Patents
Literature
150 results about "Bounding volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
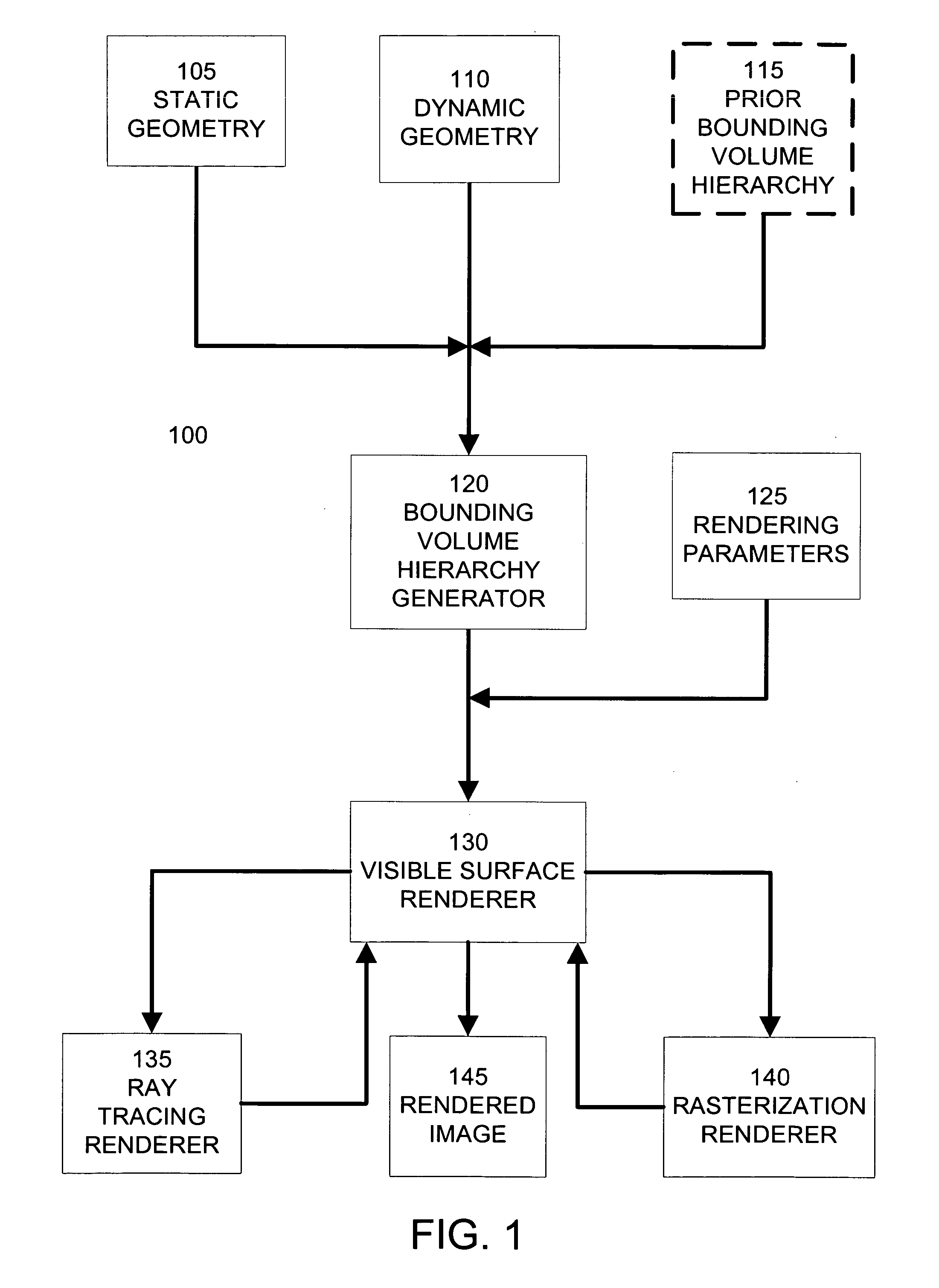
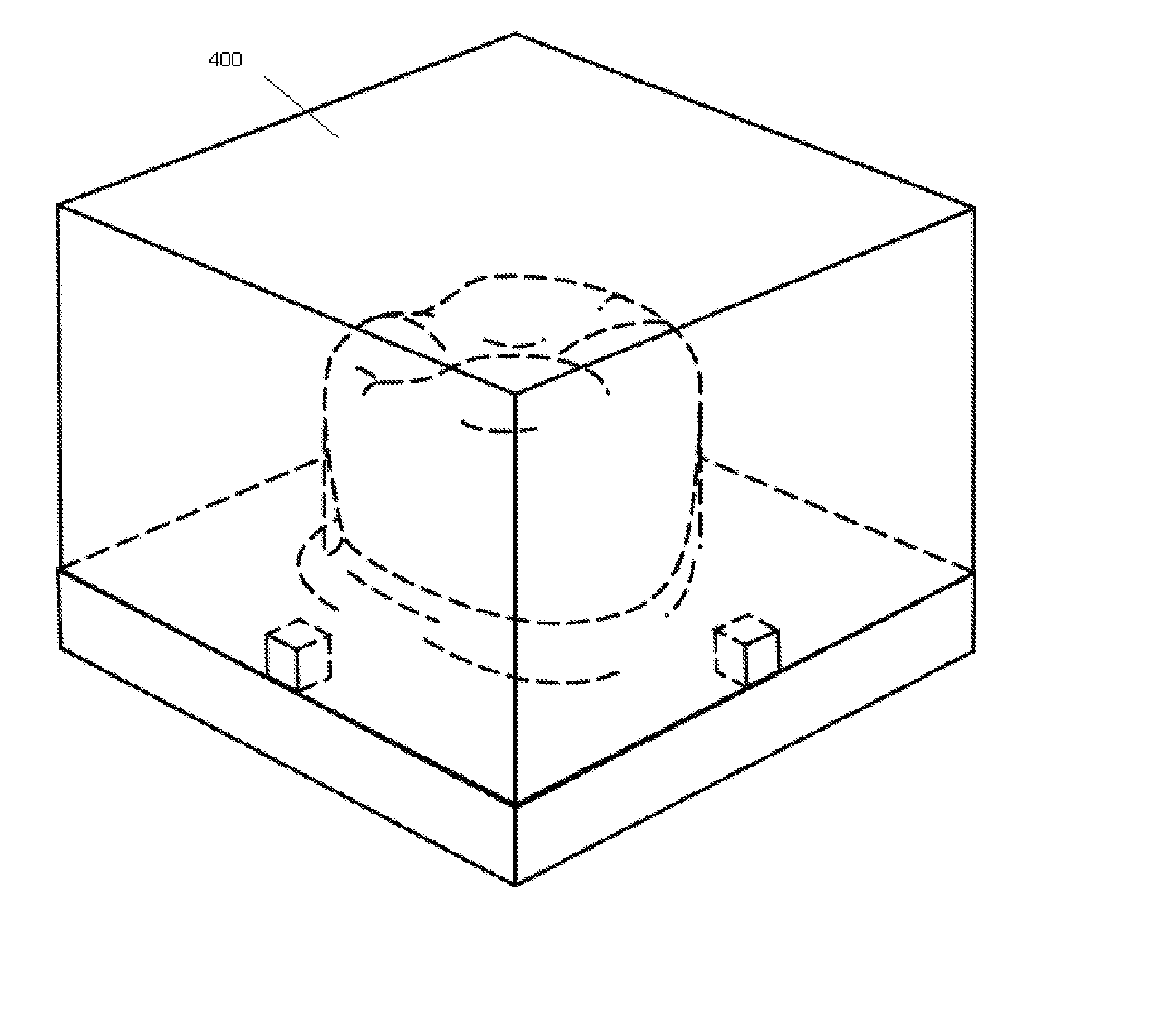
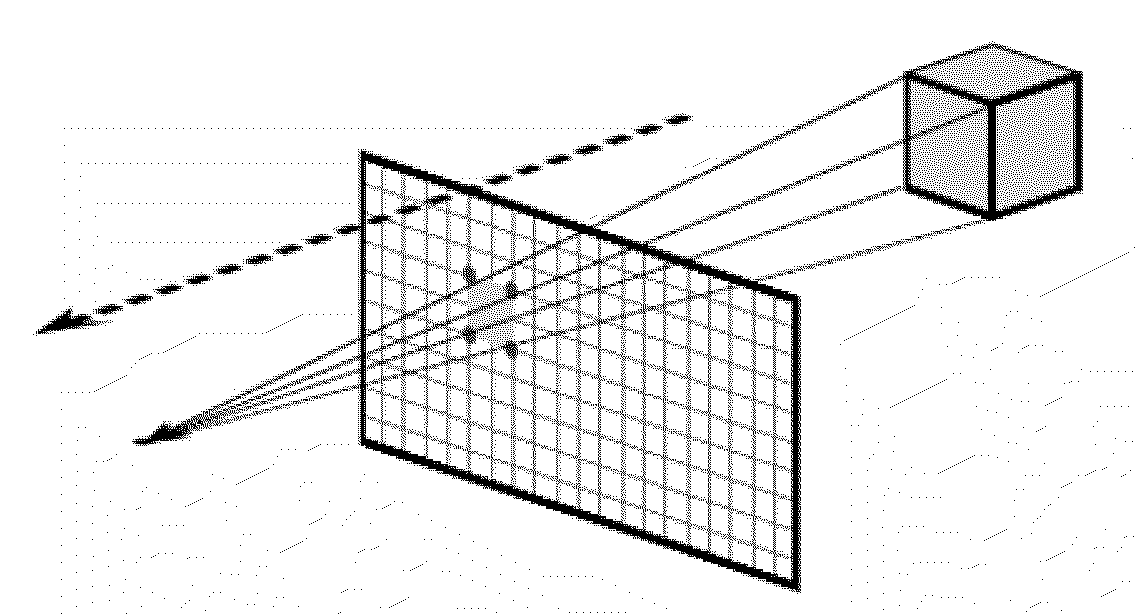
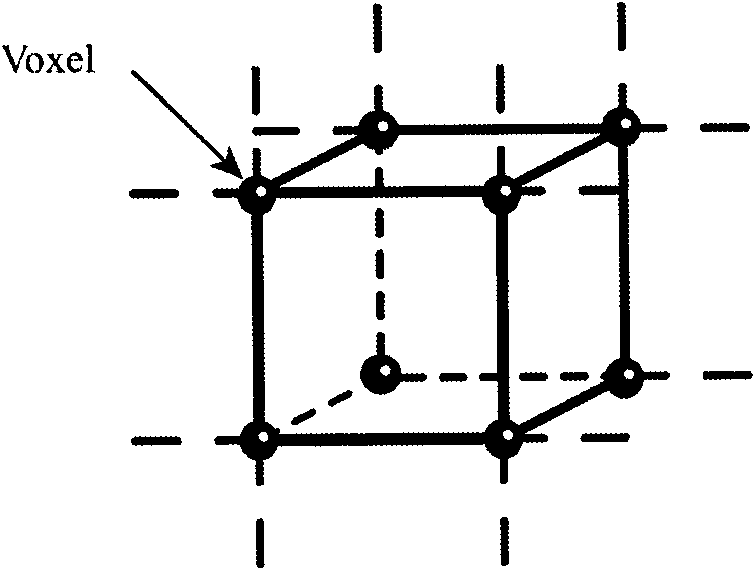
In computer graphics and computational geometry, a bounding volume for a set of objects is a closed volume that completely contains the union of the objects in the set. Bounding volumes are used to improve the efficiency of geometrical operations by using simple volumes to contain more complex objects. Normally, simpler volumes have simpler ways to test for overlap.
Method for improving spatial index efficiency by jittering splitting planes
Embodiments of the invention provide methods and apparatus to improve the efficiency of a ray tracing image processing system. According to one embodiment of the invention, when building a spatial index the position of a splitting plane used to create a bounding volume may be jittered or moved along an axis to determine if a more efficient location for the splitting plane exists. After jittering the splitting plane a number of primitives intersected by the splitting plane may be calculated. The number of primitives intersected by the splitting plane for each location may be compared, and the location with the fewest intersected primitives may be chosen for the final position of the splitting plane. By choosing the location with the fewest intersected primitives the number of ray-primitive intersection tests necessary when performing ray tracing may be reduced. Consequently, the efficiency of the image processing system may be improved.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
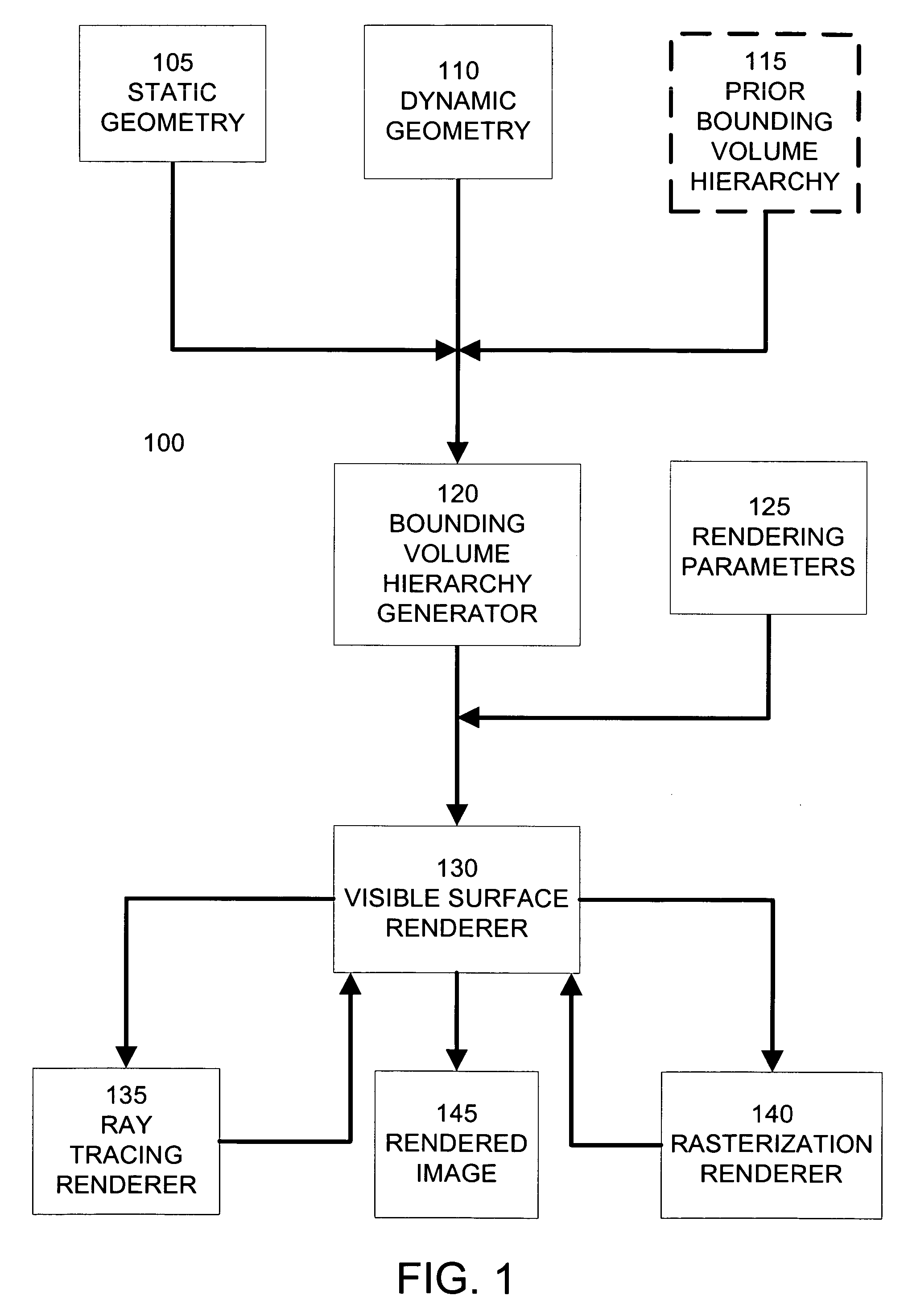
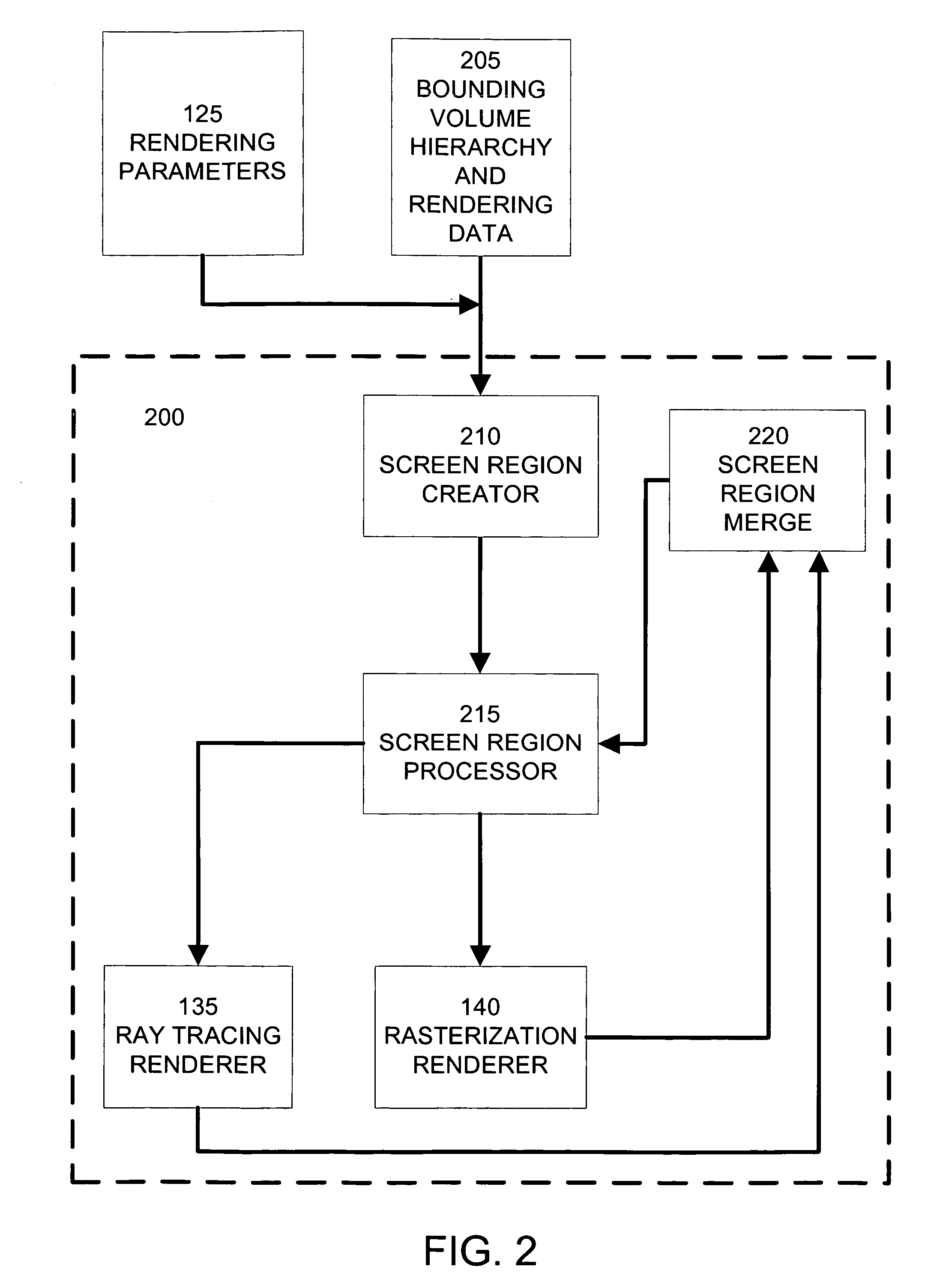
Statistical rendering acceleration
ActiveUS20060256112A1Estimate costCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGeometric primitiveComputer science
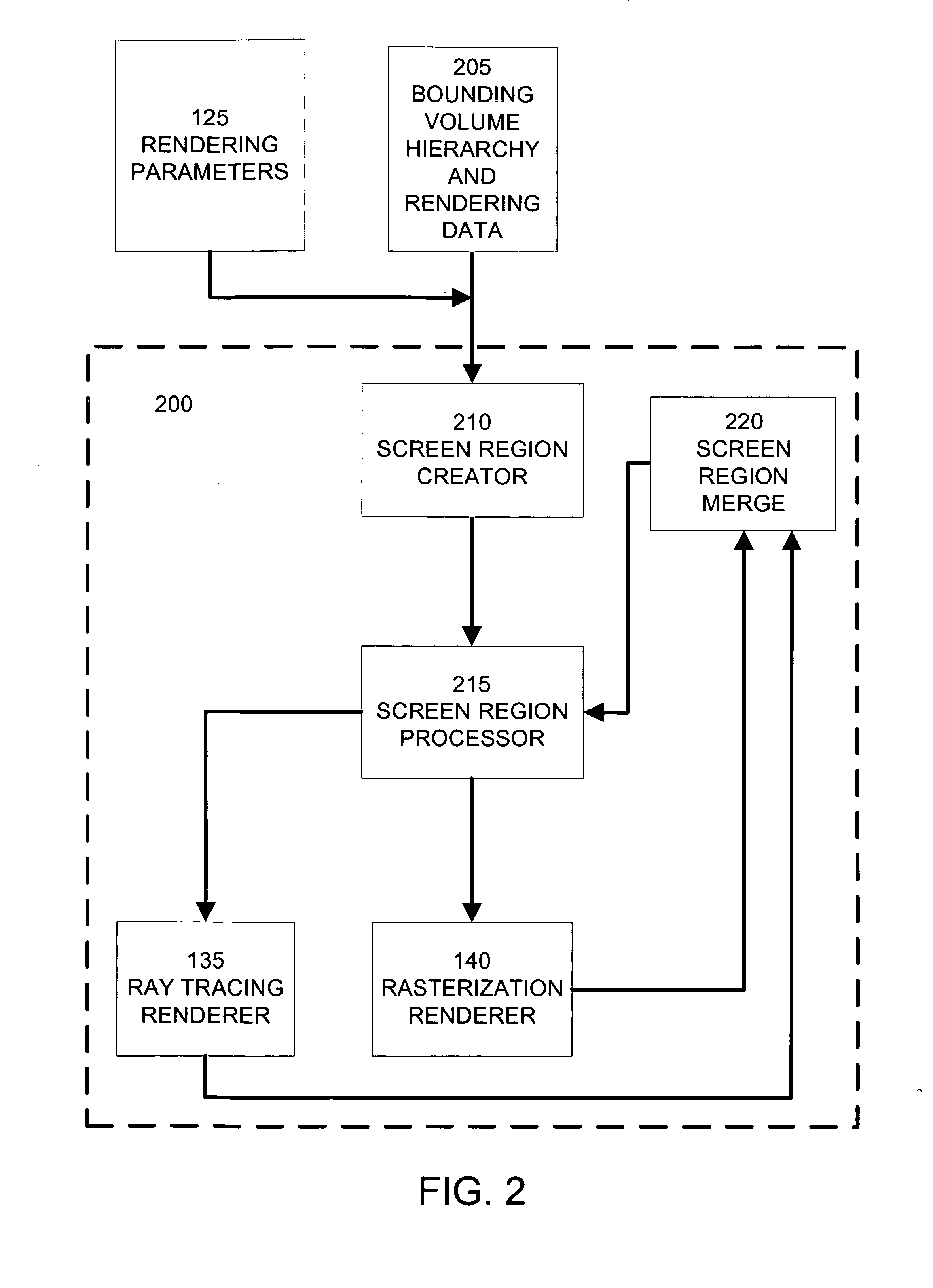
Different rendering techniques are selected for portions of a scene based on statistical estimates of the portions' rendering costs. A scene is partitioned into a bounding volume hierarchy. Each bounding volume includes a statistical model of the spatial distribution of geometric primitives within the bounding volume. An image to be rendered is partitioned into screen regions and each screen region is associated with one or more bounding volumes and their statistical models. The associated statistical models of a screen region are evaluated to estimate the rendering cost, such as the probable number of geometric primitives per pixel, for the screen region. Based on the rendering cost, the screen region is assigned to a dense geometry renderer, such as a ray tracing renderer, or a sparse geometry renderer, such as a rasterization renderer. Rendered screen regions are combined to form a rendered image.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Digital impression for remote manufacturing of dental impressions
A “digital impression” is provided in lieu of a physical “dental” impression. A 3D digitizer is used to capture the digital impression, e.g., by scanning in a patient's oral cavity. A digital impression “data set” is formed using a computer-implemented method. The method begins by generating a three dimensional (3D) restoration model. Then, a bounding volume of the restoration model is computed. The bounding volume is defined as at least a minimum 3D volume that contains the 3D model. Thereafter, a lower solid 3D model, and an upper solid 3D model are created; these lower and upper models have a predetermined relationship with one another. In particular, when superimposed upon one another within the bounding volume, the lower and upper 3D models define a cavity into which the restoration model is adapted to fit. The restoration model, the lower solid 3D model and the upper solid 3D model are then aggregated into the data set to form the digital impression. Typically, the digital impression is generated at a first location, i.e., a dental office, and then transmitted to a second location, a dental laboratory, remote from the first location. Such transmission is conveniently done over a network, such as a TCP / IP network (e.g., the Internet). A dental item is then manufactured at the second location. Thus, for example, the lower solid 3D model may be used to build a coping, or the restoration model itself used to build a restoration. In the latter case, information in the data set may be used to check a fit of the restoration.
