Patents
Literature
106 results about "Multifocals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
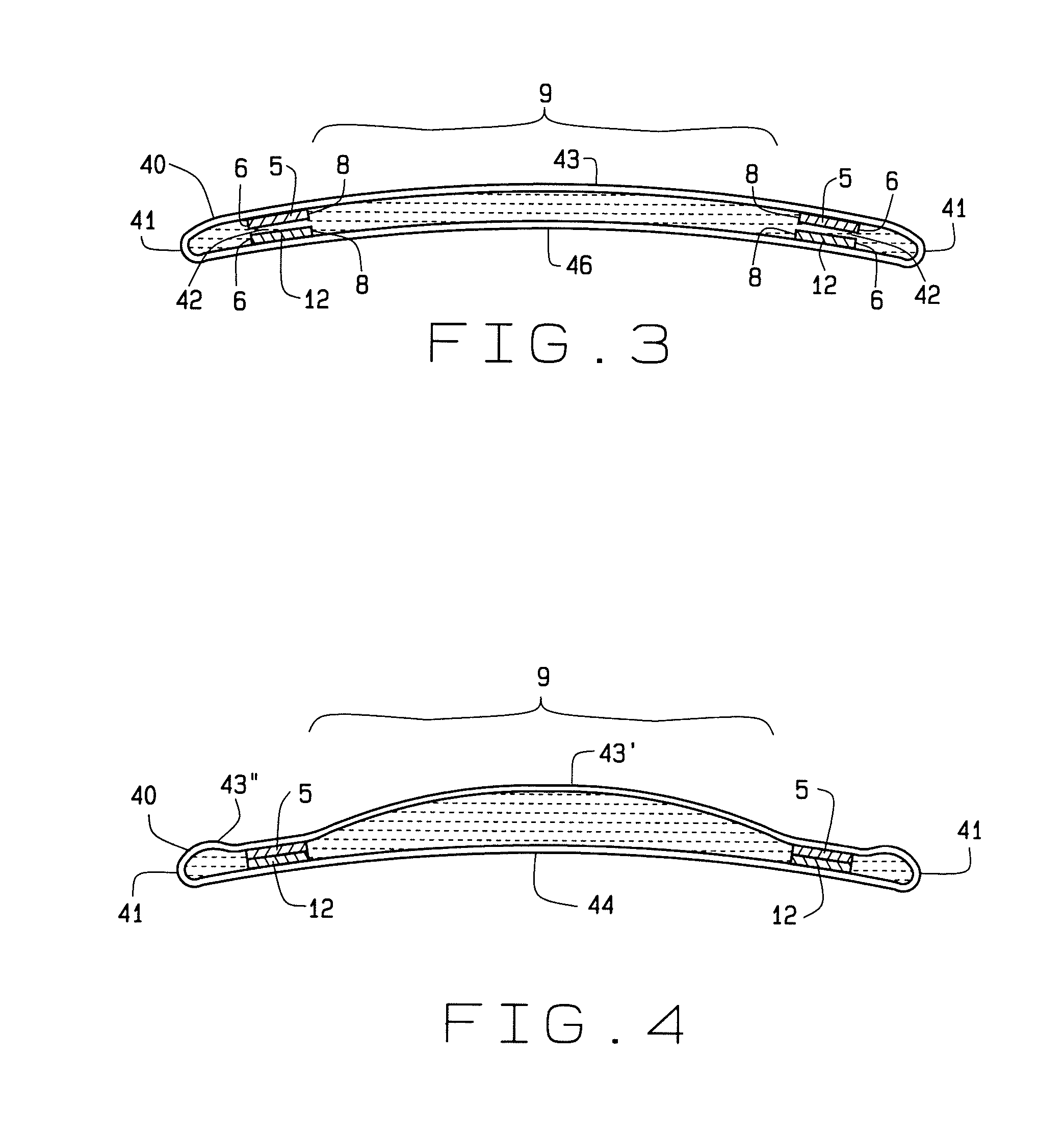
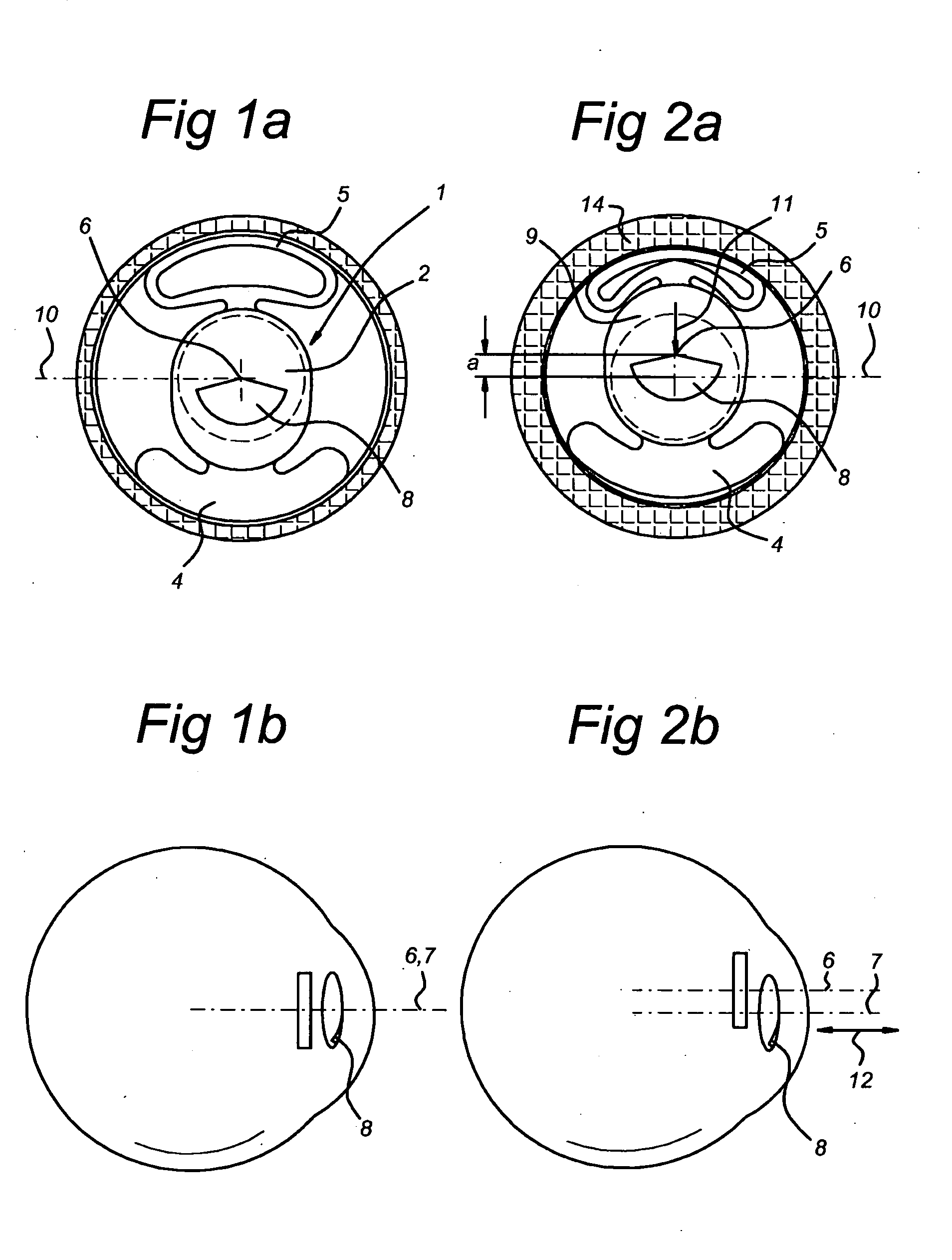
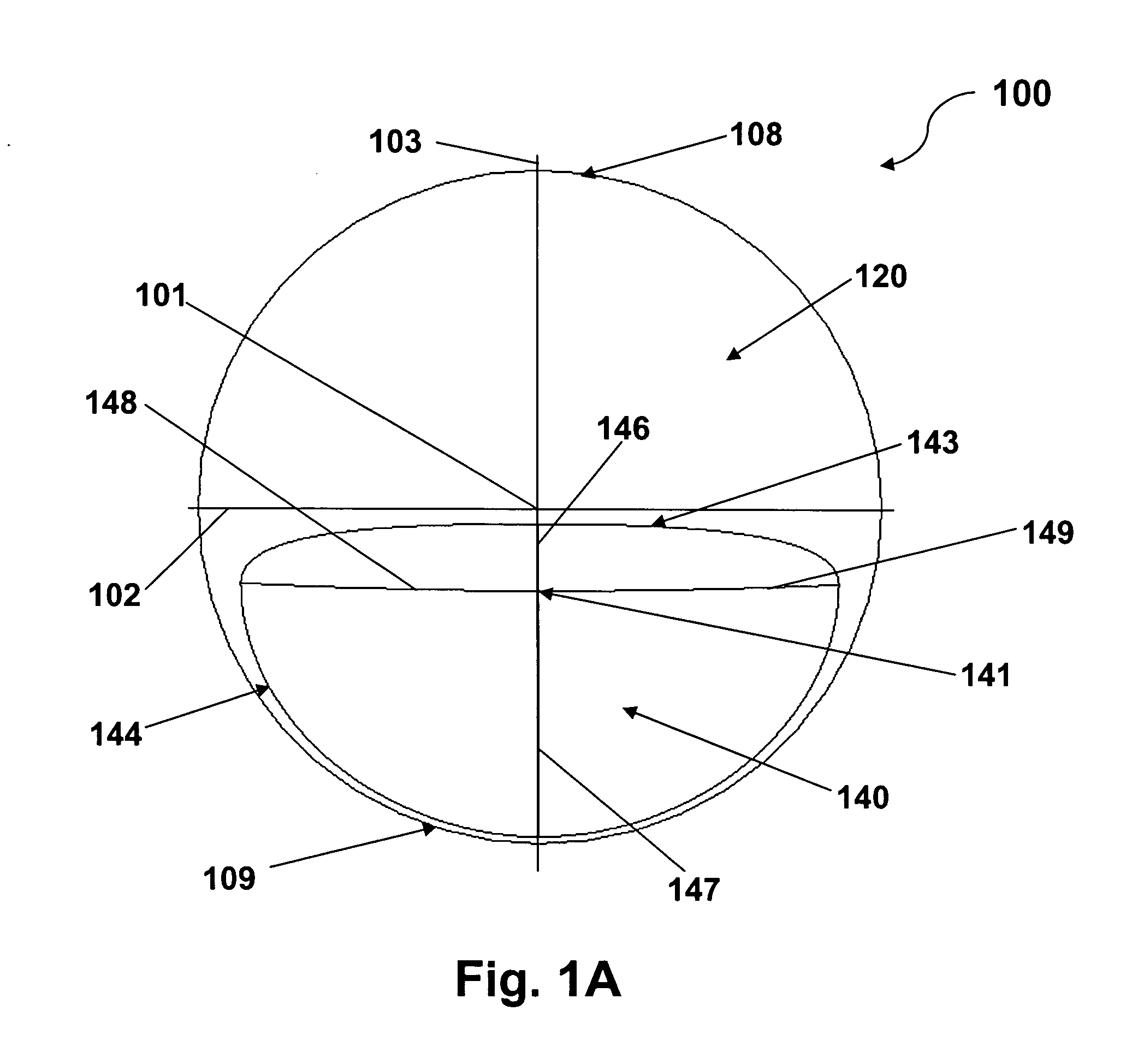
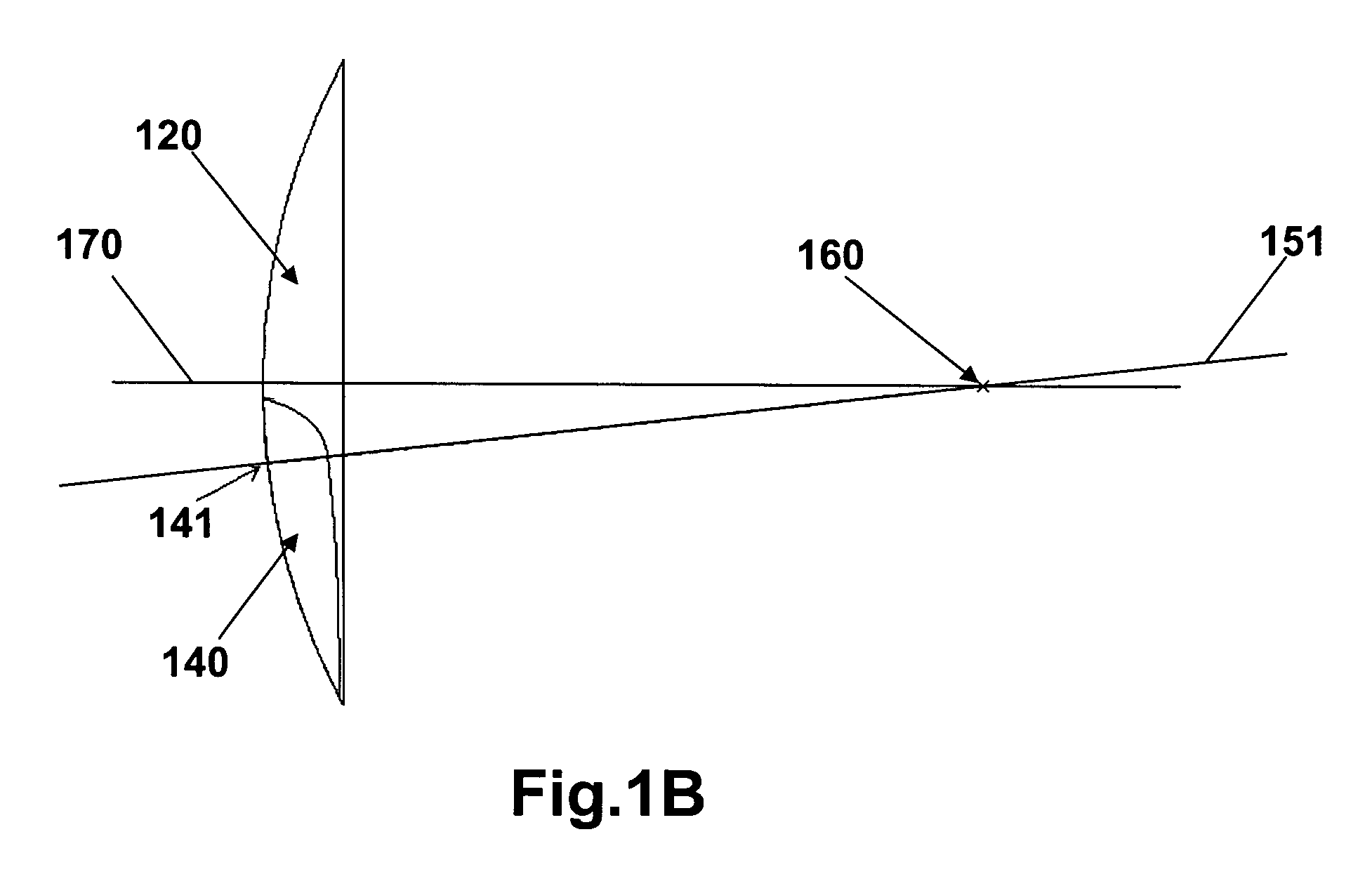
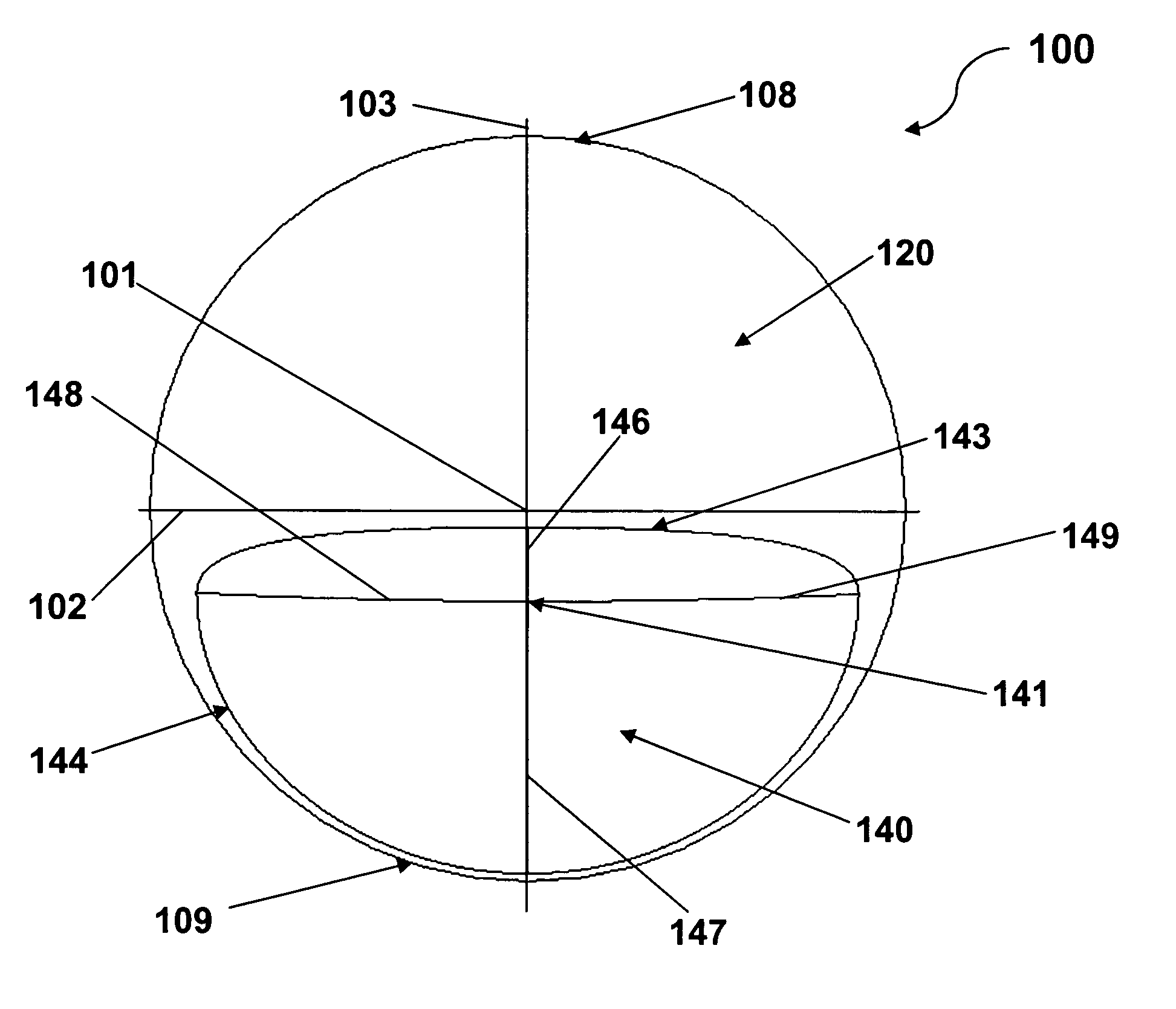
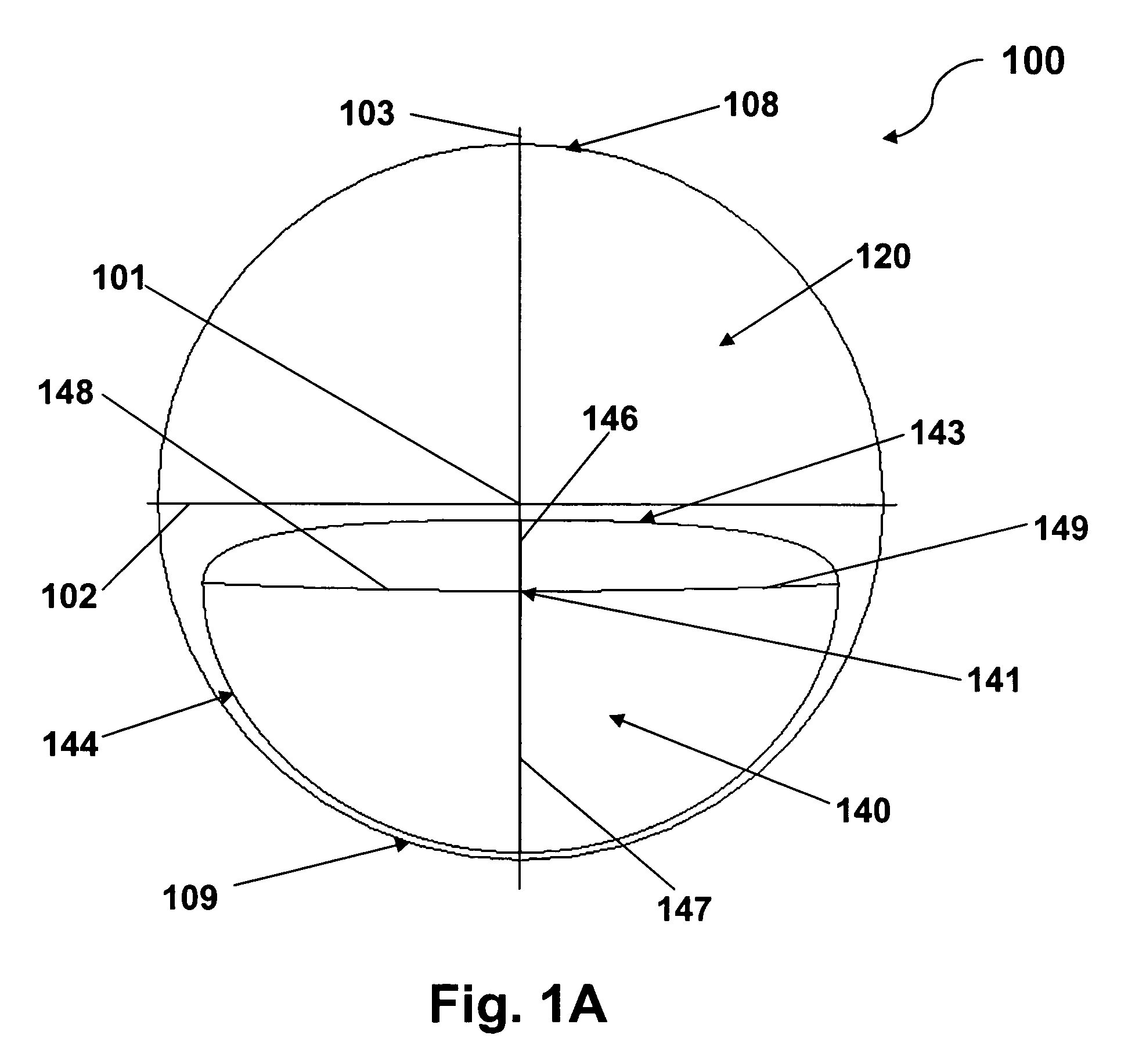
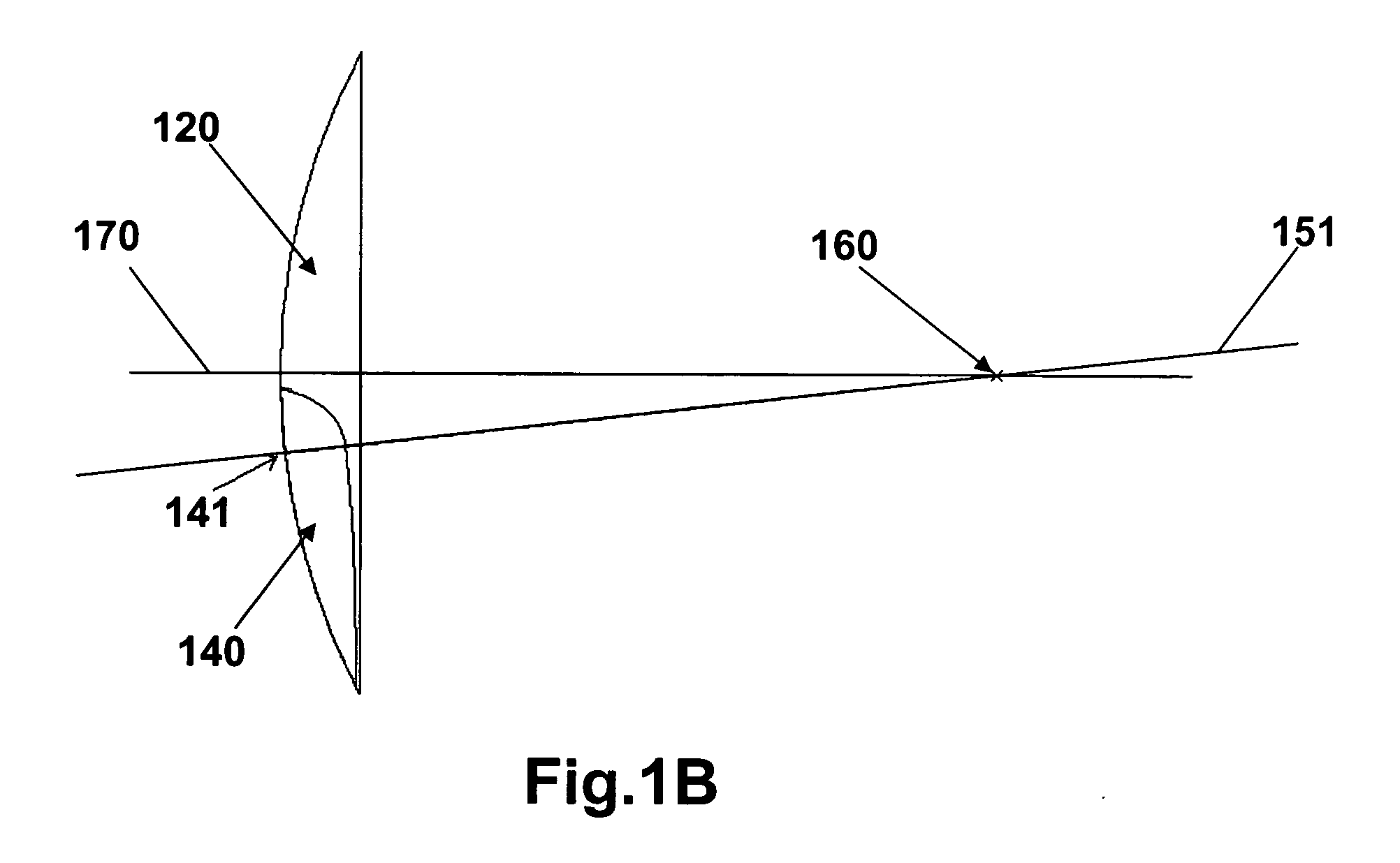
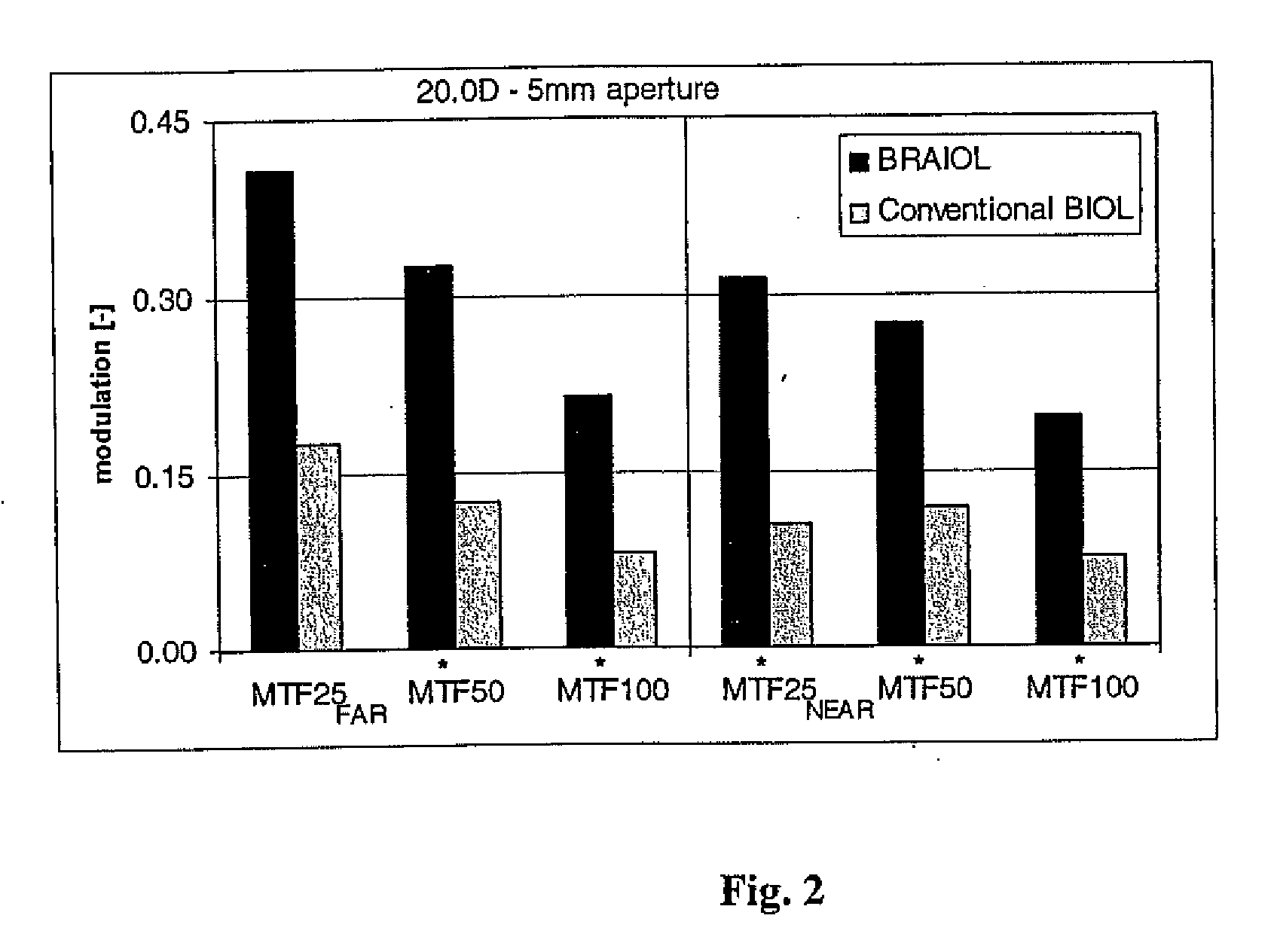
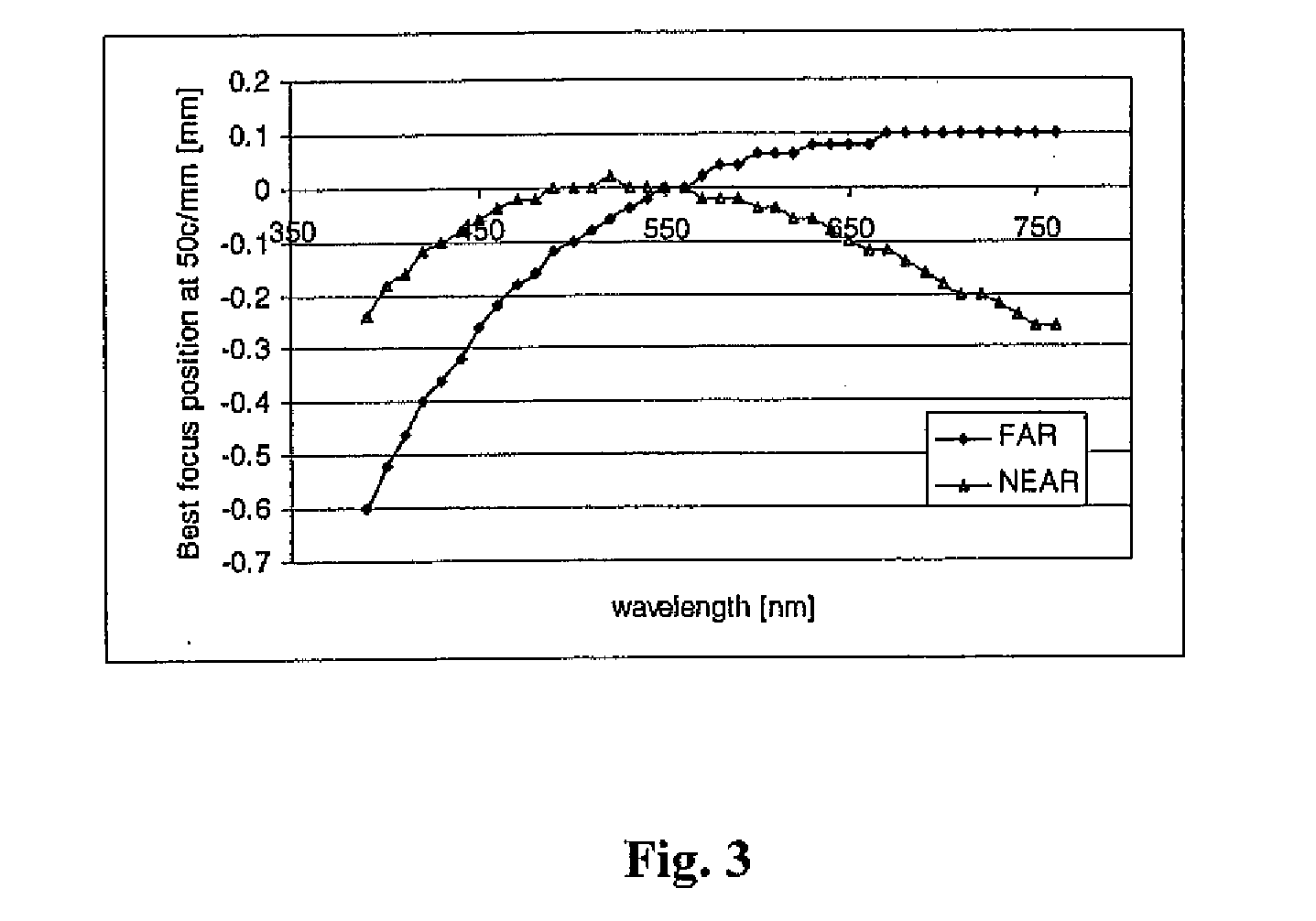
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20040156014A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
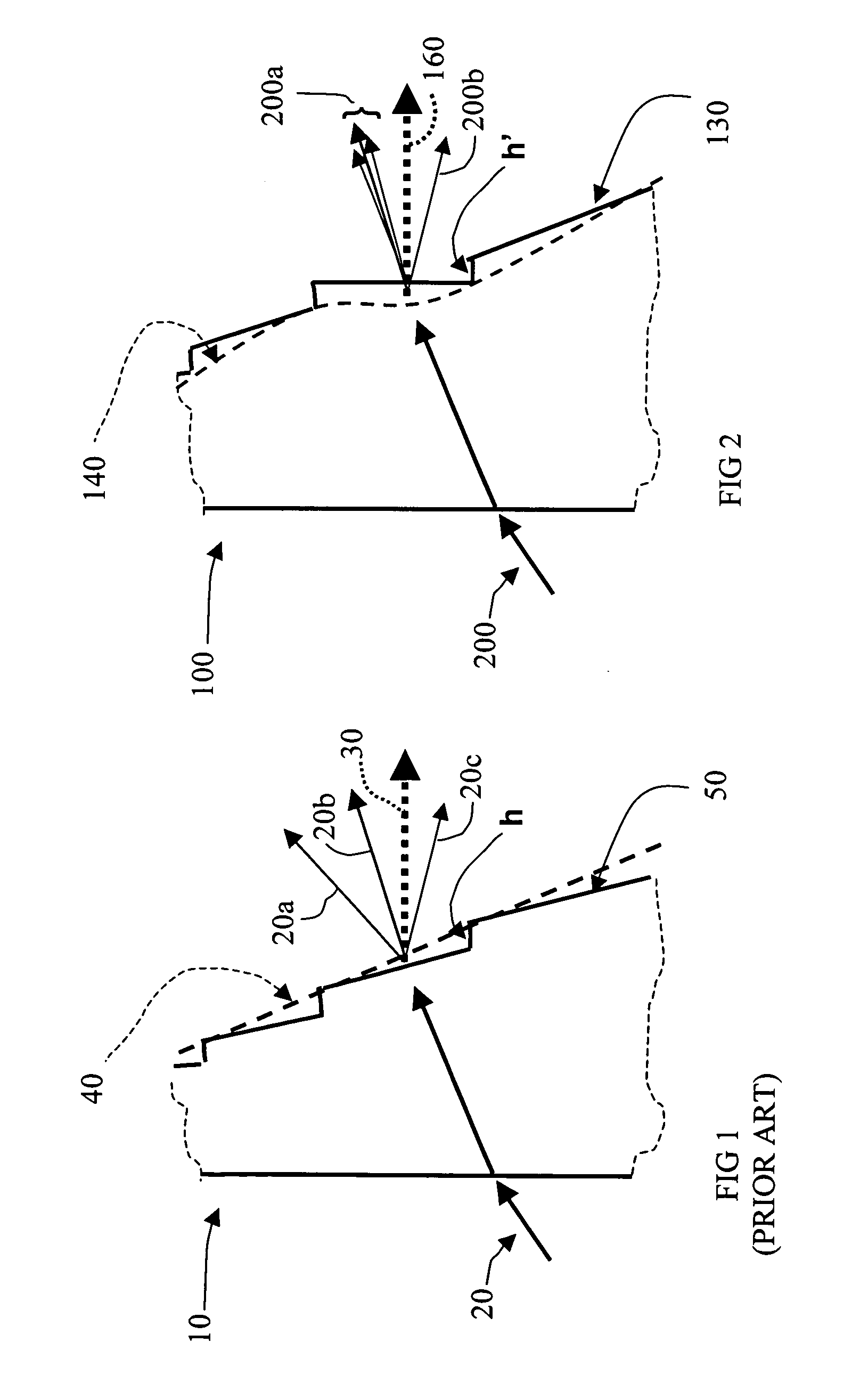
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Multifocal imaging systems and method
InactiveUS20070057211A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLow noiseGrating
