Patents
Literature
76 results about "Virtual slide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
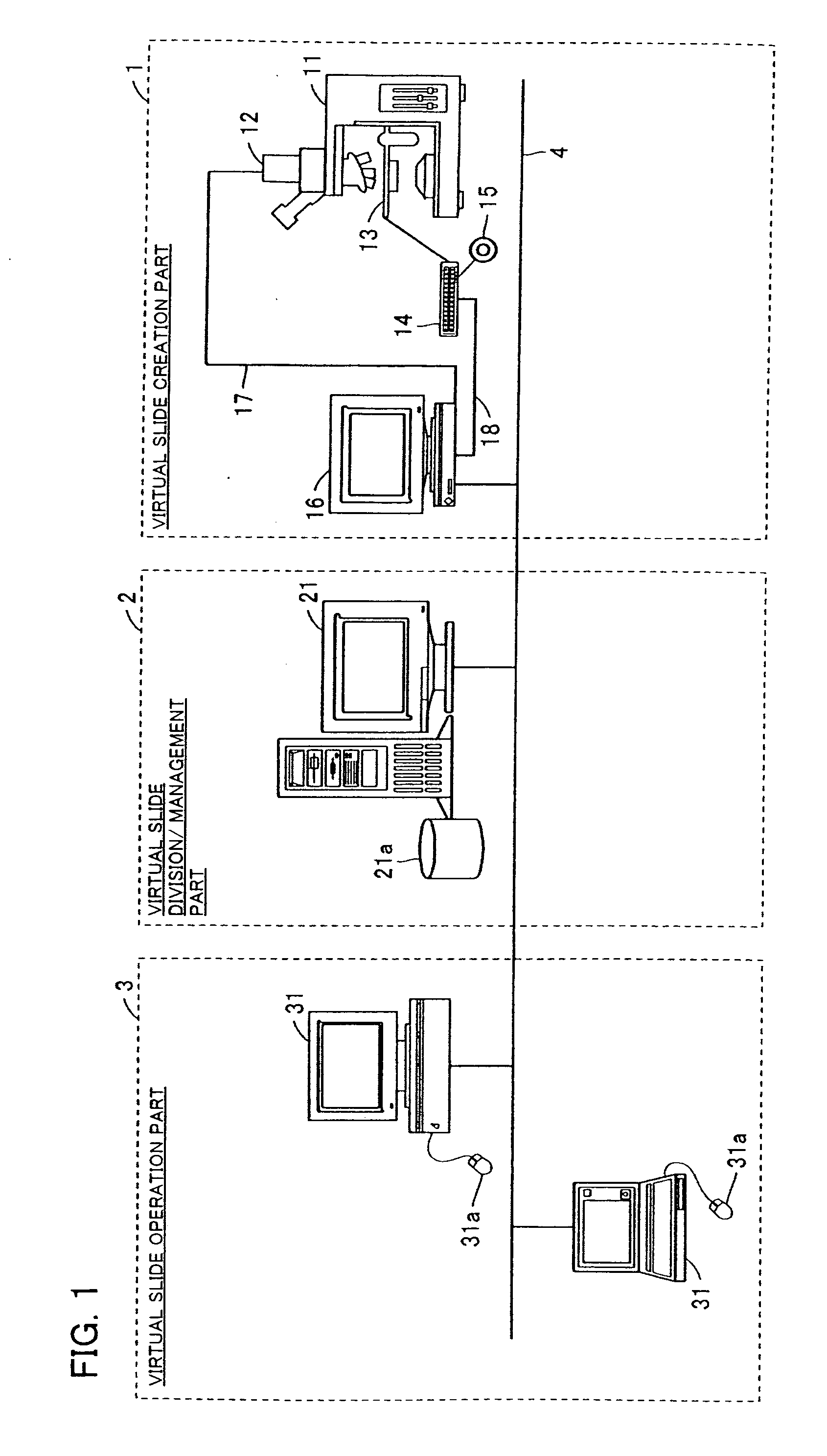
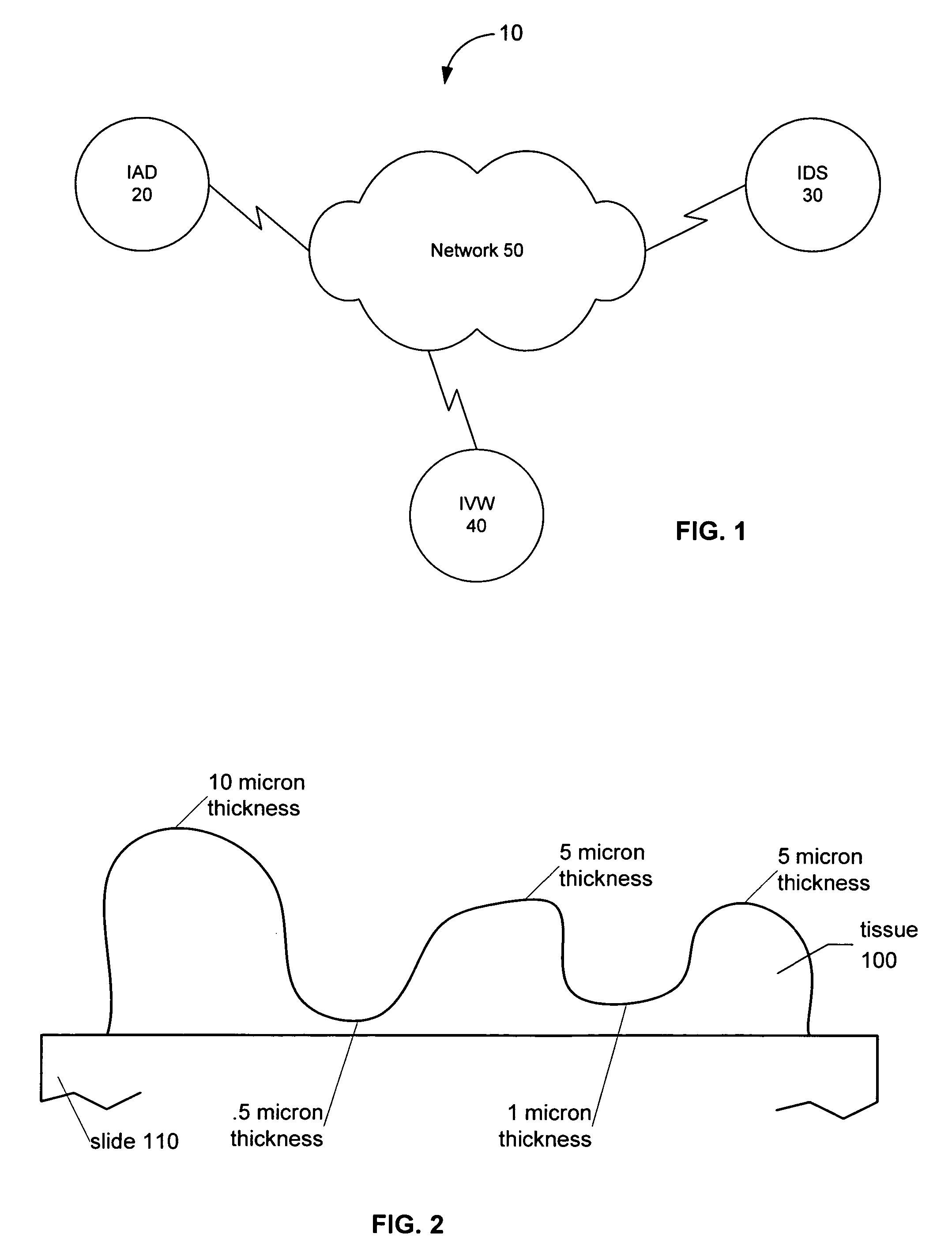
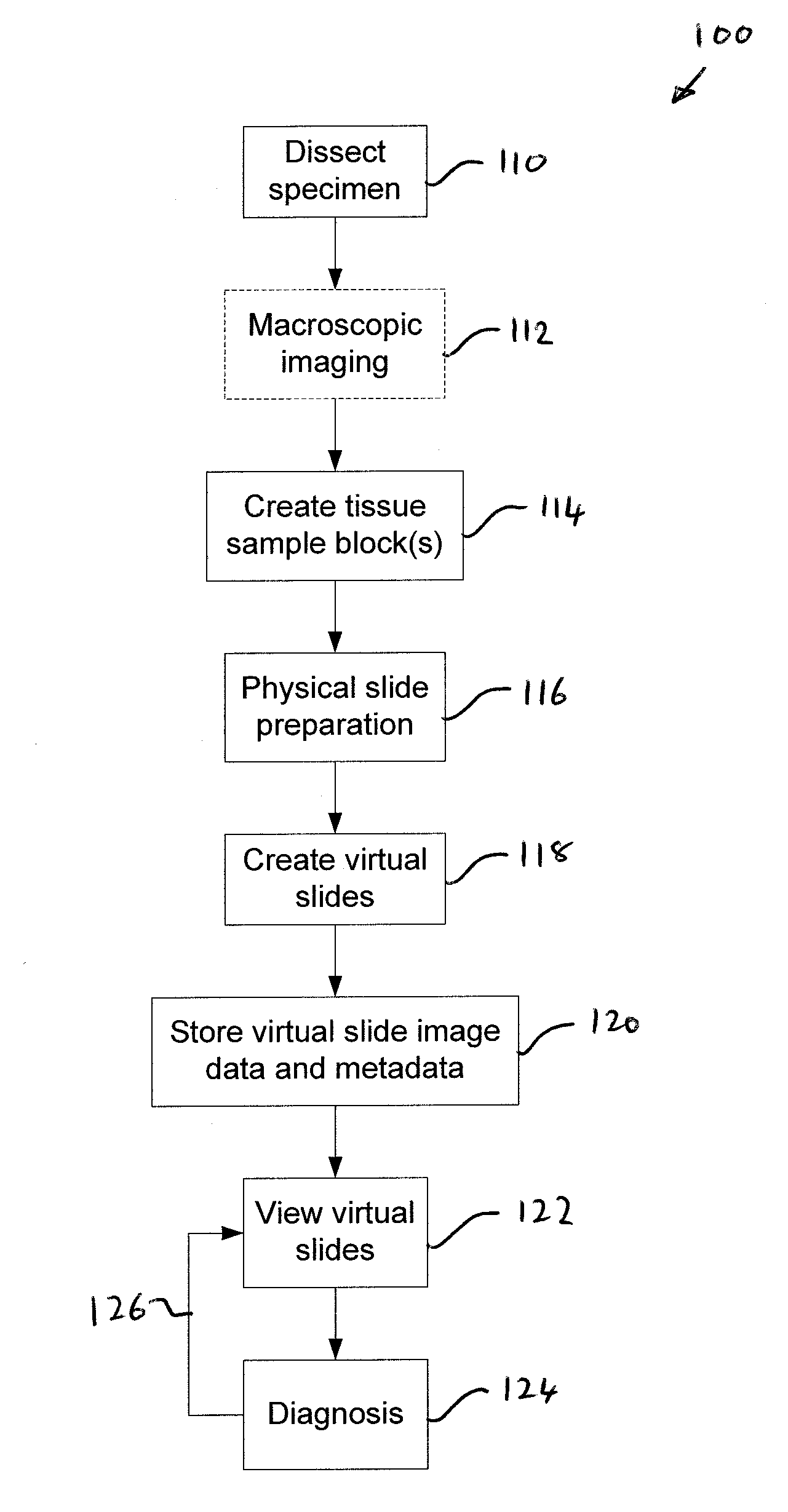
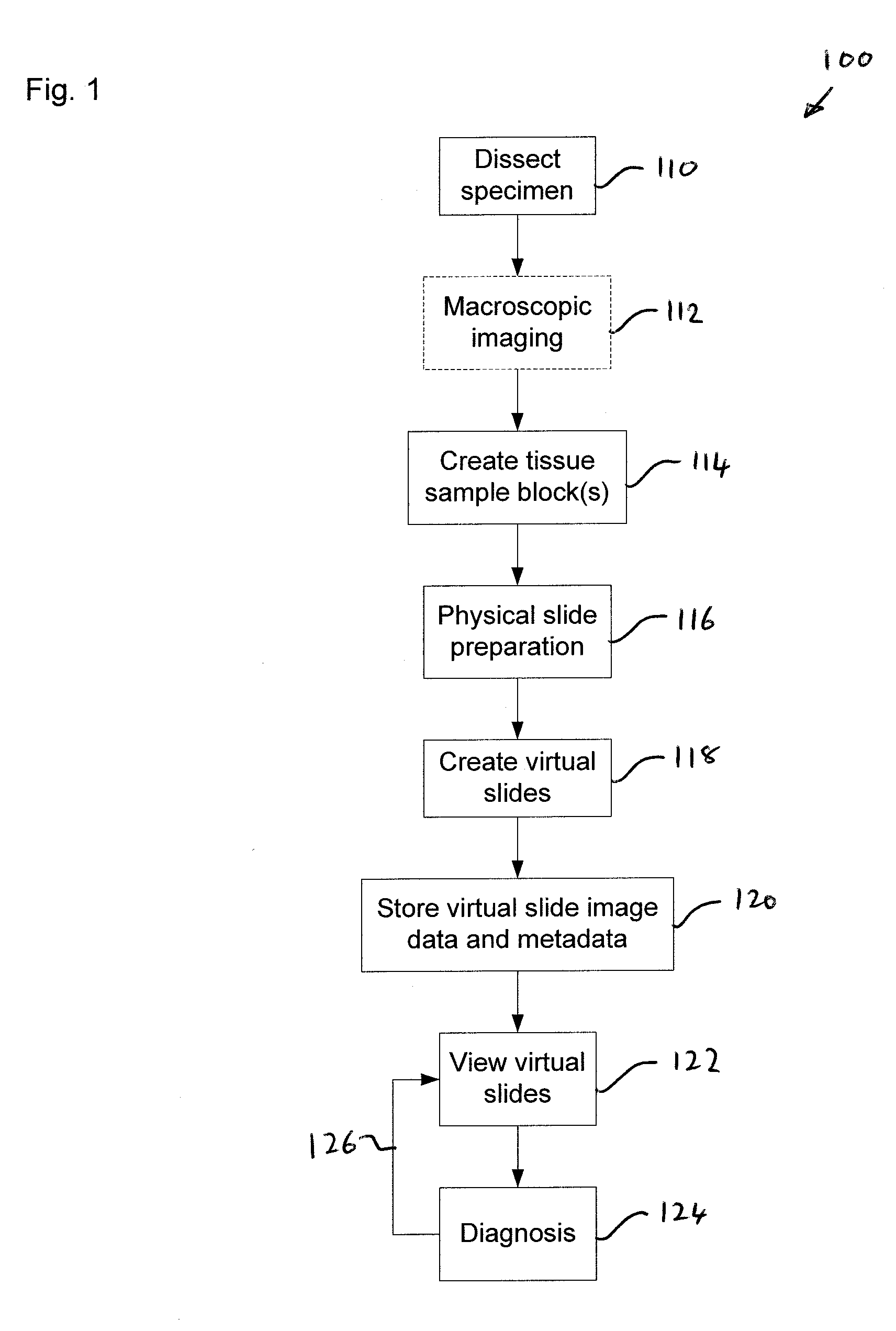
A virtual slide is created when glass slides are digitally scanned in their entirety to provide a high resolution digital image using a digital scanning system for the purpose of medical digital image analysis. Digital slides can be retrieved from a storage system, and viewed on a computer screen, by running image management software on a standard web browser, and assessed in exactly the same way as on a microscope. Digital slides can be used as an alternative to traditional viewing for the purpose of teleconsultation.
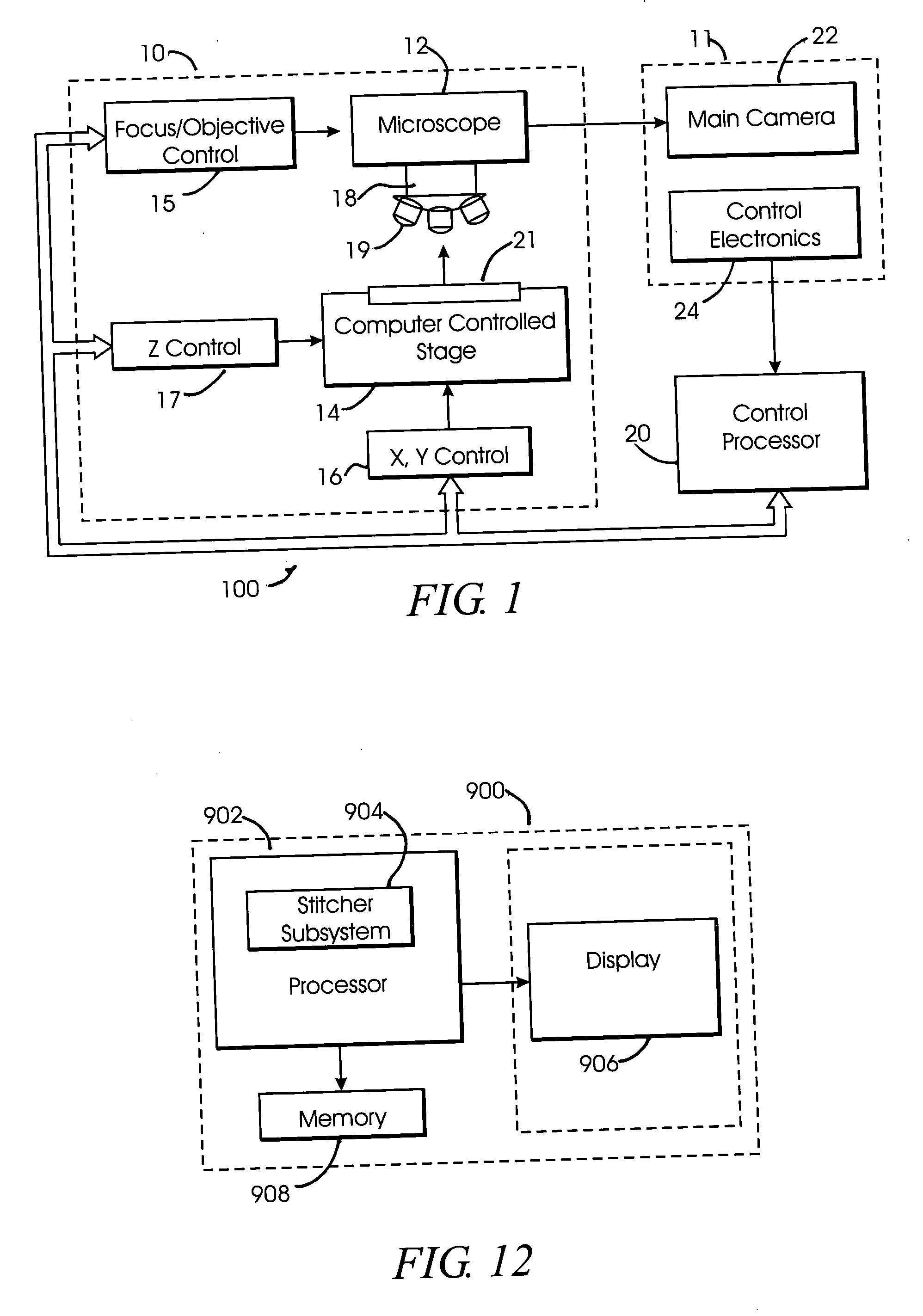
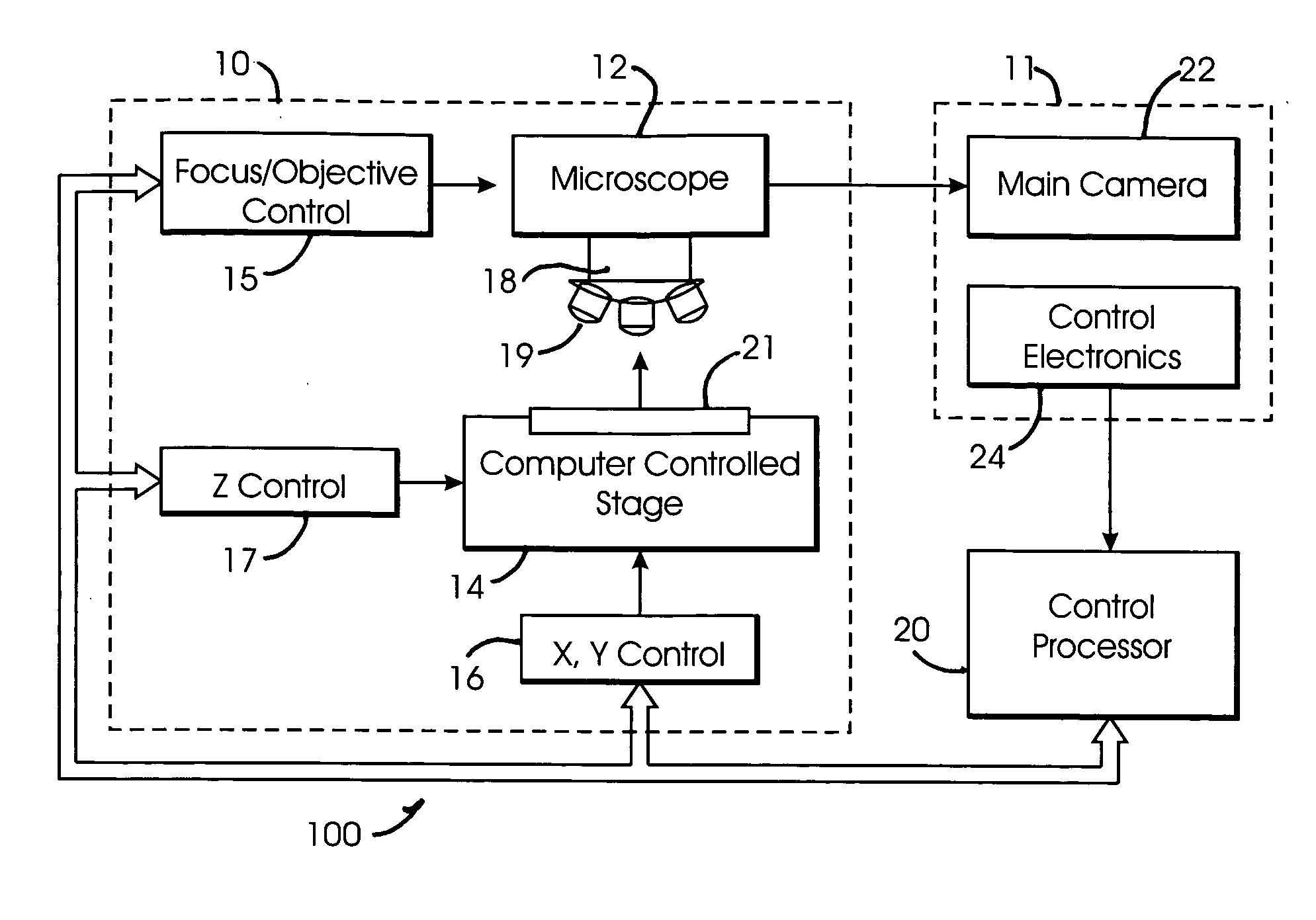
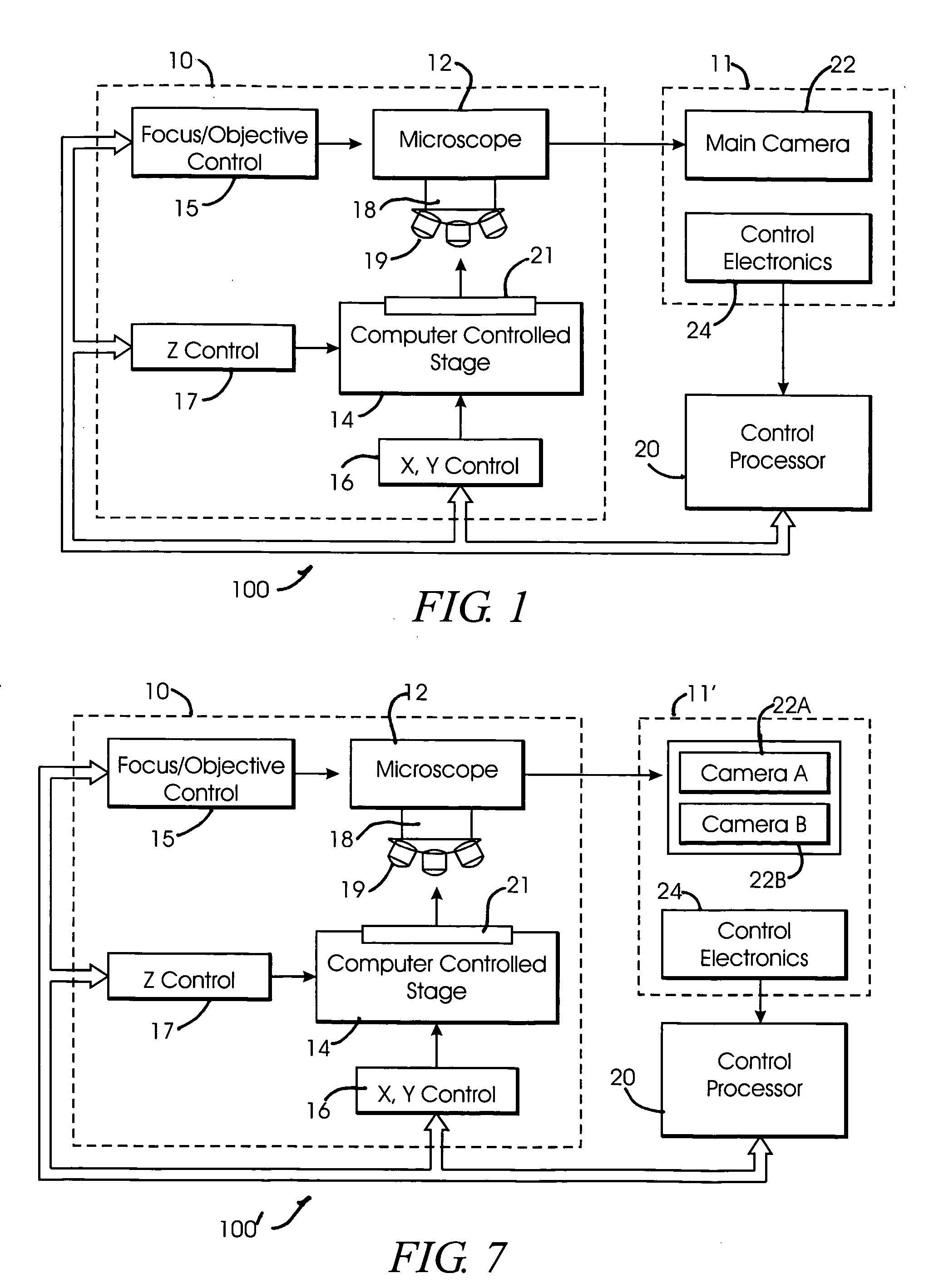
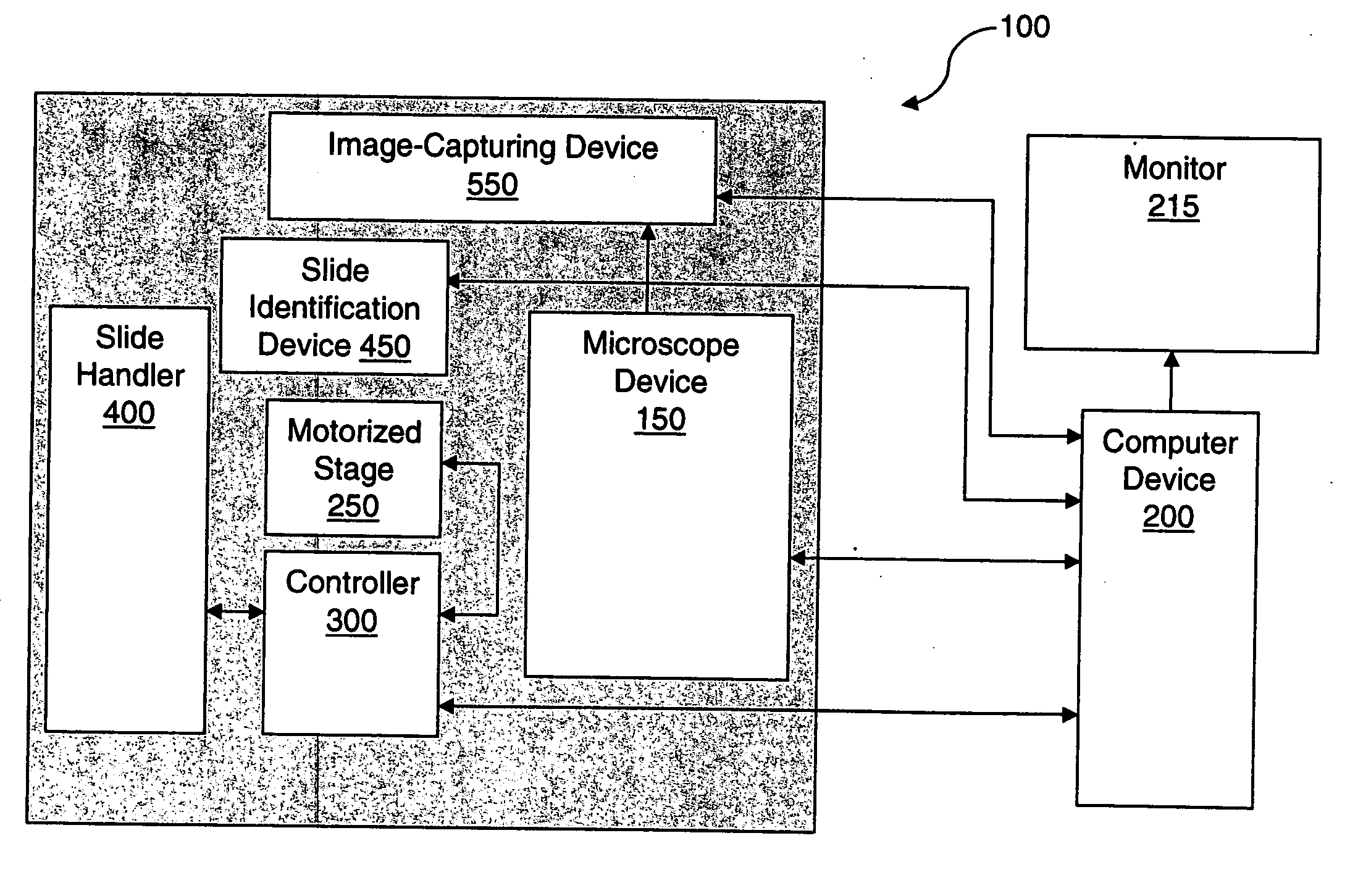
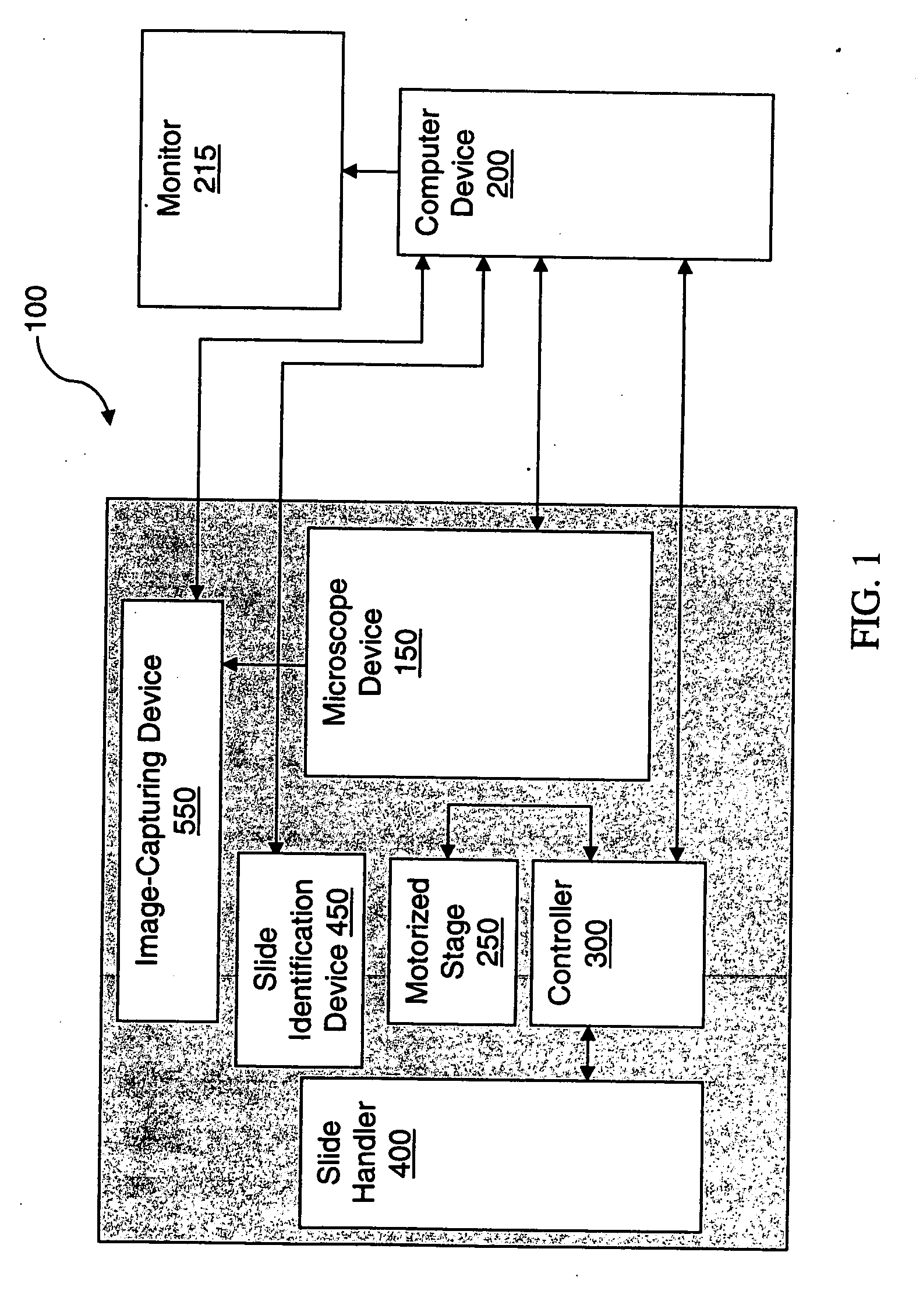
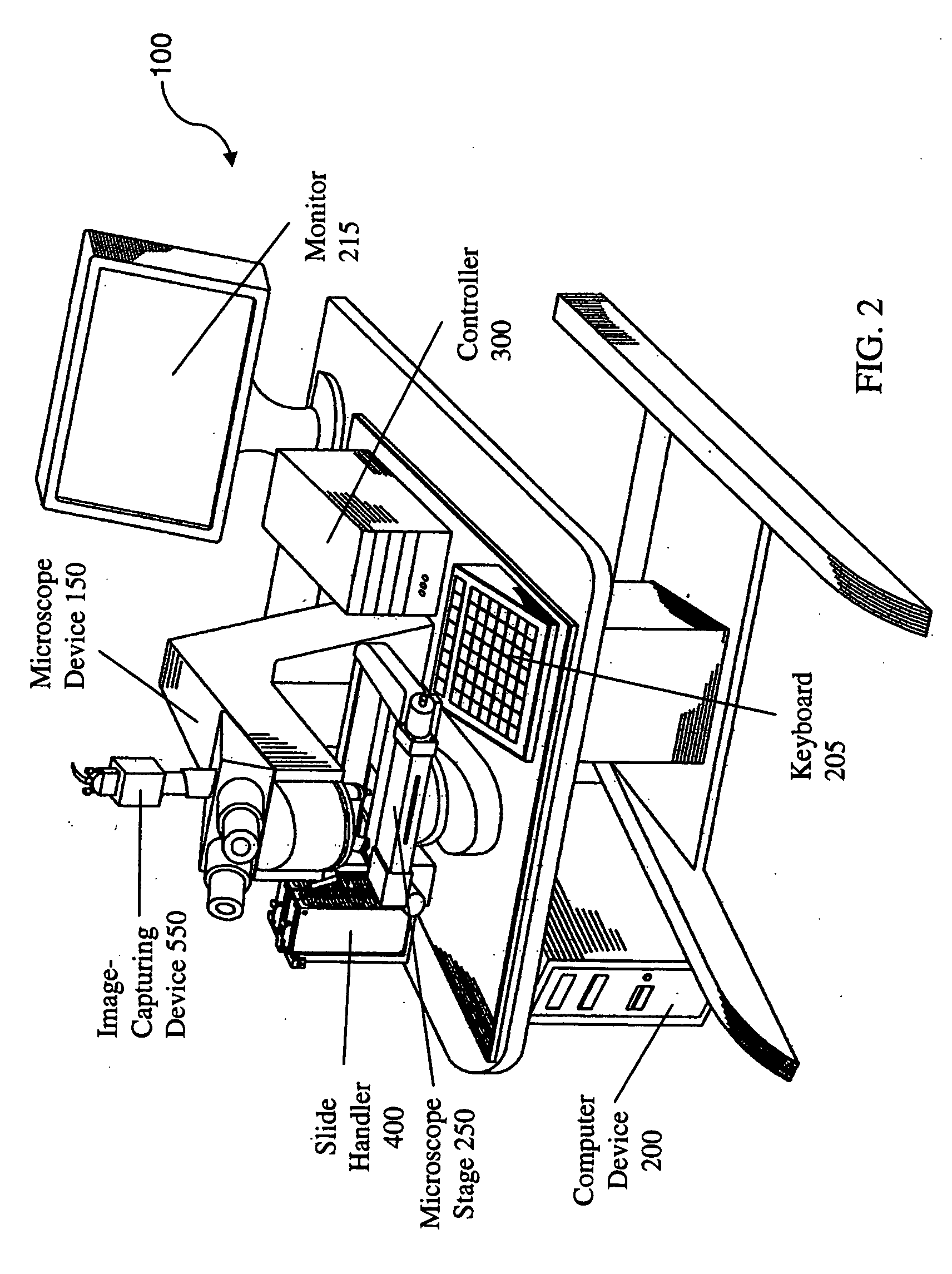
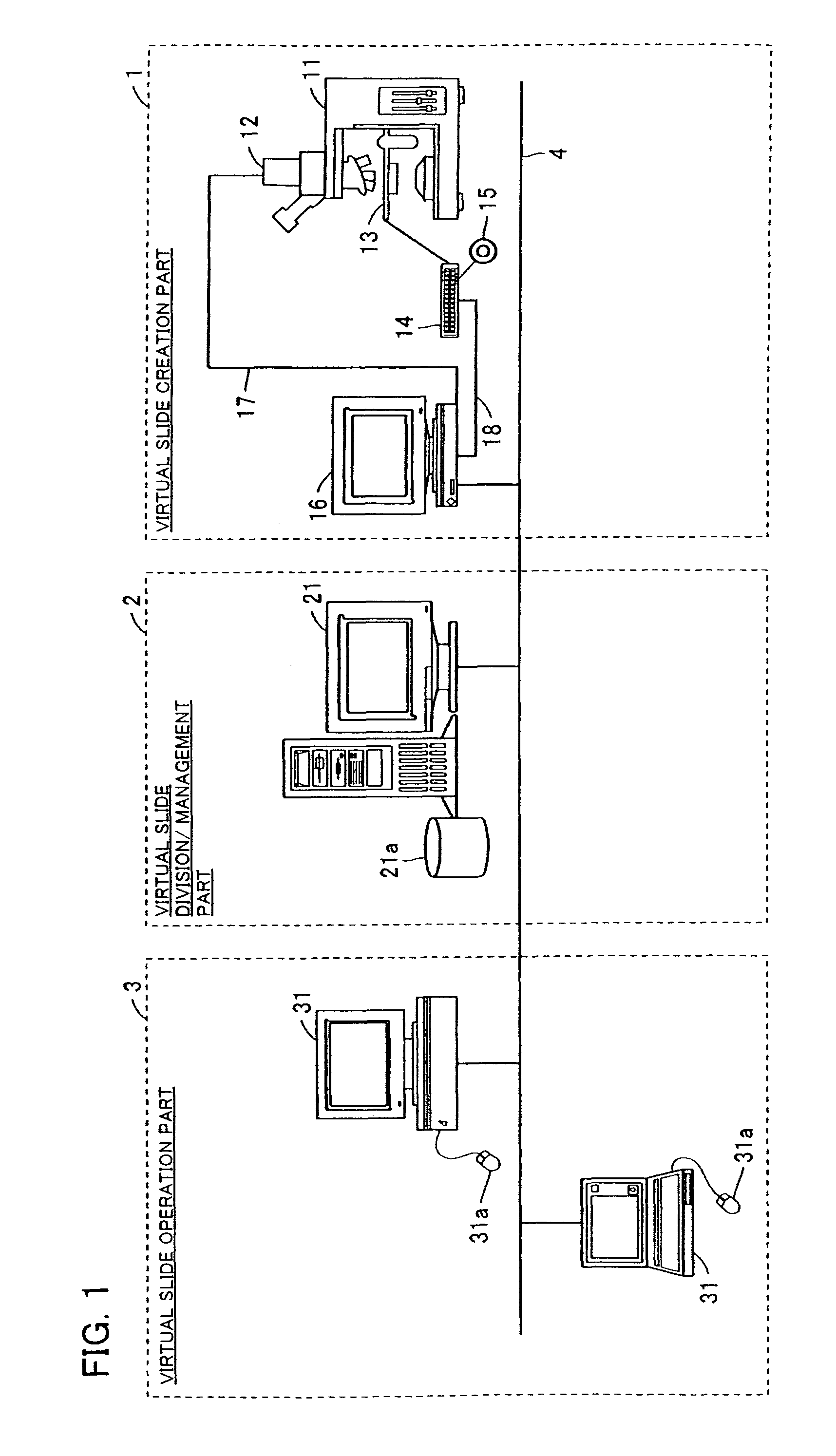
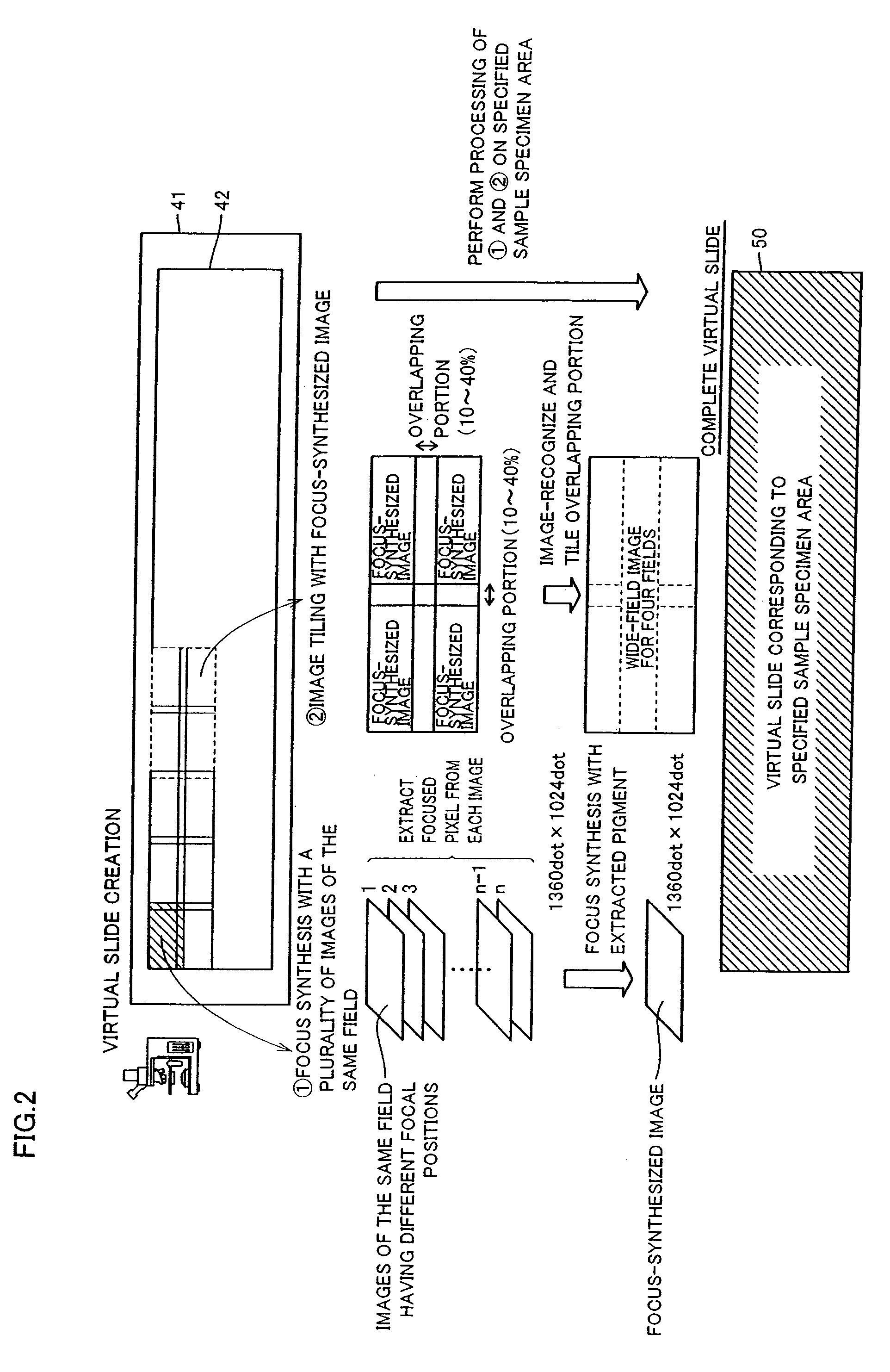
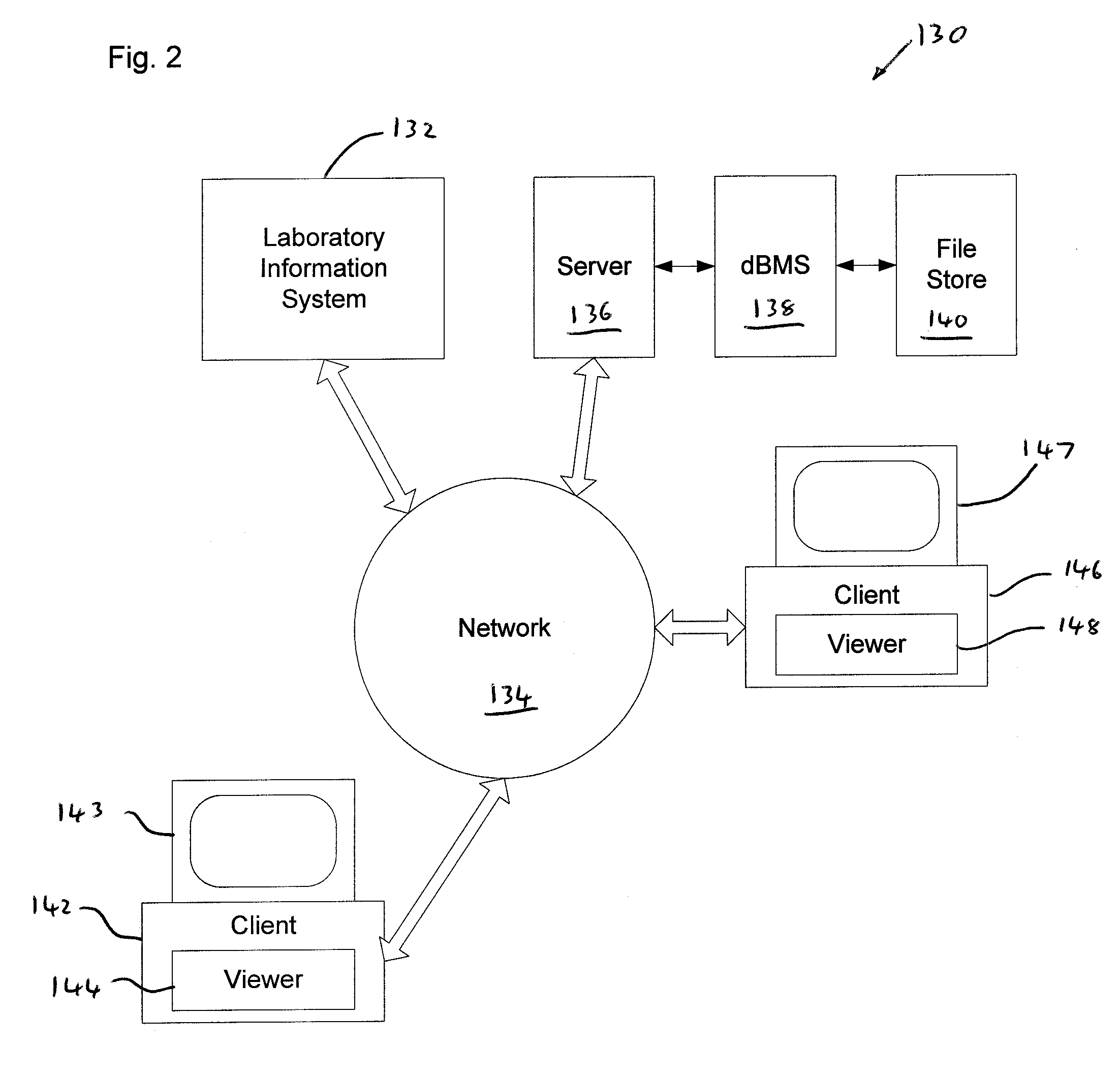
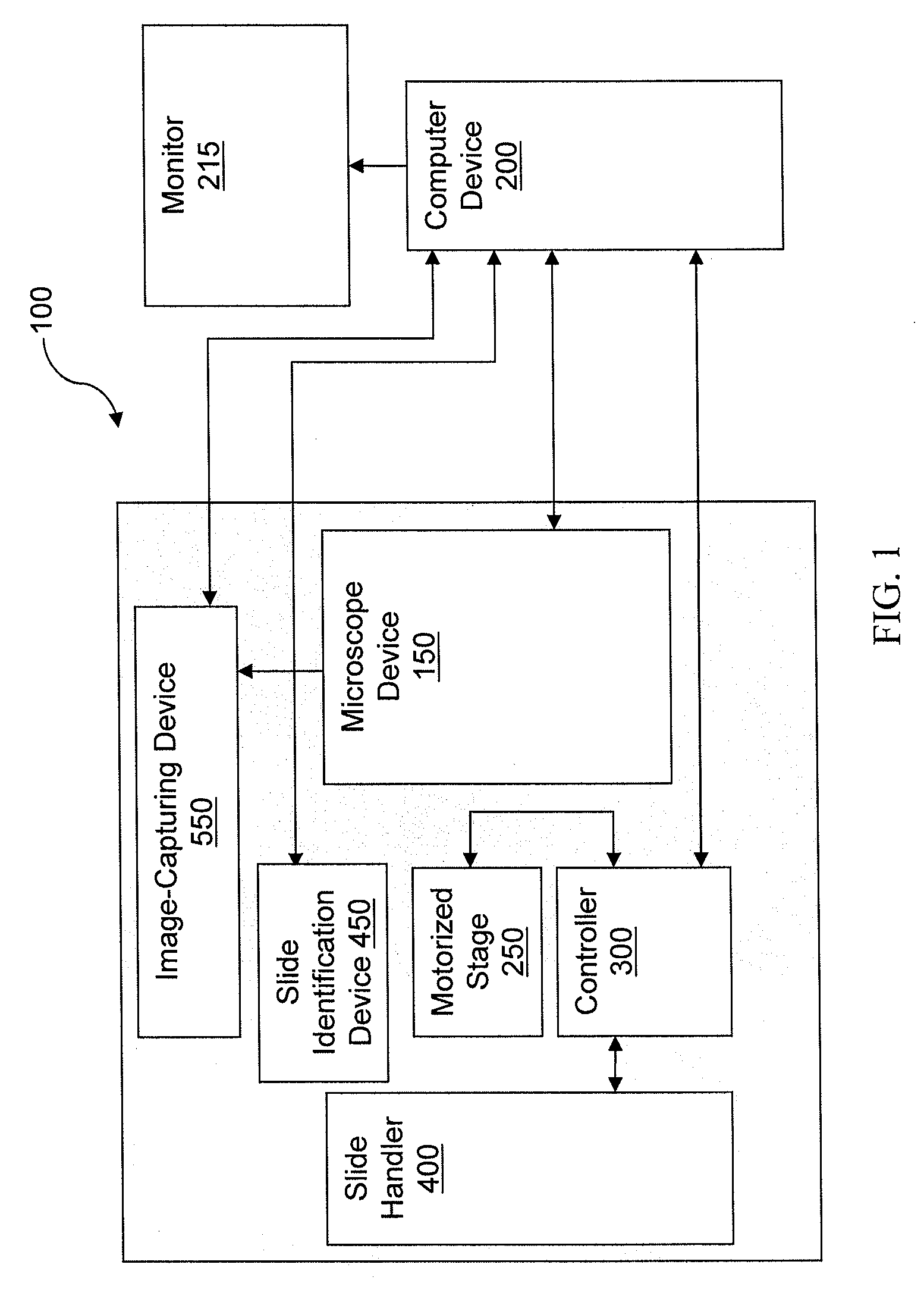
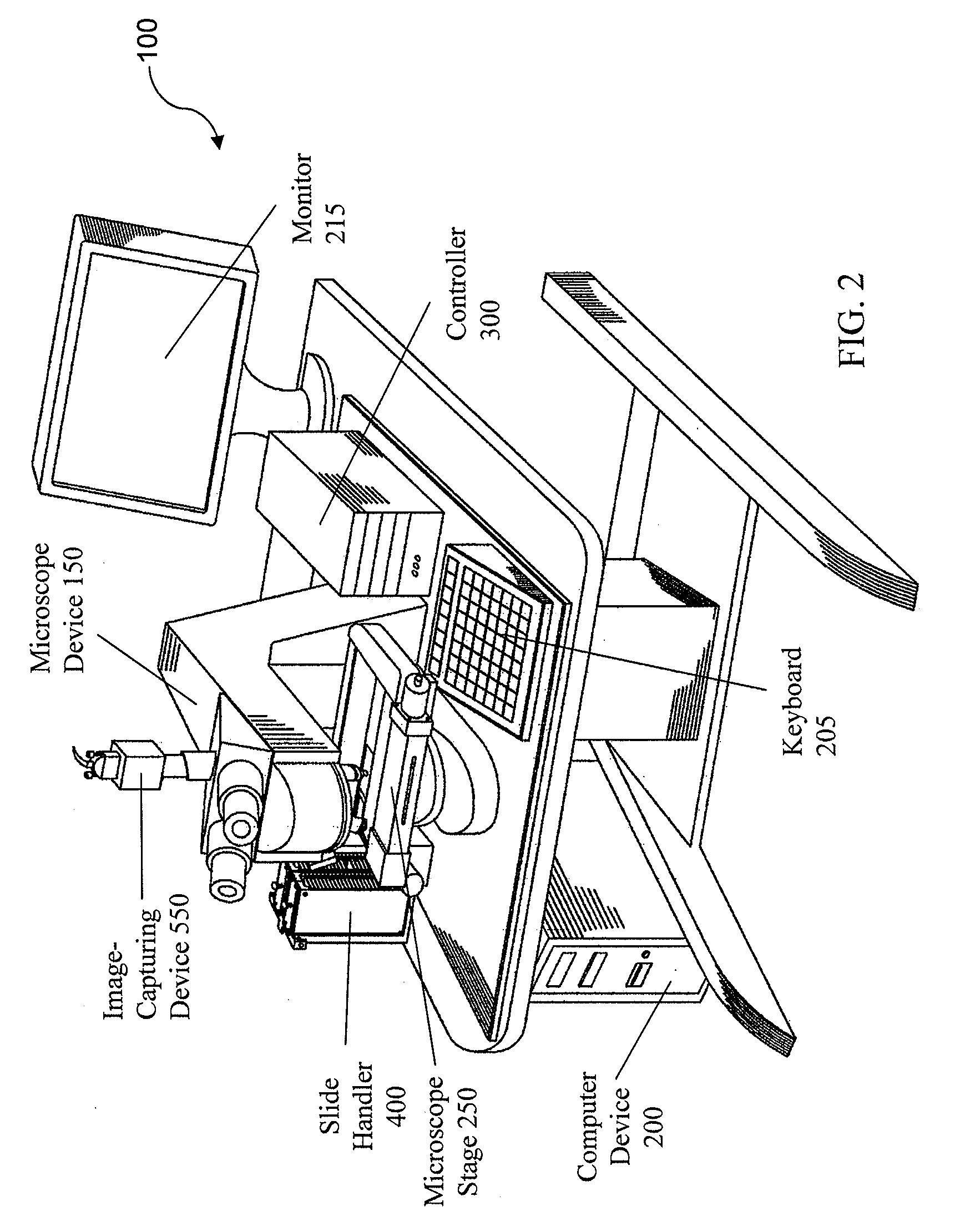
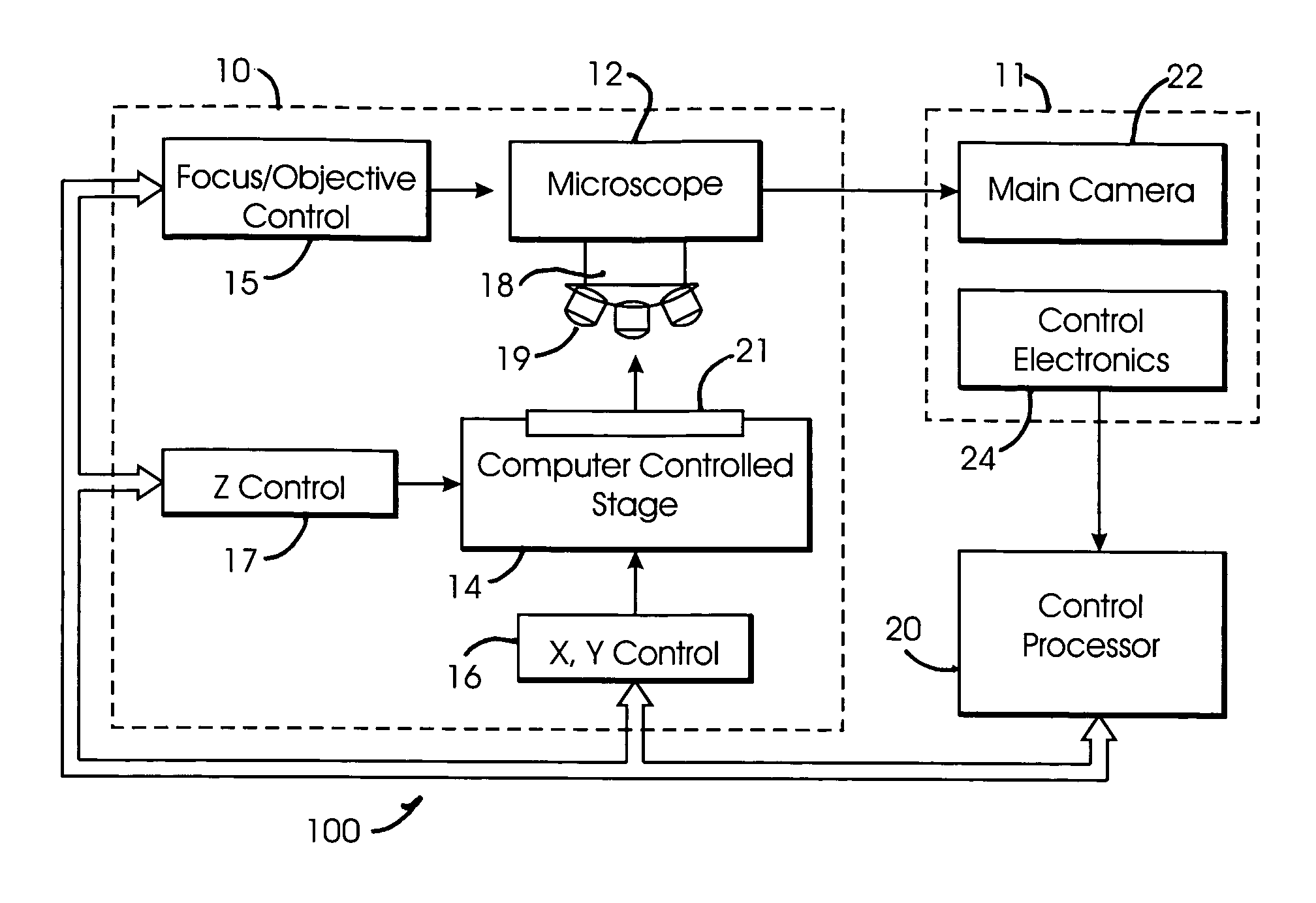
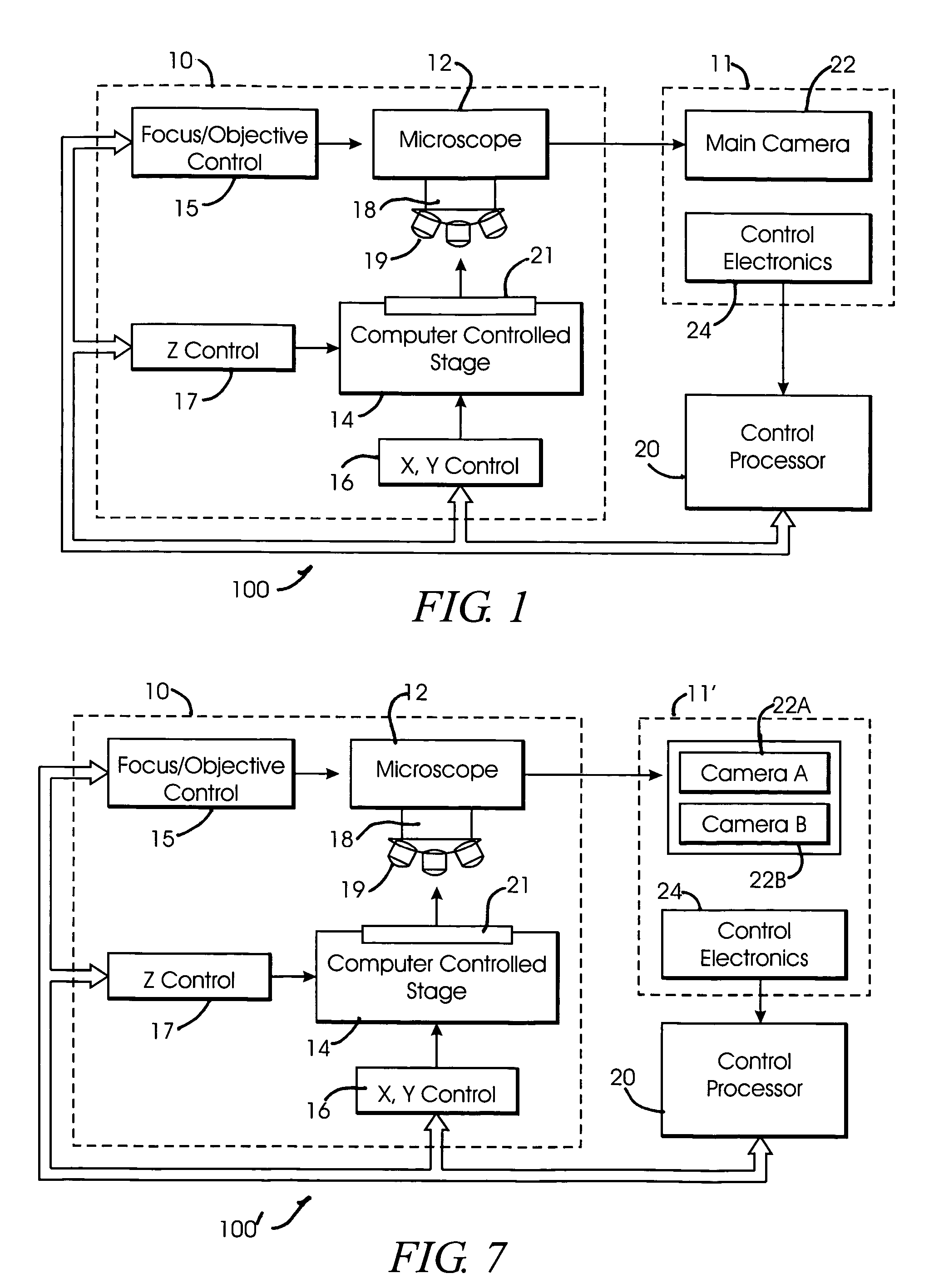
System and method for generating digital images of a microscope slide
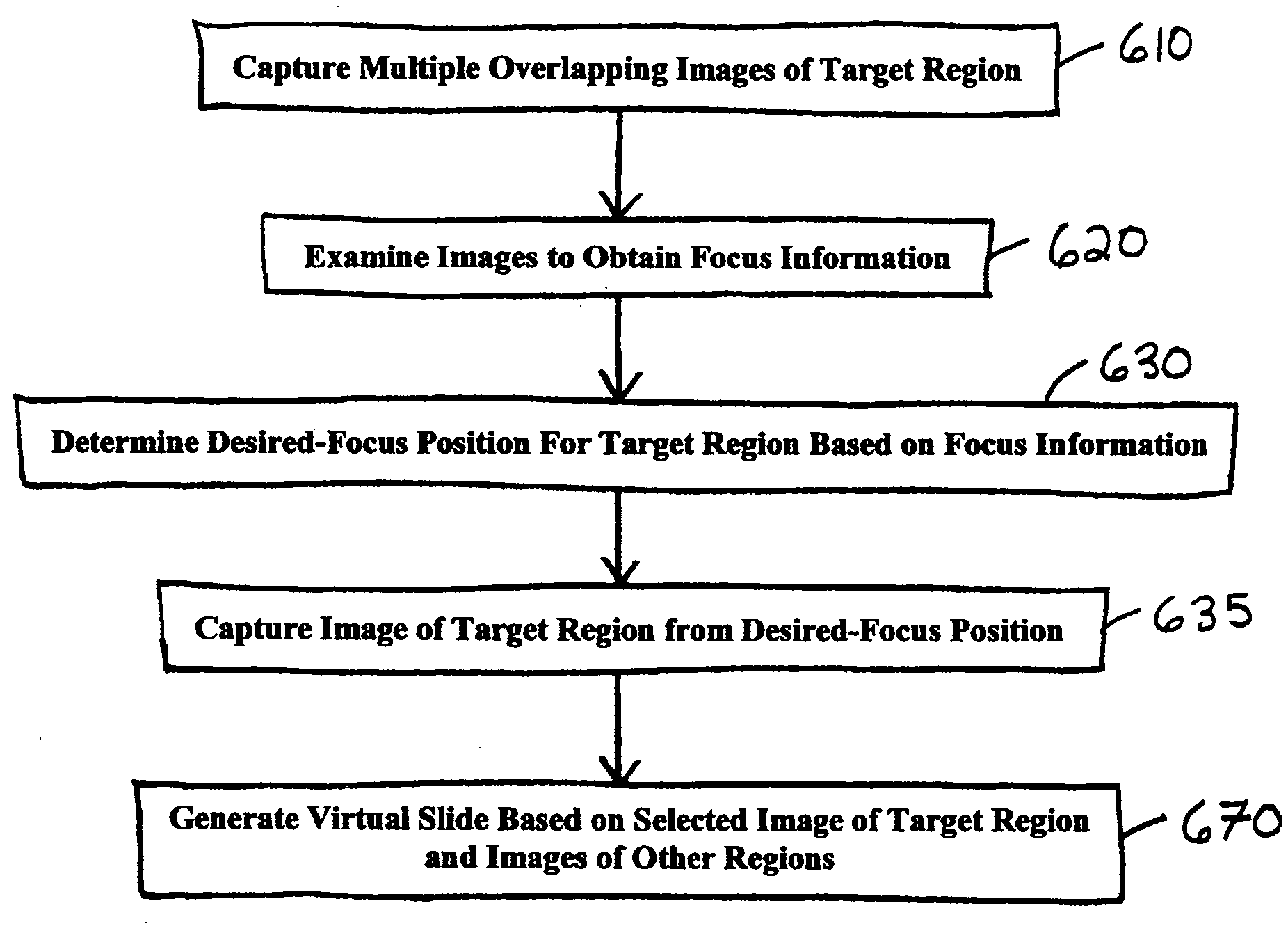
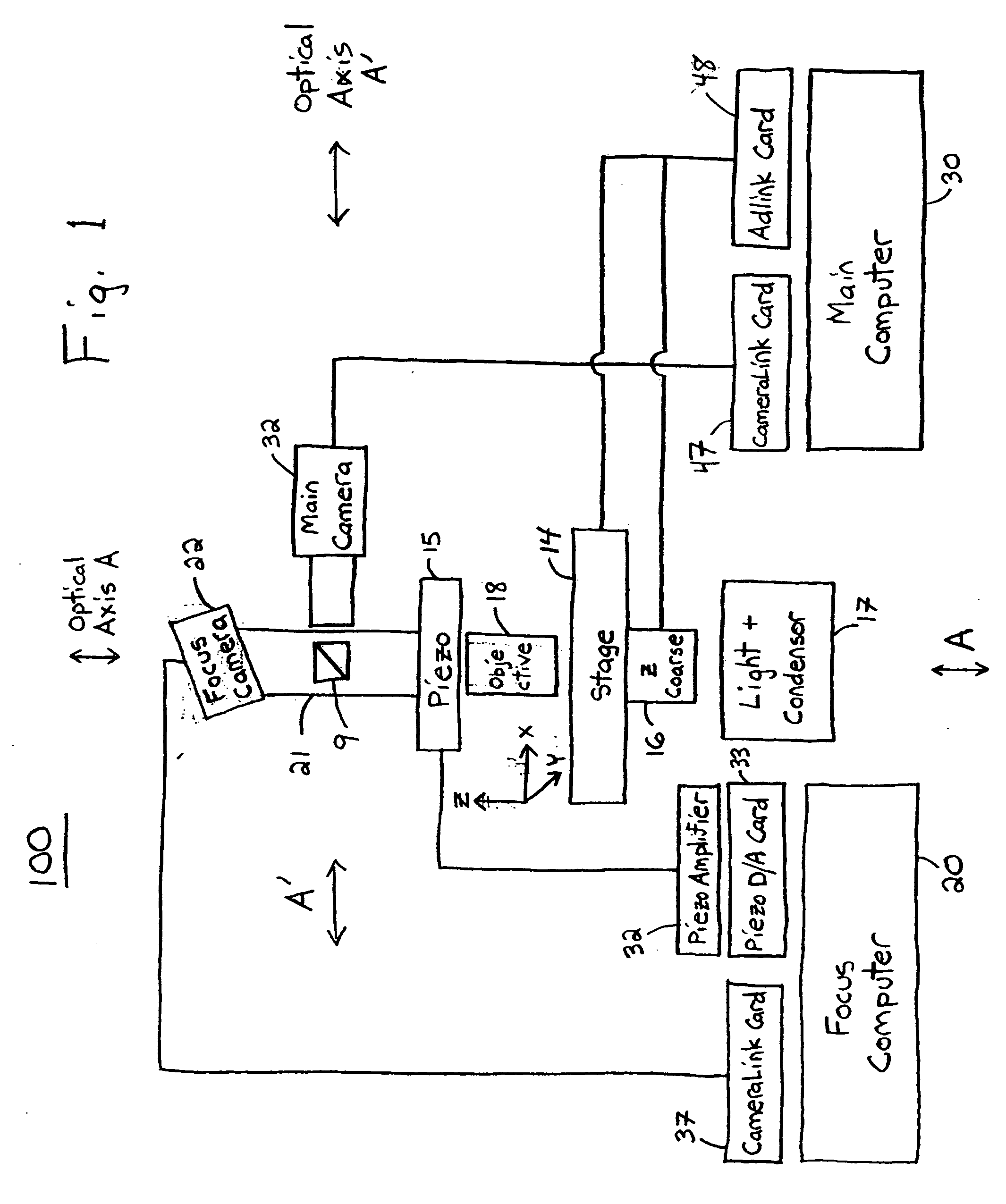
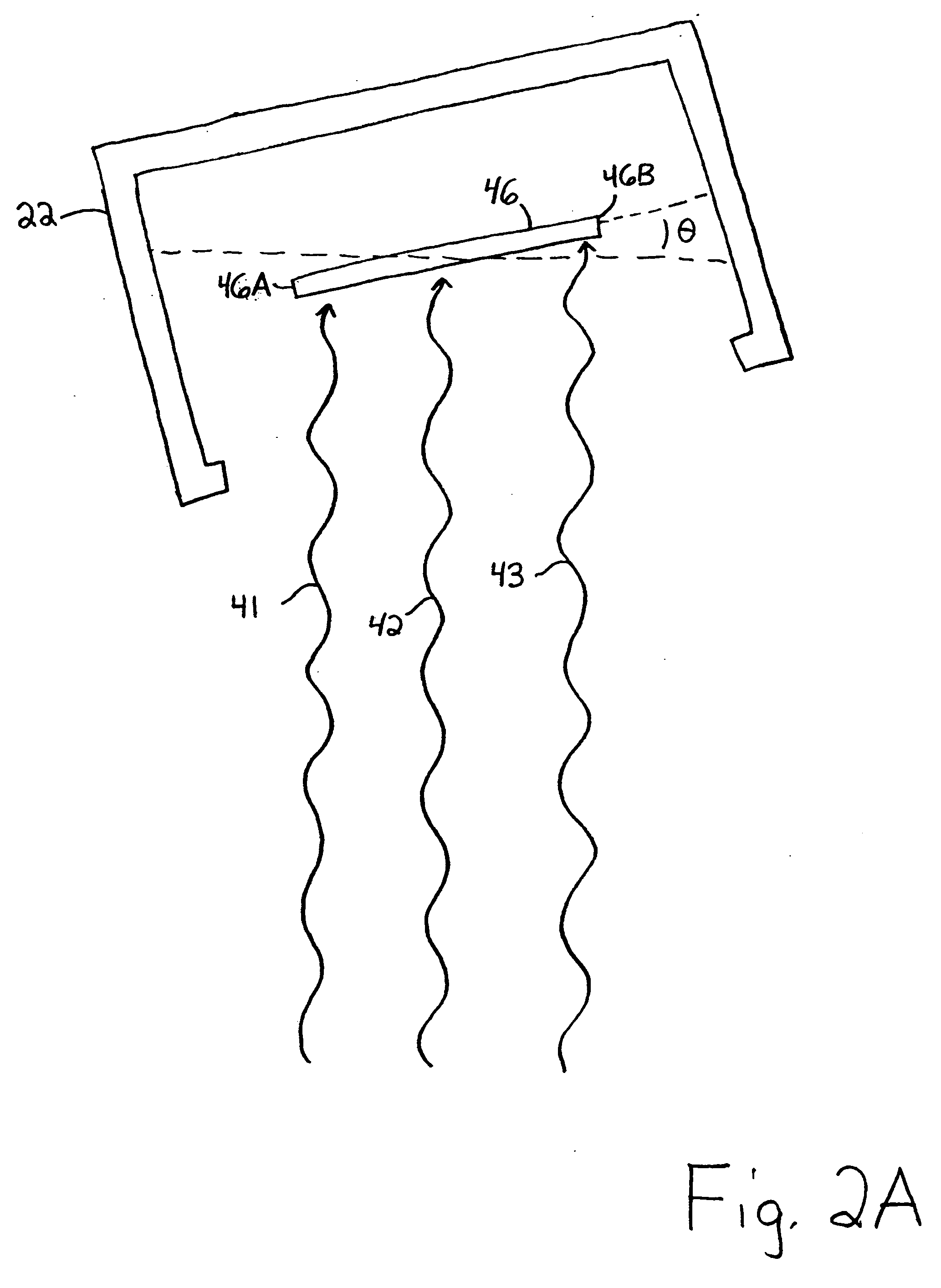
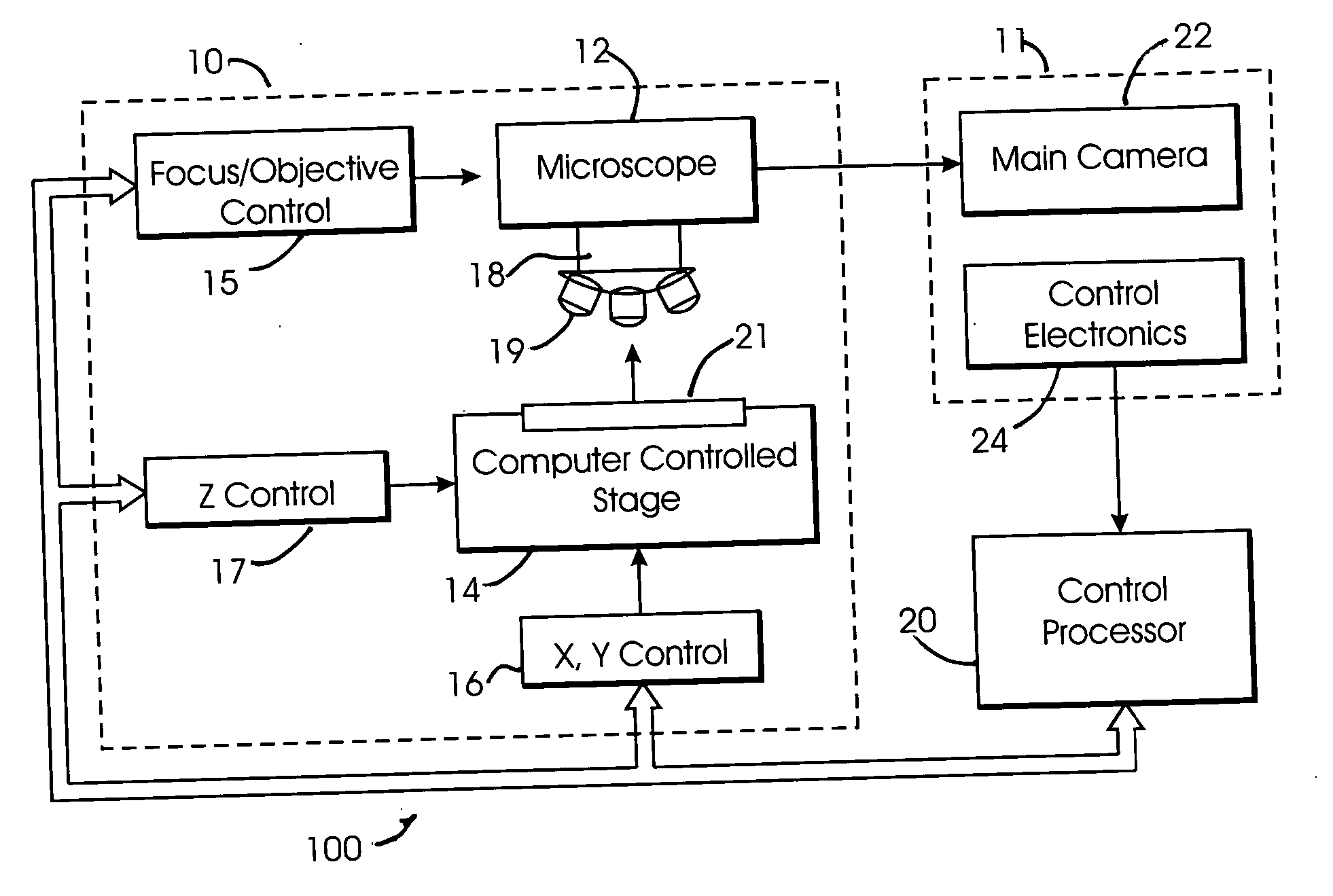
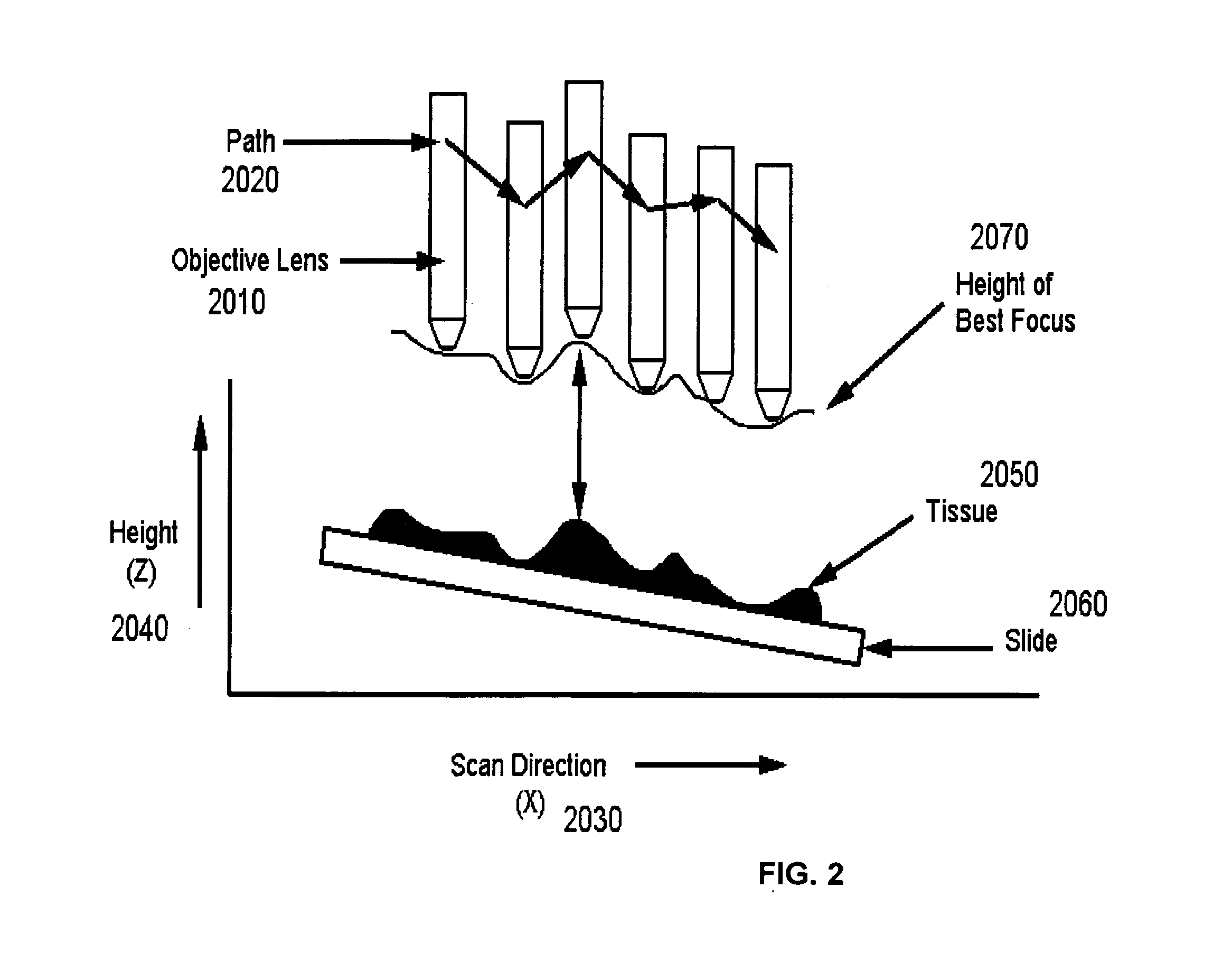
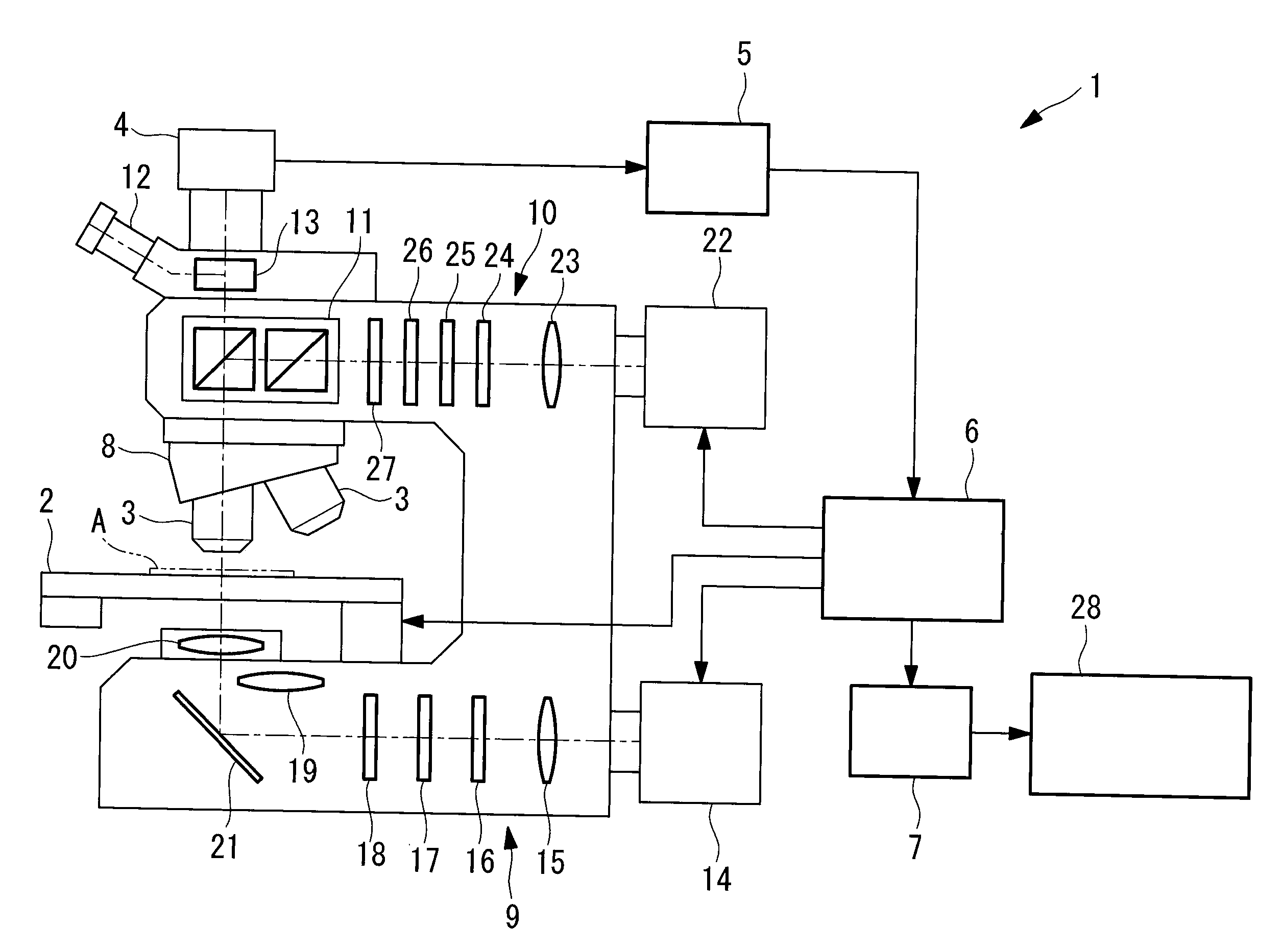
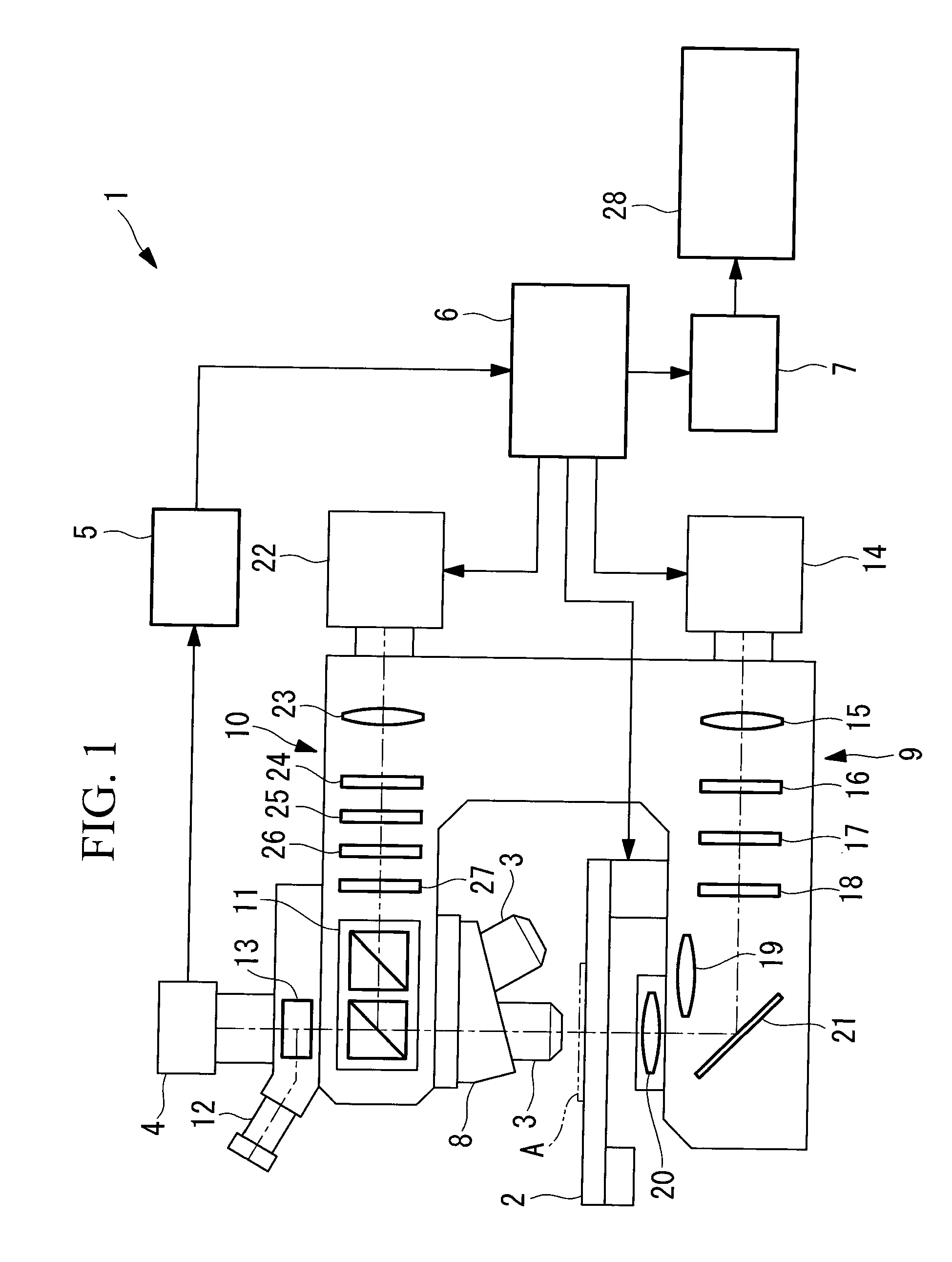
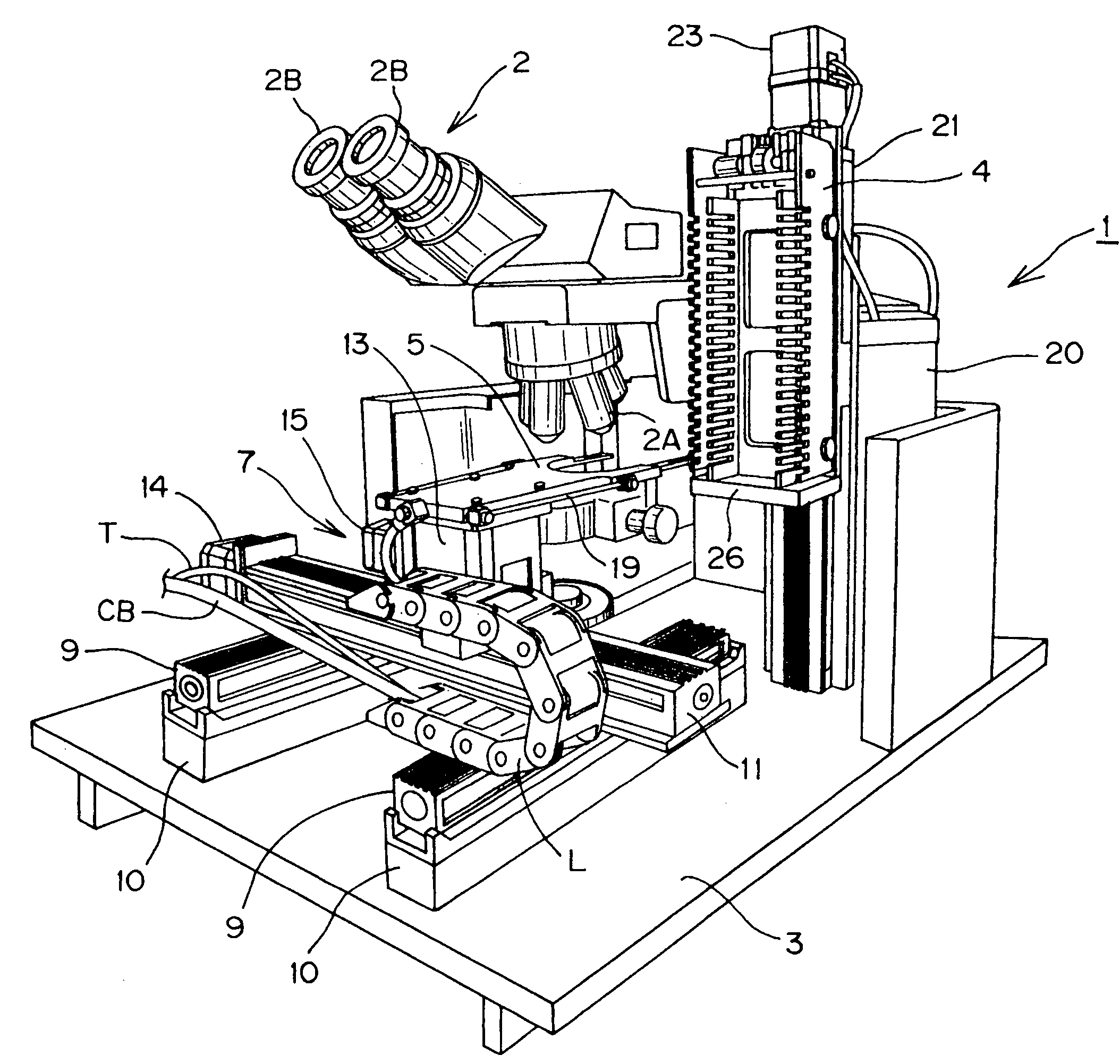
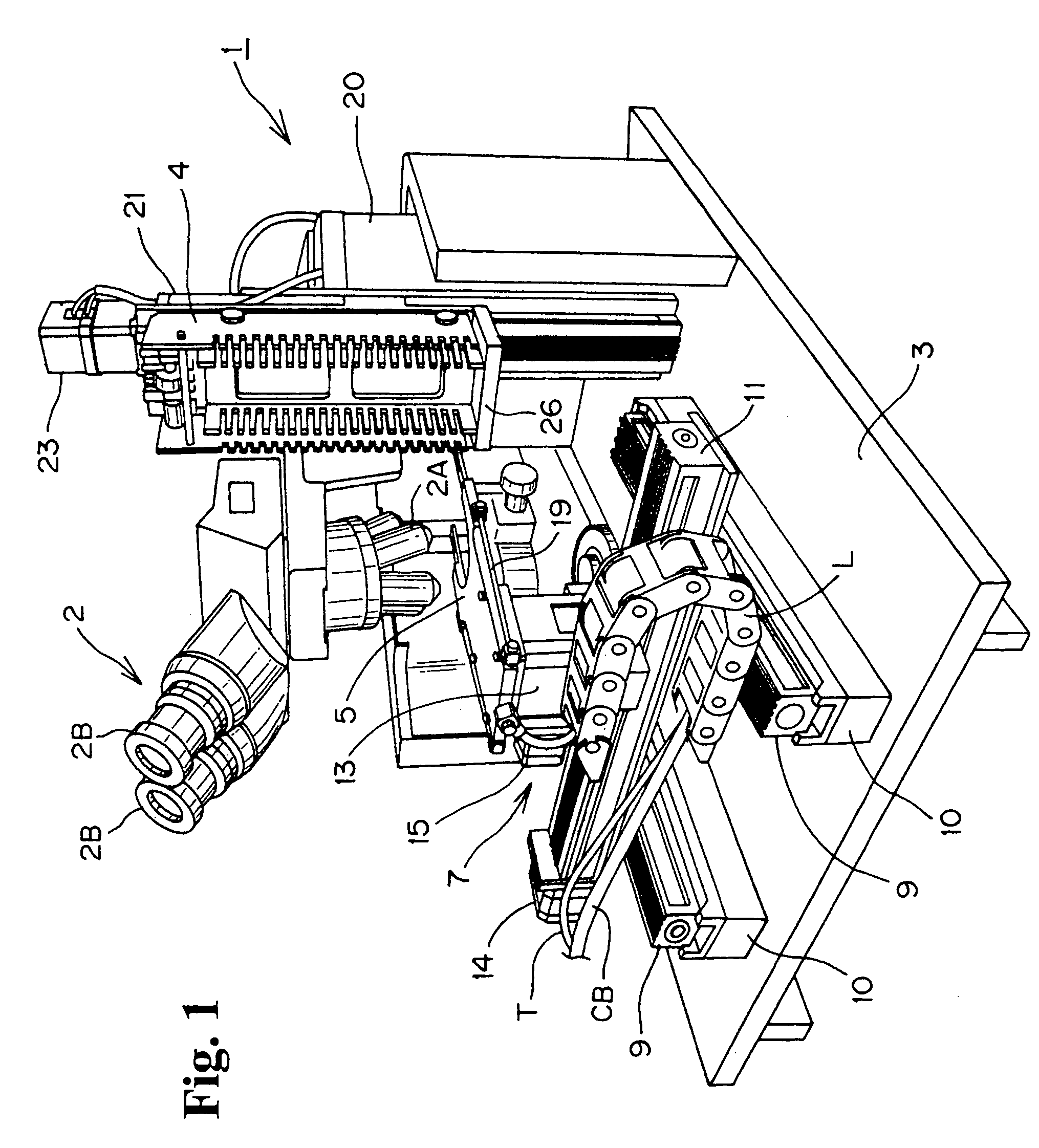
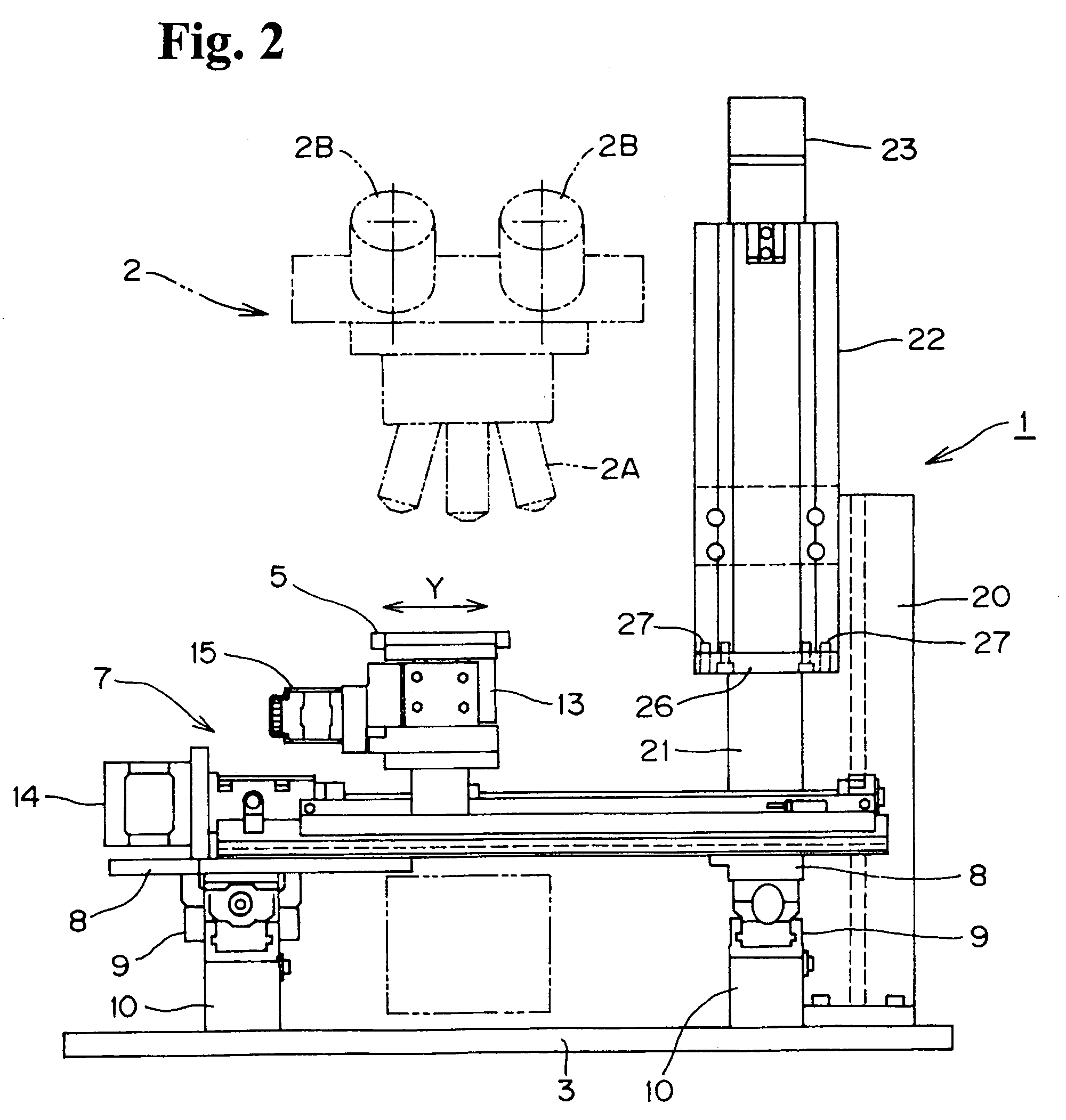
An improved system and method for obtaining images of a microscope slide are provided. In one embodiment, a focus camera includes an optical sensor that is tilted relative to the focal plane of a scanning camera. A scan of a target region is performed, and multiple overlapping images of the target region are captured from a plurality of x-y positions. Each image contains information associated with multiple focal planes. Focus information is obtained from the images, and a desired-focus position is determined for the target region based on the focus information. The scanning camera then captures an image of the target region from the desired-focus position. This procedure may be repeated for selected regions on the microscope slide and the resulting images of the respective regions are merged to create a virtual slide.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS
Systems and methods for stitching image blocks to create seamless magnified images of a microscope slide
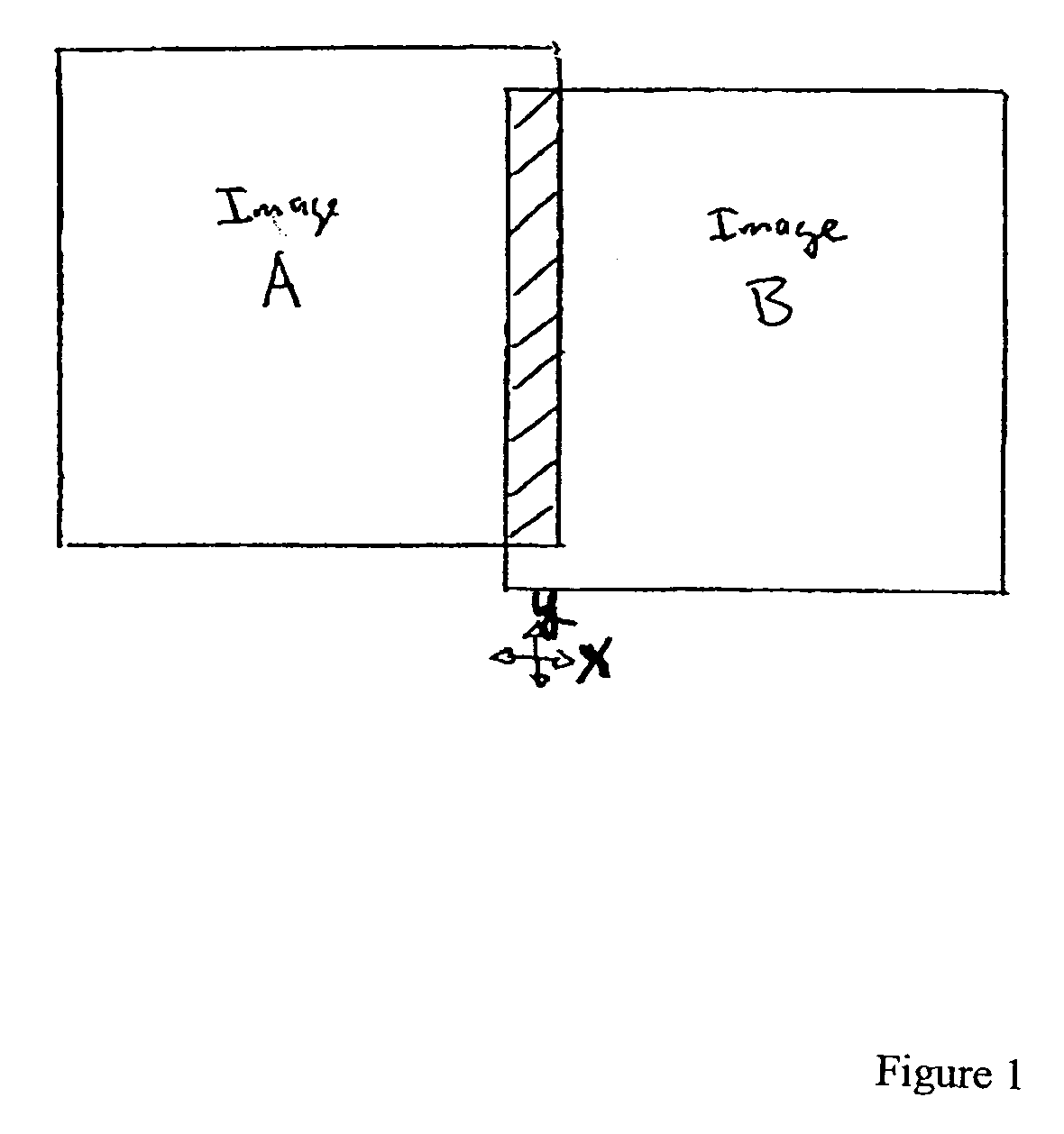
Scanned image portions of a virtual slide are stored in accord with a positional index metric associated to each image's location in a mosaic representation of the entire physical slide and a normalized correlation search is performed on next neighbor regional image blocks. A set of relative positional offset values and a correlation coefficient is determined for a regional image block and a next neighbor regional image block. A portion of the regional image blocks is viewed as a field of view of a display and a composite of the portion of regional image blocks is stitched together in accord with the set of relative positional offset values and the correlation coefficient, such that only the blocks comprising the portion are stitched. Moving the field of view of the display causes additional regional image blocks to be displayed, where image stitching is subsequently performed only with respect to the additional regional image blocks brought into the new field of view.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS +1
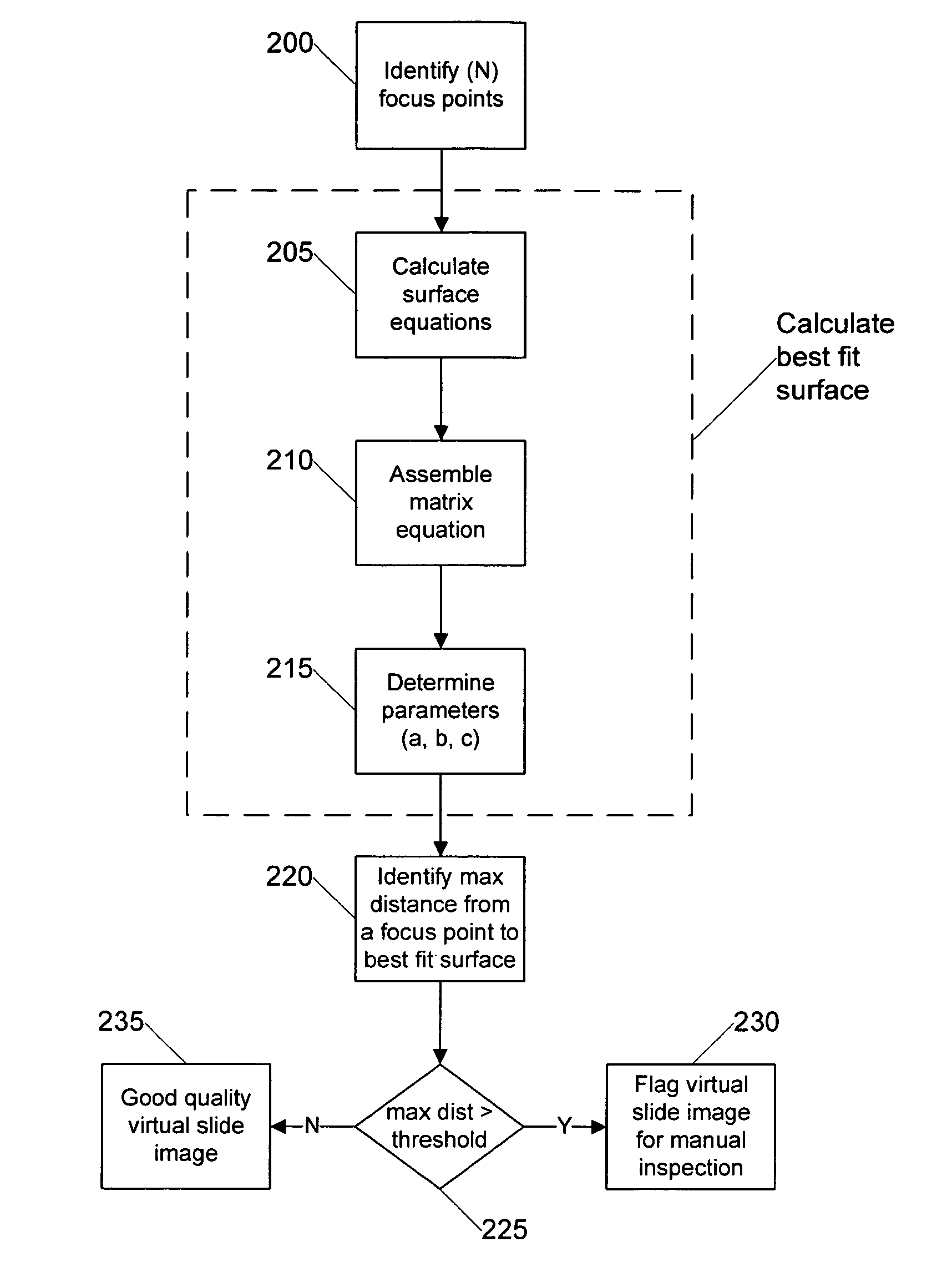
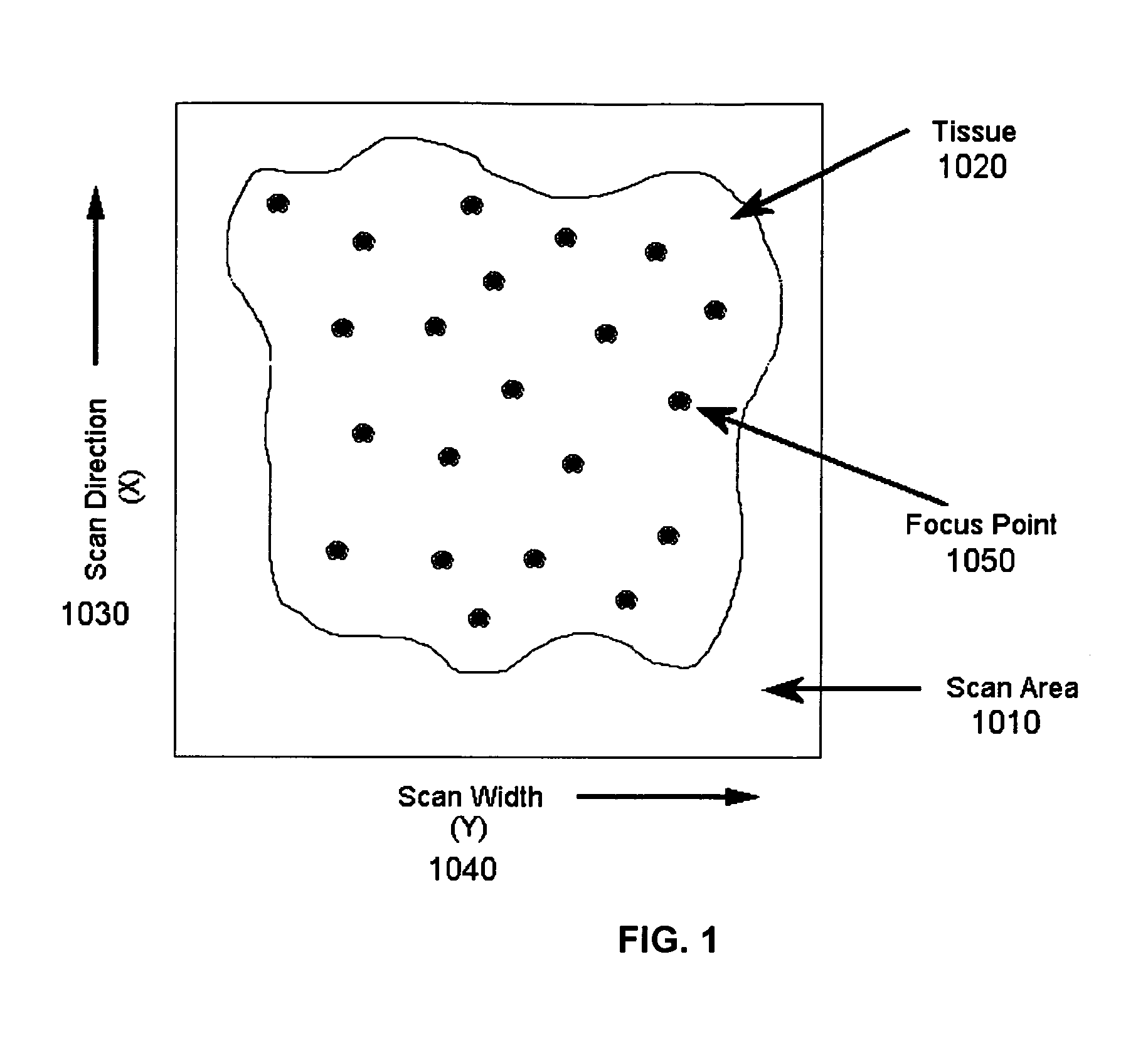
System and method for assessing virtual slide image quality
InactiveUS7668362B2Raise the possibilityEasy to demonstrateTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionVirtual slideImaging quality
