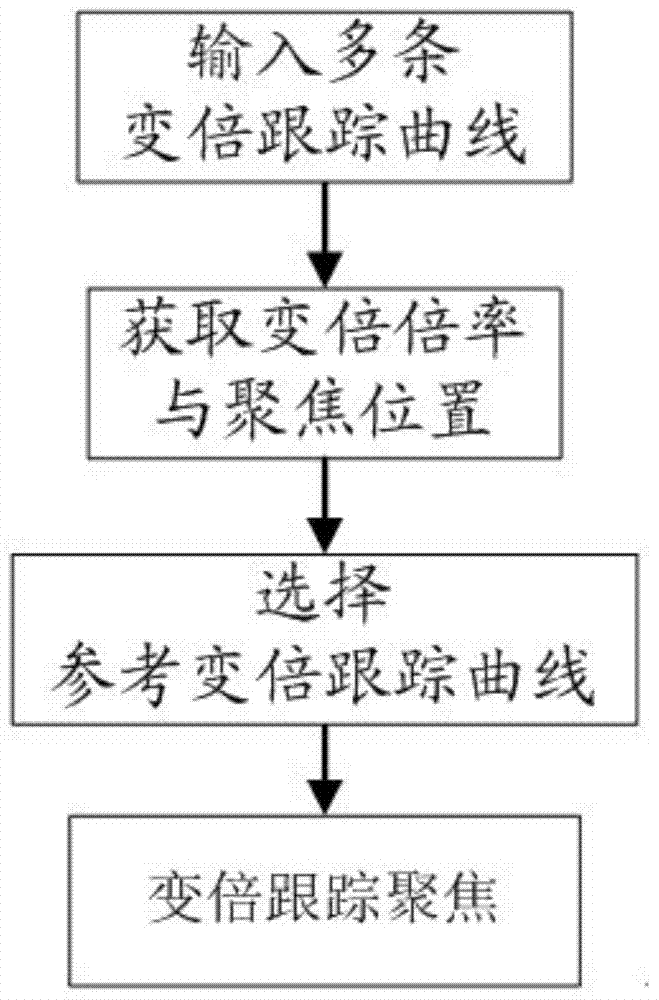
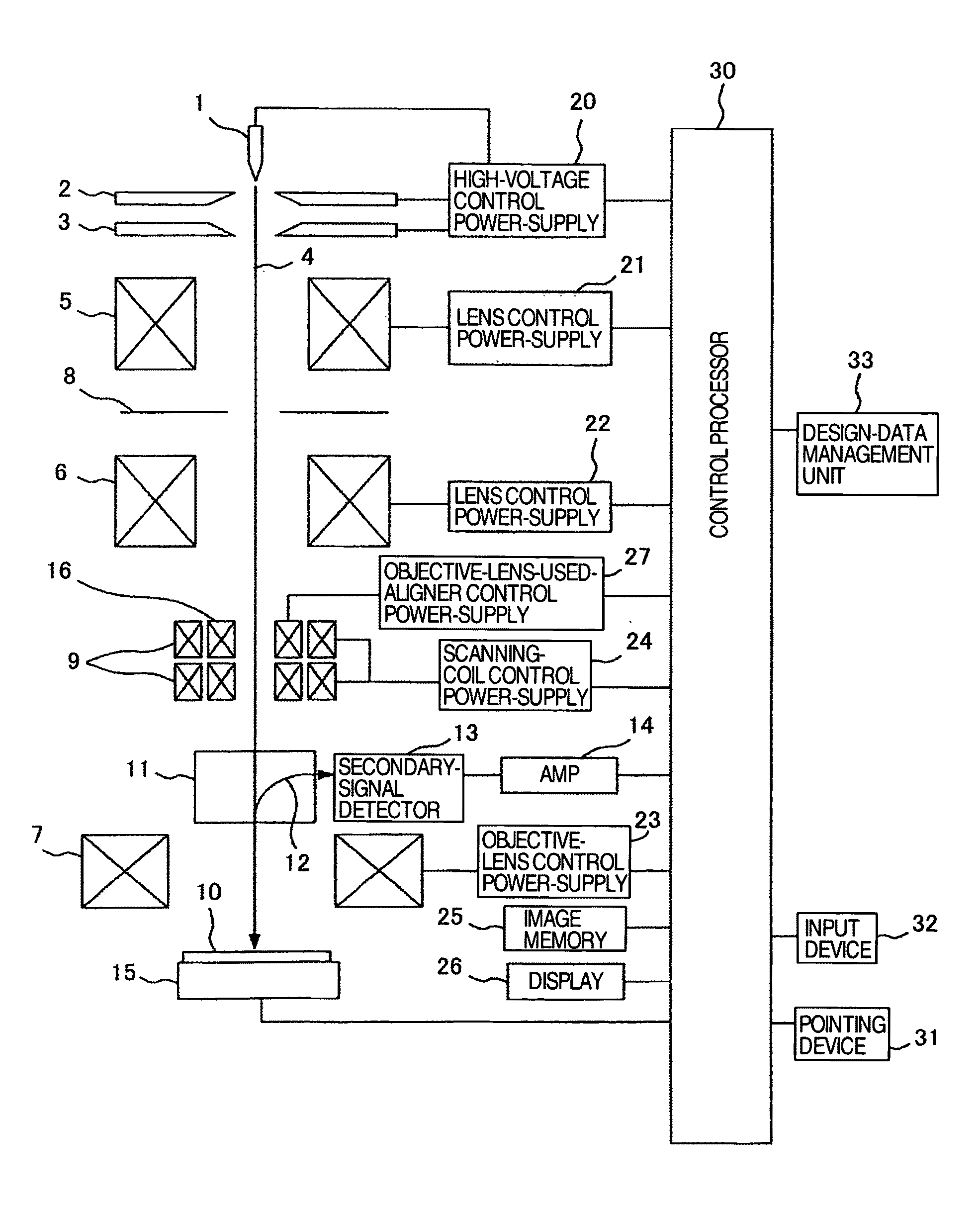
Patents
Literature
1035 results about "High magnification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High magnification is a useful feature for revealing very fine details in target subjects. Typical applications include biomedical research, material analysis, electronics inspection, or any similar applications that require the examination of intricate structures.
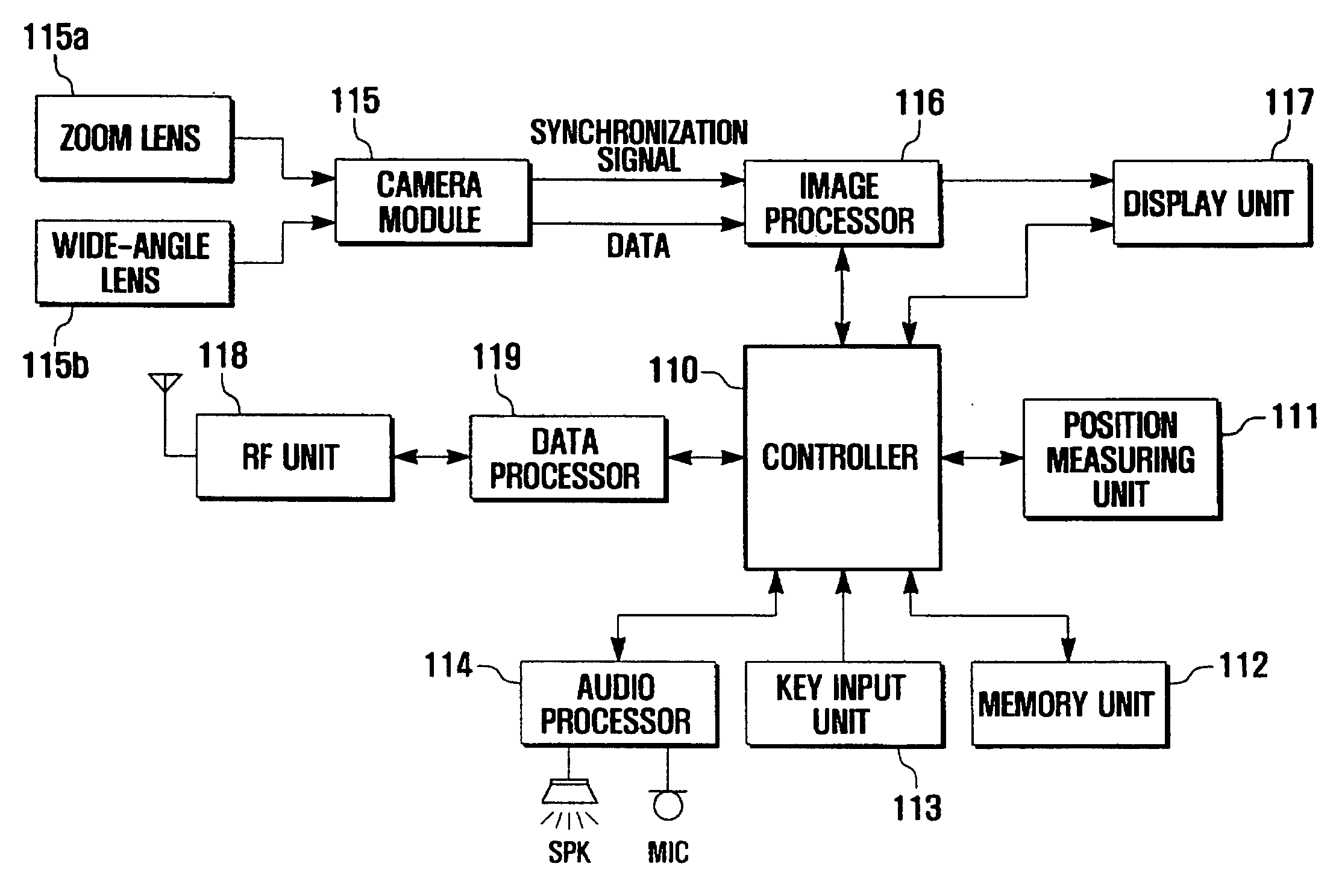
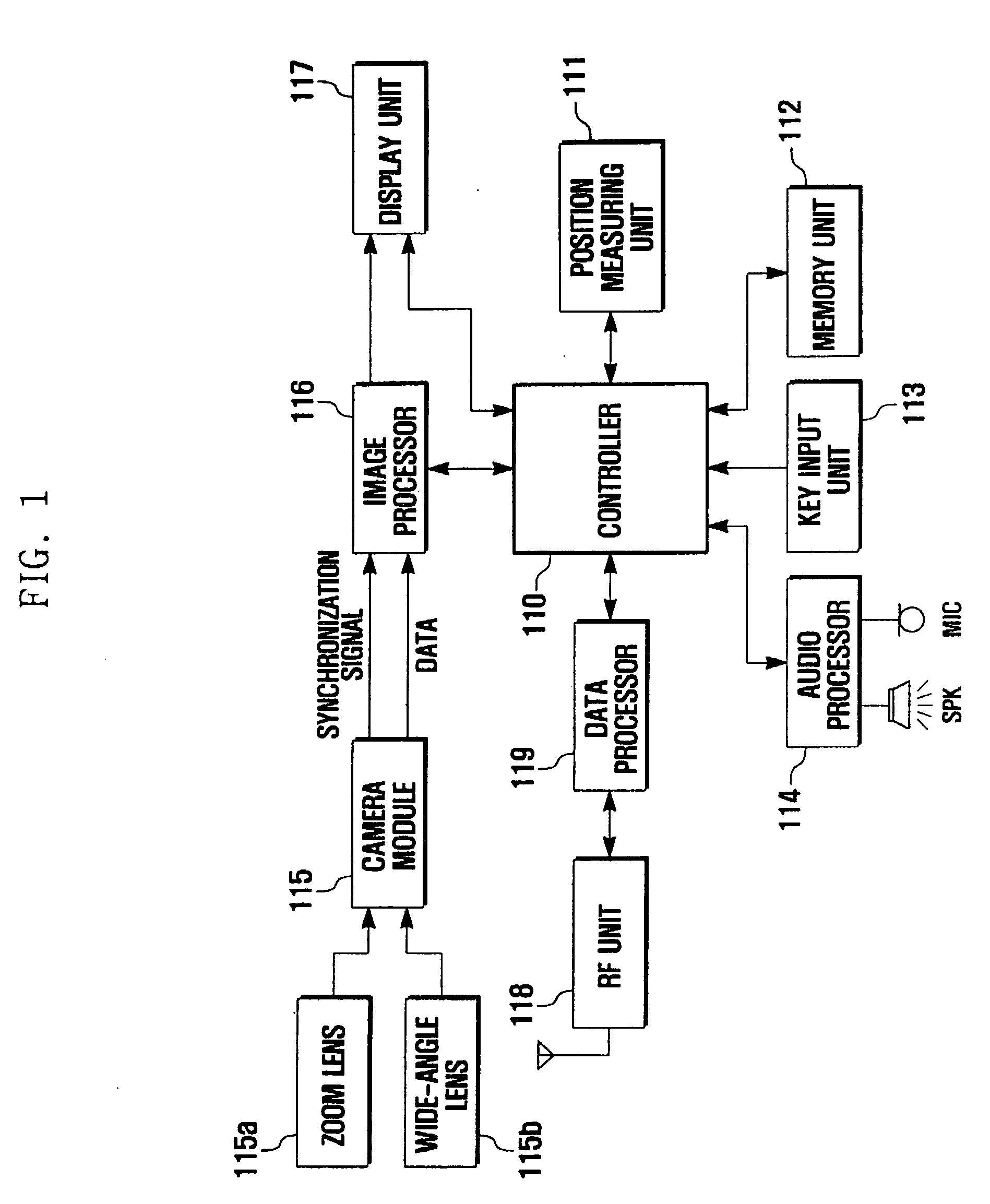
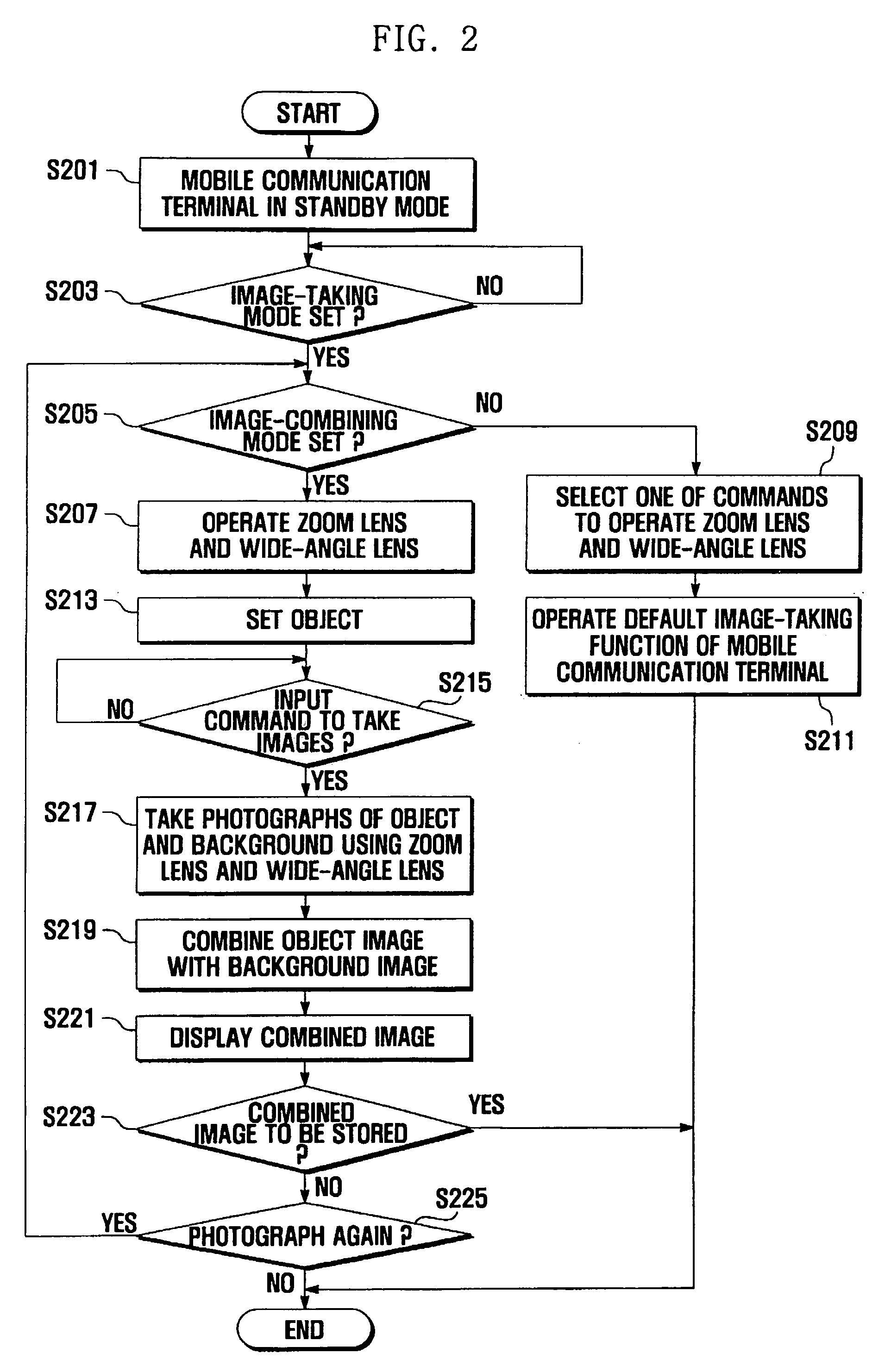
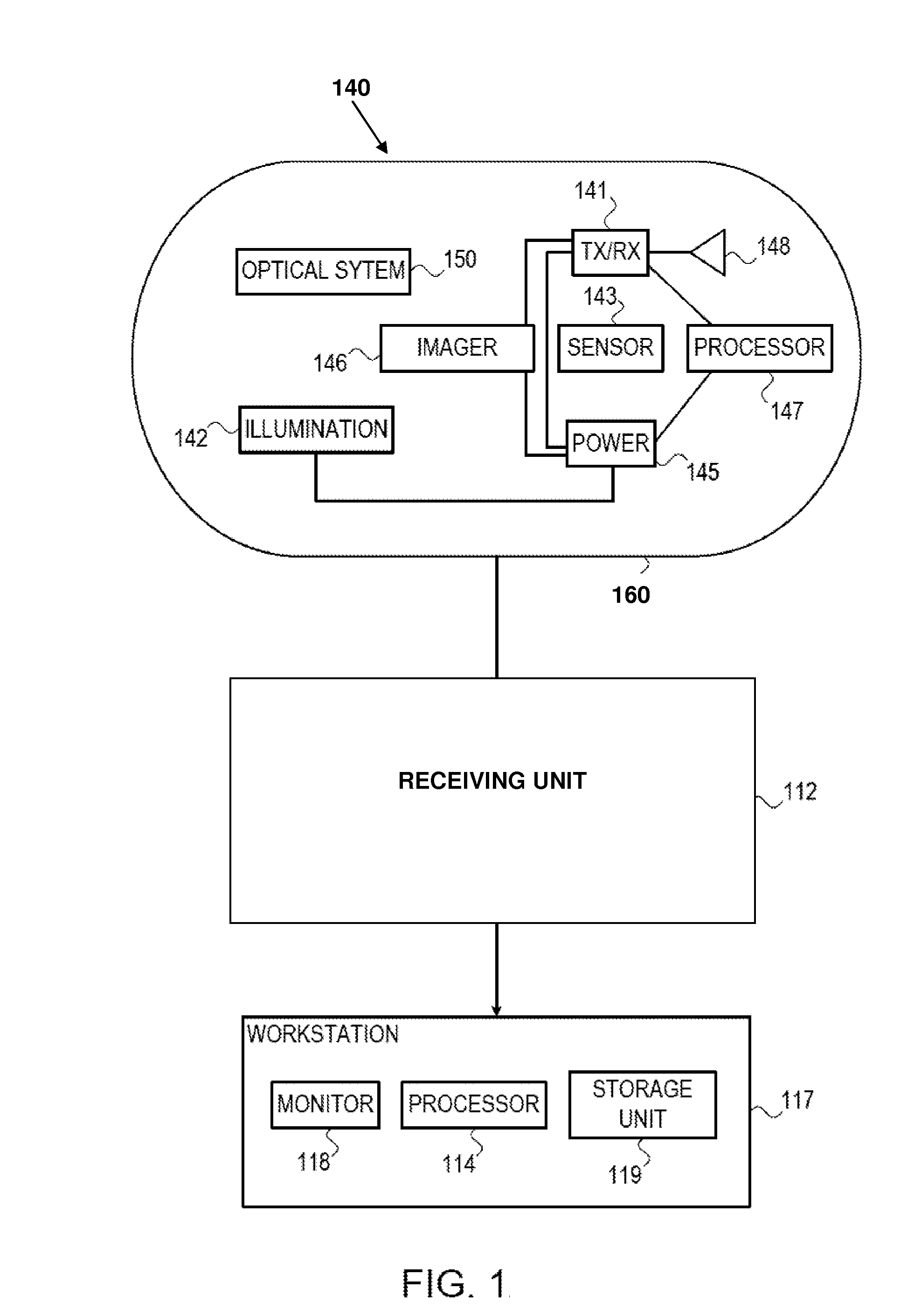
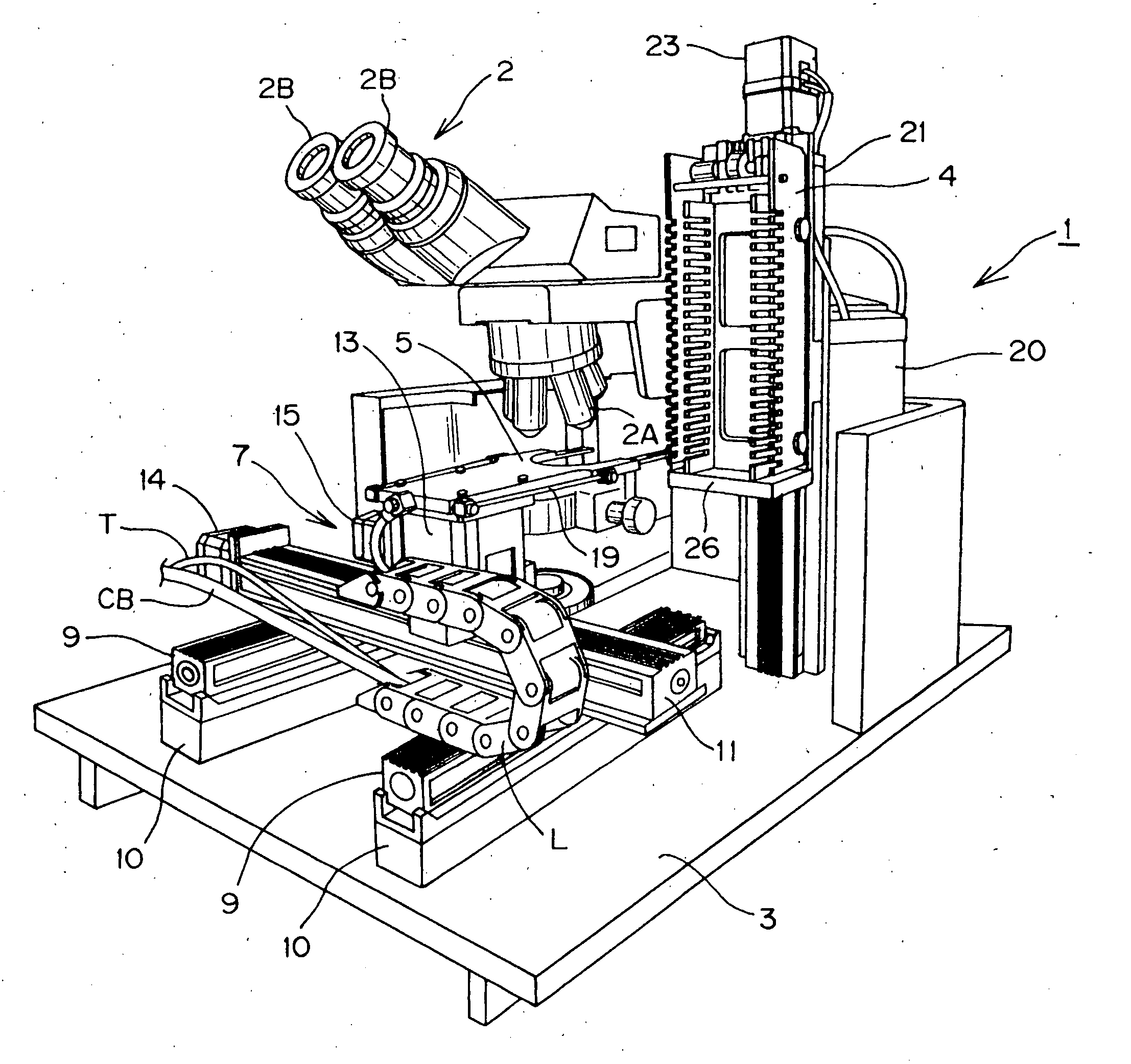
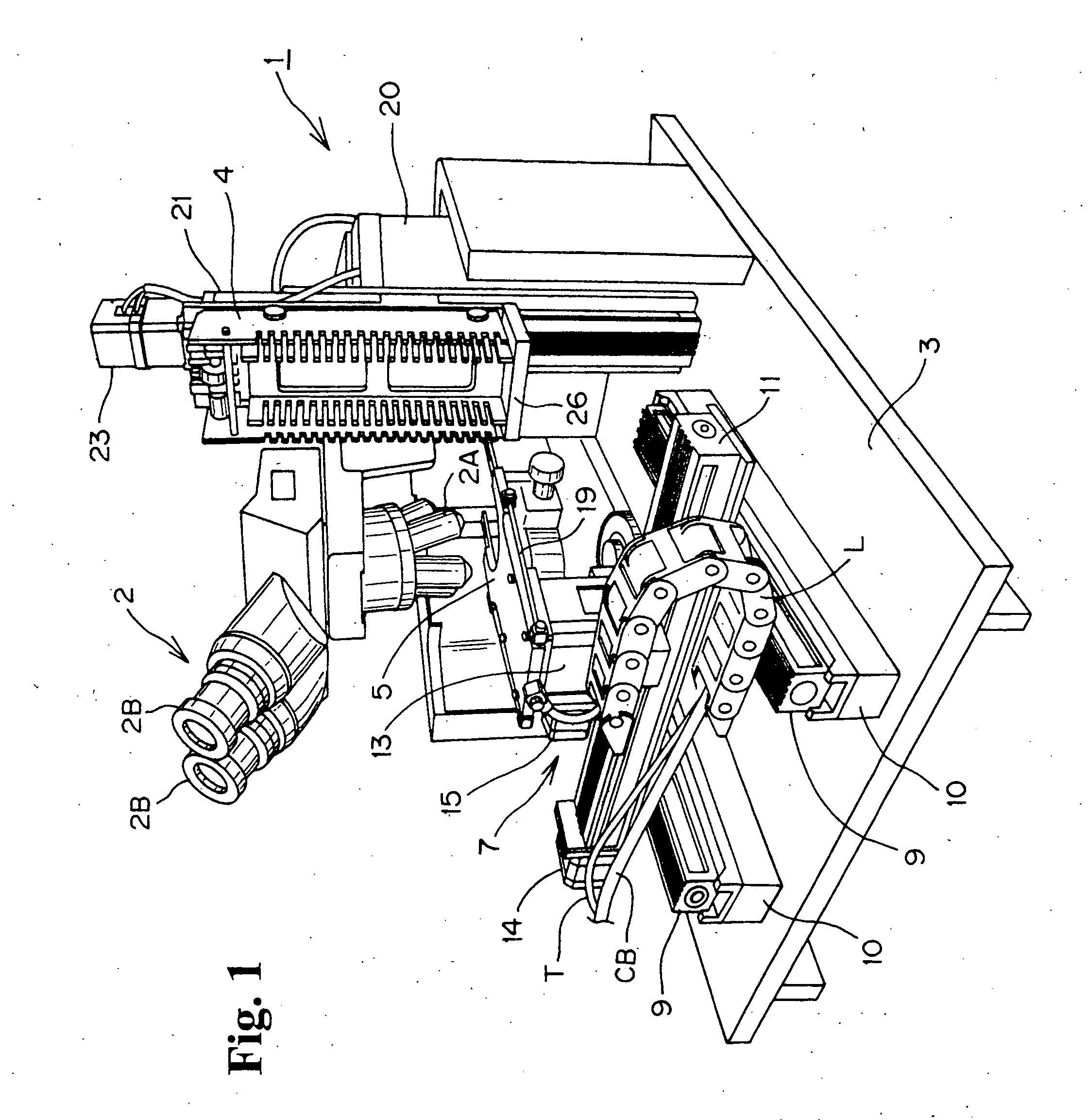
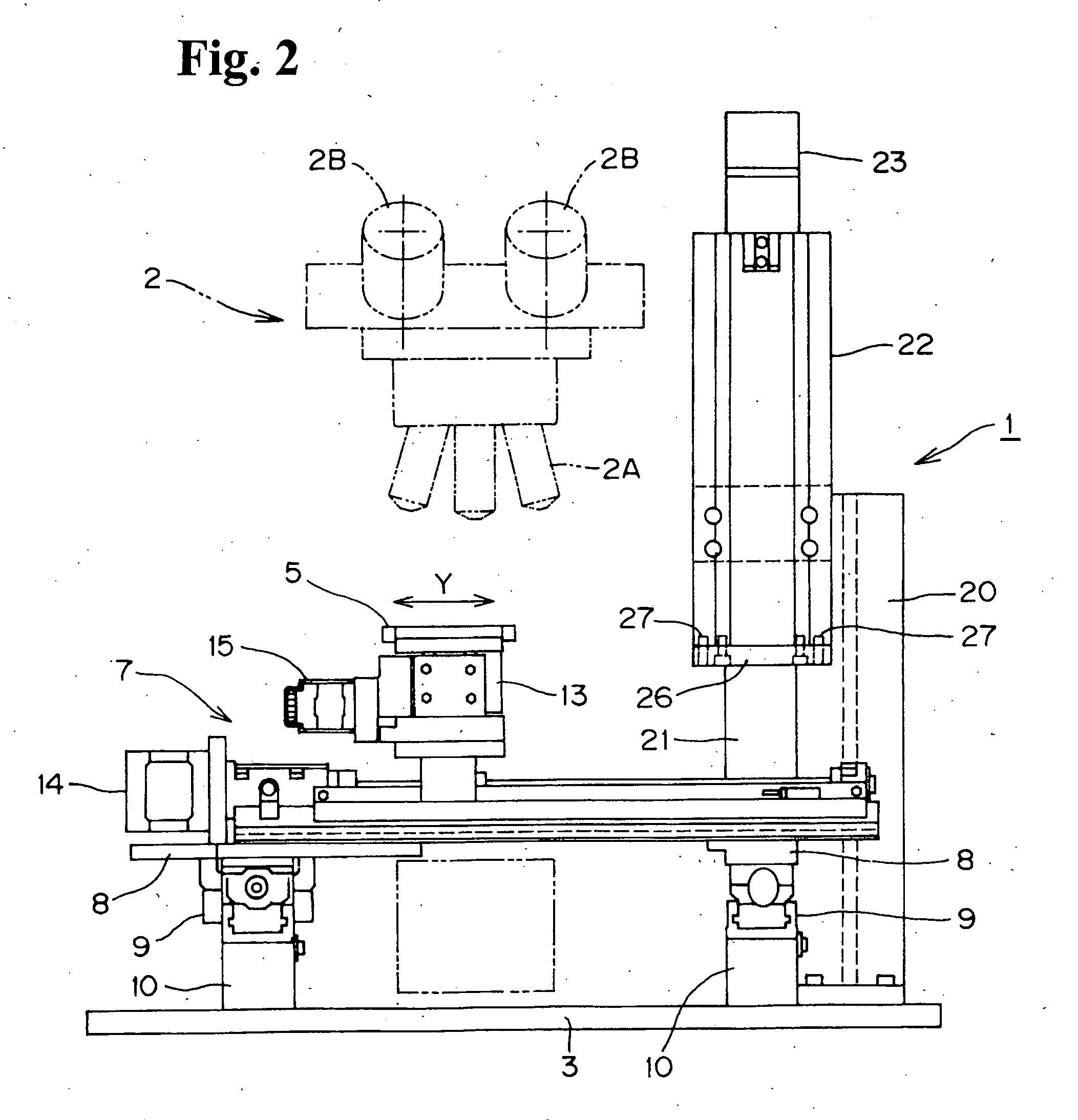
Method and apparatus for taking images using mobile communication terminal with plurality of camera lenses
InactiveUS20070285550A1Television system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensVisual perception
Provided are a method and apparatus for taking images using a mobile communication terminal with a plurality of camera lenses, that can visually emphasize the shape of an object by photographing a specific object and its surrounding background using a zoom lens and a wide-angle lens, respectively, and combining the photographed images. The method includes setting the mobile communication terminal to an image-taking mode, entering into an image-combining mode, operating the plurality of camera lenses, setting an object, taking images using the plurality of camera lenses, and combining together the images obtained using the plurality of lenses. The method and apparatus enables visual emphasis of a specific object in an entire image by photographing the specific object with a zoom lens and a background containing the object with a wide-angle lens, and then combining the photographed images so as to display the specific object at a higher magnification ratio than that of the background.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
In-vivo imaging device with double field of view and method for use
An in-vivo imaging device incorporating a double field of view imaging system, having a wide field of view with moderate magnification, and a narrow field of view with substantially higher magnification, axially superimposed thereon. A single imaging array is used for both fields of view. At least some of the optical elements are shared between both of the two different field of view imaging systems. The imaging elements for the high magnification system, being of substantially smaller diameters than those of the low magnification system, are disposed coaxially with the imaging elements of the low magnification system, and can thus use the same imaging array without the need for deflection mirrors, beam combiners or motion systems. Their location on the axis of the low magnification system means that a small part of the imaging plane, around its central axis, is blocked out by the high magnification components.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Integrated camera device and self-adapting automatic focus method
ActiveCN101494737AOvercoming the difficulty of judging the focus directionOvercome speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensSelf adaptive
The present invention relates to an integrated video camera device and self-adapting automatic focus method. The method includes: using climbing method to a curve composed of an evaluation function evaluating the definition and the definition evaluation values of multiple images acquired continuously, selecting a focus method base on the zooming situation, searching the peak of the curve and driving the lens to reach the focusing position corresponding to the peak of the curve, performing real time motion detection to the lens scenes upon searching the peak, driving the lens motor to startup a new cycle of automatic focus process when a certain degree of fuzzy is judged to appear on the lens scene or the moving scene varies and at a non-focus status. The invention has beneficial effects that the device and the method can effectively determine the focus direction in a variety of zoom magnifications, can 'recognize' images at fuzzy status and accelerate them out of the fuzzy status, and overcomes the problems of the traditional focus method that it is difficult to judge focus direction in the fuzzy region under high magnifications, and the traditional focus method has slow focus velocity and repeated oscillation.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20100261958A1Efficient collectionGuaranteed normal transmissionSurgeryEndoscopesFluorescenceImage resolution