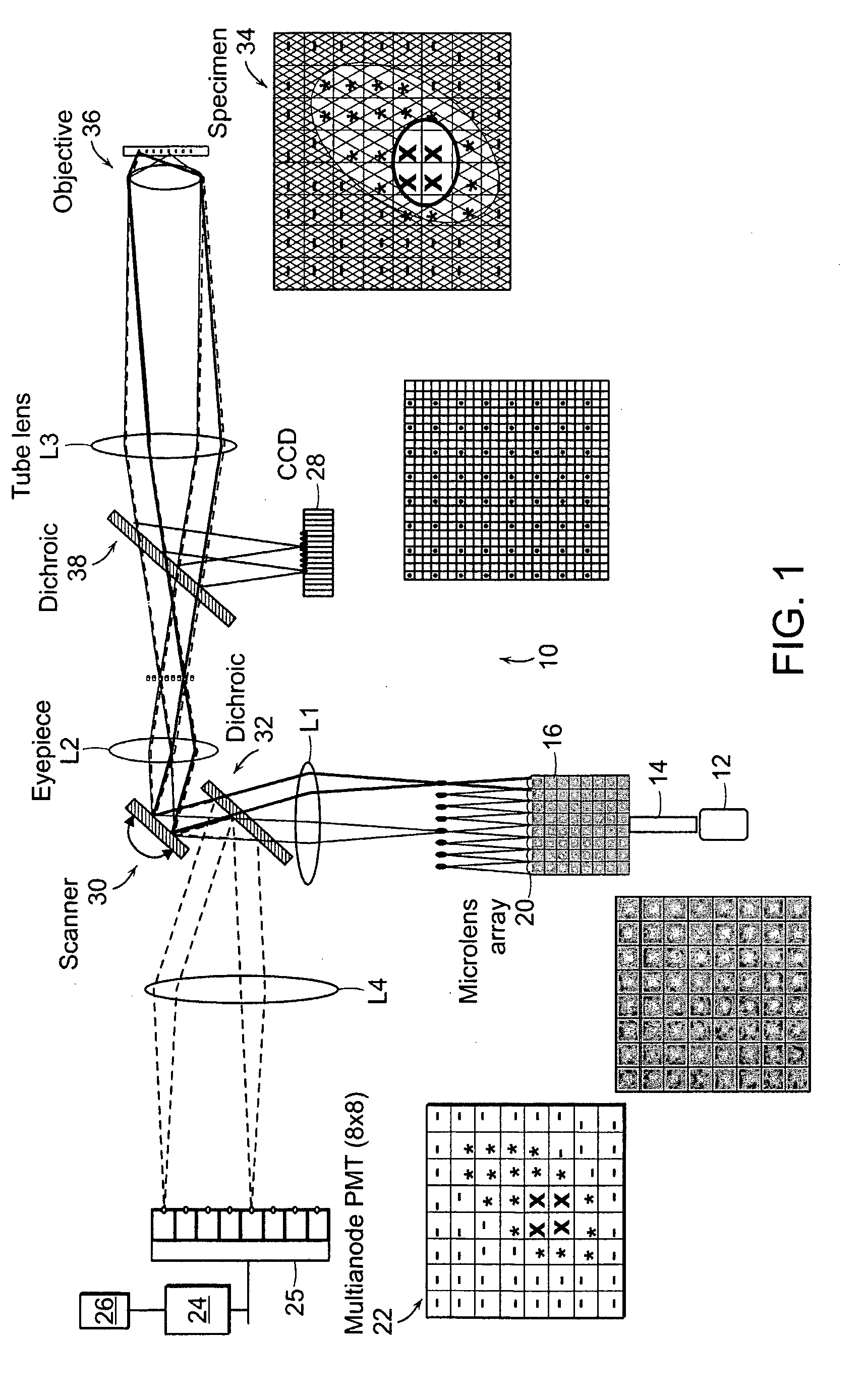
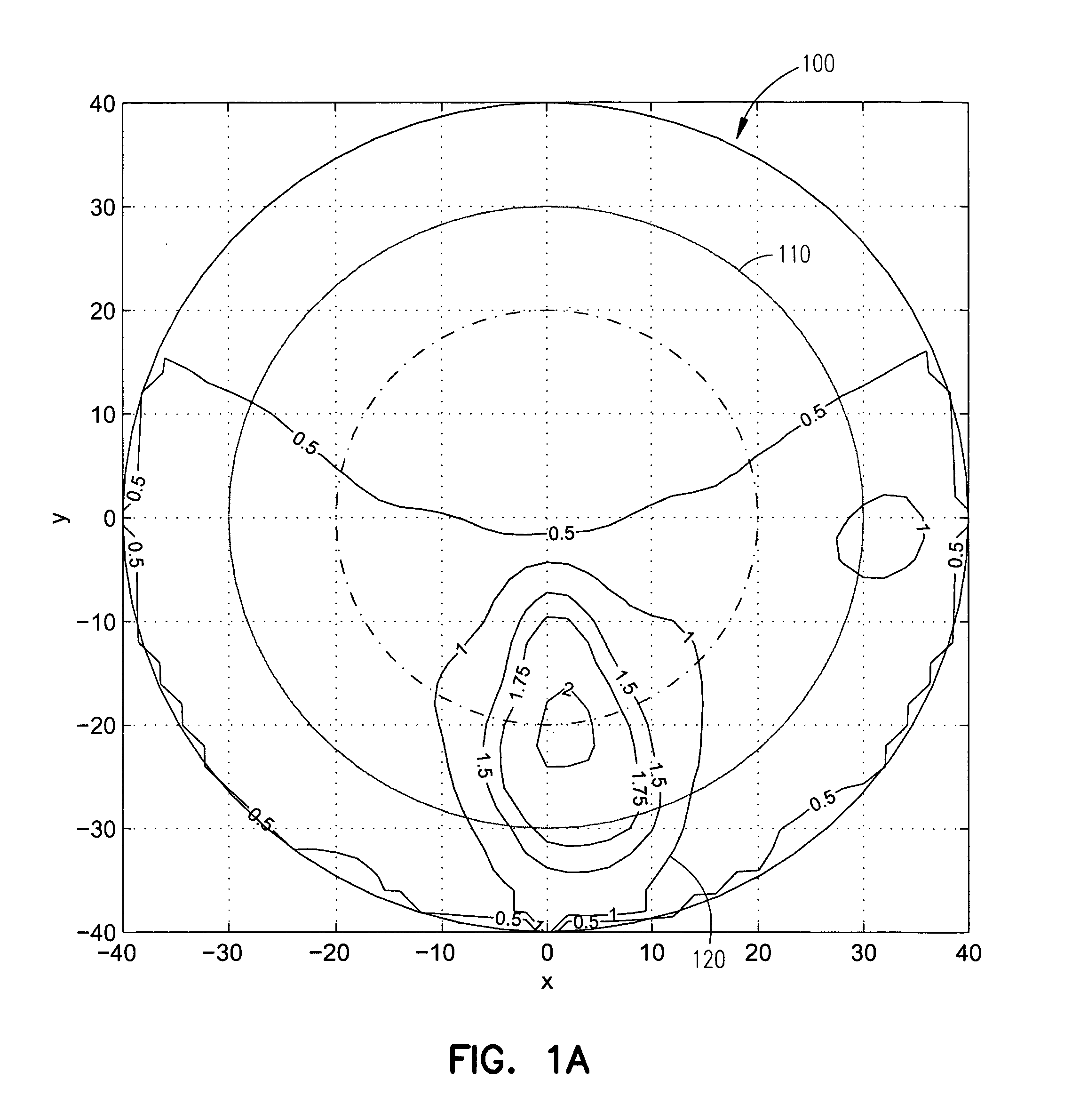
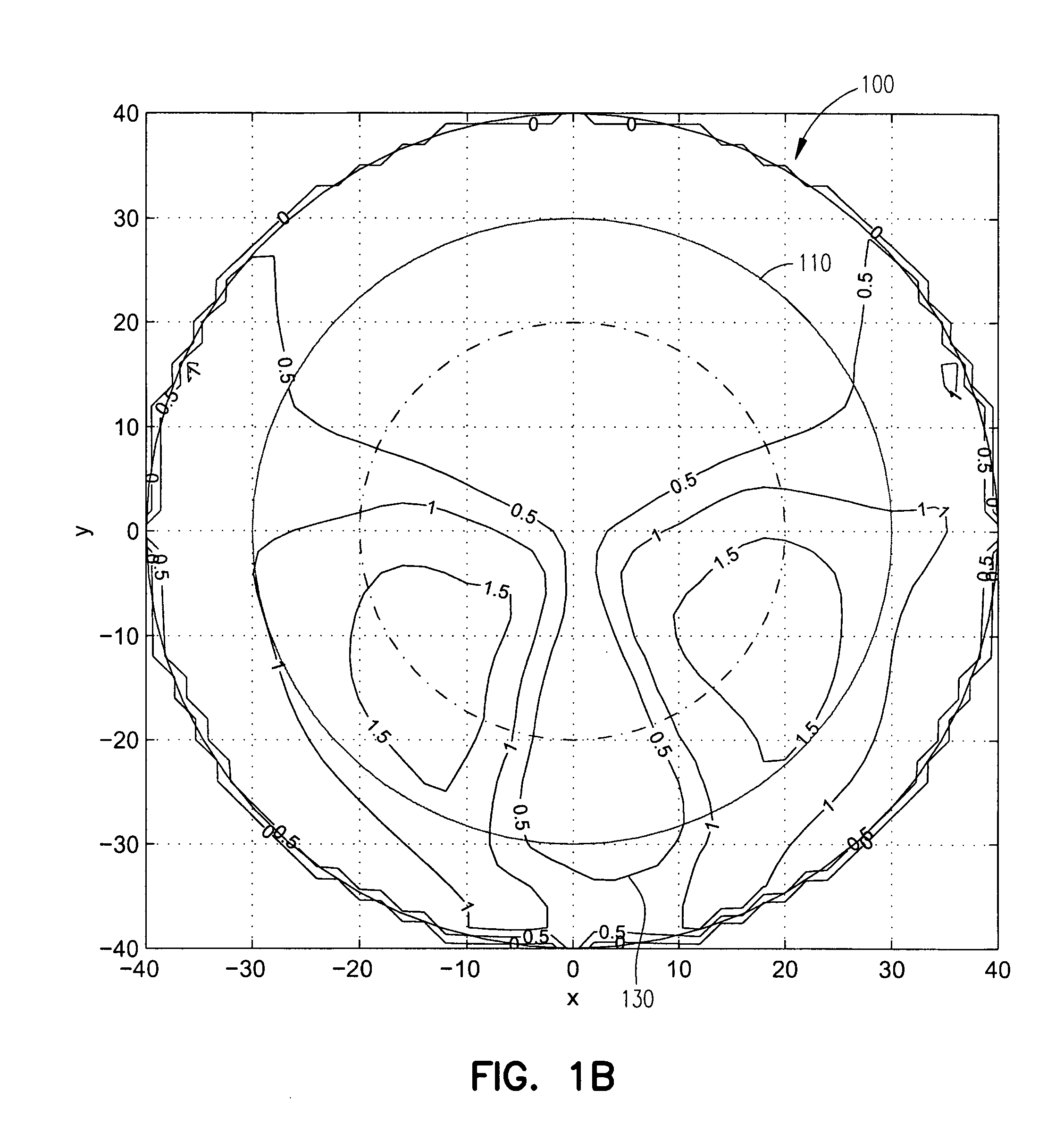
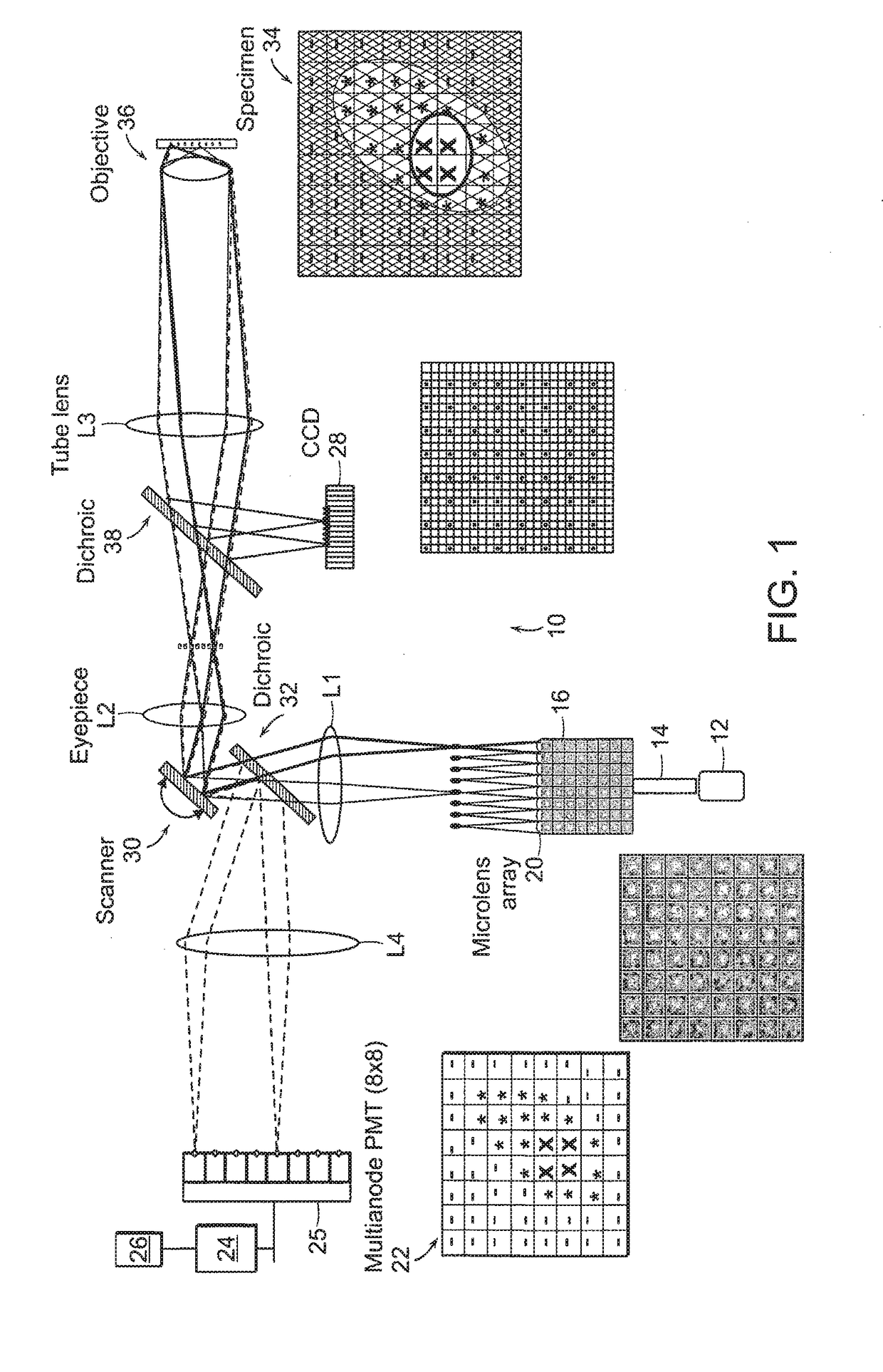
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS20060050409A1Increase contrastReduce image contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spreadIntermediate image
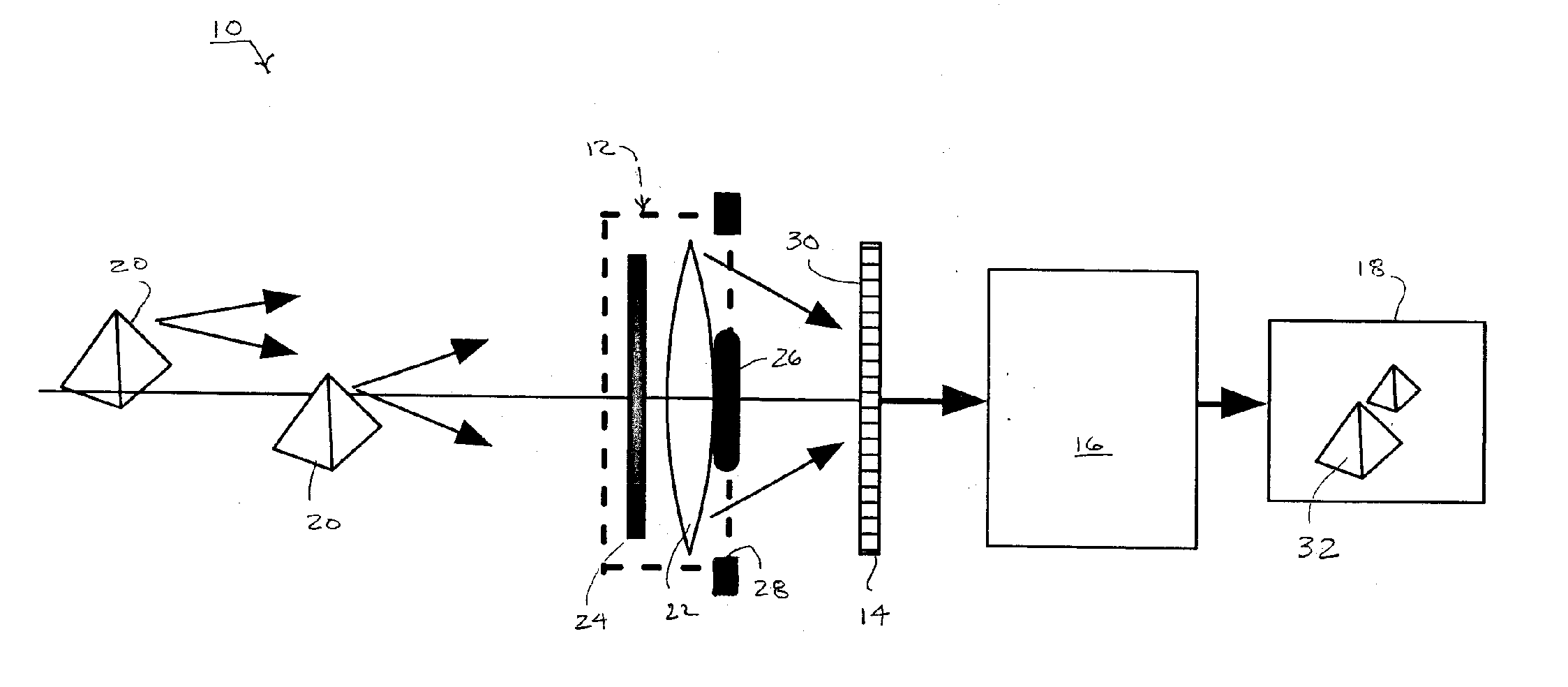
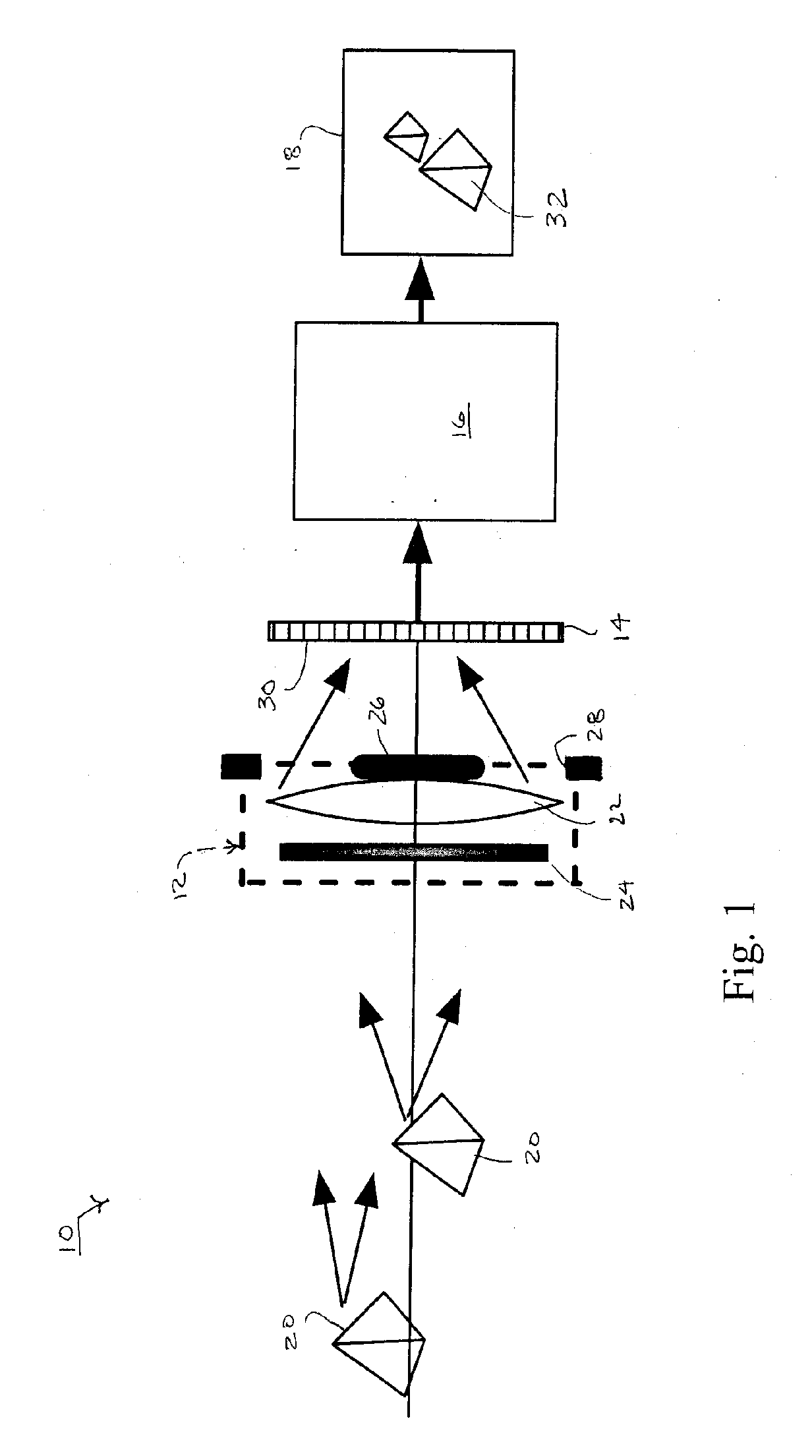
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS7377641B2Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Aspheric multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20070258143A1Increase depth of focusAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensAnterior surfaceRefractive index
