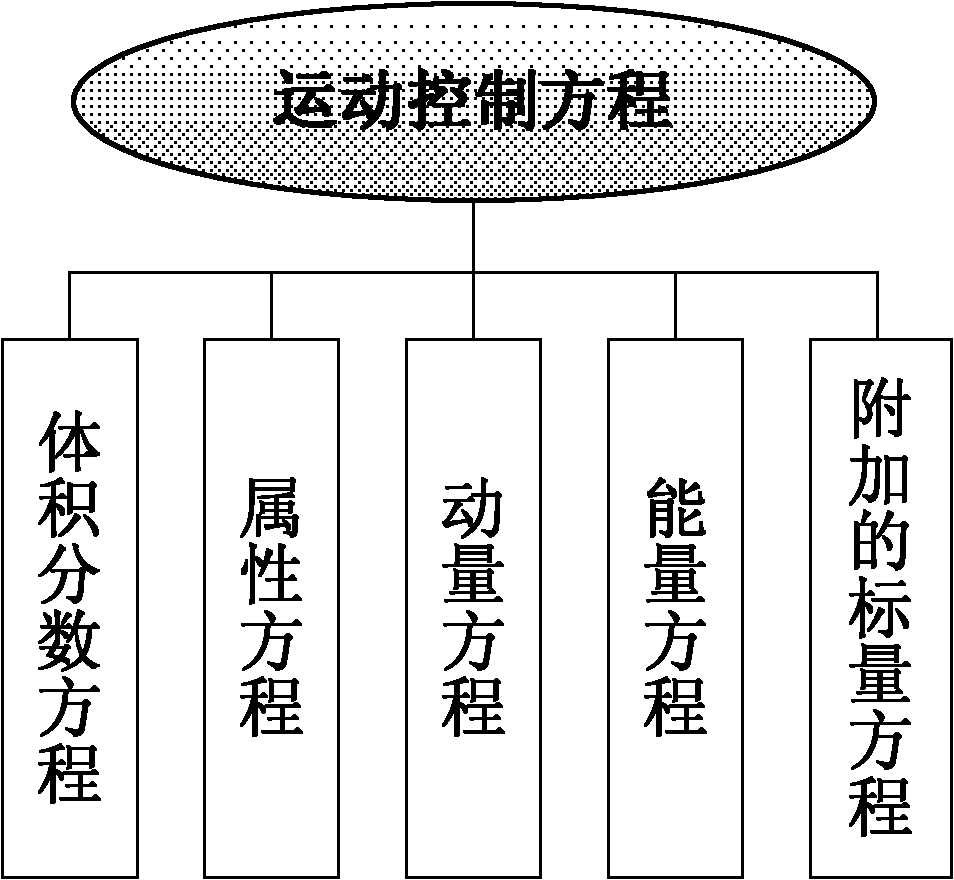
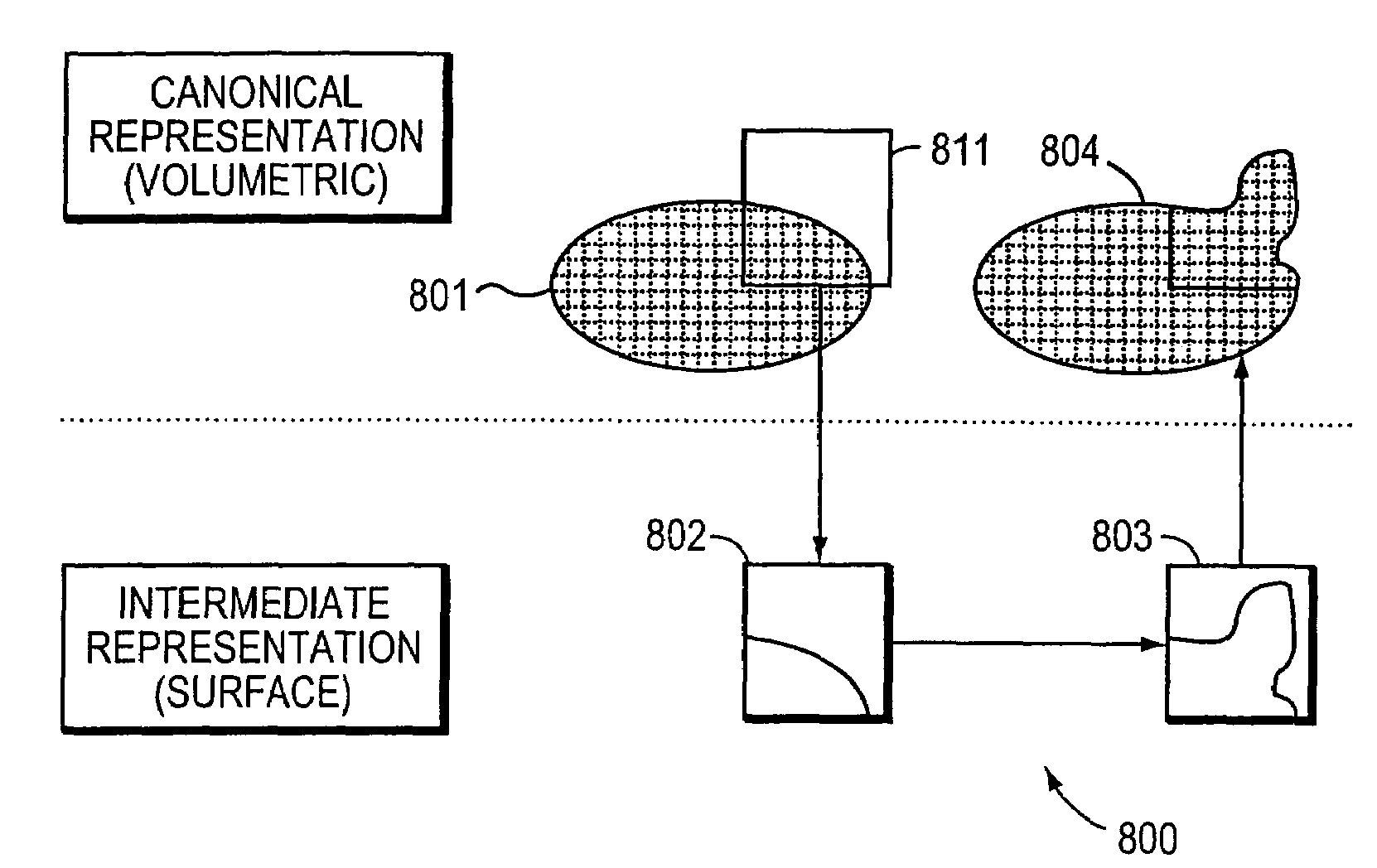
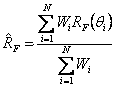Patents
Literature
90 results about "Volumetric model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for dynamic modeling of an object
InactiveUS6295464B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalogue computers for chemical processesModel dynamicsDynamic motion
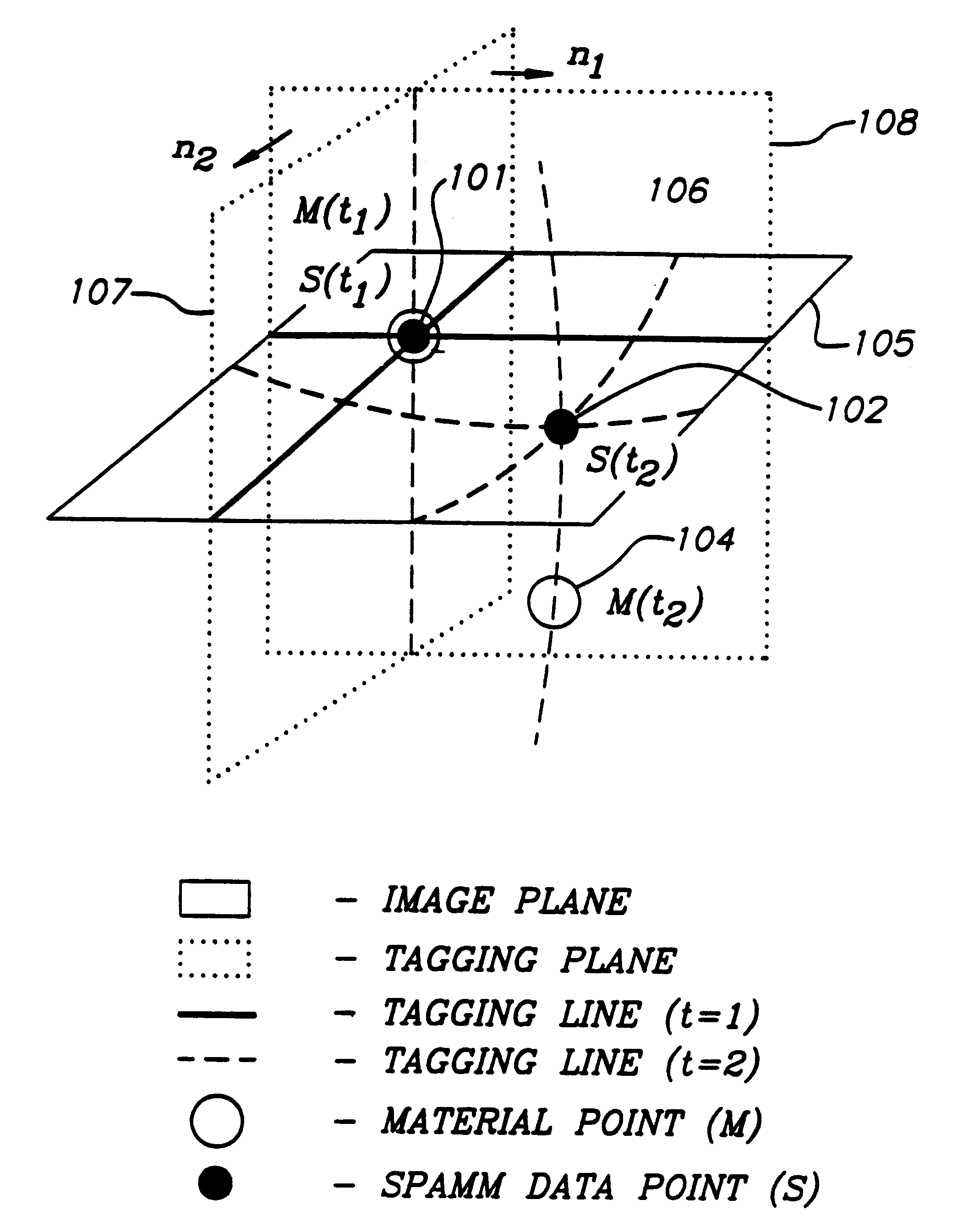
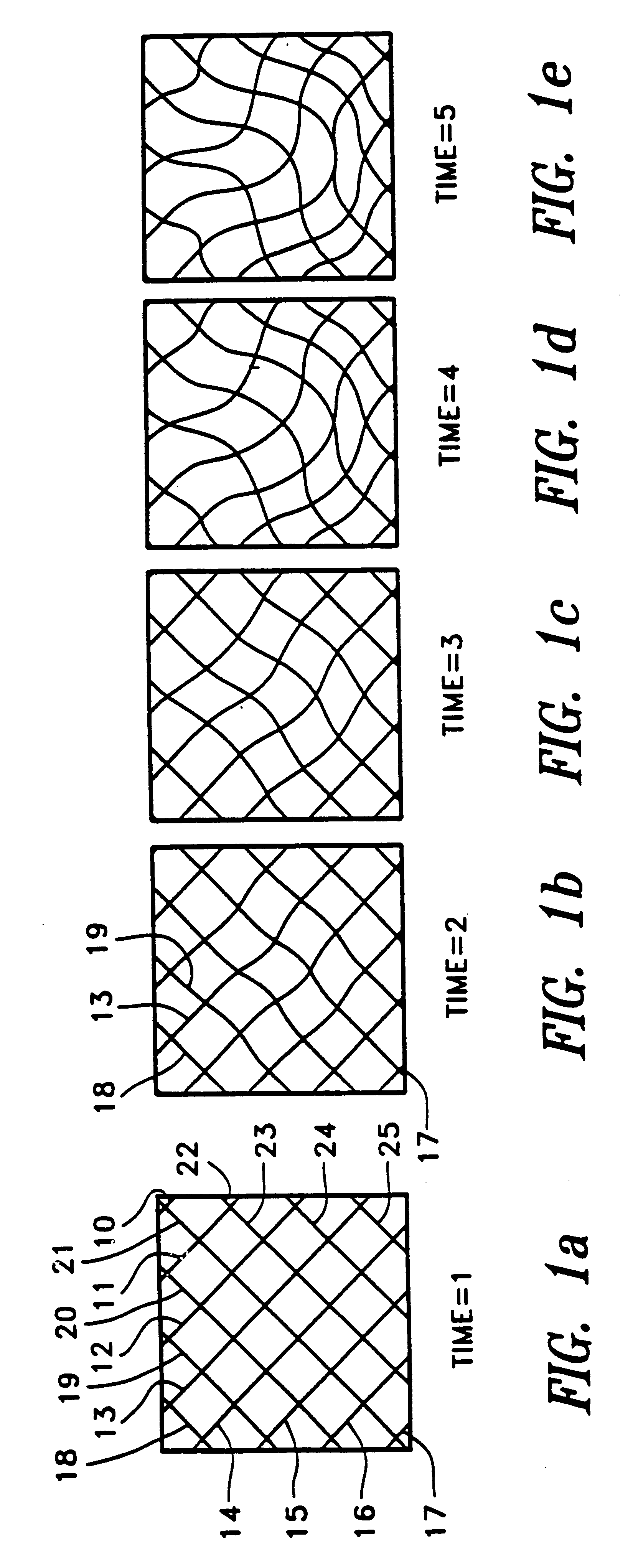
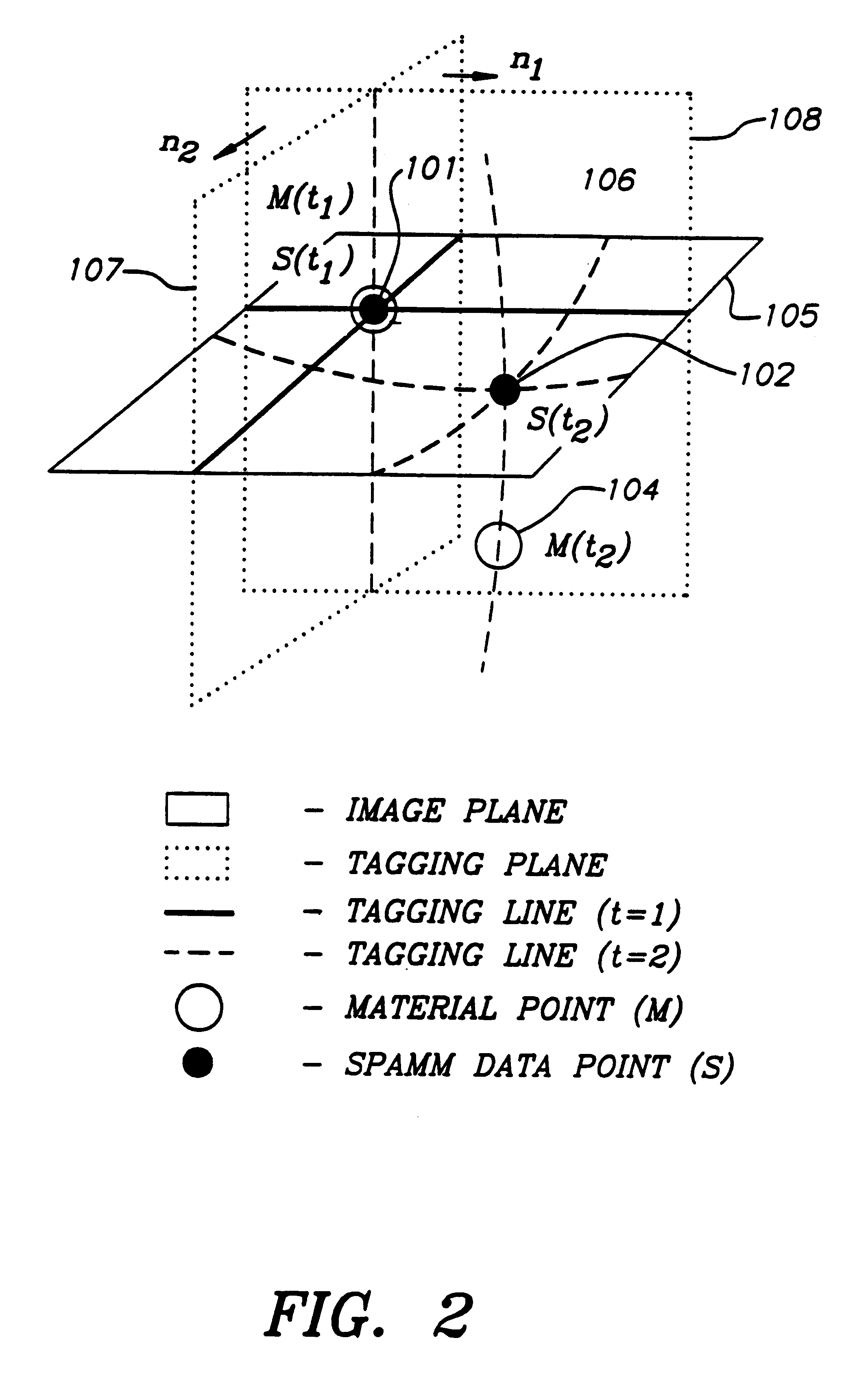
A method and apparatus for dynamic modeling of an object having material points. The method includes receiving signals from a sensor which correspond to respective material points; providing a volumetric model, having functions as parameters, representative of the object; and adapting the parameters to fit a changing model shape. This method of dynamic shape modeling dynamic motion modeling or both includes shape estimation and motion analysis. The apparatus includes a signal processor for receiving signals from a sensor, a second signal processor for providing a volumetric model having functions as parameters representative of the object and a third signal processor for receiving sensed signals and adapting the model and providing a dynamic representation.
Owner:METAXAS DIMITRI
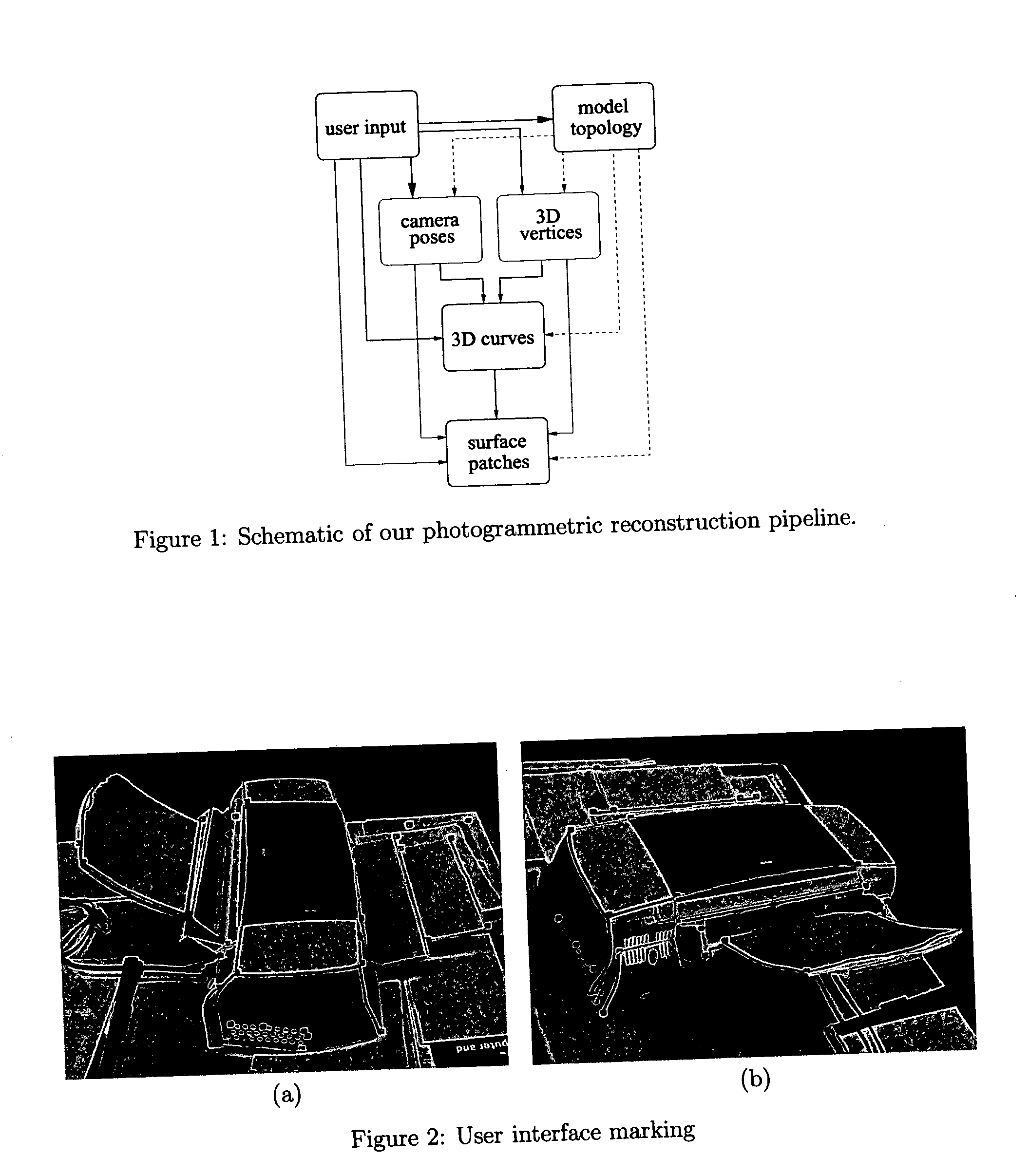
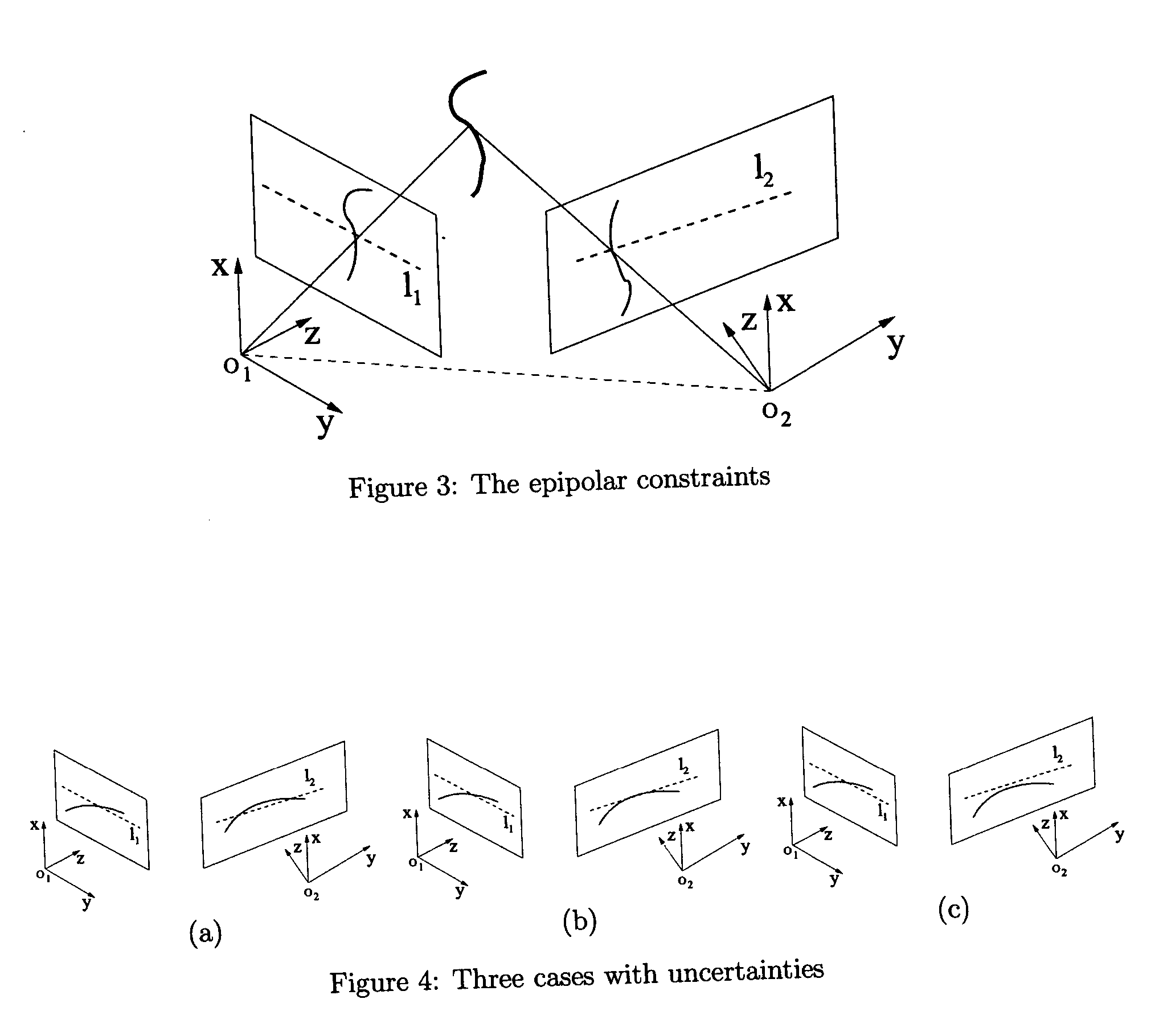
Photogrammetric reconstruction of free-form objects with curvilinear structures
InactiveUS20050140670A1Easy to useModeling free-form objects more accurate3D-image rendering3D modellingViewpointsFree form
