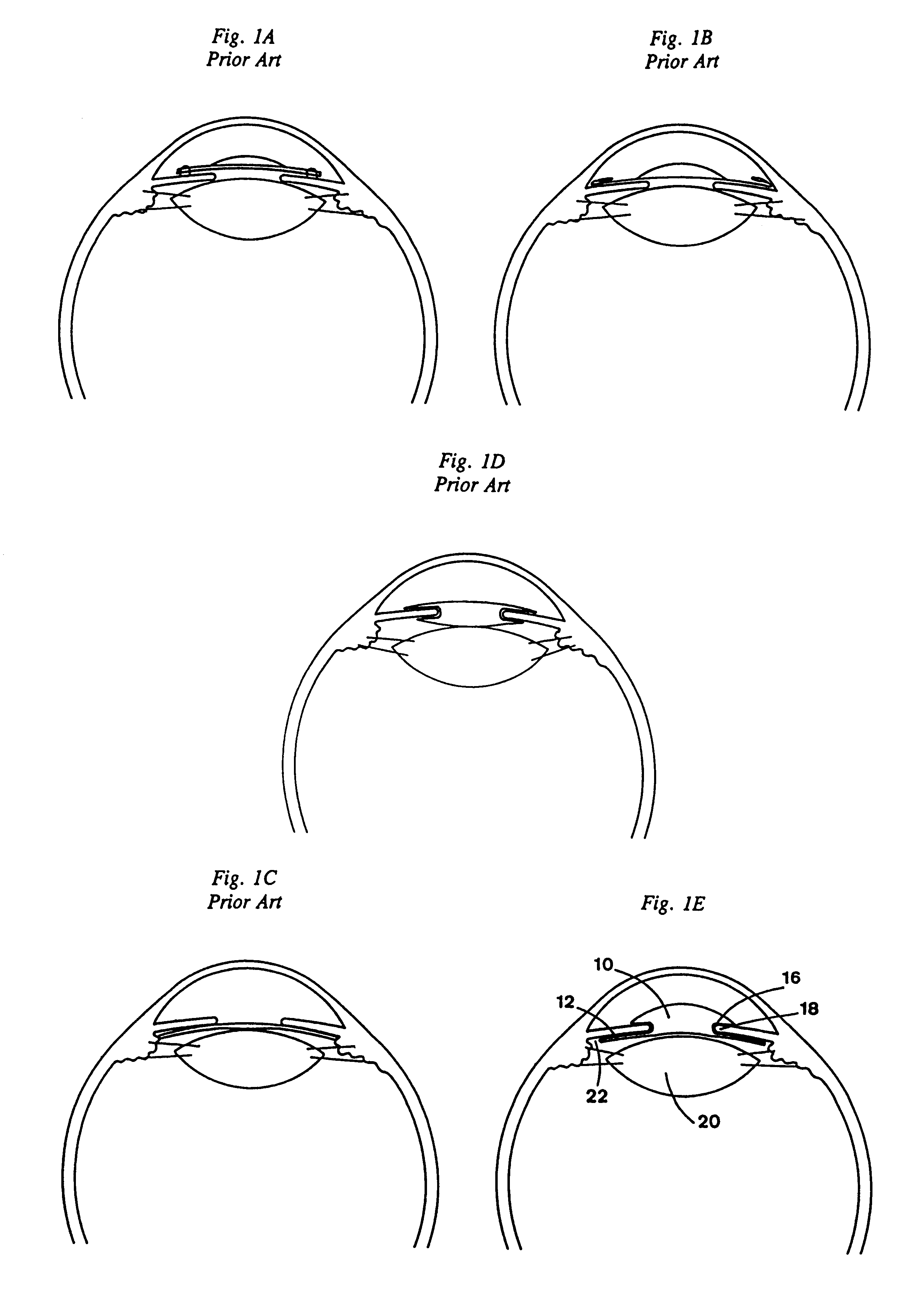
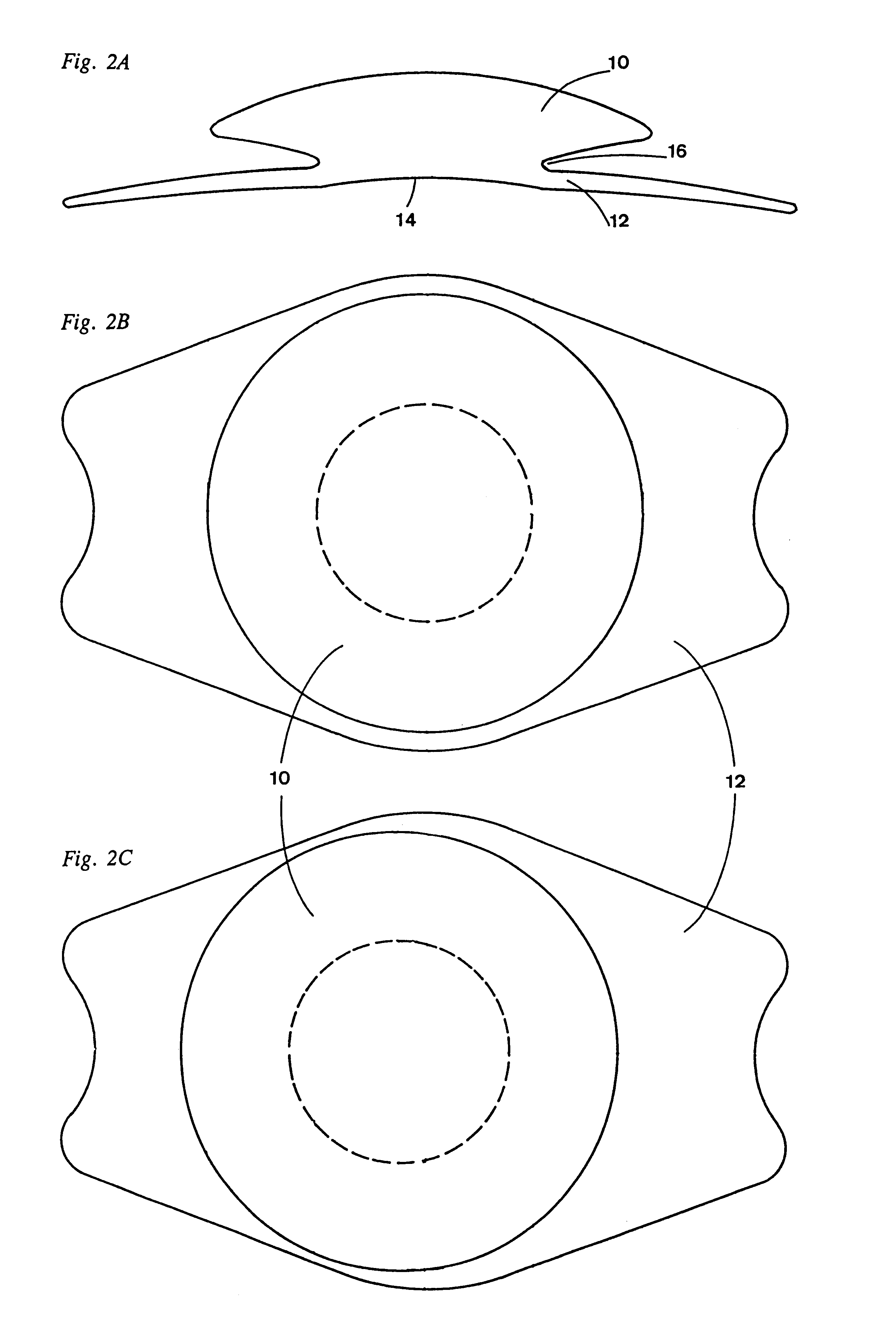
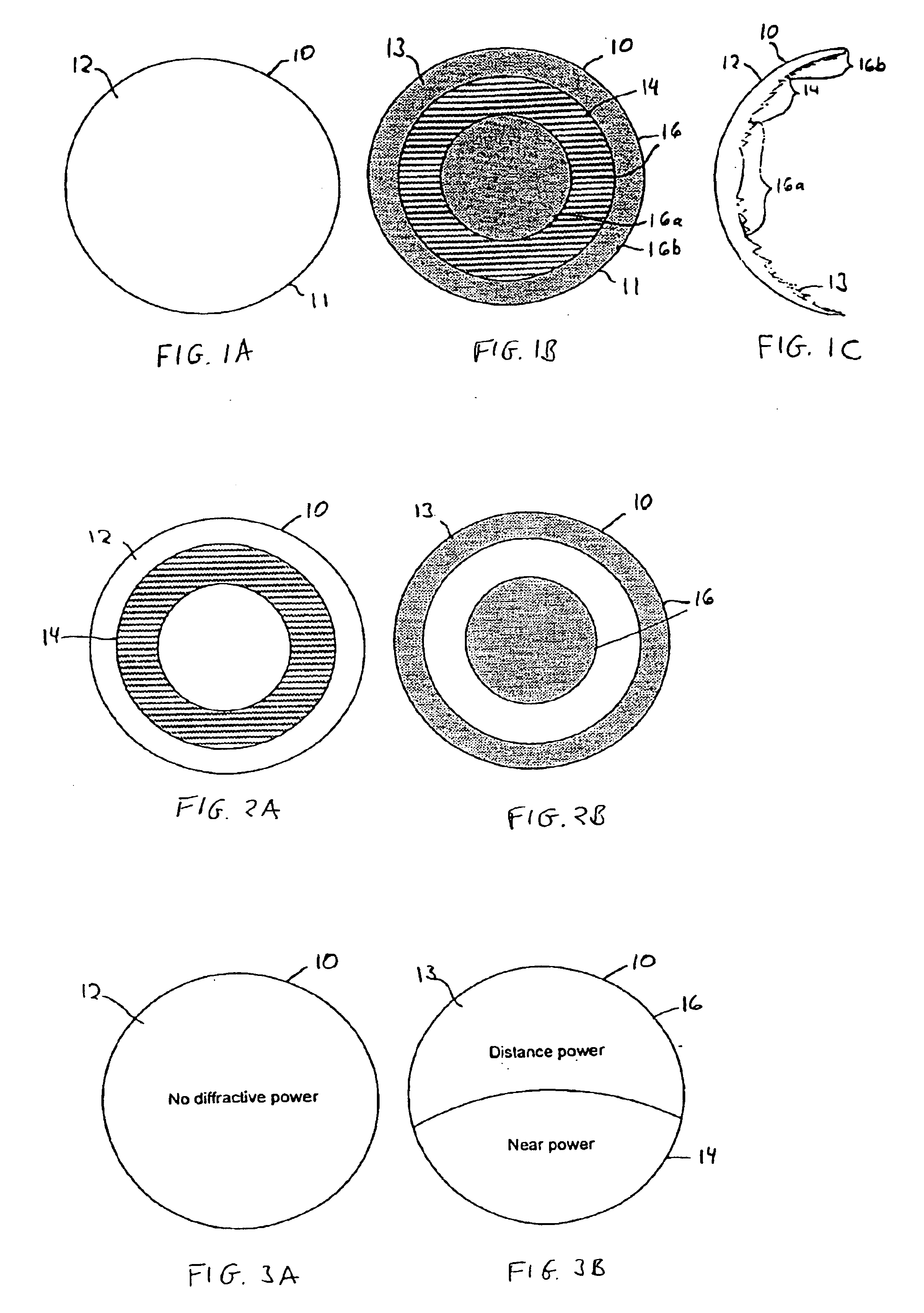
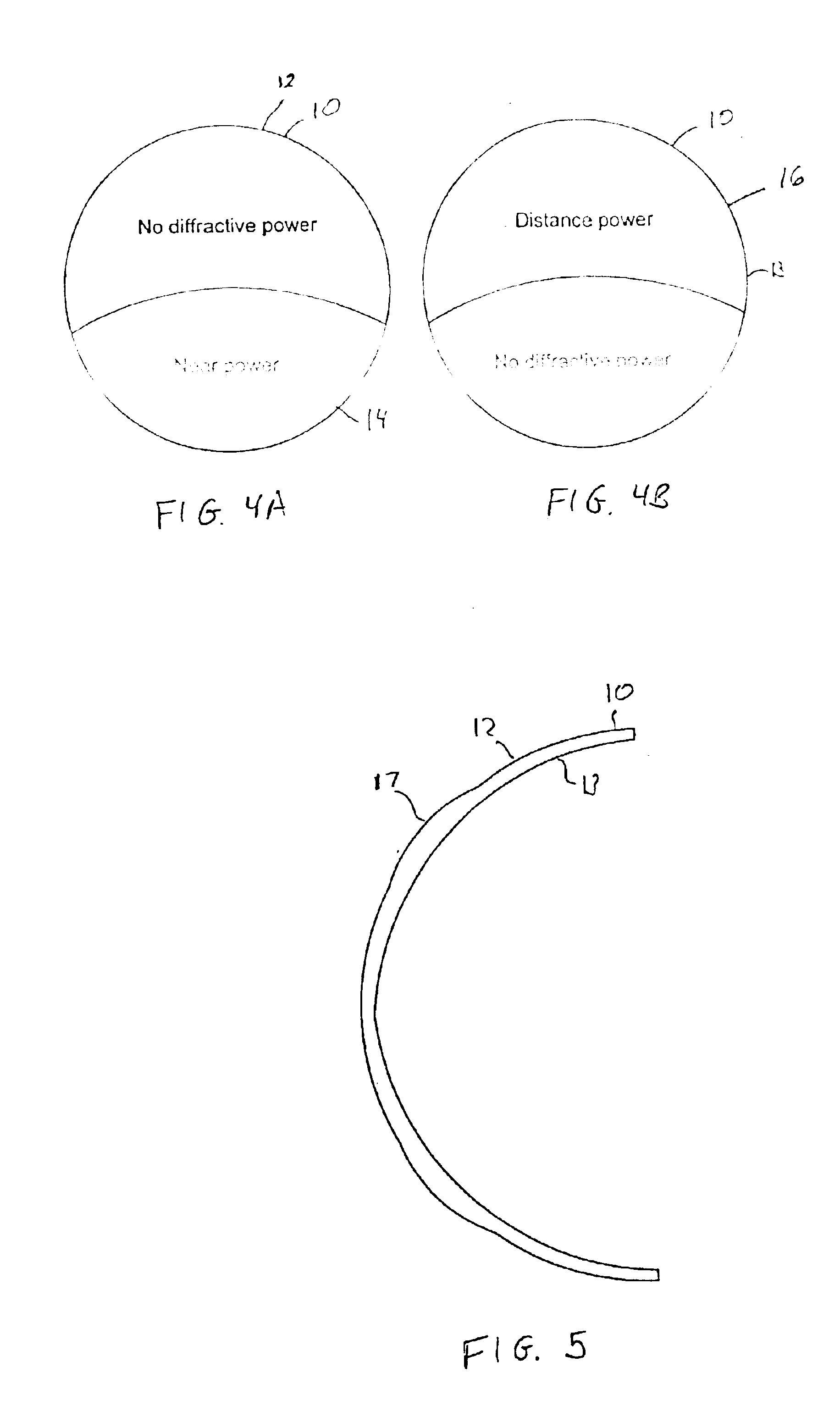
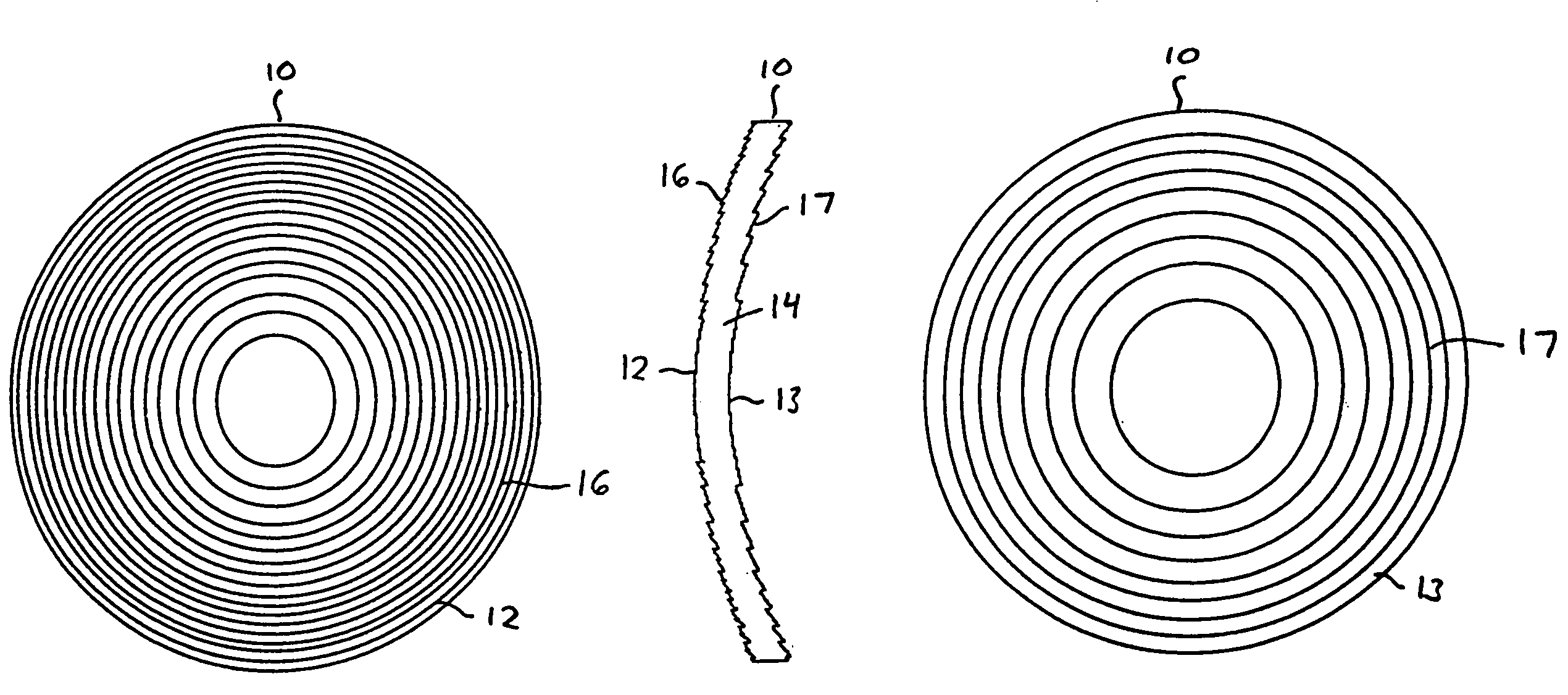
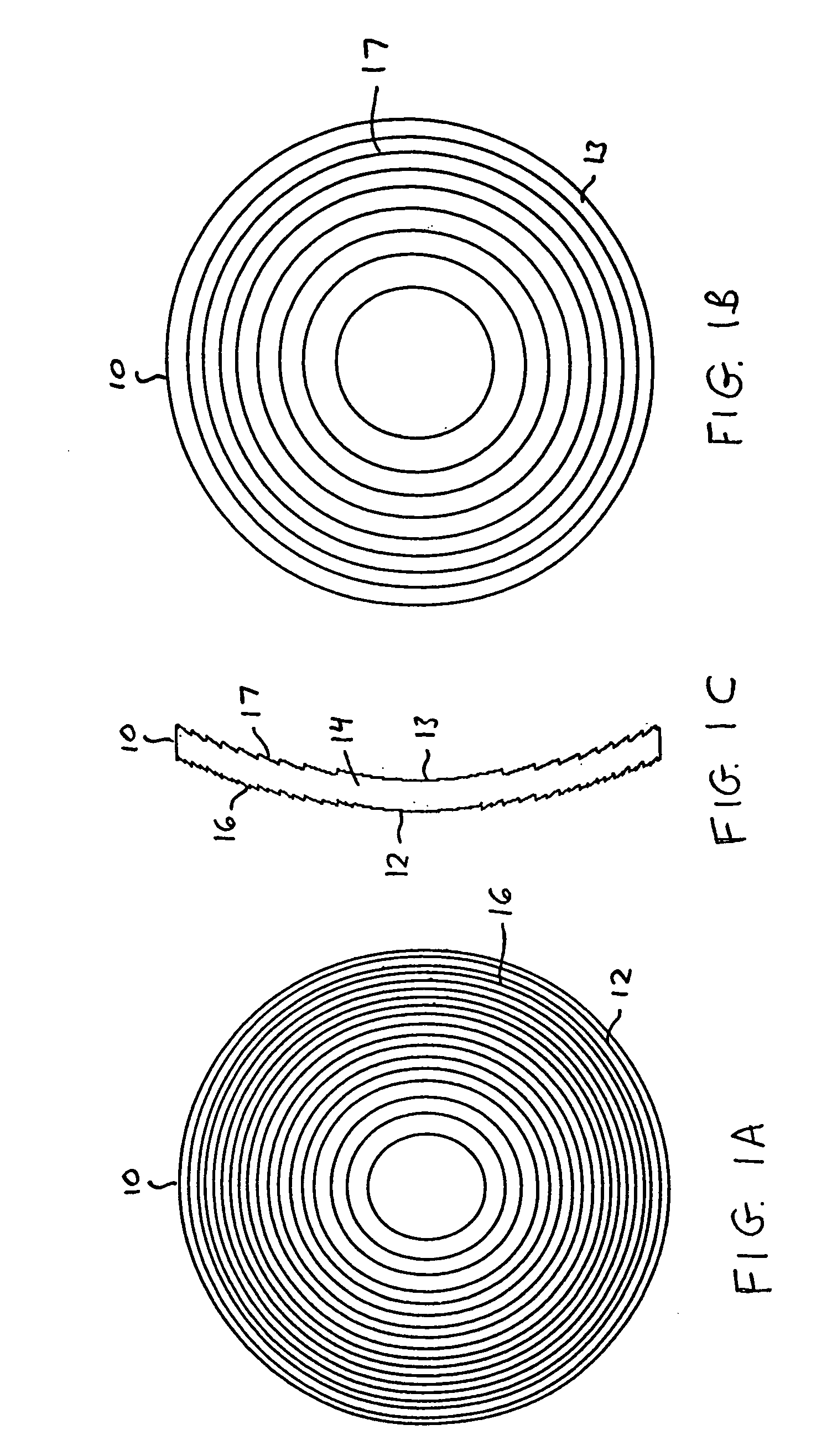
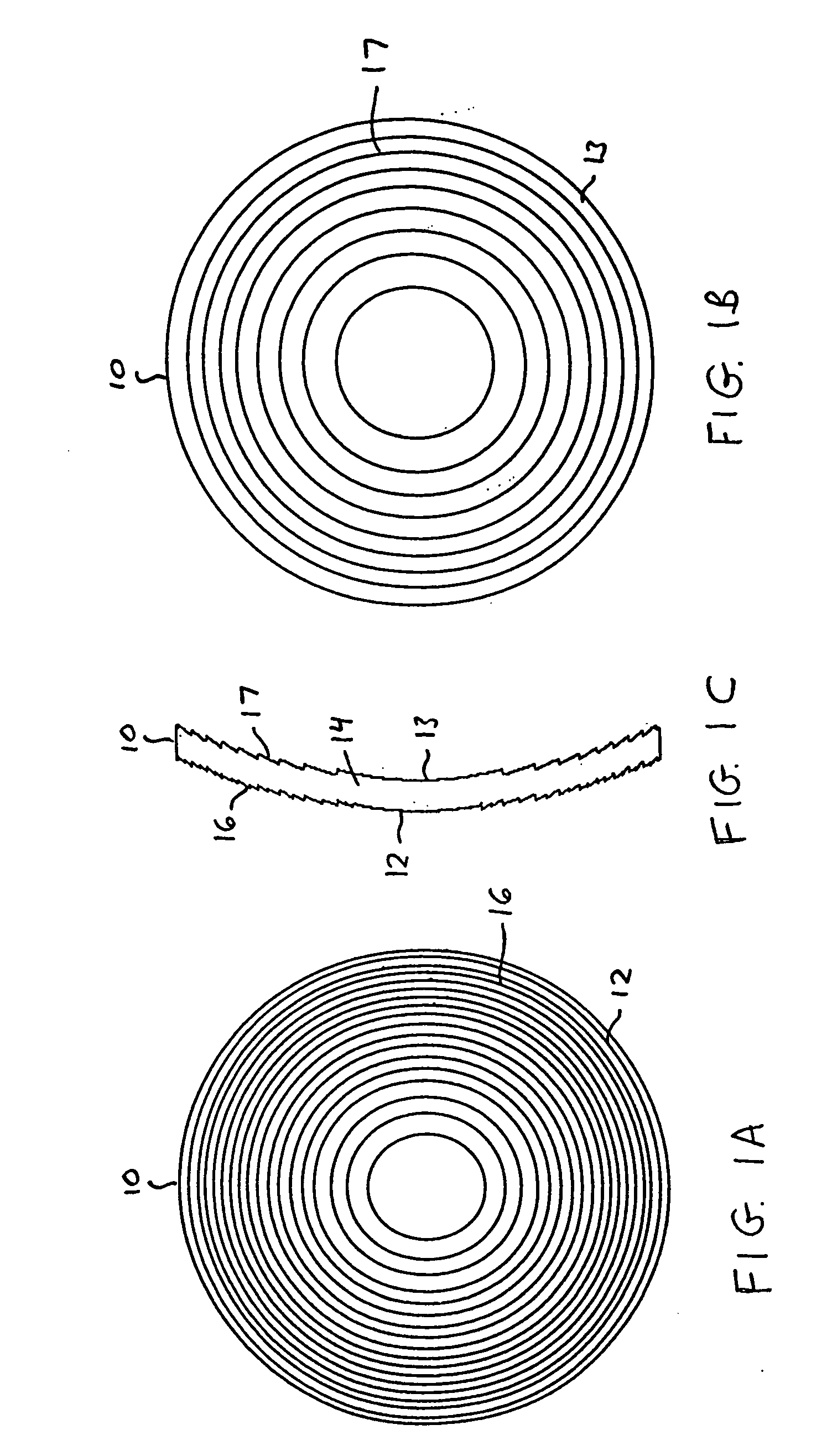
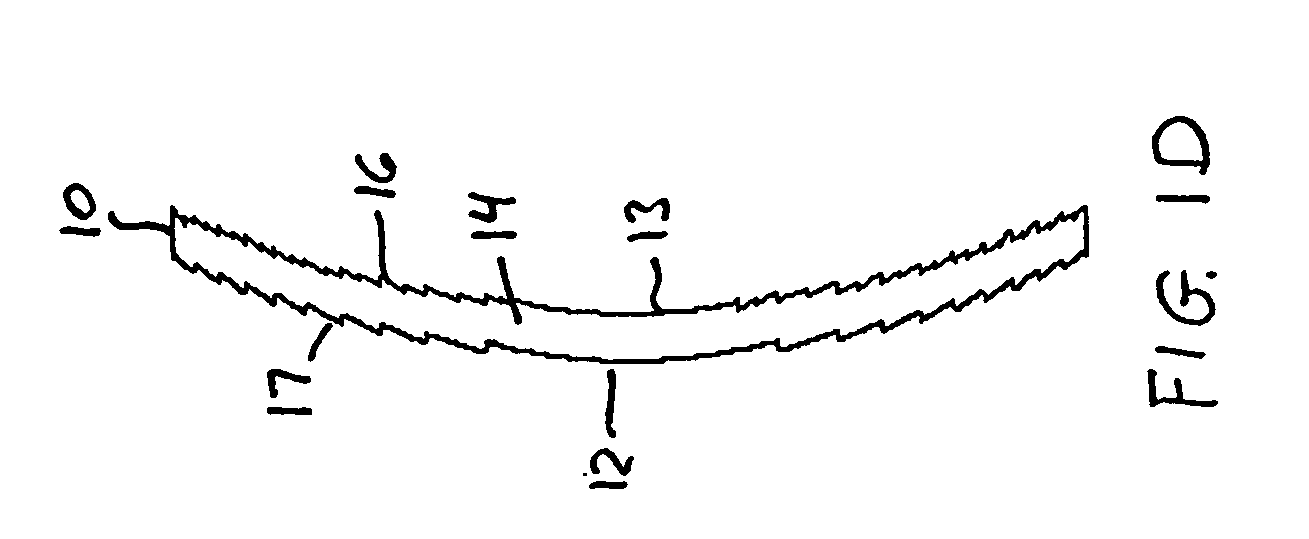
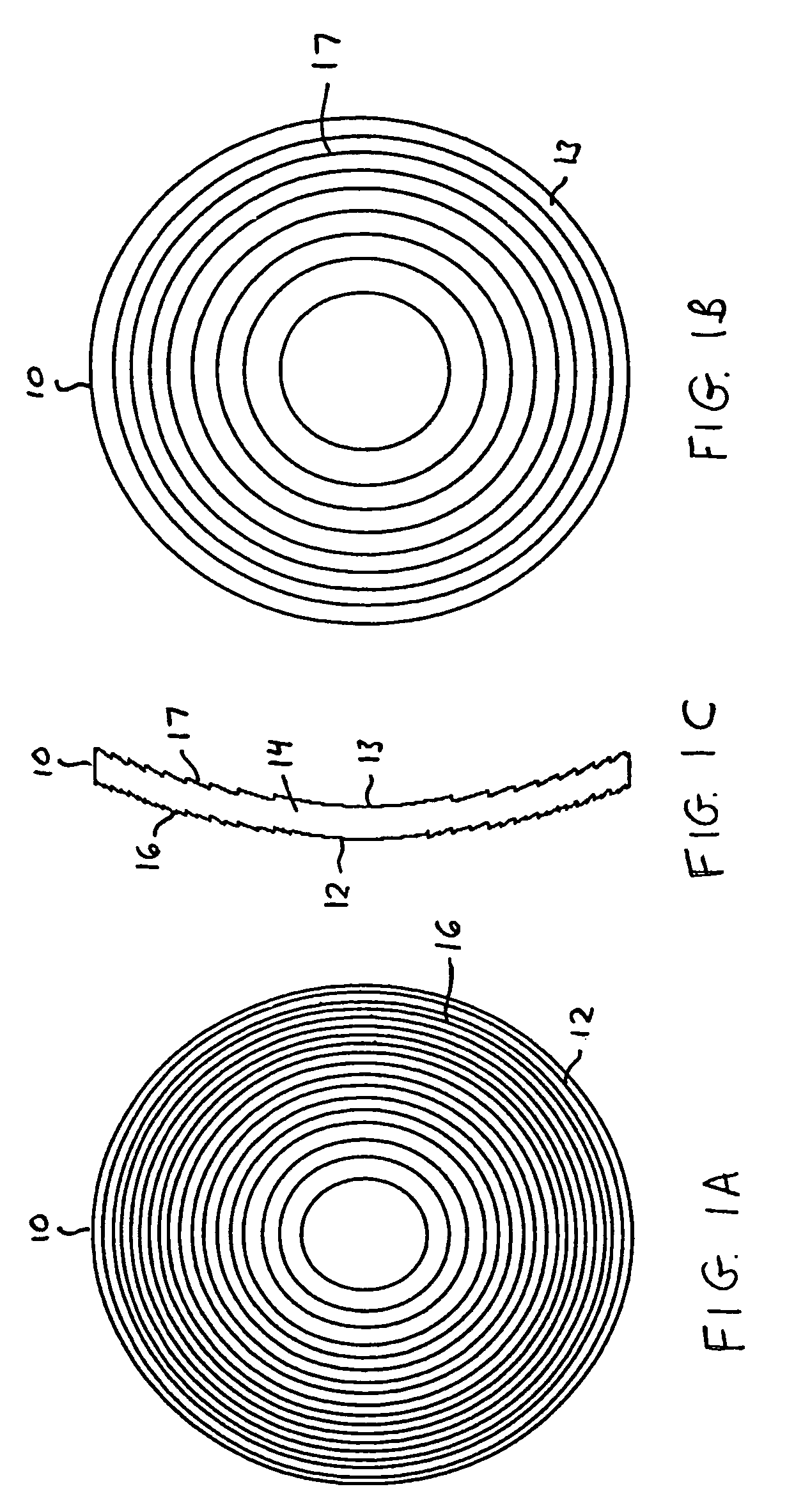
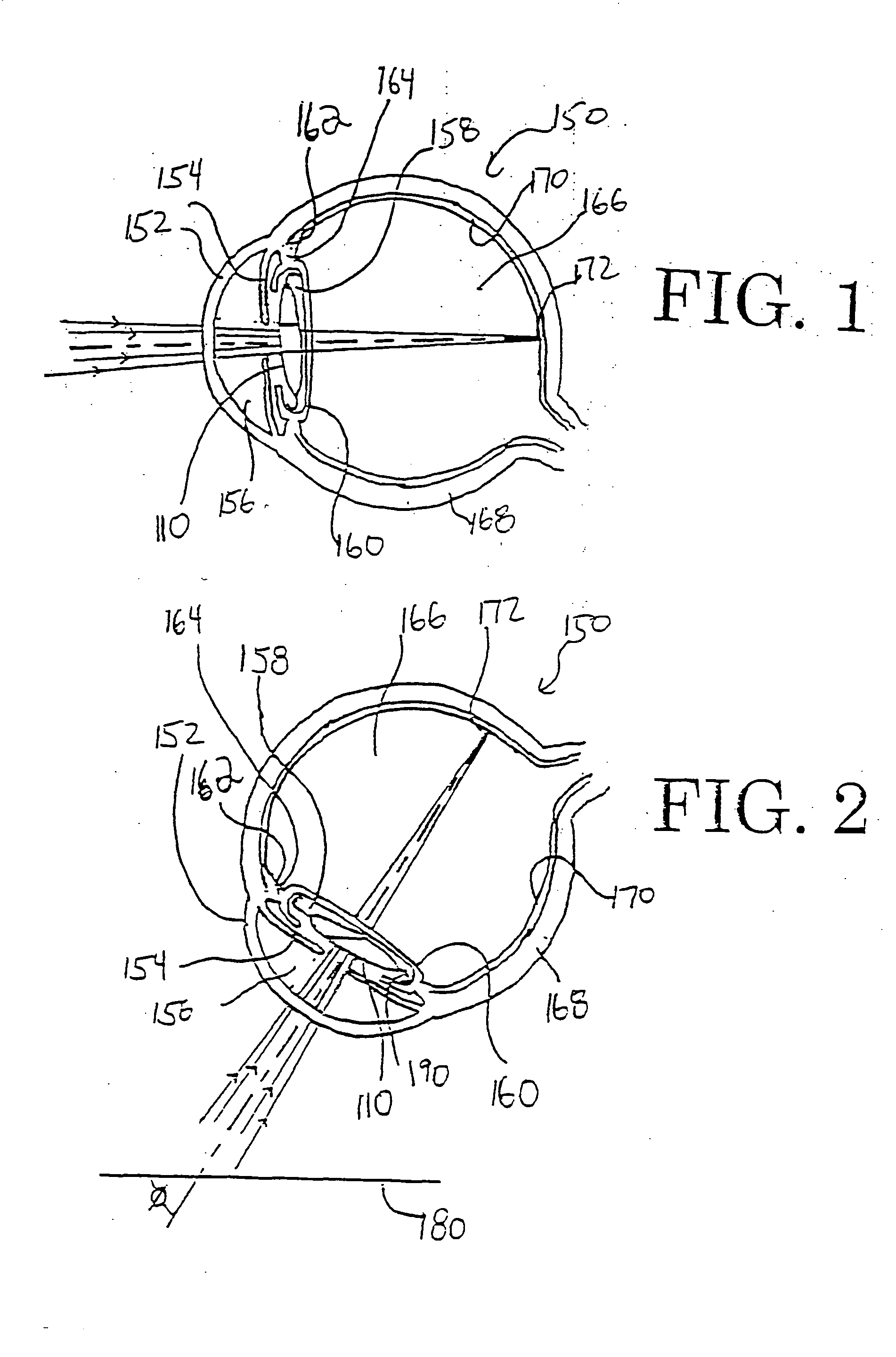
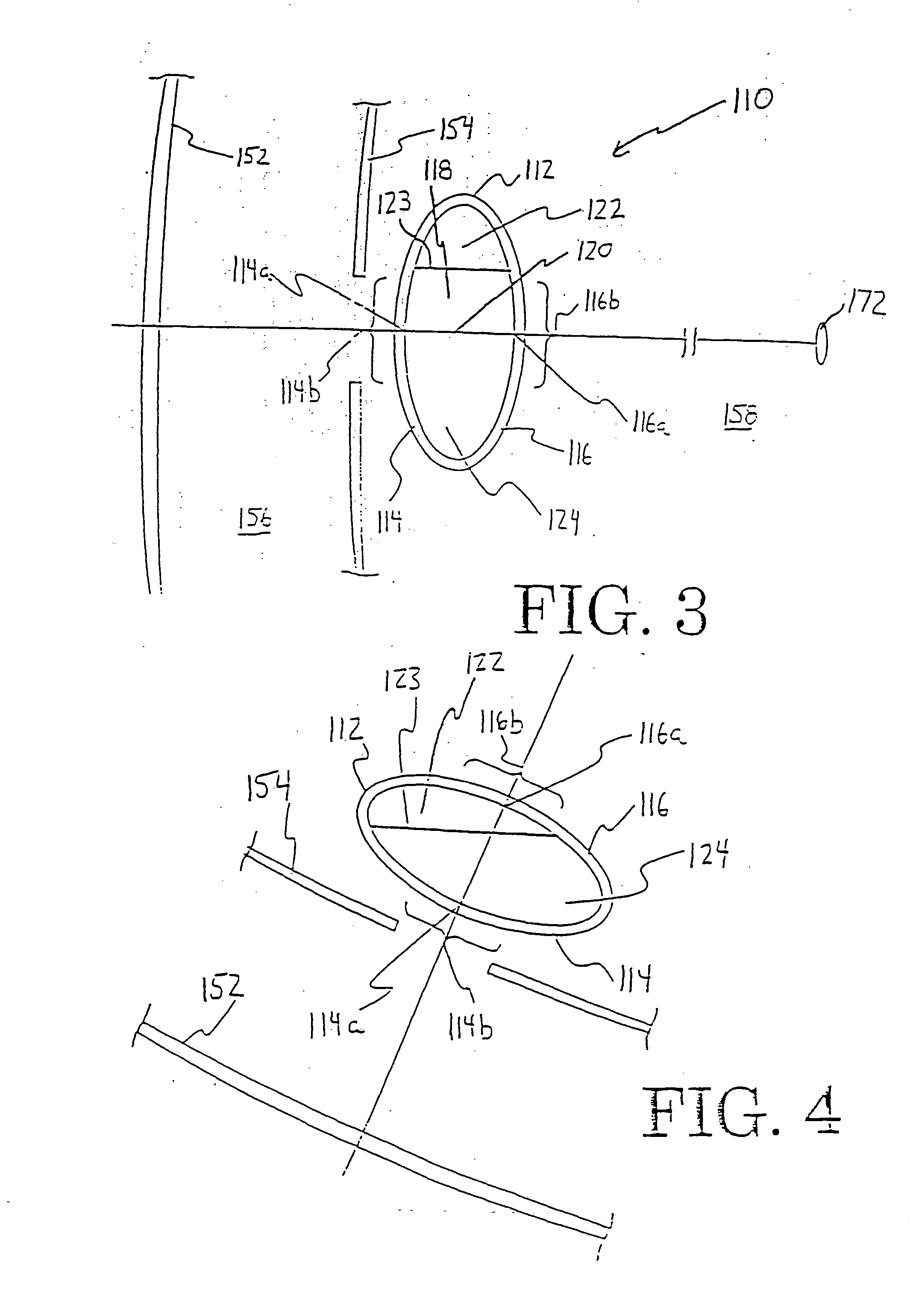
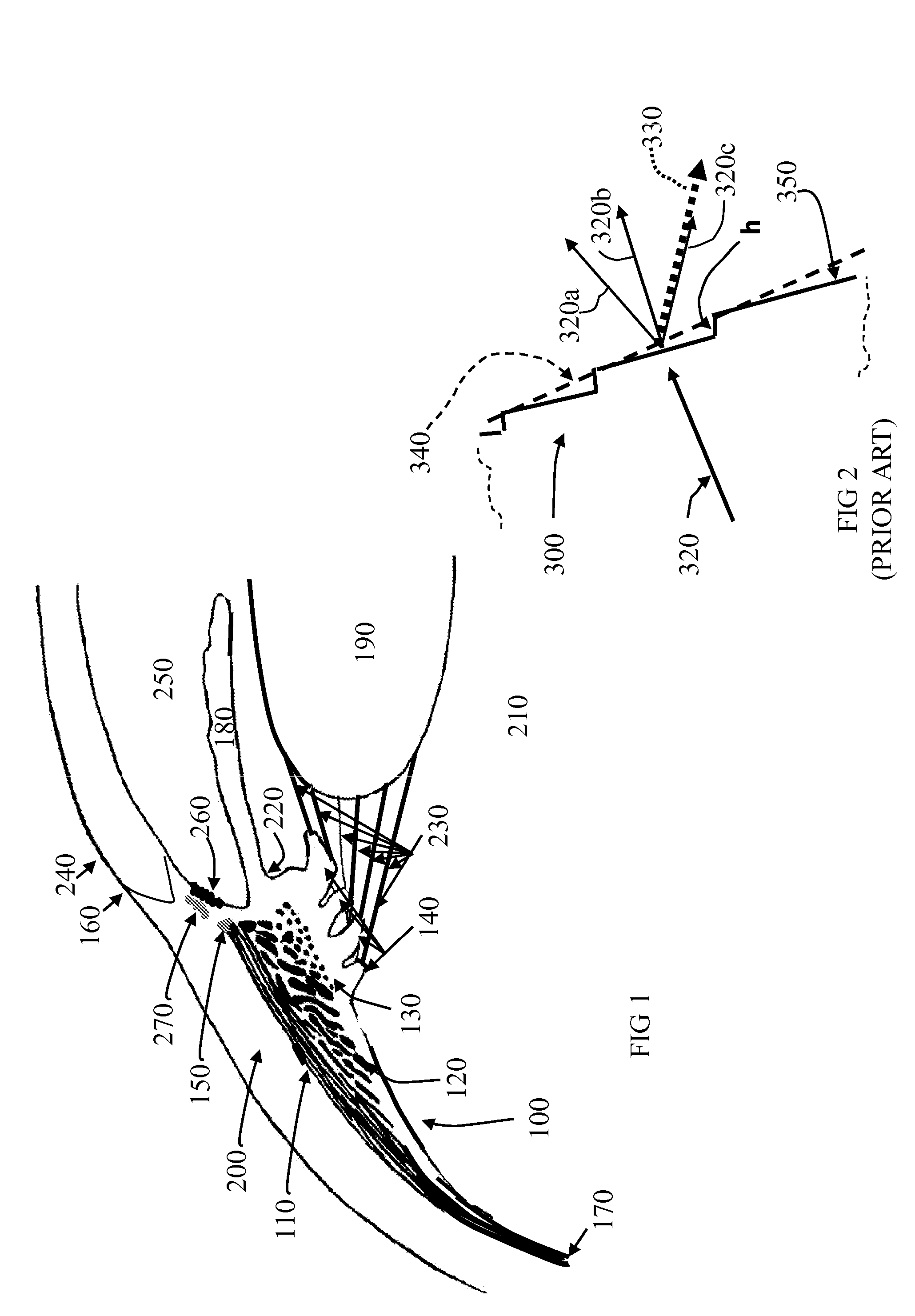
Intraocular lens with accommodative properties
InactiveUS6200342B1Focus assistPrevent excessive lateral movement and luxationIntraocular lensPupil diameterIntraocular lens
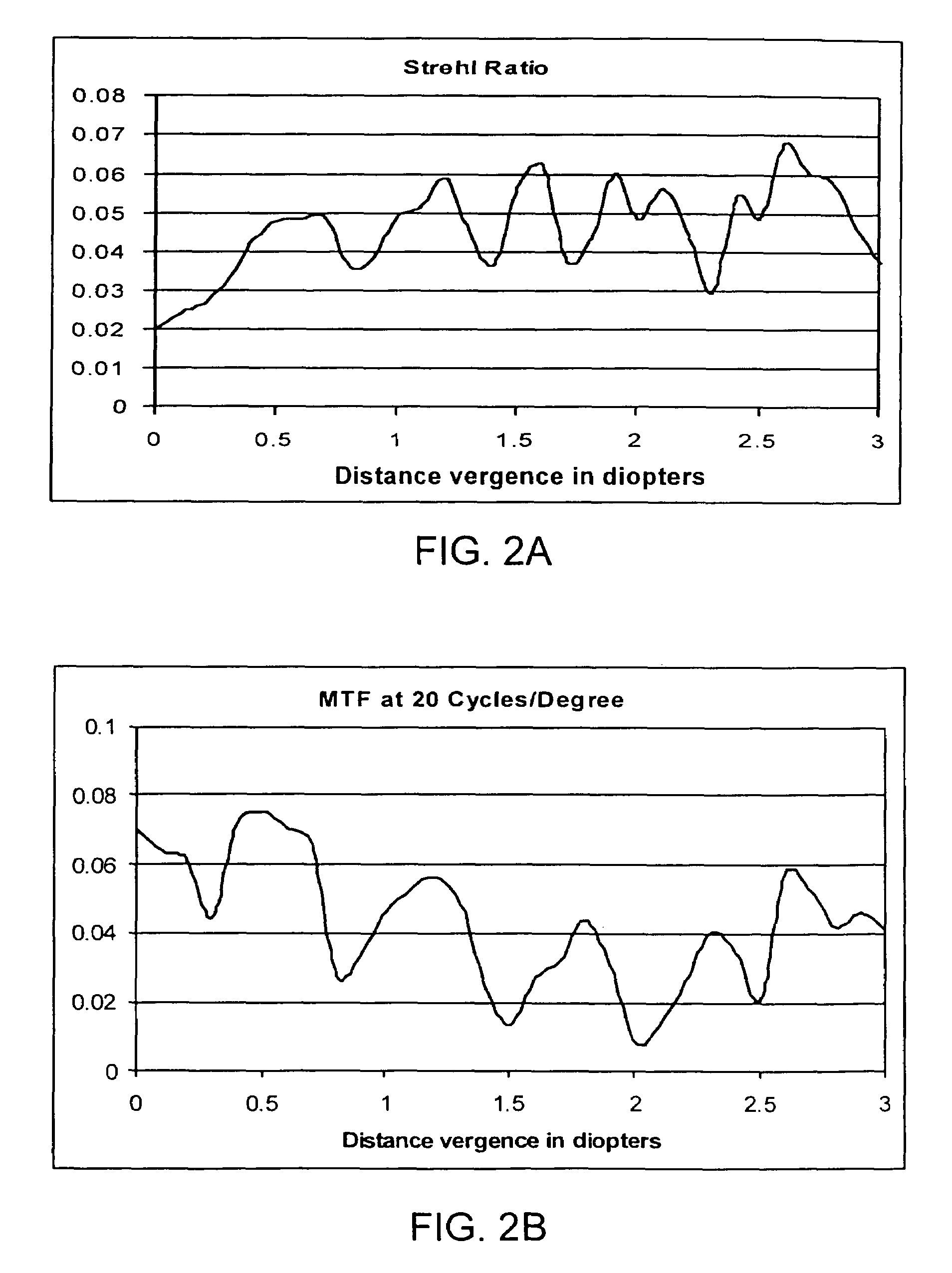
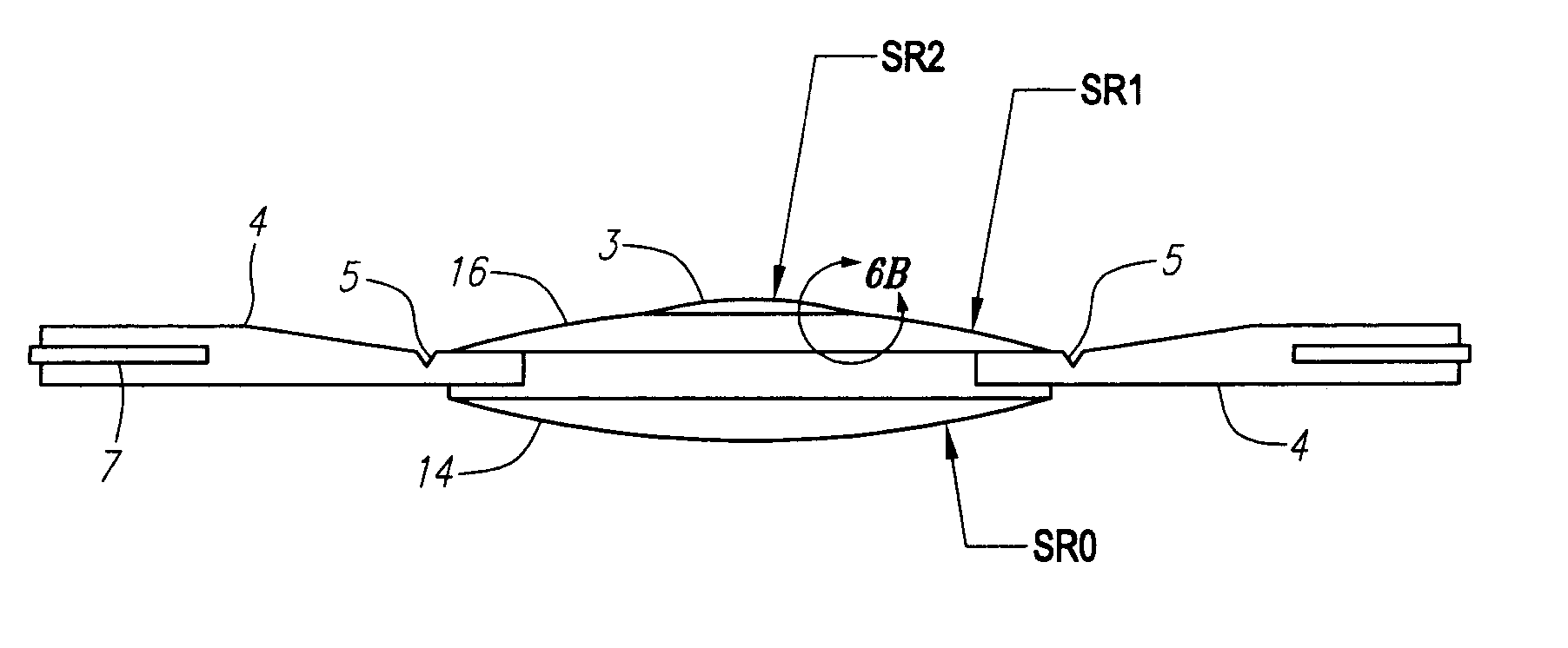
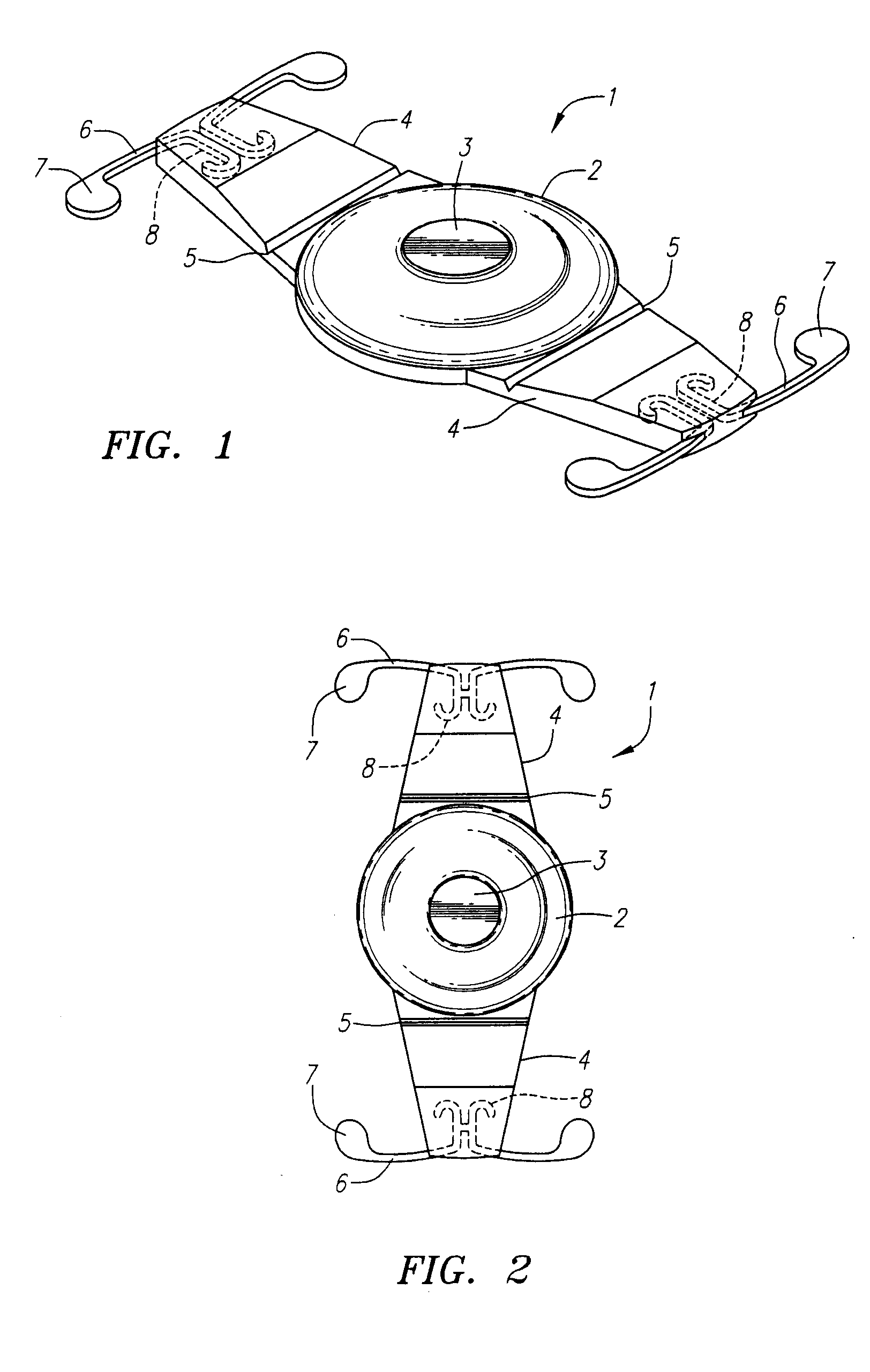
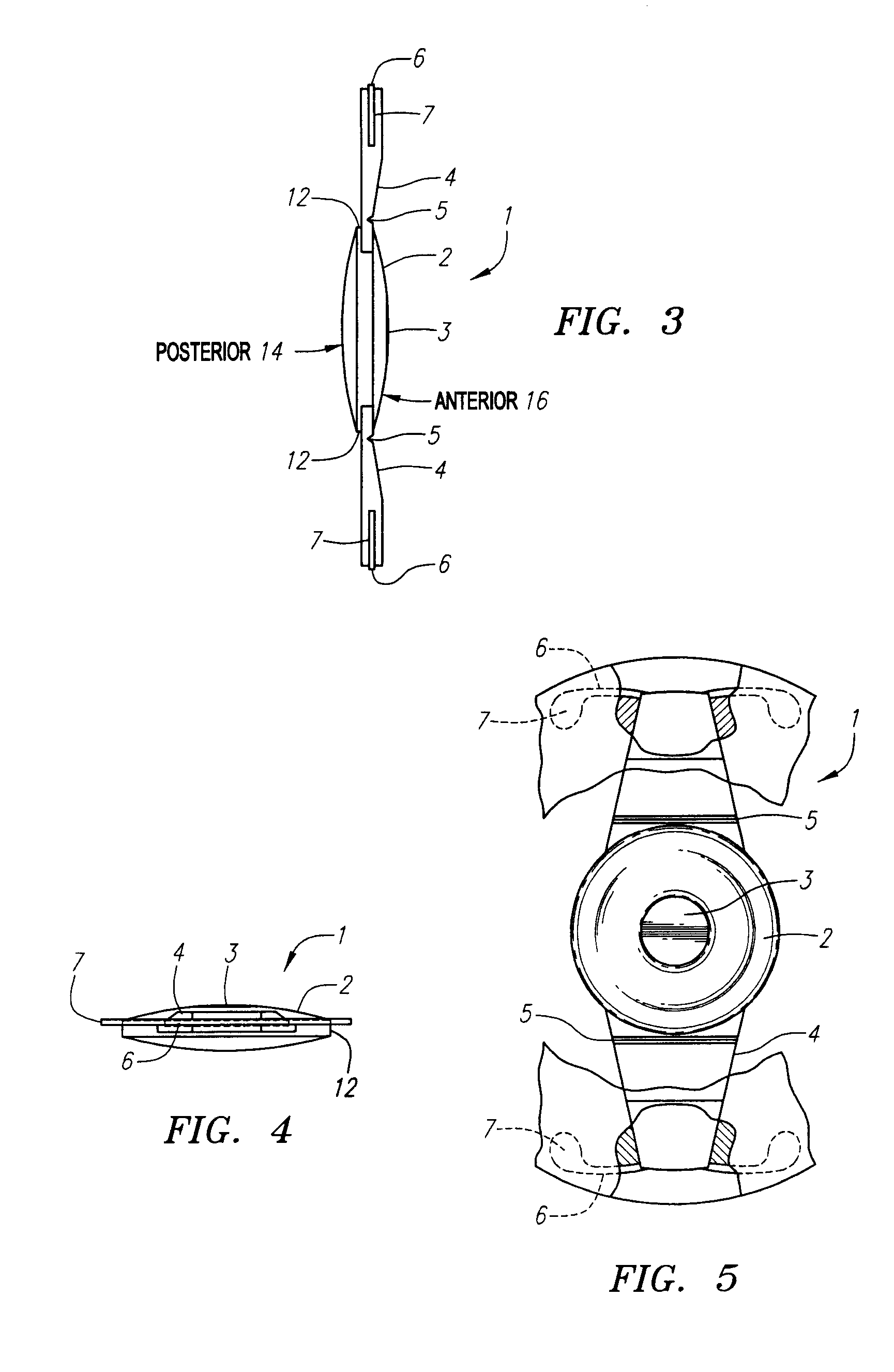
