Patents
Literature
43 results about "Multiphoton imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
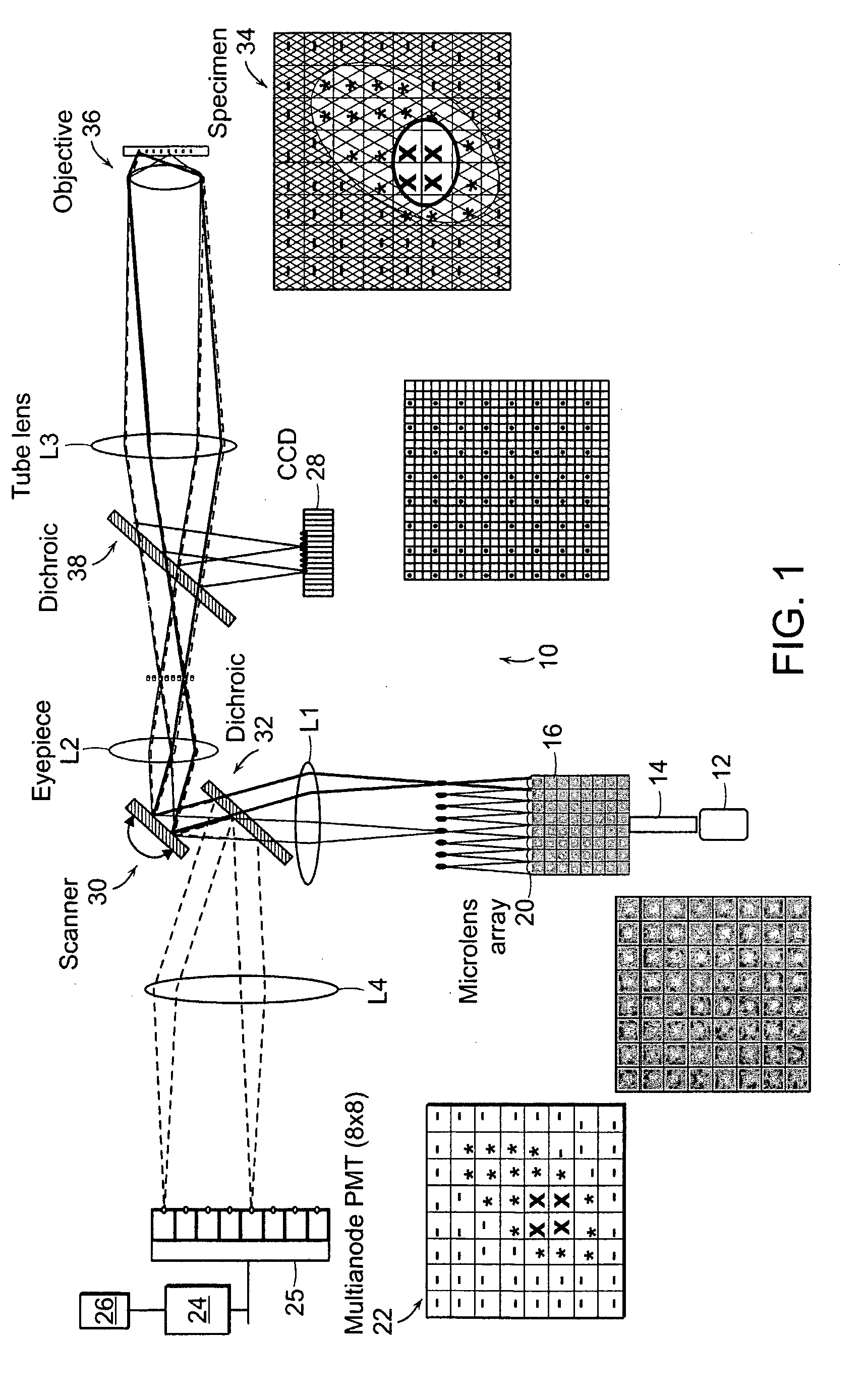
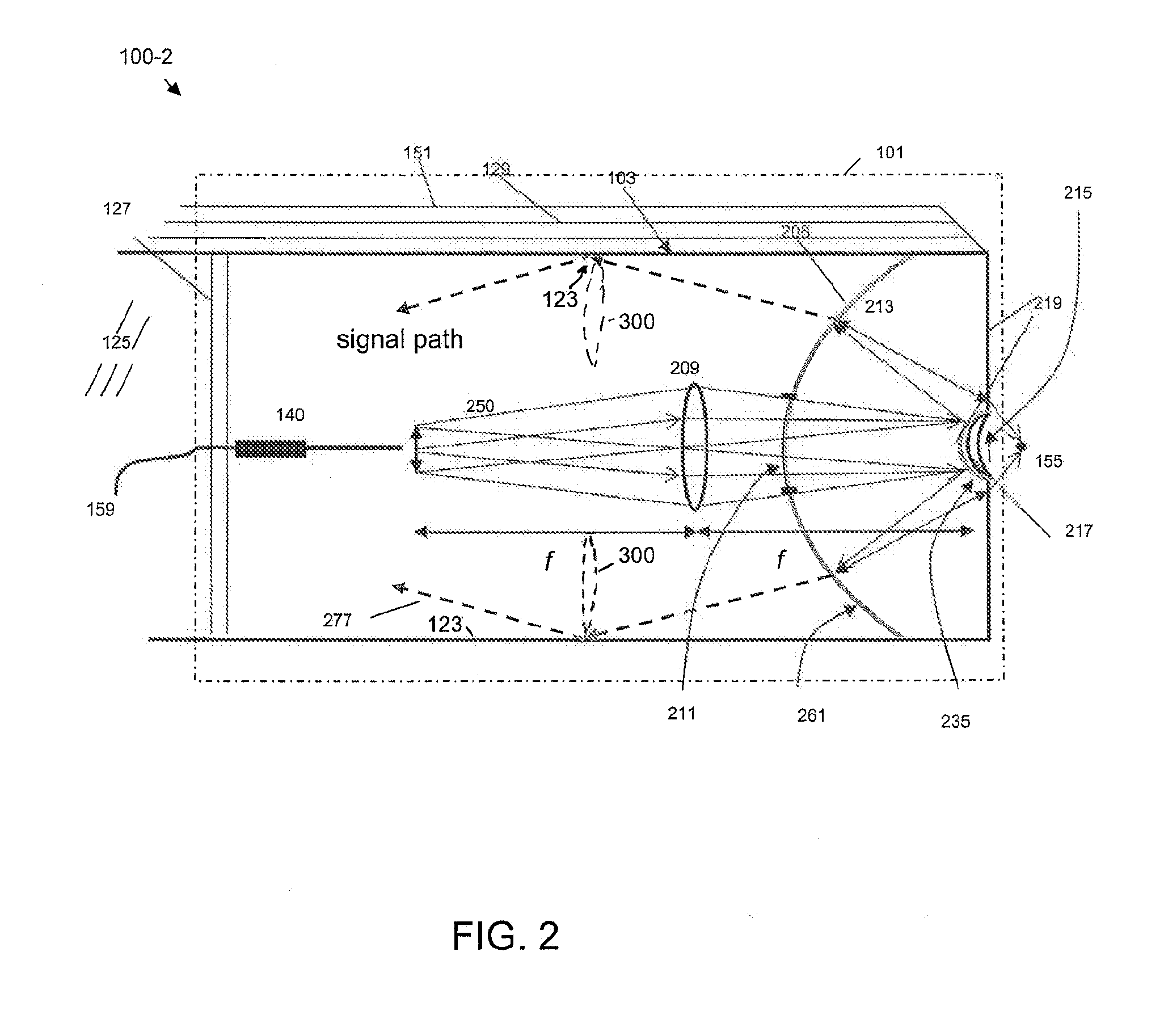
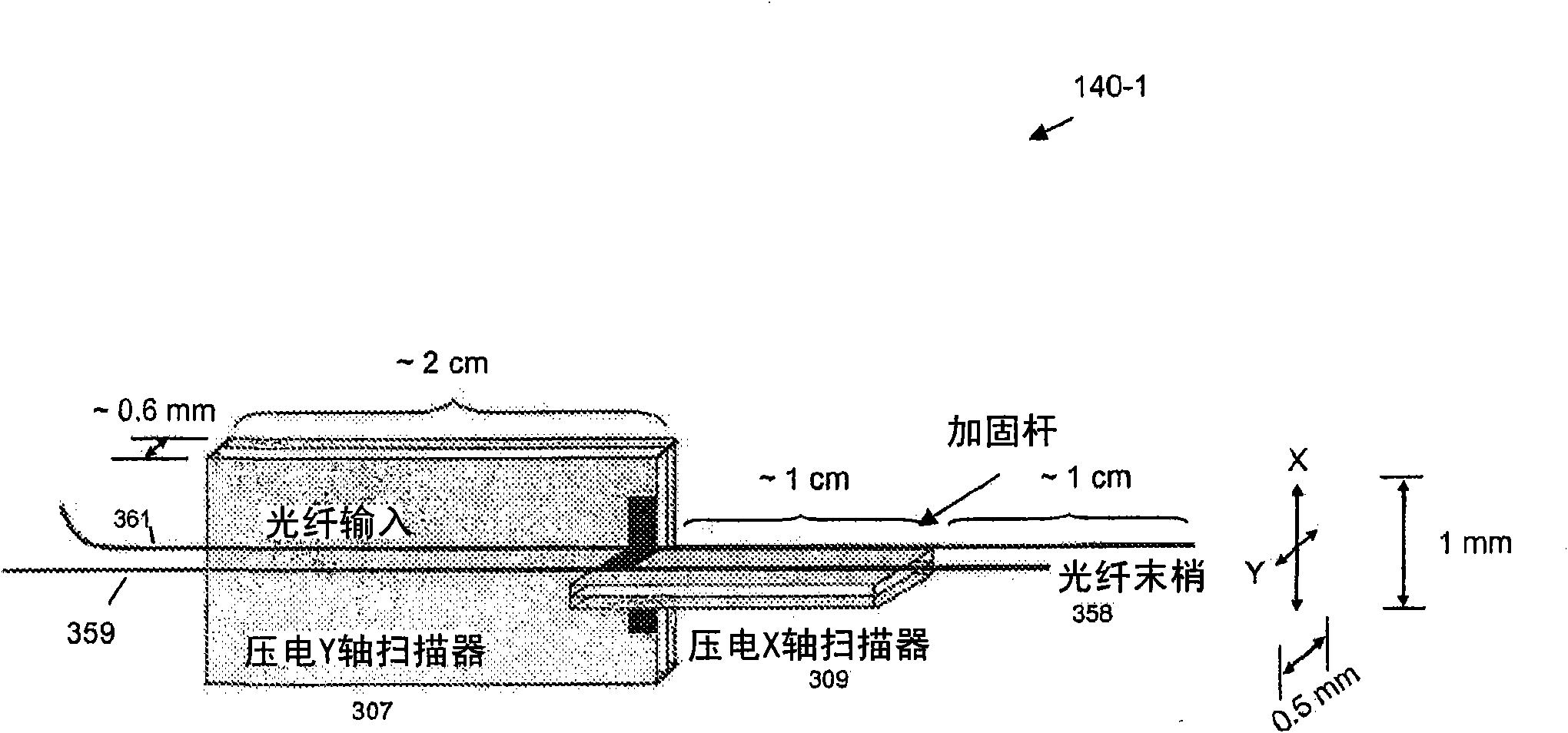
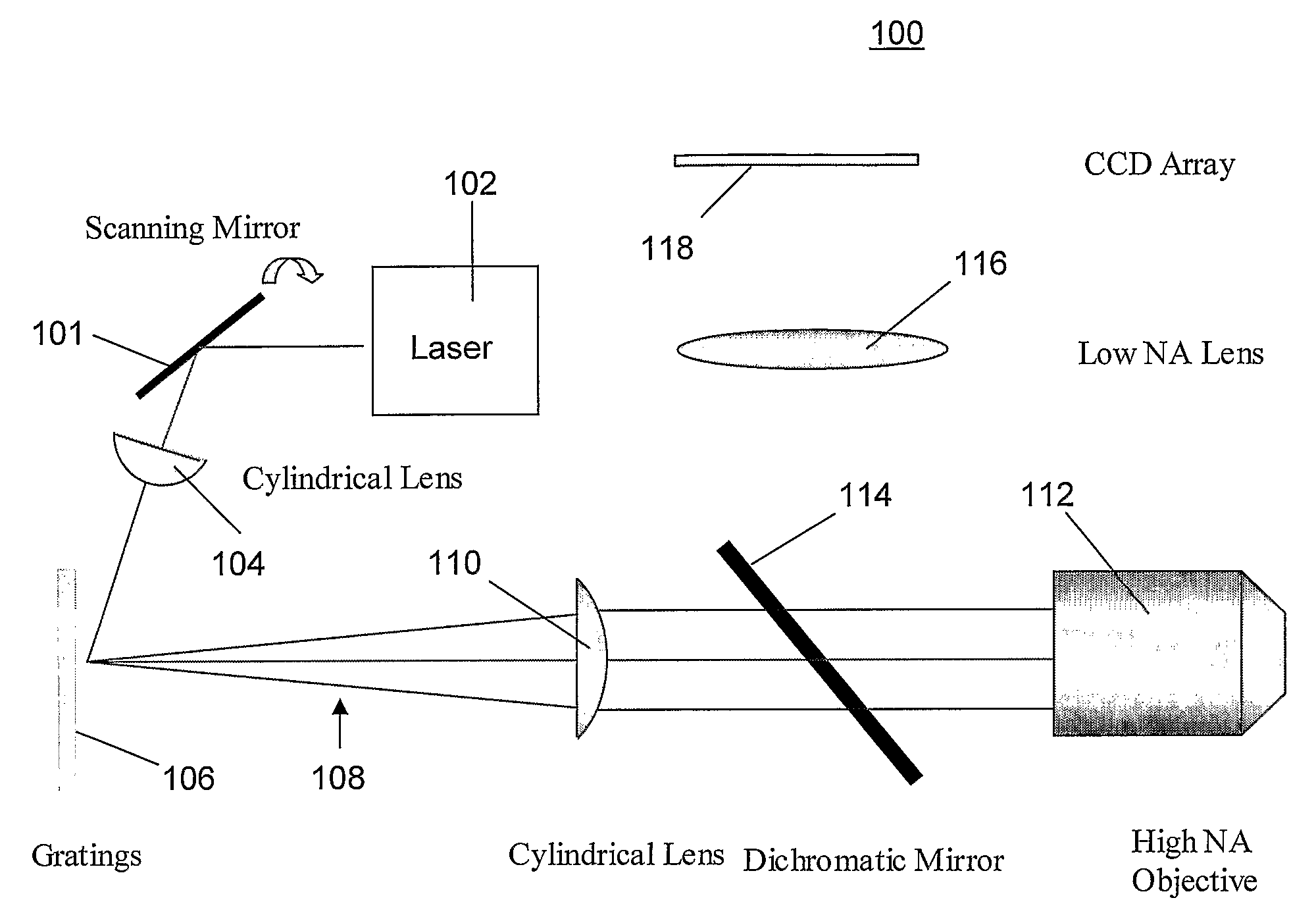
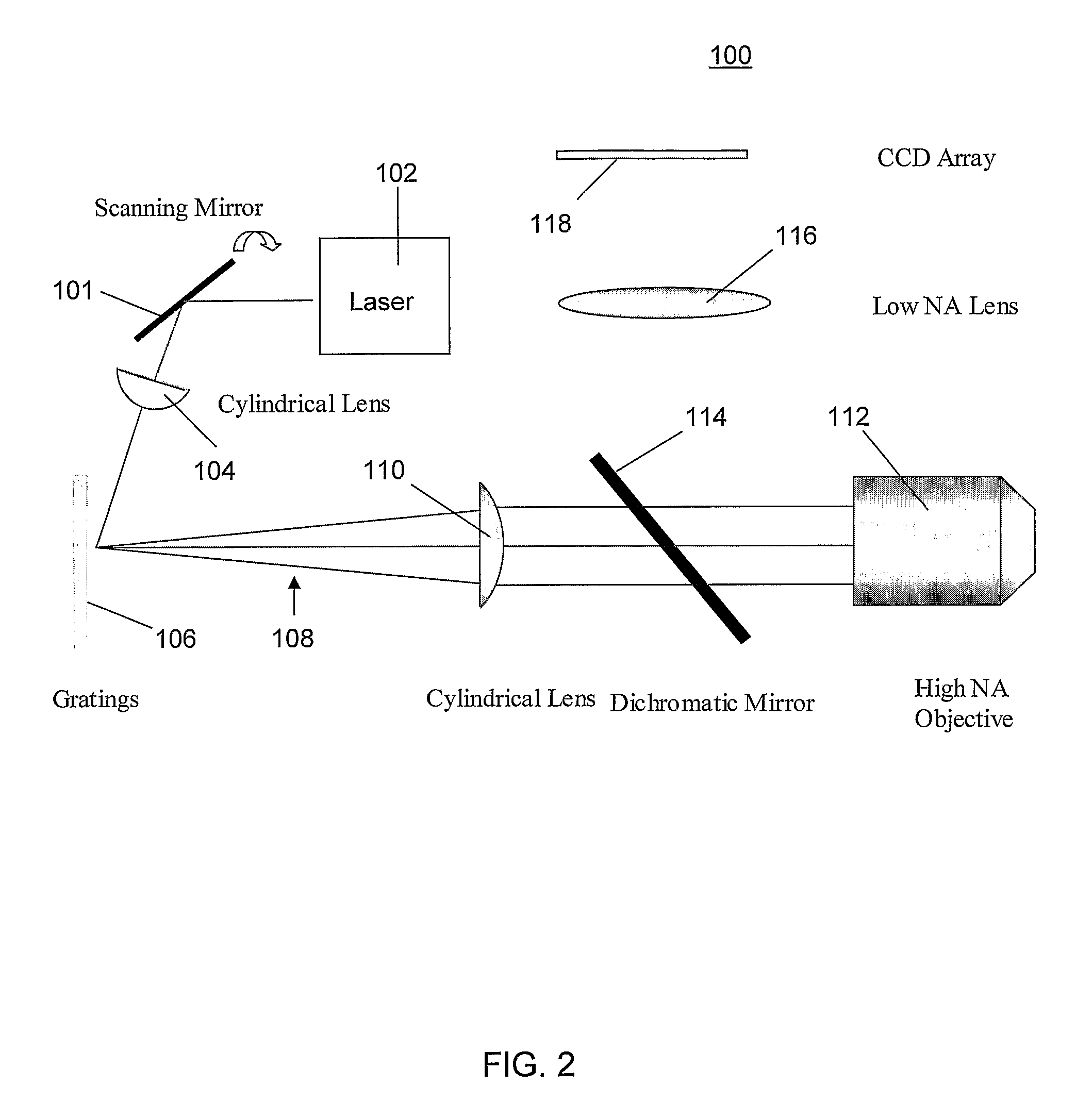
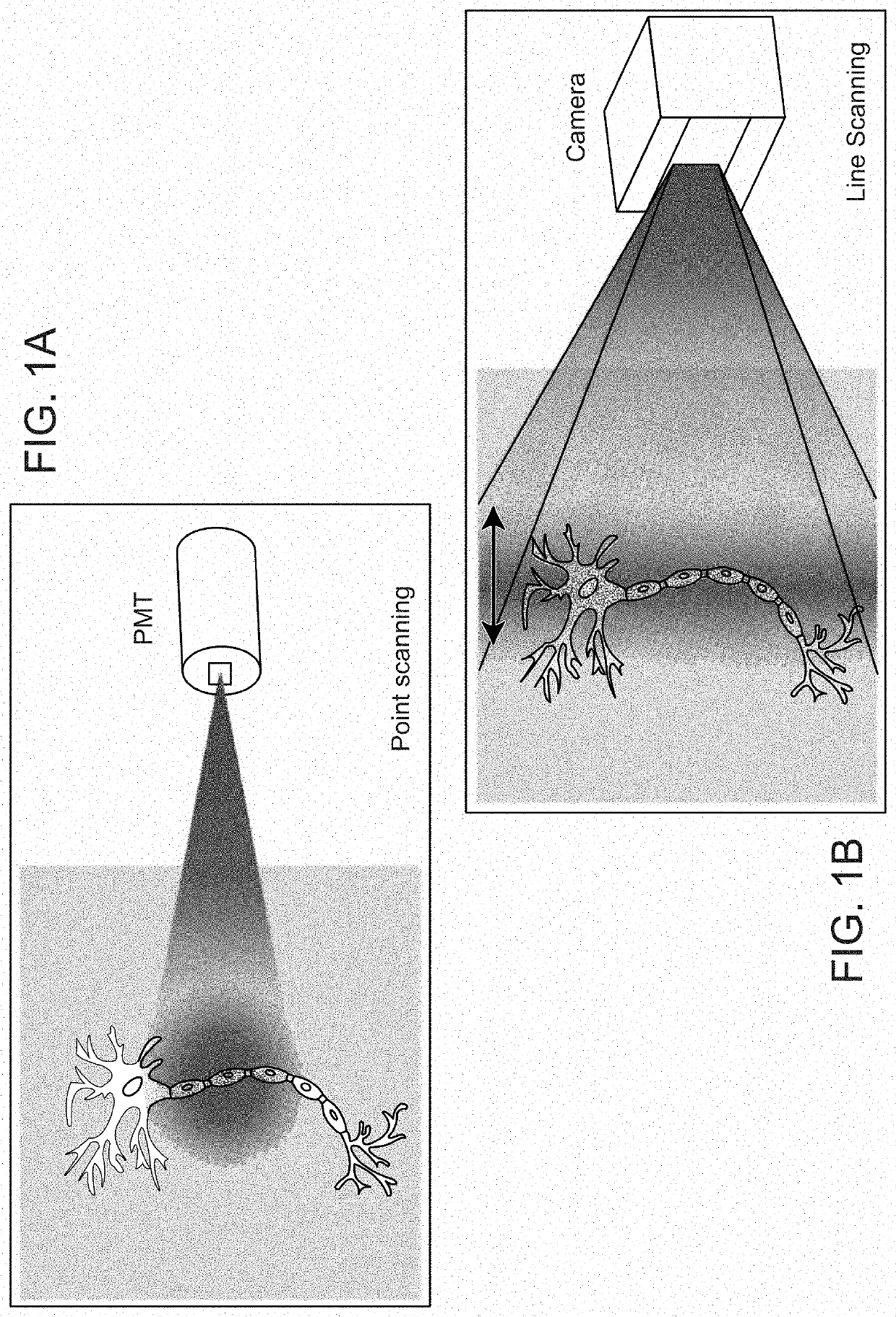
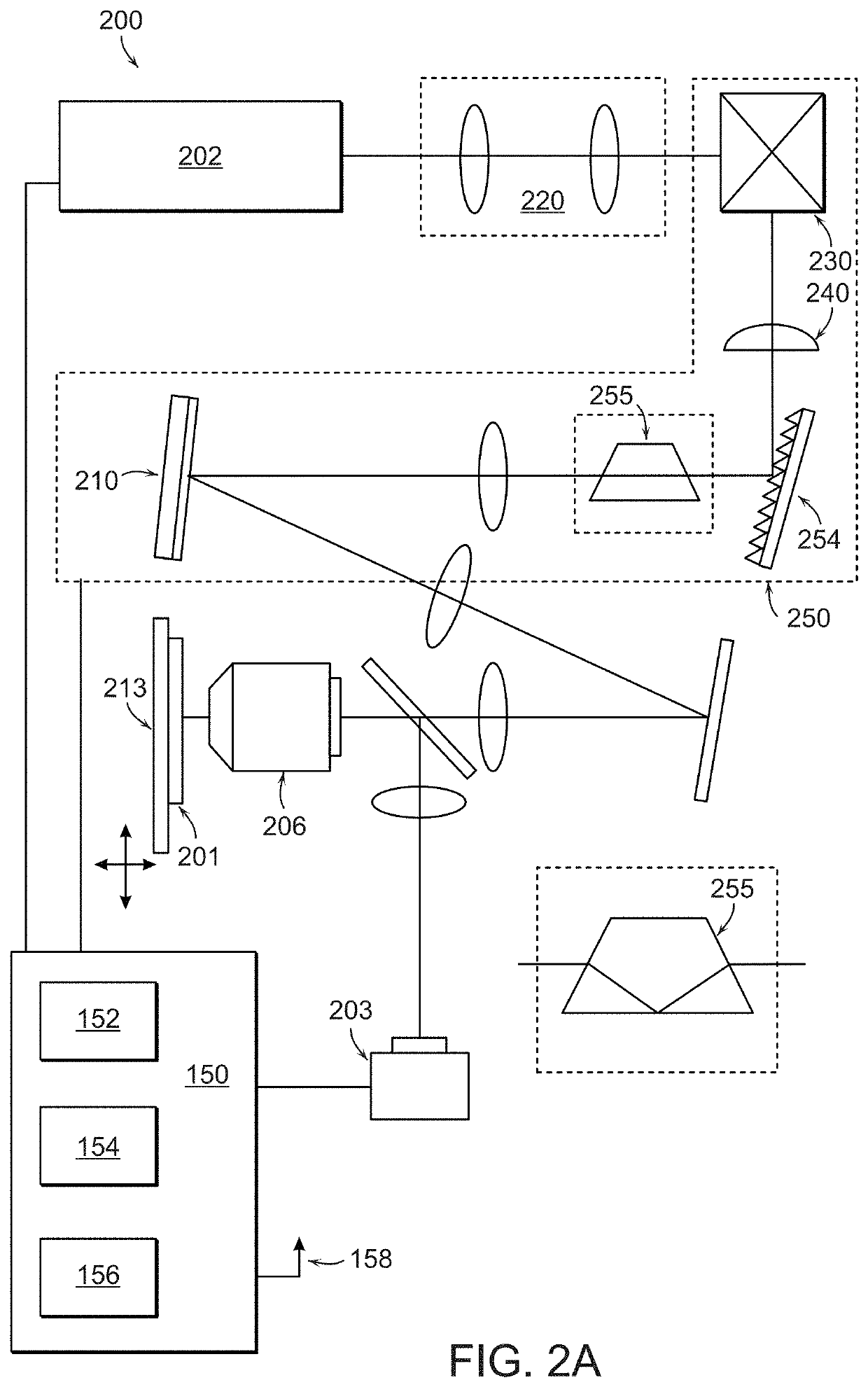
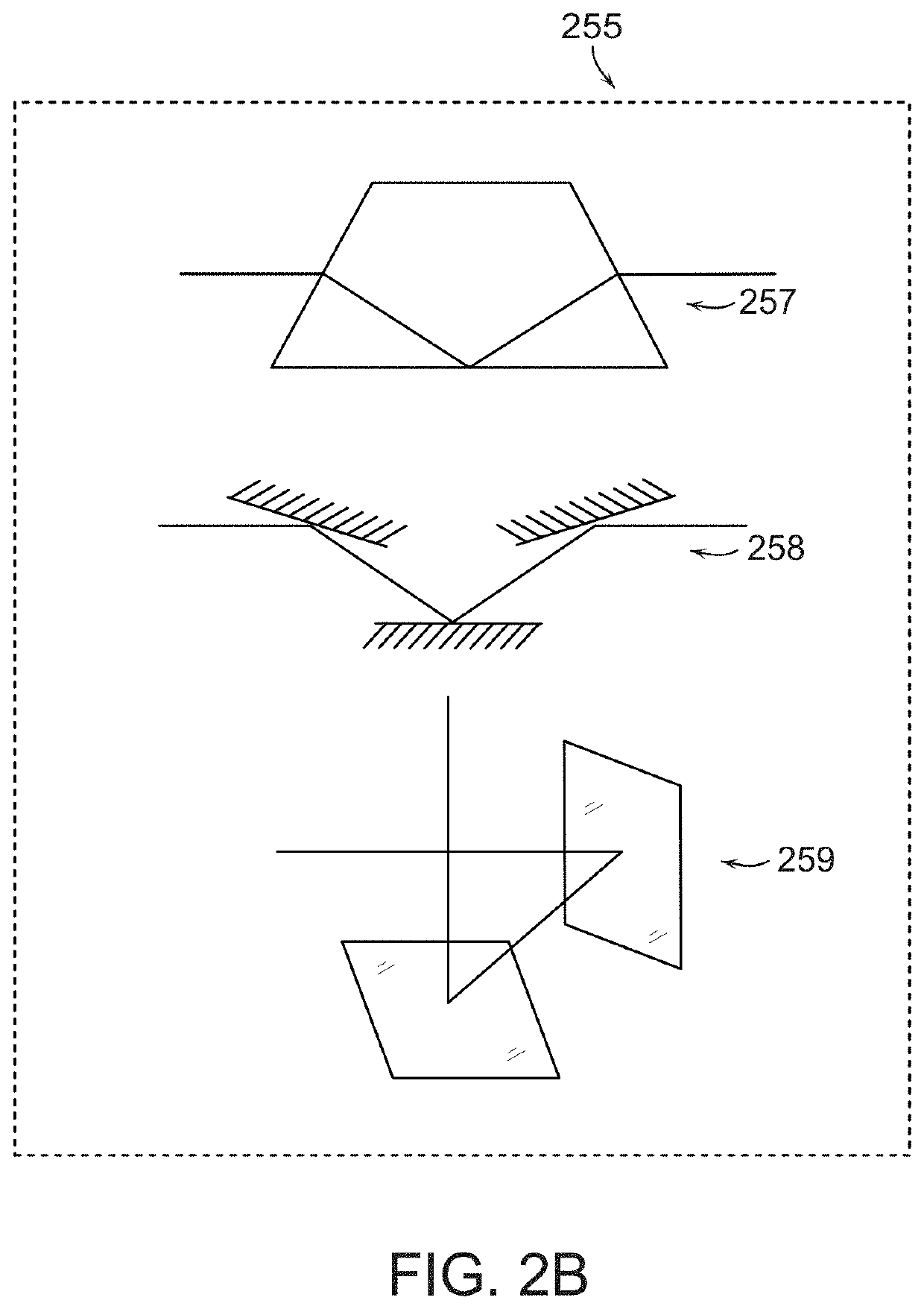
Multifocal imaging systems and method
InactiveUS20070057211A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLow noiseGrating
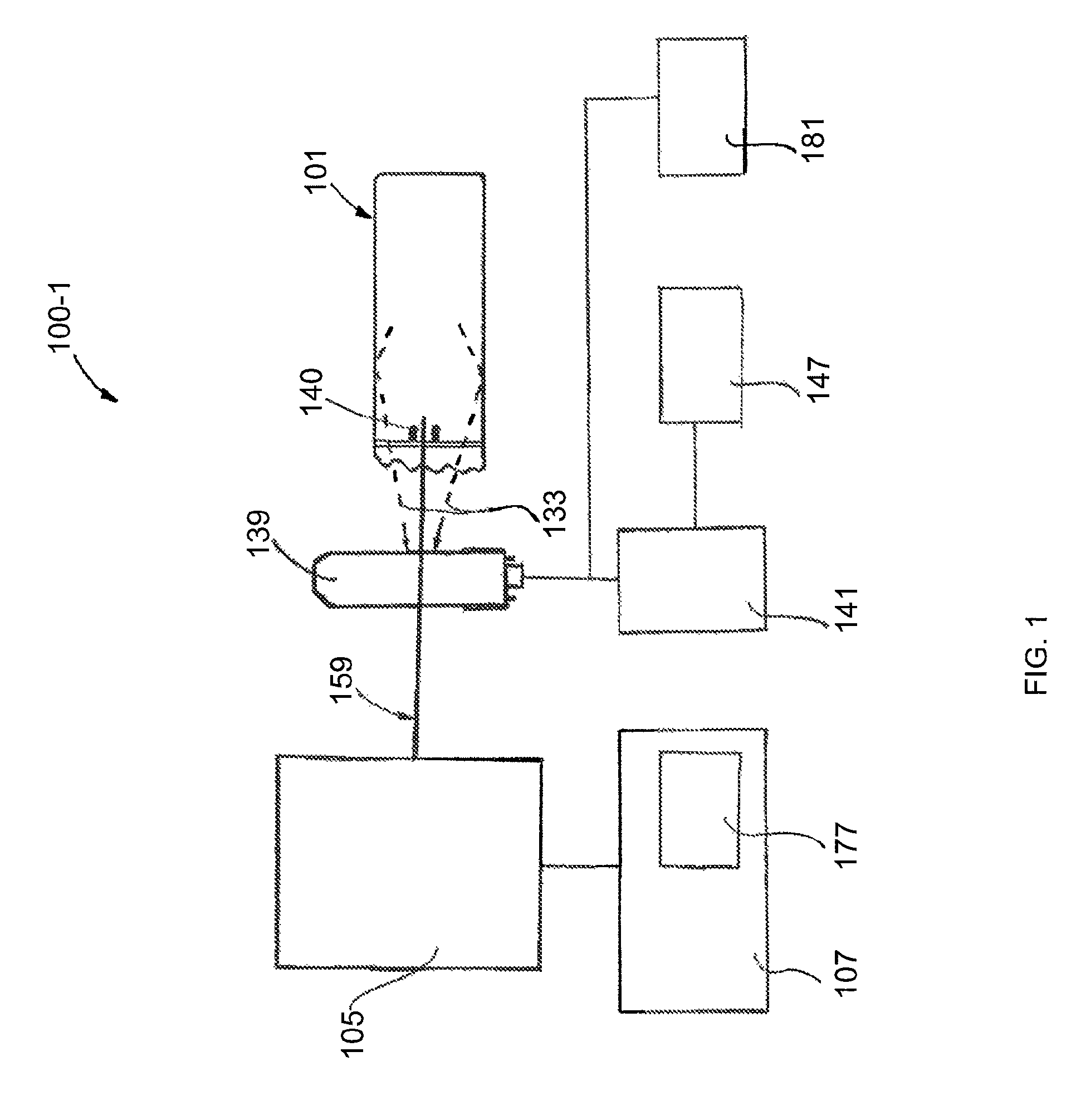
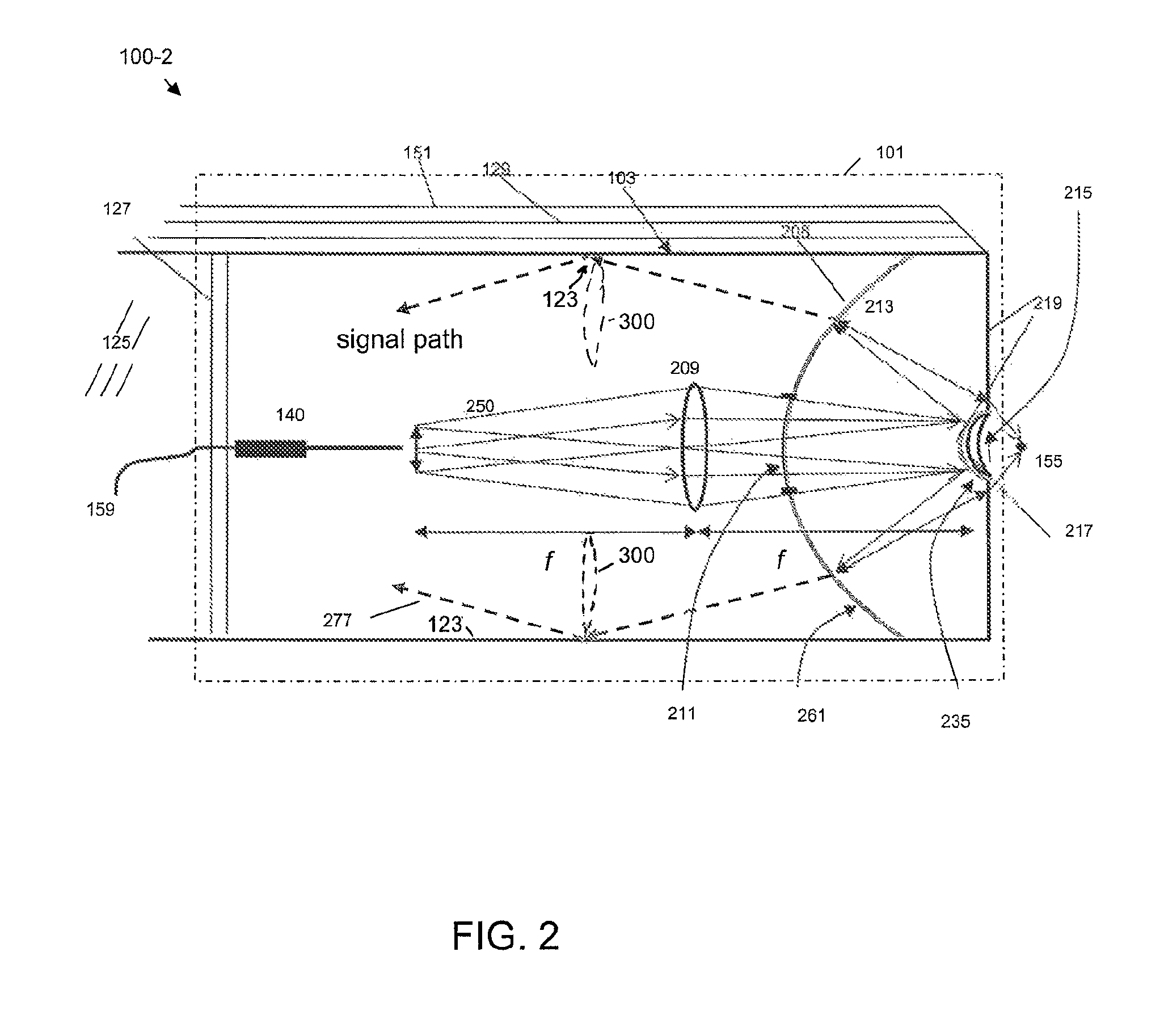
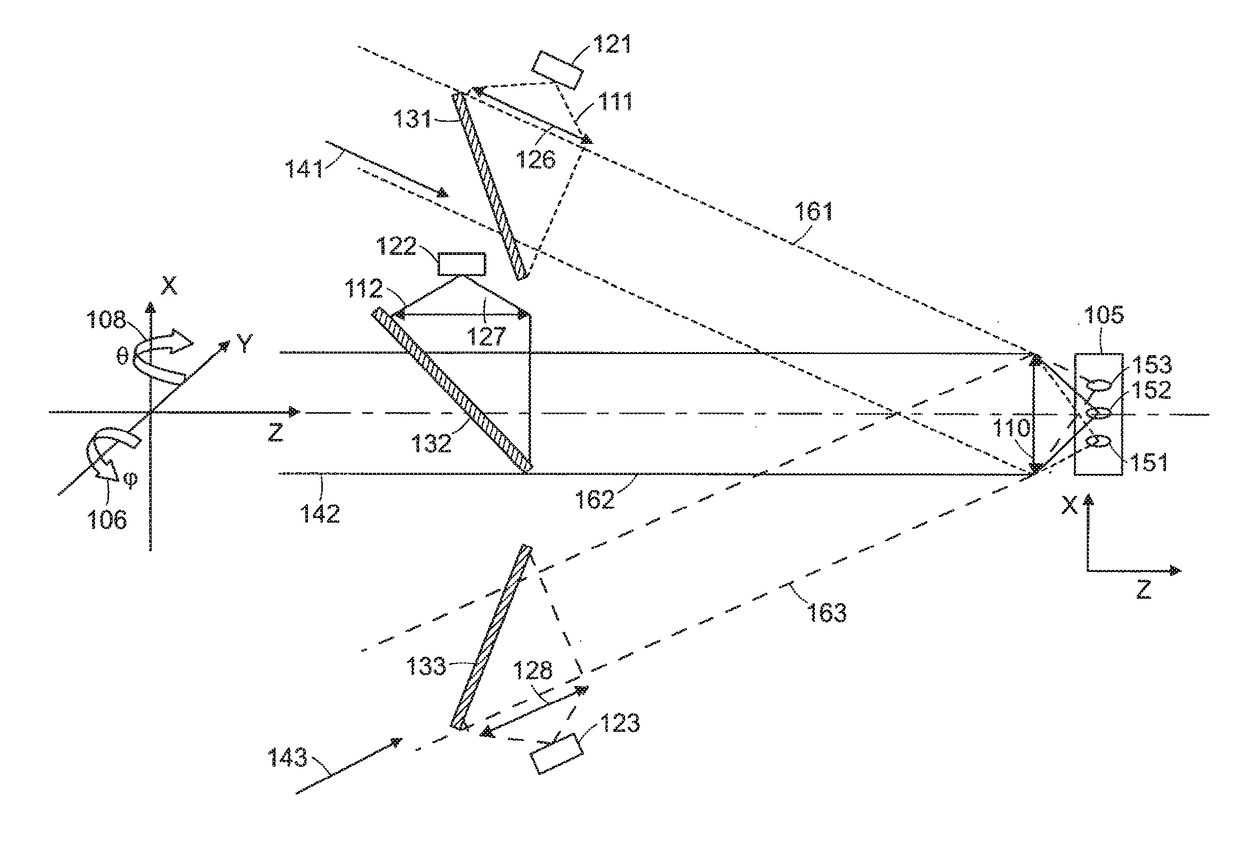
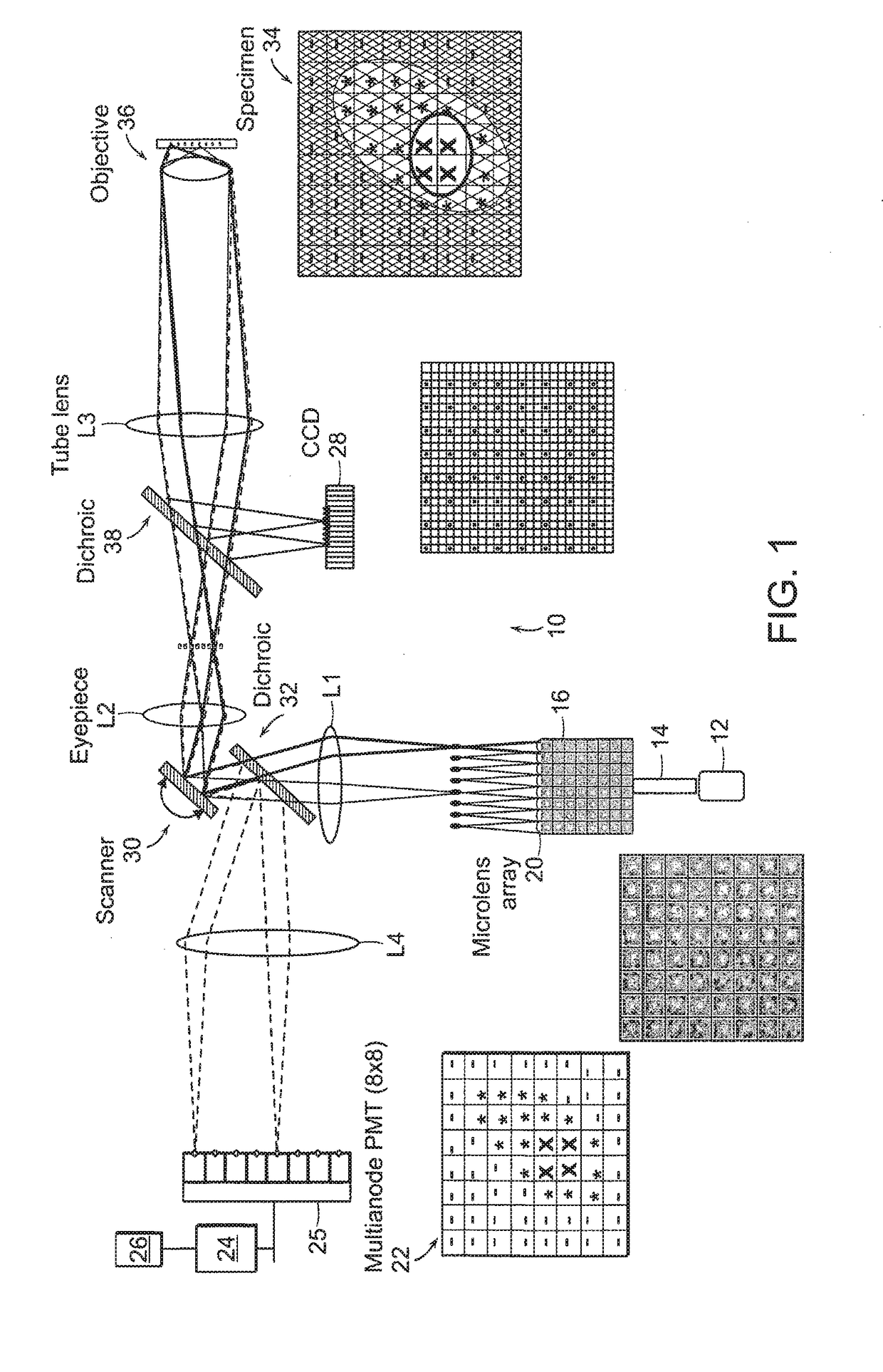
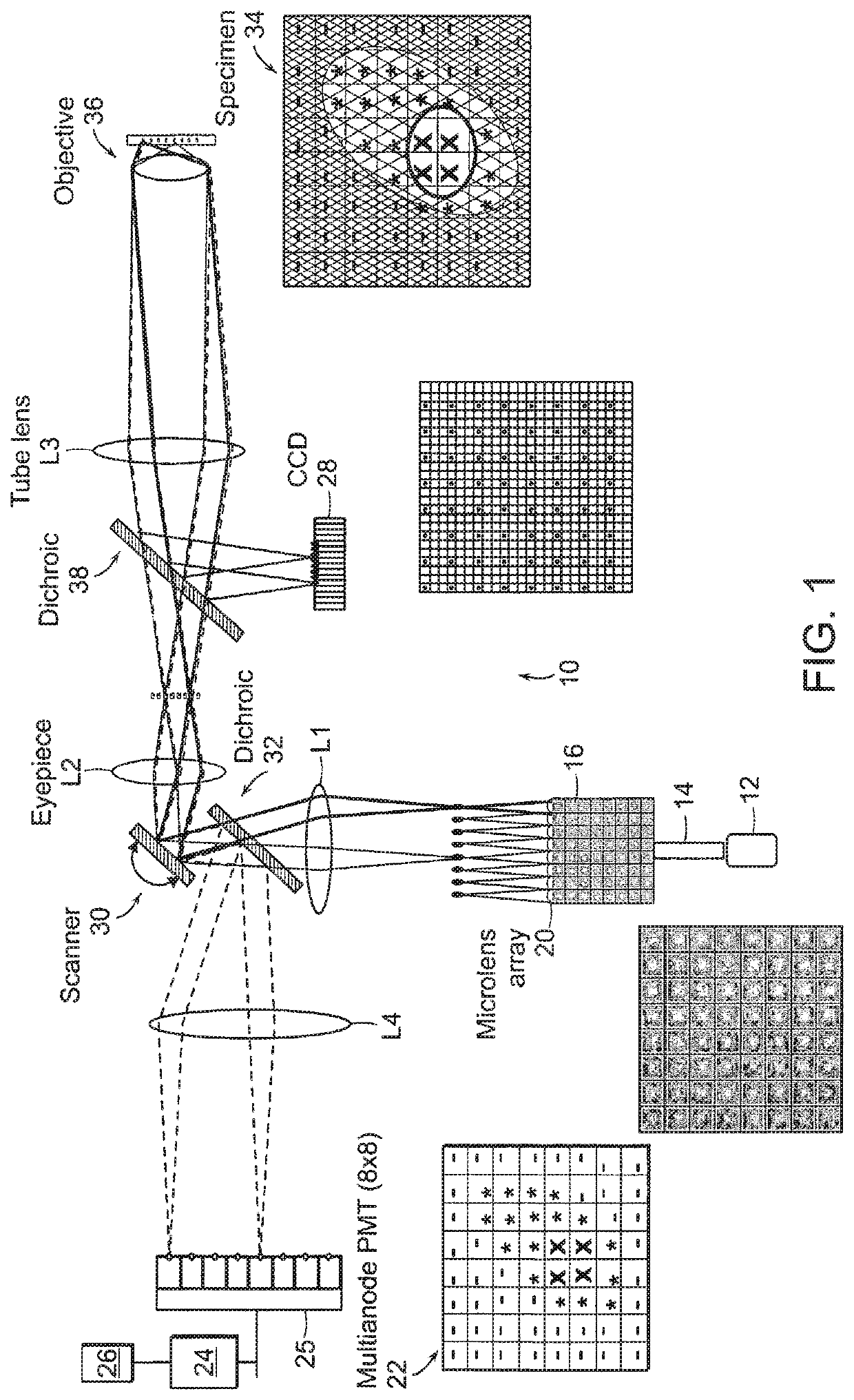
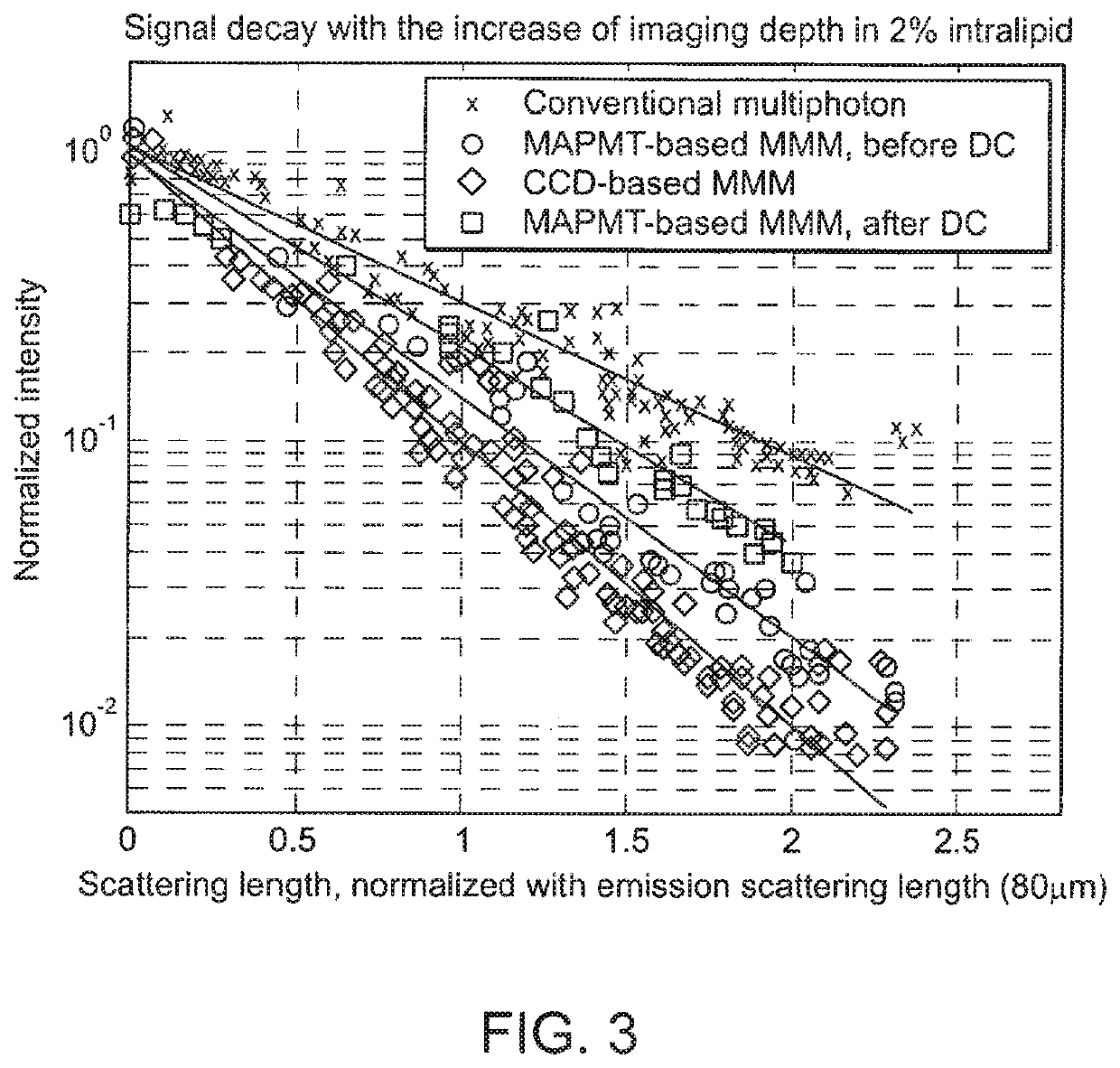
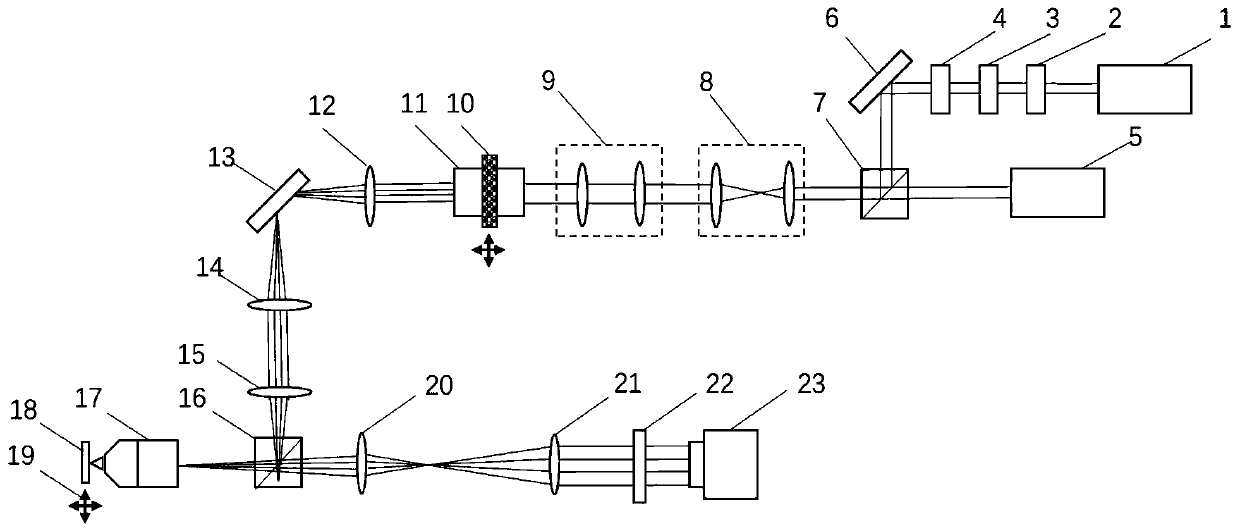
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
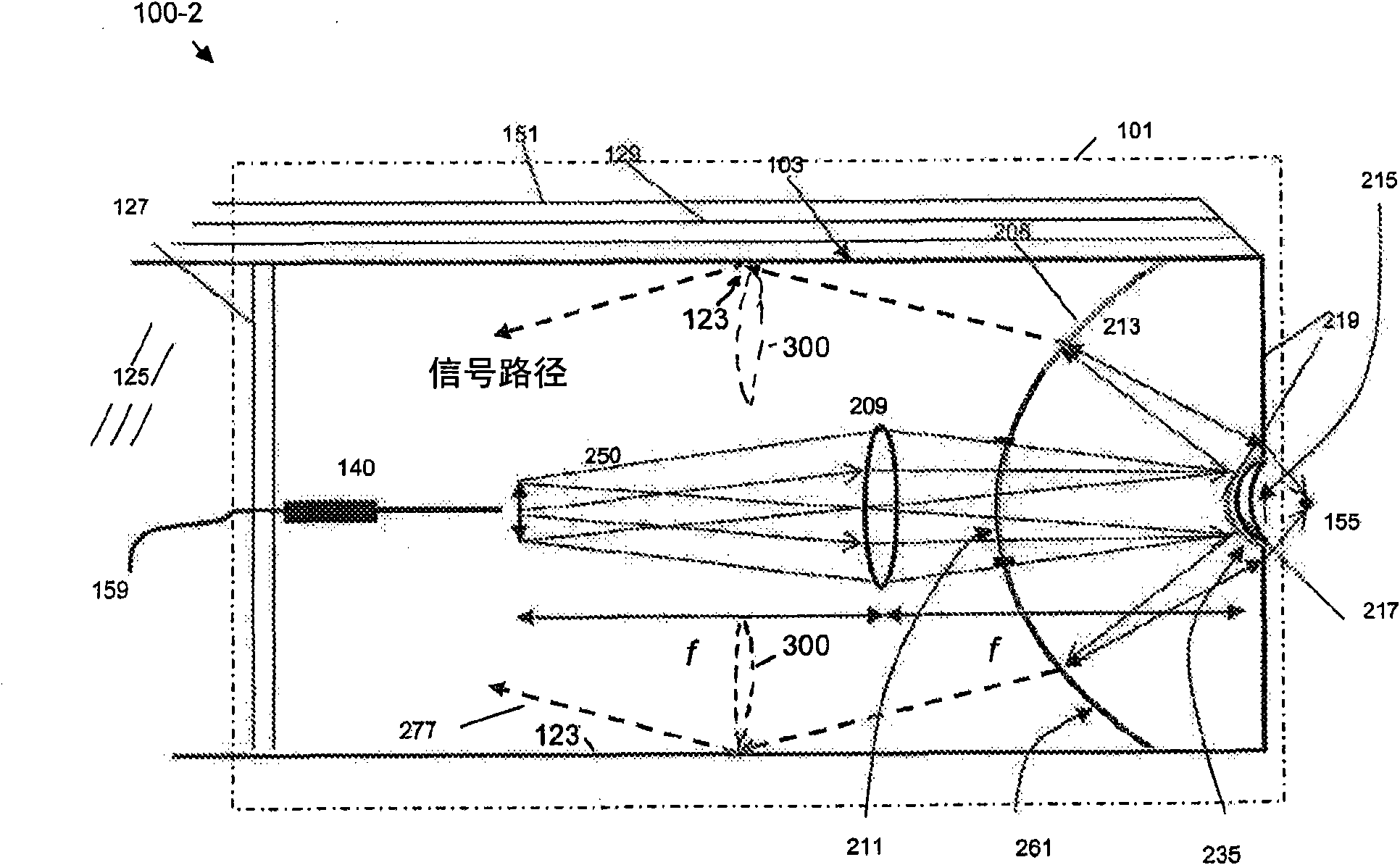
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20100261958A1Efficient collectionGuaranteed normal transmissionSurgeryEndoscopesFluorescenceImage resolution
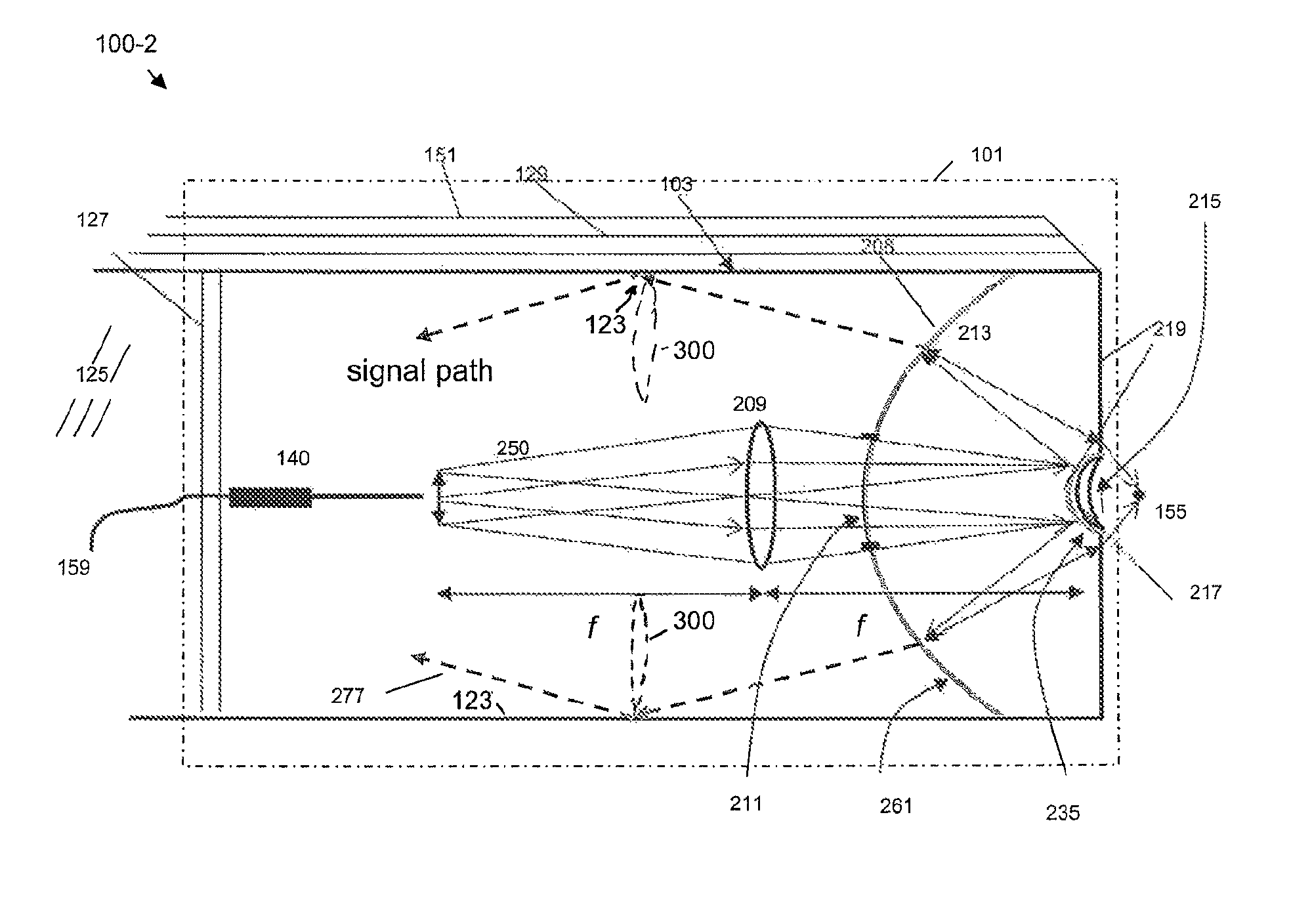
Embodiments of the invention include an optical system and an optical system module, coupled to a distal end of a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus, an optical waveguide-based fluorescence emission endoscopy system, and a method for remotely-controlled, multi-magnification imaging of a target or fluorescence emission collection from a target with a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus. An exemplary system includes an objective lens disposed in a distal end of an endoscope apparatus. The lens is adapted to transmit both a visible target illumination and a fluorescence-emission-inducing target illumination as well as fluorescence-emission and visible light from the target. The system can thus simultaneously provide low magnification, large field of view imaging and high magnification, high-resolution multiphoton imaging with a single lens system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
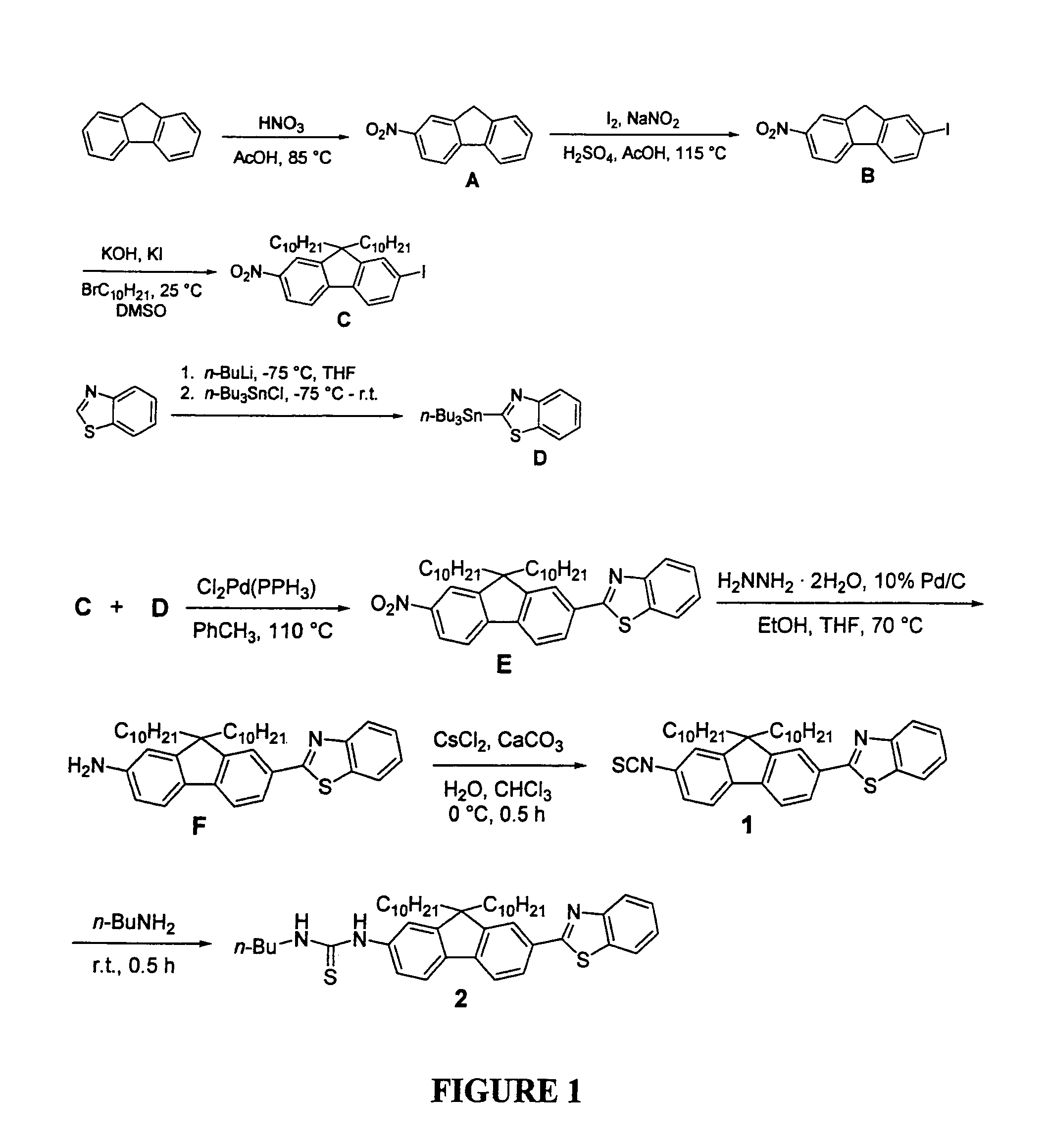
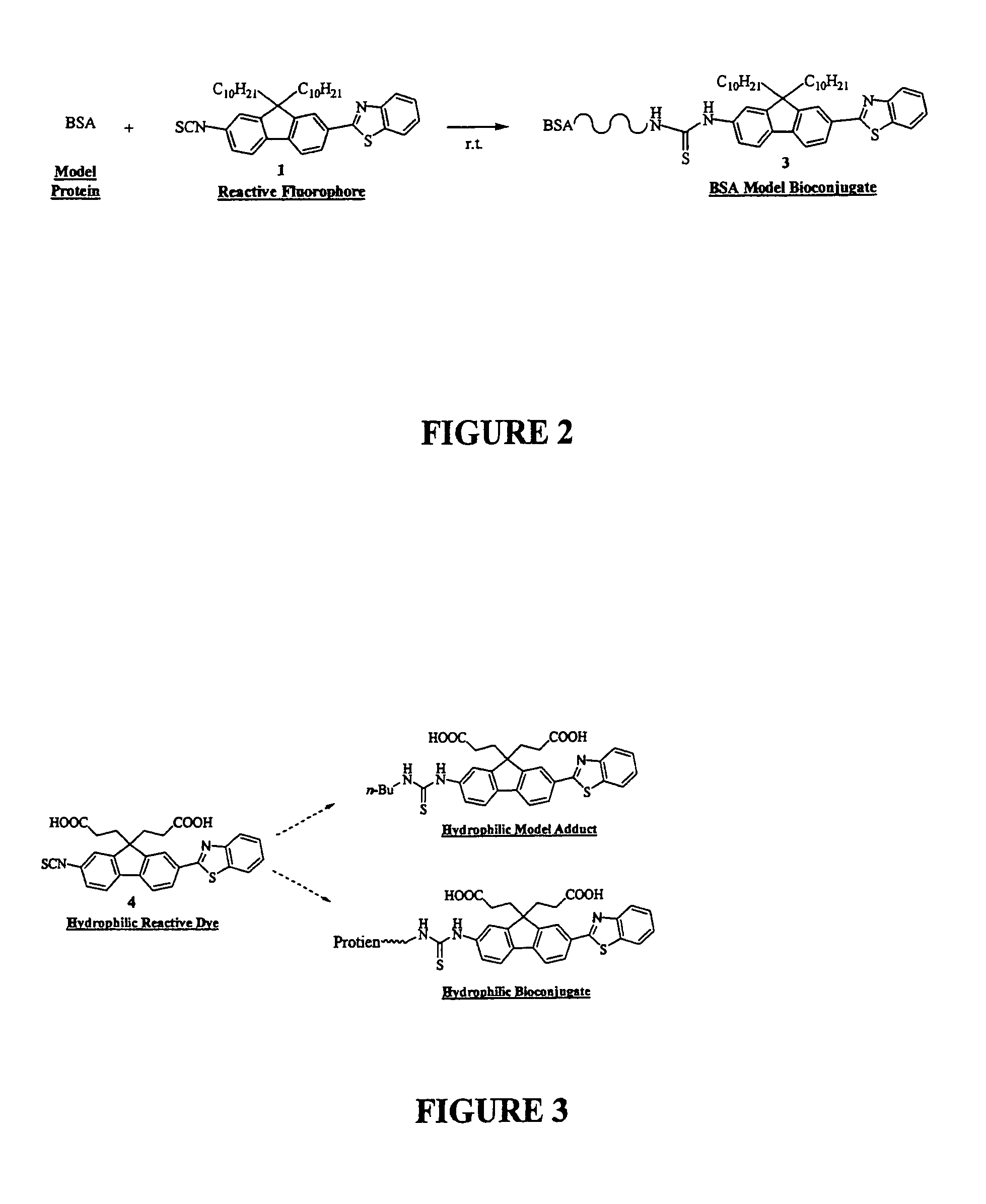
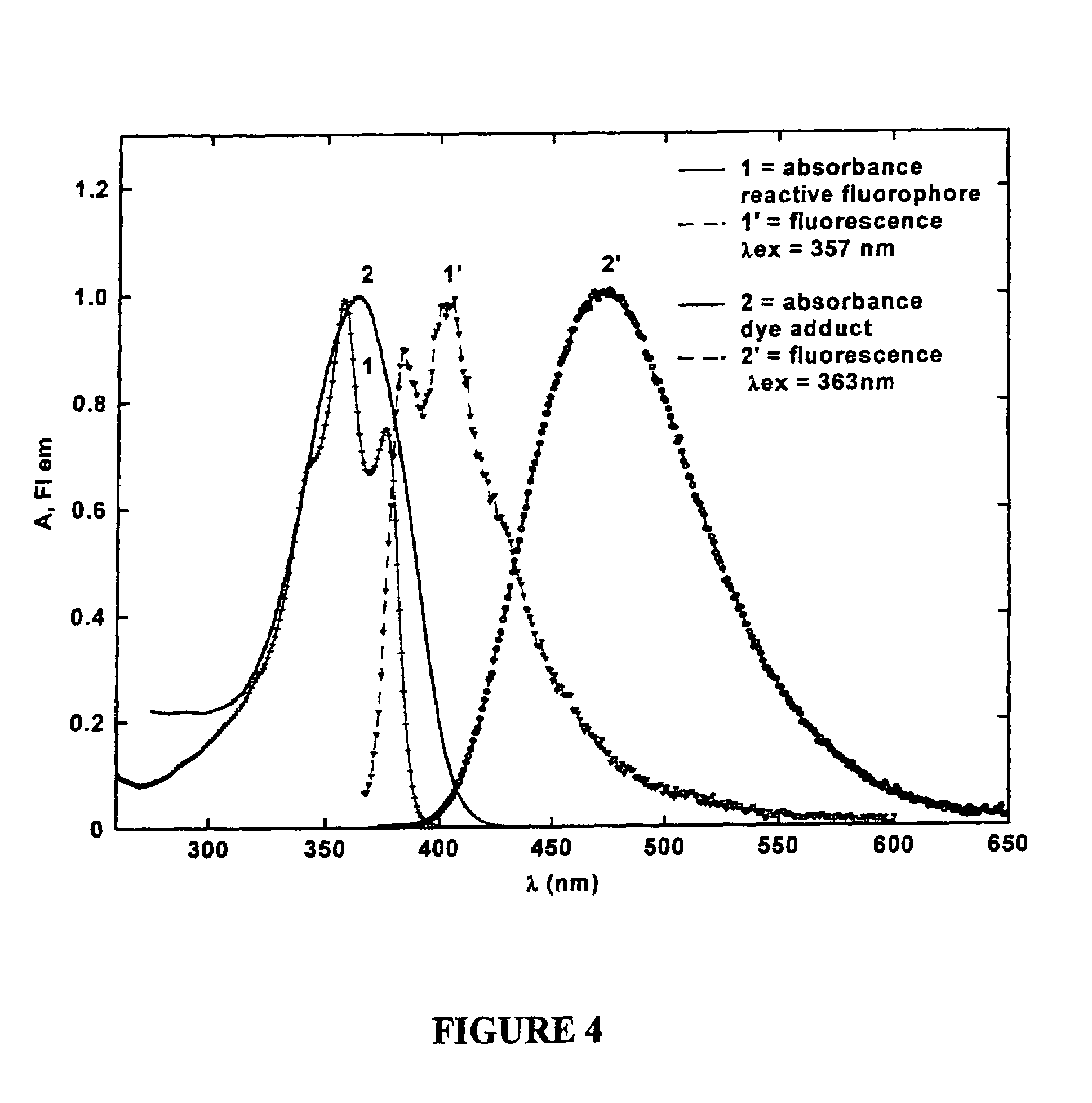
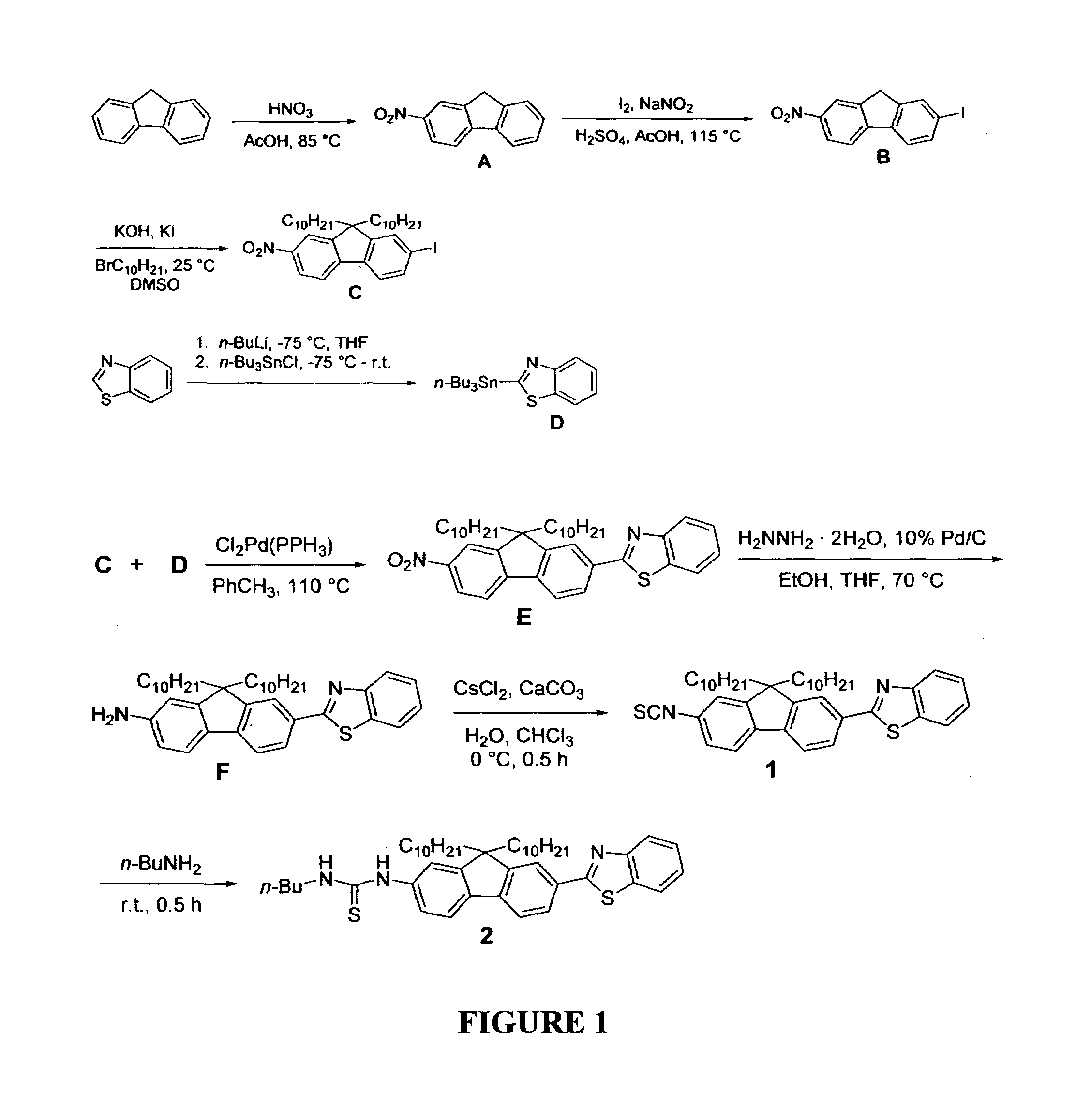
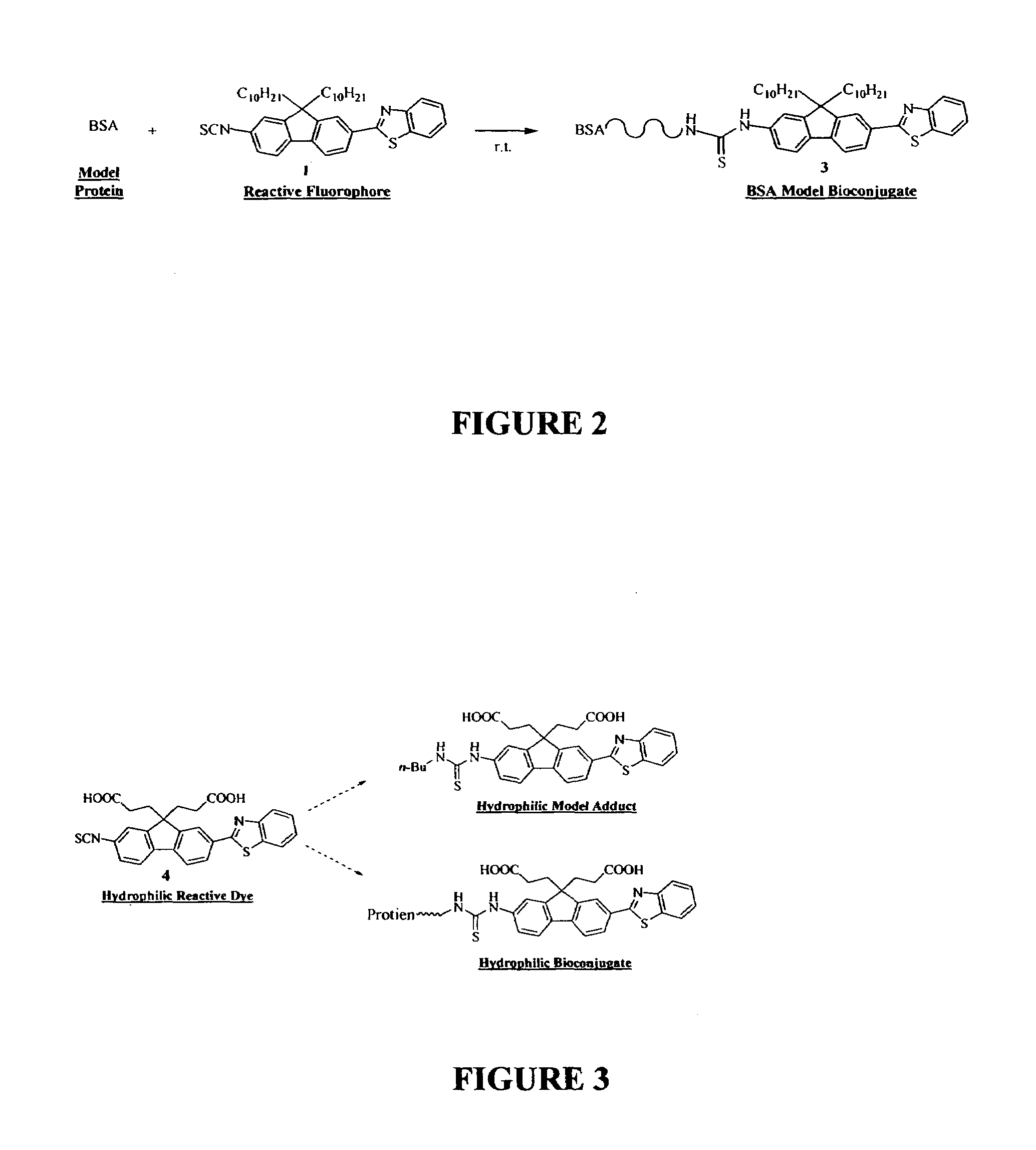
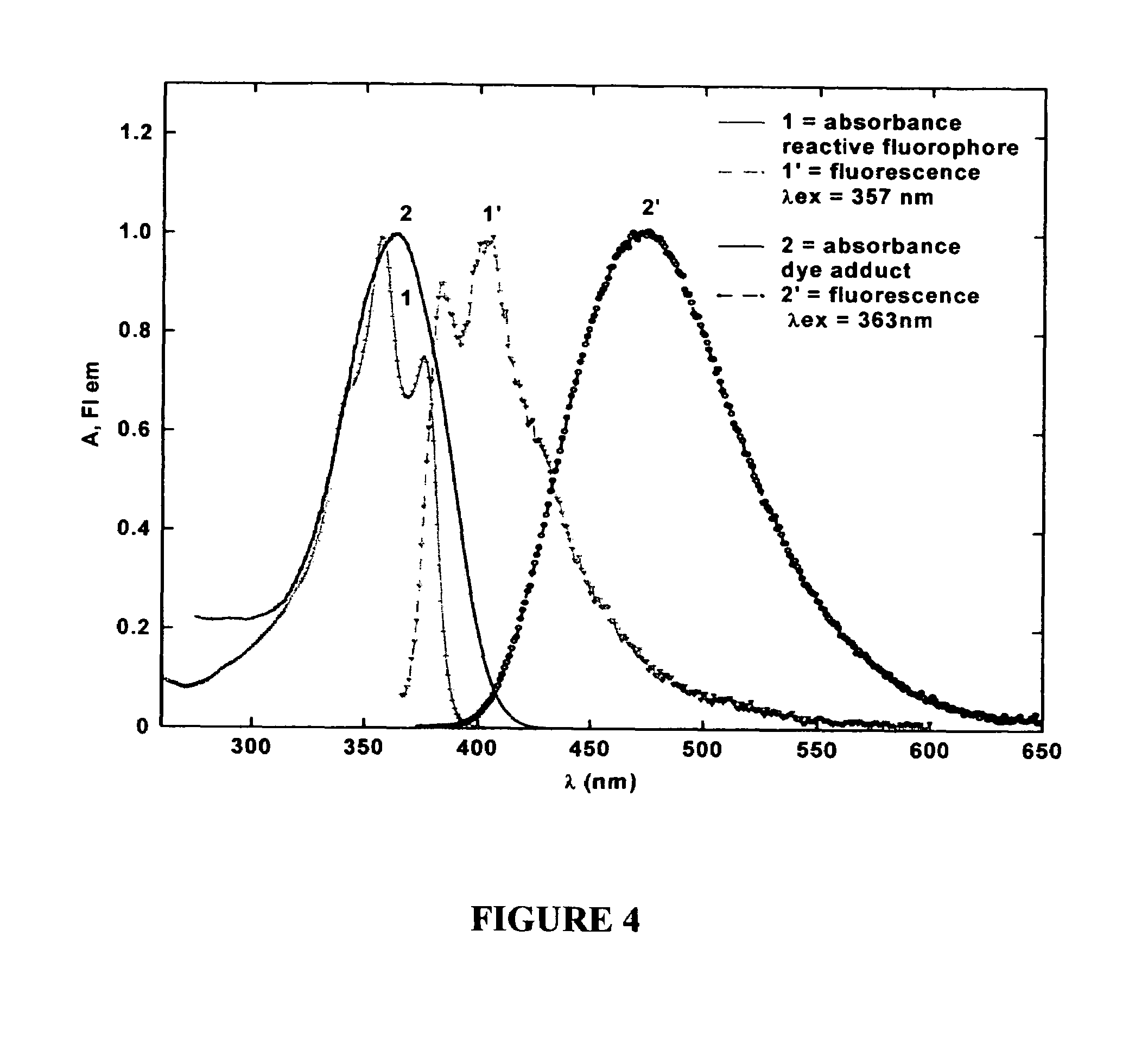
Reactive probes for two-photon fluorescent imaging and sensing
InactiveUS7282514B1High fluorescence quantum yieldBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsQuantum yieldBovine serum albumin
Fluorescent dyes and probes are key components in multiphoton based fluorescence microscopy imaging of biological samples. In order to address the demand for better performing dyes for two-photon based imaging, a new series of reactive fluorophores tailored for multiphoton imaging has been disclosed. These fluorophores are based upon the fluorene ring system, known to exhibit high fluorescence quantum yields, typically >0.7, and possess high photostability. They have been functionalized with moieties to act, e.g., as efficient amine-reactive fluorescent probes for the covalent attachment onto, e.g., proteins and antibodies. The synthesis and the single-photon spectral characteristics, as well as measured two-photon absorption cross sections of the reactive fluorophores in solution are presented. Spectral characterizations of bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugated with the new reactive probe is presented.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
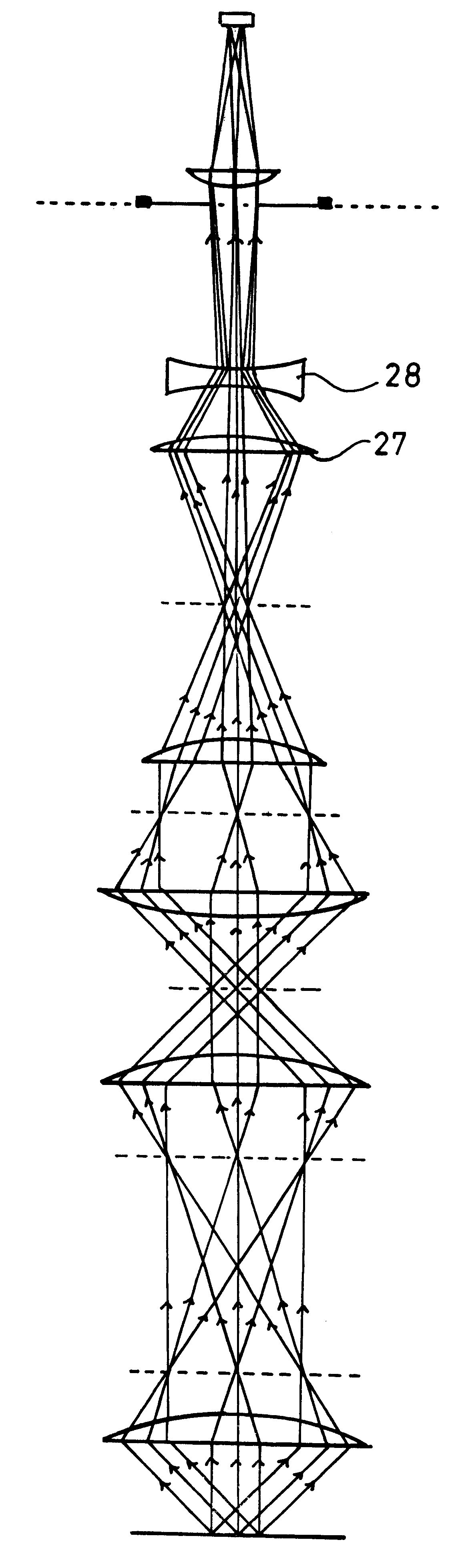
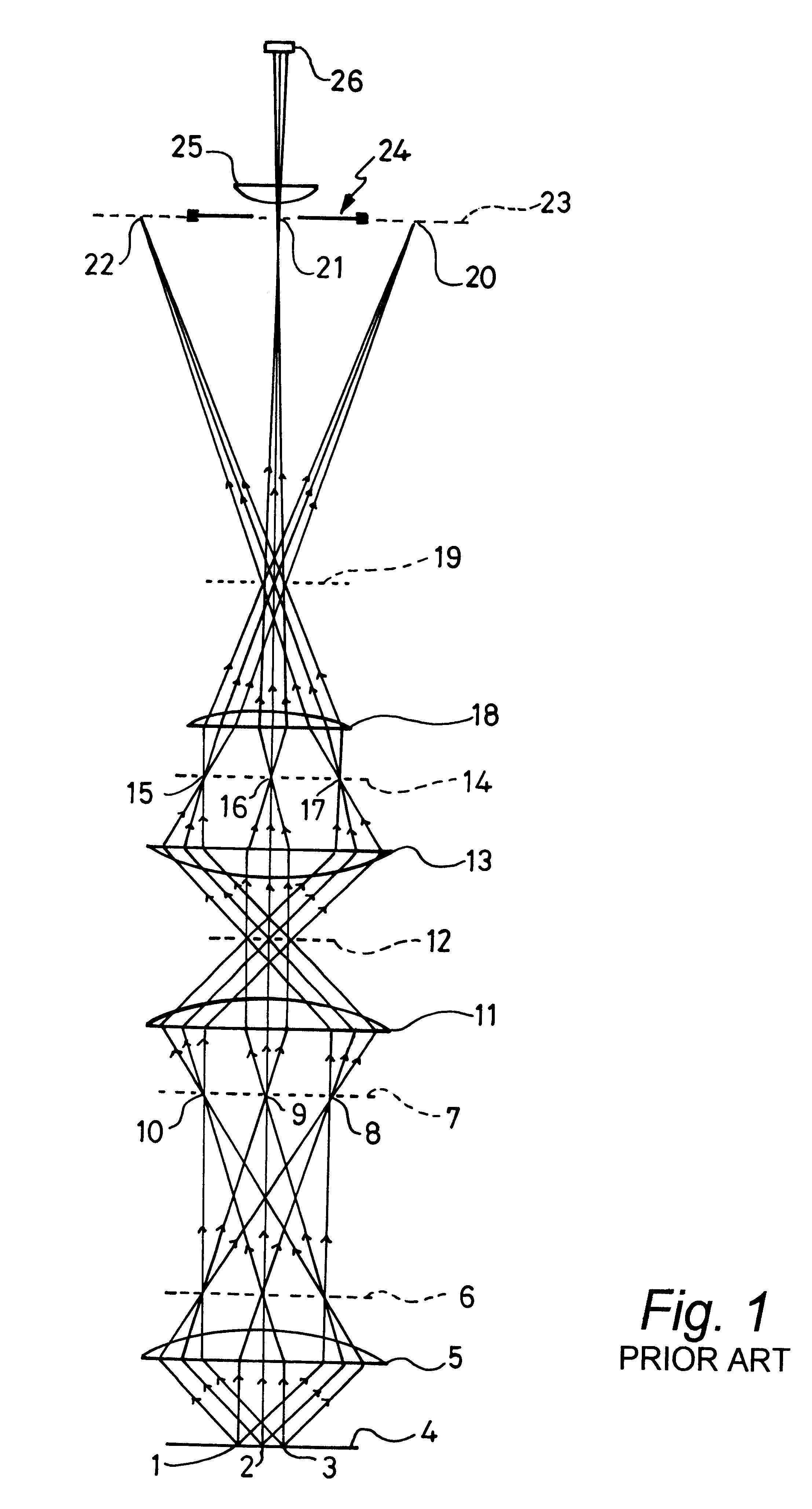
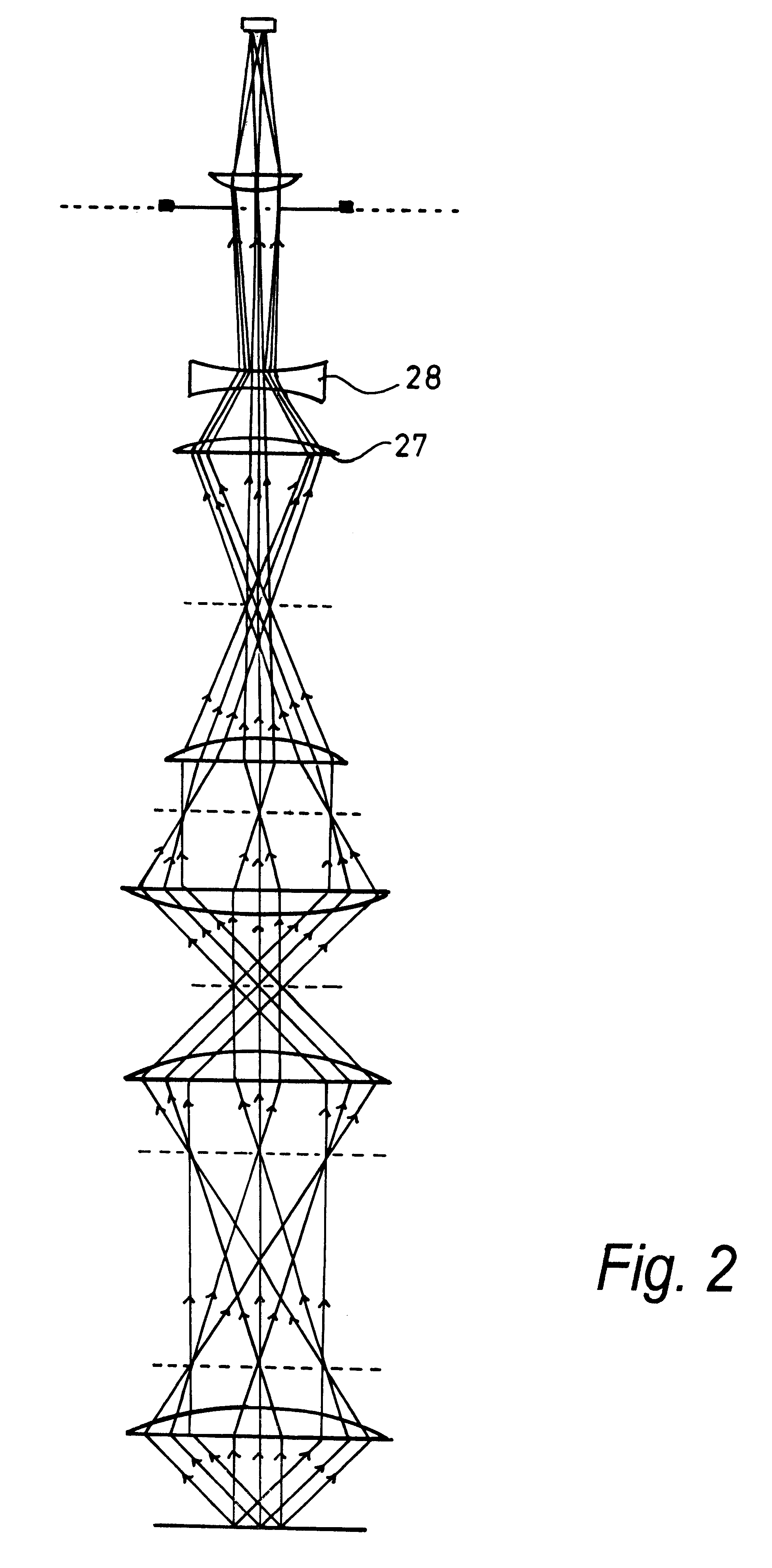
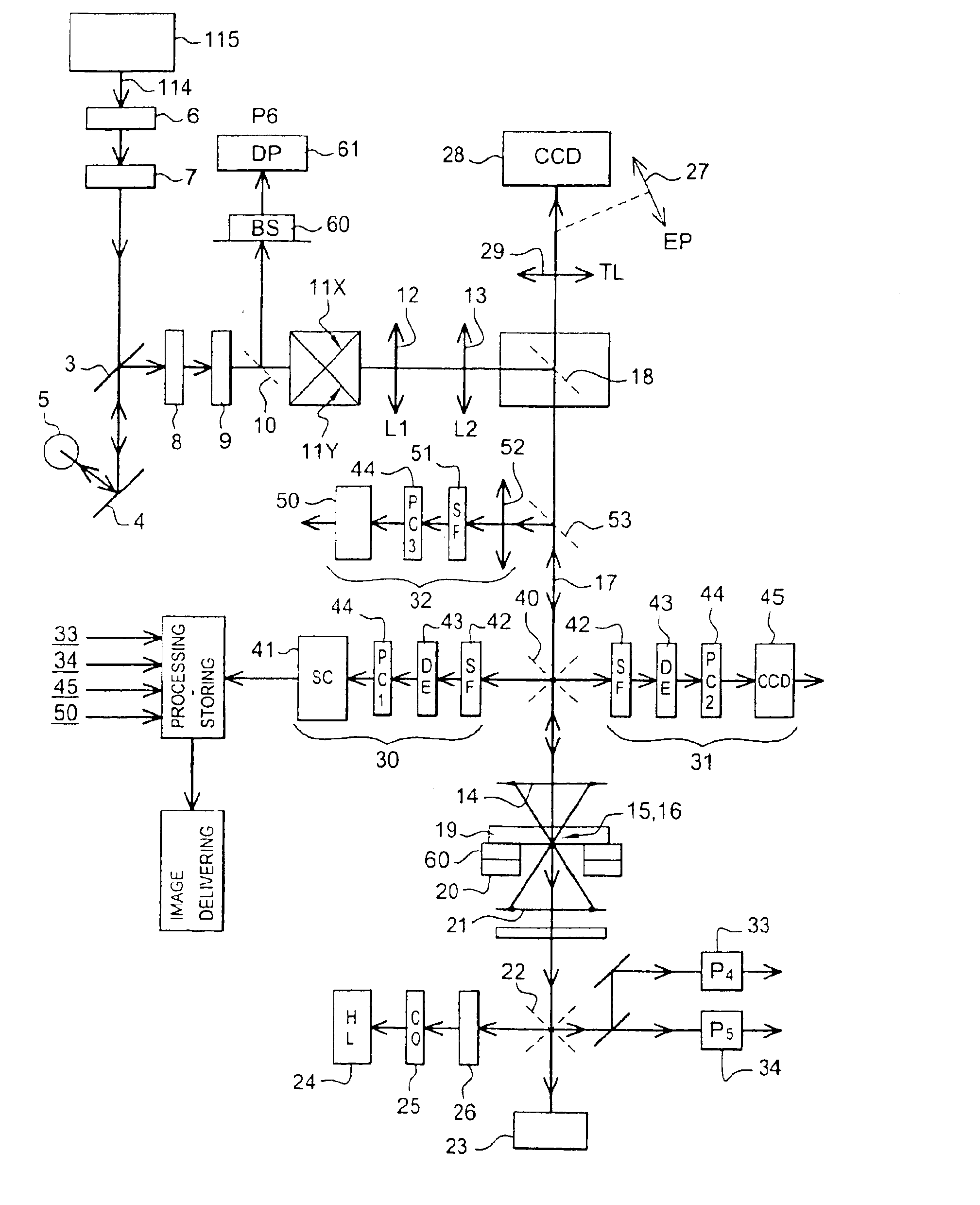
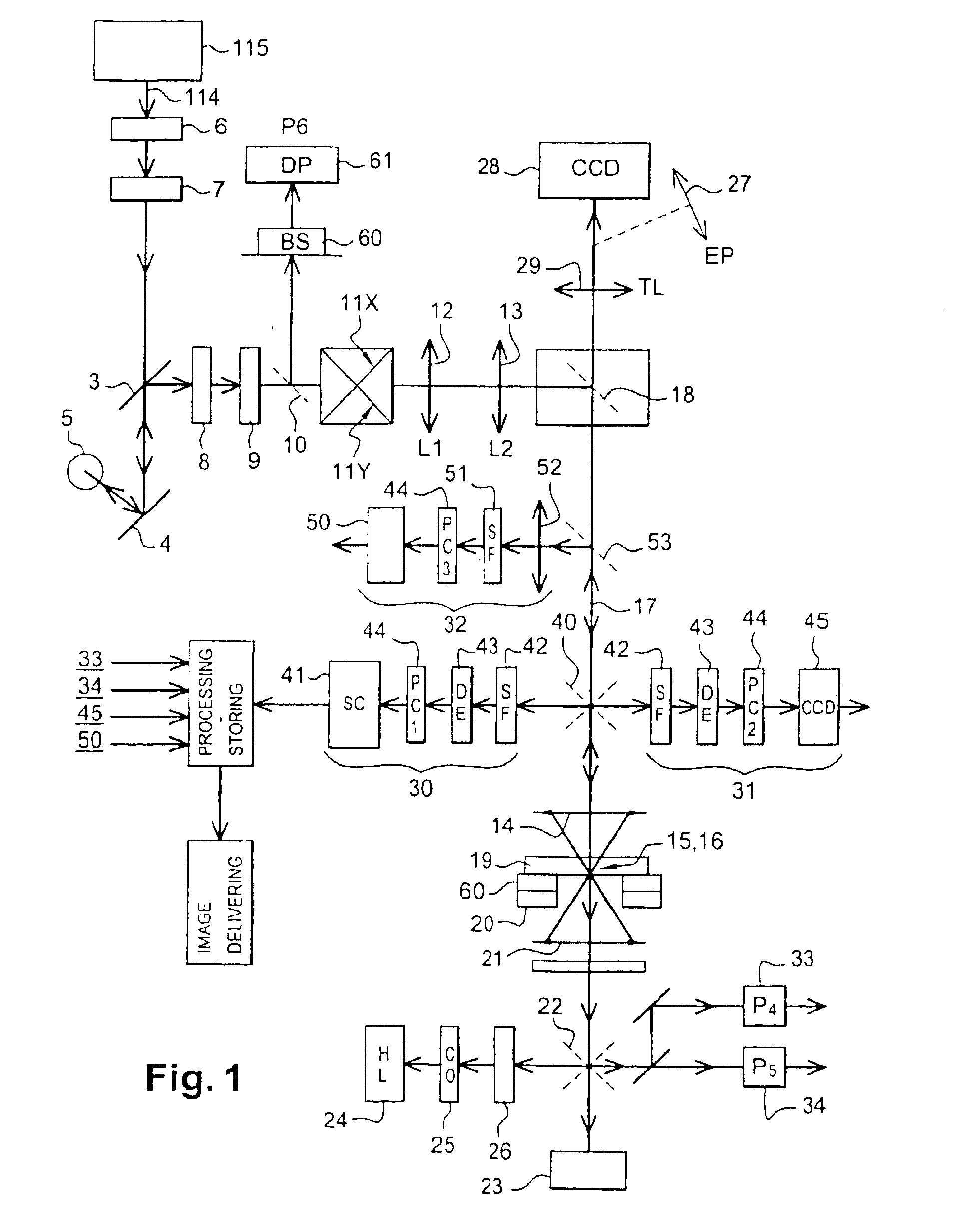
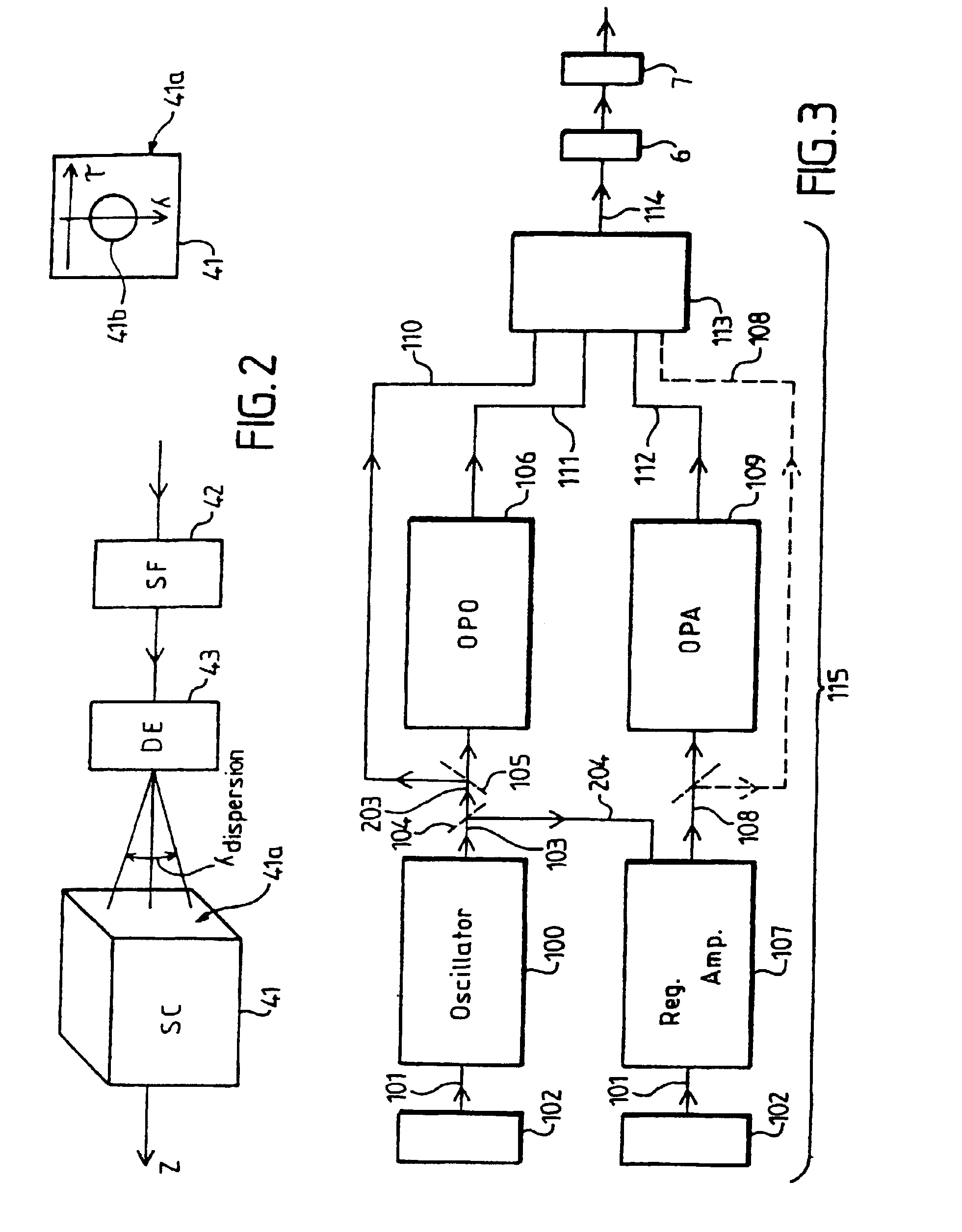
Multi-photon imaging installation
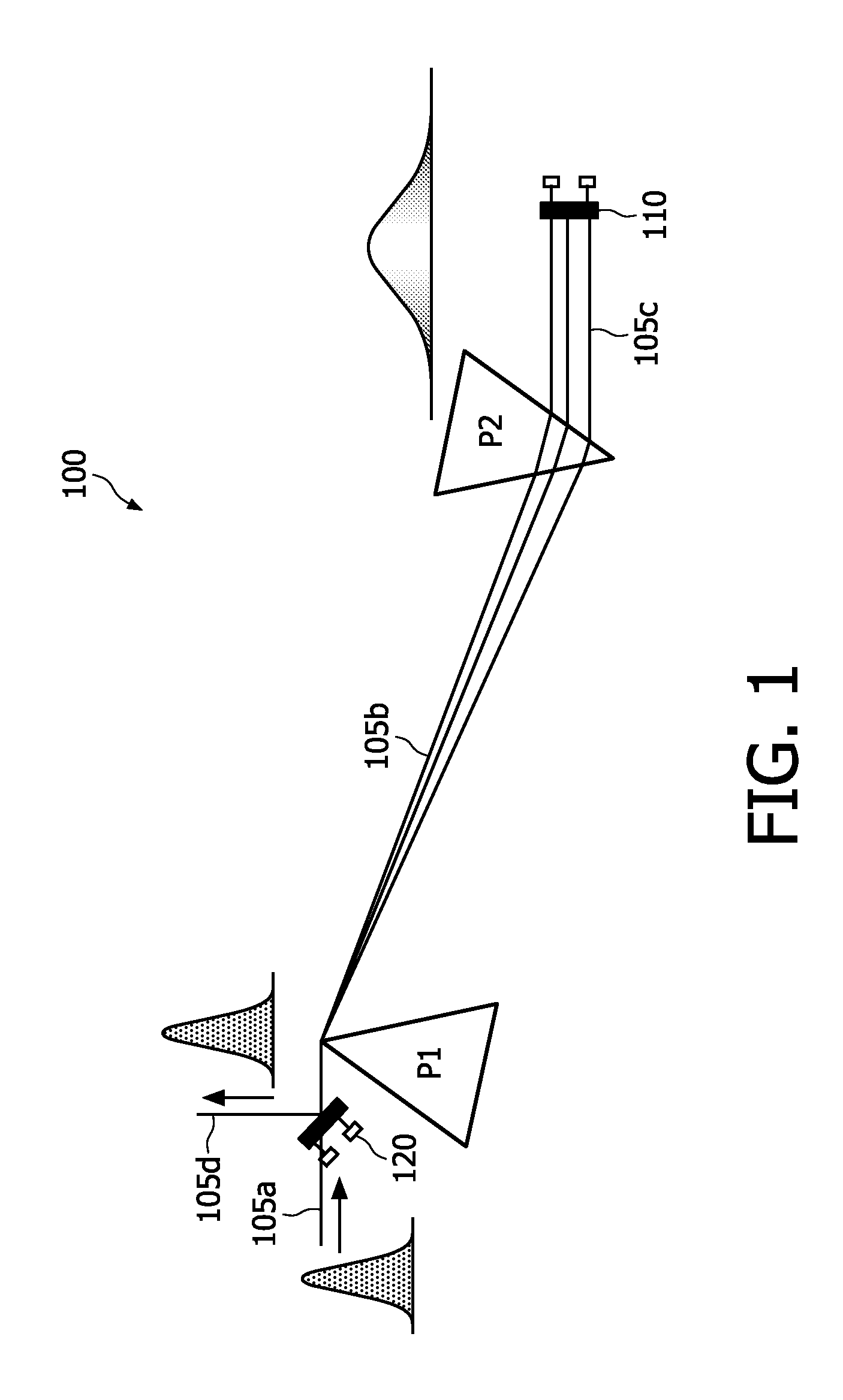
