Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
a fluorescence emission endoscopy and multi-magnification technology, applied in the field of multi-photon fluorescence and/or nonlinear harmonic emission endoscopy apparatus and methods, can solve the problems of inconvenient use of high-energy light, inability to provide a compact endoscope, and inability to adapt to the architecture of switchable optical systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
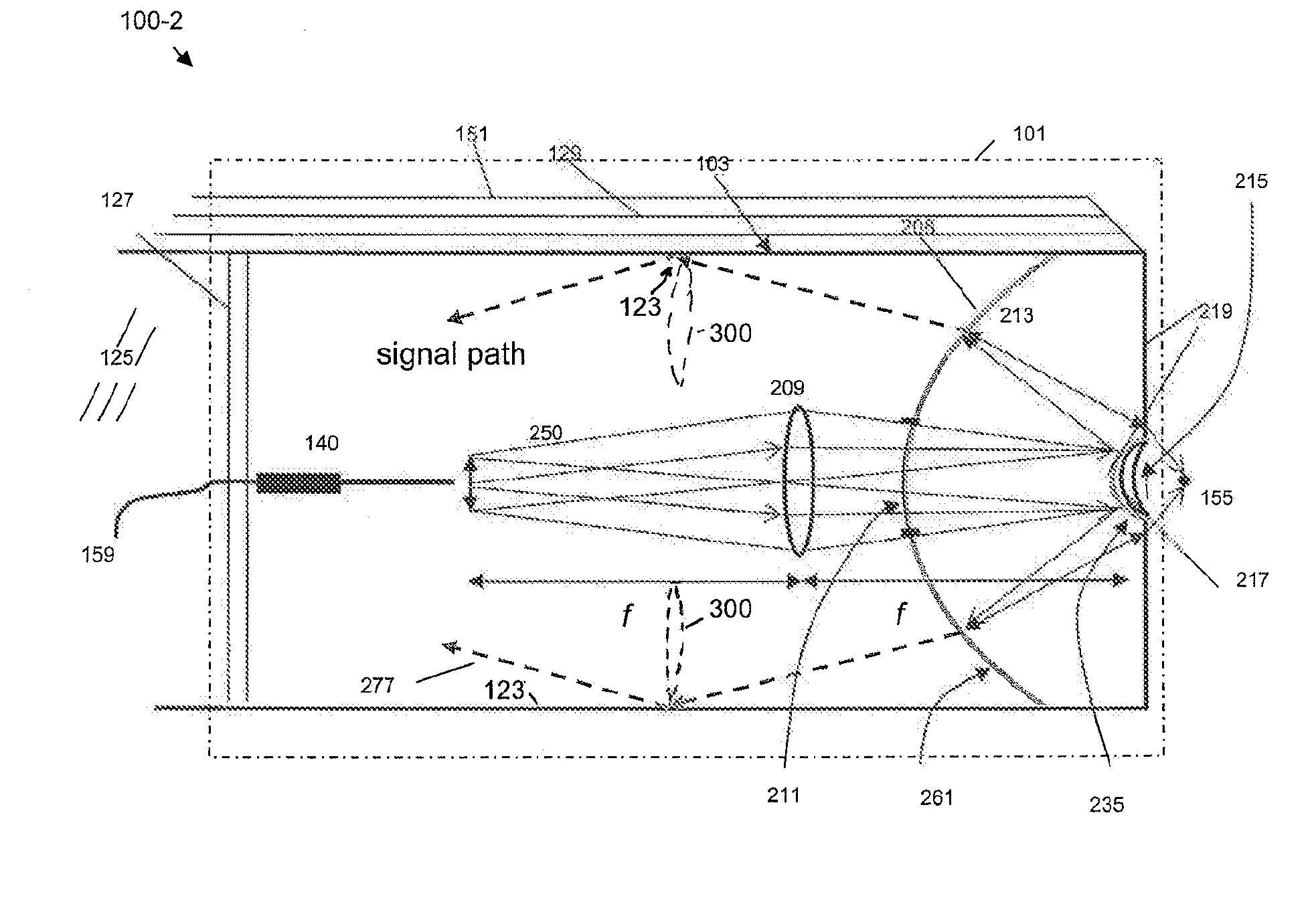
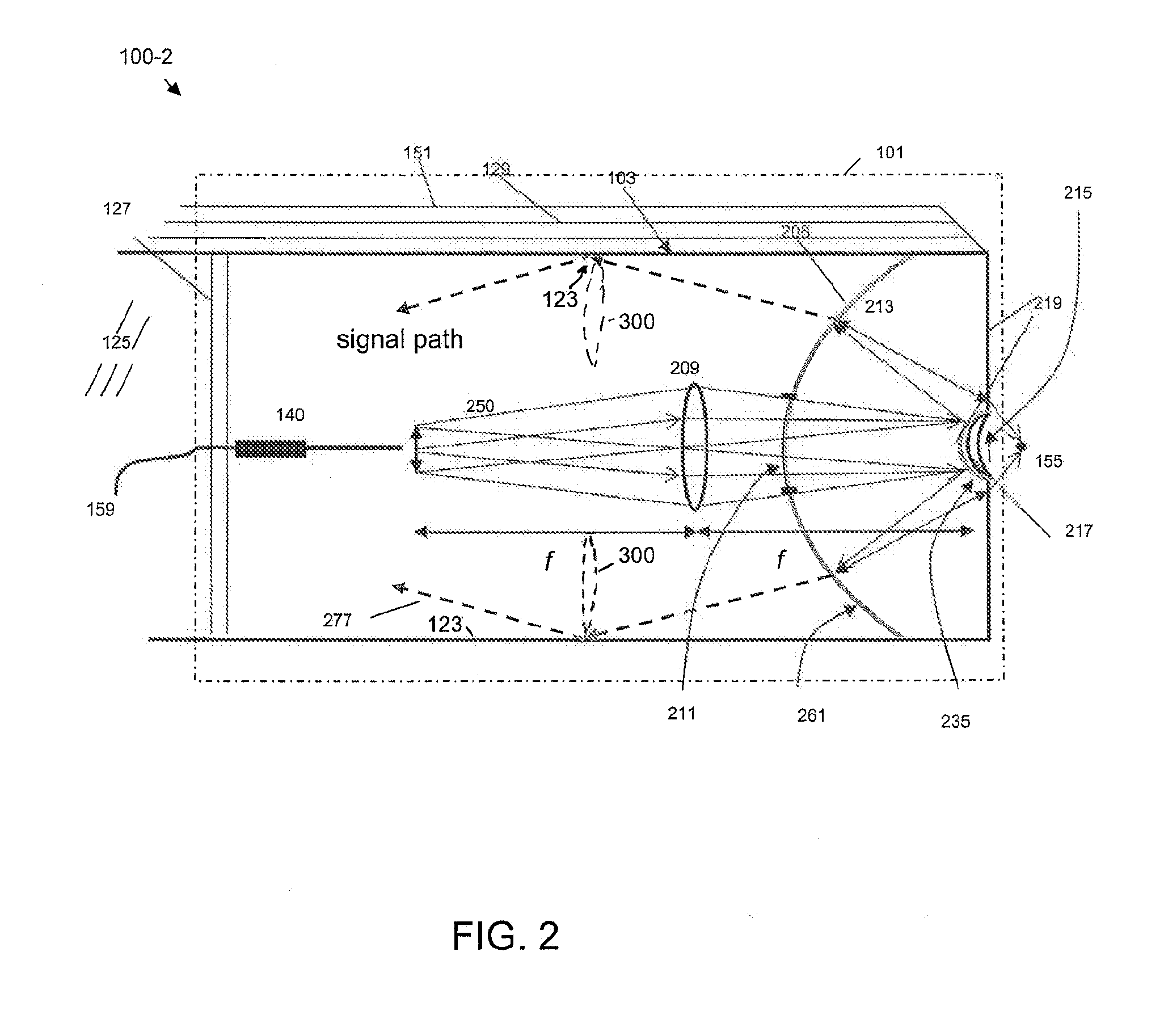
[0015]As used herein, the term “fluorescence emission” will be used to refer to multiphoton (particularly, two-photon but not excluding higher order) fluorescence emission as well as optical second harmonic generation (SHG) (but not excluding higher-order harmonic generation) from a target medium under conditions suitable to excite such fluorescence emission.