The shapes of many natural or man-made objects have curve features. The images of such curves usually do not have sufficient distinctive features to apply conventional feature-based reconstruction algorithms. In this paper, we introduce a photogrammetric method for recovering free-form objects with curvilinear structures. Our method chooses to define the topology and recover a sparse 3D wireframe of the object first instead of directly recovering a surface or volume model. Surface patches covering the object are then constructed to interpolate the curves in this wireframe while satisfying certain heuristics such as minimal bending energy. The result is an object surface model with curvilinear structures from a sparse set of images. We can produce realistic texture-mapped renderings of the object model from arbitrary viewpoints. Reconstruction results on multiple real objects are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Owner:HONG WU +1
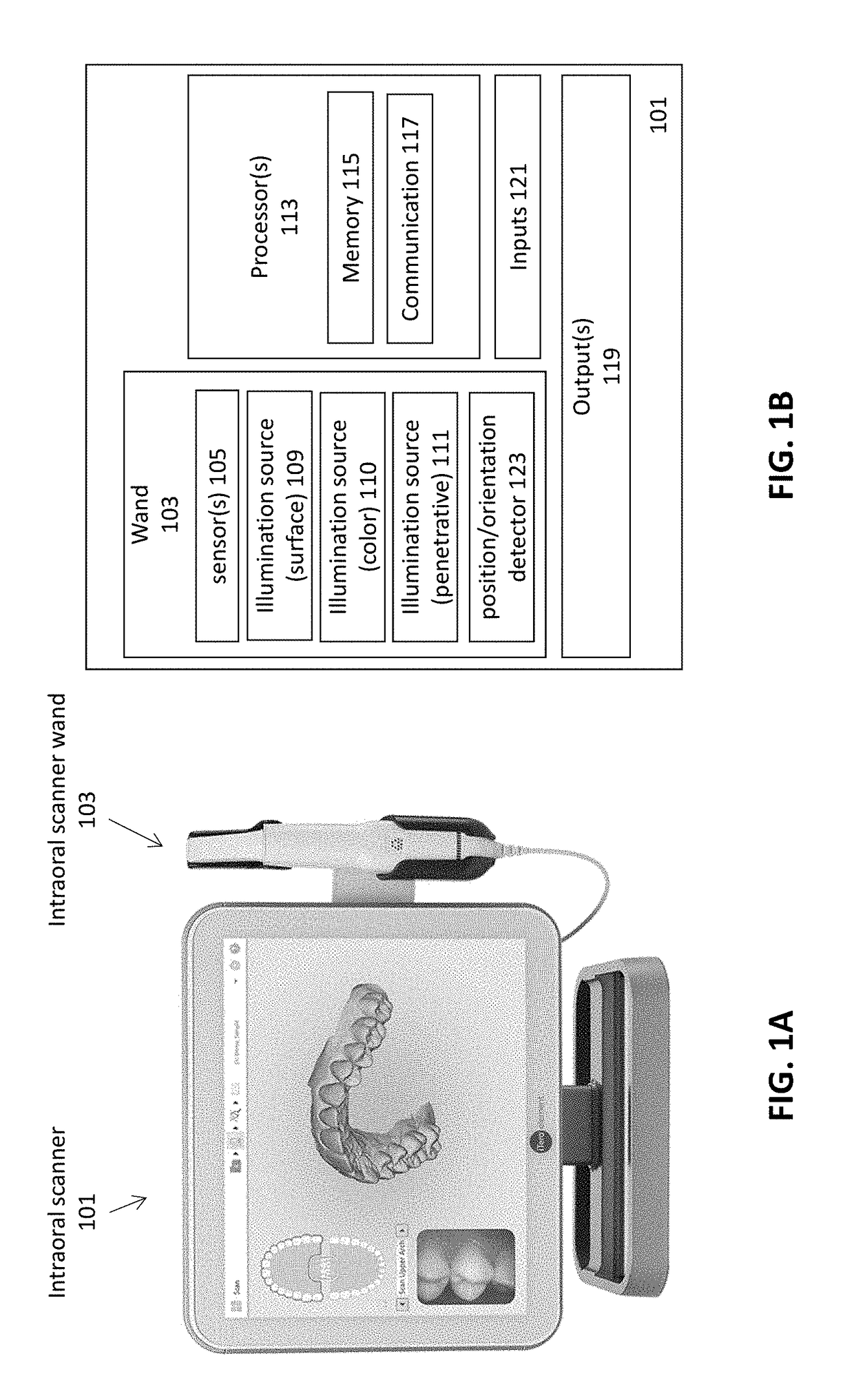
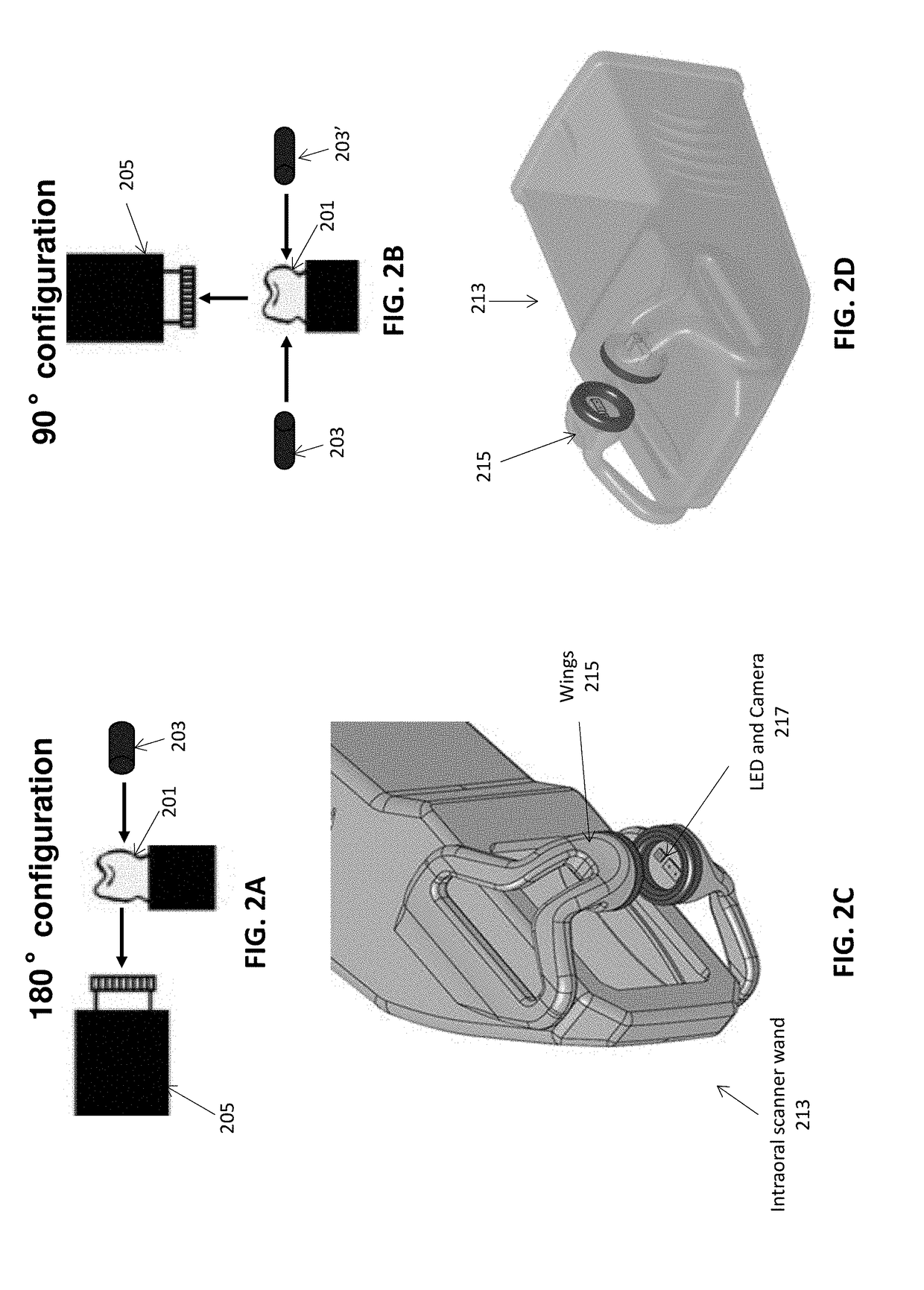
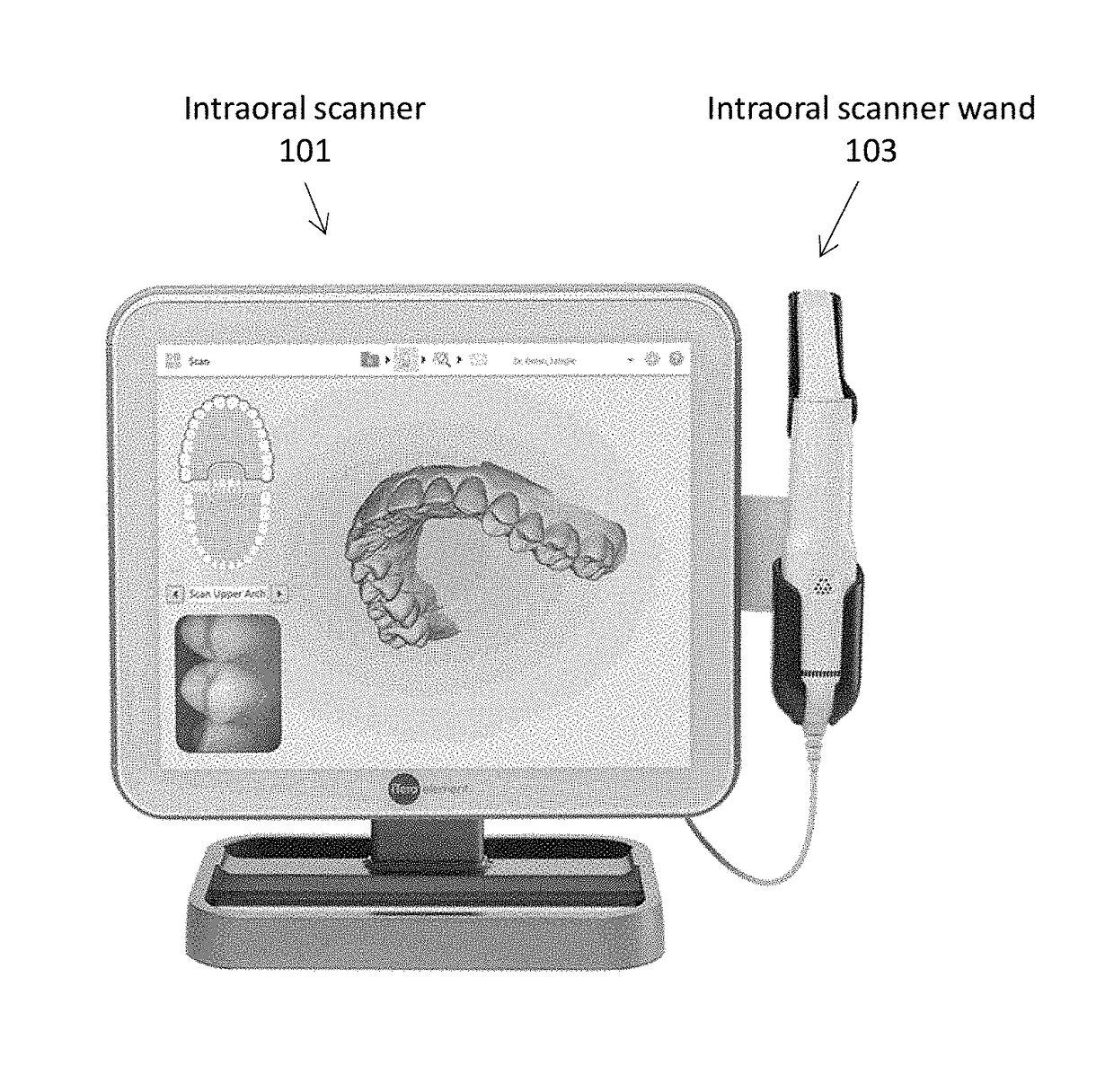
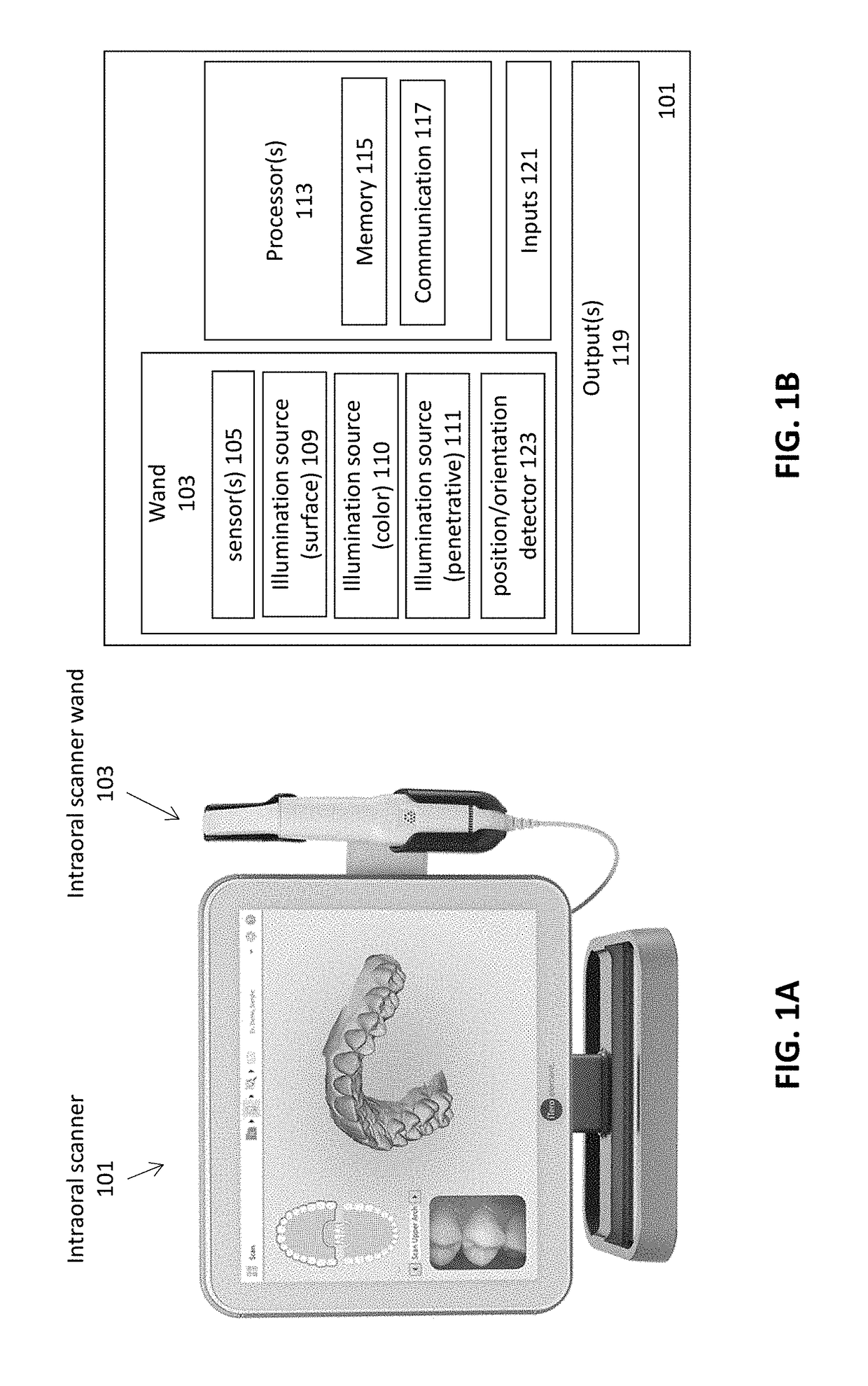
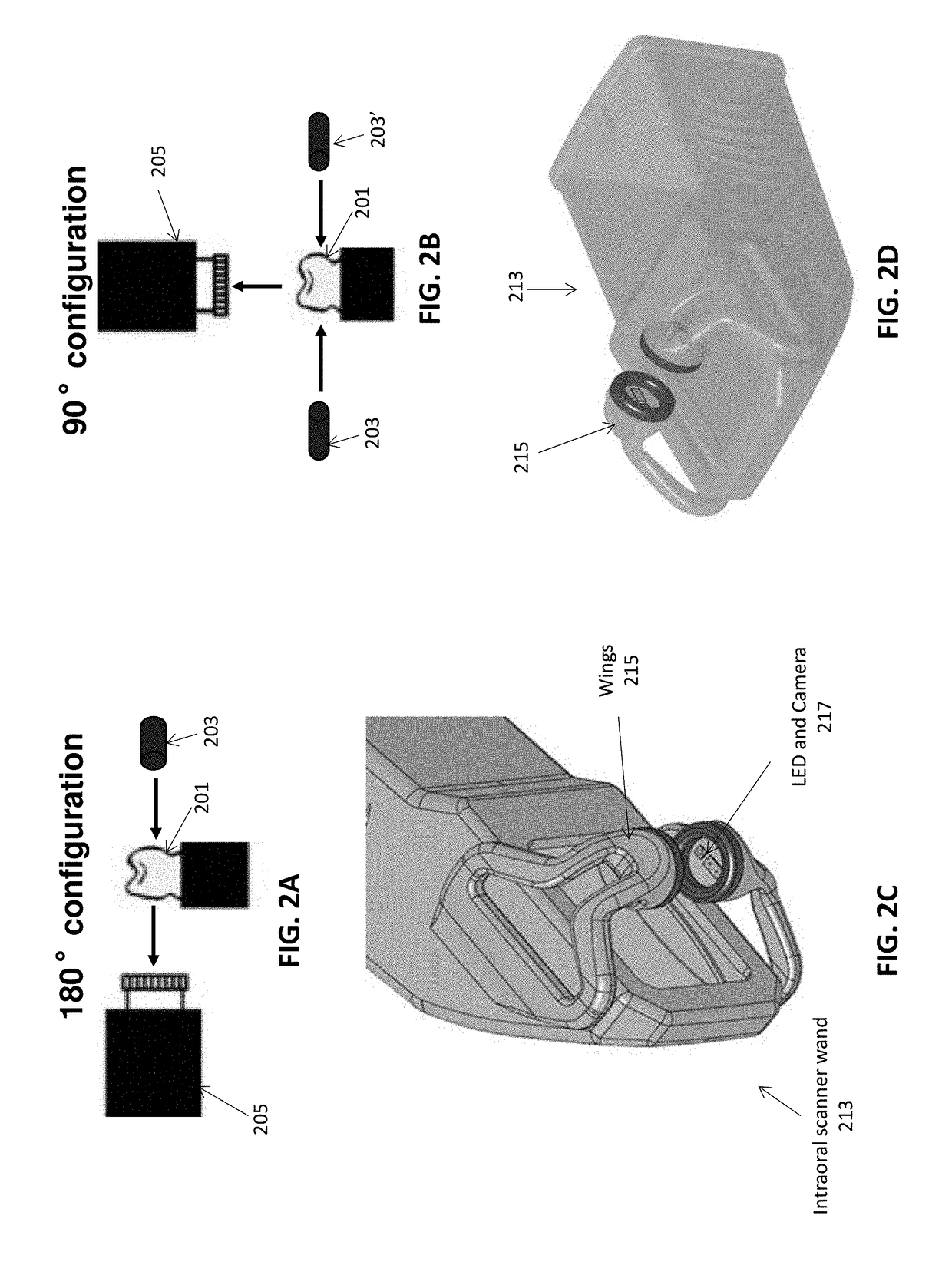
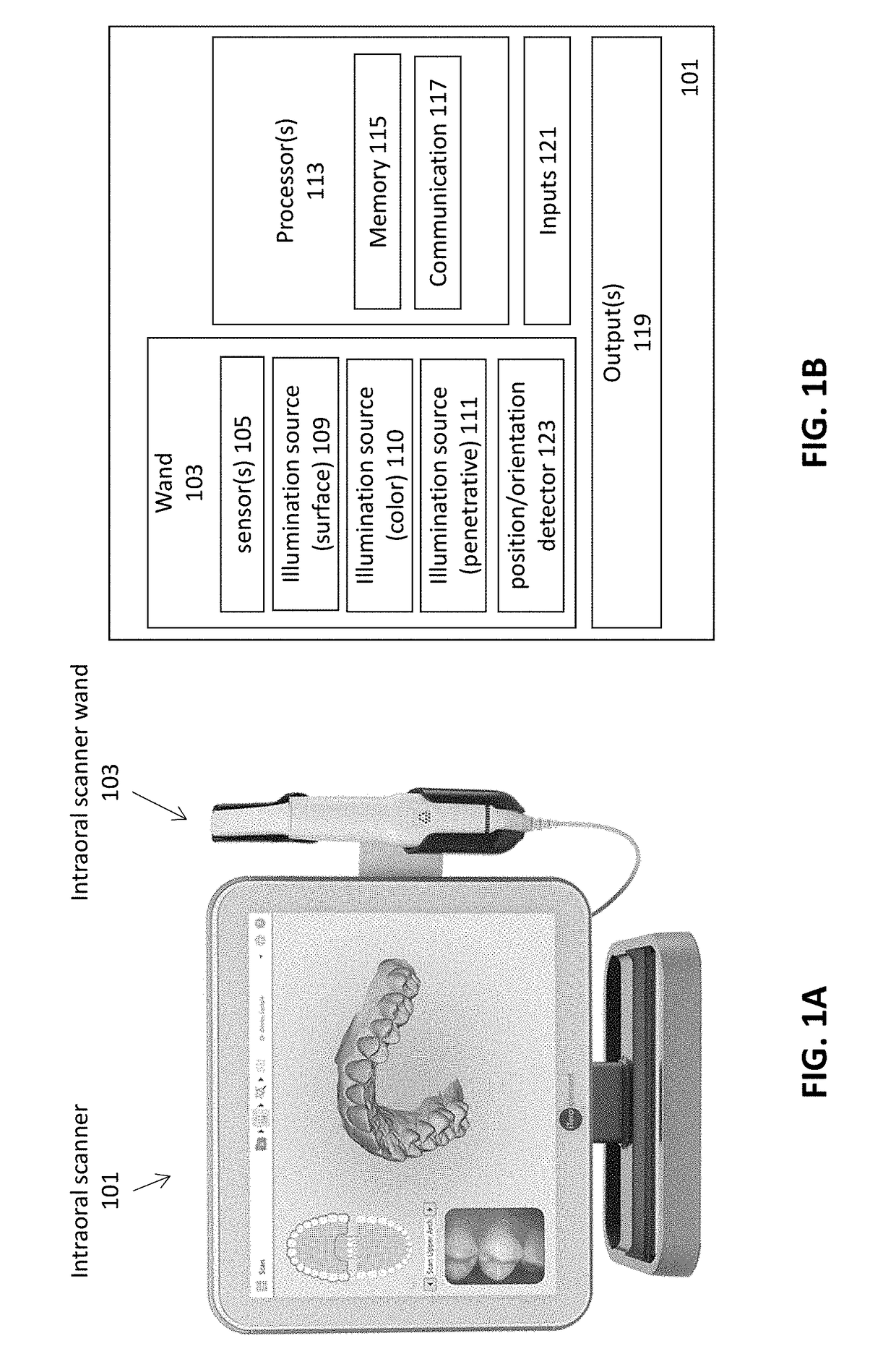
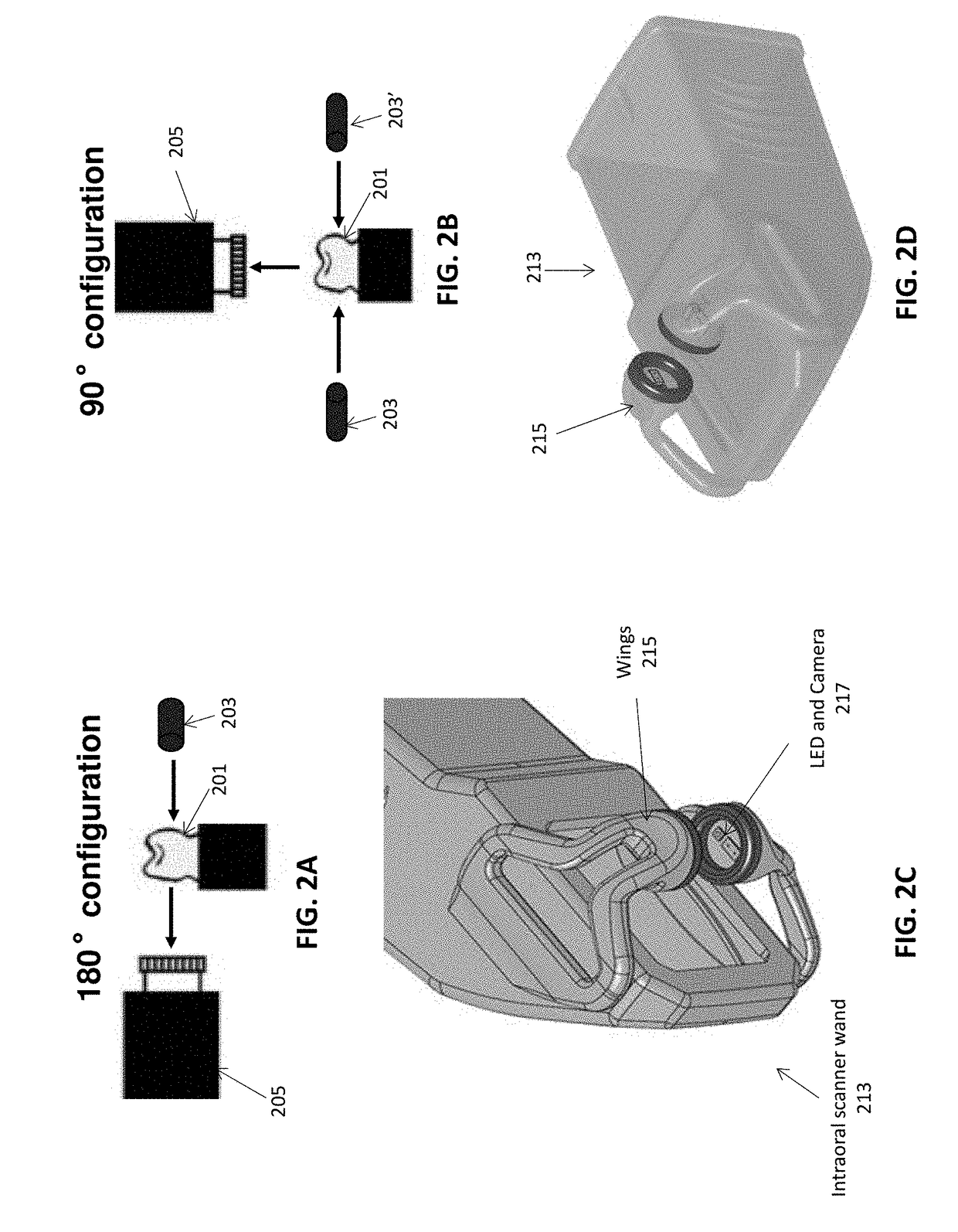
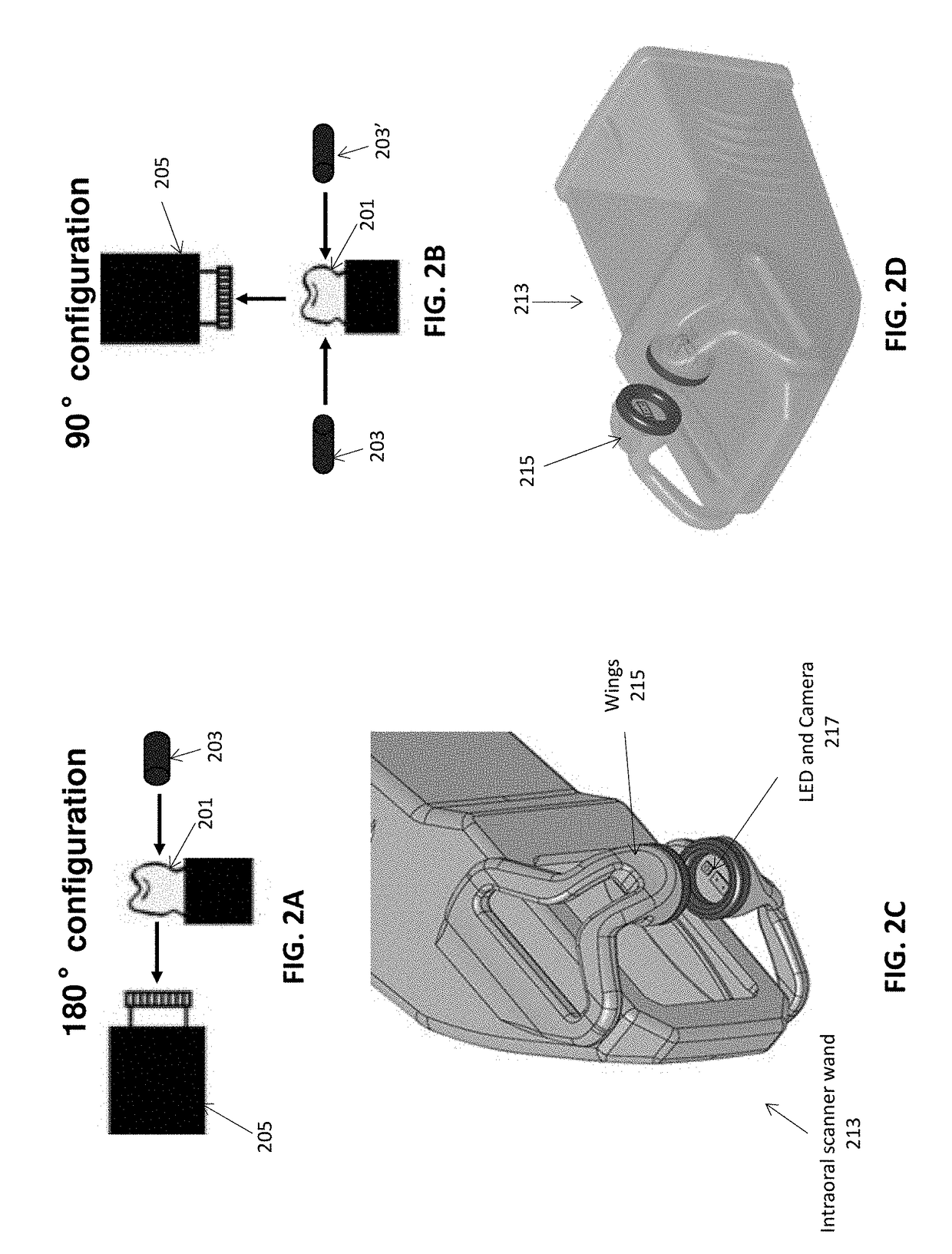
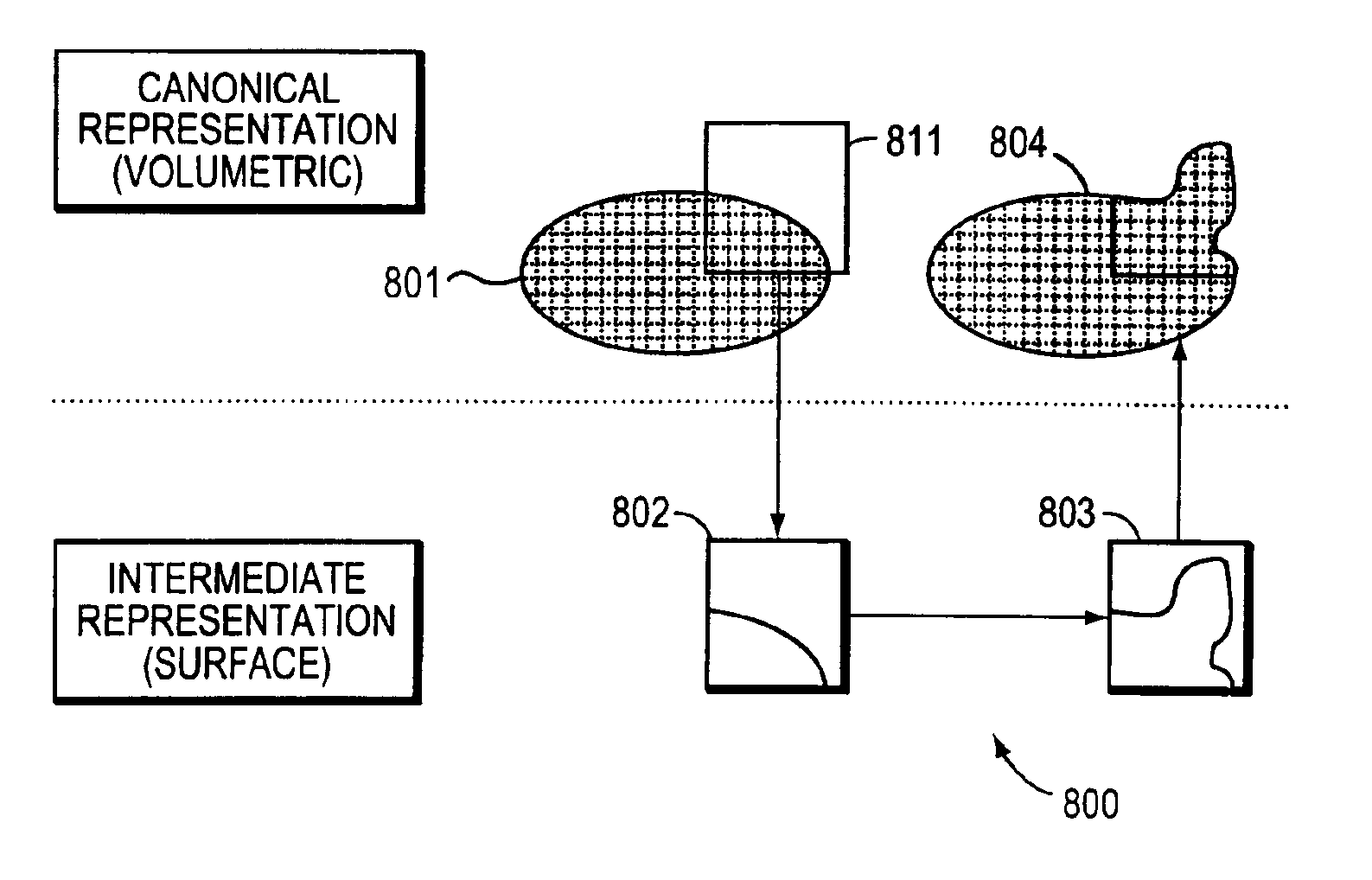
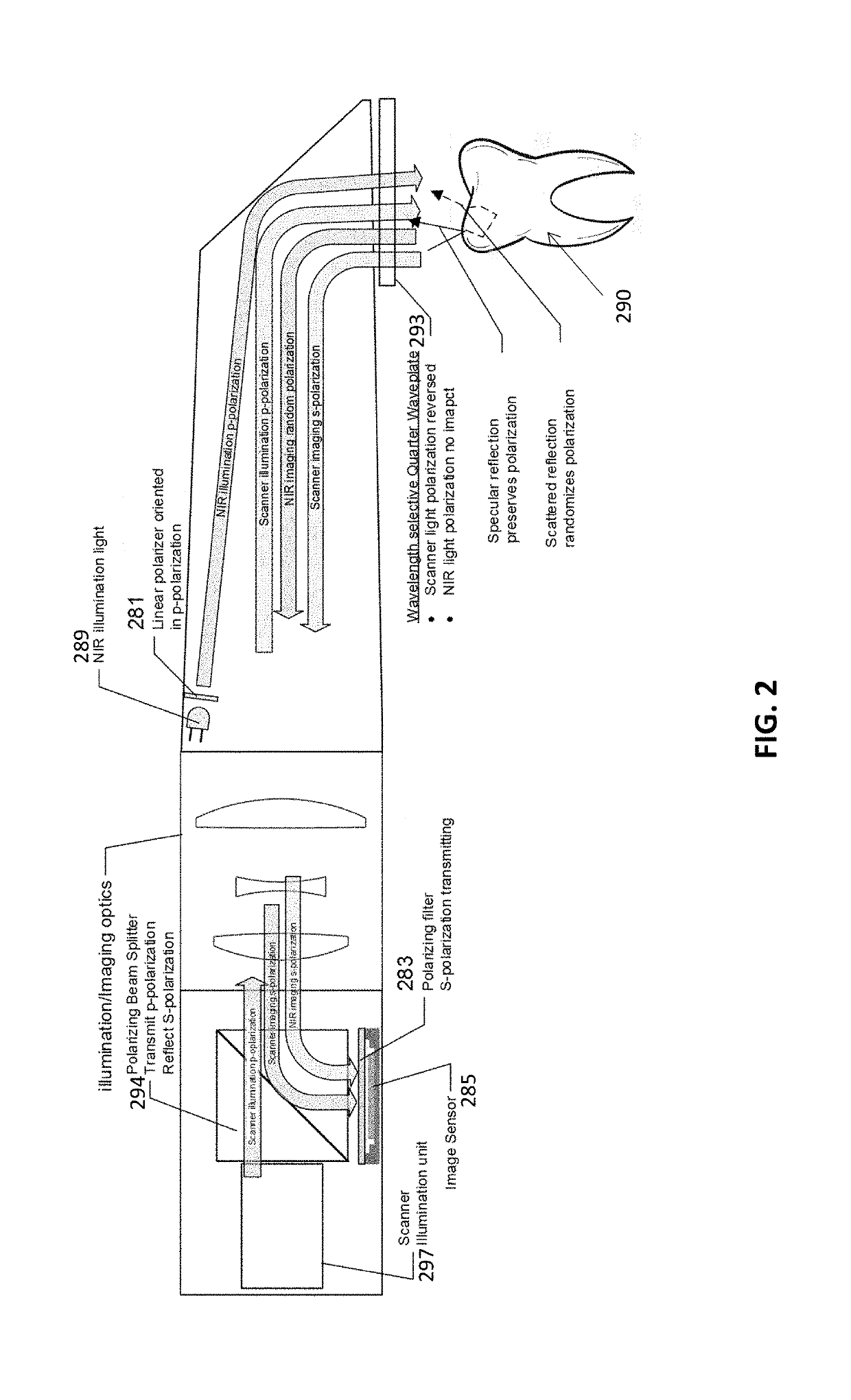
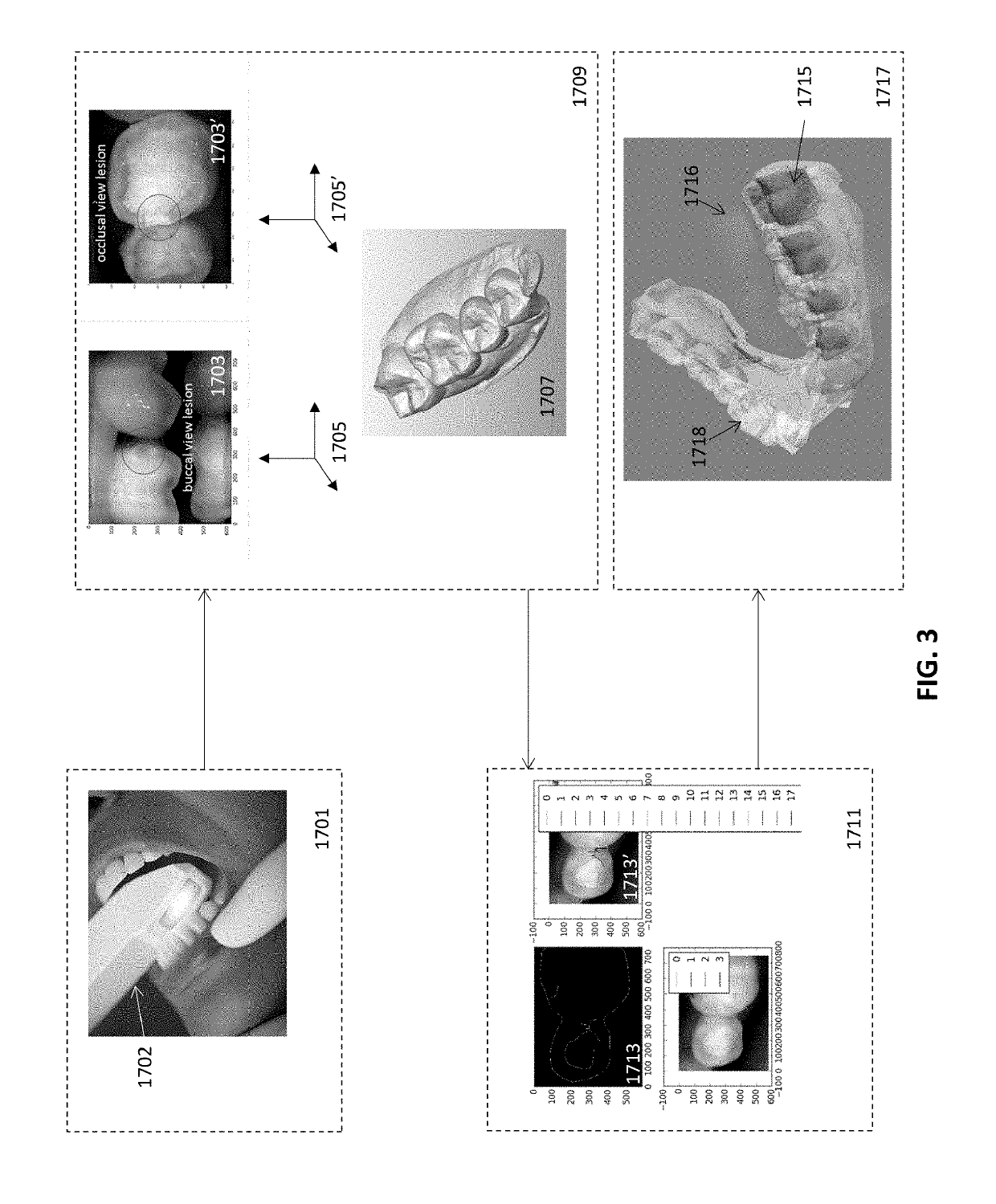
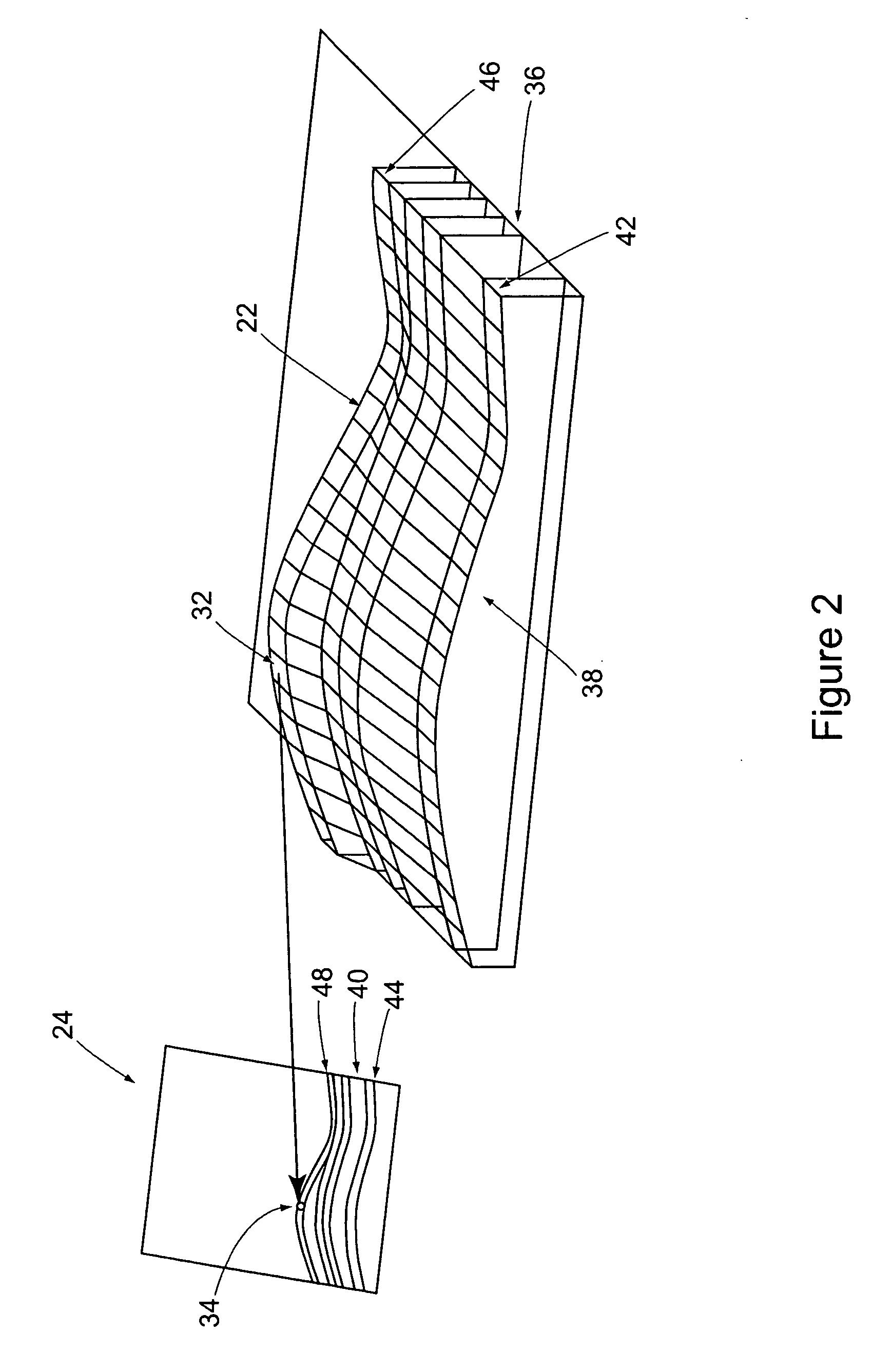
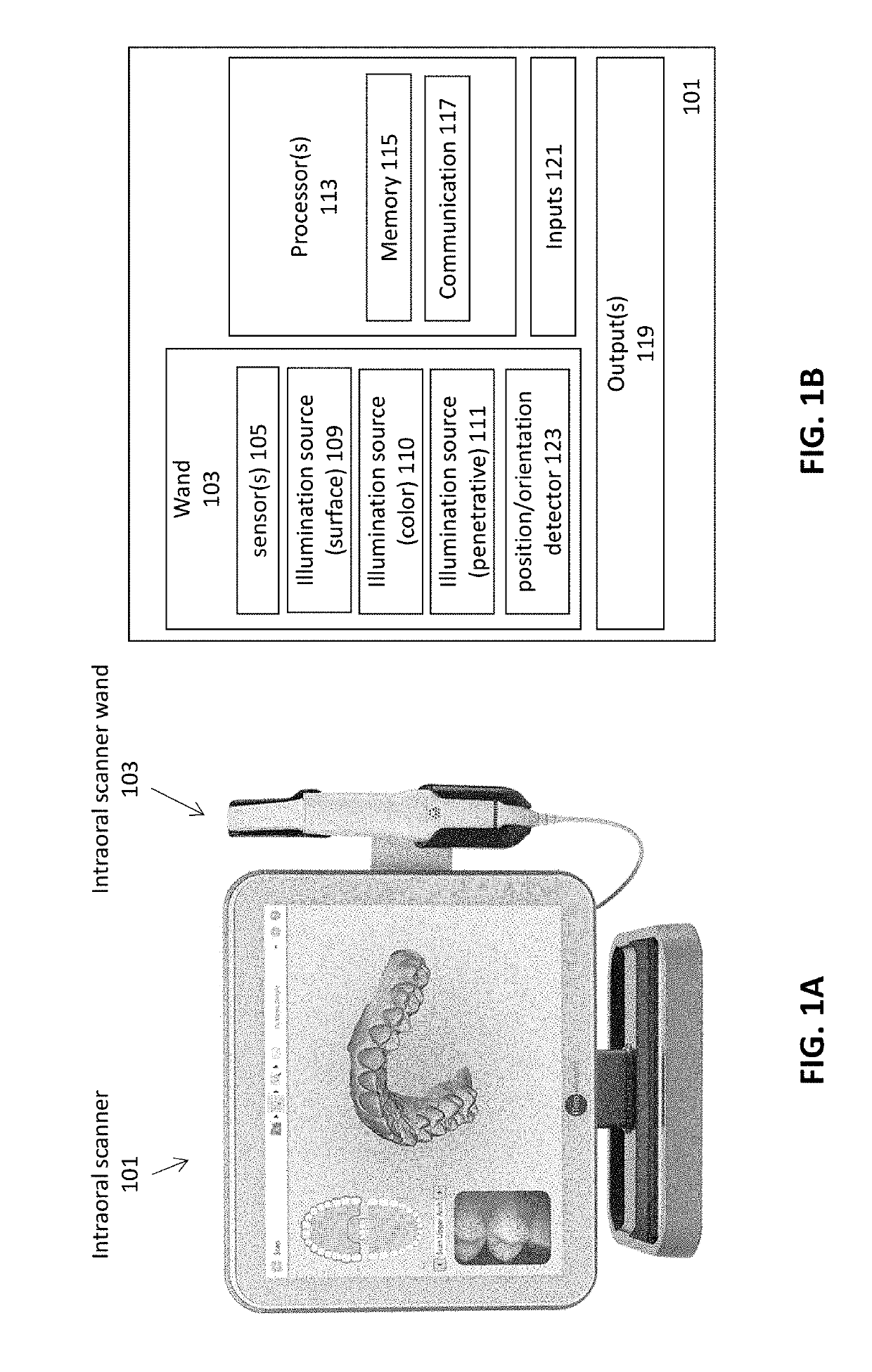
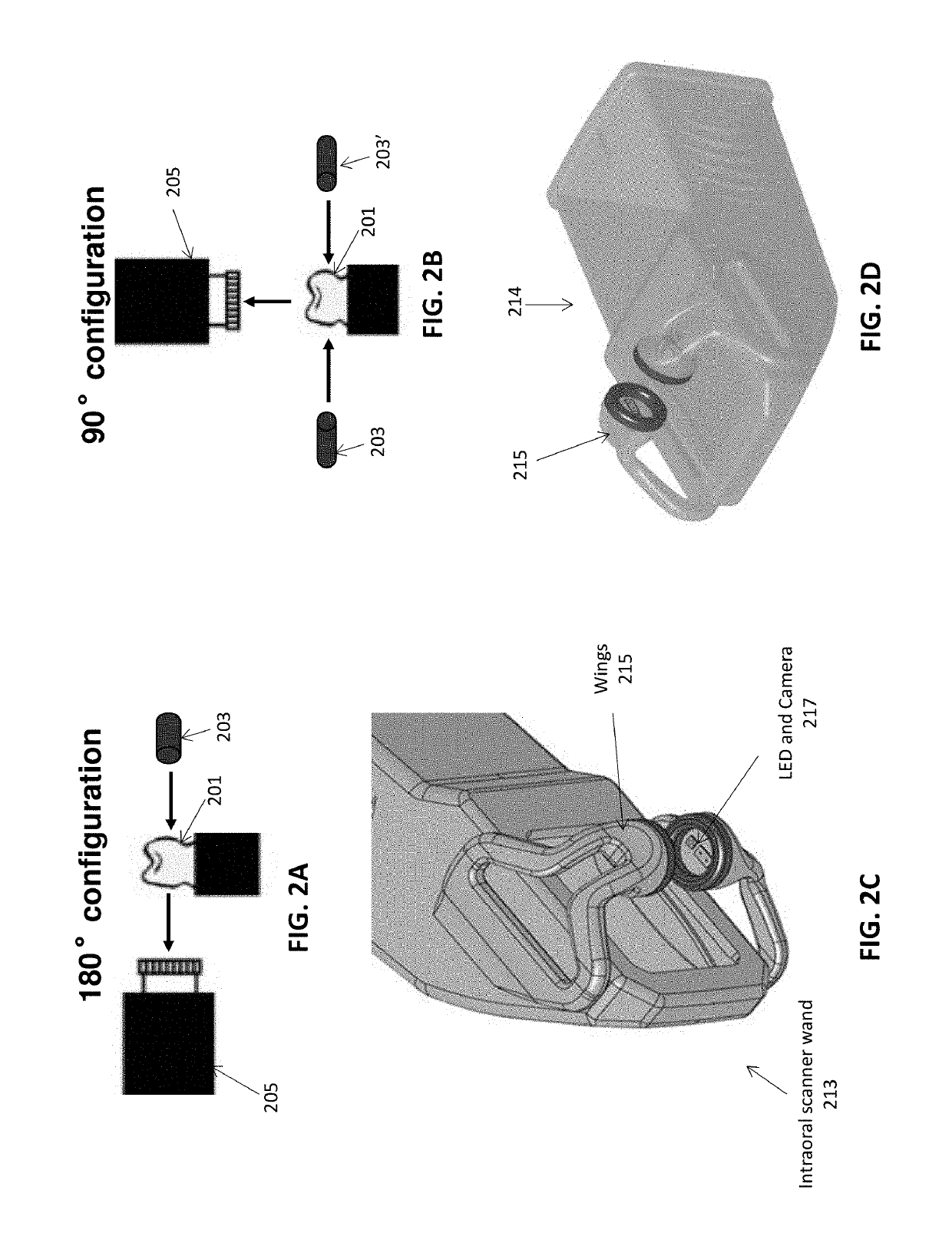
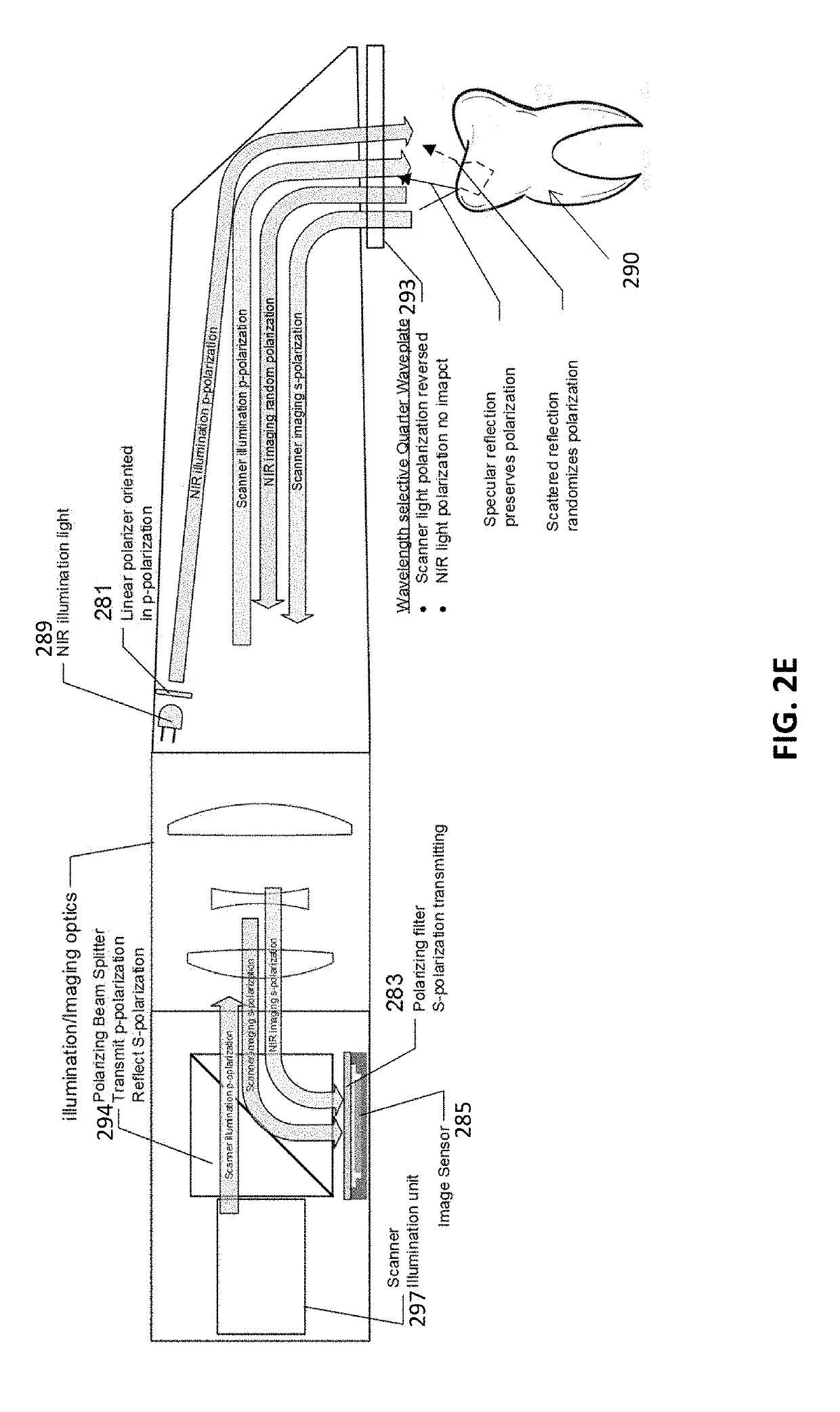
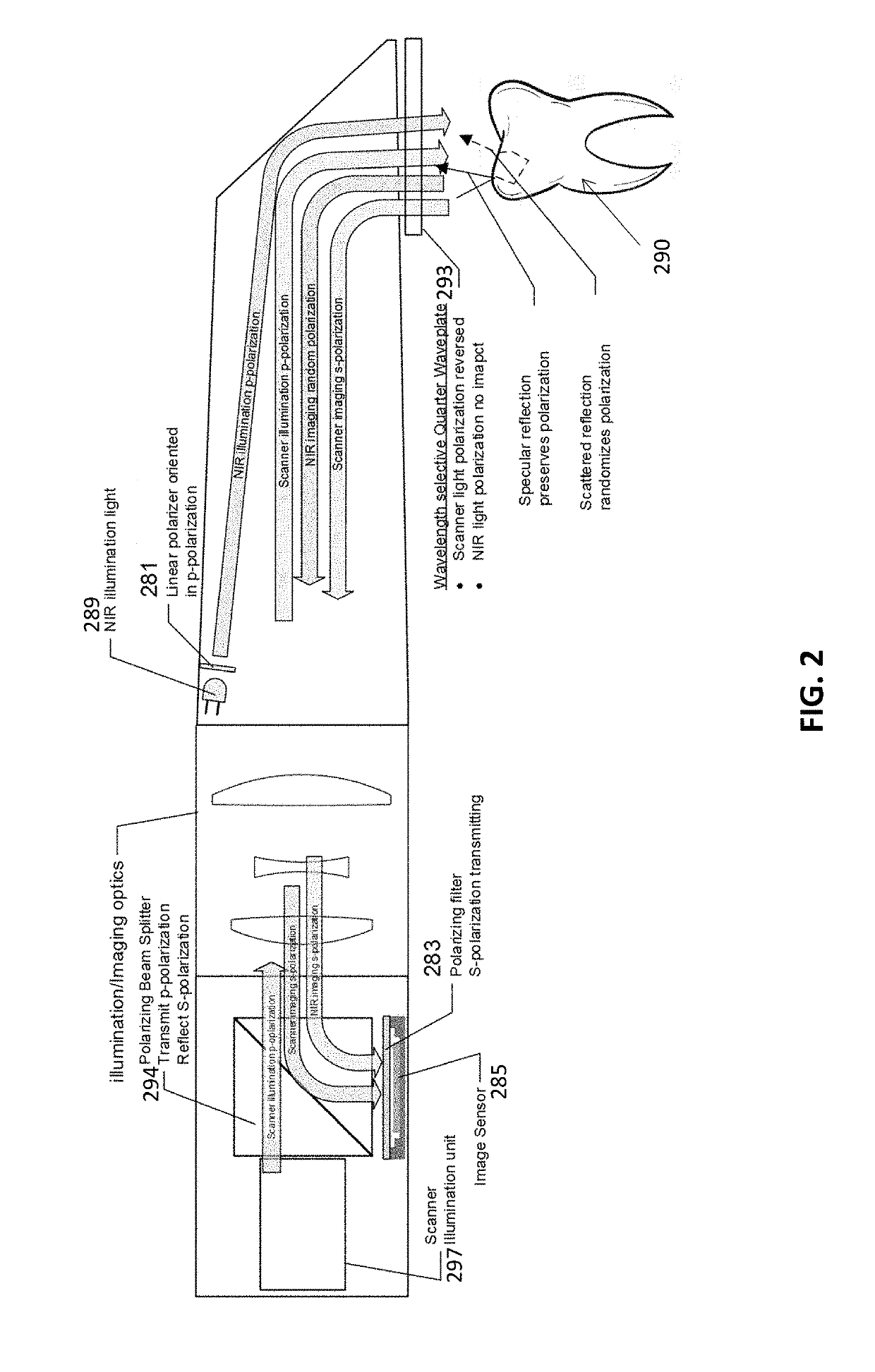
Methods and apparatuses for forming a three-dimensional volumetric model of a subject's teeth
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Fusing virtual content into real content
ActiveCN102419631AInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