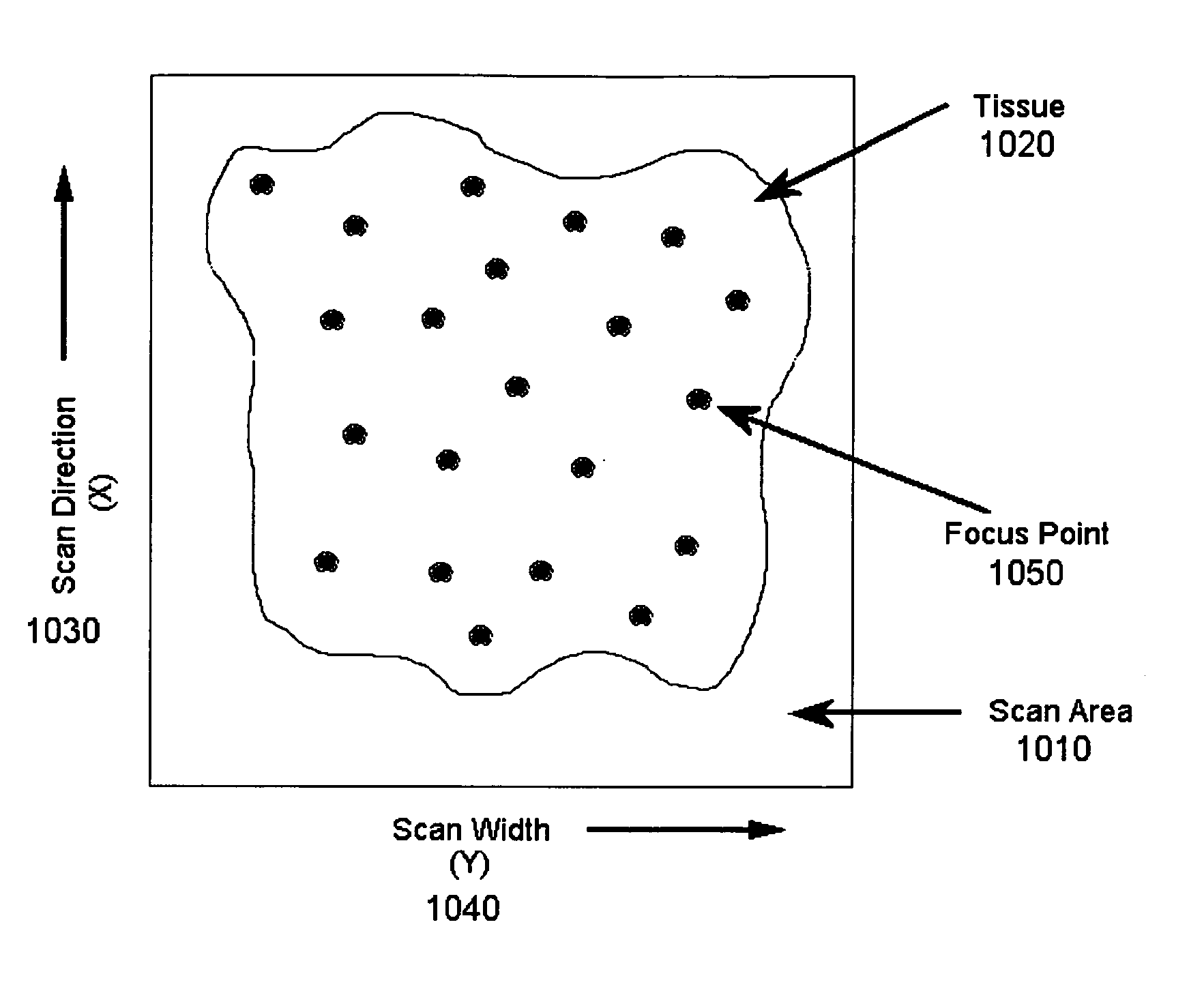
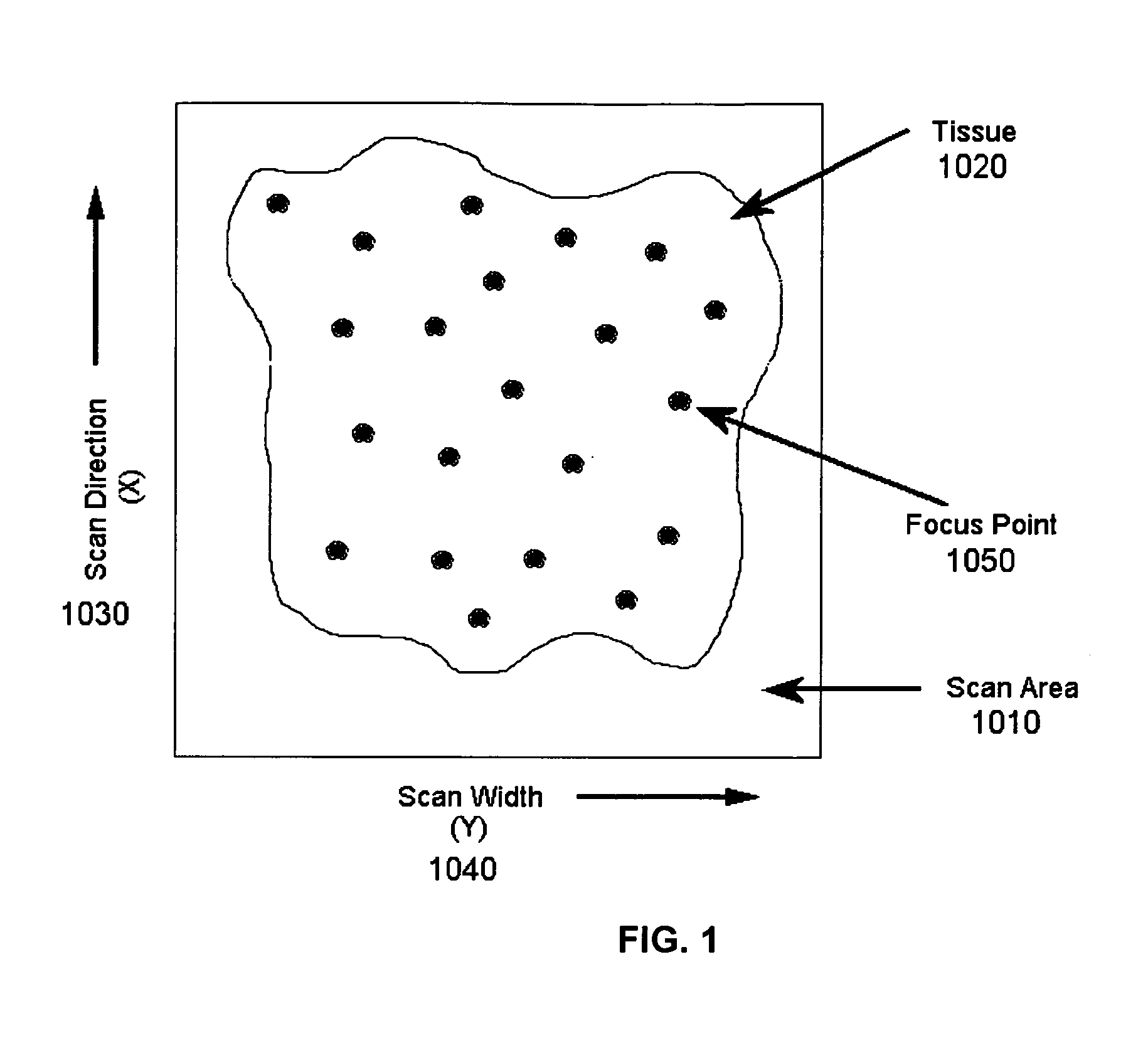
Systems and methods for assessing virtual microscope slide image quality are provided. In order to determine whether a virtual slide image has any out of focus areas and is therefore a candidate for manual inspection, the various focus points used to scan the virtual slide image are used to calculate a best fit surface for the virtual slide image. The distance of each focus point from the best fit surface is then calculated and the largest distance is compared to a predetermined value. If the largest distance from a focus point to the best fit surface is larger than the predetermined value, then the virtual slide image is designated as needing a manual inspection and possible re-scan.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
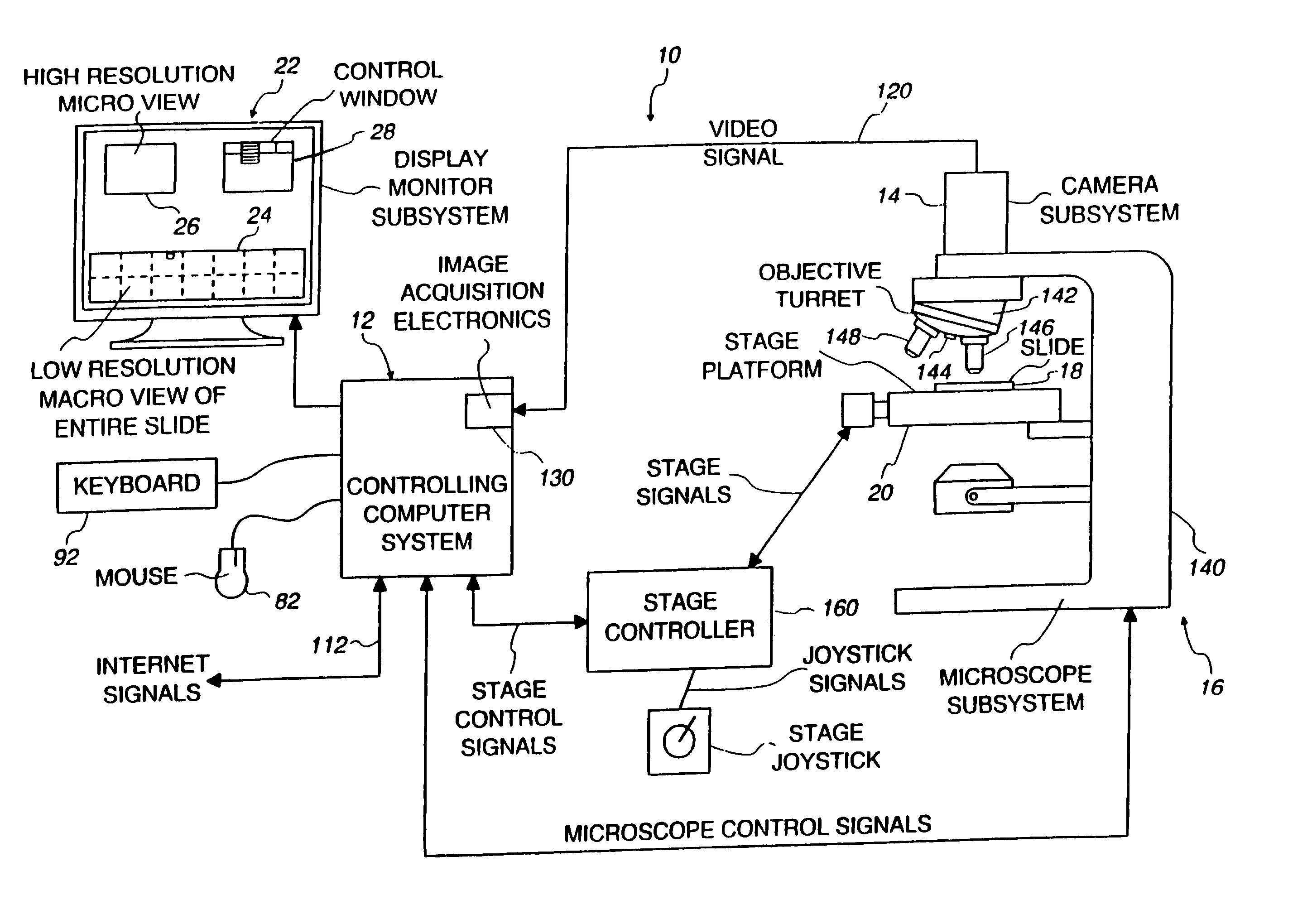
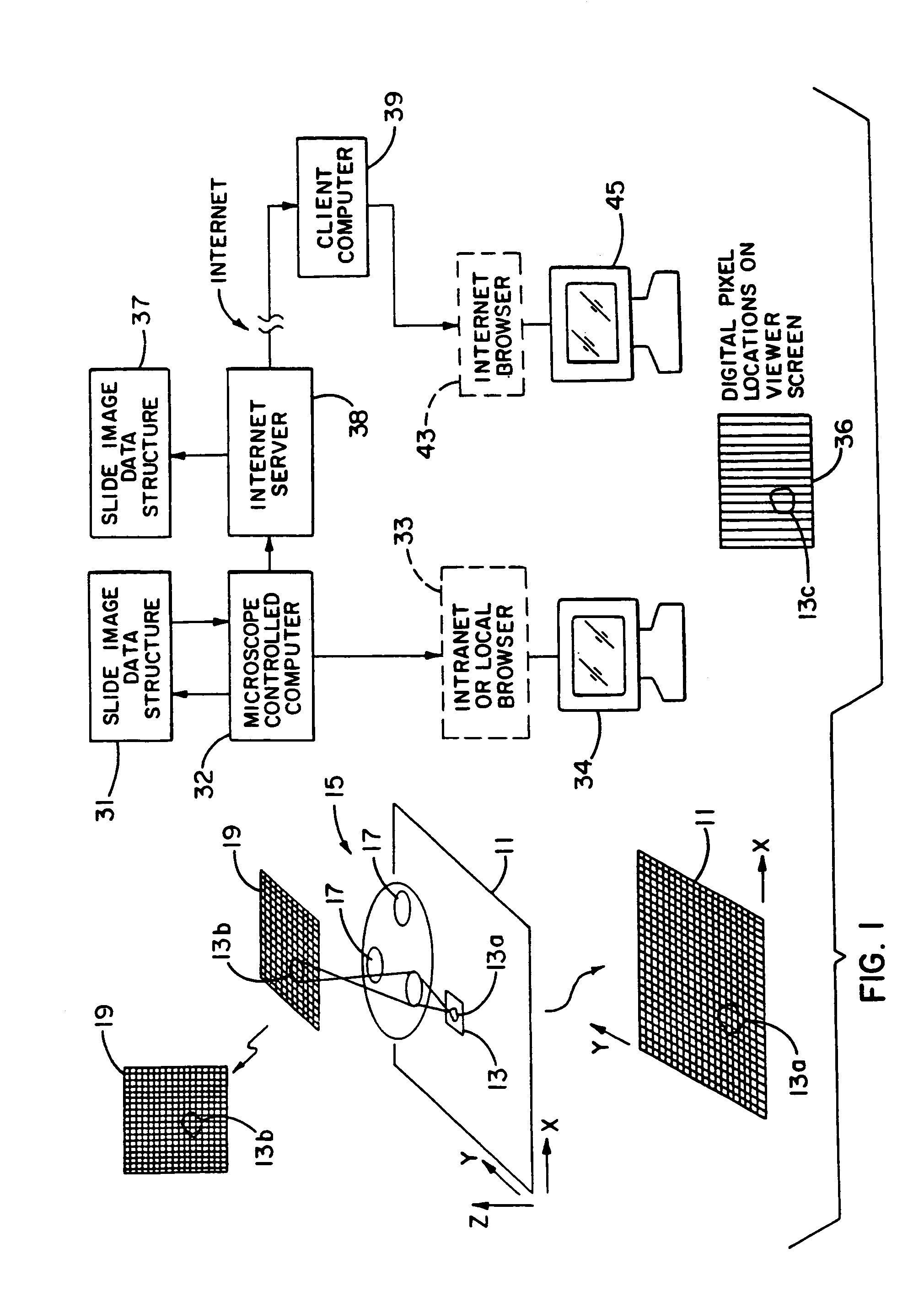
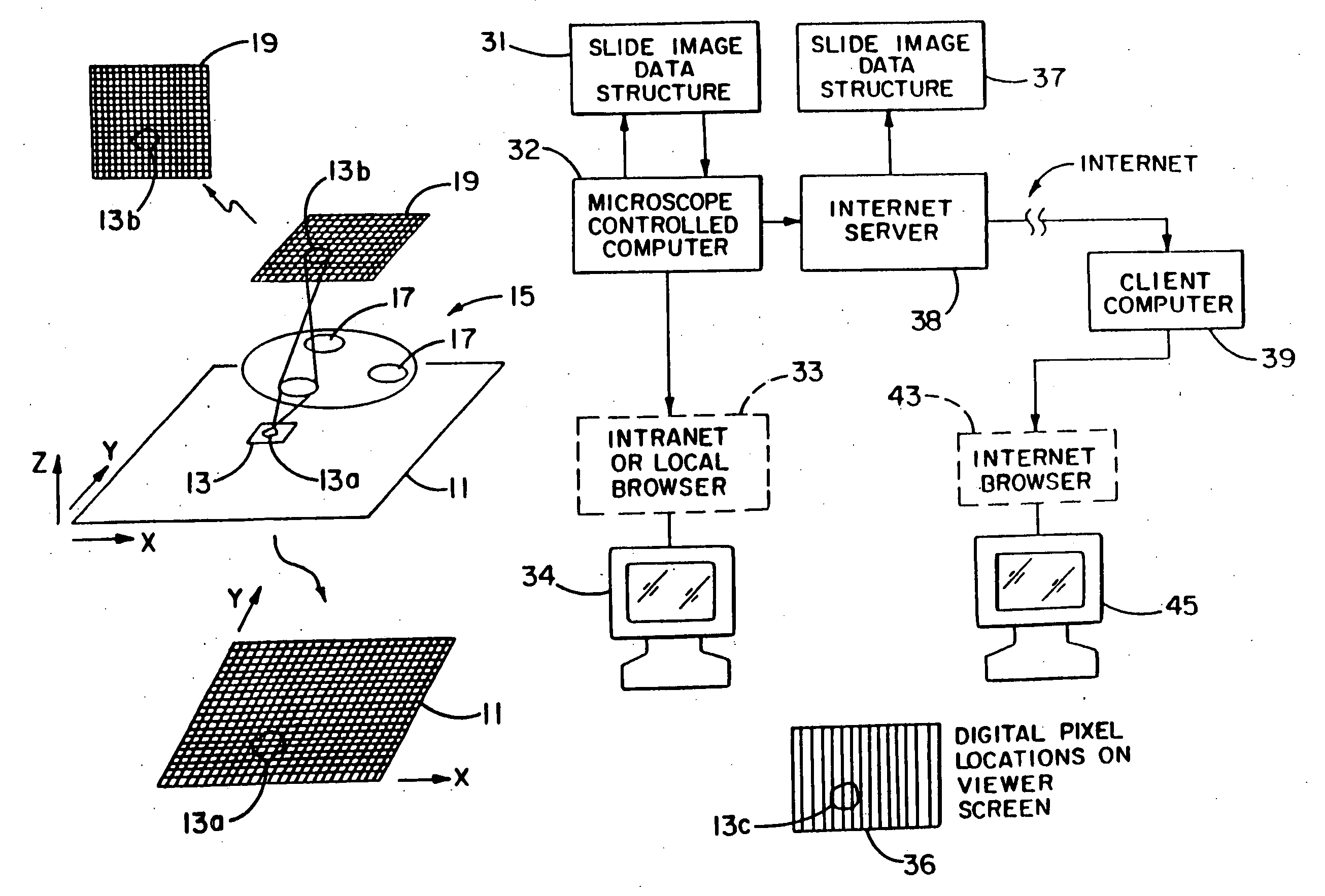
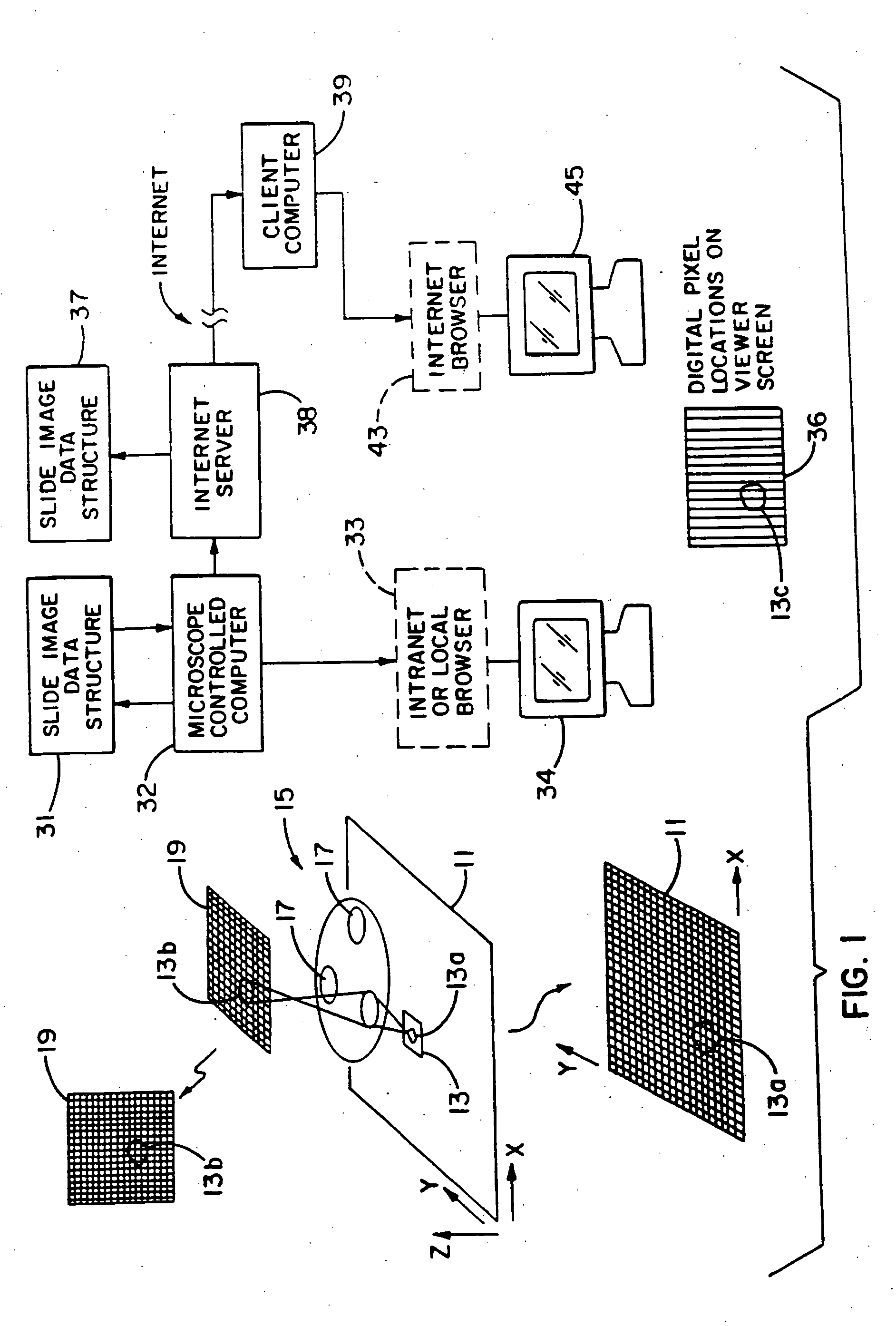
Method and apparatus for internet, intranet, and local viewing of virtual microscope slides
A method of and apparatus for viewing microscopic images include transmitting tiled microscopic images from a server to a client. The client assembles the tiled images into a seamless virtual slide or specimen image and provides tools for manipulating image magnification and viewpoint. The method and apparatus also provides a virtual multi-headed microscope function which allows scattered viewers to simultaneously view and interact with a coherent magnified microscopic image.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
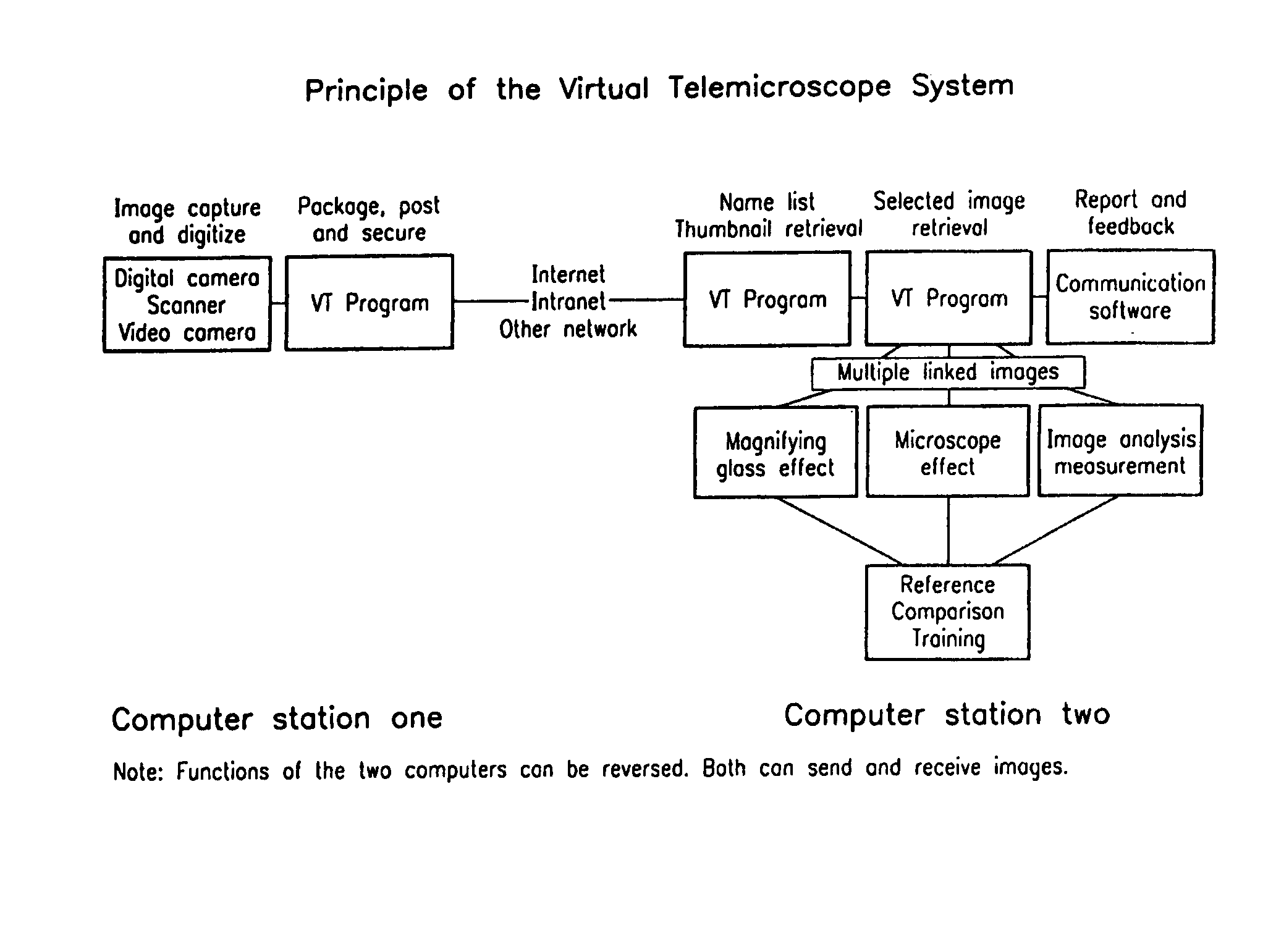
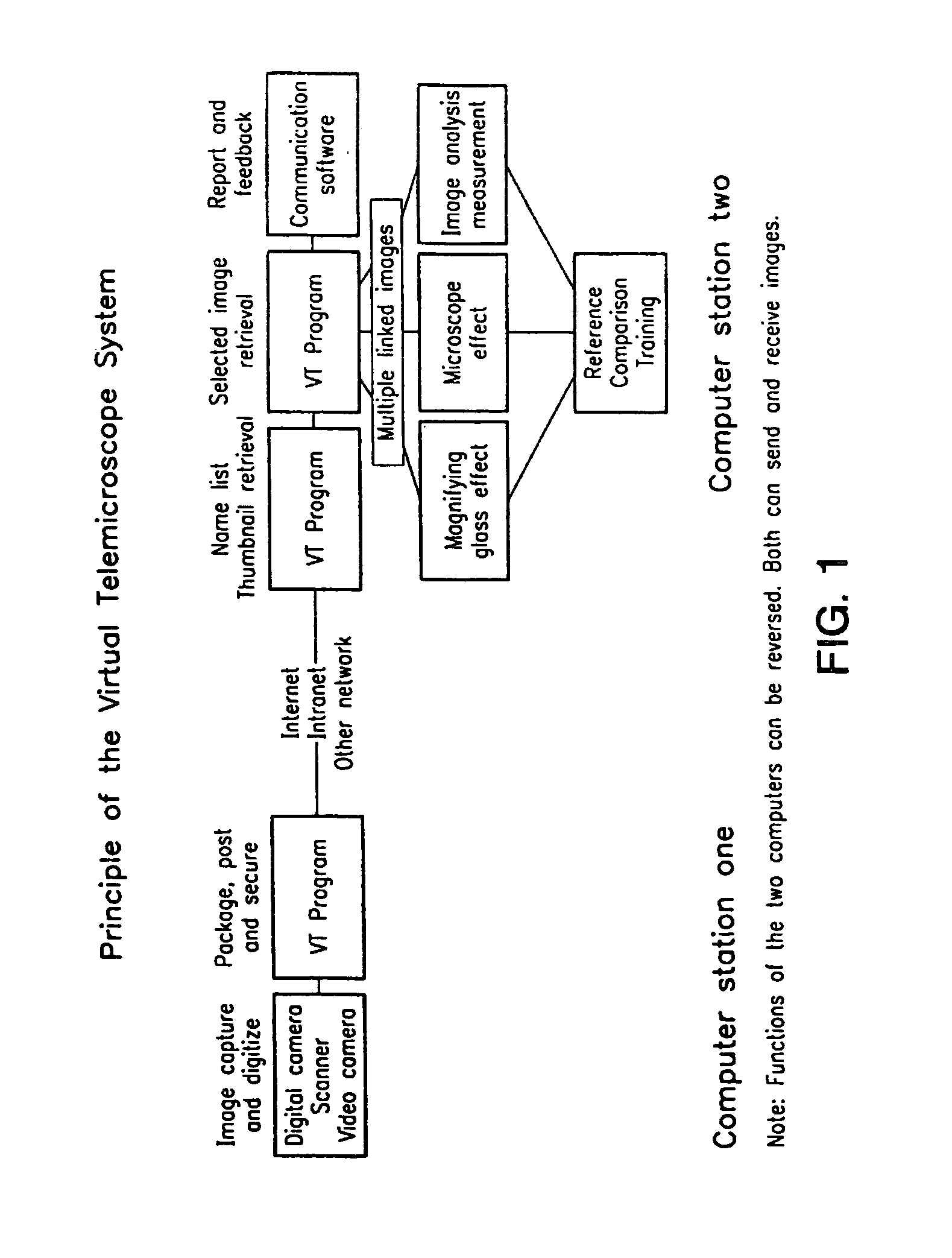
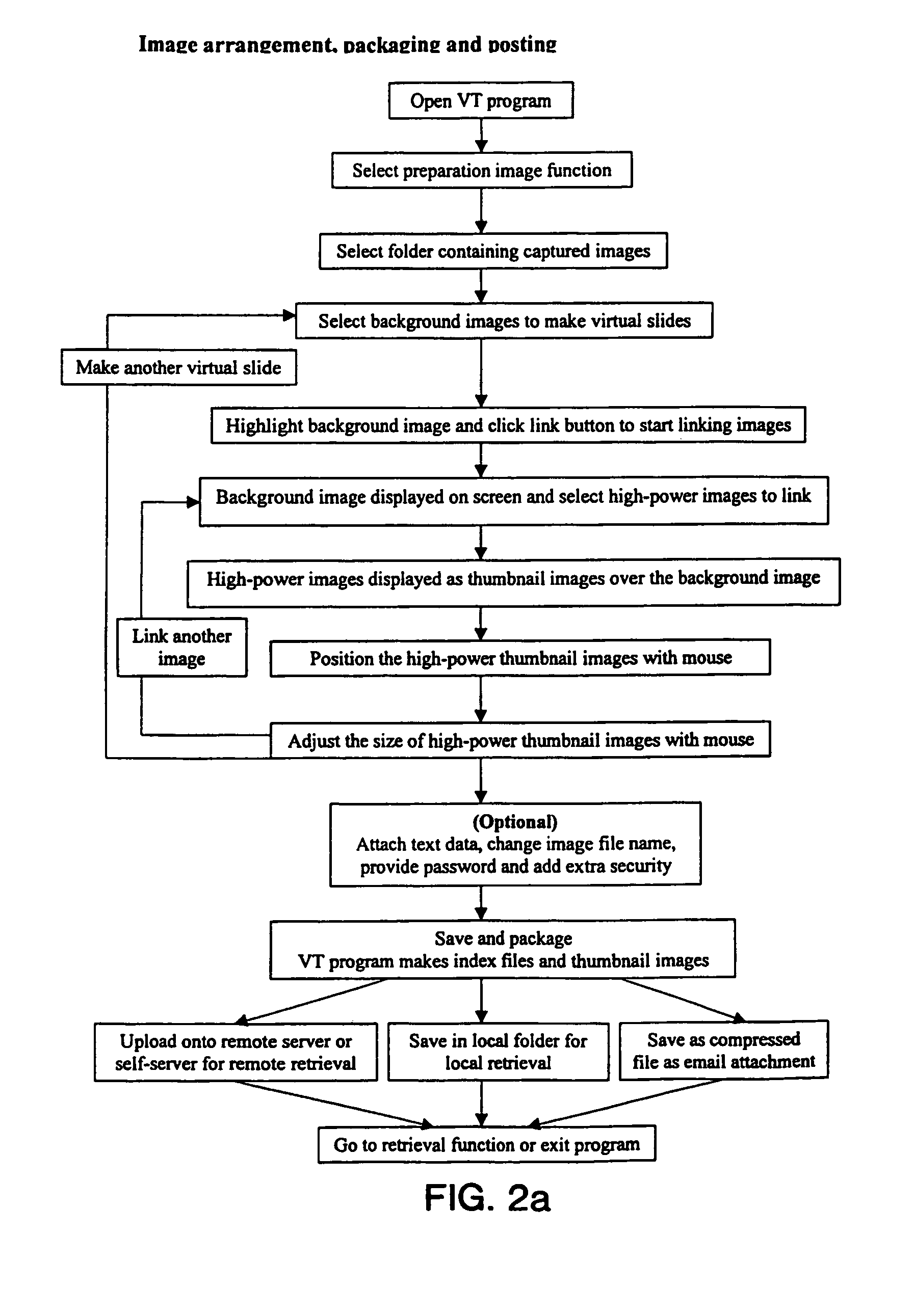
Virtual telemicroscope
InactiveUS7292251B1Different magnification levelCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingMagnifying glassVirtual slide
A method and system that uses a computer system as a telemicroscope. A plurality of images of a specimen are captured (Digital camera scanner video camera). The images correspond to the entire specimen and a plurality of segments of the specimen (Multiple linked images). The high-resolution images corresponding to said plurality of segments have different magnification levels and locations (magnifying glass effect); a linking map is generated between said images (Multiple linked images). The linking map comprises information regarding geographical location of the images in relation to the specimen's structure (Image geographical measurement); and images and said linking map are transmitted to a remote user via a computer network thereby allowing the user to view the images with different magnification levels without compromising in image clarity (Computer station one and computer station two). The transmitted images are viewed in a dynamic manner, permitting the user to navigate, enlarge, measure, compare, annotate and exam the digitized images on a virtual slides displayed on a computer screen (Image analysis measurement). The operation of the system closely mimics that of a light microscope.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
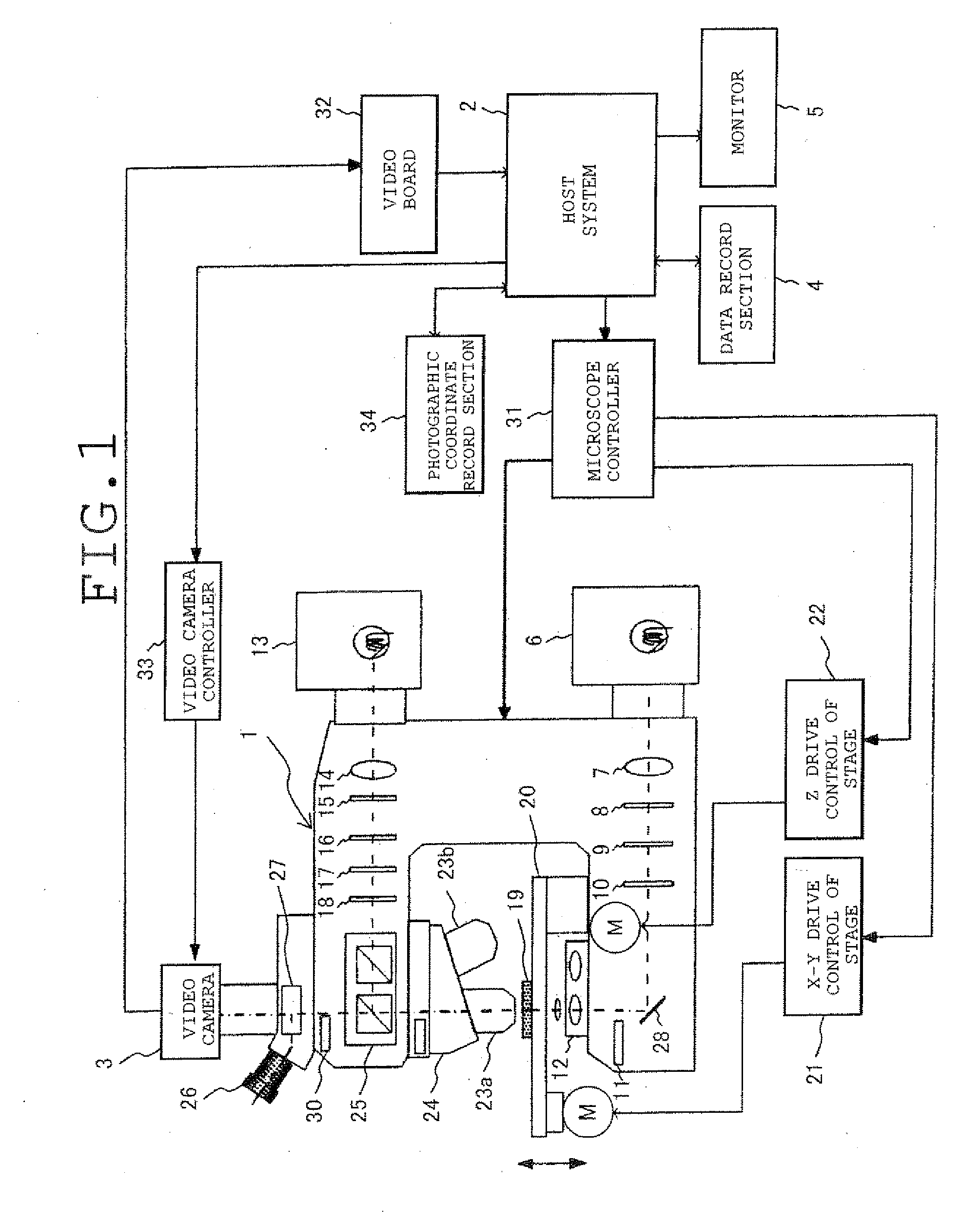
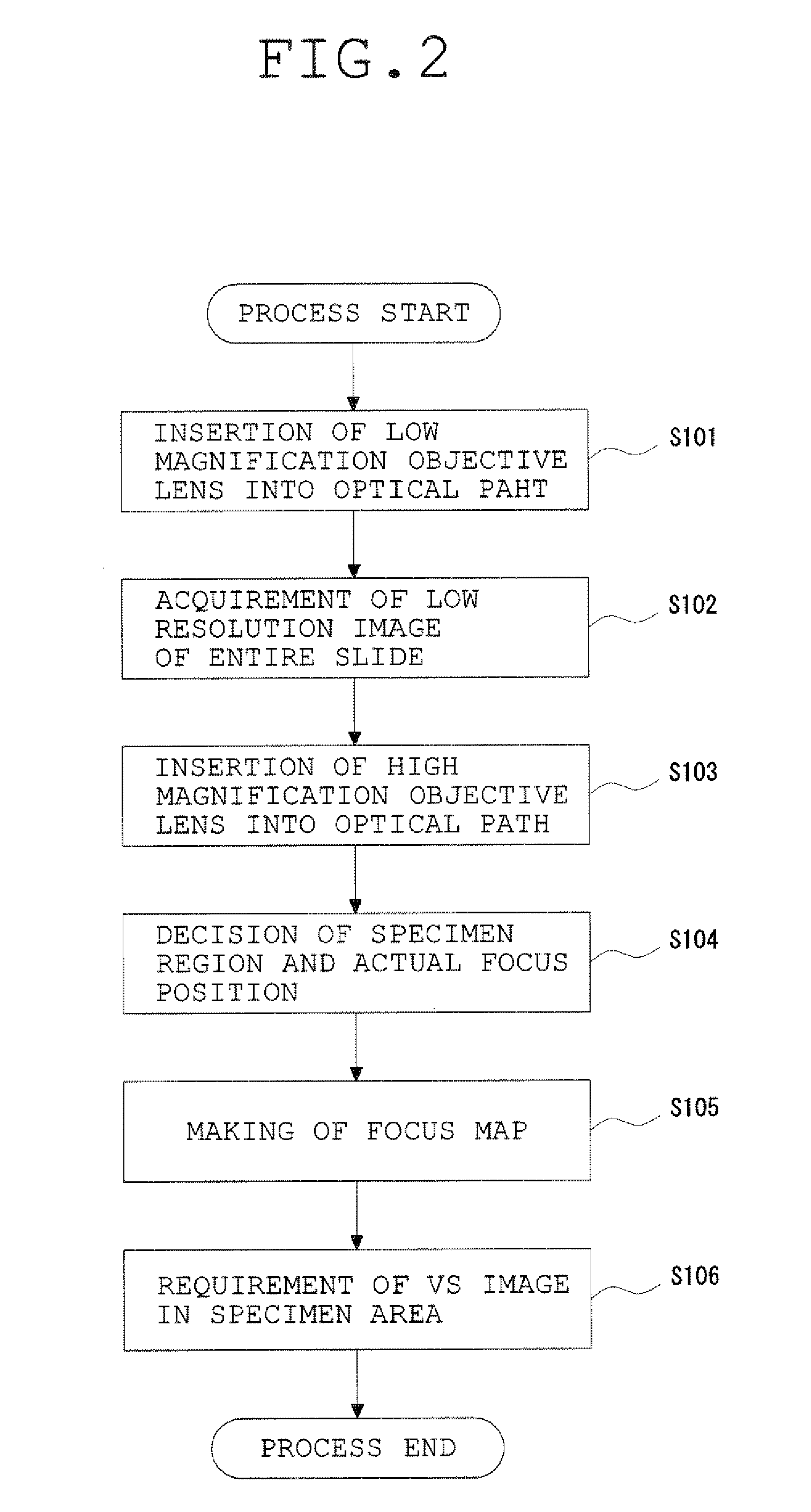
Microscope System, Image Generating Method, and Program for Practising the Same
ActiveUS20090213214A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsVirtual slideOptical axis
A microscope system has a VS image generation means for generating a virtual slide image of a specimen which is constructed by mutually connecting a plurality of microscope images with a first photomagnification photographed and acquired whenever an objective lens and the specimen are relatively moved in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis and which represents the entire image of the specimen, an object-of-interest set means setting an object of interest with respect to the entire image of the specimen represented by the VS image, and a three-dimensional VS image generation means for generating a three-dimensional VS image which is constructed by connecting the microscope images at different focal positions in accordance with the same focal position and which is constructed from the microscope images with a second photomagnification higher than the first photomagnification and represents the image of the object of interest.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
