Patents
Literature
687results about "Radiation diagnostic clinical applications" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
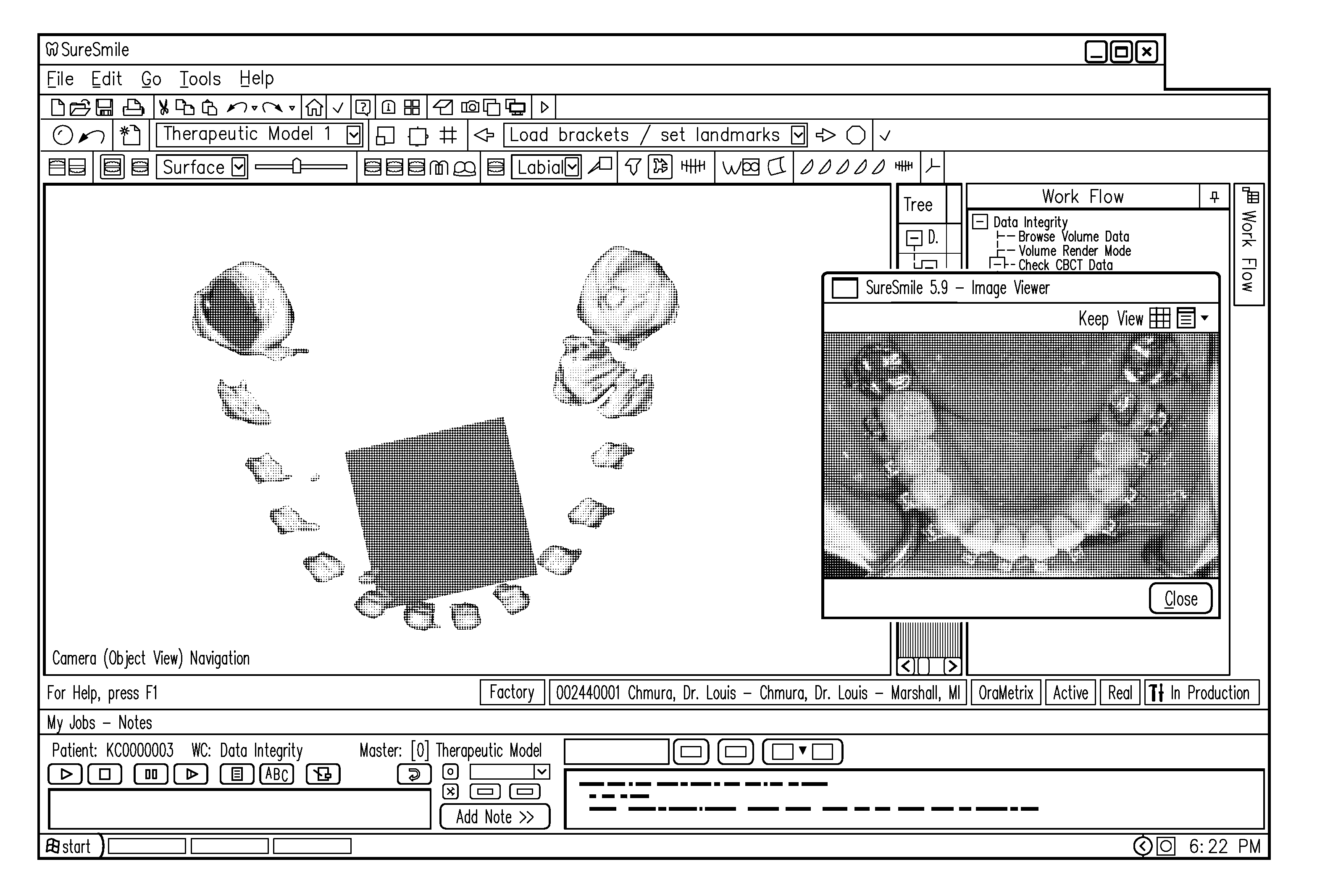
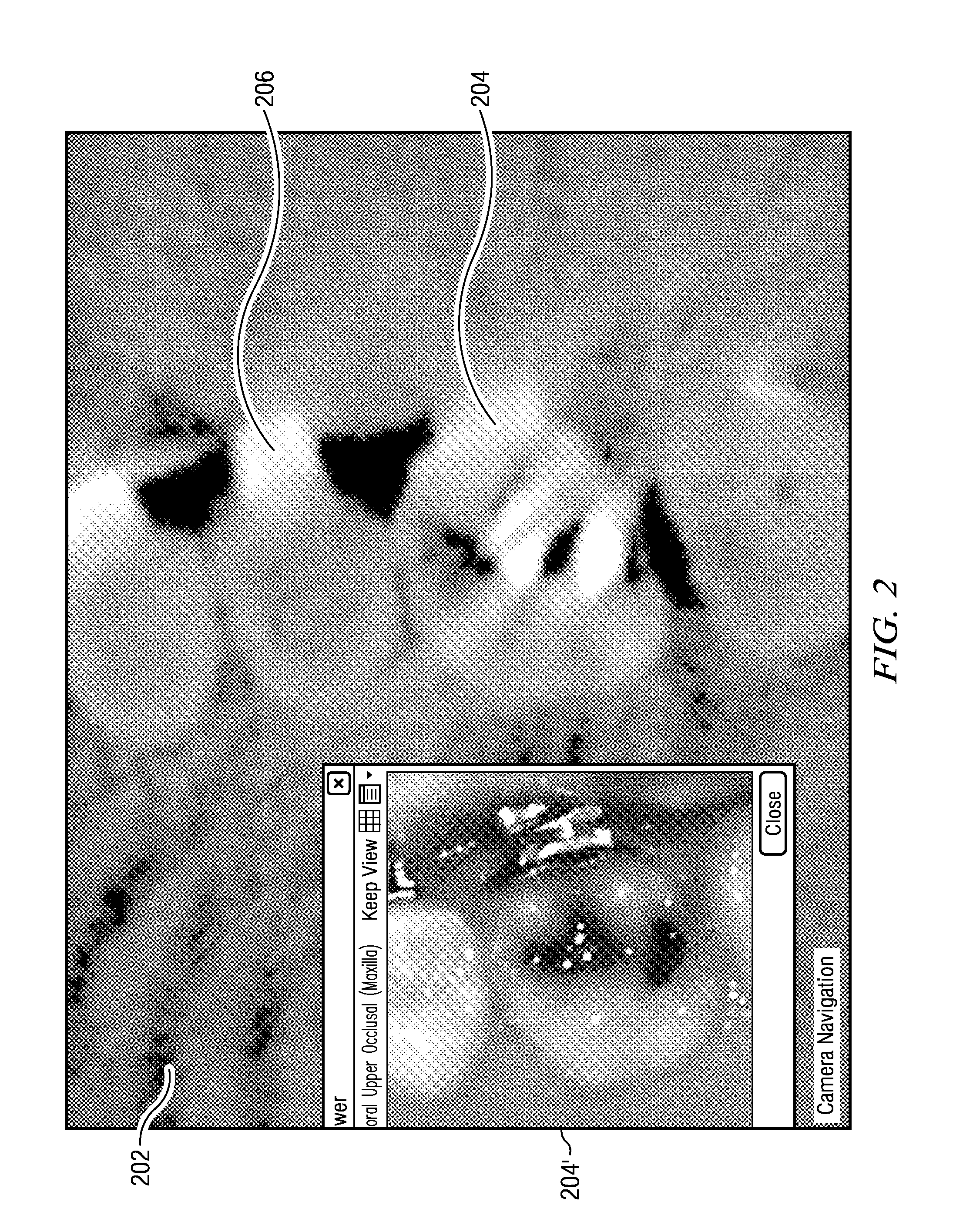
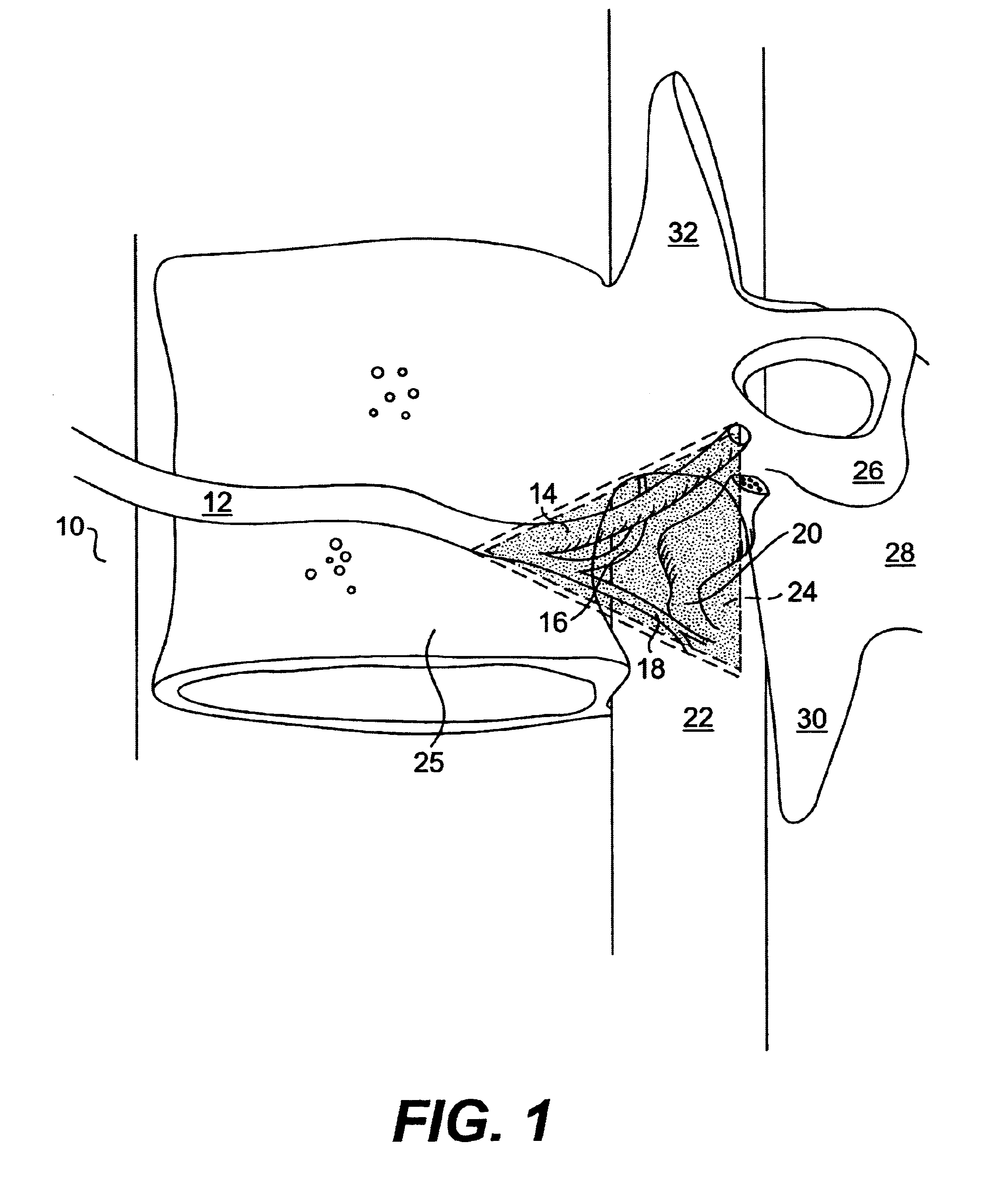
Unified three dimensional virtual craniofacial and dentition model and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120015316A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImpression capsFacial bone structureFunctional anatomy
A method and apparatus are disclosed enabling an orthodontist or a user to create an unified three dimensional virtual craniofacial and dentition model of actual, as-is static and functional anatomy of a patient, from data representing facial bone structure; upper jaw and lower jaw; facial soft tissue; teeth including crowns and roots; information of the position of the roots relative to each other; and relative to the facial bone structure of the patient; obtained by scanning as-is anatomy of craniofacial and dentition structures of the patient with a volume scanning device; and data representing three dimensional virtual models of the patient's upper and lower gingiva, obtained from scanning the patient's upper and lower gingiva either (a) with a volume scanning device, or (a) with a surface scanning device. Such craniofacial and dentition models of the patient can be used in optimally planning treatment of a patient.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
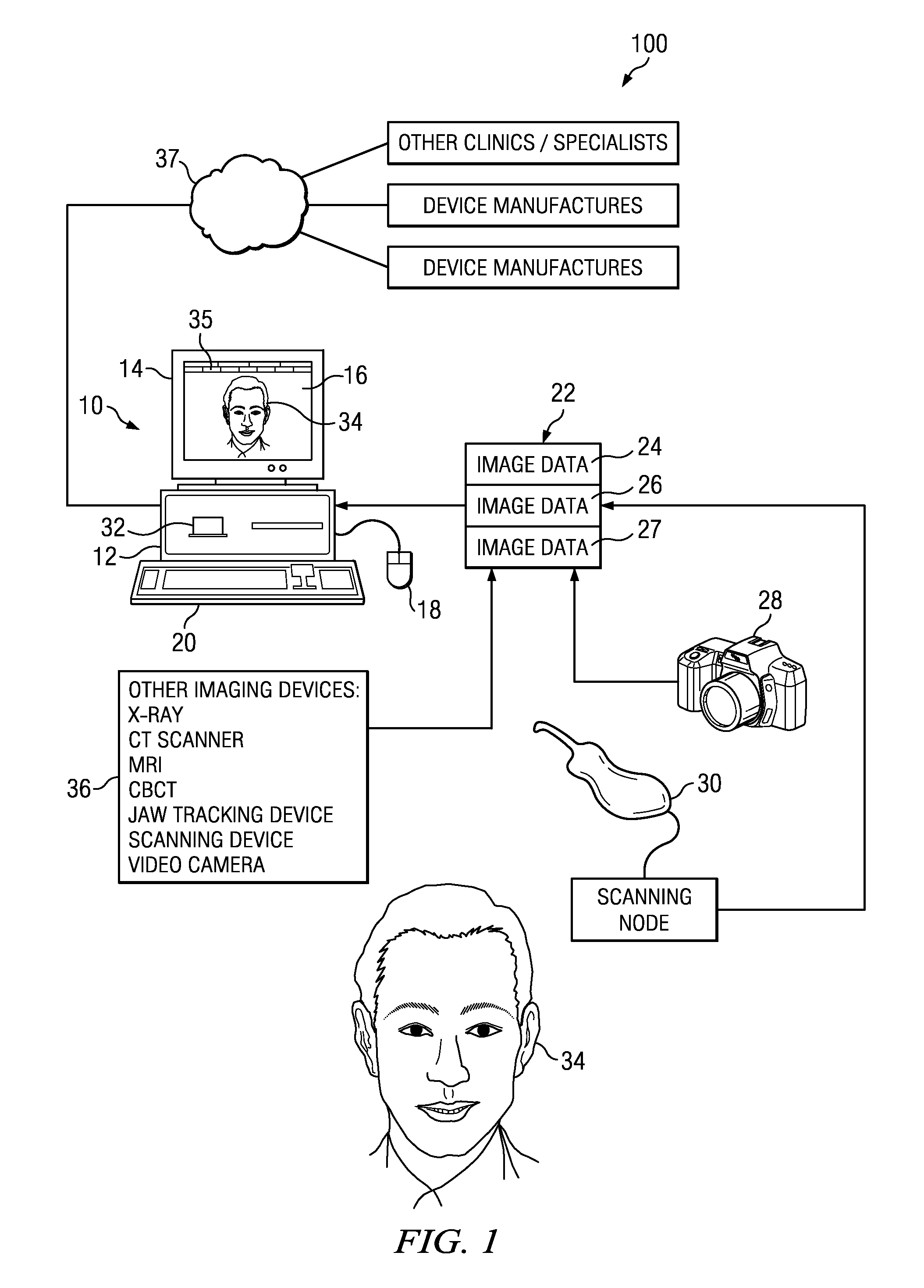
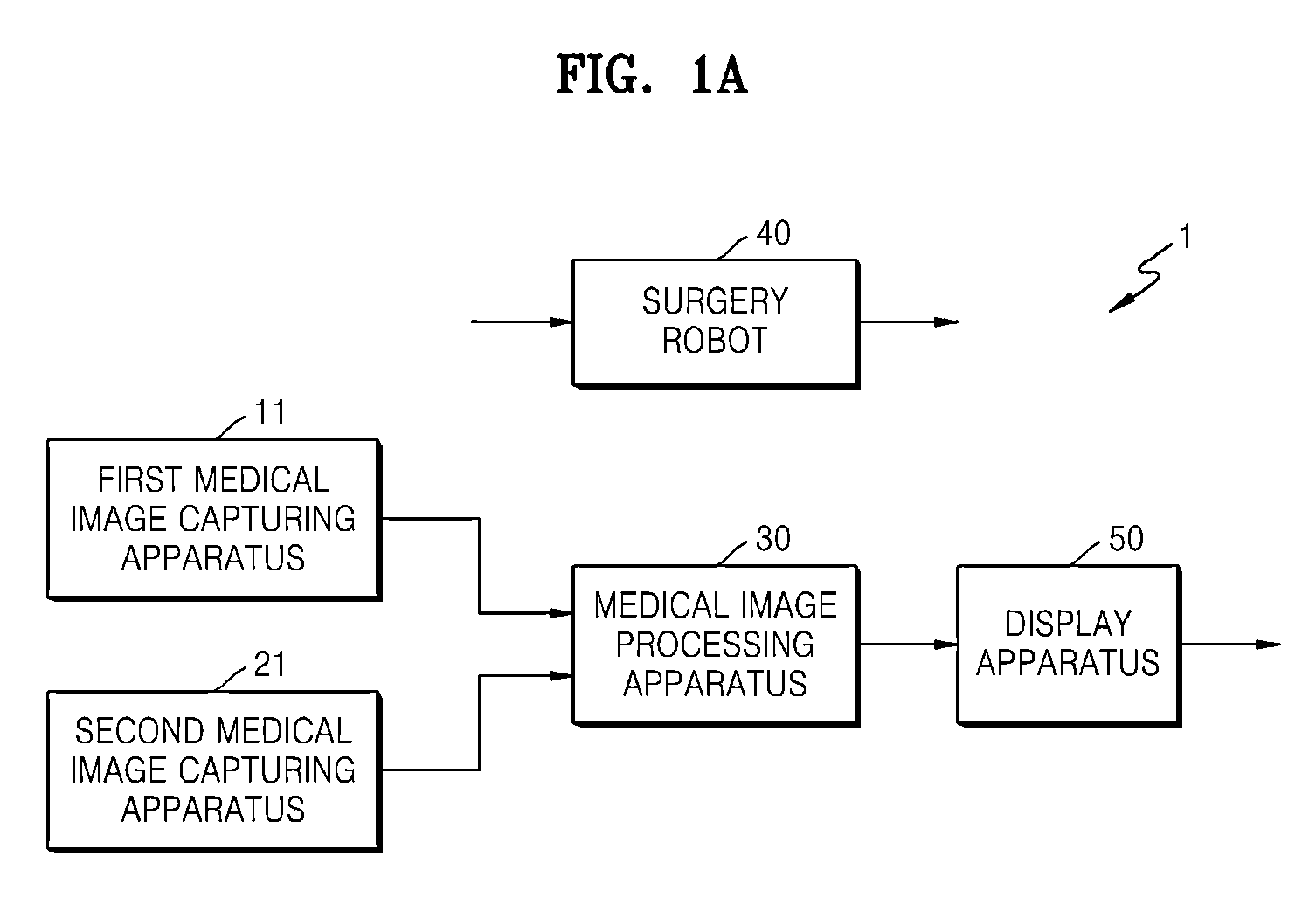
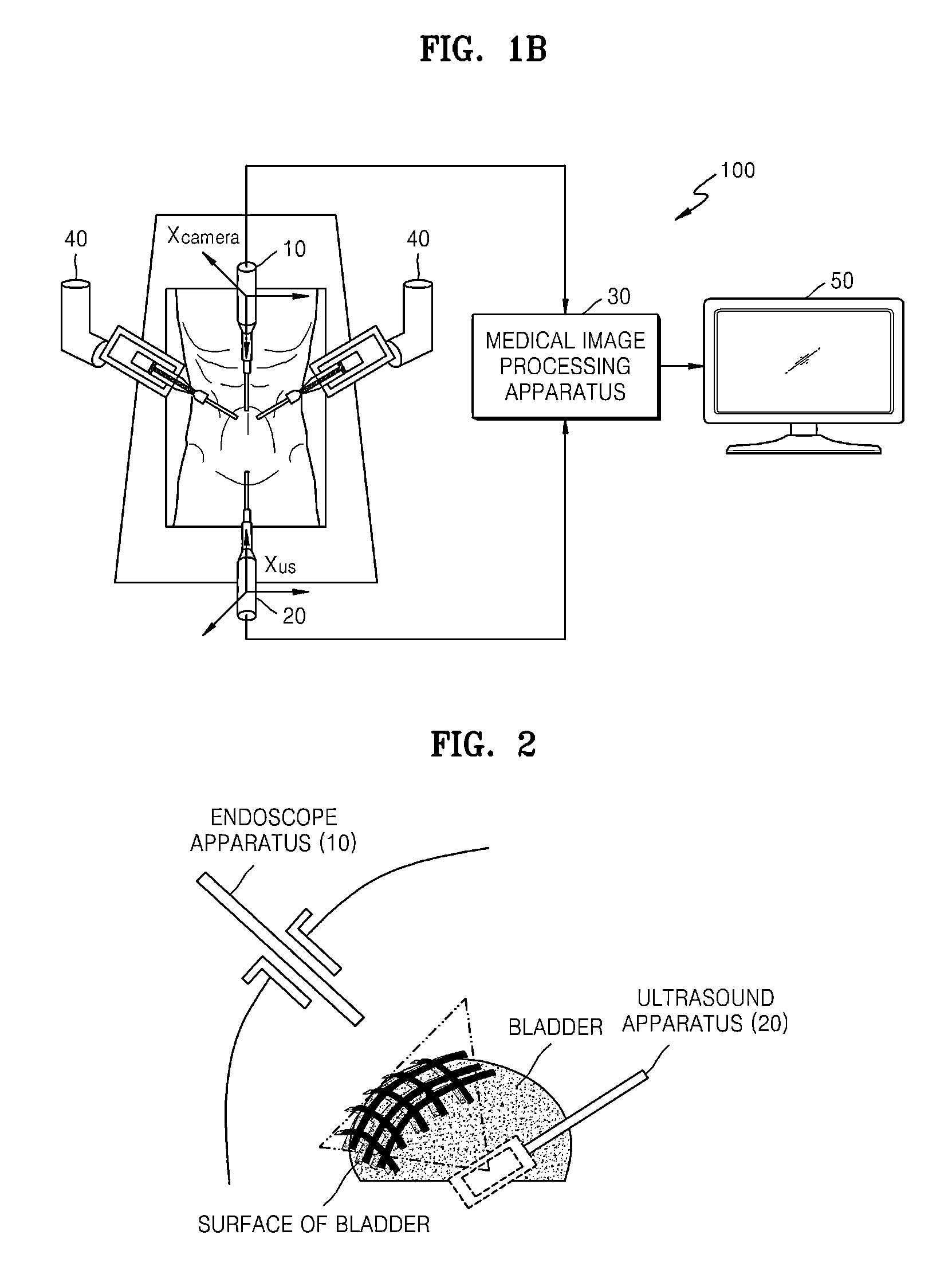
Method and apparatus for processing medical image, and robotic surgery system using image guidance
InactiveUS20130035583A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsImage guidanceImage capture
A synthesis image in which medical images captured using different medical image capturing apparatuses are registered is generated by mapping the medical images to each other. The synthesis image may be used for image guidance while a diagnosis or a robotic surgery of a patient is being performed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
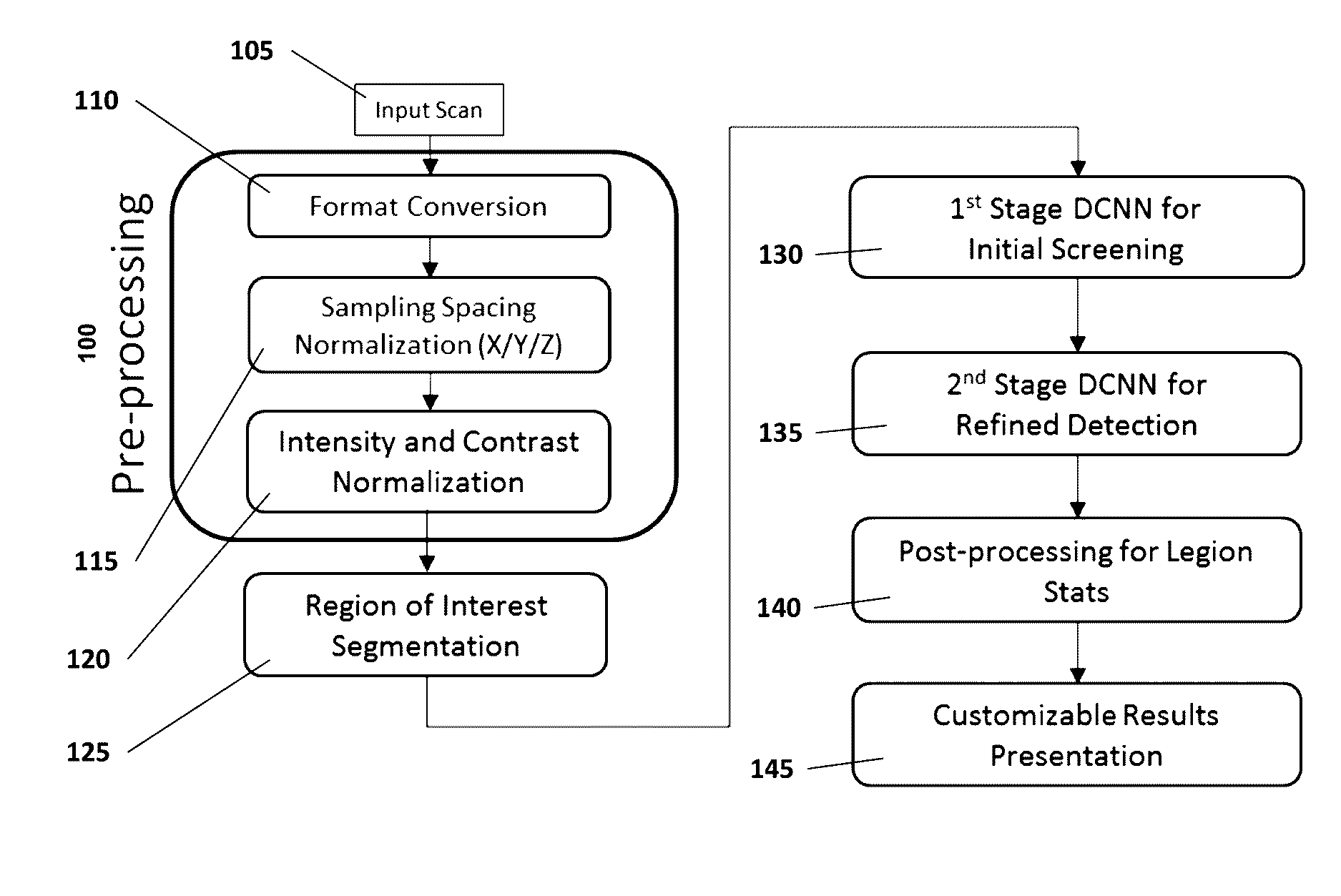
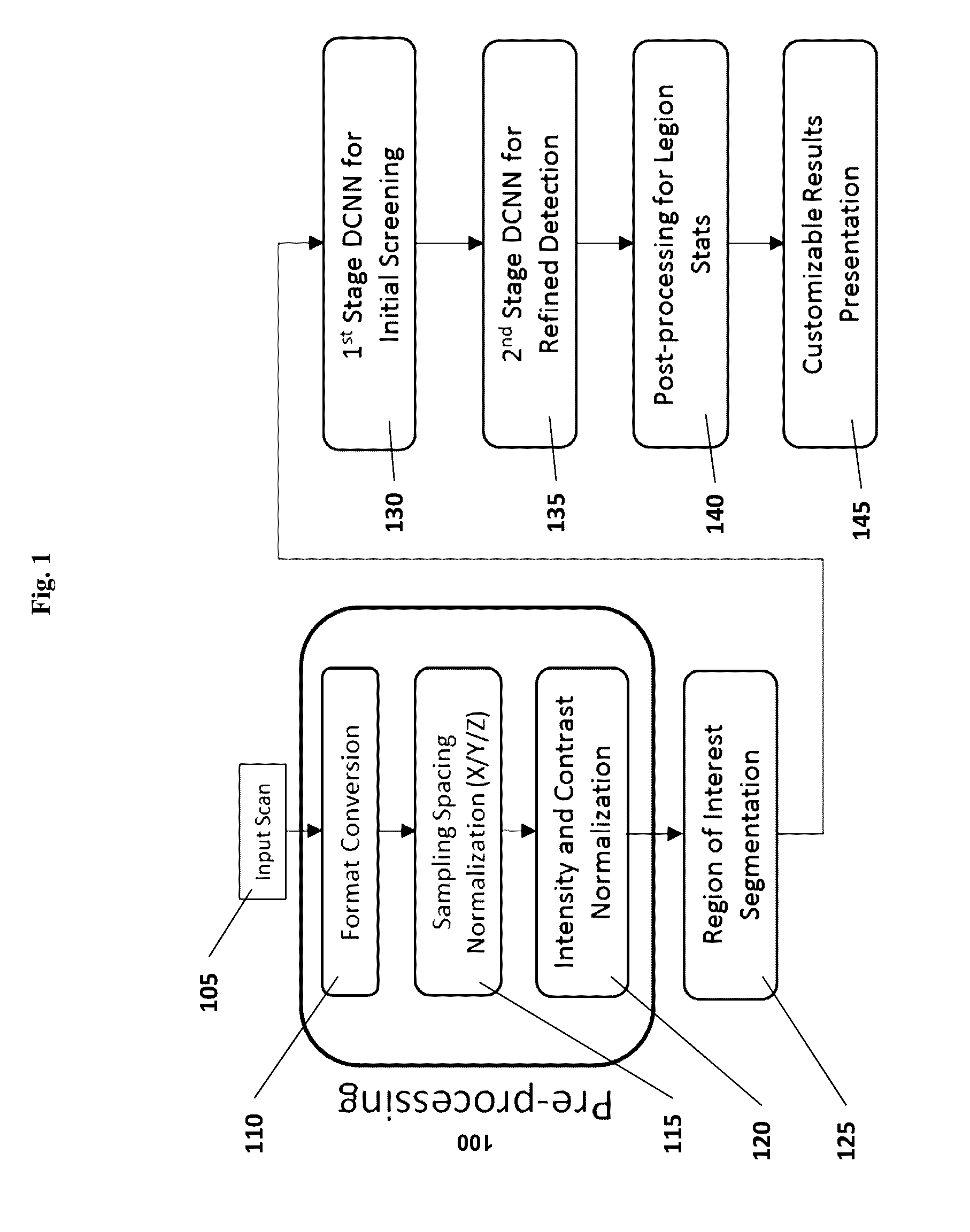
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveUS9589374B1Examination time can be shortenedImprove diagnostic accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionAided diagnosis
Owner:12 SIGMA TECH
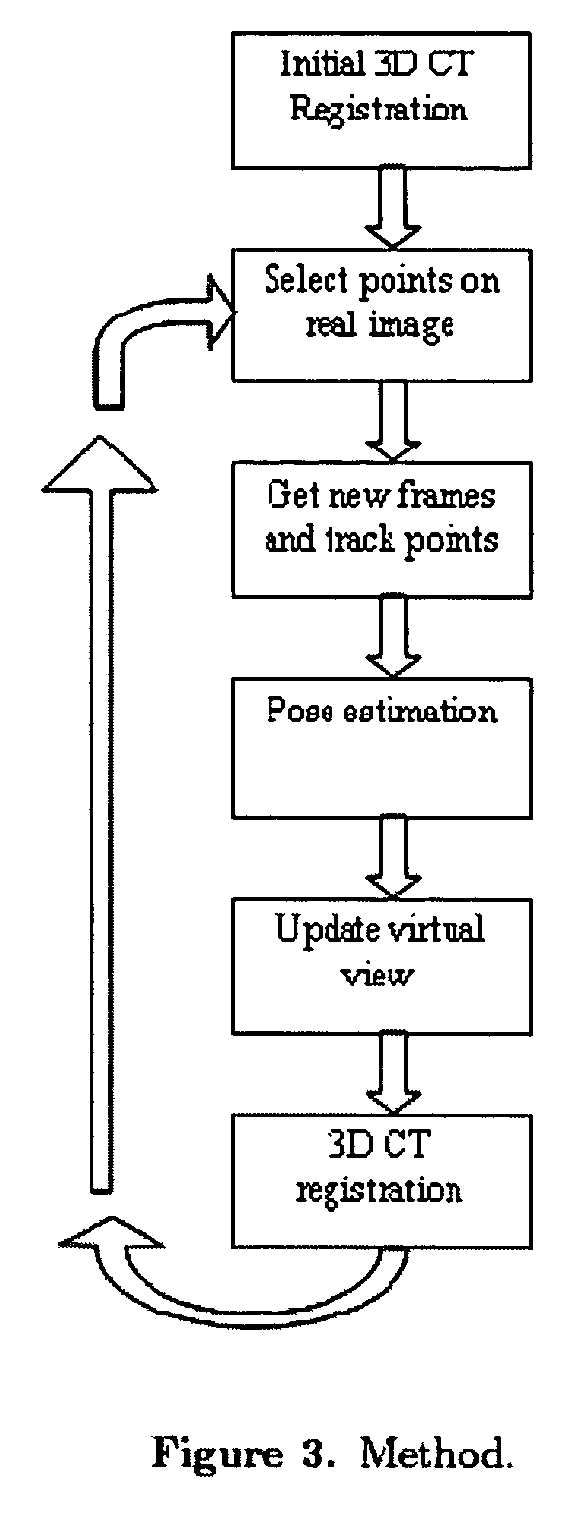
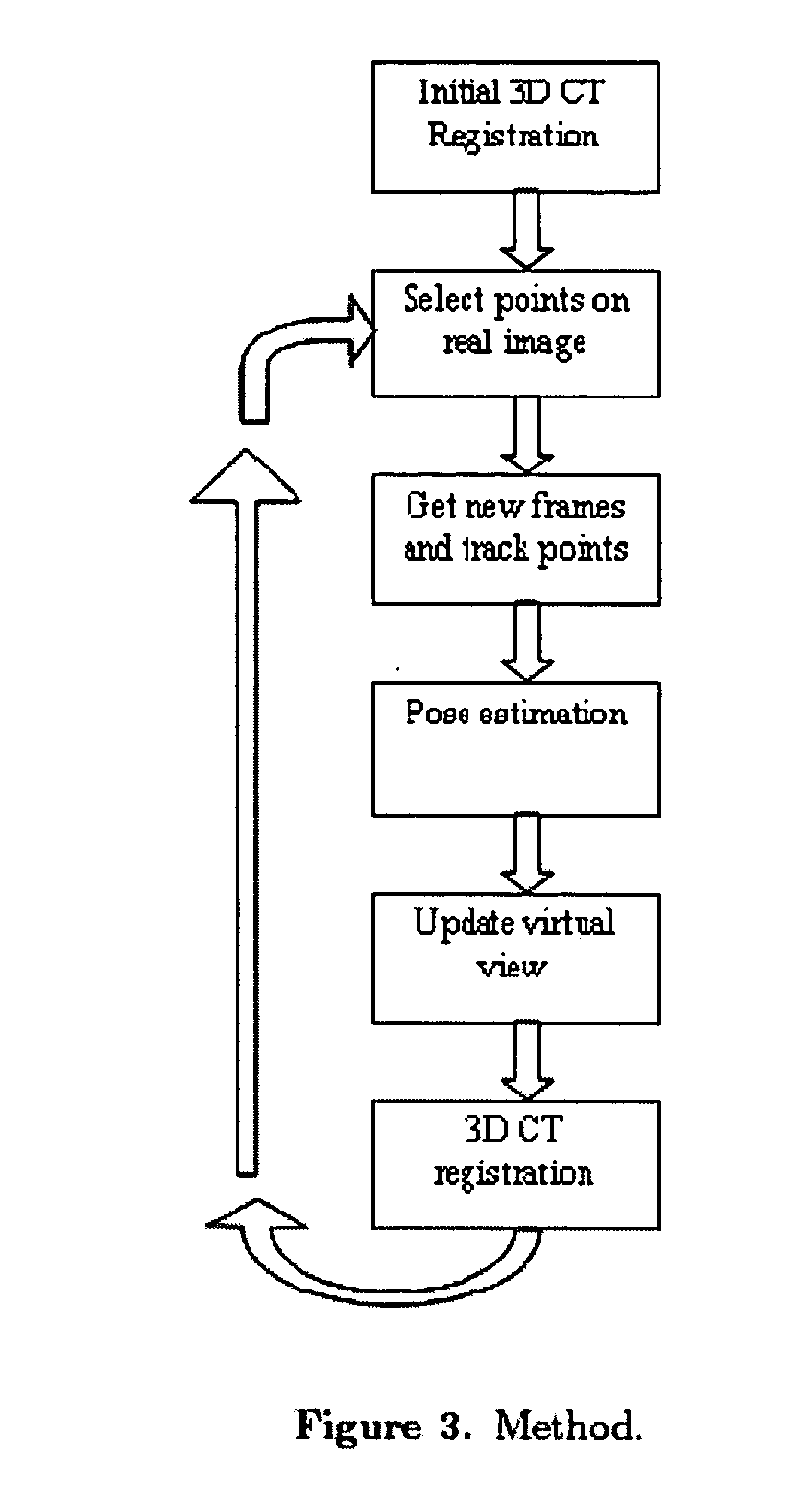
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS7756563B2Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
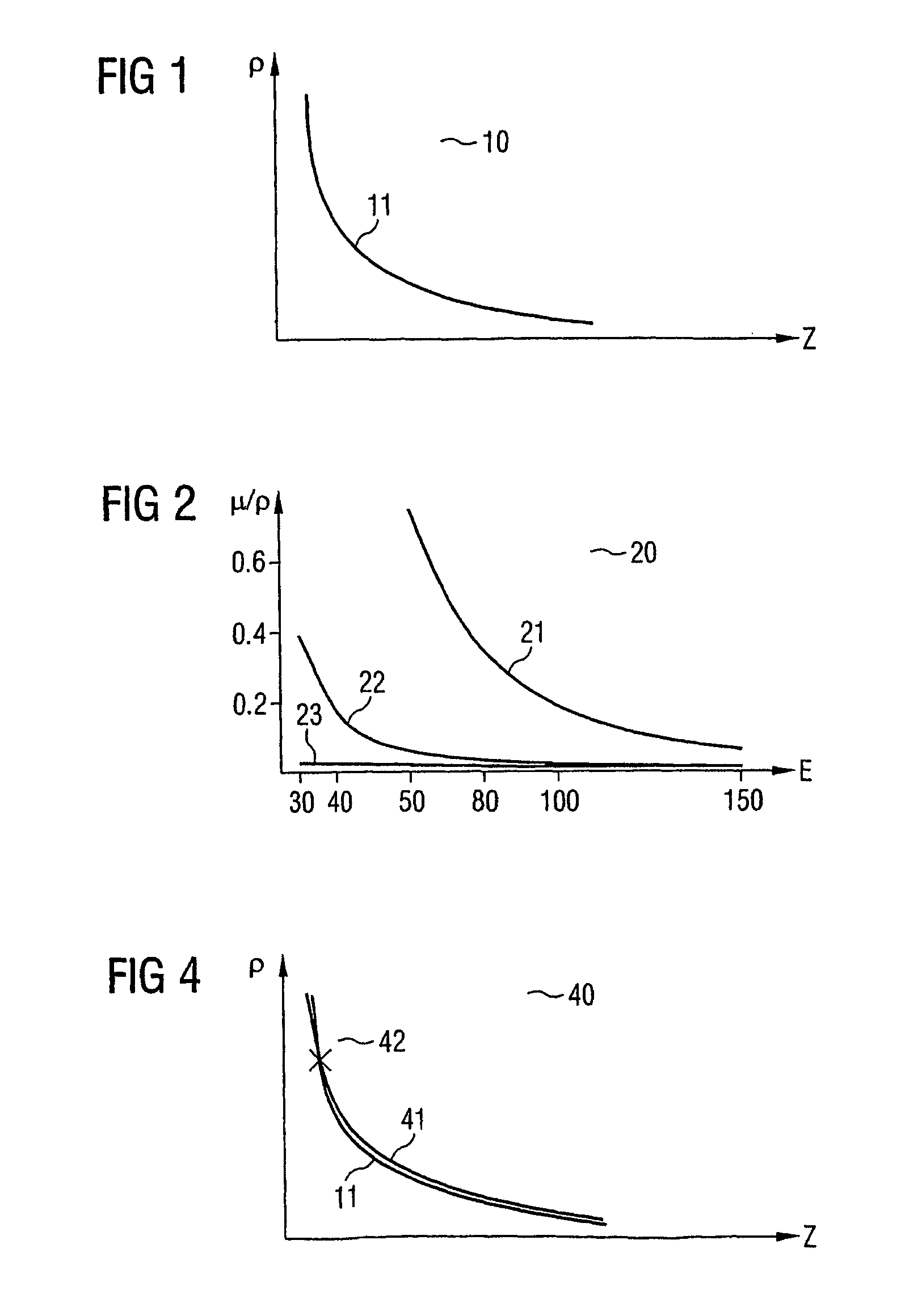
Method for determining density distributions and atomic number distributions during radiographic examination methods
InactiveUS7158611B2Accurate measurementSatisfactory resolutionRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsComputerised tomographsRadiographic ExamDensity distribution