Owner:D4D TECH LP
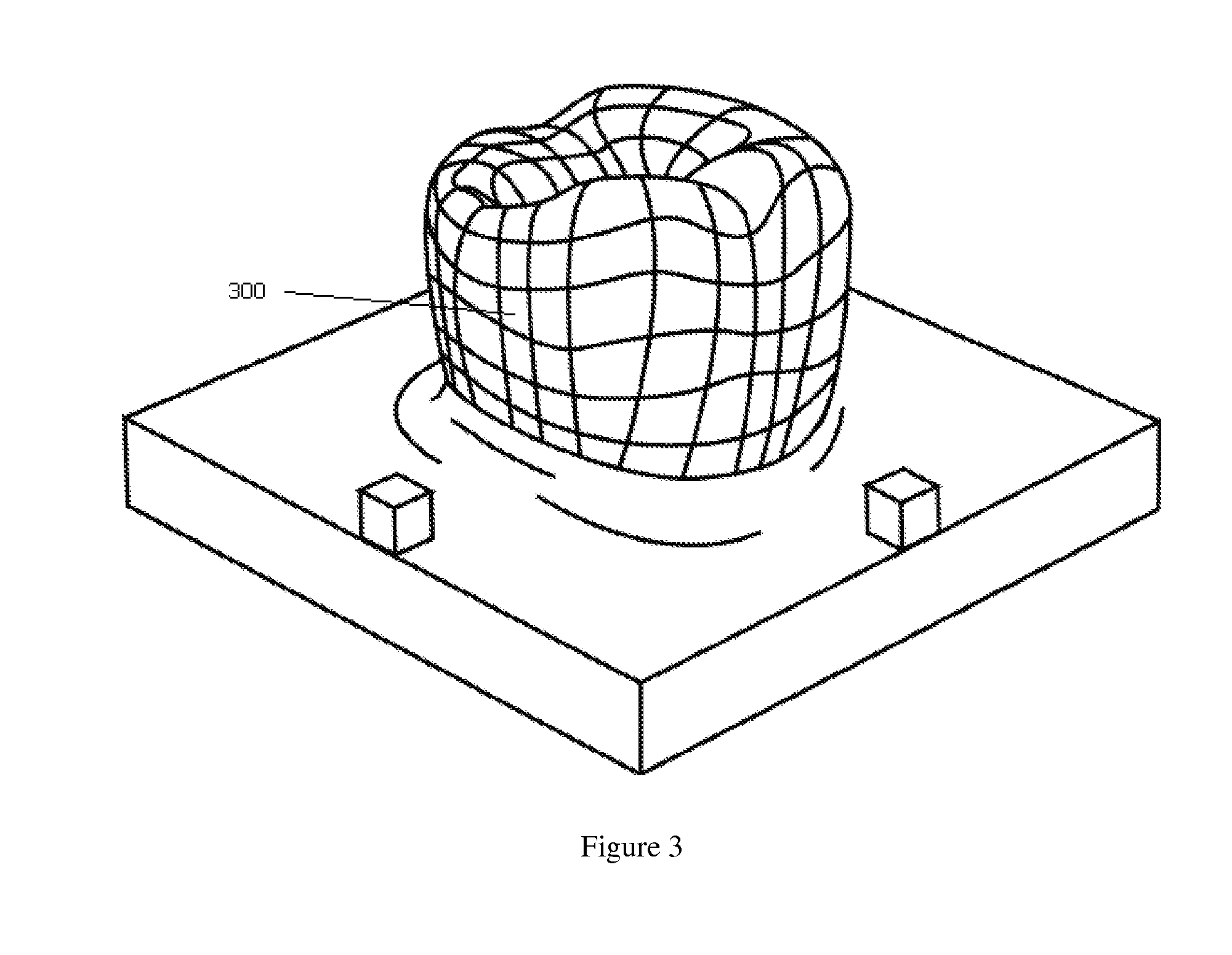
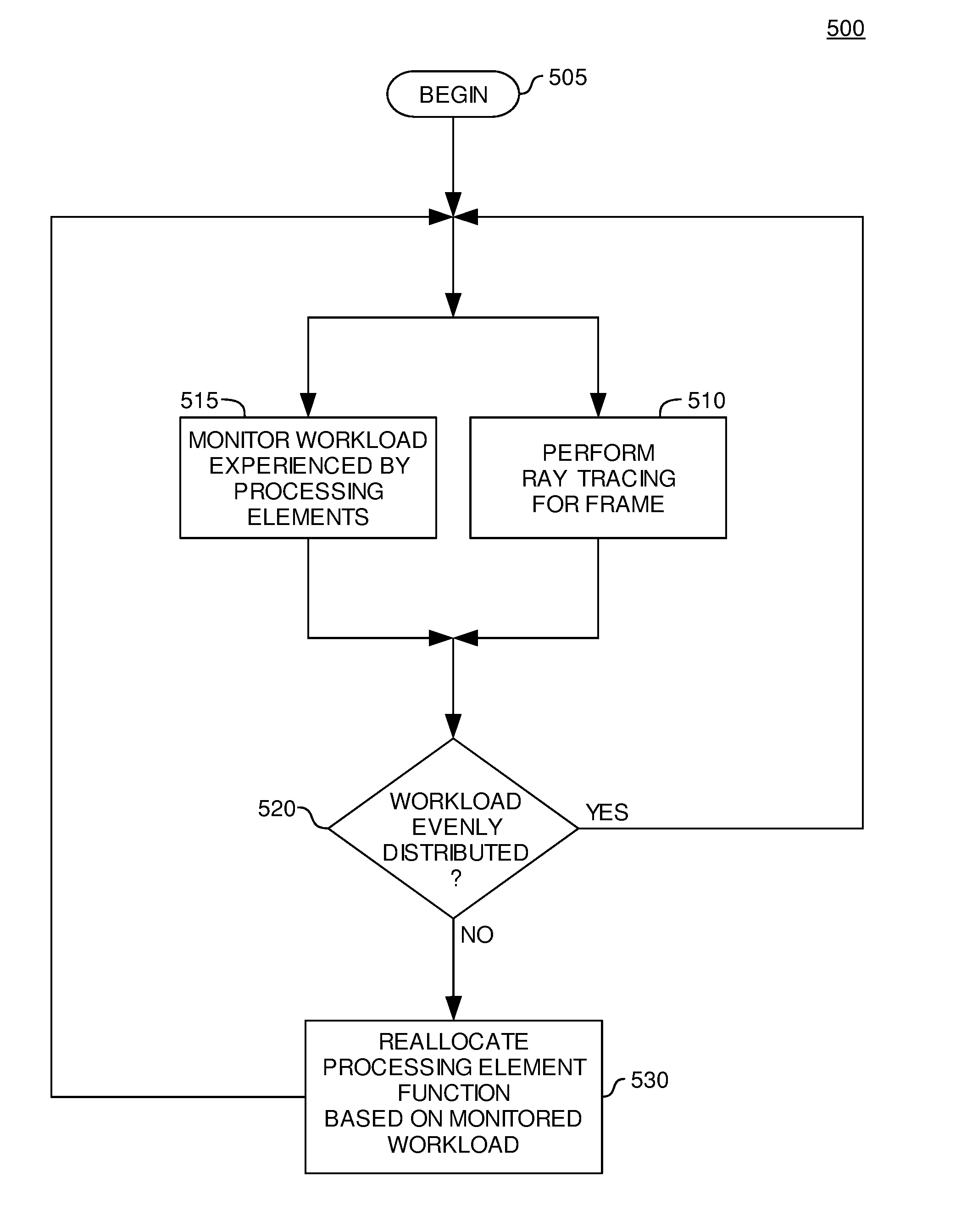
Dynamic reallocation of processing cores for balanced ray tracing graphics workload
InactiveUS20080088622A1Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingGraphicsProcessing core
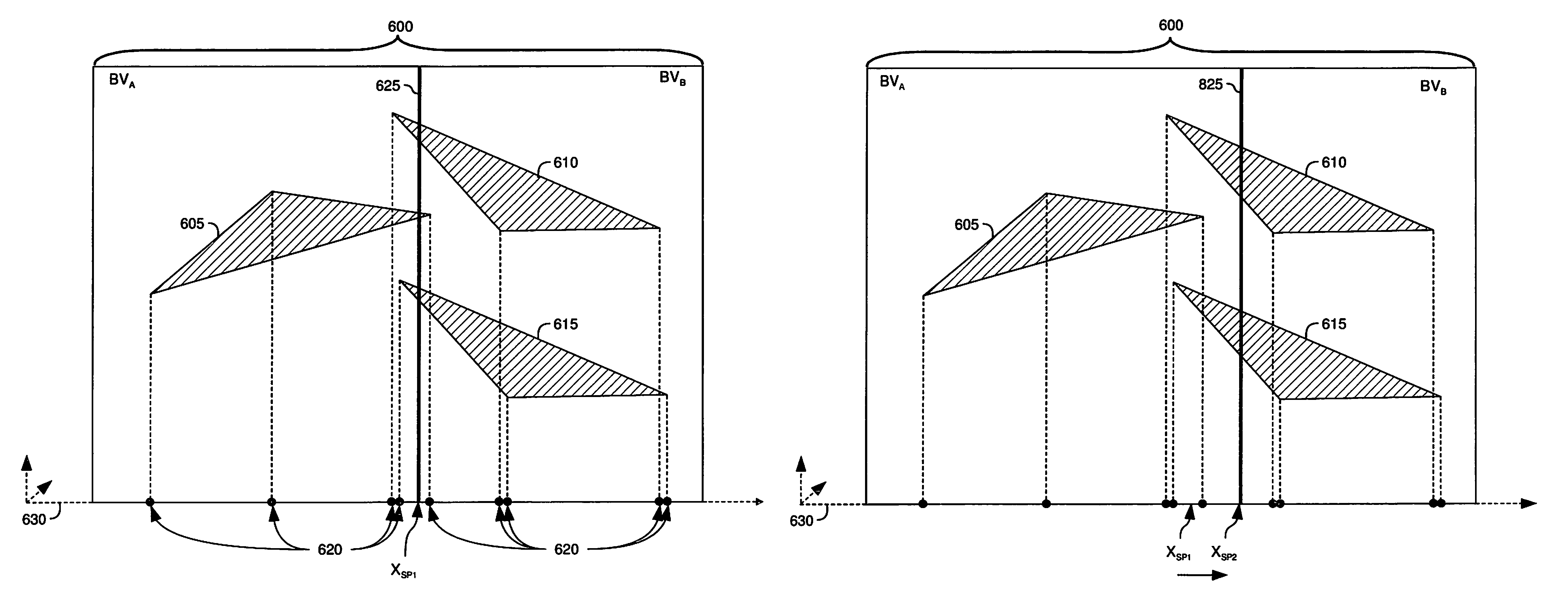
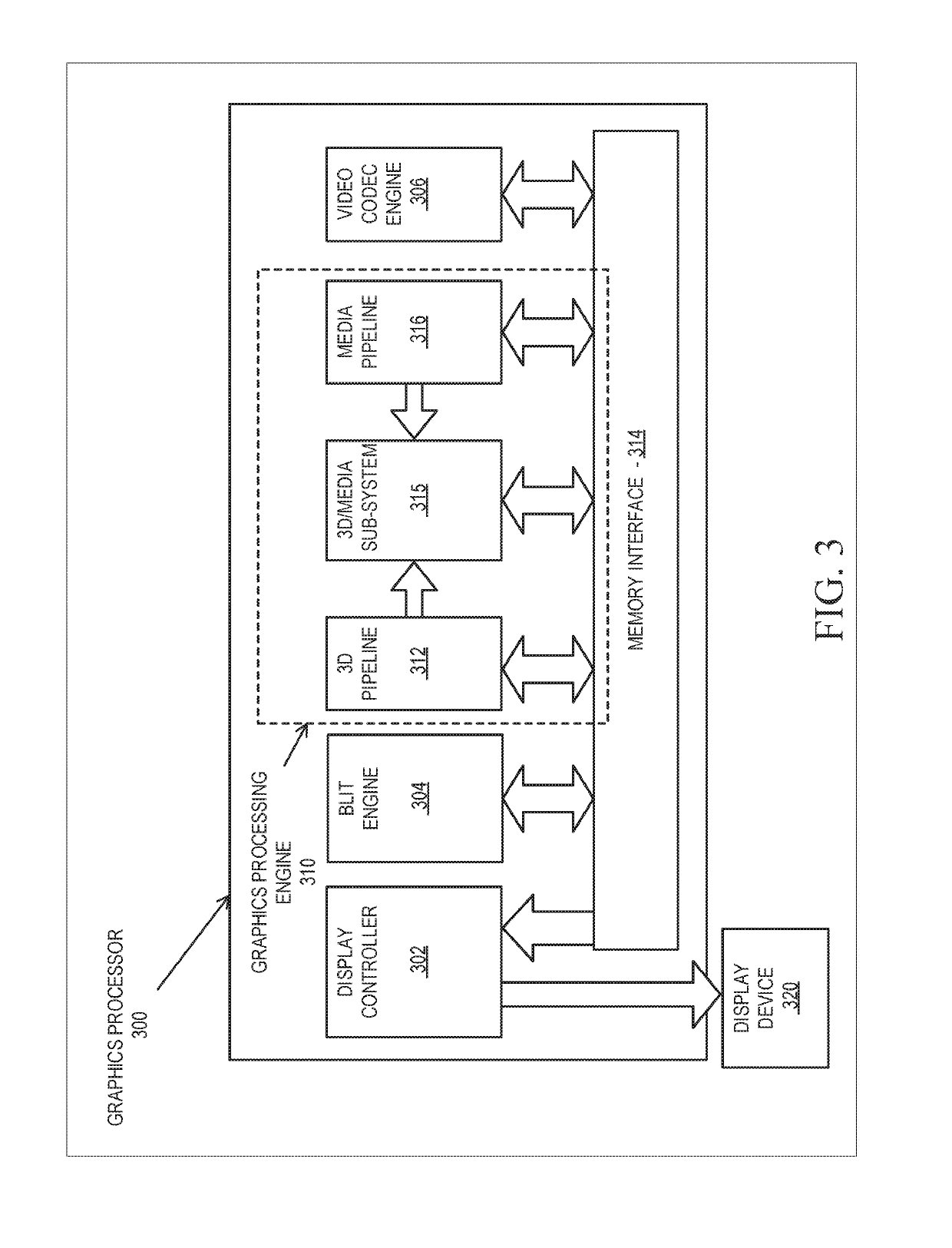
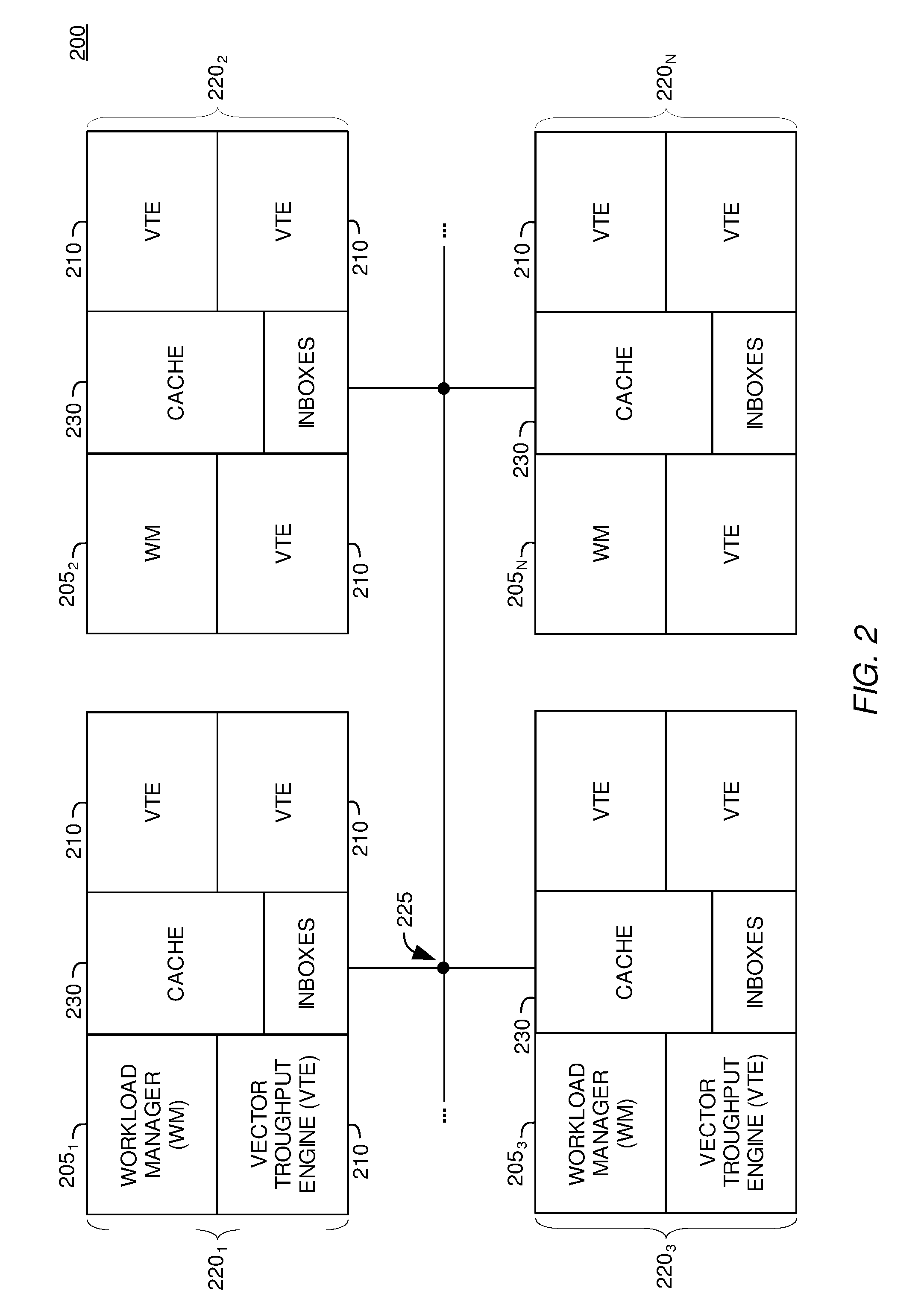
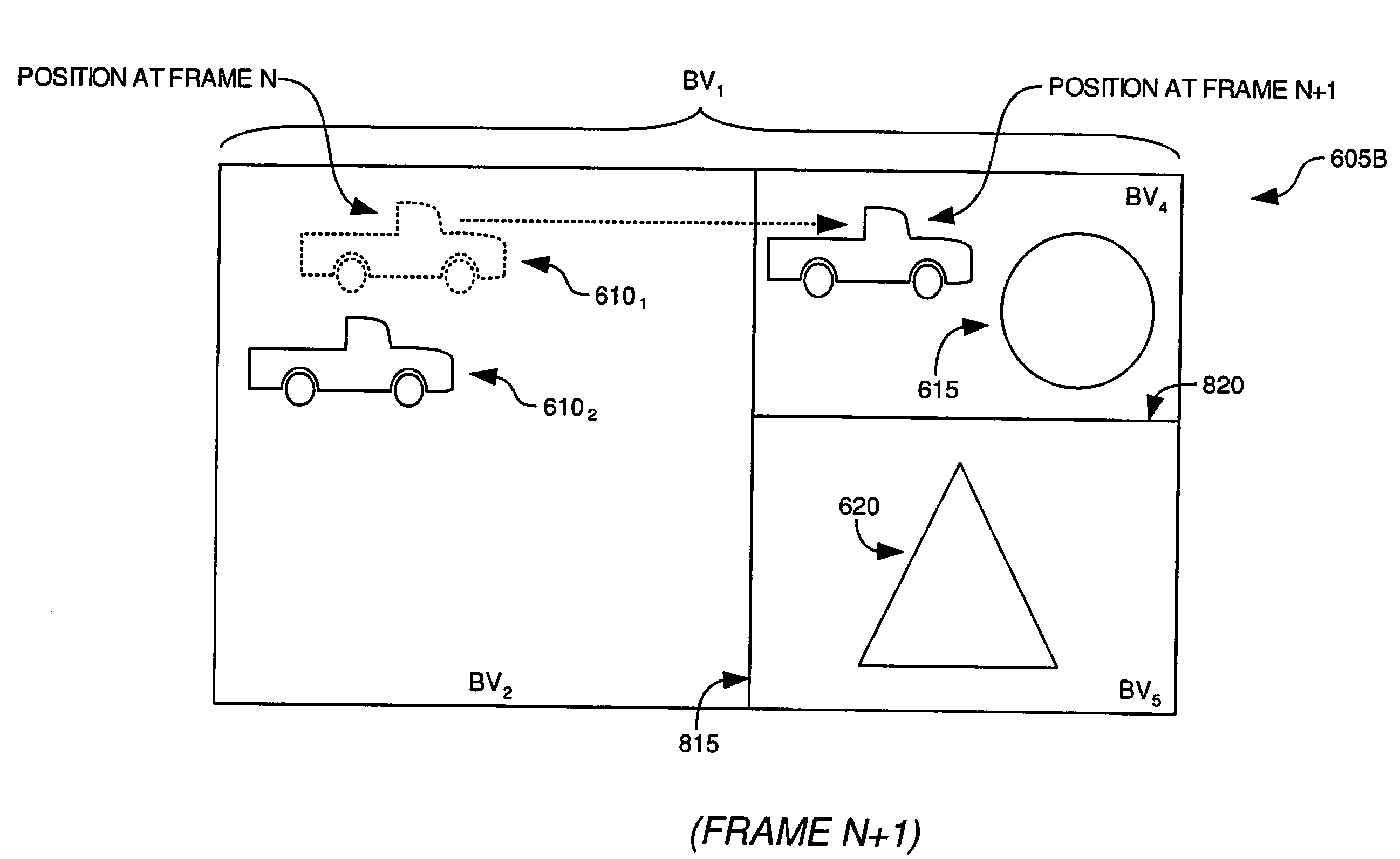
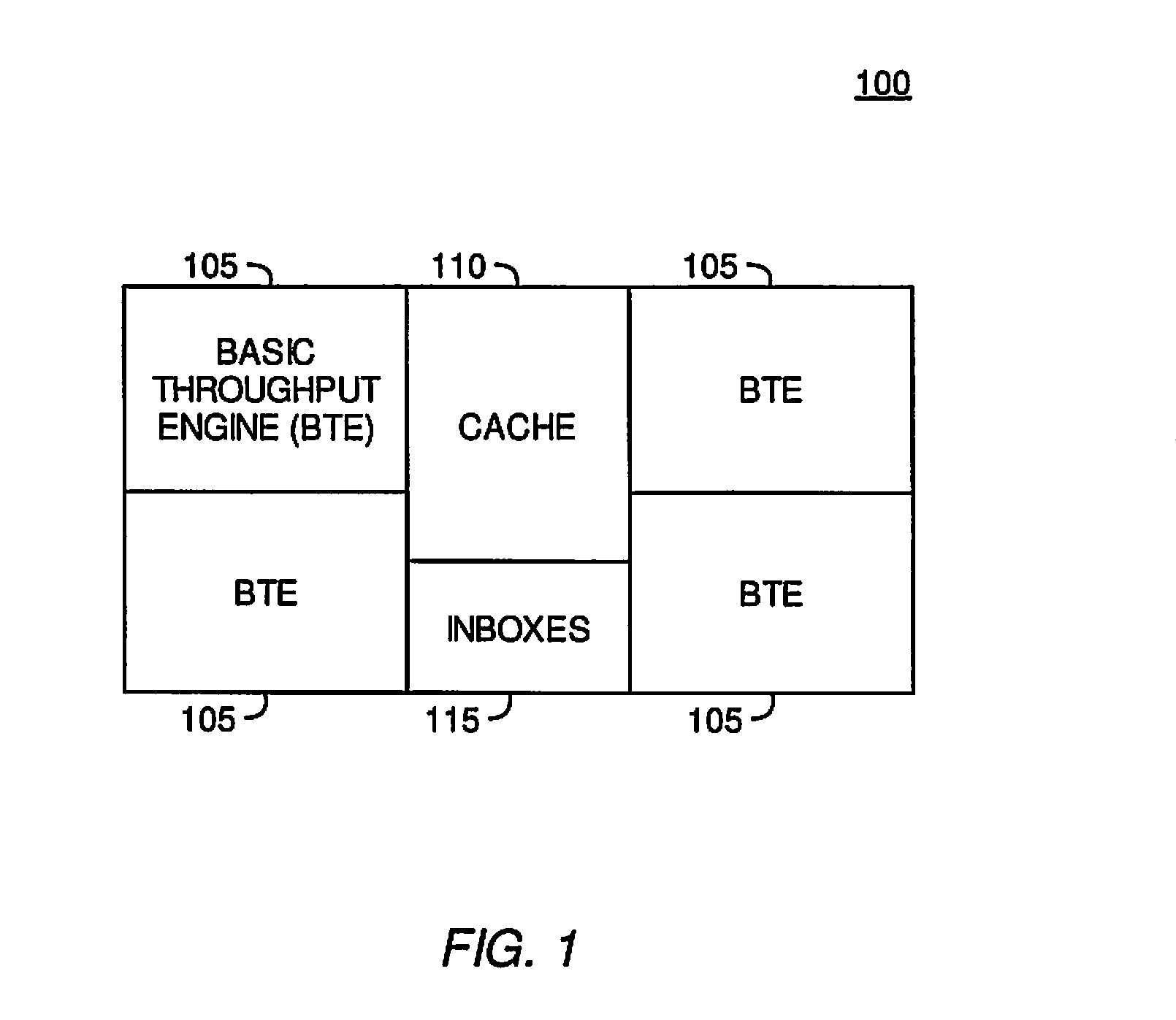
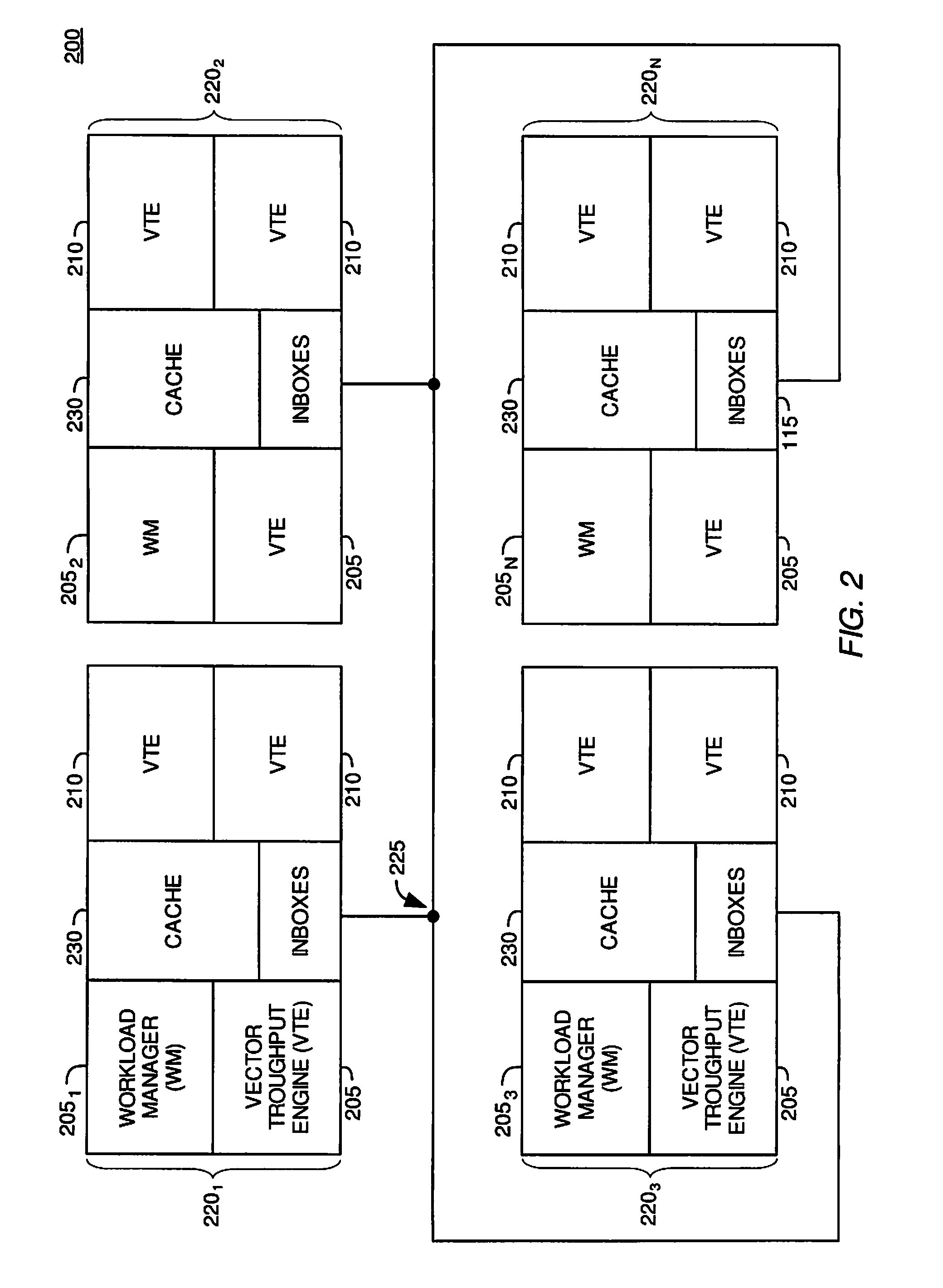
A ray tracing image processing system may use a plurality of processing elements to render a two dimensional image from a three dimensional scene. A first portion of the processing elements may function as workload managers responsible for performing operations relating to traversing a ray through a spatial index, and a second portion of the processing elements may function as vector throughput engines responsible for performing operations relating to determining if a ray intersects primitives contained within bounding volumes. By monitoring workloads experienced by the processing elements for a particular frame, processing element function may be reallocated such that for a subsequent frame the workload experienced by processing elements in the image processing system may be balanced. Balanced workload may improve the performance of the image processing system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Accelerated ray tracing using shallow bounding volume hierarchies
InactiveUS20100053162A1Increasing arityReduce memory requirementsImage data processing detailsImage generationAlgorithmBounding volume hierarchy
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program code (software) products enable acceleration of ray tracing by using acceleration data structures with high arity to enable processing of nodes using streaming SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) instructions with reduced memory requirements.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Ray tracing hierarchy
InactiveUS7164420B2Quality improvementExtension of timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage generationAlgorithmImaging quality
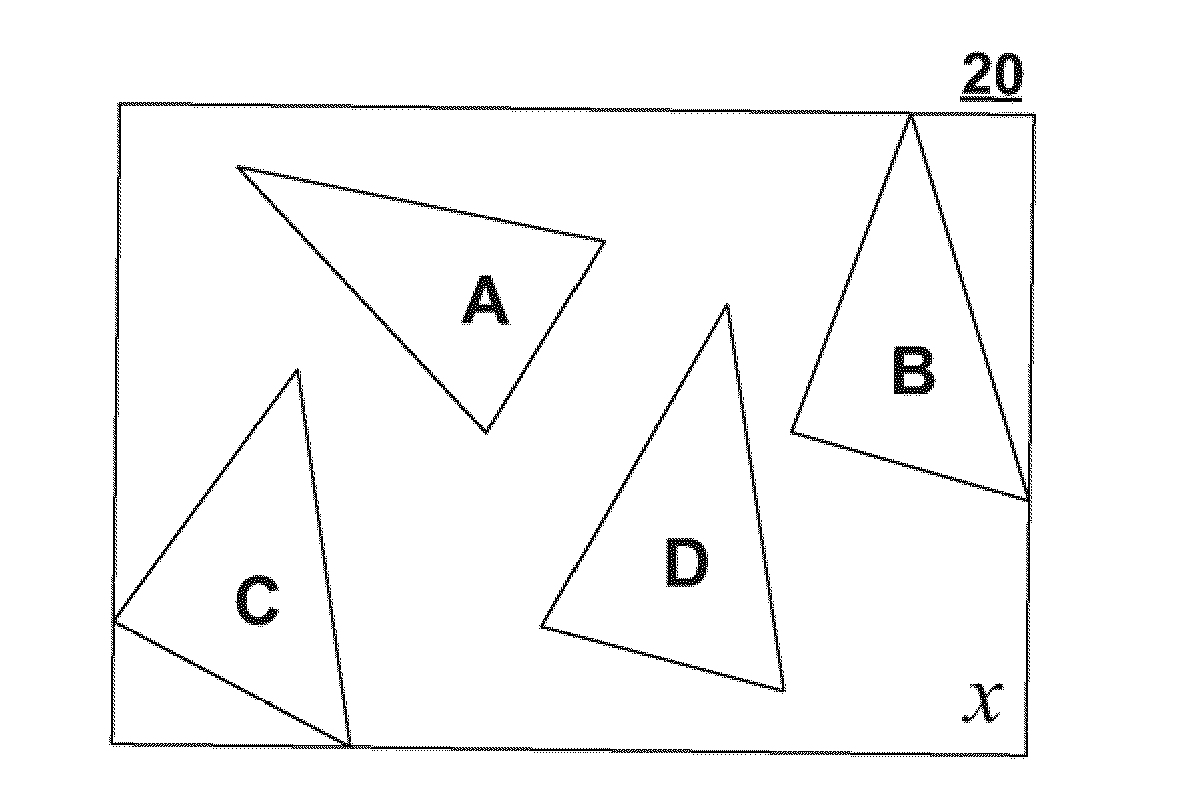
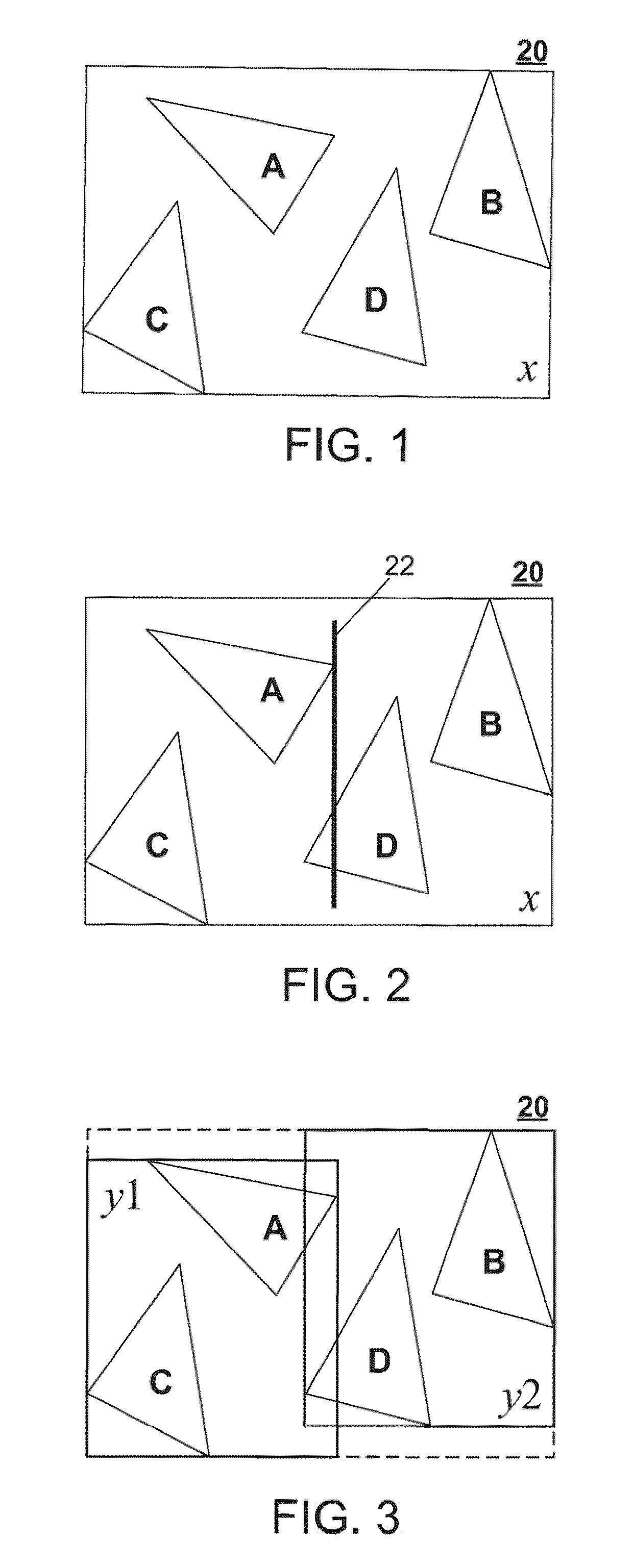
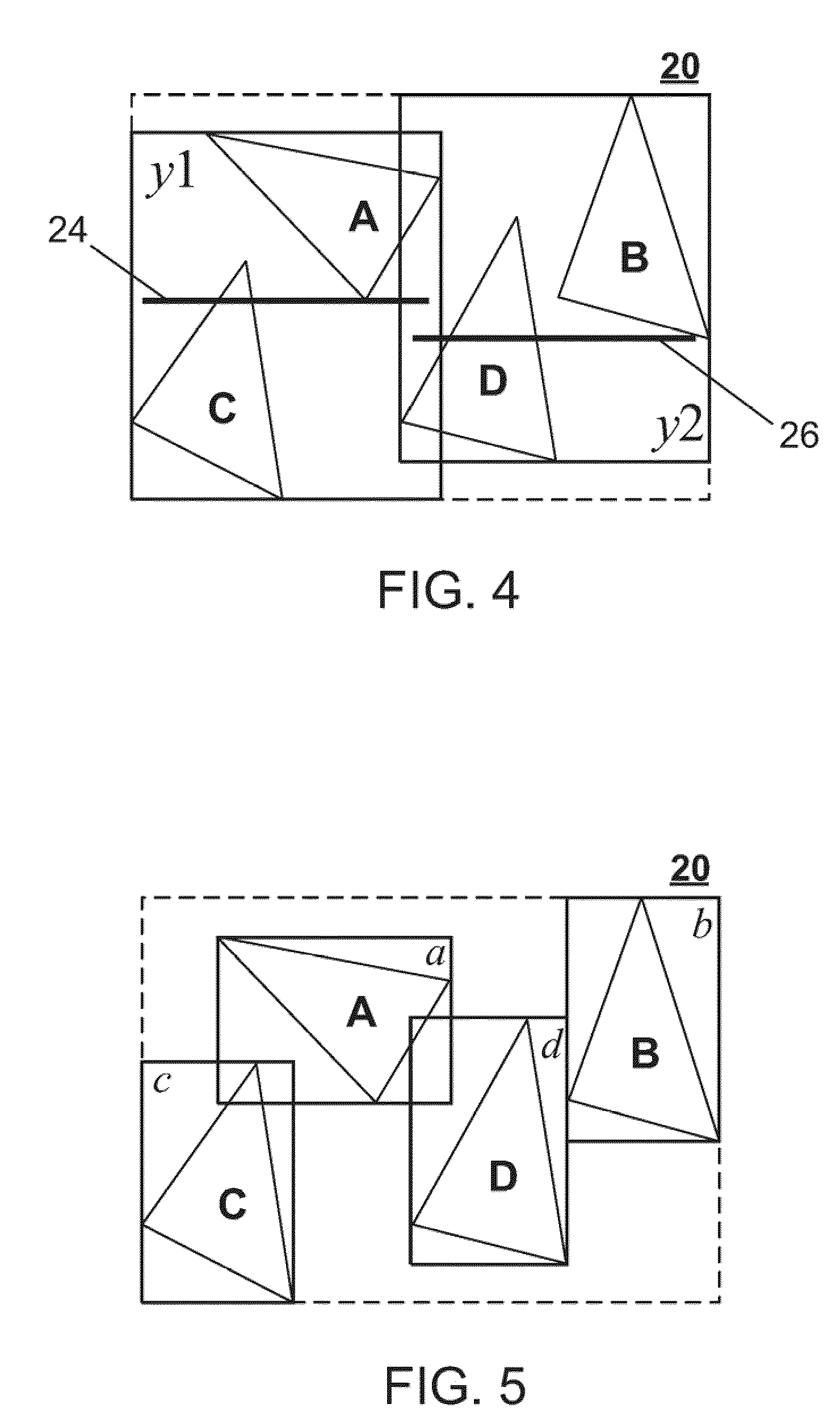
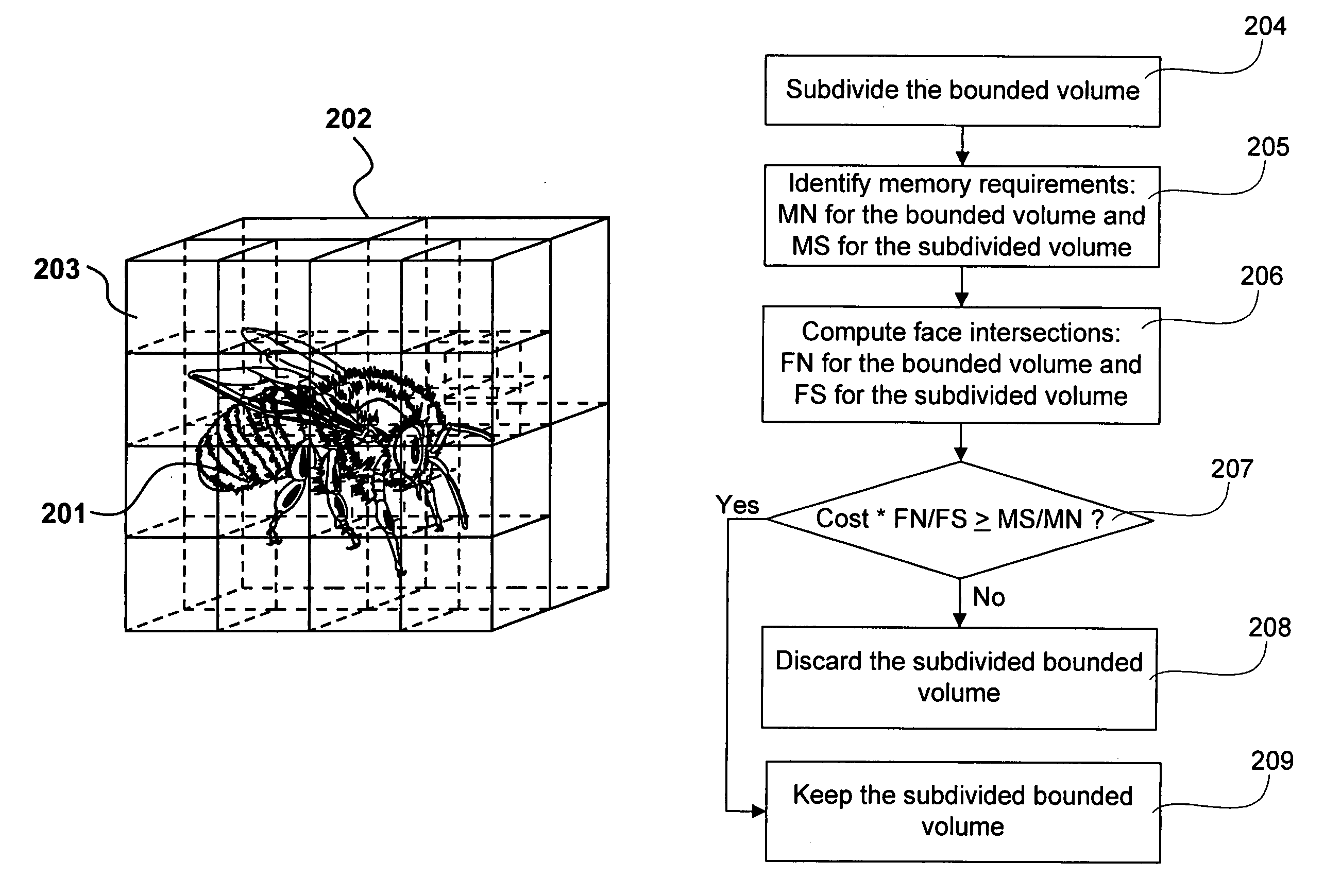
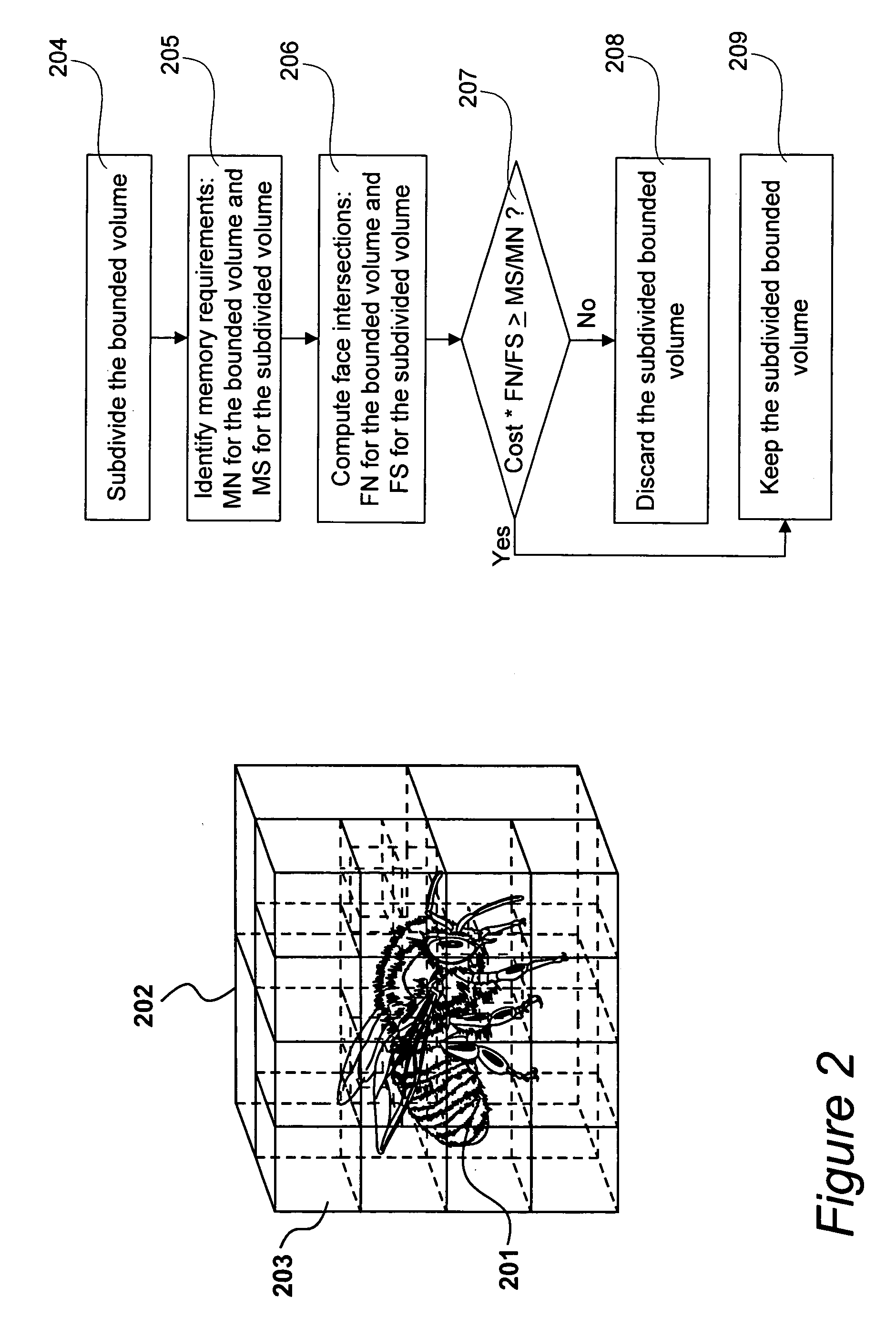
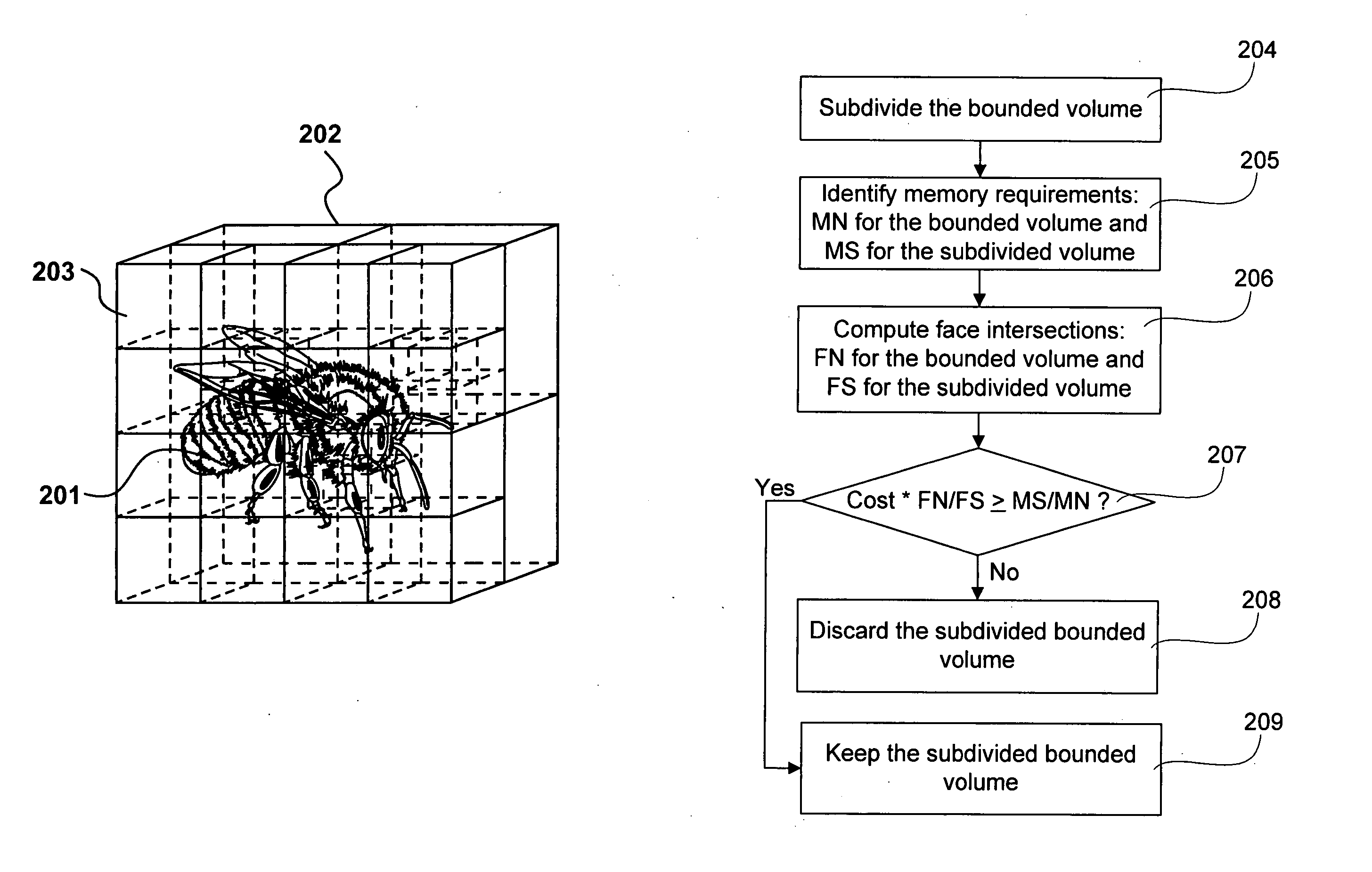
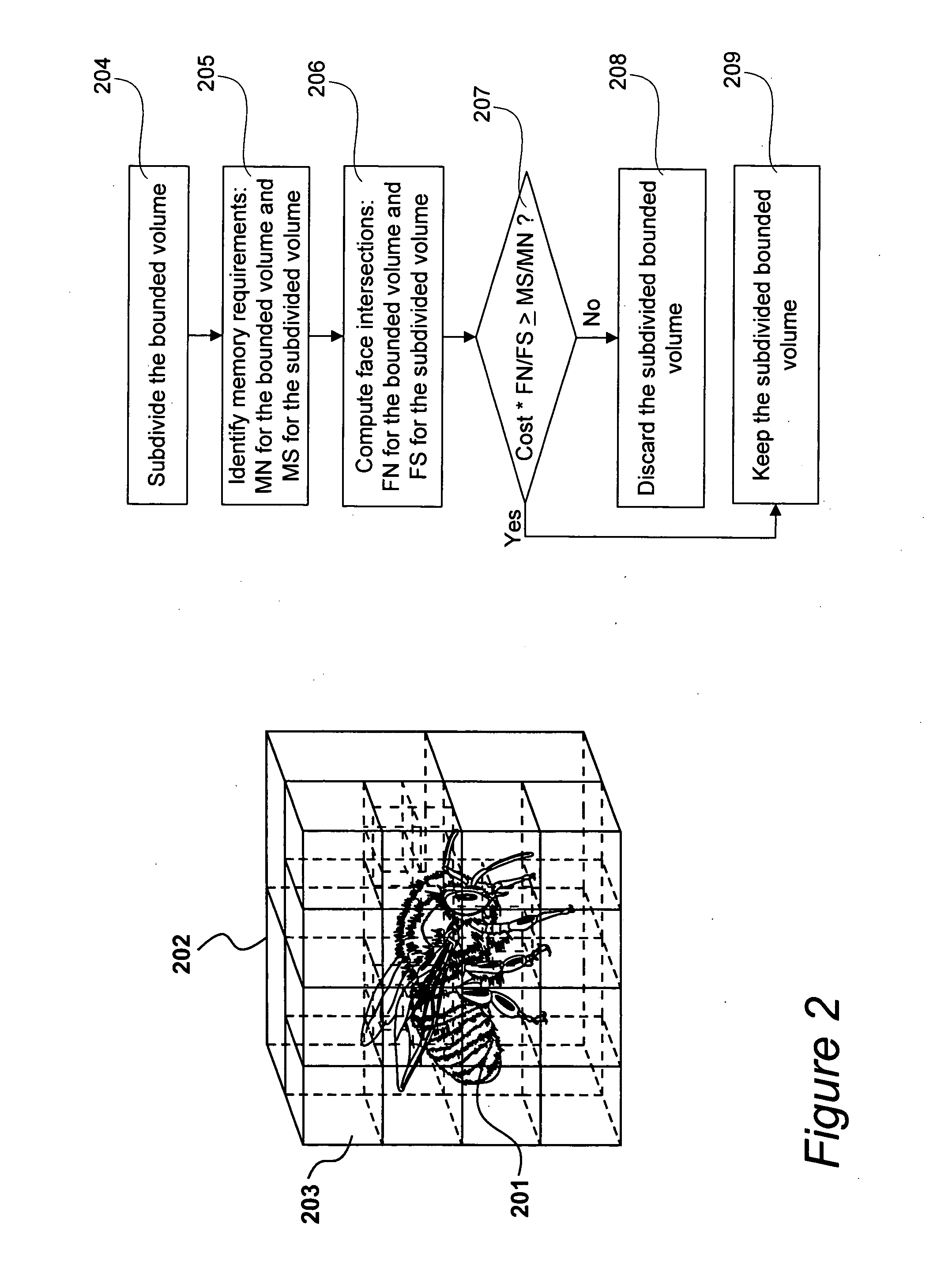
