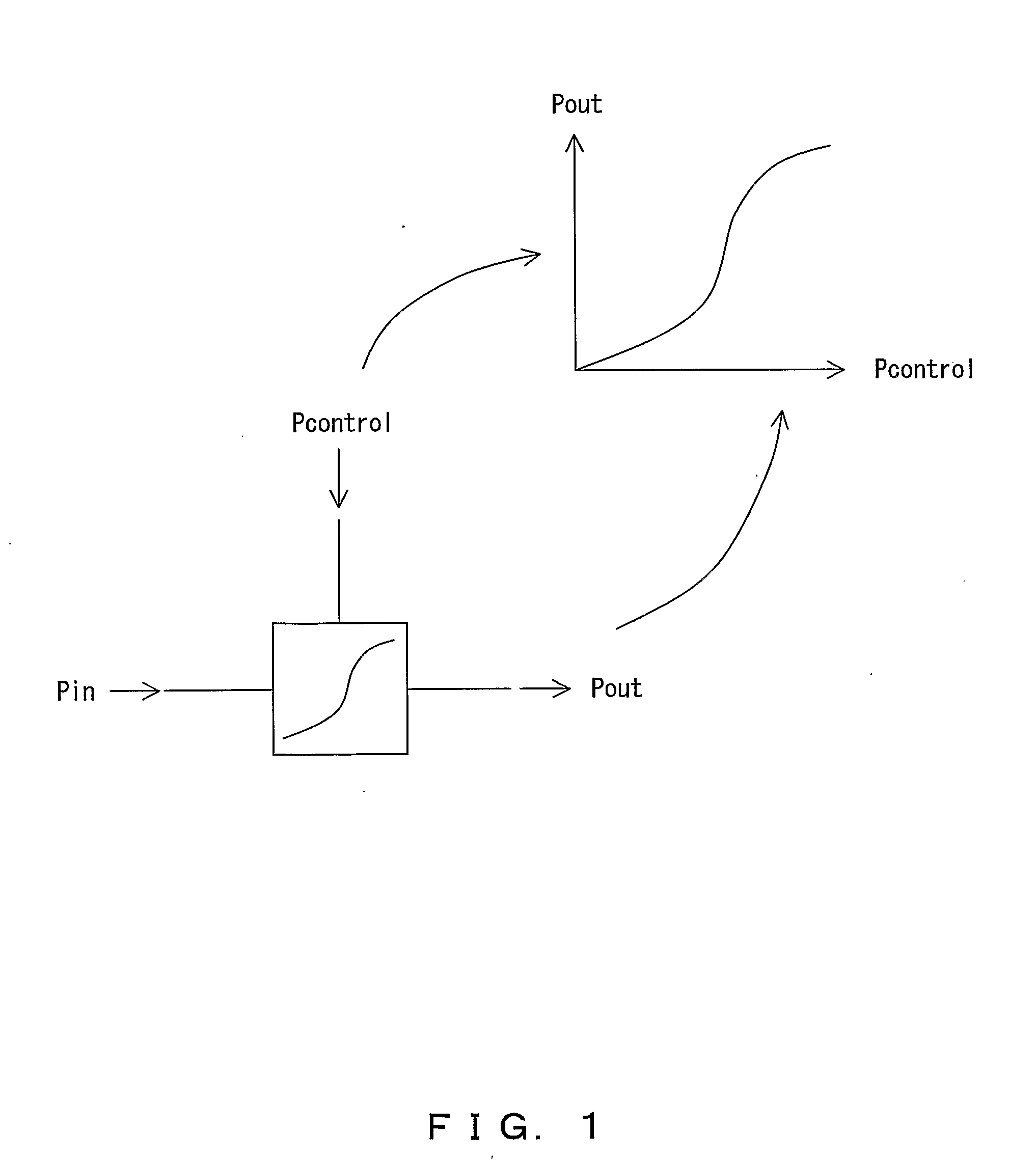
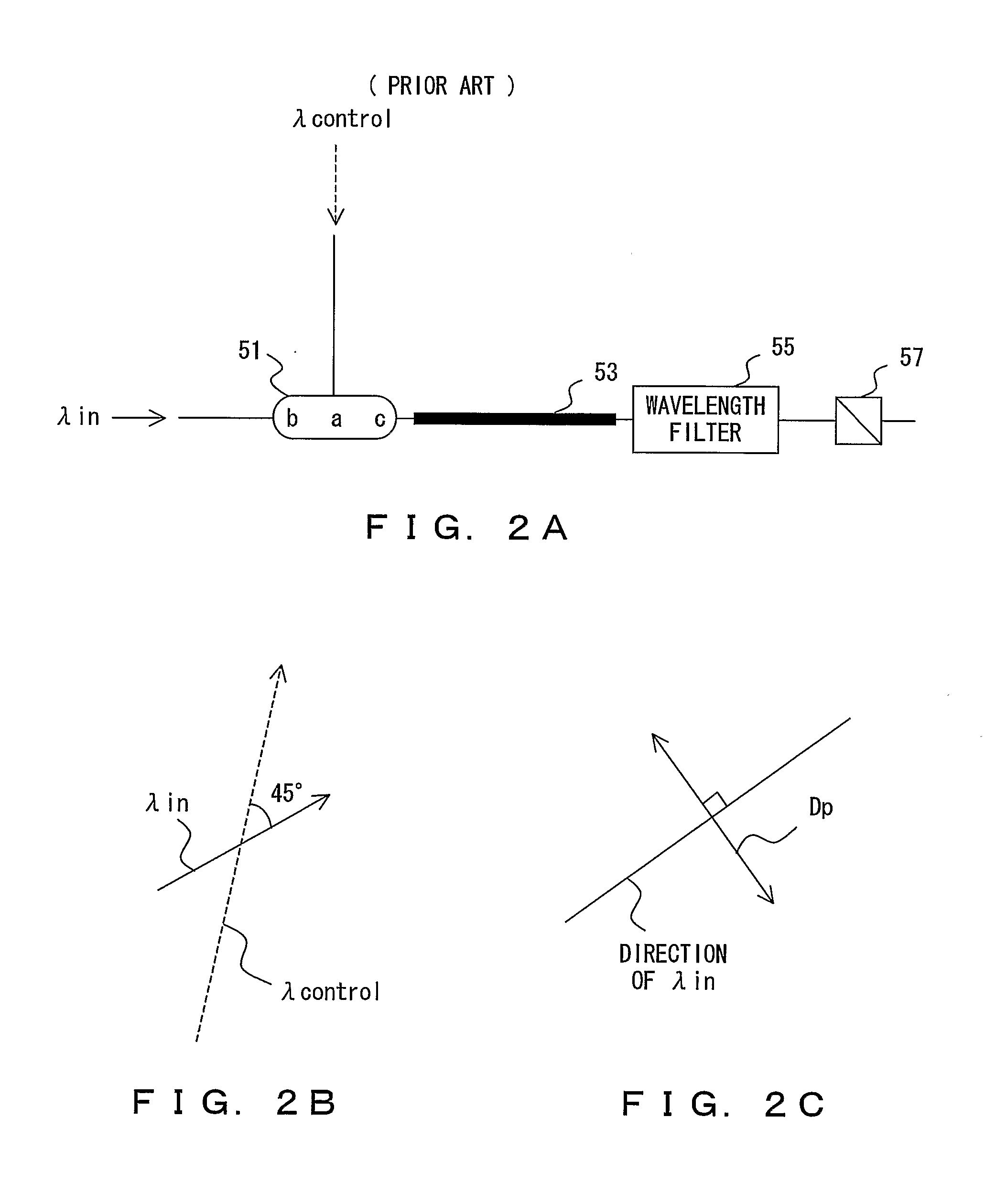
Patents
Literature
111 results about "Cross-phase modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cross-phase modulation (XPM) is a nonlinear optical effect where one wavelength of light can affect the phase of another wavelength of light through the optical Kerr effect. When the optical power from a wavelength impacts the refractive index, the impact of the new refractive index on another wavelength is known as XPM.
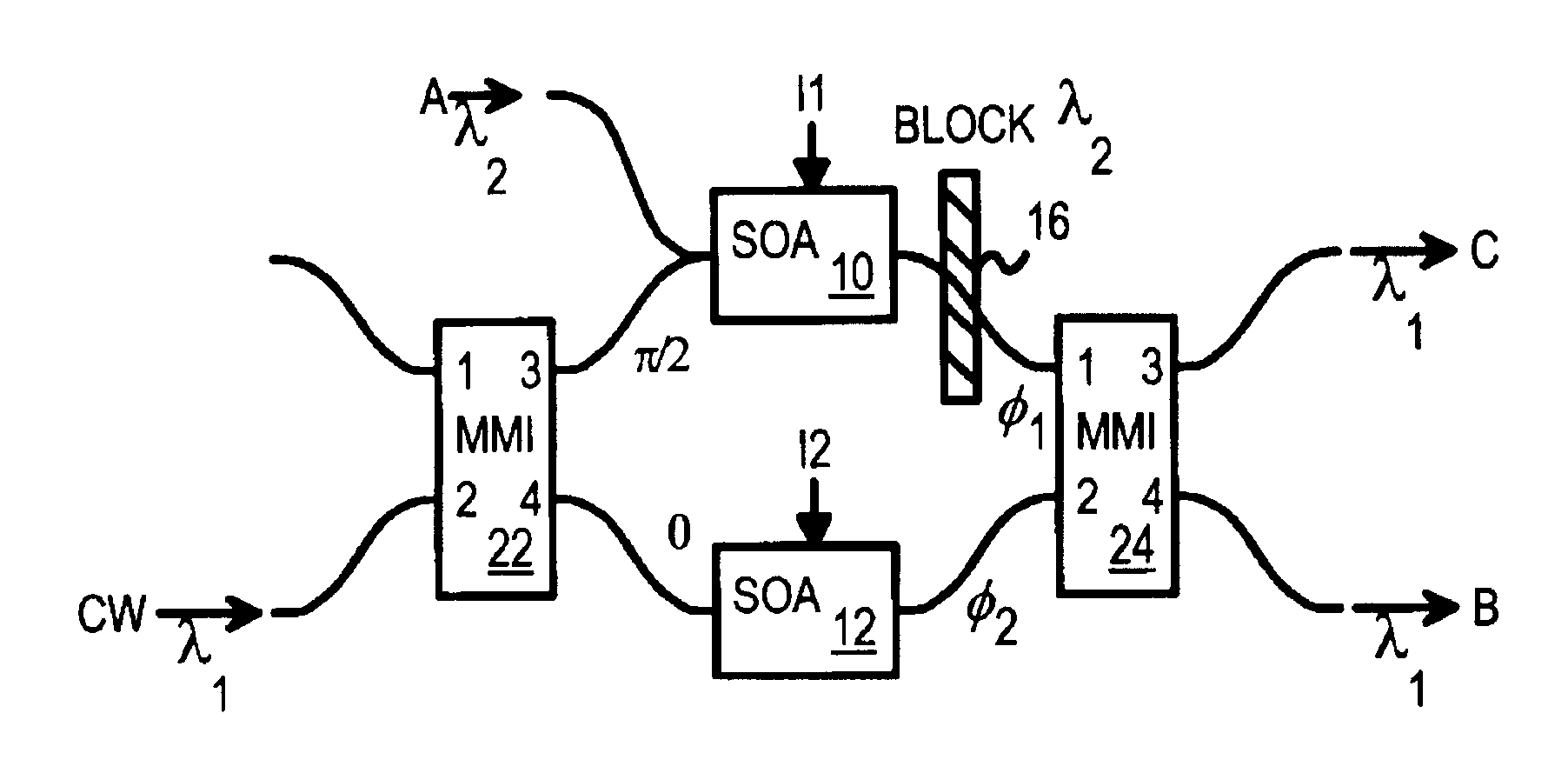
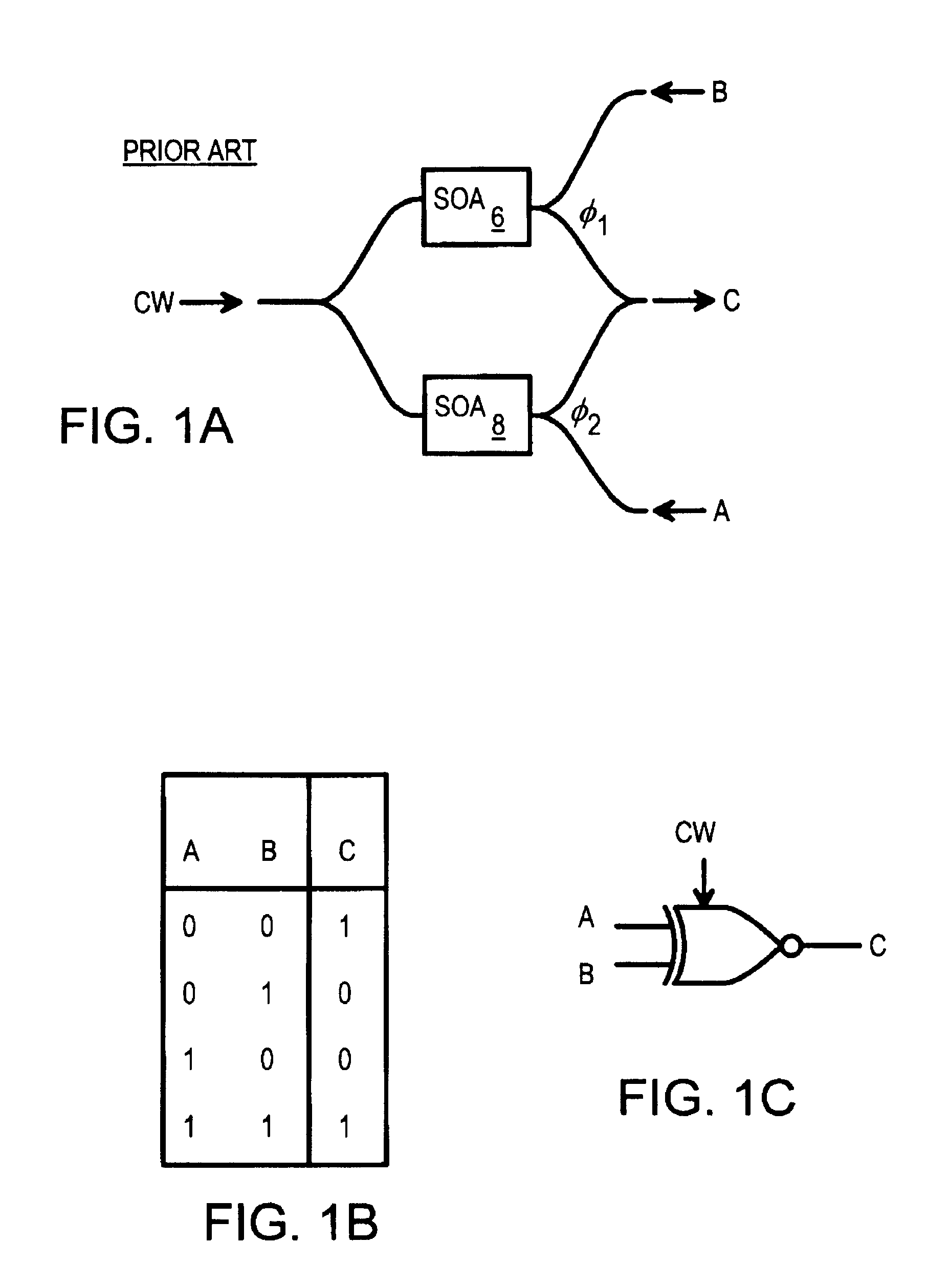
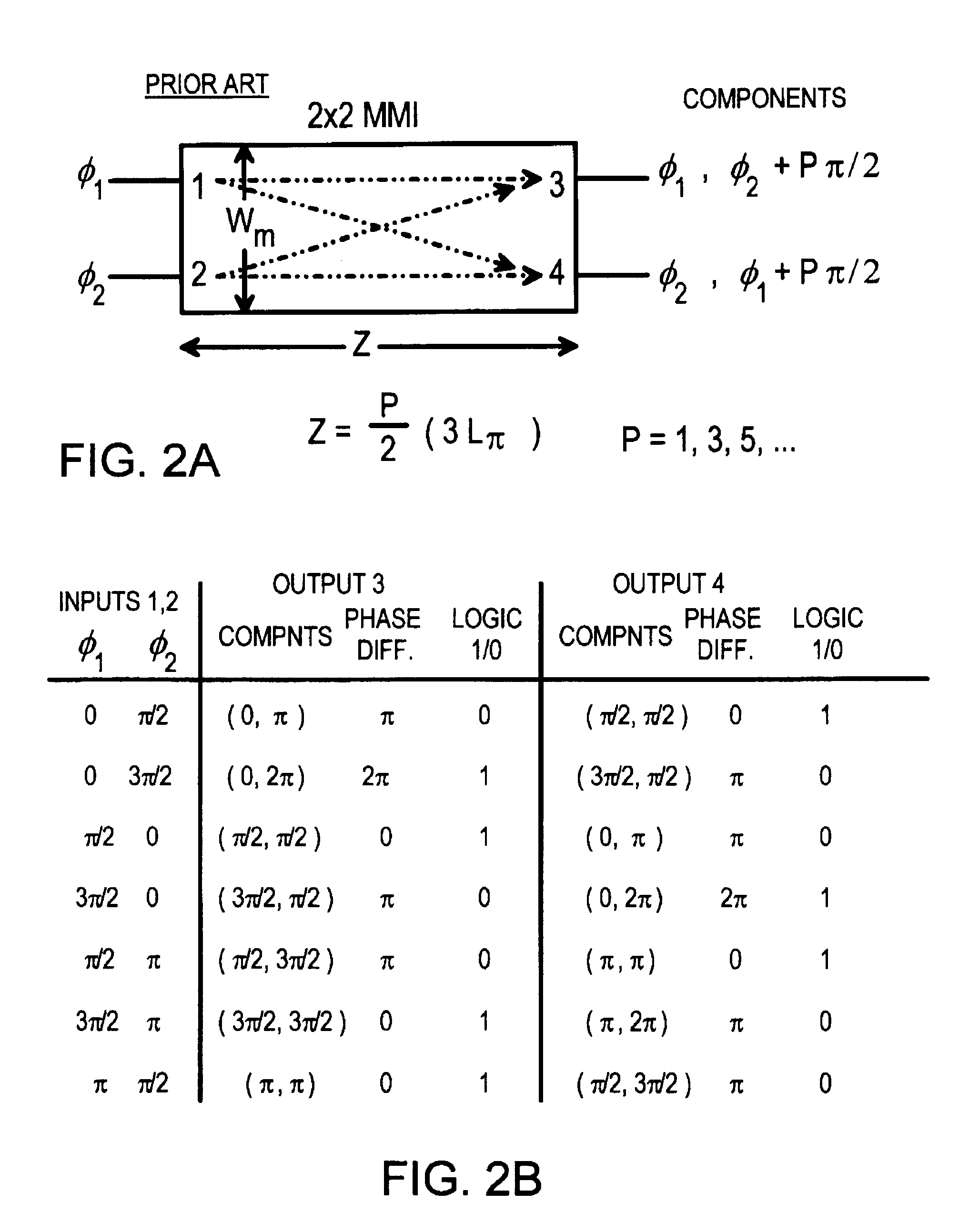
All optical logic using cross-phase modulation amplifiers and mach-zehnder interferometers with phase-shift devices
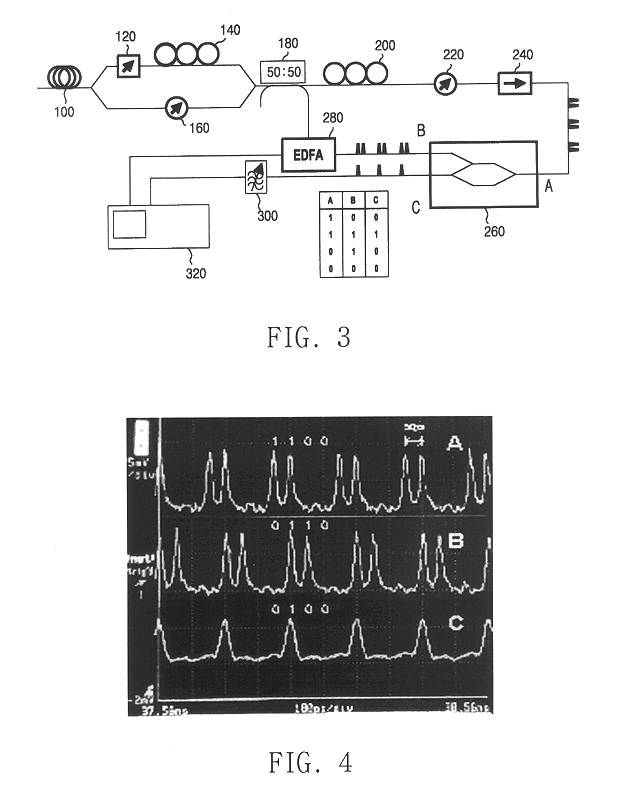
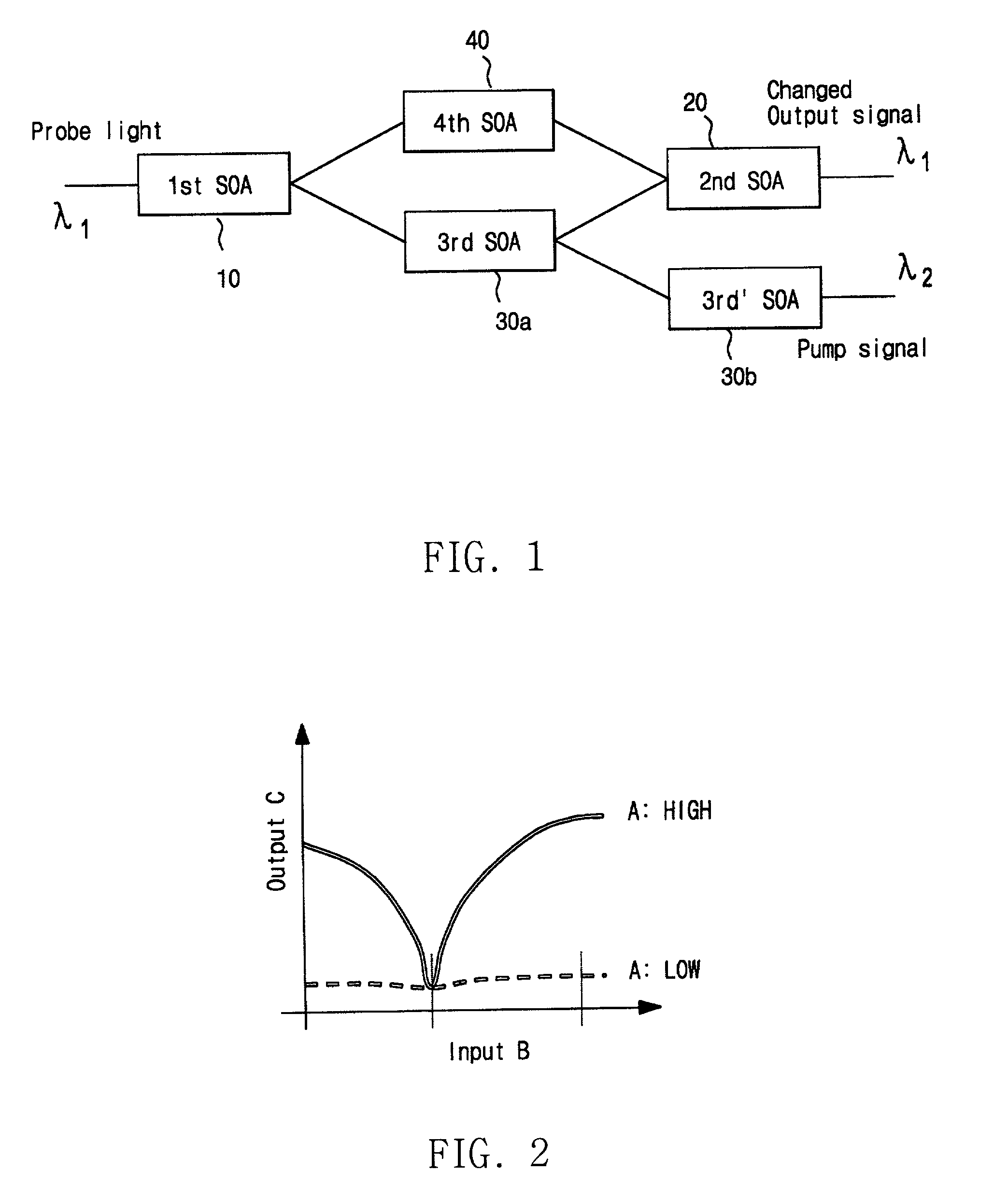
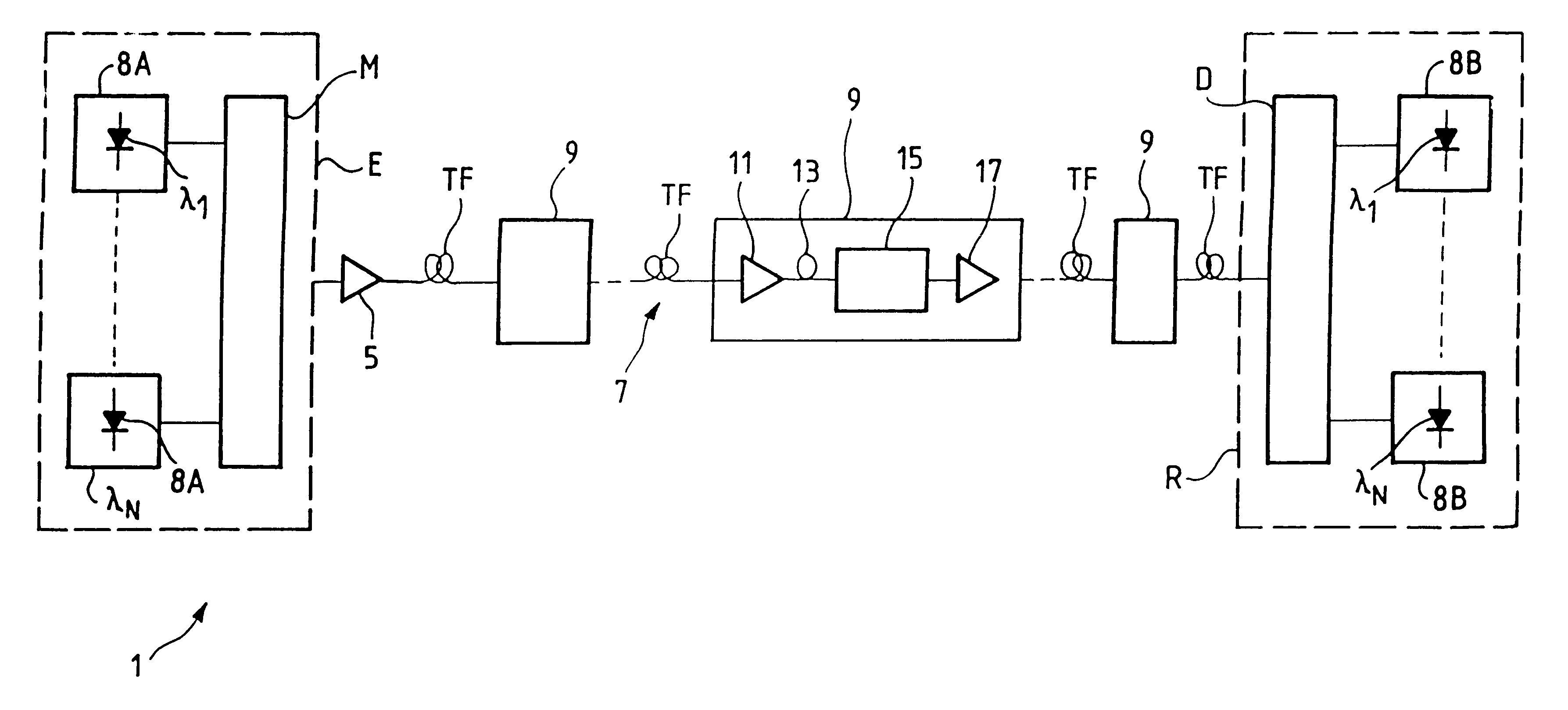
Optical logic gates are constructed from Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) optical circuits. A multi-mode interference (MMI) splitter divides a continuous-wave input into two branches of the interferometer. Each branch has a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). When a logic input having a logic-high power level is applied to one of the SOA's, cross-phase modulation occurs in the SOA. The phase shift increases through the SOA. The branch coupled to the logic input has a relative phase shift of pi compared with the other branch. When two branches with the pi phase difference are combined, destructive interference occurs, producing a logic low. An MMI combiner or an equivalent phase shifter is used to combine the two branches. The MMI splitter adds a phase shift of pi / 2 to the upper branch but not to the lower branch, while the MMI combiner also adds pi / 2 shifts.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
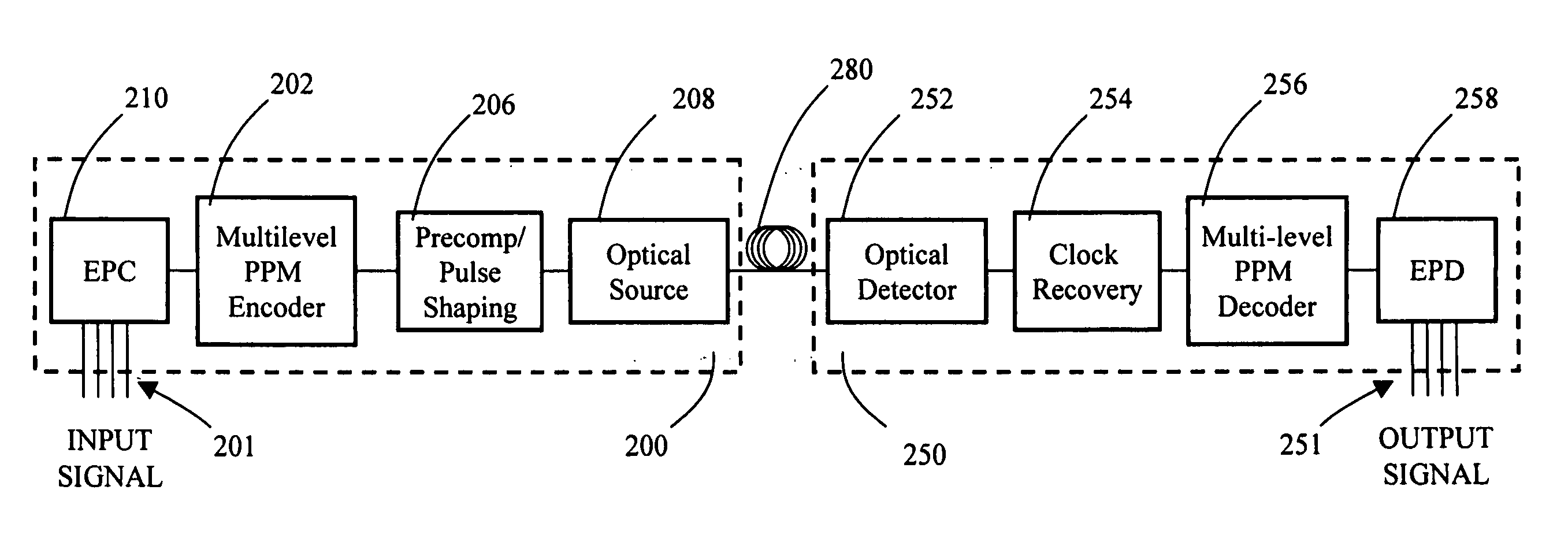
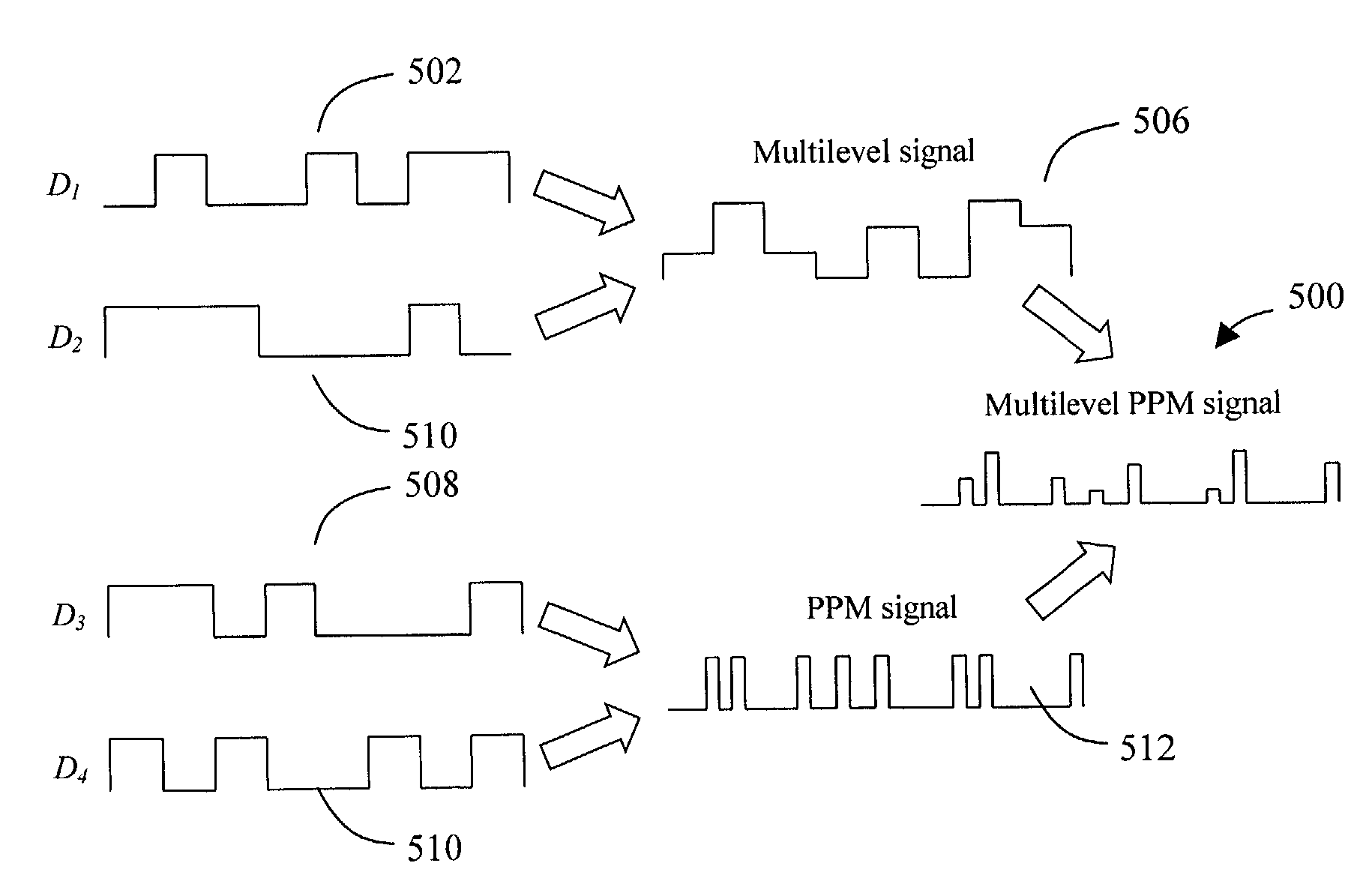
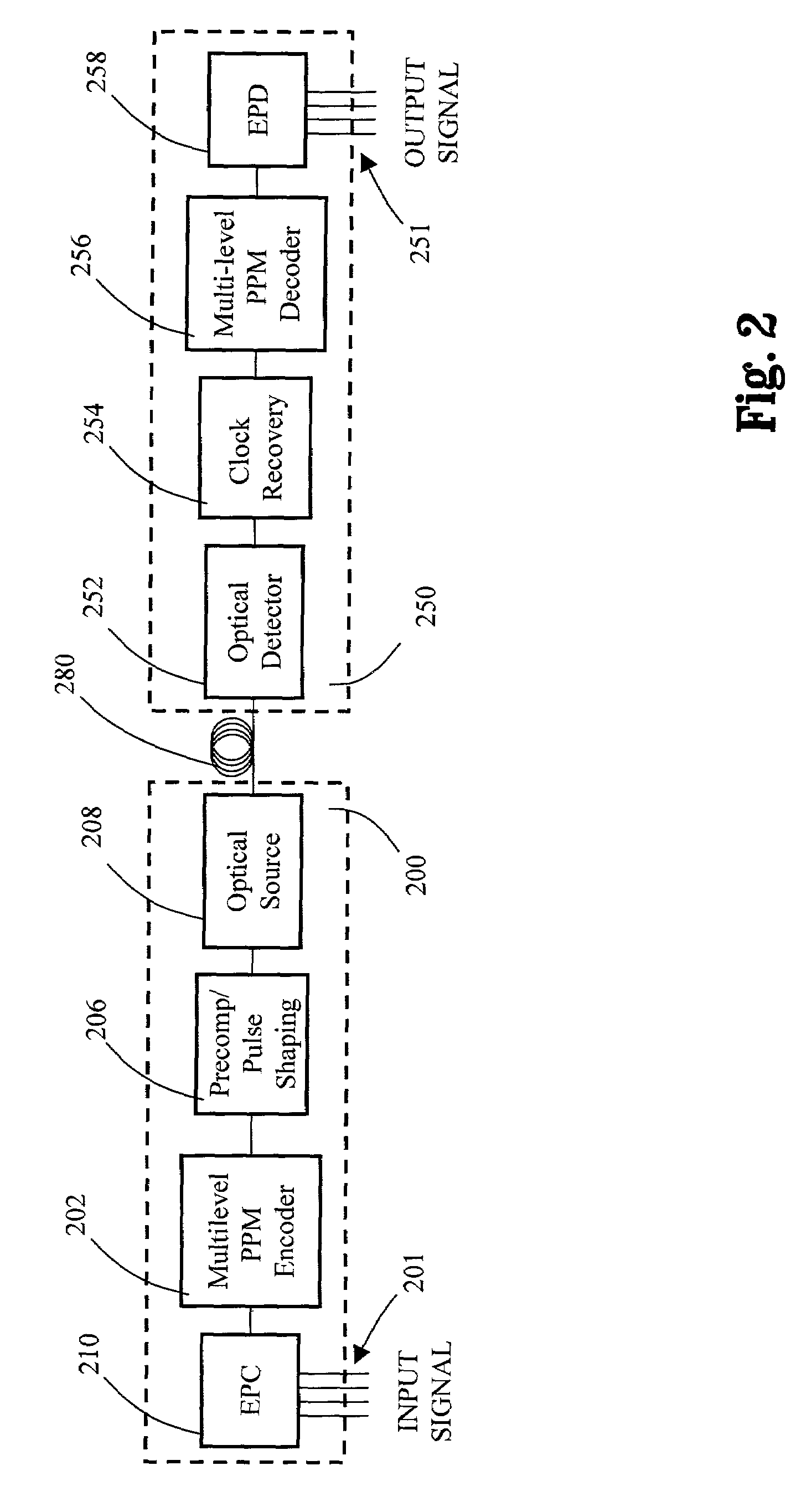
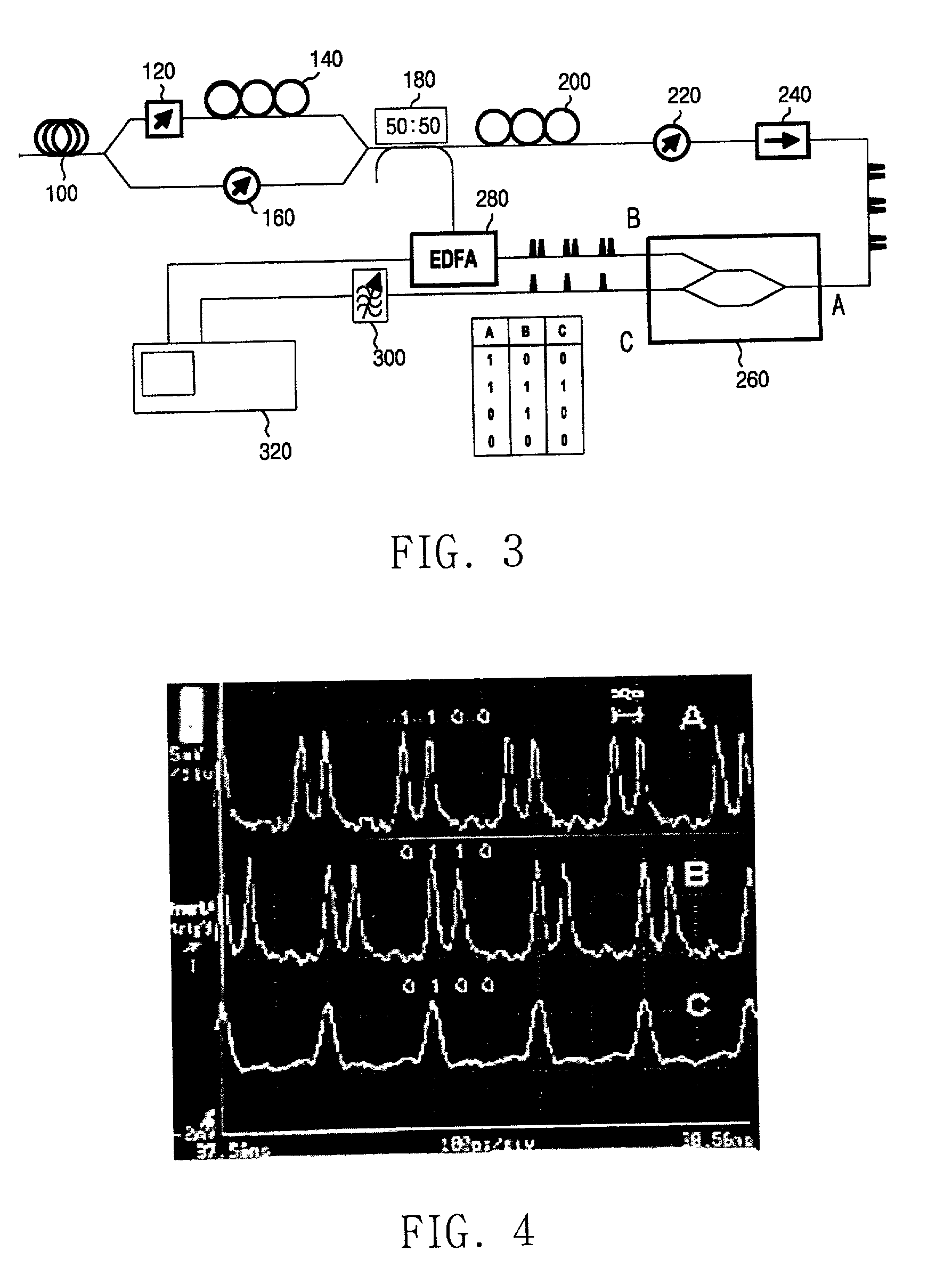
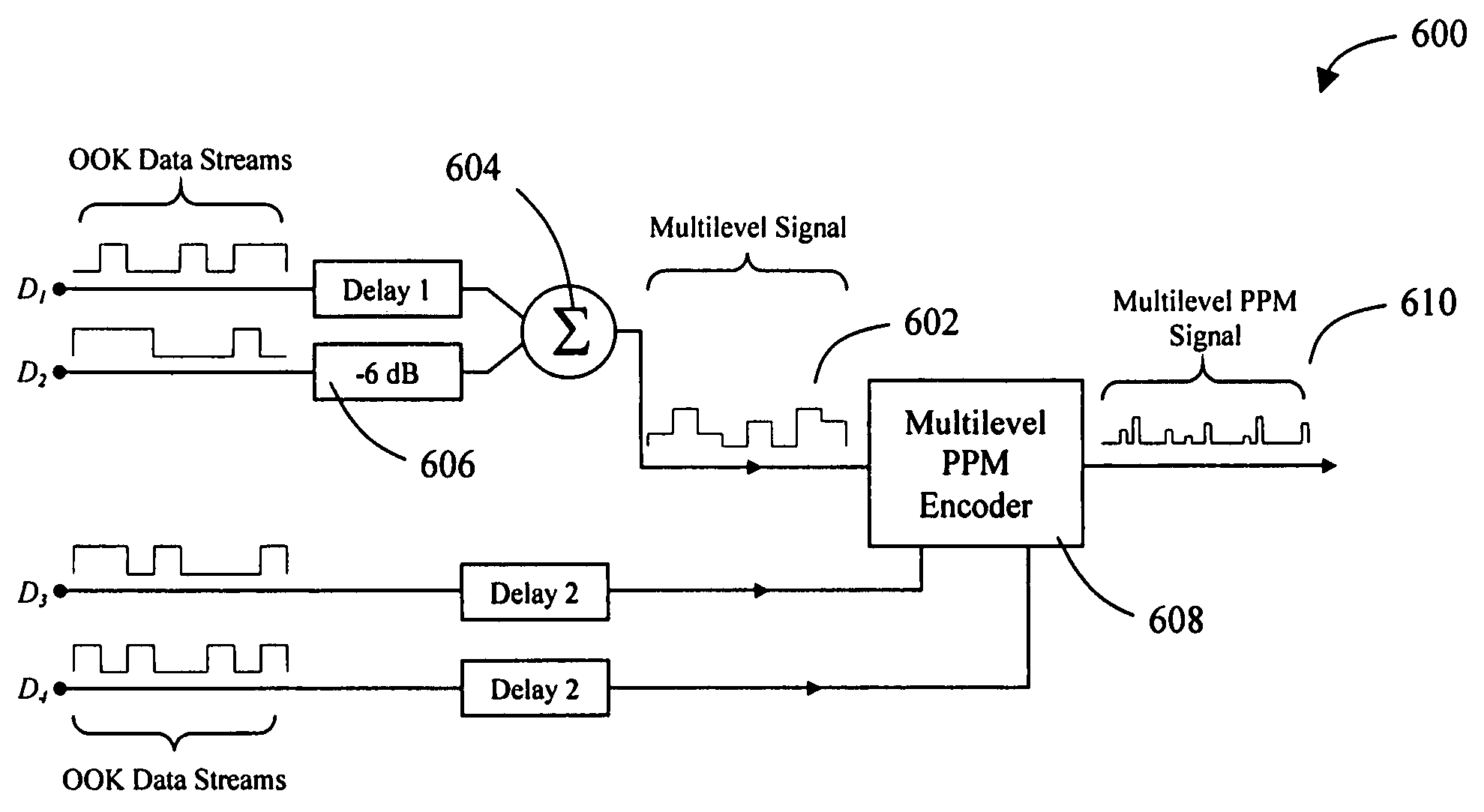
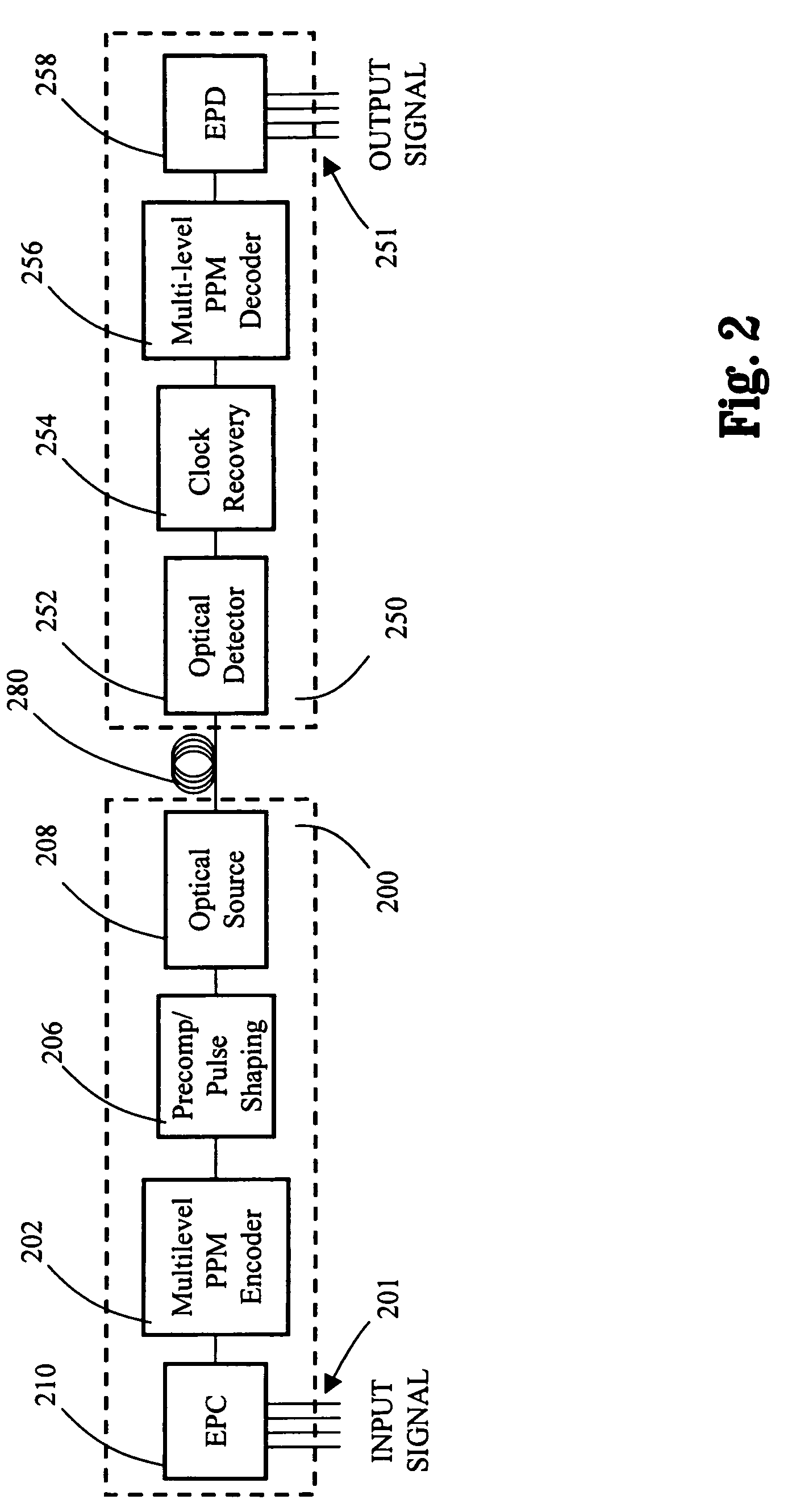
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS20070092265A1Increasing aggregate data rateReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
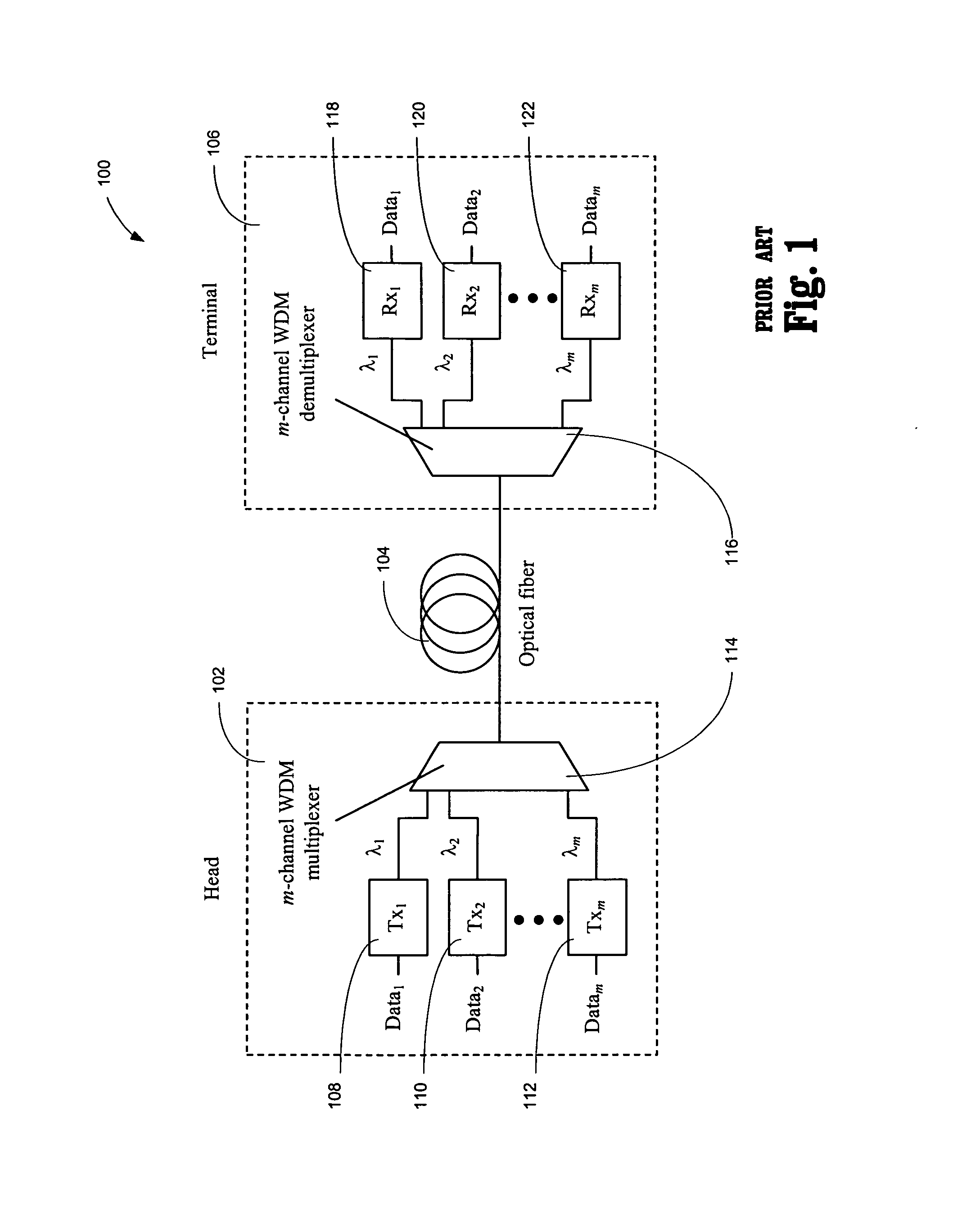
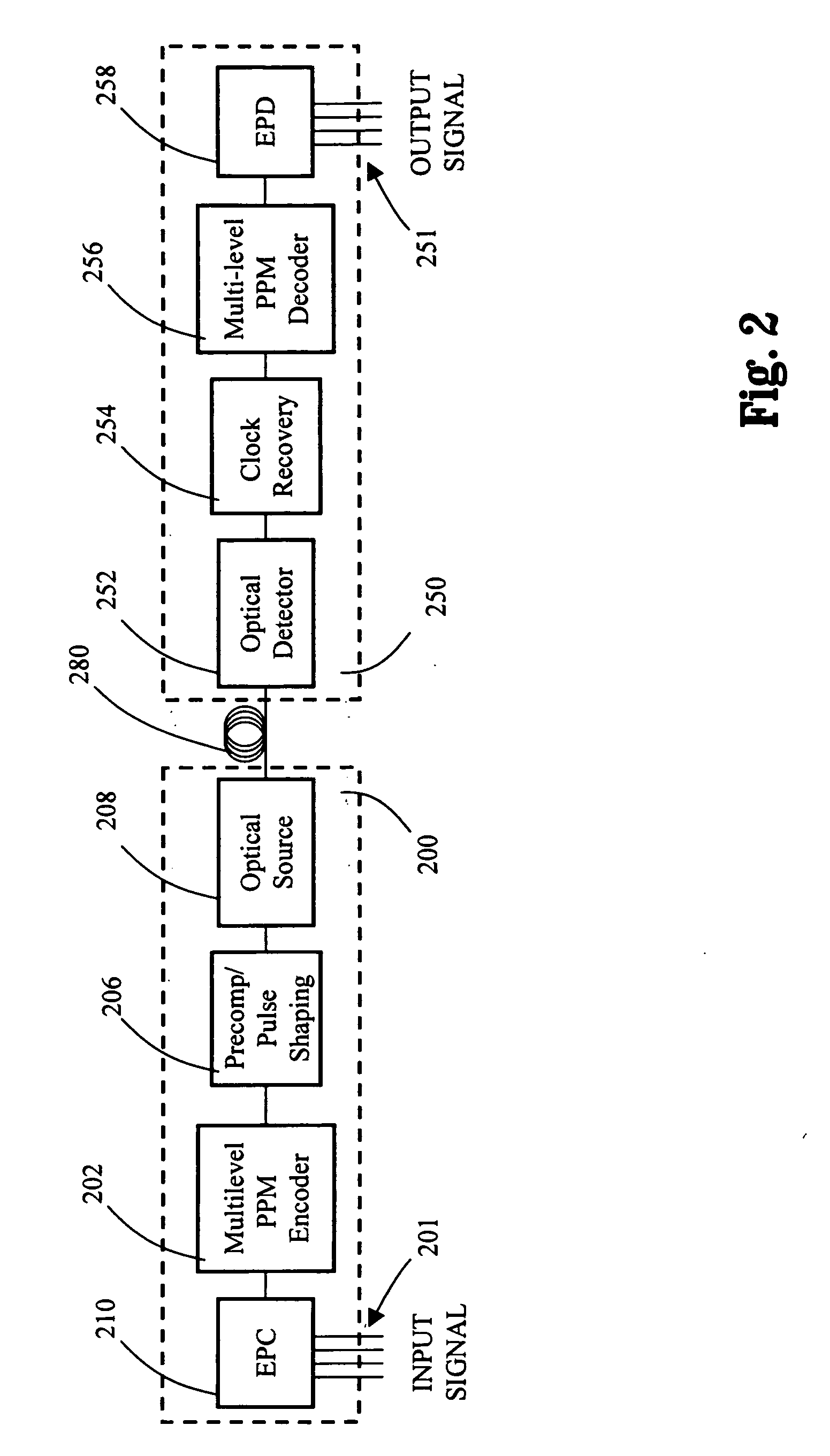
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Optical switch and optical waveform monitoring device utilizing optical switch
InactiveUS20060045445A1Improve switching efficiencyReduce lossesTime-division optical multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical parametric amplifierPolarizer
