Patents
Literature
446 results about "Dentin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
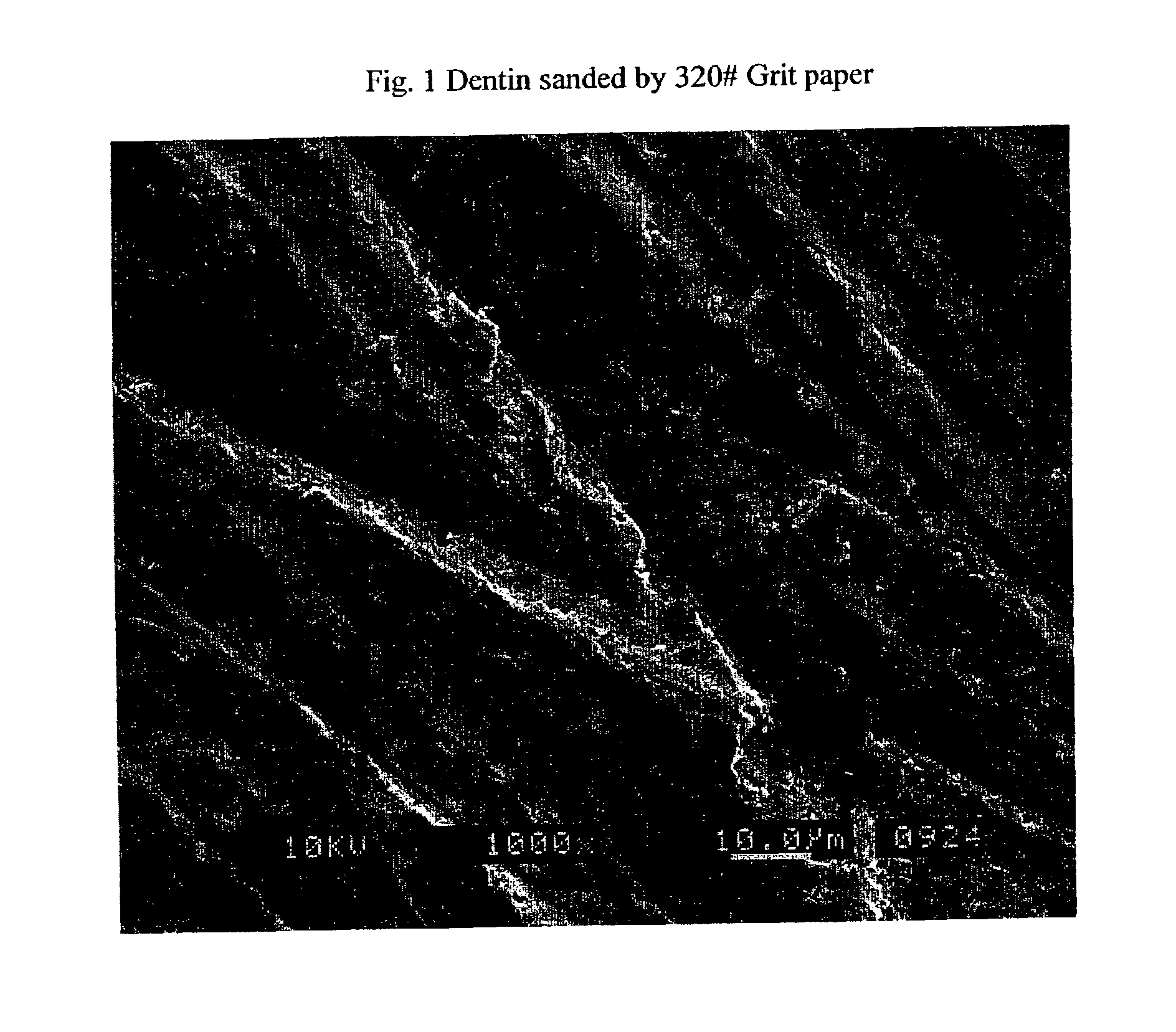
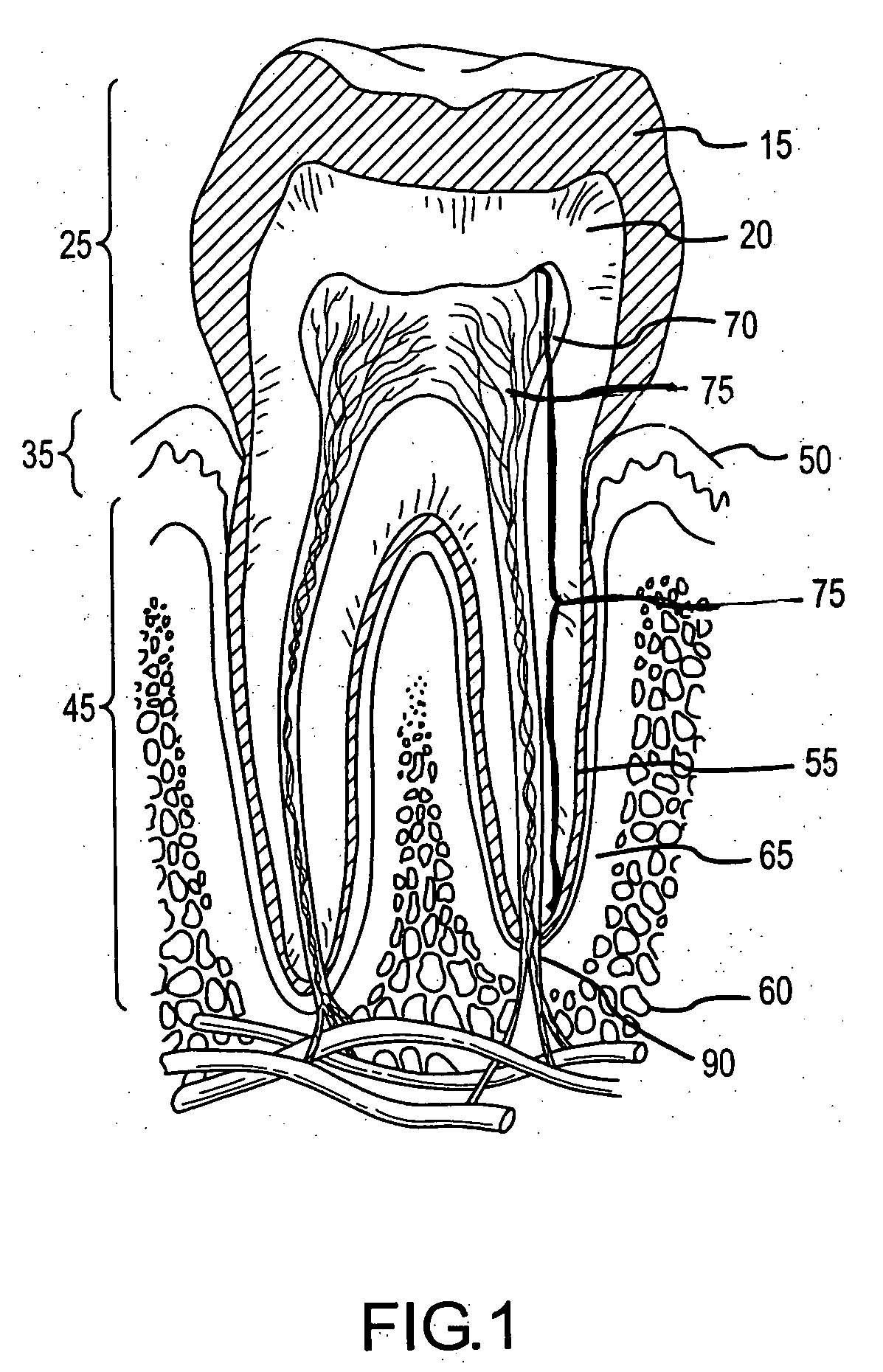
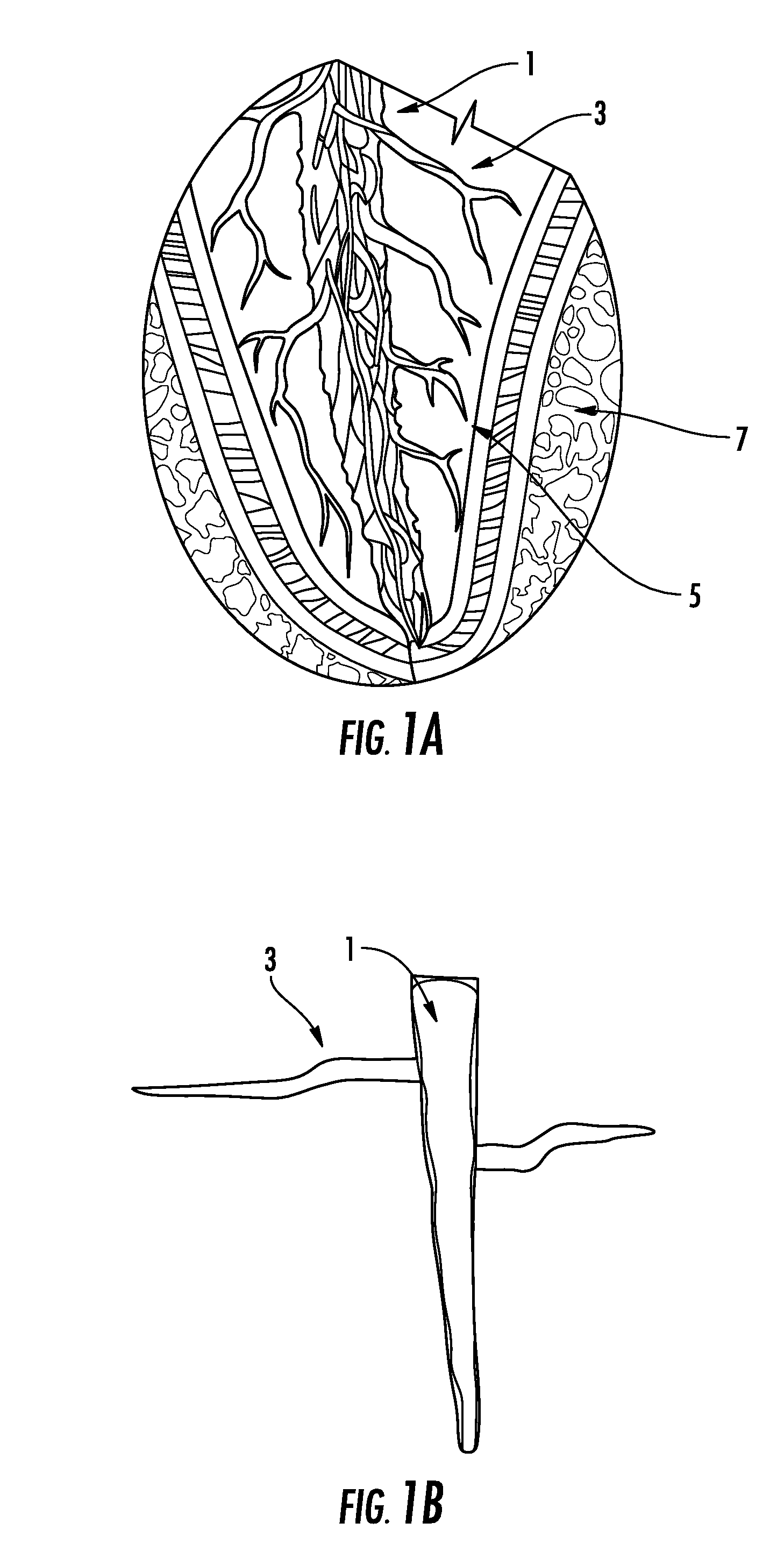
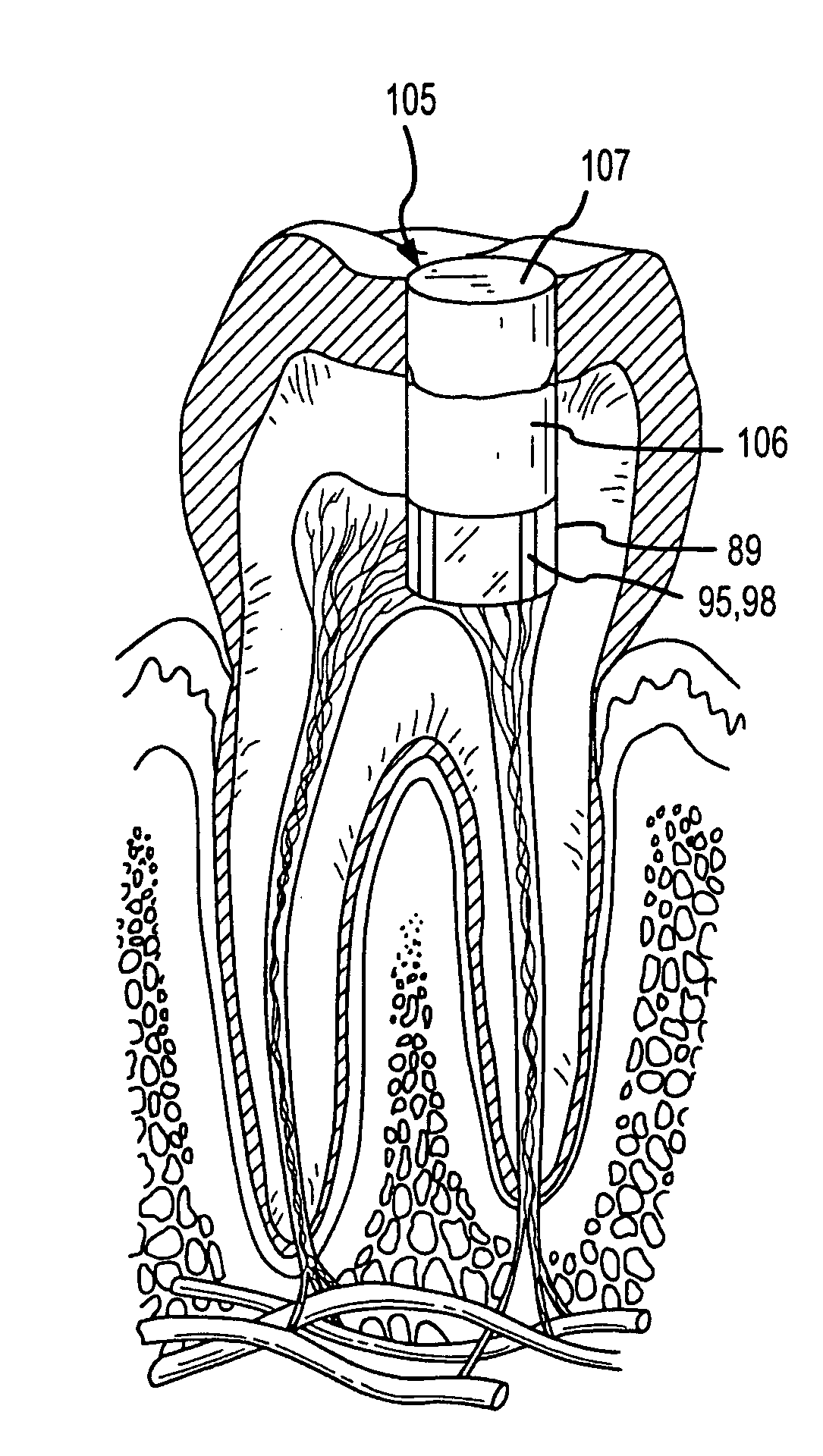
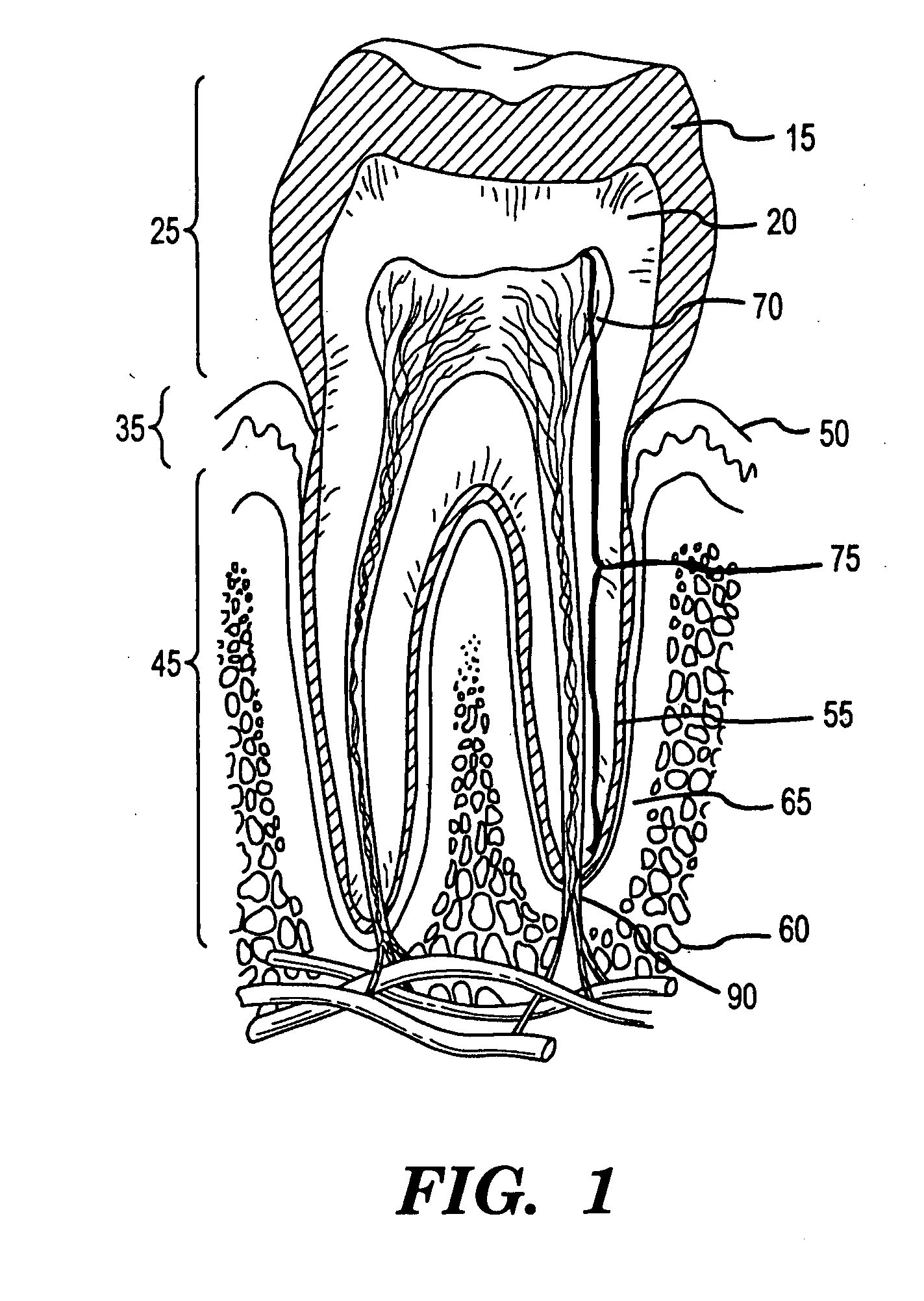
Dentin (/ˈdɛntɪn/) (American English) or dentine (/ˈdɛnˌtiːn/ or /ˌdɛnˈtiːn/) (British English) (Latin: substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxylapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive.