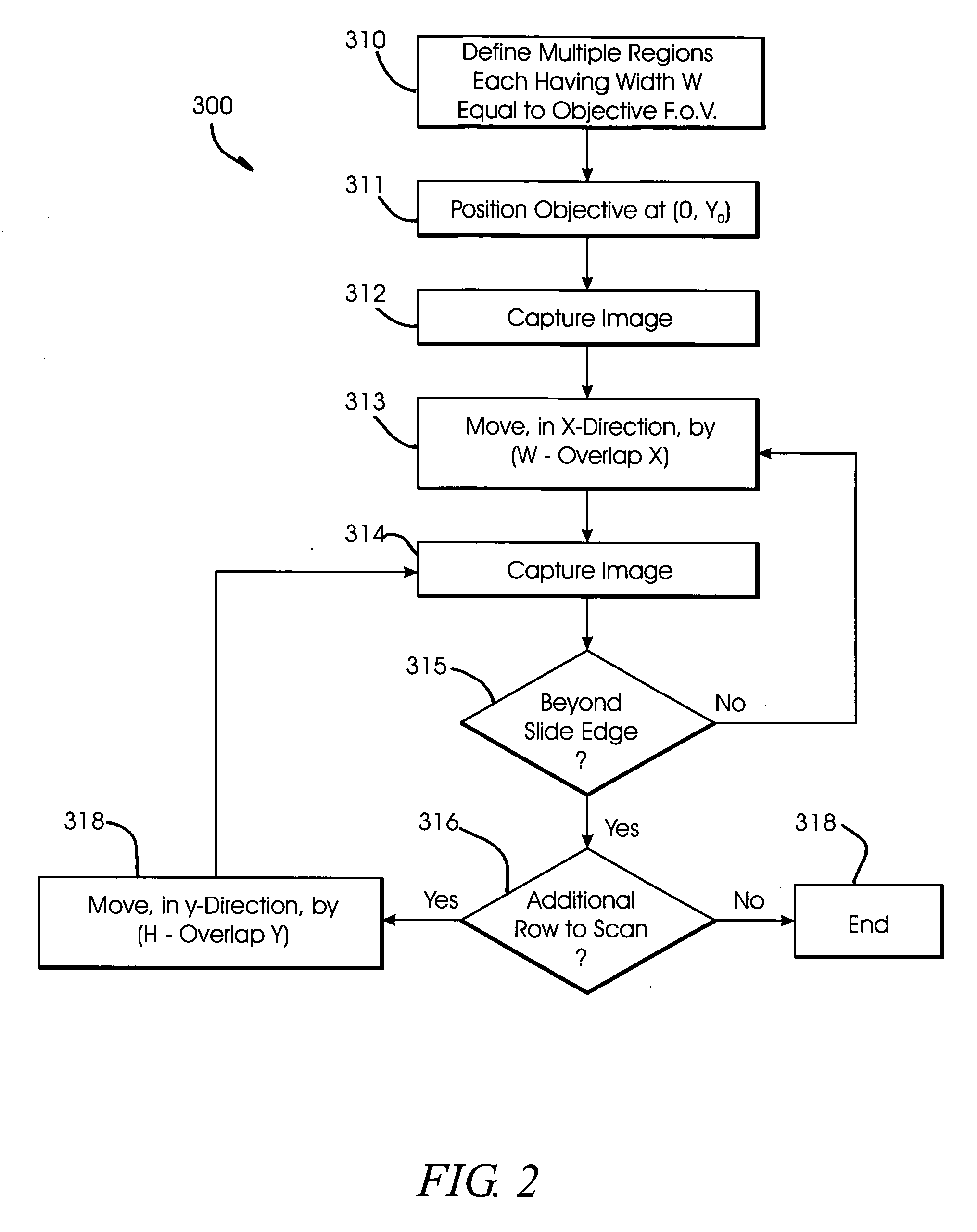
System and method for creating magnified images of a microscope slide
InactiveUS20060045505A1Optimum image quality characteristicImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscope slideRegion selection
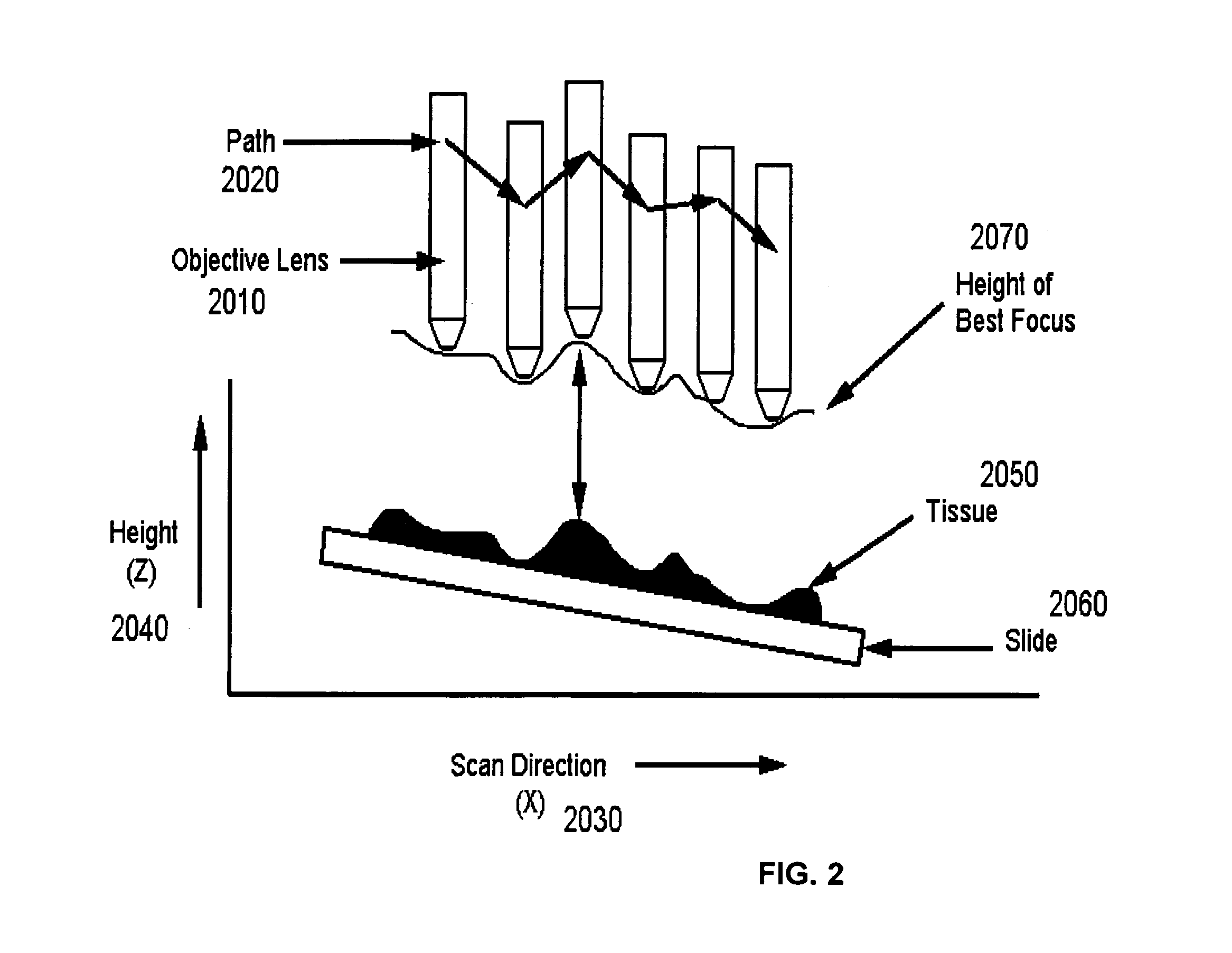
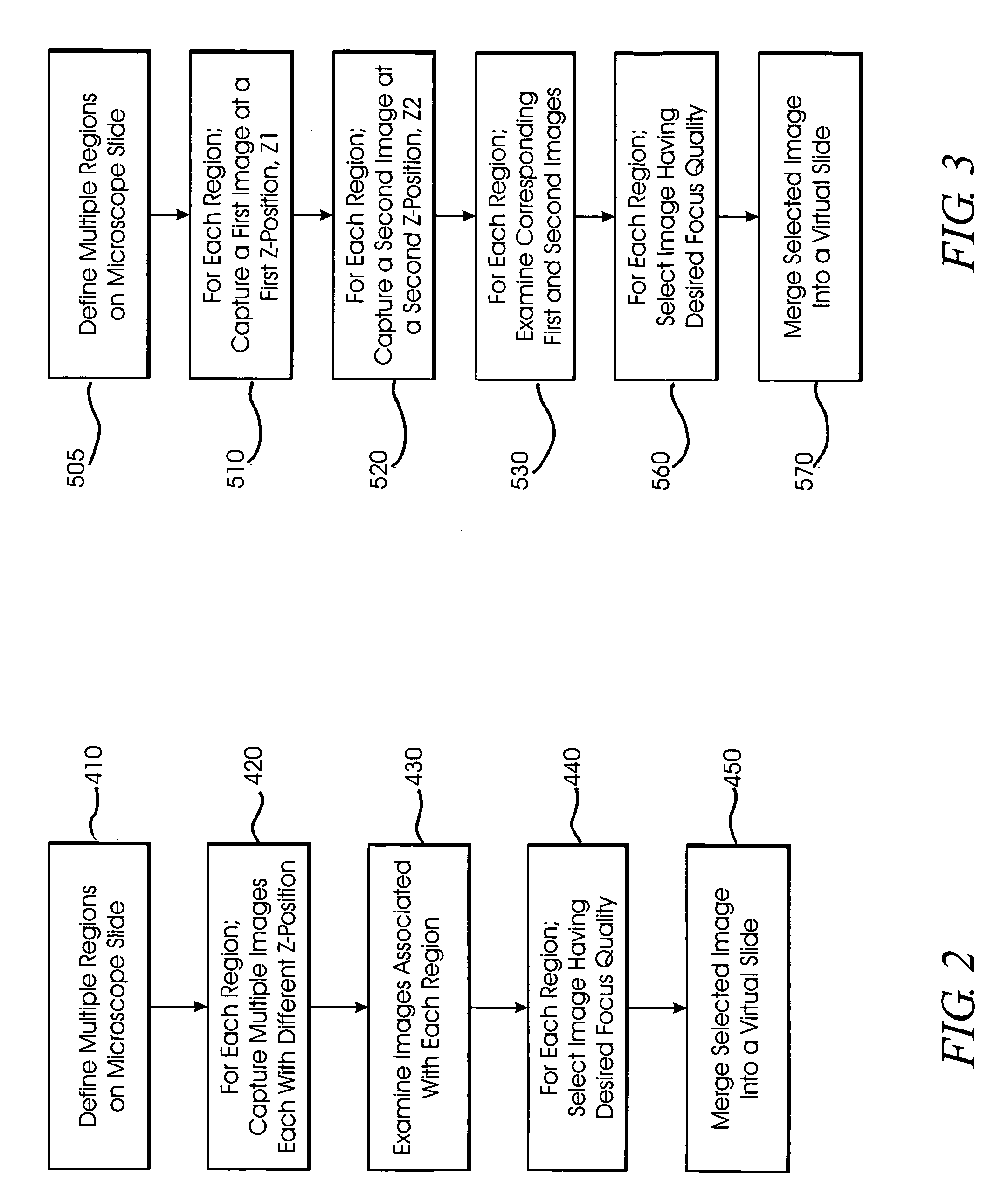
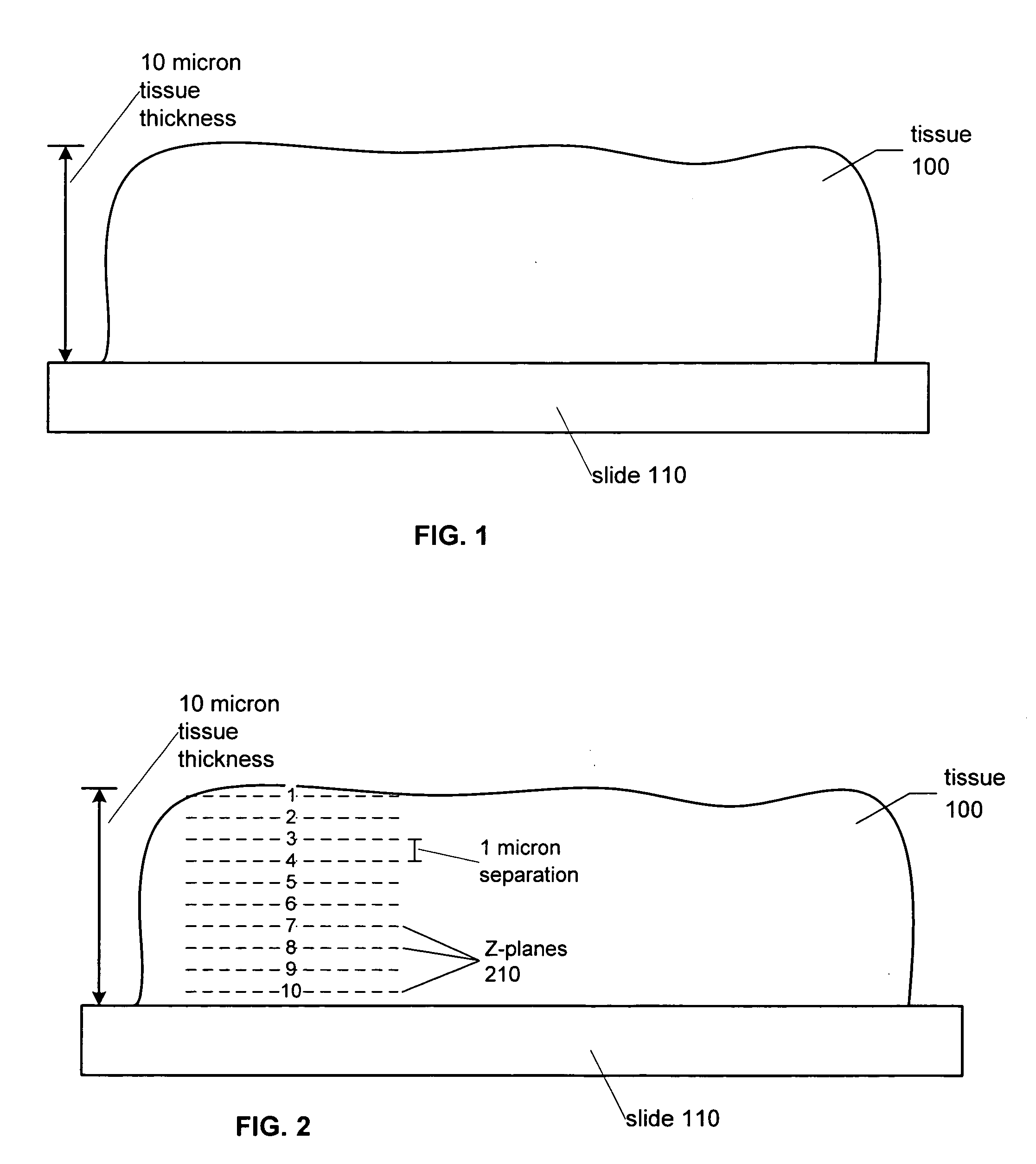
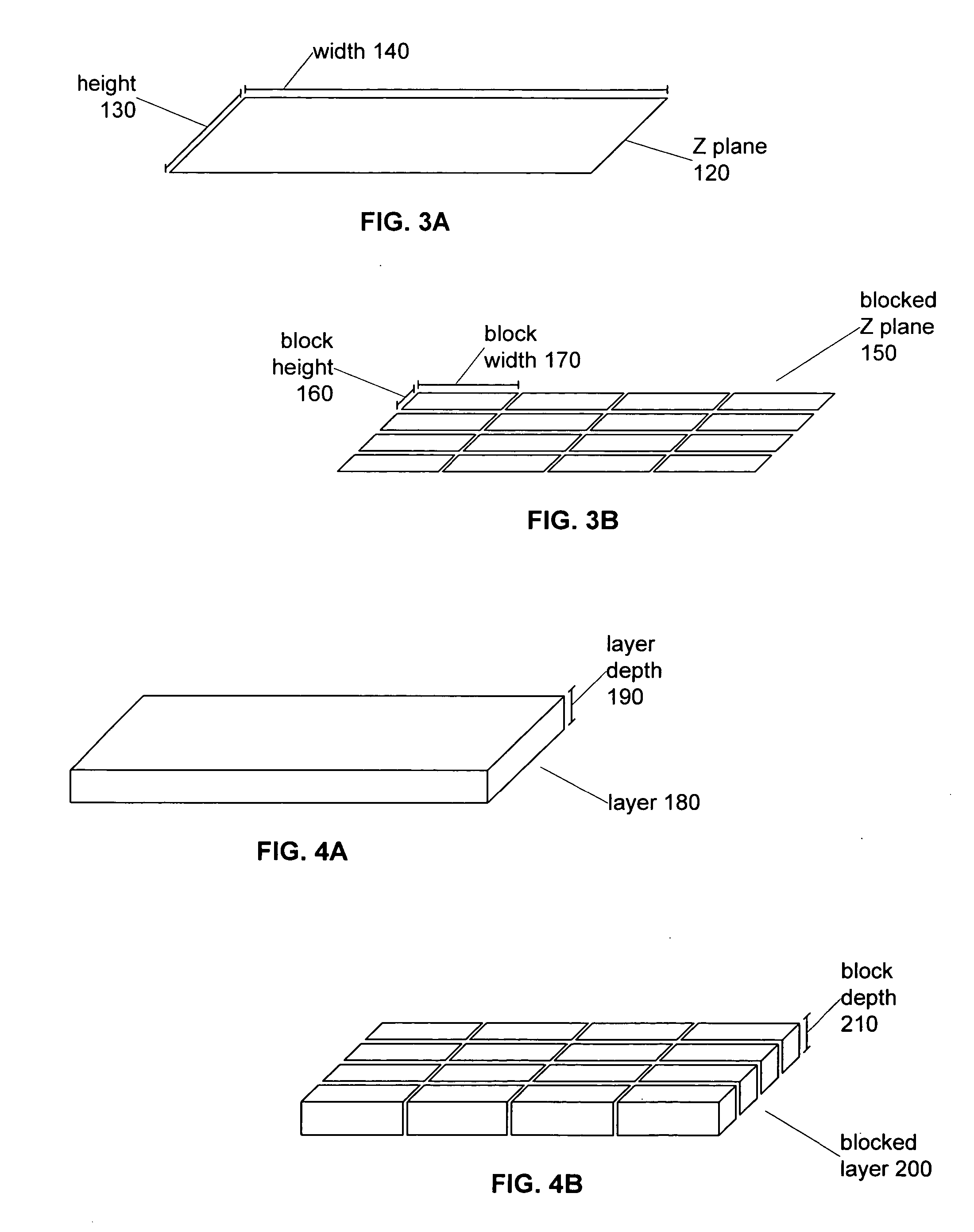
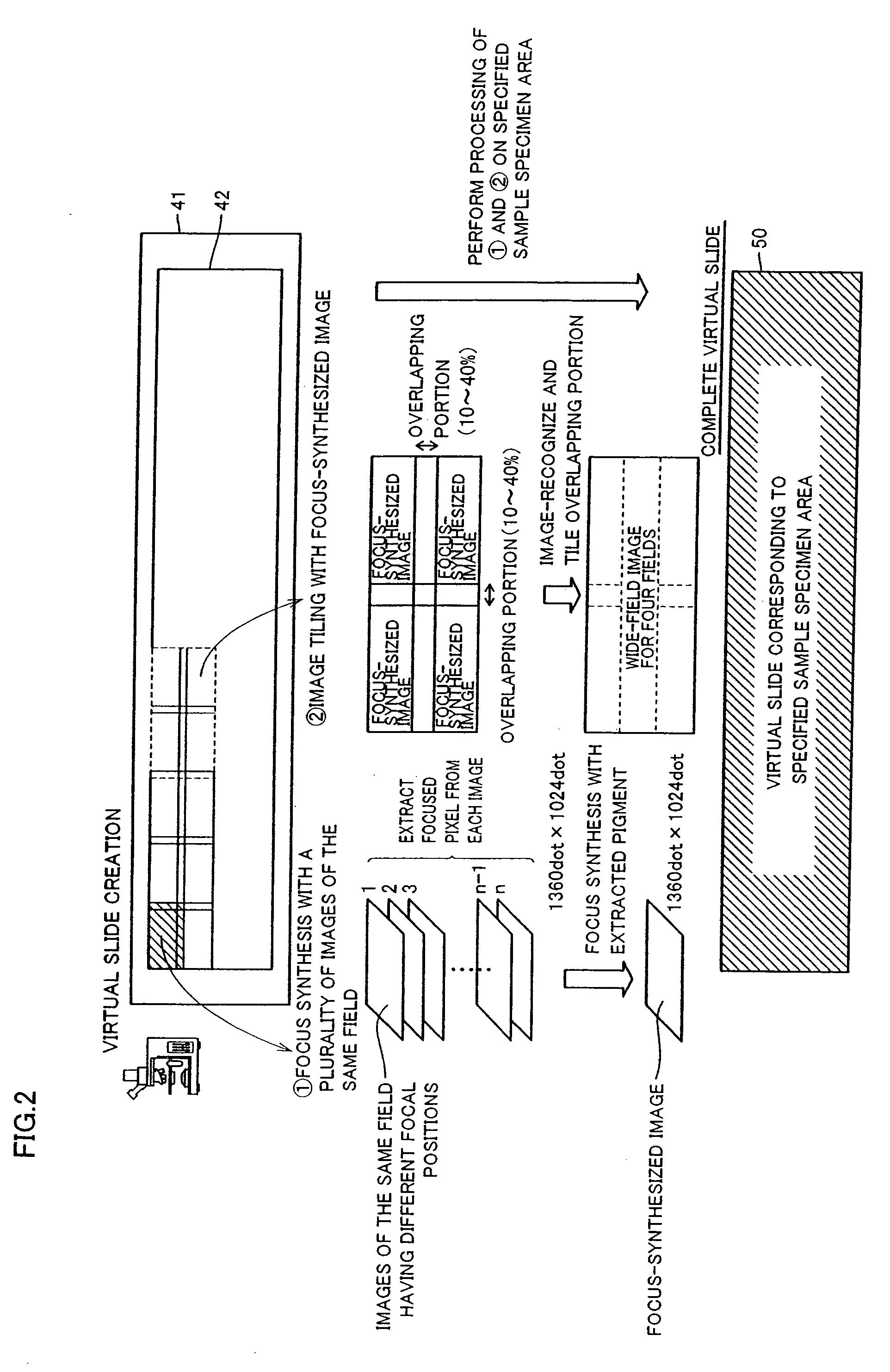
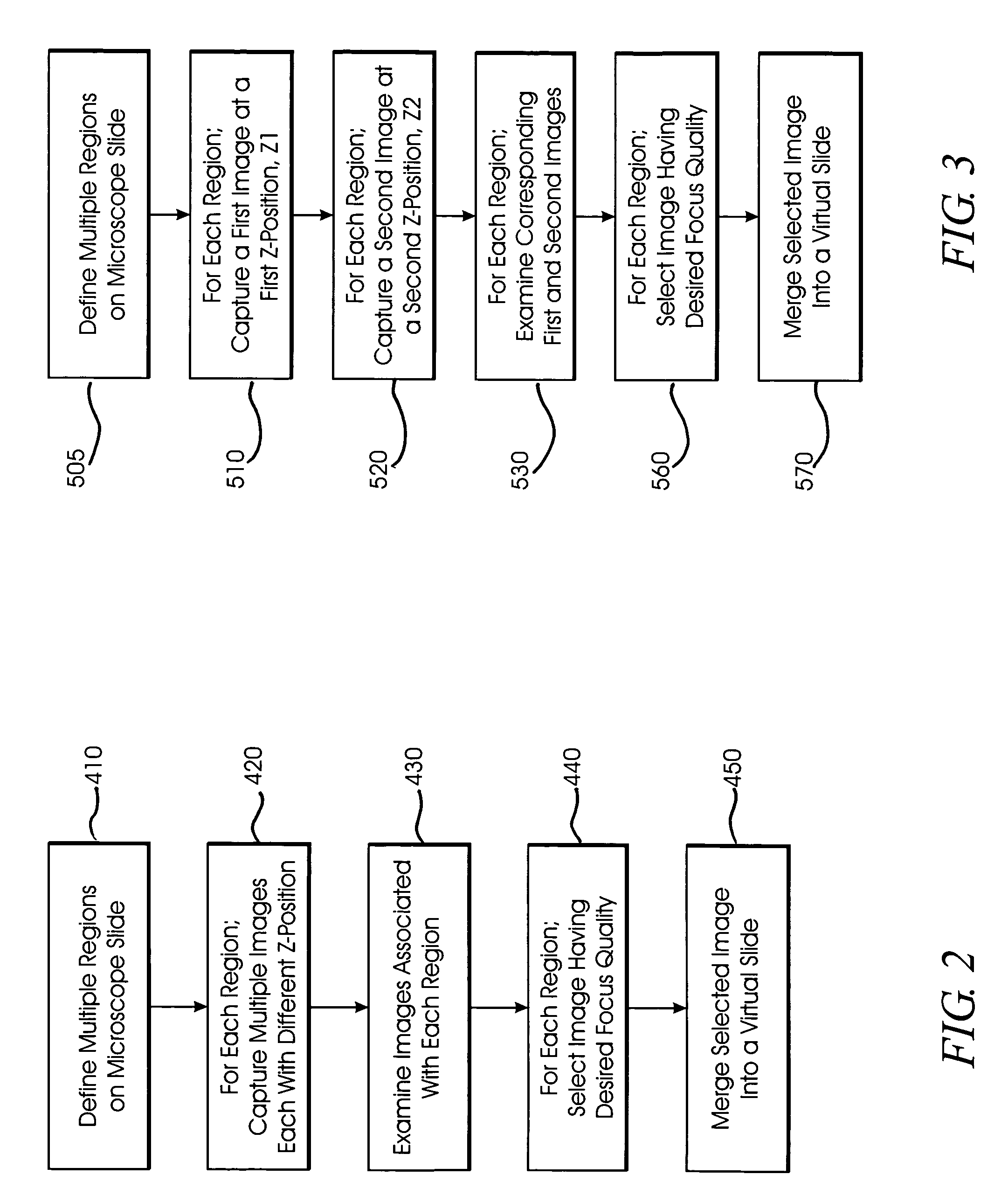
A method and system for creating a digital, virtual slide having optimum image quality characteristics. Multiple regions of a physical slide are identified as well as at least two focus z-positions z1, and z2. Each region of the physical slide is scanned (imaged) at the first z position, so as to produce a first set of digital images of each defined region. Each region of the physical slide is also scanned (imaged) at the second z position, so as to produce a second set of digital images of each defined region. Each image of each set is evaluated against a focus quality metric and, for each region, either the first or second image, corresponding to that region, is selected that exhibits a focus quality metric corresponding to a desired focus quality. These images are then merged into a digital virtual slide. Additional focus z-positions may be included, and the multiple z-positions may be scanned seriatim, sequentially, and / or in overlapping fashion.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Microscopy system having automatic and interactive modes for forming a magnified mosaic image and associated method
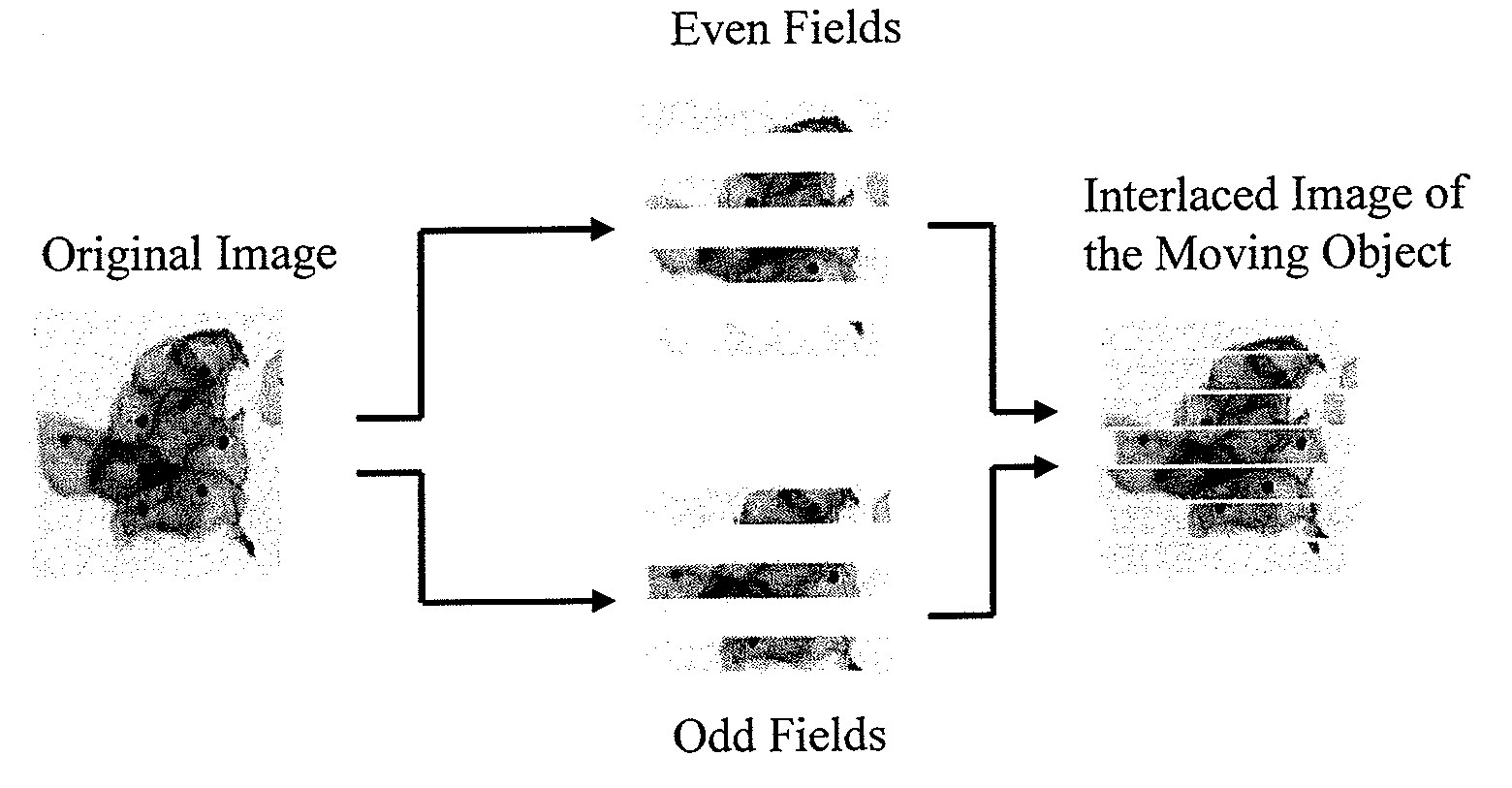
InactiveUS20060133657A1Quality improvementMeet needsAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsMicroscopesInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
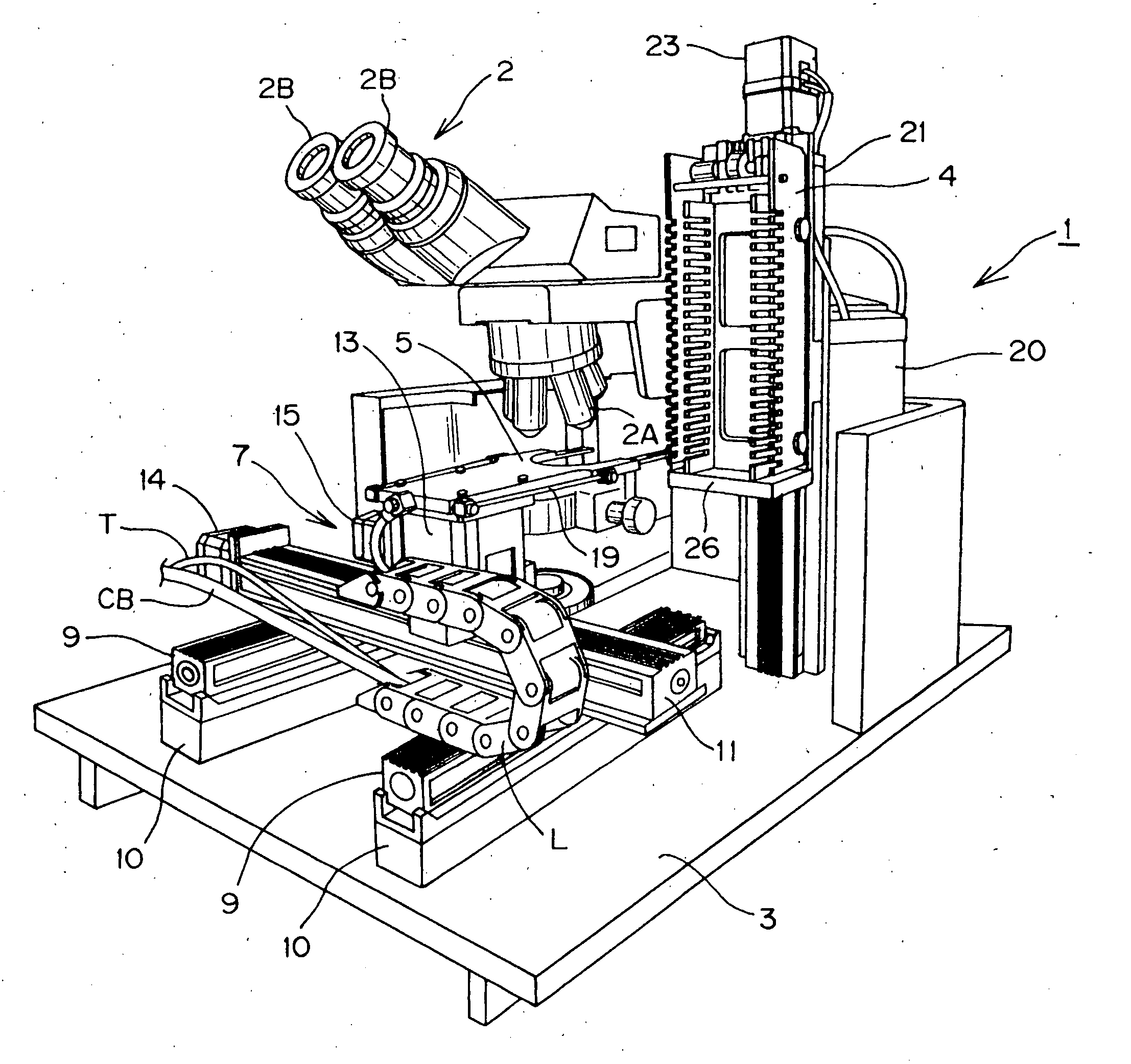
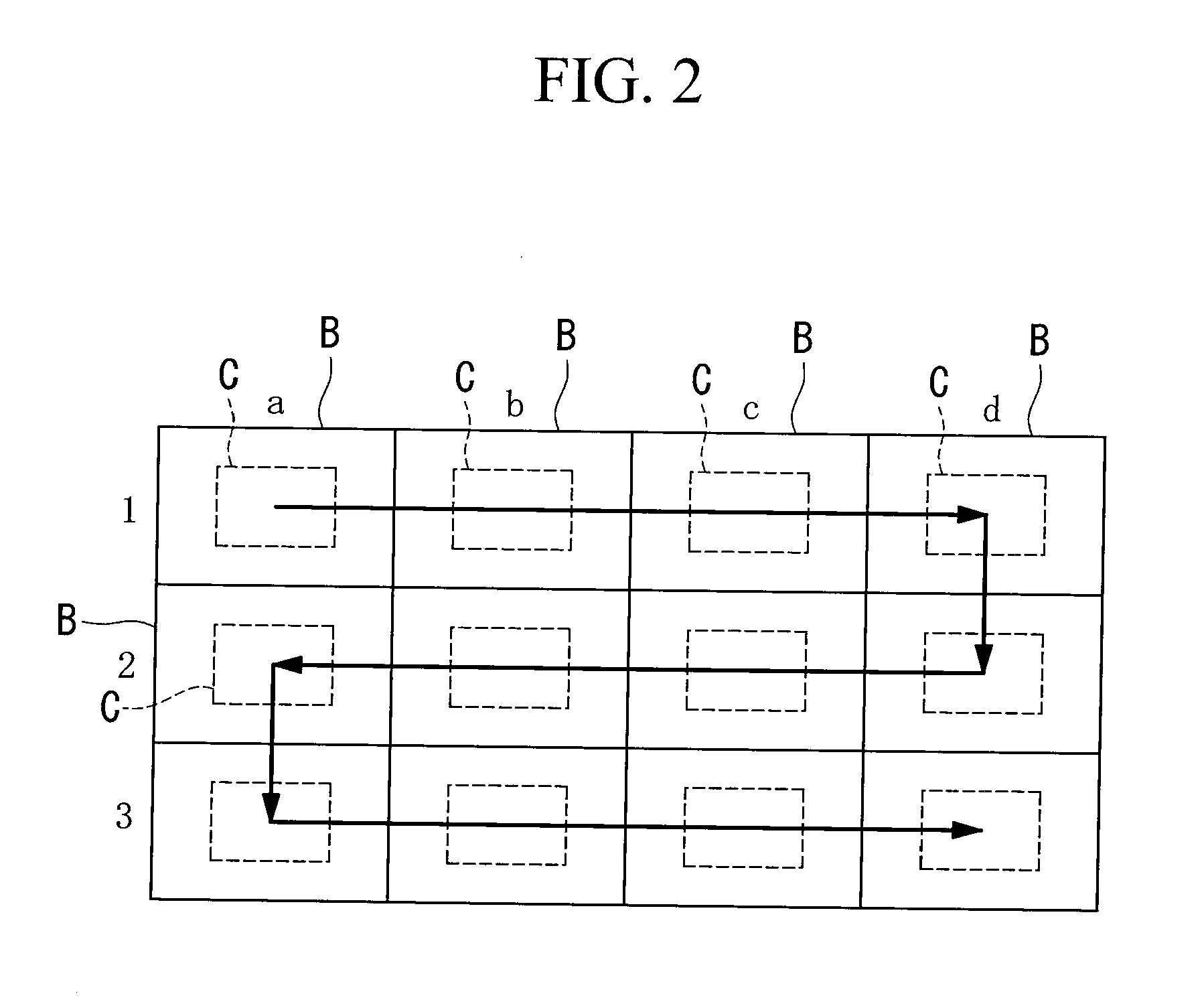
A scanning device for biological slides is provided, which can be operated in an interactive routine mode as well as in an unsupervised high speed automatic mode. In the first case, typical components, which the pathologist is used to operating manually, such as the microscope, the stage and the focus, and which have to be motorized for the automatic unsupervised system mode, are configured to simulate manual use, operation, and response. A non-interlaced area scan camera supports the interactive selection and acquisition of individual images in the manual mode, as well as the continuous high-speed scan motion for the rare event detection and virtual slide scan applications of the system. Due to the particular requirements to accommodate both operational modes, methods are described for constructing the virtual slide out of image tiles with varying overlap areas in the x- and y-directions.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
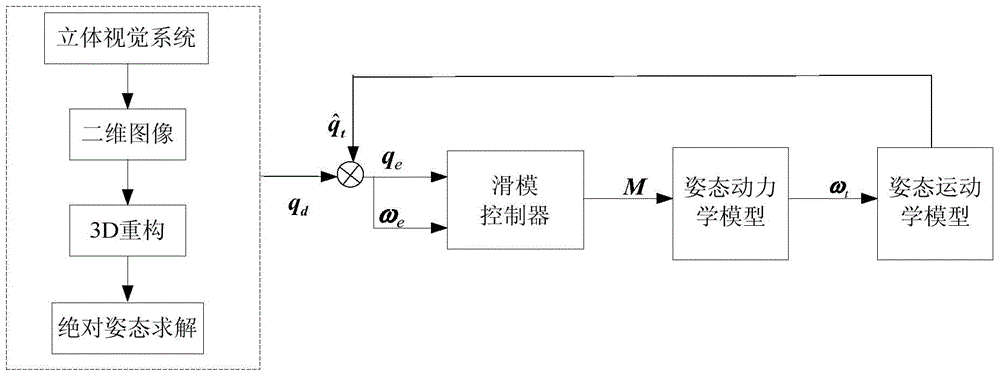
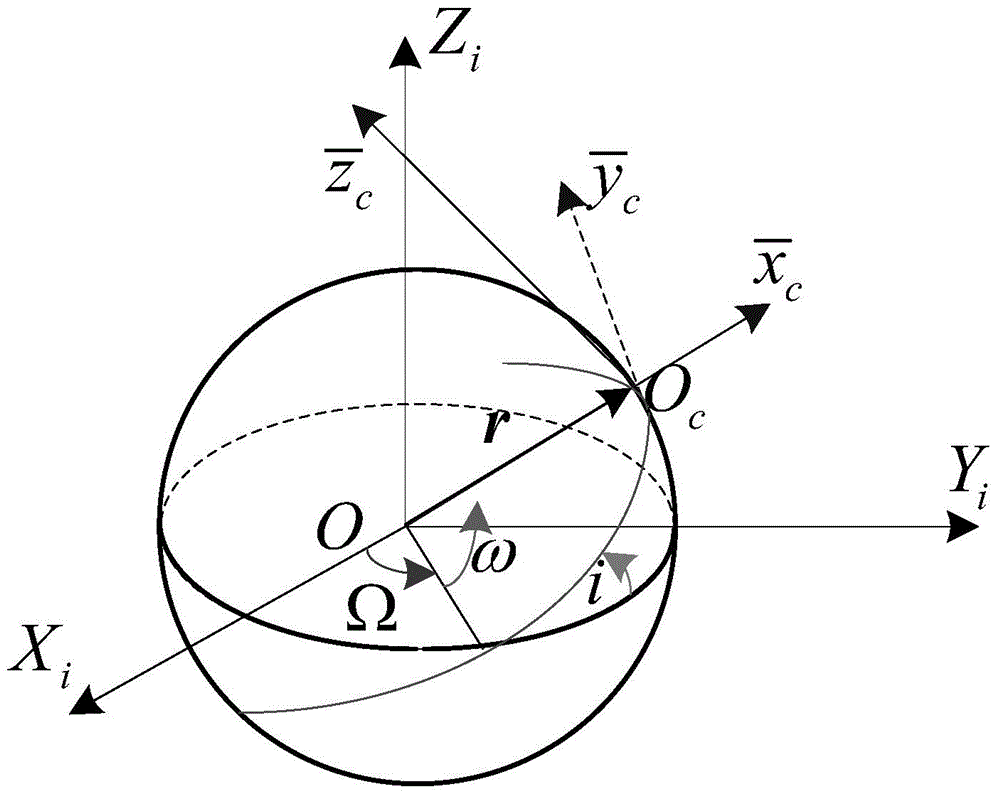
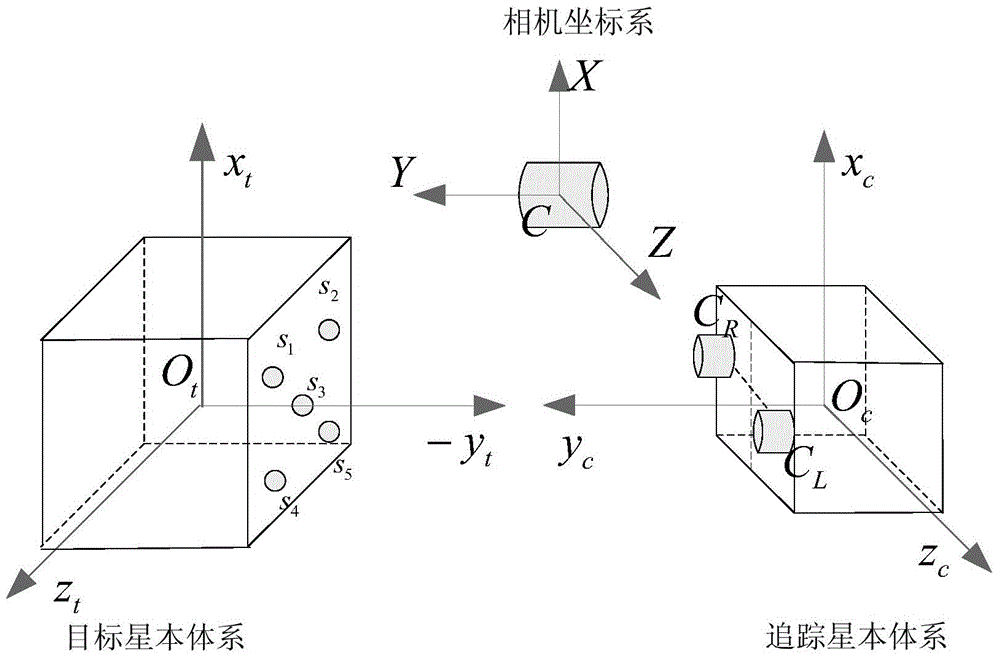
Non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method based on virtual sliding mode control
InactiveCN104406598AAccurate timingSmall amount of calculationInstruments for comonautical navigationMode controlVirtual slide