A hierarchy of bounding volumes for objects is generated for use during ray tracing. The hierarchy of bounding volumes improves image quality and well as processing time during rendering. A memory cost factor is identified that relates to the increase in the amount of memory for a subdivided volume compared to its undivided form. An estimate is made of the average number of surface intersections made with a ray passing through the undivided volume and the divided volume, and a factor is evaluated that measures the reduction in such intersections resulting from the subdivisions. A comparison between the memory cost factor and the intersection reduction factor determines whether or not a bounding volume is further subdivided. These tests are then applied recursively to the newly created bounding volumes.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Ray tracing hierarchy
InactiveUS20050017971A1Quality improvementExtension of timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage generationImaging qualityReduction factor
A hierarchy of bounding volumes for objects is generated for use during ray tracing. The hierarchy of bounding volumes improves image quality and well as processing time during rendering. A memory cost factor is identified that relates to the increase in the amount of memory for a subdivided volume compared to its undivided form. An estimate is made of the average number of surface intersections made with a ray passing through the undivided volume and the divided volume, and a factor is evaluated that measures the reduction in such intersections resulting from the subdivisions. A comparison between the memory cost factor and the intersection reduction factor determines whether or not a bounding volume is further subdivided. These tests are then applied recursively to the newly created bounding volumes.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Multi-dimensional mechanic operating collision avoidance method suitable for airborne collision avoidance system
InactiveCN103337199AImprove limitationsIncrease flexibilityAircraft traffic controlJet aeroplaneSimulation
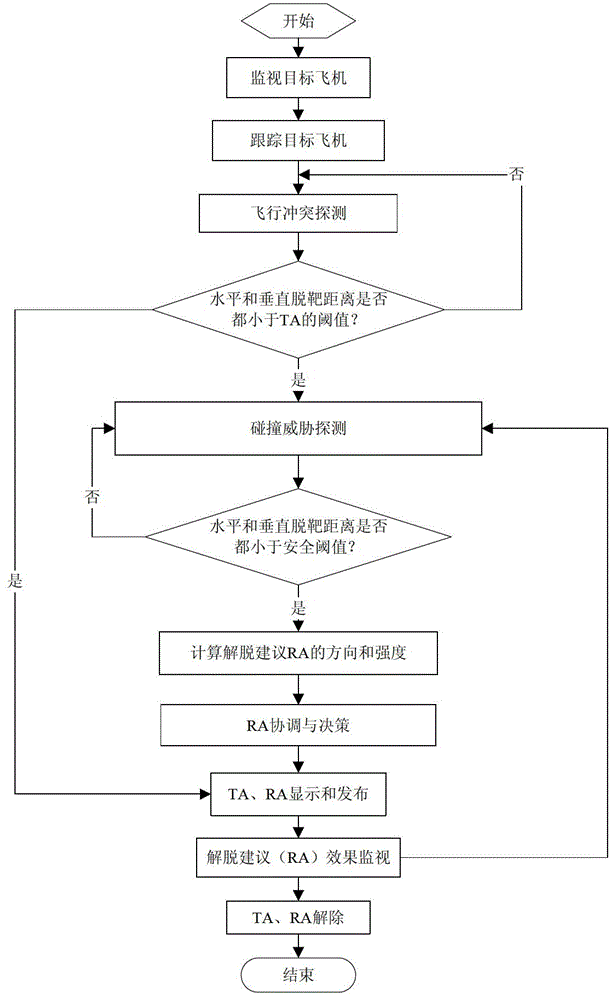
A multi-dimensional mechanic operating collision avoidance method suitable for an airborne collision avoidance system belongs to the field of air traffic safety technology, and comprises the following steps: monitoring and tracking a native and a target airplane; adopting a protection area model based on a surrounding body to conduct flight conflict detection; adopting a real-time collision detection method to conduct collision threat detection; using a four-dimensional space-time mechanic operating collision avoidance model to calculate and evaluate the manner and the strength of a release advise RA; conducting coordination and decision-making of the release advise RA; displaying and publishing a traffic advise TA and the release advise RA; conducting omnidistance monitoring for collision release effect after adopting a mechanic operating collision avoidance measure of the native; relieving the traffic advise TA and the release advise RA. The method improves the limitation of only being able to provide two release advises of climbing / descending vertically of a conventional airborne collision avoidance system, so as to allow the airborne collision avoidance system to be able to provide six release advises (climbing / descending vertically, speeding up / speeding down horizontally, or turning left / turning right), and has the advantages of more flexible and effective.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning method based on improved mechanical arms D*
