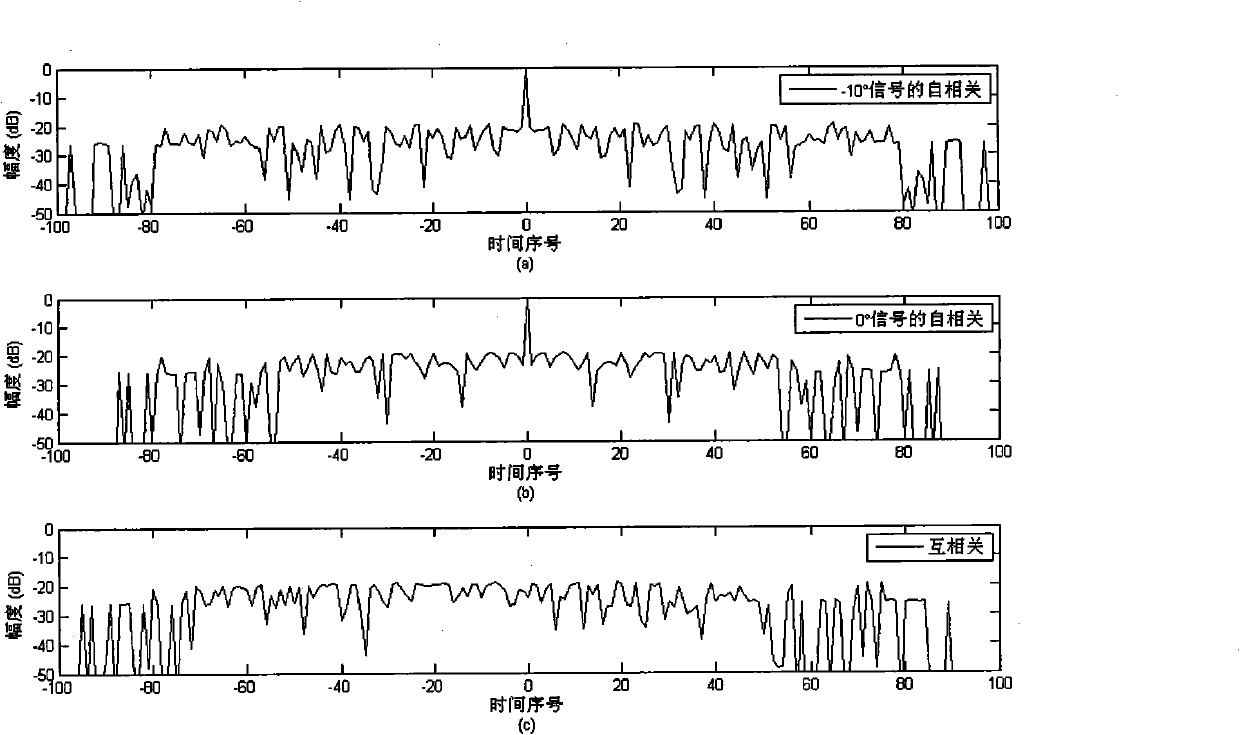
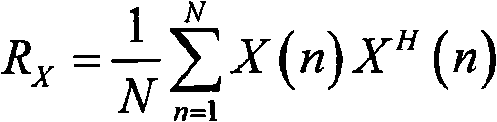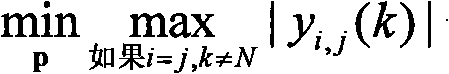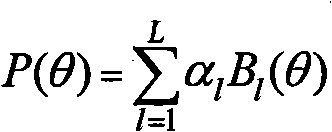Patents
Literature
1561 results about "Signal wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Signal wave. [′sig·nəl ‚wāv] (communications) A wave whose characteristics permit some intelligence, message, or effect to be conveyed.
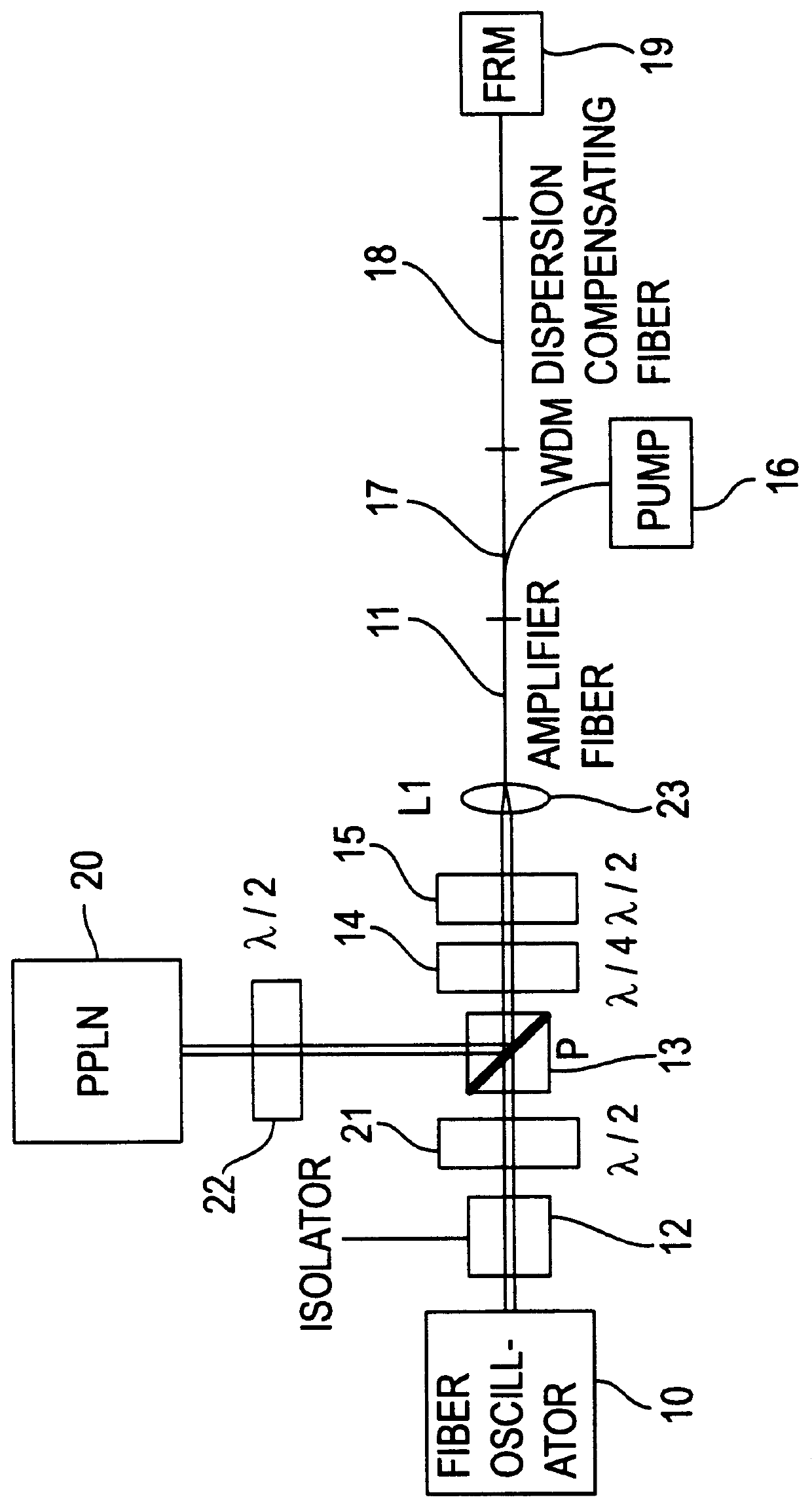
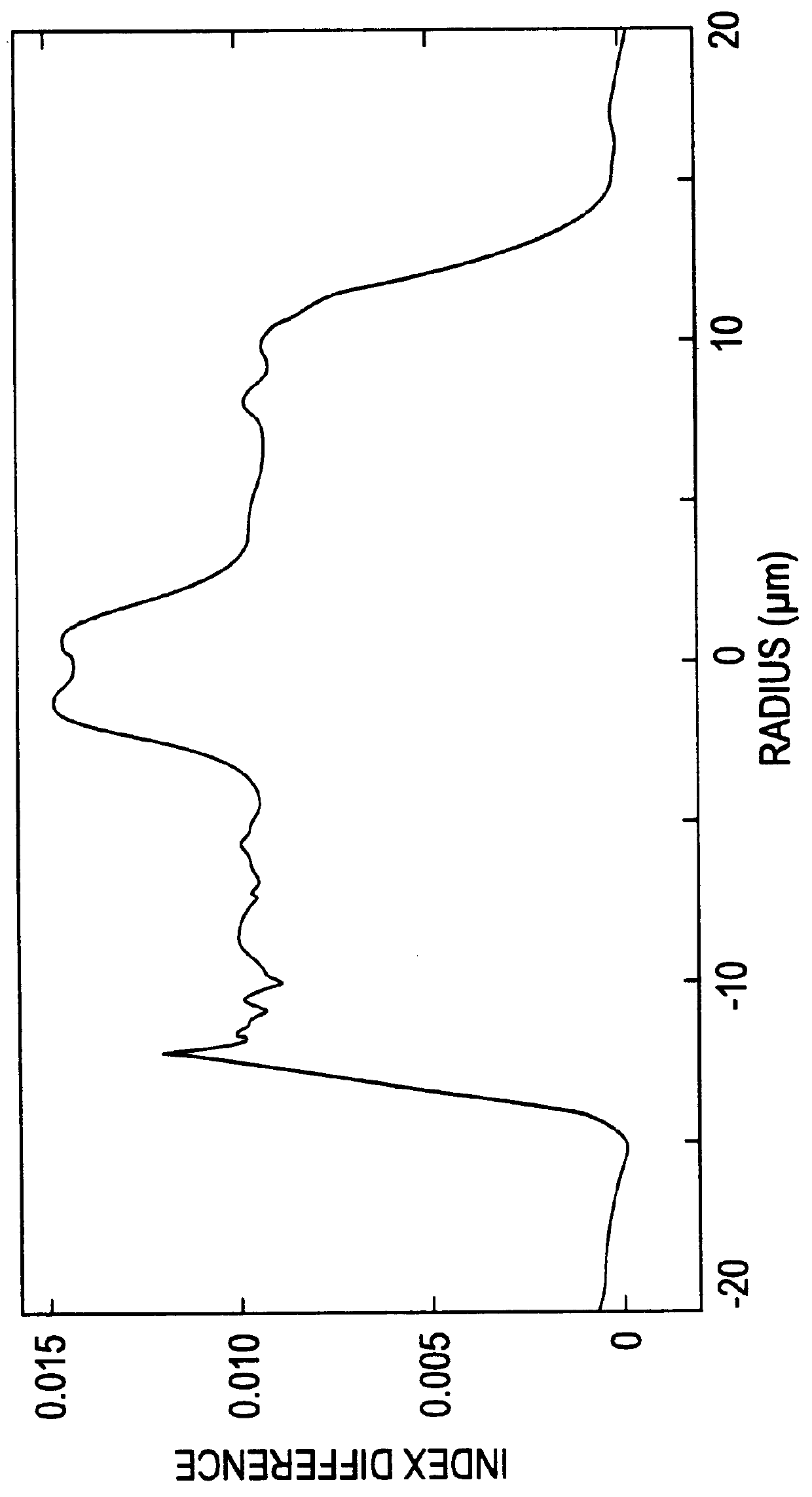
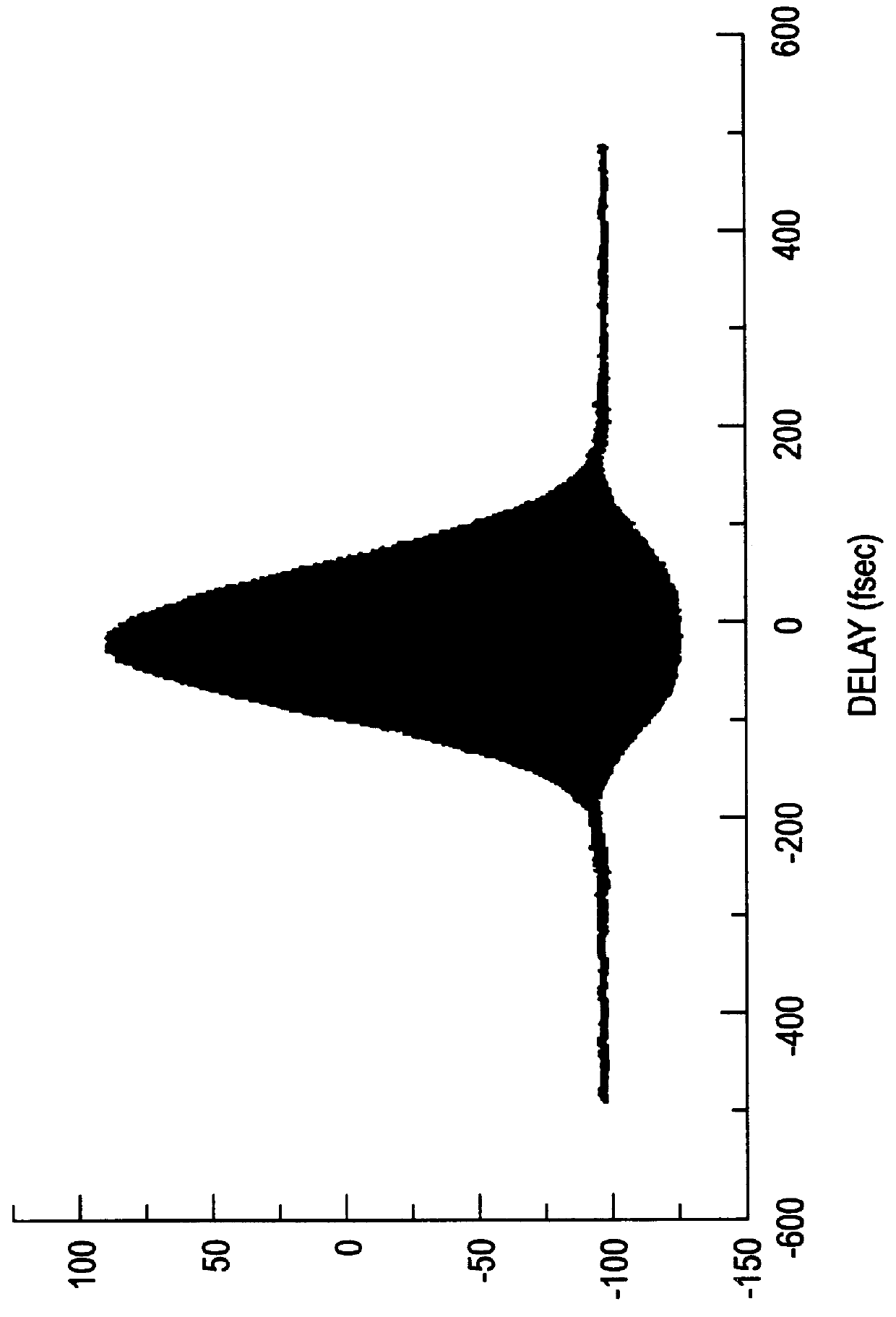
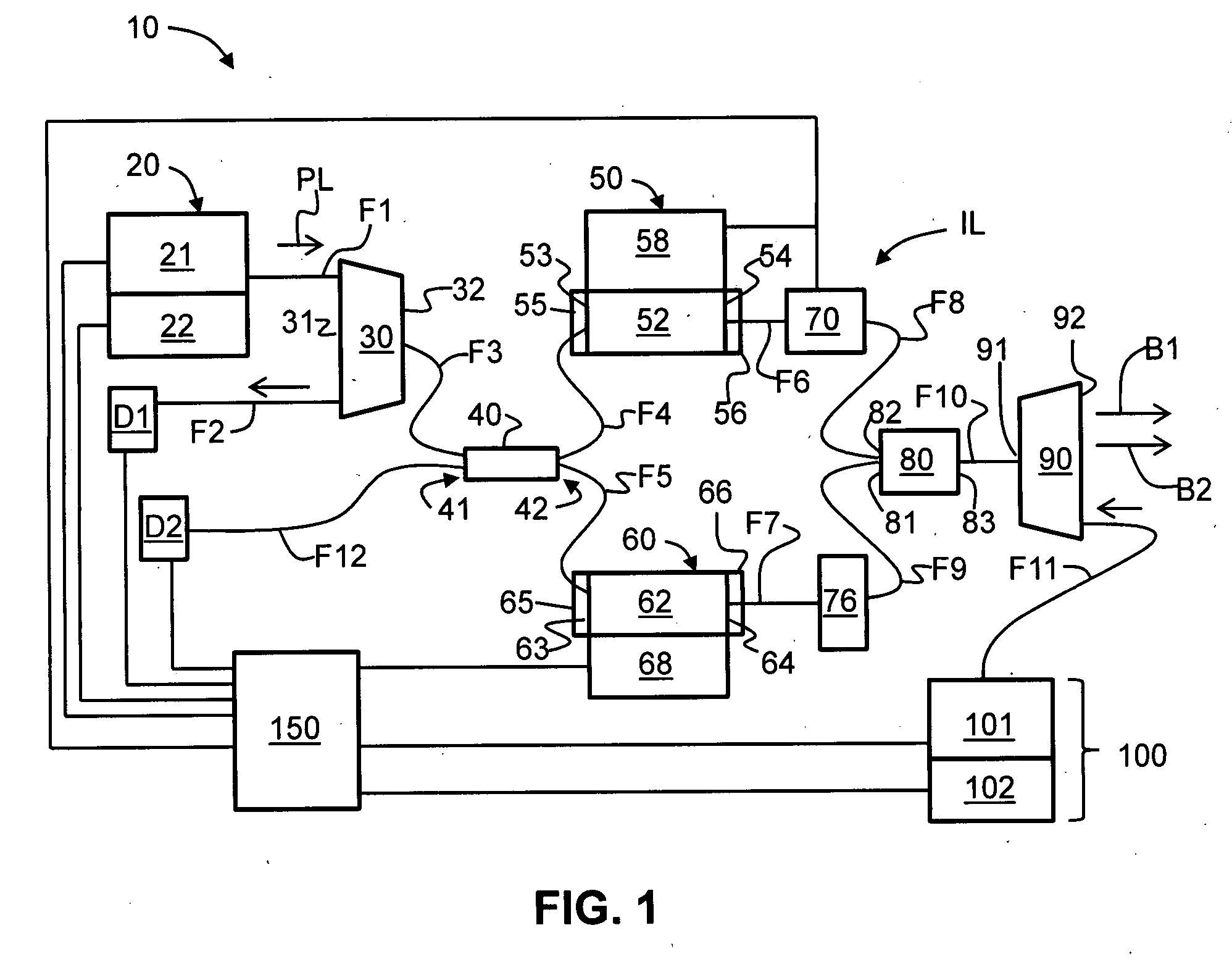
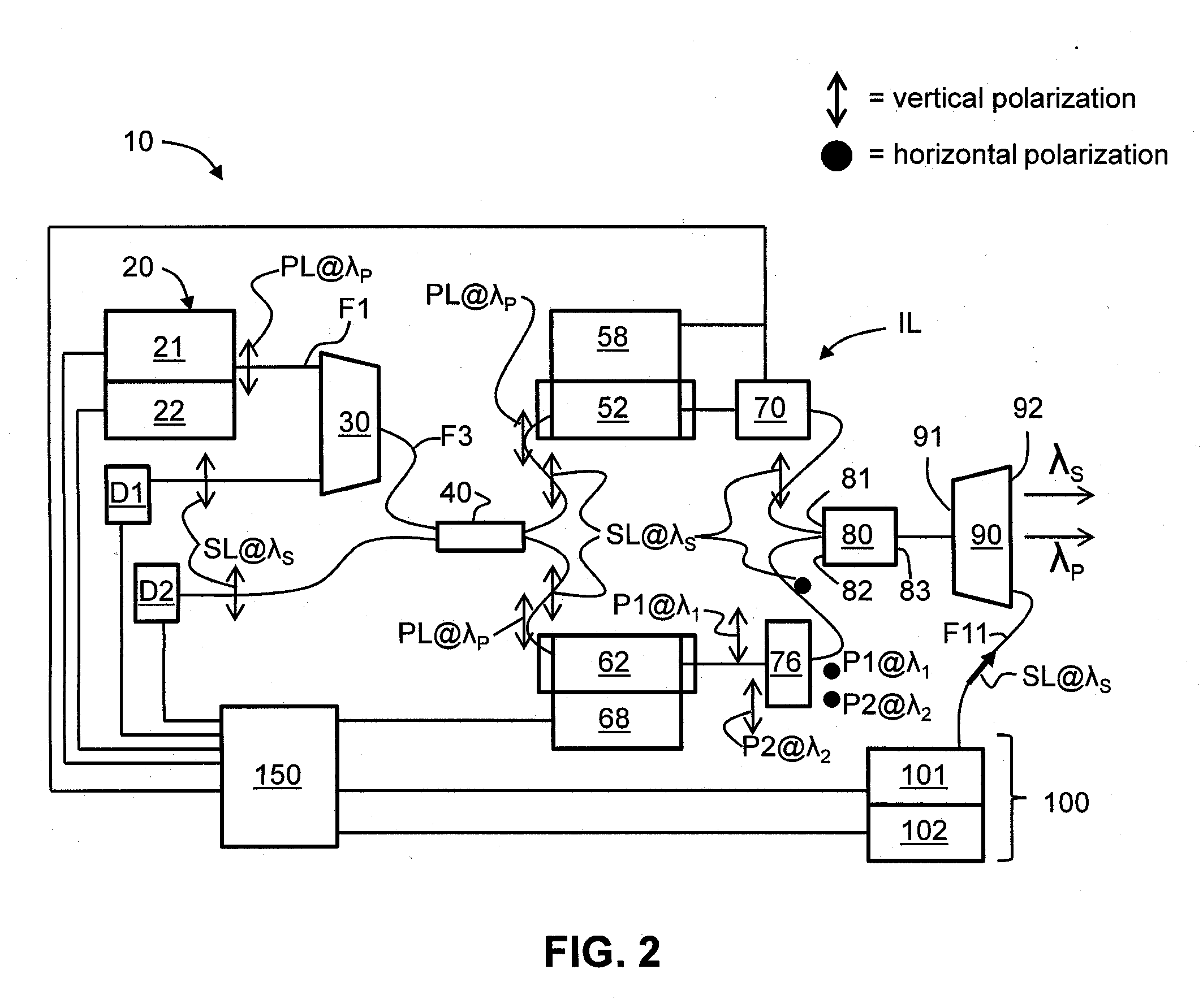
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
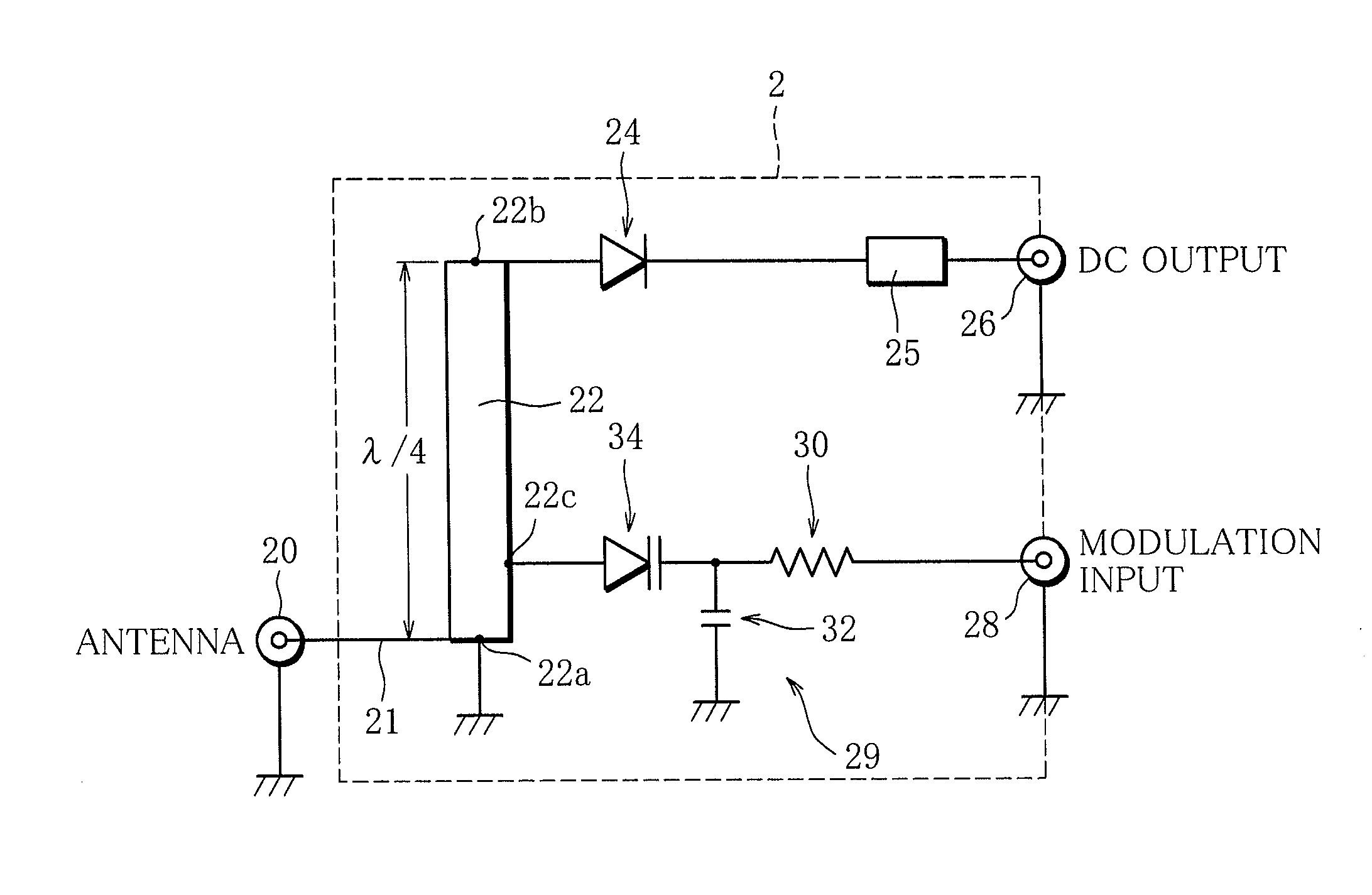
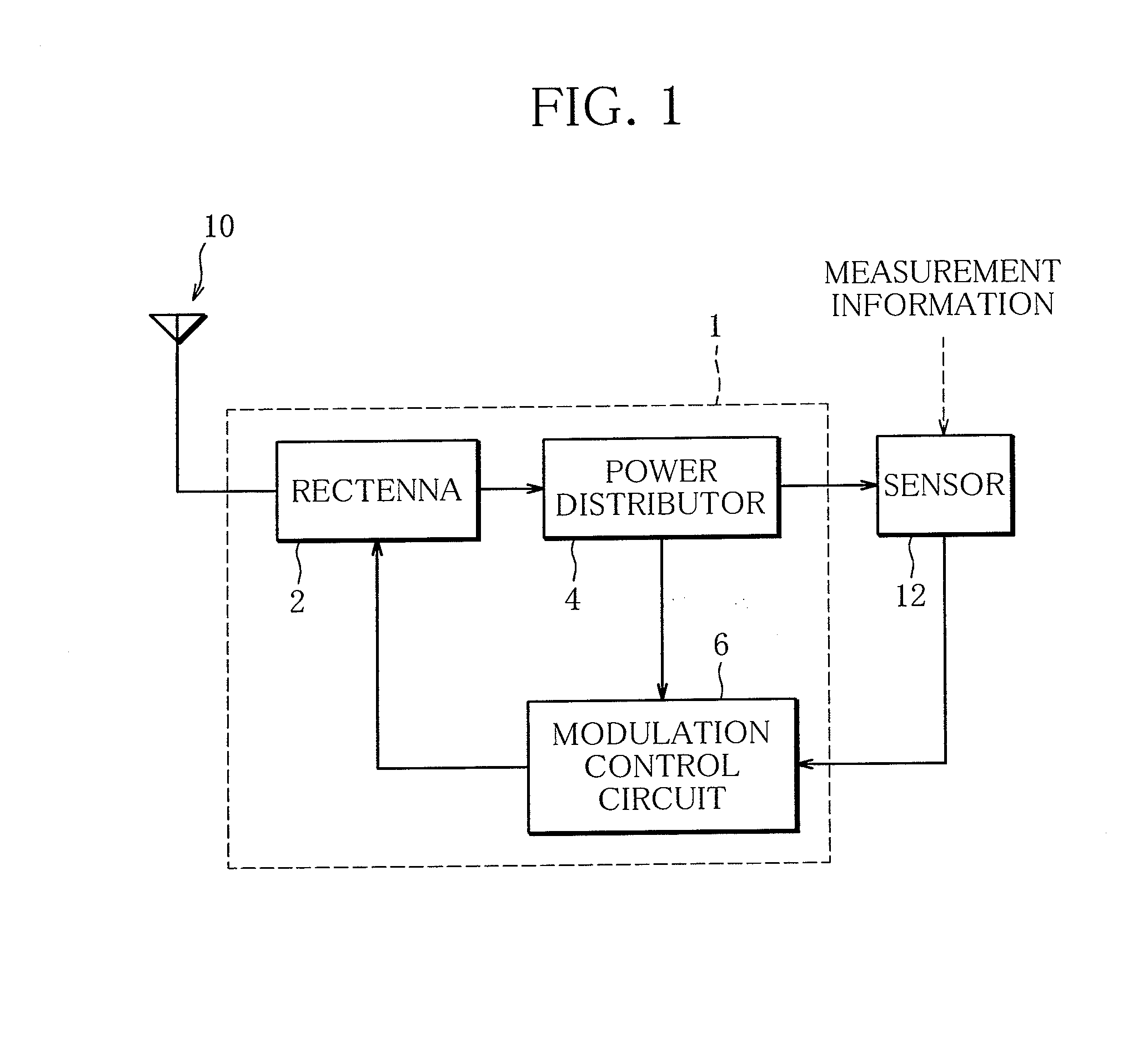
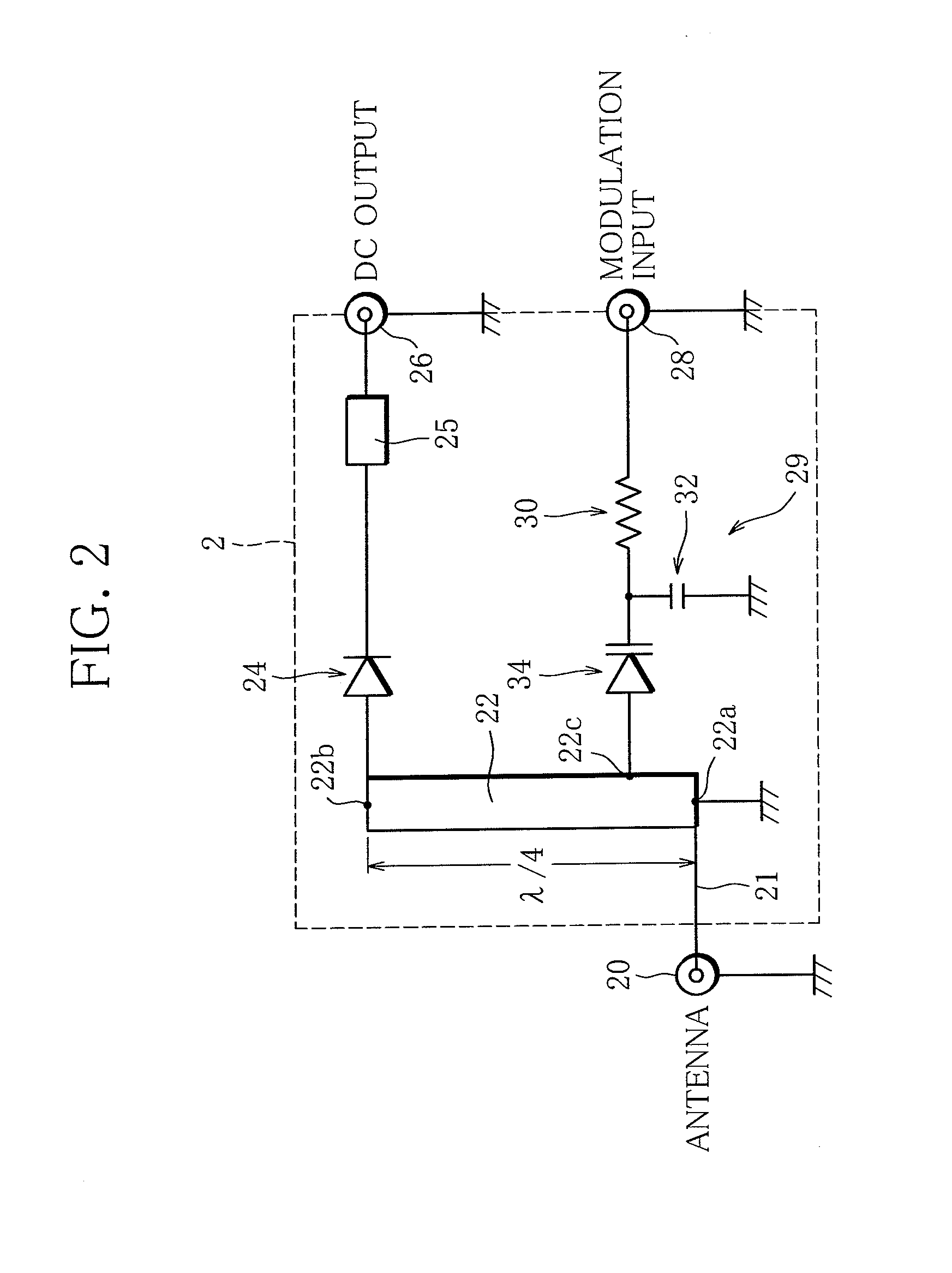
Rectenna
InactiveUS20140001876A1Small sizeProlong lifeElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersSignal waveCapacitance
A rectenna includes an antenna configured to receive a radio wave, a rectifier circuit configured to rectify the radio wave received by the antenna, a transmission line connected to the antenna and the rectifier circuit, and a modulation input circuit including a variable capacitance element. The variable capacitance element is connected at one end to a portion of the transmission line between an antenna connecting portion at which the antenna is connected to the transmission line and a rectifier circuit connecting portion at which the rectifier circuit is connected to the transmission line, and is configured such that the capacitance thereof varies in accordance with the voltage of a modulated signal wave input to the other end of the variable capacitance element.