A system that includes a head mounted display device and a processing unit connected to the head mounted display device is used to fuse virtual content into real content. In one embodiment, the processing unit is in communication with a hub computing device. The system creates a volumetric model of a space, segments the model into objects, identifies one or more of the objects including a first object, and displays a virtual image over the first object on a display (of the head mounted display) that allows actual direct viewing of at least a portion of the space through the display.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
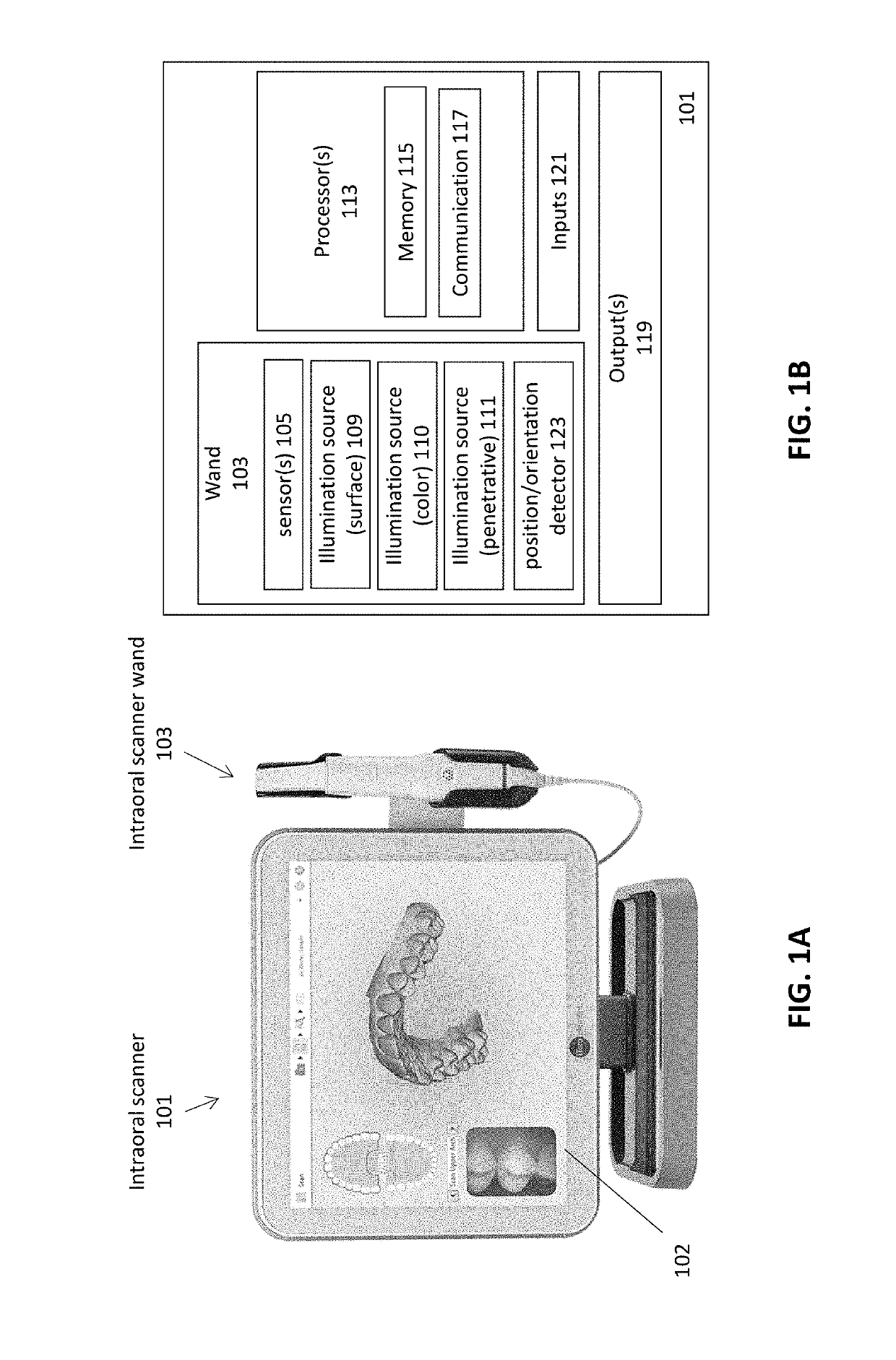
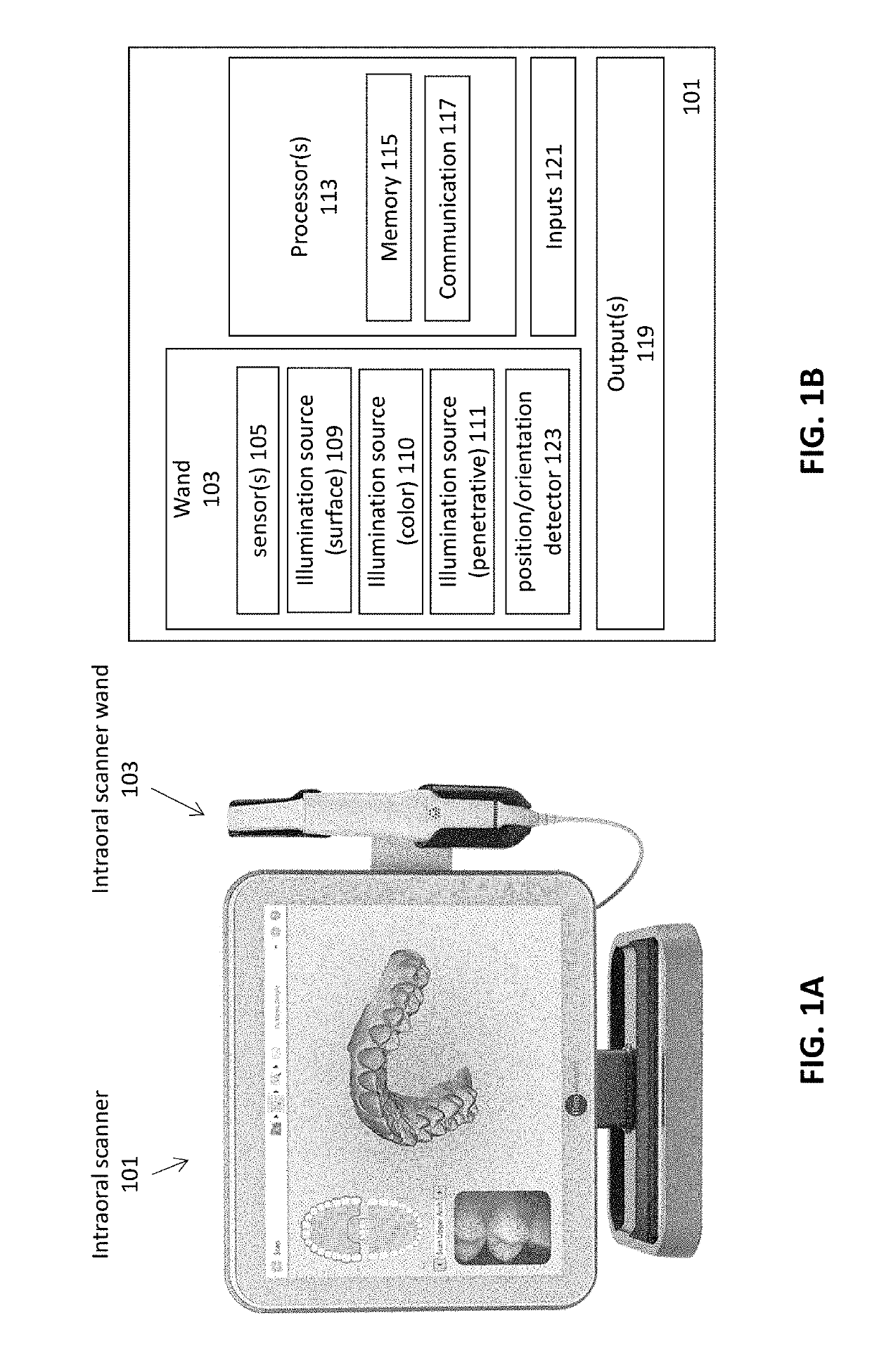
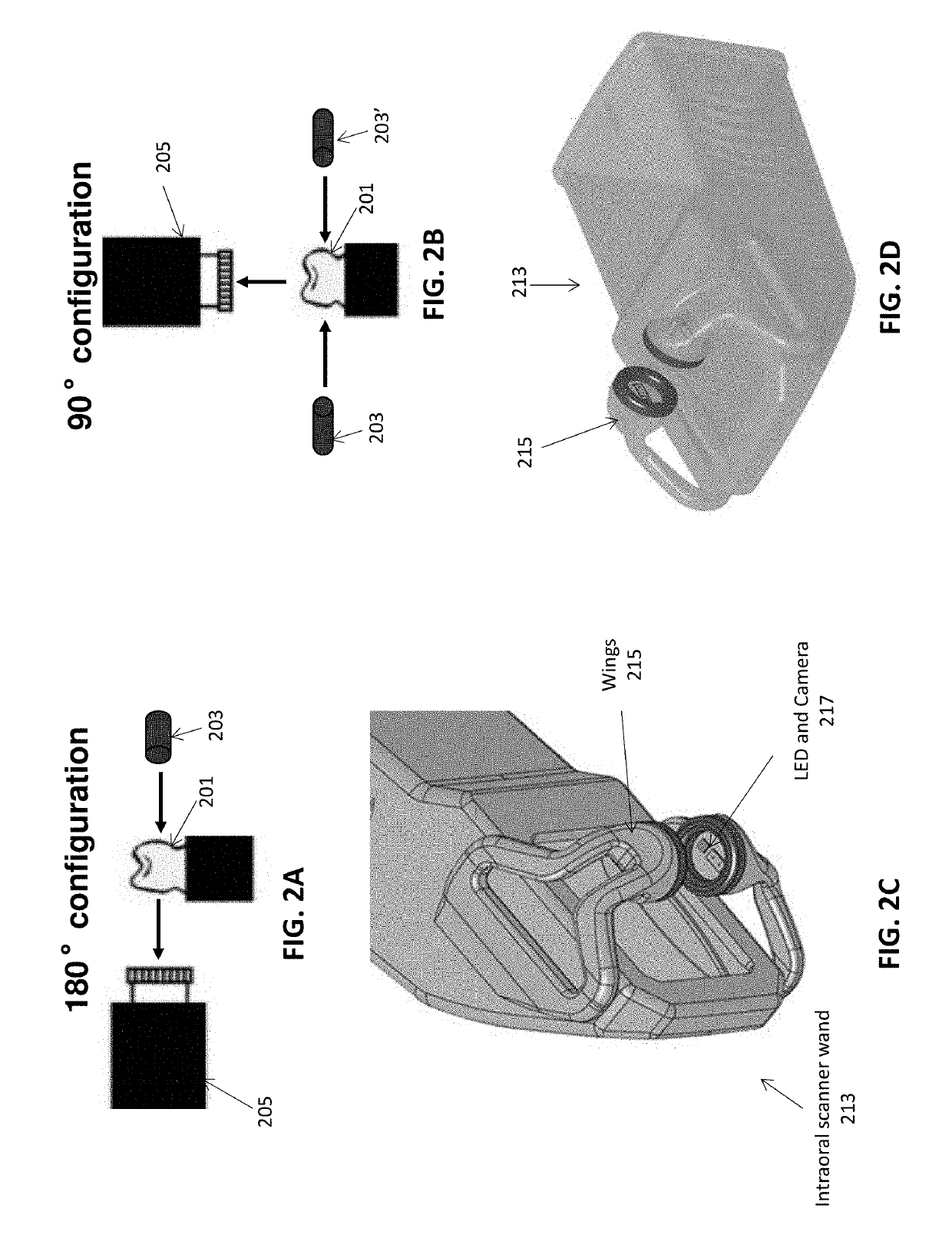
Intraoral scanner with dental diagnostics capabilities
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Incorporating video meta-data in 3D models
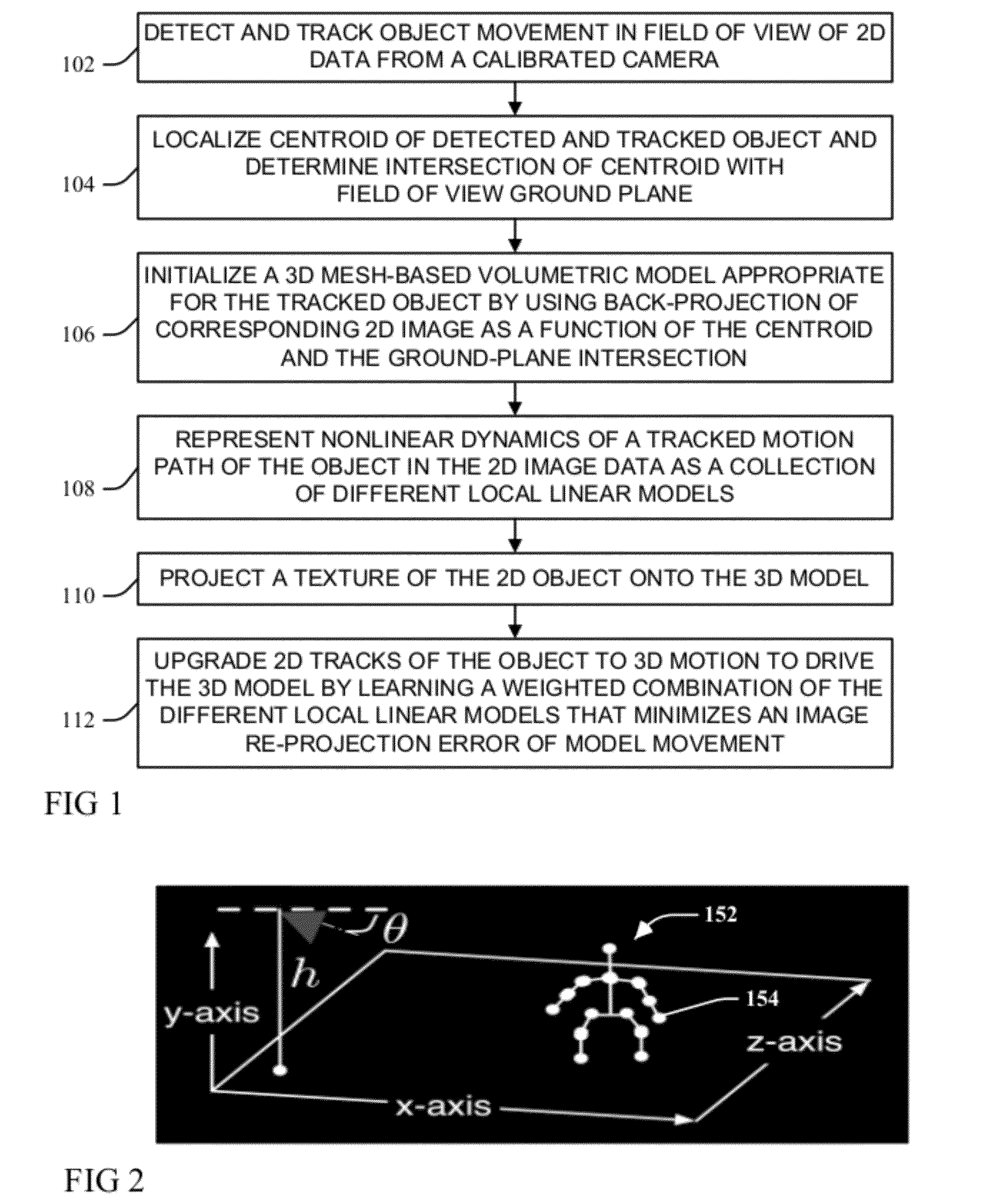
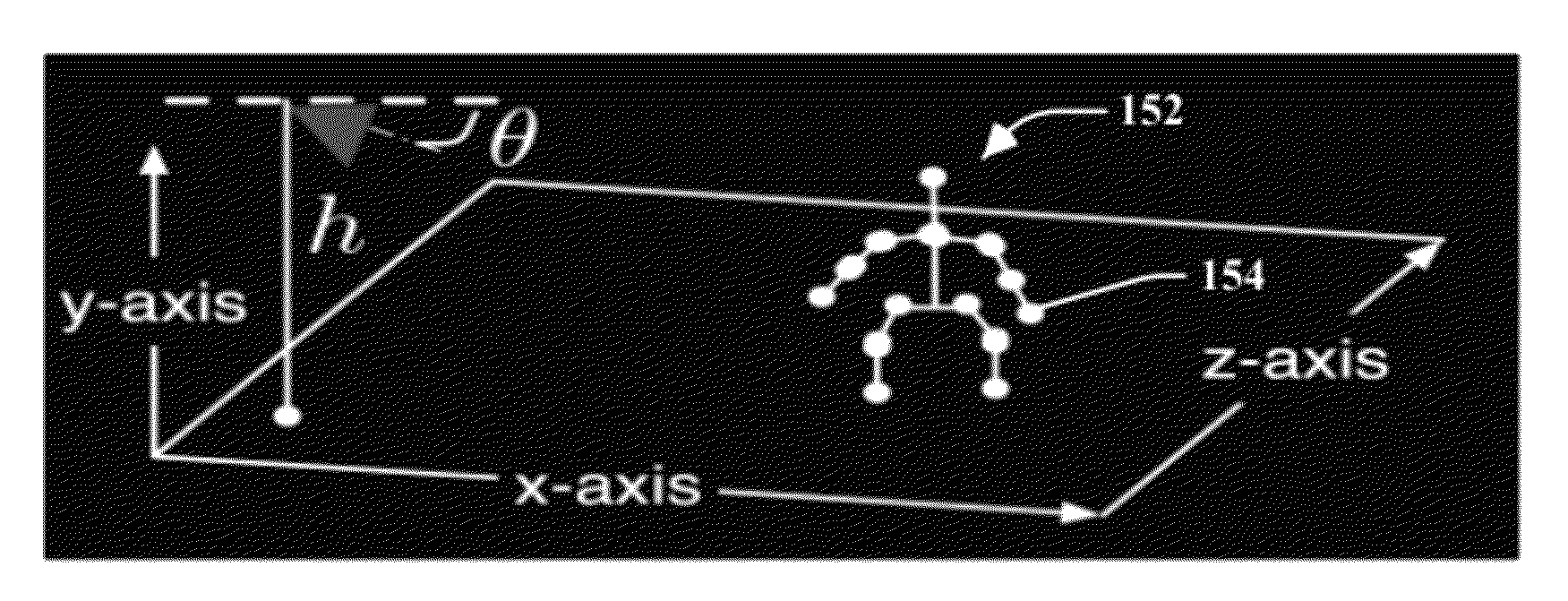
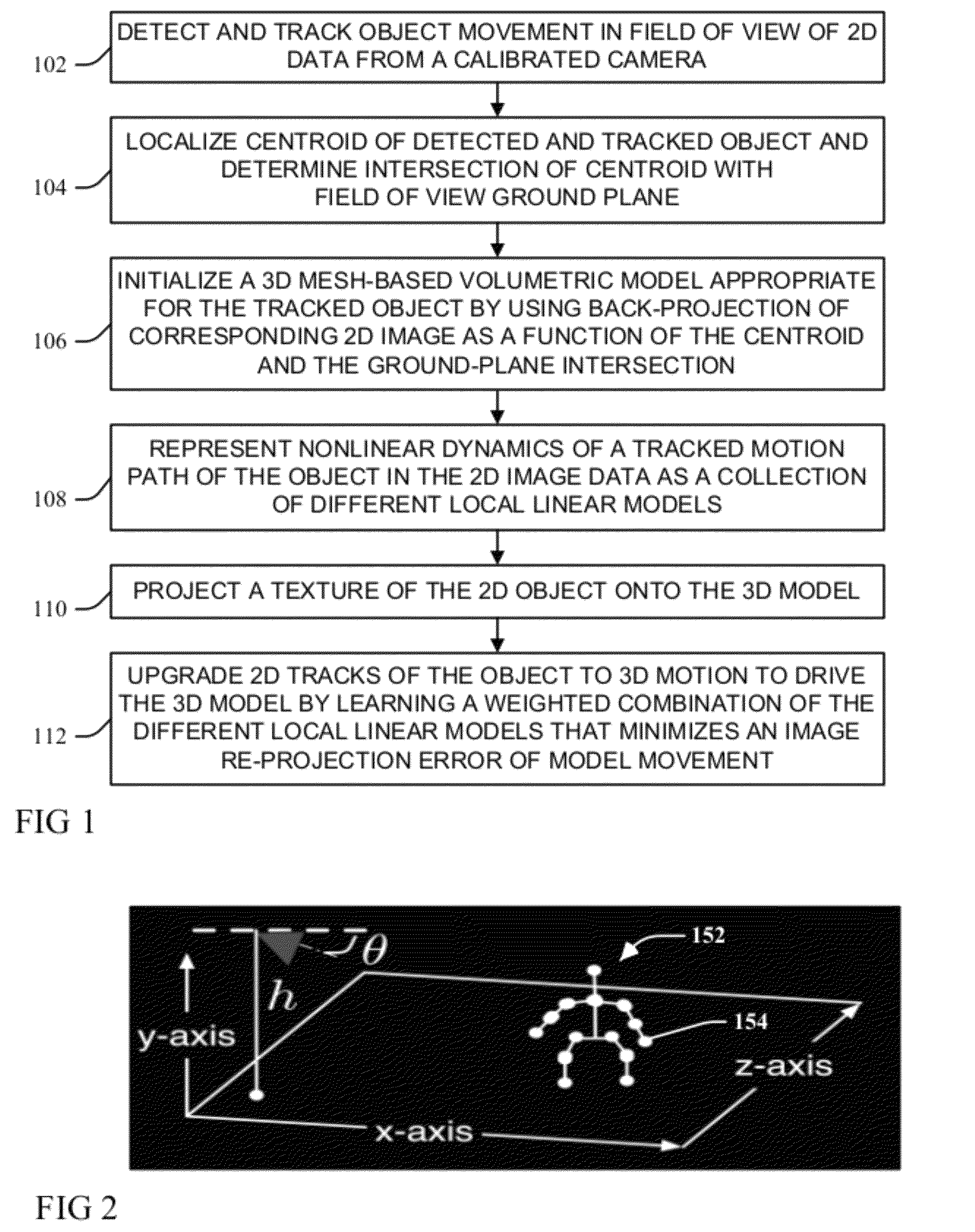
ActiveUS20120281873A1Minimizes an image re-projection error of model movementImaging errorTelevision system detailsImage analysisNon linear dynamicIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
A moving object detected and tracked within a field of view environment of a 2D data feed of a calibrated video camera is represented by a 3D model through localizing a centroid of the object and determining an intersection with a ground-plane within the field of view environment. An appropriate 3D mesh-based volumetric model for the object is initialized by using a back-projection of a corresponding 2D image as a function of the centroid and the determined ground-plane intersection. Nonlinear dynamics of a tracked motion path of the object are represented as a collection of different local linear models. A texture of the object is projected onto the 3D model, and 2D tracks of the object are upgraded to 3D motion to drive the 3D model by learning a weighted combination of the different local linear models that minimizes an image re-projection error of model movement.