The invention discloses a non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method based on virtual sliding mode control, and belongs to the technical field of non-cooperative spacecraft navigation. The non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method comprises the following steps: utilizing a virtual control sliding mode controller based on the Lyapunov principle; using target satellite absolute attitude obtained by a stereoscopic vision system as a control objective; according to motion characteristics of the target satellite, establishing a virtual satellite motion model of the target satellite; using a kinetic model of the virtual satellite as a controlled member to obtain attitude parameters of the virtual satellite; using attitude parameters estimated by the virtual satellite and the target satellite absolute attitude obtained by the stereoscopic vision system as controlled input, and calculating the virtual revolving moment on the motion model of the virtual satellite through the virtual sliding mode controller, so as to realize the estimation of the target satellite attitude parameters by the virtual control sliding mode controller. The non-cooperative spacecraft attitude estimation method disclosed by the invention is low in calculated amount, and can still achieve higher convergence rate and higher precision when the initial error of the state variables is high or the system error emerges, so as to meet the requirements of the high performance navigation system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
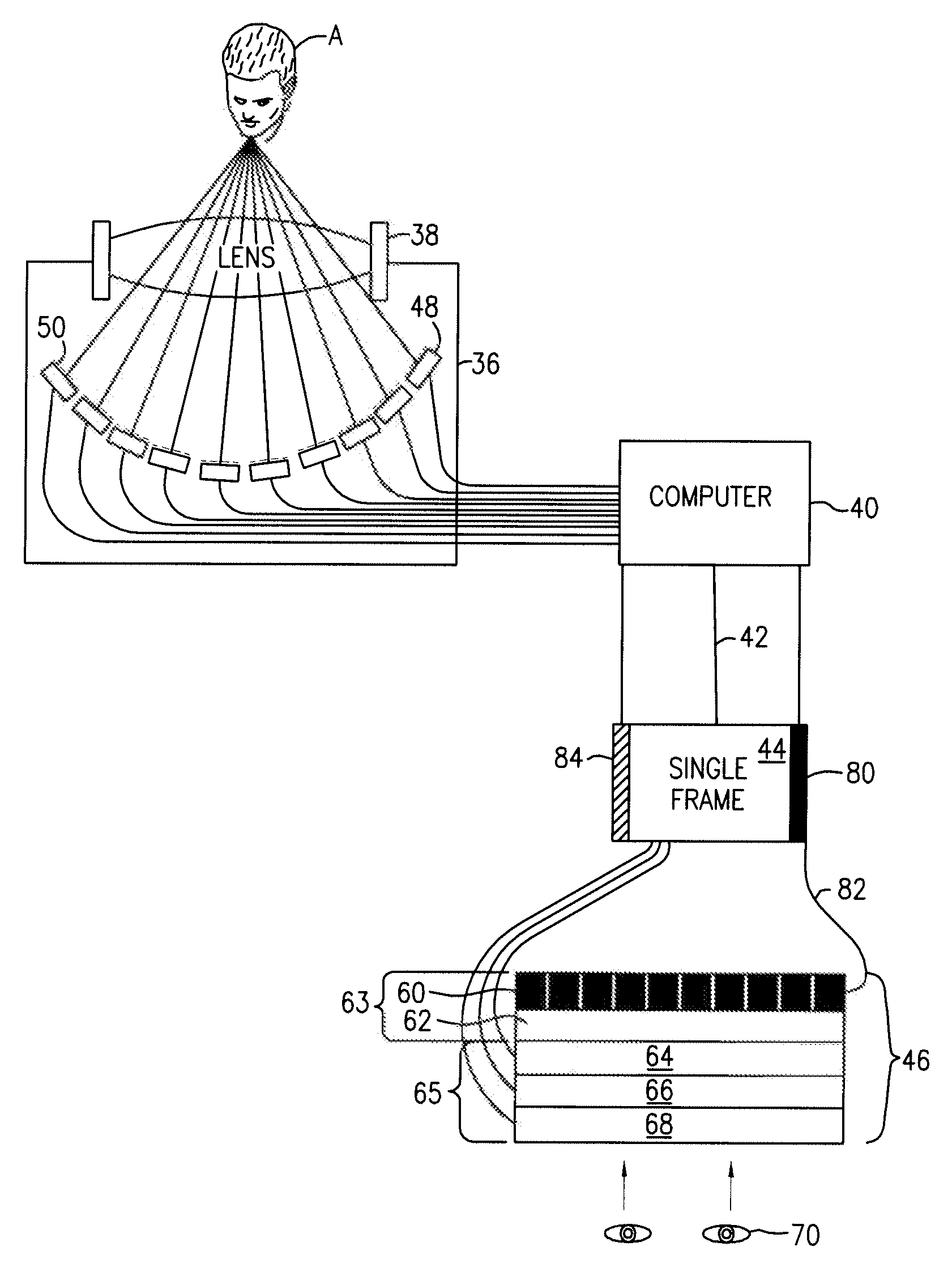
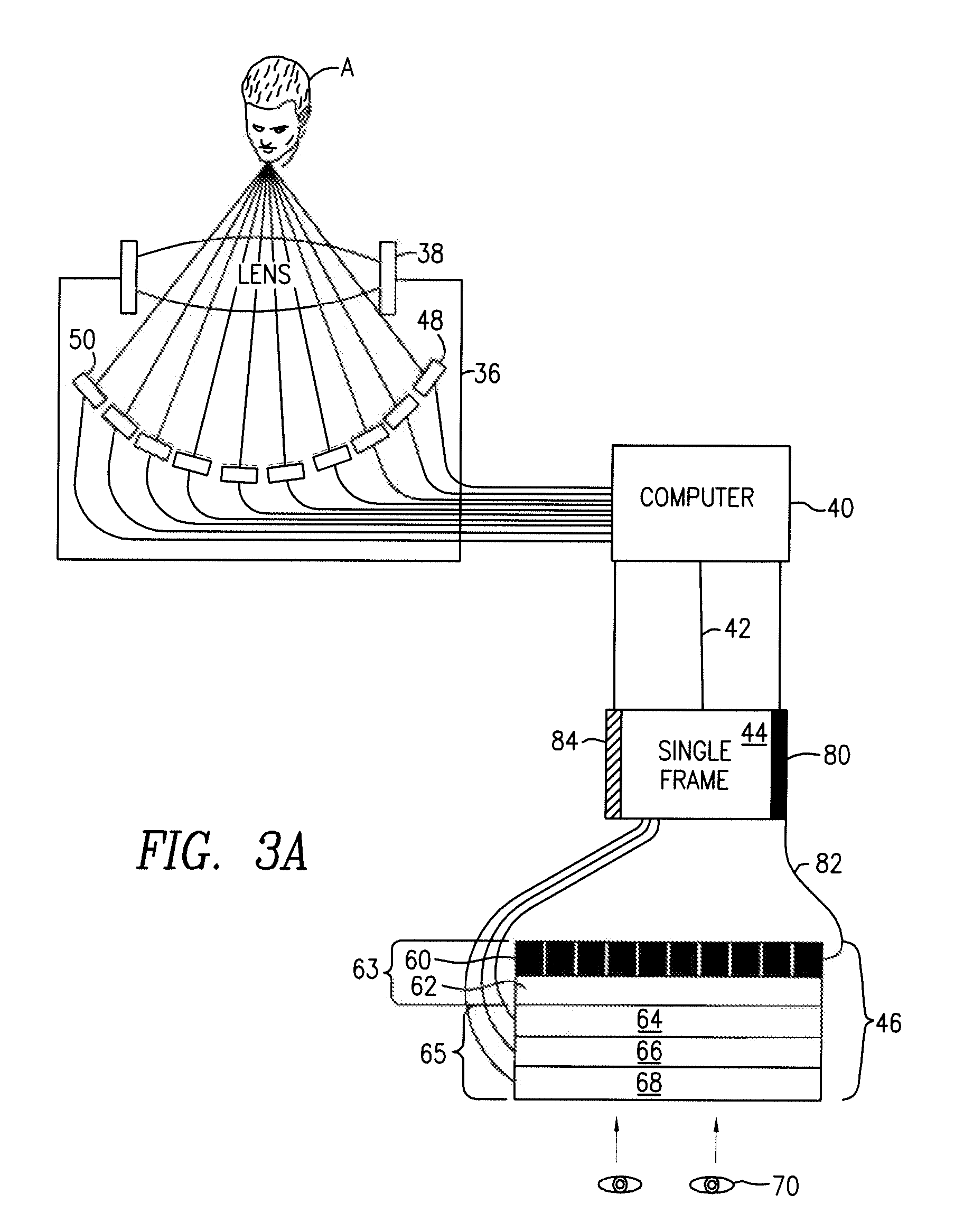
Microscope optical system, microscope, and virtual slide forming system
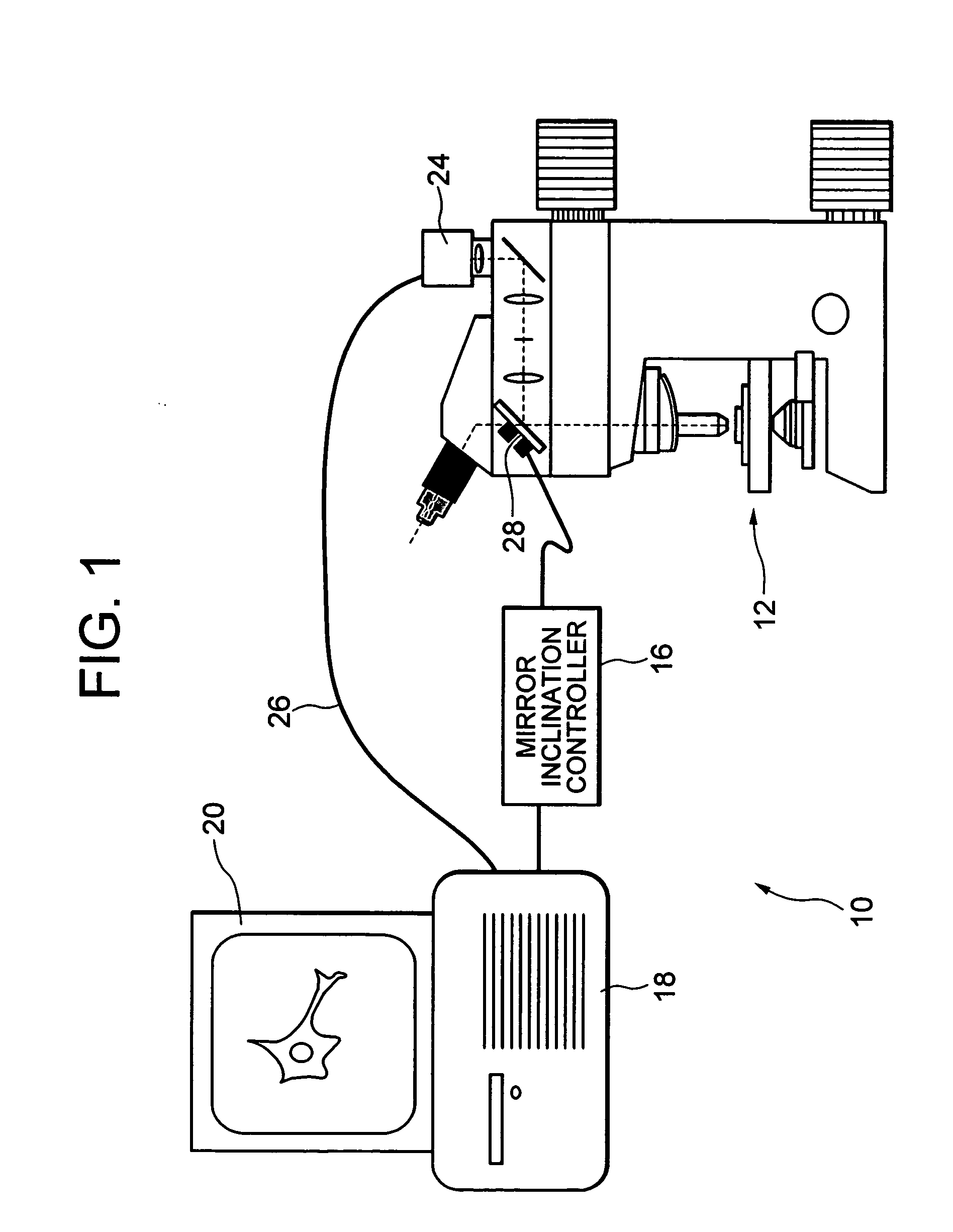
The purpose is to move an observation field of view of a microscope without moving or changing an objective lens without varying position or state of a sample. A microscope optical system according to the present invention has a mirror that changes the direction of the optical path by reflection and locates in the optical path between an objective lens of the microscope and an image to be observed. The mirror is able to be tilted with changing the position of a reflecting surface of the mirror. Accordingly, the observation field of view is moved by tilting the mirror. In other words, the observation field of view can be moved without changing positional relation between the objective lens of the microscope and the sample.
Owner:NIKON CORP
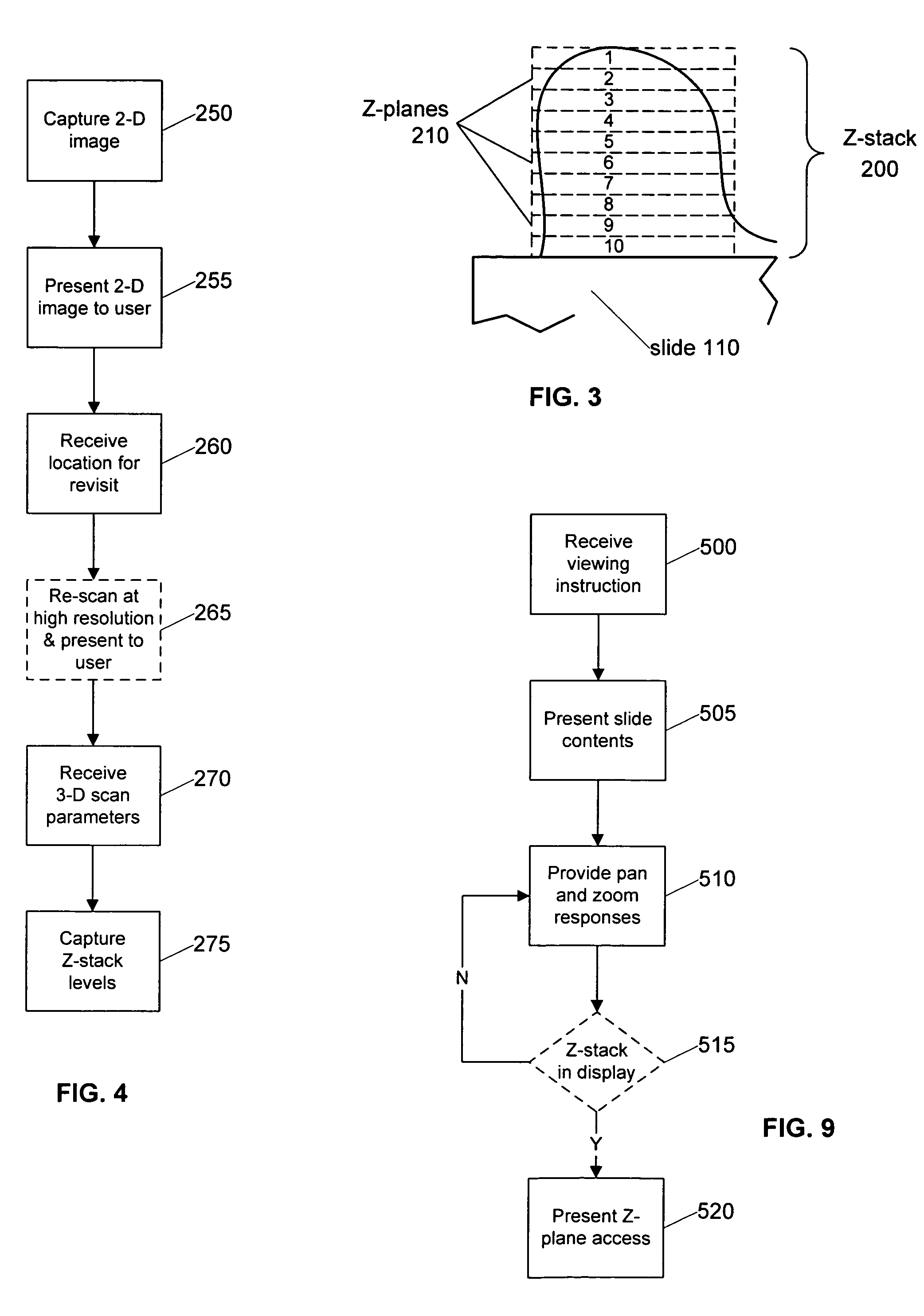
Systems and methods for viewing three dimensional virtual slides
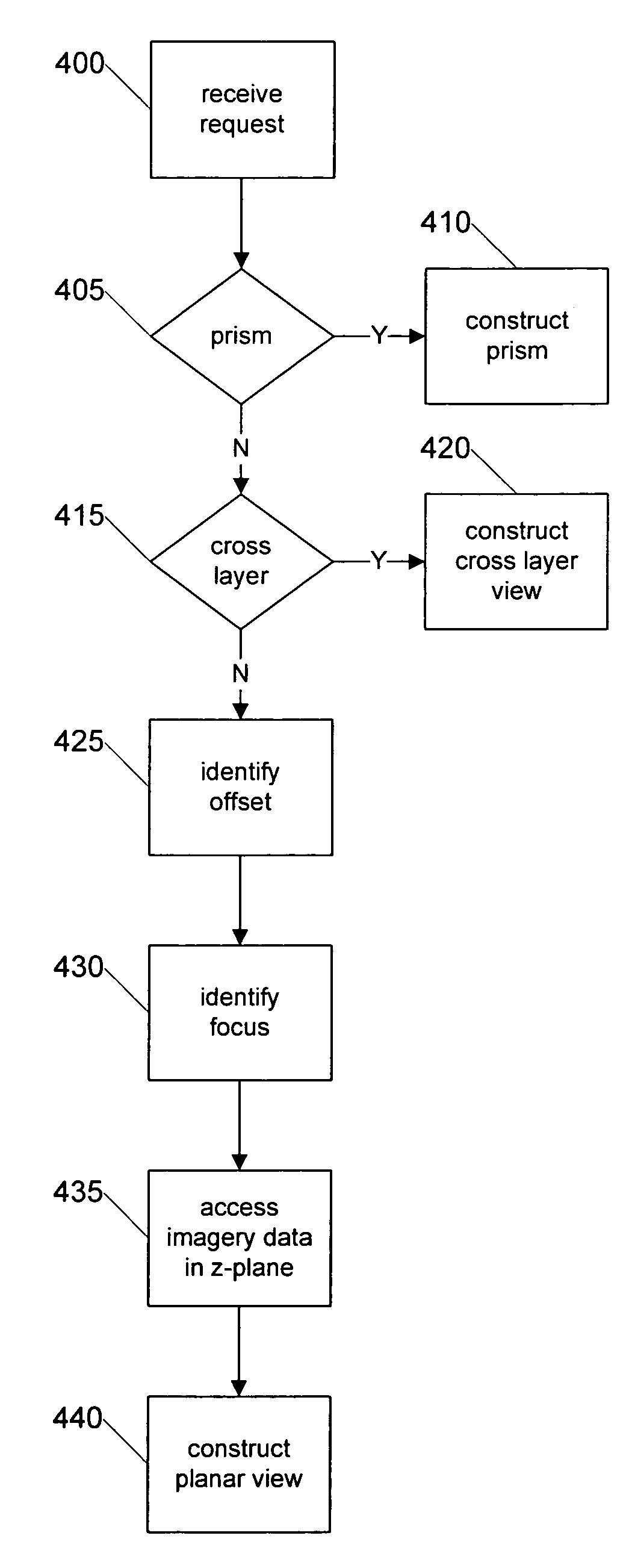
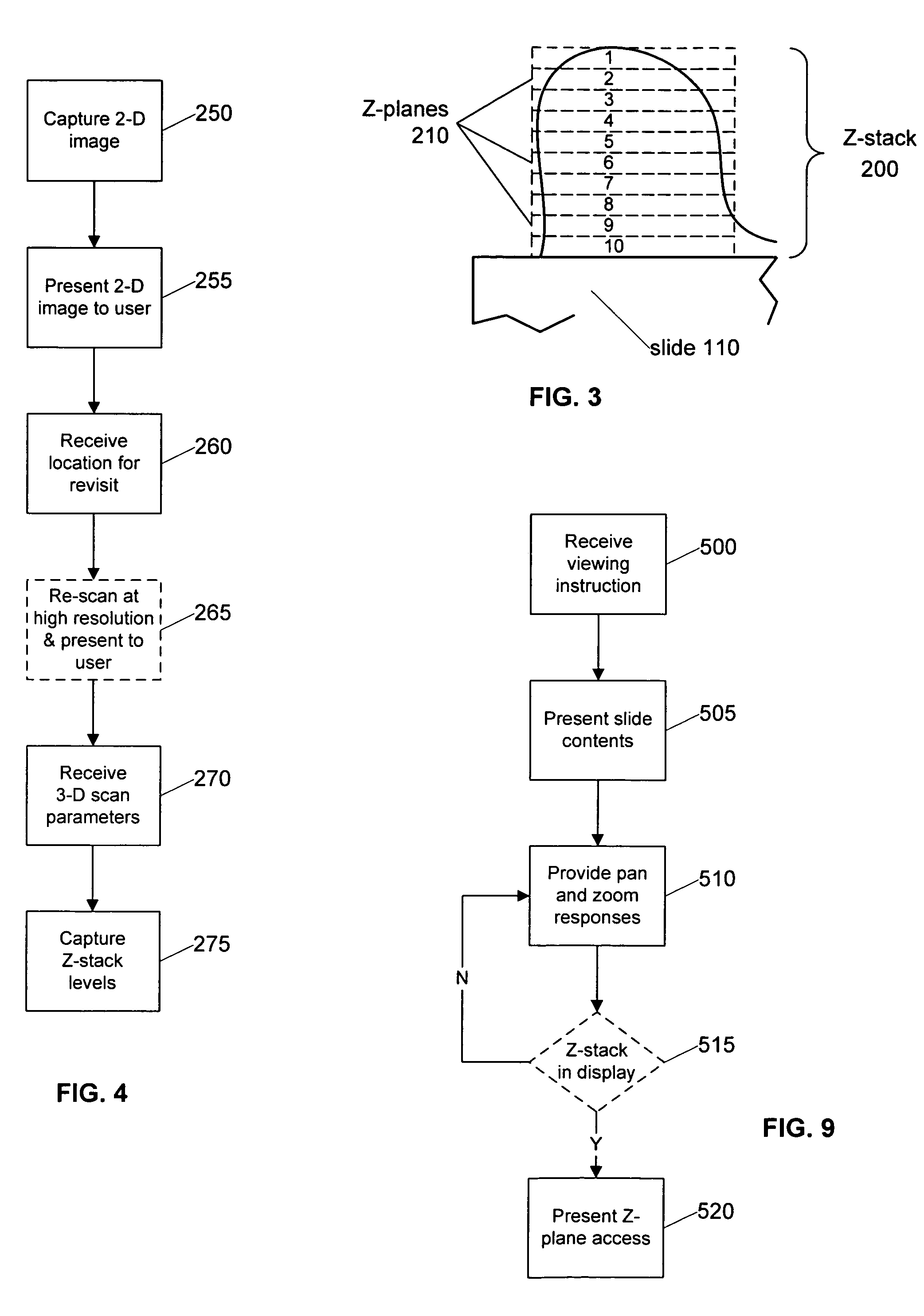
Systems and methods for retrieving, manipulating, and viewing 3D image objects from 3D virtual microscope slide images are provided. An image library module provides access to the imagery data in a 3D virtual slide and constructs 3D image objects that are coextensive with the 3D virtual slide or a 3D sub-portion thereof. From within the 3D image object, cross layer planar views spanning various depths of the 3D virtual slide are constructed as well as 3D prisms and other shaped image areas. The image library module allows a 3D image object to be sliced into horizontal and vertical views, skewed cross layer views and regular and irregular shaped 3D image areas for viewing by a user.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Systems and methods for creating and viewing three dimensional virtual slides
ActiveUS7463761B2High bandwidthQuick ViewMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsMicroscope slideAcquisition apparatus
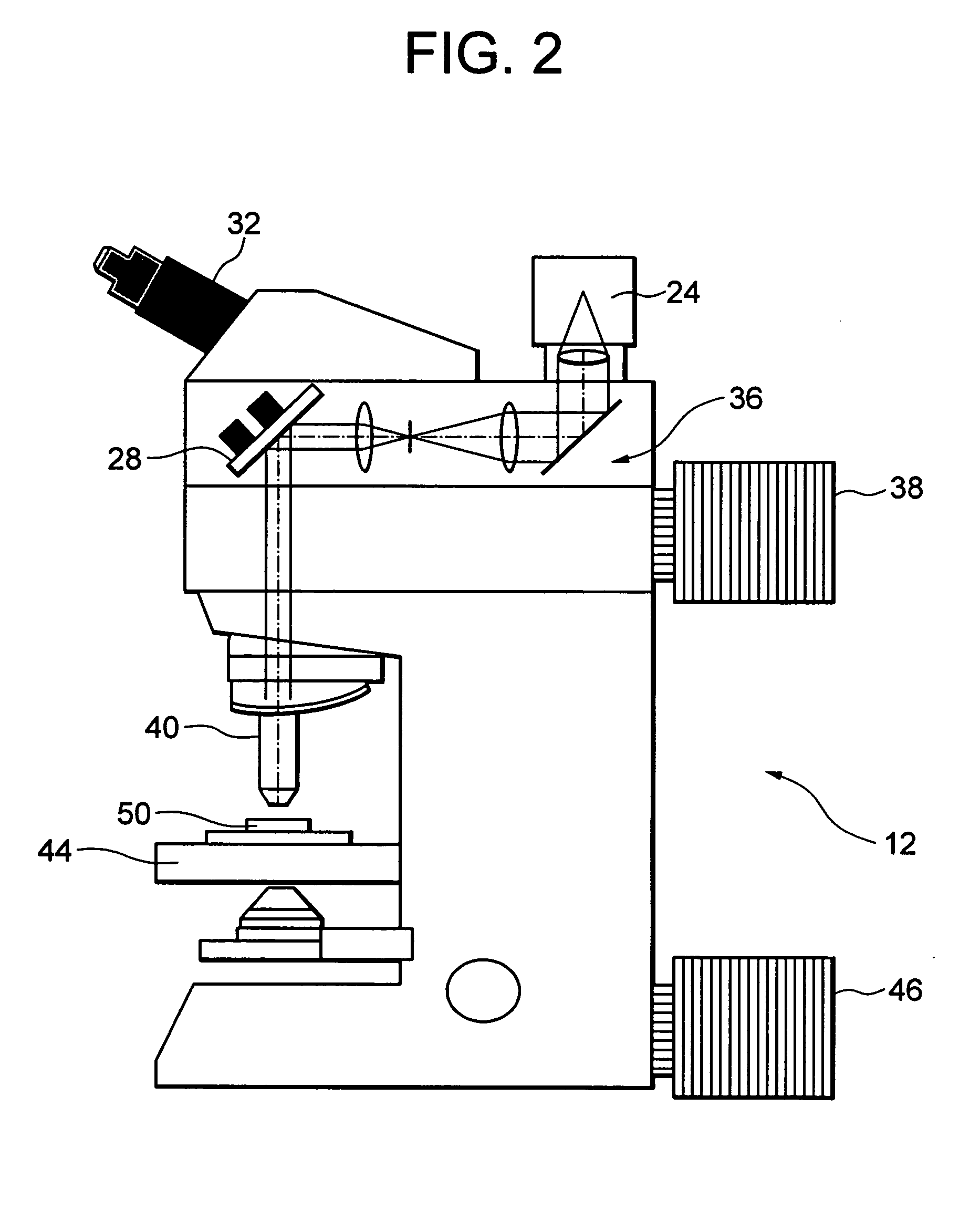
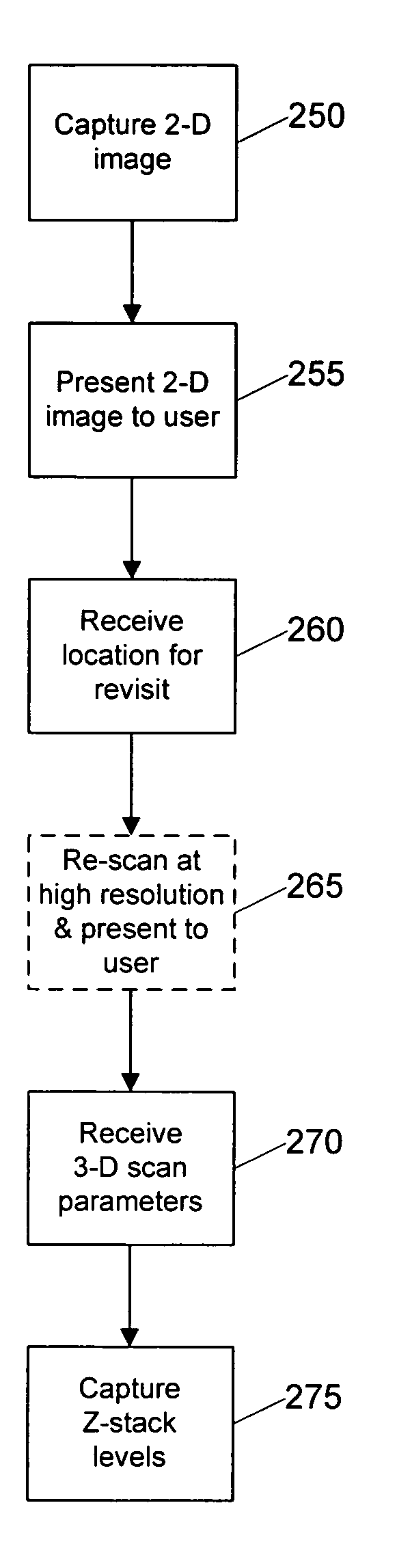
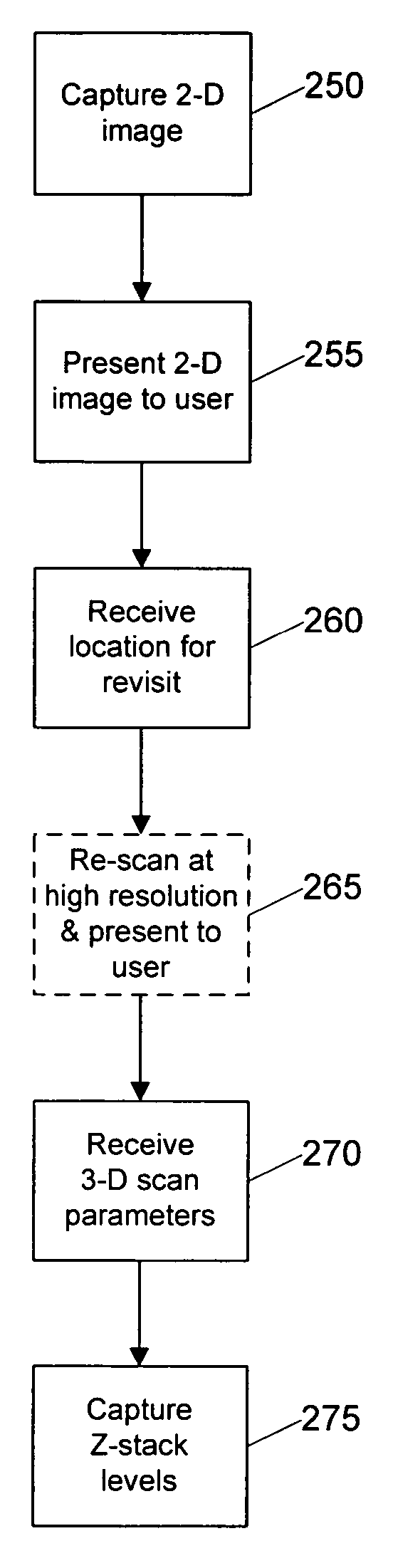
Systems and methods for creating and viewing three dimensional virtual slides are provided. One or more microscope slides are positioned in an image acquisition device that scans the specimens on the slides and makes two dimensional images at a medium or high resolution. This two dimensional images are provided to an image viewing workstation where they are viewed by an operator who pans and zooms the two dimensional image and selects an area of interest for scanning at multiple depth levels (Z-planes). The image acquisition device receives a set of parameters for the multiple depth level scan, including a location and a depth. The image acquisition device then scans the specimen at the location in a series of Z-plane images, where each Z-plane image corresponds to a depth level portion of the specimen within the depth parameter.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