ActiveCN106166750AFast Collision DetectionSolve the problem that the dynamic meridian planning cannot be completedProgramme-controlled manipulatorPlanning approachHeuristic function
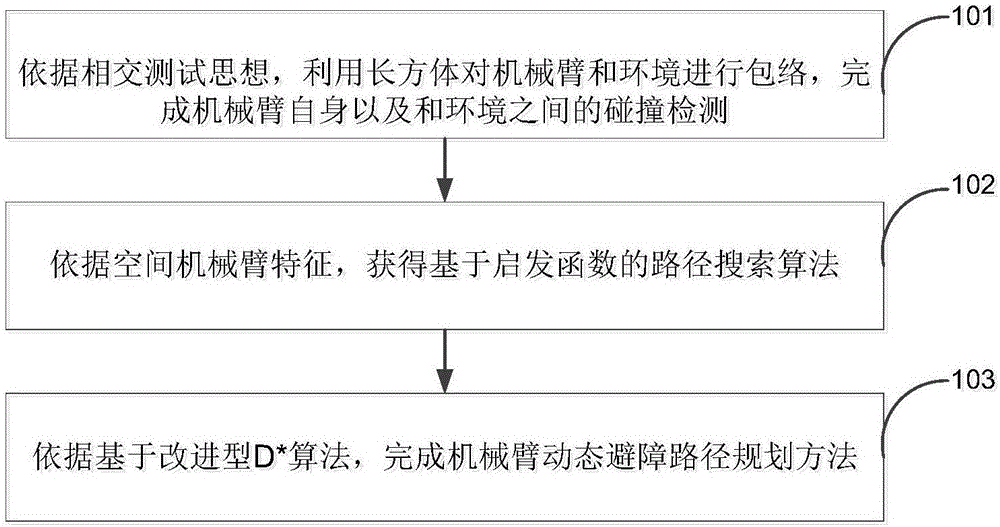
The embodiment of the invention provides an obstacle avoidance path planning method based on improved mechanical arms D* for achieving dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning of mechanical arms. The method comprises the steps that all components of the mechanical arms and obstacles in the environment are converted into a cuboid envelope through a hierarchical bounding volume method, and a relevant algorithm is designed for achieving fast collision detection between the mechanical arms and between the mechanical arms and the environment; according to spatial mechanical arm characteristics, a path search algorithm based on a heuristic function is obtained; obstacle avoidance path planning applied to seven-freedom-degree mechanical arms D* is improved, and dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning of the seven-freedom-degree mechanical arms is completed. According to the technical scheme, the method is used for achieving dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning of the seven-freedom-degree mechanical arms based on the improved mechanical arms D*.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
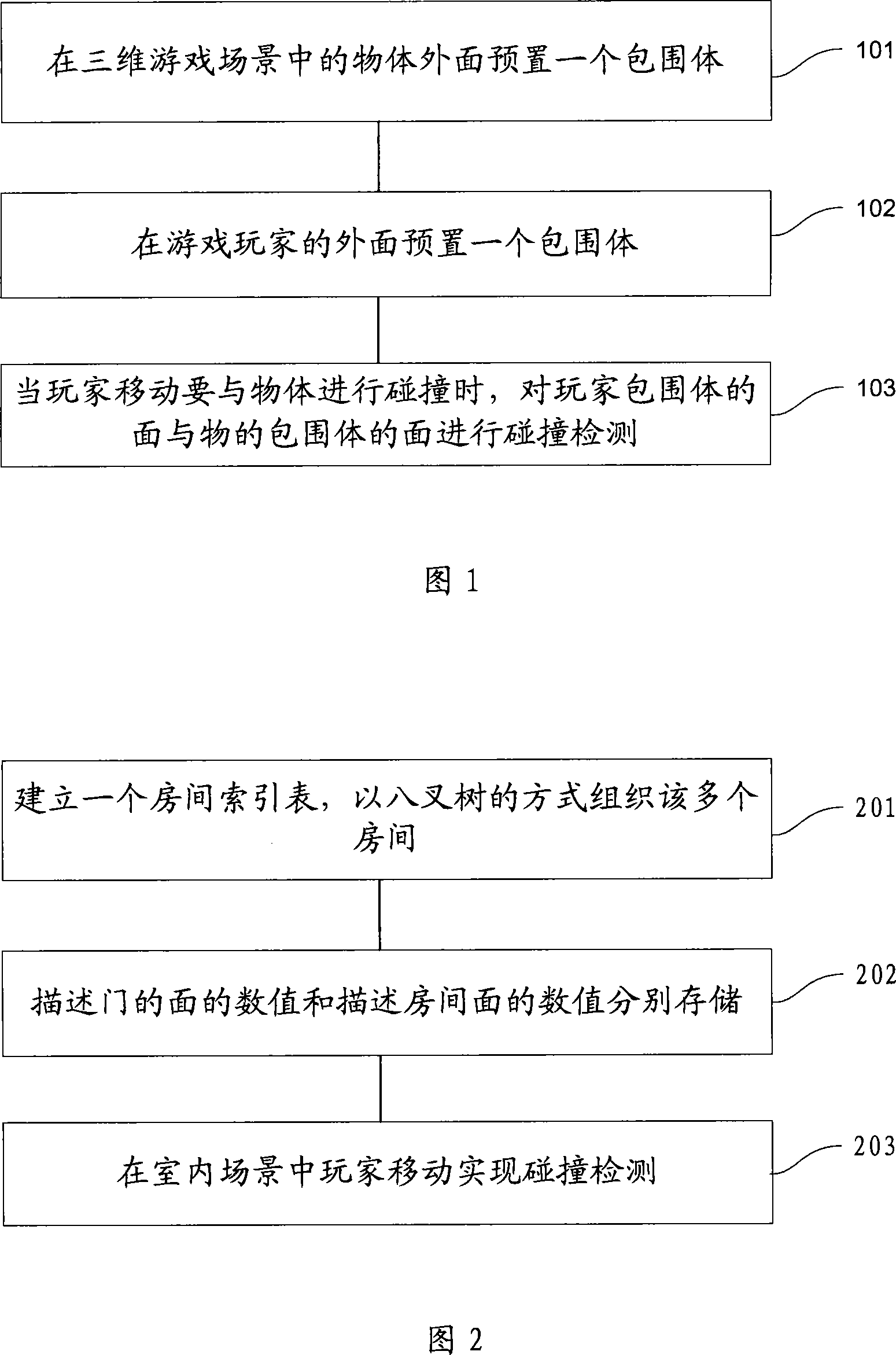
Method for realizing three-dimensional game collision detection at server end
This invention provides a method which can realize games collision detection in server-side in the three-dimensional, including the following steps: 3D gaming scene in the pre-positioning objects outside a bounding box, referred to the bounding box of siege or a major part of that siege the face value of the documents stored on the map in the game; gamers outside preset a bounding box, which covers the bounding box player or players surrounded the main part of the plane that bounding box Numerical documents stored on the game map ; When mobile gamers collisions with objects, the players bounding box of the surface and the surface bounding box for collision detection. By optimizing the game scenes, the game will be the scene of various complex objects and gamers 'description' into a bounding box, thus change collision between complex objects into collision between the limited surface of the siege, then greatly reducing burden of the computer data processing.
