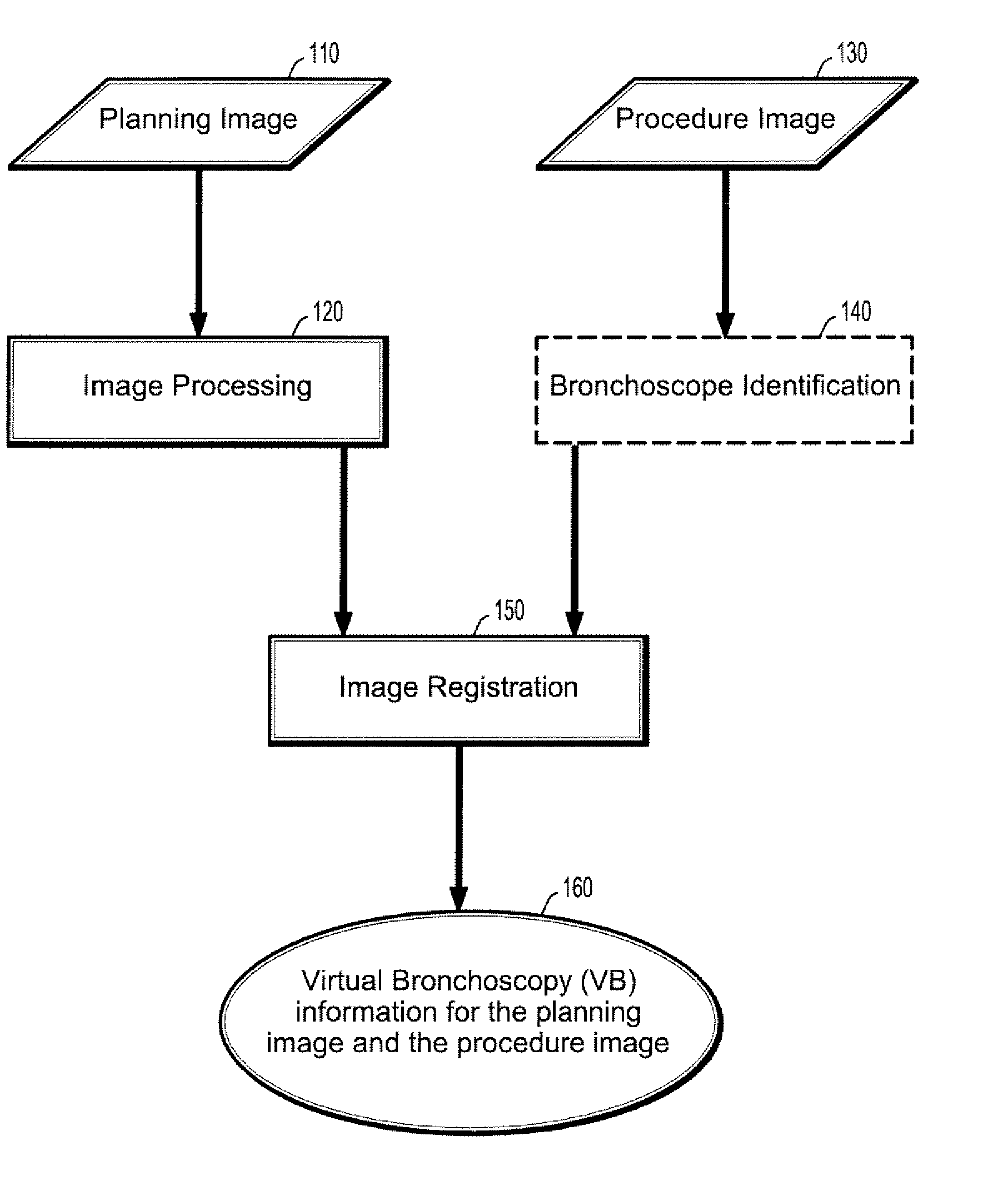
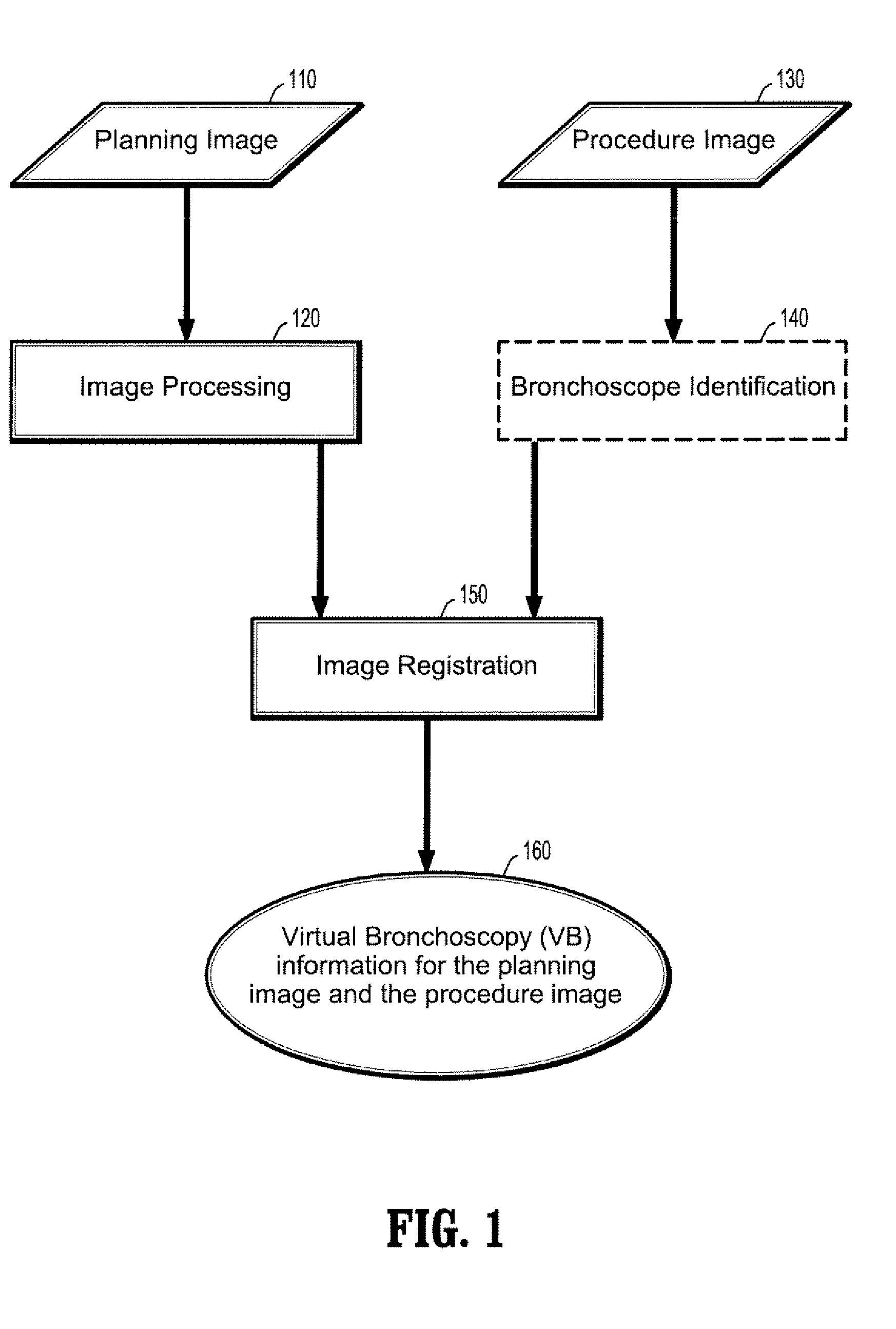
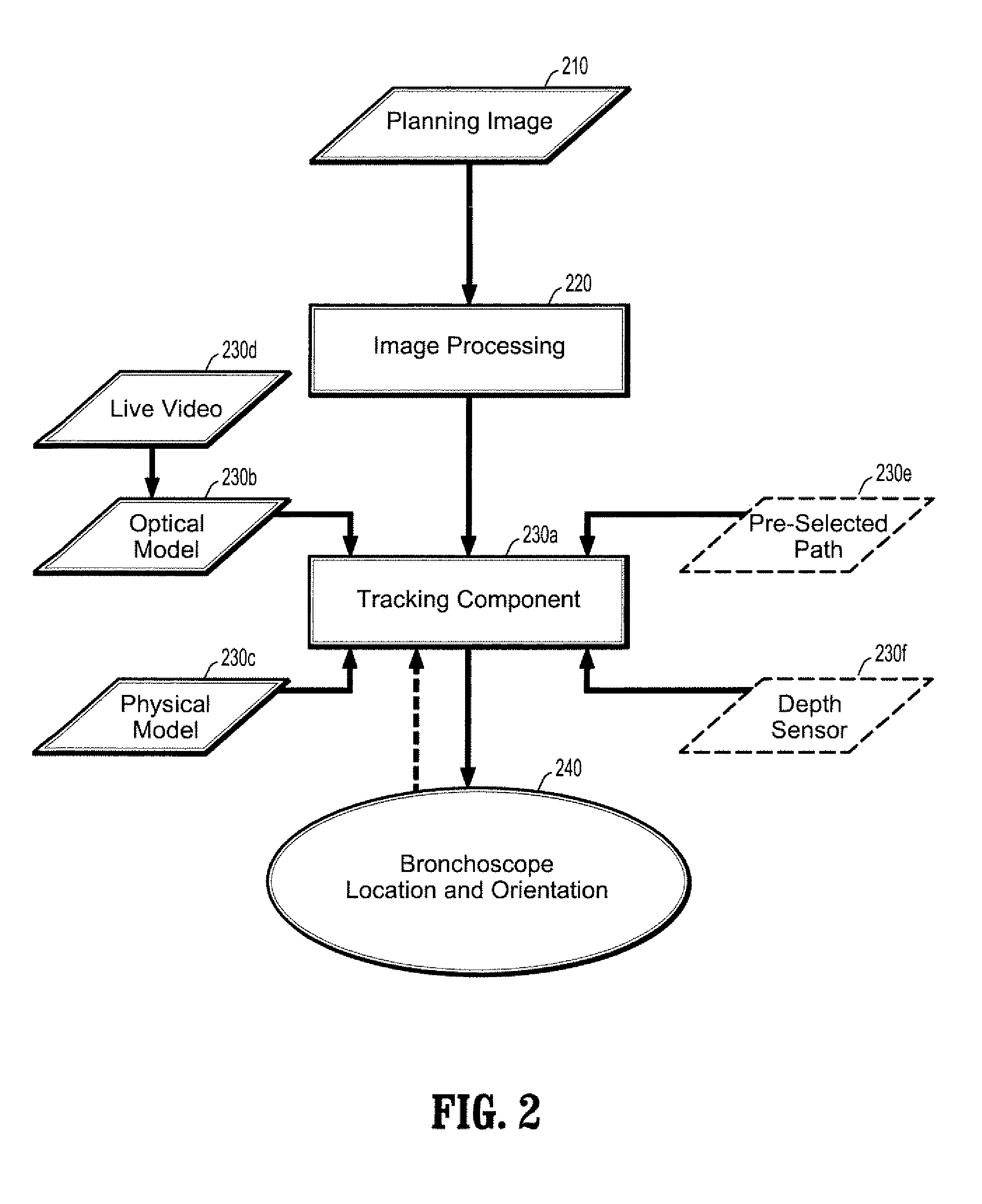
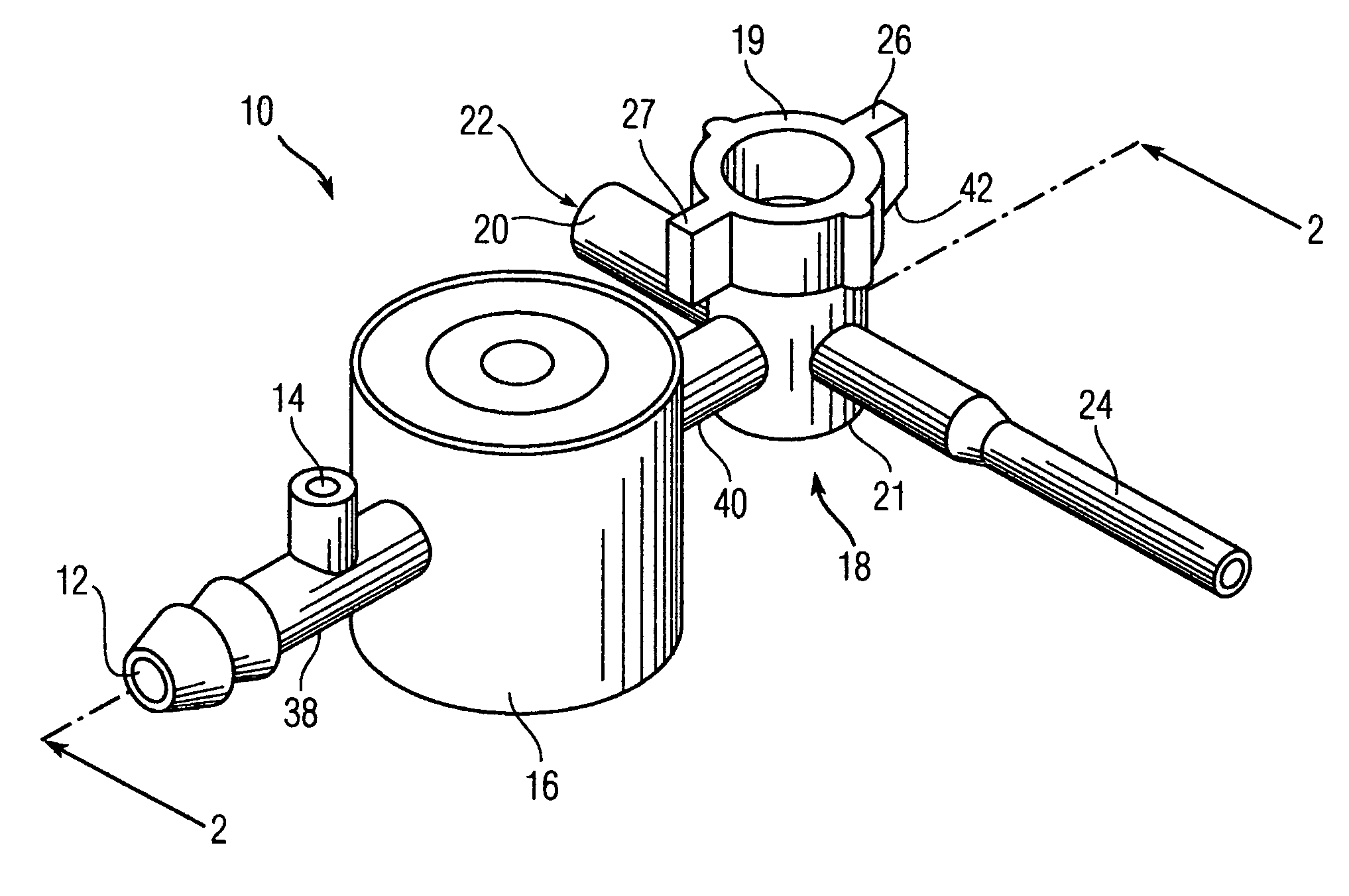
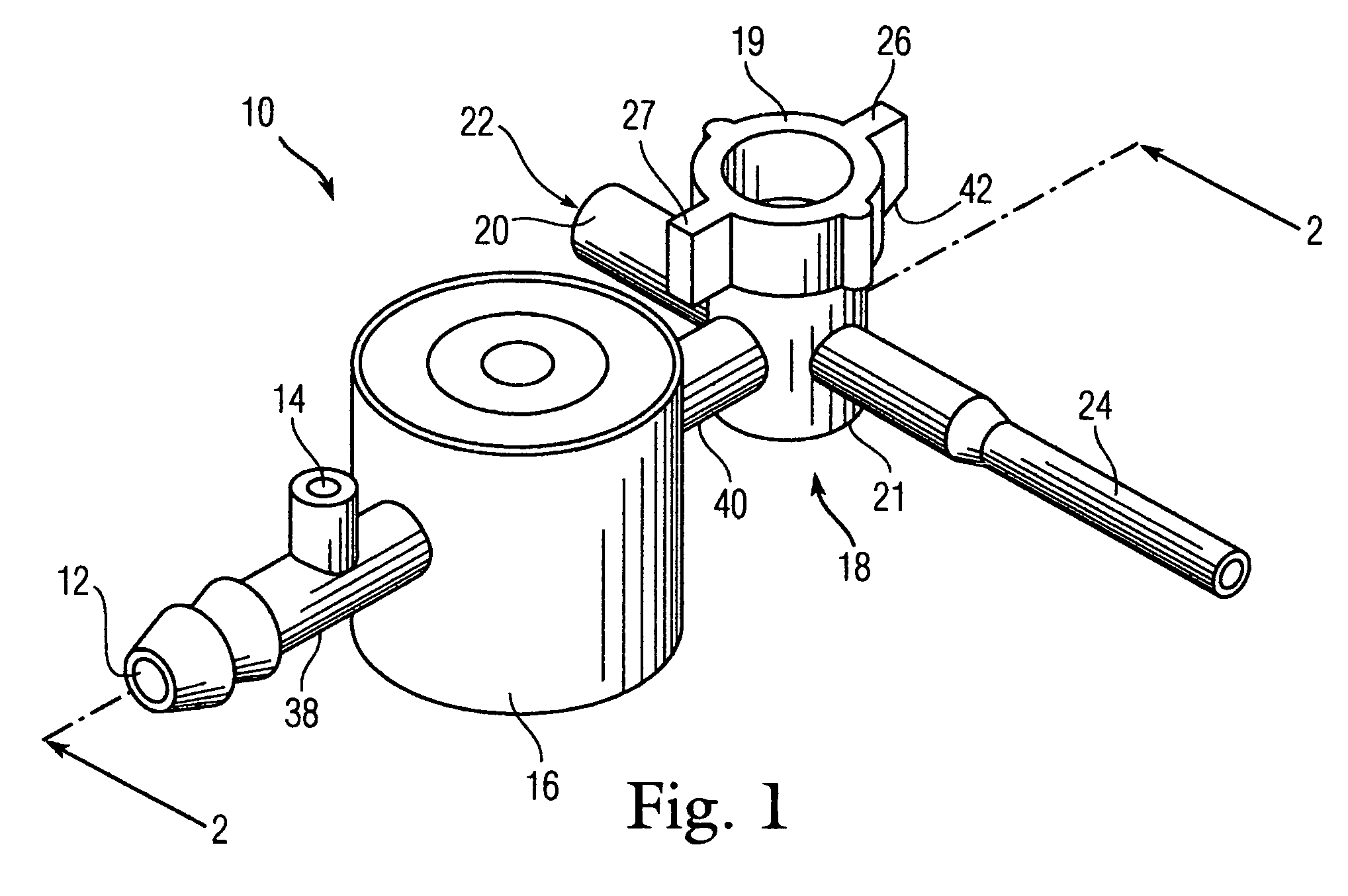
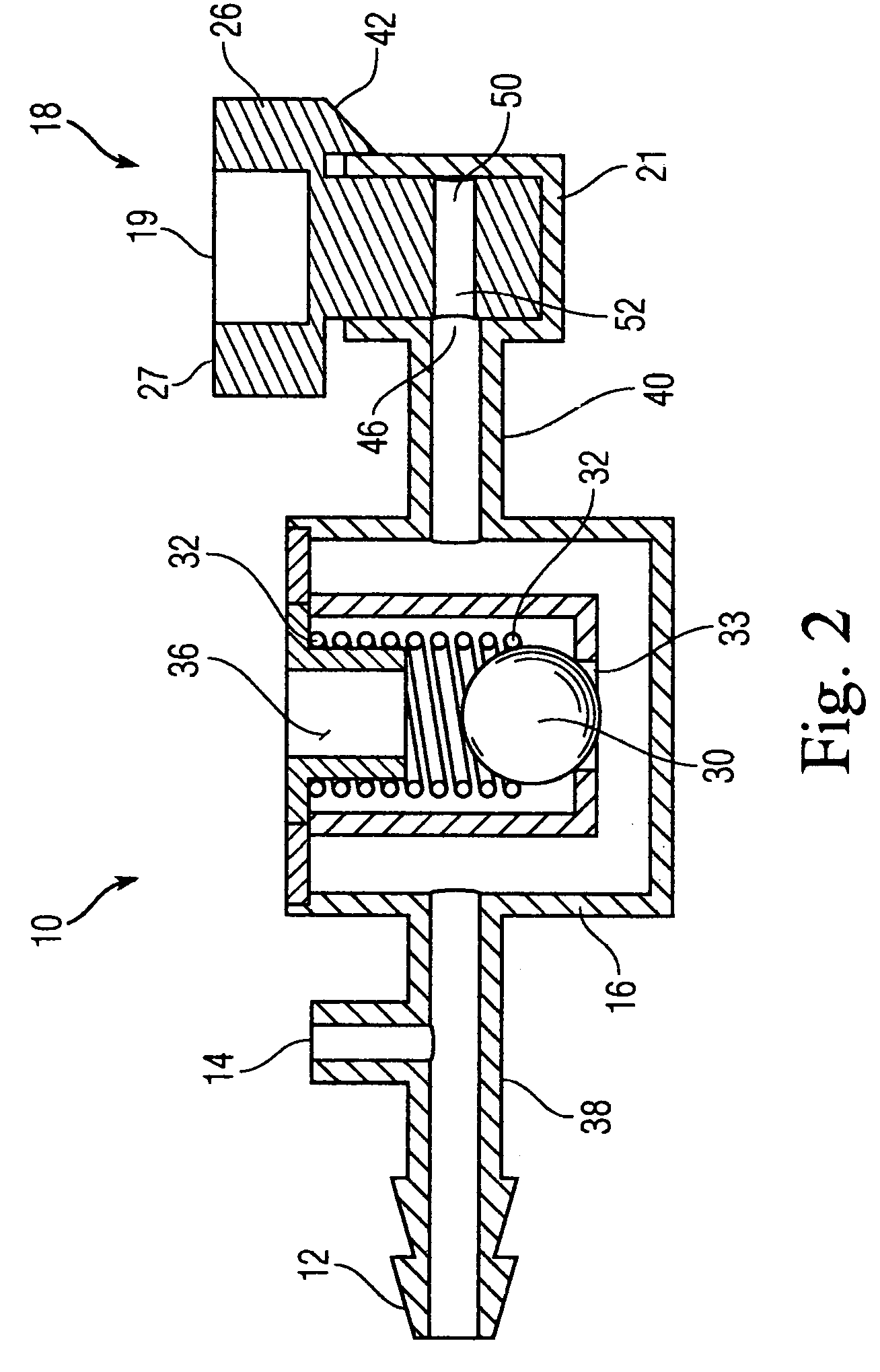
Patents
Literature
140 results about "Bronchoscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
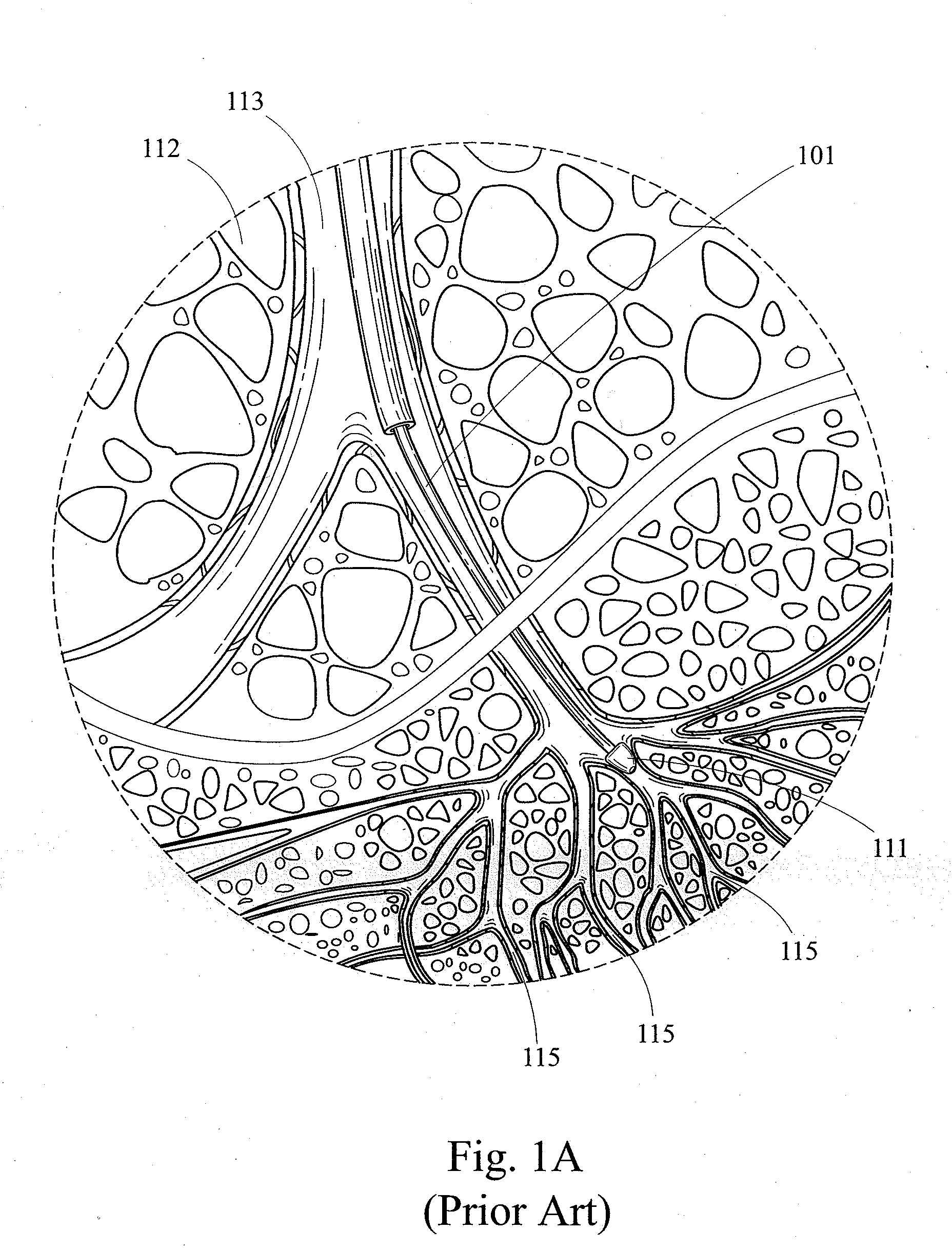
<ul><li>Normal results show healthy lungs with normal cells and fluid.</li><li>Abnormal results may show bacterial, viral, parasitic or other infection, inflammation from different disorders, damage from allergic reactions, narrowing of the airways etc.</li></ul>
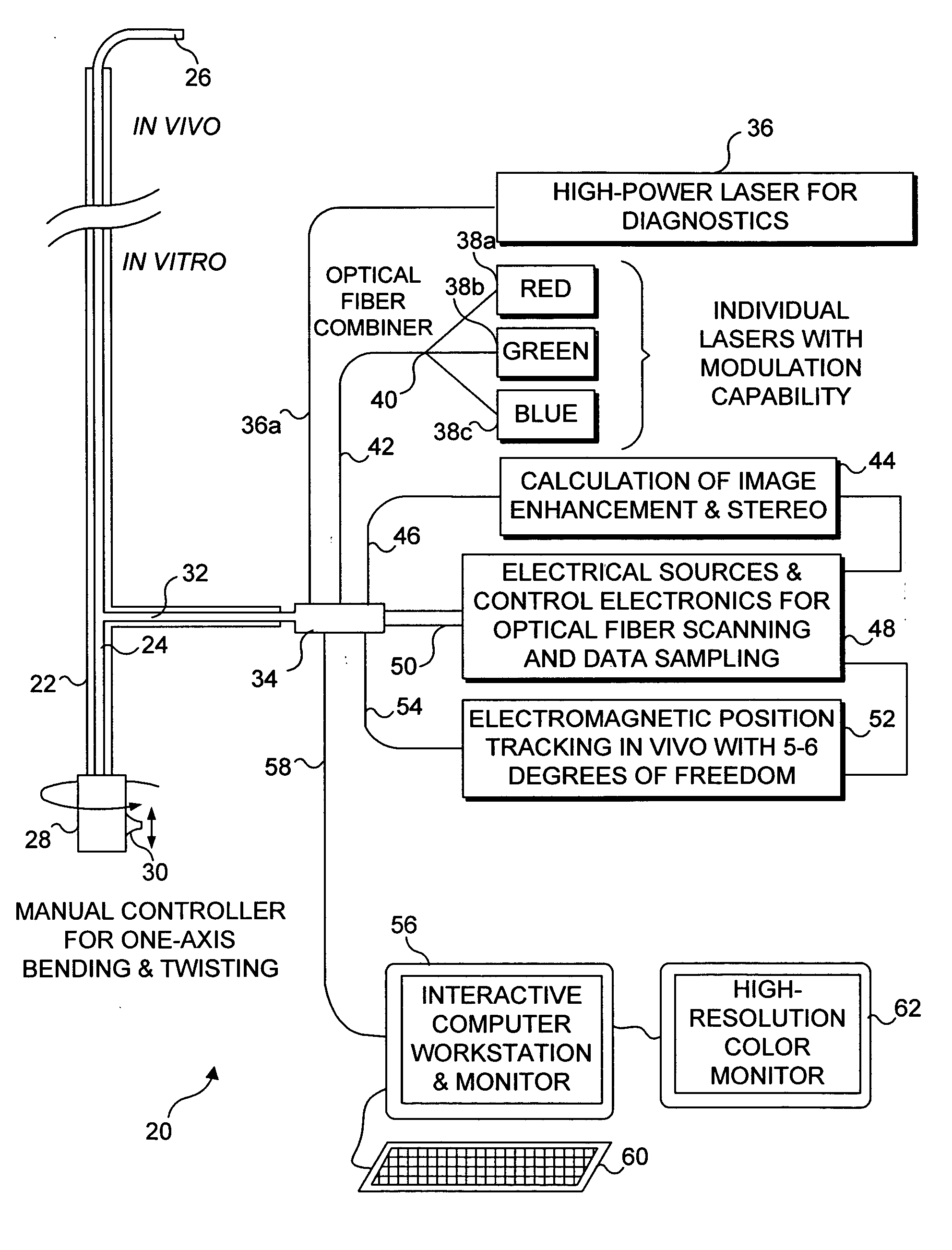
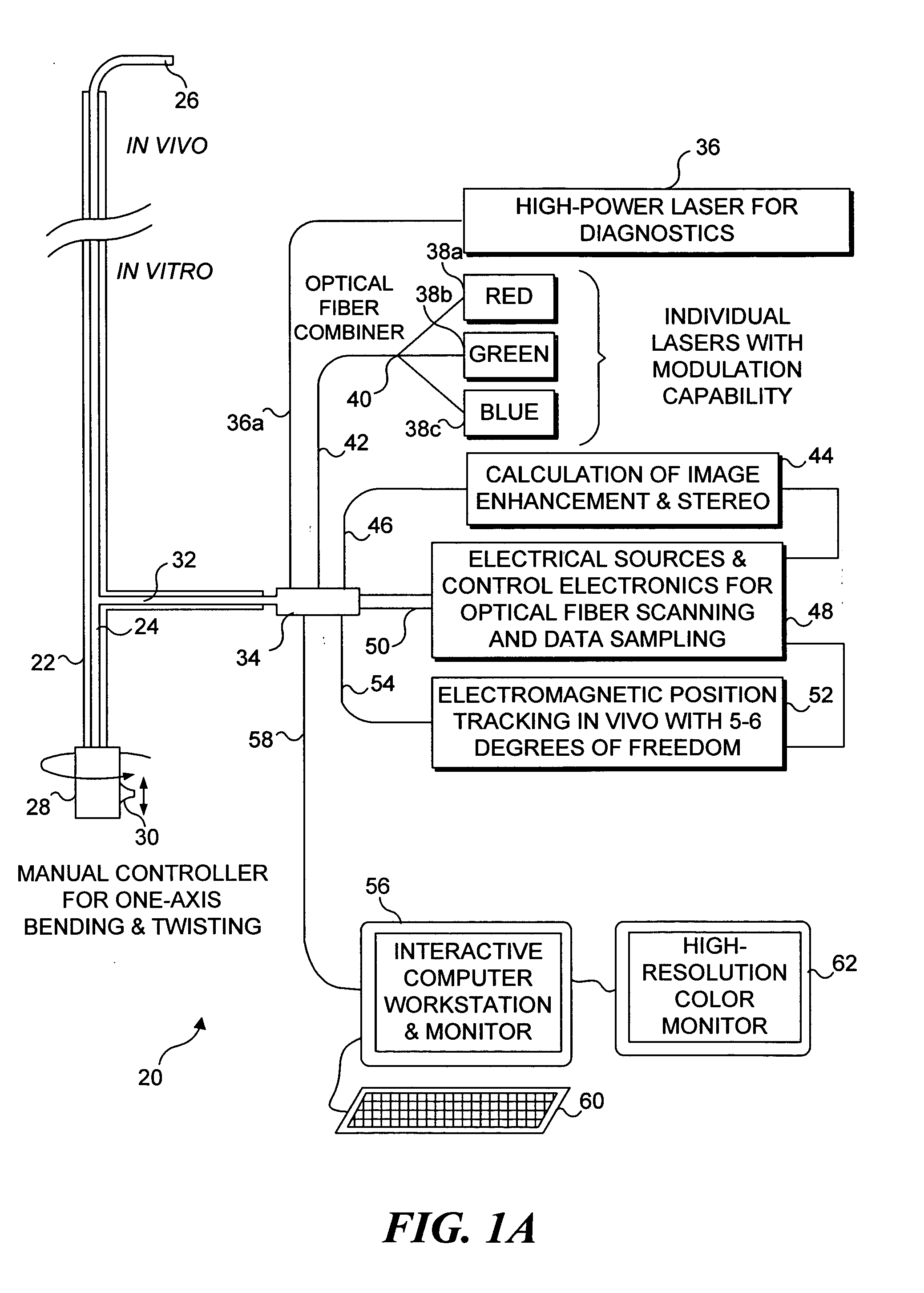
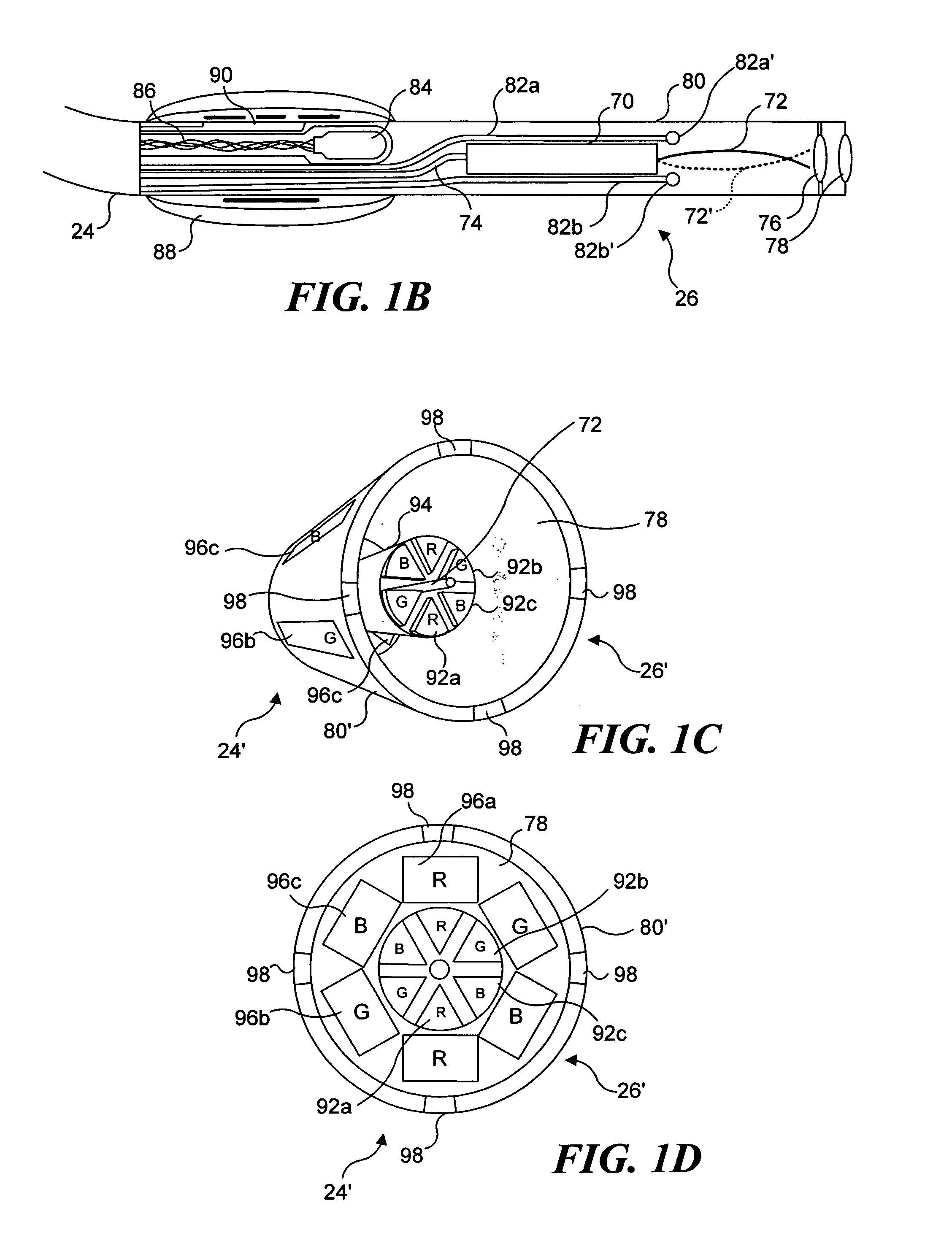
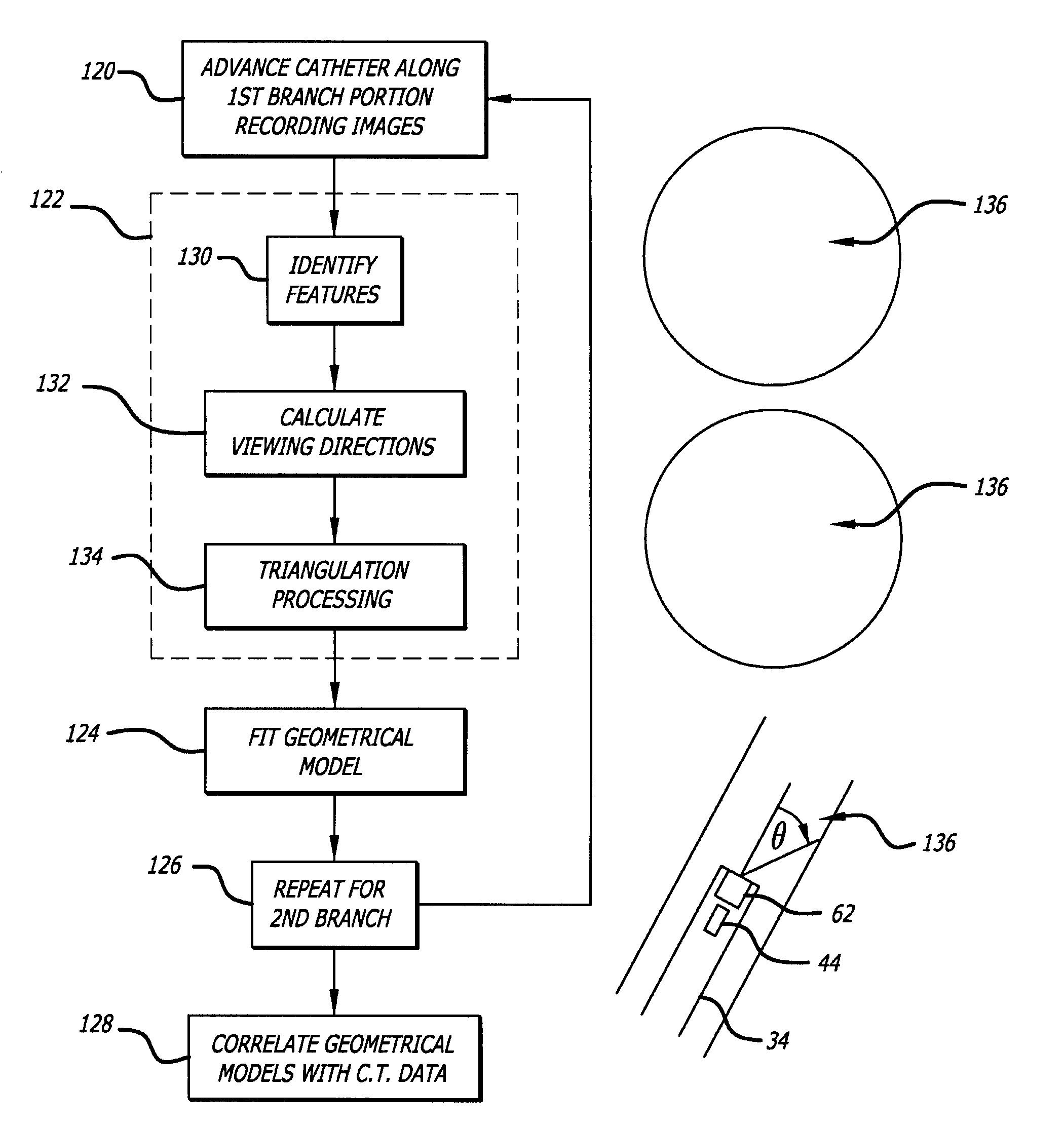
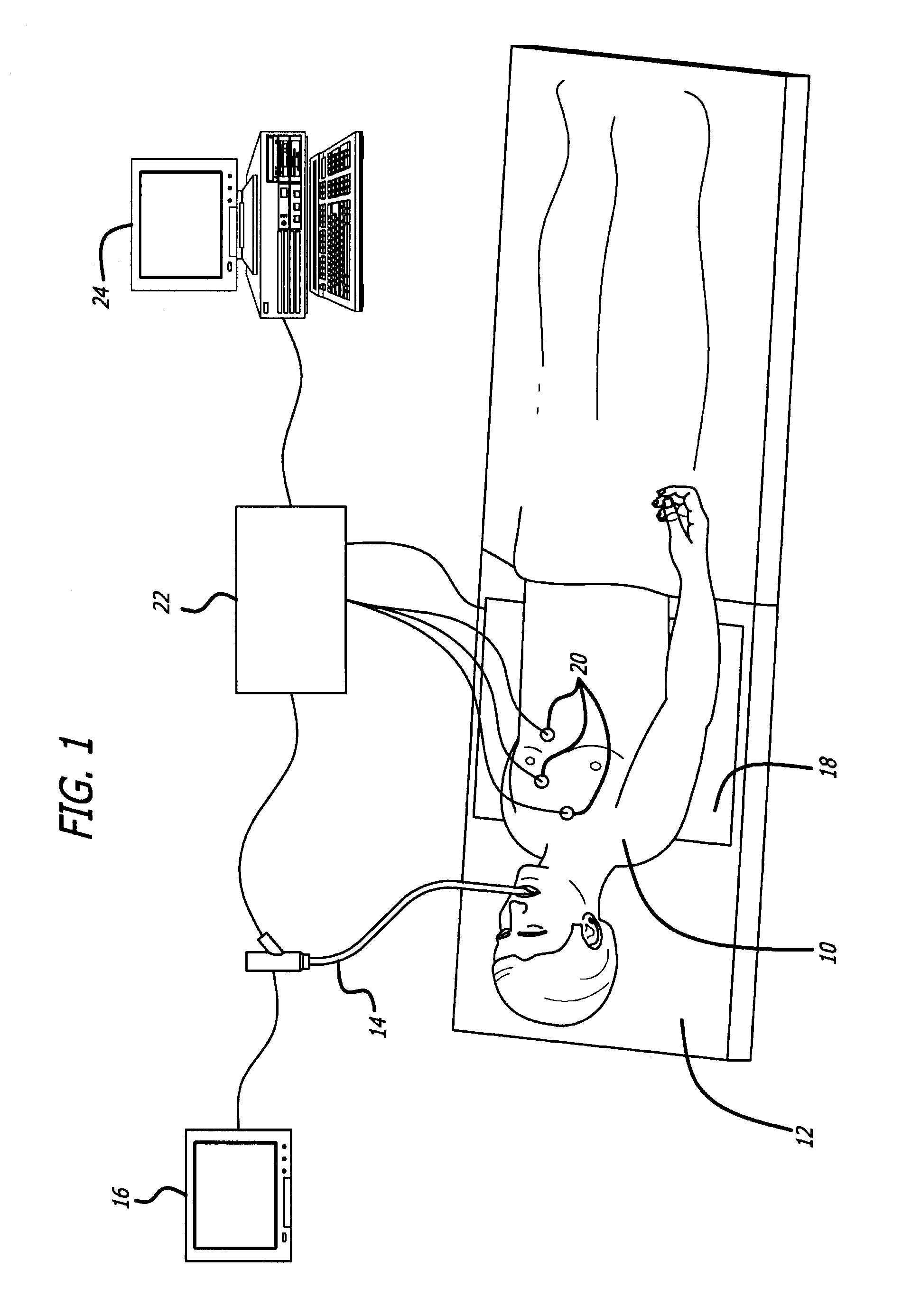
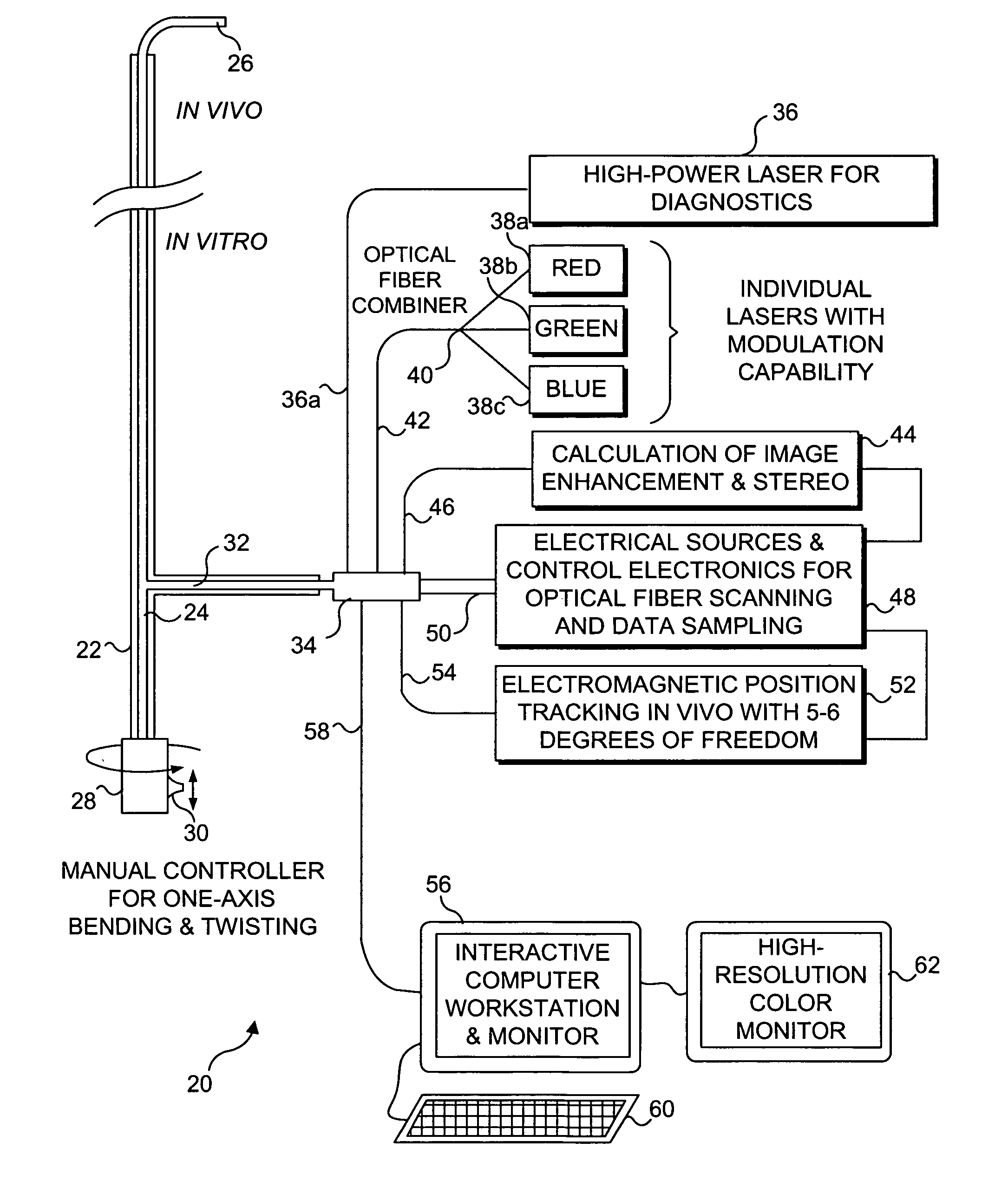
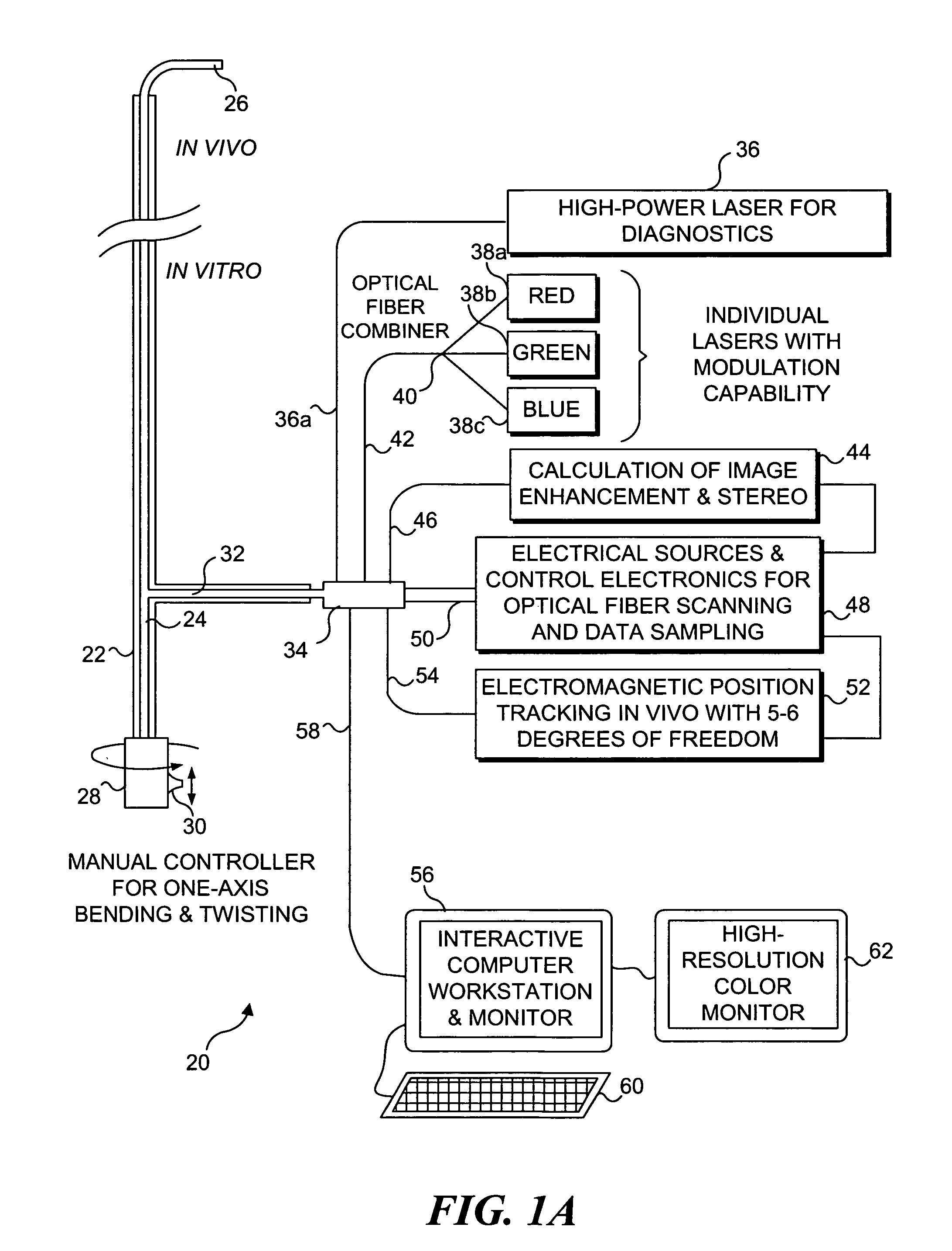
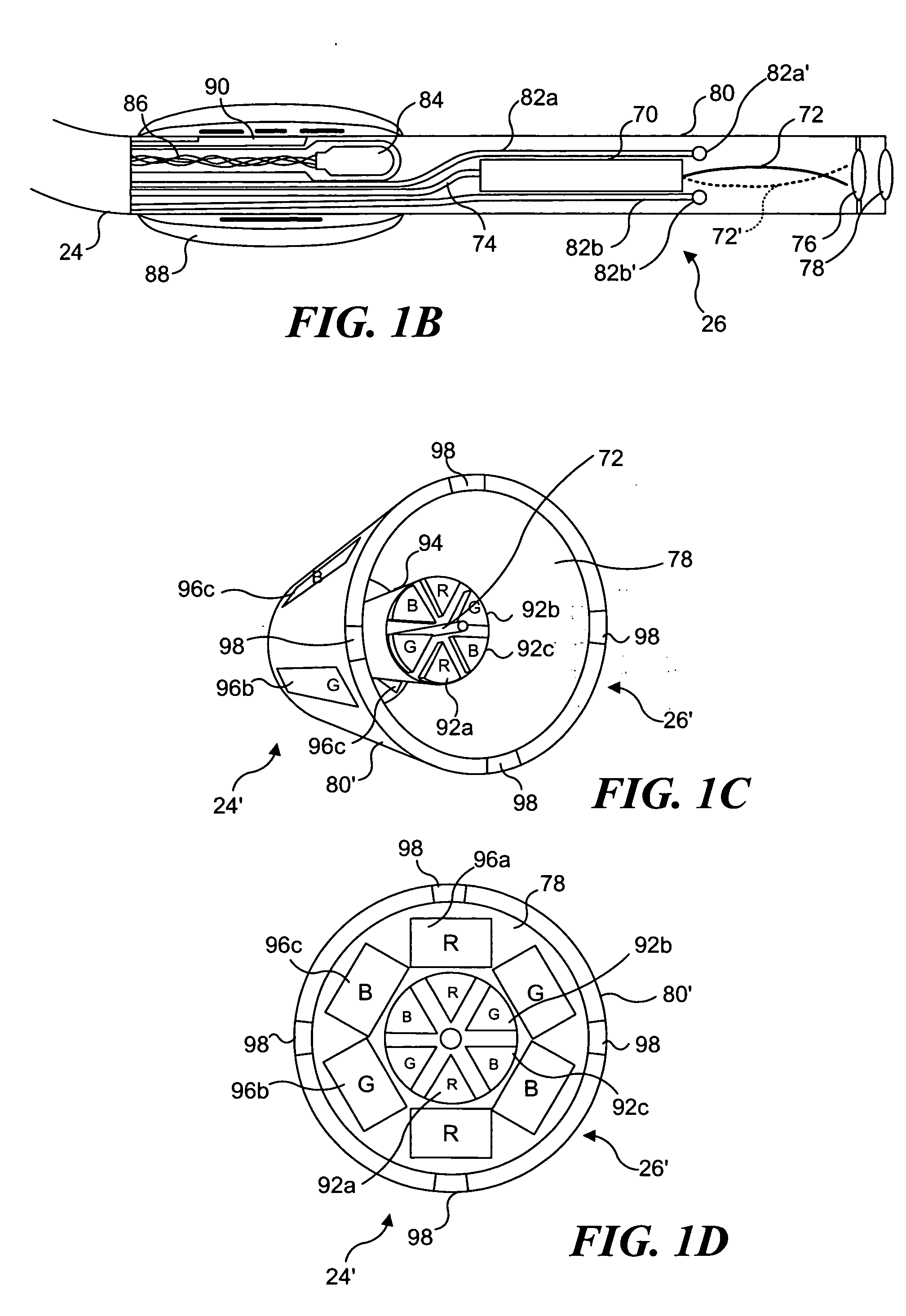
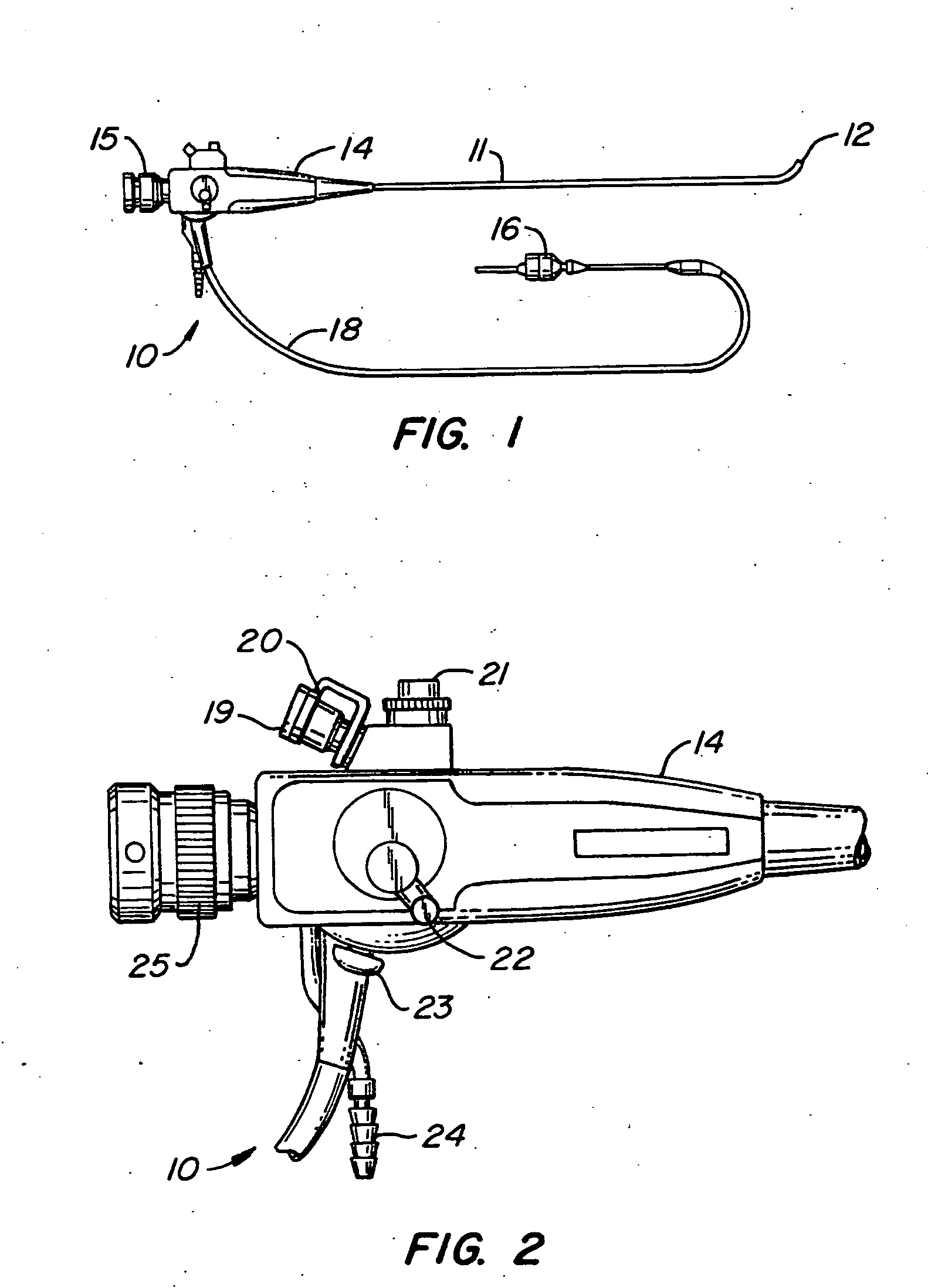
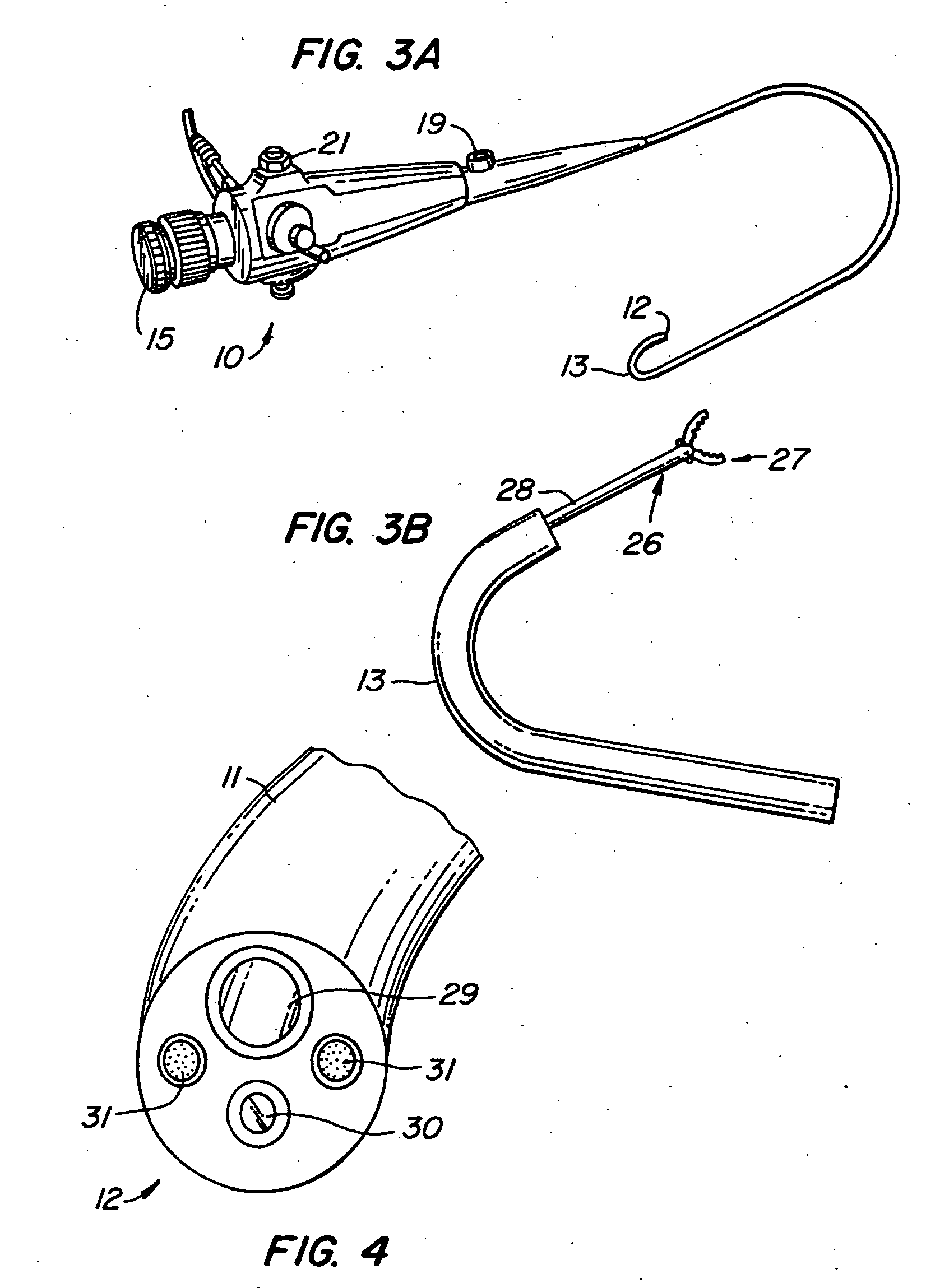
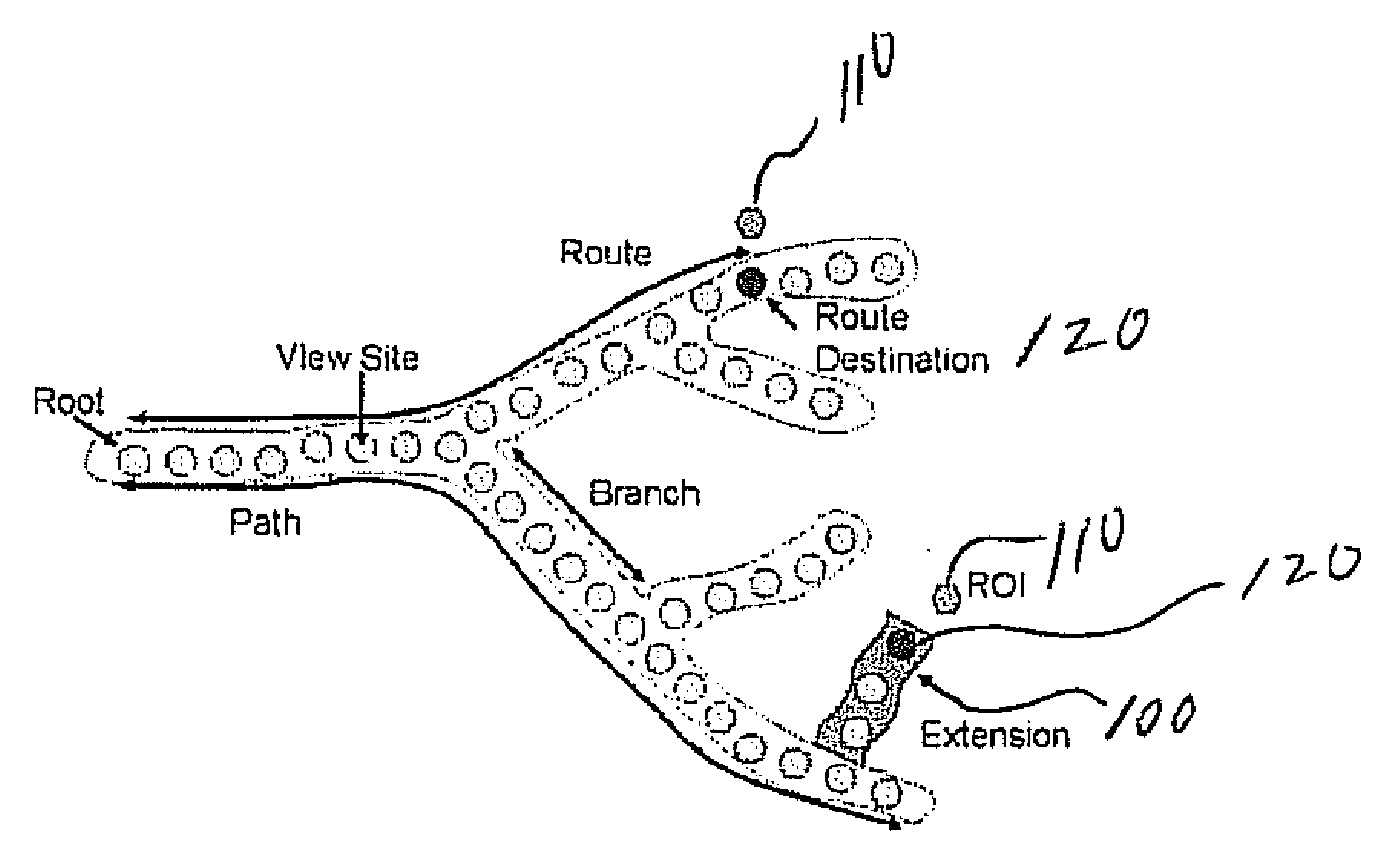
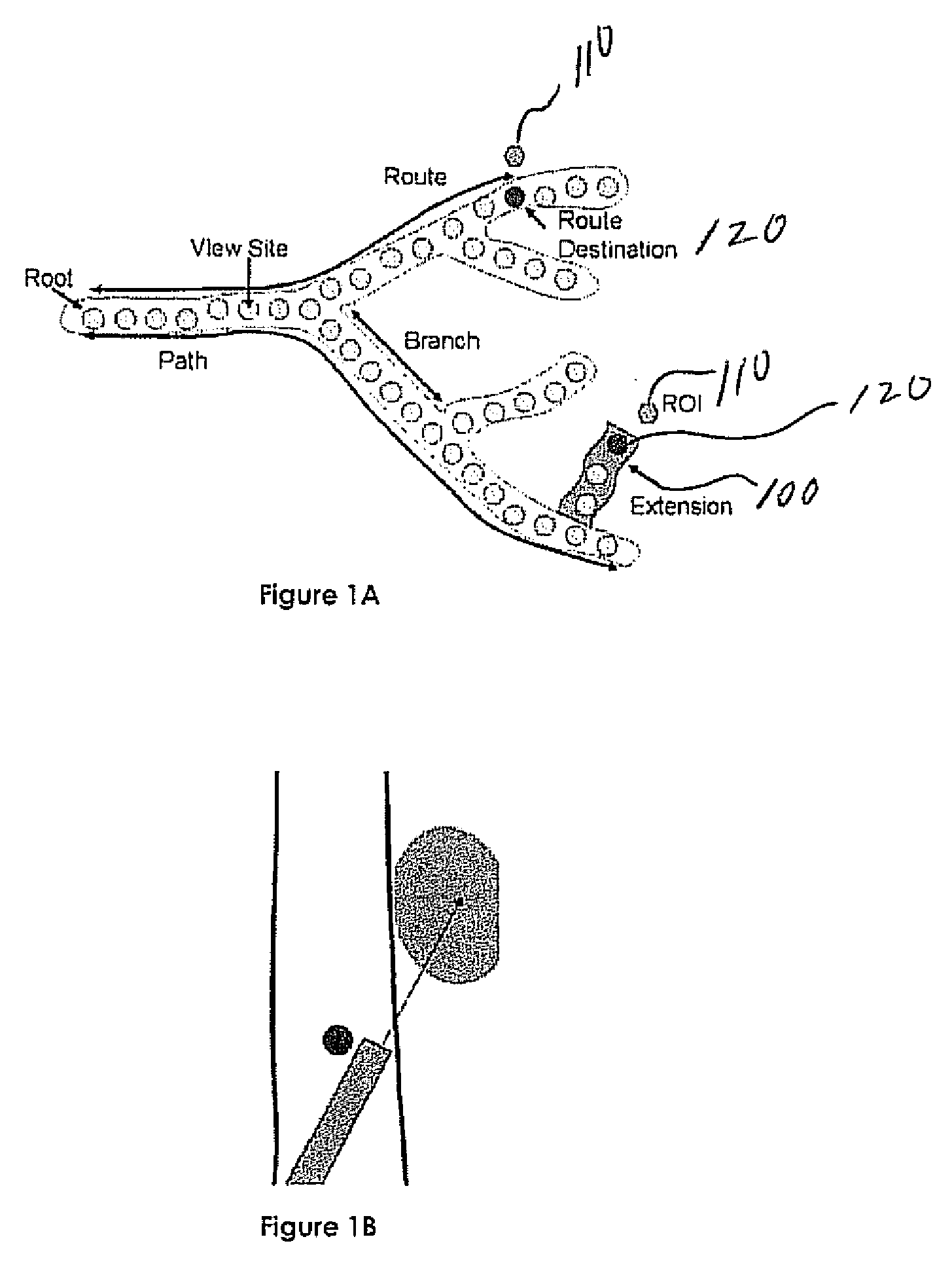
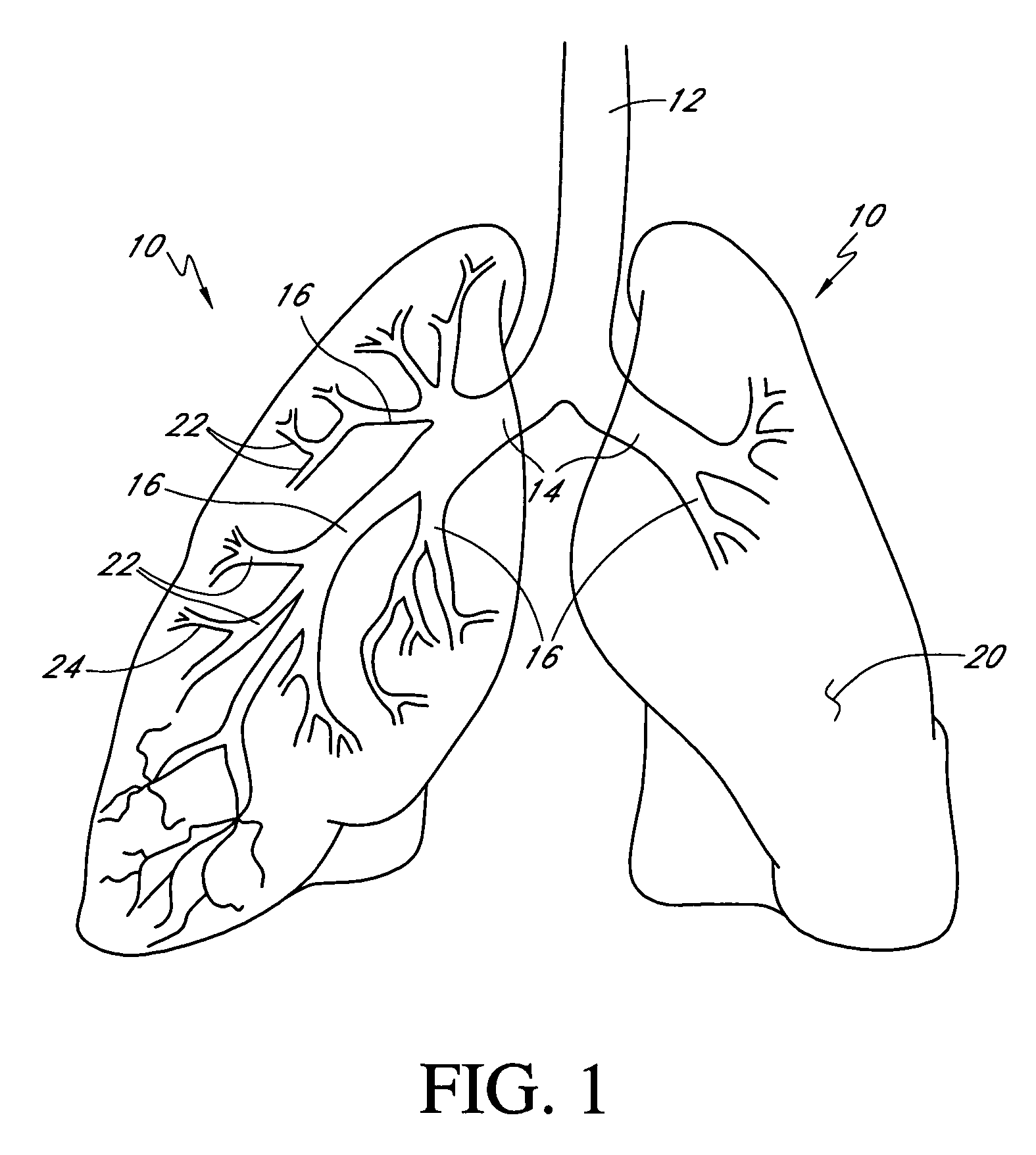
Catheterscope 3D guidance and interface system
ActiveUS20050182295A1Effective steeringReduce errorsBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesHigh-resolution computed tomographyGraphics
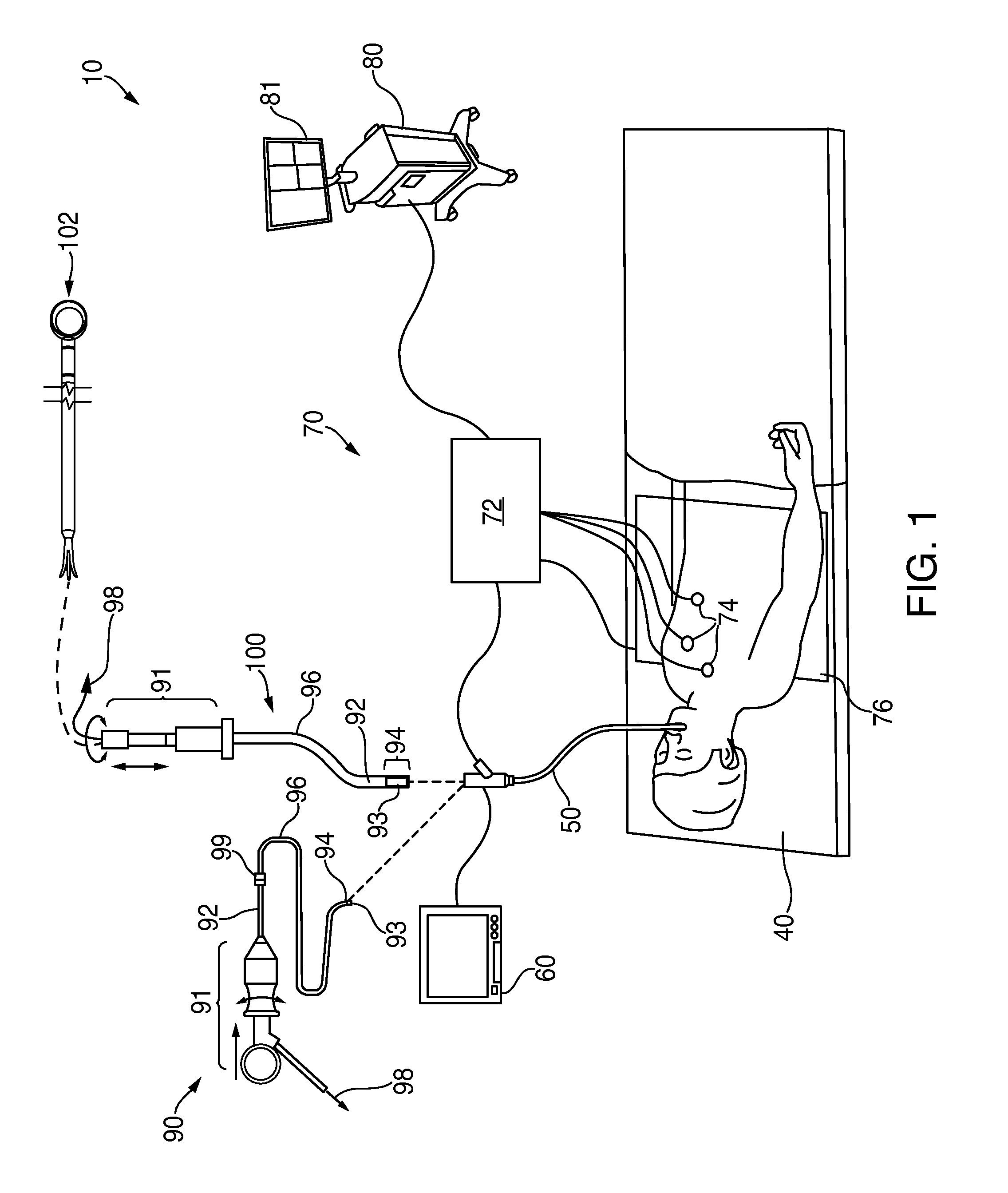
Visual-assisted guidance of an ultra-thin flexible endoscope to a predetermined region of interest within a lung during a bronchoscopy procedure. The region may be an opacity-identified by non-invasive imaging methods, such as high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) or as a malignant lung mass that was diagnosed in a previous examination. An embedded position sensor on the flexible