Embodiments of the invention include an optical system and an optical system module, coupled to a distal end of a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus, an optical waveguide-based fluorescence emission endoscopy system, and a method for remotely-controlled, multi-magnification imaging of a target or fluorescence emission collection from a target with a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus. An exemplary system includes an objective lens disposed in a distal end of an endoscope apparatus. The lens is adapted to transmit both a visible target illumination and a fluorescence-emission-inducing target illumination as well as fluorescence-emission and visible light from the target. The system can thus simultaneously provide low magnification, large field of view imaging and high magnification, high-resolution multiphoton imaging with a single lens system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
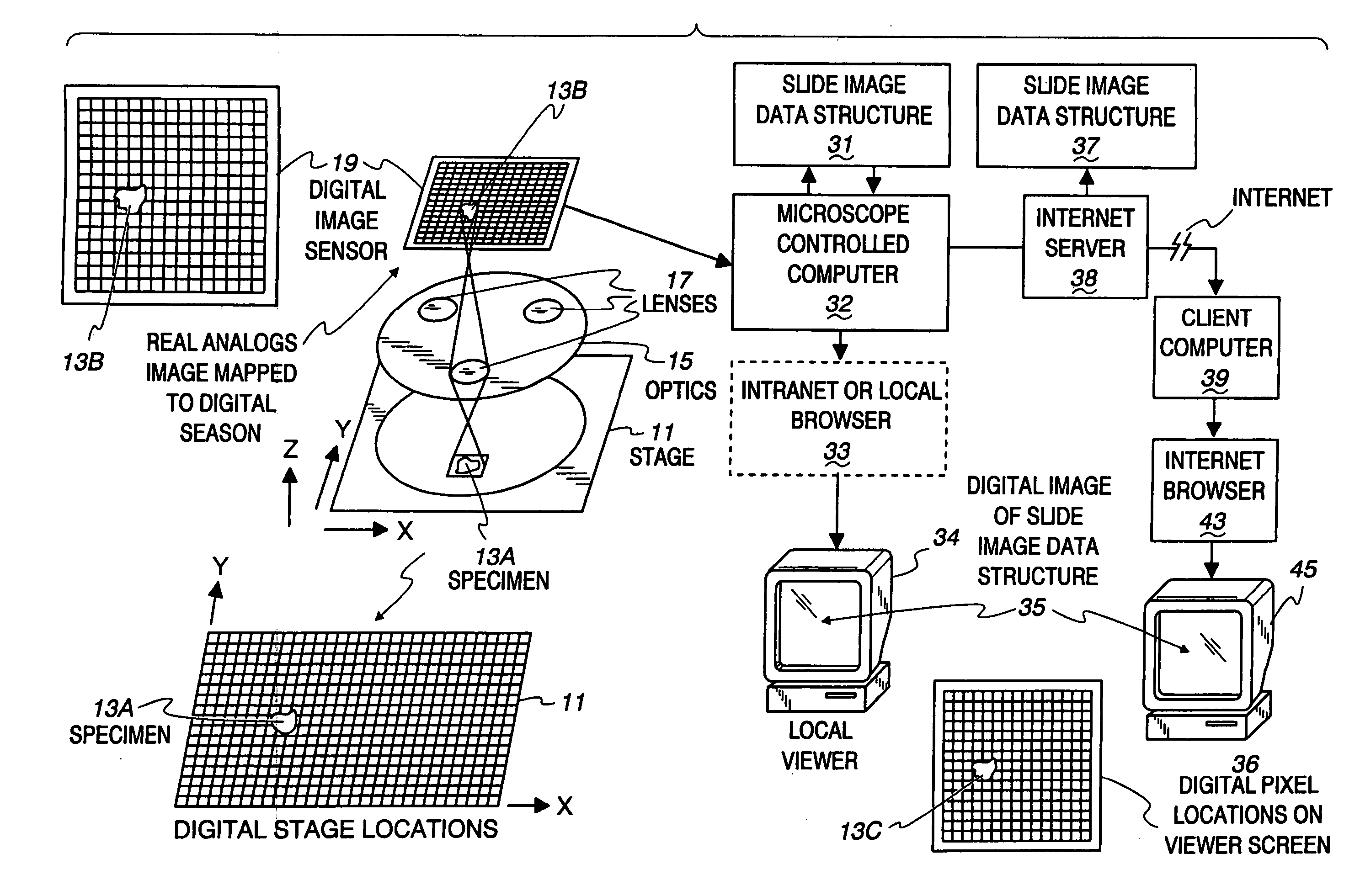
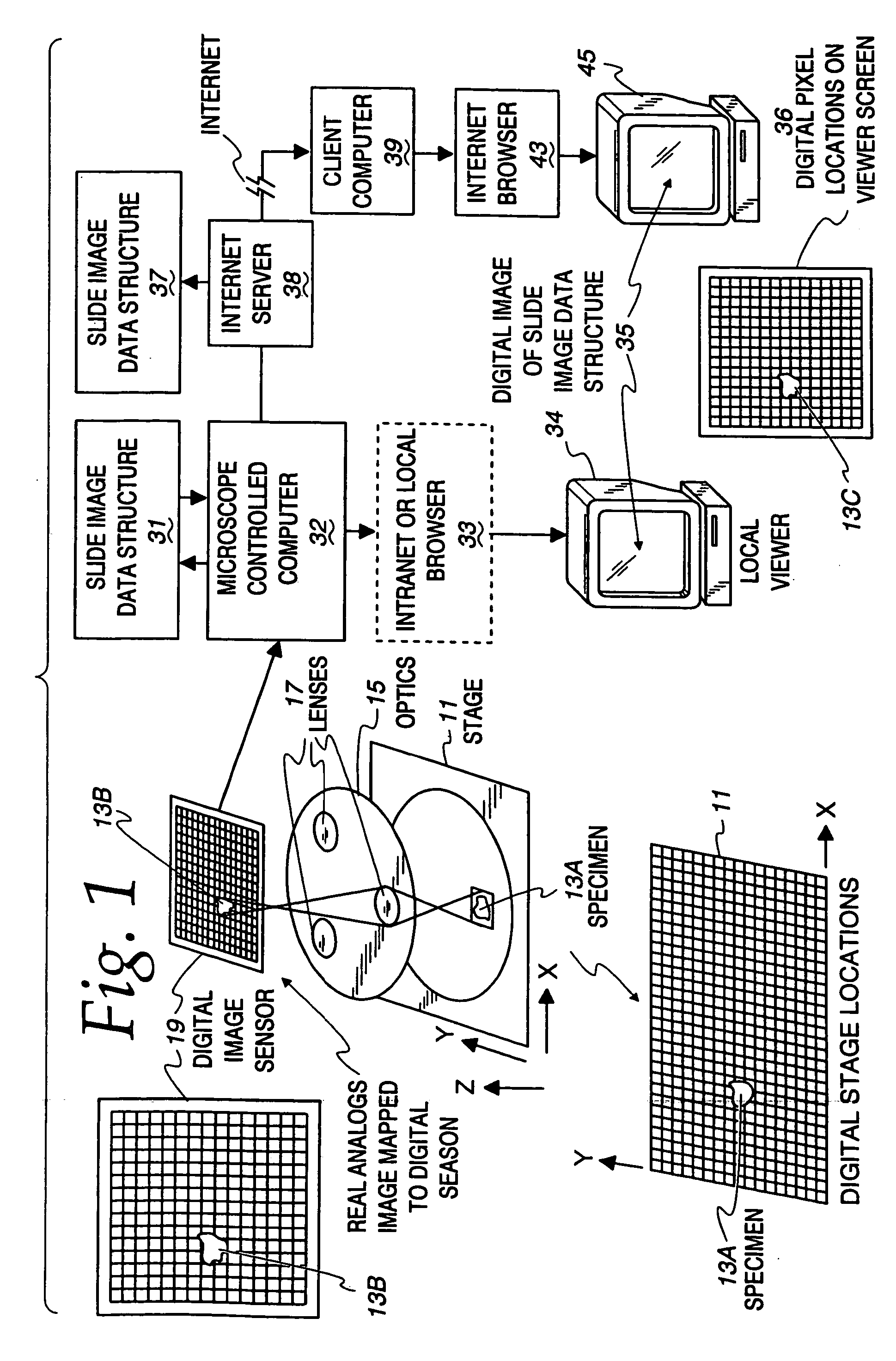
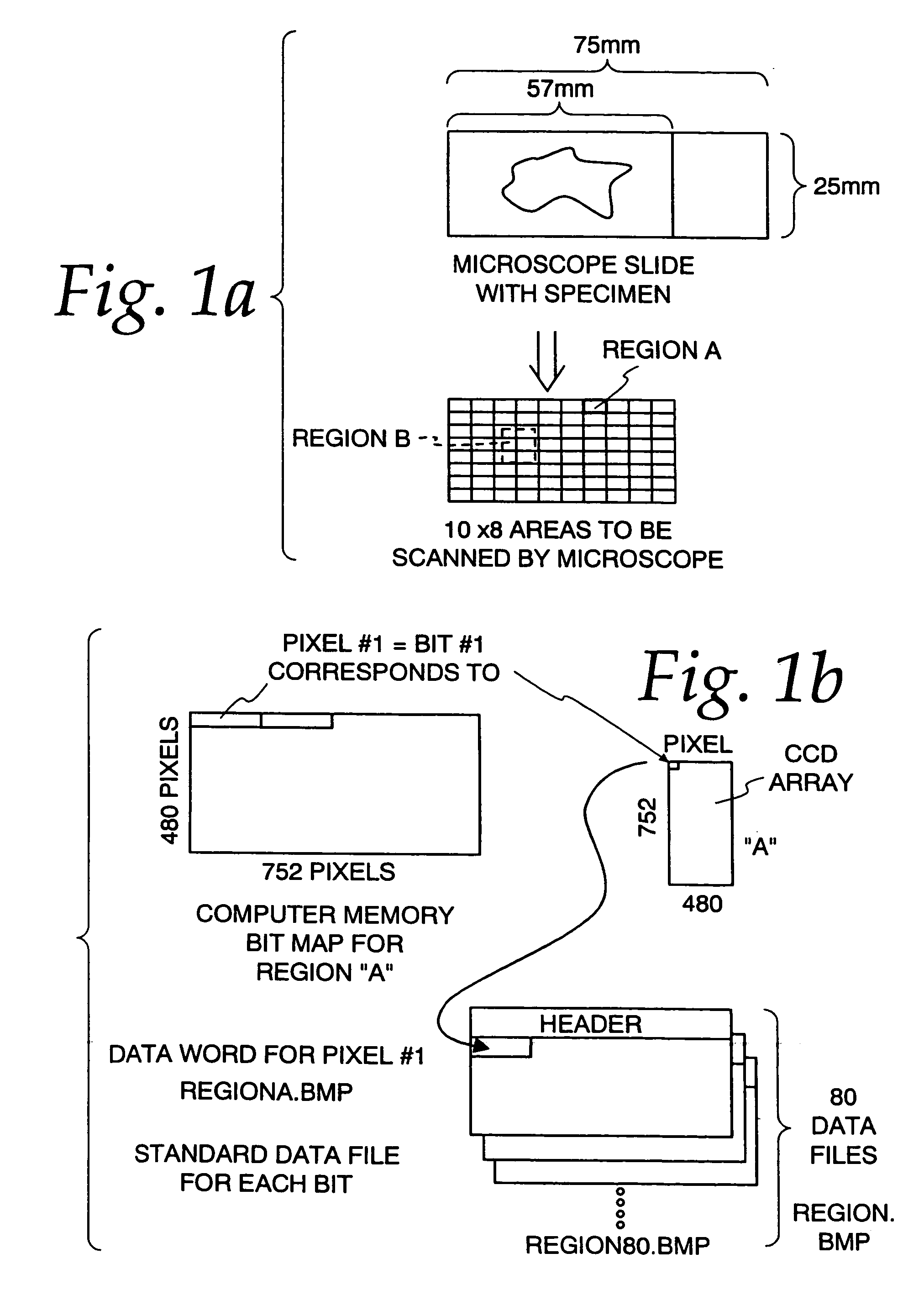
Method and apparatus for creating a virtual microscope slide
InactiveUS7146372B2Reduce in quantityHigh resolutionGeometric image transformationDigital data processing detailsComputer graphics (images)The Internet
A method and apparatus are disclosed for making and using a virtual microscope slide data structure having data for an overall image of the specimen or a substantial portion thereof along with data for higher magnification images of selected areas within the overall image and along with data useable for correlating, linking and / or coherently assembling low magnification, overall image segments with the higher image segments. This latter data may comprise a control program for manipulating images to allow zooming different, higher magnification images into view, scrolling adjacent high magnification images into view or marking the location of a displayed higher magnification view on the overall image to assist in navigation by a viewer to locate and quickly display suspicious areas within the specimen. The data structure may be sent over the Internet.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
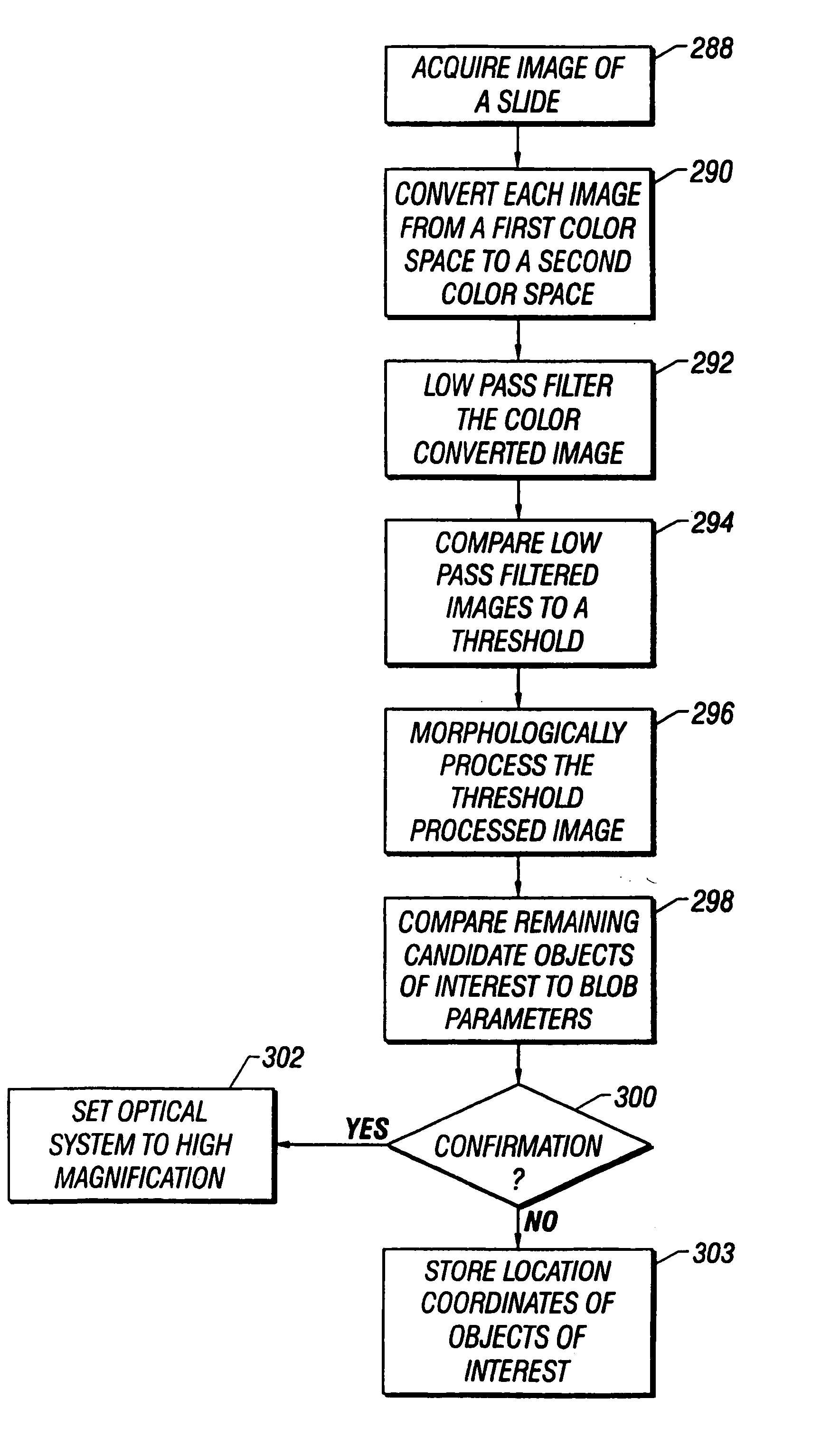
Method and apparatus for automated image analysis of biological specimens
InactiveUS6920239B2High degreeQuickly and accurately scanImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationColor transformationLow-pass filter
A method and apparatus for automated cell analysis of biological specimens automatically scans at a low magnification to acquire images which are analyzed to determine candidate cell objects of interest. The low magnification images are converted from a first color space to a second color space. The color space converted image is then low pass filtered and compared to a threshold to remove artifacts and background objects from the candidate object of interest pixels of the color converted image. The candidate object of interest pixels are morphologically processed to group candidate object of interest pixels together into groups which are compared to blob parameters to identify candidate objects of interest which correspond to cells or other structures relevant to medical diagnosis of the biological specimen. The location coordinates of the objects of interest are stored and additional images of the candidate cell objects are acquired at high magnification. The high magnification images are analyzed in the same manner as the low magnification images to confirm the candidate objects of interest which are objects of interest. A high magnification image of each confirmed object of interest is stored for later review and evaluation by a pathologist.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
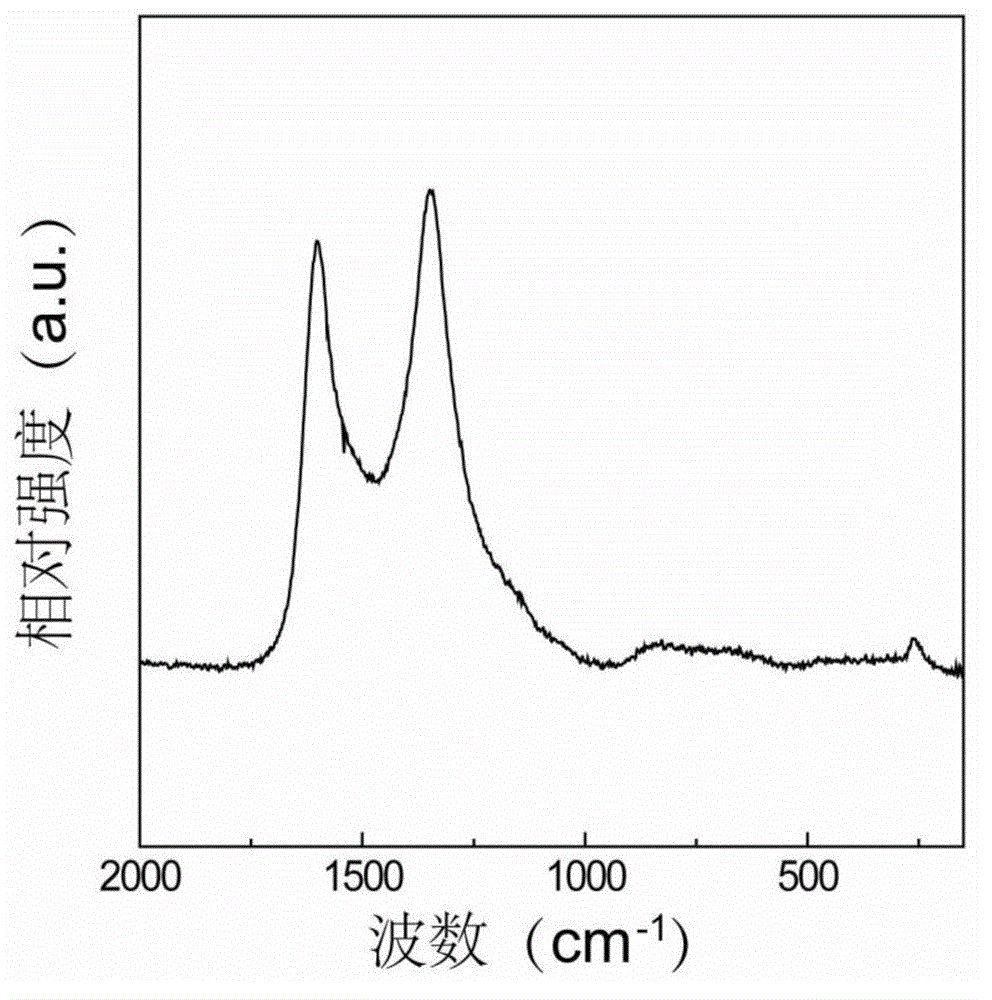
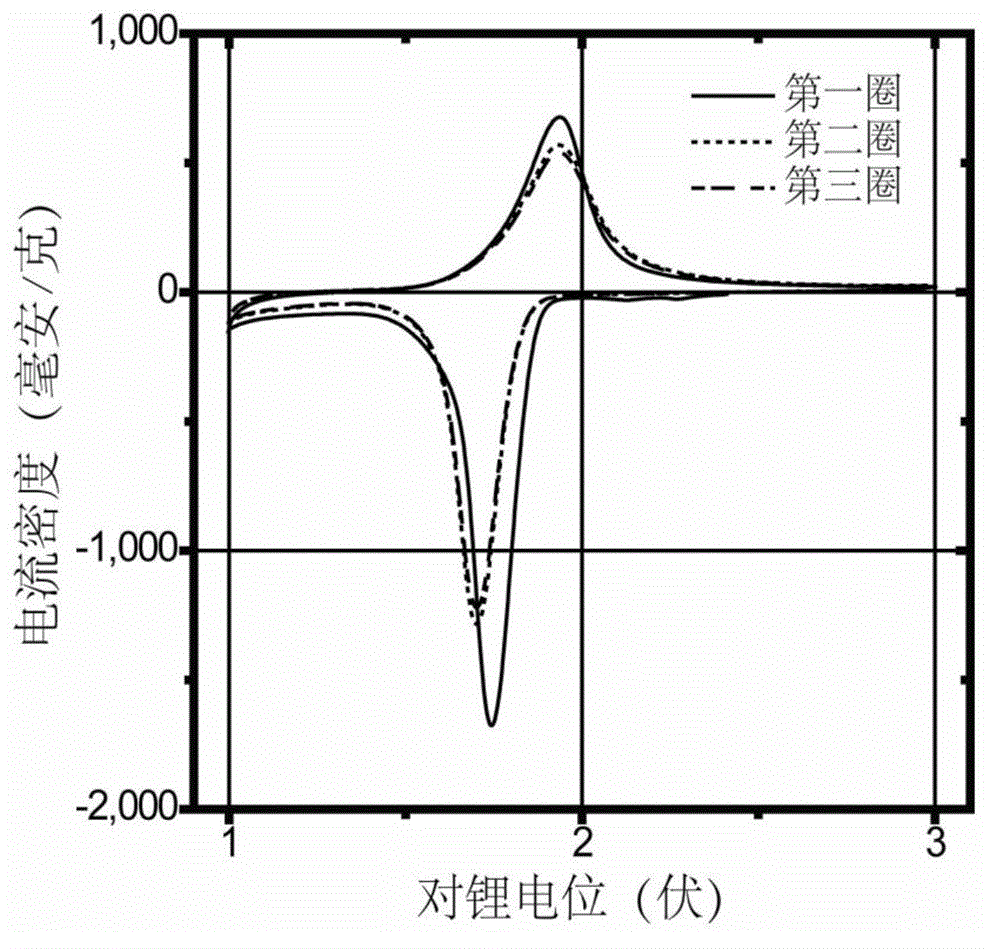
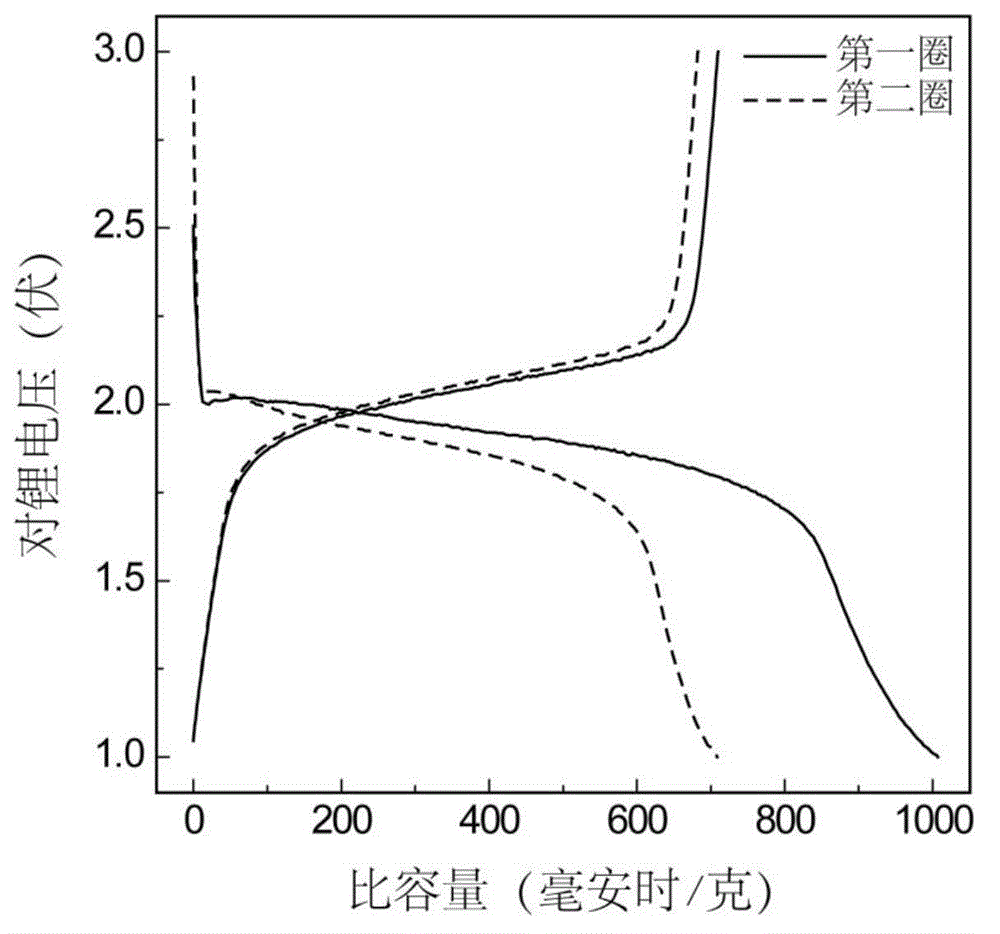
Synthesis and surface modification method of lithium excessive laminar oxide anode material
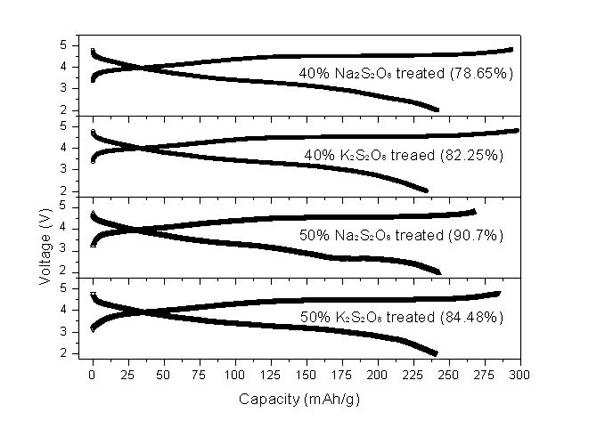
