Patents
Literature
664 results about "Cross layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cross-layer integrated collision free path routing
InactiveUS7339897B2Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTPower managementQuality of serviceSelf adaptive
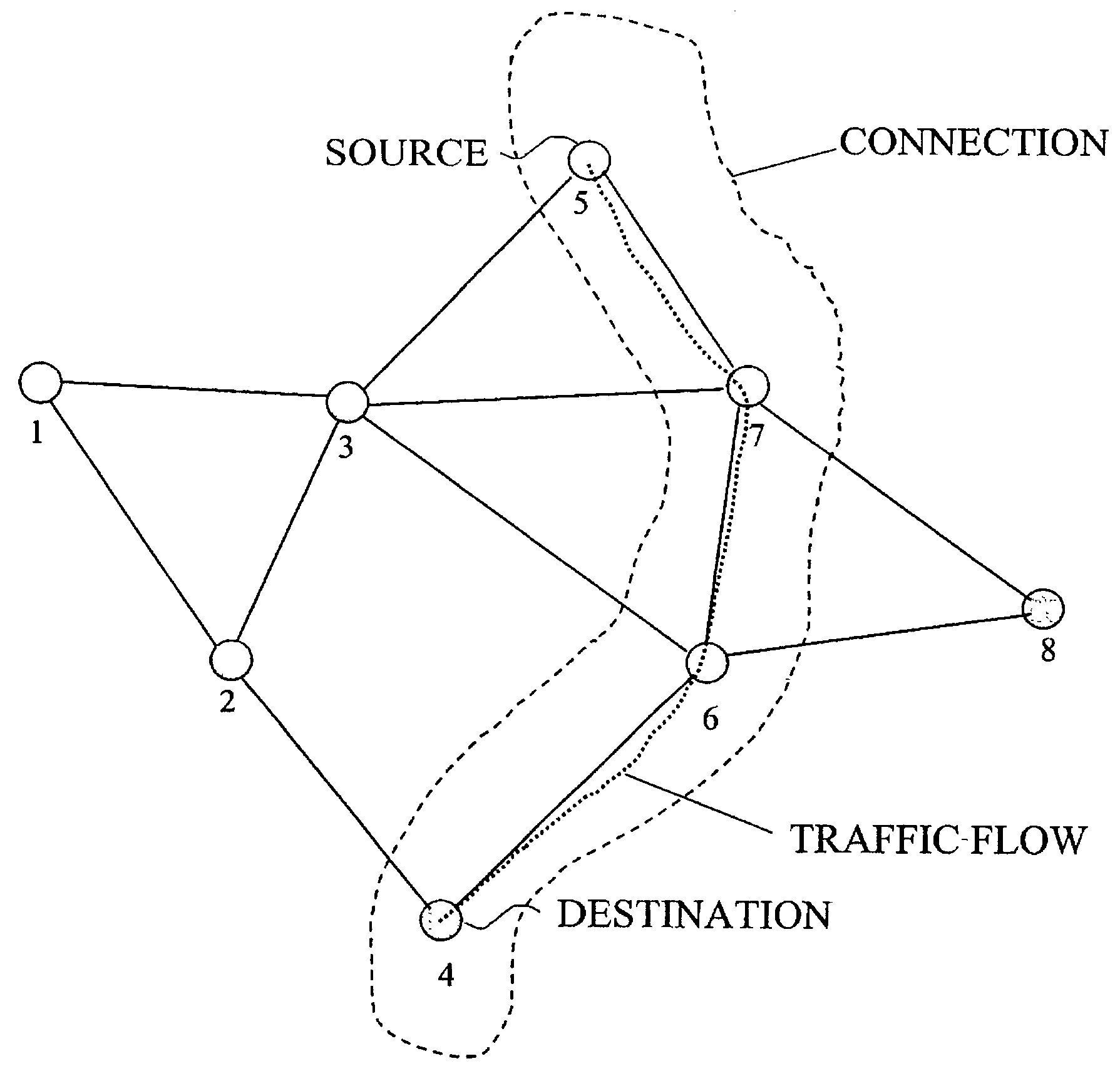
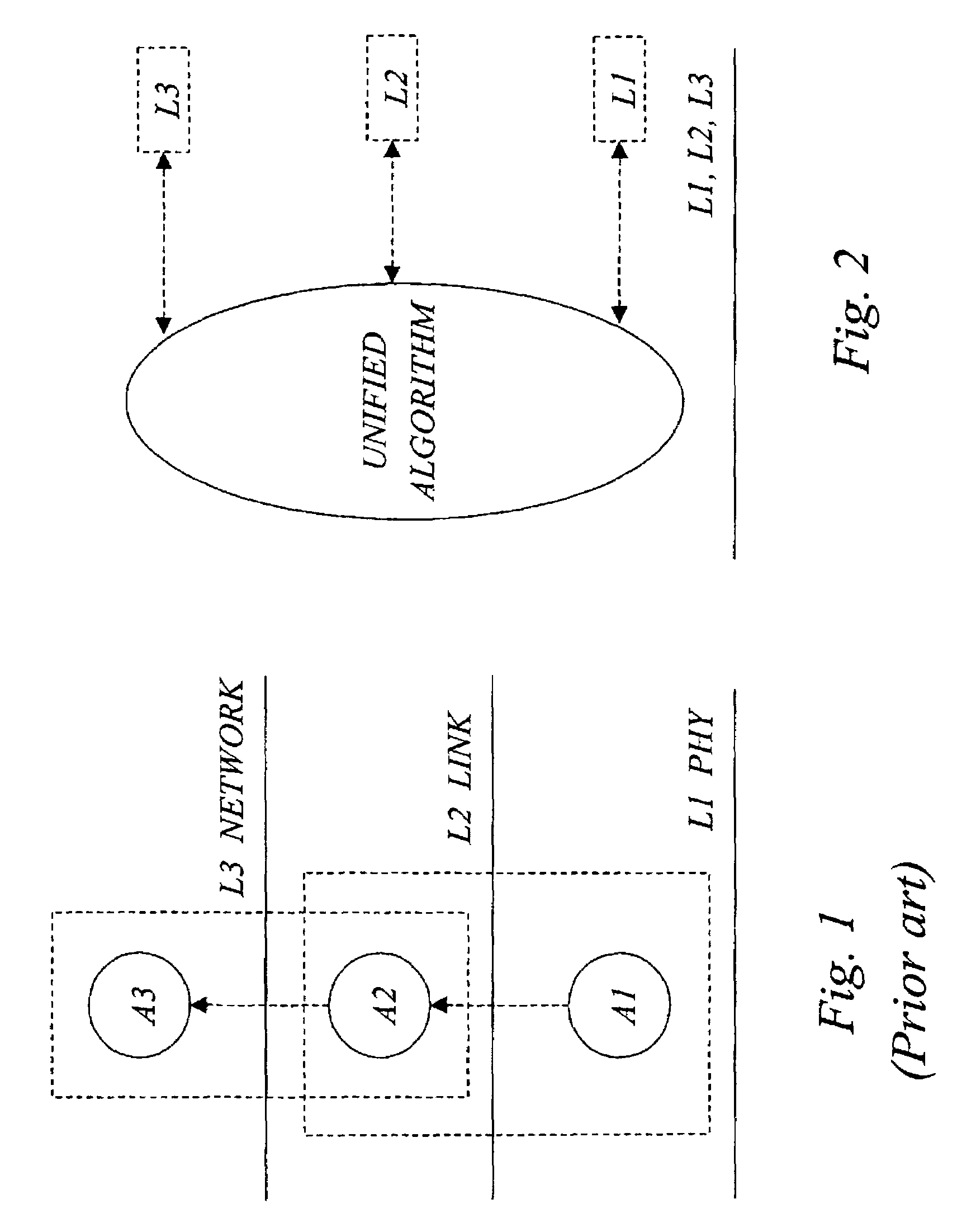
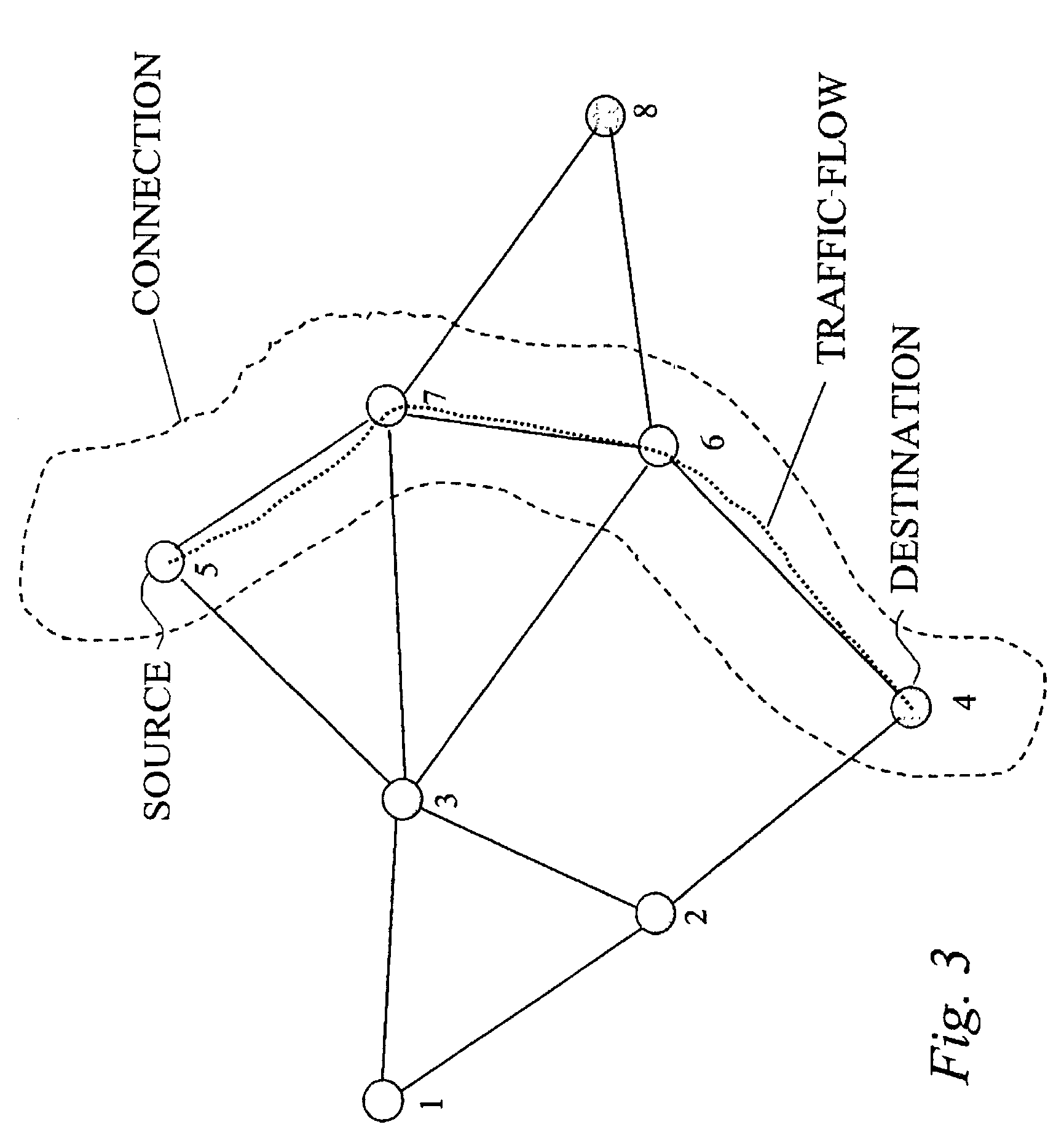
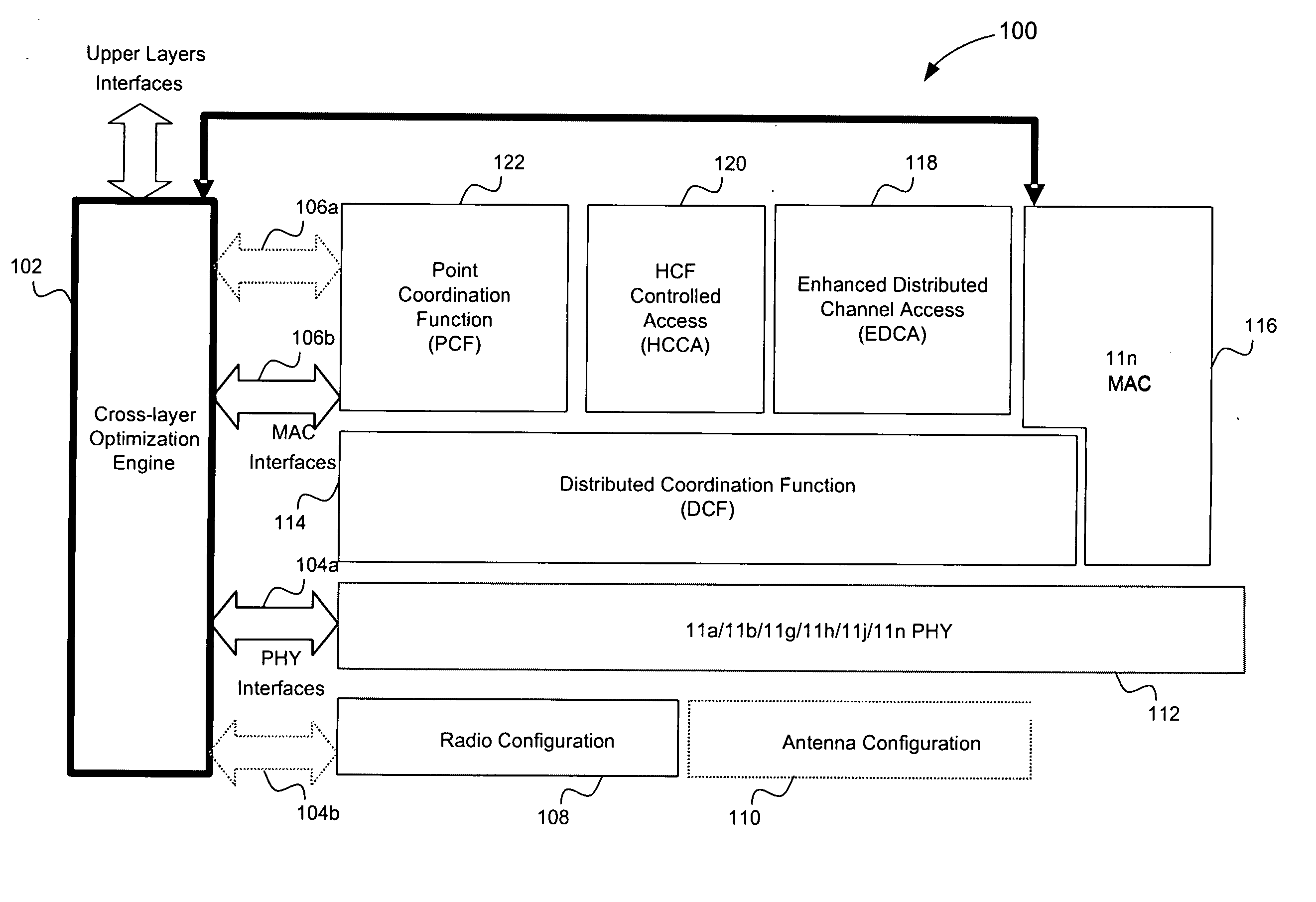
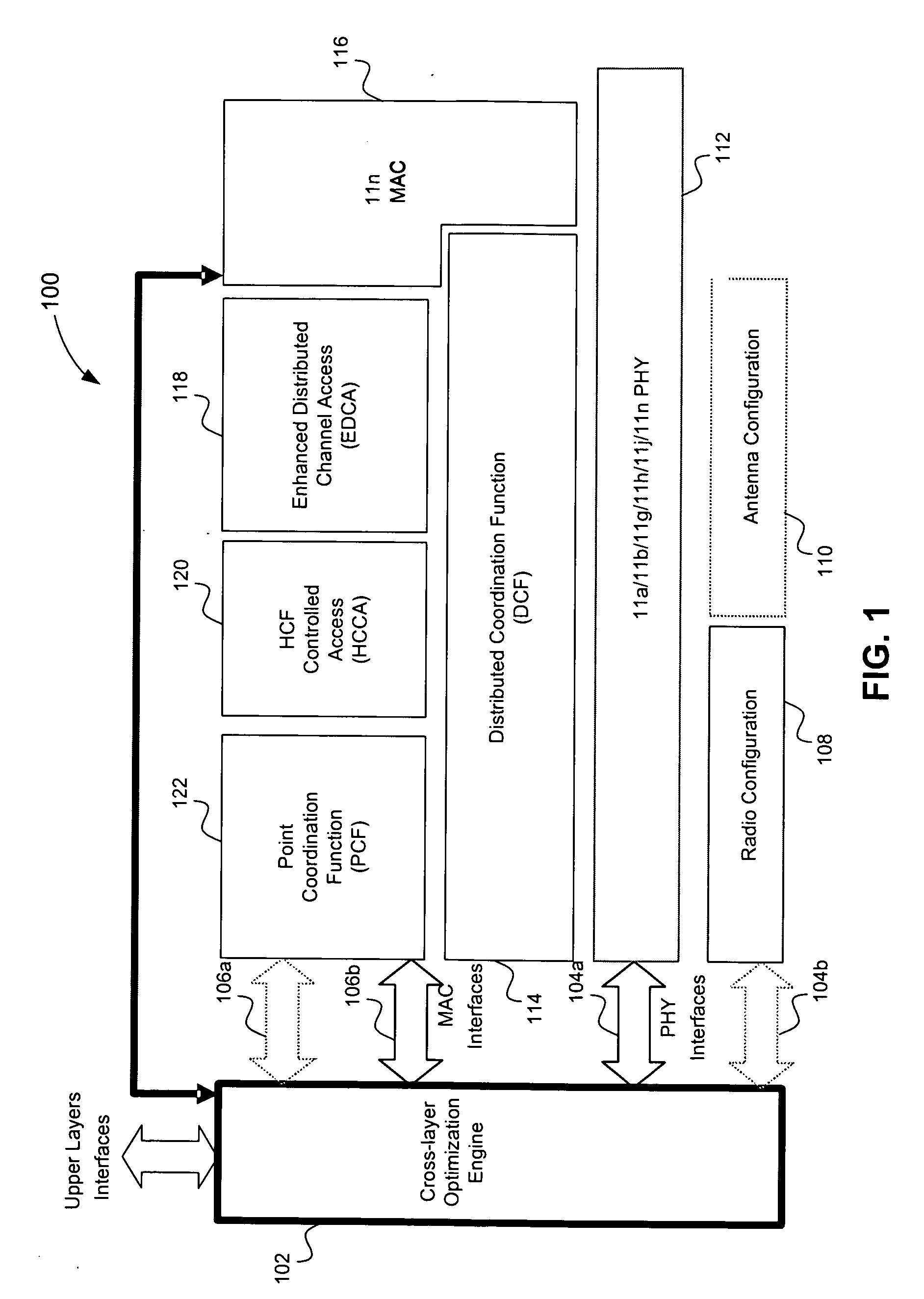
A true cross-layer integration of functions is provided on several protocol layers within a network, thus providing a unified approach to Quality of Service (QoS) provisioning in a multihop network. In the unified approach, connections are preferably determined by integrated optimization of a given objective function with respect to connection parameters on at least three protocol layers within the network. Preferably, the optimization involves routing (path selection), channel access as well as adaptation of physical link parameters. By incorporating physical connection parameters together with properly designed constraints, the issue of interference can be carefully considered. It is thereby possible to determine connection parameters that ensure substantially non-interfering communication with respect to existing connections as well as the new connection.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Mobile television broadcast system
ActiveUS20090013356A1Efficiently specifiedFunction increaseCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresCurrent channelSystem configuration
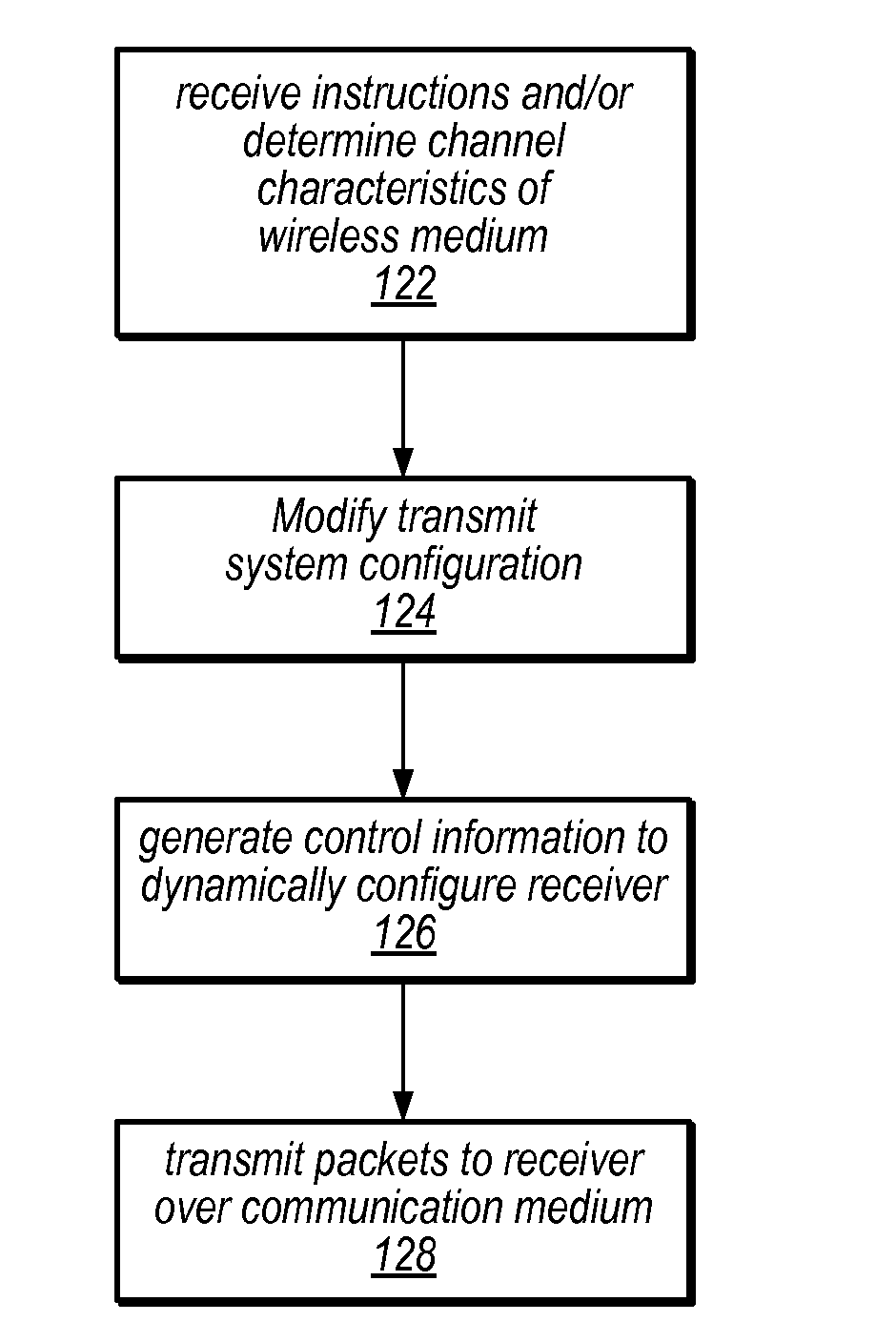
A digital television broadcast system with transmission and / or reception of digital television signals for improved mobile reception. The communication layers in the transmit and receive portions of the transmission system can be dynamically modified, e.g., based on usage patterns or current channel characteristics. The transmission system also provides for cross layer control, whereby parameters in various of the communication layers are analyzed to determine appropriate updates to the system configuration.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Multiple-hypothesis cross-layer prediction
InactiveUS20080089411A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionCoding block
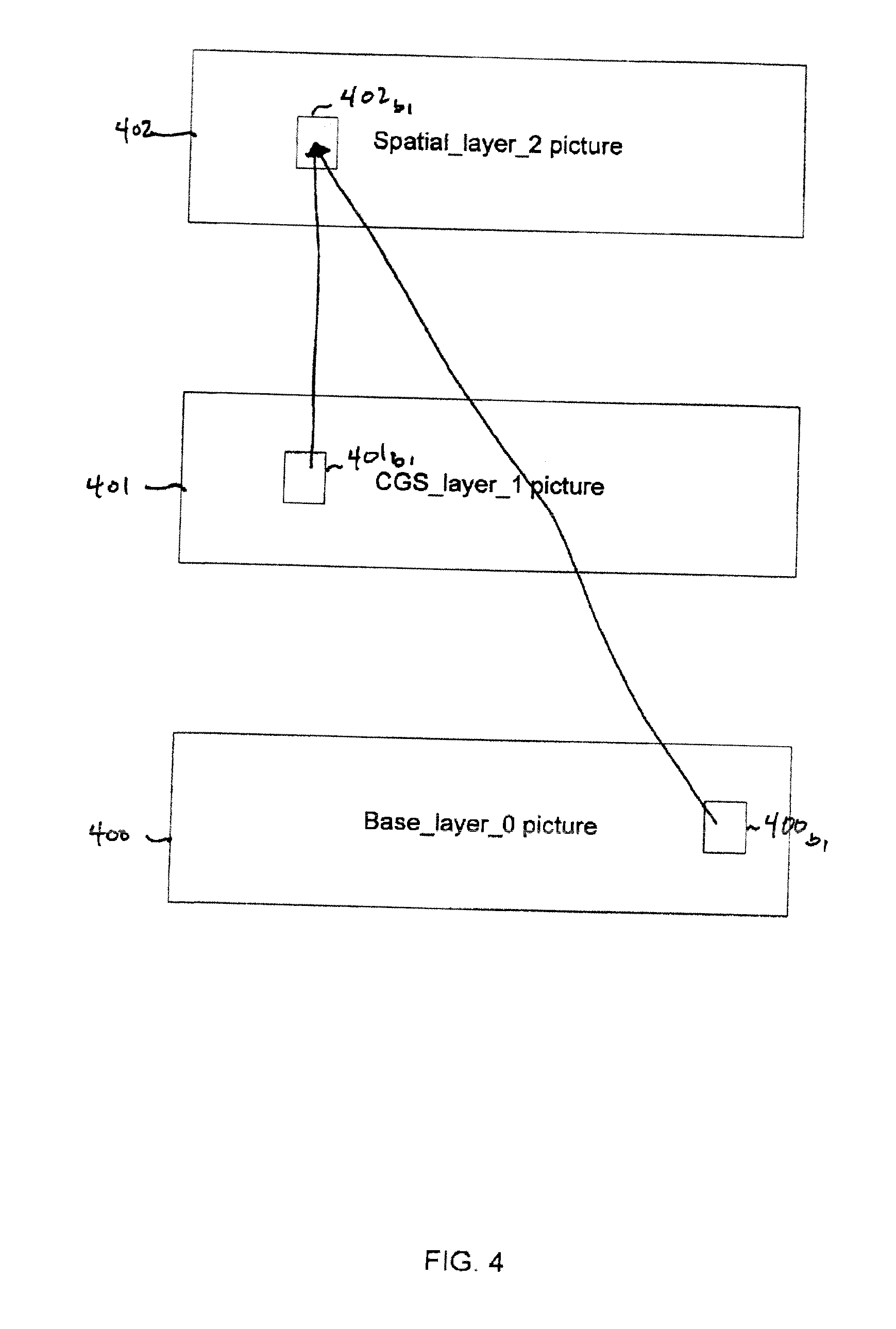
A system and method for predicting an inter-layer predicted slice of image data from at least two different reference layers, where the inter-layer predicted slice of image data itself resides on yet another layer, different from either of the two reference layers. At least one coded block from the inter-layer predicted slice of image data is encoded with an indication, indicating to a decoder that the at least one coded block is to be inter-layer multi-predicted from the at least two different reference layers. Identifications and corresponding prediction weights of the at least two different reference layers are also signaled to the decoder either in the coded block itself, or in the inter-layer predicted slice of image data.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Methods and apparatus for centralized and coordinated interference mitigation in a WLAN network
InactiveUS20110090885A1Facilitate communicationEasy to interferePower managementNetwork topologiesBroadcast channelsPrecoding
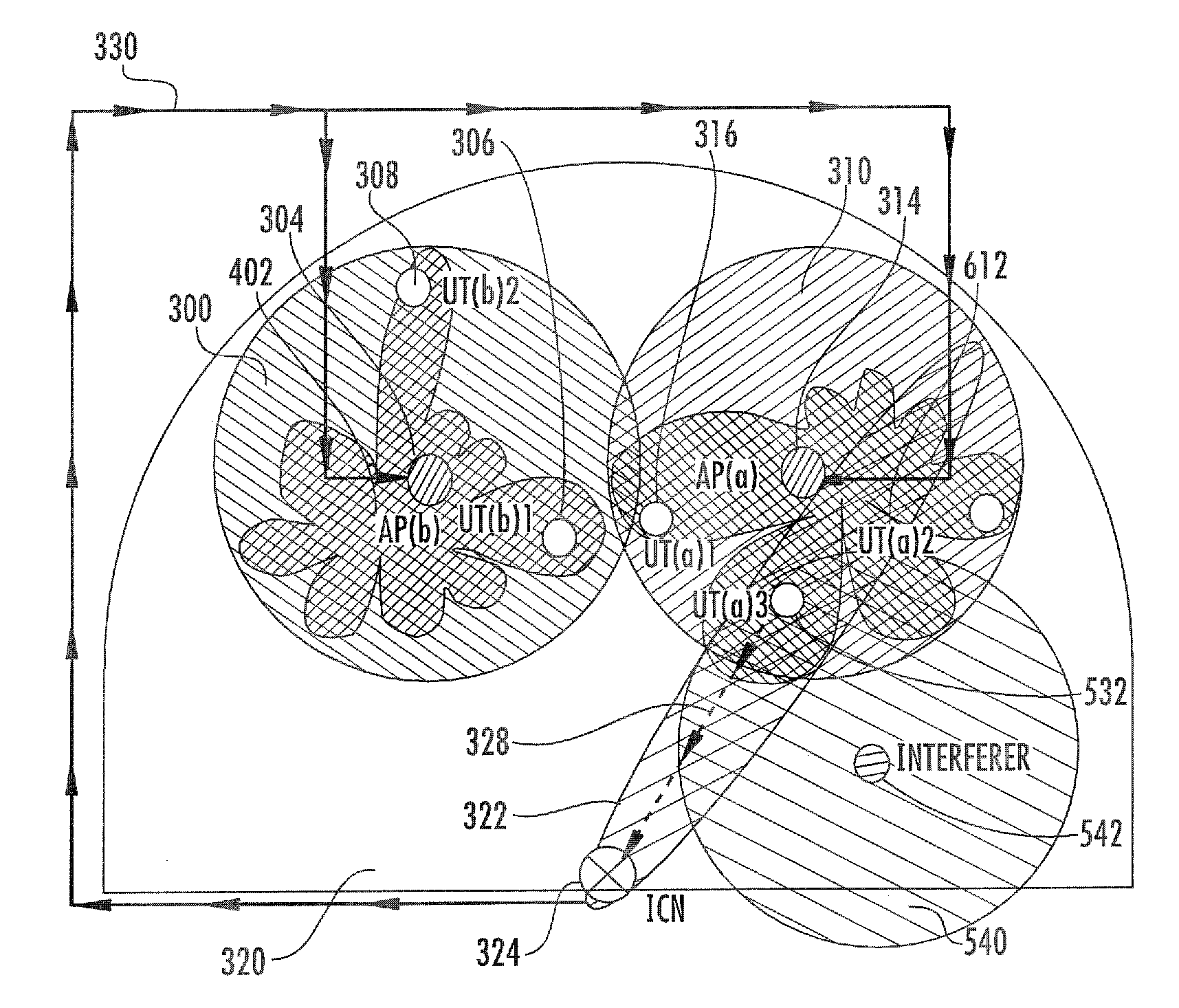
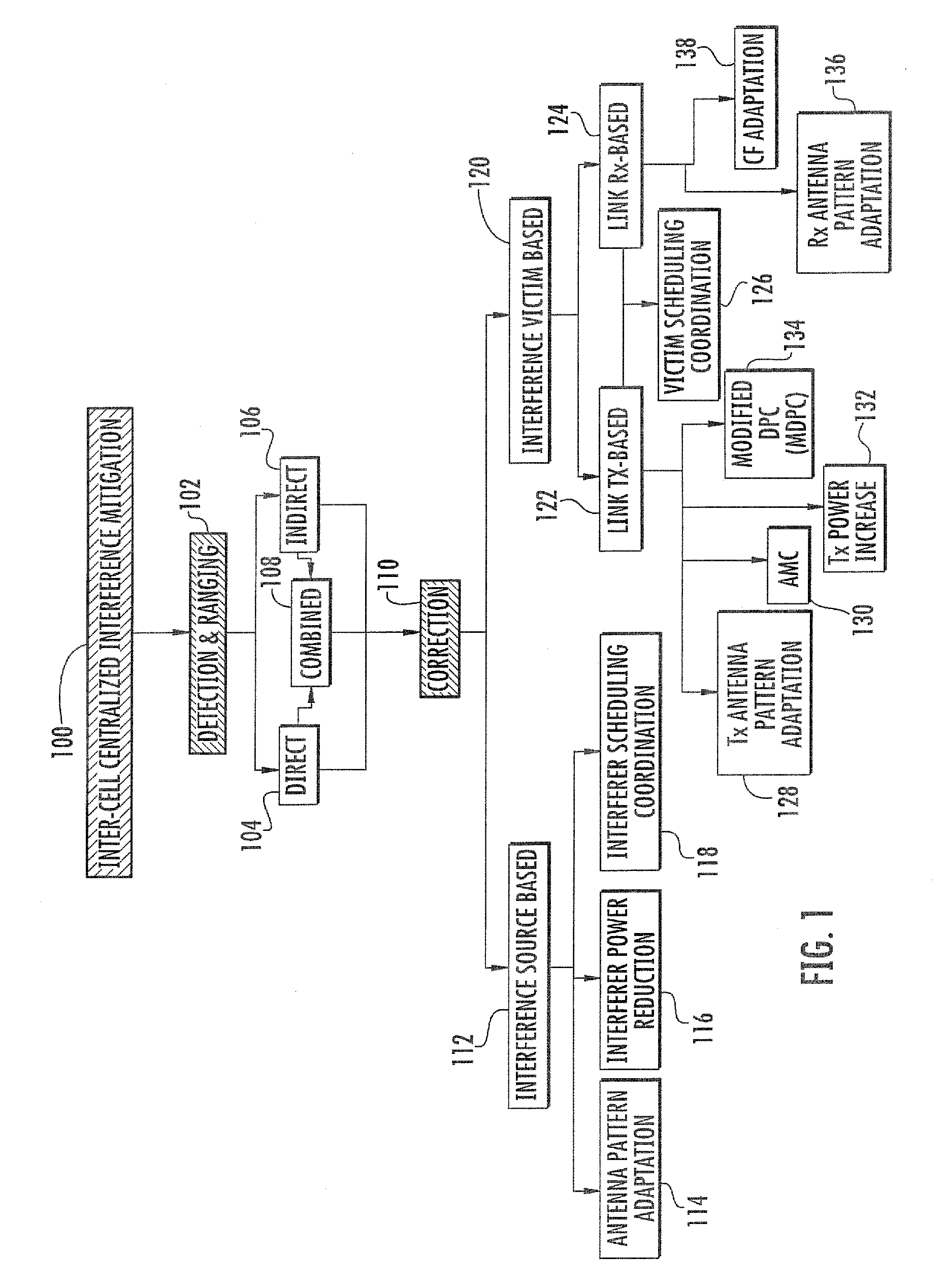
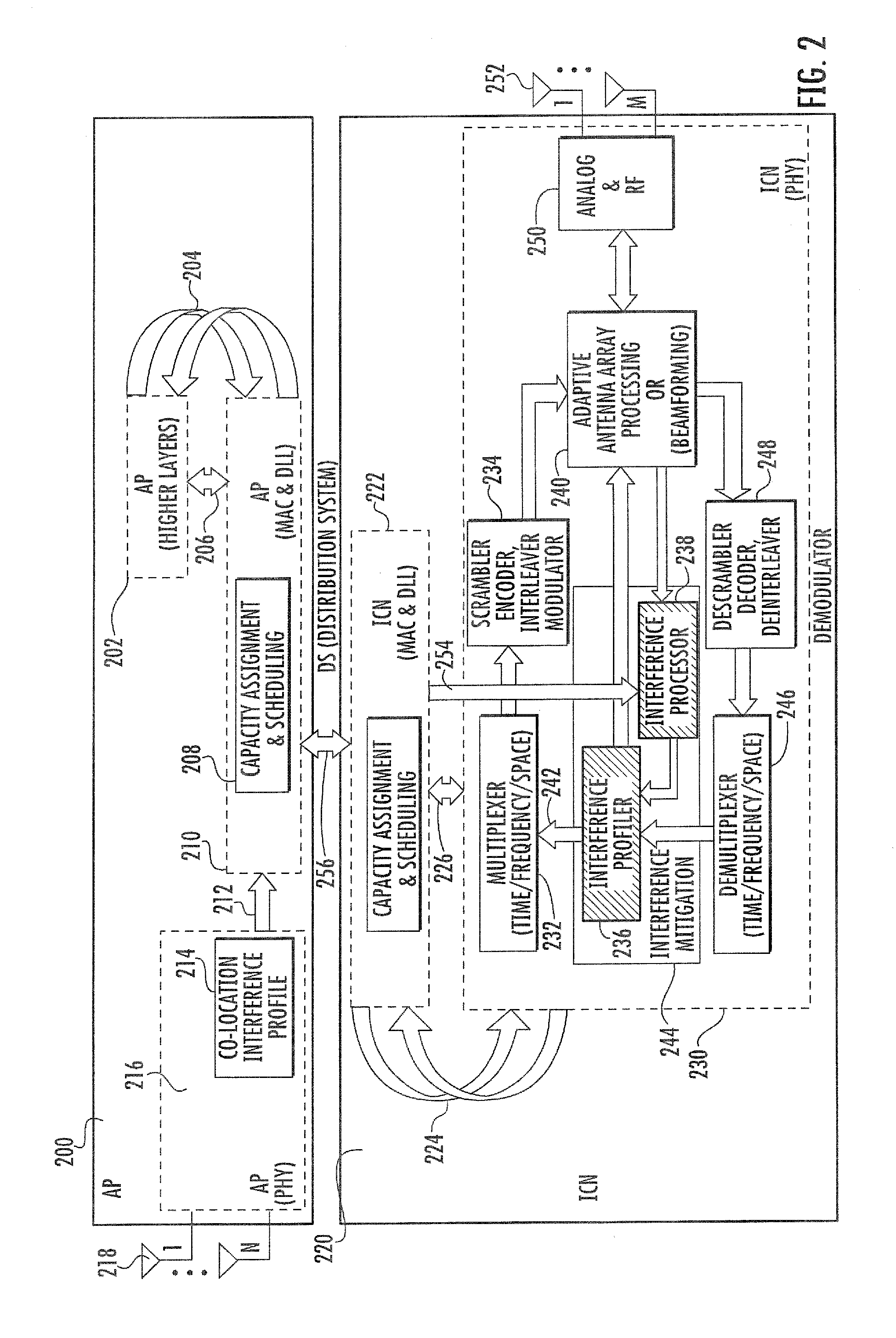
Method and apparatus for interference mitigation in wireless local area networks (such as WLANs). In one embodiment, a centralized interference measurement and mitigation method is disclosed. The method may involve spectral sensing, beamforming, MIMO, power control, MAC scheduling using a cross-layer approach, and / or broadcast channel precoding, employed towards performance enhancement of WLAN networks in presence of interference. In one variant, different actions at interference mitigation are selected based on the source of the interference (e.g., inter-network or intra-network).