An installation is provided for multi-dimensional non-linear imaging of a material comprising intrinsic chromophores, using laser scanning. This installation comprises i) at least one source (115) of time stamp pulses of synchronized photons, ii) means (12-14) for locally focusing the pulses on a material to cause its intrinsic chromophores to absorb groups of at least two synchronized photons to produce response photons, iii) means (22, 40, 53) for directing the response photons to at leat one collecting zone, iv) means (30-34) for collecting the response photons in the collecting zone(s) whatever their energy, v) processing means for converting the collected photons into data at least representative of their number and storing them in correspondence with at least the time stamp pulses that cause the material to produce the response photons, vi) means for scanning (11, 20) the pulses through a chosen area of the material, and vii) means for delivering from said data stored an image representative of said material chosen area, with a sub-millimeter resolution, and in function of the respective time stamp pulses of data.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +1
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
Embodiments of the invention include an optical system and an optical system module, coupled to a distal end of a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus, an optical waveguide-based fluorescence emission endoscopy system, and a method for remotely- controlled, multi -magnification imaging of a target or fluorescence emission collection from a target with a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus. An exemplary system includes an objective lens disposed in a distal end of an endoscope apparatus. The lens is adapted to transmit both a visible target illumination and a fluorescence-emission-inducing target illumination as well as fluorescence-emission and visible light from the target. Thee system can thus simultaneously provide low magnification, large field of view imaging and high magnification, high-resolution multiphoton imaging with a single lens system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Reactive probes for two-photon fluorescent imaging and sensing
InactiveUS7253287B1High fluorescence quantum yieldImprove light resistanceOrganic chemistryQuantum yieldBovine serum albumin
Fluorescent dyes and probes are key components in multiphoton based fluorescence microscopy imaging of biological samples. In order to address the demand for better performing dyes for two-photon based imaging, a new series of reactive fluorophores tailored for multiphoton imaging has been disclosed. These fluorophores are based upon the fluorene ring system, known to exhibit high fluorescence quantum yields, typically >0.7, and possess high photostability. They have been functionalized with moieties to act, e.g., as efficient amine-reactive fluorescent probes for the covalent attachment onto, e.g., proteins and antibodies. The synthesis and the single-photon spectral characteristics, as well as measured two-photon absorption cross sections of the reactive fluorophores in solution are presented. Spectral characterizations of bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugated with the new reactive probe is presented.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
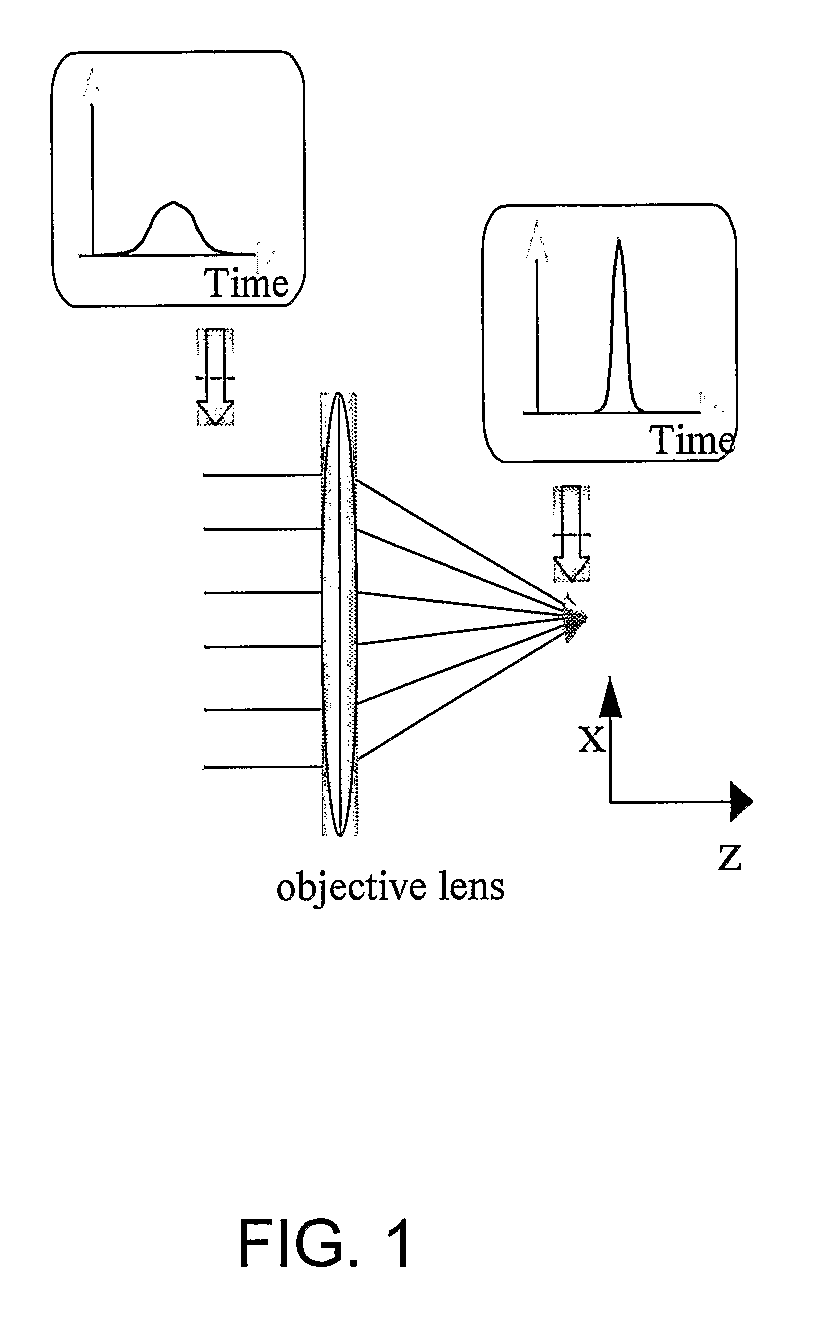
Simultaneous Spatial and Temporal Focusing of Femtosecond Pulses
InactiveUS20080151238A1Improve SBRReducing background excitationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationRainbowFemtosecond pulse shaping
A technique for simultaneous spatial and temporal focusing of femtosecond pulses improves the signal-to-back-ground ratio (SBR) in multiphoton imaging. This is achieved by spatially separating spectral components of pulses into a “rainbow beam” and recombining these components at the spatial focus of an imaging system. The temporal pulse width becomes a function of distance, with the shortest pulse width confined to the spatial focus. The technique can significantly improve the axial confinement and reduce the background excitation in multiphoton microscopy, and thereby increase the imaging depth in highly scattering biological specimens.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and device for improving multiphoton fluorescence microscope imaging resolution
InactiveCN103645136AMaintain imaging depthIncreased super-resolution imaging capabilitiesMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceImage resolution
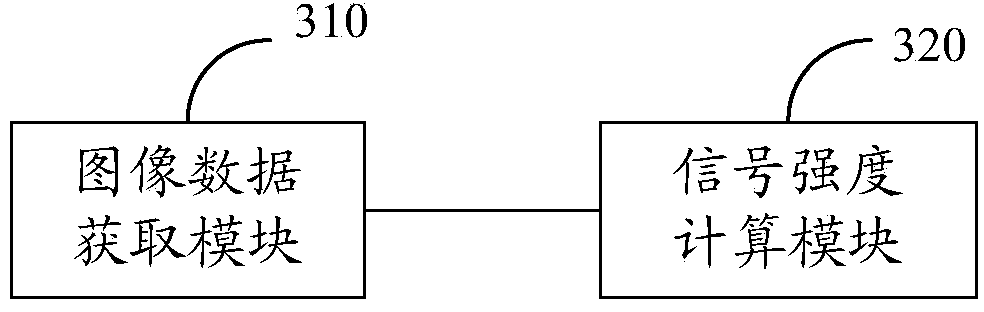