System and method for assessing virtual slide image quality
InactiveUS20060007345A1Raise the possibilityEasy to demonstrateTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityVirtual slide
Systems and methods for assessing virtual microscope slide image quality are provided. In order to determine whether a virtual slide image has any out of focus areas and is therefore a candidate for manual inspection, the various focus points used to scan the virtual slide image are used to calculate a best fit surface for the virtual slide image. The distance of each focus point from the best fit surface is then calculated and the largest distance is compared to a predetermined value. If the largest distance from a focus point to the best fit surface is larger than the predetermined value, then the virtual slide image is designated as needing a manual inspection and possible re-scan.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
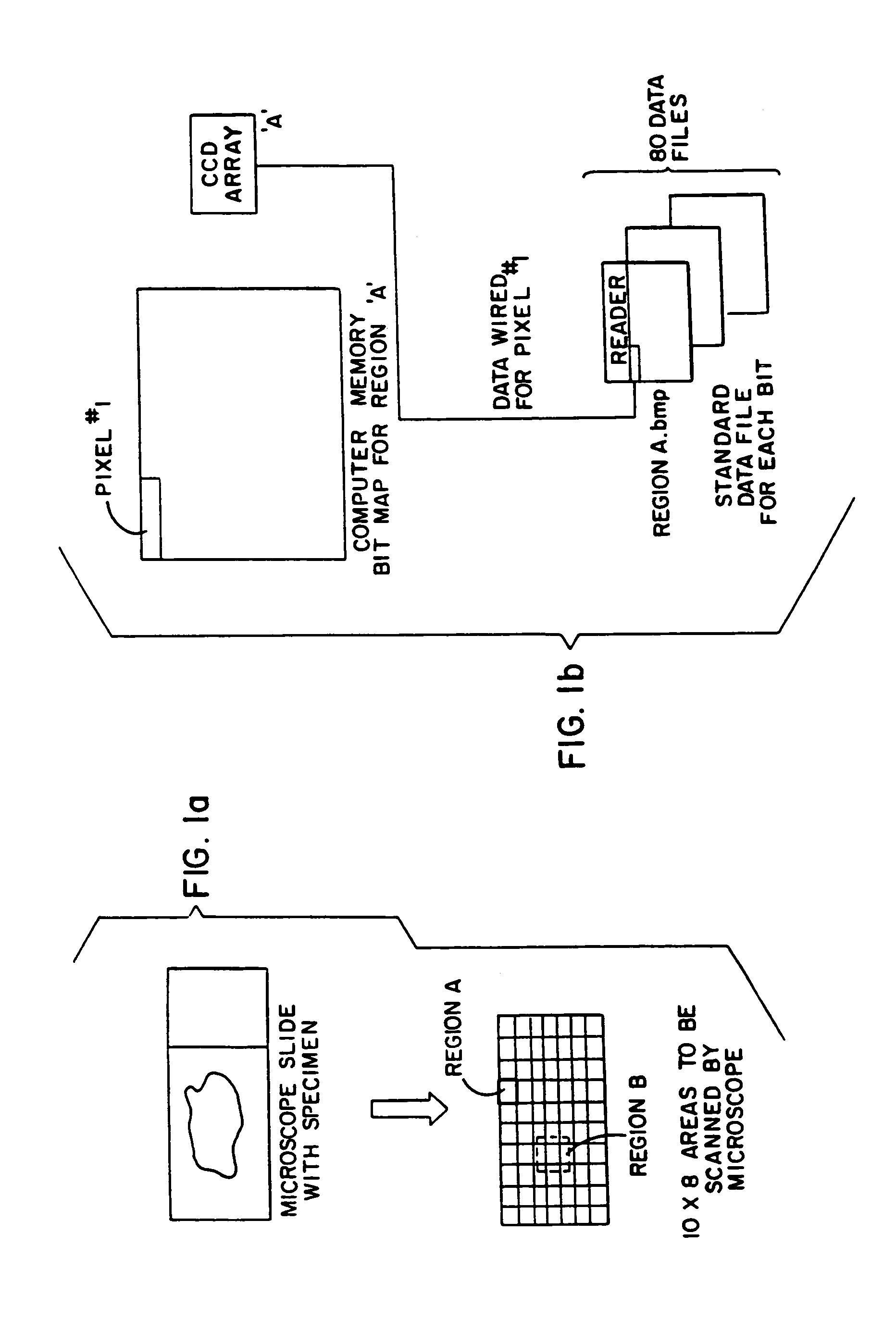
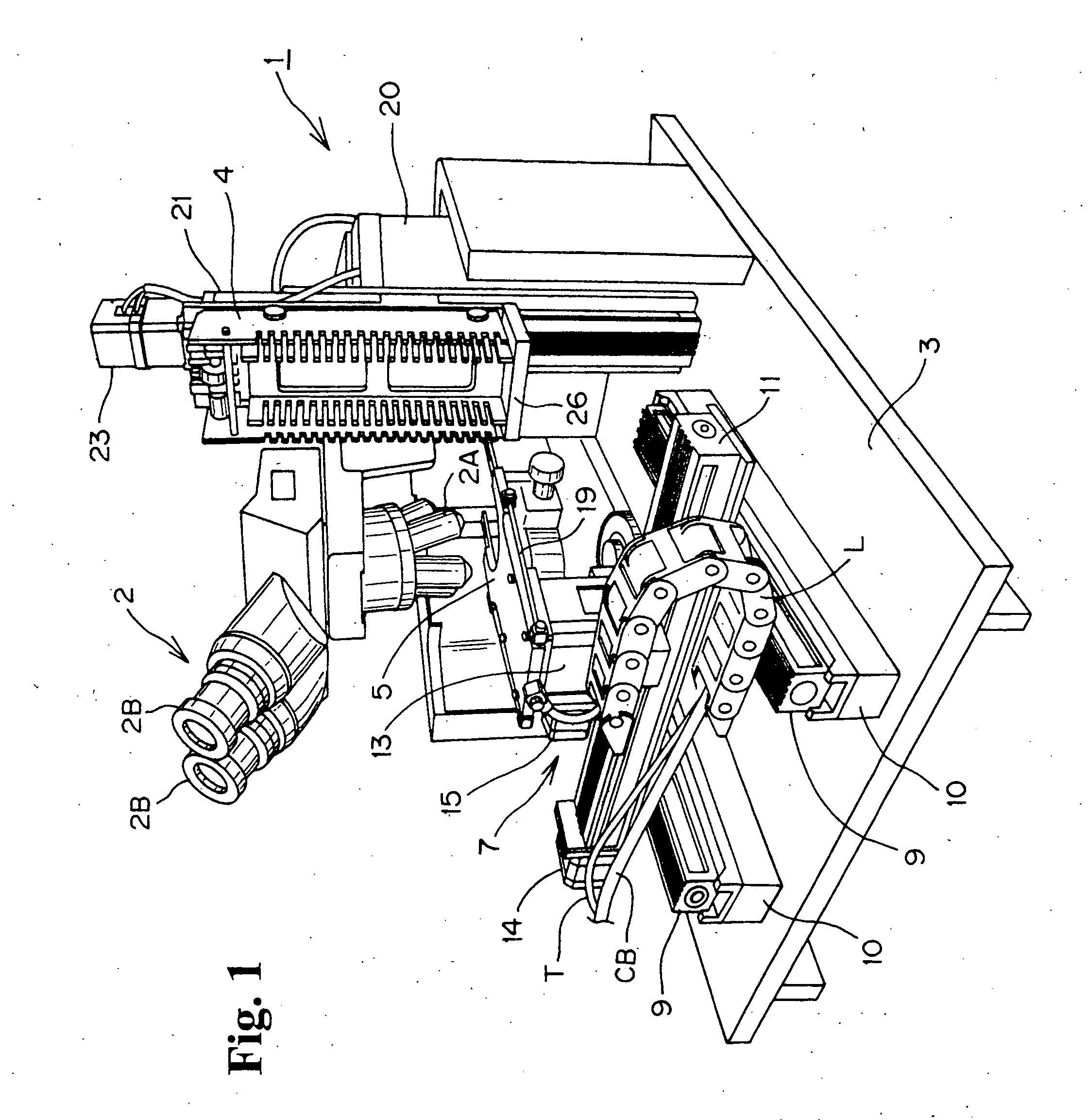
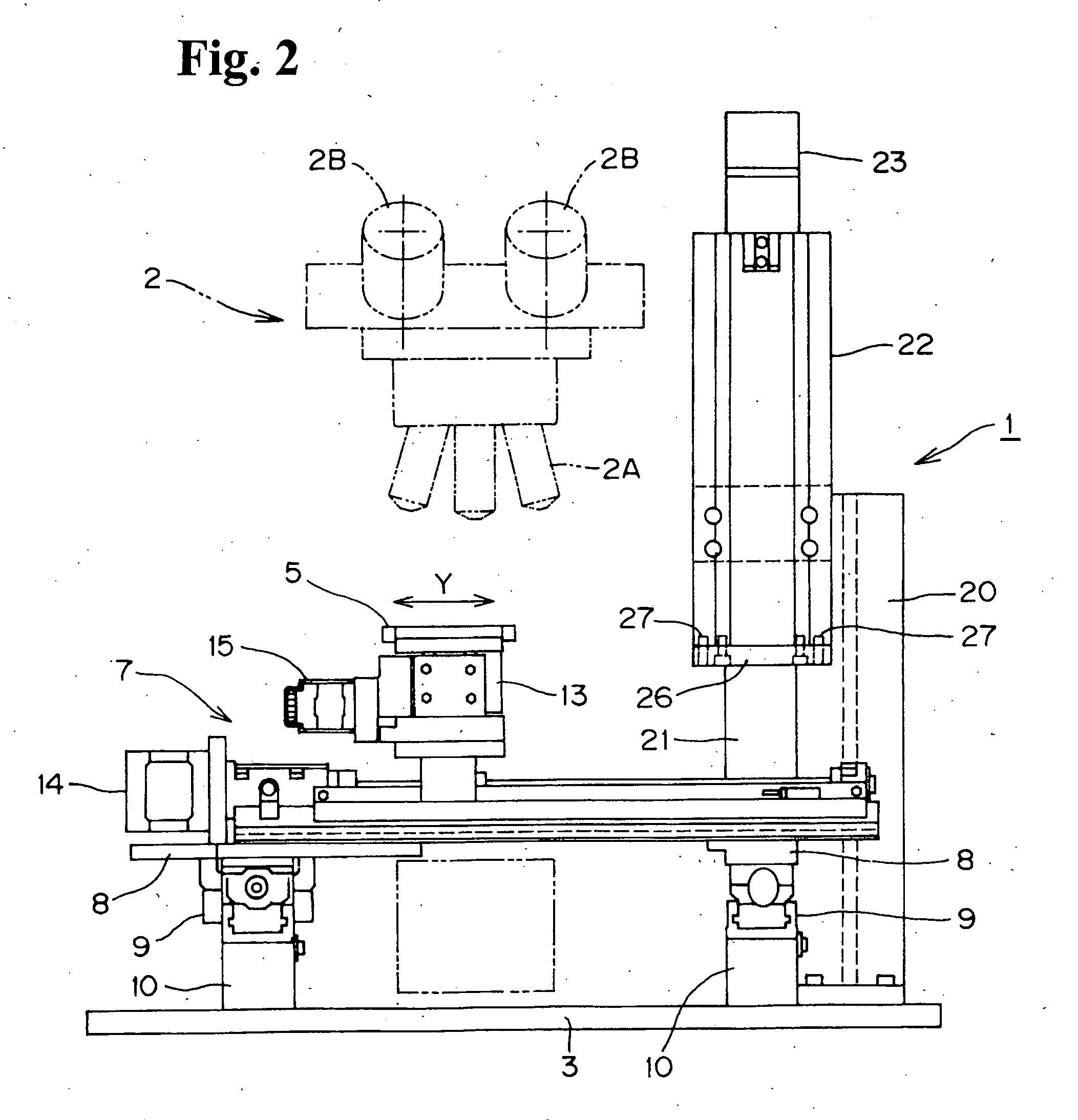
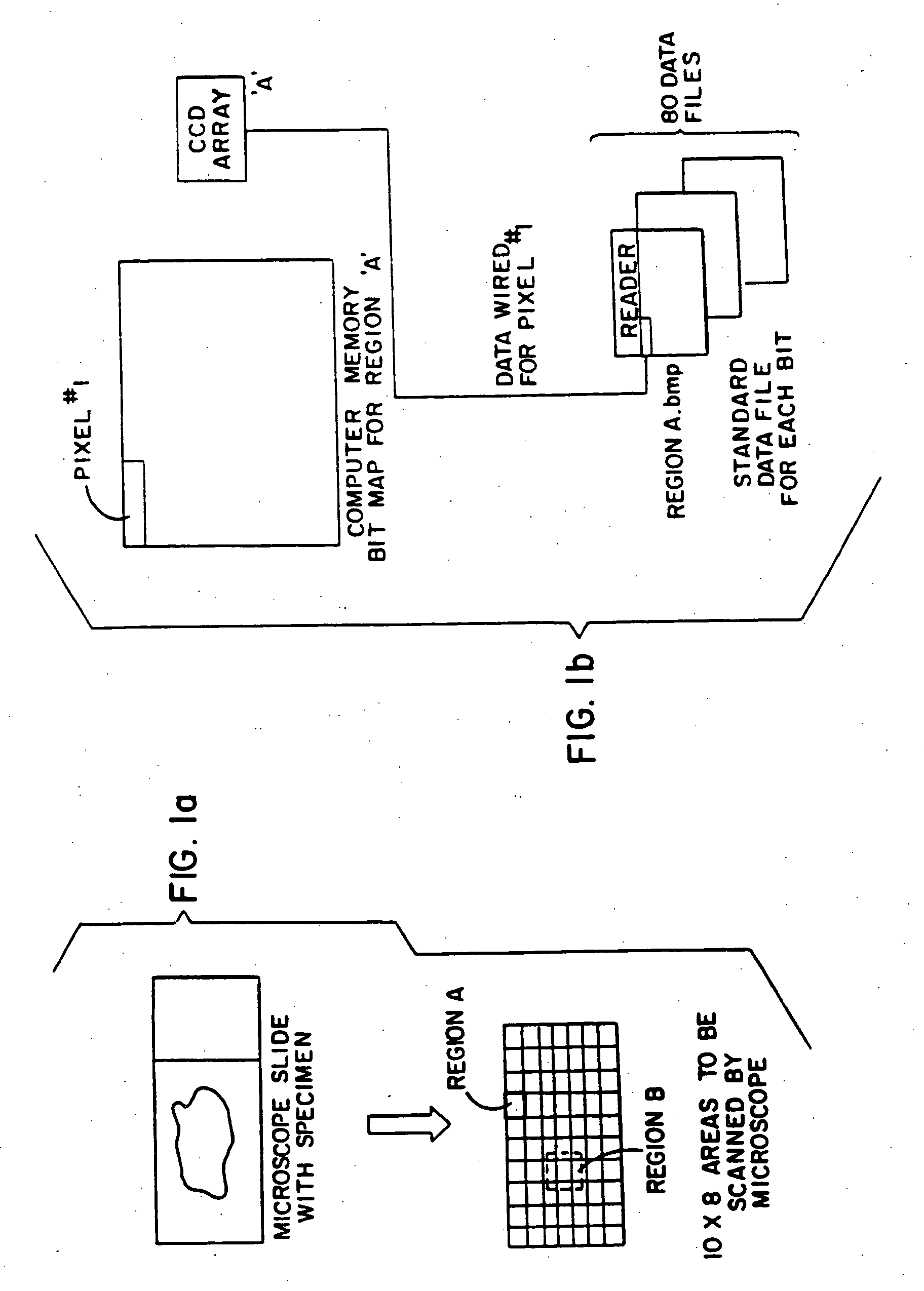
Slide photograph data creation system, and slide photograph data
InactiveUS20060228107A1Efficiently perform workEfficient executionSamplingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Virtual slide
A slide photograph data creation system includes a digital camera for making high-magnification photographs of samples, a sample transporter for holding and transporting samples, a controller for controlling the camera and the sample transporter so as to provide overlapping photographs, a pasting information generator for recognizing the margin by which the photographs overlap and for generating pasting-together information, and a photograph file generator for storing in a single file a plurality of high-magnification photographs and the pasting-together information. The system facilitates the examination and photography of large numbers of samples, and enables discrimination of the three-dimensional structure of a sample. Since the photographic data is managed with a database, virtual slide photographs and their attributes information can be browsed over a network or the Internet.
Owner:CLARO
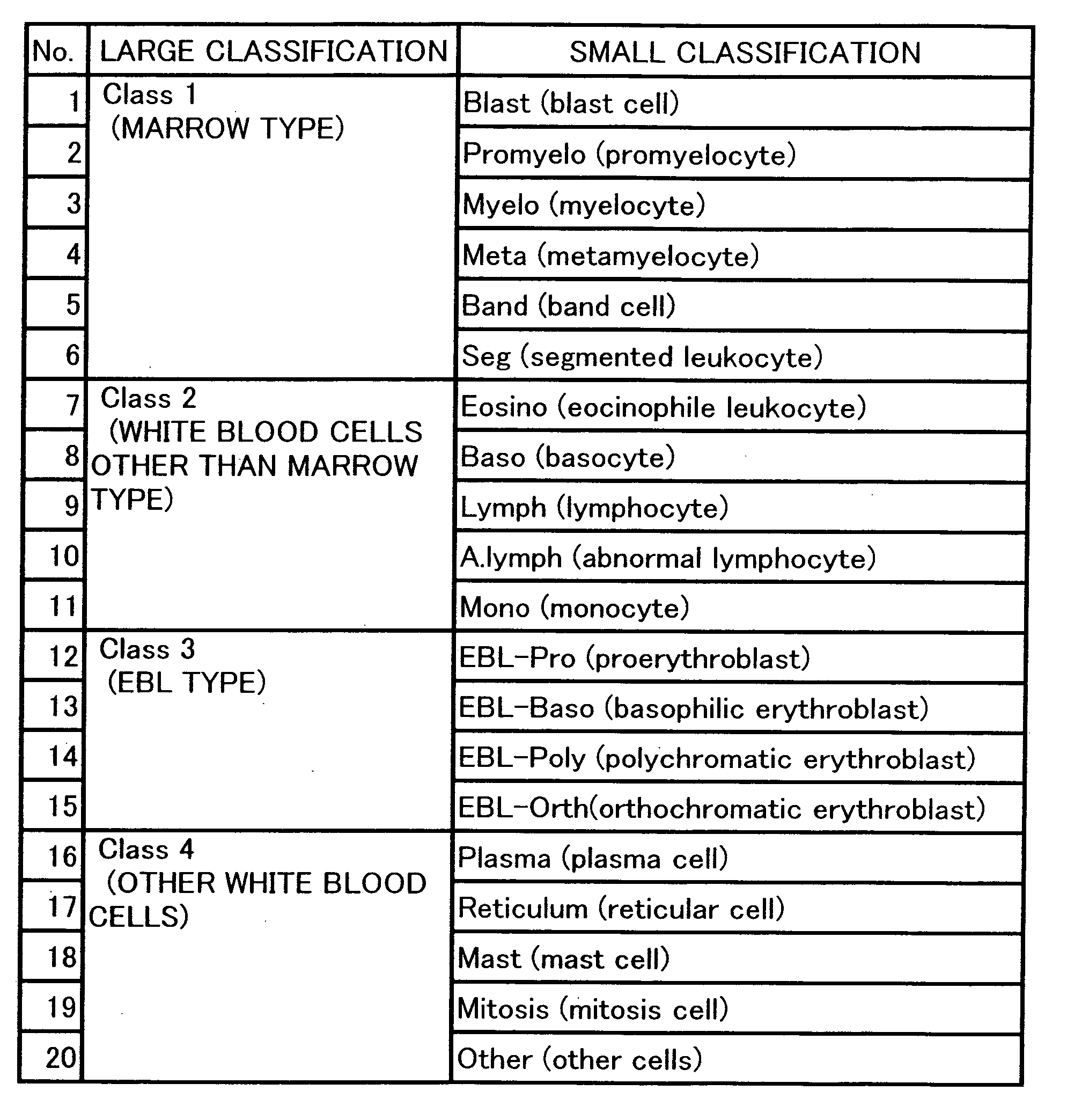
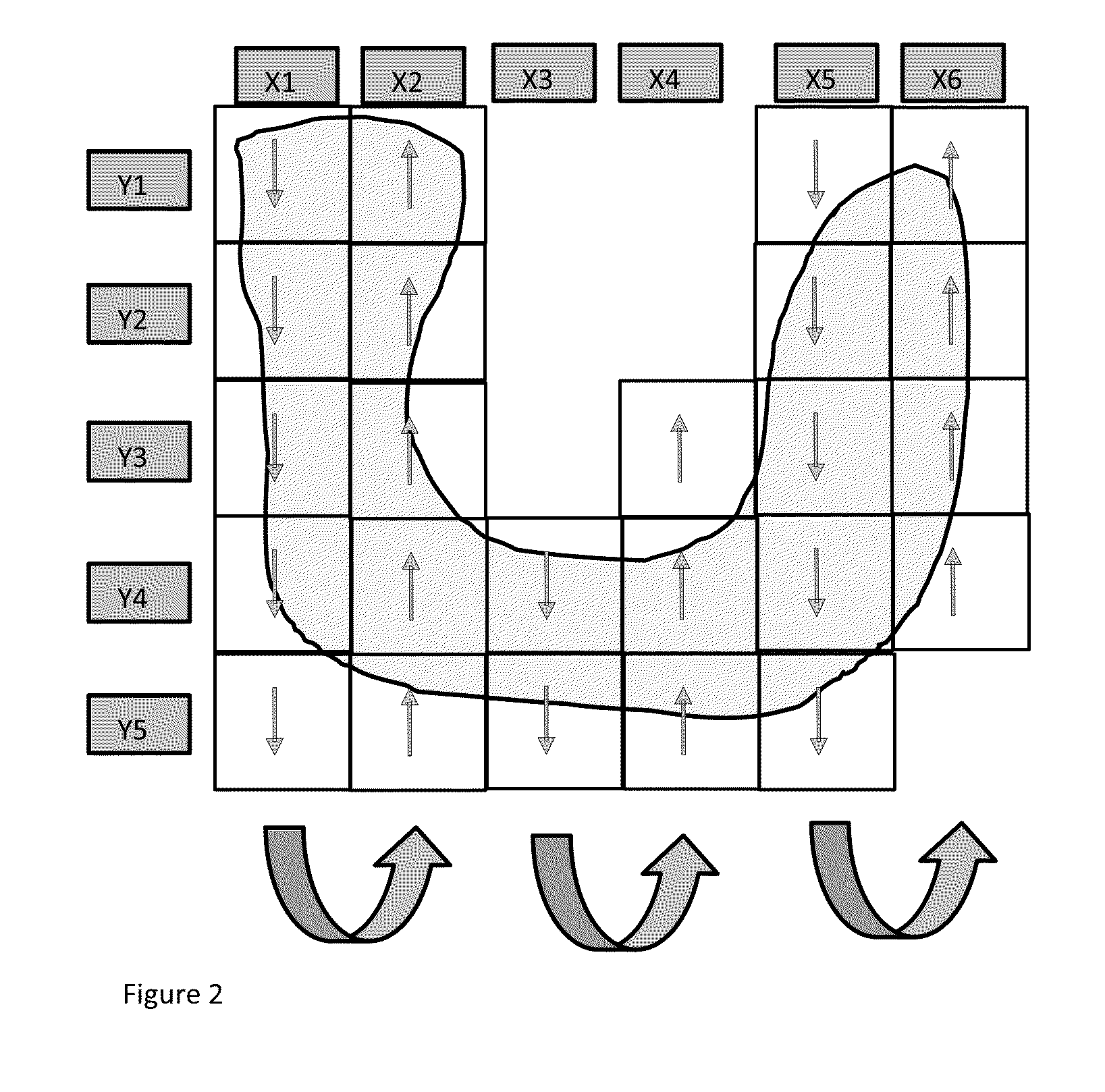
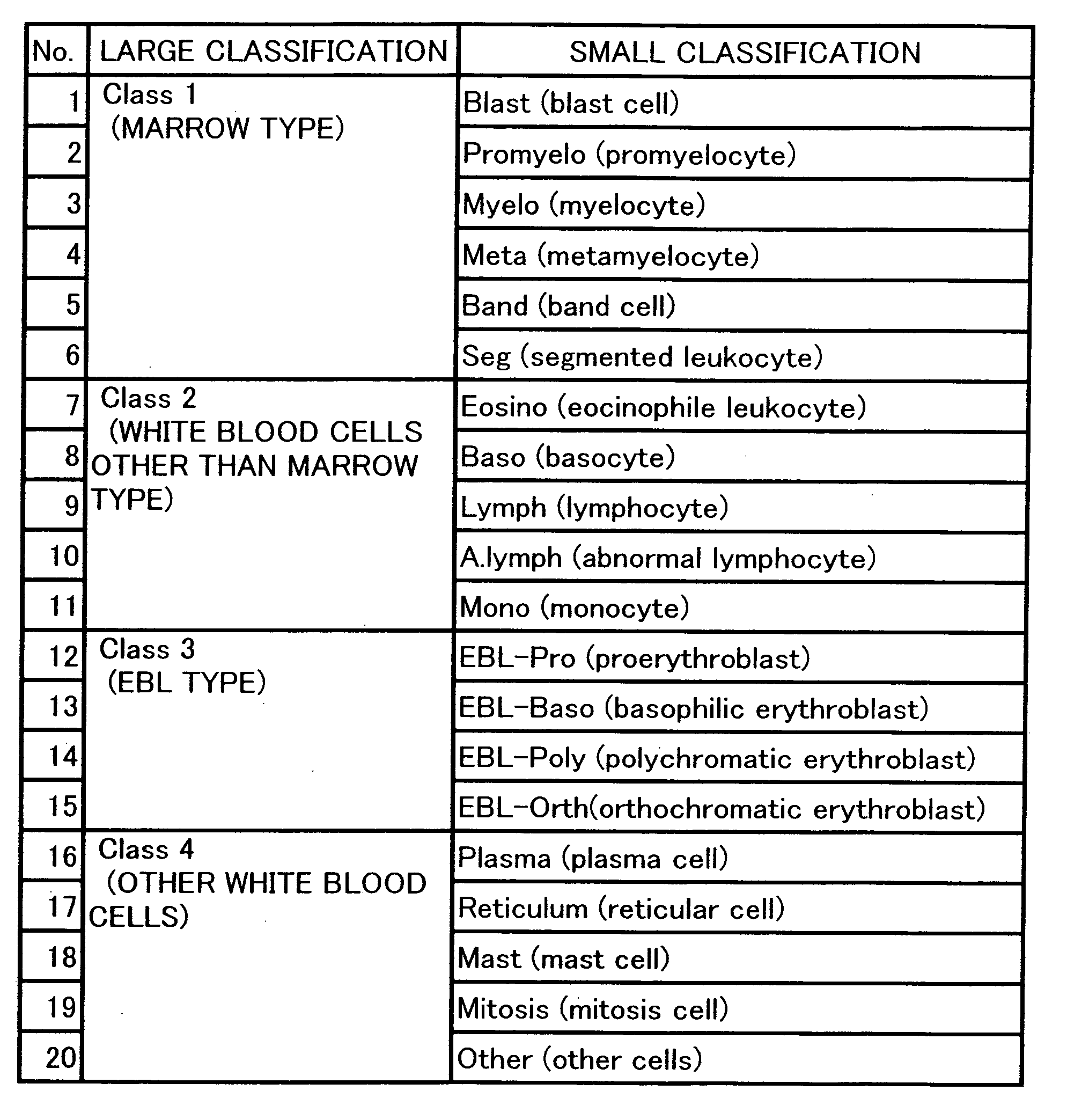
Method for displaying virtual slide and terminal device for displaying virtual slide
ActiveUS20060050948A1Convenience to workGuaranteed to workCharacter and pattern recognitionMaterial analysisOphthalmologyVirtual slide
The invention relates to a method for displaying a virtual slide capable of storing positional information of a prescribed cell in a virtual slide photographed with a magnification capable of recognizing cell morphology and a terminal device for displaying the virtual slide; or a method for displaying the virtual slide capable of classifying the prescribed cell in the virtual slide photographed with a magnification capable of recognizing cell morphology by a simple operation; or a terminal device for displaying the virtual slide.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
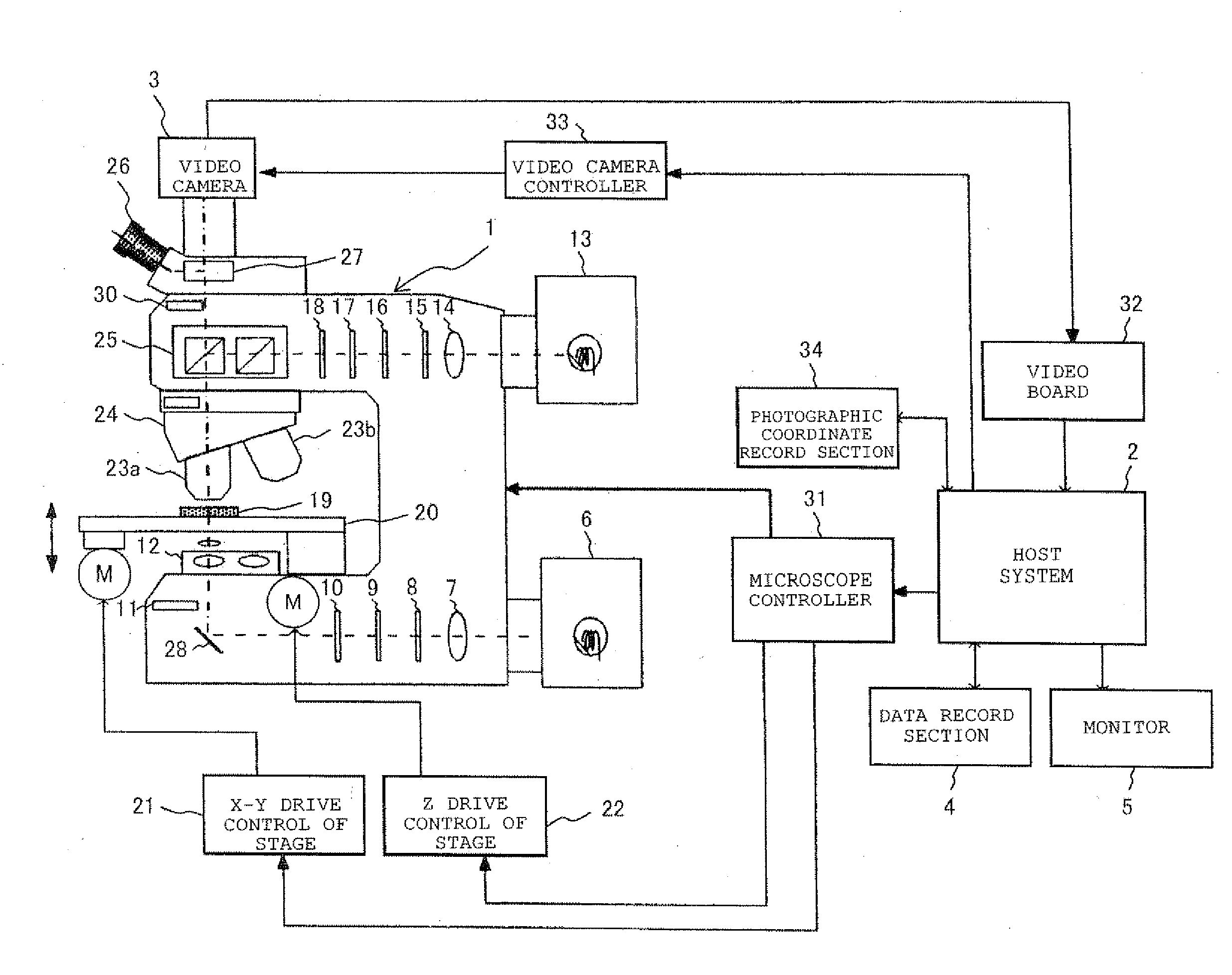
Microscope Apparatus and Microscope Observation Method
ActiveUS20110102571A1Adjustment is limitedColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVirtual slideMicroscopic observation
The number of seams between magnified images in a created virtual slide is reduced to make the virtual slide clear and sharp. Provided is a microscope apparatus including an objective lens that collects light from a sample on a slide; a focus position detecting section that detects a focus position of the objective lens with respect to the sample; a focus state adjustment section that adjusts a focus state with respect to the sample based on a detection result from the focus position detecting section; and a magnified-image acquisition section that acquires a magnified image of each part of the sample, in which, if the focus position detected by the focus position detecting section is changed by more than a predetermined threshold with respect to a focus state in which an adjacent magnified image was obtained, the focus state adjustment section limits the adjustment in the focus state to the predetermined threshold or less.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Image processing and analysis framework
