Patents
Literature
79 results about "Aberrations of the eye" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
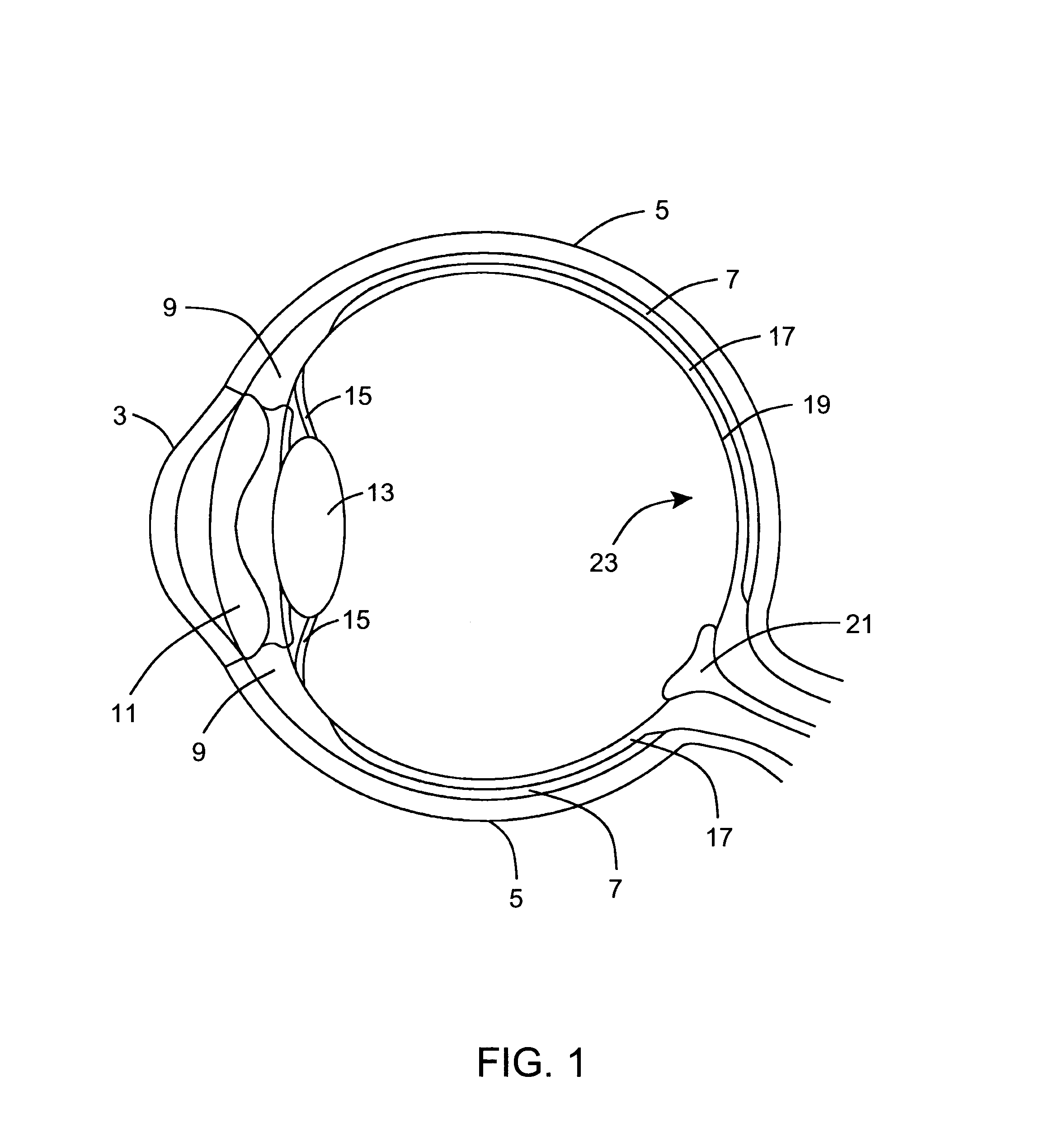
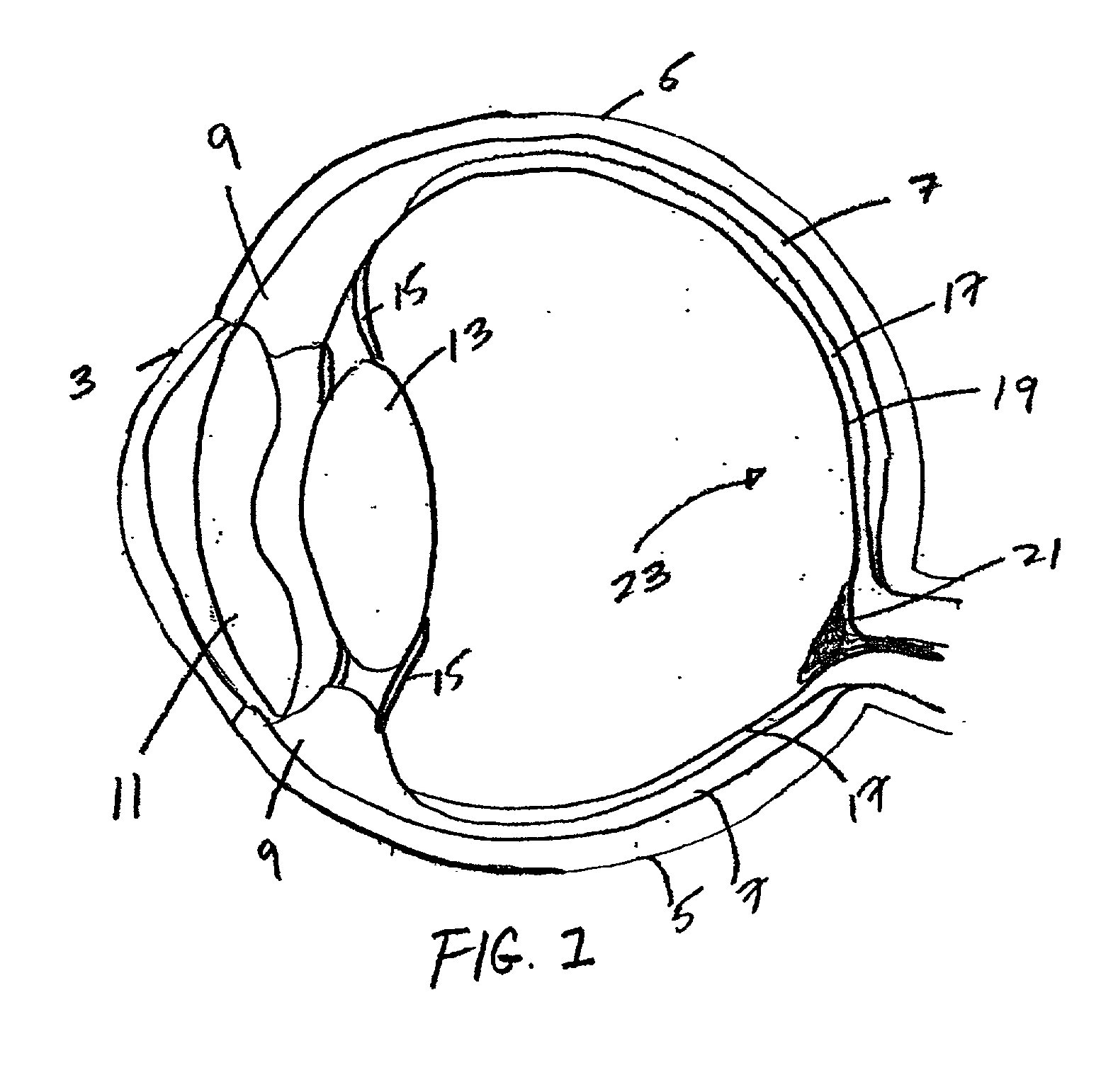
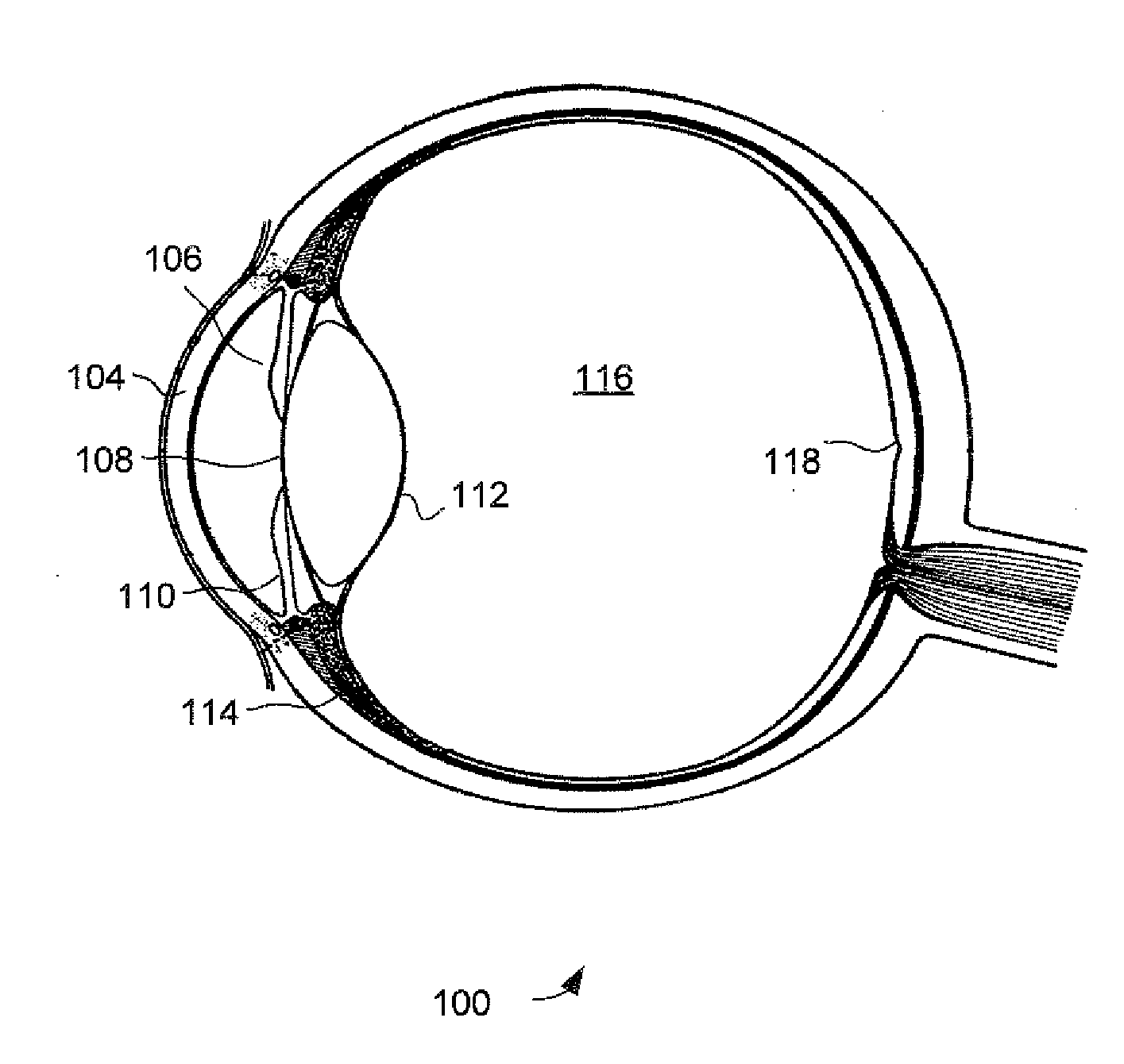
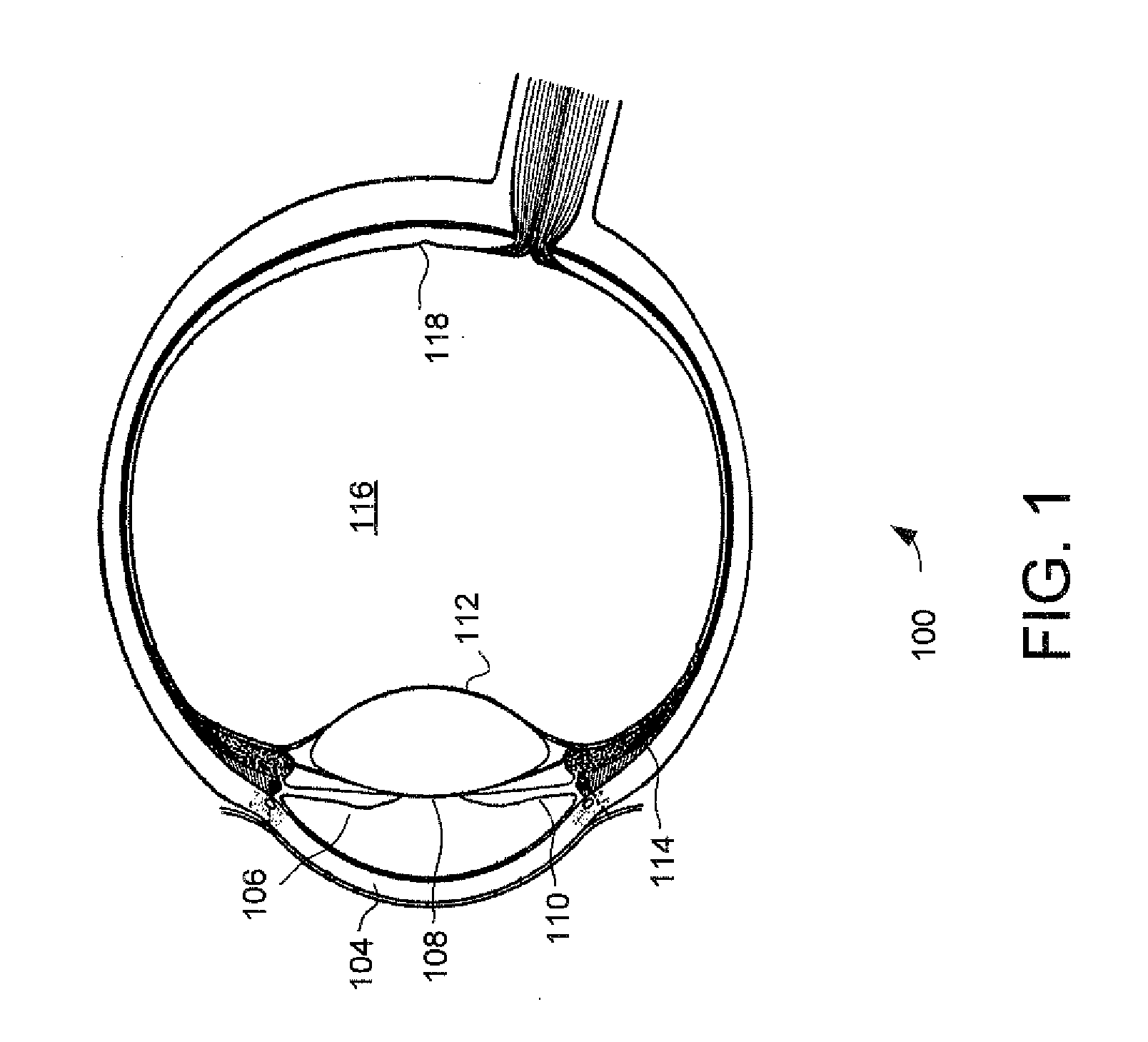
The eye, like any other optical system, suffers from a number of specific optical aberrations. The optical quality of the eye is limited by optical aberrations, diffraction and scatter. Correction of spherocylindrical refractive errors has been possible for nearly two centuries following Airy's development of methods to measure and correct ocular astigmatism. It has only recently become possible to measure the aberrations of the eye and with the advent of refractive surgery it might be possible to correct certain types of irregular astigmatism.
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20040156014A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
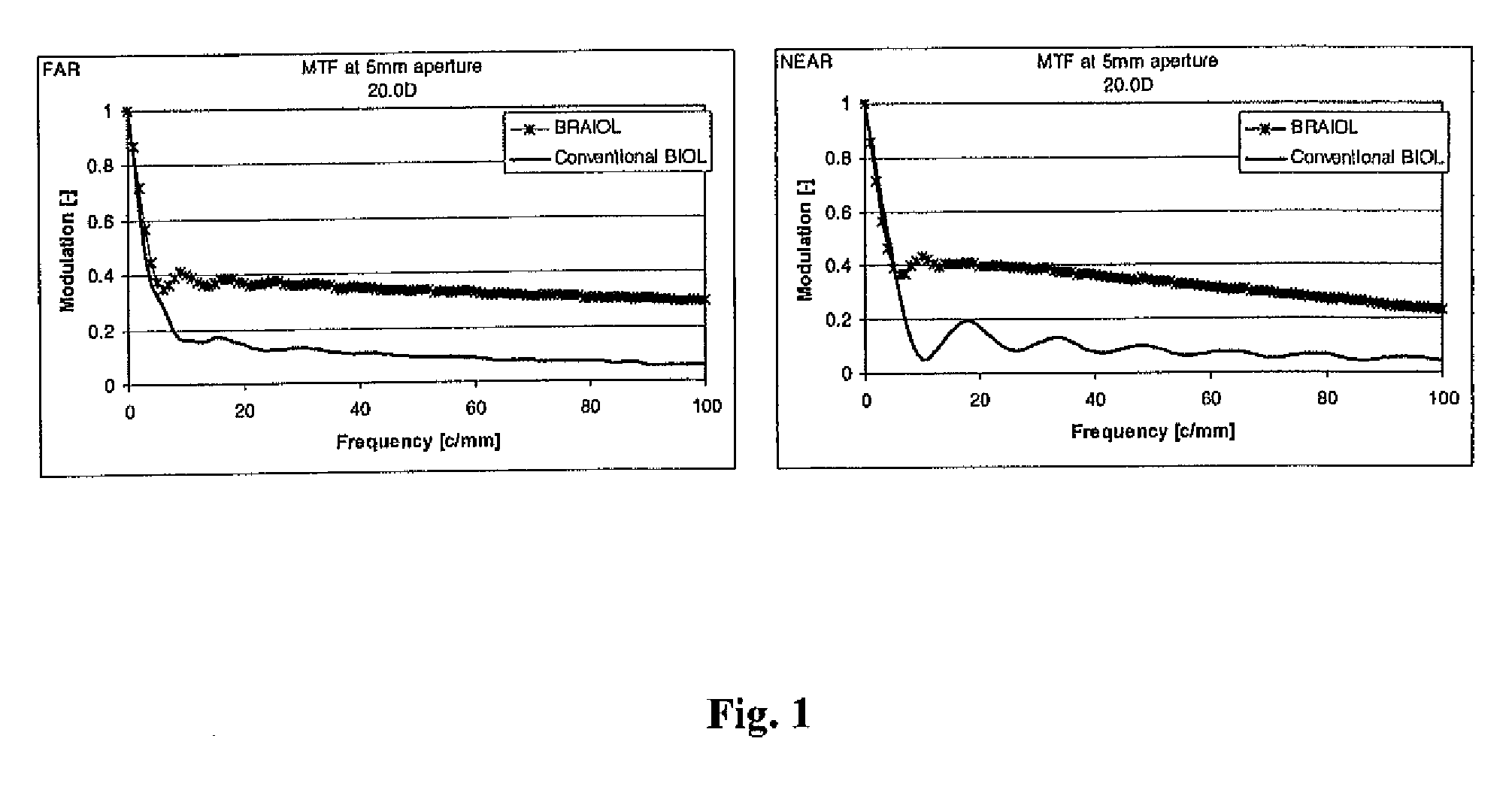
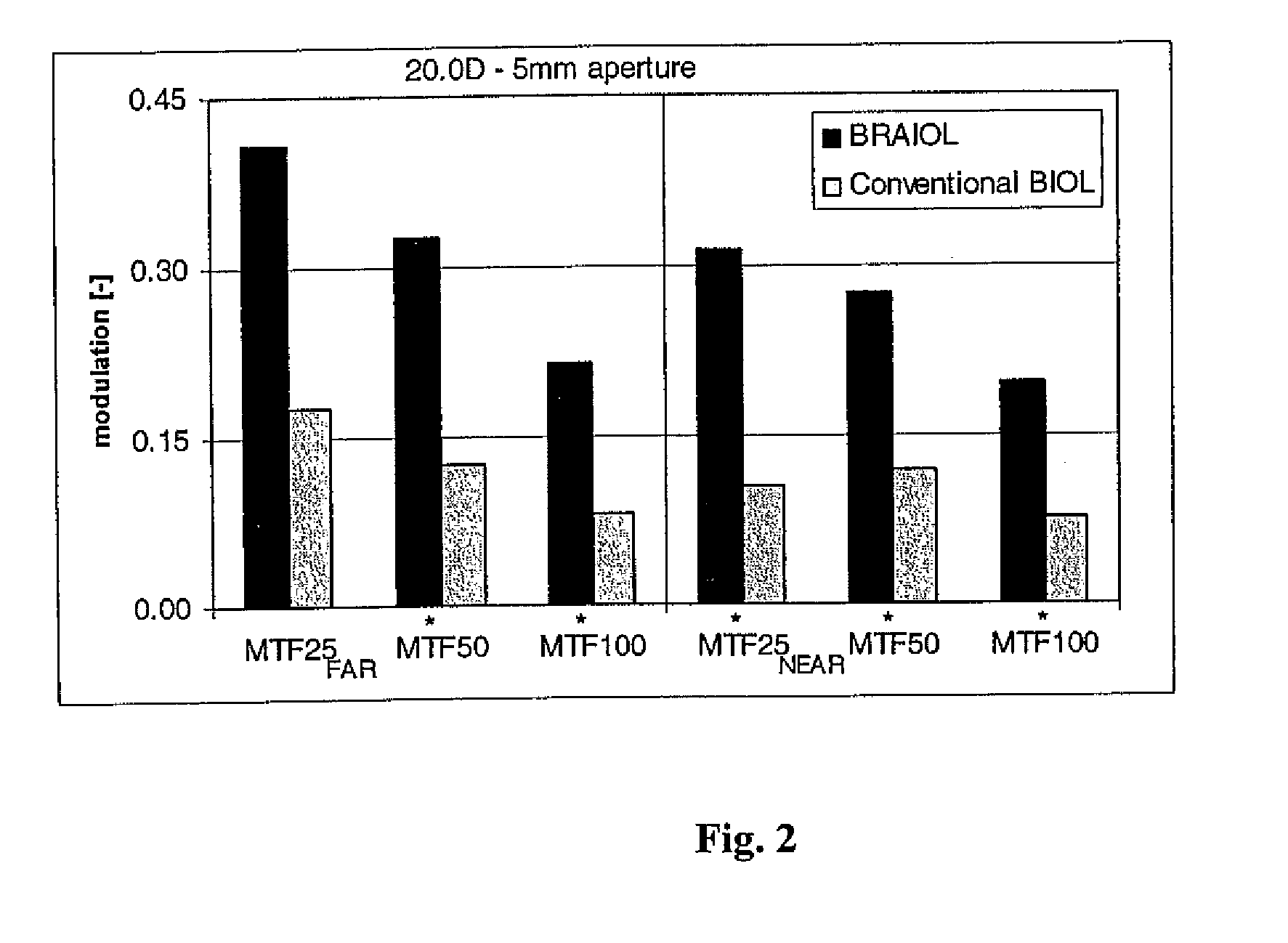
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
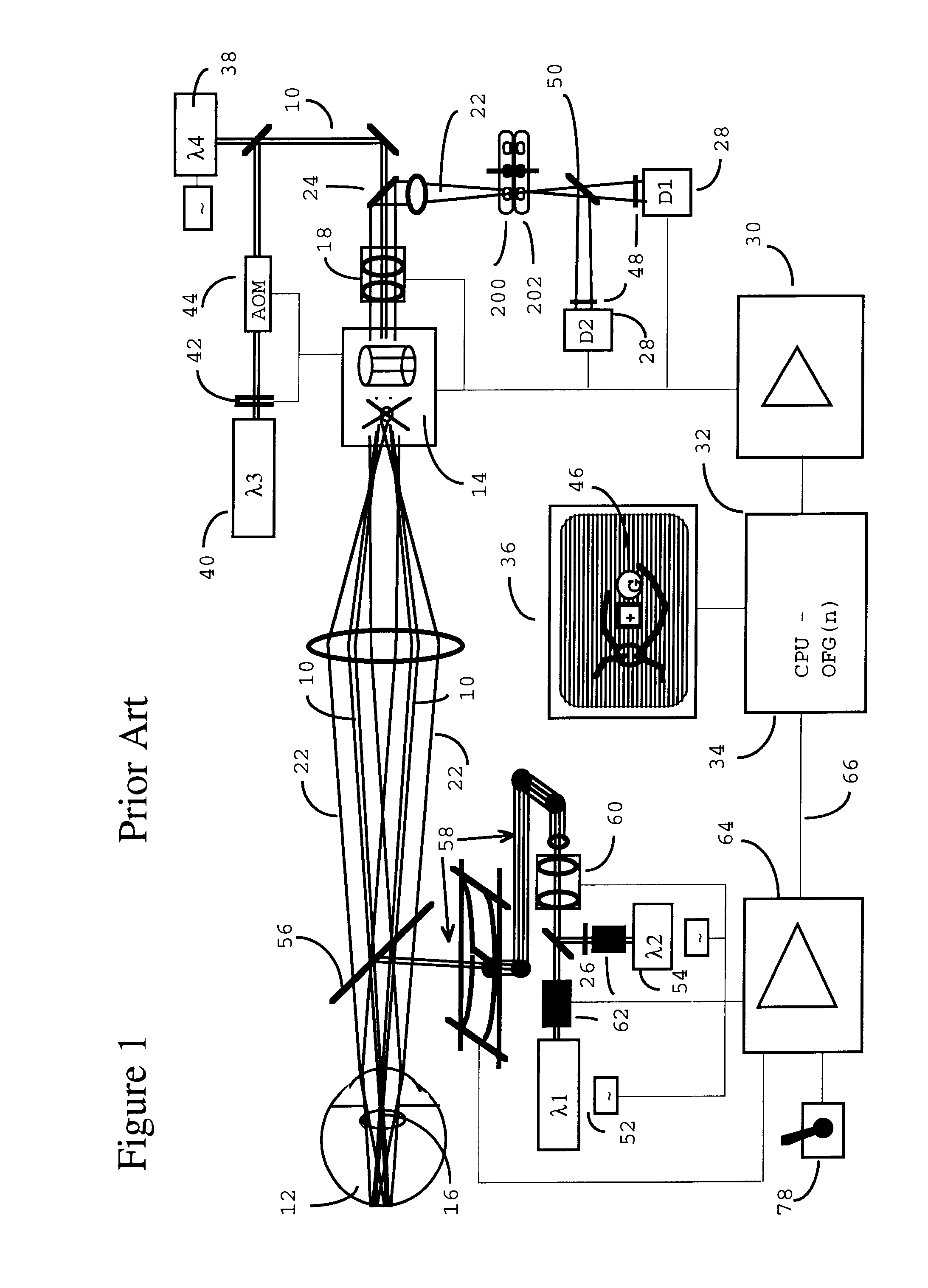
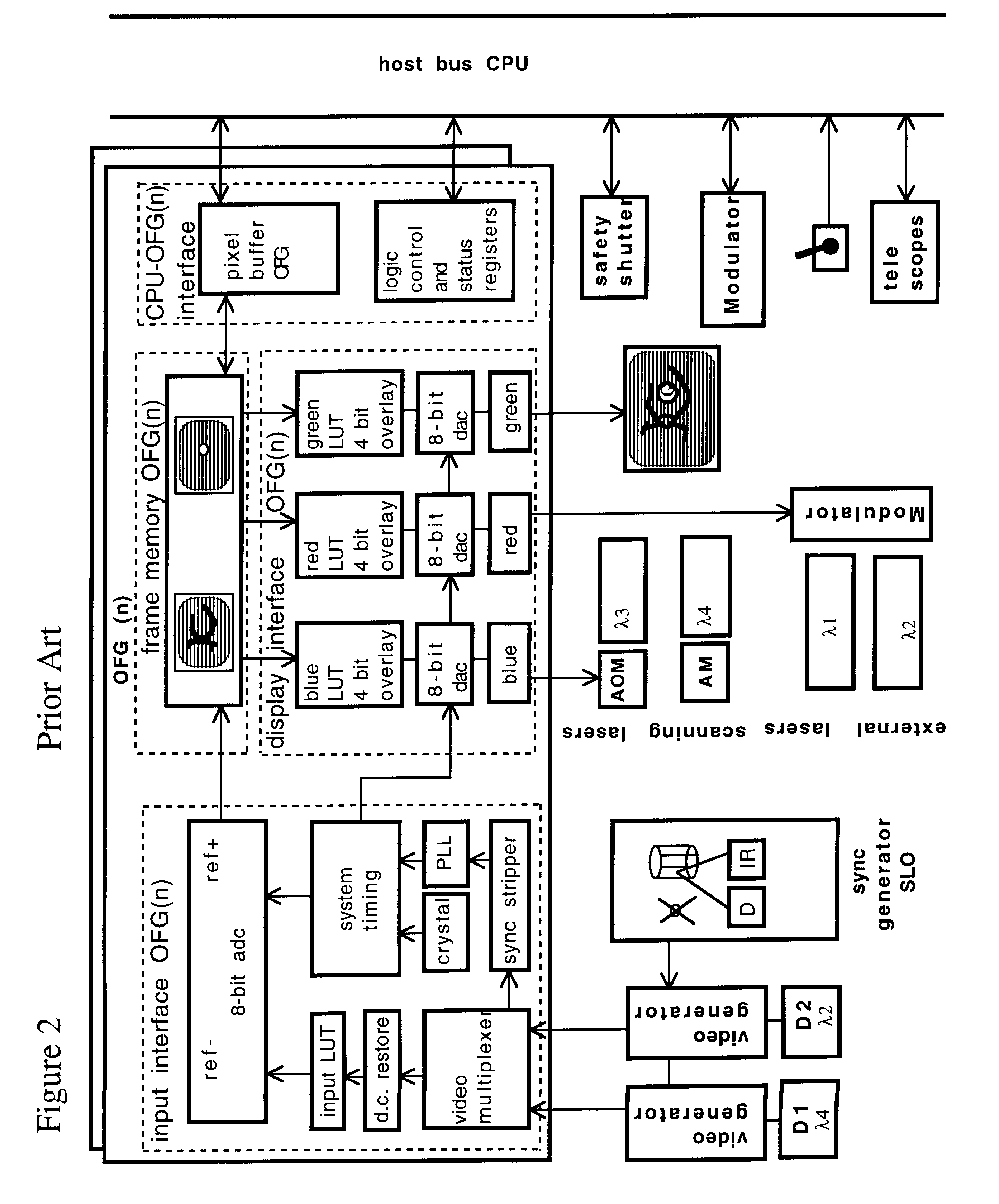
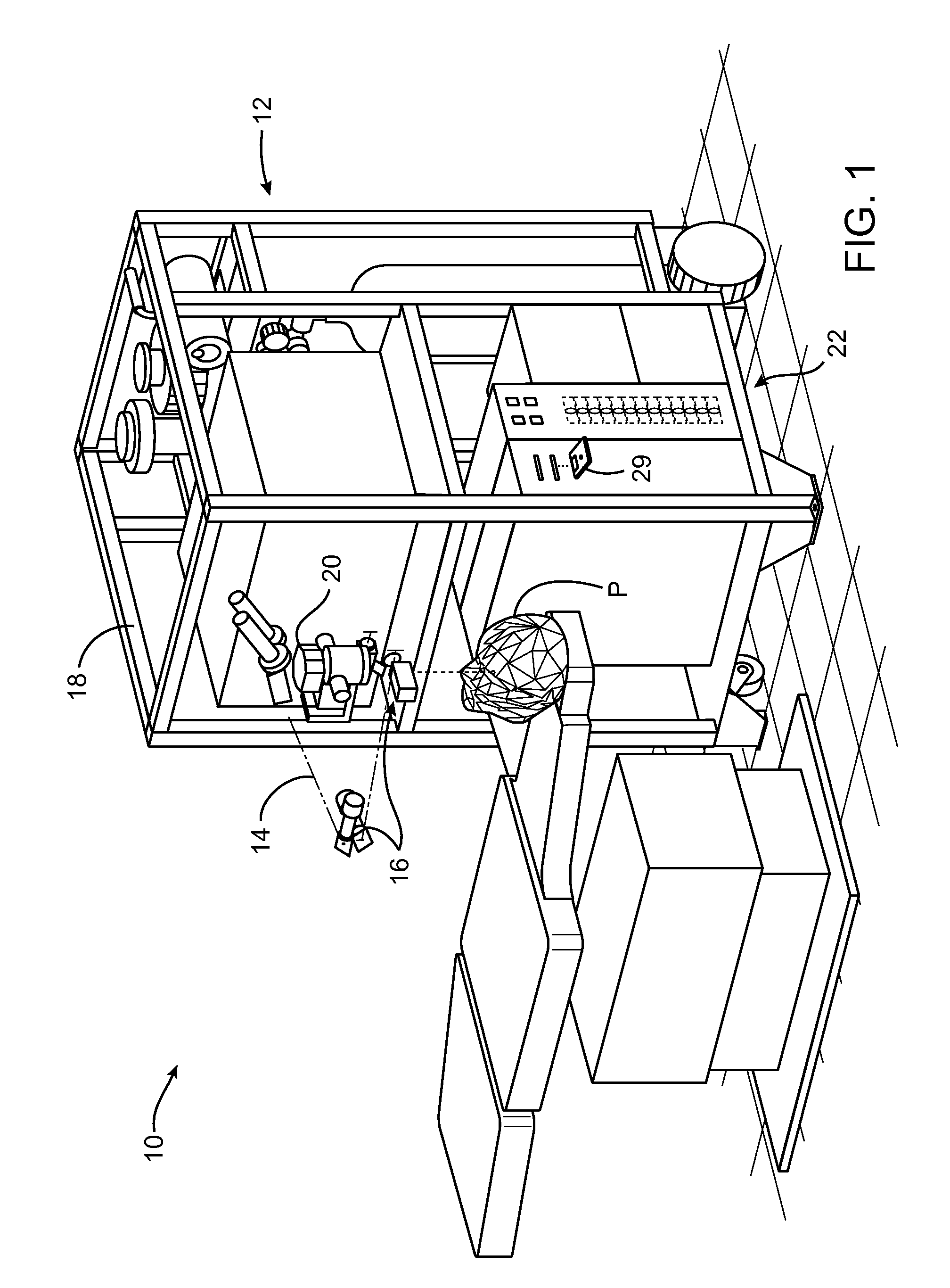
Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for selective therapeutic laser
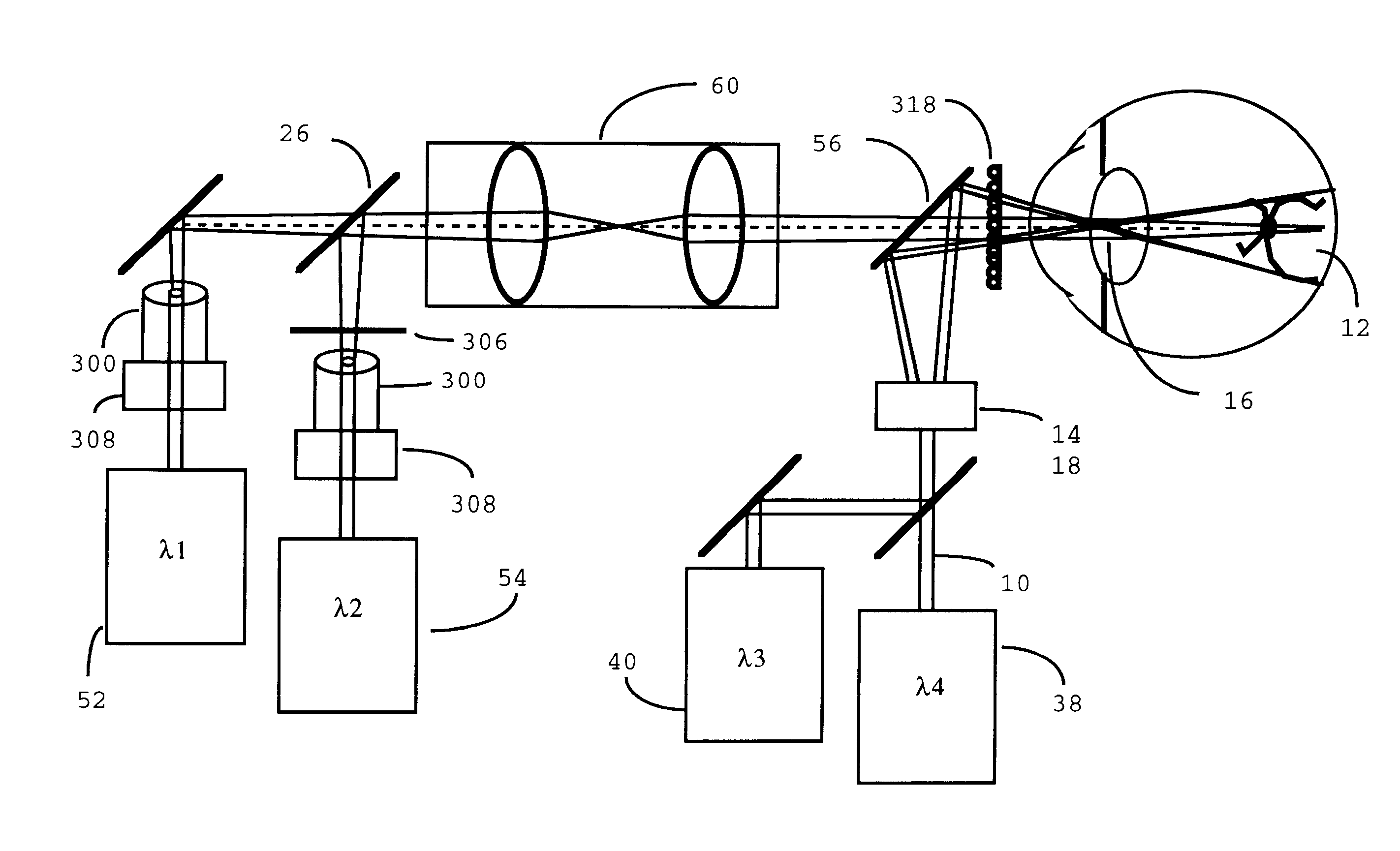
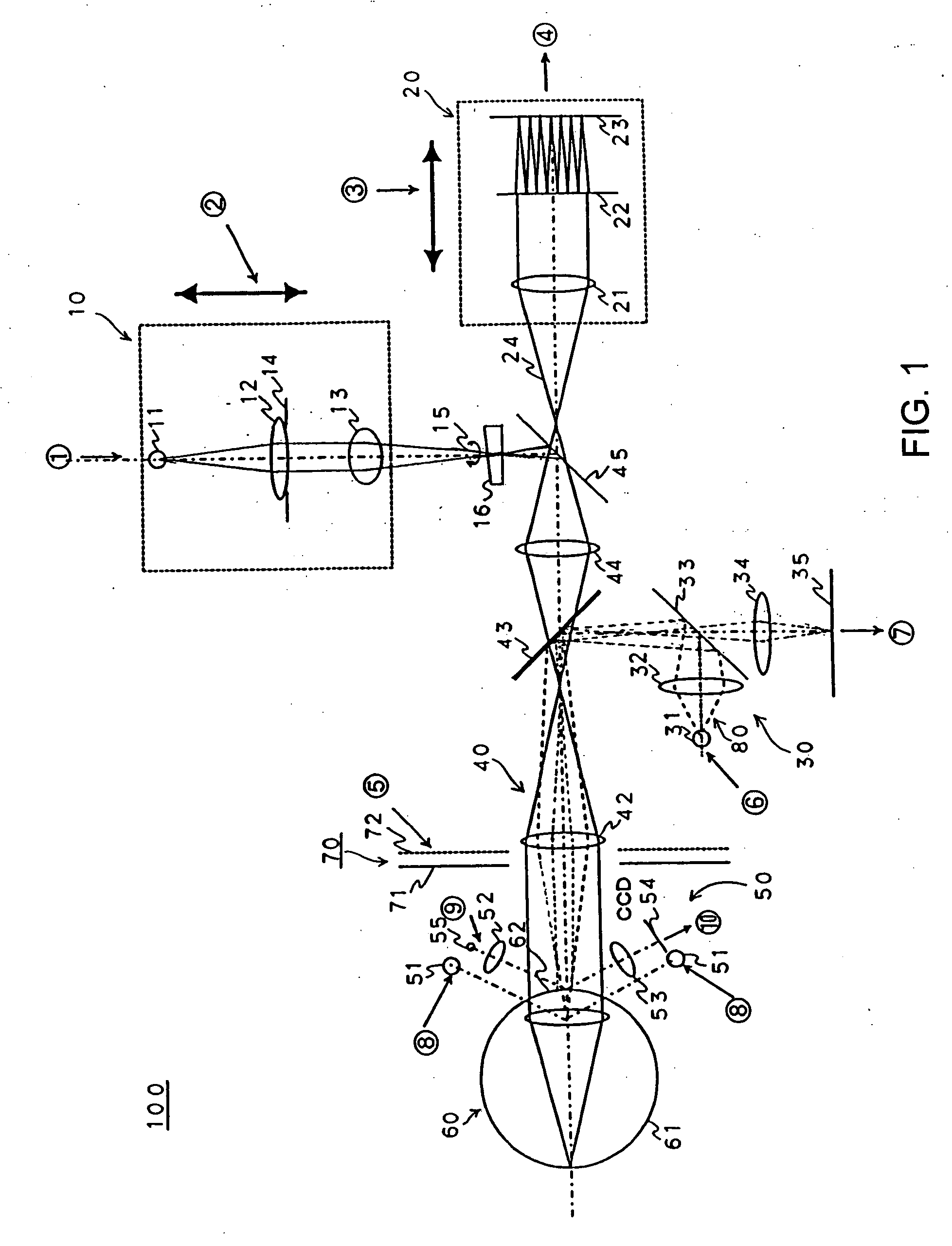