The invention relates to a synthesis and surface modification method of a lithium rich anode material Li1+xM1-xO2 (M is one or more of Ni, Co and Mn, and X is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 / 3) for a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a precursor by using a carbonate precipitation method, mixing the precursor and a lithium salt, and calcining for 2 to 20 hours at the temperature of between 800 and 1,100 EG C to obtain a lithium rich material, wherein the prepared lithium rich material has controllable particle size and higher reversible capacity; and dissolving persulfate or sulfate in an amount which is 5 to 80 mass percent of the lithium rich material into deionized water, adding the lithium rich material, stirring for 2 to 100 hours at the temperature of between 25 and 80 DEG C, heating the materials to the temperature of between 100 and 500 DEG C in a muffle furnace, calcining the materials for 2 to 20 hours, fully filtering the obtained materials, and washing off impurities to obtain the surface modified anode material Li1+x-yM1-xO2. The synthesized lithium rich material has controllable particle size; the first charge / discharge efficiency of the lithium rich material and the discharge specific capacity and the cyclical stability under high magnification can be improved; and the method is simple, low in cost, convenient for operation and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HKUST FOK YING TUNG RES INST
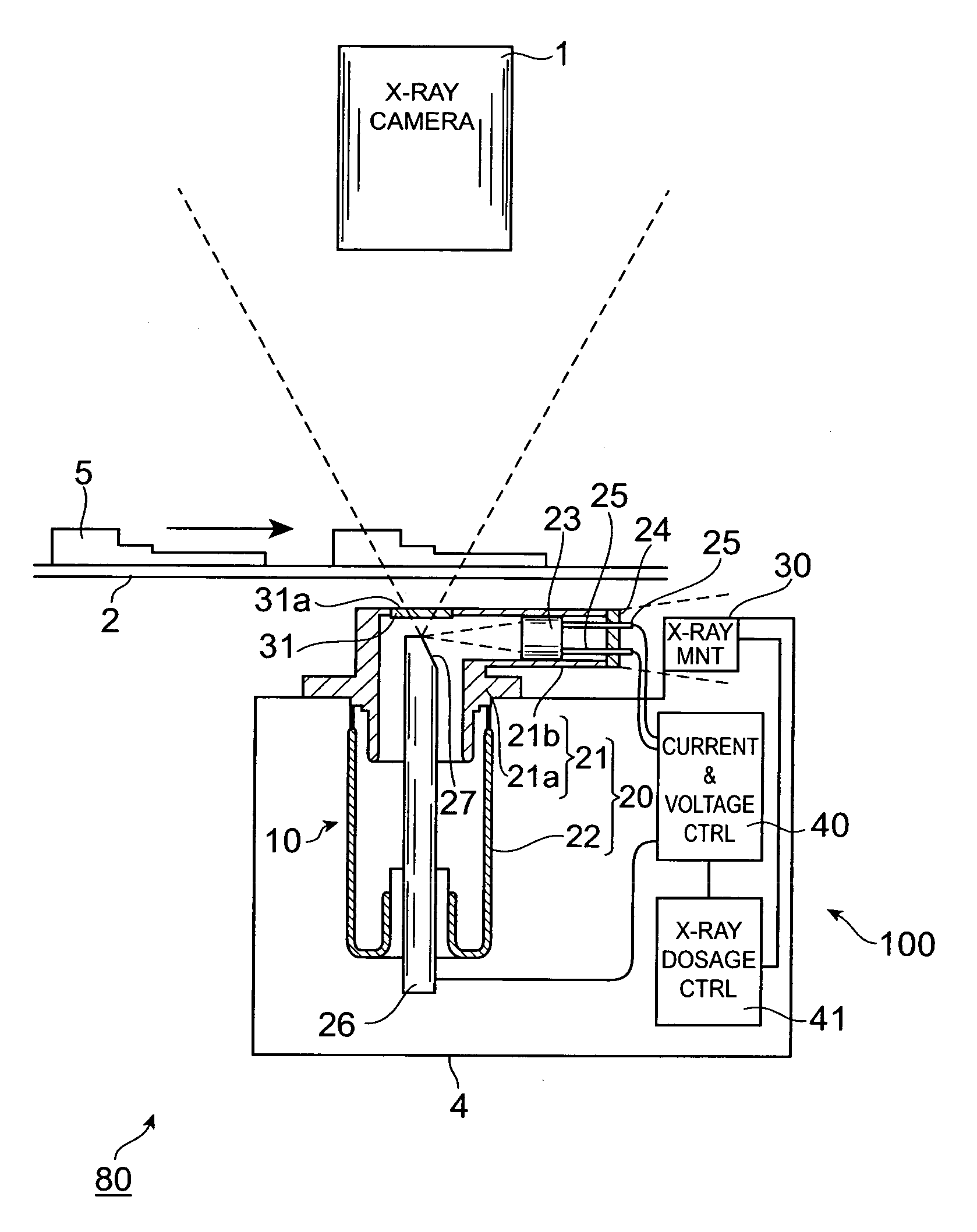
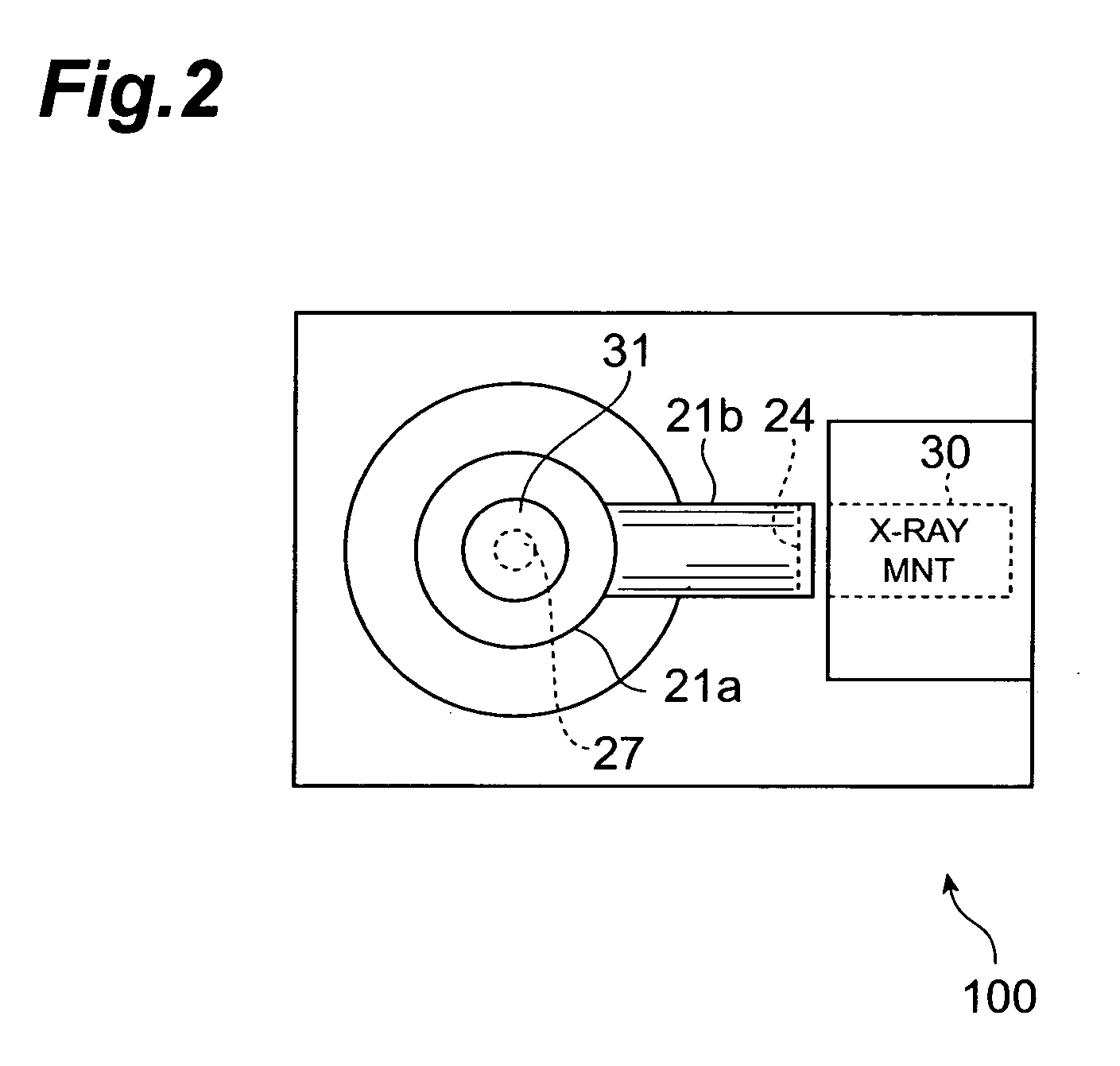
X-ray generator
InactiveUS20050163284A1High strengthImprove precision monitoringX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX ray imageX-ray generator
An X-ray generator of this invention has an X-ray monitor that monitors a state of an X-ray emitted from a target. Hence the state of the X-ray can be monitored in real time to maintain the X-ray in a constant state. The X-ray monitor is positioned off the path on which an X-ray transmitted from a first exit window travels. Hence, when the X-ray is emitted from the first exit window to an object to be inspected, the X-ray monitor does not obstruct the approaching of the object to the first exit window. This makes it possible to acquire X-ray images of high magnification.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Defect detecting apparatus, defect detecting method, information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program therefor
InactiveUS20100074516A1Highly accurate and efficient detectionAccurately determineImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingProtein chip
A defect detecting apparatus captures an image of a protein chip formed on each die of a wafer with a low magnification for every first division region obtained by dividing each die in plurality; stores each obtained image as an inspection target image together with an ID for identifying each first division region; creates a model image for every first division region by calculating an average luminance value of pixels of each inspection target image; extracts a difference between the model image and each inspection target image as a difference image; determines presence of a defect by extracting a Blob having an area larger than a preset value from the difference image; captures a high-magnification image of every second division region; creates a model image again and extracts a Blob; and determines the kind of the defect based on a feature point of the defect.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Cathode material for lithium-ion power and energy storage battery and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a cathode material for a lithium-ion power and energy storage battery and a preparation method thereof, aiming to solve the problem on how to improve the high-magnification charge-discharge property of the battery and how to enable the battery to have good cycle property. The cathode material is obtained by carbonizing asphalt containing a catalyst at 500-1,300 DEG C. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: raising the temperature and the pressure to have a carbonized thermal polycondensation reaction; washing, extracting and then washing; drying to obtain mesophase microbead precursors; and then carbonizing to obtain the cathode material for the lithium-ion power and energy storage battery. Compared with the prior art, the invention reduces the production cost; because the mesophase soft carbon materials obtained by low-temperature carbonization are adopted, the interior of the cathode material is in a turbostratic structure capable of charging and discharging with high power and high current; and the main raw material of the mesophase soft carbon material is asphalt, so that compared with other hard carbons such as the resin type, the plant, and the like, the cathode material has yield improved by 3-5 times, low cost and higher specific capacity.