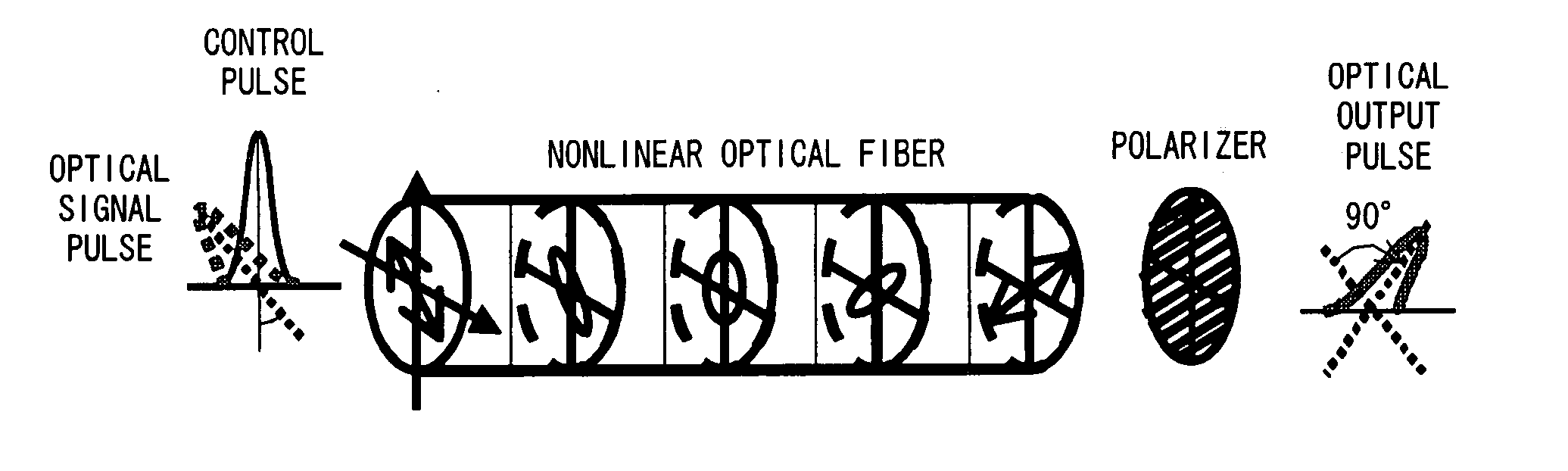
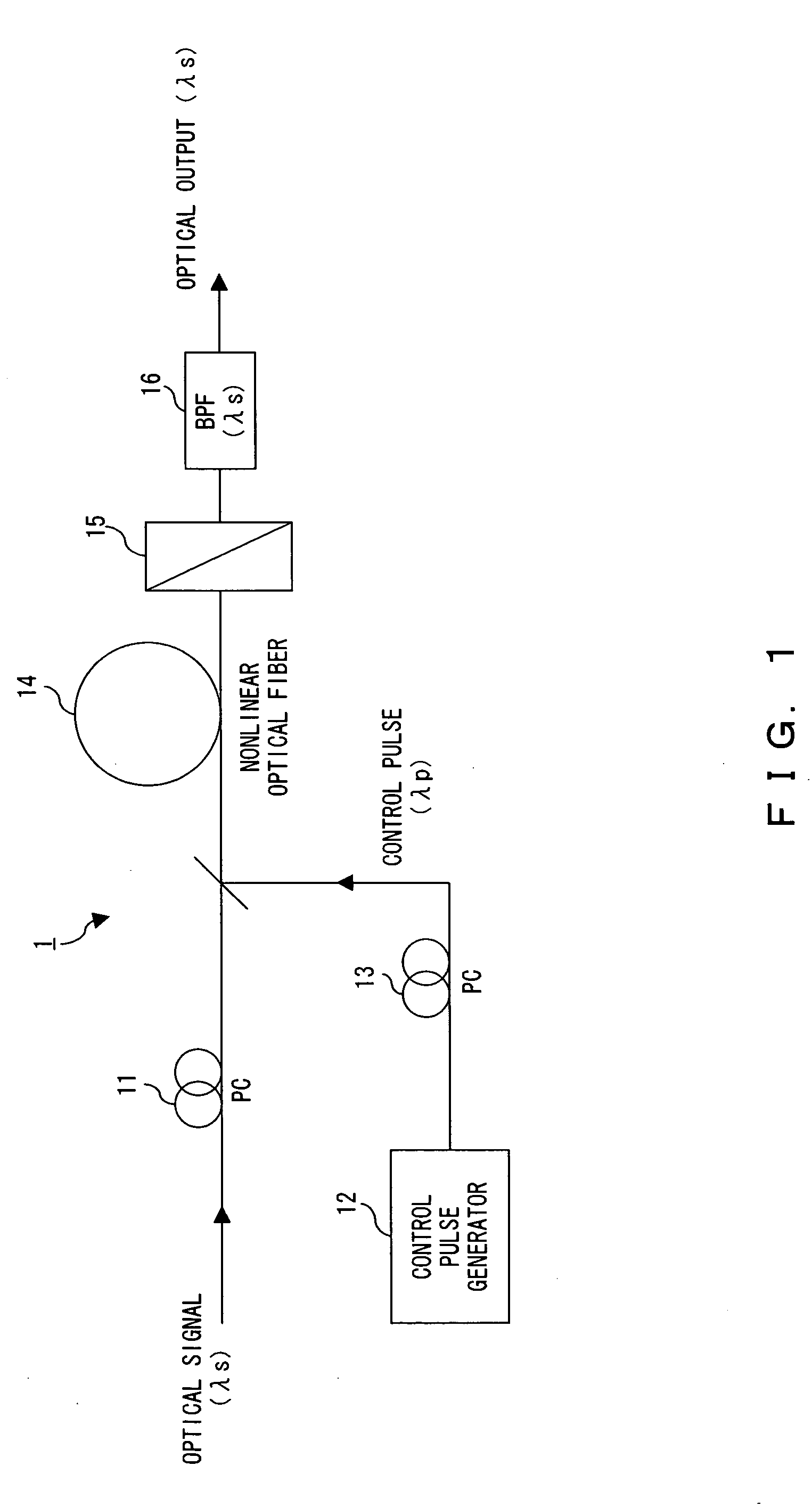
The polarization direction of a signal is rotated by a polarization controller so as to be orthogonal to the main axis of a polarizer. A control pulse generator generates control pulses from control source with a wavelength which is different from the wavelength of the signal. The signal and the control pulse are input to a nonlinear optical fiber. In the nonlinear optical fiber, the signal, during the time period in which the signal and the control pulse coincide, has its polarization direction rotated by cross phase modulation, and is amplified by optical parametric amplification. The signal, during the time period in which the signal and the control pulse coincide, passes through the polarizer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
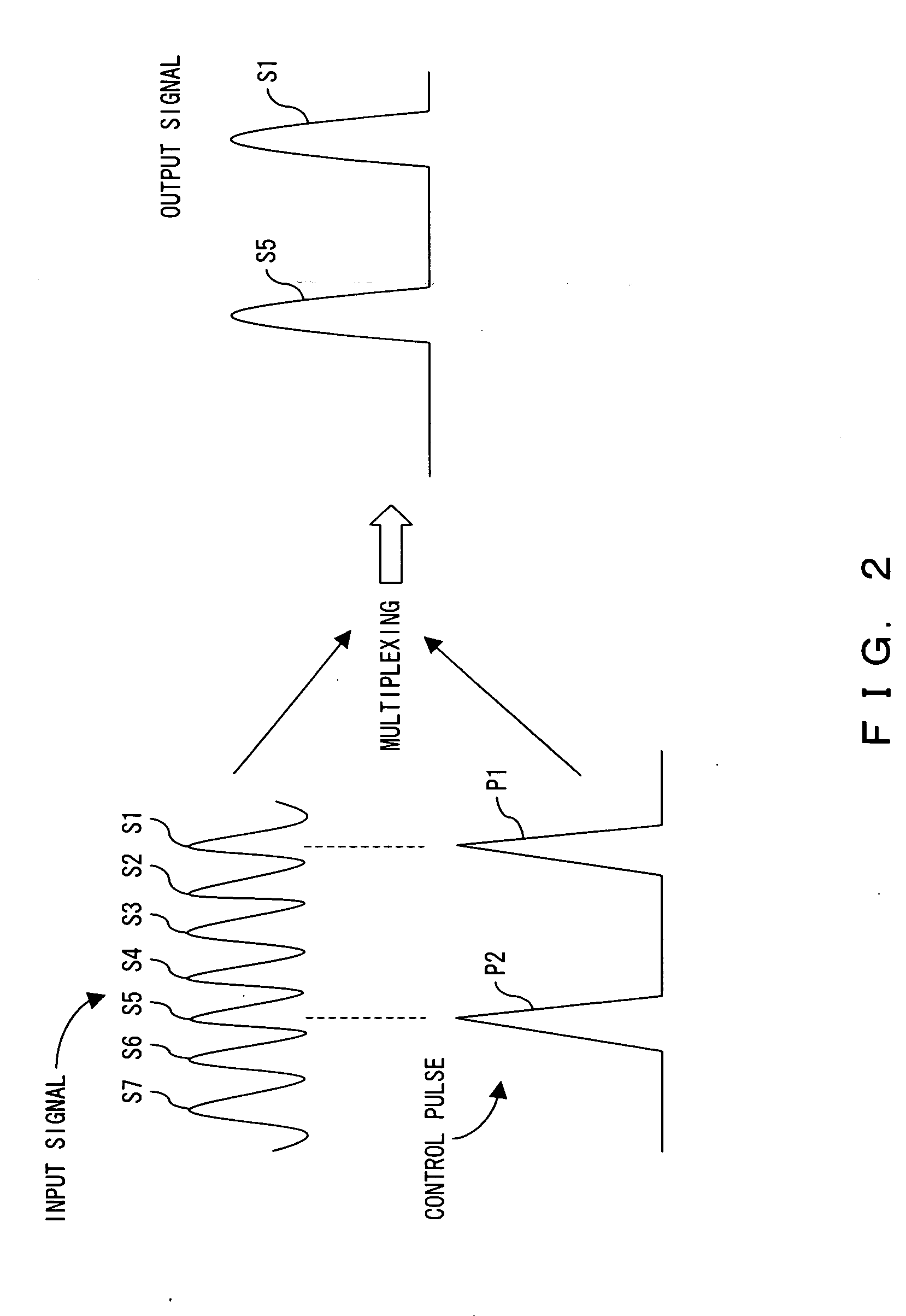
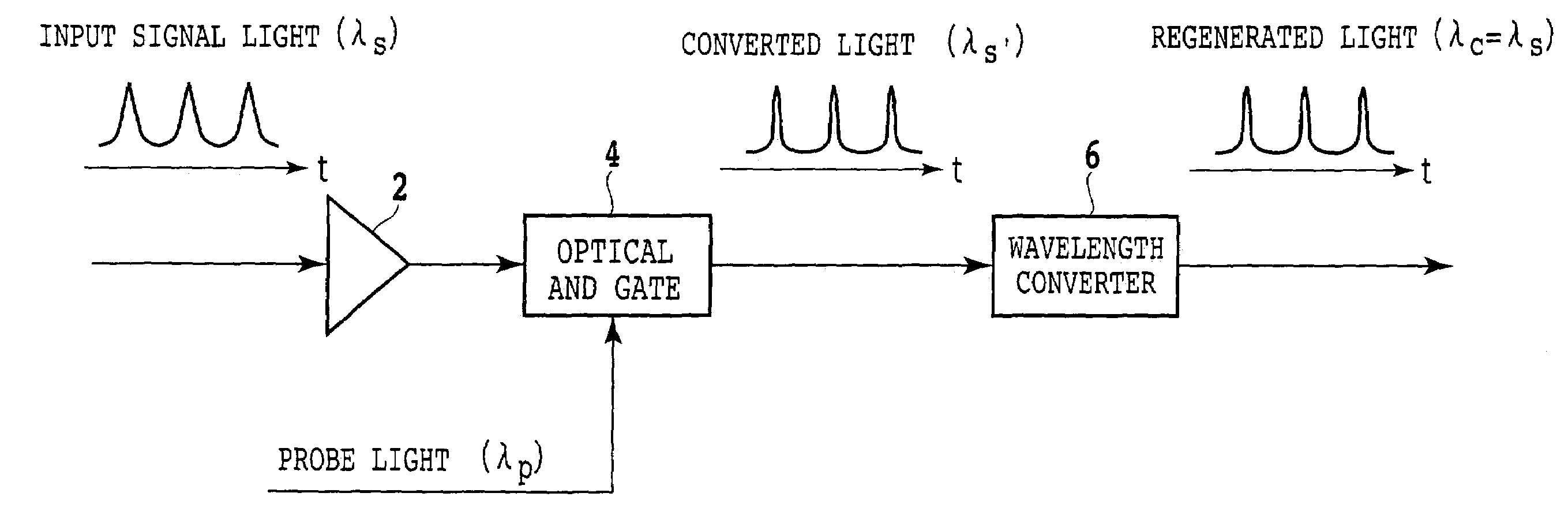
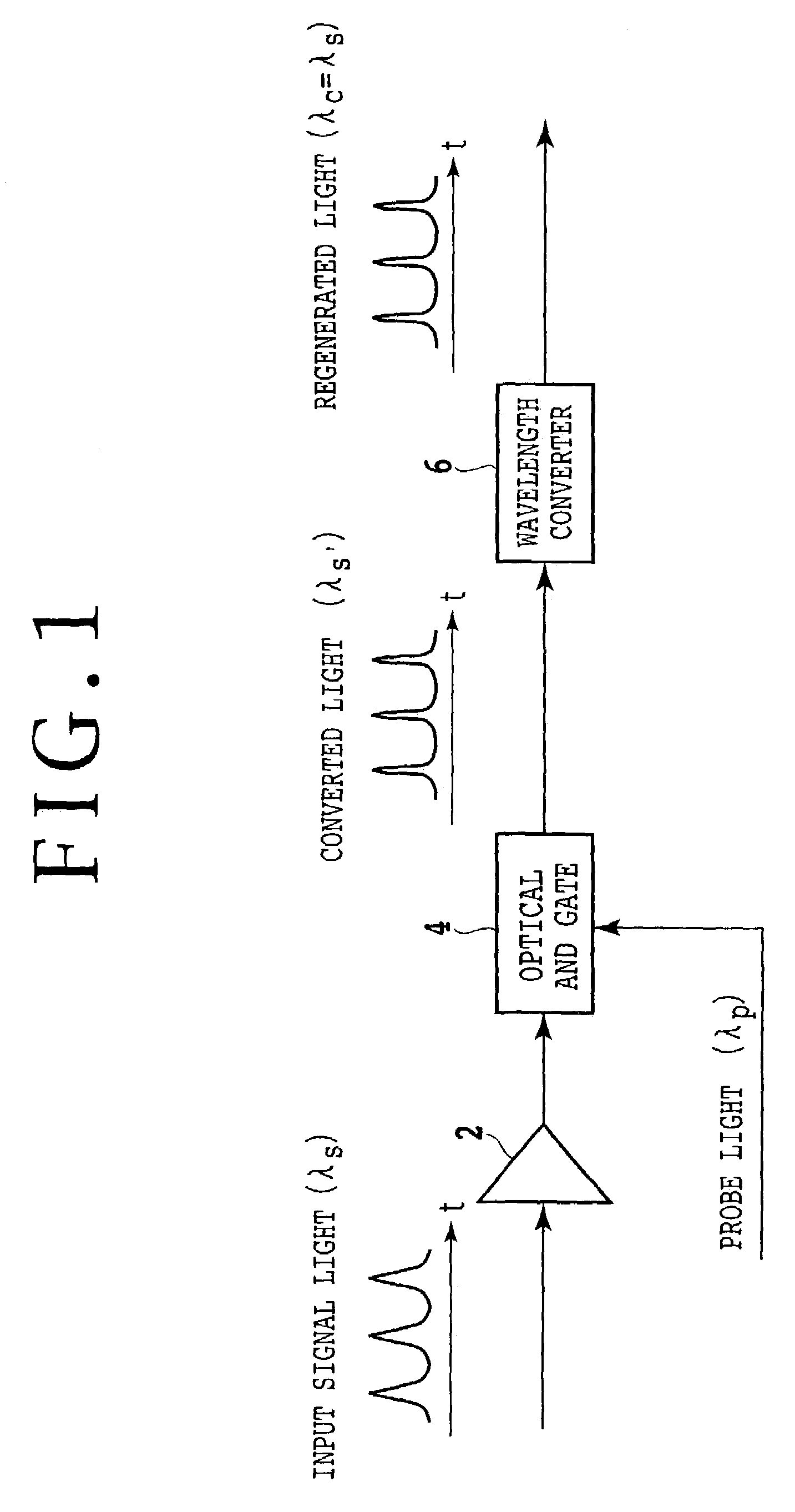
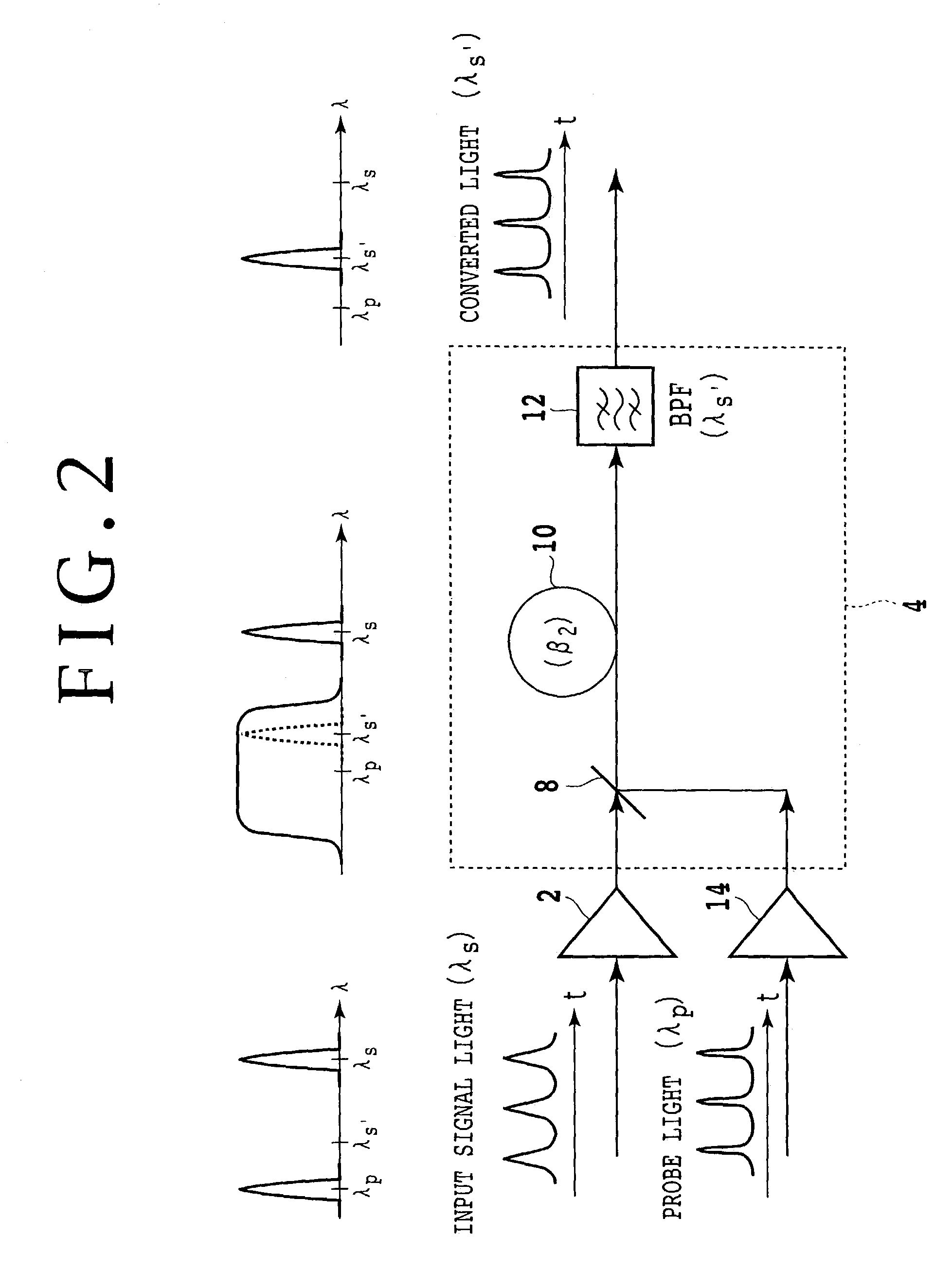
Optical AND gate and waveform shaping device
InactiveUS6987607B2Promote conversionLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesElectromagnetic transmissionWaveform shapingSignal light
The method according to the present invention includes the steps of inputting an optical signal having a first wavelength and probe light having a second wavelength different from the first wavelength into a nonlinear optical medium, broadening the spectrum of the probe light through cross phase modulation between the optical signal and the probe light inside the nonlinear optical medium, and extracting a signal component including a modulated component of the optical signal and having a band narrower than the band of the spectrum broadened. According to the present invention it can be possible to provide a method and device which can easily convert the wavelength of signal light into an arbitrary wavelength in performing optical 3R functions.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS7149256B2Reduce transmit powerIncreasing aggregate data rateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
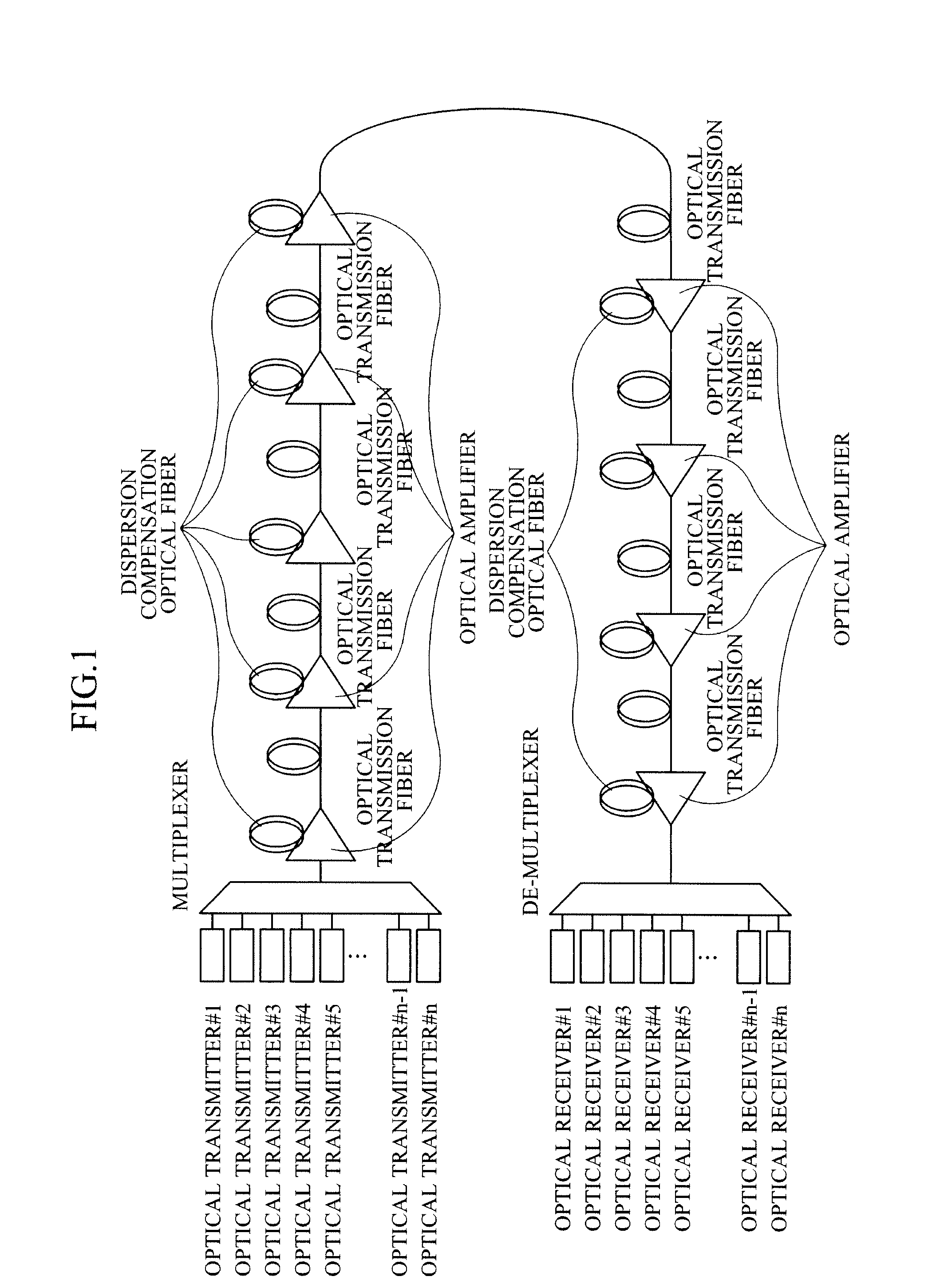
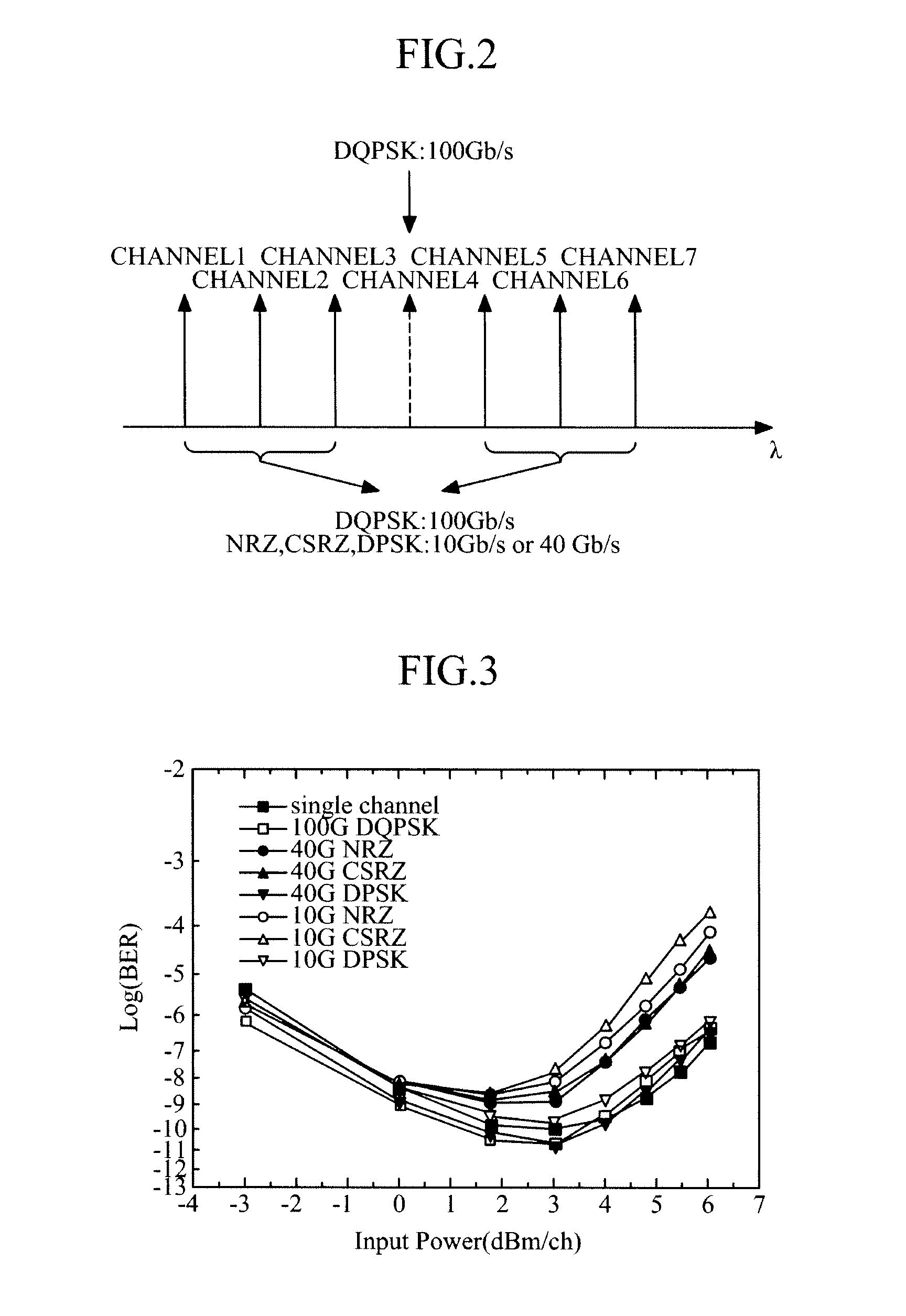
Channel assignment method and apparatus for wavelength-division-multiplexed transmission system
InactiveUS20100158531A1Suppress interferenceImprove transmission performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexEngineeringLength wave