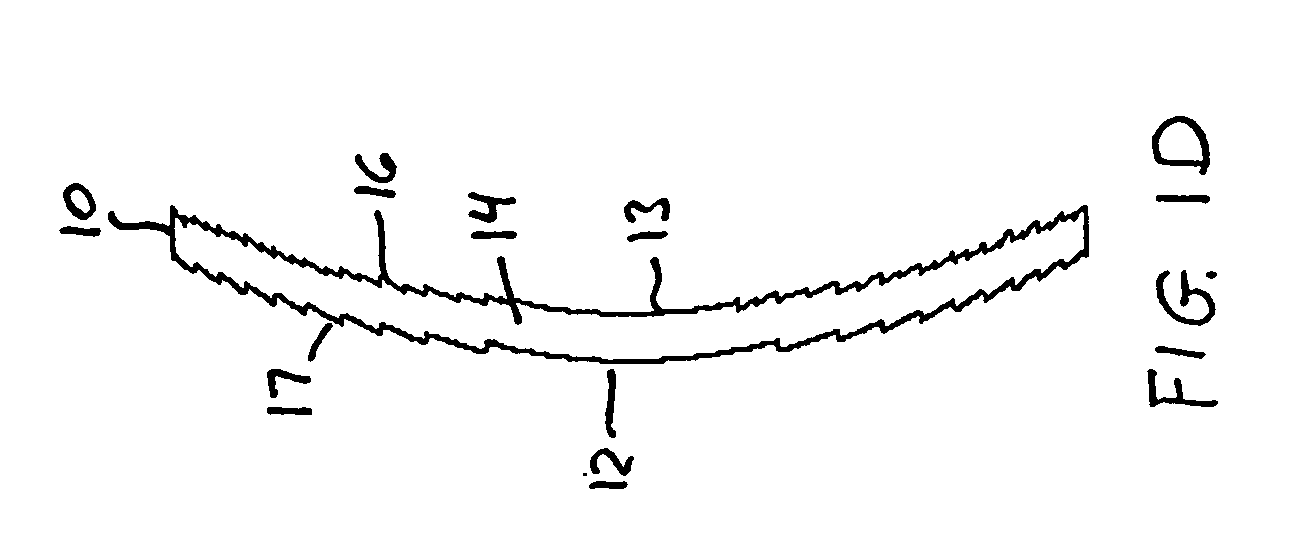
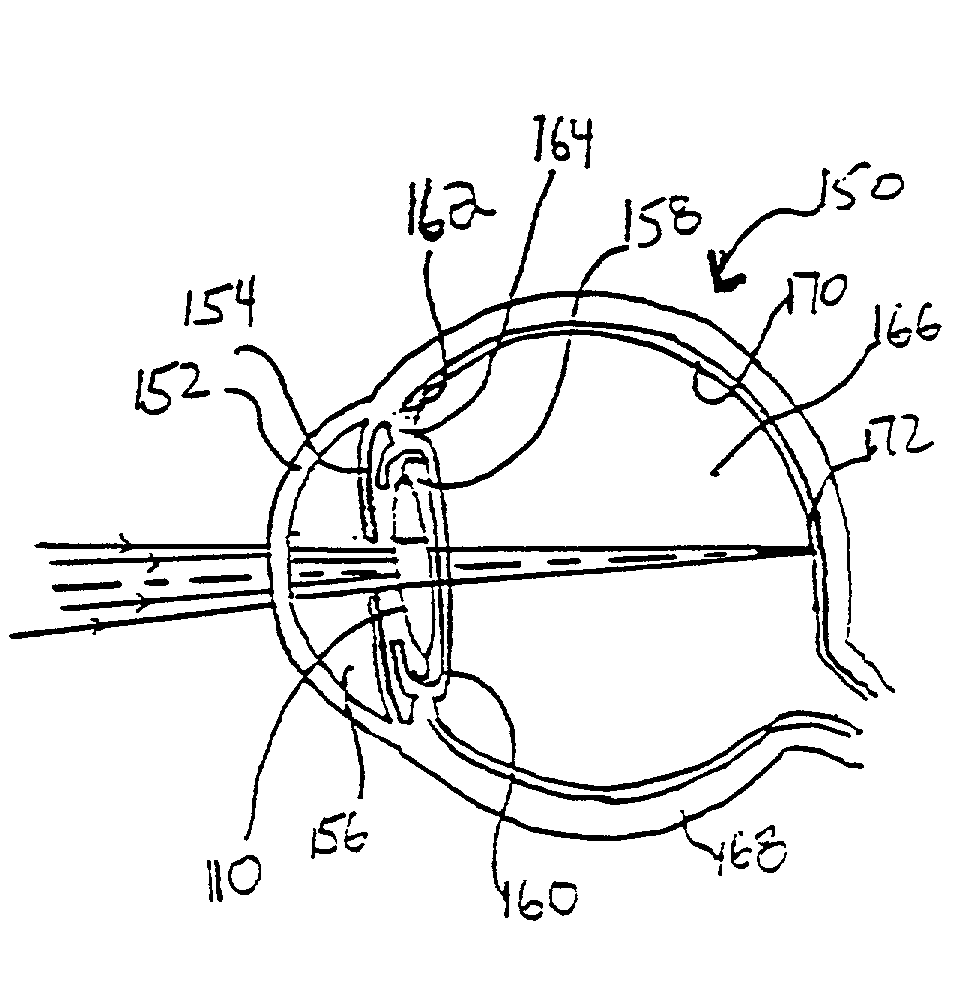
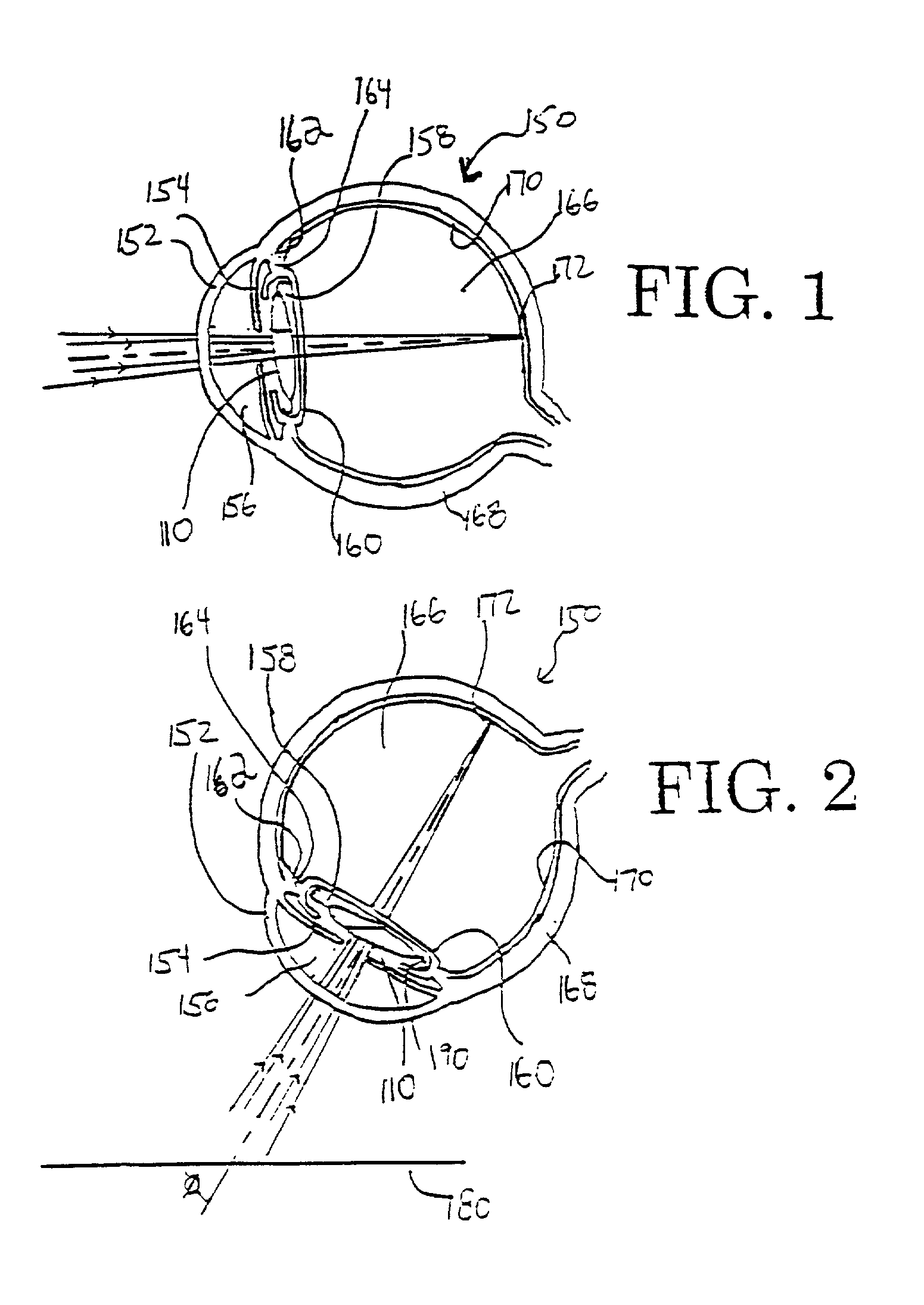
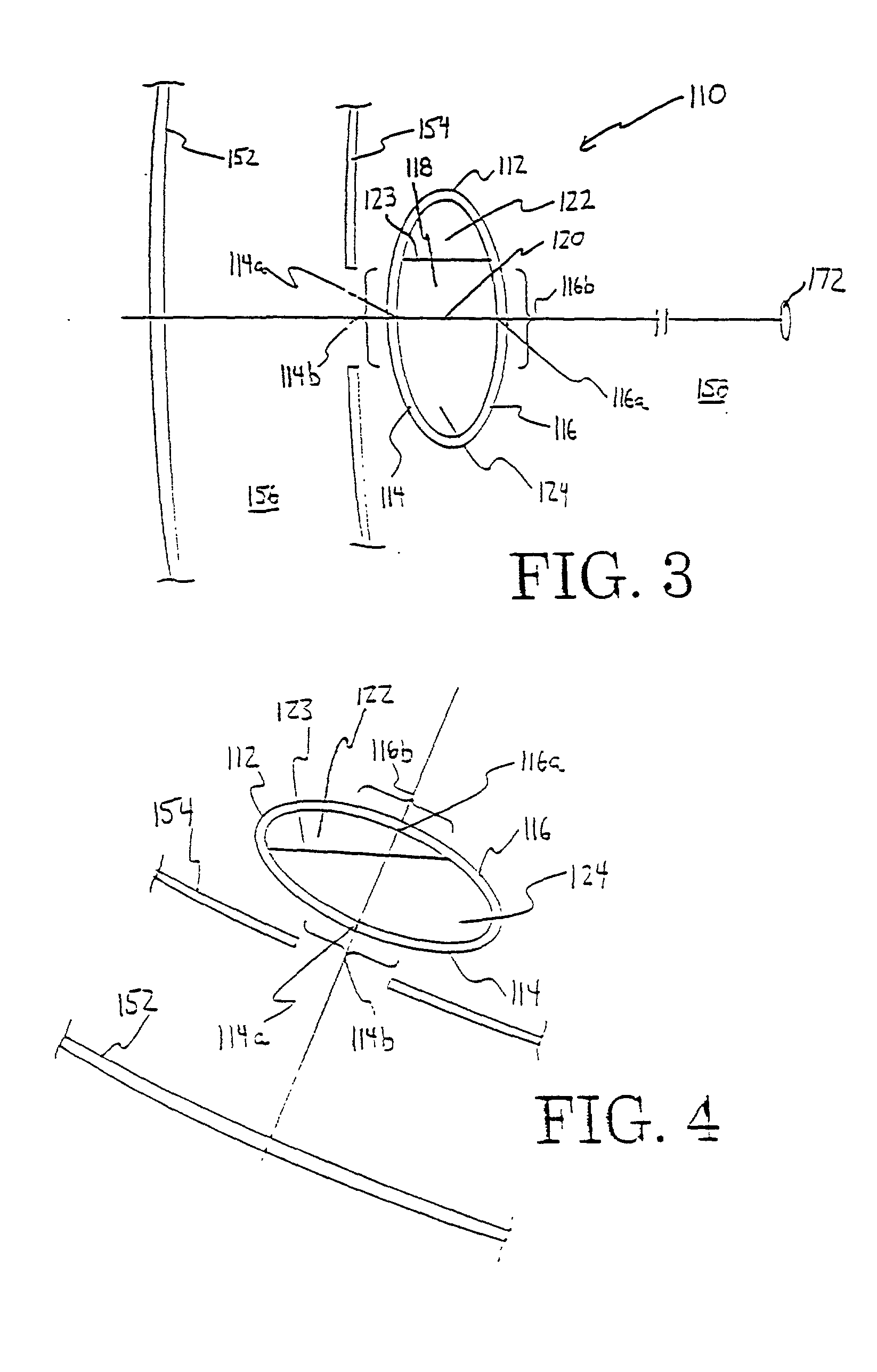
A new lens design and method of implantation uses the change in pupil diameter of the eye concurrent with the changes induced by a contraction of the ciliary muscle during the accommodative reflex, in order to assist in focusing of nearby objects. This new intraocular lens consists of two parts. The posterior part or haptic part is inserted behind the iris and in front of the natural lens or artificial implant. Its main purpose is to participate in the accommodative mechanism and to prevent excessive lateral movement and luxation of the lens. An anterior or optical part is made of flexible material and is placed before the iris. Its diameter is variable but should be large enough to cover the pupillary margins to some degree under various conditions of natural dilation. The anterior and posterior part of the lens are separated by a compressible circular groove in which the iris will settle. The diameter of this groove is slightly larger than the pupillary diameter measured under normal photopic daylight conditions and for distance vision. Since the pupil becomes smaller in near vision, the iris will exert a slight pressure at the level of the groove of the lens which will cause a progressive and evenly distributed flexing of the anterior part of the intraocular lens, as the diameter of the compressible circular groove slightly decreases. This flexing will induce an increase in refractive power which corresponds to a variable part of the amount necessary for focusing nearby objects.