Owner:BEIJING KINGSOFT SOFTWARE +3
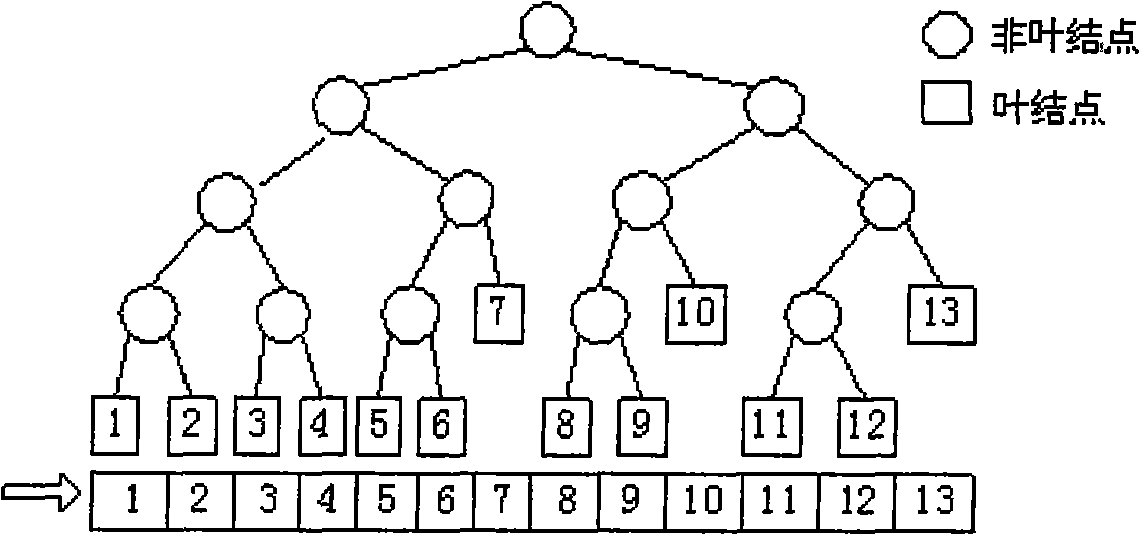
Balanced binary tree-based method for detecting collisions in large-scale virtual environment
InactiveCN101593366AHigh precisionSolve the degradation problem3D modellingTime complexityBinary tree
The invention relates to a balanced binary tree-based method for detecting collisions in a large-scale virtual environment. According to the characteristics of large object quantity and complex object types in a large-scale visual environment, the method adopts an expanded balanced binary tree to improve a bounding volume hierarchy tree, accelerates the detection of object collisions and reduces time complexity, caused by environmental changes, of tree reconstruction for overcoming the drawbacks of the conventional bounding volume hierarchy method in the real-time detection of collisions in a dynamic environment. The method adopts different bounding volumes according to hierarchy, combines the simplicity and compactibility of the bounding volumes, and improves a collision method as well as the accuracy of collision detection. Concrete processing flow is described in drawings in the abstract.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
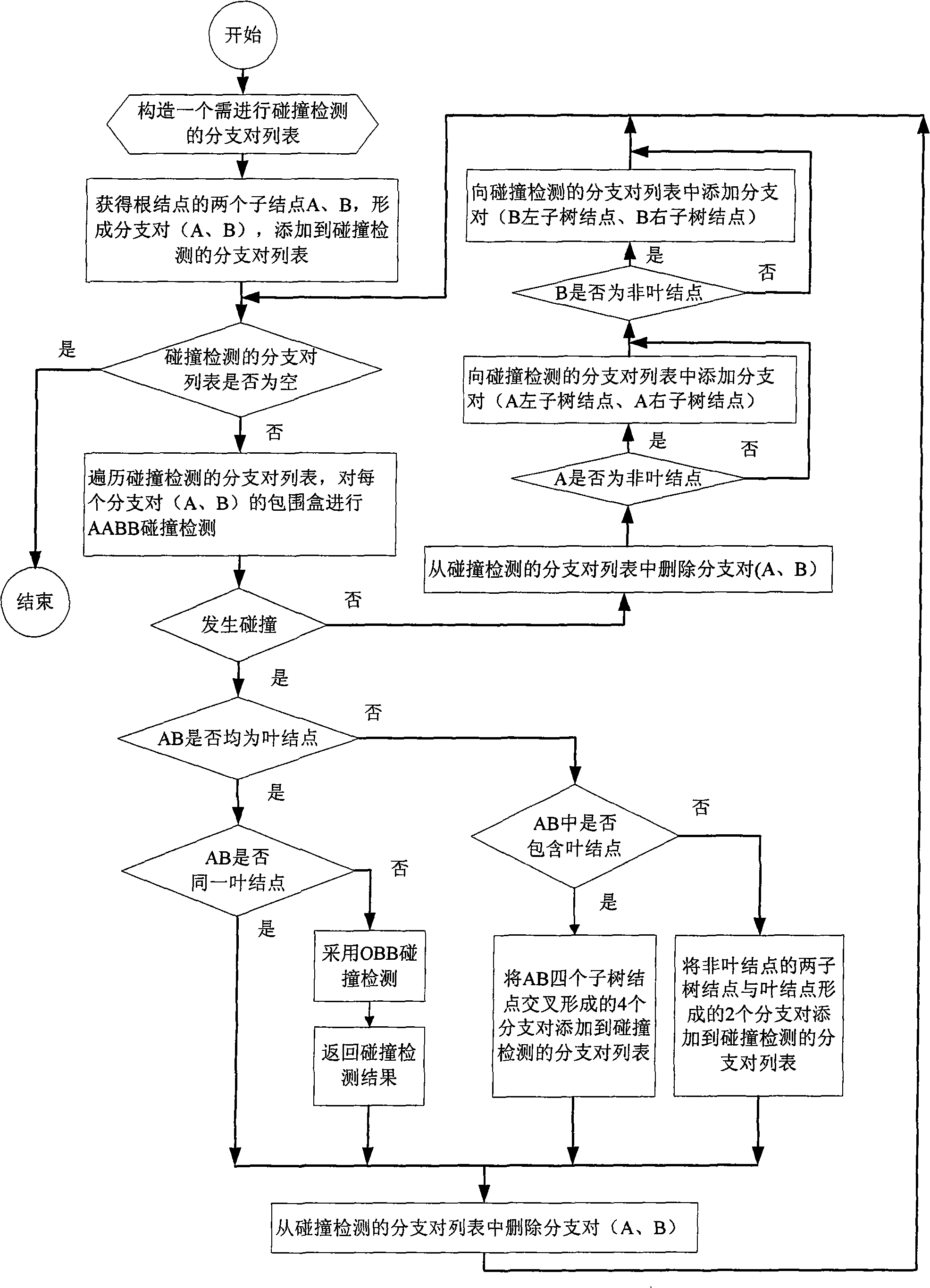
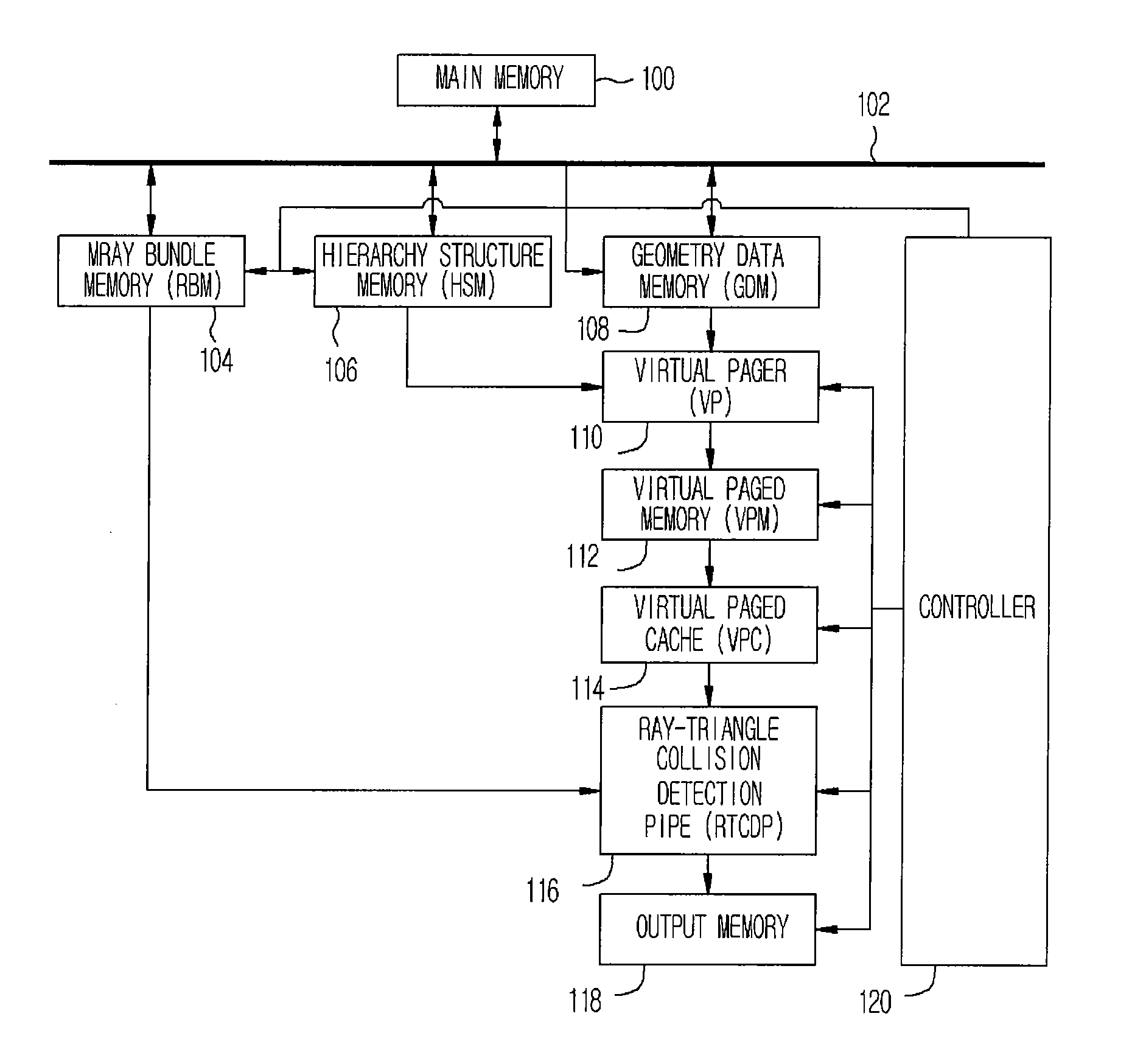
Apparatus and method of ray-triangle collision detection for ray-tracing
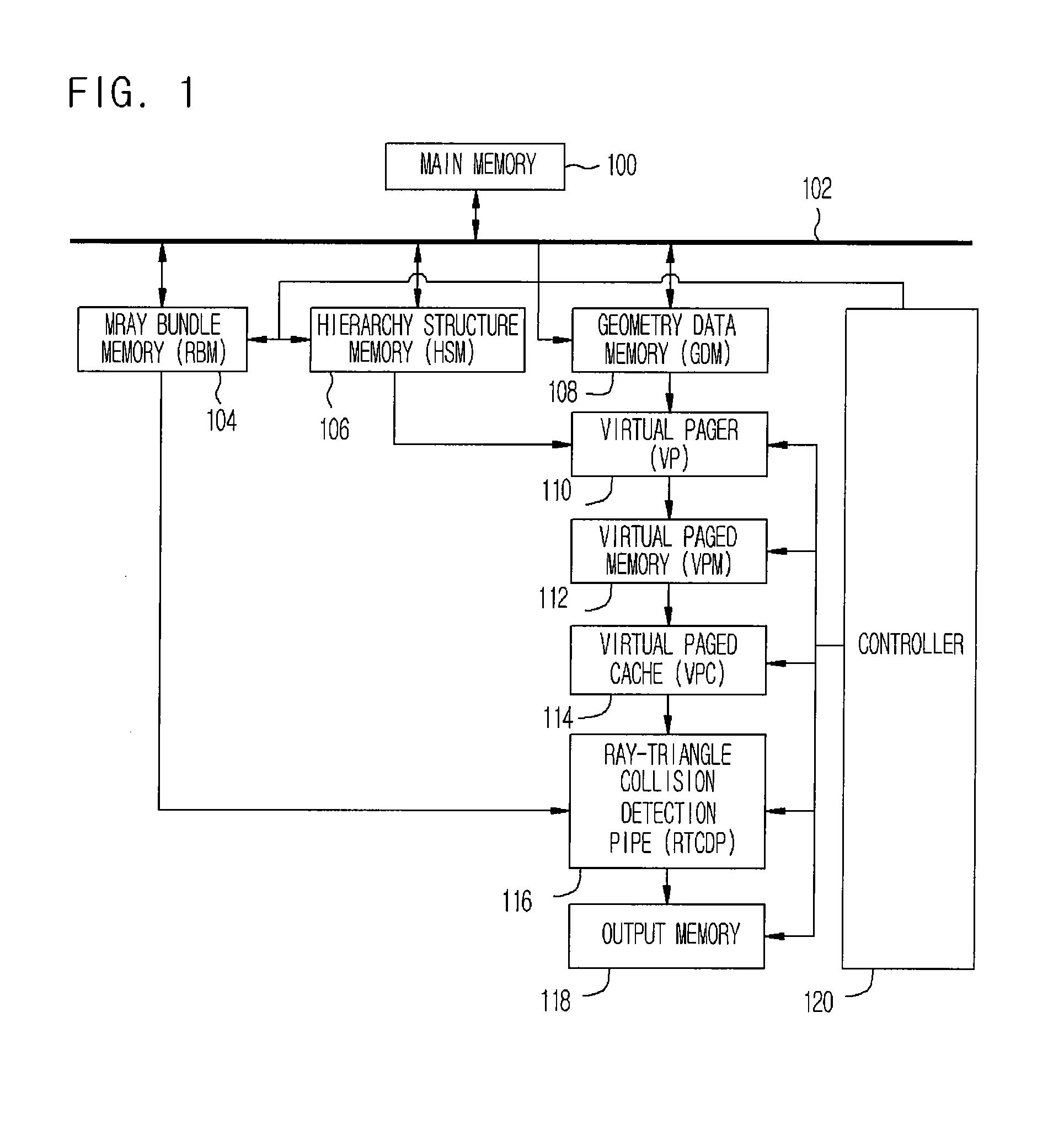
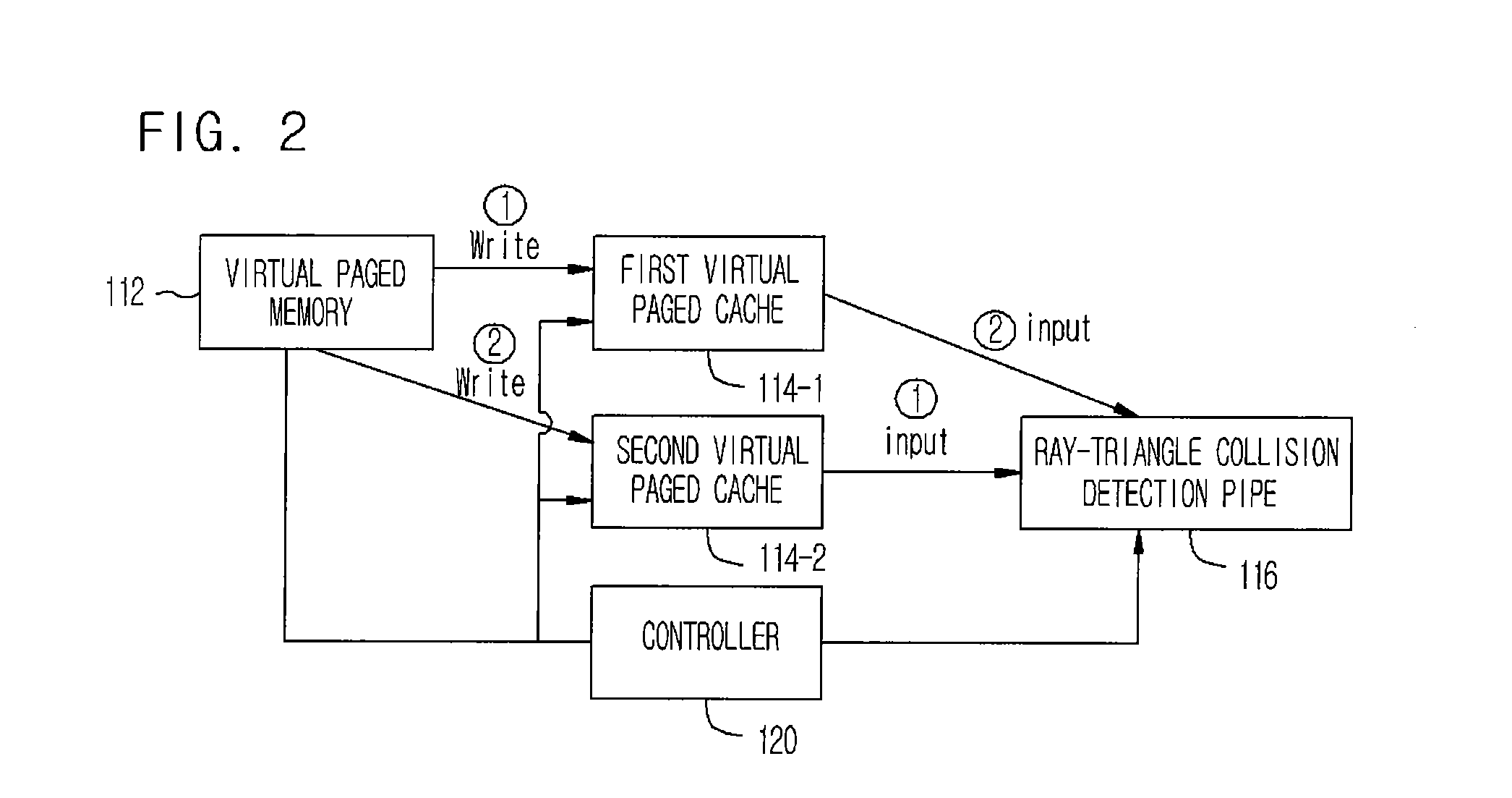
InactiveUS20080129734A1Data input efficientlyEfficient inputDrawing from basic elementsProcessor architectures/configurationPagerComputer graphics (images)
Provided are an apparatus and method for detecting ray-triangle collision for ray-tracing. The apparatus includes a ray bundle memory for storing ray bundle, a geometry data memory for storing geometry triangle data, a hierarchy structure memory for storing space subdivision and bounding volume hierarchy structure information, a virtual pager for receiving the geometry triangle data, the space subdivision and bounding volume hierarchy structure information, and the bounding hierarchical structure information by rearranging geometry triangle data by final end nodes, a virtual paged memory for receiving the rearranged data, forming page memories, and storing triangle data by pages, a virtual page cache for processing the page data in a pipe line manner, and previously storing a page memory for collision detection, a ray-triangle collision detection pipe for detecting a ray-triangle collision based on the page memory and the ray bundle, and an output memory for storing the ray-triangle collision detection result.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
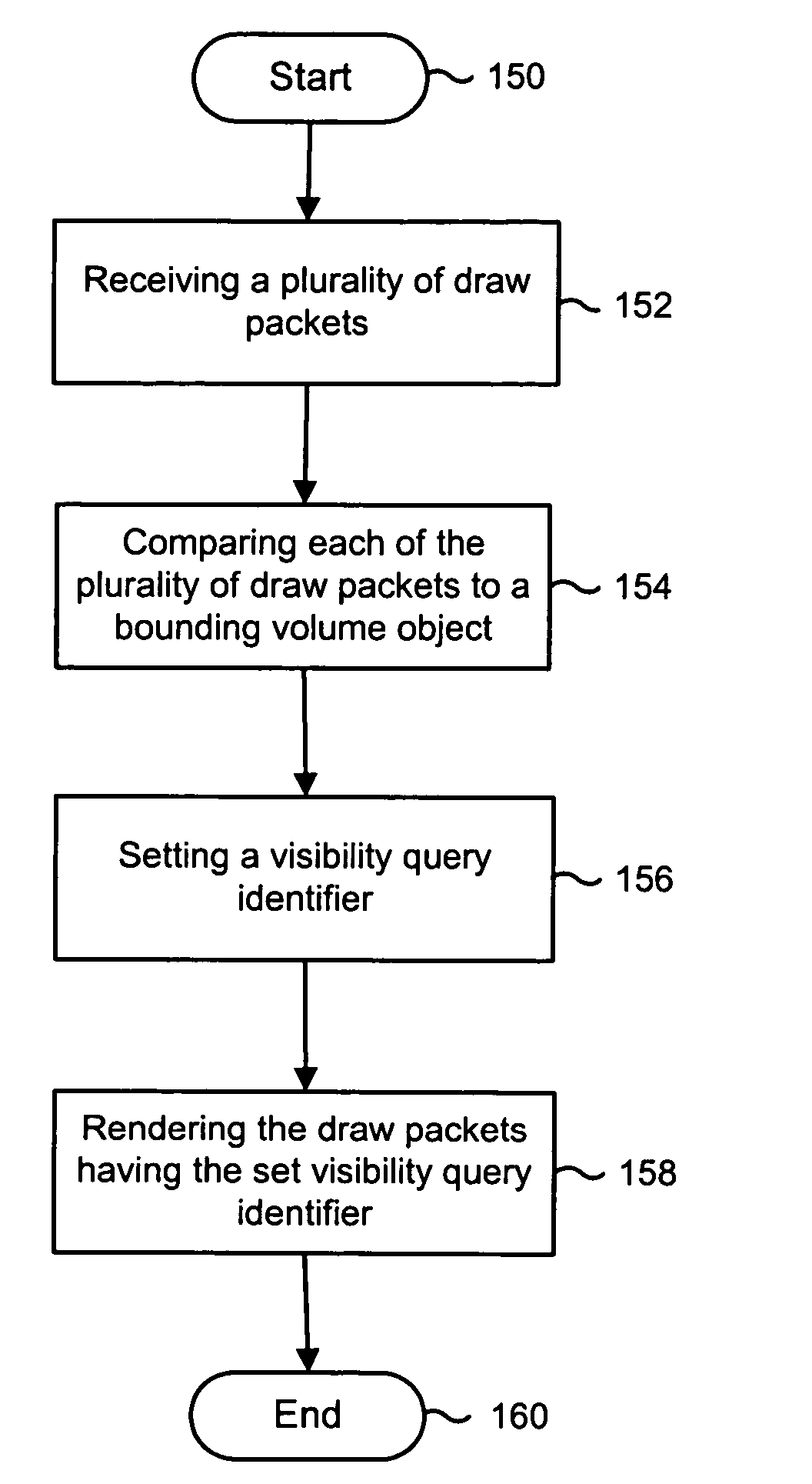
Method and apparatus for object based visibility culling
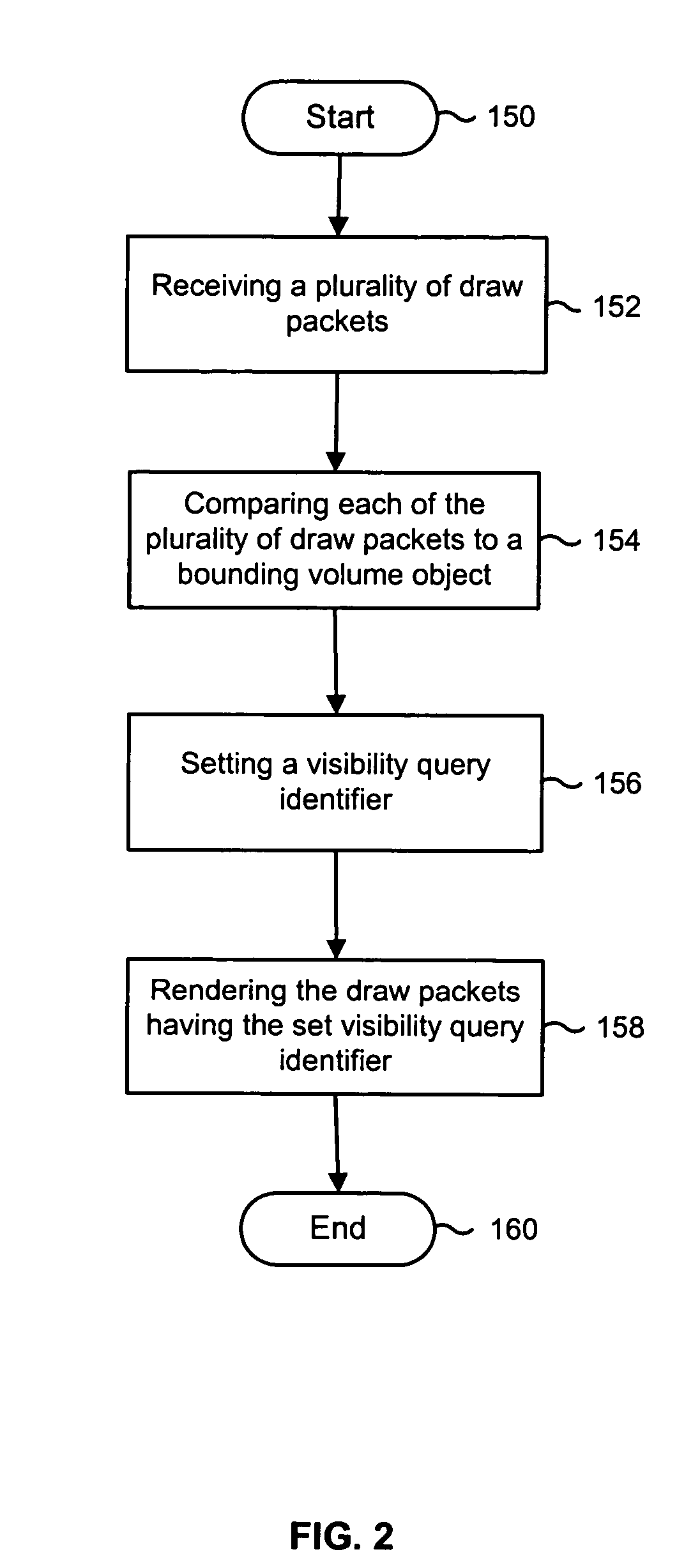
A method and apparatus for object-based visibility culling includes receiving a plurality of draw packets, such as pixels or vertices. The method and apparatus further includes comparing each of the plurality of draw packets to a bounding volume object, wherein the bounding volume object may be a low resolution geometric representation of a specific object. Whereupon, for each of the plurality of draw packets, if the draw packet is deemed potentially visible, setting a visibility query identifier and rendering the draw packets having the set visibility query identifier.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Depth image-based modeling method and apparatus
A depth image-based modeling method and apparatus. A depth information-based modeling method using a three-dimensional (3D) polygonal mesh includes: extracting a bounding volume (BV) for the 3D polygonal mesh; obtaining a 3D grid by dividing the BV using a plurality of sampling lines; selecting some of a plurality of vertices of the 3D grid that intersect the 3D polygonal mesh as valid vertices; obtaining depth information and color information of the valid vertices by using a plurality of vertices of the 3D polygonal mesh; and modeling an object using the depth information and the color information of the valid vertices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Physical Rendering With Textured Bounding Volume Primitive Mapping
InactiveUS20100238169A1Reduce overheadReduce memory usageImage data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Memory footprint
A circuit arrangement, program product and circuit arrangement utilize a textured bounding volume to reduce the overhead associated with generating and using an Accelerated Data Structure (ADS) in connection with physical rendering. In particular, a subset of the primitives in a scene may be mapped to surfaces of a bounding volume to generate textures on such surfaces that can be used during physical rendering. By doing so, the primitives that are mapped to the bounding volume surfaces may be omitted from the ADS to reduce the processing overhead associated with both generating the ADS and using the ADS during physical rendering, and furthermore, in many instances the size of the ADS may be reduced, thus reducing the memory footprint of the ADS, and often improving cache hit rates and reducing memory bandwidth.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image rendering method and system
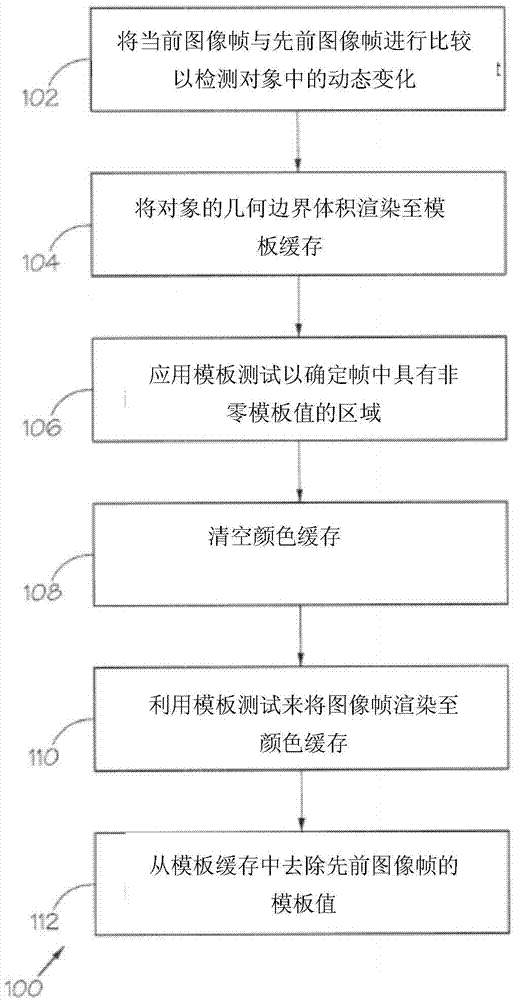
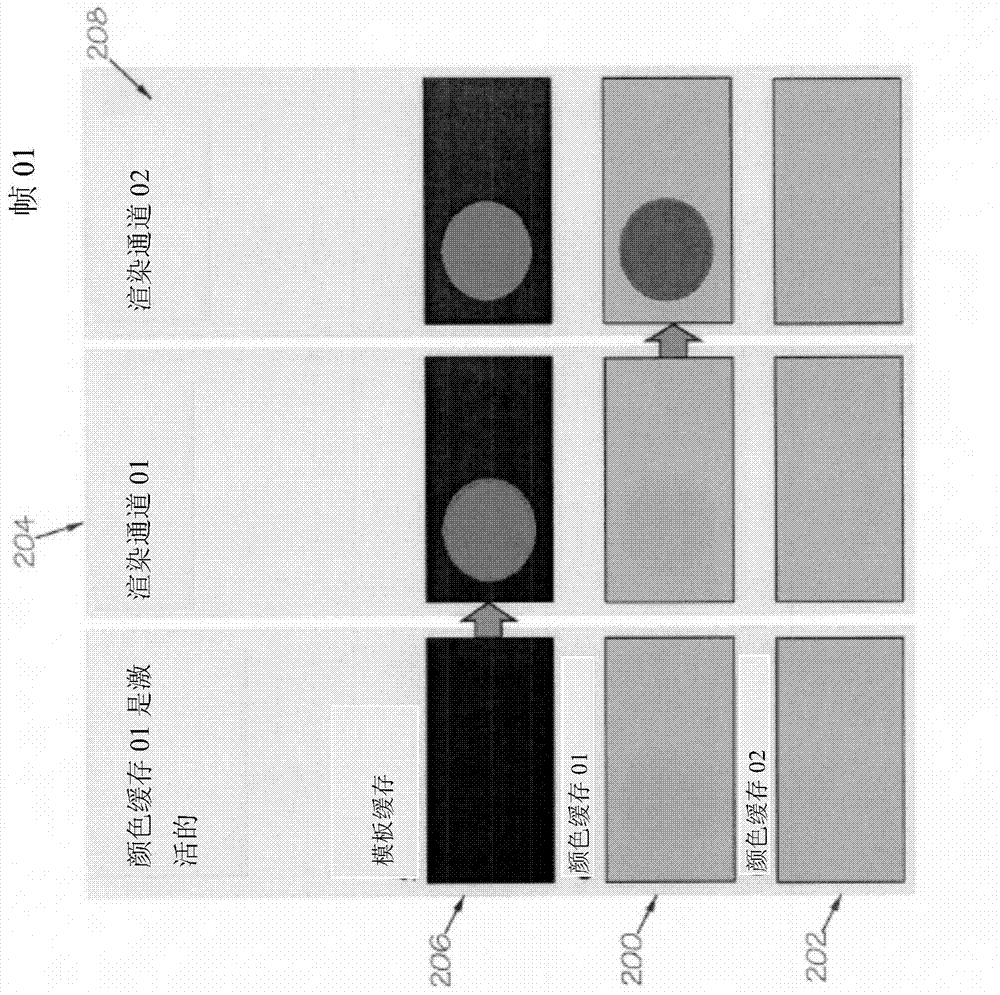
An image rendering method is provided, comprising comparing a current image frame with a previous image frame to detect a dynamic change in an object in the image frames, with each image frame being defined by a scene graph and each object having an associated geometric bounding volume. If a dynamic change in an object is detected, the method comprises rendering the object's geometric bounding volume to a stencil buffer for each dynamically changed object, using a stencil value assigned to the current image frame. A stencil is then applied to determine areas in the frames having non-zero stencil values. The method further comprises clearing a color buffer with respect to the areas in the previous image frame that have been redrawn and with respect to areas in the current frame that need to be overdrawn, rendering the image frame to the color buffer using a stencil test, so that only the areas with non-zero stencil values are redrawn, and then removing the stencil values from a previous image frame from the stencil buffer.