The functional dependency of a first X-ray absorption value of density and atomic number is determined in the instance of a first X-ray spectrum, and at least the functional dependency of a second X-ray absorption value of density and atomic number is determined in the instance of a second X-ray spectrum. Based on a recording of a first distribution of X-ray absorption values of the object to be examined in the instance of a first X-ray spectrum, and on a recording of at least one second distribution of X-ray absorption values of the object to be examined in the instance of a second X-ray spectrum, the values for density and atomic number are determined by comparing the functional dependency of a first X-ray absorption value of the first distribution of X-ray absorption values with the functional dependency(ies) of the X-ray absorption values, which are assigned to the first X-ray absorption value, of the second and / or other distributions of X-ray absorption values.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Reducing incremental measurement sensor error
ActiveUS20140264081A1Reduce measurement errorReduce volatilityOptical radiation measurementRadiation measurementFiberOrientation measurement
For position sensors, e.g., a fiber-based system, that build a shape of an elongated member such as a catheter using a sequence of small orientation measurements, a small error in orientation at the proximal end of the sensor will cause large error in position at distal points on the fiber. Exemplary methods and systems are disclosed which may provide full or partial registration along the length of the sensor to reduce the influence of the measurement error. Additional examples are directed to applying selective filtering at a proximal end of the elongated member to provide a more stable base for distal measurements and thereby reducing the influence of measurement errors.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
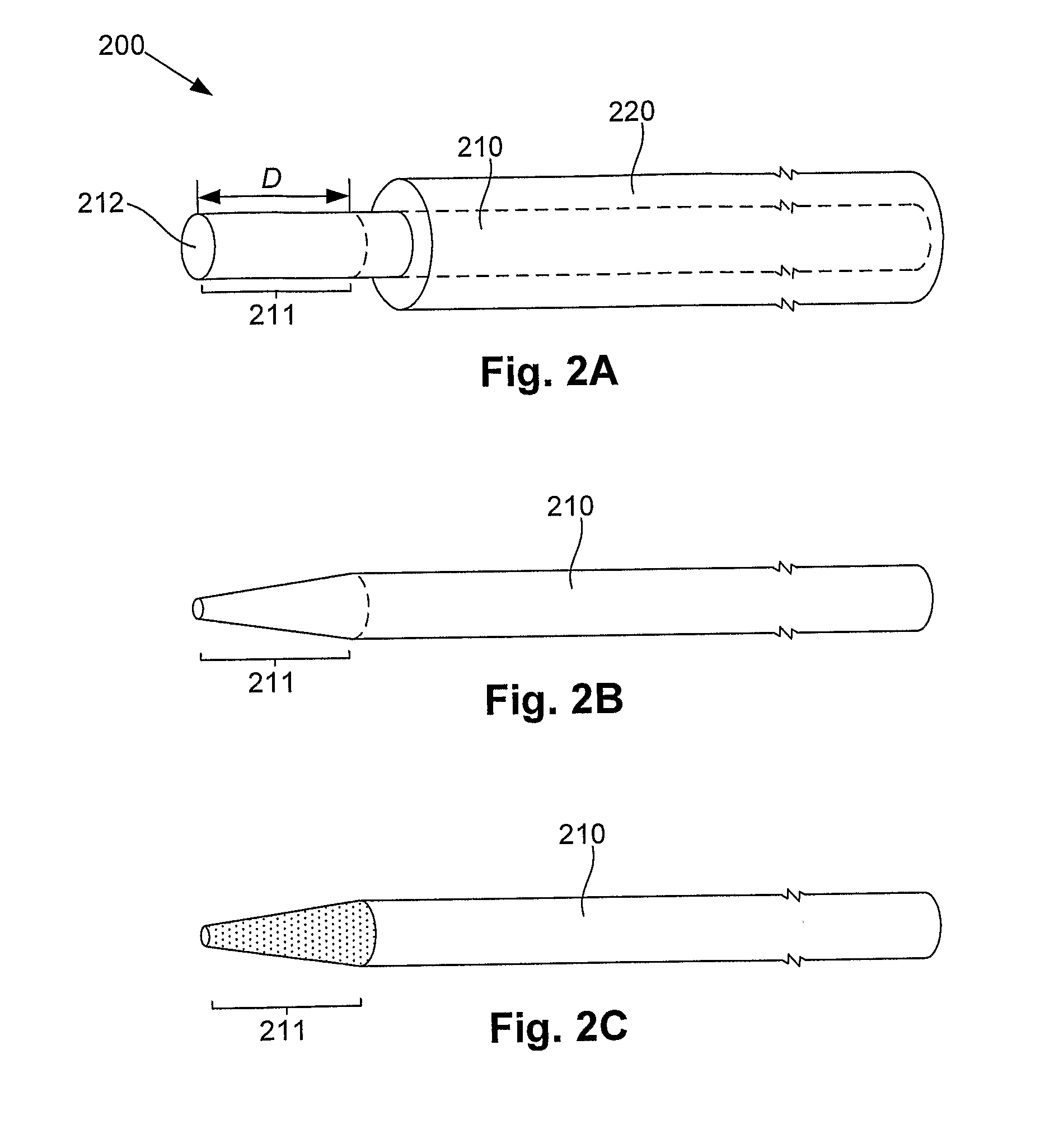
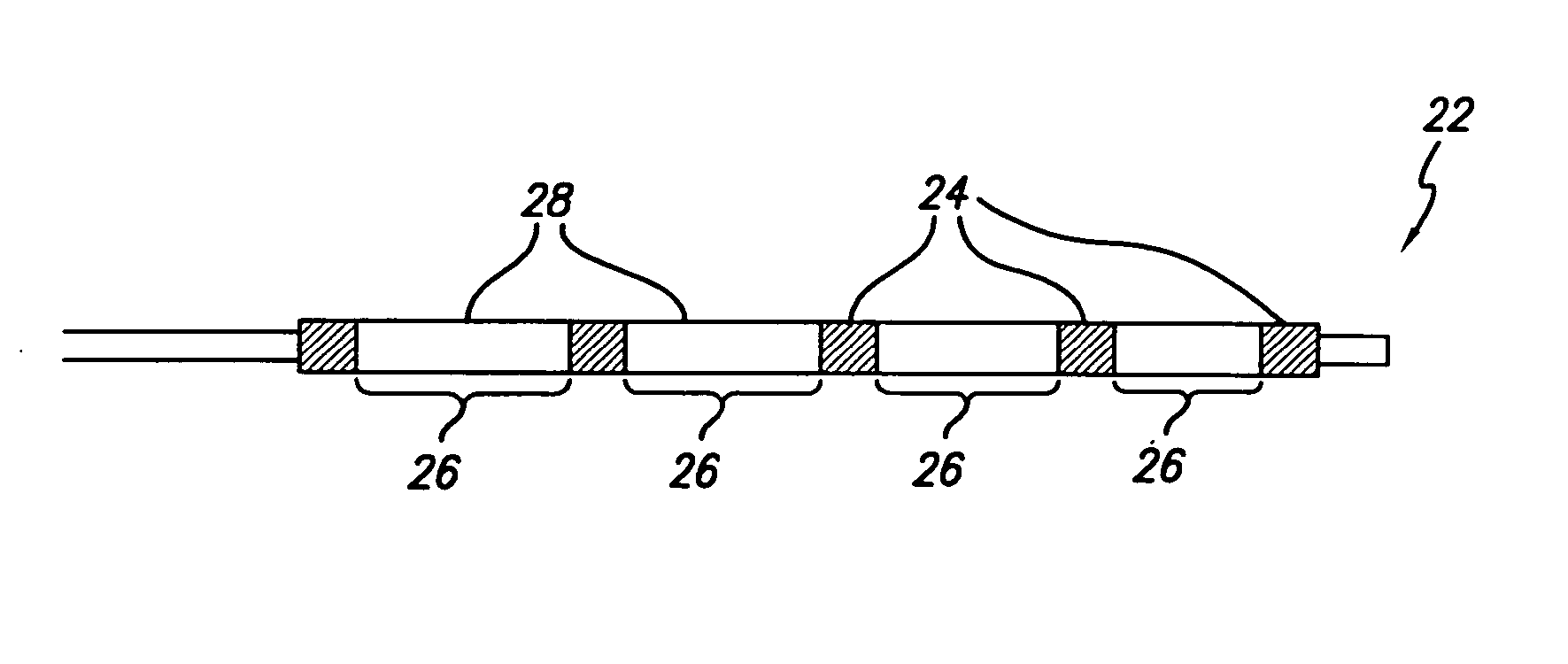
Polymeric marker with high radiopacity for use in medical devices
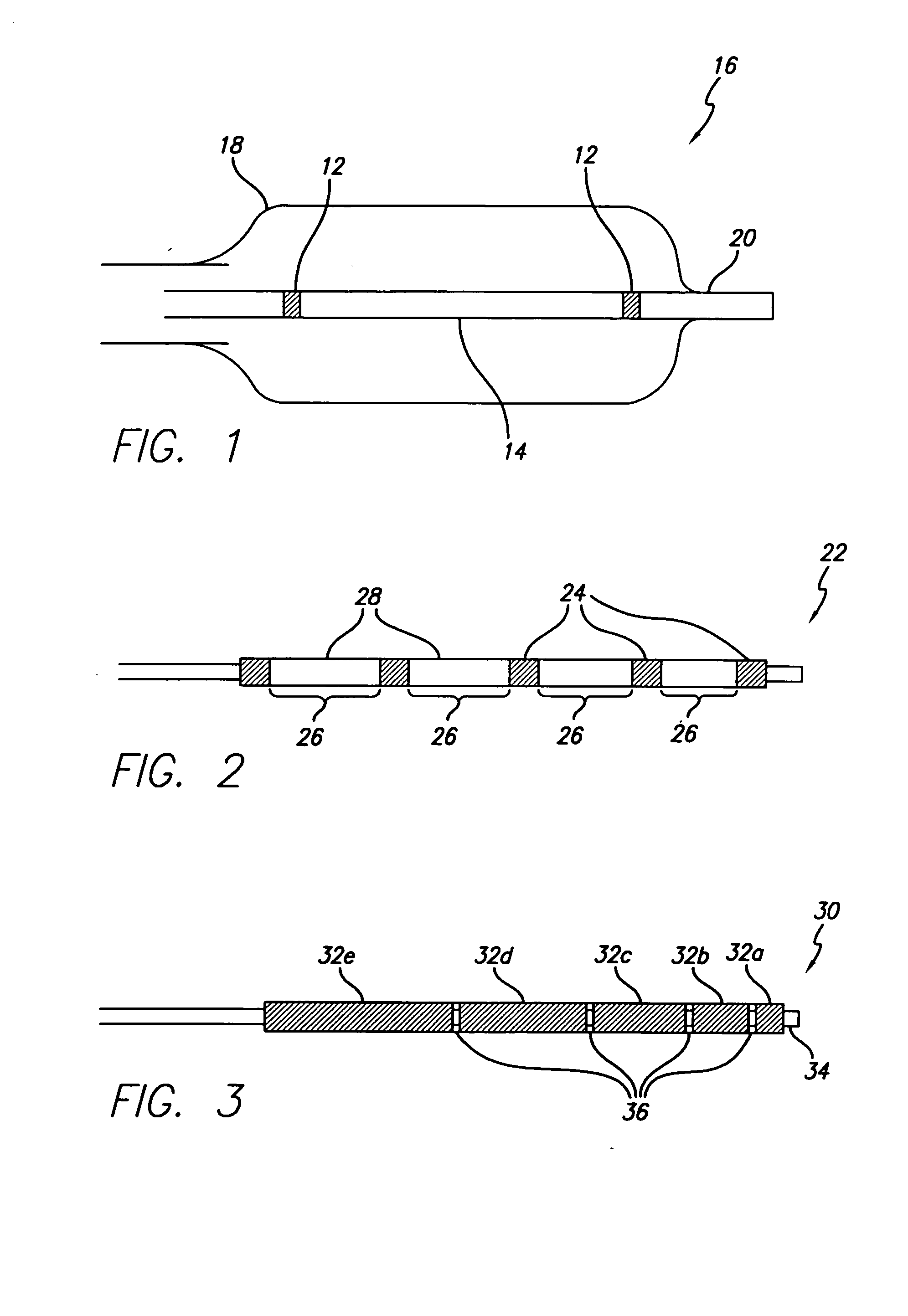
ActiveUS7303798B2Overcomes shortcomingEnhance wetting and adhesive and flow propertyMedical devicesDischarge tube main electrodesPolymer resinRadiopaque agent
High radiopacity is achieved in a polymeric marker by combining a polymeric resin, a powdered radiopaque agent having uniformly shaped particles of a specific particle size distribution and a wetting agent. The method to produce the marker calls for the blending and pelletization of these materials followed by extrusion onto support beading. The resulting supported tubing is subsequently cut to length with the beading still in place. After ejection of the beading remnant the marker is slipped into place on the device to be marked and attached by melt bonding. Marking of a guidewire allows lesions to be measured while the marking of balloon catheters allow the balloon to be properly positioned relative to a lesion.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Visualizing different types of airway wall abnormalities
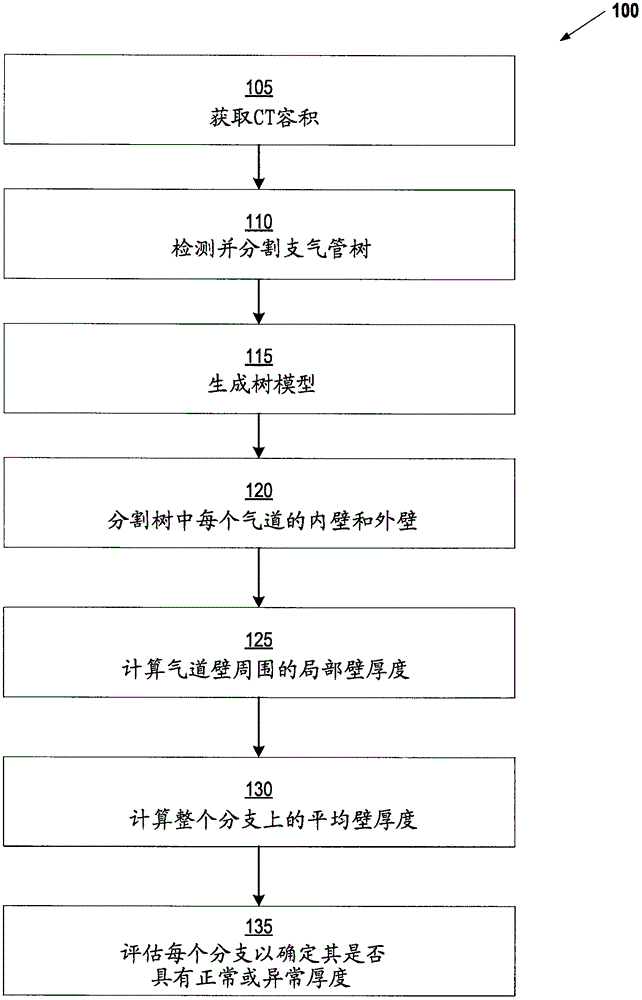
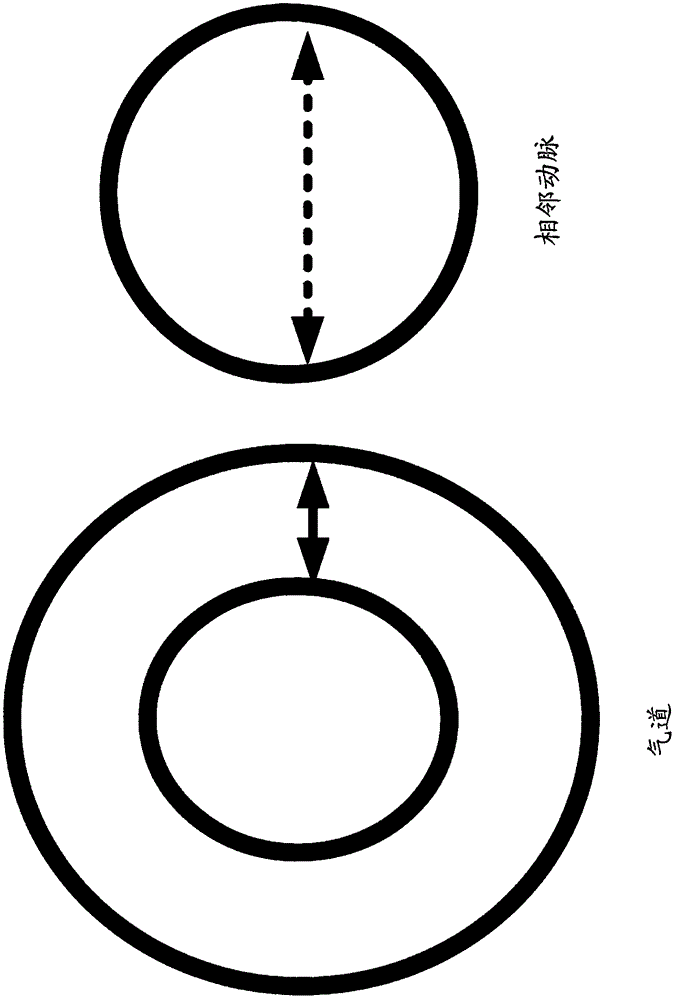
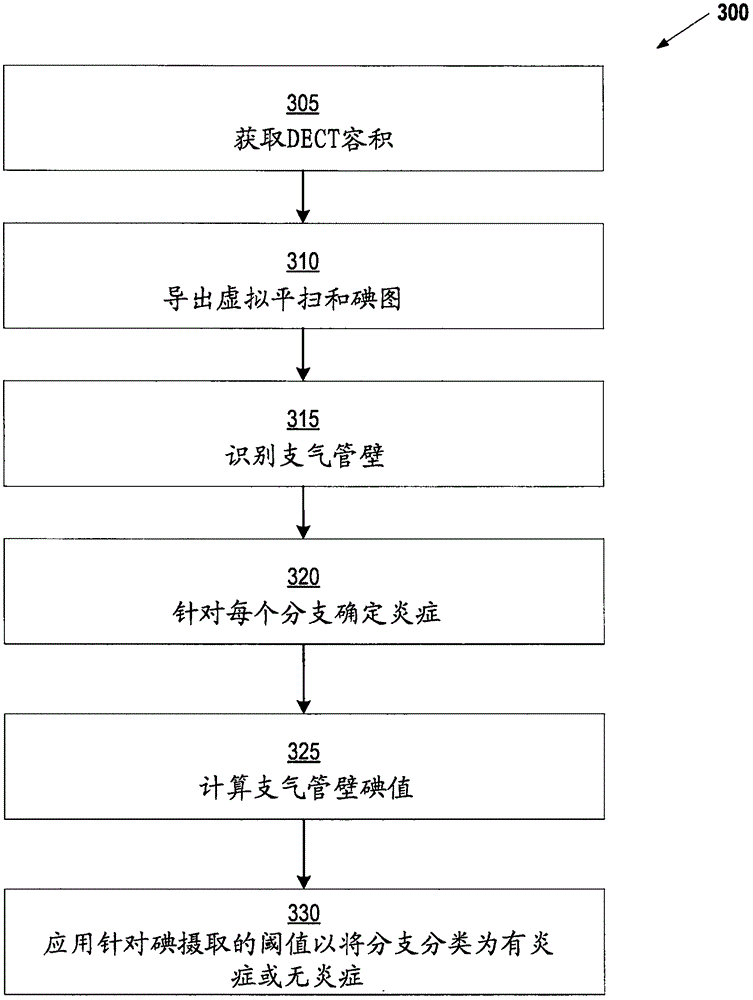