endoscope indicates the position of the distal tip of the probe in a Cartesian coordinate system during the procedure. A visual display is continually updated, showing the present position and orientation of the marker in a 3-D graphical airway model generated from image reconstruction. The visual display also includes windows depicting a virtual fly-through perspective and real-time video images acquired at the head of the endoscope, which can be stored as data, with an audio or textual account.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
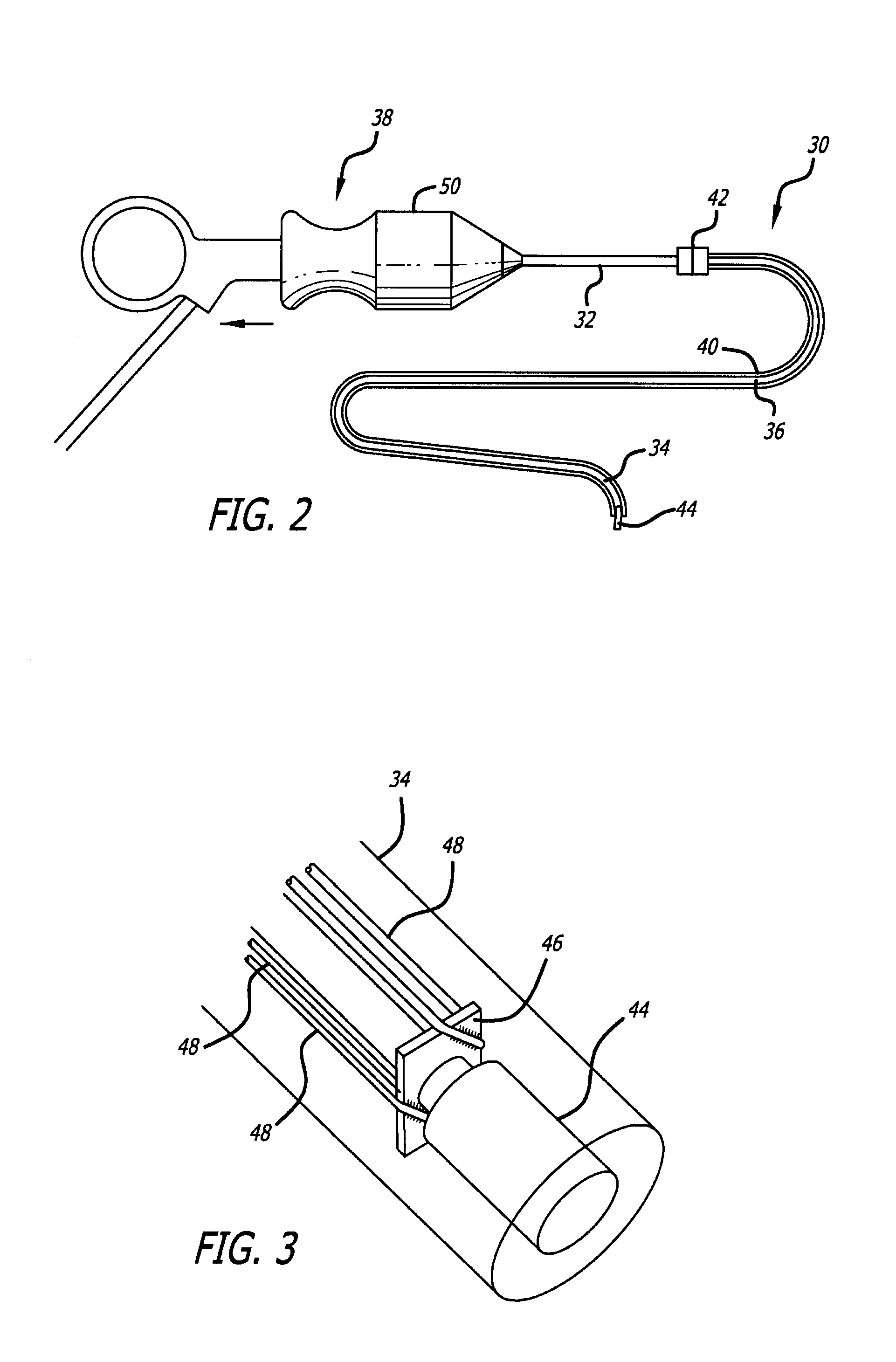
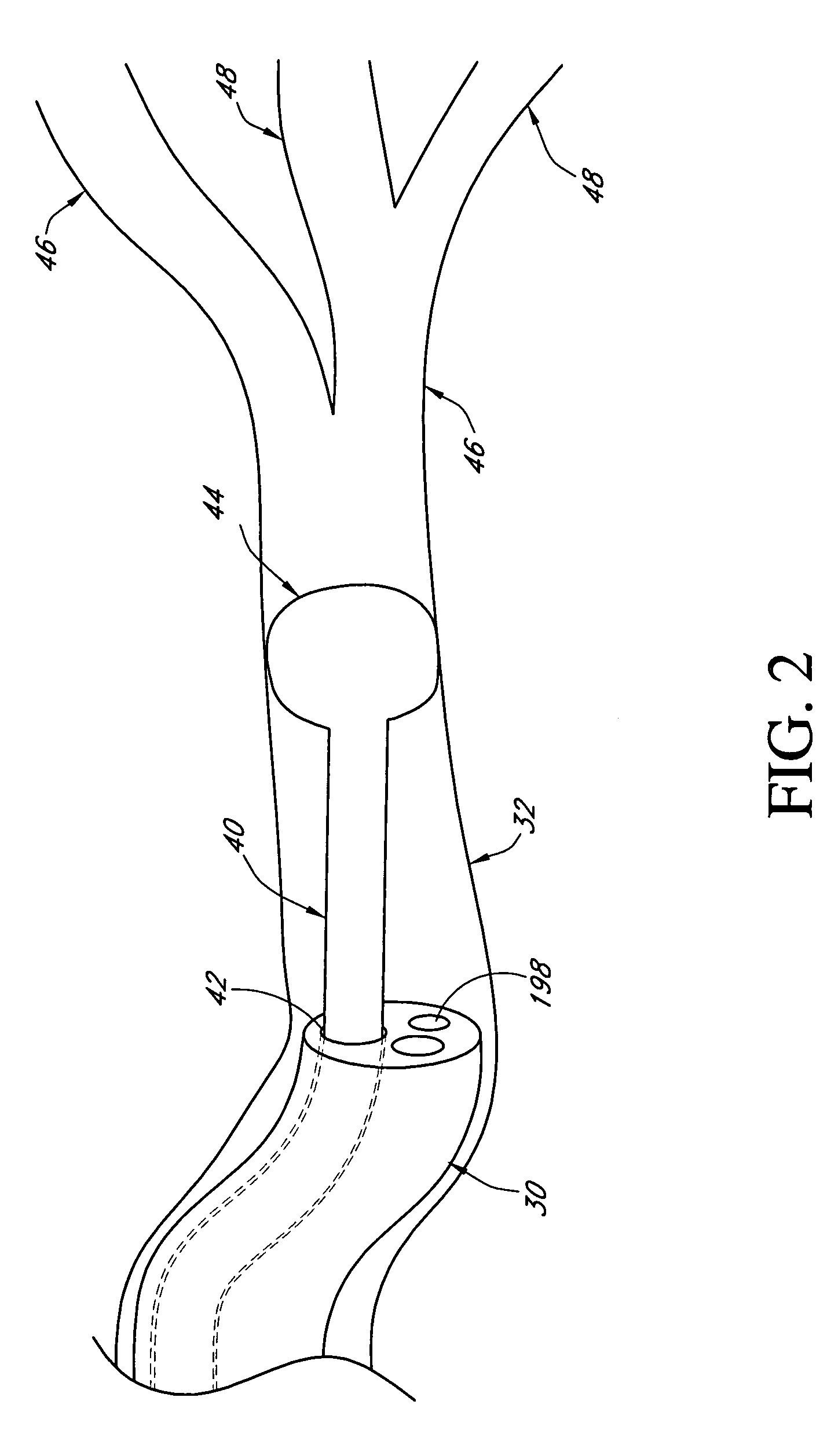
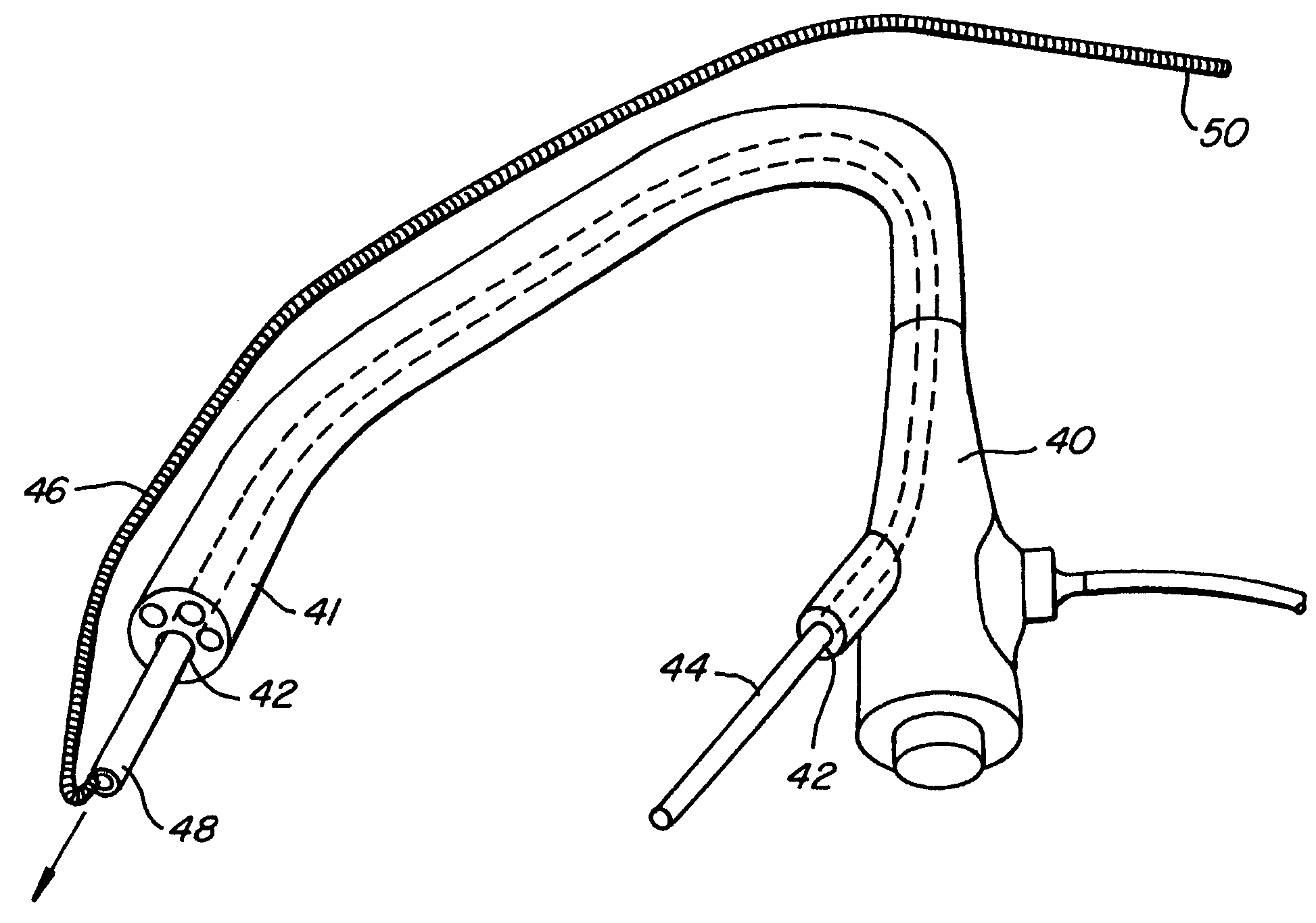
Endoscope structures and techniques for navigating to a target in branched structure
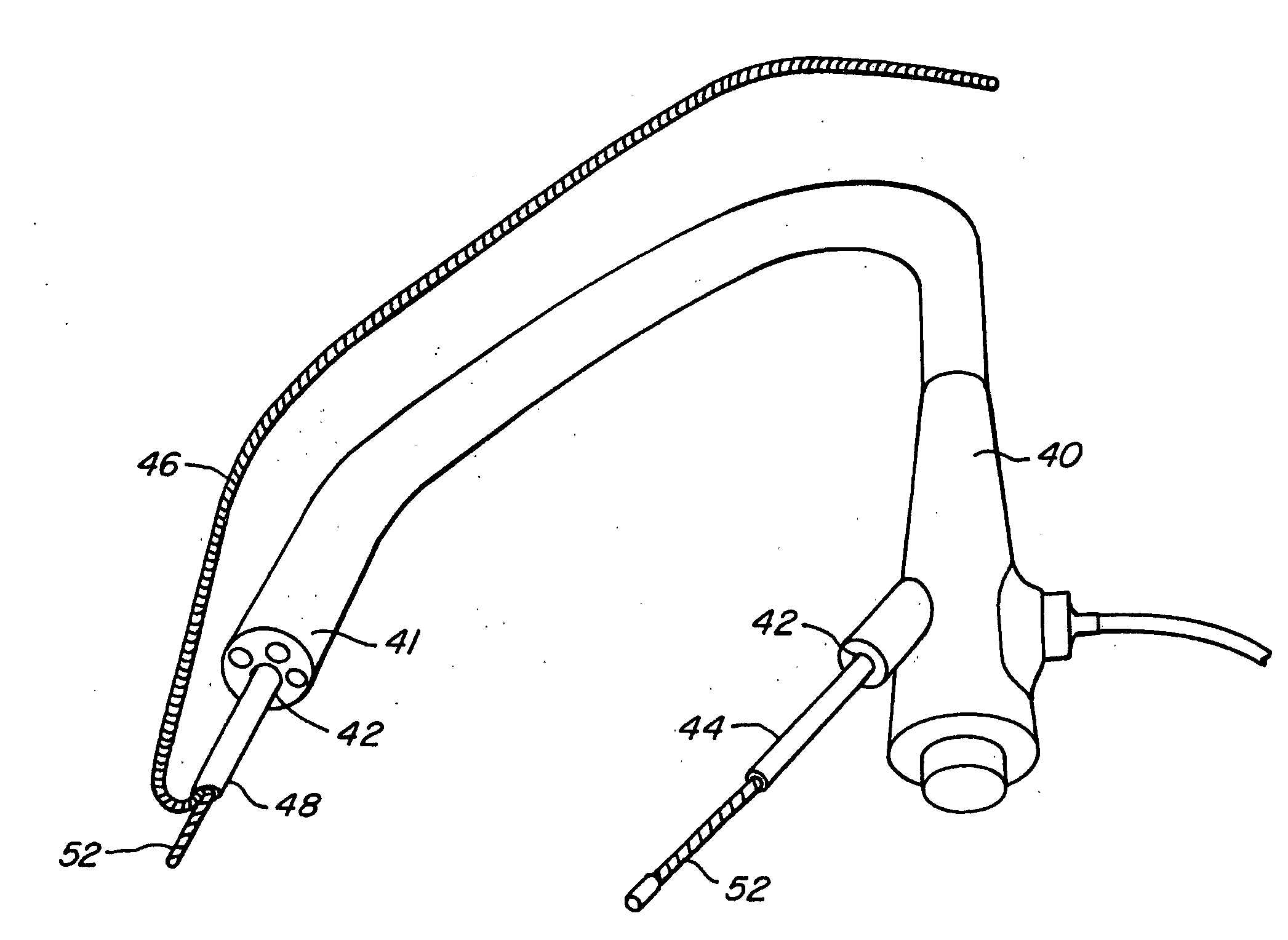
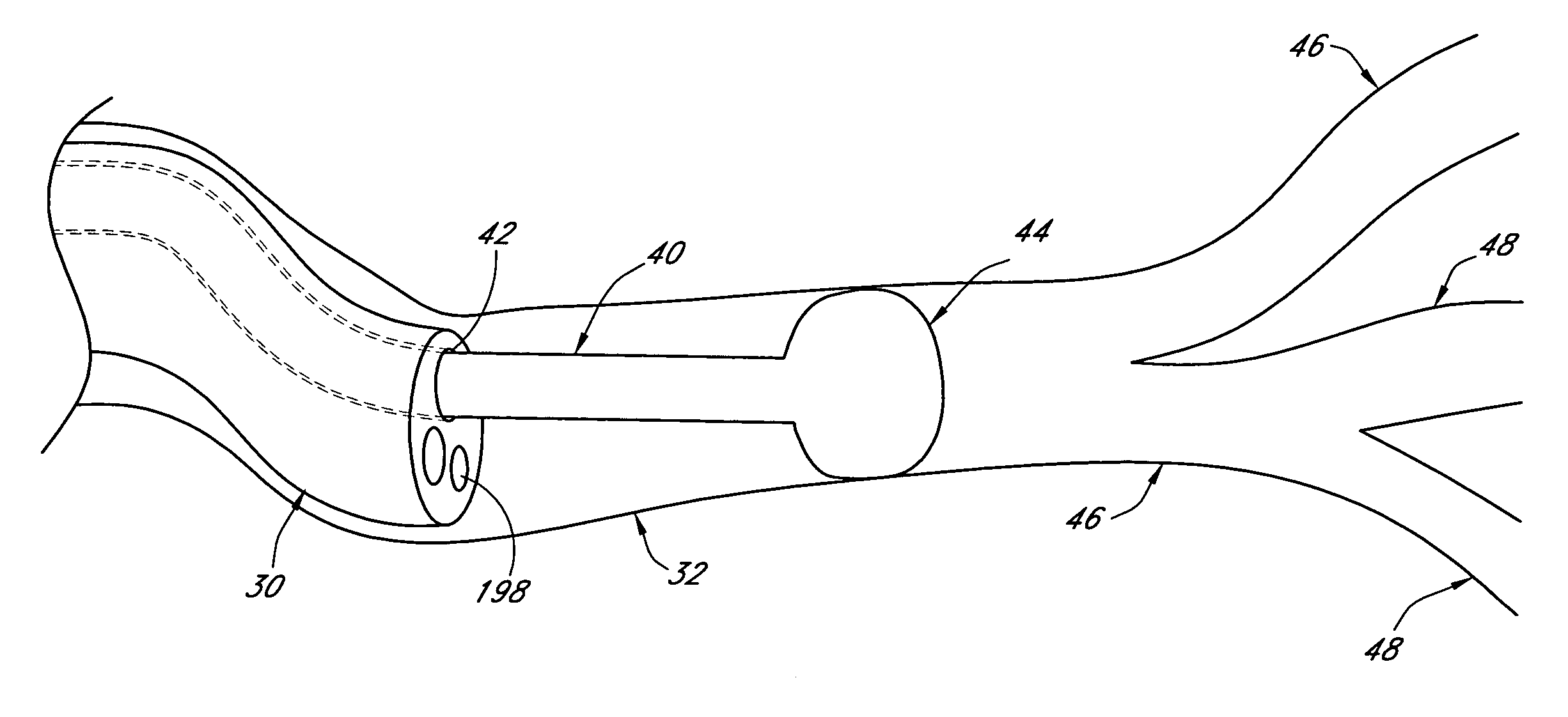
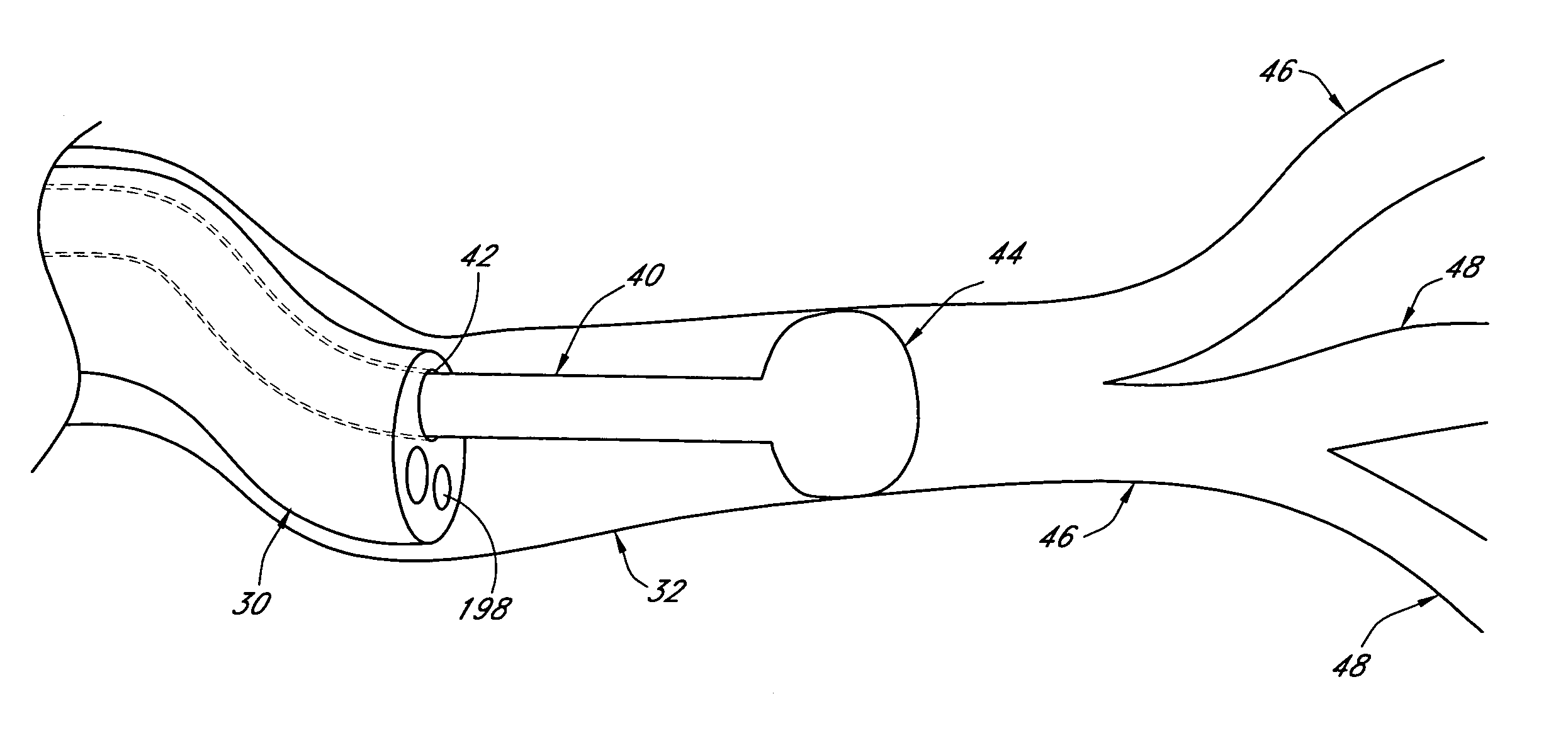
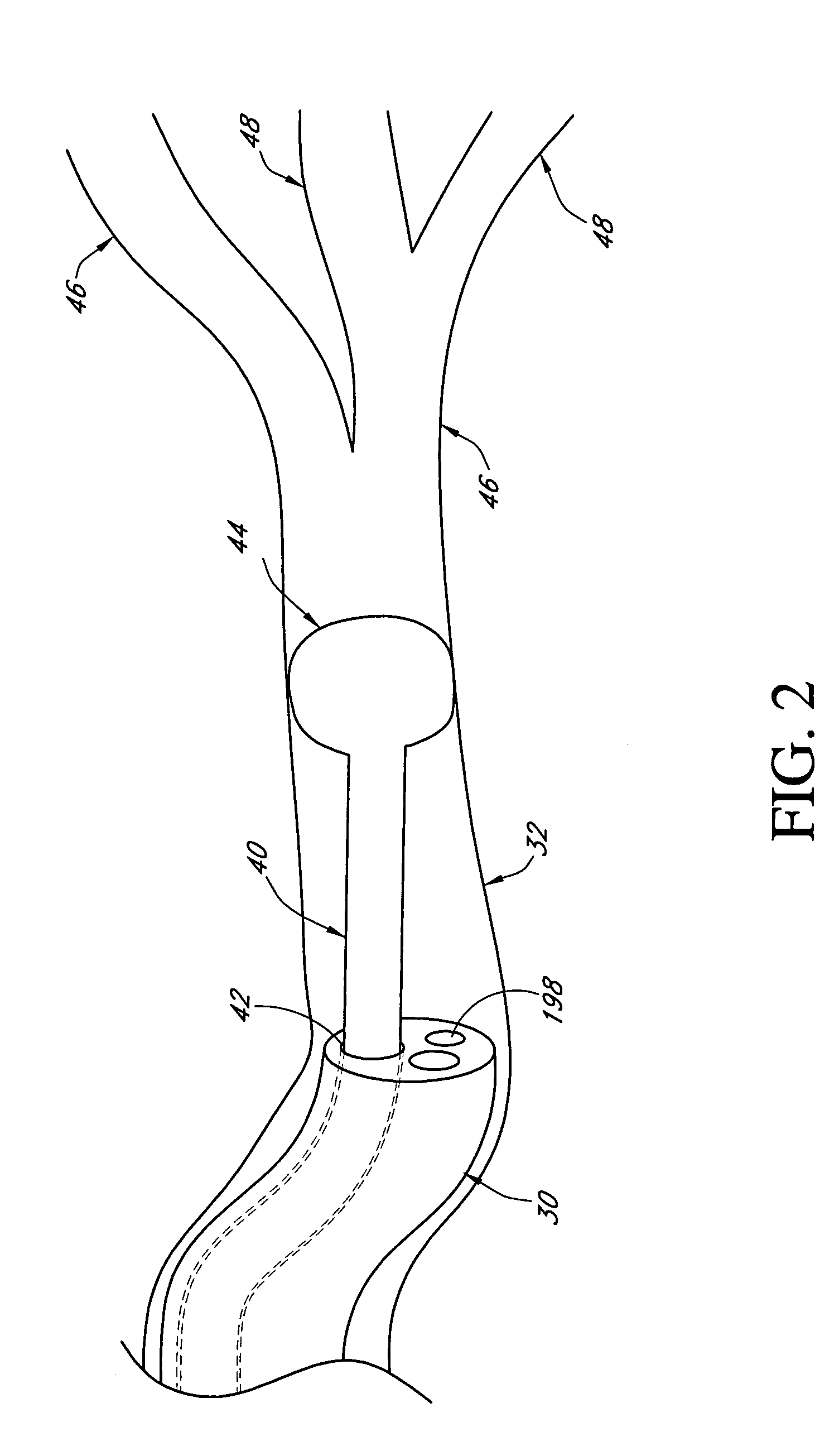
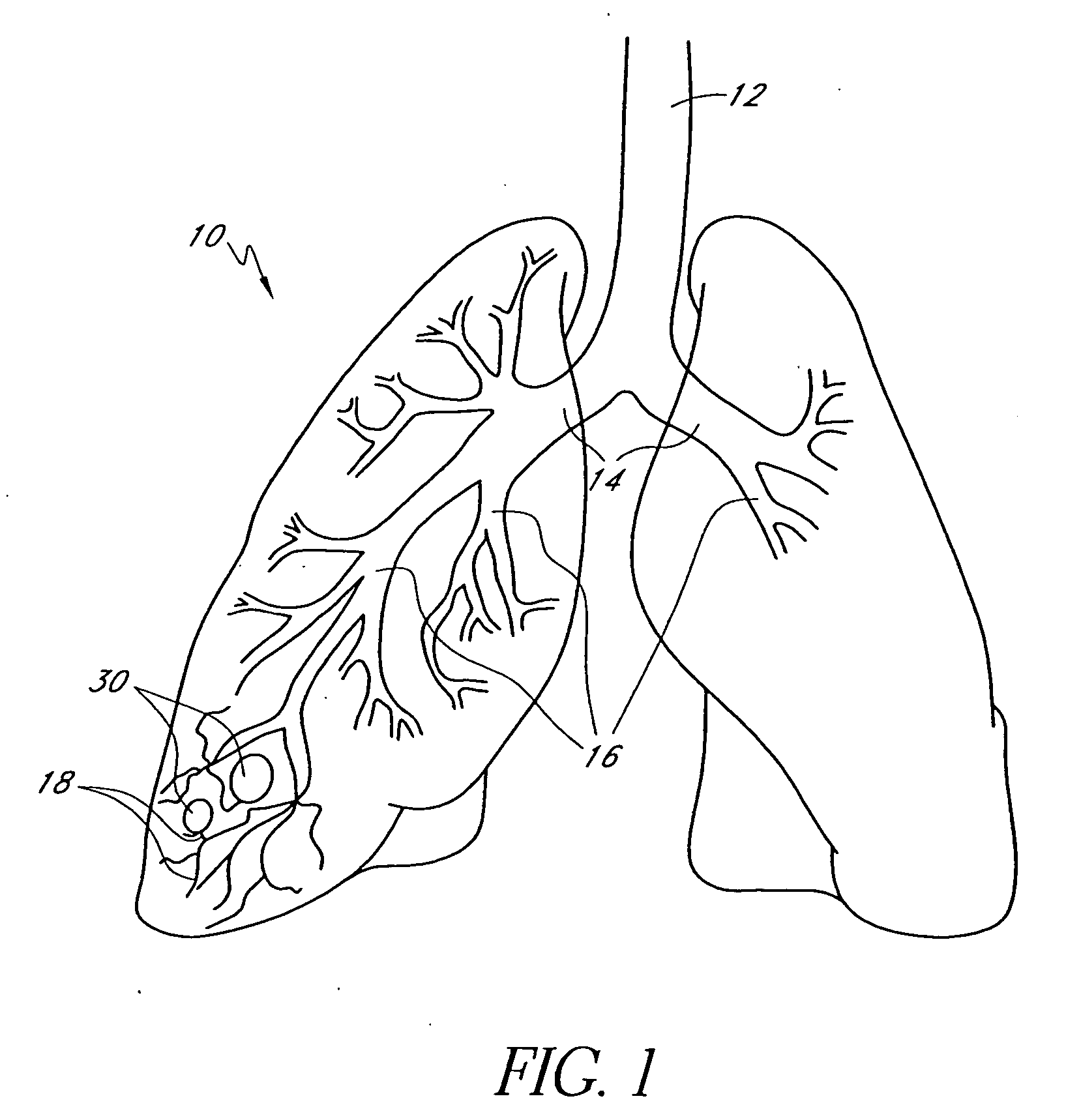
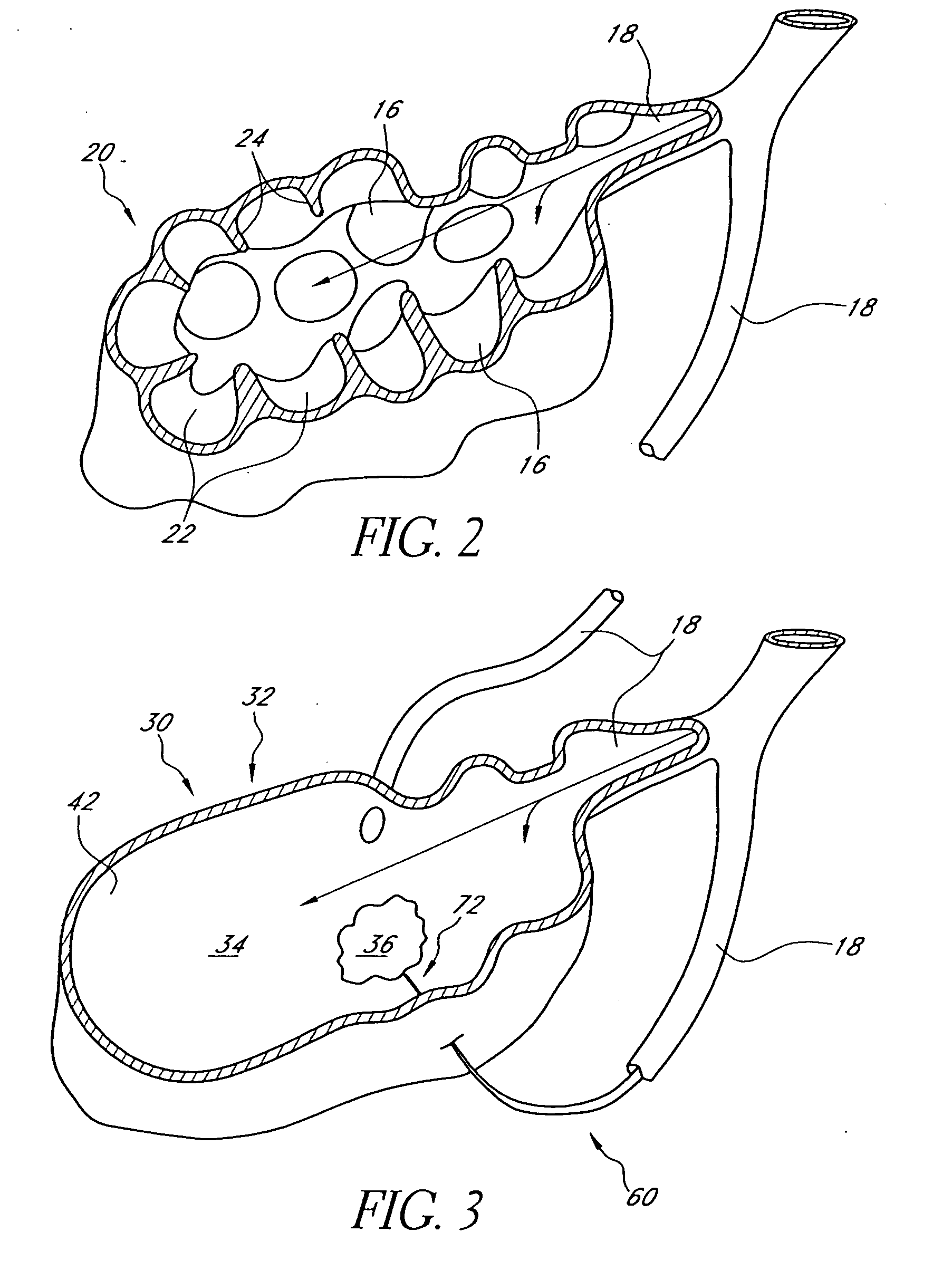
Systems and methods employing a small guage steerable catheter (30) including a locatable guide (32) with a sheath (40), particularly as an enhancement to a bronchoscope (14). A typical procedure is as follows. The location of a target in a reference coordinate system is detected or imported. The catheter (30) is navigated to the target which tracking the distal tip (34) of the guide (32) in the reference coordinate system. Insertion of the catheter is typically via a working channel of a convention bronchoscope. Once the tip of the catheter is positioned at the target, the guide (32) is withdrawn, leaving the sheath (40) secured in place. The sheath (40) is then used as a guide channel to direct a medical tool to target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Catheterscope 3D guidance and interface system