Methods and compositions for culturing a biological tooth
Tooth tissues include the pulp mesenchyme that forms the dentin and an epithelium that is responsible for enamel formation. Cells from these tissues were obtained from porcine third molars and were seeded onto a biodegradable scaffold composed of a polyglycolic acid—polylactic acid copolymer. Cell polymer constructs were then surgically implanted into the omentum of athymic nude rats so that the constructs would have a blood supply and these tissues were allowed to develop inside the rats. Infrequently, columnar epithelial cells were observed as a single layer on the outside of the dentin-like matrix similar to the actual arrangement of ameloblasts over dentin during early tooth development. Developing tooth tissues derived from such cell polymer constructs could eventually be surgically implanted into the gum of an edentulous recipient where the construct would receive a blood supply and develop to maturity, providing the recipient with a biological tooth replacement.
Owner:FORSYTH DENTAL INFARY FOR CHILDREN +2
Preparation for being fastened on a natural tooth part or tooth and corresponding fastening method
ActiveUS6955540B2Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsRelieve stressDental implantsImpression capsStress concentrationNatural tooth
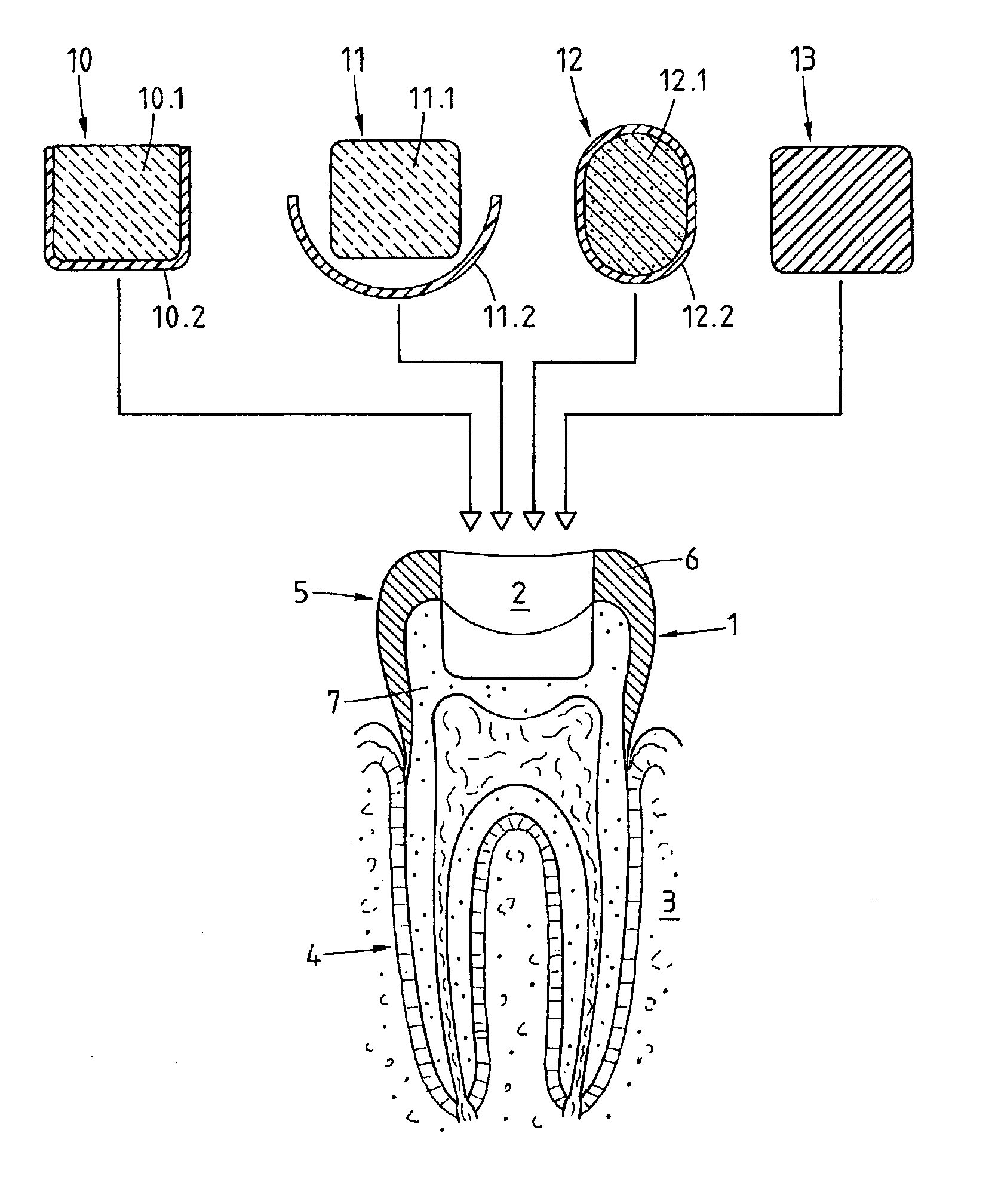
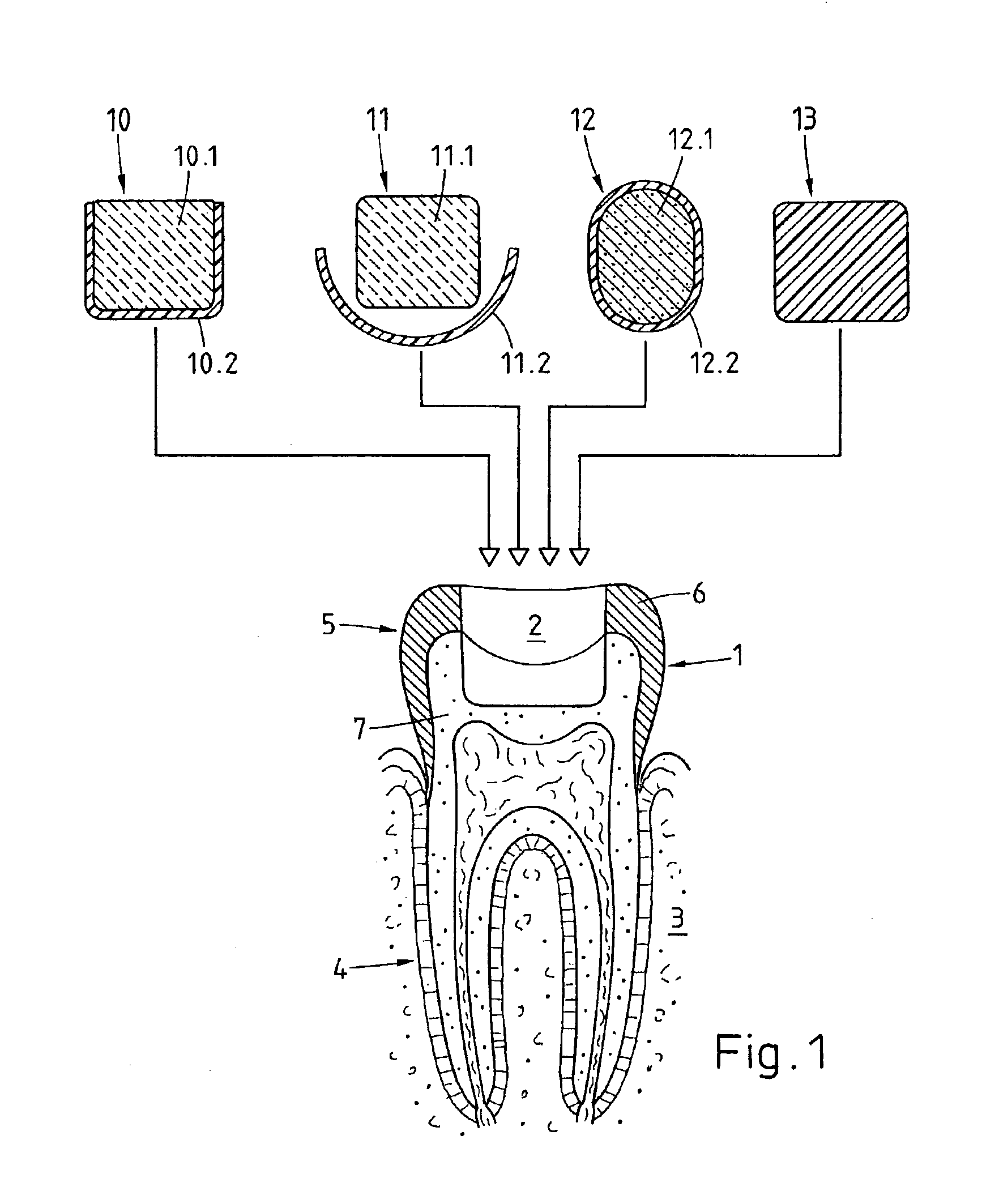
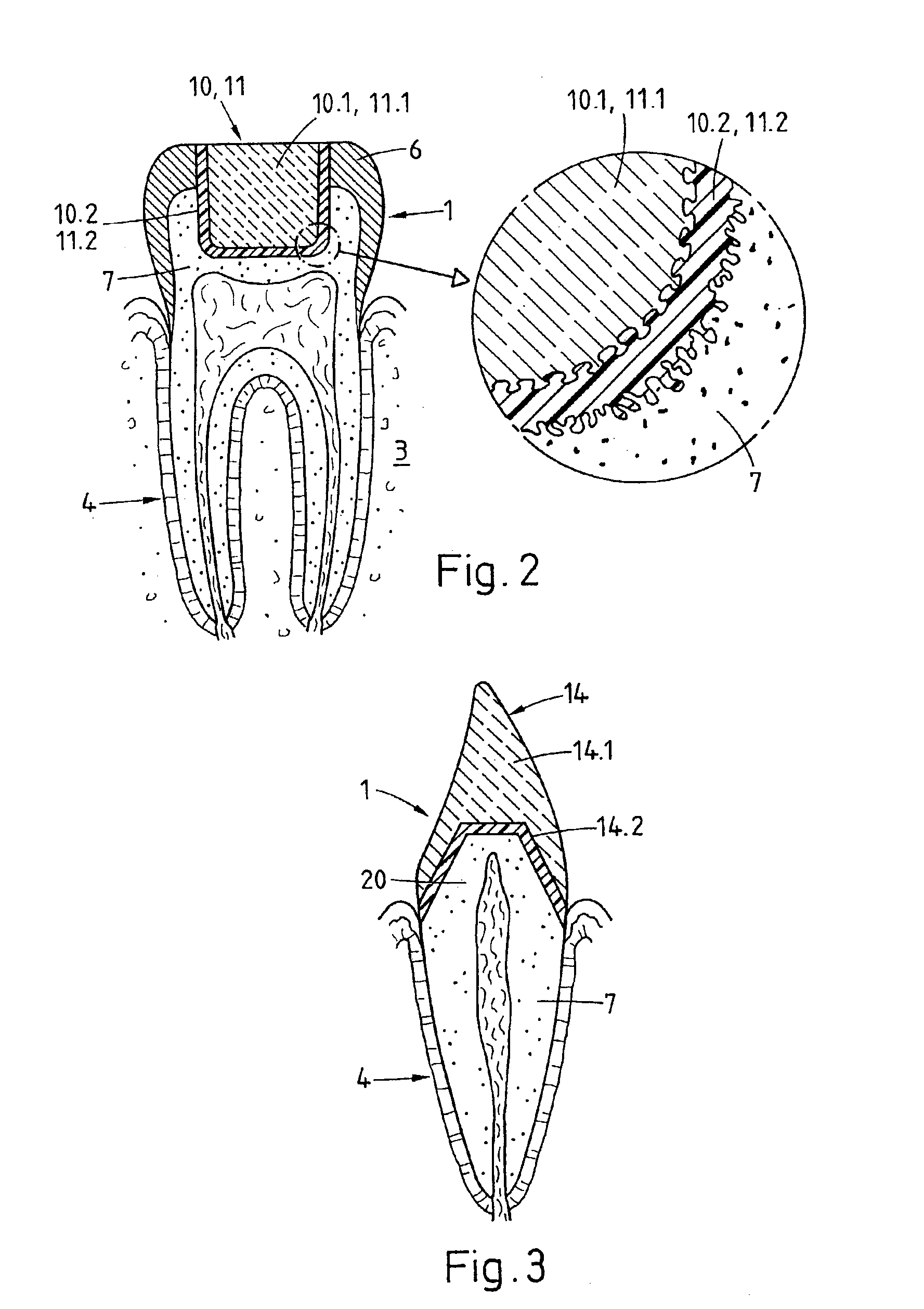
A preparation (10, 11,12,13) to be fixed to a natural tooth part or tooth, in particular for the replacement of a load-bearing tooth part, is for example a filling for a drilled-out tooth (1), a crown, bridge or prosthesis to be placed on a tooth stub, or a tooth pin to be fixed in a tooth root for fastening an artificial tooth, a bridge or a prosthesis. The preparation has surface regions which consist of a material with thermoplastic properties. The preparation (10, 11, 12,13) is designed in a manner such that it has oscillation properties with such low damping losses that for a liquefaction of the material with thermoplastic properties by way of oscillations there are local stress concentrations required, and in a manner such that such stress concentrations only occur in the region of the preparation surface. The preparation is positioned on a suitably prepared natural tooth part in a manner such that the material with the thermoplastic properties is in contact or may be brought into contact with the dentin surface and / or enamel surface. The preparation is then made to mechanically oscillate and is simultaneously pressed against the natural tooth part, whereby the material with the thermoplastic properties is at least partly liquefied and brought into intimate contact with the dentin or enamel surface in a manner such that after solidification it forms a positive fit and / or material fit connection. Teeth restored with such preparations have a high stability and a long life, which in particular is attributed to the fact that the thermoplastic material, in contrast to cements used for the same purpose, shrinks less and has the ability to relieve internal stress by creeping.
