Patents
Literature
122 results about "Far-sightedness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
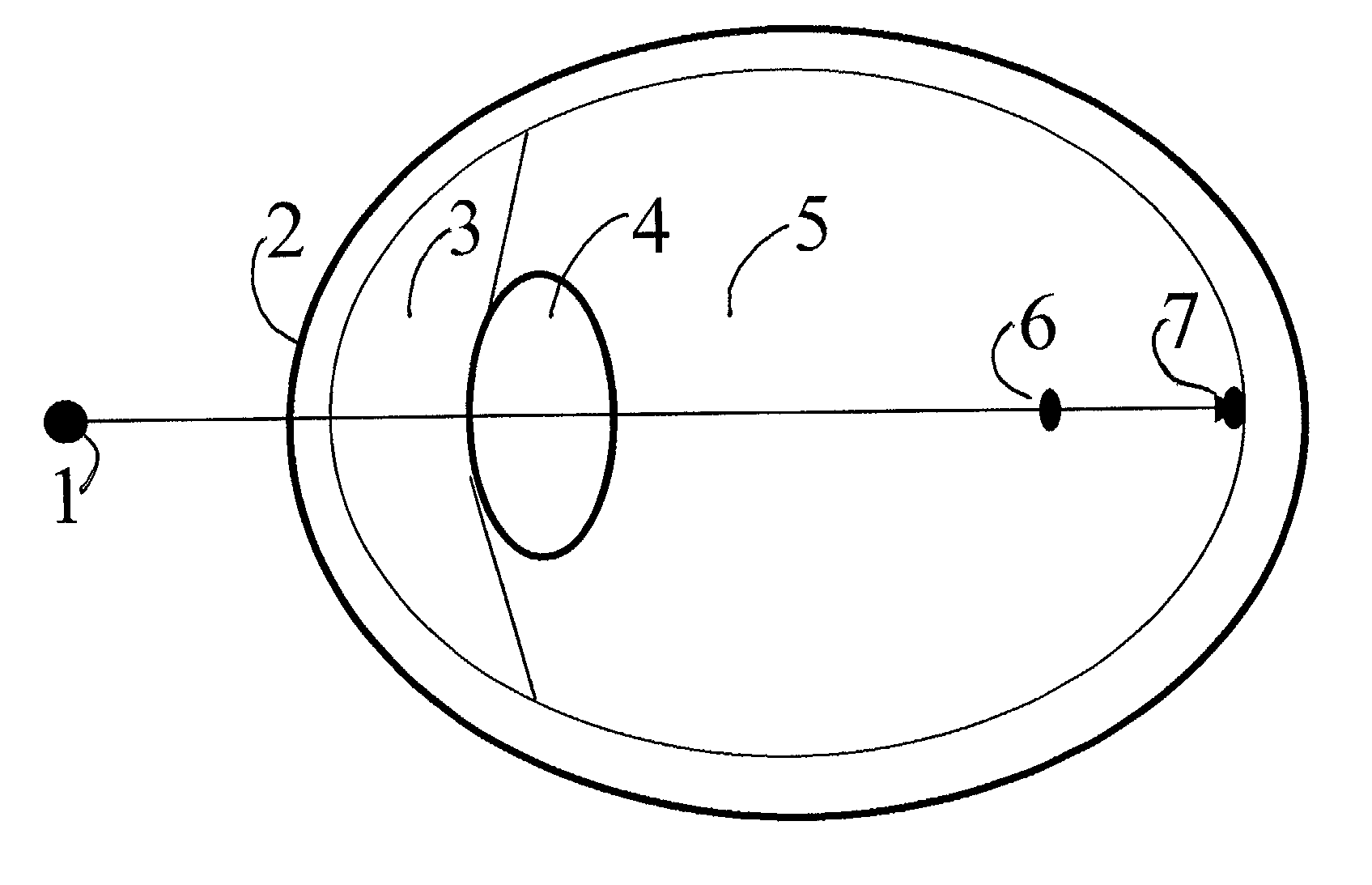
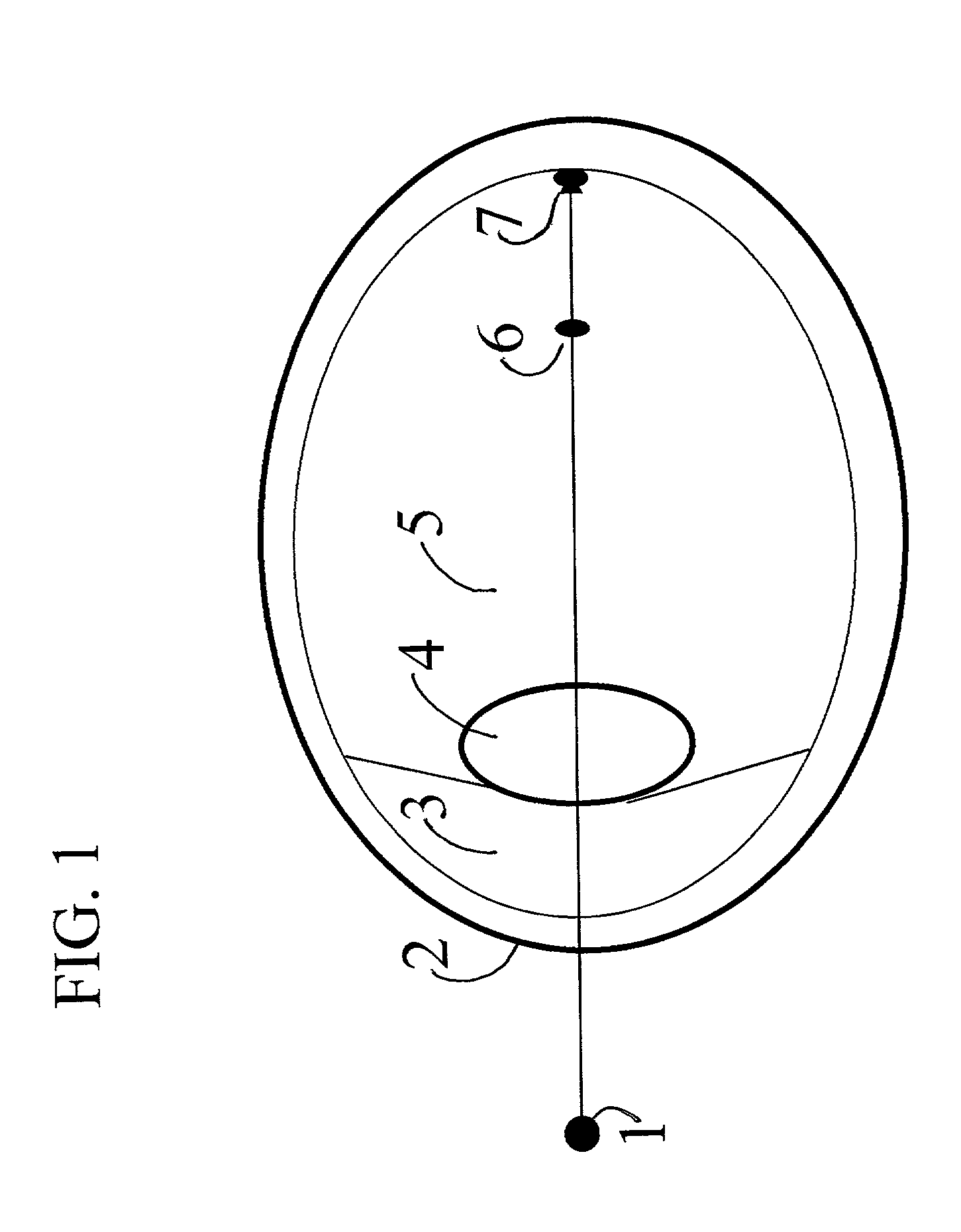
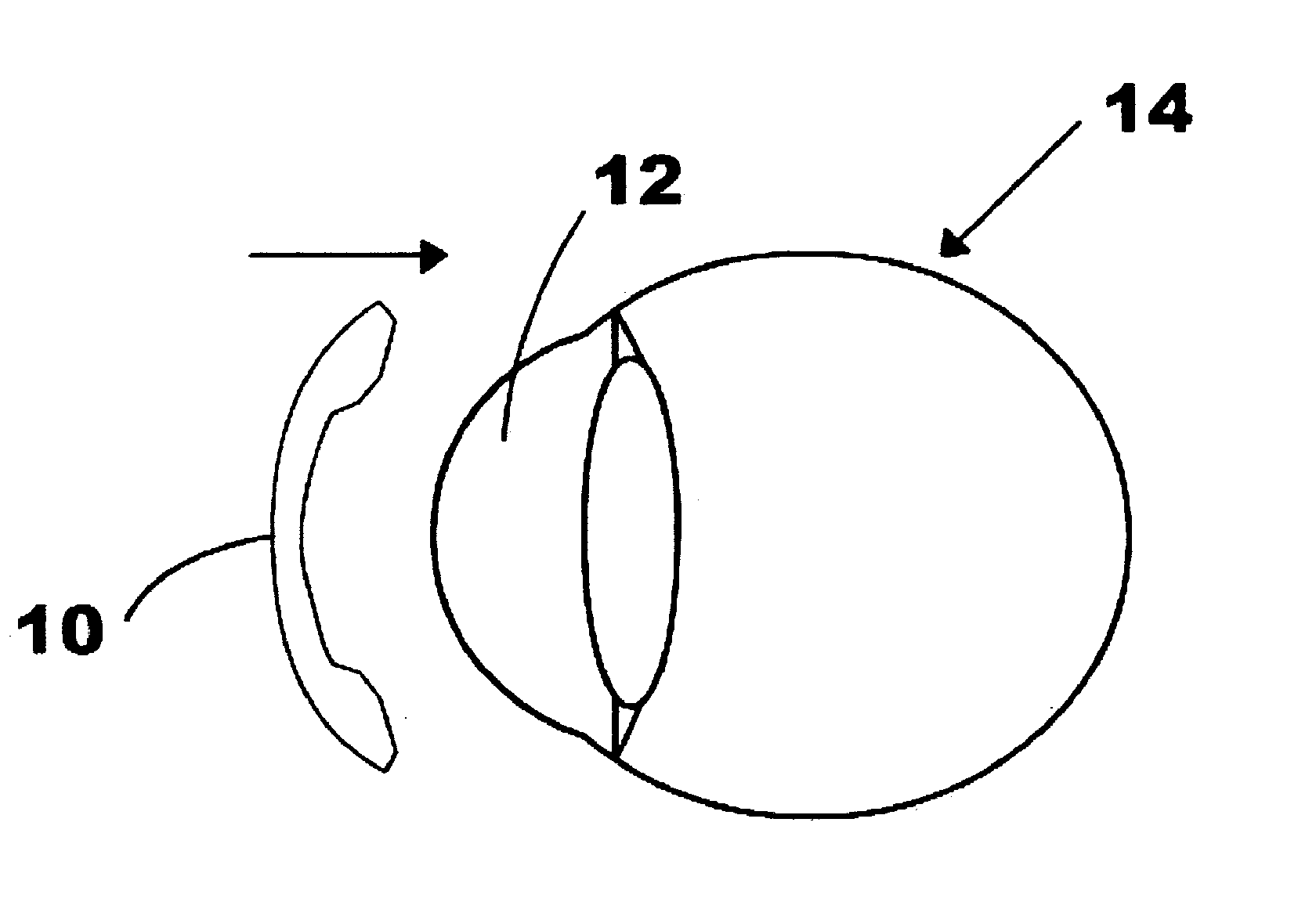
Far-sightedness, also known as hyperopia, is a condition of the eye in which light is focused behind, instead of on, the retina. This results in close objects appearing blurry, while far objects may appear normal. As the condition worsens, objects at all distances may be blurry.
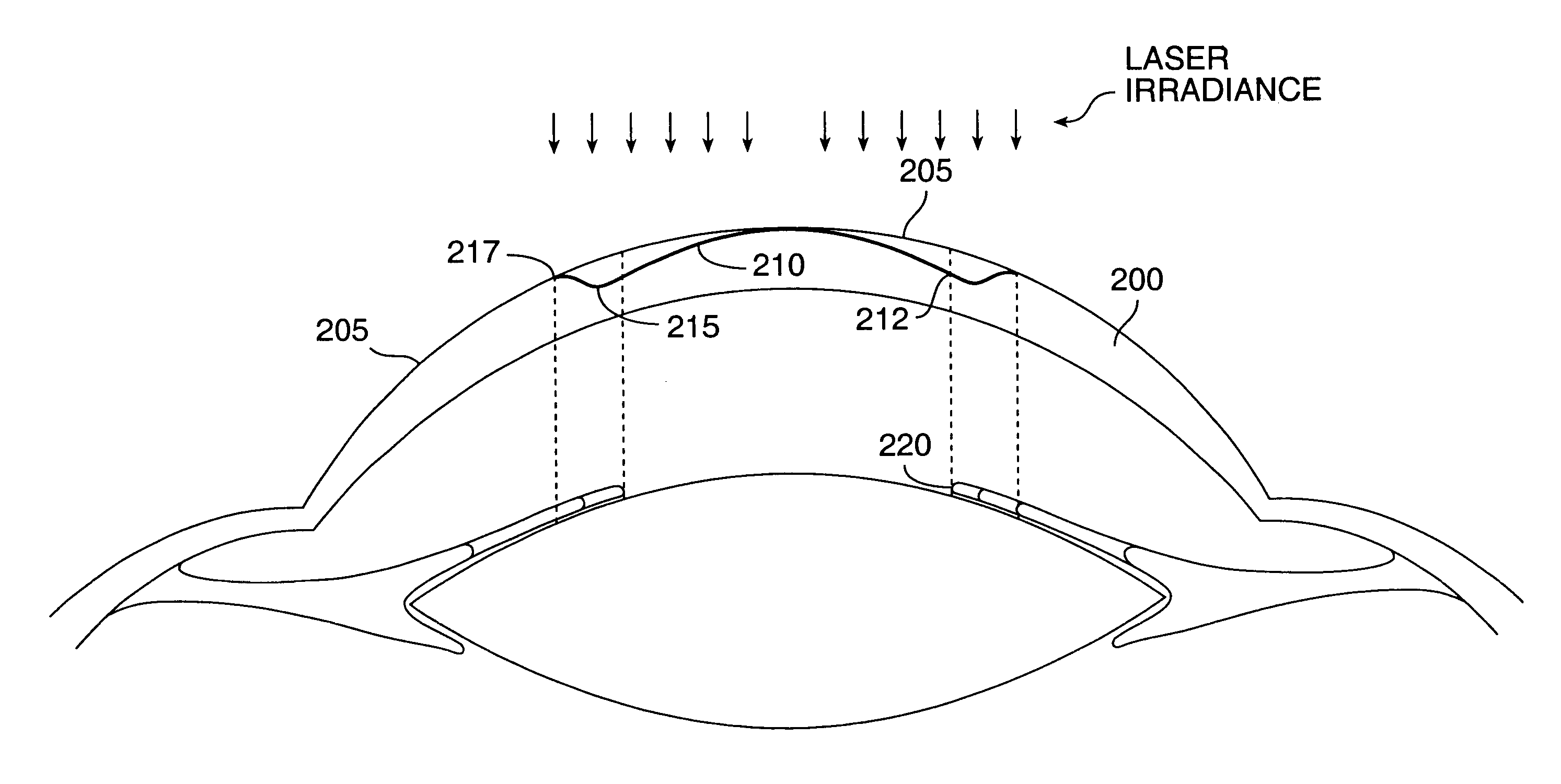
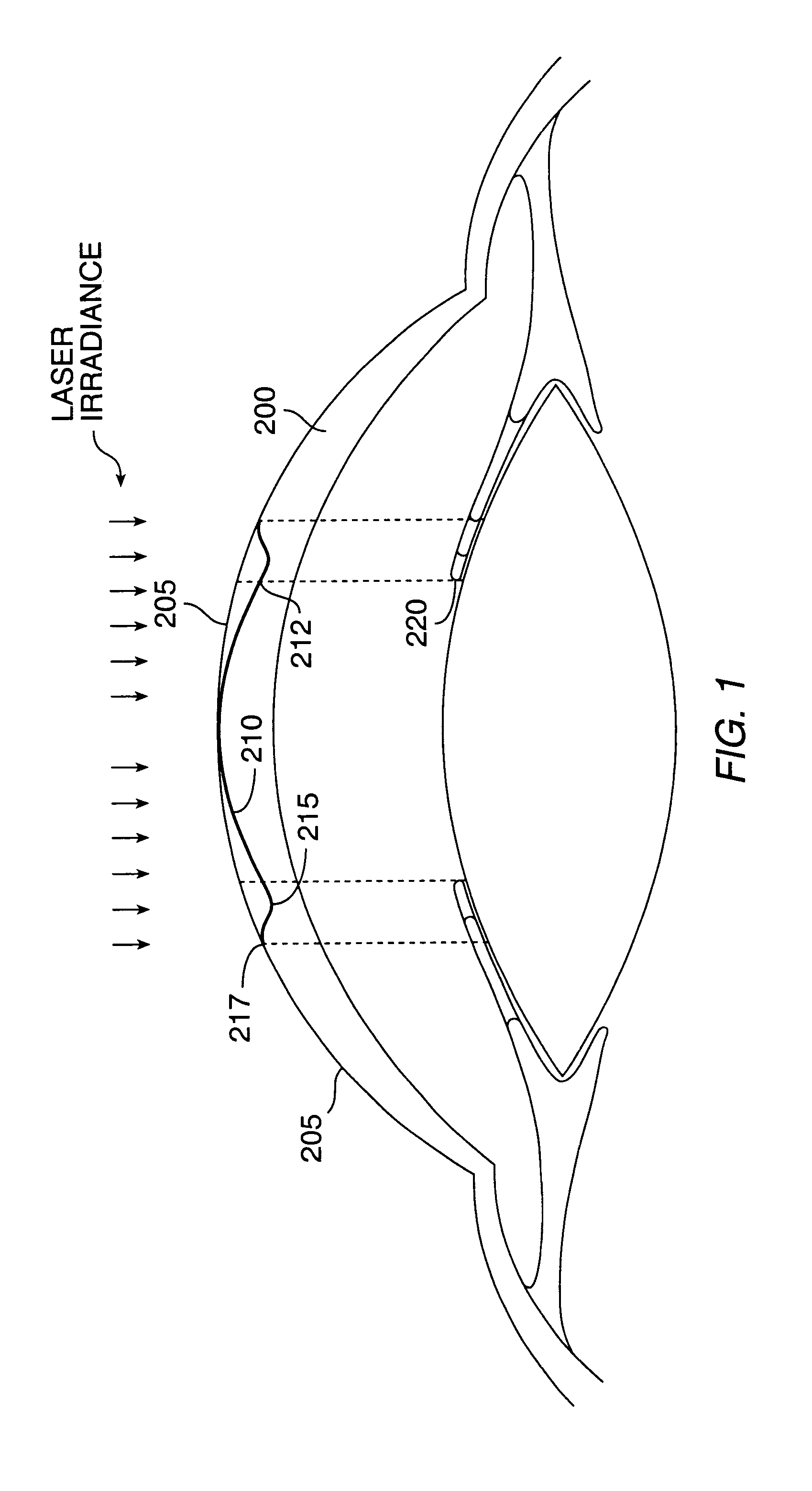
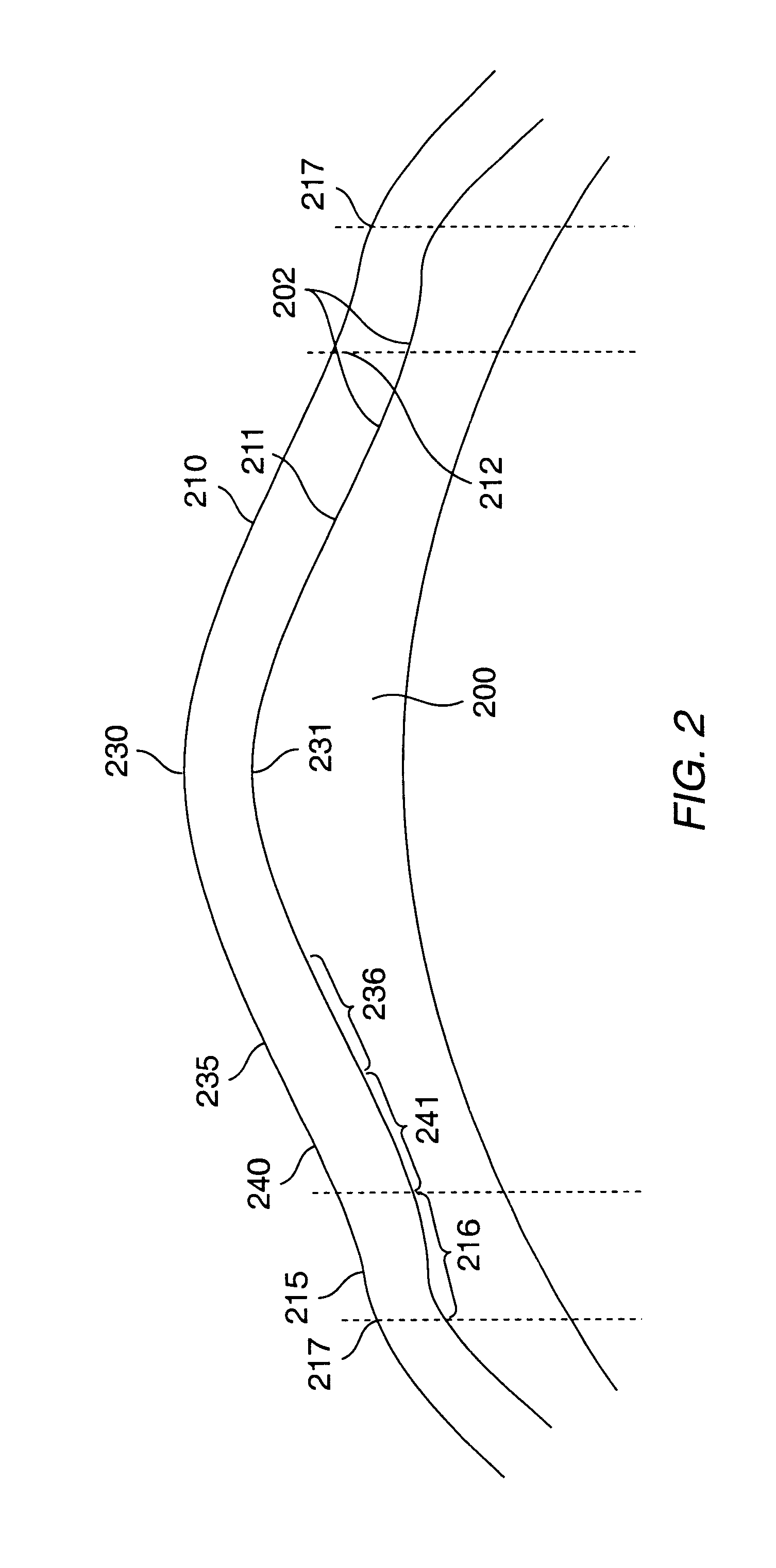
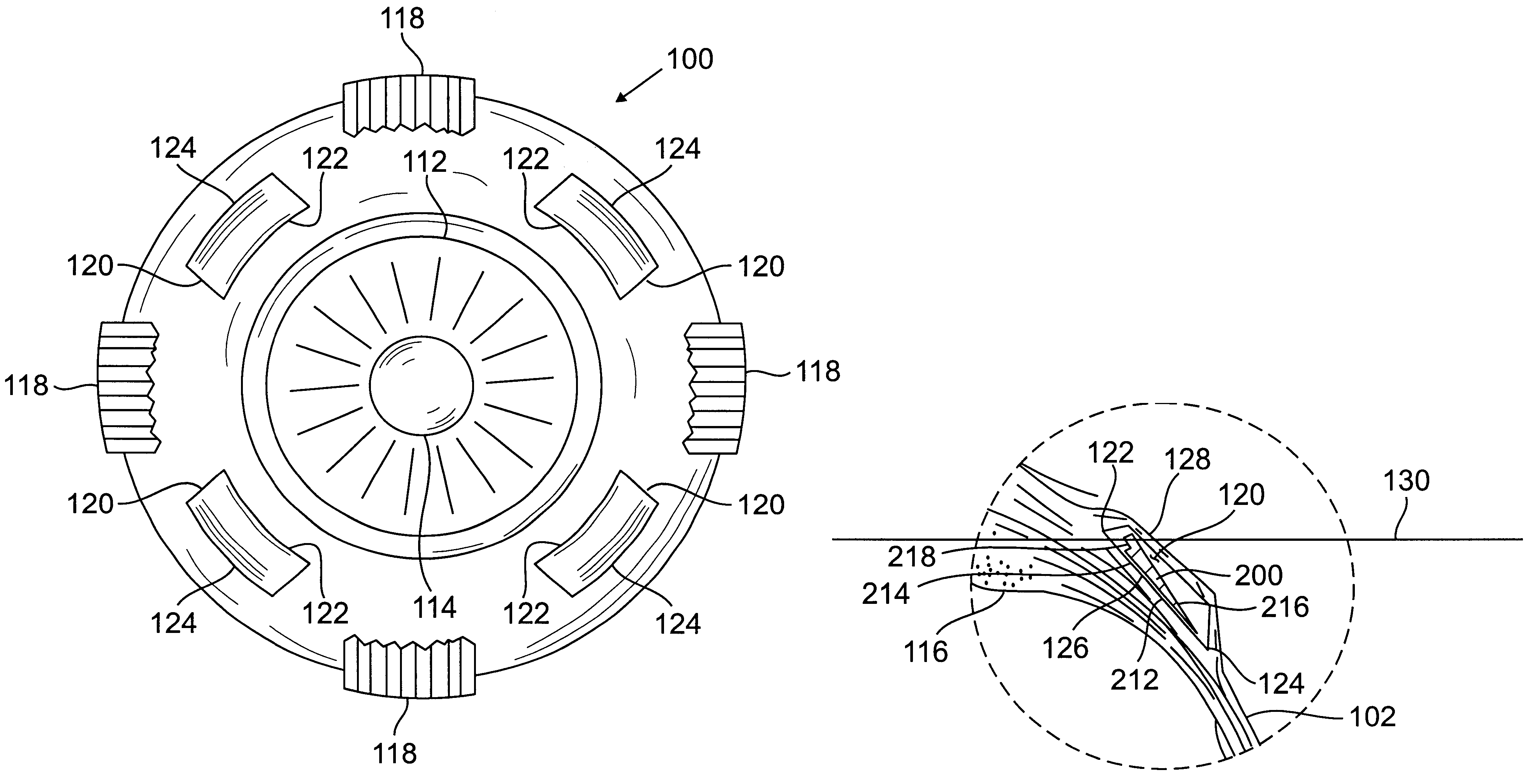
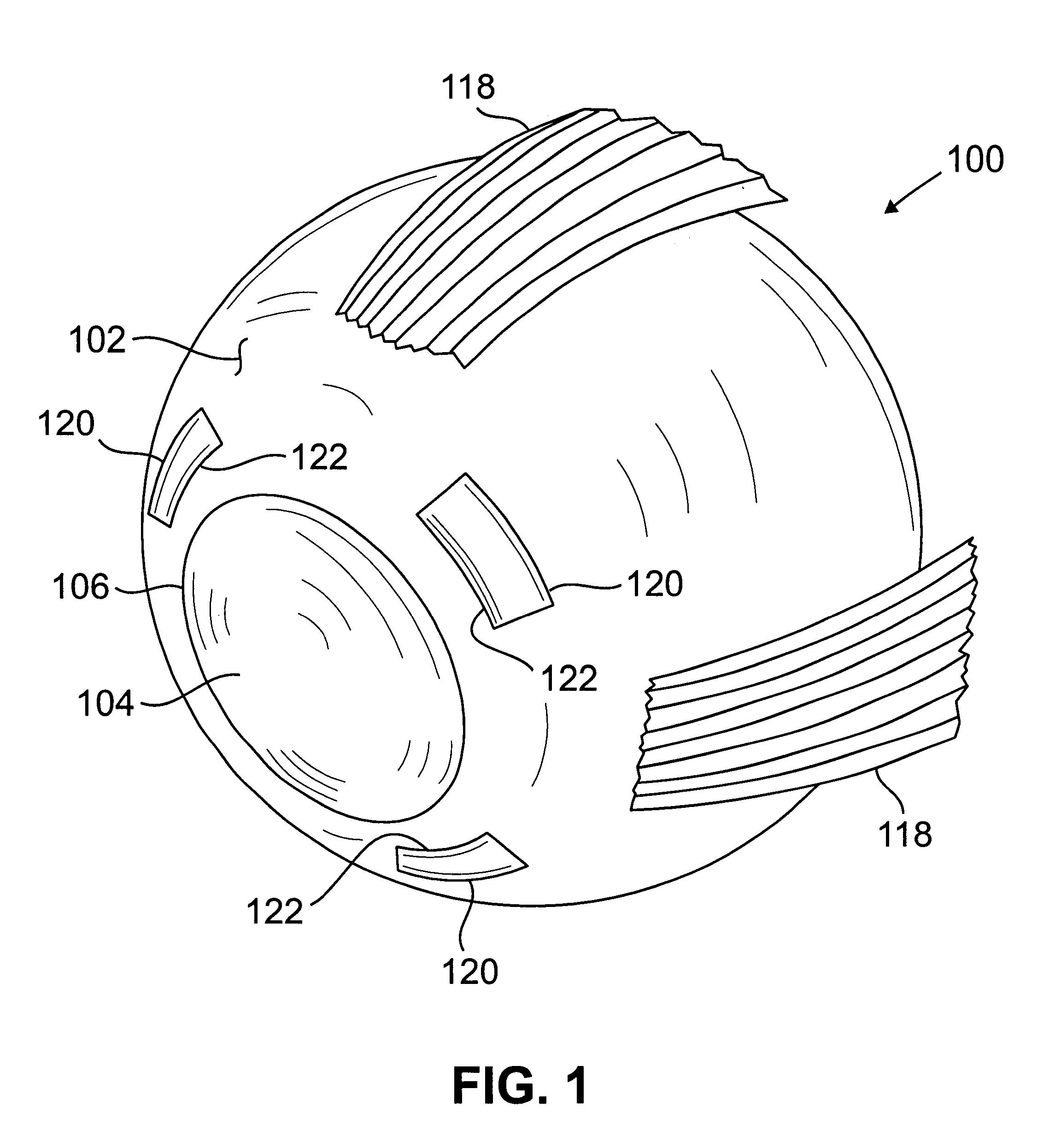
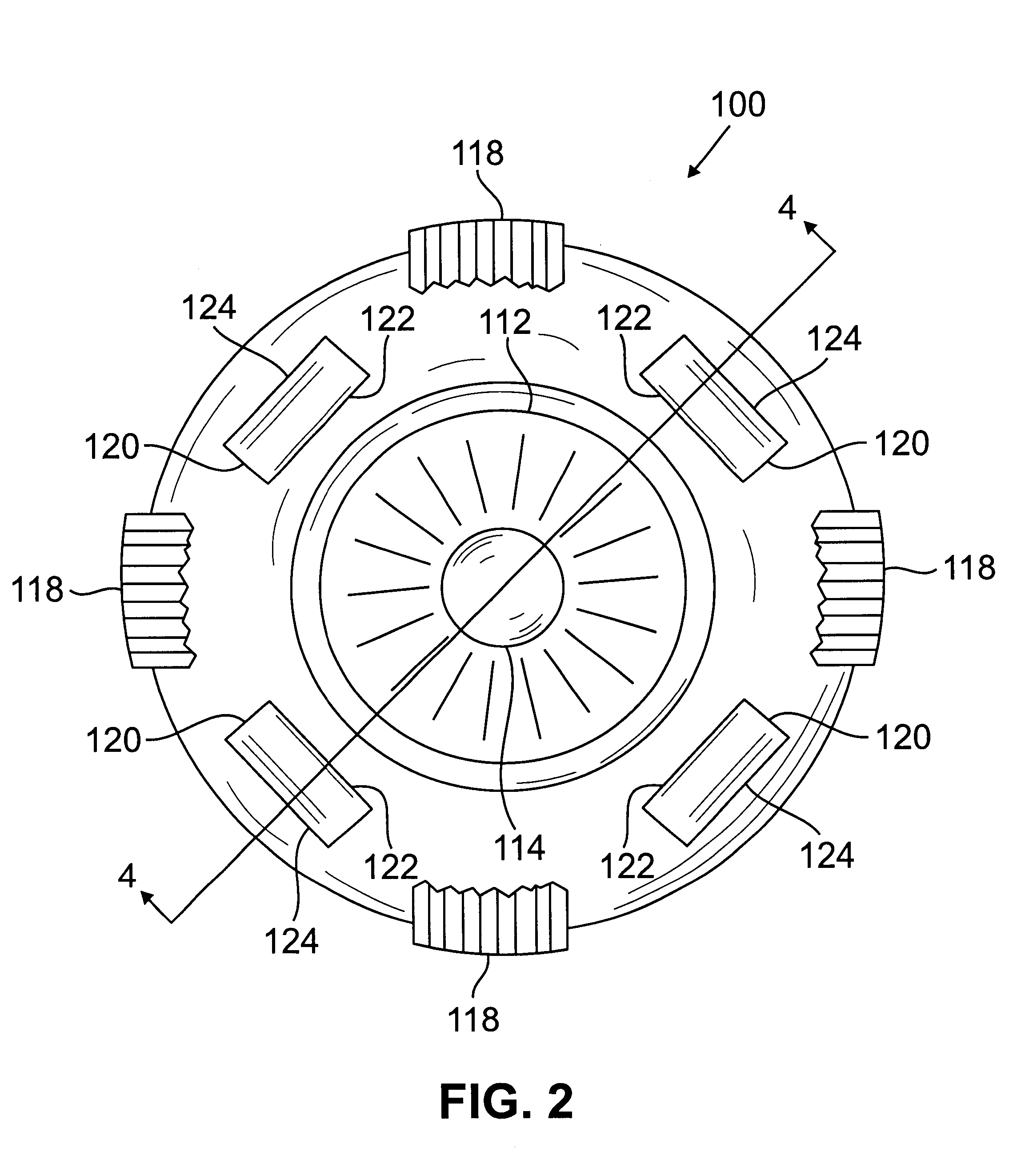
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Scleral prosthesis for treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders
InactiveUS6280468B1Increase the effective working distanceIncrease the working distanceLaser surgeryEye implantsDiseaseOpen angle glaucoma
Presbyopia is treated by implanting within a plurality of elongated pockets formed in the tissue of the sclera of the eye transverse to a meridian of the eye, a prosthesis having an elongated body having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface to contact the base and flap of the scleral pocket. The first and second surfaces are spaced apart a distance so that the implanted prosthesis exerts an outward force on the flap of the scleral pocket which results in an outward traction on at least the anterior margin of the scleral pocket. The combined effect of the implanted prostheses is to exert a radially outward traction on the sclera in the region overlying the ciliary body which expands the sclera in the affected region together with the underlying ciliary body. The expansion of the ciliary body restores the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle in the presbyopic eye and thereby increases the amplitude of accommodation. Hyperopia, primary open angle glaucoma and / or ocular hypertension can be treated by increasing the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle according to the invention. A preferred embodiment of the scleral prosthesis has a major surface adapted to contact the base or flap of the pocket and an opposite surface or ridge spaced from the major surface.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Drug delivery implants for inhibition of optical defects
InactiveUS20100114309A1Avoid side effectsInhibition releaseSenses disorderEye surgeryFar-sightednessHomatropine
An implant for use with an eye comprises an implantable structure and a therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent is deliverable from the structure into the eye so as to therapeutically effect and / or stabilize a refractive property of the eye. In many embodiments, the refractive property of the eye may comprise at least one of myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism. The therapeutic agent can comprise a composition that therapeutically effects or stabilizes the refractive property of the eye. The therapeutic agent may comprise at least one of a mydriatic or a cycloplegic drug. For example, the therapeutic agent may include a cycloplegic that comprises at least one of atropine, cyclopentolate, succinylcholine, homatropine, scopolamine, or tropicamide. In many embodiments, a retention element can be attached to the structure to retain the structure along a natural tissue surface.