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
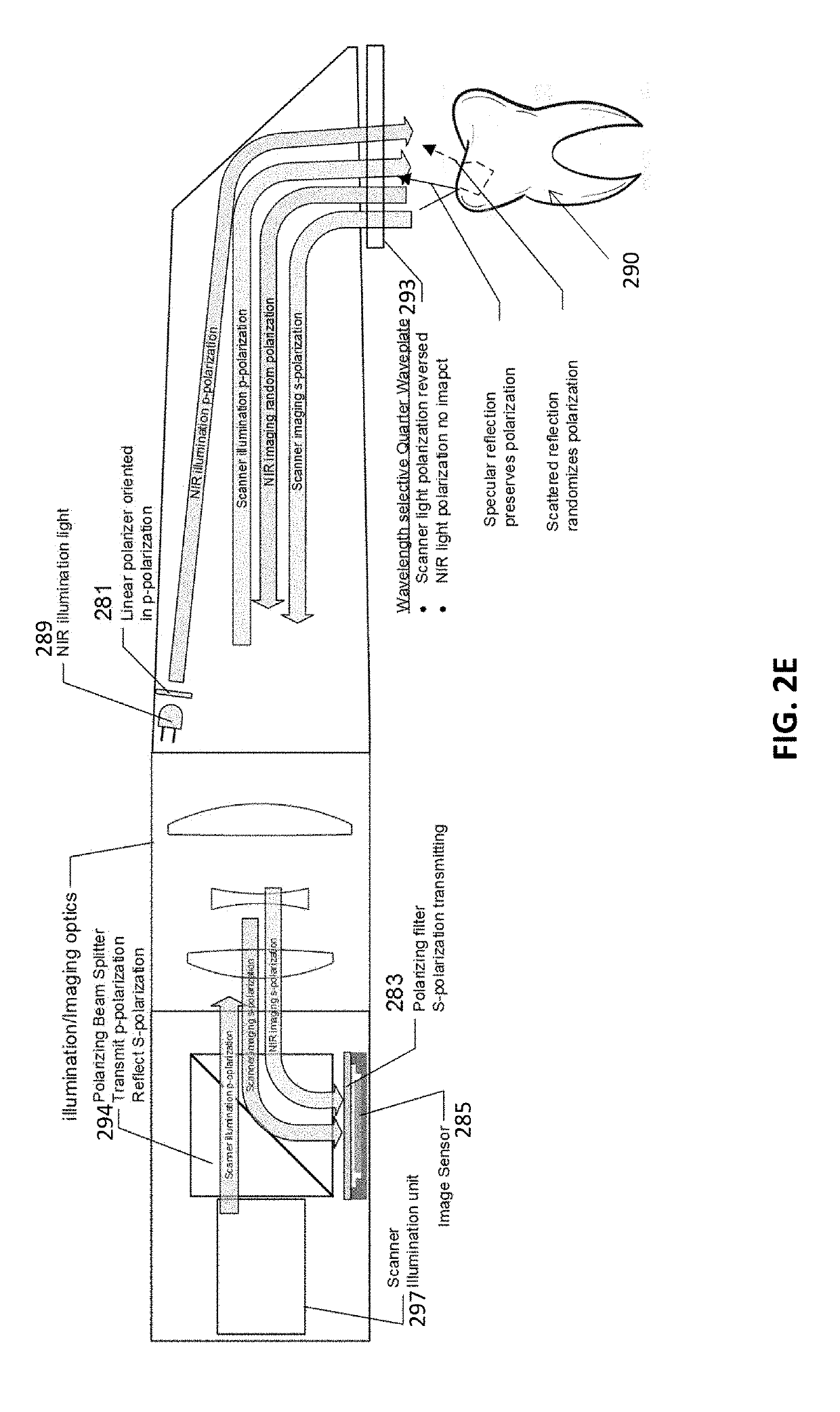
Methods for dental diagnostics
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Intraoral scanner with dental diagnostics capabilities
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Systems and methods for three-dimensional modeling
InactiveUS6958752B2Increase flexibilityMaintaining representationVisual presentationAnimationDimensional modelingObject store
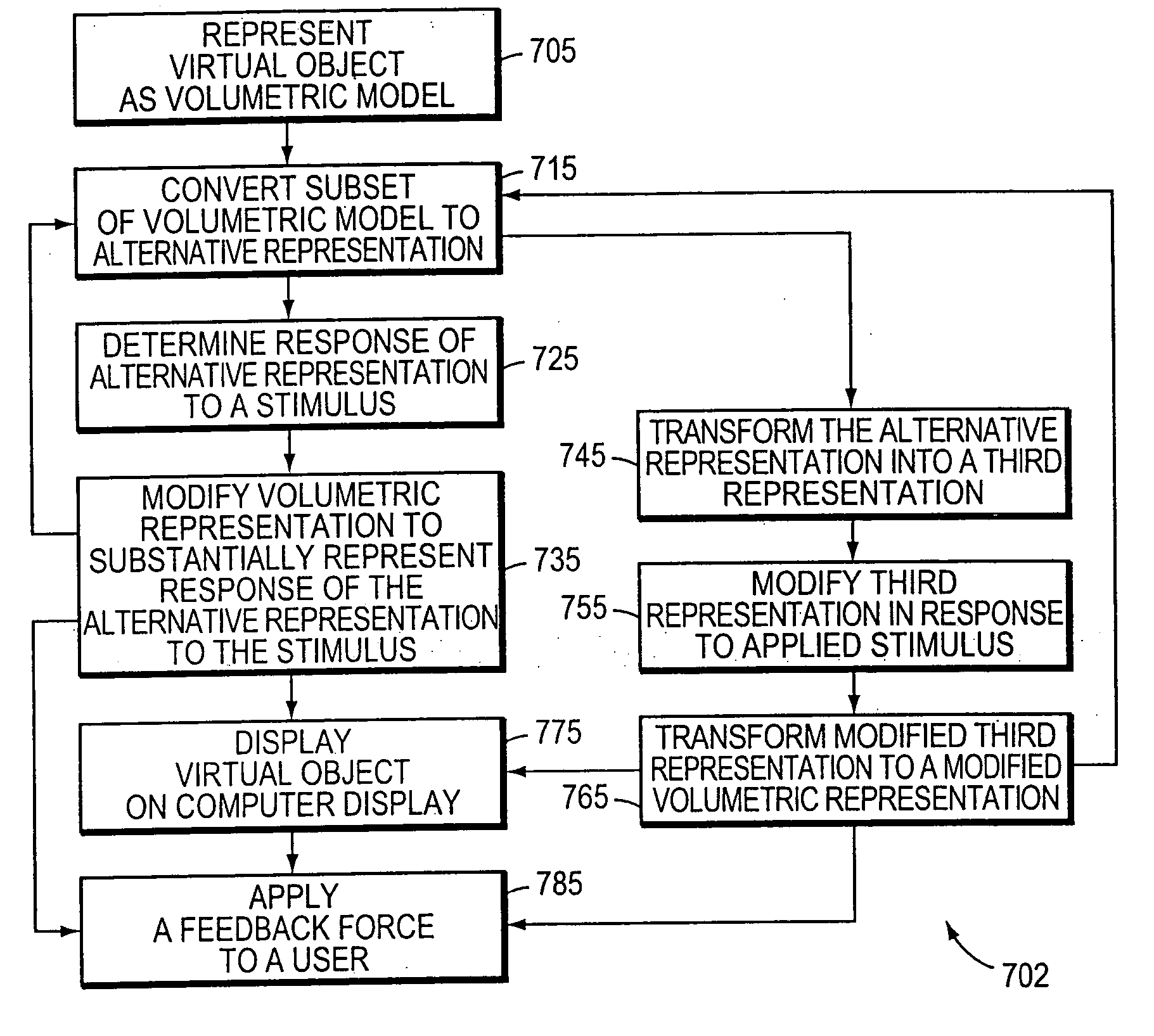
Systems and methods for modifying a virtual object stored within a computer. The systems and methods allow virtual object modifications that are otherwise computationally inconvenient. The virtual object is represented as a volumetric representation. A portion of the volumetric model is converted into an alternative representation. The alternative representation can be a representation having a different number of dimensions from the volumetric representations. A stimulus is applied to the alternative representation, for example by a user employing a force-feedback haptic interface. The response of the alternative representation to the stimulus is calculated. The change in shape of the virtual object is determined from the response of the alternative representation. The representations of the virtual object can be displayed at any time for the user. The user can be provided a force-feedback response. Multiple stimuli can be applied in succession. Multiple alternative representations can be employed in the system and method.