ActiveUS7116440B2Limited accessRich diversityDigitally marking record carriersDigital data processing detailsImaging processingVirtual slide
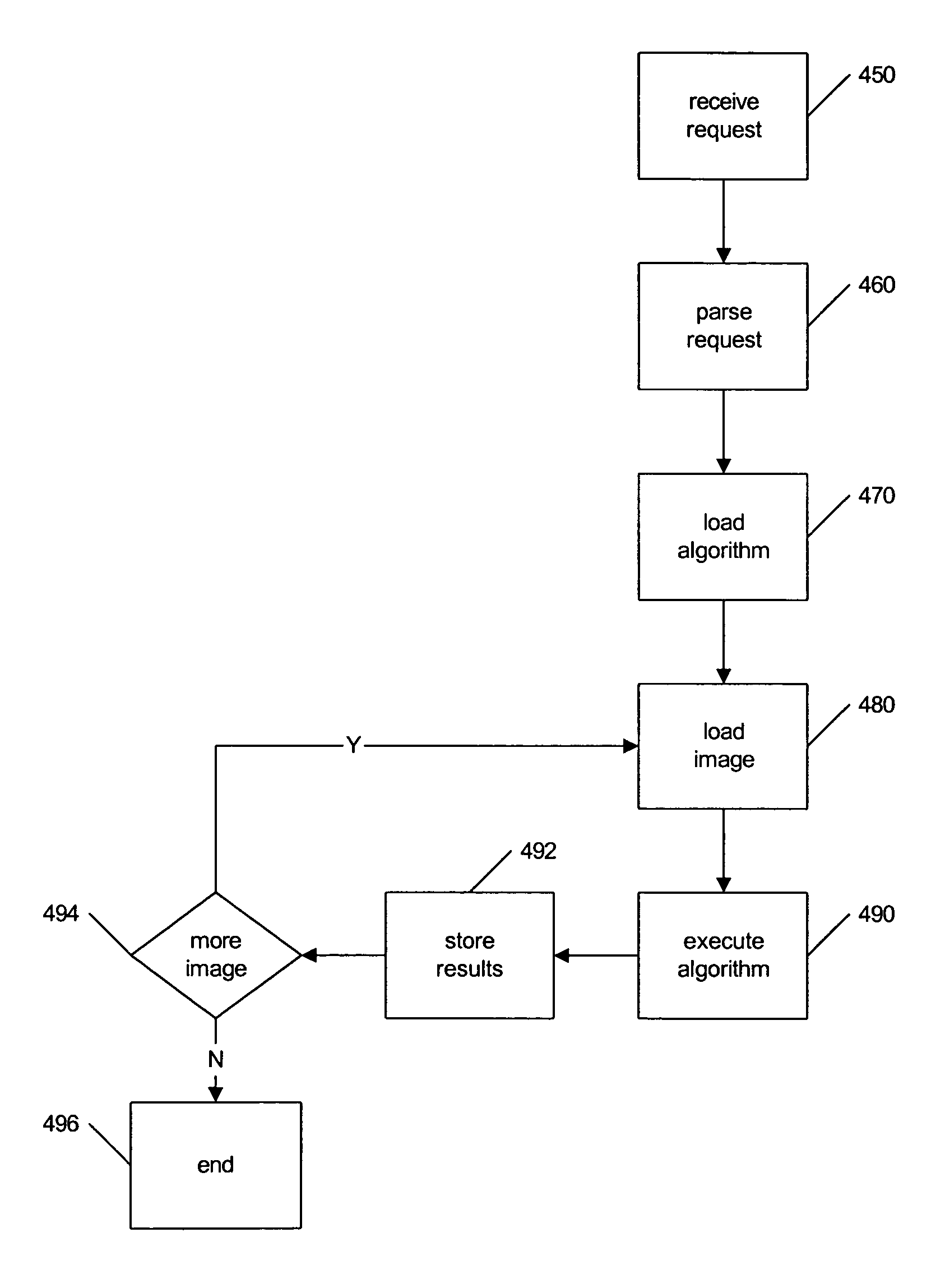
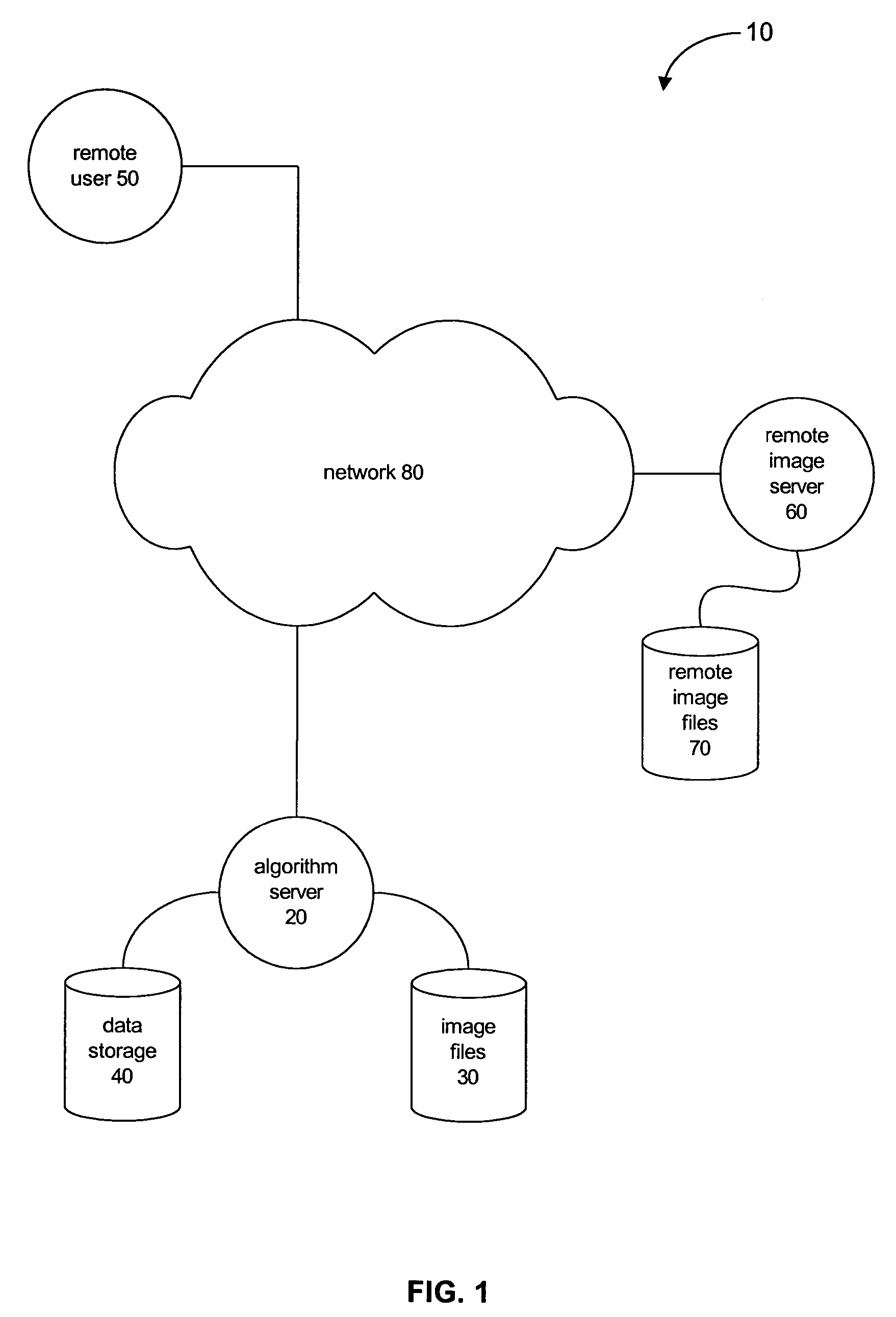
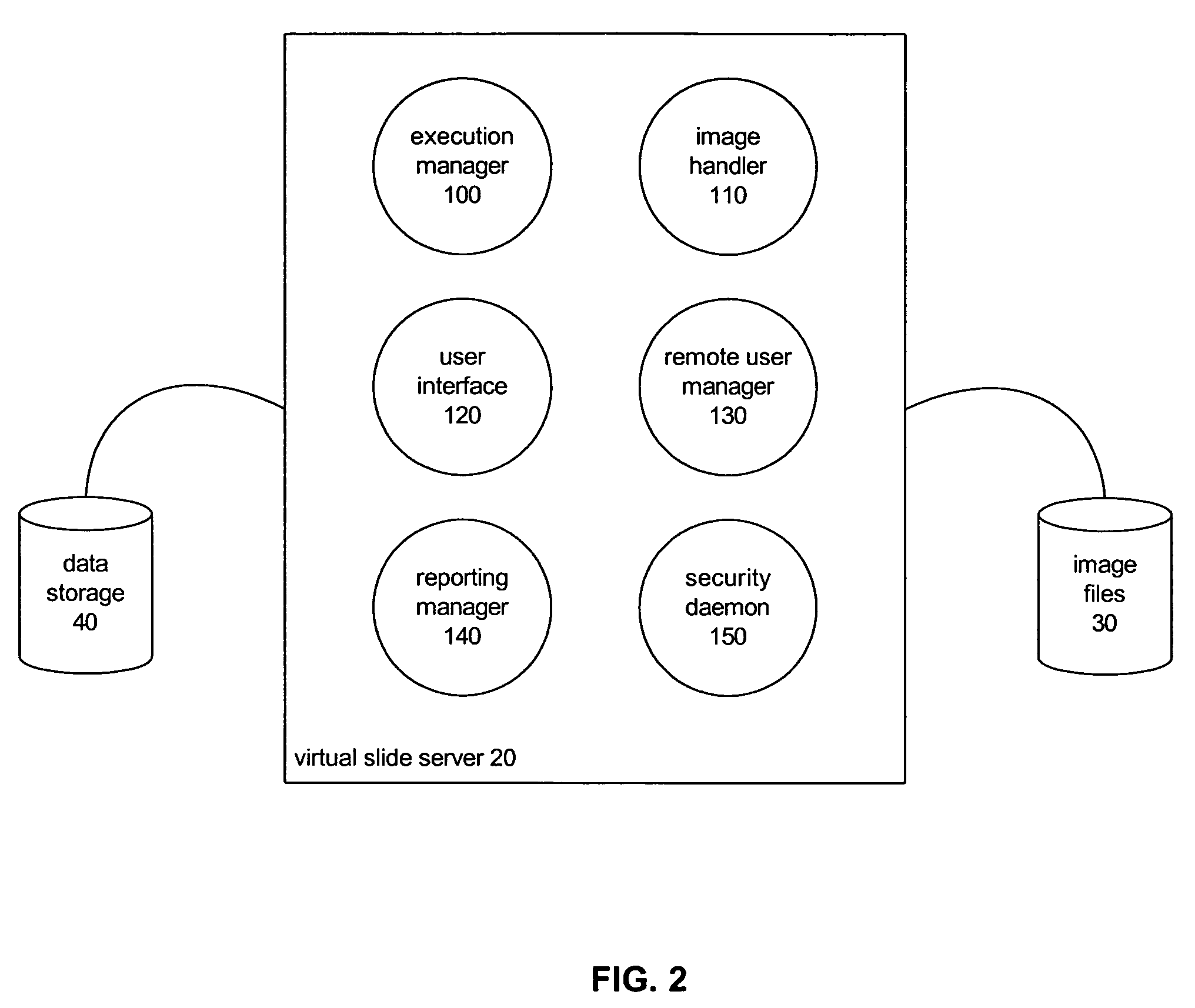
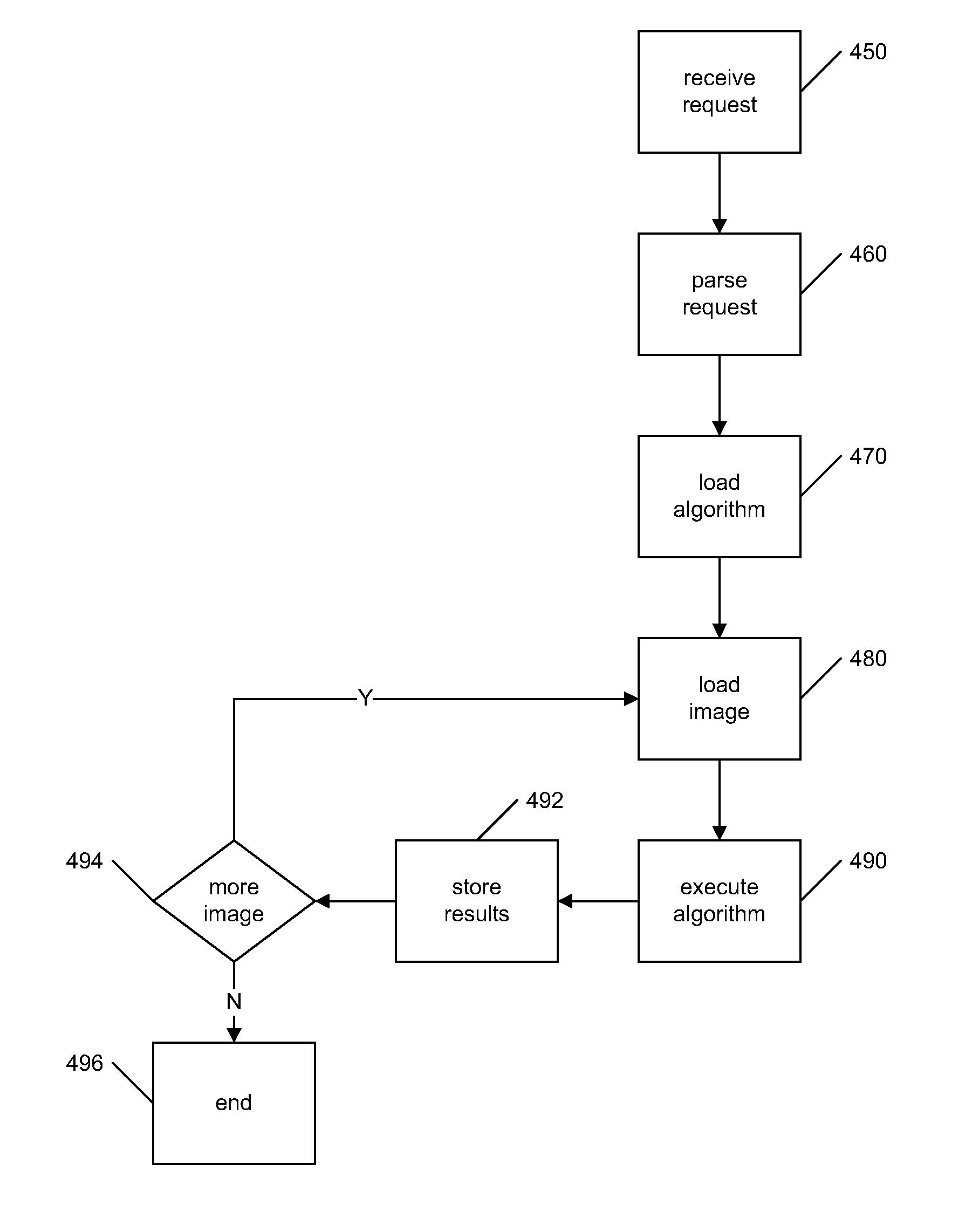
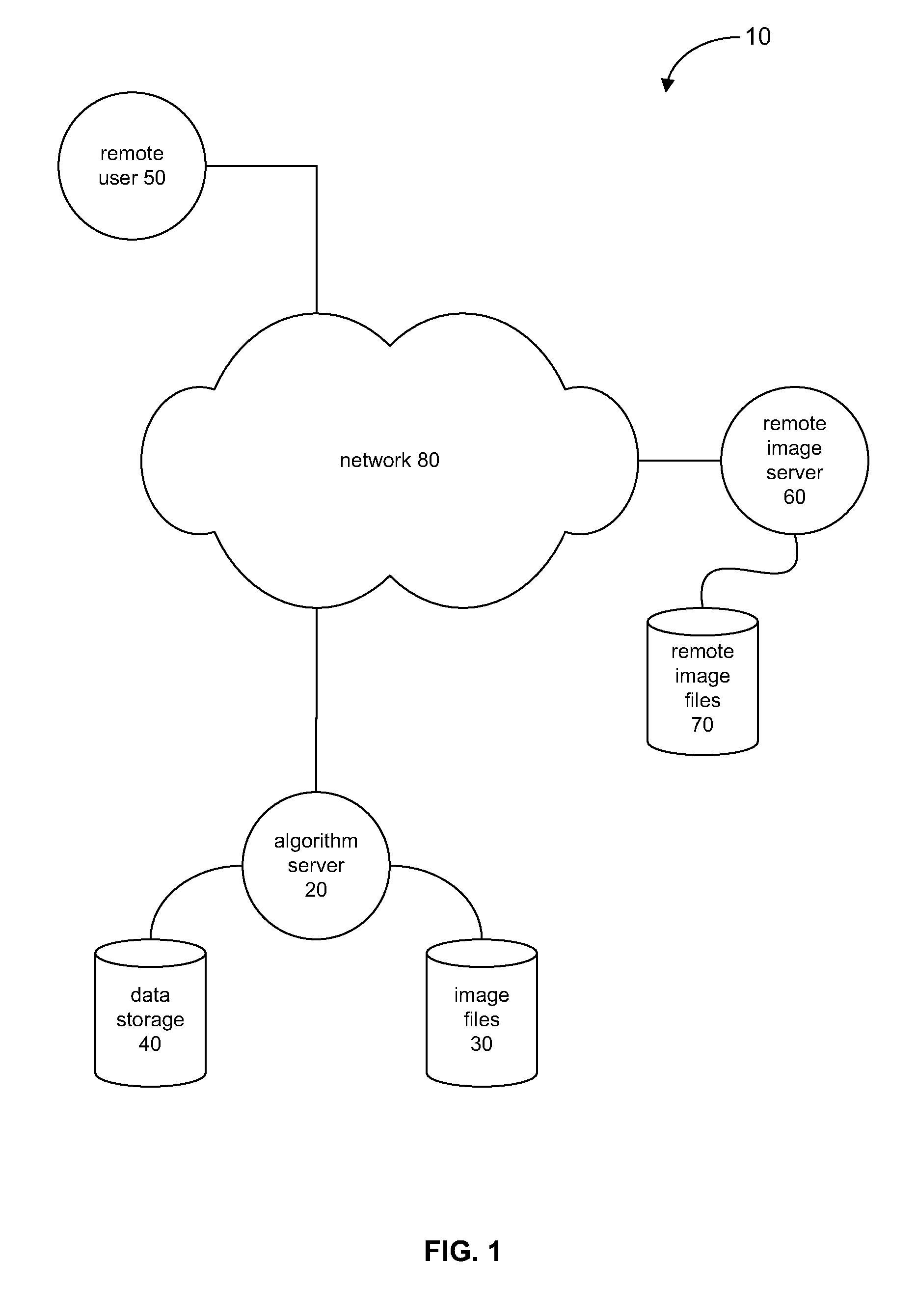
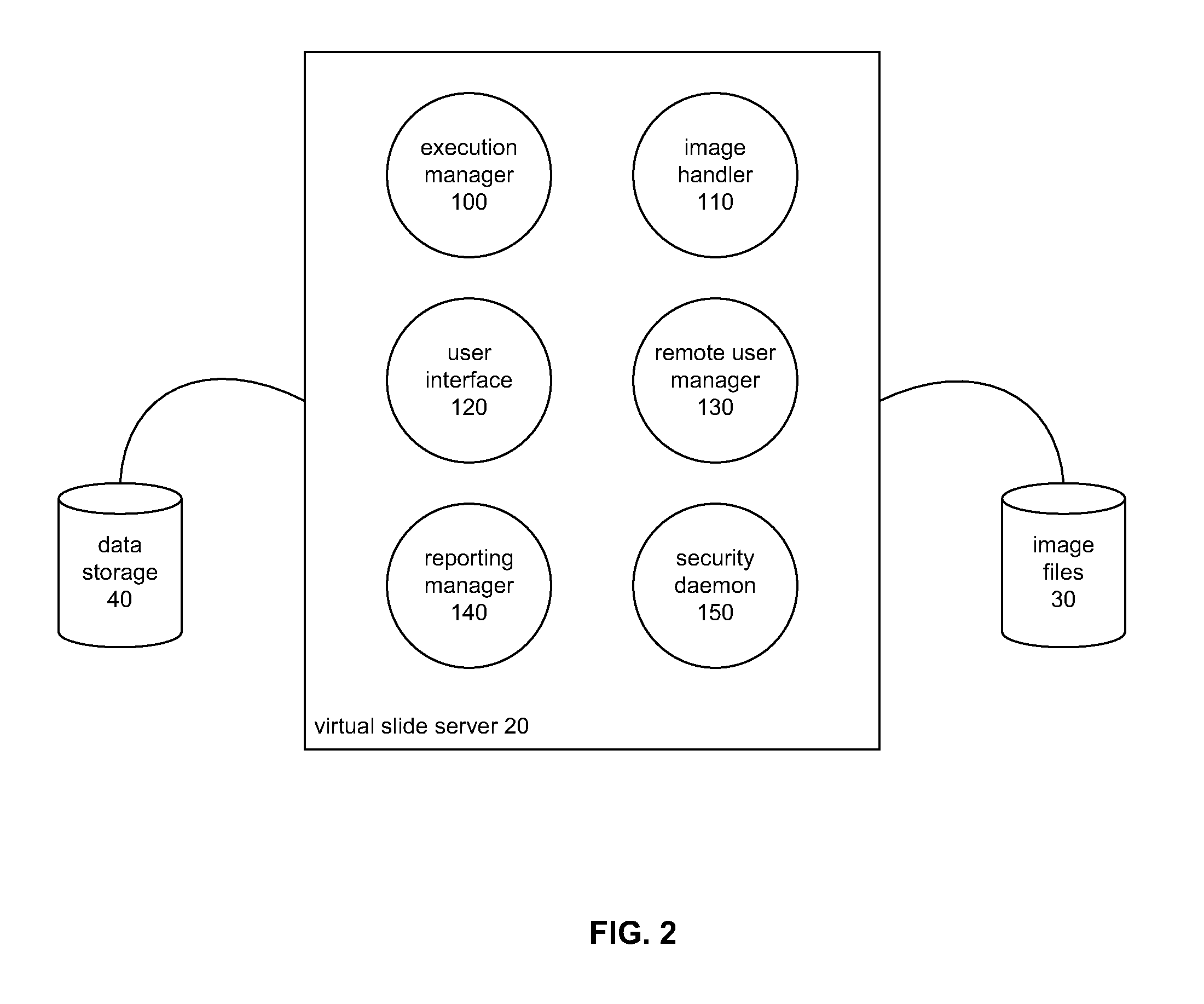
A system and method for processing and analyzing virtual microscopy digital images (“virtual slides”) is provided. The system comprises an algorithm server that maintains or has access to a plurality of image processing and analysis routines. The algorithm server additionally has access to a plurality of virtual slides. The algorithm server executes a selected routine on an identified virtual slide and provides the resulting data. The virtual slide can be accessed locally or remotely across a network. Similarly, the image processing routines can be obtained from local storage or across a network, or both. Advantageously, certain common sub-routines may be stored locally for inclusion in other local or remotely obtained routines. Access to image processing and analysis may be restricted through a monitor process that authenticates requests to process or view virtual slides. Variations in restrictions to images provide a rich diversity in access levels that allow sharing of virtual slides and demonstrations of image processing algorithms.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Systems and methods for creating and viewing three dimensional virtual slides
ActiveUS20060007533A1High bandwidthQuick ViewMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsMicroscope slideVirtual slide
Systems and methods for creating and viewing three dimensional virtual slides are provided. One or more microscope slides are positioned in an image acquisition device that scans the specimens on the slides and makes two dimensional images at a medium or high resolution. This two dimensional images are provided to an image viewing workstation where they are viewed by an operator who pans and zooms the two dimensional image and selects an area of interest for scanning at multiple depth levels (Z-planes). The image acquisition device receives a set of parameters for the multiple depth level scan, including a location and a depth. The image acquisition device then scans the specimen at the location in a series of Z-plane images, where each Z-plane image corresponds to a depth level portion of the specimen within the depth parameter.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Scan Order Optimization and Virtual Slide Stitching
Virtual microscopy and other system may benefit from a system that can build the large mosaic by stitching images, and overcoming positioning error of stages used to provide the images. In particular, these systems may benefit from scan order optimization and virtual slide stitching techniques. A method can include analyzing, by a machine, a low resolution image of a sample. The method can also include determining, by the machine, a scan pattern for the sample based on analysis of the low resolution image of the sample. The method can further include controlling, by the machine, the scan based on the scan pattern, wherein the scan pattern is configured to minimize an amount of back-stitching of scans in the scan pattern.
Owner:OLYMPUS INTEGRATED TECH AMERICA
Method for displaying virtual slide and terminal device for displaying virtual slide
ActiveUS7925070B2Convenience to workGuaranteed to workCharacter and pattern recognitionMaterial analysisOphthalmologyVirtual slide
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Virtual microscope system
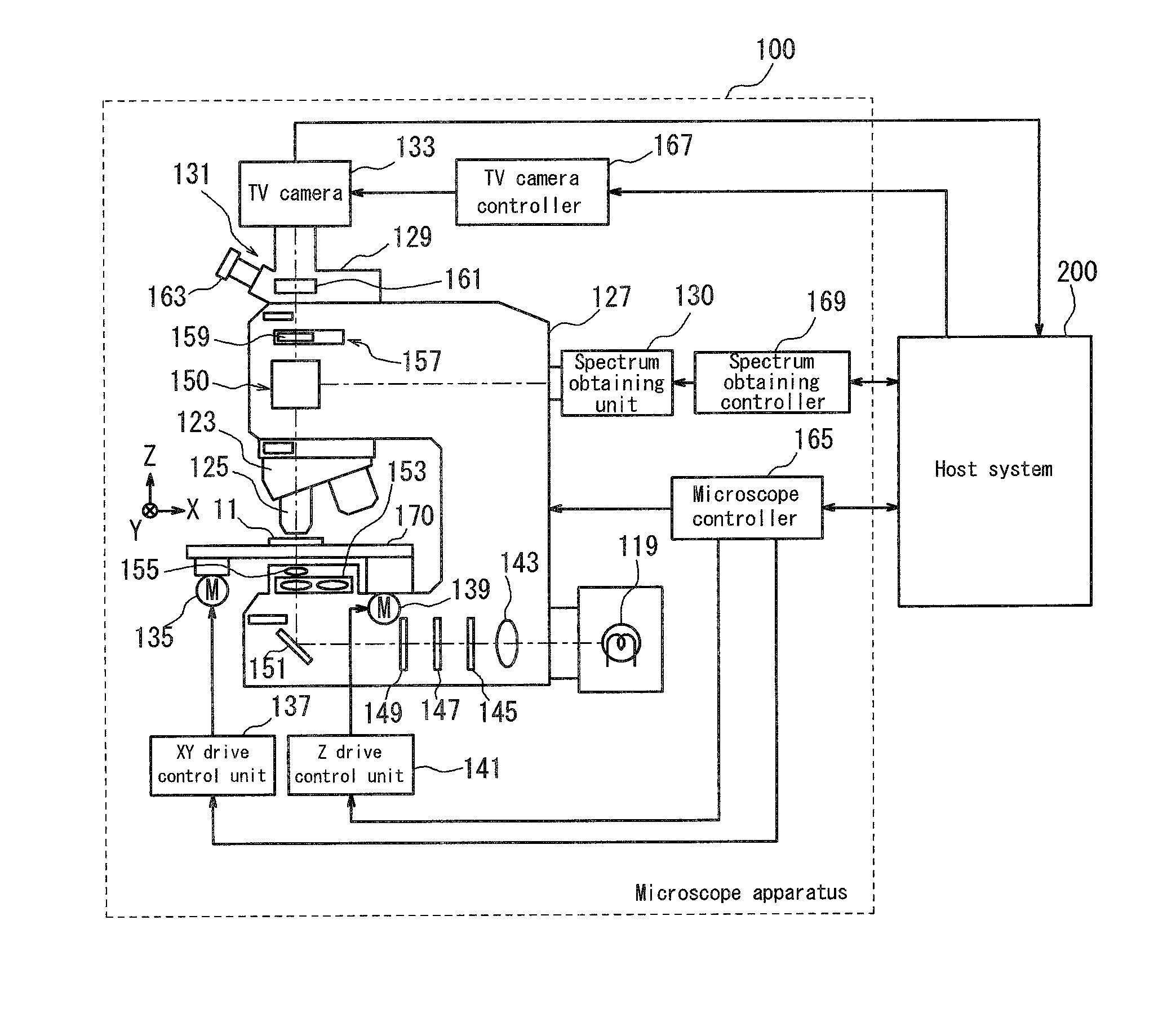
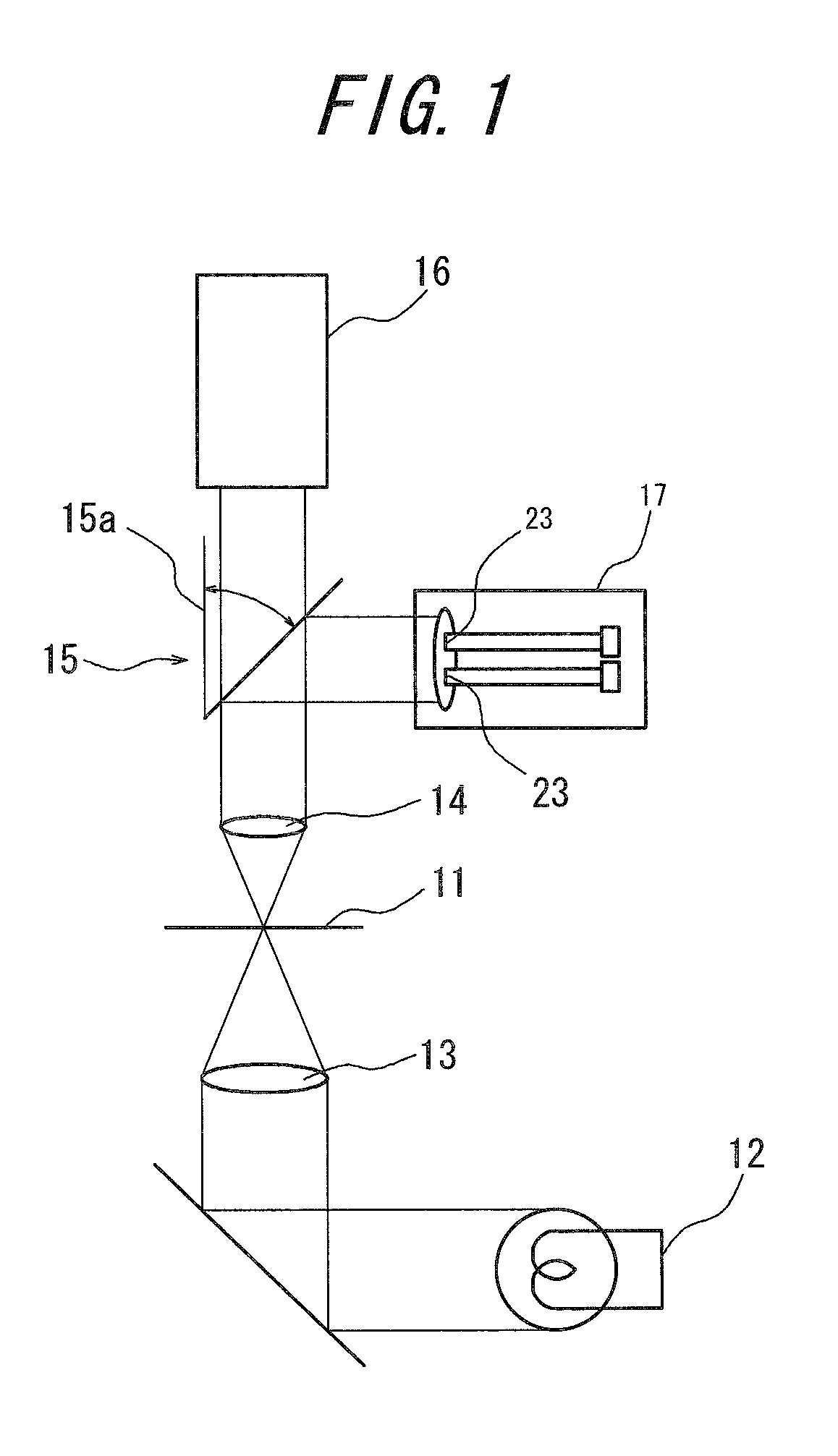