A combination of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope and external laser sources (52) is used for microphotocoagulation and photodynamic therapy, two examples of selective therapeutic laser. A linkage device incorporating a beamsplitter (56) and collimator-telescope (60) is adjusted to align the pivot point (16) of the scanning lasers (38, 40) and external laser source (52). A similar pivot point minimizes wavefront aberrations, enables precise focusing and registration of the therapeutic laser beam (52) on the retina without the risk of vignetting. One confocal detection pathway of the scanning laser ophthalmoscope images the retina. A second and synchronized detection pathway with a different barrier filter (48) is needed to draw the position and extent of the therapeutic laser spot on the retinal image, as an overlay (64). Advanced spatial modulation increases the selectivity of the therapeutic laser. In microphotocoagulation, an adaptive optics lens (318) is attached to the scanning laser ophthalmoscope, in proximity of the eye. It corrects the higher order optical aberrations of the eye optics, resulting in smaller and better focused applications. In photodynamic therapy, a spatial modulator (420) is placed within the collimator-telescope (60) of the therapeutic laser beam (52), customizing its shape as needed. A similar effect can be obtained by modulating a scanning laser source (38) of appropriate wavelength for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:VAN DE VELDE JOZEK F
Method and apparatus for controlling ablation in refractive surgery
InactiveUS20050107775A1Minimize spatial overlapThe result is accurateLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorFarsightedness
The present invention relates to laser ablation patterns to correct refractive errors of the eye (60) such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and higher order aberrations of the eye (60). The laser ablation patterns used to control the laser (10) prevent induced aberrations by compensating for post-procedure epithelial smoothing. The position of laser pulses (12) is also controlled to optimize the achievement of the intended ablation pattern.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
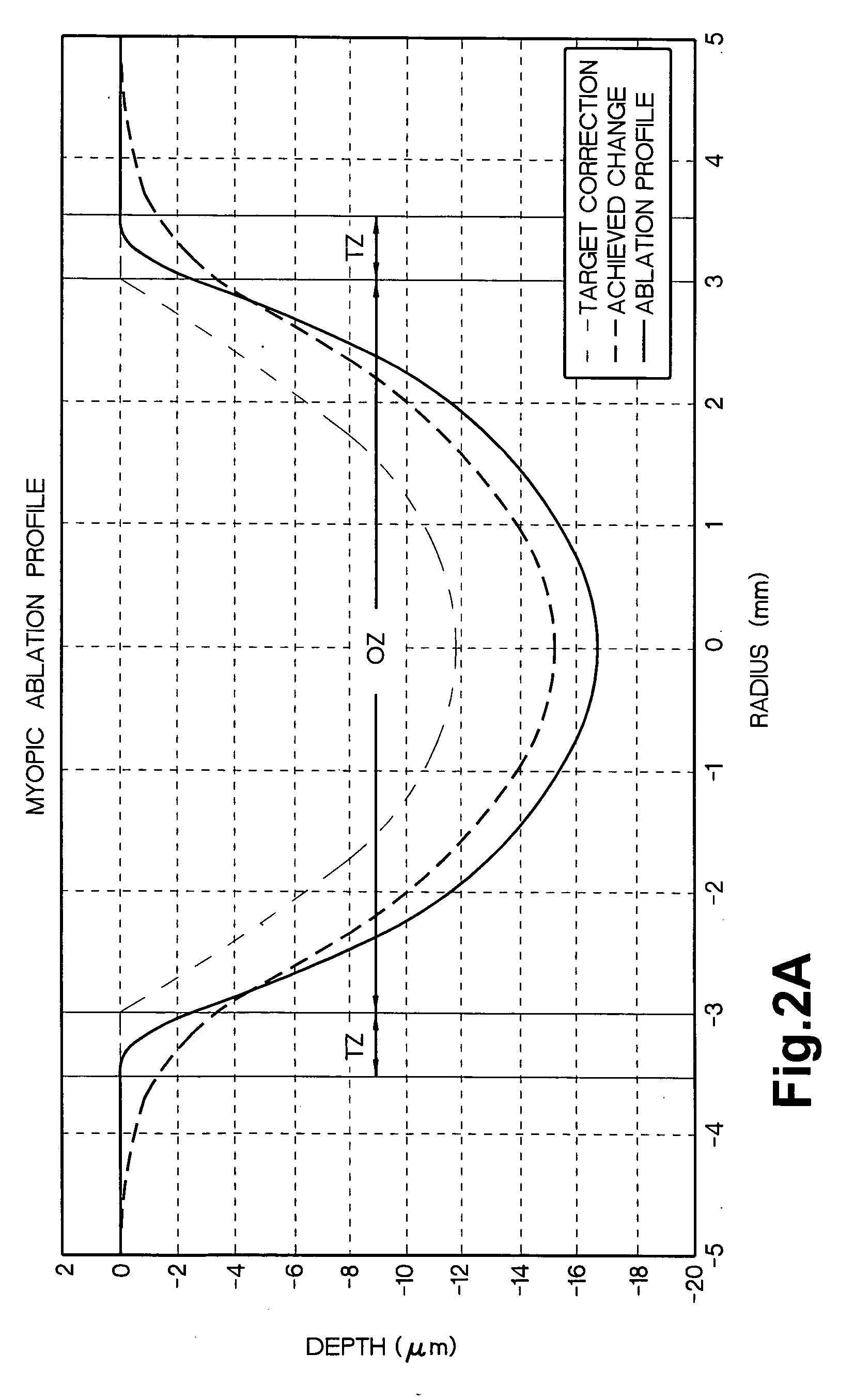
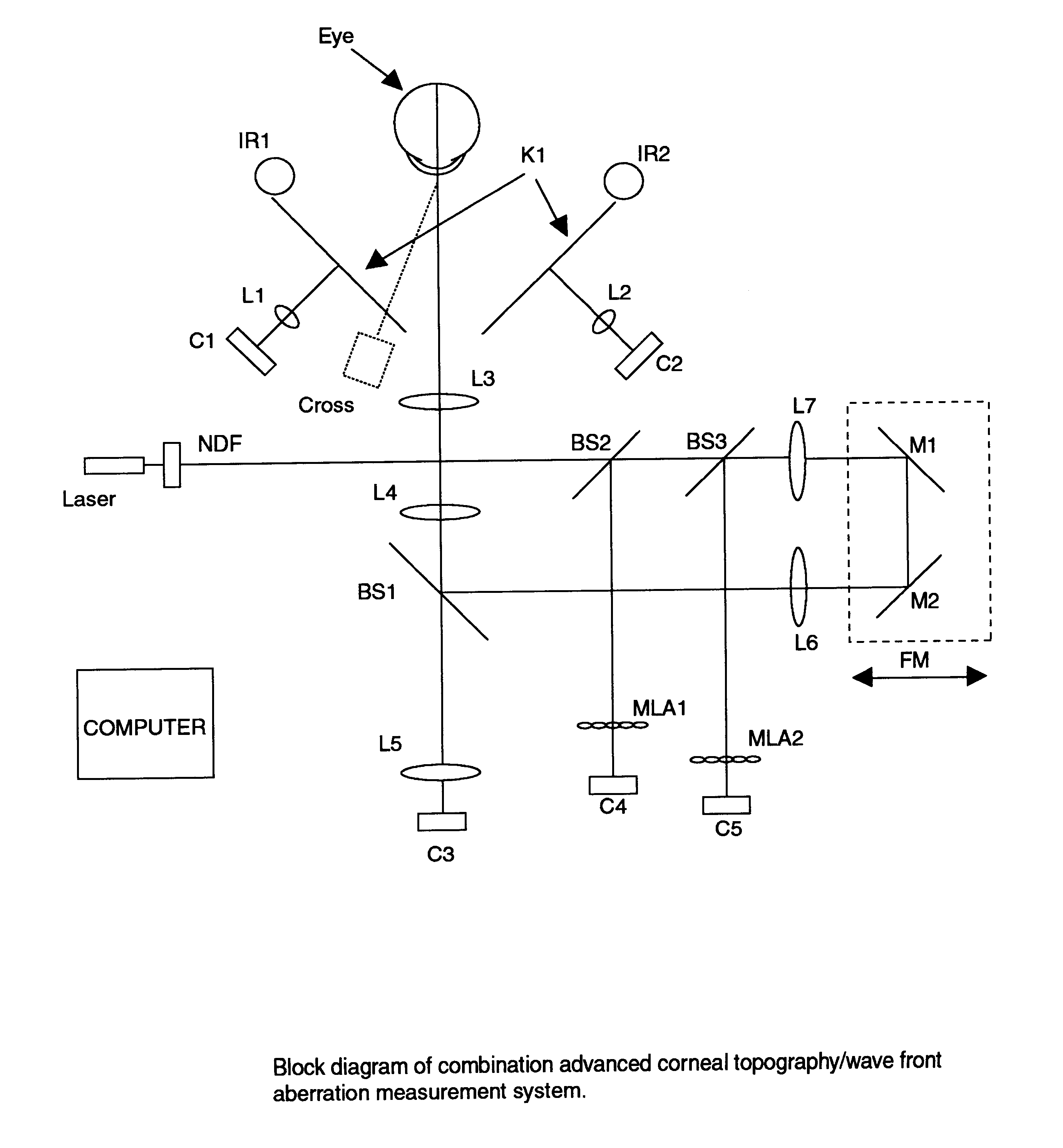
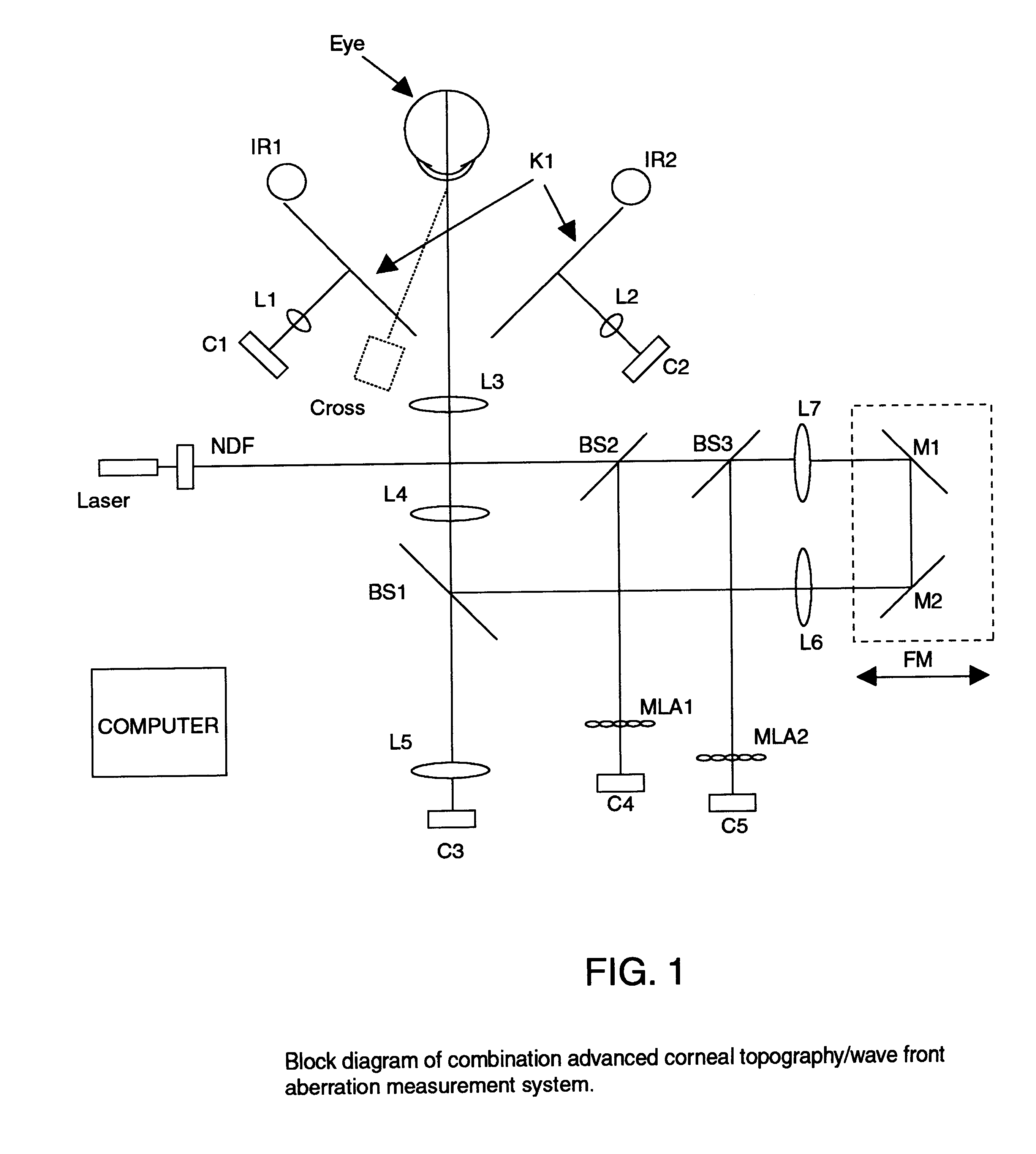
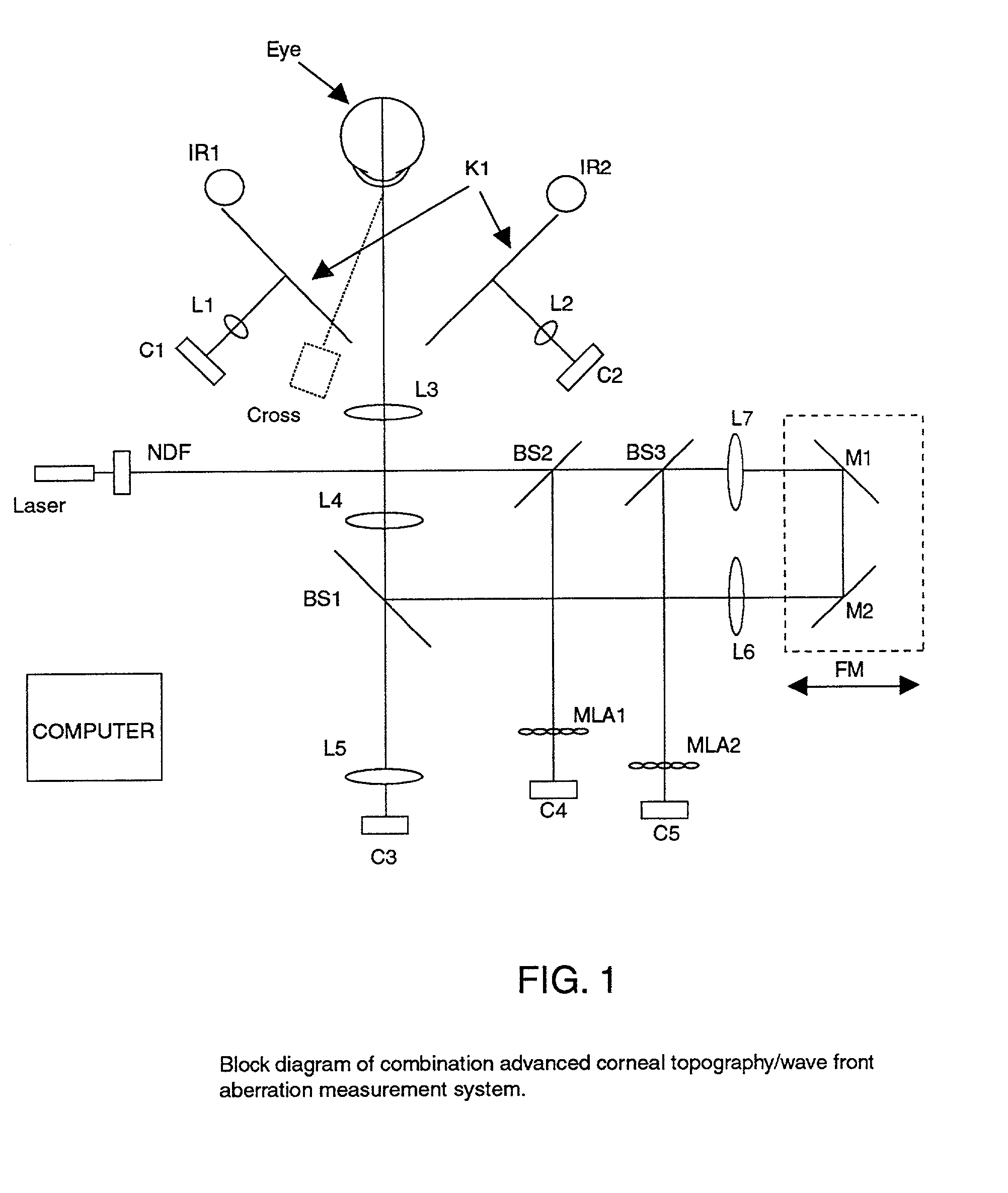
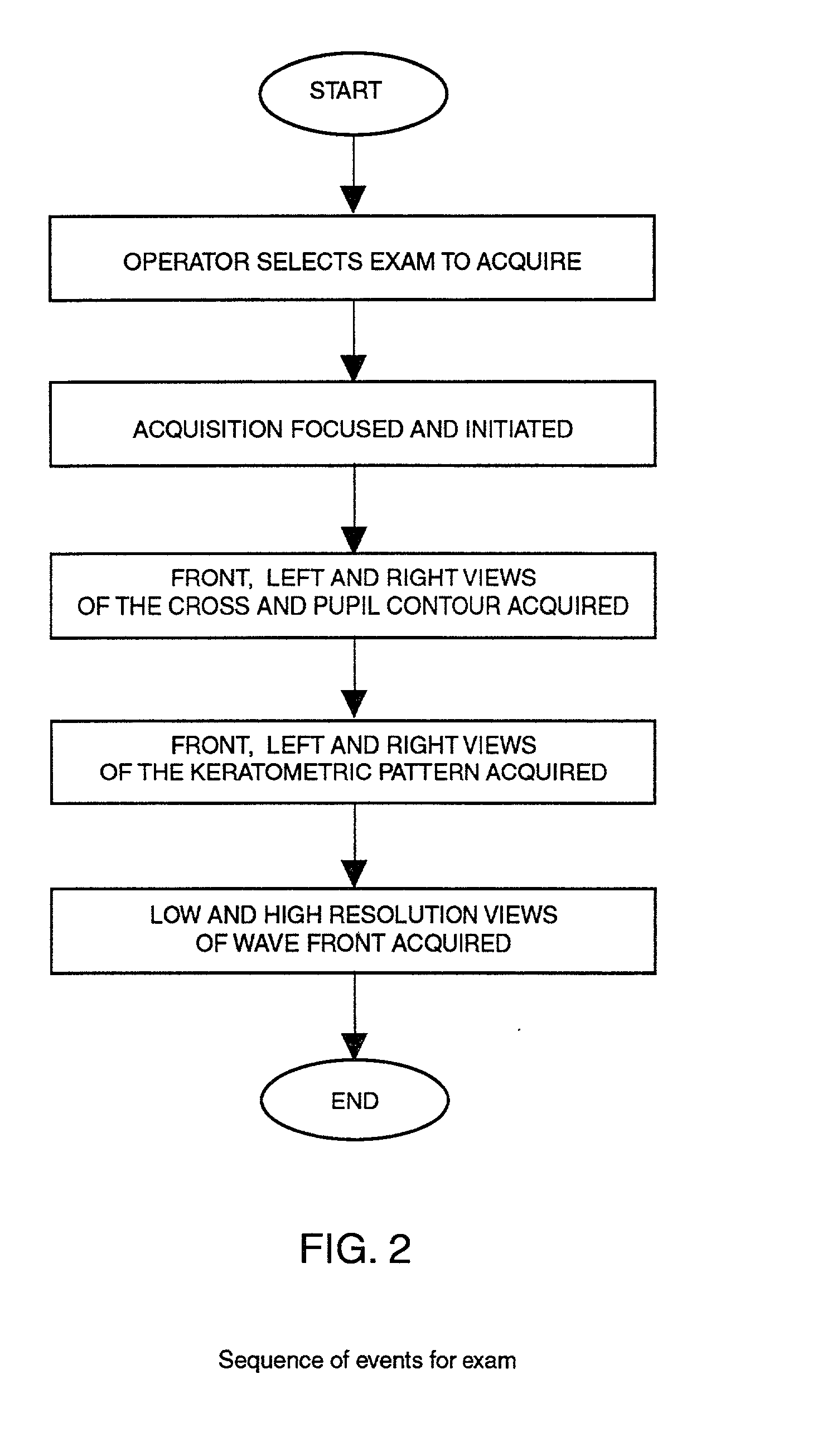
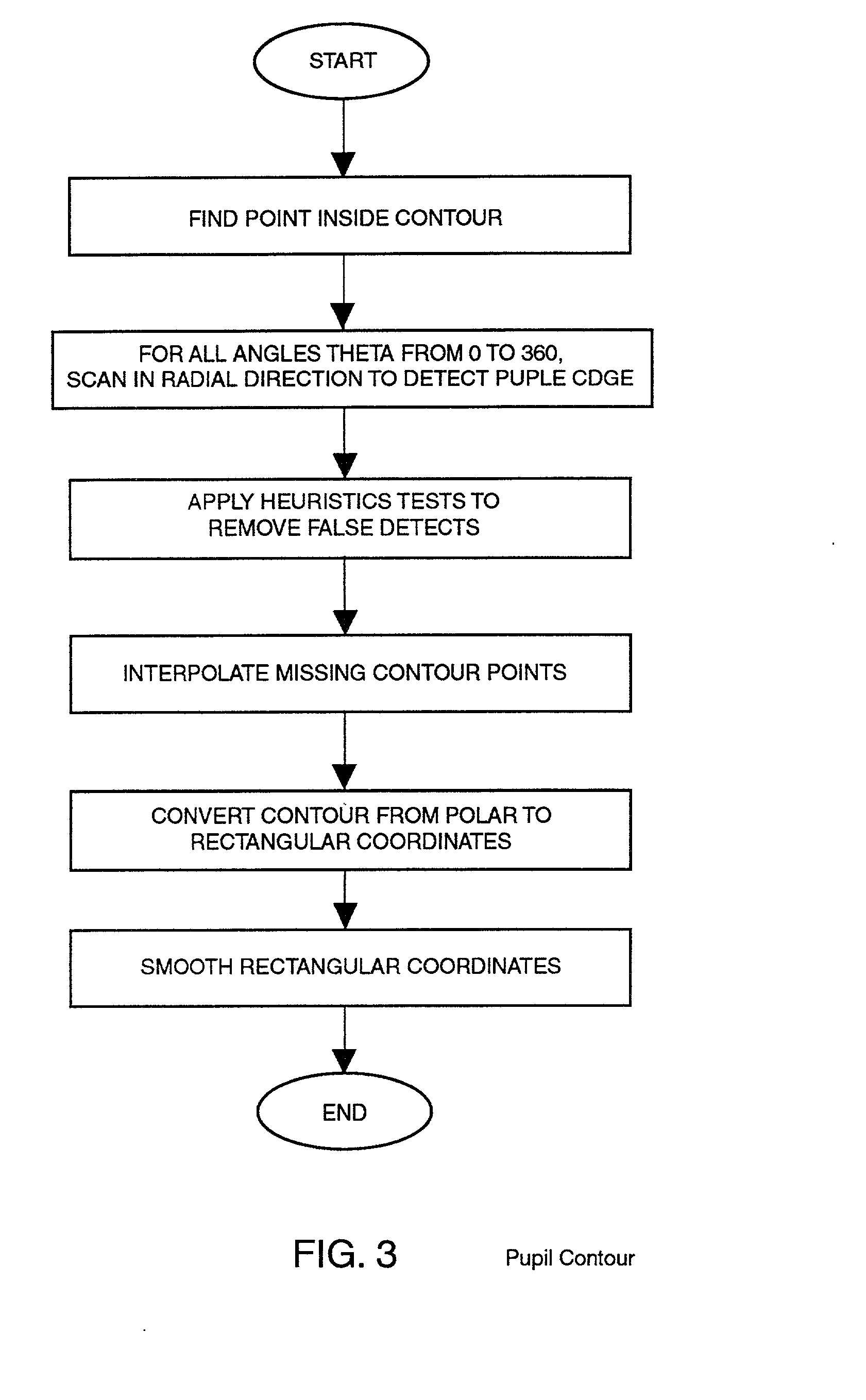
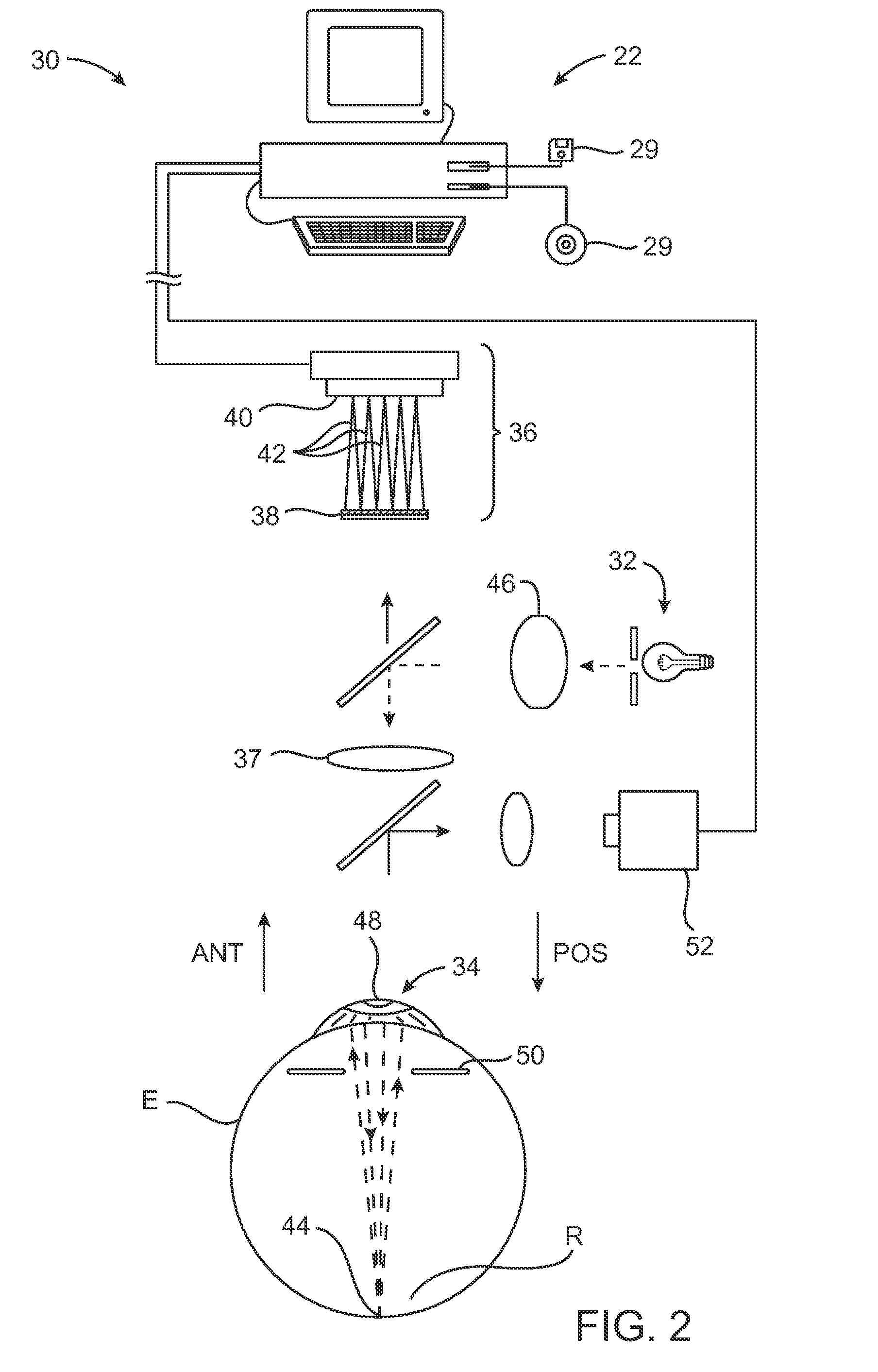
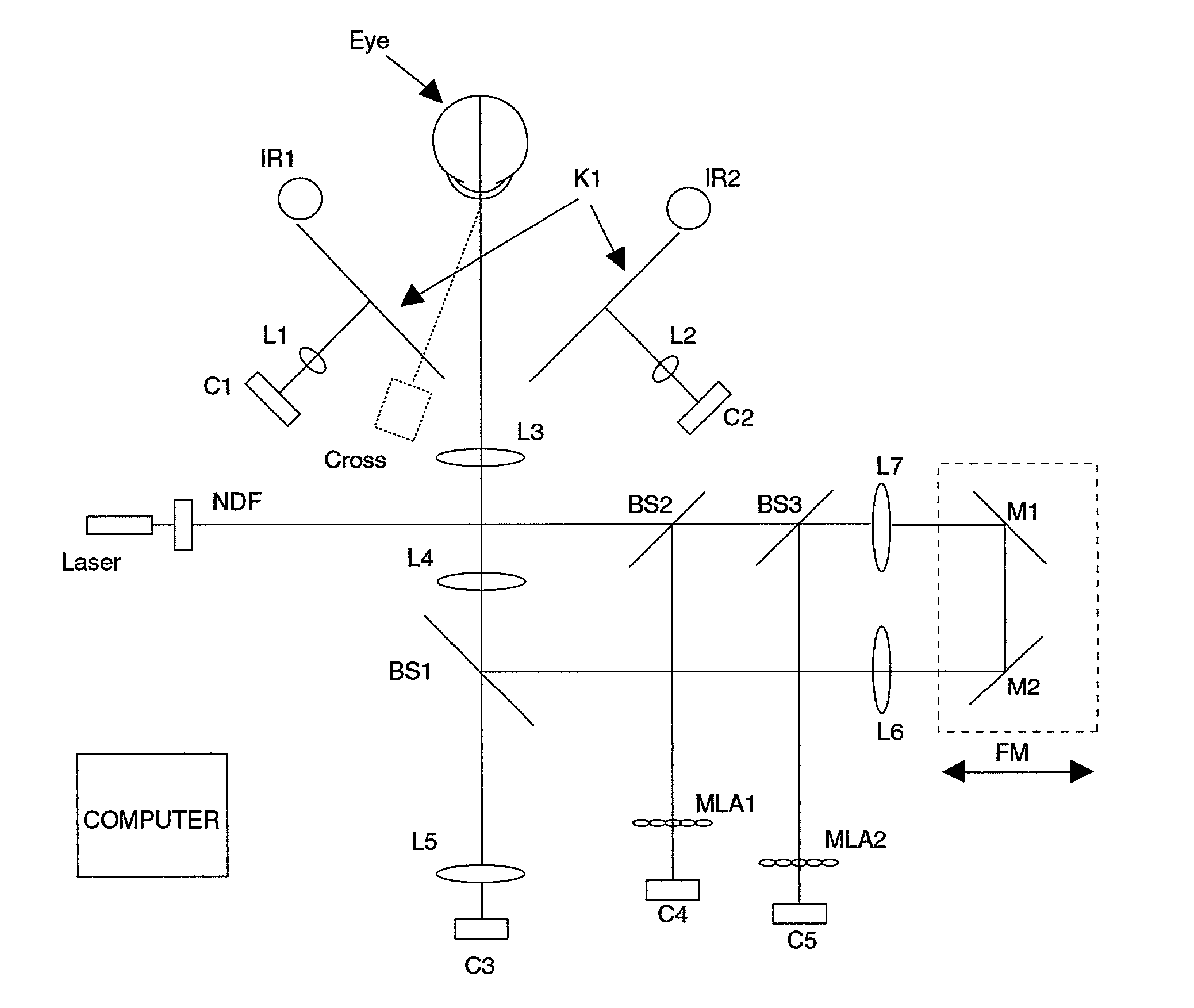
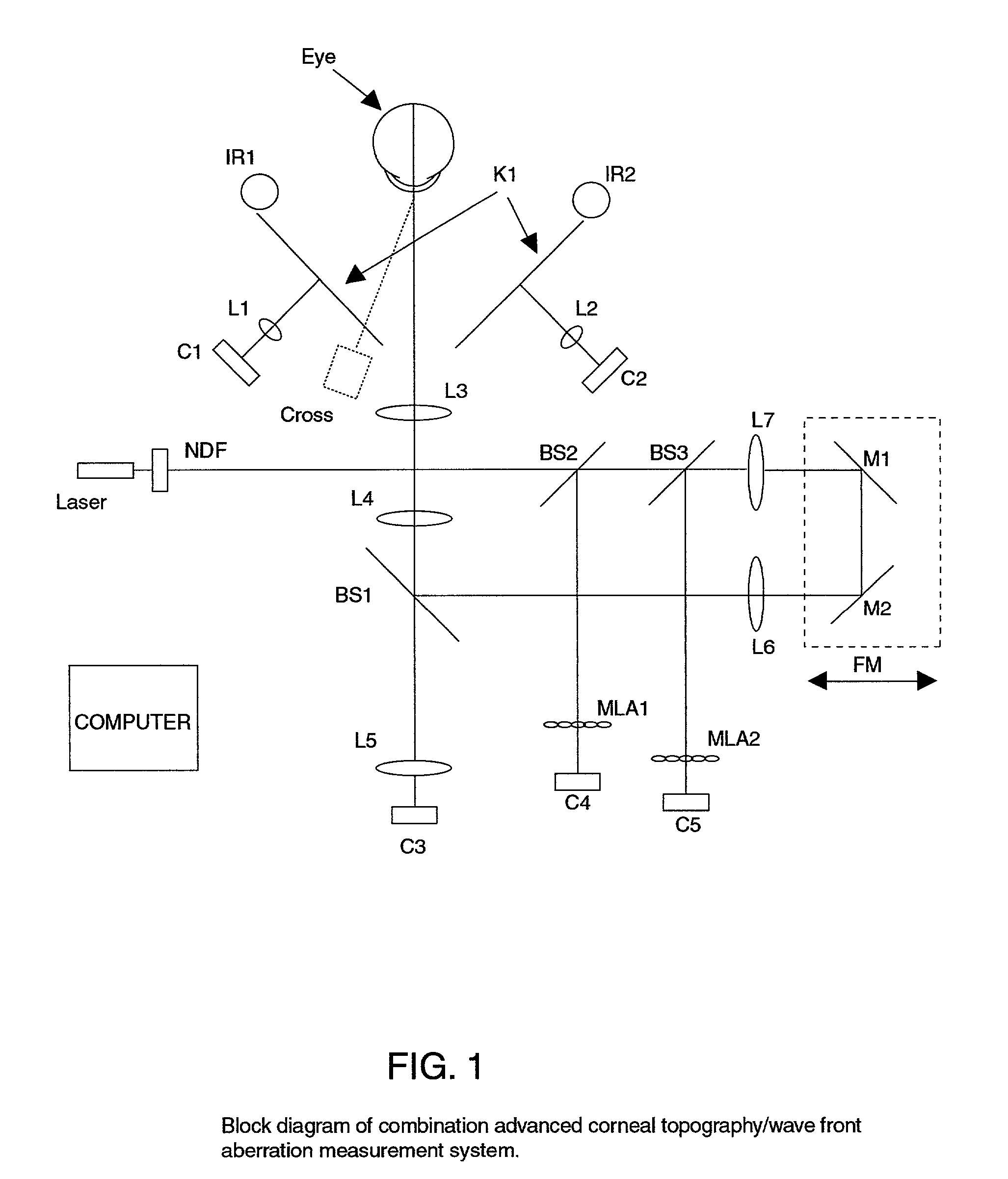
Combination advanced corneal topography/wave front aberration measurement
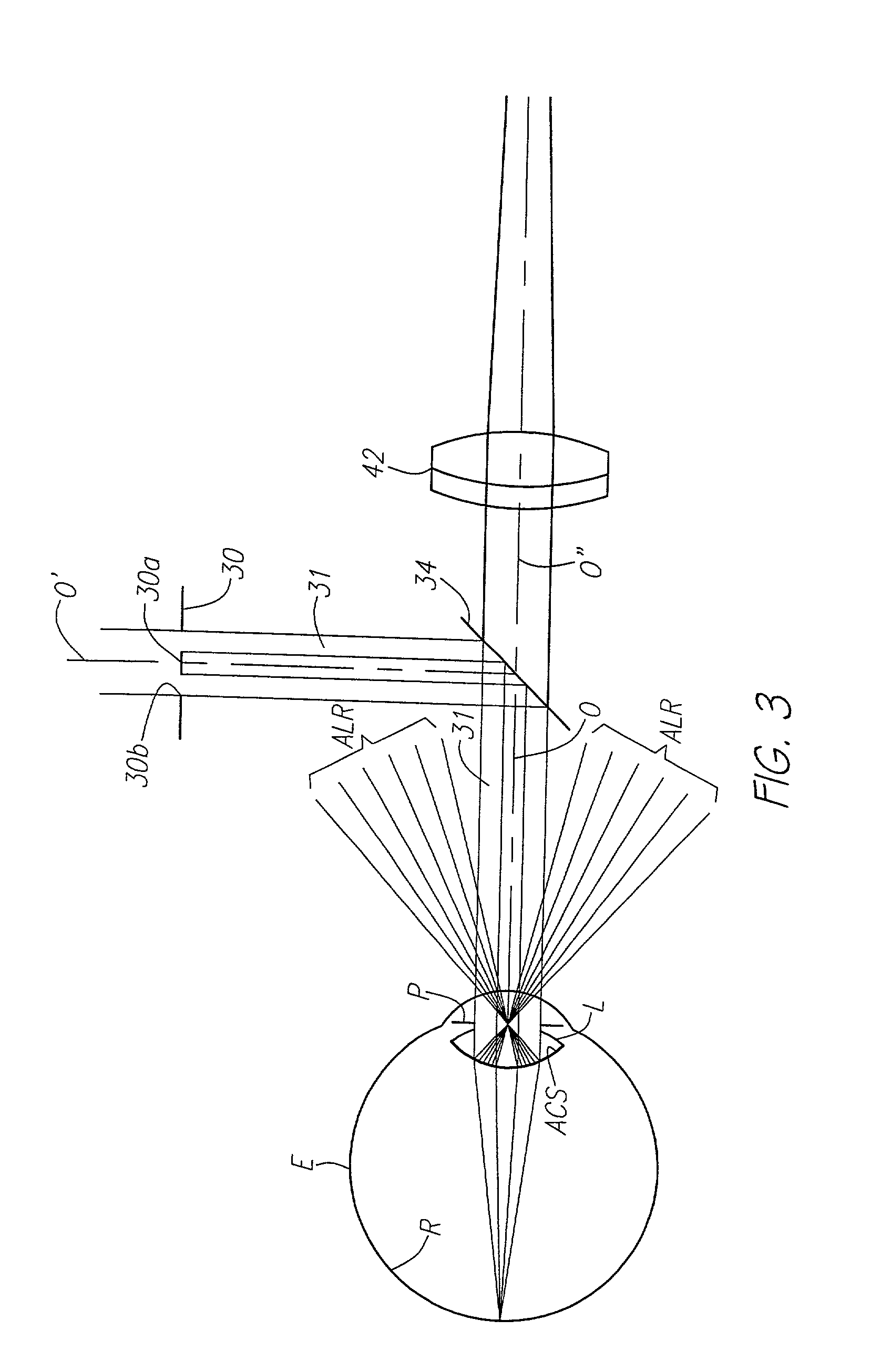
A method for the simultaneous measurement of the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces, corneal thickness, and optical aberrations of the eye. The method employs direct measurements and ray tracing to provide a wide range of measurements for use by the ophthalmic community.