Owner:3D SYST INC
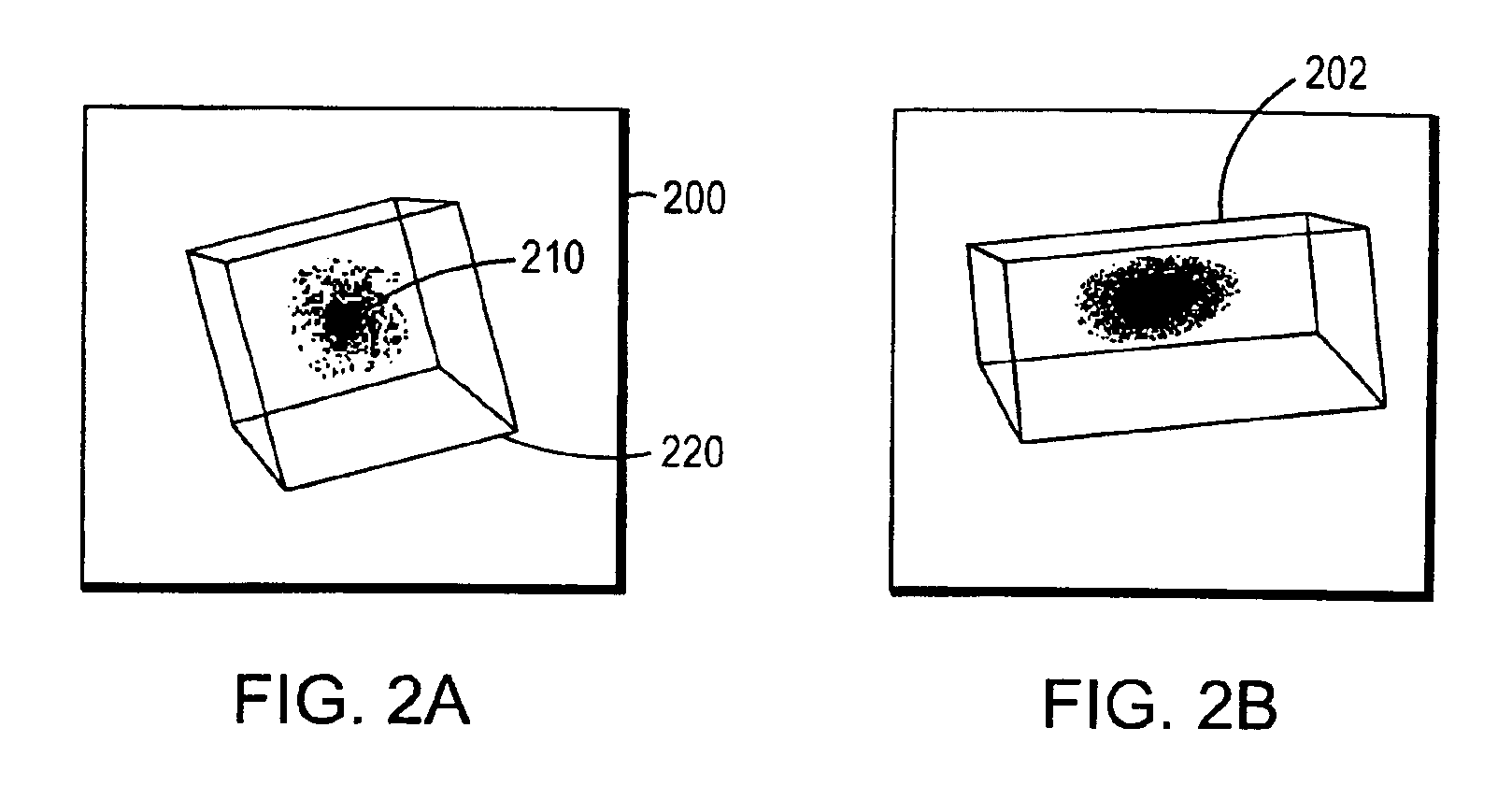
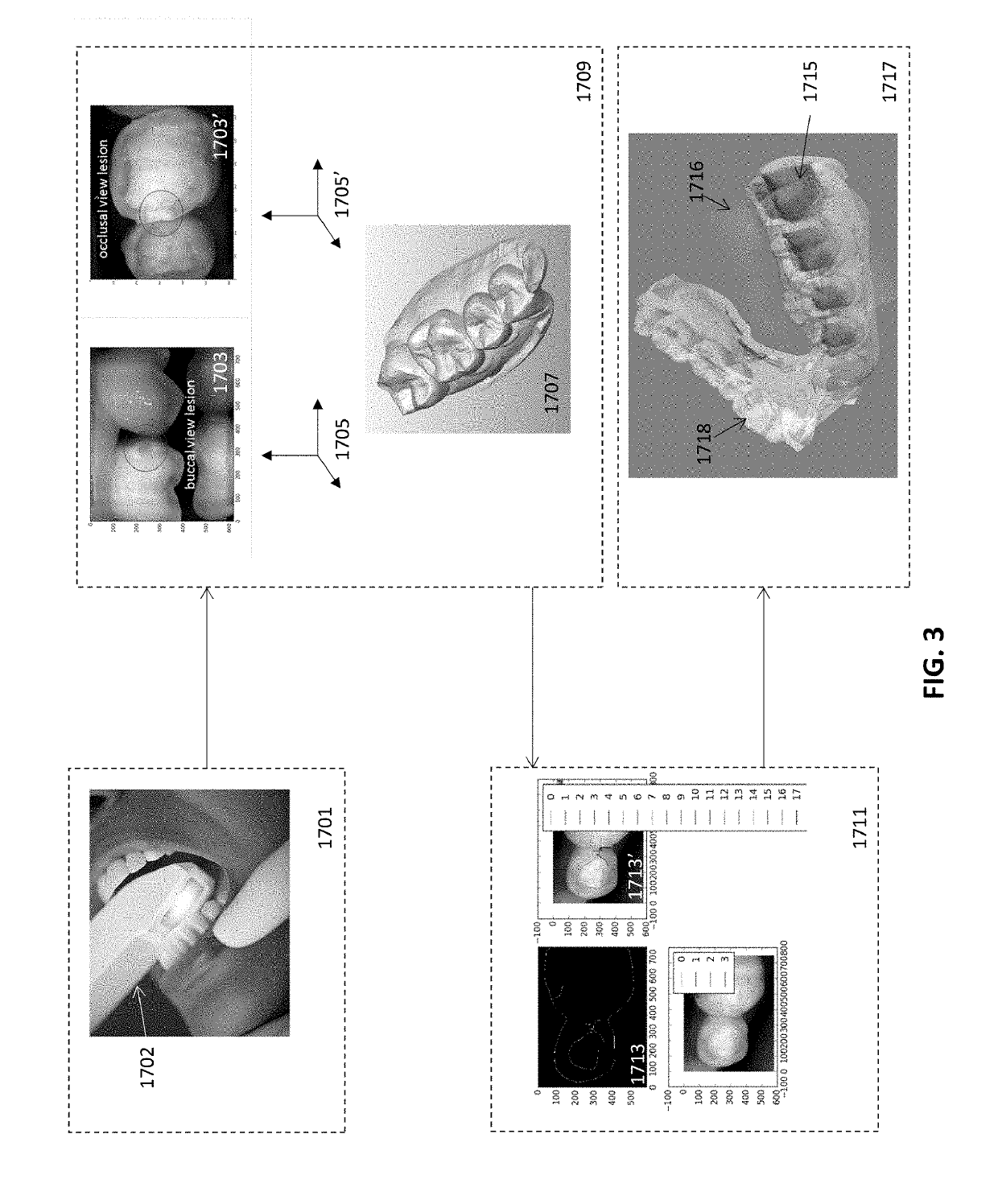
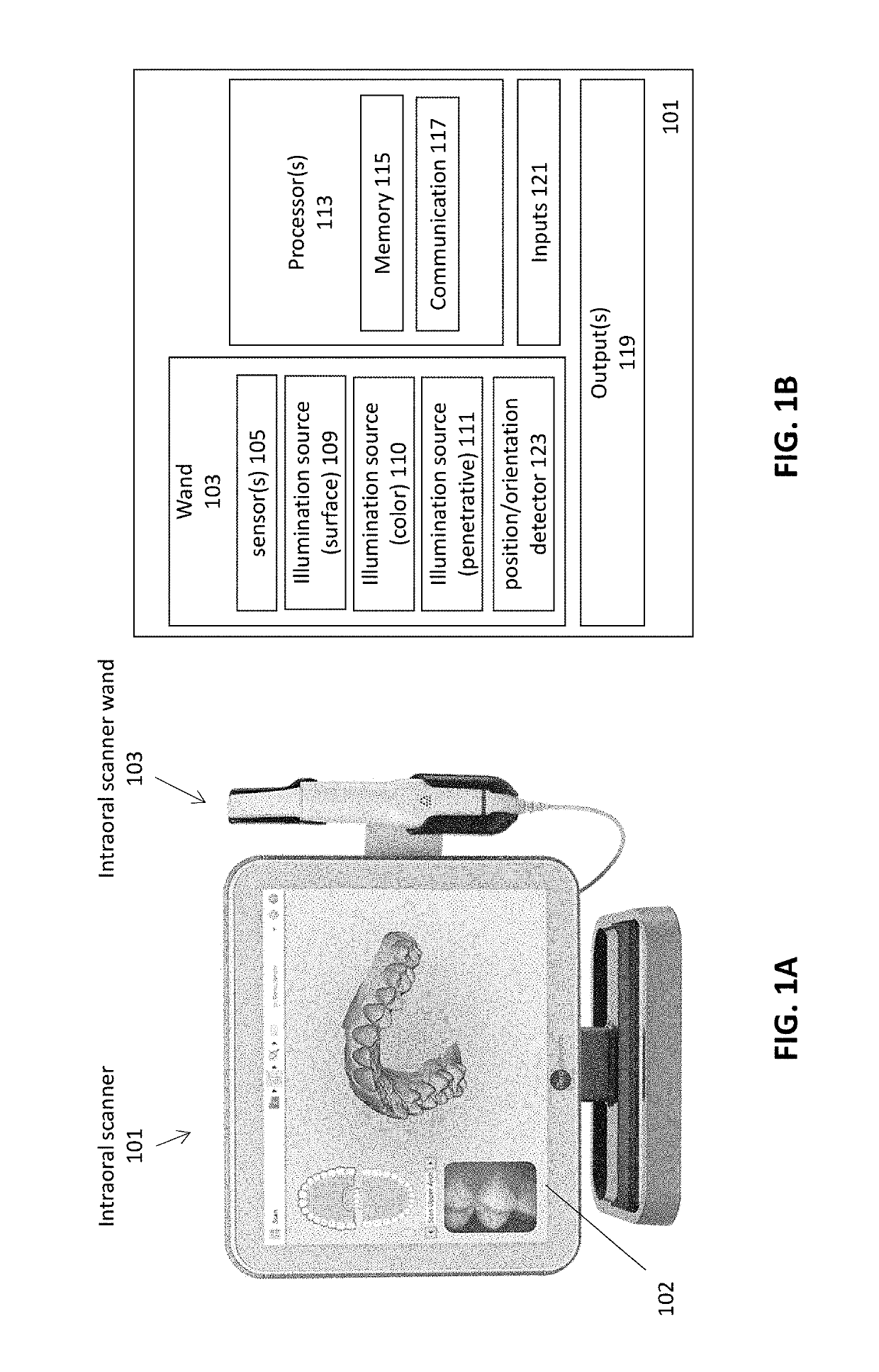
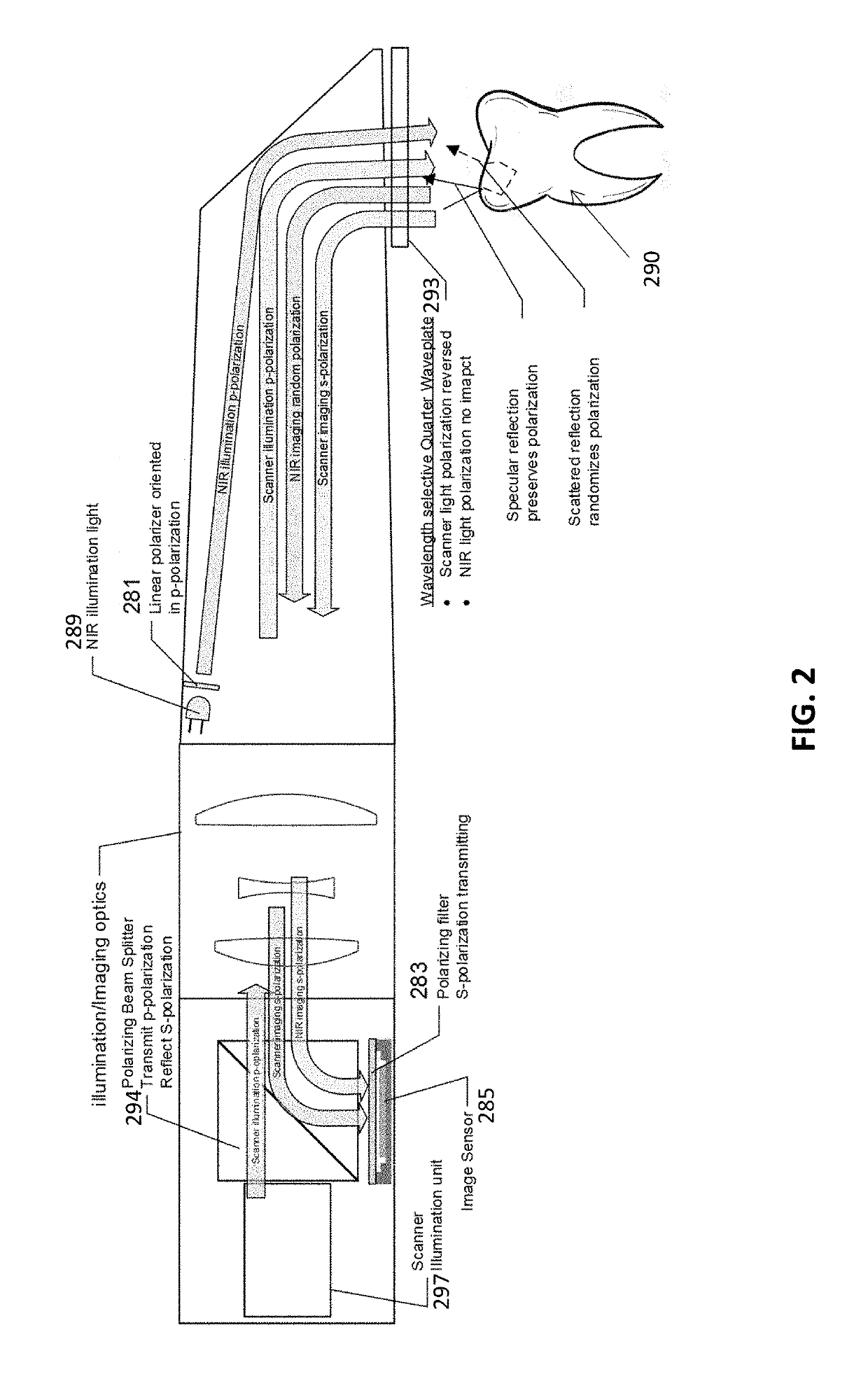
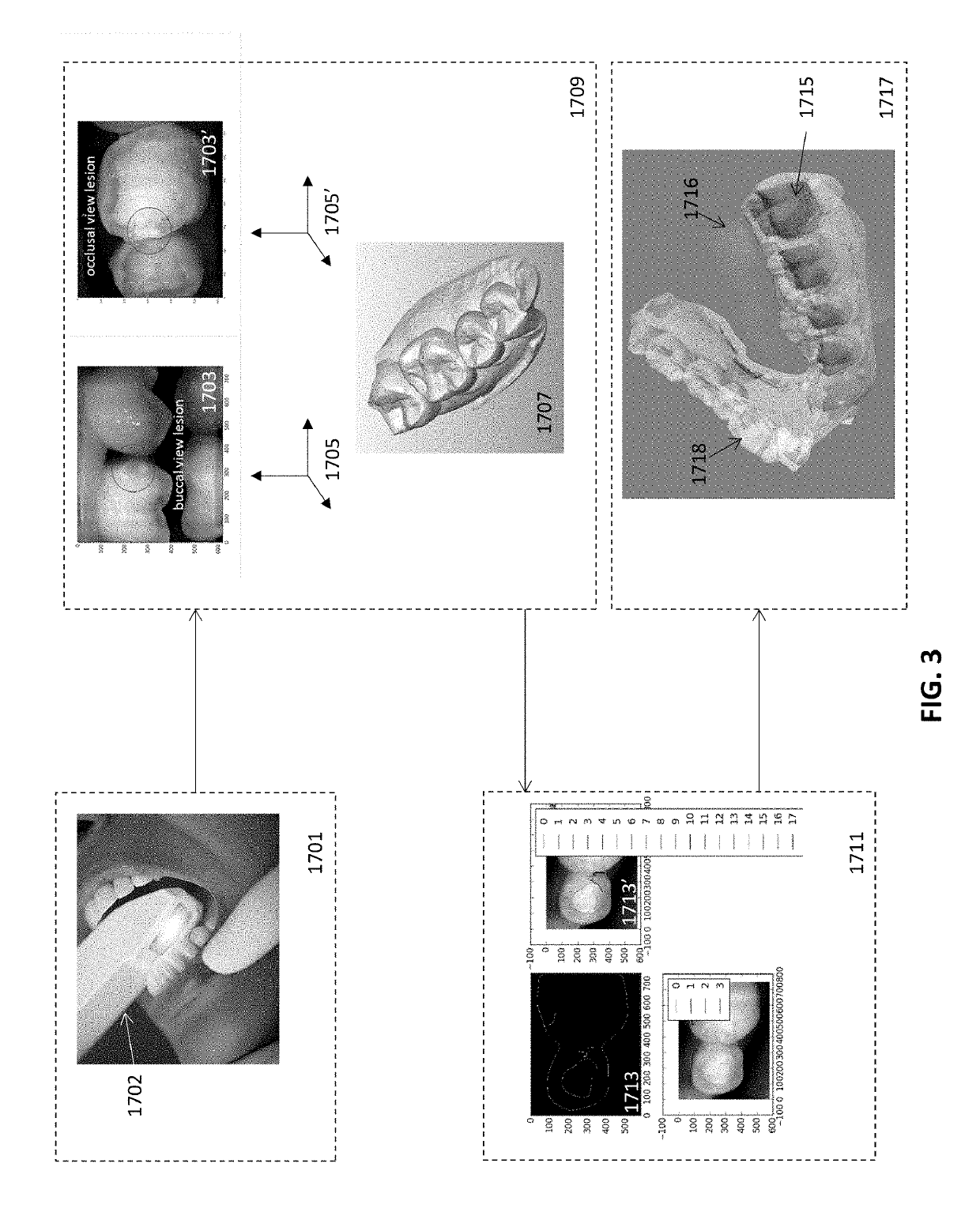
Diagnostic intraoral scanning
Methods and apparatuses for taking, using and displaying three-dimensional (3D) volumetric models of a patient's dental arch. A 3D volumetric model may include surface (e.g., color) information as well as information on internal structure, such as near-infrared (near-IR) transparency values for internal structures including enamel and dentin.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Method and system for interactive simulation of materials and models
ActiveUS20130187930A1Overcome problemsDesign optimisation/simulationAnimationAnimationVisual perception
A method and system for drawing, displaying, editing animating, simulating and interacting with one or more virtual polygonal, spline, volumetric models, three-dimensional visual models or robotic models. The method and system provide flexible simulation, the ability to combine rigid and flexible simulation on plural portions of a model, rendering of haptic forces and force-feedback to a user.