A multifocal ophthalmic lens includes a lens element having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, a refractive zone, or base surface having aspherically produced multifocal powers disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces; and a near focus diffractive multifocal zone disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces.
Owner:VISION ADVANCEMENT LLC
Multifocal contact lens designs utilizing pupil apodization
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Stochastic scanning apparatus using multiphoton multifocal source
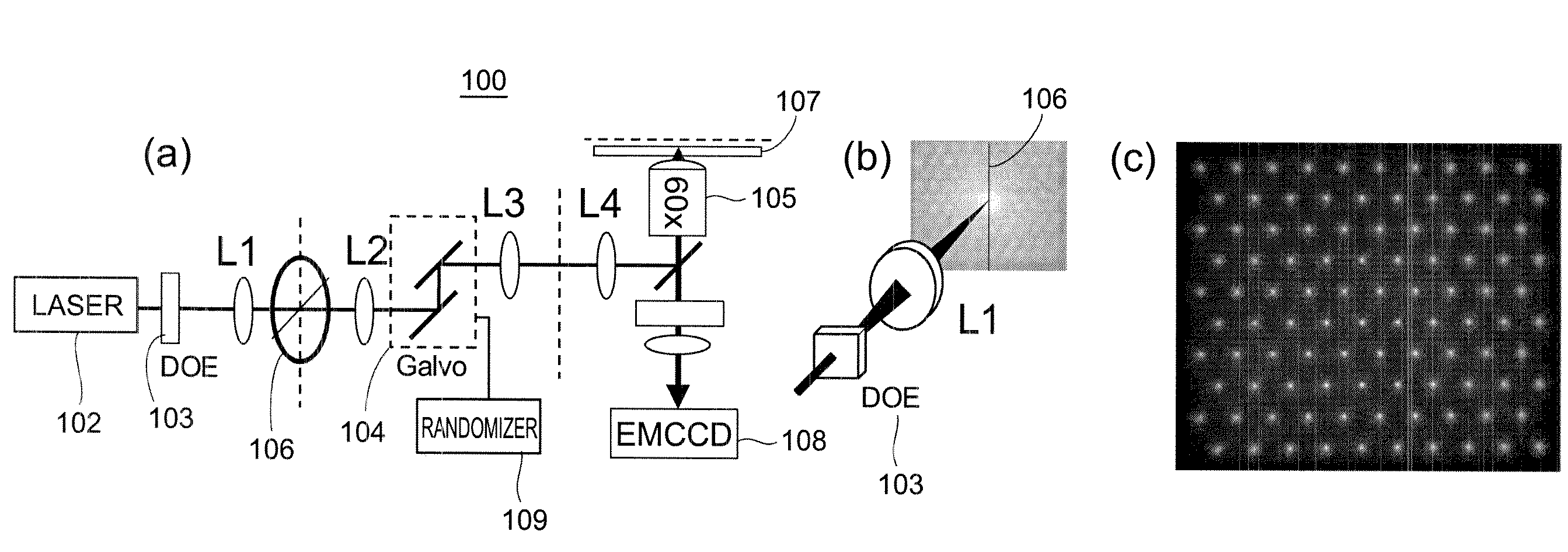
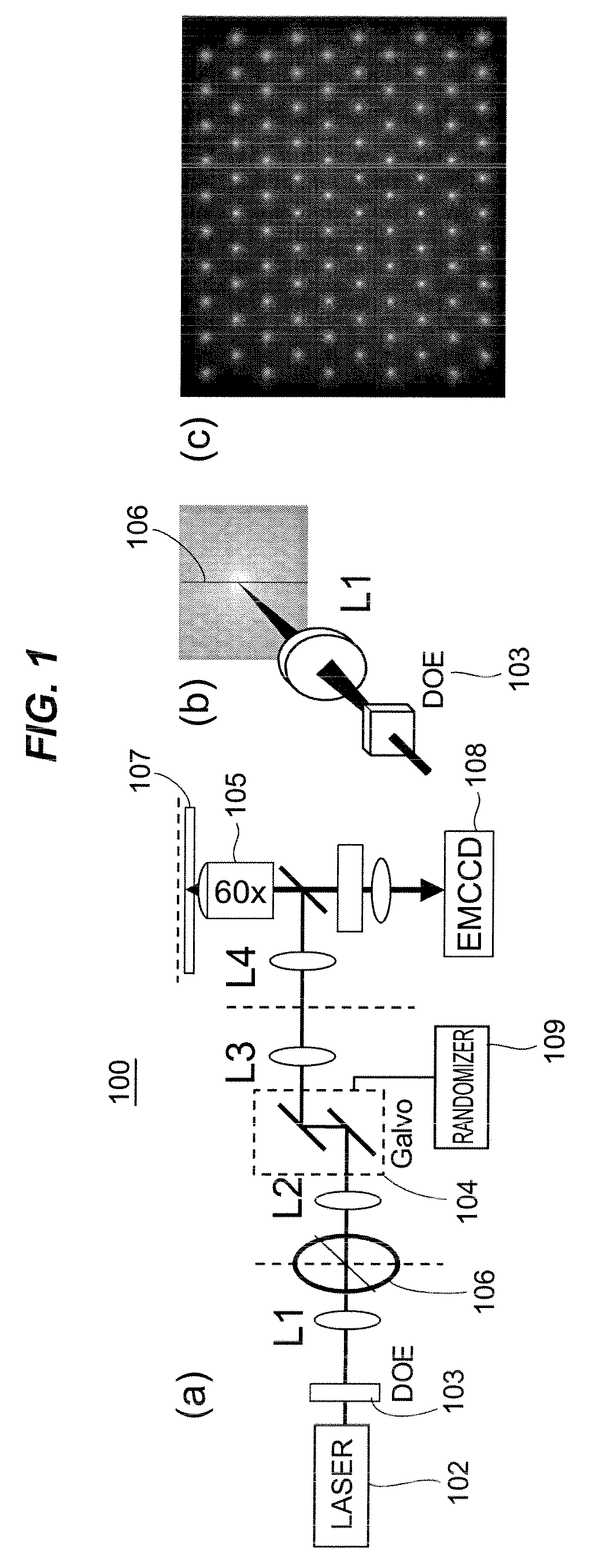
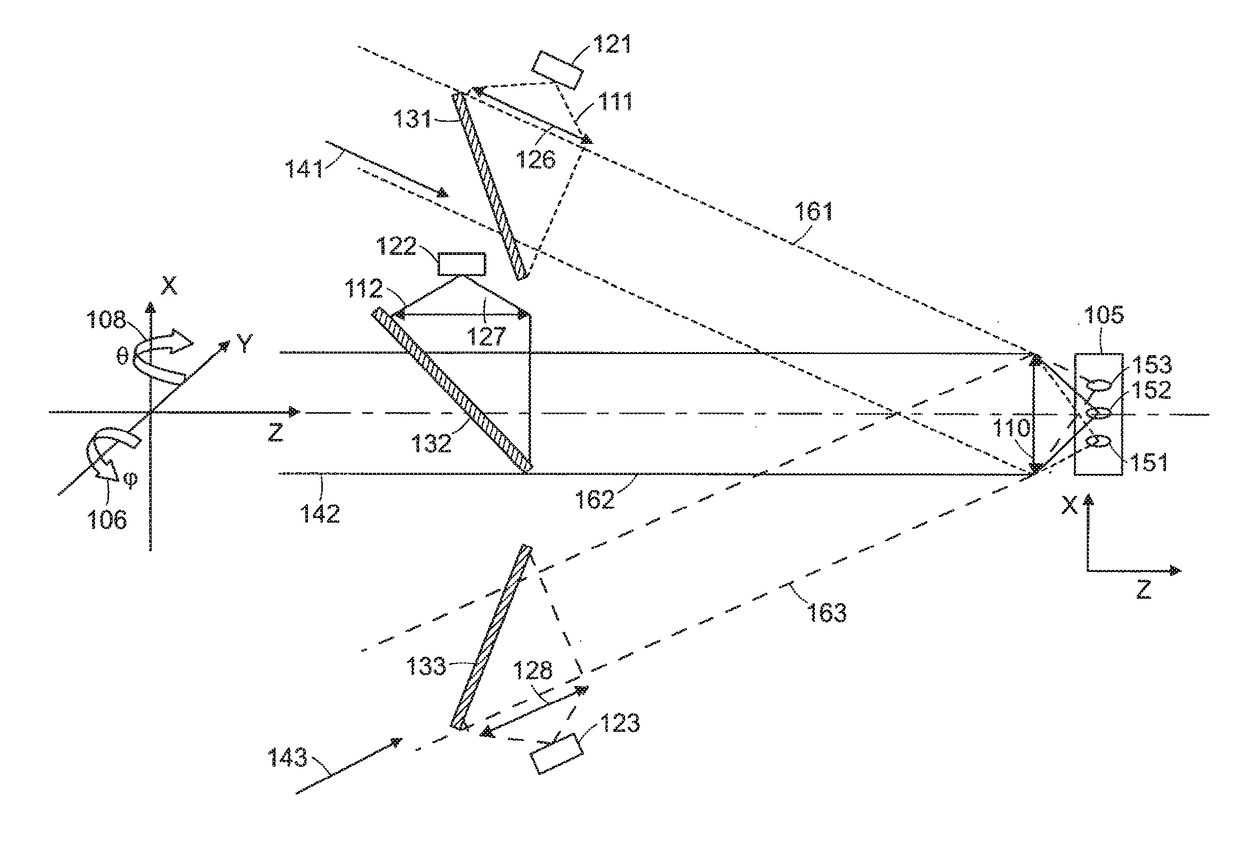
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Photochromic multifocal optical article
Describes a multifocal optical article, e.g., an ophthalmic article such as a lens, in which the article includes (1) a rigid optical substrate, e.g., a transparent polymeric substrate, such as a thermoset or thermoplastic substrate, adapted to possess at least one light influencing property on at least a portion of at least one surface of the substrate, e.g., a photochromic and / or polarizing layer, and (2) a multifocal layer of an optical quality material on said substrate having the light influencing property. Describes also the aforedescribed optical article having an abrasion-resistant coating on the multifocal layer, e.g., an abrasion-resistant coating comprising an organo silane. A method for preparing the multifocal optical article comprising curing optical quality material between a multifocal mold and a preform comprising an optical substrate possessing the light influencing property is also described.