Owner:IHI AEROSPACE CO LTD
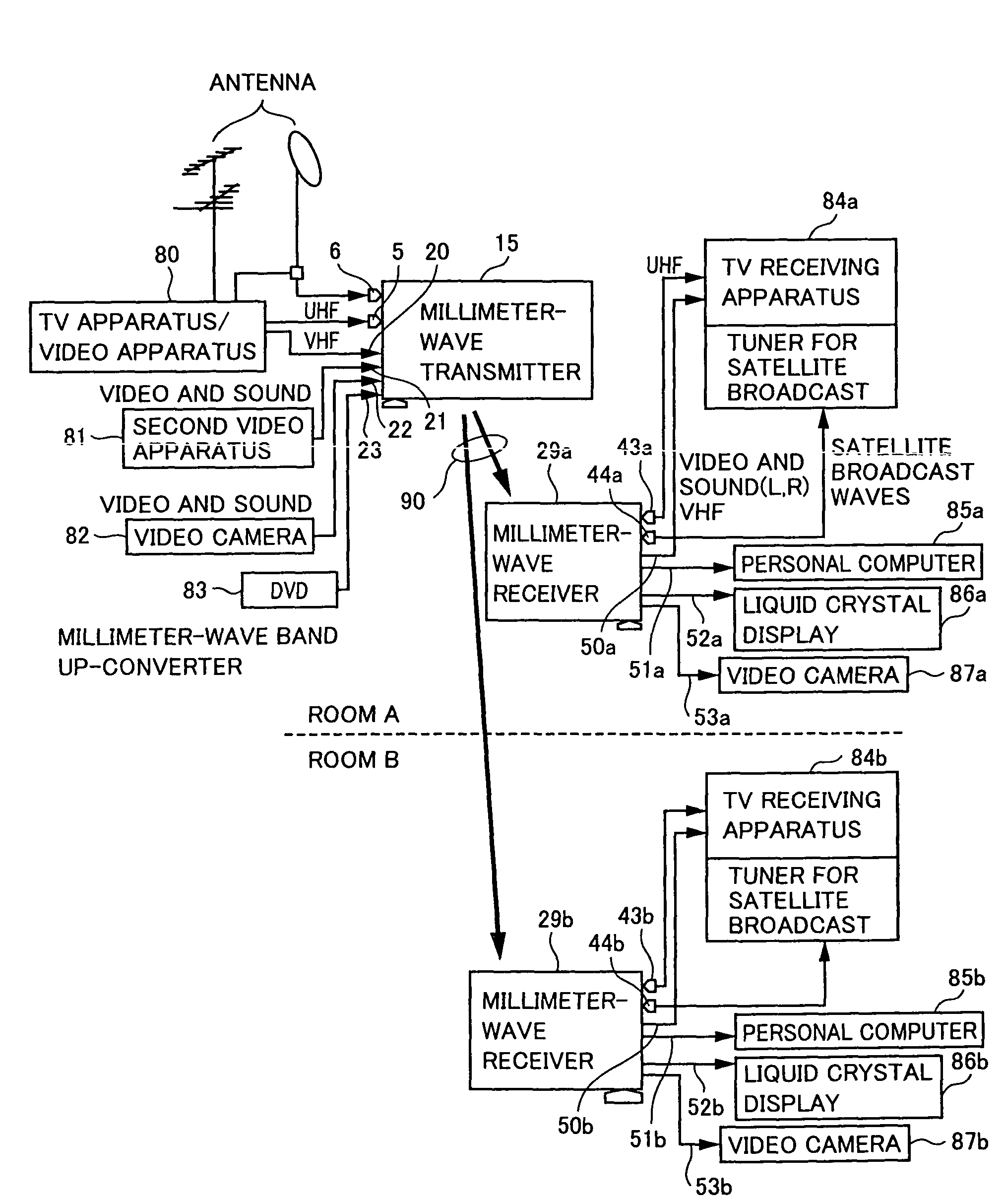
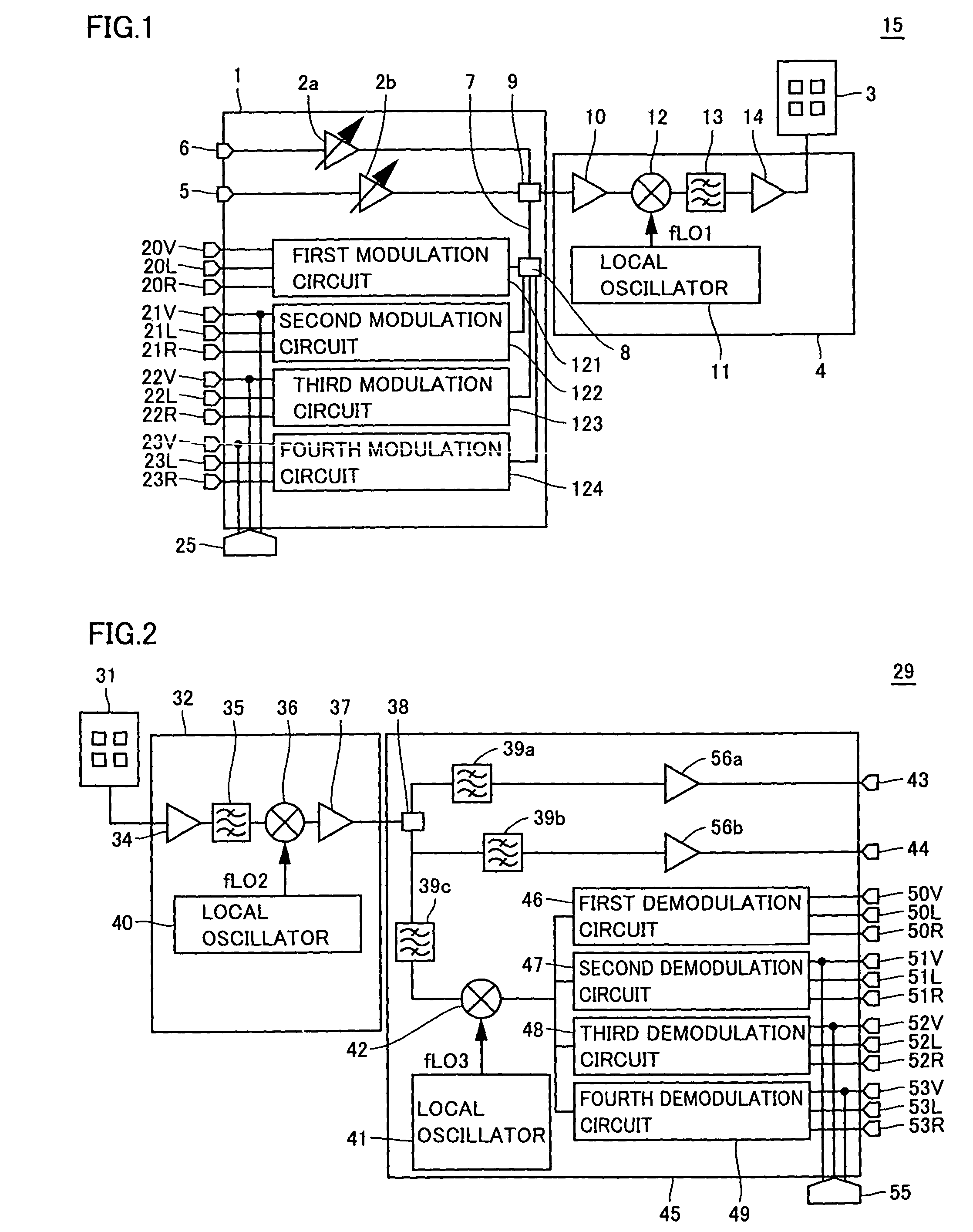
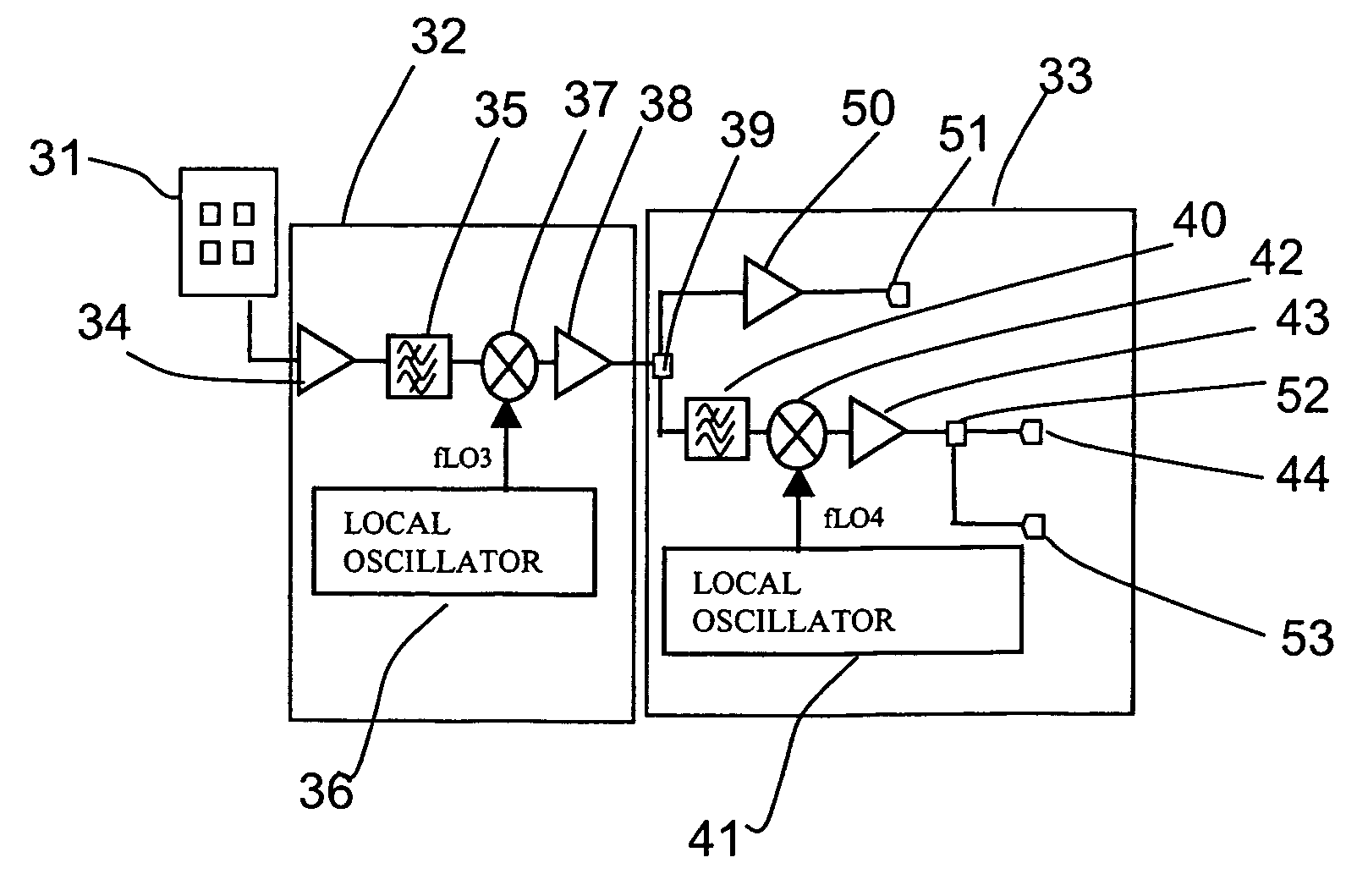
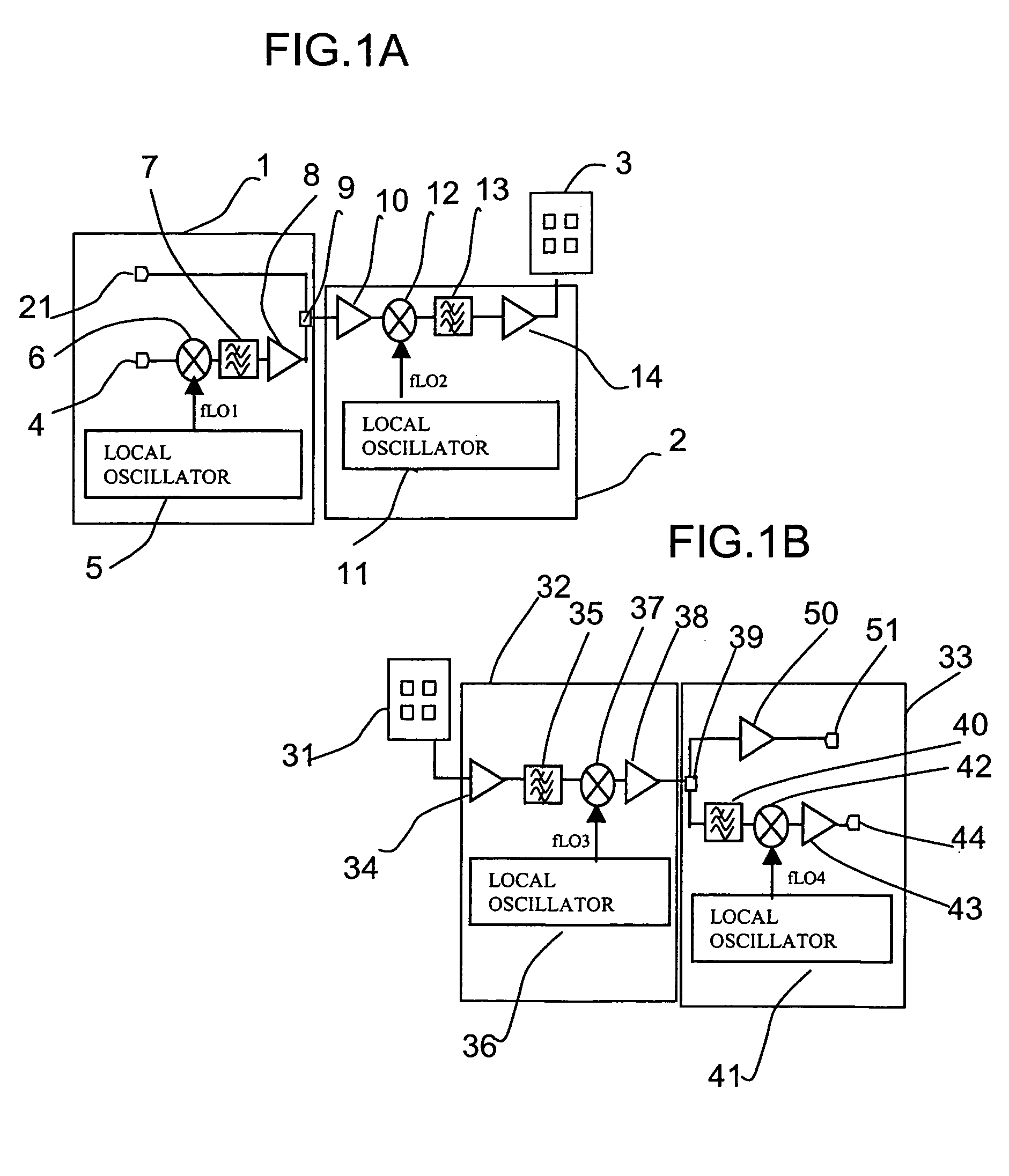
Radio communication apparatus, transmitter apparatus and receiver apparatus
InactiveUS7697574B2Improve frequency stabilityTelevision system detailsActive radio relay systemsMultiplexingSignal wave
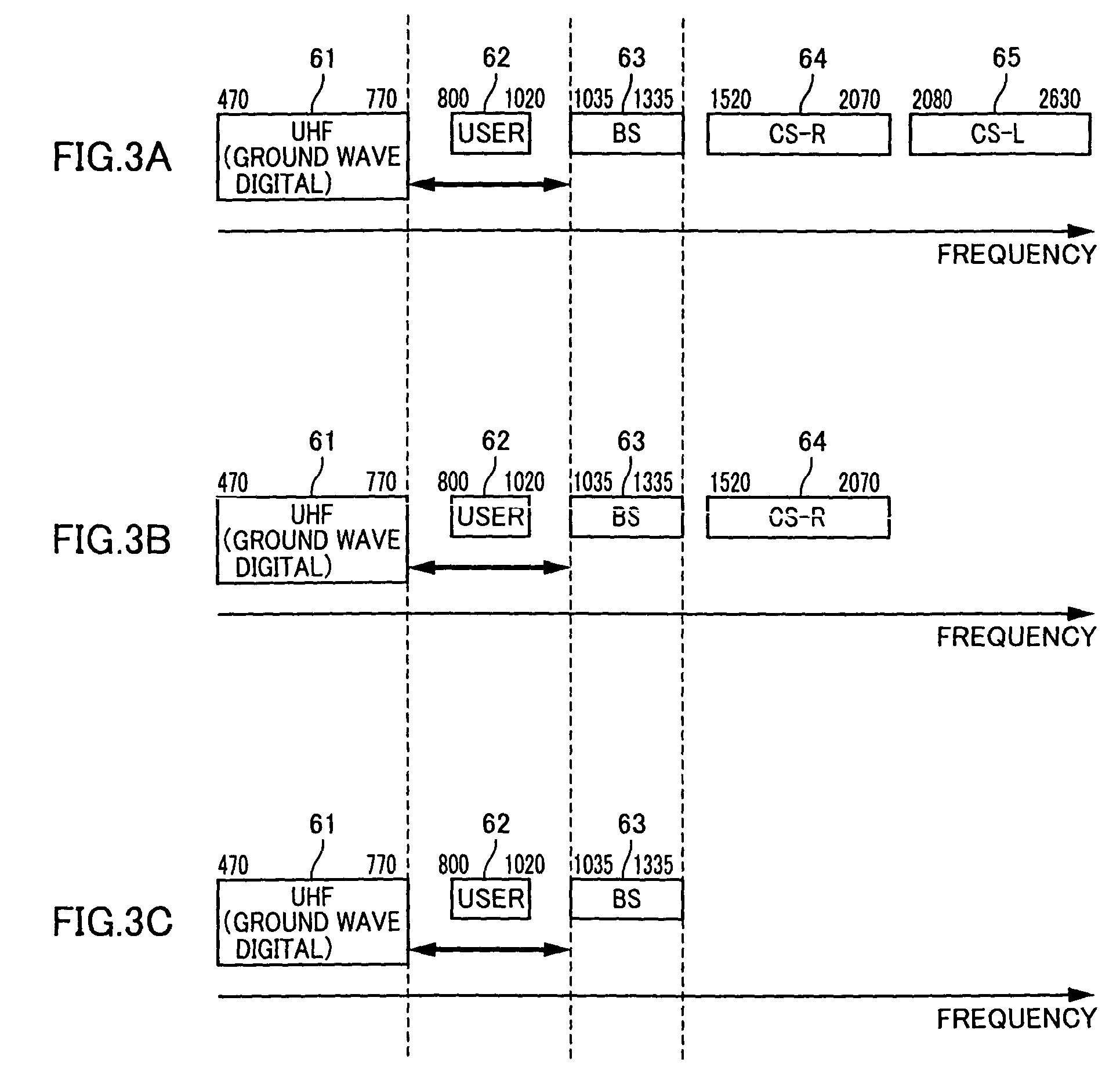
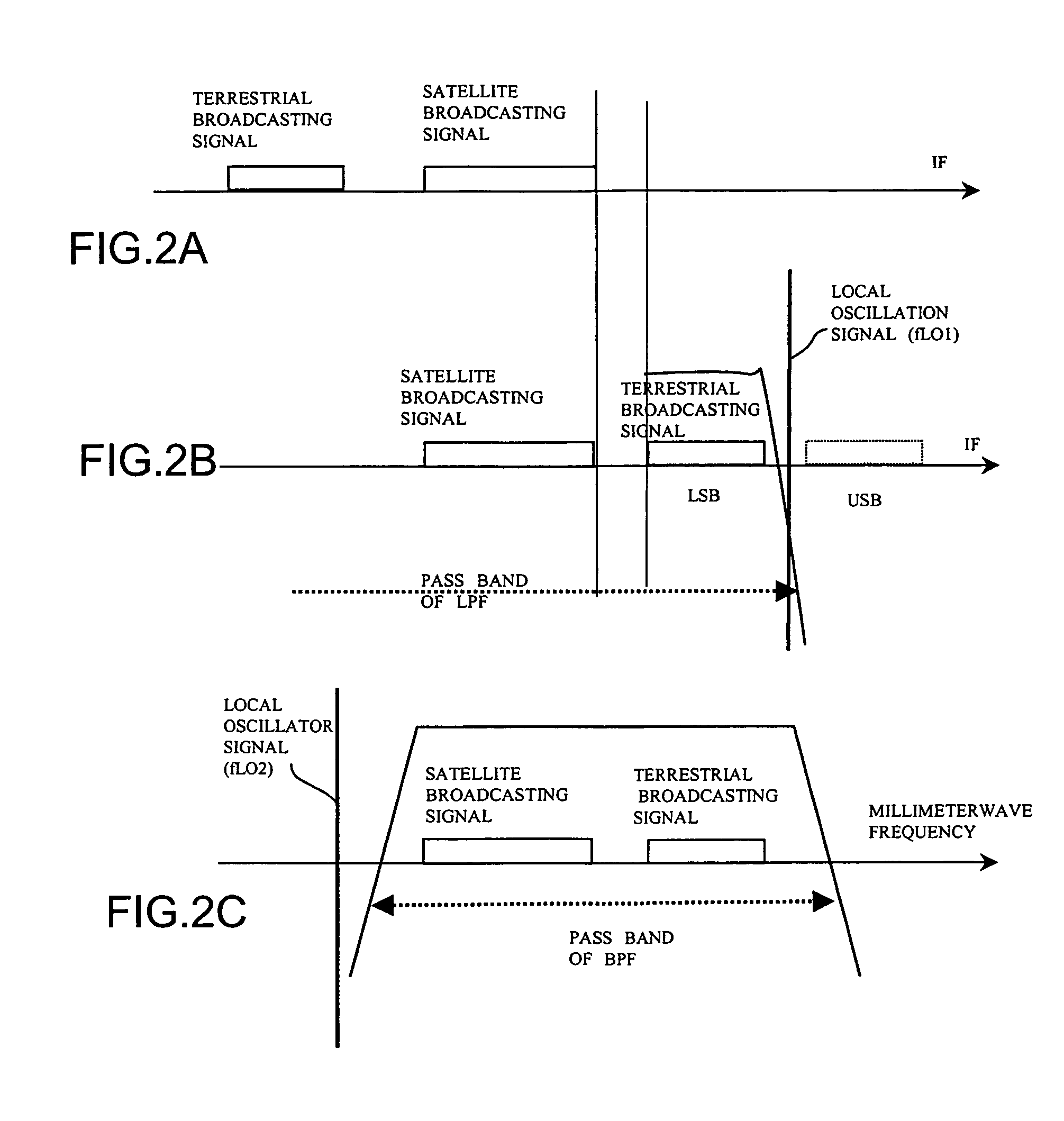
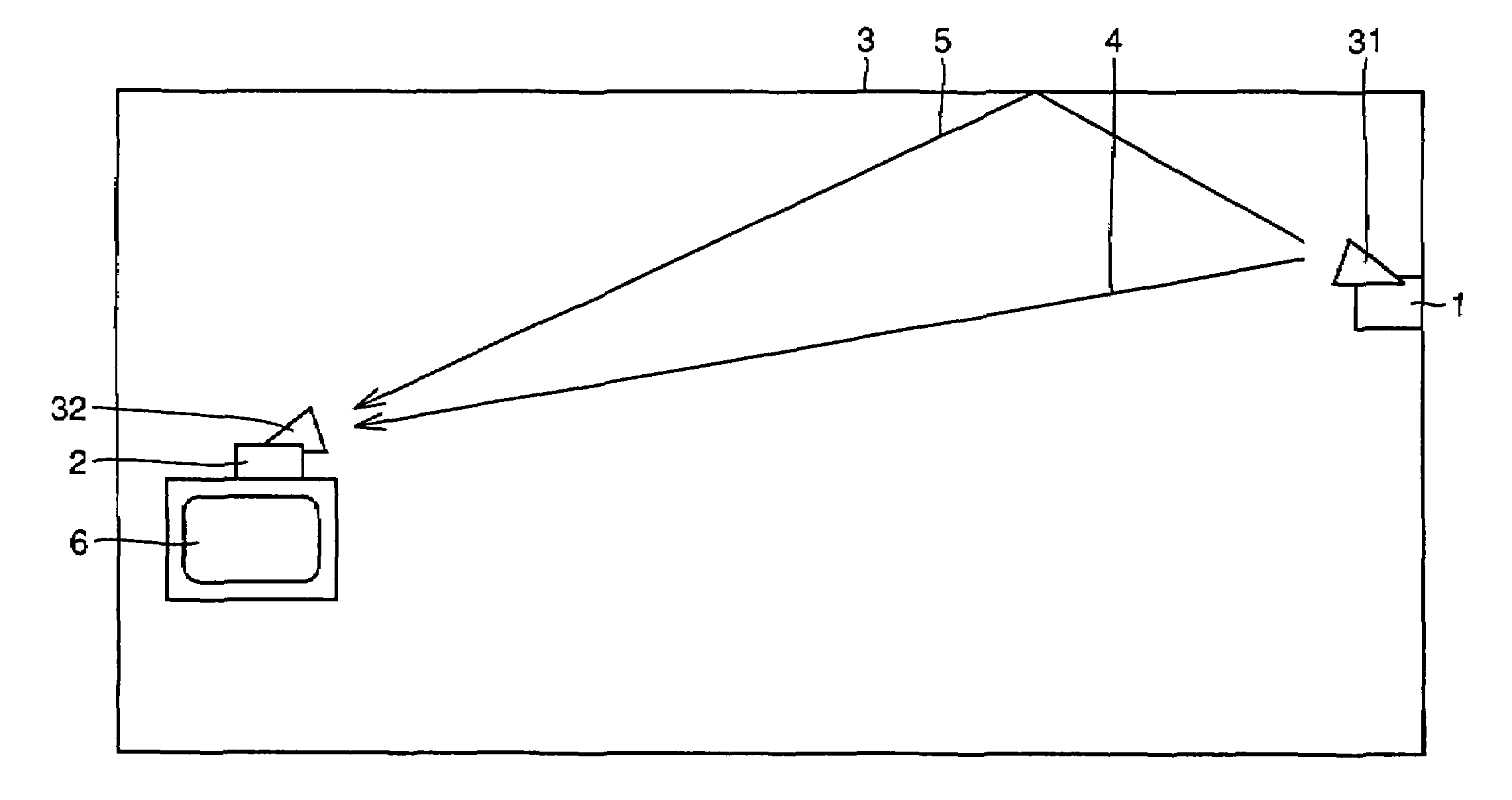
The present invention provides a radio communication device, a transmitter and a receiver capable of handling a plurality of signal waves. A radio communication device has a millimeter-wave transmitter (15) and a millimeter-wave receiver (29). Millimeter-wave transmitter (15) includes a multiplexing circuit (1), a millimeter-wave up-converter (4) and an antenna (3), and the millimeter-receiver includes an antenna (31), a millimeter-wave down-converter (32) and an output processing circuit (45). The signal waves dedicated to the user are modulated by a modulation circuit (121 to 124) so as to be allocated between the ground broadcast waves and satellite broadcast waves. The frequencies are multiplexed in an intermediate frequency band, after that, the multiplexed frequencies are converted into a millimeter-wave band and the resultant is transmitted. On the reception side, the multiplexed waves are down-converted, separated to signal waves and demodulated.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
Optical fiber pump multiplexer
InactiveUS20050105854A1Lower refractive indexLaser detailsCoupling light guidesSignal waveDouble-clad fiber
One or more single mode few-moded or multimode fibers are incorporated into a bundle to carry input to a fiber amplifier or output from a fiber amplifier or a fiber laser. The input is at the signal wavelength, which is the wavelength where amplification or lasing occurs. Each of the fibers in the bundle is cleaved individually or as a group and fiber ends are aligned in the same plane. The fiber amplifier or fiber laser may include a double clad fiber and the other fibers of the bundle couple light for cladding pumping. The device may also include a mode filter for controlling the output mode.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Sulfur hexafluoride discharge decomposed gas component analysis system and its usage method
InactiveCN101059485AImprove sealingGuaranteed validityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationTransformerSulfur hexafluoride
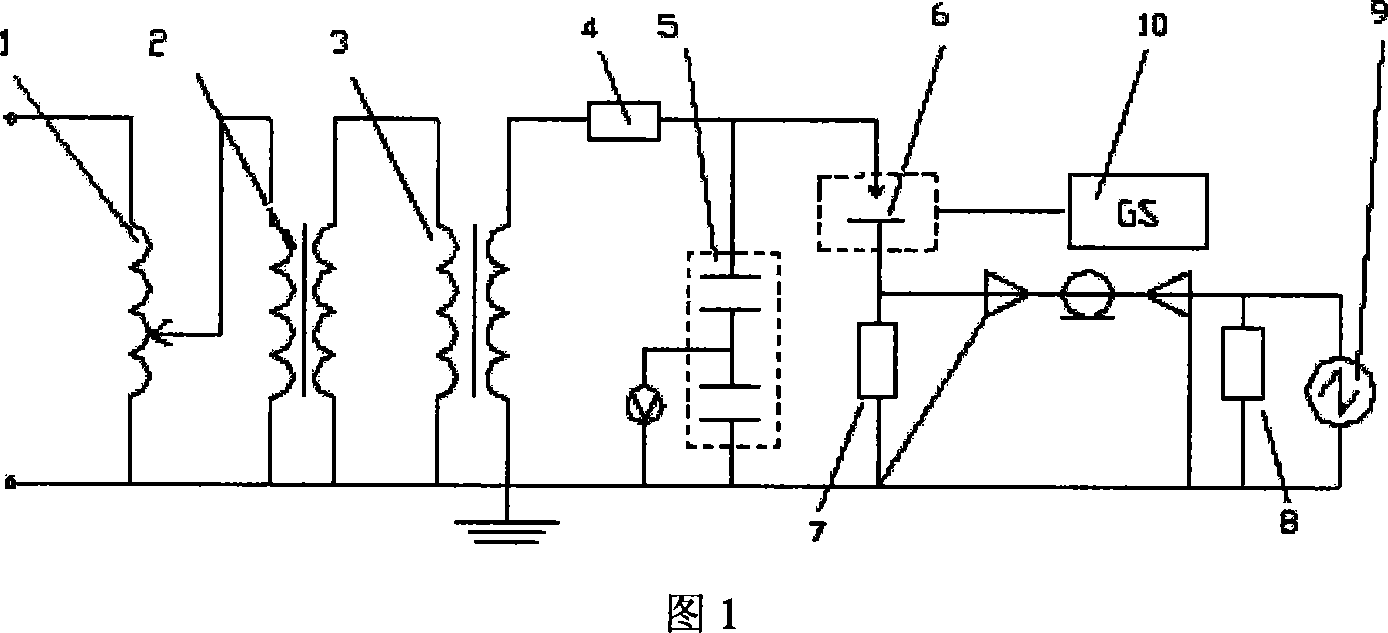
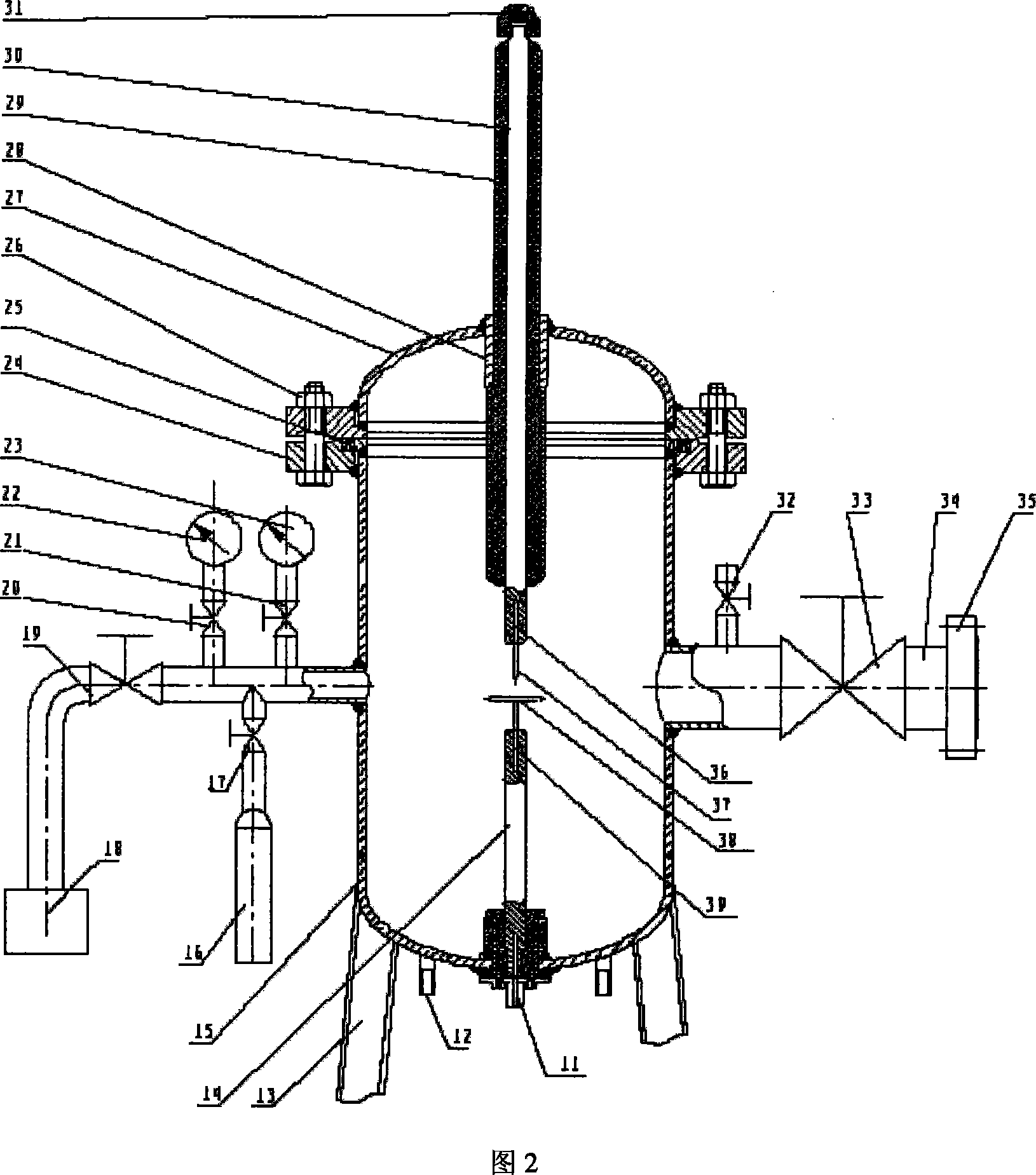
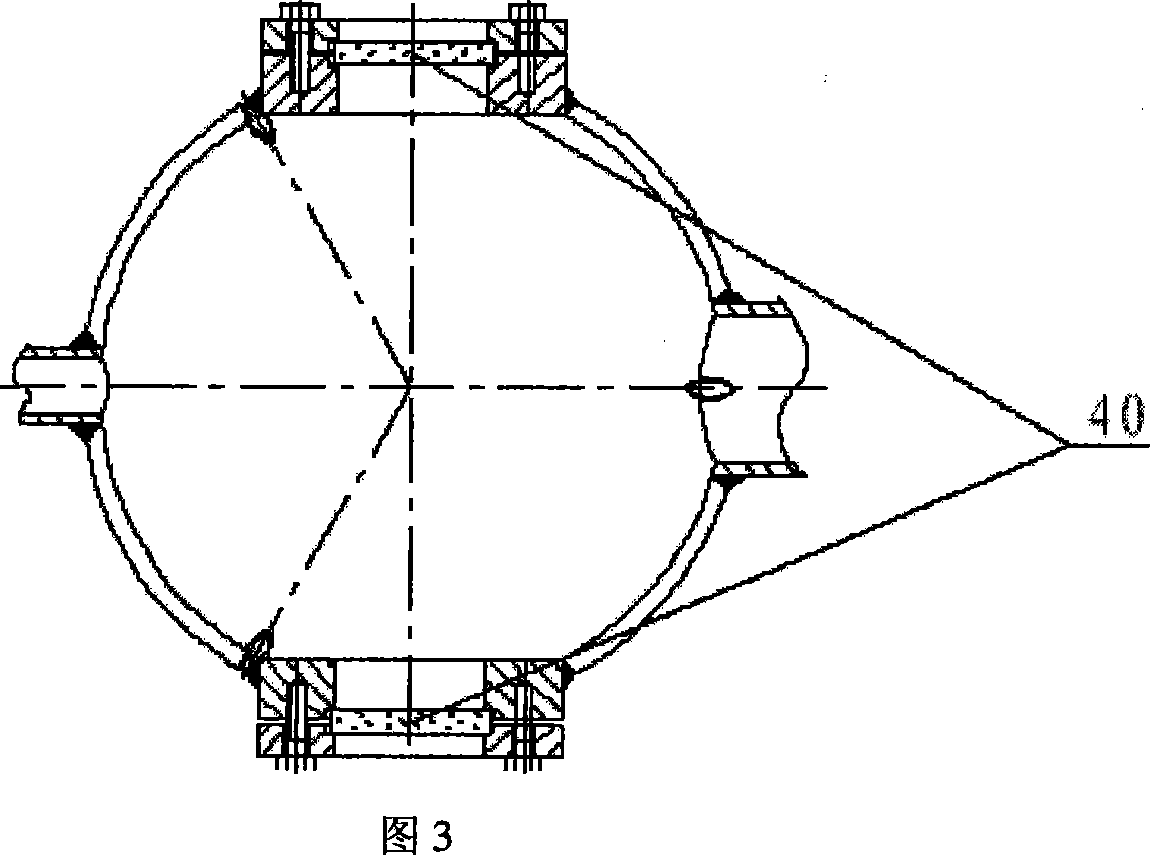