Owner:MILLMAN ALAN
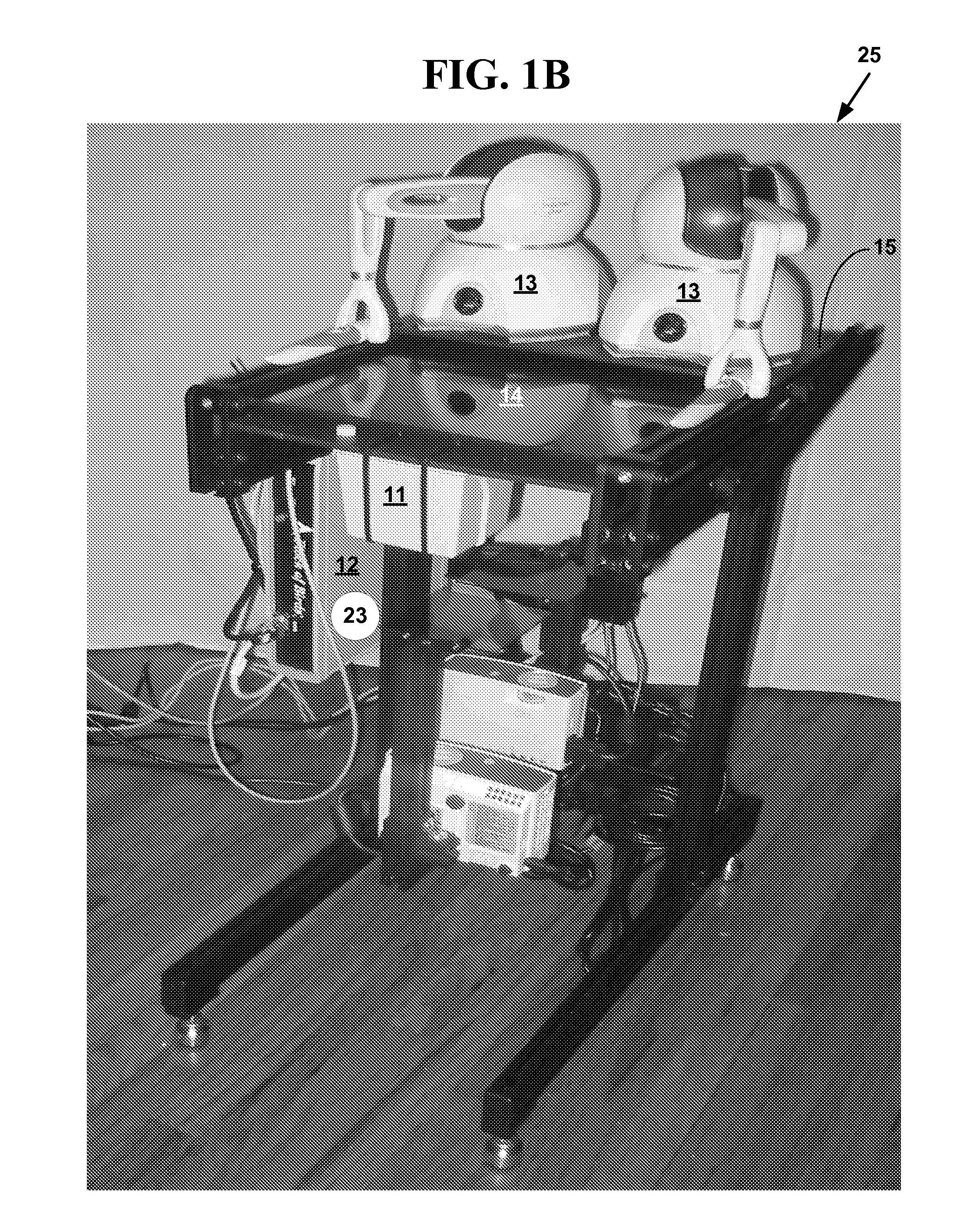
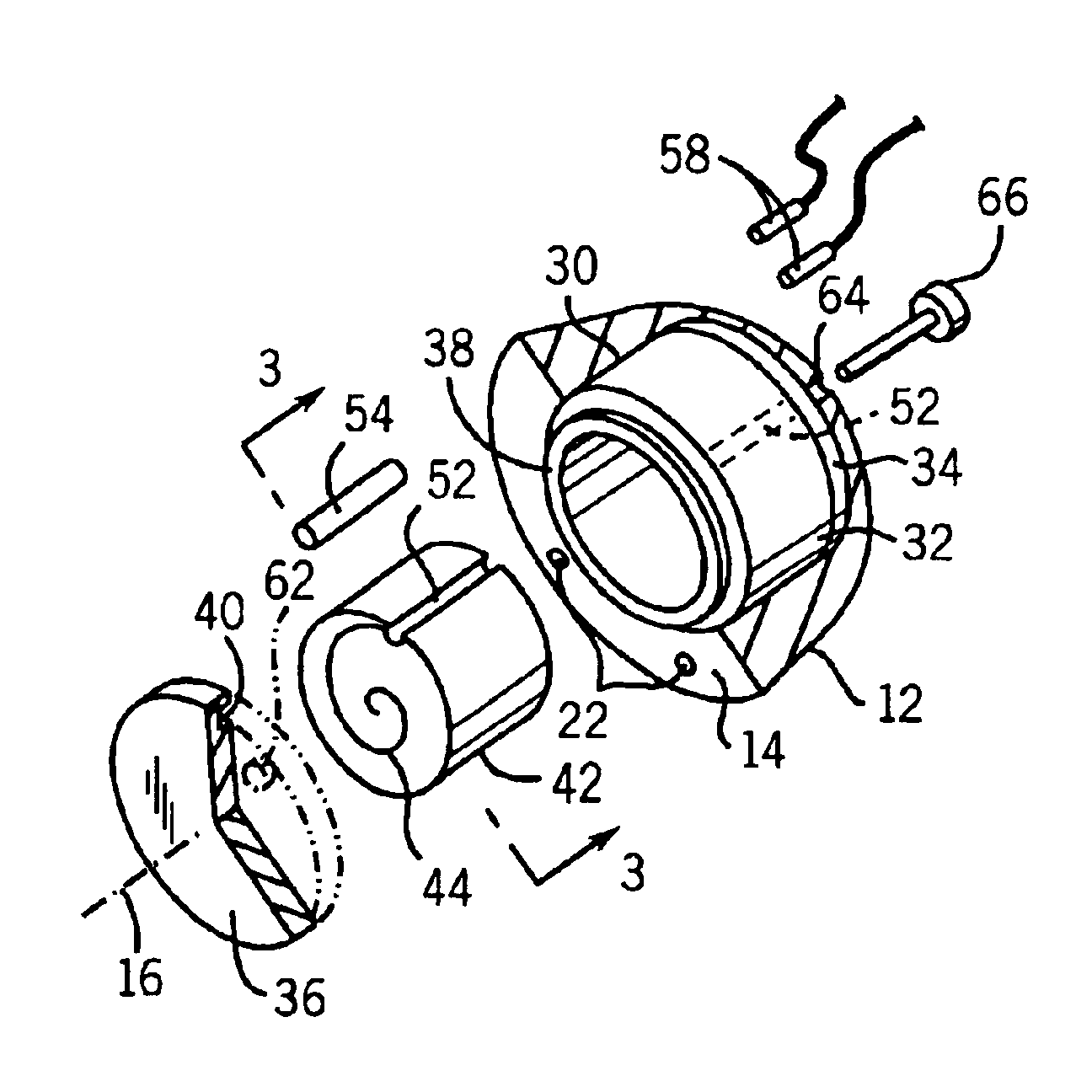
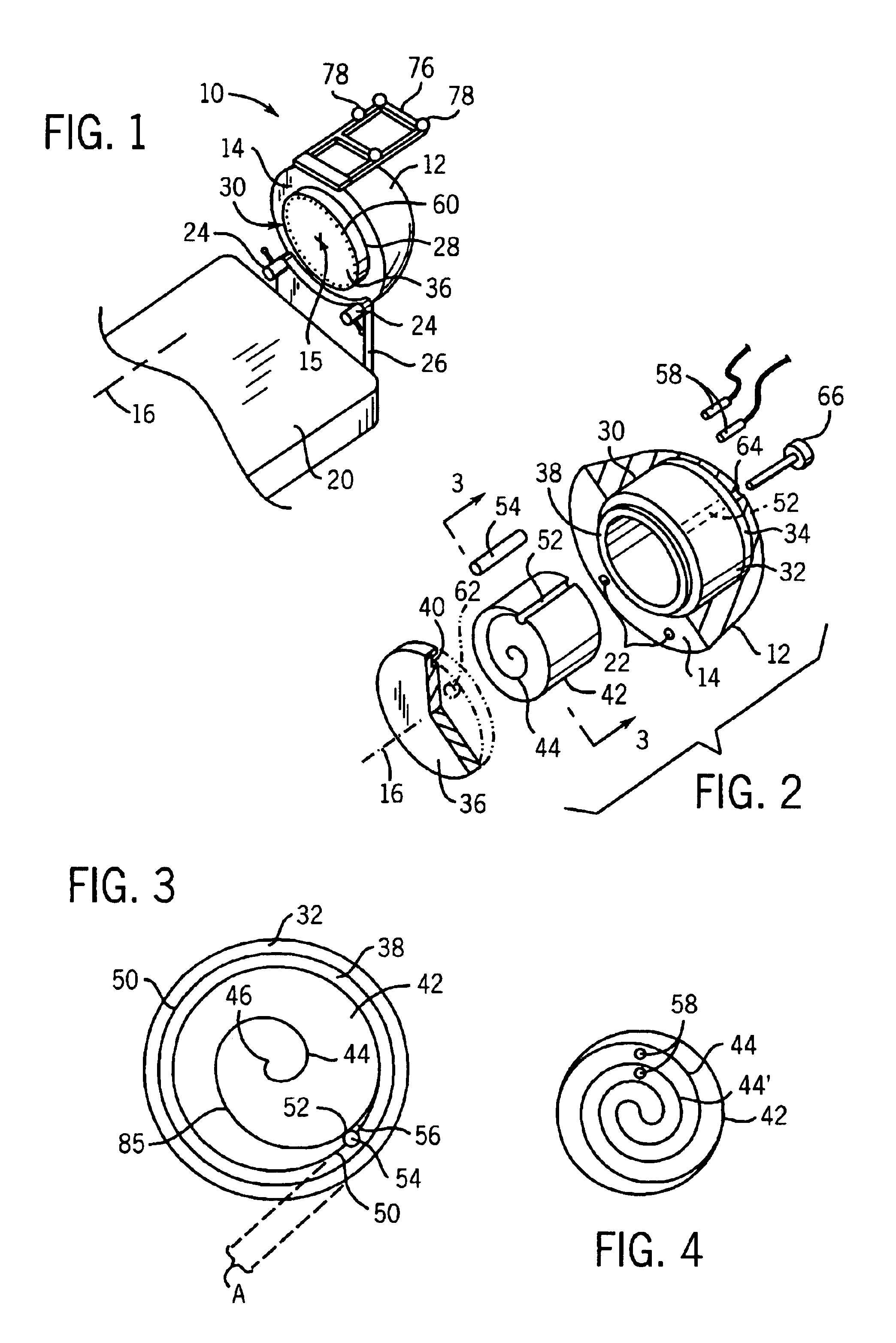
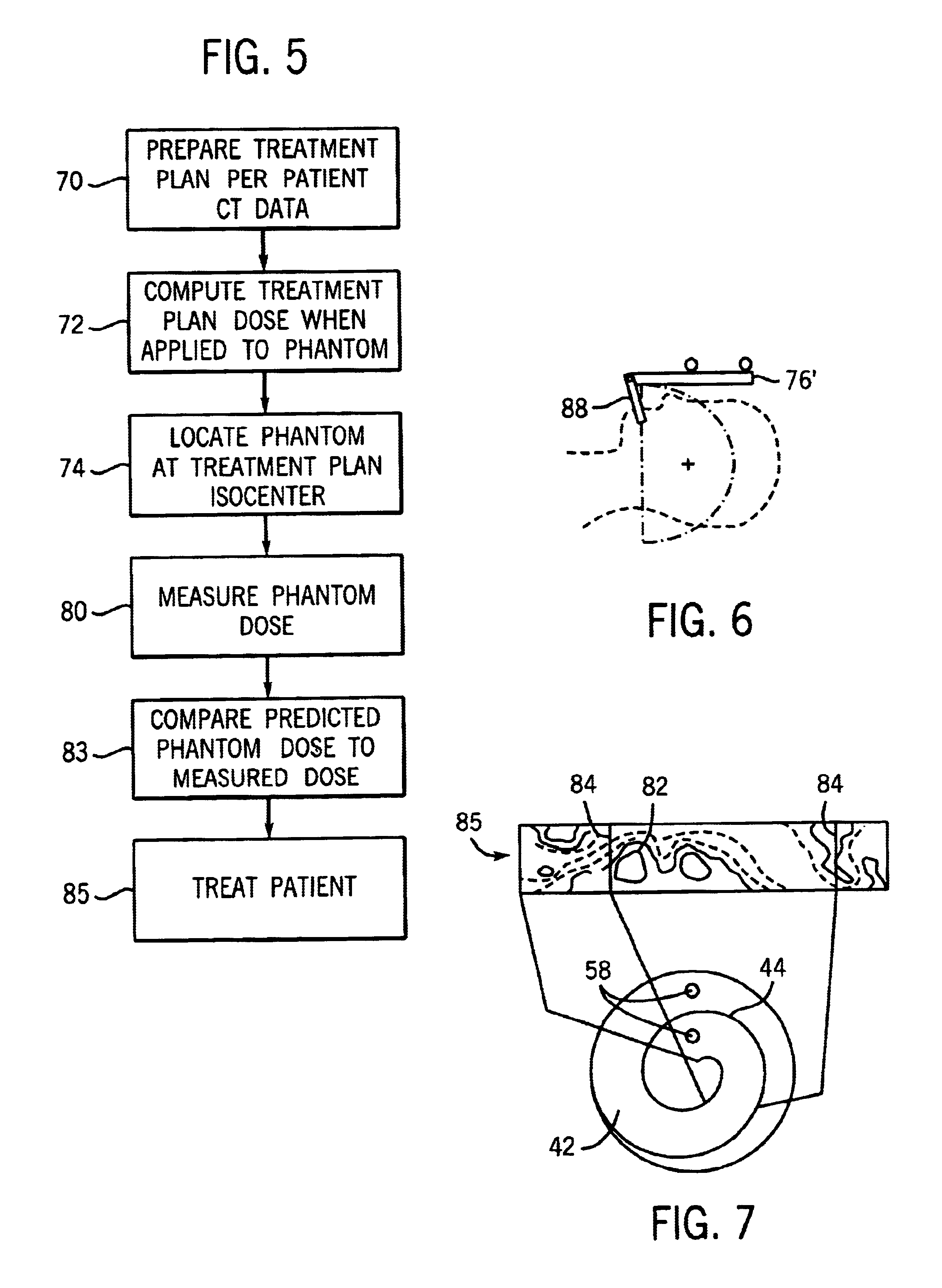
Radiation therapy volume phantom using film
InactiveUS6974254B2High quantitative accuracyMore uniform sensitivity of the film to radiationX-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationModeling and simulationRadiation therapy
A volume phantom for radiation therapy verification employs film held in a spiral configuration within a equalizing ring of attenuating material. The ring provides improved uniformity in radiation measurement and may be extended, for example, to a hemisphere to provide improved modeling and simulation of treatments in the region of the head.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
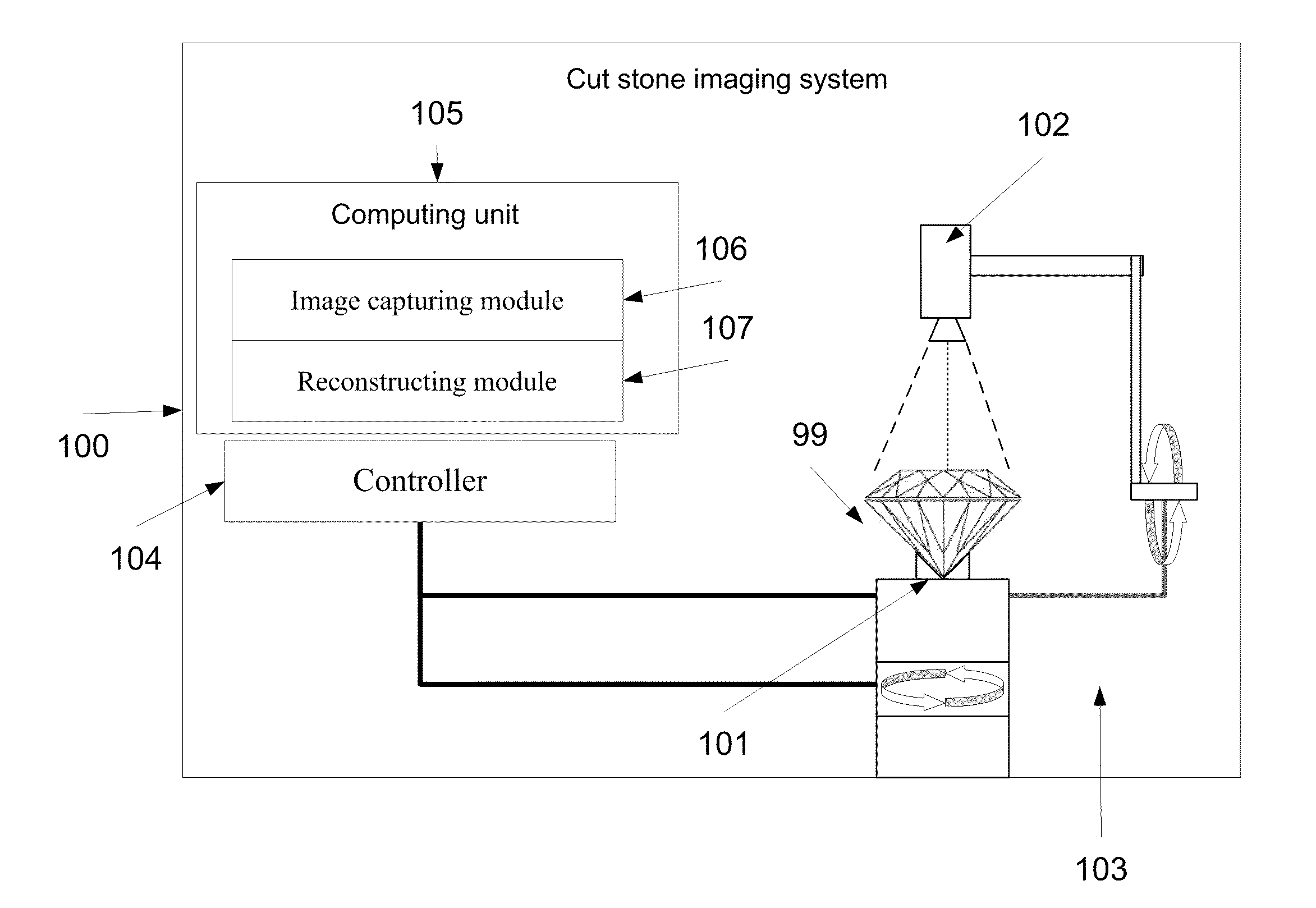
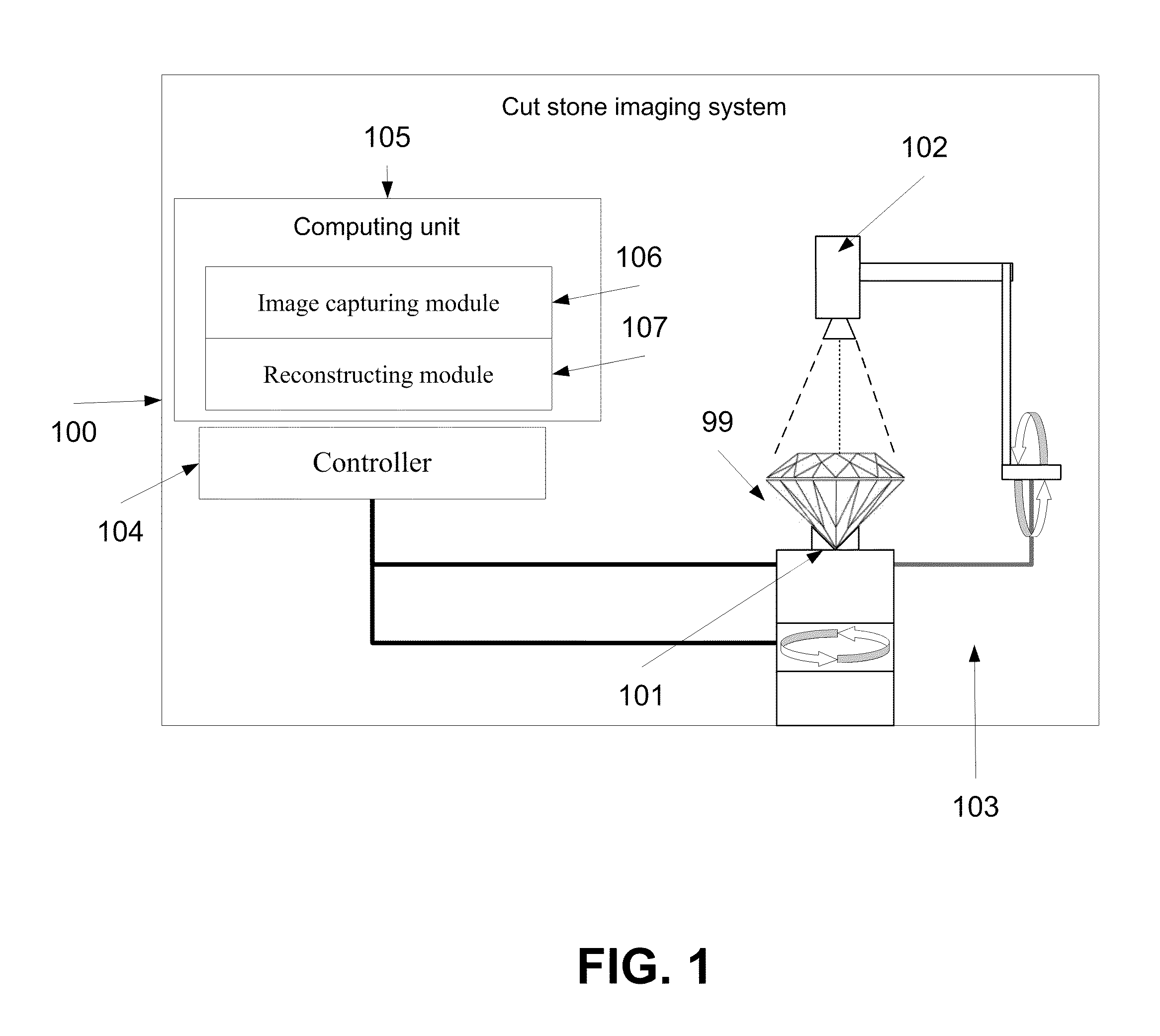
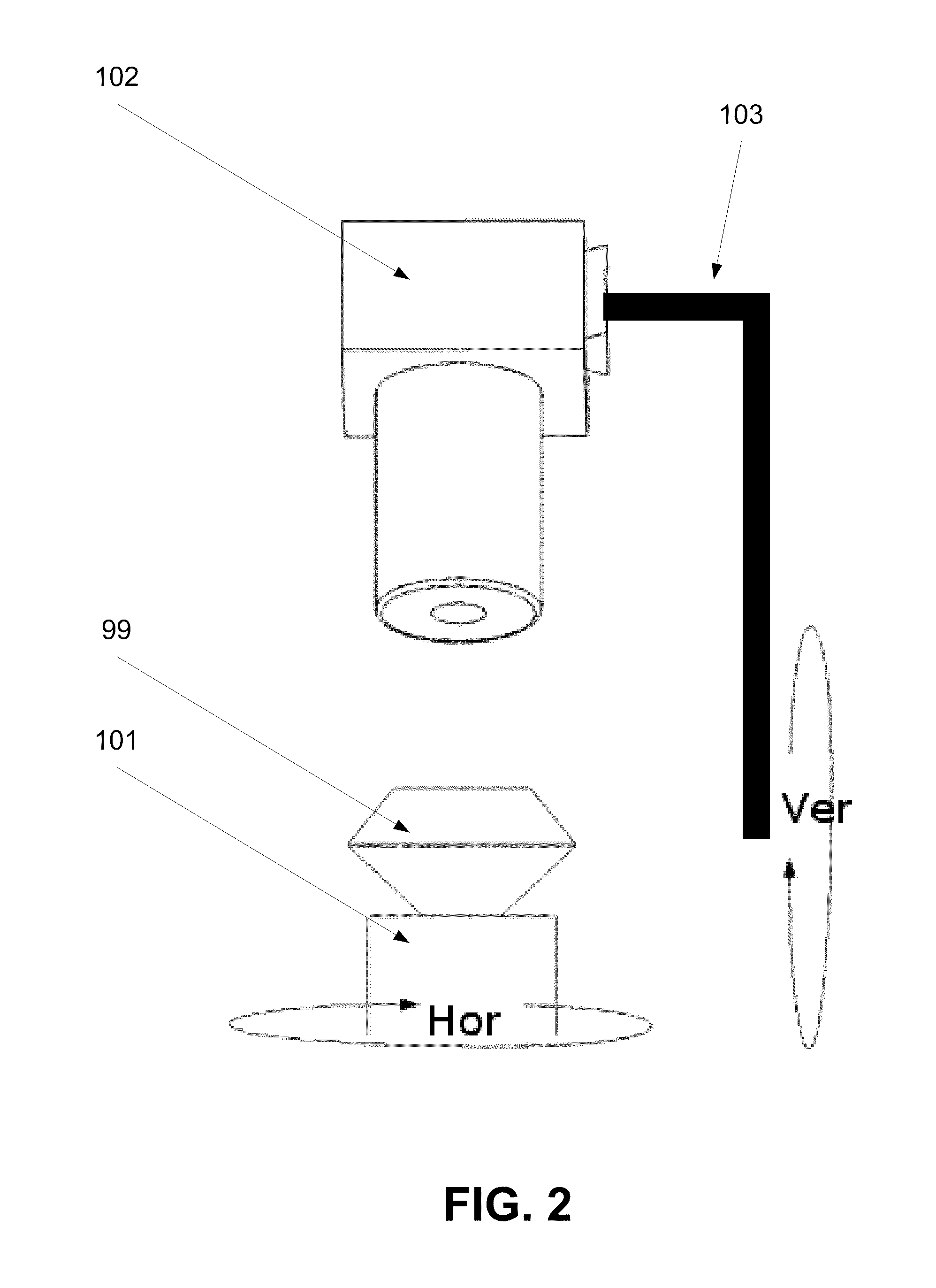
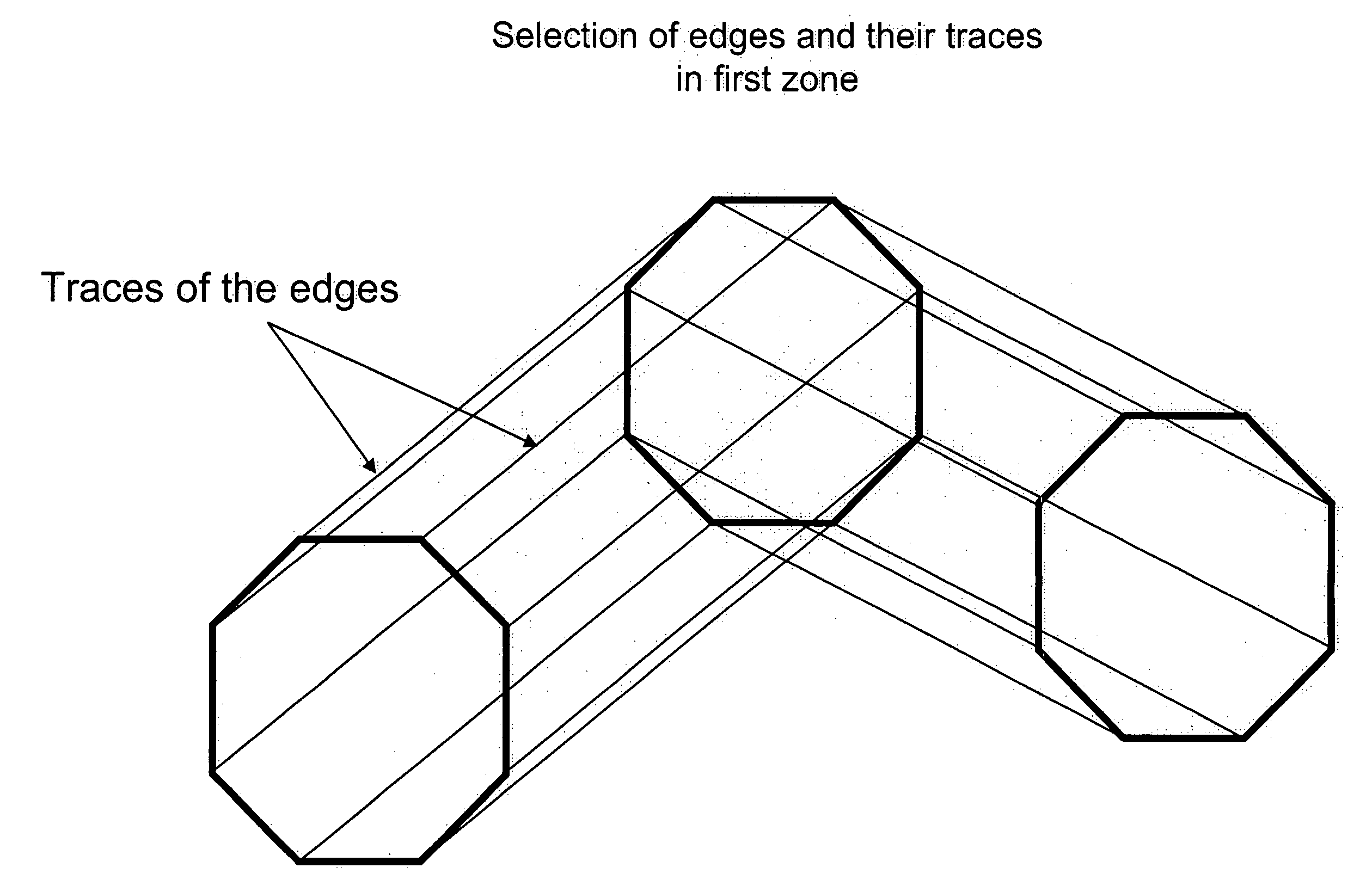
Methods and systems of imaging cut stones
ActiveUS20120007971A1Increase exposureImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMethod of imagesVolumetric model
A method of imaging a cut stone. The method comprises a) identifying an orientation of a cut stone, b) creating a volumetric model of the cut stone according to the orientation, c) capturing a plurality of images of the cut stone from a plurality of viewing angles around the cut stone, d) cropping a plurality of segments depicting the cut stone from the plurality of images using the volumetric model, and e) generating a volumetric image of the cut stone from the plurality of segments.