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
Pseudo-accommodative IOL having multiple diffractive patterns
ActiveUS20070182924A1Reduce spherical aberrationSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensFar-sightednessFocal area
Owner:ALCON INC
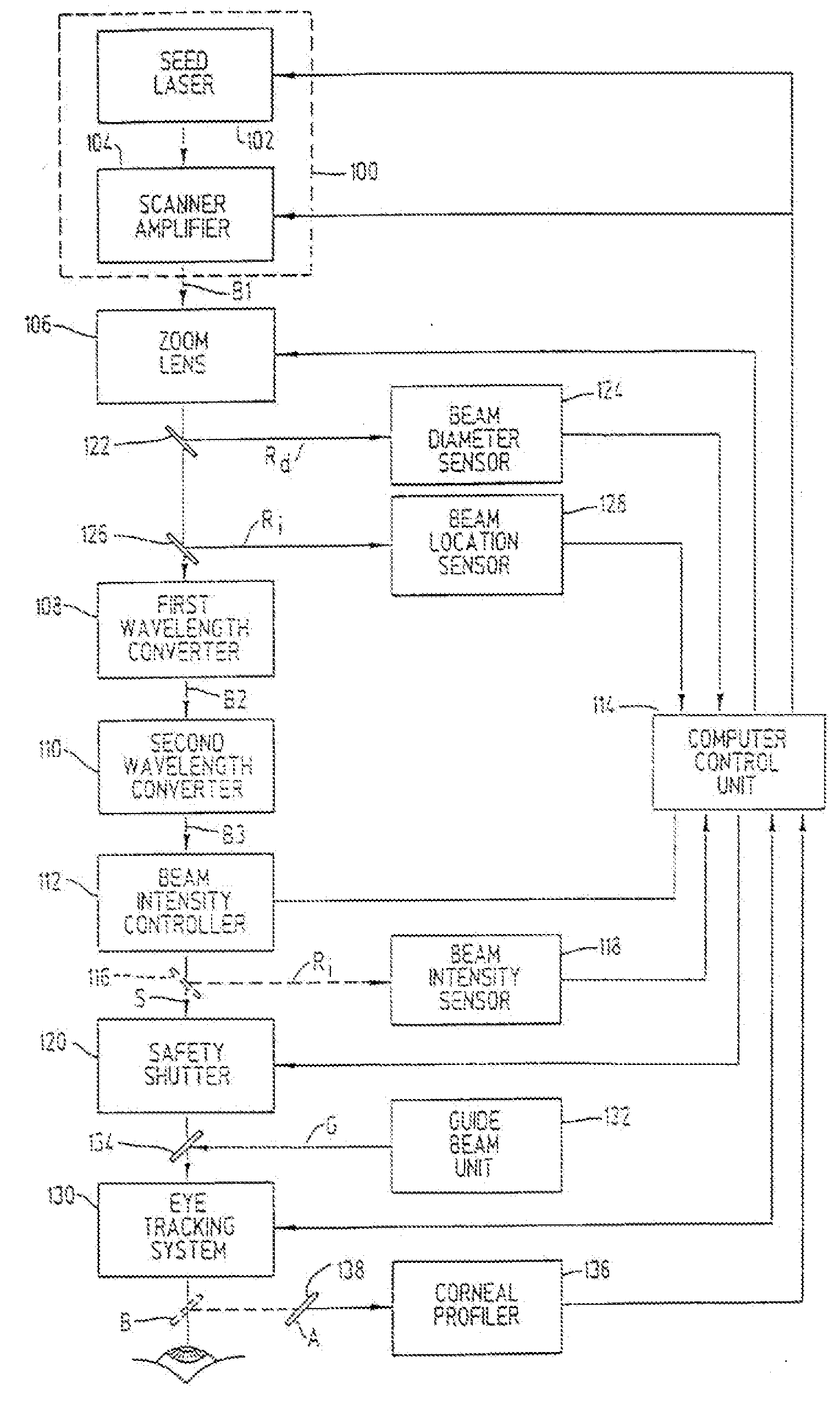
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
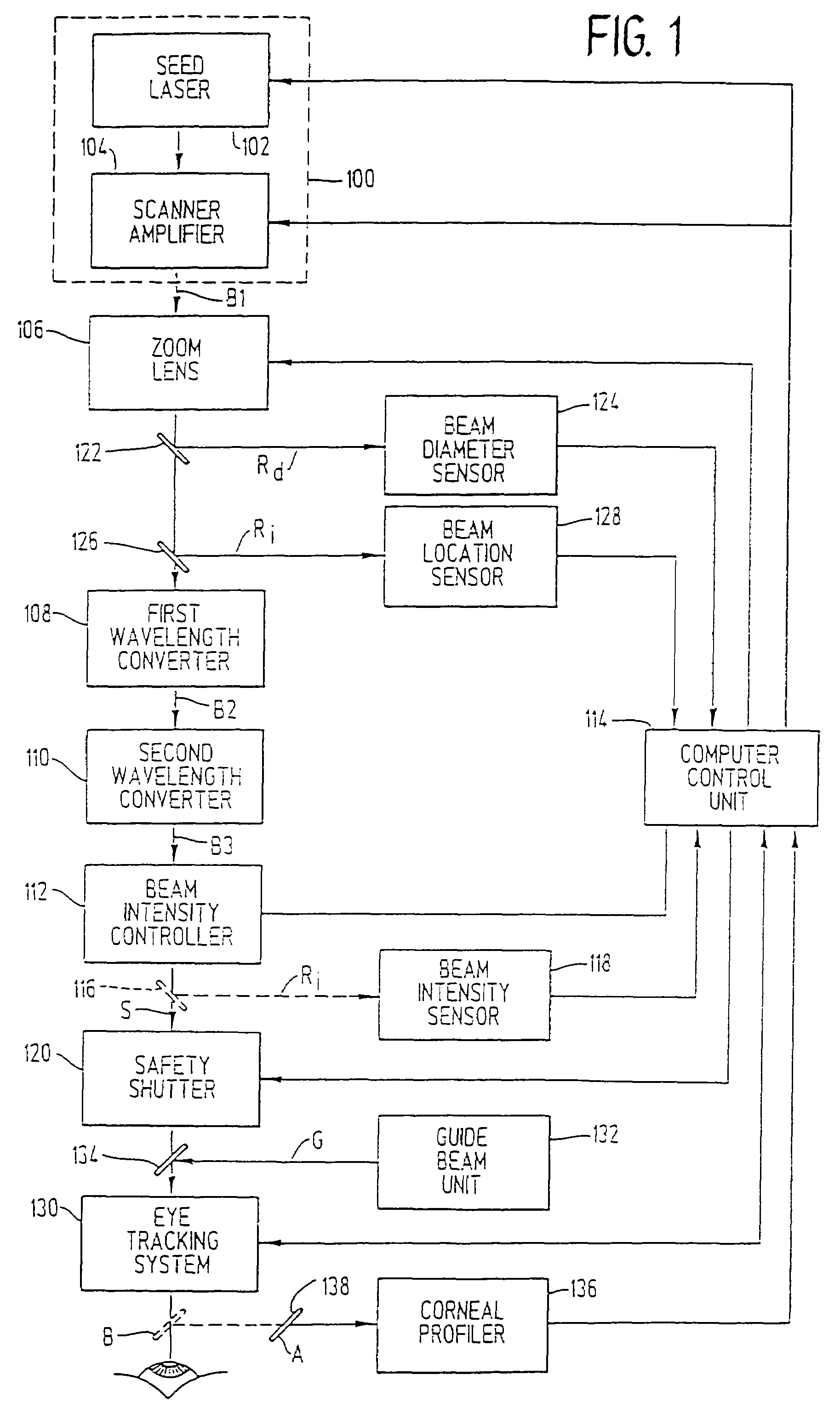
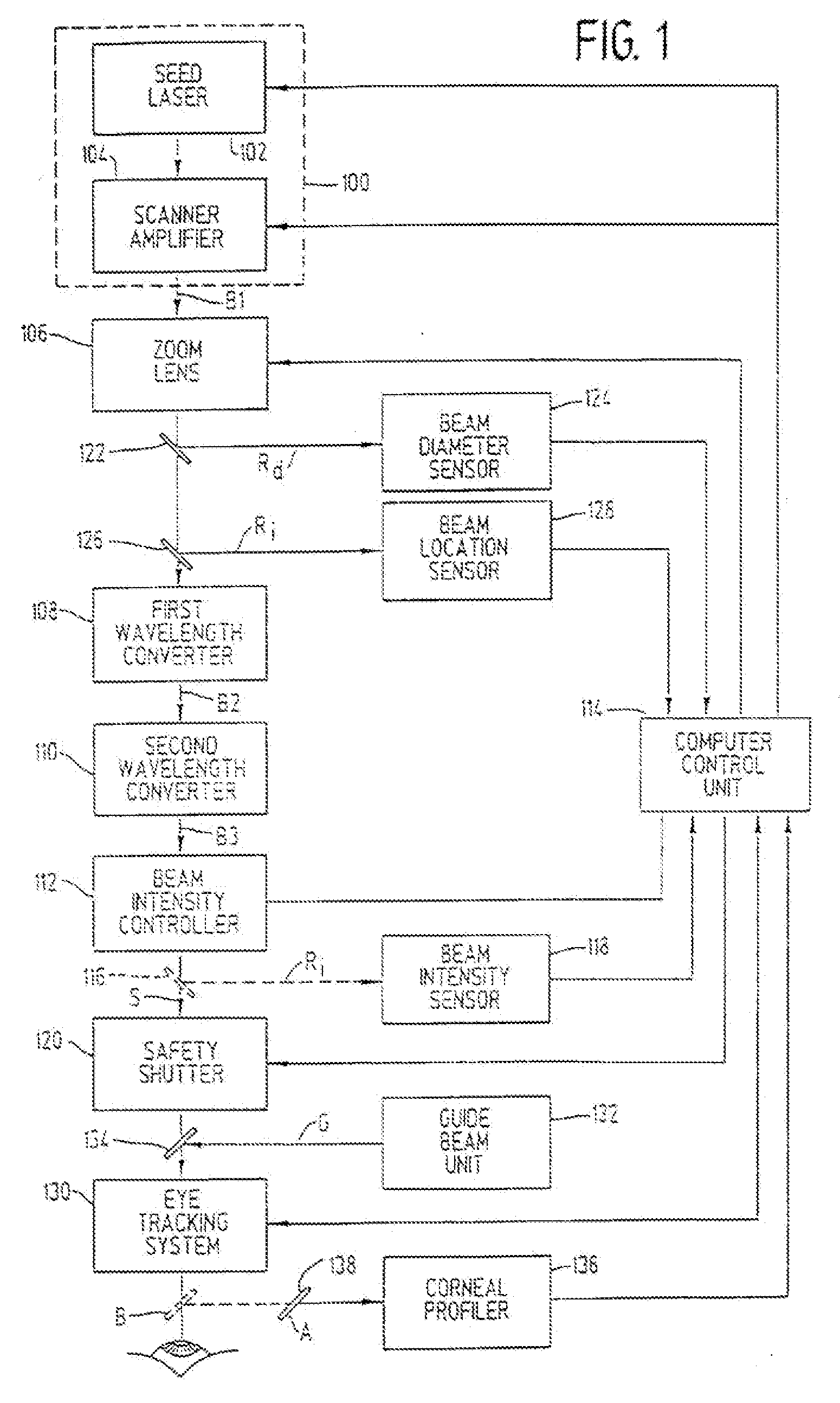
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Scleral prosthesis for treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders
InactiveUS6299640B1Increase the effective working distanceIncrease the working distanceLaser surgeryEye implantsDiseaseOpen angle glaucoma
Presbyopia is treated by implanting within a plurality of elongated pockets formed in the tissue of the sclera of the eye transverse to a meridian of the eye, a prosthesis having an elongated base member having an inward surface adapted to be placed against the inward wall of the pocket and having a ridge on the inward surface of the base extending along at least a major portion of the major dimension of the base. The combined effect of the implanted prostheses is to exert a radially outward traction on the sclera in the region overlying the ciliary body which expands the sclera in the affected region together with the underlying ciliary body. The expansion of the ciliary body restores the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle in the presbyopic eye and thereby increases the amplitude of accommodation. Hyperopia, primary open angle glaucoma and / or ocular hypertension can be treated by increasing the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle according to the invention.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
Treatment device for operatively correcting defective vision of an eye, method for producing control data therefor and method for operatively correcting defective vision of an eye
ActiveUS20100331831A1Improve optical qualityMore volumeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFar-sightednessTherapeutic Devices
A treatment apparatus for operatively correcting myopia or hyperopia in an eye includes a laser device controlled by a control device and that separates the corneal tissue by applying a laser beam. The control device controls the laser device to emit the laser beam into the cornea such that a lenticule-shaped volume is isolated in the cornea. The control device, when controlling the laser device, predefines the lenticule-shaped volume such that the volume has a minimum thickness of between 5 and 50 μm. For myopia correction, the minimum thickness occurs on the edge of the volume, and for hyperopia correction the minimum thickness occurs in the region of the visual axis.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
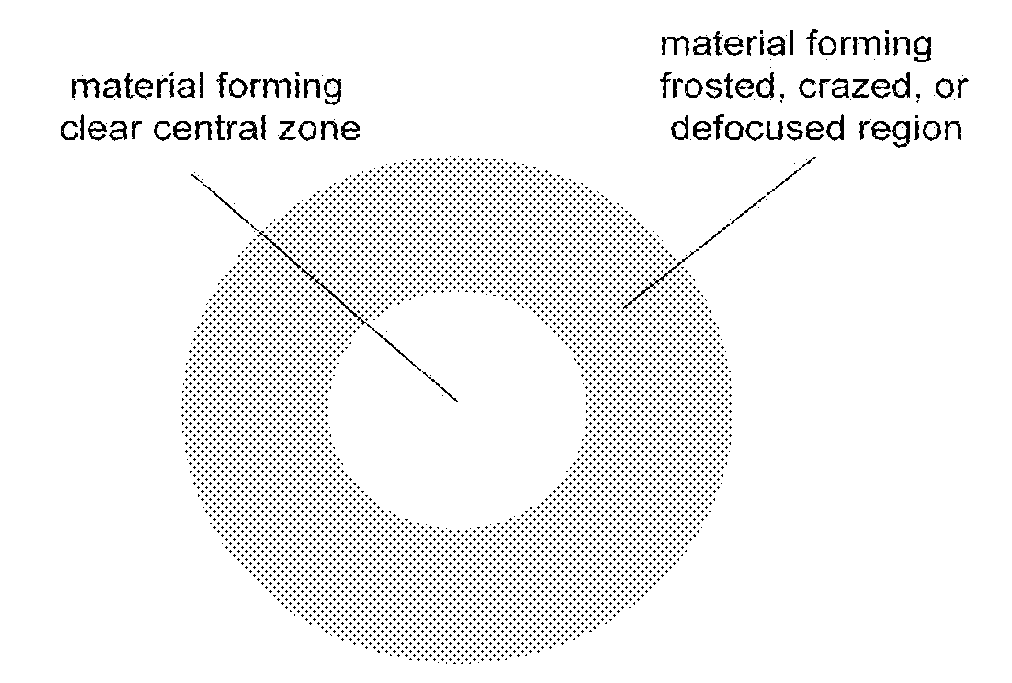
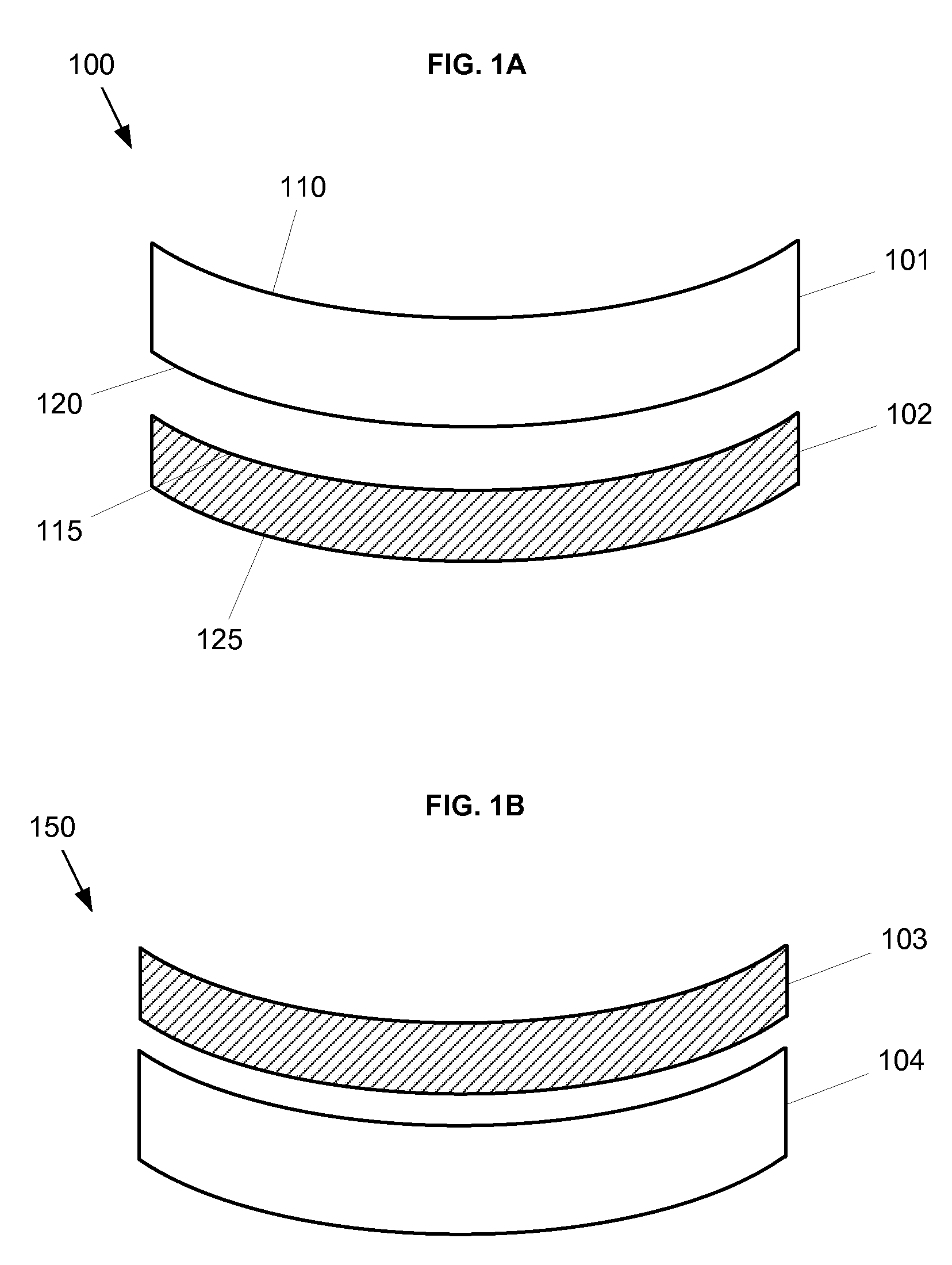