Provided is a channel assignment method in a wavelength-division-multiplexed transmission system. The channel assignment method includes obtaining information about signal modulation schemes from a plurality of optical transmitters, and assigning channels to the respective optical transmitters in consideration of the obtained information about the signal modulation schemes. Accordingly, in transmission of channels of different modulation formats, cross phase modulation is minimized, thereby reducing inter-channel interference.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
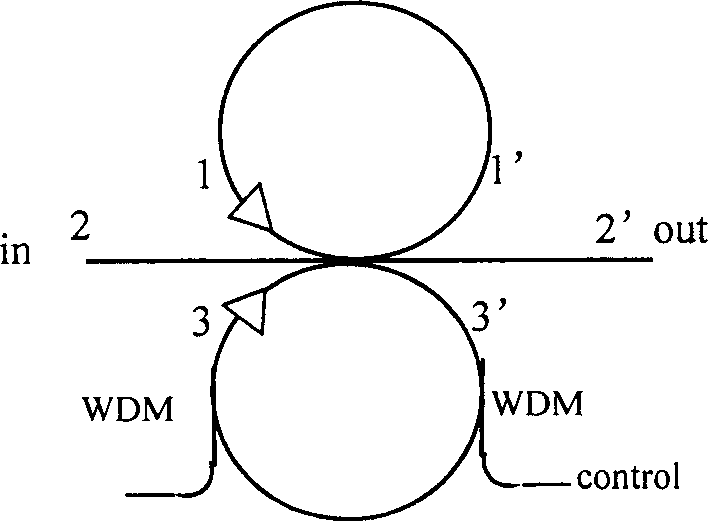
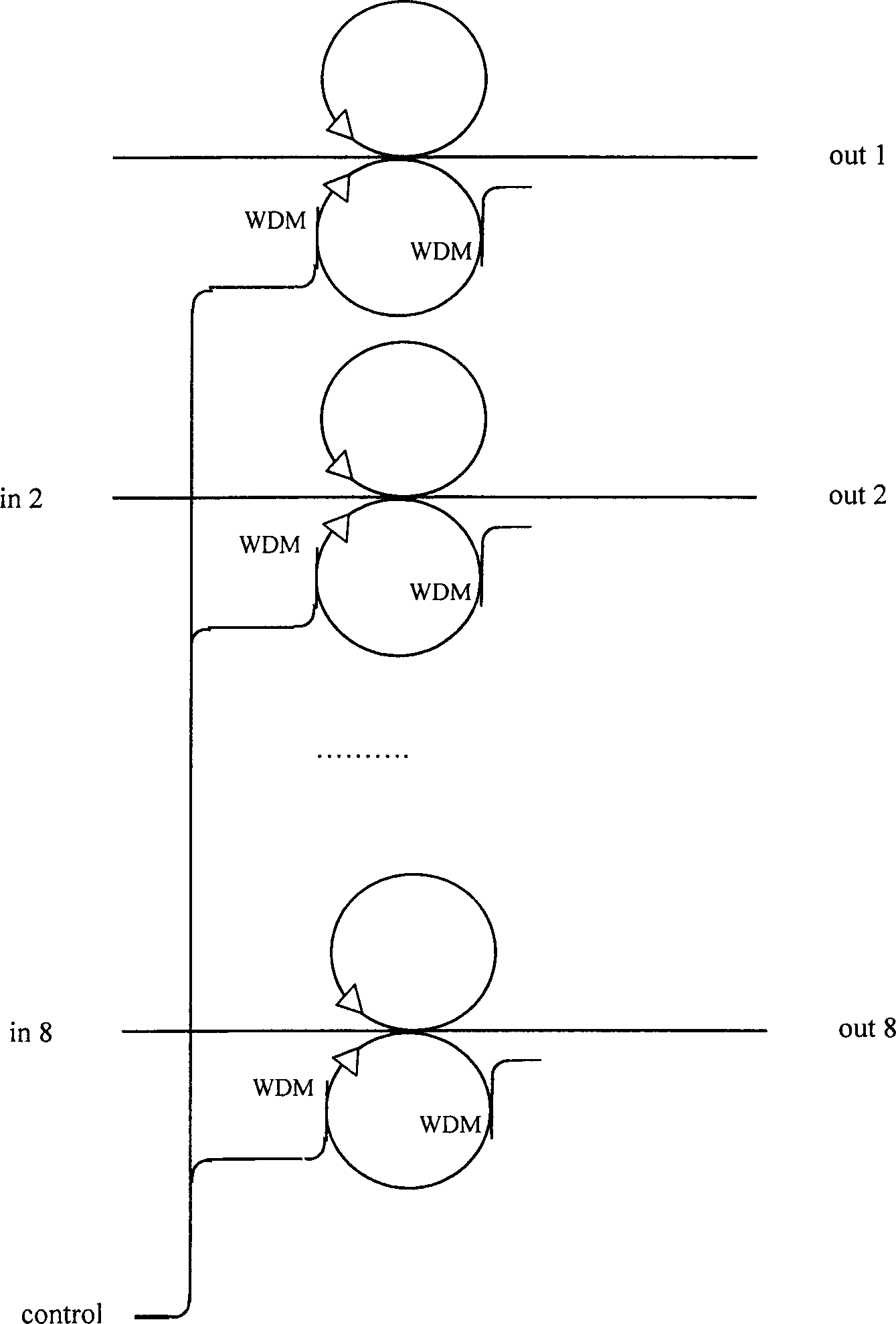
Double-ring coupled all optical buffer storage
InactiveCN1417604AExtended storage timeGood symmetryCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionFiber couplerPhase difference
The double-ring coupled all optical buffer storage based on 3x3 fiber coupler stores light signal has its read / write operation under control of one other light signal. Two side ports of the 3x3 fibercoupler constitute the double-ring structure via fiber feedback and the middle ports are used as the input and output of the buffer storage. Control light is led in and led out one fiber ring via twoWDM fiber coupler, and the phase difference between the two ring light signals is altered by means of cross phase modulation effect to realize the write-in and real-out of light signal in fiber ring.The control light signal may be positive logic one or negative logic one. If necessary, light amplifier may be added into the fiber ring for power compensation. Several buffer storages can be constituted into one parallel signal light buffer storage.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Compensation of Optical Transmission Impairments Using Digital Backward Propagation
ActiveUS20100239262A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingFiber chromatic dispersionTransmission channel
Systems and method of compensating for transmission impairment are disclosed. One such method comprises receiving a wavelength-division multiplexed optical signal. The received optical signal has been distorted in the physical domain by an optical transmission channel. The method further comprises propagating the distorted optical signal backward in the electronic domain in a corresponding virtual optical transmission channel. The backward propagation fully compensates for fiber dispersion, self-phase modulation, and cross-phase modulation (XPM) and partially compensates for four-wave mixing (FWM).
