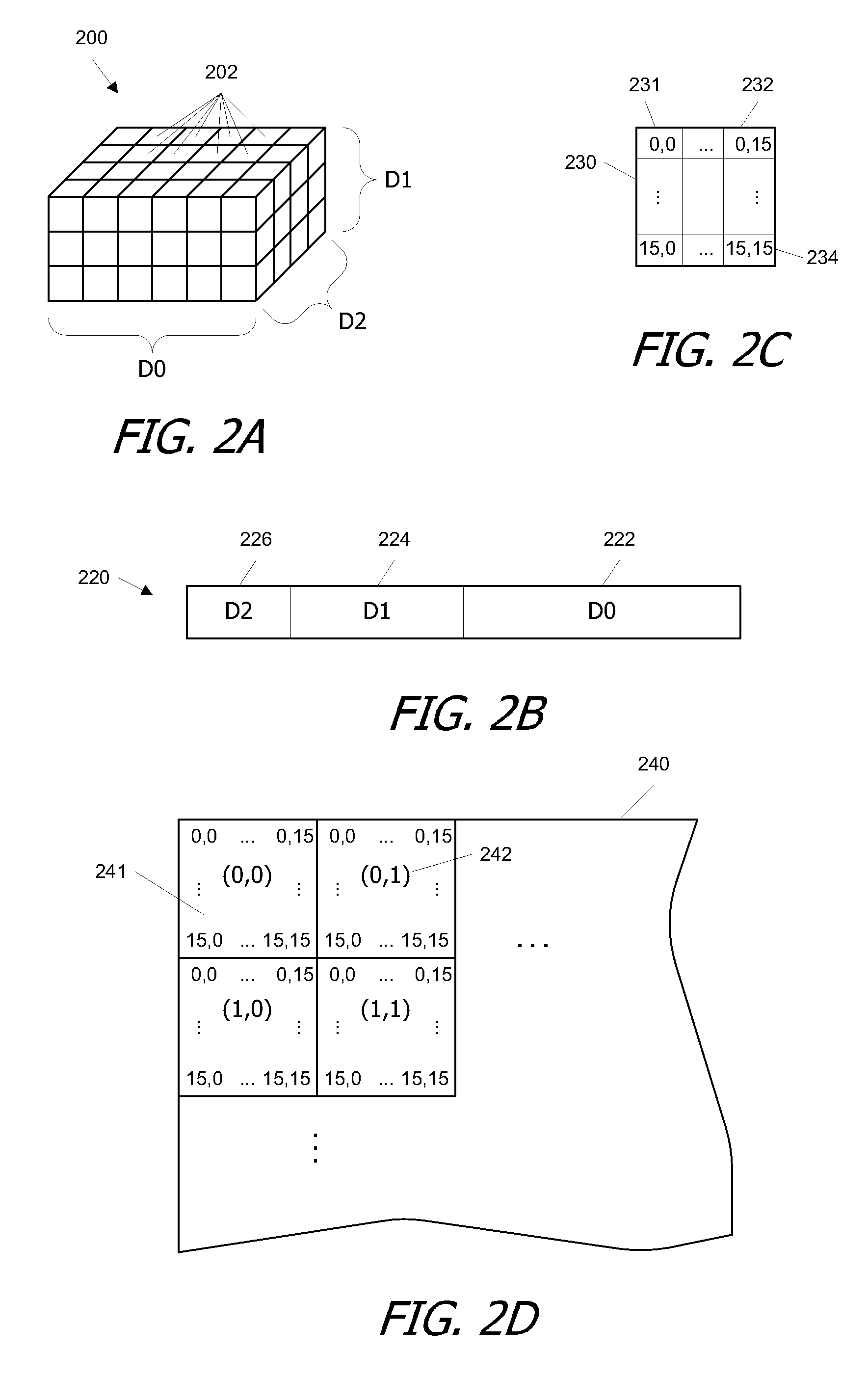
Patents
Literature
584 results about "SIMD" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
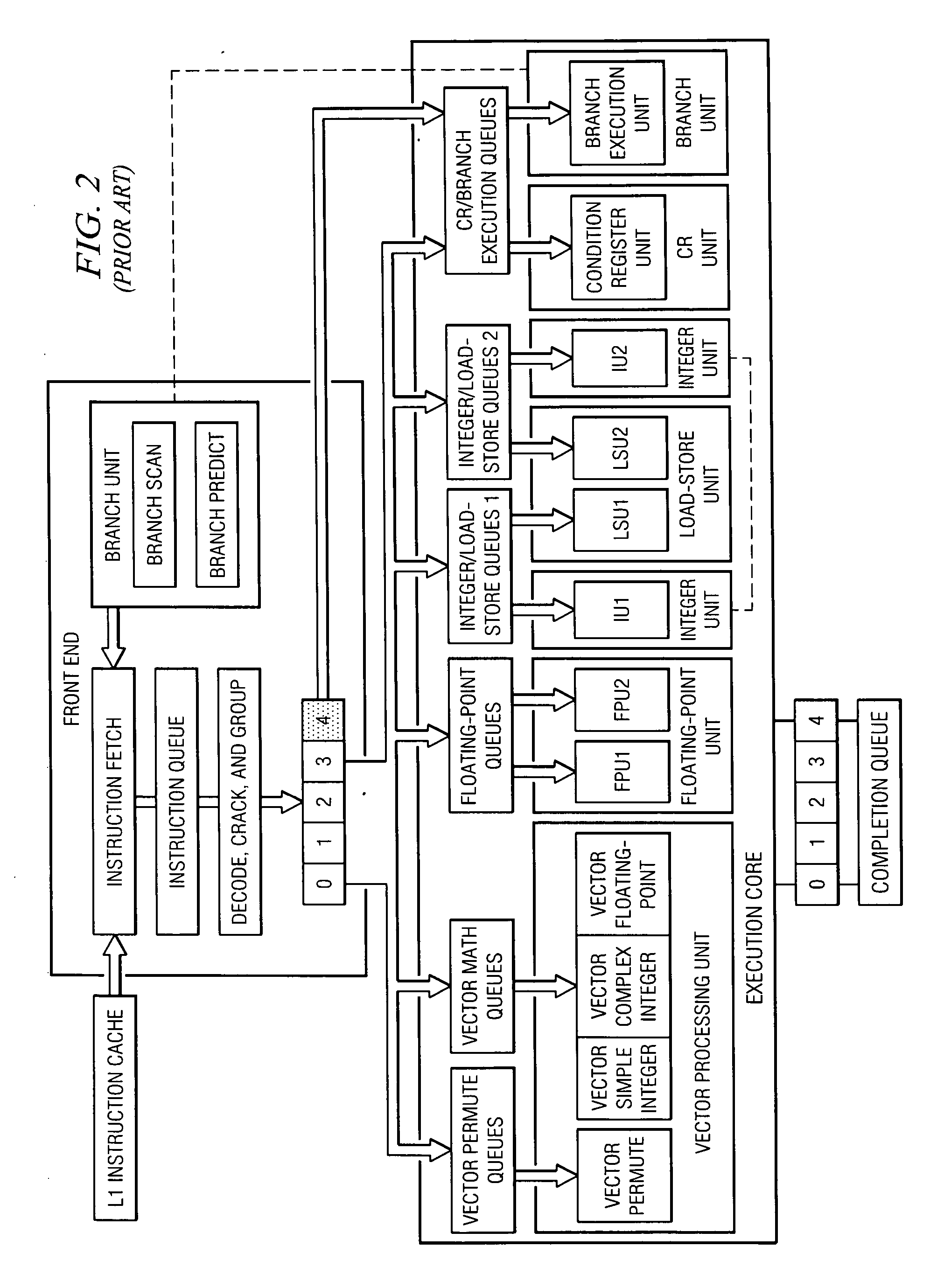
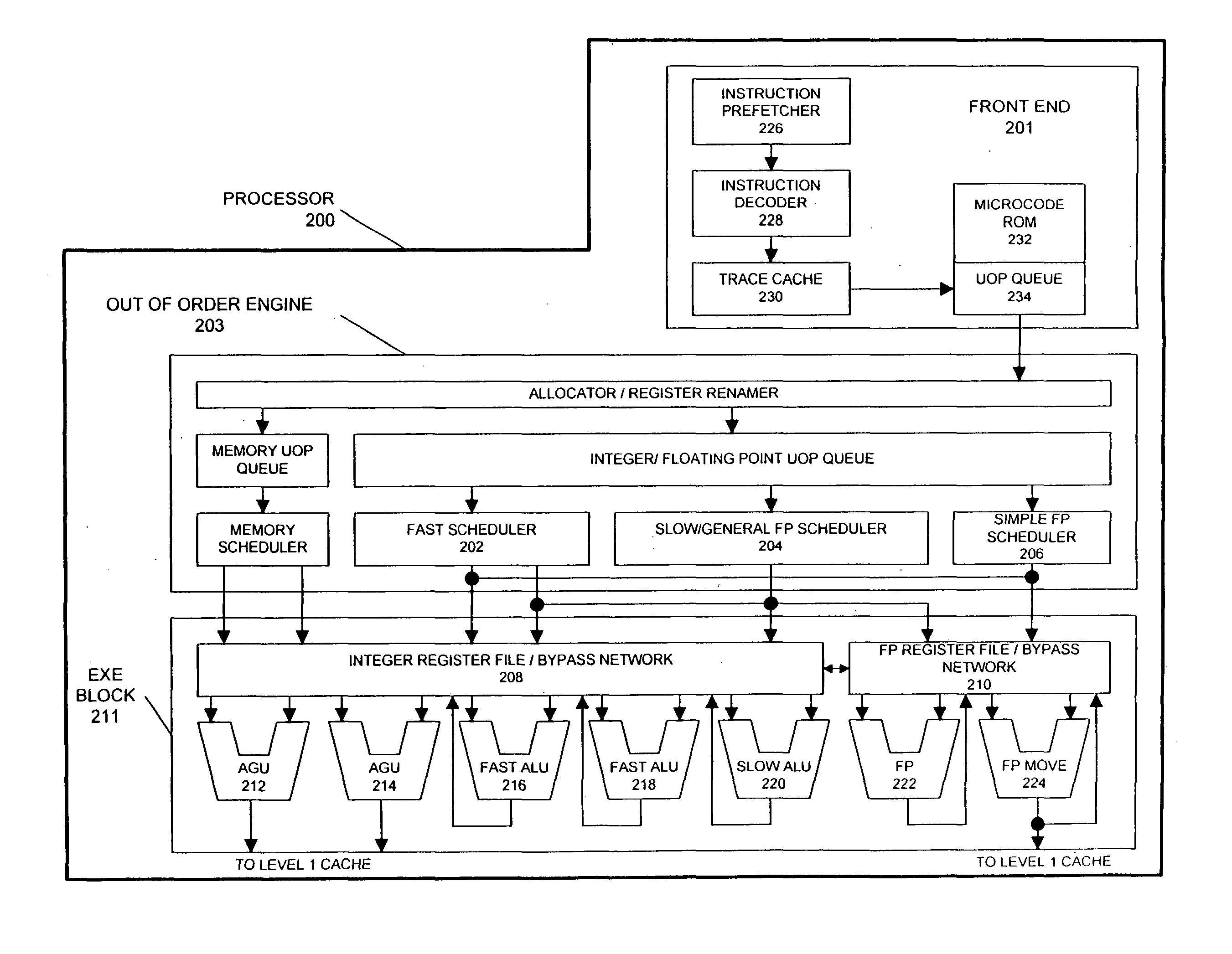
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a class of parallel computers in Flynn's taxonomy. It describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. Such machines exploit data level parallelism, but not concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but only a single process (instruction) at a given moment. SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Most modern CPU designs include SIMD instructions to improve the performance of multimedia use. SIMD is not to be confused with SIMT, which utilizes threads.
