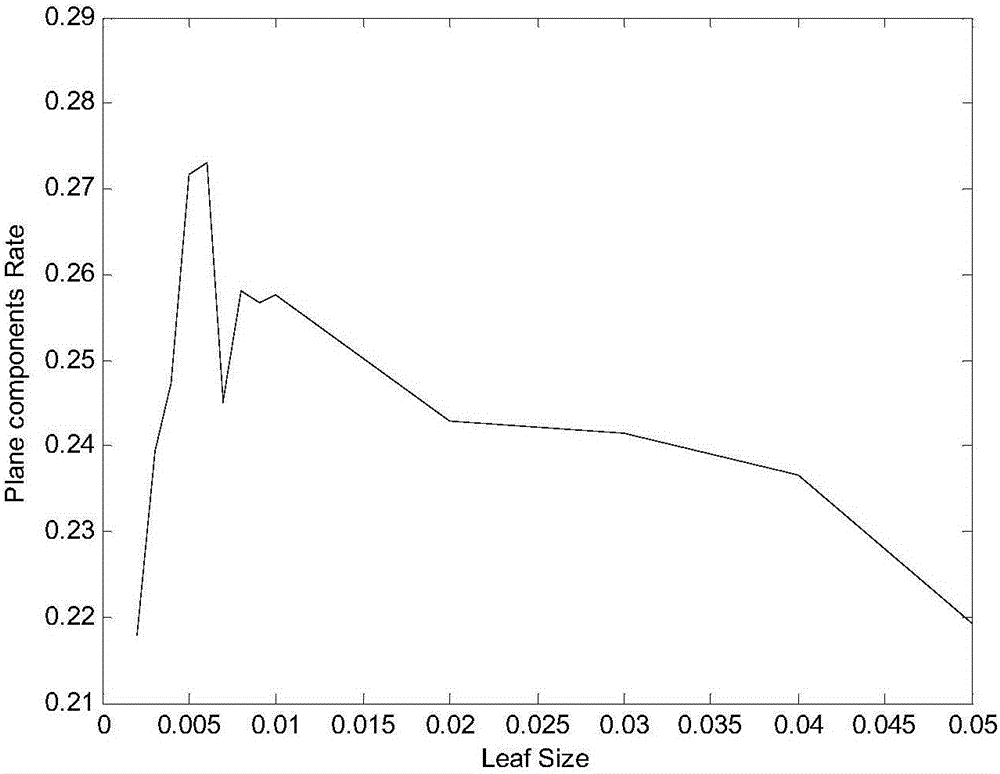
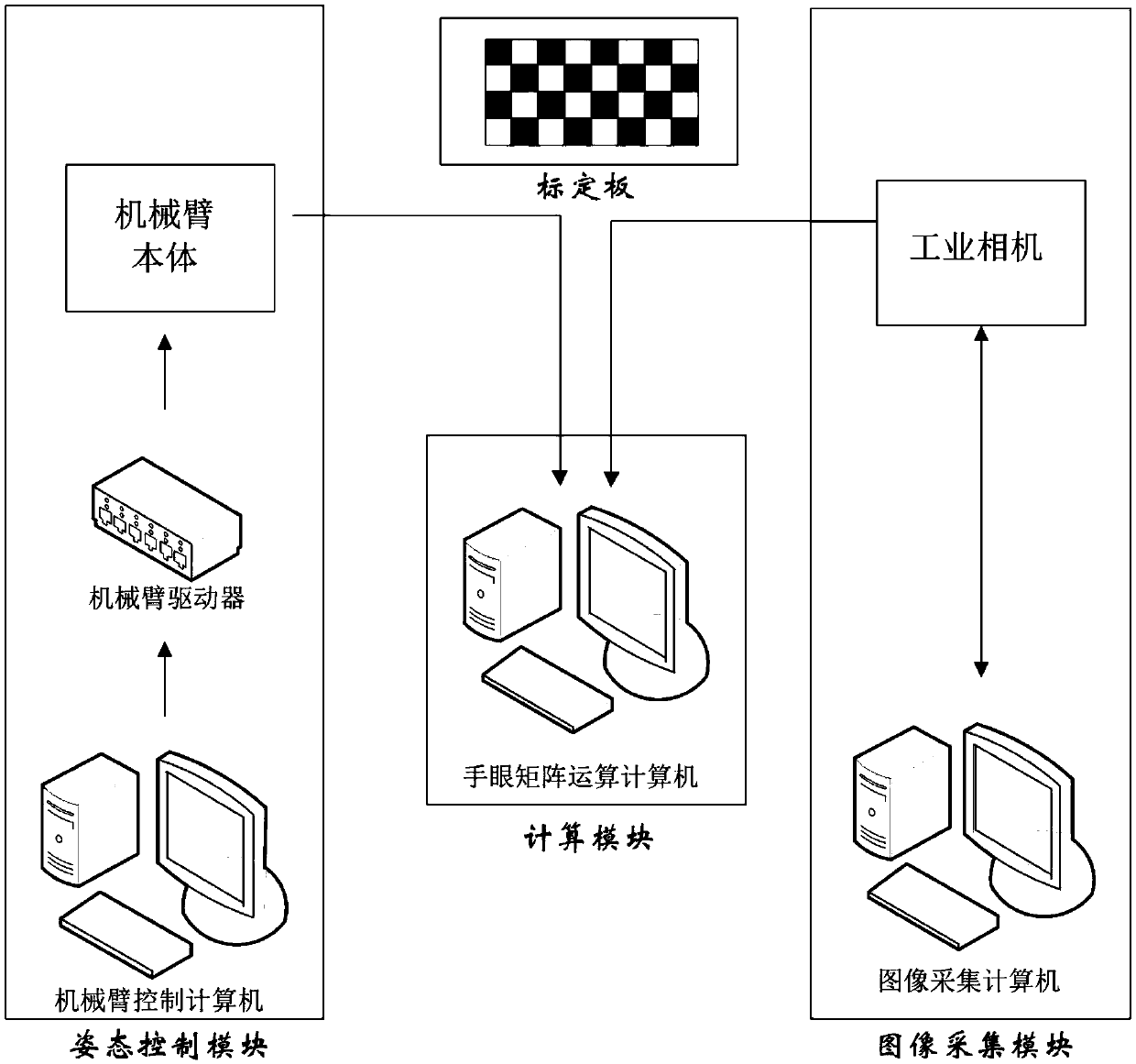
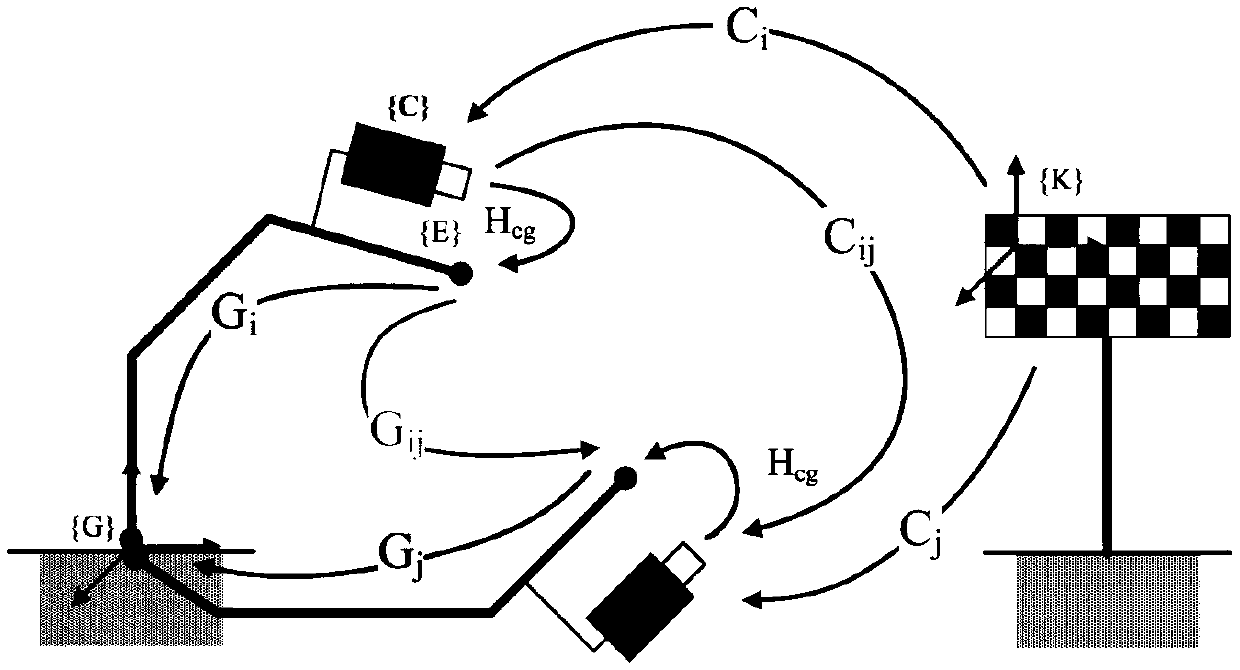
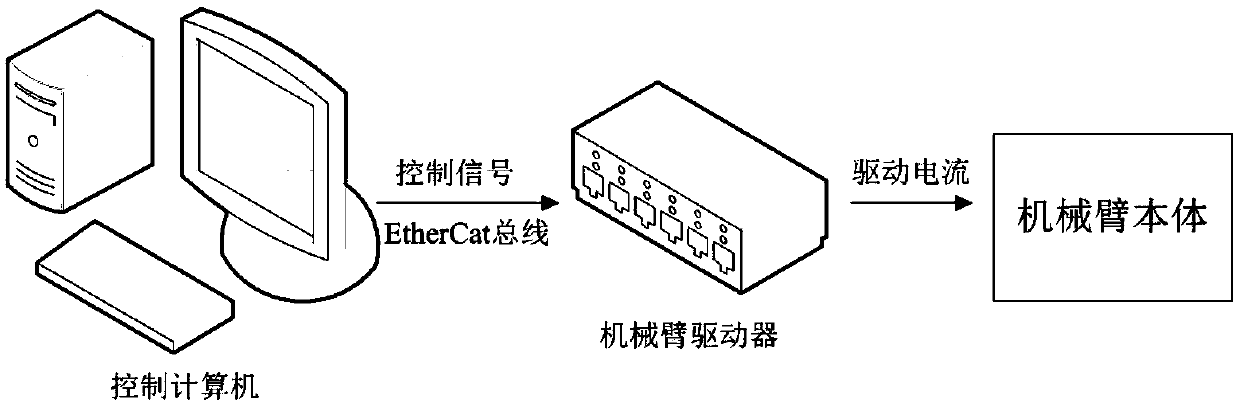
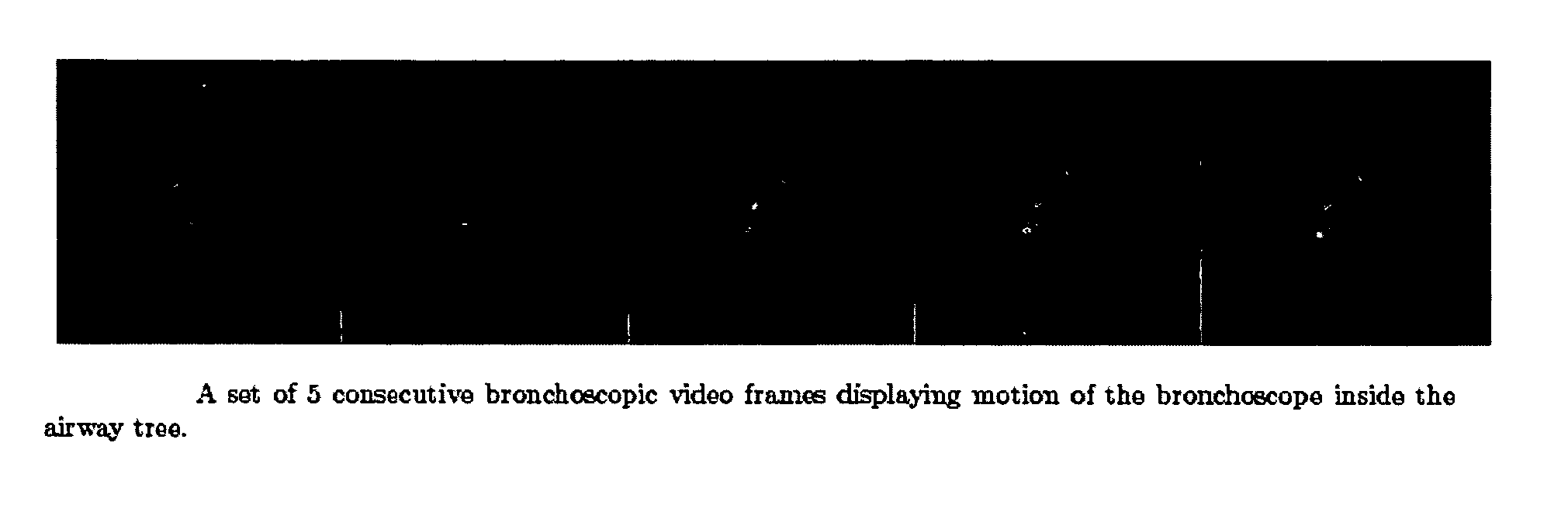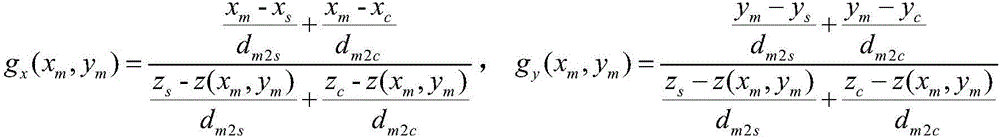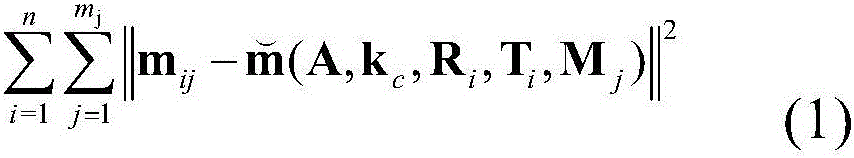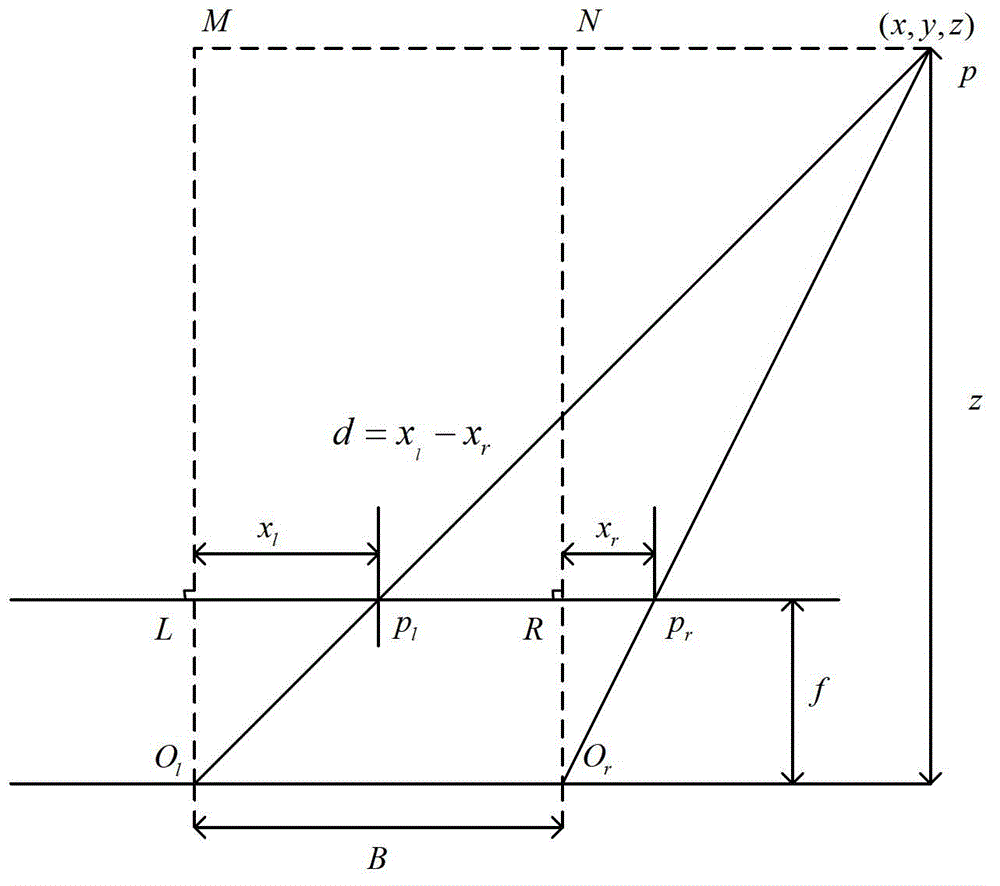Patents
Literature
1191 results about "Rotation matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
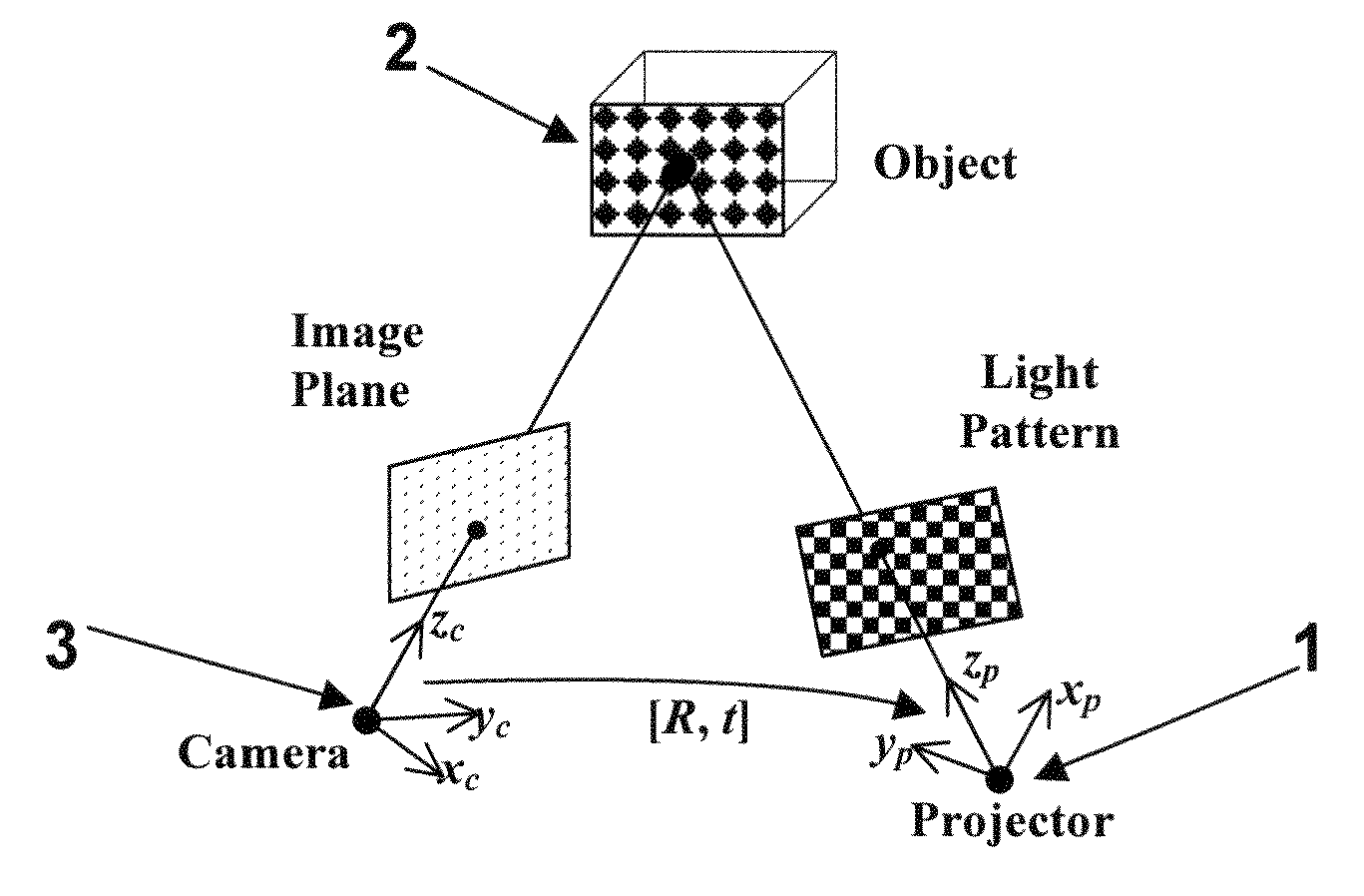
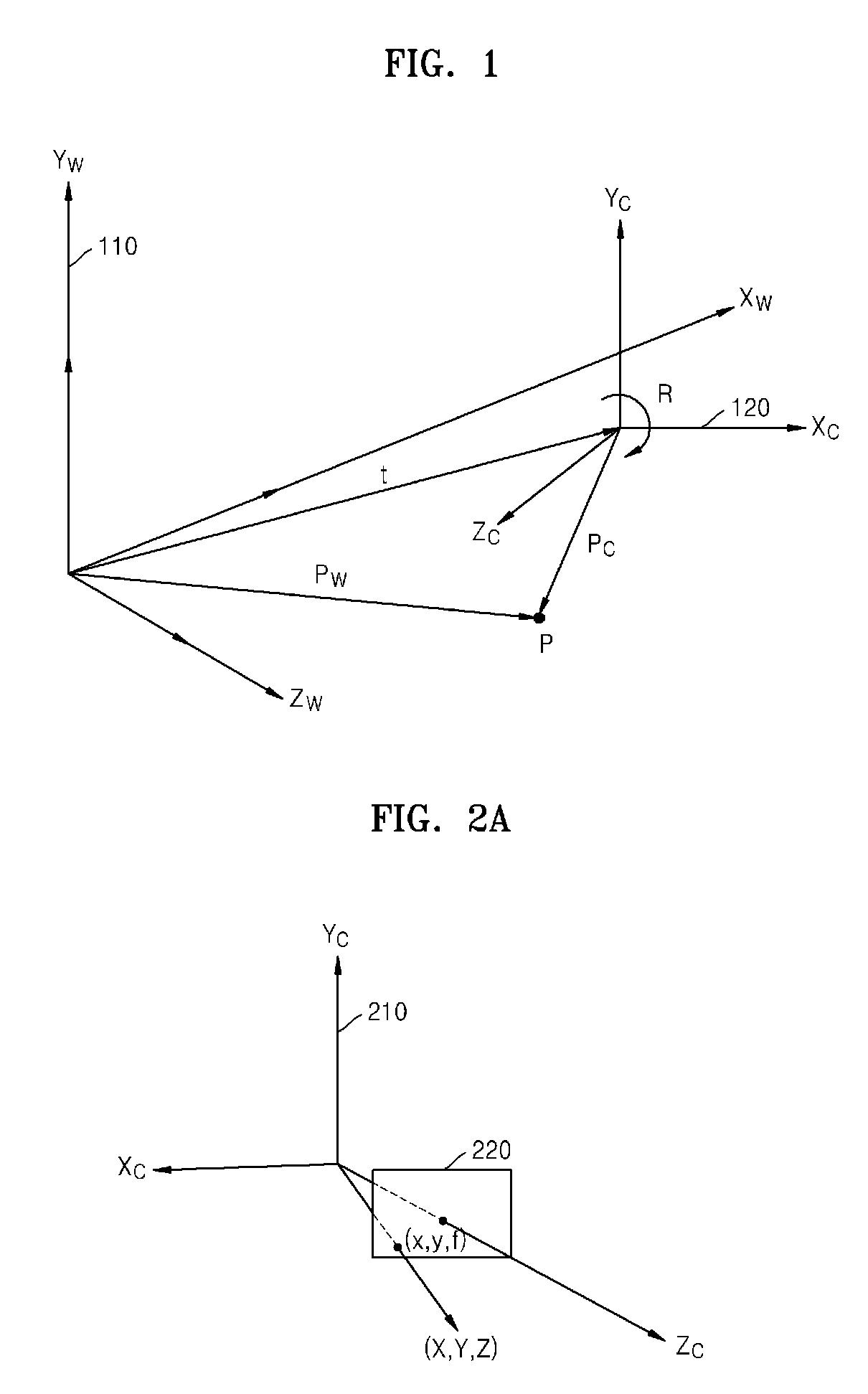
In linear algebra, a rotation matrix is a matrix that is used to perform a rotation in Euclidean space. rotates points in the xy-plane counterclockwise through an angle θ about the origin of a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.