The invention relates to visualizing different types of airway wall abnormalities. A method for visualizing airway wall abnormalities includes acquiring Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) imaging data comprising one or more image volumes representative of a bronchial tree. An iodine map is derived using the DECT imaging data and the bronchial tree is segmented from the image volume(s). A tree model representative of the bronchial tree is generated. Then, for each branch, this tree model is used to determine an indicator of normal or abnormal thickness. Locations corresponding to bronchial walls in the bronchial tree using the tree model are identified. Next, for each branch, the locations corresponding to bronchial walls in the bronchial tree and the iodine map are used to determine an indicator of normal or abnormal inflammation. A visualization of the bronchial tree may be presented with visual indicators at each of the locations corresponding to bronchial walls indicating whether a bronchial wall is thickened and / or inflamed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveCN106897573AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementNerve networkComputer vision
Owner:图兮深维医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Method and apparatus for implementing digital video modeling to generate an optimal healthcare delivery model
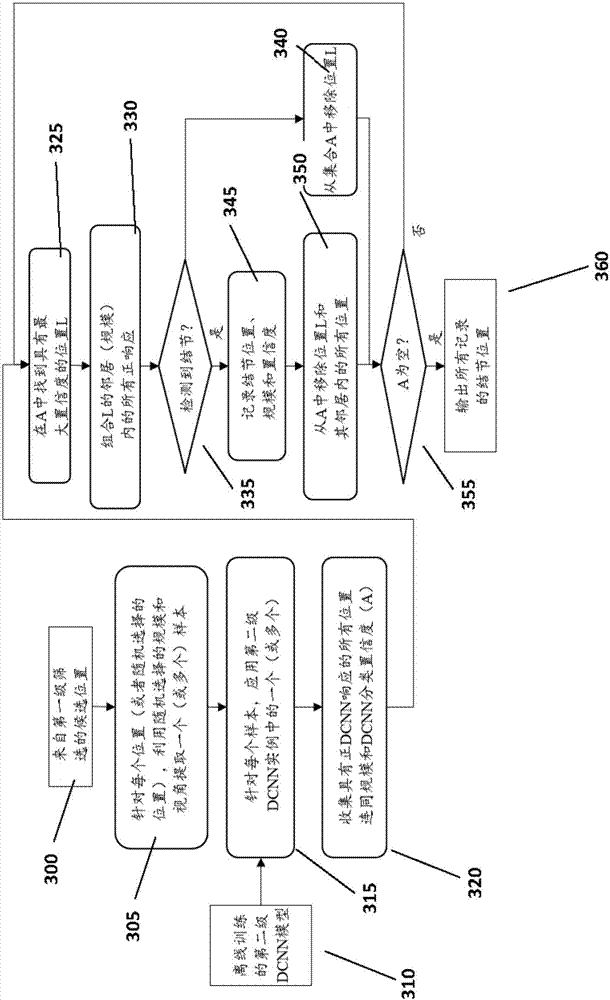
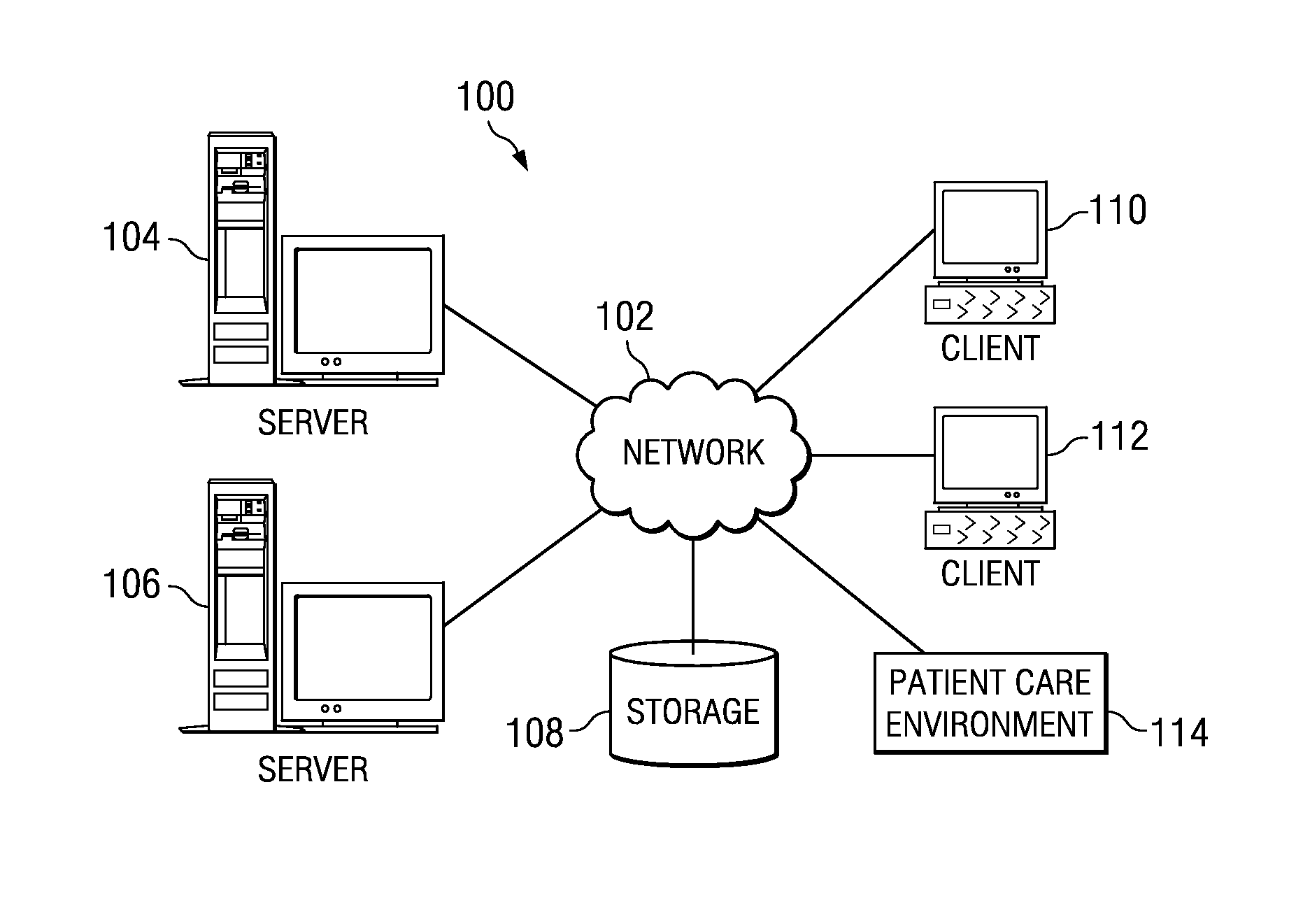
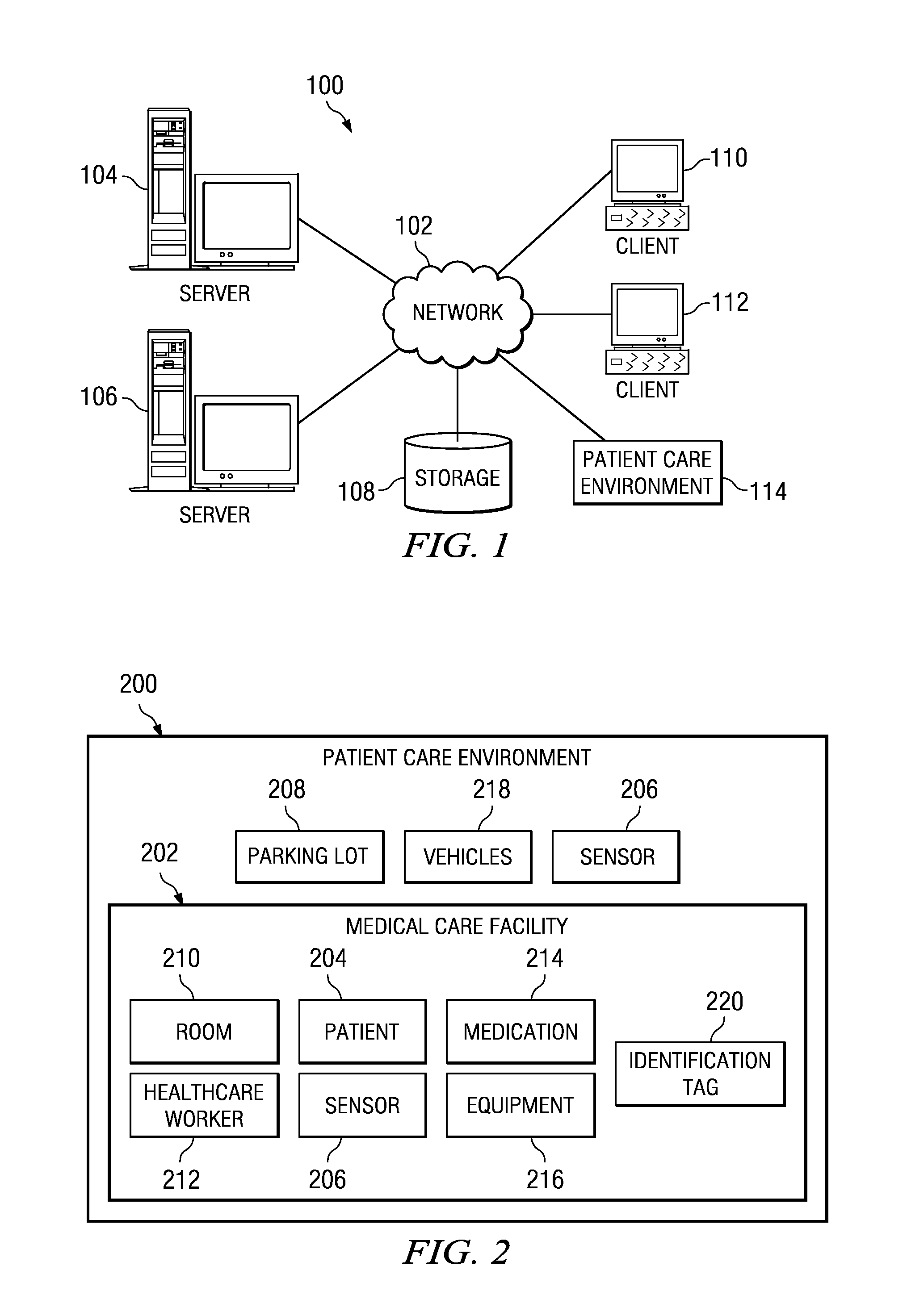
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer program product for generating an optimal healthcare delivery model. The process parses event data derived from video data to identify patterns of events, wherein the event data comprises metadata describing events associated with a medical care facility. The process then identifies a subset of patterns of events from the patterns of events that achieves a target outcome to form a set of optimized patterns of events. The process generates an optimized healthcare delivery strategy using the set of optimized patterns of events to form the optimized healthcare delivery model for the medical care facility.
Owner:IBM CORP
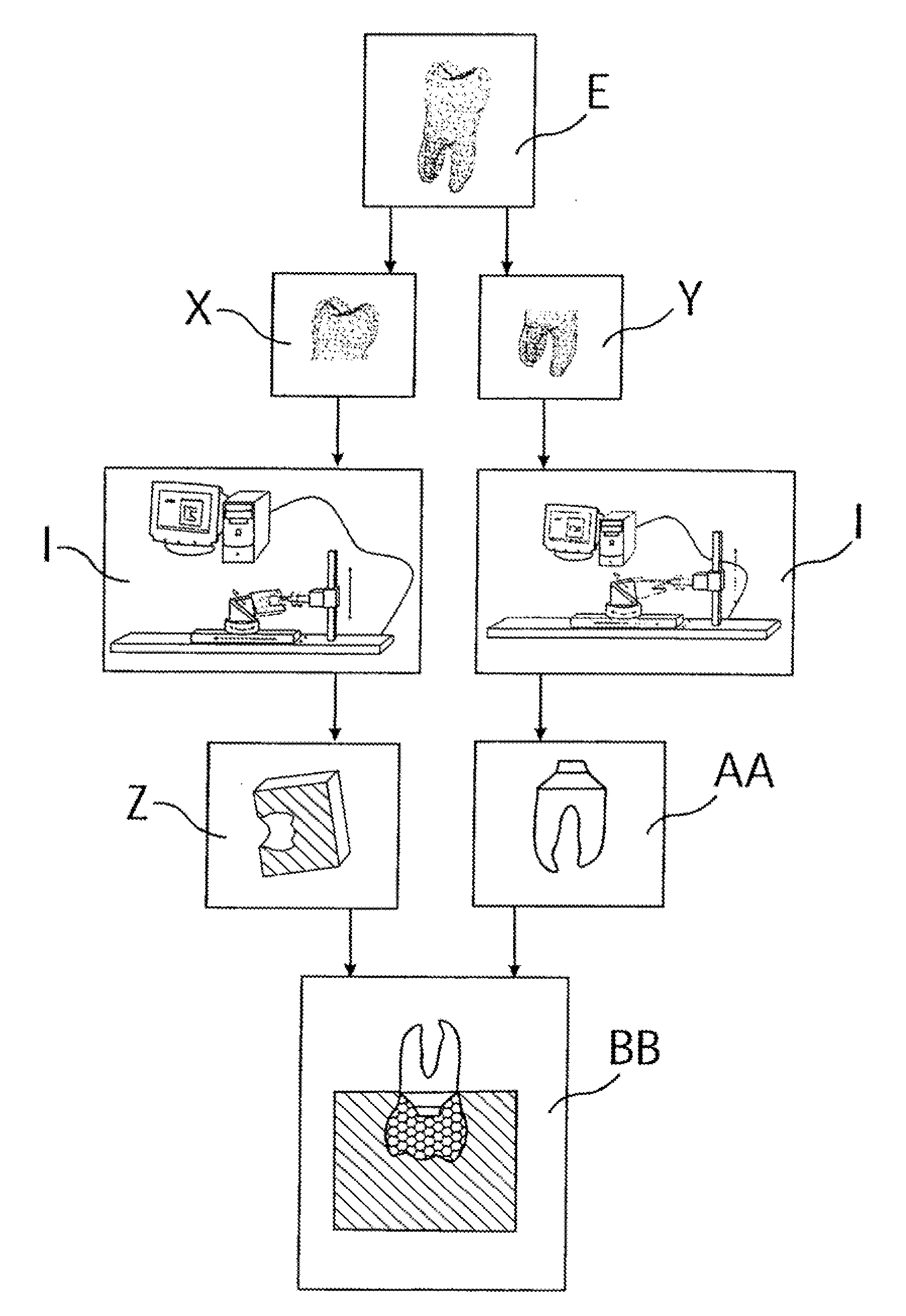
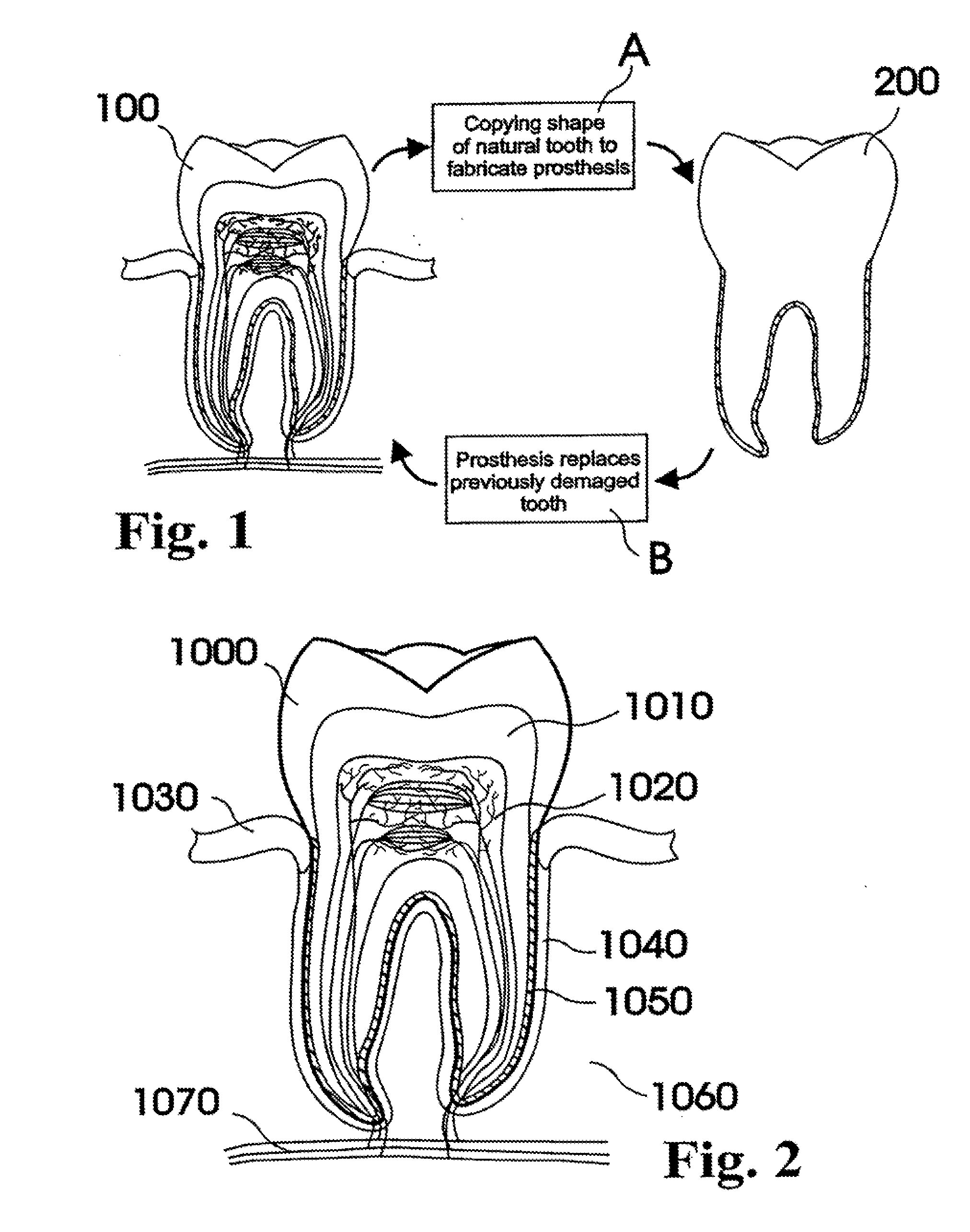
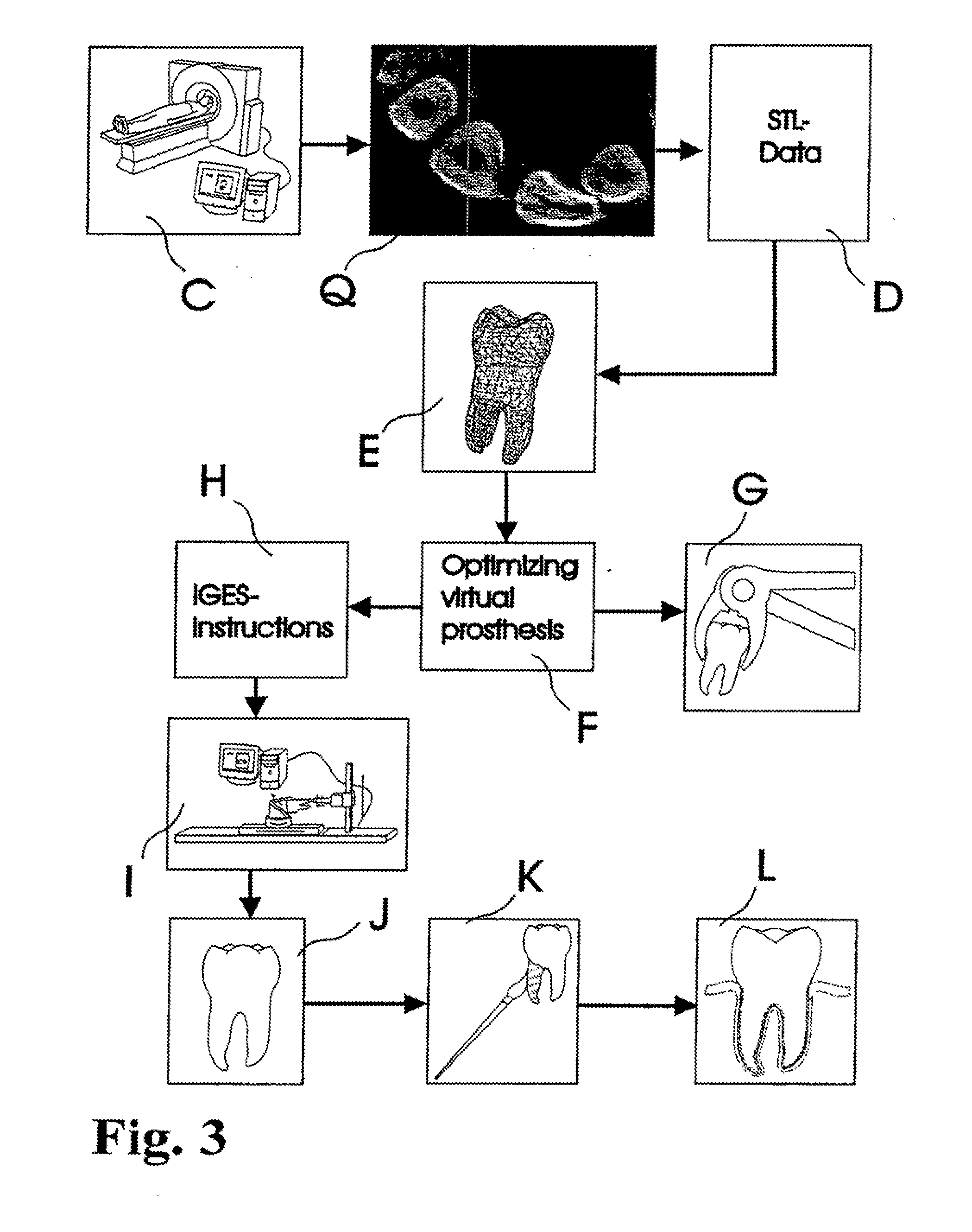
Customized Dental Prosthesis for Periodontal or Osseointegration and Related Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20100203478A1Great primary stabilityQuality improvementDental implantsImpression capsOsseointegrationProsthesis
Dental prosthesis, systems, and methods of forming and using a dental prosthesis, are provided. An example of a dental prosthesis includes a first manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a root of a tooth to be replaced and a second manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a crown of the tooth. Furthermore, customized manufactured splints to position and fixate a tooth-shaped prosthesis, are provided. Furthermore, a CAD / CAM based methods of and a systems for manufacturing a customized dental prosthesis are provided. The tooth can be scanned to determine its three-dimensional shape and substantially copied using an imaging system in-vitro like a 3D scanner or in-vivo like a cone beam CT system and CNC machinery. Biocompatible material that is suitable to be integrated into the extraction socket and adopted by existing tissue forming the socket can be manufactured or engineered.