Owner:SAFAVI SAEID
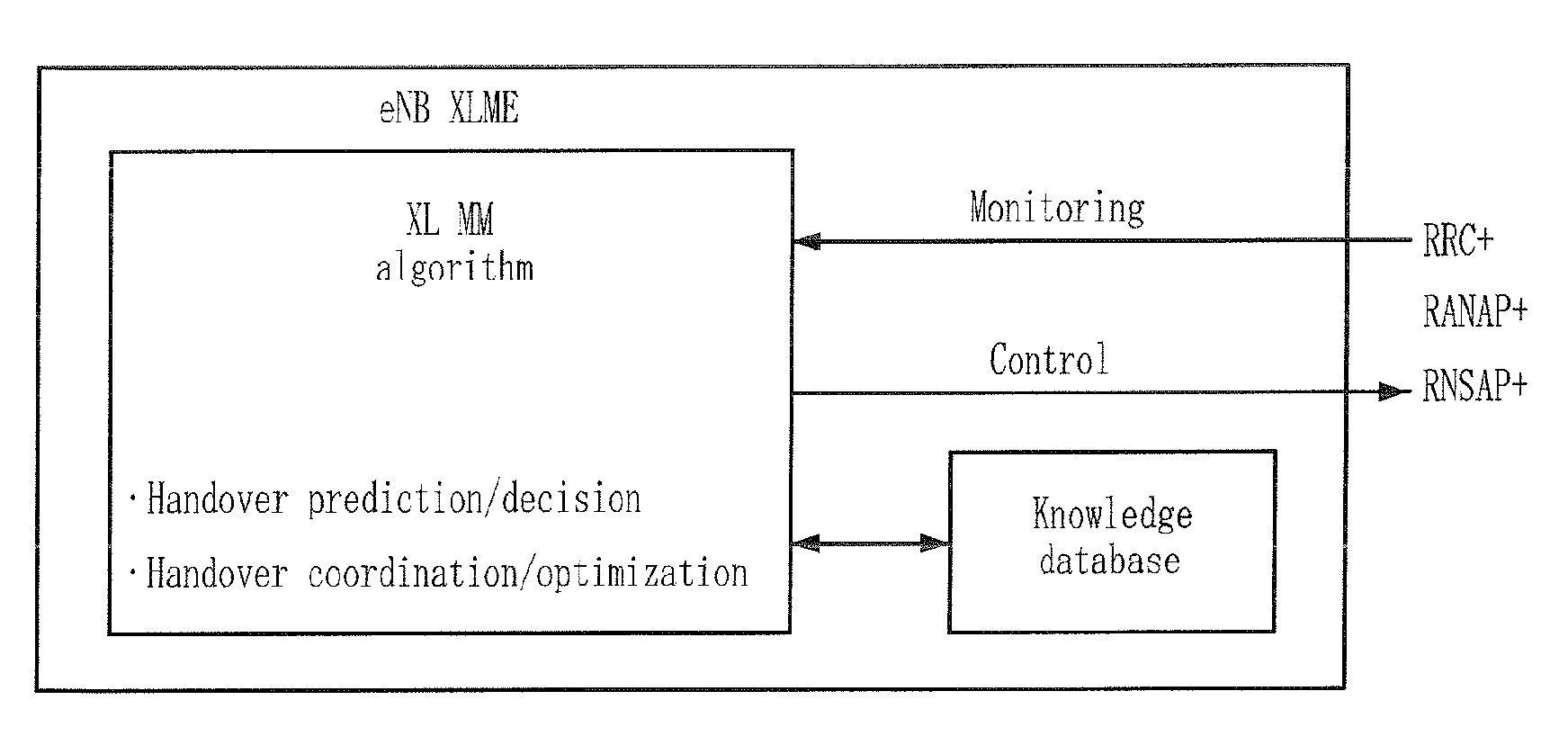
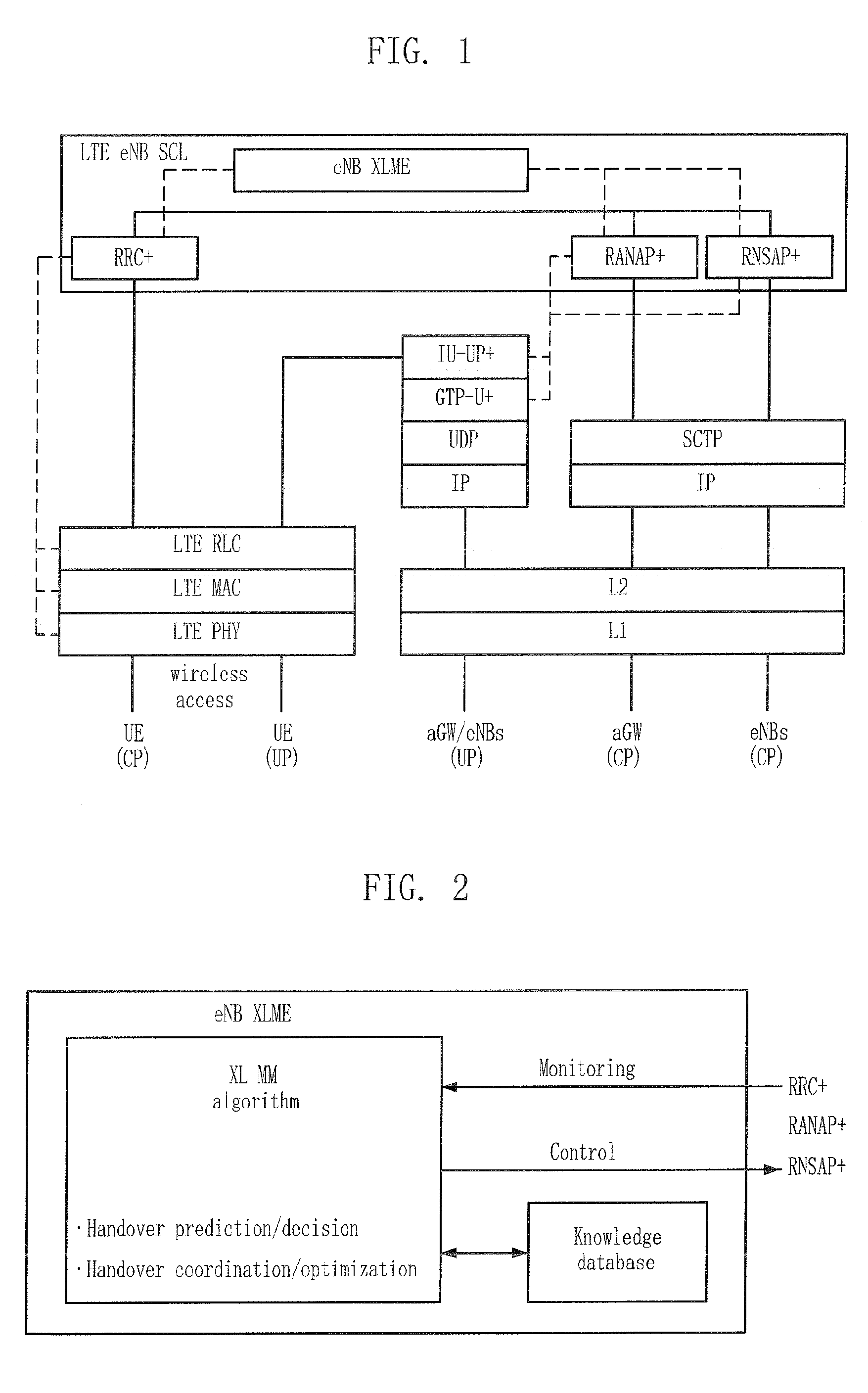
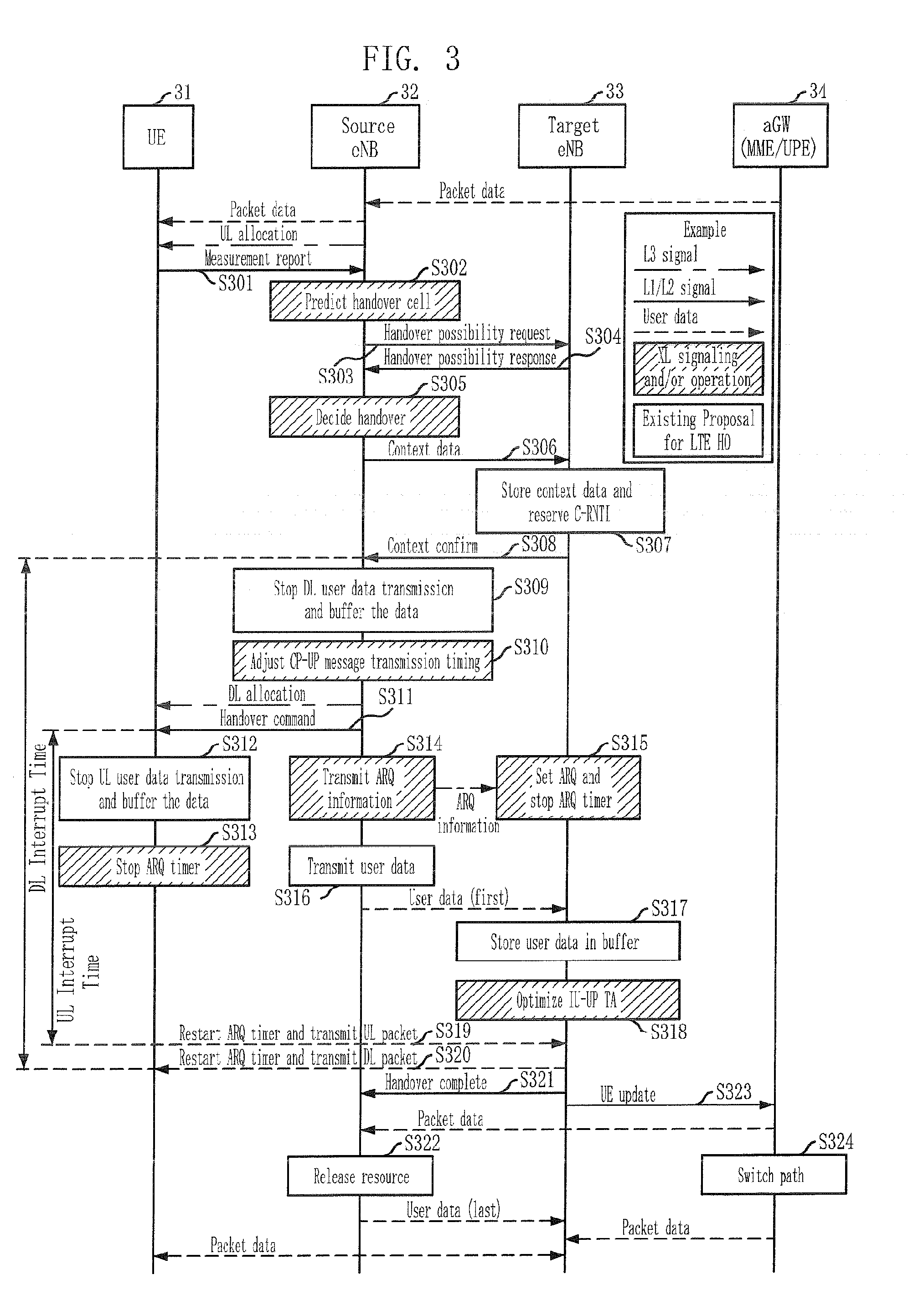
Method for managing cross-layer handover
ActiveUS20080130585A1Rapid and lossless and optimal handoverEasy to moveRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesHandoverSignal strength
Provided is a method for managing a cross-layer handover. The method includes the steps of: managing a predetermined number of neighbor cells as a handover candidate set based on signal strength and route estimation; transmitting a Measurement Report message having the handover candidate set information to a source base station according to a reporting event; and performing a handover according to a Handover Command message received from the source base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Frame level multimedia decoding with frame information table
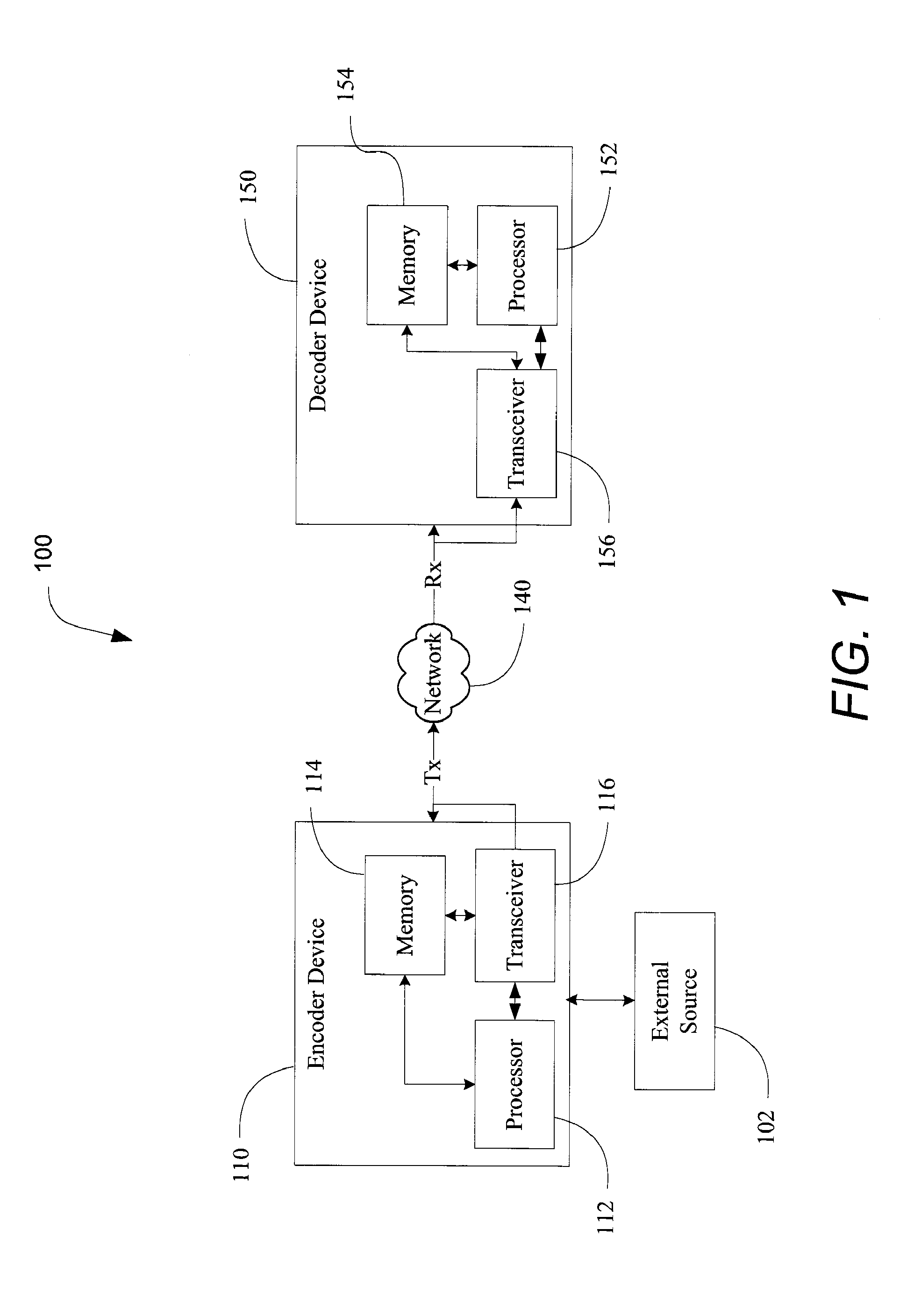
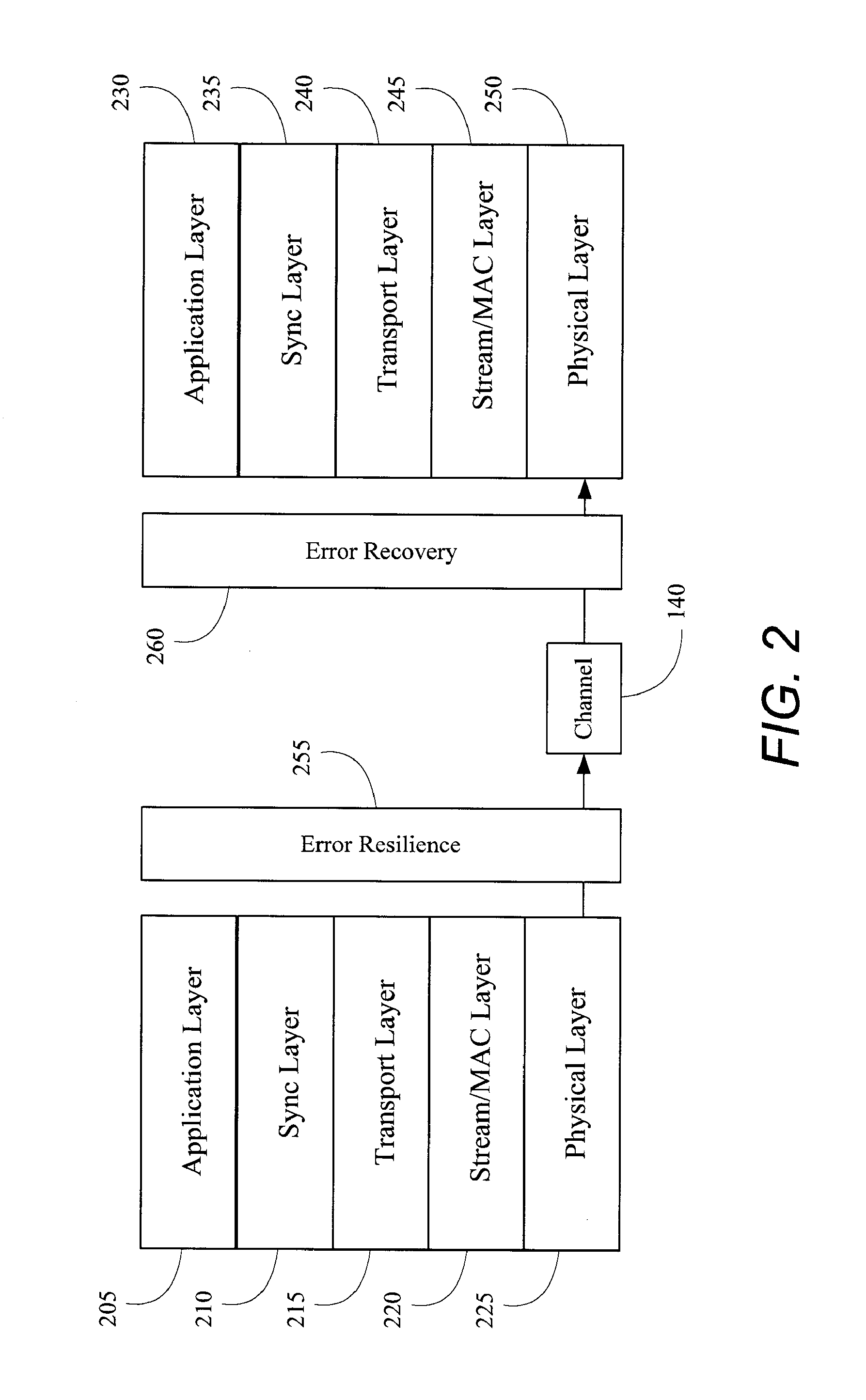
ActiveUS20070291836A1Improve errorImprove efficiencyError preventionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesScalable compressionEncoder decoder
Apparatus and method to decode video data while maintaining a target video quality using an integrated error control system including error detection, resynchronization and error recovery are described. Robust error control can be provided by a joint encoder-decoder functionality including multiple error resilience designs. In one aspect, error recovery may be an end-to-end integrated multi-layer error detection, resynchronization and recovery mechanism designed to achieve reliable error detection and error localization. The error recovery system may include cross-layer interaction of error detection, resynchronization and error recovery subsystems. In another aspect, error handling of a scalable coded bitstream is coordinated across a base-layer and enhancement layer of scalable compressed video.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
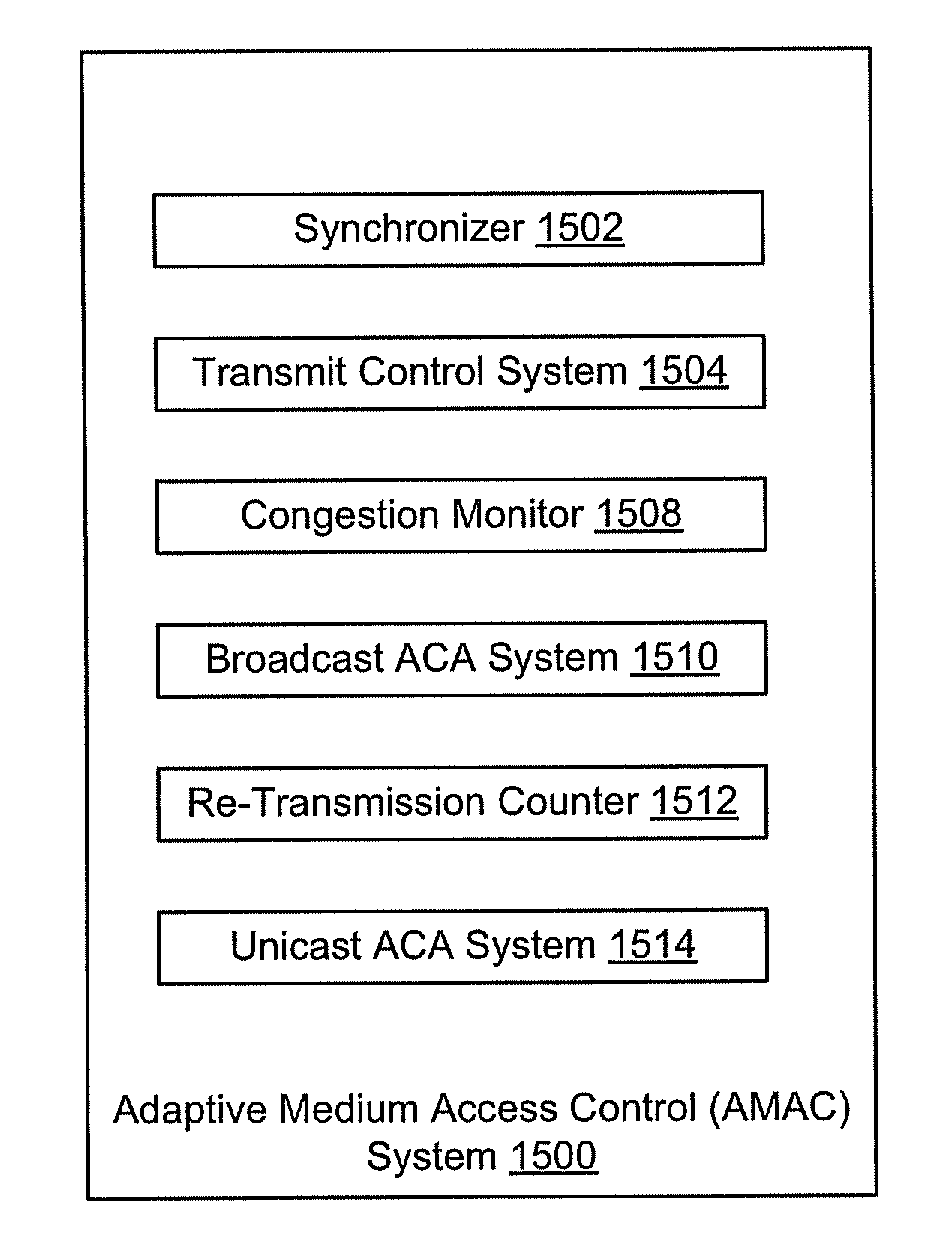
Adaptive Medium Access Control
ActiveUS20120182867A1Controlling the riskError preventionTransmission systemsPerformance enhancementTraffic flow
Bandwidth allocation configuration and fully decentralized adaptive medium access control (AMAC) systems and methods with support for time critical applications, spectrum efficiency, scalability enhancements, and fair allocation of bandwidth among nodes sharing a common channel. The methods fully integrate TDMA and CSMA / CA channel access approaches and incorporate adaptive congestion and collisions avoidance scheme to reduce bandwidth wastage and diminish adverse cross layers interactions. AMAC improves support for multi-media traffic while allowing higher transmission incidents from large number of transmitting devices sharing a common channel, with fair distribution of the available bandwidth, to enable improved multi-level-security connectivity over a common multi-hop wireless network, provide end-to-end performance enhancement for constant bit rate traffic, variable bit rate traffic, and distribute bandwidth fairly amongst competing TCP traffic flows that traverse varying length paths in multi-hop ad-hoc wireless networks.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A pedestrian and vehicle detection method and system based on improved YOLOv3
ActiveCN109815886ADetection matchHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMulti-label classificationVehicle detection
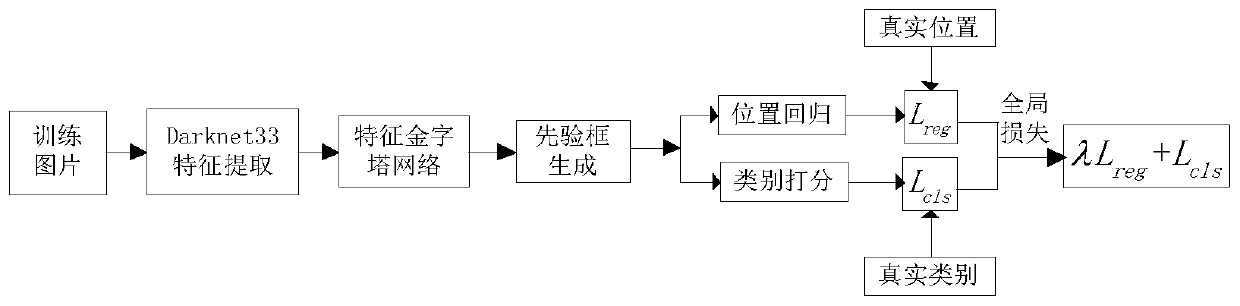
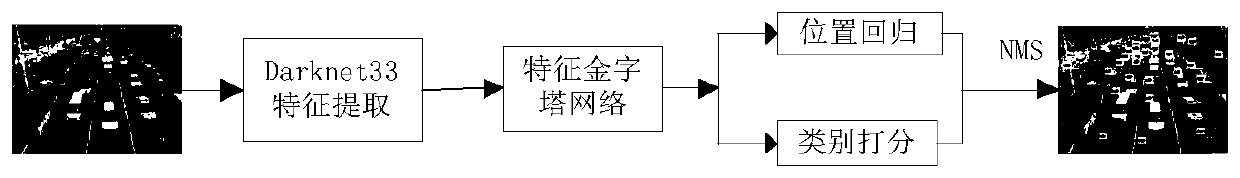