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
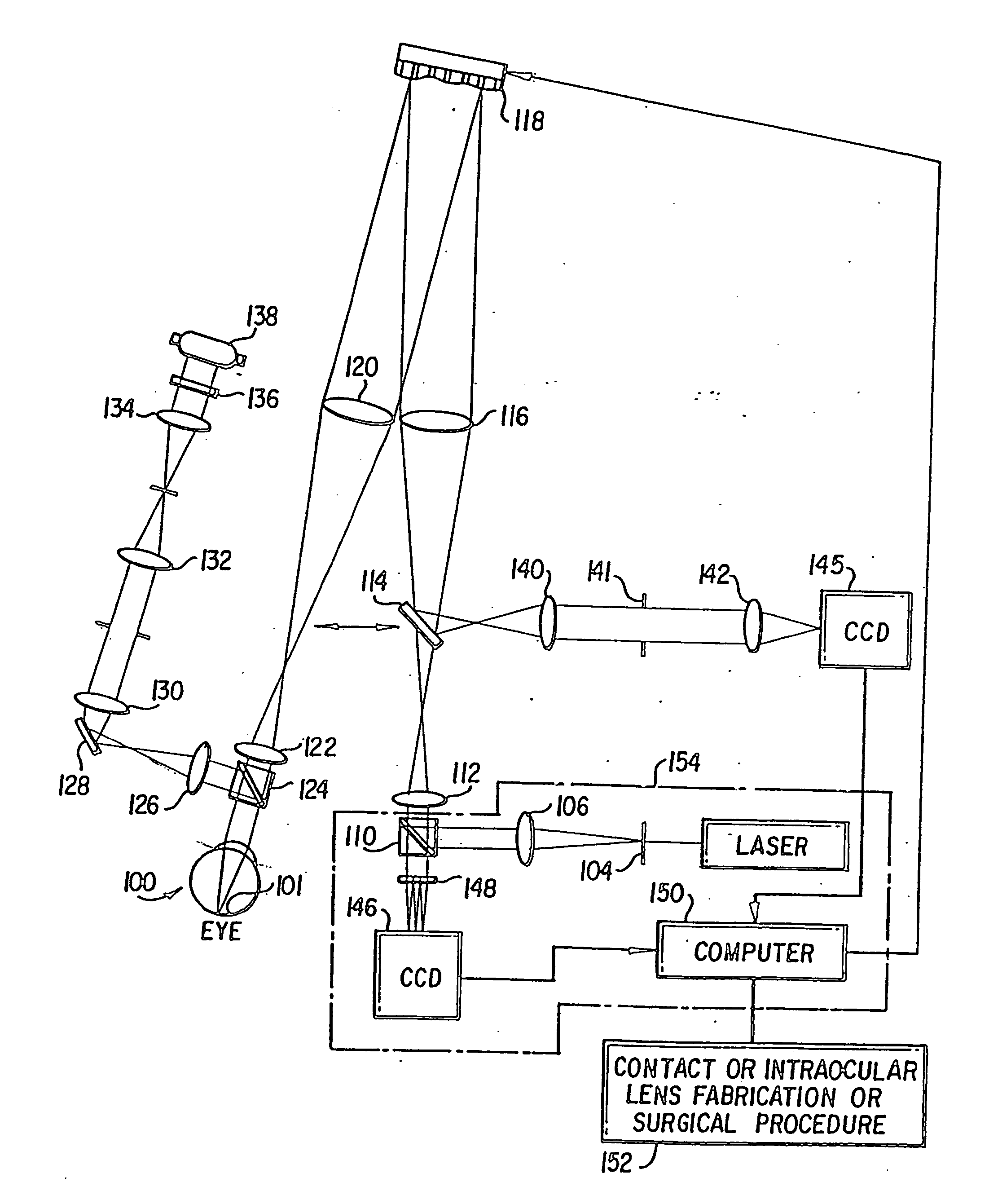
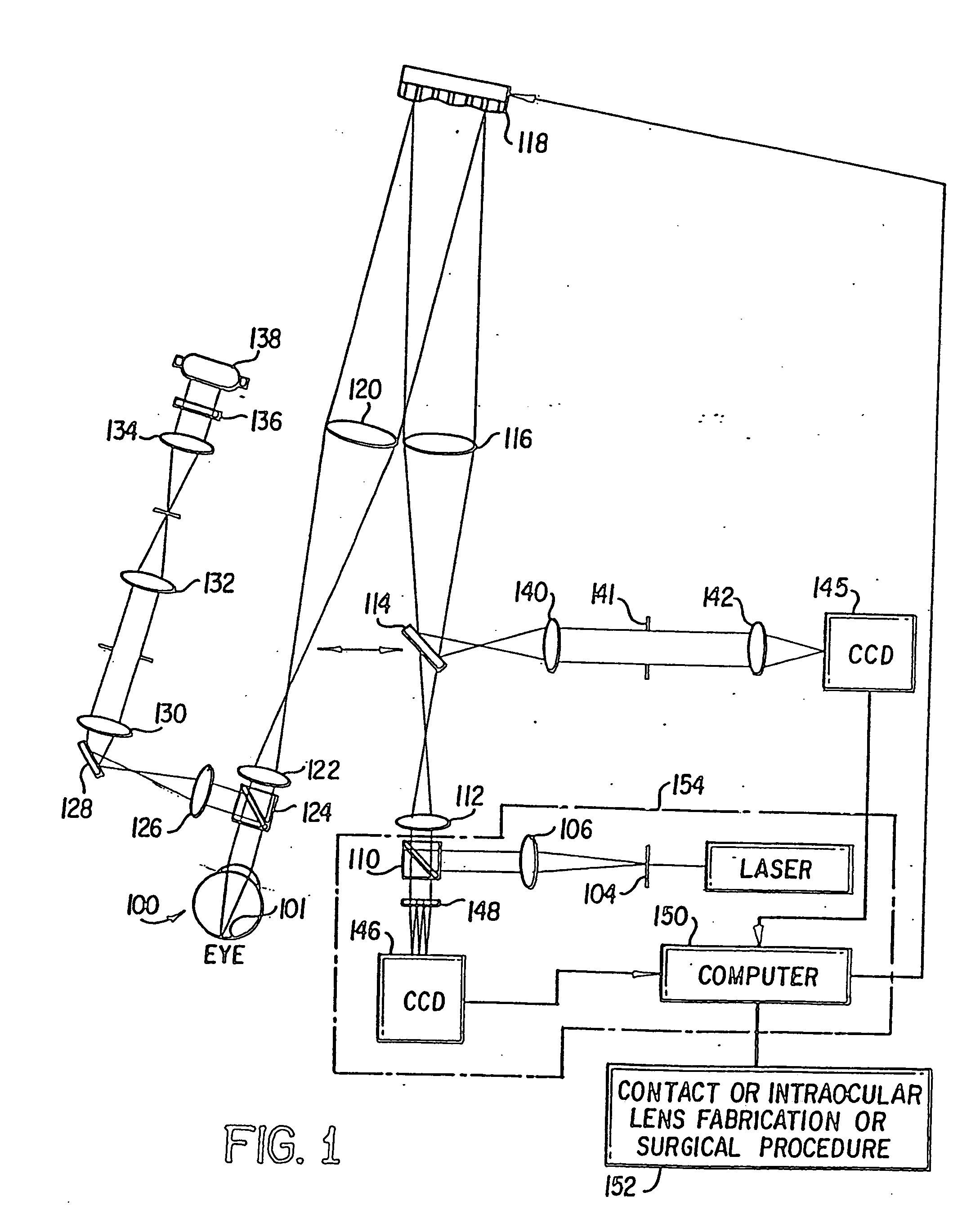
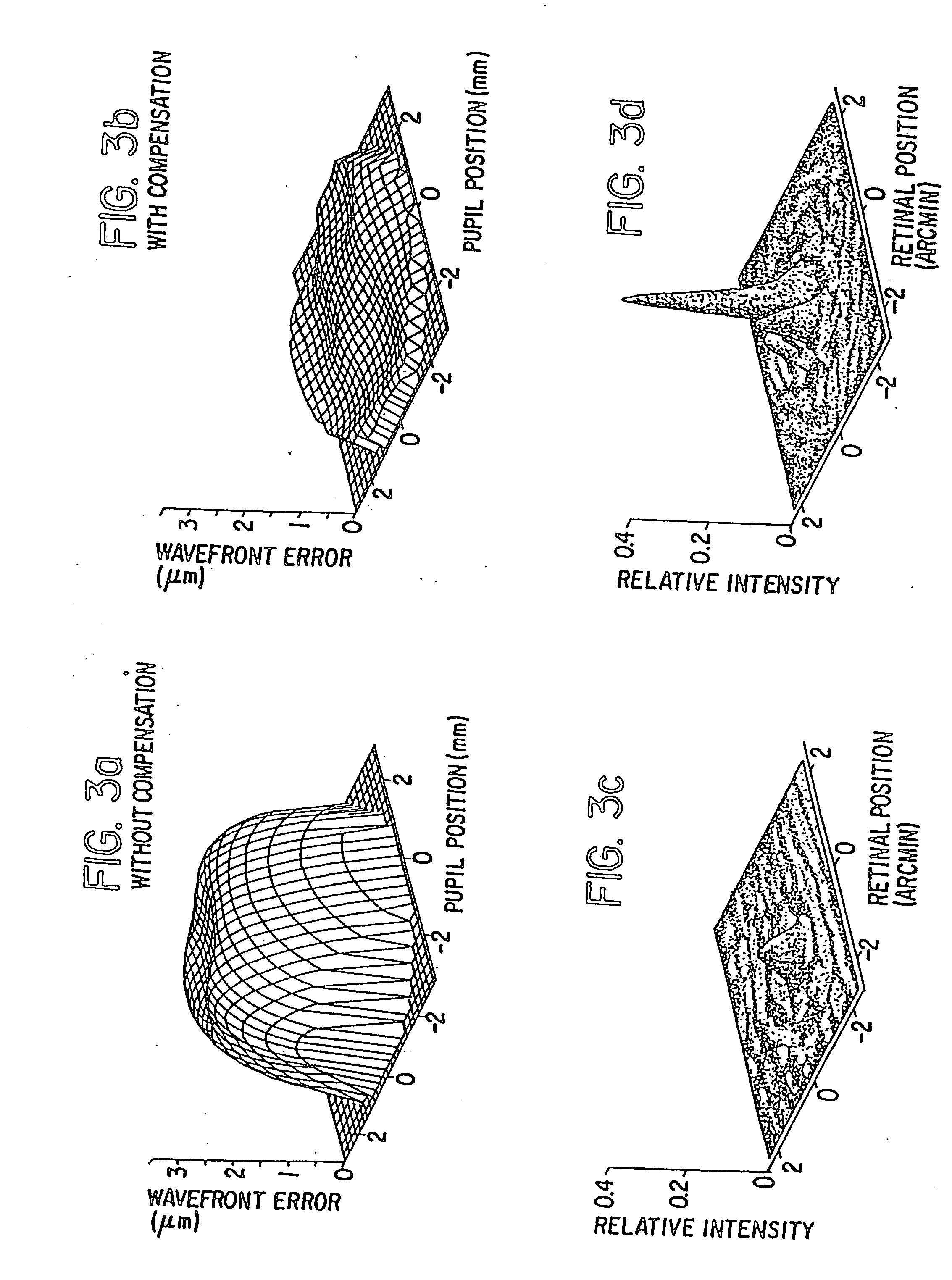
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
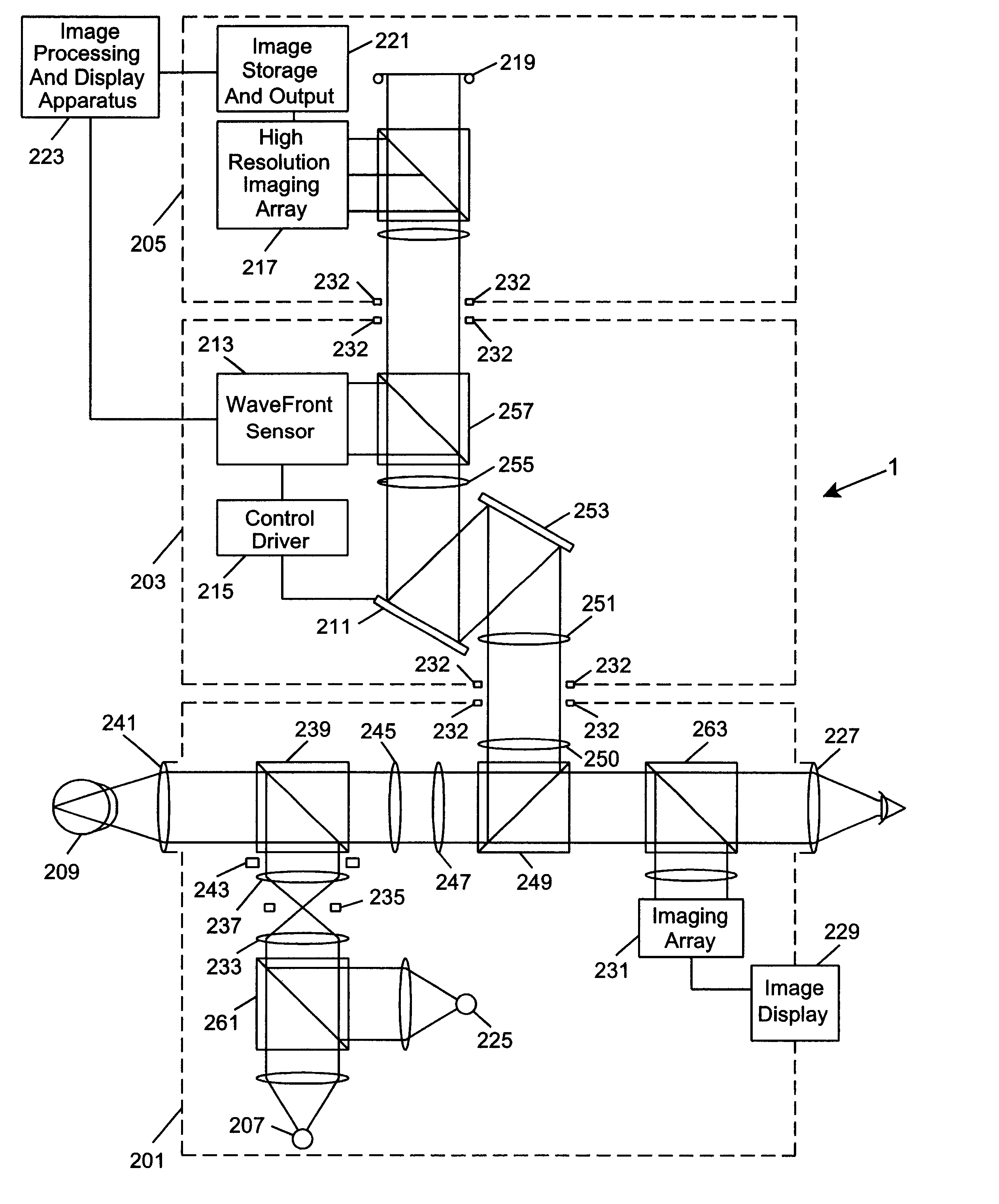
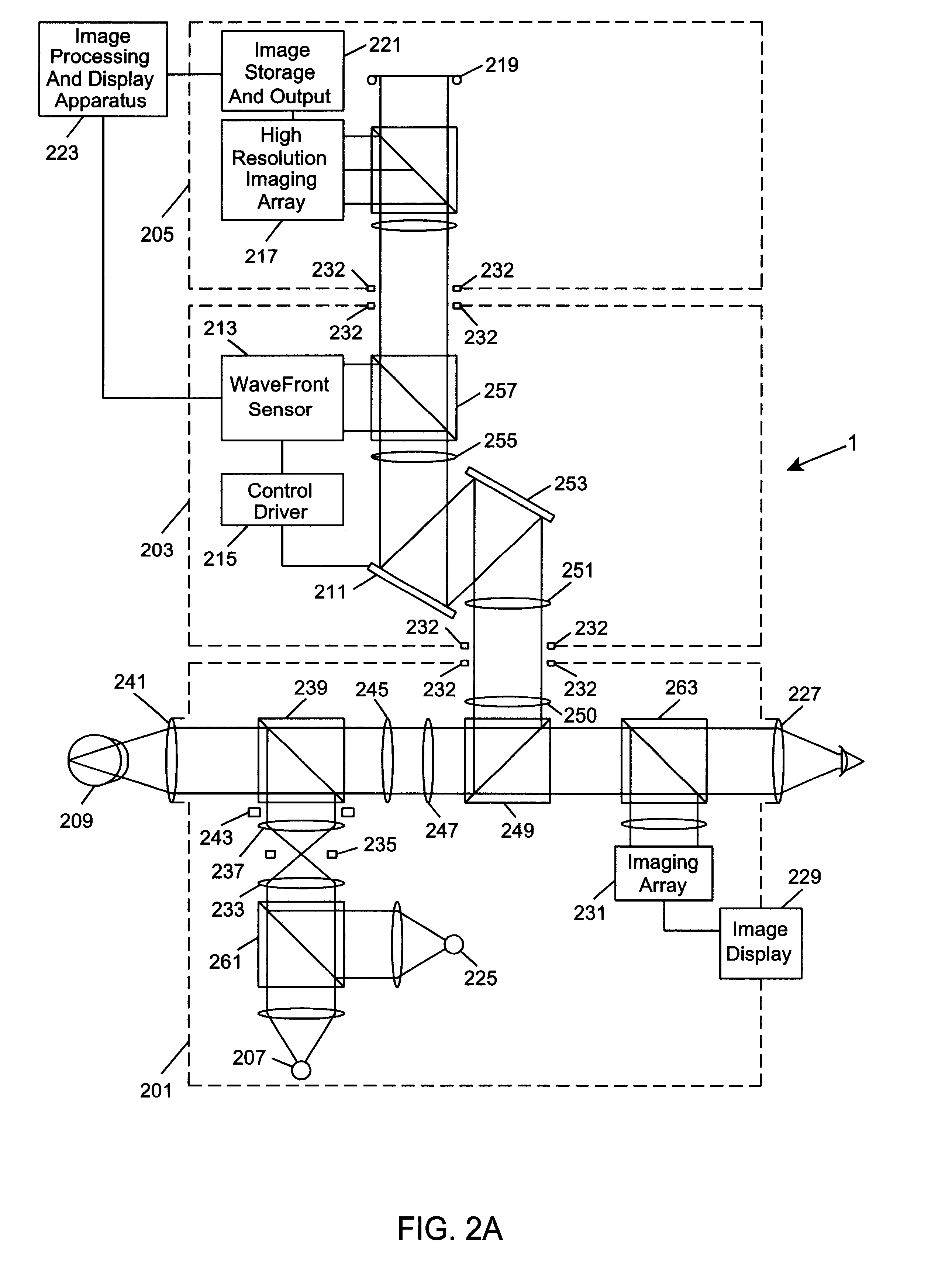
Ophthalmic instrument having an integral wavefront sensor and display device that displays a graphical representation of high order aberrations of the human eye measured by the wavefront sensor
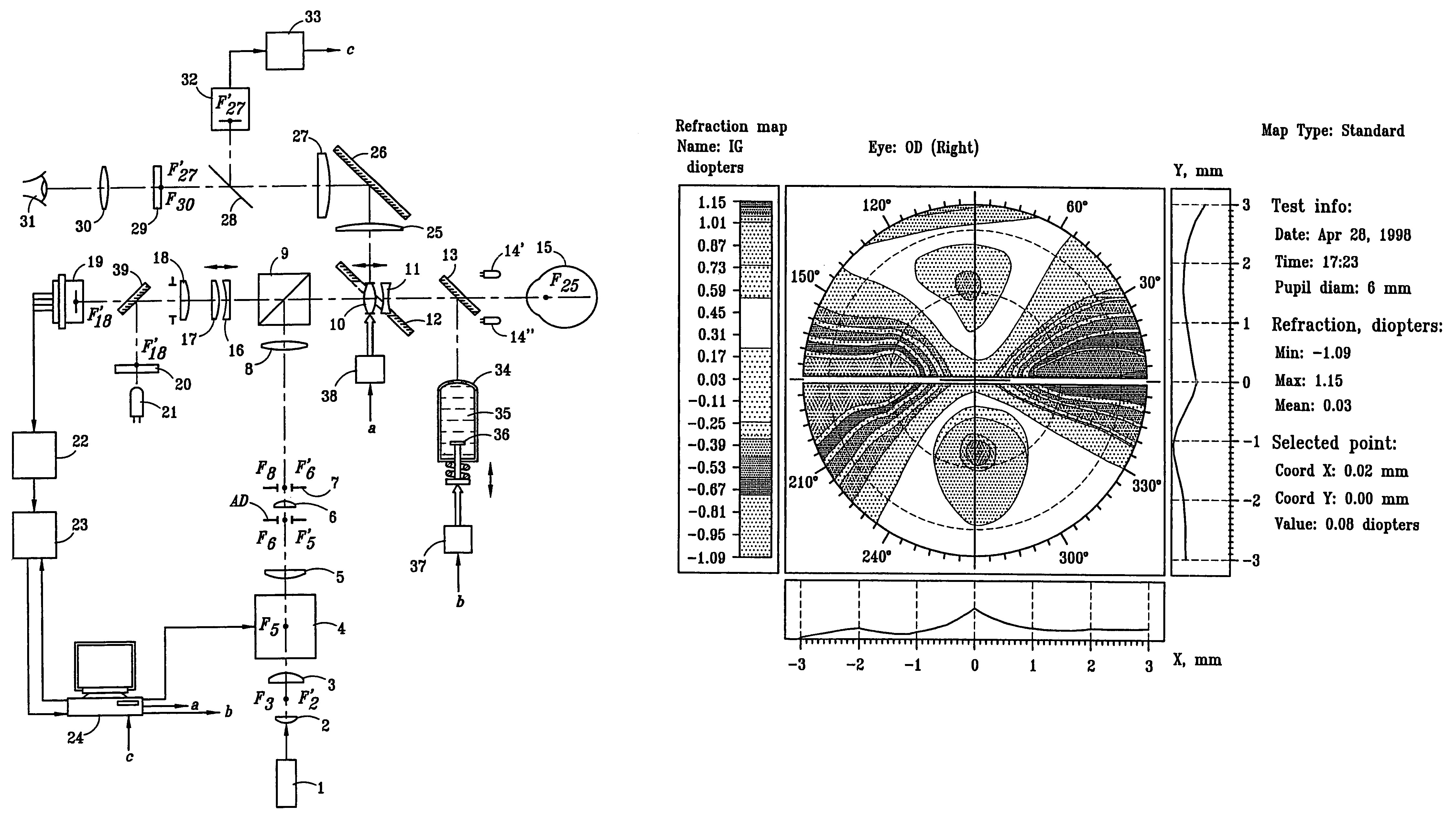
An improved ophthalmic instrument including an integral wavefront sensor and display device, wherein the wavefront sensor measures phase aberrations in reflections directed thereto to characterize aberrations of the eye and is operably coupled to the display device, which displays a graphical representation of the aberrations of the eye. Such graphical representation may include: two dimensional contour maps that graphically depict contribution of pre-specified terms (such as spherical aberration, astigmatism and coma) for the aberrations of the eye, coefficients corresponding to such pre-specified terms that characterize the aberrations of the eye, or predefined two-dimensional icons that provide a general graphical depiction of such prespecified terms. Such graphical representations provide the practitioner with valuable information characterizing the high order optical errors of the eye (which is far beyond the diopter information typically provided by current ophthalmic instruments) for use in diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities and disease in the eye.
Owner:ADAPTIVE OPTICS ASSOC
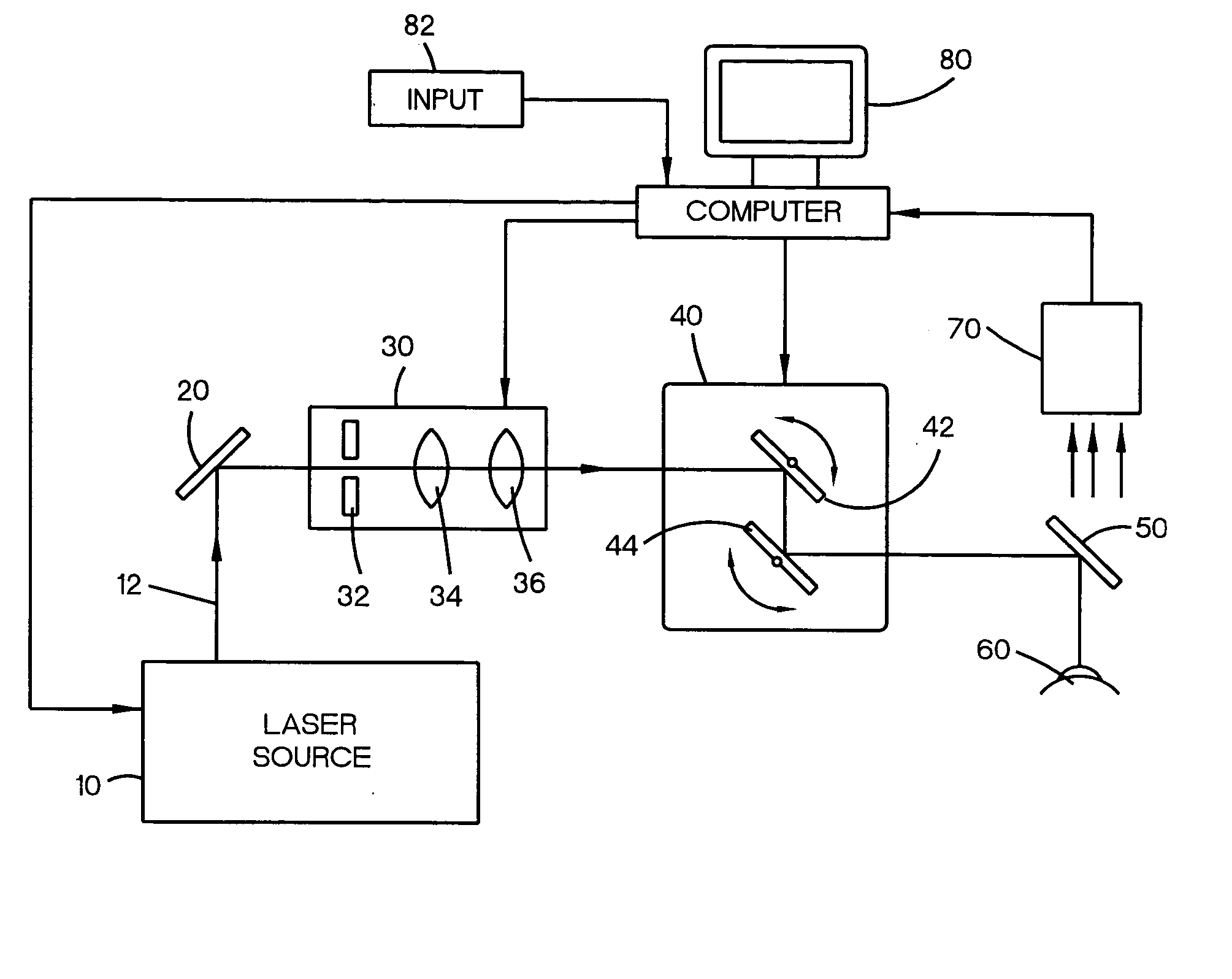
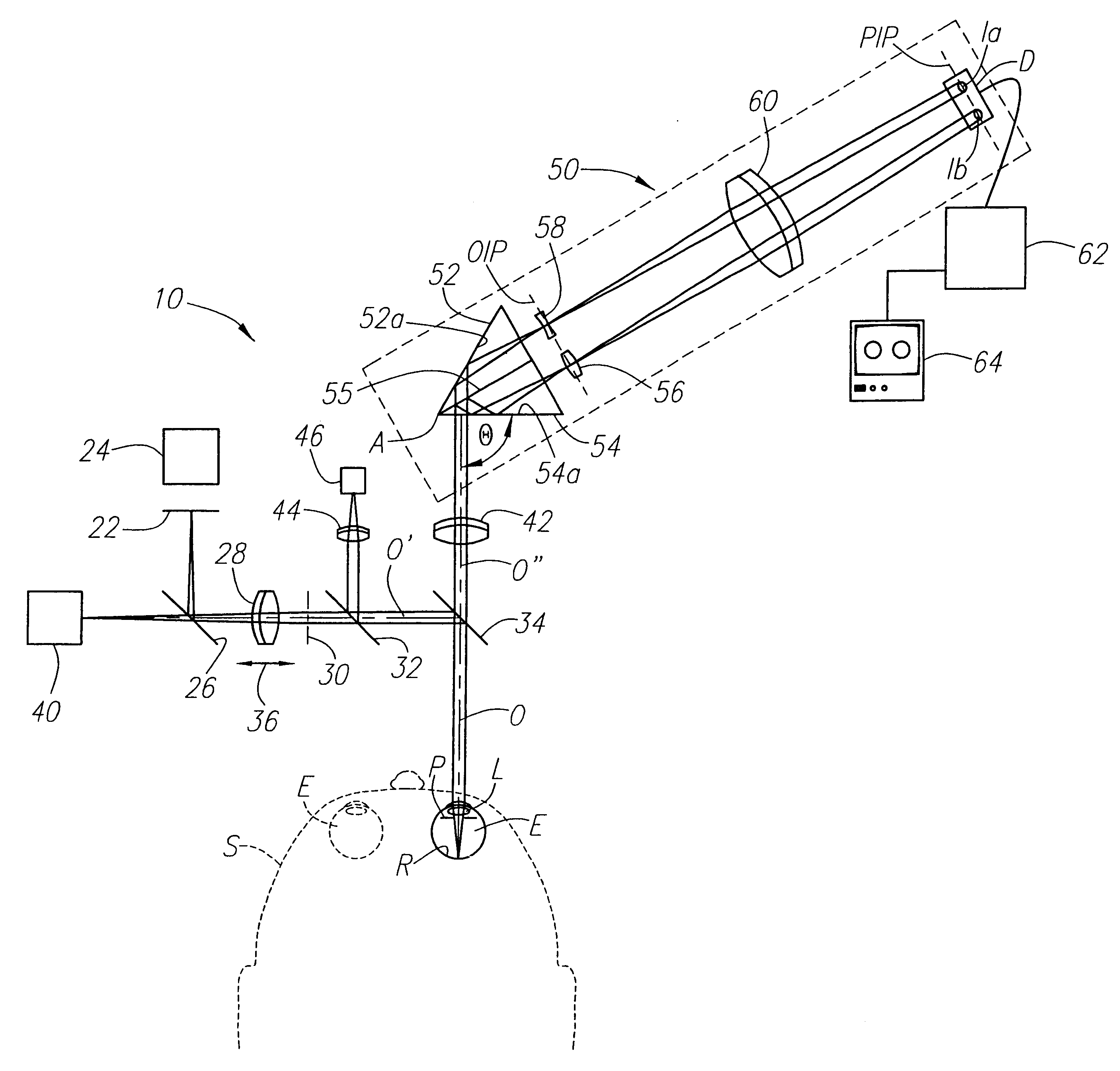
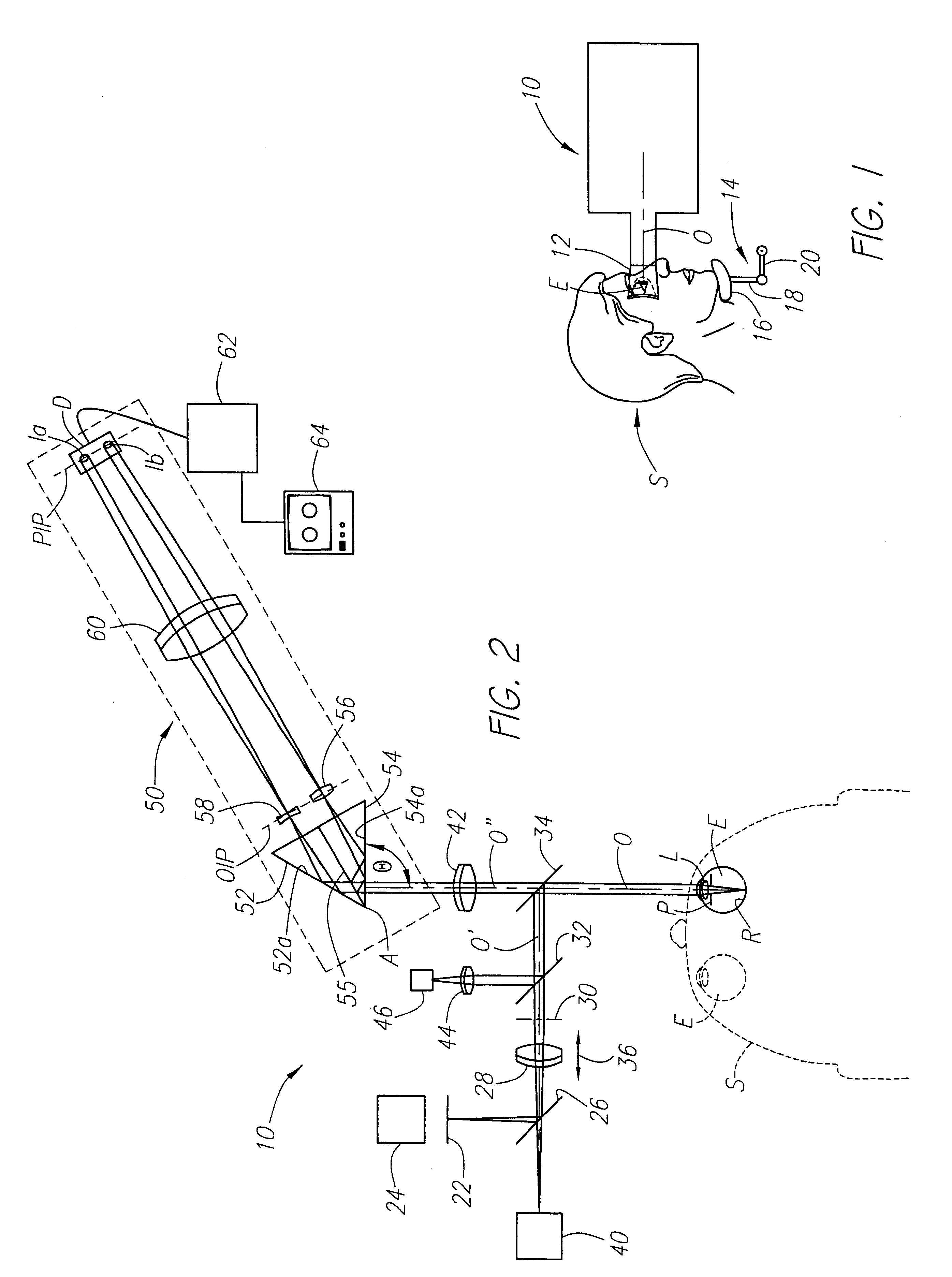
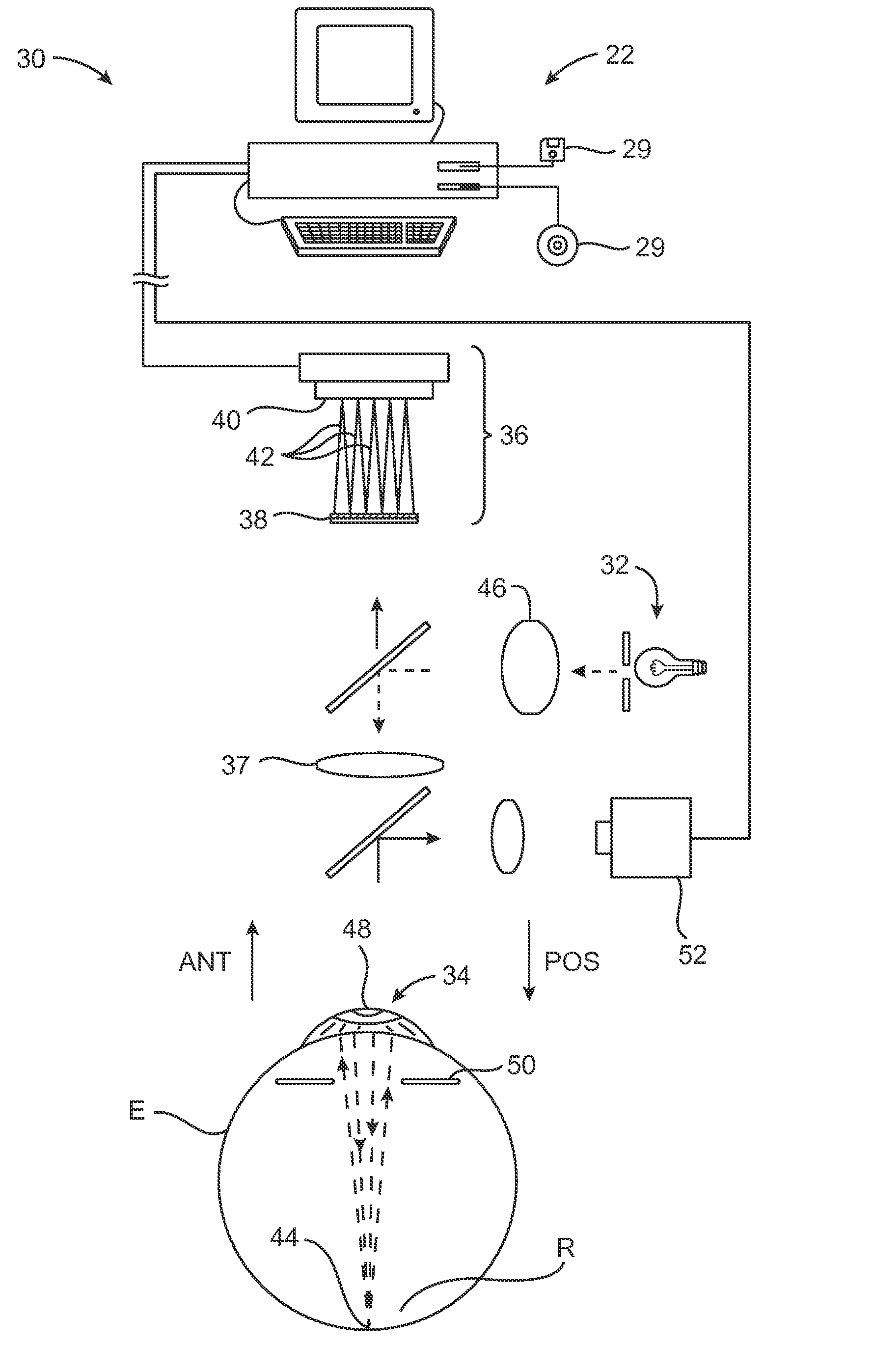
Method and apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye
InactiveUS6439720B1Quickly and accurately measuringMaximize accuracyRefractometersSkiascopesLight spotImage detection
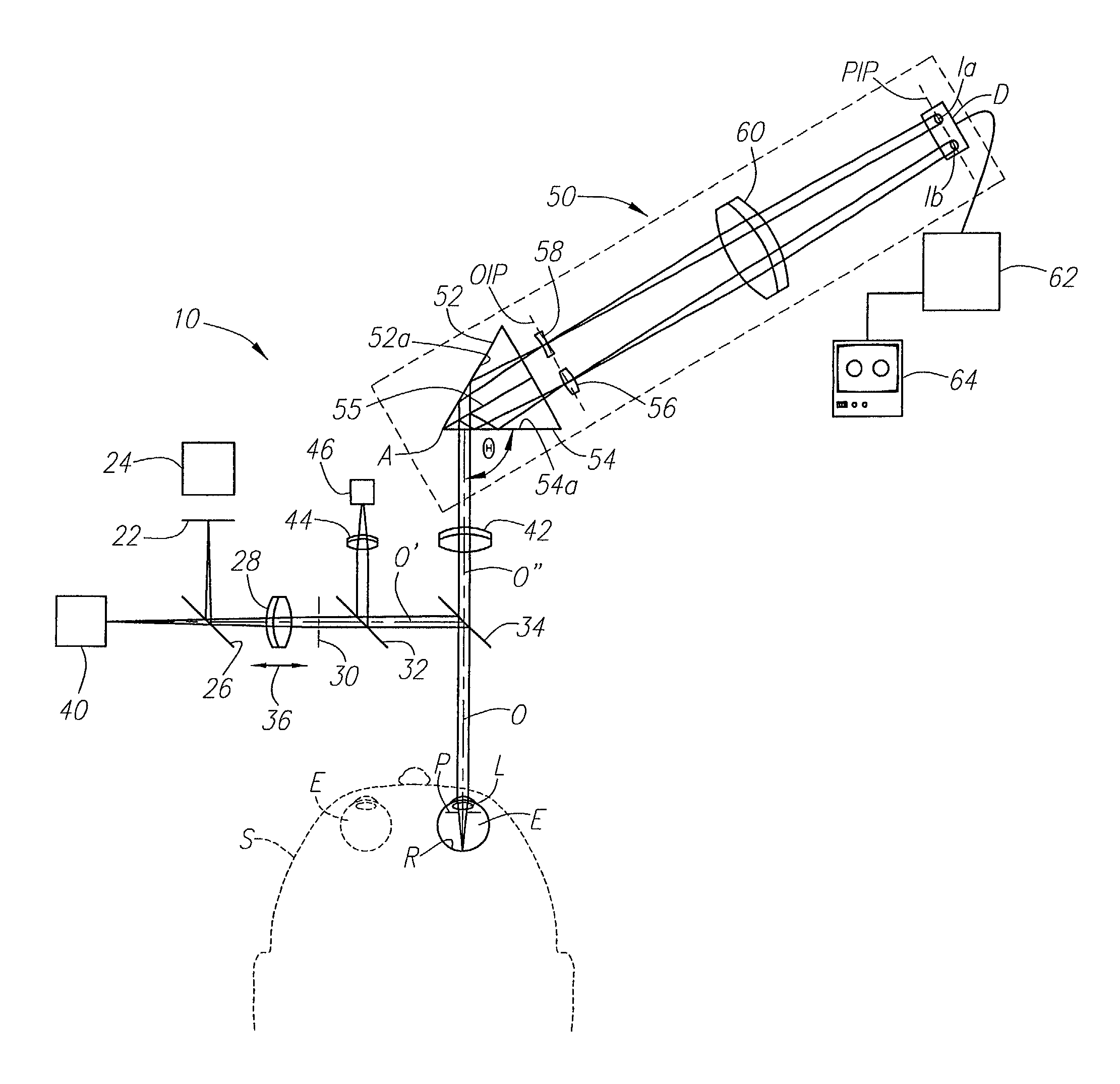
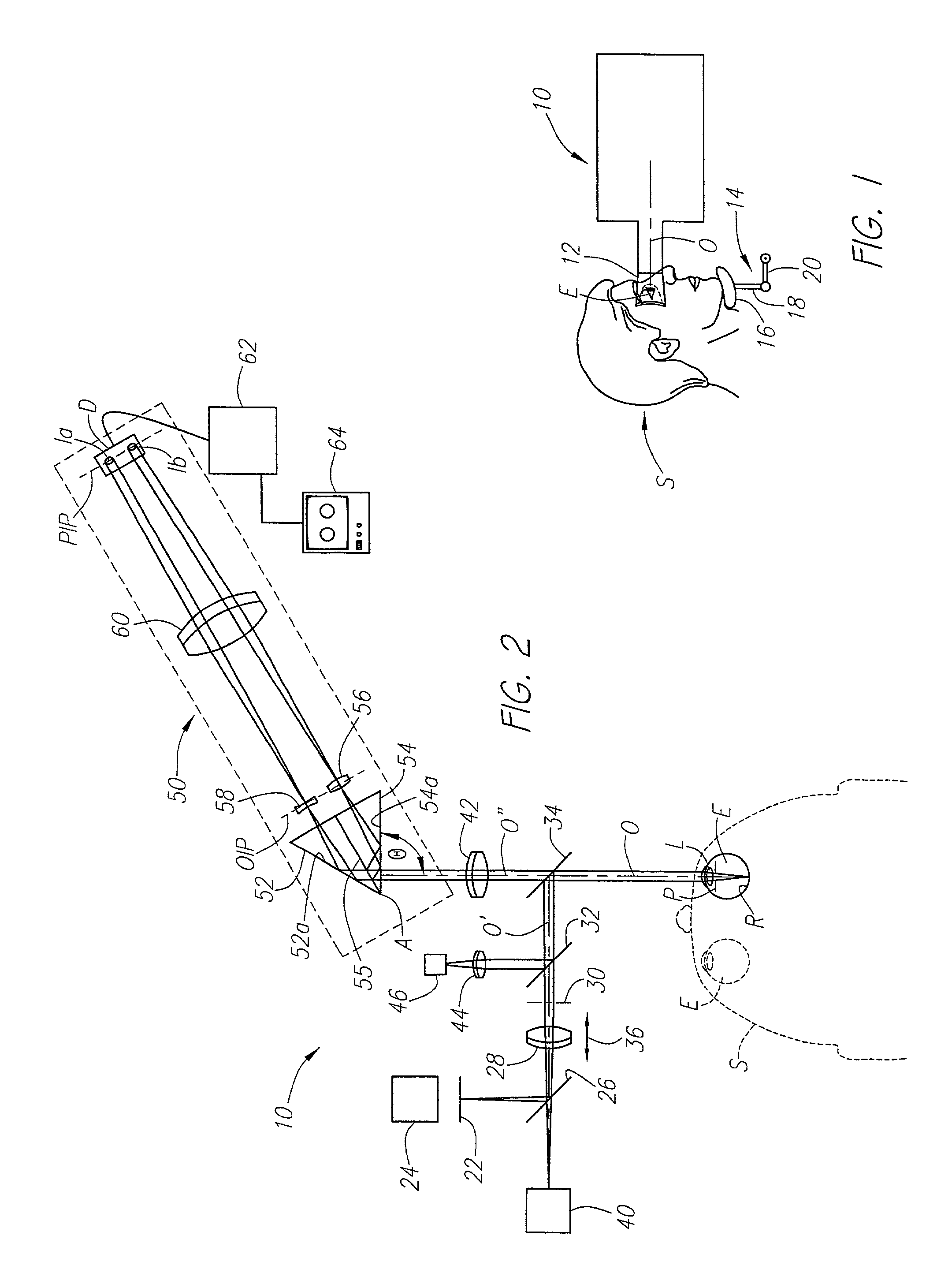
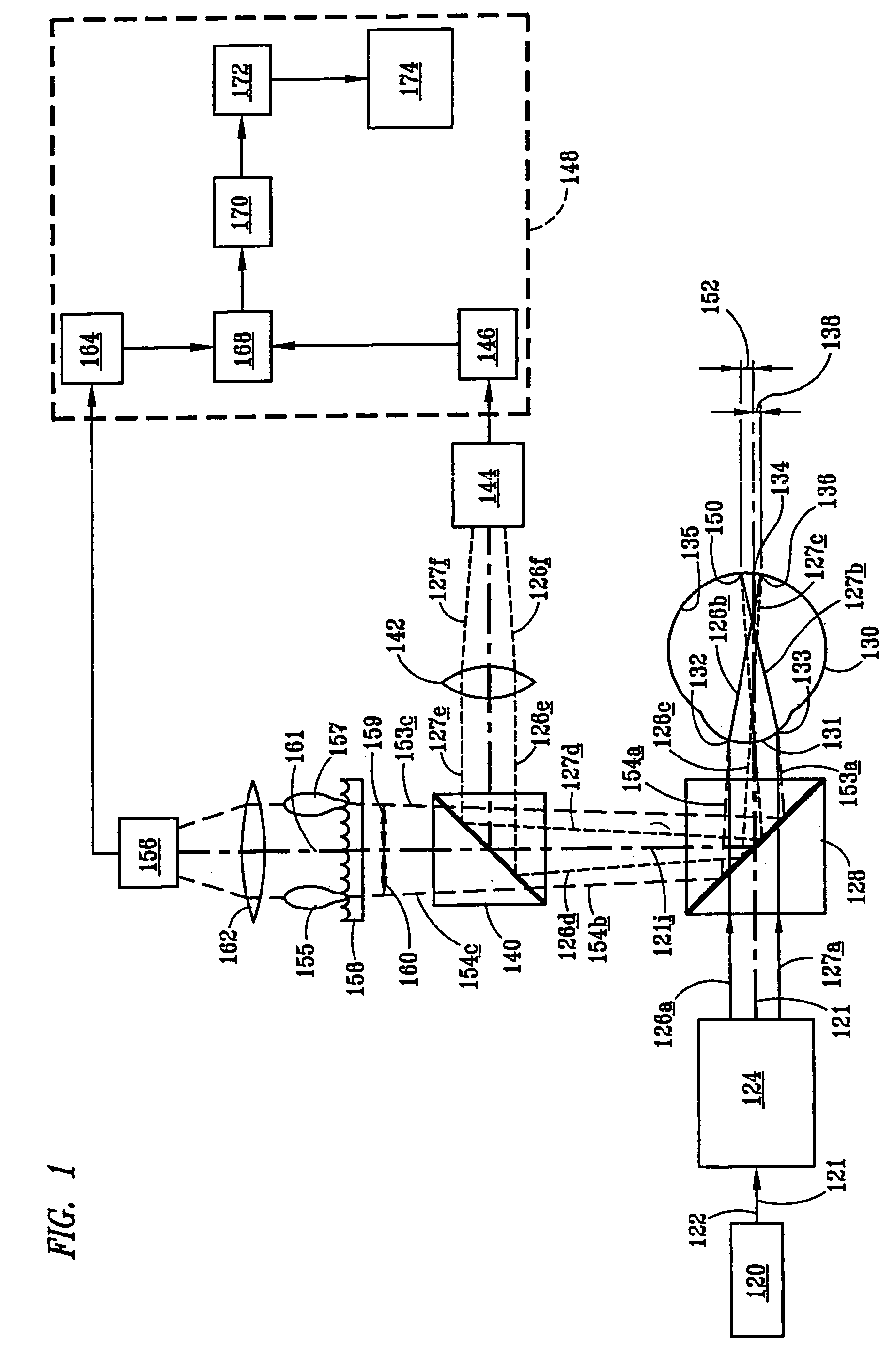
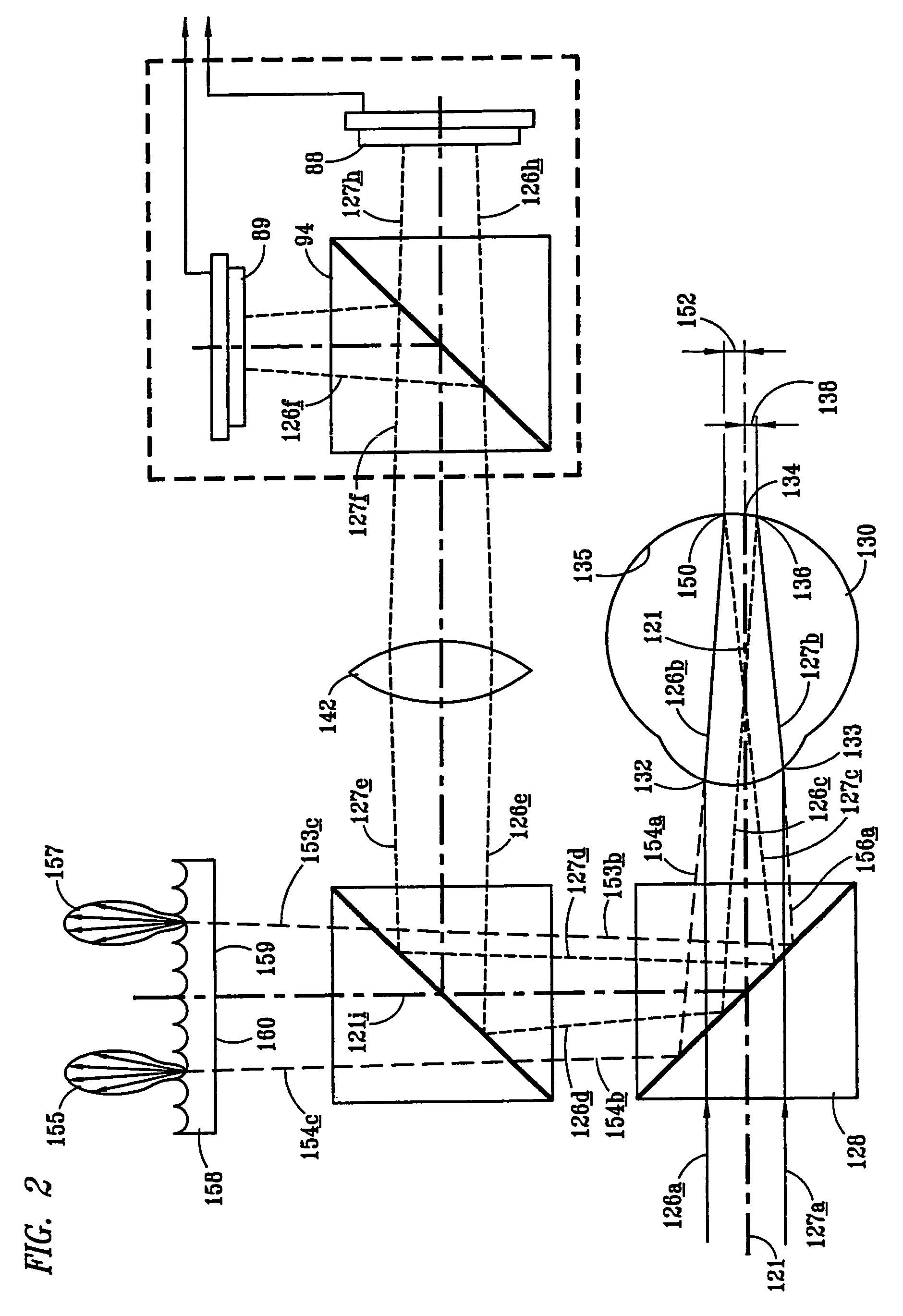
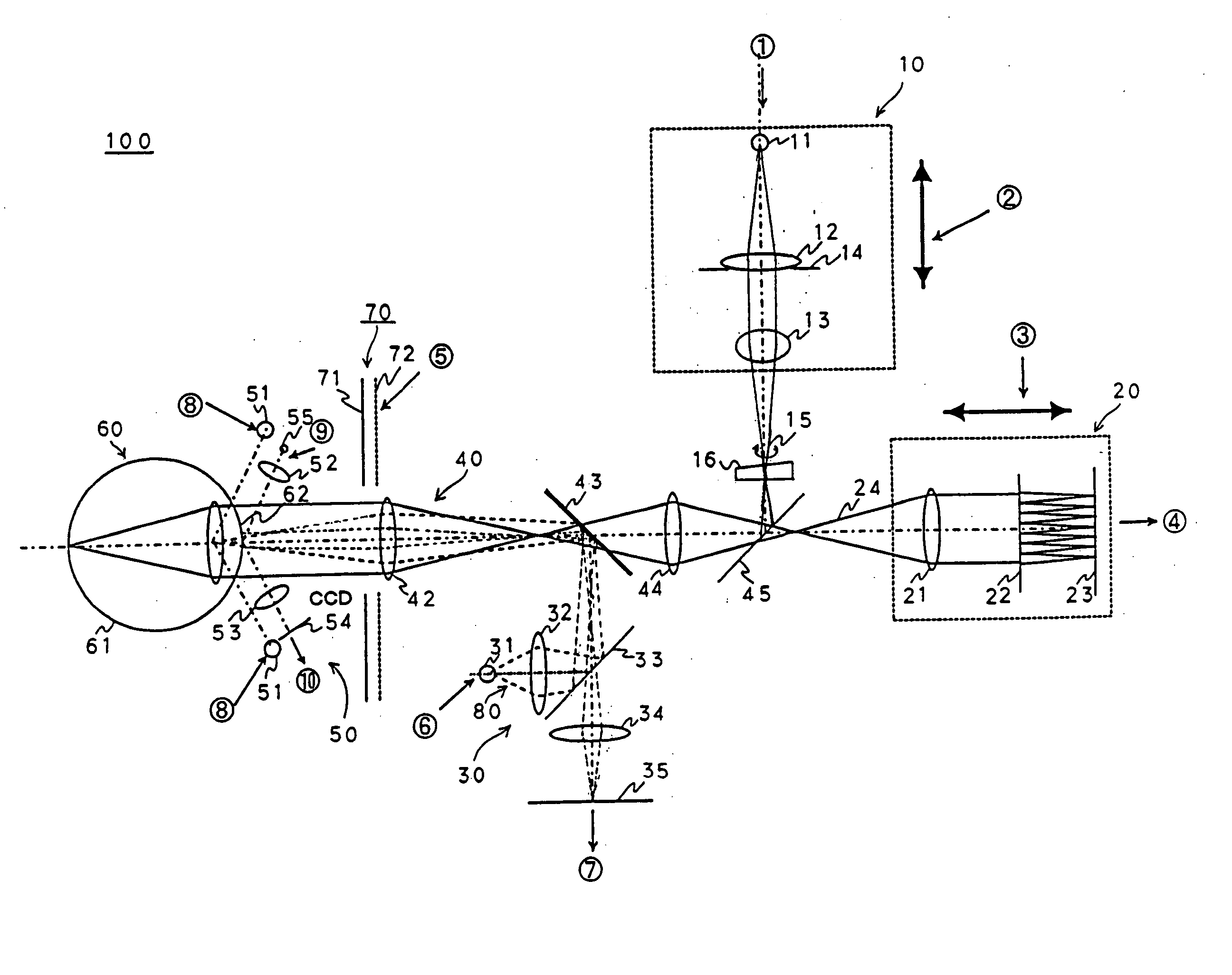
An apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye wherein the person positions his or her eye on an optical axis of the apparatus and looks at an illuminated target on the optical axis that is visible to the eye for allowing the eye to focus on the target and establish a position of the eye. A collimating lens on the optical axis is movable along the optical axis for adjusting the apparent optical distance between the eye and the target. A light source directs a predetermined light beam along the optical axis into the eye and onto the retina of the eye as a spot of light. A lens reimages the light scattered from the light spot on the eye retina into a wavefront curvature sensor that forms two oppositely defocused images on an image detector, and a computer processes and analyzes the two defocused images for measuring the optical aberrations of the eye.
Owner:AOPTIX TECH
Method and device for determining refractive components and visual function of the eye for vision correction
A method and an instrument is provided for measuring aberration refraction of an eye with a first device for measuring the total aberration refraction of the eye and a second device for measuring the aberration refraction of the cornea of the eye. The component of aberration refraction caused by the lens caused by the lens is calculated using the measured total eye aberration refraction and the measured component of aberration refraction of the cornea mapped over the optical surfaces of the eye. Each component portion of the aberration refraction provides information usable for making appropriate corrective actions at the cornea, at the lens, or both as indicated by the mapped measurements and calculations.
Owner:TRACEY TECH
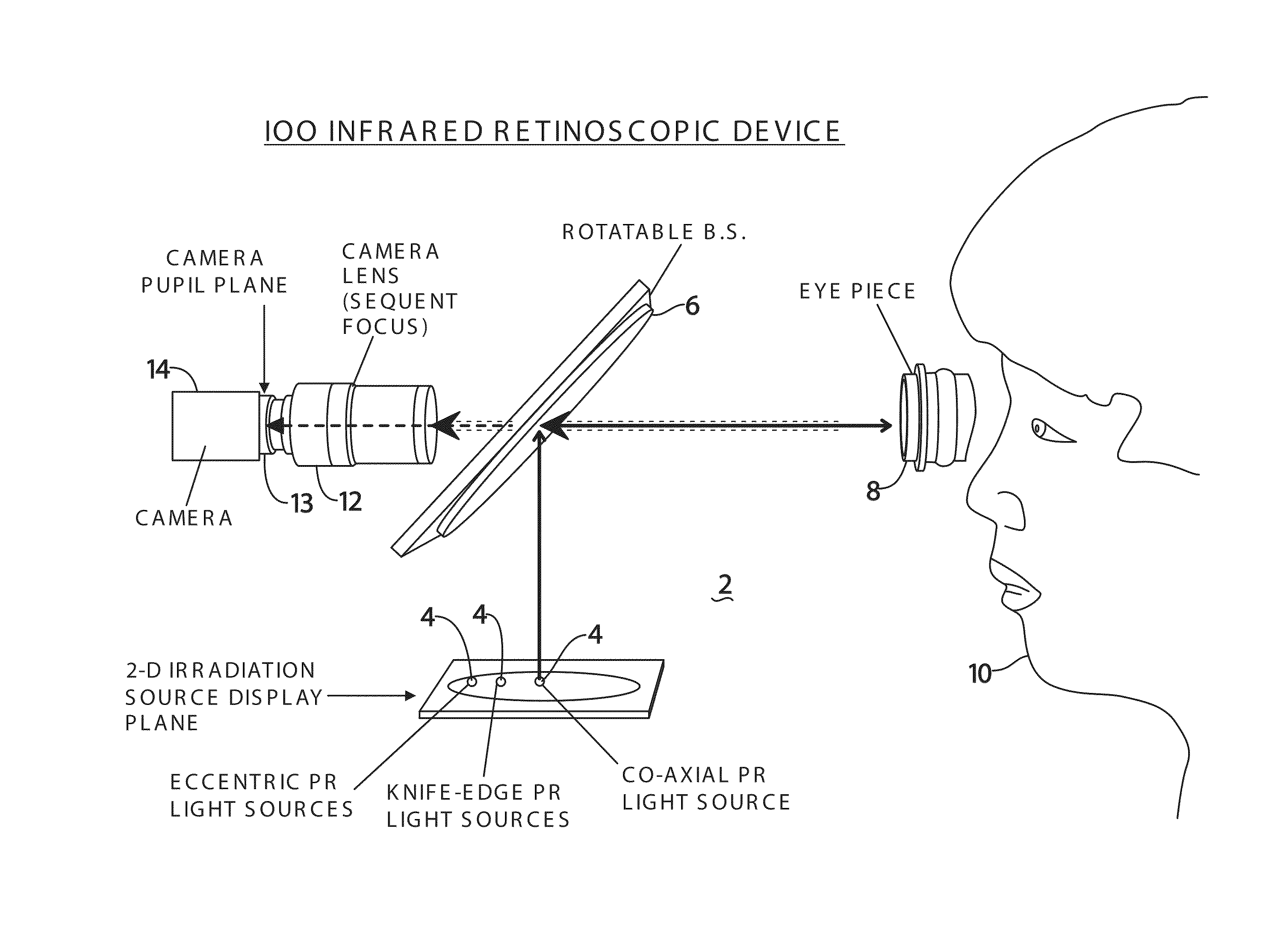
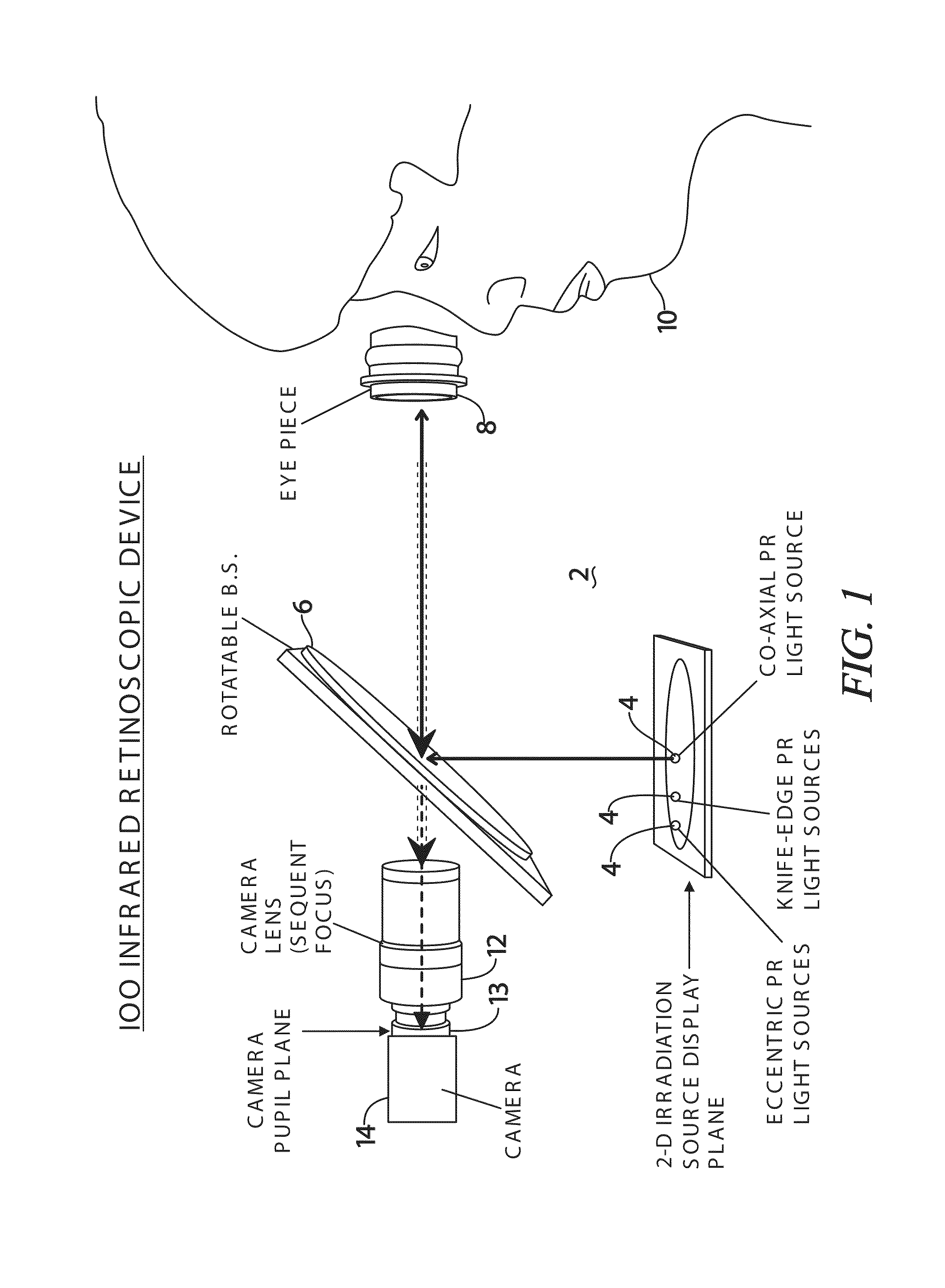
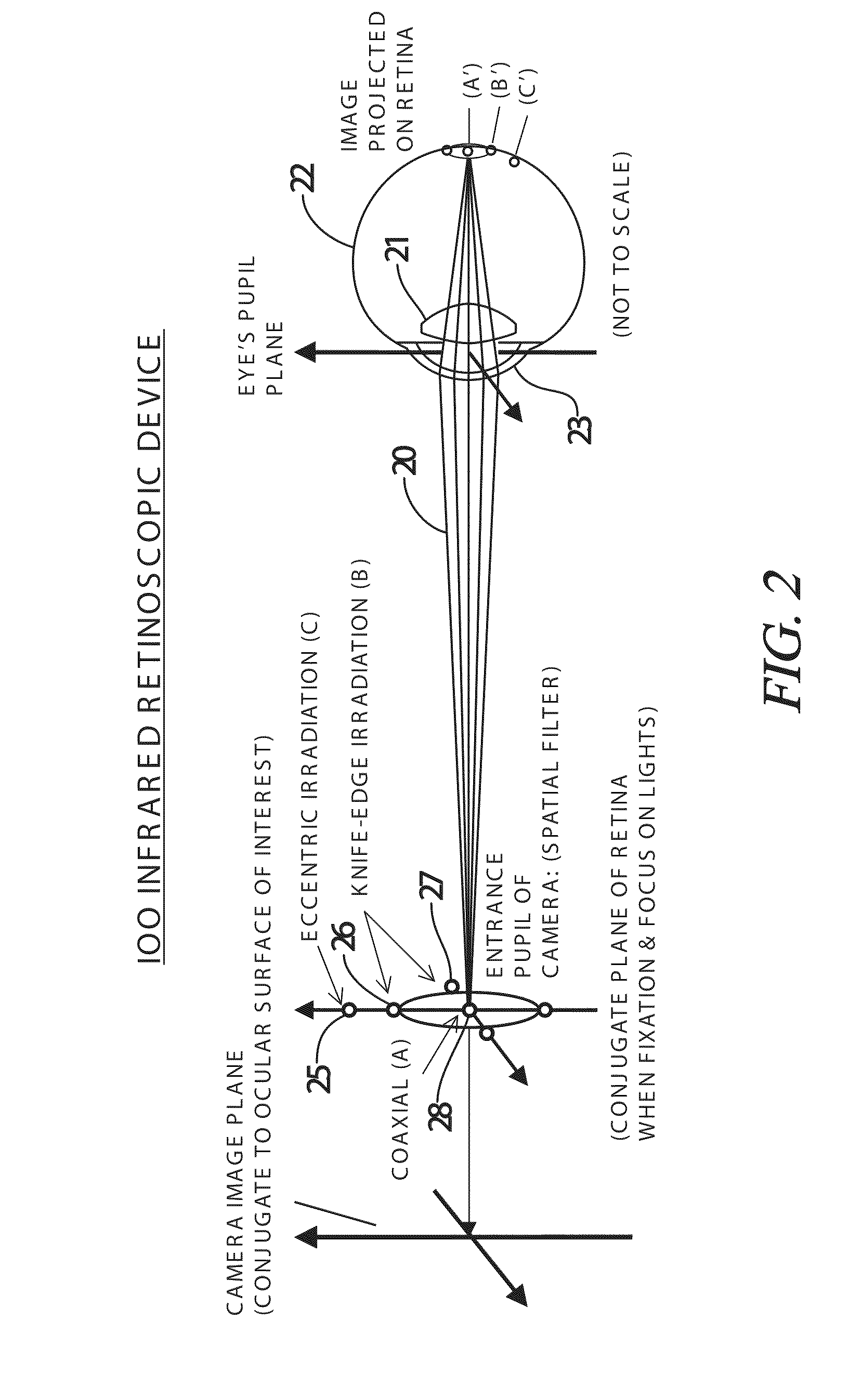
Adaptive infrared retinoscopic device for detecting ocular aberrations
An ocular system for detecting ocular abnormalities and conditions creates photorefractive digital images of a patient's retinal reflex. The system includes a computer control system, a two-dimensional array of infrared irradiation sources and a digital infrared image sensor. The amount of light provided by the array of irradiation sources is adjusted by the computer so that ocular signals from the image sensor are within a targeted range. Enhanced, adaptive, photorefraction is used to observe and measure the optical effects of Keratoconus. Multiple near-infrared (NIR) sources are preferably used with the photorefractive configuration to quantitatively characterize the aberrations of the eye. The infrared light is invisible to a patient and makes the procedure more comfortable than current ocular examinations.