Owner:NATURAL DENTAL IMPLANTS
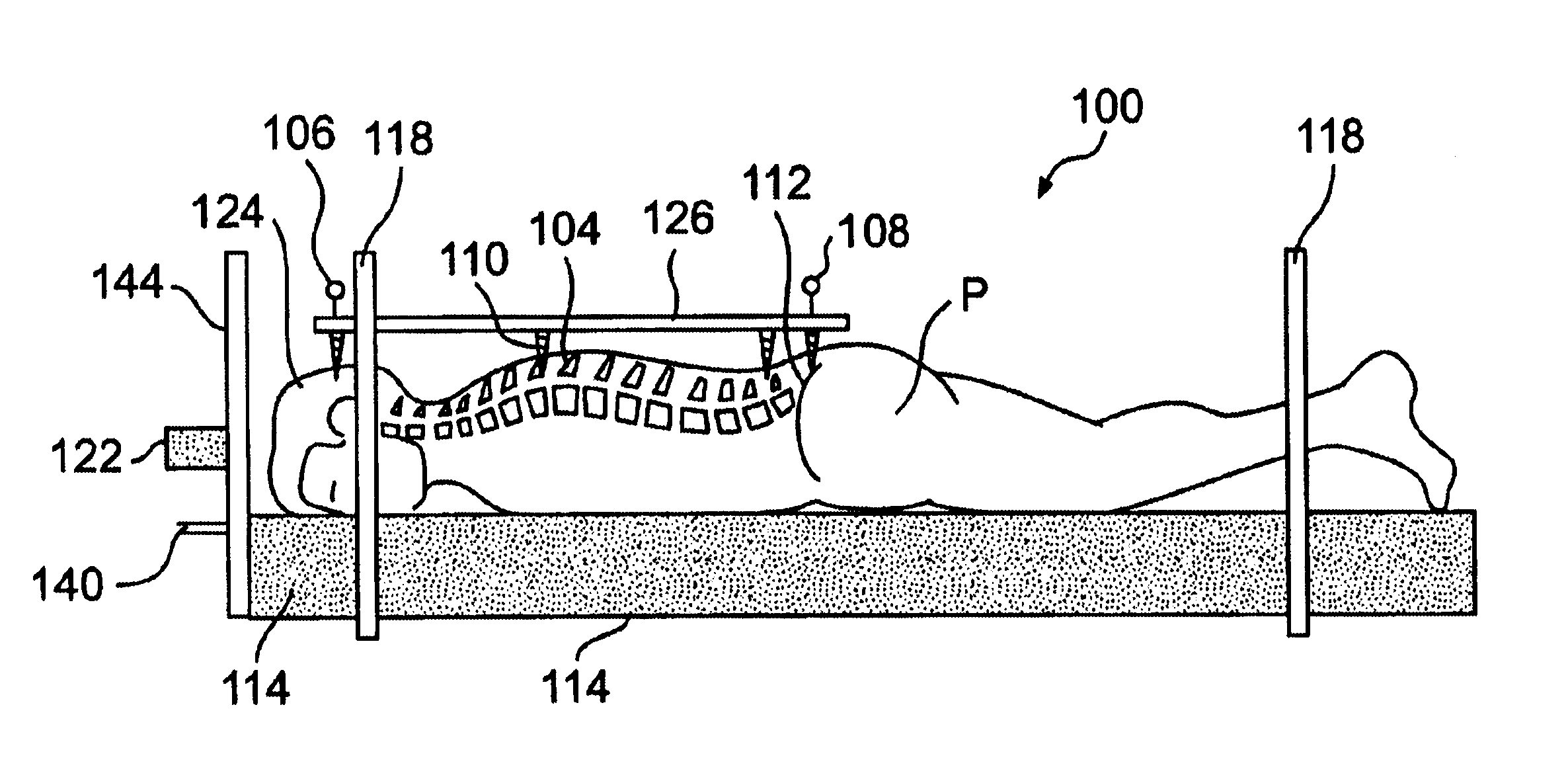
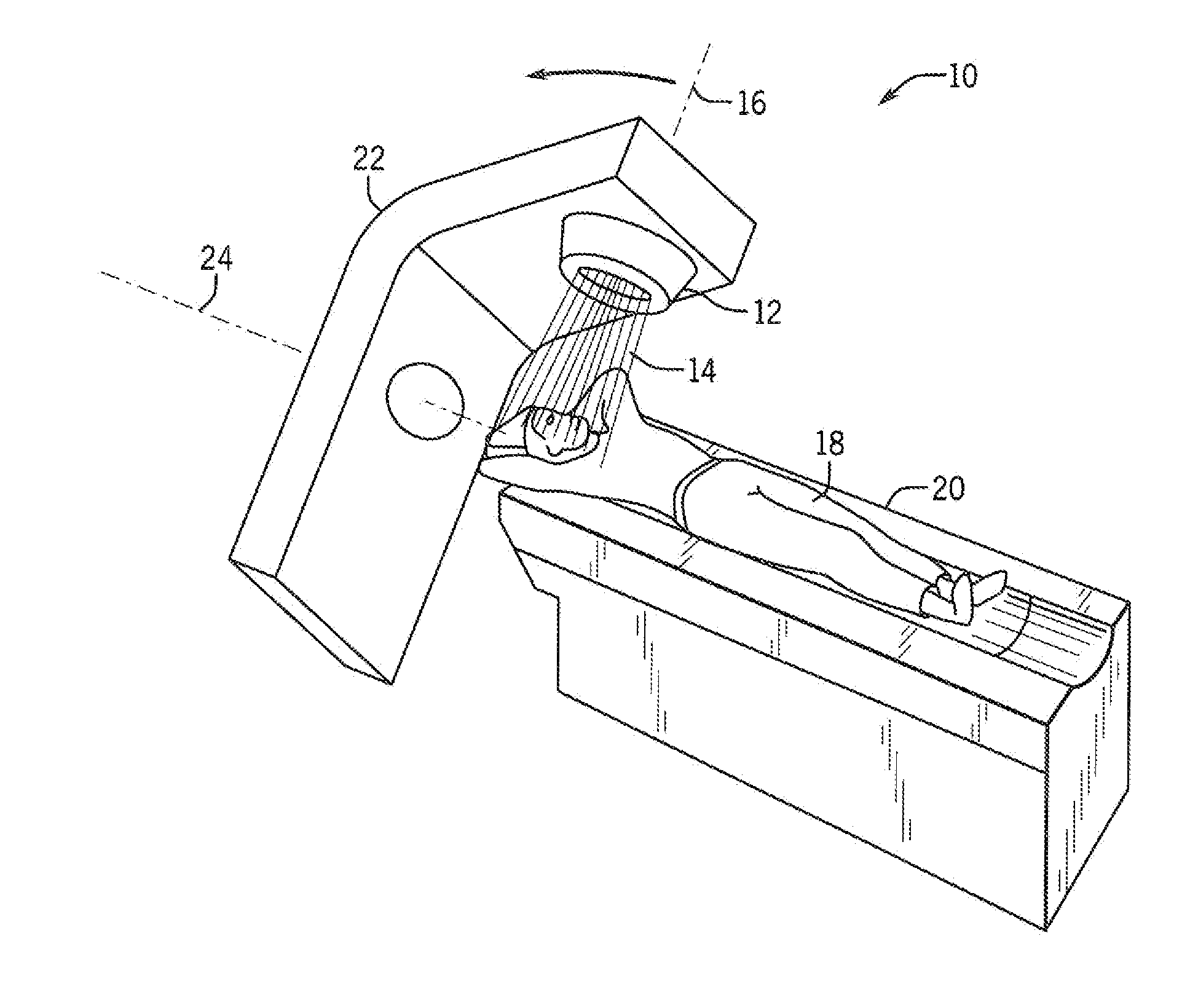
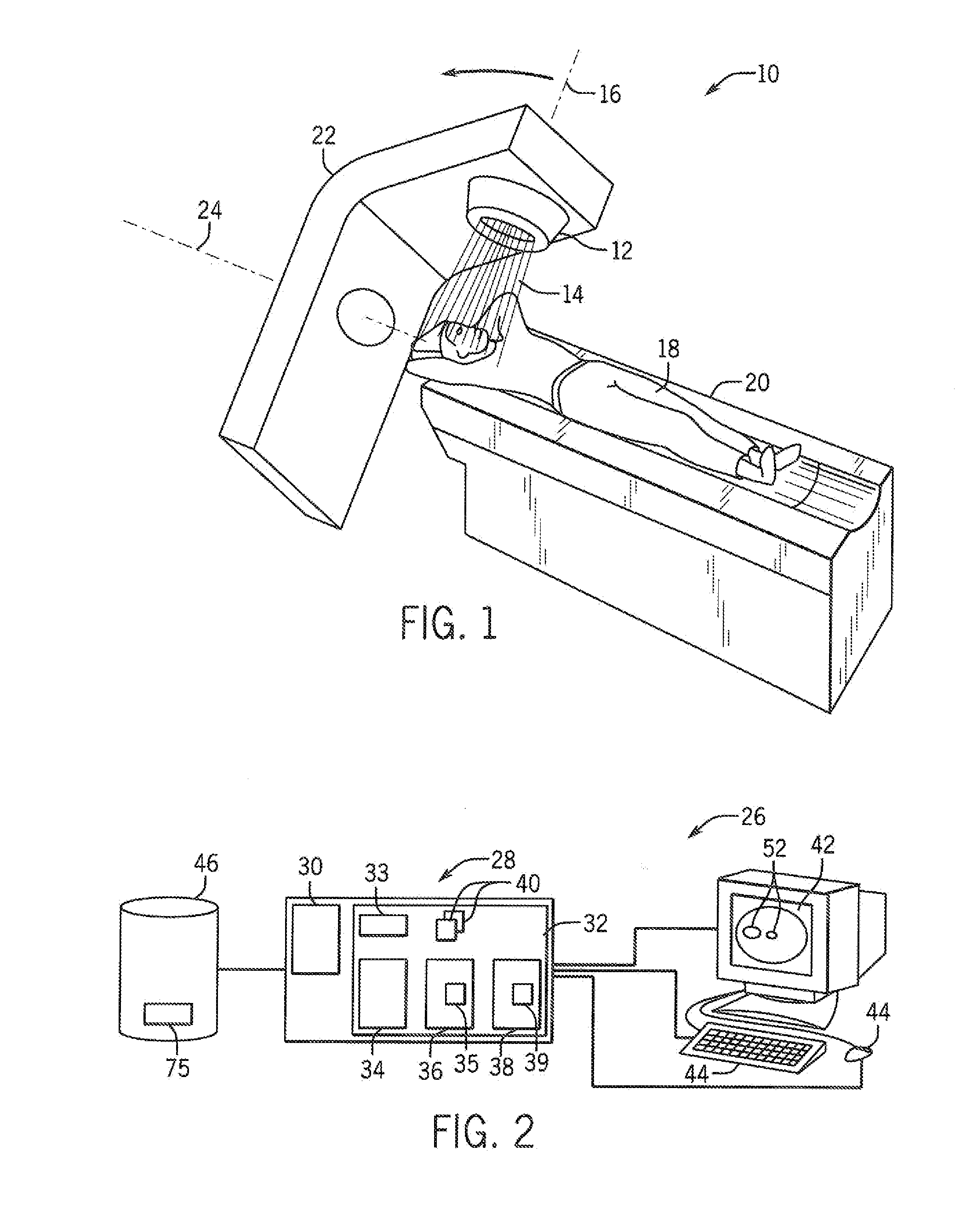
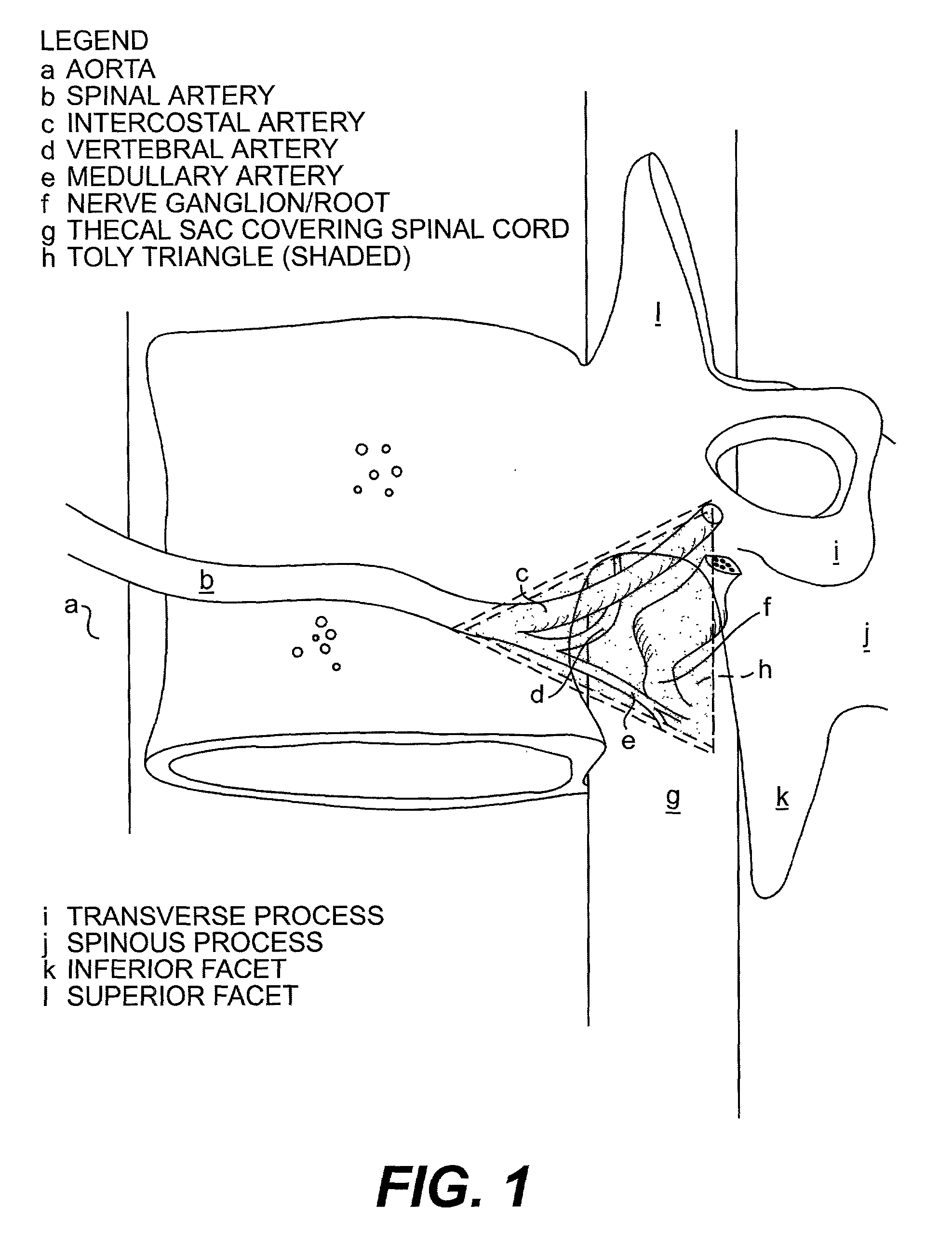
Radiosurgery methods that utilize stereotactic methods to precisely deliver high dosages of radiation especially to the spine
InactiveUS6665555B2Reduce decreaseAvoiding and minimizing deliveryRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgeryRadiosurgeryStereotaxis
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
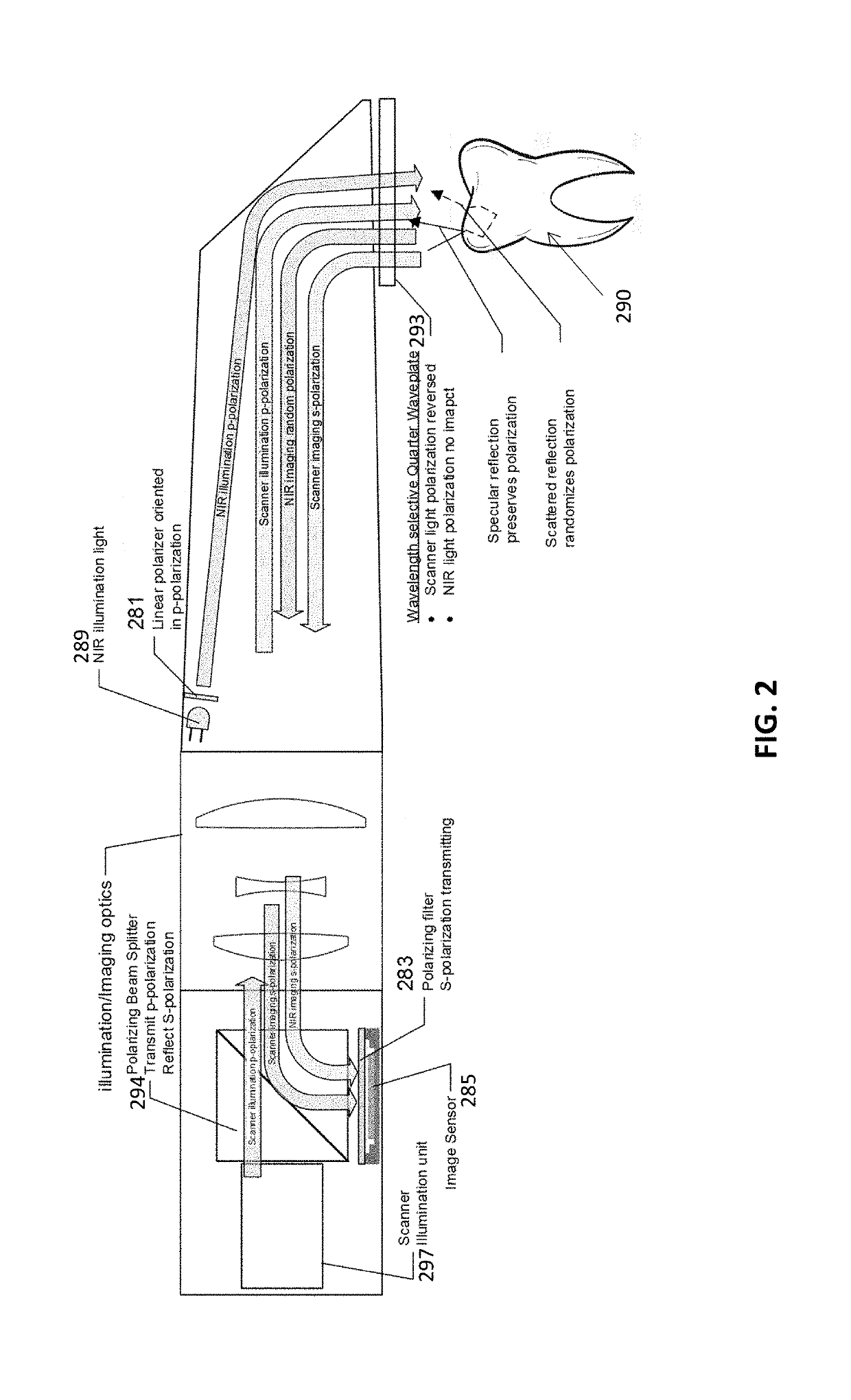
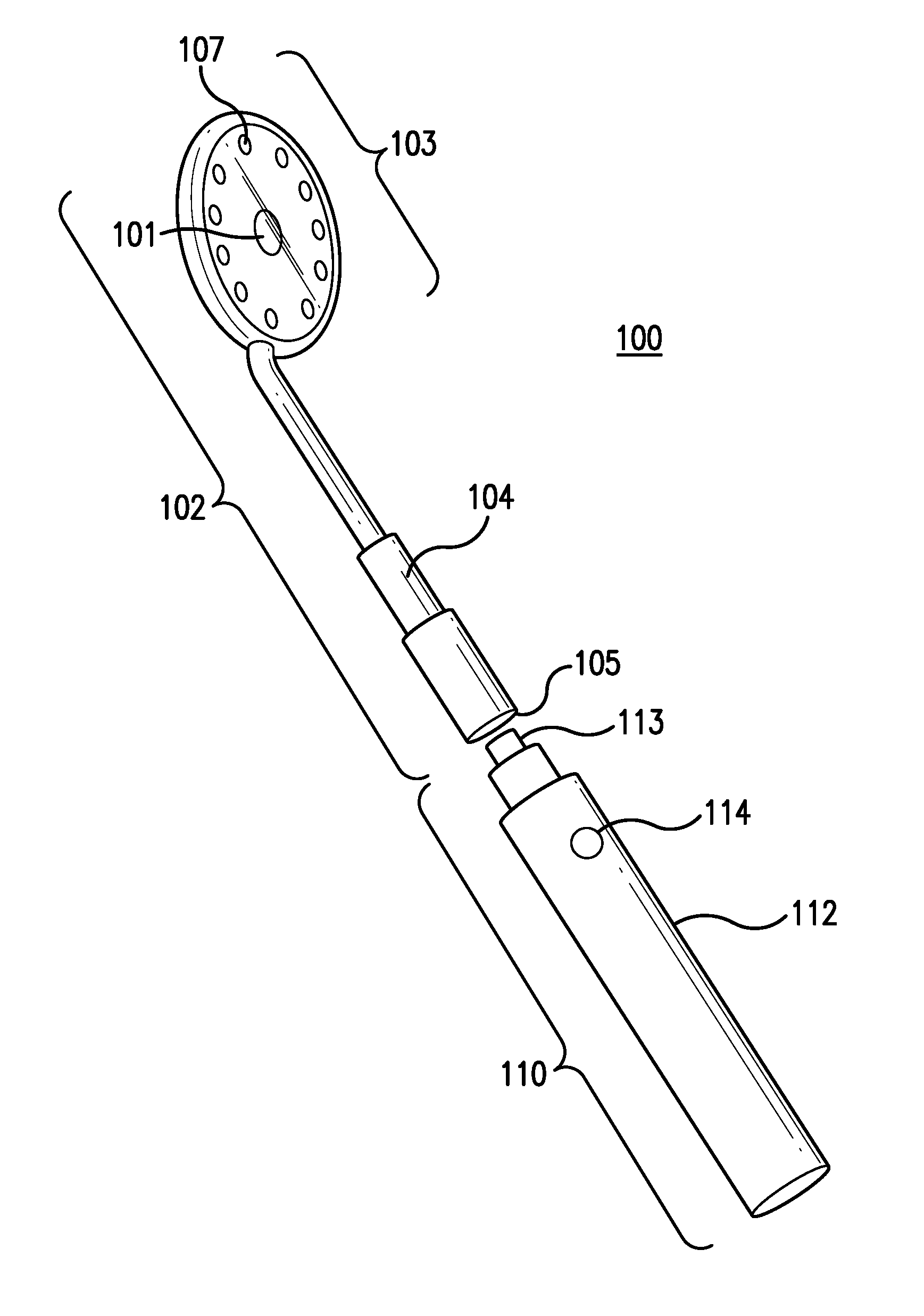
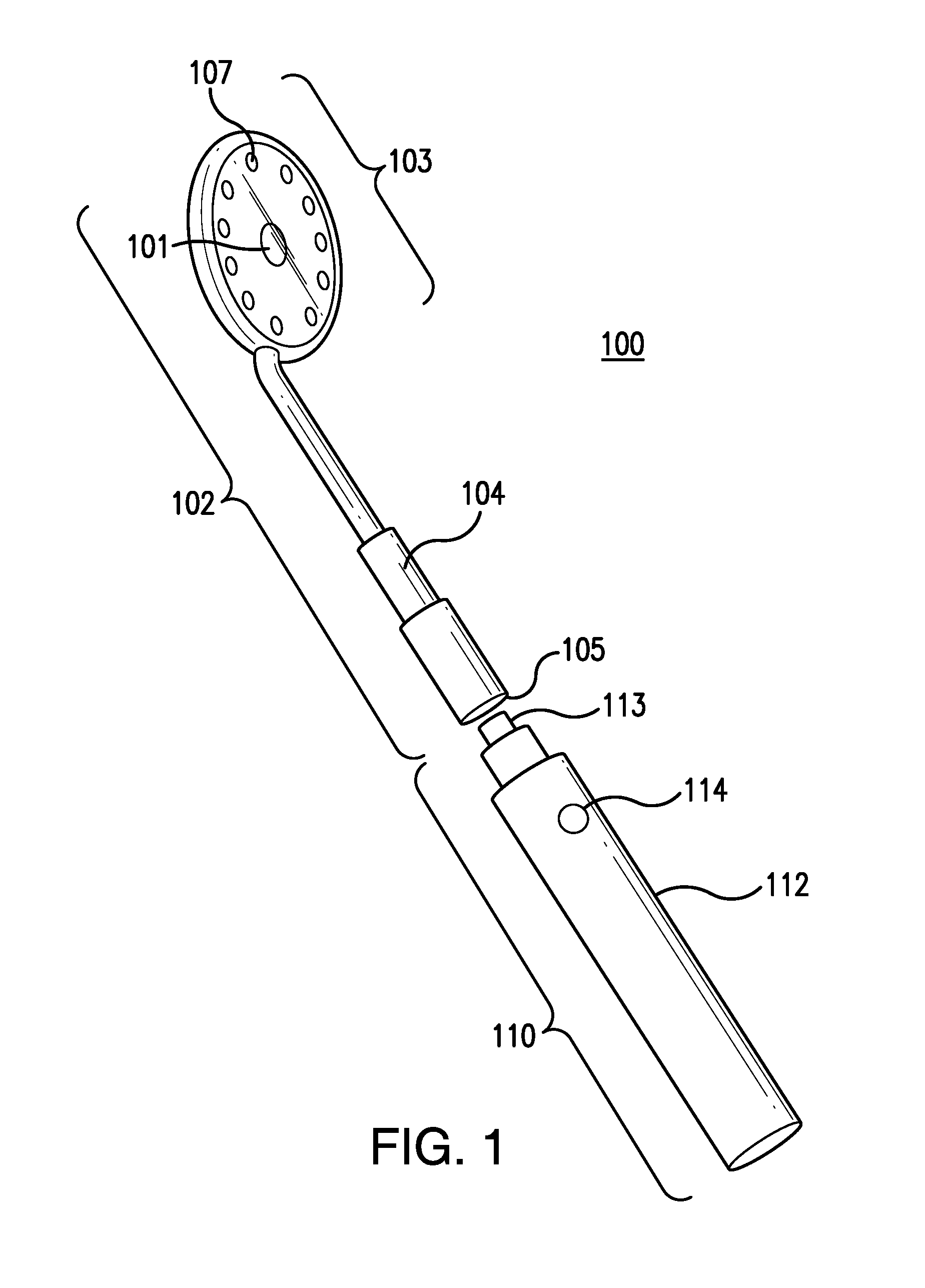
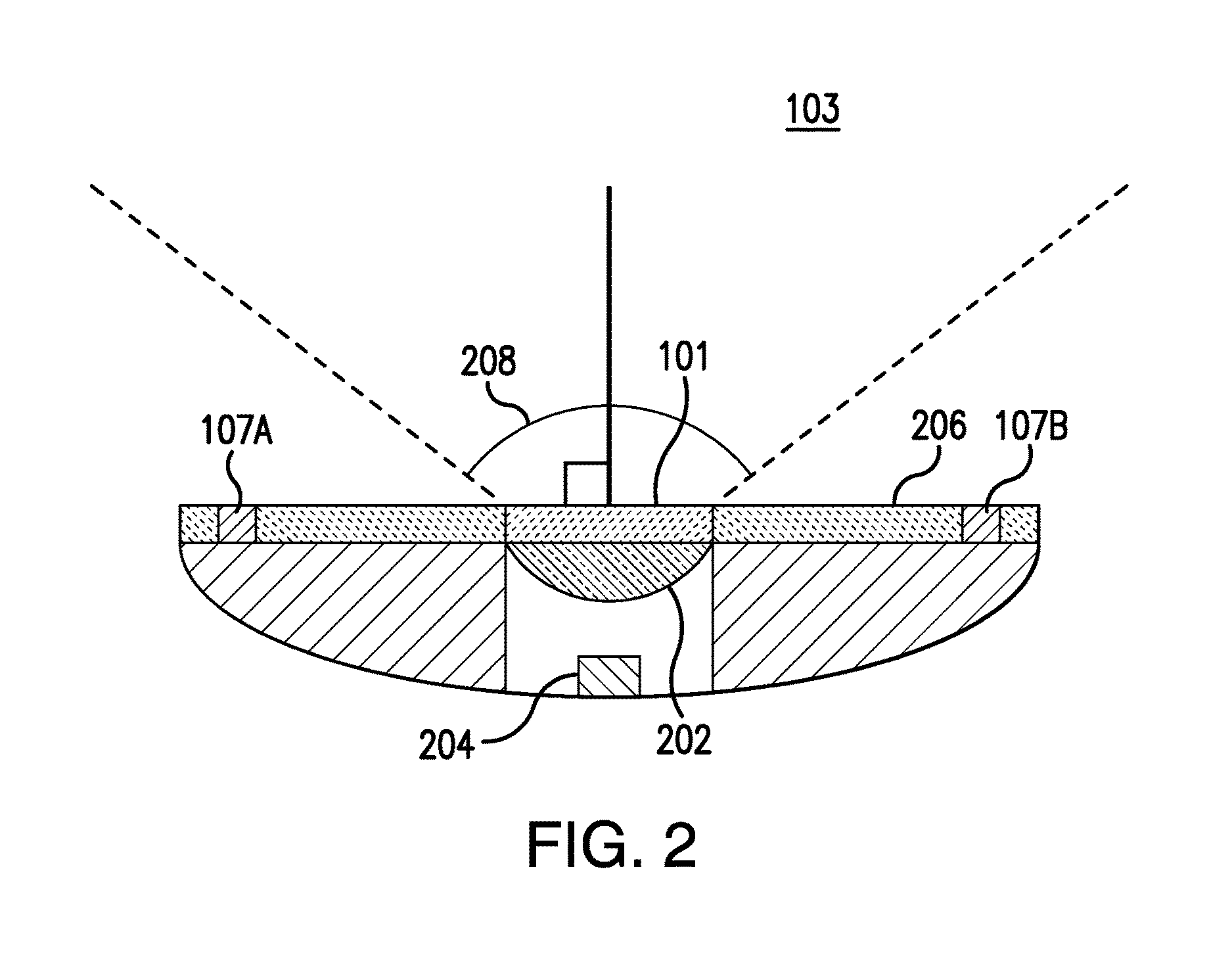
Living Body Observing Apparatus, Intraoral Imaging Apparatus and Medical Treatment Appliance
InactiveUS20080017787A1High diagnosticHigh clinical valueOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceBiological bodyFluorescence
A medical living body observation apparatus, an intraoral photography system and a medical treatment appliance which can be used conveniently by a general user at home as well as a technician, e.g. a dentist or a physician. There is provided an irradiation means (2) comprising an exciting light emission section (2a) emitting an exciting light for causing a lesion to radiate fluorescence, and an illumination light emission section (2b) emitting a light for illuminating the periphery of the lesion. The irradiating means (2) can simultaneously irradiate the illumination light and the exciting light.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS20070015997A1Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
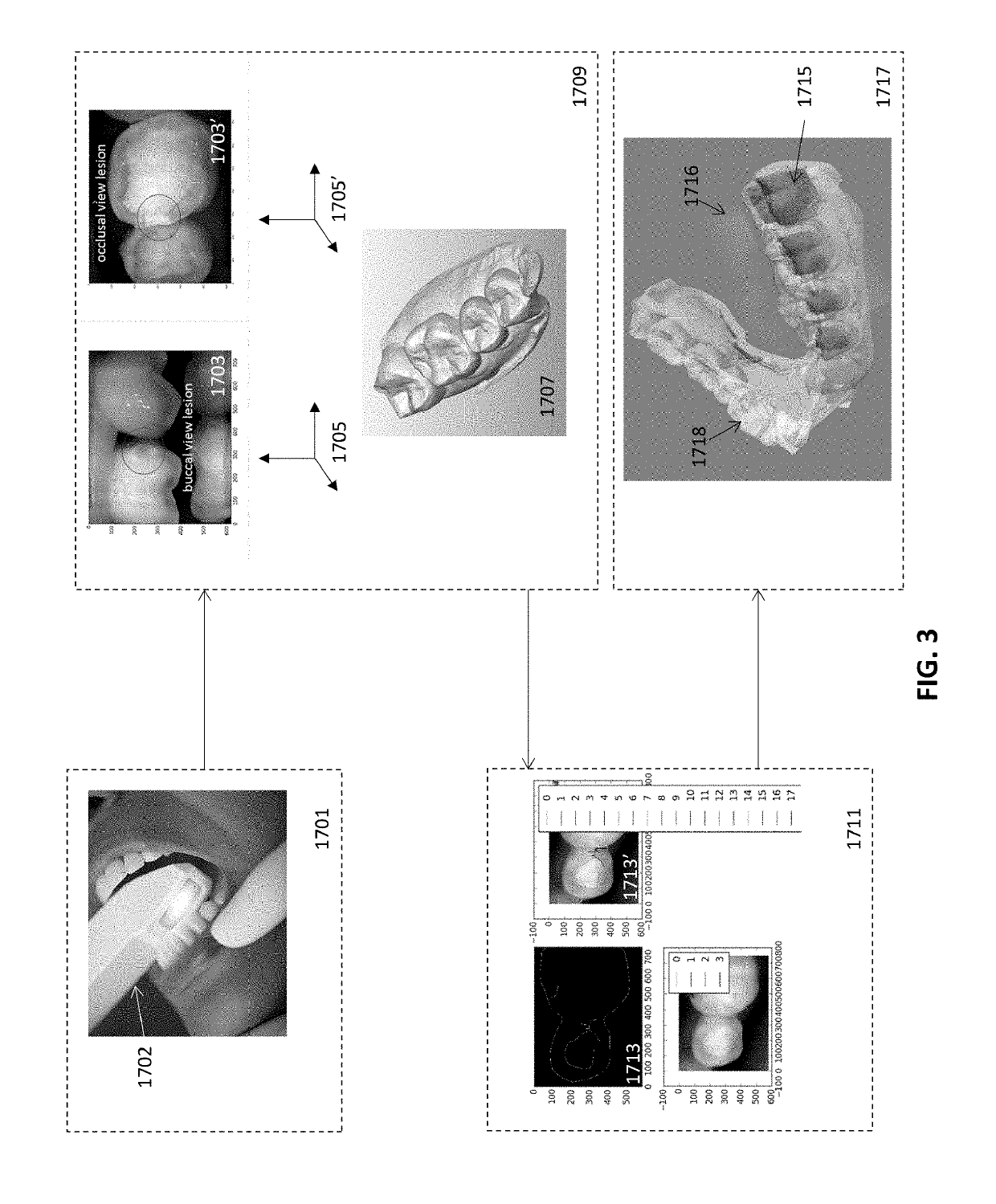
Diagnostic intraoral scanning
Methods and apparatuses for taking, using and displaying three-dimensional (3D) volumetric models of a patient's dental arch. A 3D volumetric model may include surface (e.g., color) information as well as information on internal structure, such as near-infrared (near-IR) transparency values for internal structures including enamel and dentin.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
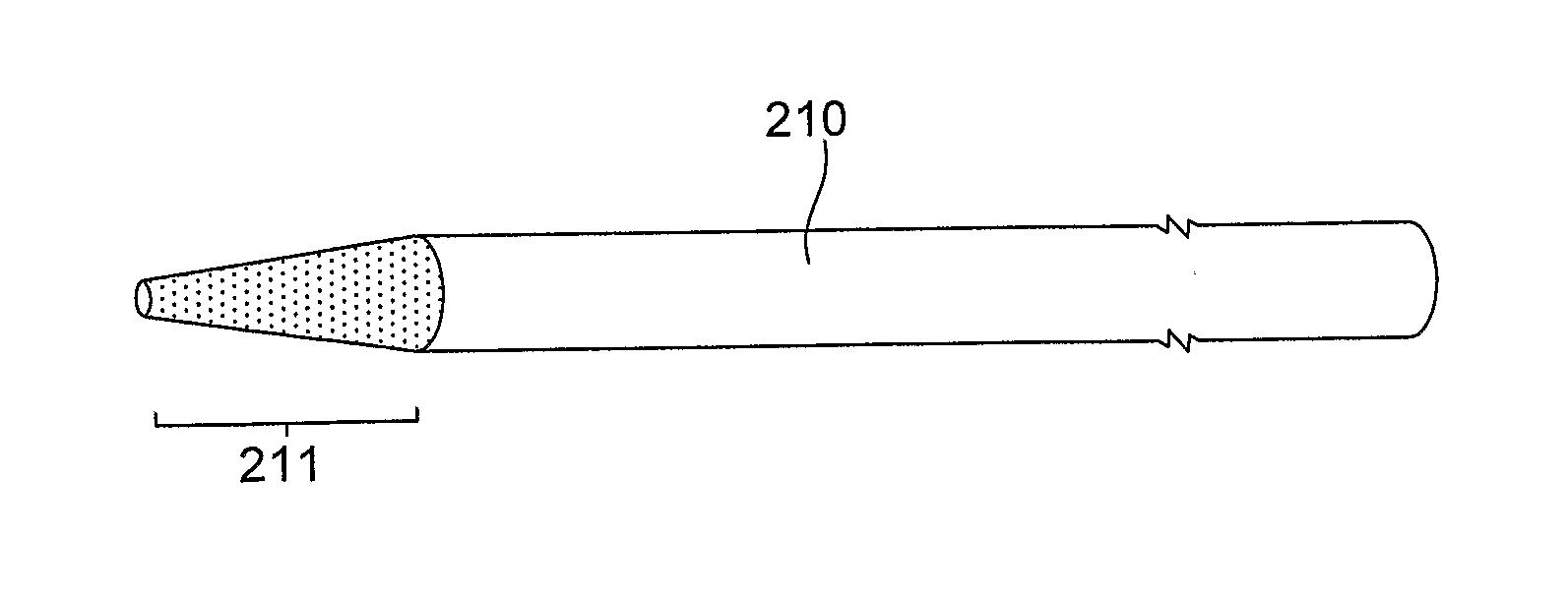
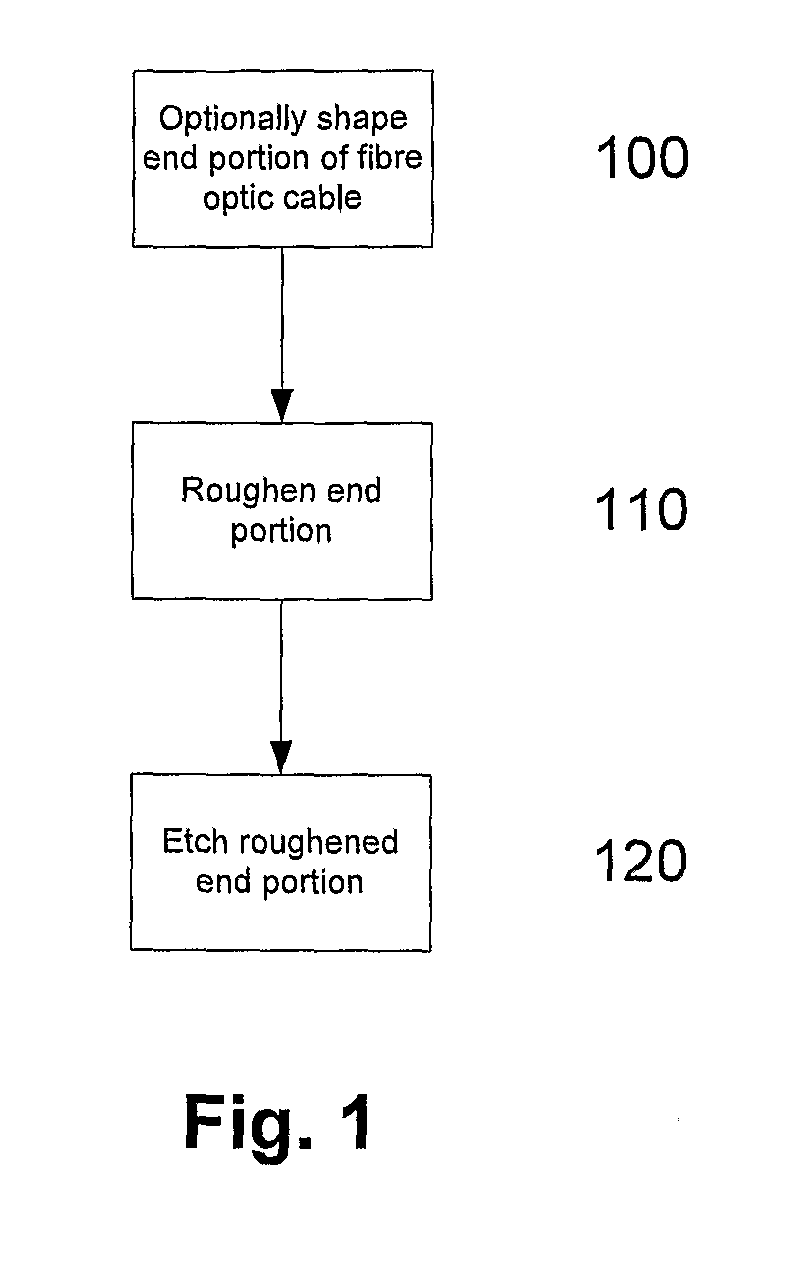
Surface structure modification
A method of forming an optical fibre tip, the method including, roughening at least part of an end portion of the optical fibre; and, etching the roughed end portion to thereby form an optical fibre tip.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
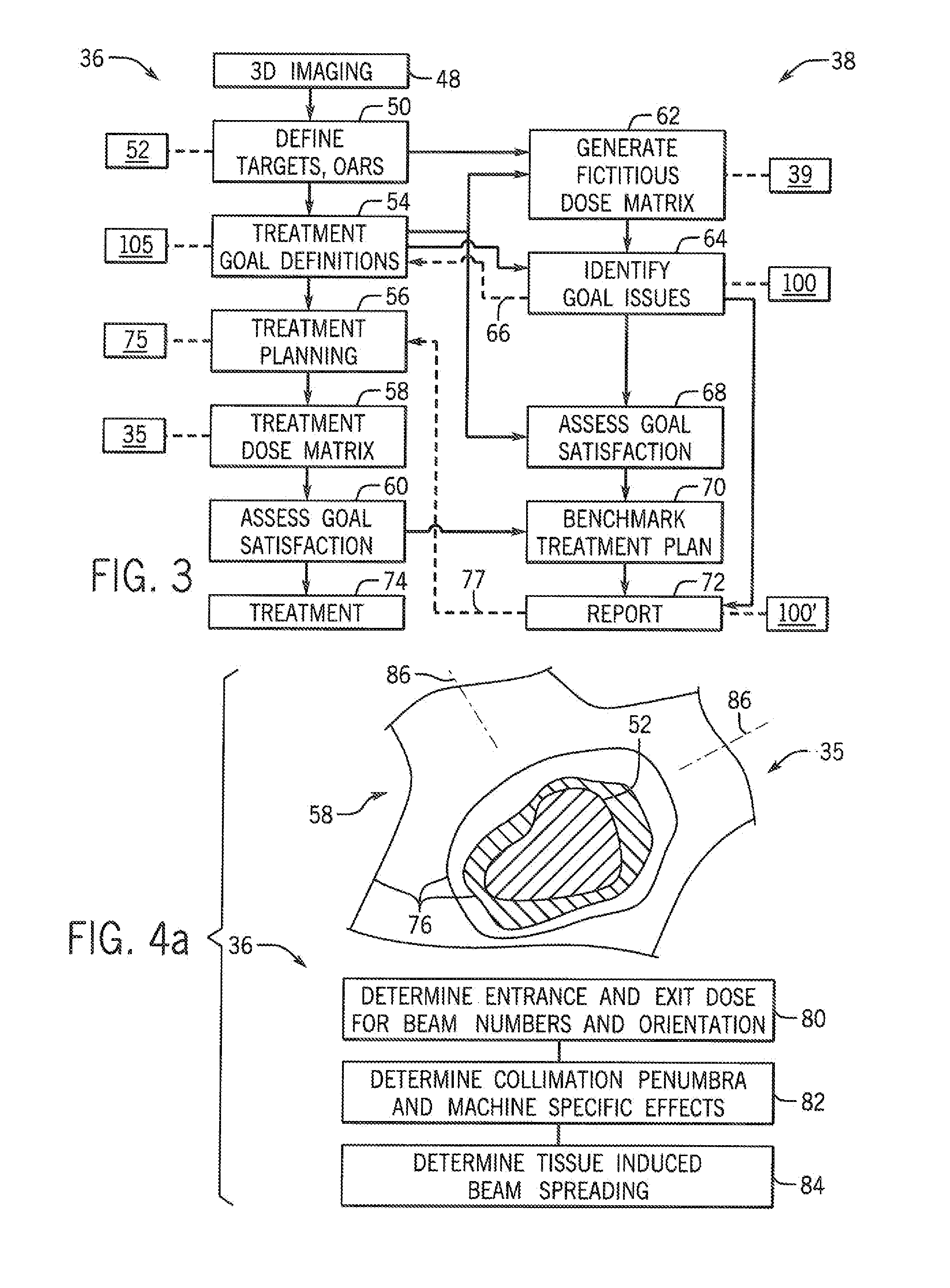
Benchmark system for radiation therapy planning
ActiveUS20150087879A1Reduce impactSimple modelRadiation diagnostics testing/calibrationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsRadiation treatment planningBaseline system