Relating to the field of optical technologies, the embodiment of the invention discloses a method for improving the multiphoton fluorescence microscope imaging resolution. The method includes: scanning a sample through a microscope repeatedly, acquiring the data of scanned multiple images, and acquiring the pixel point signal strength of sample target points in the multiple images according to the obtained multiple image data; and calculating the signal strength of sample target points in a reconstructed image obtained by processing the data of the multiple images according to the pixel point signal strength of the sample target points in the multiple images. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a device for improving the multiphoton fluorescence microscope imaging resolution. By means of the method and the device provided by the invention, and through specific mathematical calculation formulas, fusion of a multiphoton imaging technology and a structured illumination imaging technology is realized, while keeping the advantage of multiphoton original imaging depth, a super-resolution imaging ability is increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS8553337B2Efficient collectionGuaranteed normal transmissionSurgeryEndoscopesFluorescenceImage resolution
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Multifocal imaging systems and method
ActiveUS20180202935A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLow noiseGrating
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
New use of neodymium ion sensitized up-conversion nanocrystal, and high-resolution multi-photon microscopic system
ActiveCN105004704ALower requirementEase of high-order multiphoton imagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageBiological imaging
The invention discloses a new use of a neodymium ion sensitized up-conversion nanocrystal, and a high-resolution multi-photon microscopic system. The above neodymium ion sensitized up-conversion nanomaterial can be excited by short-wavelength stable laser with the center wavelength being shorter than 800nm to generate multi-photon visible light, so the nanomaterial has large multi-photon absorption cross section and multi-photon saturated excitation power, and makes higher-order multi-photon imaging easy, so the above new characteristic can be used in multi-photon microscopic imaging to greatly reduce the cost of the system and greatly improves the microscopic imaging resolution. The multi-photon microscopic imaging system comprises a short-wavelength stable laser with the center wavelength being shorter than 800nm, and the neodymium ion sensitized up-conversion nanomaterial is adopted as a sample. The short-wavelength stable laser is used to construct the cheap and simple multi-photon microscopic system for the first time, the neodymium ion sensitized up-conversion luminescence nanomaterial is used to carry out ultrahigh-resolution multi-photon microscopic imaging, and the material can also be introduced to cells, tissues or other matrixes in order to carry out high-resolution biological imaging.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multifocal imaging systems and method
ActiveUS10598597B2Fast imagingEfficient collectionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLow noiseHemt circuits
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multi-mode array type scanning imaging device combined with multi-photon excitation
InactiveCN110941100AFast scanningMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention discloses a multi-mode array type scanning imaging device combined with multi-photon excitation, and belongs to the field of optical microscopic measurement. Aiming at different imagingrequirements of a transparent thin sample and a thick scattering sample, the multi-mode imaging device combining multi-photon excitation imaging and common wide-field fluorescence imaging is designedthrough selection of different light sources, and the two light sources can realize switching of multiple modes through combination of a beam splitter. A fixed micro-lens array is used for accuratelycontrolling an illumination mode and the position of an excitation point so as to generate sparse focus illumination, rapid scanning of a sample is completed, rapid double-resolution imaging of a transparent sample and a thick sample is achieved, and meanwhile the image contrast of the thick scattering sample is improved. Moreover, an adaptive aberration correction unit is introduced into the imaging system, so that the aberration of the system is reduced or eliminated, and the imaging depth and the imaging quality in a multi-photon imaging mode are improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fast two-photon imaging by diffracted swept-laser excitation