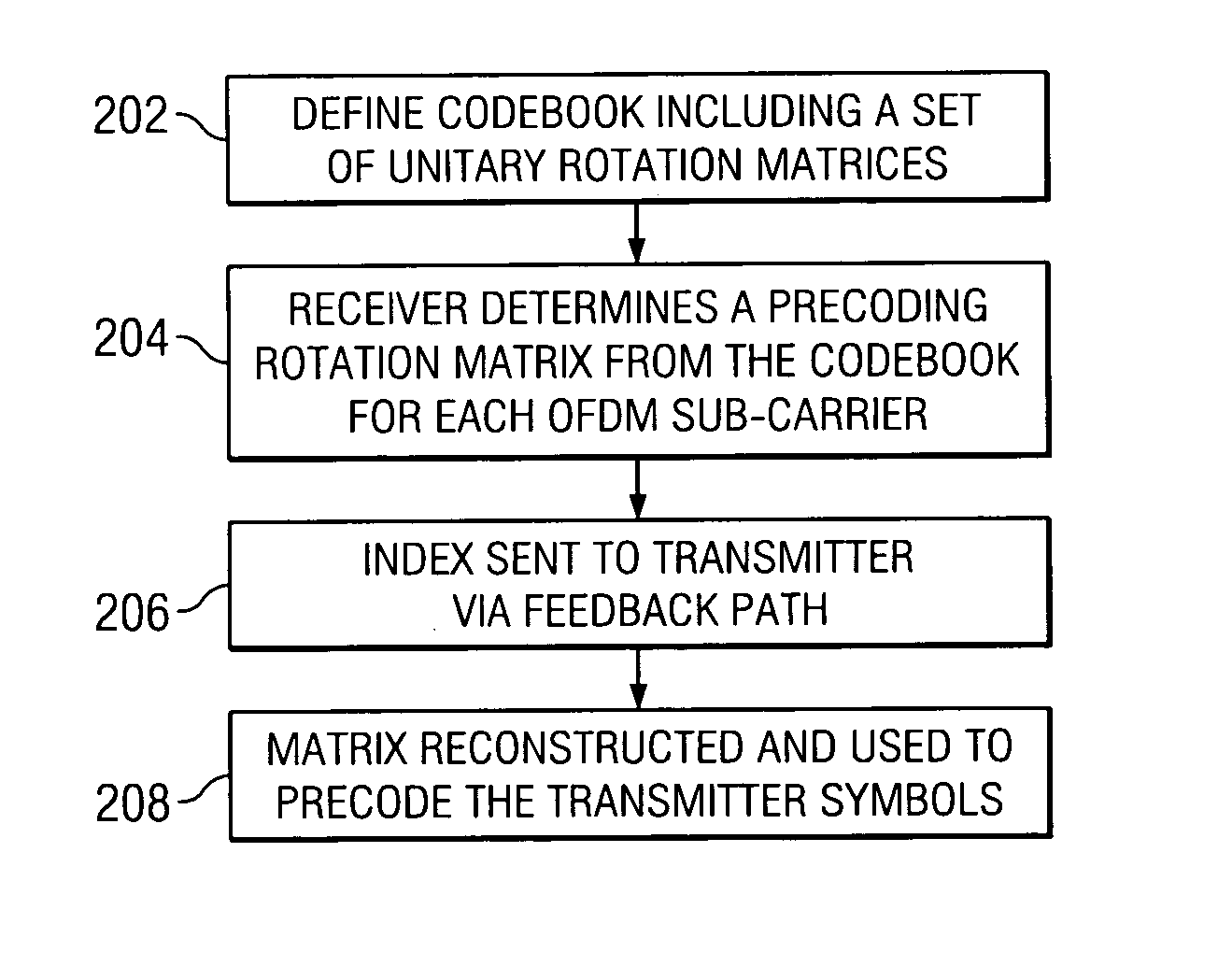
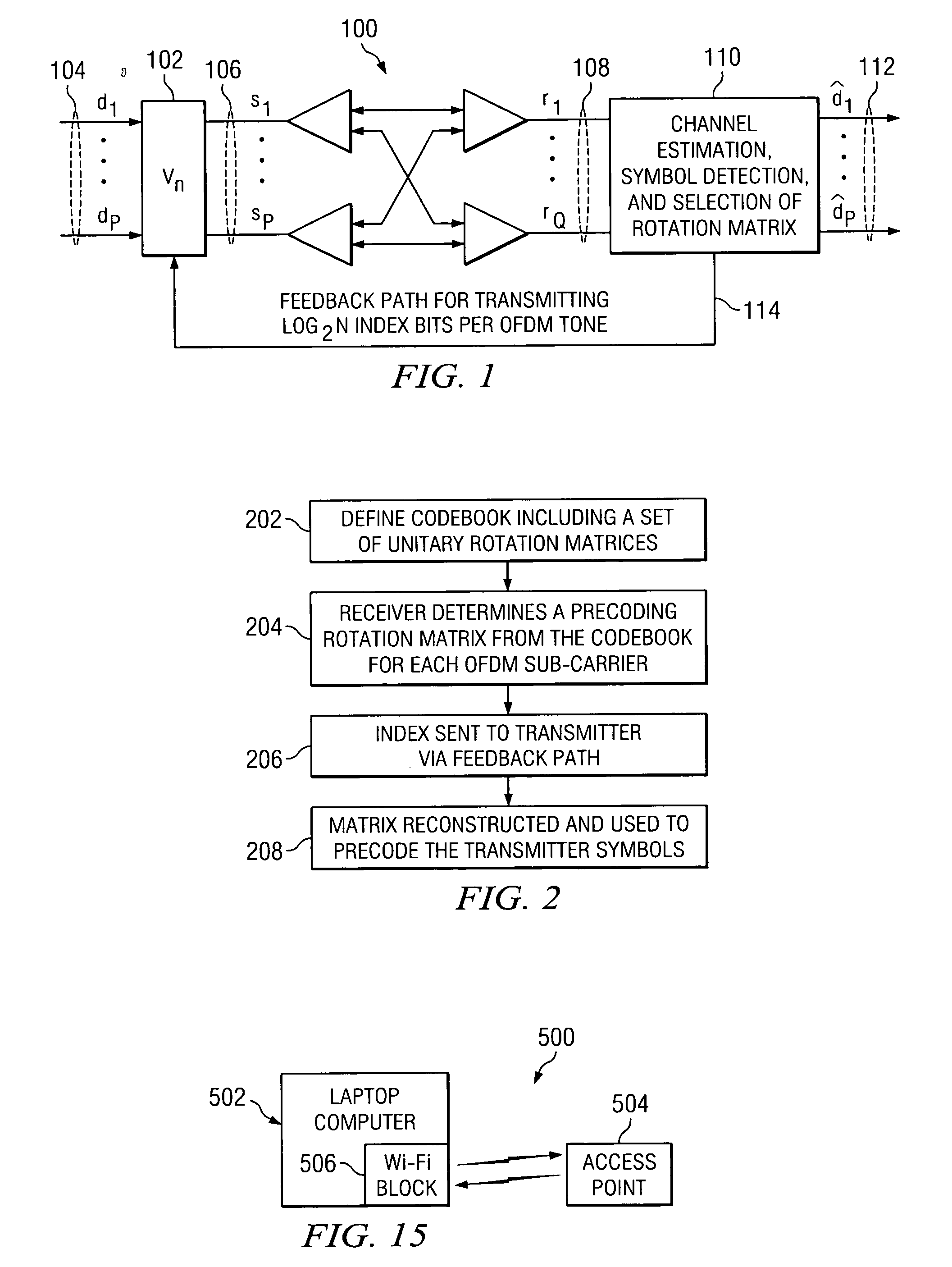
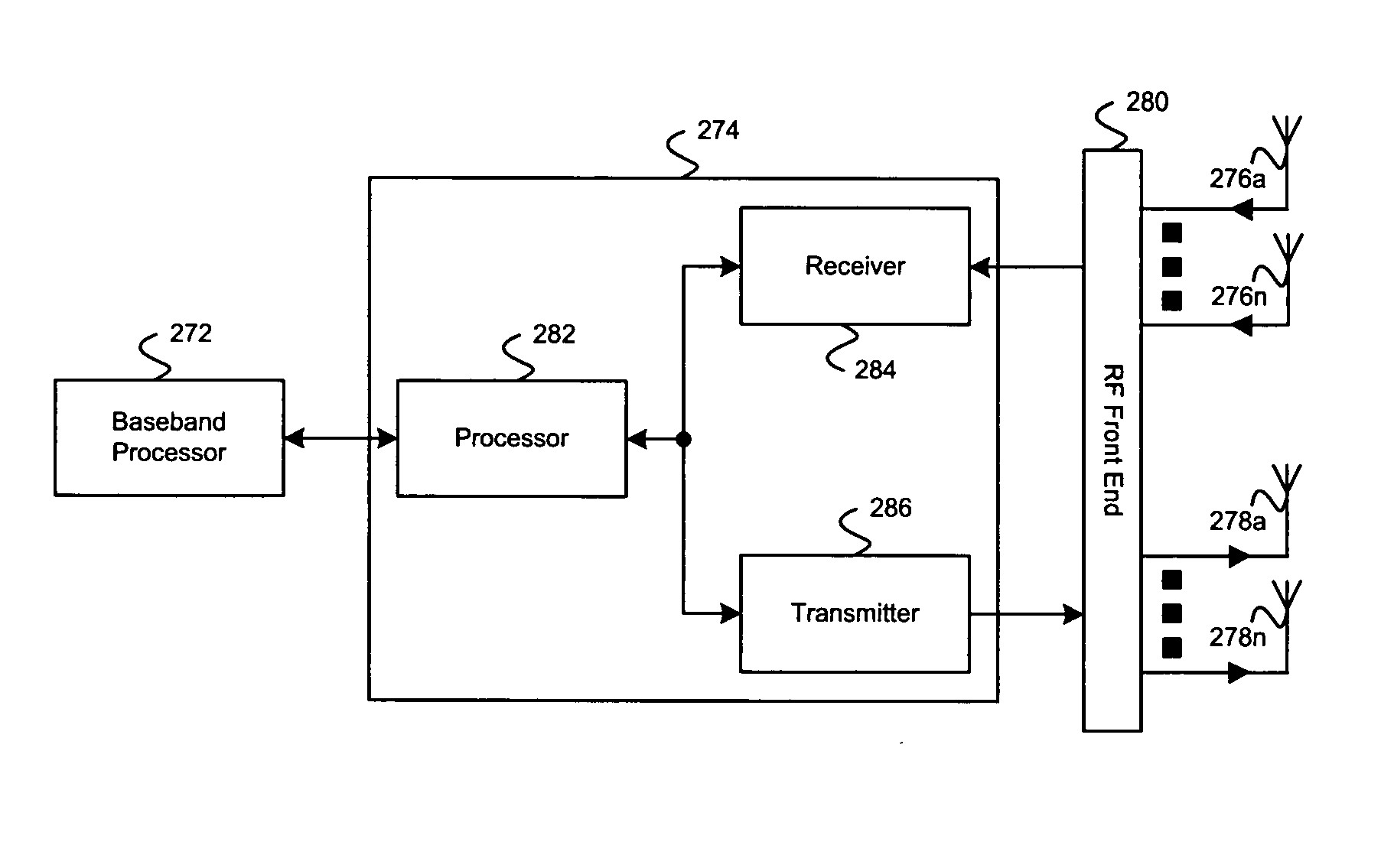
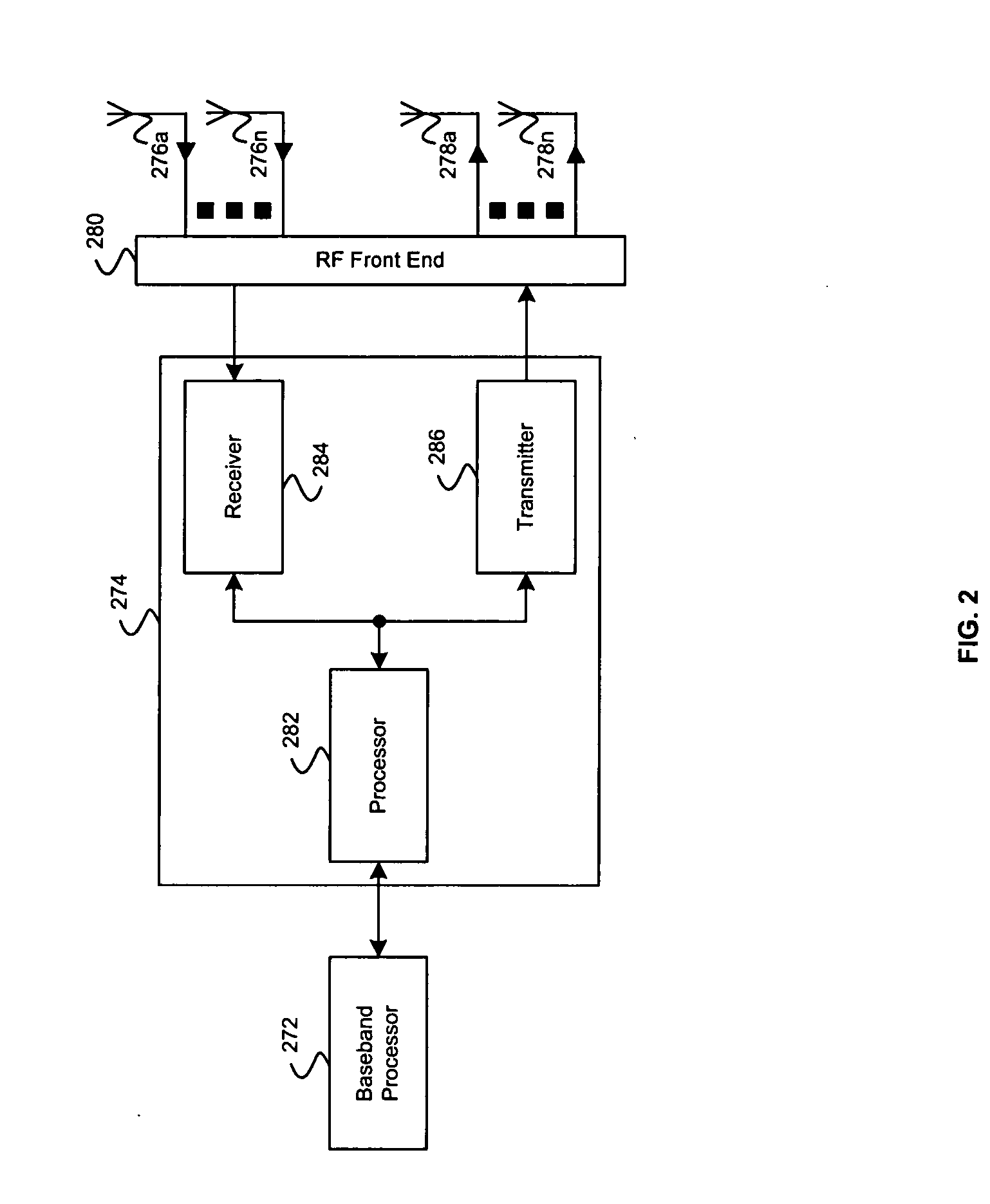
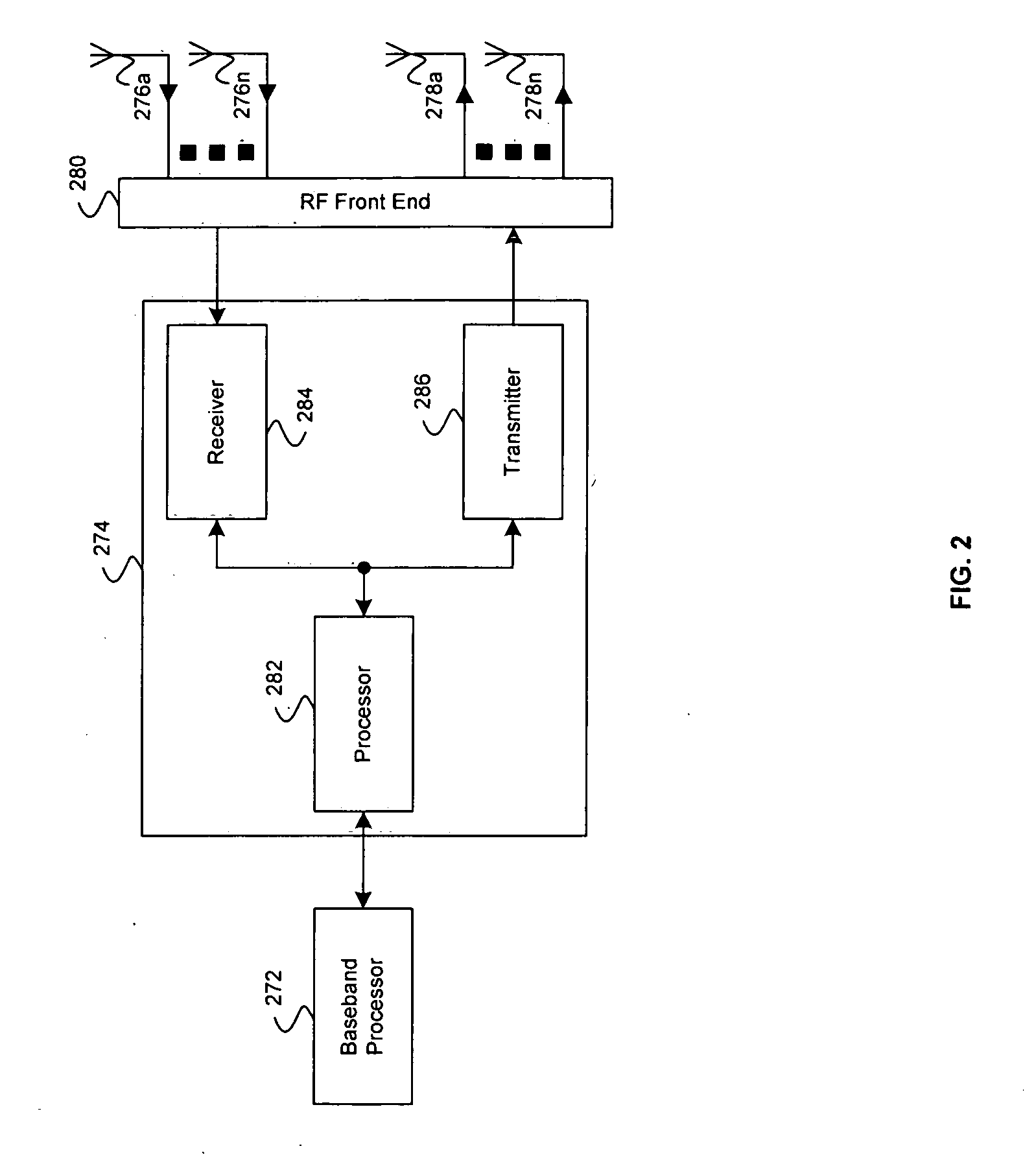
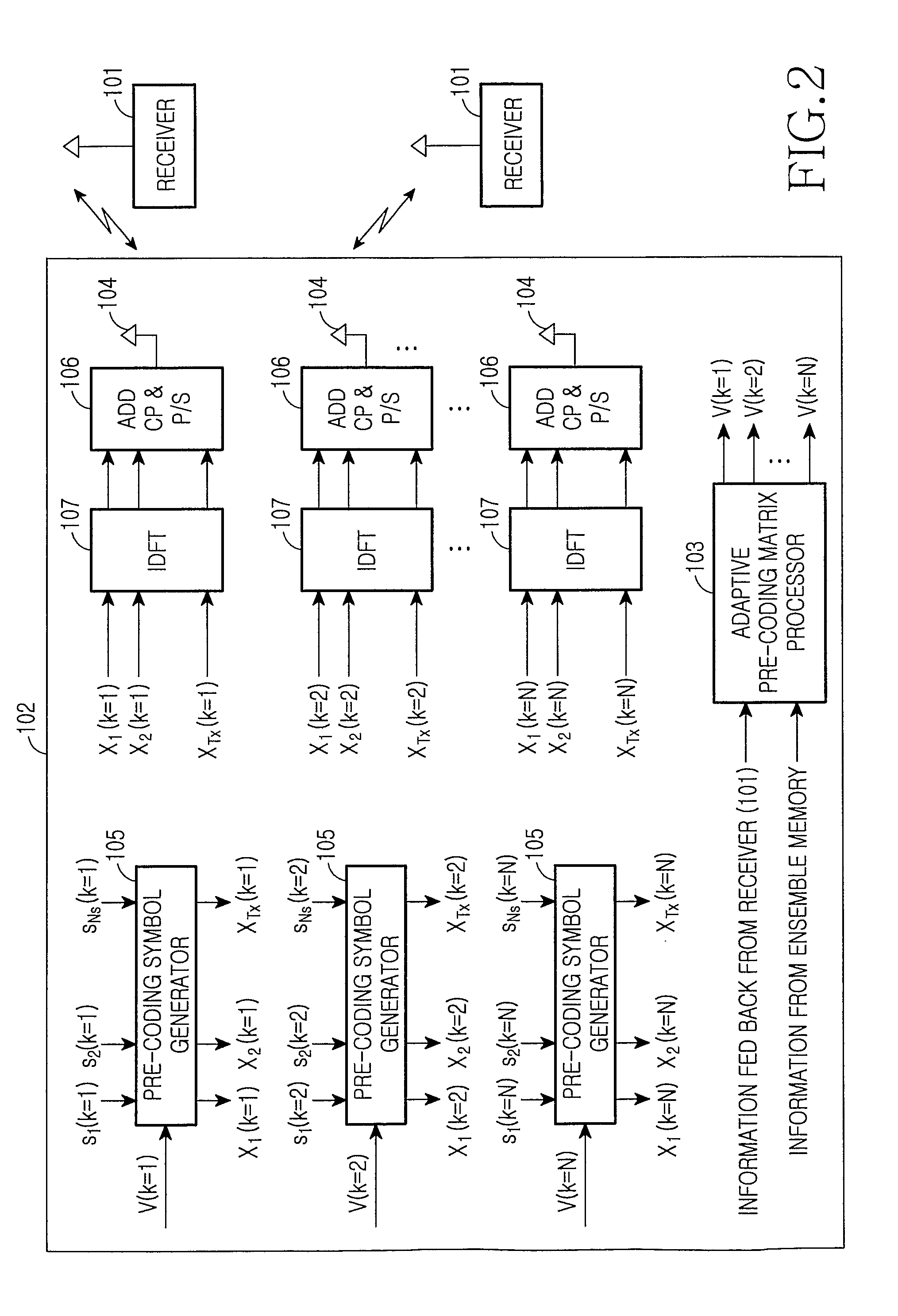
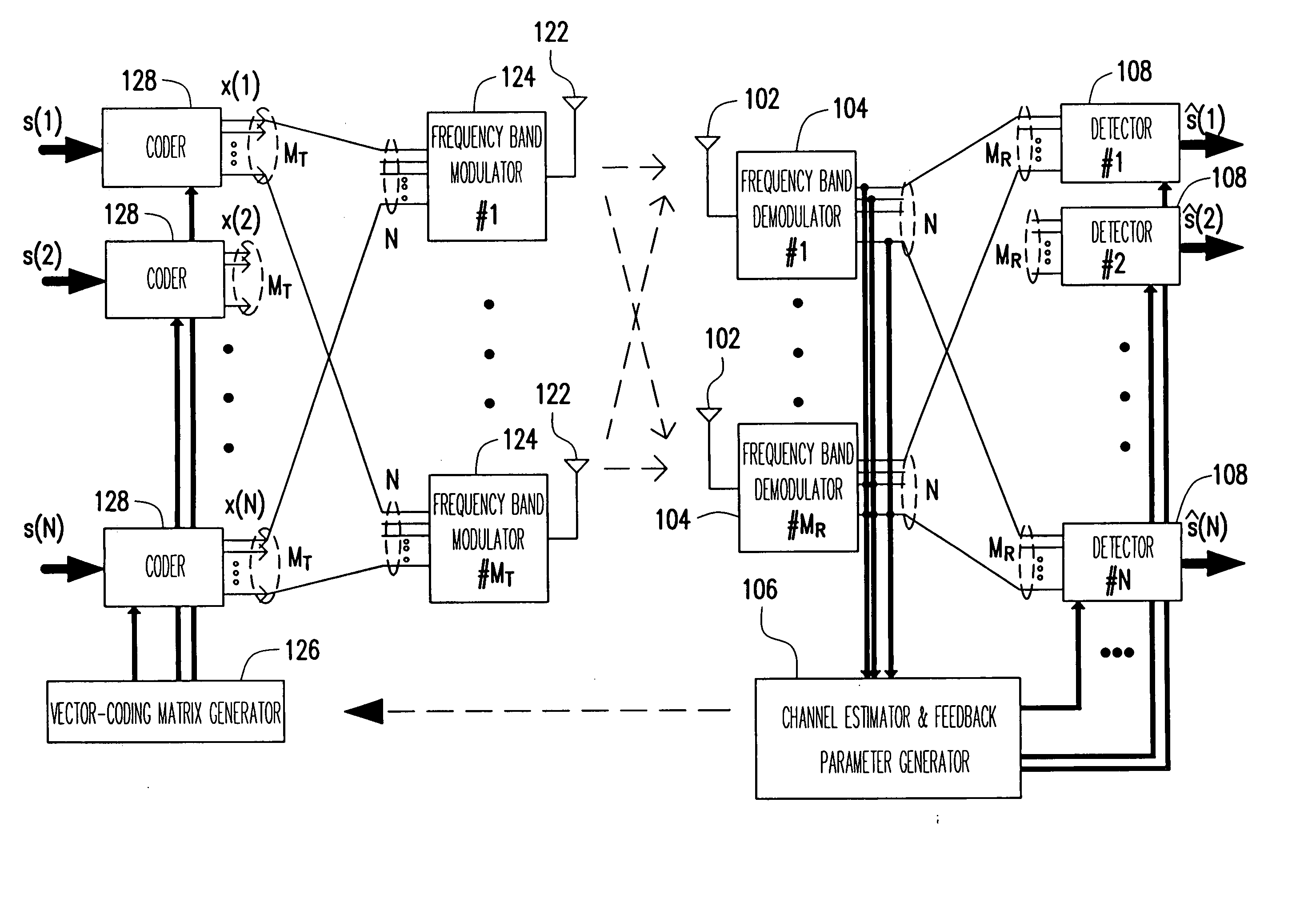
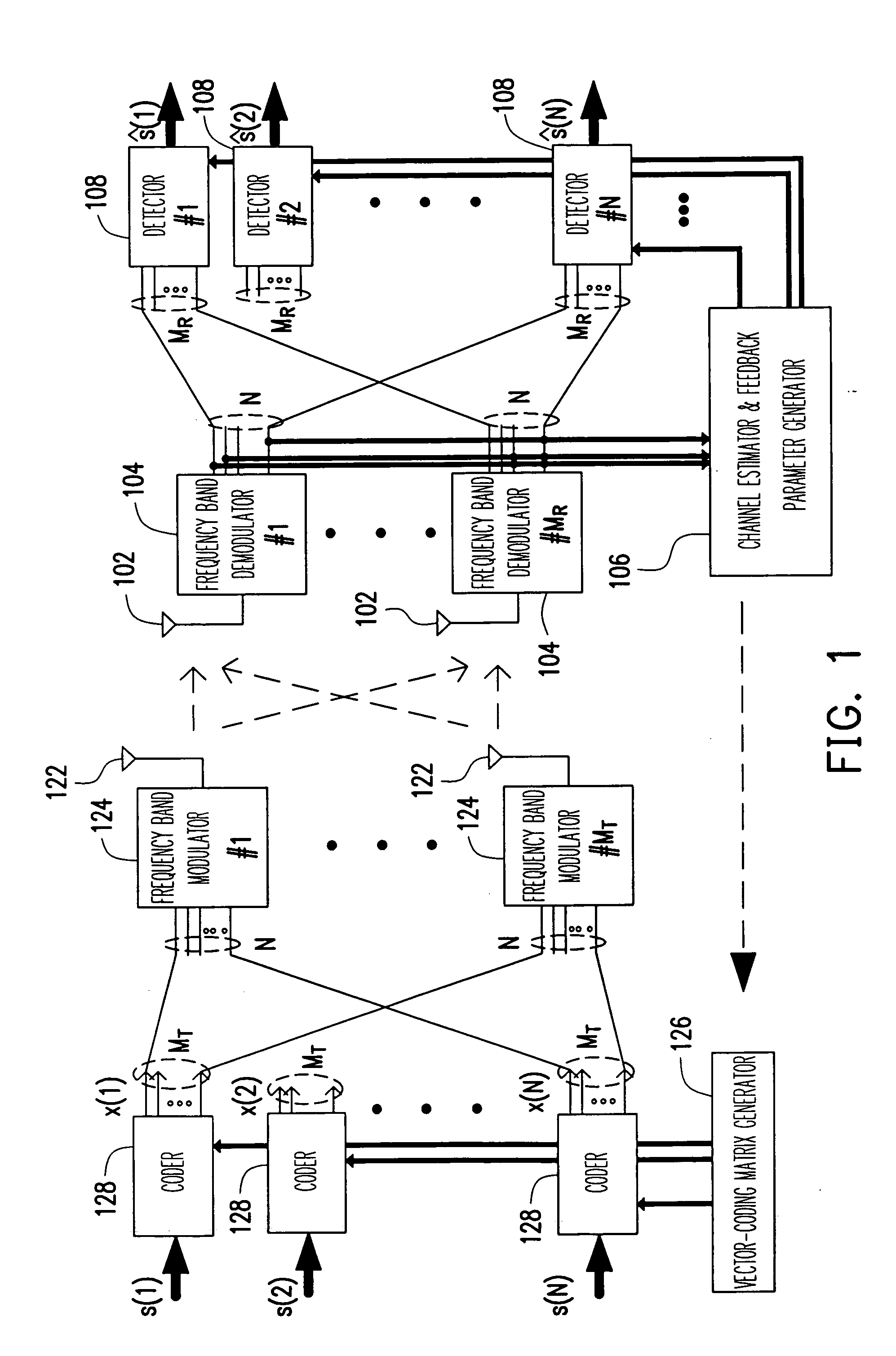
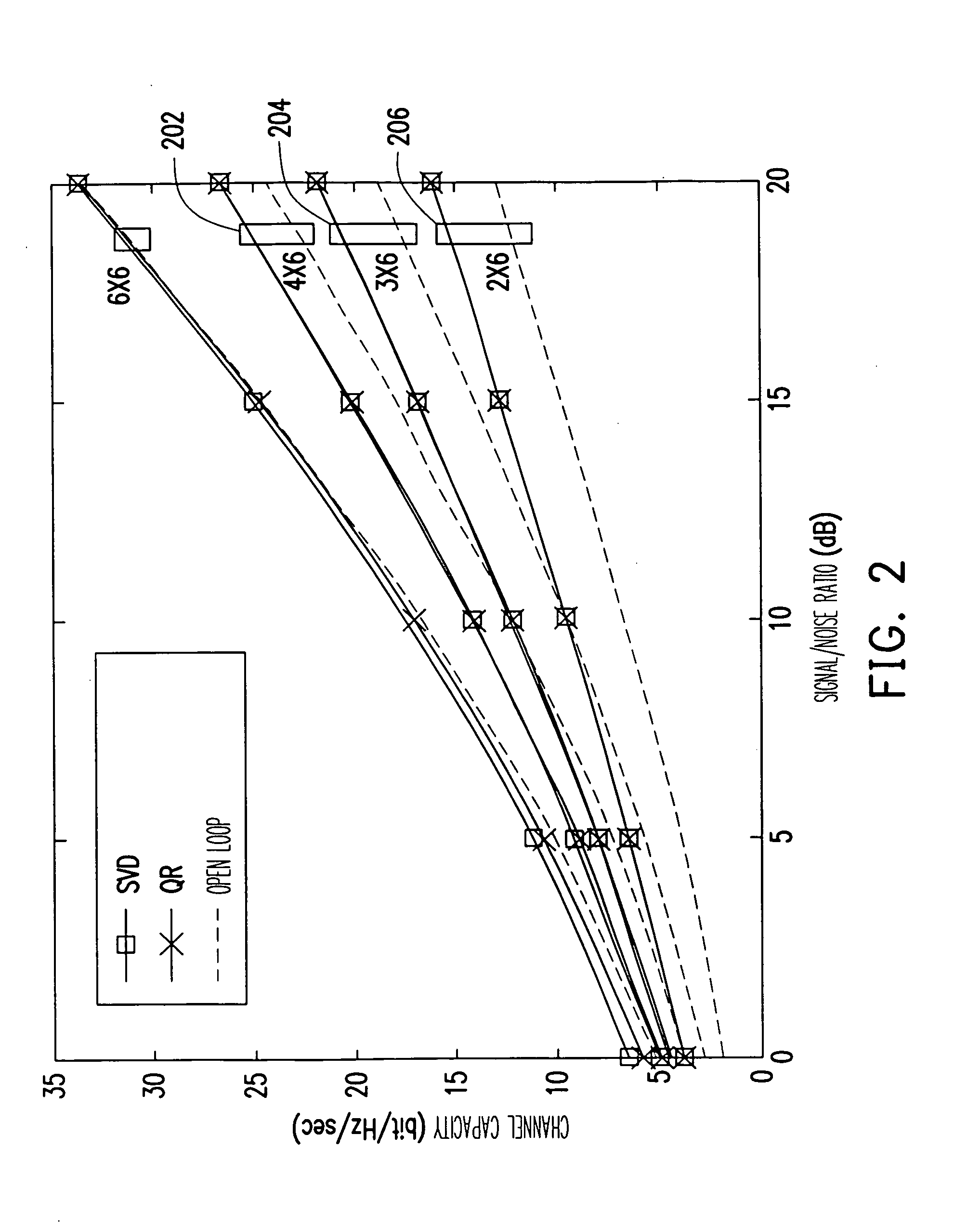
Method and apparatus for providing closed-loop transmit precoding
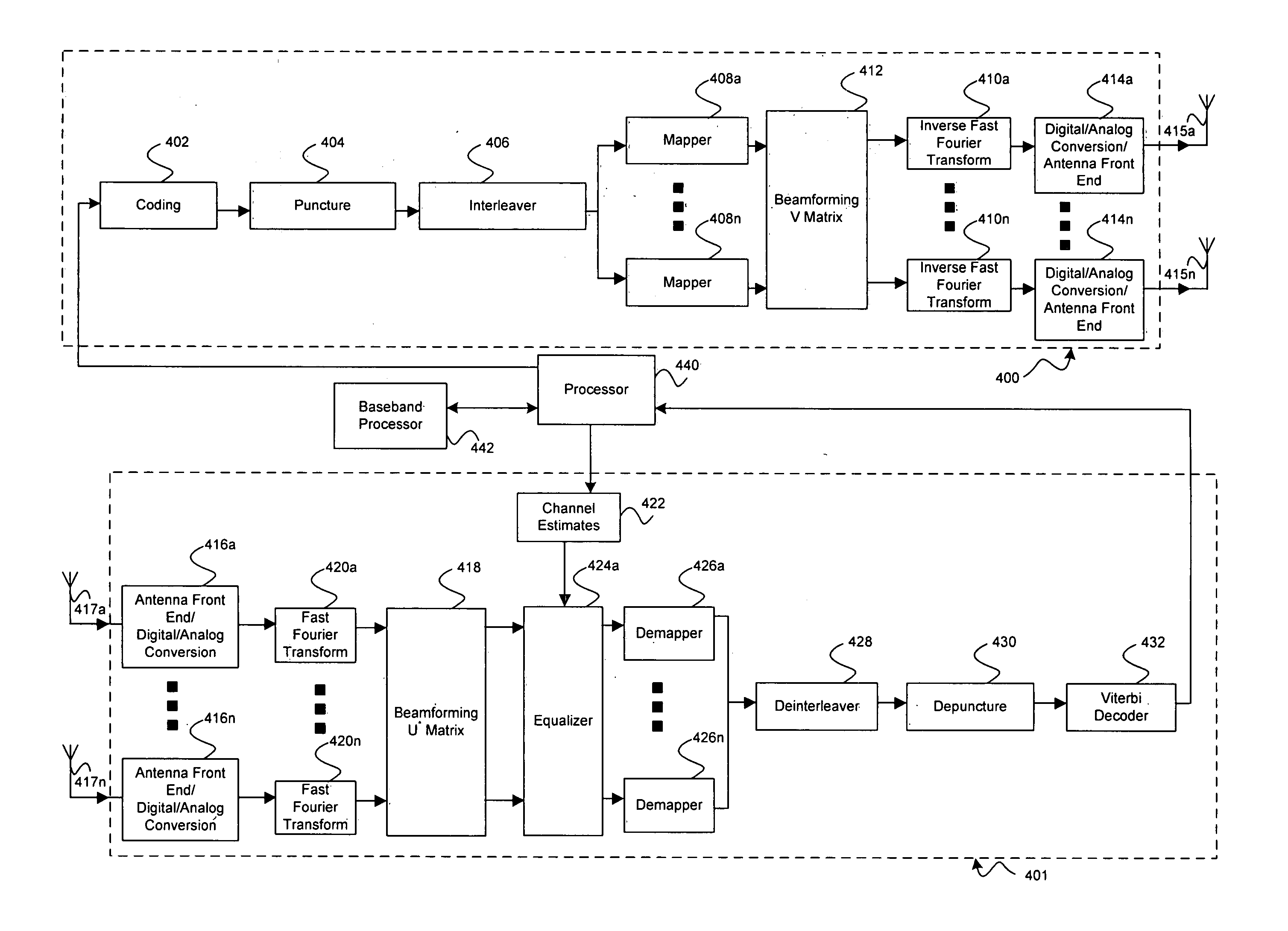
A method for providing closed-loop transmit precoding between a transmitter and a receiver, includes defining a codebook that includes a set of unitary rotation matrices. The receiver determines which preceding rotation matrix from the codebook should be used for each sub-carrier that has been received. The receiver sends an index to the transmitter, where the transmitter reconstructs the precoding rotation matrix using the index, and precodes the symbols to be transmitted using the preceding rotation matrix. An apparatus that employs this closed-loop technique is also described.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
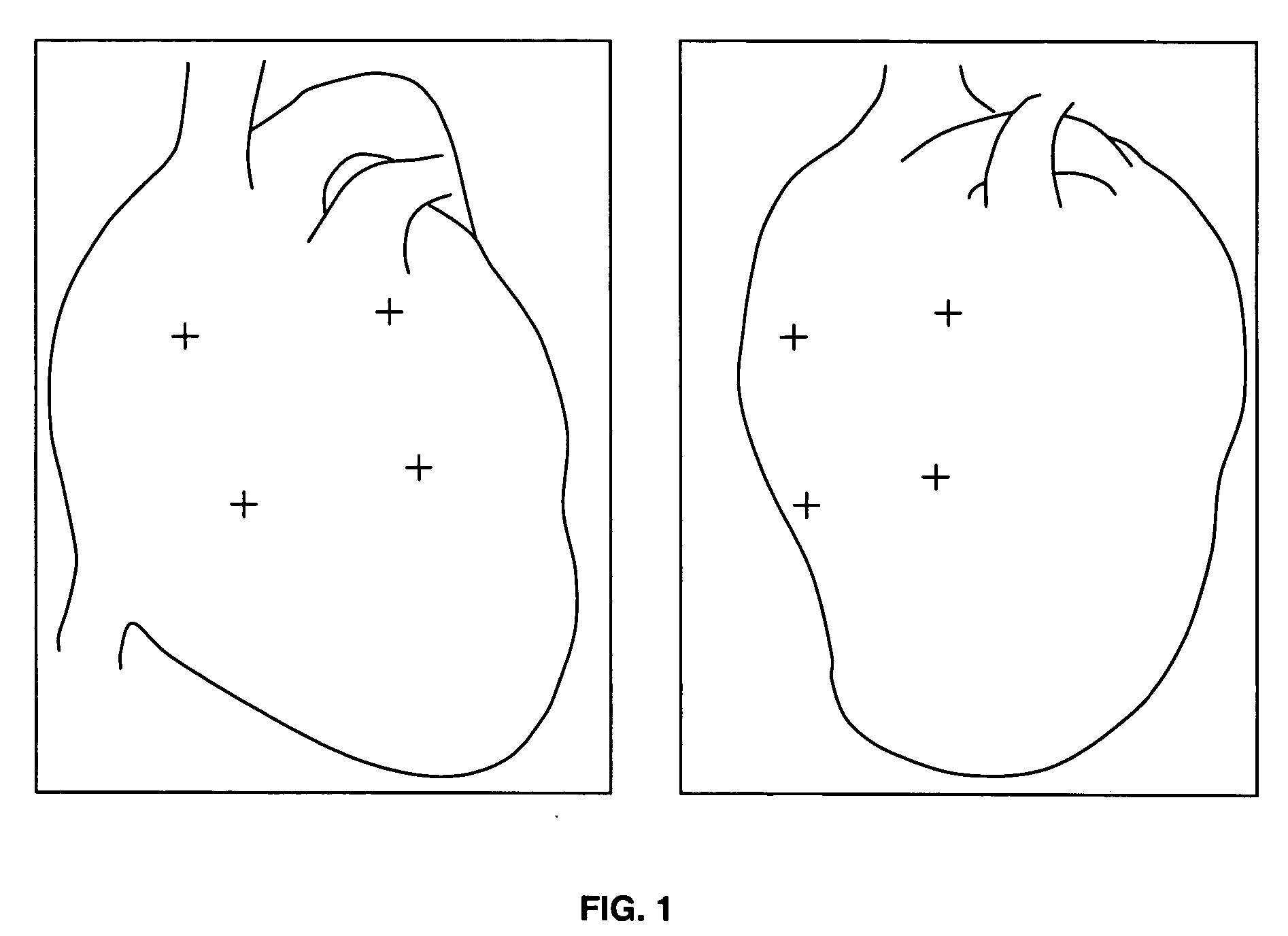
Method for surgical navigation utilizing scale-invariant registration between a navigation system and a localization system
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Method for surgical navigation utilizing scale-invariant registration between a navigation system and a localization system
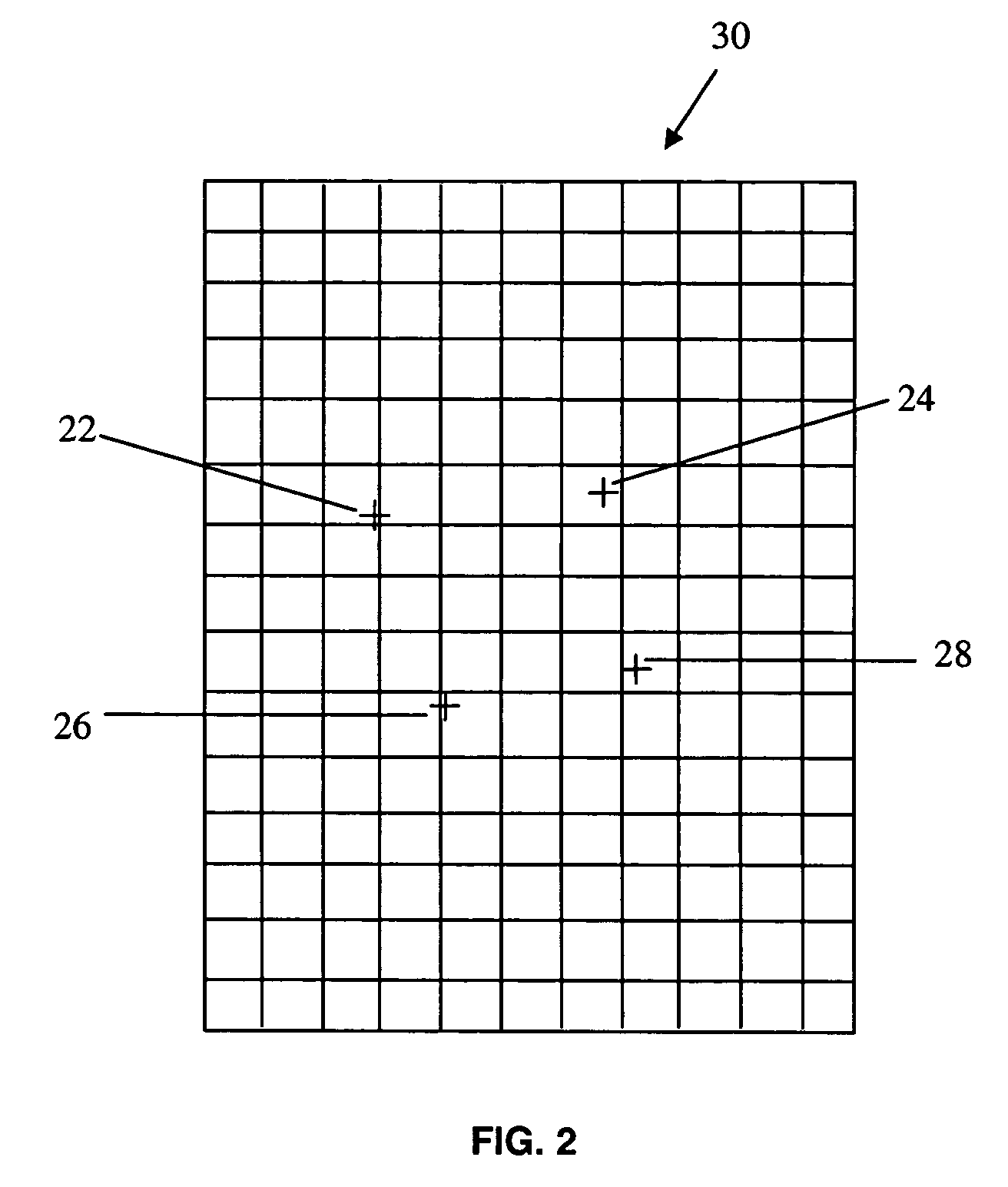
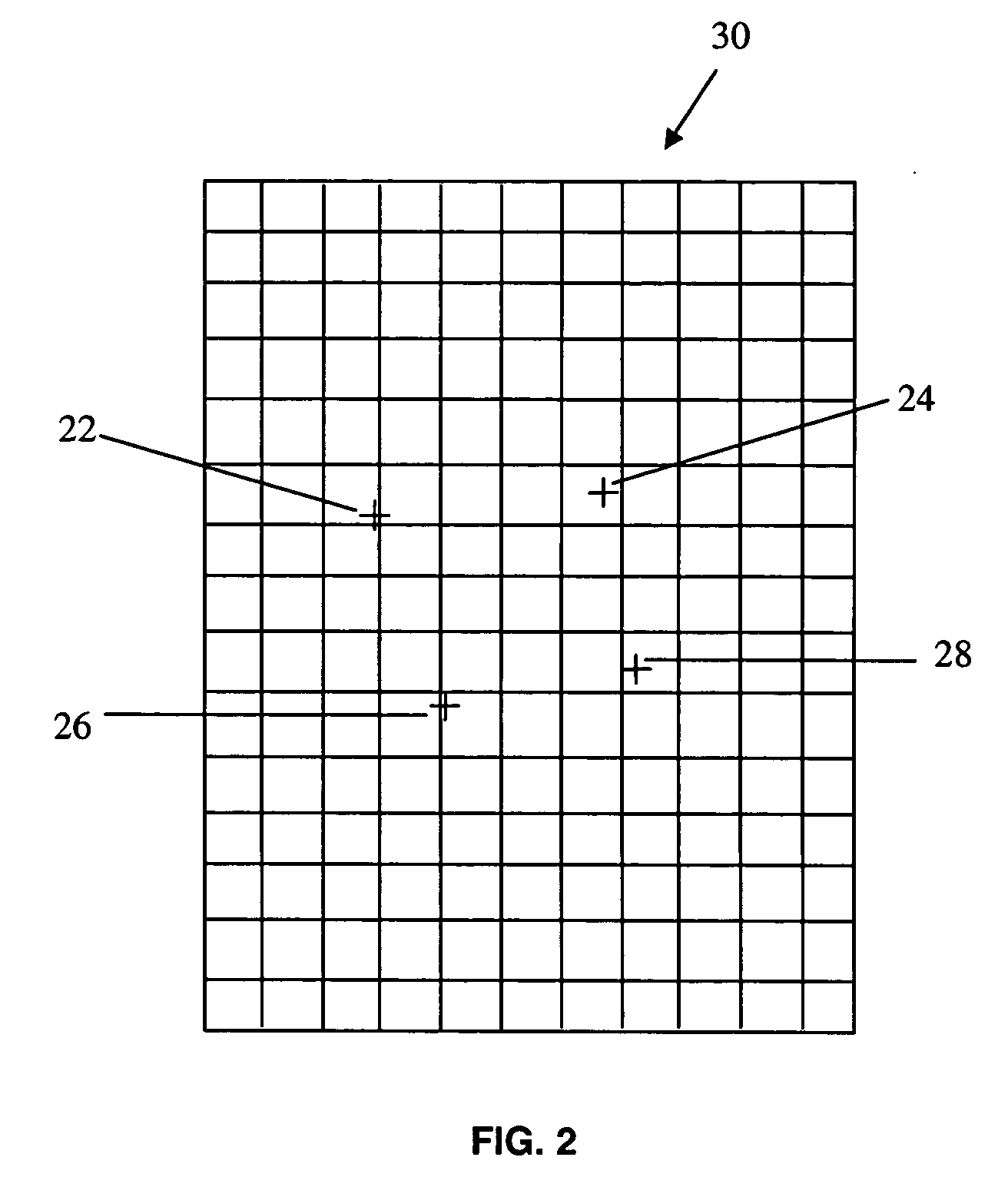
ActiveUS20060058646A1Precise NavigationAccurate operationImage analysisCatheterLocalization systemDisplay device
A system for navigating a medical device through the lumens and cavities in an operating region in a subject, comprising an imaging system for displaying an image of the operating region, including a representation of the distal end of the medical device in the operating region. The system also includes a localization system for determining the position of the medical device in a frame of reference translatable to the displayed image. Finally, the system includes an algorithm for evaluating one or more rotation matrix using a cost function to determine an optimum rotation matrix for performing transformation of a vector in the local frame of the localization system to that of the reference frame of the navigation system. The rotation matrix can then provide a scale invariant transformation or “registration” of the coordinate systems of the localization system and the navigation system. This allows navigation to be performed to a significant extent from the localization system display alone, which avoids the frequent x-ray irradiation that occurs during the use of fluoro imaging for navigation purposes.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
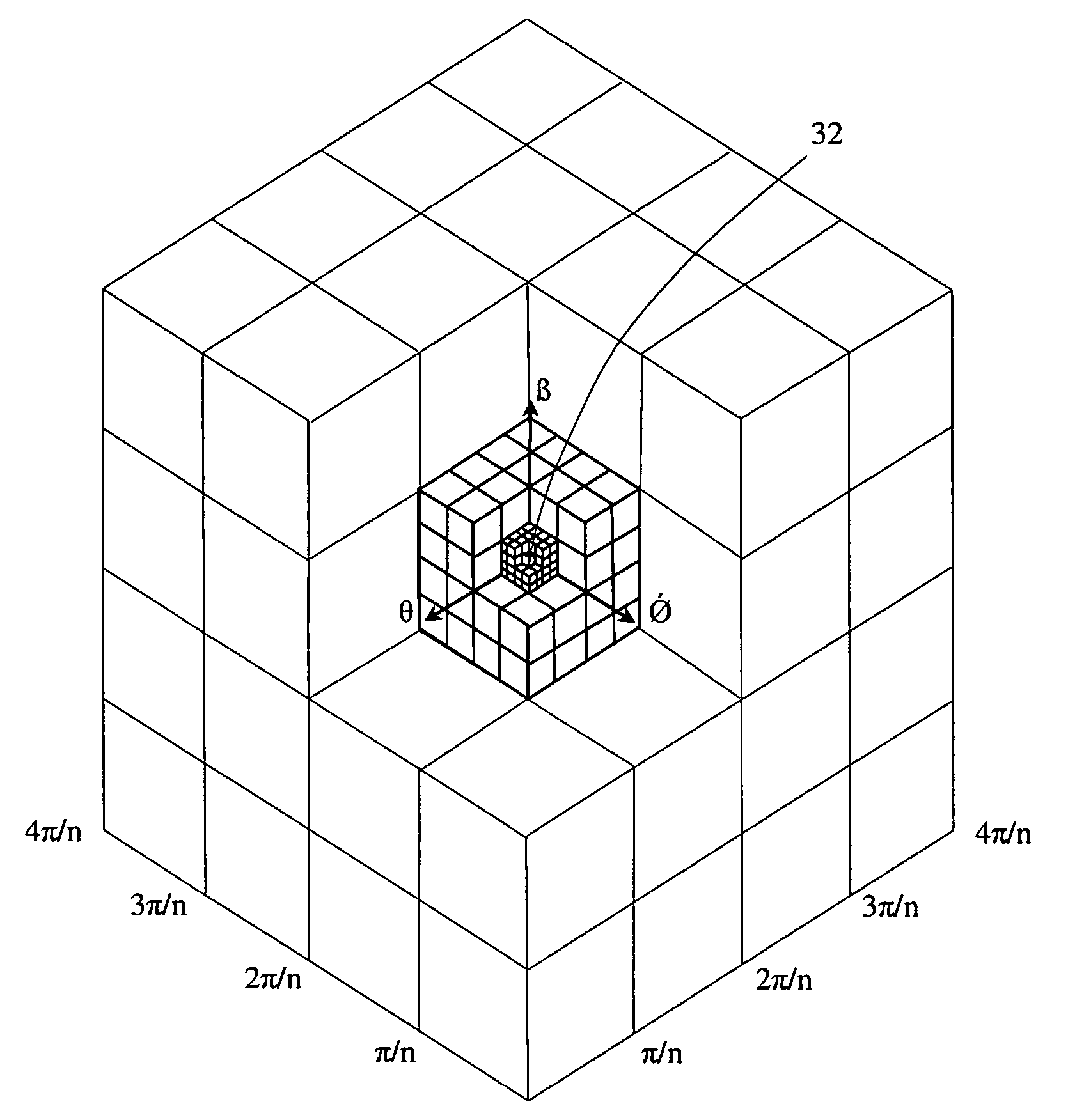
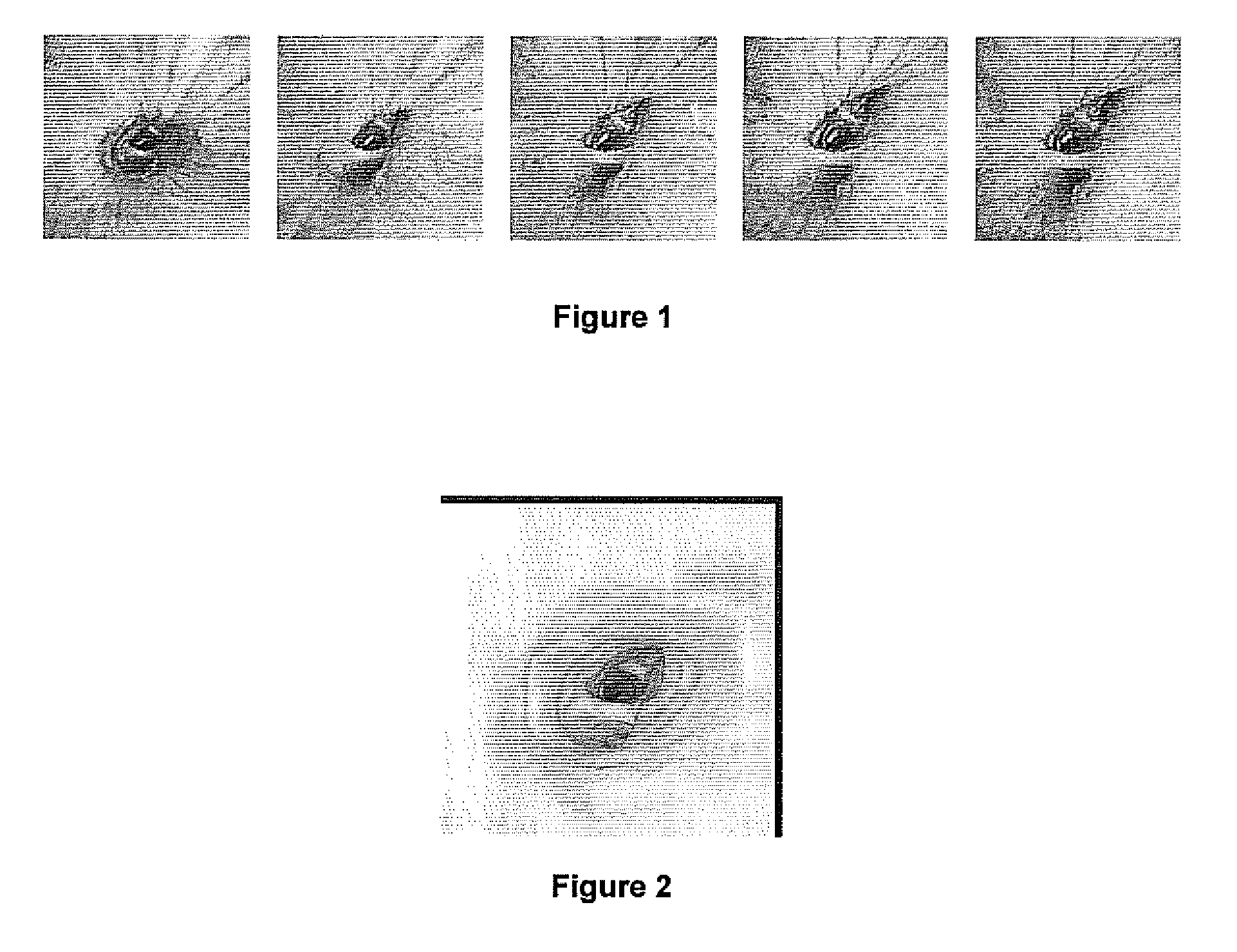
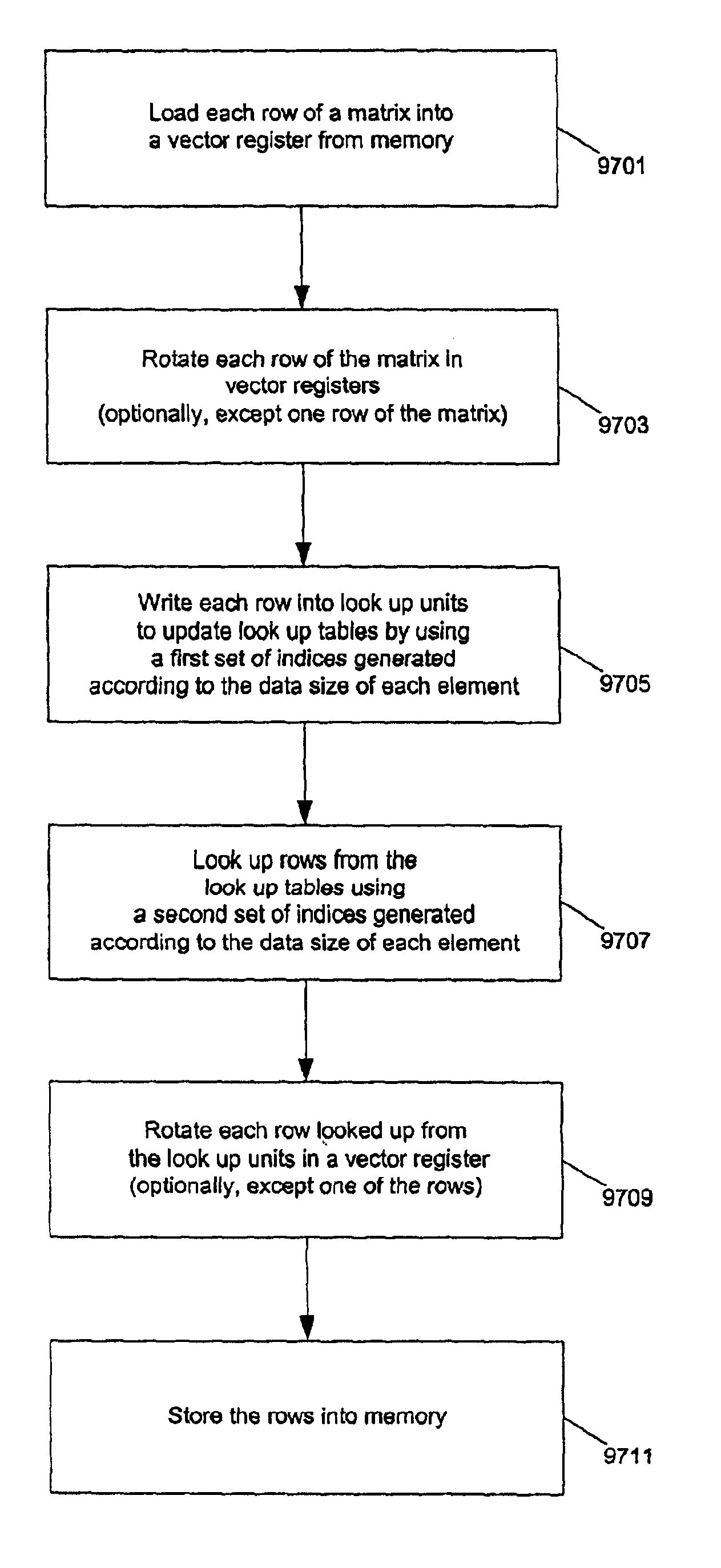
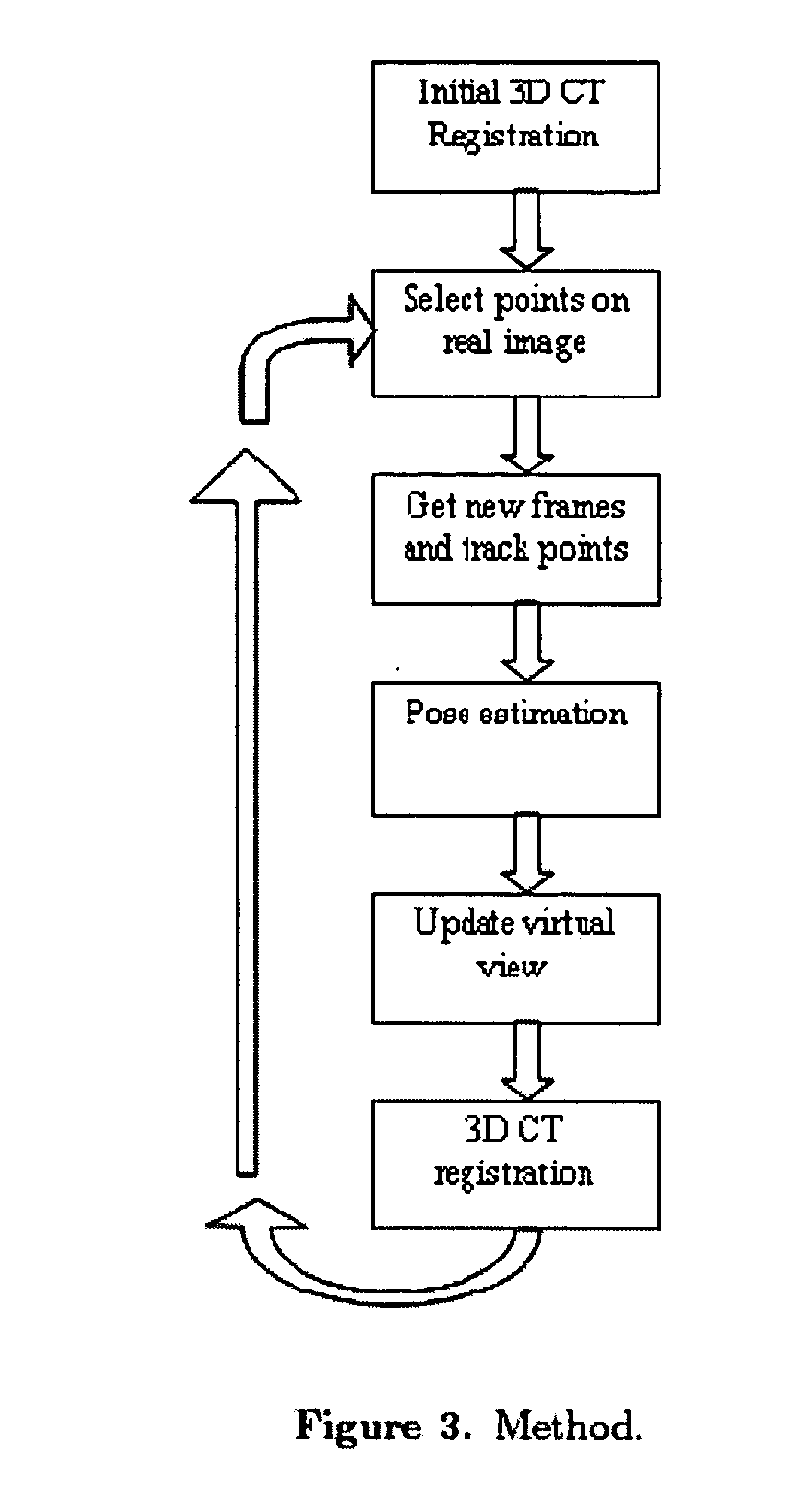
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS7756563B2Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for matrix transposition
InactiveUS6877020B1Handling data according to predetermined rulesComplex mathematical operationsComputer scienceRotation matrix
Owner:APPLE INC
Joint measurement method based on laser radar and binocular visible light camera
ActiveCN108828606AAccurate locationIncrease workloadPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryElectromagnetic wave reradiationBinocular stereoVisual perception
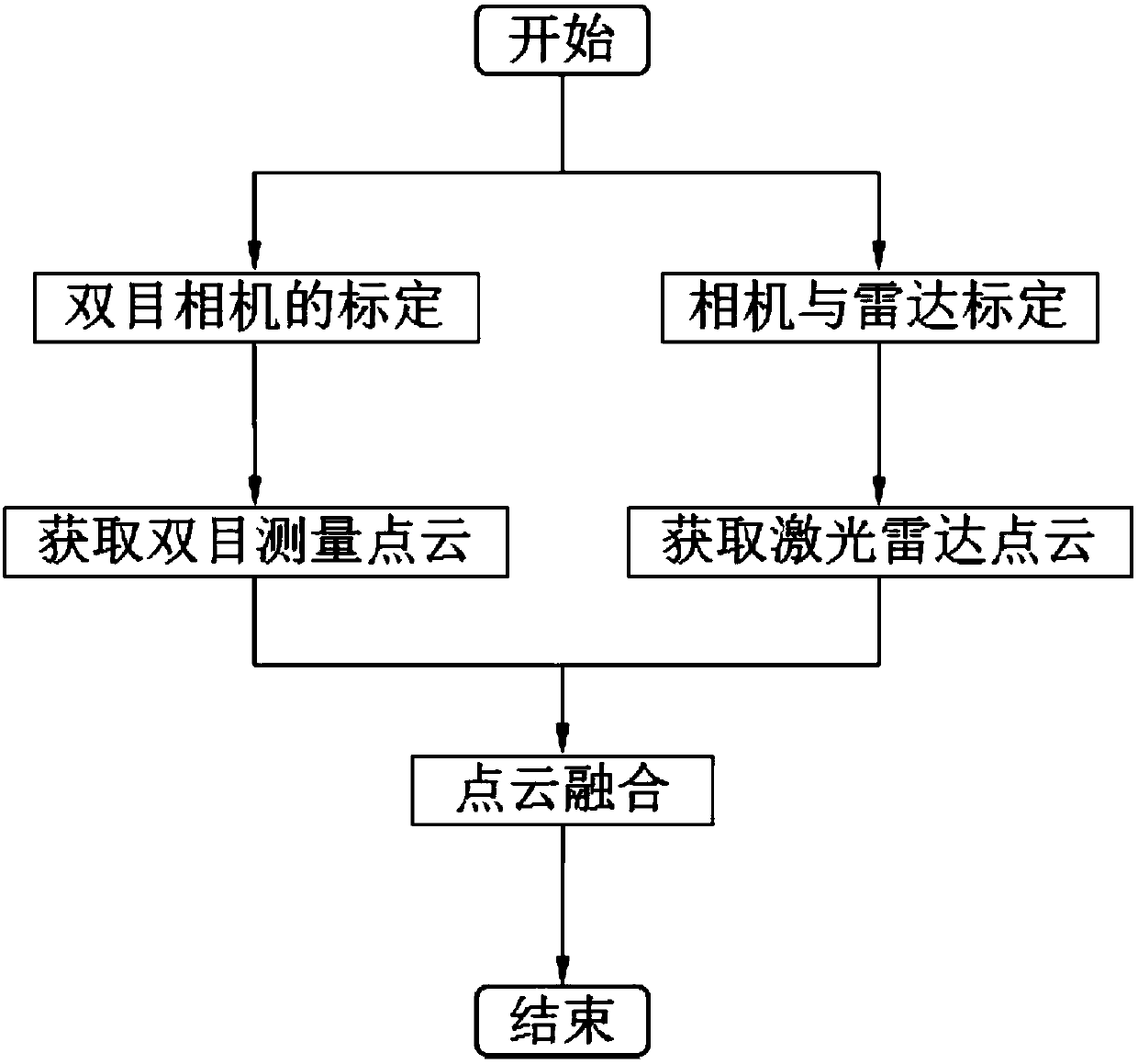
The invention provides a joint measurement method based on a laser radar and a binocular visible light camera to obtain accurate and dense three-dimensional information simply and efficiently. The joint measurement method comprises assuming that the laser radar is a camera device with a fixed internal reference; directly projecting three-dimensional point cloud data into a two-dimensional image, calculating rotation and translation relationships between the laser radar device and the binocular camera by using an image processing method and the matching between the two-dimensional images; creatively introducing an idea for obtaining a matrix norm and a matrix trace to solve a rotation matrix; finally fusing laser radar and binocular stereo vision point cloud data. The method not only can obtain an accurate position and attitude information, but also can reconstruct the special texture and feature information of a target surface, which has a high application value for spacecraft dockingand hostile satellite capture in the military field and workpiece measurement and unmanned driving in the civilian field.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information