ActiveUS20060149134A1Effective steeringReduce errorsBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesHigh-resolution computed tomographyGraphics
Visual-assisted guidance of an ultra-thin flexible endoscope to a predetermined region of interest within a lung during a bronchoscopy procedure. The region may be an opacity-identified by non-invasive imaging methods, such as high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) or as a malignant lung mass that was diagnosed in a previous examination. An embedded position sensor on the flexible endoscope indicates the position of the distal tip of the probe in a Cartesian coordinate system during the procedure. A visual display is continually updated, showing the present position and orientation of the marker in a 3-D graphical airway model generated from image reconstruction. The visual display also includes windows depicting a virtual fly-through perspective and real-time video images acquired at the head of the endoscope, which can be stored as data, with an audio or textual account.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
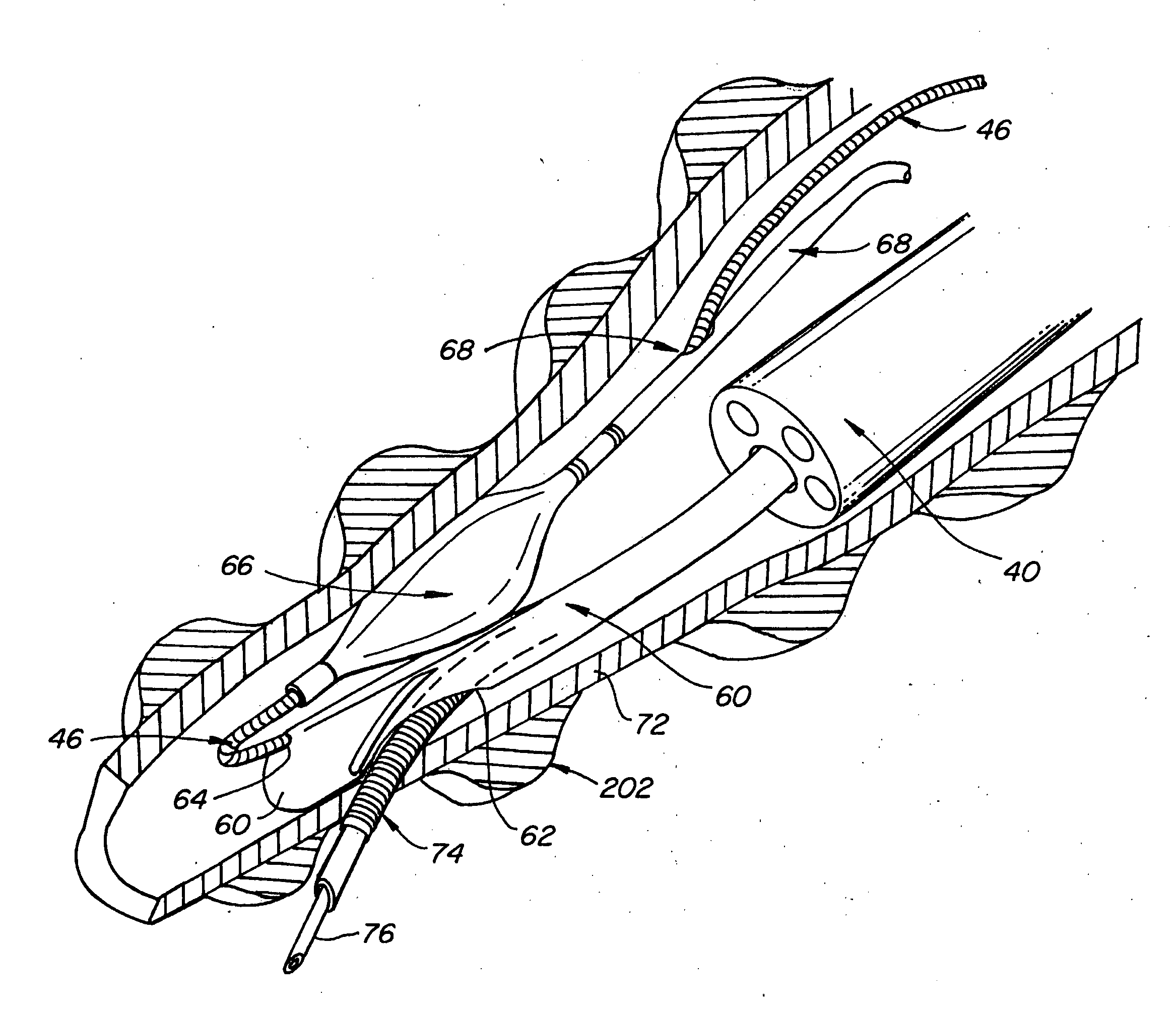
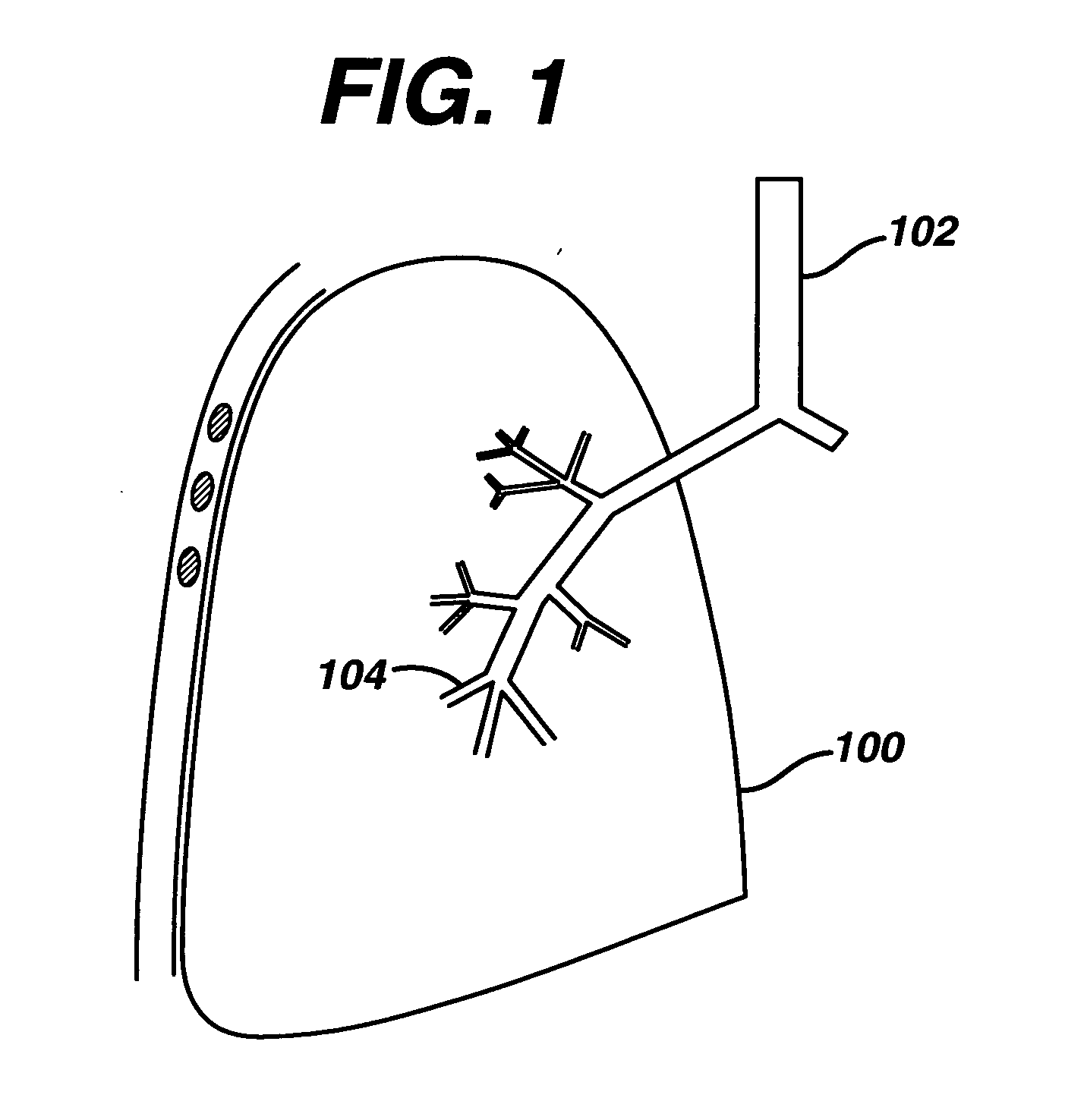
Guided access to lung tissues
InactiveUS20050288549A1Facilitate spreading apart anatomical featureBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesLung tissueMediastinal space
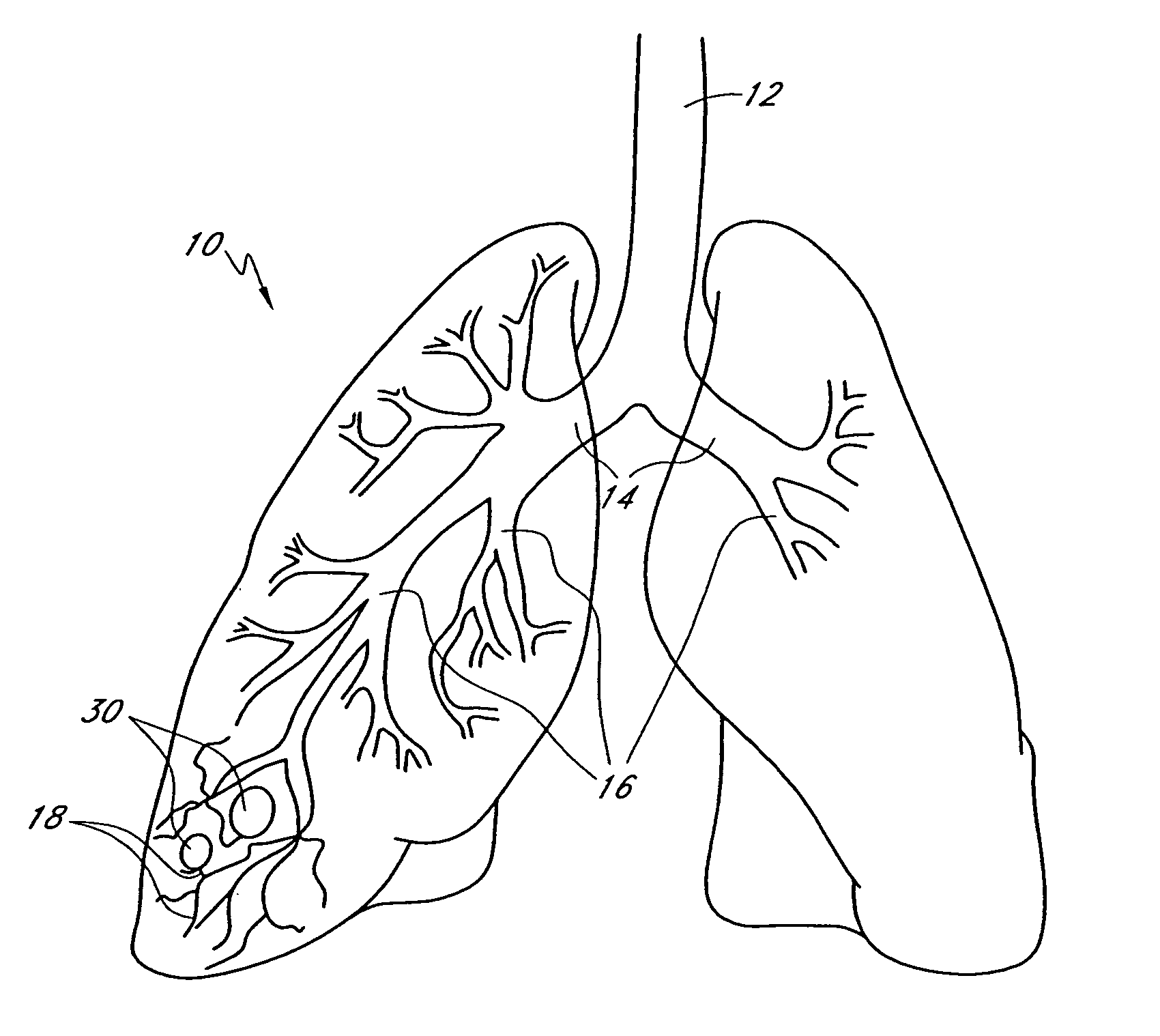
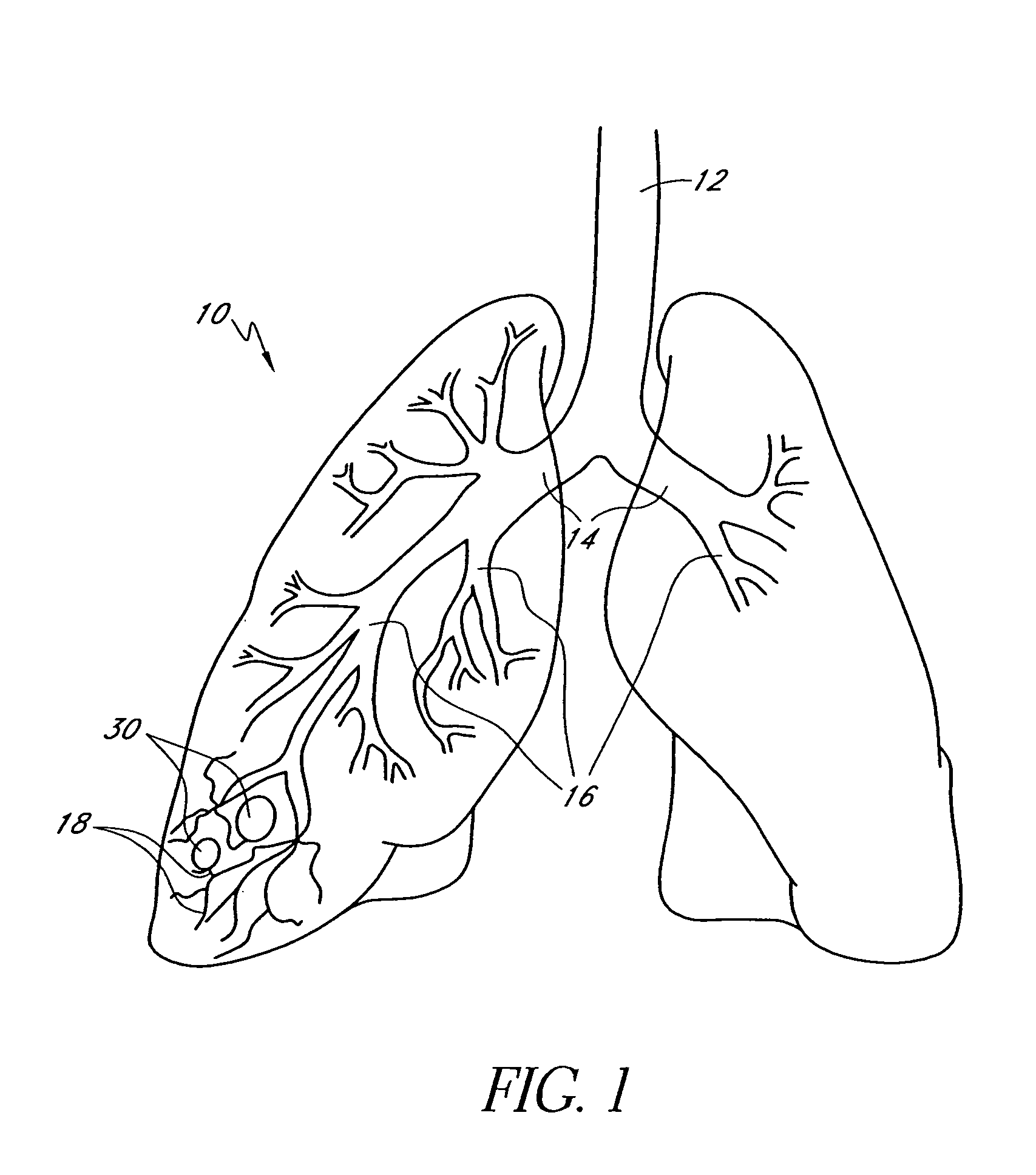
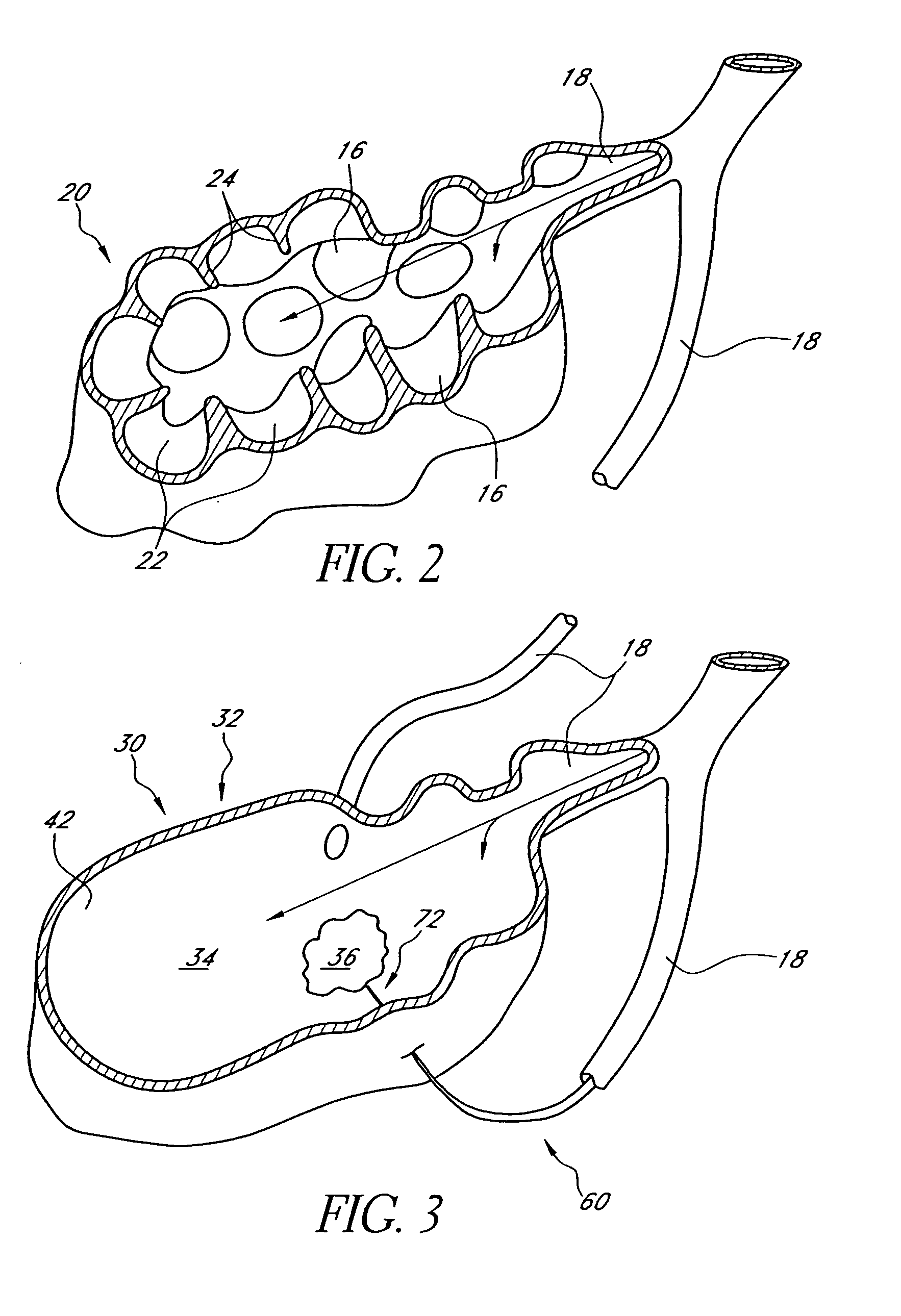
This invention relates generally to lung access devices and methods of using the devices to gain access to the interior of a lung or to the mediastinal space around the lung. In particular, the invention relates to auxiliary access devices and tools for use with conventional bronchoscopes or other endoscopes to enable the delivery of more and larger devices to a target site than is currently possible through a typical endoscope or bronchoscope.