A sulfur hexafluoride discharge decomposition gas component analysis system is composed of a pressure adjuster console 1, an insulation transformer 2, a non-blooming test transformer 3, a non-local-discharge protective resistance 4, a capacitor bleeder 5, a sulfur hexafluoride discharge decompose device 6, a non-inductive check resistance 7, a match resistance 8, an oscillometer 9, and a gas spectrometer 10. And the method comprises that (1), using a vacuum pump 18 to vacuum the sulfur hexafluoride discharge decompose device 6, (2), using an inlet needle valve 17 to feed SF6 gas into the sulfur hexafluoride discharge decompose device 6, (3), measuring maximum external test voltage and initial PD voltage, (4), generating PD under different electrodes, (5), collecting gas, (6), analyzing gas components, (7), collecting PD pulse signal wave shape, diagnosing accident and recognizing mode. The invention has wide application in research, teach, academy and industry, used in theory analysis and research of PD online state check of GIS device.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Wireless communications antenna assembly generating minimal back lobe radio frequency (RF) patterns
InactiveUS6885352B2Increase installation costCumbersome set-up procedureAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysSignal wavePower cable
An antenna assembly for wireless communications has various components to minimize signal influence when transmitting signals to minimize undesirable loop formation phenomena caused by (positive) feedback of signals. Signal wave scattering and diffraction causing back lobe radio frequency (RF) patterns are minimized by a particular antenna assembly structure having a reflector and at least one attenuating structural member, a metallic mesh wrapping the power cable of a feeder, a non-conductive antenna support structure, or any combination thereof. The dimensions of the various components, in particular the reflector and attenuators, can be varied according to desired wireless communications environment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Device and procedure for visual three-dimensional presentation of ECG data
ActiveUS7266408B2Easy to useElectrocardiographyMedical report generationSignal waveThree-dimensional space
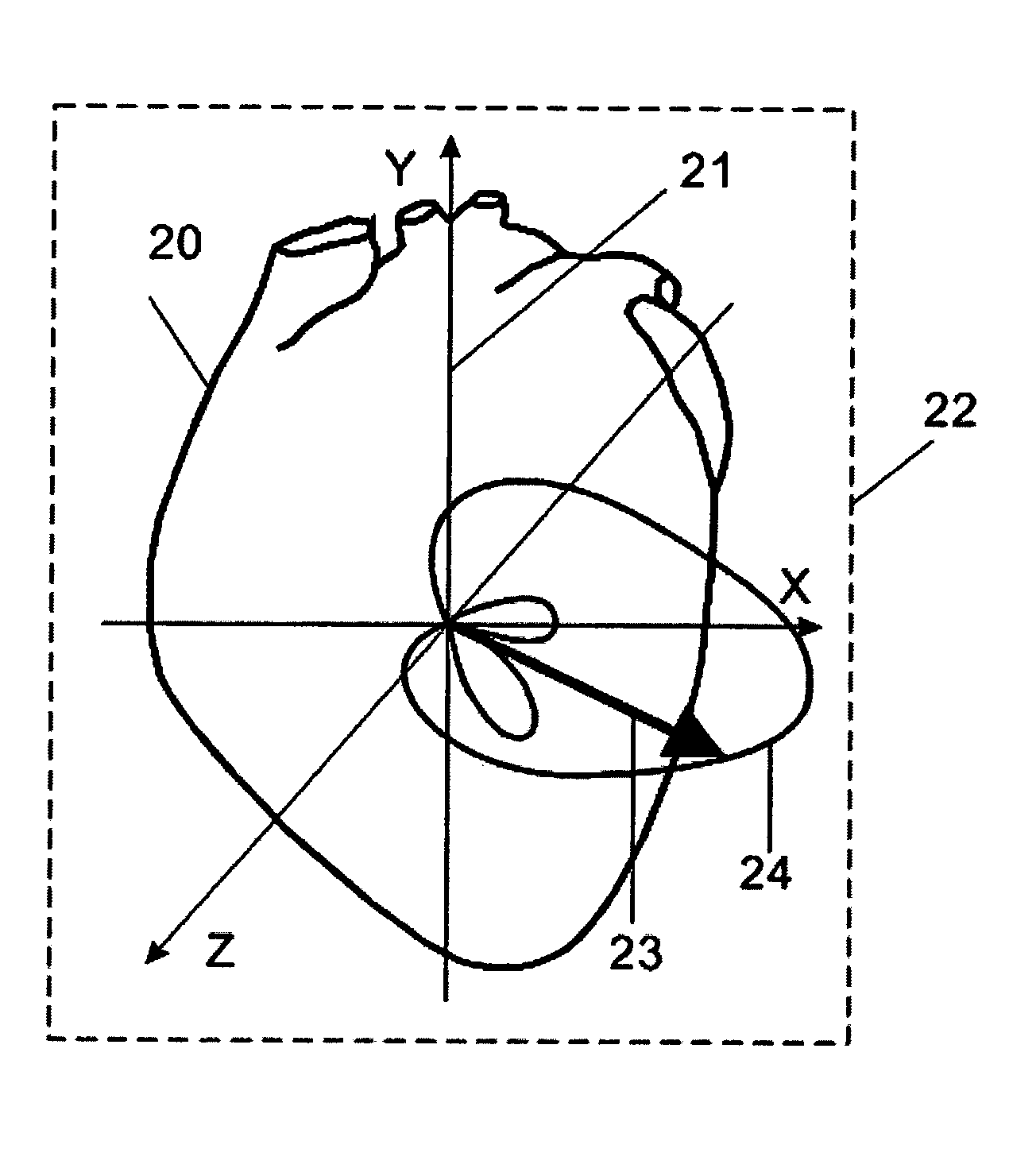
The invention relates to the analysis of ECG data by exploiting computerized three-dimensional spatial presentation of the measured data using the vector concept. A three-dimensional presentation of the human heart may be correlated with waveforms specific for standard ECG or derived ECG signals based on the dipole approximation of the heart electrical activity. The three-dimensional heart model may be rotated, and the ECG signals are interactively linked to the model. In the visualization process, different types of signal presentation may be used, including graphical presentation of the heart vector hodograph, graphical presentation of the signal waveform in an arbitrary chosen point on the heart, and graphical presentation of the map of equipotential lines on the heart in a chosen moment. Additional tools for analyzing ECG data are also provided which may be interactively used with the display tools.