ActiveUS20070160011A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFormation matrixSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Aspects of a method and system for utilizing Givens rotation expressions for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information. In one aspect of the invention, feedback information is computed at the receiving MIMO wireless device based on a geometric mean decomposition (GMD) method. The feedback information may include a matrix that describes a wireless medium. The matrix may represent a multiplicative product of at least one rotation matrix and at least one diagonal phase rotation matrix. Each of the rotation matrices may include at least one matrix element whose value is based on Givens rotation angle. The transmitting MIMO wireless device may subsequently transmit a plurality of signals via the wireless medium based on the received matrix information. The signal strength and / or signal to noise ratio (SNR) measurement (as measured in decibels, for example) associated with each of the transmitted plurality of signals may be about equal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Camera-based inertial sensor alignment for pnd
An apparatus and method to enhance dead-reckoning navigation using inertial sensor measurements based on images from a camera are disclosed. A camera build into a mobile device is used to calibrate inertial sensors and rotation matrices. Images from a camera may be used (1) to remove a gravitational element from accelerometer measurements; (2) to set a scaling factor and an offset for a gyrometer; and (3) to set initial and updated values for rotation matrices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for utilizing givens rotation expressions for asymmetric beamforming matrices in explicit feedback information
Aspects of a method and system for utilizing Givens rotation expressions for asymmetric beamforming matrices in explicit feedback information are presented. In one aspect of the invention, Givens matrices may be utilized to reduce a quantity of information communicated in explicit feedback information via an uplink RF channel. The explicit feedback information may include specifications for a feedback beamforming matrix that may be utilized when transmitting signals via a corresponding downlink RF channel. The feedback beamforming matrix may represent a rotated version of an un-rotated matrix. The Givens matrices may be utilized to apply one or more Givens rotations to un-rotated matrix. The feedback beamforming matrix may be computed based on a matrix product of a plurality of Givens matrices. The feedback beamforming matrix may be encoded utilizing fewer bits than may be required to encode the un-rotated matrix.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Three-dimensional rebuilding method based on laser and camera data fusion
InactiveCN101581575AReal-time acquisitionReduce mistakesPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryUsing optical meansPoint cloudRadar
A three-dimensional rebuilding method based on laser and camera data fusion is characterized in that the rebuilding method comprises the following steps: (1) a C++ language is adopted to compile a laser data automatic collecting platform based on a radar principle; (2) a rotation matrix R and a translation vector T are arranged between a camera coordinate system and a laser coordinate system; (3) a motion object is extracted and subdivided by utilizing an optical flow field region merging algorithm, thus further subdividing the point cloud corresponding to the motion object; and (4) guarantee of point cloud and image texture on the precise positioning is provided for the three-dimensional image texture mapping, thus realizing the three-dimensional rebuilding system based on data fusion. The three-dimensional rebuilding method has the advantages of quickly and automatically collecting and processing laser data, quickly completing the external labeling of the laser and CCD, effectively extracting and subdividing effective point clouds of the object in complex environment and exactly completing the three-dimensional rebuilding of the laser and CCD data of the object.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method and device for pre-coding in multiple input multiple output system
InactiveUS20100266061A1Effectively settlingReduce in quantityModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCarrier signalEngineering
A signal processing method in an MIMO multi-carrier system is disclosed comprising: receiving by a receiver signals of a plurality of sub-carriers transmitted from a transmitter; dividing the sub-carriers into a plurality of sub-carrier blocks according to the correlation between adjacent sub-carriers, each sub-carrier block containing K sub-carriers; selecting a feedback sub-carrier pre-coding matrix ( ) and a rotation matrix ( ) for each sub-carrier block, and then sending the information on the pre-coding matrix and the rotation matrix back to the transmitting end. The present invention provides the method and device for effectively settling the feedback problem in an MIMO / OFDMA system, thereby greatly reducing the number of pre-coding weight matrices needed to feed back to the transmitting device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
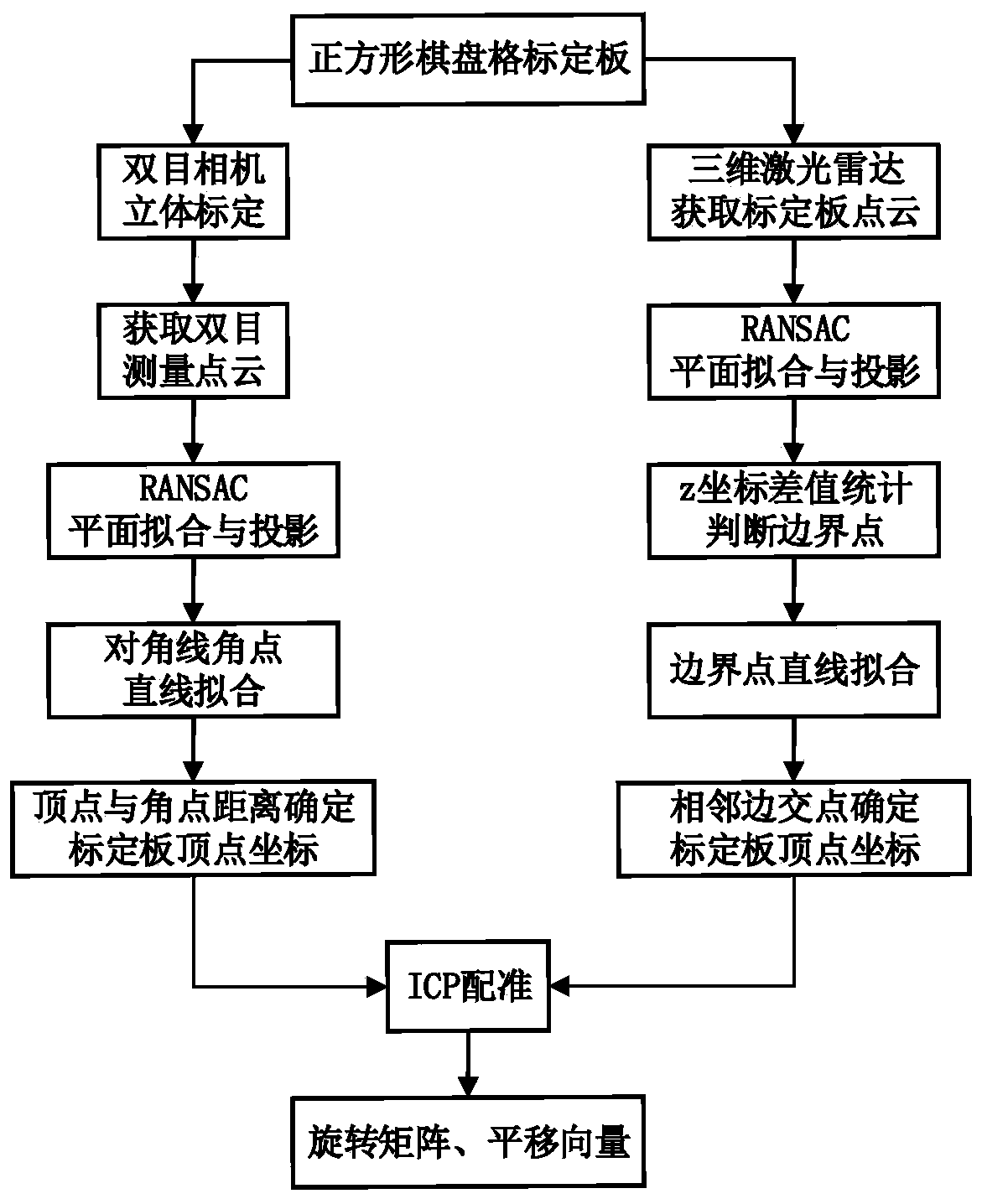
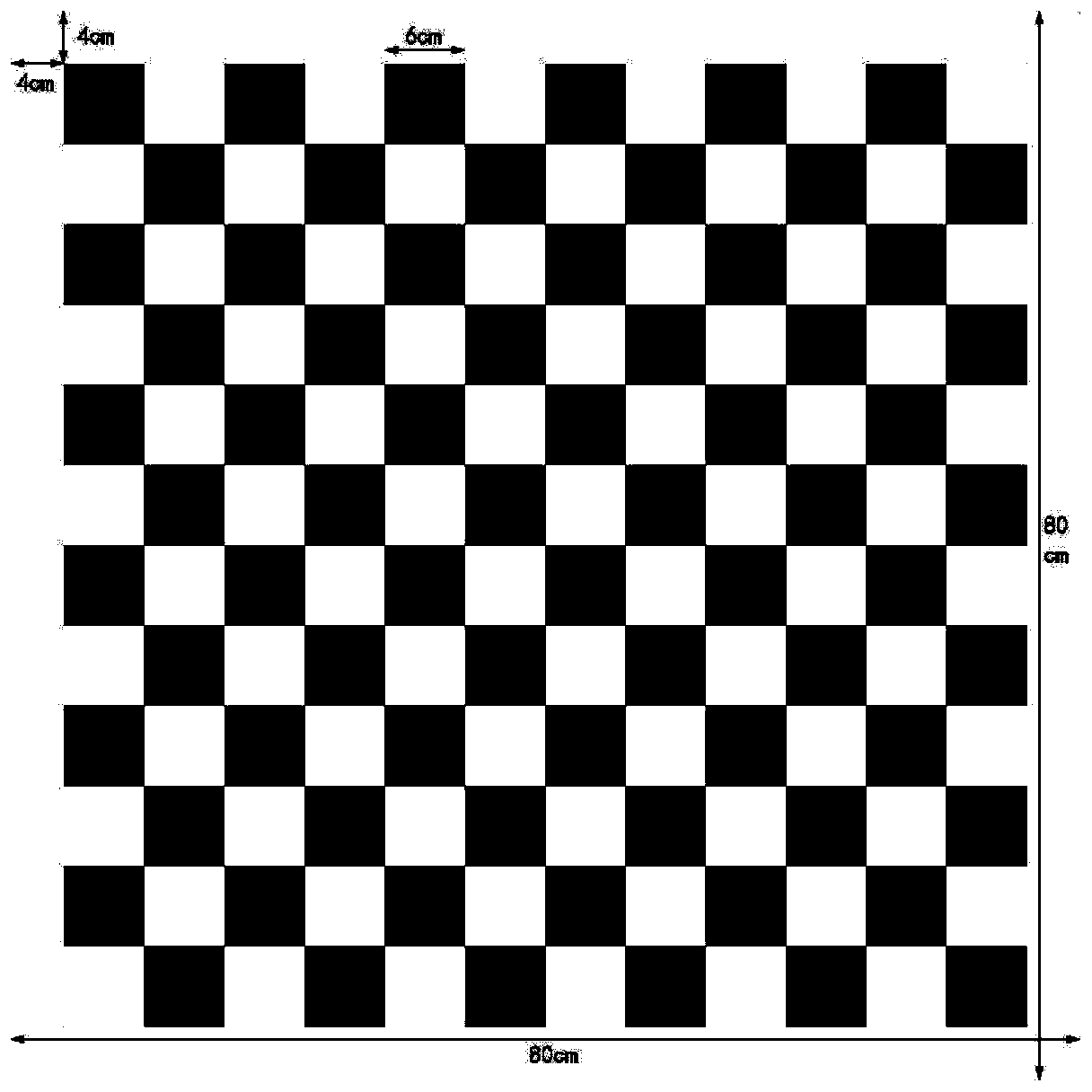
Fusion calibration method of three-dimensional laser radar and binocular visible light sensor