Ophthalmic lens element for myopia correction
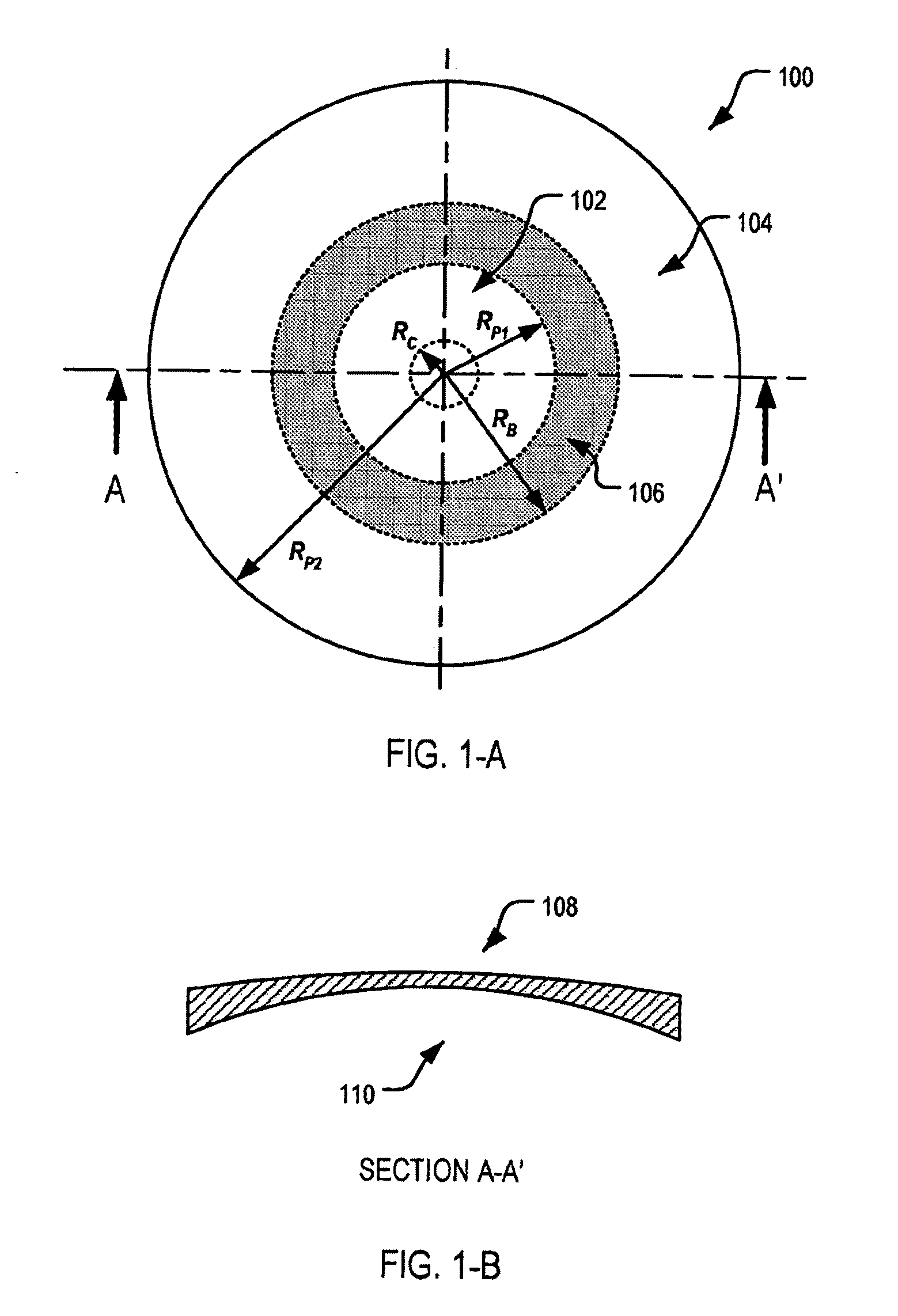
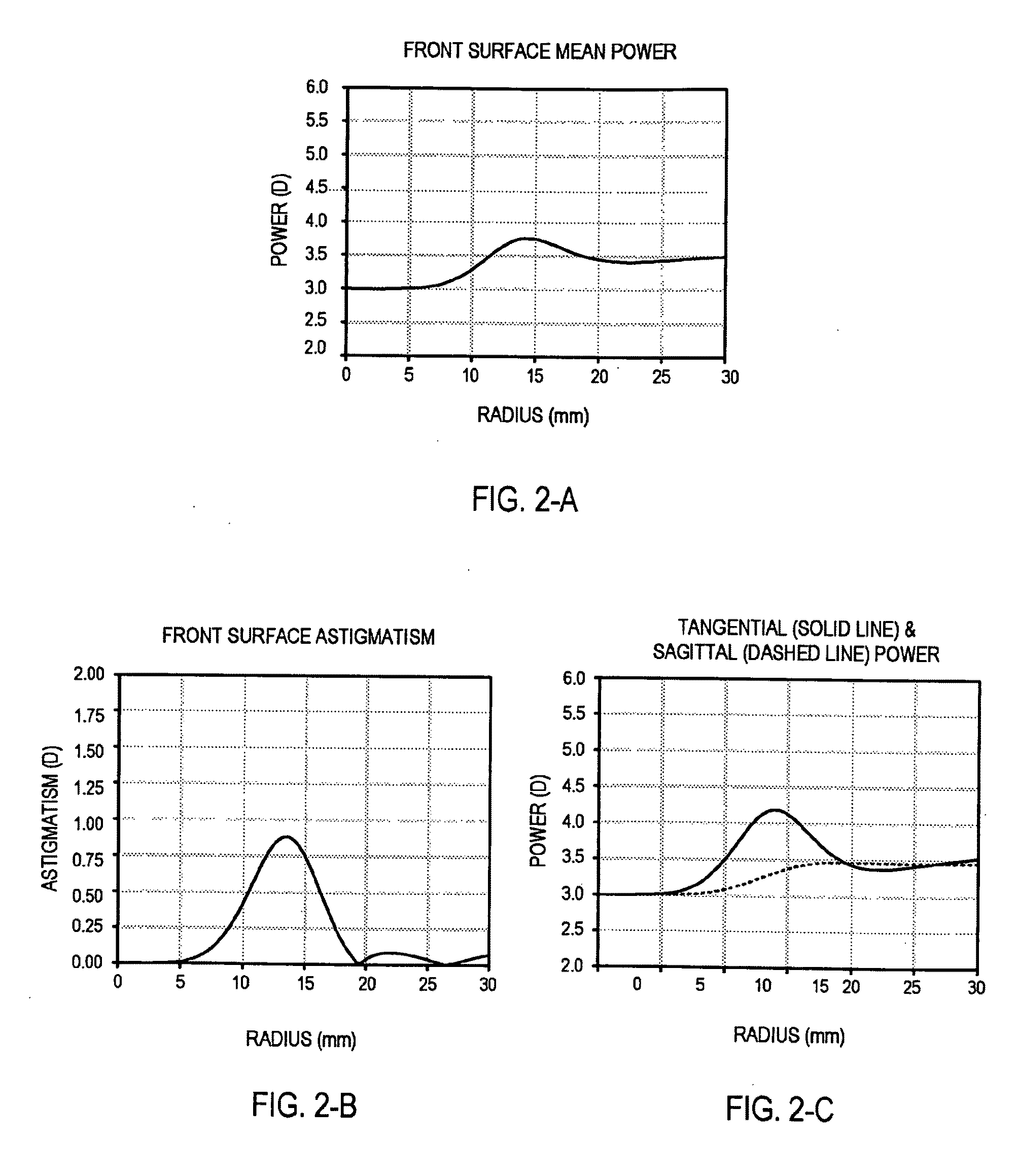
ActiveUS7862171B2Improve concentrationCorrects, orSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessOptical correction
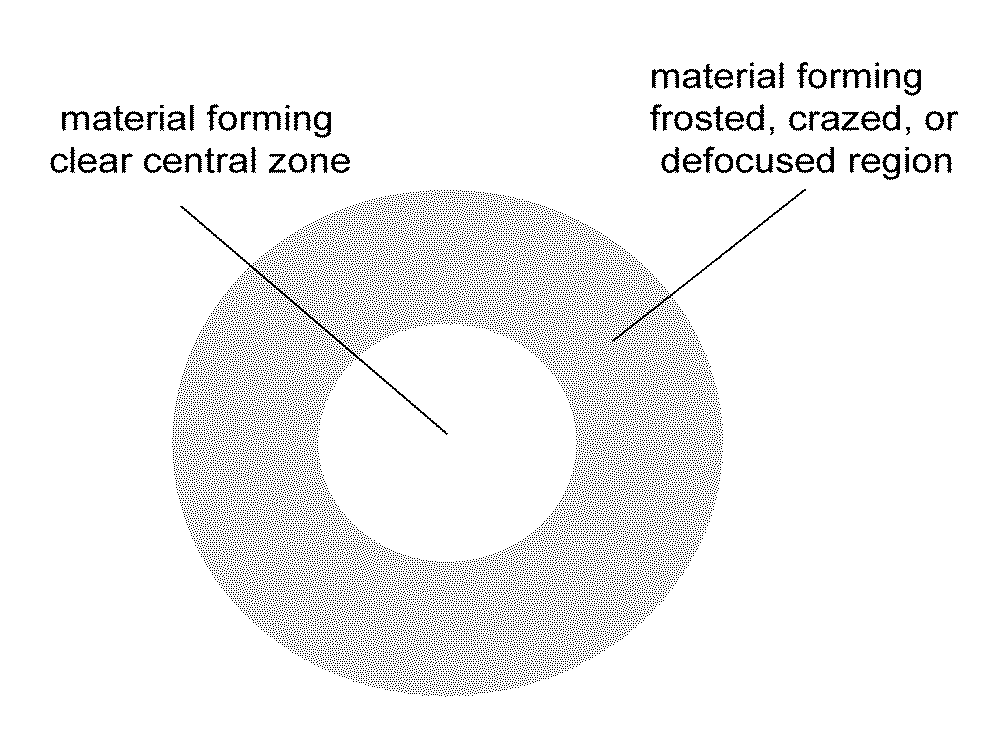
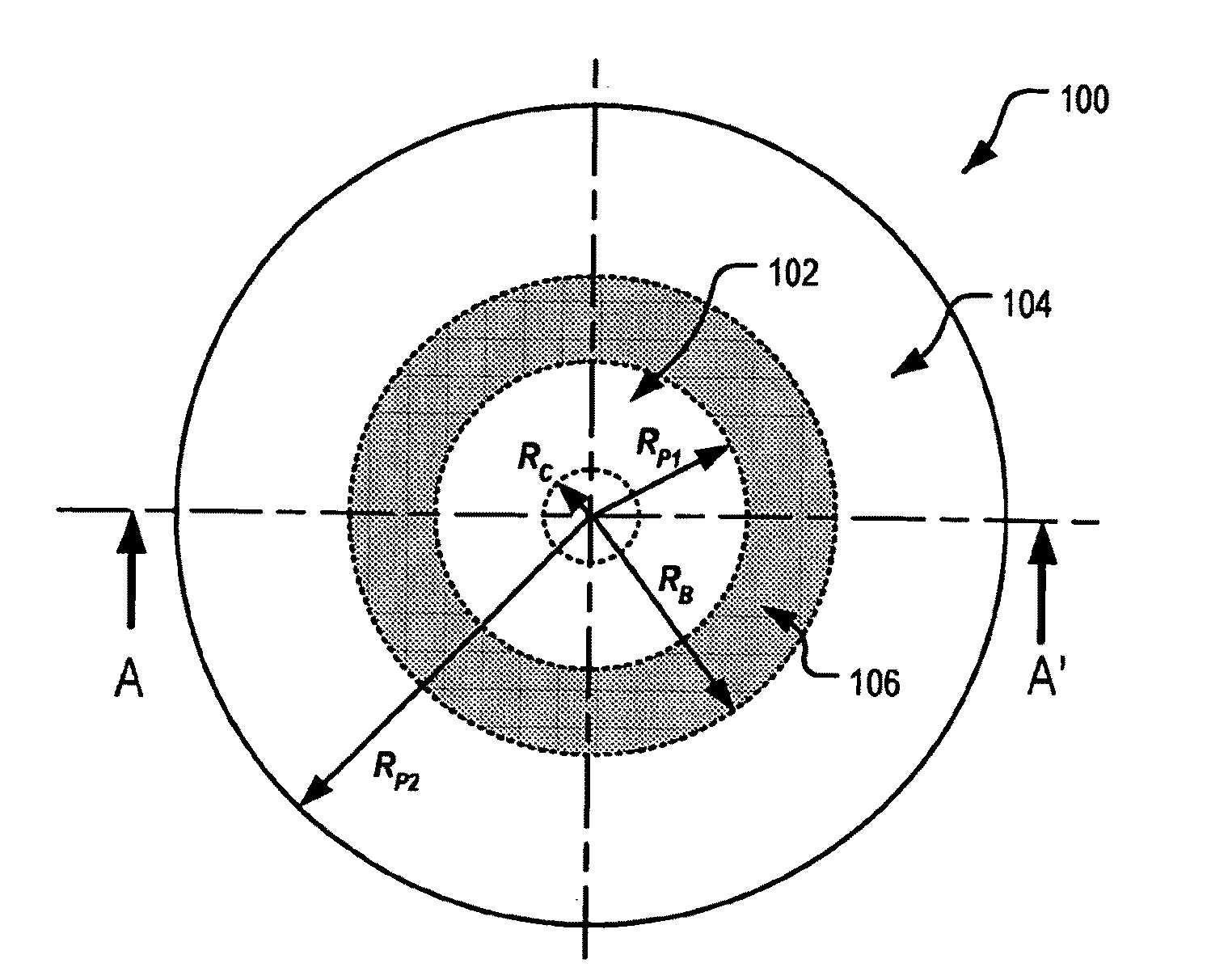
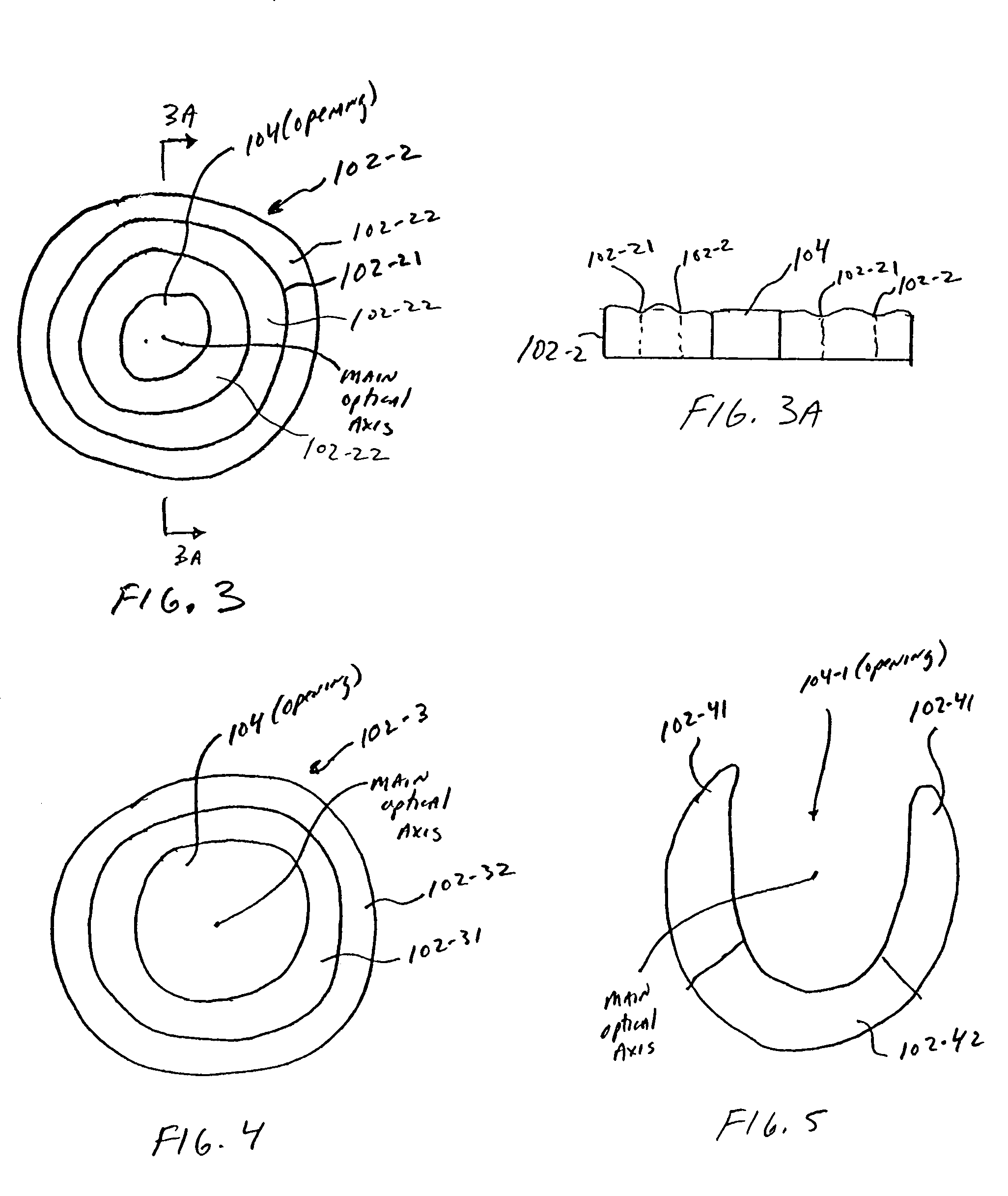
An ophthalmic lens element (100) for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is disclosed. The lens element (100) includes a central zone (102) and a peripheral zone (104). The central zone (102) provides a first optical correction for substantially correcting myopia associated with the foveal region of the wearer's eye. The peripheral zone (104) surrounds the central zone (102) and provides a second optical correction for substantially correcting myopia or hyperopia associated with a peripheral region of the retina of the wearer's eye. A system and method for dispensing or designing an ophthalmic lens element for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO +1
Method and Apparatus for Laser Surgery of the Cornea
InactiveUS20060217688A1Correction of myopiaCorrected astigmatismLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm.sup.2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100-50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198-300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1-5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Method for correcting hyperopia and presbyopia using a laser and an inlay outside the visual axis of eye
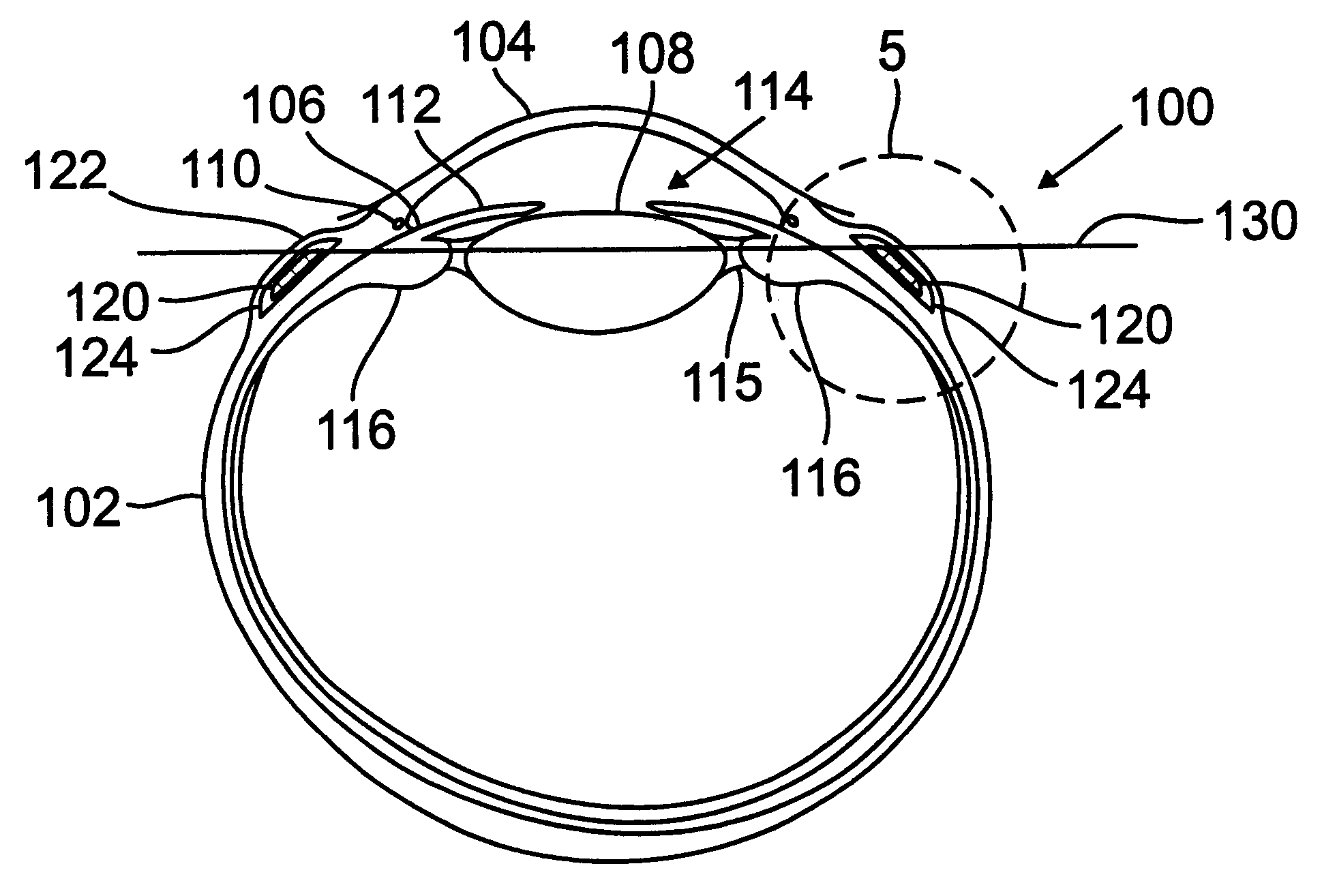
A cornea is reshaped by first creating a first cut in the cornea using an ultra-short pulse laser. The first cut is located below the surface of the cornea and does not extend through the epithelium. A second cut is then created using the ultra-short pulse laser. The second cut creates a corneal flap and intersects with the first cut to create a substantially severed portion of the cornea located between the first cut and the second cut. The severed portion of the cornea is located outside of the visual axis of the eye. The corneal flap is lifted away from the severed portion, and the severed portion is removed from the eye. The corneal flap is moved into the space on the cornea previously occupied by the severed portion. The cornea is thereby reshaped, and the reshaped portion of the cornea has an increased refractive power, correcting for hyperopic and presbyopic conditions.
Owner:MINU
Treatment device for surgically correcting ametropia of an eye and method for creating control data therefore
ActiveUS20100331830A1Decreased regressionEfficient removalLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorFar-sightedness