Owner:ERESTECH +1
Chest diagnostic support information generation system
A chest diagnostic support information generation system includes: a radiography section which radiographs a chest portion of a subject; an image analysis section which generates a diagnostic support information based on an image data generated by the radiography section; and a display which displays the diagnostic support information, wherein the radiography section obtains a plurality of frame images which show a motion state of the chest of the subject, and the image analysis section includes: a breathing information generation section which generates the diagnostic support information relating to breathing of the subject based on a difference value of the pixel or the block corresponded with each other between image frames temporally adjacent among the plurality of frame images; and a blood flow information generation section which generates the diagnostic support information relating to blood flow of the subject based on a generated output signal wave form.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Optical switch and optical waveform monitoring device utilizing optical switch
InactiveUS20060045445A1Improve switching efficiencyReduce lossesTime-division optical multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical parametric amplifierPolarizer
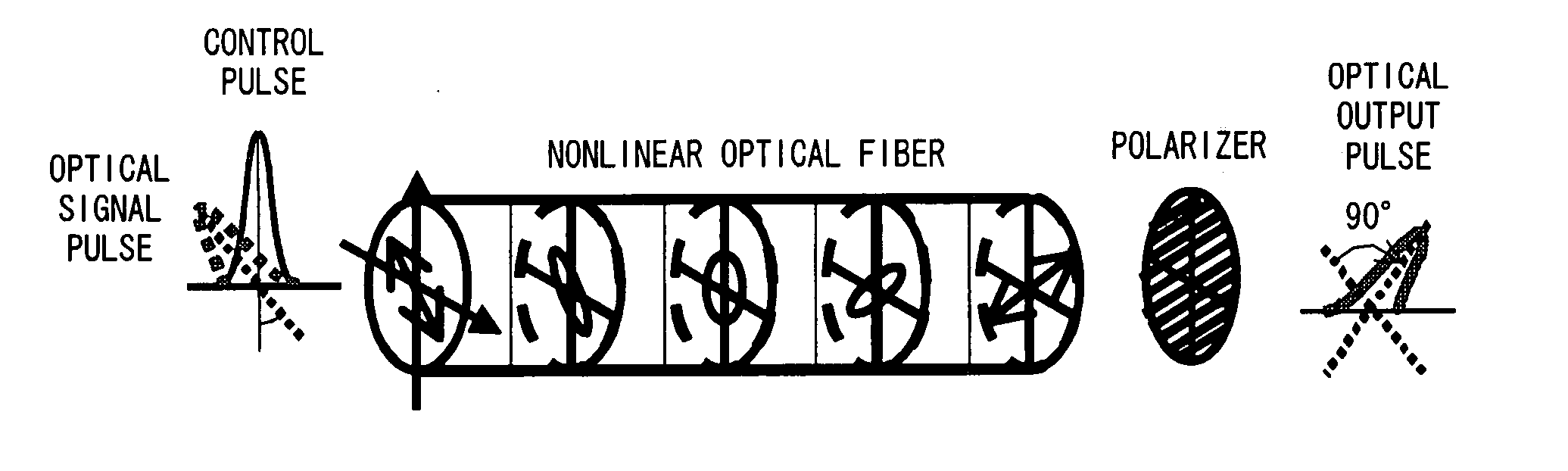
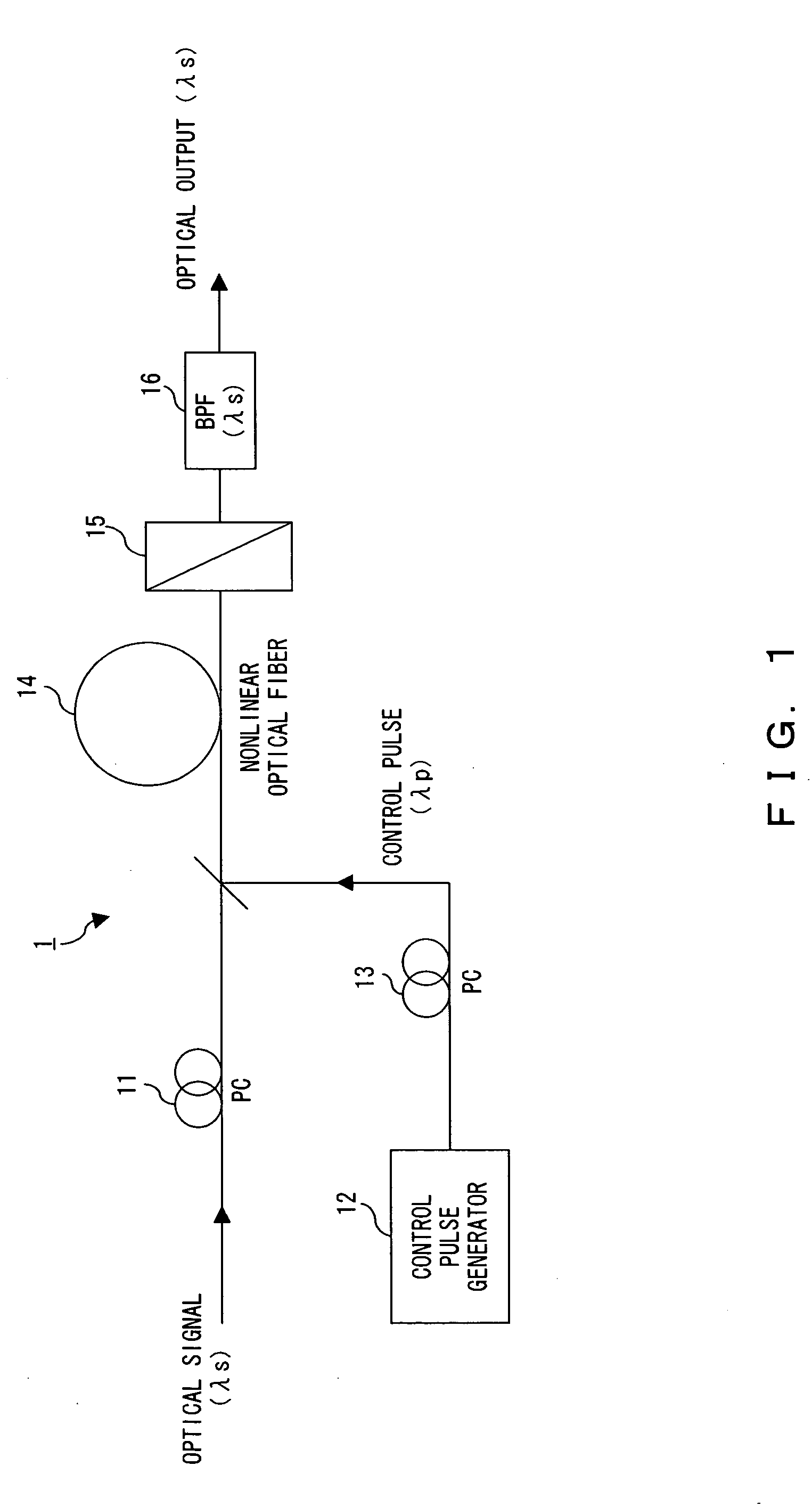
The polarization direction of a signal is rotated by a polarization controller so as to be orthogonal to the main axis of a polarizer. A control pulse generator generates control pulses from control source with a wavelength which is different from the wavelength of the signal. The signal and the control pulse are input to a nonlinear optical fiber. In the nonlinear optical fiber, the signal, during the time period in which the signal and the control pulse coincide, has its polarization direction rotated by cross phase modulation, and is amplified by optical parametric amplification. The signal, during the time period in which the signal and the control pulse coincide, passes through the polarizer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, method of manufacturing electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker, method of reproducing sound signal, and super-directivity sound system, and display device
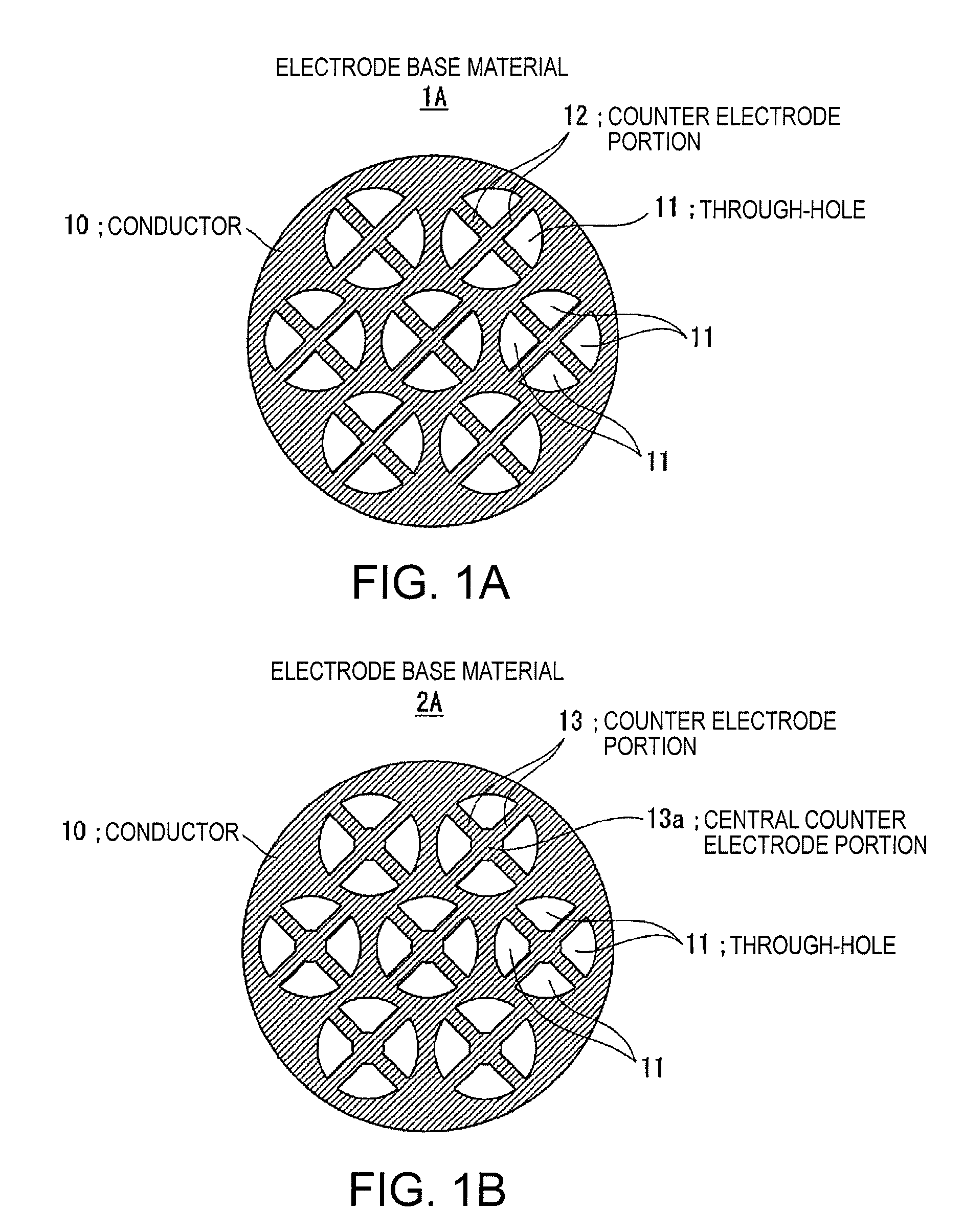
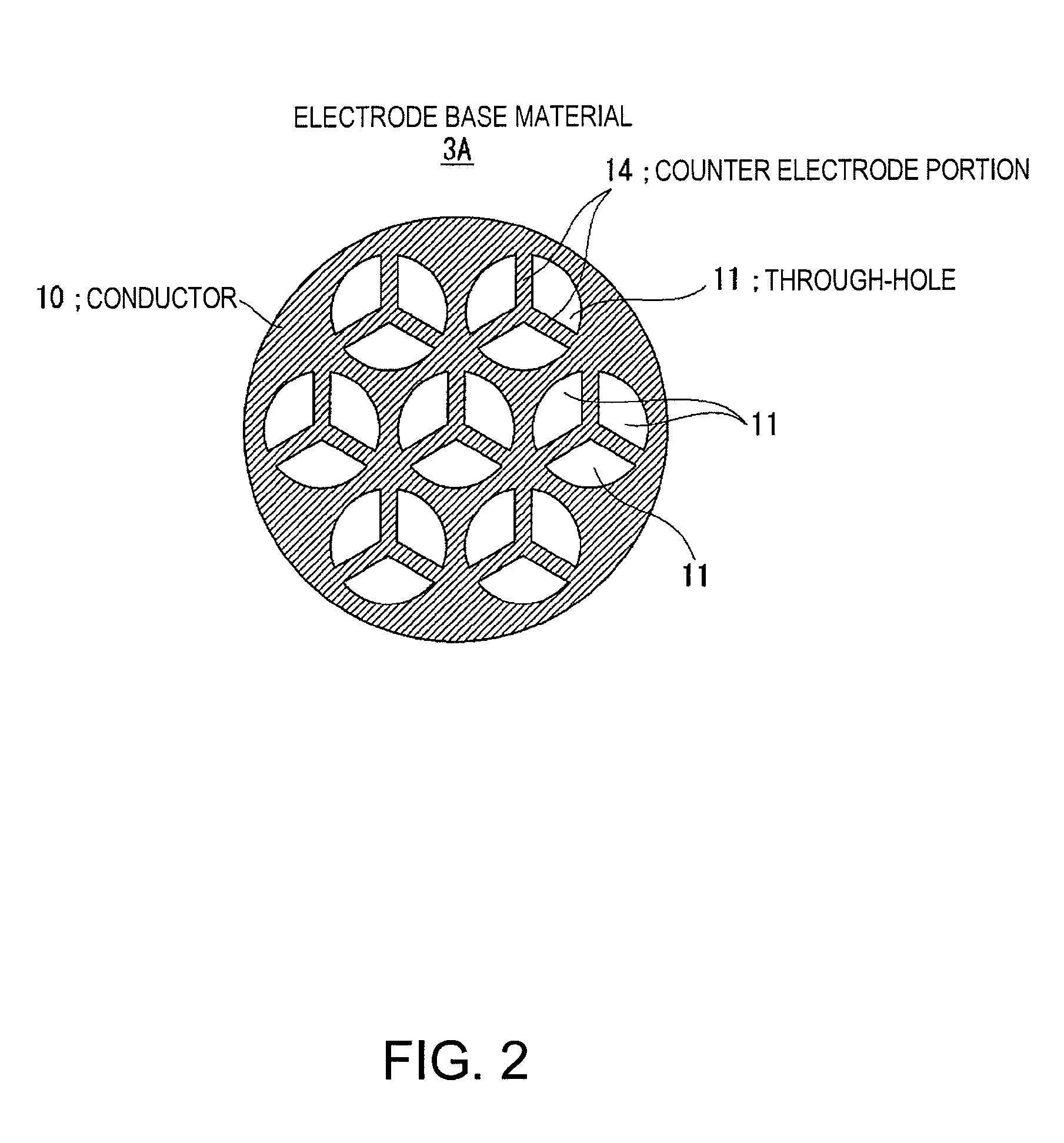
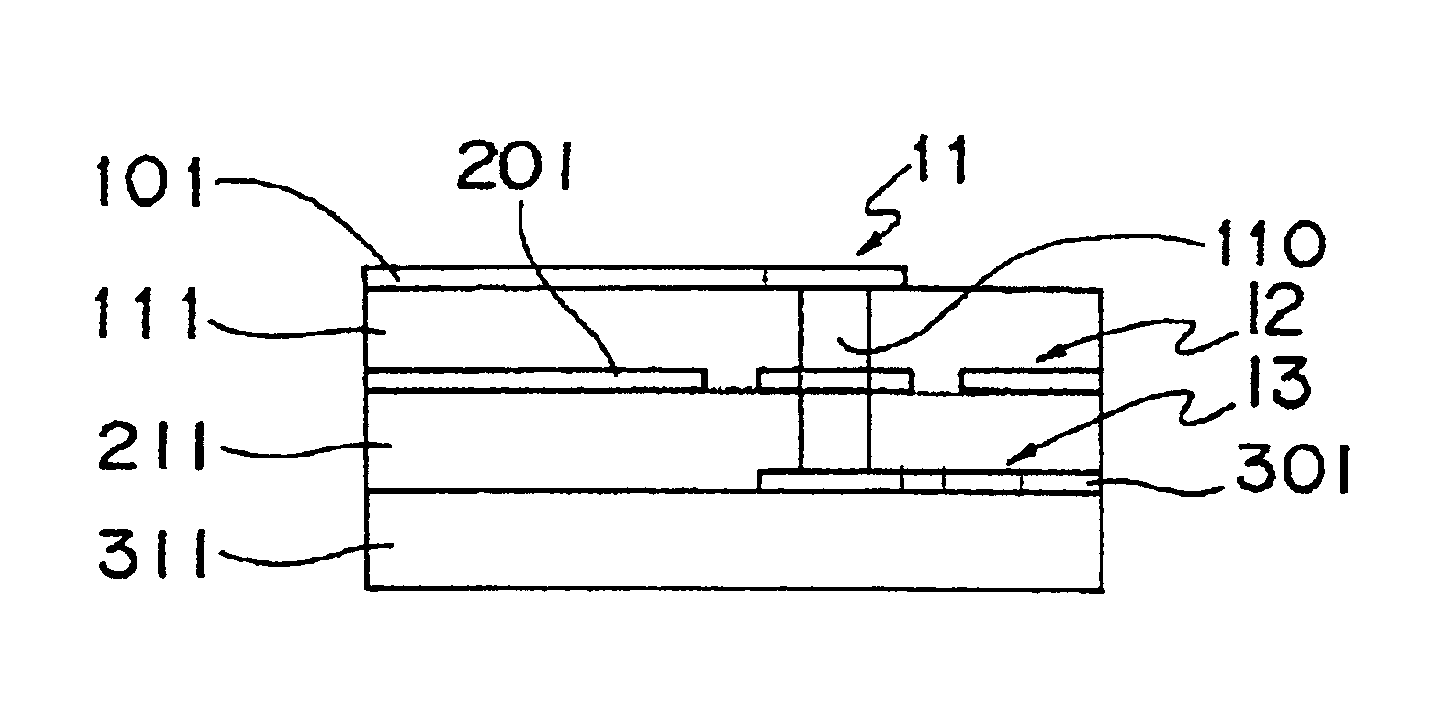
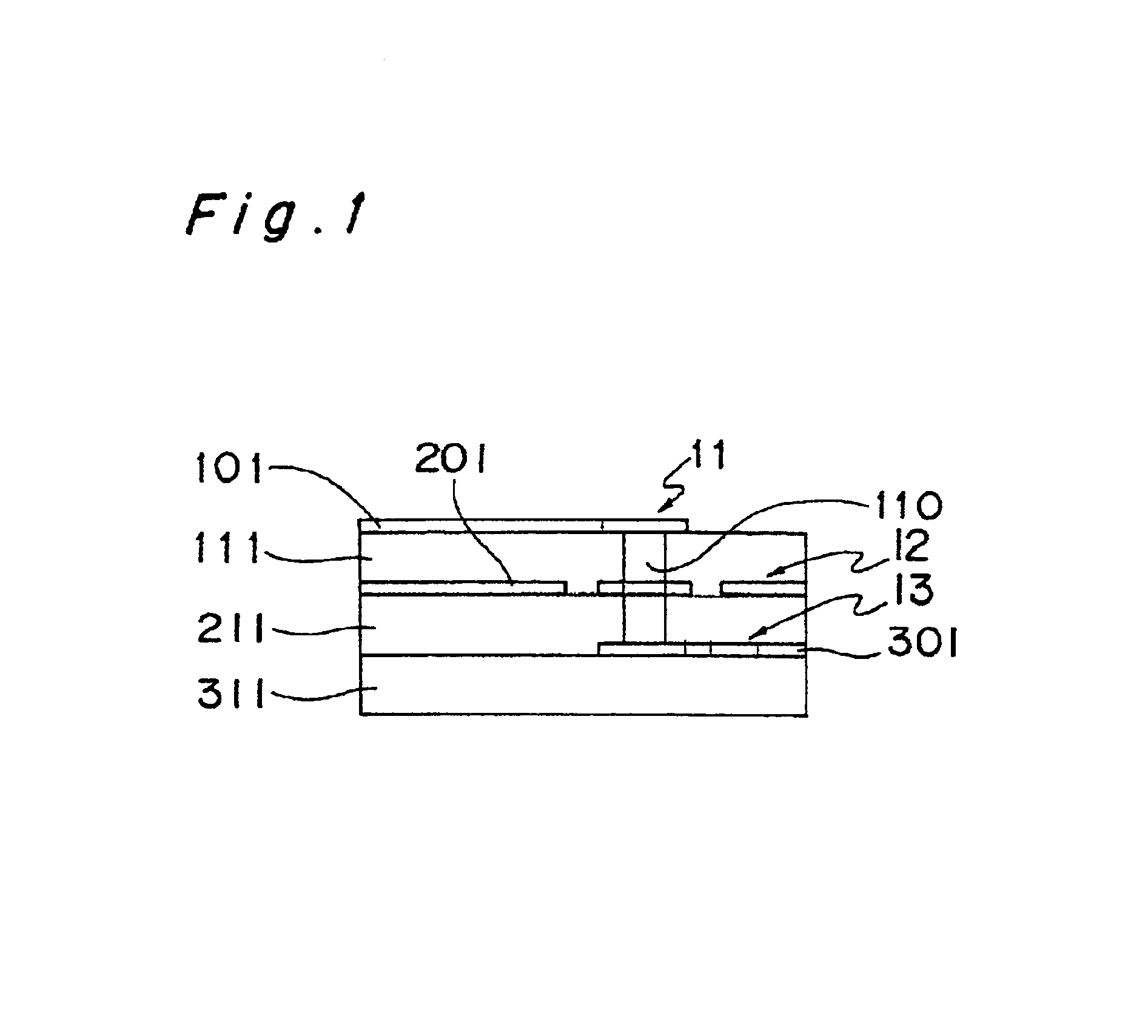
InactiveUS20070195976A1Increase the output sound pressureEfficiently displacedElectrostatic transducersTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsVibrating membraneSignal wave
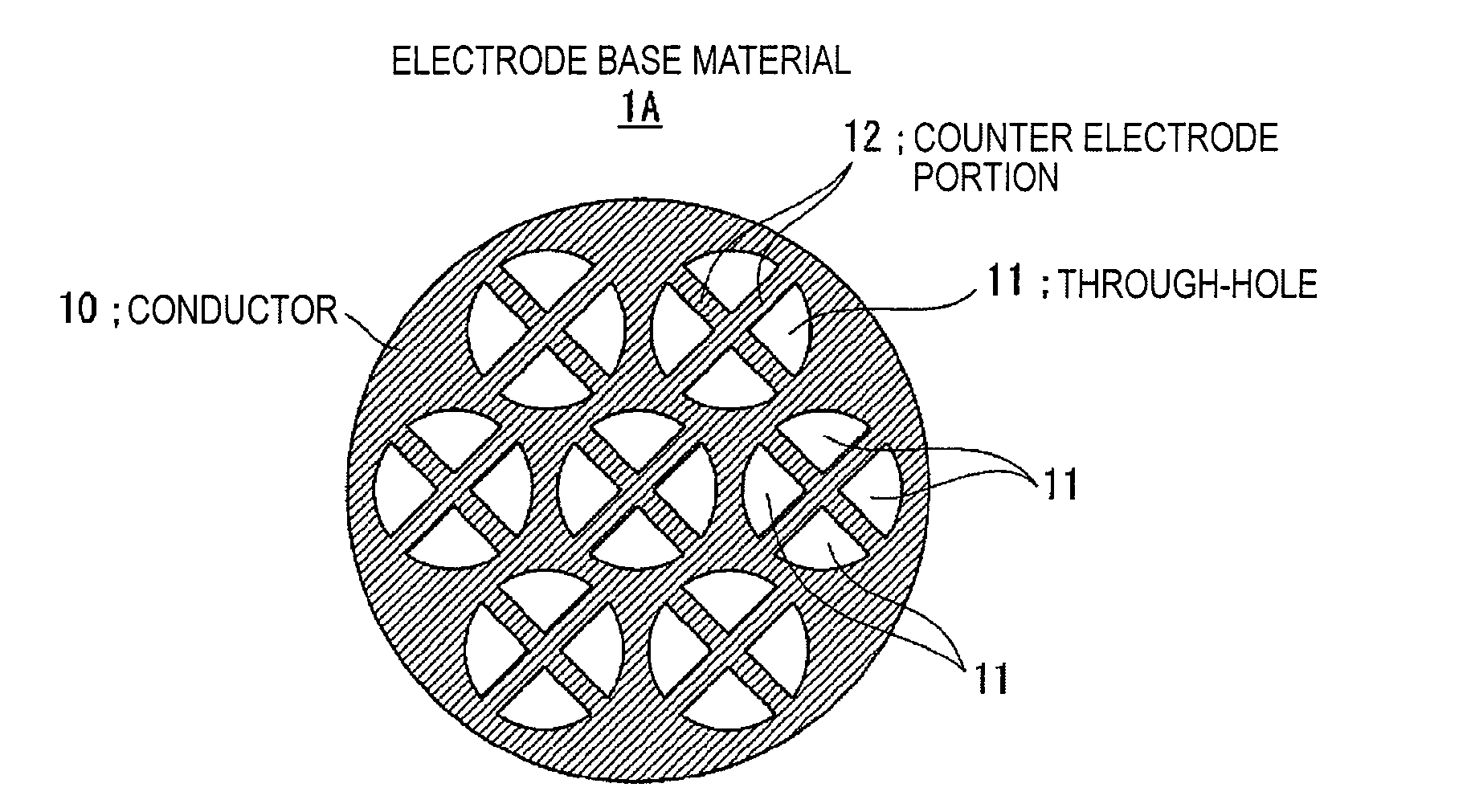
An electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a first electrode that has through-holes, a second electrode that has through-holes, and a vibrating membrane that is disposed such that the through-holes of the first electrode and the through-holes of the second electrode form a pair, interposed between a pair of electrodes composed of the first electrode and the second electrode, and having a conductive layer applied with a direct current bias voltage. The first electrode and the second electrode each have counter electrode portions that are formed in the through-holes to face the vibrating membrane, and a modulated wave, which is obtained by modulating a carrier wave in an ultrasonic frequency band with a signal wave in an audible frequency band, is applied between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
High-frequency multilayer circuit substrate
InactiveUS6856210B2Improve matchSimple structureMultiple-port networksHigh frequency circuit adaptationsSignal waveImpedance matching
A high-frequency multilayer circuit substrate having a plurality of circuit layers includes a via hole for connection between the circuit layers, a metal pad, an impedance matching transmission line, rectangular stubs and a signal transmission line. A via hole connecting portion is constructed of the via hole, the rectangular stubs and the impedance matching transmission line. A characteristic impedance of the via hole connecting portion is matched to a characteristic impedance of the signal transmission line by adjusting widths and lengths of the impedance matching transmission line and the rectangular stubs. Thereby, the reflection of the signal wave in the via hole connecting portion is reduced to decrease a transmission loss.
Owner:SHARP KK
Signal processing using non-linear regression with a sinusoidal model
InactiveUS7574253B2Low costImprove spatial resolutionSpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementFull cycleLinear regression
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method and device for detecting and processing signal waves
InactiveUS7012738B1Small sizeLow costOptical measurementsModulated-carrier systemsSignal waveSignal source
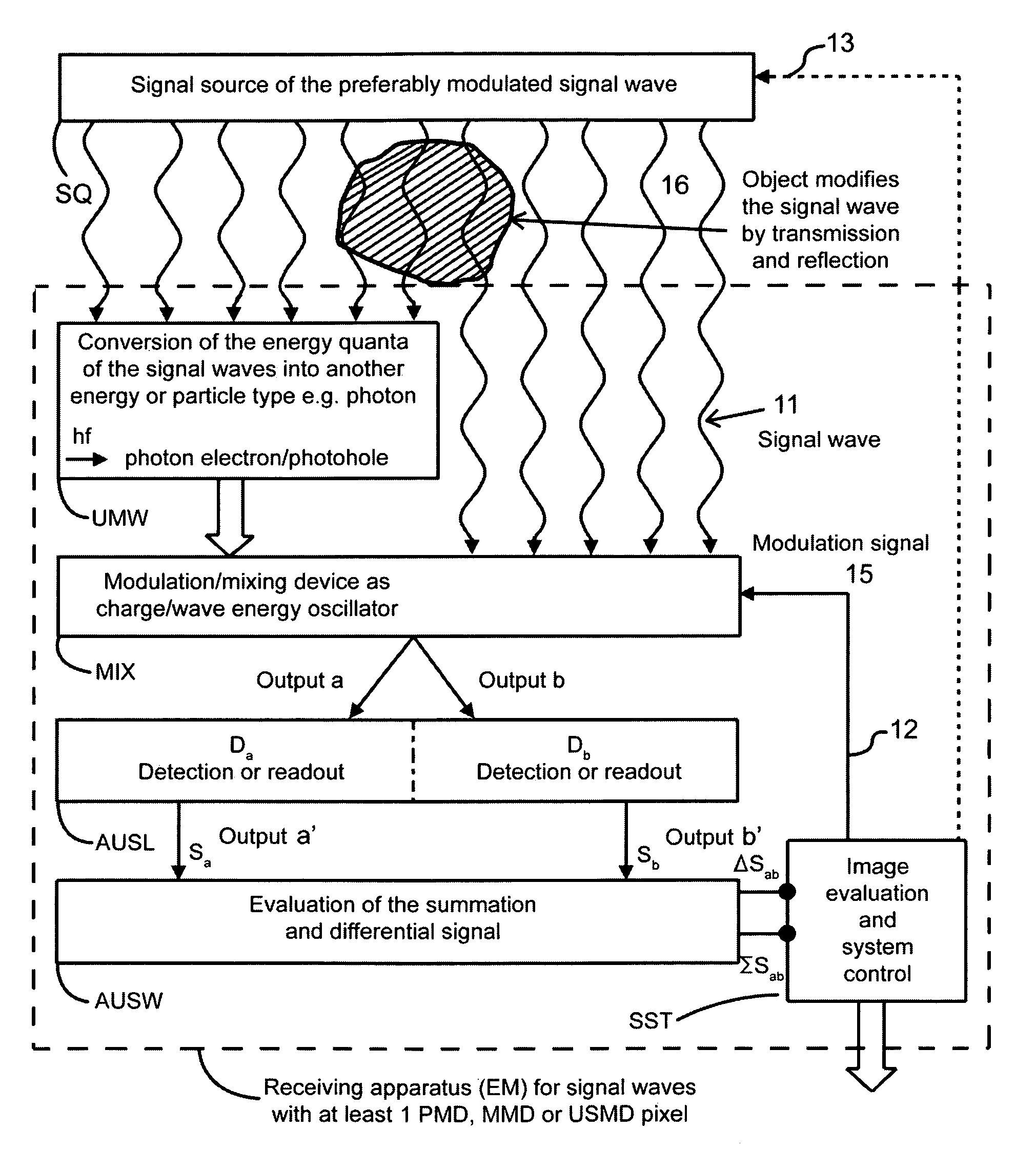
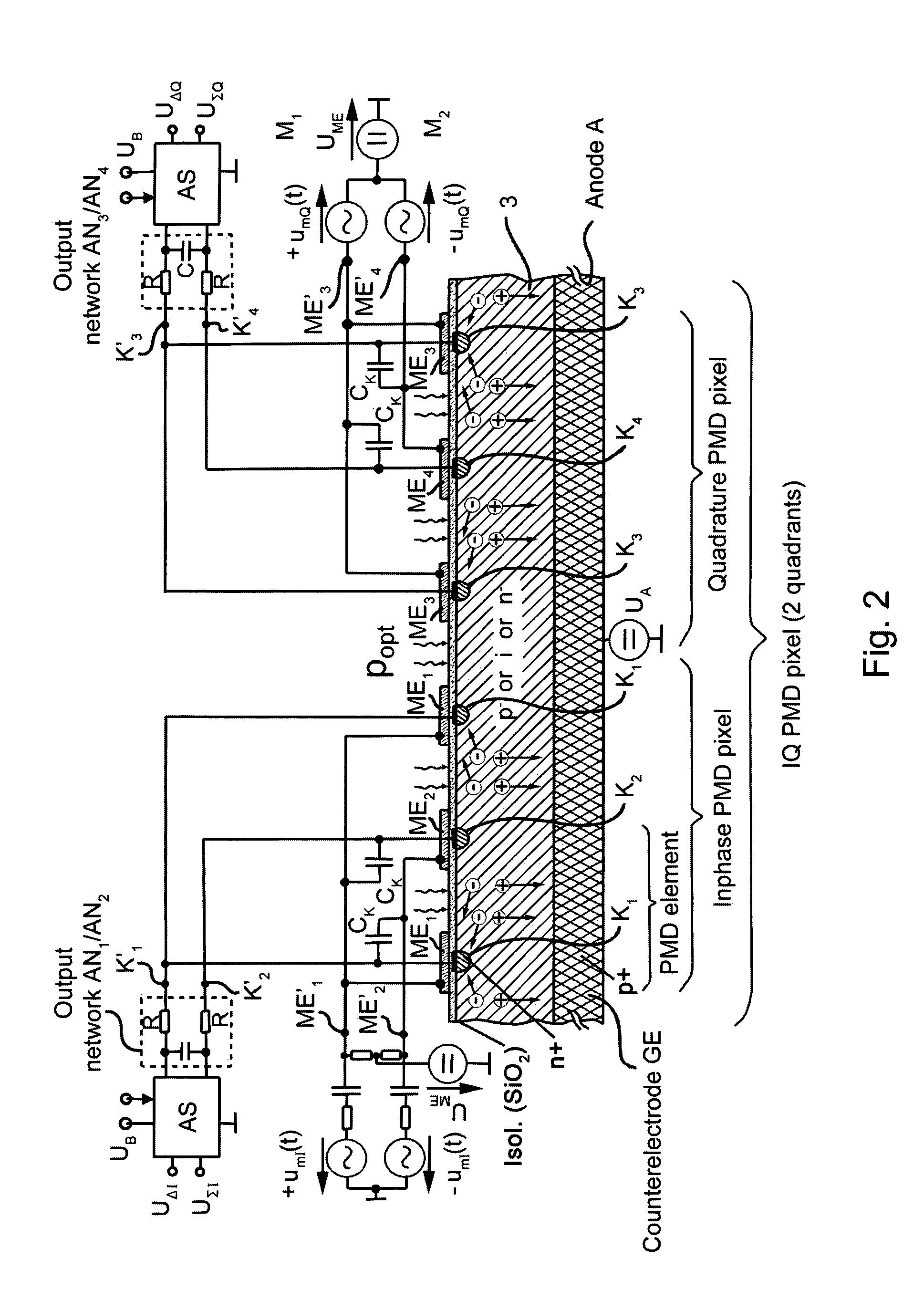
The invention relates to a method for detecting and processing the amplitude and phase of signal waves. A Modulated signal source generates the signal waves which are modified by transmission medium or by reflection and scattering by at least one object. The modified signal waves are received and demodulated using a modulation signal. The amplitude of the modulated signal waves and their phase relationship to the modulation signal are measured and evaluated. The demodulated signal wave is converted into an electrical charge or charge displacement in the receiving medium and is distributed in accordance with a modulation signal to at least two readout outputs and fed to an evaluation unit. The evaluation unit produces the sum and difference of the output signals thus applying the value of the intensity and the phase position of the signal wave that has been scattered, reflected or delayed by the object.