A system for evaluating radiation treatment planning generates a fictitious treatment dose matrix with a quality of dose placement beyond that achievable with physically realizable radiation therapy machines. Such a fictitious treatment dose matrix provides an objective measure that is readily tailored to different clinical situations, and although unattainable, thereby provides a benchmark allowing evaluation of radiation plan goals and the radiation plans between different multiple clinical situations and individuals.
Owner:SUN NUCLEAR
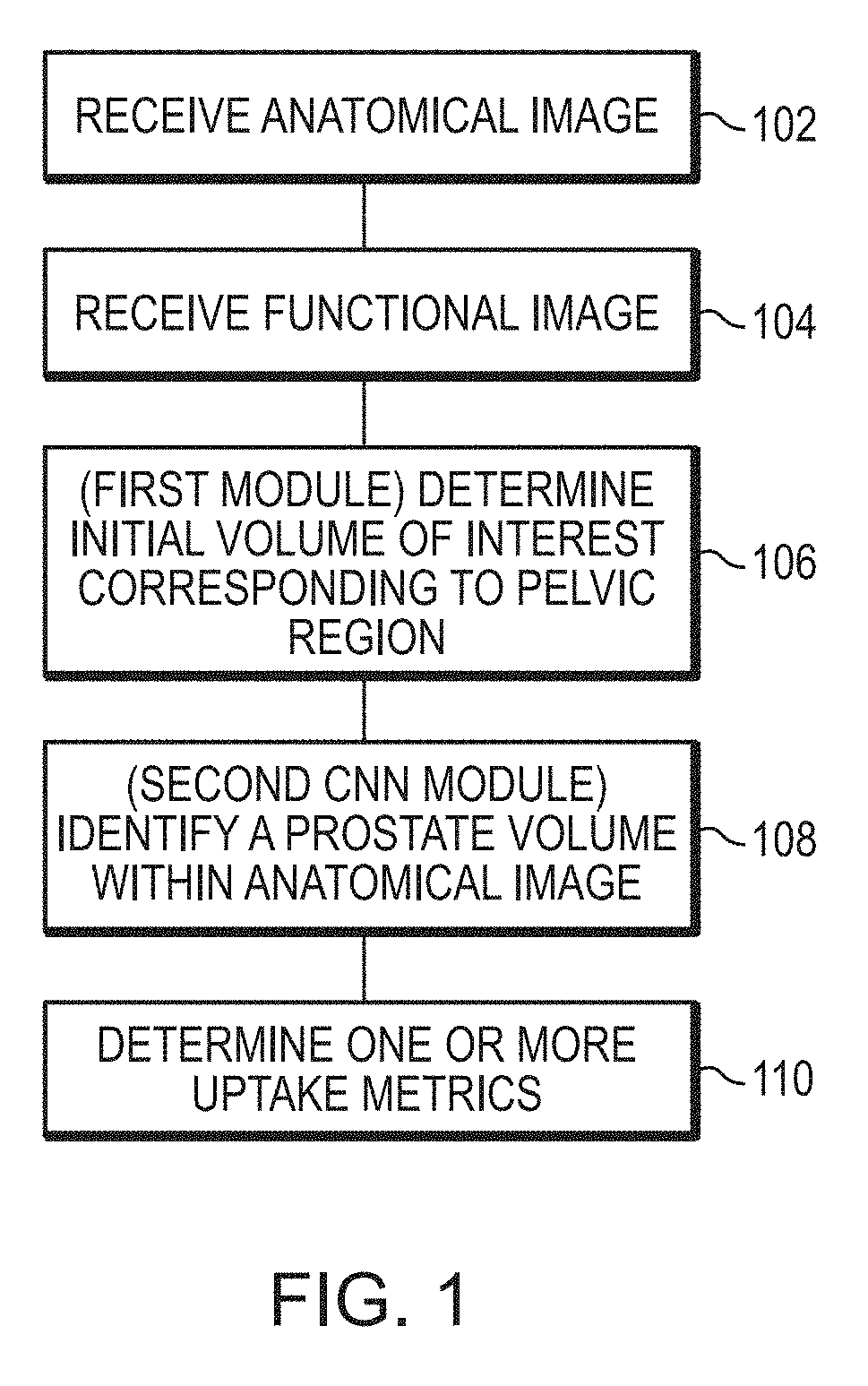
Systems and methods for rapid neural network-based image segmentation and radiopharmaceutical uptake determination
ActiveUS20190209116A1Improve computing efficiencyPrecise processingImage enhancementImage analysisDisease3d image
Presented herein are systems and methods that provide for automated analysis of three-dimensional (3D) medical images of a subject in order to automatically identify specific 3D volumes within the 3D images that correspond to specific organs and / or tissue. In certain embodiments, the accurate identification of one or more such volumes can be used to determine quantitative metrics that measure uptake of radiopharmaceuticals in particular organs and / or tissue regions. These uptake metrics can be used to assess disease state in a subject, determine a prognosis for a subject, and / or determine efficacy of a treatment modality.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS +1
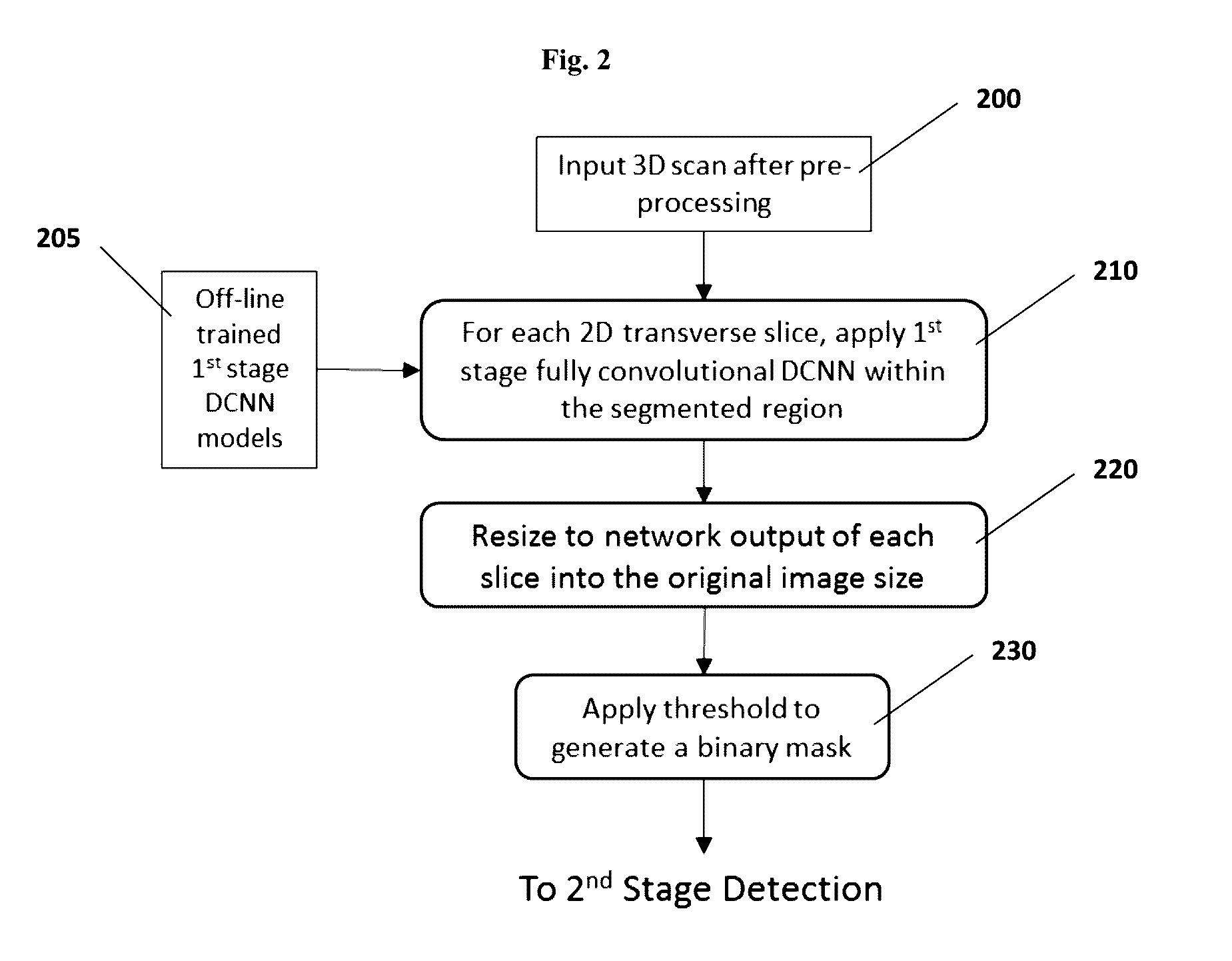
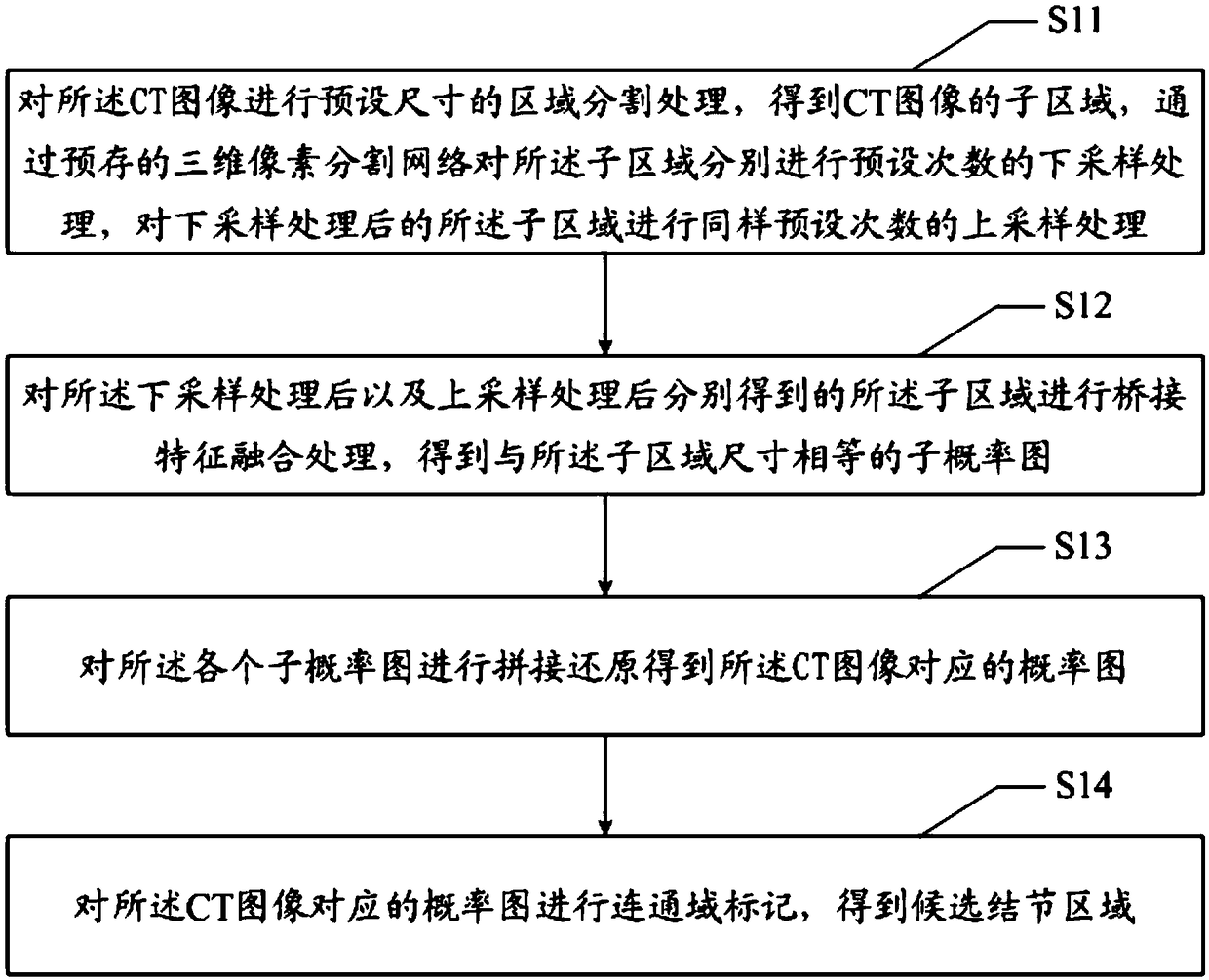
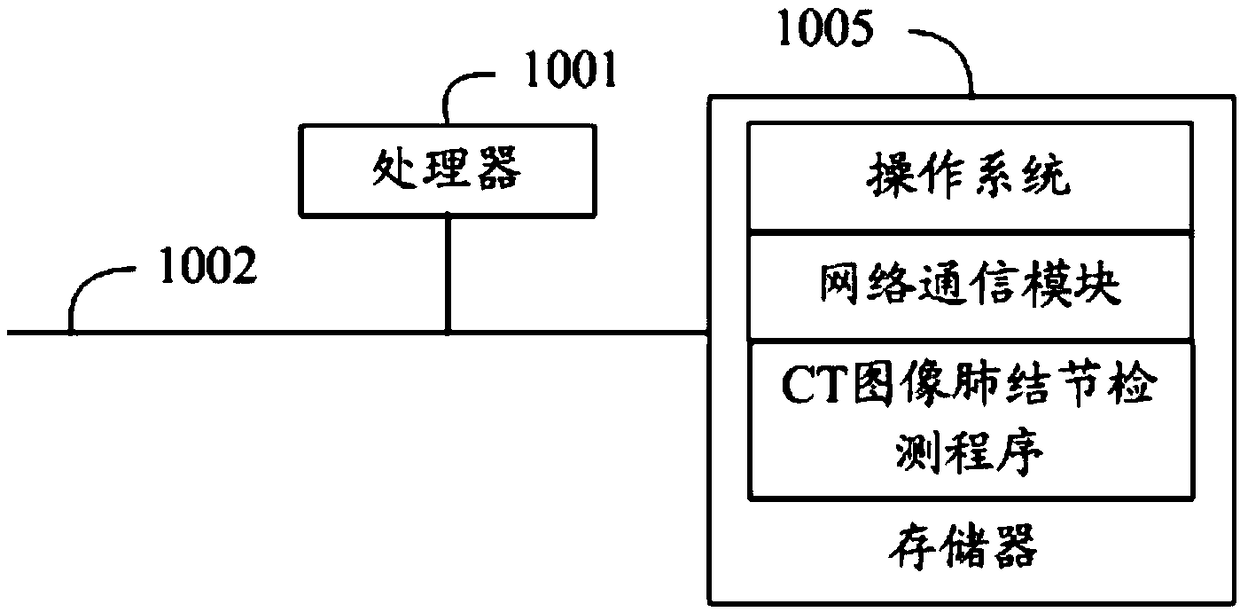
CT image pulmonary nodule detection method and device, apparatus, and readable storage medium
ActiveCN109003260AAvoid the phenomenon of low detection accuracyTroubleshoot technical issues with poor accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleNeural network classifier
The invention provides a CT image pulmonary nodule detection method and device, an apparatus, and a readable storage medium. The CT image pulmonary nodule detection method comprises the following step: acquiring a CT image to be detected, performing pixel segmentation processing on the CT image through a pre-stored three-dimensional convolution neural pixel segmentation network to obtain a probability map corresponding to the CT image, and marking the probability map with a connectivity domain to obtain a candidate nodule region; predicting the candidate nodule region by a plurality of modelscorresponding to different pre-stored three-dimensional convolution neural network classifiers, obtaining each probability prediction value corresponding to the candidate nodule region, and fusing theprobability prediction values to obtain a classification result of the candidate nodule region. The invention solves the technical problem of poor accuracy of automatic detection of lung nodules based on CT images.