Owner:AW HEALTHCARE MANAGEMENT LLC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS7377641B2Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Method and apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye
InactiveUS20020047992A1Measure quickly and accuratelyQuickly and accurately measuringRefractometersSkiascopesLight spotImage detection
An apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye wherein the person positions his or her eye on an optical axis of the apparatus and looks at an illuminated target on the optical axis that is visible to the eye for allowing the eye to focus on the target and establish a position of the eye. A collimating lens on the optical axis is movable along the optical axis for adjusting the apparent optical distance between the eye and the target. A light source directs a predetermined light beam along the optical axis into the eye and onto the retina of the eye as a spot of light. A lens reimages the light scattered from the light spot on the eye retina into a wavefront curvature sensor that forms two oppositely defocused images on an image detector, and a computer processes and analyzes the two defocused images for measuring the optical aberrations of the eye.
Owner:AOPTIX TECH
Method and device for determining refractive components and visual function of the eye for vision correction
A method and an instrument is provided for measuring aberration refraction of an eye with a first device for measuring the total aberration refraction of the eye and a second device for measuring the aberration refraction of the cornea of the eye. The component of aberration refraction caused by the lens caused by the lens is calculated using the measured total eye aberration refraction and the measured component of aberration refraction of the cornea mapped over the optical surfaces of the eye. Each component portion of the aberration refraction provides information usable for making appropriate corrective actions at the cornea, at the lens, or both as indicated by the mapped measurements and calculations.
Owner:TRACEY TECH
Control of Myopia Using Contact Lenses
InactiveUS20090141235A1Prevention of controllingControl progressSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentAberrations of the eyeEyelid
Devices and methods for controlling myopia are provided. The devices and methods relate to the inventors discovery of the relationship between near work, the forces applied to the eye by the eyelids and myopia. The devices include a contact lens comprising a region that disperses force applied to the eye by an eyelid. The devices also include a device designed by measuring first wavefront aberrations of an eye before pre-near work and measuring second measured wavefront aberrations of the eye post-near work. The methods include a method for controlling myopia including identifying optical changes associated with near work and correcting the optical changes with an optical device.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
Methods of obtaining ophthalmic lenses providing the eye with reduced aberrations
InactiveUS7241311B2Reduce aberrationEasy to identifySpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
The present invention discloses methods of obtaining ophthalmic lens capable of reducing the aberrations of the eye comprising the steps of characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model, calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model, selecting the optical power of the intraocular lens. From this information, an ophthalmic lens is modeled so a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and corneal model obtains reduced aberrations in the eye. Also disclosed are ophthalmic lenses as obtained by the methods which are capable reducing aberrations of the eye.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Control of myopia using contact lenses
InactiveUS8485662B2Prevention of controllingControl progressSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentEyelidAberrations of the eye
Devices and methods for controlling myopia are provided. The devices and methods relate to the inventors discovery of the relationship between near work, the forces applied to the eye by the eyelids and myopia. The devices include a contact lens comprising a region that disperses force applied to the eye by an eyelid. The devices also include a device designed by measuring first wavefront aberrations of an eye before pre-near work and measuring second measured wavefront aberrations of the eye post-near work. The methods include a method for controlling myopia including identifying optical changes associated with near work and correcting the optical changes with an optical device.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
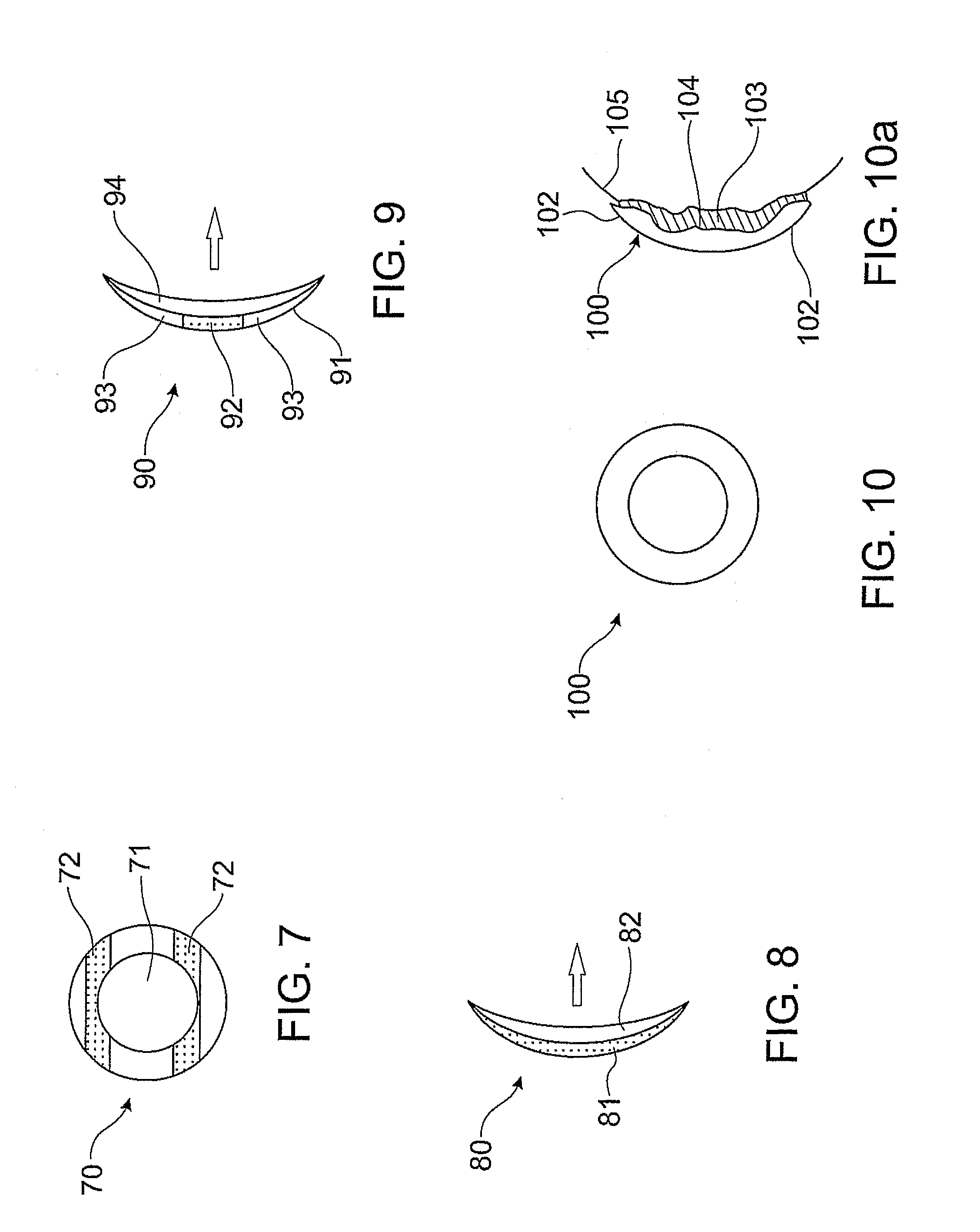
Combination advanced corneal topography/wave front aberration measurement
InactiveUS20010033362A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
Accommodation compensation systems and methods
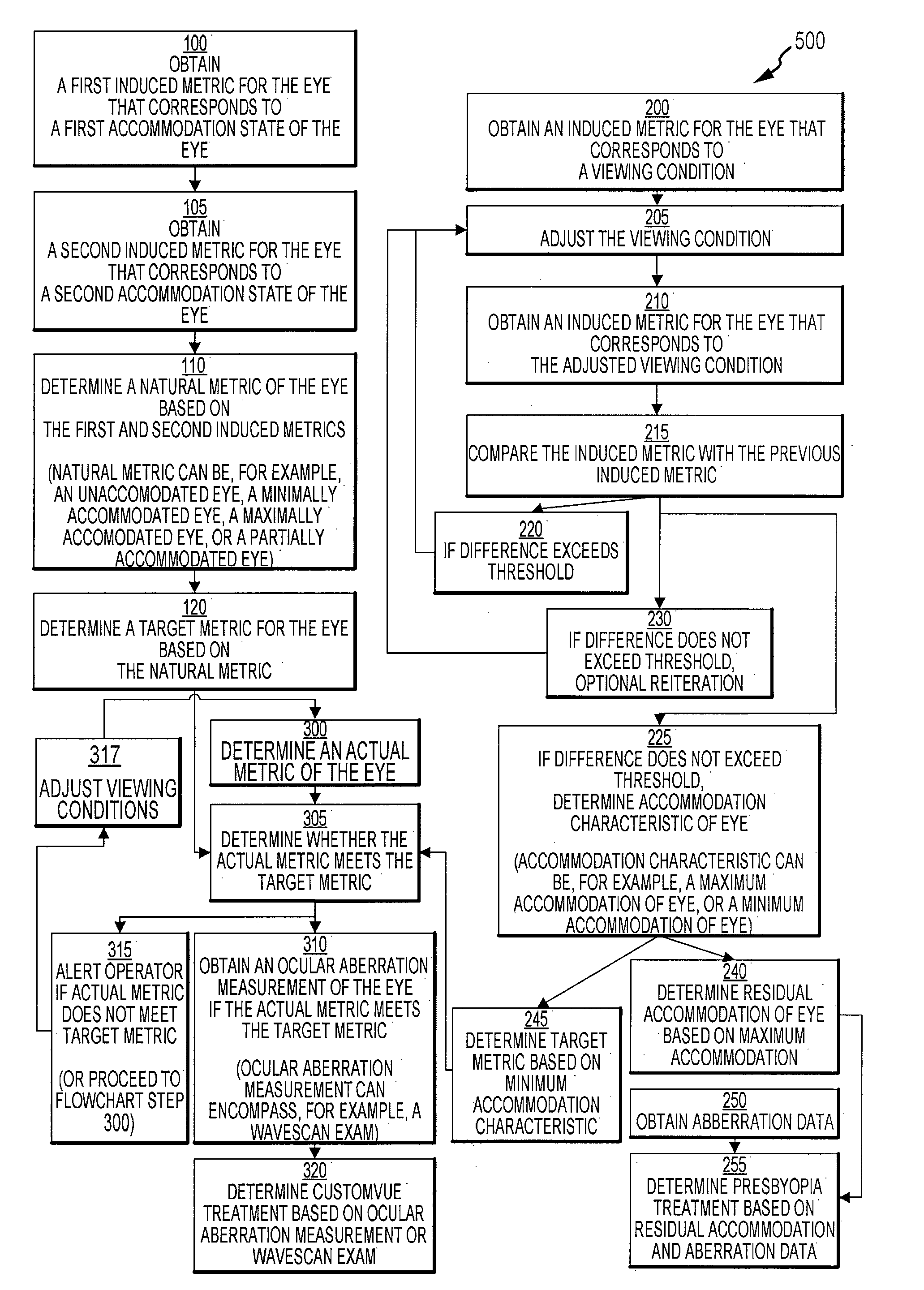
ActiveUS20080291395A1Improve treatment of patientReduced accommodationLaser surgeryEye diagnosticsAberrations of the eyePupil
Methods and systems for obtaining an ocular aberration measurement of an eye of a patient are provided. Exemplary techniques involve obtaining a first induced metric for the eye that corresponds to a first accommodation state of the eye, obtaining a second induced metric for the eye that corresponds to a second accommodation state of the eye, and determining a natural metric of the eye based on the first and second induced metrics. An induced metric may include a pupil size or a spherical aberration. Techniques can also include determining a target metric for the eye base on the natural metric, determining whether an actual metric of the eye meets the target metric, obtaining an ocular aberration measurement of the eye if the actual metric meets the target metric, and determining a treatment for the eye based on the ocular aberration measurement.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Opthalmological apparatus