A treatment device for the surgical correction of hyperopia in the eye comprising a laser device controlled by a control device. The laser device separating corneal tissue by applying laser radiation. The control device controls the laser device for emitting the laser radiation into the cornea such that a lenticule-shaped volume is isolated. Removal thereof effects the desired correction. The control device (12) predefines the volume such that a posterior surface and an anterior surface are connected via an edge surface that has a width in projection along the visual axis that is wider than the one which a straight line in the same projection, that is perpendicular at the edge of the posterior or the anterior surface would have relative to the associated surface and connects the anterior surface to the posterior surface or to the perceived extension thereof.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Multi-element lens of controlling defocus and eye diopter and application thereof
ActiveUS20150160477A1Easy to useSimple structureSpectales/gogglesOptical partsFarsightednessFar-sightedness
A multi-element lens for controlling defocus and eye diopter for prevention and treatment of myopia and hyperopia. The multi-element lens includes one large unit convex lens for generating large defocus. One small unit concave lens for generating small defocus or focus through combination is combined on the lens of the large unit convex lens, or one small single lens is separately provided on the large unit convex lens. When an eye watches different distances through the lens, the central view region is in a small nearsightedness defocus or focus state, or a small farsightedness defocus or focus state, whereas the equatorial view region is always in a nearsightedness or farsightedness defocus state. Through the special influences of light on the view regions of human eyes, the growth of the ocular axis can be effectively controlled, which achieves the characteristics of good and fast prevention and treatment of myopia and hyperopia.
Owner:DAI MINGHUA
Method and Device for Cornea Reshaping by Intrastromal Tissue Removal
A method and device for flapless, intrastromal keratomileusis for the correction of myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism, i.e., for vision correction by corneal reshaping without creating a flap. Ultra-short laser pulses are used to create a temporary micro-channel extending to an end point located within the cornea. A second series of ultra-short laser pulses are then delivered to photo-ablate material in the vicinity of the micro-channel end-point. The photo-ablated material may exit through the micro-channel used to deliver the laser pulses, or via a separate micro-channel. With the micro-channel oriented substantially normal to the optical axis of the cornea, and by continuing to supply the ultra-short laser pulses in the appropriate number while moving the point of ablation along the micro-channel, the photo-ablation of the intrastromal tissue may continue in a controlled fashion and the cornea reshaped in a predetermined manner without creating a flap.