The invention discloses a pedestrian and vehicle detection method and system based on improved YOLOv3. According to the method, an improved YOLOv3 network based on Darknet-33 is adopted as a main network to extract features; the cross-layer fusion and reuse of multi-scale features in the backbone network are carried out by adopting a transmittable feature map scale reduction method; and then a feature pyramid network is constructed by adopting a scale amplification method. In the training stage, a K-means clustering method is used for clustering the training set, and the cross-to-parallel ratio of a prediction frame to a real frame is used as a similarity standard to select a priori frame; and then the BBox regression and the multi-label classification are performed according to the loss function. And in the detection stage, for all the detection frames, a non-maximum suppression method is adopted to remove redundant detection frames according to confidence scores and IOU values, and an optimal target object is predicted. According to the method, a feature extraction network Darknet-33 of feature map scale reduction fusion is adopted, a feature pyramid is constructed through feature map scale amplification migration fusion, and a priori frame is selected through clustering, so that the speed and precision of the pedestrian and vehicle detection can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for power management using distributed generation
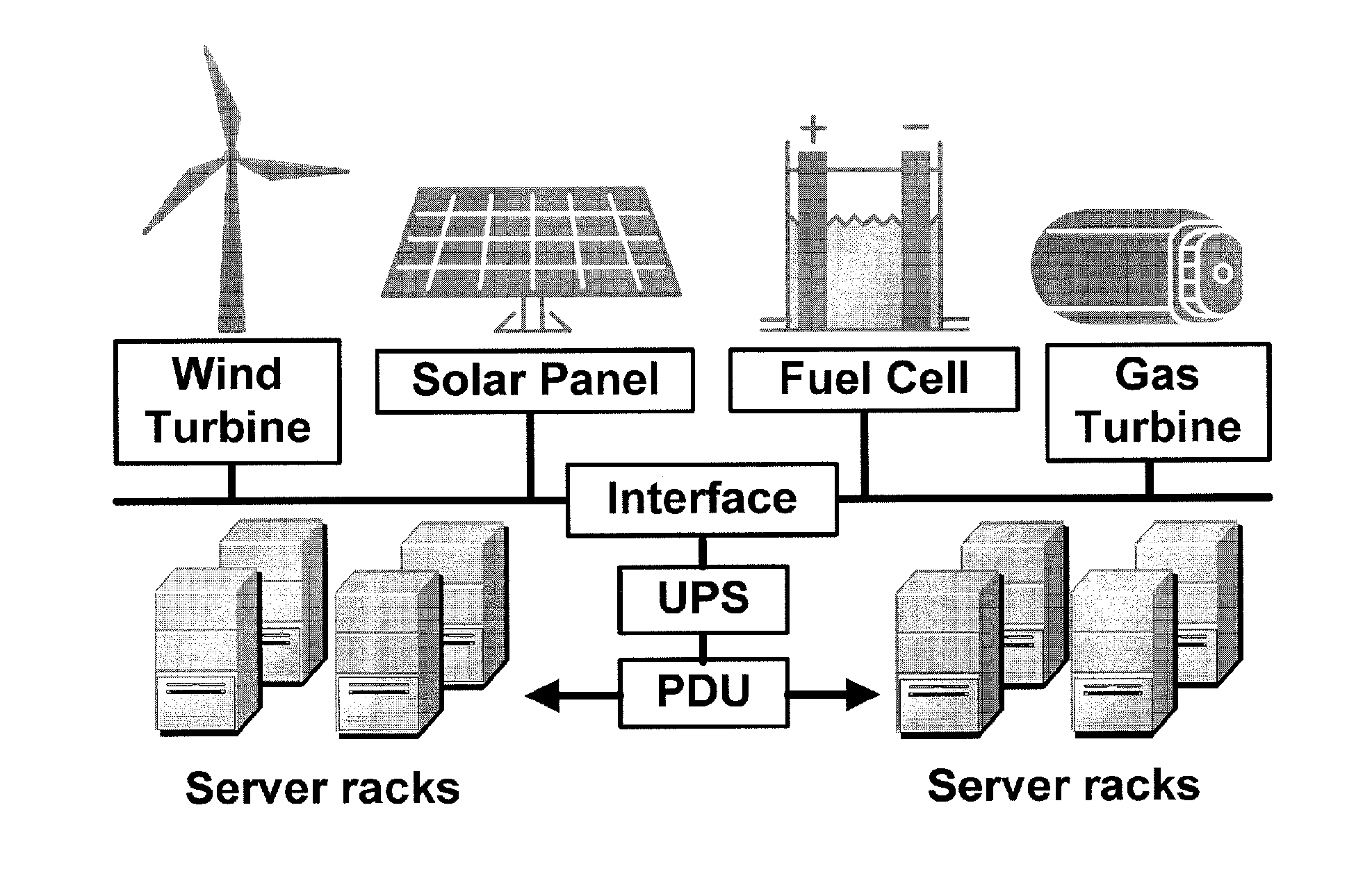
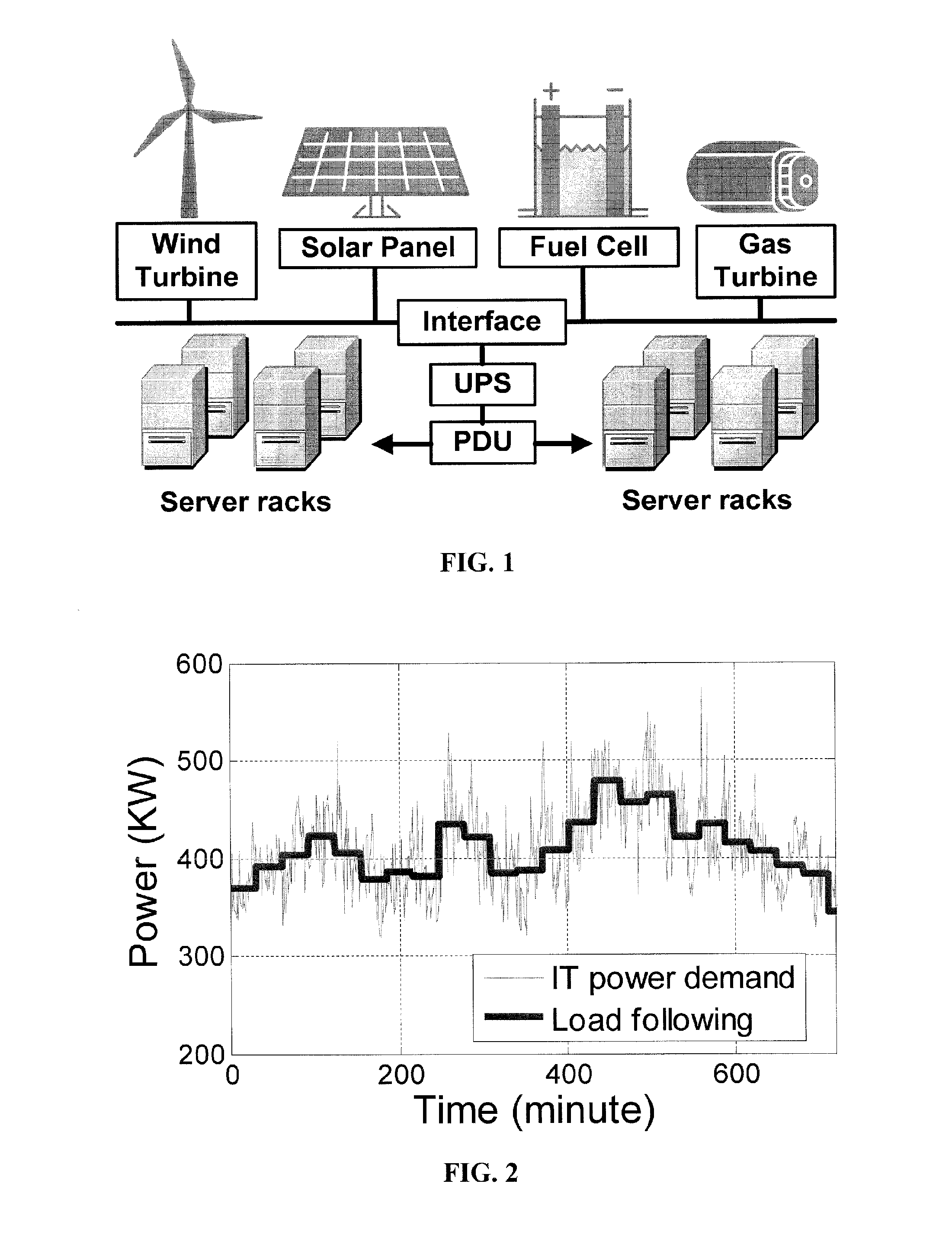
ActiveUS9800052B2Improve performanceReduce electricity loadGeneration forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsData centerEngineering
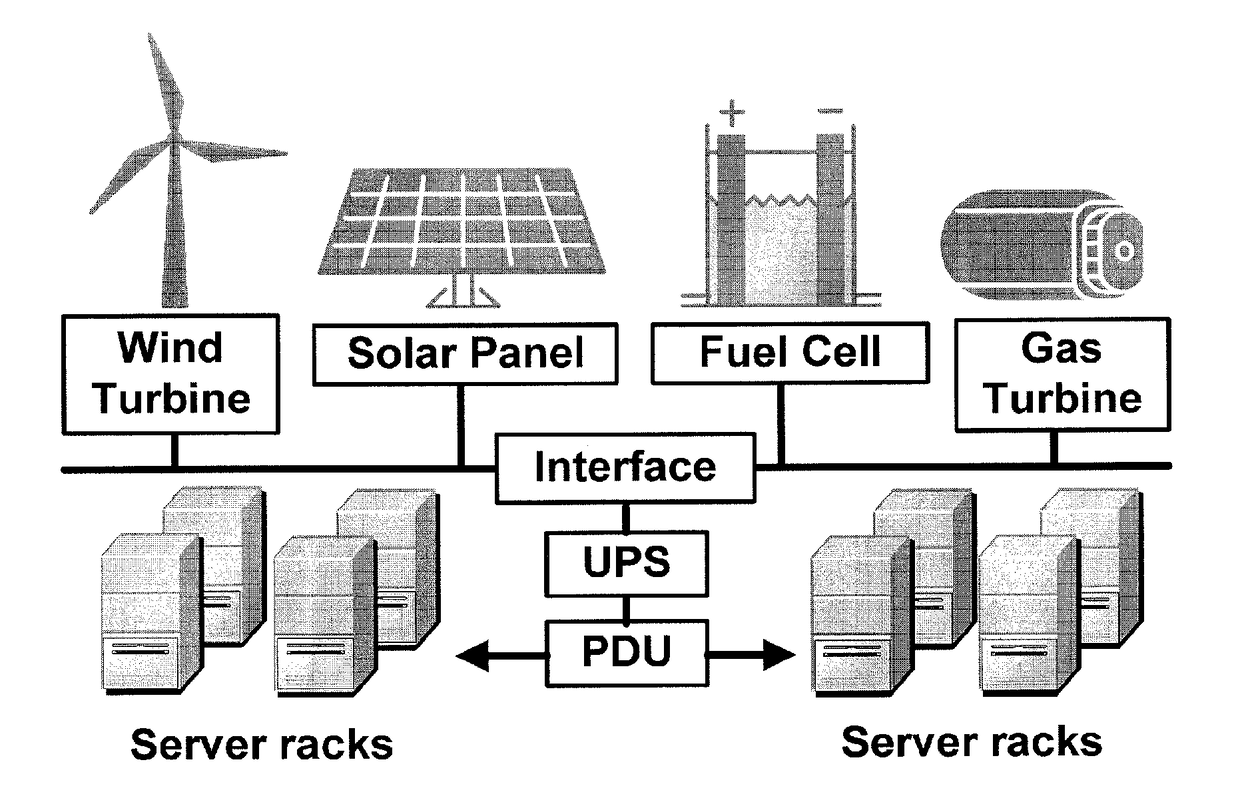
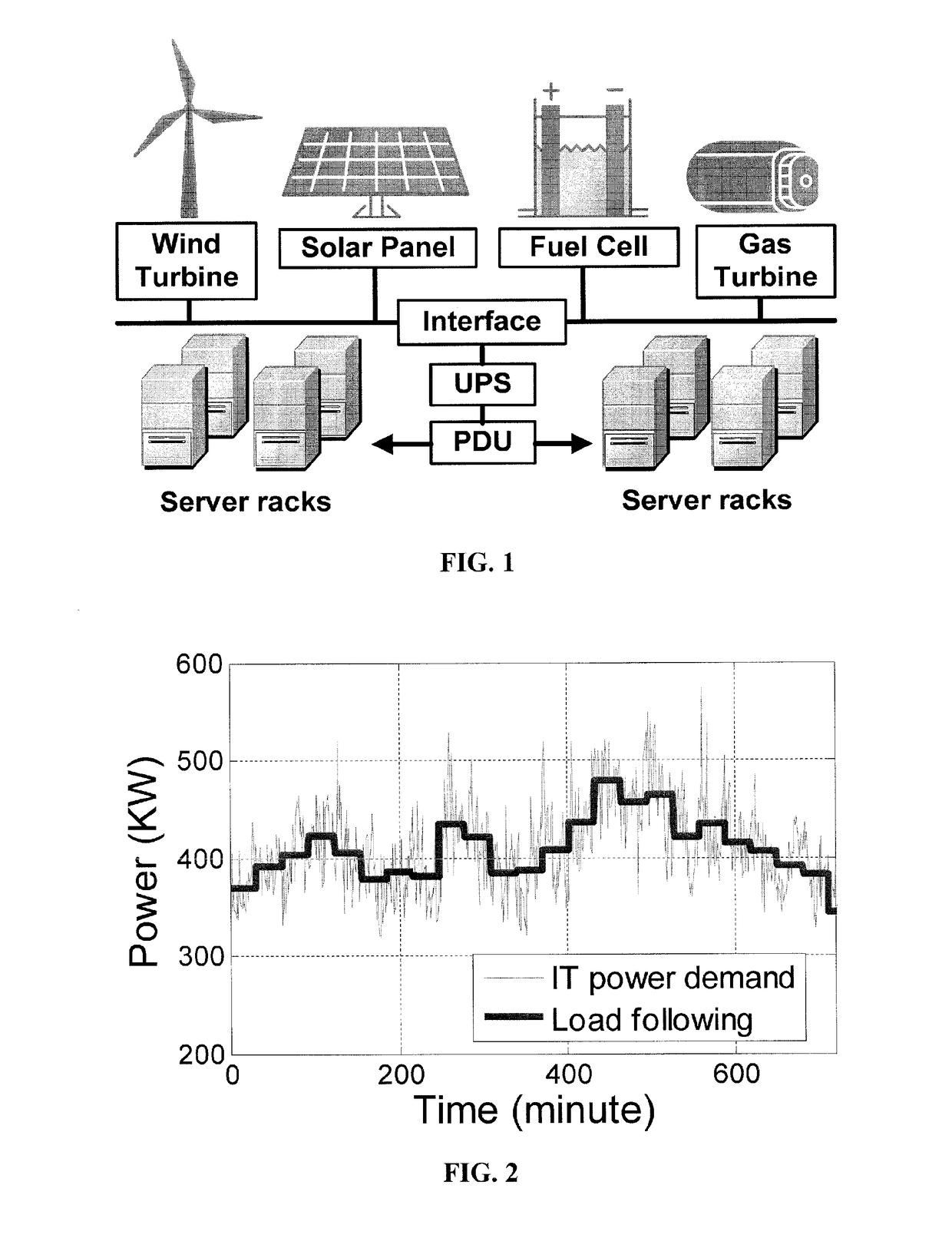
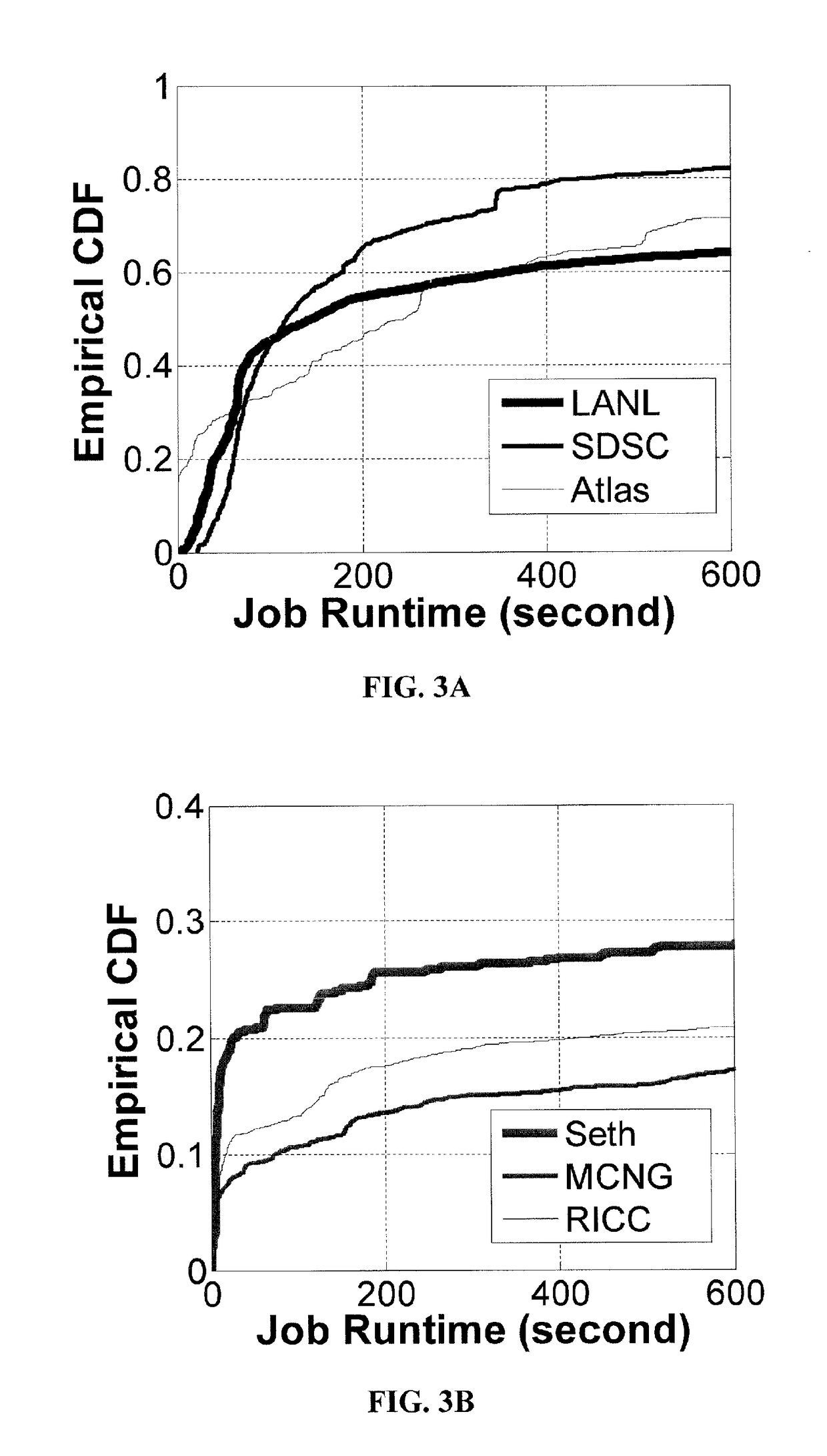
Embodiments relate to a method and system for power demand shaping (PDS) so as to manage power generation and use. Specific embodiments relate to data center power demand shaping to achieve high-performance low-overhead data center operation. Specific embodiments can incorporate standard (utility power) energy sources, renewable energy sources, or a combination of standard (utility power) energy sources and renewable energy sources. Embodiments of the subject PDS techniques can incorporate trimming the data center load power so as to allow DG systems to follow the power demand efficiently and / or incorporate two adaptive load tuning schemes that can boost data center performance and enable near-oracle operation during power demand trimming process. To implement a cross-layer power optimization scheme, embodiments of the subject invention relate to a power management module that can reside between front-end distributed generation and back-end computing facilities to provide a coordinated tuning between the supply and load.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Adaptive network system with online learning and autonomous cross-layer optimization for delay-sensitive applications
InactiveUS20110019693A1Sub-optimal performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexReliable transmissionNetworked system
A network system providing highly reliable transmission quality for delay-sensitive applications with online learning and cross-layer optimization is disclosed. Each protocol layer is deployed to select its own optimization strategies, and cooperates with other layers to maximize the overall utility. This framework adheres to defined layered network architecture, allows layers to determine their own protocol parameters, and exchange only limited information with other layers. The network system considers heterogeneous and dynamically changing characteristics of delay-sensitive applications and the underlying time-varying network conditions, to perform cross-layer optimization. Data units (DUs), both independently decodable DUs and interdependent DUs, are considered. The optimization considers how the cross-layer strategies selected for one DU will impact its neighboring DUs and the DUs that depend on it. While attributes of future DU and network conditions may be unknown in real-time applications, the impact of current cross-layer actions on future DUs can be characterized by a state-value function in the Markov decision process (MDP) framework. Based on the dynamic programming solution to the MDP, the network system utilizes a low-complexity cross-layer optimization algorithm using online learning for each DU transmission.