Owner:JIXI BTR GRAPHITE IND PARK CO LTD +2
Magnifying attachment
The object of this invention is to provide a magnifying attachment to be attached to a camera by which a high magnification image can be obtained without appearing a part having no image in the image. The magnifying attachment has a magnifying objective lens (21A), a field lens (21B) for converting a light passed through the objective lens (21A) into collimated light, and a converging lens (21C) for focusing the collimated light on a camera lens (42). Light passed through the converging lens (21C) is converged on a pupil (42X) of the camera lens (42) with a solid angle exceeding the view angle of the camera lens (42).
Owner:SCALAR CORP
Long working distance incoherent interference microscope
ActiveUS7034271B1Low costShorten the timeMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesElectron probe microanalysisProbe card
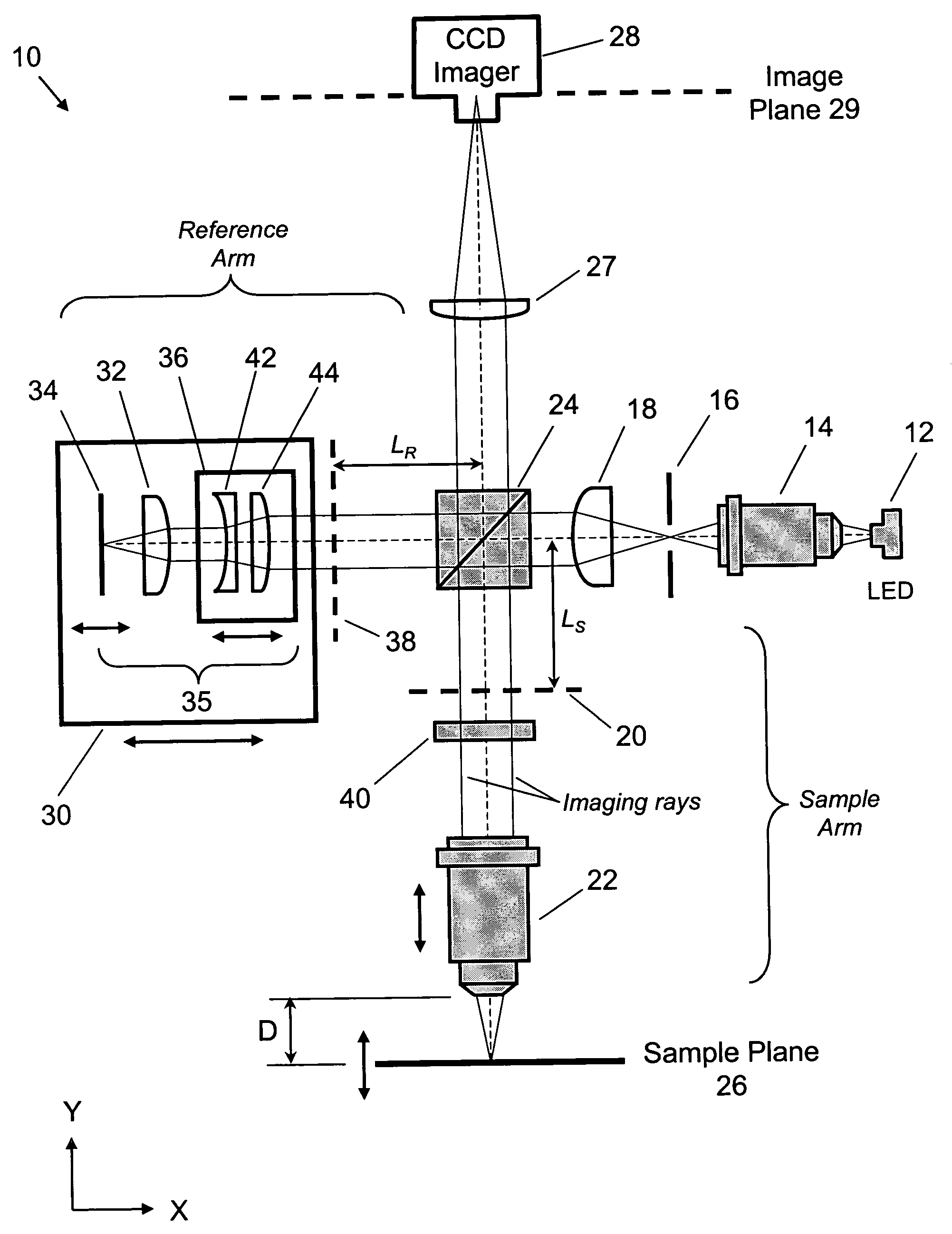
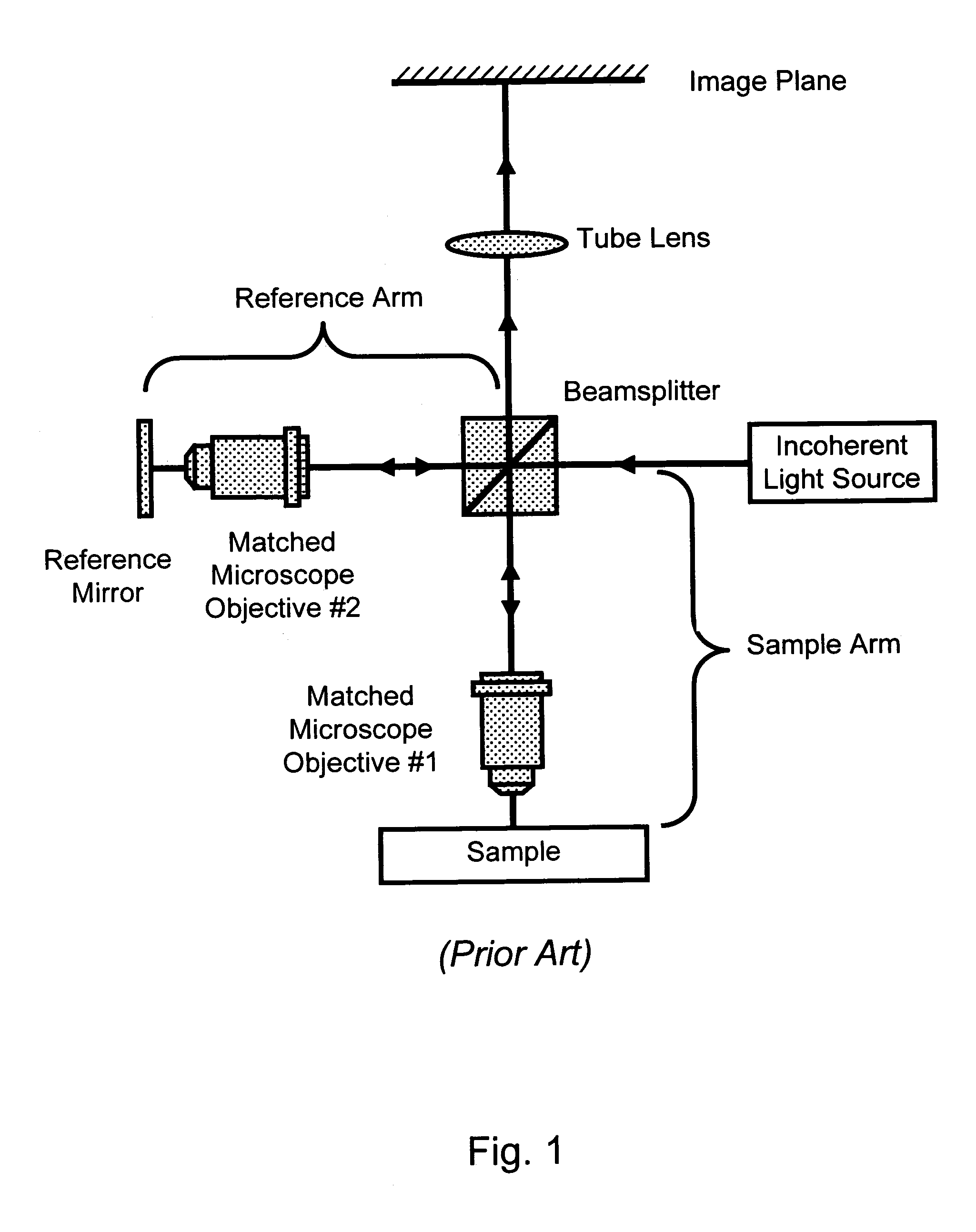
A full-field imaging, long working distance, incoherent interference microscope suitable for three-dimensional imaging and metrology of MEMS devices and test structures on a standard microelectronics probe station. A long working distance greater than 10 mm allows standard probes or probe cards to be used. This enables nanometer-scale 3-dimensional height profiles of MEMS test structures to be acquired across an entire wafer while being actively probed, and, optionally, through a transparent window. An optically identical pair of sample and reference arm objectives is not required, which reduces the overall system cost, and also the cost and time required to change sample magnifications. Using a LED source, high magnification (e.g., 50×) can be obtained having excellent image quality, straight fringes, and high fringe contrast.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multitask KSVD (K singular value decomposition) dictionary learning
ActiveCN102156875AReduce refactoring timeReduce the numberImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionFeature vector
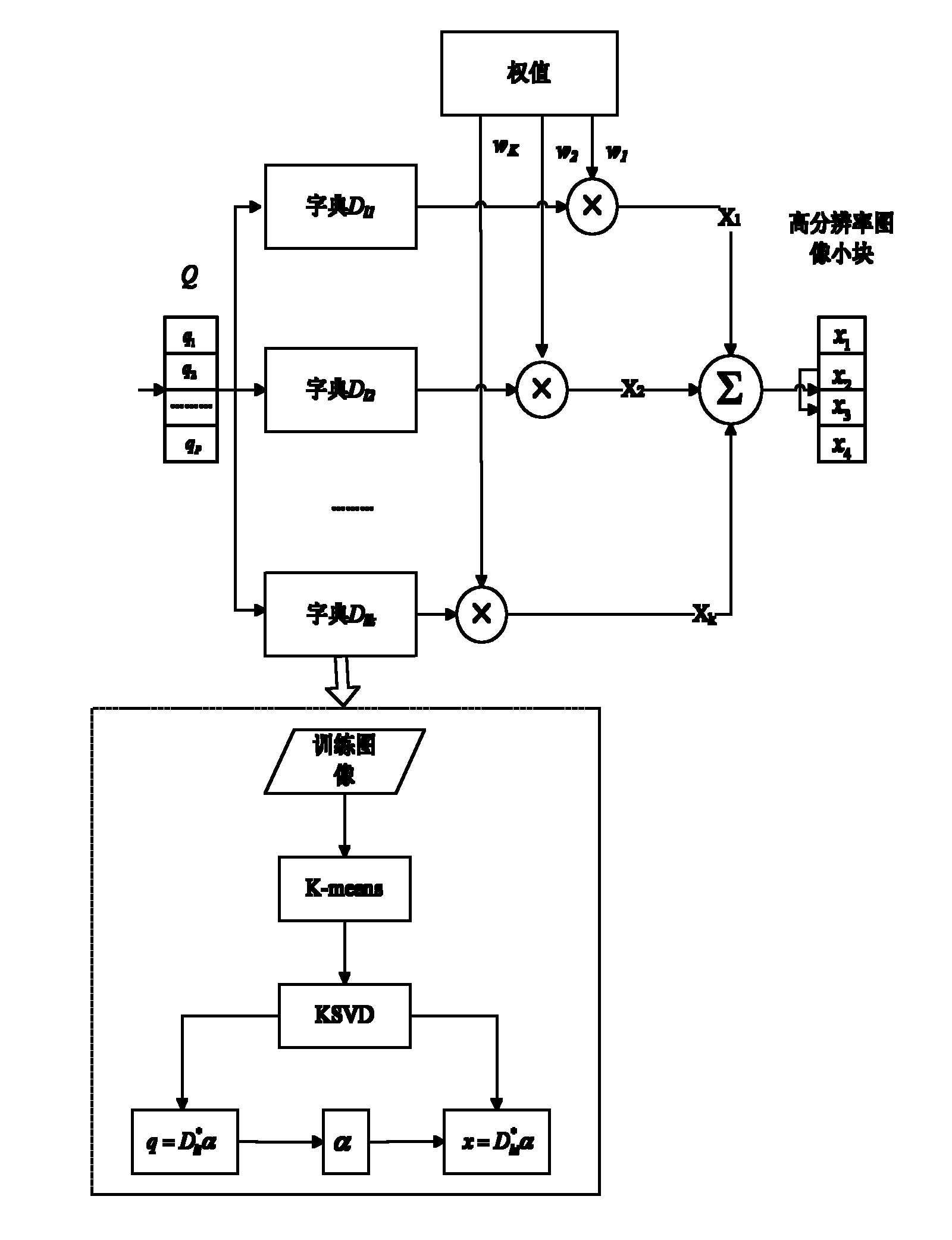
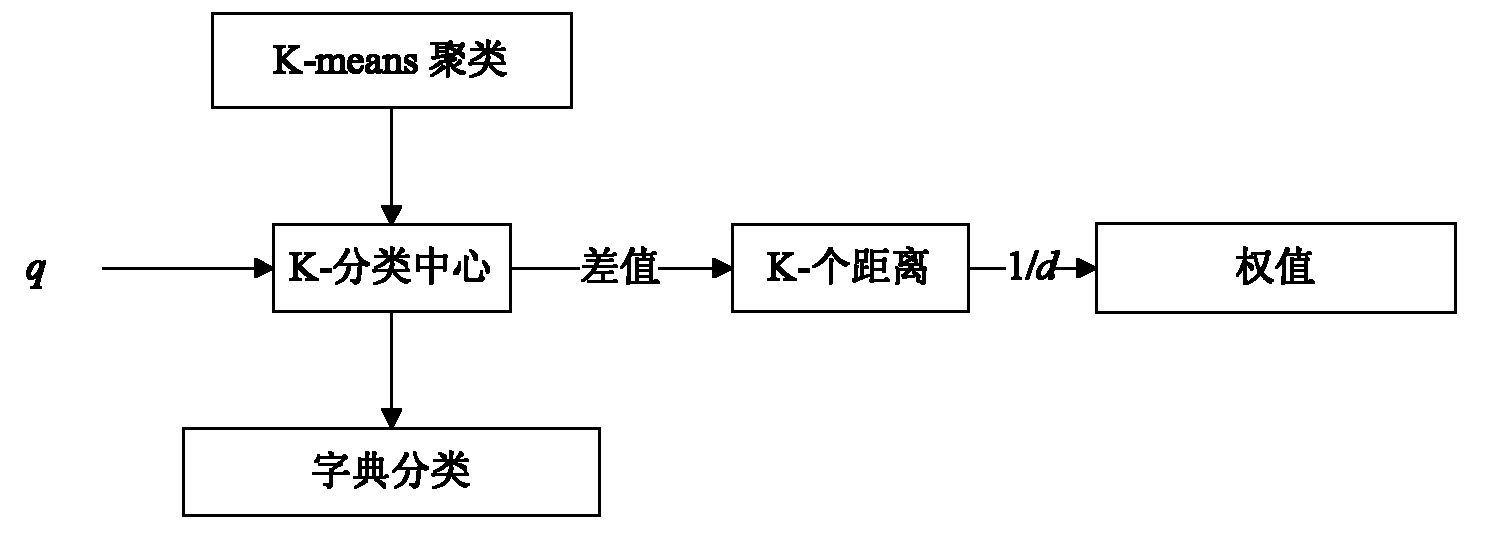
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multitask KSVD (K singular value decomposition) dictionary learning, mainly aims at solving the problem that the quality of a reconstructed image of the existing method is relatively reduced seriously under a high-magnification factor. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting a training image, filteringthe image to extract characteristics; extracting tectonic characteristics vector sets of small characteristic blocks, and clustering to obtain sample pair sets {(H1, L1), (H2, L2), ..., (HK, LK)} of K to high resolution and low resolution; developing K high-resolution dictionaries Dh1, Dh2, ..., DhK and corresponding low-resolution dictionaries Dl1, Dl2, ..., DlK from the K groups of sample pair sets by means of a KSVD method; encoding low-resolution patterns input in the low-resolution dictionaries Dl1, Dl2, ..., DlK; obtaining an initial reconstruction image by encoding and high-resolution dictionaries Dh1, Dh2, ..., Dh; then implementing local constrained optimization of the initial reconstruction image; and compensating residual errors and implementing global optimization treatment toobtain a final reconstruction image. The image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multitask KSVD dictionary learning has the advantages that the various natural images can be reconstructed, the quality of the reconstructed image can be effectively improved under the condition of a high-magnification factor, and the method can be applied to the recover and identification of human, animal, plant and building and other target objects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