Owner:TASSIGNON MARIE JOSE B
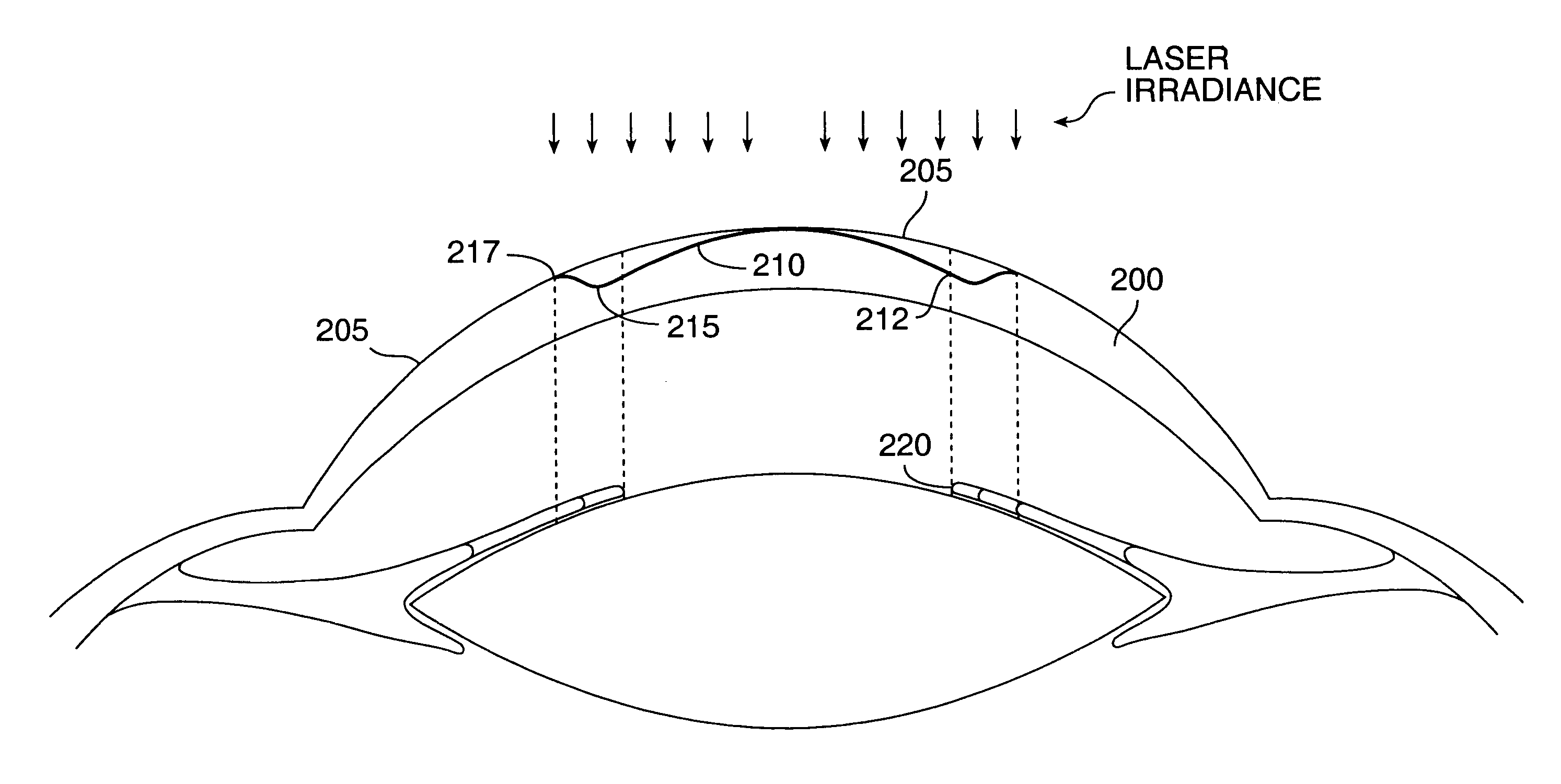
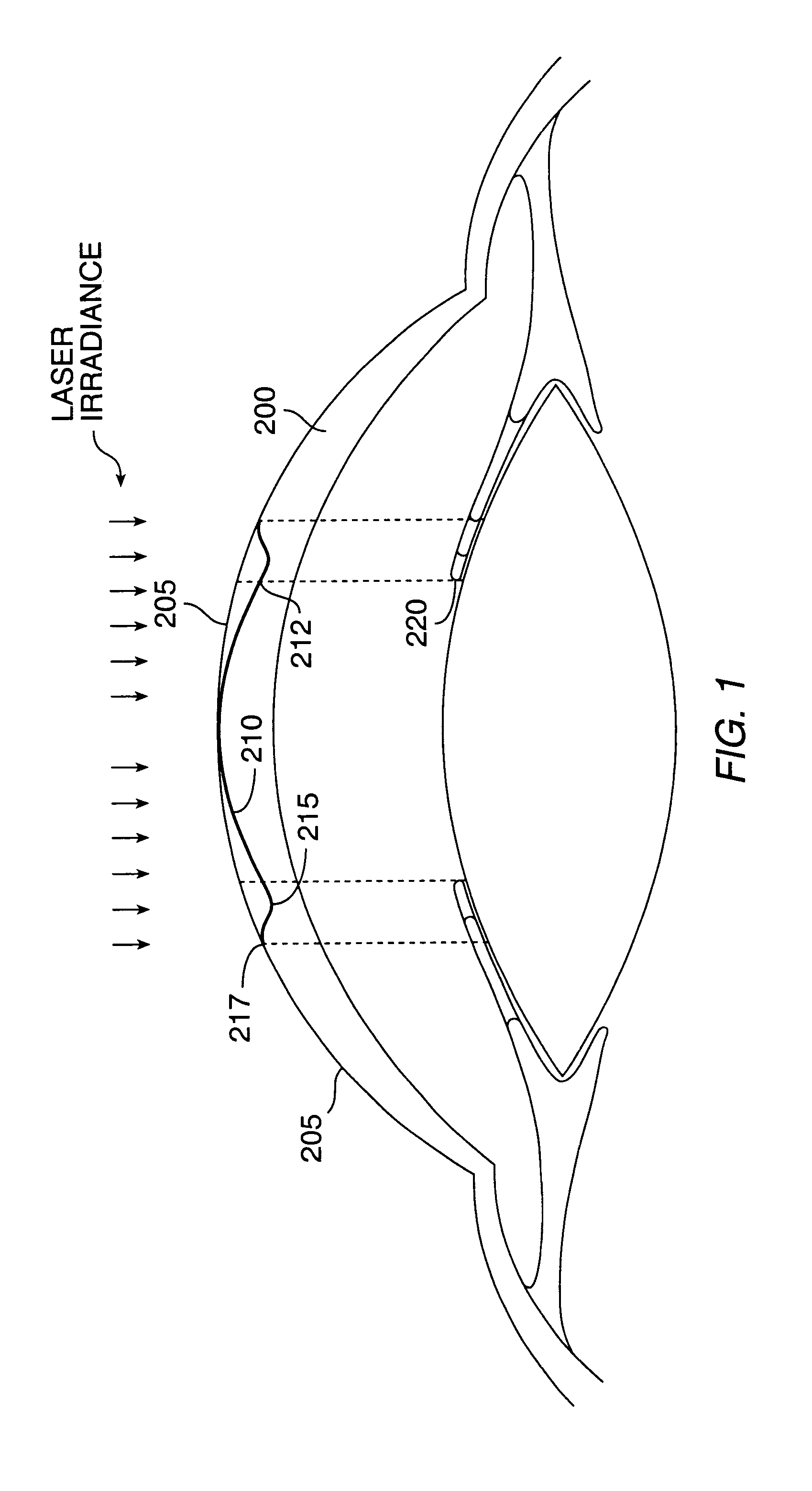
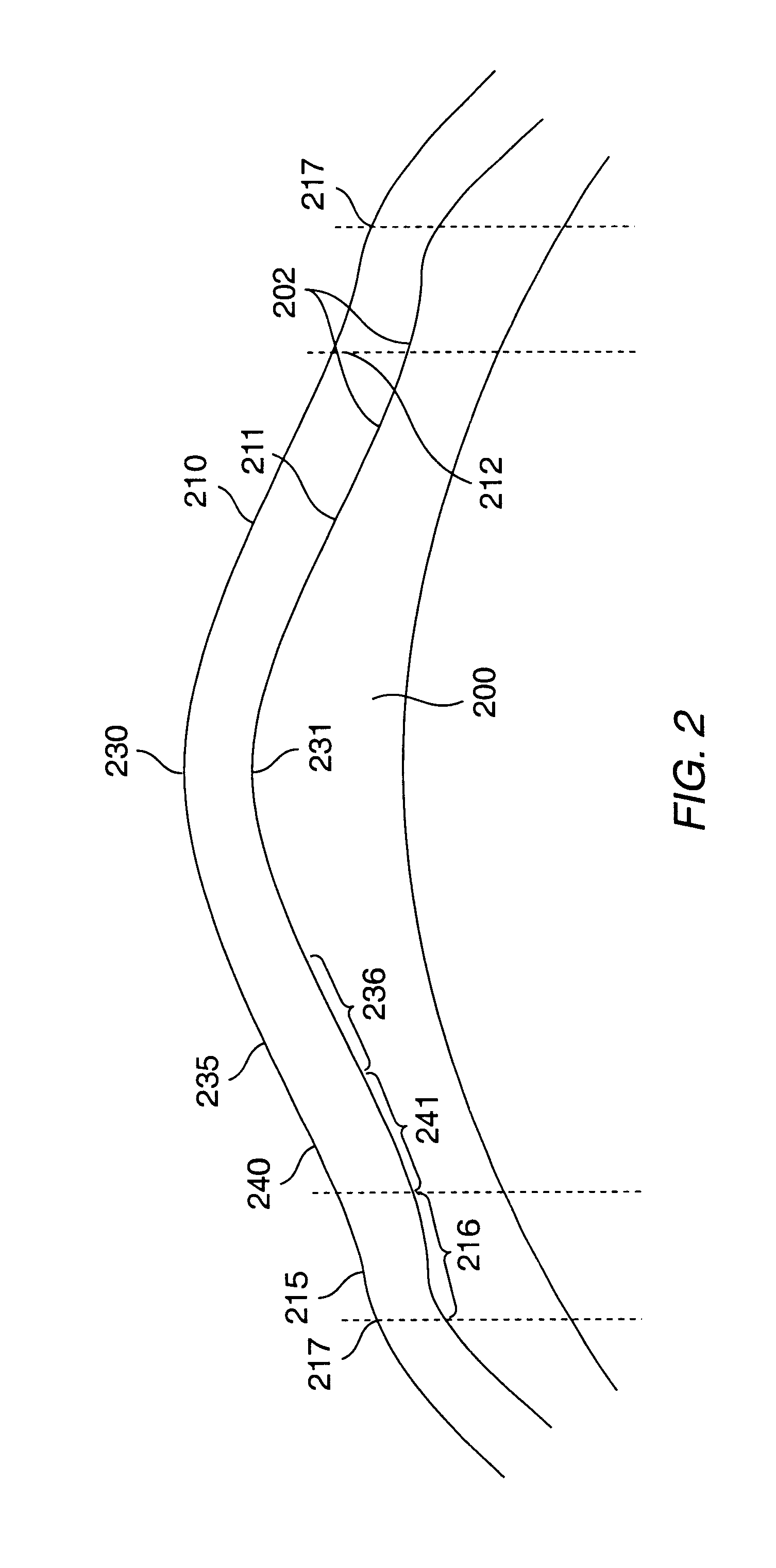
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
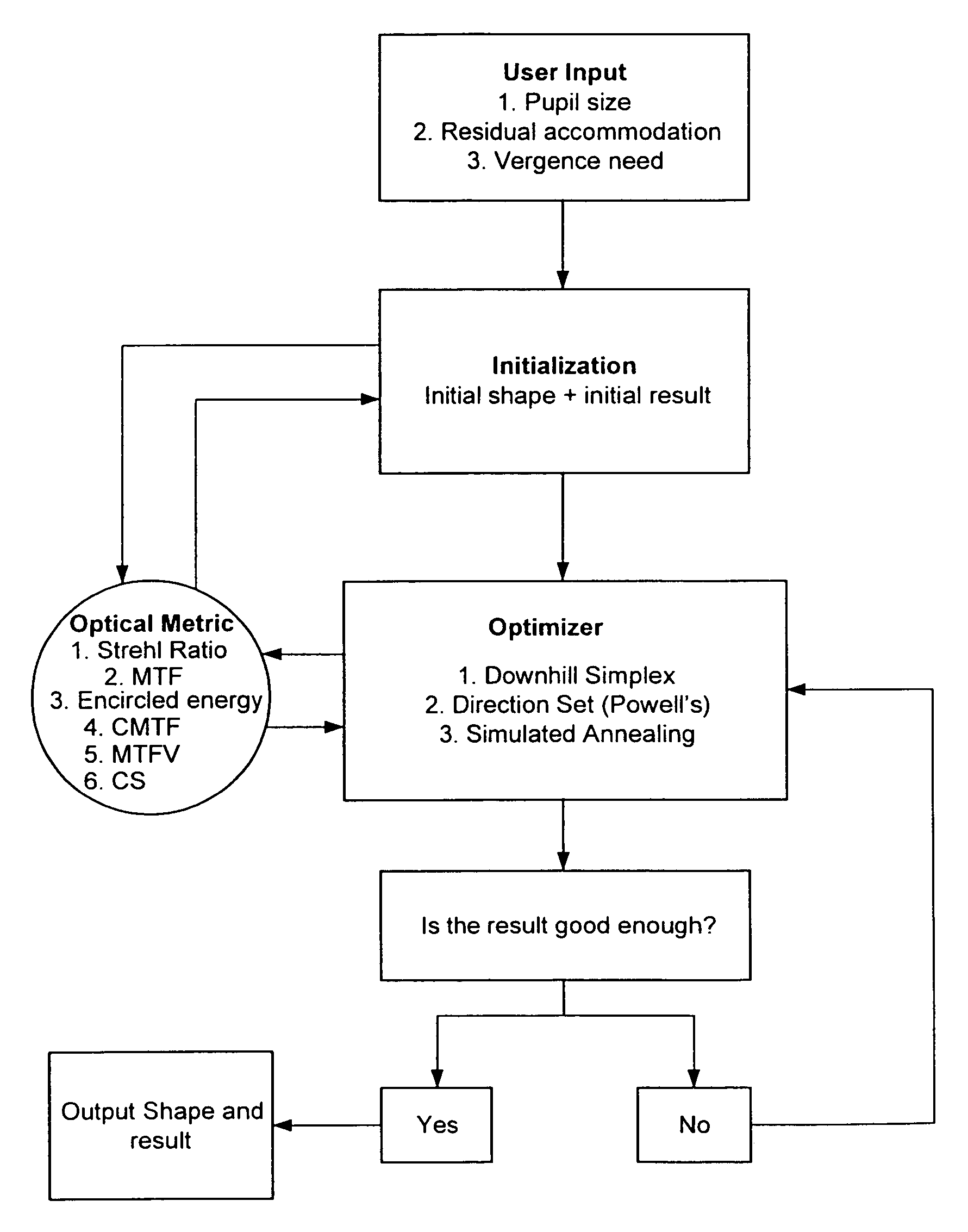
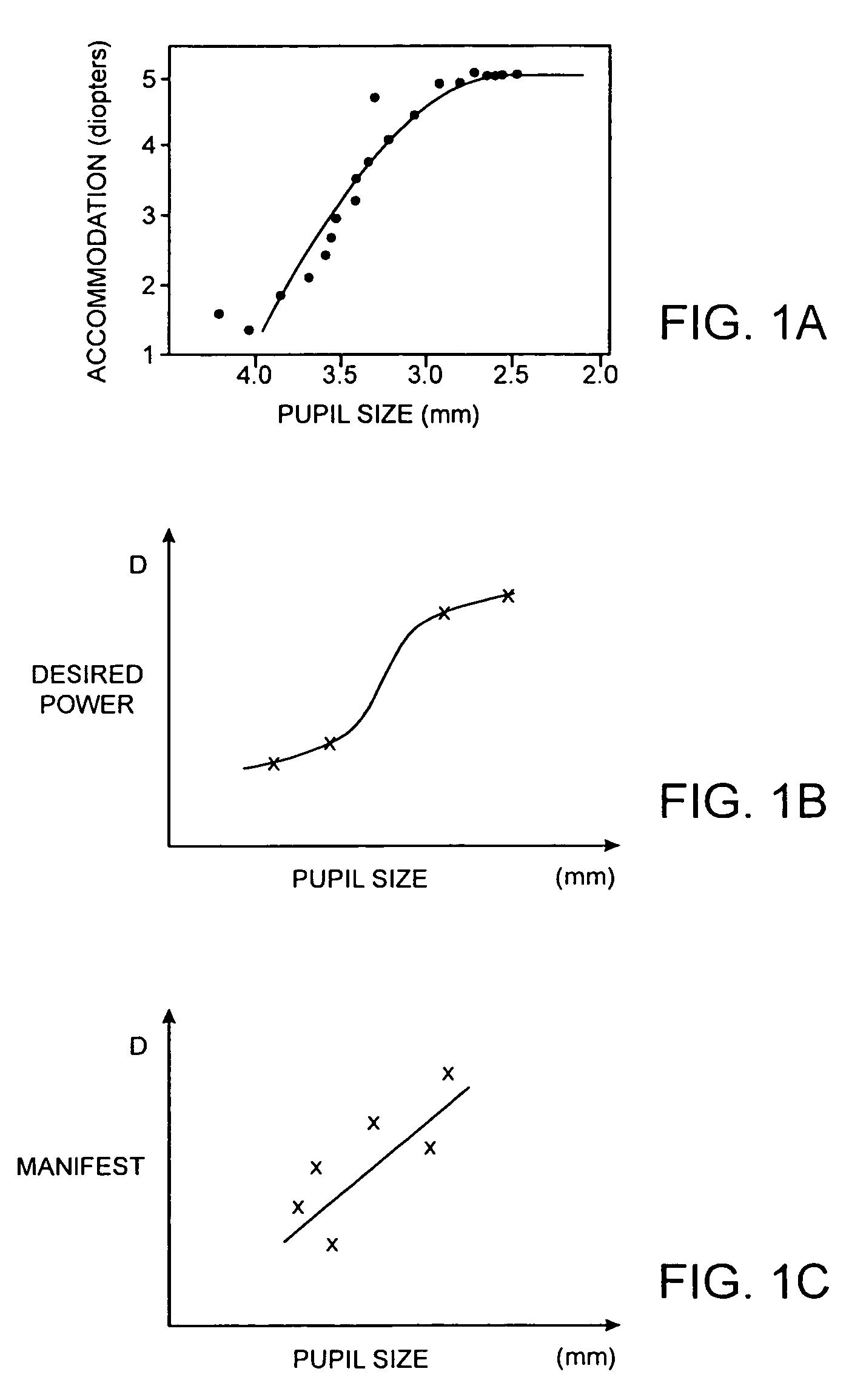
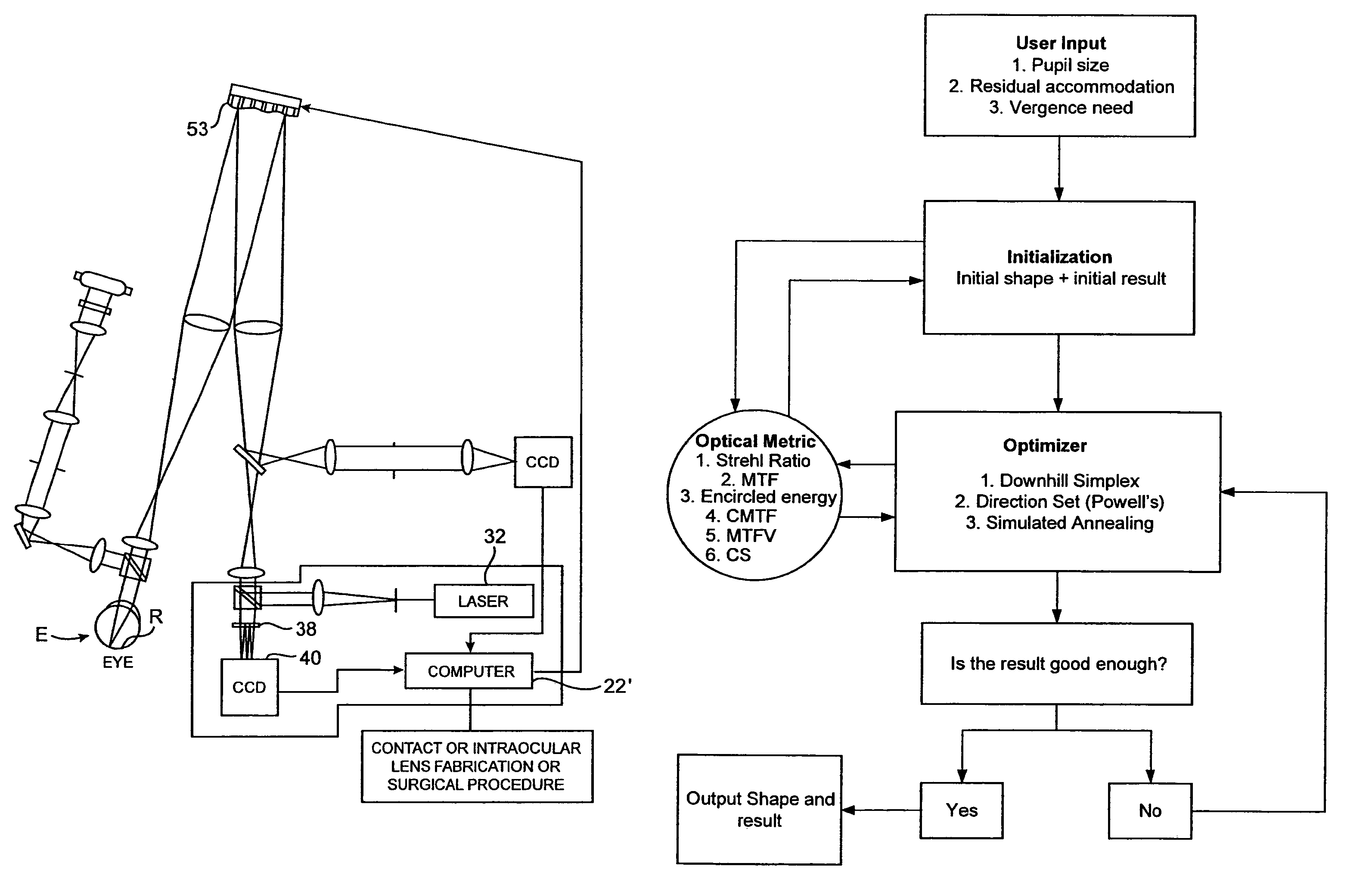
Presbyopia correction using patient data
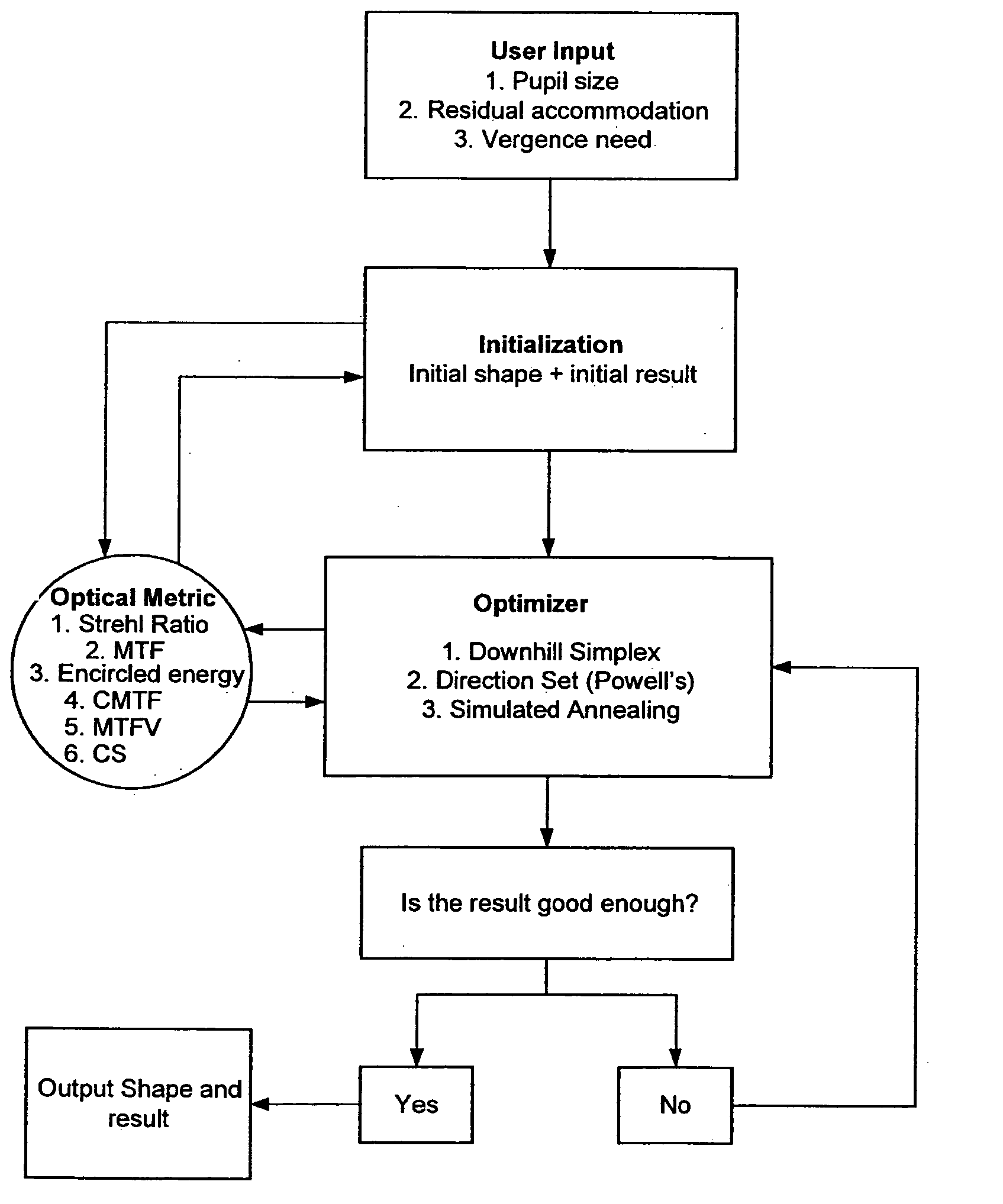
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats presbyopia in a particular patient. The combination of distance vision and near vision in a patient can be improved, often based on input patient parameters such as pupil size, residual accommodation, and power need. Iterative optimization may generate a customized corrective optical shape for the patient.