Owner:RIGHTWARE
Apparatus and method for compressing leaf nodes of a bounding volume hierarchy (BVH)
ActiveUS20190318445A1Improve performanceImage codingConcurrent instruction executionGraphicsTheoretical computer science
Apparatus and method for compressing an acceleration data structure such as a bounding volume hierarchy (BVH). For example, one embodiment of a graphics processing apparatus comprises: one or more cores to execute graphics instructions including instructions to perform ray tracing operations; and compression circuitry to compress lowest level nodes of a hierarchical acceleration data structure comprising a plurality of hierarchically arranged nodes, each of the lowest level nodes comprising pointers to leaf data; the compression circuitry to quantize the lowest level nodes to generate quantized lowest level nodes and to store each quantized lowest level node and associated leaf data without the pointers to the leaf data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
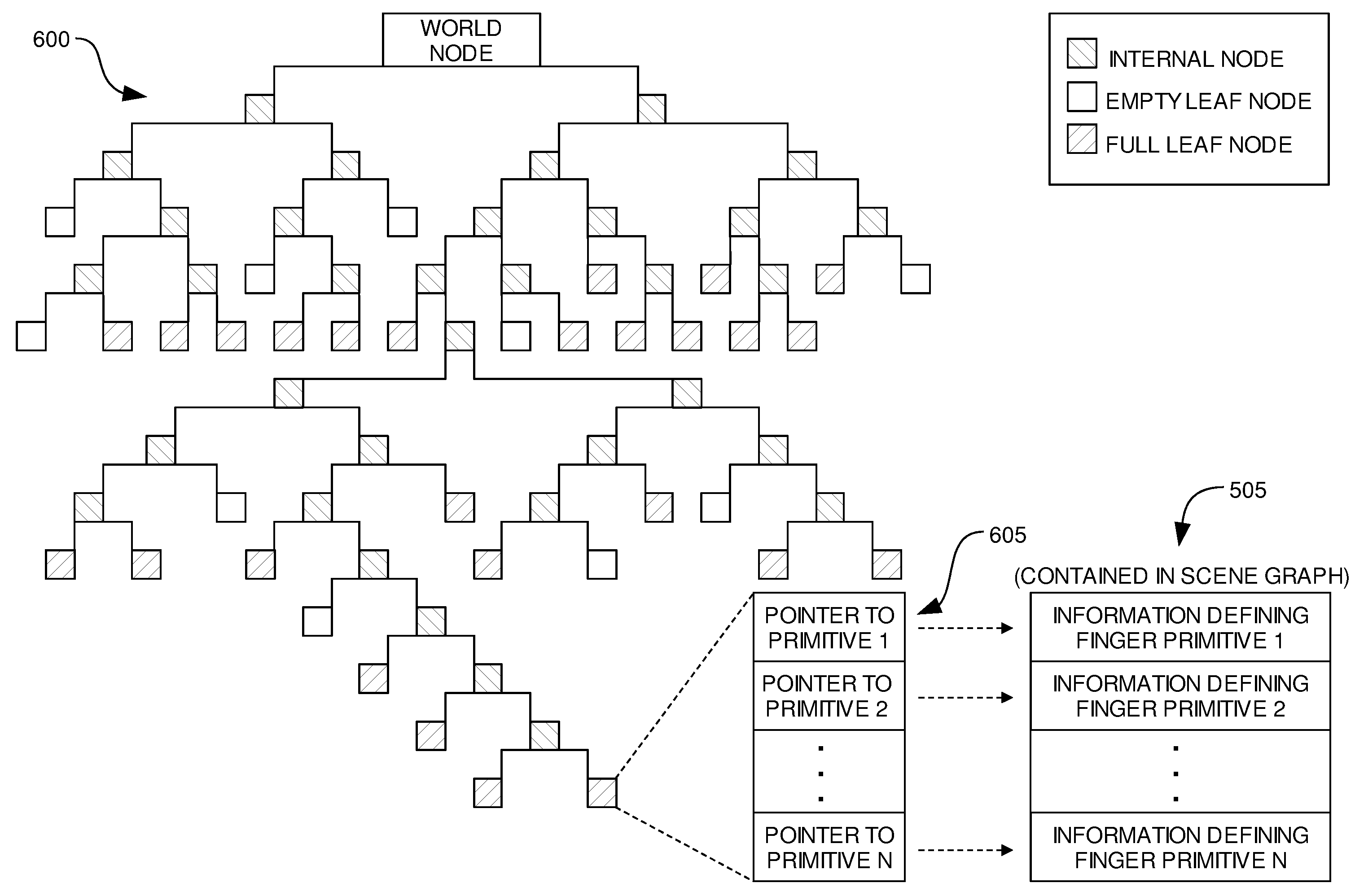
Methods and Systems for Referencing a Primitive Located in a Spatial Index and in a Scene Index
Embodiments of the invention provide methods and systems to reduce the amount of space necessary to store a spatial index. According to embodiments of the invention, a spatial index may store pointers to information defining primitives which are located within bounding volumes defined by leaf nodes in the spatial index. The pointers may be smaller in size in contrast to information which defines the primitives, and the pointers may point to locations within a scene graph which contains information defining the primitives. Therefore, by storing pointers to primitives in the spatial index rather than the information which defines the primitives, the amount of space required to store the spatial index may be reduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
Integrated Acceleration Data Structure for Physics and Ray Tracing Workload
According to embodiments of the invention, a data structure may be created which may be used by both an image processing system and by a physics engine. The data structure may have an initial or upper portion representing bounding volumes which partition a three dimensional scene and a second or lower portion representing objects within the three dimensional scene. The integrated acceleration data structure may be used by an image processing system to render a two dimensional image from a three dimensional scene, and by a physics engine to perform physics based calculations in order to simulate physical phenomena in the three dimensional scene. Furthermore, the physics engine may update the integrated acceleration data structure in response to changes in position or shape of objects due to physical phenomena.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ray-aggregation for ray-tracing during rendering of imagery
A computer-enabled method for rendering a scene of objects representing physical objects includes projecting a first plurality of rays against a scene and aggregating a second plurality of rays that intersect a bounding volume, wherein the bounding volume encloses an object of the scene, and wherein the second plurality of rays is a portion of the first plurality of rays. The method further includes determining or computing intersections of the second plurality of aggregated rays with the object when the number of the second plurality of aggregated rays exceeds a predetermined value. The method also includes rendering the scene based on the determined intersections of the rays with the object. The second plurality of rays may be aggregated in a bounding volume aggregate data structure for processing.
Owner:DREAMWORKS ANIMATION LLC
Image Processing Techniques
InactiveUS20150145873A1Processor architectures/configurationImage generationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
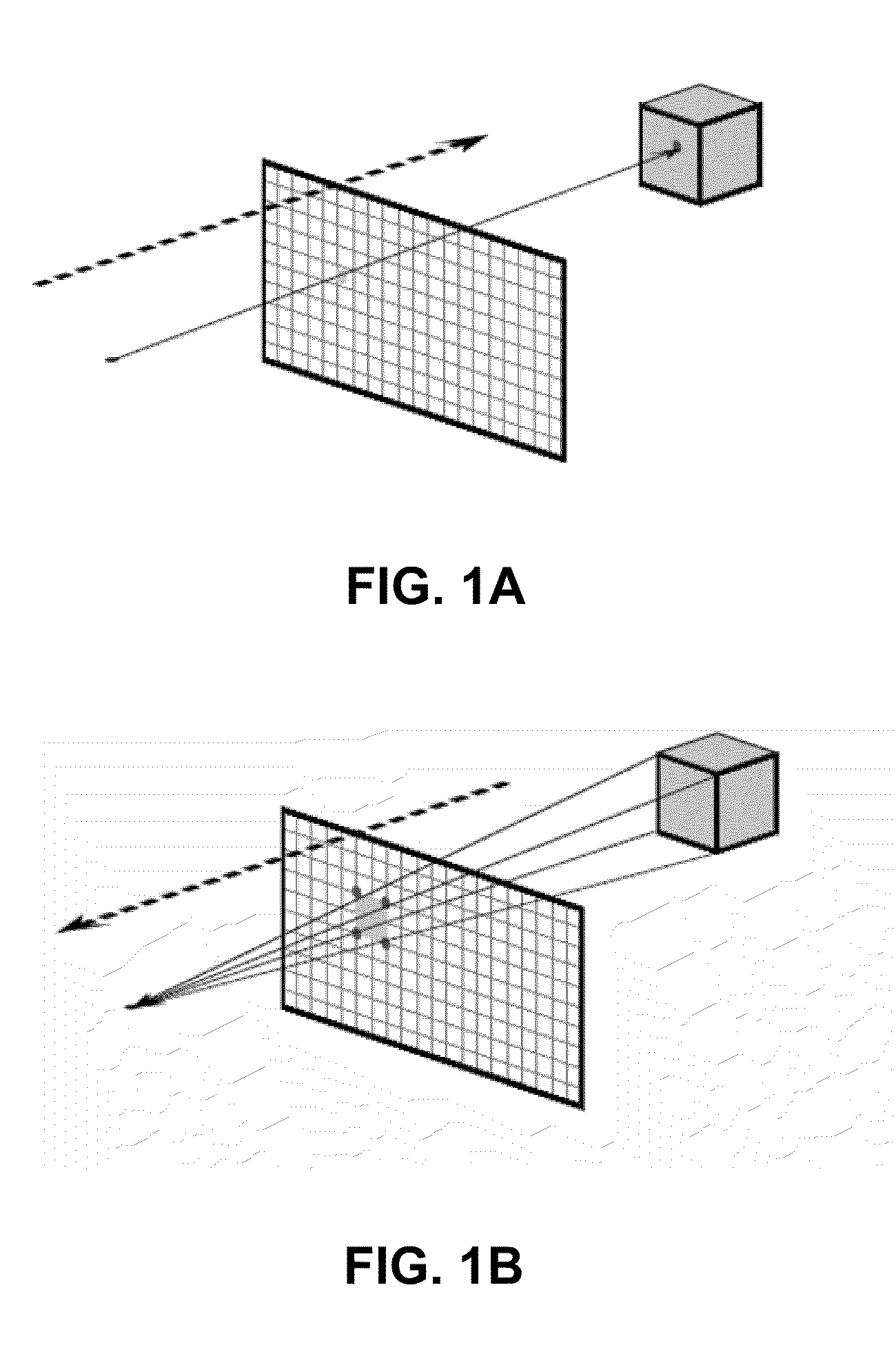
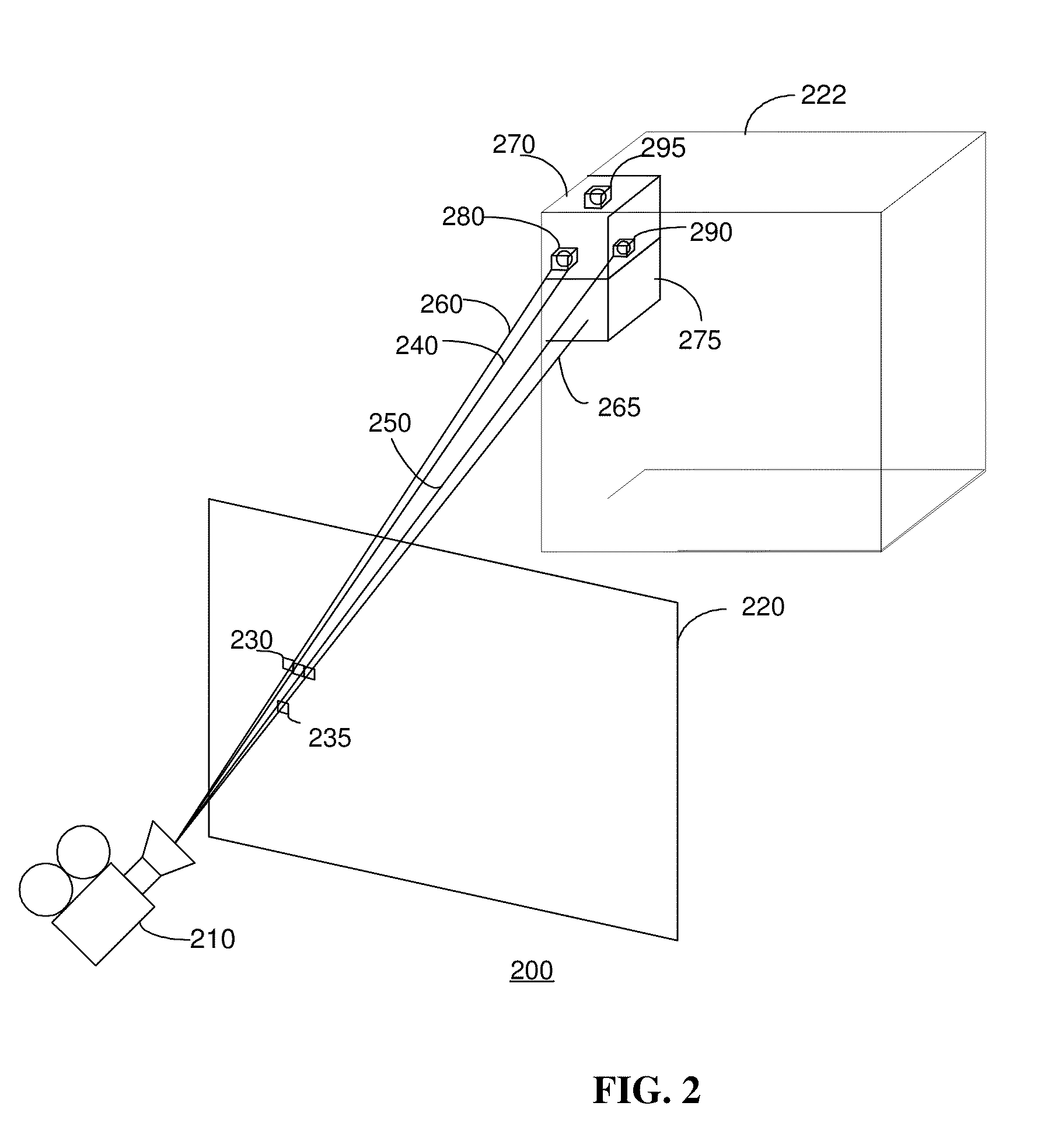
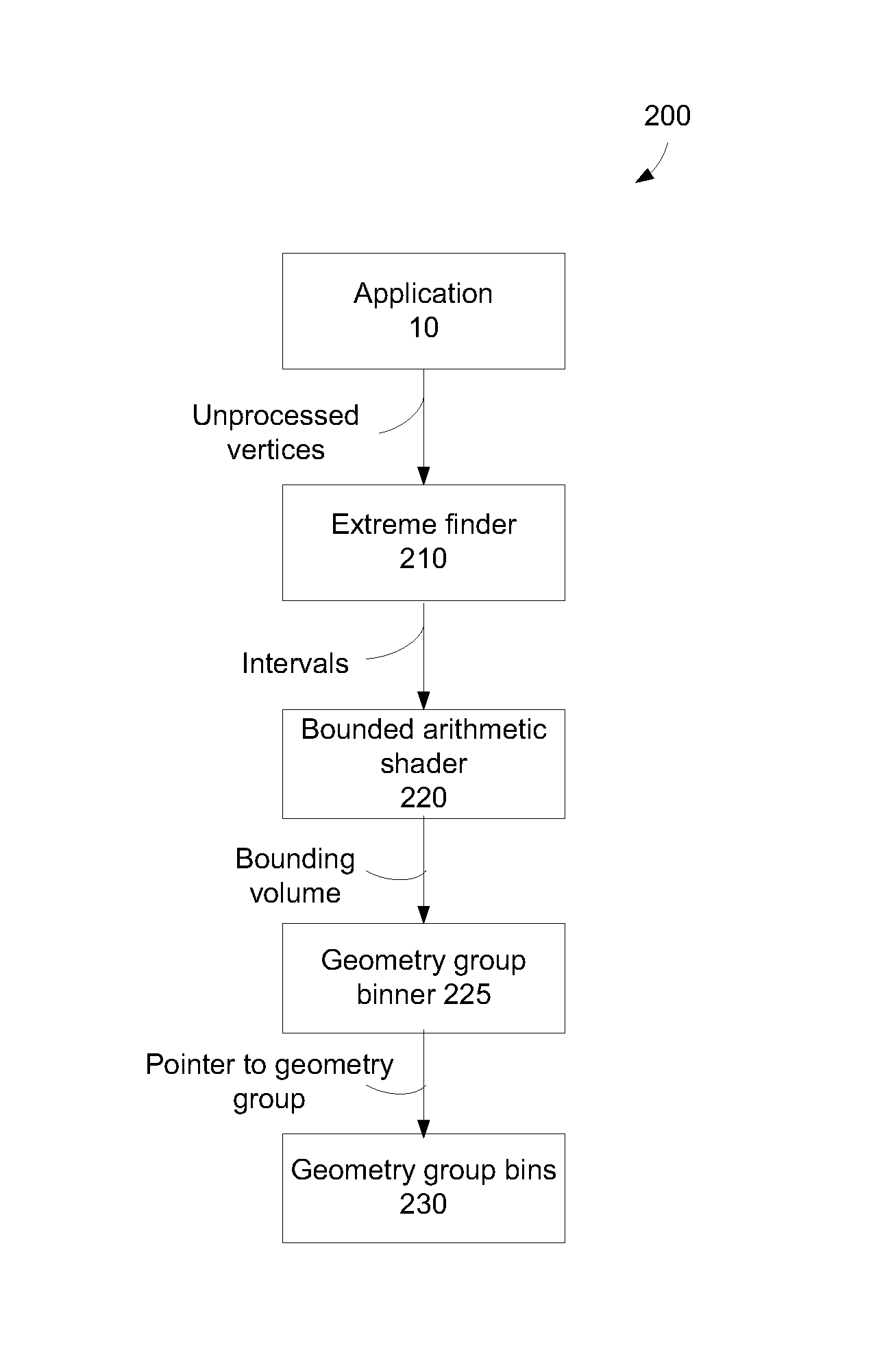
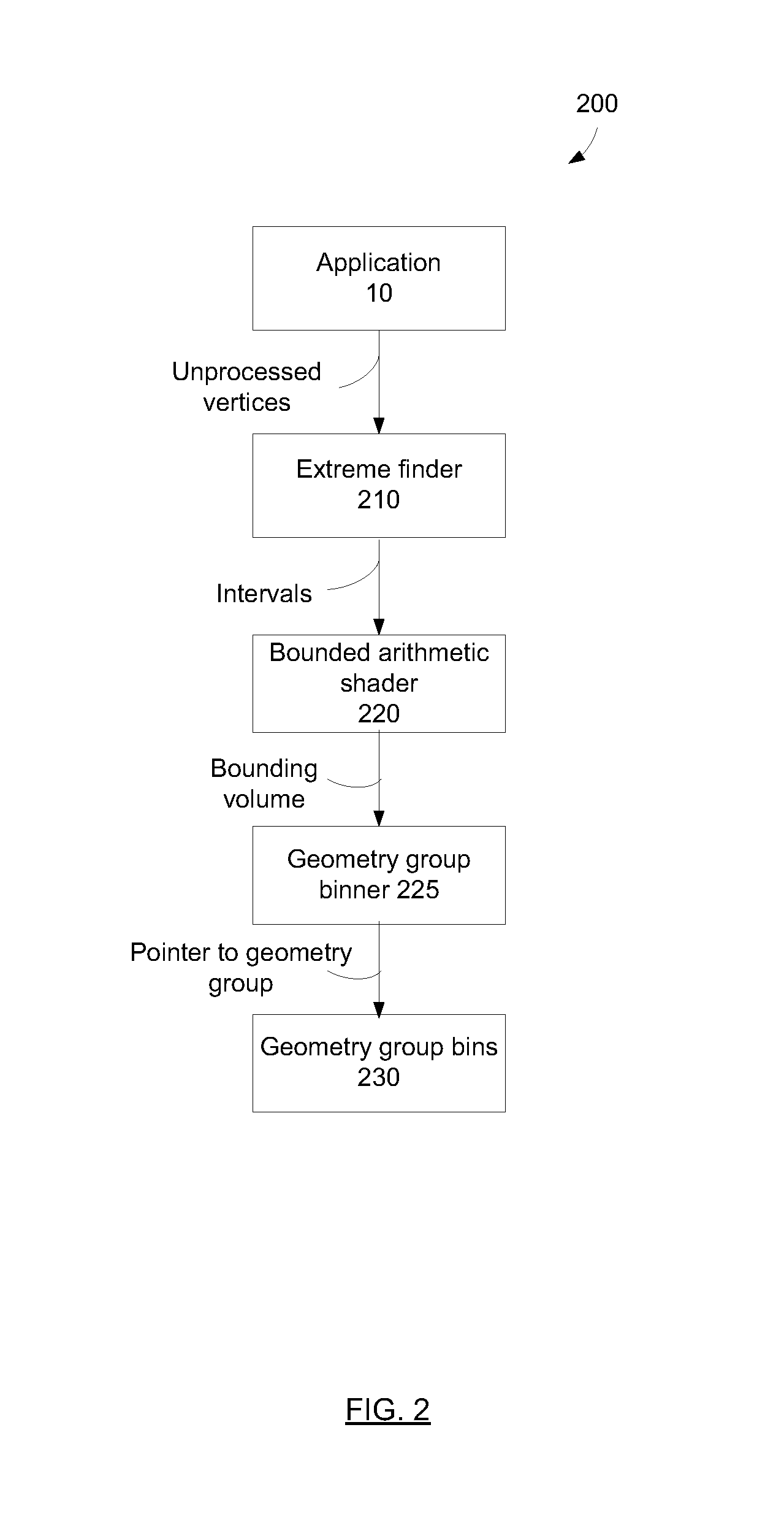
Techniques are described that can delay or even prevent use of memory to store triangles associated with tiles as well as processing resources associated with vertex shading and binning triangles. The techniques can also provide better load balancing among a set of cores, and hence provide better performance. A bounding volume is generated to represent a geometry group. Culling takes place to determine whether a geometry group is to have triangles rendered. Vertex shading and association of triangles with tiles can be performed across multiple cores in parallel. Processing resources are allocated for rasterizing tiles that have been vertex shaded and binned triangles over tiles that have yet to be vertex shaded and binned triangles. Rasterization of triangles of different tiles can be performed by multiple cores in parallel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Self collision detection method based on triangle mesh deformation body
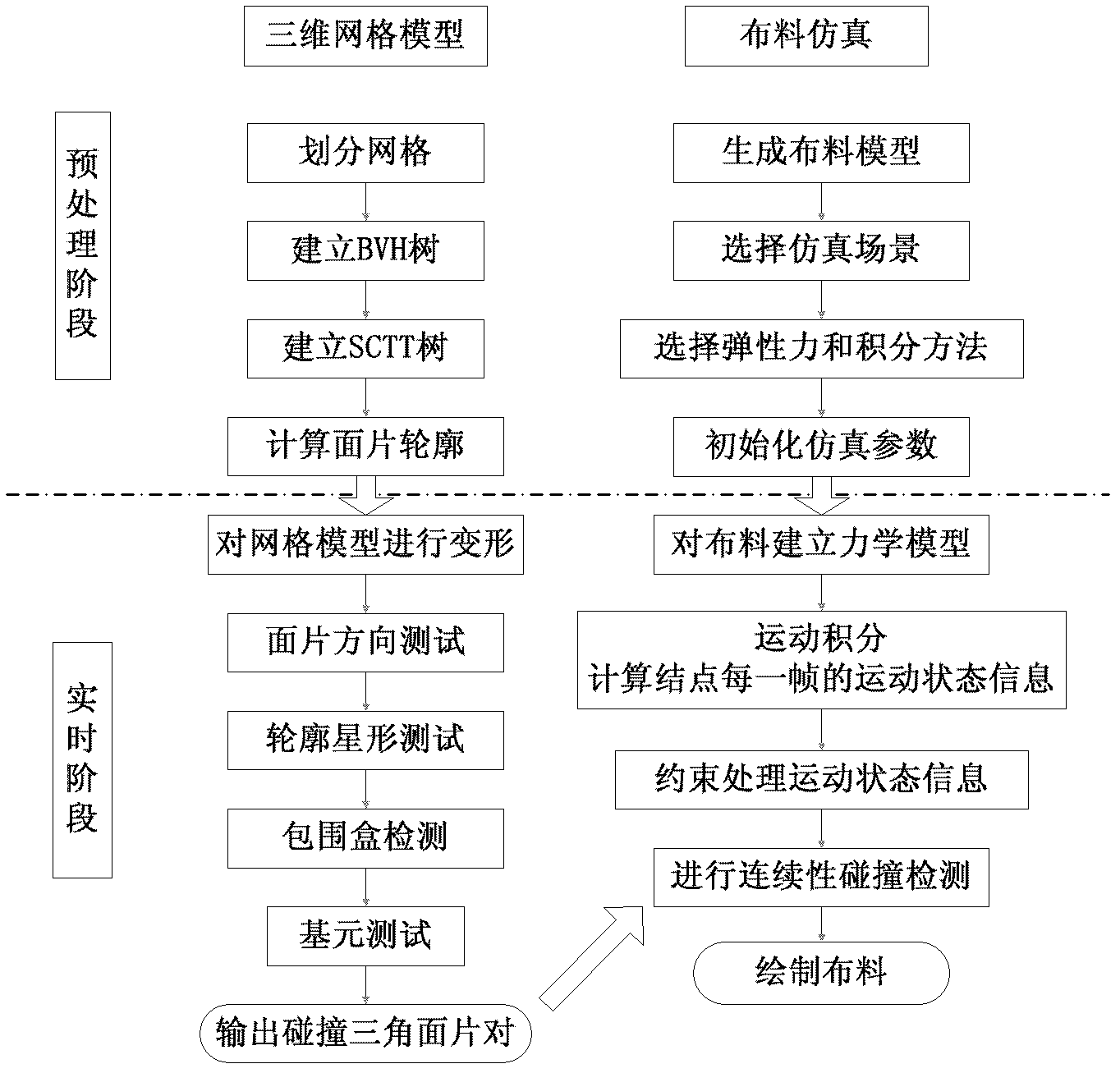
InactiveCN102609992ASpeed up the self-collision detection processImprove accuracyImage data processingGrid deformationCollision test
The invention discloses a self collision detection method based on a triangle mesh deformation body, comprising the steps of (1), constructing a data structure based on a hierarchical hounding volume (BVH); constructing an xBVH (expanded bounding volume hierarchy); constructing an SCTT (self-collision test tree)); optimizing star-shaped outline; (2), pre-processing self-collision detection based on the star-shaped outline; (3), performing self-collision test based on the star-shaped outline in real time. The method can detect the self-collision phenomenon during the deformation of the triangle mesh deformation body effectively in real time, accurately locates collision generation point and updates the collision information in real time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Statistical rendering acceleration