The invention discloses a fusion calibration method of a three-dimensional laser radar and a binocular visible light sensor. According to the invention, the laser radar and the binocular visible lightsensor are used to obtain the three-dimensional coordinates of the plane vertex of the square calibration plate, and then registration is carried out to obtain the conversion relation of the two coordinate systems. In the calibration process, an RANSAC algorithm is adopted to carry out plane fitting on the point cloud of the calibration plate, and the point cloud is projected to a fitting plane,so that the influence of measurement errors on vertex coordinate calculation is reduced. For the binocular camera, the vertex of the calibration plate is obtained by adopting an angular point diagonalfitting method; for the laser radar, a distance difference statistical method is adopted to judge boundary points of the point cloud on the calibration board. By utilizing the obtained vertex coordinates of the calibration plate, fusion calibration can be accurately carried out on the three-dimensional laser radar and the binocular visible light sensor, a rotation matrix and a translation vectorof coordinate systems of the three-dimensional laser radar and the binocular visible light sensor are obtained, and a foundation is laid for realizing data fusion of three-dimensional point cloud anda two-dimensional visible light image.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
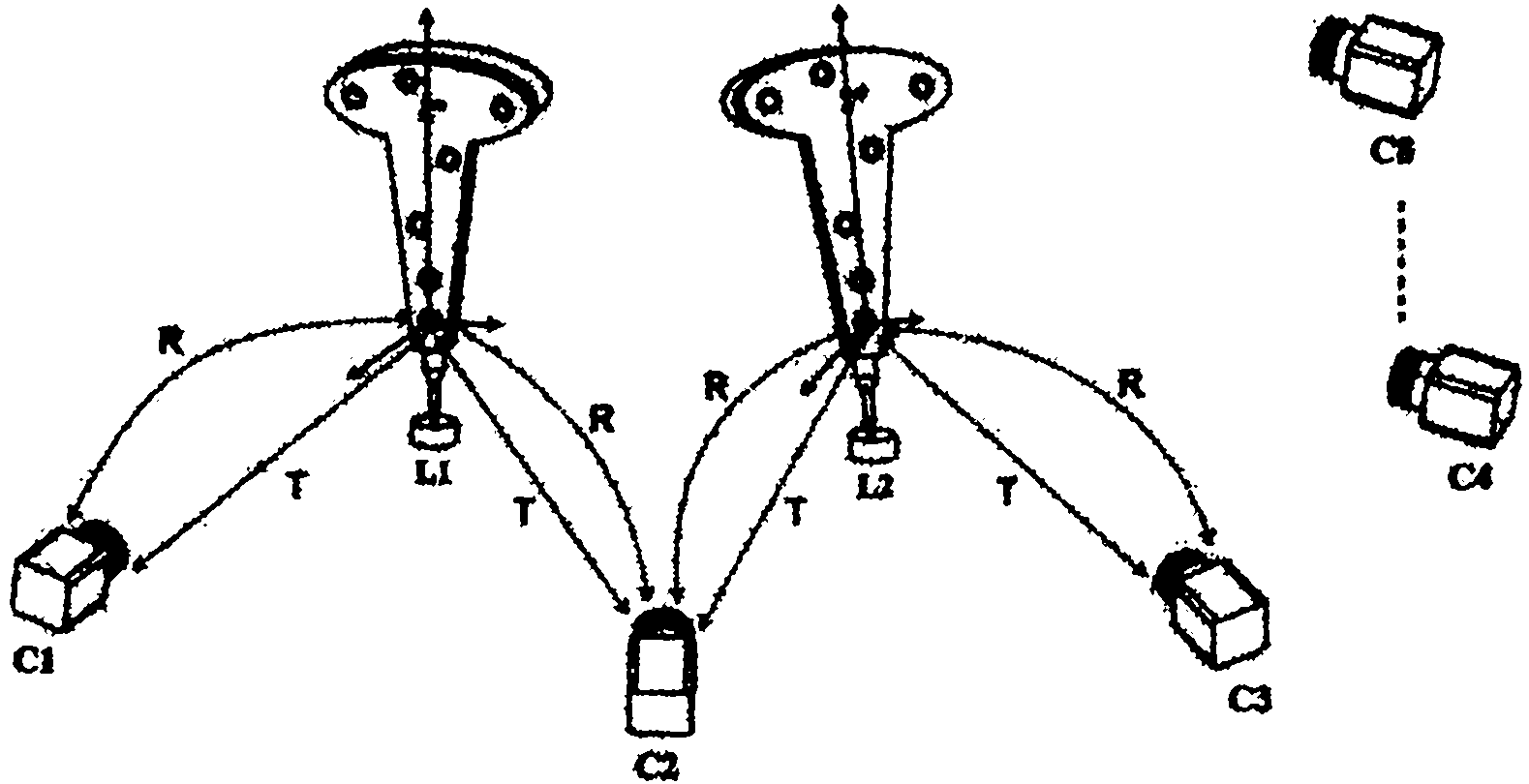
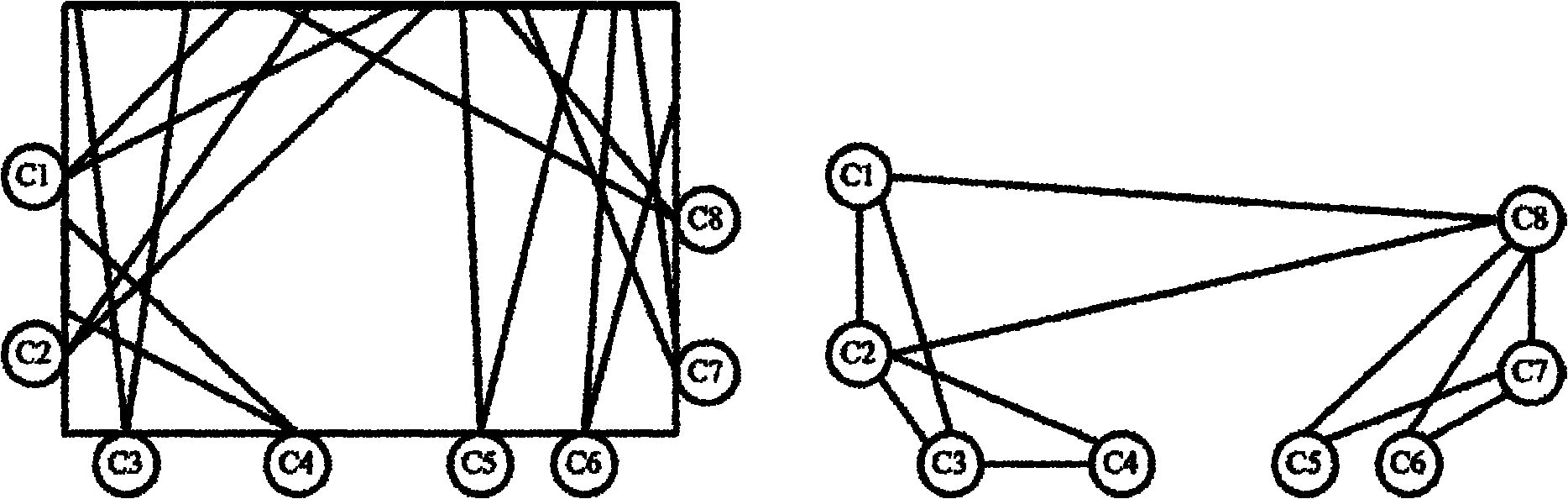
Multi-camera system calibrating method based on optical imaging test head and visual graph structure
ActiveCN102034238AHigh precisionImprove robustnessImage analysisStereoscopic photographyEssential matrixMulti camera
The invention provides a multi-camera system calibrating method based on an optical imaging test head and a visual graph structure. The method comprises the following steps: independently calibrating each camera by the optical imaging test head to obtain the initial values of the internal parameter and aberration parameter of each camera; calibrating the multiple cameras two by two, and obtaining the fundamental matrix, polar constraint, rotation matrix and translation vector between every two cameras with a plurality of overlapped regions at a view field by means of linear estimation; building the connection relationship among the multiple cameras according to the graph theory and the visual graph structure, and estimating the rotation vector quantity initial value and translation vector quantity initial value of each camera relative to the referred cameras by a shortest path method; and optimally estimating all the internal parameters and external parameters of the all cameras and the acquired three-dimensional sign point set of the optical imaging test head by a sparse bundling and adjusting algorithm to obtain a high-precision calibrating result. The multi-camera system calibrating method is simple in a calibrating process from the partial situation to the overall situation and from the robust to the precise, ensures high-precise and robust calibration, and is applied to calibrating multi-camera systems with different measurement ranges and different distribution structures.
Owner:SUZHOU DEKA TESTING TECH CO LTD
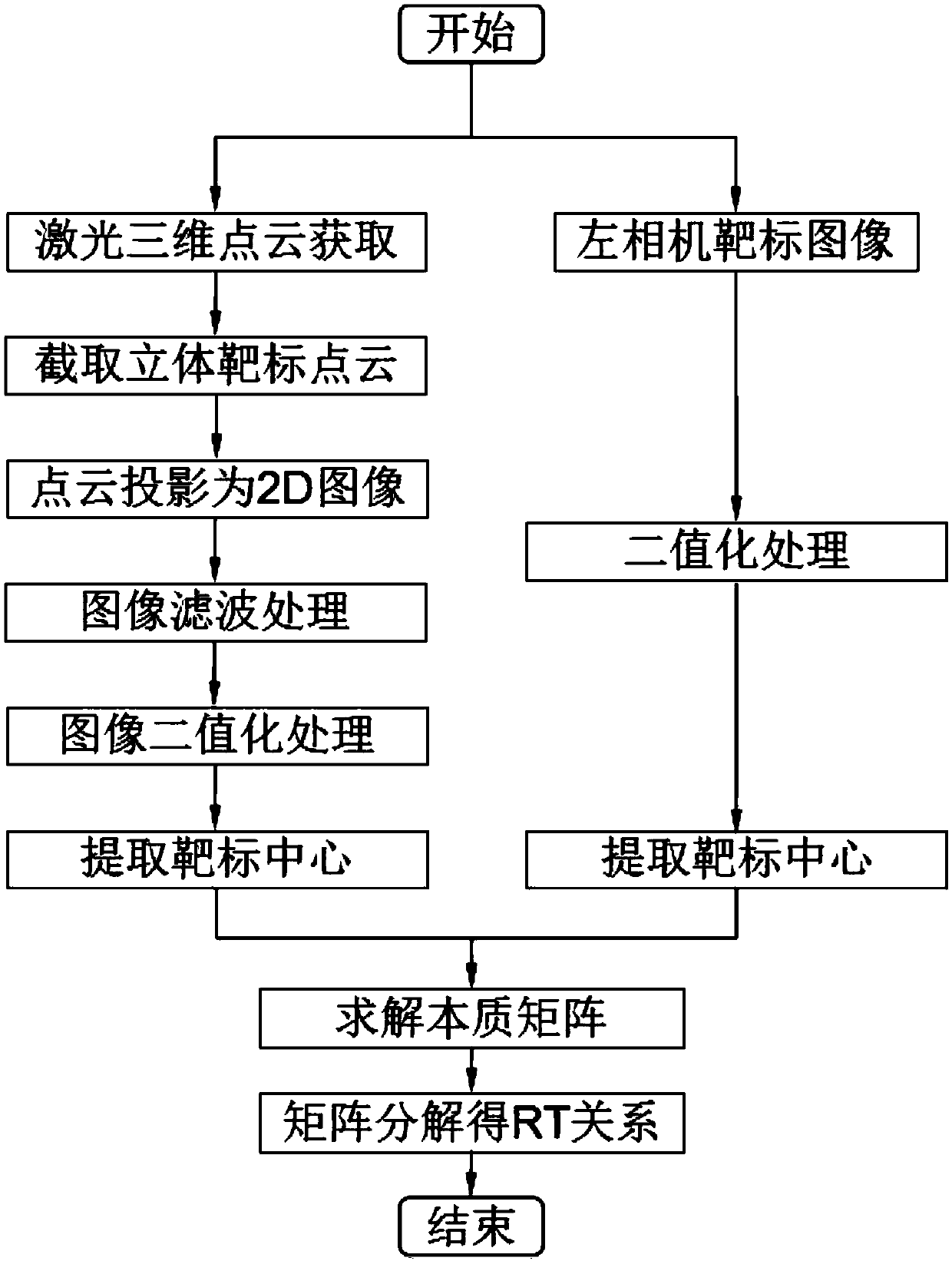
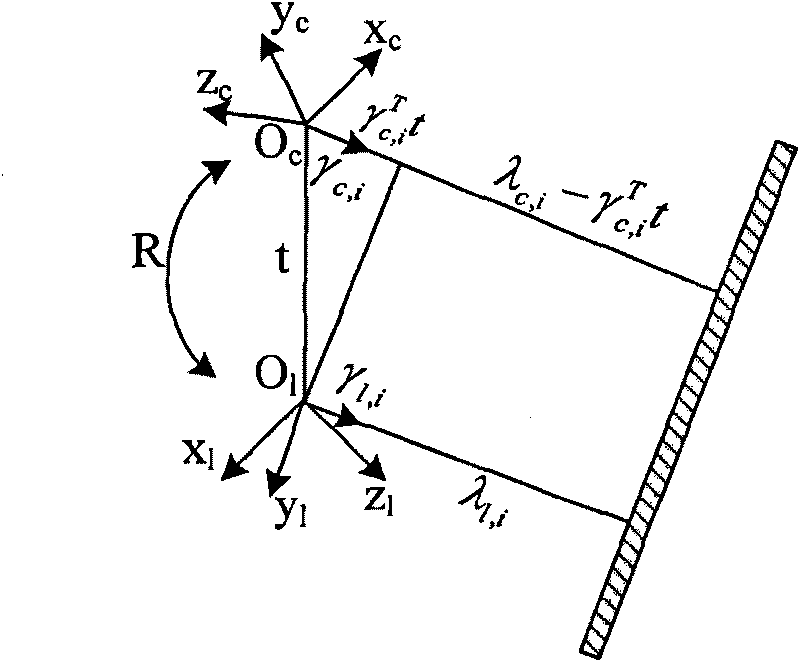
Method and system for calibrating external parameters based on camera and three-dimensional laser radar
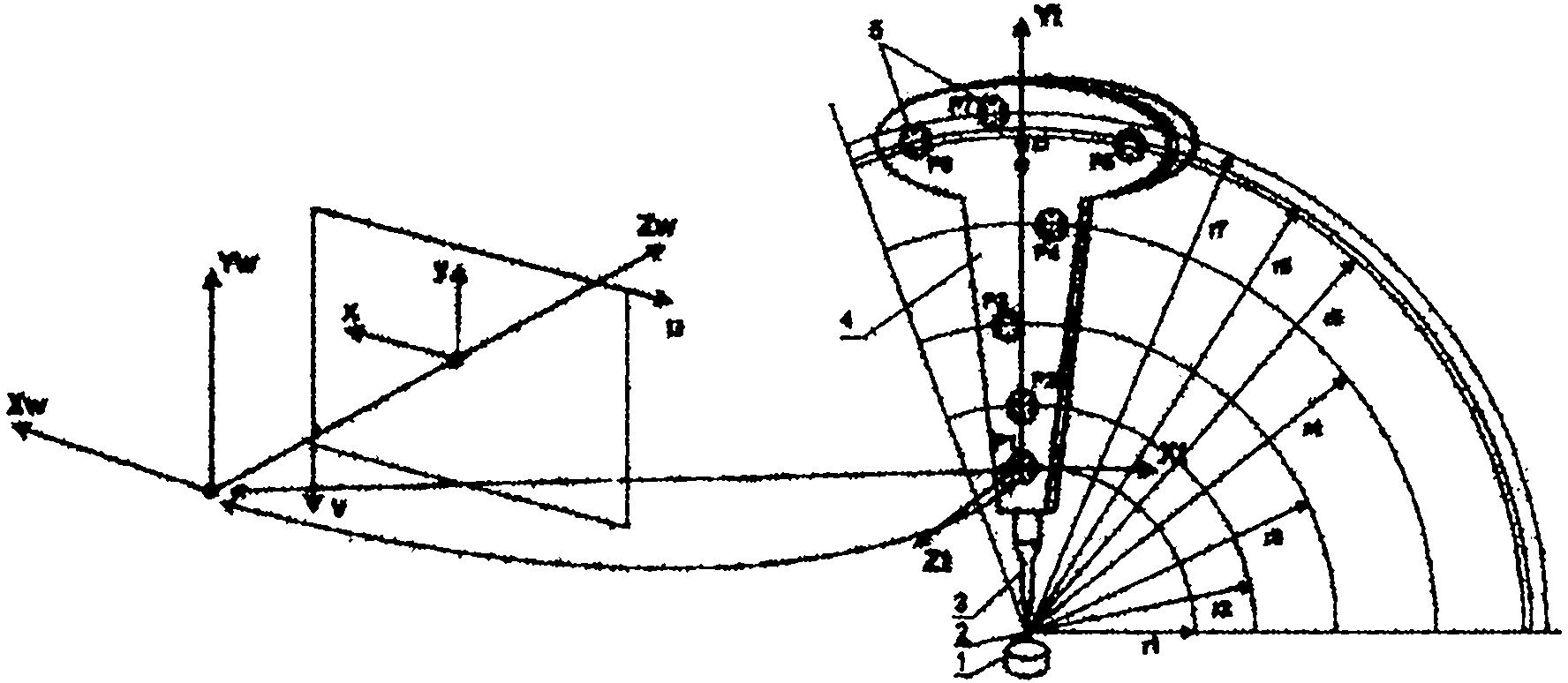
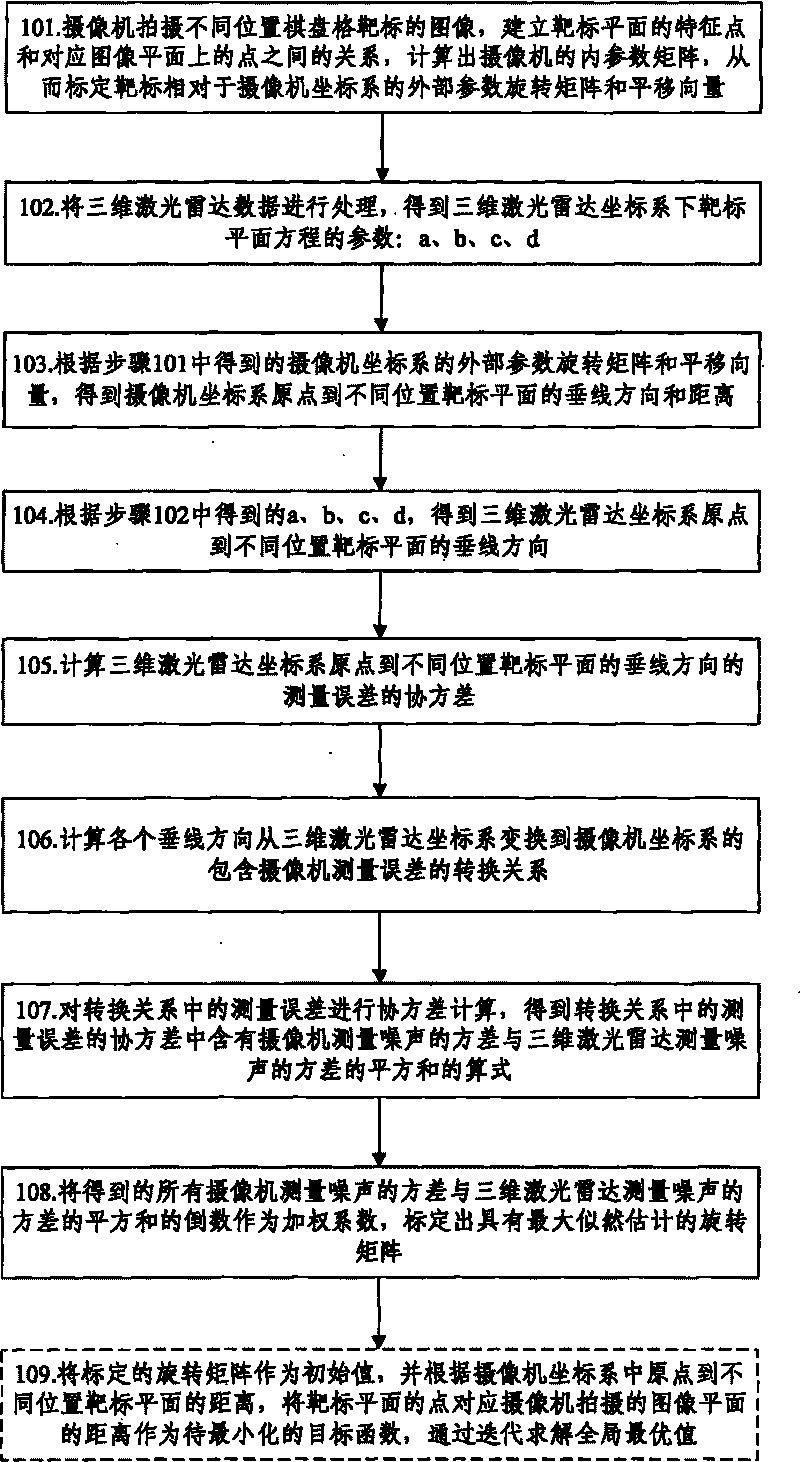
InactiveCN101699313AImprove accuracyThe result is accurateImage analysisWave based measurement systemsObservational errorClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for calibrating external parameters based on a camera and a three-dimensional laser radar, which comprises the following steps: according to a covariance of measurement errors in the perpendicular line direction from a three-dimensional laser radar coordinate system origin to different position target planes and a covariance of measurement errors in a conversion relationship from a three-dimensional laser radar coordinate system to a camera coordinate system in the perpendicular line direction, acquiring an equation of a quadratic sum of the variance including the variance of the camera measurement noise and the variance of the three-dimensional laser radar measurement noise in the covariance of the measurement errors in the conversion relationship; and calibrating a rotation matrix with maximum likelihood estimate by using the reciprocal of the quadratic sum of the variances of all obtained measurement noise as a weighting coefficient. The invention also discloses a system for calibrating the external parameters based on the camera and the three-dimensional laser radar at the same time. The effect of the measurement errors on the rotation matrix to be calibrated is taken into consideration during calibrating, and the algorithm of the maximum likelihood estimate is adopted for the measurement errors in the calibrated result of the rotation matrix, so the calibrating result is more accurate.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
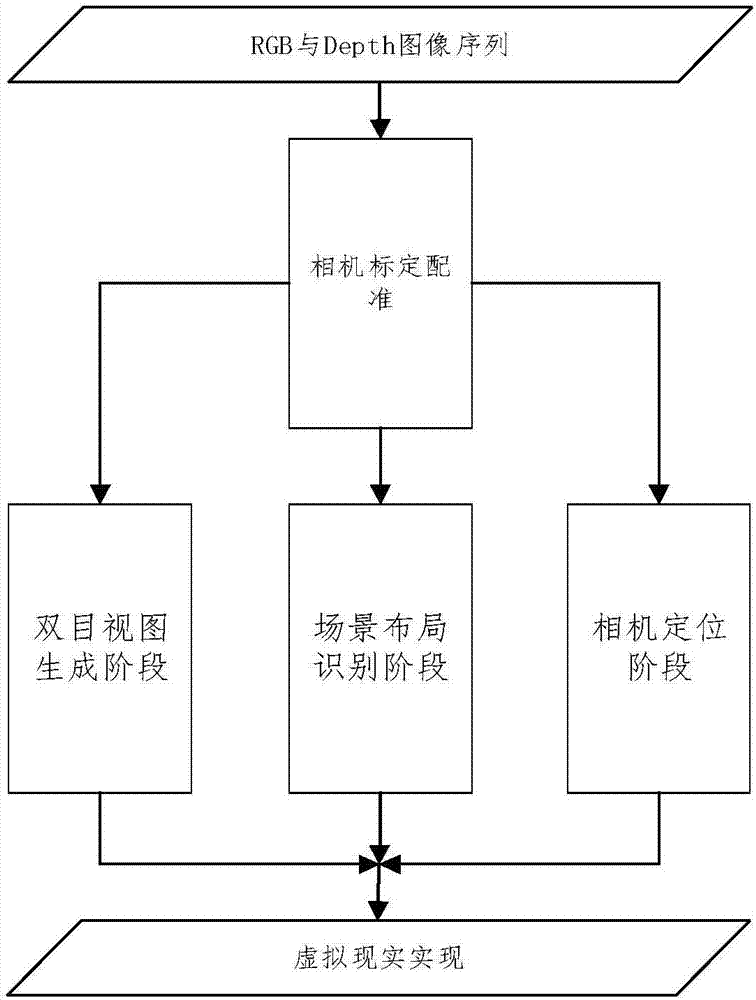
Virtual reality realization method based on augmented reality