Owner:SCHWARTE RUDOLF
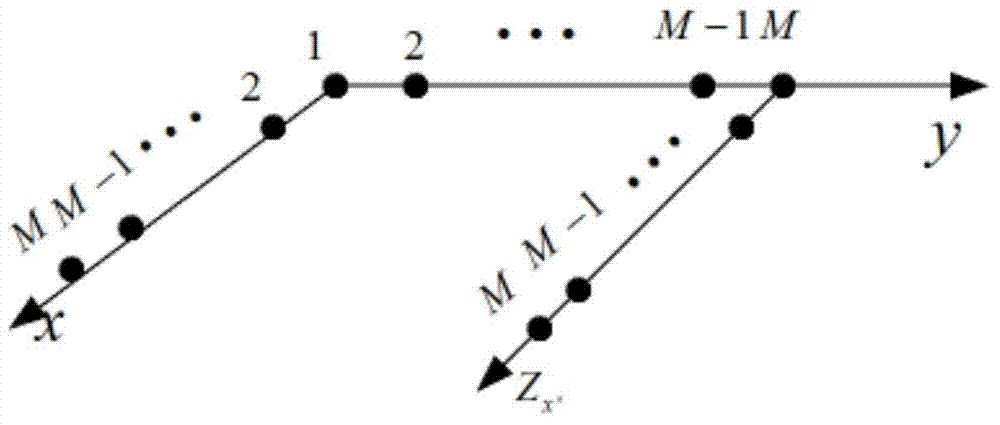
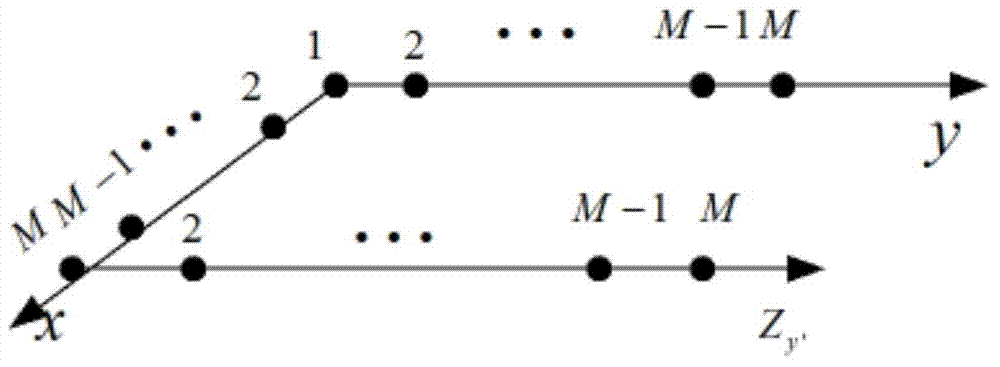
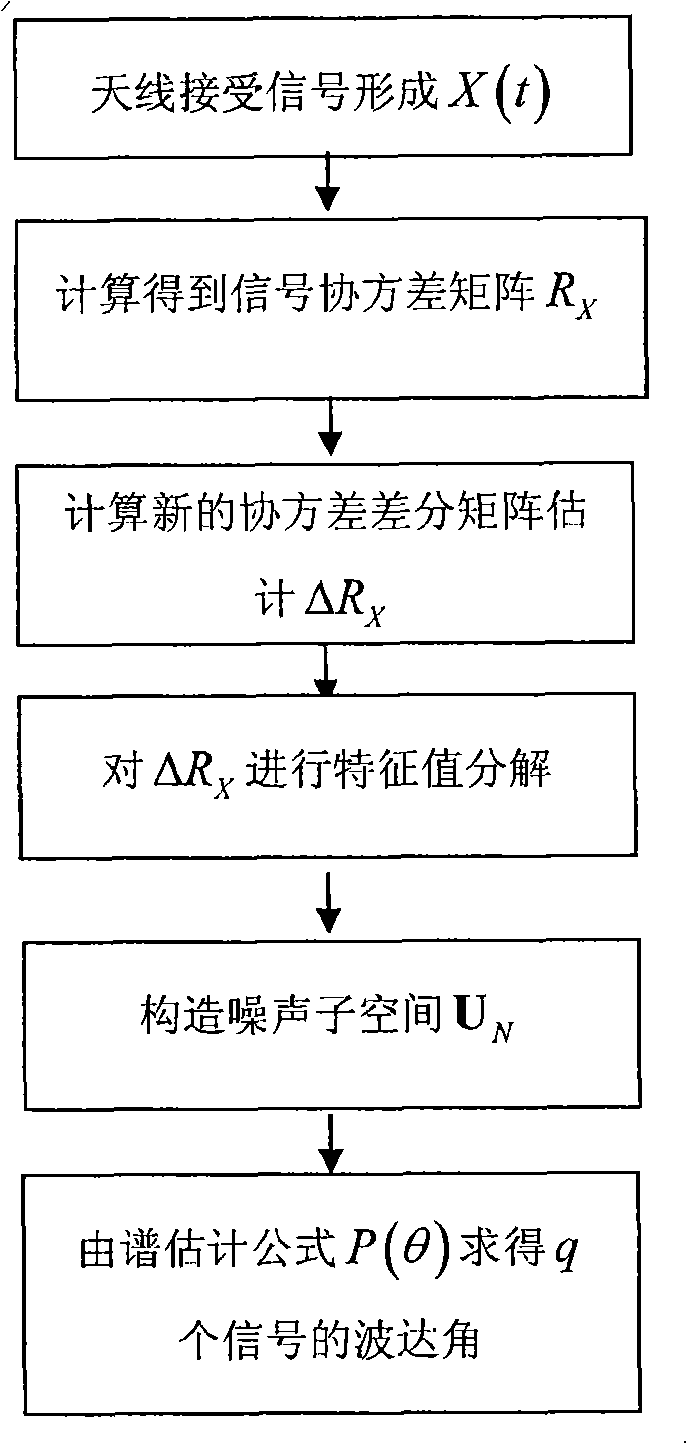
Virtual array DOA estimation method based on L type array
InactiveCN104730491AReduce complexityLarge apertureDirection/deviation determination systemsDecompositionSignal subspace
The invention discloses a virtual array DOA estimation method based on an L type array. The method comprises the steps that 1, based on the shift invariant property, a subarray Zx and a subarray Zy of the L type array horizontally shift to obtain a virtual array Zx' and a virtual array Zy', rotation invariance of two sub signals is formed due to the shift invariant property of the subarrays, and the virtual subarray signals are equal to the L type subarray Zx and L type subarray Zy input signals multiplied by a twiddle factor respectively; 2, the output of the four subarrays are combined to form a virtual array output signal Z (t); 3, the signal subspace and the noise subspace can be described by decomposing the features of covariance matrixes output by the array, mutual correlation processing is carried out on the array output signal Z(t) to obtain Rzz, and eigenvalue decomposition is carried out to obtain signal subspaces; 4, the twiddle factor is solved through linear operation, and the signal wave arrival direction can be obtained through the diagonal element of the twiddle factor. According to the virtual array DOA estimation method, no spectral function needs to be calculated, the phenomenon that the wave arrival direction is indirectly calculated without searching for the peak value is avoided, the complexity is lowered, the equipment complexity and cost are reduced, and the positioning precision is high.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Millimeter wave band transmitter, millimeter wave band receiver and millimeter wave band communication apparatus carrying out radio communication in millimeter wave band region
InactiveUS6973328B1Improve transmission efficiencySpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency changerSignal wave
A millimeter wave band communication apparatus includes a millimeter wave band transmitter receiving a plurality of input modulation signal waves to transmit a millimeter wave band multiplex signal wave, and a millimeter wave band receiver receiving the transmitted millimeter wave band multiplex signal wave to restore the plurality of input modulation signal waves. The millimeter wave band transmitter includes a frequency arranging circuit generating a multiplex signal wave having respective frequency bands of the plurality of input modulation signal waves arranged on the frequency axis independent of each other, a frequency up-converter up-converting the generated multiplex signal wave to the millimeter wave band, and a transmission circuit transmitting the millimeter wave band multiplex signal wave. The millimeter wave band receiver includes a reception circuit receiving the millimeter wave band multiplex signal wave, a frequency down-converter down-converting the millimeter wave band multiplex signal wave from the millimeter wave band, and a frequency rearranging circuit restoring the down-converted multiplex signal wave into the plurality of input modulation signal waves respectively having the former frequency bands.
Owner:SHARP KK
Antenna assembly
InactiveUS20040113840A1Improve shielding effectEasy to manufactureSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSignal waveEngineering
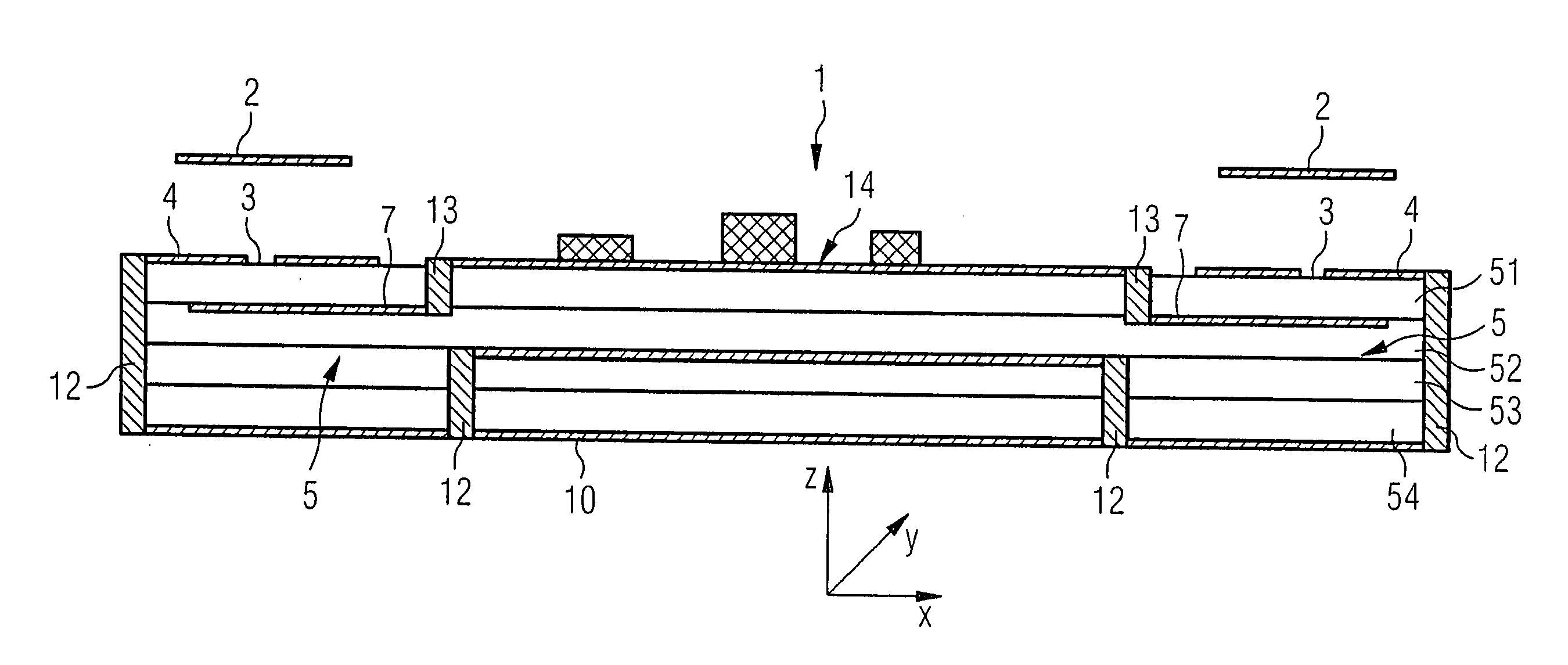
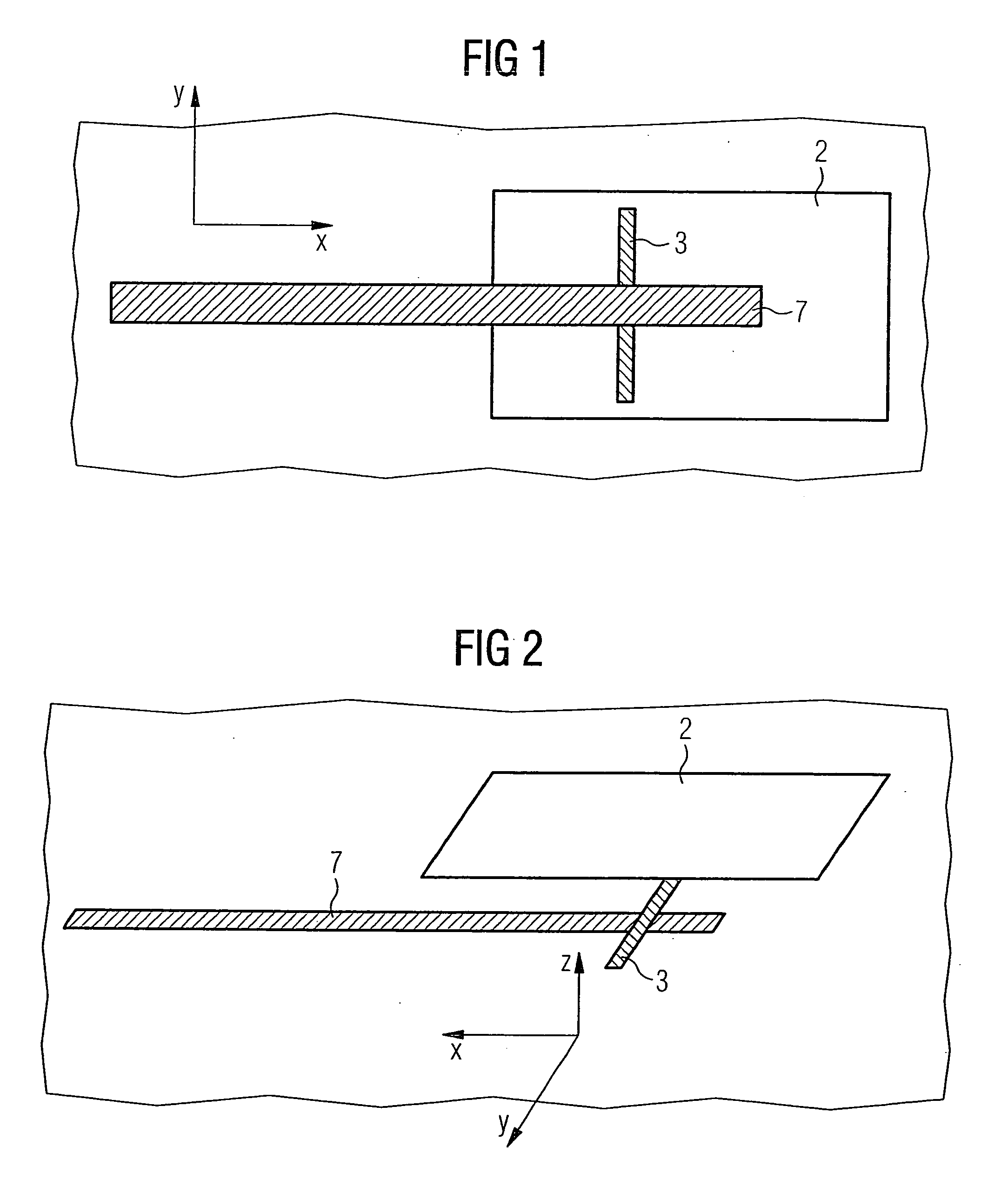
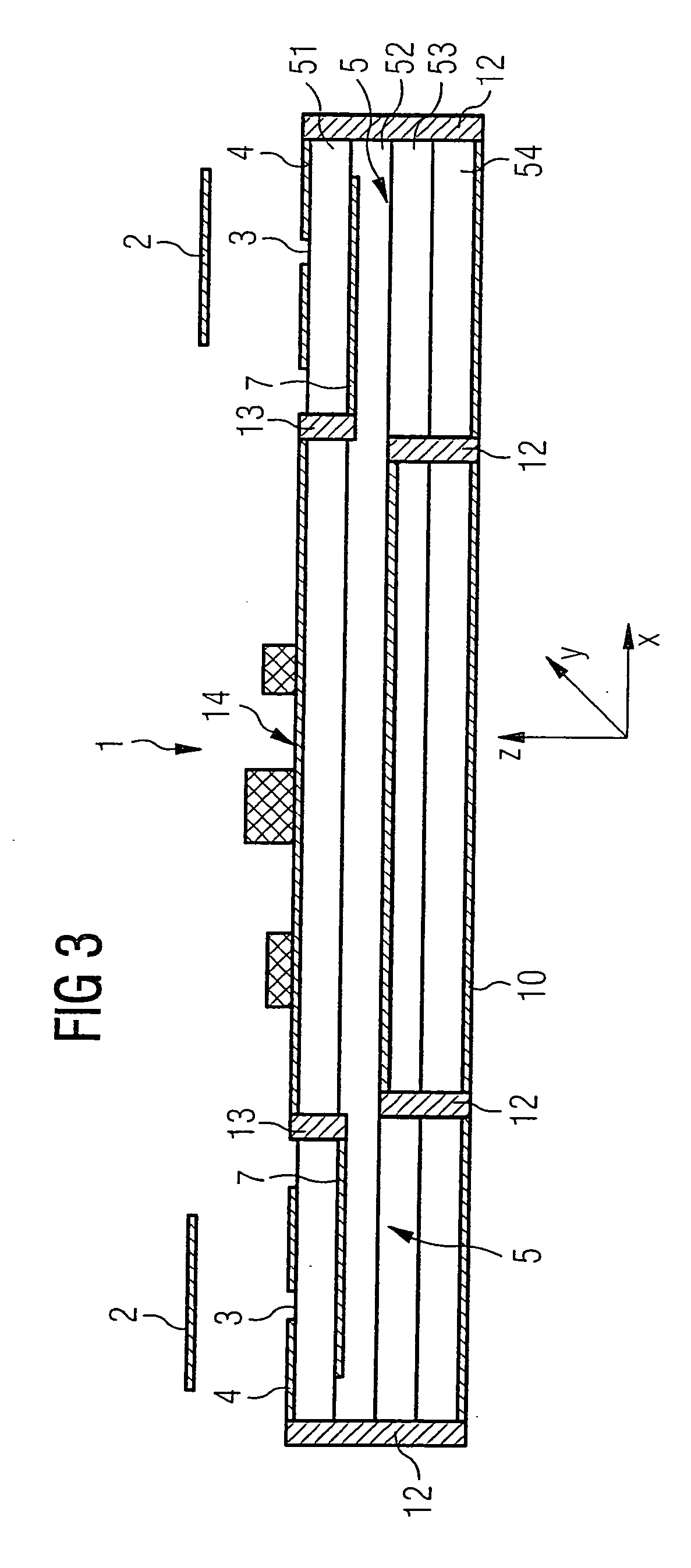
The present invention provides an antenna array for ascertaining the distance between vehicles and their speed, which includes devices for receiving or transmitting signal waves, a multi-layer carrier situated underneath the devices, a first potential surface, which is at ground and which is situated on the surface of the carrier facing the devices, coupling devices located in the first potential surface, electrical connecting sections disposed as closely as possible underneath the first potential surface, and a second potential surface which is located underneath the connecting sections and is at mass.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Millimeter band signal transmitting/receiving system having function of transmitting/receiving millimeter band signal and house provided with the same
InactiveUS7164932B1Easy to set upConvenient ArrangementTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversitySignal waveSide lobe
A millimeter band transmitter transmits one or more indirect path signal waves from the main lobe of a transmit antenna, and a direct path signal wave is transmitted in a side lobe of the transmit antenna. A receiver simultaneously receives each of the indirect and direct path signal waves if the receive antenna is unobstructed. If the direct line of sight path between the transmitter and receiver is blocked, the receiver only receives one or more of the indirect path signal waves.