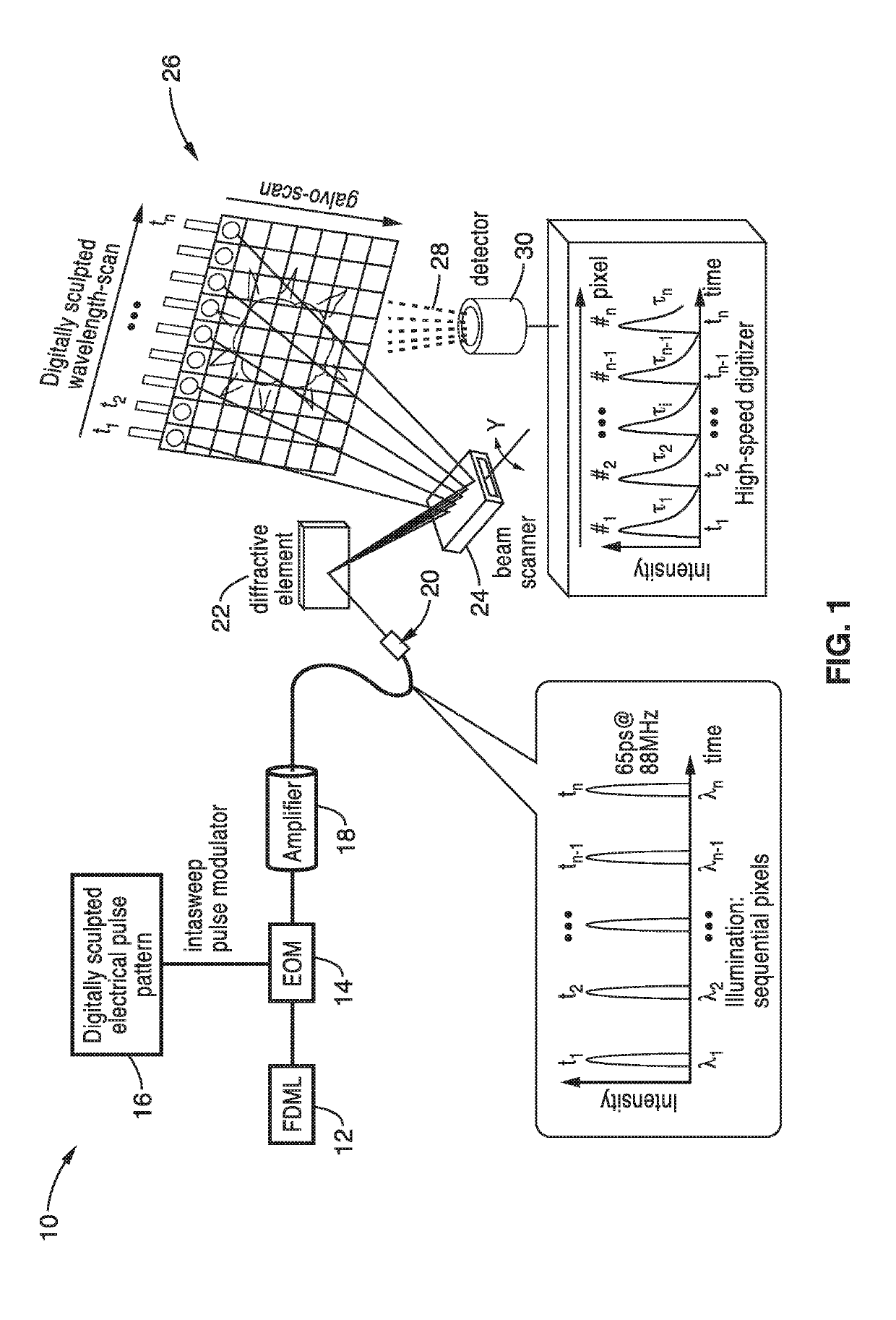
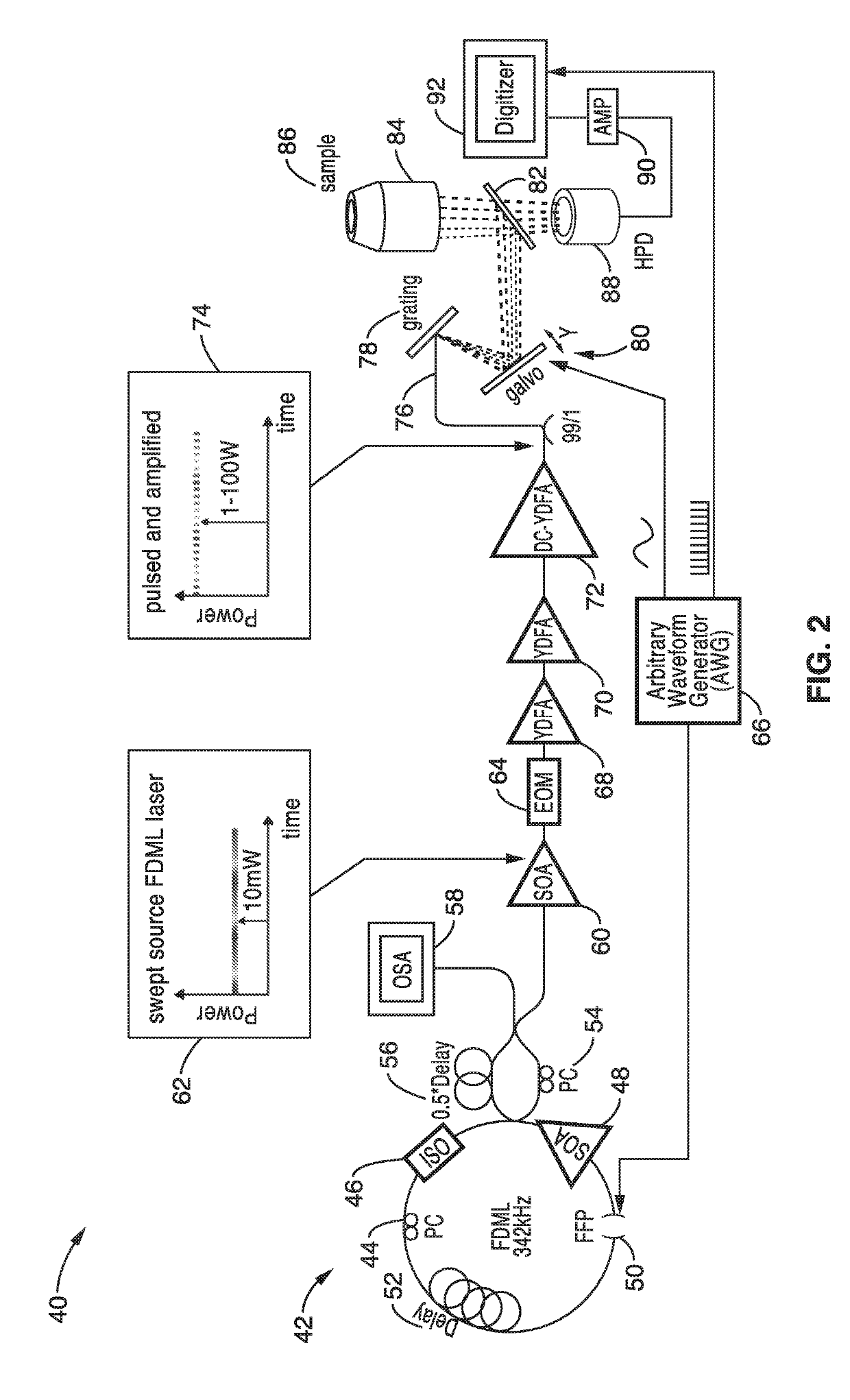
ActiveUS20190226989A1Faster non-linear imaging speedElimination speedDiagnostics using spectroscopyDianostics using fluorescence emissionPhotonTwo photon fluorescence
An apparatus and methods for high-speed non-linear spectrally encoded multi-photon imaging that are particularly suited for use in two photon fluorescence and fluorescence lifetime imaging. The system is capable of optical image compression and scale invariant digital zoom. A wavelength agile laser with digitally synthesized electro-optic modulation in a master oscillator-power amplifier configuration is combined with spectral encoding to eliminate the speed limitations of inertial scanning. The technique for fast two photon fluorescent imaging with simultaneous lifetime imaging independently detects the location, amplitude and lifetime of fluorescent emission by synthesizing a sequential excitation beam via digital electro-optic modulation of a quasi-CW swept source followed by time encoded detection. For fluorescent imaging, spectral and temporal mappings are employed separately, with quasi-CW spectral encoding used for pumping and time encoding for constructing the image at fluorescence wavelength.
Owner:UNIV ZU LUBECK +1
Systems and methods to reduce scattering in temporal focusing multiphoton microscopy
ActiveUS20200342205A1Enhance the imageInhibition effectSamplingSurgeryHigh resolution imageMaterials science
Systems and methods herein provide improved, high-throughput multiphoton imaging of thick samples with reduced emission scattering. The systems and methods use structured illumination to modify the excitation light. A reconstruction process can be applied to the resulting images to recover image information free of scattering. The disclosed systems and methods provide high throughput, high signal-to-noise ratio, and high resolution images that are depth selective.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
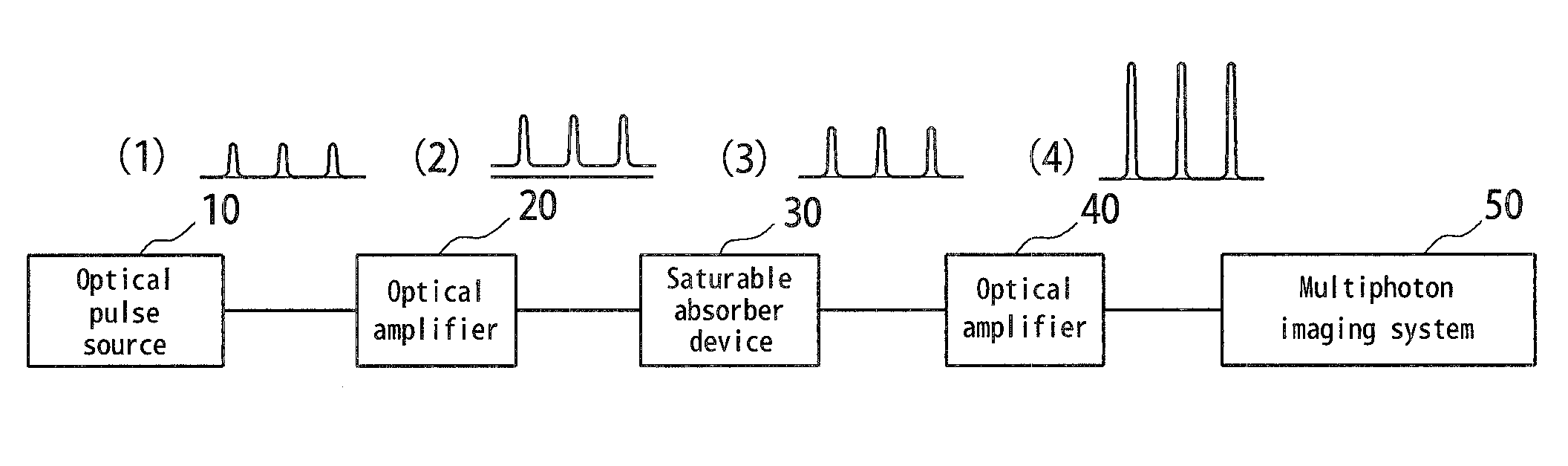
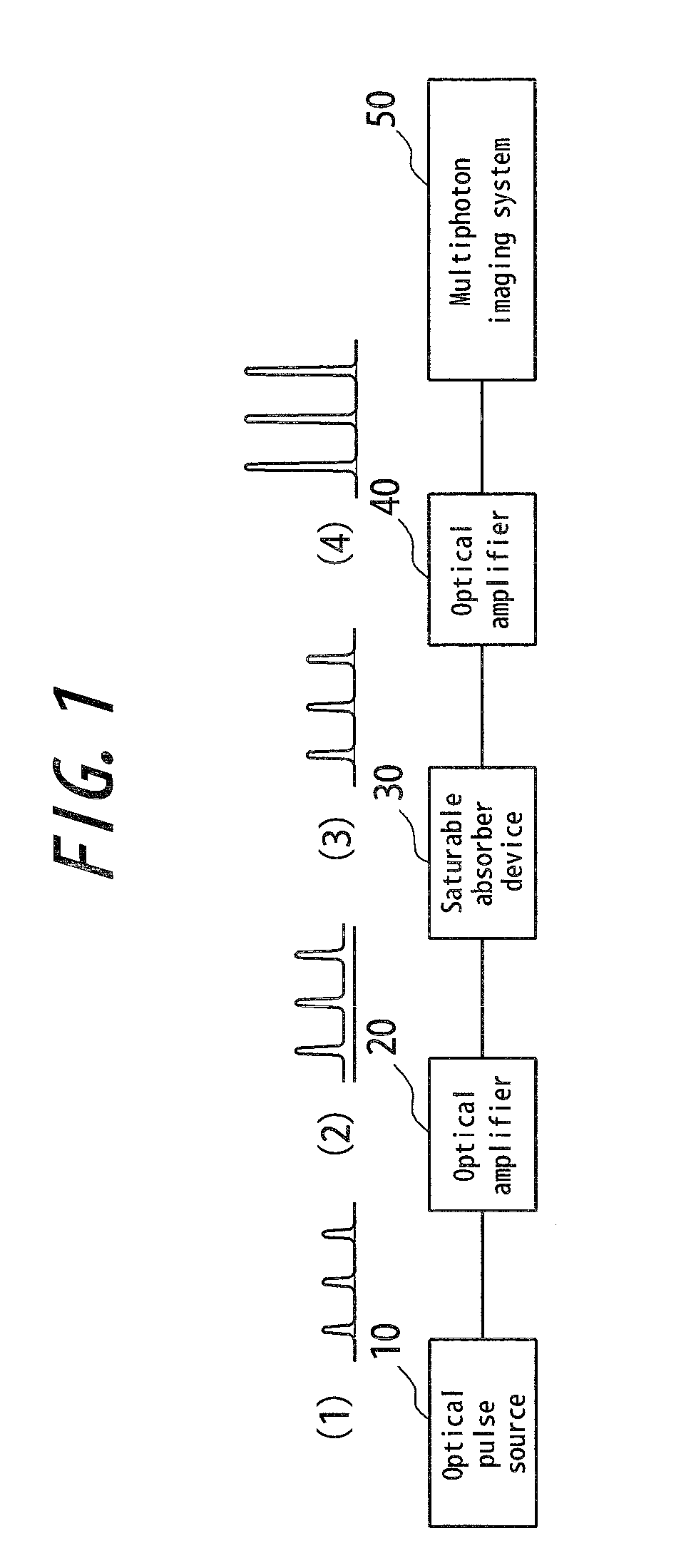
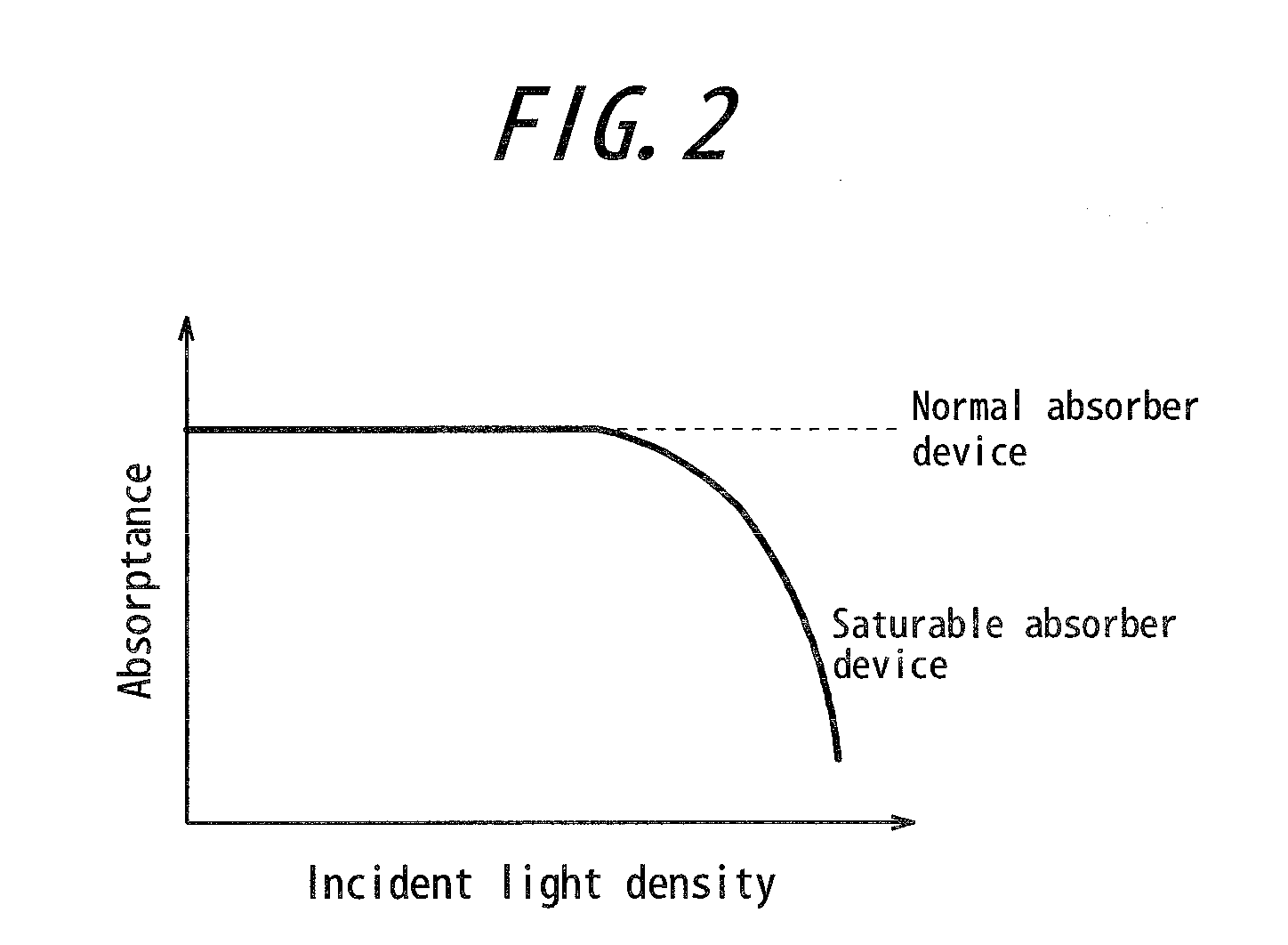
Optical pulse source device
InactiveUS20100195193A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSimple configurationLaser detailsFibre transmissionActive timePhoton
An optical pulse source device comprising an optical pulse source (10) emitting an optical pulse train, optical amplifying means (20, 40) amplifying the optical pulse train and a saturable absorber device (30) removing noise floor in the optical pulse train. There is provided an optical pulse source device for multiphoton imaging system being of small size and high stability and capable of improving the SNR by its relatively simple configuration without using a synchronous circuit or an active time gate.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
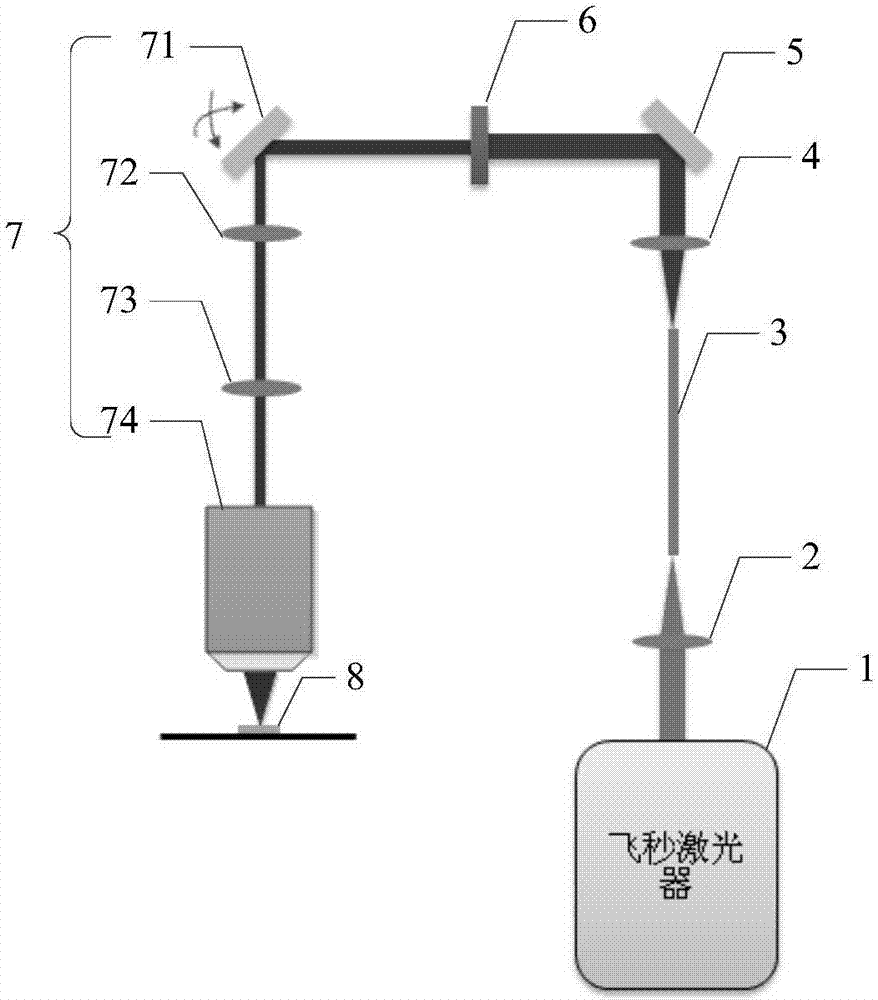
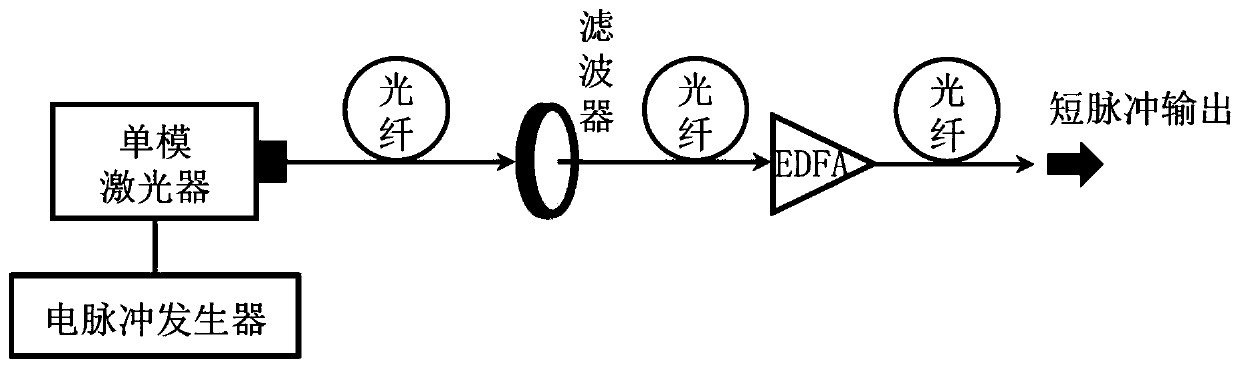
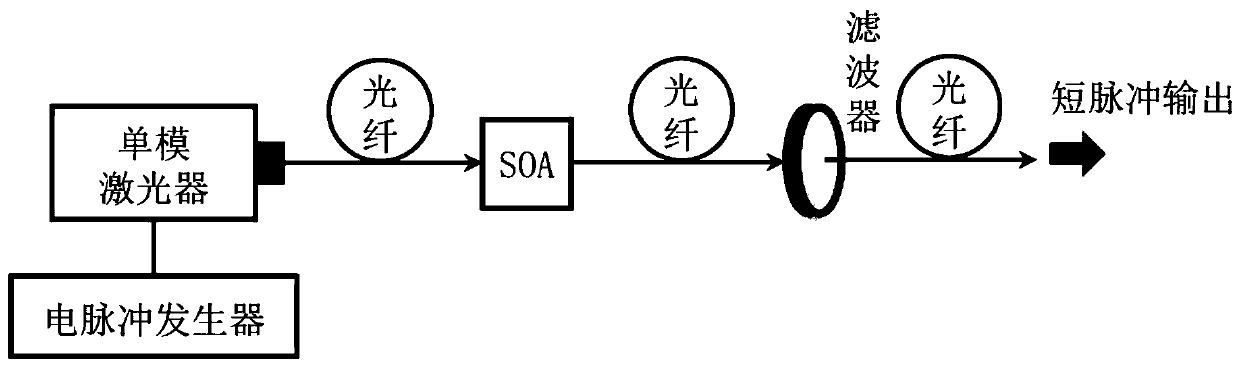
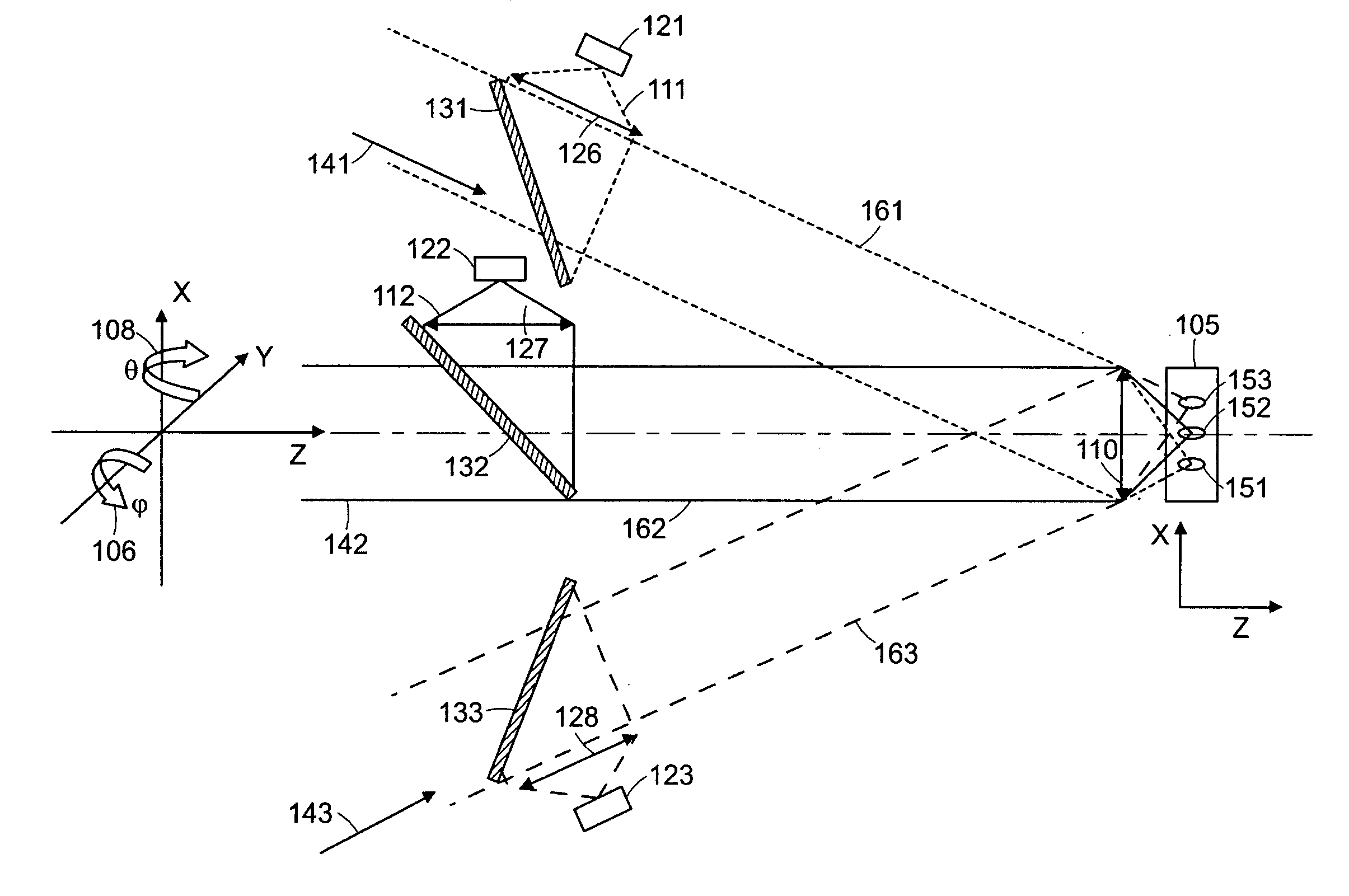
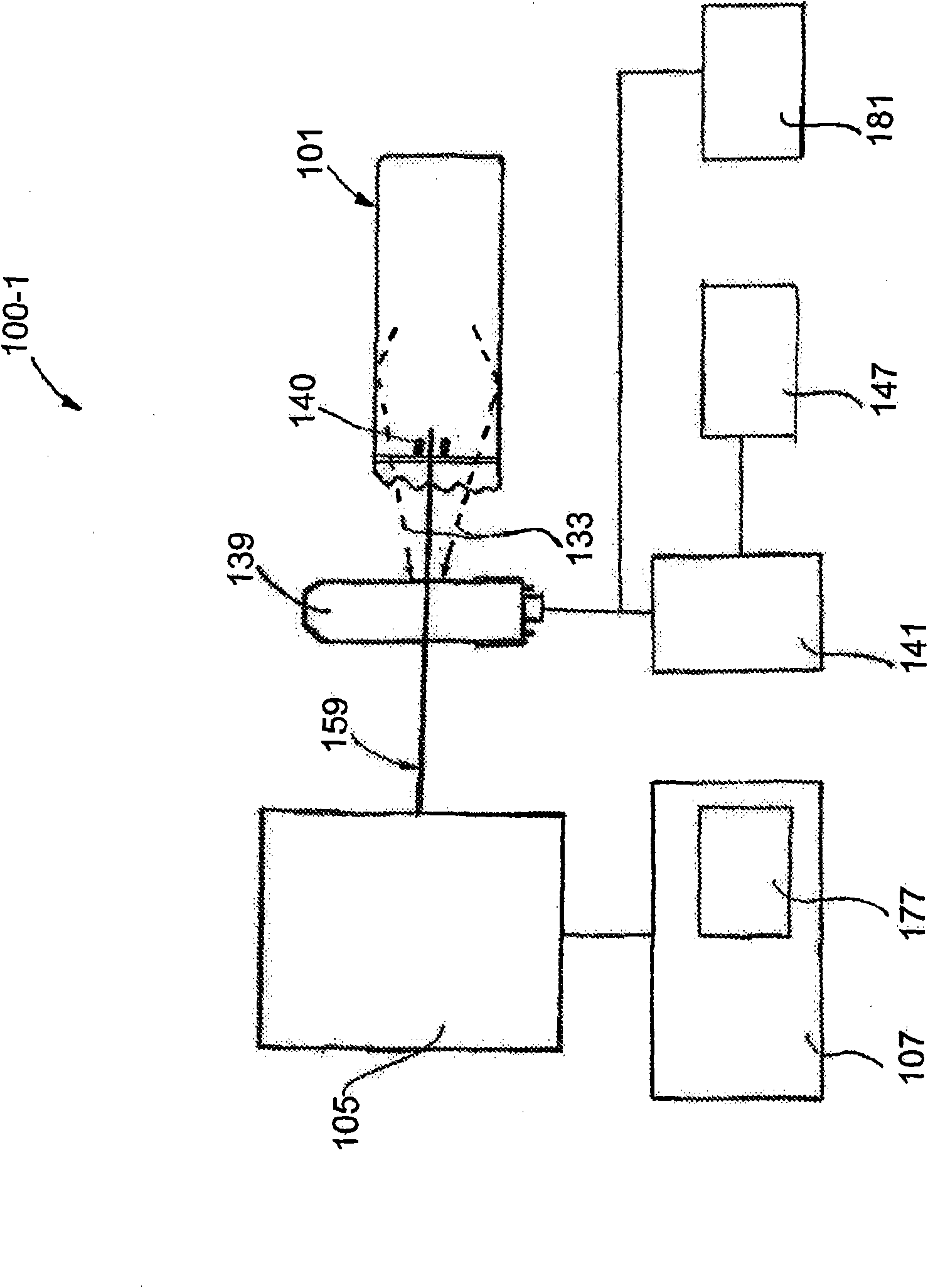
Mode-locked fiber laser of 1.7[mu]m based on thulium-doped silica fiber
ActiveCN109687269AGuaranteed growthGuaranteed one-way operationActive medium shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserBand-pass filter
The invention relates to a mode-locked fiber laser of 1.7[mu]m based on thulium-doped silica fiber. The mode-locked fiber laser specifically and structurally and mainly comprises a signal source of 1.7[mu]m, a first coupler, a pumping source, a wavelength division multiplexer, the thulium-doped silica fiber, a band-pass filter, a first polarization controller, a polarization dependent isolator, asecond polarization controller, common single-mode fiber, a second coupler and a fiber wire jumper head. The mode-locked fiber laser can realize short wavelength 1.7 [mu]m mode-locked fiber laser output operation in the thulium-doped silica fiber. The laser is of an all-fiber structure, the whole optical path has a simple and compact structure, operability is high, cost is low, long-term stable operation is achieved, and the laser is particularly suitable for integrated development, and has important application prospects in the fields such as multi-photon imaging and optical coherence tomography.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Confocal optical microscope, magnifying attachment therefor and method of use thereof