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Accommodative Intraocular Lens
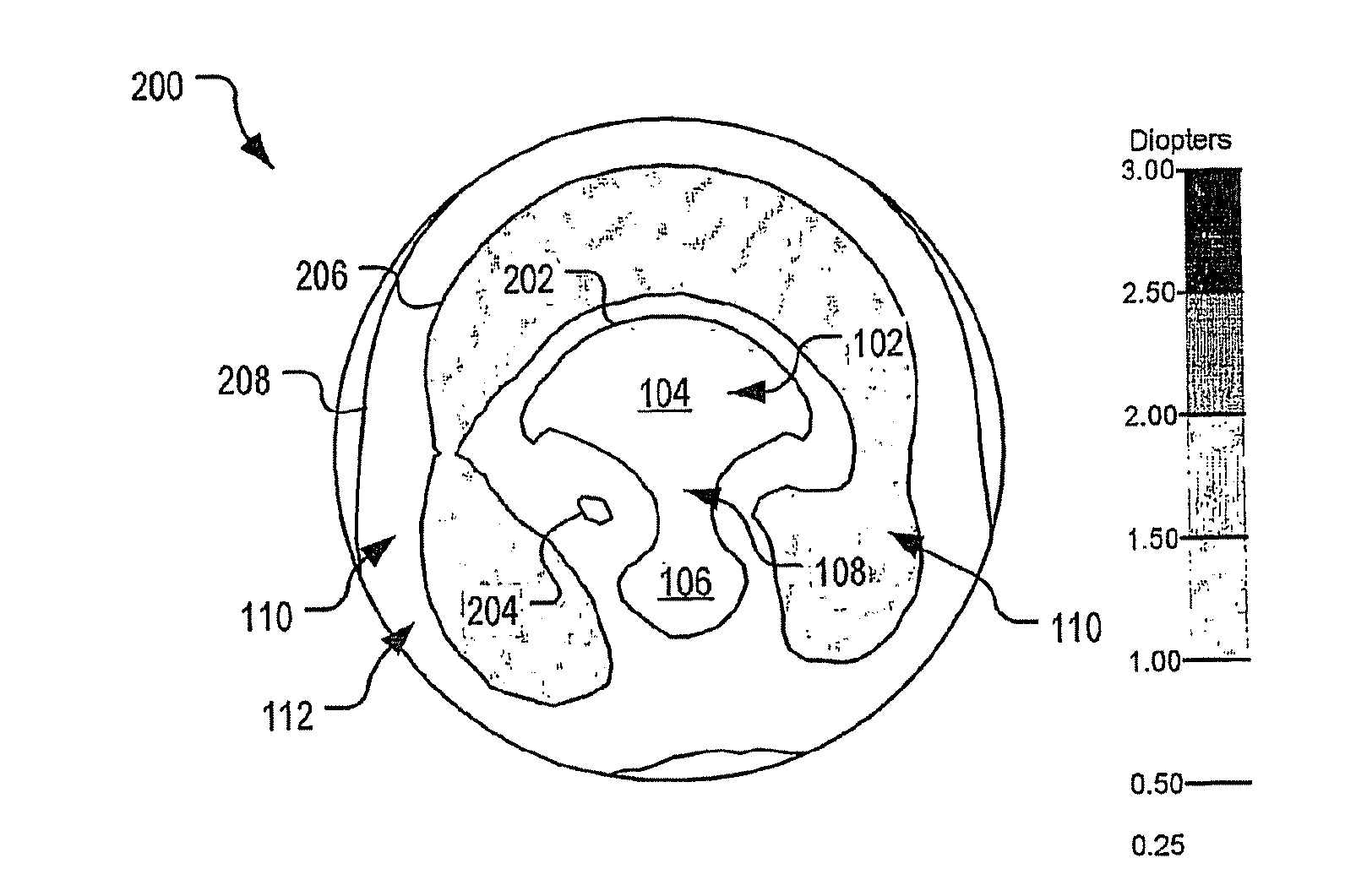
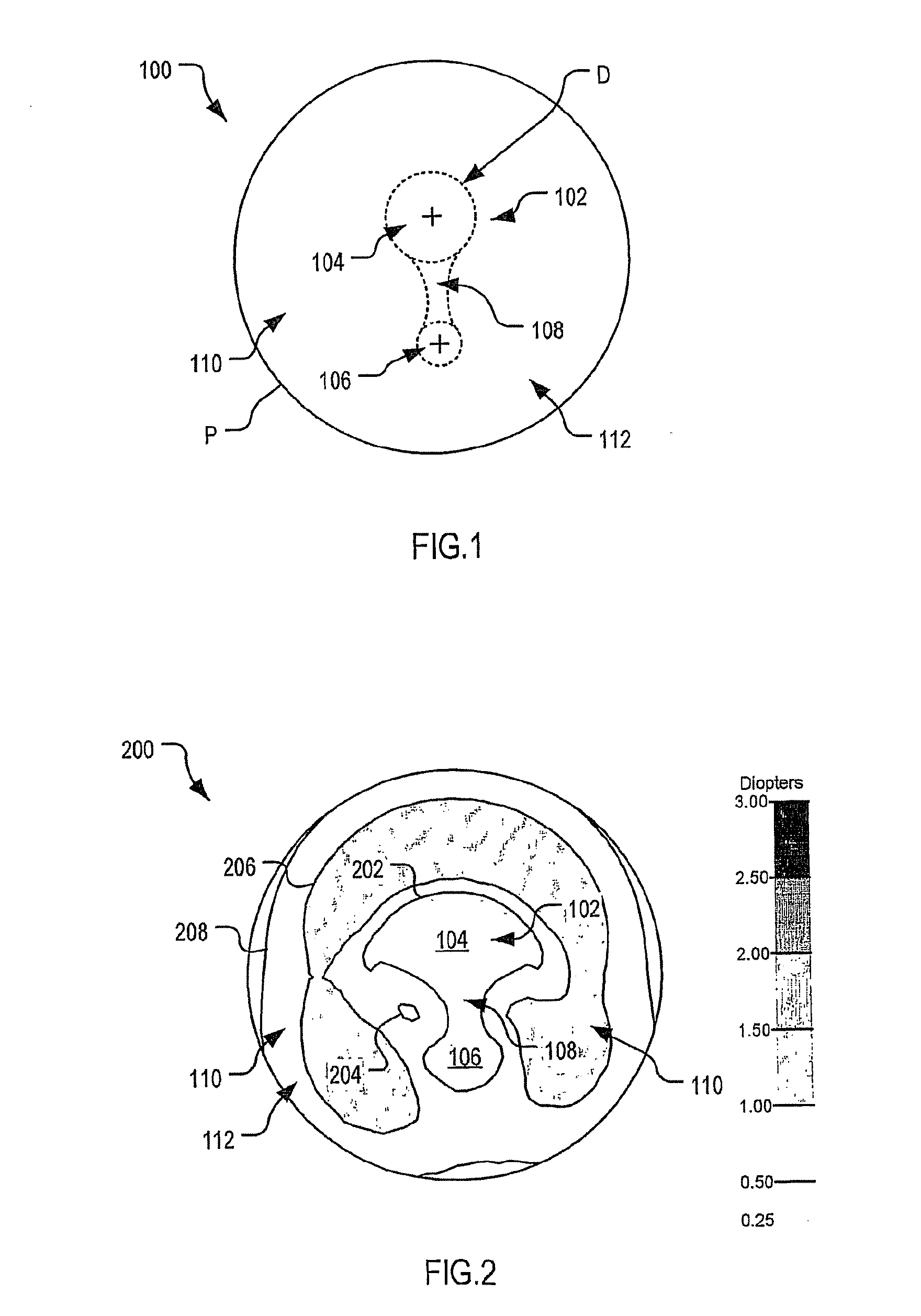
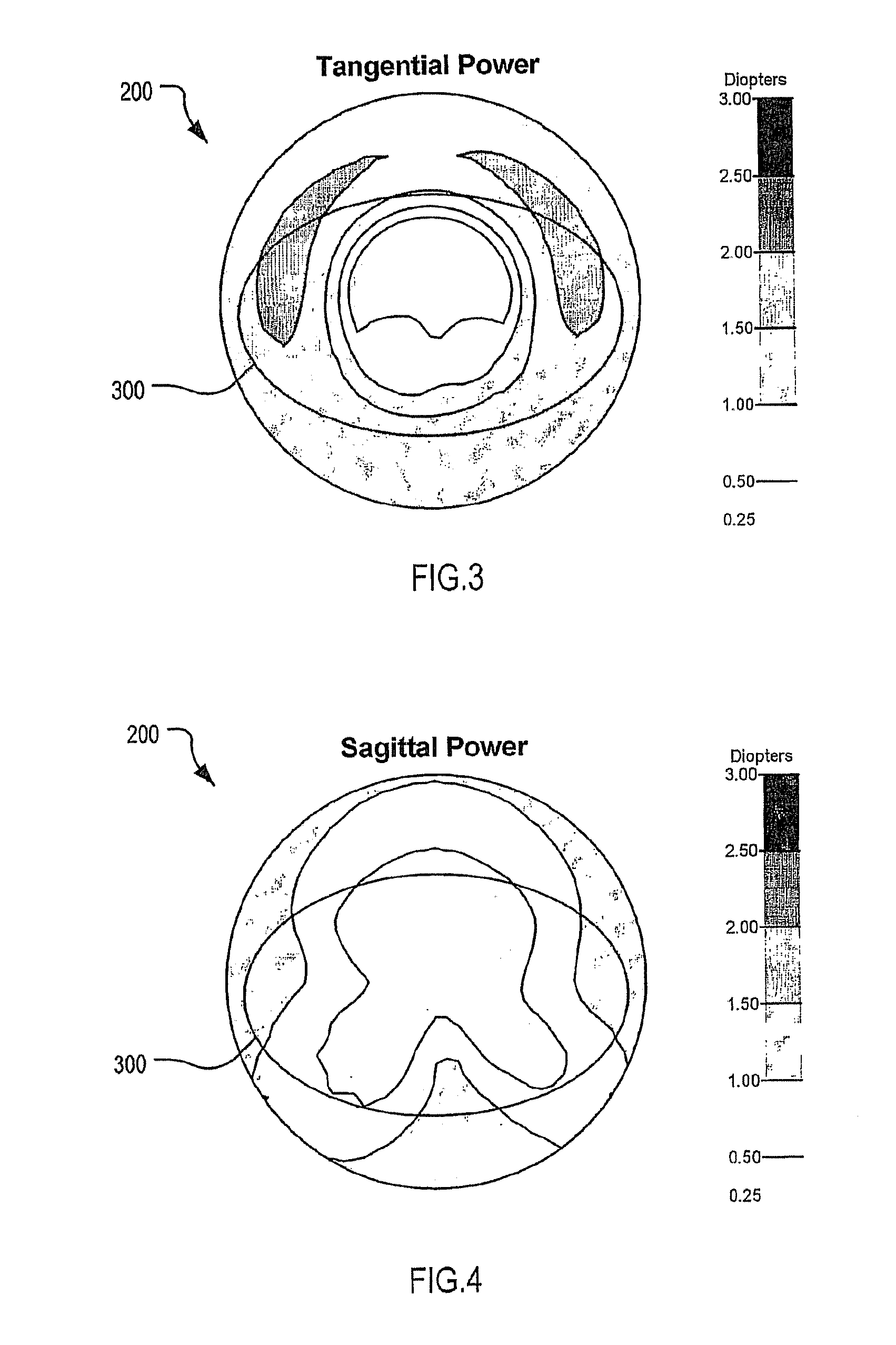
An accommodating intraocular lens where the optic is moveable relative to the outer ends of the extended portions. The lens comprises an optic made from a flexible material combined with extended portions that is capable of multiple flexions without breaking. The optic has a central area of increased power of less than 1.0 diopter aid near vision. A method is disclosed of implanting the present lens in the non-dominant eye of a patient.