In an ophthalmological apparatus, how scattering at an eye under measurement and a contact lens affects how the eye sees is shown by measuring scattering when the contact lens is worn and by comparing a retinal image obtained with aberration and the scattering taken into account and a retinal image obtained with only the aberration taken into account. An aberration measurement section obtains the aberration of the eye under measurement. An other-components measurement section obtains other components other than the aberration component based on a point light-source image caused by each Hartmann plate. A scattering-level calculation section obtains a coefficient expressing the level of scattering based on the other components and the aberration. A simulation section generates a retinal image or data indicating how the eye under measurement sees with the measured aberration and the other components taken into account, based on the aberration and the coefficient.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Ophthalmic instrument having an integral wavefront sensor and display device that displays a graphical representation of high order aberrations of the human eye measured by the wavefront sensor
An improved ophthalmic instrument including an integral wavefront sensor and display device, wherein the wavefront sensor measures phase aberrations in reflections directed thereto to characterize aberrations of the eye and is operably coupled to the display device, which displays a graphical representation of the aberrations of the eye. Such graphical representation may include: two dimensional contour maps that graphically depict contribution of pre-specified terms (such as spherical aberration, astigmatism and coma) for the aberrations of the eye, coefficients corresponding to such pre-specified terms that characterize the aberrations of the eye, or predefined two-dimensional icons that provide a general graphical depiction of such prespecified terms. Such graphical representations provide the practitioner with valuable information characterizing the high order optical errors of the eye (which is far beyond the diopter information typically provided by current ophthalmic instruments) for use in diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities and disease in the eye.
Owner:ADAPTIVE OPTICS ASSOC
Customized contact lenses for reducing aberrations of the eye
InactiveUS20080212024A1Improve visual qualityAvoid spreadingSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsAberrations of the eyeFigure of merit
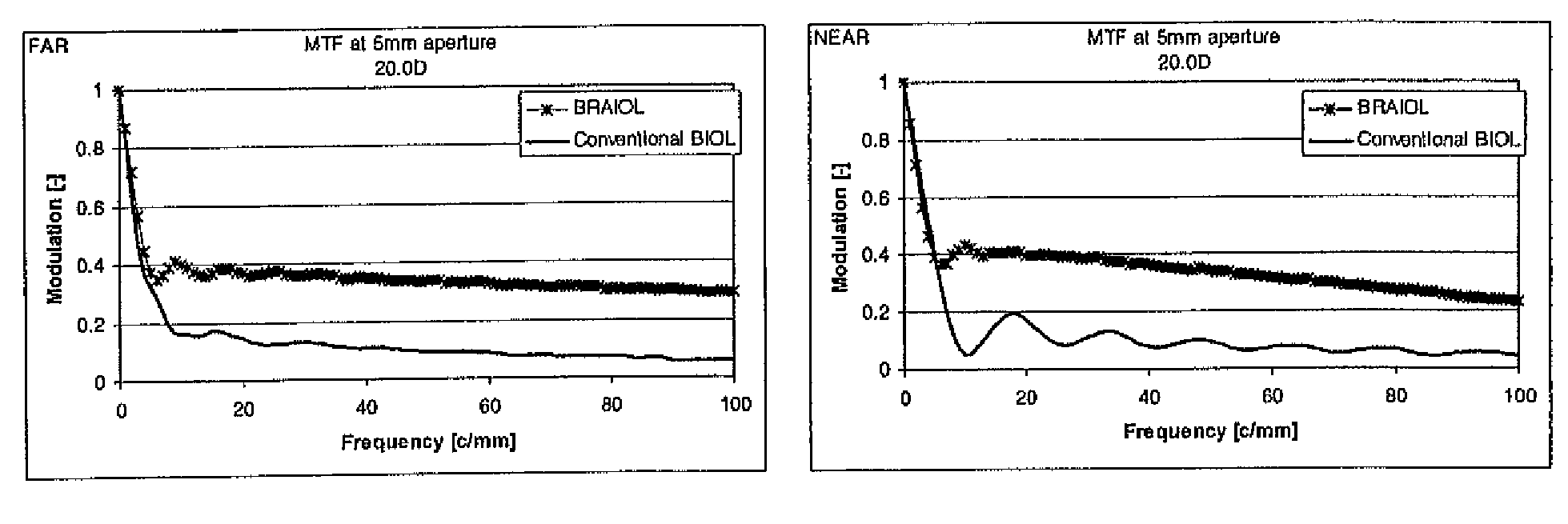
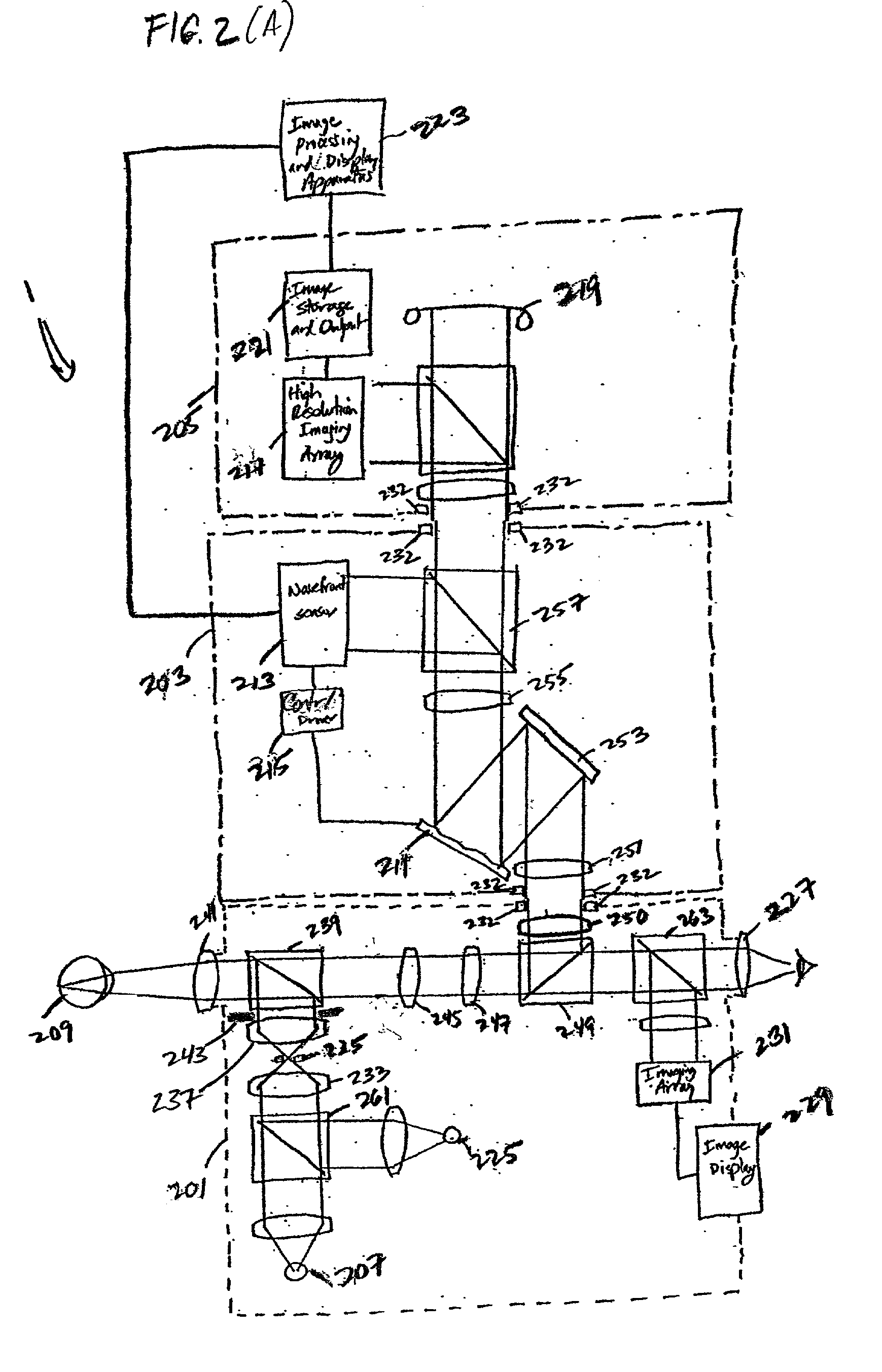
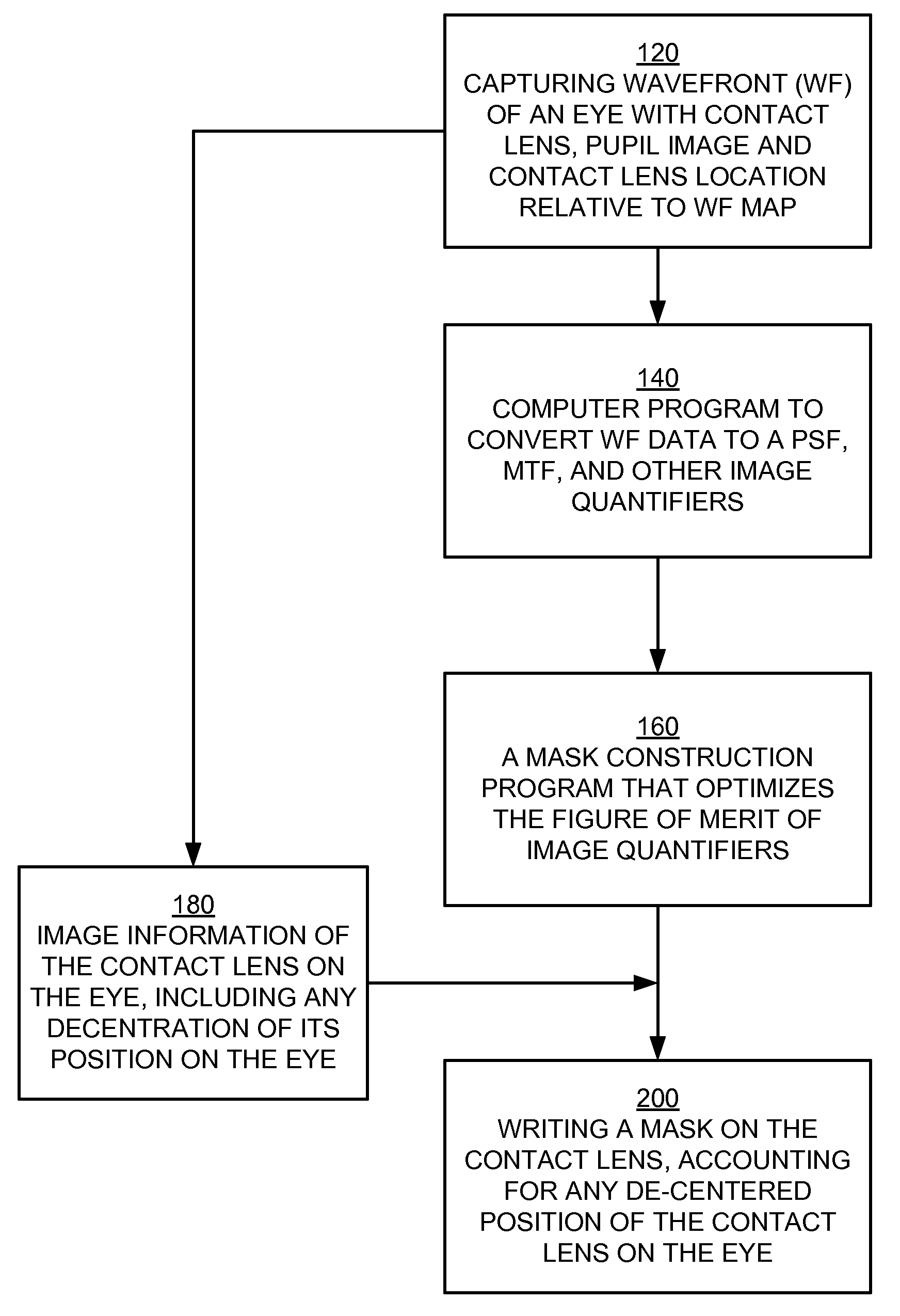
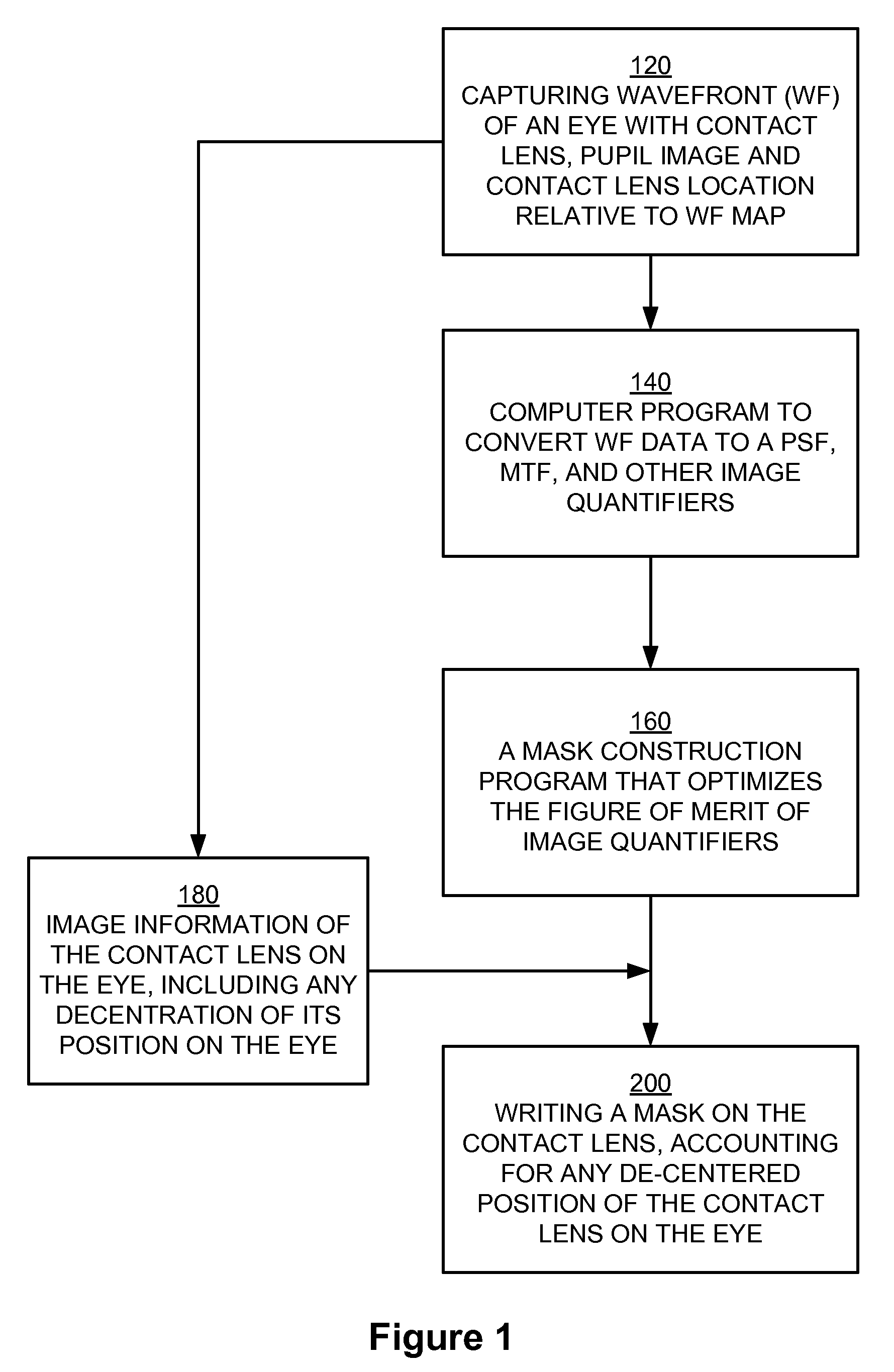
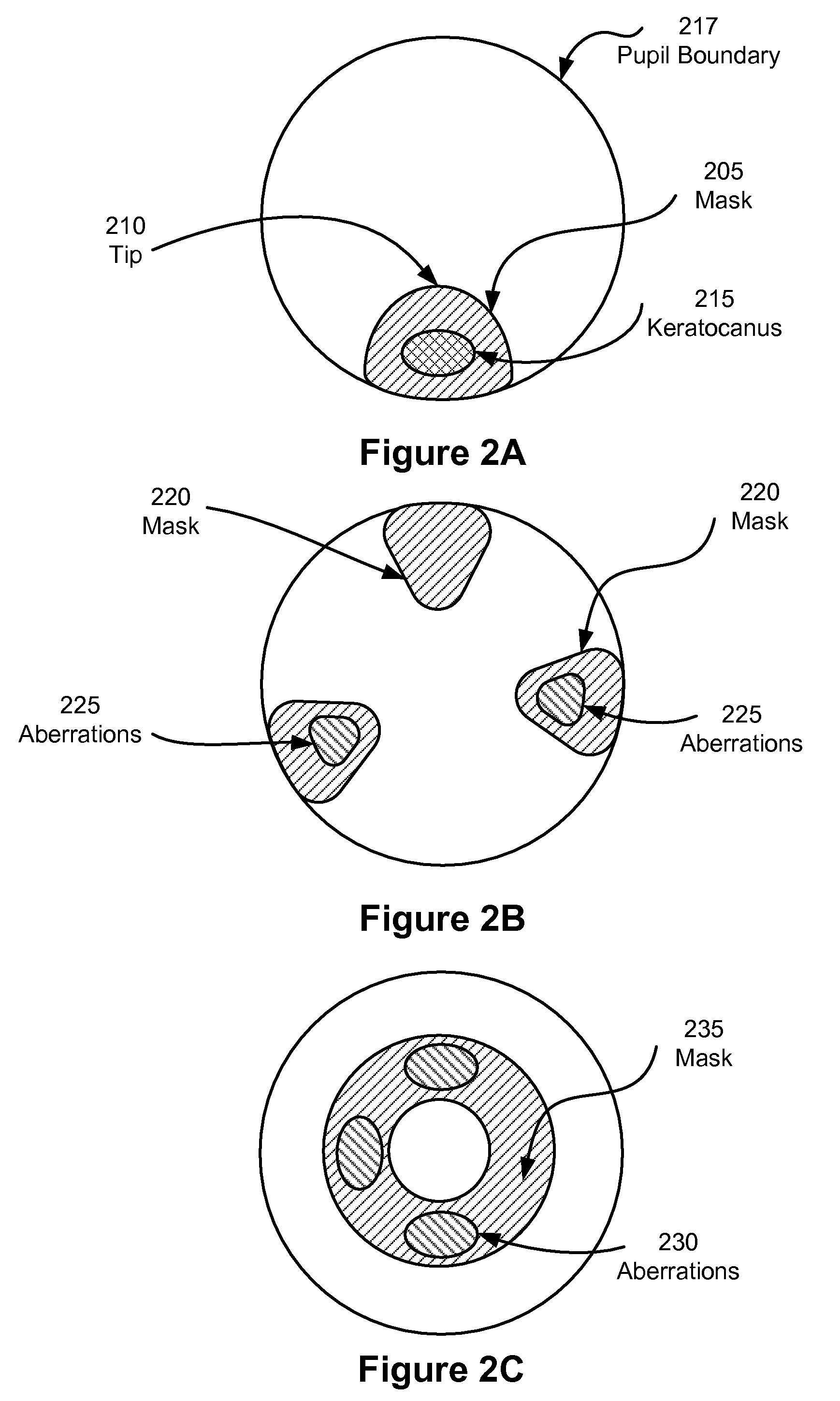
Higher order aberrations of an eye are reduced. Wavefront aberrations of the eye are measured, providing wavefront information and / or a wavefront map. A mask is derived from the wavefront information and / or wavefront map based on the measured wavefront aberrations. A customized contact lens is formed including the mask. The deriving of the mask includes optimizing a figure of merit using a PSF, a MTF, and / or another image quantifier.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
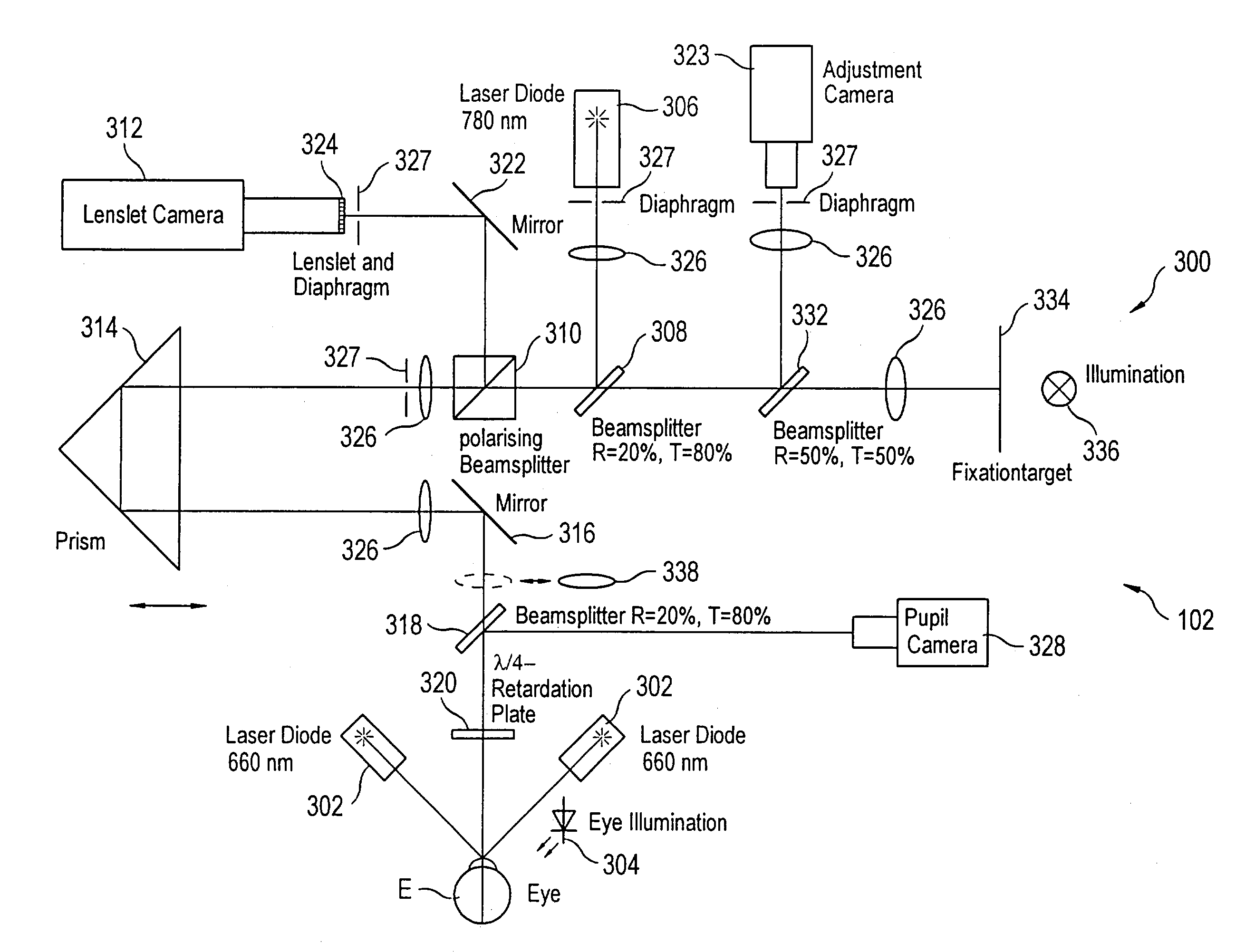
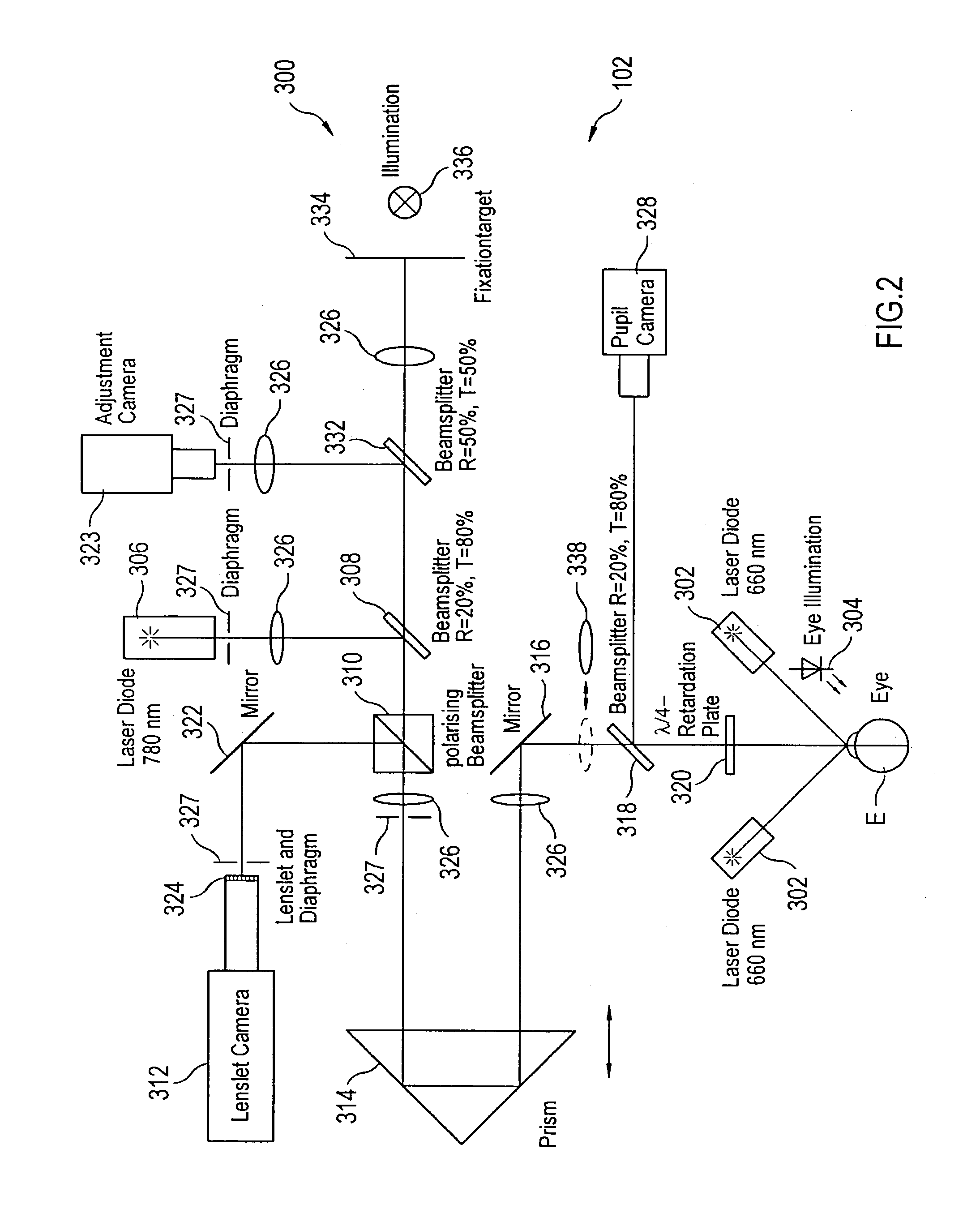
Wavefront sensor having multi-power modes, independent adjustment camera, and accommodation range measurement
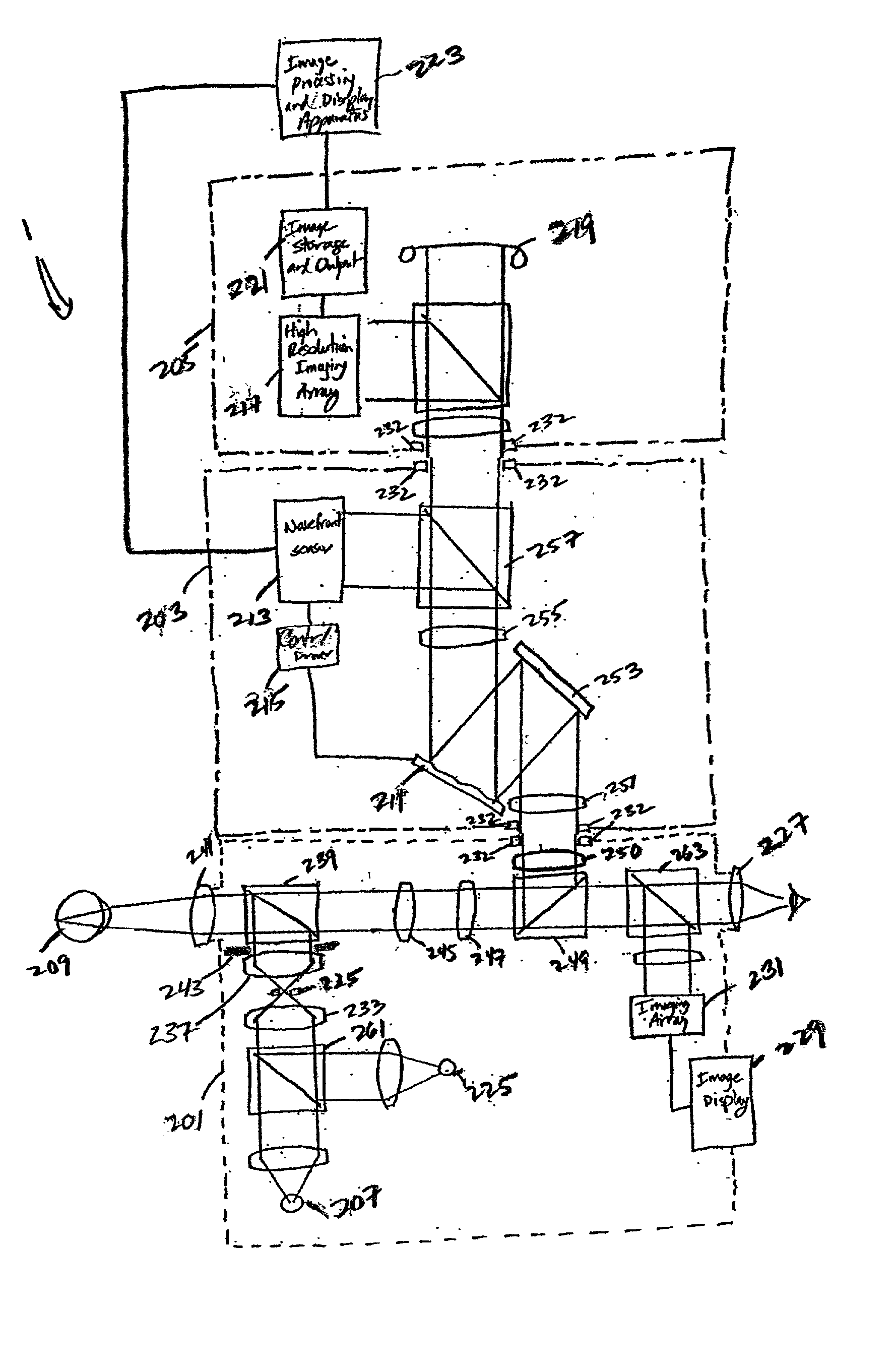
InactiveUS7036934B1Accurate focusWavefront sensor can be improvedOptical measurementsEye surgeryPower modeAberrations of the eye
An improved wavefront sensor is provided that enhances the initial focus and precision of imaged spots used to determine the monochromatic wave aberrations of the eye. The wavefront sensor includes an adjustment camera that is independent of a lenslet camera. A laser in a lower power mode is projected onto the retina of the eye and is brought into more precise or sharp focus by a control system employing data from the adjustment camera, which aids in focusing the imaged spots. “Trombone”-type optics are used to adjust the focus of the light projected onto the retina and the imaged spots onto a sensor. The laser has a higher power mode used when acquiring data of the imaged spots from the sensor.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS20060244906A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Lenses, systems and methods for providing custom aberration treatments and monovision to correct presbyopia
InactiveUS20130335701A1Improve eyesightIncrease depth of focusSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessAberrations of the eye
A lens, system and / or method for providing custom ocular aberrations for enhanced higher visual acuity. Scaled versions of a patient's aberration pattern may either attenuate or amplify the overall amount of ocular aberrations, to either correct or partially correct a patient's aberrations leading to enhanced visual acuity and / or extended depth of focus. This may be binocularly applied in order to provide high visual acuity in a patient at least at near, far and intermediate distances. The method may include obtaining an optimized binocular summation of both eyes of the patient; designing a first lens solution to correct or partially correct the dominant eye's aberrations according to an attenuated scaled version of a patient's ocular aberrations in the dominant eye; and designing a second lens solution to provide an additional customized extension of depth of focus by the induction of scaled patterns of ocular aberrations in the non dominant eye.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
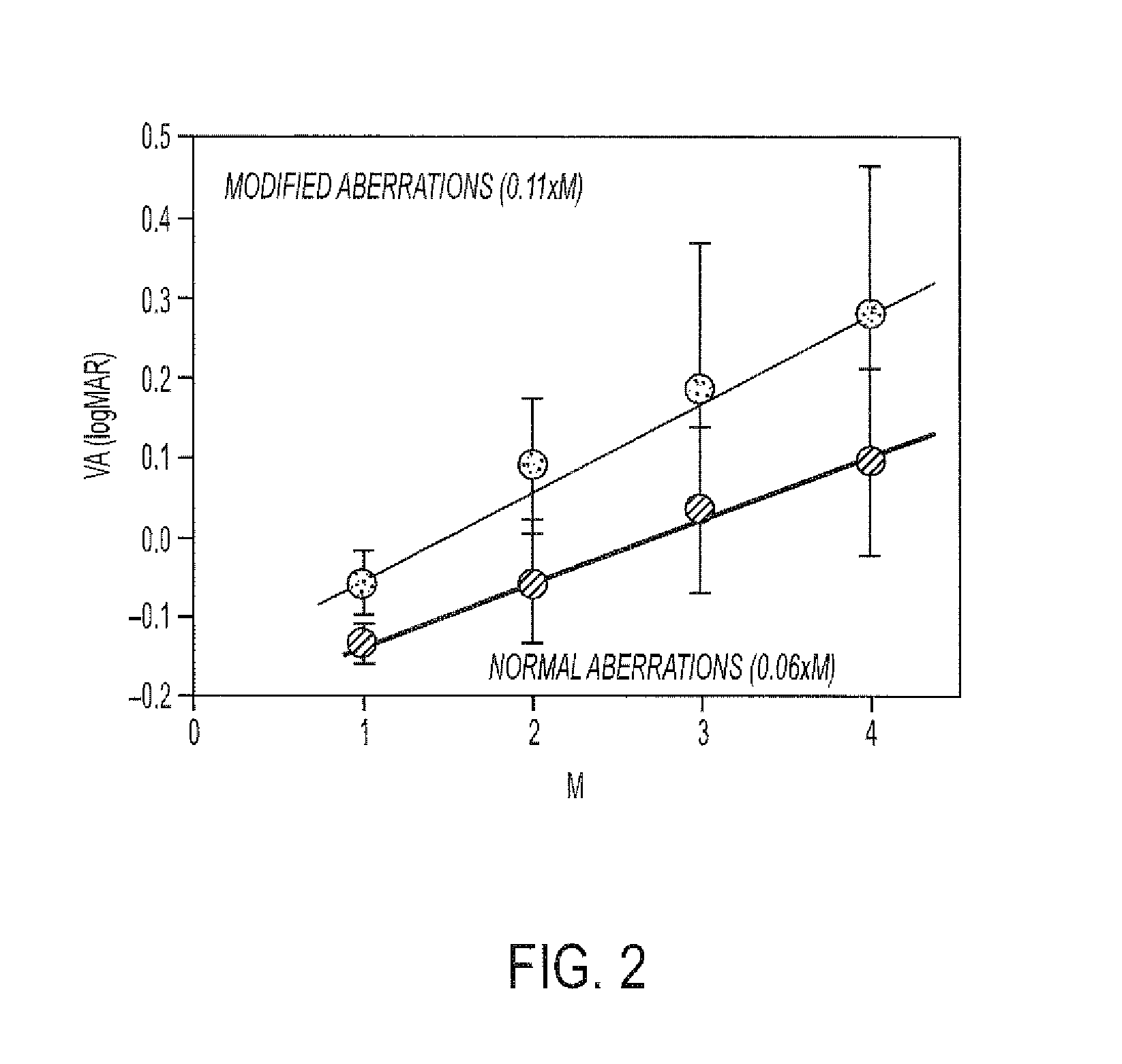
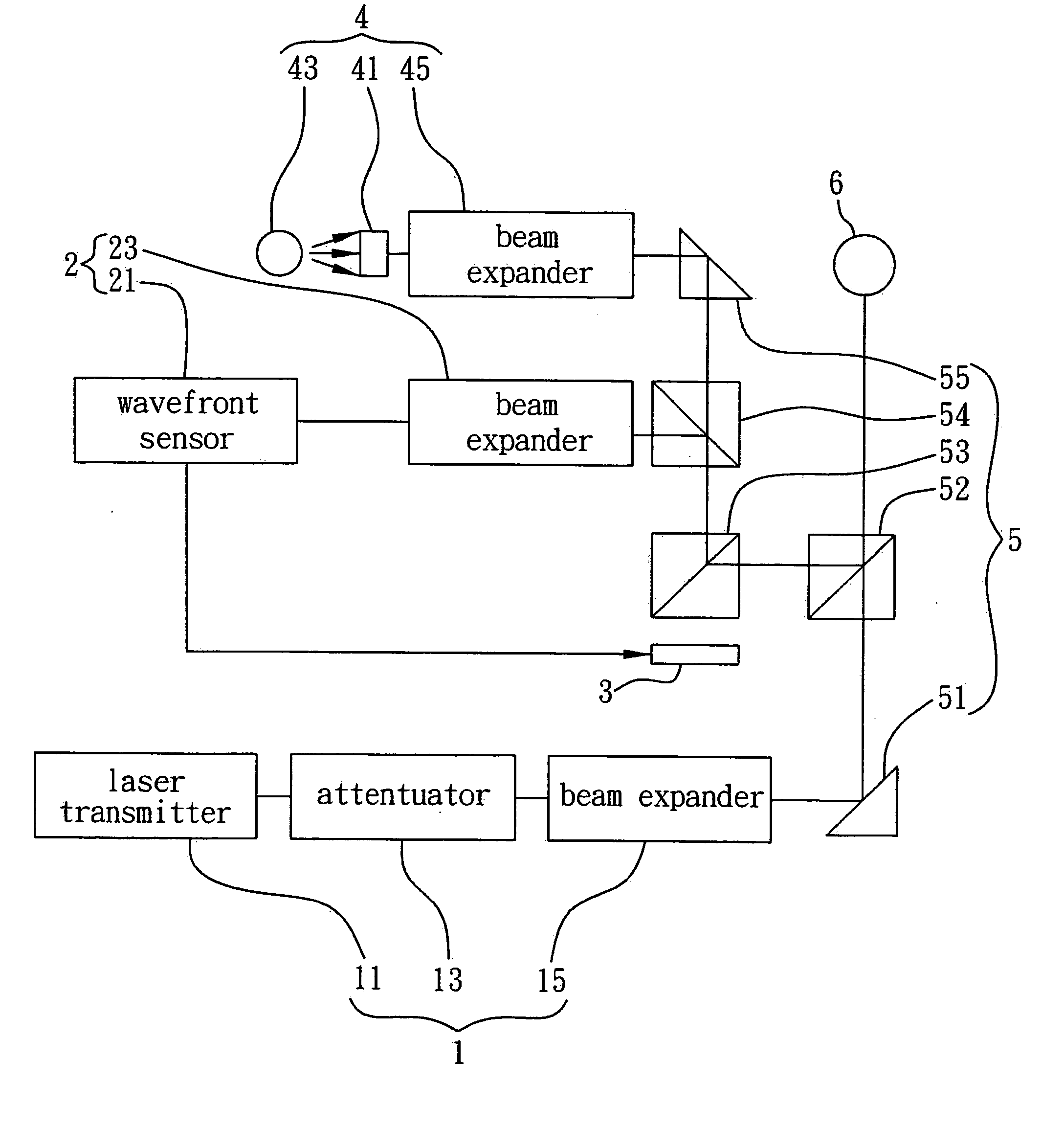
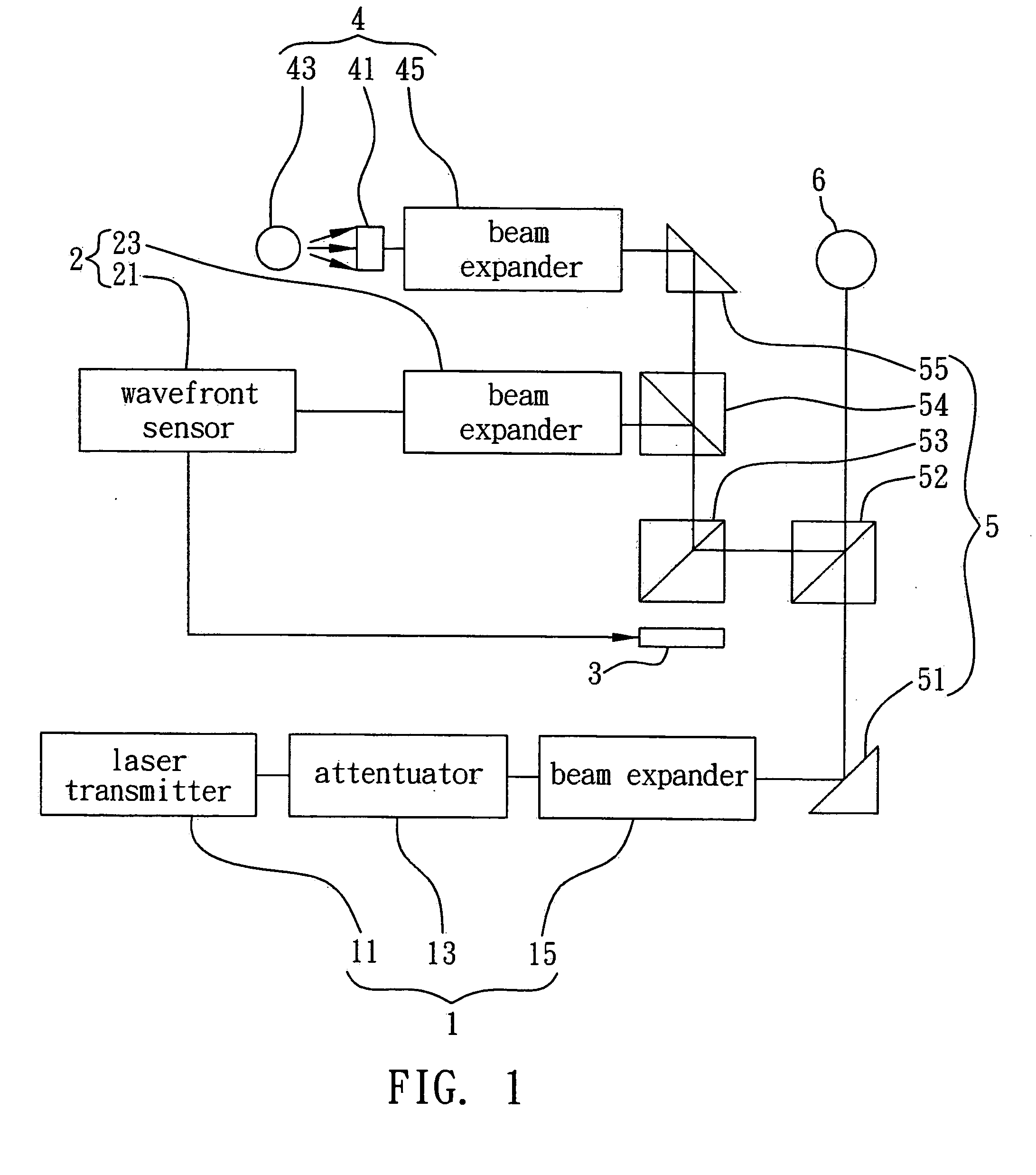
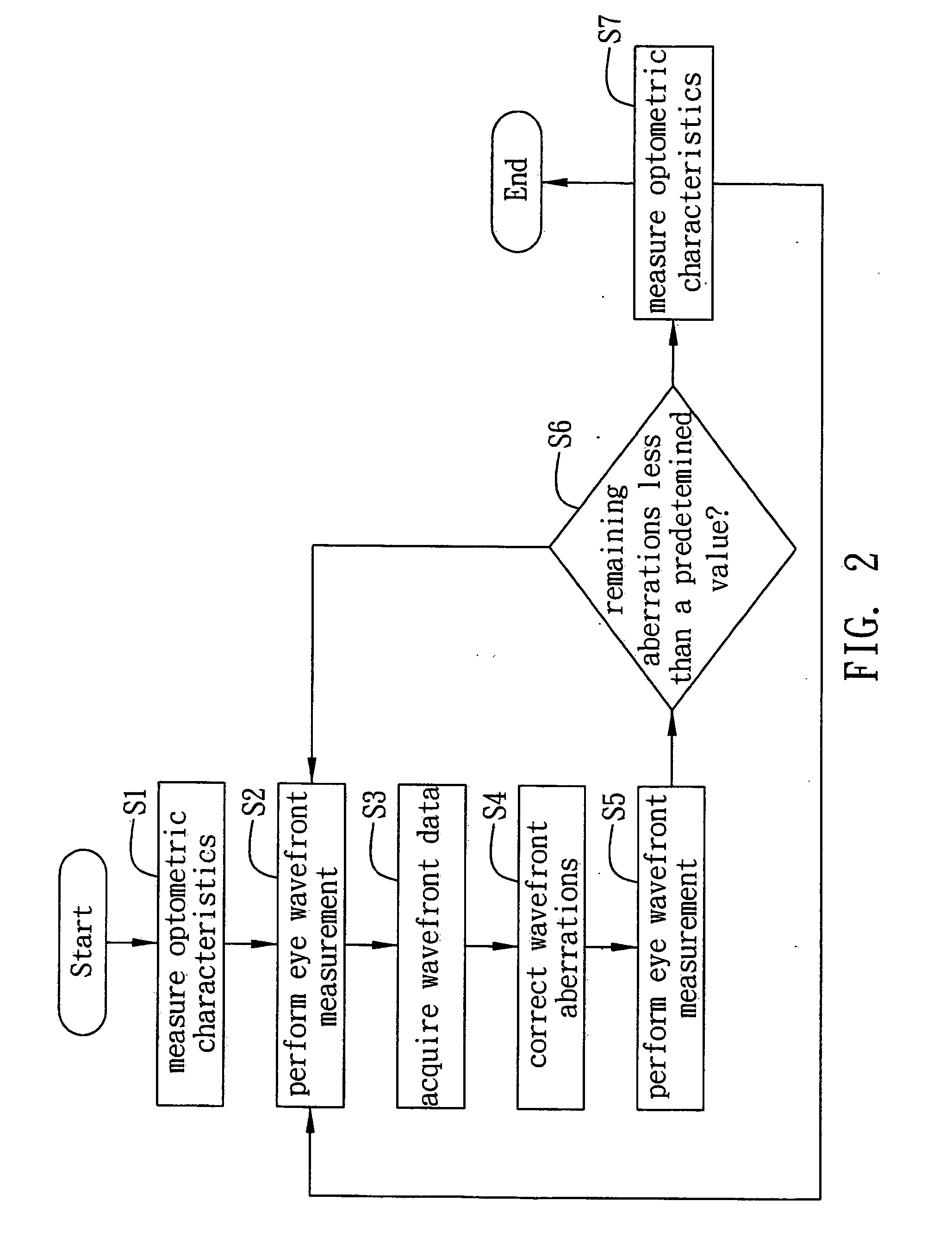
Method and device for measuring and correcting aberrations of eye
InactiveUS20070109497A1Accurate dataSimple designEye diagnosticsAberrations of the eyeWavefront aberration