InactiveUS6429967B1Maximise signal collectionImprove confocal performanceMicroscopesTelescopesMagnificationPhoton
An optical attachment unit is described which can be inserted reversibly into the detection light path of a confocal optical microscope, which has the effect of modifying the magnification of the specimen at the level of the detector iris. This modification consists in the preferred form of a demagnification, so that high sensitivity is obtained at the expense of confocal function, as is required for multiphoton imaging and other purposes. No optical telescope or other imaging system used for confocal function is disturbed or removed by the operation of inserting the unit, so that the confocal function can be restored reproducibly and rapidly.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
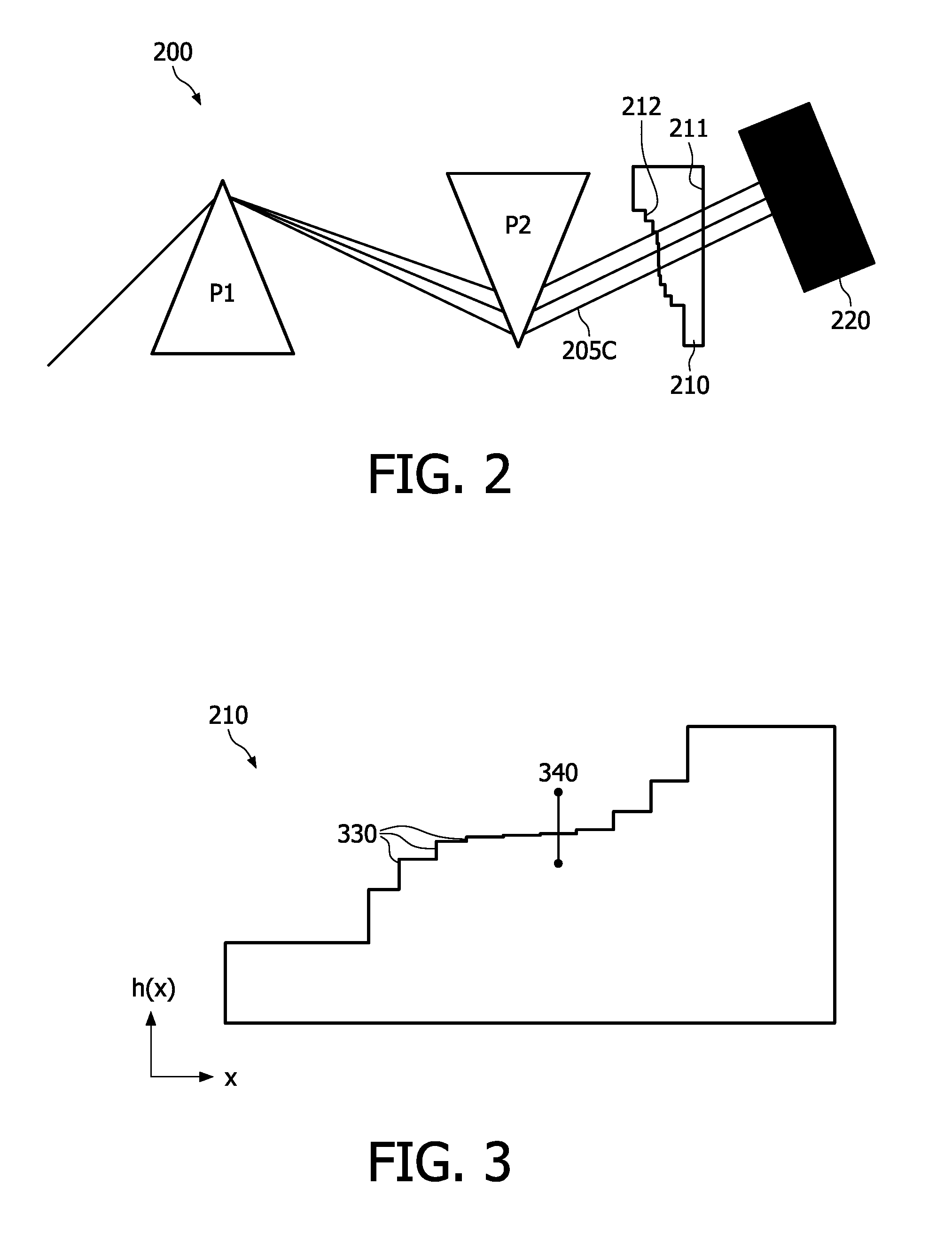
Higher order dispersion compensation device
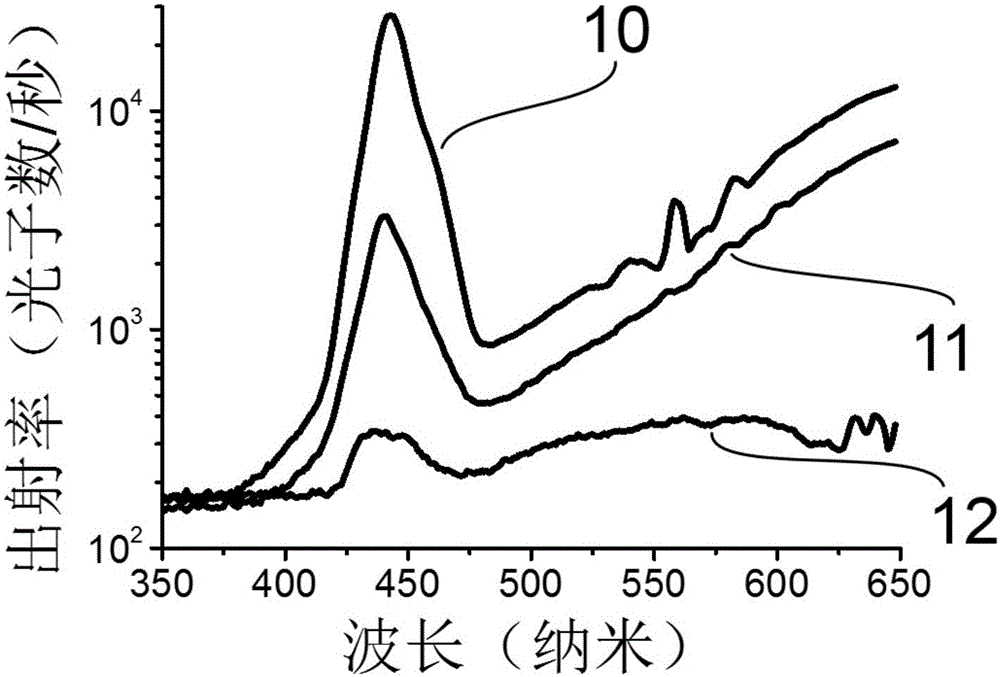
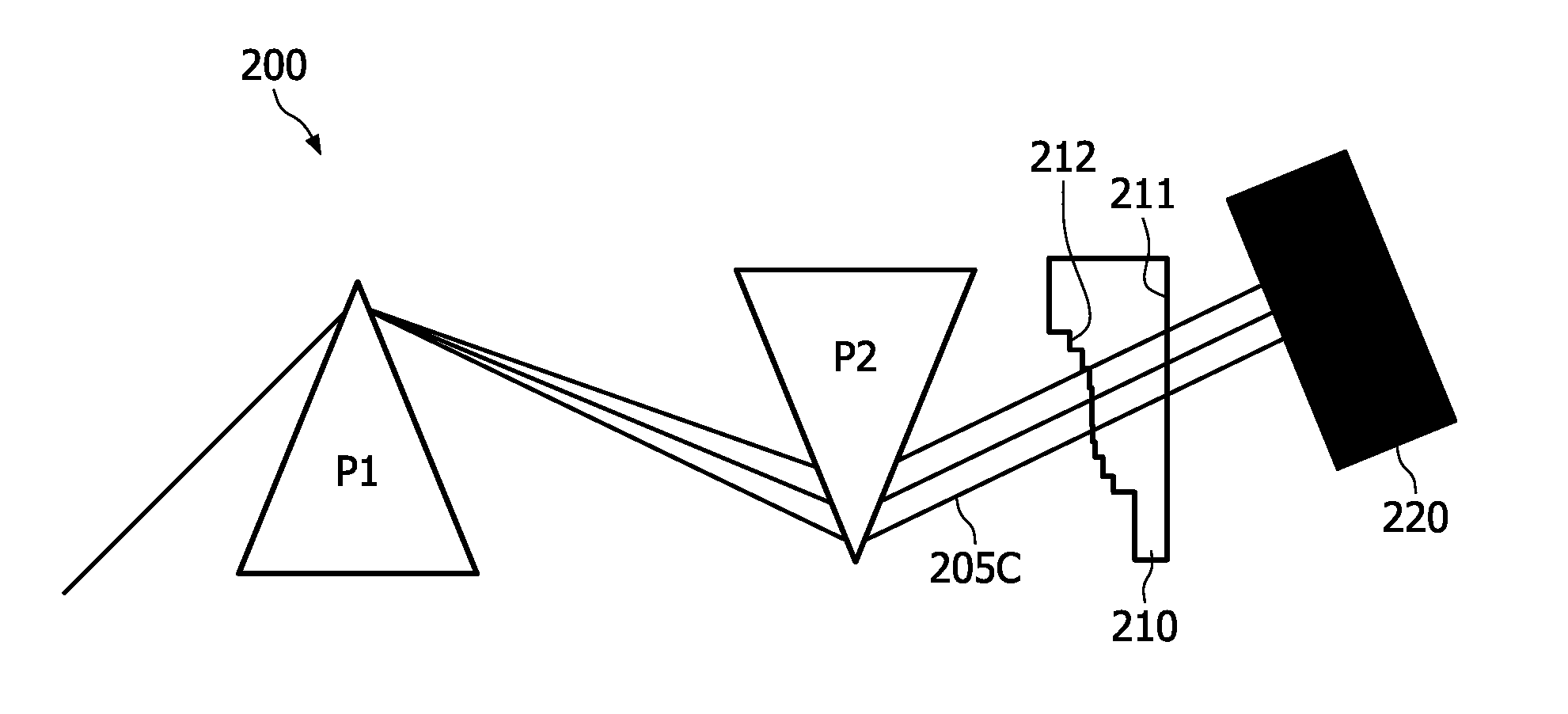
The present invention relates to a higher-order dispersion compensation device (210), the device being adapted to cooperate with a pair of optical components (P1, P2), e.g. a pair of prisms, being arranged to compensate first-order dispersion by separating different wavelengths spatially. The compensation device (210) has the form of a phase plate, wherein the phase change for each wavelength is adjusted by designing the height (h) at the corresponding position (x) of the plate so as to substantially compensate for higher-order dispersion. The invention is advantageous for obtaining a higher-order dispersion compensation device which is relatively simple to construct and use making it a quite cost-effective device. The invention also relates to a corresponding optical system and method for compensating dispersion where this is important, e.g. in a multiple-photon imaging system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
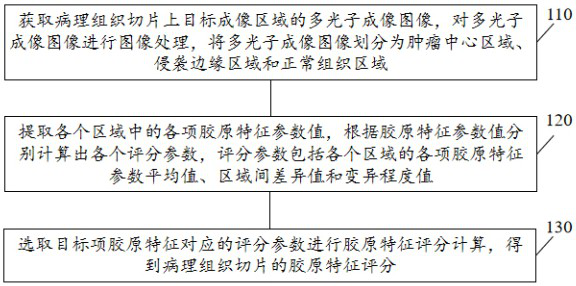
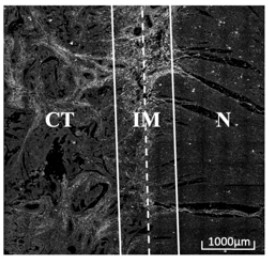
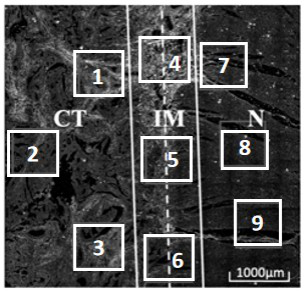
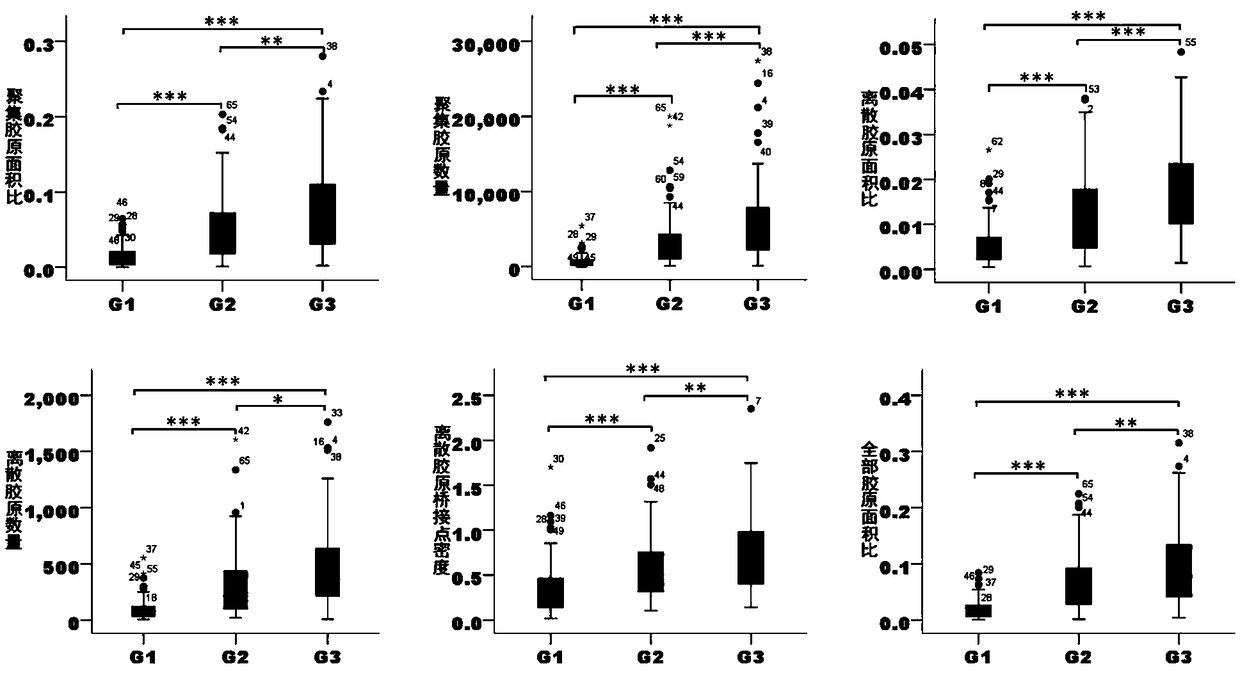
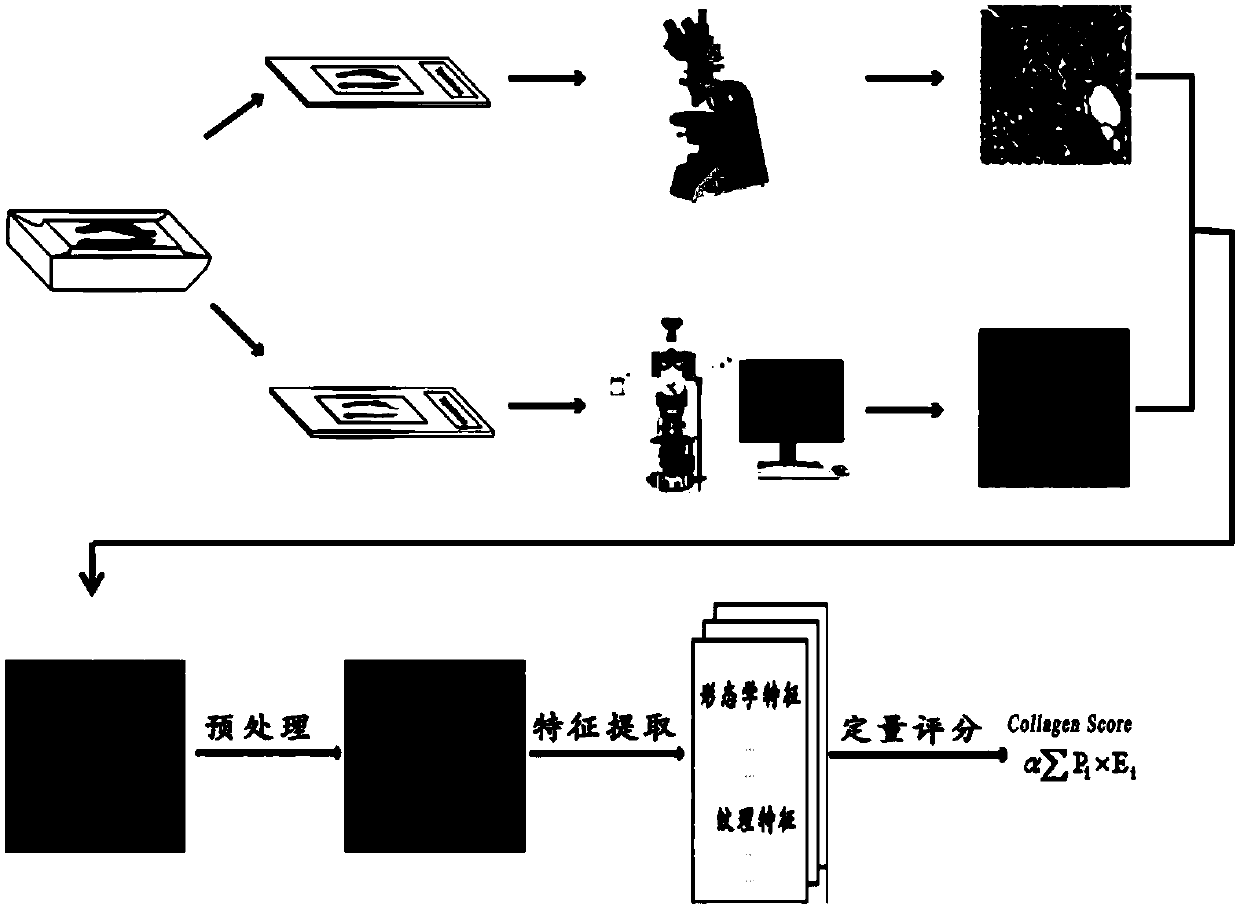
Colorectal cancer collagen evaluation and prognosis prediction device and storage medium
ActiveCN114299069ASupplementary assessment missingReduced variabilityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTNM staging systemPathology diagnosis
The invention discloses a computer readable storage medium. When the content of the computer readable storage medium is executed by the processor, multi-photon imaging can be performed on a pathological tissue section containing tumor environment information, and pathological division of a tumor microenvironment is further performed through image processing; extracting various collagen characteristic parameter values, such as morphology, energy and texture characteristic parameters, from three areas of tumor tissue, invasion edge and normal tissue; calculating differences and variation degrees among the regions according to the region feature parameters; establishing a collagen feature scoring model; calculating a collagen characteristic score through collagen characteristic parameters included in the model; the collagen feature score can well supplement the evaluation deficiency of a TNM staging system on tumor microenvironment soil, and more effectively provides reference for prognosis prediction of colorectal cancer.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Multi-photon ultra-deep tissue imaging equipment based on coherent detection and detection imaging method thereof
PendingCN113390827AFast imagingAdd depthPhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionRapid imagingLaser light
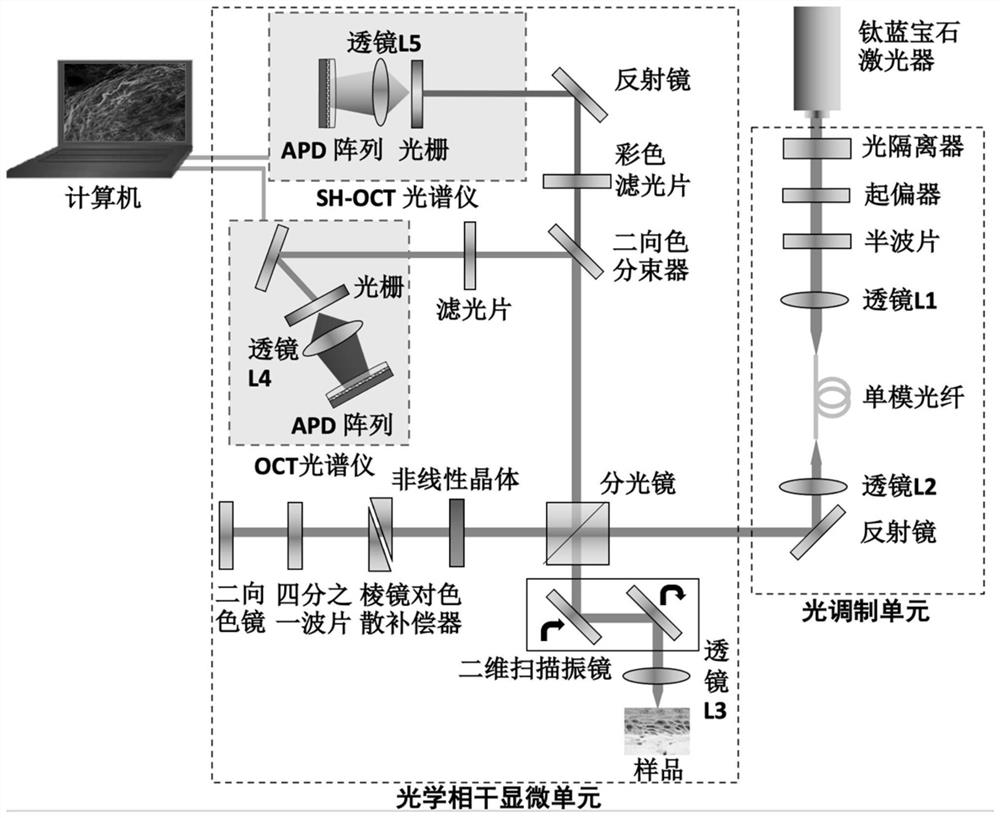