Owner:WOODWELDING
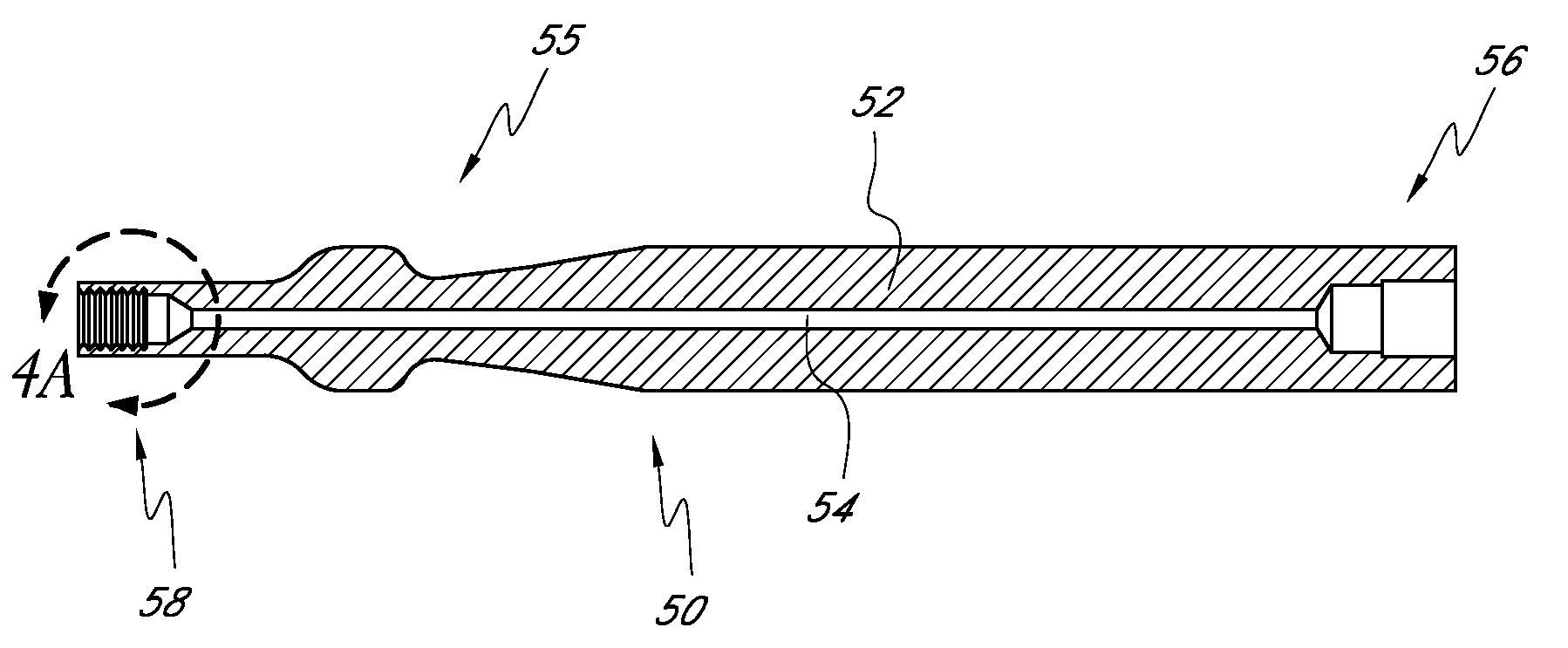
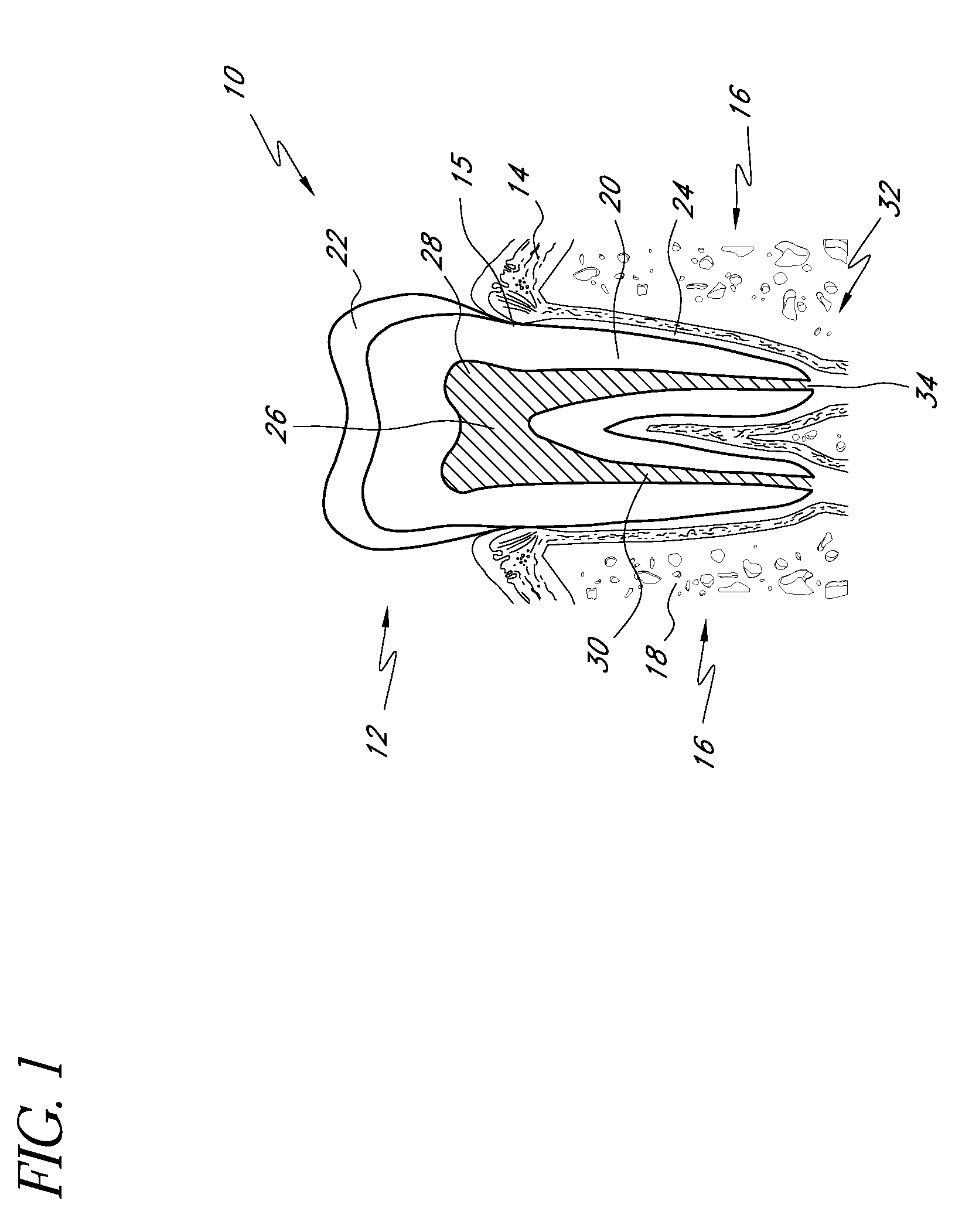
Apparatus and methods for treating root canals of teeth
Apparatus and methods for endodontic treatment of teeth provide effective cleaning of organic material (such as pulp and diseased tissue) from the root canal system. In an embodiment, a compressor system generates high pressure liquid (e.g., water) that flows through an orifice to produce a high-velocity collimated jet of liquid. The high-velocity jet is directed toward a surface of a tooth, for example, an exposed dentinal surface, and impingement of the jet onto the surface generates an acoustic wave that propagates throughout the tooth. The acoustic wave effectively detaches organic material from dentinal surfaces and tubules. The detached organic material is flushed from the root canal system by the liquid jet and / or by additional irrigation.
Owner:SONENDO
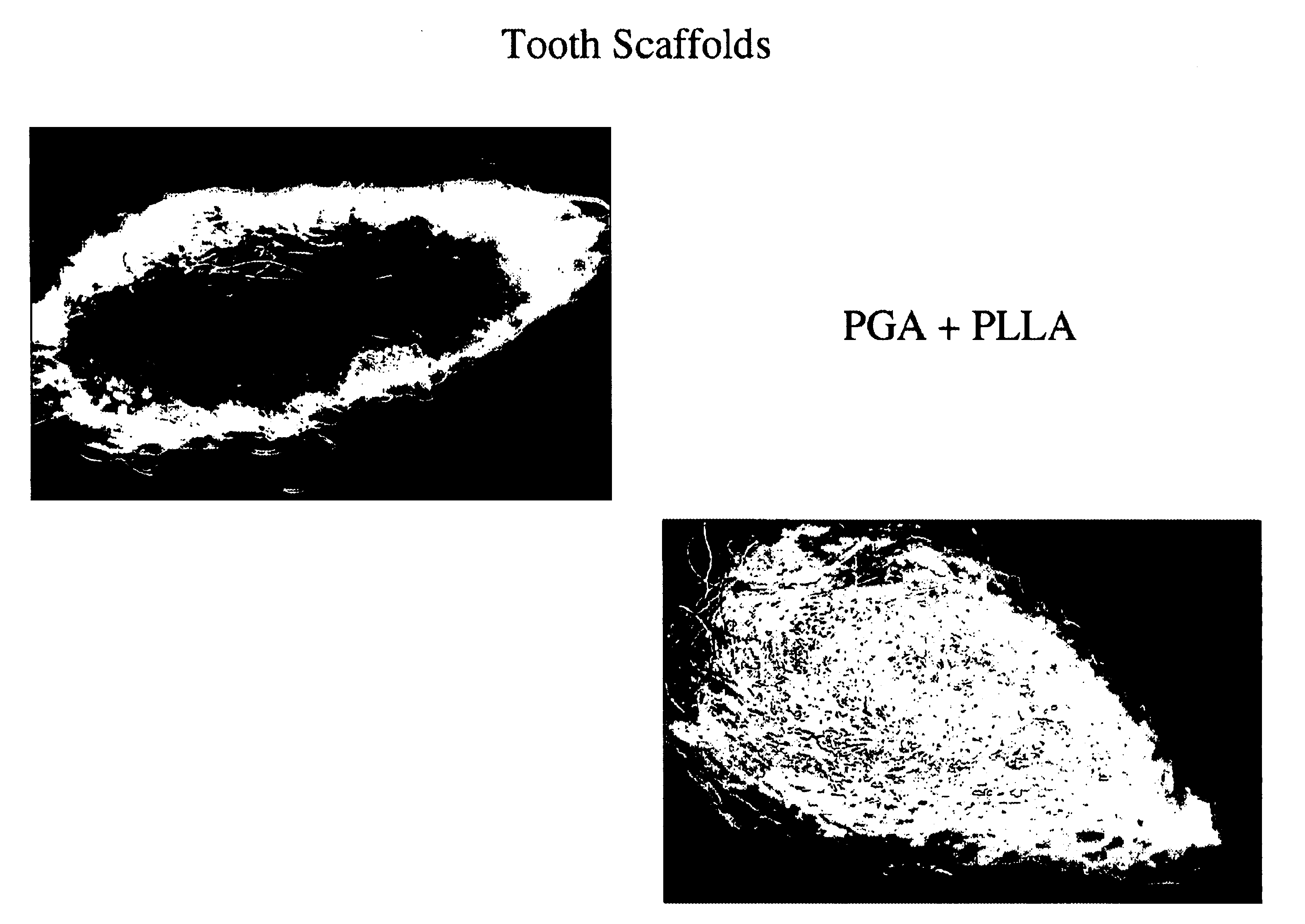
Methods for treating dental conditions using tissue scaffolds
The invention provides methods, apparatus and kits for regenerating dental tissue in vivo that are useful for treating a variety of dental conditions, exemplified by treatment of caries. The invention uses tissue scaffold wafers, preferably made of PGA, PLLA, PDLLA or PLGA dimensioned to fit into a hole of corresponding sized drilled into the tooth of subject to expose dental pulp in vivo. In certain embodiments the tissue scaffold wafer further comprises calcium phosphate and fluoride. The tissue scaffold wafer may be secured into the hole with a hydrogel, a cement or other suitable material. Either the wafer or the hydrogel or both contain a morphogenic agent, such as a member encoded by the TGF-β supergene family, that promotes regeneration and differentiation of healthy dental tissue in vivo, which in turn leads to remineralization of dentin and enamel. The tissue scaffold may further include an antibiotic or anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT INC
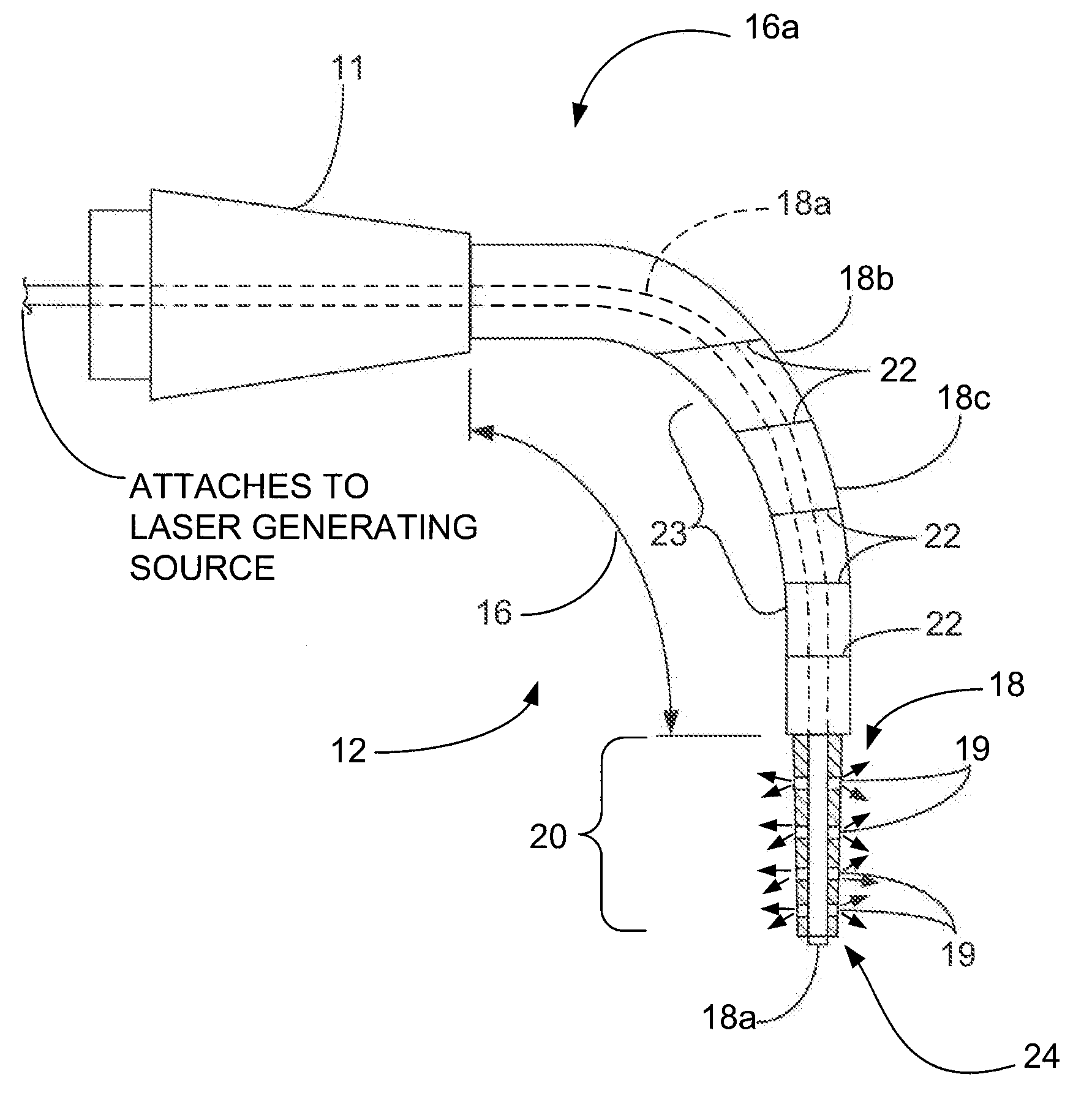
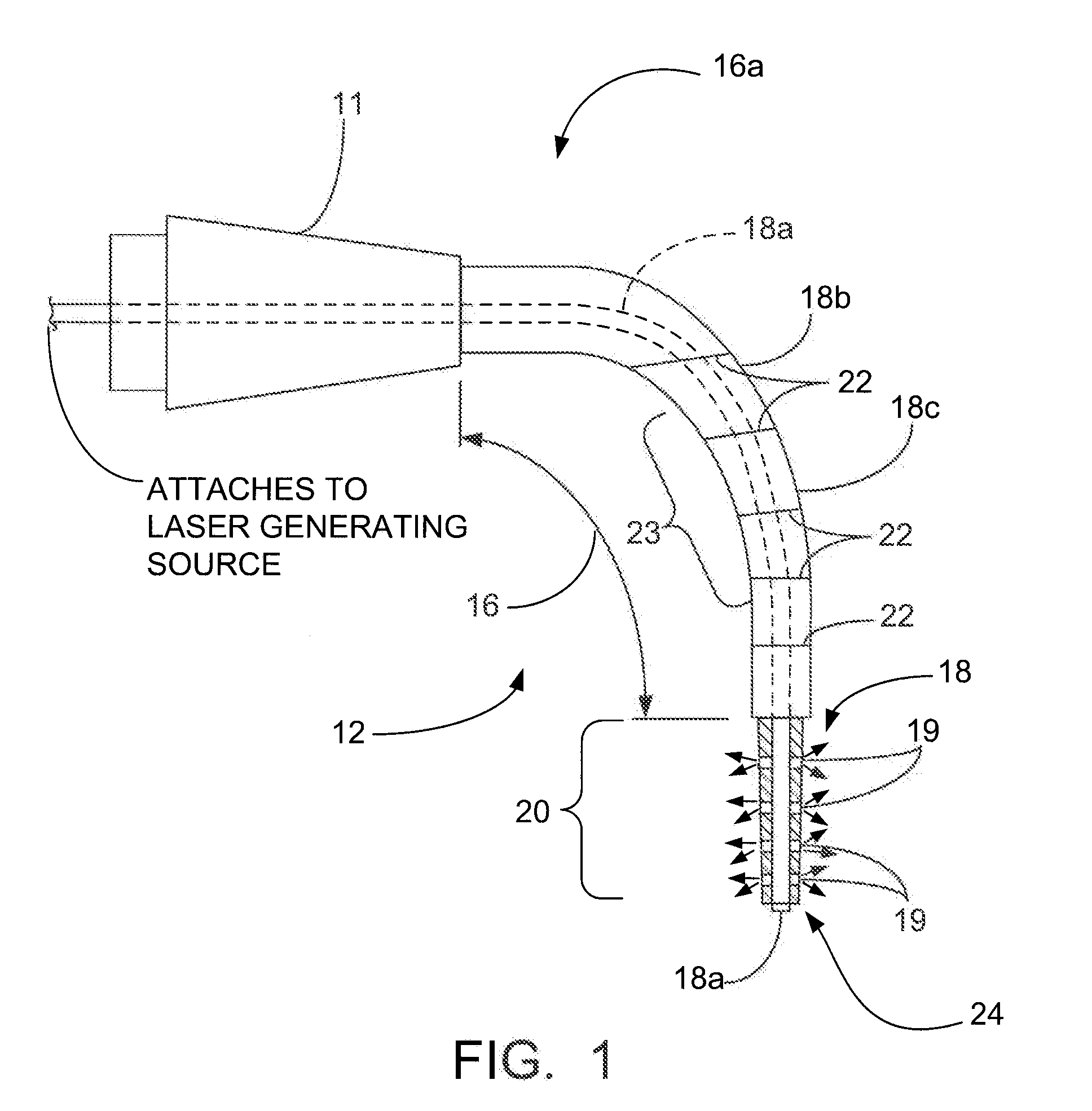
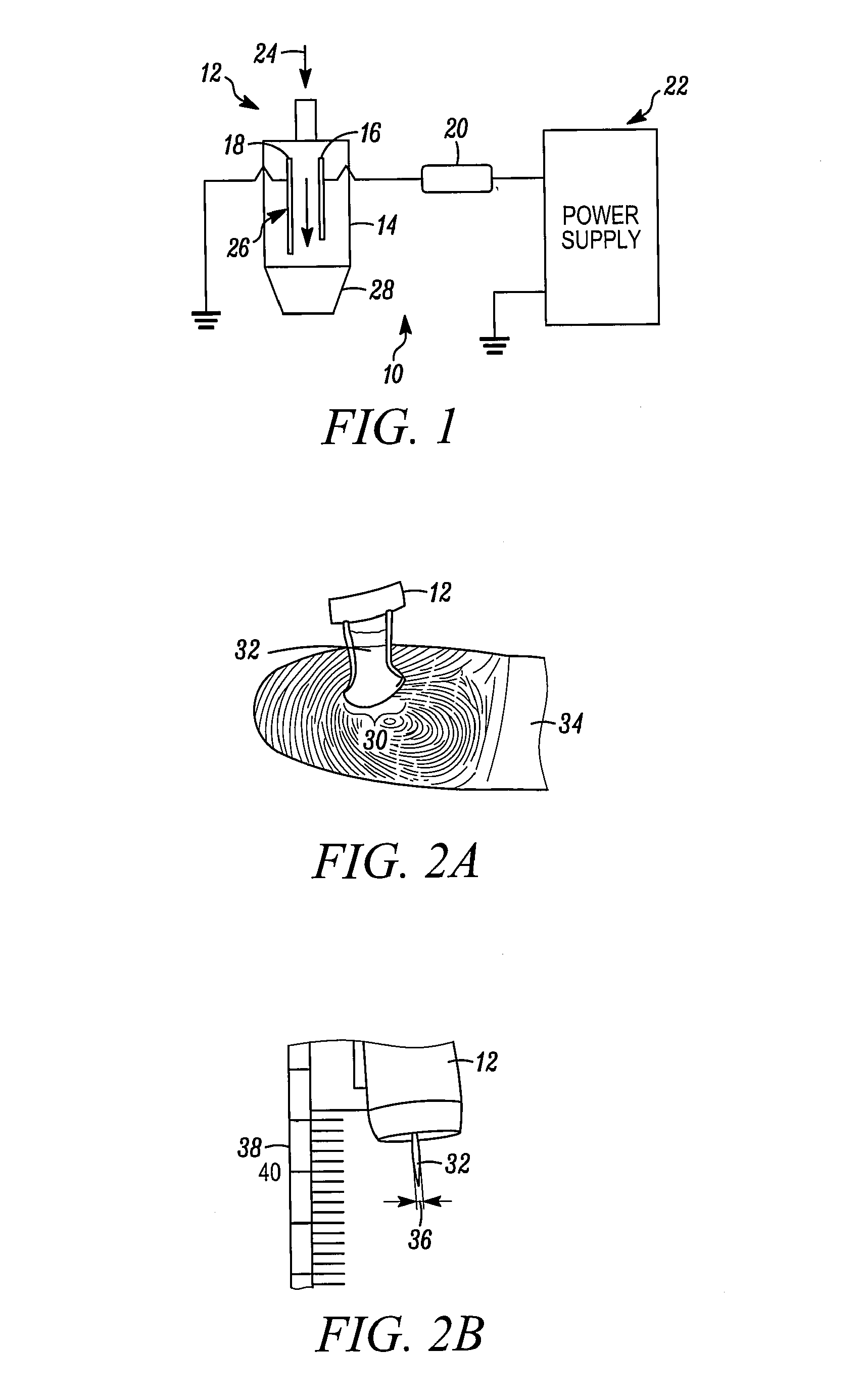
Method and Apparatus for Disinfecting or Sterilizing a Root Canal System Using Lasers Targeting Water
InactiveUS20090130622A1Sufficient deliveryEnhanced light absorptionSurgical instrument detailsDental toolsDiseaseEnergy absorption
Method and apparatus for disinfecting and / or sterilizing a root canal system by targeting the water content of disease and debris in the canals. The laser technique of employs a frequency of the wavelength emissions between about 930 to about 1065 nanometers with an optimum of 980 nm. This range of wavelengths targets the water content of tissue cells and pathogens as well as any residual organic debris in water within the root canal system after its preparation while being poorly absorbed by the surrounding dentin. The selection of the optimum wavelength produces significant effects generating and advancing treatment to the targeted aqueous environments. This is due to the rapid energy absorption by the water and the subsequent creation of gas bubbles, liberation of heat and subsequent propulsion of waves of heat and gas that impact along the canal walls and ramifications resulting in an enhanced bacterial kill and cleaning of the canal walls and ramifications. No dyes or other additives are necessary to enhance the effectiveness of the laser kill of bacteria, etc.