Owner:SANYO NORTH AMERICA CORP +1
Optimizing the usage of radio resources by cross-layer reading of information from higher level control plane protocol layer
ActiveUS20110032898A1Improve control plane related qualitySave resource costNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsCellular radioRadio networks
Methods and apparatuses relating to optimization of radio network resources between user equipments operating in a cell and nodes in a cellular radio communication network are provided. Cross-layer information is read from higher level control plane protocol layer packets being transported, before or during lower level control plane protocol layer procedures being performed between a user equipment and a node or between two nodes The lower level control plane protocol layer procedures are optimized by using the analyzed control plane information received.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
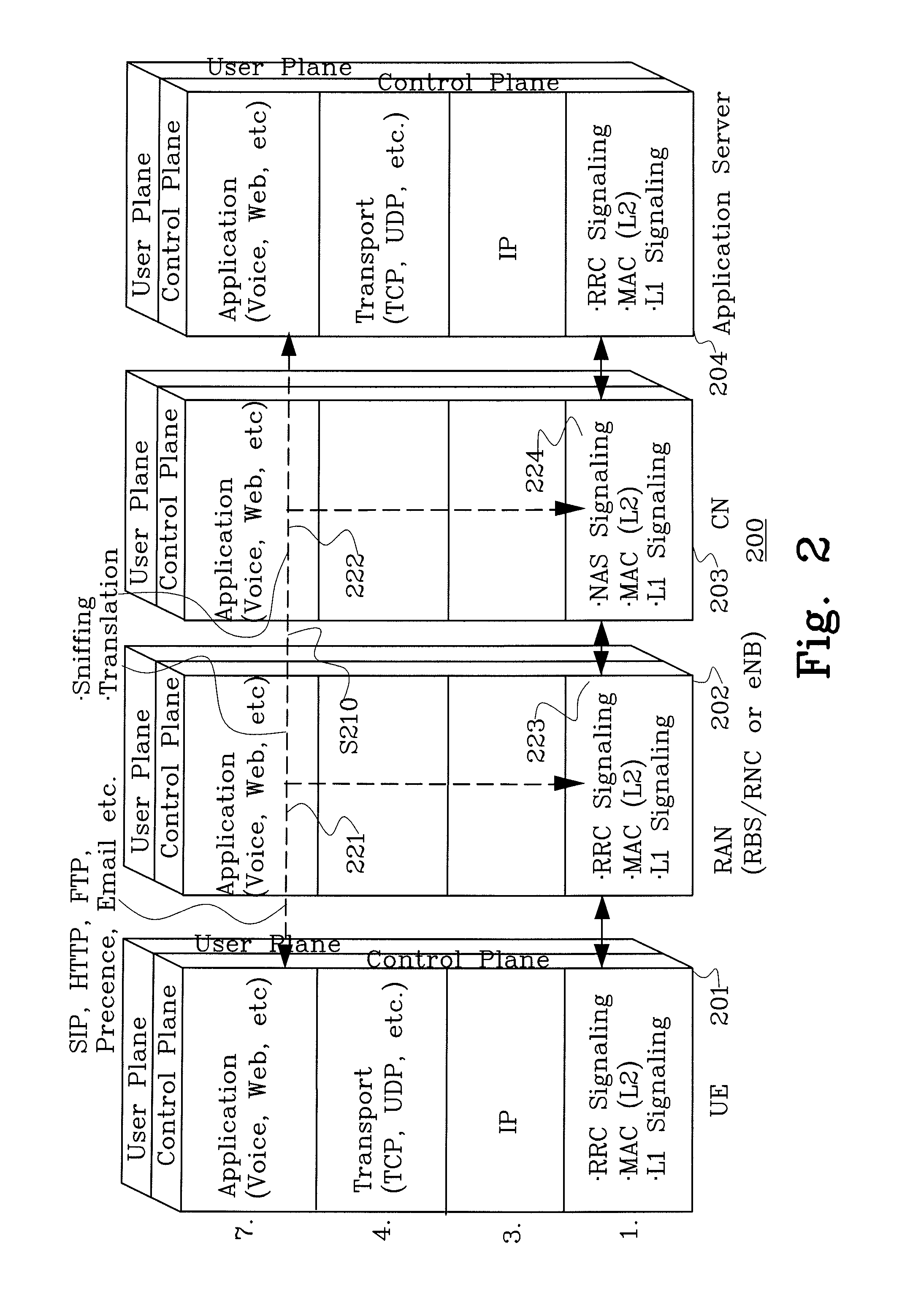
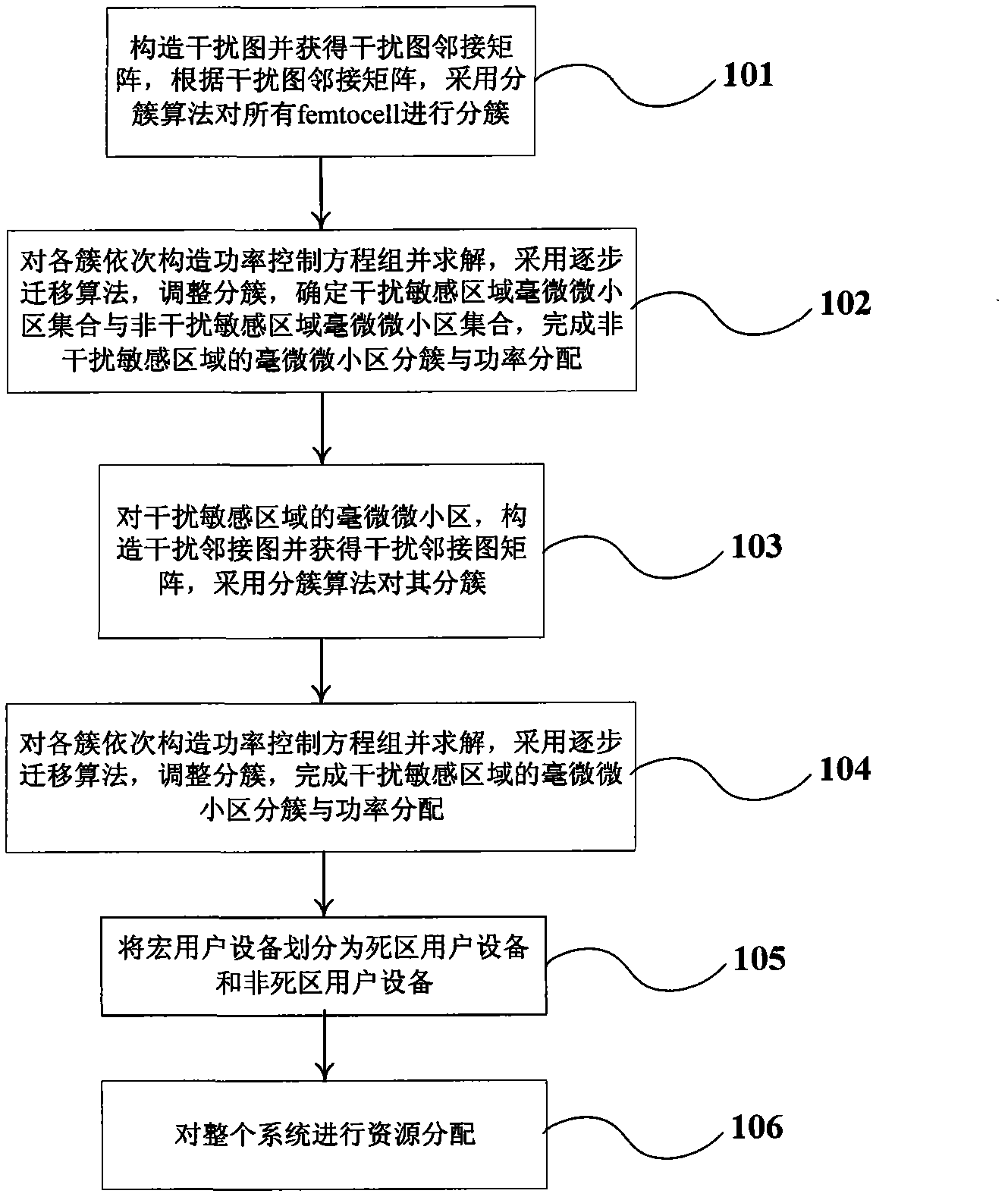
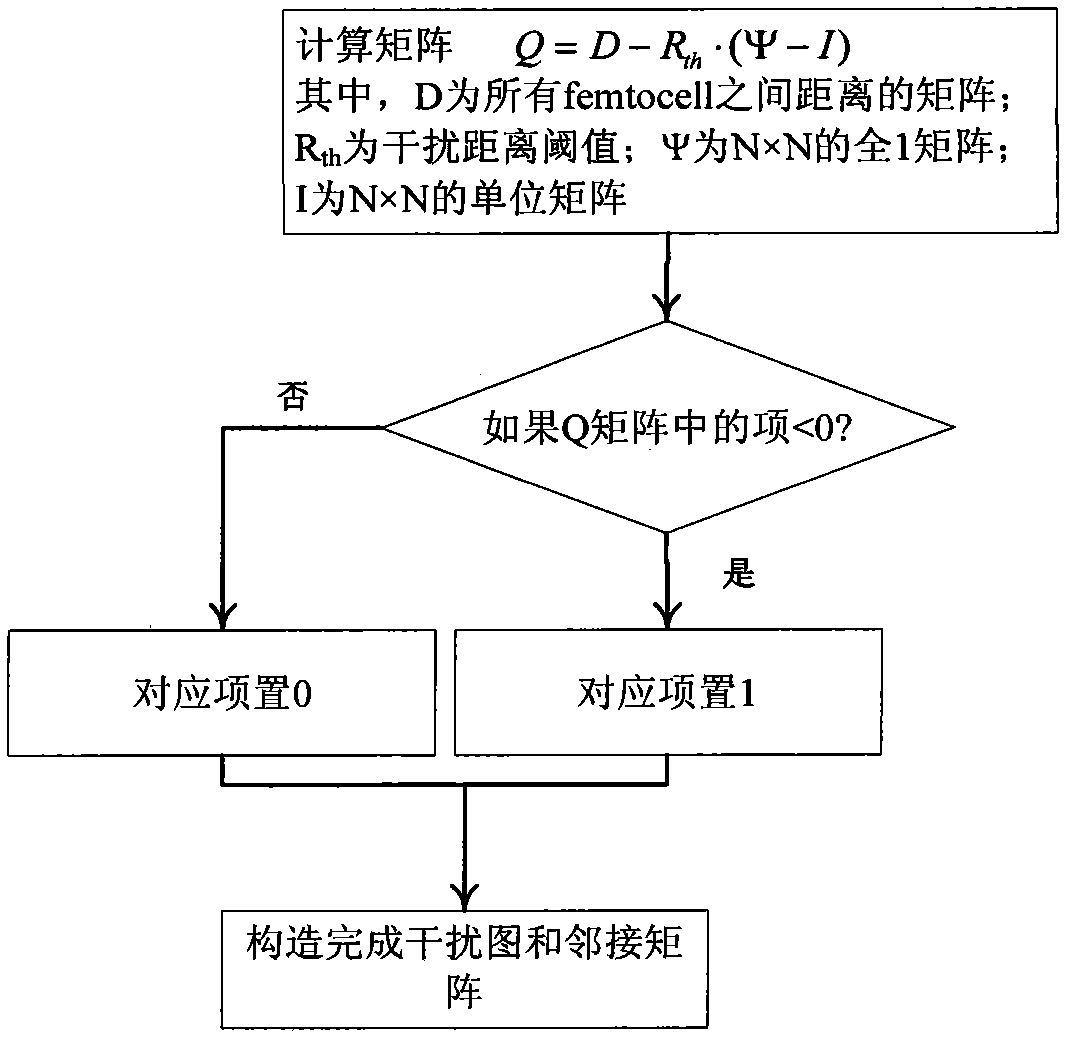
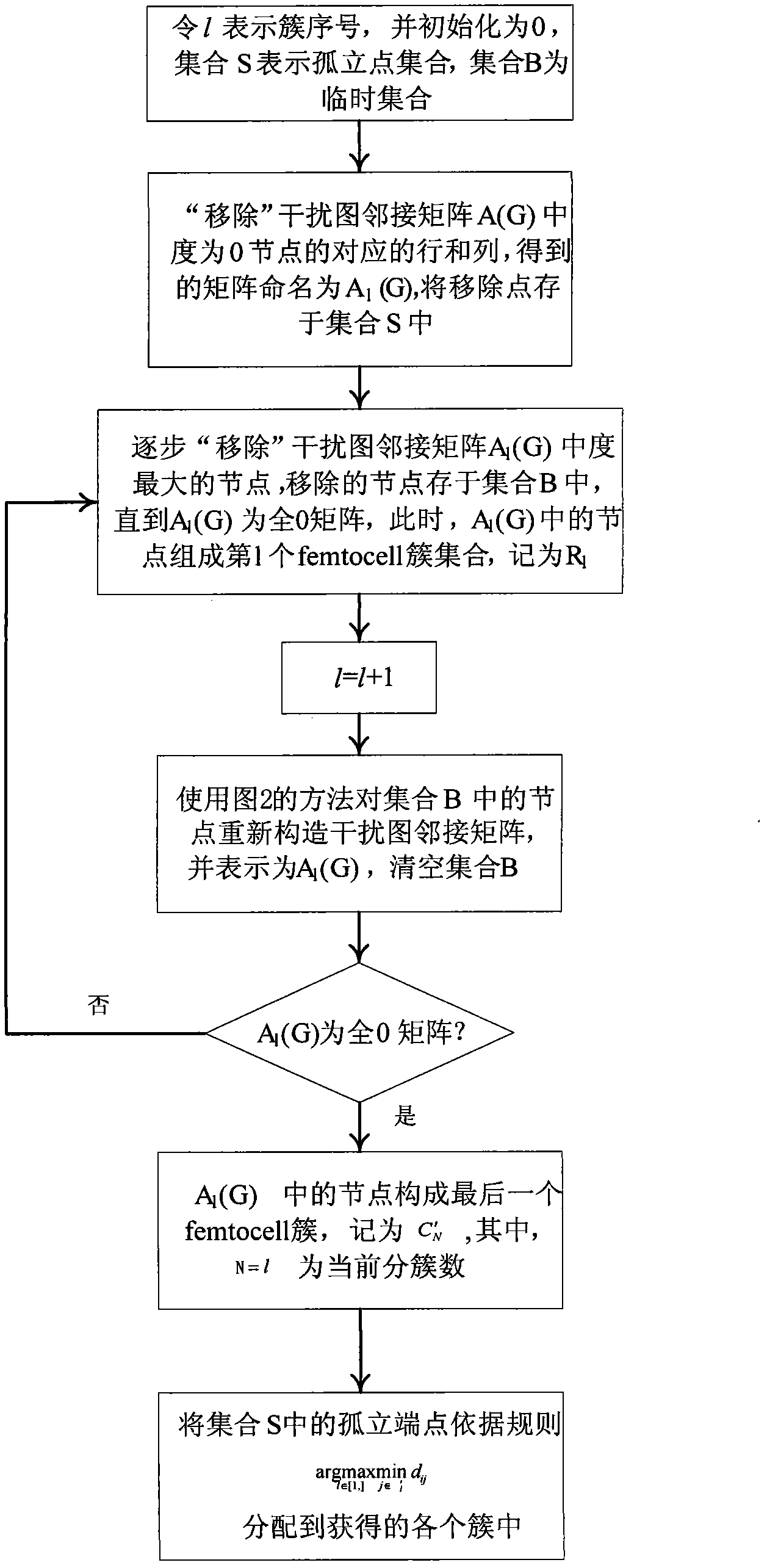
Interference suppression method of hybrid network of macrocell and Femtocell
InactiveCN102006599AImprove Spectrum Utilization EfficiencyIncrease system capacityPower managementNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
The invention discloses an interference suppression method of a hybrid network of macrocell and Femtocell. The method comprises the following steps: the Femtocell in a certain range is clustered; the transmission power of the femto base station in the cluster; the clustering situation of the Femtocell is adjusted; the Femtocell in an interference sensitive area is clustered; for the Femtocell of the clustered interference sensitive area, the transmission power of the femto base station in the cluster is controlled by using the cluster as unit; the clustering situation of the Femtocell in the interference sensitive area is adjusted, the Femtocell cluster in the interference sensitive area is determined; the micro user equipment is divided into a dead zone user equipment and a non-dead zoneuser equipment; spectrum resources are divided into three nonoverlapping parts; and the spectrum resources are distributed for the Femtocell in the interference sensitive area, the dead zone user equipment, the Femtocell in the non-interference sensitive area and the non-dead zone user equipment. By adopting the method of the invention, the spectrum utilization efficiency and system capacity of the overlapped double-layer network of the macrocell and the Femtocell, and the problems of the cross-layer interference between the macrocell and the Femtocell and the same-layer interference of the Femtocell can be effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for power management using distributed generation
ActiveUS20160013652A1Sufficient performanceImprove load following efficiencyGeneration forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsData centerEngineering
Embodiments relate to a method and system for power demand shaping (PDS) so as to manage power generation and use. Specific embodiments relate to data center power demand shaping to achieve high-performance low-overhead data center operation. Specific embodiments can incorporate standard (utility power) energy sources, renewable energy sources, or a combination of standard (utility power) energy sources and renewable energy sources. Embodiments of the subject PDS techniques can incorporate trimming the data center load power so as to allow DG systems to follow the power demand efficiently and / or incorporate two adaptive load tuning schemes that can boost data center performance and enable near-oracle operation during power demand trimming process. To implement a cross-layer power optimization scheme, embodiments of the subject invention relate to a power management module that can reside between front-end distributed generation and back-end computing facilities to provide a coordinated tuning between the supply and load.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
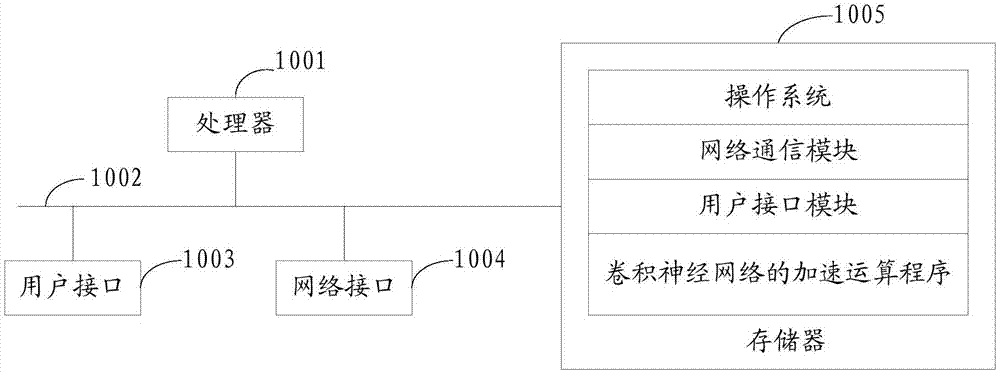
Accelerated operation method and server for convolutional neural network, and storage medium
ActiveCN107451654AIncrease computing speedImprove resource usage efficiencyNeural architecturesInteraction timeInternal memory
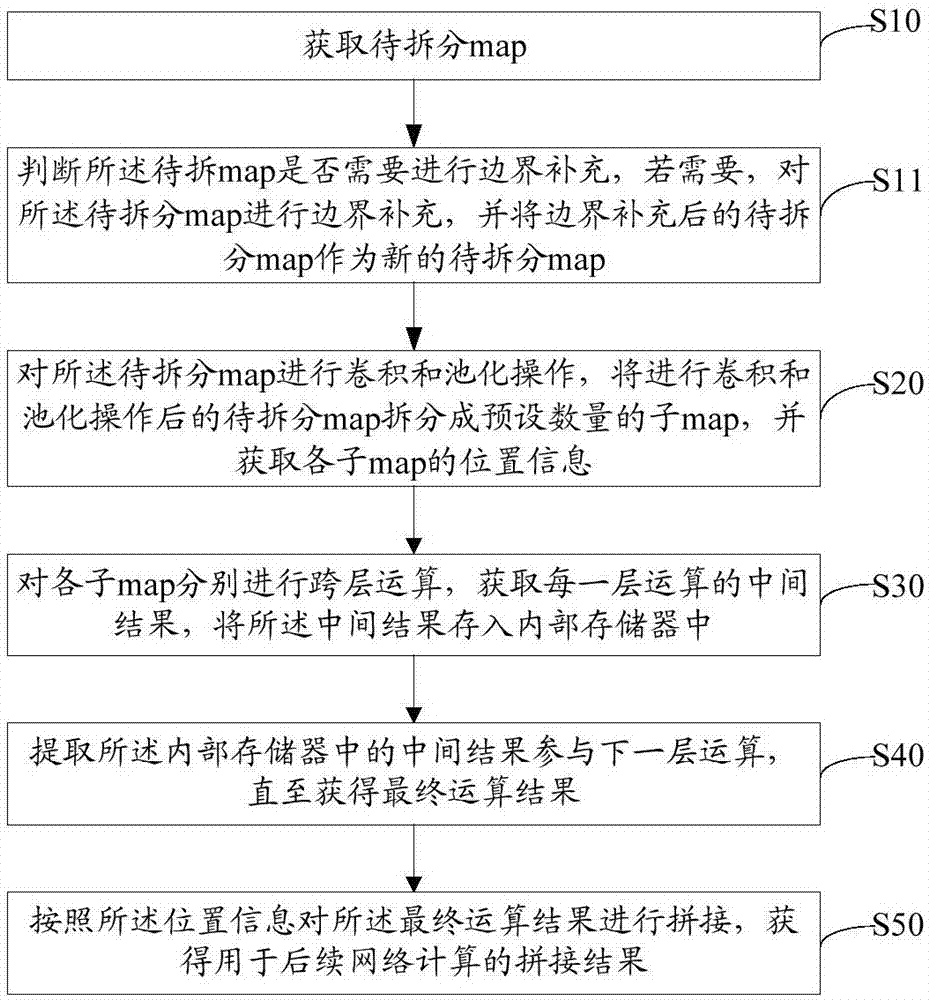
The invention discloses an accelerated operation method and server for a convolutional neural network, and a storage medium. A map to be split is split into a preset quantity of sub-maps, and the position information of each sub-map is obtained; each sub-map is independently subjected to cross-layer operation; an intermediate result of each-layer operation is obtained and is stored into an internal memory to extract the intermediate result in the internal memory so as to participate in next-layer operation; therefore, the internal memory is fully utilized, resources are reused, interaction time with an external memory is shortened, the operation speed and the resource use efficiency of the CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) are greatly improved, and therefore, the CNN can efficiently operate at a high speed in an embedded terminal.