Speed up big-number multiplication using single instruction multiple data (SIMD) architectures
InactiveUS20130332707A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsMatrix multiplicationSIMD
A processing apparatus may be configured to include logic to generate a first set of vectors based on a first integer and a second set of vectors based on a second integer, logic to calculate sub products by multiplying the first set of vectors to the second set of vectors, logic to split each sub product into a first half and a second half and logic to generate a final result by adding together all first and second halves at respective digit positions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Processing array data on SIMD multi-core processor architectures
InactiveUS8484276B2Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
SIMD datapath coupled to scalar/vector/address/conditional data register file with selective subpath scalar processing mode
InactiveUS6839828B2Not compromise SIMD data processing performanceReduce consumptionRegister arrangementsDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerOperation mode
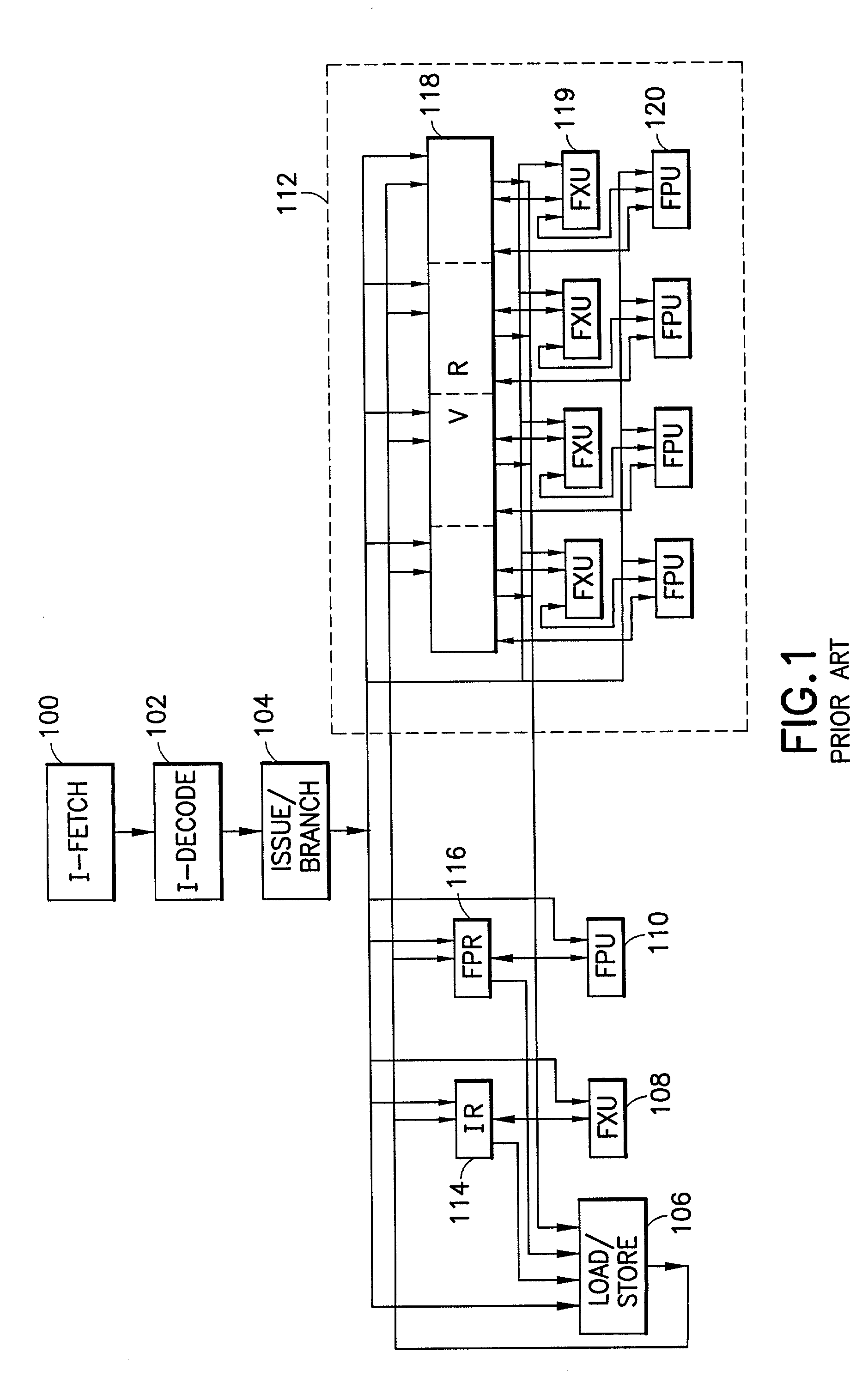
There is provided a processor designed to operate in a plurality of modes for processing vector and scalar instructions. Register files are each for storing scalar and vector data and address information. A