Owner:SARIN COLOR TECH
Swept volume model
InactiveUS6993461B1Efficient productionEfficient processingComputation using non-contact making devicesComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer scienceComputer simulation
Owner:ENTERA +1
Method for geocoding a perspective image
ActiveUS20070002040A1Without computational difficultySufficient speedPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer Aided DesignComputer graphics (images)
A method for geographically registering a perspective image of a location assigns elevation values to elements or pixels of a two dimensional array of image elements or pixels of the location. The elevation value for each image pixel is obtained using a corresponding database stored reference digital elevation model, or a three dimensional surface model of the location. The reference elevation model or surface model is composed of rows and columns of elevation values corresponding to two dimensions of location values at a sensed location shown in the image, or is composed of a three dimensional surface or volume model of the location, such as a computer-aided design model or any other means of describing the three dimensional characteristics of the sensed location.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Methods and apparatuses for forming a three-dimensional volumetric model of a subject's teeth
ActiveUS20190269485A1Change in positionImpression capsDiagnostics using lightCementum cariesSimulation
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
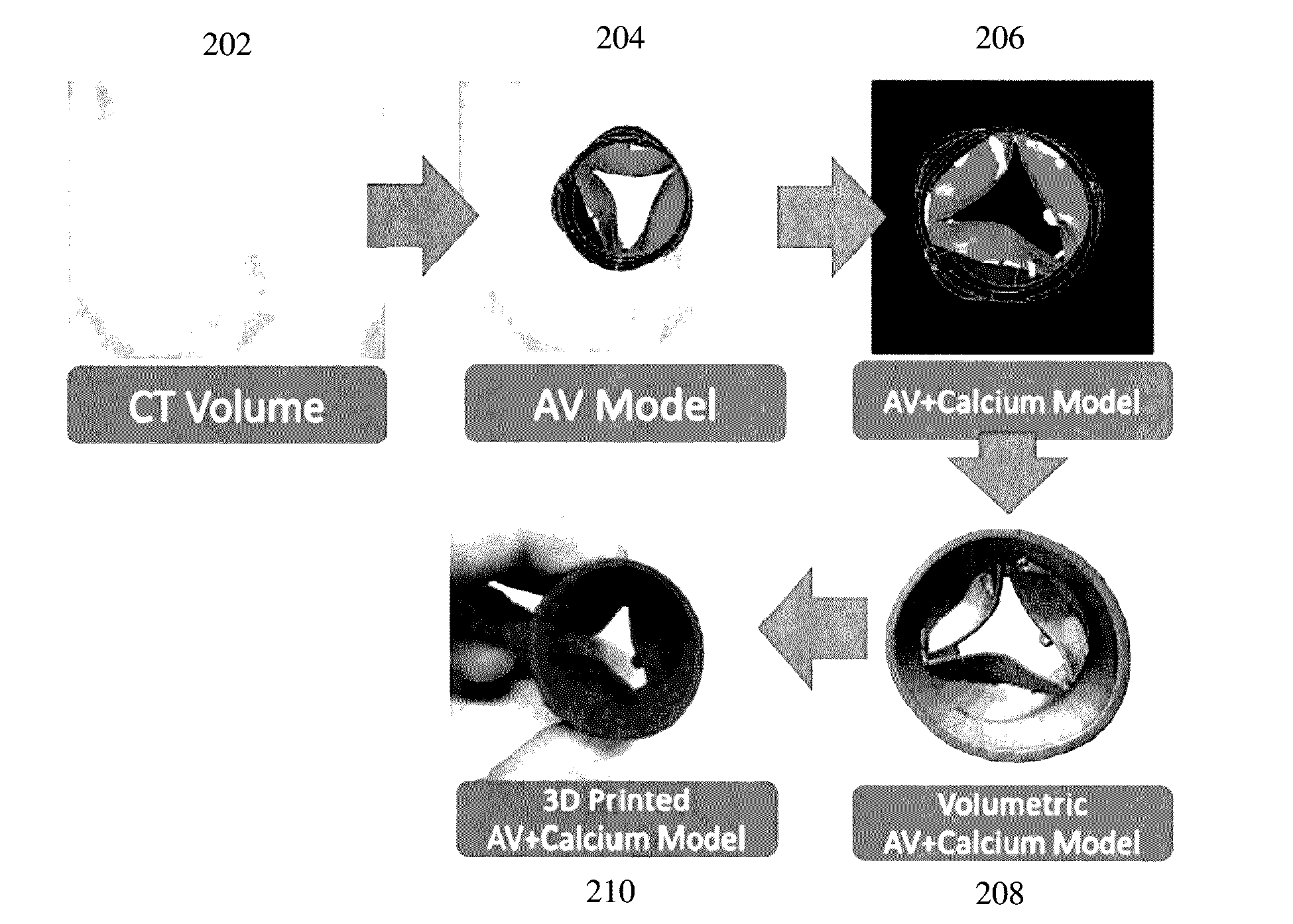
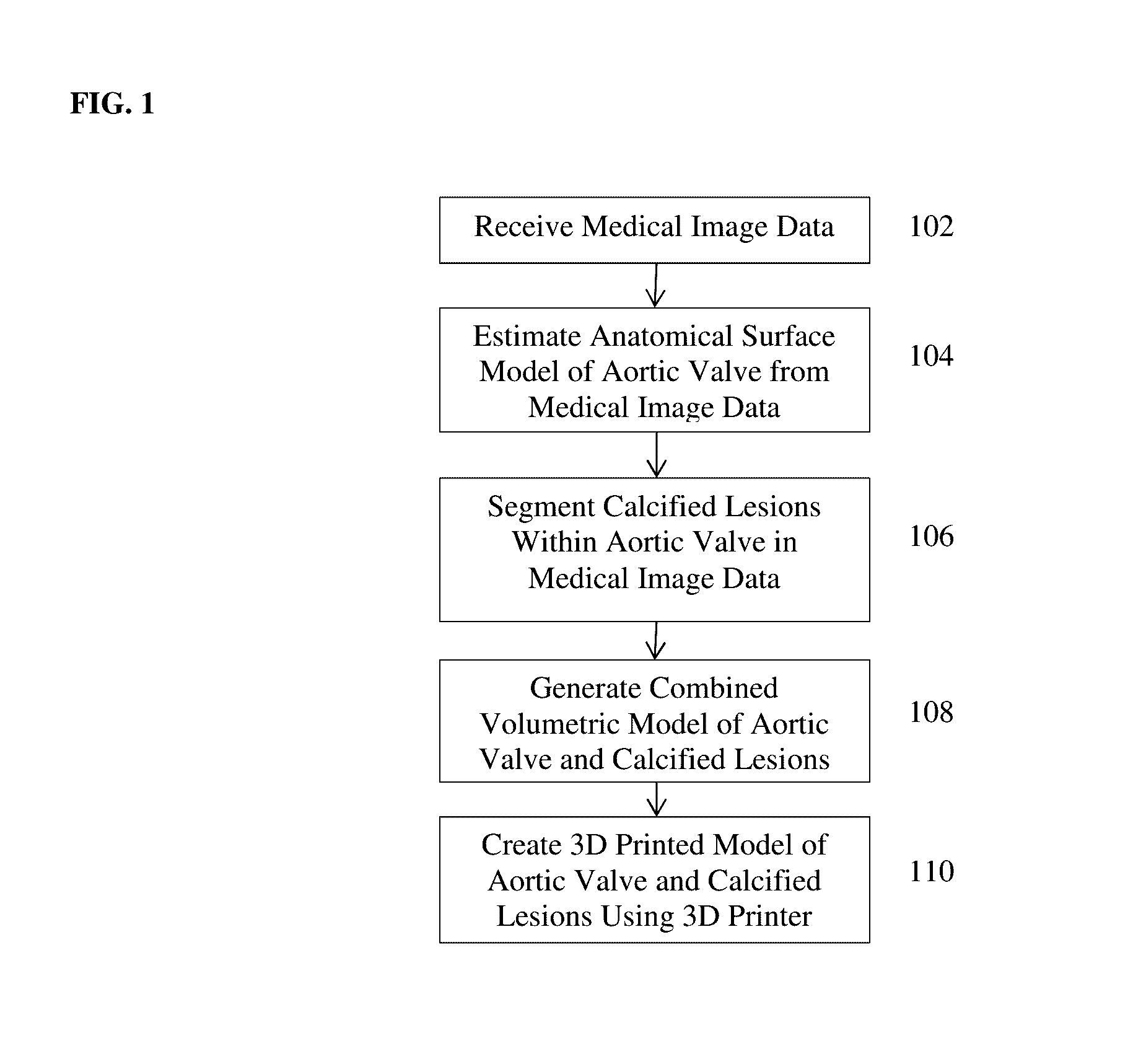
Method and System for Advanced Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Planning
A method and system for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) planning is disclosed. An anatomical surface model of the aortic valve is estimated from medical image data of a patient. Calcified lesions within the aortic valve are segmented in the medical image data. A combined volumetric model of the aortic valve and calcified lesions is generated. A 3D printed model of the heart valve and calcified lesions is created using a 3D printer. Different implant device types and sizes can be placed into the 3D printed model of the aortic valve and calcified lesions to select an implant device type and size for the patient for a TAVI procedure. The method can be similarly applied to other heart valves for any type of heart valve intervention planning.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and apparatuses for forming a three-dimensional volumetric model of a subject's teeth
Methods and apparatuses for generating a model of a subject's teeth. Described herein are intraoral scanning methods and apparatuses for generating a three-dimensional model of a subject's intraoral region (e.g., teeth) including both surface features and internal features. These methods and apparatuses may be used for identifying and evaluating lesions, caries and cracks in the teeth. Any of these methods and apparatuses may use minimum scattering coefficients and / or segmentation to form a volumetric model of the teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Diagnostic intraoral methods and apparatuses
Methods and apparatuses for taking, using and displaying three-dimensional (3D) volumetric models of a patient's dental arch. A 3D volumetric model may include surface (e.g., color) information as well as information on internal structure, such as near-infrared (near-IR) transparency values for internal structures including enamel and dentin.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Incorporating video meta-data in 3D models
ActiveUS8457355B2Minimizes an image re-projection error of model movementImaging errorTelevision system detailsImage analysisNon linear dynamicIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
A moving object detected and tracked within a field of view environment of a 2D data feed of a calibrated video camera is represented by a 3D model through localizing a centroid of the object and determining an intersection with a ground-plane within the field of view environment. An appropriate 3D mesh-based volumetric model for the object is initialized by using a back-projection of a corresponding 2D image as a function of the centroid and the determined ground-plane intersection. Nonlinear dynamics of a tracked motion path of the object are represented as a collection of different local linear models. A texture of the object is projected onto the 3D model, and 2D tracks of the object are upgraded to 3D motion to drive the 3D model by learning a weighted combination of the different local linear models that minimizes an image re-projection error of model movement.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
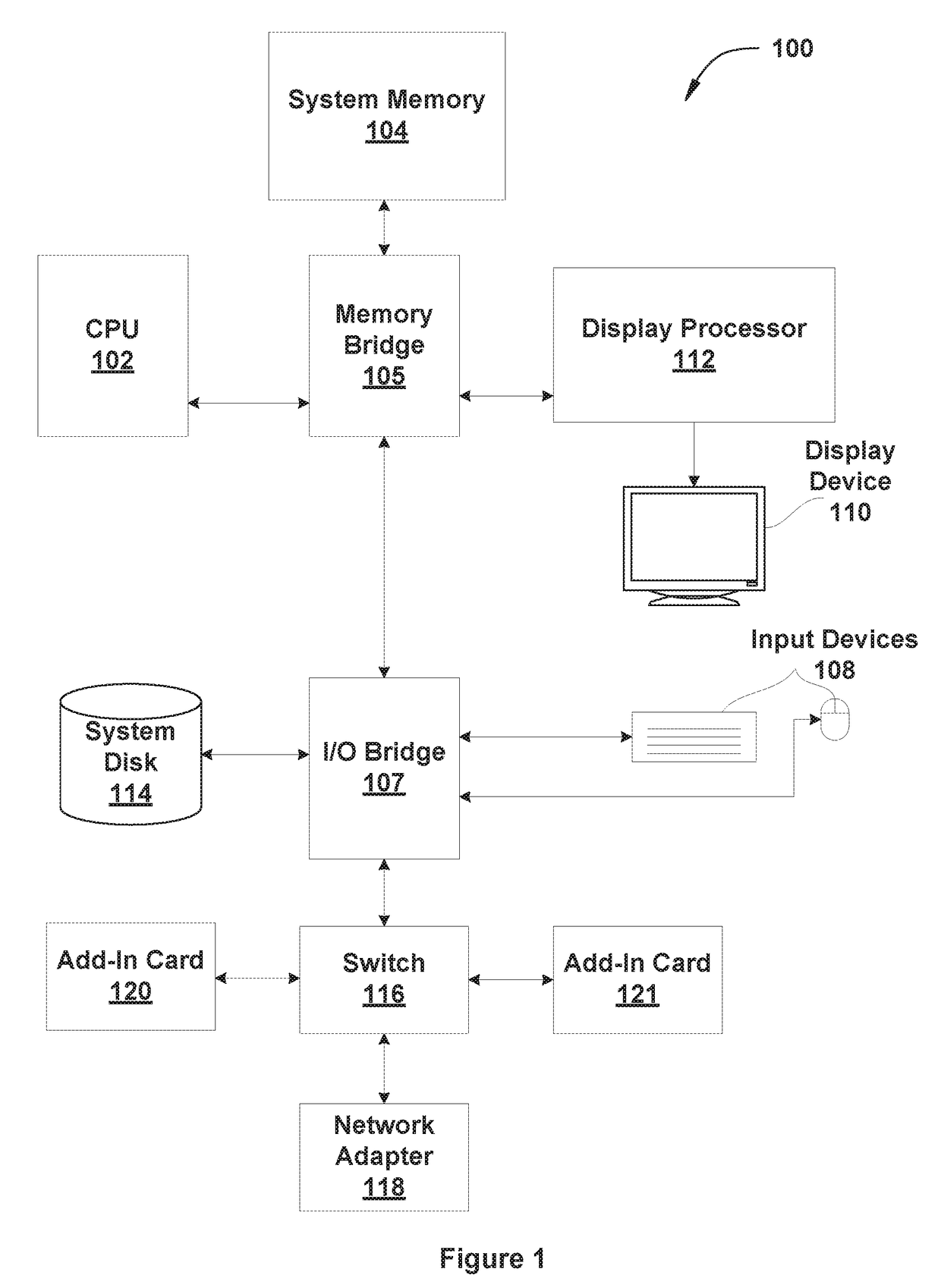
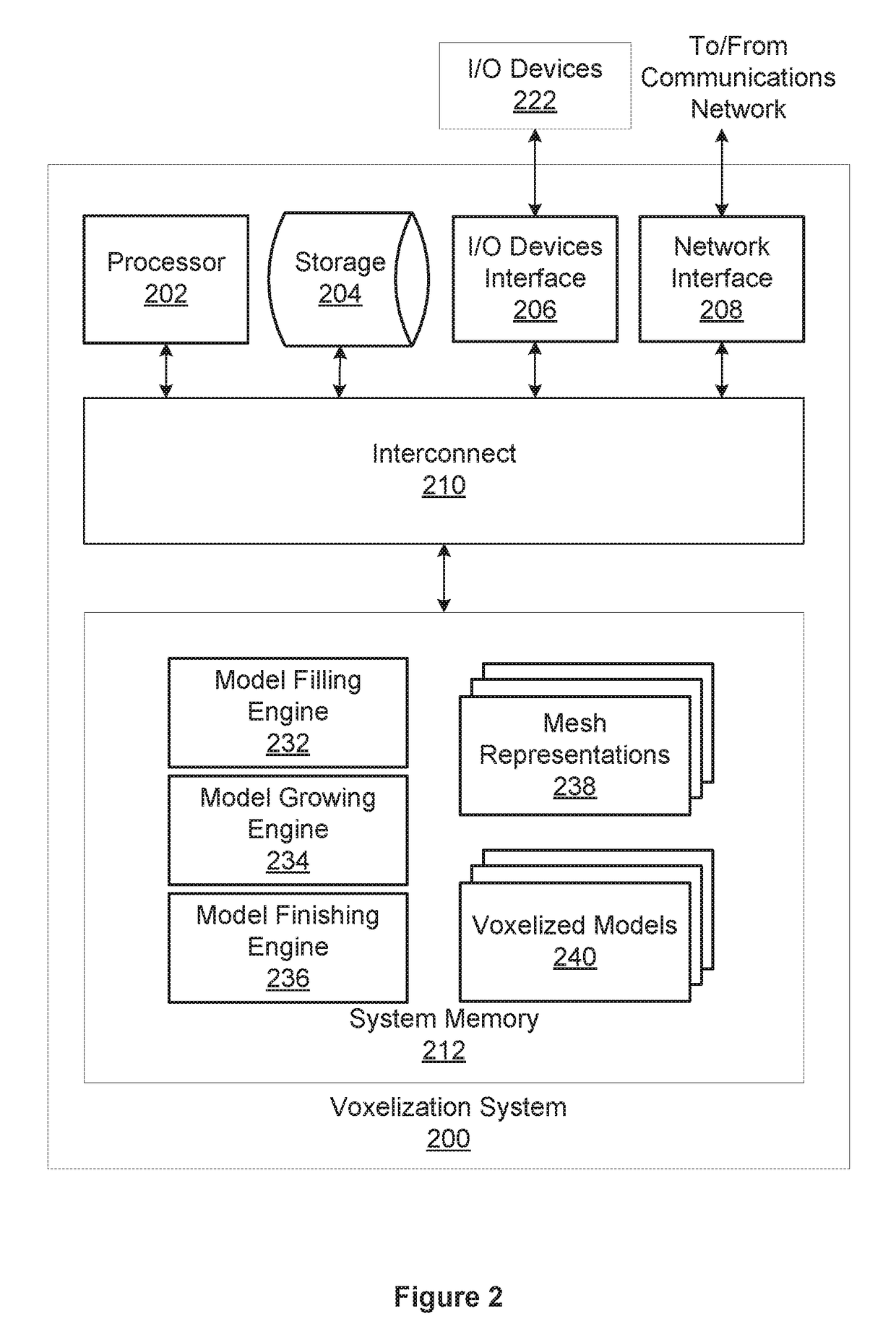
Voxelization of mesh representations
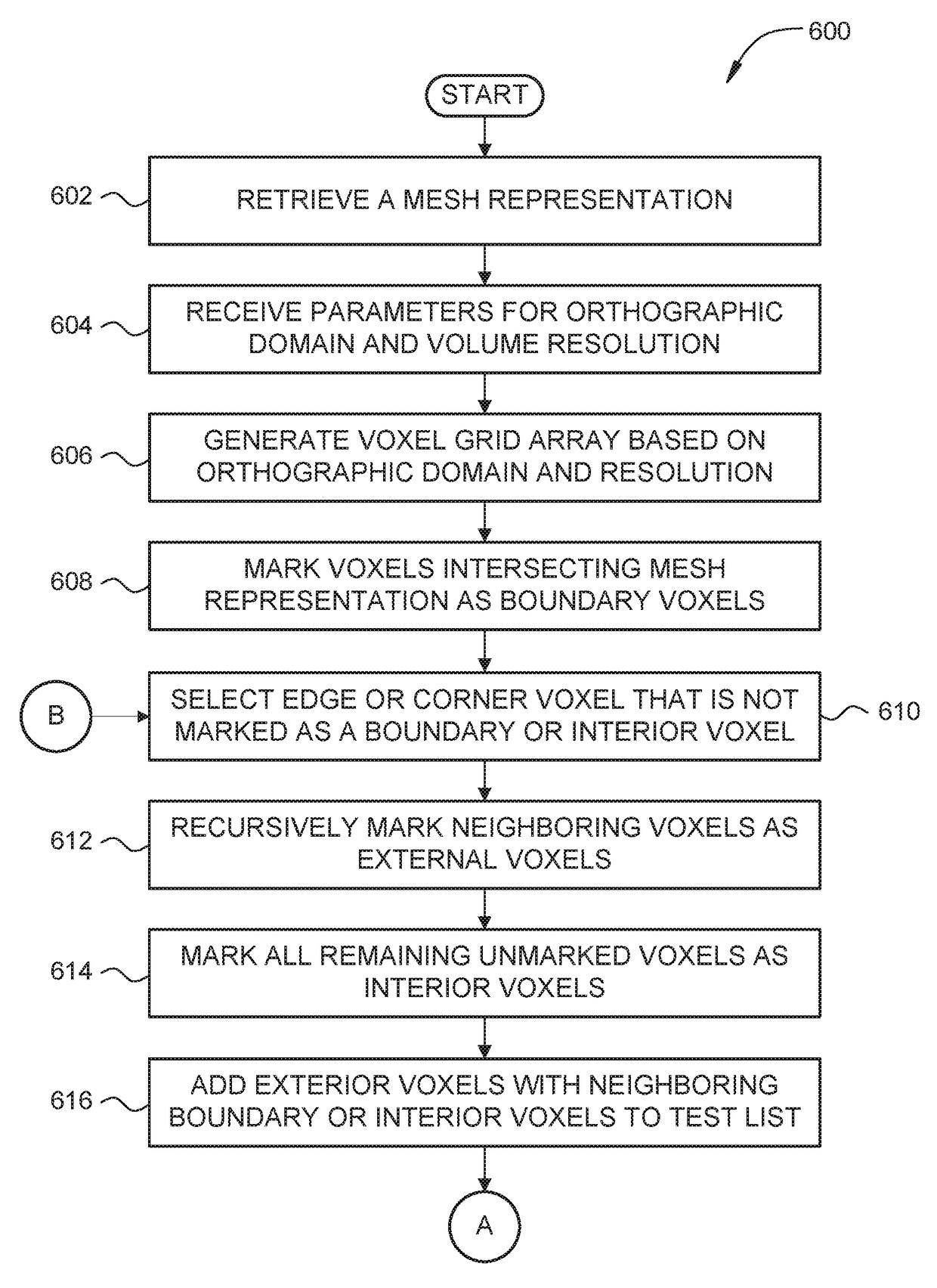
ActiveUS20170178388A1High quality volumetric modelLow cost3D-image rendering3D modellingComputational scienceVoxel
One embodiment of the invention disclosed herein provides techniques for voxelizing a mesh representation associated with a three-dimensional model to generate a volumetric model. A model filling engine associated with a voxelization system identifies a first voxel included in a voxel grid array that intersects with the mesh representation. The model filling engine selects a second voxel at an exterior boundary of the voxel grid array that is not identified as a boundary voxel. The model filling engine marks the second voxel as an exterior voxel. The model filling engine marks all unmarked voxels that are adjacent to the second voxel as exterior voxels. The model filling engine marks all remaining voxels as interior voxels. A model finishing engine associated with the voxelization system generates a volumetric model based at least in part on the first voxel.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Device in-orbit single event upset rate predicating method based on composite sensitive volume model
ActiveCN103729503ACorrecting for overestimationImprove forecast accuracySpecial data processing applicationsLogic cellSimulation
The invention provides a device in-orbit single event upset rate predicating method based on a composite sensitive volume model. The method includes: acquiring charge deposition borne by a device on an actual flight orbit by means of event transportation simulation; combining a single event effect simulation means of a device logic unit to acquire sensitive parameters of the device logic unit, establish the composite sensitive volume model, and describe incident event decomposition charge collection situation; after sample event upset of the logic unit is obtained, adopting a weighted statistic method to obtain a device in-orbit upset rate prediction result. Accuracy in in-orbit upset rate prediction of space navigation components and particularly of high-integration-level small-feature-size deep submicron devices is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
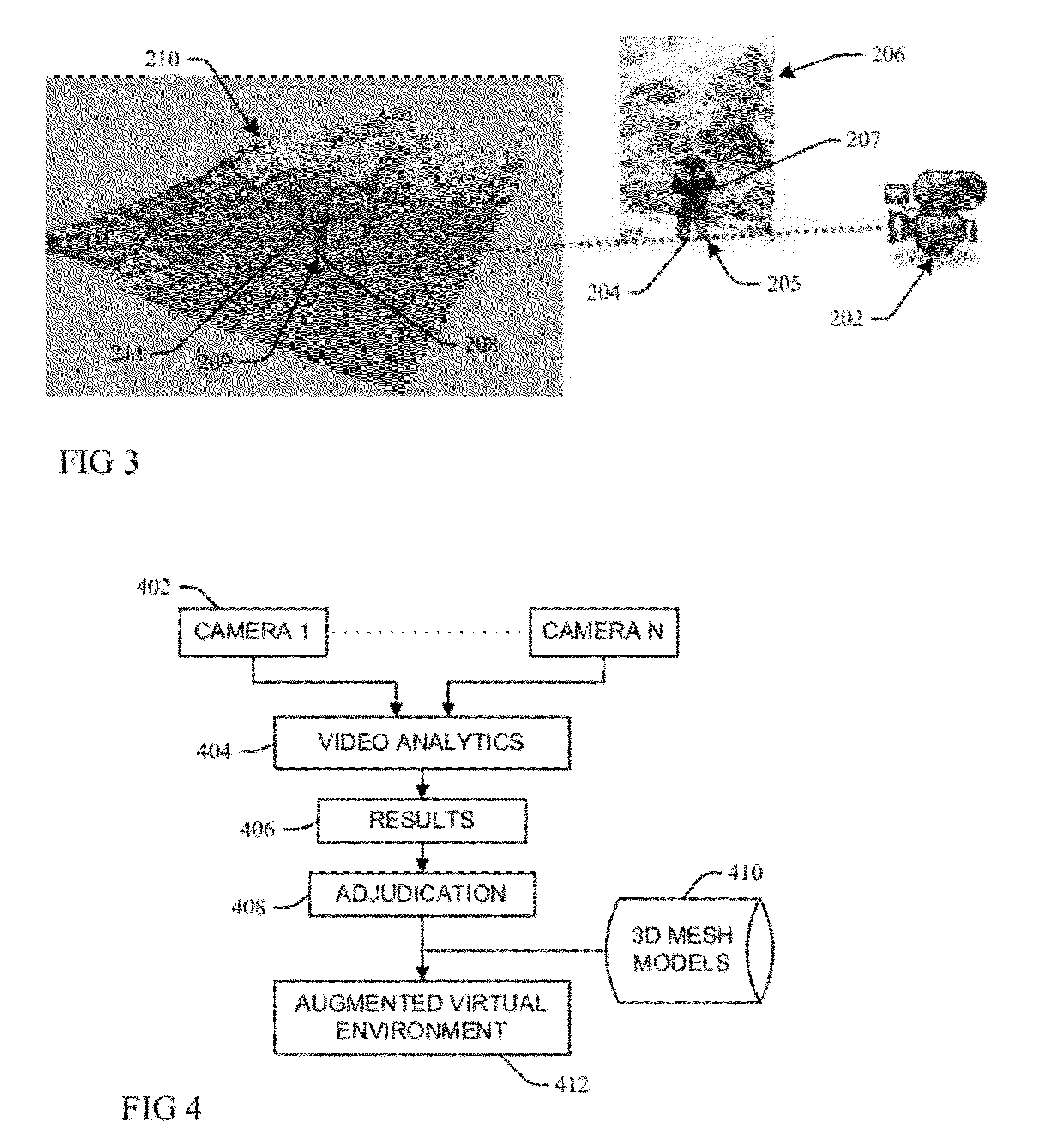
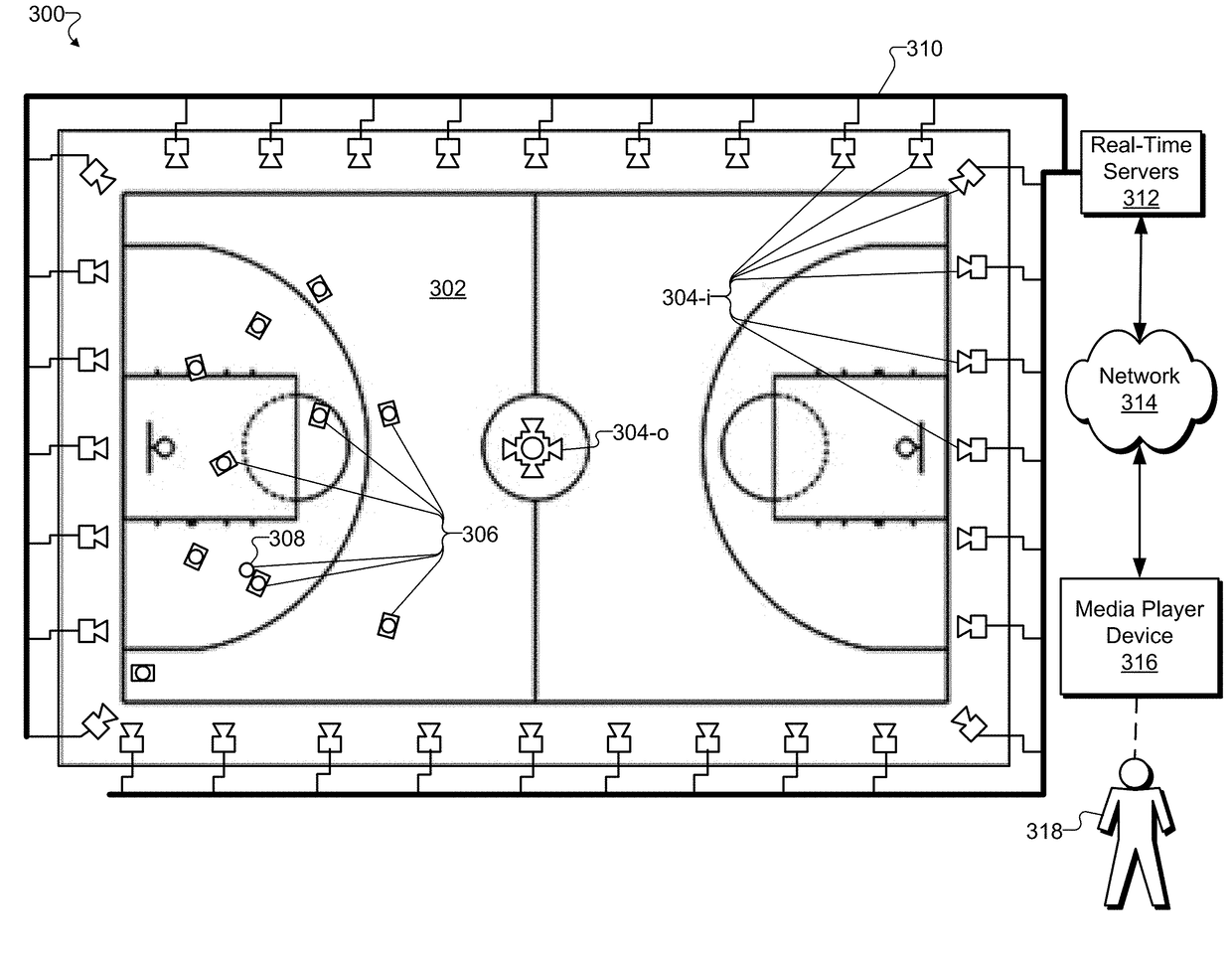
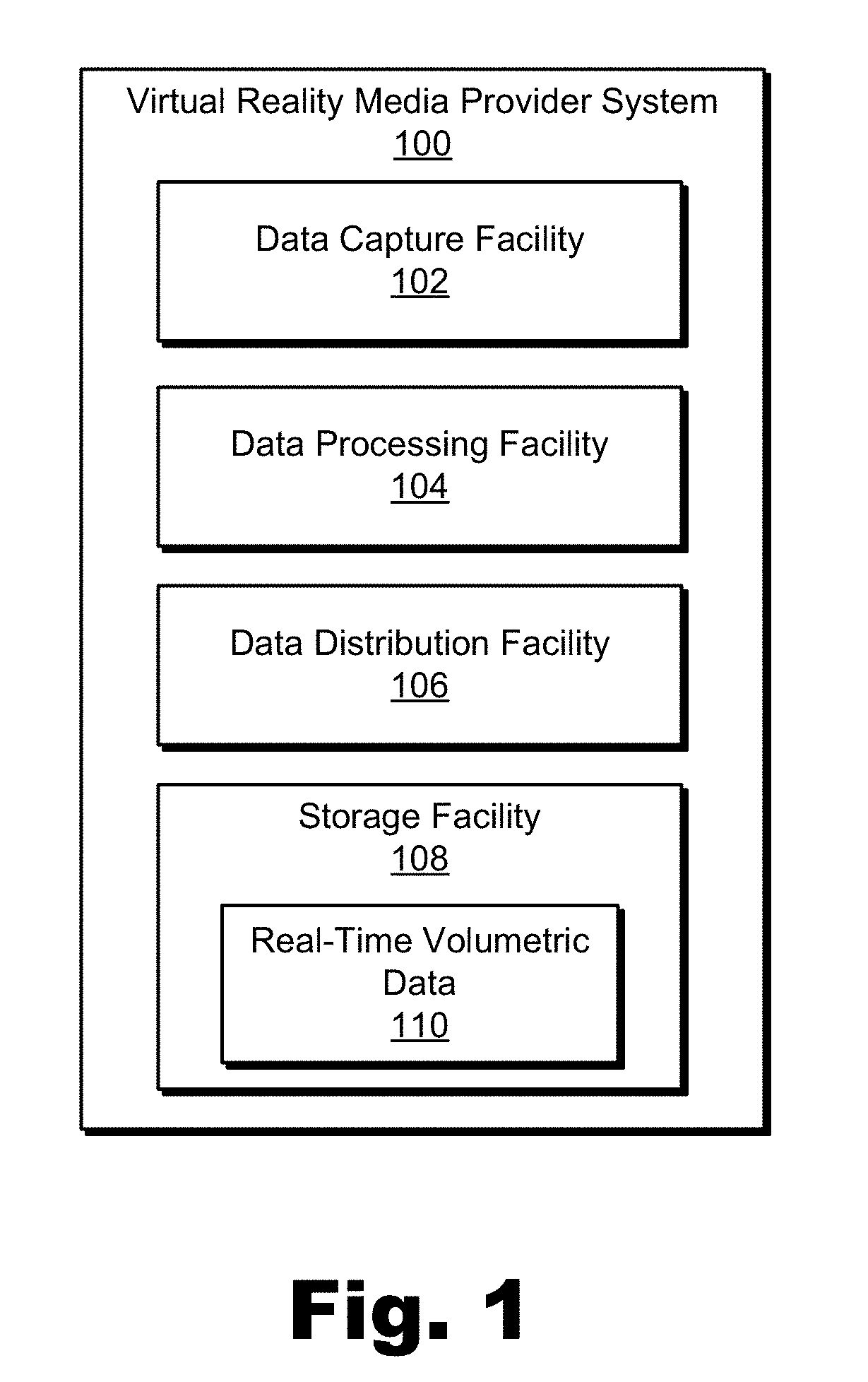
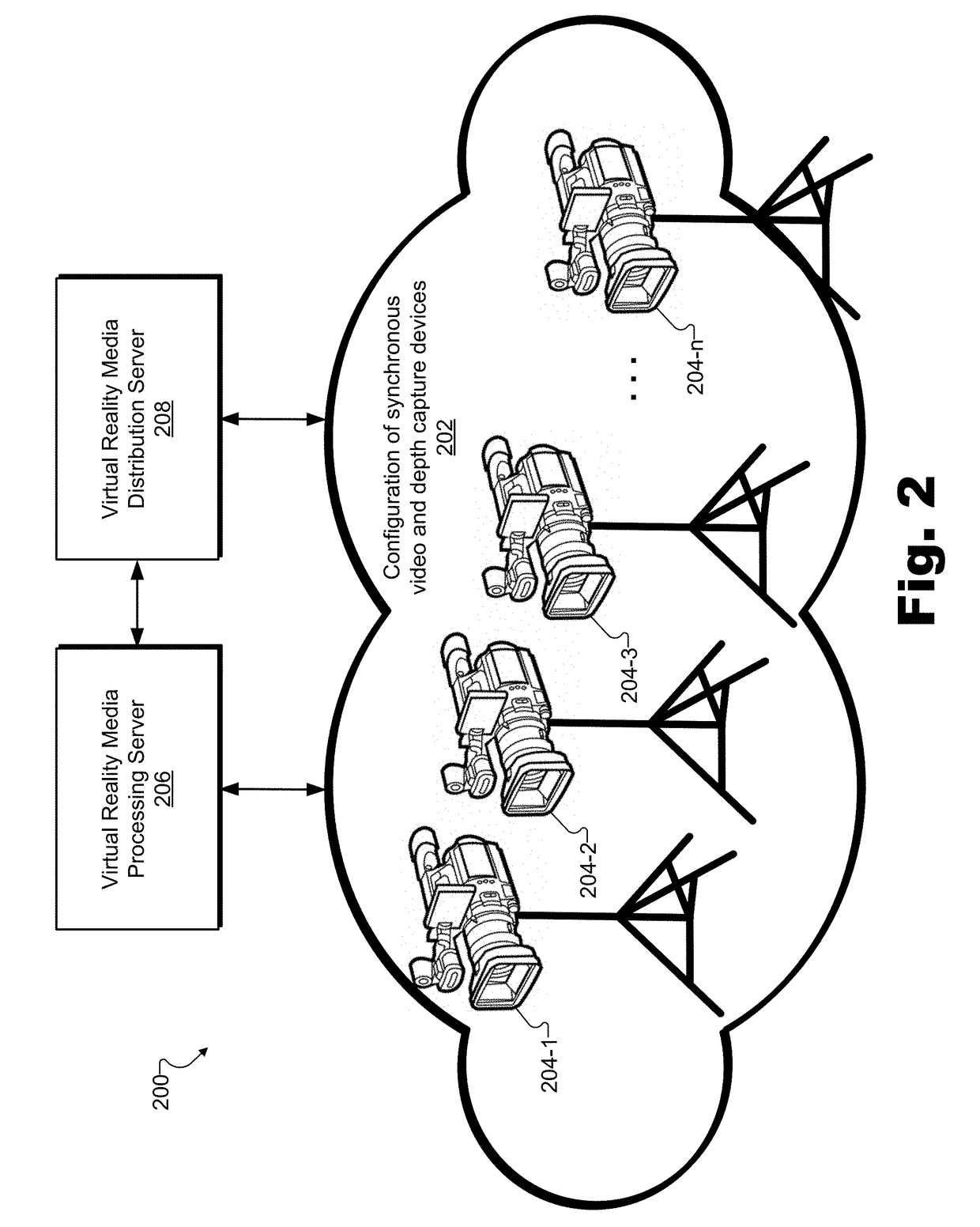
Methods and Systems for Creating and Providing a Real-Time Volumetric Representation of a Real-World Event
An exemplary virtual reality media provider system (“system”) includes a configuration of synchronous video and depth capture devices disposed at fixed positions at a real-world event. In real time, the video and depth capture devices capture two-dimensional video data and depth data for surfaces of objects at the real-world event. The system generates a real-time volumetric data stream representative of a dynamic volumetric model of the surfaces of the objects at the real-world event in real time based on the captured two-dimensional video data and captured depth data. The dynamic volumetric model of the surfaces of the objects at the real-world event is configured to be used to generate virtual reality media content representative of the real-world event as experienced from a dynamically selectable viewpoint corresponding to an arbitrary location at the real-world event and selected by a user experiencing the real-world event using a media player device.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Parallel processing method drawn by pre-projection light ray projection body