Owner:深圳市自行科技有限公司
Intelligent demand response and demand side optimizing operation system
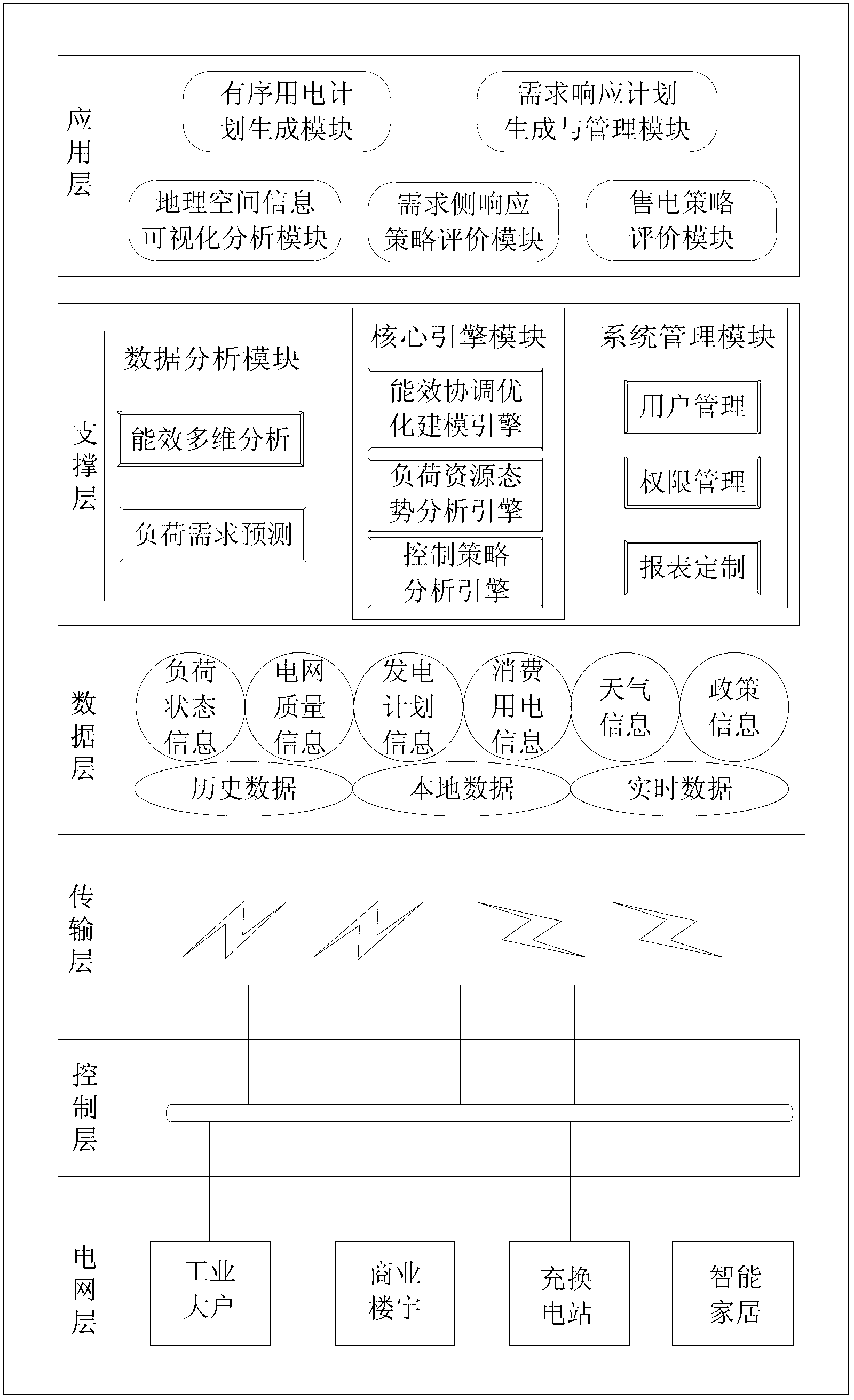
ActiveCN103259335AWide rangeLarge areaAc network load balancingSystems intergating technologiesSystems designControl layer
The invention provides an intelligent demand response and demand side optimizing operation system which comprises a power grid layer, a control layer, a transmission layer, a data layer, a supporting layer and an application layer. The layers can be divided scientifically, reasonably and clearly so that system design can be optimized and a procedure is standardized. Each layer is relatively independent. Each layer offers service for the upper layer through an interface and each layer calls the service of the lower layer through an interface, so that a data flow is transmitted between two adjacent layers. Cross-layer calling does not exist. The layers are divided reasonably, so that compatibility and expansibility are enhanced and coupling degree among different networks is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
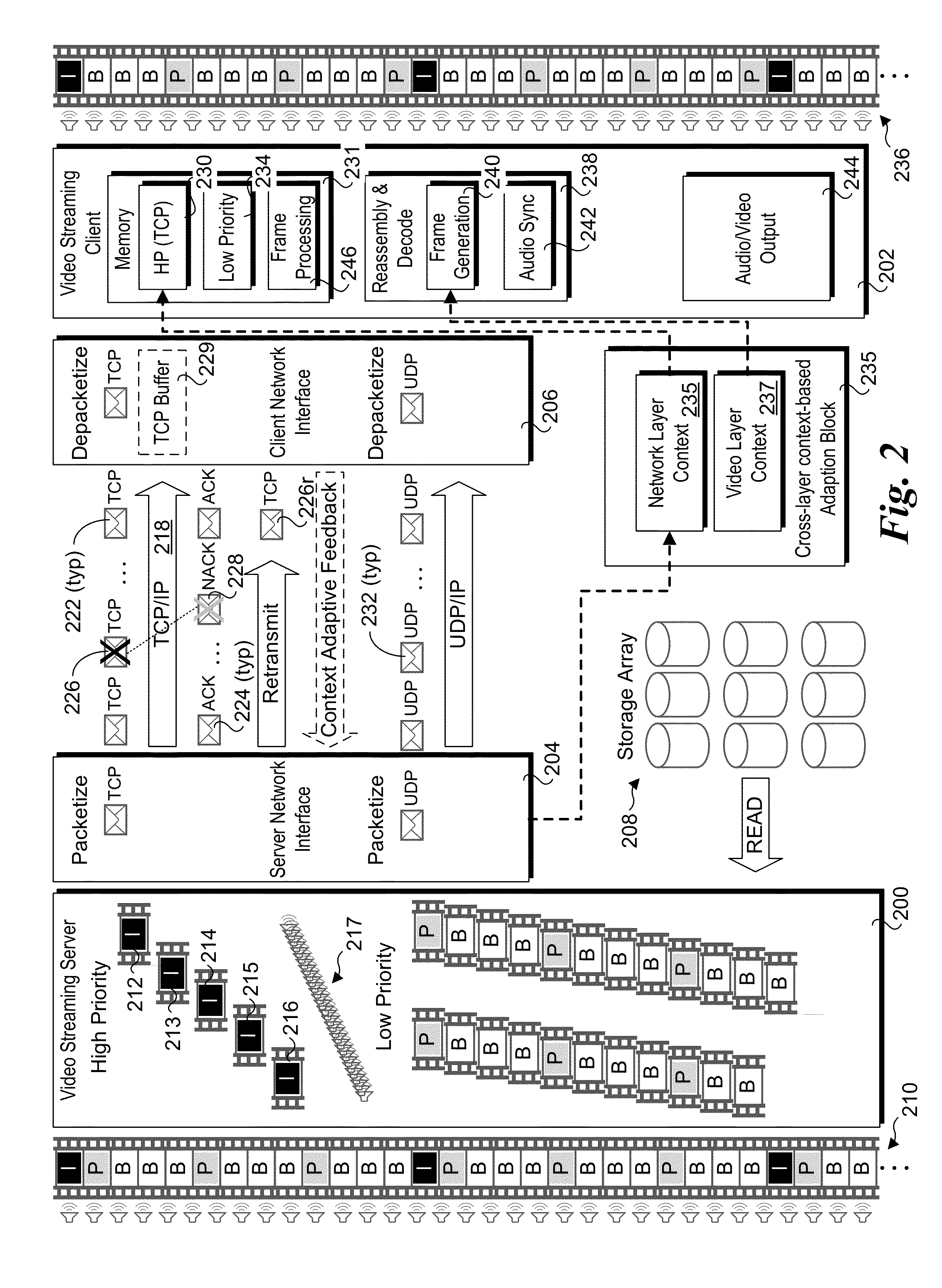
Multiple network transport sessions to provide context adaptive video streaming
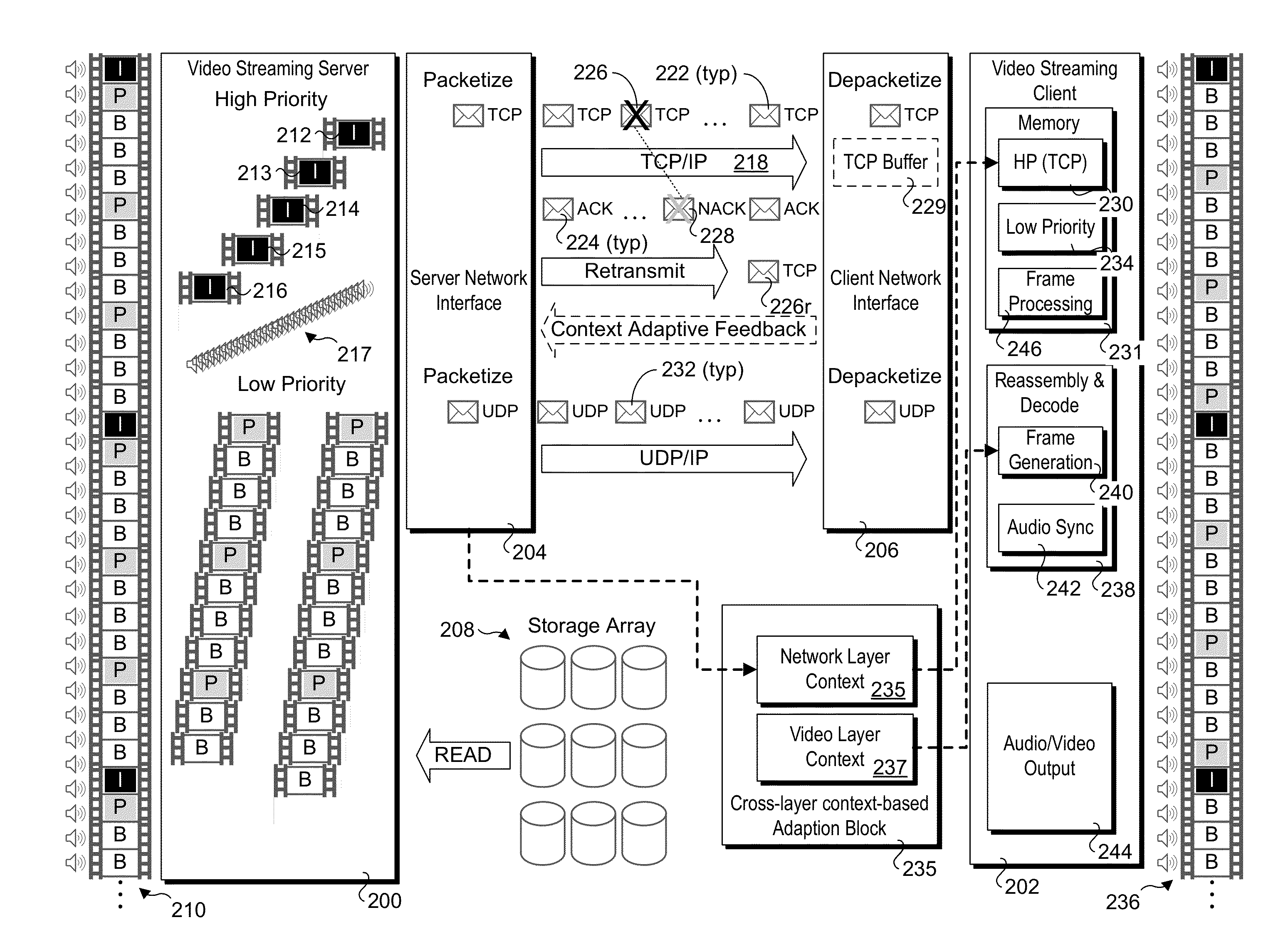
Methods, apparatus, systems, and software for implementing context adaptive video streaming using multiple streaming connections. Original video content is split into multiple bitstreams at a video streaming server and streamed to a video streaming client. Higher-importance video content, such as I-frames and the base layer for scalable video coder (SVC) content are streamed over a high-priority streaming connection, while lower-importance video content is streamed over a low-priority streaming connection. The high-priority streaming connection may employ a reliable connection protocol such as TCP protocol, while the lower-priority connection may employ UDP or a modified TCP protocol under which some portions of the bitstream may be dropped. Cross-layer context adaptive streaming may be implemented under which context data such as network context and video application context information may be considered to adjust parameters associated with implement one or more streaming connections.
Owner:INTEL CORP
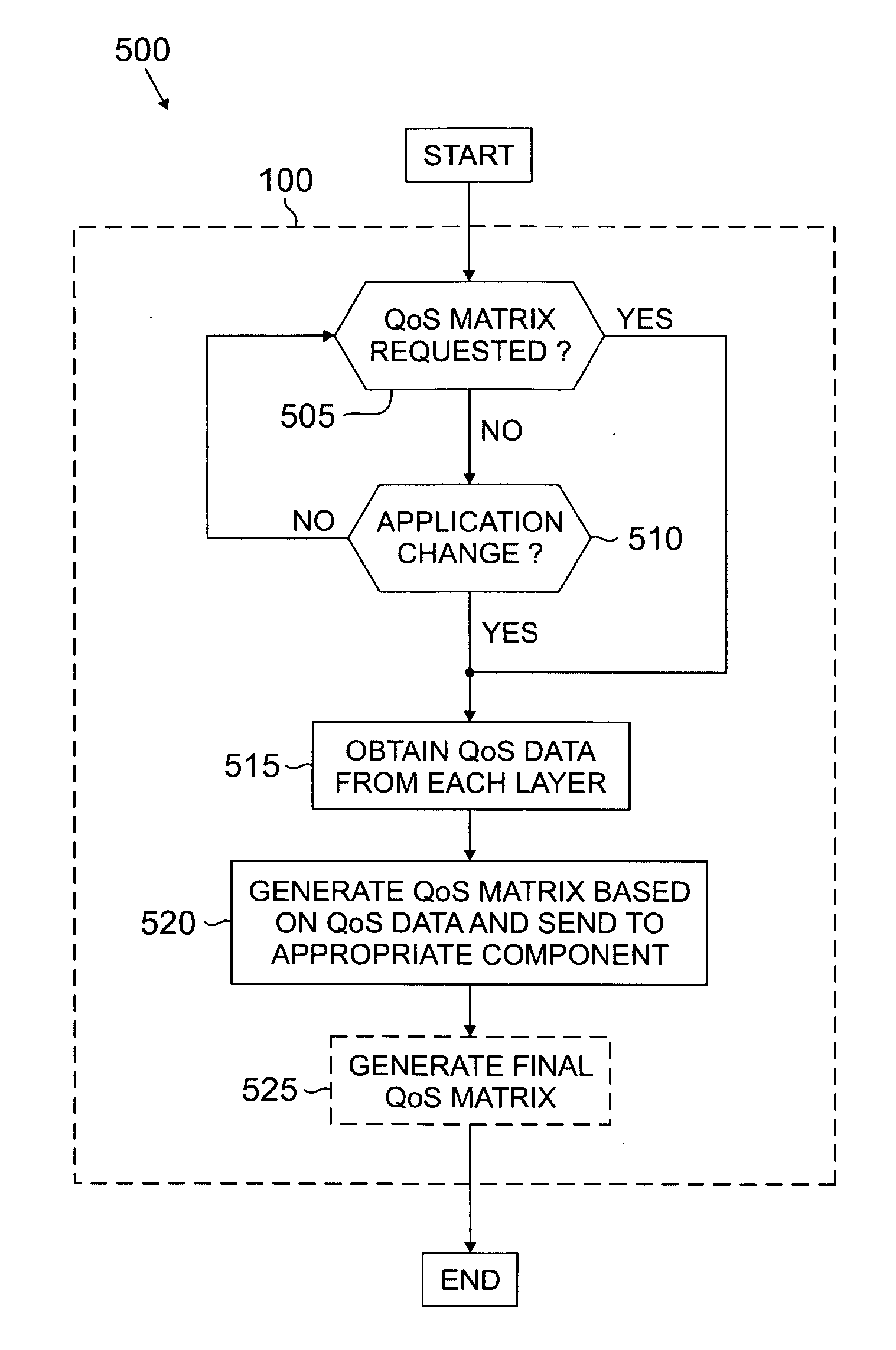
Method and system for providing cross-layer quality-of-service functionality in a wireless network
InactiveUS20050286438A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceNetsniff-ng
A method for providing cross-layer quality-of-service (QoS) functionality in a wireless network is provided. The method includes obtaining QoS data from each layer of an application stack for a particular application. A QoS matrix is generated based on the obtained QoS data. Packet distribution for the particular application may then be prioritized based on the QoS matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive cross-layer cross-node optimization
ActiveUS20070266134A1Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsCross-layer optimizationCommunications system
Methods and systems for adaptive cross-layer cross-node optimization in wireless communication systems are provided. Adaptive cross-layer cross-node optimization allows for conventional cross-layer optimization coupled with the ability to adaptively optimize cross-layer interactions across node boundaries. In one aspect, adaptive cross-layer cross-node optimization includes adaptively and dynamically shifting functions / layers among nodes in a network, so that a global network objective is achieved. In another aspect, adaptive cross-layer cross-node optimization includes adaptively and dynamically distributing functions / layers across a network, according to changes and / or events in the network. In a further aspect, adaptive cross-layer cross-node optimization includes dynamically defining or changing individual node functions within a network, so that a global network functionality may emerge.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
Method and Apparatus for Cross Layer Resource Allocation for Wireless Backhaul Networks
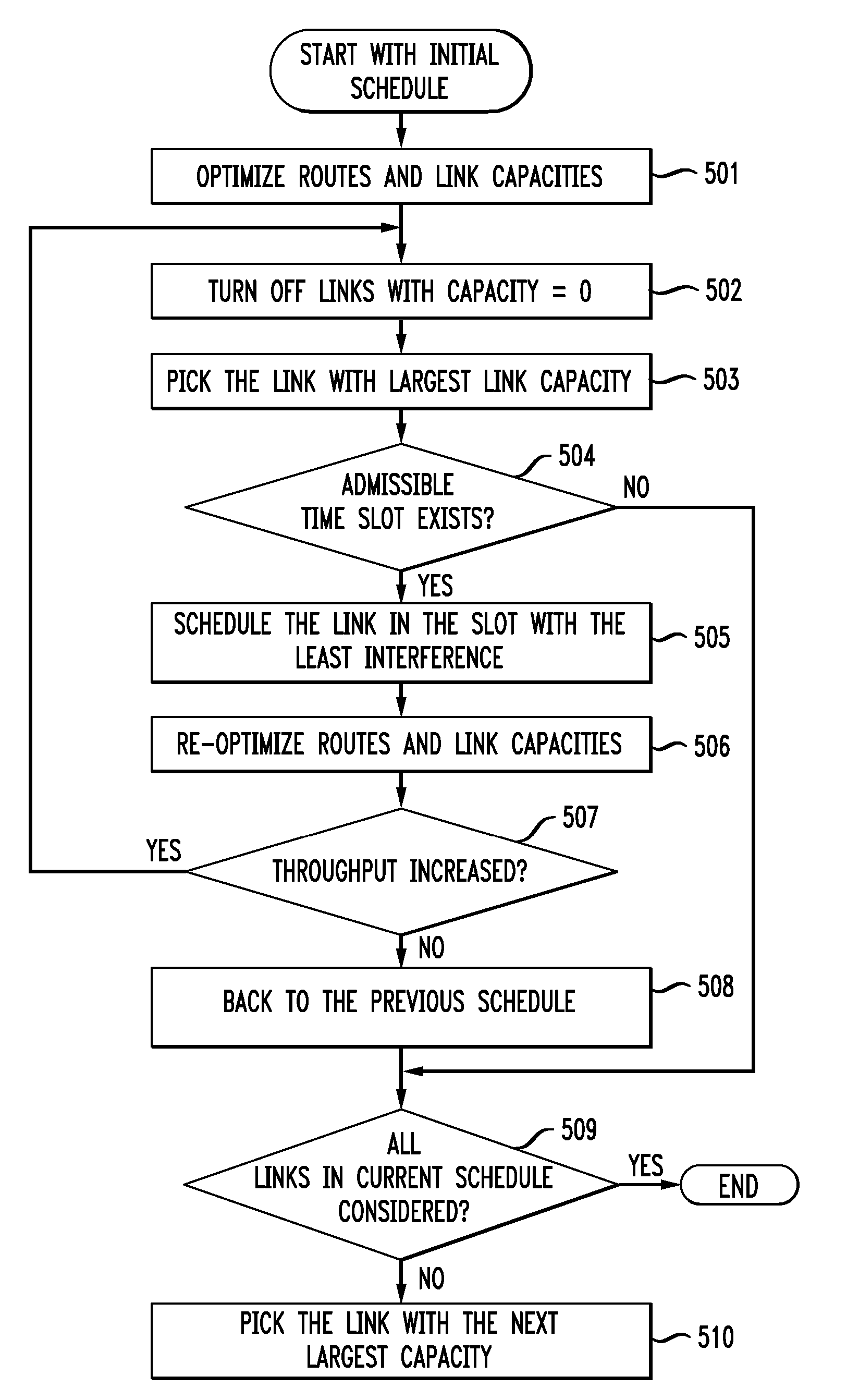
InactiveUS20070111757A1Optimal transmission throughputSet become largePower managementNetwork topologiesTransmitted powerWeighted independent set
Owner:NEC CORP
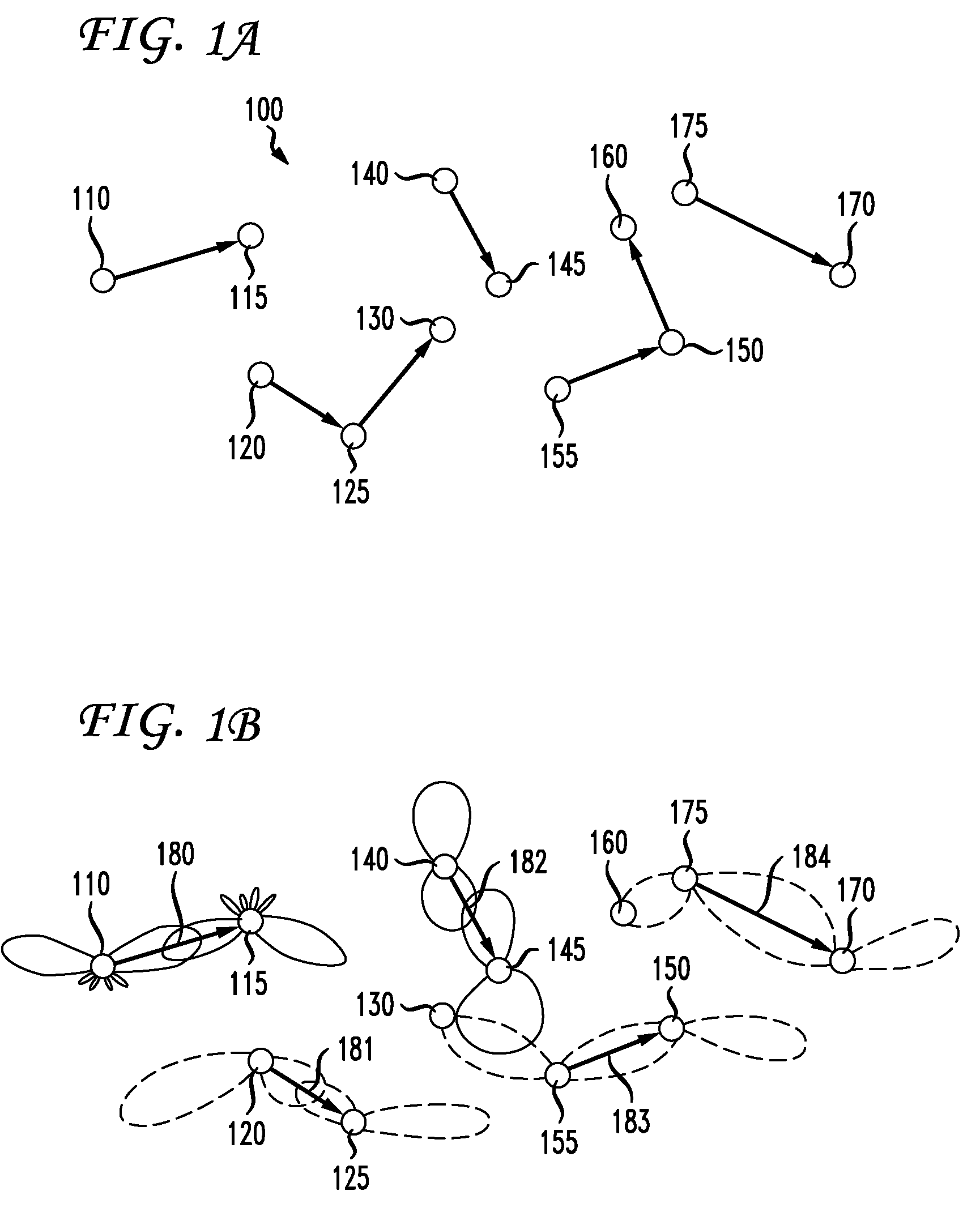
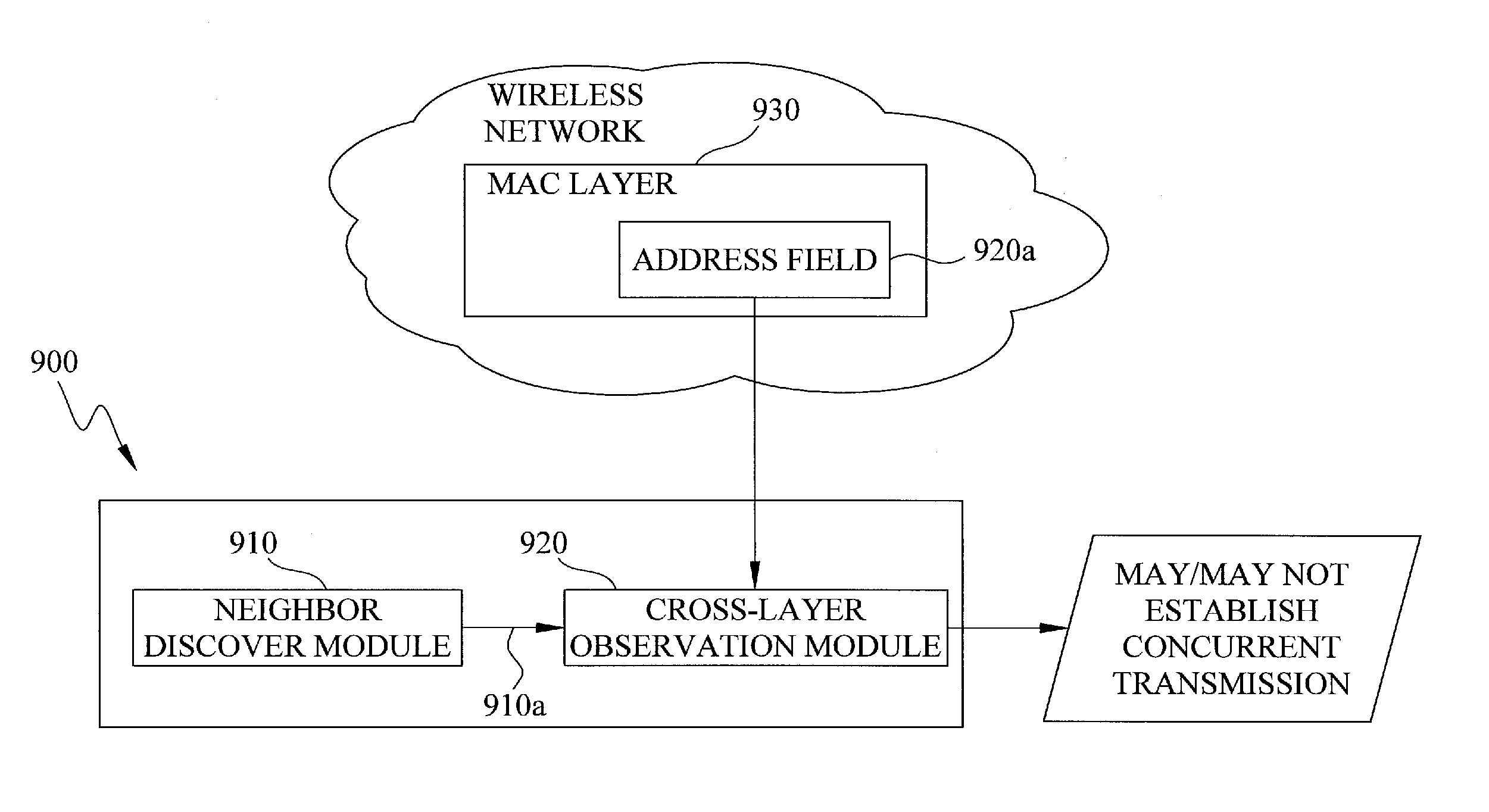
Apparatus And Method For Neighbor-Aware Concurrent Transmission Media Access Control Protocol
InactiveUS20110038358A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesTopology informationMedia access control