InactiveCN107016704AEasy retrievalEasy to understandInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementThree-dimensional spaceComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a virtual reality realization method based on the augmented reality. The method includes: 1) acquiring a depth image sequence and a RGB sequence of a scene through a camera; 2) generating a RGBD four-channel image sequence of the scene according to the acquired depth image sequence and the RGB sequence; 3) calculating a rotation matrix and a translation vector of the camera between two frames according to the RGBD, recognizing a target object and a planar structure in the scene and position information thereof in the three-dimensional space from the RGBD of the scene, and converting the RGBD to a binocular view sequence; and 4) presenting the binocular view sequence on a screen of the camera, drawing a virtual three-dimensional model of the target object in the scene according to the position information of the planar structure in the three-dimensional space in the scene, transforming the virtual three-dimensional model according to the rotation matrix and the translation vector of the camera, and enabling the virtual three-dimensional model and the attached planar structure to be relatively static. According to the method, the image to be presented can be accurately and rapidly calculated.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
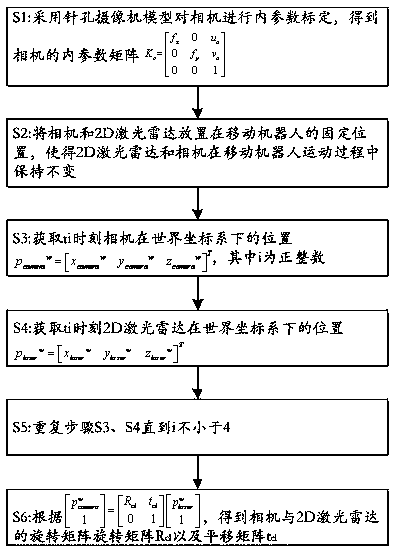
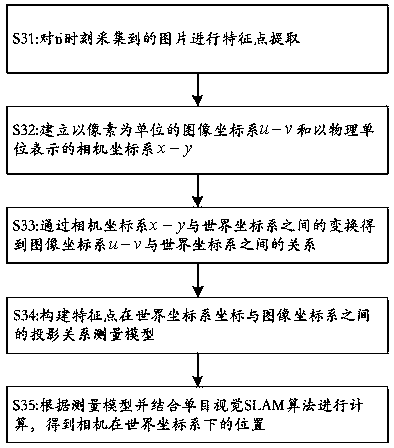
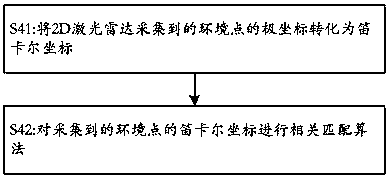
Combined calibration method for multiple sensors of mobile robot
The application of the invention discloses a combined calibration method for multiple sensors of a mobile robot. The mobile robot comprises a 2D laser radar and a camera. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, performing internal parameter calibration on the camera by use of a pinhole cameramodel, so as to obtain an internal parameter matrix, which is as shown in the description, of the camera; S2, placing the camera and the 2D laser radar on fixed positions of the mobile robot, and keeping the 2D laser radar and the camera constant in a movement process of the mobile robot; S3, acquiring the position of the camera in a world coordinate system at a moment ti, wherein the position of the camera is as shown in the description, and I is a positive integer; S4, acquiring the position of the 2D laser radar in a world coordinate system at the moment ti, wherein the position of the 2D laser radar is as shown in the description; S5, repeating the S3 and S4 until i is not less than 4; and S6, obtaining a rotation matrix Rcl and a translation matrix tcl of the camera and the 2D laser radar according to an equation as shown in the description. The technical scheme of the application of the invention completely breaks away from the restriction of a calibration target, calibration can be performed under various environments, real-time calibration can be performed in a use process, the problem that positioning error is caused since parameters of existing mobile robots are calibrated only before leaving factory and the parameters fluctuate in the later stage, and users can perform calibration conveniently in the use process.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN 3IROBOTICS CO LTD
Auto-calibration method for a projector-camera system
ActiveUS20090245690A1Quality improvementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionProjector camera systemsVisual perception
A method for self-recalibration of a structured light vision system including a camera and a projector. A camera plane and a projector plane are defined, a Homography matrix between the camera plane and the projector plane is computed, and a translation vector and a rotation matrix are determined from Homography-based constraints. A computer vision system implementing the method is also described.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
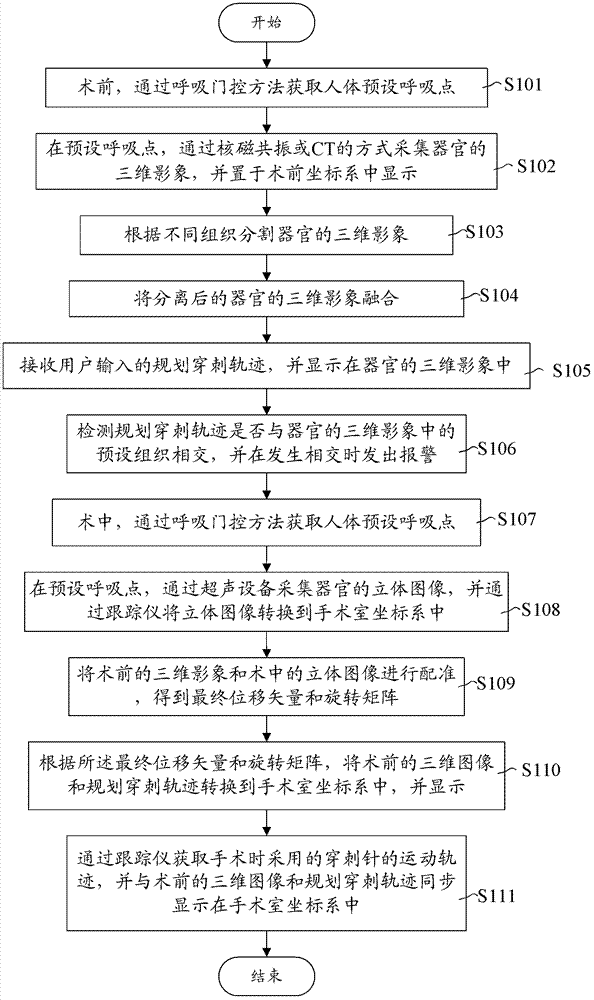
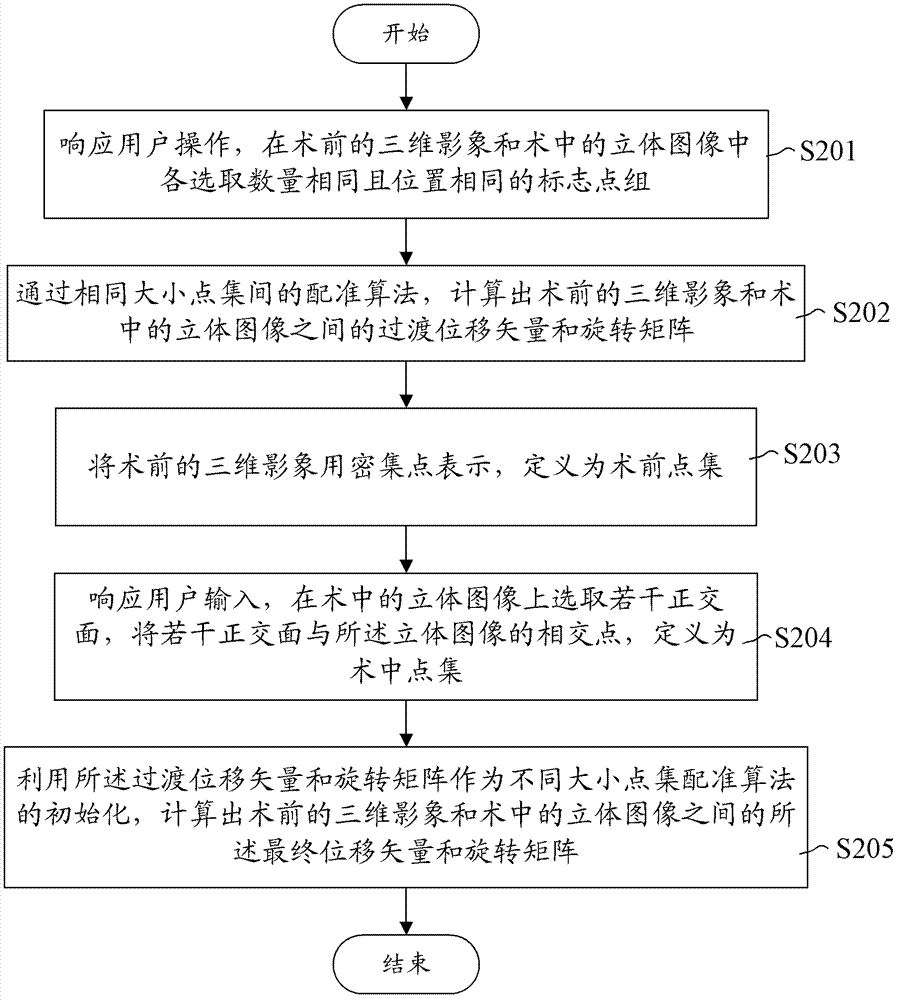
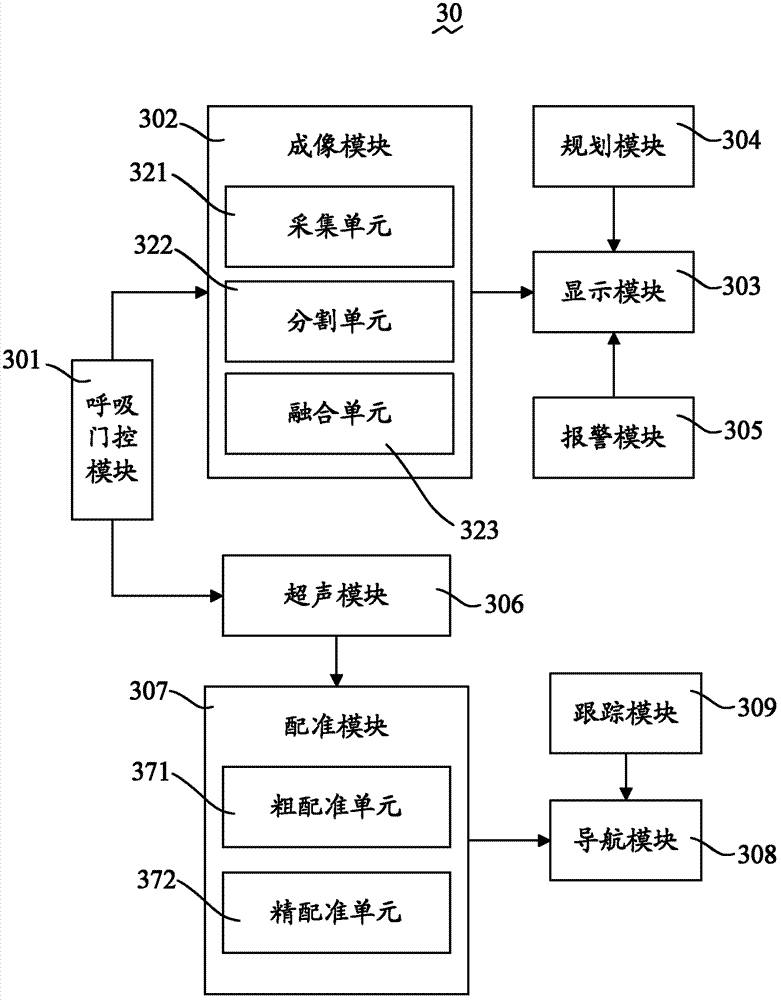
Surgical navigation method and system
ActiveCN103356284ASolve unclear problemsSolve the speed problemDiagnosticsSurgeryNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSonification
A surgical navigation method comprises collecting the three-dimensional images of an organ through nuclear magnetic resonance or CT (computed tomography) before an operation; receiving a planned puncture trace input by a user and displaying the planned puncture trace in the three-dimensional images; collecting the three-dimensional images of the organ through an ultrasonic device during the operation, and converting the three-dimensional images into an operating room coordinate system through a tracer; registering the three-dimensional images before the operation with the three-dimensional images during the operation to obtain final displacement vectors and rotation matrixes; according to the final displacement vectors and the rotation matrixes, converting the three-dimensional images and the planned puncture trace into the operating room coordinate system for displaying; obtaining the motion trace of a puncture needle utilized during the operation through the tracer and displaying the motion trace, the three-dimensional images before the operation and the planned puncture trace in the operating room coordinate system synchronously. The invention also provides a corresponding surgical navigation system. According to the surgical navigation system, blurred images during the operation are replaced by clear images before the operation to provide great help to aspects such as operation, time and image clearness.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