A device and method for measuring and correcting eye aberrations integrate wavefront sensing, wavefront aberration correction and optometric testing into one another and configure the optical paths of wavefront sensing and optometric testing as aplanatic structures, such that under optometric testing conditions both wavefront sensing and aberration correction can be performed simultaneously, and final optometric testing is conducted on wavefront aberration-corrected optometric parameters to verify if the wavefront aberration-corrected optometric parameters fall within normal visual range, thus ensuring the accuracy and high repetition of the measured optometric parameters.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Subjective Wavefront Refraction Using Continuously Adjustable Wave Plates of Zernike Function
A wavefront device produces adjustable amplitudes in optical path differences and adjustable axis orientation angles. two substantially identical wave plates have a wavefront profile of at least the third order Zernike polynomial function which are not circularly symmetric, as denoted by Z(i,j) where i≧3 and j≠0. The wave plates are mounted in rotatable mounts with their optical centers substantially aligned with each other. An subjective wavefront refraction instrument and method are provided to correct low and high order aberrations of the eye, using the adjustable wave plates that have astigmatism and higher order Zernike function optical path difference wavefront profiles.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
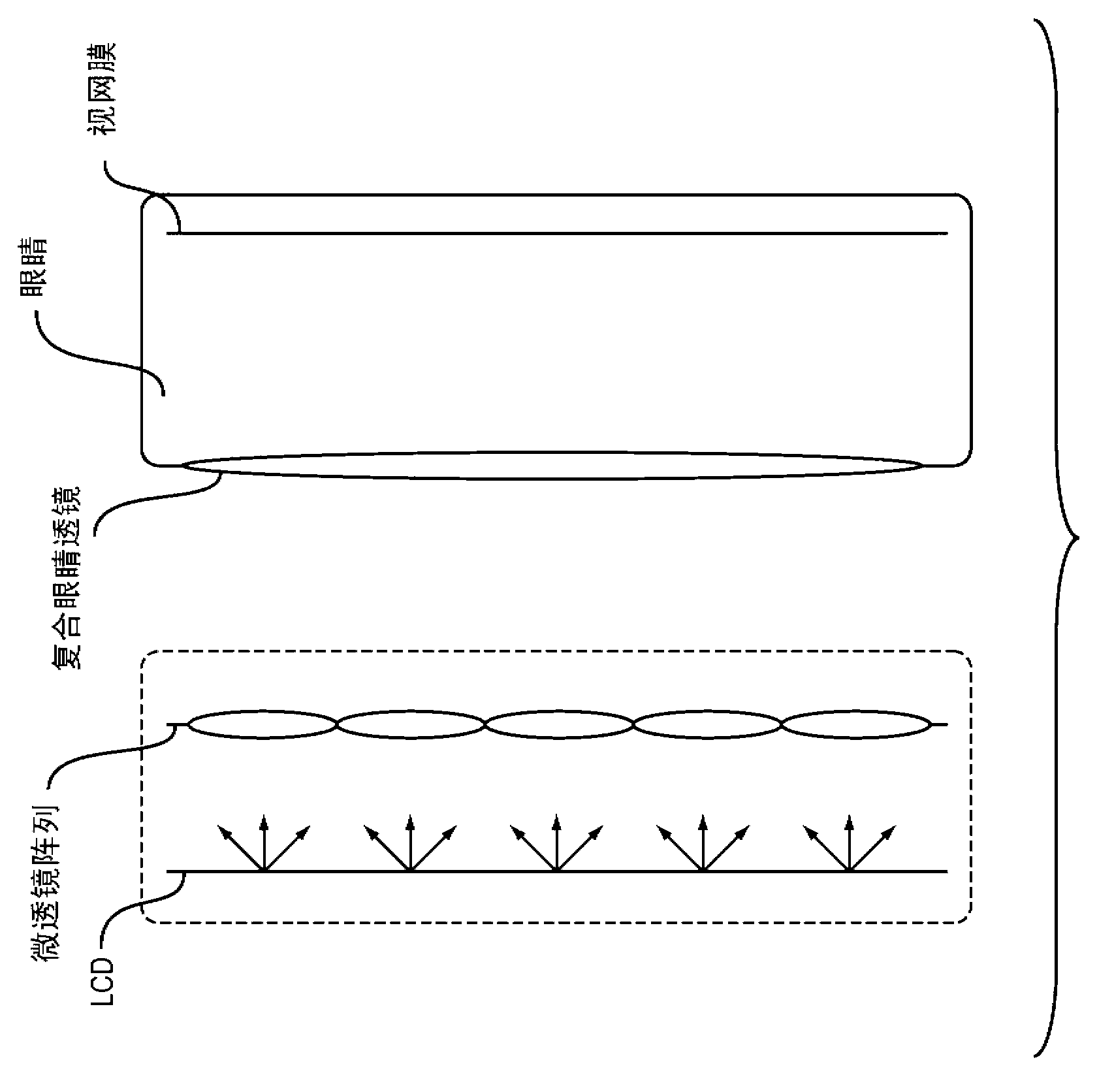
Near eye tool for refractive assessment
In exemplary implementations, this invention is a tool for subjective assessment of the visual acuity of a human eye. A microlens or pinhole array is placed over a high- resolution display. The eye is brought very near to the device. Patterns are displayed on the screen under some of the lenslets or pinholes. Using interactive software, a user causes the patterns that the eye sees to appear to be aligned. The software allows the user to move the apparent position of the patterns. This apparent motion is achieved by pre- warping the position and angle of the ray-bundles exiting the lenslet display. As the user aligns the apparent position of the patterns, the amount of pre-warping varies. The amount of pre-warping required in order for the user to see what appears to be a single, aligned pattern indicates the lens aberration of the eye.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Closed Loop System and Method for Ablating Lenses with Aberrations
The present invention comprises a closed loop system and method for assessing a performance of a refractive surgical system that is capable of correcting lower and higher order aberrations of the eye. In one embodiment, the refractor surgical system comprises a corneal re-shaping laser system and a refractor system that is capable of measuring low and higher order aberrations of the eye. A software application is capable of transforming the measurements of the refractor system to a treatment plan to control and guide the corneal re-shaping laser system. The systems and methods of the present invention may include a lens that is created by the corneal reshaping laser system and can be measured by the refractor system.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Combination advanced corneal topography/wave front aberration measurement
A method and apparatus for the simultaneous measurement of the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces, corneal thickness, and optical aberrations of the eye. The method employs direct measurements and ray tracing to provide a wide range of measurements for use by the ophthalmic community.
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
System and method for ocular aberrometry and topography using plenoptic imaging
ActiveUS20140268044A1Improve efficiencyAccurate ocular topographyRefractometersSkiascopesCorneal surfaceAberrations of the eye
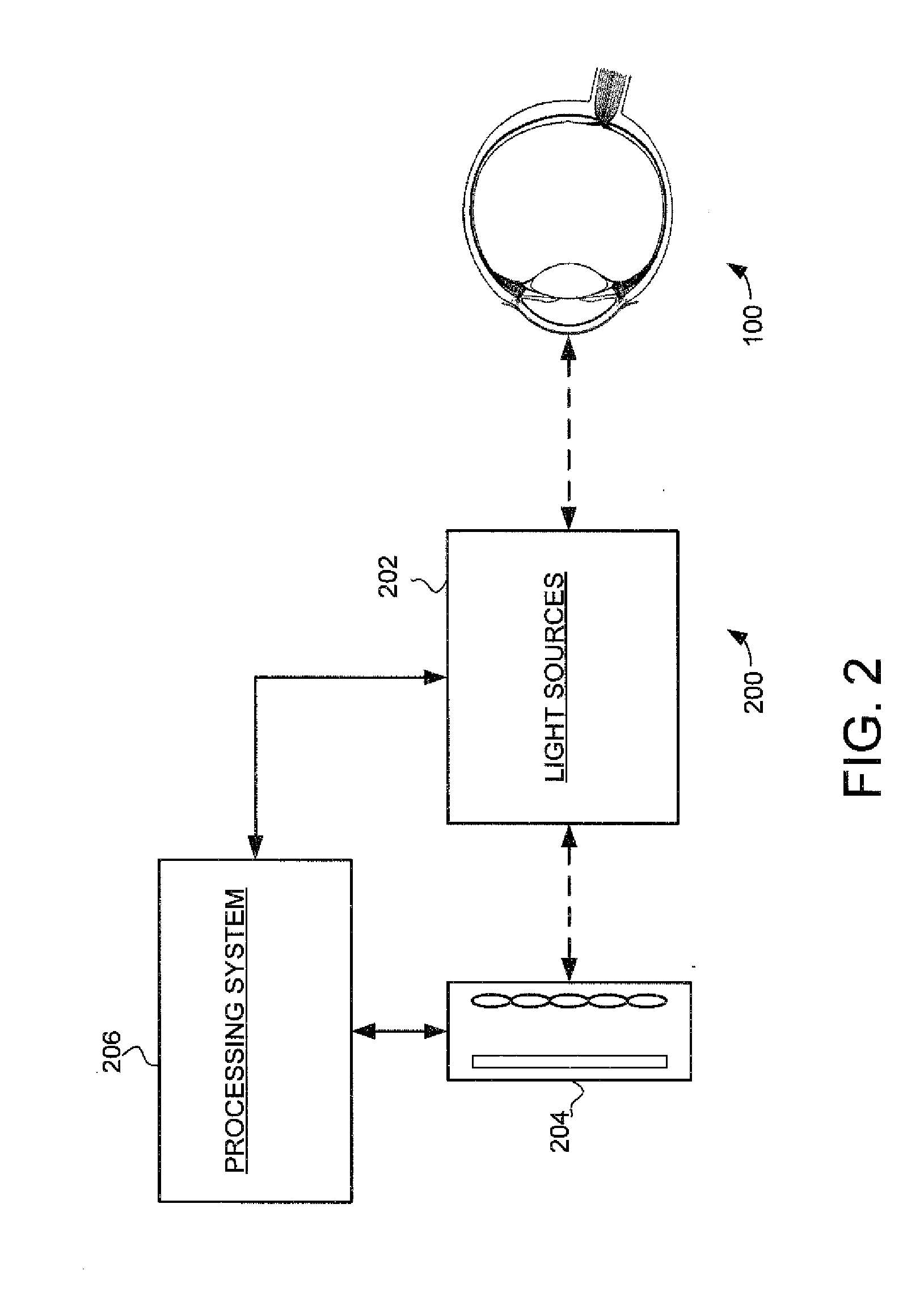
Improved systems and methods for ocular topography and using a plenoptic detector are provided. For example, a multifunction ocular topography and aberrometry system can comprise a first set of light sources, a second light source, a plenoptic detector and a processing system coupled to the plenoptic detector. The first set of light sources and the second light source are configured to selectively illuminate an eye. The plenoptic detector is configured to selectively receive images of the first set of light sources reflected from a corneal surface of the eye and generate first plenoptic image data representing the images of the first set of light sources. The plenoptic detector is further configured receive images of the second light source reflected from a retina of the eye and generate second plenoptic image data representing the images of the second light source.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
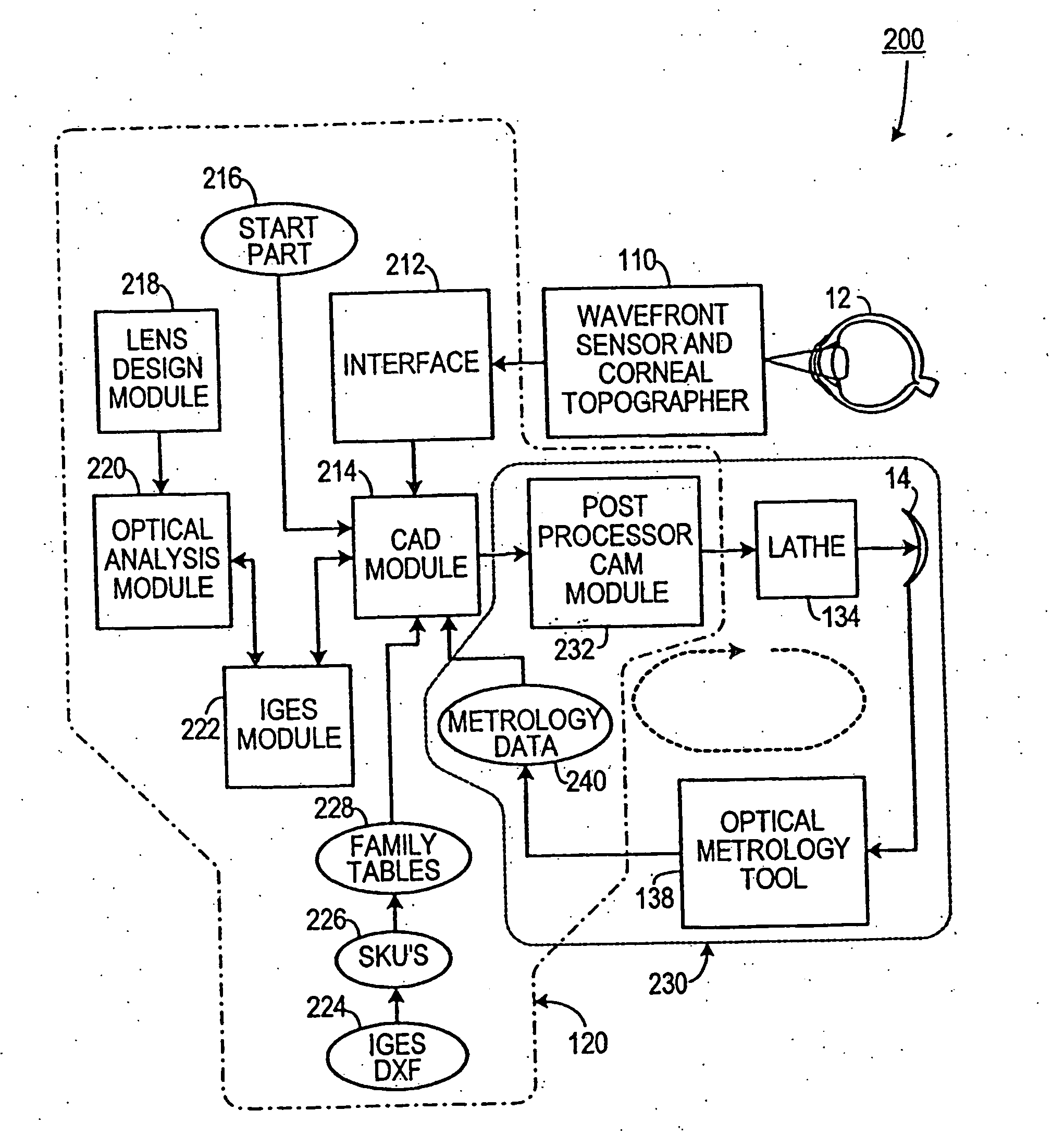
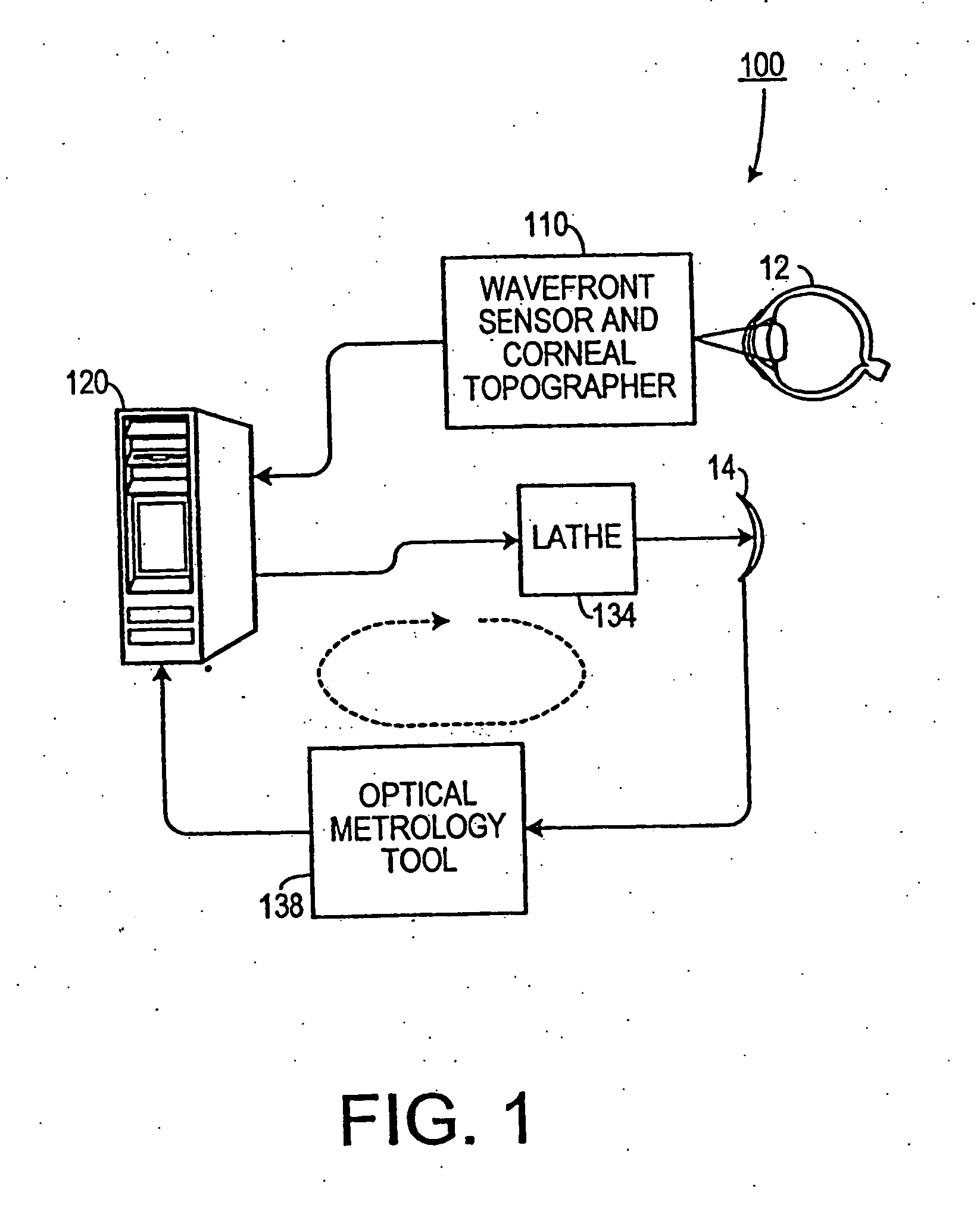
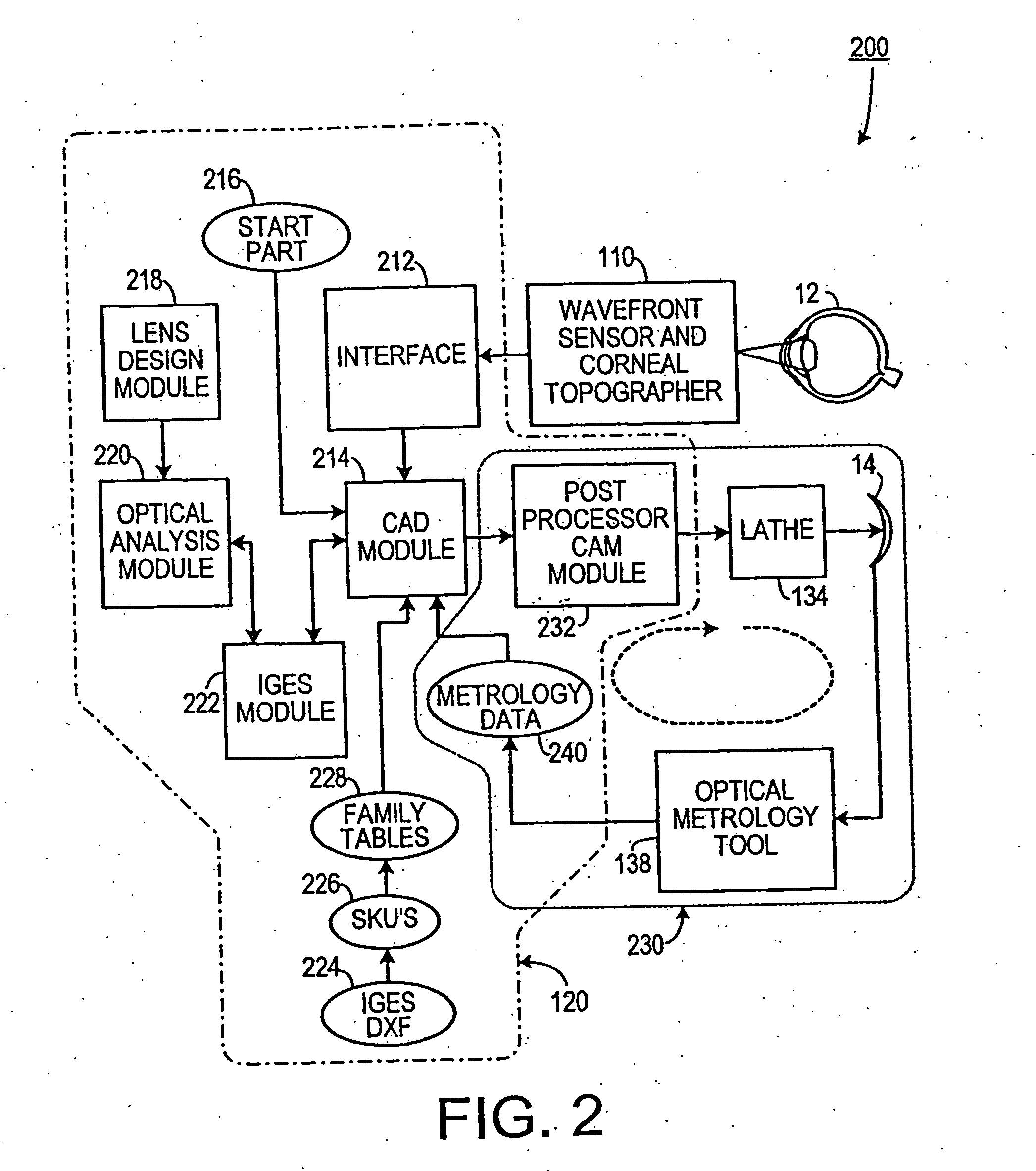
Automatic lens design and manufacturing system
The present invention provides a method for designing and making a customized ophthalmic lens, such as a contact lens or an intraocular lens, capable of correcting high-order aberrations of an eye. The posterior surface of the customized contact lens is designed to accommodate the corneal topography of an eye. The design of the customized ophthalmic lens is evaluated and optimized in an optimizing routine using a computational model eye that reproduces the aberrations and corneal topography of an eye. The present invention also provides a system and method for characterizing the optical metrology of a customized ophthalmic lens that is designed to correct aberrations of an eye. Furthermore, the present invention provides a business model and method for placing an order for a pair of customized ophthalmic lenses.
Owner:ALCON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com