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
Stochastic Scanning Apparatus Using Multiphoton Multifocal Source
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Multifocal contact lenses
The invention provides methods for correcting presbyopia and lenses for such correction in which production of a full range of multifocal lenses is accomplished using three rotationally symmetric, aspheric back surfaces, the design of which base curves is a function of refractive power.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
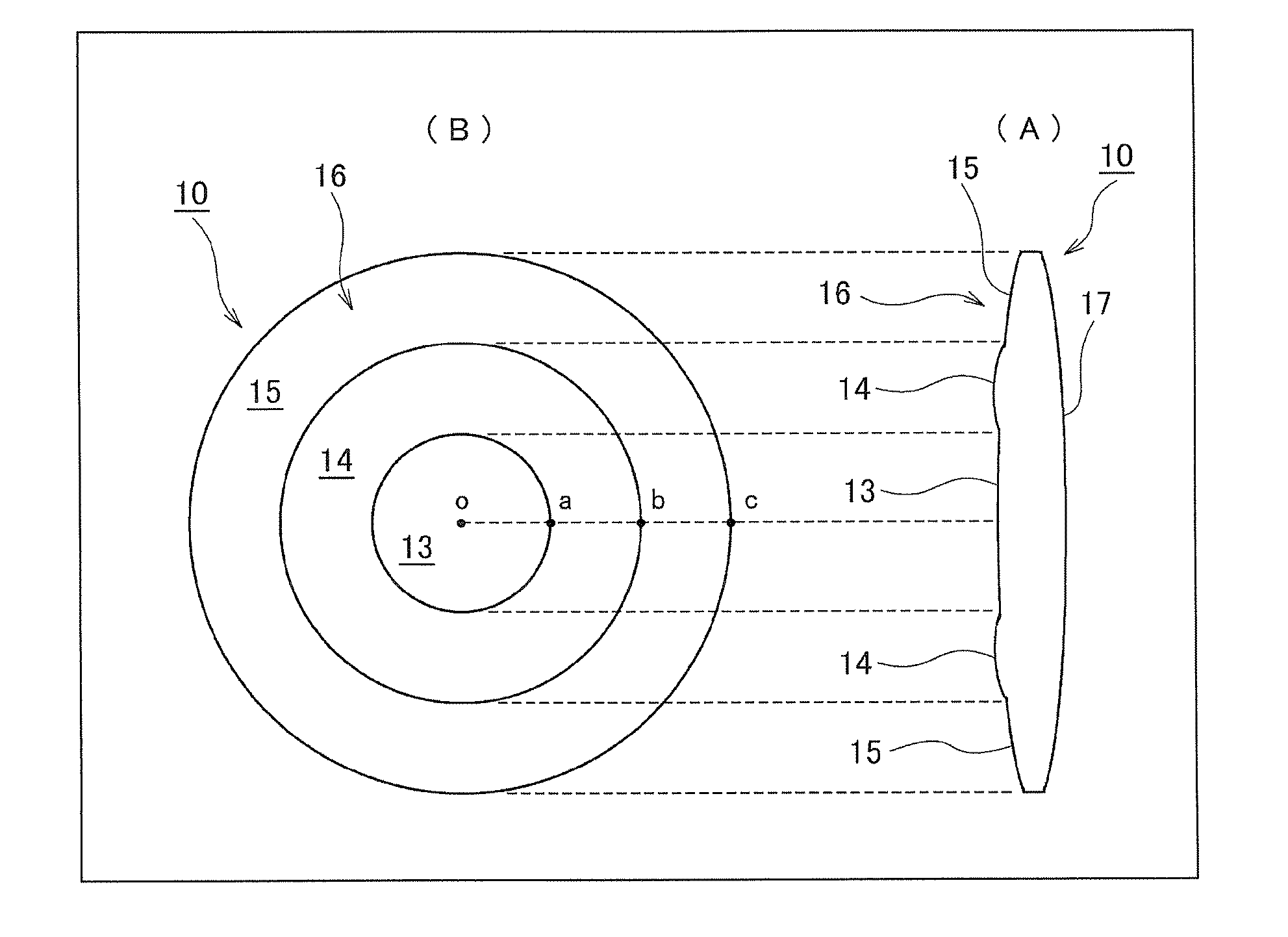
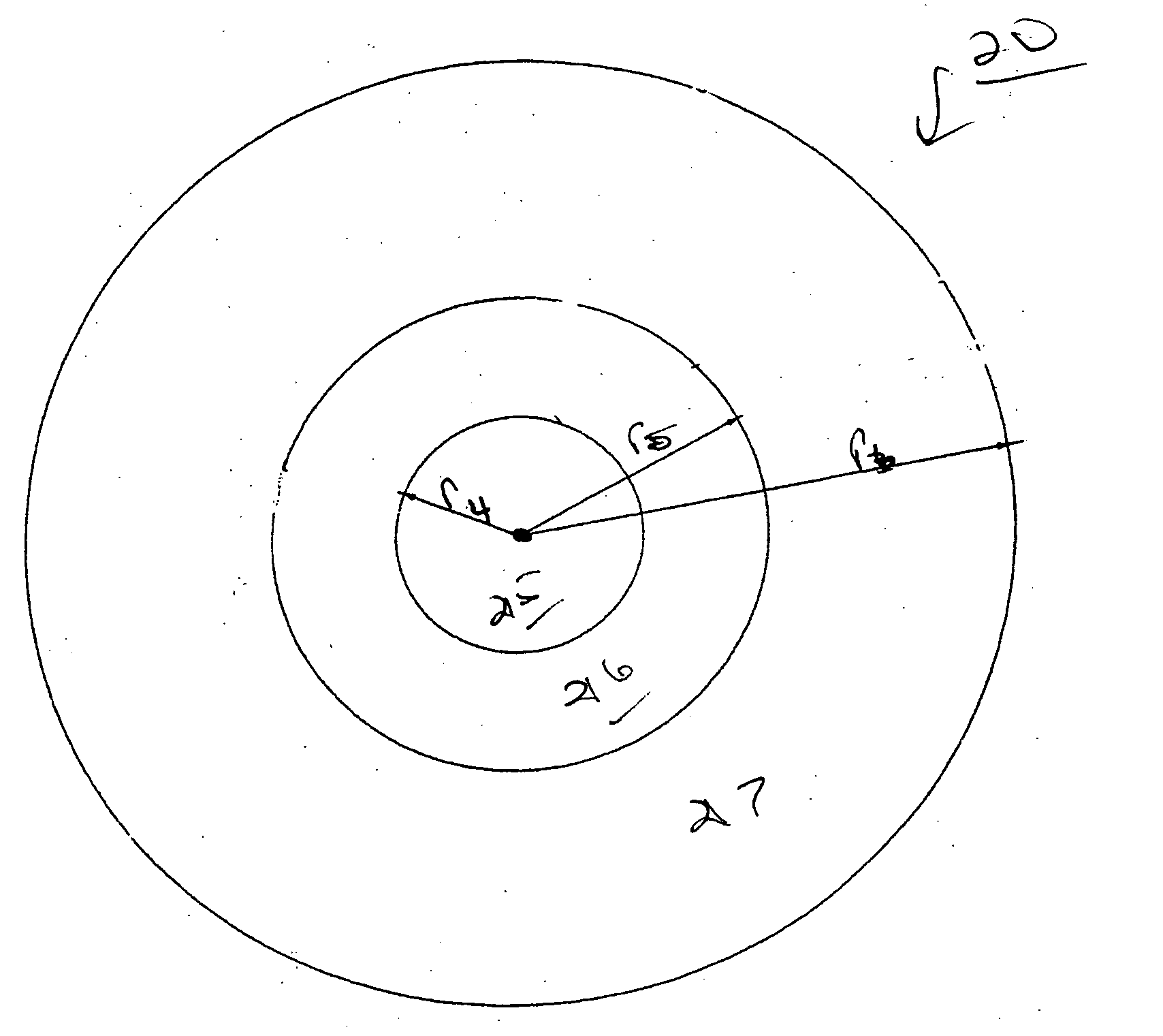
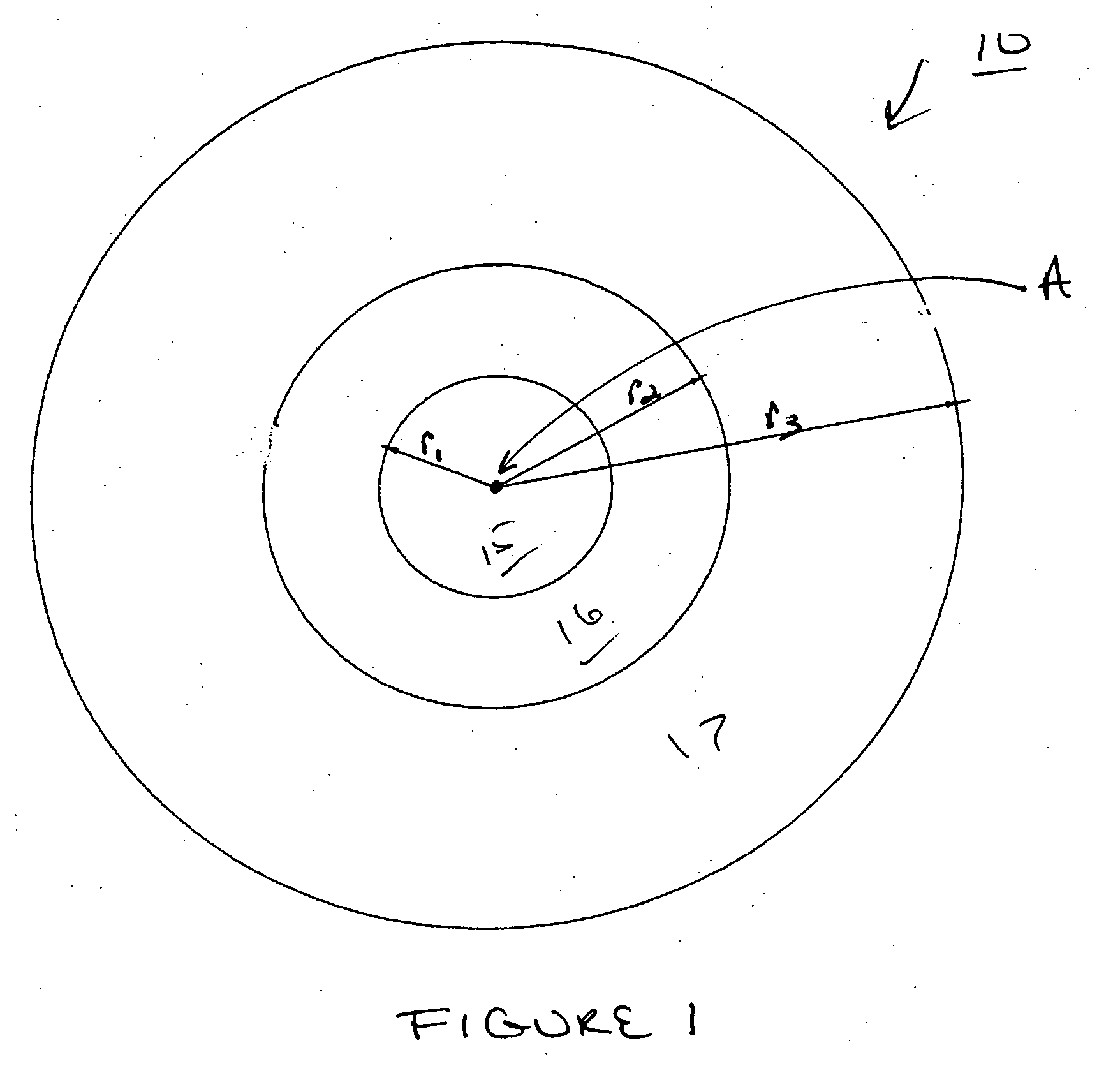
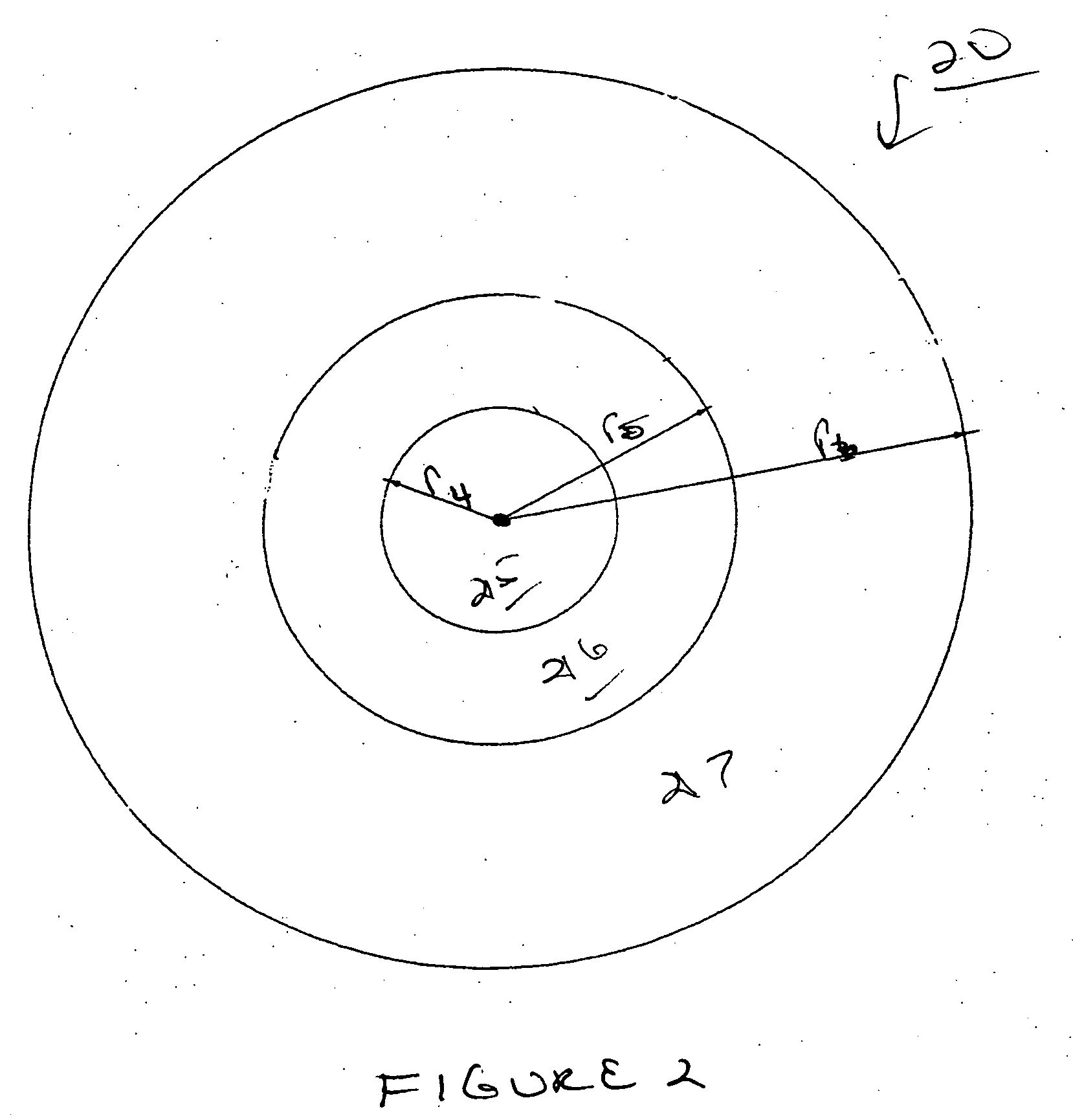
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
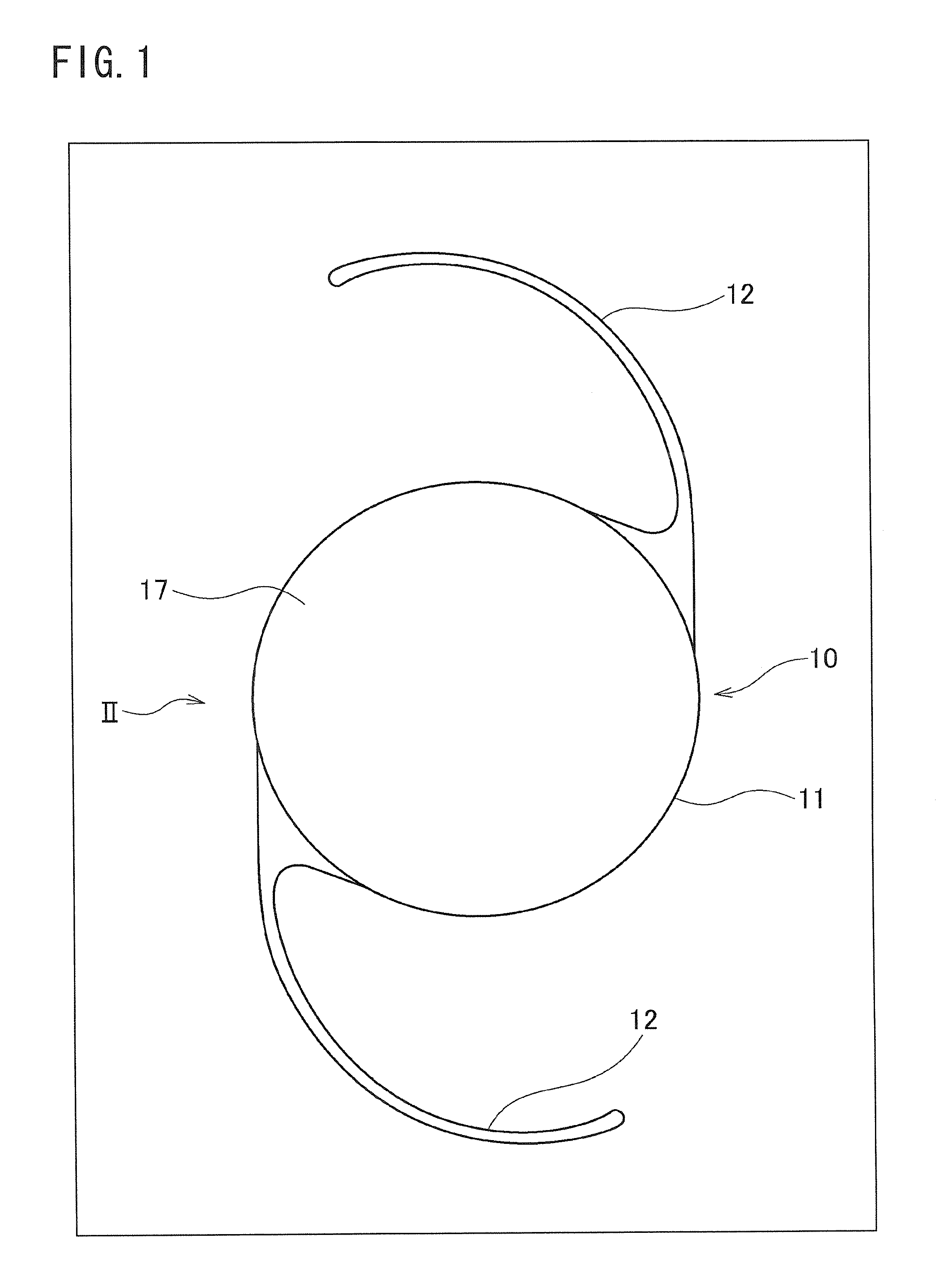
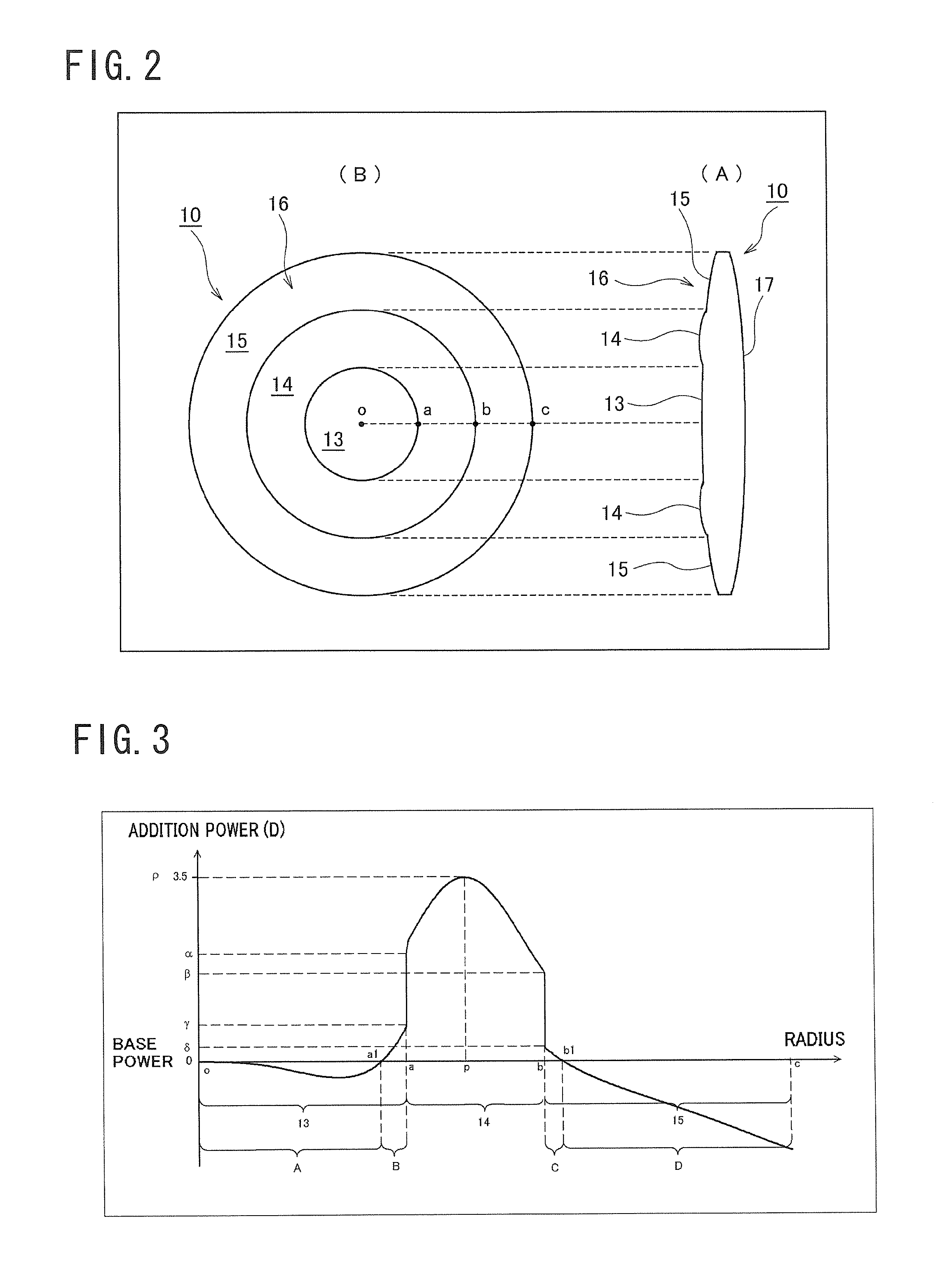
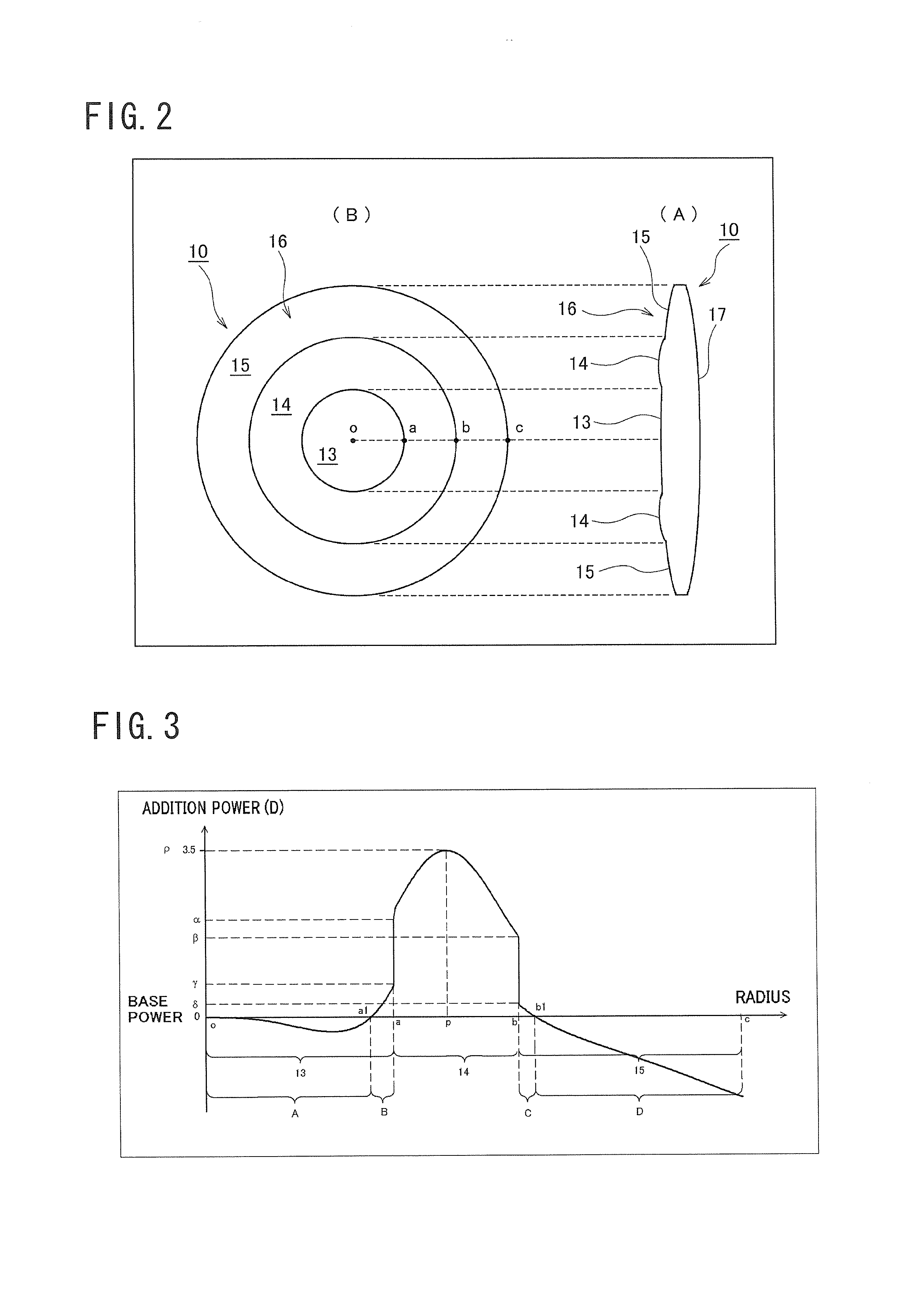