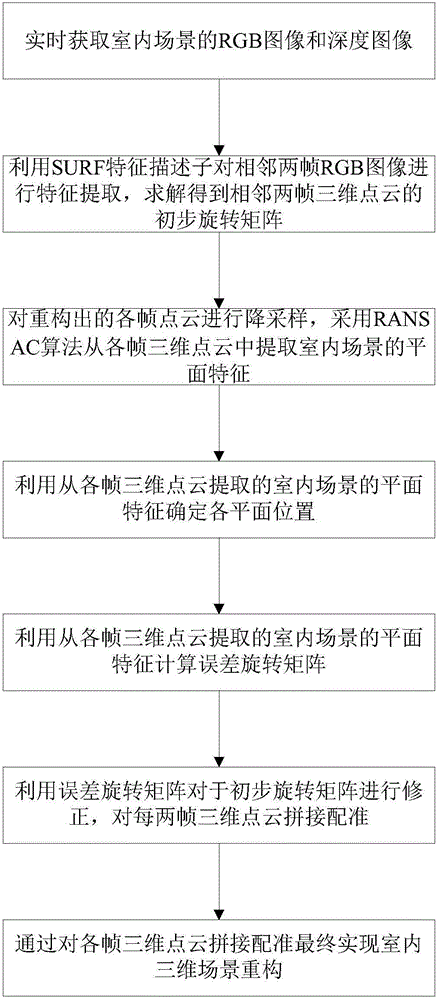
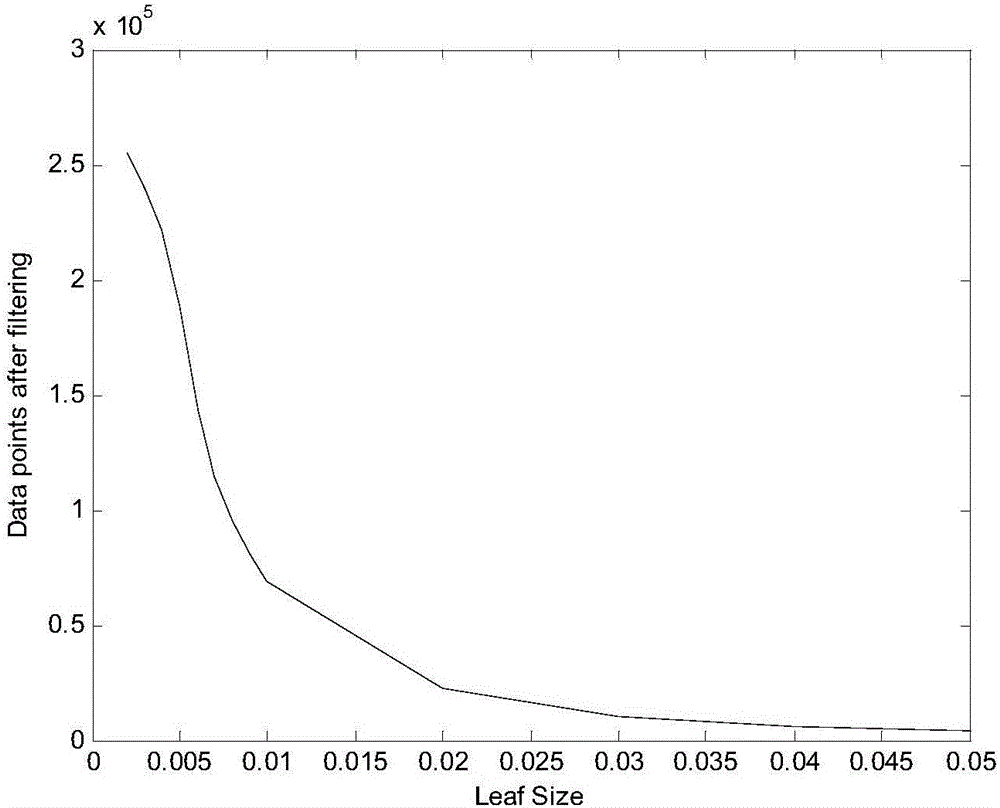
Indoor three-dimensional scene reconstruction method employing plane characteristics
InactiveCN105913489AIncrease speedQuick and efficient extractionDetails involving processing steps3D modellingFeature extractionPoint cloud
The invention provides an indoor three-dimensional scene reconstruction method employing plane features, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an RGB image and a depth image of an indoor scene in real time, and completing the reconstruction of a single-frame three-dimensional point cloud; carrying out the feature extraction of two adjacent RGB images, and obtaining the initial rotating matrixes of the two adjacent three-dimensional point clouds; carrying out the downsampling of each three-dimensional point cloud, and extracting the plane features of the indoor scene from each three-dimensional point cloud; determining each plane position; calculating an error rotating matrix; correcting the initial rotating matrixes, and carrying out the jointing and registering of each two three-dimensional point clouds; and finally achieving the reconstruction of the indoor three-dimensional scene through the jointing and registering of each three-dimensional point cloud. The method carries out the error elimination through employing the geometric features of the point clouds, and extracts the plane features of the point clouds quickly and effectively. The success rate of the matching of the plane features of the current and former point clouds is higher. According to the plane features, the method judges the type of the planes, calculates the error matrix, corrects the initial rotating matrix, and obtains a more accurate indoor three-dimensional point cloud map.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Mechanical arm tail end camera hand-eye calibration method and system
InactiveCN109658460ASolve the problem of hand-eye relationship calibrationProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage analysisHand eye calibrationManipulator
The embodiment of the invention provides a mechanical arm tail end camera hand-eye calibration method and system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a calibration image collected by a calibration area when a mechanical arm performs translation and rotation for multiple times at the same time; Obtaining a hand-eye calibration matrix based on the mechanical arm pose information and the calibration image external parameter information; And calibrating the hand-eye relationship of the tail end of the mechanical arm by using the hand-eye calibration matrix. According to the scheme, the calibration of the camera is completed by utilizing spatial motion and image acquisition at a plurality of different positions; According to the principle that the hand-eye relationship is constrainedby multiple spatial relative positions, only the positions of at least three spatial positions relative to the base and external parameters of the camera need to be obtained in the calibration process, and the calibration process can be universal for different mechanical arm models, the number of freedom degrees and camera models; According to the scheme, translation and rotation matrix transformation is utilized, the mechanical arm tail end coordinates are projected to the pixel coordinates, and calibration of the hand-eye relation between the camera and the mechanical arm tail end when the mechanical arm tail end has rotation and translation movement at the same time is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO MEASUREMENT
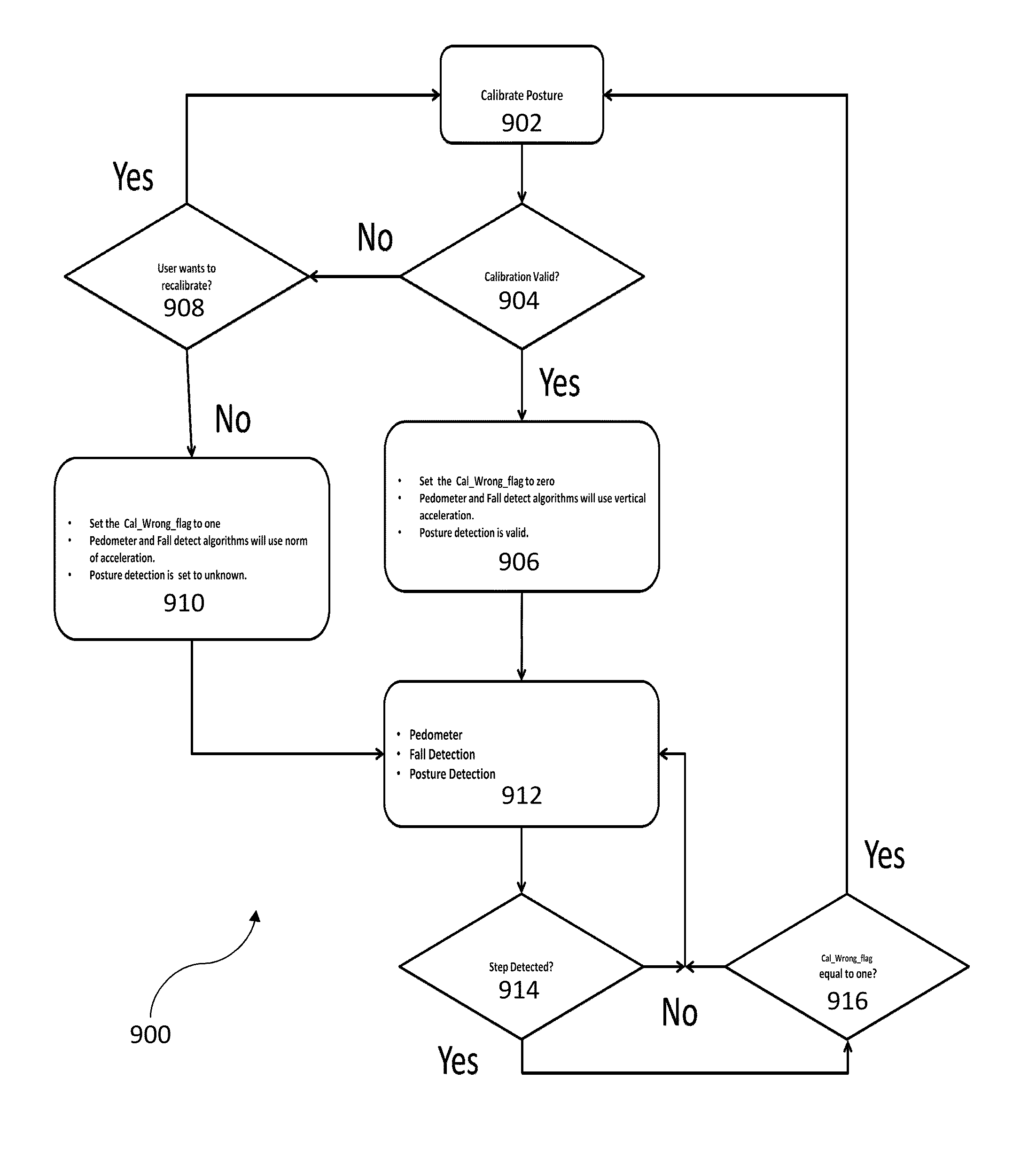
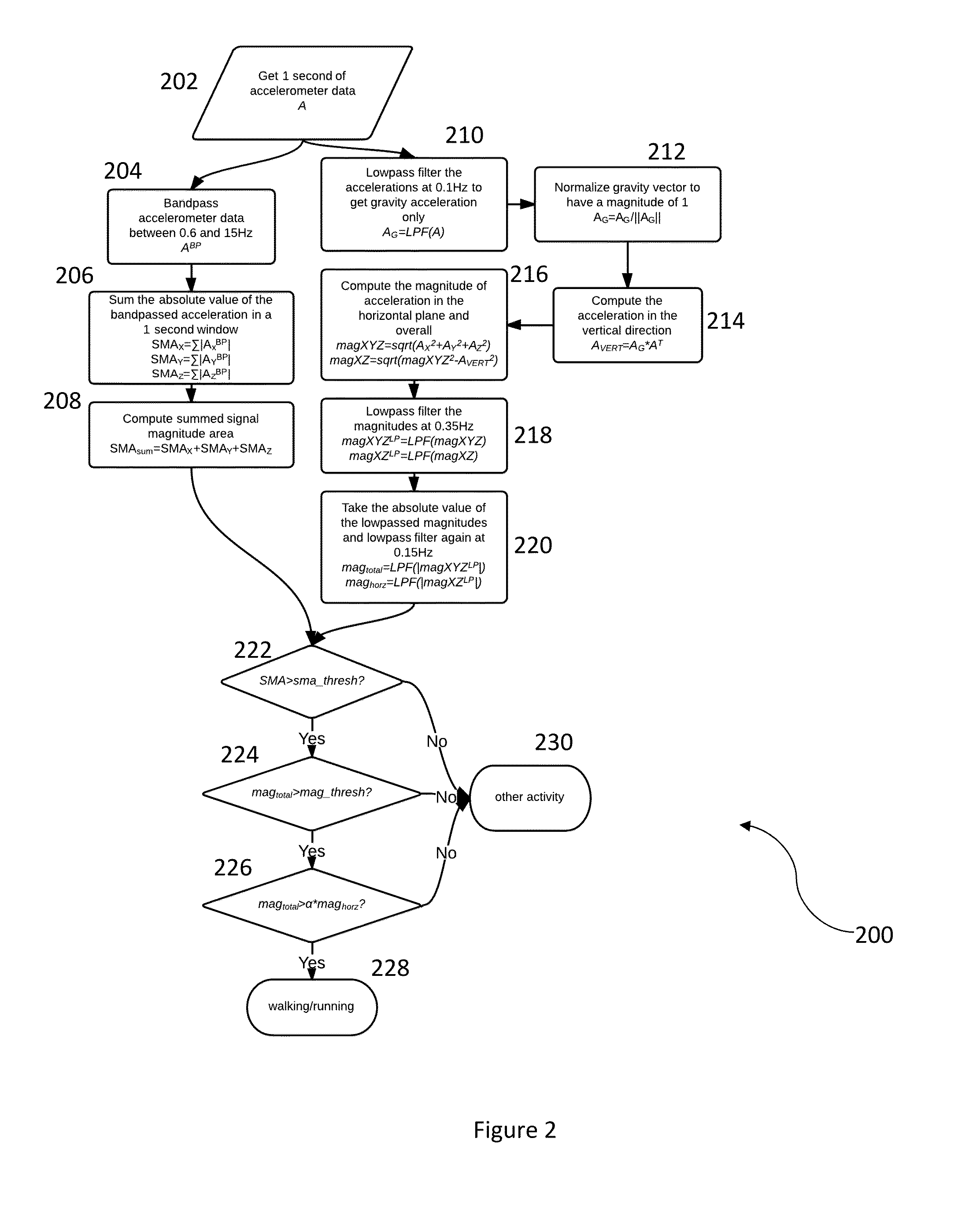
Calibration of a chest-mounted wireless sensor device for posture and activity detection
ActiveUS20140019080A1Registering/indicating time of eventsTesting/calibration apparatusLine sensorBody axis
A method and system for calibrating a wireless sensor device are disclosed. In a first aspect, the method comprises determining a vertical calibration vector and determining a rotation matrix using the vertical calibration vector to line up native axes of the wireless sensor device with body axes. In a second aspect, a wireless sensor device comprises a processor and a memory device coupled to the processor, wherein the memory device includes an application that, when executed by the processor, causes the processor to determine a vertical calibration vector and to determine a rotation matrix using the vertical calibration vector to line up native axes of the wireless sensor device with body axes.