The invention discloses multi-photon ultra-deep tissue imaging equipment based on coherent detection and a detection imaging method thereof. A multi-photon imaging technology is combined with an optical coherence tomography technology to realize ultra-deep and high-molecular specific imaging of a detected sample. The equipment comprises an ultrashort pulse femtosecond laser light source, a light modulation unit and an optical coherence microscopic unit. The light modulation unit modulates input laser to generate continuous spectrum laser. The optical coherence microscopic unit is used for conducting coherent detection on a biological sample. The system can detect OCT and SH-OCT signals of a tissue at the same time and obtain the specific structure of the tissue and the molecular micro-environment information of the surrounding environment of the tissue, and can quantitatively characterize the structure and function of the tissue through an image analysis method. The equipment can reflect the ultra-deep structure and functional information of the tissue, has the advantages of ultra depth, strong molecular specificity recognition capability, high temporal-spatial resolution, rapid imaging and the like, and provides the tissue structure and function information and the molecular specificity information at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
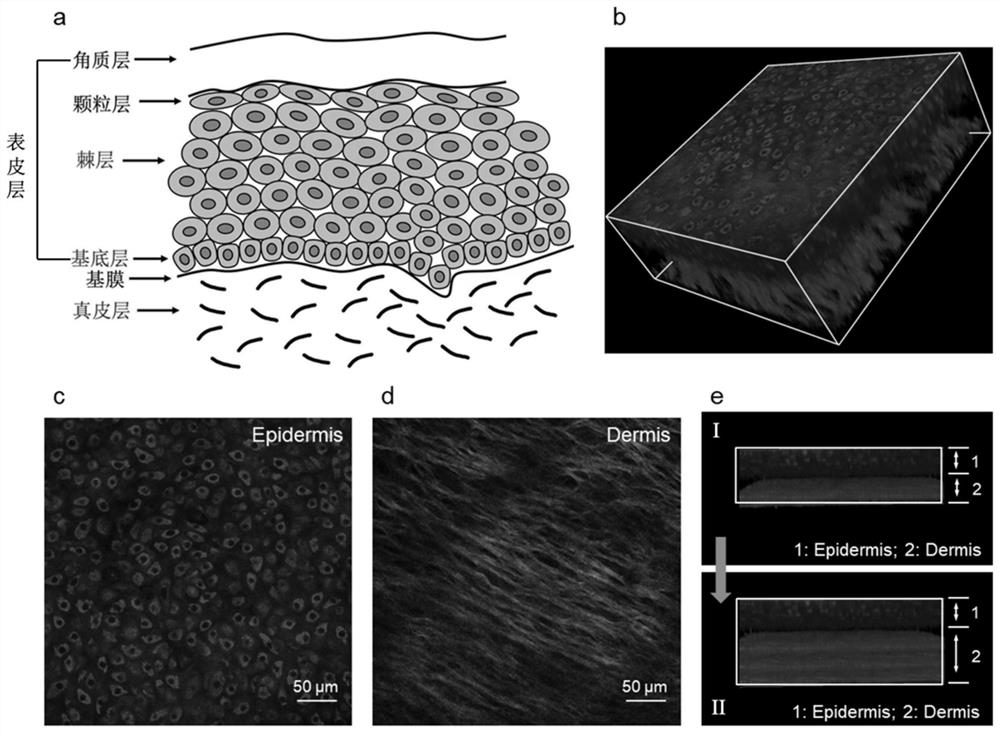
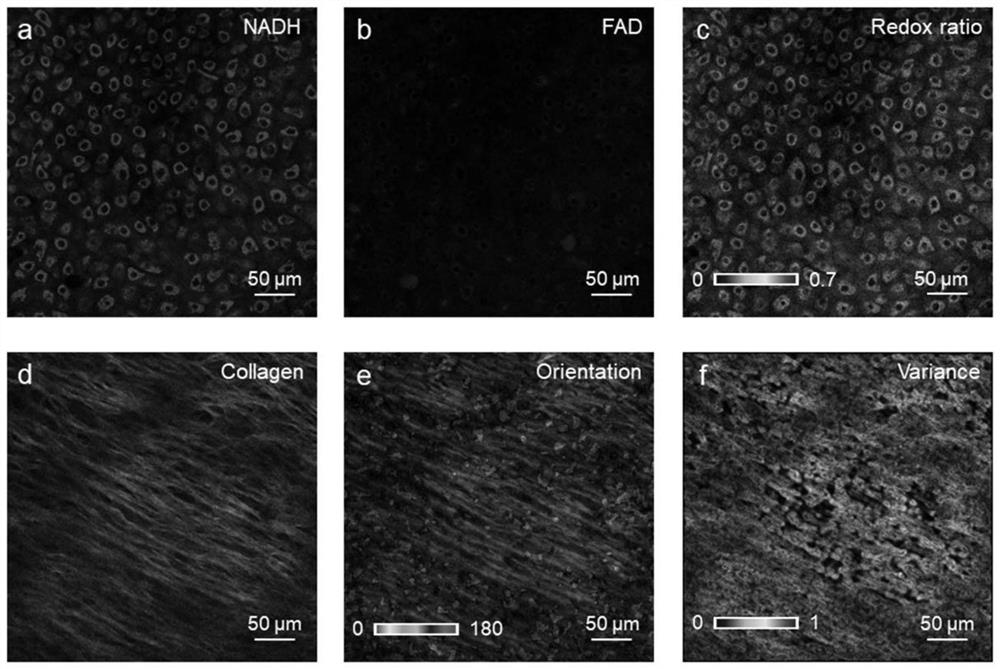
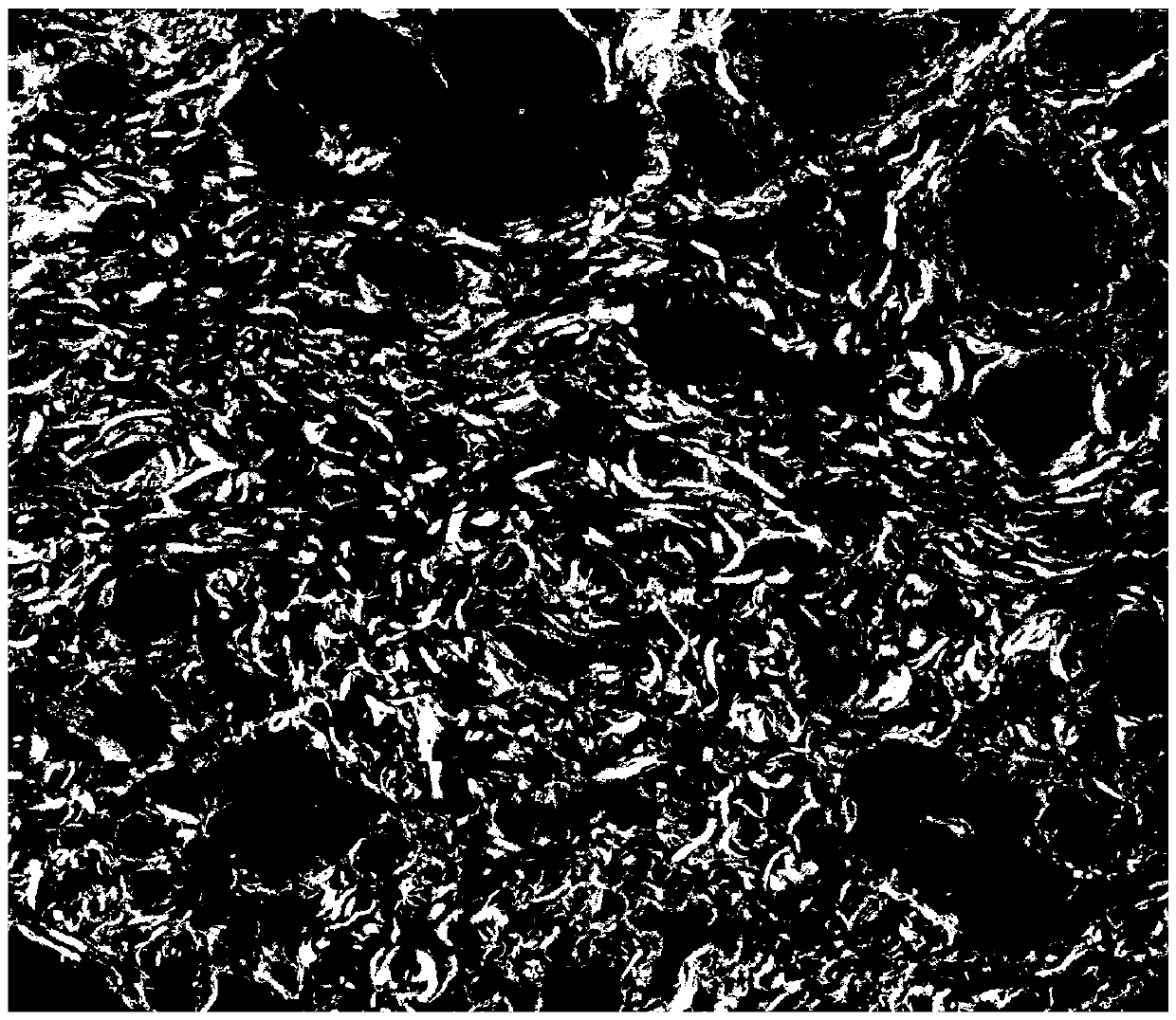
Method for discriminating liver cancer differentiation grades by using multiphoton imaging technology
InactiveCN108426862AOvercoming time consumingOvercome missed diagnosisPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationStatistical analysisWilms' tumor
The invention relates to a method for discriminating liver cancer differentiation grades by using a multiphoton imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out quick freezing film shooting processing on a fresh liver cancer specimen subjected to surgical excision or puncture sampling; secondly, obtaining a collagen fiber MPM image inside a tumor by multiphoton microscopic imaging, processing the image, extracting features and then carrying out statistical analysis and discrimination by using Mann-Whitney inspection and Boxplot. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the multiphoton microscopic imaging and an image processing algorithm are utilized to be combined with a statistical analysis method for evaluating different differentiation grades of liver cancer; liver cancer differentiation grade data obtained by a label-free quick discrimination method are compared with pathologist diagnostic result data so as to achieve the aim of objectively evaluating the liver cancer differentiation grades; and the defects of time consumption, missed diagnosis and high subjectivity of a current clinical biopsy technique are effectively overcome.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
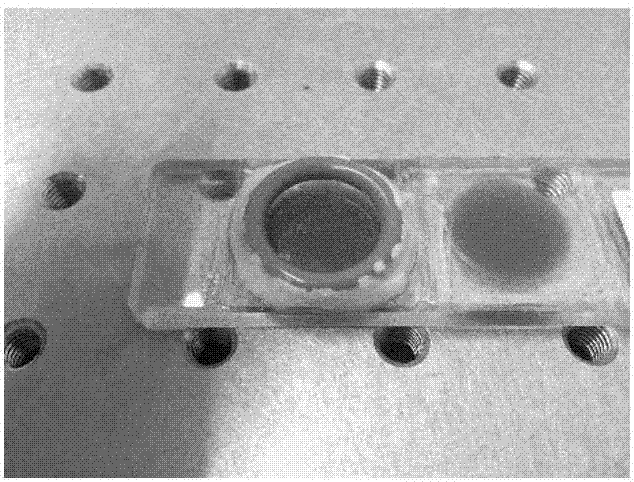
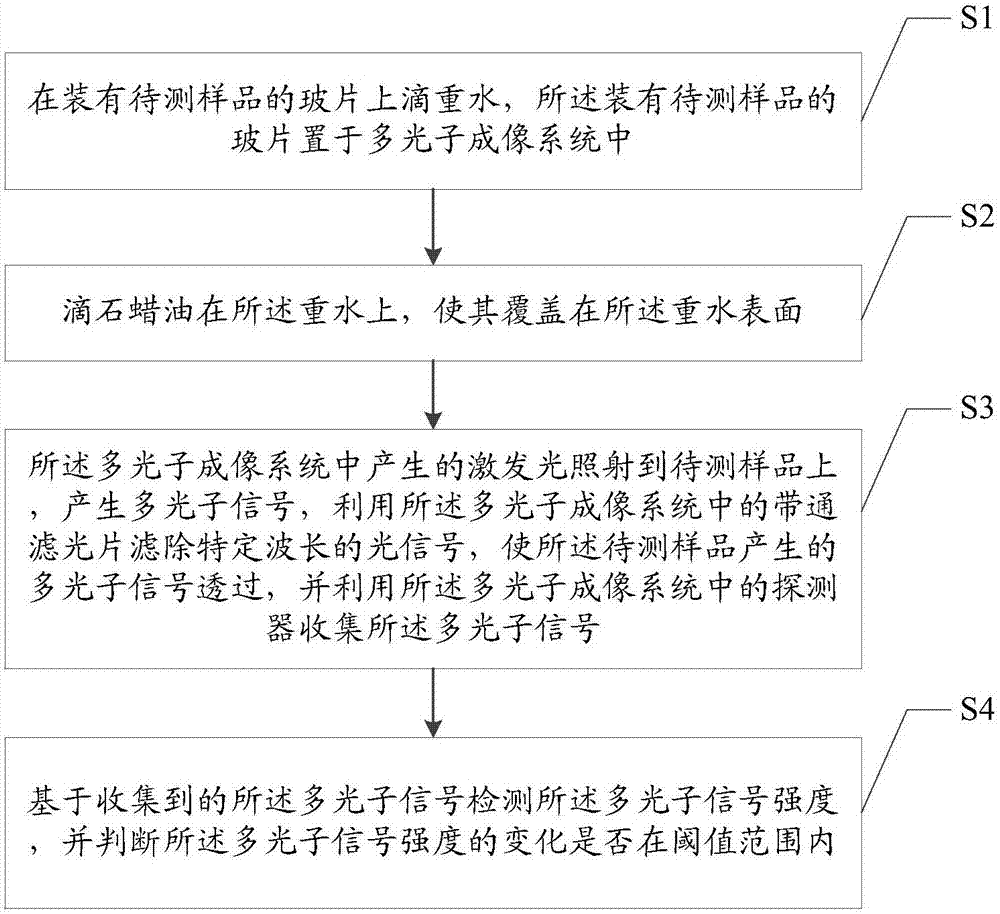
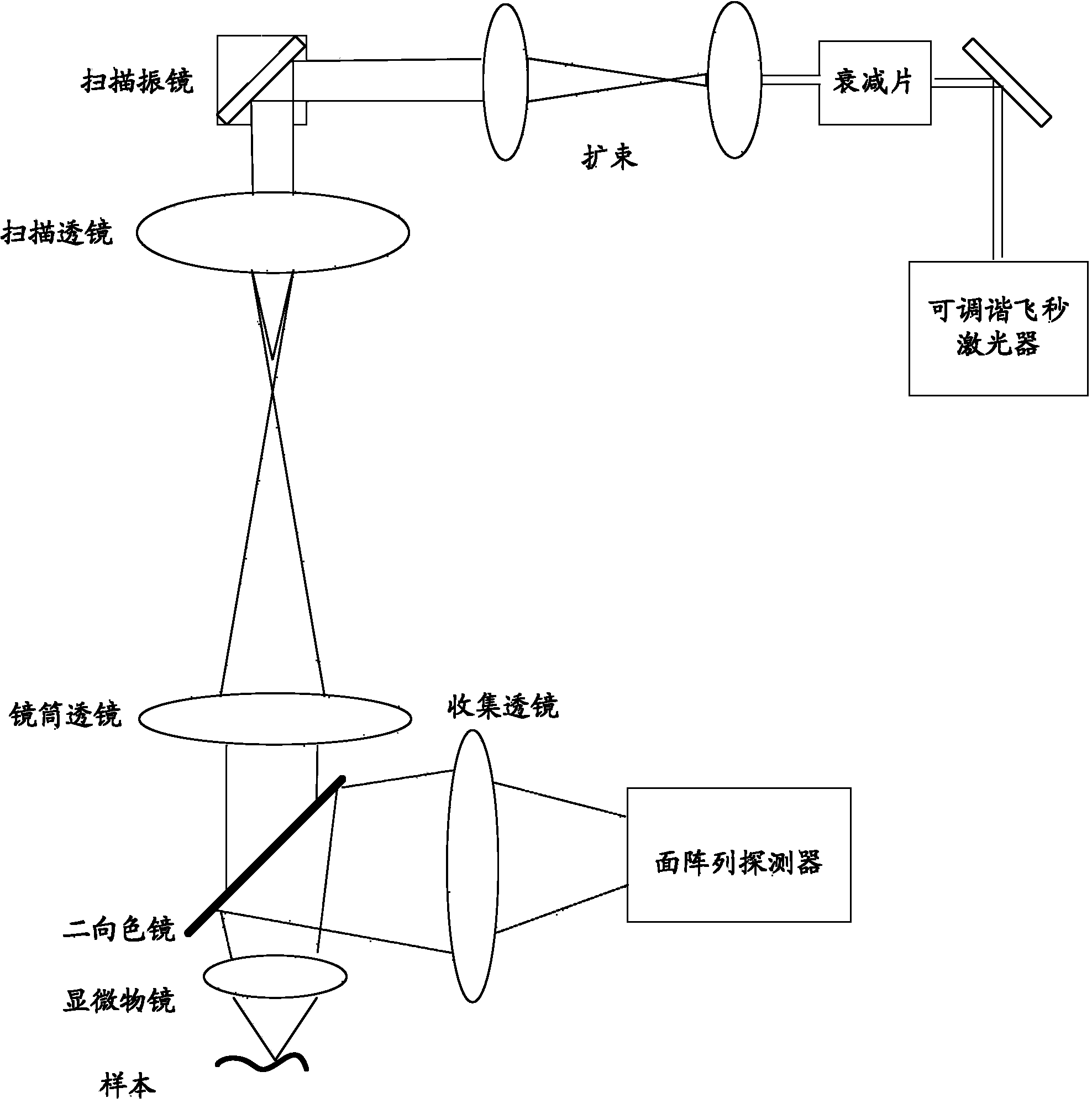
Heavy water sealing method and method for detecting multi-photon signal strength in multi-photon imaging
ActiveCN107144451AFacilitates time kinetic measurementsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationTest sampleUltimate tensile strength
The invention is applicable to the technical field of biophotonics and provides a heavy water sealing method. The heavy water sealing method comprises the step of dripping paroline to the surface of heavy water to cover the surface of the heavy water. The invention further provides a method for detecting multi-photon signal strength in multi-photon imaging. The method comprises the following steps: dripping the heavy water to a slide provided with a to-be-tested sample, and putting the slide provided with the to-be-tested sample into a multi-photon imaging system; dripping paroline to the surface of the heavy water to cover the surface of the heavy water; irradiating the to-be-tested sample by virtue of laser generated by the multi-photon imaging system so as to generate multi-photon signals, and collecting the multi-photon signals by virtue of a detector in the multi-photon imaging system; and detecting the multi-photon signal strength based on the collected multi-photon signals, so as to judge whether the change of the multi-photon signal strength is in a threshold range. According to the detection method, paroline has a very good effect on sealing the heavy water, so that the strength of the generated multi-photon signals is not attenuated along with time.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
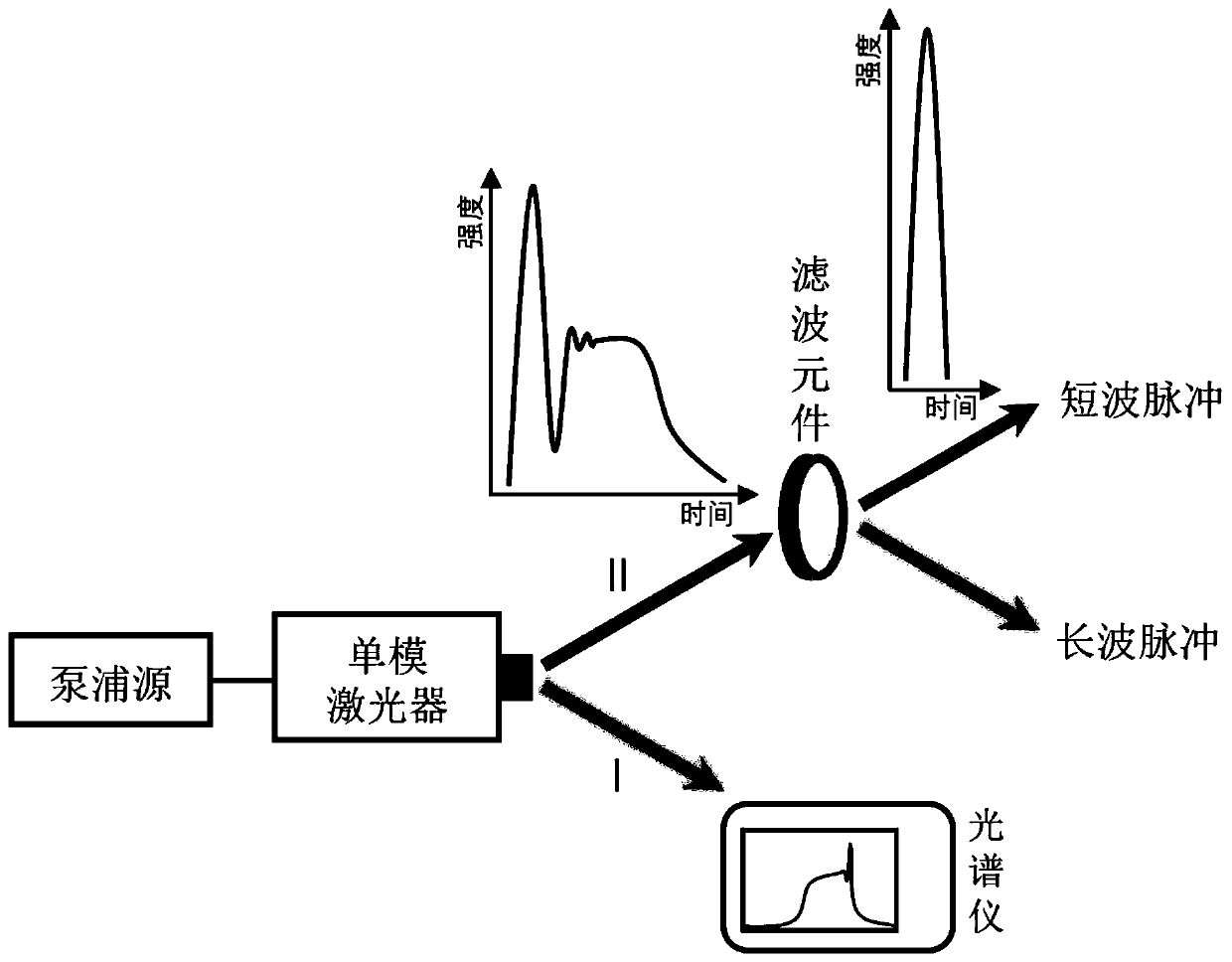
Method for shortening pulse and obtaining adjustable picosecond pulse