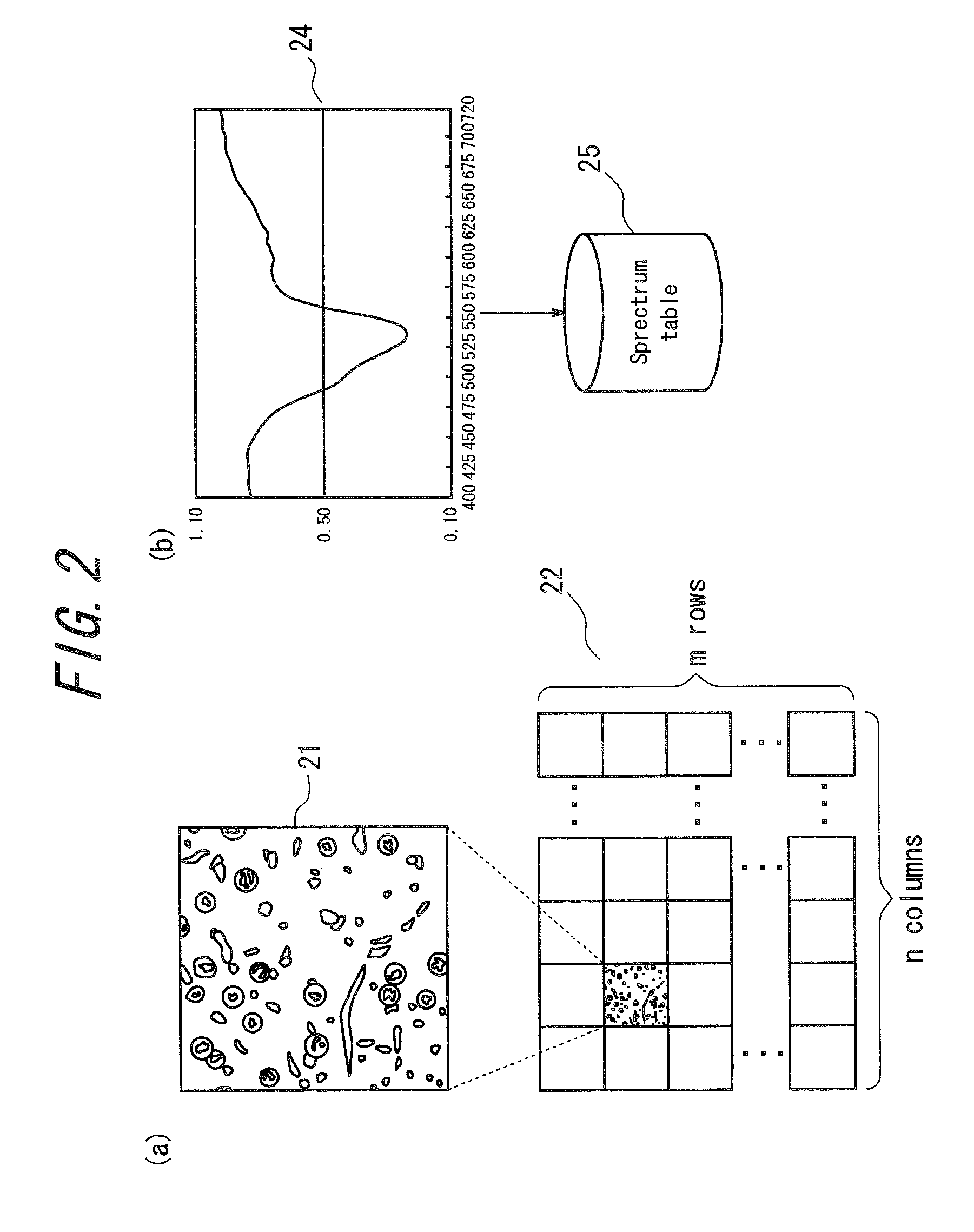
ActiveUS20110109735A1Increase speedColor television detailsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyLight fluxVirtual slide
A virtual microscope system capable of obtaining a stained sample image and a statistical data of spectra in a short period of time is provided, the virtual microscope system includes an image obtaining unit for obtaining a stained sample image, a spectrum obtaining unit for obtaining a spectrum of the stained sample image, an optical path setting unit for setting an optical path of a light flux passed through the stained sample with respect to the image obtaining unit and the spectrum obtaining unit and a control unit for controlling to repeat obtaining the stained sample image by the image obtaining unit and obtaining the spectrum of the stained sample image by the spectrum obtaining unit in the observation field of the stained sample to create a virtual slide and a spectrum table of the stained sample.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Method and apparatus for Internet, intranet, and local viewing of virtual microscope slides
A method of and apparatus for viewing microscopic images include transmitting tiled microscopic images from a server to a client. The client assembles the tiled images into a seamless virtual slide or specimen image and provides tools for manipulating image magnification and viewpoint. The method and apparatus also provides a virtual multi-headed microscope function which allows scattered viewers to simultaneously view and interact with a coherent magnified microscopic image.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
Virtual microscopy
ActiveUS20120320094A1Easy to browseHigh magnificationImage enhancementImage analysisUser inputVirtual slide
Computer implemented methods and data processing apparatus are described for displaying virtual slide images. Images of a plurality of slides are automatically displayed in a first region of a display device at a first magnification. The slides comprise all the slides including material from a same specimen. An image of at least one of the slides is displayed in a second region at a second magnification greater than the first magnification. At least the image displayed in the second region is changed responsive to receiving user input. Methods for automatically determining a slide layout pattern and methods for virtually melding glass slide images into a single image are also described.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Advance in Transmission and Display of Multi-Dimensional Images for Digital Monitors and Television Receivers using a virtual lens
The present invention provides an advance in multi-dimensional displays for digital monitors and televisions. In general, the present invention provides image capture devices arranged at different angles about a target image, or in a straight line, to capture images at pre-designated angles. Each captured image is combined into a composite image using hardware such as a computer. The composite image and a virtual lens are then transmitted together to a display means to be viewed having stereoscopic characteristics.
Owner:3 D VIRTUAL LENS TECH
Microscopy system having automatic and interactive modes for forming a magnified mosaic image and associated method
InactiveUS20090196526A1Easy to handleWell equipped with system memoryAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsSedimentation analysisInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
A scanning device for biological slides is provided, which can be operated in an interactive routine mode as well as in an unsupervised high speed automatic mode. In the first case, typical components, which the pathologist is used to operating manually, such as the microscope, the stage and the focus, and which have to be motorized for the automatic unsupervised system mode, are configured to simulate manual use, operation, and response. A non-interlaced area scan camera supports the interactive selection and acquisition of individual images in the manual mode, as well as the continuous high-speed scan motion for the rare event detection and virtual slide scan applications of the system. Due to the particular requirements to accommodate both operational modes, methods are described for constructing the virtual slide out of image tiles with varying overlap areas in the x- and y-directions.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