Owner:VITAL CONNECT
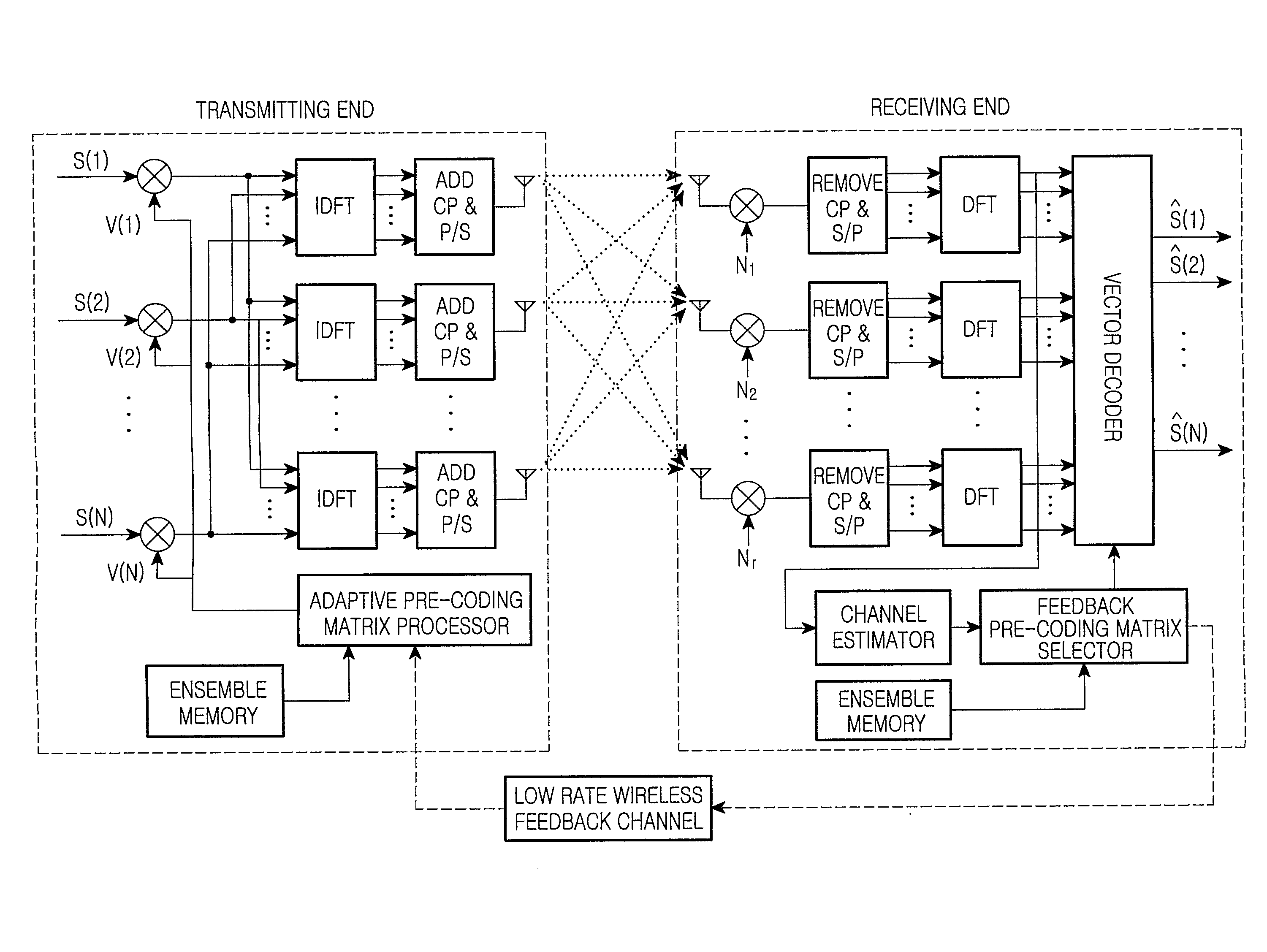
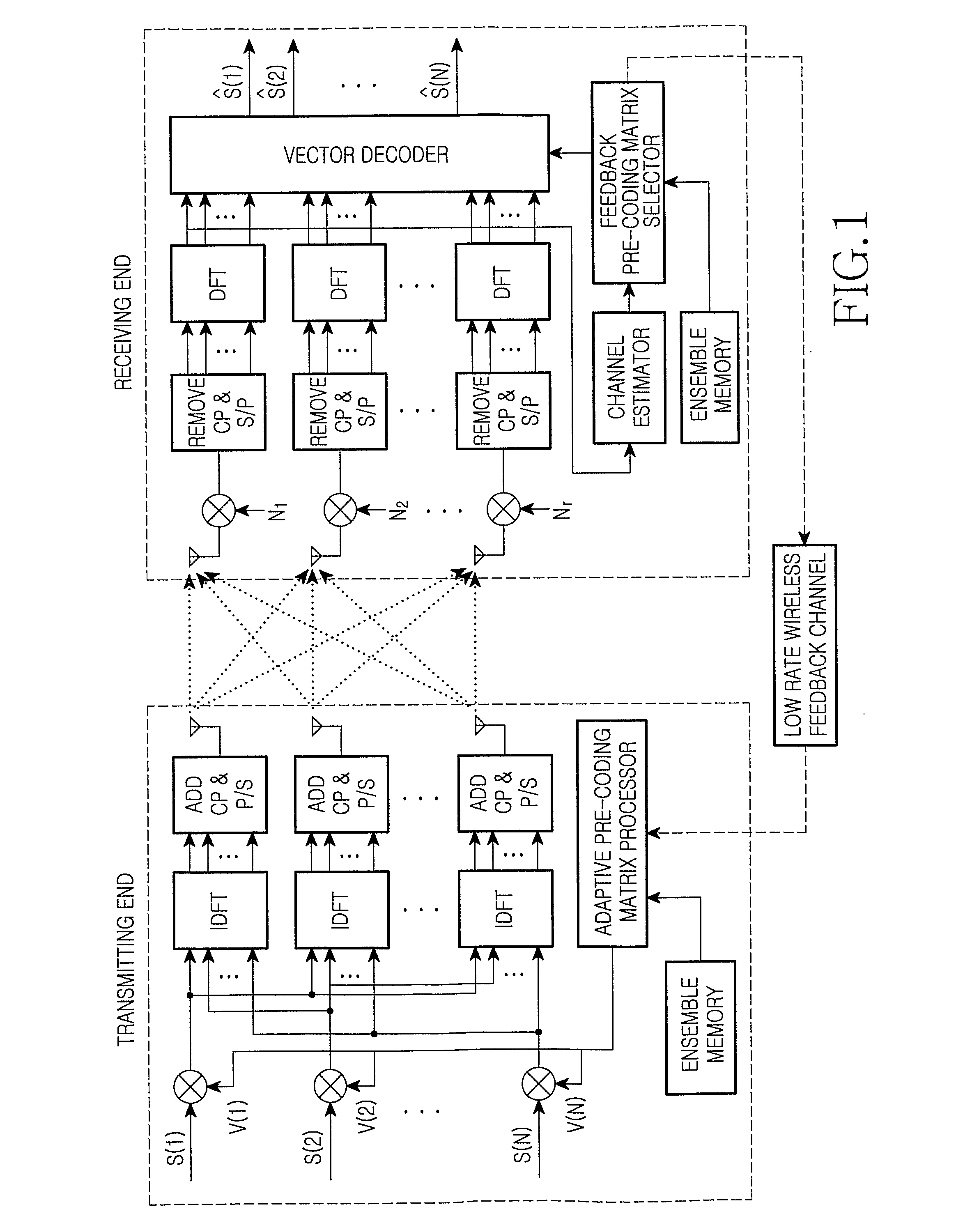
MIMO-OFDM system and pre-coding and feedback method therein
InactiveUS20070115799A1Better respondReduce complexityModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionChannel state informationRound complexity
The present invention provides an antenna-array-based multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal-frequency-division-multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) system and a pre-coding and feedback method used in the same. The present invention uses QR decompositions of the MIMO channel matrixes to parameterize the channel state information (CSI) of every OFDM frequency band. In addition, the present invention feeds back the information related to θ and φ in the Givens rotation matrixes of the partial frequency bands and then uses an interpolation method to generate θ and φ in the Givens rotation matrixes of all the frequency bands, which further is able to represent the CSI of all the frequency bands. In this way, the present invention has advantages of low complexity and low feedback rate requirement.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS20070015997A1Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
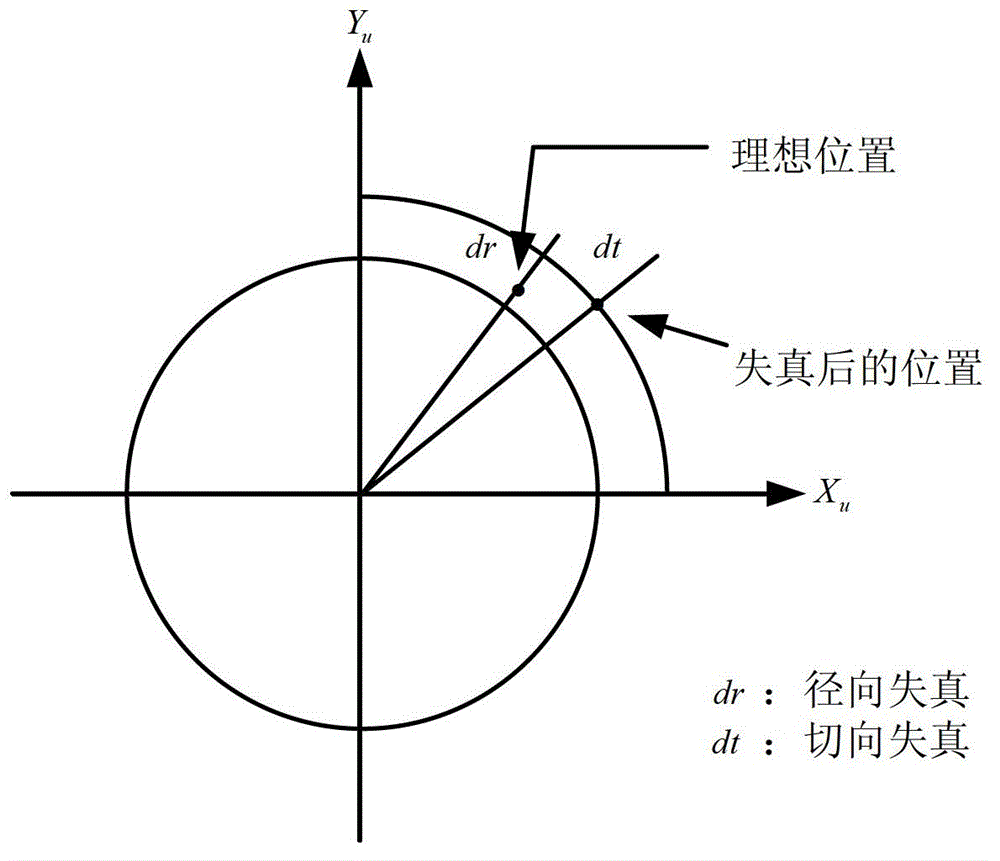
Device and method of measuring surface topographies of mirror and mirror-like objects
InactiveCN105783775AIncreased complexityGuarantee authenticityUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring surface topographies of mirror and mirror-like objects. Phase measurement deflectometry is adopted to measure mirror and mirror-like surface shapes, a combination between a liquid crystal display and a planar mirror serves as a calibration plate, the liquid crystal display is fixed and can not move, the planar mirror moves freely for four times, an image reflected by the planar mirror is photographed by a CCD detector, linear solution and beam method adjustment are then used for completing calibration on inner parameters of the camera, global pose estimation is used for completing calibration on the relative relation between the liquid crystal display and the camera, and finally, a three-dimensional topography of a to-be-detected mirror surface is calculated and obtained through a gradient integral of the phase measurement deflectometry. According to the device and the method of the invention, defects that the calibration plate is needed and a precise positioning control point is attached to the planer mirror during the calibration process in the traditional method are overcome, the measurement cost is low, and he measurement speed is quick; and constraint conditions such as rotation matrix orthogonality during a perspective imaging process and a fourier transform method are introduced for corresponding point matching, and influences by high noise and multiframe processing on three-dimensional topography recovery can be overcome.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Calibration method of camera and inertial sensor integrated positioning and attitude determining system
InactiveCN102162738AAvoid System Calibration ErrorsHigh precisionImage analysisMeasurement devicesIntrinsicsComputer vision
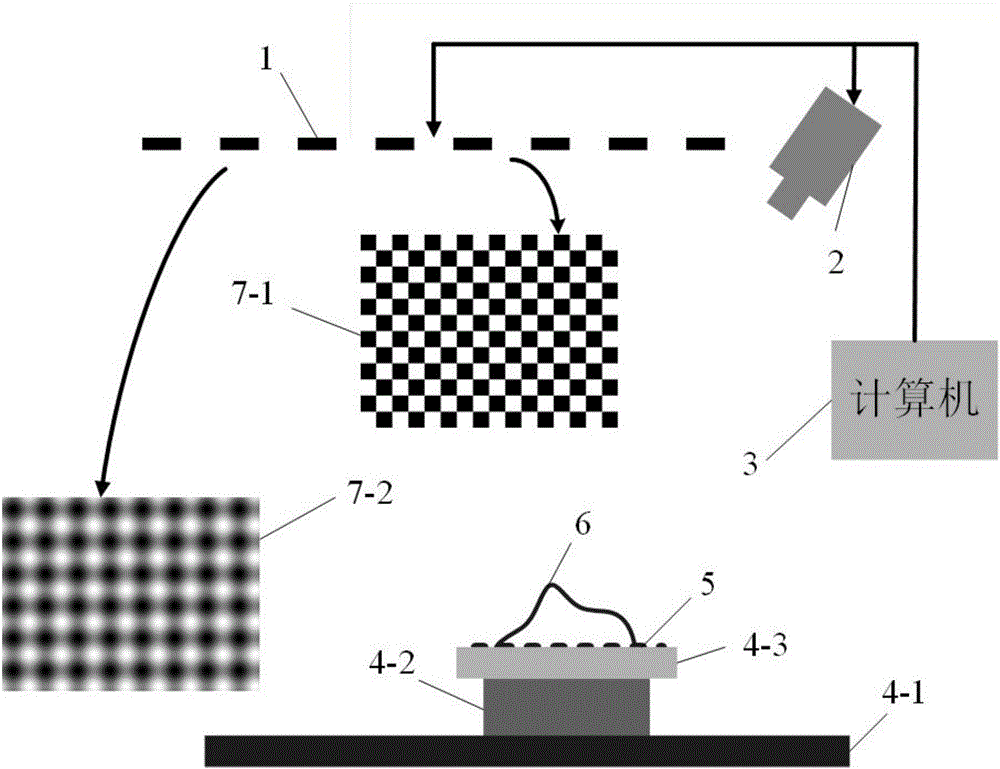
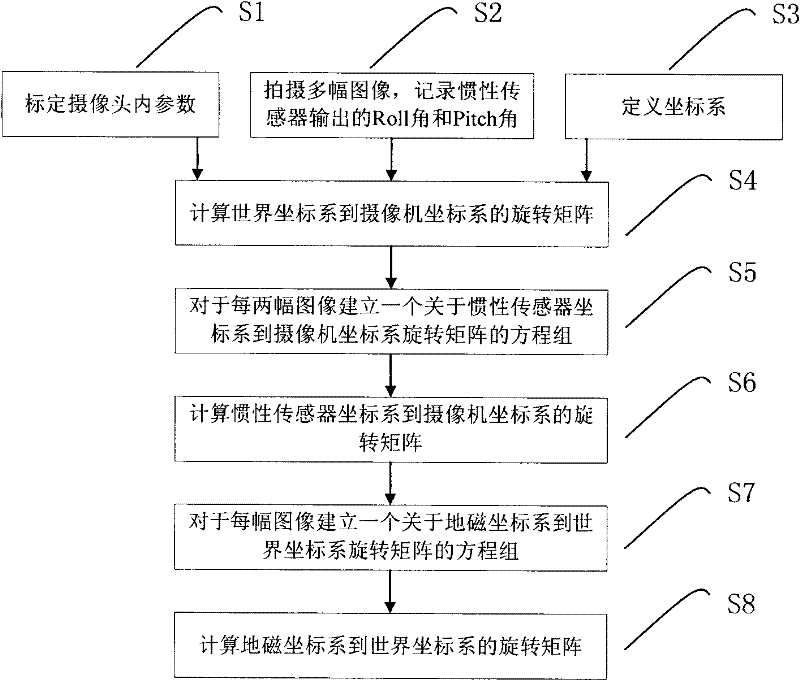
The invention provides a calibration method of a camera and inertial sensor integrated positioning and attitude determining system. The method comprises the following steps: calibrating the intrinsic matrix of the camera; shooting a plurality of images of a calibration object with known dimensions from different angles, and recording the roll angle and the pitch angle output by the inertial sensor when each image is shot; defining a world coordinate system, a camera coordinate system, an inertial sensor coordinate system and a geomagnetic coordinate system; calculating the rotation matrix from the world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system at the moment based on the image information and spatial information of the calibration object in each image; integrating the shot images pairwise, establishing an equation set with respect to the rotation matrix from the inertial sensor coordinate system to the camera coordinate system for each group, and solving the equation set to calculate the rotation matrix from the inertial sensor coordinate system to the camera coordinate system; and establishing an equation set with respect to the rotation matrix from the geomagnetic coordinate system to the world coordinate system for each image, and solving the equation set to calculate the rotation matrix from the geomagnetic coordinate system to the world coordinate system.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
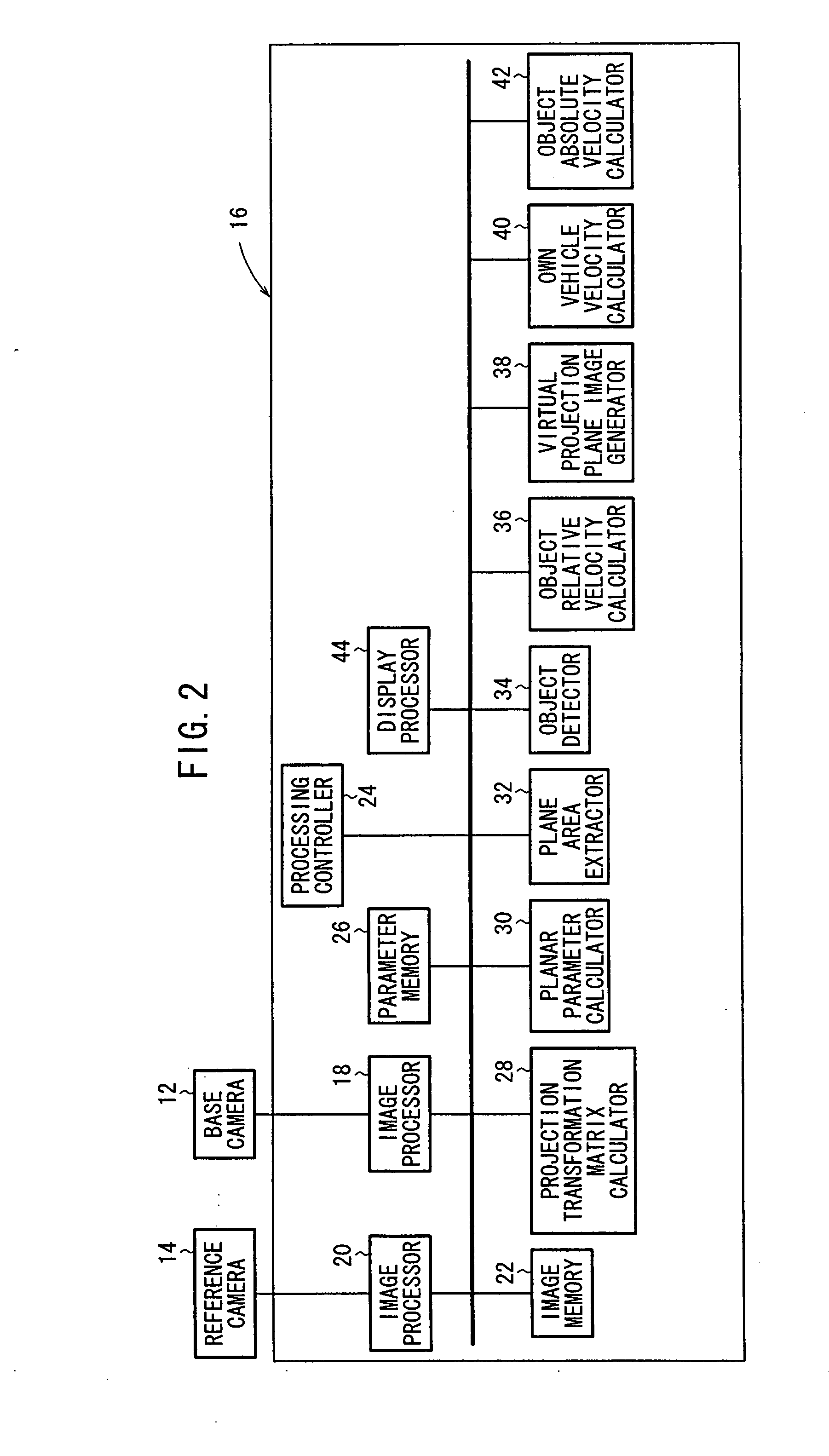
Plane Detector and Detecting Method
InactiveUS20080253606A1Short timeAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringMechanical engineering
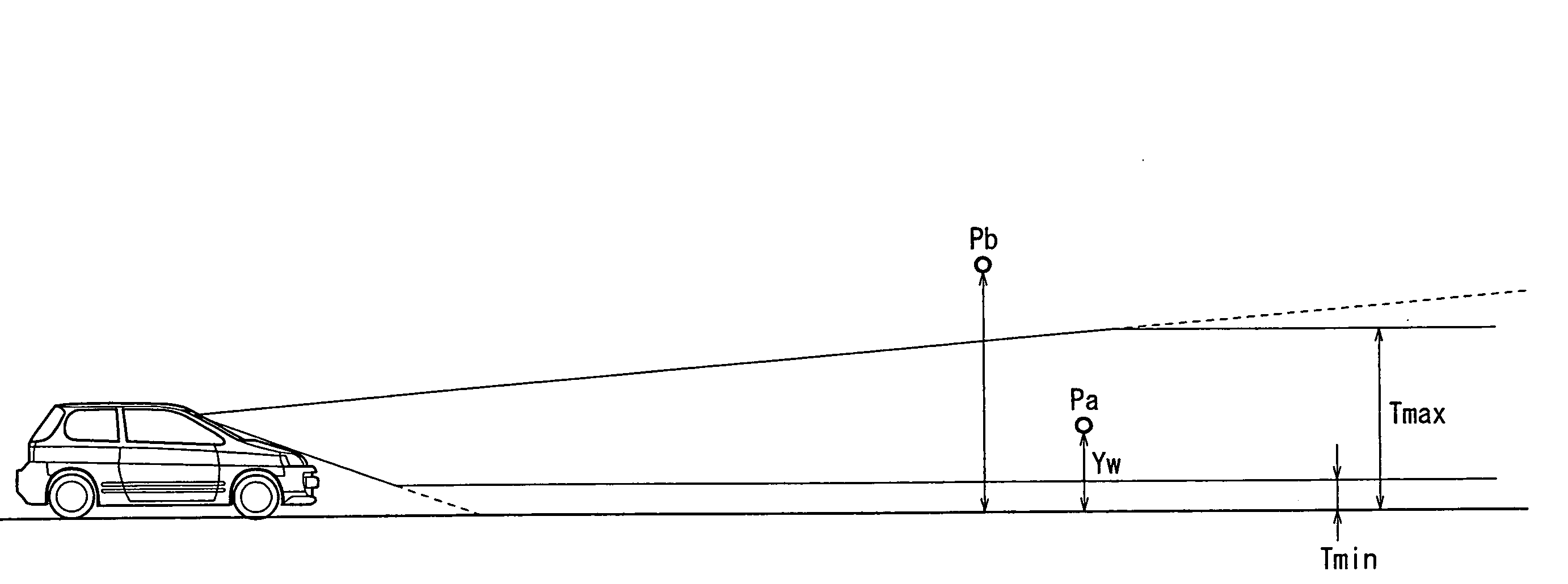
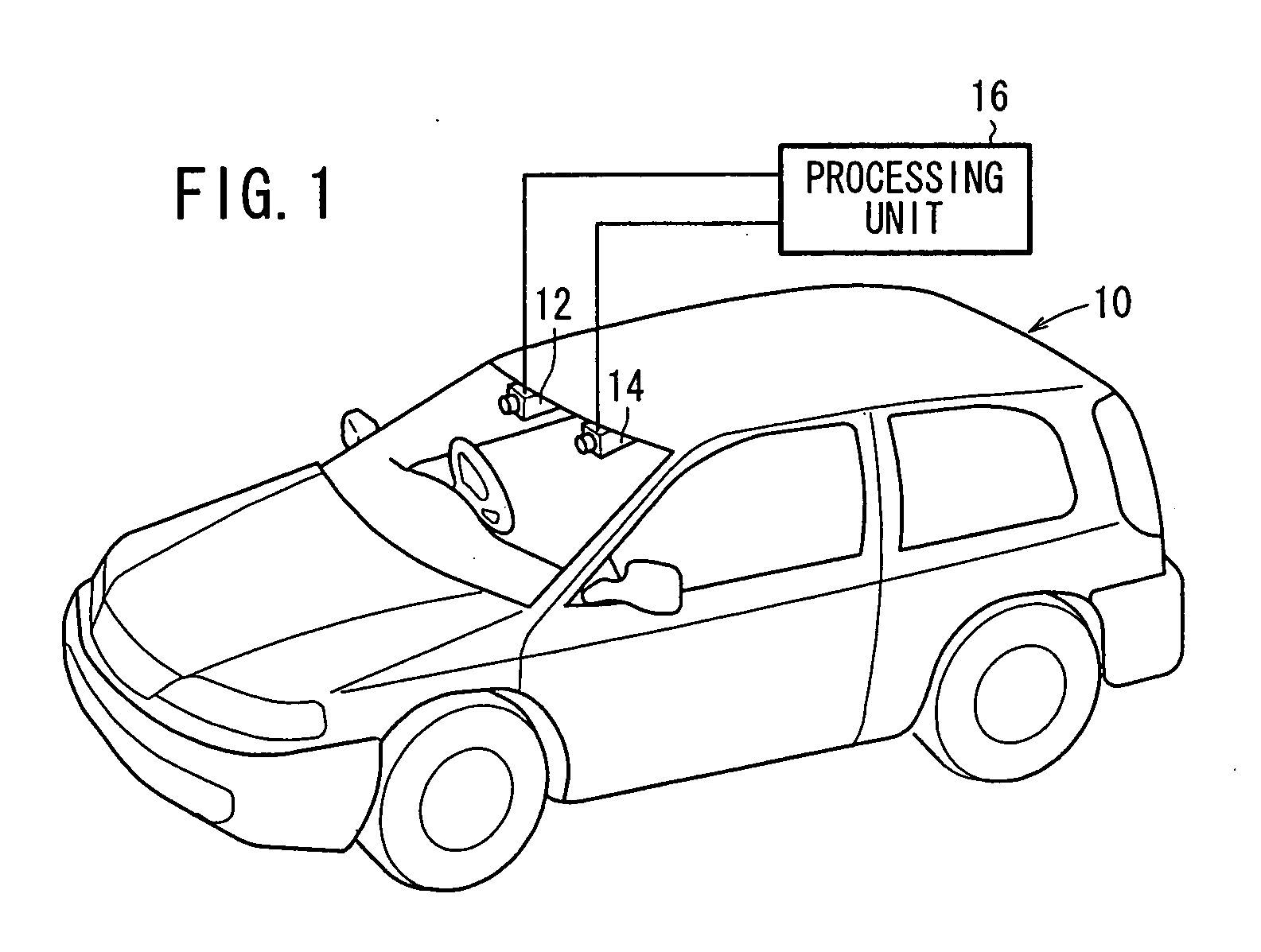
A rotation matrix and a translation vector between a basic camera (12) and a reference camera (14) are read out from a parameter storage section (26). At a projection conversion matrix calculating section (28), a projection conversion matrix capable of overlapping the road plane area included in images picked up by the basic camera (12) and the reference camera (14) is calculated by using the rotation matrix and the translation vector.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