Owner:SHARP KK
System for monitoring loosening part of nuclear reactor and coolant system
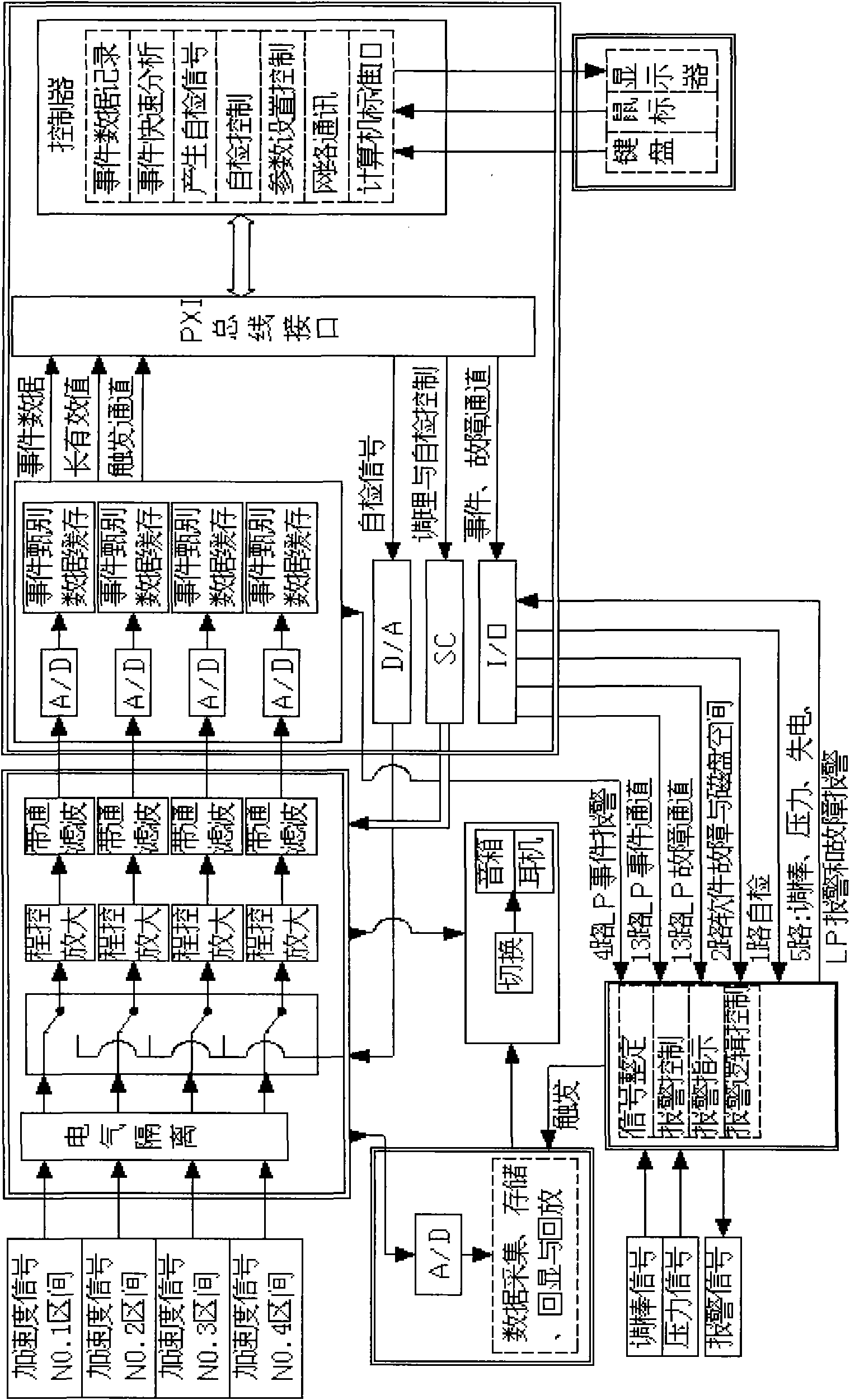
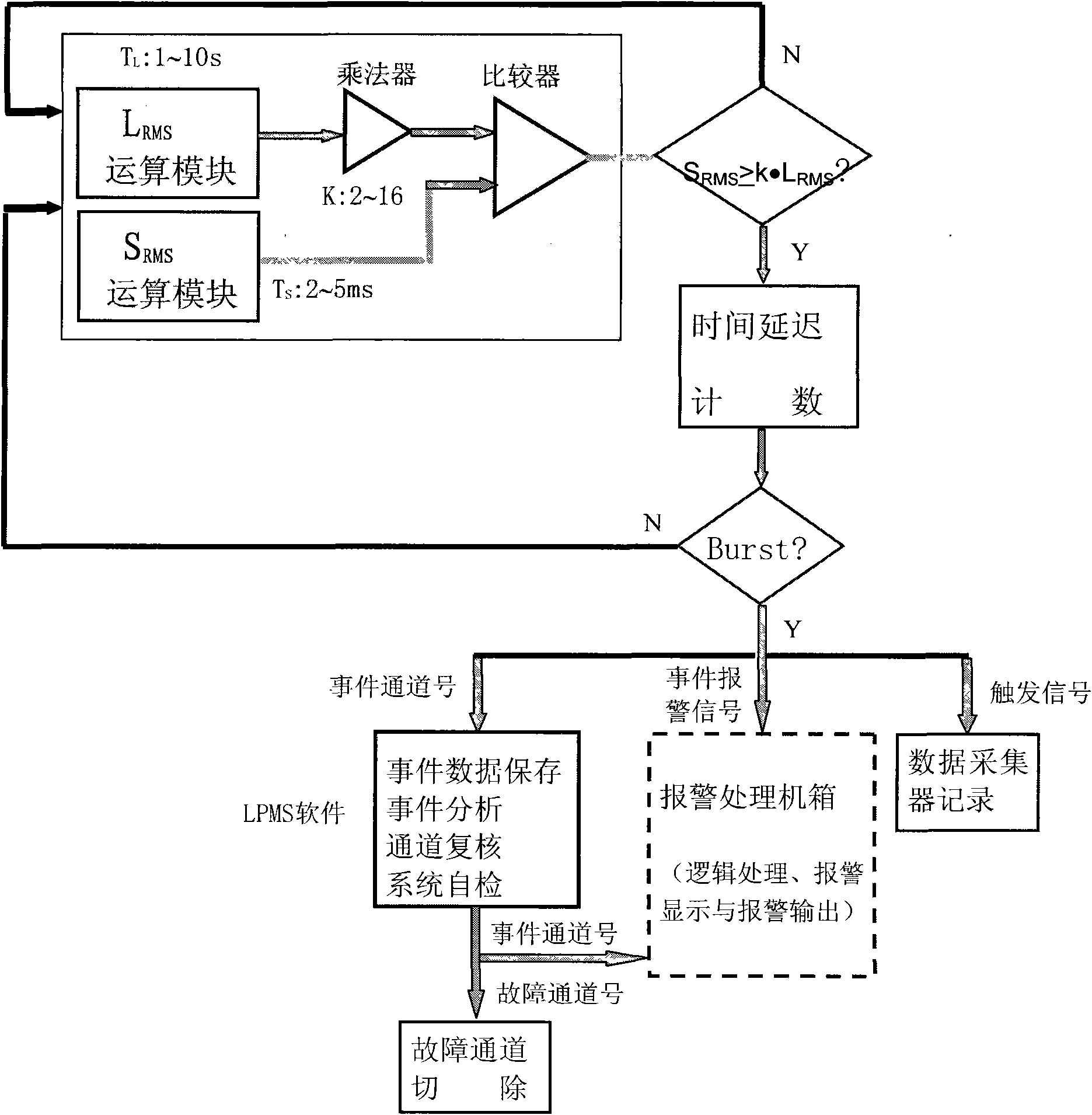
ActiveCN101685679AEasy to replaceEliminate systematic errorsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreAccelerometer
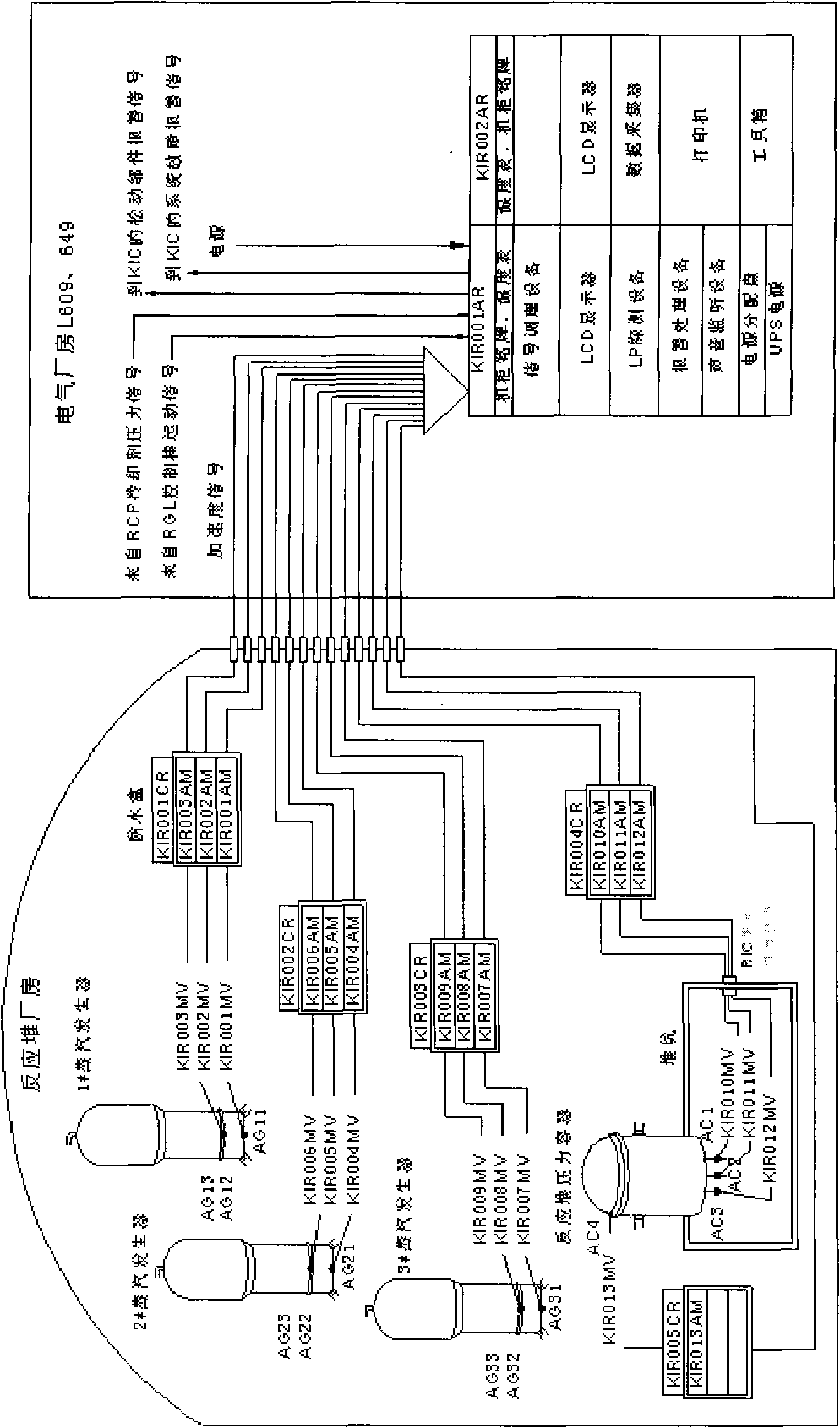
The invention provides a system for monitoring loosening parts of a nuclear reactor and a coolant system, solving the problems of reliability, compatibility, stability and maintenance convenience andcomprising an accelerometer, a charge amplifier, signal conditioning equipment, loosening part detection equipment, alarm processing equipment, sound monitor equipment, data collection equipment, a display, loosening part monitor software and the like. The system adopts a PXI bus technology so as to enable every two modules to be synchronized; a signal conditioning module adopts an FPGA programmable technology; a DSP digital technology is adopted to discriminate a loosening part event; loosening part signal length effective value floating discrimination, time delay, channel recheck combination discrimination, alarm prohibition caused by alarm channel recheck, control rod motion or coolant low pressure, and the like ensure that the system has a strong wrong alarming resistance capacity; the data collection equipment collects data to replace tape records so as to ensure the integrity of event signal records; and event signal waveform display and data storage can carry out display back and secondary analysis on signals.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Electrostatic ultrasonic transducer drive control method, electrostatic ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic speaker using the same, audio signal reproduction method, ultra-directional acoustic system, and display device
InactiveUS20070154036A1High strengthImprove energy conversion efficiencyMicrophonesSignal processingSonificationUltrasonic sensor
A Push-Pull-type electrostatic ultrasonic transducer includes a first electrode having a through hole, a second electrode having a through hole making a pair with the through hole of the first electrode, and a vibration film held between a pair of electrodes composed of the first and the second electrodes and having a conductive layer to which a direct-current bias voltage is applied, and holds the pair of electrodes and the vibration film. Assuming that λ is the wavelength of the carrier wave having a frequency shifted as a predetermined amount of frequency from the resonance frequency, which is the mechanical resonance frequency of the vibration film, the thickness t of each of the pair of electrodes is set to (λ / 4)·n or roughly (λ / 4)·n (where, λ is the wavelength of the ultrasonic wave, n is a positive odd number), and an alternating-current signal, which is a modulated wave obtained by modulating the carrier wave in the ultrasonic frequency band with a signal wave in an audible frequency band, is applied between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
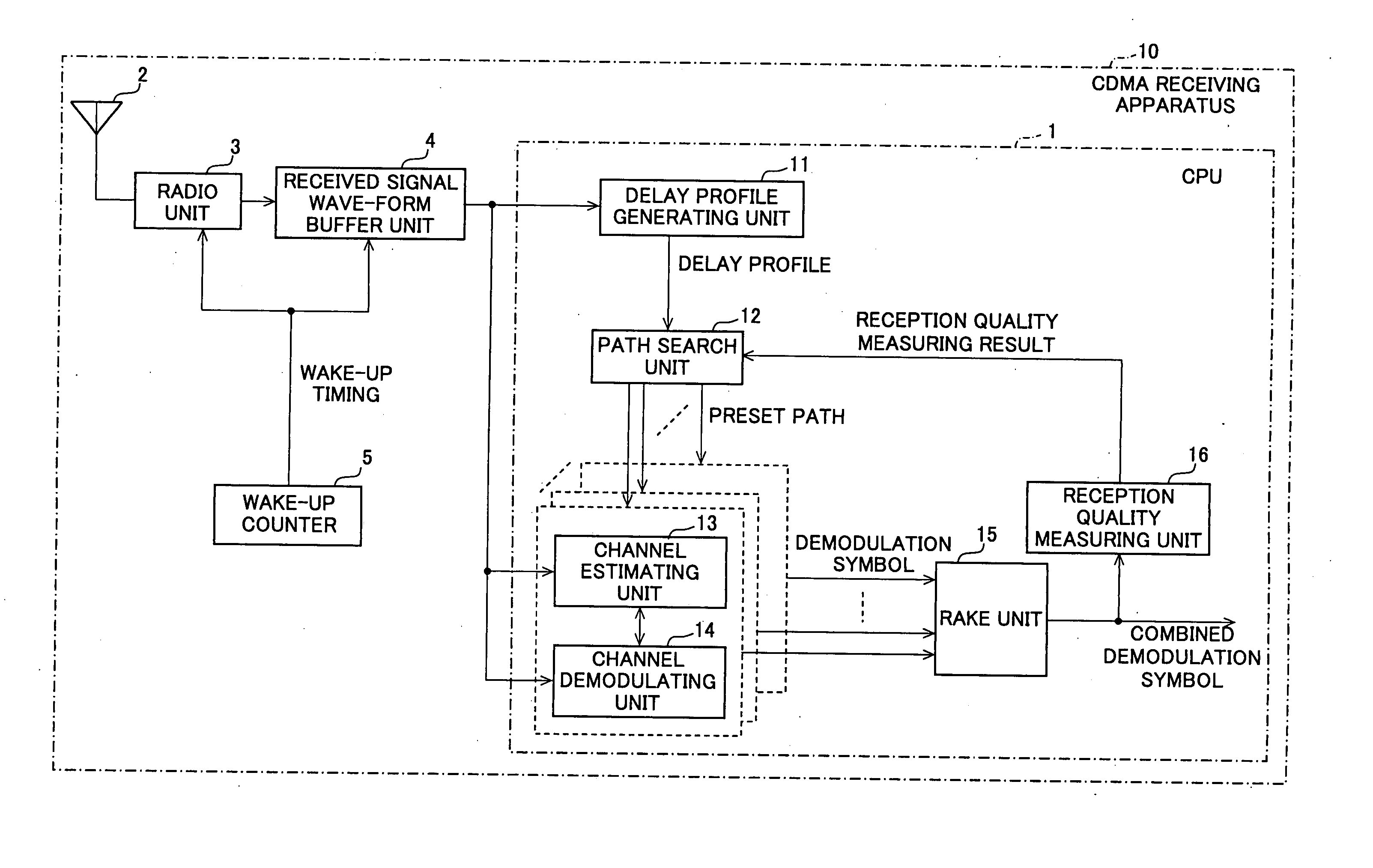
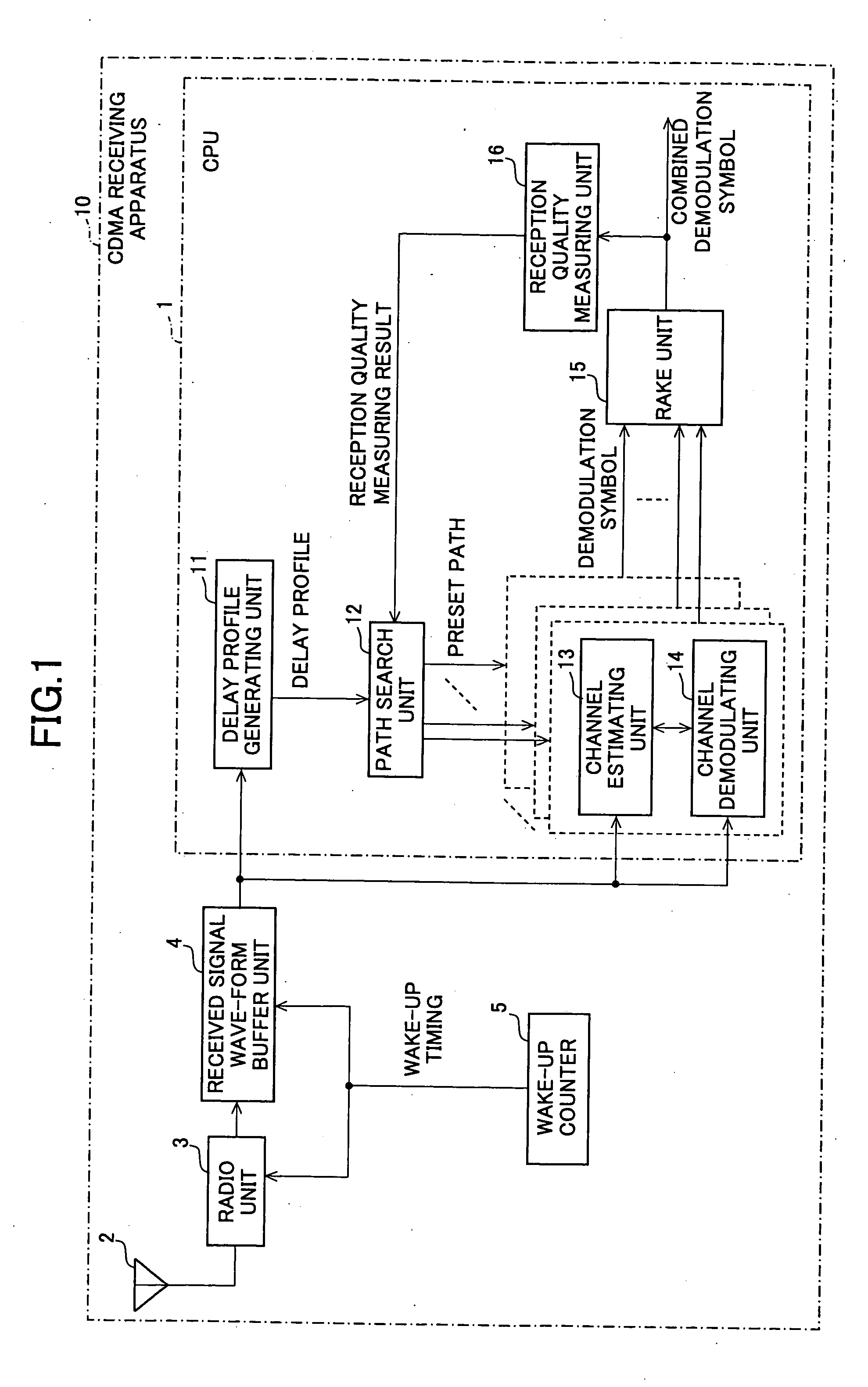
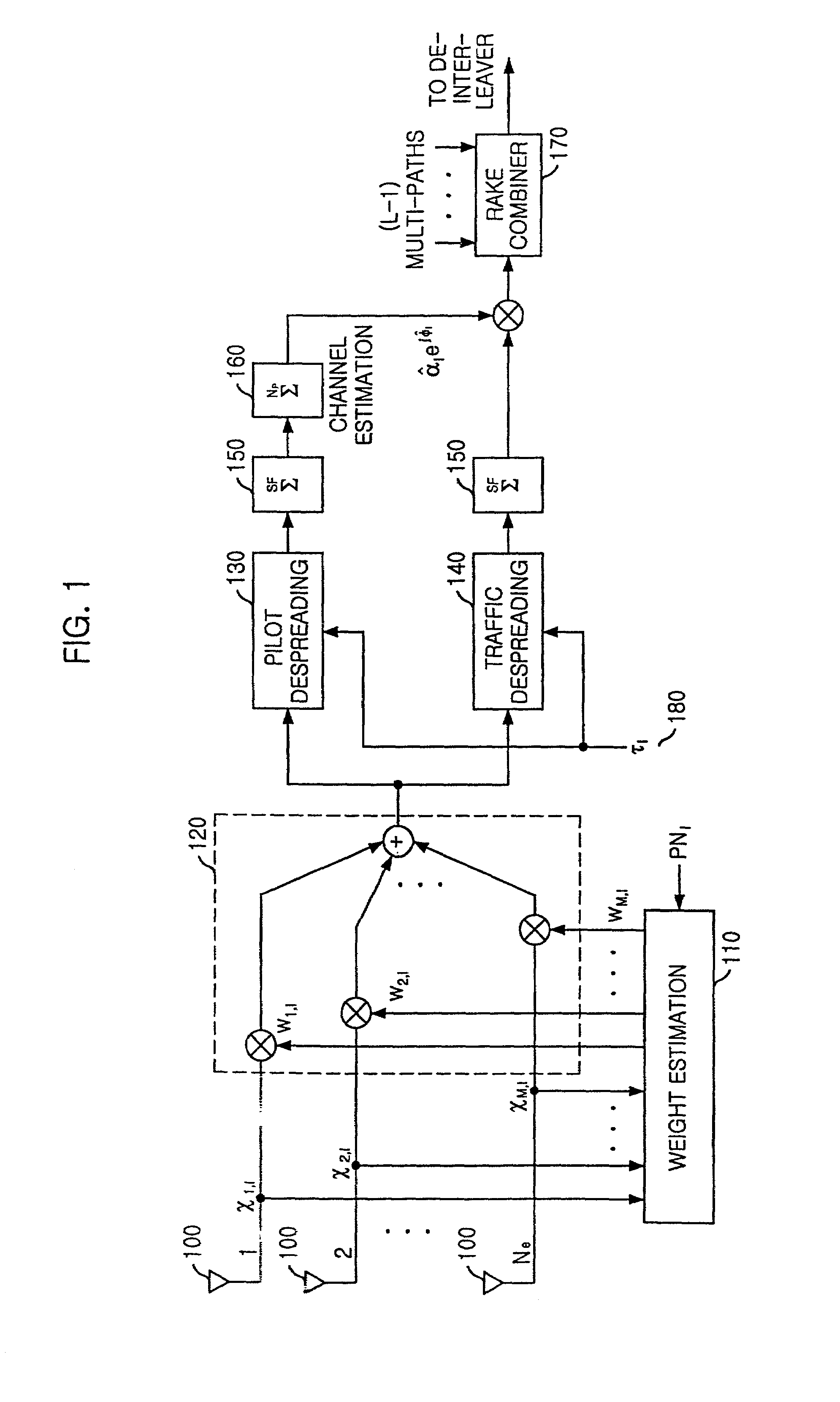
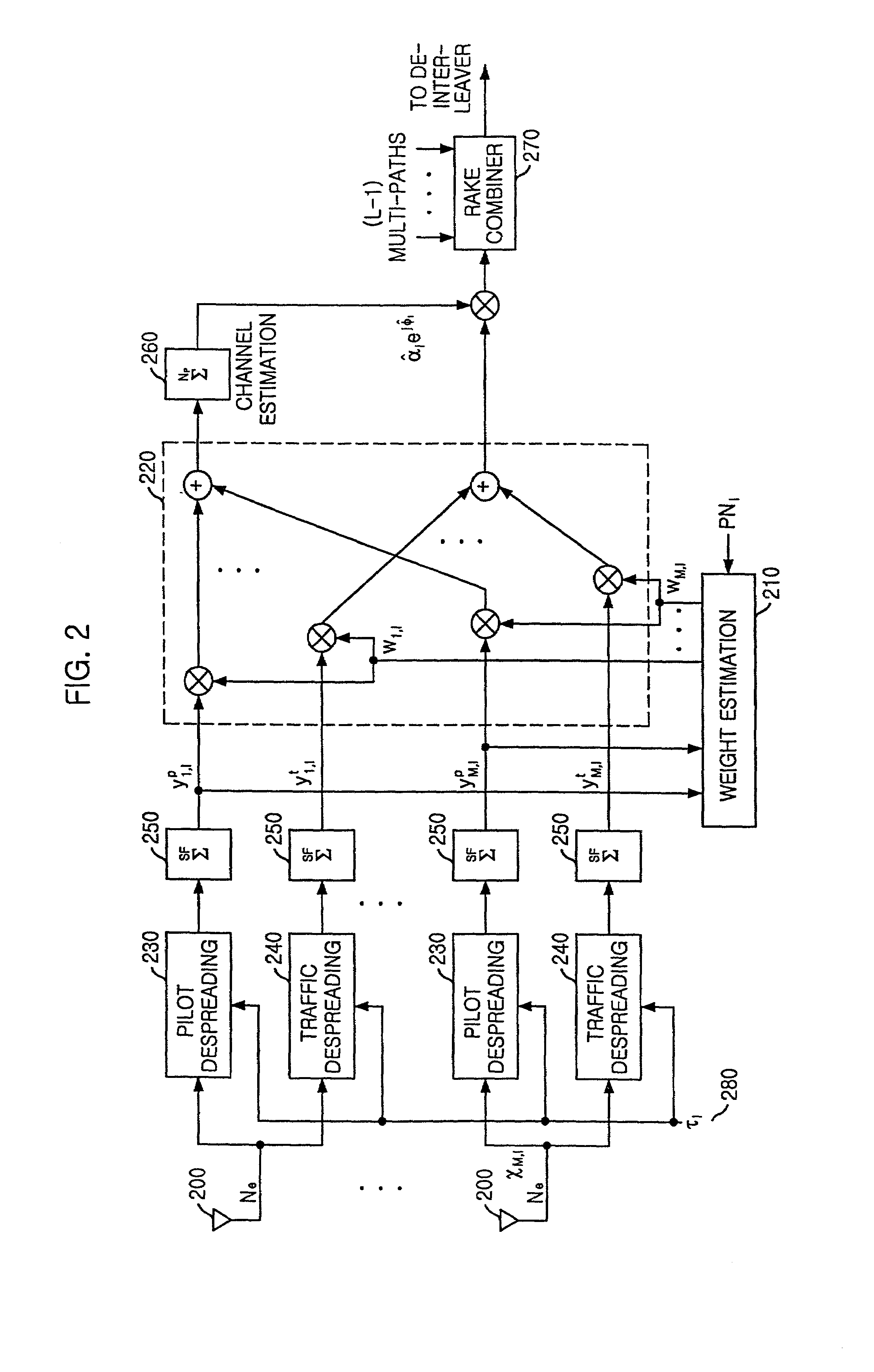
CDMA receiving apparatus, method, program and recording medium
InactiveUS20050047488A1Improve featuresReduce power consumptionRadio transmission for post communicationSynchronising arrangementSignal waveEngineering
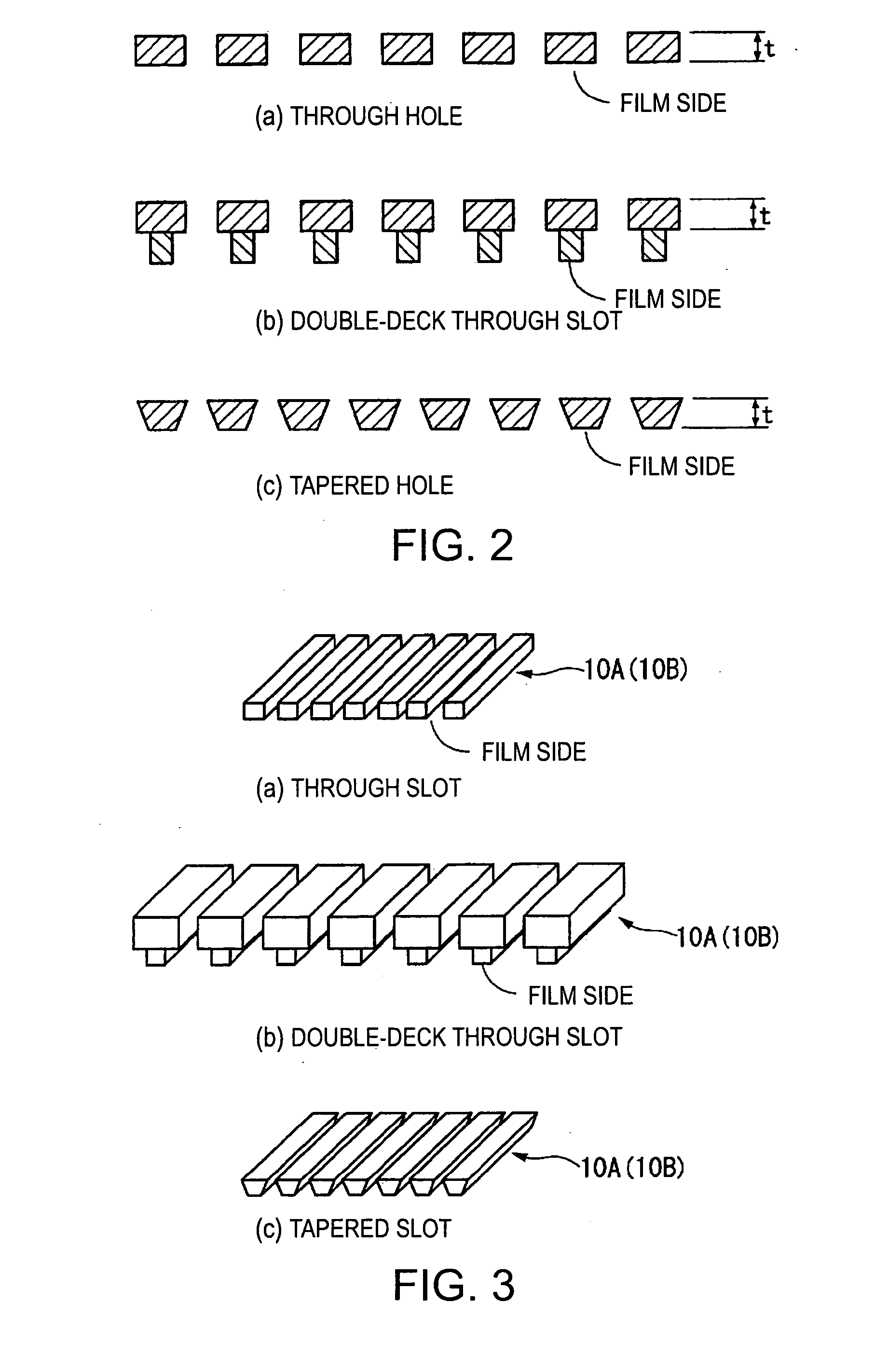
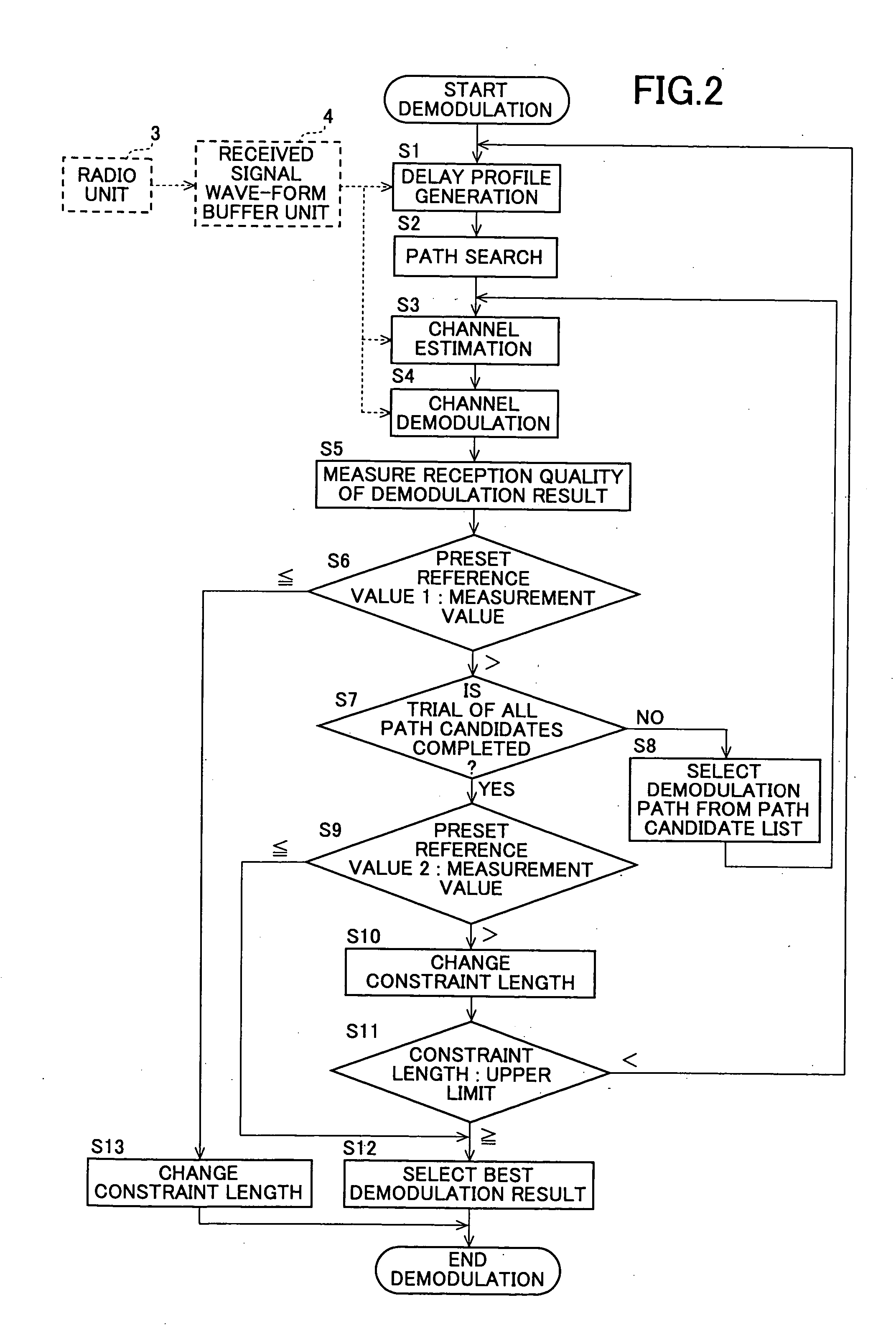
In a CDMA receiving apparatus, a delay profile using a desired constraint length is generated by a delay profile generating unit from received signal wave-form data recorded on a received signal wave-form buffer unit. Several demodulation paths are selected at peak position of the delay profile by the path search unit. Demodulation symbols which are generated from received signal wave-form data of each demodulation path by the channel demodulating unit are brought into in-phase by an adjustment angle which is obtained by the channel estimating unit. If the reception quality which is measured by the reception quality measuring unit is lower than a predetermined value for a combined demodulation symbol which is combined by a RAKE unit, the combination of said selected demodulation paths or the constraint length is changed to repeat the demodulation operation of the same received signal wave-form data.