Owner:FEMTO VISION LTD
Intracorneal lens placement method and apparatus
InactiveUS7207998B2Minimal disturbance of setupEasy to keepEye surgerySurgeryRefractive indexEngineering
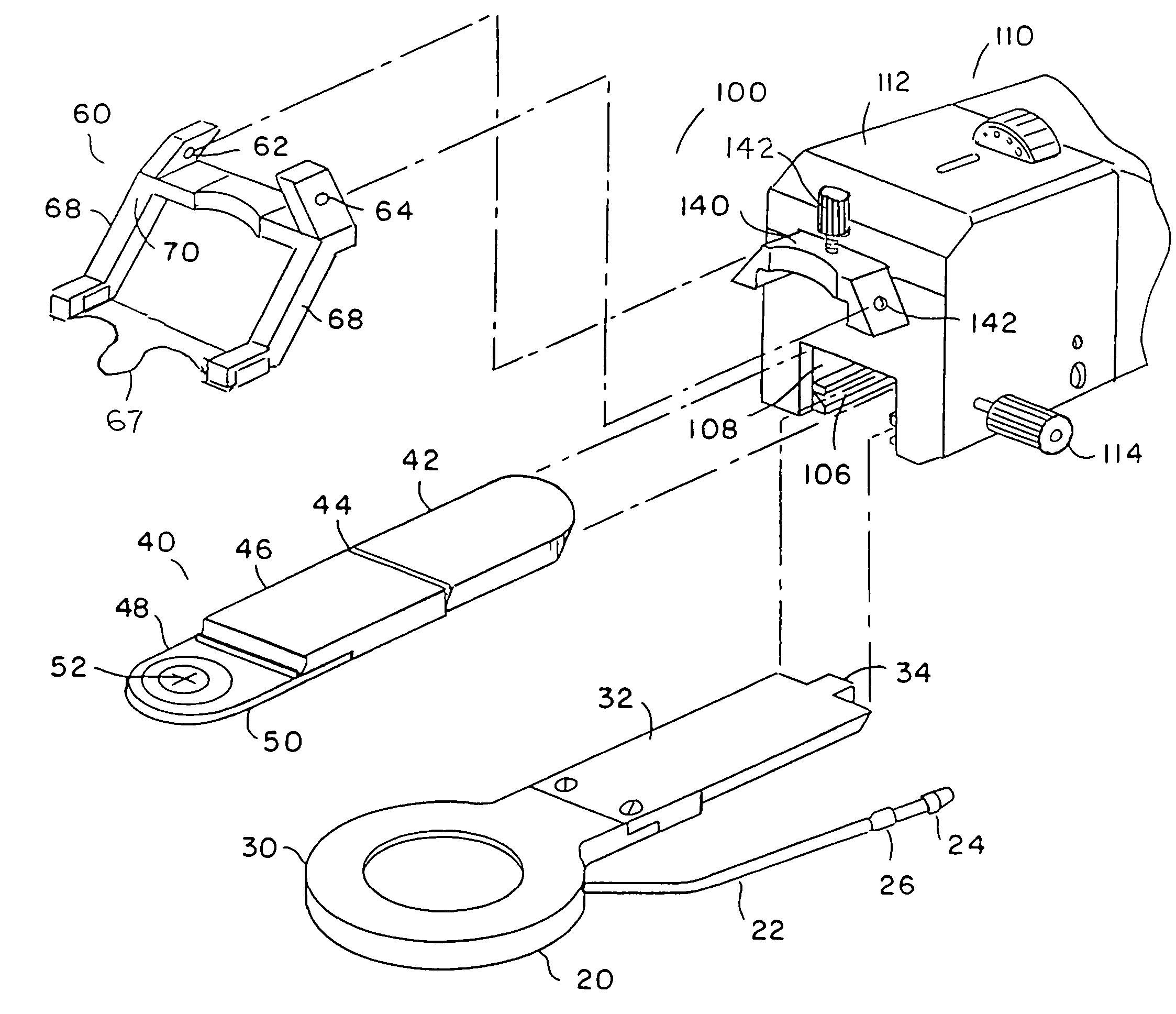
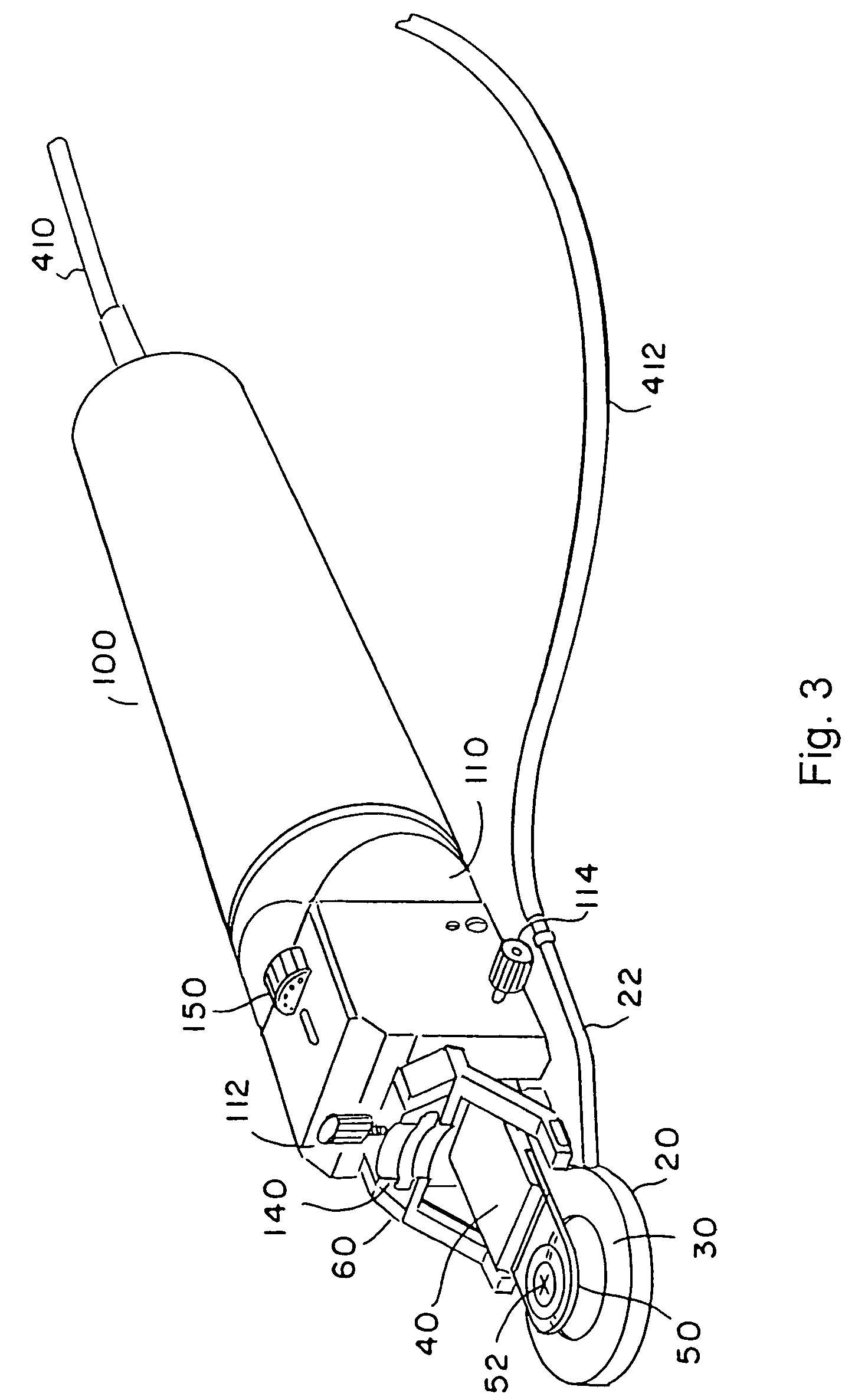
A method and apparatus for correcting vision, including a corneal-pocket keratome device to create a corneal pocket and a lens to be inserted and retained in the corneal pocket to effect correction. The corneal-pocket keratome includes a drive unit having cutting head elements which contact the subject eye during corneal pocket formation. The cutting head elements may be removeable and may be disposable. The cutting head elements include a corneal restraint device, which may be a positioning ring to position an eyeball with the cornea protruding through the ring; a keratome blade assembly with a corneal-pocket blade; and may also include an applanation shoe surface to restrain the cornea, in addition or instead of the positioning ring. The applanation shoe may be pivotable away from the surgical area. The corneal-pocket blade may include a guide which travels with the blade. The blade assembly oscillates laterally while extending forward into the cornea to form the pocket, and the amplitude of the lateral oscillation is preferably increased as the blade goes beyond an opening incision into the cornea. Lenses for this invention preferably include a feature to impede accidental lens movement after the lens is disposed within the corneal pocket, which may be a swelling after insertion or a circumferential irregularity. Lenses may be of Fresnel or non-Fresnel type, and may employ annular changes in the index of refraction of the lens material, as well as changes in refractive shape which may be annular or not, to effect variations in focal length for relieving presbyopia, astigmatism, and combinations of those as well as myopia and hyperopia. Drive control and vacuum for the positioning ring are provided under user command by a control unit having user inputs.
Owner:BIOVISION AG
Ophthalmic Lens Element for Myopia Correction
ActiveUS20090257026A1Improve concentrationShorten the progressSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessOptical correction
An ophthalmic lens element (100) for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is disclosed. The lens element (100) includes a central zone (102) and a peripheral zone (104). The central zone (102) provides a first optical correction for substantially correcting myopia associated with the foveal region of the wearer's eye. The peripheral zone (104) surrounds the central zone (102) and provides a second optical correction for substantially correcting myopia or hyperopia associated with a peripheral region of the retina of the wearer's eye. A system and method for dispensing or designing an ophthalmic lens element for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO +1
Intraocular lens for correcting presbyopia
An intraocular lens for modifying the refractive abilities of a natural lens or an existing artificial lens in an eye to correct for vision disorders such as presbyopia, myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism. Specifically, the lens system can be configured so that it does not effect far vision, while effecting near vision using a plus lens to correct for presbyopia. The lens system includes a lens portion and fastening members, with the lens portion being movably secured to at least one of the fastening members so that the position of the lens portion can be modified with respect to the optical axis, and the overall length of the lens system can be increased or decreased.
Owner:MINU
Methods and viewing systems for inhibiting ocular refractive disorders from progressing
InactiveUS20140039361A1Reducing hyperopiaChiropractic devicesEye exercisersFar-sightednessRefractive disorders
A method for retarding or reversing progression of myopia of a viewer includes providing an object in front of the viewer; providing a transparent layer between the viewer and the object; and providing a primary image on the transparent layer, the transparent layer allows the viewer to see the object as a secondary image simultaneously with the primary image, wherein the secondary image is focused in front of the central region of the retina. A method for reducing hyperopia of a viewer includes providing an object in front of the viewer to provide a primary image; providing a transparent layer between the viewer and the object; providing a secondary image on the transparent layer, the transparent layer allows the viewer to see the primary image simultaneously with the secondary image, wherein the secondary image is focused behind the central region of the retina. Other systems are also described herein.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Biocompatible polymeric compositions for use in making anterior chamber intraocular lenses
Biocompatible polymers useful for making anterior chamber intraocular lenses (AC-IOL) are provided. The biocompatible polymers are generally composed of one or more acrylate monomers, crosslinked with at least one diacrylate ester and may include one or more additional components such as ultraviolet light and / or blue-violet light absorbing dyes. The AC-IOLs made using the biocompatible polymers disclosed herein are suitable for placement in phakic or aphakic eyes and are intended for refractive correction including myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatisms.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Apparatus and methods for vision correction using refractive index effects
A method and apparatus for performing vision correction by selecting means of changing the refractive index includes medical, mechanical, optical or chemical method. Detail theoretical calculation with clinical predictions are presented for quantitative index changes required to correct myopia, hyperopia and presbyopia. The key parameters of the radius and thickness of the cornea, lens and indices of the lens, cornea and humor chambers and the effect due aging are proposed.
Owner:LIN J T
Orthokeratology and bi-focal contact lens
InactiveUS20050105046A1Effective reduction of hyperopia and presbyopiaShort correction timeEye treatmentOptical partsFar-sightednessFocal Contacts
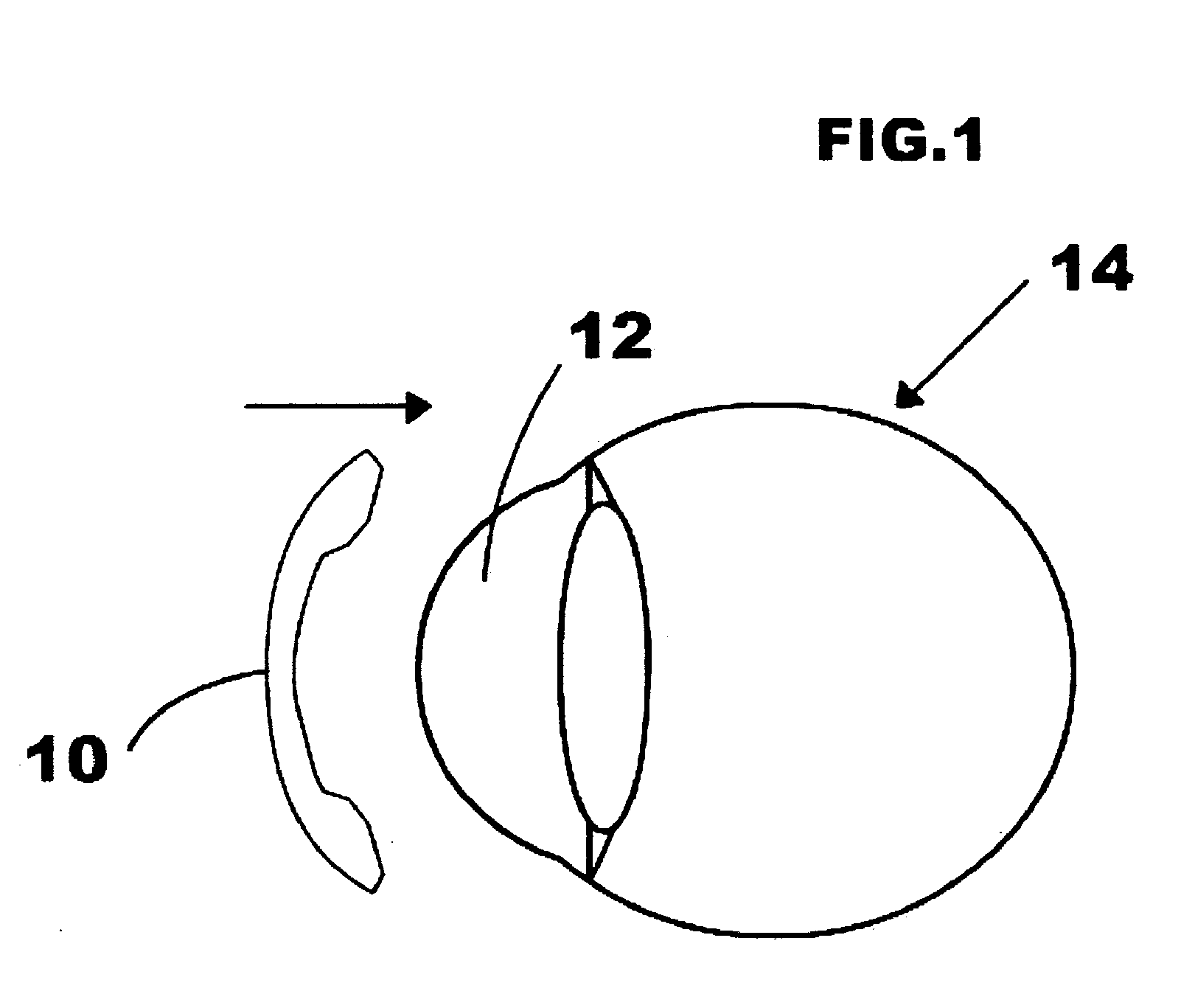
A contact lens is fitted to a cornea of a patient's eye to gradually alter the patient's cornea during continued wear to reshape the cornea to reduce the hyperopia and / or presbyopia condition. The contact lens has a plurality of zones that includes one or two optical zones, a plateau zone, a fitting zone, an alignment zone and a peripheral zone. The one or more optical zones are utilized to redistribute cornea tissue to cause the cornea to have a steepened central portion surrounded by a flat mid-peripheral ring The plateau zone helps steepening the central cornea by two ways: a positive molding effect of pushing the cornea tissue inward to pile up and a negative molding effect to flatten the mid-peripheral cornea for enhancing.