Owner:EKOS CORP
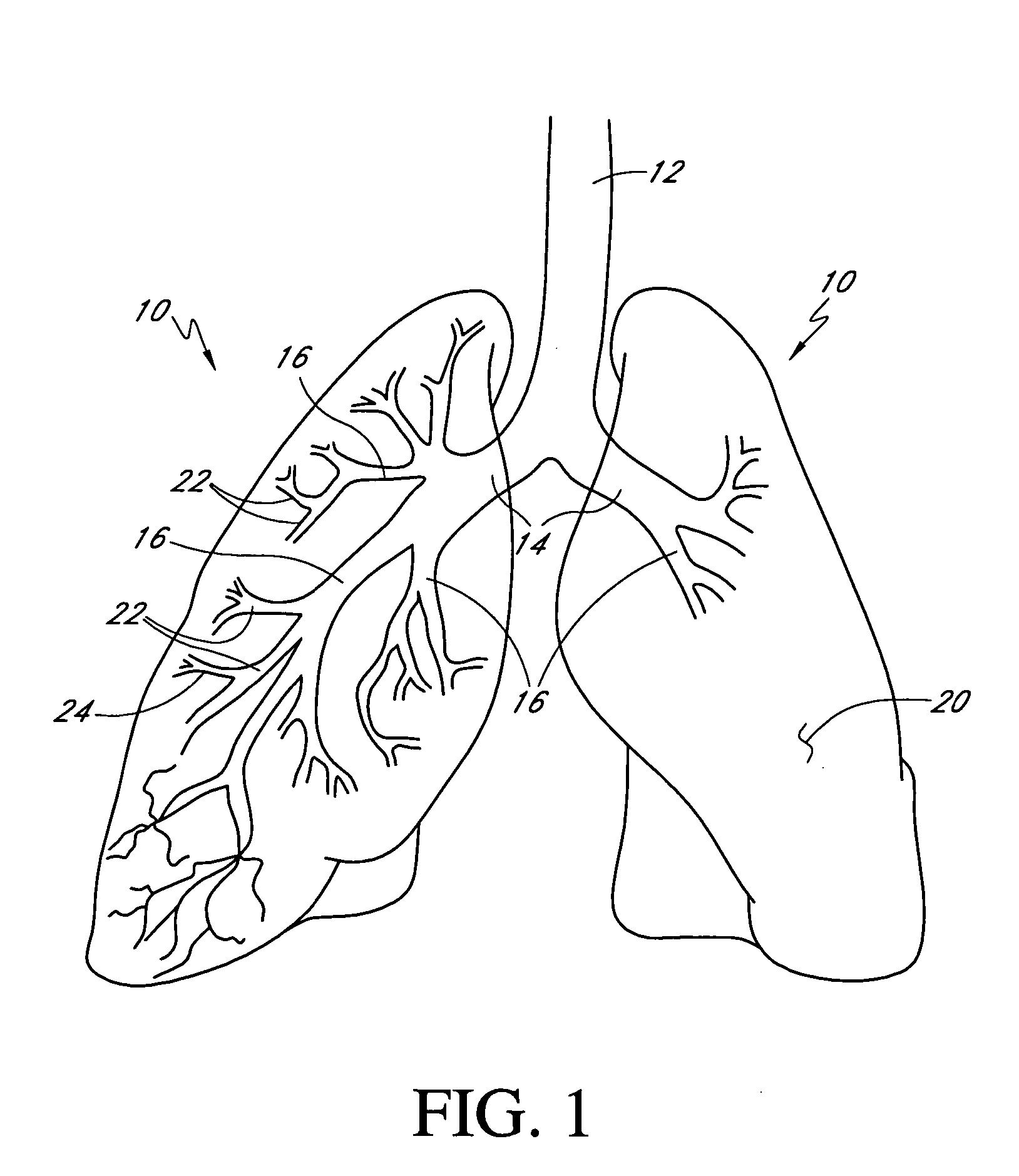
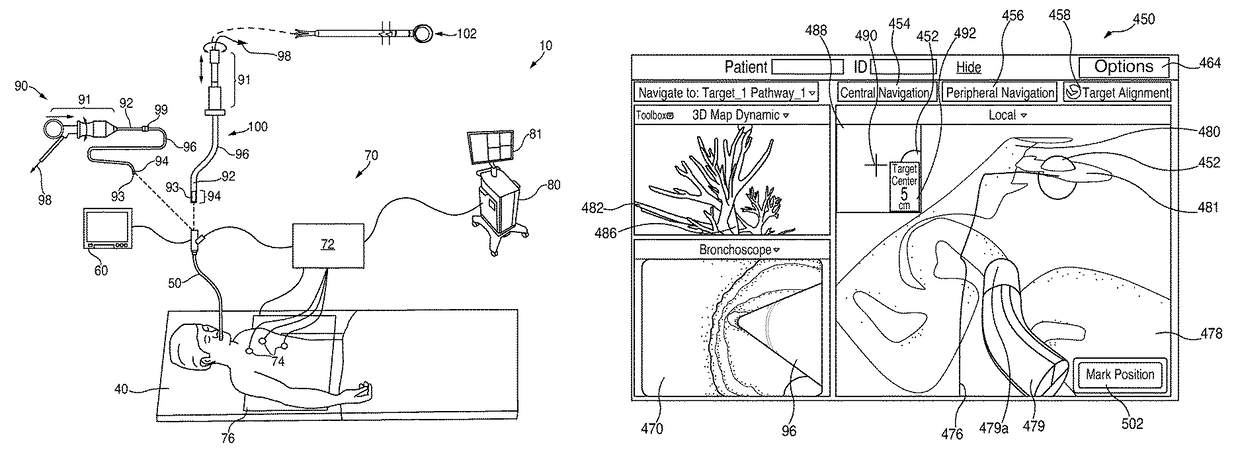
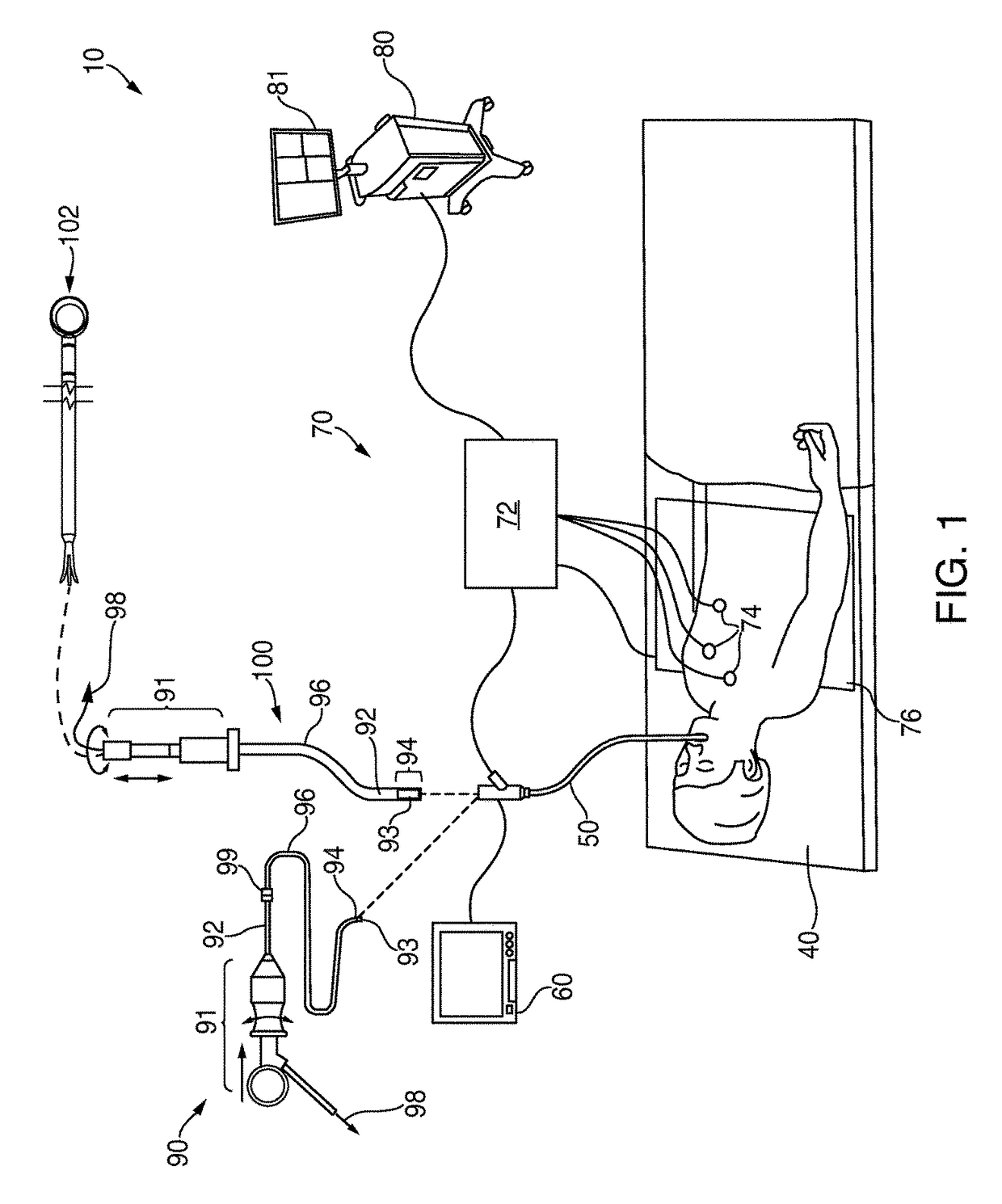
System and method for navigating within the lung
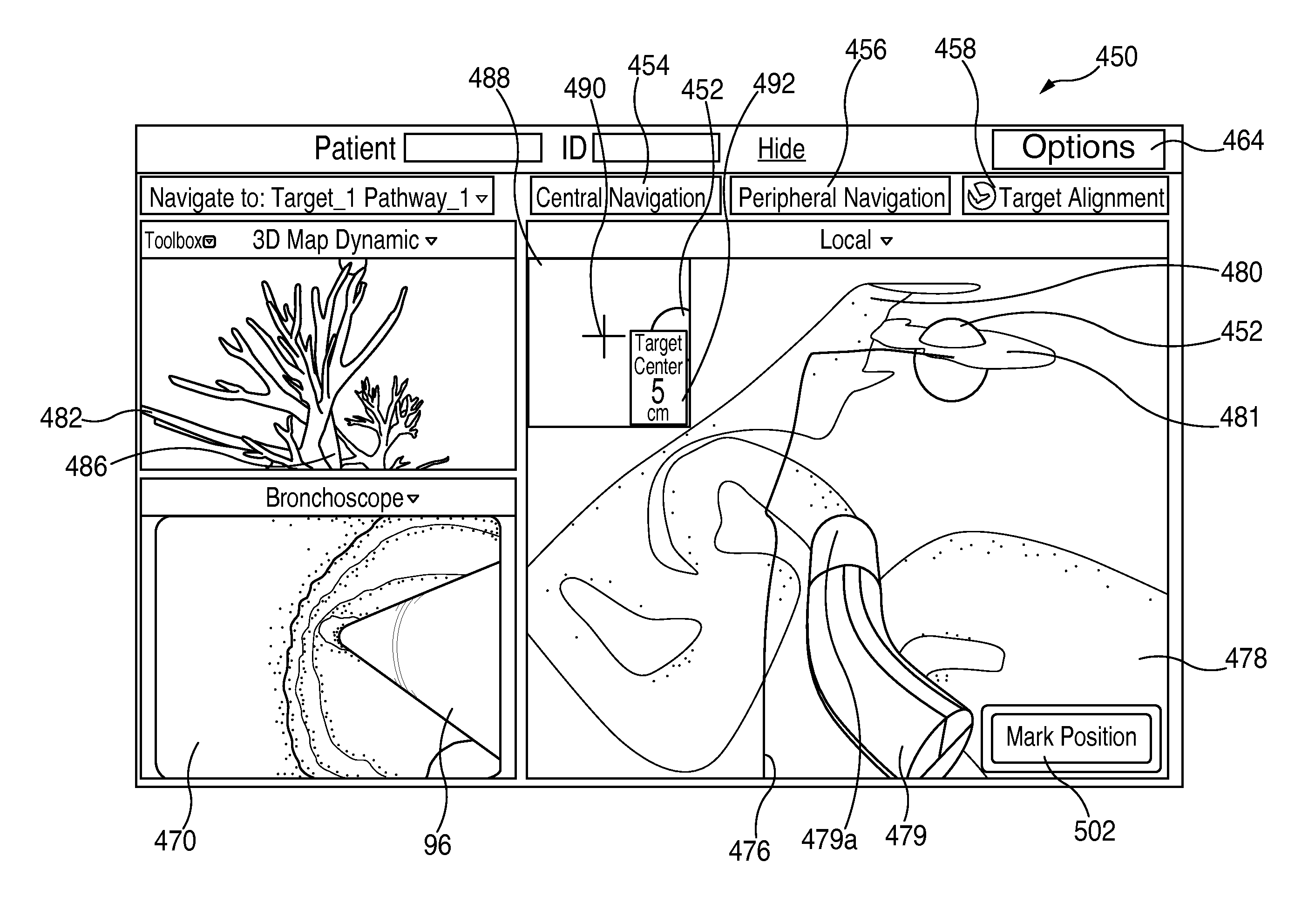
Methods and systems for navigating to a target through a patient's bronchial tree are disclosed including a bronchoscope, a probe insertable into a working channel of the bronchoscope and including a location sensor, and a workstation in operative communication with the probe and the bronchoscope, the workstation including a user interface that guides a user through a navigation plan and is configured to present a central navigation view including a plurality of views configured for assisting the user in navigating the bronchoscope through central airways of the patient's bronchial tree toward the target, a peripheral navigation view including a plurality of views configured for assisting the user in navigating the probe through peripheral airways of the patient's bronchial tree to the target, and a target alignment view including a plurality of views configured for assisting the user in aligning a distal tip of the probe with the target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Lung access device
This invention relates generally to lung access devices and methods of using the devices to gain access to the interior of a lung or to the mediastinal space around the lung. In particular, the invention relates to auxiliary access devices and tools for use with conventional bronchoscopes or other endoscopes to enable the delivery of more and larger devices to a target site than is currently possible through a typical endoscope or bronchoscope.