Owner:BOLLINGER JAMES EDWIN +2
Classified silica for improved cleaning and abrasion in dentifrices
InactiveUS20060140878A1Improve uniformityPrecision cleaningCosmetic preparationsSilicaToothpastePhysical chemistry
A method of making precipitated silica abrasive compositions having excellent cleaning performance and lower abrasiveness with post-reactor sizing of the abrasive particles being performed via air classification techniques is provided. By targeting a specific particle size range, it has been determined that higher pellicle film cleaning levels may be achieved without also increasing the dentin abrasion properties of the silica products themselves. As a result, dentifrices including such classified abrasive silica products, and exhibiting particularly desirable cleaning benefits, can be provided for improved tooth polishing, whitening, and the like, without deleteriously affecting the hard tooth surfaces. Also encompassed within this invention also are products of this selective process scheme and dentifrices containing such classified silica products.
Owner:J M HUBER CORP
High-cleaning silica materials made via product morphology control and dentifrice containing such
InactiveUS20060110307A1Excellent thickening propertyDesirable abrasivePigmenting treatmentCosmetic preparationsClean teethViscosity
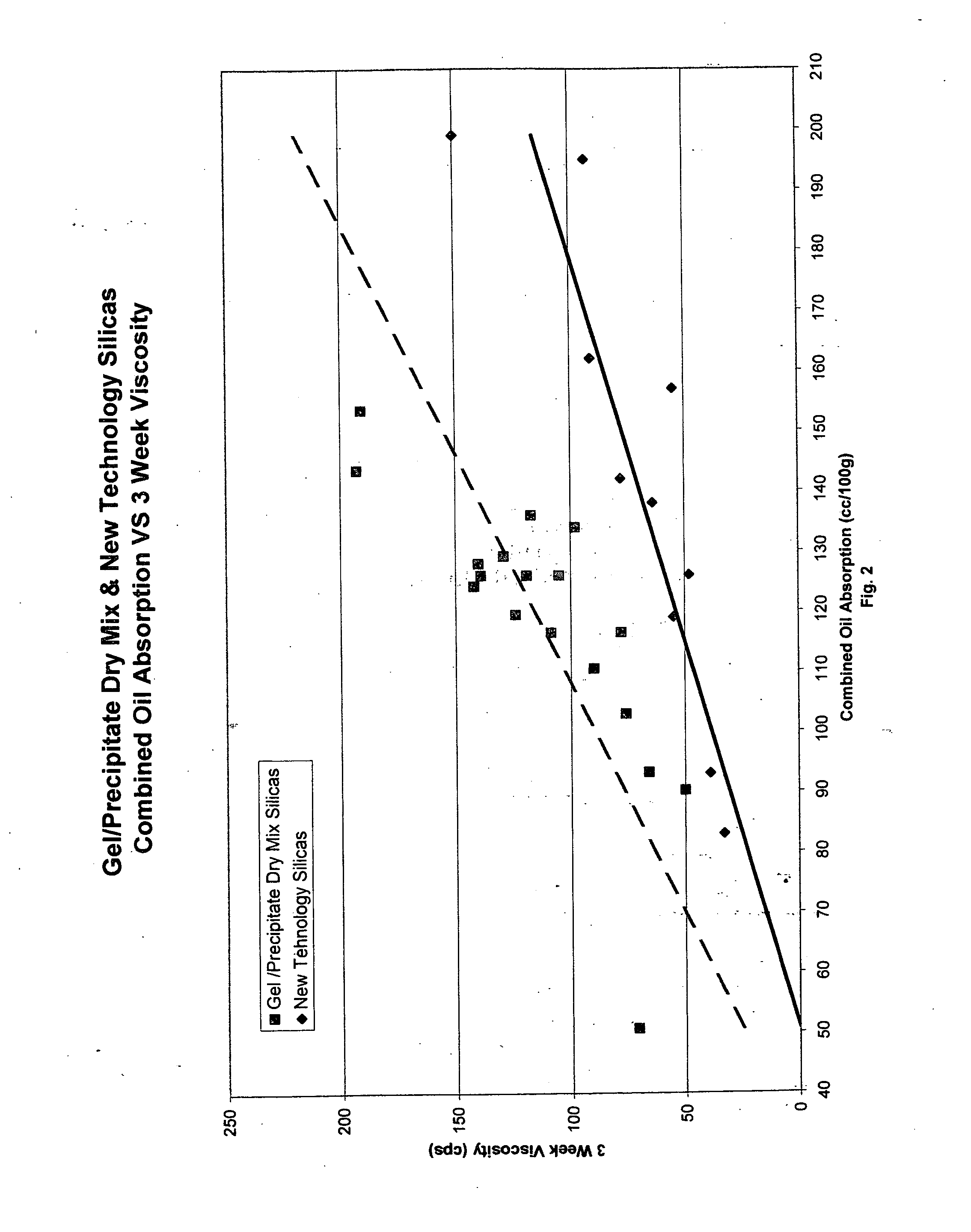
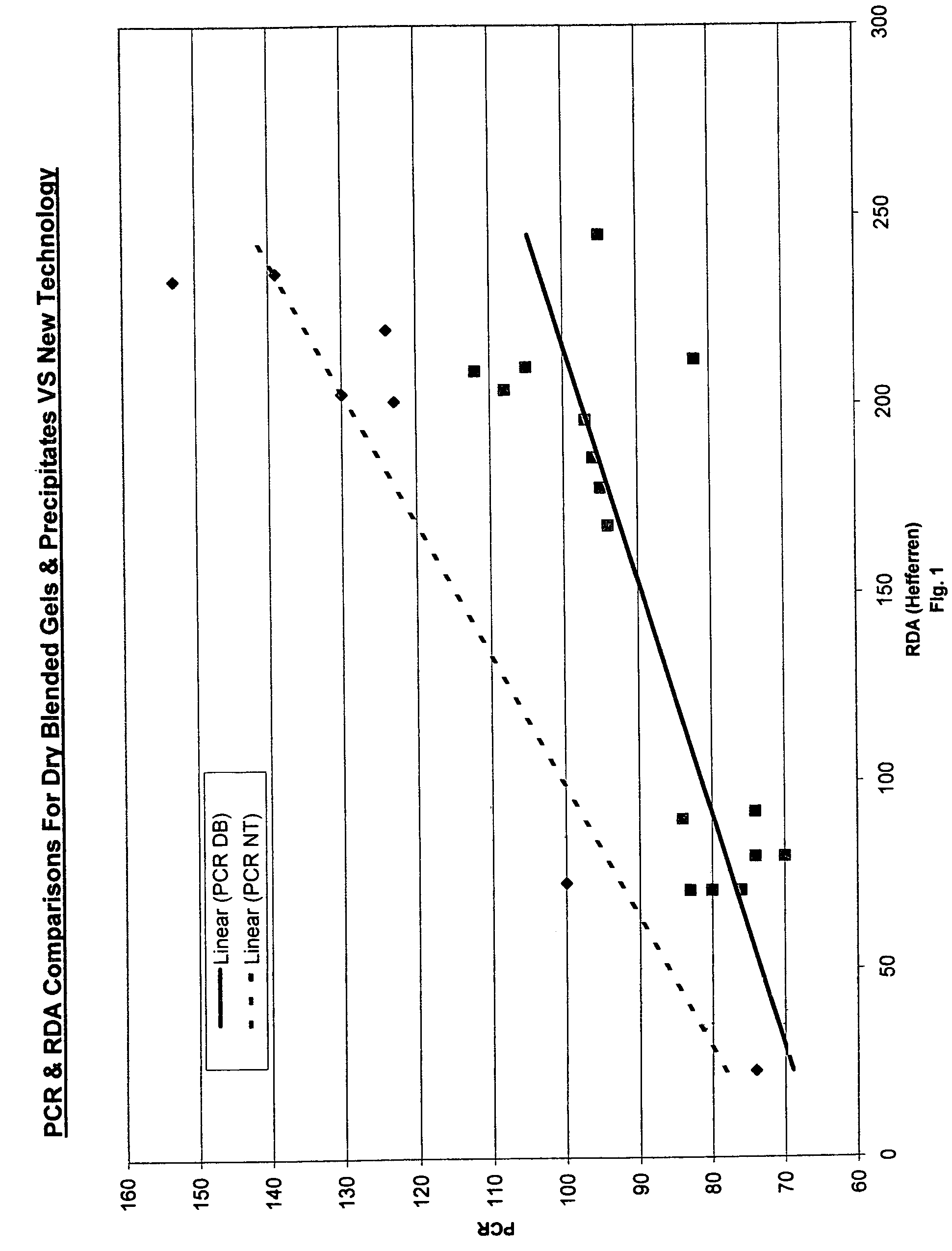
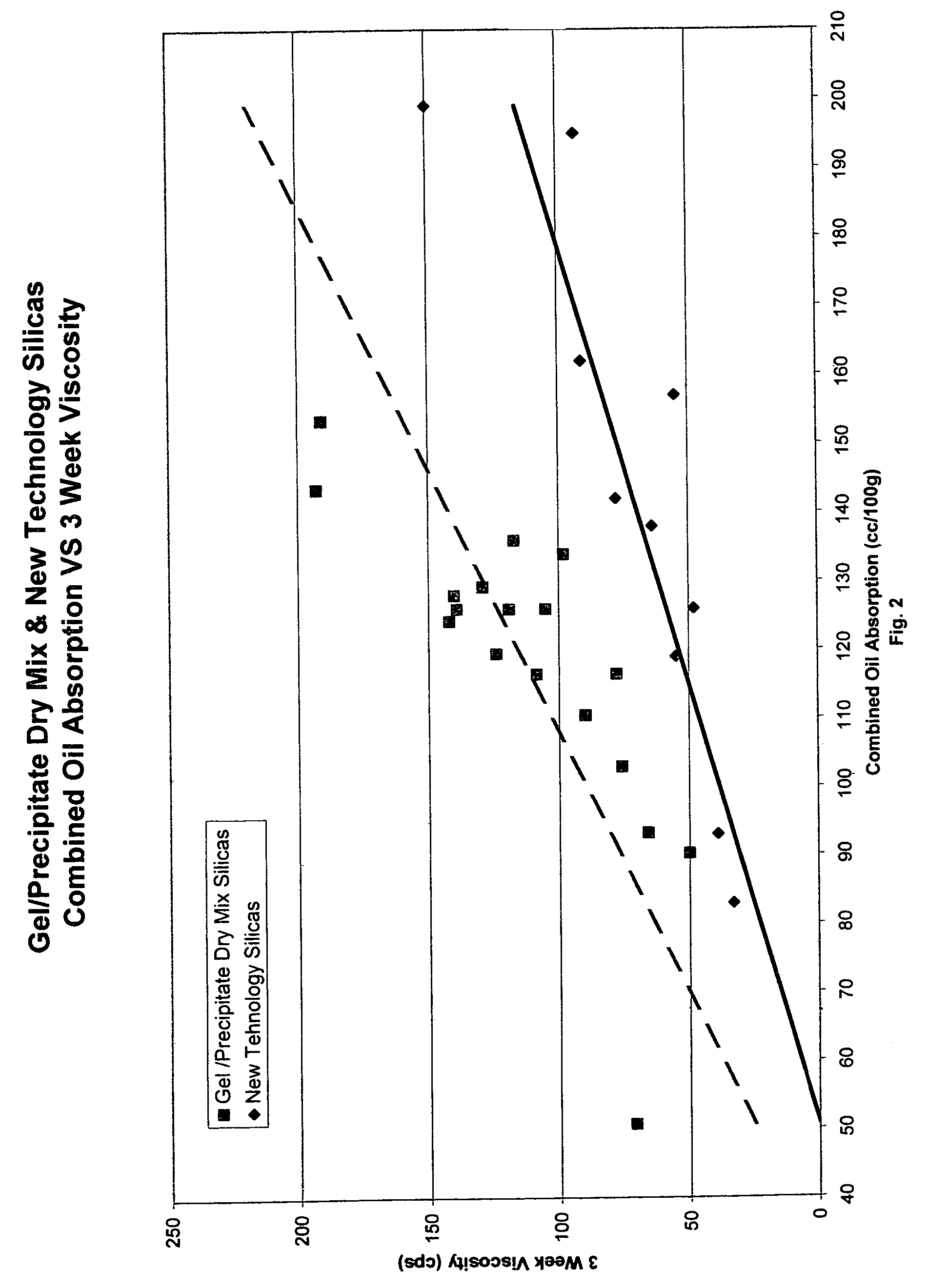
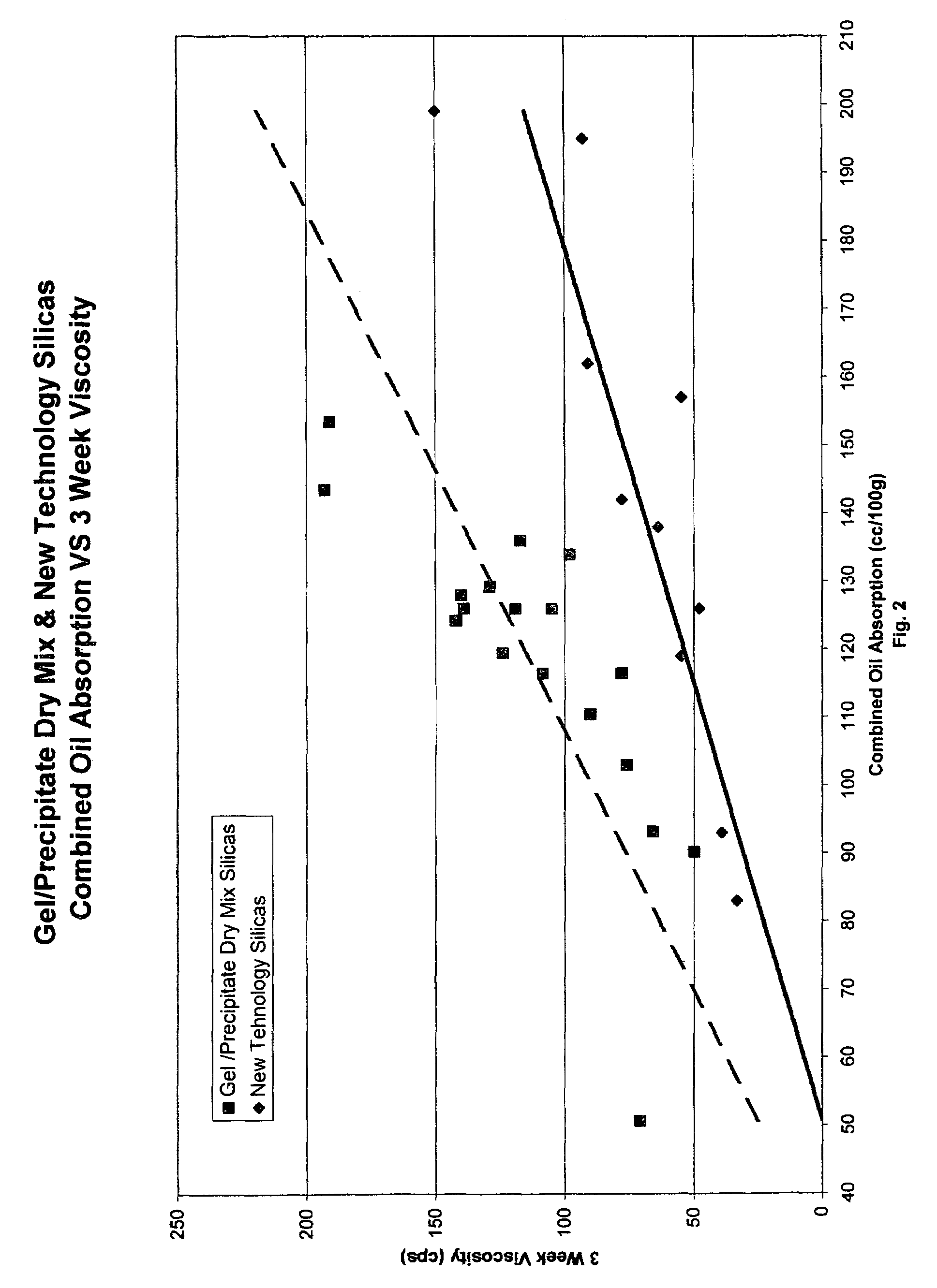
Unique abrasive and / or thickening materials that are in situ generated compositions of precipitated silicas and silica gels are provided. Such compositions exhibit different beneficial characteristics depending on the structure of the composite in situ generated material. With low structured composites (as measured via linseed oil absorption levels from 40 to 100 ml oil absorbed / 100 g composite), simultaneously high pellicle film cleaning properties and moderate dentin abrasion levels are possible in order to accord the user a dentifrice that effectively cleans tooth surfaces without detrimentally abrading such surfaces. Increased amounts of high structure composite materials tend to accord greater viscosity build and thickening benefits together with such desirable abrasion and cleaning properties, albeit to a lesser extent than for the low structure types. Thus, mid-range cleaning materials will exhibit oil absorption levels from an excess of 100 to 150, and high thickening / low abrasion composite exhibit oil absorption properties in excess of 150. Such an in situ, simultaneously produced precipitated silica / silica gel combination provides such unexpectedly effective low abrasion and high cleaning capability and different thickening characteristics as compared to physical mixtures of such components. Encompassed within this invention is a unique method for making such gel / precipitated silica composite materials for such a purpose, as well as the different materials within the structure ranges described above and dentifrices comprising such.