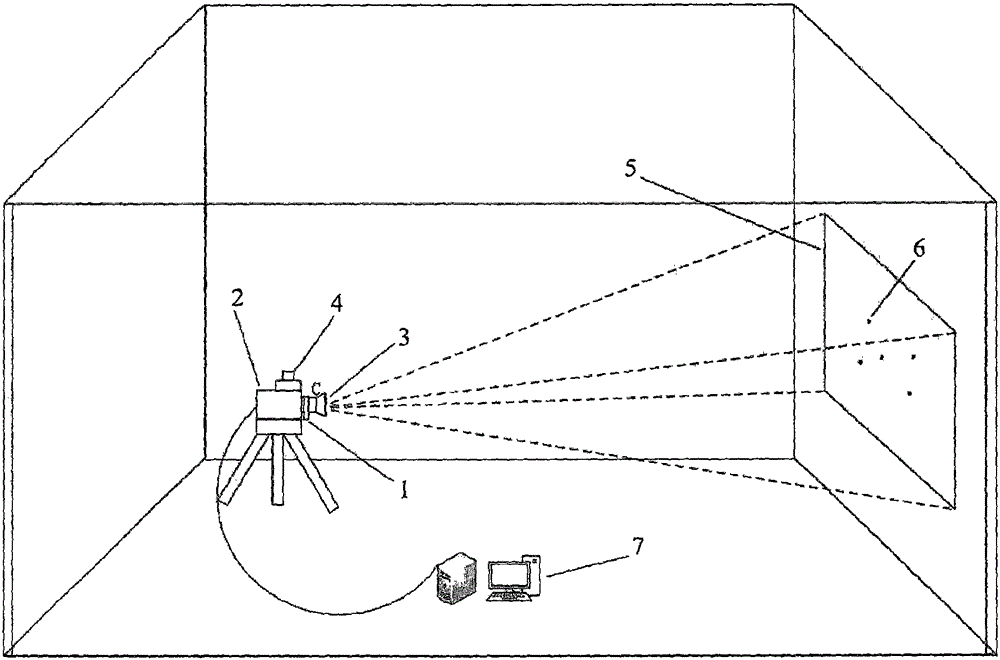
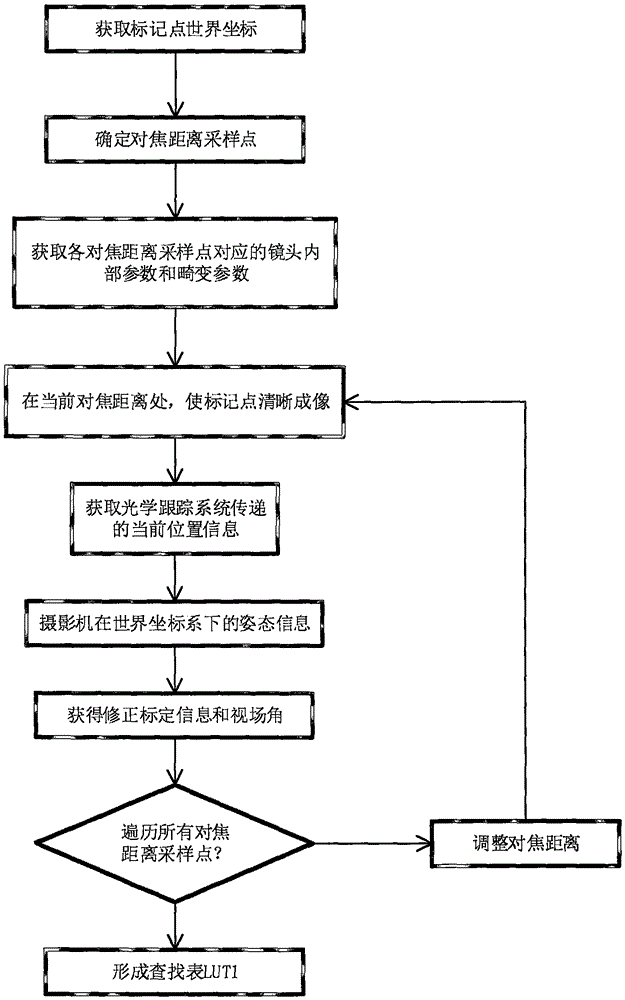
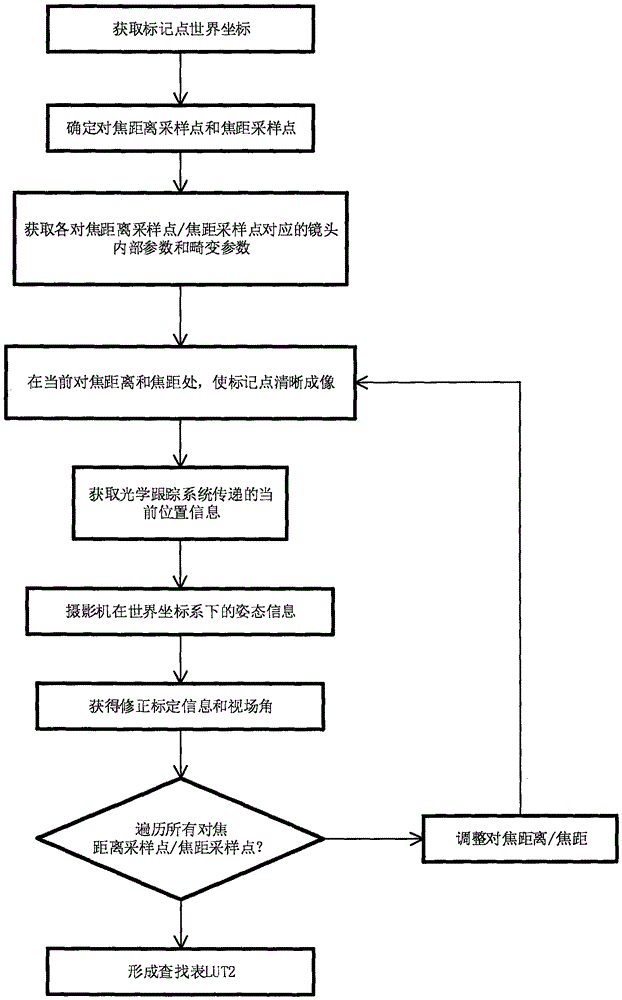
Camera positioning correction calibration method and system
ActiveCN105118055AFully automatedReal-time computingImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensOptical tracking
The present invention discloses a camera positioning correction calibration method and a system for realizing the method, belonging to the technical field of image virtual production. Through the intrinsic relationship among a lens parameter, an imaging surface and an optical tracking device, by using the world coordinate and image point coordinate of N mark points on a background screen and the internal parameter and lens distortion parameter of a camera lens, the rotation matrix between a camera coordinate system and a world coordinate system and the translation vector of a camera perspective center in the world coordinate system are obtained, combined with the current position information given by a camera posture external tracking device in a current state, camera correction calibration information and viewing angle are obtained, the lookup table with a focusing distance and a focus length relationship is established, thus when a camera position, a lens focal distance and a focusing distance change, the position of the virtual camera of the virtual production system is fully automatically positioned and corrected, and thus a real video frame picture and a virtual frame image generated by a computer can be matched perfectly.
Owner:BEIJING FILM ACAD
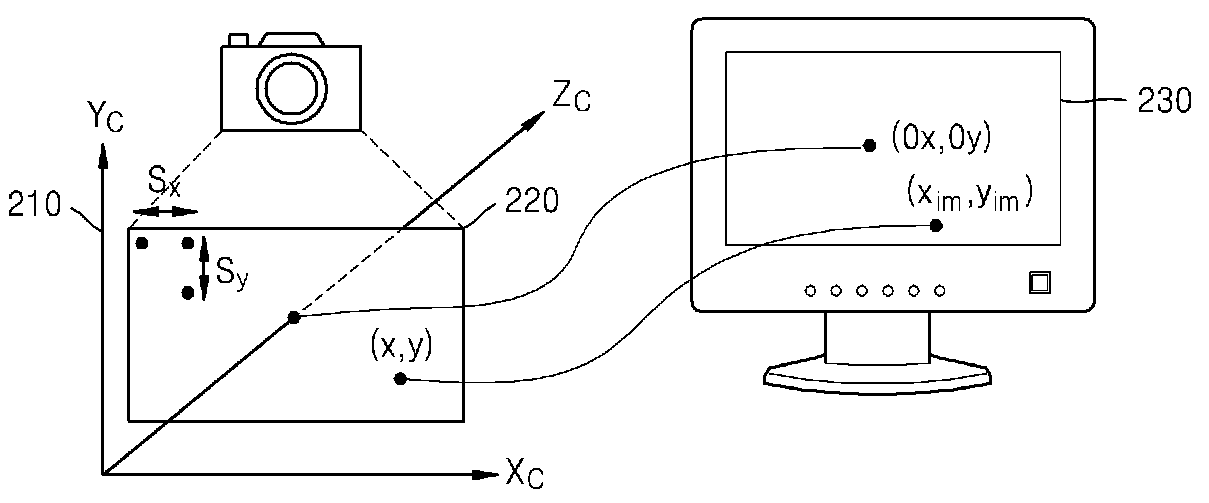
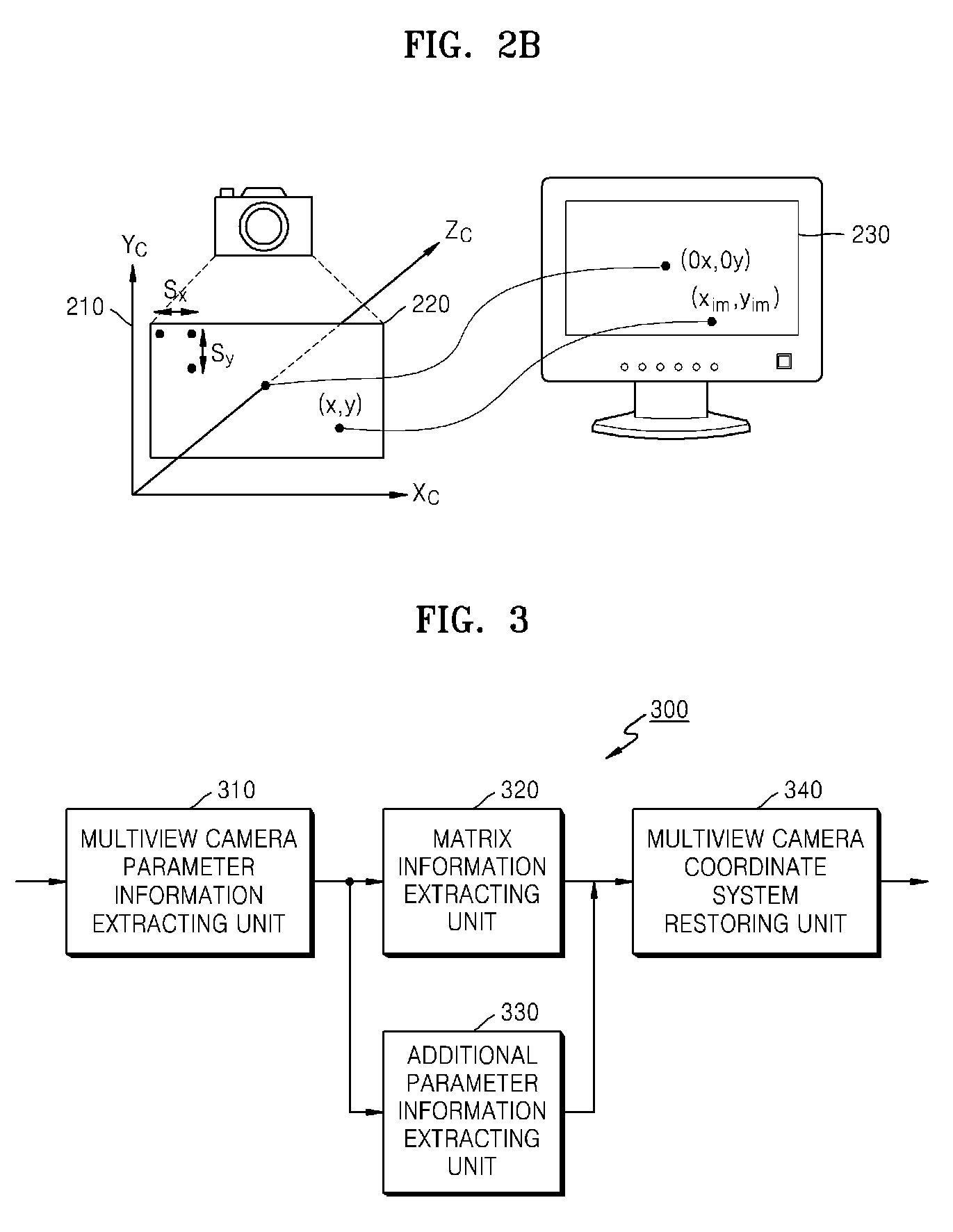
Method and apparatus for receiving multiview camera parameters for stereoscopic image, and method and apparatus for transmitting multiview camera parameters for stereoscopic image
ActiveUS20090092311A1Efficient representationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamComputer vision
Provided is a method of receiving multiview camera parameters for a stereoscopic image. The method includes: extracting multiview camera parameter information for a predetermined data section from a received stereoscopic image data stream; extracting matrix information including at least one of translation matrix information and rotation matrix information for the predetermined data section from the multiview camera parameter information; and restoring coordinate systems of multiview cameras by using the extracted matrix information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
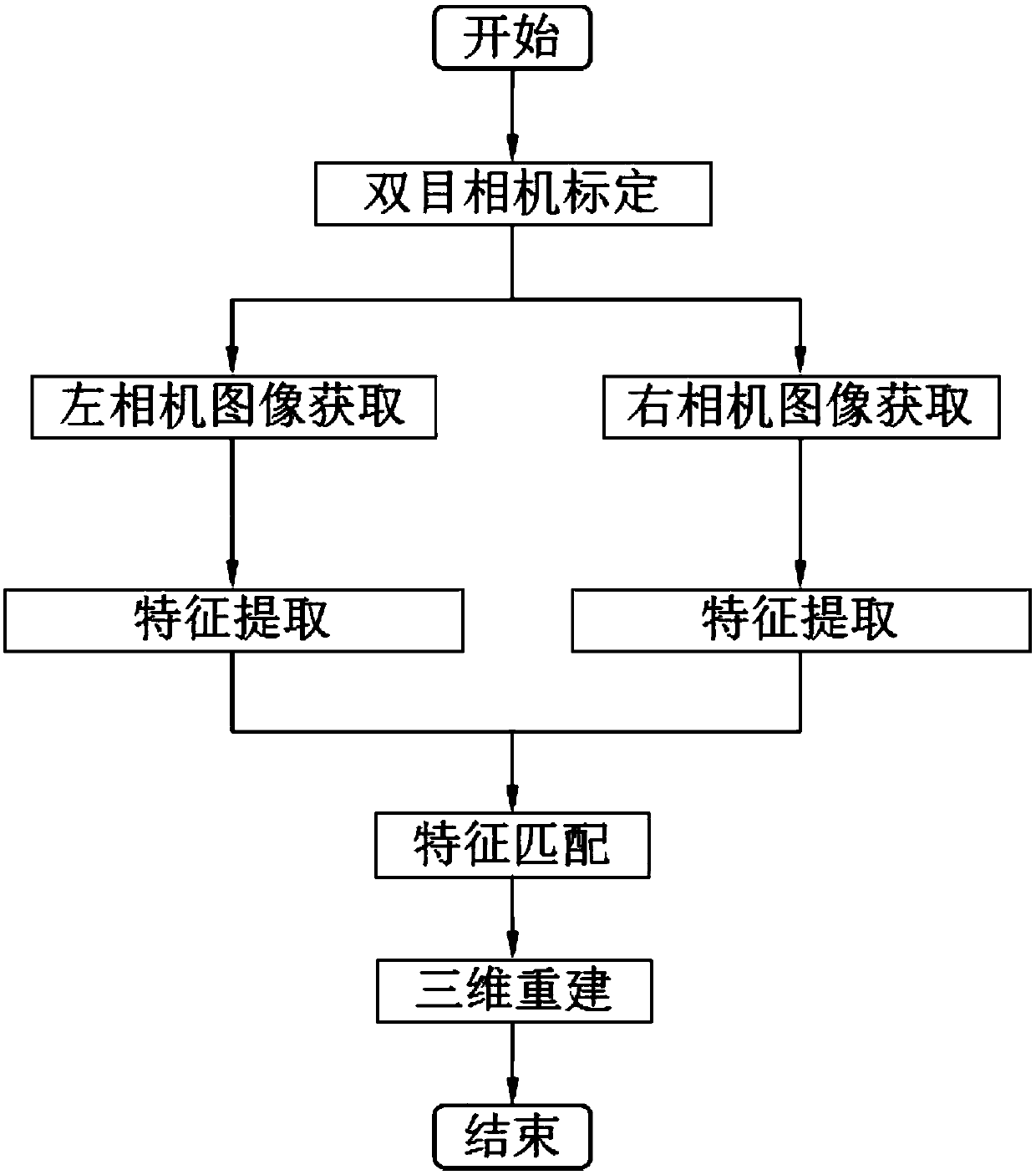
Method for measuring geometric parameters of spatial circle based on technique of binocular stereoscopic vision
InactiveCN101093160ARealize fully automatic detectionReduce measurement errorUsing optical means3D-image renderingObservational errorAutonomous Navigation System
A method for measuring space-circle geometric parameter based on binocular stereo-vision includes confirming parameter and one-order radial distortion parameter separately in left-right video cameras, calculating out rotary matrix and translation vector presenting relative position relation of left-right video cameras, utilizing left-right video cameras to obtain two frame of images containing space-circle oval image and carrying out distortion calibration on two obtained images and directly calculating out all geometric parameters of space-circle in linear way by adapting oval image of distortion-calibrated image plane.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
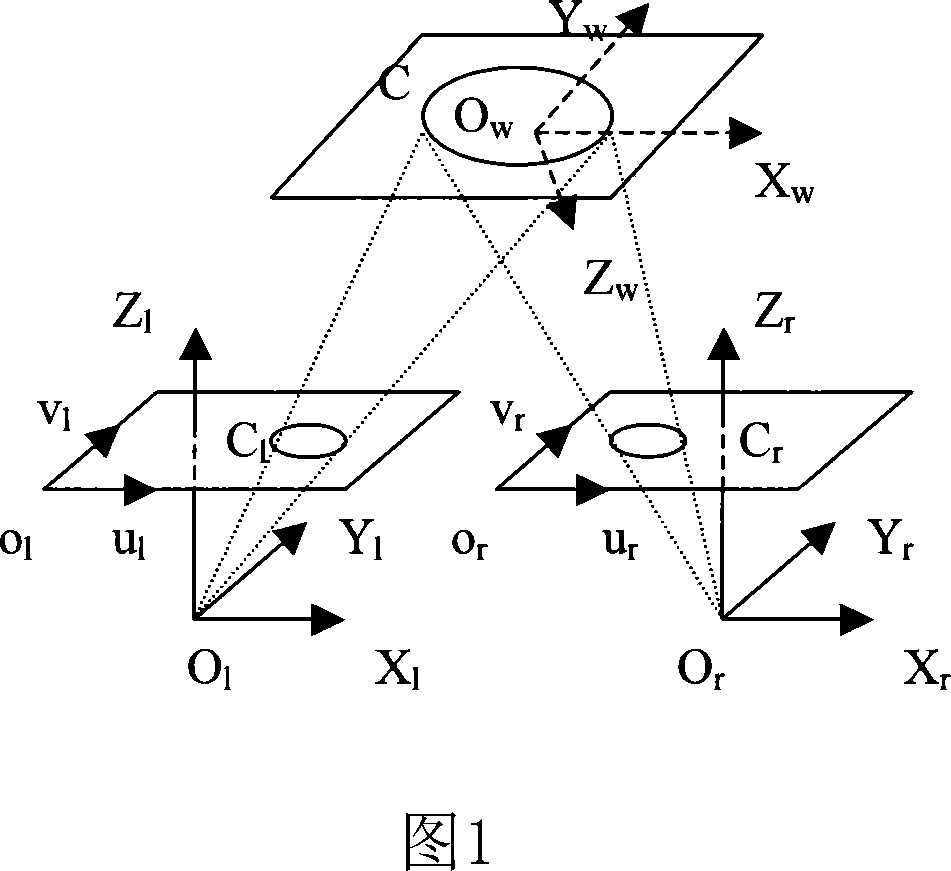
Method for establishing relation between scene stereoscopic depth and vision difference in binocular stereoscopic vision system
InactiveCN102867304AAchieve accurate recoveryRealize 3D reconstructionImage analysis3D modellingRelational modelMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses a method for establishing a relation between a scene stereoscopic depth and a vision difference in a binocular stereoscopic vision system. the method comprises the steps of firstly, solving inner parameters, and relative rotary matrixes and translation vectors of left and right cameras; then, analyzing a main error source and an error model of the binocular stereoscopic vision system; then, analyzing influences of the main error on a base line length and the vision difference of the parallel binocular stereoscopic vision system; then, establishing a common relation model of the scene stereoscopic depth and the vision difference in the binocular stereoscopic vision system; obtaining depth information by a laser distance measuring instrument by selecting a certain amount of demarcation points and carrying out demarcation based on a least square method to solve a relation model between the scene stereoscopic depth and the vision difference in the binocular stereoscopic vision system; and finally, solving the vision difference in left and right images through a corresponding fixed matching method so as to realize accurate recovery and three-dimensional reestablishment of the scene stereoscopic depth. The method has the beneficial effect of directly, simply, accurately and extremely improving the accuracy of the stereoscopic depth recovery and the three-dimensional reestablishment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com