Owner:EKOS CORP
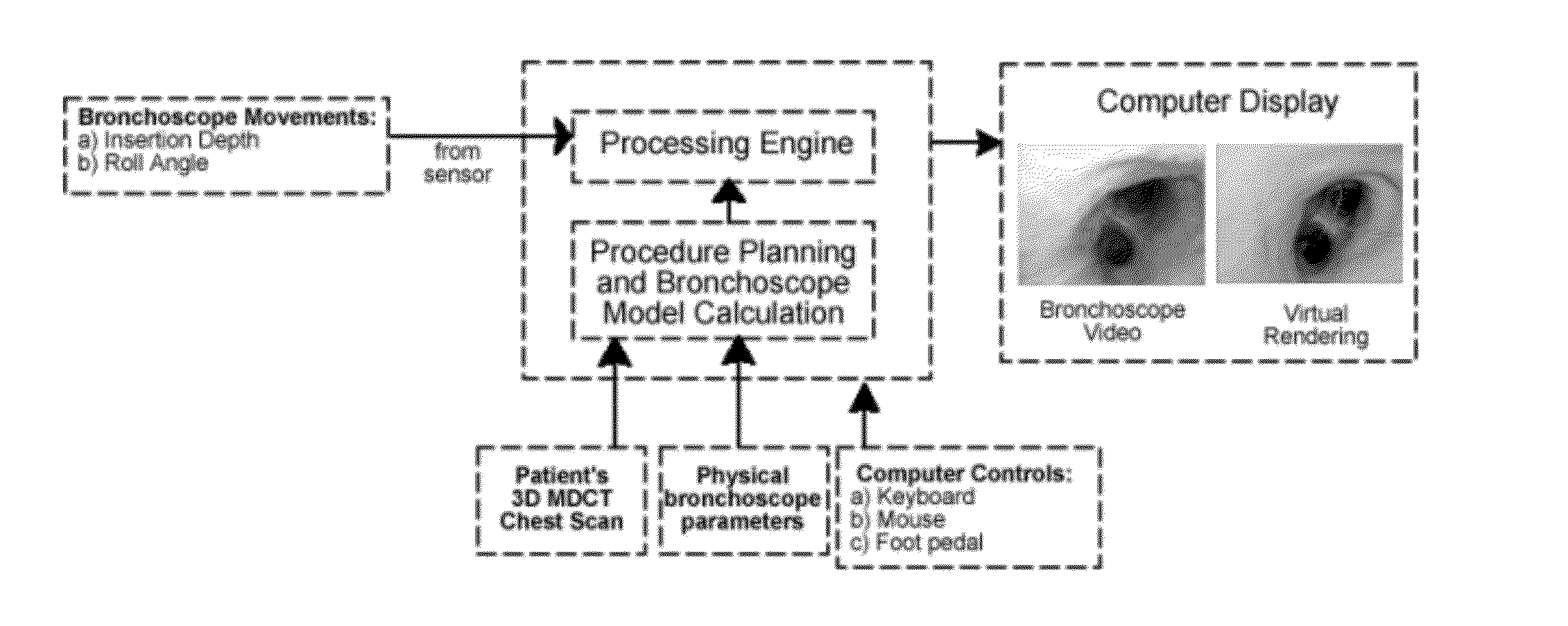
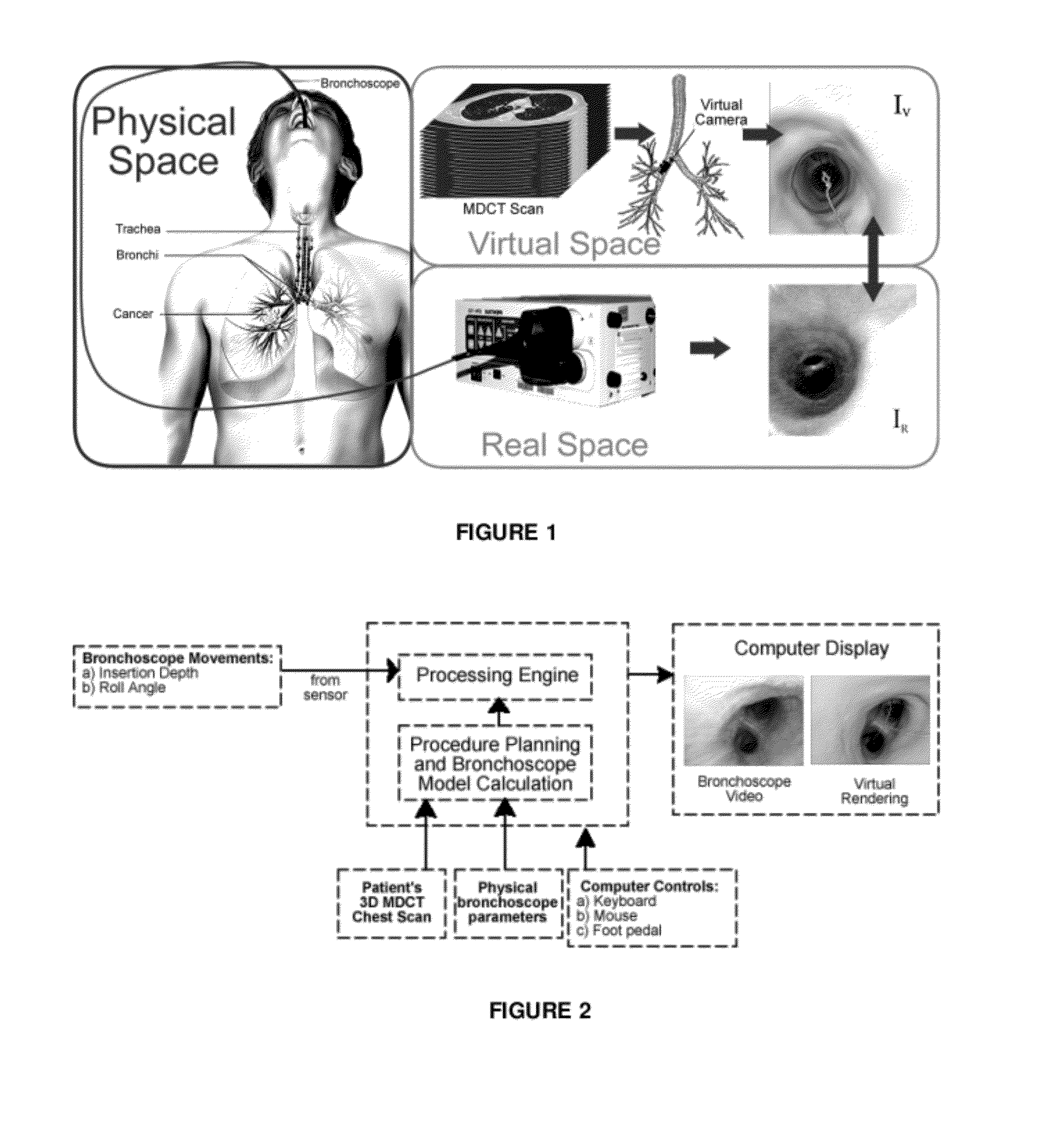
Method and device for determining the location of an endoscope
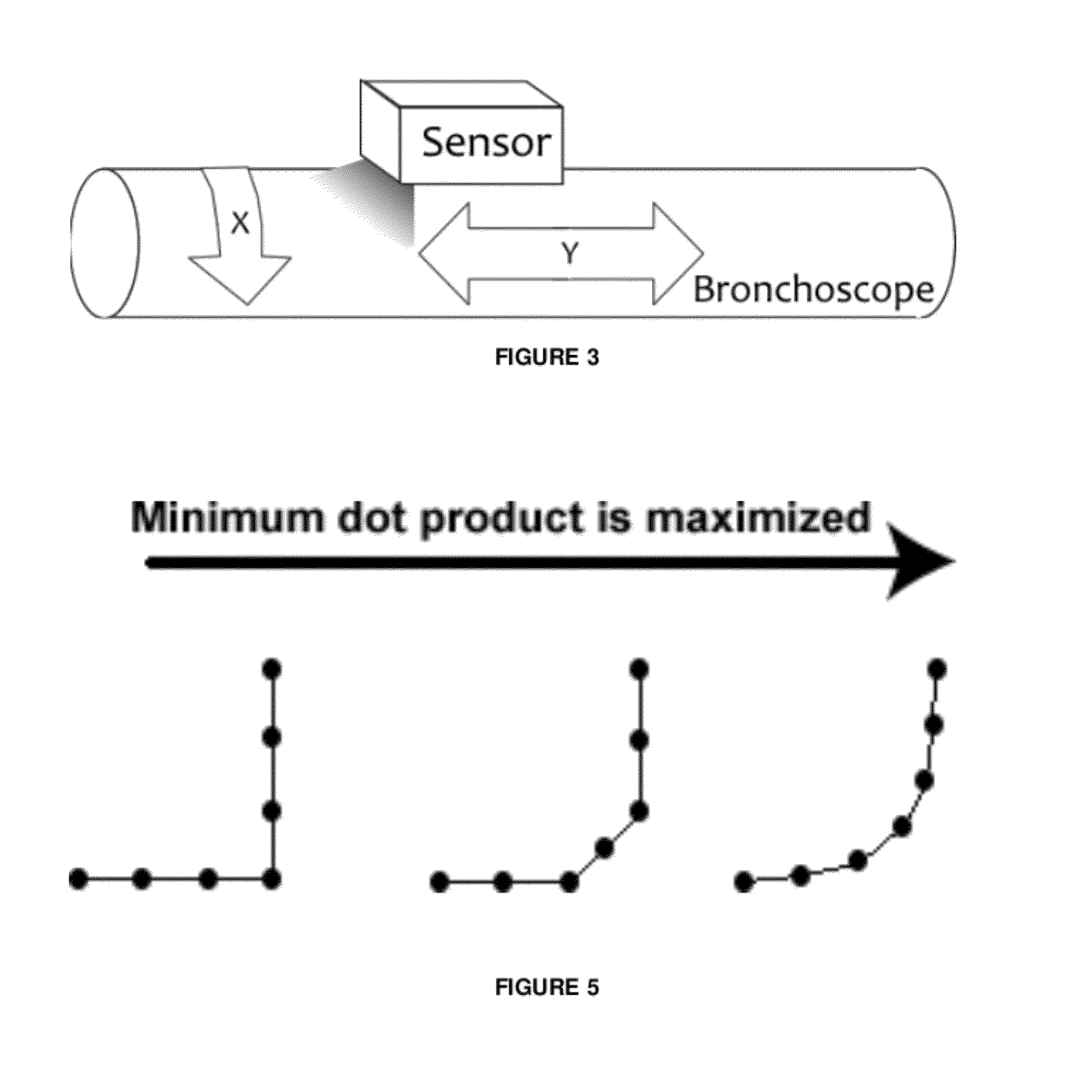
A technician-free strategy enables real-time guidance of bronchoscopy. The approach uses measurements of the bronchoscope's movement to predict its position in 3D virtual space. To achieve this, a bronchoscope model, defining the device's shape in the airway tree to a given point p, provides an insertion depth to p. In real time, the invention compares an observed bronchoscope insertion depth and roll angle, measured by an optical sensor, to precalculated insertion depths along a predefined route in the virtual airway tree to predict a bronchoscope's location and orientation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction method
InactiveUS7100616B2Reduce riskEffective lung volume reductionRespiratorsBronchiAirway occlusionAtmospheric air
A method of minimally invasively reducing a volume of a hyper-inflated target section of diseased lung comprising the steps of introducing a bronchoscope into a patient's airway to a position adjacent the target section and equilibrating air within the target section with atmospheric air to at least partially deflate the target lung section; injecting an inflammation-causing substance into the target section to precipitate adhesion of the walls within the target lung section, preventing substantial re-inflation of the target section by occluding an airway upstream of the target section for a period of time, and removing the airway occlusion after the target section has substantially permanently been reduced in volume. The injected substance can be autologous blood or a constituent thereof.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
System and Method For Bronchoscopic Navigational Assistance
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
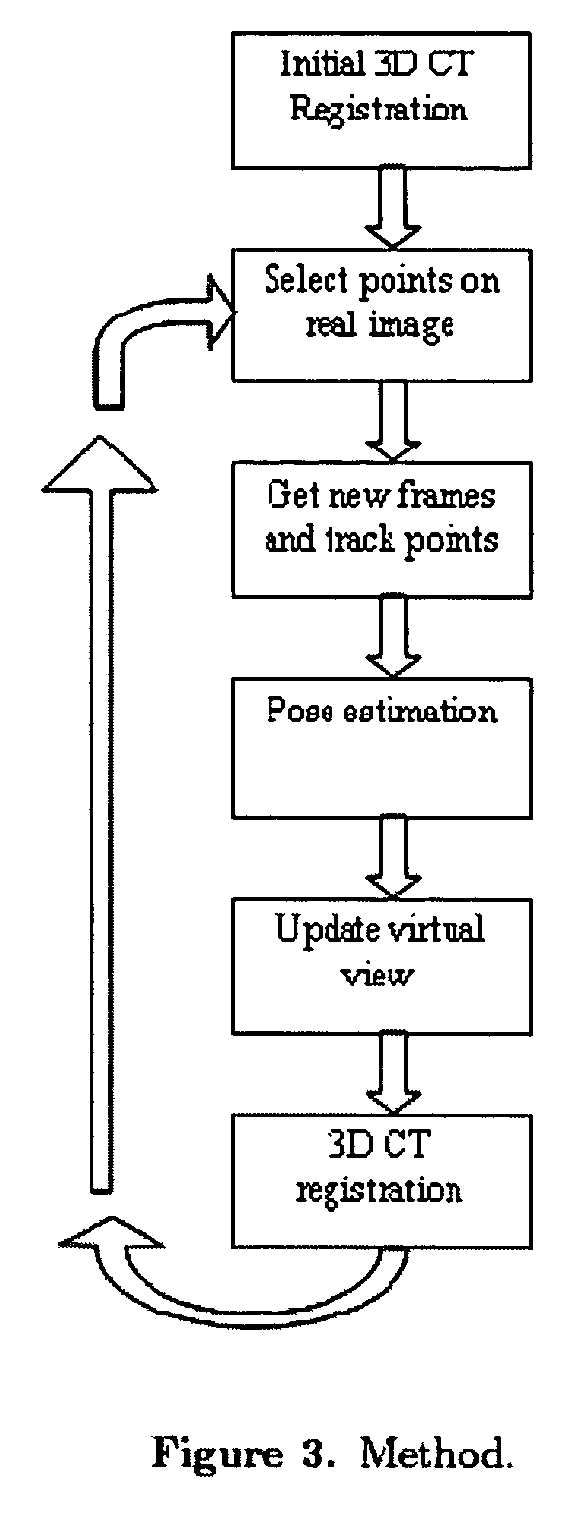
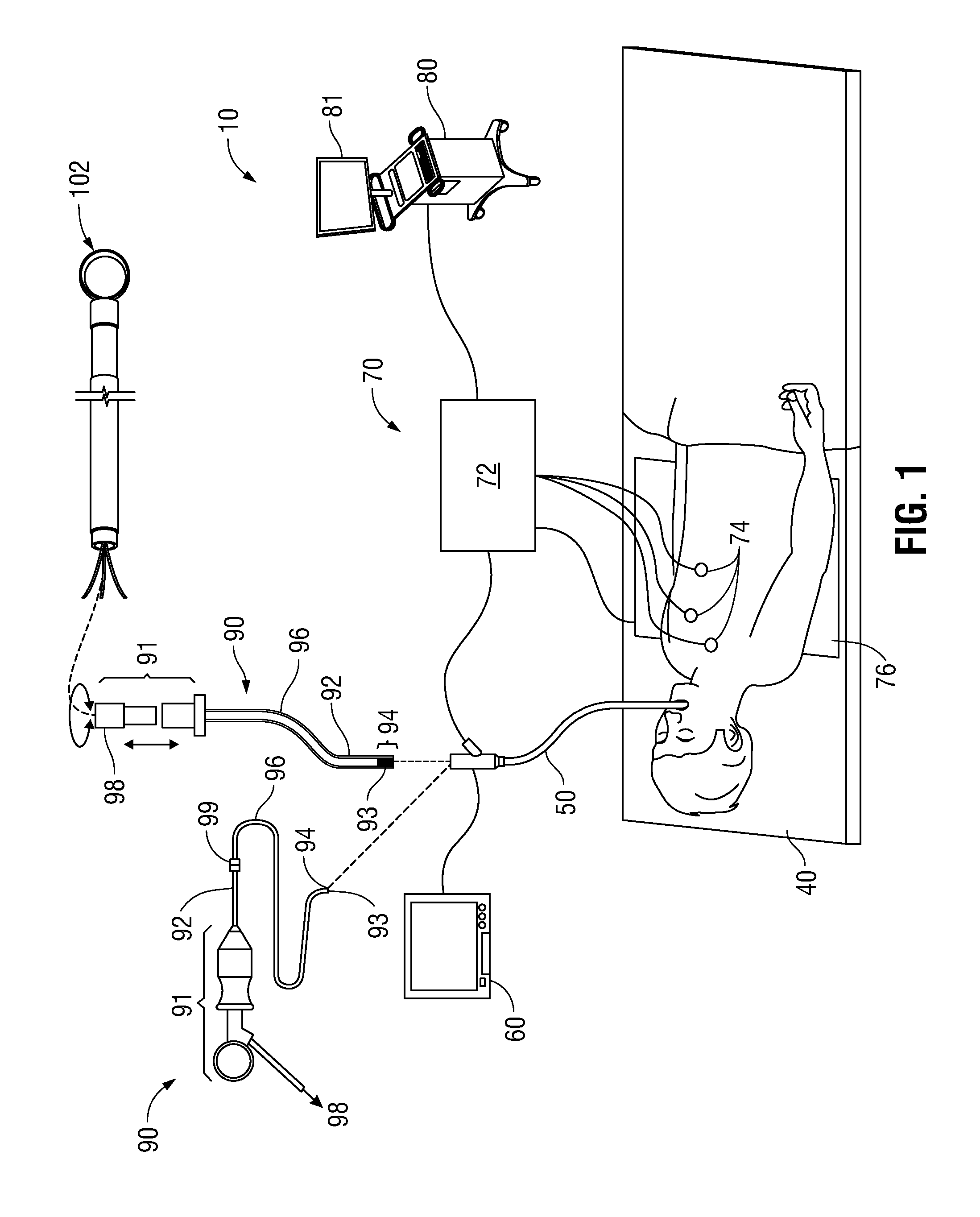
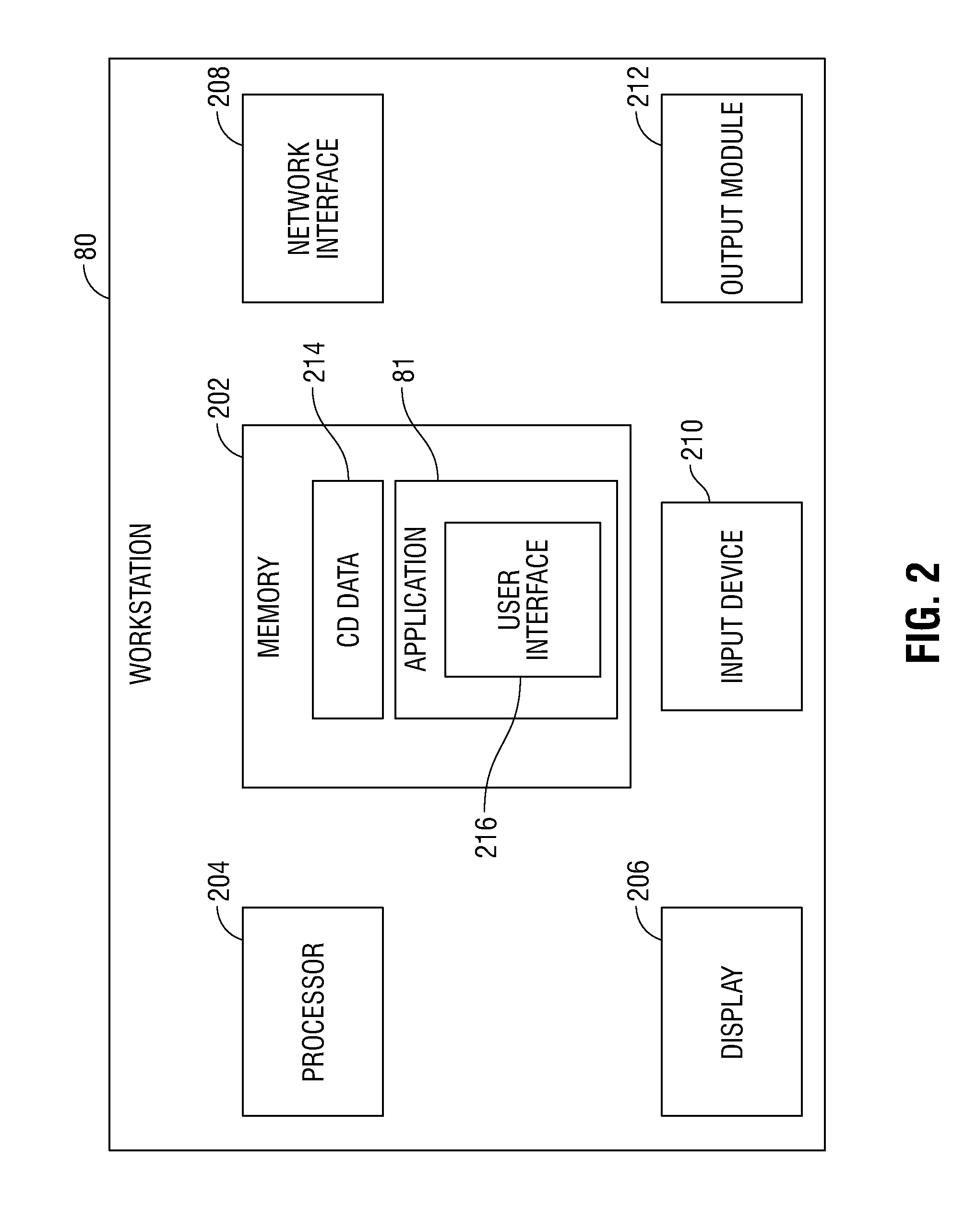
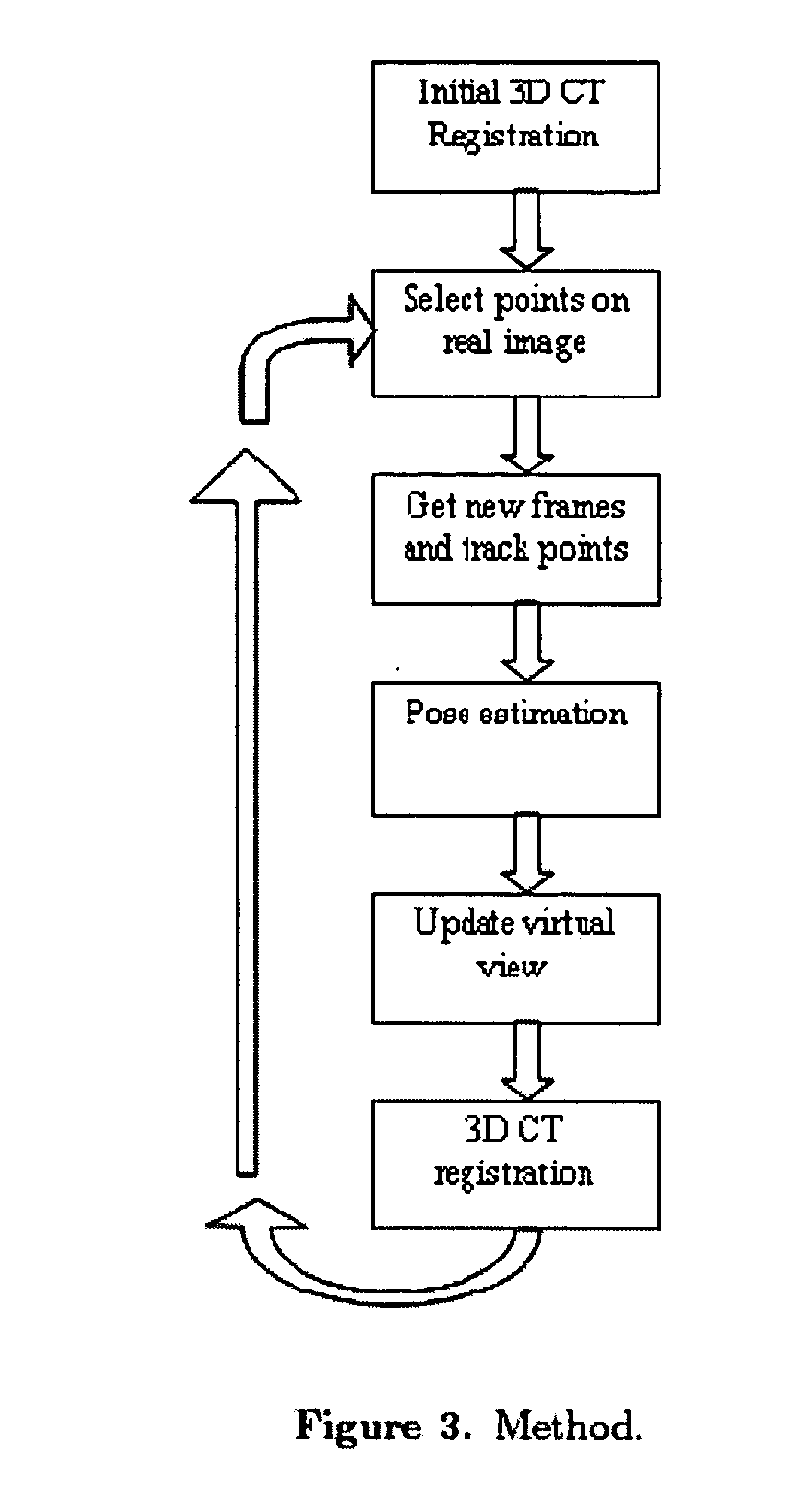
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS7756563B2Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
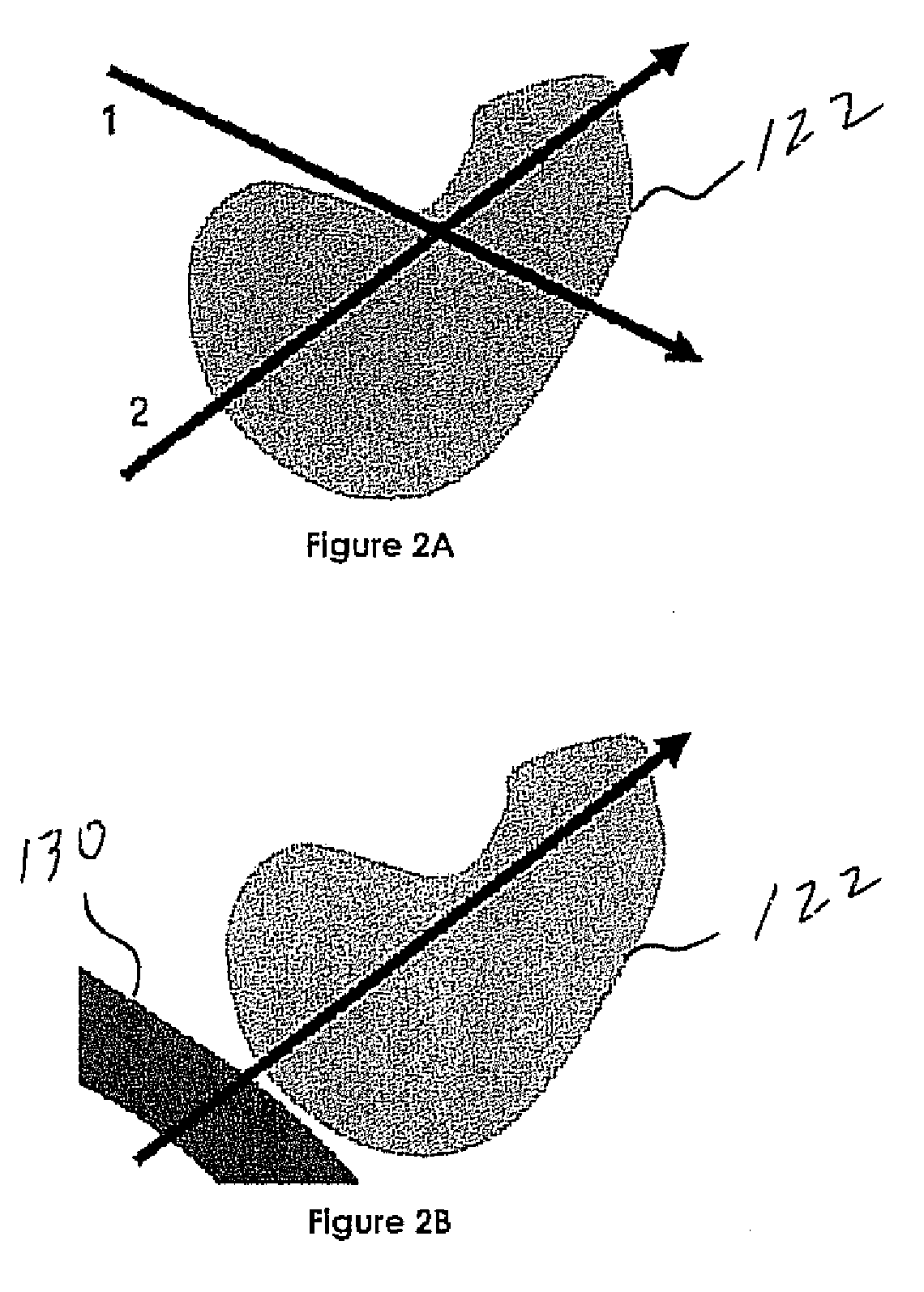
Precise endoscopic planning and visualization
InactiveUS20090156895A1Ensure safetyLarge depthImage enhancementImage analysisThree vesselsPostural orientation
Endoscopic poses are used to indicate the exact location and direction in which a physician must orient the endoscope to sample a region of interest (ROI) in an airway tree or other luminal structure. Using a patient-specific model of the anatomy derived from a 3D MDCT image, poses are chosen to be realizable given the physical characteristics of the endoscope and the relative geometry of the patient's airways and the ROI. To help ensure the safety of the patient, the calculations also account for obstacles such as the aorta and pulmonary arteries, precluding the puncture of these sensitive blood vessels. A real-time visualization system conveys the calculated pose orientation and the quality of any arbitrary bronchoscopic pose orientation. A suggested pose orientation is represented as an icon within a virtual rendering of the patient's airway tree or other structure. The location and orientation of the icon indicates the suggested pose orientation to which the physician should align during the procedure.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
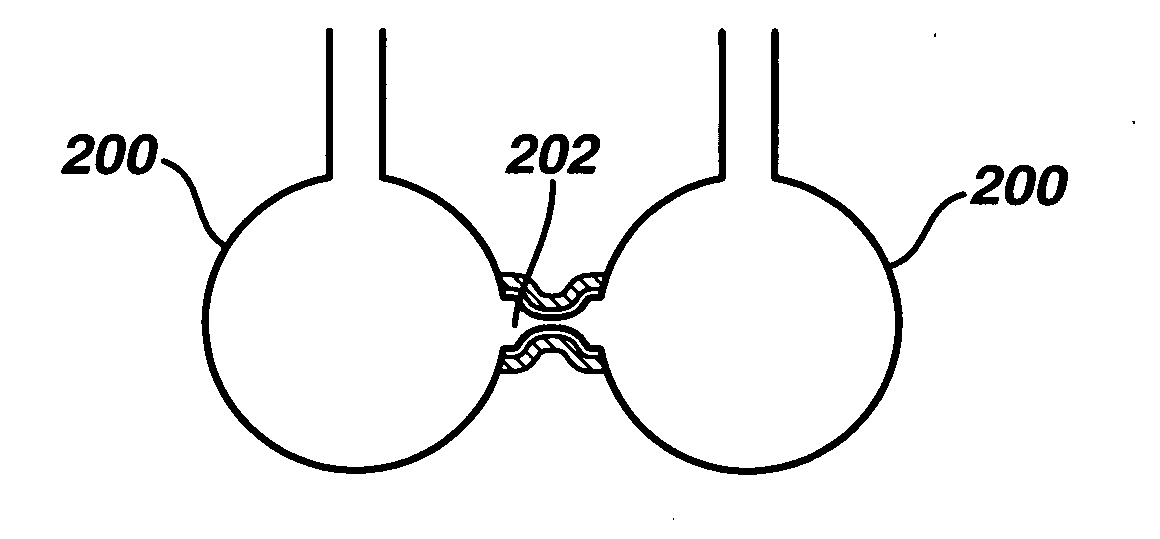
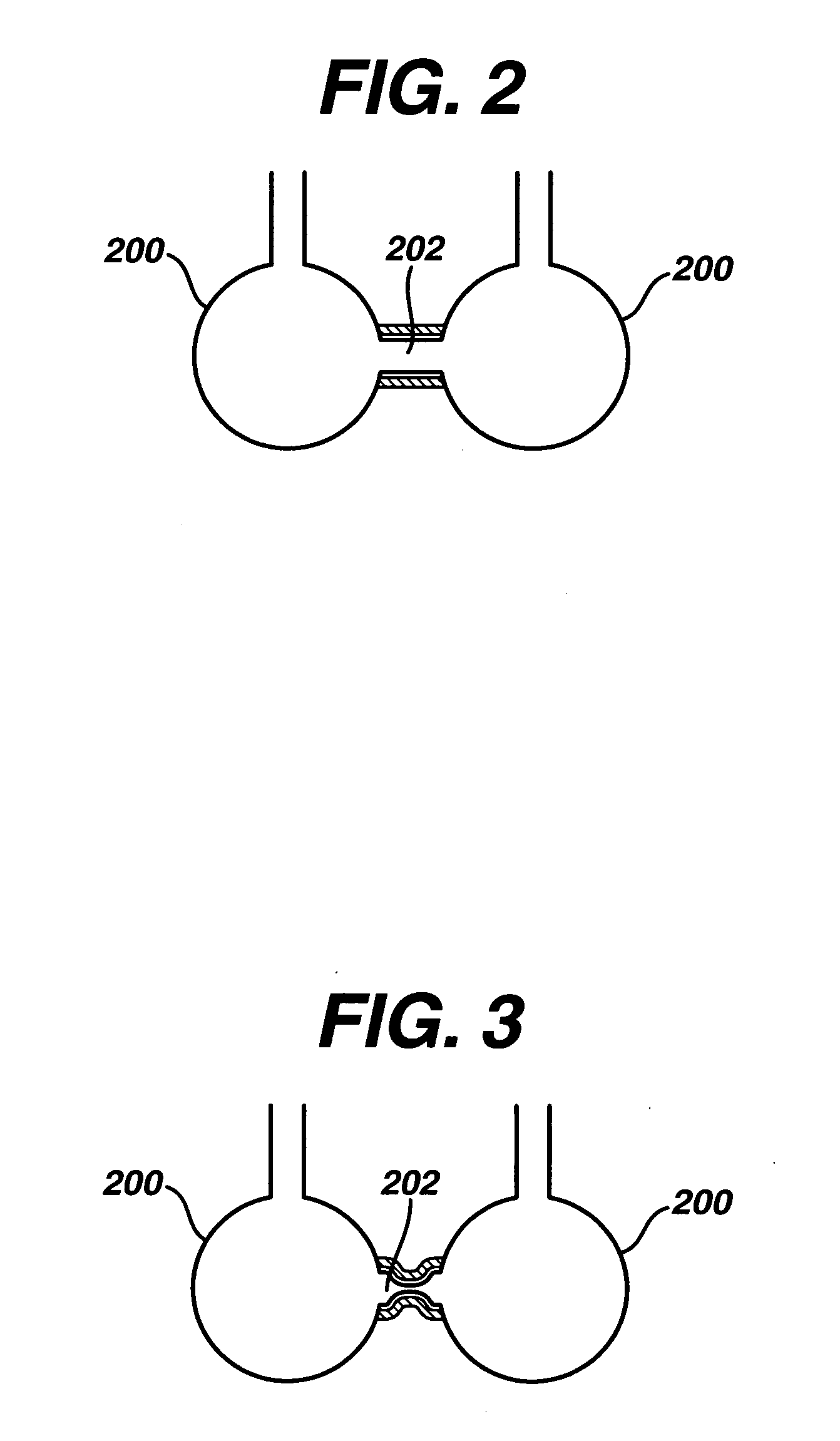
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction valve
ActiveUS20070096048A1Permit flowAvoid flowStentsBronchiPorous coatingBronchoscopic lung volume reduction
A valve to perform lung volume reduction procedures is described. The valve is formed of a braided structure that is adapted for endoscopic insertion in a bronchial passage of a patient's lung. The braided structure has a proximal end and a distal end and is covered with a non porous coating adapted to prevent flow of air into the. A constricted portion of the braided structure is used to prevent flow of air through a central lumen of the structure, and to define at least one funnel shaped portion. The funnel shaped portion blocks the flow of air towards the constriction, i.e. towards the core of the lung. At least one hole is formed in the braided structure to permit flow of mucus from the distal end to the proximal end, to be expelled out of the lungs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Bronchoscopic repair of air leaks in a lung
ActiveUS7533671B2Minimizes dislodgingSmall sizeRespiratorsBronchiAirway occlusionIntensive care medicine
Methods and systems for minimally invasively treating an air leak in a lung comprise the steps of detecting an air leak in a lung; locating an airway in fluid communication with the air leak, introducing a bronchoscope into a patient's airway to a position adjacent the target section and occluding an airway upstream of the air leak for a period of time. The airway occlusion is preferably removed after the air leak has substantially permanently healed. The method can also include the injection of a substance into the airway on a distal side of the occlusion.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Lung access device
This invention relates generally to lung access devices and methods of using the devices to gain access to the interior of a lung or to the mediastinal space around the lung. In particular, the invention relates to auxiliary access devices and tools for use with conventional bronchoscopes or other endoscopes to enable the delivery of more and larger devices to a target site than is currently possible through a typical endoscope or bronchoscope.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Global and semi-global registration for image-based bronchoscopy guidance
Two system-level bronchoscopy guidance solutions are presented. The first incorporates a global-registration algorithm to provide the physician with updated navigational and guidance information during bronchoscopy. The system can handle general navigation to a region of interest (ROI), as well as adverse events, and it requires minimal commands so that it can be directly controlled by the physician. The second solution visualizes the global picture of all the bifurcations and their relative orientations in advance and suggests the maneuvers needed by the bronchoscope to approach the ROI. Guided bronchoscopy results using human airway-tree phantoms demonstrate the potential of the two solutions.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Methods and devices for controlling collateral ventilation
InactiveUS20060118126A1Improve efficiencyReduce riskRespiratorsBronchoscopesCollateral ventilationAnesthesia
Chemical lung volume reduction may be utilized to control collateral ventilation so that trapped air in diseased lungs can be removed. The chemical or therapeutic agent may be locally delivered to the site or sites of highest collateral ventilation utilizing any number of methods including bronchoscopic delivery.