Owner:J M HUBER CORP
Dental and Medical Treatments and Procedures
ActiveUS20090220908A1Sufficient amountUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsLaser lightDentin
A method treating a root canal in a tooth by introducing into the pulp chamber of a tooth and pulsing a laser light into the fluid reservoir so as to disintegrate pulp within the root canal without generation of any significant heat in said liquid fluid so as to avoid elevating the temperature of any of the dentin, tooth, or other adjacent tissue more than about 5° C.
Owner:PIPSTEK LLC
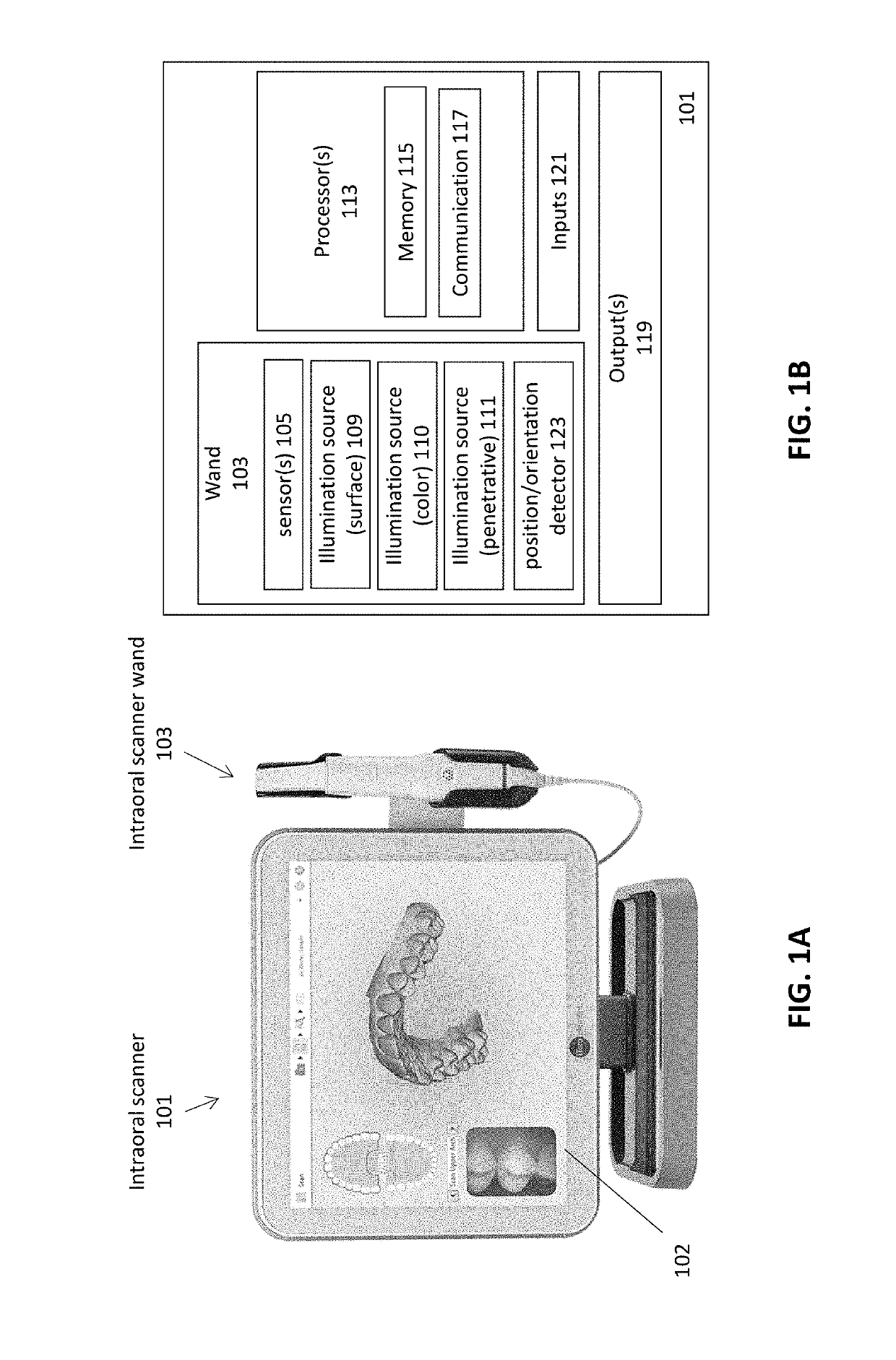
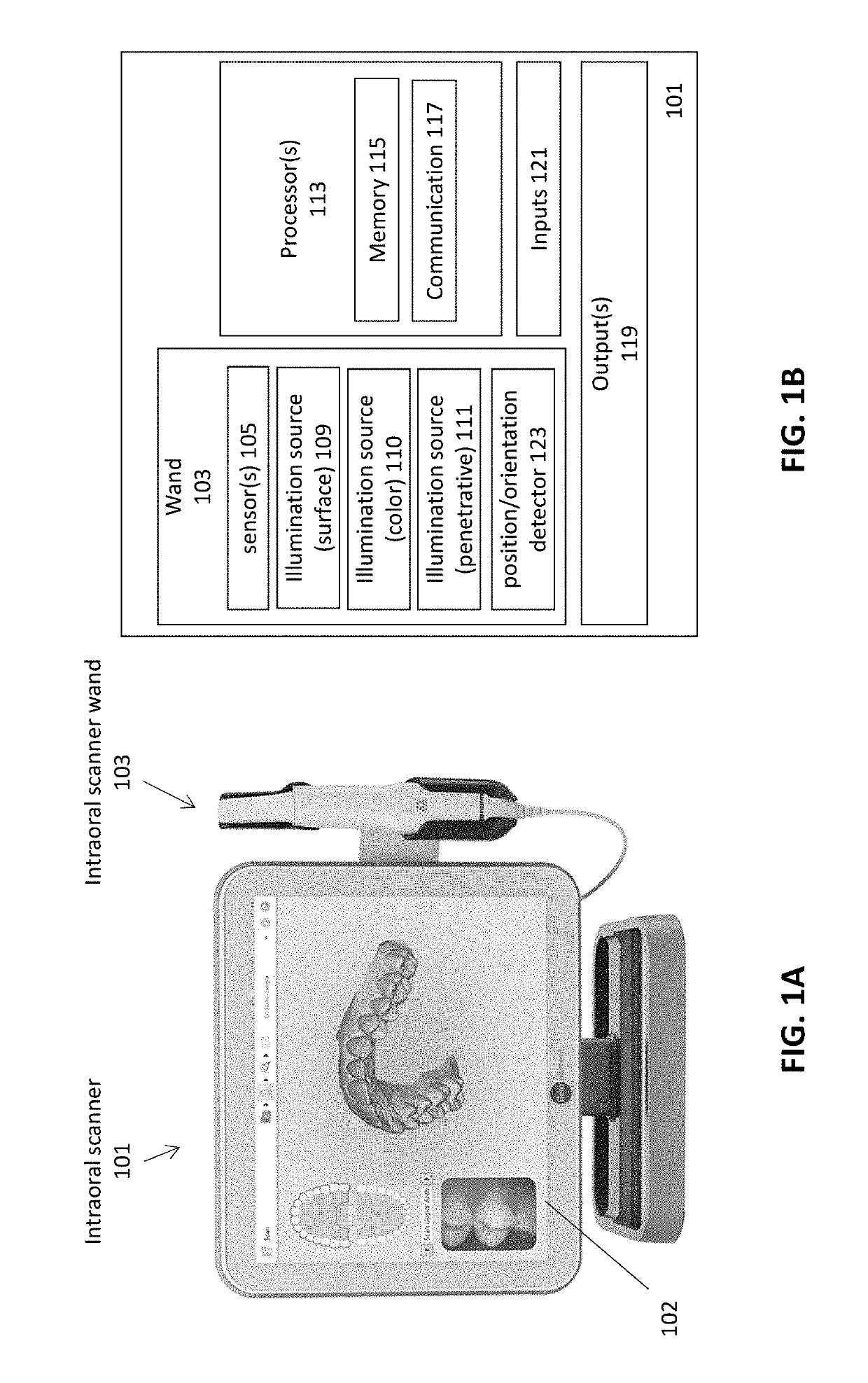
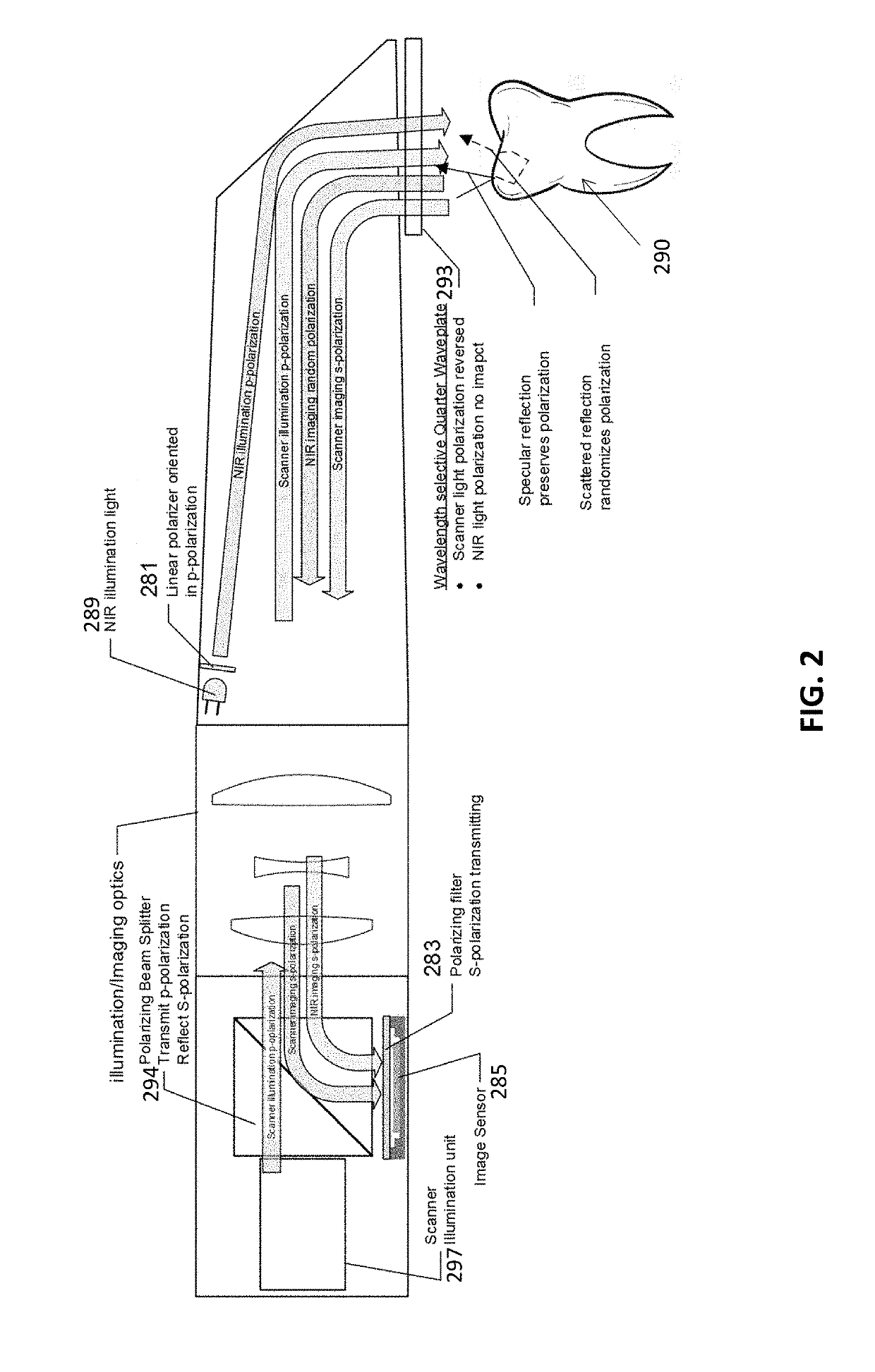
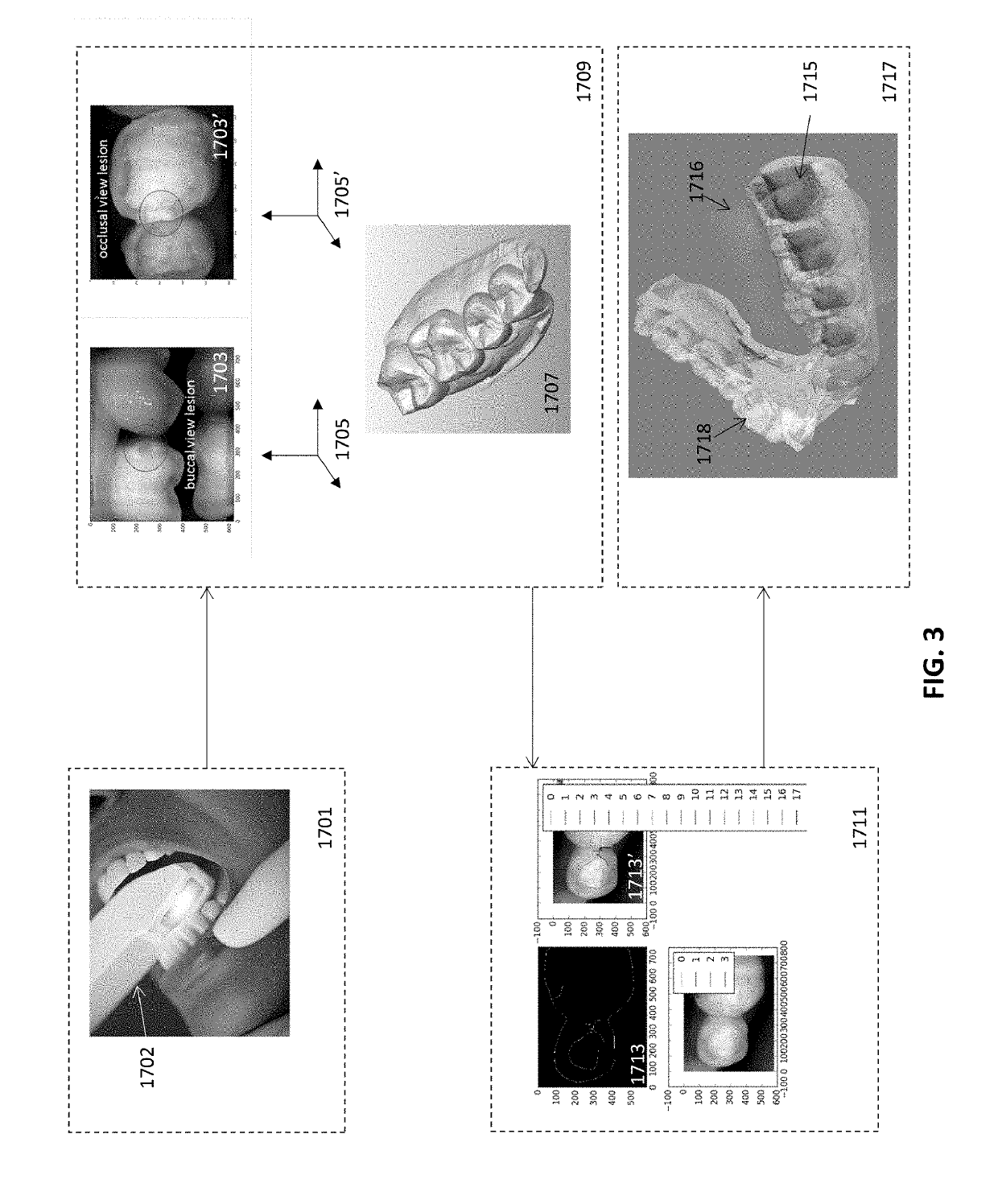
Diagnostic intraoral scanning
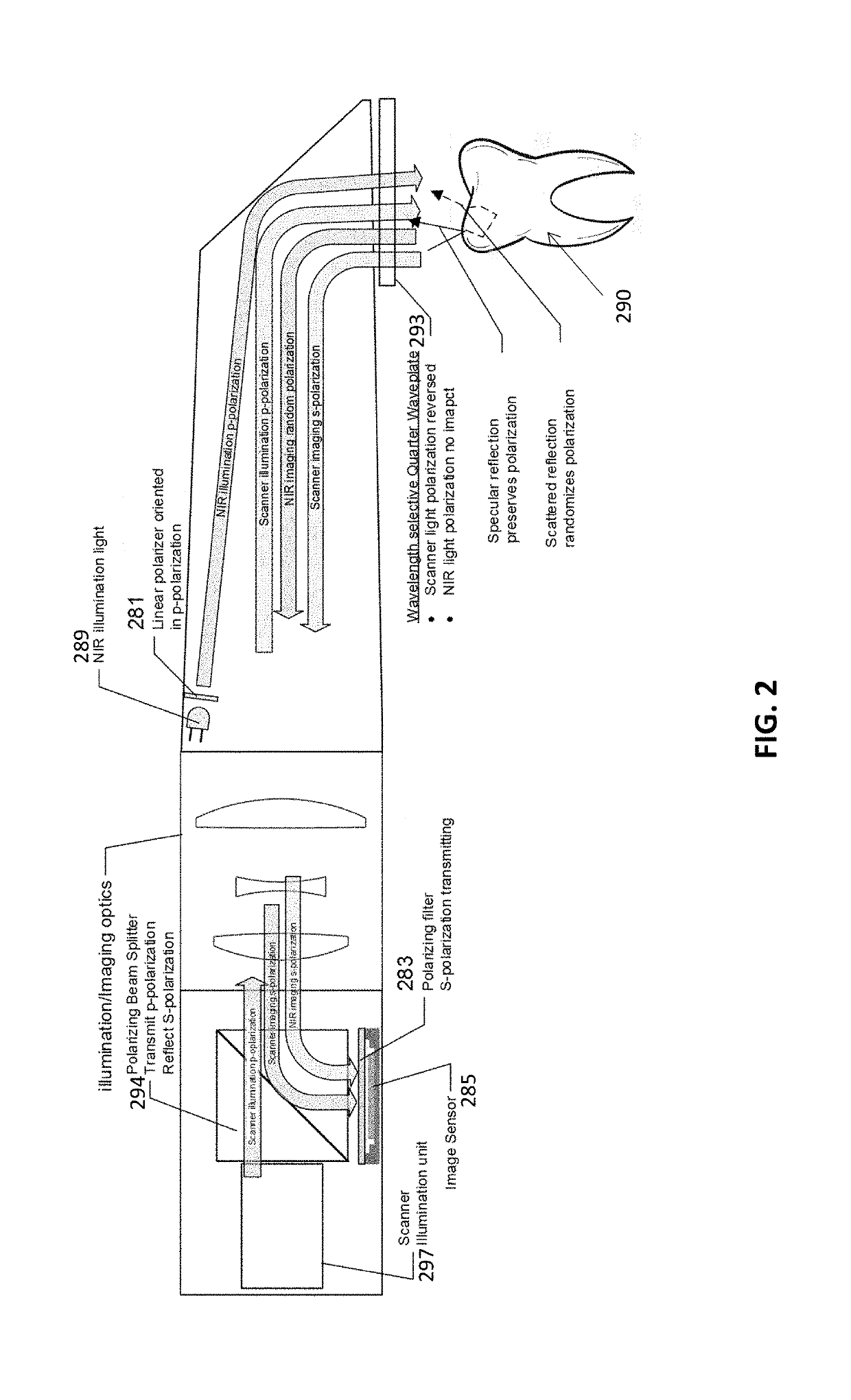
Methods and apparatuses for taking, using and displaying three-dimensional (3D) volumetric models of a patient's dental arch. A 3D volumetric model may include surface (e.g., color) information as well as information on internal structure, such as near-infrared (near-IR) transparency values for internal structures including enamel and dentin.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Adhesive antimicrobial and/or reparative dentin stimulating dental compositions and methods for forming and using such compositions
InactiveUS6071528AEffective and reliable sealEffective and reliable sealingPowder deliveryBiocideAntibiotic YBond strength
Adhesive antimicrobial dental compositions and methods for forming and using compositions are disclosed. The compositions are primarily useful as pulp caps and dentin liners. The composition includes an alkyl methacrylate having an oxyphosphorus group, a polymerization initiator and an antimicrobial agent. The antimicrobial agent can be organohalogens, antibiotics, alkali metal hydroxides, alkaline earth metal oxides and alkaline earth metal hydroxides. The compositions have high dentin tensile bond strength, are stable as a single component or package system, can be polymerized in situ, prevent ingress by microorganisms into an area of a tooth treated with the compositions and can be syringe delivered.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Dental and medical treatments and procedures
A method treating a root canal in a tooth by introducing into the pulp chamber of a tooth and pulsing a laser light into the fluid reservoir so as to disintegrate pulp within the root canal without generation of any significant heat in said liquid fluid so as to avoid elevating the temperature of any of the dentin, tooth, or other adjacent tissue more than about 5° C.
Owner:PIPSTEK LLC
Stable self-etching primer and adhesive bonding resin compositions, systems, and methods
InactiveUS6994551B2High bonding strengthExtended shelf lifeImpression capsTeeth fillingDental AdhesivesTooth enamel
Stable self-etching copolymerizable primer compositions are provided including compounds having a polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated groups and acidic groups, and optionally comonomers and suitable solvents. Such compositions are used in conjunction with dental adhesives to provide one or multi-component dental systems capable of etching or decalcifying tooth dentin and enamel without the need for a separate rinse step. Methods of use of such compositions according to the present invention include application for priming and imparting enhanced adhesion between the primers, adhesives, and the tooth substrates such as dentin or cut or uncut enamel, and subsequently applied dental composites, restoratives or other dental components.
Owner:BISCO
Self-etch amphiphilic dental adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103622837AHigh bonding strengthDentin bonding effect is goodImpression capsDentistry preparationsAcid etchingAdhesive
The invention discloses a self-etch amphiphilic dental adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The adhesive is a one-component adhesive and comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of polymerizable monomer, 0.2 to 0.8 part of photoinitiator, 0.1 to 0.5 parts of an accelerating agent, 0.001 to 0.5 parts of a polymerization inhibitor and 1 to 20 parts of filler; the polymerizable monomer comprises the following components in weight percent: 40% to 60% of resinous monomer, 1% to 10% of amphiphilic monomer, 2% to 10% of acidic monomer and 35% to 50% of dilute monomer. The self-etch amphiphilic dental adhesive provided by the invention can be used for acid etching of dentin, has the characteristic of amphipathicity, and is relatively high in bonding strenth; not only does the development of the adhesive update the conventional clinical adhesive, but also the adhesive has a relatively good dentin bonding effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Compositions, methods and kits for hemostasis and sealing of pulp during invasive dental procedures
InactiveUS6309221B1Strong adhesionAvoid infectionImpression capsTeeth fillingPropylhexedrine hydrochlorideSealant