ActiveCN101324962AReduce processingProcessing speedProcessor architectures/configuration3D-image renderingVolumetric modelBounding volume
The invention discloses a pre-projection ray casting volume rendering parallel processing method. The following steps are included in the volume rendering data handling procedure: calculating bounding volume of a three dimensional volumetric model; projecting the bounding volume in the screen space; storing the corresponding coordinates of a projection area; and conducing the parallel processing of volume rendering data. The method adopts the parallel processing manner of pre-projection, so that all the computing nodes do not need to wait for all tasks to be calculated and finished and then transmit the result data to a main node without waiting, and instead, the computing nodes send intermediate result data to the main node immediately after a task block is calculated and start the calculation for the next task block. Fewer task blocks are distributed to the main node at first. The method provides the optimum estimation for the number of task blocks distributed to each computing node, thereby greatly reducing the processing volume of data and improving the processing speed of data.
Owner:广东碳中和研究院(韶关)
Method of evaluating volumes of components in mud shale
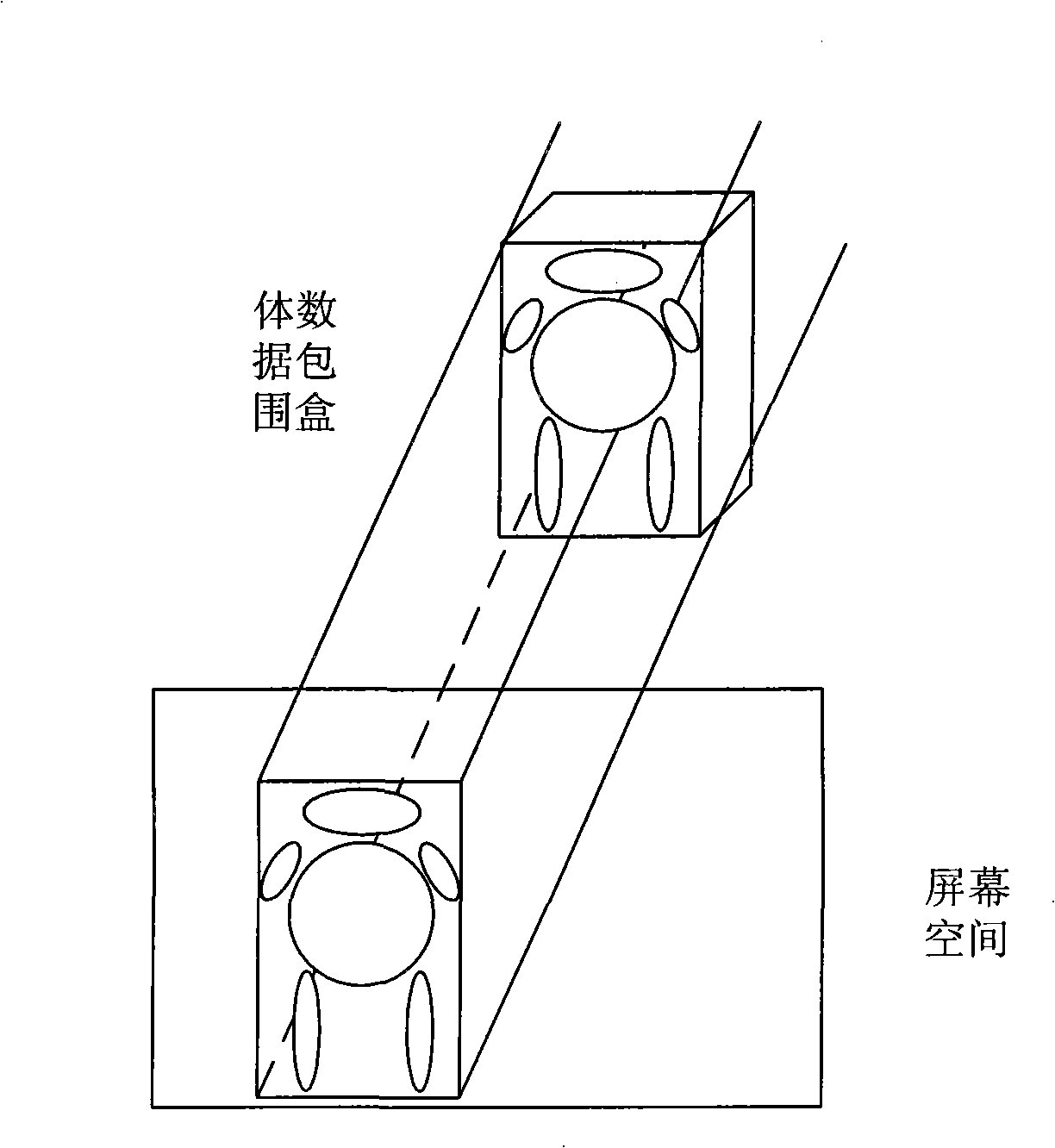
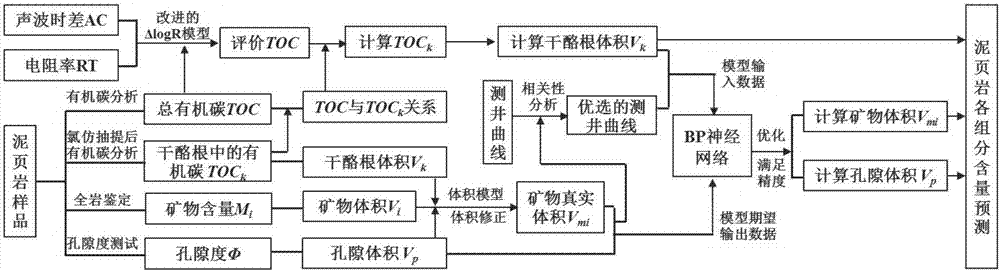
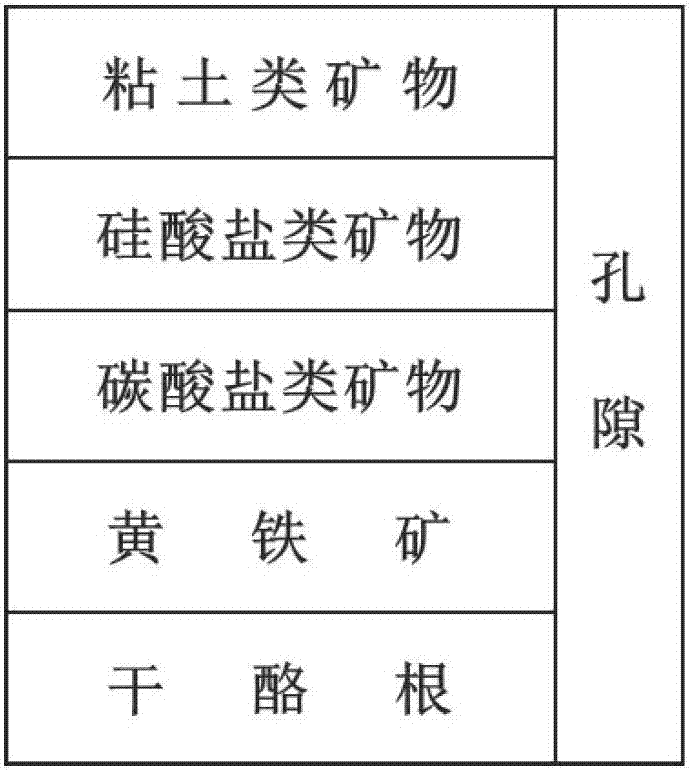
ActiveCN106950347ASolve complex nonlinear problemsSolve nonlinear problemsEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityKerogen
The invention belongs to the technical field of evaluation of components in mud shale, and discloses a method of evaluating volumes of components in mud shale by means of a conventional logging curve. The method includes the steps of: 1) on the basis of organic carbon analysis, porosity test and total rock inspection test of the mud shale after extraction, with combination of densities of the components in the mud shale, calibrating the volumes of the components in the mud shale and establishing a component volume model of the mud shale; 2) on the basis of evaluation of total organic carbon content with a [delta]logR method, with combination of a relationship of organic carbon before and after the extraction, calculating volume of kerogen, and performing optimizing calculation to obtain a BP neural network model of mineral components and pore volumes in a cross validation manner. The method, on the basis of ensuring that the sum of the volumes of the components in mud shale is 1, achieves the advantages of multiple inputs and multiple outputs of the BP neural network and solves a complex nonlinear problem between the components in mud shale and logging response.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Systems and methods for three-dimensional modeling
InactiveUS20060109269A1Highly flexible editingVisual presentationAnimationObject storeDimensional modeling
Systems and methods for modifying a virtual object stored within a computer. The systems and methods allow virtual object modifications that are otherwise computationally inconvenient. The virtual object is represented as a volumetric representation. A portion of the volumetric model is converted into an alternative representation. The alternative representation can be a representation having a different number of dimensions from the volumetric representations. A stimulus is applied to the alternative representation, for example by a user employing a force-feedback haptic interface. The response of the alternative representation to the stimulus is calculated. The change in shape of the virtual object is determined from the response of the alternative representation. The representations of the virtual object can be displayed at any time for the user. The user can be provided a force-feedback response. Multiple stimuli can be applied in succession. Multiple alternative representations can be employed in the system and method.
Owner:3D SYST INC
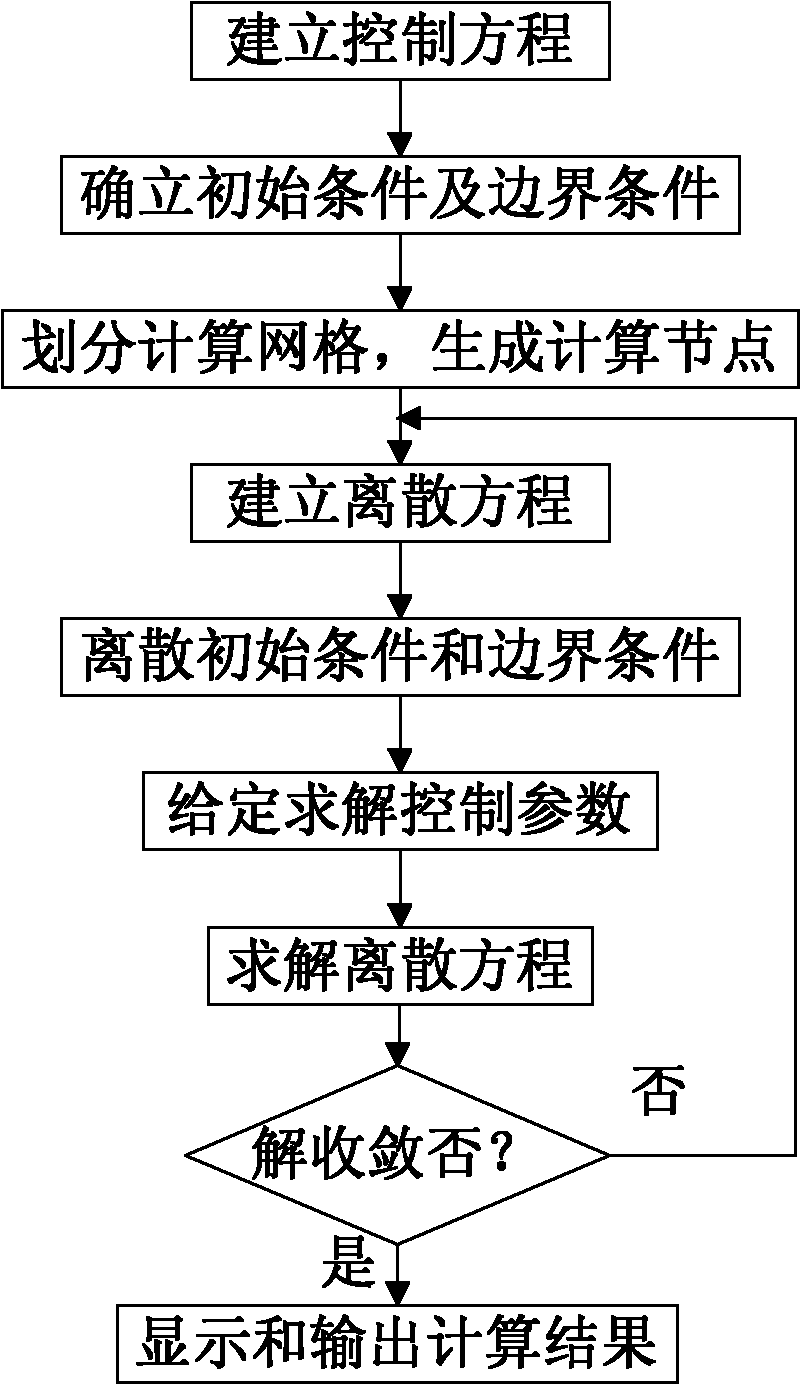
Control method for precision processing of micro-flow path abrasive flow based on flow volume mould
ActiveCN101833605AImprove processing efficiencyImprove economySpecial data processing applicationsTime domainMathematical model
The invention relates to a control method for precision processing of micro-flow path abrasive flow based on a fluid volume mould, comprising the following steps: (1) establishment of a mathematical model of abrasive flow movement based on the fluid volume mould; (2) solution process of the abrasive flow, which particularly comprises: 2.1) original conditions and boundary conditions; 2.2) grid division; 2.3) establishment of a discrete equation; 2.4) the original discrete conditions and the boundary conditions; 2.5) setting of solution control parameters; 2.6) calculation of the discrete equation; and 2.7) convergence of discontinuous solutions: the solution for a steady-state problem or the solution for an instant problem on a certain special time step can be obtained through multi-iterations; the solution for the instant problem can be obtained if an explicit scheme is used to conduct integration on a time domain; and the iteration process is finished after a solution value reaches designated precision. The control method has the advantages of low cost and rapid speed, and can achieve observation of abrasive manifold.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for three-dimensional modeling
InactiveUS7710415B2Highly flexible editingVisual presentationAnimationDimensional modelingObject store
Systems and methods for modifying a virtual object stored within a computer. The systems and methods allow virtual object modifications that are otherwise computationally inconvenient. The virtual object is represented as a volumetric representation. A portion of the volumetric model is converted into an alternative representation. The alternative representation can be a representation having a different number of dimensions from the volumetric representations. A stimulus is applied to the alternative representation, for example by a user employing a force-feedback haptic interface. The response of the alternative representation to the stimulus is calculated. The change in shape of the virtual object is determined from the response of the alternative representation. The representations of the virtual object can be displayed at any time for the user. The user can be provided a force-feedback response. Multiple stimuli can be applied in succession. Multiple alternative representations can be employed in the system and method.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method and system for interactive simulation of materials and models
A method and system for drawing, displaying, editing animating, simulating and interacting with one or more virtual polygonal, spline, volumetric models, three-dimensional visual models or robotic models. The method and system provide flexible simulation, the ability to combine rigid and flexible simulation on plural portions of a model, rendering of haptic forces and force-feedback to a user.
Owner:MILLMAN ALAN
Diagnostic intraoral scanning
Methods and apparatuses for taking, using and displaying three-dimensional (3D) volumetric models of a patient's dental arch. A 3D volumetric model may include surface (e.g., color) information as well as information on internal structure, such as near-infrared (near-IR) transparency values for internal structures including enamel and dentin.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com