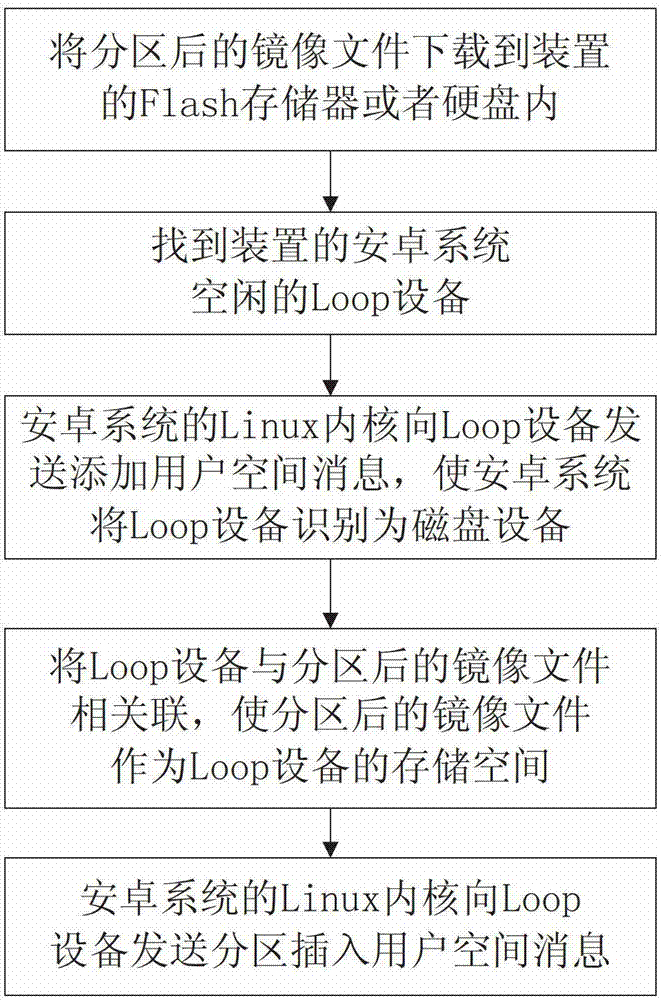
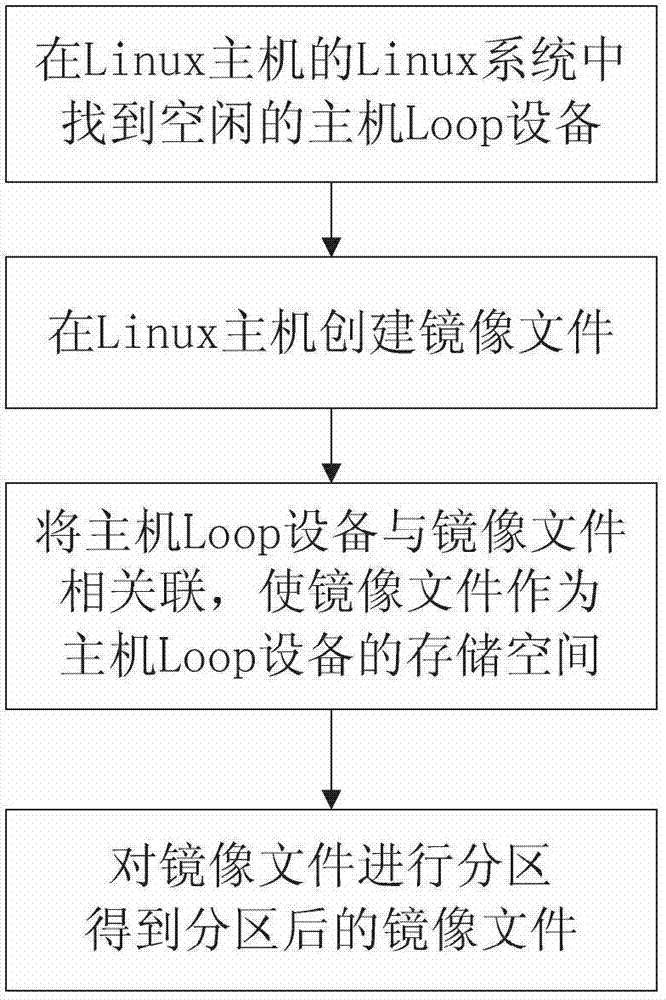
Method of virtual SD (Security Digital) card on device with android system
ActiveCN102880498ALow access speedFast accessProgram loading/initiatingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtual slideLinux kernel
Owner:深圳市佳创软件有限公司
System and method for creating magnified images of a microscope slide
A method and system for creating a digital, virtual slide having optimum image quality characteristics. Multiple regions of a physical slide are identified as well as at least two focus z-positions z1, and z2. Each region of the physical slide is scanned (imaged) at the first z position, so as to produce a first set of digital images of each defined region. Each region of the physical slide is also scanned (imaged) at the second z position, so as to produce a second set of digital images of each defined region. Each image of each set is evaluated against a focus quality metric and, for each region, either the first or second image, corresponding to that region, is selected that exhibits a focus quality metric corresponding to a desired focus quality. These images are then merged into a digital virtual slide. Additional focus z-positions may be included, and the multiple z-positions may be scanned seriatim, sequentially, and / or in overlapping fashion.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Slide photograph data creation system, and slide photograph data
InactiveUS7426345B2Attach and detachDisplaySamplingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Virtual slide
A slide photograph data creation system includes a digital camera for making high-magnification photographs of samples, a sample transporter for holding and transporting samples, a controller for controlling the camera and the sample transporter so as to provide overlapping photographs, a pasting information generator for recognizing the margin by which the photographs overlap and for generating pasting-together information, and a photograph file generator for storing in a single file a plurality of high-magnification photographs and the pasting-together information. The system facilitates the examination and photography of large numbers of samples, and enables discrimination of the three-dimensional structure of a sample. Since the photographic data is managed with a database, virtual slide photographs and their attributes information can be browsed over a network or the Internet.
Owner:CLARO
System for remote viewing and display of a slide
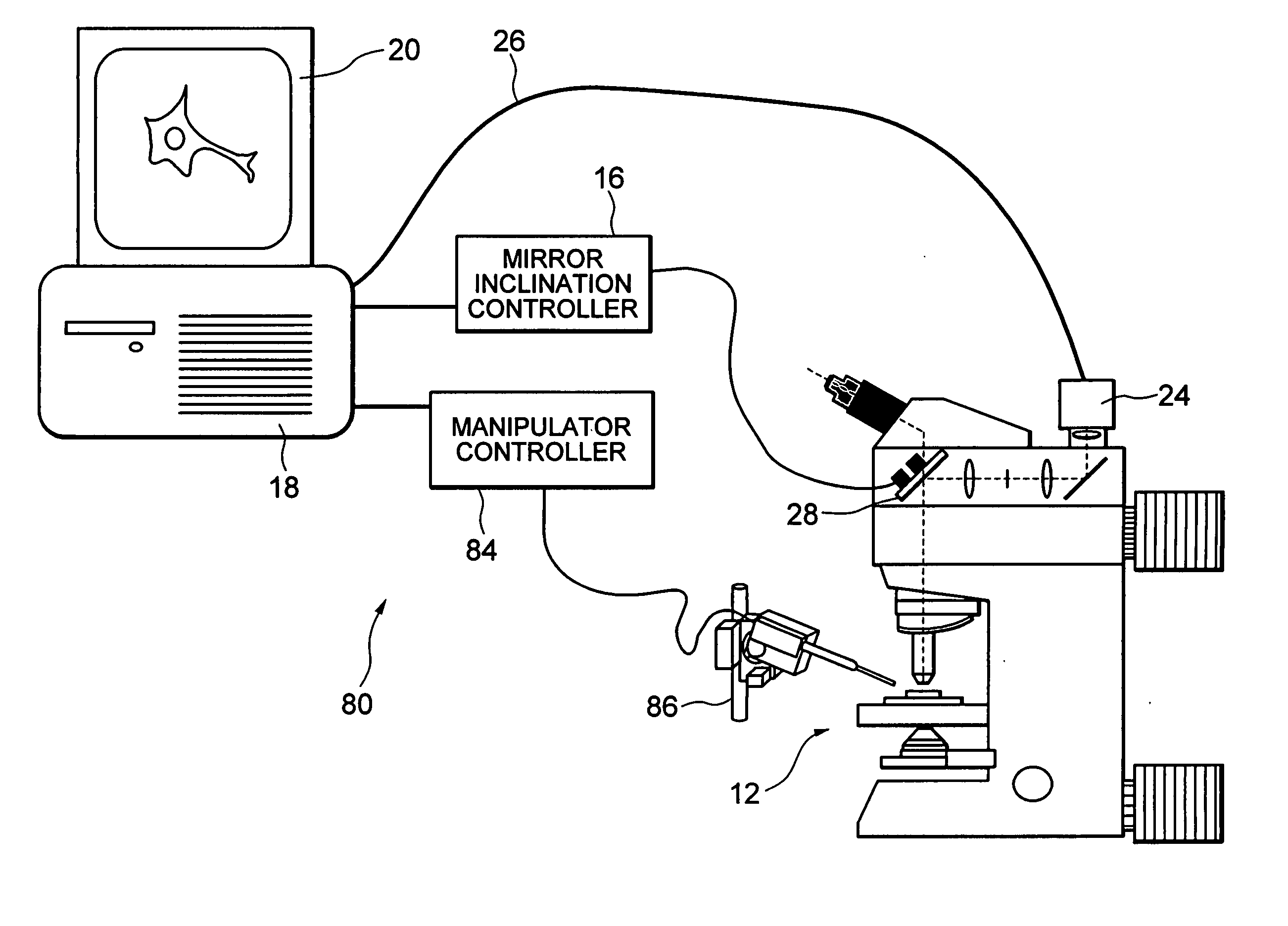
A method for creating a virtual slide is provided. A virtual slide is a digital representation of an area of interest of a microscope slide. One method is to use a motorized microscope that can move a specimen with respect to a microscope objective. With such a system, one can capture one or more images through a microscope objective, such that a region of interest is imaged. Each image is then joined together to form a composite or “virtual image.” In one embodiment, after a virtual slide is created, a user may fully utilize the full capabilities of the remote microscope. Among these capabilities is a set of “optical objectives” and “virtual objectives.” Optical objectives are images created by digitizing an image through a microscope objective in real time. Virtual objectives are digitally created magnifications created by utilizing the existing virtual slide data to digitally create a field of view.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS
Image Processing and Analysis Framework
ActiveUS20070030529A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingVirtual slide
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com