Owner:RESPIRA
Bronchoscopic repair of air leaks in a lung
ActiveUS20050137714A1Minimizes dislodgingSmall sizeBronchiOcculdersAirway occlusionIntensive care medicine
Methods and systems for minimally invasively treating an air leak in a lung comprise the steps of detecting an air leak in a lung; locating an airway in fluid communication with the air leak, introducing a bronchoscope into a patient's airway to a position adjacent the target section and occluding an airway upstream of the air leak for a period of time. The airway occlusion is preferably removed after the air leak has substantially permanently healed. The method can also include the injection of a substance into the airway on a distal side of the occlusion.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
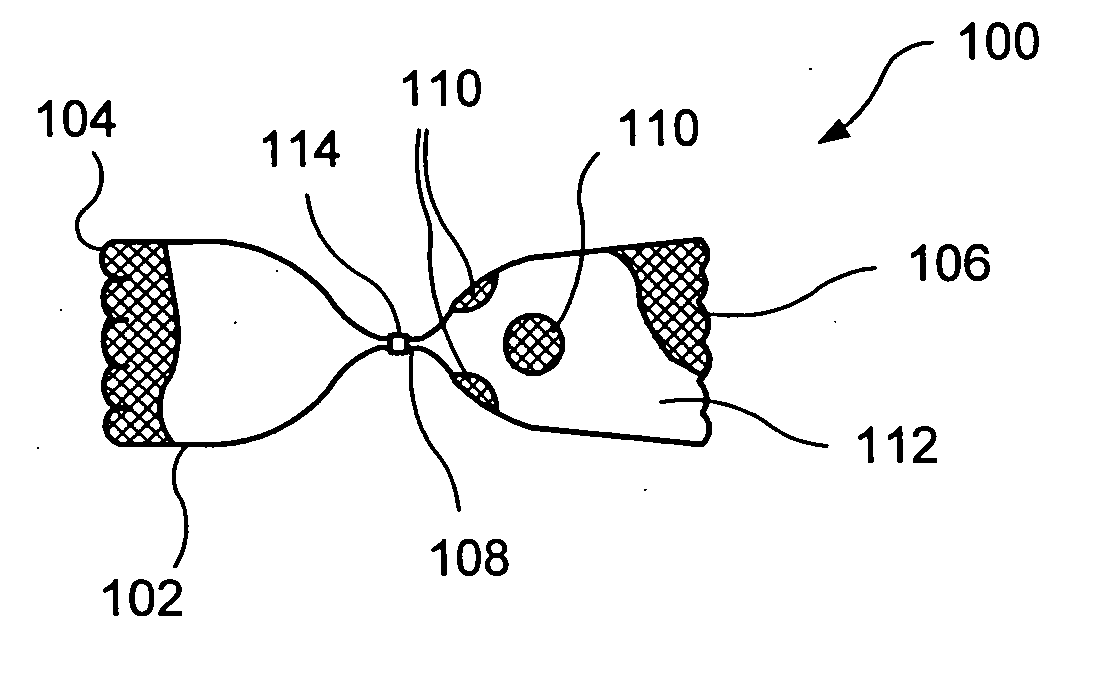
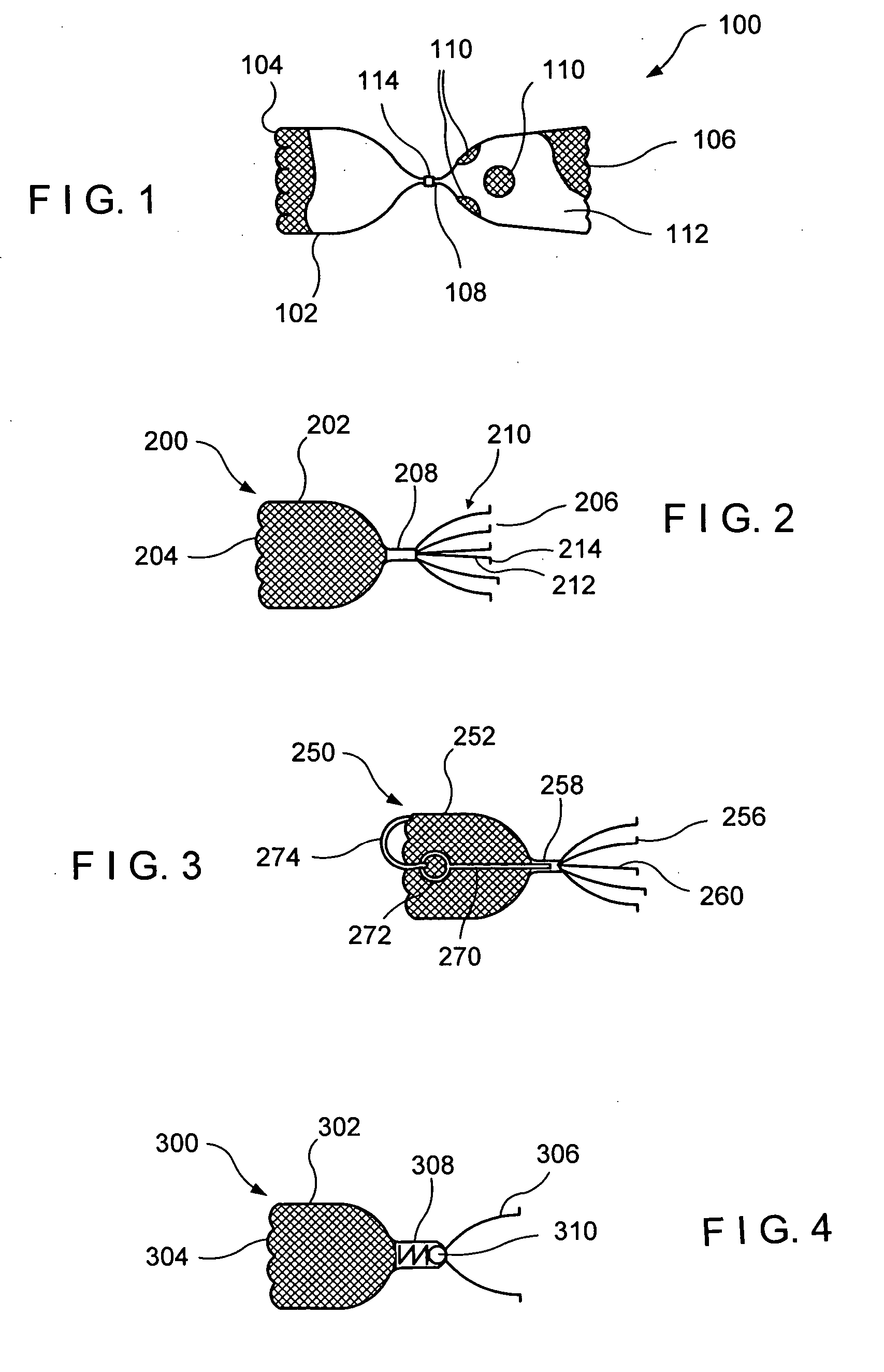
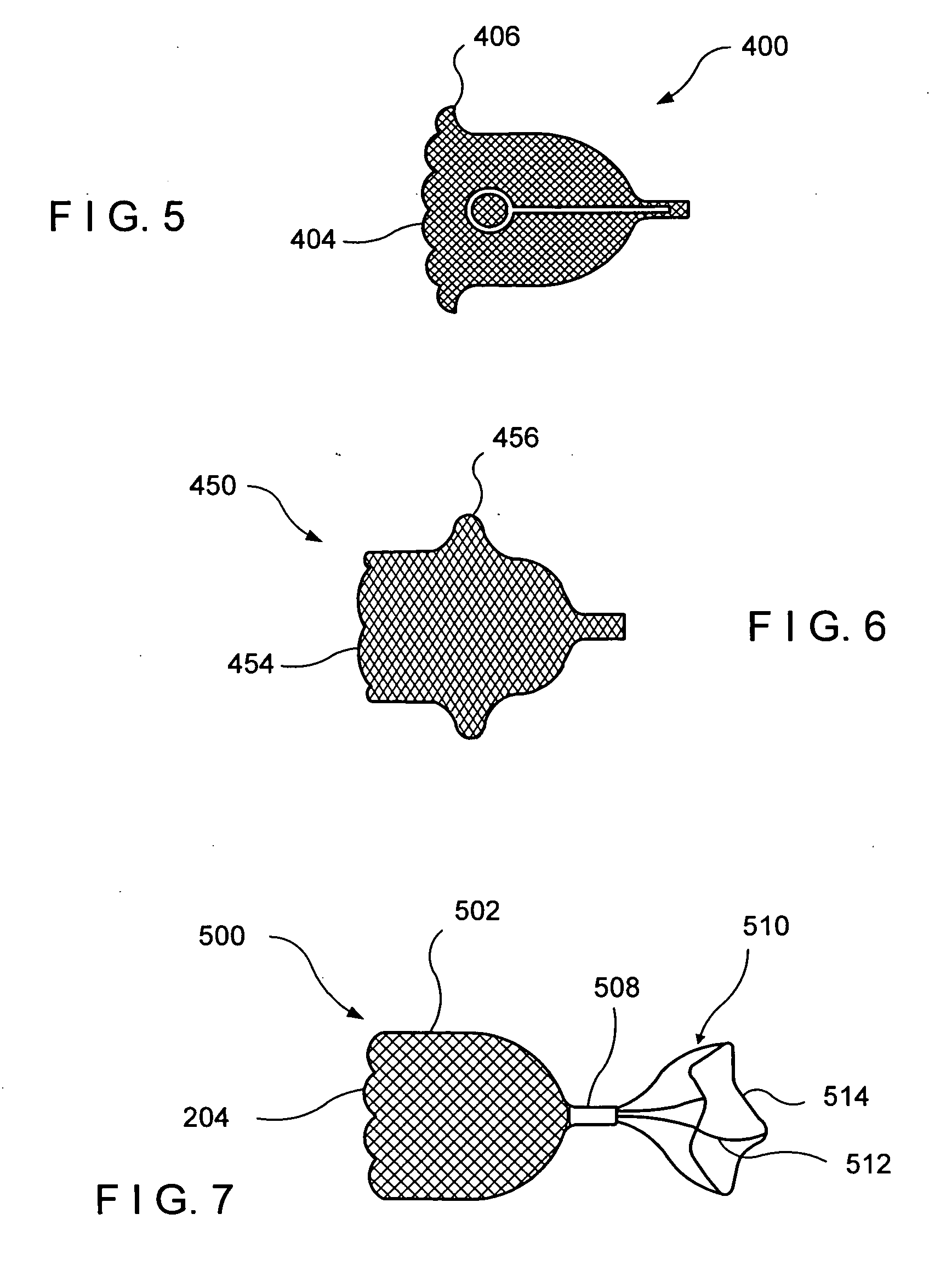
Bronchoalveolar lavage catheter assembly
A catheter assembly configured for use in a non-bronchoscopic bronchoalveolar lavage procedure. The catheter assembly may include an inner catheter member having an inner catheter lumen and an outer catheter member having an outer catheter lumen, where the inner catheter member is disposed longitudinally and coaxially through at least a lengthwise portion of the outer catheter lumen, a distal end portion of the outer catheter includes an atraumatically-shaped disruptable seal—which seal includes at least a pair of overlapping slits that extend at least partially through an internal distal end wall portion of the outer catheter—and where a distal end portion of the inner catheter includes a wedging structure configured to at least partially sealingly contact an inner circumference of a passage in a lower portion of a patient lung.
Owner:CAREFUSION 2200 INC
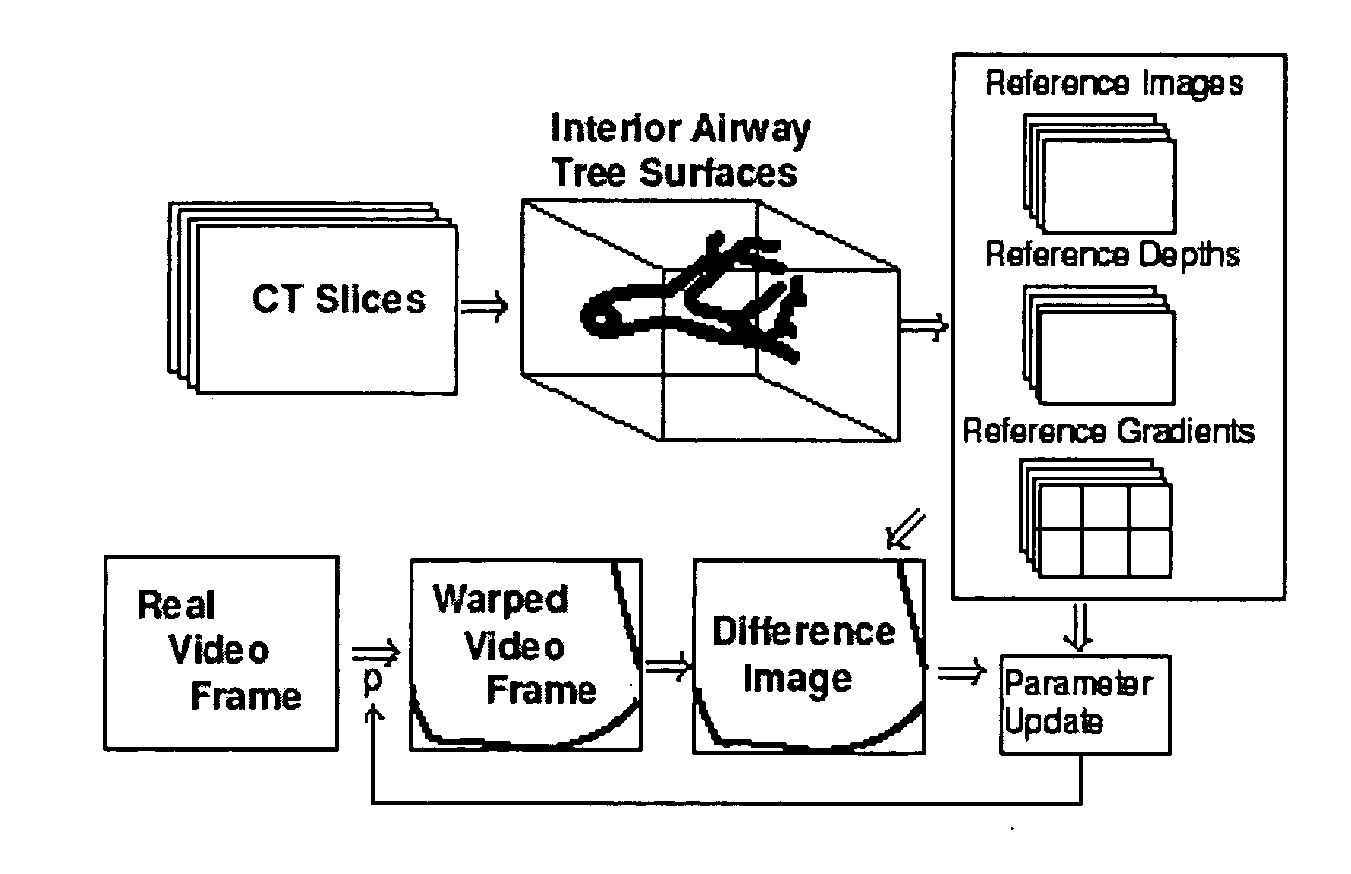
Fast 3D-2D image registration method with application to continuously guided endoscopy
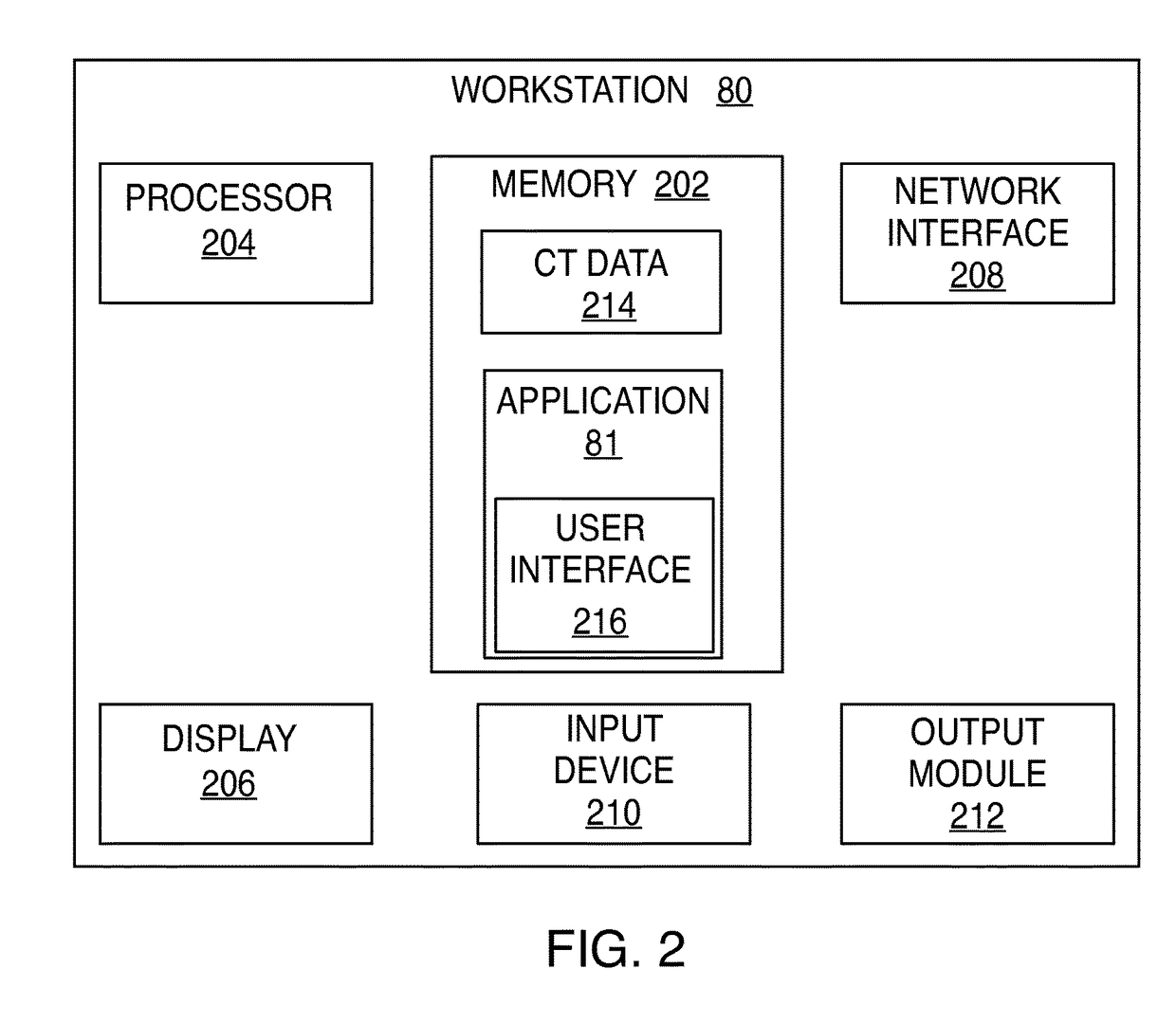
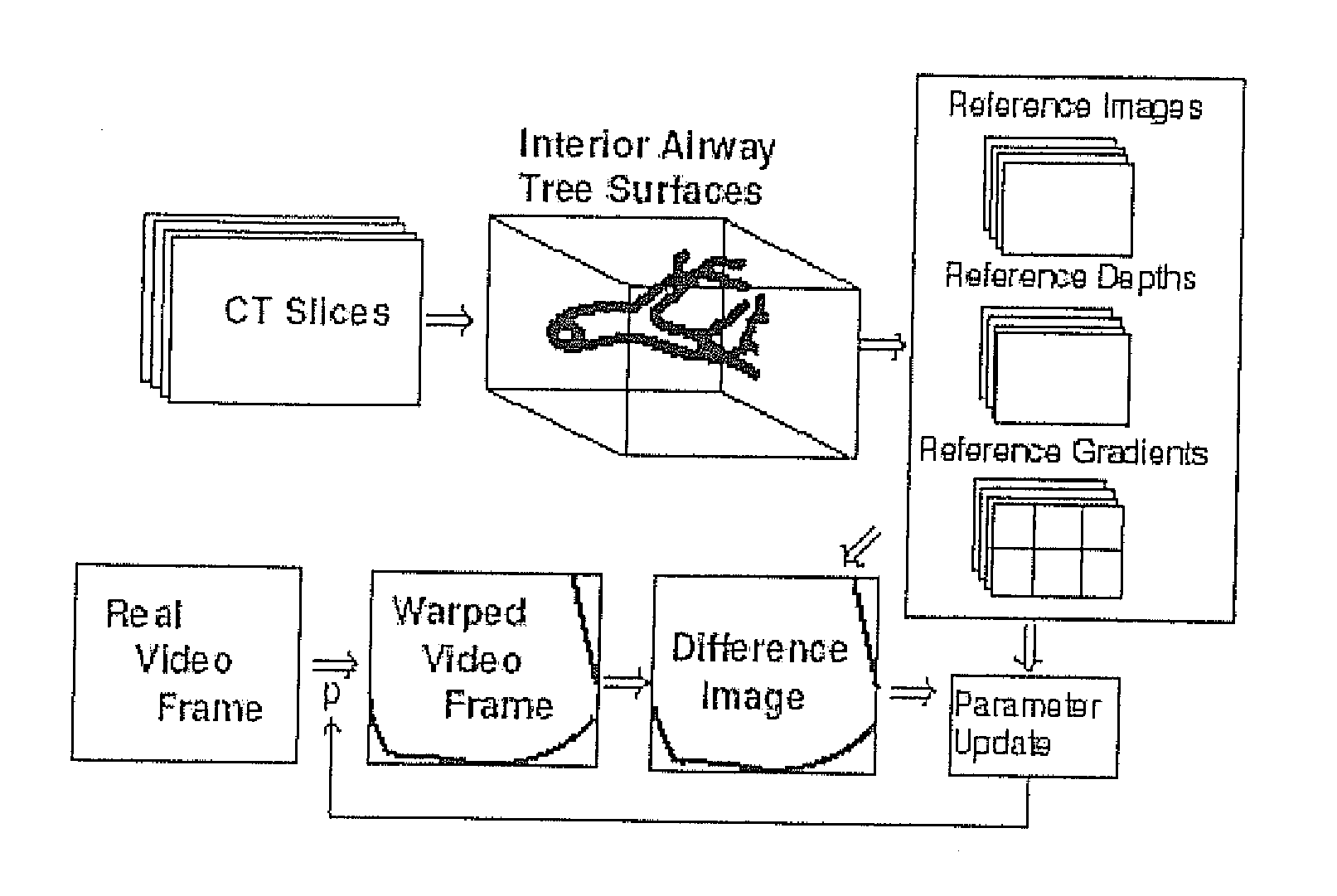
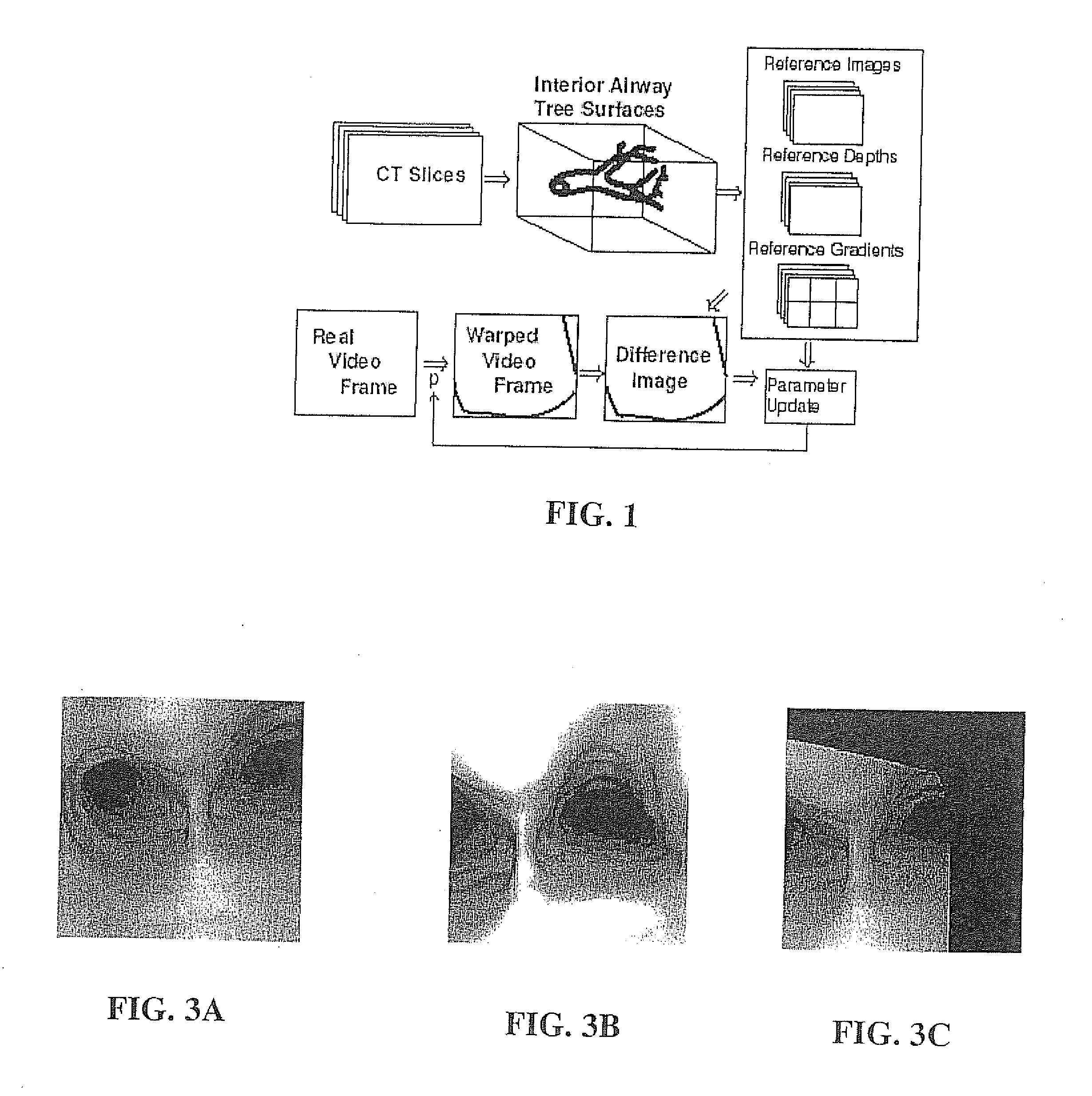
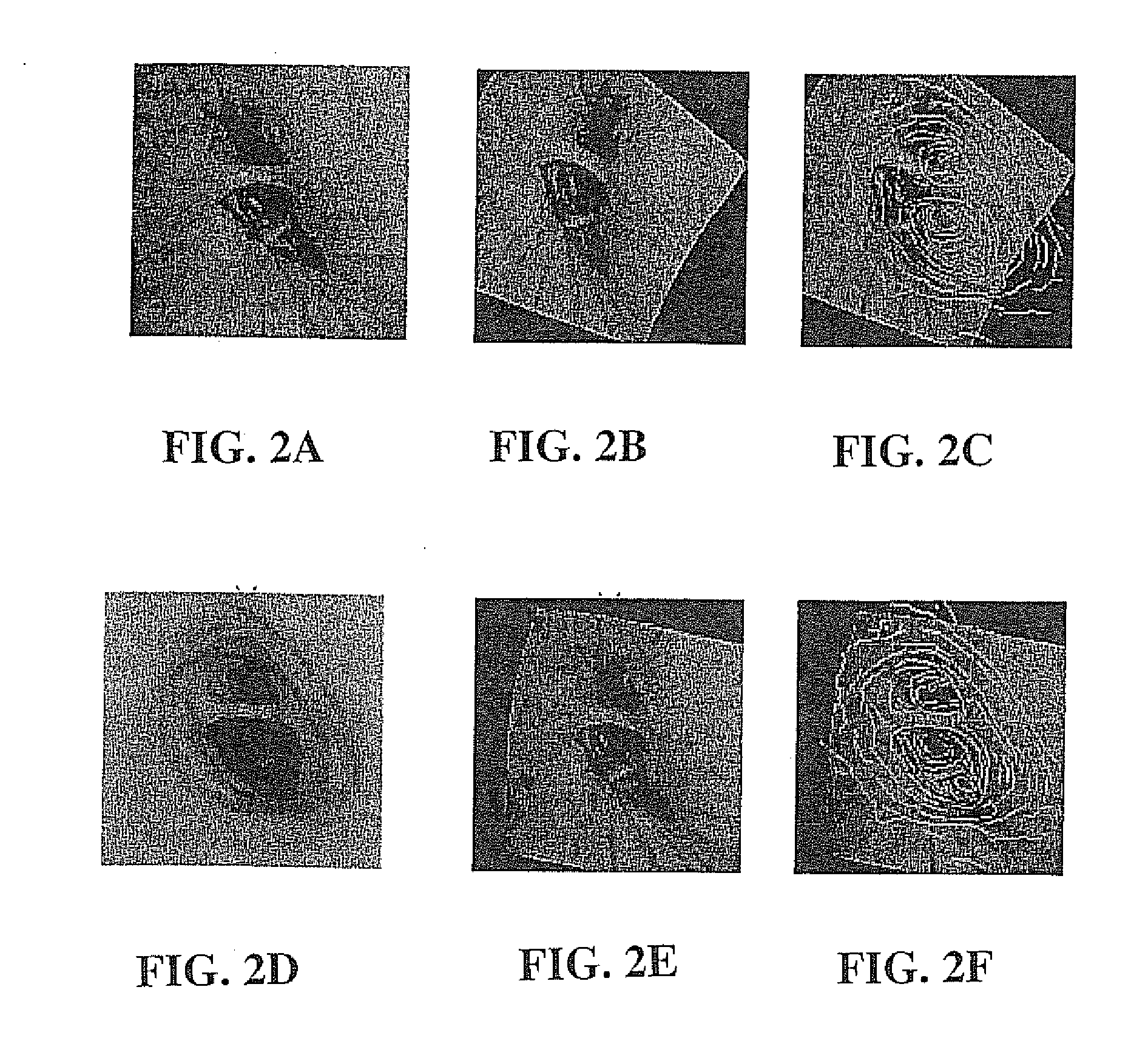
A novel framework for fast and continuous registration between two imaging modalities is disclosed. The approach makes it possible to completely determine the rigid transformation between multiple sources at real-time or near real-time frame-rates in order to localize the cameras and register the two sources. A disclosed example includes computing or capturing a set of reference images within a known environment, complete with corresponding depth maps and image gradients. The collection of these images and depth maps constitutes the reference source. The second source is a real-time or near-real time source which may include a live video feed. Given one frame from this video feed, and starting from an initial guess of viewpoint, the real-time video frame is warped to the nearest viewing site of the reference source. An image difference is computed between the warped video frame and the reference image. The viewpoint is updated via a Gauss-Newton parameter update and certain of the steps are repeated for each frame until the viewpoint converges or the next video frame becomes available. The final viewpoint gives an estimate of the relative rotation and translation between the camera at that particular video frame and the reference source. The invention has far-reaching applications, particularly in the field of assisted endoscopy, including bronchoscopy and colonoscopy. Other applications include aerial and ground-based navigation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
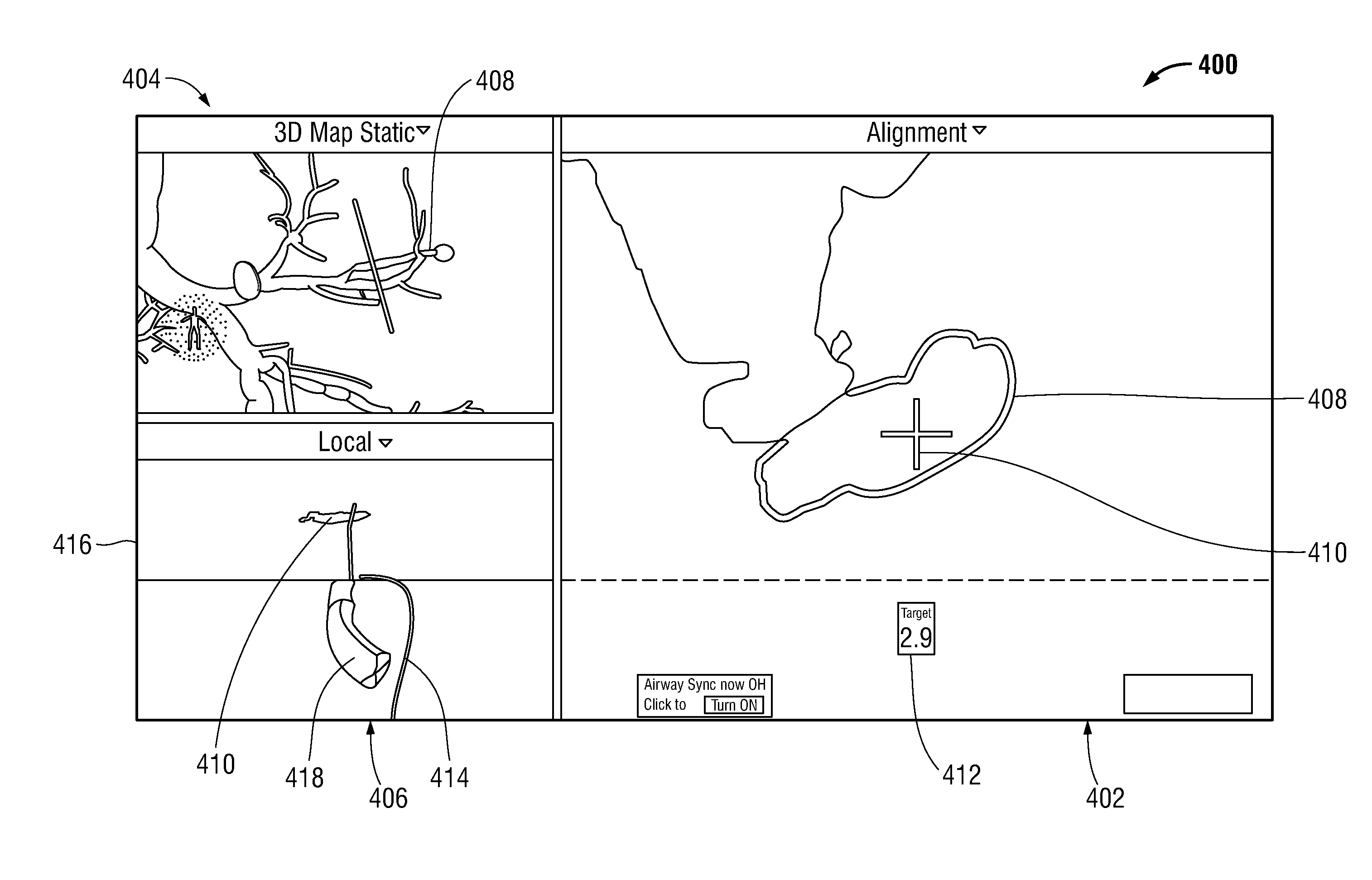
Alignment ct
Methods and systems for navigating to a target through a patient's bronchial tree are disclosed including a bronchoscope, a probe insertable into a working channel of the bronchoscope including a location sensor, and a workstation in operative communication with the probe and the bronchoscope the workstation including a user interface that guides a user through a navigation plan and is configured to present a three-dimensional (3D) view for displaying a 3D rendering of the patient's airways and a corresponding navigation plan, a local view for assisting the user in navigating the probe through peripheral airways of the patient's bronchial tree to the target, and a target alignment view for assisting the user in aligning a distal tip of the probe with the target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS20070015997A1Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for guiding an instrument to a target in the lung