Compositions, methods and kits for providing hemostasis and sealing of exposed tooth pulp and / or pink dentin. The inventive methods and kits employ propylhexedrine as a hemostatic agent, such as in the form of an aqueous composition of propylhexedrine hydrochloride, and an adhesive sealant composition. The propylhexedrine solution is advantageously applied to the exposed pulp and pink dentin by means of a cotton pellet or other absorbent applicator. The adhesive sealant composition is advantageously applied to exposed pulp and pink dentin, which has been previously treated with the propylhexedrine solution, by means of a syringe. The adhesive sealant composition may include an alkyl methacrylate having an oxyphosphorus group, a polymerization initiator and an antimicrobial agent, such as calcium hydroxide. The adhesive sealant composition can be polymerized in situ and is used to prevent ingress by microorgaism into an area of the tooth being treated.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
High-cleaning/low abrasive silica and materials and dentifrice containing such materials
InactiveUS7267814B2Excellent abrasionImprove rendering capabilitiesCosmetic preparationsPigmenting treatmentCleaned teethLinseed oil
Unique abrasive and / or thickening materials that are in situ generated compositions of precipitated silicas and silica gels are provided. Such compositions exhibit different beneficial characteristics depending on the structure of the composite in situ generated material. With low structured composites (as measured via linseed oil absorption levels from 40 to 100 ml oil absorbed / 100 g composite), simultaneously high pellicle film cleaning properties and moderate dentin abrasion levels are possible in order to accord the user a dentifrice that effectively cleans tooth surfaces without detrimentally abrading such surfaces. Increased amounts of high structure composite materials tend to accord greater viscosity build and thickening benefits together with such desirable abrasion and cleaning properties, albeit to a lesser extent than for the low structure types. Thus, mid-range cleaning materials will exhibit oil absorption levels from an excess of 100 to 150, and high thickening / low abrasion composite exhibit oil absorption properties in excess of 150. Such an in situ, simultaneously produced precipitated silica / silica gel combination provides such unexpectedly effective low abrasion and high cleaning capability and different thickening characteristics as compared to physical mixtures of such components. Encompassed within this invention is a unique method for making such gel / precipitated silica composite materials for such a purpose, as well as the different materials within the structure ranges described above and dentifrices comprising such.
Owner:J M HUBER CORP
Endodontic instrument having notched cutting surfaces
InactiveUS20050266375A1Trend downGood curative effectTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFile designRasp
A fluteless endodontic file is provided, formed from a tapered shaft of material having a prismatic shape generally defined by three or more side surfaces and three or more interposed corners. A plurality of notches are cut into one or more corners defining cutting surfaces, points and / or edges. The notched cutting surfaces are formed such that the file, when rotated and / or reciprocated within a root canal, effectively cuts / debrides hard tissue (known in the art as dentin) as well as soft tissue, thus, forming an optimal canal shape. The cutting surfaces are also preferably formed at an angle to the centerline of the instrument to provide optimal cutting efficiency and material removal. The fluteless file design exhibits increased efficacy, with less tendency to bind and break within the root canal and also significantly reduces manufacturing and capital equipment costs.
Owner:BROCK G MATTHEW +1
High-cleaning/moderate abrasive silica materials and dentifrice containing such materials
InactiveUS7306788B2Excellent abrasionImprove rendering capabilitiesCosmetic preparationsSilicaLinseed oilSilica gel
Unique abrasive and / or thickening materials that are in situ generated compositions of precipitated silicas and silica gels are provided. Such compositions exhibit different beneficial characteristics depending on the structure of the composite in situ generated material. With low structured composites (as measured via linseed oil absorption levels from 40 to 100 ml oil absorbed / 100 g composite), simultaneously high pellicle film cleaning properties and moderate dentin abrasion levels are possible in order to accord the user a dentifrice that effectively cleans tooth surfaces without detrimentally abrading such surfaces. Increased amounts of high structure composite materials tend to accord greater viscosity build and thickening benefits together with such desirable abrasion and cleaning properties, albeit to a lesser extent than for the low structure types. Thus, mid-range cleaning materials will exhibit oil absorption levels from an excess of 100 to 150, and high thickening / low abrasion composite exhibit oil absorption properties in excess of 150. Such an in situ, simultaneously produced precipitated silica / silica gel combination provides such unexpectedly effective low abrasion and high cleaning capability and different thickening characteristics as compared to physical mixtures of such components. Encompassed within this invention is a unique method for making such gel / precipitated silica composite materials for such a purpose, as well as the different materials within the structure ranges described above and dentifrices comprising such.