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Systems and methods for the compensation of nonlinear cross polarization and cross phase modulation in dual polarization coherent channels
ActiveUS20140050476A1Improve toleranceOptimize channel performancePolarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization multiplexedEngineering
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for the compensation of signal distortion in fiber optic communication systems and the like. More specifically, the present disclosure provides an orthogonal polarization detection and broadband pilot (OPDBP) technique for the compensation of nonlinear cross polarization (i.e. nonlinear cross polarization modulation) (XPolM) induced noise and nonlinear nonlinear cross phase modulation (XPM) induced noise in a high data rate polarization multiplexed (PM) multilevel-quadrature amplitude modulated (M-QAM) channel due to neighboring channels. This approach allows for the compensation of both XPolM and XPM simultaneously, providing several dBs of optical reach extension. The approach uses a pilot tone based orthogonal polarization detection scheme with broadband (i.e. a few GHz wide) filtering of the pilot tones.
Owner:CIENA
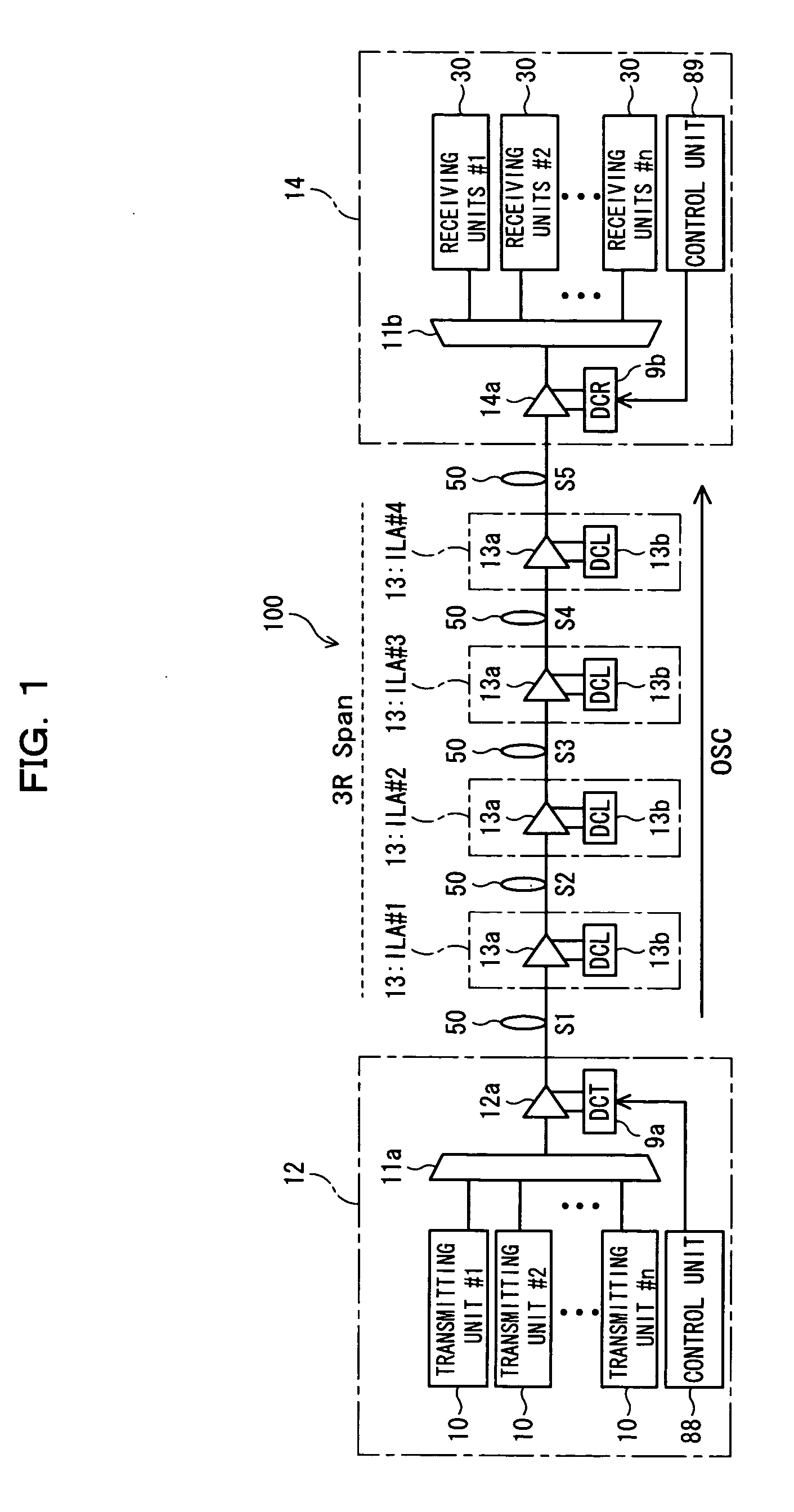
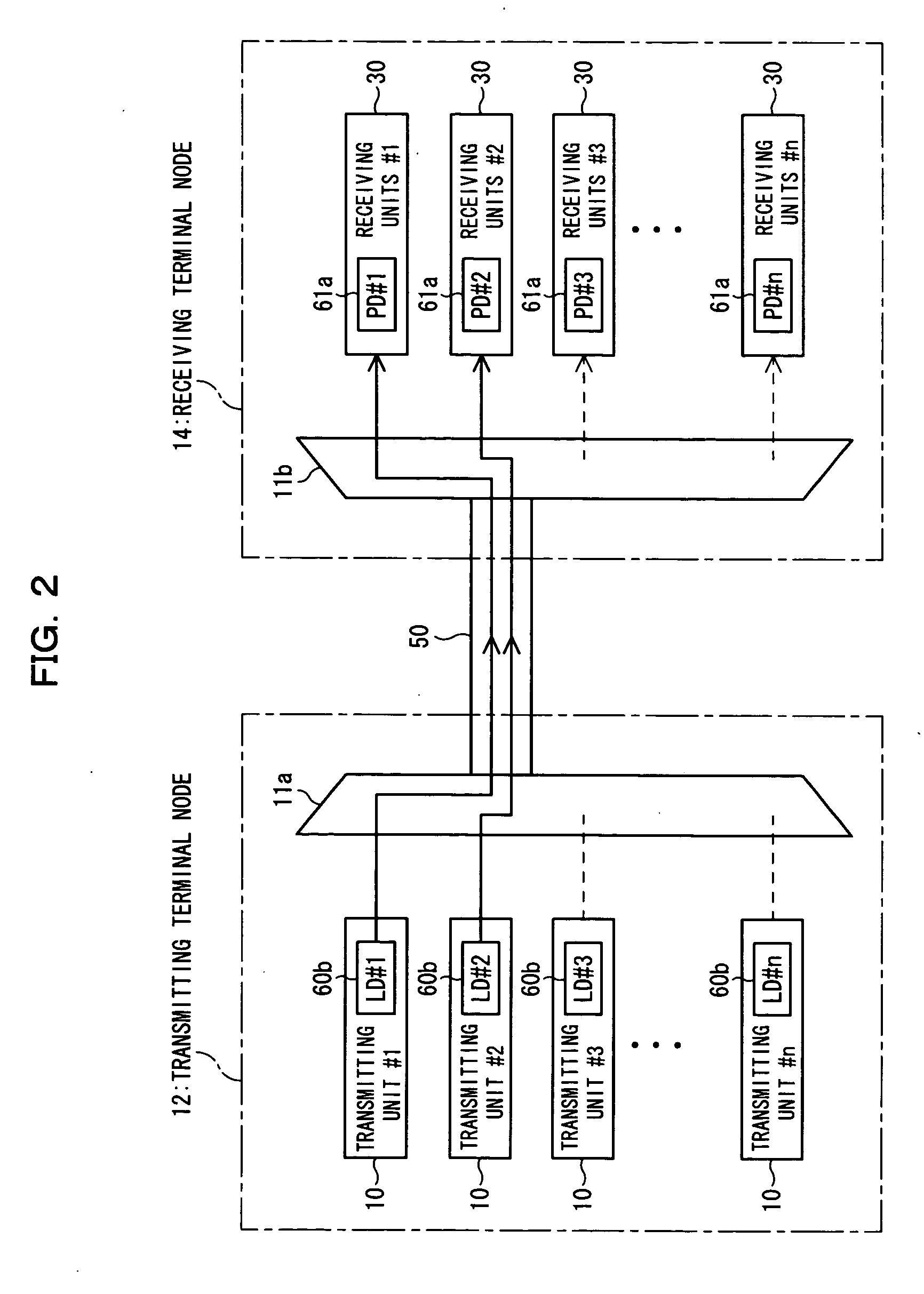
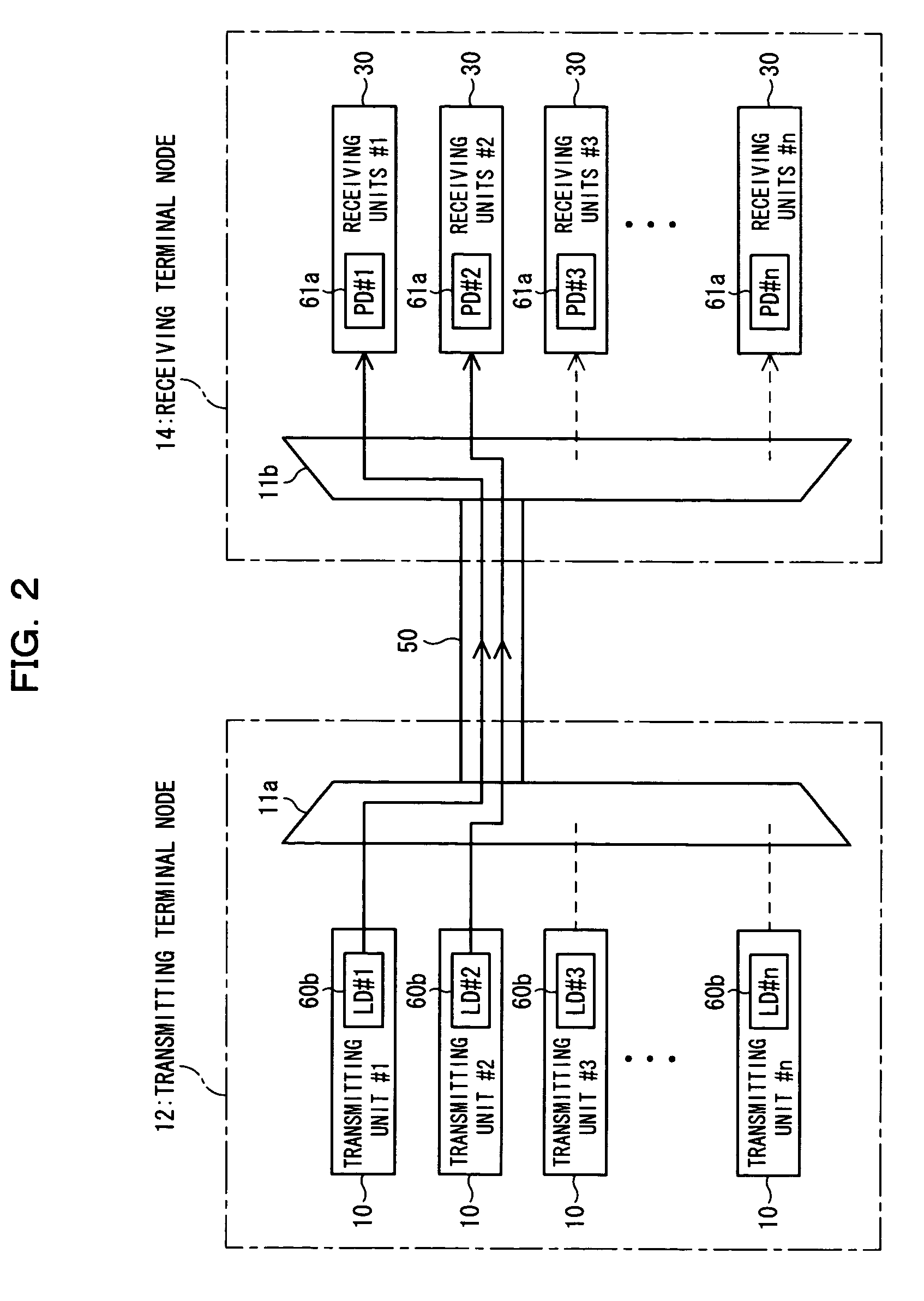
Dispersion compensation quantity setting method, receiving terminal station, and wavelength-multiplexing optical transmission system
InactiveUS20050238362A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationWdm transmission systemsTransport system
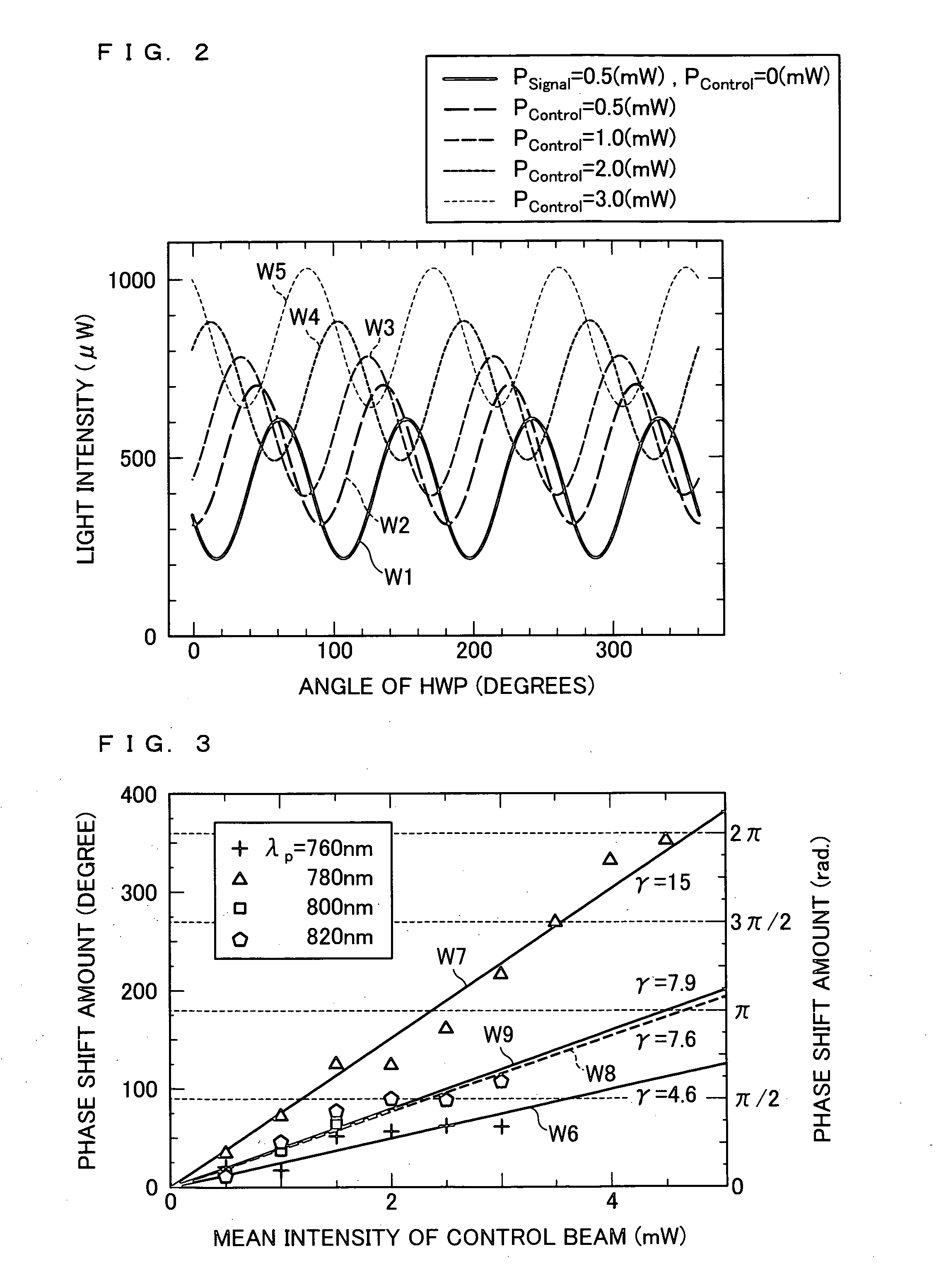
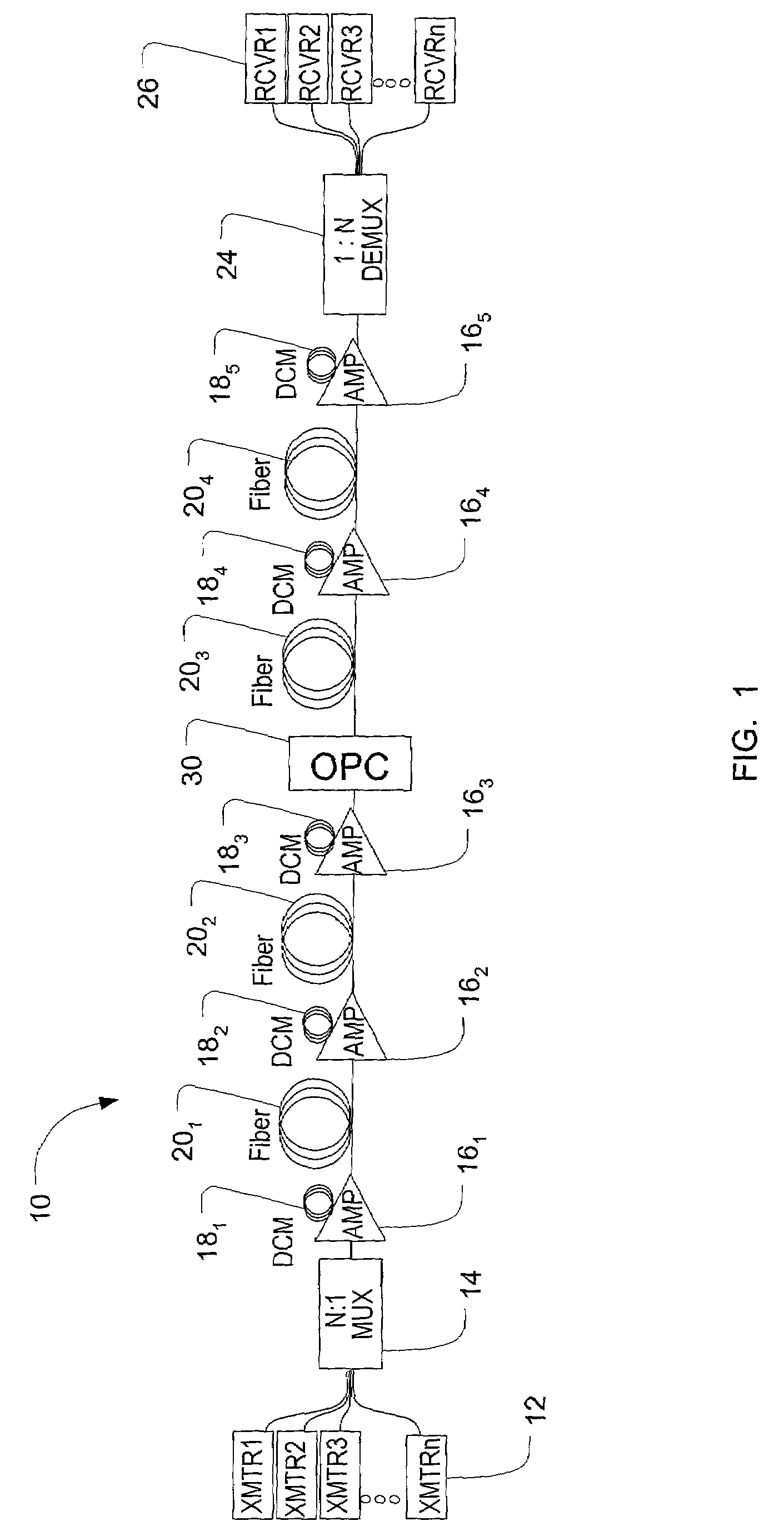
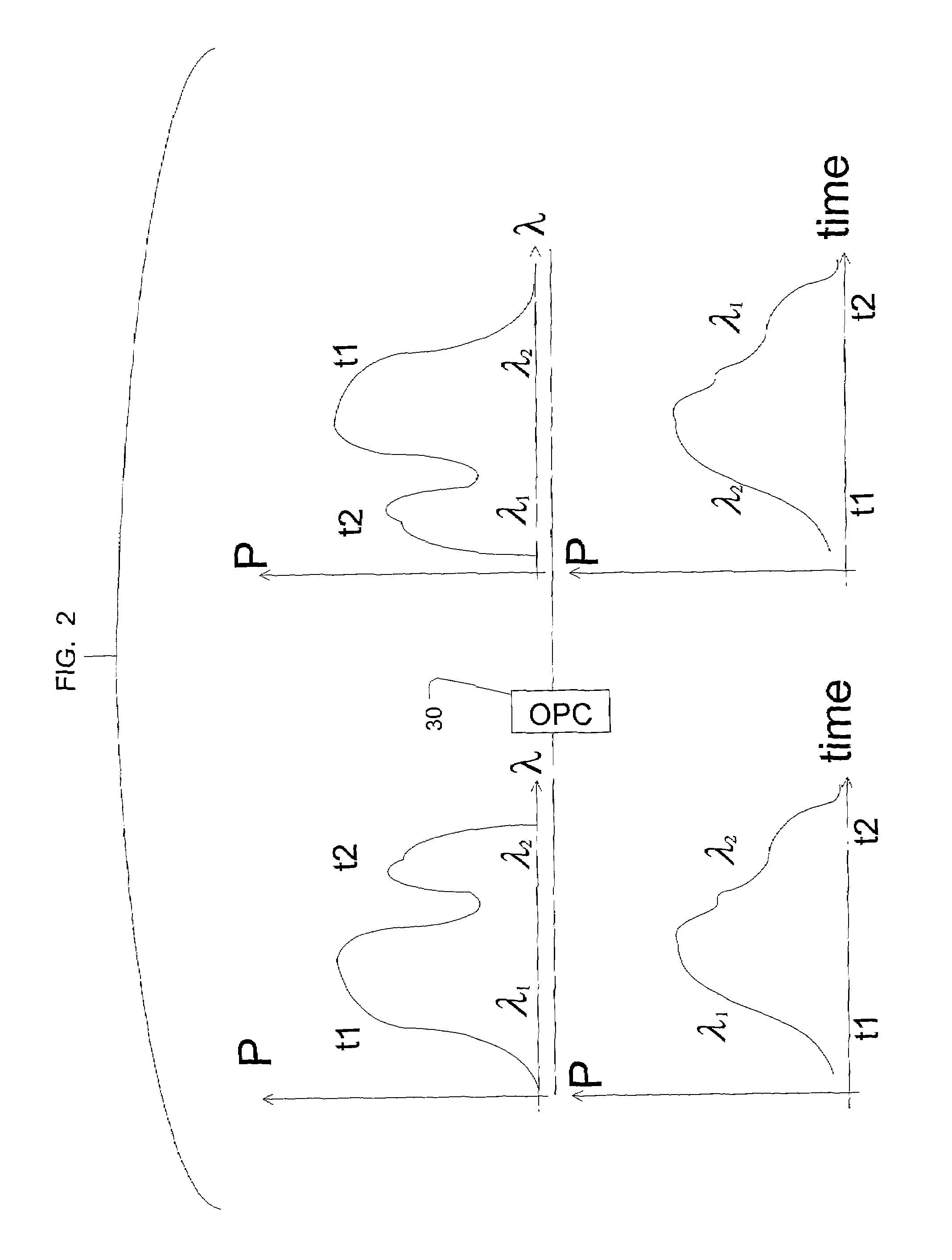
In a dispersion compensation quantity setting technique for use in a WDM transmission system, a transmitting terminal node transmits CW light and modulated light obtained by modulation using a modulation pattern signal, while a receiving terminal node detects a physical quantity stemming from cross phase modulation occurring between the transmitting terminal node and the receiving terminal node on the basis of a variation of an intensity of the transmitted CW light and sets a dispersion compensation quantity on the basis of a variation of the detected physical quantity. Moreover, this optimizes the crosstalk, suppresses the output power of transmitted light, eliminates the nonlinear optical effect of the transmitted light, and carries out dispersion compensation superior in cost performance.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
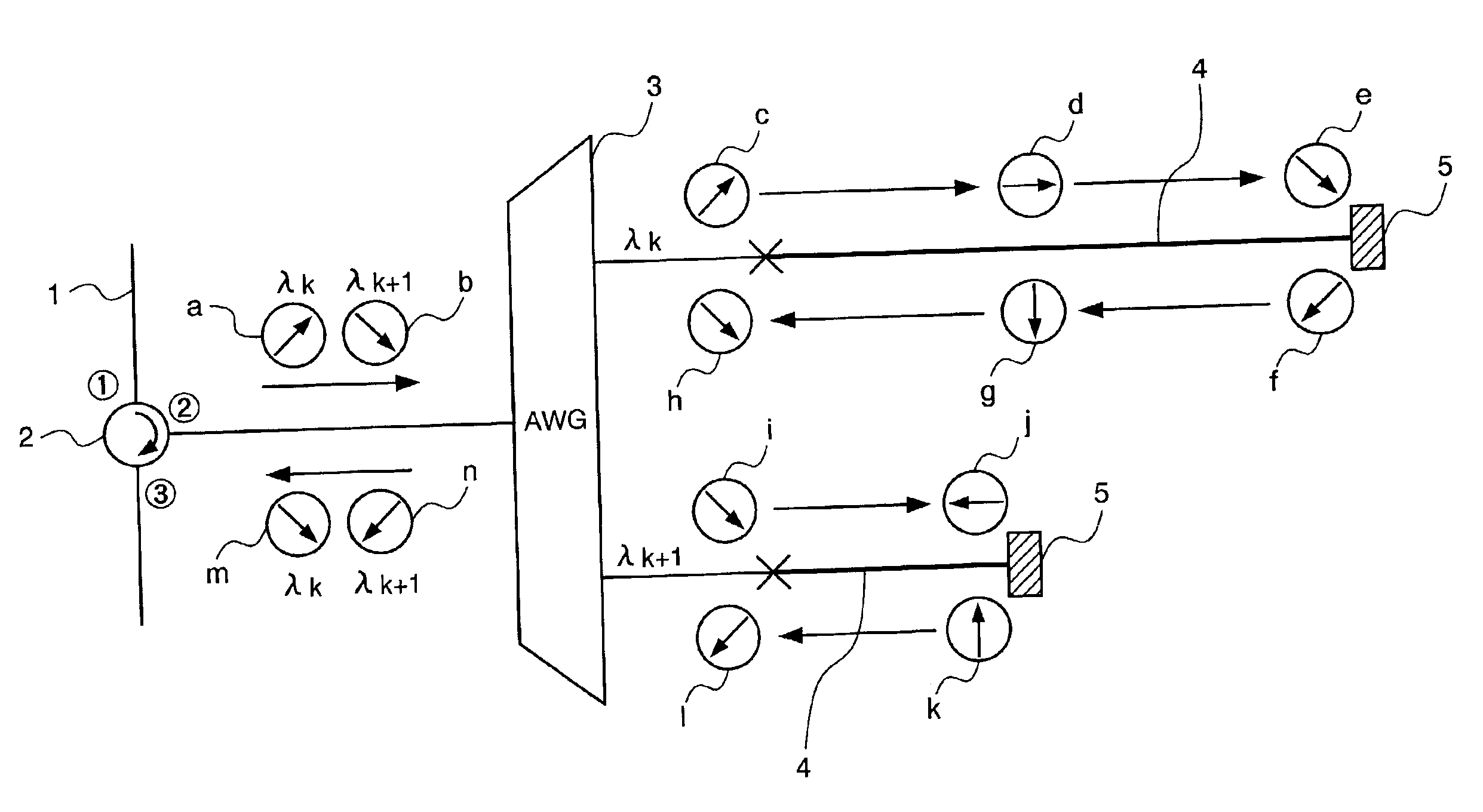
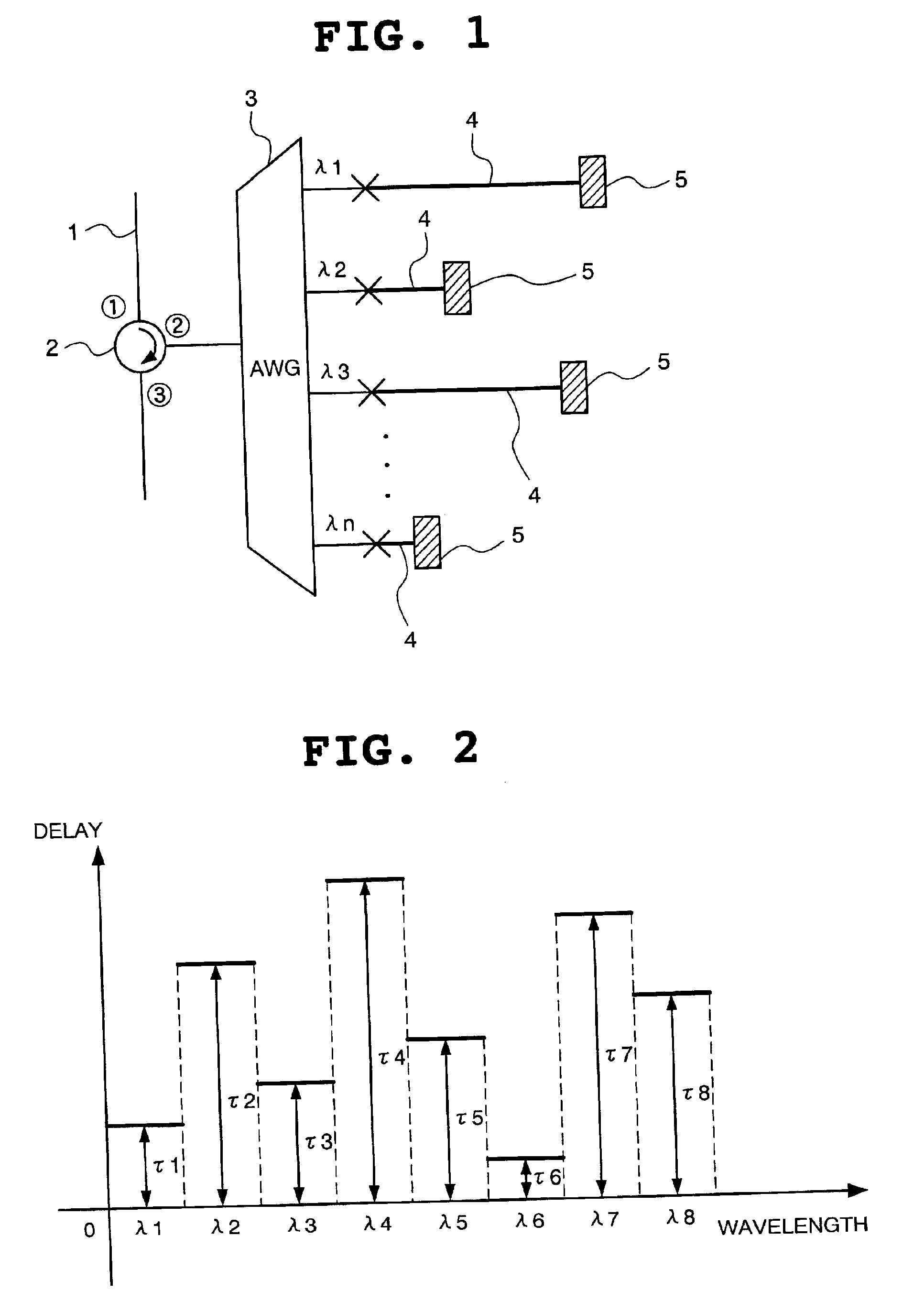
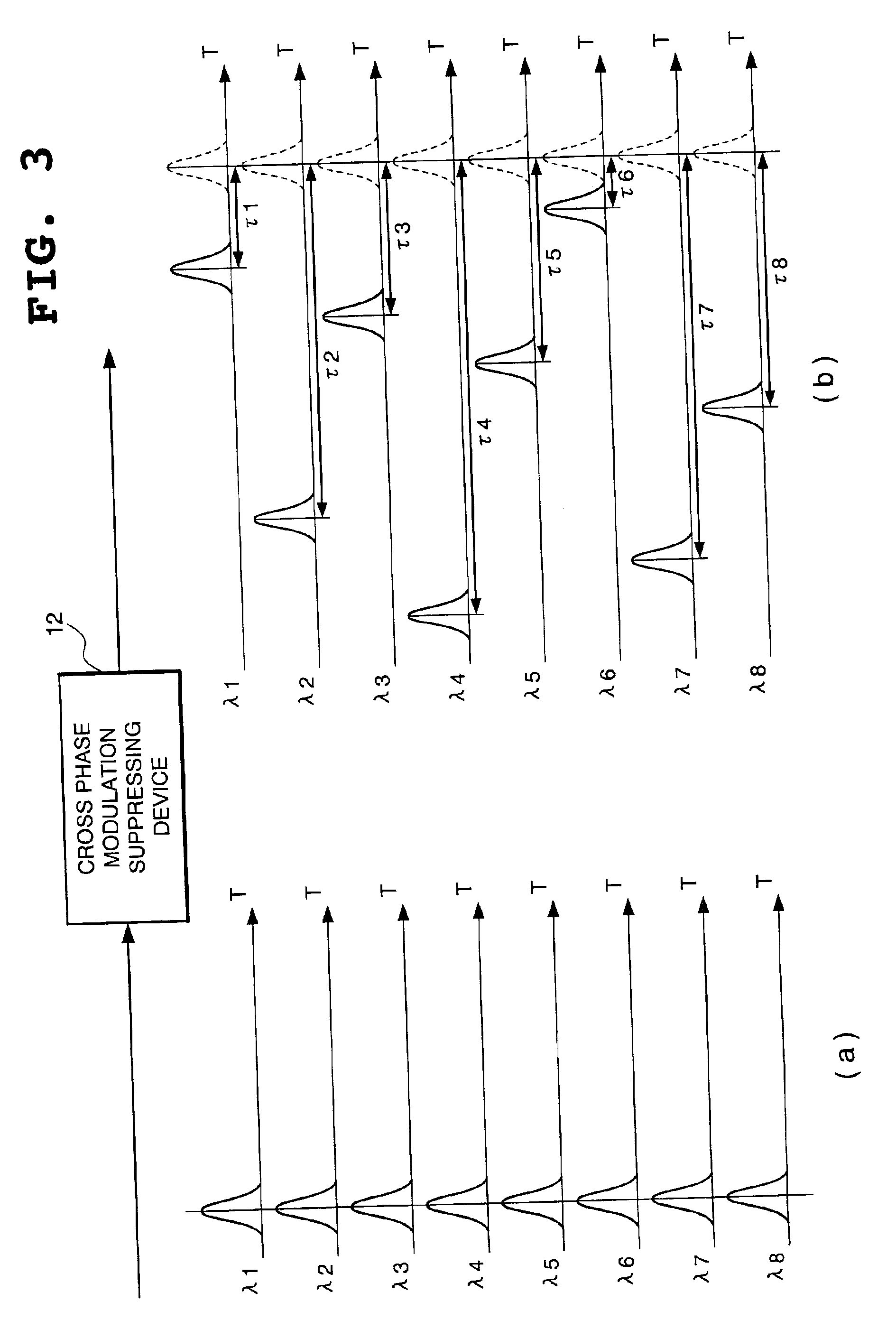
Cross phase modulation suppressing device in wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system and optical communication system
InactiveUS6920261B2Improve transmission qualityReduce lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesCommunications systemOptical circulator
According to the cross phase modulation suppressing device of the present invention, the wavelength multiplexing optical signal from an optical fiber having polarization orthogonality between the adjacent channels is split for every channel and the split optical signals are led to delaying optical waveguides of different lengths by the AWG (Arrayed Waveguide Grating) connected to a second port of an optical circulator, and the split optical signals with each delay added are reflected by the Farraday mirrors in polarization states orthogonal to each other and again led to the delaying optical waveguides. The reflected lights are combined by the AWG and supplied to a third port of the optical circulator as the wavelength multiplexing optical signal with orthogonality of polarization states kept between the adjacent channels.