Different rendering techniques are selected for portions of a scene based on statistical estimates of the portions' rendering costs. A scene is partitioned into a bounding volume hierarchy. Each bounding volume includes a statistical model of the spatial distribution of geometric primitives within the bounding volume. An image to be rendered is partitioned into screen regions and each screen region is associated with one or more bounding volumes and their statistical models. The associated statistical models of a screen region are evaluated to estimate the rendering cost, such as the probable number of geometric primitives per pixel, for the screen region. Based on the rendering cost, the screen region is assigned to a dense geometry renderer, such as a ray tracing renderer, or a sparse geometry renderer, such as a rasterization renderer. Rendered screen regions are combined to form a rendered image.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Tree Insertion Depth Adjustment Based on View Frustrum and Distance Culling
A method, program product and system for conducting a ray tracing operation where the rendering compute requirement is reduced by varying the size of bounding volumes into which image data is divided and / or by varying a number of primitives included within nodes of an acceleration data structure that correspond to the bounding volumes.
Owner:IBM CORP
Enhanced shape characterization device and method
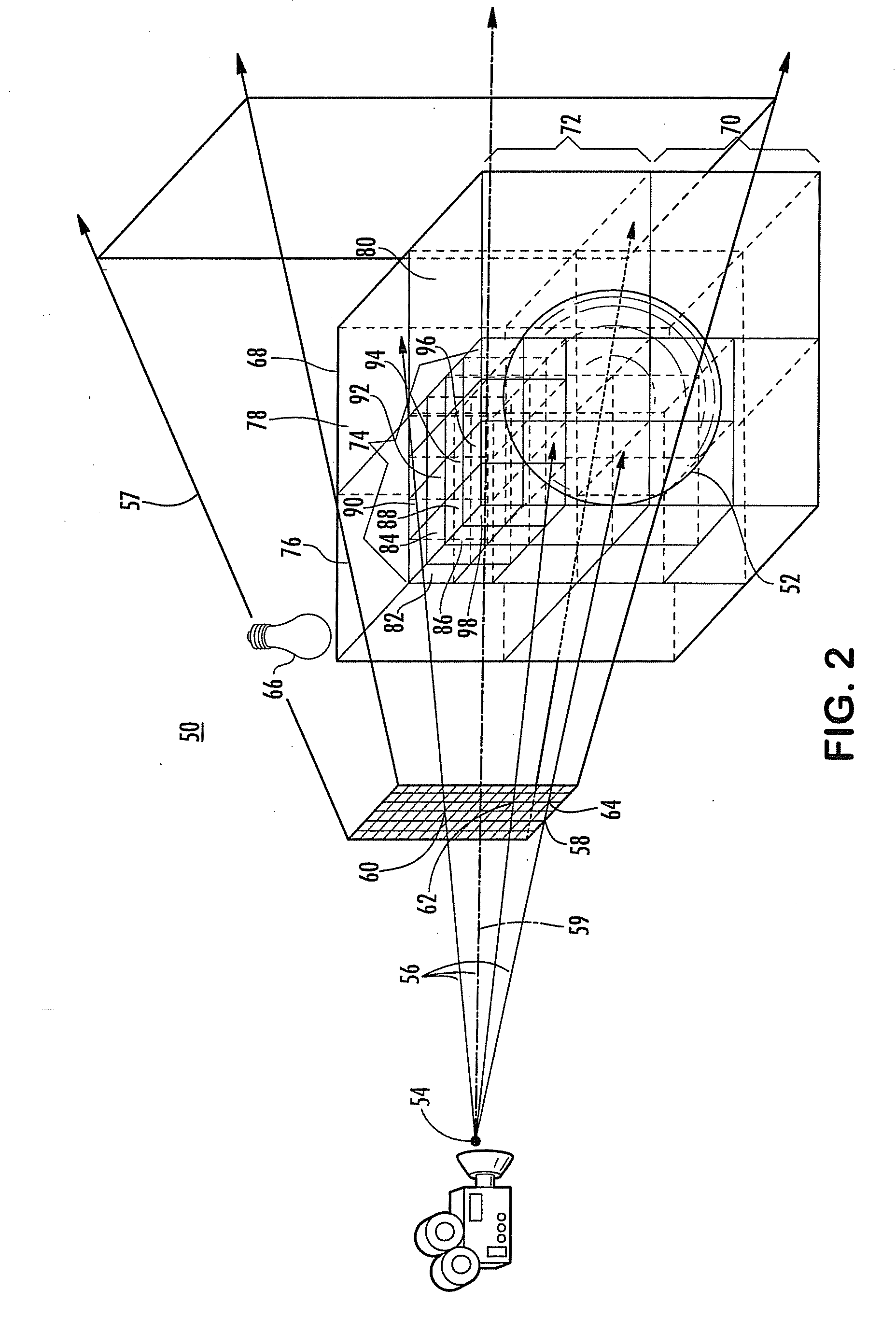
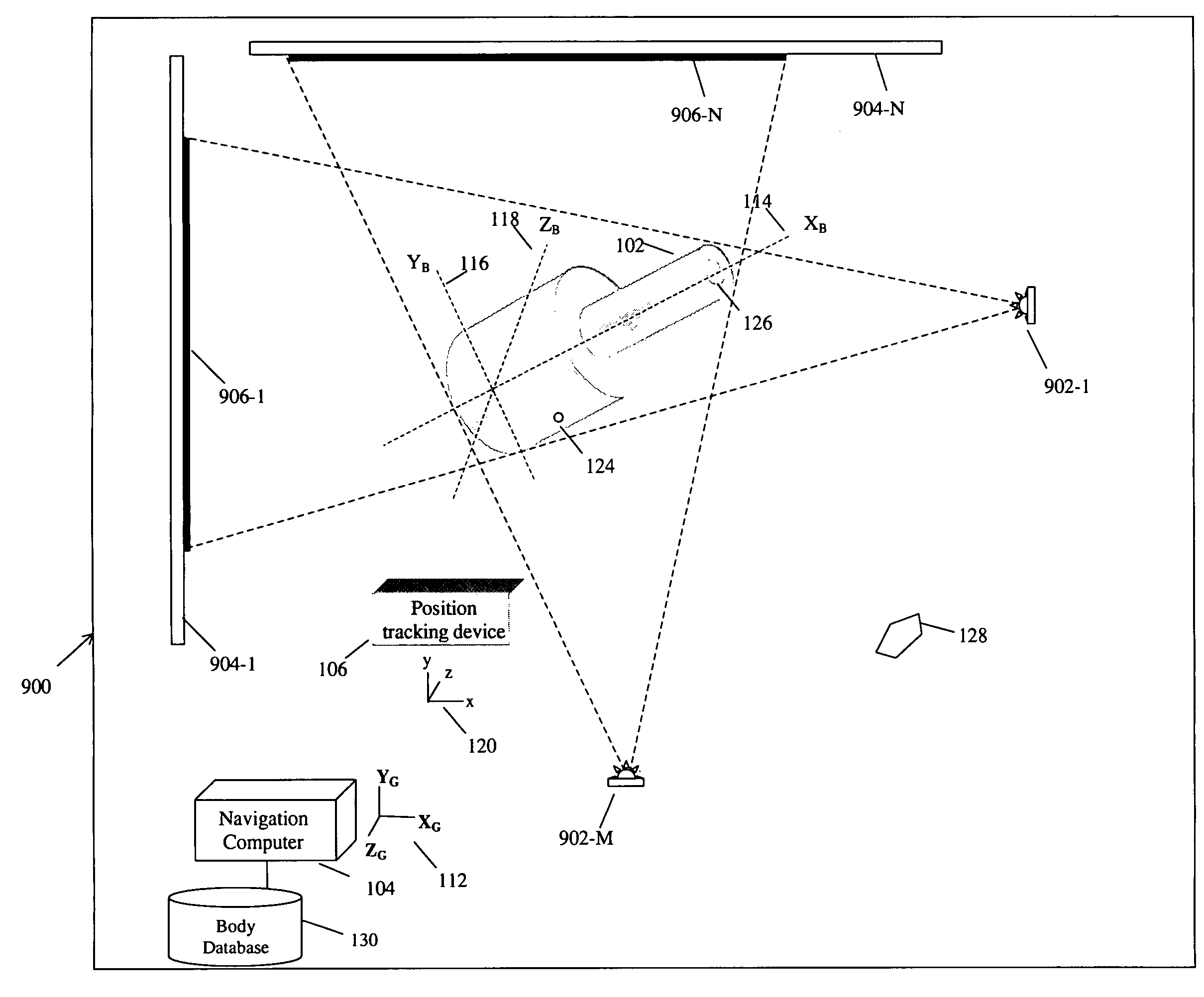
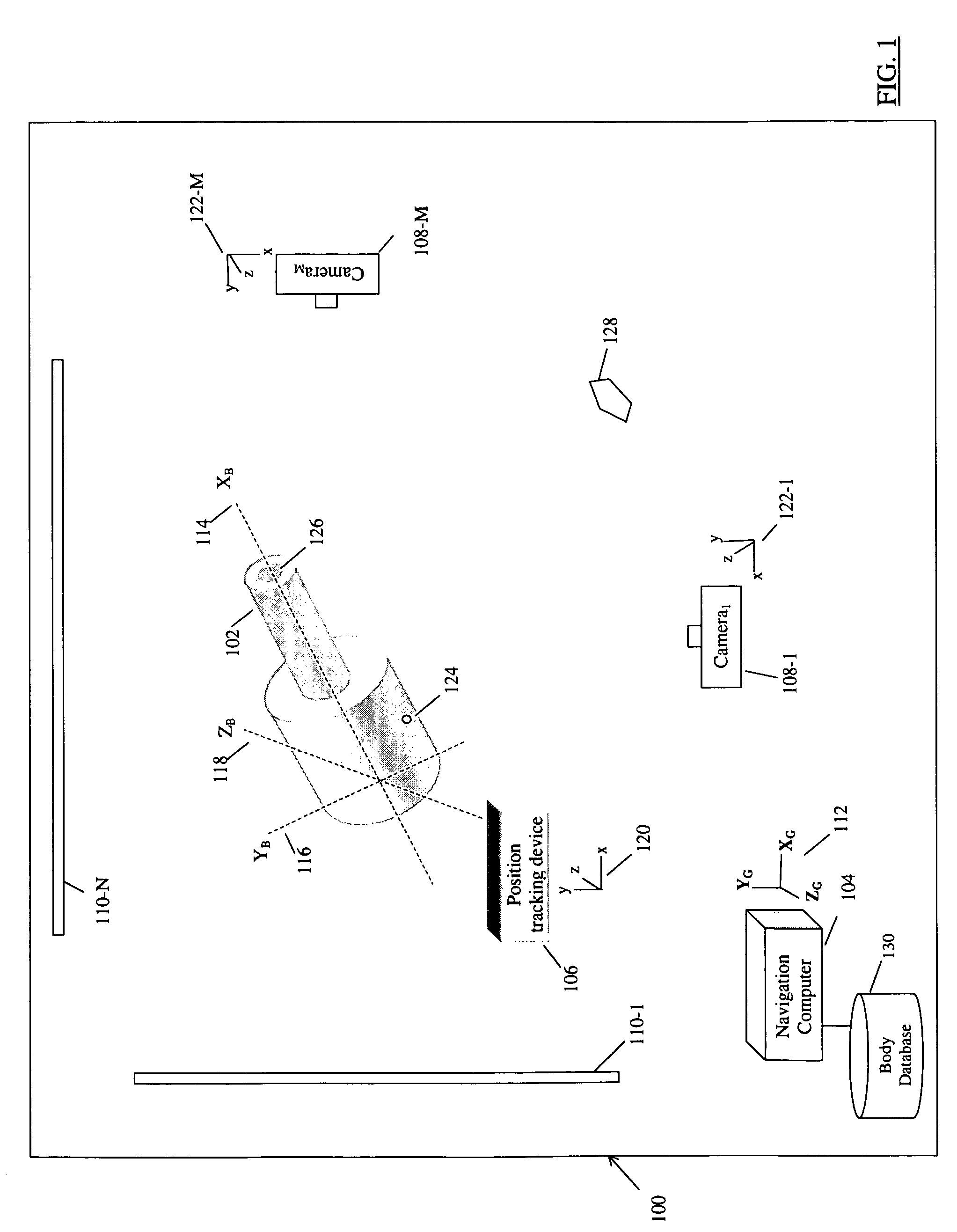
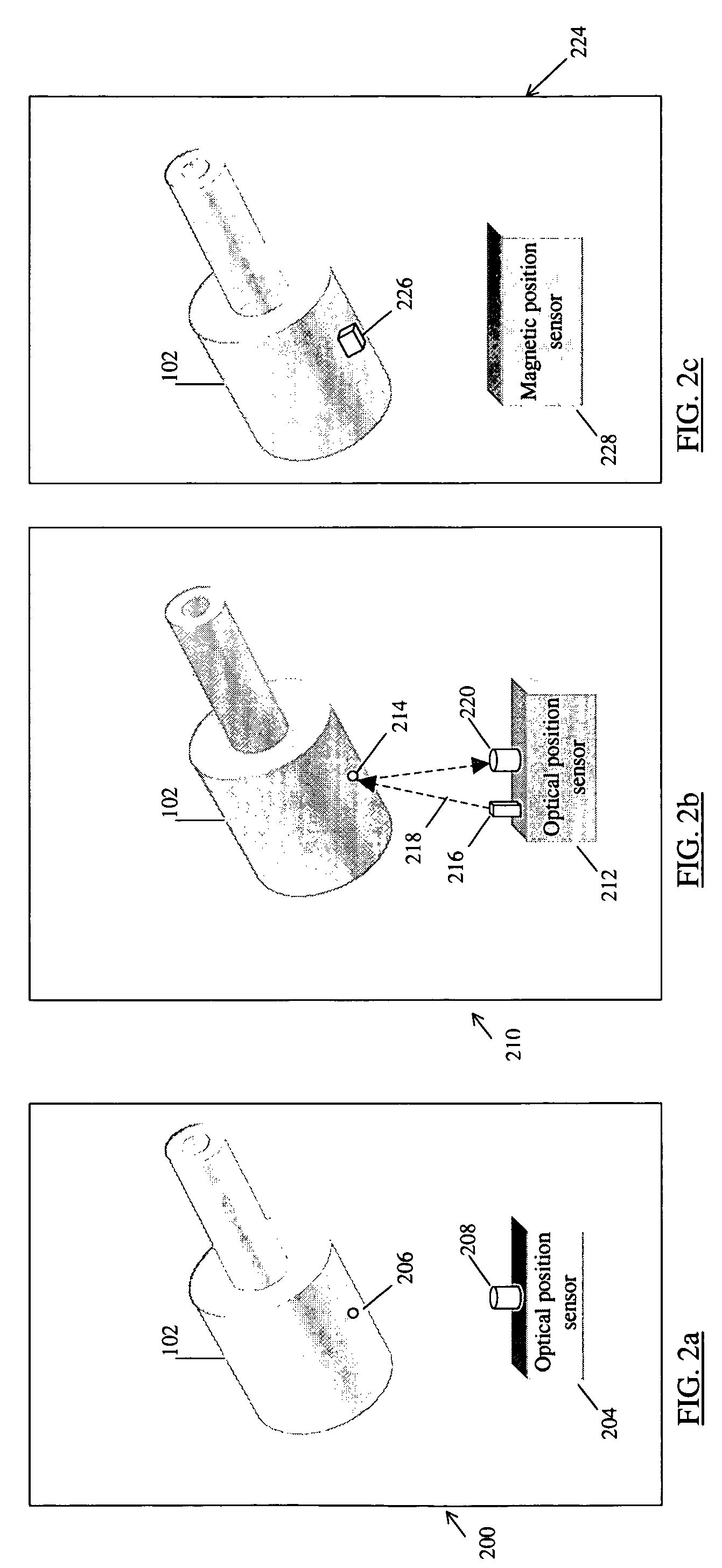
The shape and orientation of rigid or nearly rigid moveable bodies are determined using a shape characterization. Sensors capture a plurality of representations of different perspectives of the body that are analyzed to determine a bounding volume of the body. The shape of the body is determined from the bounding volume. The position of the body is determined using tracking devices that sense the position of the body. The bounding volume and position information are combined to define the shape and orientation in space of the body, and in particular the position of a point of interest on the body.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Collision detection method based on bounding volume tree
InactiveCN102446122AImprove collision detection speedImprove detection efficiencyError detection/correctionTree rootAlgorithm
The invention provides a collision detection method based on a bounding volume tree, which performs detection from the root portion to the branch extreme end and includes that: step a building the bounding volume tree of two objects; step b obtaining current nodes of the bounding volume tree of the two objects for performing detection with two nodes as a group, judging whether the two nodes collide, and turning to step c if collision happens, otherwise, turning to step d; step c judging whether the current nodes are leaf nodes, recording the nodes if the current nodes are leaf nodes, returning and performing accurate detection to determine whether collision really happens, otherwise, taking all sub nodes of the current nodes as the current nodes of the tree and recursively executing the step b; and step d calculating node information including 'nearest distance', 'speed' and 'whether nodes are collided' if the current nodes do not contain undetected brother nodes and returning, otherwise, sequentially taking next brother nodes as the current nodes of the tree and recursively executing the step b. A method for performing detection from the branch extreme end to the root portion is further provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Expanding Empty Nodes in an Acceleration Data Structure
InactiveUS20080192051A1Image generation3D-image renderingTheoretical computer scienceAcceleration Unit
Embodiments of the invention may update an ADS (e.g., spatial index) when an object moves into an empty bounding volume by partitioning the empty bounding volume and adding corresponding nodes to an ADS. The added nodes may be branched to from an empty leaf node which corresponds to the empty bounding volume. Furthermore, embodiments of the invention may update an ADS when an object moves out of the empty bounding volume by removing the nodes which were added when the object moved into the empty bounding volume. In order to locate the nodes which were added, embodiments of the invention may assert a bit in a data structure associated with the empty leaf node when the nodes are added to the ADS.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for drawing volume rendering cutting surface
ActiveCN102074039AEasy to integrateReduce judgment3D-image rendering3D modellingSpatial logicLight treatment
The invention provides a method for drawing a volume rendering cutting surface. Aiming at two conventional cutting modes, an in-and-out intersection point quick jumping cutting method is adopted, and the cutting surface is subjected to special light treatment so as to draw the cutting surface. The method has a high speed and a drawing result is favorable for observation and medical diagnosis. A one-time surrounding body method and deep judgment are adopted, the one-time surrounding body is needed to be solved for data volume, the method is well integrated with a ray tracing algorithm, multiple times of repetitive computation and the judgment of spatial logic are reduced, judgment in the ray tracking is not needed for a view angle cutting surface, logic operation is reduced, and the cutting surface is subjected to special illumination computation, so that the drawn cutting surface has a smooth effect and is convenient to observe.