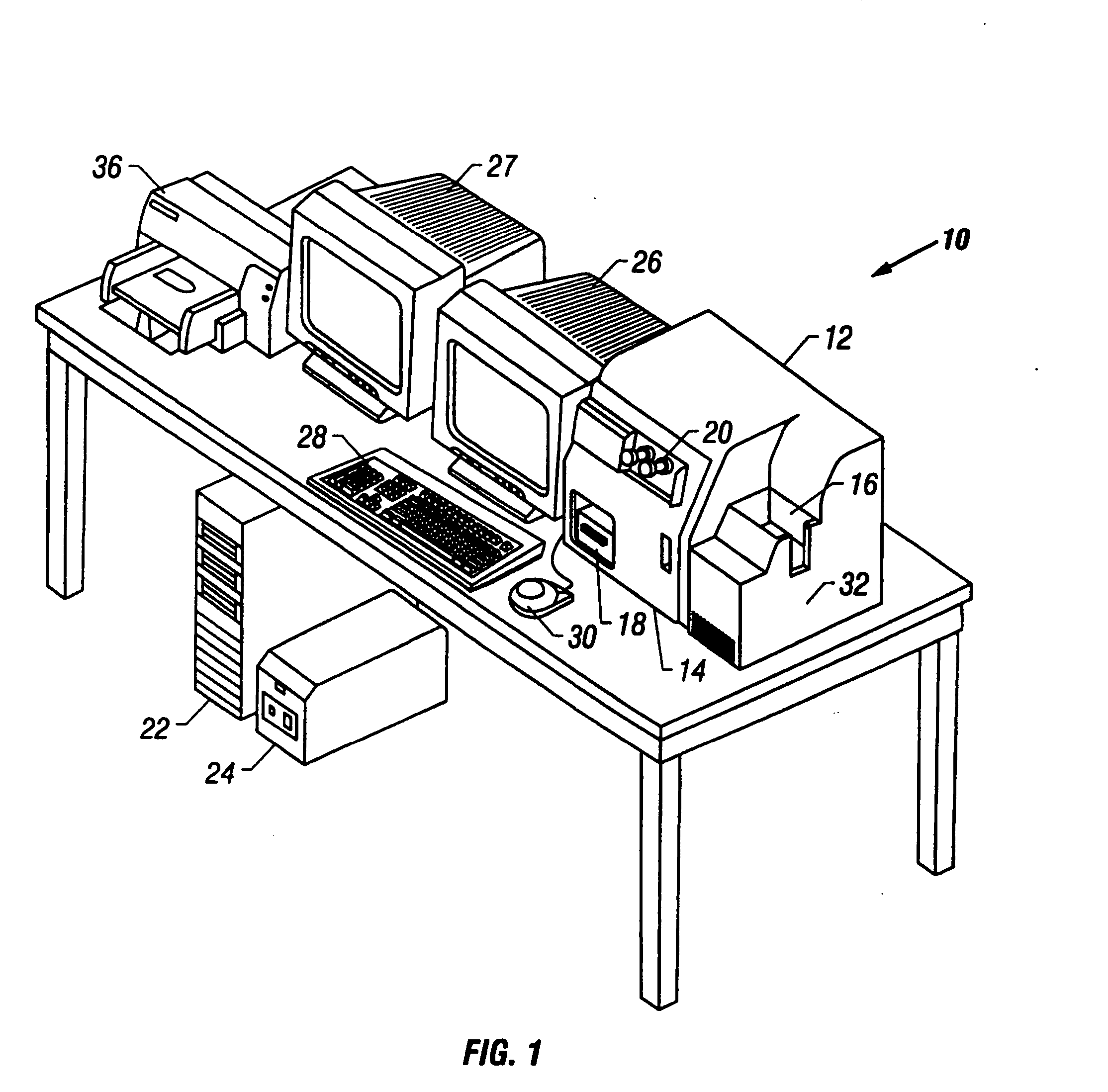
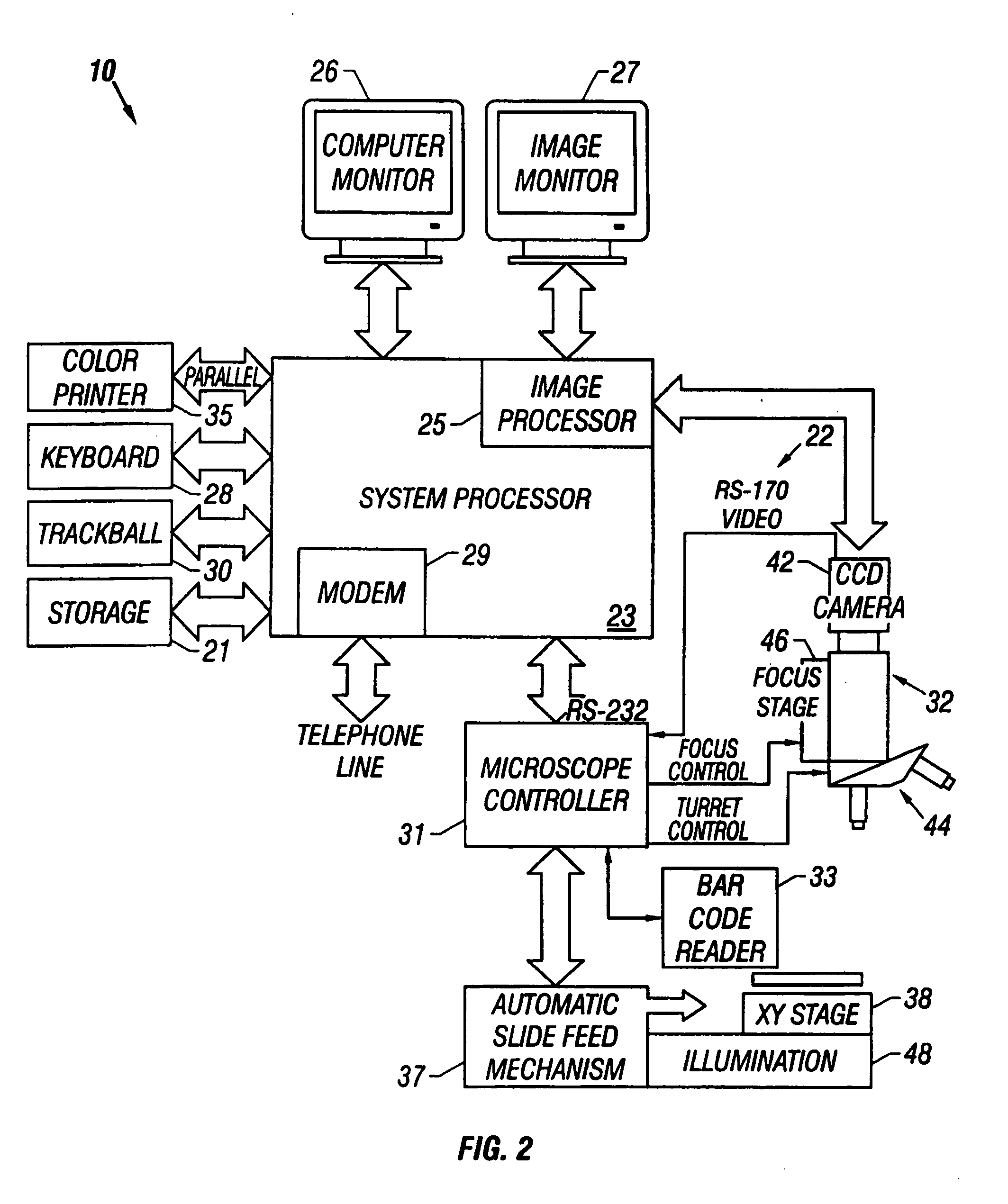
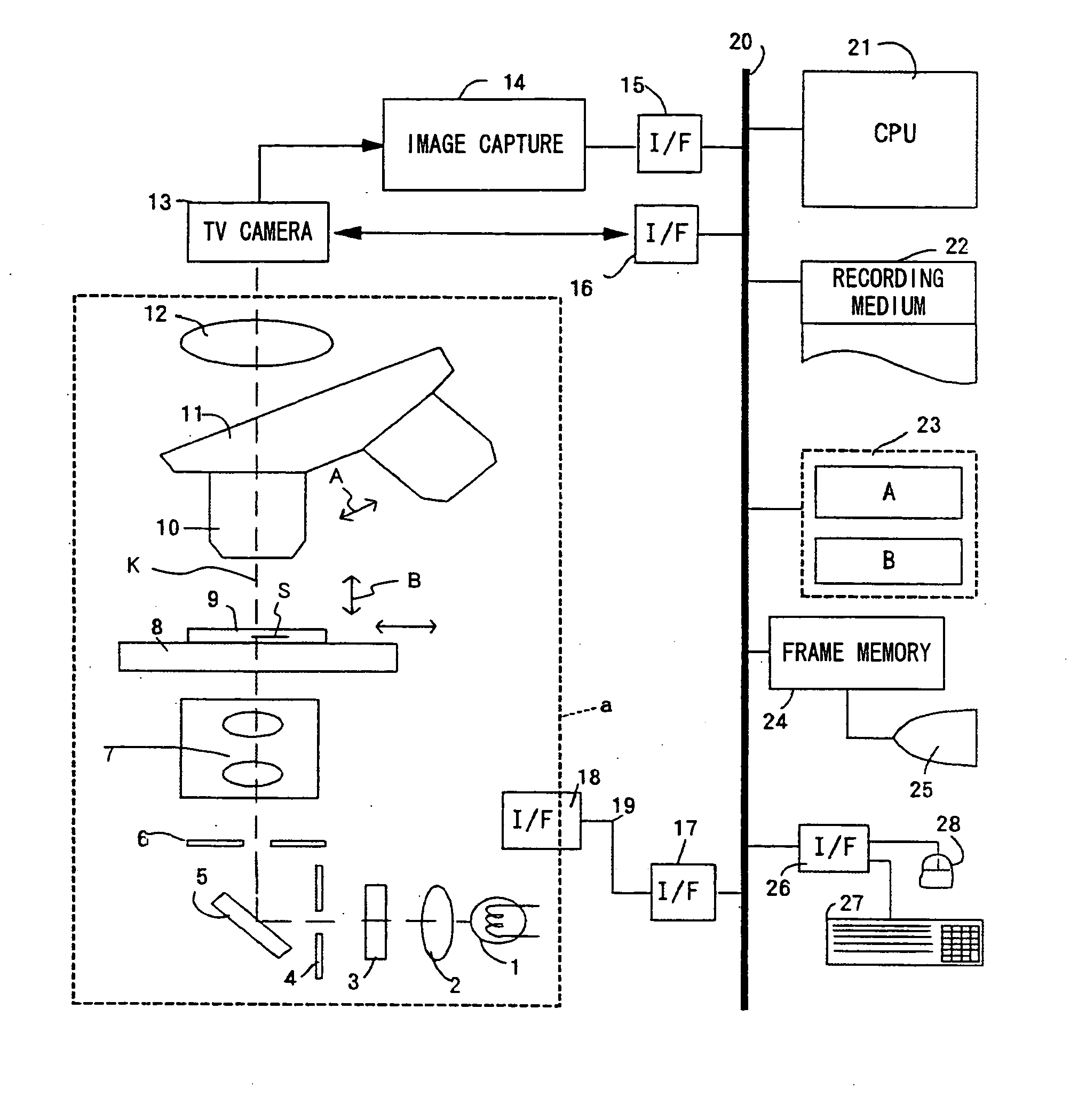
Apparatus for remote control of a microscope
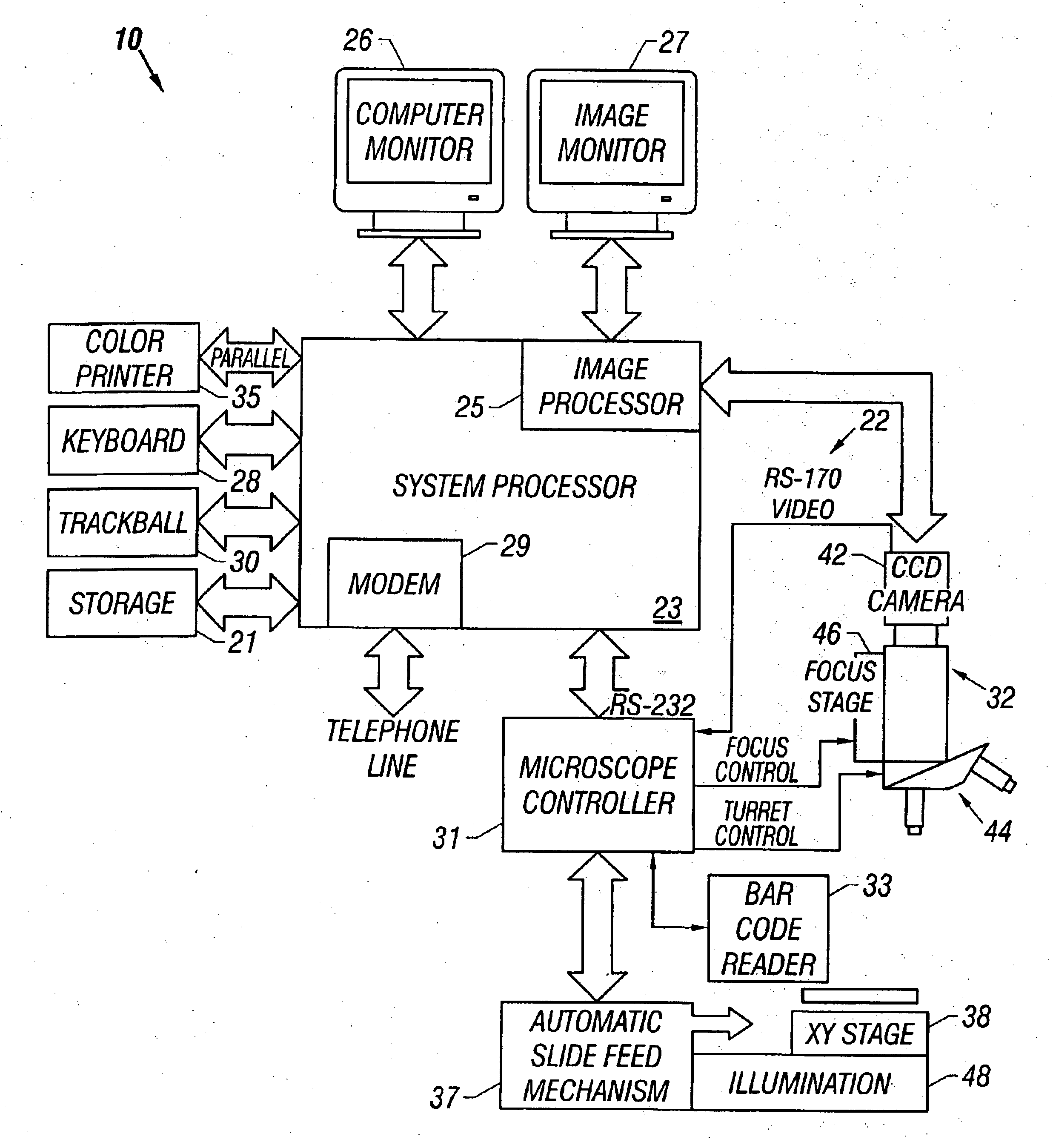
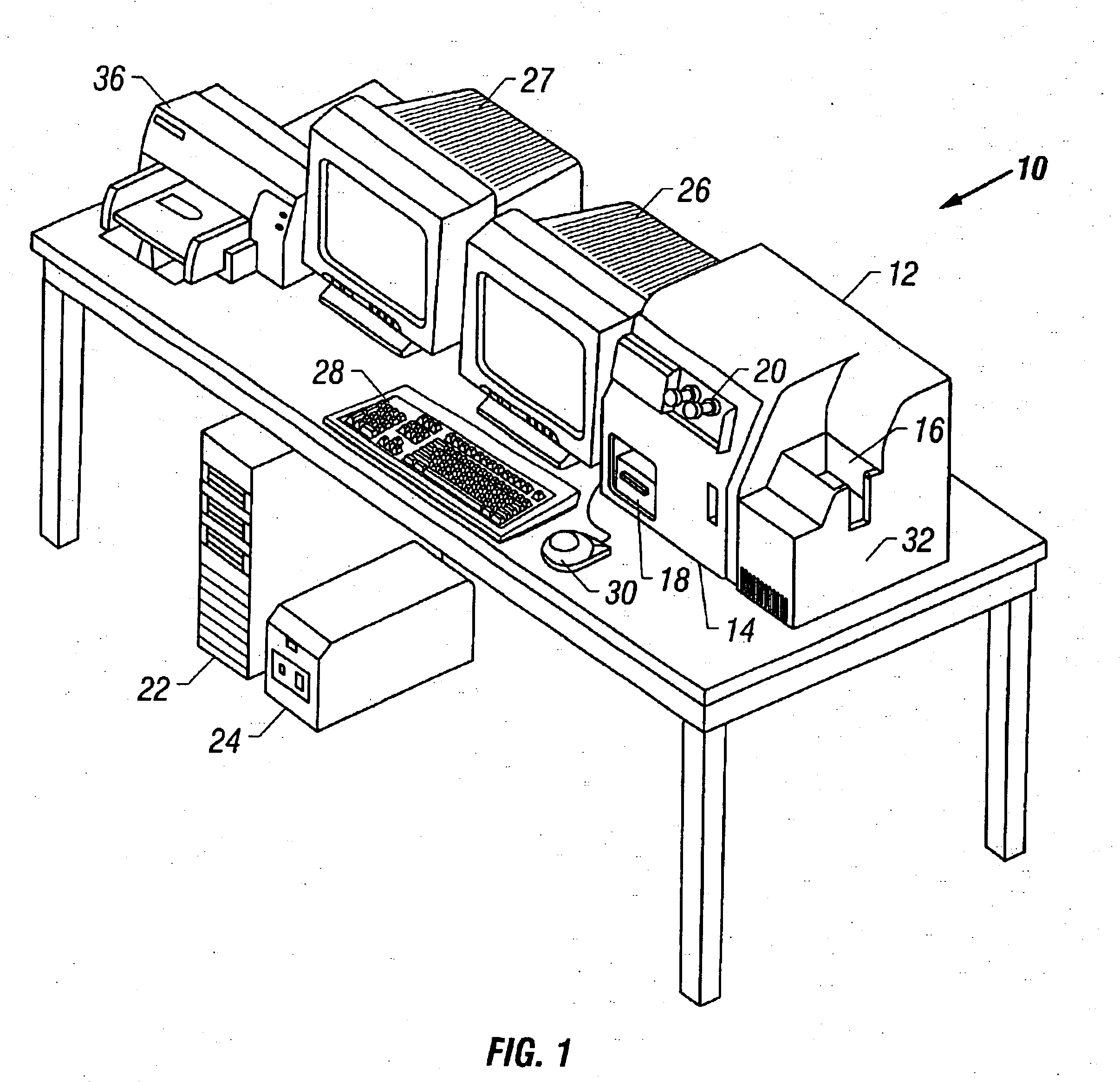
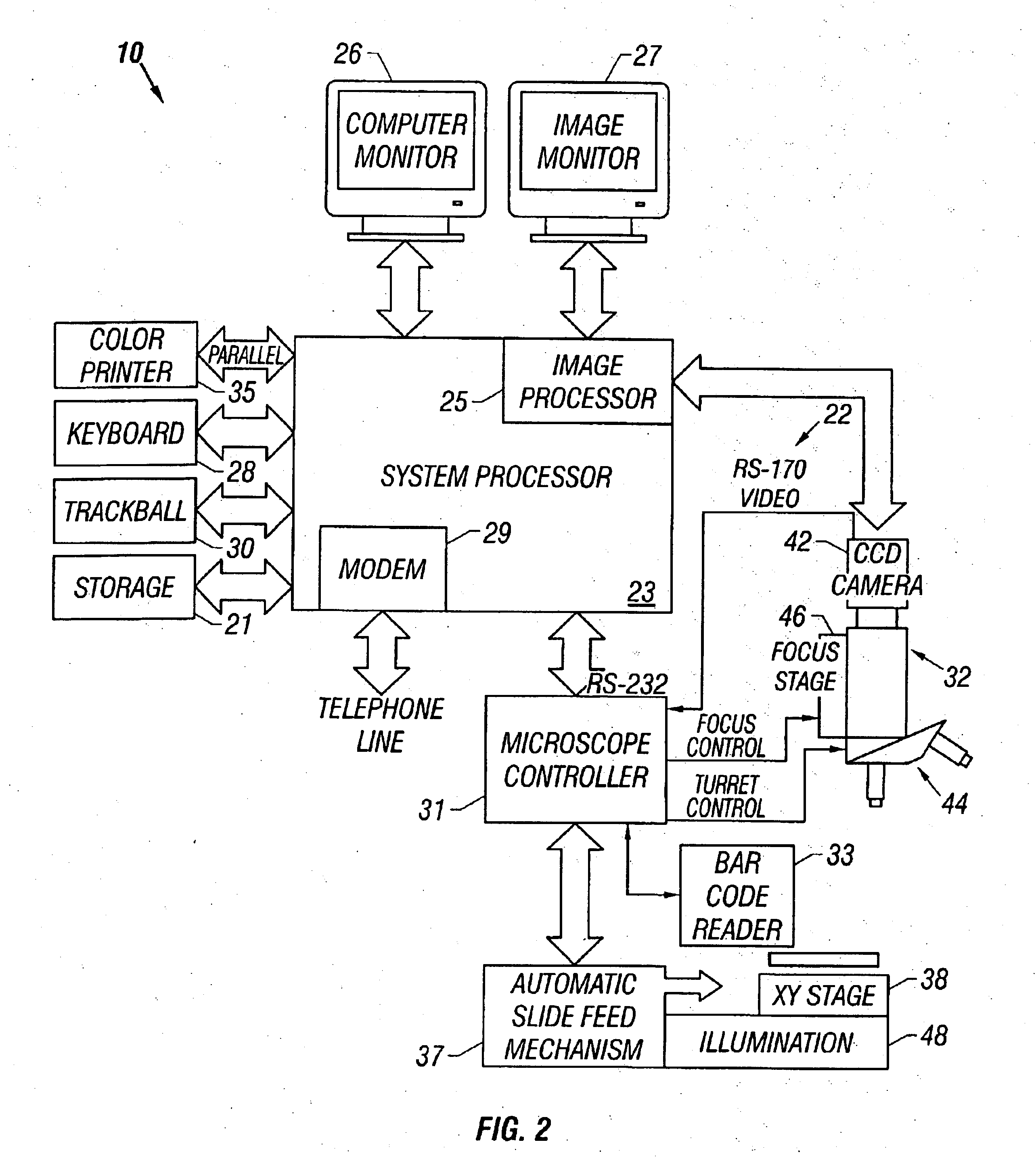
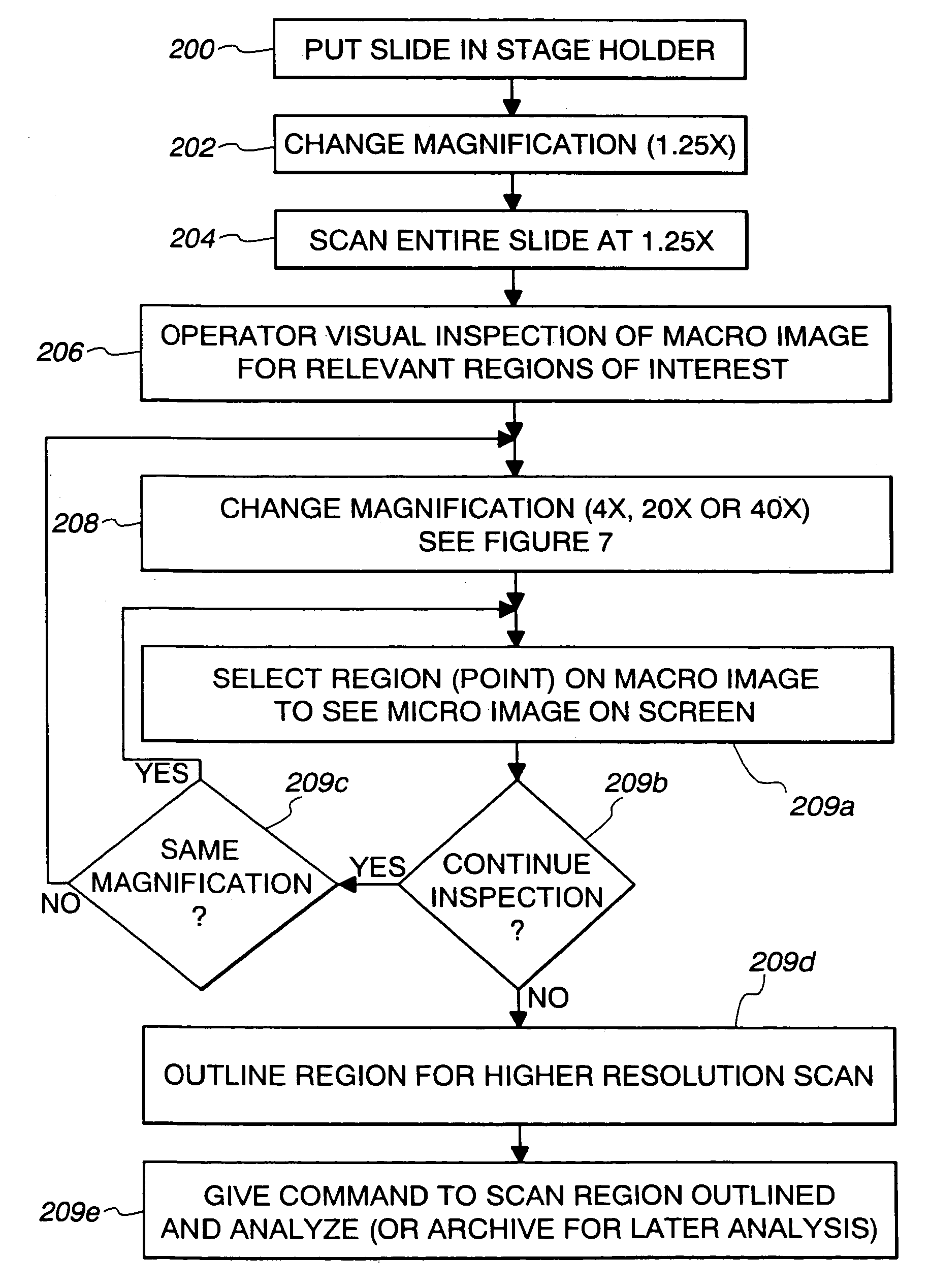
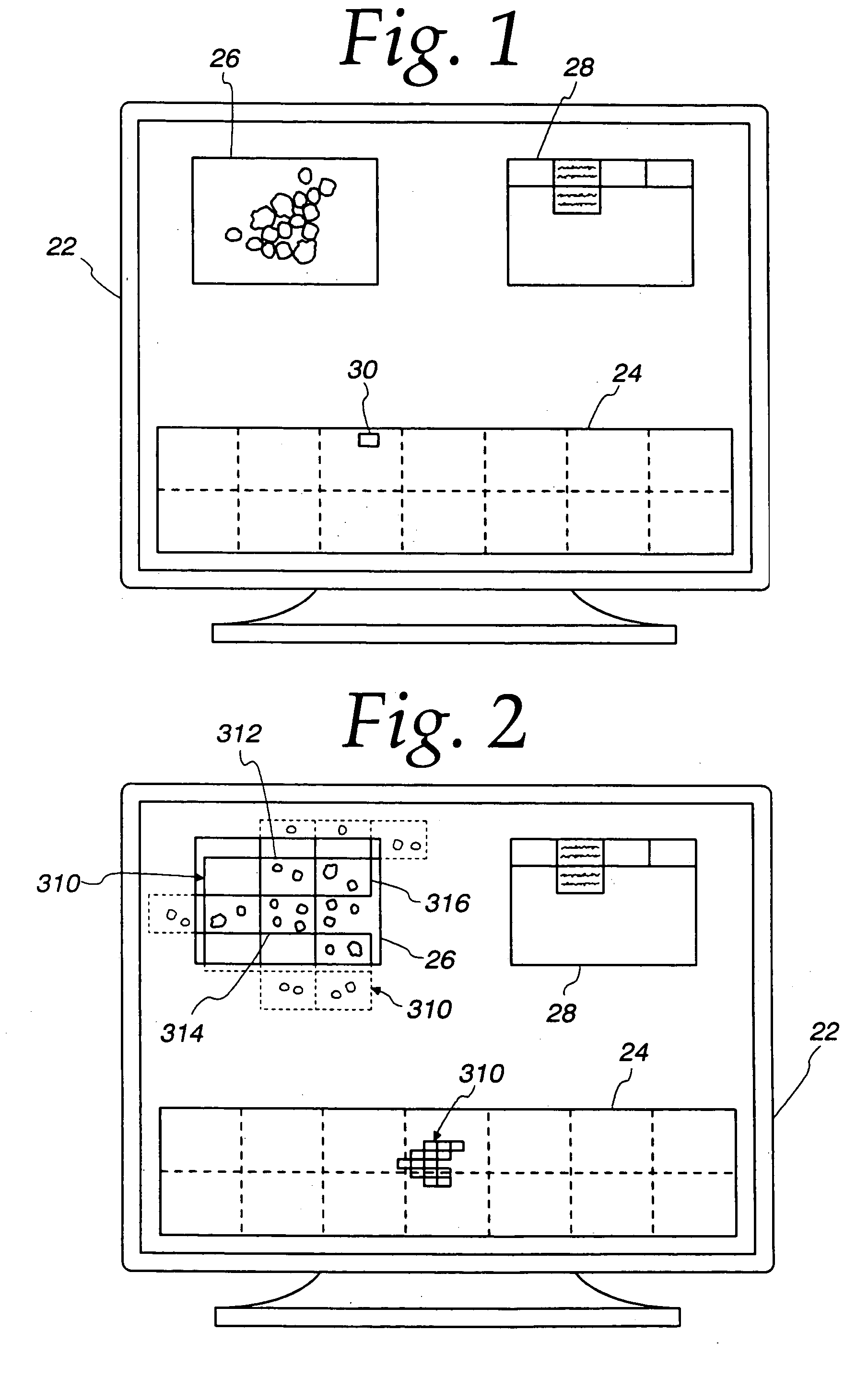
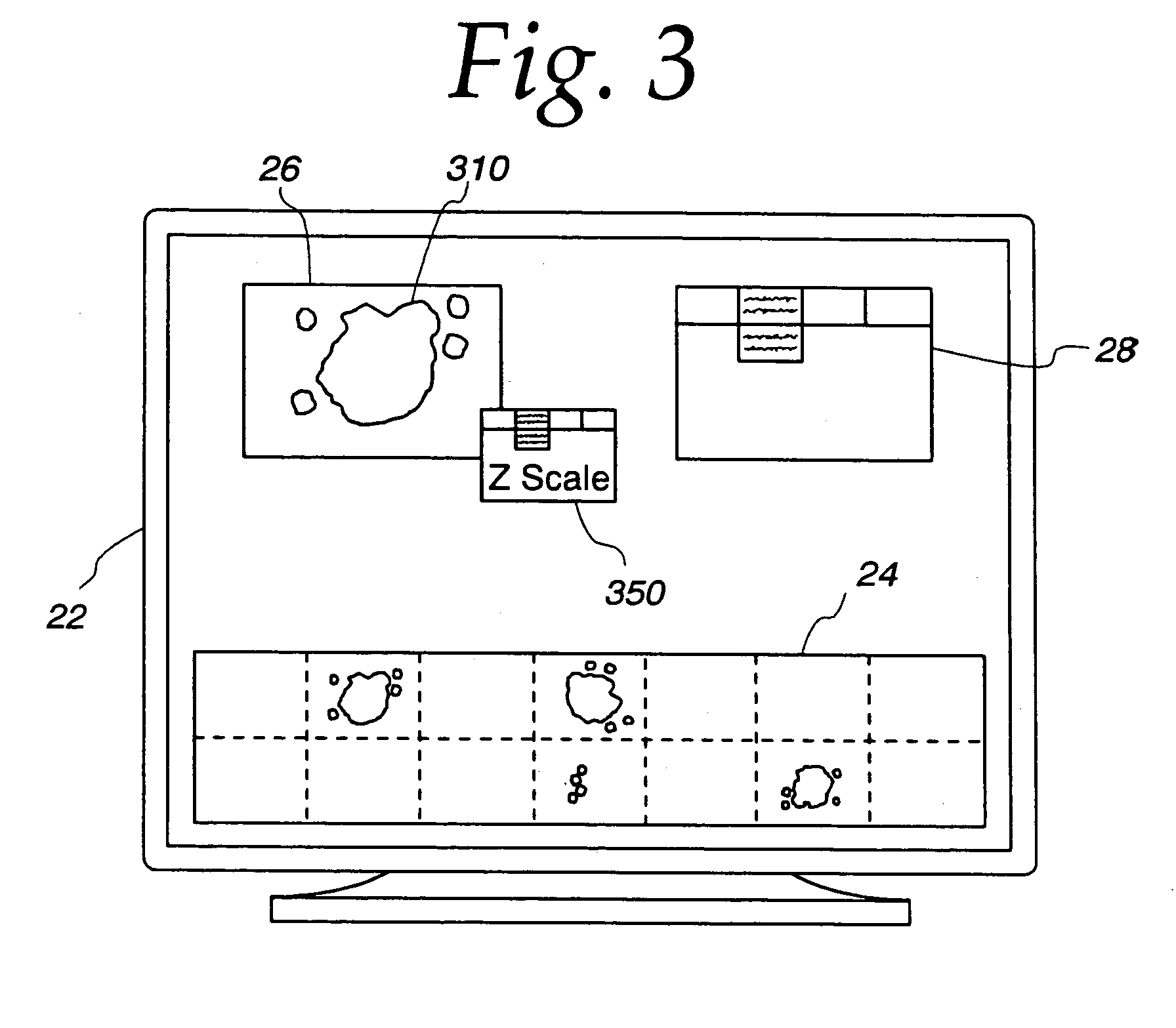
InactiveUS7110586B2Small field of viewLow magnificationImage analysisGeometric image transformationSoftware systemDisplay device
An apparatus and method acquires and stores multiple resolution images from a specimen on a support and provides to the user a low magnification, reconstructed macro image of the entire specimen, or a large portion thereof, to aid the person in selecting points of interest to be viewed or analyzed at higher magnifications and resolution. The reconstructed image is formed of a large number of tiled, stored images which are coordinated and assembled to form the macro image of the specimen which is displayed on a monitor. Preferably, the stored, reconstructed image is reduced further in size by a software system before it is displayed to the user. The display may be on a local monitor over a local area network or sent over the Internet to the user who is typically a pathologist. The user selects by a marker such as a cursor the defined area of interest or region and then views higher magnification images or has them analyzed. Preferably, the pathologist can scroll to shift digitized, adjacent image tiles into view on the monitor. A fully computer-controlled microscope is used to acquire and store the digitized images and the illustrated microscope can be remotely controlled to change objective lenses, focus, light intensity, filters, field diaphragm, and to shift the microscope stage by a controller.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
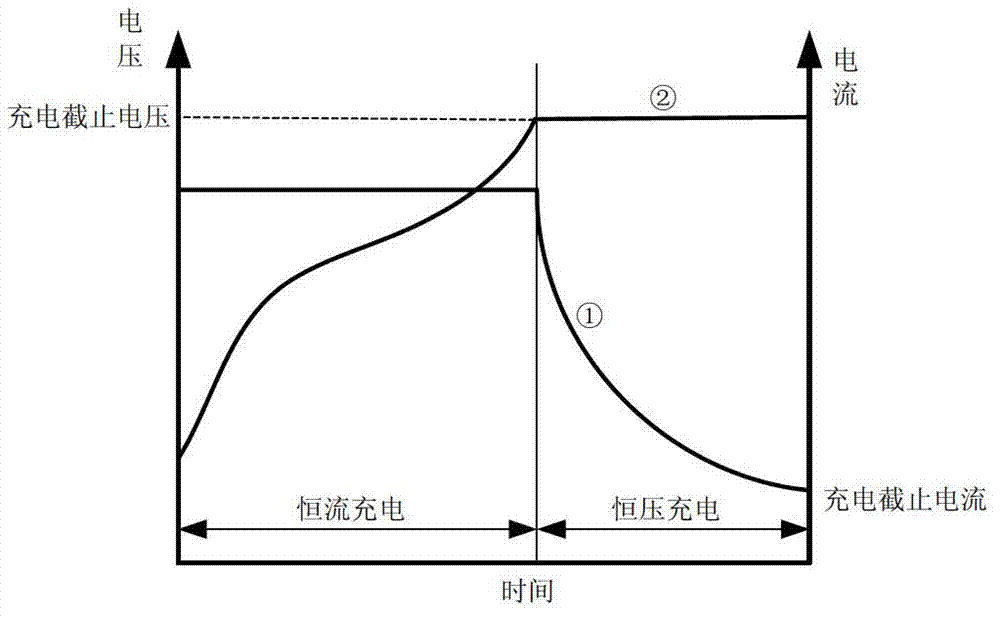
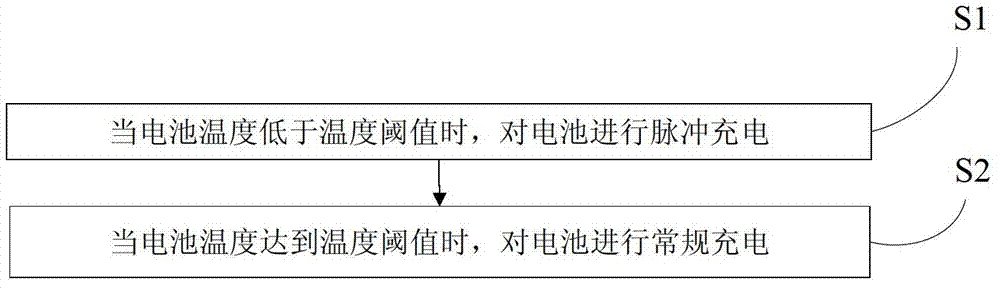
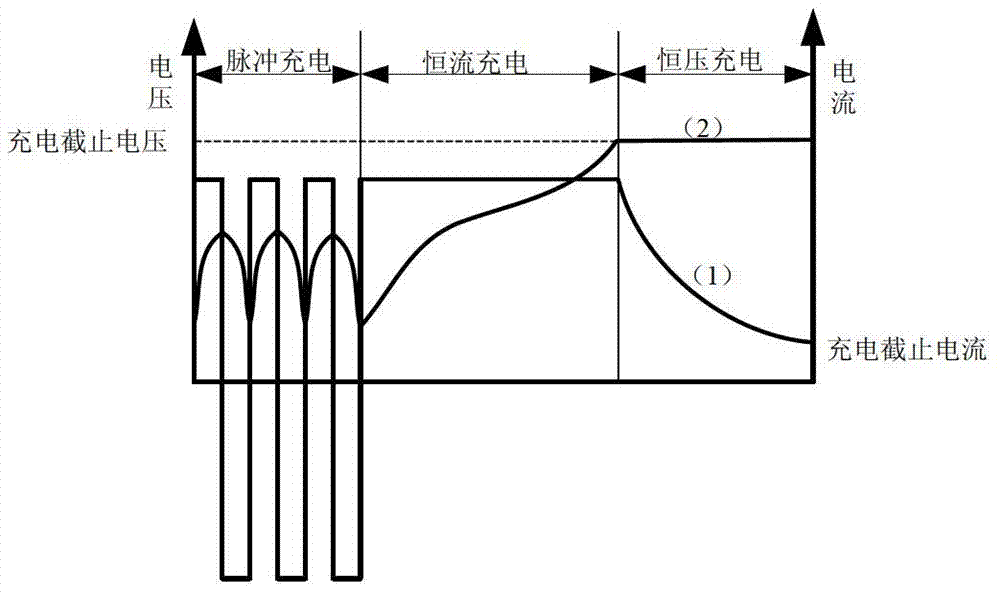
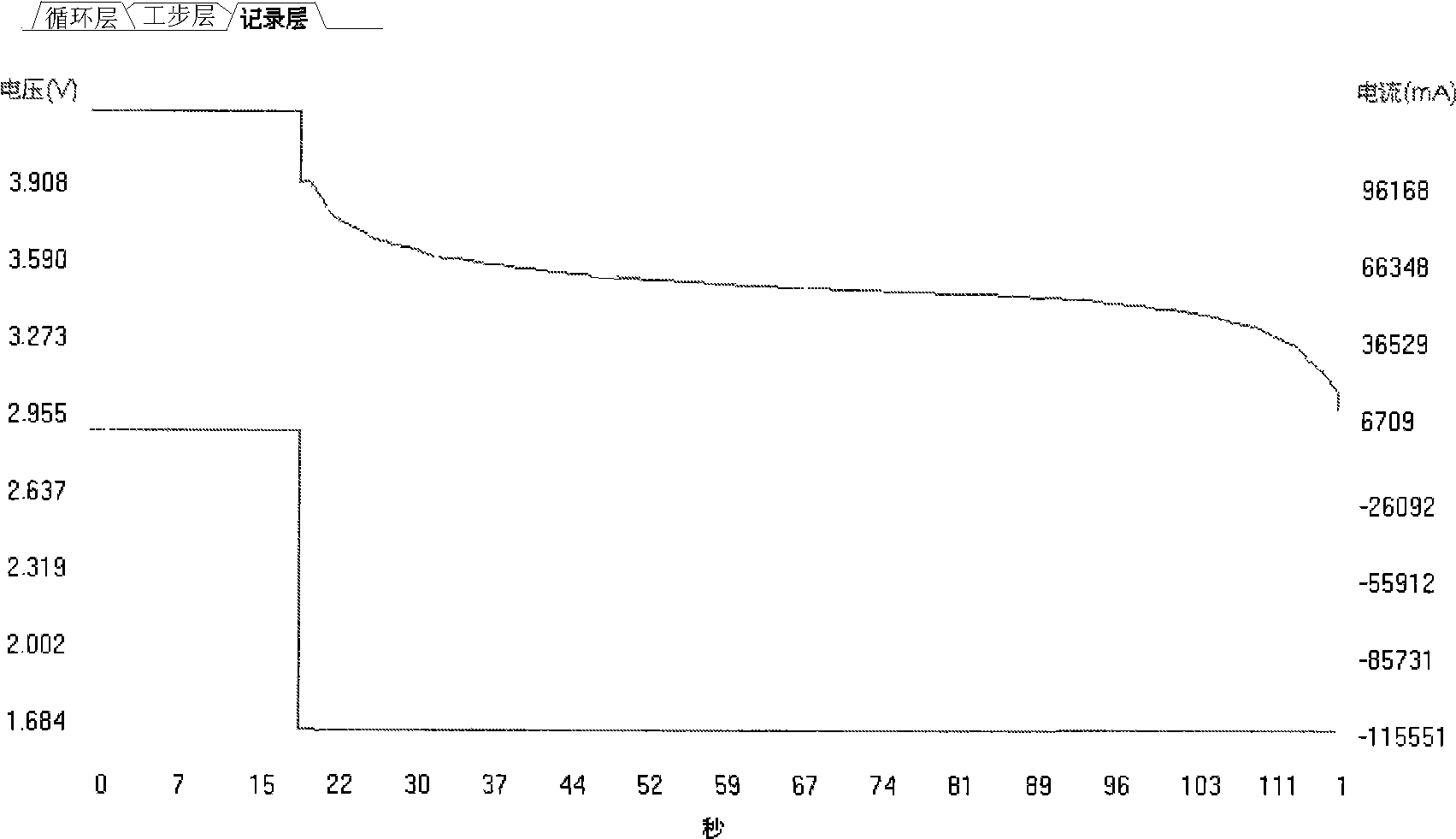
Low-temperature battery charging method
InactiveCN103117421AExtend your lifeMonitor voltage in real timeSecondary cells charging/dischargingLithiumThermal threshold
The invention discloses a low-temperature battery charging method which comprises the following steps that: when the battery temperature is lower than a temperature threshold, a battery is subjected to pulsed charging; and when the battery temperature reaches the temperature threshold, the battery is charged normally. The low-temperature battery charging method provided by the invention can be used for charging a battery at a low temperature according to the super long cycle service of the novel battery and avoidance of side effects of separation out of lithium ions at a negative electrode in high-magnification charging at a low temperature and the like, and the battery can be charged at a low temperature to a degree which is equivalent to that of charging at a normal temperature. The low-temperature battery charging method has the advantages of safety, reliability, high charge efficiency and prolongation of service life of the battery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
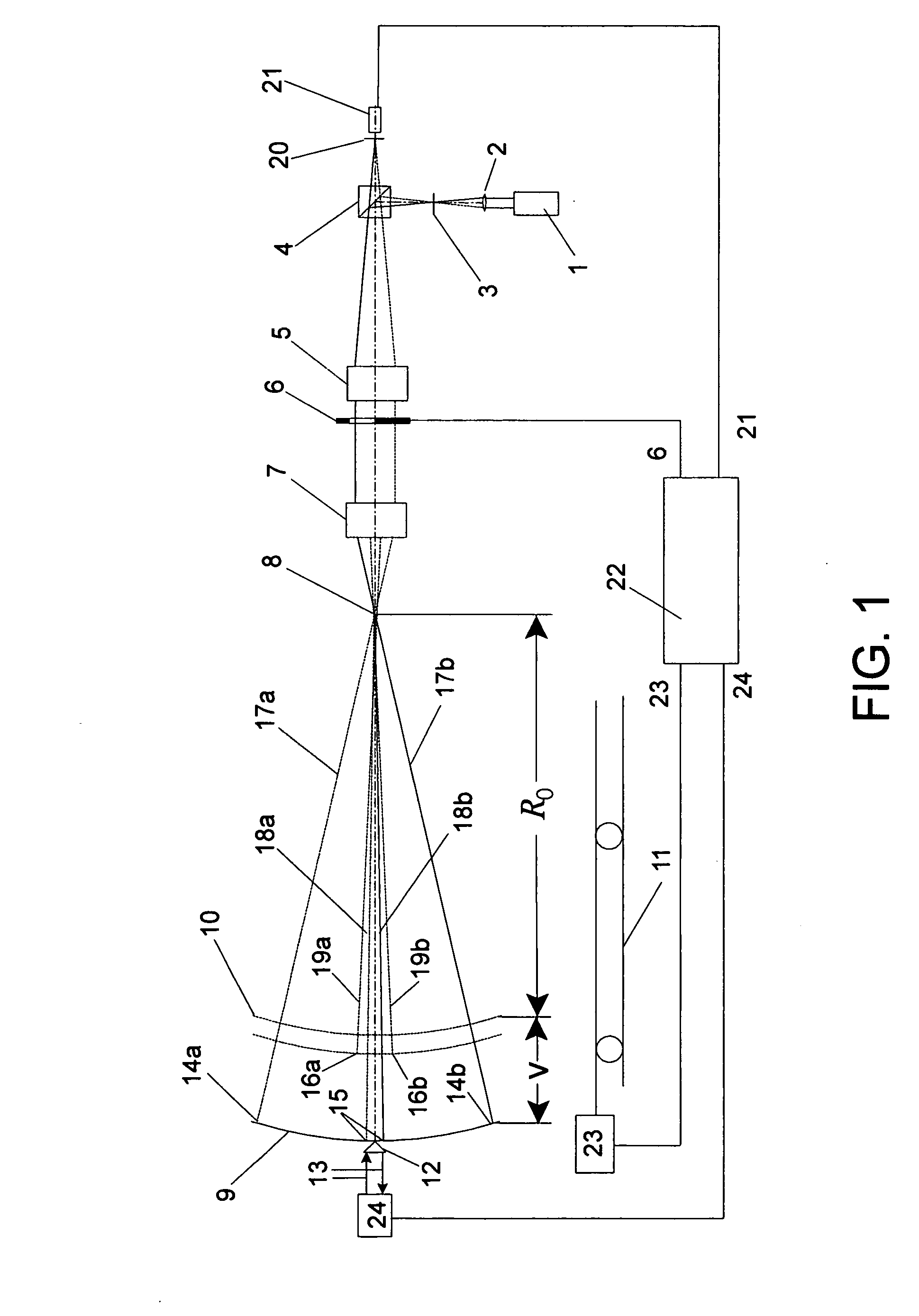
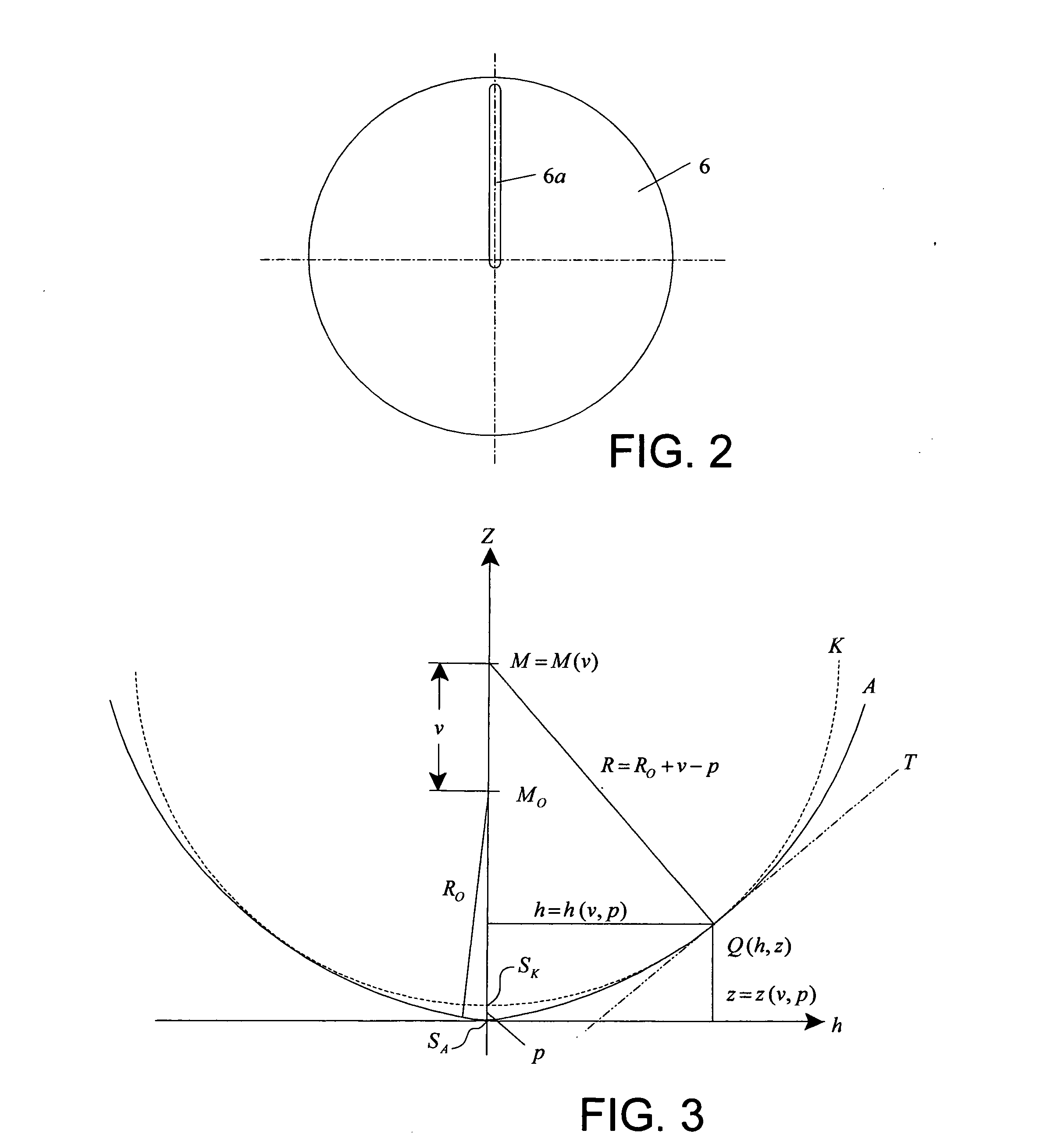
Scanning interferometer for aspheric surfaces and wavefronts
Interferometric scanning method(s) and apparatus for measuring rotationally and non-rotationally symmetric test optics either having aspherical surfaces or that produce aspherical wavefronts. A spherical or partial spherical wavefront is generated from a known location along a scanning axis though the use of a decollimator carrying a spherical reference surface. The test optic is aligned with respect to the scanning axis and selectively moved along it relative to the known origin so that the spherical wavefront intersects the test optic at the apex of the aspherical surface and at radial zones where the spherical wavefront and the aspheric surface possess common tangents. The test surface is imaged onto a space resolving detector to form interferograms containing phase information about the differences in optical path length between the spherical reference surface and the test surface while the