Owner:NEC CORP
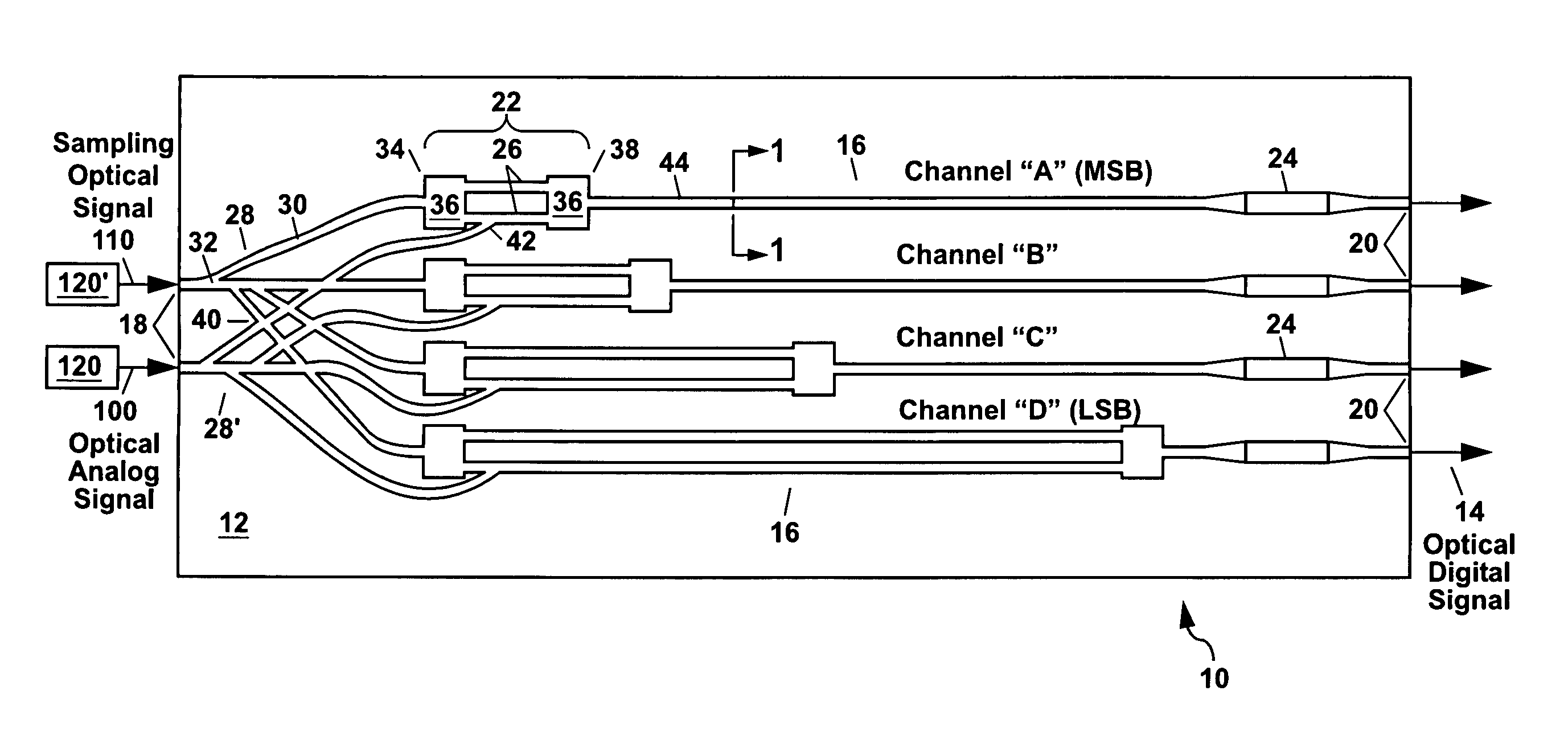
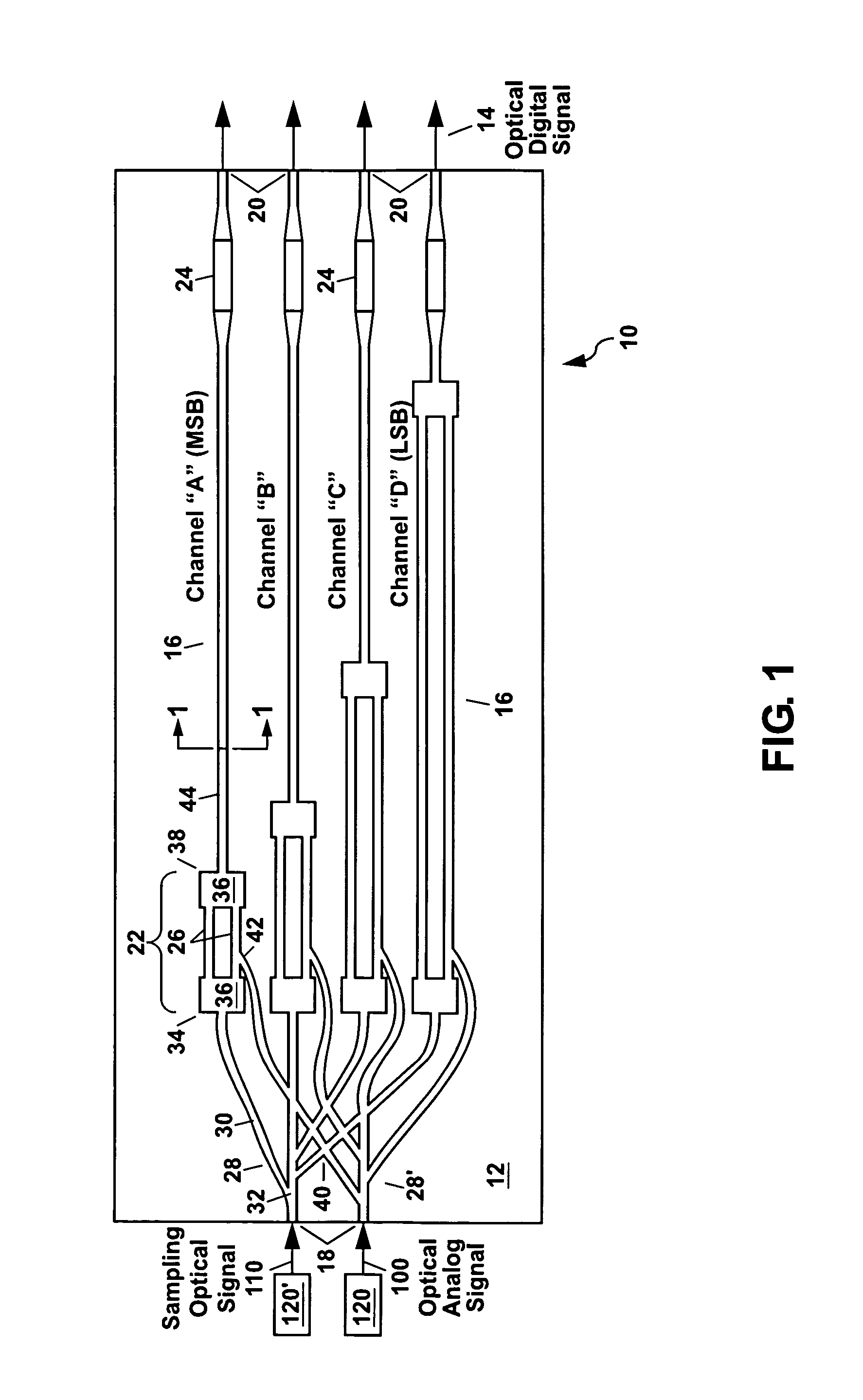
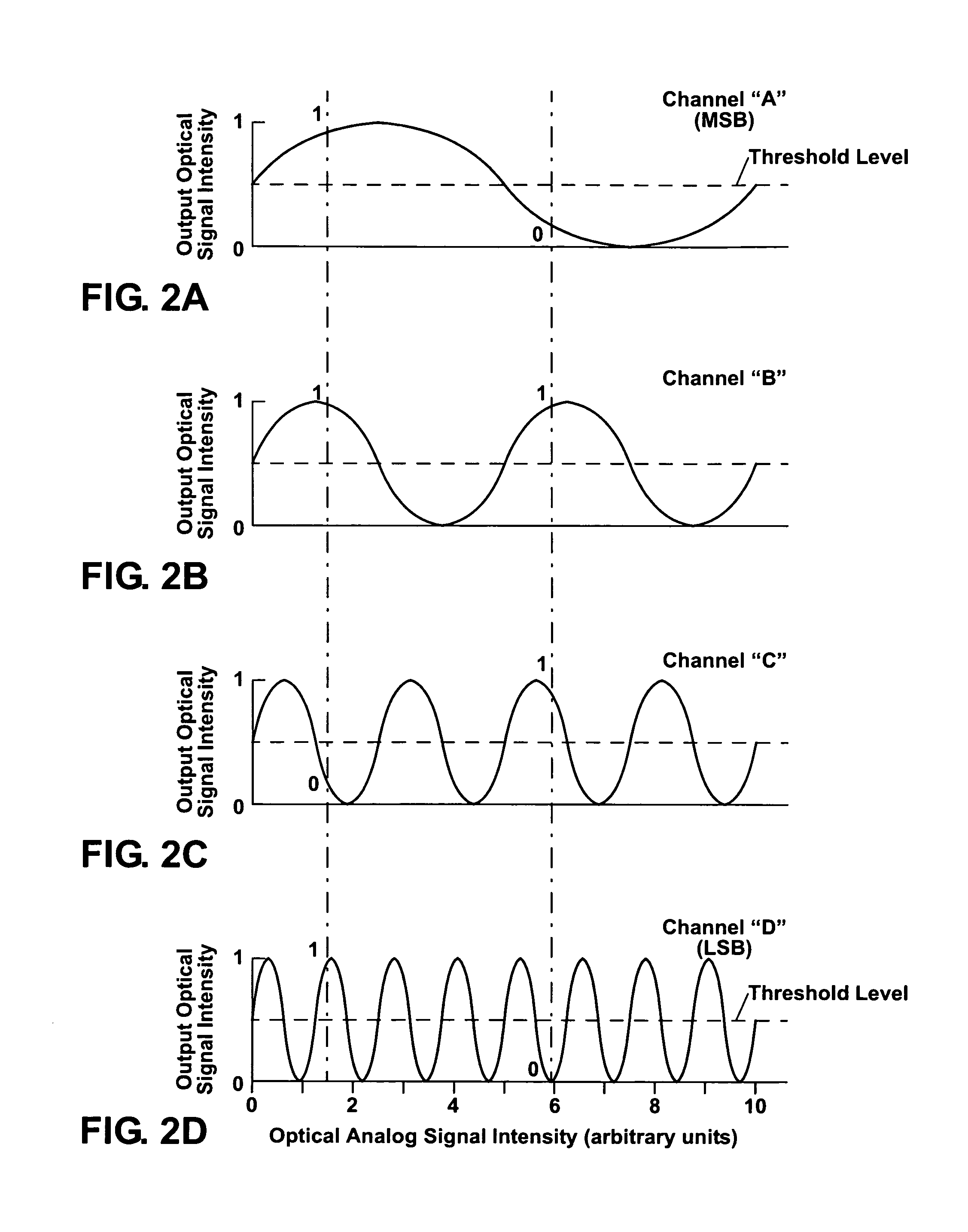
Optical analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS7564387B1Electric signal transmission systemsOptical analogue/digital convertersDigital down converterAudio power amplifier
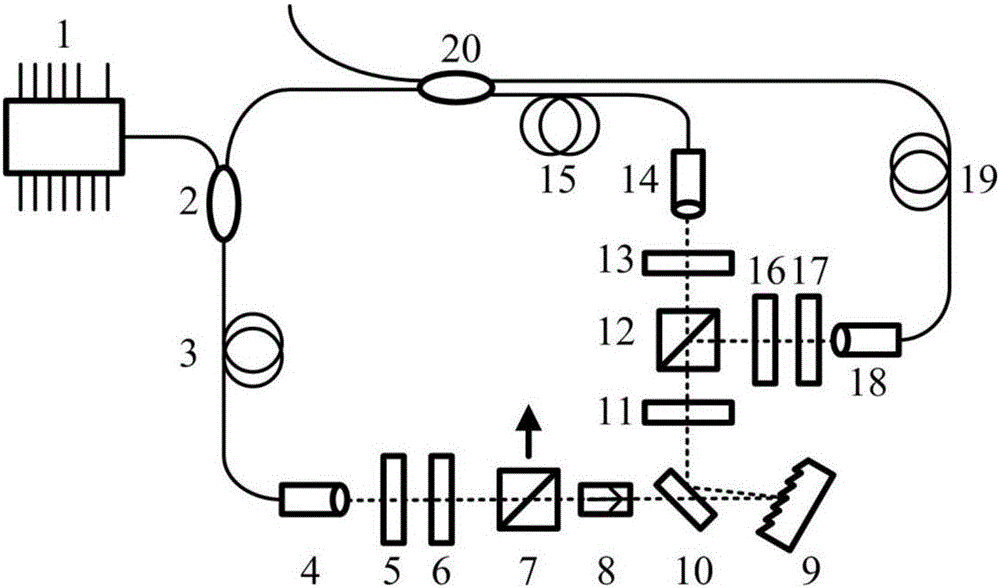
An optical analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is disclosed which converts an input optical analog signal to an output optical digital signal at a sampling rate defined by a sampling optical signal. Each bit of the digital representation is separately determined using an optical waveguide interferometer and an optical thresholding element. The interferometer uses the optical analog signal and the sampling optical signal to generate a sinusoidally-varying output signal using cross-phase-modulation (XPM) or a photocurrent generated from the optical analog signal. The sinusoidally-varying output signal is then digitized by the thresholding element, which includes a saturable absorber or at least one semiconductor optical amplifier, to form the optical digital signal which can be output either in parallel or serially.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
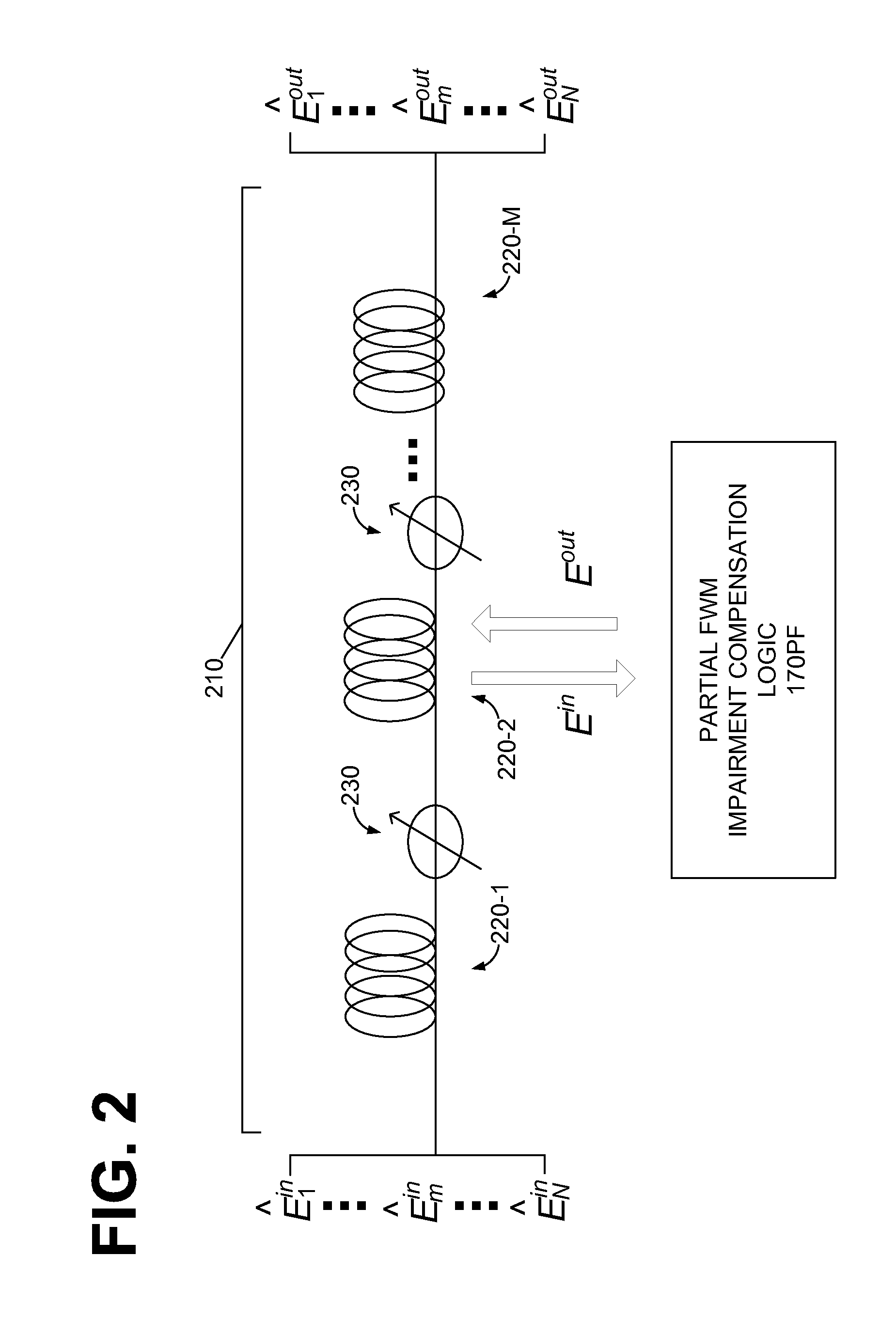
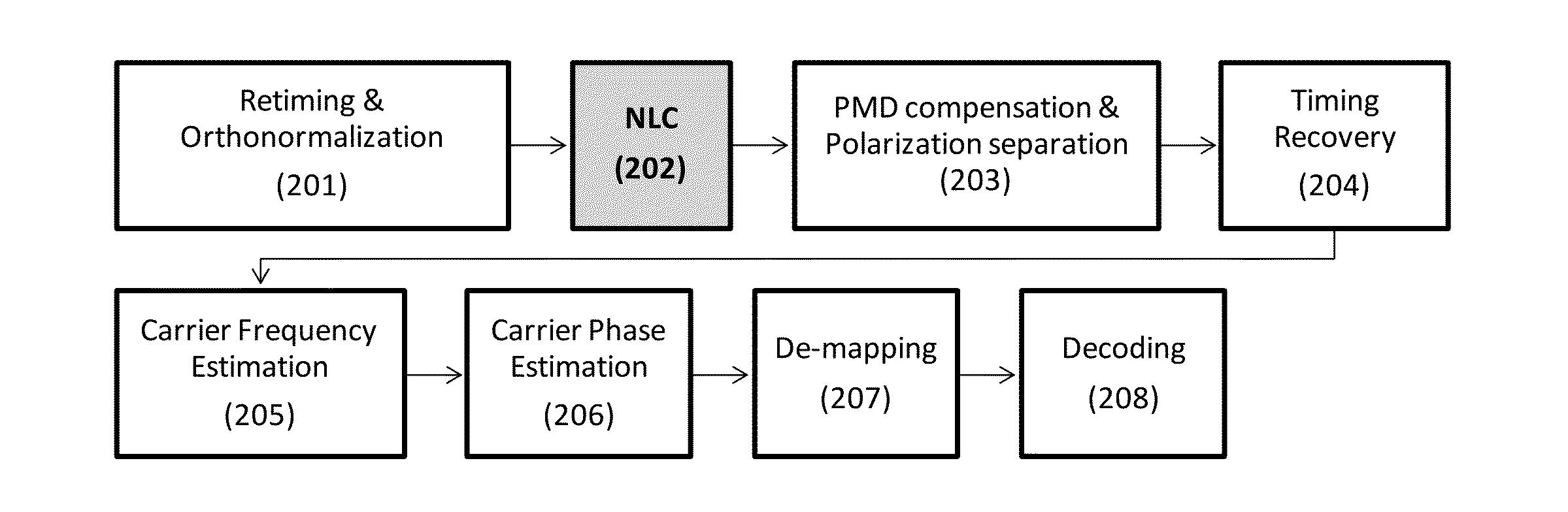
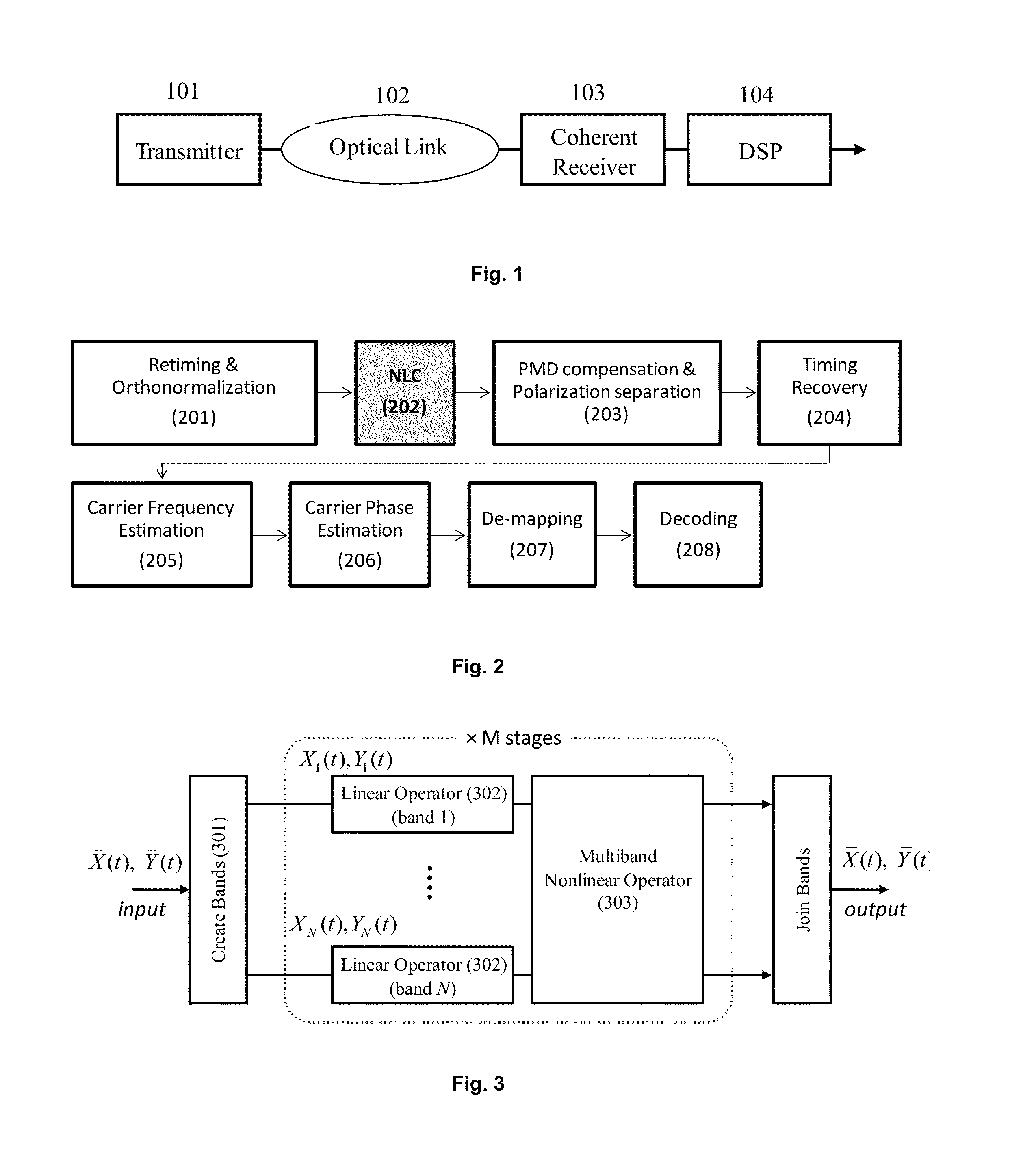
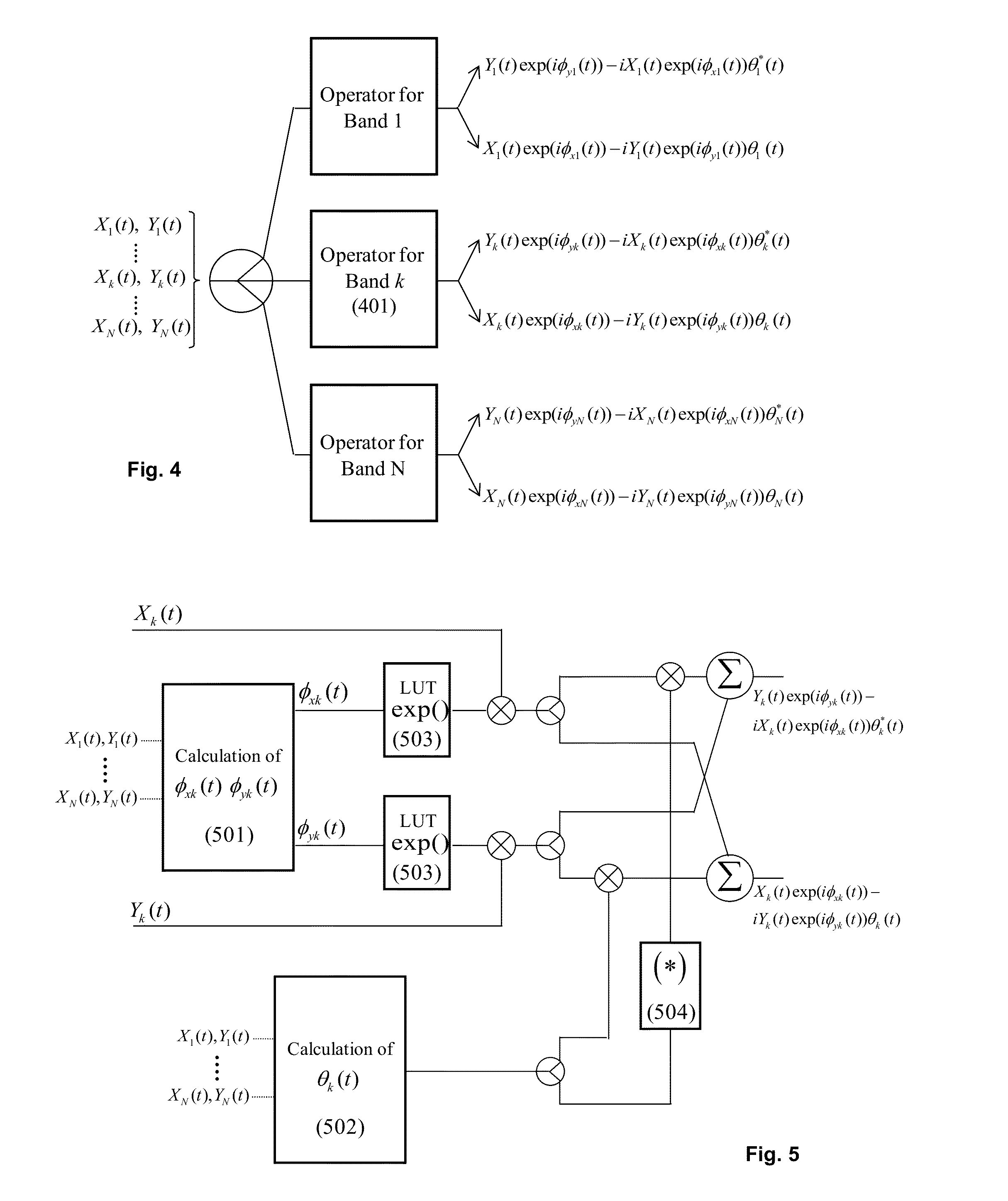
Inter-band cross-phase modulation compensation for the mitigation of intra-channel nonlinear impairments in optical fiber transmission
ActiveUS20140099128A1Increase capacityImprove transmission distanceElectromagnetic receiversFiberCommunications system
An optical communication system includes a digital signal processer coupled to the coherent receiver, said coherent receiver including a nonlinearity compensation module for compensating for nonlinear effects in fiber in the optical link for increasing capacity or transmission distance of the fiber, the nonlinearity compensation module includes a spectral slicing of the signal into bands, computing nonlinear interaction between the bands with parameters opposite to those of the fiber to reverse the non-linear effects in the fiber, and only certain nonlinear interactions between bands are considered thereby reducing complexity of the nonlinearity compensation.