ActiveUS8611983B2Precise positioningImprove accuracyBronchoscopesGuide wiresBronchoscopyMarine navigation
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction method
A method of minimally invasively reducing a volume of a hyper-inflated target section of diseased lung comprising the steps of introducing a bronchoscope into a patient's airway to a position adjacent the target section and equilibrating air within the target section with atmospheric air to at least partially deflate the target lung section; injecting an inflammation-causing substance into the target section to precipitate adhesion of the walls within the target lung section, preventing substantial re-inflation of the target section by occluding an airway upstream of the target section for a period of time, and removing the airway occlusion after the target section has substantially permanently been reduced in volume. The injected substance can be autologous blood or a constituent thereof.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
System and method for navigating within the lung
Methods and systems for navigating to a target through a patient's bronchial tree are disclosed including a bronchoscope, a probe insertable into a working channel of the bronchoscope and including a location sensor, and a workstation in operative communication with the probe and the bronchoscope, the workstation including a user interface that guides a user through a navigation plan and is configured to present a central navigation view including a plurality of views configured for assisting the user in navigating the bronchoscope through central airways of the patient's bronchial tree toward the target, a peripheral navigation view including a plurality of views configured for assisting the user in navigating the probe through peripheral airways of the patient's bronchial tree to the target, and a target alignment view including a plurality of views configured for assisting the user in aligning a distal tip of the probe with the target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Fast 3d-2d image registration method with application to continuously guided endoscopy
A novel framework for fast and continuous registration between two imaging modalities is disclosed. The approach makes it possible to completely determine the rigid transformation between multiple sources at real-time or near real-time frame-rates in order to localize the cameras and register the two sources. A disclosed example includes computing or capturing a set of reference images within a known environment, complete with corresponding depth maps and image gradients. The collection of these images and depth maps constitutes the reference source. The second source is a real-time or near-real time source which may include a live video feed. Given one frame from this video feed, and starting from an initial guess of viewpoint, the real-time video frame is warped to the nearest viewing site of the reference source. An image difference is computed between the warped video frame and the reference image. The viewpoint is updated via a Gauss-Newton parameter update and certain of the steps are repeated for each frame until the viewpoint converges or the next video frame becomes available. The final viewpoint gives an estimate of the relative rotation and translation between the camera at that particular video frame and the reference source. The invention has far-reaching applications, particularly in the field of assisted endoscopy, including bronchoscopy and colonoscopy. Other applications include aerial and ground-based navigation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
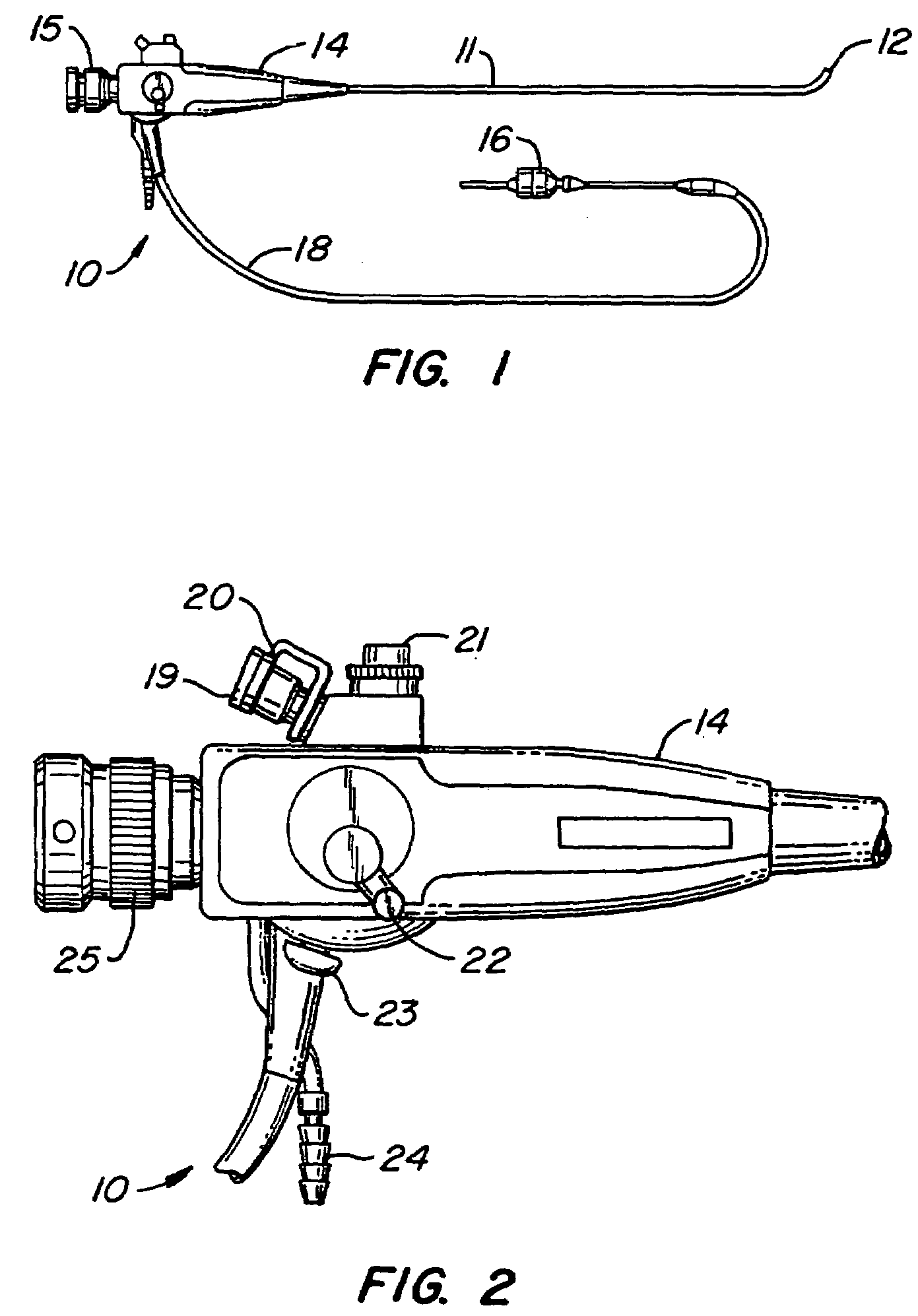
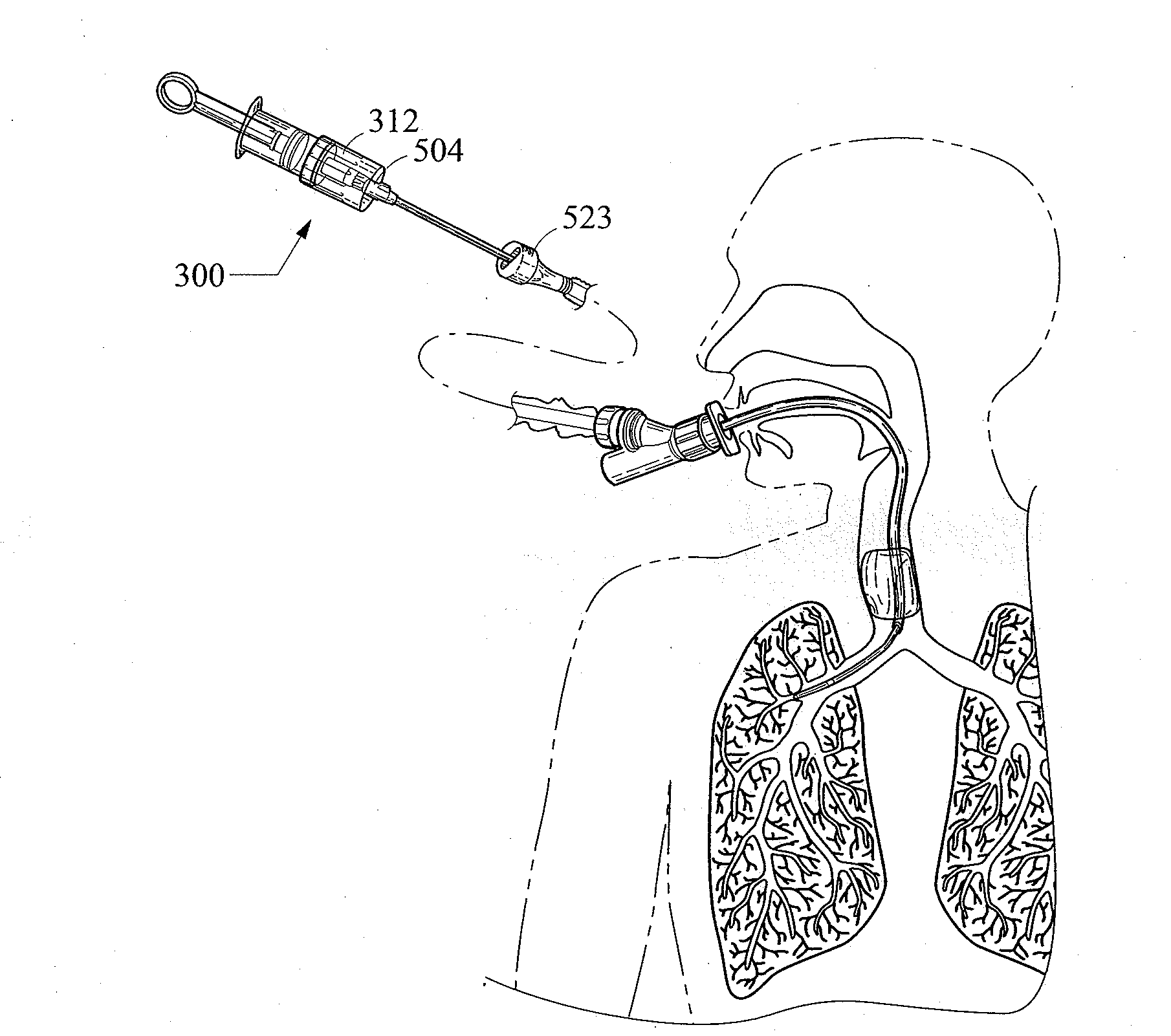
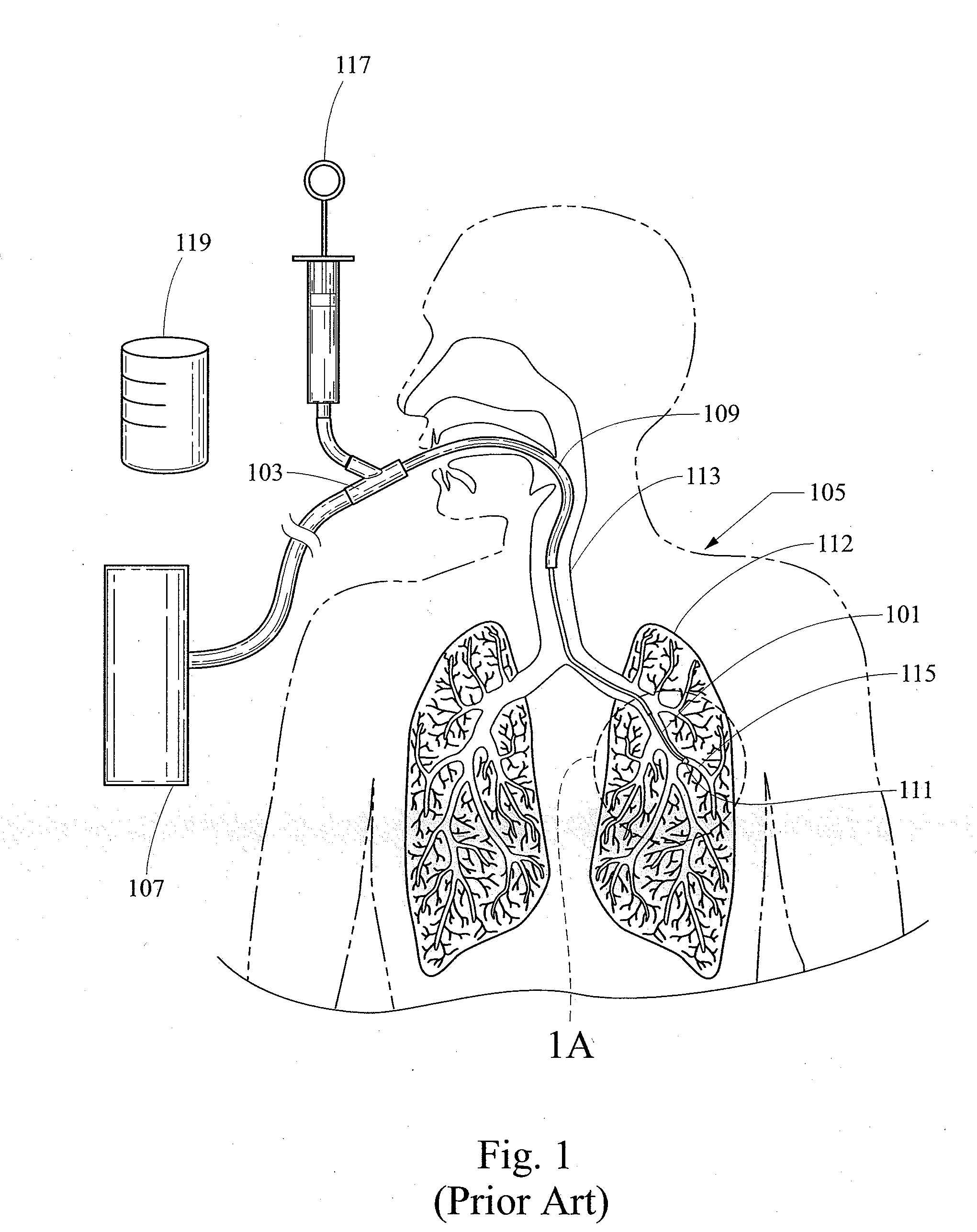
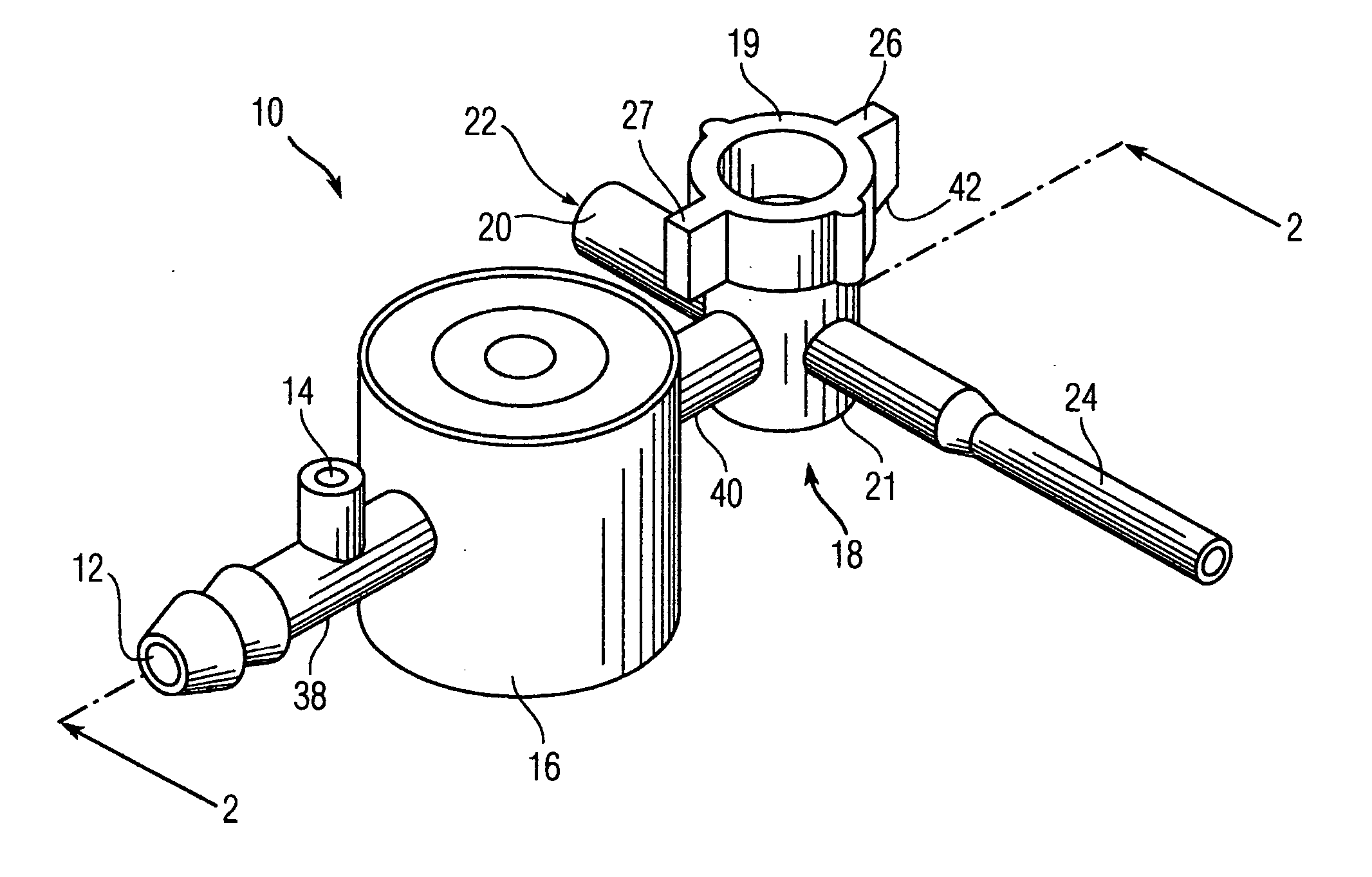
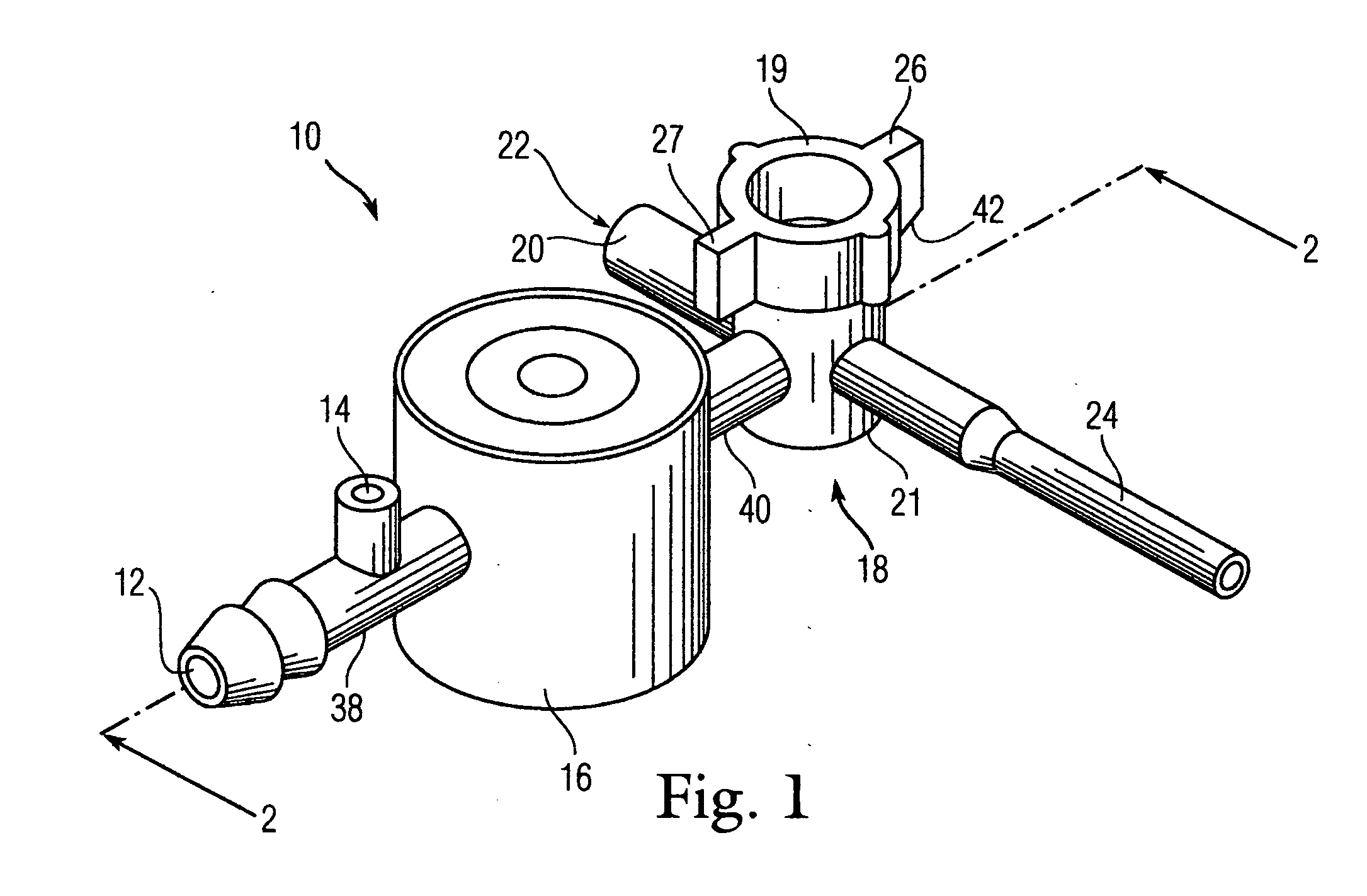
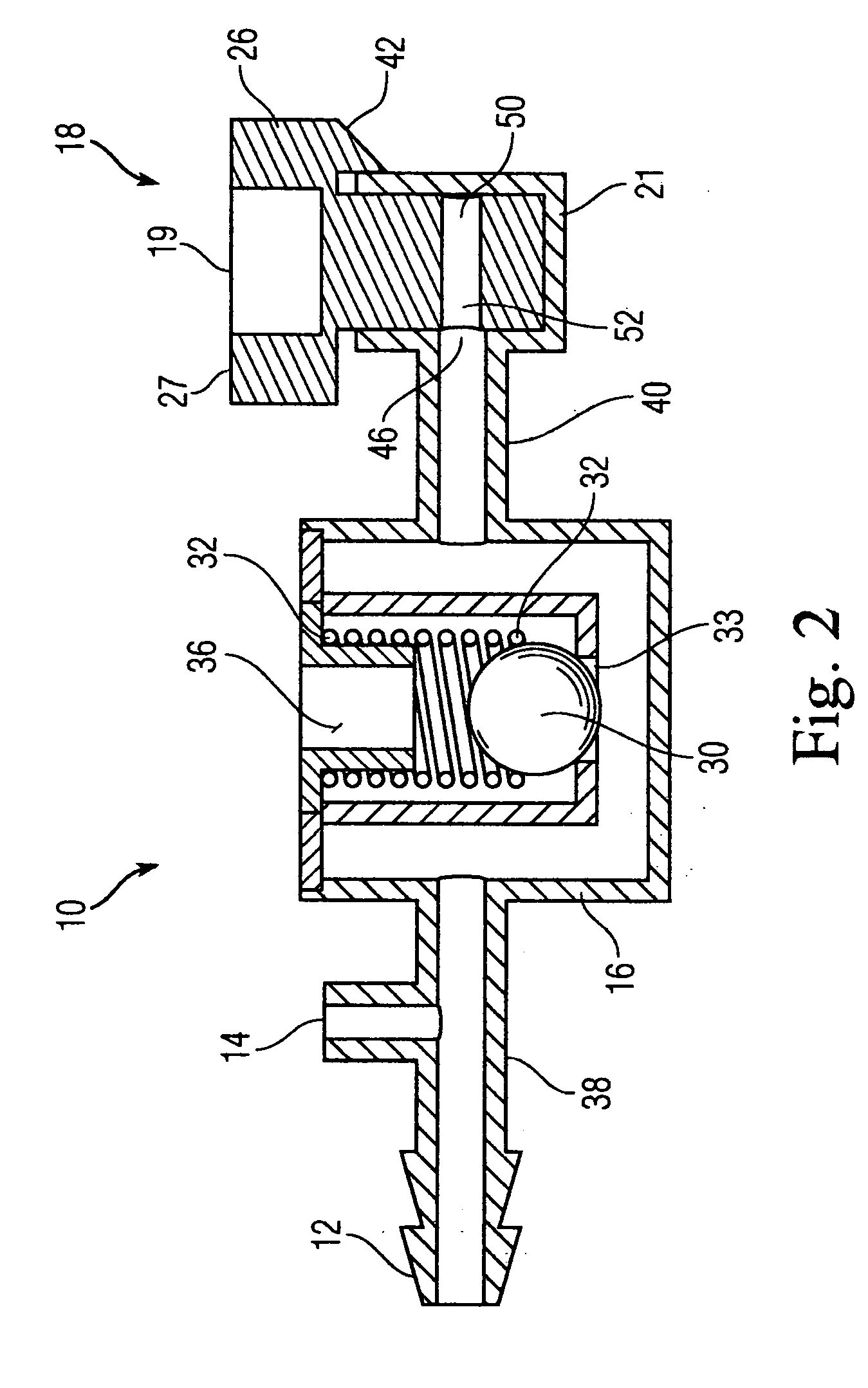
Bronchoscopy oxygenation system
A bronchoscopy oxygenation system having a channel for inserting alternately an instrument or fluids and for delivering oxygen to a patient. The system being provided with pressure relief vent and a pressure relief valve for the relief of excessive oxygen pressure. The bronchoscopy oxygenation system may be used during bronchoscopy and with patient suctioning, bronchoalveolar lavage or biopsy. The bronchoscopy oxygenation system is intended to be used with a conventional bronchoscope.