ActiveUS20100321632A1Improved near visionImprove comfortIntraocular lensOptical partsLens platePower difference
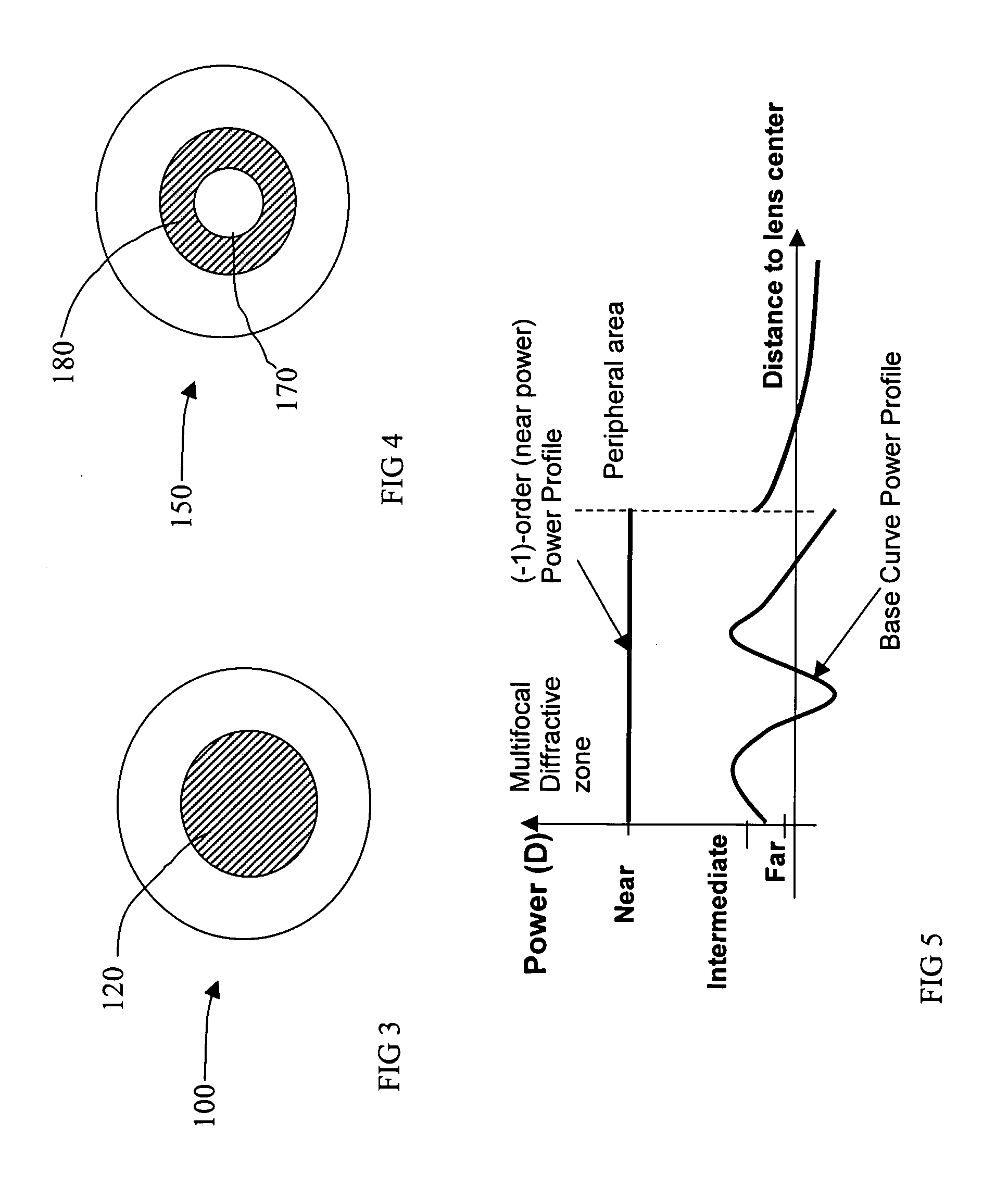
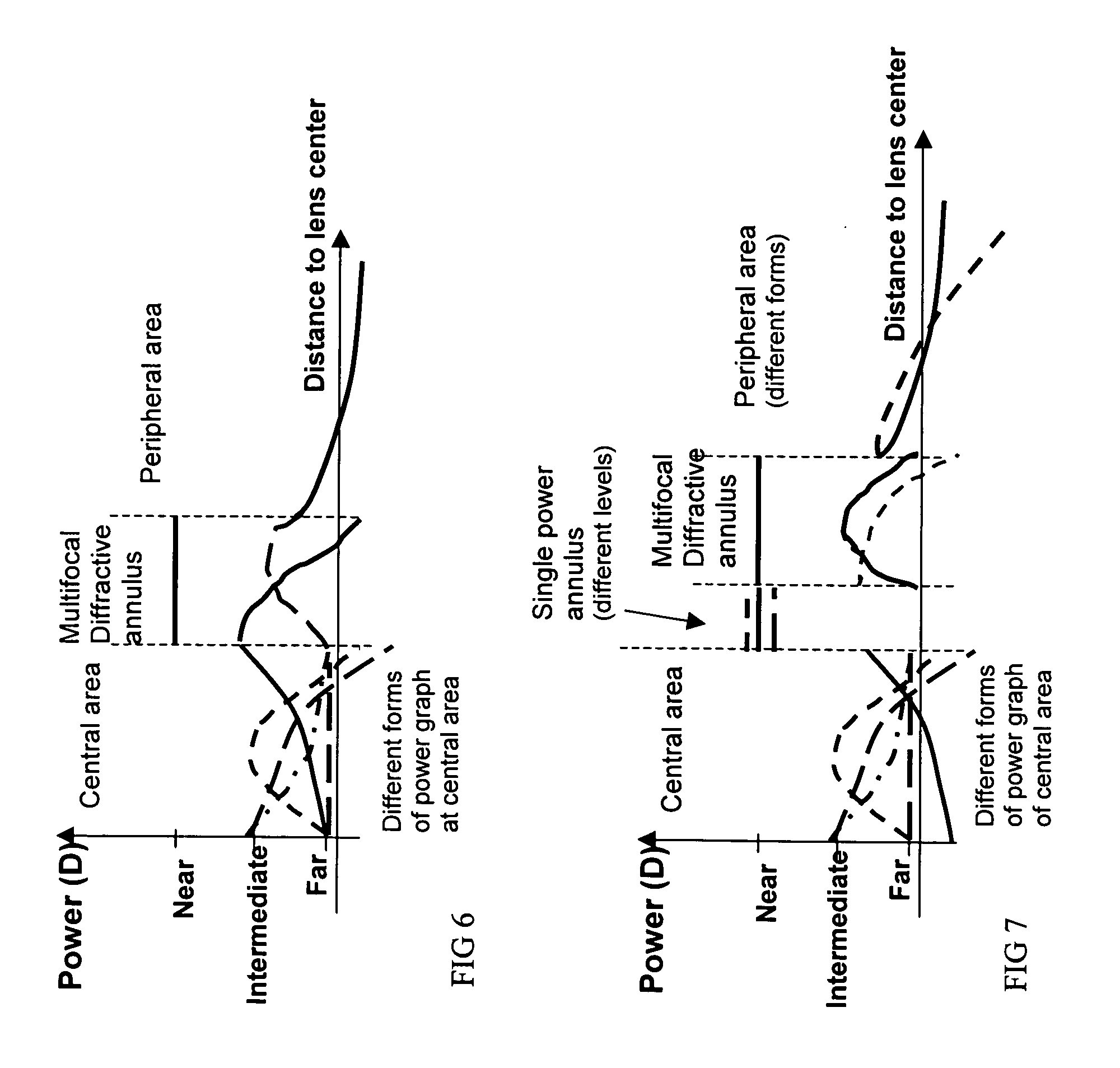
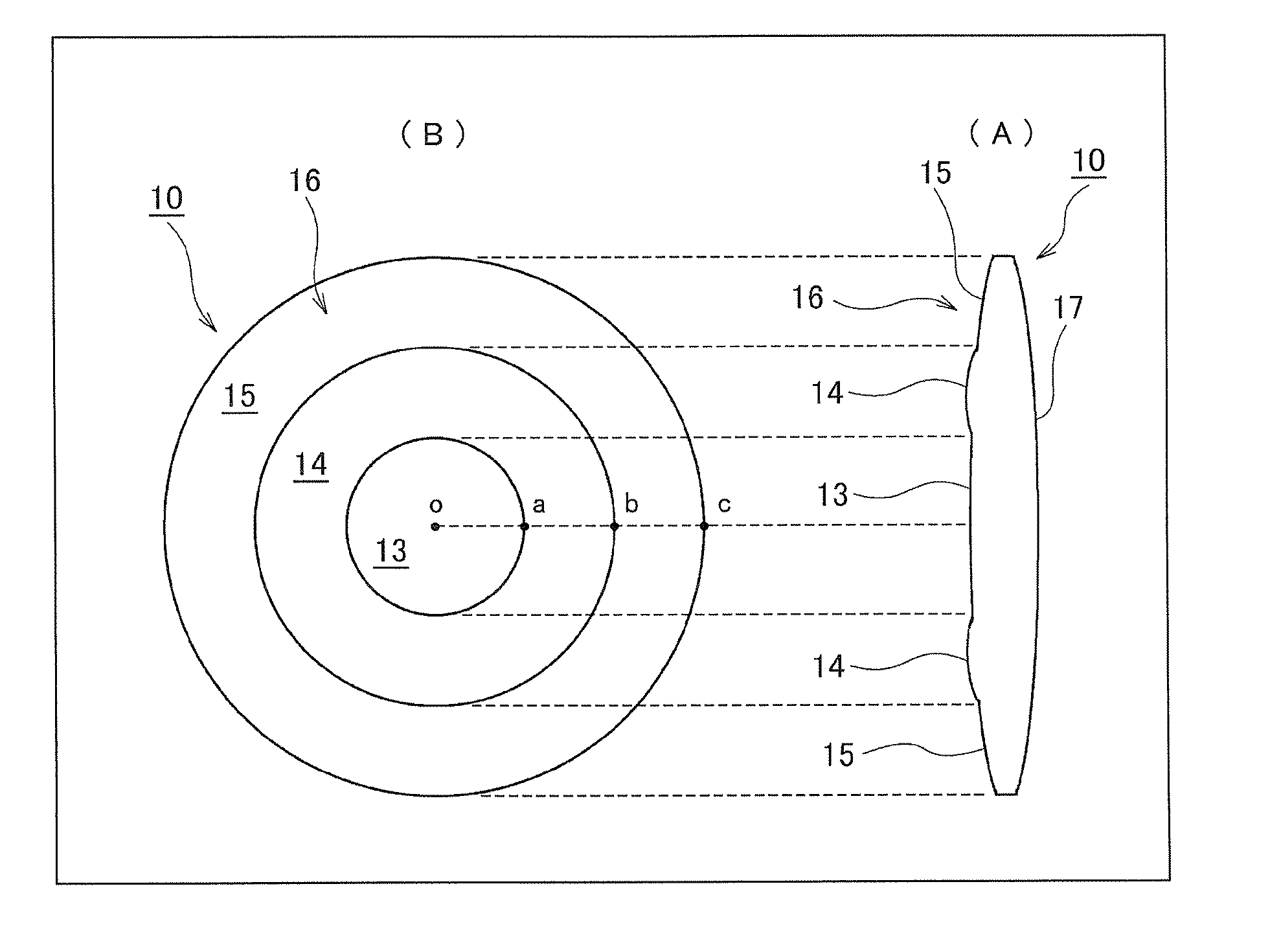
A multifocal ophthalmic lens, including: a far zone for correcting a far vision; and a near zone for correcting a near vision, arranged concentrically in an optical region of the lens, wherein a power distribution is set to vary progressively in radial direction of the far zone and the near zone; power is altered discontinuously to have a stepwise power difference at a boundary between the far zone and the near zone, the value of the power difference at the boundary between the far zone and the near zone is not greater than a maximum value of an intermediate power for correcting an intermediate vision.