Owner:GLOBAL OK VISION
Lenses, systems and methods for providing custom aberration treatments and monovision to correct presbyopia
InactiveUS20130335701A1Improve eyesightIncrease depth of focusSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessAberrations of the eye
A lens, system and / or method for providing custom ocular aberrations for enhanced higher visual acuity. Scaled versions of a patient's aberration pattern may either attenuate or amplify the overall amount of ocular aberrations, to either correct or partially correct a patient's aberrations leading to enhanced visual acuity and / or extended depth of focus. This may be binocularly applied in order to provide high visual acuity in a patient at least at near, far and intermediate distances. The method may include obtaining an optimized binocular summation of both eyes of the patient; designing a first lens solution to correct or partially correct the dominant eye's aberrations according to an attenuated scaled version of a patient's ocular aberrations in the dominant eye; and designing a second lens solution to provide an additional customized extension of depth of focus by the induction of scaled patterns of ocular aberrations in the non dominant eye.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Diopter-adjustable optical system for helmet display
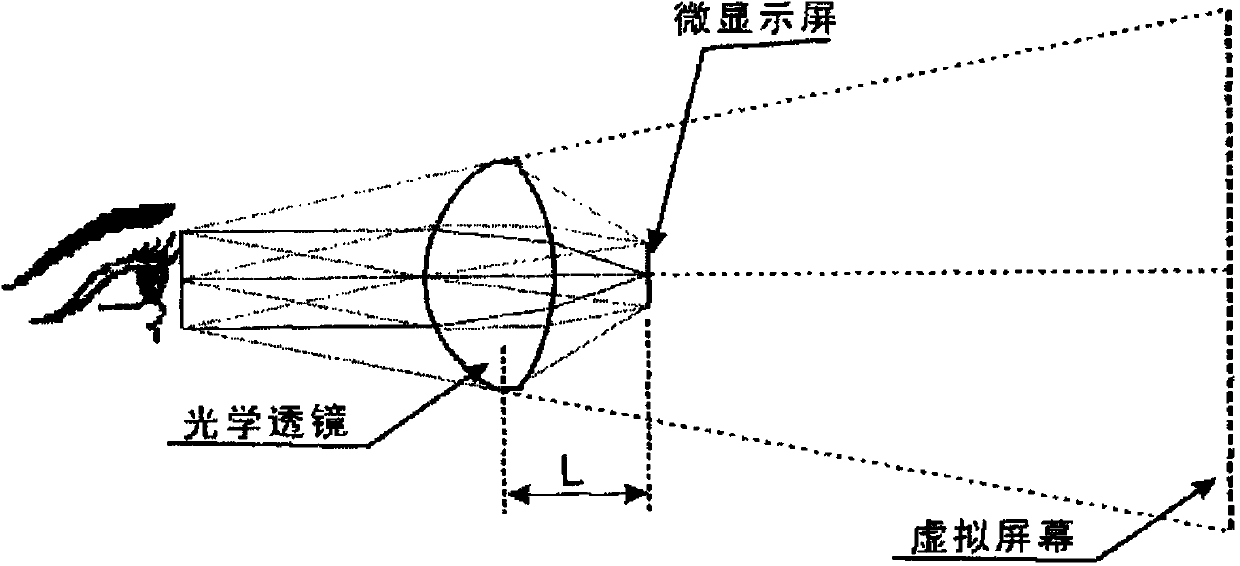
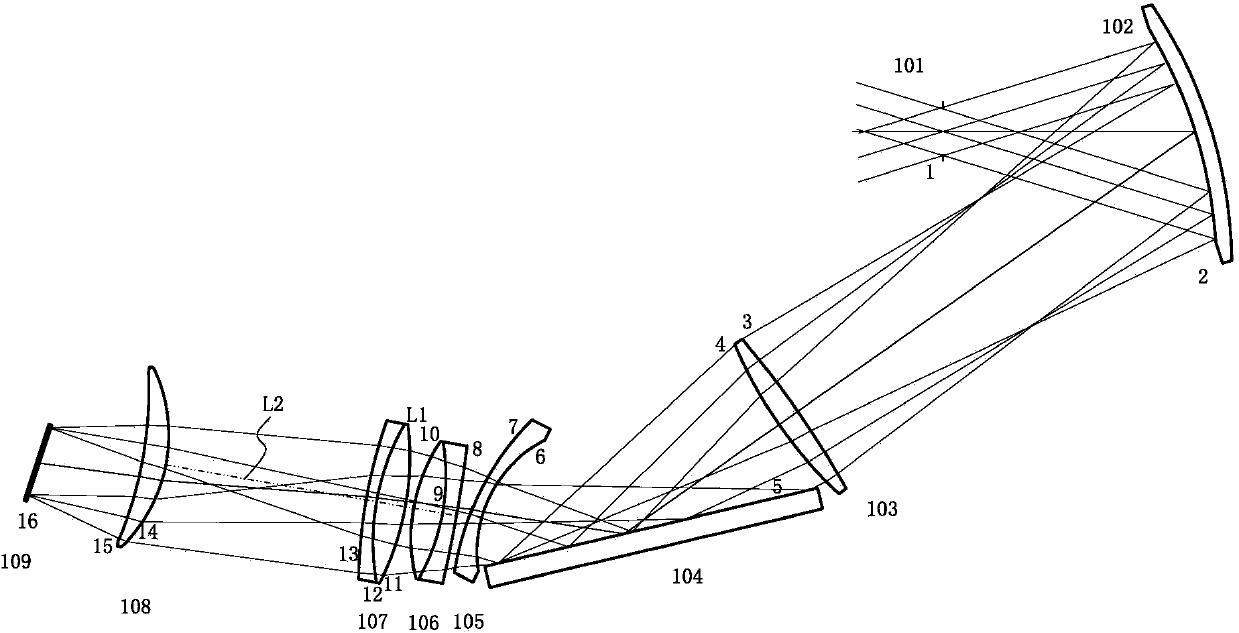
ActiveCN103995355AReduce complexitySimple structureMountingsMagnifying glassesFar-sightednessDisplay device
The invention provides a diopter-adjustable optical system for a helmet display. The diopter-adjustable optical system comprises a glasses-shaped lens and a relay lens set. The glasses-shaped lens is arranged before the human eyes, and the relay lens set is arranged between a micro-display and the inner surface of the glasses-shaped lens. Image light rays sent by the micro-display of the helmet display are transmitted to the inner surface of the glasses-shaped lens by the relay lens set, and then the glasses-shaped lens is used for reflecting the light rays to the human eyes. The relay lens set is used for imaging an image of the micro-display to the position between the glasses-shaped lens and the relay lens set, and the glasses-shaped lens is used for magnifying the real image into a virtual image before the human eyes. The distance between the virtual image and the human eyes is changed according to the vision level of a user through zooming of the relay lens set, and therefore people with the normal eyes, the myopic eyes and the hypermetropic eyes can clearly see the image of the micro-display. Imaging and zooming of the relay lens set can be achieved by adopting six lenses, the complex degree of the relay lens set is reduced, and the structure is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING NEDPLUSAR DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus to automatically insert a probe into a cornea
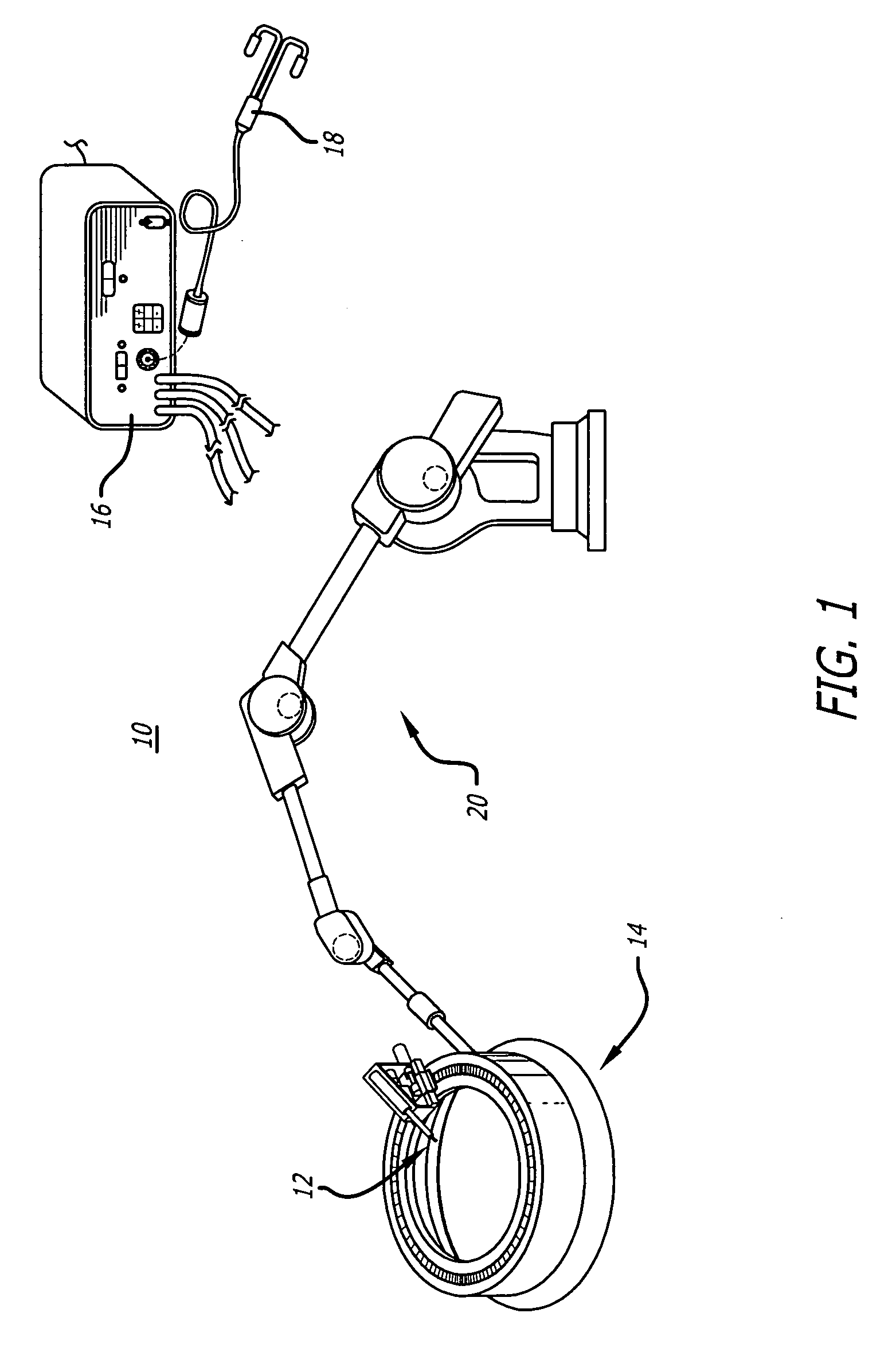
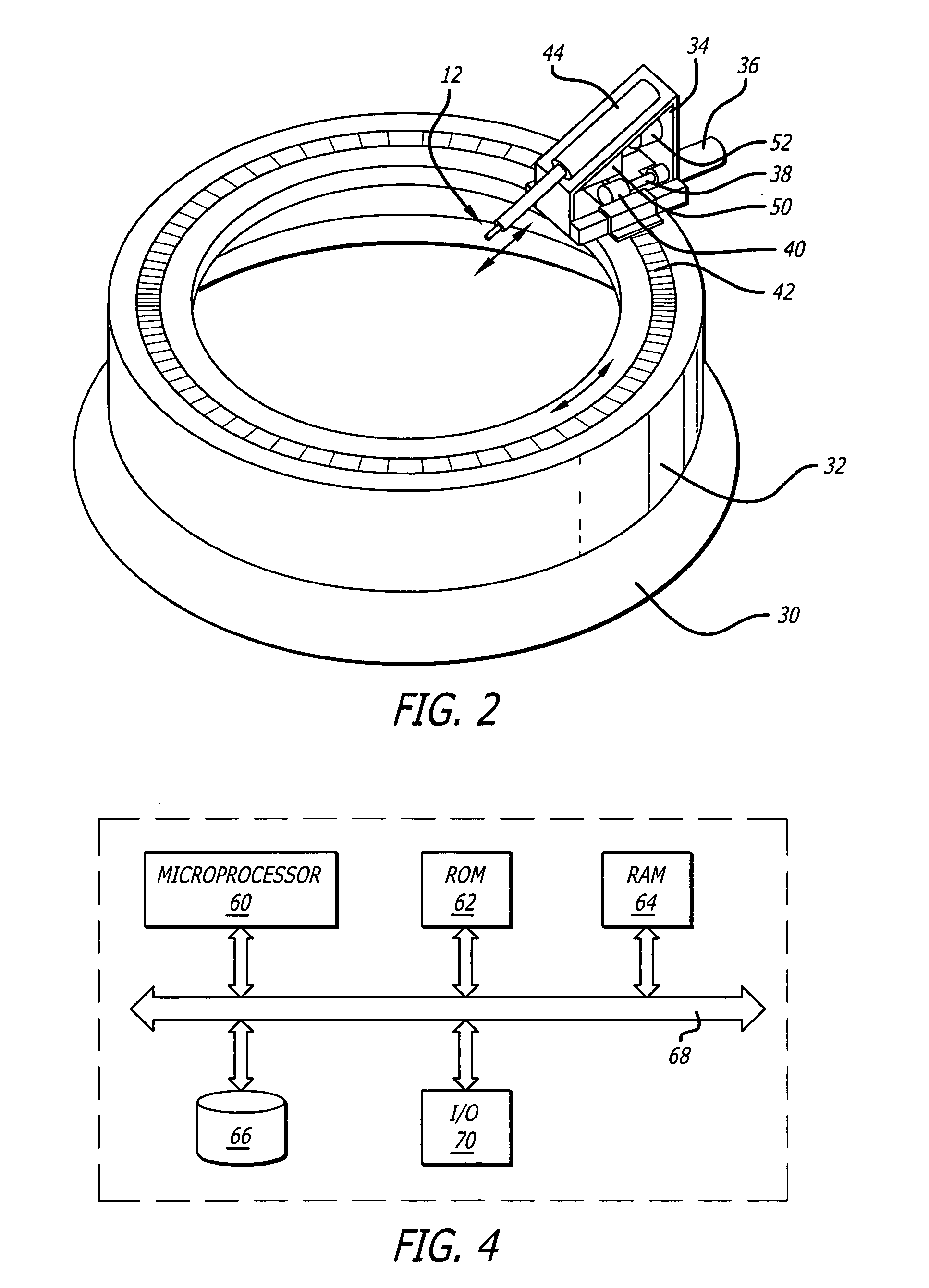
An apparatus that is used to perform a medical procedure on a cornea. The apparatus may include a ring that can be placed on a cornea and a probe that can deliver energy to denature corneal tissue. The probe can be moved about the ring and cornea by a first actuator. A second actuator may move the probe into contact with the cornea to deliver energy and denature tissue. The process of moving the probe and delivering energy can be repeated to create a circular pattern of denatured areas. The circular pattern of denatured areas may correct for hyperopia. The actuators may be controlled by a controller that operates in accordance with a program to move the probe and create the circular pattern of denatured areas in an automated process.
Owner:REFRACTEC
Orthokertology and bi-focal contact lens
InactiveUS7070275B2Effective reduction of hyperopia and presbyopiaShort correction timeEye treatmentOptical partsFar-sightednessFocal Contacts
A contact lens is fitted to a cornea of a patient's eye to gradually alter the patient's cornea during continued wear to reshape the cornea to reduce the hyperopia and / or presbyopia condition. The contact lens has a plurality of zones that includes one or two optical zones, a plateau zone, a fitting zone, an alignment zone and a peripheral zone. The one or more optical zones are utilized to redistribute cornea tissue to cause the cornea to have a steepened central portion surrounded by a flat mid-peripheral ring The plateau zone helps steepening the central cornea by two ways: a positive molding effect of pushing the cornea tissue inward to pile up and a negative molding effect to flatten the mid-peripheral cornea for enhancing.