Owner:J M HUBER CORP
Method of inducing biomineralization method of inducing bone regeneration and methods related thereof
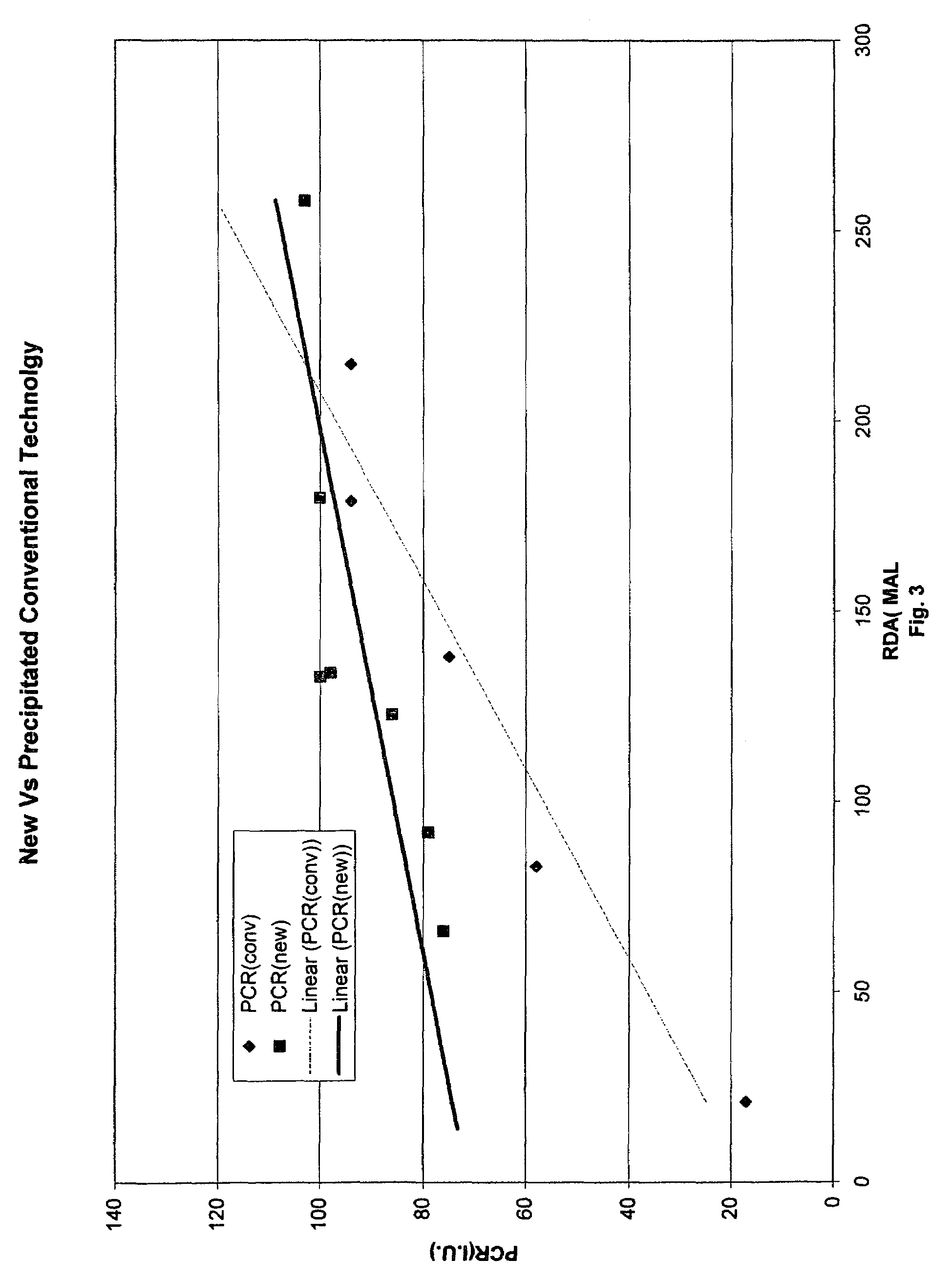
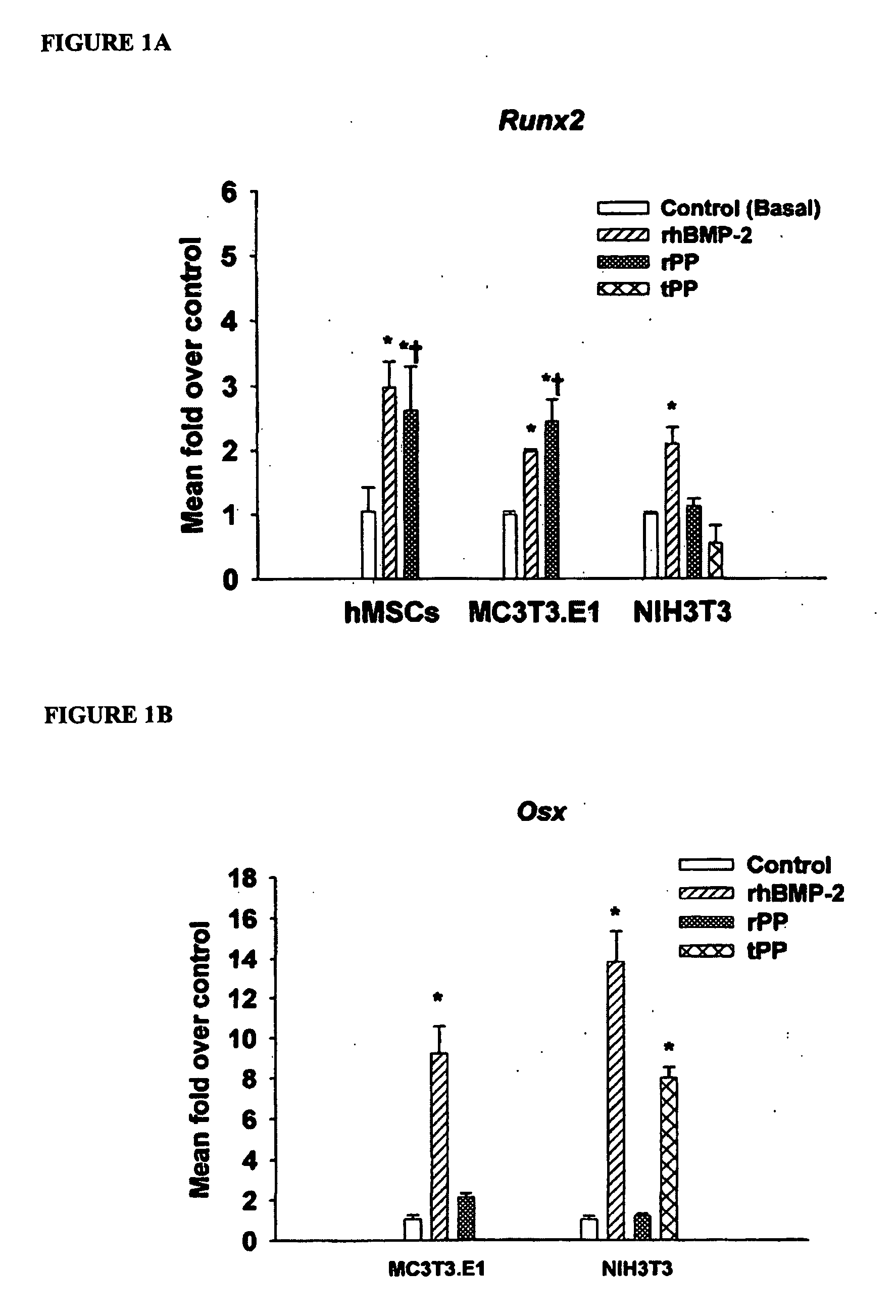
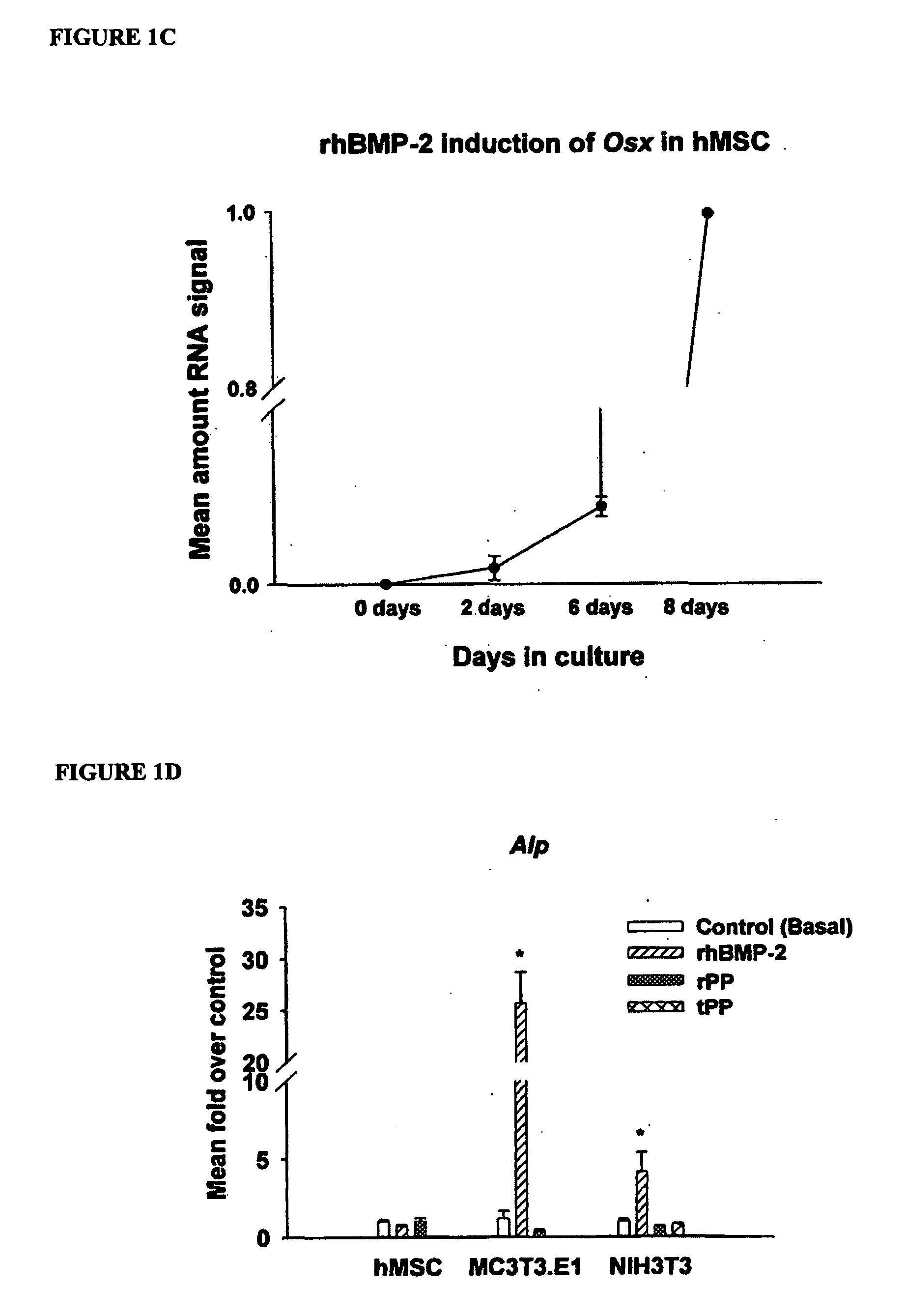
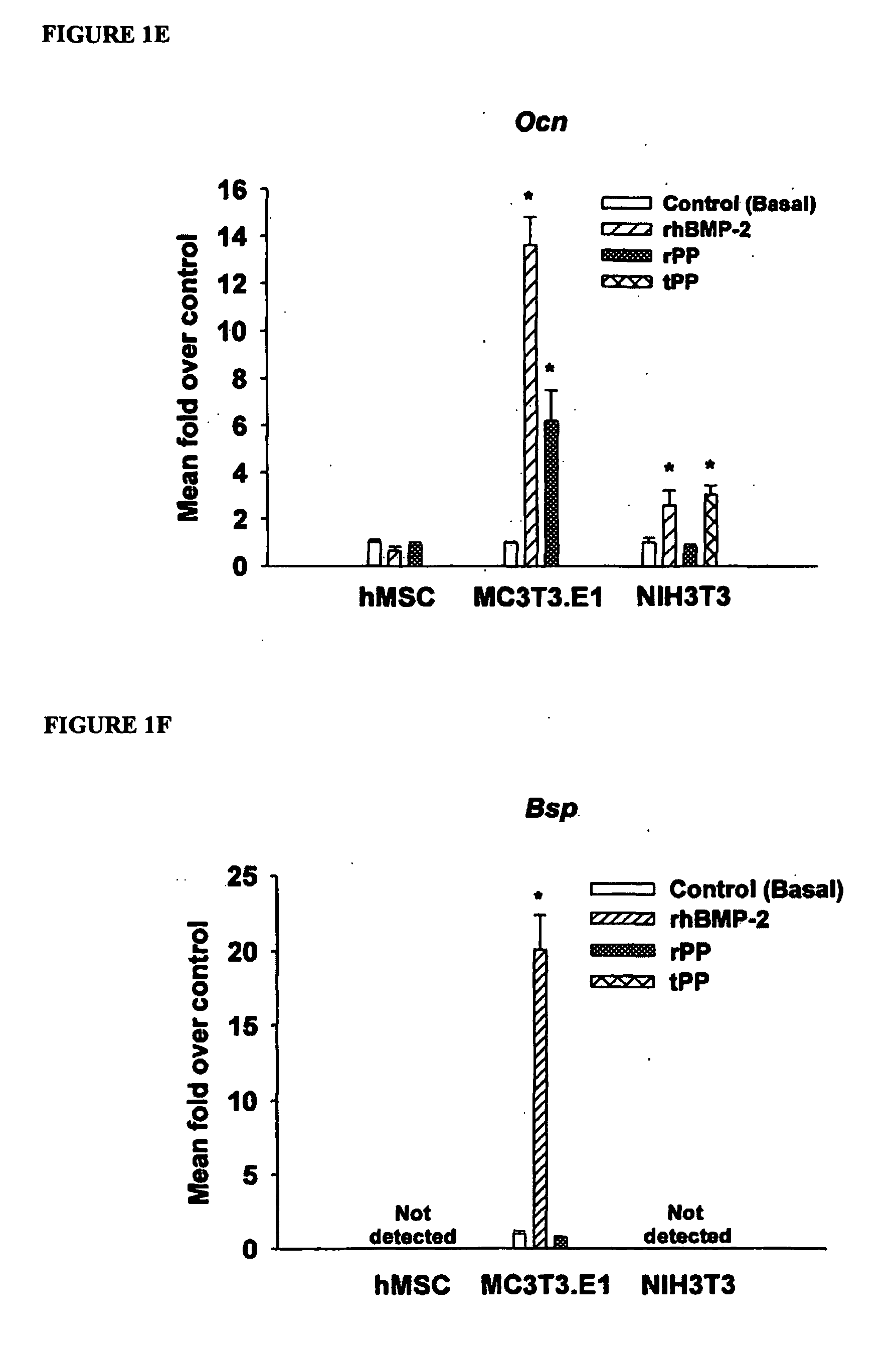
A method of inducing biomineralization in a tissue, which method comprises administering to the tissue a source of Phosphophoryn (PP) in an amount sufficient to induce biomineralization; a method of treating tooth sensitivity or injured pulp tissue; a method of inducing differentiation of a cell into an osteogenic cell or odontogenic cell; a method of inducing bone or dentin regeneration; a method of inducing periodontal regeneration; a method of inducing differentiation of a cell into a cementoblast, osteoblast, or periodontal ligament cell; and a composition comprising a source of PP and a carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Remineralizing material for organomineral tissues
InactiveUS6413498B1Facilitated releaseIncreased microhardnessCosmetic preparationsImpression capsDental flossingToothpaste Product
Together with other accessory products, includes a mixture of ion-exchange resins, cationic and anionic, charged with Ca2+, F- and PO43- ions, in an approximate molar ratio of 2:1:1, respectively. Particularly preferred is a material in which the resins also have a charge of Zn2+ ions representing a proportion of less than 1%, preferably close to 0.2% of the dry weight of the resin. The preferred resins are those whose base is cross-linked polystyrene with 2-14% divinylbenzene. The material is useful as first filler in the treatment of caries, especially deep caries, leading to remineralization of the dentin with a composition very close to the original composition, together with high microhardness. It is also useful as a component of dentifrice products such as pastes, elixirs and dental floss.
Owner:SOC PARA EL DESARROLLO CIENTIFICO APLICADO
Diagnostic intraoral methods and apparatuses
Methods and apparatuses for taking, using and displaying three-dimensional (3D) volumetric models of a patient's dental arch. A 3D volumetric model may include surface (e.g., color) information as well as information on internal structure, such as near-infrared (near-IR) transparency values for internal structures including enamel and dentin.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
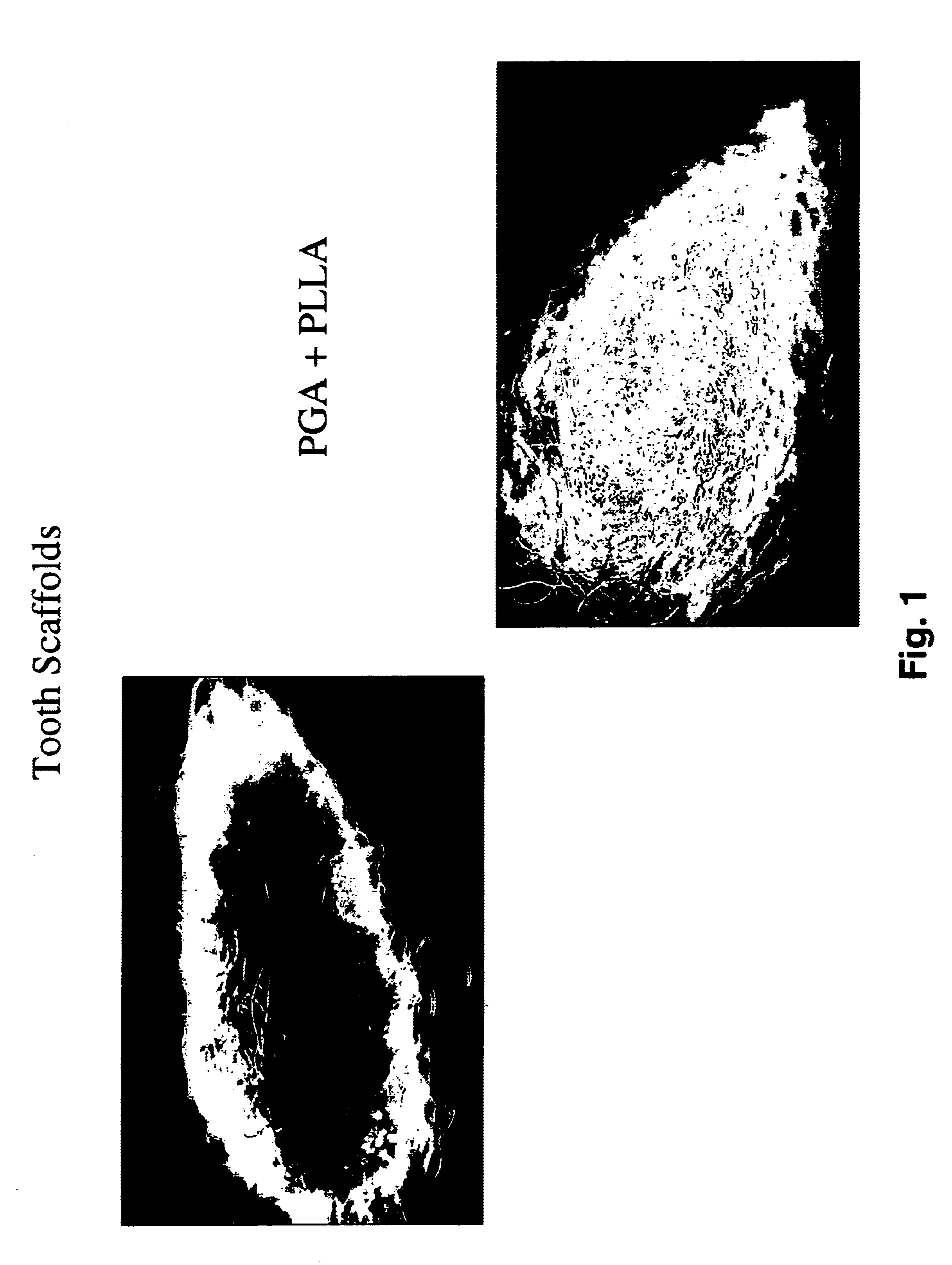
Methods for treating dental conditions using tissue scaffolds
The invention provides methods, apparatus and kits for regenerating dental tissue in vivo that are useful for treating a variety of dental conditions, exemplified by treatment of caries. The invention uses tissue scaffold wafers, preferably made of PGA, PLLA, PDLLA or PLGA dimensioned to fit into a hole of corresponding sized drilled into the tooth of subject to expose dental pulp in vivo. In certain embodiments the tissue scaffold wafer further comprises calcium phosphate and fluoride. The tissue scaffold wafer may be secured into the hole with a hydrogel, a cement or other suitable material. Either the wafer or the hydrogel or both contain a morphogenic agent, such as a member encoded by the TGF-β supergene family, that promotes regeneration and differentiation of healthy dental tissue in vivo, which in turn leads to remineralization of dentin and enamel. The tissue scaffold may further include an antibiotic or anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT INC
Dual component dentinal desensitizing dentifrice
A two component dental composition is disclosed which eliminates or substantially reduces the discomfort and pain associated with dentinal hypersensitivity which composition comprises a first dentifrice component having an alkaline pH, a second dentifrice component having an acid pH and at least one of the components containing a potassium ion releasable compound, the first and second components being maintained separate from each other until dispensed and combined for application to teeth requiring relief from dentine hypersensitivity, whereby heightened desensitization is experienced by the user.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Borate bioactive glass and methods of use for dentin and enamel restoration
A borate bioactive glass is described, and may be used in the form of particles in an acidic mixture to form a borate bioactive glass paste. The borate bioactive glass paste may be used for the restoration of dentin and enamel on a tooth surface by the precipitation of calcium phosphate. The borate bioactive glass may also be used as a bone grafting material.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Atmospheric Non-Thermal Gas Plasma Method for Dental Surface Treatment
The provision of dental restorations can be improved by generating a cold atmospheric plasma inside the mouth of the patient and then applying that cold atmospheric plasma onto a dental restoration site. The dental restoration site can be composed of either or both of dentin and enamel. Further, the provision of dental restorations can also be improved by introducing a dental adhesive onto a dental restoration site and treating it with a cold atmospheric plasma.