Owner:HOYA CORP
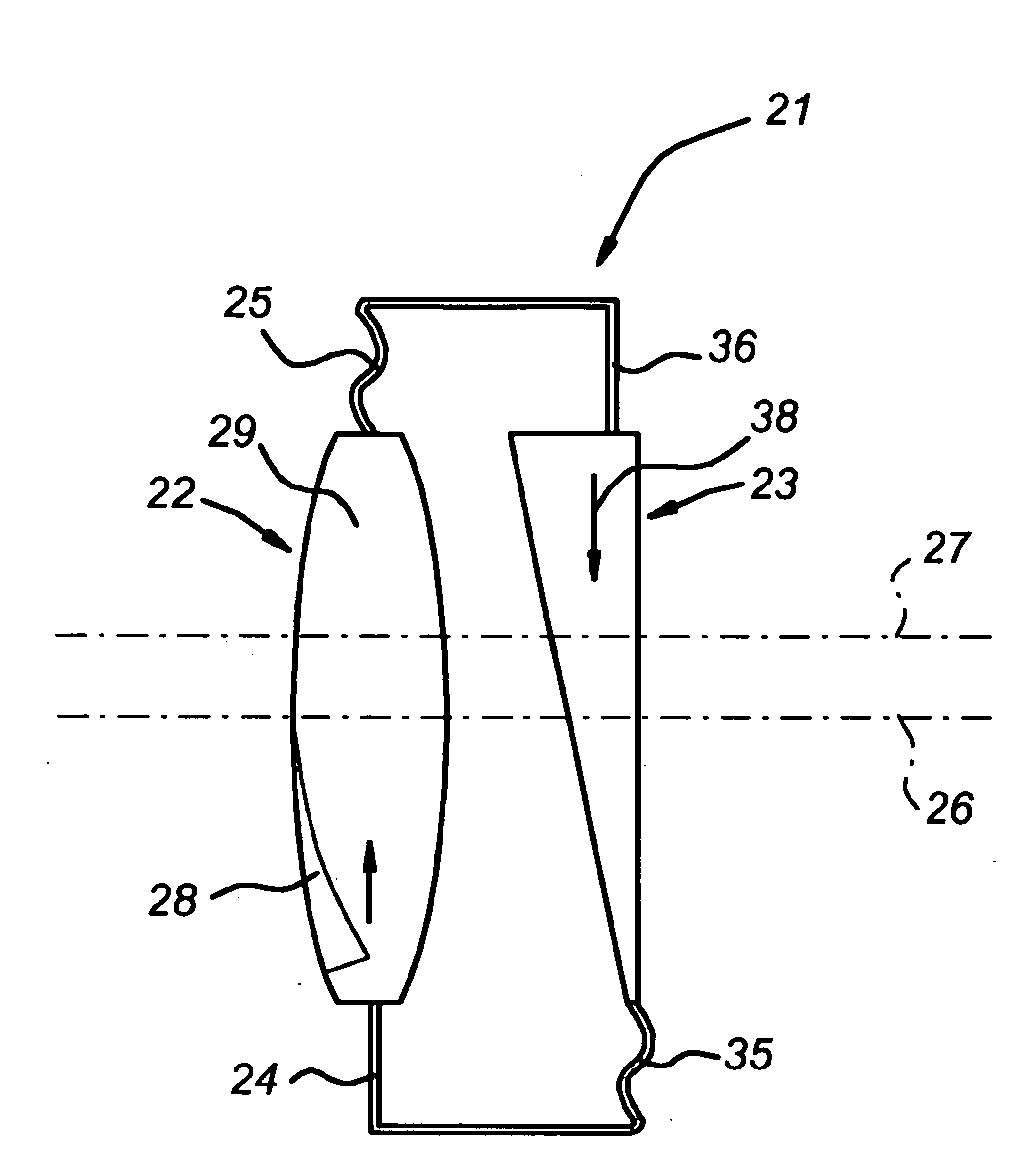
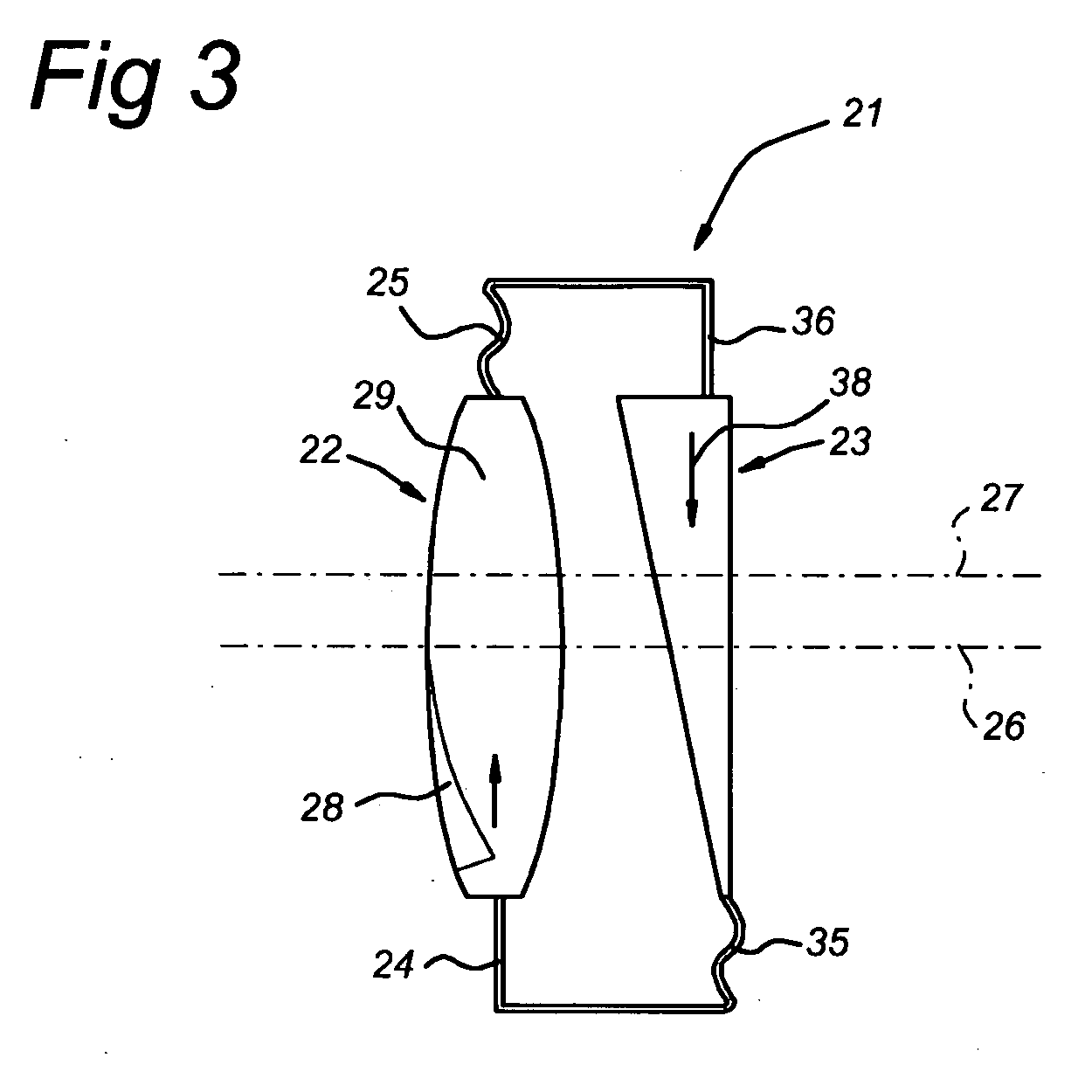
Dynamic multifocal contact lens
An dynamic multiple focus contact lens has at least one transparent layer with a first annular electromagnet and a second annular electromagnet, a transparent pupil allowing passage of light through the at least one layer, at least one loop antenna in communication with the electromagnets, and a transmitter for activating the electromagnets. The at least one layer has a first shape similar to a circular segment that follows the surface of the cornea. The first shape has a first focal length, or power. Upon initiation by a user, a transmitter sends a signal to the loop antenna which energizes the electromagnets to mutually attract causing the at least one layer to deflect and the central portion of the first layer to deform outwardly forming the layer into a second shape. The second shape has a second power, stronger than the first shape.
Owner:IWAI BENJAMIN T
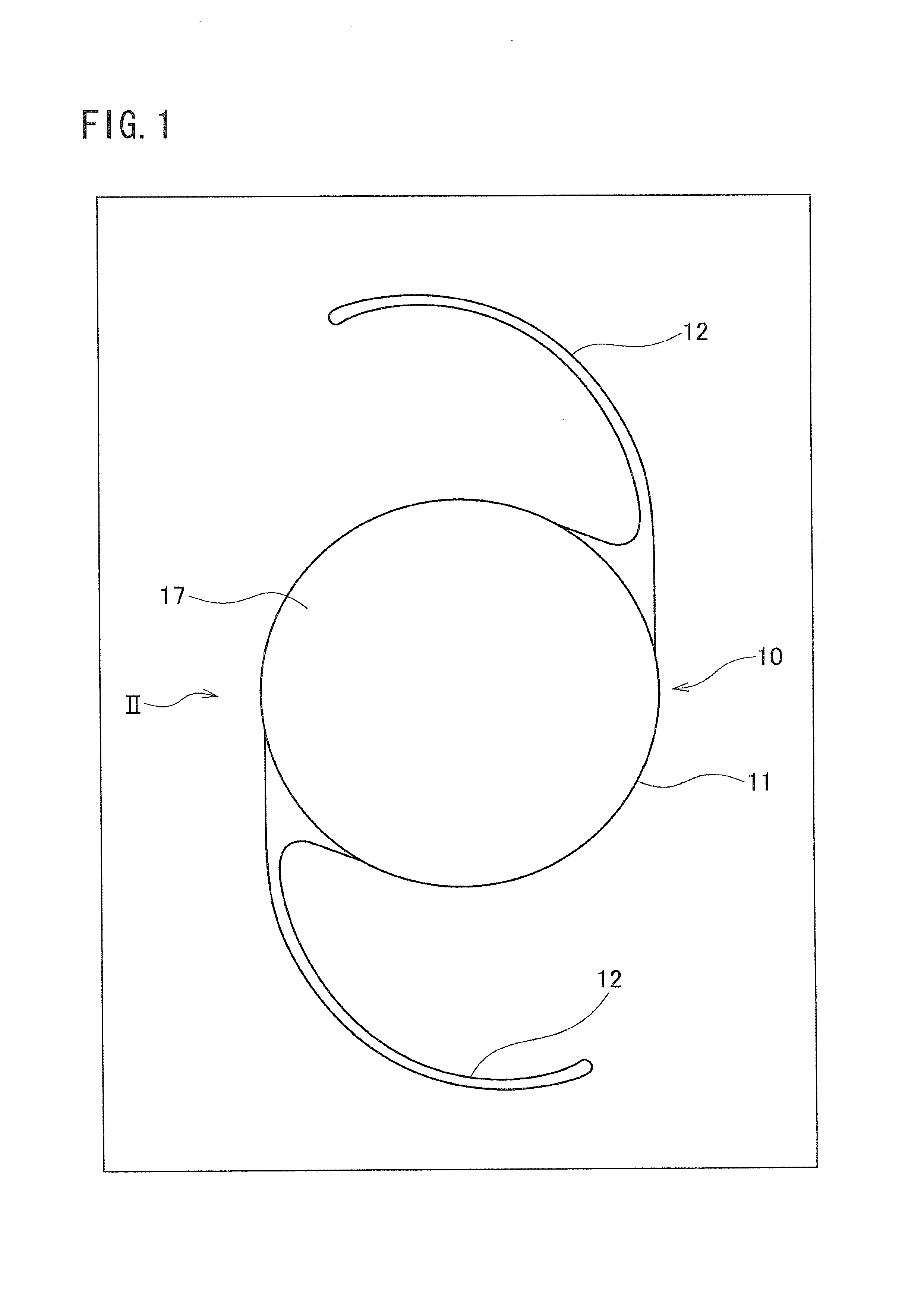
Multifocal Iol
InactiveUS20080312738A1Easy to switchImprove functional propertiesIntraocular lensIntraocular lensPhysics
Intraocular lens consisting of a centrally located lens part with supporting parts (haptics) on either side. According to the invention one supporting part is non-deformable and another supporting part, located approximately opposite said supporting part, is deformable. In this way it is achieved that when the ciliary cell contracts the reduction in the space therein is used for moving the centre of the lens part. By arranging the transition between distance and near part in a multifocal lens on said centre, switching from the distance part to the near part can be obtained for the user in an almost natural way.
Owner:OCULENTIS HLDG
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS20060244906A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Multifocal opthalmic lens
This invention is generally related to vision corrections by means of multifocal ophthalmic lenses or by means of corneal refractive surgery. In particular, the present invention provides a multifocal contact lens, a multifocal intraocular lens, a method for making a multifocal ophthalmic lens (contact lens and intraocular lens), and a method of correcting presbyopia by reshaping the cornea of an eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
A multifocal ophthalmic lens, including: a far zone for correcting a far vision; and a near zone for correcting a near vision, arranged concentrically in an optical region of the lens, wherein a power distribution is set to vary progressively in radial direction of the far zone and the near zone; power is altered discontinuously to have a stepwise power difference at a boundary between the far zone and the near zone, the value of the power difference at the boundary between the far zone and the near zone is not greater than a maximum value of an intermediate power for correcting an intermediate vision.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Photochromic multifocal optical article
Describes a multifocal optical article, e.g., an ophthalmic article such as a lens, in which the article includes (1) a rigid optical substrate, e.g., a transparent polymeric substrate, such as a thermoset or thermoplastic substrate, adapted to possess at least one light influencing property on at least a portion of at least one surface of the substrate, e.g., a photochromic and / or polarizing layer, and (2) a multifocal layer of an optical quality material on said substrate having the light influencing property. Describes also the aforedescribed optical article having an abrasion-resistant coating on the multifocal layer, e.g., an abrasion-resistant coating comprising an organo silane. A method for preparing the multifocal optical article comprising curing optical quality material between a multifocal mold and a preform comprising an optical substrate possessing the light influencing property is also described.