Owner:SHARP KK
Wave time division mixed multiplexing passive optical network system
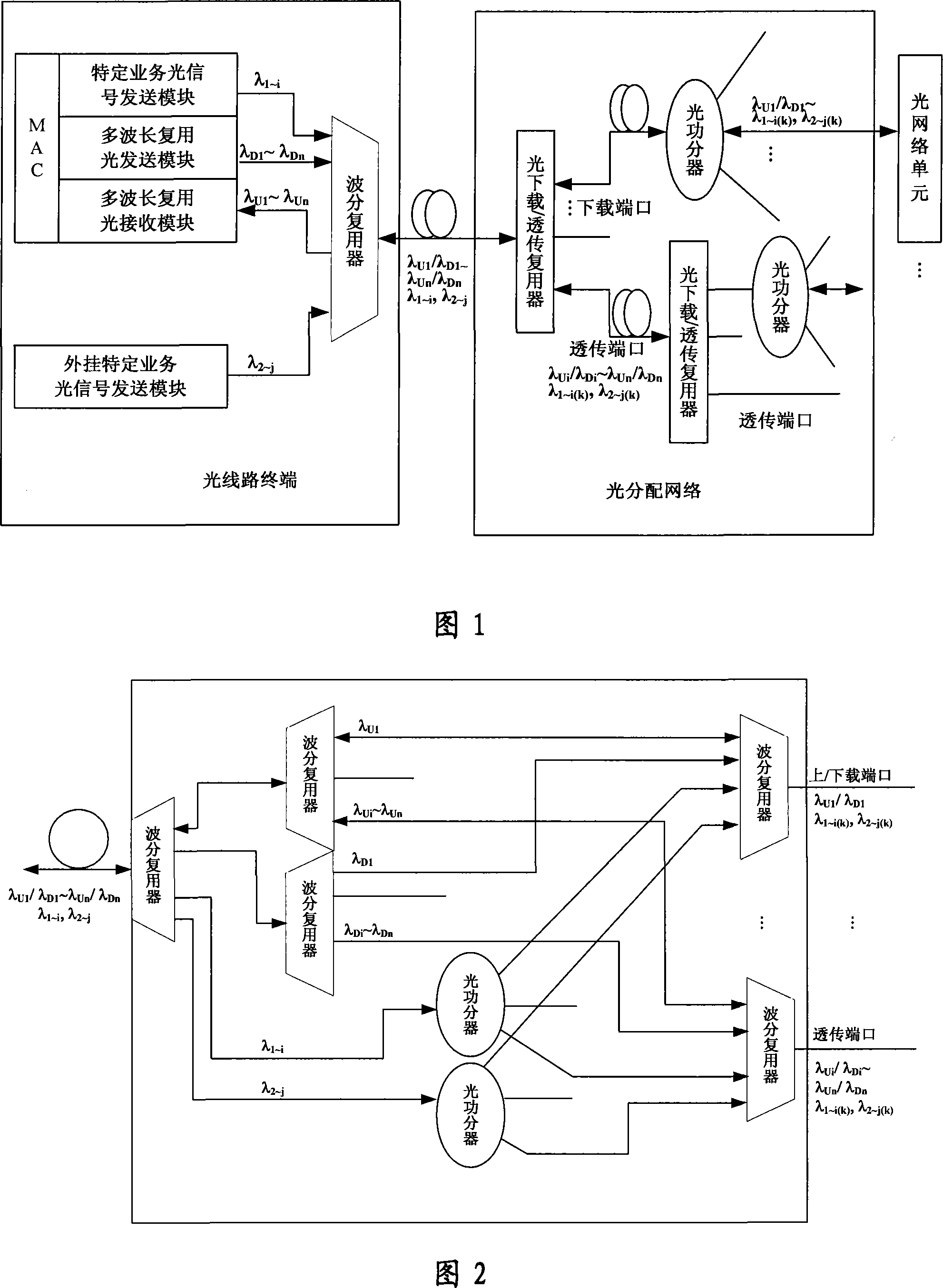
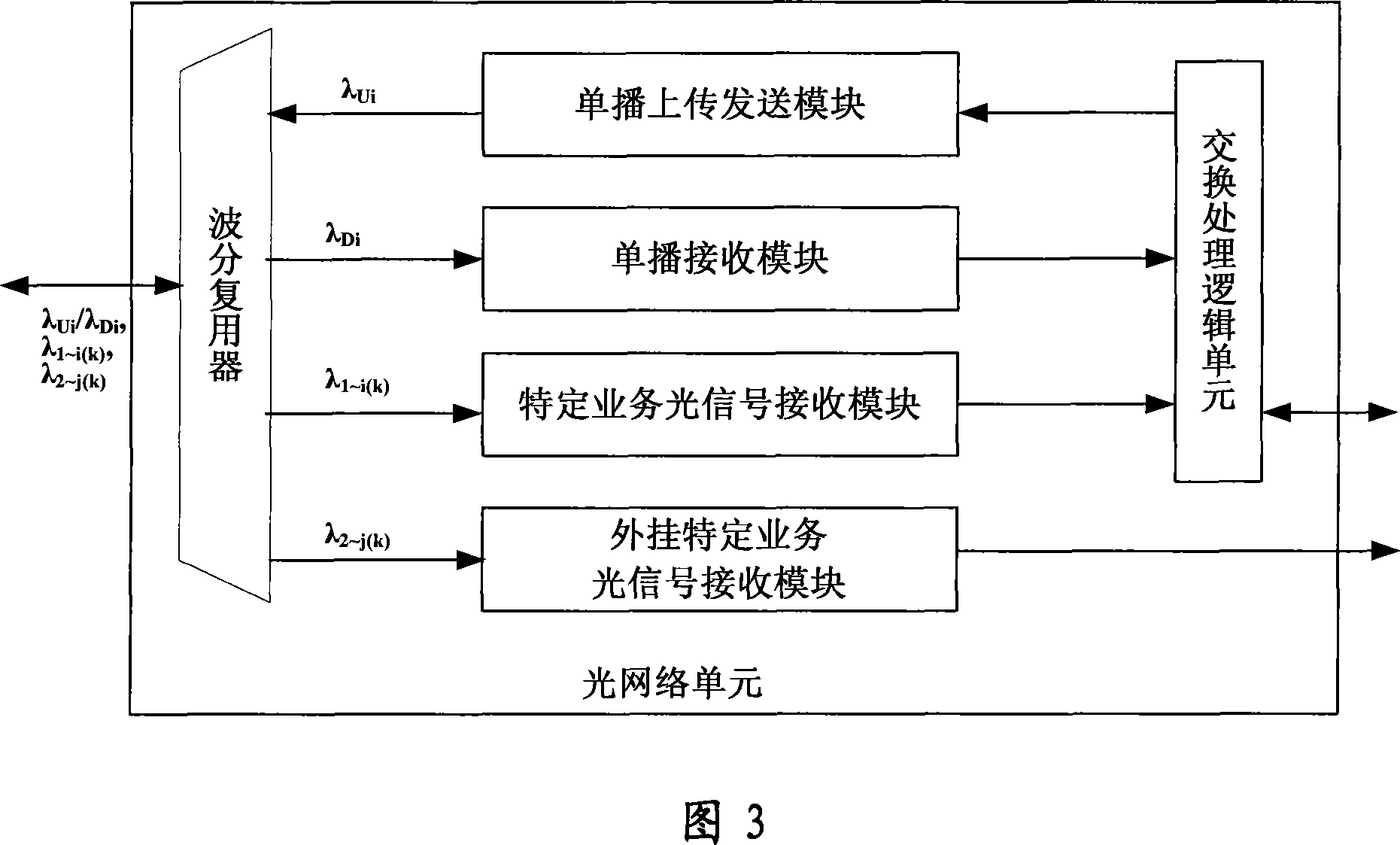
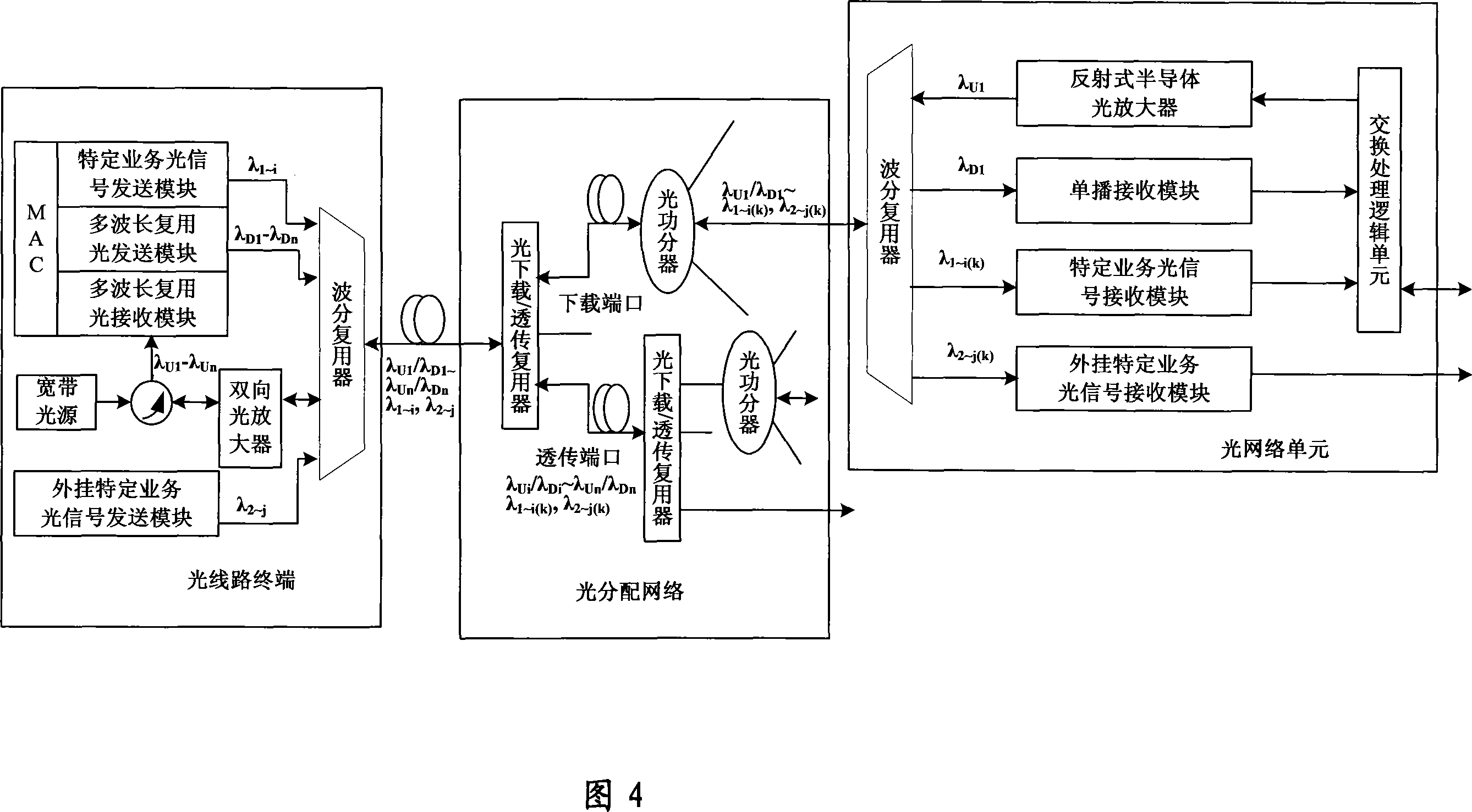
InactiveCN101237293AImprove transmission efficiencyReduce construction costsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical line terminationPhysics
The invention discloses a wavelength-division time-division mixed multiplexing passive optical network system, which at least comprises an optical line terminal, an optical distribution network and a plurality of optical network units. The optical line terminal is used to send downlink optical signal wave bands of a plurality of services, make multiplexing wave coupling to the optical signal wave bands of the plurality of services, then allow the optical signal wave bands to enter the same single fiber and transmit the optical signal wave bands to the optical distribution network; the optical distribution network is used to demultiplex an optical signal which is received from the optical line terminal and wave-coupled, then makes multi-level selective download and transparent transmission to one or a plurality of optical signals after the demultiplexing, and makes power division of one or the plurality of demultiplexed optical signals to the optical network units; the optical network units are used to receive light signals of the plurality of services downloaded by the optical distribution network through a coupling fiber, and logically processes the optical signals. The wavelength-division time-division mixed multiplexing passive optical network system has the advantages of large single-fiber access capacity, low cost of network construction, easy operation maintenance and upgrade and so on.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Compact tunable high-efficiency entangled photon source
InactiveUS20080063015A1Reduce pump powerEasy transferLaser detailsUsing optical meansWaveguidePhoton source
A compact, tunable, high-efficiency entangled photon source system that utilizes first and second periodically poled waveguides rather than bulk media in order to decrease the required pump power by up to several orders of magnitude. The first and second waveguides are arranged in respective arms of an interferometer. Each waveguide has partially reflecting ends, and are each placed on the Z-face of respective periodically poled KTP or LiNBO3 crystals to form respective first and second Fabry-Perot cavities. All waves (pump, idler, and signal) are co-polarized along the z-axis of the crystals. One of the waveguides is followed by a polarization rotator (shown as a half-wave-plate in the Figures) rotating the idler and signal wave polarization by 90 degrees. The outputs from two interferometer arms are combined by a polarization beam combiner and then split by a wavelength multiplexer into two spatially separated time-bin and polarization entangled beams. Another light source, a single frequency stabilized C-band laser (stabilization laser) is used to synchronize cavities spectral modes and phase-lock their outputs.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
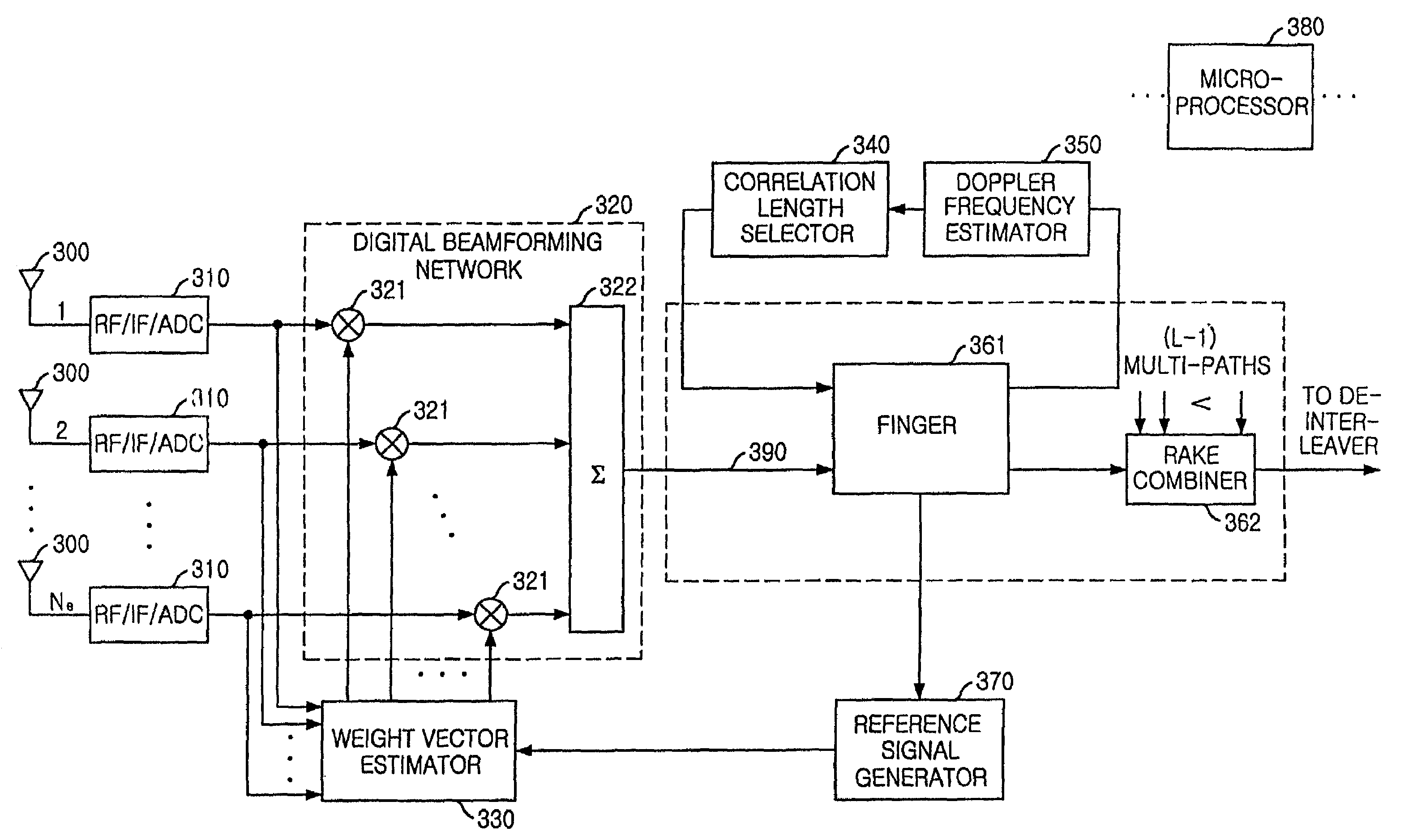
Apparatus and method for very high performance space-time array reception processing using chip-level beamforming and fading rate adaptation
InactiveUS7095814B2Increase capacityExpand coverageSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityEngineeringFading rate
An apparatus for very high performance space-time array reception processing using chip-level beamforming and fading rate adaptation is disclosed. The space-time array receiving system includes a plurality of digital beamforming networks for forming beams of signals by spatial-filtering the signals, to thereby generate spatial-filtered signals; a plurality of demodulating unit for demodulating the spatial-filtered signals to generate demodulated signals; correlating unit for estimating a fading channel signal based on pilot channel signals; Doppler frequency estimating unit for estimating Doppler frequency of the fading channel signal to generate Doppler frequency estimated values; correlation length selection unit for selecting a correlation length of the pilot channel signals based on the Doppler frequency estimated values; a plurality of reference signal generation unit for generating reference signals based on output signals from the correlating unit; and a plurality of weight vector estimating unit for generating weight vectors based on the reference signals and the signals and for providing the weight vector to the digital beamforming networks.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
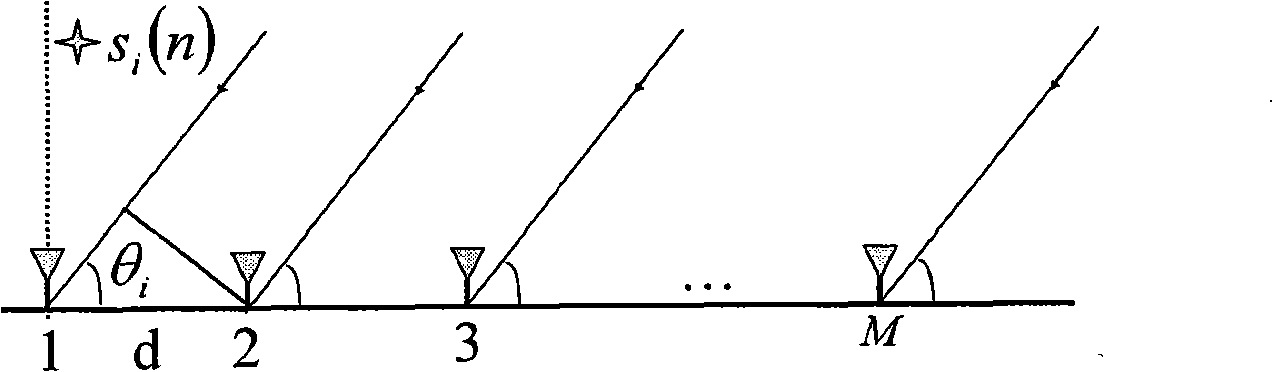
Method for estimating signal wave direction
InactiveCN101325807ARemove estimated effectsReduce arityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal waveEstimation methods
The invention provides a signal DOA estimation method. The method supposes that an unknown noise covariance matrix has a symmetrical Toeplitz matrix character; according to the difference conception of the traditional covariance matrix, an imaginary number j is introduced so that the newly constructed covariance matrix changes into a central Hermitian matrix, thereby, the character decomposition can obtain the same DOA as the incident signal numbers. The method greatly reduces the number of the antenna array element required by estimating the signal wave arrival direction, and a wave crest is only formed in the wave arrival direction of the real signal. The method can reduce cost greatly in the practical application.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar wave shape online designing method
ActiveCN101950014AImprove featuresWave based measurement systemsSpatial transmit diversitySignal waveWave shape
The invention discloses a centralized MIMO radar wave shape online designing method mainly aiming to solve the problems that a transmitting direction diagram can not be designed on line and the wave shape of a transmitted signal can not be synthesized on line by utilizing the traditional methods. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out amplitude weighting on an MIMO radar array, and constructing a fundamental wave beam bank with lower airspace sidelobe off line; (2) based on sequence quadratic programming, constructing various proportions of orthotropic fundamental wave shape banks which have low autocorrelation peak sidelobe level and low peak cross-correlation level off line; (3) solving the transmitting proportion of fundamental wave beams synthetizing the given transmitting direction diagram on line by utilizing linear programming; (4) selecting the fundamental wave shapes meeting the demand from the orthotropic fundamental wave shape banks according to the transmitting proportion of the fundamental wave beams; and (5) respectively synthetizing the transmitting direction diagram and a transmitting signal wave shape by the selected fundamental wave beams and the fundamental wave shapes. Compared with the traditional wave shape designing method, the invention can realize the online wave shape design and can be used for the self-adaption tracking of an MIMO radar on a moving target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Dual-band antenna having small size and low height