Owner:SHENZHEN IMSIGHT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
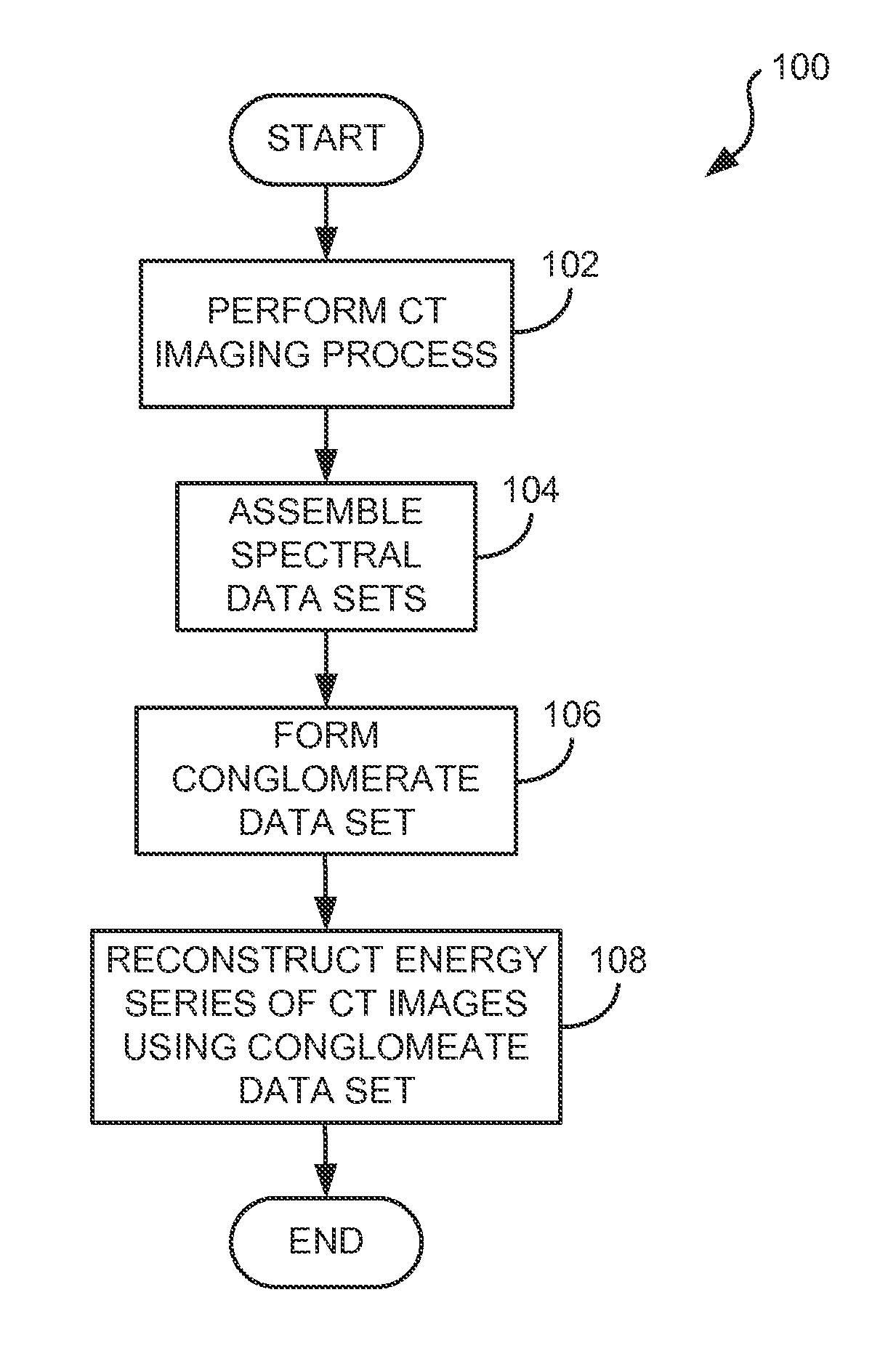
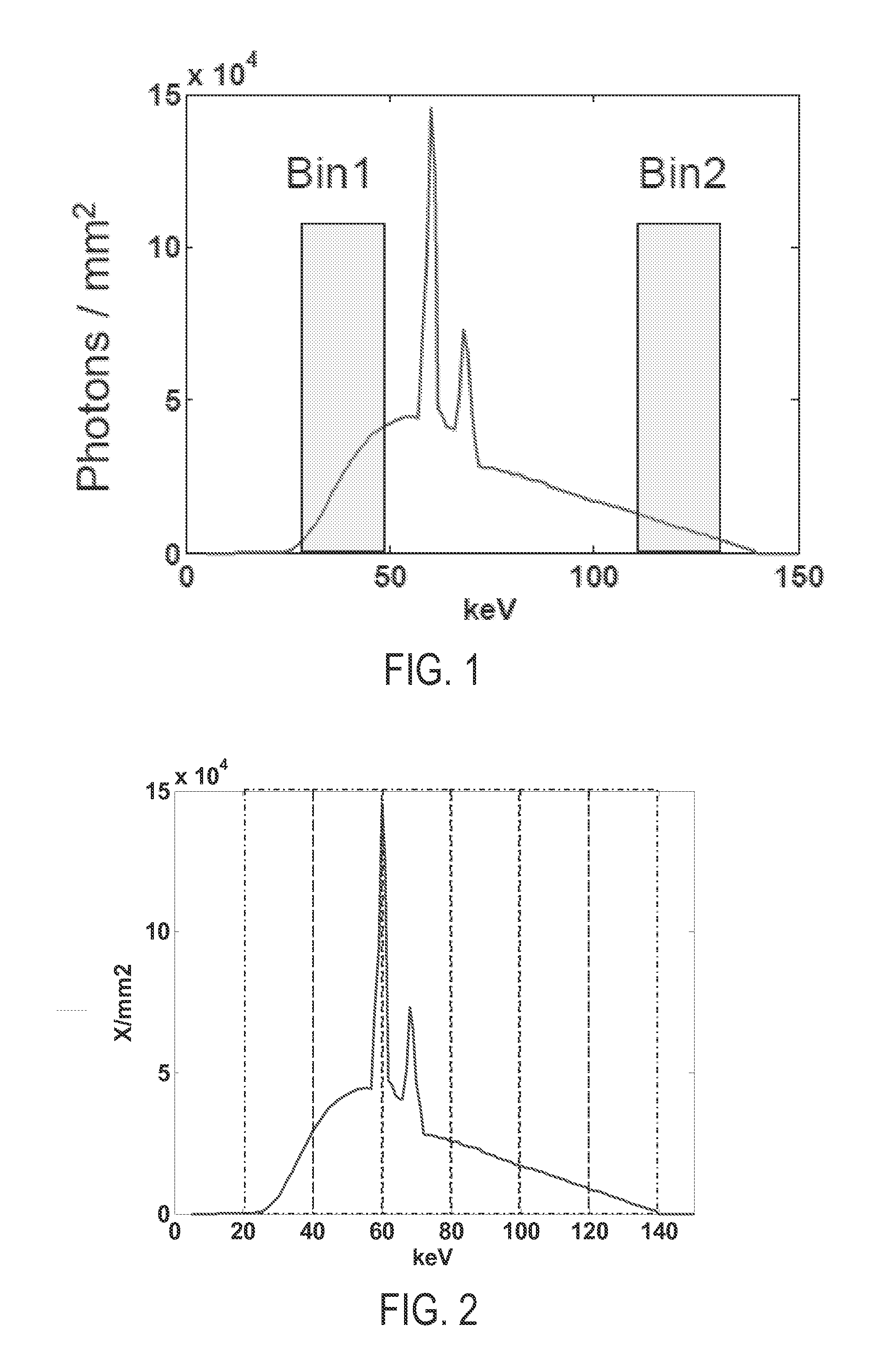
System and method for improved energy series of images using multi-energy ct
ActiveUS20130108013A1Reduce image noiseImproves material differentiationImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setComputing tomography
A method for creating an energy series of images acquired using a multi-energy computed tomography (CT) imaging system having a plurality of energy bins includes acquiring, with the multi-energy CT imaging system, a series of energy data sets, where each energy data set is associated with at least one of the energy bins. The method includes producing a conglomerate image using at least a plurality of the energy data sets and, using the conglomerate image, reconstructing an energy series of images, each image in the energy series of images corresponding to at least one of the energy data sets.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
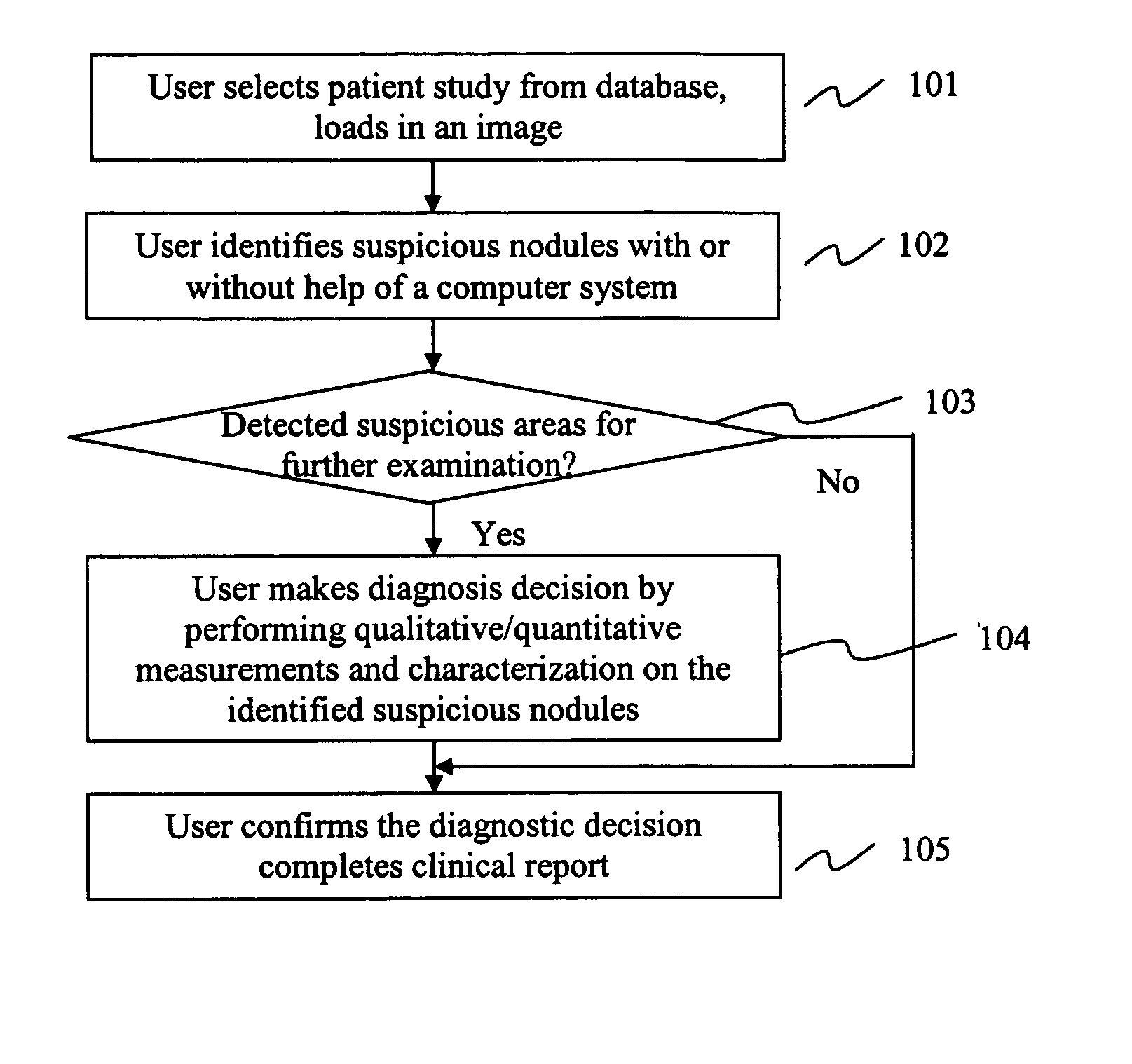
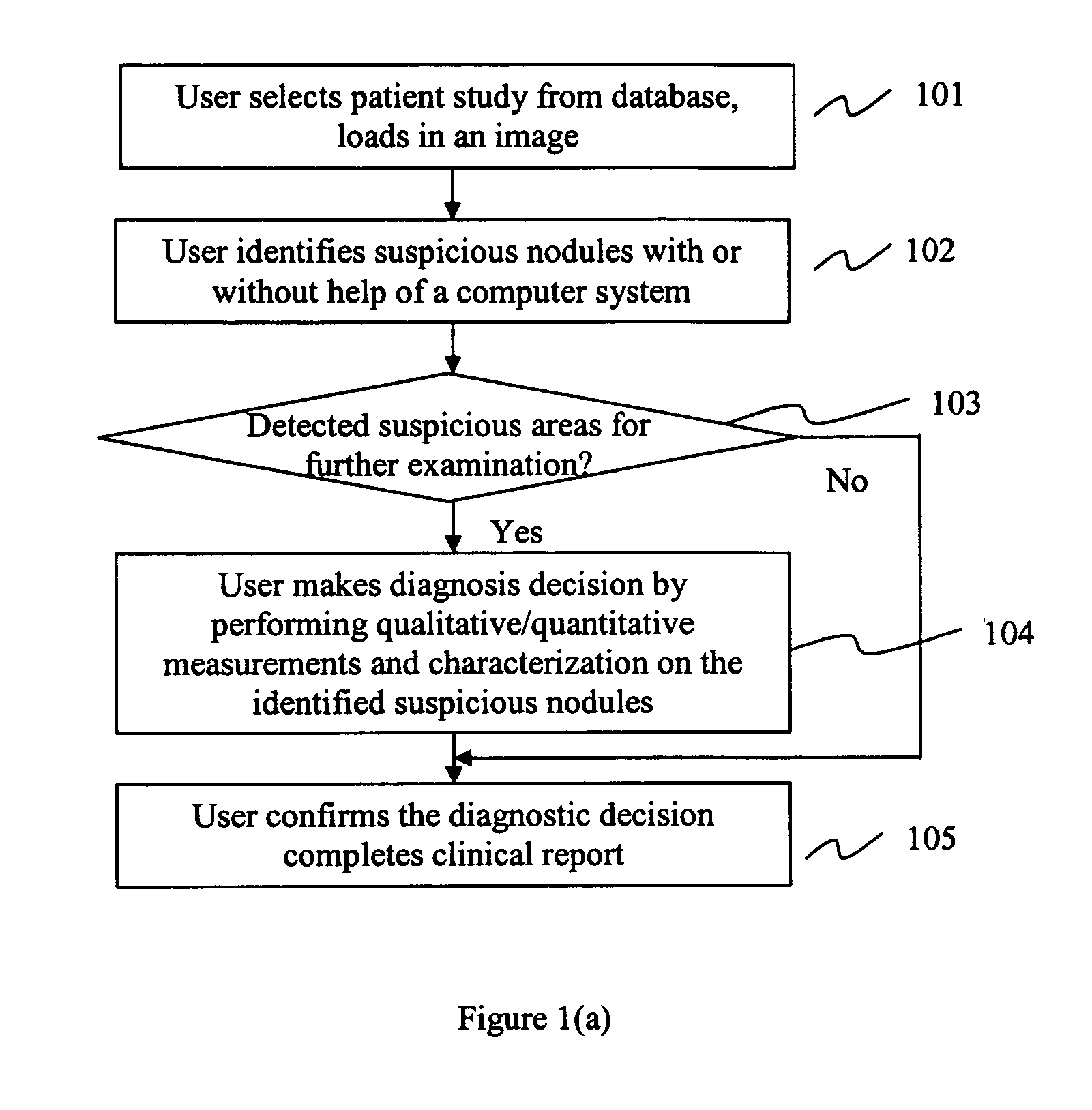
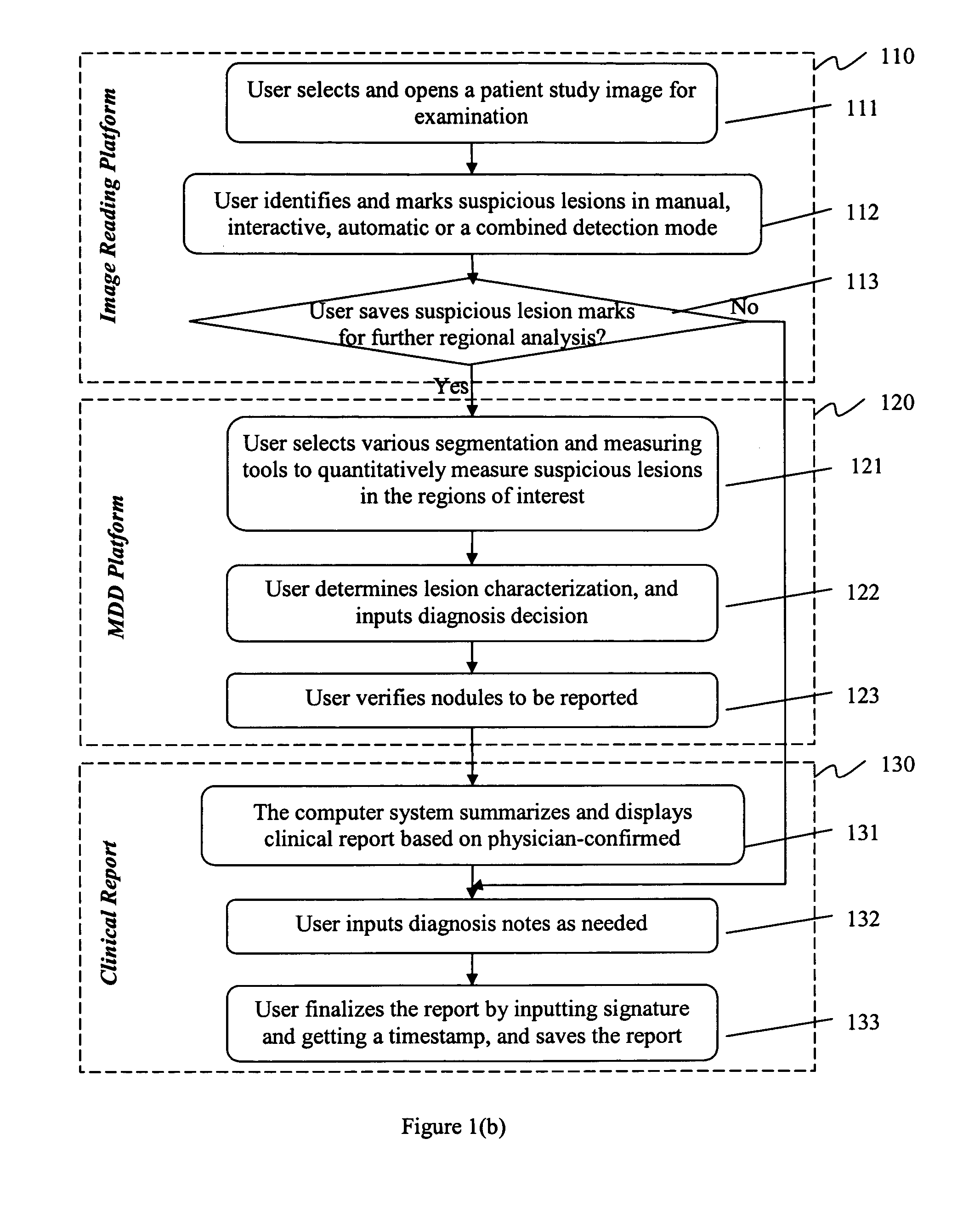
Method and system for intelligent qualitative and quantitative analysis of digital radiography softcopy reading
The present invention describes a method and system for intelligent diagnostic relevant information processing and analysis. Information associated with a patient is processed via an image reading platform. Based on such processed information, a matrix of diagnosis decisions containing diagnostic related information is generated via a matrix of diagnosis decision platform. A diagnostic decision is made based on the diagnostic relevant information. The image reading platform and / or the matrix of diagnosis decision platform encapsulate information and toolkits to be used to manipulate the information.
Owner:EDDA TECH
Polymeric marker with high radiopacity
ActiveUS20050064224A1Minimize and prevent flowingReduce wall thicknessMedical devicesDischarge tube main electrodesPolymer resinRadiopaque agent
High radiopacity is achieved in a polymeric marker by combining a polymeric resin, a powdered radiopaque agent having uniformly shaped particles of a specific particle size distribution and a wetting agent. The method to produce the marker calls for the blending and pelletization of these materials followed by extrusion onto support beading. The resulting supported tubing is subsequently cut to length with the beading still in place. After ejection of the beading remnant the marker is slipped into place on the device to be marked and attached by melt bonding. Marking of a guidewire allows lesions to be measured while the marking of balloon catheters allow the balloon to be properly positioned relative to a lesion.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
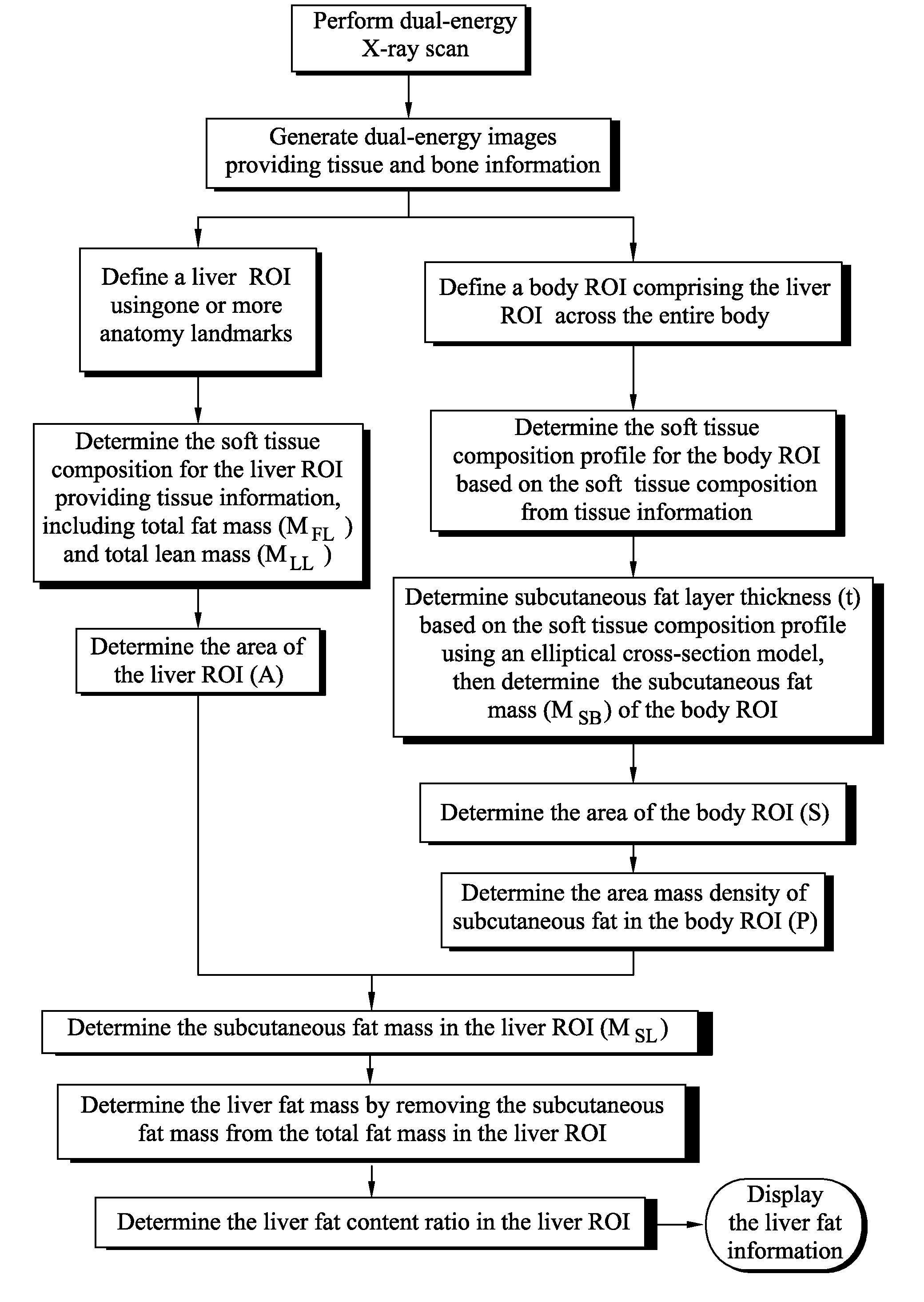
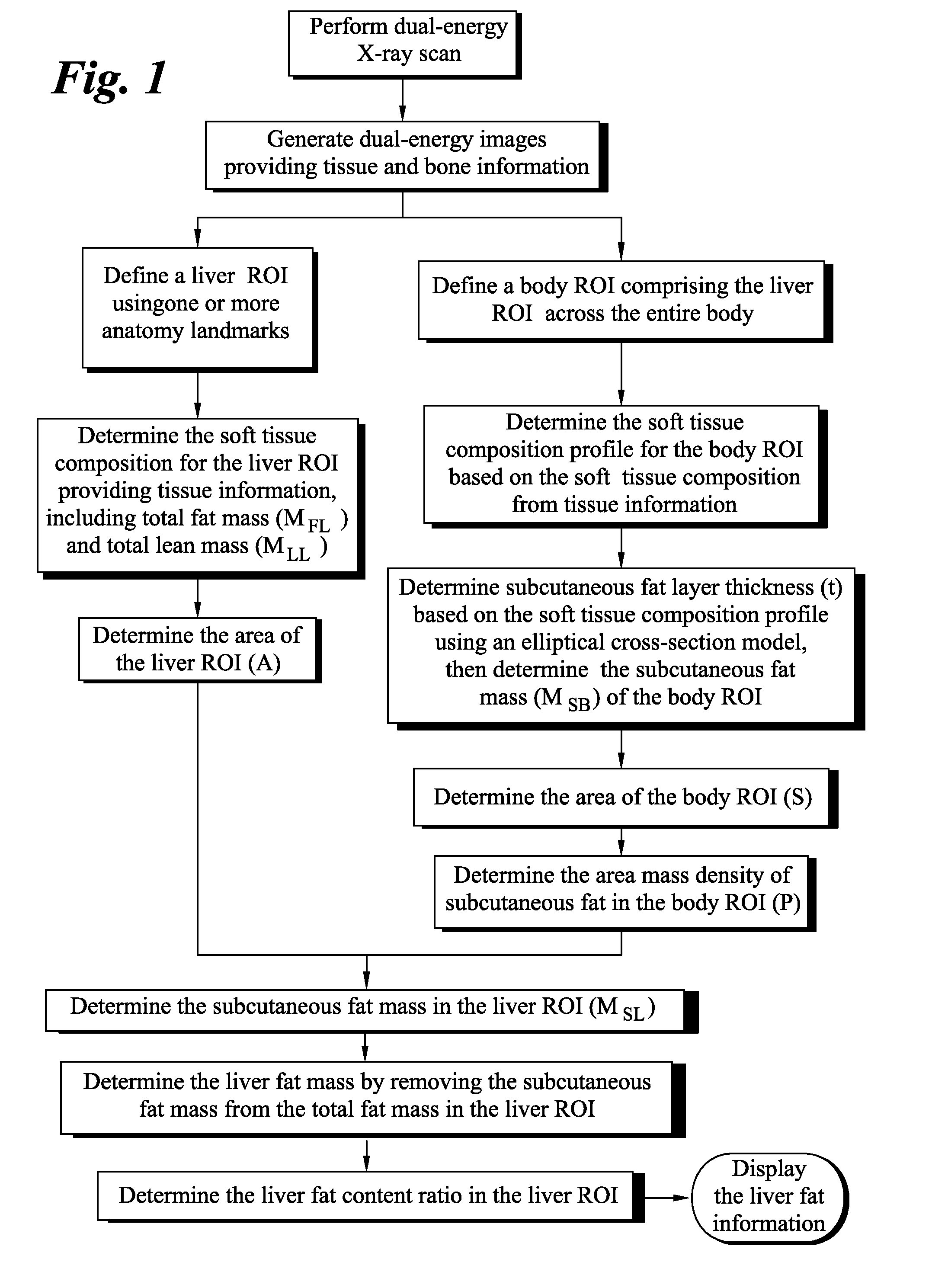
Method for measuring liver fat mass using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