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
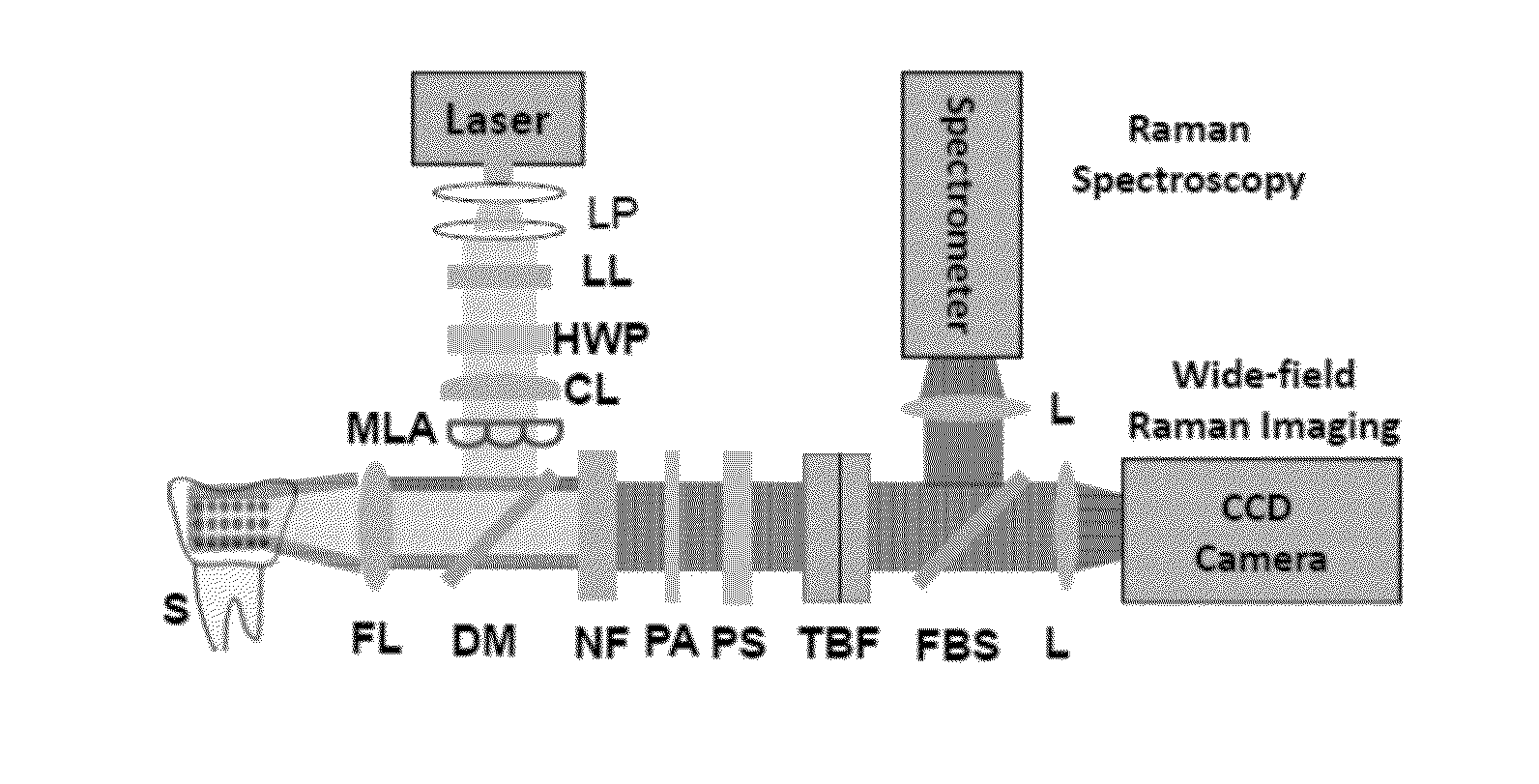
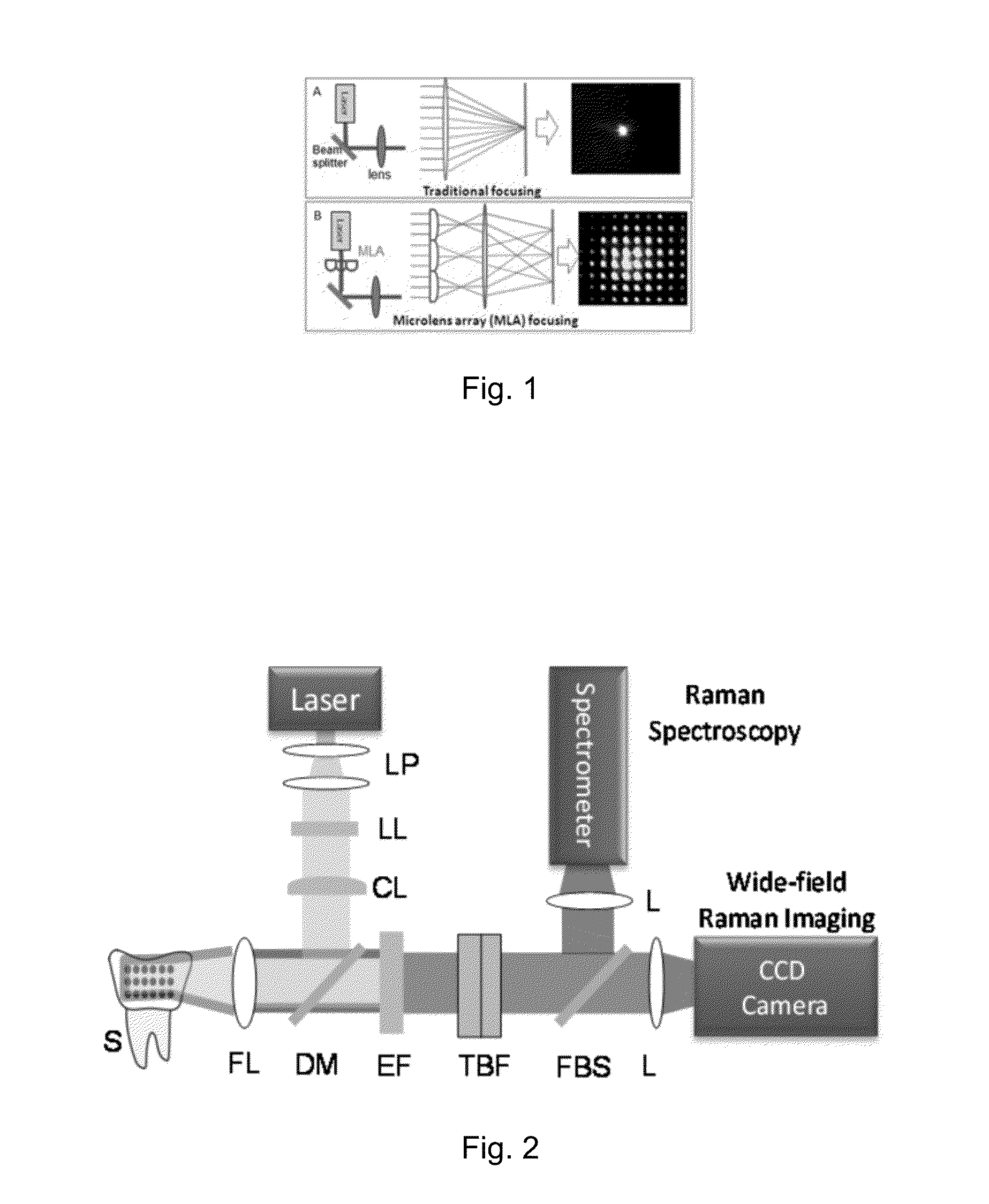
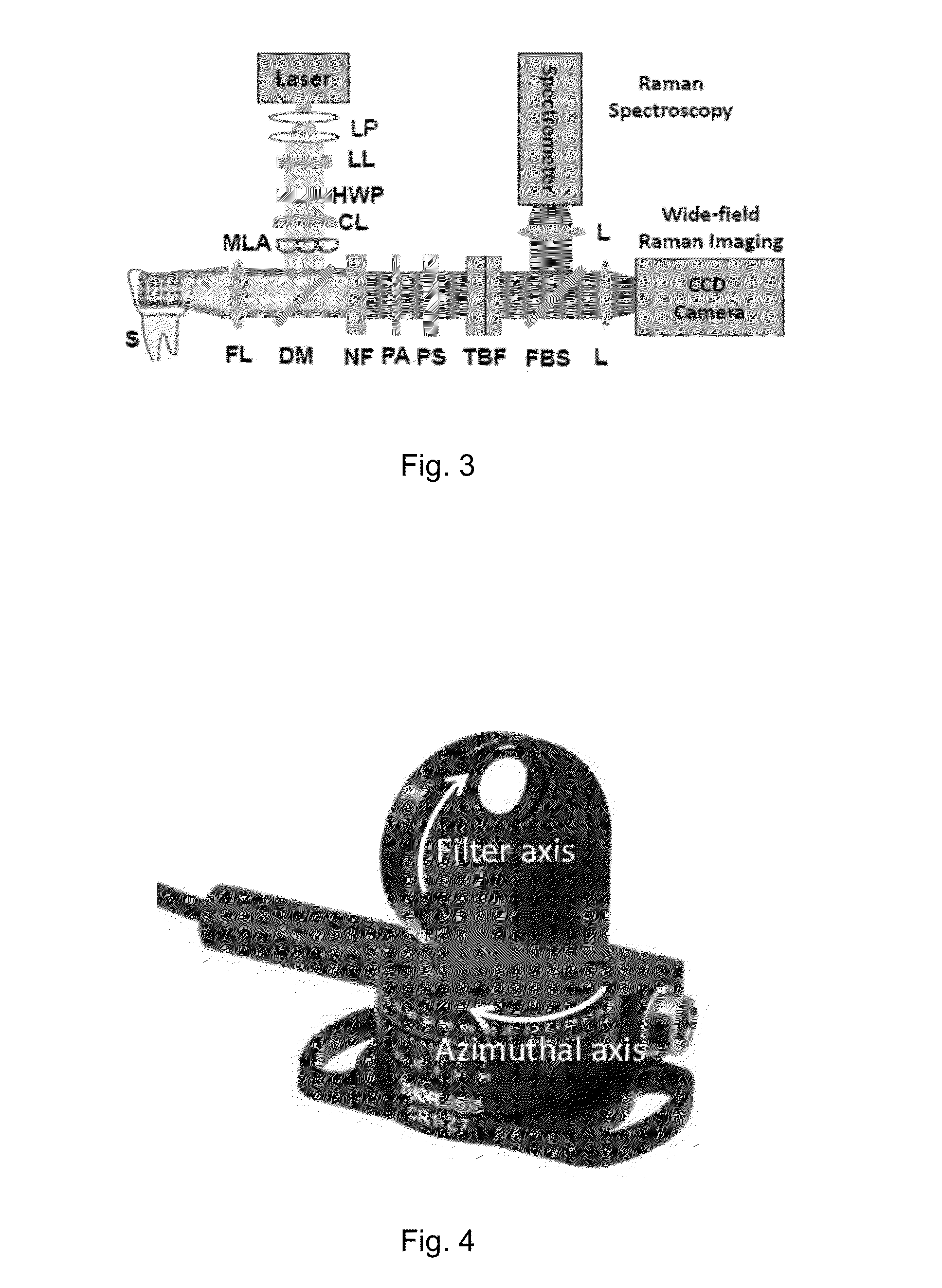
Multifocal hyperspectral raman system and methods for imaging of materials
ActiveUS20150204789A1Large field of viewReduce acquisition timeRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyRaman imagingElectricity
A hyperspectral Raman imaging system having the ability to focus on excitation laser beam over a relatively wide field of view due to the use of a lens array, in particular a microlens array. Hyperspectral selection is provided in one embodiment through the use of dual-axis controlled dielectric filtration. Methods for analyzing materials with the system are disclosed. The device or system can be used in generally any application where investigation of materials is required.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method for manufacturing multifocal lenses
InactiveUS7014317B2Accurate measurementSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsMultifocal lensesRefractive index
The present invention provides a method for the manufacture of thin multifocal lenses by deposition of a high refractive index material on a lens substrate.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Multi-focal intraocular lens system and methods
InactiveUS20090032679A1Accurately determine changeAccurately determineOptical rangefindersInvestigating moving sheetsIntraocular lensVisual perception
The invention pertains to methods, components, and operations of multi-focal intraocular lens systems, including range finding for driving same and for discriminating between multiple objects and varying brightness conditions. The invention also pertains to intraocular photosensors and range-finding methods to be used with intra-ocular lens systems, and components, that provide multi-focal IOL capabilities in dynamic visual environments.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
This invention is generally related to vision corrections by means of multifocal ophthalmic lenses or by means of corneal refractive surgery. In particular, the present invention provides a multifocal contact lens, a multifocal intraocular lens, a method for making a multifocal ophthalmic lens (contact lens and intraocular lens), and a method of correcting presbyopia by reshaping the cornea of an eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method for designing multifocal contact lenses
The invention provides methods for designing contact lenses that takes into account pupil size and vergence. The lenses of the invention augment the eye's accommodative gain and take advantage of the eye's residual accommodation amplitude.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS20060244905A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
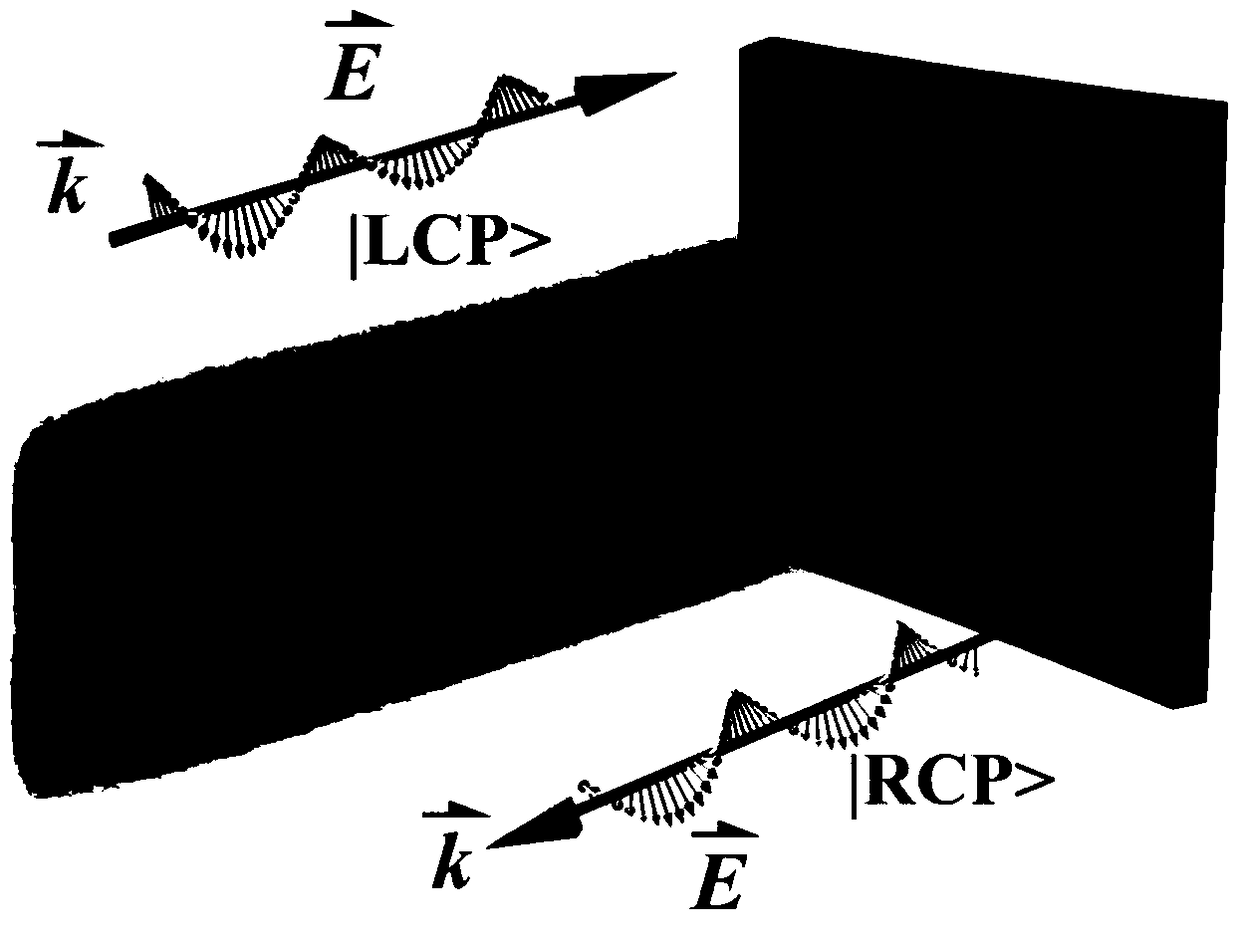
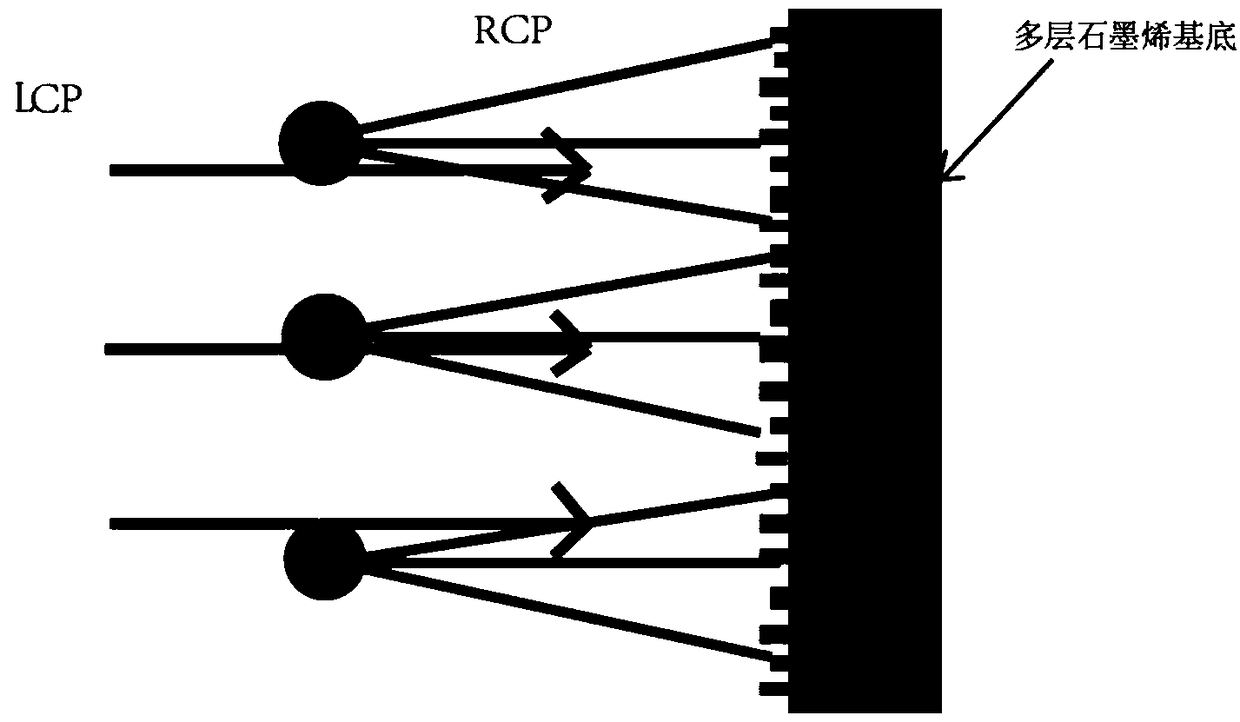
Method for constructing dynamic multifocal superlens based on medium and graphene
The invention discloses a method for constructing a dynamic multifocal superlens based on a medium and graphene. The method includes the following steps that: (1) as for incident light of different wavelengths, phase gradient distribution on a medium metasurface within an infrared wavelength range of 0.7 micron to 500 microns is calculated according to positional relations between focuses and wavelengths; (2) different periodic structures are designed for each center wavelength, specific phase values are determined according to the phase gradient distribution and Pancharatnam-Berry phases; (3)height-determined columnar structures are designed as the basic units of the medium metasurface, and then, a corresponding concrete realization structure and rotation direction are designed; and (4)according to a substrate part, multilayer graphene is adopted to form a reflection type focusing lens, and the Fermi level of the graphene can be changed such the position of a focusing point can be dynamically adjusted. According to the method of the invention, the dynamic multifocal reflective lens is realized through the medium metasurface and the multilayer graphene structure. The method has the advantages of high-efficiency focusing function, ultra-wideband performance, dynamic adjustment, easiness in integration and the like.
Owner:GUILIN G LINK TECH
Multifocal contact lens designs utilizing pupil apodization
The invention provides a contact lens that corrects for the wearer's refractive prescription by taking into account both pupil size and the Stiles Crawford effect of the first order.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Multifocal optical device design
InactiveUS20050254007A1Reduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationEye diagnosticsTriangulationEngineering
Multifocal optical device designs receive input parameters to specify a desired power distribution function, a power deviation weight function, and an astigmatism weight function over the design field. A fourth-order partial differential variational equation is linearized by defining the optical surface in terms of perturbations from a base surface such as a sphere or a toric. The solution may be expressed as piecewise quadratic splines superposed over a triangulation of the field. Evaluation of the surface may use a set of tensor-product splines. An astigmatic base surface permits both multiple magnifying powers and a prescribed astigmatism correction in a single optical surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Multifocal optical device design
InactiveUS20050052615A1Reduces computation time for accurate powersDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTriangulationEngineering
Multifocal optical device designs receive input parameters to specify a desired power distribution function, a power deviation weight function, and an astigmatism weight function over the design field. A fourth-order partial differential variational equation is linearized by defining the optical surface in terms of perturbations from a base surface such as a sphere or a toric. The solution may be expressed as piecewise quadratic splines superposed over a triangulation of the field. Evaluation of the surface may use a set of tensor-product splines. An astigmatic base surface permits both multiple magnifying powers and a prescribed astigmatism correction in a single optical surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Multifocal imaging systems and method
ActiveUS20180202935A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLow noiseGrating
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multifocal quasi-Fibonacci zone plate and construction method thereof
ActiveCN107728242ARealize regular arrangementGood pleochroismDiffraction gratingsOptical axisThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a multifocal quasi-Fibonacci zone plate and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the steps of: acquiring a Fibonacci binary (A / B) aperiodic sequencebased on a recursion mode of Fibonacci numbers; and extending a recursion mode of the Fibonacci binary sequence to obtain a new recursion rule. According to the recursion rule, a new binary aperiodicsequence can be created, which is called a quasi-Fibonacci binary sequence. Based on the new sequence, the corresponding zone plate can be constructed by means of a transmittance function. The zone plate produces a series of focal points in the direction of an optical axis of an incident light beam, the focal points have the advantage of good polychromaticity, and imaging by means of the multifocal quasi-Fibonacci zone plate can reduce the color difference of the imaging; meanwhile, the multifocal quasi-Fibonacci zone plate has the plurality of focal points with relatively great intensities in the axial direction, can be used for binding and manipulating tiny objects, and can be used for constructing a three-dimensional optical trap array, so as to realize regular arrangement of particlesin a three-dimensional space.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com