Owner:NEC CORP
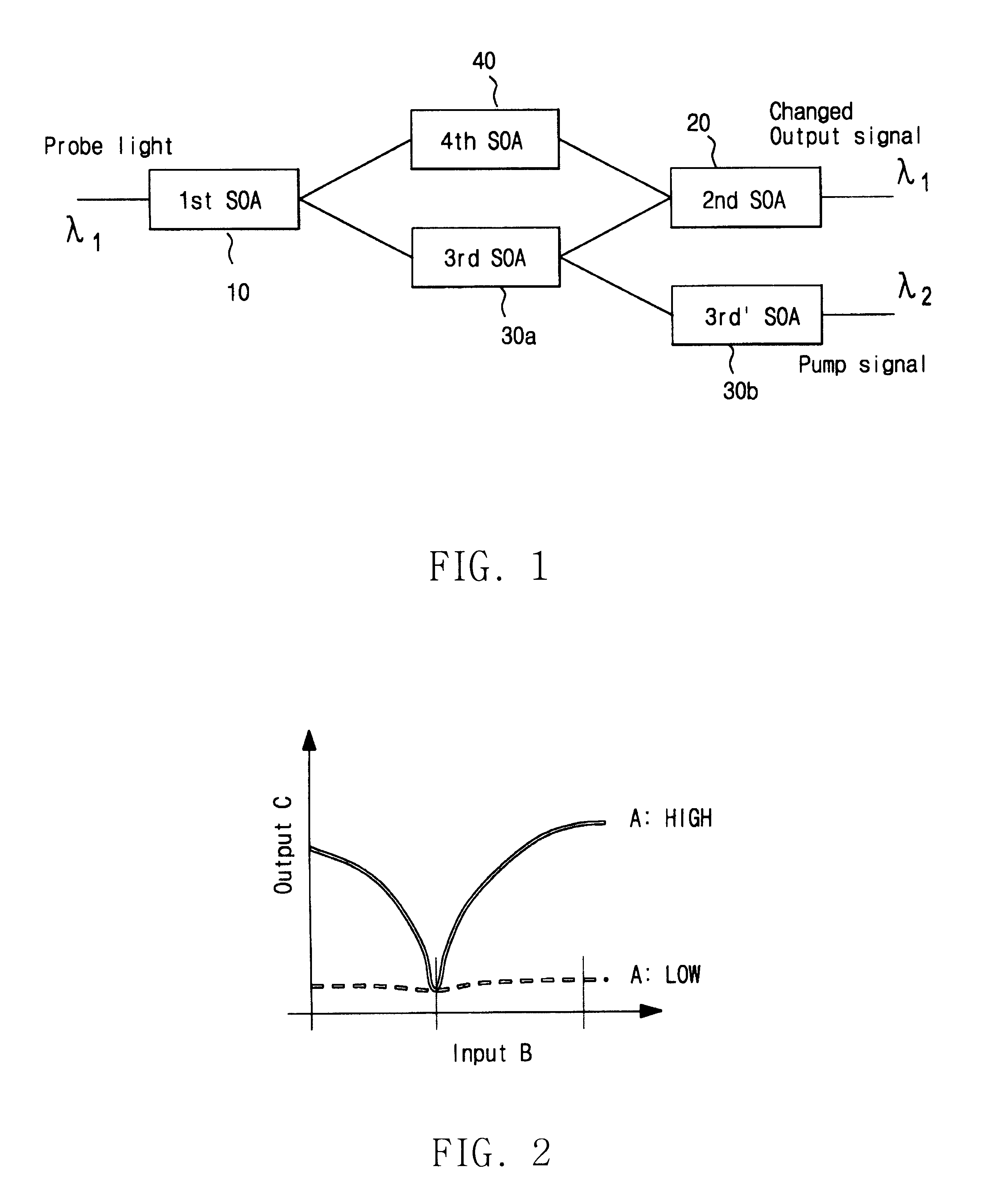
All-optical logic AND operation in a SOA-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer
InactiveUS6624929B2Laser detailsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesUltra high speedMach–Zehnder interferometer
The present invention relates to the all-optical logic AND operation in a SOA (semiconductor optical amplifier)-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. More particularly, it relates to the technology making feasible ultra high-speed logic operations while maintaining a small size and a low input power by utilizing a cross-phase modulation (XPM) wavelength converter composed of semiconductor optical amplifiers in the form of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with nonlinear characteristics.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
All-optical logic AND operation in a SOA-based mach-zehnder interferometer
InactiveUS20020118441A1Laser detailsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesUltra high speedMach–Zehnder interferometer
The present invention relates to the all-optical logic AND operation in a SOA (semiconductor optical amplifier)-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. More particularly, it relates to the technology making feasible ultra high-speed logic operations while maintaining a small size and a low input power by utilizing a cross-phase modulation (XPM) wavelength converter composed of semiconductor optical amplifiers in the form of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with nonlinear characteristics.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS7352824B2Increasing aggregate data rateReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Owner:INTERSIL INC
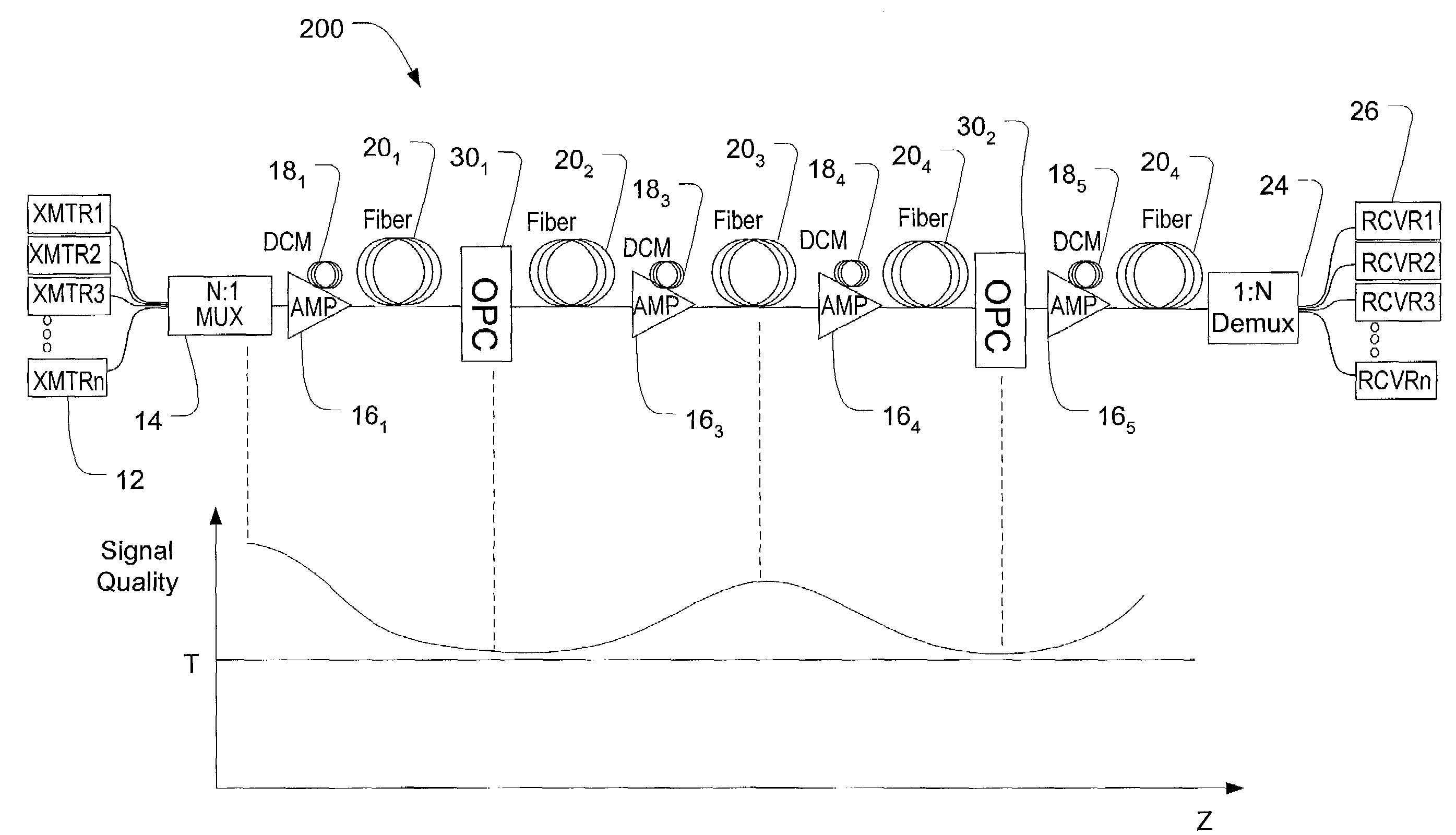
Method and apparatus for dispersion management in optical mesh networks
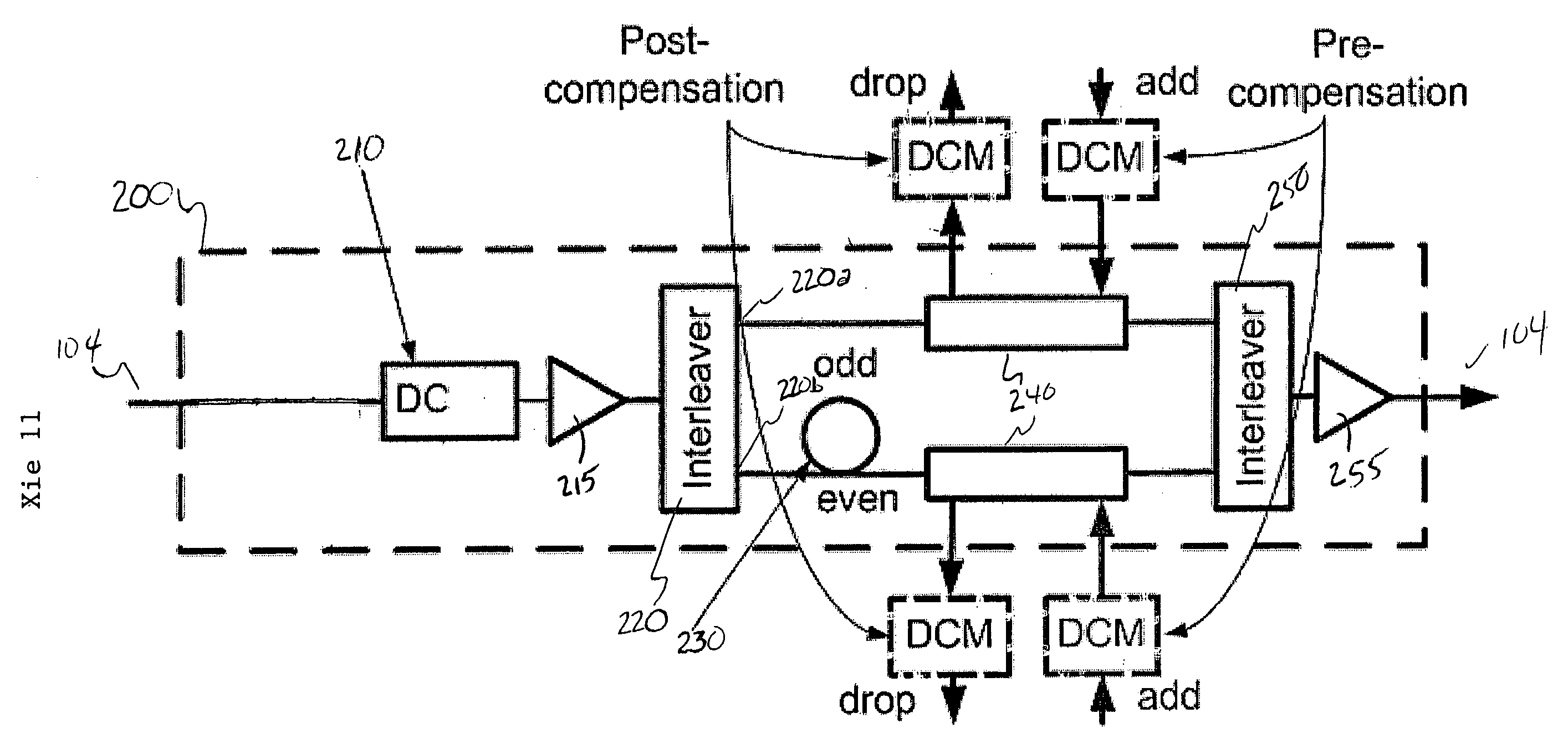
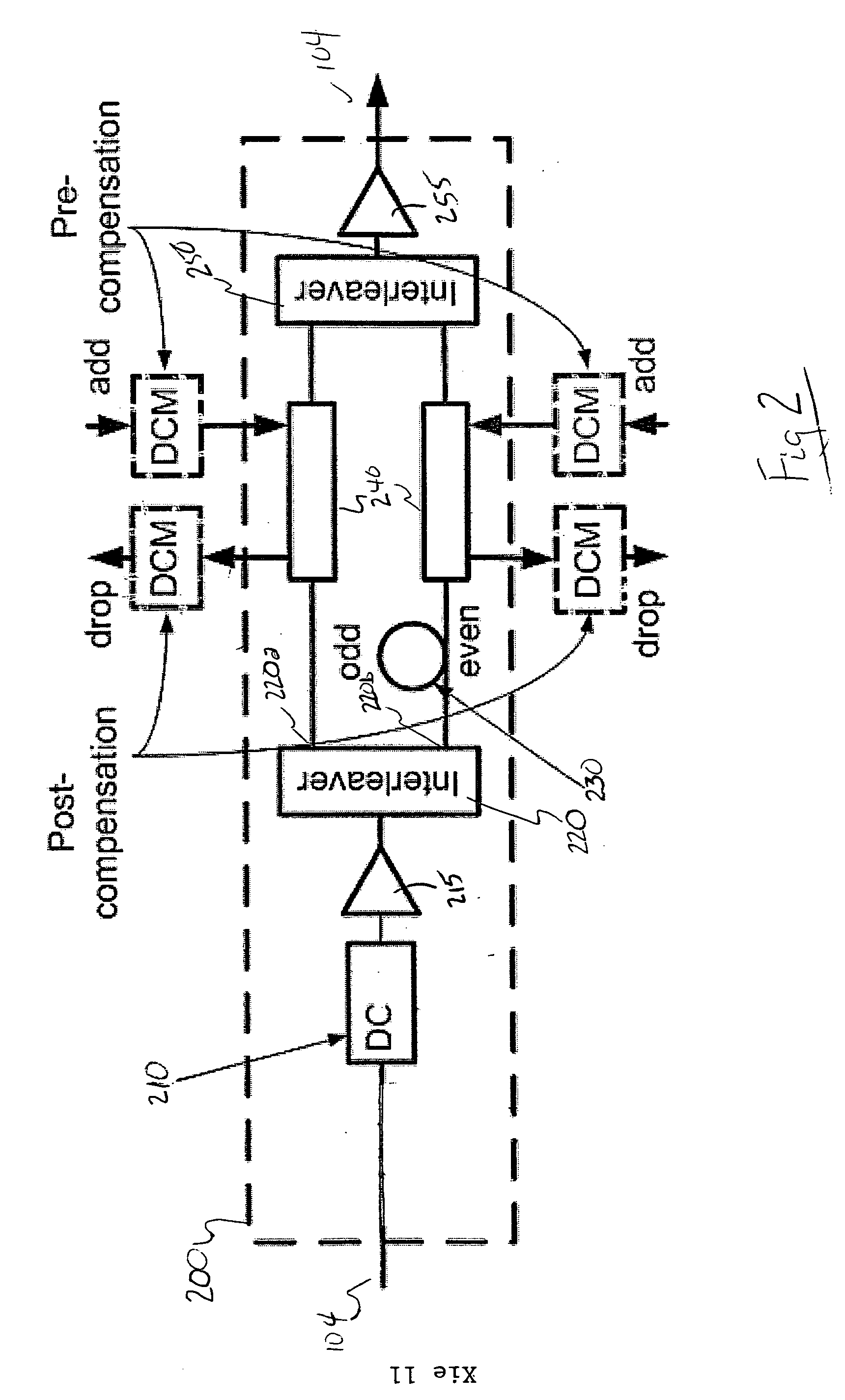
ActiveUS20060133817A1Cost effectiveSignificantly reducing inter-channel XPMElectromagnetic transmissionOptical transmissionOptical mesh networkLength wave
A method and apparatus for dispersion management in hybrid data rate long haul mesh networks are provided. The apparatus comprises a dispersion compensator for fully compensating the residual dispersion of a fiber link in the mesh network. A de-interleaver is coupled to the dispersion compensator for de-interleaving odd and even channels of wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) signals transmitted across the fiber link. A delay device is coupled to the de-interleaver for introducing a delay to the odd channels or the even channels of the WDM signals to decorrelate the odd and even channels and substantially reduce inter-channel cross-phase modulation.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Method of reducing intensity distortion induced by cross phase modulation in a WDM optical fiber transmission system
InactiveUS6626591B1Reduce intensity distortionMitigate those various drawbacksCladded optical fibreTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberLength wave
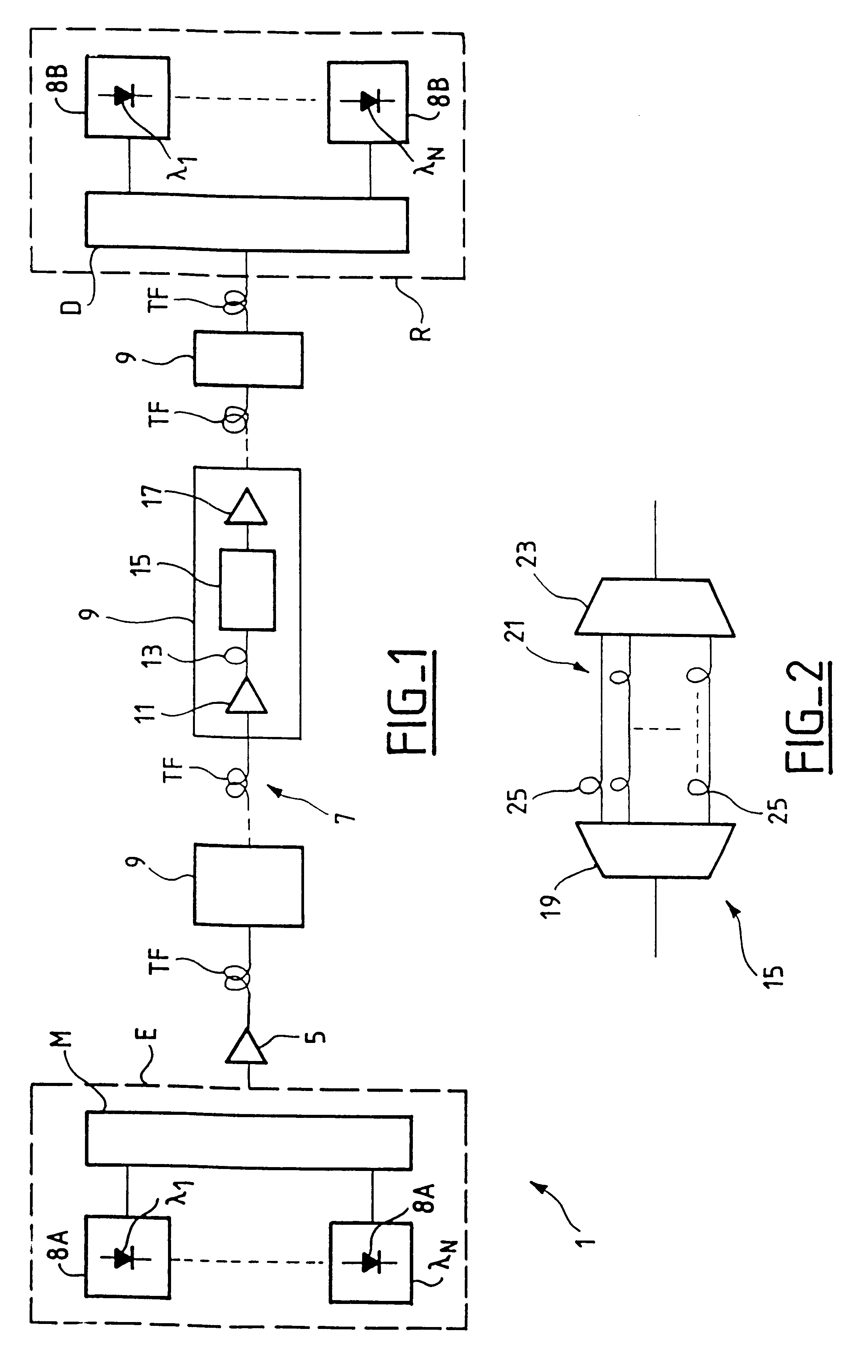
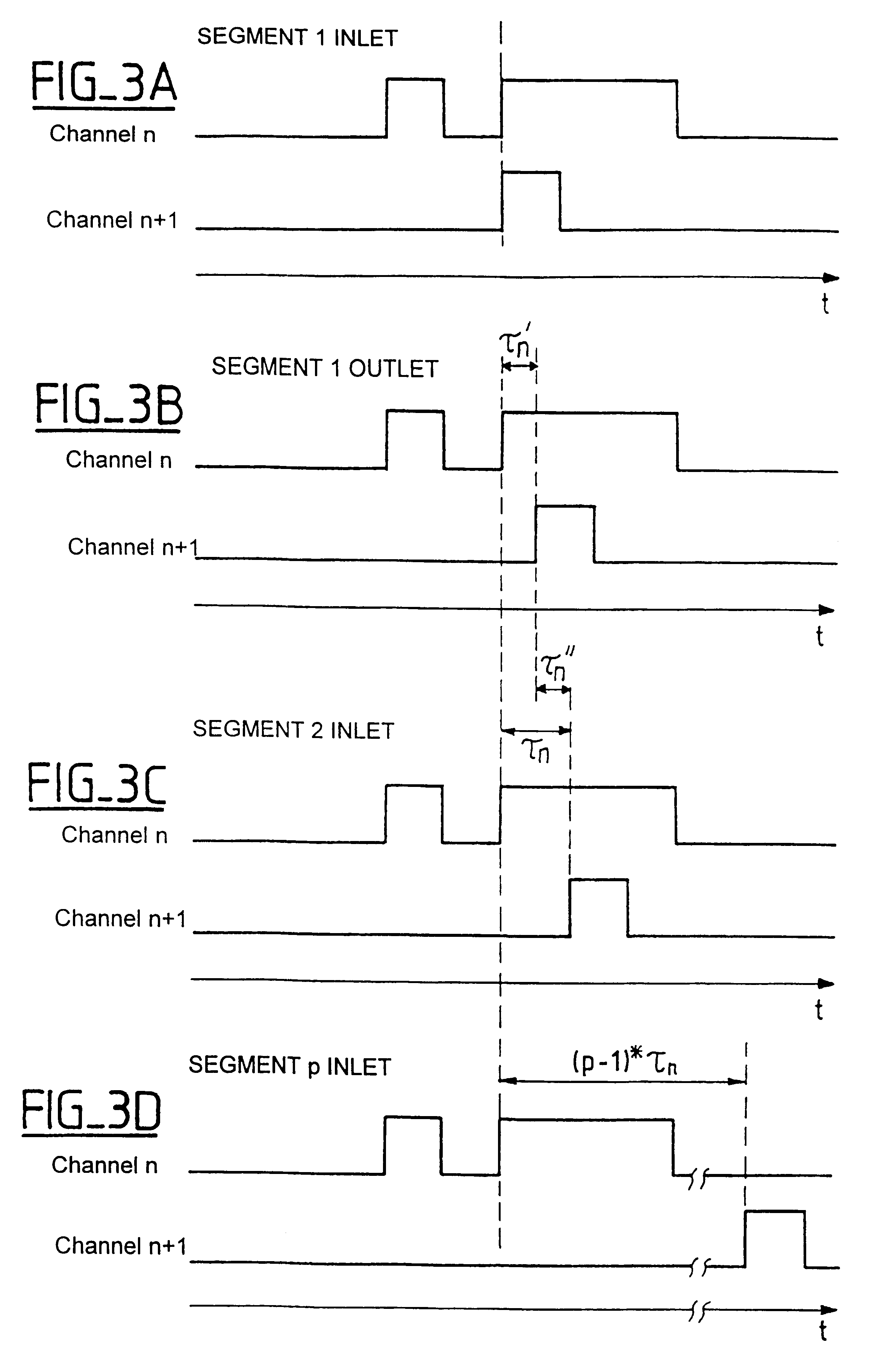
The invention relates to a method of reducing the intensity distortion induced by cross phase modulation in a wavelength division multiplexed optical fiber transmission system comprising a transmission line made up of a plurality of optical fiber segments with repeaters interposed between successive optical fiber segments, the transmission system having N different wavelength channels, where N is an integer greater than unity. In each repeater interconnecting first and second consecutive fiber segments, a time offset is introduced between the channels in such a manner that compared with the inlet of the first optical segment, the (n+1)and the nchannels are offset by taun at the inlet to the second fiber segment, where n is an integer less than or equal to N, where taun is selected to be greater than zero and less than a value that eliminates correlation between the intensity distortion contributions of each fiber segment.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
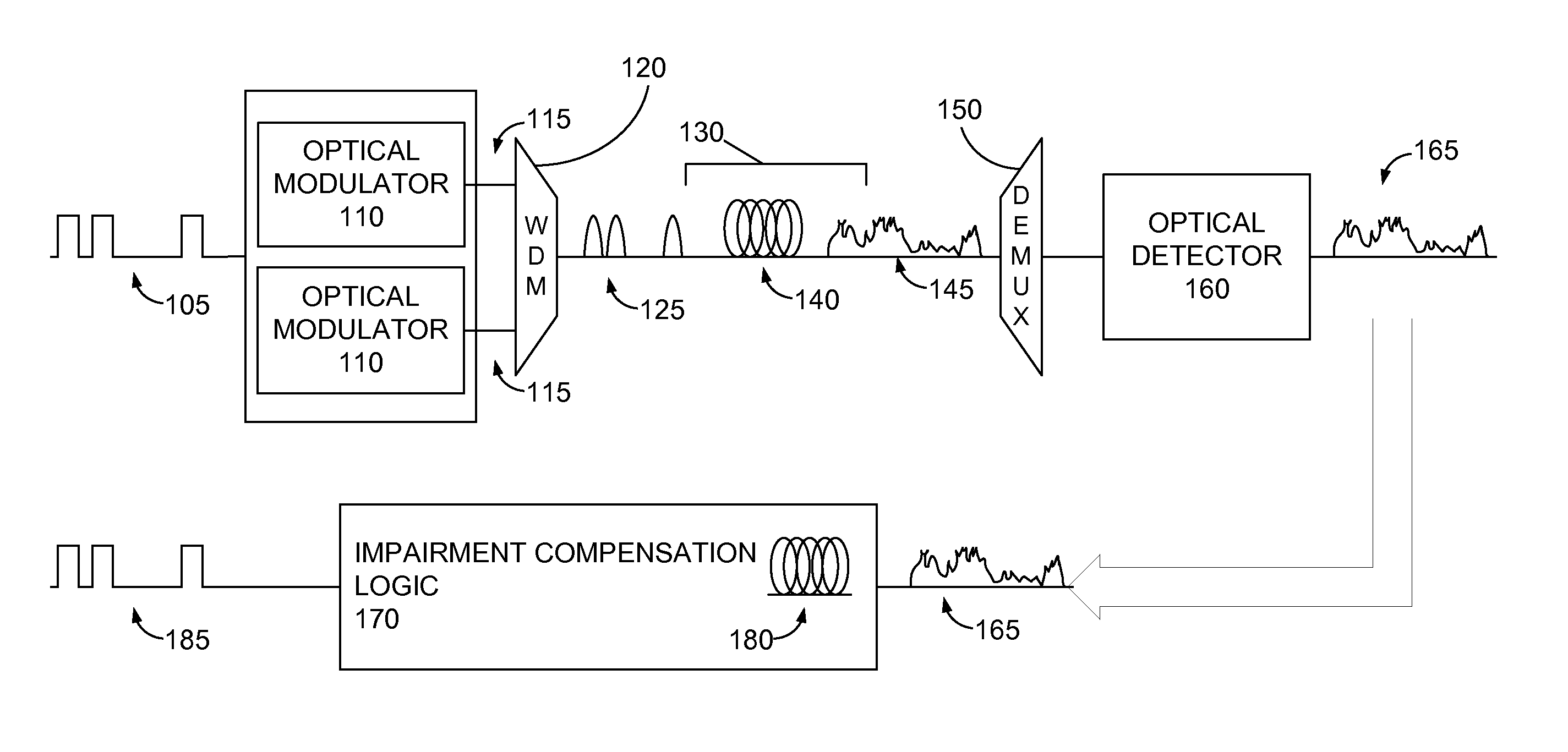
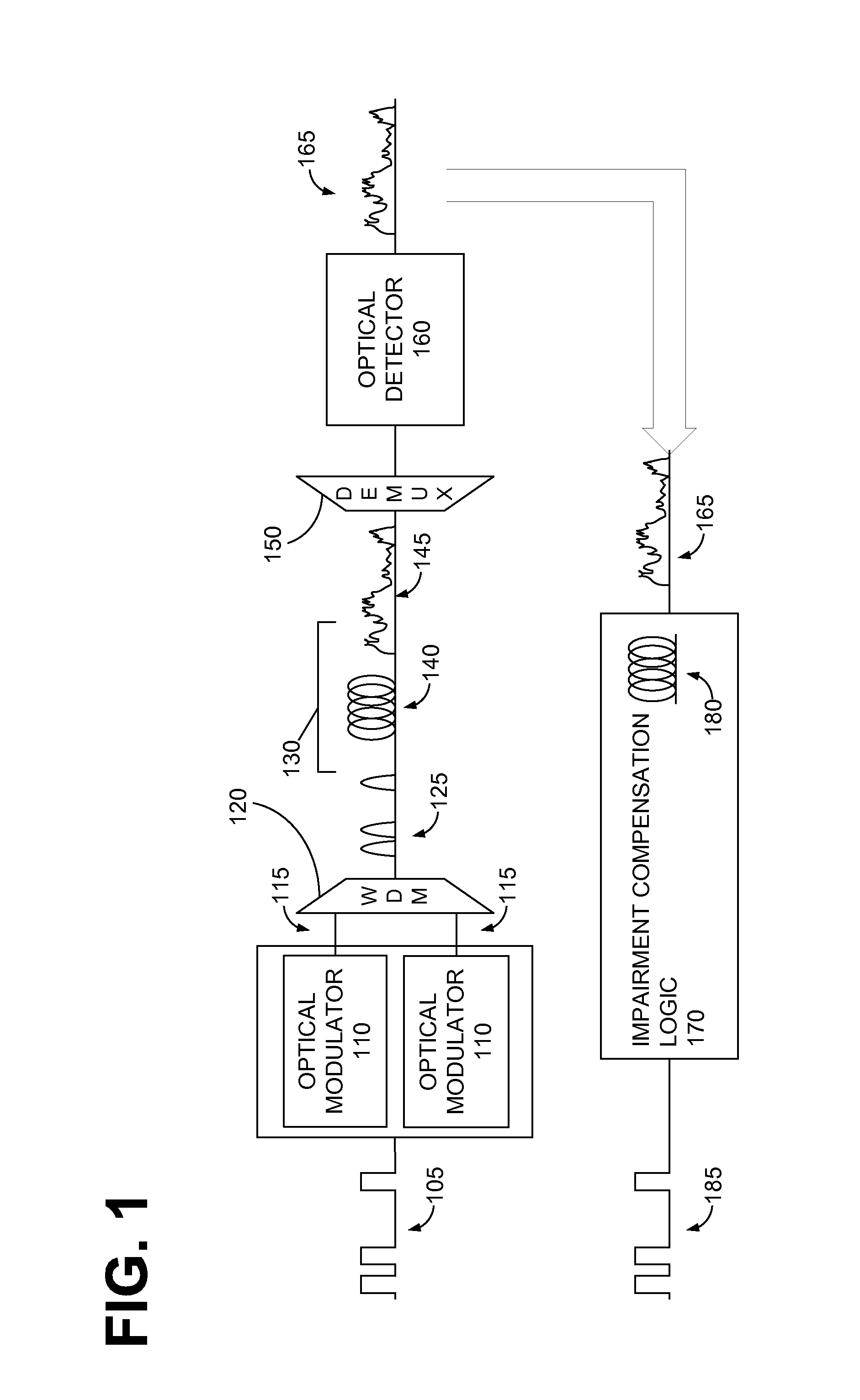
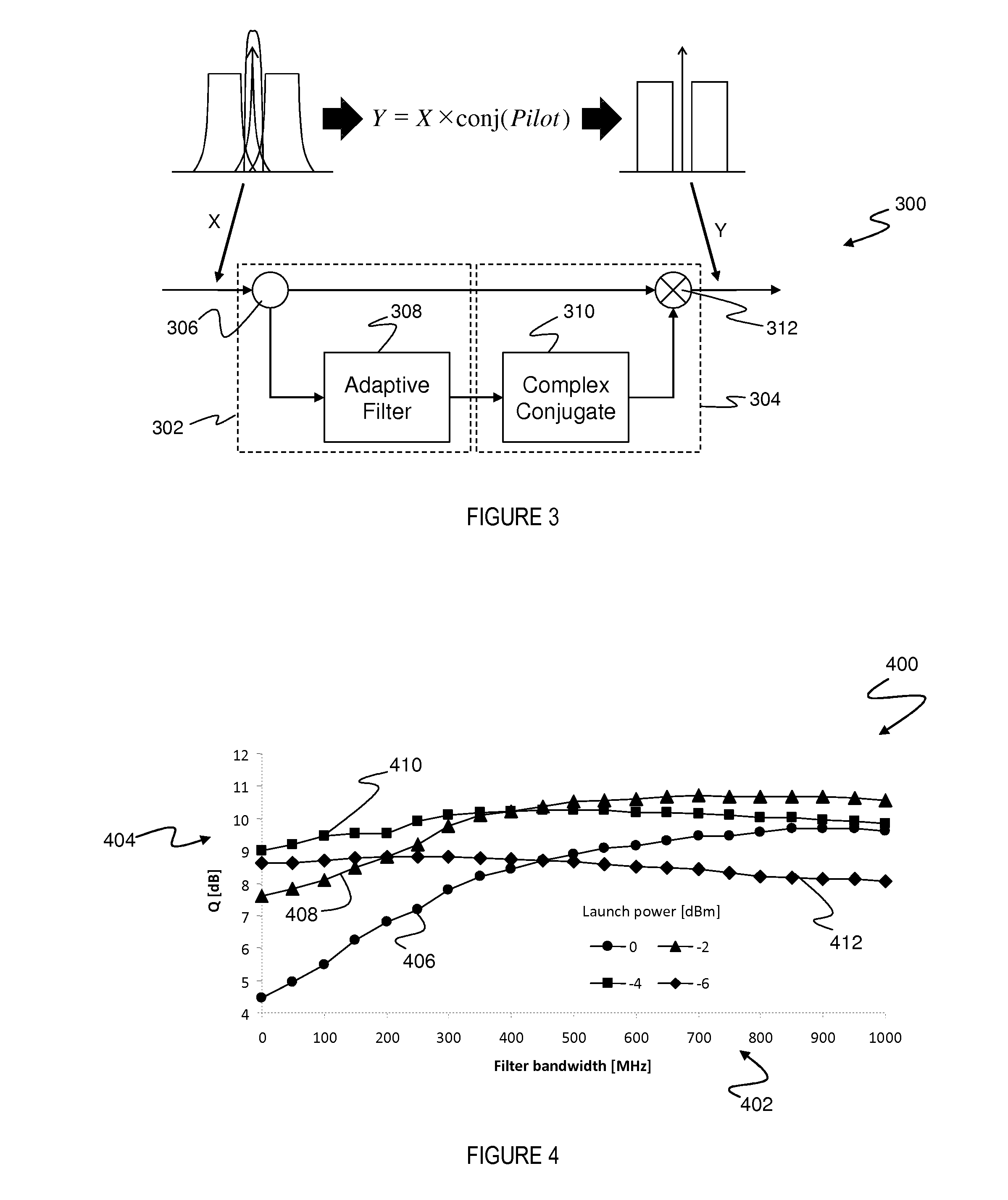
Electronic compensation of cross-phase modulation
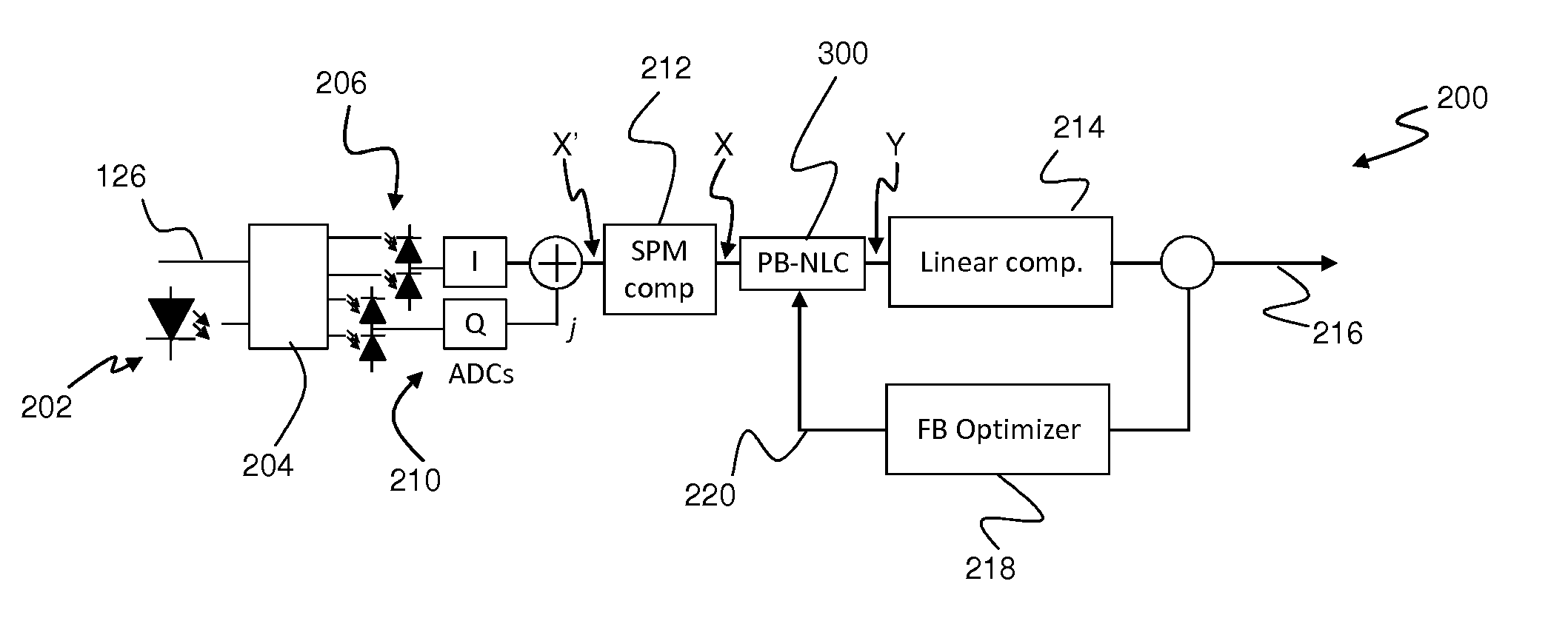
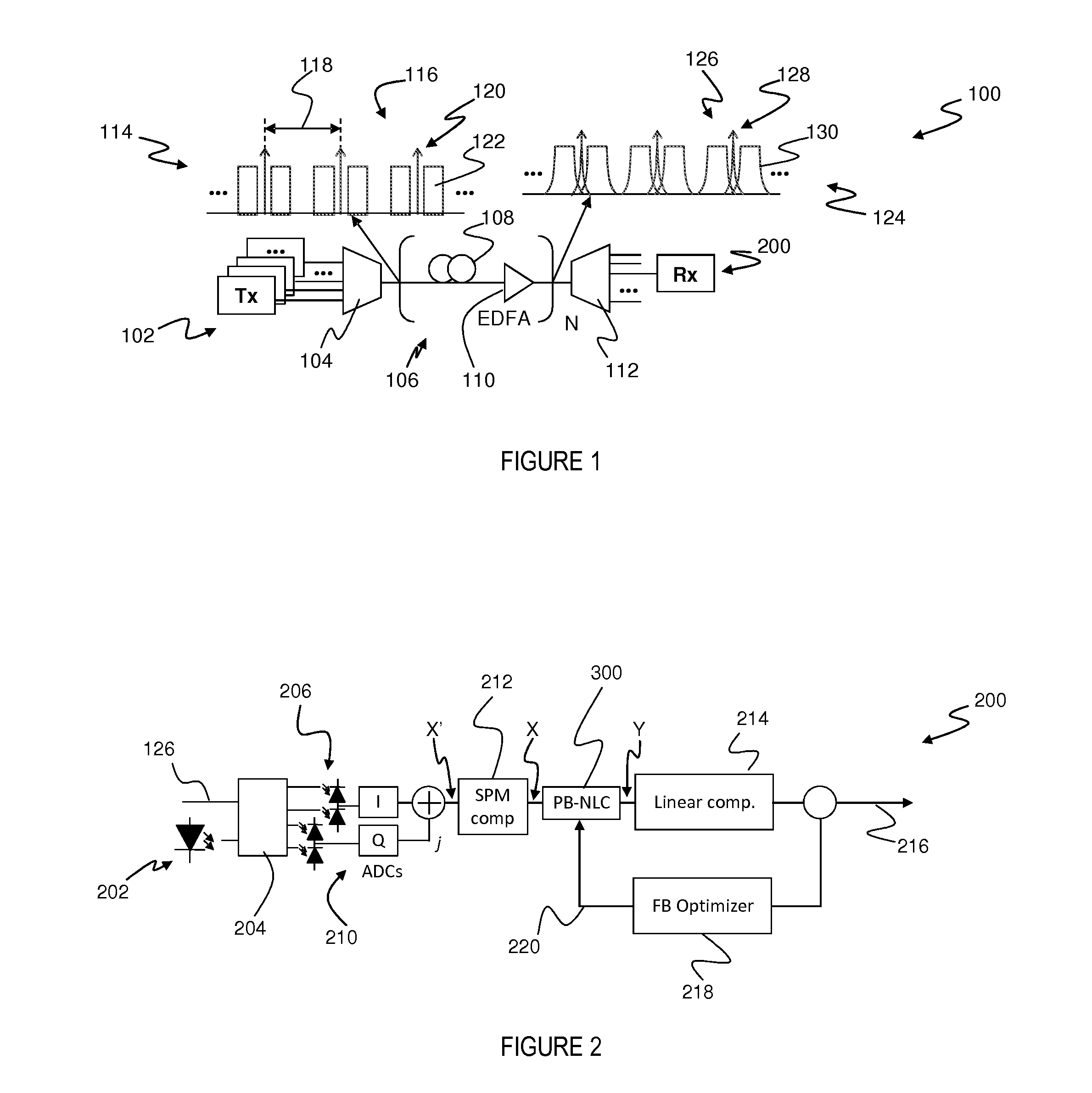
ActiveUS20140286642A1Maximizing quality measureReduce distortion problemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic receiversEngineeringNonlinear optical
An optical signal (116) is modulated with a transmitted electrical signal comprising an information-bearing component (122) and a pilot tone (120) having a predetermined frequency. Transmission of the signal results in distortion, including nonlinear optical transmission impairments. A method of receiving the signal includes detecting the optical signal to produce a received electrical signal (X) comprising a distorted variant of the transmitted electrical signal. The pilot tone is extracted from the received electrical signal using a filtering operation (308) having a predetermined characteristic, and a compensation signal determined based upon the extracted pilot tone. The compensation signal is applied to the received electrical signal (X) to produce a compensated signal (Y) having reduced distortion. The predetermined characteristic of the filtering operation (308) is represented by one or more parameters having values selected so as to substantially maximise a measure of quality of the compensated signal.
Owner:OFIDIUM PTY LTD
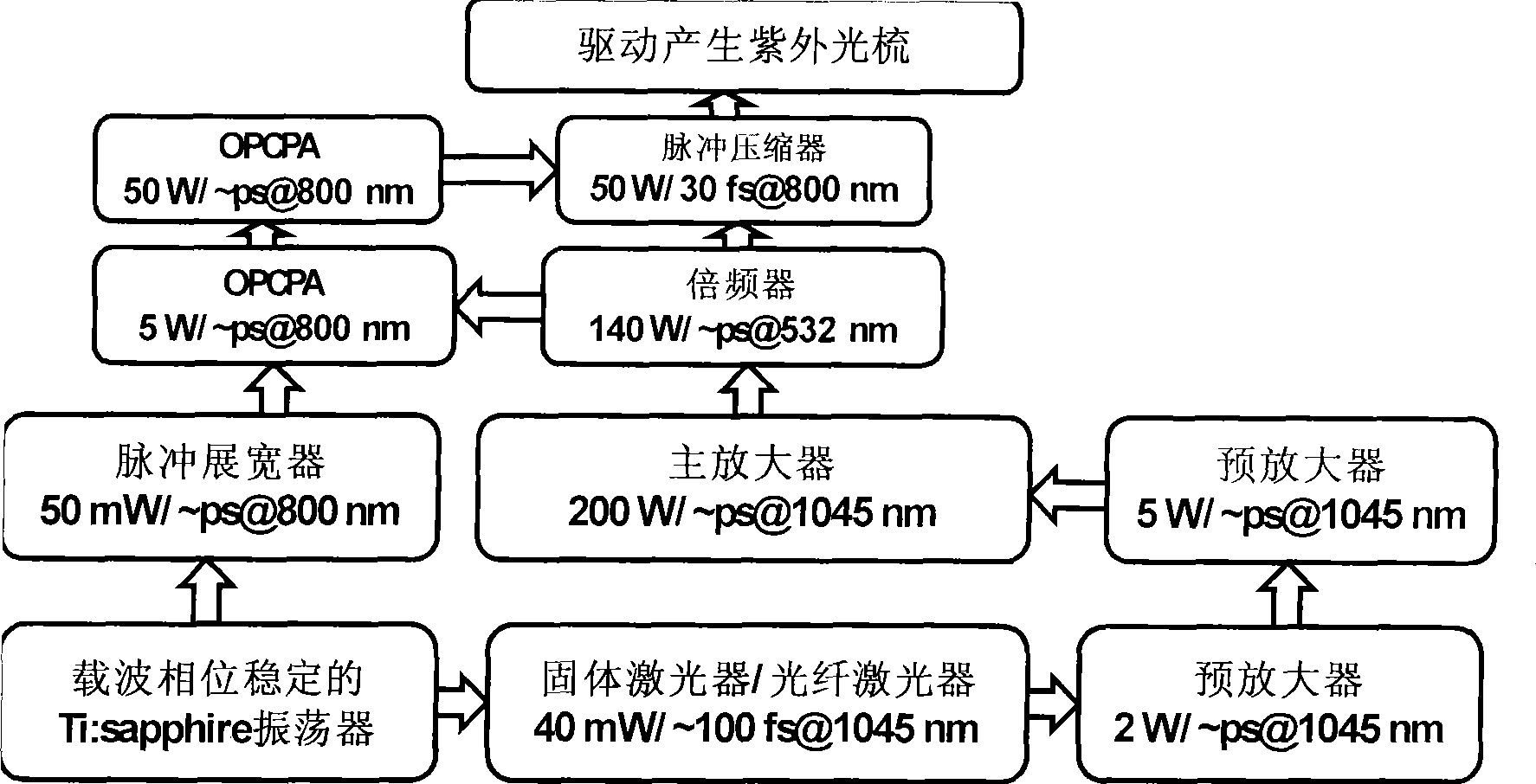
Method for generating ultraviolet optical frequency comb drive source
InactiveCN101442176AReduce the temperatureLower requirementLaser detailsGratingChirped pulse amplification
The invention relates to a method for generating a drive source of an ultraviolet optical frequency comb. The method comprises the steps of synchronous control of laser and chirped pulse amplification of optical parameters, wherein ultrashort pulses outputted by a laser with stable carrier phase are divided into two beams; one beam is used as signal light to be amplified for chirped pulse amplification of the optical parameters, and the other beam is used for generating synchronous pumping signals through crossed phase modulation or gain selective amplification; picosecond and nanosecond intense pulse laser is taken as a pumping source for chirped pulse amplification of the optical parameters; and ultrashort and ultra-intense laser output is obtained by utilization of compression of grating pairs at an output end for chirped pulse amplification of the optical parameters. The method has the advantages that the method does not need a complex circuit system, can greatly reduce the requirement on the environment and particularly on temperature and vibration, and can obtain the ultraviolet optical frequency comb which has a wider application scope, relatively high power and high repetition frequency and shorter wavelength.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for generating supercontinuum from communication band to middle infrared based on silicon nitride waveguide