Owner:WILLEFORD KENNETH L
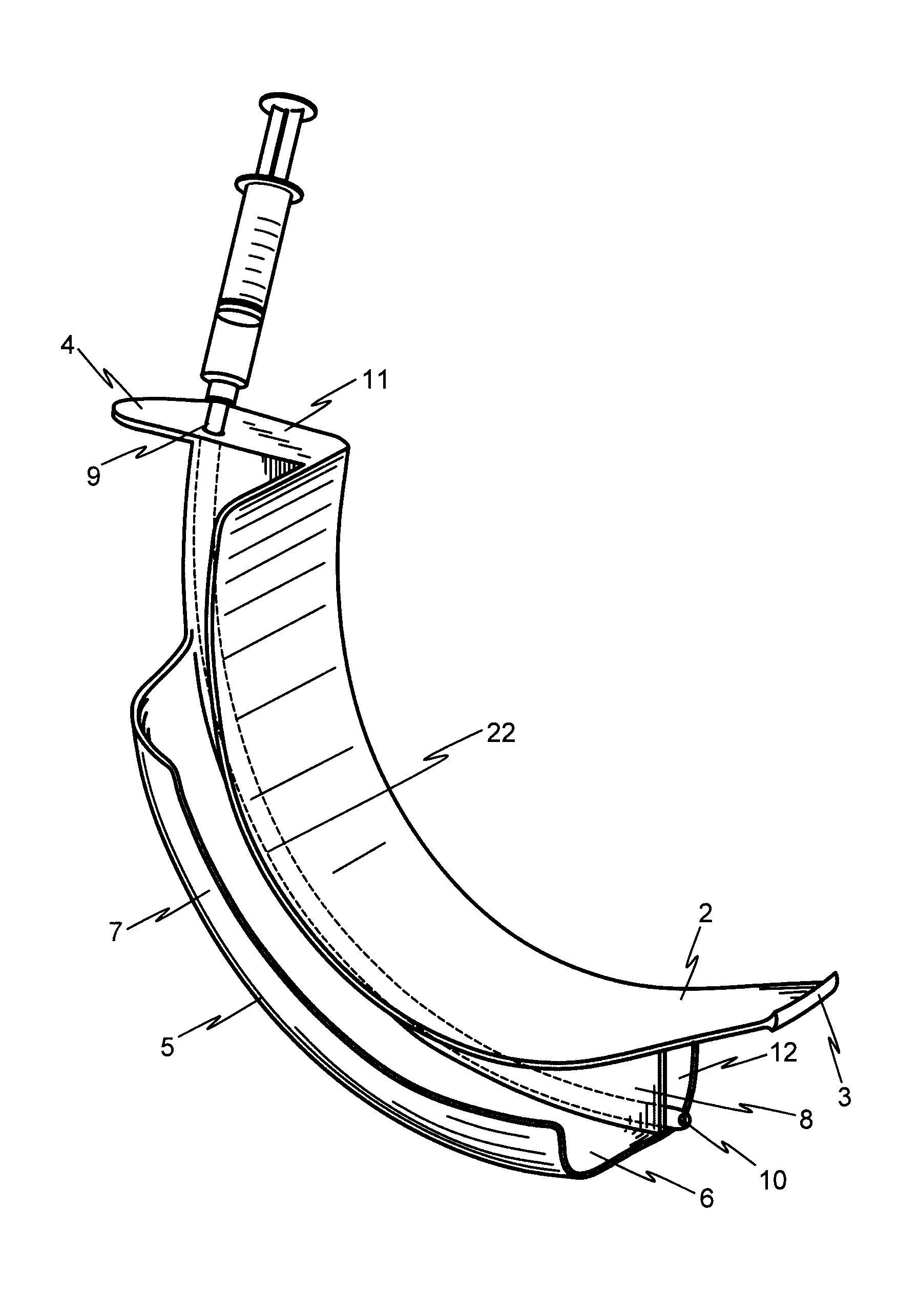
Intubating Airway
The intubating airway of the present invention has a shape of a long curved spatula with two channels underneath. The present invention its design, size, shape and adjustable depth of insertion provide it with unique ability to open the airway tract completely, reliably and consistently from the mouth to the larynx. This ability makes it a multifunction device: It can relieve any degree of airway obstruction when all available airway devices have failed. It convert fiber optic intubation and optical stylet intubation from difficult, time consuming and need a lot of experience into quick, easy and simple even by first time user could intubate with high success rate. It facilitates lighted stylet intubation and the intubation of a double lumen tube or nasal tube when it is difficult to intubate, and also facilitate the insertion of a TEE probe or gastroscope or bronchoscope.
Owner:ALEXANDER MARK
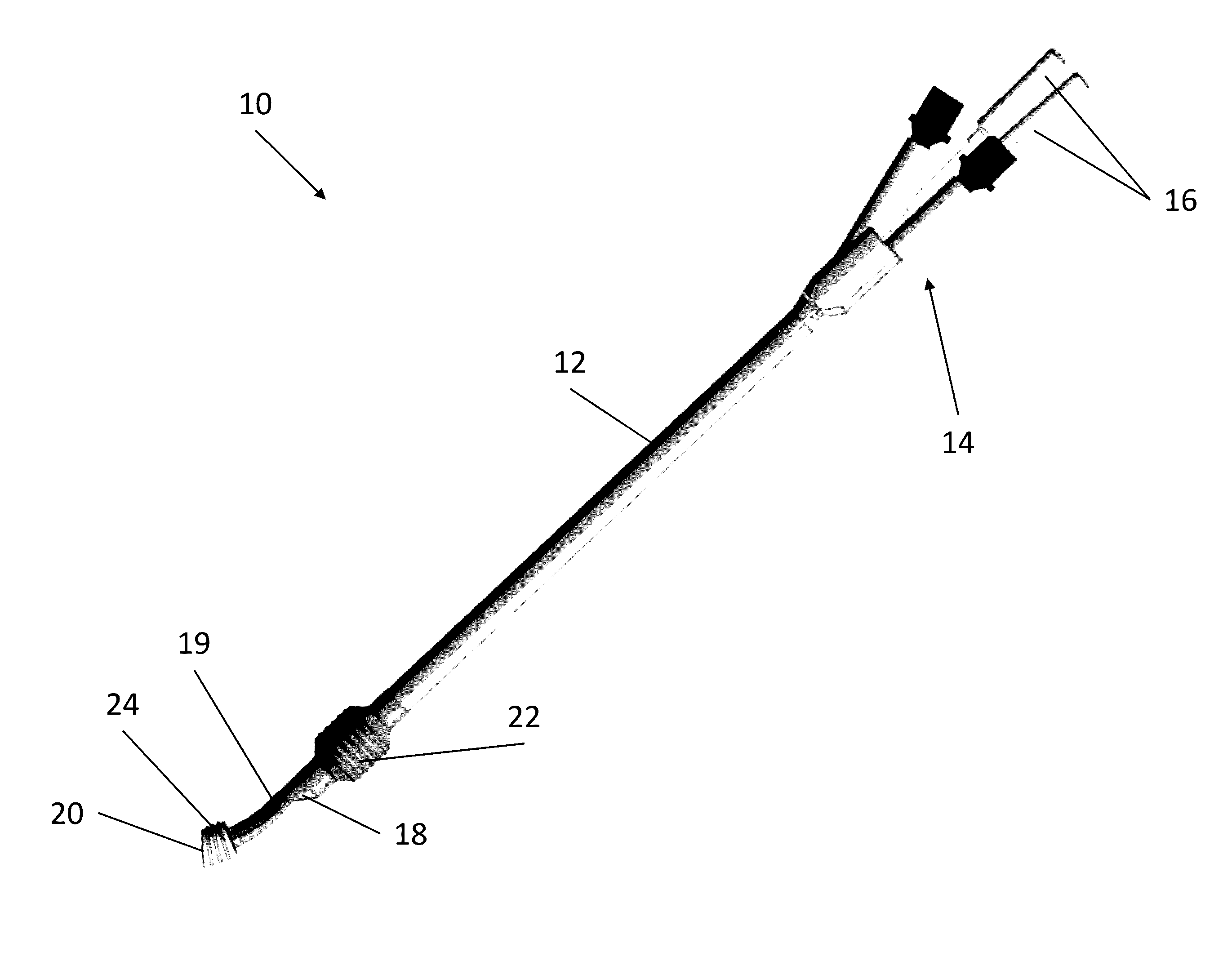
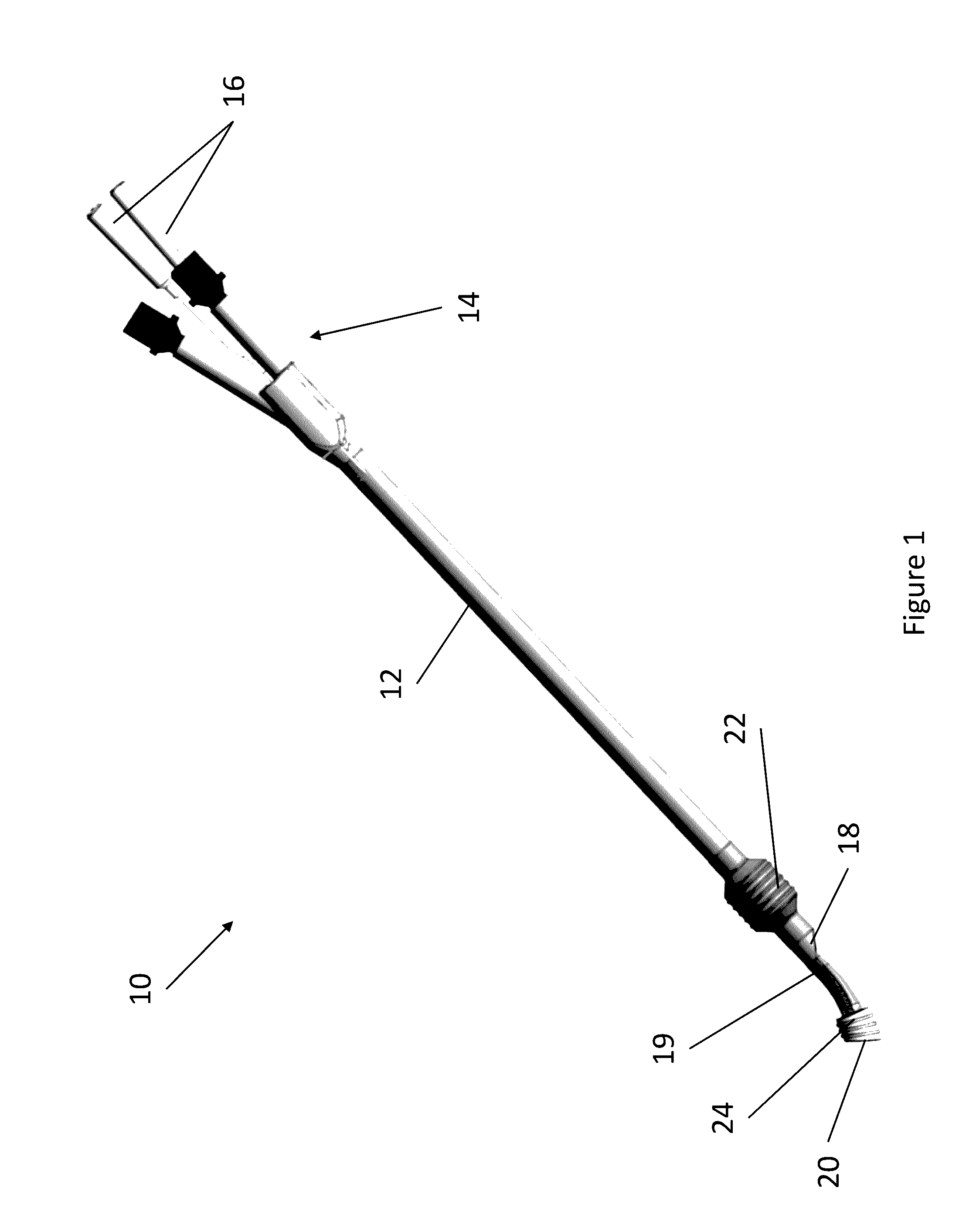
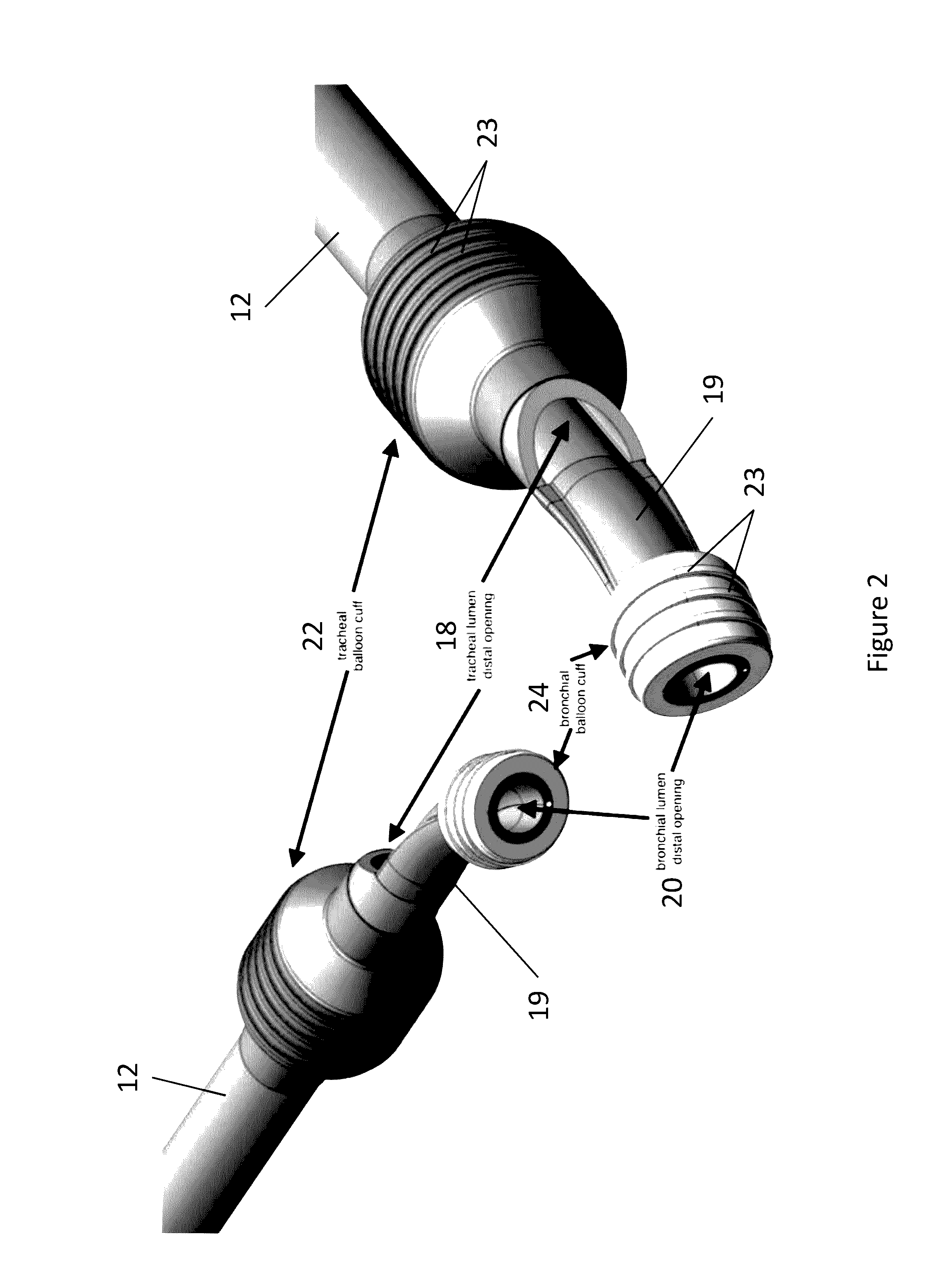
Dual Lumen Endobronchial Tube Device
The present invention provides improved dual lumen endobronchial tube devices. The dual lumen endobronchial tube devices feature a universal design for left or right mainstem bronchus insertion. The dual lumen endobronchial tube devices also feature enhanced balloon cuff designs to minimize dislodgement while maintaining proper airway sealing. The present invention also includes water activated lubricious coating inside the shaft to reduce friction during insertion of a bronchoscope into the airway. The present invention also provides improved double clamps that prevent the accidental clamping of both tubes of a Y-adapter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
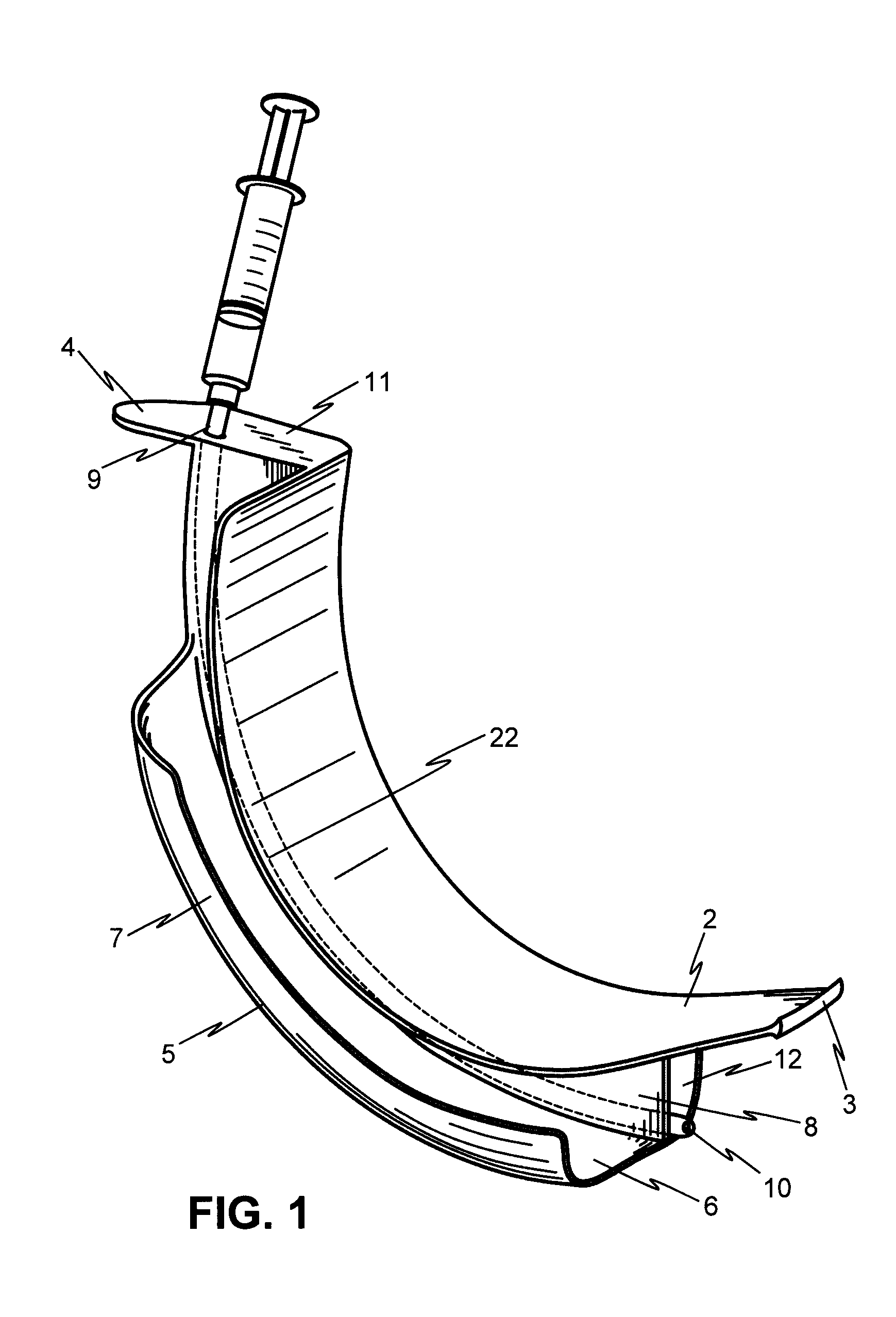
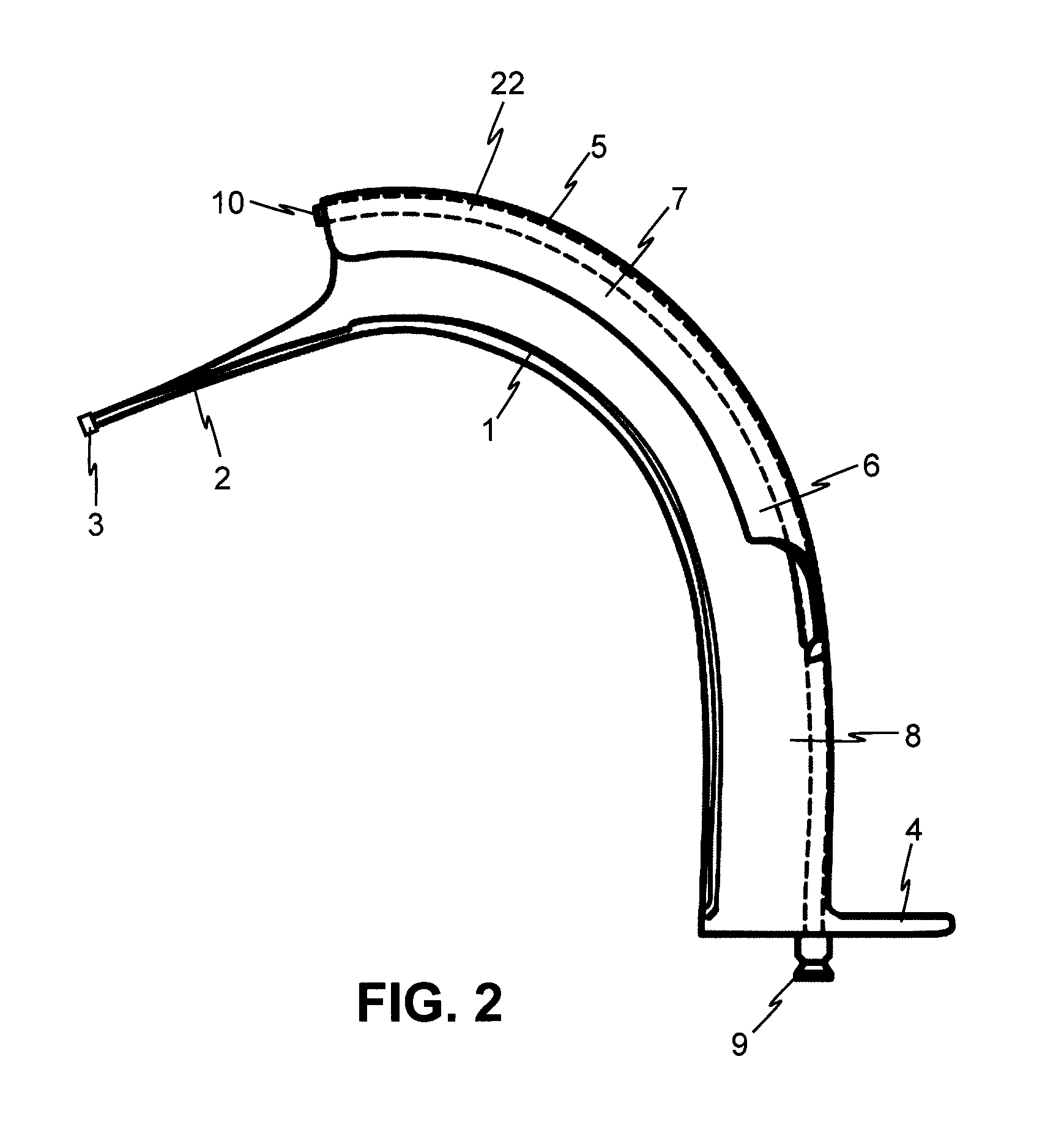
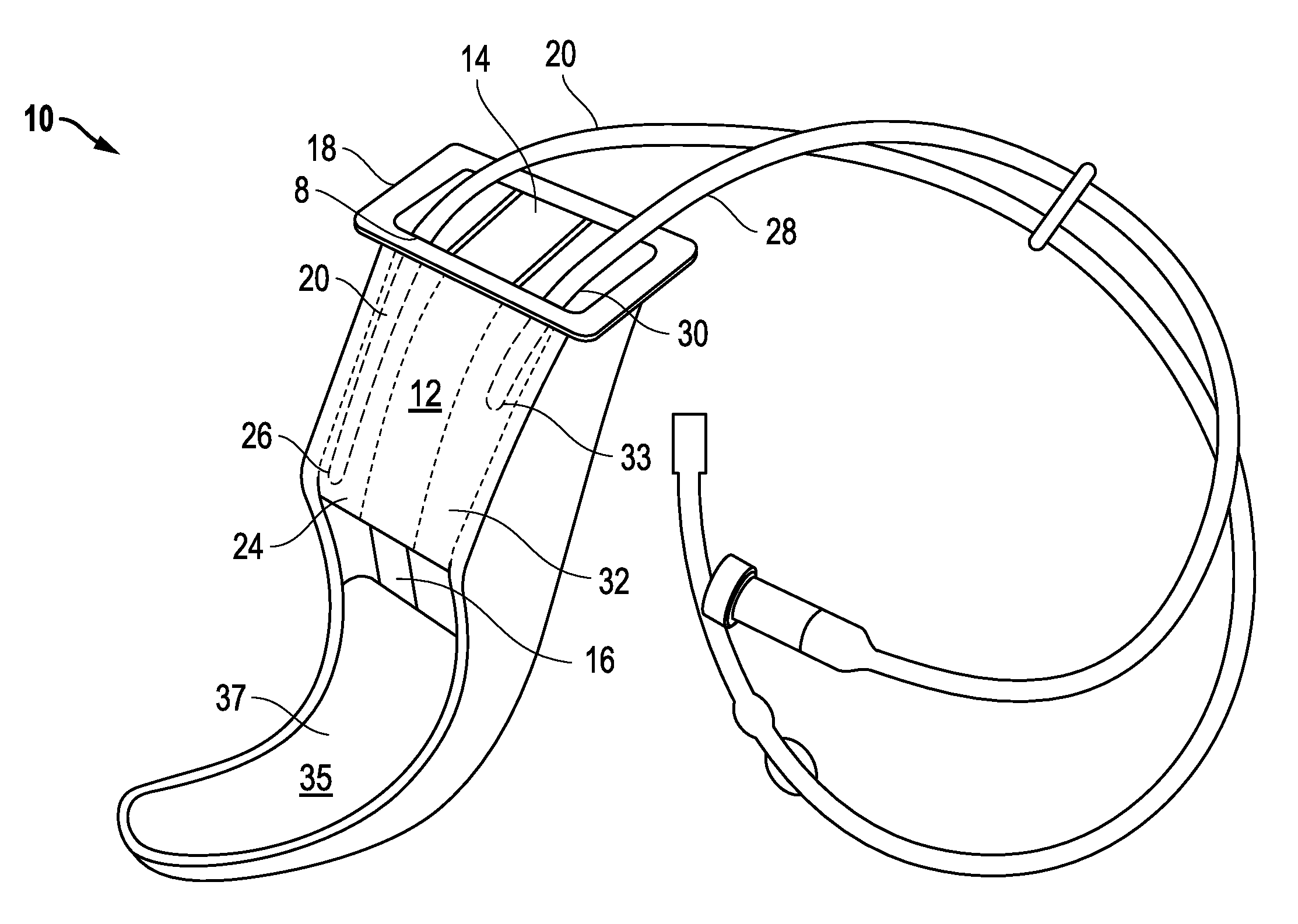
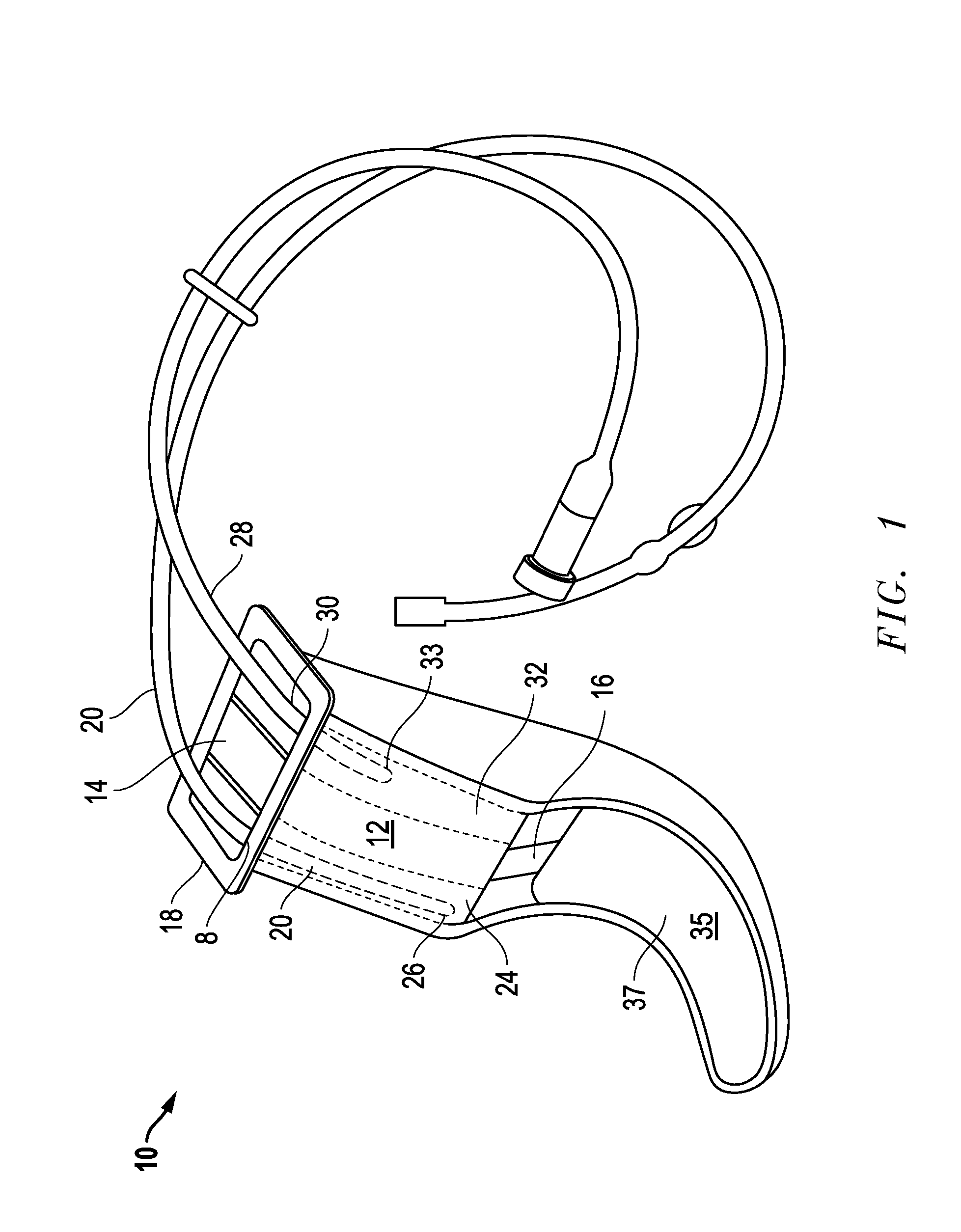
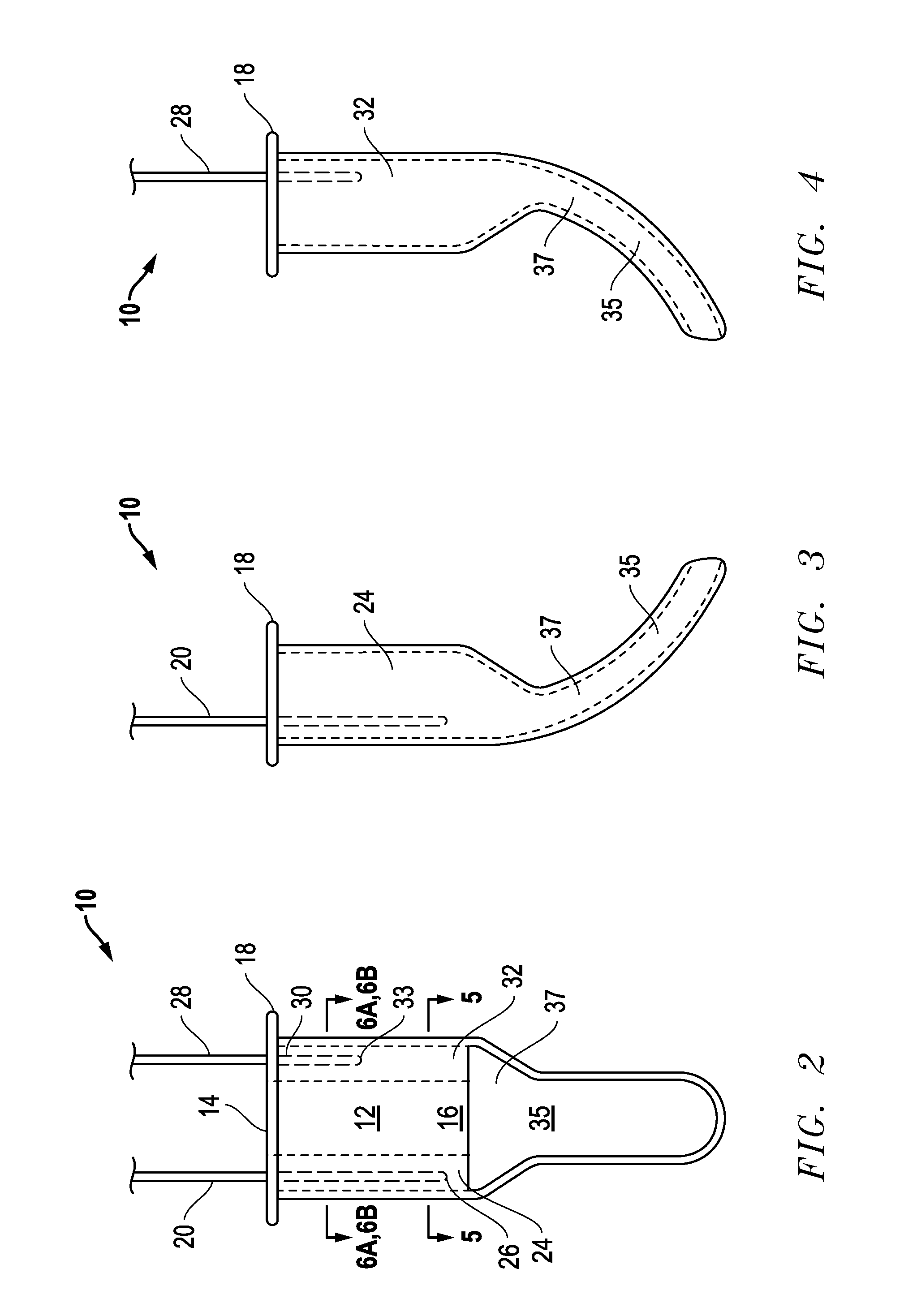
Oral airway for endoscopic and intubating procedures
An oral airway providing a patent airway to a patient, supplies oxygen to the patient and monitors expelled gases during endoscopic or intubating procedures. The oral airway includes a central lumen and two lateral breathing channels. A bracket at the proximal end of the oral airway functions to guide an oxygen supply line and an end tidal carbon dioxide monitoring line into the lateral breathing channels and to act as a barrier beyond which the airway cannot be inserted into the mouth of the patient. The airway has a straight main central lumen which serves as a guide and conduit to facilitate endoscope, bronchoscope, or fiber optic bronchoscope placement and manipulation.
Owner:CAPL MEDICAL LLC
Bronchoscopy oxygenation system
A bronchoscopy oxygenation system having a channel for inserting alternately an instrument or fluids and for delivering oxygen to a patient. The system being provided with pressure relief vent and a pressure relief valve for the relief of excessive oxygen pressure. The bronchoscopy oxygenation system may be used during bronchoscopy and with patient suctioning, bronchoalveolar lavage or biopsy. The bronchoscopy oxygenation system is intended to be used with a conventional bronchoscope.
Owner:WILLEFORD KENNETH L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com