Energy-saving MAC and routing cross-layer method for linear monitoring network
A monitoring network and linear technology, which is applied in the field of physical linear monitoring network and where the battery is not easy to replace, can solve the problems of premature node death, limited node energy, network paralysis, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
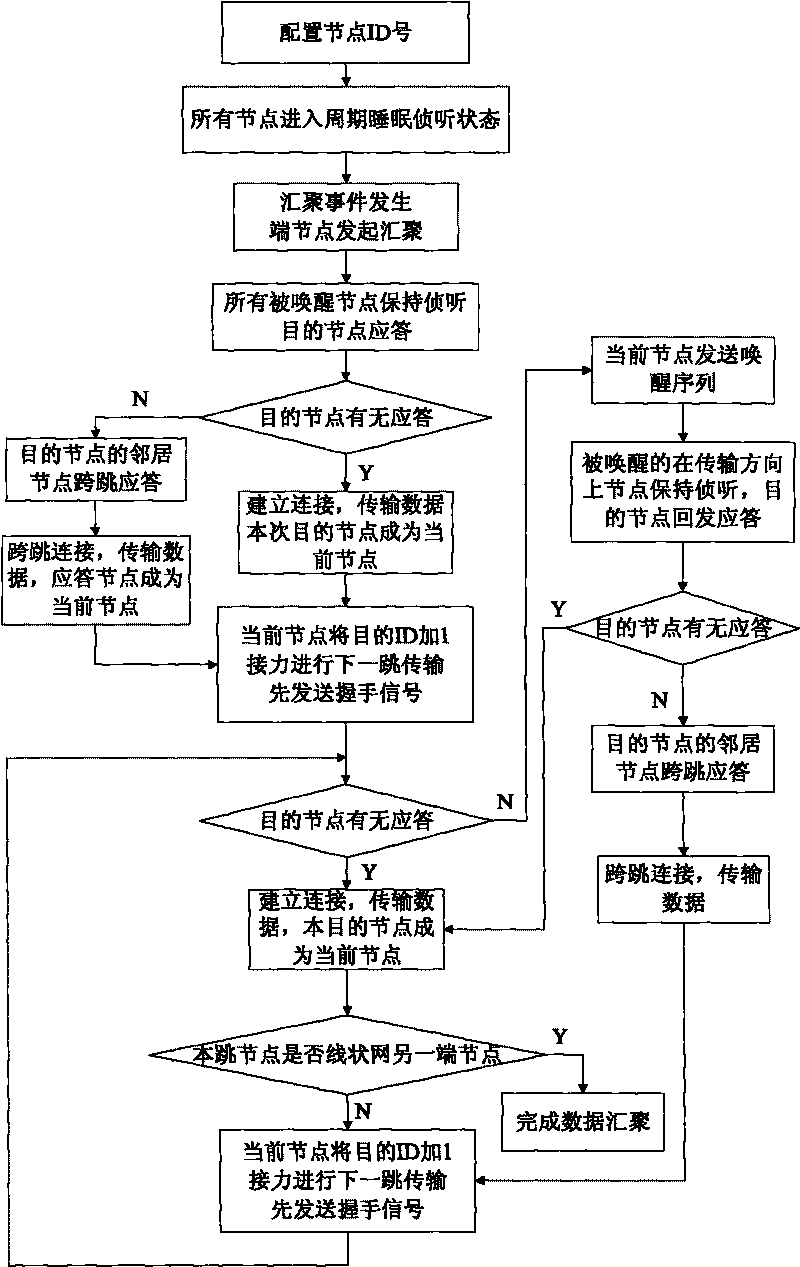
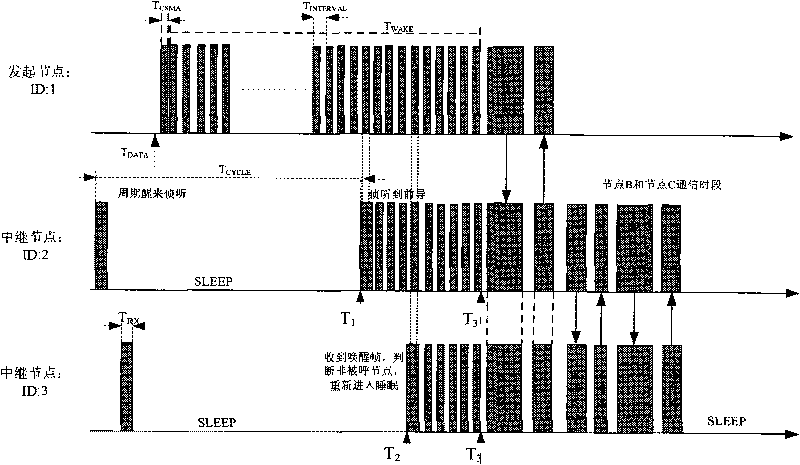
[0024] Embodiment 1: This is used for energy-saving MAC and routing of linear monitoring networks. First, all nodes need to be pre-configured with logical IDs according to their physical locations; communication is initiated by end nodes, and the MAC protocol is implemented based on the sleep wake-up mechanism, and the wake-up method is Group call, the awakened node can automatically judge whether to sleep or continue listening according to the ID and direction information in the received data. When the node selects the next hop node, the routing layer automatically selects the next hop node according to the previous hop node information in the MAC layer data. One hop; neighbor nodes can respond across hops when there is no reply from the called node; the current node integrates all previous node data and transmits it to the next level, thereby reducing sending useless information.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment Two: This embodiment is the same as Embodiment Two, and the special feature is that the specific operation steps are as follows:
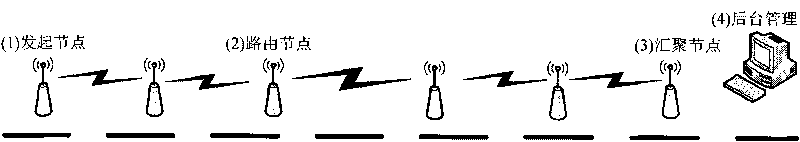
[0026] 1) First, configure the logical ID of the node according to its physical location in the network, and use the logical ID for identification in communication. According to the position in the linear network, its logical ID is incremented sequentially. The node at the end of the network, that is, the node with the smallest ID number, also acts as an initiating node in terms of logical functions, and regularly initiates data collection signals. The node in the middle of the network also acts as a routing node when performing data collection functions. All The collected data is converged one by one in the linear network, and reaches the other terminal (with the largest ID number) converging node, that is, this terminal node acts as data collection and data collection function of all nodes at the same time, and also transmits the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com