axial distance, v, by which said test optic moves relative to said spherical reference surface is interferometrically measured. Based on an analysis of the phase information contained in the interferograms and the axial distance, v, the deviation in the shape of the aspheric surface from its design in a direction normal to the aspheric surface is determined. In scanning, two cameras having different magnification are preferably used simultaneously with the one of higher magnification observing near the part axis where high fringe densities occur while that of lower magnification observes the full part surface. Special procedures are described for alternately improving accuracy near the axis.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
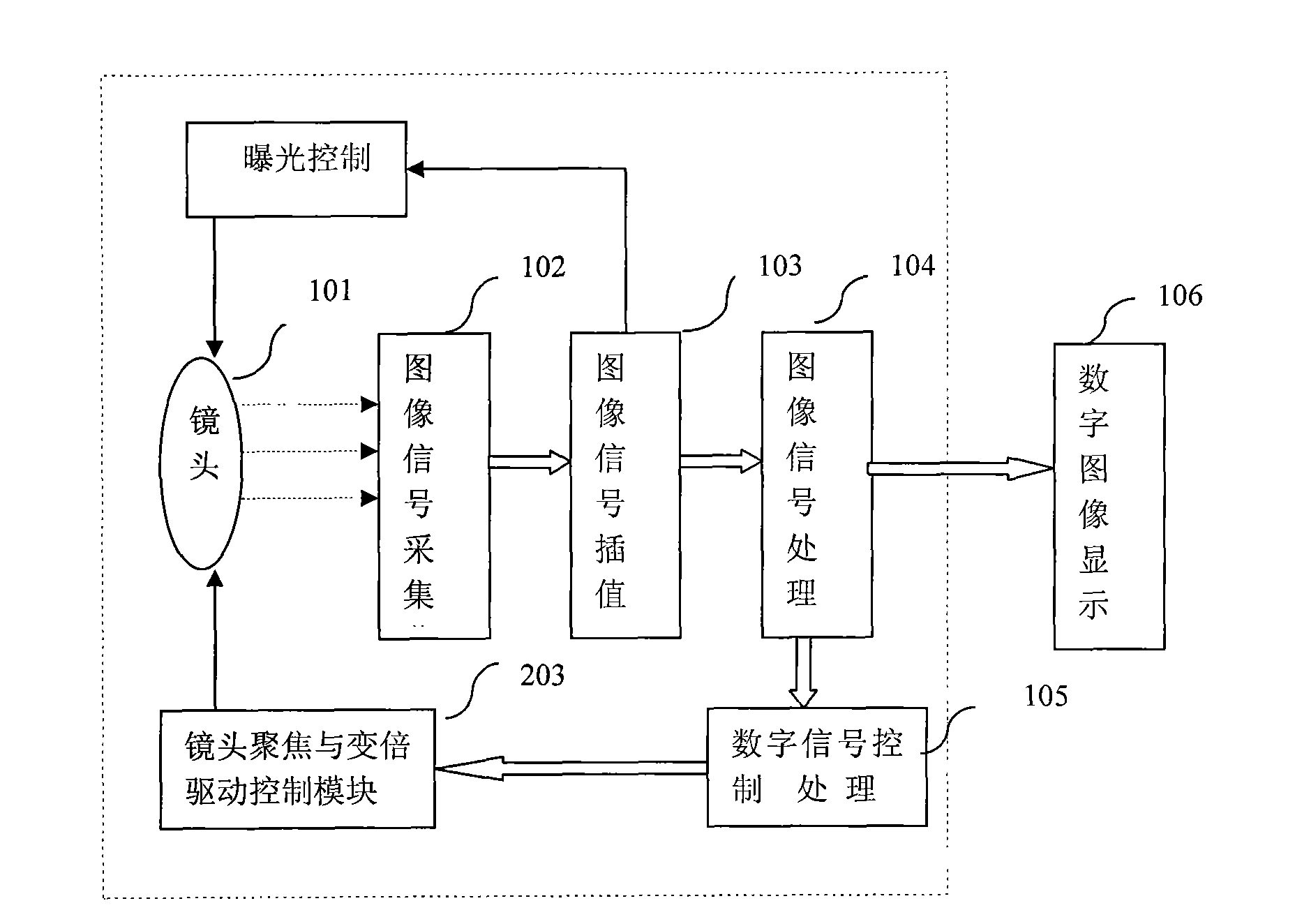
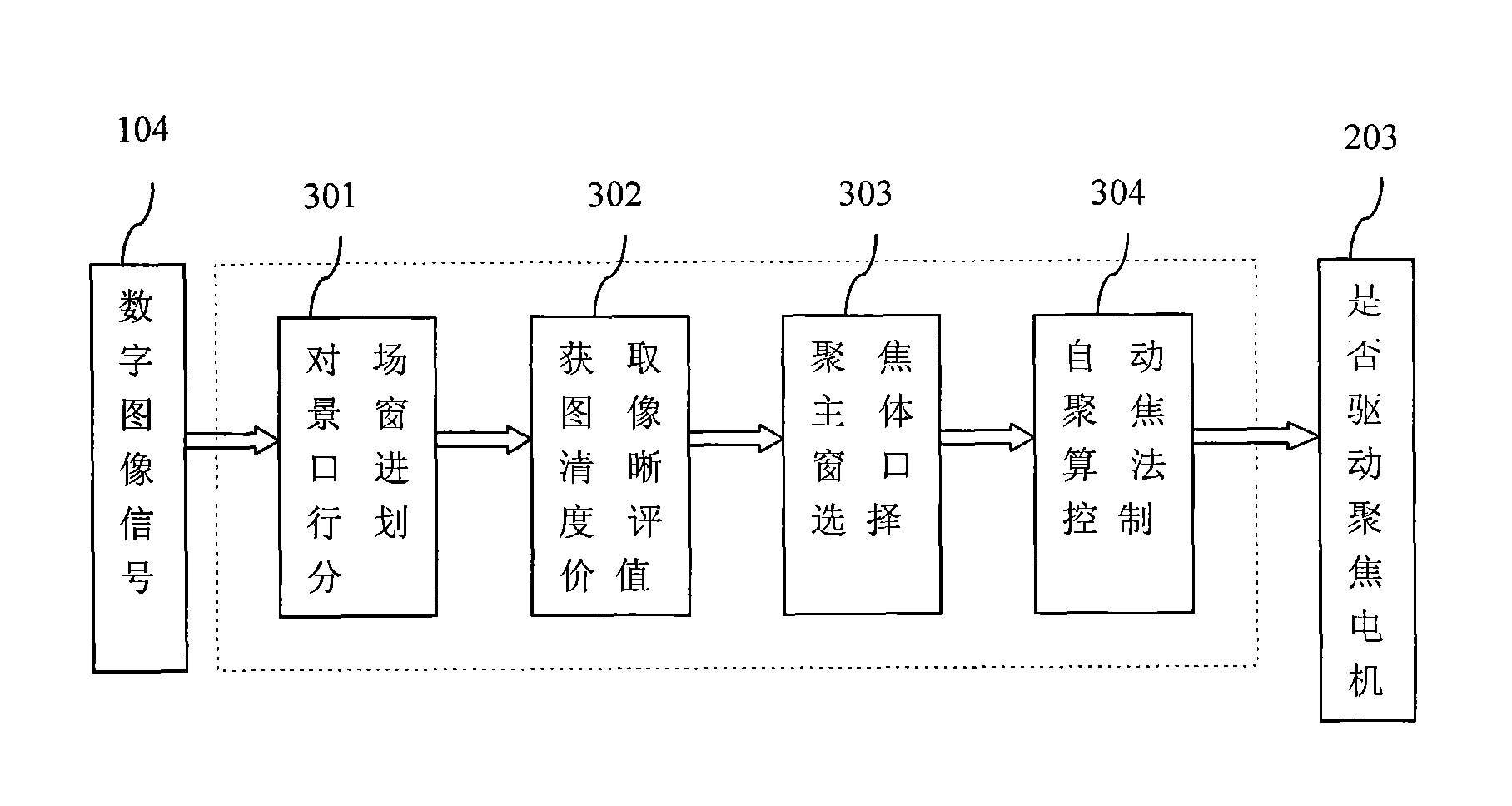
Rapid and automatic focusing method and system for camera zoom
ActiveCN103929588AImprove visual effectsFast focusingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensIlluminance
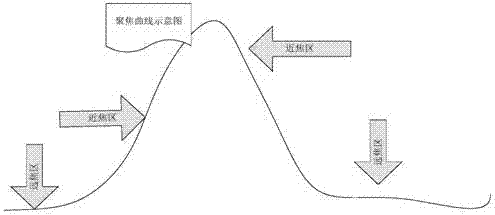
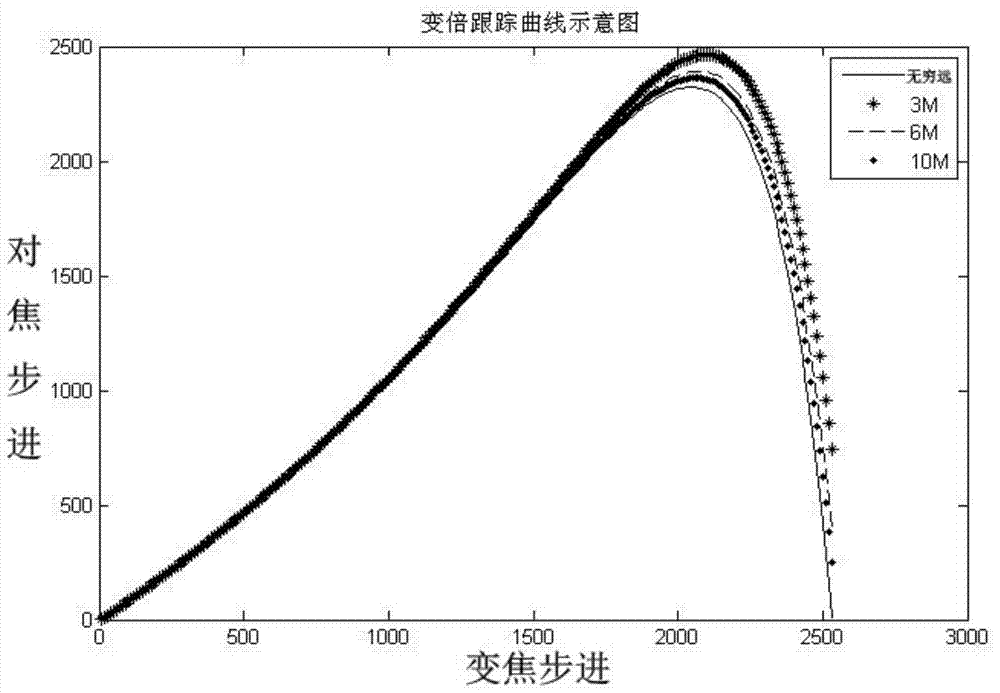
The invention provides a rapid and automatic focusing method and system for camera zoom. The rapid and automatic focusing method and system have the advantages that in the camera zoom process, the distance between a current scene center object and a lens is judged according to the last focusing position of a focusing motor, and therefore the closet tracking curve is selected for tracking; compared with the original mode that an image is significantly out of focus with high magnification due to the scheme that zoom is conducted at first and then focusing is conducted, the focusing speed can be greatly improved after zoom. The invention further provides a rapid and automatic focusing process. Different focusing modes are selected according to different illumination intensities and magnifications, and the focusing process comprises the step of rapid search of the near-focus area and the step of self-adaptive climbing. The focusing speed and accuracy and the image visual effect in the focusing process are greatly improved.
Owner:SANLI VIDEO FREQUENCY SCI & TECH SHENZHEN
Pattern measurement apparatus
ActiveUS20090039263A1High magnificationImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputer scienceHigh magnification
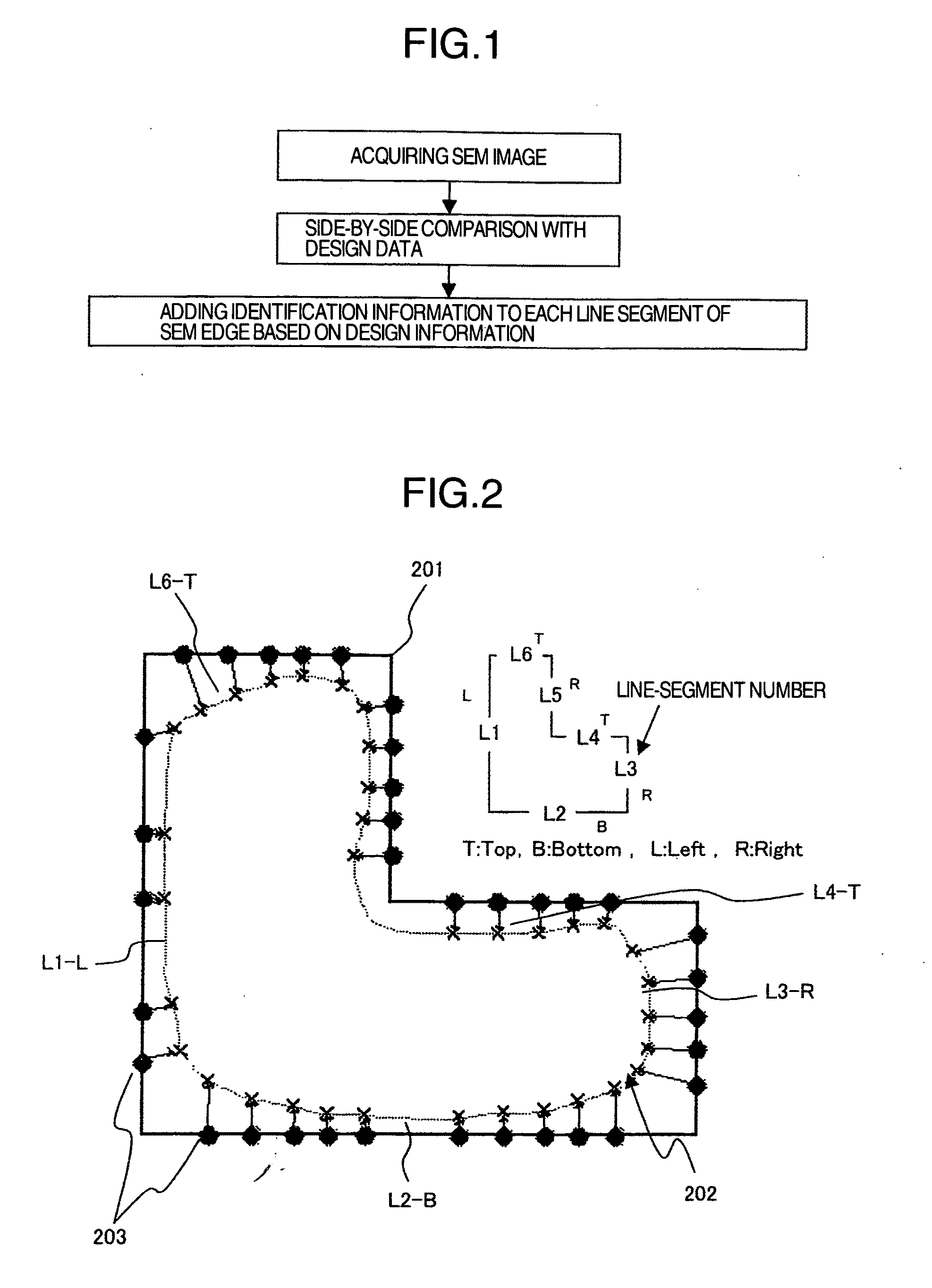
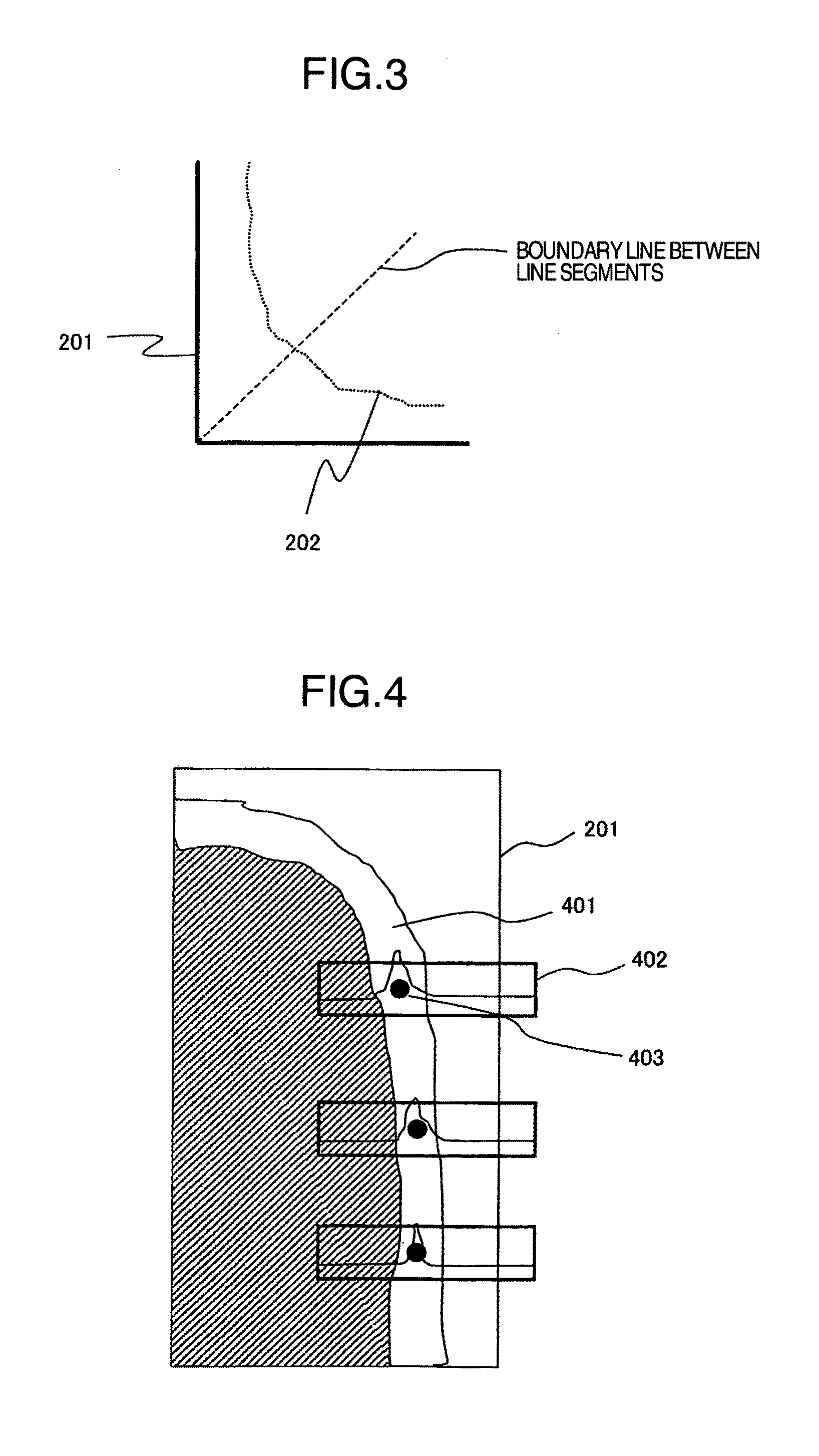
Mutual compatibility is established between the measurement with a high magnification and the measurement in a wide region. A pattern measurement apparatus is proposed which adds identification information to each of fragments that constitute a pattern within an image obtained by the SEM, and which stores the identification information in a predetermined storage format. Here, the identification information is added to each fragment for distinguishing between one fragment and another fragment. According to the above-described configuration, it turns out that the identification information is added to each fragment on the SEM image which has possessed no specific identification information originally. As a result, it becomes possible to implement the SEM-image management based on the identification information.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Ultra-high magnification lithium ion battery
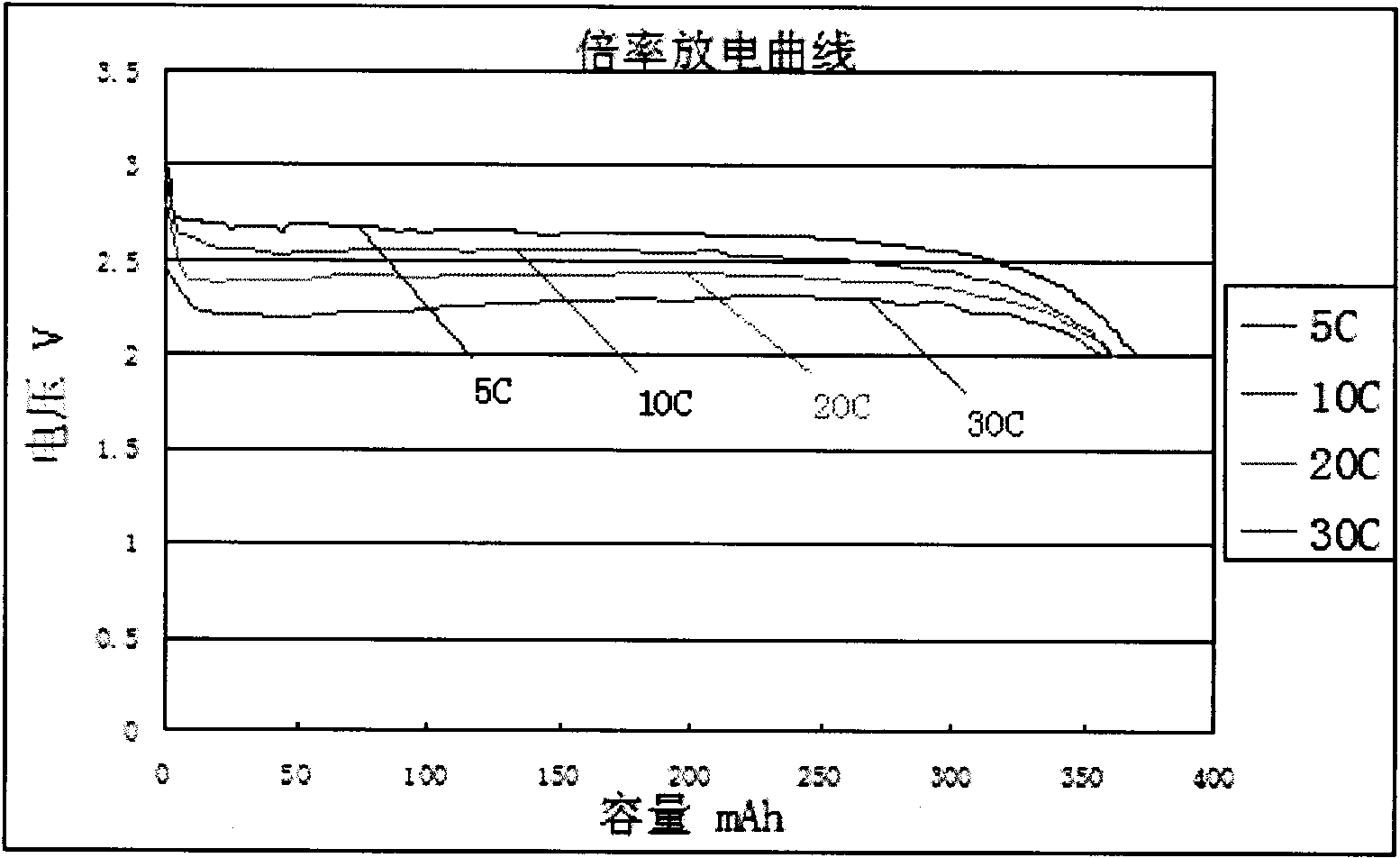
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery with superhigh multiplying power, which comprises a positive plate, a negative plate, a membrane, an electrolyte solution, a plate lug and a packing shell. The positive plate is manufactured by coating the mixed slurry of a positive active material, a conducting agent and a cementing agent on both sides of an aluminium foil; the negative plate is manufactured by coating the mixed slurry of a negative active material, the conducting agent and the cementing agent on both sides of a copper foil; and the electrolyte solution is a mixed solution of lithium and an organic solvent. The lithium ion battery is capable of discharging continually at a superhigh multiplying power and the discharge multiplying power can reach 35C-50C. The discharge capacity of the discharge multiplying power at 35C, 40C, 45C, 50C can respectively reach 96.3 percent, 95.6 percent, 95.1 percent and 94.5 percent of the discharge capacity at 1C.