parallel vector unit, coupled to the register files, includes functional units configurable to operate in a vector operation mode and a scalar operation mode. The vector unit includes an apparatus for tightly coupling the functional units to perform an operation specified by a current instruction. Under a vector operation mode, the vector unit performs, in parallel, a single vector operation on a plurality of data elements. The operations performed on the plurality of data elements are each performed by a different functional unit of the vector unit. Under a scalar operation mode, the vector unit performs a scalar operation on a data element received from the register files in a functional unit within the vector unit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
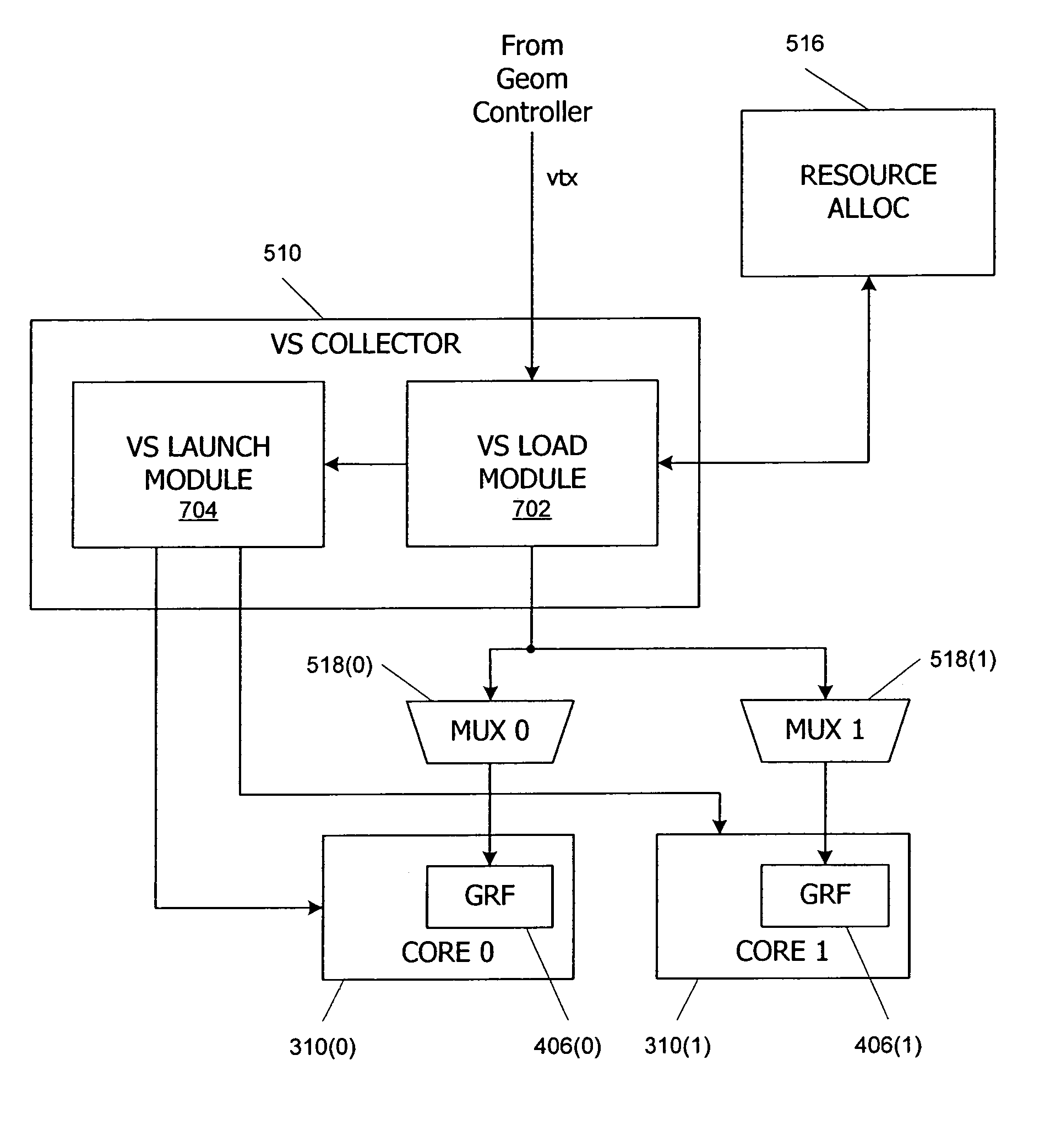
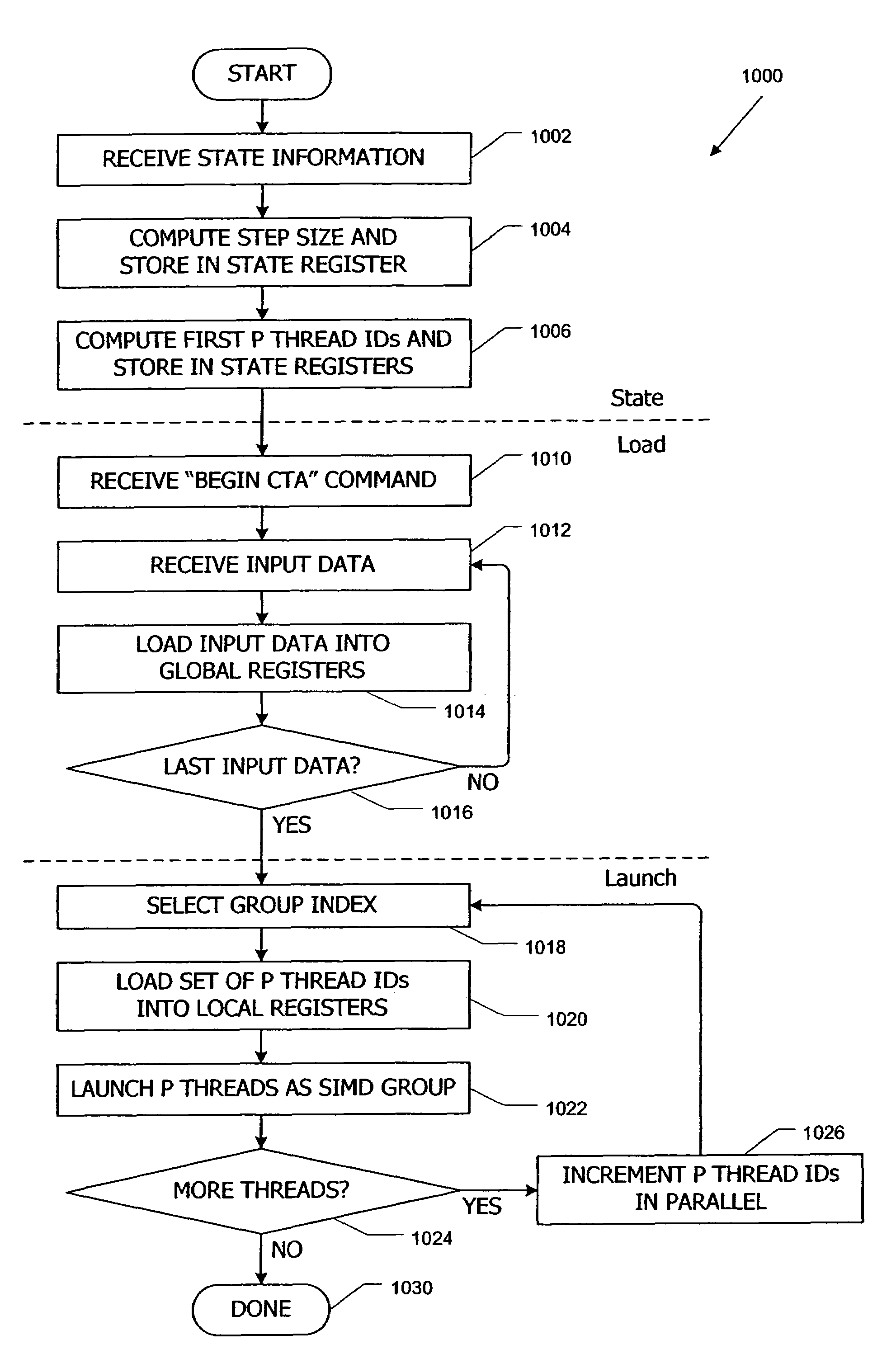
Multithreaded SIMD parallel processor with loading of groups of threads
ActiveUS7447873B1Management loadRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessing coreProcessor register
In a multithreaded processing core, groups of threads are executed using single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) parallelism by a set of parallel processing engines. Input data defining objects to be processed received as a stream of input data blocks, and the input data blocks are loaded into a local register