Owner:C& C VISION INT
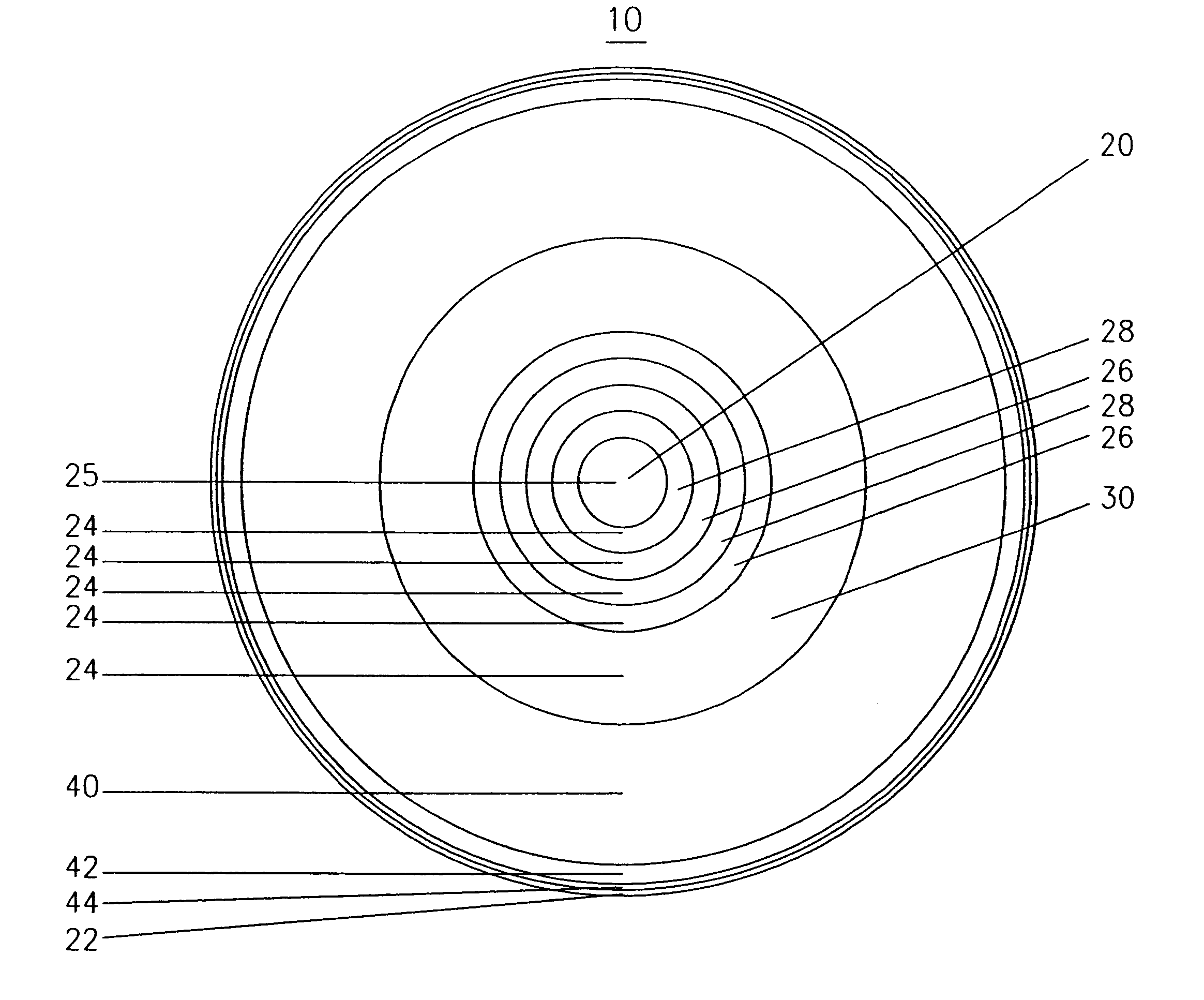
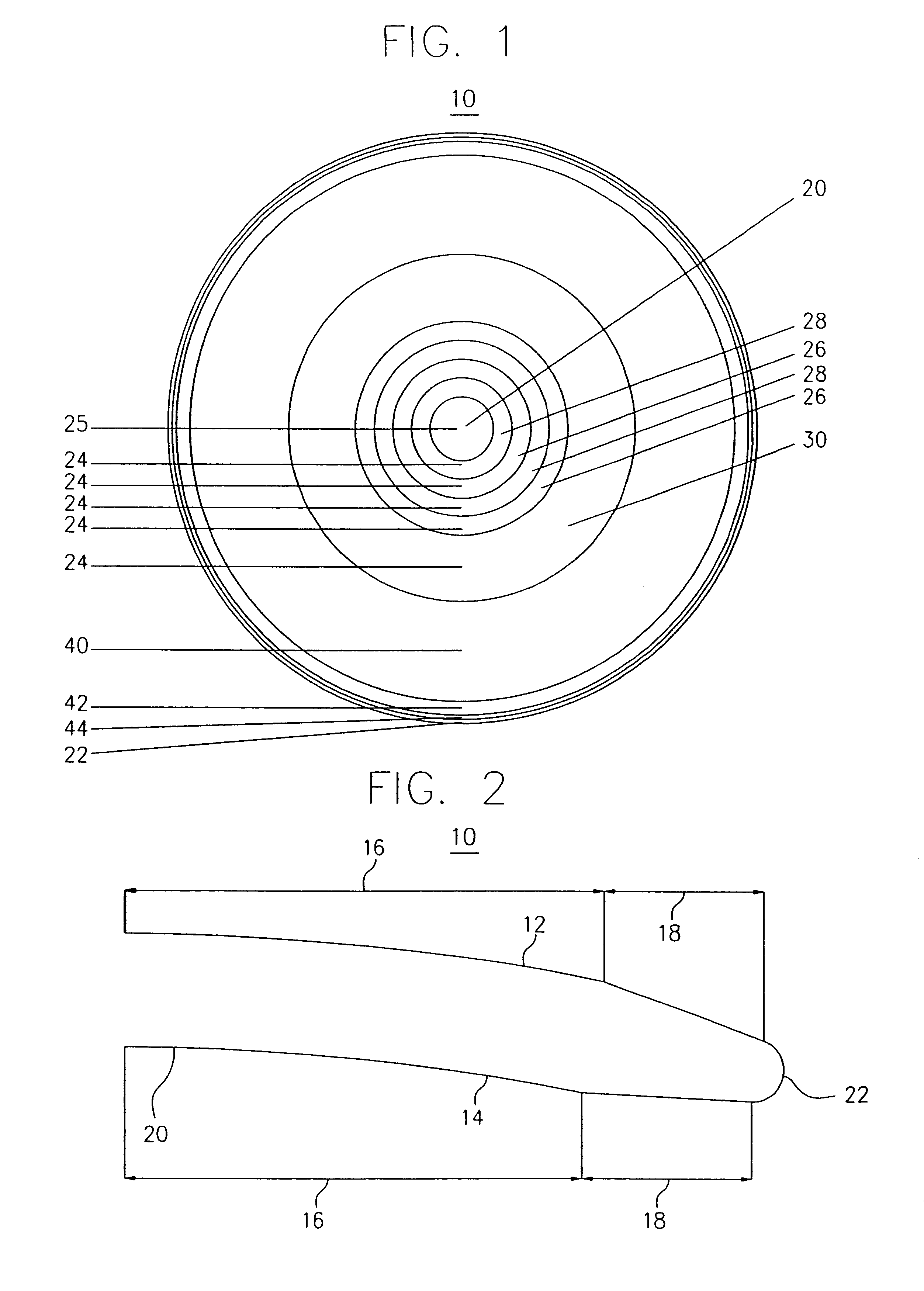
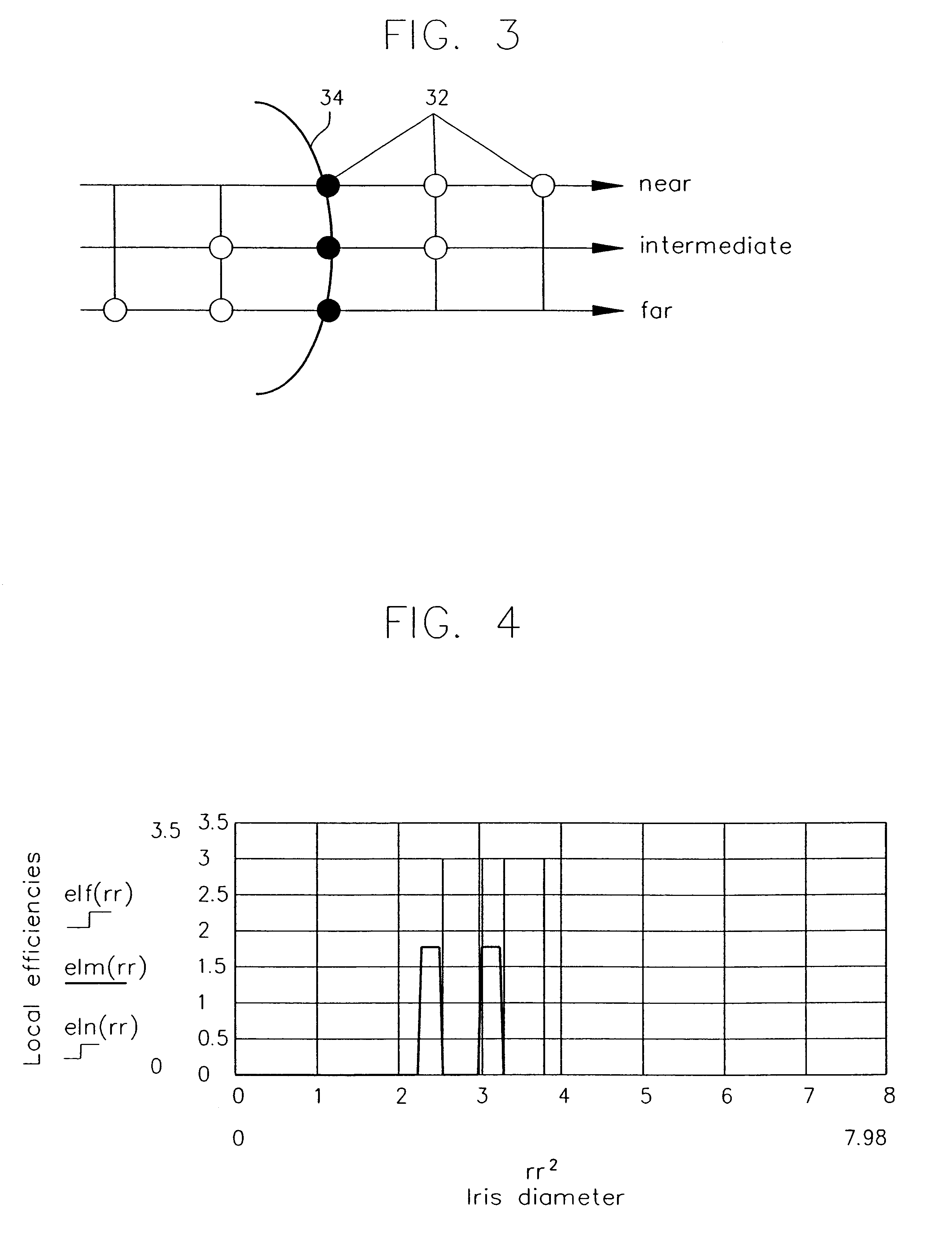
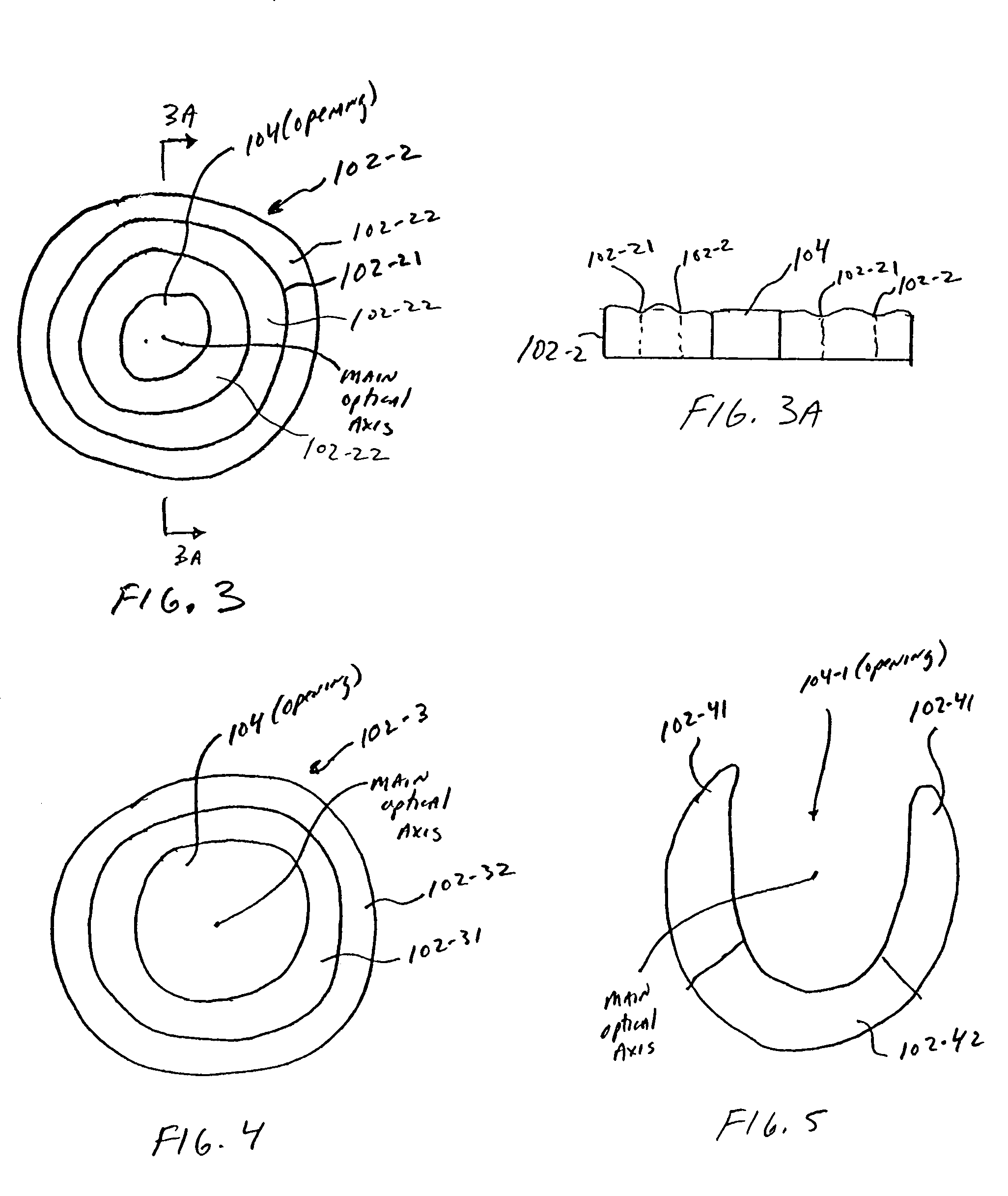
Pupil dependent diffractive lens for near, intermediate, and far vision
InactiveUS20120140166A1Reduce light scatterImproved patient visionSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensMultifocal diffractive lensOptical power
A multifocal diffractive lens comprises a multifocal diffractive structure coupled to a refractive component. The refractive component comprises at least one curved surface. The multifocal diffractive structure comprises a first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having a first optical power for near vision correction and a second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes for far vision correction. The first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes combined with the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes can provide a multifocal diffractive profile having decreased light scatter, chromatic aberration, and diffraction to non-viewing orders such that dysphotopsia is substantially inhibited. A third plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having an intermediate optical power can be combined with the first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes and the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
ActiveUS7156516B2Smooth edgesEasy to manufactureSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensSquare waveformDiffraction order
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. The first diffractive structure may have blazed (i.e., sawtooth), sinusoidal, sinusoidal harmonic, square wave, or other shape profile. A sinusoidal harmonic diffractive structure is particularly useful in applications where smooth rather than sharp edges are desirable.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
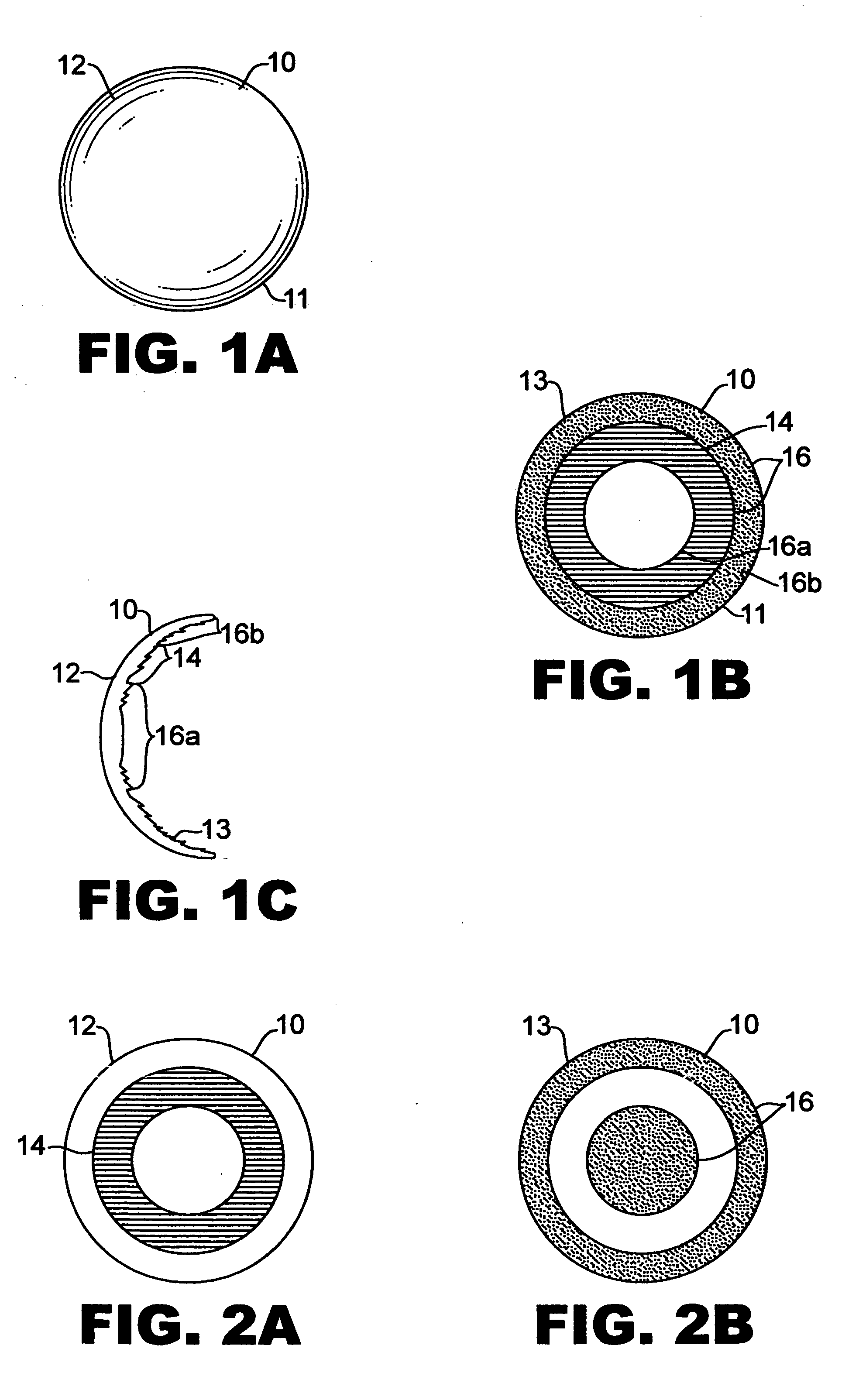
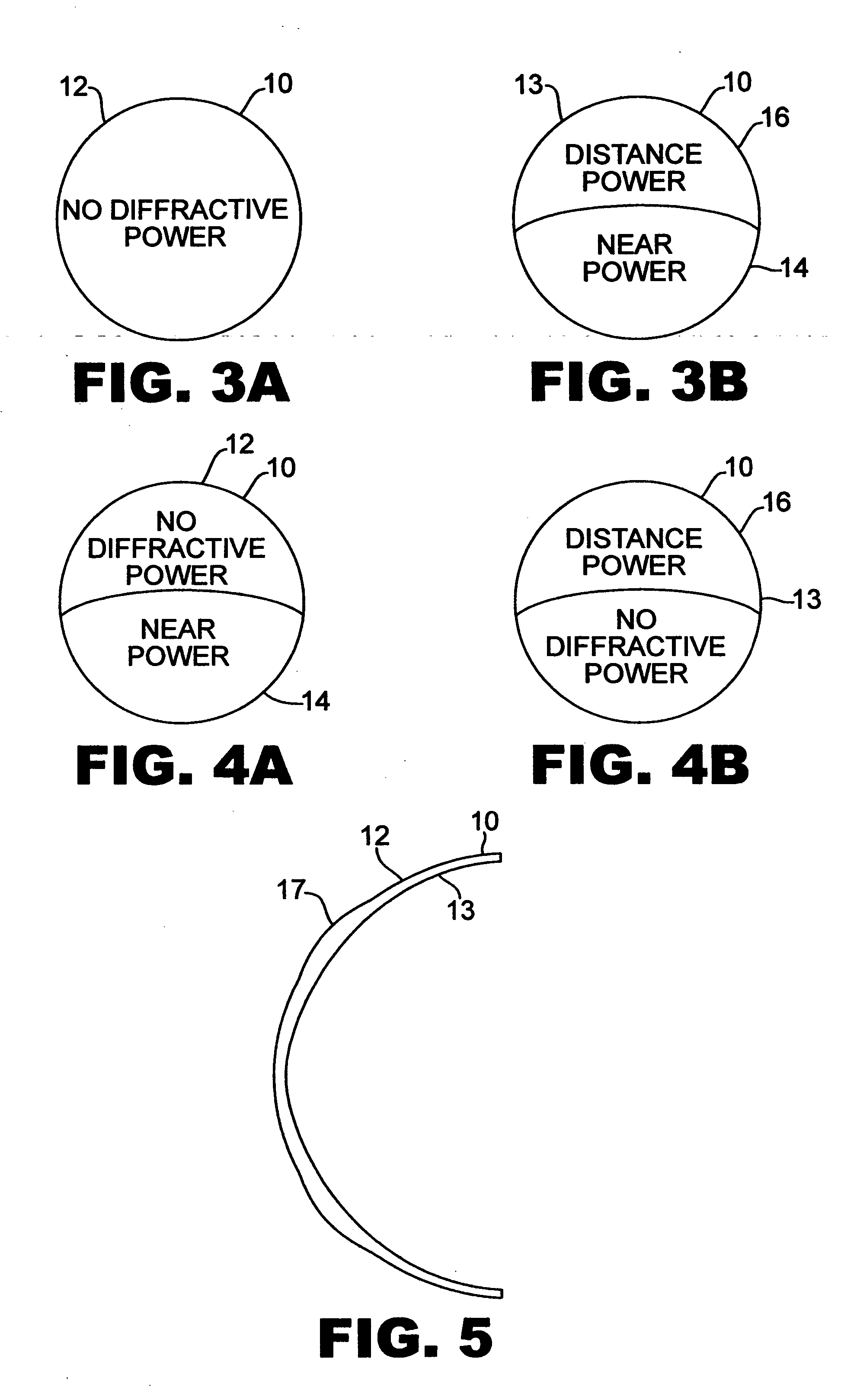
Multifocal ophthalmic lenses
The invention provides lenses for correcting presbyopia in which the near vision segments interfere at least about 50% less with distance vision than do the near vision segments in conventional contact lenses.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Simultaneous multifocal contact lens and method of utilizing same for treating visual disorders
A simultaneous multifocal contact lens for correcting vision acuity of an individual is disclosed. The contact lens comprises a central region radially surrounded by at least one far vision focal region and at least one near vision focal region, wherein a near vision additional correction of the at least one near vision focal region is overcorrected by at least 10% with respect to the near vision additional correction prescribed for the
Owner:HOLO OR
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
ActiveUS20060055883A1Smooth edgesEasy to manufactureSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensSquare waveformDiffraction order
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. The first diffractive structure may have blazed (i.e., sawtooth), sinusoidal, sinusoidal harmonic, square wave, or other shape profile. A sinusoidal harmonic diffractive structure is particularly useful in applications where smooth rather than sharp edges are desirable.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
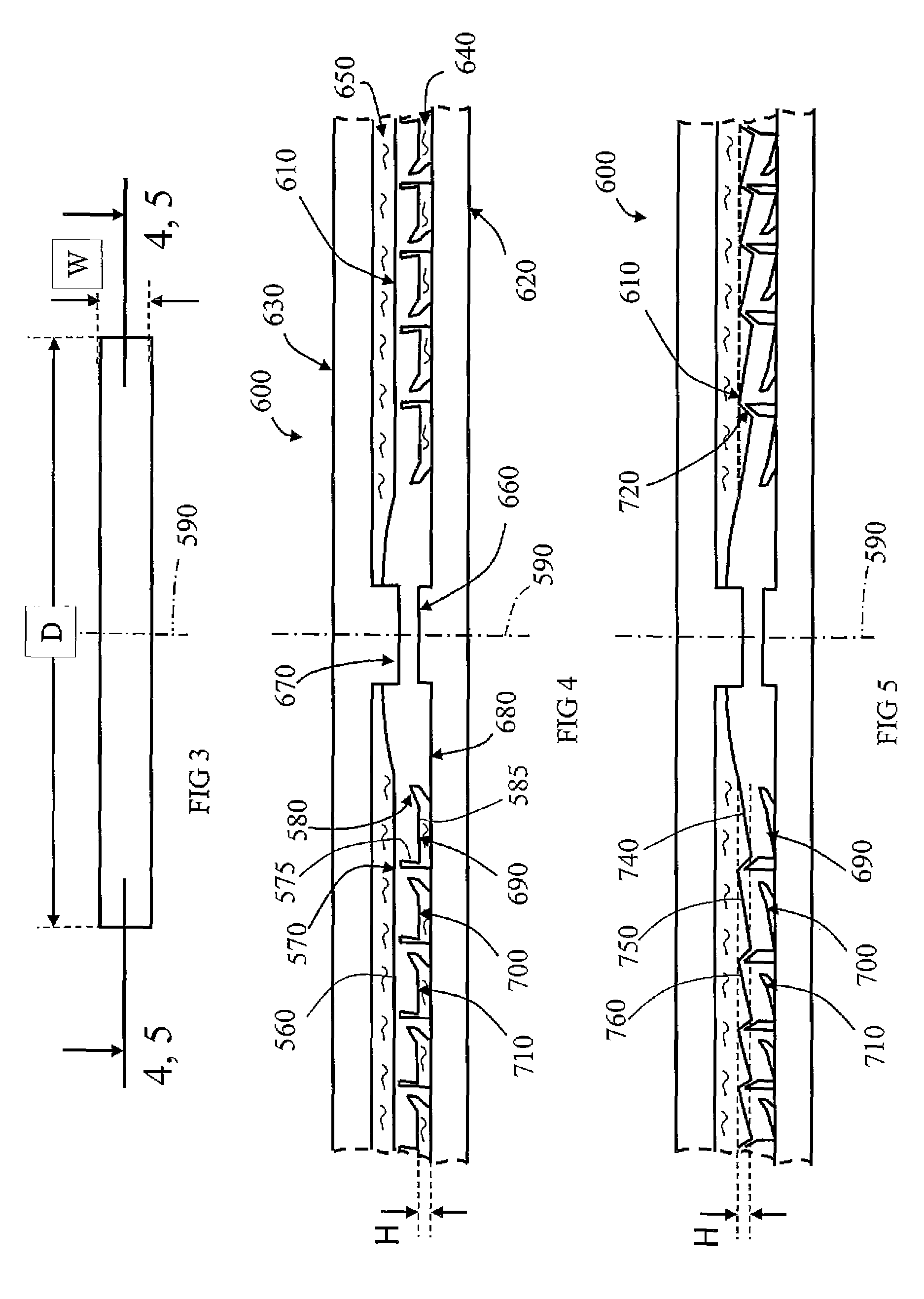
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS6855164B2Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensOptical axisRefractive index
This intraocular lens includes an optic body having anterior and posterior walls, a chamber, and optically transmissive primary and secondary fluids, and method for making and using the same. The secondary fluid is substantially immiscible with the primary fluid and has a different density and a different refractive index than the primary fluid. The primary fluid is present in a sufficient amount that orienting optical body optical axis horizontally for far vision positions the optical axis through the primary fluid, thereby immersing the anterior and posterior optical centers in the primary fluid. The secondary fluid is contained in the optic body in a sufficient amount that orienting the optical axis at a range of effective downward angles relative to the horizontal for near vision positions the optical axis to extend through the primary fluid and the secondary fluid, thus changing the focus of the intraocular lens.
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling peripheral image position for reducing progression of myopia
ActiveUS7665842B2Improve visual effectsGood and useful visionSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryRefractive errorCentral vision
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Accommodating Intraocular Lens (Aiol), and Aiol Assemblies Including Same
InactiveUS20070244561A1Natural positive diopter strengthReduced strengthIntraocular lensCiliary epitheliumEngineering
An accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL) including a biasing mechanism for elastically deforming an elastically deformable shape memory disk-like optical element for affording the AIOL a natural positive diopter strength for near vision. The AIOL is intended to be implanted in a human eye such that relaxation of its ciliary body causes its capsular diaphragm to apply an accommodation force for overcoming the biasing mechanism to reduce the AIOL's natural positive diopter strength for distance vision.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Switchable diffractive accommodating lens
InactiveUS20130035760A1Improve image contrastReduces halo and glareSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensPressure differenceRefractive index matching
A lens in accordance with the present invention includes an accommodating cell having two chambers with at least one chamber filled with optical fluid with the refractive index matching the refractive index of the accommodating element separating them. The accommodating element has a diffractive surface with surface relief structure that maintains its period but changes its height due a pressure difference between the chambers to redirect most of light that passes through the lens between different foci of far and near vision. The invention also includes a sensor cell that directly interacts with the ciliary muscle contraction and relaxation to create changes in pressure between the accommodating cell chambers that results in changing surface relief structure height and the lens accommodation.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
Accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL), and AIOL assemblies including same
InactiveUS7815678B2Natural positive diopter strengthFacilitate accommodationIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCiliary body
An accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL) including a biasing mechanism for elastically deforming an elastically deformable shape memory disk-like optical element for affording the AIOL a natural positive diopter strength for near vision. The AIOL is intended to be implanted in a human eye such that relaxation of its ciliary body causes its capsular diaphragm to apply an accommodation force for overcoming the biasing mechanism to reduce the AIOL's natural positive diopter strength for distance vision.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Multifocal ophthalmic lenses
The invention provides multifocal lenses for correction of presbyopia. Each of the lenses of the invention provide both distance and near vision correction by providing both a first multifocal region, a monofocal region, and a second multifocal region within the same lens.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Residual accommodation threshold for correction of presbyopia and other presbyopia correction using patient data
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats presbyopia in a particular patient. The combination of distance vision and near vision in a patient can be improved, often based on input patient parameters such as pupil size, residual accommodation, and power need. Iterative optimization may generate a customized corrective optical shape for the patient. Threshold residual accommodation is established for presbyopia treatment.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. An optical element, such as a substrate or coating, may be integrated along one or both surfaces of the lens to provide the lens with smooth outer surface(s).
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20050071002A1Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensLens crystallineOptical axis
An intraocular lens is provided that includes an optic body having anterior and posterior walls, a chamber, and optically transmissive primary and secondary fluids, and method for making and using the same. The secondary fluid is substantially immiscible with the primary fluid and has a different density and a different refractive index than the primary fluid. The primary fluid is present in a sufficient amount that orienting optical body optical axis horizontally for far vision positions the optical axis through the primary fluid, thereby immersing the anterior and posterior optical centers in the primary fluid. The secondary fluid is contained in the optic body in a sufficient amount that orienting the optical axis over a range of effective downward angles relative to the horizontal for near vision positions the optical axis to extend through the primary fluid and the secondary fluid, thus changing the focus of the intraocular lens.
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
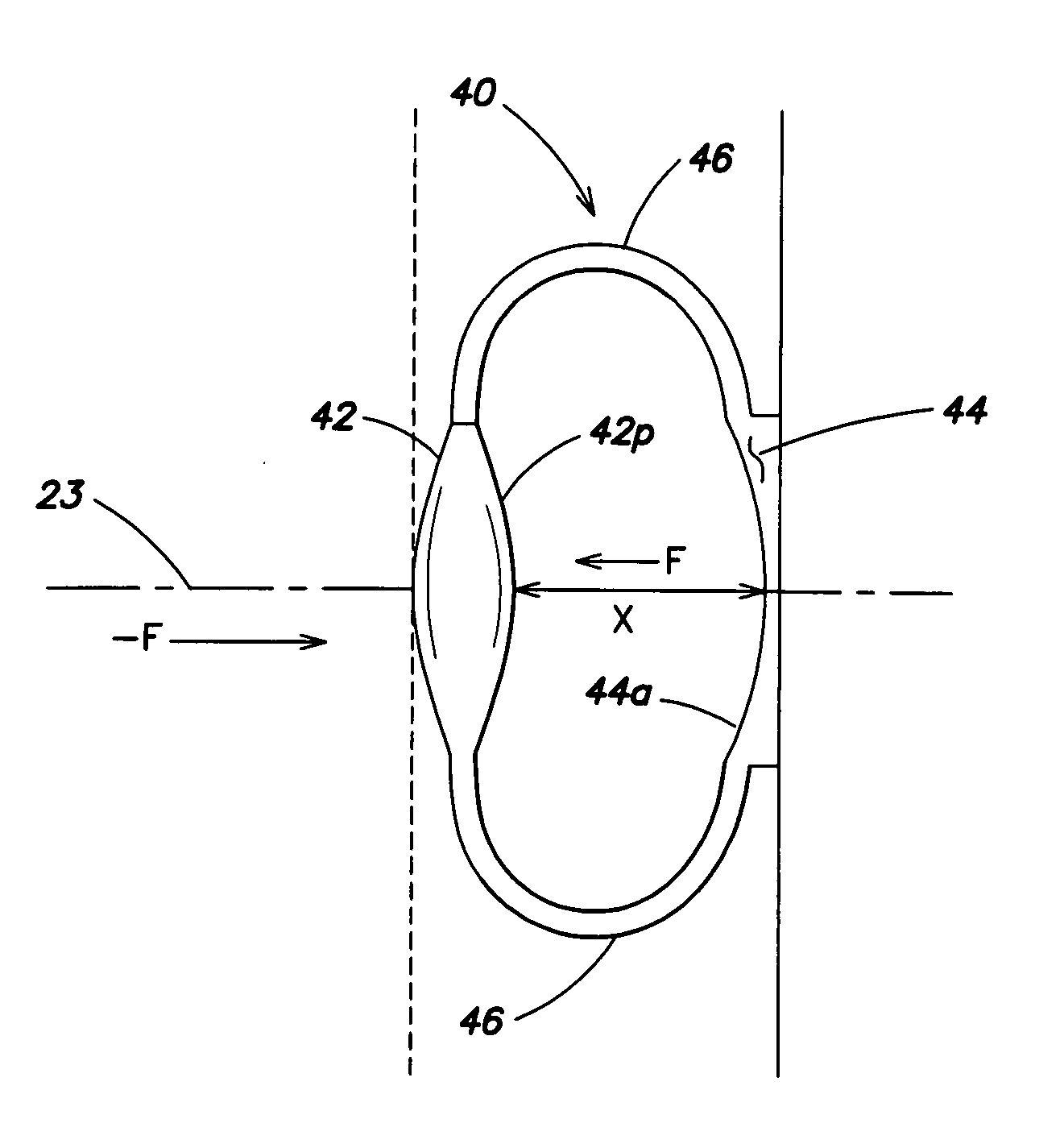
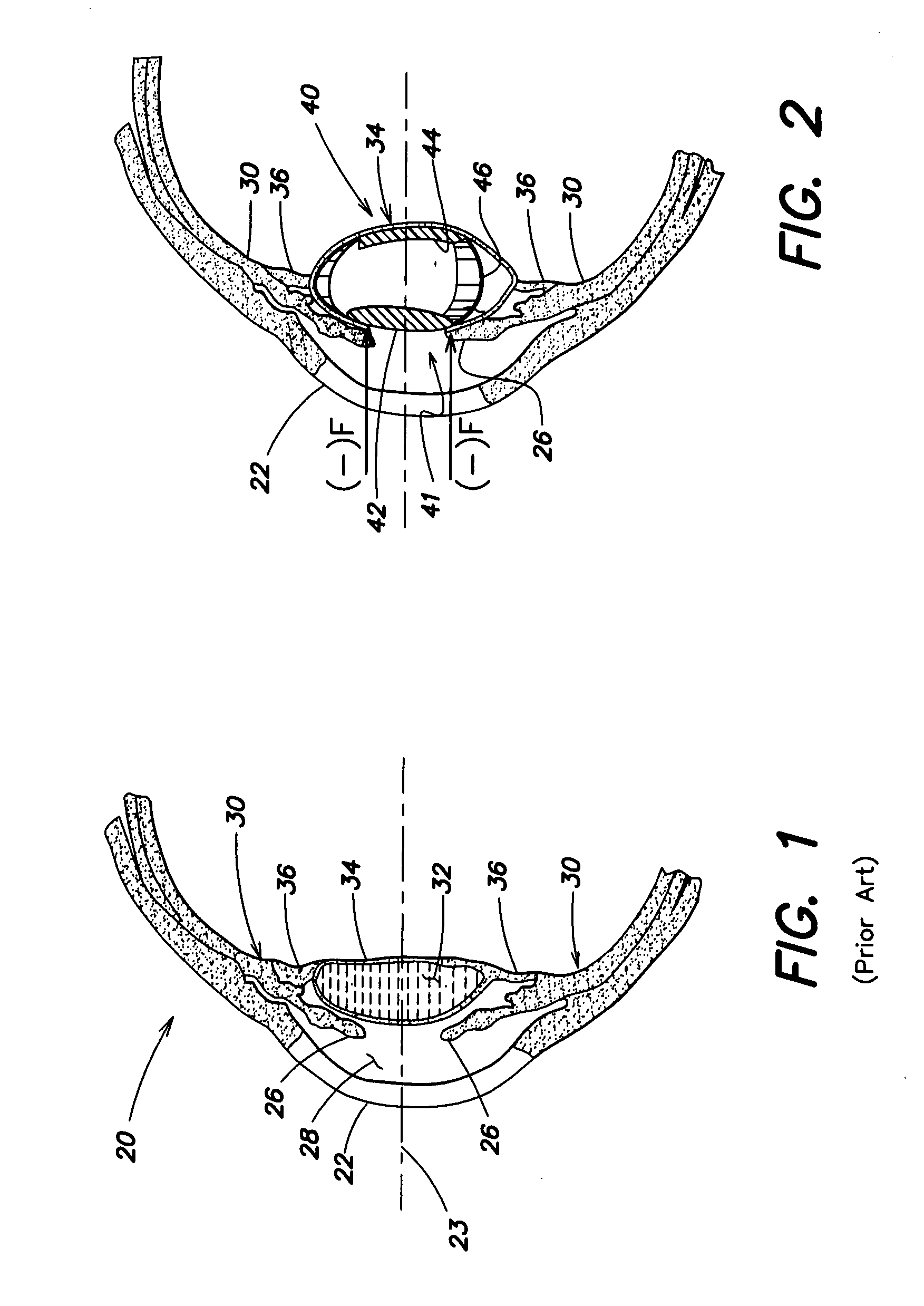
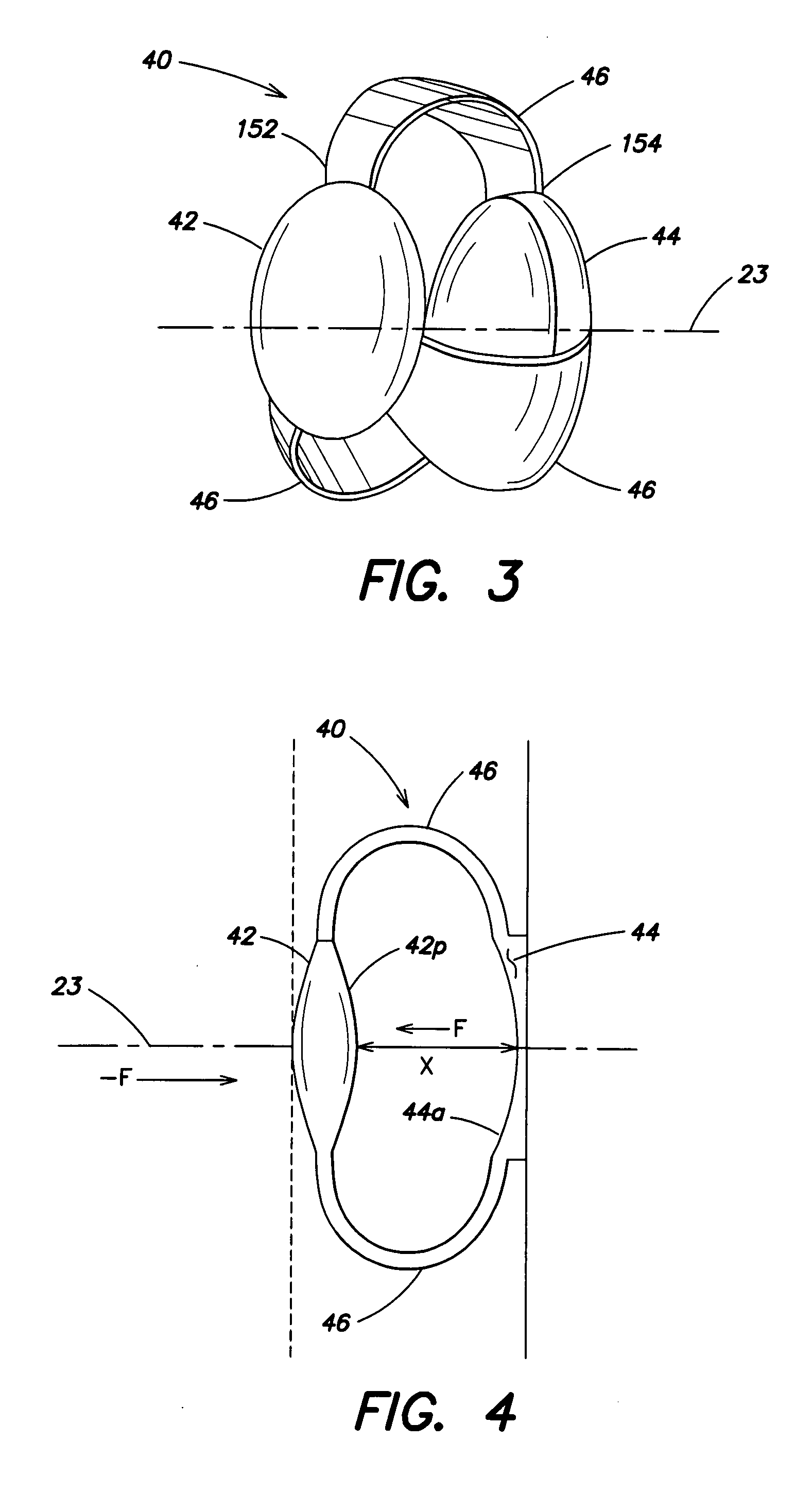
Accommodative Intraocular Lens Having Defined Axial Compression Characteristics
A multi-optic accommodating intraocular lens (A-IOL) for implantation in a capsular bag of an eye having an optical axis, includes a posterior component, an anterior component that is translatable relative to the posterior component along an optical axis of the A-IOL, and a biasing element that joins at least a portion of the anterior component and at least a portion of the posterior component. The A-IOL is quantitatively characterized by an axial compression characteristic such as a spring constant or an axial restoring force. The axial compression characteristic is capable of keeping the components sufficiently vaulted apart for enabling near vision yet weak enough to allow the eye's accommodative mechanism to pull the optics close together for distance vision.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20030093149A1Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensOptical axisRefractive index
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Residual accommodation threshold for correction of presbyopia and other presbyopia correction using patient data
InactiveUS20050270491A1Improved near visionImproved distance visionLaser surgeryEye diagnosticsPatient dataOptical surface
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats presbyopia in a particular patient. The combination of distance vision and near vision in a patient can be improved, often based on input patient parameters such as pupil size, residual accommodation, and power need. Iterative optimization may generate a customized corrective optical shape for the patient. Threshold residual accommodation is established for presbyopia treatment.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
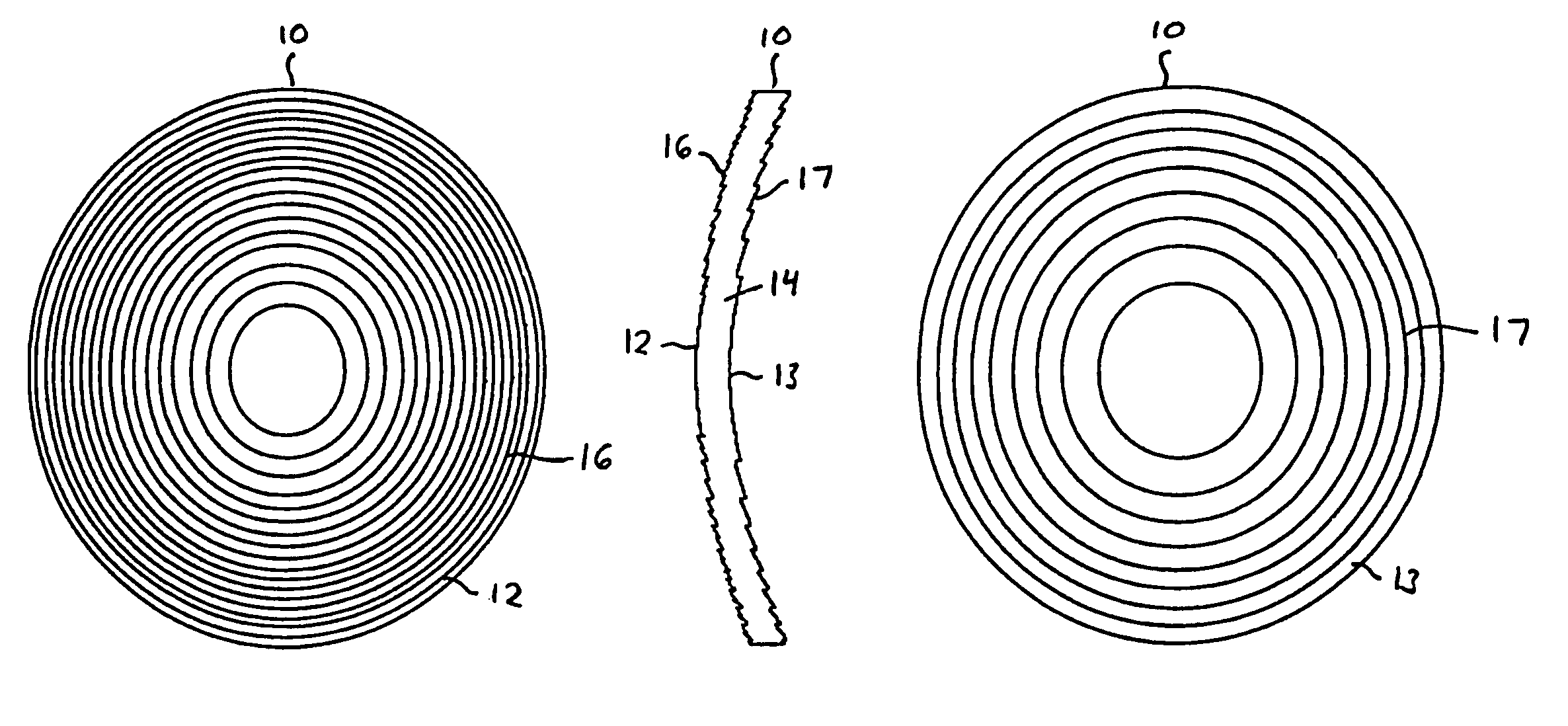
Progressive lens elements and methods for designing and using same
InactiveUS6074062ALower surfaceImprove performanceSpectales/gogglesOptical partsMultifocal lensesAstigmatism
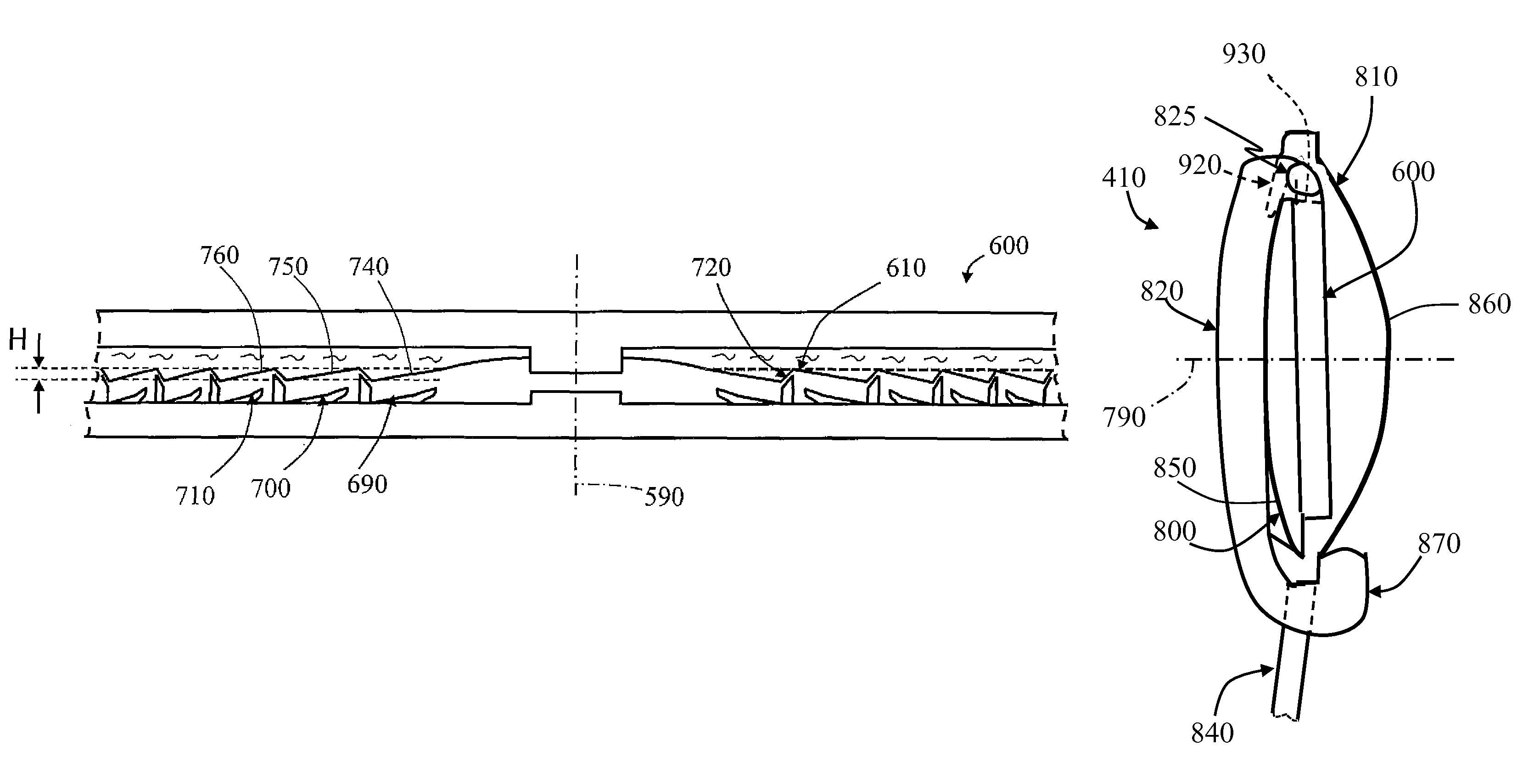
A series of progressive ophthalmic lens elements, each lens element including a lens surface having an upper viewing zone having a surface power to achieve a refracting power corresponding to distance vision; a lower viewing zone having a greater surface power than the upper viewing zone to achieve a refracting power corresponding to near vision; a corridor of relatively low surface astigmatism connecting the upper and lower zones, said corridor having a surface power varying from that of the upper viewing zone to that of the lower viewing zone; the progressive ophthalmic lens series including a first set of lens elements having a base curve(s) suitable for use in providing a range of distance prescriptions for a first category of patient; and a second set of lens elements having a base curve(s) suitable for use in providing a range of distance prescriptions for a second category of patient; each lens element within a set differing in prescribed addition power and including a progressive design, in at least one of the upper and lower viewing zones, depending upon the addition power of the lens element; the lens elements in the first set differing substantively in progressive design from the corresponding lens elements in the second set due to the differences in base curve(s).