An apparatus and method for neighbor-aware concurrent transmission media access control (MAC) protocol is provided, which determines whether a plurality of communication connections may be established concurrently in a wireless network, where each node in the network obtains the topology information of its multi-hop neighbors via a neighbor discover module. A cross-layer observation module integrates the physical and virtual carrier sensing, observes the address field of a control frame of a MAC layer in the wireless network, and compares the address field information of the control frame against the topology information obtained by the neighbor discover module to determine whether a plurality of connections may be established for concurrent transmission.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
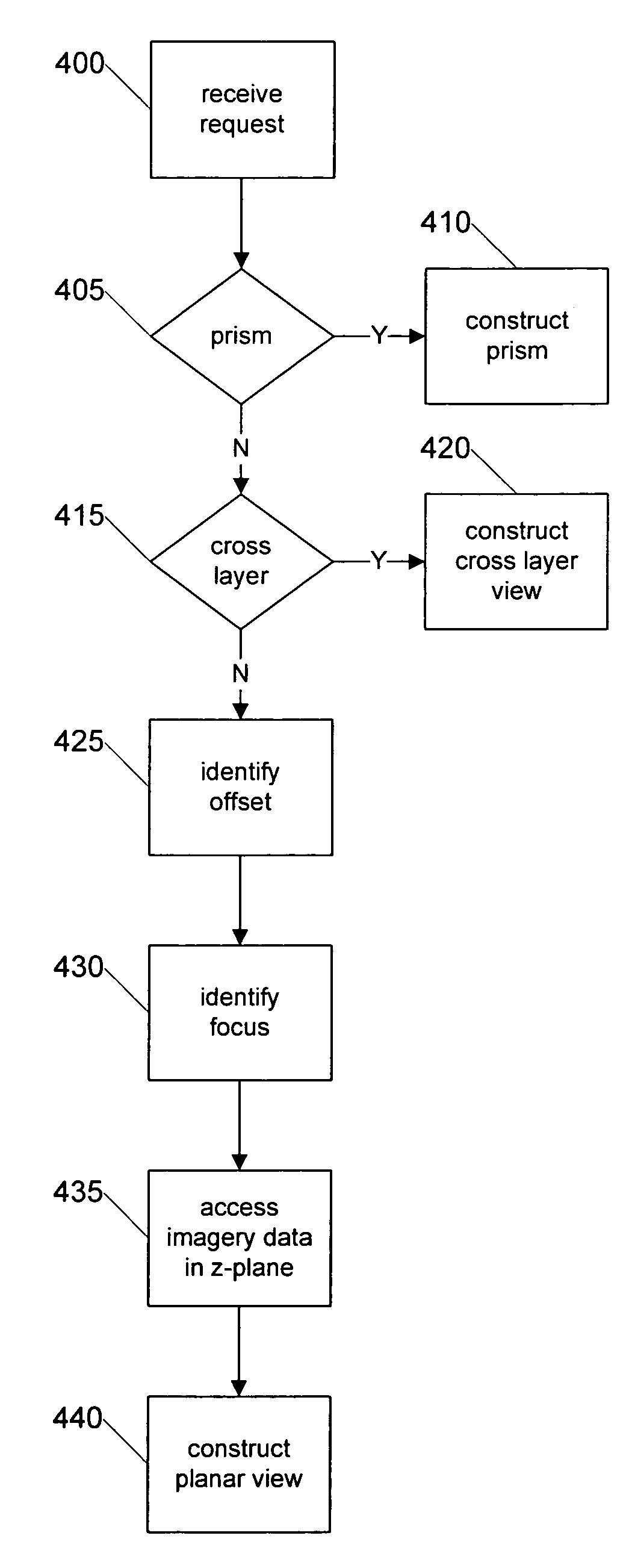
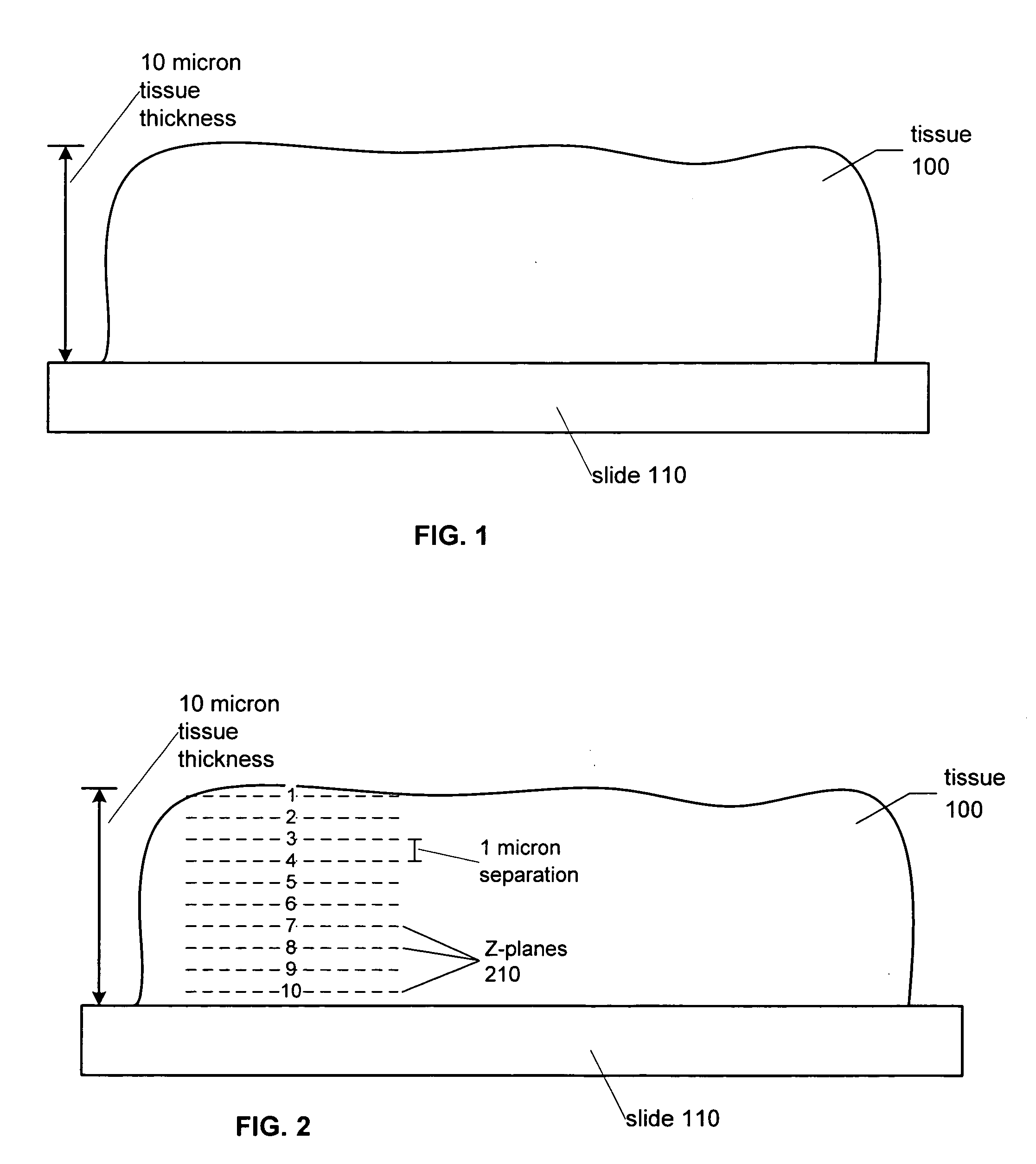
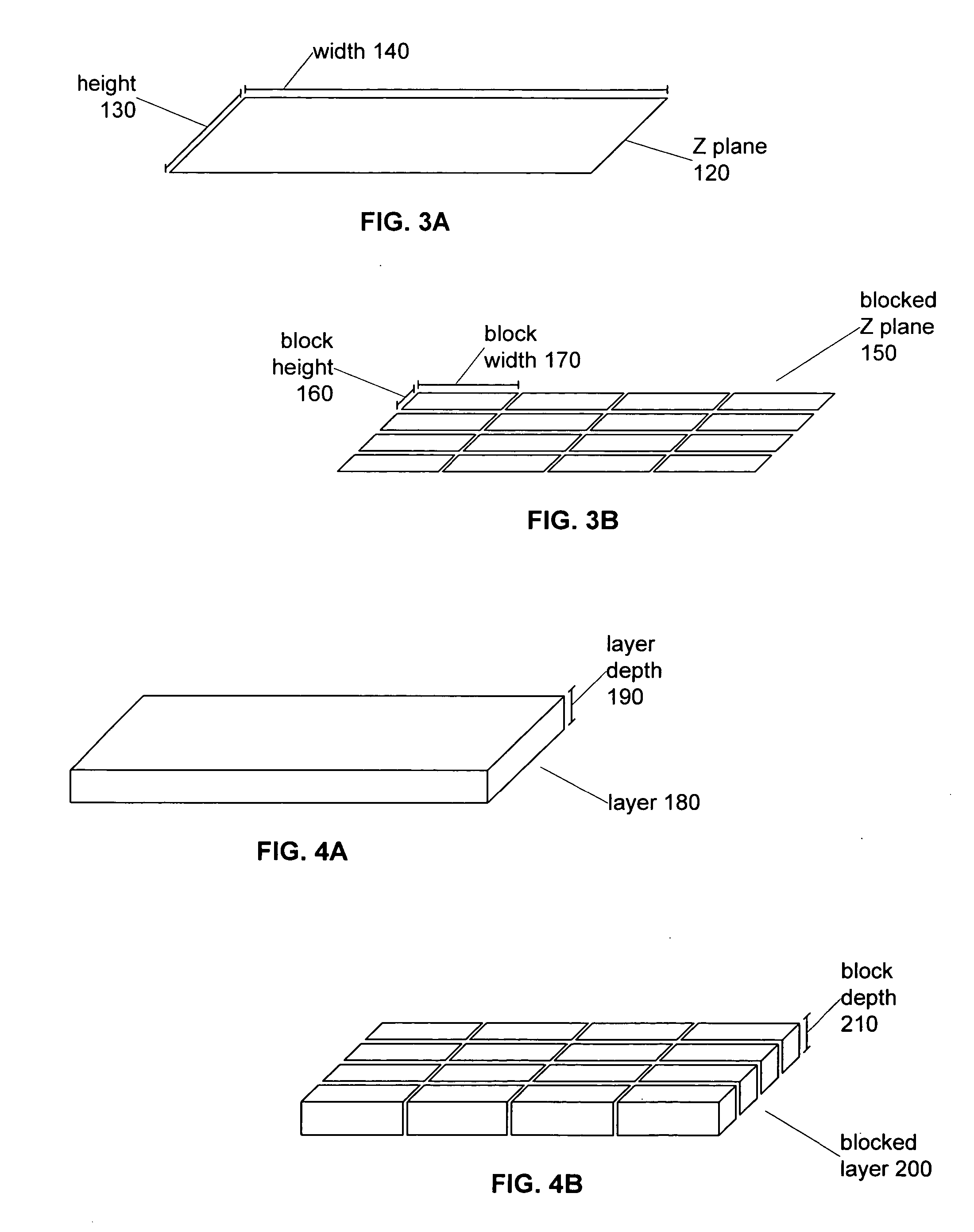
Systems and methods for viewing three dimensional virtual slides
Systems and methods for retrieving, manipulating, and viewing 3D image objects from 3D virtual microscope slide images are provided. An image library module provides access to the imagery data in a 3D virtual slide and constructs 3D image objects that are coextensive with the 3D virtual slide or a 3D sub-portion thereof. From within the 3D image object, cross layer planar views spanning various depths of the 3D virtual slide are constructed as well as 3D prisms and other shaped image areas. The image library module allows a 3D image object to be sliced into horizontal and vertical views, skewed cross layer views and regular and irregular shaped 3D image areas for viewing by a user.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
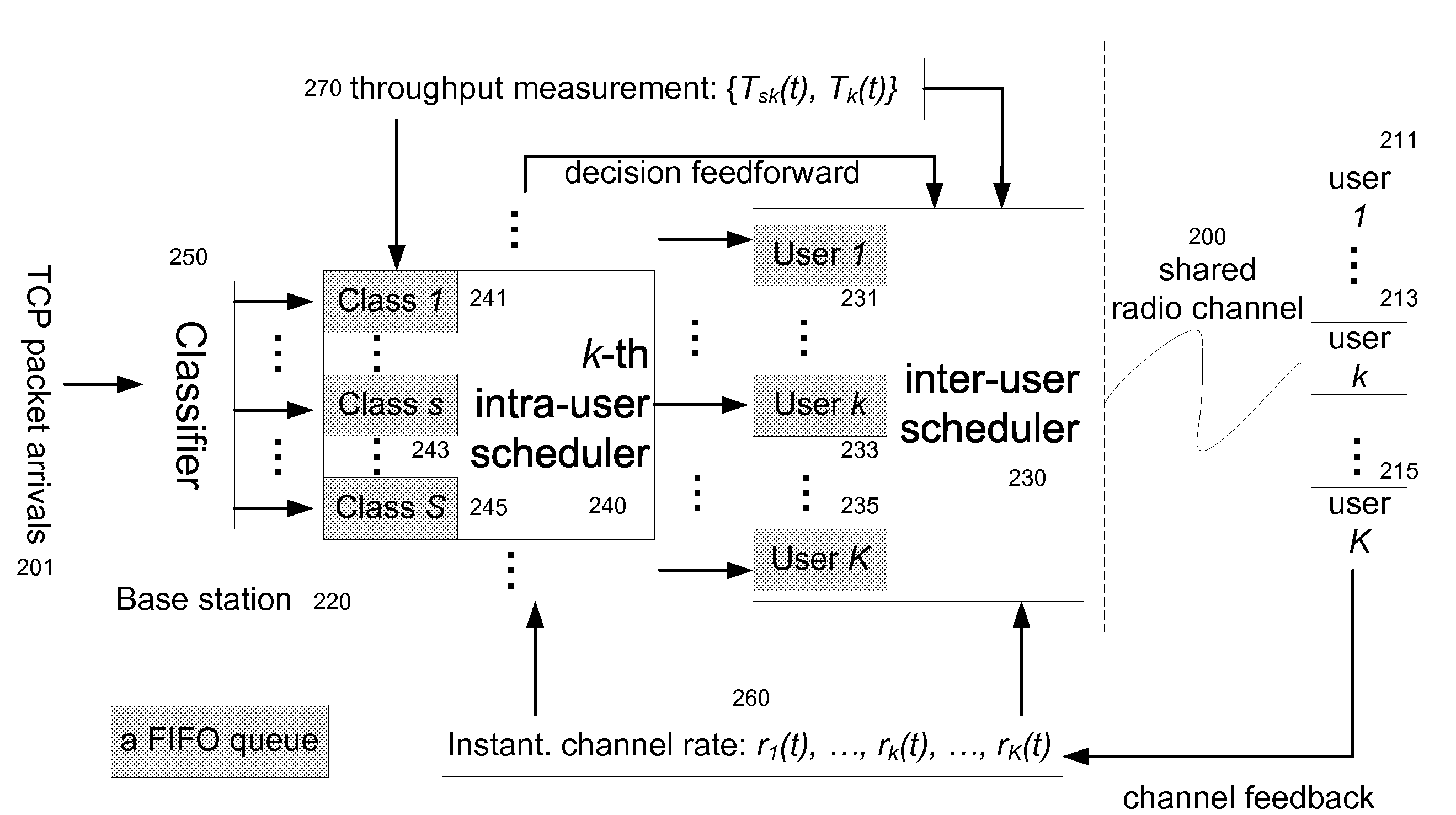
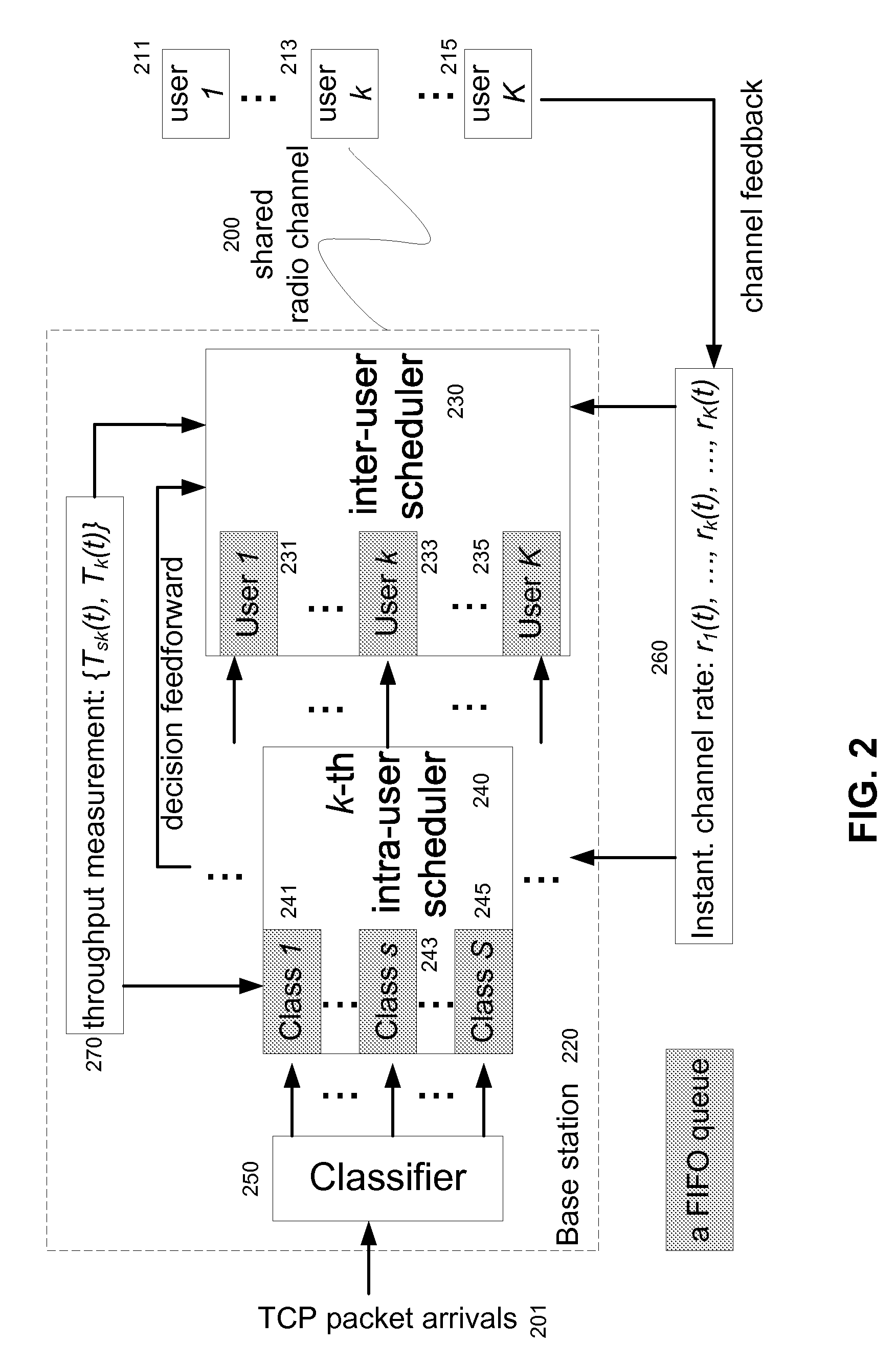
Service Differentiated Downlink Scheduling in Wireless Packet Data Systems
InactiveUS20060242319A1Improve user perceptionAvoid hungerDigital computer detailsNetwork connectionsCommunications systemPattern perception
A base station design for a wireless communication system is disclosed with a hierarchical scheduler for packet data services which is advantageously both traffic-aware and channel-dependent in a manner which enhances the users' perception of network performance. In one embodiment, a cross-layer hierarchical scheduler is disclosed which further comprises an intra-user scheduler and an inter-user scheduler.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Stream table entry generating method and device
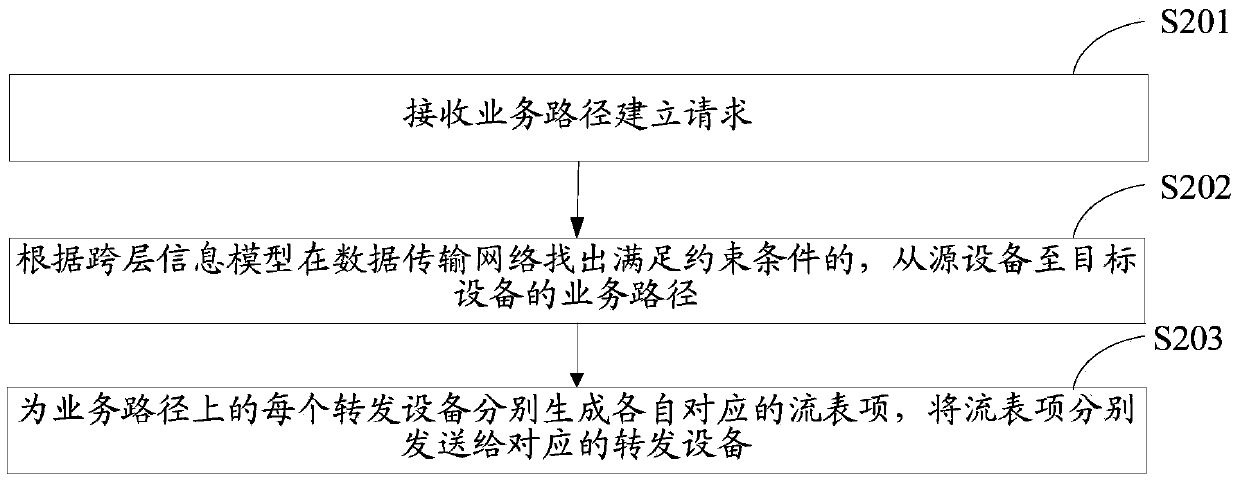
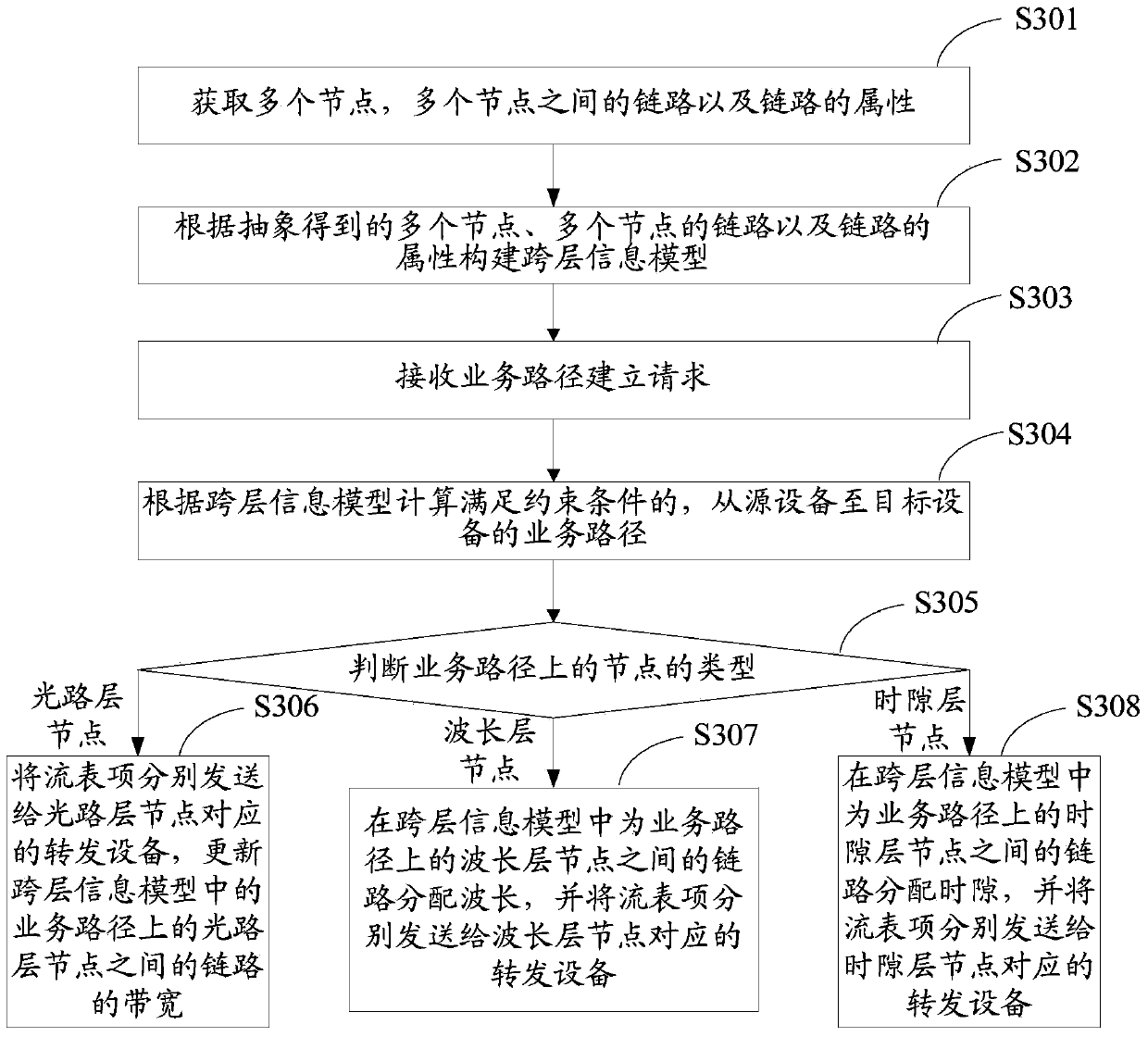
ActiveCN103812778AReduce time complexityImprove computing efficiencyHybrid transportTime complexityData transmission
The invention discloses a stream table entry generating method and device. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a service path establishing request, wherein the service path establishing request comprises a constraint condition, source equipment and target equipment; finding a service path which satisfies the constraint condition and ranges from the source equipment to the target equipment in a data transmission network according to a cross-layer information model, wherein the cross-layer information model is a model describing an integral topological relation between an IP (Internet Protocol) layer and a light layer on the same level; generating a respective stream table entry corresponding to each piece of forwarding equipment respectively on the service path, and transmitting the stream table entries to corresponding forwarding equipment respectively. According to the scheme, resources of the IP layer and resources of the light layer are considered during calculation of the service path according to the cross-layer information model in which the resources of the IP layer and the resources of the light layer are on the same level, thereby greatly lowering the time complexity of business path calculation, increasing the service path calculation efficiency, and increasing the generation efficiency of the stream table entries.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Across layer self-adapting paralleling channel allocating method of cognized radio system
InactiveCN101257714AReduce distractionsIncrease capacityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCross layerParallel channel
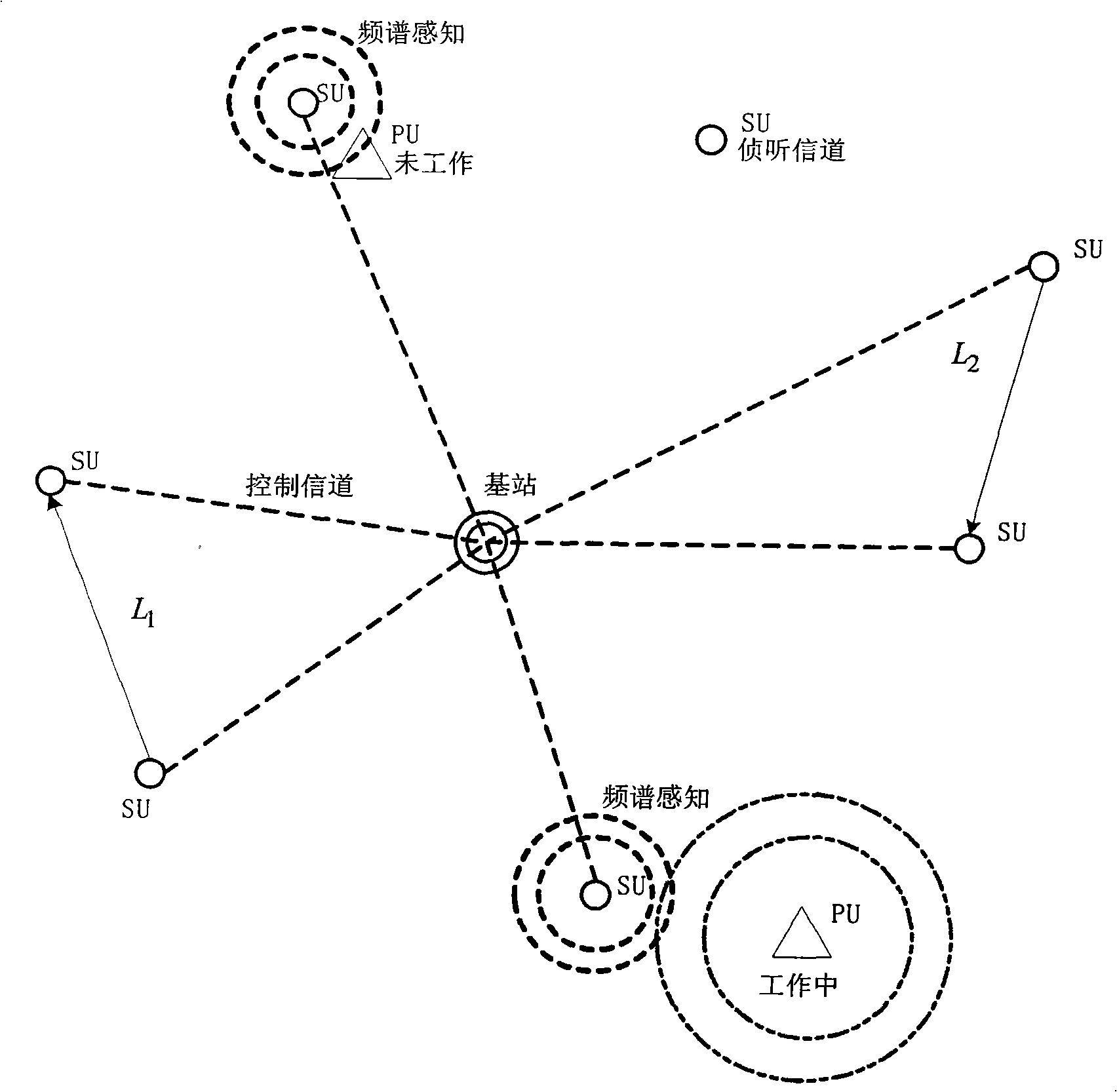
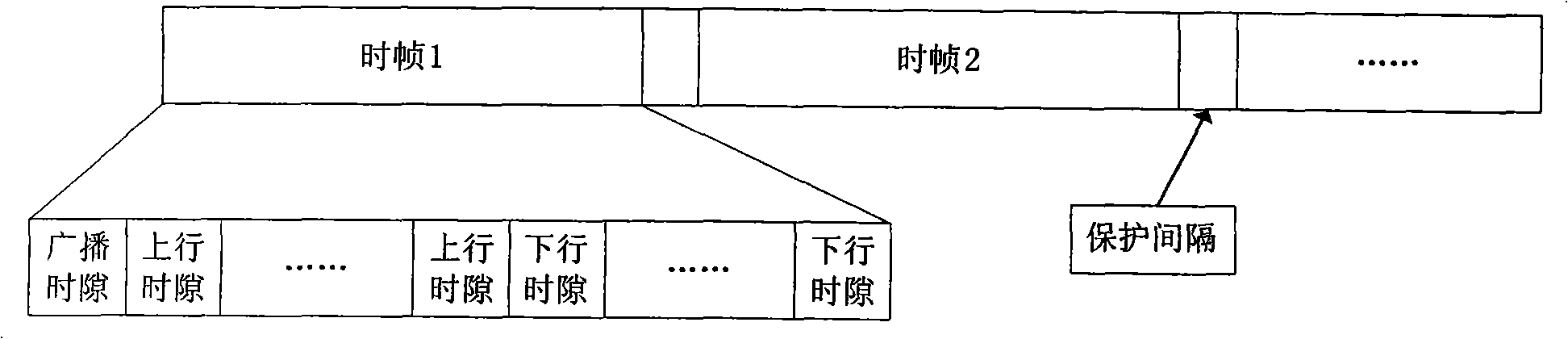
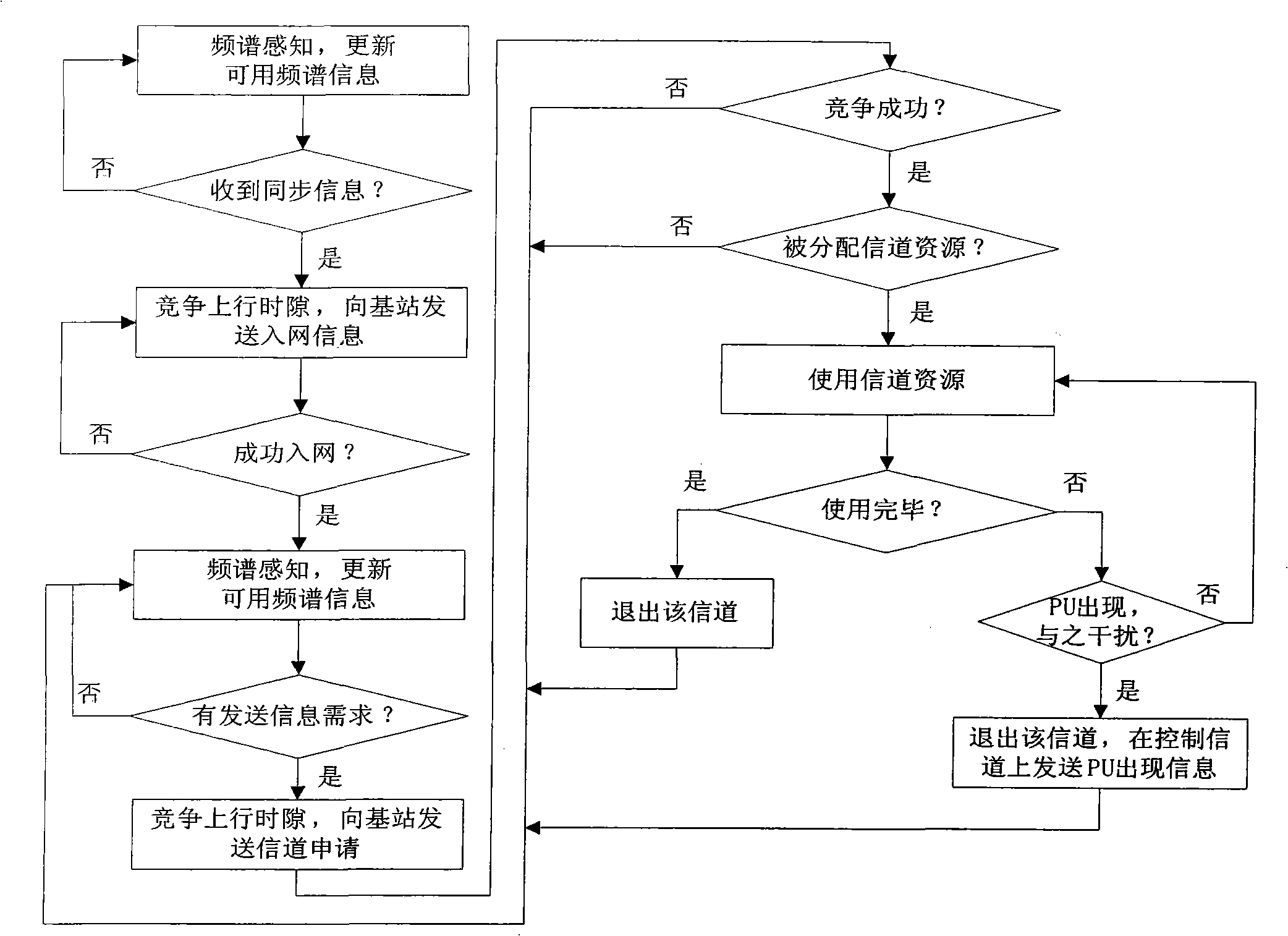