Owner:XIAN SAFTY ENERGY TECH
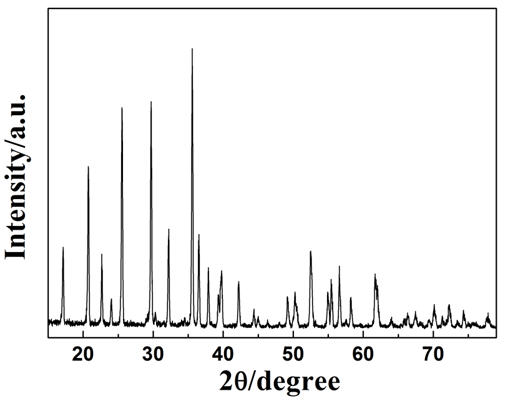
Resource-saving glazed ceramic tile having antiskid effect on surface and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105837172AAchieve anti-slip effectGood quality glazeCeramic materials productionClaywaresBrickSludge
A resource-saving glazed ceramic tile having an antiskid effect on surface and a preparation method thereof. Without great change on production process of the glazed ceramic tiles, formula composition of a blank body, composition of ground and cover glaze frits and formula composition of ground and cover glaze are regulated and optimized focusedly, so that the glazed ceramic tile, which has excellent performance and the antiskid effect, can be prepared even large quantity sludge residue is added to the blank body. Through a high-magnification scanning electronic microscopy for observing the surface of glaze on the product, it is found that projects which are hard and needle-like and look like aluminum spinel crystal are formed on the surface, and the glaze is 0.8 in antiskid coefficient and is R12 in antiskid level when a less quantity of water is sprayed on the glaze. The glazed ceramic tile has good antiskid effect, can reach 4000 r / four grade in wear-resisting revolution through detection, and has good anti-wear performance, surface anti-fouling performance and water permeation resistance. The glaze has no defects such as needle pores, bubbles and the like, has clear decorative pattern grains and is highly stone-simulated. The technology has strong adaptability and is easy to promote in the field.
Owner:GUANGDONG WINTO CERAMICS +3
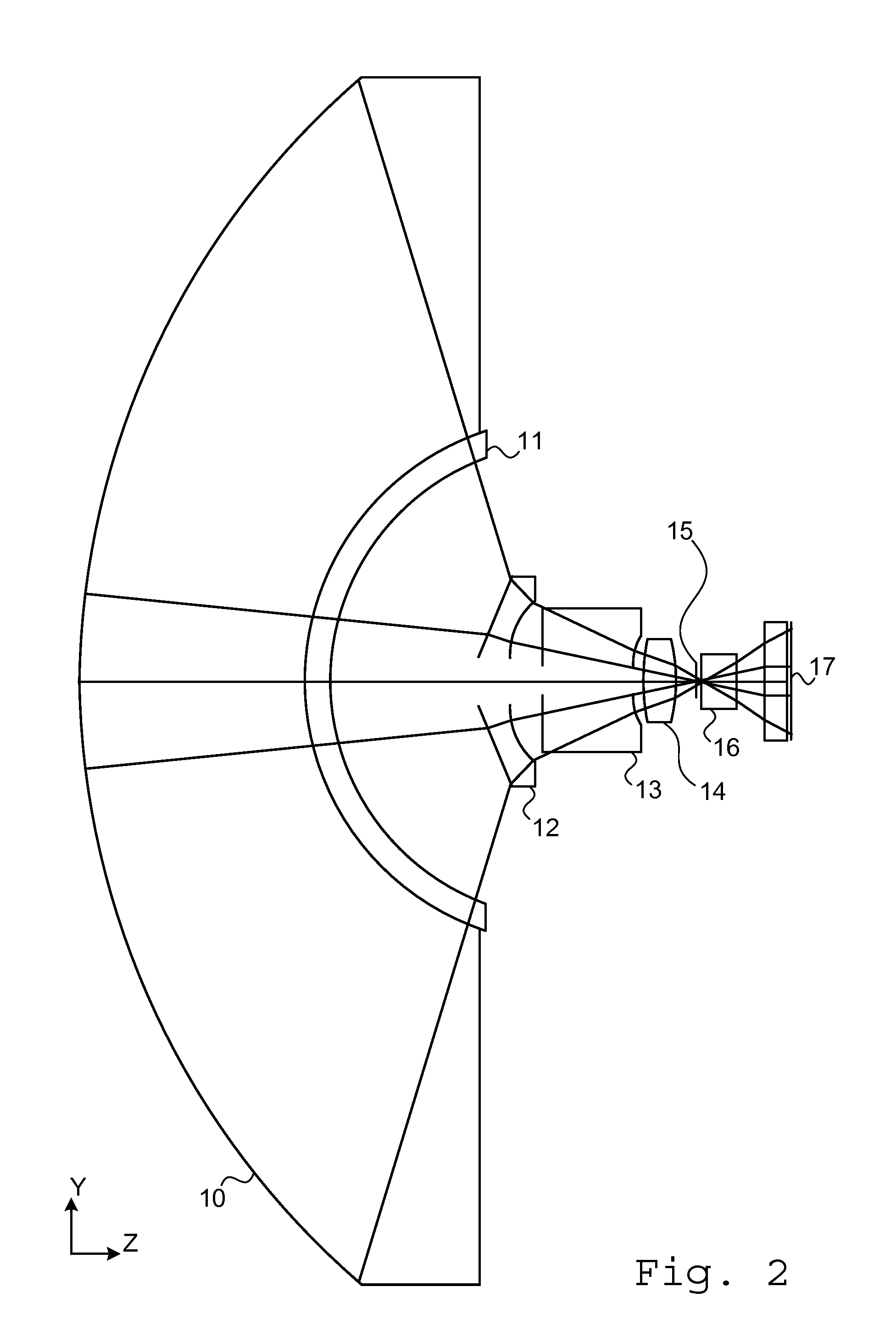
Ophthalmic photography apparatus
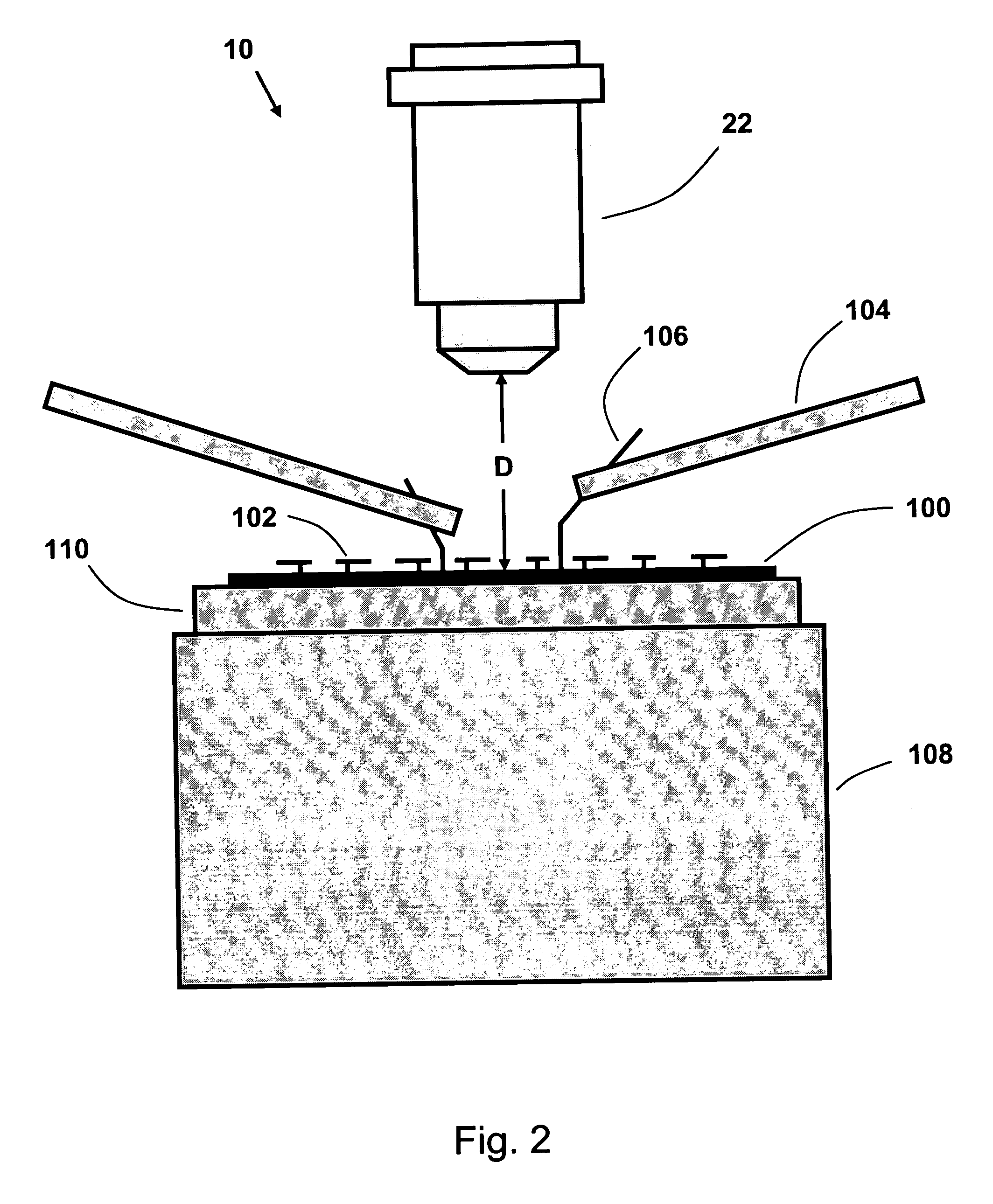
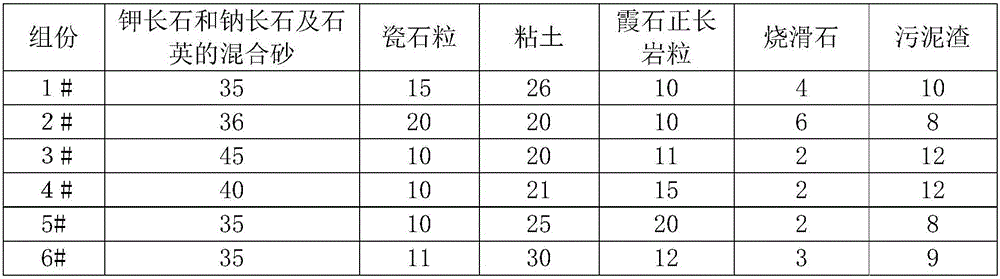
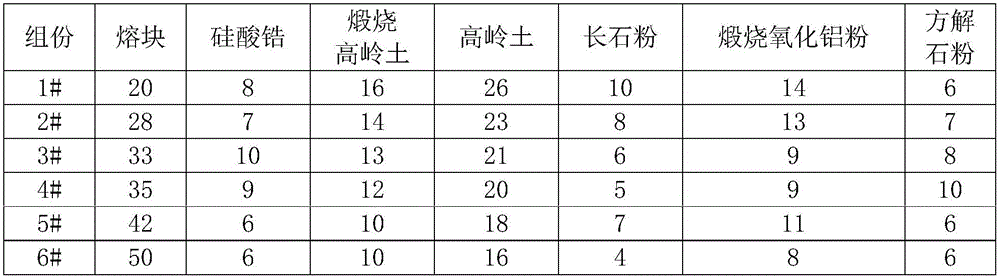
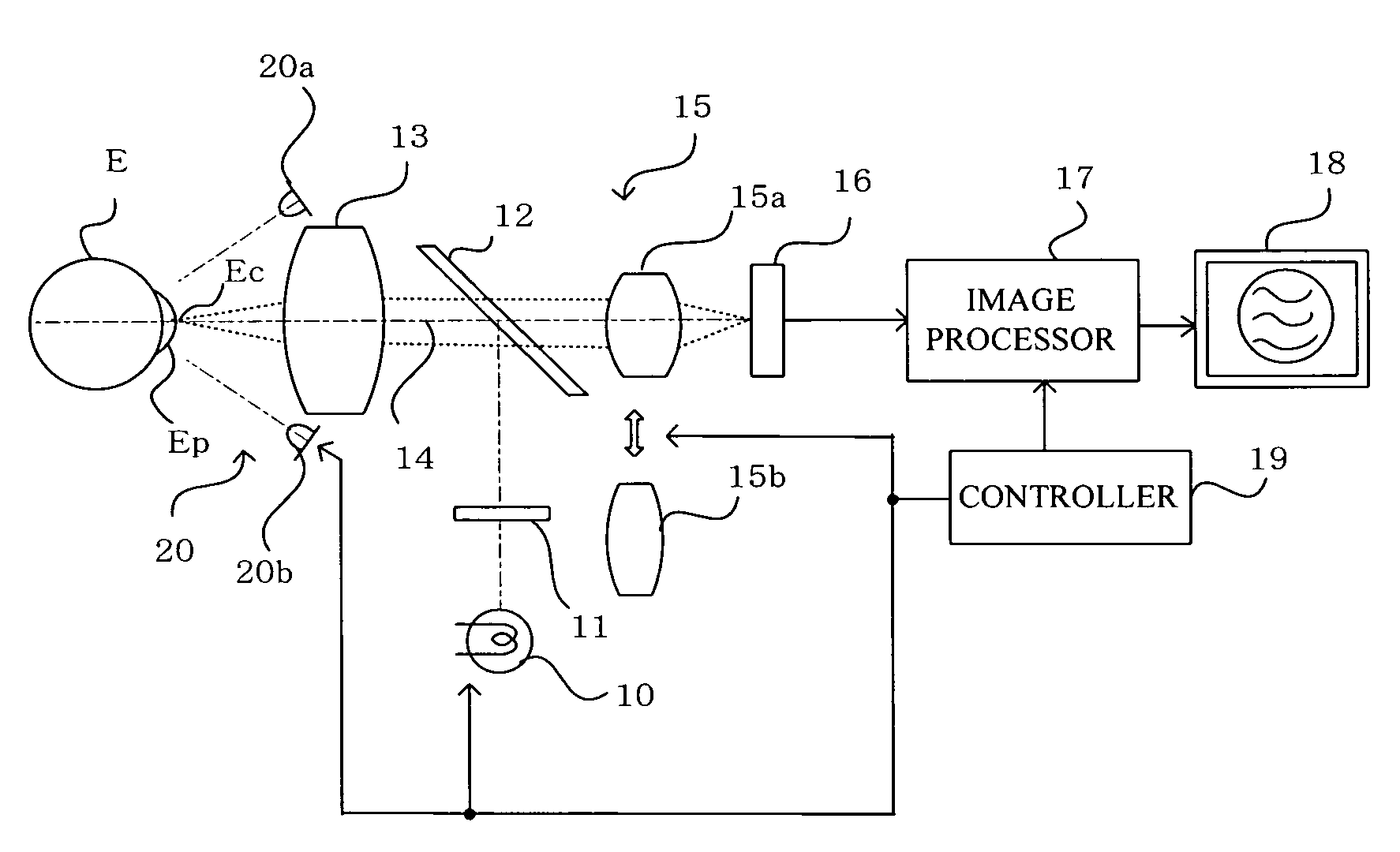
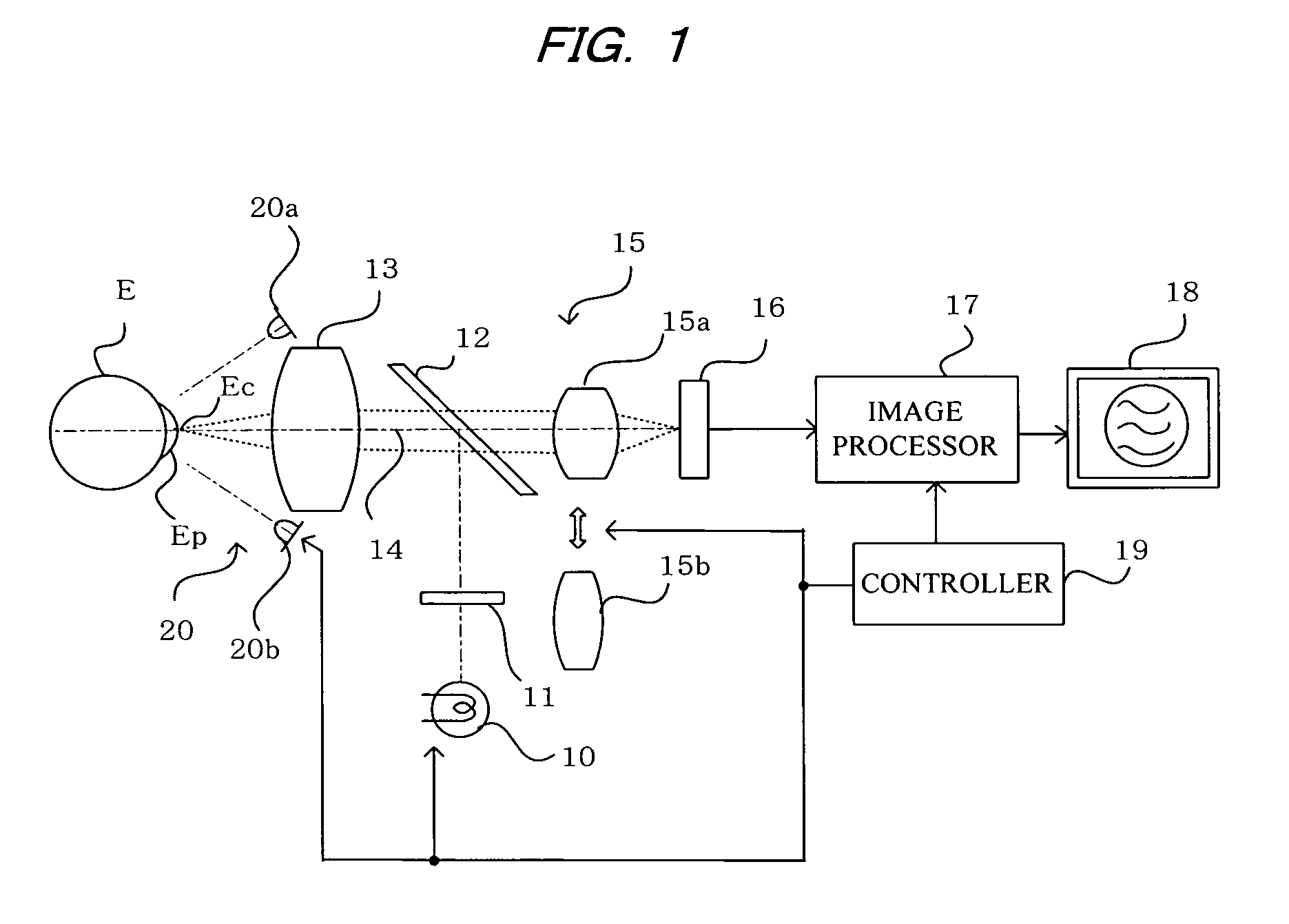
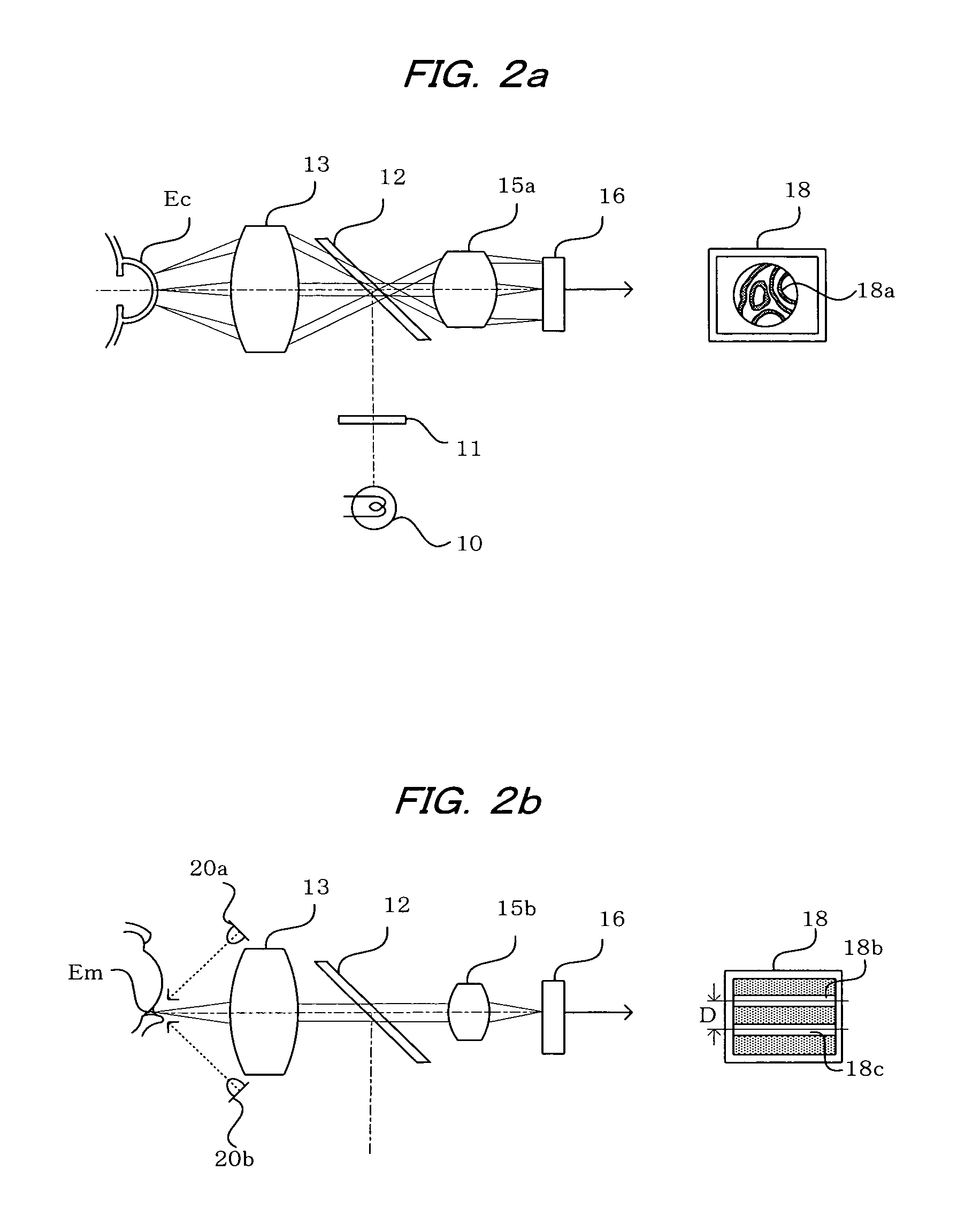
To observe interference stripes produced by tear fluid, a low magnification light source 10 is turned on to illuminate the outermost layer of a tear film on the cornea Ec of a subject's eye. Light reflected from the cornea Ec forms an image on a CCD 16, and an interference stripes pattern 18a created by the lipid film on the cornea is displayed on a monitor 18. To measure the amount of tear fluid, light-emitting elements 20a, 20b of a high-magnification light source are turned on to irradiate a tear fluid meniscus Em that has accumulated on the lower eyelid portion of the anterior ocular segment. Light reflected on the surface of the meniscus Em forms an image on the CCD 16, and images 18b, 18c of the light-emitting elements 20a, 20b are displayed on the monitor 18 as clear images separated by an interval D. The amount of tear fluid can be quantitatively measured by measuring the interval D. A single such structure allows interference stripes created by the tear film of the anterior ocular segment to be observed and the amount of tear fluid to be measured.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Method and apparatus for reviewing defects of semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070031026A1Effective reviewPrevent false detectionImage enhancementImage analysisDevice materialReference image
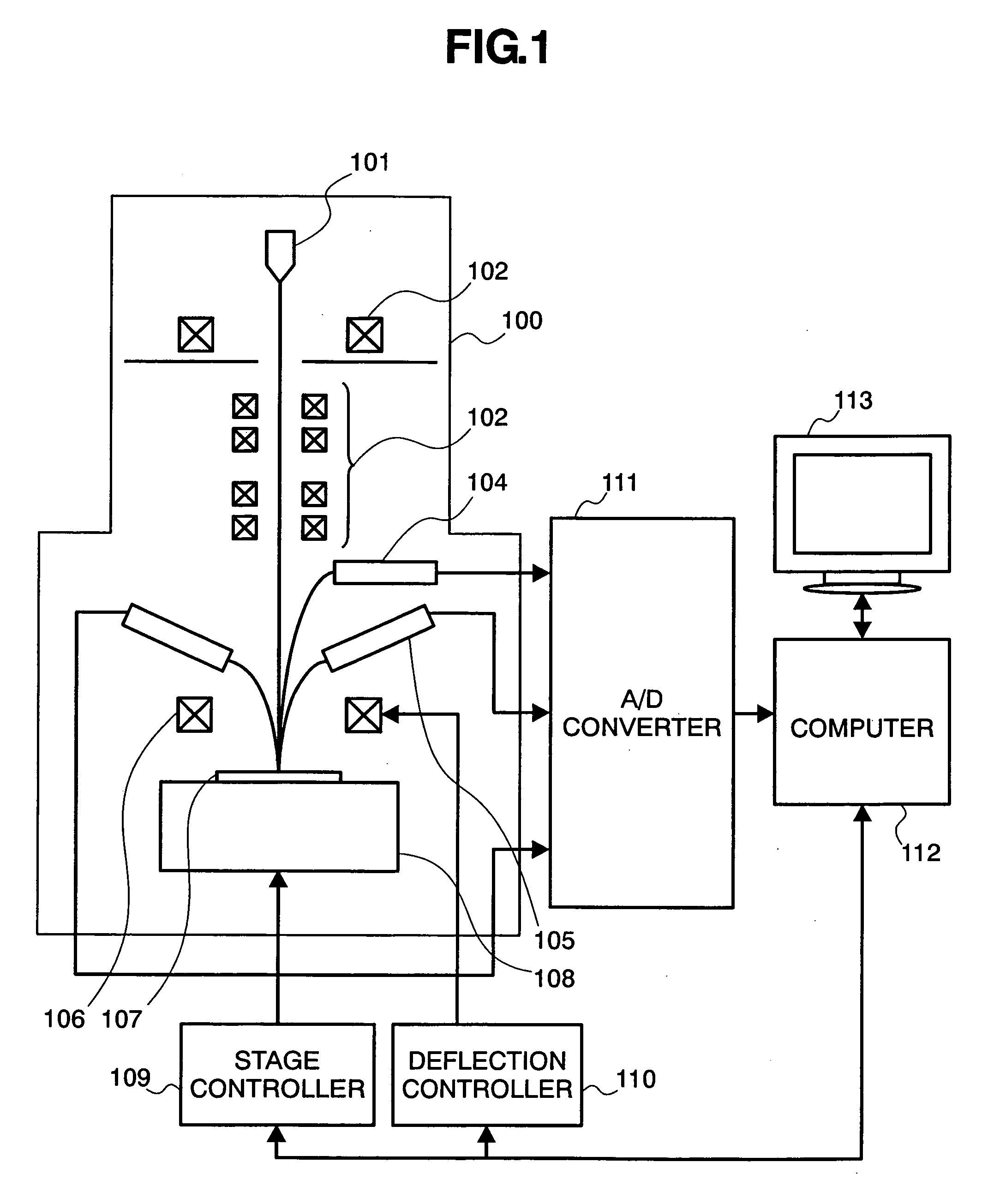
A method and apparatus for reviewing defects of a semiconductor device is provided which involves detecting a defect on a SEM image taken at low magnification, and reviewing the defect on a SEM image taken at high magnification, and which can review a lot of defects in a short period of time thereby to improve the efficiency of defect review. In the present invention, the method for reviewing defects of a semiconductor device includes the steps of obtaining an image including a defect on the semiconductor device detected by a detection device by use of a scanning electron microscope at a first magnification, making a reference image from the image including the defect obtained at the first magnification, detecting the defect by comparing the image including the defect obtained at the first magnification to the reference image made from the image including the defect at the first magnification, and taking an image of the detected defect at a second magnification that is larger than the first magnification.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for providing zoom functionality in a portable device display
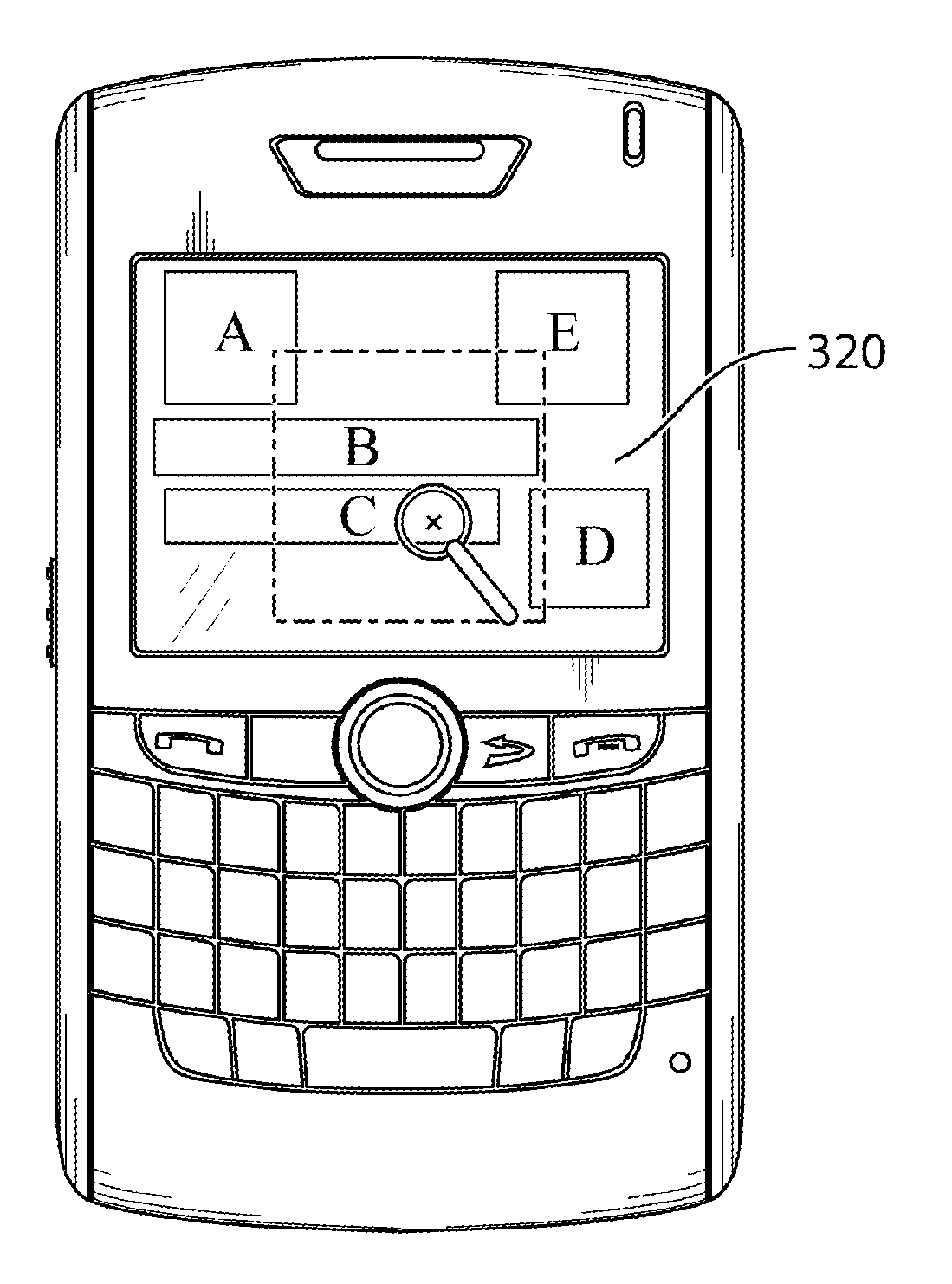
InactiveUS20090089707A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsMagnifying glassData file
A method and apparatus for providing zoom functionality in a mobile device display are described. In the method, a data file is displayed on the portable device display in a full layout view. A cursor is displayed in the layout view as a zoom icon, such as a magnifying glass cursor, with which any portion of the layout view can be selected by positioning the icon and triggering a zoom tool in response to actuation of an input device, such as trackball, on a mobile communications device. In response to actuation of the trackball, the selected portion is displayed in the portable device display at a next higher magnification. The process can be repeated to successively zoom in on a desired portion of the data file, until a maximum magnification is reached.