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
Multifocal contact lens
A multifocal contact lens includes a first, central zone for distance and intermediate vision and a second, outer zone for near vision. The first and second zones are conic sections joined tangentially at their junction. The power in the distance subregion is relatively constant, while the power throughout the intermediate subregion is a monotonically increasing function which reaches the near power correction at the junction. The second zone includes an aspheric surface having an eccentricity calculated to minimize or eliminate spherical aberration. The slope or power gradient in the intermediate subregion is calculated to provide a smooth transition from the lower power distance subregion to the junction between the intermediate subregion and the near power correction zone.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Ophthalmic lens element
ActiveUS7992997B2Effective retardingEffective arrestingSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentOptical correctionHigh surface
An ophthalmic lens element is disclosed. The, ophthalmic lens element includes a central region of low surface astigmatism and a peripheral region. The central region includes an upper viewing zone for providing a first power suitable for a wearer's distance vision tasks. The peripheral region has a positive power relative to the first power, and surrounds the central region. The peripheral region provides an optical correction for retarding or arresting myopia for a wearer and includes one or more regions of relatively higher surface astigmatism, a lower or near viewing zone of low surface astigmatism, and a corridor of low surface astigmatism having a surface power varying from that of the upper viewing zone to that of the lower viewing zone. The lower viewing zone is for a wearer's near vision tasks.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
Switchable diffractive accommodating lens
InactiveUS8608800B2Stable maintenanceImprove image contrastSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCamera lensPressure difference
A lens in accordance with the present invention includes an accommodating cell having two chambers with at least one chamber filled with optical fluid with the refractive index matching the refractive index of the accommodating element separating them. The accommodating element has a diffractive surface with surface relief structure that maintains its period but changes its height due a pressure difference between the chambers to redirect most of light that passes through the lens between different foci of far and near vision. The invention also includes a sensor cell that directly interacts with the ciliary muscle contraction and relaxation to create changes in pressure between the accommodating cell chambers that results in changing surface relief structure height and the lens accommodation.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
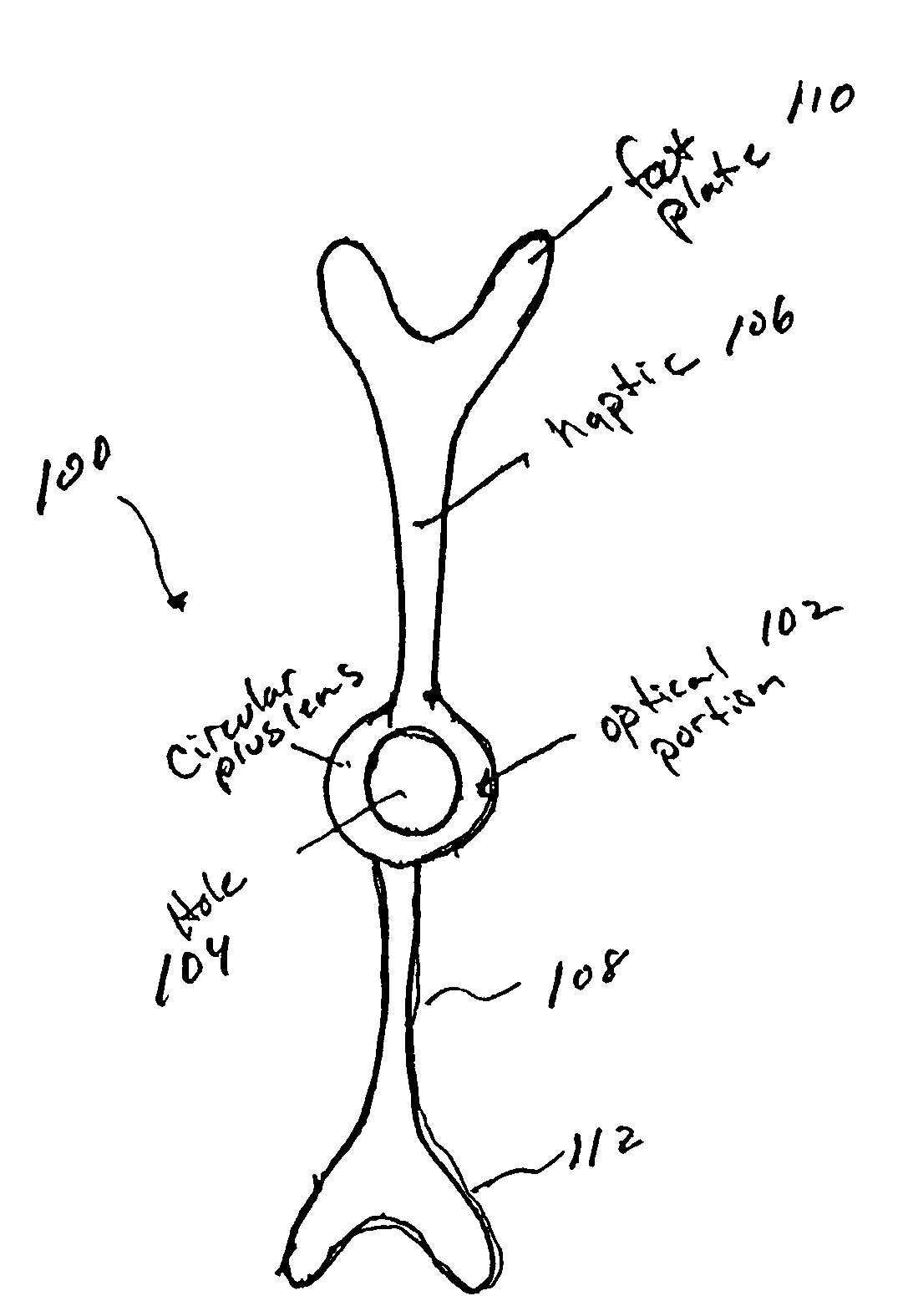
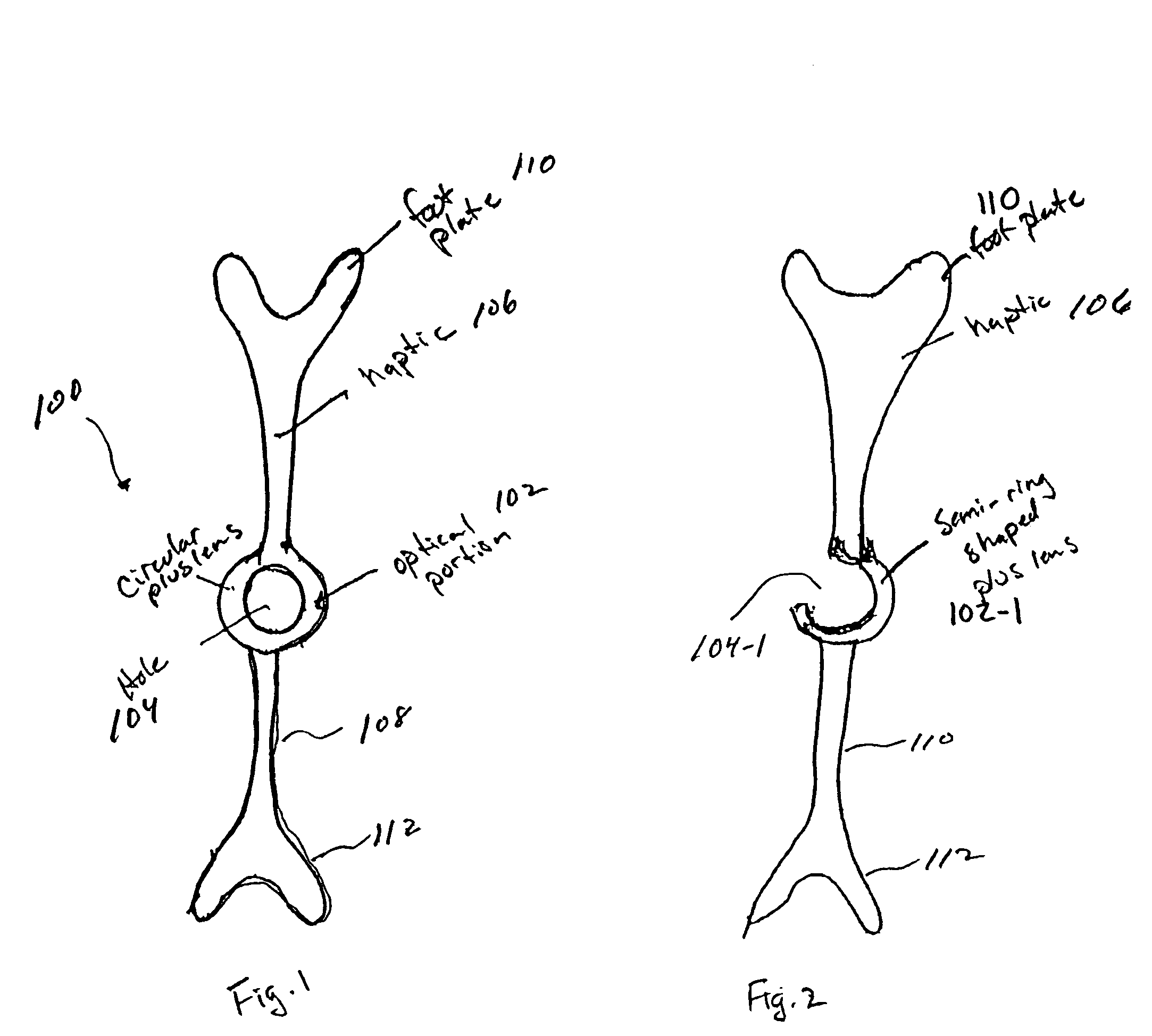
Intraocular lens for correcting presbyopia
An intraocular lens for modifying the refractive abilities of a natural lens or an existing artificial lens in an eye to correct for vision disorders such as presbyopia, myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism. Specifically, the lens system can be configured so that it does not effect far vision, while effecting near vision using a plus lens to correct for presbyopia. The lens system includes a lens portion and fastening members, with the lens portion being movably secured to at least one of the fastening members so that the position of the lens portion can be modified with respect to the optical axis, and the overall length of the lens system can be increased or decreased.
Owner:MINU
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. Such one or more first regions may represent one or more annular rings, or other portion of the lens, and the second region may occupy the portion of the lens aperture outside the first region. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. When multiple optical elements are used, the multiorder diffractive structures may be located along an interior surface of the lens. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. The lens may represent a contact lens, a spectacle lens, or the optic portion of an intraocular implant (IOL). Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for performance for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Presbyopic treatment system
A method and system for treating Presbyopia and pre-Presbyopia are provided that do not compromise the wearer's intermediate or distance vision. The system is a lens and a lens series, wherein the power profiles of the lenses are tailored to provide an amount of positive ADD power in the near vision zone that is slightly less than that which is normally required for near vision accommodation, while also providing an amount of negative spherical aberration in the peripheral optical zone. The dynamic ocular factors of the wearer's eye work in conjunction with the positive ADD power provided by the central optical zone and with the effective ADD gained from the negative spherical aberration provided by the peripheral optical zone to induce a minimally discernible amount of blur that is tuned to maximize the wearer's depth of focus.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Free-form progressive multifocal refractive lens for cataract and refractive surgery
InactiveUS20140135919A1Improve acuityIncrease distanceIntraocular lensOptical partsPresent dayKeratorefractive surgery
A new type of multi-focal lens that has a free-form progressive multifocal front surface consisting of a 16th order polynomial superimposed on a standard conic base surface is described. The center region of the lens is optimized for distance vision, while simultaneously optimizing the rest of the lens for near vision. The resulting free-form even asphere polynomial surface is smooth, unlike present day diffractive multifocal designs. Additionally, this lens design is suitable for both refractive and cataract surgeries.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com