The invention provides a method for allocating cross-layer adaptive parallel channels of a cognitive radio system. The method includes steps that a base station receives channel requests of each unauthorized subscriber SU in an uplink time slot analyzes the channel request information, and allocates available channel resources adaptively on the premise that SU do not disturb each other and do not disturb patchusers PU. The invention adopts the method of dividing uplink and downlink time slots of time division duplexing TDD, analyzing the signal noise ratio information of available channel resources by the base station, adopts transmission set portion, channel parallel allocation, adaptive adjustment of the optimized channel, maximizing transmission efficiency and determining optimum transmission modes for each SU, provides optimum channel resources, and utilizes SU to monitor presence of PU in real time, reduces interference at the lowest to the PU, improves capacity of radio cognitive networks and channel utilization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Energy-saving MAC and routing cross-layer method for linear monitoring network
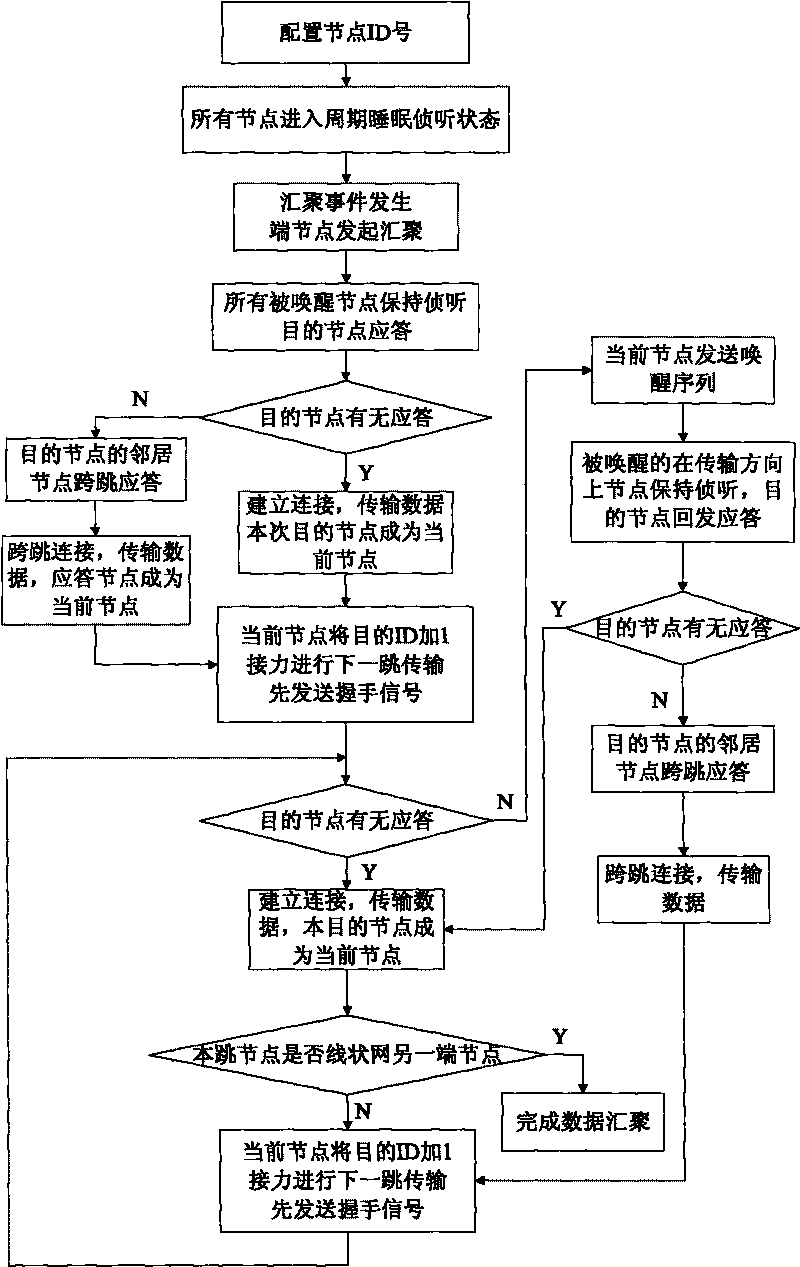
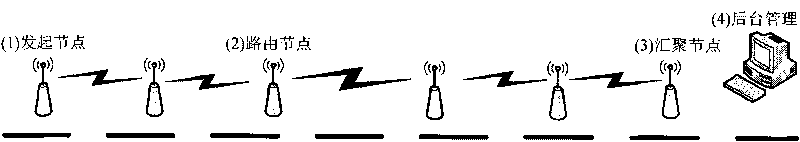
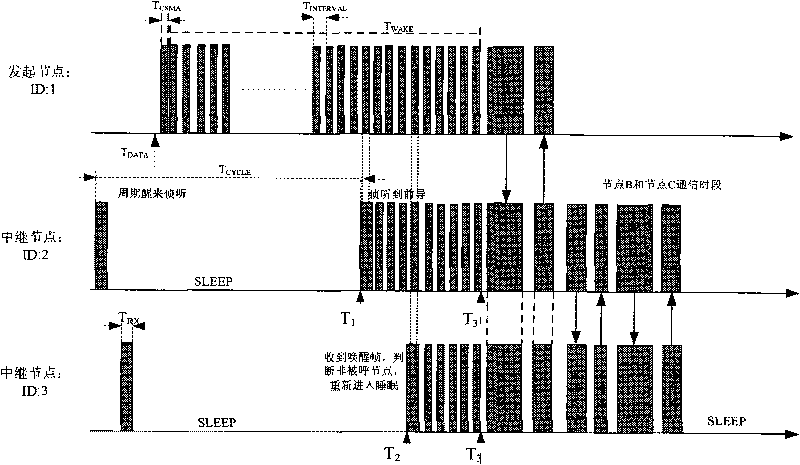
ActiveCN101742544AProlong lifeSave monitoring node energyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementEnergy consumptionCross layer
The invention relates to an energy-saving MAC and routing cross-layer method for a linear monitoring network. The method comprises that: all nodes are configured with a logic ID in advance according to the physical positions; the communication is initiated by an end node, the MAC protocol is realized based on a sleep wakeup mechanism, the wakeup method is group wakeup, the wakened nodes automatically judge whether to sleep or continuously monitor according to the ID in the received data and the directional information, and a routing layer automatically selects the next hop according to the last hop node information in the MAC layer data when the node selects the next hop node; the neighbor node can jump the hop to respond when the called node has no response; and the current node fuses all the past node data and transmits the data to the next stage so as to reduce the transmission of useless information and improve the efficiency of energy consumption. The method can be widely applied to the places of pipeline survey, road survey, fuel gas wireless network acquisition systems and the like, and has the advantages of saving the energy of the survey node, prolonging the life cycle of the node and effectively improving the work efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
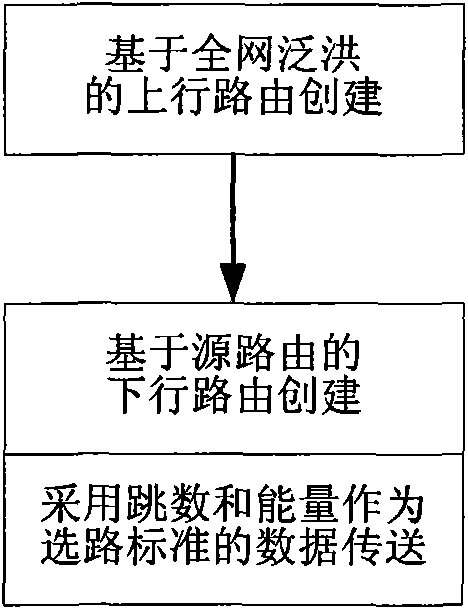
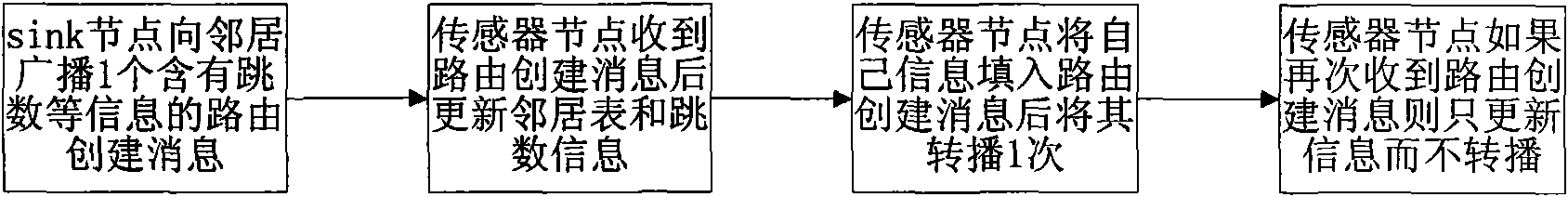
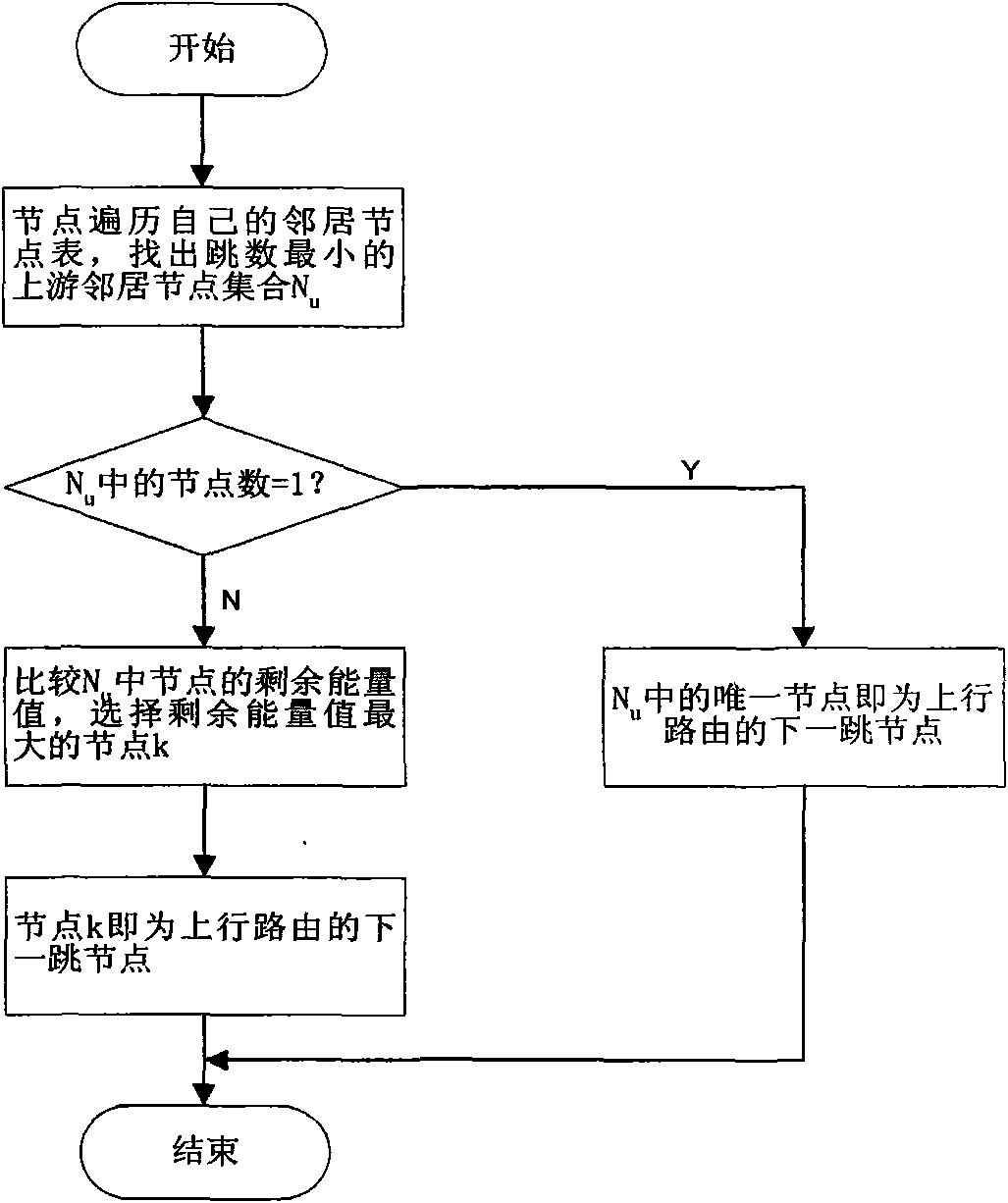
Cross-layer and bi-directional routing method based on hop number and energy in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101562861AImprove bandwidth utilizationExtend your lifeEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesLine sensorRest energy
The invention asks for protecting a cross-layer and bi-directional routing method in a wireless sensor network and relates to the technical field of communication. The existing wireless sensor network has the disadvantages that no downlink route is established in route establishing process, function of inquiring a sink node can not be supported, extra-cost occurs when energy information is updated by adopting node energy as the routing standard, and the cost of controlling the system is slightly larger. The method adopts source routing and cross-layer information share manner and uses smaller cost to establish the downlink route from the sink node to a sensor node without using special control group, the function of inquiring the sink node is added, and regular acquiring, releasing and updating of the rest energy information of the node are realized, when routing, the hop number and the rest energy of the node are both used as the measure standards, the energy consumption when forwarding the node is balanced when reducing the node energy and the network bandwidth consumption, and the service life of the wireless sensor network can be prolonged, and the network bandwidth utilization rate is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
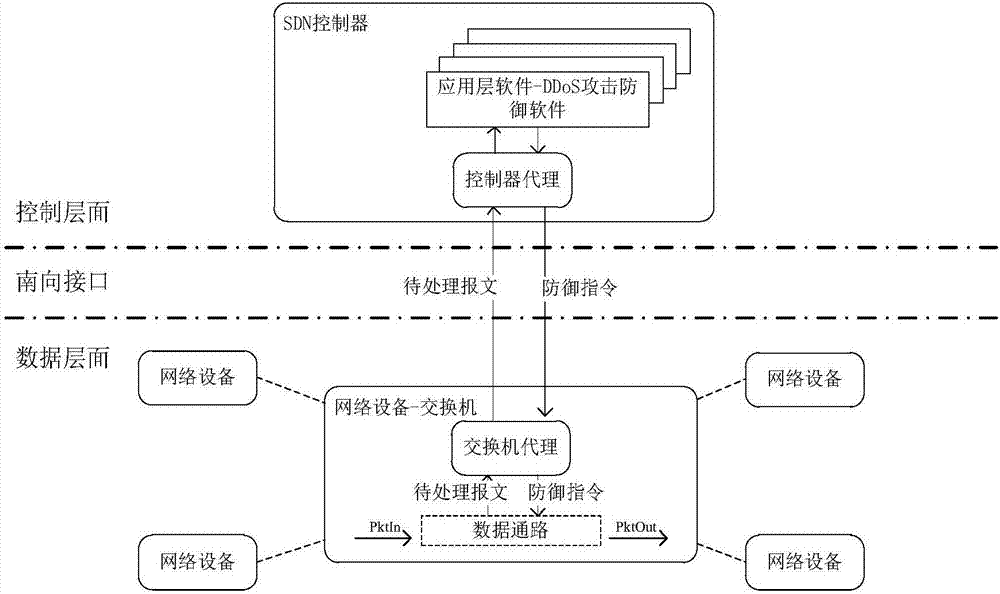
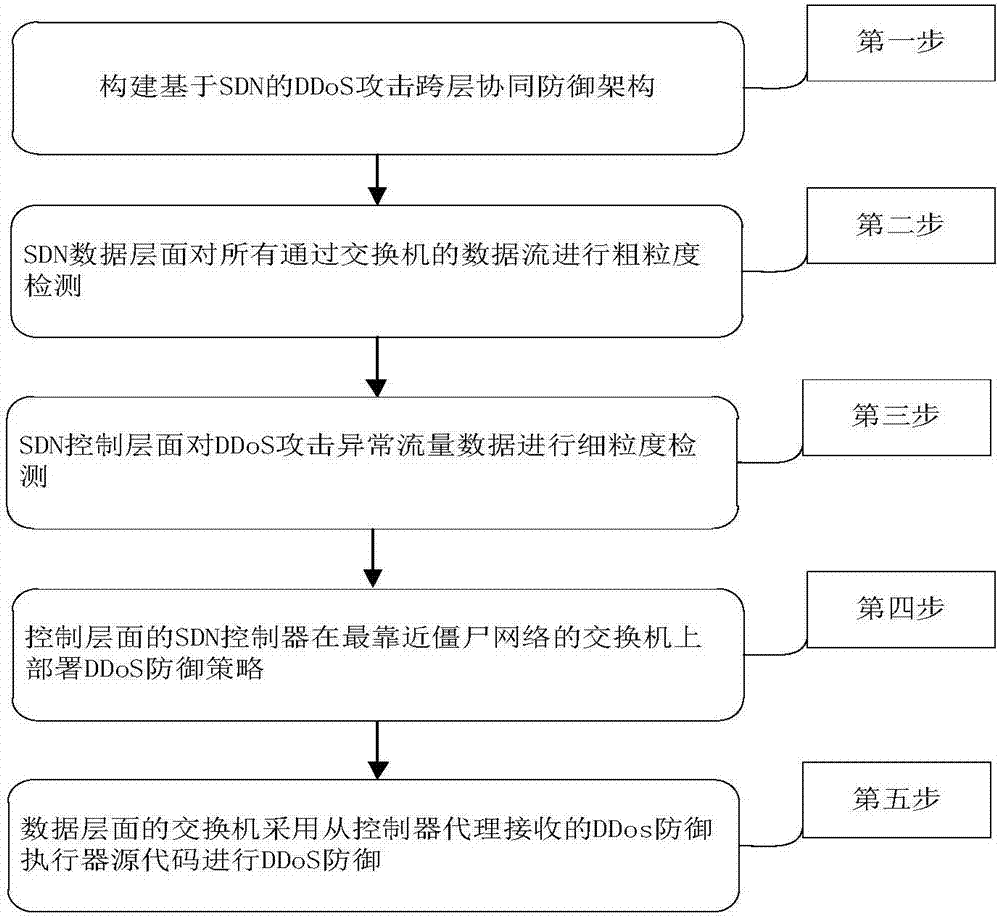
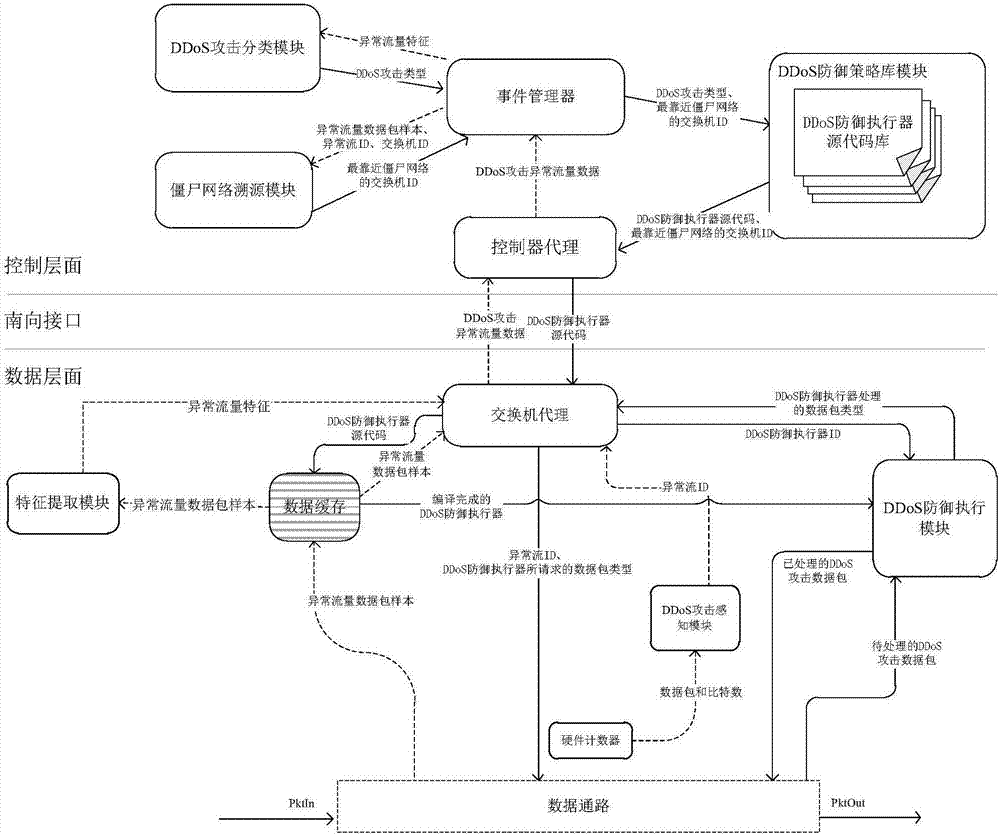
Software defined network-based DDoS attack cross-layer cooperative defense method