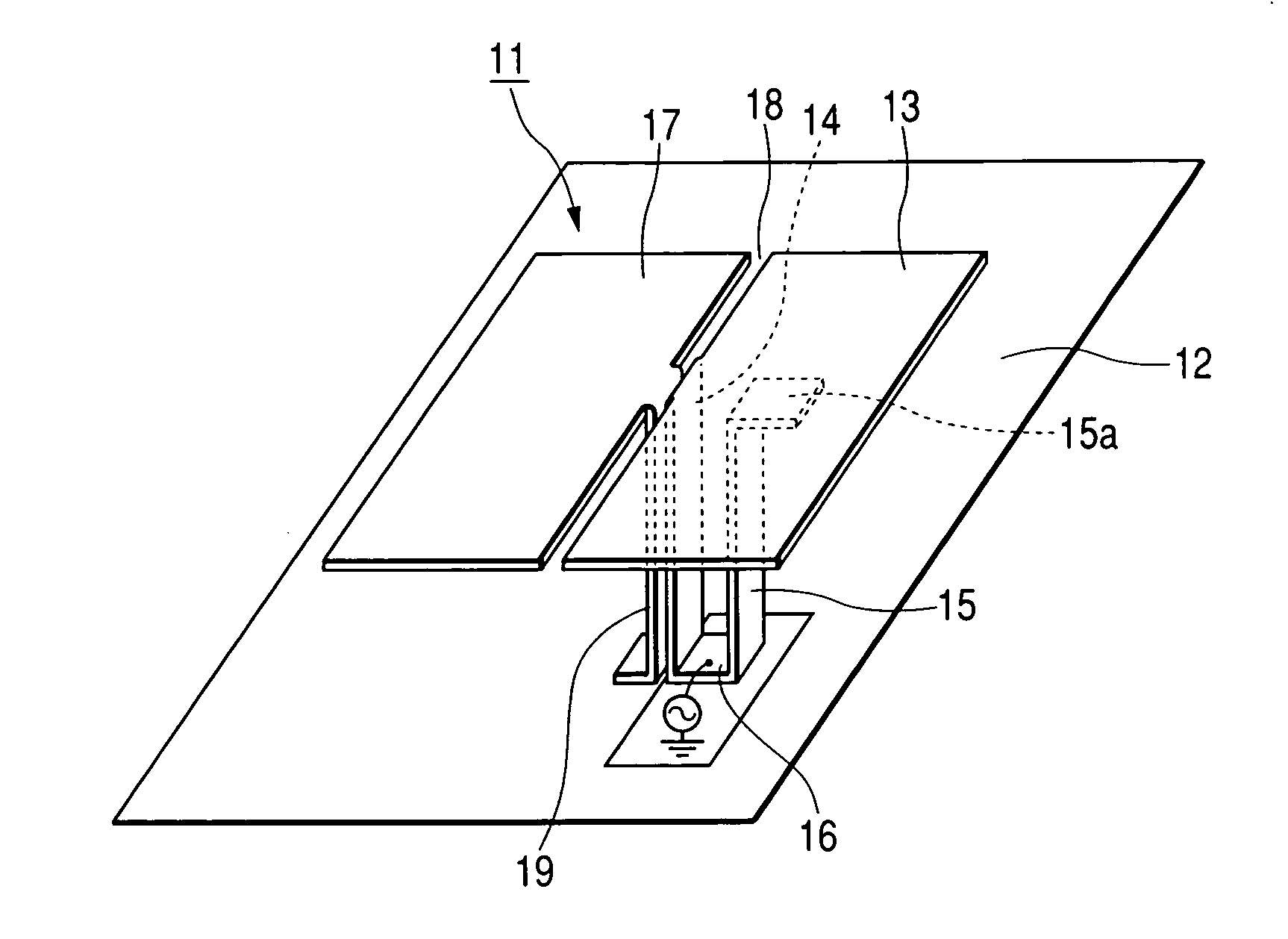
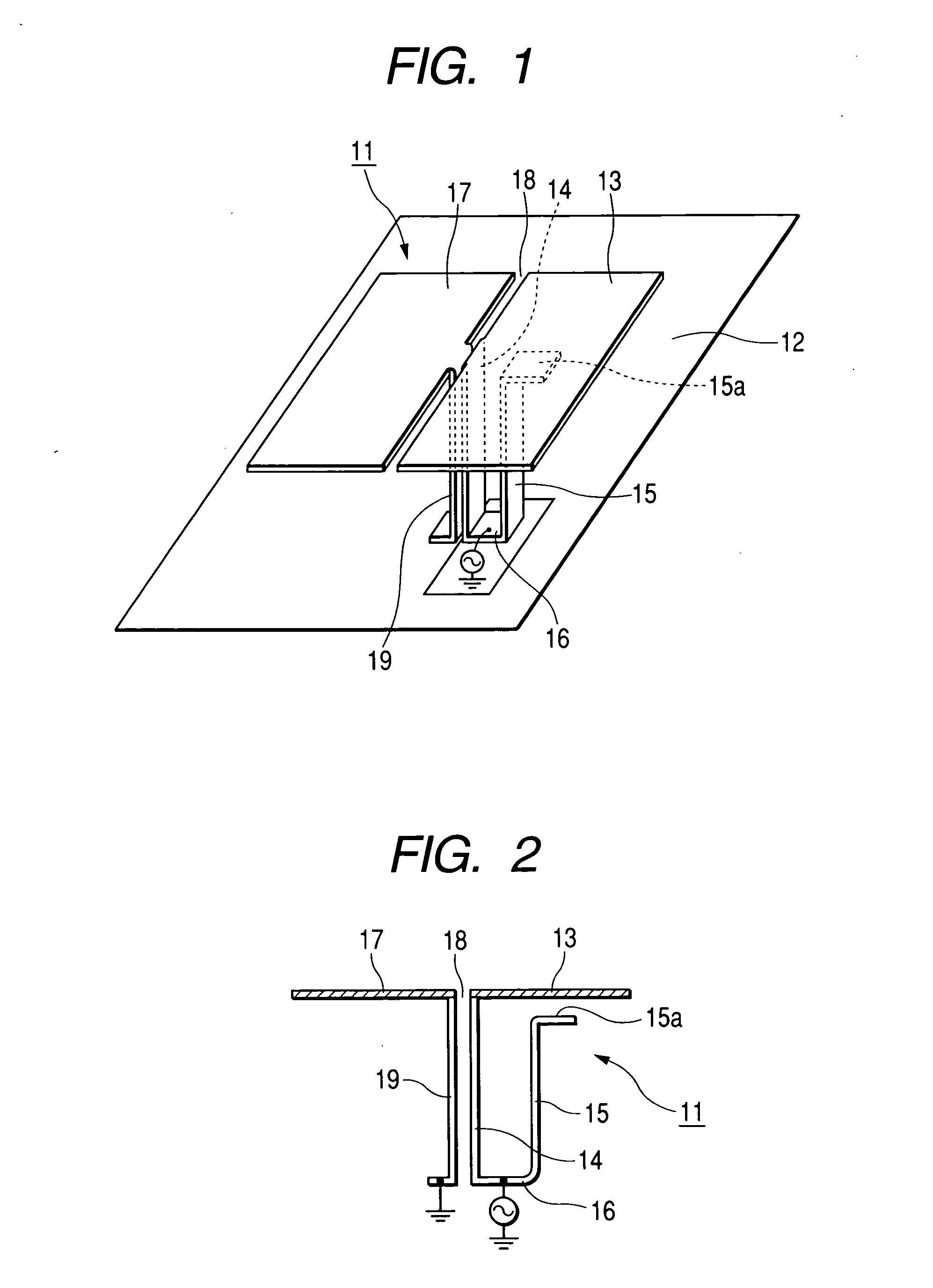
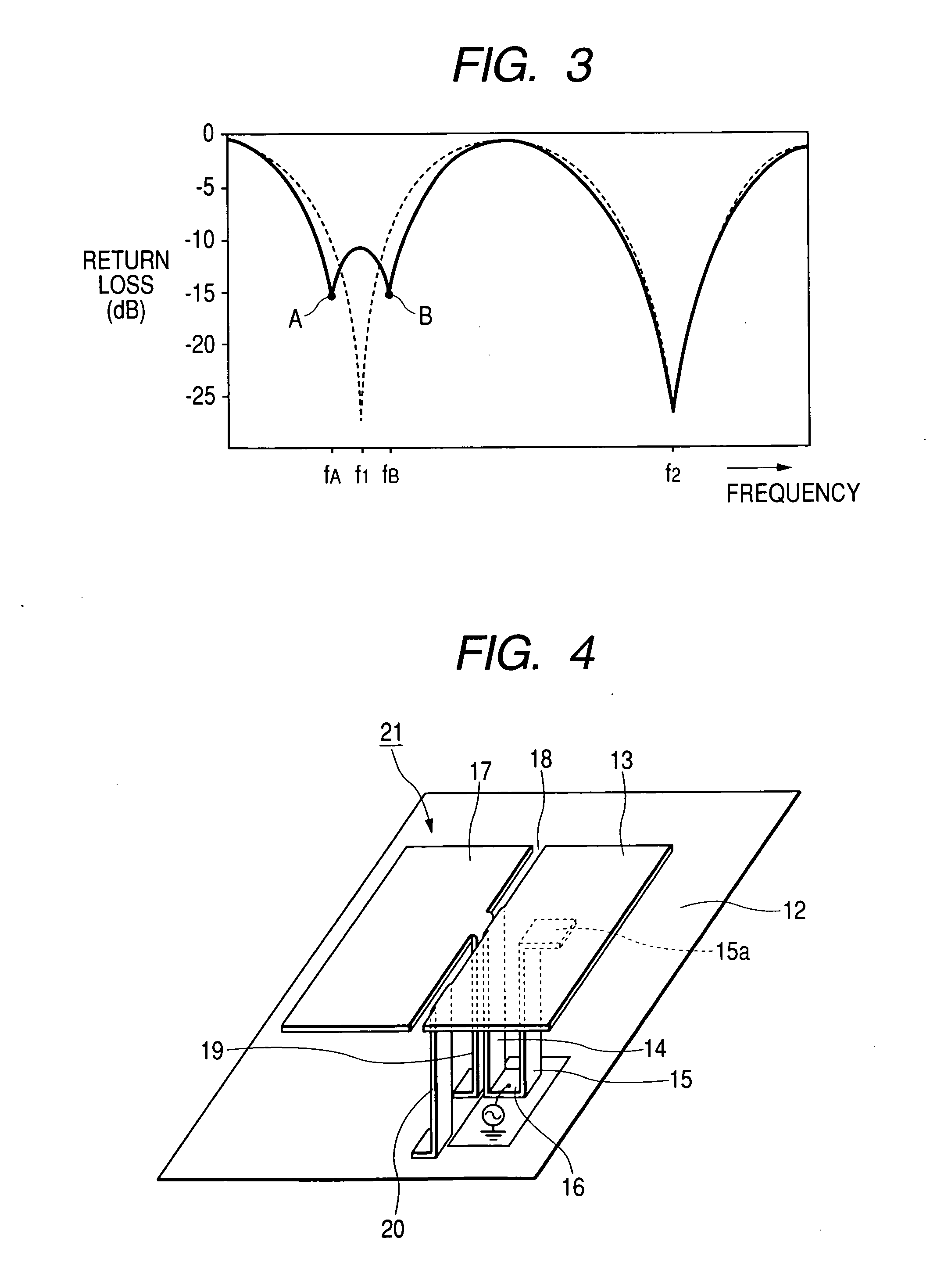
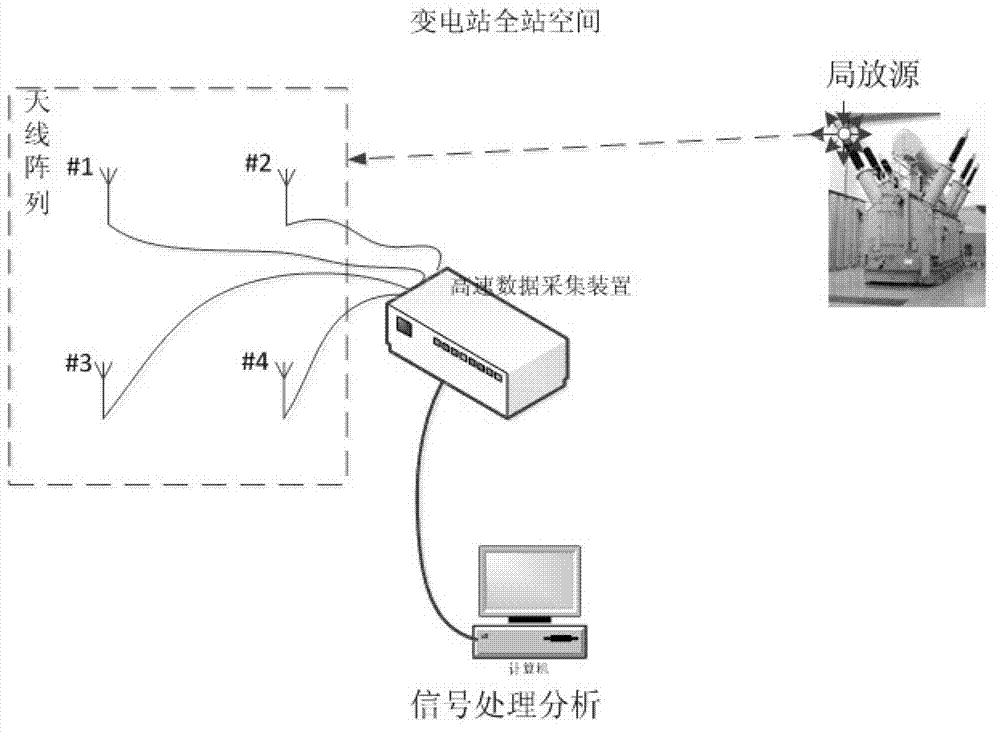
ActiveUS20050057400A1Easy to secure desired bandwidthHigh gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSignal waveDual frequency
There is provided a dual-band antenna having small size and low height which has a characteristic of not affecting a bandwidth of signal waves of a low band in its miniaturized state. In a dual-band antenna 11, a first radiating conductive plate 13 is arranged to oppose a surface of a grounding conductor 12 in an approximately parallel manner, being excited at a first frequency. A feeding conductive plate 14 extends approximately orthogonally from an outer edge of the first radiating conductive plate 13 and is connected to a feeding circuit A second radiating conductive plate 15 is stood downward the first radiating conductive plate 13, whose lower end is connected to the feeding conductive plate 14. The second radiating conductive plate 15 is excited at a second frequency. A third radiating conductive plate 17 is arranged to oppose the surface of the grounding conductor 12 in an approximately parallel manner on a surface of the grounding conductor and to be adjacent to the first radiating conductive plate 13. A slit 18 is interposed between both radiating conductive plates 13 and 17. A shorting conductive plate 19 extends approximately orthogonally from an outer edge of the third radiating conductive plate 17 and is connected to the surface of the grounding conductor 12. The feeding conductive plate 14 and the shorting conductive plate 19 is arranged close to each other, such that, when a power is supplied, the feeding conductive plate 14 and the shorting conductive plate 19 is electromagnetically coupled.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
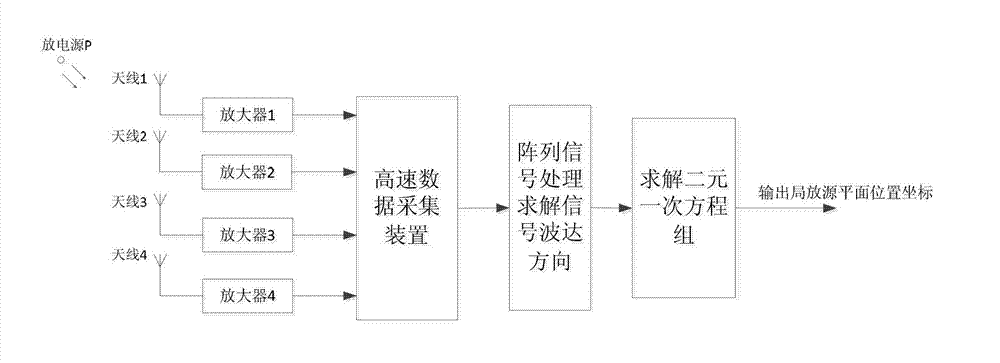
Transformer substation local discharge positioning method based on electromagnetic antenna array signal processing
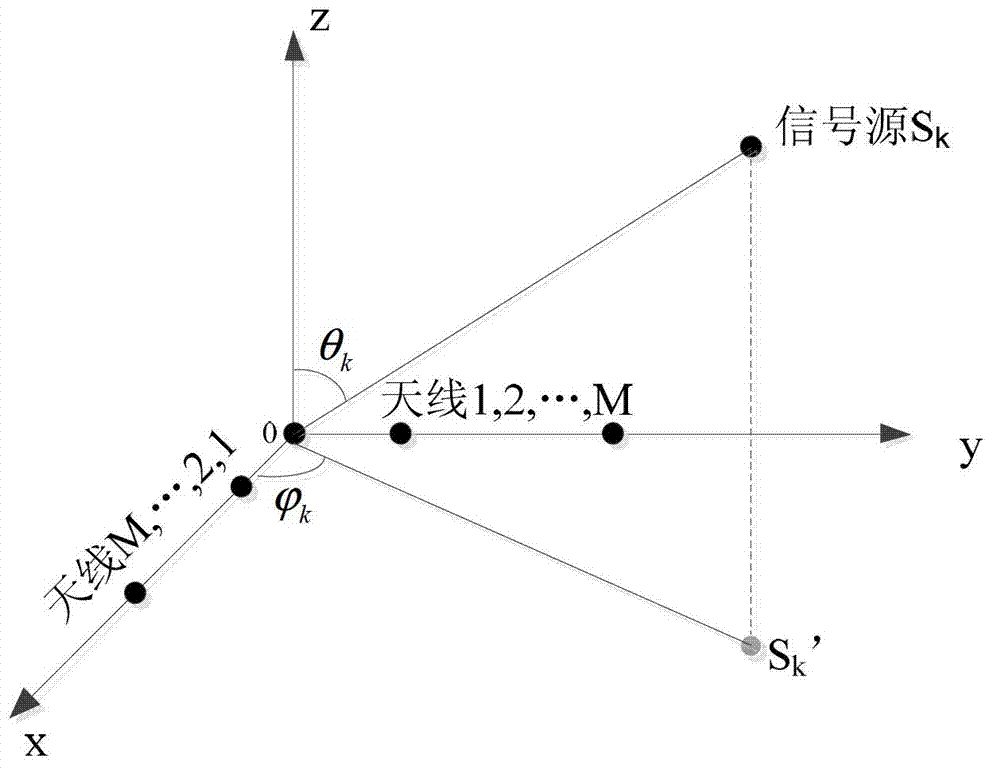
ActiveCN102830333AReduced sampling rate requirementsSolve the blockageTesting dielectric strengthTransformerTime delays
The invention discloses a transformer substation local discharge positioning method based on electromagnetic antenna array signal processing. The transformer substation local discharge positioning method is finished by a local discharge detection device, and the local discharge detection device comprises an omnidirectional antenna array, a built-in amplifier, a super-high-speed data sampling unit and a data processing unit which are mounted in a transformer substation. The positioning method comprises the steps as follows: constructing a matrix according to a concept of working out a signal wave arrival direction by a rotation invariant technology based on L-shaped antenna array signal processing; obtaining an azimuth angle of a local discharge source arriving at an antenna; and finishing planar location of the local discharge source of the transformer substation. A time delay sequence of a signal does not need to be calculated, so that the requirement on a sampling rate of an acquisition system can be lowered; and a plane coordinate of the local discharge source is obtained by working out a linear cross point in two wave arrival directions, namely working out a linear equation set in two unknowns, so that calculation of a nonlinear equation set is avoided.
Owner:上海迈内能源科技有限公司
Elongated twin feed line RFID antenna with distributed radiation perturbations
ActiveUS20100060457A1Promote polarizationReduce distractionsResonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsConductive materialsLength wave
An RFID antenna comprising an elongated structure existing along an axis that is long compared to the signal wavelength and including twin ribbon-like feed lines of electrically conductive material, the feed lines being in a common plane and being uniformly laterally spaced from one another, and a plurality of radiating perturbations associated with the feed lines at a plurality of locations spaced along the feed lines, at each location each feed line has its own individual perturbation or portion of a perturbation.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB +1
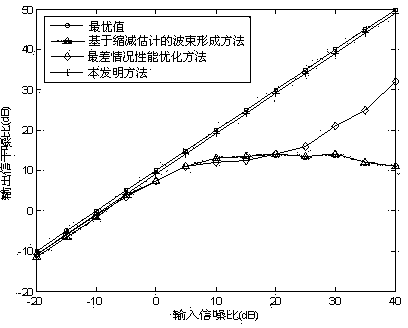
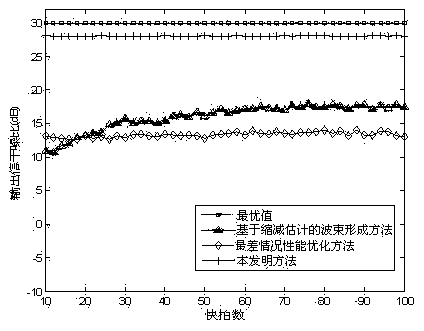
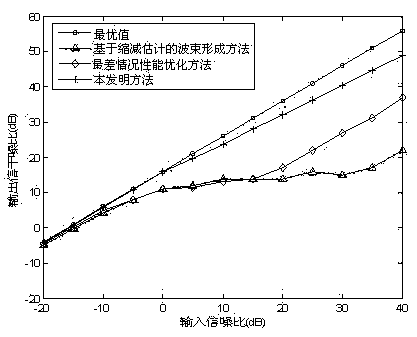
Interference noise matrix reconstitution-based self-adaptive wave beam forming method
InactiveCN103778102AImprove robustnessComplex mathematical operationsSignal classificationEngineering
The invention relates to an interference noise matrix reconstitution-based self-adaptive wave beam forming method and belongs to the field of array signal processing. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing the signal model of a minimum variance distortionless response wave beam forming problem, then under the condition that the angle range of an expected signal wave arrival direction is known, utilizing a multiple signal sorting spatial spectrum to reconstitute an interference noise covariance matrix in a region without containing expected signals, based on the matrix, solving the estimation value of a guide vector of the real expected signal by using the maximizing of an array output power and the constrain condition that the estimation value of the guide vector of the expected signal is prevented from being converged to the guide vector of any interference or the linear combination of the interference. According to the method, a simulation result shows that when random pointing errors and local scattering of the expected signal and a interference source exist, the output signal to interference plus noise power ratio in a very large input signal-to-noise ratio range is still close to a theoretical value and is superior to that of other self-adaptive wave bean forming methods.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
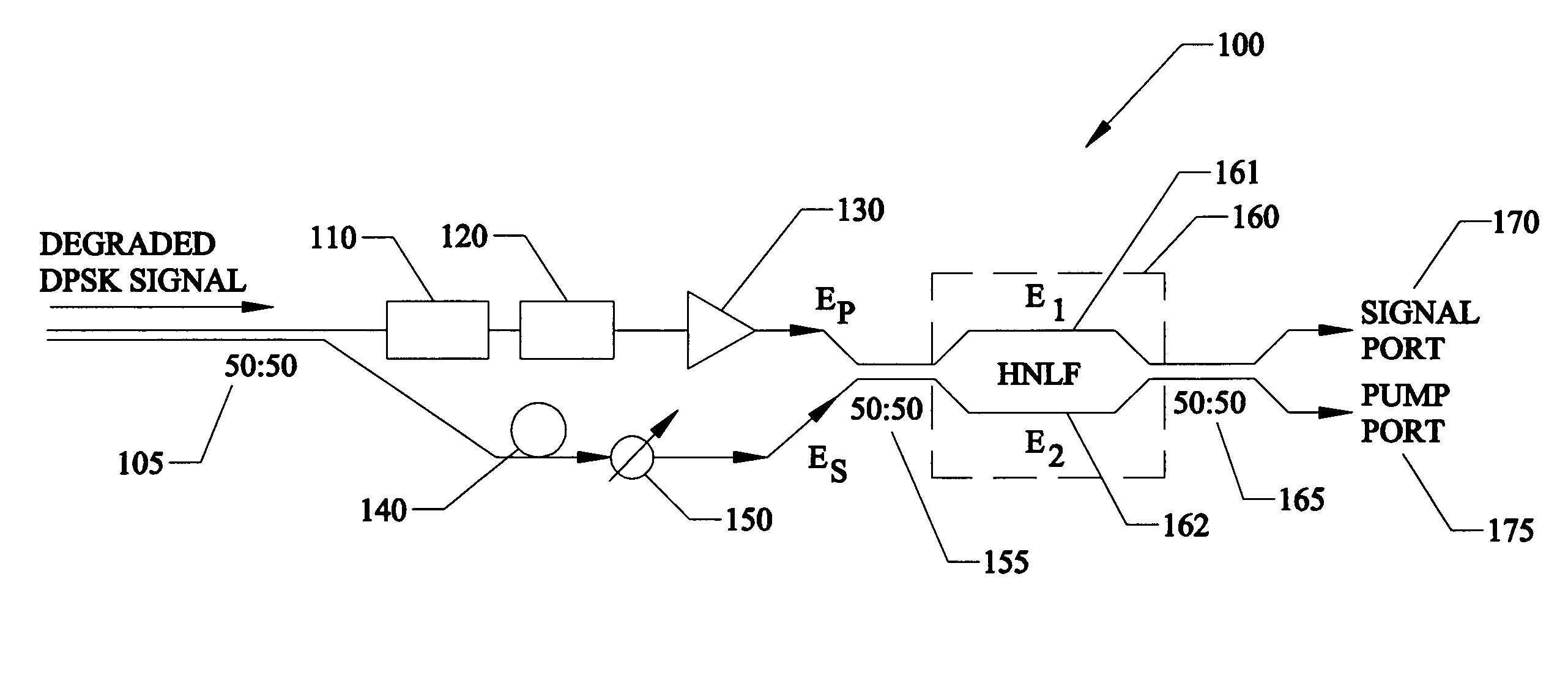
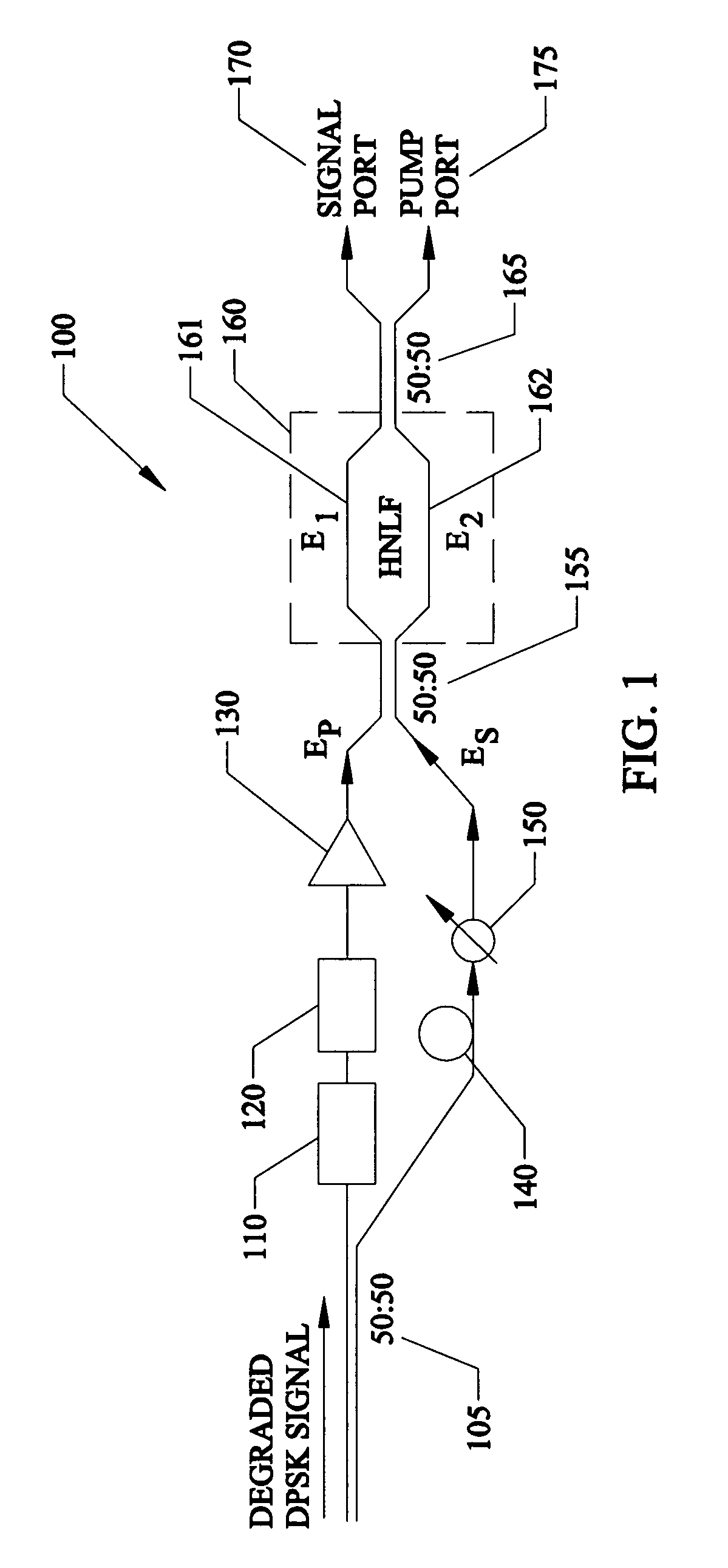
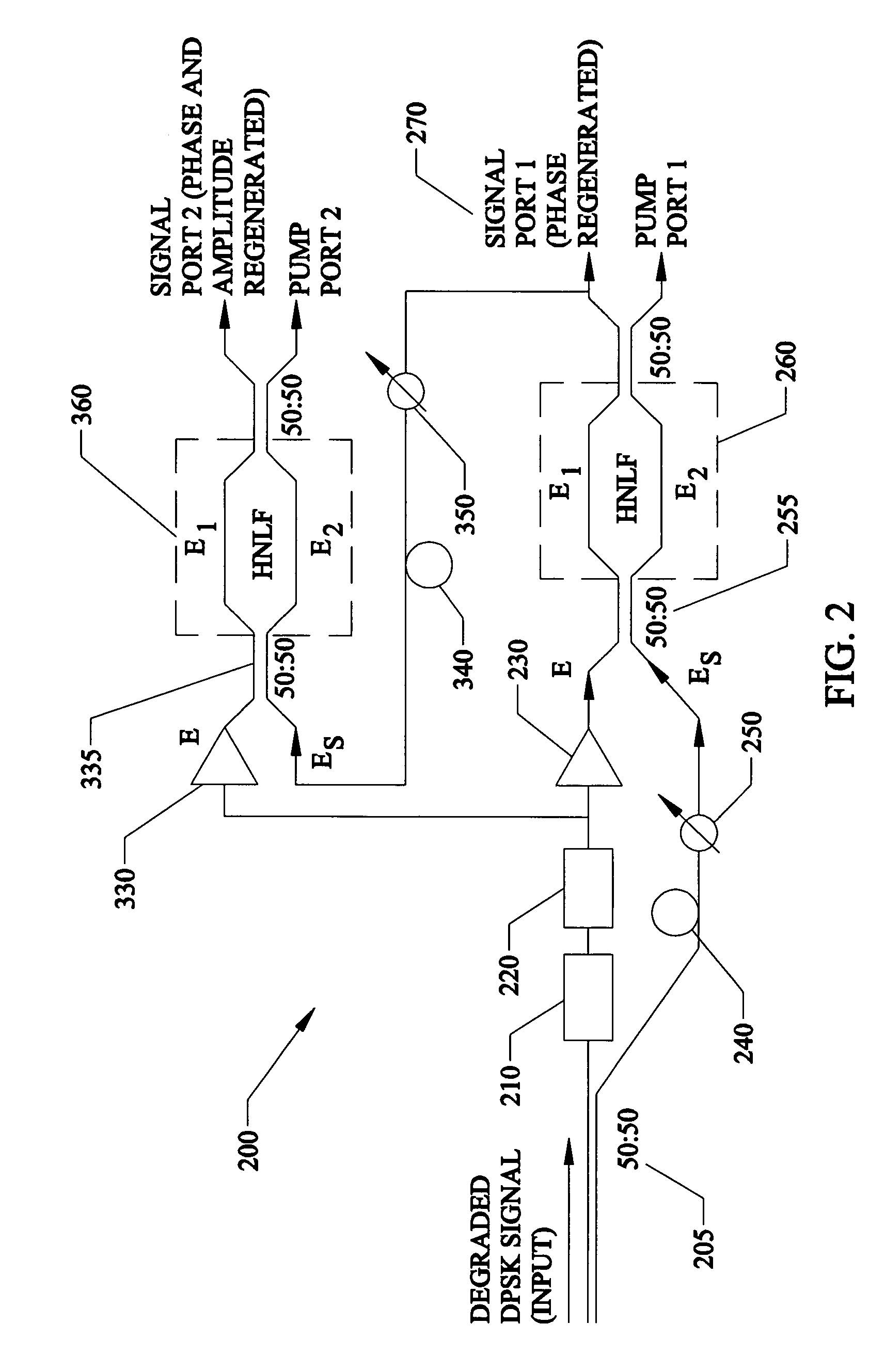
Regeneration of optical phase modulated signals
InactiveUS7369779B1Minimized amplitudeNoise minimizationLaser detailsCladded optical fibrePhase differencePhase sensitive
A regenerator for restoring the originally encoded optical phase of a differential-phase-shift-keyed signal. In an embodiment, the regenerator simultaneously provides limiting amplification and reduces amplitude noise based on a phase-sensitive optical amplifier that combines a weak signal field of a degraded input data with a strong pump field supplied by a local oscillator in a nonlinear interferometer. The two fields interact through degenerate four-wave mixing, and optical energy is transferred from the pump to the signal and vice versa. The phase sensitive nature of the optical gain leads to amplification of a specific phase component of the signal, determined by the input pump-signal phase difference and the incident signal phase is restored to two distinct states, separated by 180° according to the original encoding. Simultaneously, gain saturation of the pump wave by the signal wave results in limiting amplification of the signal wave for removing signal amplitude noise.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com