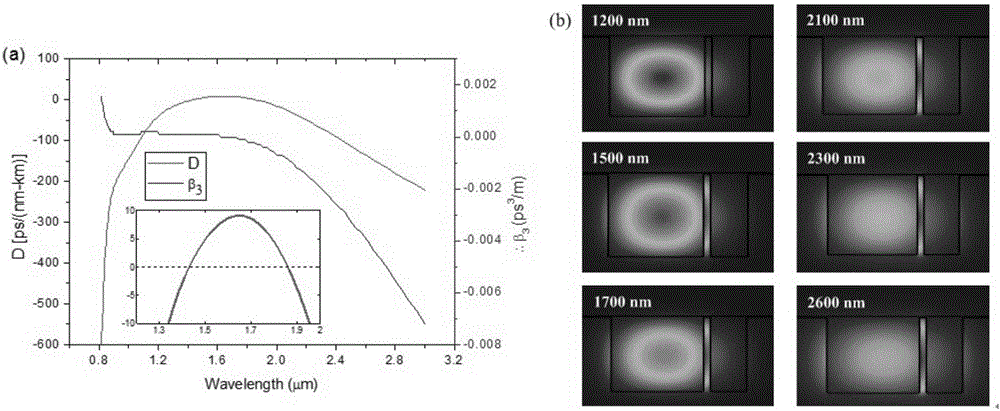
ActiveCN106647098AHigh nonlinear coefficientReduce the effective areaNon-linear opticsLight dispersionMiddle infrared
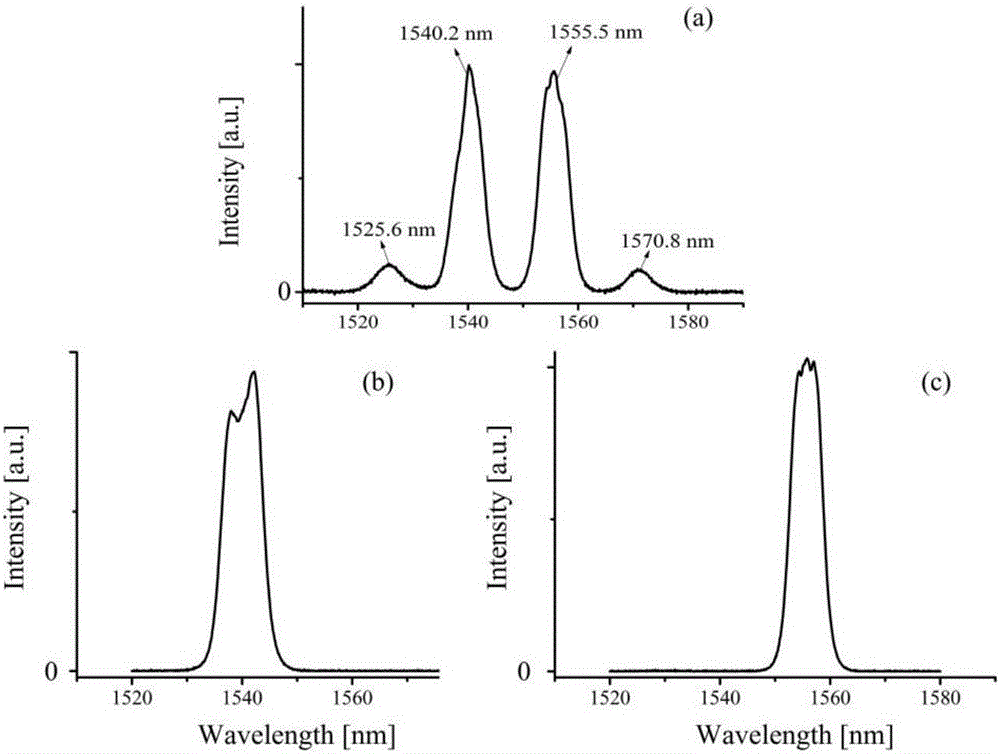
The invention discloses a method for generating supercontinuum from the communication band to the middle infrared based on a silicon nitride waveguide. The method comprises the steps of step 1, using an ultrashort pulse light source to emit the light which has a frequency of 8-12MHz, and a central wavelength of 1.4-2.2 micrometer, step 2, conducting lens coupling of ultrashort femtosecond pulses which is then infused into a ridge / groove hybrid reverse silicon nitride waveguide with a flat light dispersion, wherein the structure of the silicon nitride waveguide comprises a silica oxide layer arranged on a silicon plate, the grooves containing a single silica ridge is formed on the surface of the silica. The silicon nitride waveguide applies the structure of the ridge / groove hybrid to make the effect area of the light field small, and achieve a big non-linear coefficient of the waveguide. After high peak power femtosecond optical pulses are introduced into the waveguide, non-linear processes of self phase modulation, cross phase modulation, four-wave mixing, soliton frequency shift, dispersive wave generation and the like occur, and finally the supercontinuum from the communication band to the middle infrared is formed.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
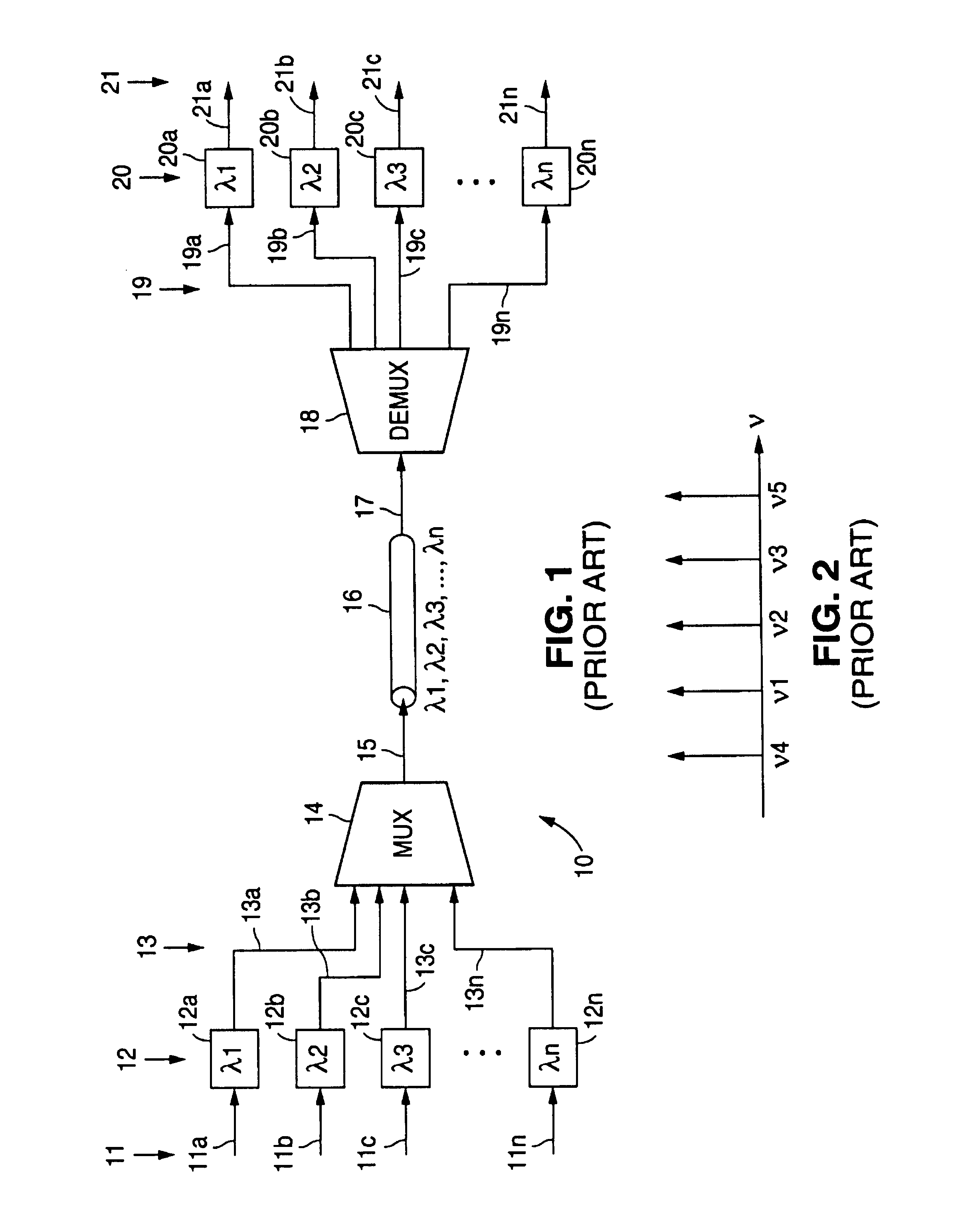
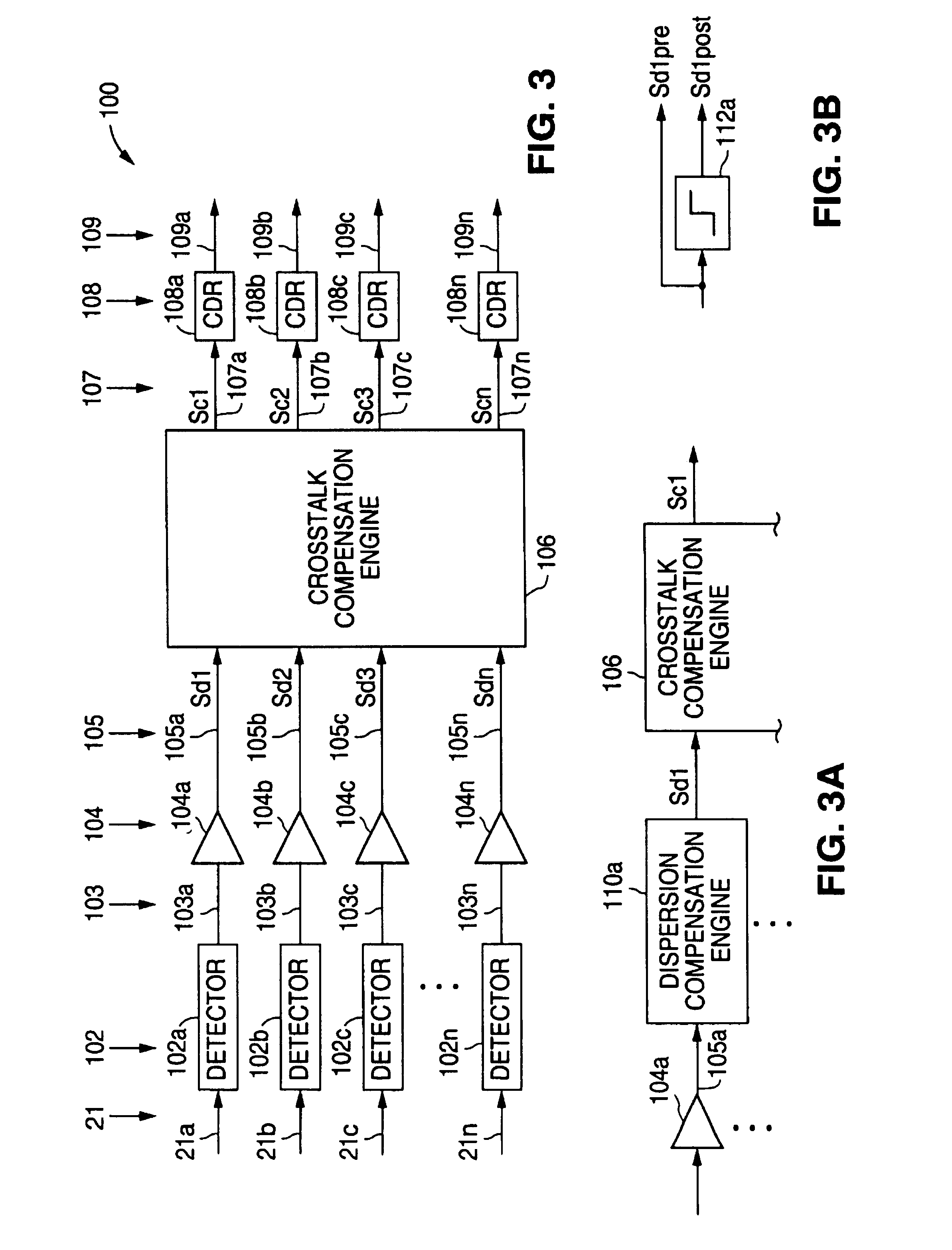
Crosstalk compensation engine for reducing signal crosstalk effects within a data signal
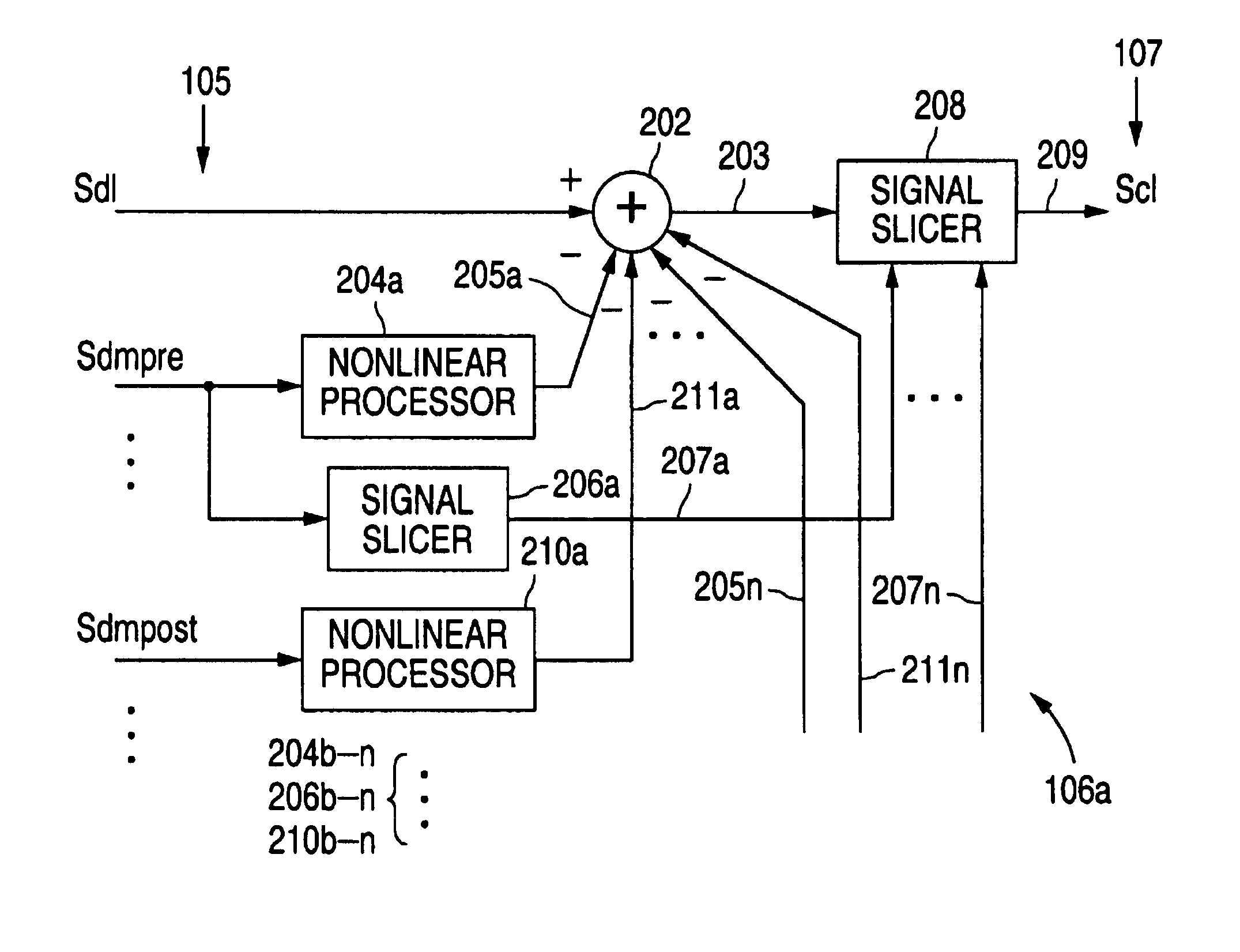
InactiveUS7020402B2Reduce signal crosstalk effectsReduce one or more signal crosstalk productsFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingData signal
A crosstalk compensation engine for reducing signal crosstalk effects within a data signal. Demultiplexed data signals corresponding to multiplexed data signals received via a signal transmission medium are processed to significantly reduce one or more signal crosstalk products related to one or more interactions among the multiplexed data signals within the signal transmission medium. Such signal crosstalk products include those resulting from dense wavelength-division mutiplexing of the data signals used to provide the multiplexed data signals, four-wave mixing among the multiplexed data signals within the signal transmission medium, and cross-phase modulation among the multiplexed data signals within the signal transmission medium.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Link damage perception energy efficiency routing method for distinguishing services in elastic optical network
ActiveCN108322392AReduce performanceReduce the effects of cross-phase modulationMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksDifferentiated servicesFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a link damage perception energy efficiency routing method for distinguishing services in an elastic optical network, and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber communications. The method designs a path weight formula based on load balancing for comprehensively considering the link frequency spectrum state and the transmission damage, so as to reduce the nonlineardamage among different channels. Based on the path weight formula, an edge-separated maximum weight path is selected for high-quality services; and an edge-separated shortest energy efficiency path isselected for low-quality services. During spectrum allocation, the spectrum is partitioned according to the ratio of the service rate, and a spectrum allocation mode combining first-time hit and tail-end hit is adopted to reduce the cross-phase modulation between the services of different transmission rates. At the same time, in order to reduce the probability that existing services are blocked since the current transmission service causes damage to the existing services in the network, an optical path reconfiguration mechanism of a physical damage blocking service is designed. The link damage perception energy efficiency routing method for distinguishing the services in the elastic optical network provided by the invention effectively improves the spectrum resource utilization rate and reduces the bandwidth blocking rate and the service transmission energy consumption.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for estimating cross-phase modulation impairments
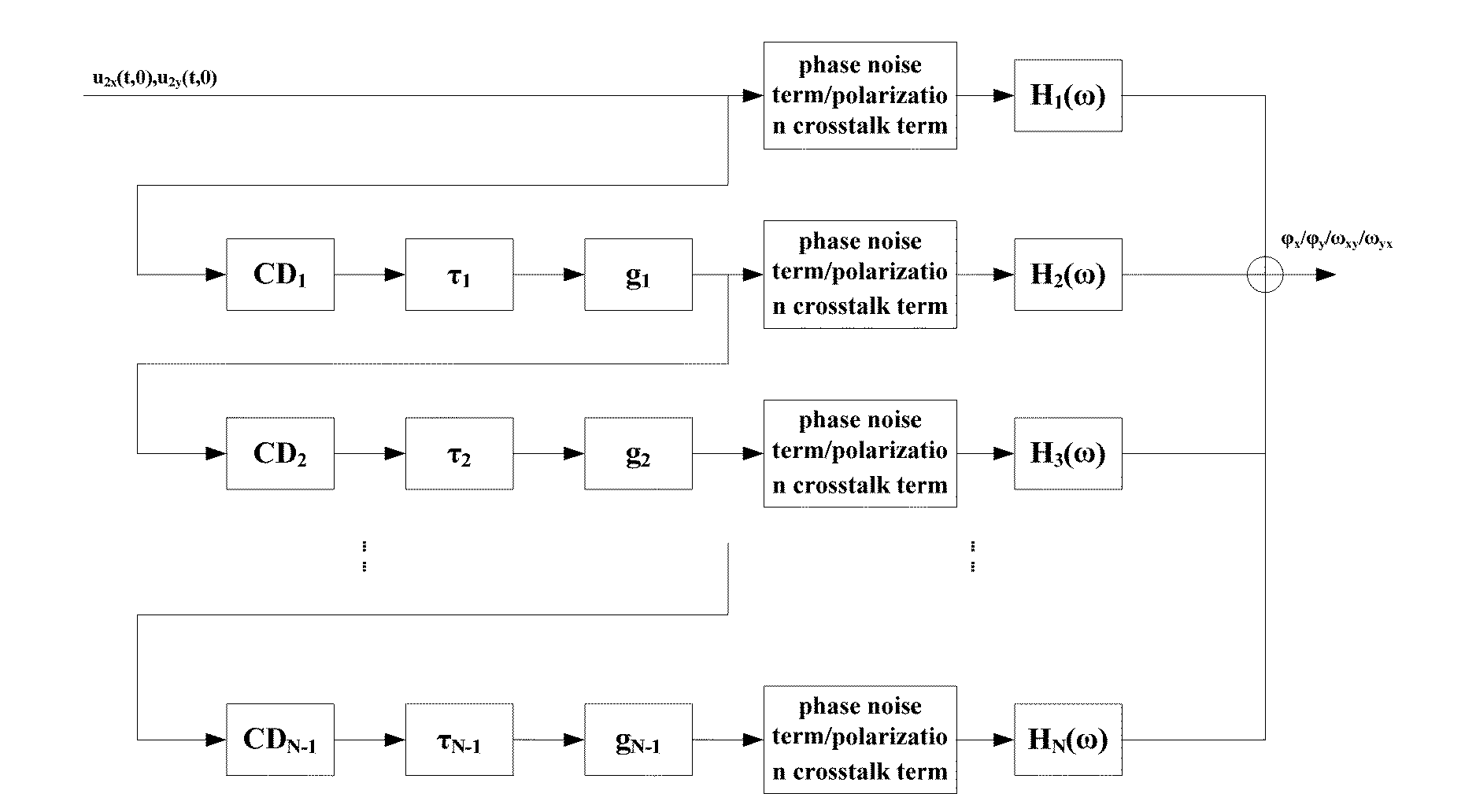
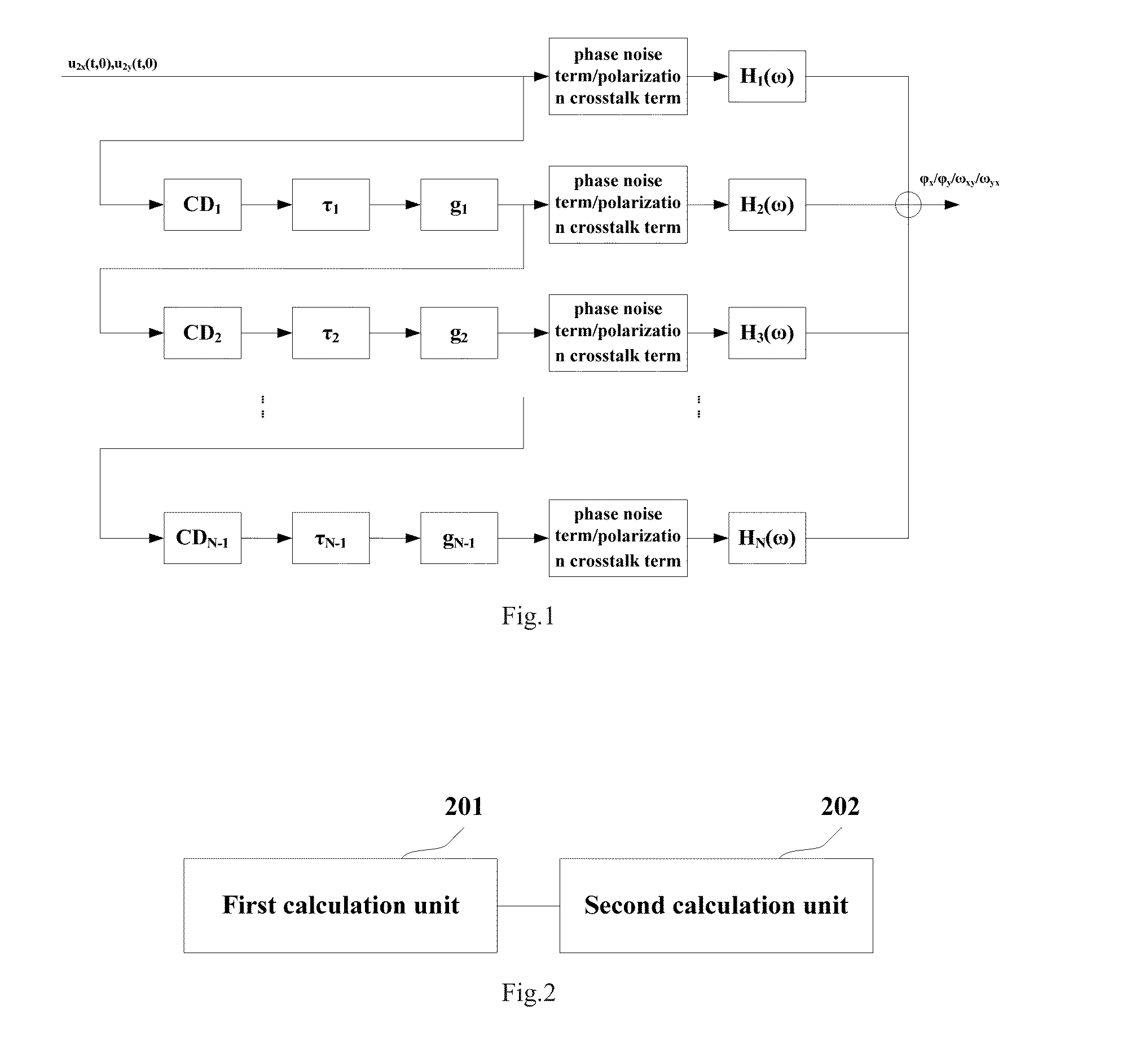
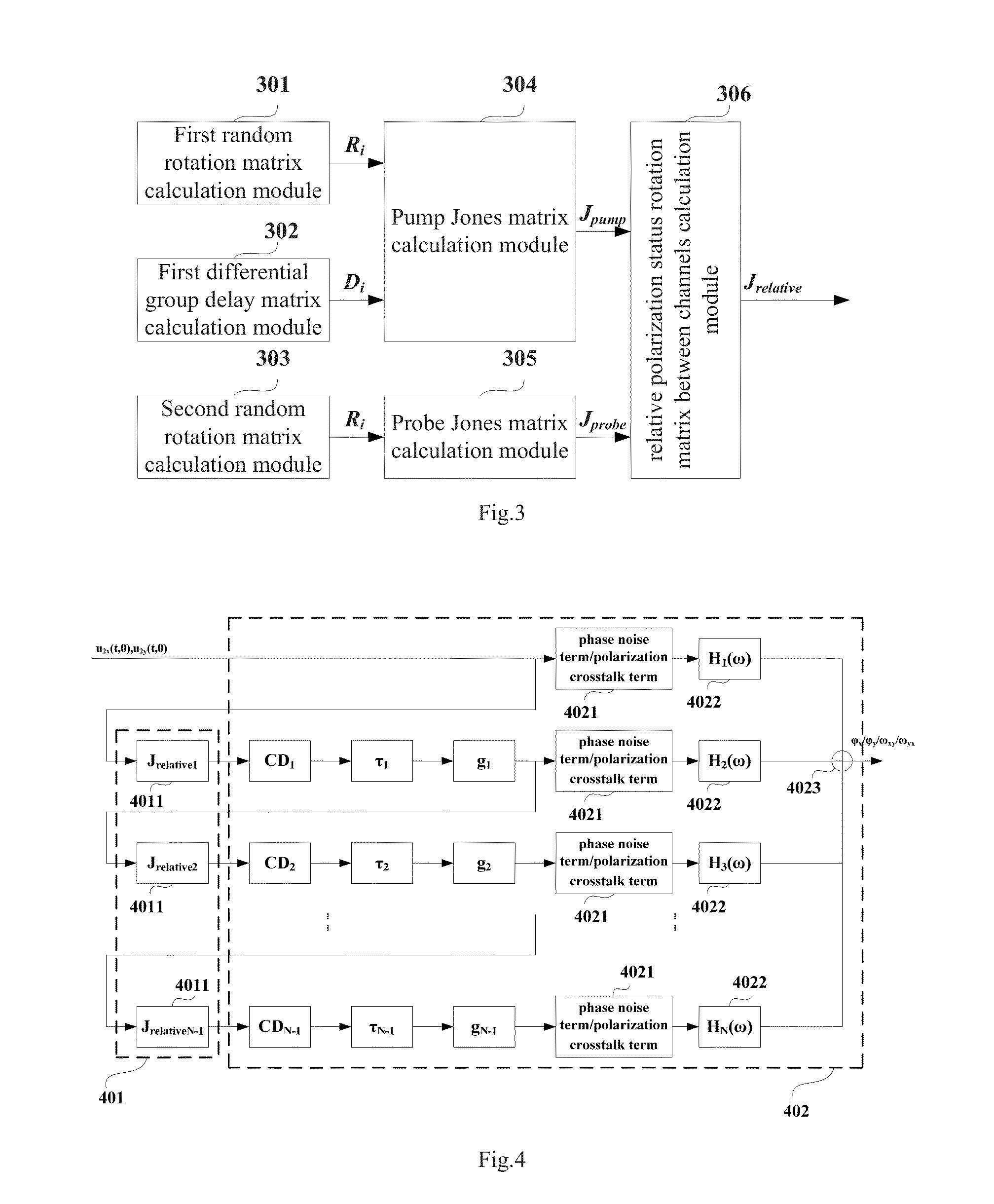
ActiveUS20130266311A1Quickly and accurately estimatedTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsRelative polarizationPhase noise
A system for estimating cross-phase modulation (XPM) impairments, wherein the method comprises: determining, according to a pump Jones matrix of a pump channel and a probe Jones matrix of a probe channel of each of fiber spans except for the first fiber span in a fiber transmission system, a polarization mode dispersion (PMD)-induced relative polarization status rotation matrix between channels of the each of fiber spans; and determining, according to the rotation matrix of the each of fiber spans, dispersion of a pump signal of the each of fiber spans, differential delay of the pump signal relative to a probe signal of the each of fiber spans and a gain of the each of fiber spans, polarization crosstalk and phase noise of the XPM impairments in the fiber transmission system. This allows the XPM impairments in the effect of the polarization mode dispersion to be quickly and accurately estimated,
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Transient crossing phase modulation type full gloss half-adder
InactiveCN1928689ALow costSimple structureLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesInstrumentsBand-pass filterFiber amplifier