ActiveUS20140371570A1Health-index calculationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsX-rayDual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Methods for measuring liver fat mass are provided. One method includes acquiring dual-energy two-dimensional (2D) scan information from a dual-energy X-ray scan of a body and generating a dual-energy X-ray image of the body using the 2D scan information. The method further includes identifying a region of interest using the dual-energy X-ray image and determining a subcutaneous fat mass for each of a plurality of sections of the region of interest. The method also includes determining a liver fat mass for the region of interest based on the determined subcutaneous fat mass for each of the plurality of sections.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
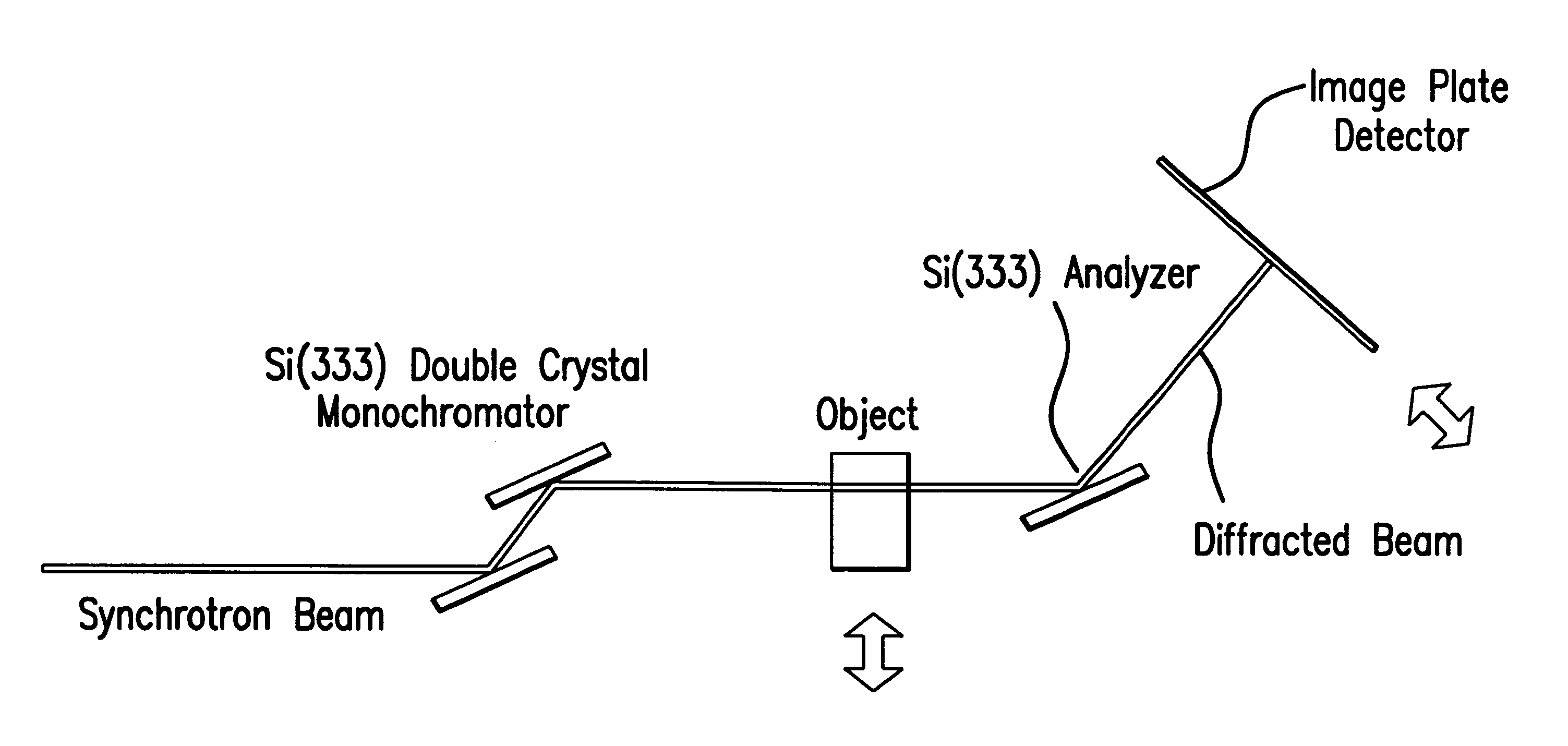
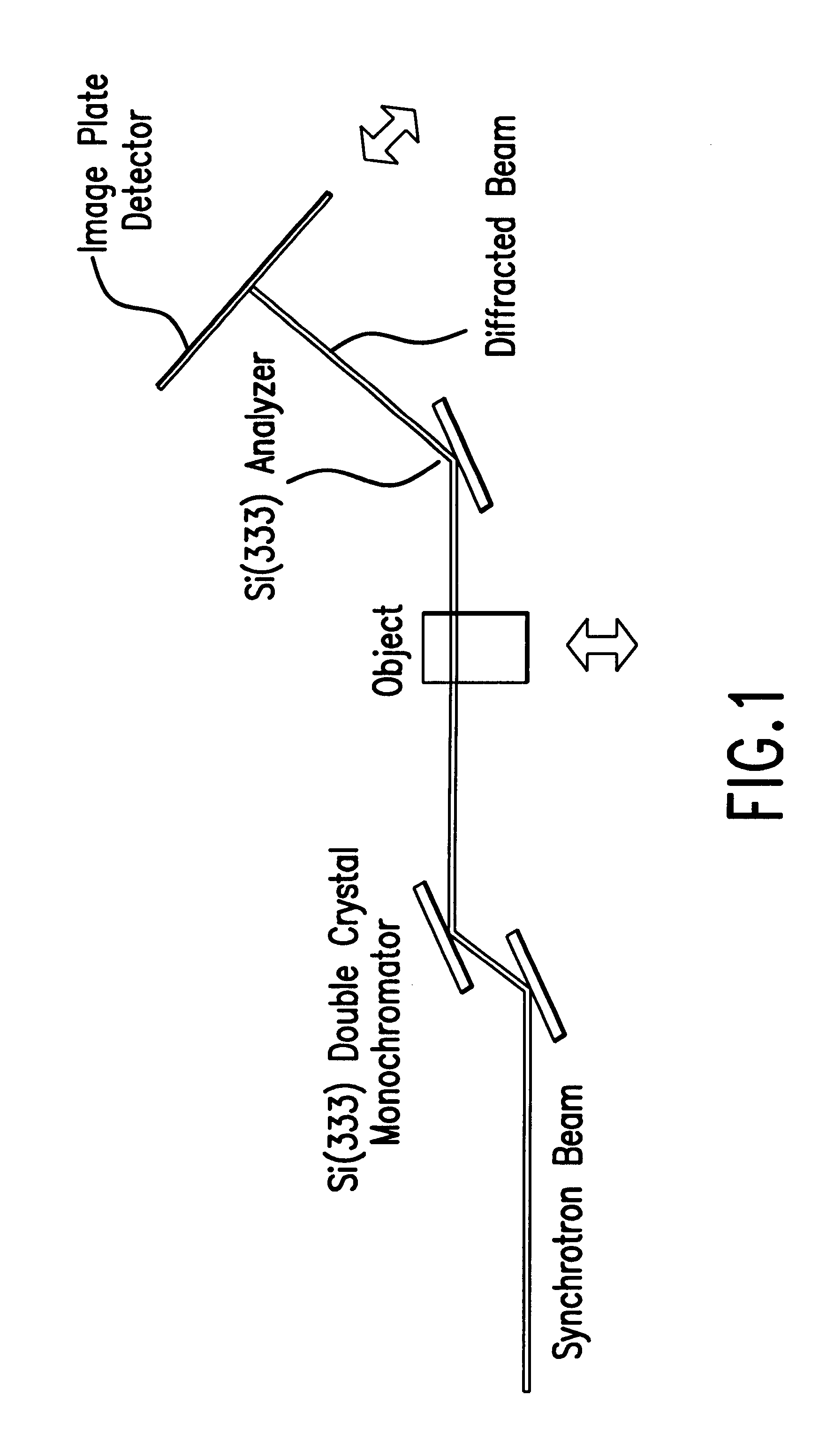
Diffraction enhanced x-ray imaging of articular cartilage
InactiveUS6577708B2Imaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementRocking curveAngle of incidence
A method and system for detecting an image of an object, particularly a soft tissue material. A generated x-ray beam is transmitted through the soft tissue material. A transmitted beam is directed at an angle of incidence upon a crystal analyzer. An image of the object is detected from a beam diffracted from the crystal analyzer either at or near a peak of a rocking curve of the crystal analyzer. The method and system of this invention is particularly useful for analyzing images of cartilage.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +2
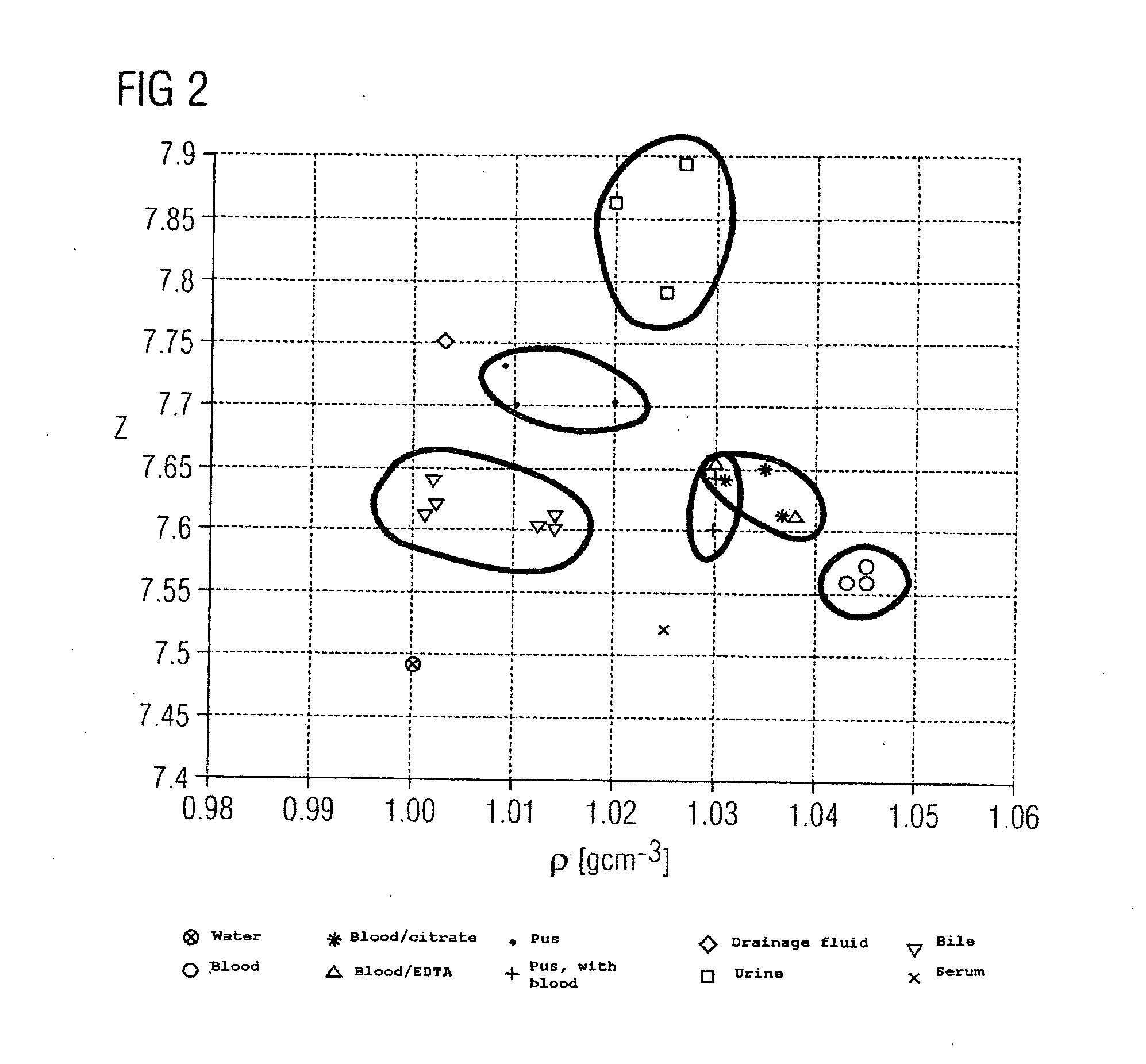
Method and device for determining the type of fluid in a fluid mass in an object
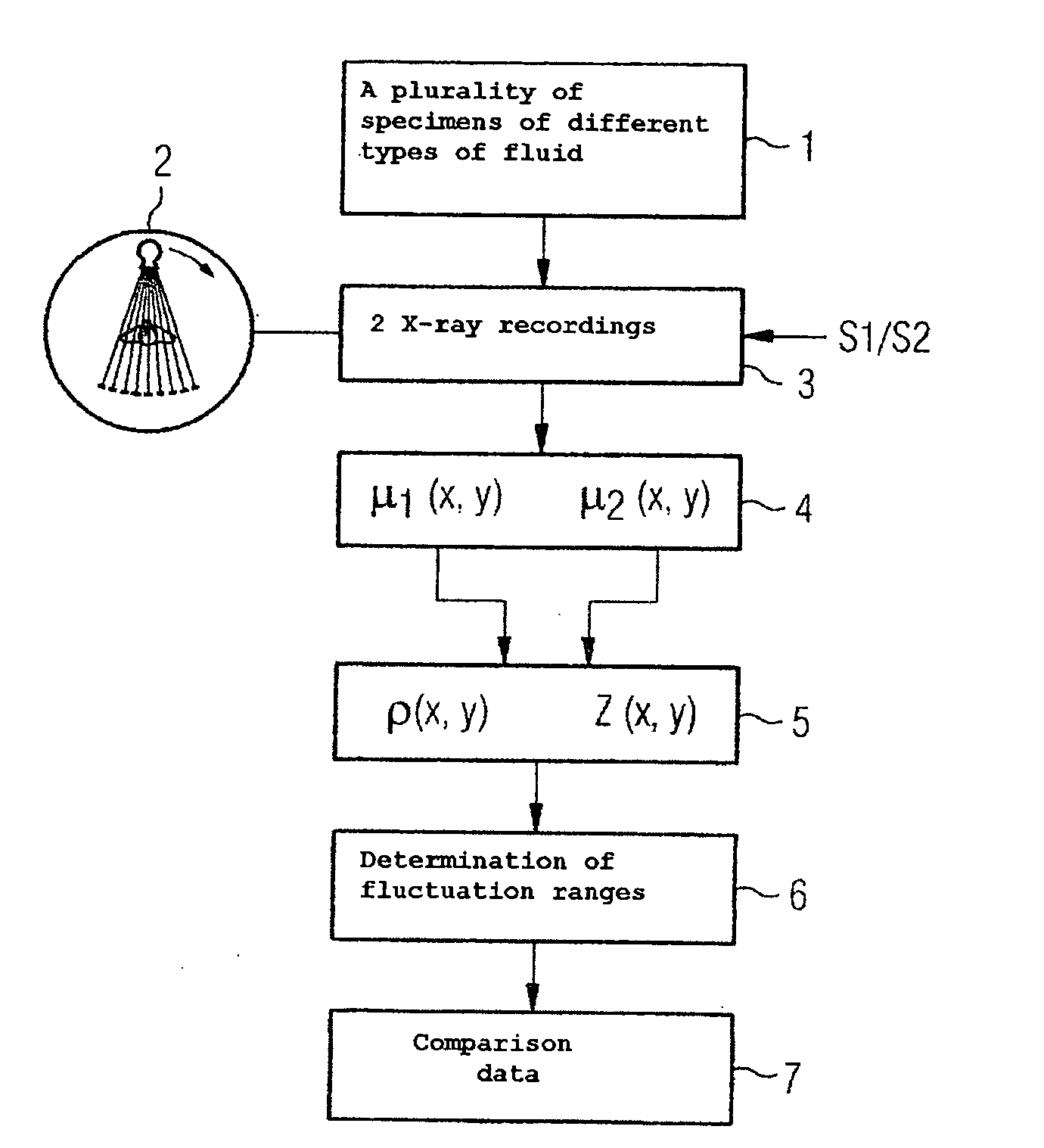
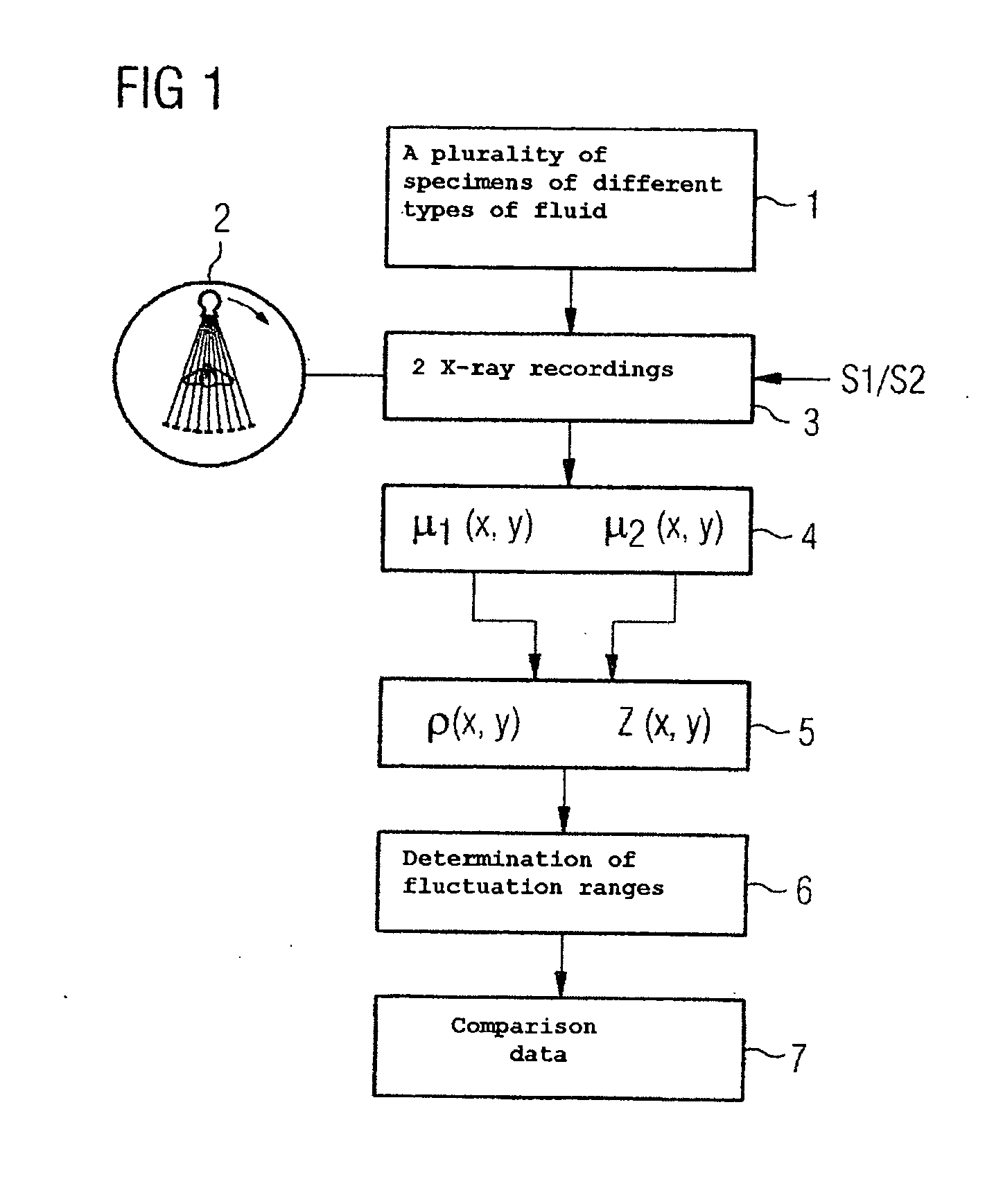
InactiveUS20050084063A1High resolutionQuick changeRadiation/particle handlingRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsX ray spectraVolumetric Mass Density
A method and a device are proposed for determining the type of fluid in a fluid mass in an object. X-ray attenuation data is supplied from one or a plurality of X-ray recordings of an object area including the fluid mass in the object, which were acquired with at least two different X-ray spectra or detector weightings. The X-ray attenuation data is used to determine values for effective atomic number and density for the fluid mass and average these to obtain a mean value for effective atomic number and density for the fluid mass. Comparison data is also supplied, which indicates fluctuation ranges for combinations of effective atomic number and density for different types of fluid. The mean values for effective atomic number and density of the fluid mass are compared with the comparison data to determine the fluctuation range and thereby the type of fluid, into which the two mean values fall. The method and associated device can be used to determine the type of fluid in a fluid mass in an object in a reliable and unambiguous manner.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Novel radiosurgery methods that utilize stereotactic methods to precisely deliver high dosages of radiation especially to the spine
InactiveUS20020032378A1Reduce decreaseAvoiding and minimizing deliveryRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgeryRadiosurgeryStereotaxis
A system for delivery of high dosage of radiation to a targeted spinal area is provided. This is accomplished by a system which provides for precise immobilization and positioning of the treated spinal area during dose planning and treatment via stereotactic radiosurgery. Advantages of the system include convenience to the patient, enhanced efficacy, and reduced risk of radiotoxicity to non-target tissues.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Avoiding dazzle from lights affixed to an intraoral mirror, and applications thereof