The invention discloses a software defined network-based DDoS attack cross-layer cooperative defense method and aims to solve the problems of over high communication pressure of a southbound interfaceand a control plane as well as over high calculation pressure of an SDN controller. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: constructing an SDN-based DDoS attackcross-layer cooperative defense framework comprising a data plane and a control plane, performing coarse-grained detection on data flow by the data plane to acquire DDoS attack abnormal flow data, andperforming fine-grained detection on the DDoS attack abnormal flow data by the control plane to acquire an exchanger closest to a bot network; deploying a DDoS defense strategy on the exchanger closest to the bot network by the SDN controller of the control plane, and performing DDoS defense according to the DDoS defense strategy by the SDN exchanger of the data plane. Through cooperation of thedata plane and the control plane, the cooperative defense advantage of the SDN is completely utilized and the problems of high pressure of the SDN southbound interface and too large burden of the SDNcontroller are solved, so that the exchanger can perform automatic defense intelligently.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Communication station and method providing flexible compression of data packets
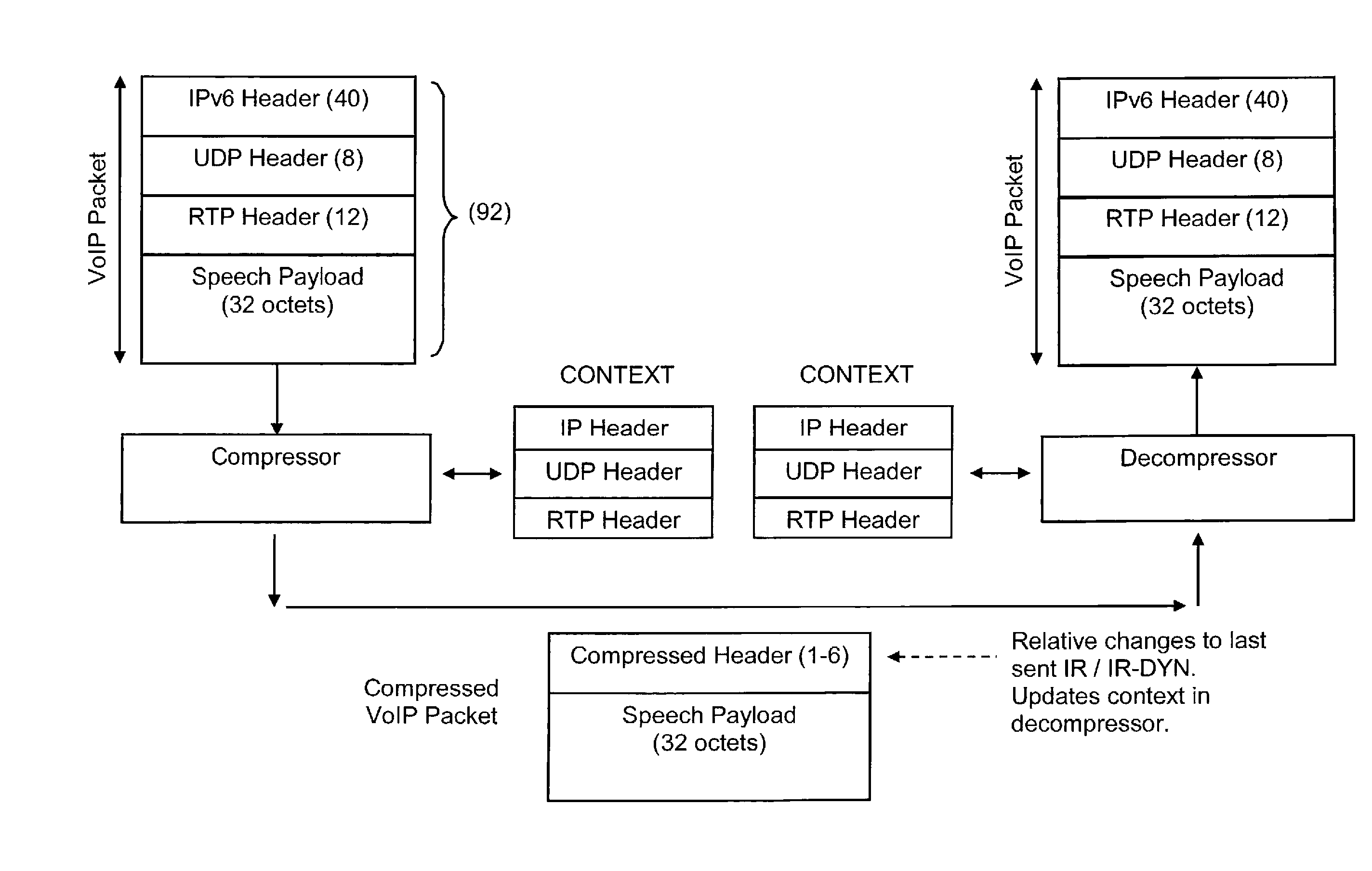
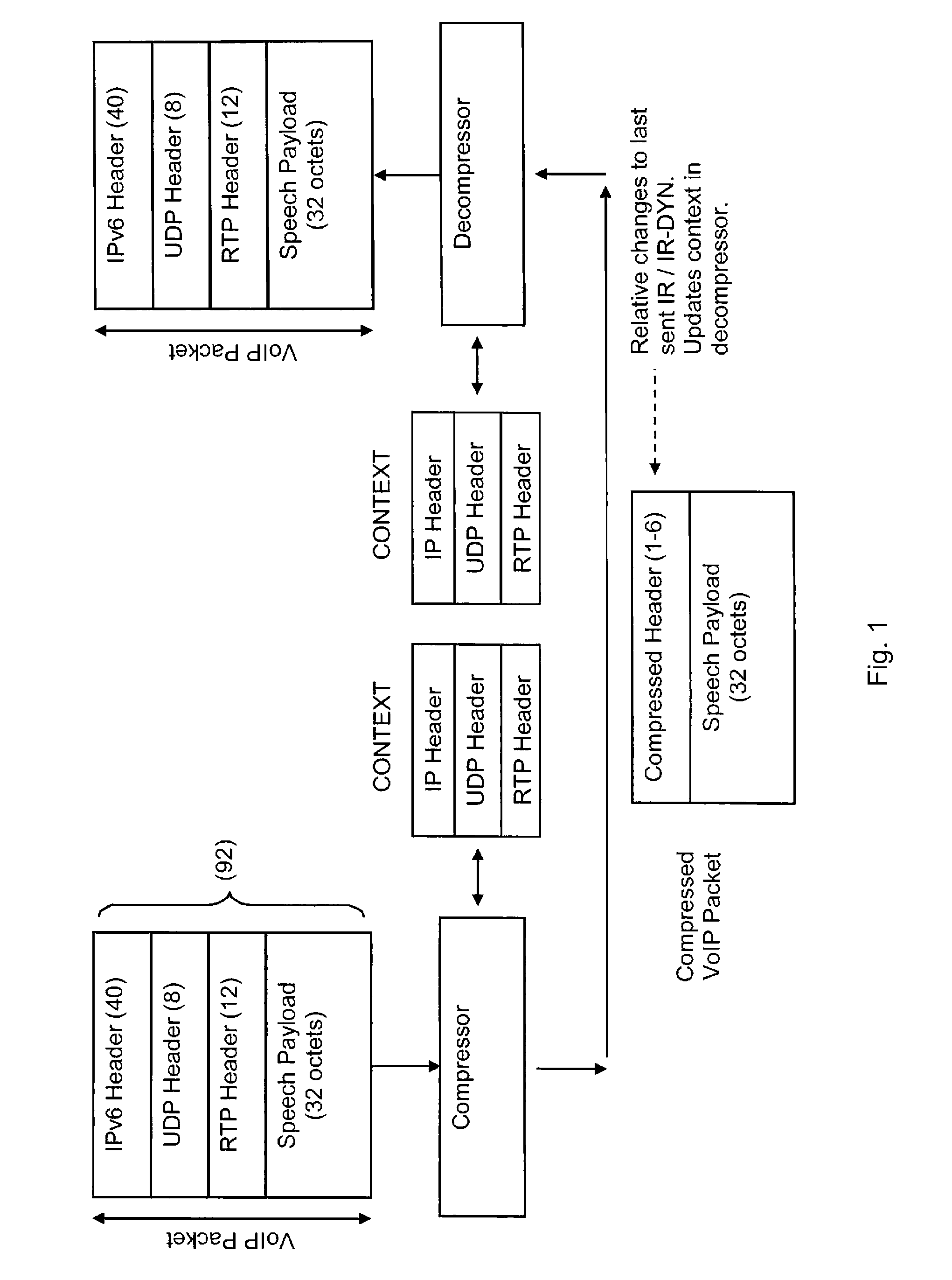
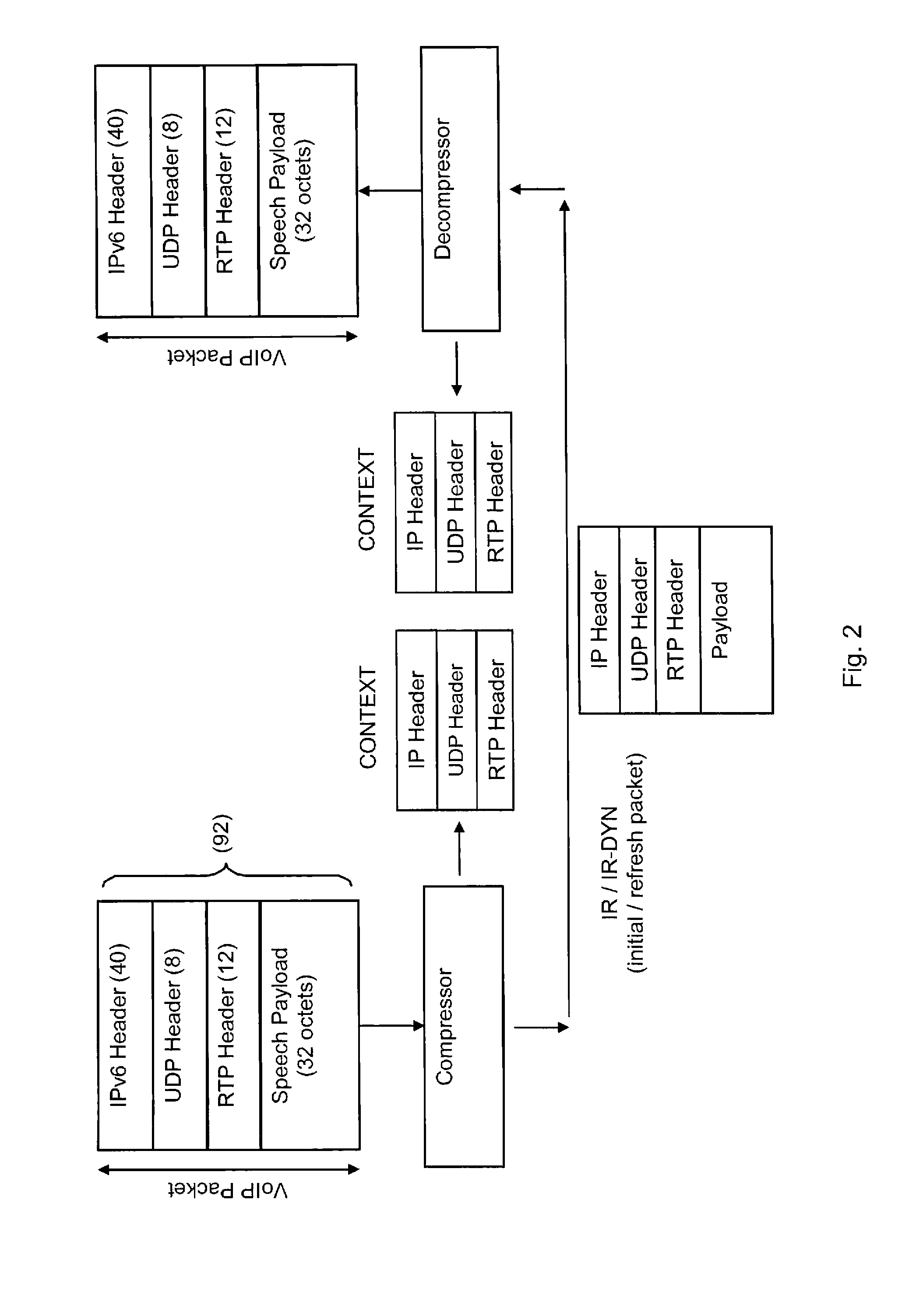
ActiveUS20070211724A1Reducing bandwidth fluctuationQuick SetupError preventionTransmission systemsComputer hardwareCross layer
A method and a communication station for determining a packet format of a data packet based on at least one compressed header information field. A header packet format of a data packet is determined based on the determined packet format of a partially or completely compressed header information part. The station may also determine a codec rate based on the result of a previously performed compression of at least one header information field. In one embodiment, internal cross-layer signaling from a header generator module to a payload generator module in the communication station is used for signaling information associated with determining the header packet format of the data packet. The method reduces bandwidth fluctuations associated with services such as text messaging audio, or audiovisual services; lowers the delay variations and the erasure rates for application media streams; and provides for faster set-up of sessions.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Carrier-aggregation-based method for scheduling upstream cross-layer resources in LTE-Advanced system
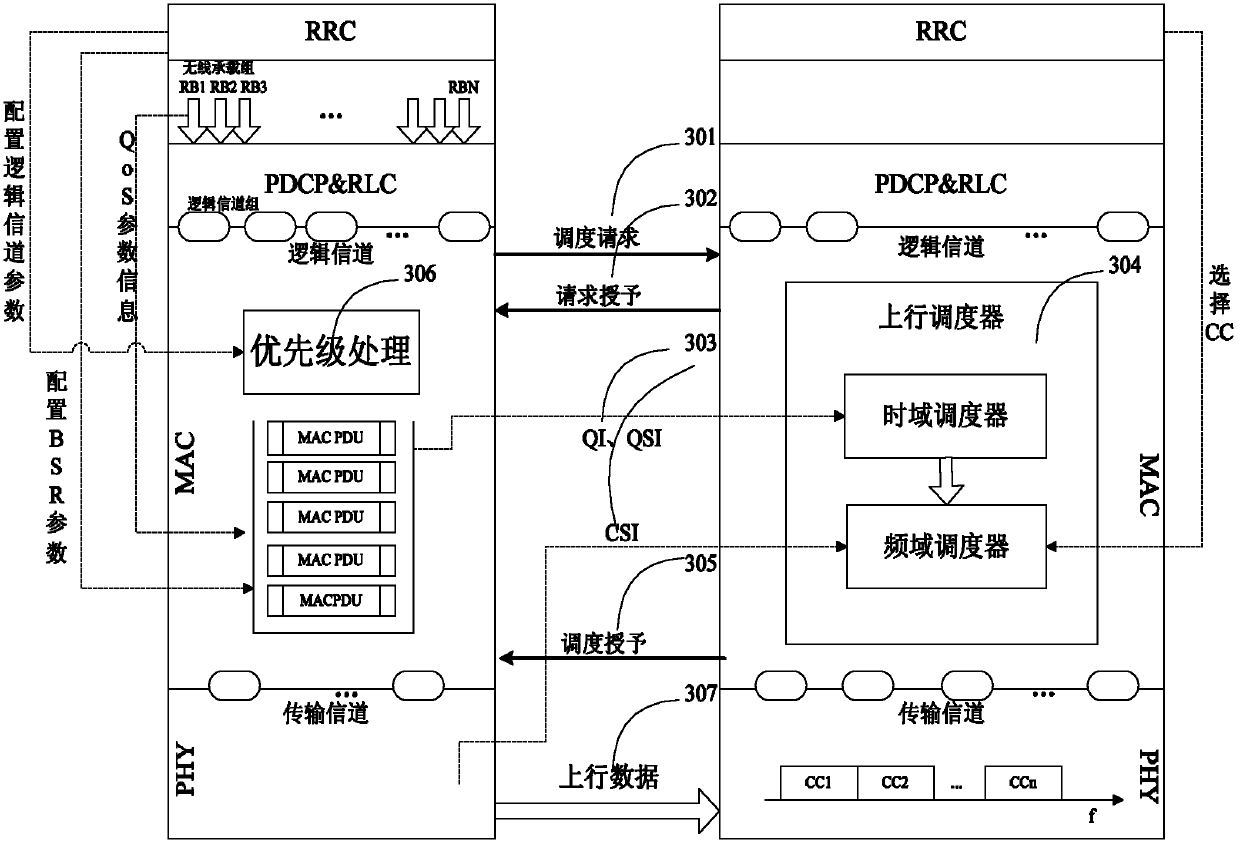
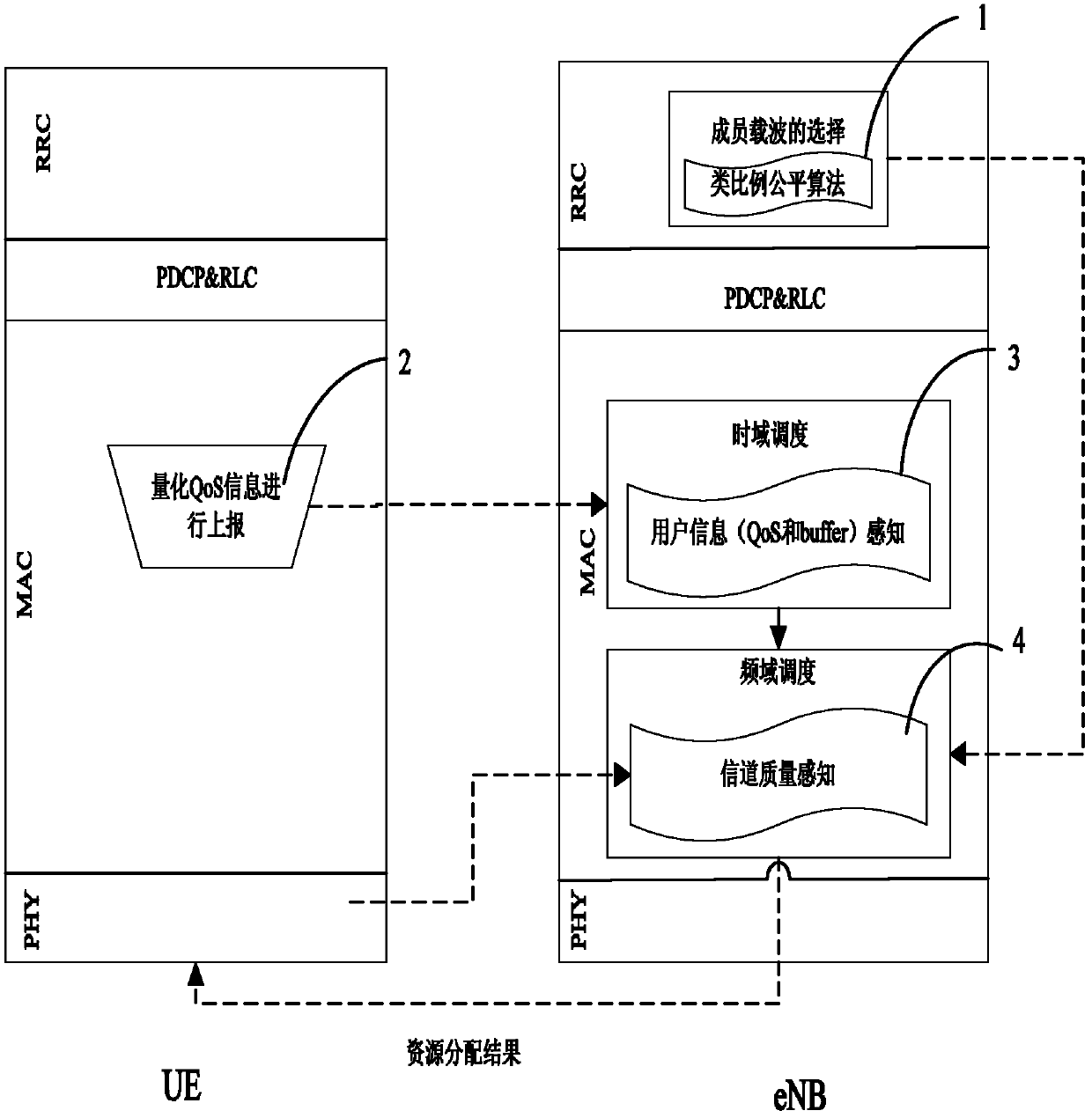
InactiveCN102612093AEnsure fairnessGuaranteed minimum QoS requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceTime domain
The invention discloses a carrier-aggregation-based method for scheduling upstream cross-layer resources in an LTE-Advanced system, wherein the QoS (quality of service) information of a user is obtained by an upstream scheduler by adopting the method of reporting quantized QoS under the condition of not bringing additional signaling expenditure and increasing the system complexity. Meanwhile, the selection of CC (component carrier) is carried out by adopting the method of class proportional fair of taking account of both efficiency and fairness on an RRC (radio resource control) layer of eNB, then the scheduling is divided into time domain scheduling and frequency domain scheduling, wherein the time domain scheduling is used for calculating the optimization of a user to be scheduled by sensing the QoS and the queue status information, and the distribution of the radio resources are carried out in the frequency domain scheduling by sensing the channel information, and finally the optimization of the distribution of the radio resources is realized. While the system performance is improved, the fairness of the distribution of the resources is guaranteed, and the requirement of the minimum QoS of the user is met.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for cross layer resource allocation for wireless backhaul networks
A method and apparatus is disclosed whereby the scheduling of network transmissions in a wireless backhaul network is determined using a cross-layer optimization algorithm. In a first embodiment, the algorithm assumes a good MAC layer transmit schedule has been provided and computes optimal network layer routes as well as transmit beam patterns and transmit powers in a semi-distributed manner. According to this embodiment, the optimization goal is the throughput from each access point, or node in the network, to the core network. In another embodiment, an independent set of transmitting nodes is determined at the MAC layer in a way such that no link in the set interferes with another link and no link is scheduled to transmit and receive at the same time. According to this embodiment, a column generation algorithm is used to find a maximal weighted independent set and to achieve optimal network transmission throughput.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com