The disclosed transient-cross phase-modulation full-light half-adder comprises: two ultrashort pulse sources are modulated to output RZ codes as two path data signals; after coupling by a coupler, these data signals are injected into a semiconductor amplifier together with continual laser beam through another coupler; the output power of the amplifier is divided into two parts; after amplifying and filtering by fiber amplifier and light band-pass filter respectively, it obtains light logic 'AND' and 'OR' operators detected by an optical receiver. This invention simplifies structure greatly, saves cost, and can achieve 100Gb / s speed in theory.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
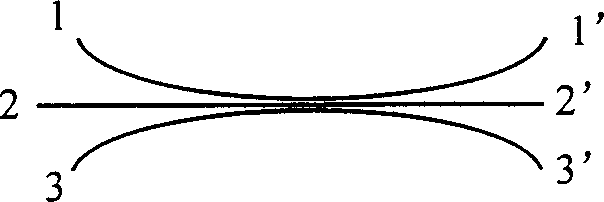
All-optical polarization rotation switch using a loop configuration
All-optical polarization rotation switch is disclosed. A linearly polarized probe light is split by a polarization beam splitter (PBS) into two orthogonal linear polarization components, which are coupled with respective ends of a nonlinear optical fiber in loop configuration. A linearly polarized control pump light is launched into one direction of the fiber. The probe light component co-propagating with the control light pulse undergoes a nonlinear phase shift due to cross phase modulation (XPM). The phase shift of the light co-propagating with the control pulse thus causes a rotation of the recombined light output from the PBS. The rotation is detected by using a polarizer. Exploiting XPM instead of the nonlinear birefringence enables the use of highly nonlinear PM fiber.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical nonlinear evaluation device and optical switching element
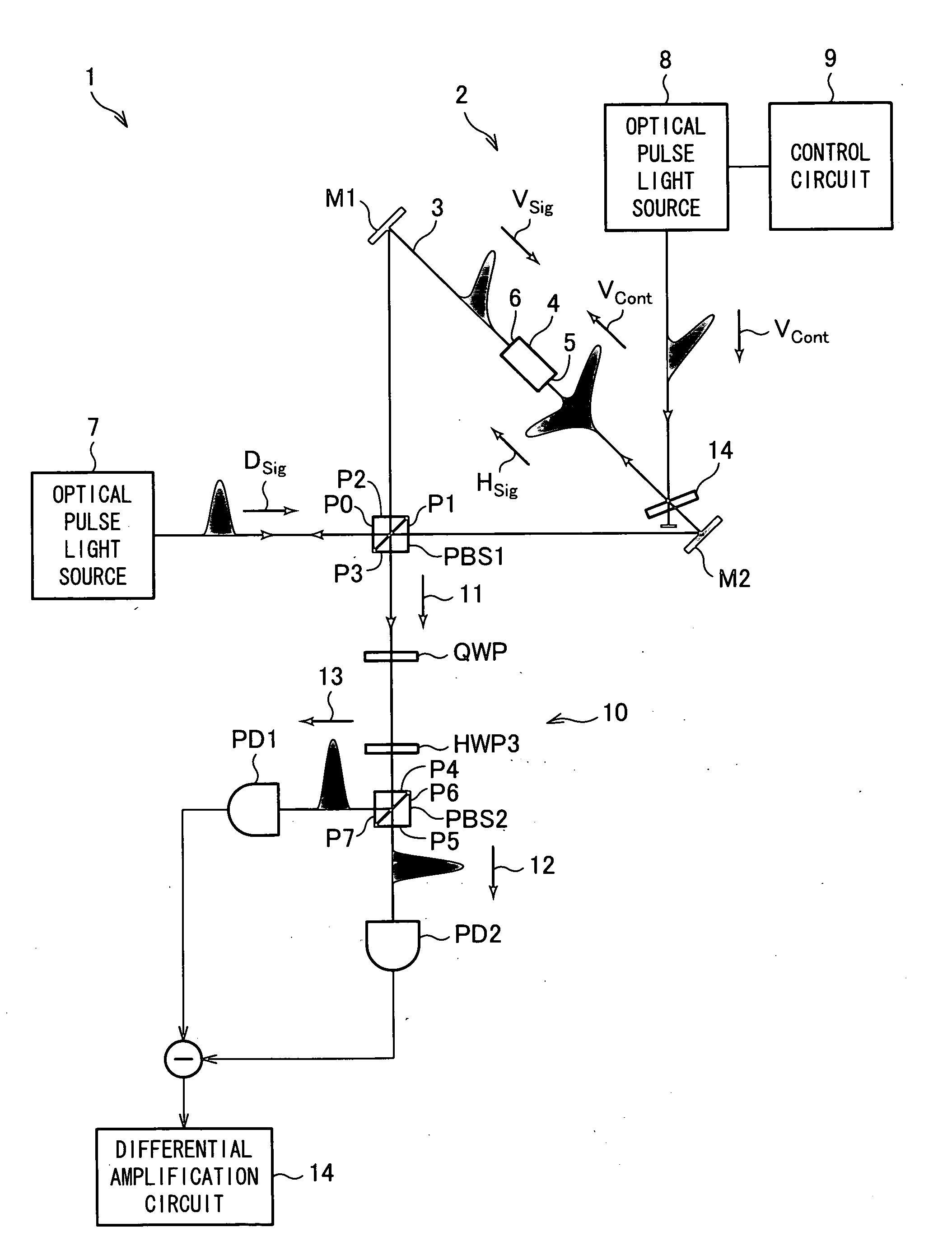
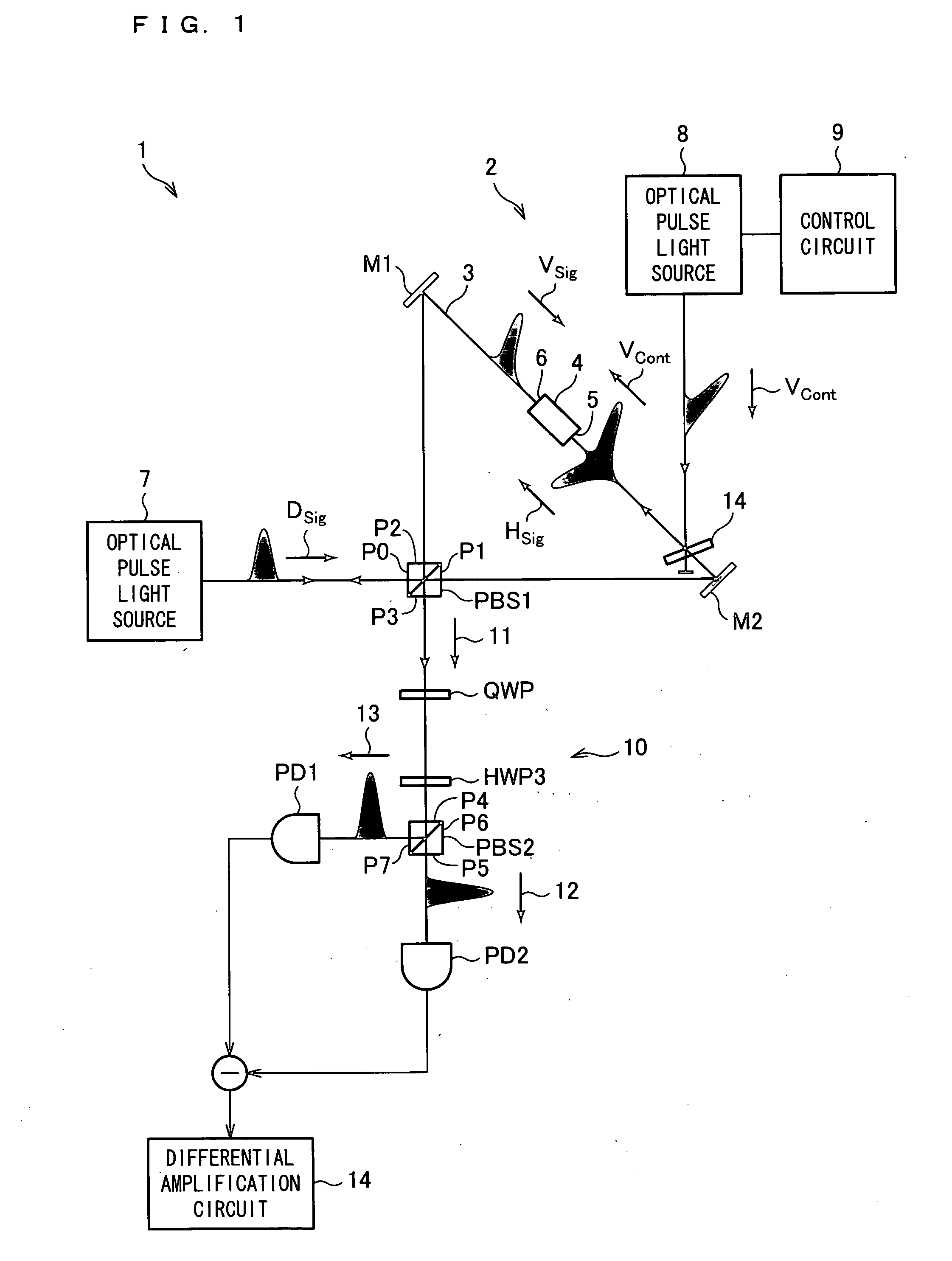
InactiveUS20090251703A1Low detection sensitivityHigh-speed switchingOptical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase differenceLight beam
An optical nonlinear evaluation device (1) capable of accurately evaluating the optical nonlinearity of a Kerr medium in accordance with a phase difference caused by cross-phase modulation generated in the Kerr medium includes: a polarization Sagnac interference path (3) provided with a Kerr medium (4); an optical pulse light source (7) for supplying a signal beam (Dsig); a polarization beam splitter (PBS1) for splitting the signal beam (Dsig) into a signal beam (Hsig) and a signal beam (Vsig) polarized in a direction orthogonal to the signal beam (Hsig), for supplying the signal beam (Hsig) to a first side of the Kerr medium (4), and for supplying the signal beam (Vsig) to a second side of the Kerr medium (4); a glass plate (14) for entering, onto the signal beam (Hsig), a control beam (Vcont) for causing a change in phase difference between the signal beam (Hsig) and the signal beam (Vsig); separating means for separating the control beam (Vcont) from the signal beam (Hsig) having traveled through the Kerr medium (4); and a detection section (10) provided so as to detect the phase difference between the signal beam (Hsig) and the signal beam (Vsig).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Multi-wavelength synchronous output fiber laser based on nonlinear polarization rotation mode locking
ActiveCN106058620AImprove stabilityIncrease long offset rangeActive medium shape and constructionGratingBeam splitting
The invention relates to a multi-wavelength synchronous output fiber laser based on nonlinear polarization rotation mode locking, which comprises a semiconductor laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a gain fiber, a first collimating mirror, a first half wave plate, a first quarter wave plate, a first polarization beam splitter, a Faraday isolator, a glaring grating, and a silver mirror. According to the first half wave plate, a nonlinear polarization rotation technology is adopted for mode locking, a saturable absorber which is likely to be damaged can be prevented from being used, and the stability of the laser is enhanced. According to the same laser gain fiber and the nonlinear polarization mode locking device, the distance between two wavelengths under mutual cross phase modulation effects in the laser cavity is increased, and thus, a cavity length misadjustment range for two laser cavities in the case of synchronous mode locking can be increased. Through changing the angle of a beam-splitting grating, the output wavelength of the laser can be tuned, the gap between the two wavelengths can be changed through changing the position of the collimator in the spectral space, and through changing the position of the collimator away from the beam-splitting grating, the pulse spectral width and the pulse width of laser output pulses can be changed.
Owner:SICHUAN GUANGZHENG TECH
Method and system for using optical phase conjugation in an optical communications network
A optical communications network including at least one optical phase conjugator for compensating for non-linear effects. The optical communications network includes at least one dispersion compensation module before the optical phase conjugator and at least one dispersion compensation module after the optical phase conjugator. The dispersion compensation modules compensate for linear effects of the transmission path such as dispersion and dispersion slope. This allows the optical phase conjugator to be designed to compensate for non-linear effects such as self-phase modulation and cross-phase modulation. The separate compensation of linear and non-linear effects provides enhanced control of these effects.
Owner:CIENA
Dispersion compensation quantity setting method, receiving terminal station, and wavelength-multiplexing optical transmission system
InactiveUS7394993B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationTransport systemEngineering
In a dispersion compensation quantity setting technique for use in a WDM transmission system, a transmitting terminal node transmits CW light and modulated light obtained by modulation using a modulation pattern signal, while a receiving terminal node detects a physical quantity stemming from cross phase modulation occurring between the transmitting terminal node and the receiving terminal node on the basis of a variation of an intensity of the transmitted CW light and sets a dispersion compensation quantity on the basis of a variation of the detected physical quantity. Moreover, this optimizes the crosstalk, suppresses the output power of transmitted light, eliminates the nonlinear optical effect of the transmitted light, and carries out dispersion compensation superior in cost performance.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com