The invention discloses a method for shortening a pulse and obtaining an adjustable picosecond pulse, which comprises the steps of firstly modulating a pumping source to generate an optical pulse or an electric pulse to excite a gain switch type semiconductor laser, generating pulse laser with a chirp pulse component and a steady-state pulse component, then leading the pulse laser to a filter element through a light path, and obtaining short wave laser or long wave laser after filtering treatment, wherein the short wave laser is from the initial pulse component, has extremely short pulse widthcan achieve the purpose of shortening the pulse, and the filtering parameters are adjusted to change the wavelength and the pulse width of the short wave pulse laser so as to achieve pulse adjustment. The method can be applied to a single-mode gain switch semiconductor laser. Compared with common methods such as chirp compensation and pulse compression, the method has the advantages of simplicity, high feasibility and low cost, can conveniently obtain the adjustable picosecond pulse with high spectral purity, narrow optical pulse width and weak pulse jitter, combines the technologies such asoptical amplification and wavelength transfer, and can be applied to many fields such as multiphoton imaging and time resolution spectrum.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
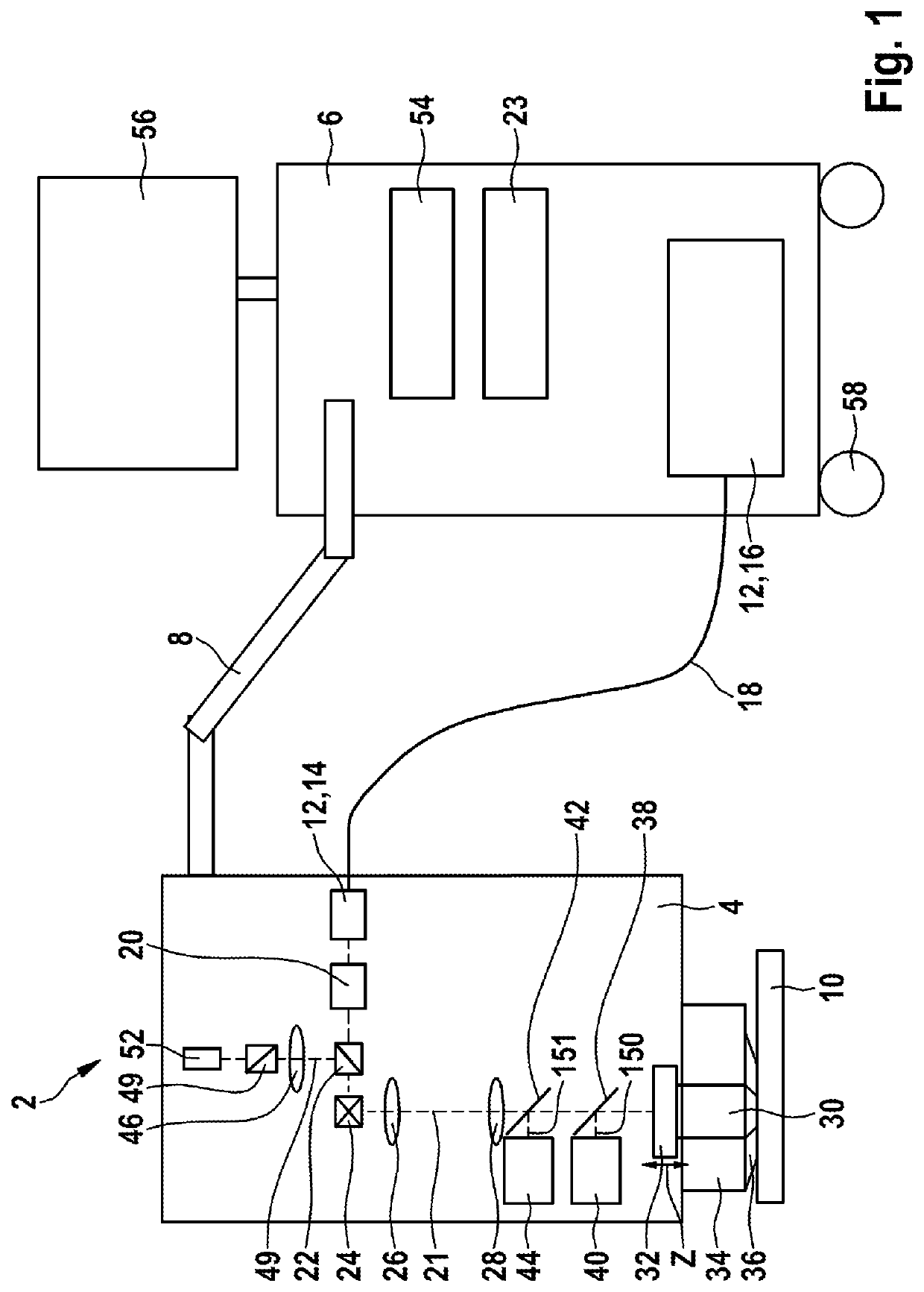
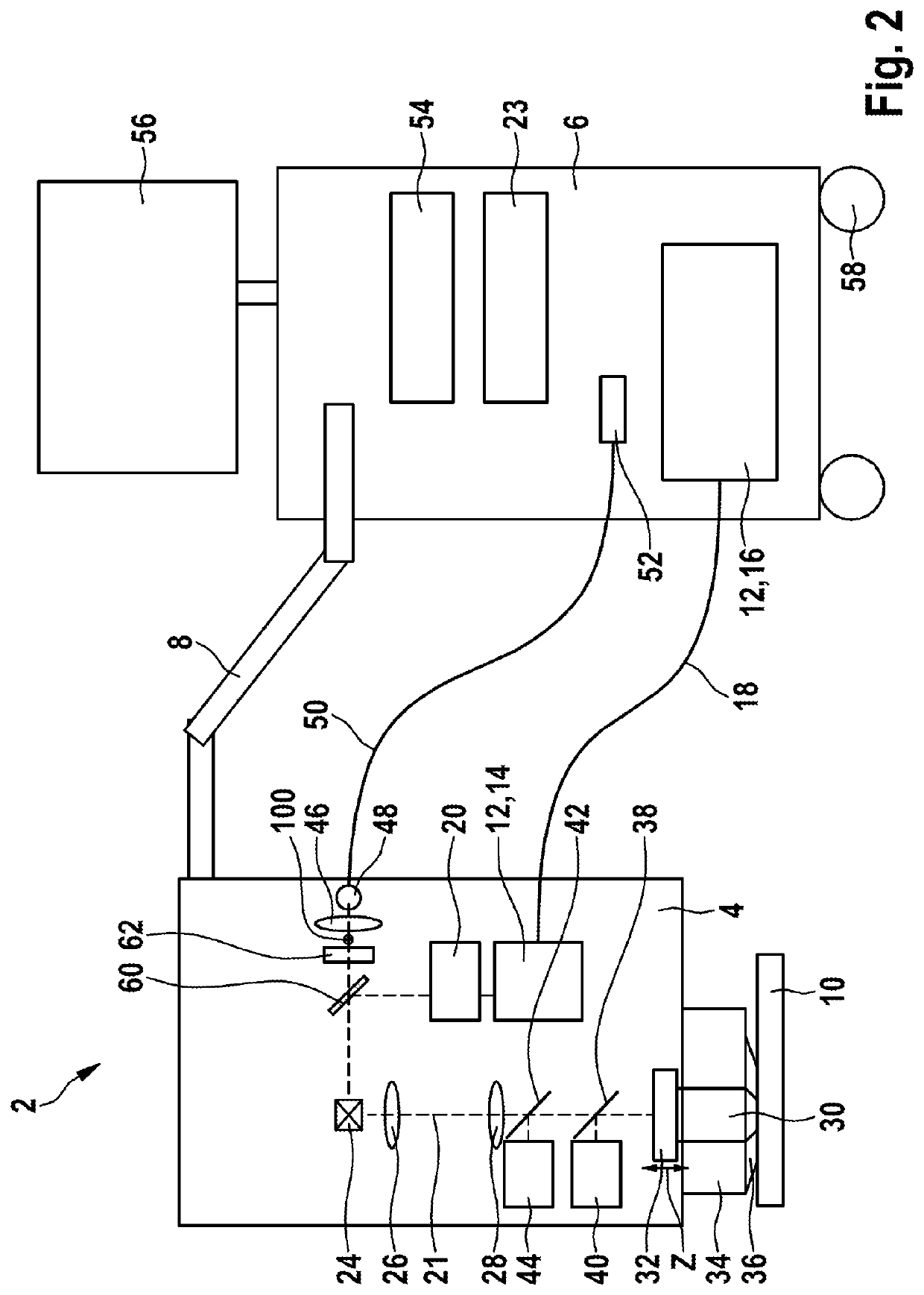
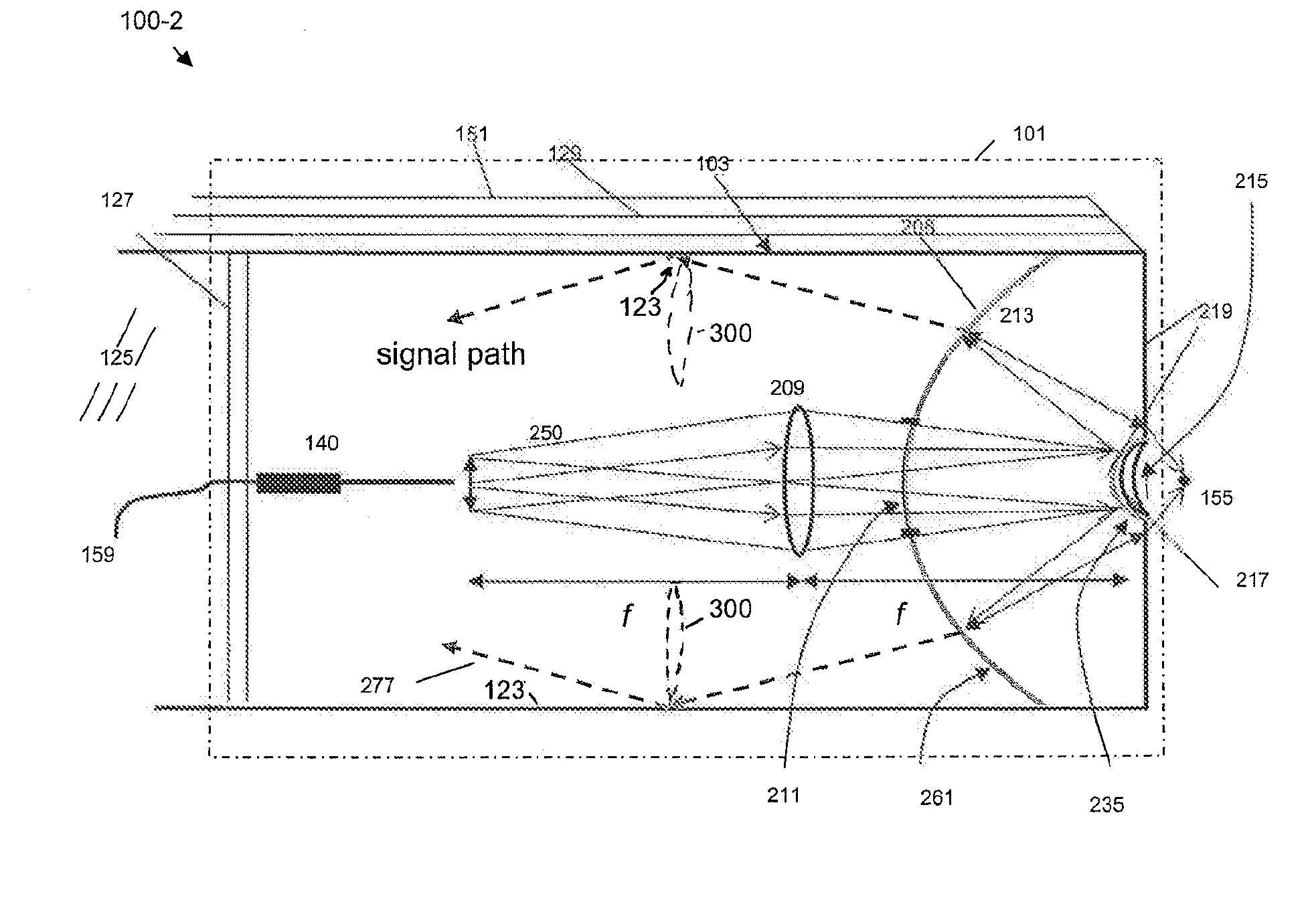
Multi-Modal Imaging System and Method for Non-Invasive Examination of an Object to be Examined
PendingUS20210052160A1Facilitate different imaging modeMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiffuse reflectionNon invasive
The invention relates to a multi-modal imaging system (2) for non-invasive examination of an examination object (10), comprising a multi-photon imaging system for providing high-resolution detailed images of the examination object (10), which imaging system comprises a radiation source (12), the latter generating an excitation beam (21) of near infrared femtosecond laser radiation for triggering secondary radiation emitted by the examination object (10), and a focusing optical unit (30), by means of which the radiation of the radiation source (12) is directable at a measurement position of the examination object (10), wherein the focusing optical unit (30) and a laser head (14) of the radiation source (12) are provided in a measuring head (4), which is pivotable, rotatable and flexibly positionable freely in space such that the examination of the examination object (10) is performable under any desired solid angle, and comprising at least one confocal detection device, which is at least partly integrated in the measuring head (4) as well and which is configured to receive a signal of the excitation beam (21) of near infrared femtosecond laser radiation, which was diffusely reflected by the examination object (10).Moreover, a method is specified for non-invasive examination of an examination object (10) using a multi-modal imaging system (2), as is the use of the multi-modal imaging system (2) for examining living matter of the examination object (10)
Owner:JENLAB
Evaluation method of paracancerous collagenous tissue of early gastric cancer excision specimen
ActiveCN107907395AImprove the quality of lifeReduce the chance of tumor recurrencePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceWilms' tumorPathology diagnosis
The invention provides an evaluation method of a paracancerous collagenous tissue of an early gastric cancer excision specimen, and relates to the technical field of pathology identification. The evaluation method of the paracancerous collagenous tissue of the early gastric cancer excision specimen can analyze and evaluate a morphological feature and a texture feature of a multiphoton imaging of the early gastric cancer paracancerous collagenous tissue, and timely find out the change of the early gastric cancer paracancerous collagenous change, and is good for making the clinic workers learn about if the patient has the risk of lymphatic metastasis, thereby providing reference of in-operation selection and subsequent treatment of clinic doctors, providing more individual treatment plan forpatients, and finally reaching the purpose of improving patient living quality and reducing cancer recurrent probability; the evaluation method is reasonable in design, mature in technology, simple and easy to practice, wide in clinic application prospect and good in scientific research and promotion value.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for tissue evaluation of collagen at incisal edge of rectal cancer resection specimen