ActiveUS9585549B1Effective displayImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Computer science
Disclosed embodiments integrate a camera into an intraoral mirror. Integrating a camera into an intraoral mirror provides an efficient way to record and display what is visible to the healthcare provider in the mirror.
Owner:DENTAL SMARTMIRROR INC
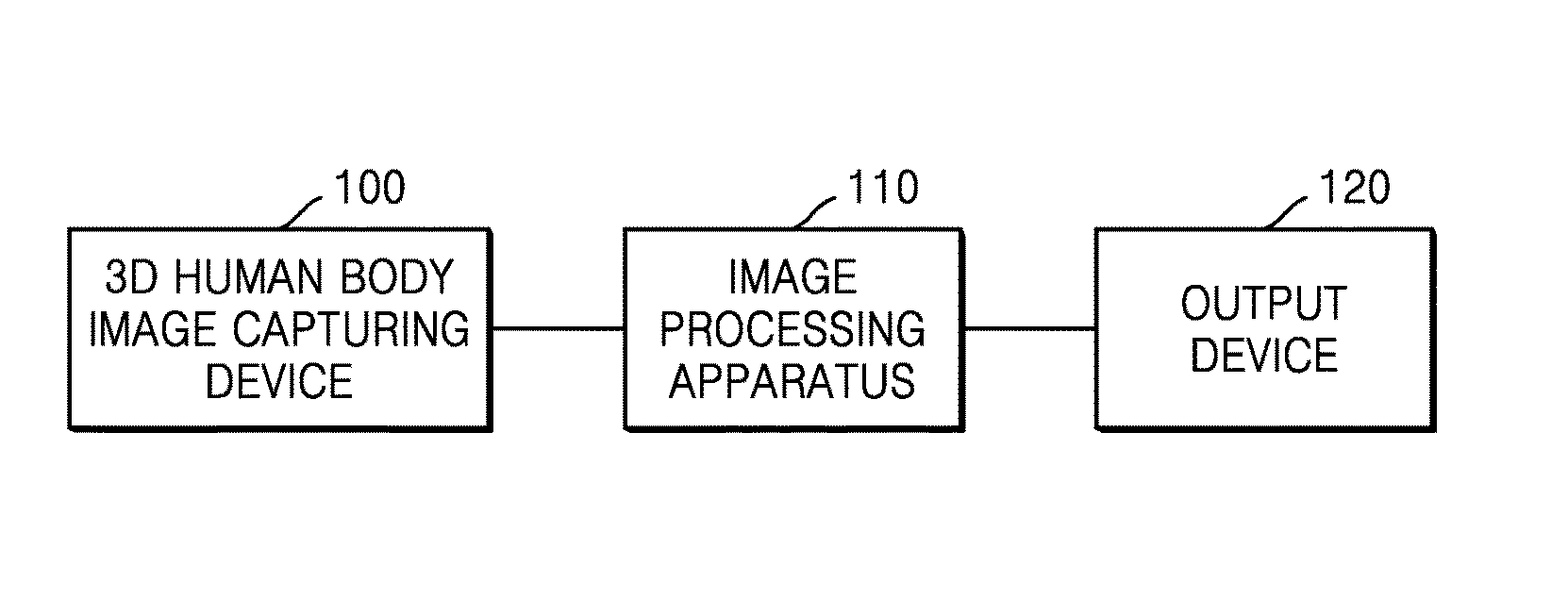
Method for Extracting Airways and Pulmonary Lobes and Apparatus Therefor
ActiveUS20160189373A1Accurate segmentationAccurate analysisImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyImaging processing
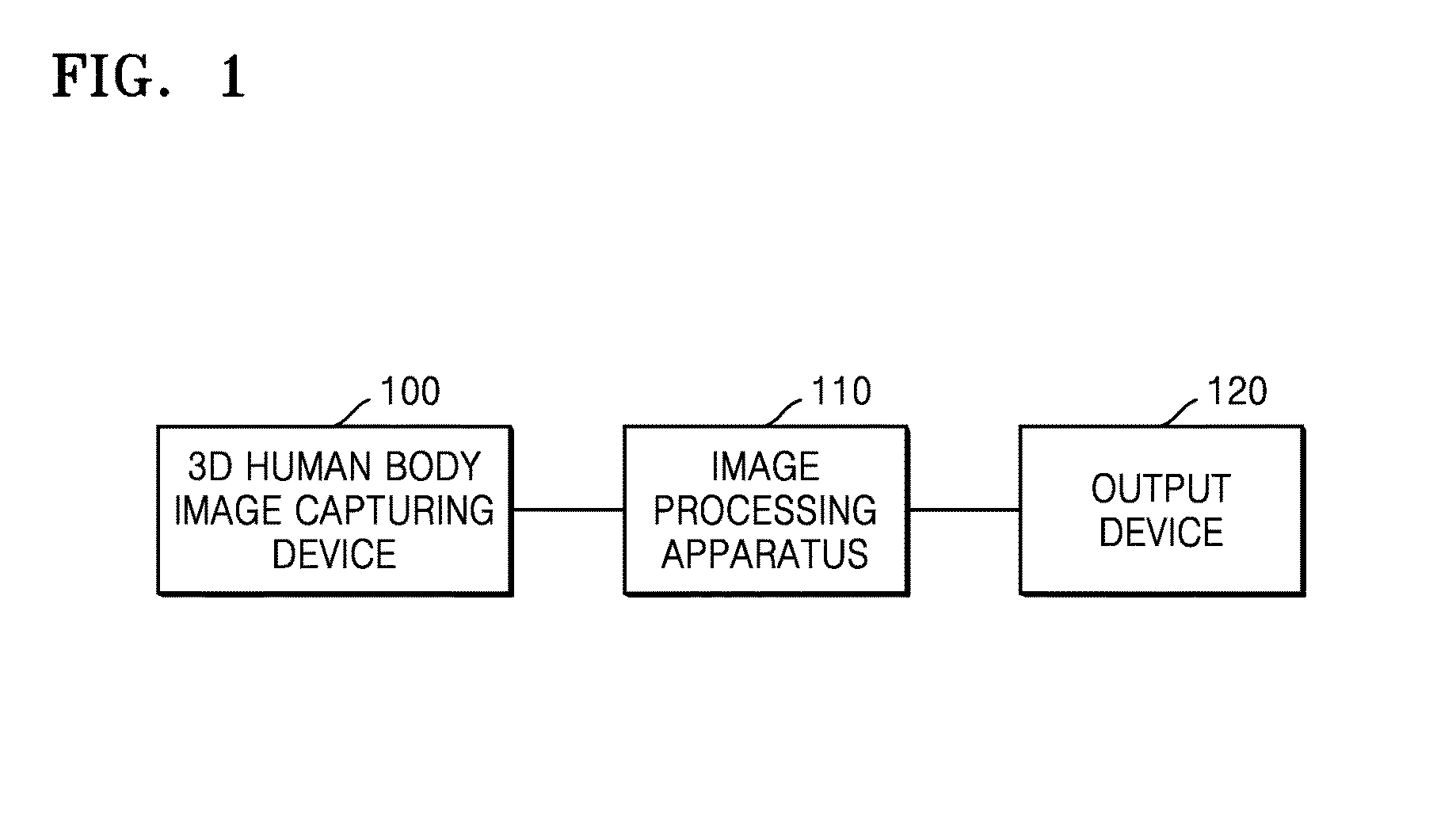
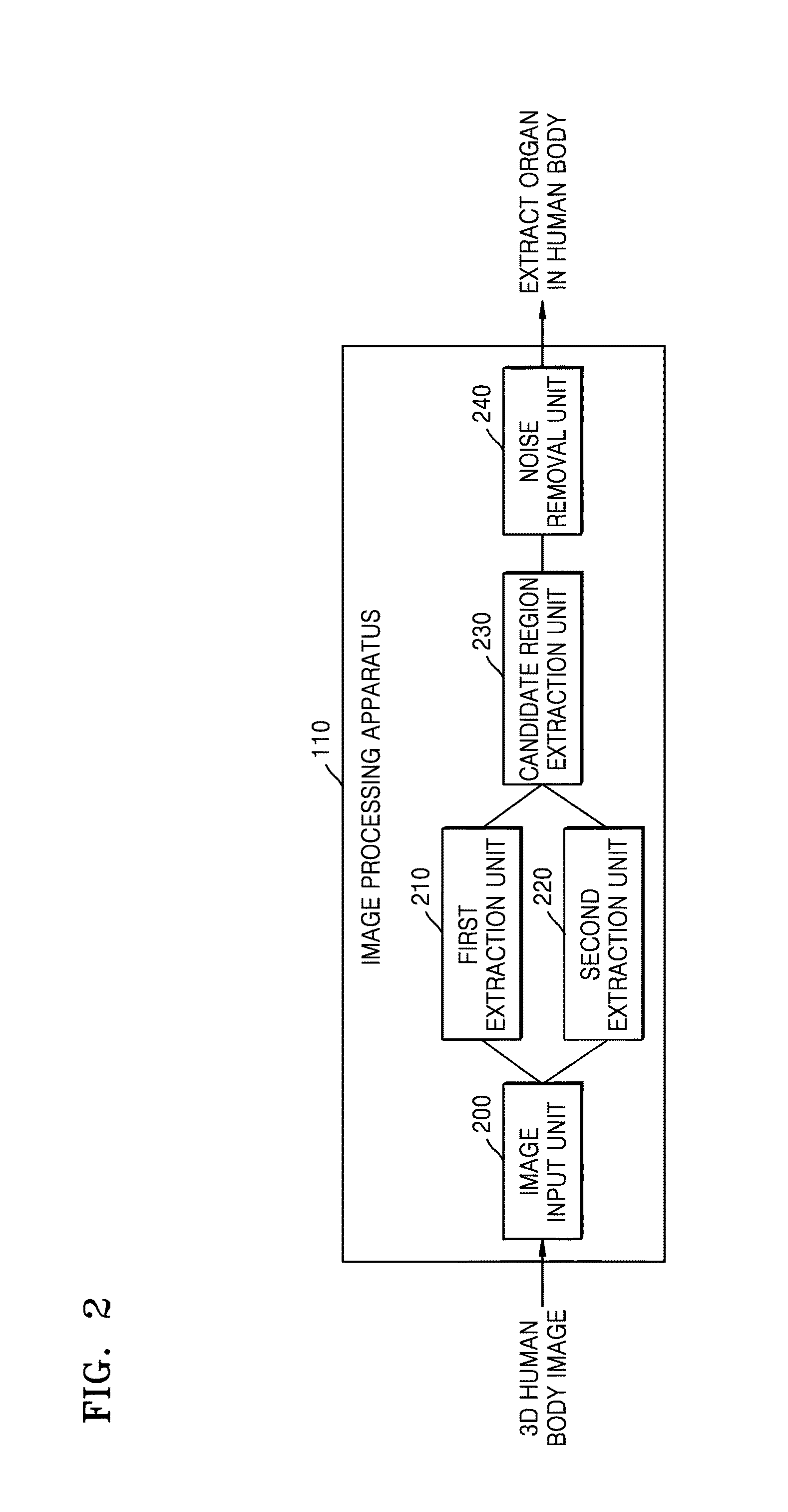
Provided is a method and apparatus for segmenting airways and pulmonary lobes. An image processing apparatus obtains a first candidate region of an airway from a three-dimensional (3D) human body image by using a region growing method, obtains a second candidate region of the airway based on a directionality of a change in signal intensity of voxels belonging to a lung region segmented from the 3D human body image, segments an airway region by removing noise based on similarity of a directionality of a change in signal intensity of voxels belonging to a third candidate region acquired by combining together the first and second candidate regions. Furthermore, the image processing apparatus segments a lung region from a 3D human body image by using a region growing method, obtains a fissure candidate group between pulmonary lobes based on a directionality of a change in signal intensity of voxels belonging to the lung region, reconstructs an image of the lung region including the fissure candidate group into an image viewed from a front side of a human body and generates a virtual fissure based on a fissure candidate group shown in the reconstructed image, and segments the pulmonary lobes by using the virtual fissure.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
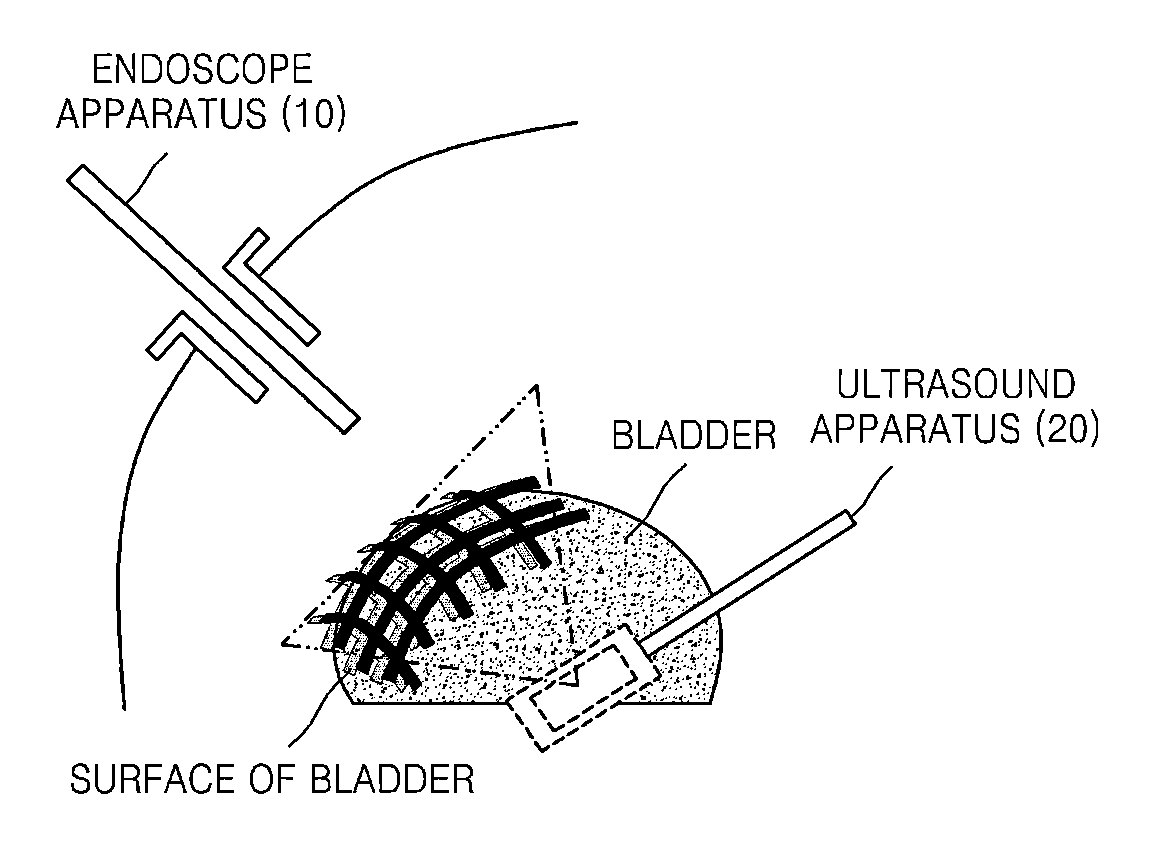
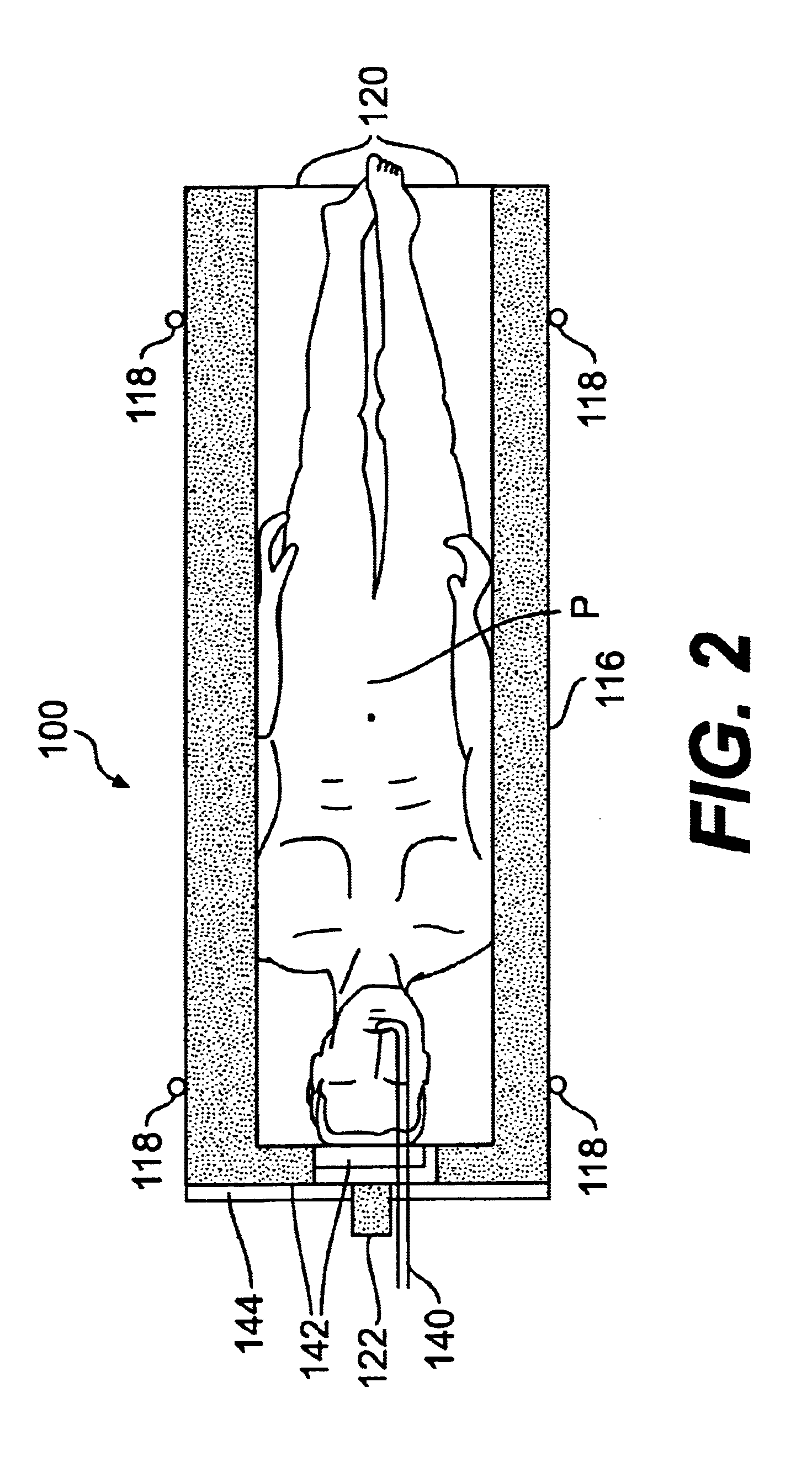
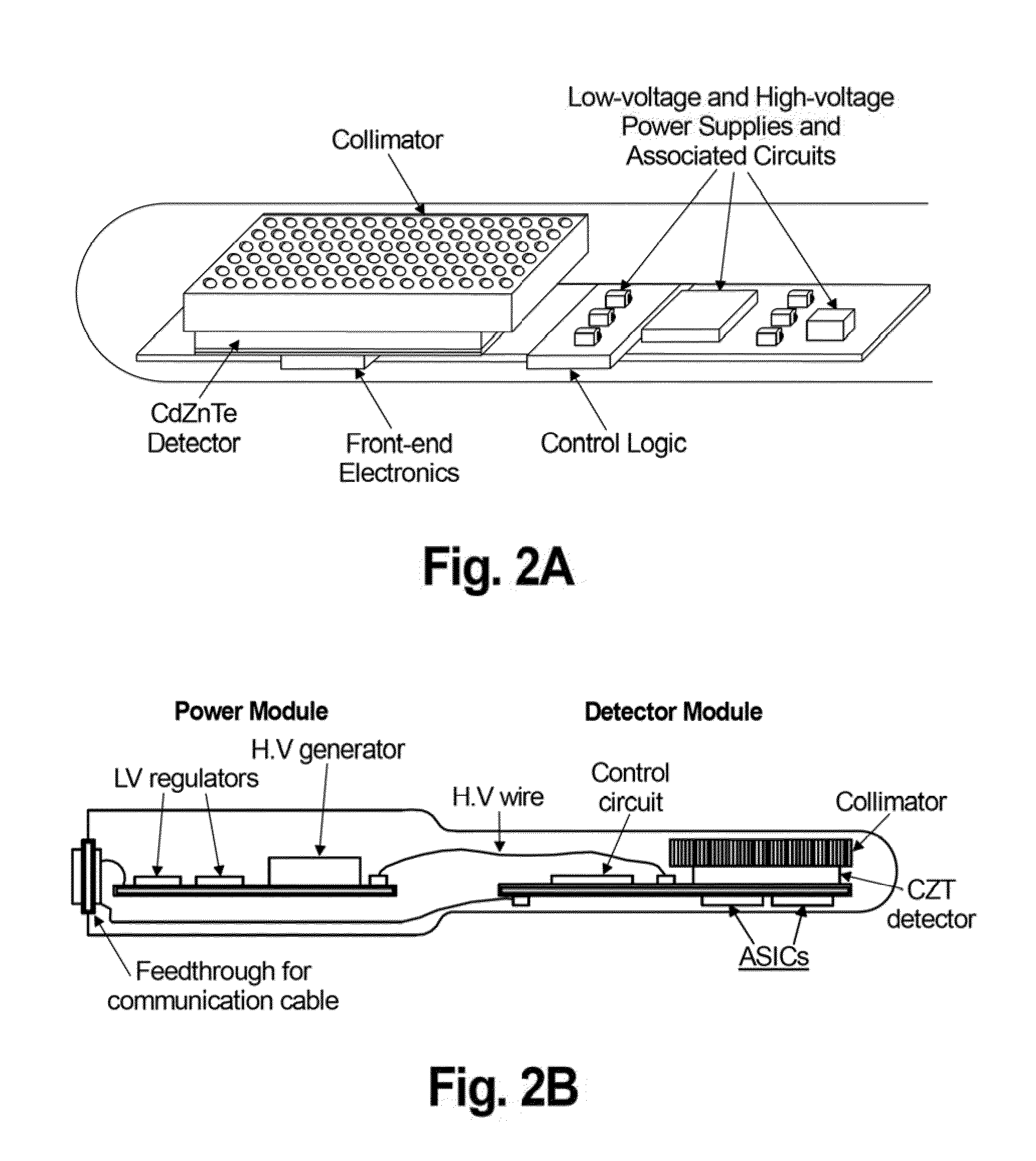
Compact Endocavity Diagnostic Probes for Nuclear Radiation Detection
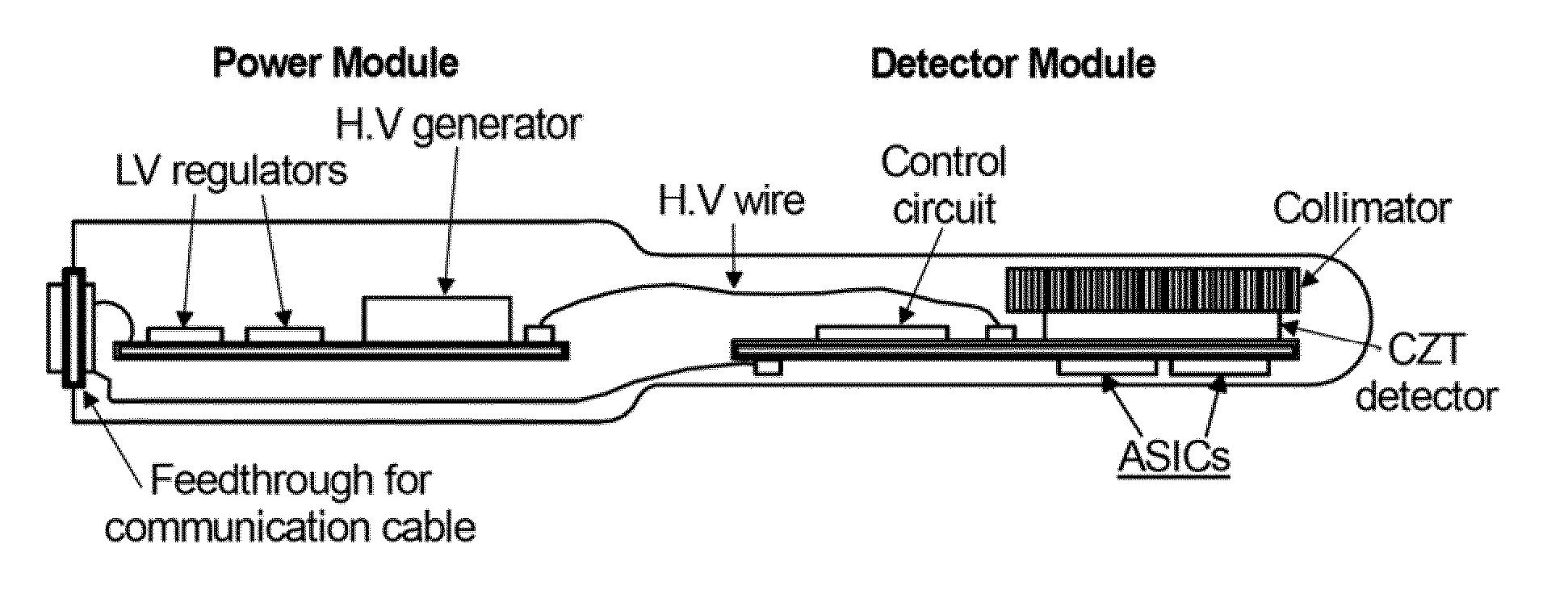
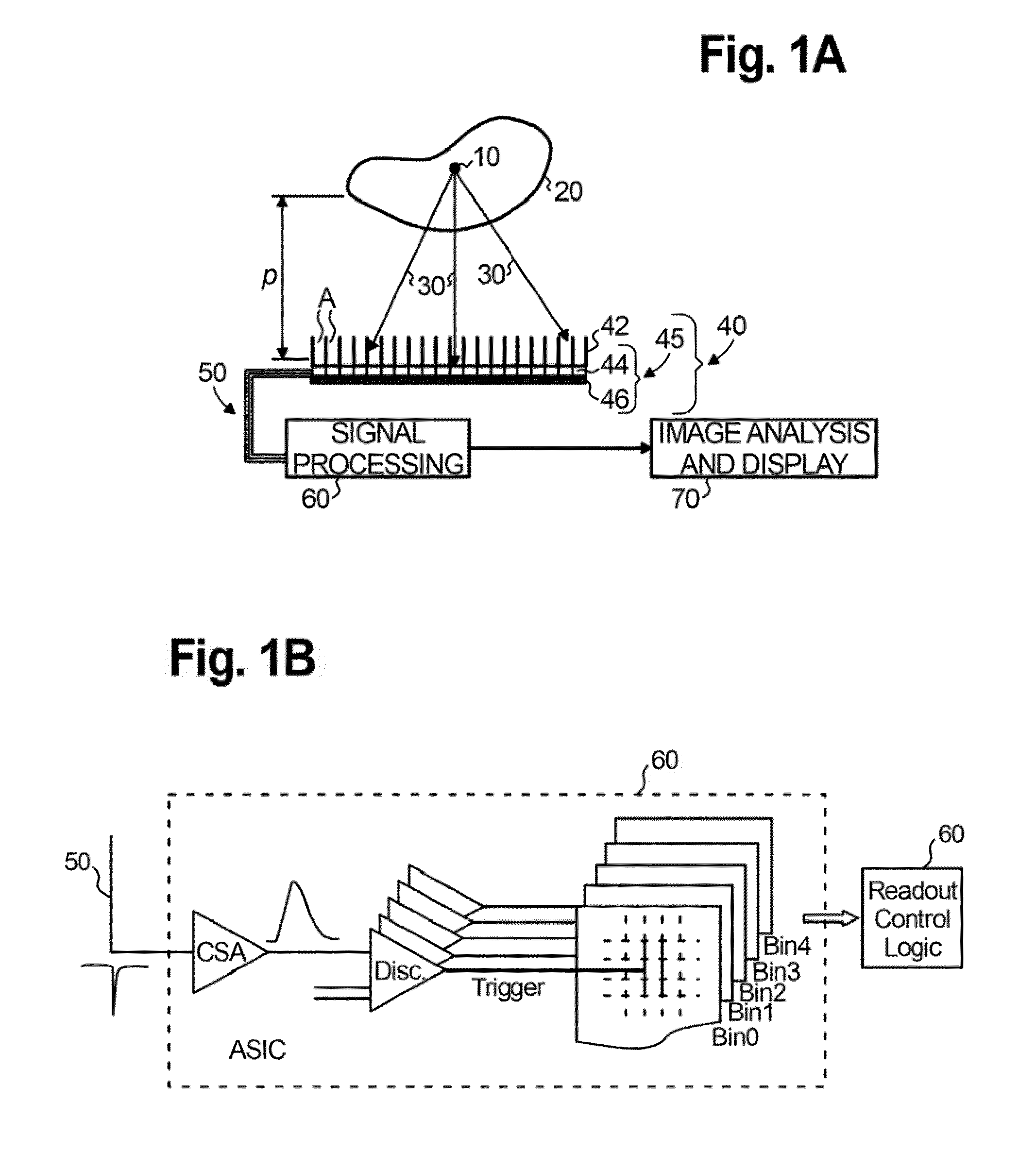
ActiveUS20110286576A1Improve image qualityEasy to carrySolid-state devicesEndoscopesNuclear radiationRadiation imaging
This invention relates to the field of radiation imaging. In particular, the invention relates to an apparatus and a method for imaging tissue or an inanimate object using a novel probe that has an integrated solid-state semiconductor detector and complete readout electronics circuitry.
Owner:HYBRIDYNE IMAGING TECH
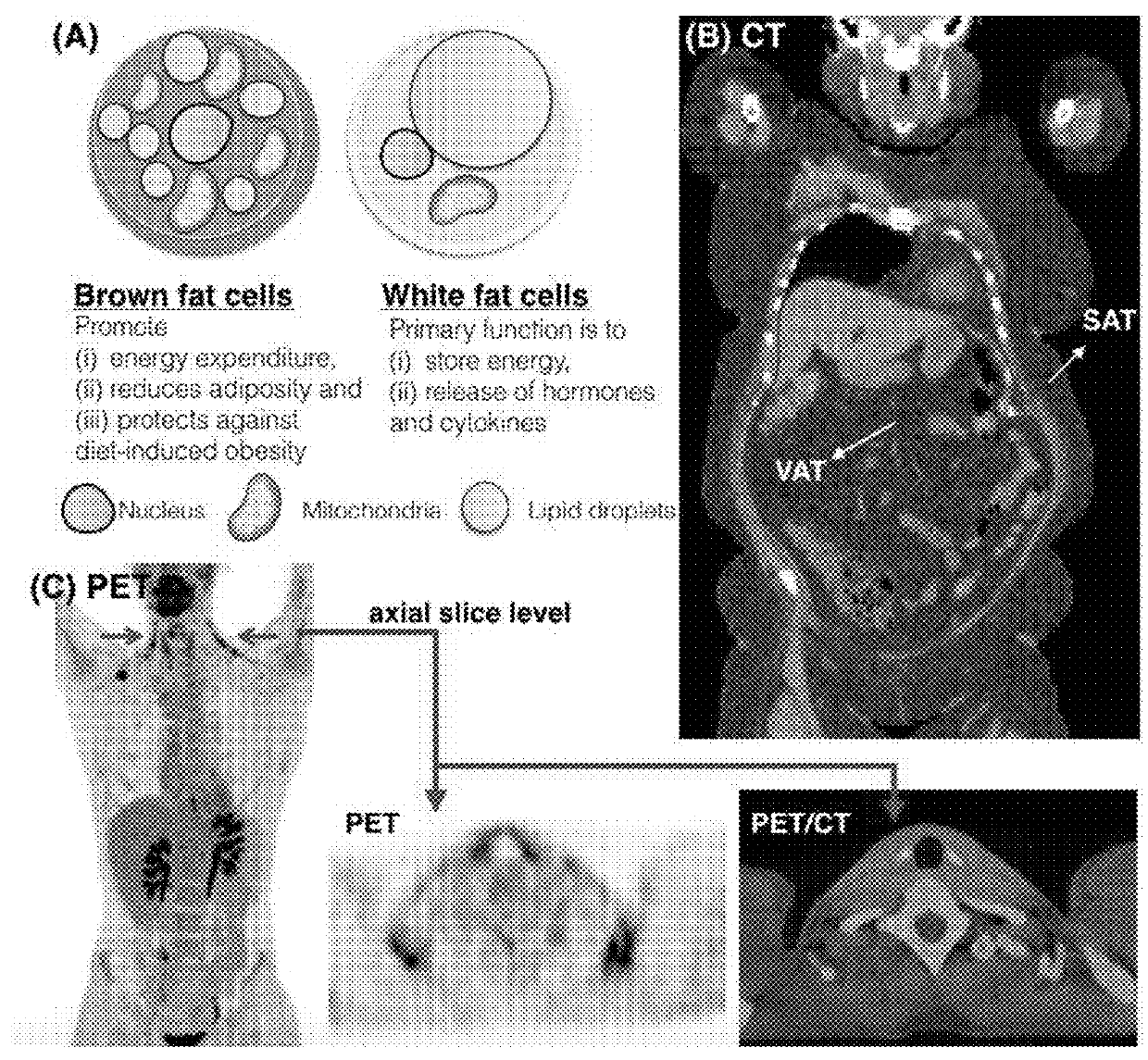
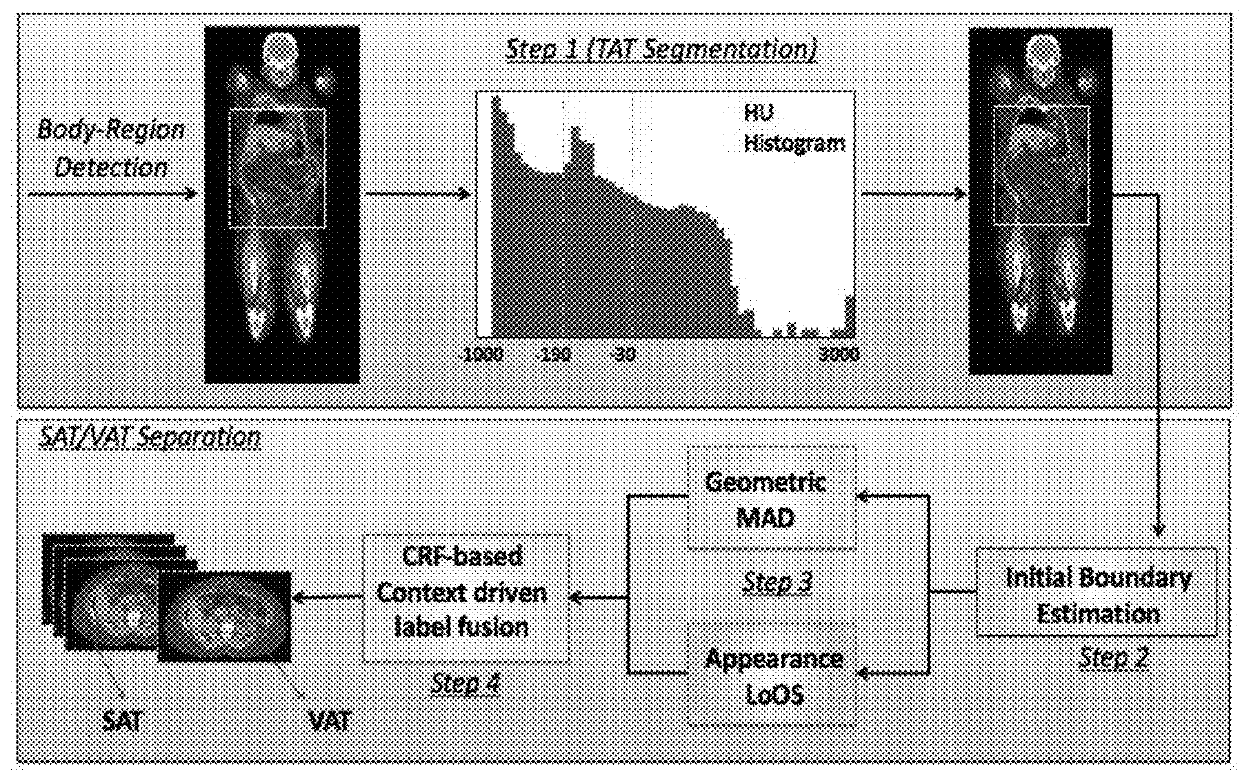
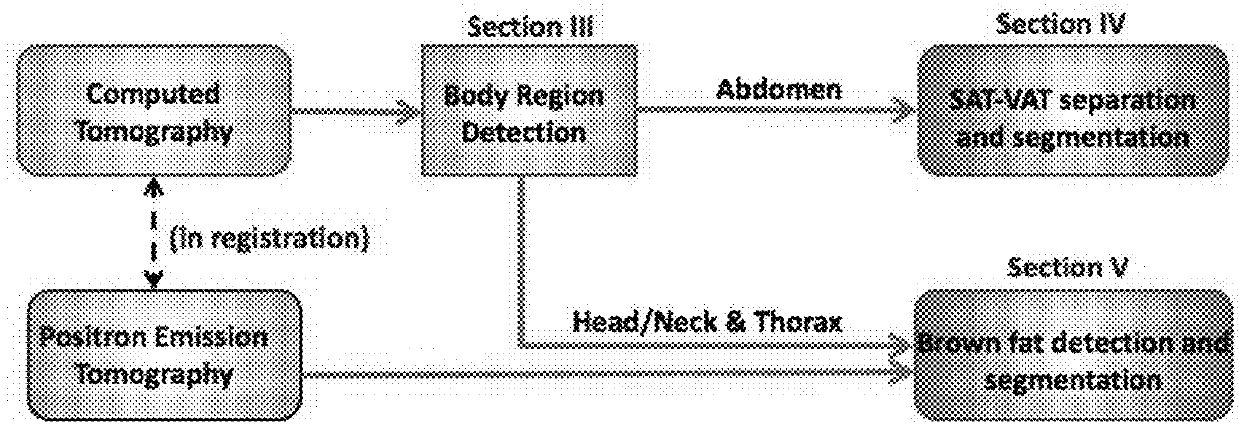
System and method for image-based quantification of white and brown adipose tissue at the whole-body, organ and body-region levels
InactiveUS20180165808A1Increases default detection rateHigh level of detectionImage enhancementImage analysisWhole bodyMedicine
A system and method for automatically detecting and quantifying adiposity distribution is presented herein. The system detects, segments and quantifies white and brown fat adipose tissues at the whole-body, body region, and organ levels.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com