Owner:NANOVA +1
Integrated porcelain system for a dental prosthesis
An integrated dental porcelain system for making dental prostheses and restorations is provided. The system includes three universal major components: a) opaque porcelain composition; b) pressable dentin ingot; and c) veneering porcelain composition that can be used interchangeably for making restorations. Techniques for making the prostheses and restorations include porcelain fused-to-metal (PFM), press-to-metal (PTM), and either pressed and / or machined all-ceramic methods. The system uses both a hand-layering of veneering porcelain (PFM technique) and a hot-pressing process (PTM and all-ceramic technique) to fabricate the prostheses and restorations.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Method for extracting panoramic image from three-dimensional conical beam CT data of dentistry department
ActiveCN105608747AIdentify anatomyStructural solutionDetails involving 3D image dataGeometric image transformationAnatomical structuresThree dimensional ct
The invention relates to a method for extracting panoramic image from three-dimensional conical beam CT data of a dentistry department, and the method comprises the following steps: (1), generating a dental arch curve according to the three-dimensional conical beam CT data of the dentistry department; (2), extracting a three-dimensional oral cavity panoramic curved surface according to the generated dental arch curve; (3), expanding the three-dimensional oral cavity panoramic curved surface and obtaining an oral cavity panoramic image. The method can extract a tooth curved surface faultage image through the three-dimensional CT data, solves problems of structure overlapping and image fuzzy, and improves the diagnosis precision. The method can obtain a single-frame oral cavity panoramic image, and the single-frame oral cavity panoramic image can display all teeth. The method can clearly recognize the anatomical structure of teeth, such as enamel, dentin and dental pulp, effectively avoids image fuzzy caused by perspective, and has no structure overlapping.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
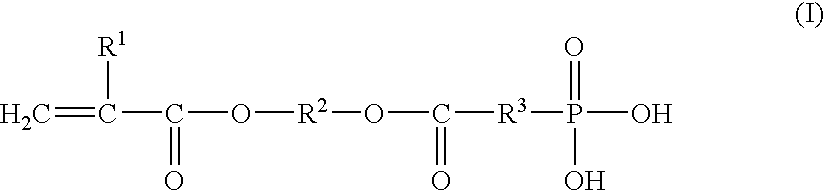
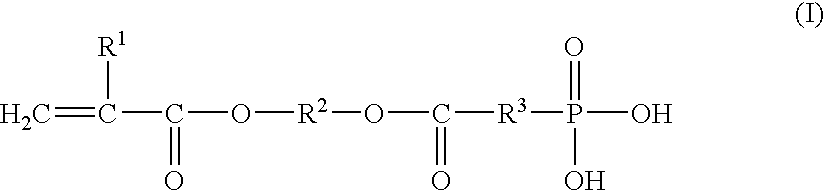
Dental materials
A dental composition is provided comprising (a) a part A comprising fluoroaluminosilicate glass that has been surface treated with agents selected from the group consisting of silane, silanol and combinations thereof, and at least one fatty acid; and (b) a part B comprising at least one polyacid. The composition further comprises resin that can be curable or non-curable and at least one initiator. The composition exhibits adhesion to dentin, and the treated FAS glass contained therein does not settle out with time.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Abrasive System for Oral Care Compositions
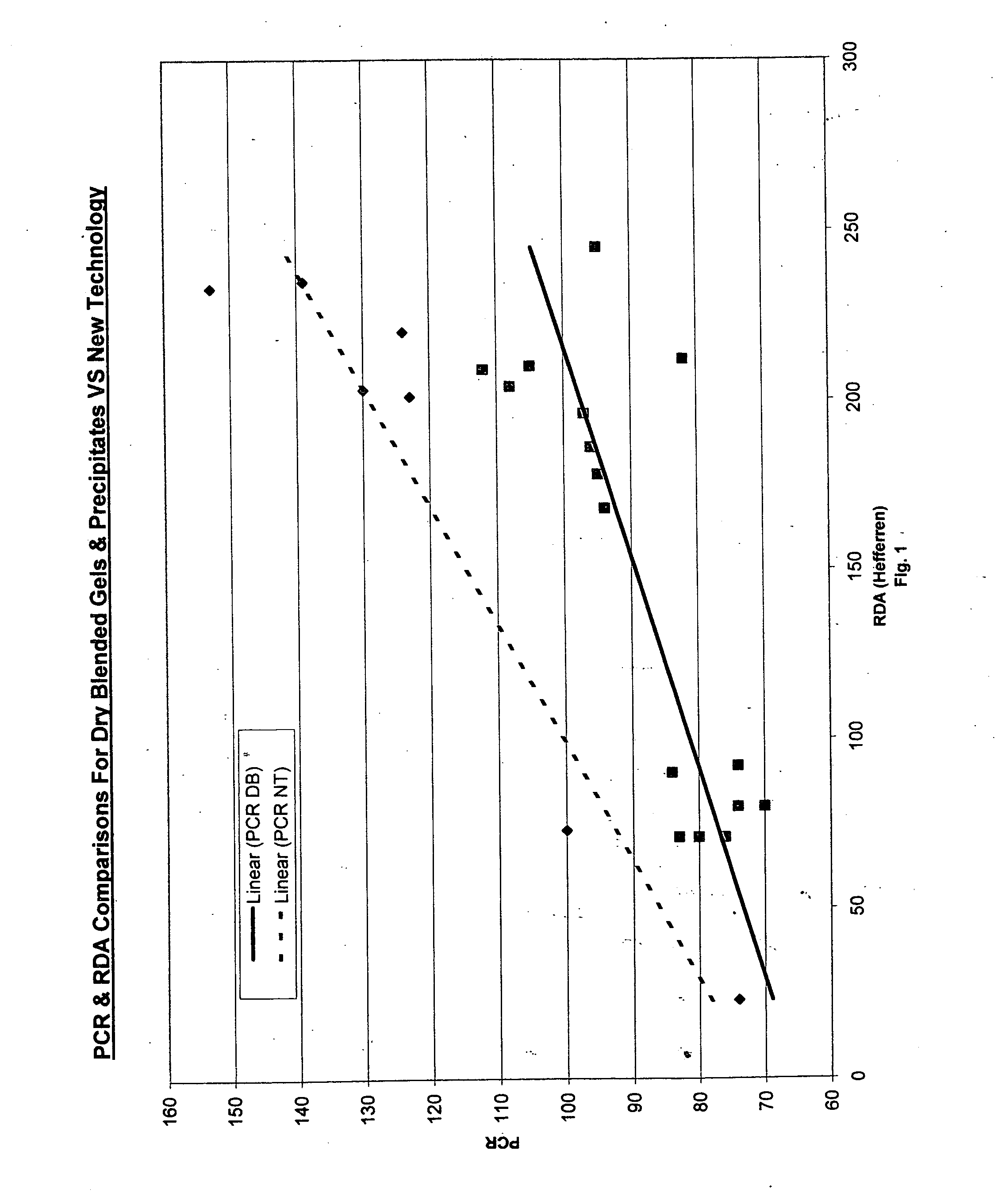
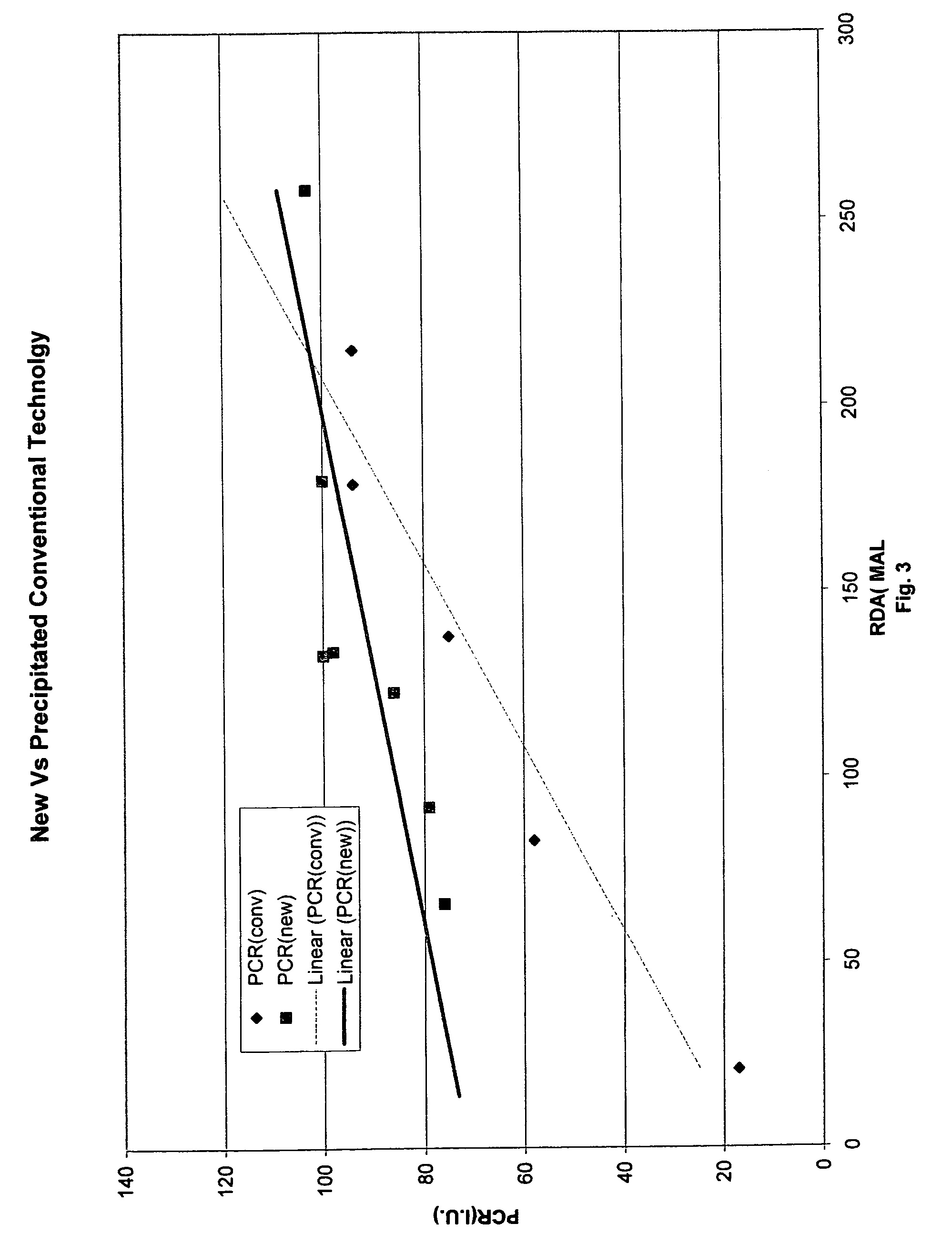
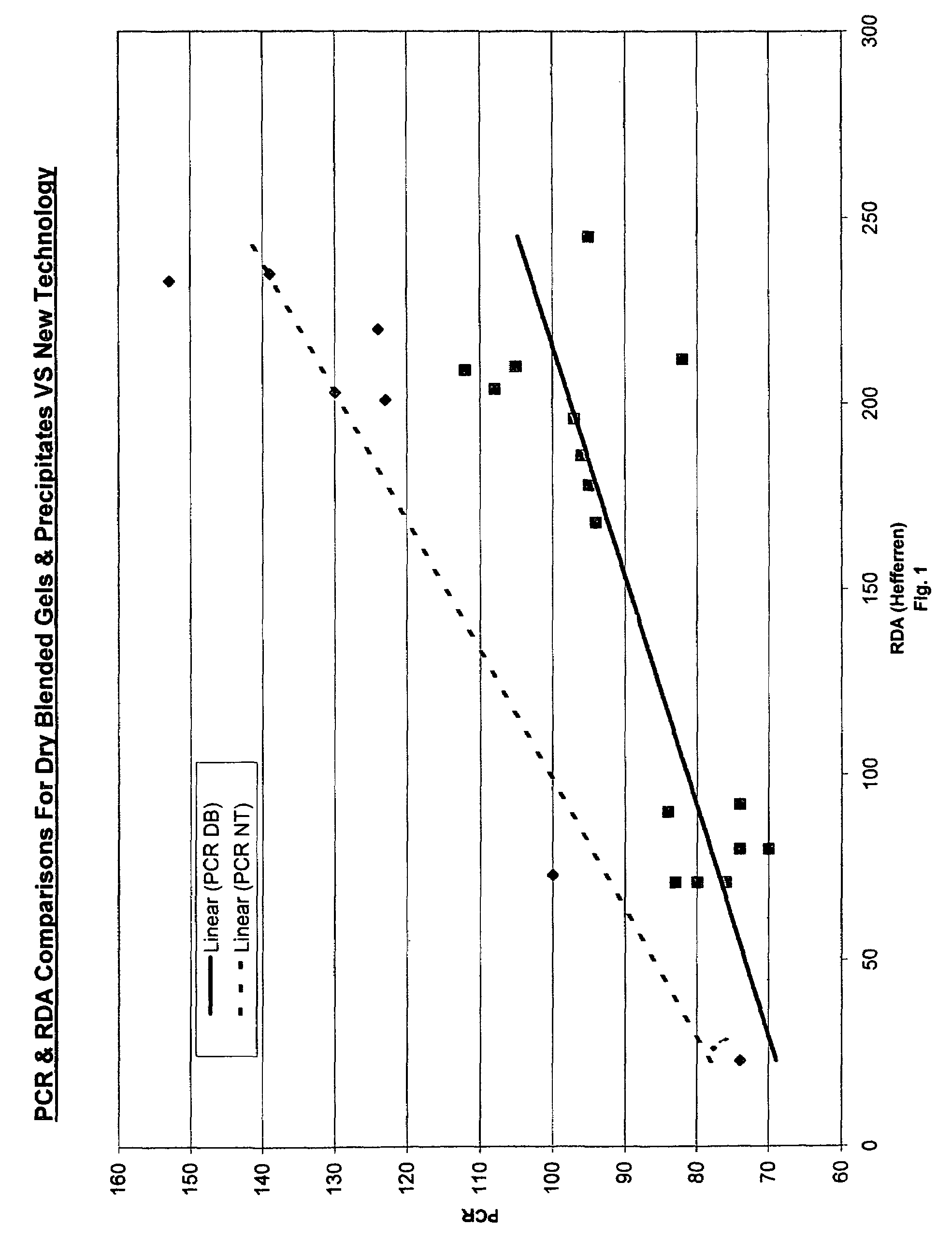
Oral compositions comprising a first and a second abrasive are provided. The first abrasive preferably has an Einlehner hardness of greater than about 5 mg loss per 100,000 revolutions, and the second abrasive preferably has an Einlehner hardness of less than about 5 mg loss per 100,000 revolutions. A ratio of the first abrasive to the second abrasive ranges from about 1:1.6 to about 1.6:1, and the first and second abrasives are preferably present in the oral composition at an amount of about 13% to about 21% by weight, respectively. The pellicle cleaning ratio of the oral composition is greater than 100 and the radioactive dentin abrasiveness is preferably less than 200, and in certain embodiments, preferably less than about 175. Methods of using the oral compositions are also provided.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Dental Composite Resin Cement, Dental Primer and Dental Adhesive Kit Containing Them
ActiveUS20090048366A1Improve adhesionRich in hydrophilicityImpression capsOther chemical processesResin cementMaterials science
The present invention provides a dental resin cement which is excellent in a mechanical strength, workability and storage stability, and a dental primer which significantly improves adhesiveness of the dental resin cement both to enamel and dentin of a tooth. According to the present invention, a salt of barbituric acid is used as a polymerization initiator in the dual-cure two-paste type dental resin cement being excellent in workability and storage stability to improve the storage stability, and a primer containing barbituric acid and amine is applied to a surface of a tooth to significantly improve adhesiveness of the dental resin cement both to enamel and dentin of teeth.
Owner:SHOFU INC
Predominantly platelet-shaped, sparingly water-soluble calcium salts and/or composite materials thereof comprising them
InactiveUS20090042169A1Good biocompatibilityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsFine structureTooth enamel
The invention relates to sparingly water-soluble calcium salts and / or composite materials comprising them, characterized in that the calcium salts are present in the form of single crystals or in the form of particles comprising a multitude of said crystals and having a mean particle diameter in the region of below 1,000 nm, preferably below 300 nm, the calcium salt particles being predominantly platelet-like. The inventive calcium salts and / or composite materials comprising these calcium salts, owing to their composition and fine structure, are particularly suitable for promoting the restoration of bone and tooth material, especially enamel and dentine.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com