Owner:LANWON TECH
Parallel processing method drawn by pre-projection light ray projection body
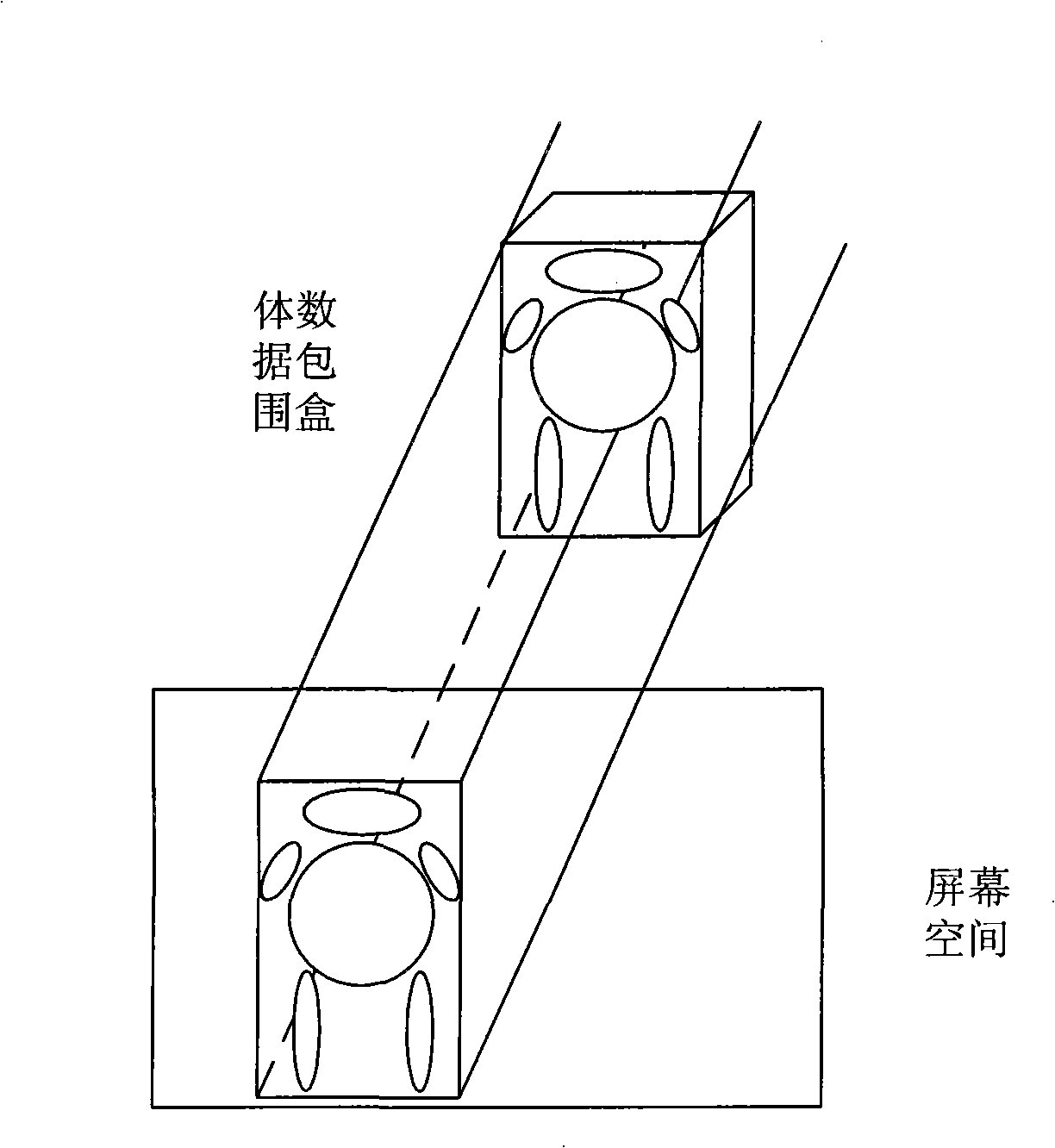
ActiveCN101324962AReduce processingProcessing speedProcessor architectures/configuration3D-image renderingVolumetric modelBounding volume
The invention discloses a pre-projection ray casting volume rendering parallel processing method. The following steps are included in the volume rendering data handling procedure: calculating bounding volume of a three dimensional volumetric model; projecting the bounding volume in the screen space; storing the corresponding coordinates of a projection area; and conducing the parallel processing of volume rendering data. The method adopts the parallel processing manner of pre-projection, so that all the computing nodes do not need to wait for all tasks to be calculated and finished and then transmit the result data to a main node without waiting, and instead, the computing nodes send intermediate result data to the main node immediately after a task block is calculated and start the calculation for the next task block. Fewer task blocks are distributed to the main node at first. The method provides the optimum estimation for the number of task blocks distributed to each computing node, thereby greatly reducing the processing volume of data and improving the processing speed of data.
Owner:广东碳中和研究院(韶关)
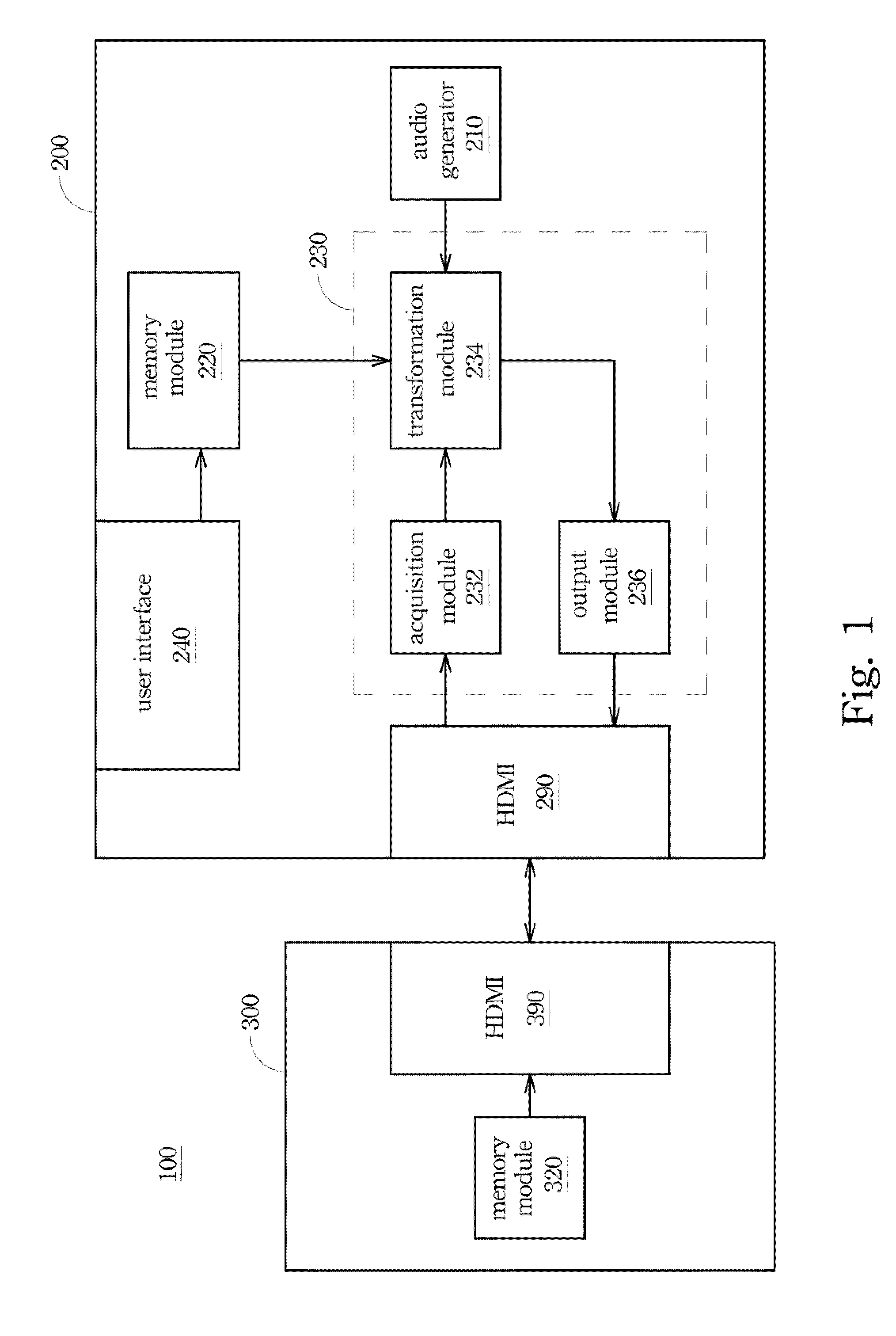
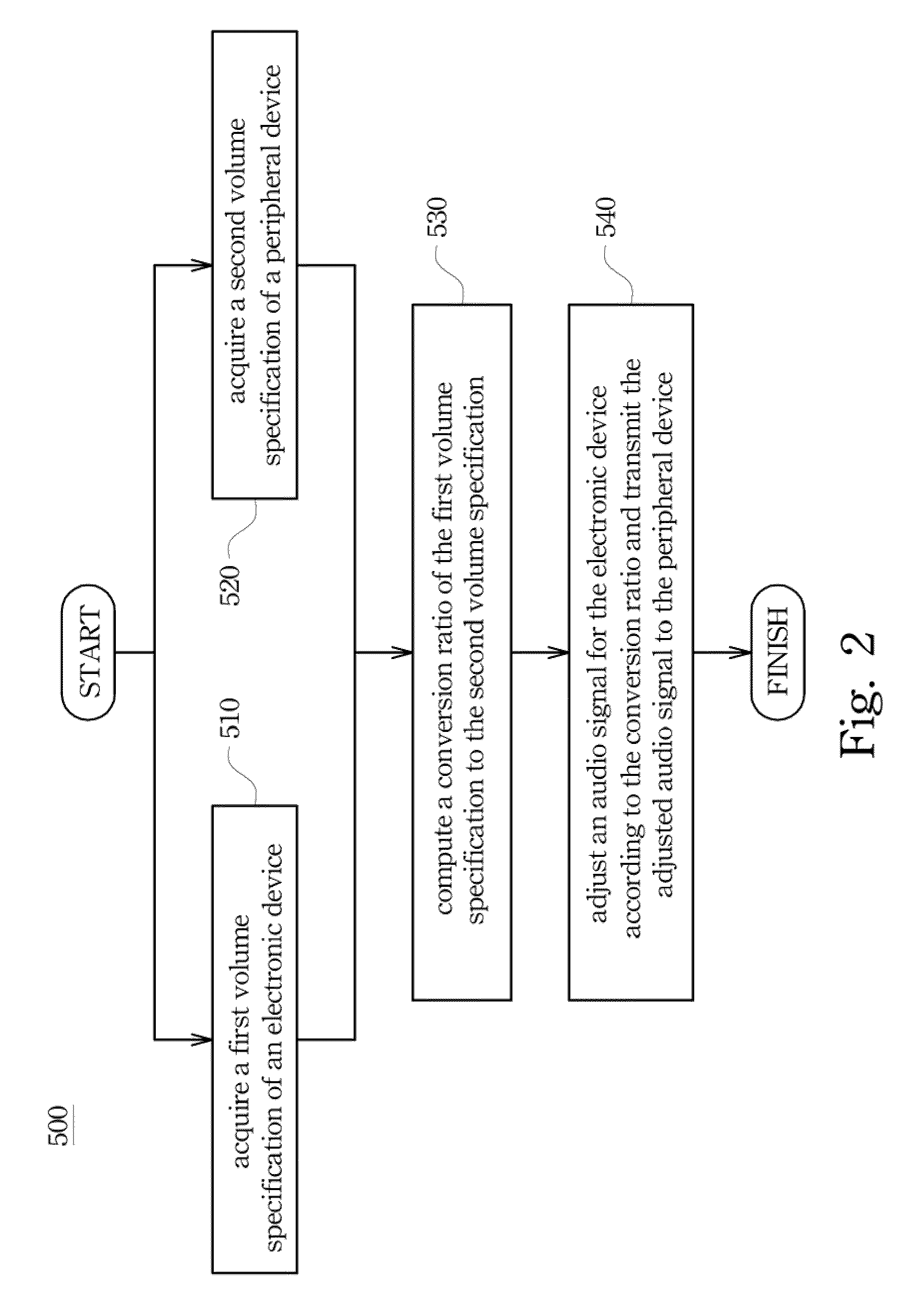
Electronic device, control volume system and method
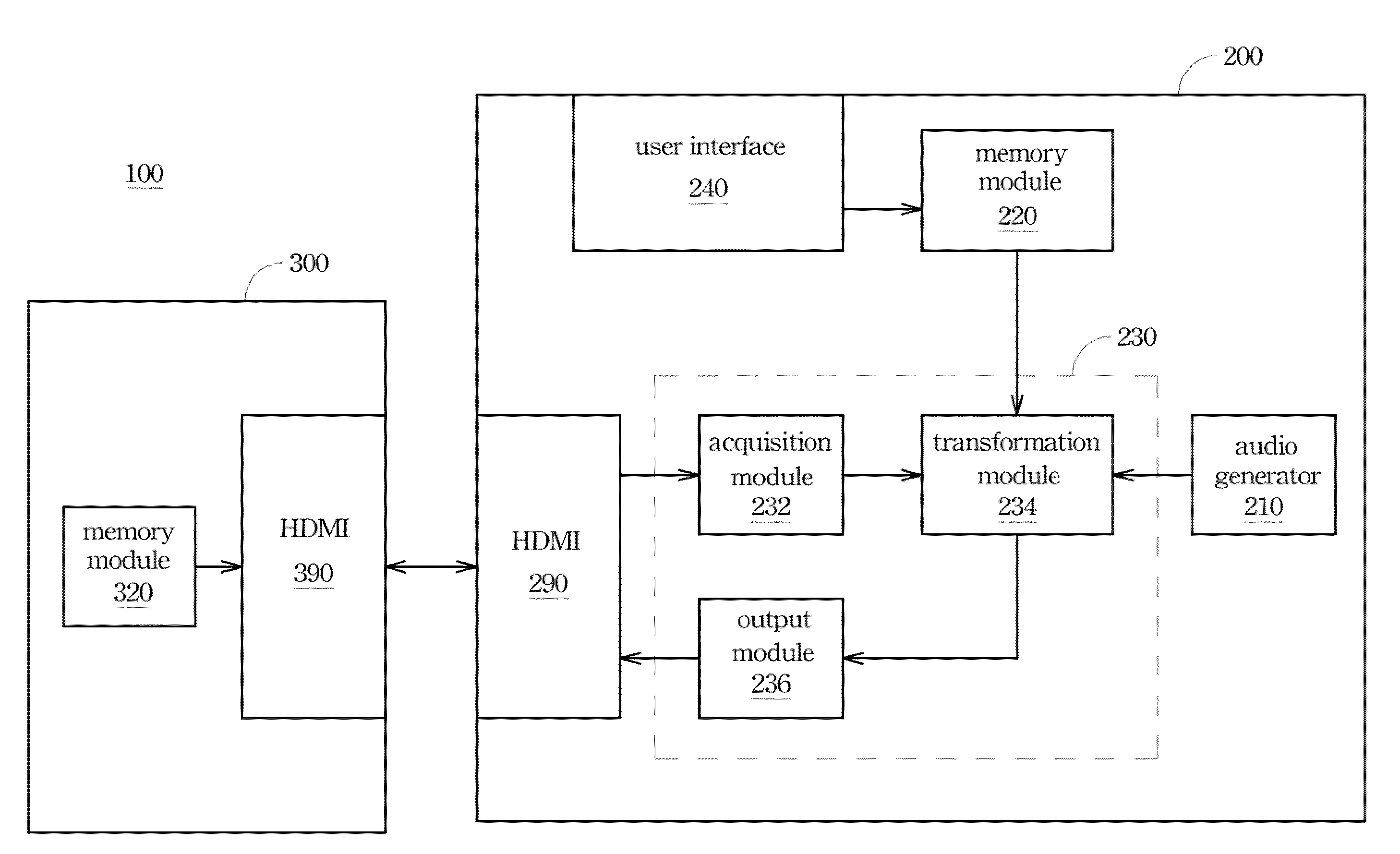
ActiveUS20100157172A1Easy to appreciateTelevision system detailsGain controlComputer scienceBounding volume
In the specification and drawing a control volume system is described and shown for synchronizing a sound volume of an electronic device and another sound volume of the peripheral device according to a volume specification of the electronic device and another volume specification of the peripheral device. Moreover, a control volume method and the electronic device are also disclosed in the specification and drawing.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com