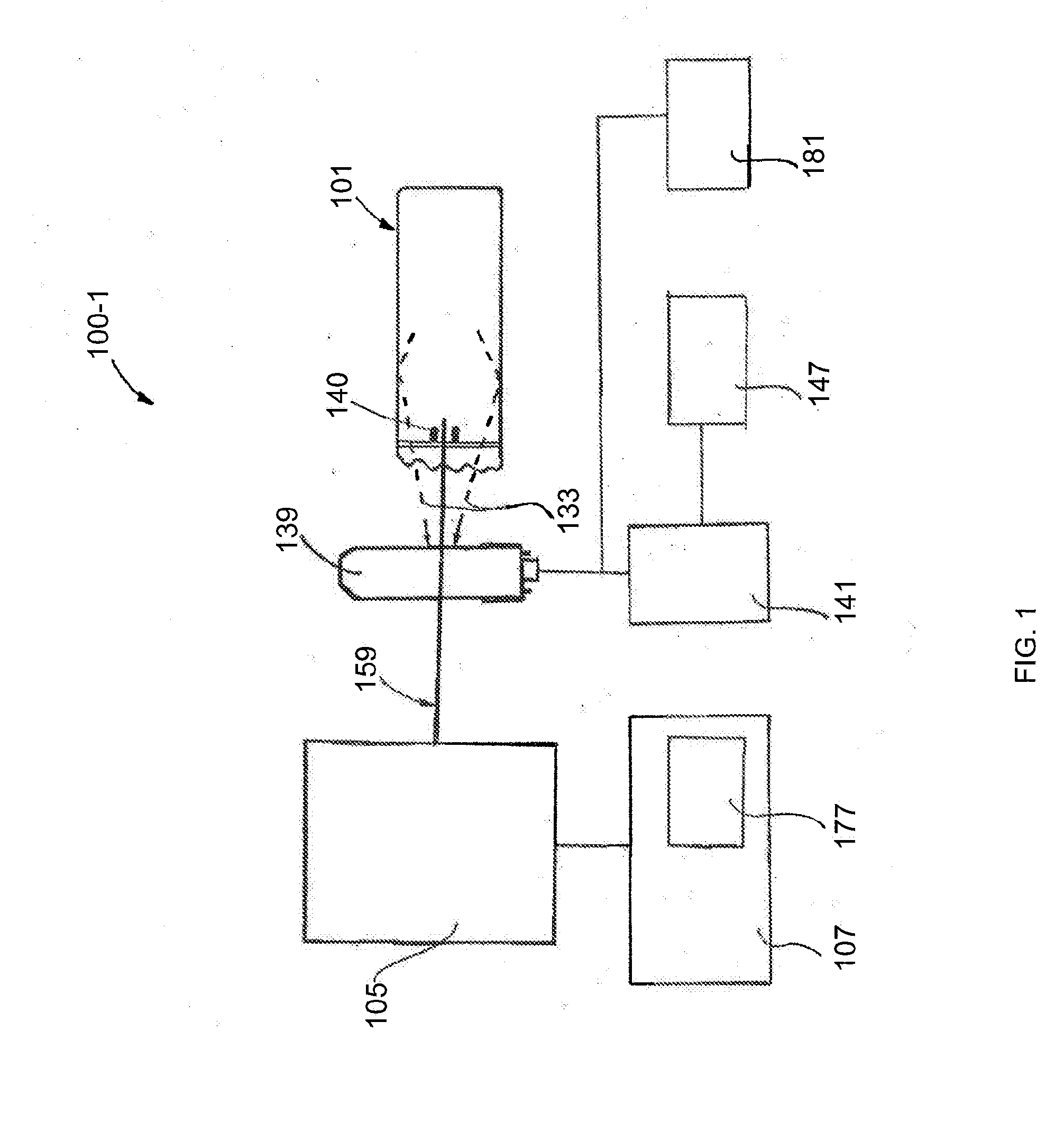
[0016]Illustrative embodiments of the invention include, but are not limited to, an optical system disposed in, or at, a distal end of a fluorescence emission endoscope, an optical system module for use in, or with, a fluorescence emission endoscope, an optical waveguide-based fluorescence emission endoscopy system, and a method for remotely-controlled, multi-magnification imaging of a target or fluorescence emission collection from a target with a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus.
[0017]An embodiment of the invention is an optical system disposed in, or at, a distal end of a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com