Owner:GLOBAL OK VISION
Generating scanning spot locations for laser eye surgery
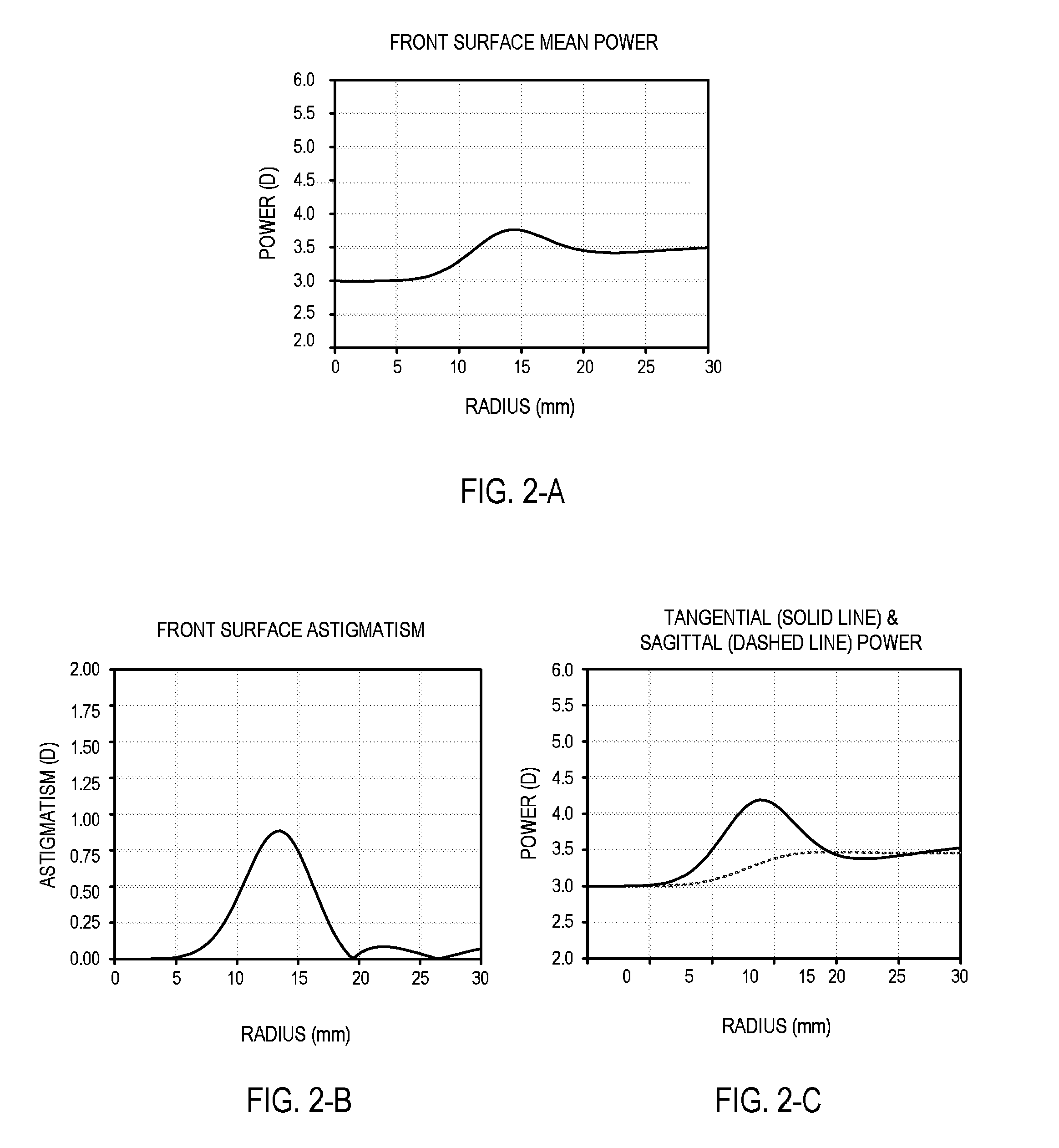
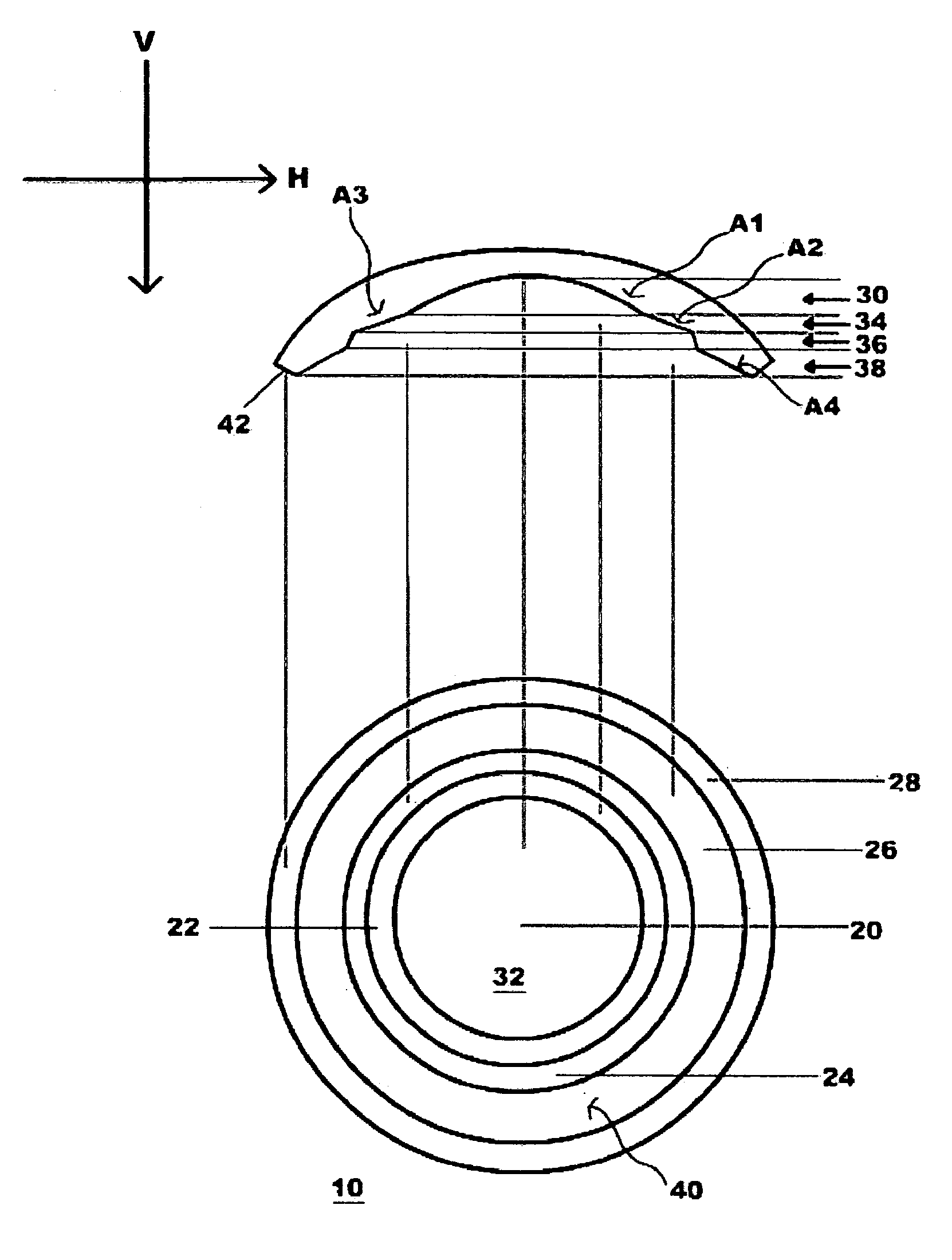
InactiveUS7008415B2Easy to analyzeVariable shapeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFar-sightednessLens plate
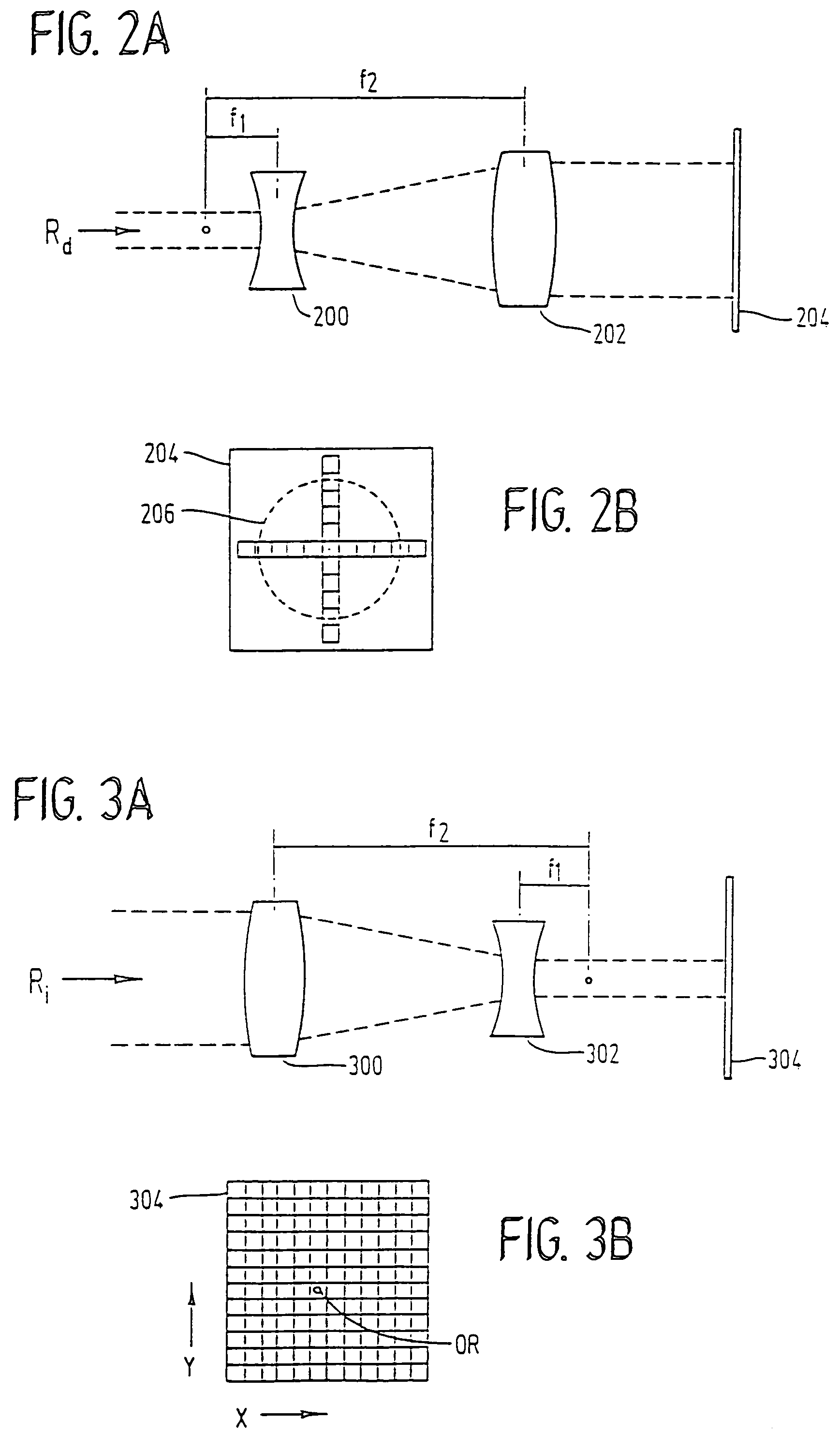
Scanning spot locations are generated for ablating tissue using a scanning laser beam over a treatment region by taking a target function representing a desired lens profile of ablation with a basis function representing a treatment profile produced by overlapping scanning spots in a particular treatment pattern. In some embodiments, the basis function is a two-dimensional function representing a two-dimensional section of a three-dimensional treatment profile, which has symmetry with respect to the two-dimensional section extending along the treatment pattern. For example, the treatment pattern is generally straight for myopic and hyperopic cylinders, and is generally circular for myopia and hyperopia. The fit produces ablation depths for discrete scanning spots, which are used to calculate the number of pulses at each reference position along the two-dimensional section. The pulses are distributed along the treatment pattern to produce the desired overlapping effect.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Methods and viewing systems for inhibiting ocular refractive disorders from progressing
ActiveUS20160143801A1Reducing hyperopiaChiropractic devicesEye exercisersFar-sightednessRefractive disorders
A method for retarding or reversing progression of myopia of a viewer includes providing an object in front of the viewer; providing a transparent layer between the viewer and the object; and providing a primary image on the transparent layer, the transparent layer allows the viewer to see the object as a secondary image simultaneously with the primary image, wherein the secondary image is focused in front of the central region of the retina. A method for reducing hyperopia of a viewer includes providing an object in front of the viewer to provide a primary image; providing a transparent layer between the viewer and the object; providing a secondary image on the transparent layer, the transparent layer allows the viewer to see the primary image simultaneously with the secondary image, wherein the secondary image is focused behind the central region of the retina. Other systems are also described herein.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Vision-corrective Polarizing Lens
The present invention provides a PC vision-corrective polarizing lens consisted of a polarizing film and an optical substrate, wherein said polarizing film includes protection layer, PVA base and adhesive layer bonding on the surface of the PC optical substrate by injection-molding. The present invention with simple structure and widely adapting to near-sighted lens, far-sighted lens, presbyopia lens and gradual near-sighted lens and so on, not only corrects the poor vision, but also makes the visual object more clear under the cooperating of the polarizing function without visual-tire happened on the eyes.
Owner:WANG WEI CHEN
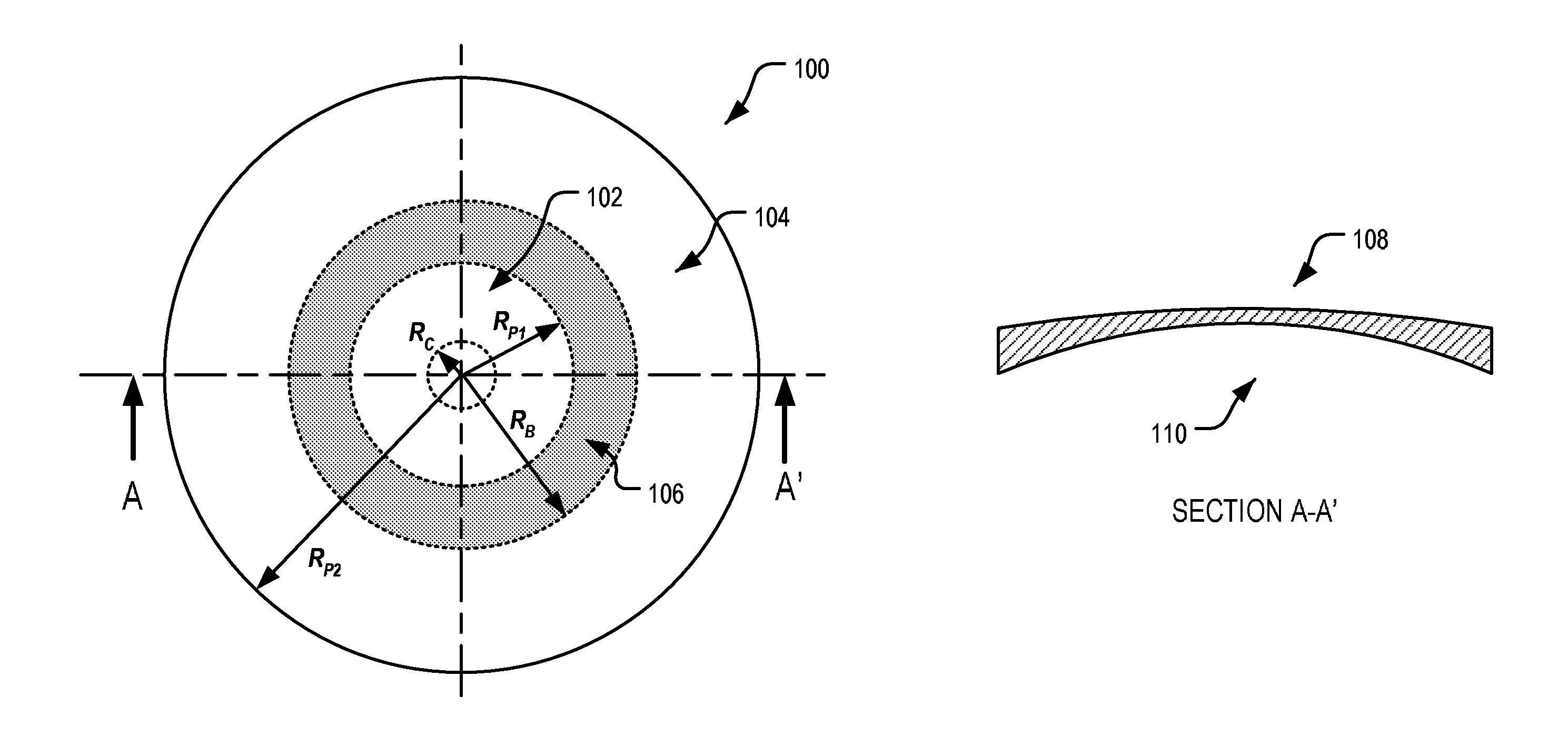
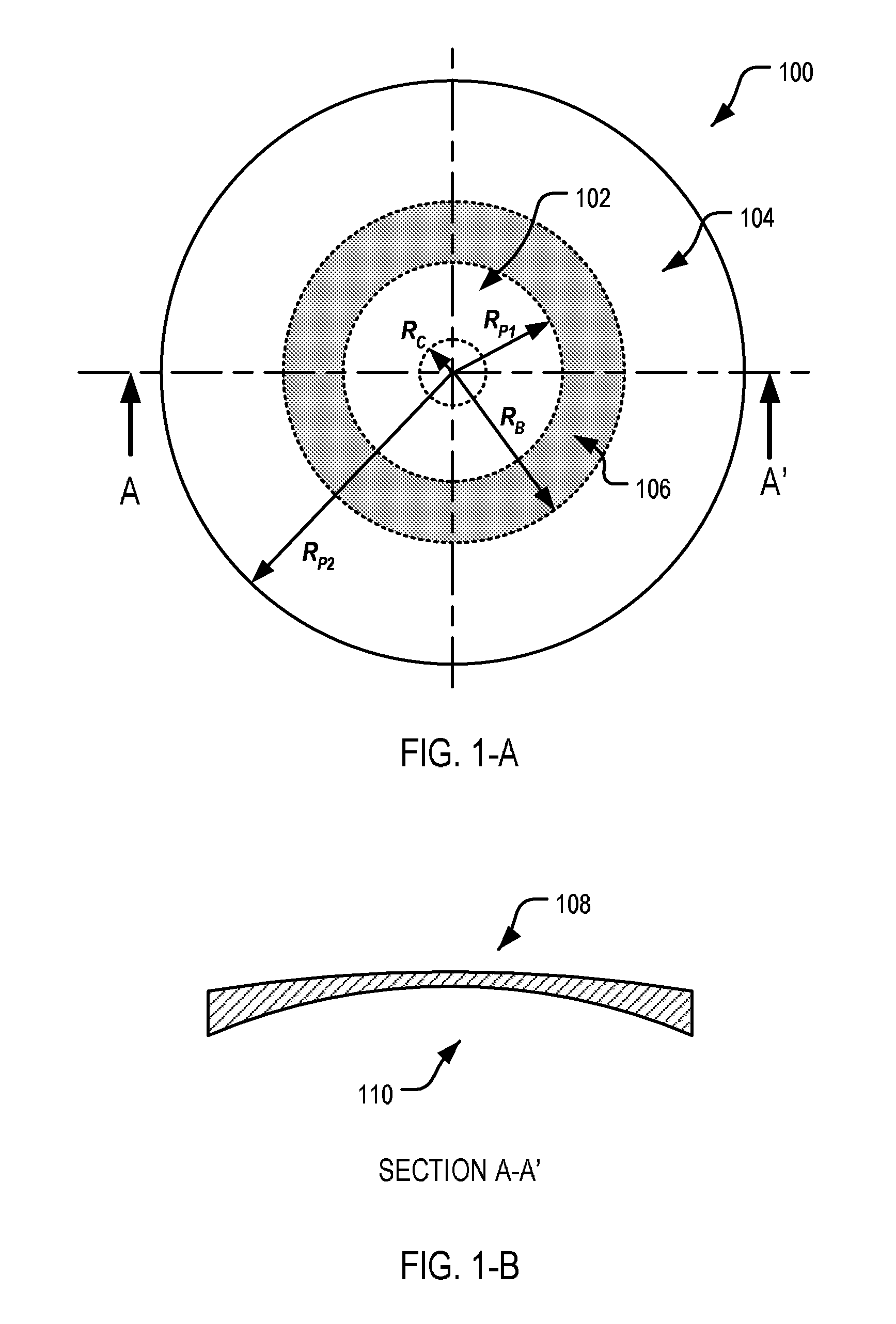
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS20090216217A1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
An ophthalmic surgery system and method for treating presbyopia by performing ablative photodecomposition of the corneal surface. The offset image of a variable aperture, such as a variable width slit and variable diameter iris diaphragm, is scanned in a preselected pattern to perform ablative sculpting of predetermined portions of a corneal surface. The scanning is performed to ablate an optical zone sized to match the patient pupil with a peripheral transition zone outside the pupil. The shape of the ablated optical zone is different from the shape of the final optical correction on the anterior surface of the cornea. The optical zone corrects for near-vision centrally and far-vision peripherally. A movable image displacement mechanism enables radial displacement and angular rotation of the profiled beam exiting from the variable aperture. The invention enables wide area treatment with a laser having a narrower beam than the treatment area, and can be used in the treatment of many conditions in conjunction with presbyopia such as hyperopia, hyperopic astigmatism and irregular refractive aberrations.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com