Owner:RES IN MOTION LTD
Sensing method and device for micro inner cavity size and three-dimensional coordinate based on two-dimensional micro-focus collimation
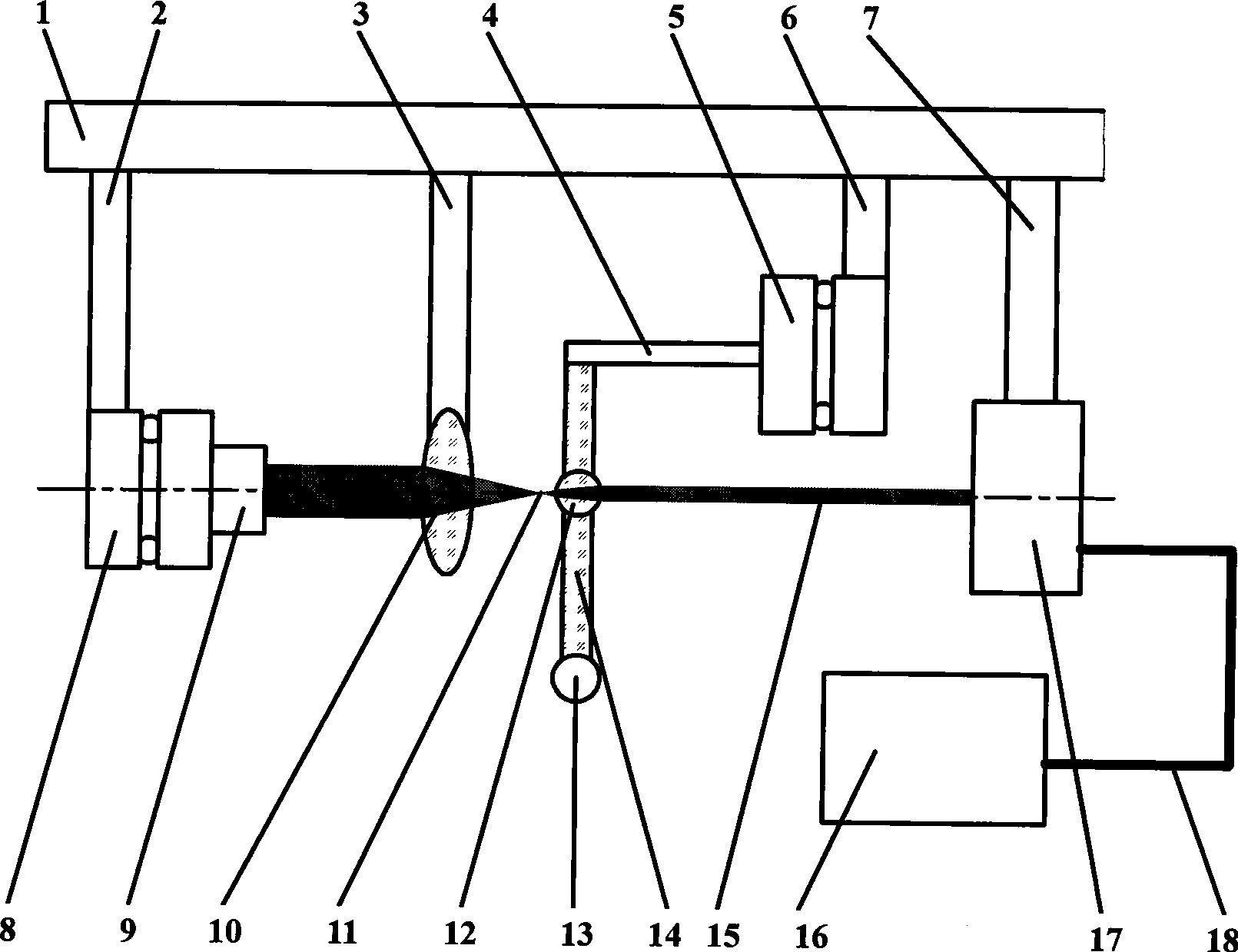
InactiveCN101520313AGenerate displacement sensitivityEfficient extractionUsing optical meansPoint lightThree dimensional measurement
The invention relates to a sensing method and a device for micro inner cavity size and three-dimensional coordinate based on two-dimensional micro-focus collimation, belonging to the technical filed of precise instrument manufacture and measurement, in particular to a sensing method and a device for micro and complex inner cavity size and three-dimensional coordinate in the filed of sub-macroscopy, which is especially suitable for the three-dimensional detection of blind holes with large depth-diameter ratio. The device combines a micro spherical biconvex lens and an optical fiber probe measuring rod, and establishes a point light two-dimensional micro-focus collimation imaging light path by using the micro spherical biconvex lens, thereby realizing the high magnification and the sensing for the three-dimensional displacement of the optical fiber probe measuring rod by utilizing the light path. The invention has the characteristics of small measured force of a single optical fiber probe, easy miniaturization, large measured depth-diameter ratio, simple system structure, good real-time performance, easy practical application, and has obvious advantages for carrying out the quick and ultra-precise measurement and calibration for the inner cavity micro-size and the three-dimensional coordinate. Especially, the top of the resolution capability can reach the deep sub-nanometer magnitude, and an absolute zero position exists in the three-dimensional measurement direction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Modification method for improving high-temperature cycle performance and ionic conductance of lithium iron phosphate material
The invention discloses a modification method for improving the high-temperature cycle performance and ionic conductance of a lithium iron phosphate material. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: mixing an organic compound which contains silicon, aluminum and titanium with lithium iron phosphate; performing certain heat treatment; and coating silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide or titanium oxide onto the surface of the lithium iron phosphate material to fulfill the aim of improving the electrochemical performance of the lithium iron phosphate material. The high-temperature cycle performance and the high-magnification charging-discharging current cycle capacity of coating-modified lithium iron phosphate are enhanced, and the impedance of a prepared electrode is remarkably reduced. The lithium iron phosphate material can be applied to more fields. A coating method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, stable and controllable product performance and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for automated image analysis of biological specimens
InactiveUS20050185832A1Low costQuickly and accurately scanImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationColor transformationLow-pass filter
A method and apparatus for automated cell analysis of biological specimens automatically scans at a low magnification to acquire images which are analyzed to determine candidate cell objects of interest. The low magnification images are converted from a first color space to a second color space. The color space converted image is then low pass filtered and compared to a threshold to remove artifacts and background objects from the candidate object of interest pixels of the color converted image. The candidate object of interest pixels are morphologically processed to group candidate object of interest pixels together into groups which are compared to blob parameters to identify candidate objects of interest which correspond to cells or other structures relevant to medical diagnosis of the biological specimen. The location coordinates of the objects of interest are stored and additional images of the candidate cell objects are acquired at high magnification. The high magnification images are analyzed in the same manner as the low magnification images to confirm the candidate objects of interest which are objects of interest. A high magnification image of each confirmed object of interest is stored for later review and evaluation by a pathologist.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS
Selenium-micropore carrier composite, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a lithium-selenium battery and a preparation method thereof. A lithium-selenium battery comprises a metal lithium cathod, a selenium-micropore carrier composite anode and organic electrolyte. The selenium-micropore carrier composite anode is prepared by mixing selenium and a micropore carrier and heating; and the selenium is uniformly dispersed inside micropore channels of the micropore carrier in a short-chain molecule manner. The micropore carrier comprises a carbon micropore carrier, a non-carbon micropore carrier and a composition. The lithium-selenium battery can maintain a high circulation capacity, excellent stable circulation property and good high-magnification (large-current density charging and discharging) property in a large-temperature range such as room temperature and the like; the main composite part, namely, the selenium-micropore carrier composite anode, is simple in preparation method, easily accessible in raw material, applicable to large-scale production and has very high practicability.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
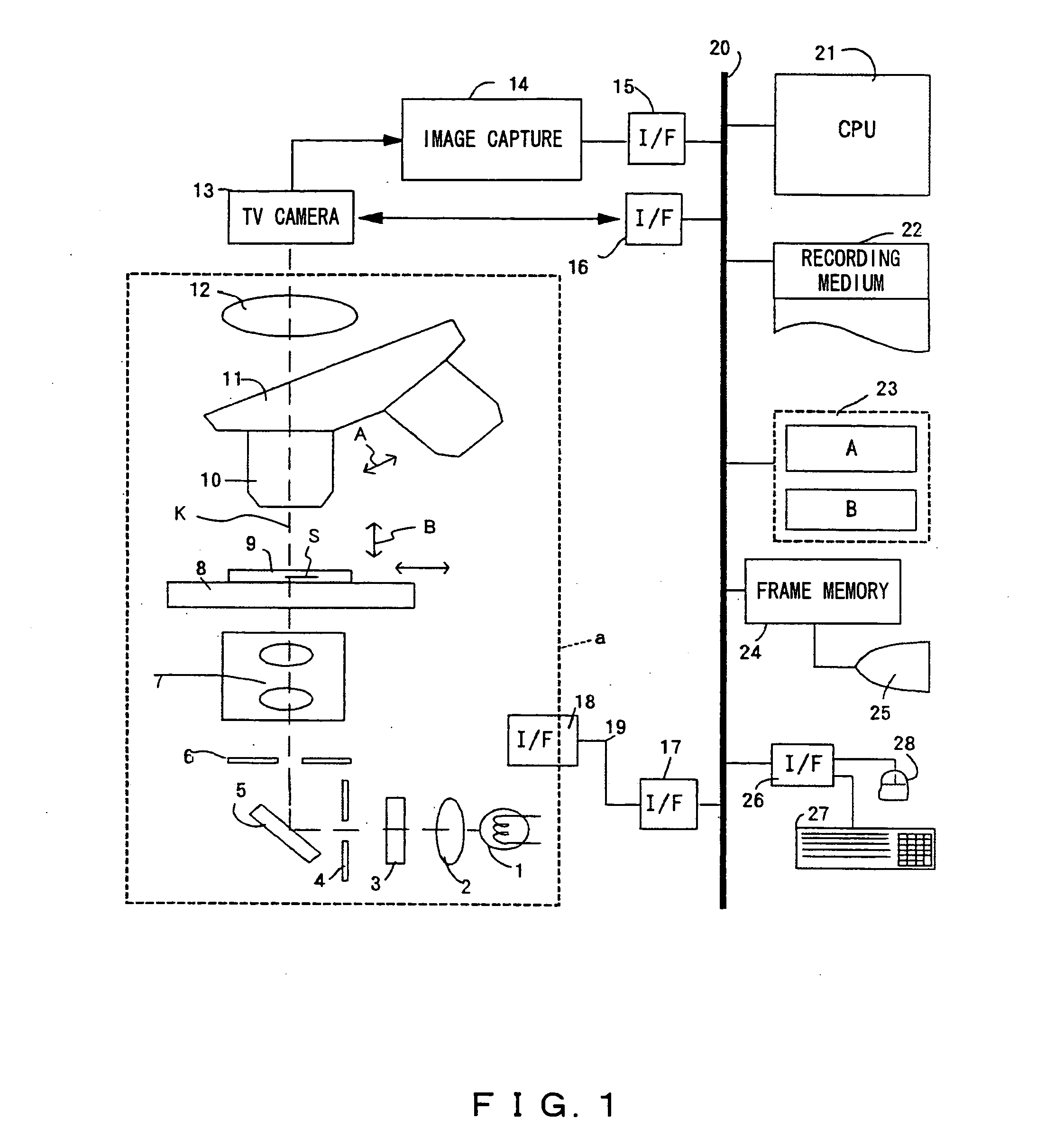
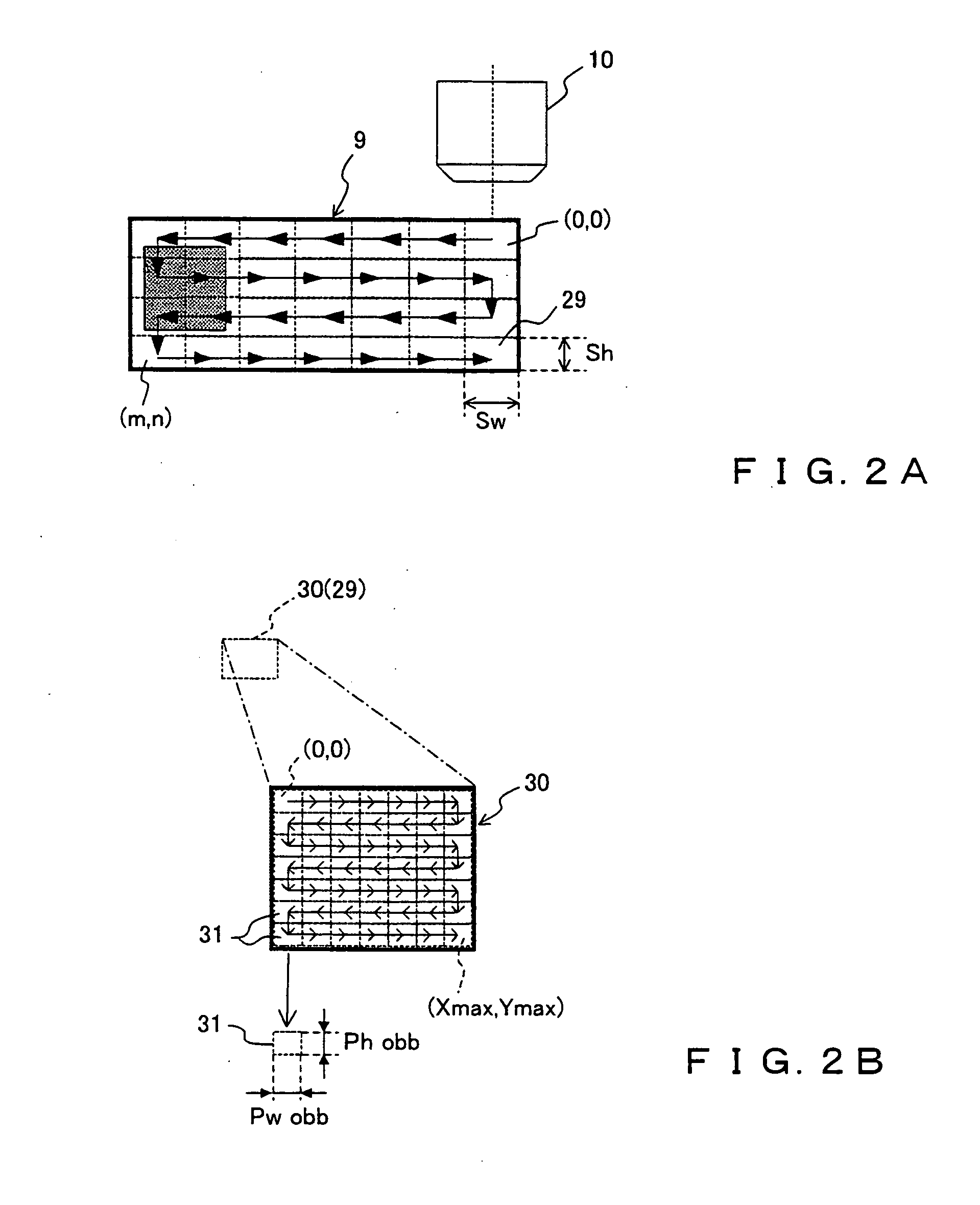
Microscopic image capture apparatus and microscopic image capturing method
ActiveUS20050190437A1High precision imagingLong is wastedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageField size
A microscopic image capture apparatus and a microscopic image capturing method allow a wide-angle field and high-precision microscope digital image to be efficiently captured. First, the entire area of a slide glass on a stage is divided into field size sections (low-magnification sections) of a low-powered objective lens, the stage is sequentially transferred perpendicular to an optical axis, image information is obtained for each low-magnification section of the entire area, each low-magnification section is divided into high-magnification size sections (high-magnification sections), a high-magnification image is captured using a high-powered objective lens only on a high-magnification section including simultaneously in the high-magnification sections, a high-magnification image is generated by correctly maintaining the relative position between the obtained image information and the area of a high-magnification section which is not captured, and a high-magnification composite image information about a sample on the slide glass is generated.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
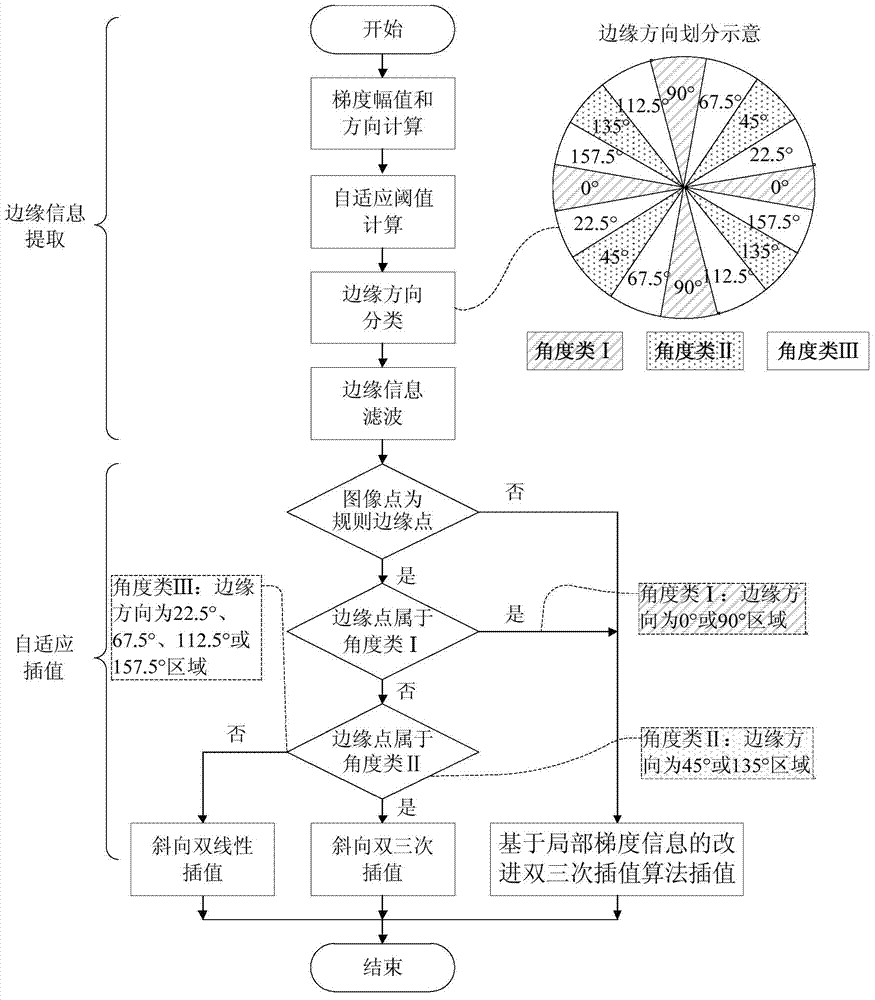
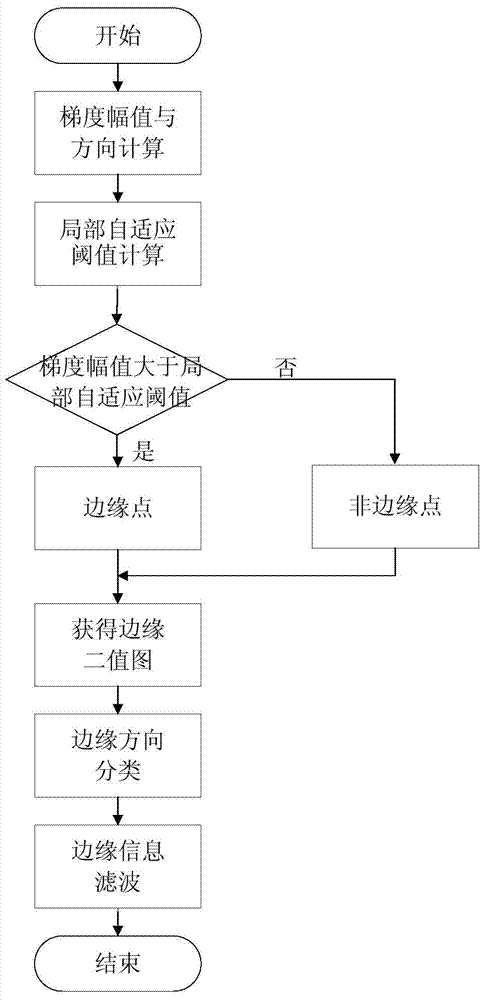
Margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method and VLSI implementation device thereof
ActiveCN103500435AGuaranteed accuracyProtectImage enhancementImage analysisVlsi implementationsSynchronous control
The invention discloses a margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method and a VLSI implementation device thereof. The method comprises the steps that the gradient magnitude and the gradient direction of a source image pixel are computed, and marginal information is obtained by comparing the gradient magnitude and a local self-adaptive threshold value, wherein the marginal direction is perpendicular to the gradient direction; the marginal direction is classified, filtering is conducted through the marginal information, and an image is divided into a regular marginal area and a non-marginal area; the regular marginal area interpolation is conducted in the marginal direction, and an improved bicubic interpolation method, a slant bicubic interpolation method and a slant bilinear interpolation method based on local gradient information are adopted to conduct image interpolation according to the classification of the marginal information; image interpolation is conducted on the non-marginal area through the improved bicubic interpolation method based on the local gradient information. The VLSI implementation device comprises a marginal information extraction module, a self-adaptive interpolation module, an input line field synchronous control module and an after-scaling line field synchronous control module. The margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method and the VLSI implementation device of the margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method can effectively improve the effect of image interpolation with high-magnification scaling, and is beneficial to integrated circuit framework achieving.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Slide photograph data creation system, and slide photograph data
InactiveUS20060228107A1Efficiently perform workEfficient executionSamplingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Virtual slide
A slide photograph data creation system includes a digital camera for making high-magnification photographs of samples, a sample transporter for holding and transporting samples, a controller for controlling the camera and the sample transporter so as to provide overlapping photographs, a pasting information generator for recognizing the margin by which the photographs overlap and for generating pasting-together information, and a photograph file generator for storing in a single file a plurality of high-magnification photographs and the pasting-together information. The system facilitates the examination and photography of large numbers of samples, and enables discrimination of the three-dimensional structure of a sample. Since the photographic data is managed with a database, virtual slide photographs and their attributes information can be browsed over a network or the Internet.
Owner:CLARO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com