ActiveCN107941760AUnderstand the degree of local fibrosisLearn about healingPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationFibrosisSevere complication
The invention provides a method for tissue evaluation of collagen at the incisal edge of a rectal cancer resection specimen, belonging to the technical field of pathological differentiation. Accordingto the method, tissue evaluation is carried out on collagen at the incisal edge of a rectal cancer resection specimen obtained after neoadjuvant therapy of the rectal cancer in virtue of a combination of Masson dyeing and multiphoton imaging analysis, so clinical workers are allowed to learn about the local fibration degree of the rectum tissue of patients and the healing status of anastomotic parts; and thus, reference is provided for clinical doctors in selection of surgical methods and in subsequent diagnosis and treatment, better individual-based treatment schemes are provided for patients, and the purposes of improving the living quality of patients and maximally avoiding severe complications are eventually achieved. The method provided by the invention is reasonable in design, mature in technology and easy to practice and has good clinical application prospects and high promotion value in scientific research.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
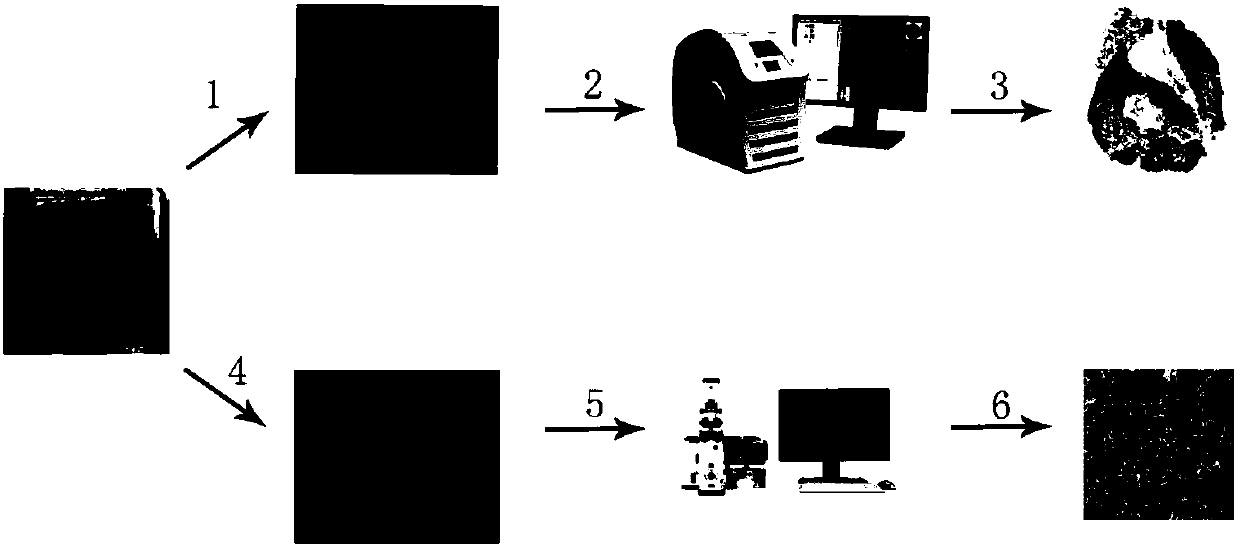
Method for evaluating completeness of mesorectum specimen after colorectal cancer
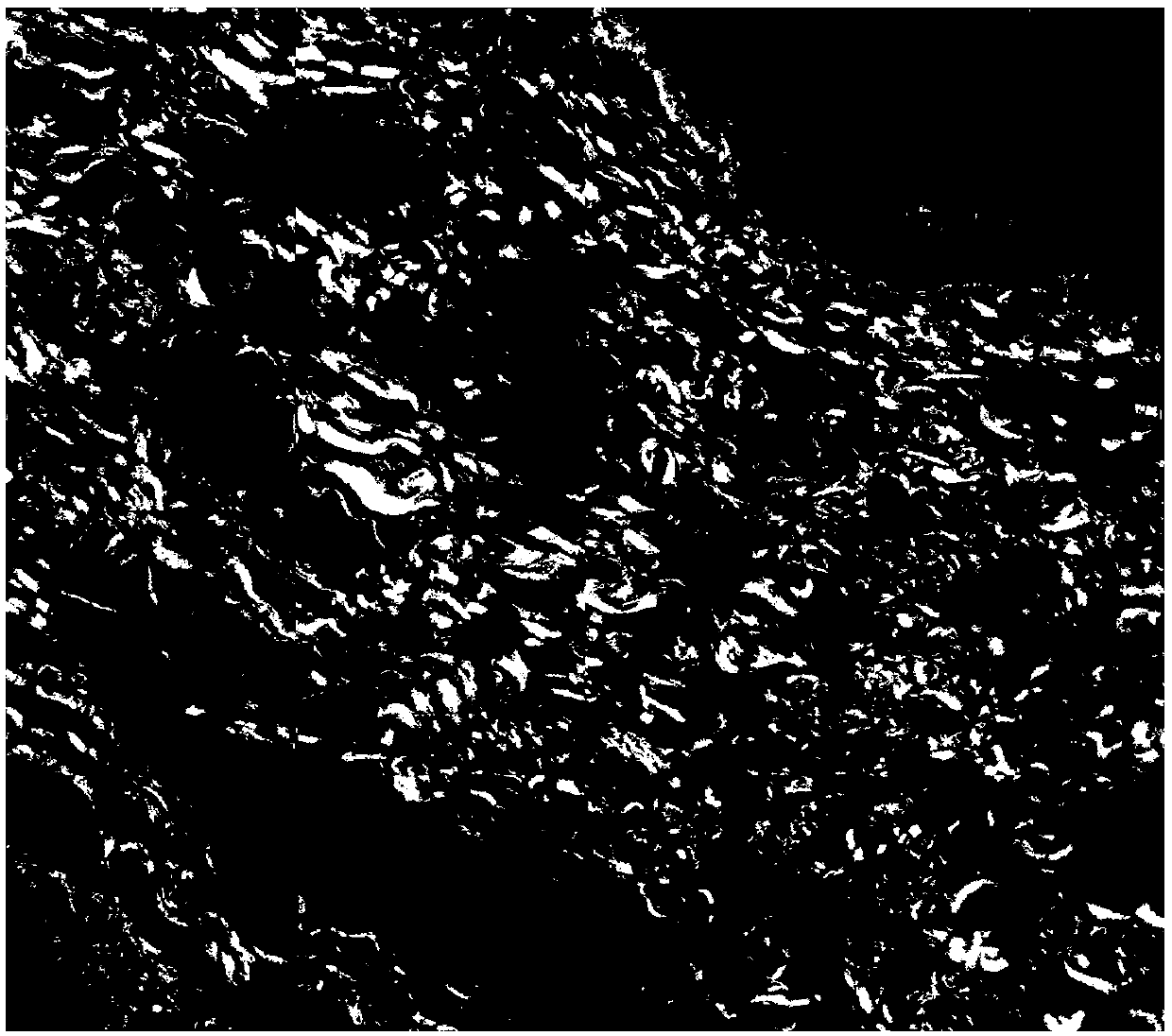
InactiveCN107677648AEase subjectivityMitigation accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationMicro imagingImaging technology
The invention provides a method for evaluating completeness of a mesorectum specimen after colorectal cancer and relates to the technical field of medical imaging. According to the method, the mesorectum specimen after colorectal cancer is subjected to tissue evaluation on the basis of a multi-photon imaging technology in combination with staining sections, wherein the staining sections can be used for macroscopic analysis of gross structure and overall proportion of collagen of the mesorectum; multi-photon imaging can be used for micro-imaging the collagen of the mesorectum and analyzing thefine structure of the collagen; with combination of the two collagen analysis methods, completeness of the mesorectum can be distinguished from the macroscopic level and the microcosmic level, then the problem that the conventional naked eye based evaluation standards have obvious subjectivity and is lack of certain accuracy is solved, a clinical worker can be helped to know whether total mesorectal excision is realized in a colorectal cancer operation, and radical operation for colorectal cancer is more standardized.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
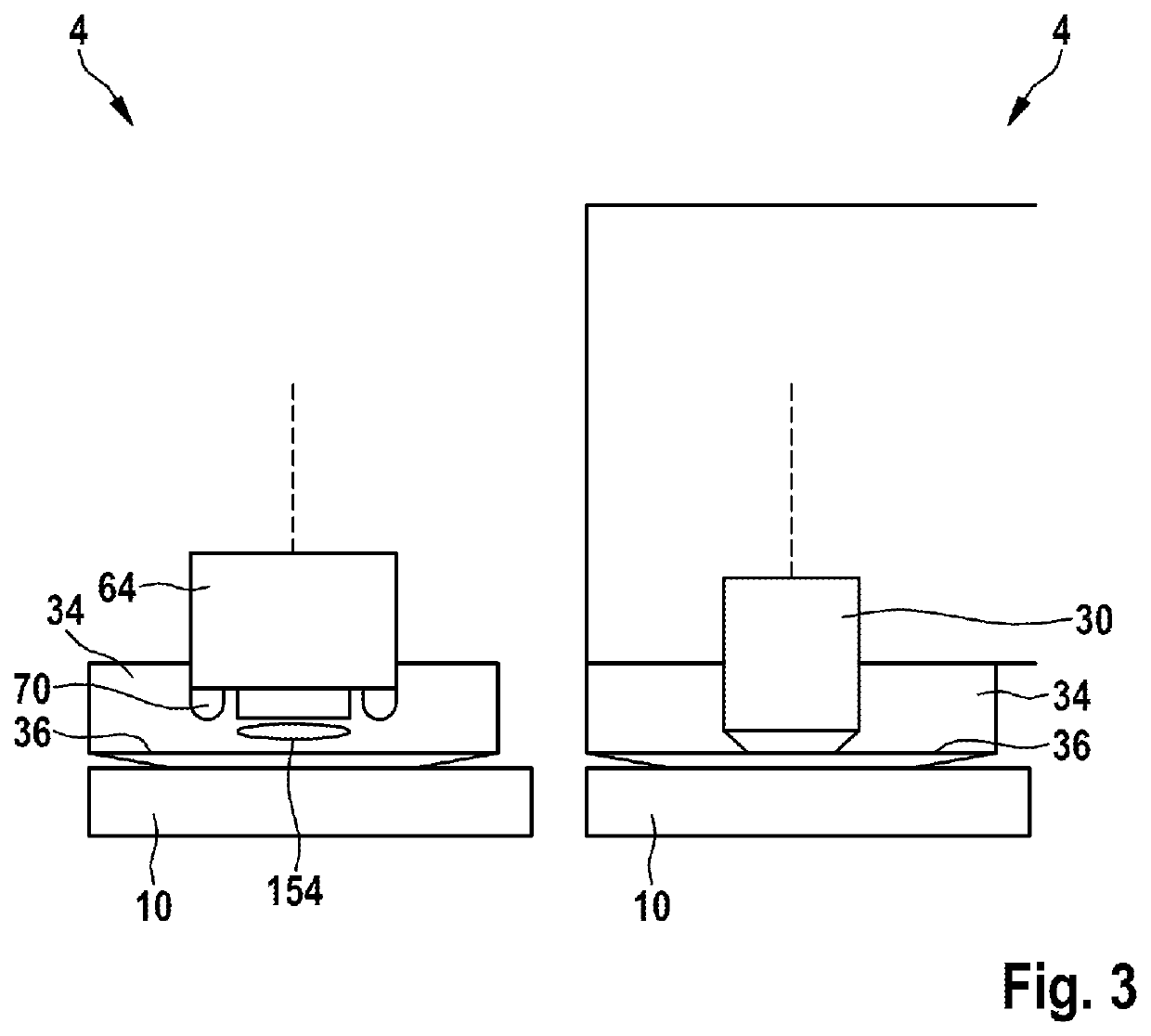
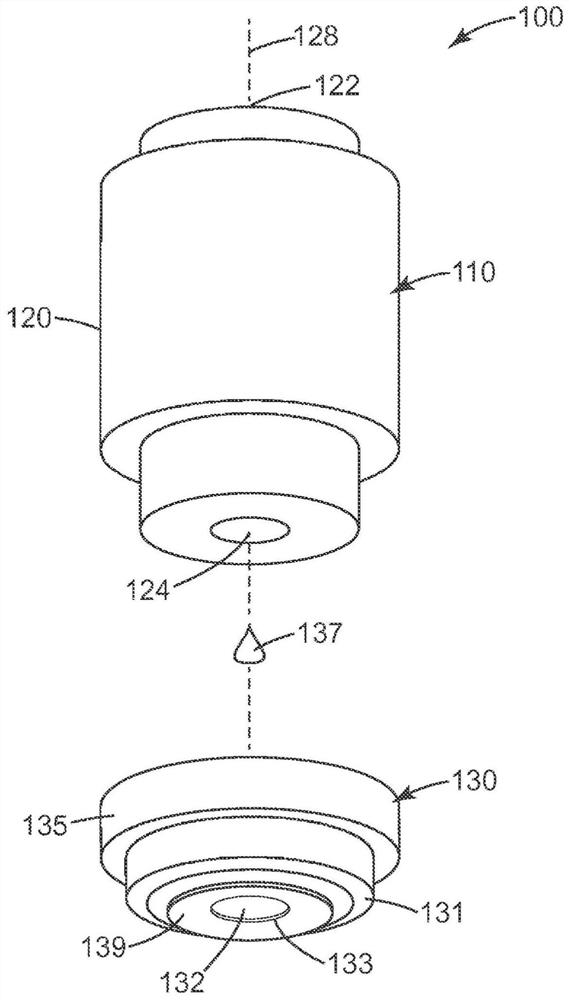
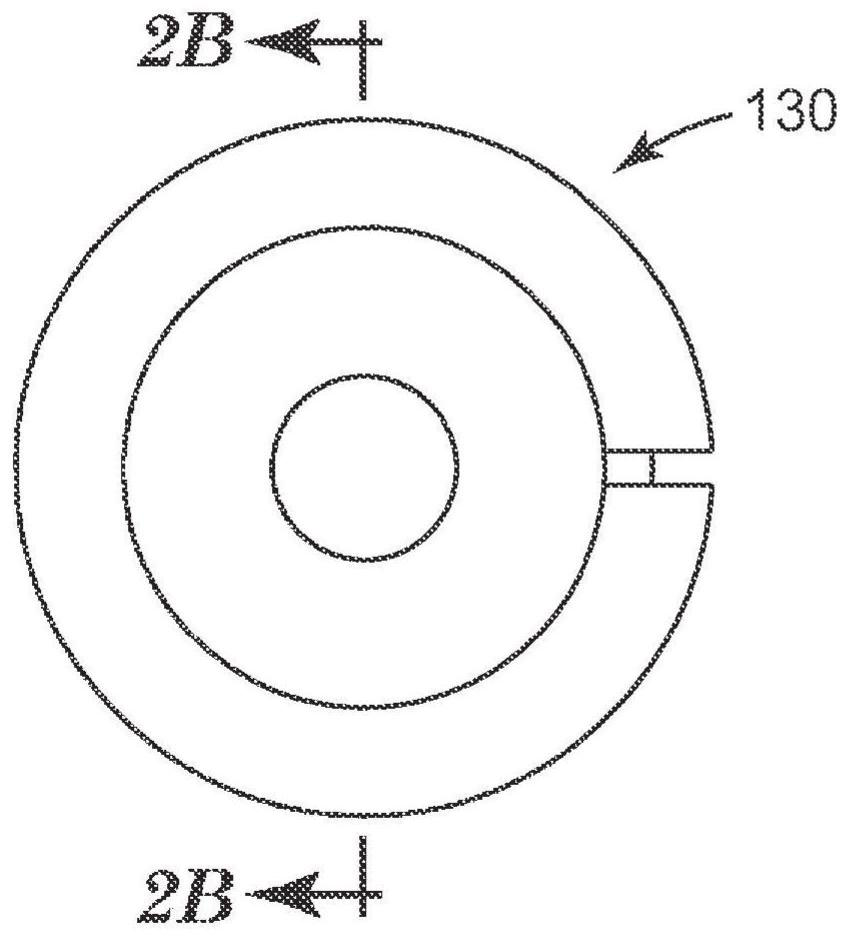
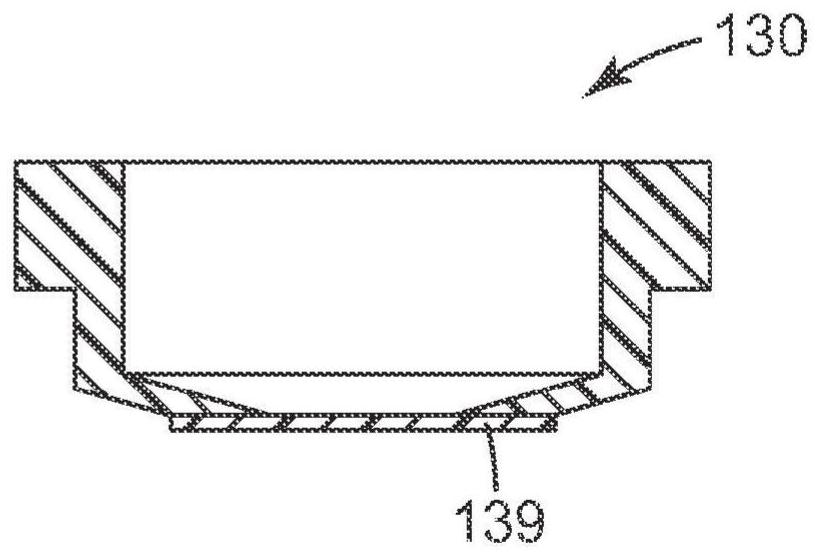
Semi-submersible microscope objective with protective element and use of the same in multiphoton imaging method
The invention relates to a semi-submersible microscope objective with a protective element and uses of the same in a multiphoton imaging method, and provides a semi-submersible microscope objective (100). The semi-submersible microscope objective includes a microscope objective having a protective barrel (120) with an optical inlet (122) and optical outlet (124), and a protective element (130) affixed to the microscope objective, sealing the optical outlet (124) but not the optical inlet (122). A transparent portion (132) of the protective element is aligned with the optical exit (124). The protective element is separable from the microscope objective without damaging the microscope objective. Use of the semi- submersible microscope objective in a multiphoton imaging method is also disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Mode-locked fiber laser of 1.7[mu]m based on thulium-doped silica fiber Mode-locked fiber laser of 1.7[mu]m based on thulium-doped silica fiber](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/afeb13cb-e459-42c8-b402-3d055ef756fe/HDA0001956648800000011.png)