file in the core such that all of the data for one of the input objects is accessible to one of the processing engines. The input data can be loaded directly into the local register file, or the data can be accumulated in a buffer and loaded after accumulation, for instance during a launch operation for a SIMD group. Shared input data can also be loaded into a shared memory in the processing core.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Scalar hardware for performing SIMD operations
InactiveUS6292886B1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionProcessor registerExecution unit
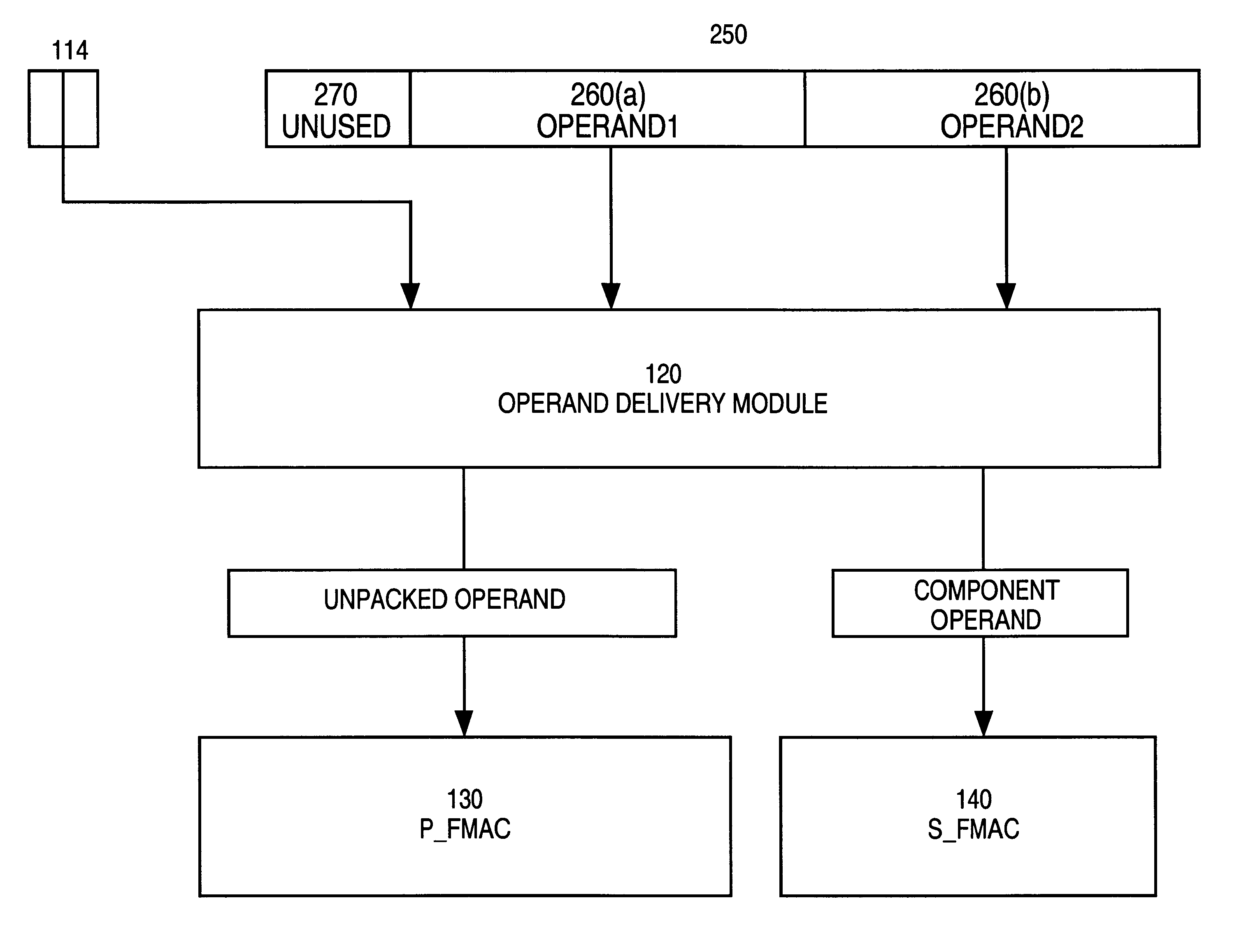
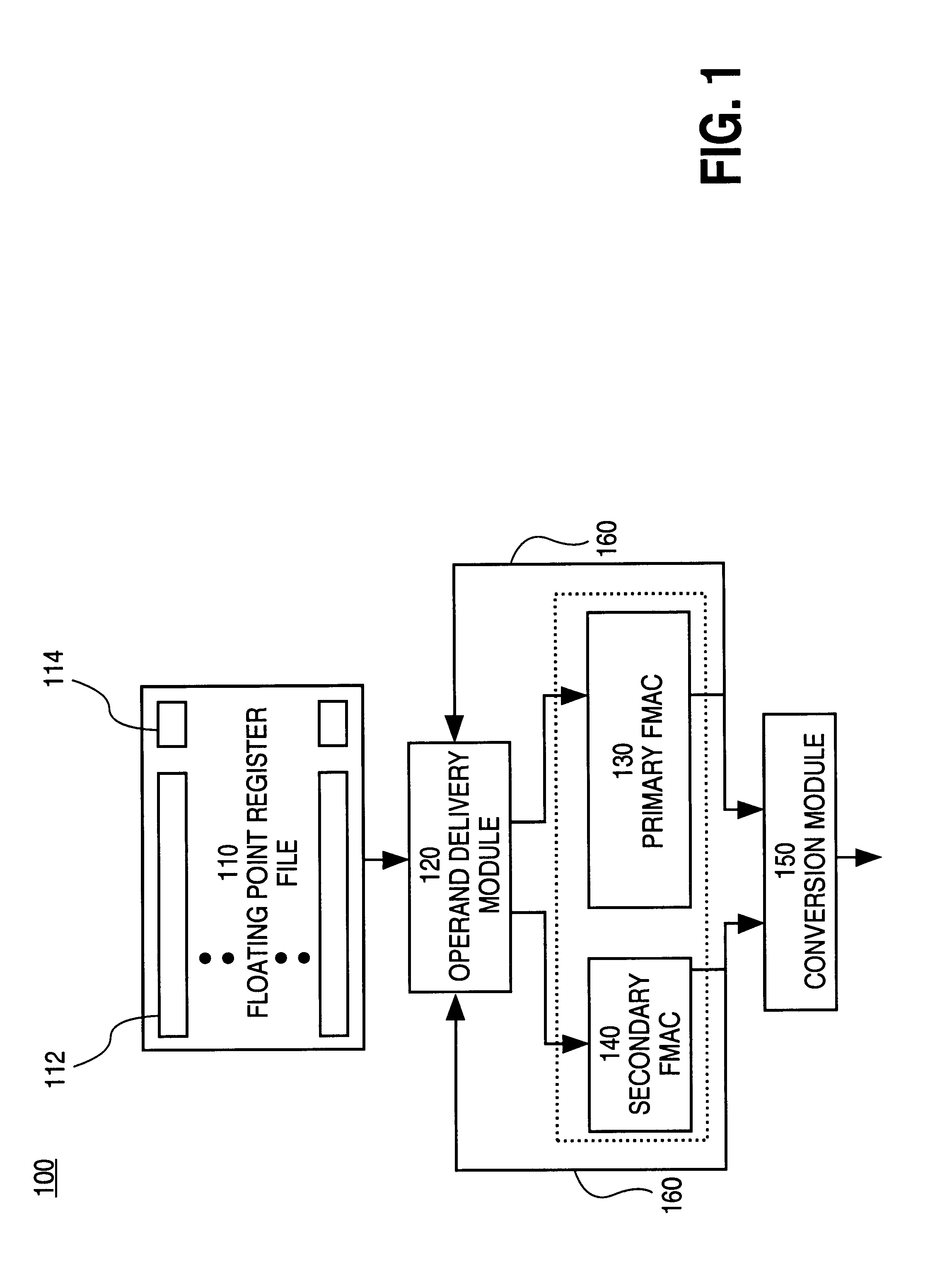
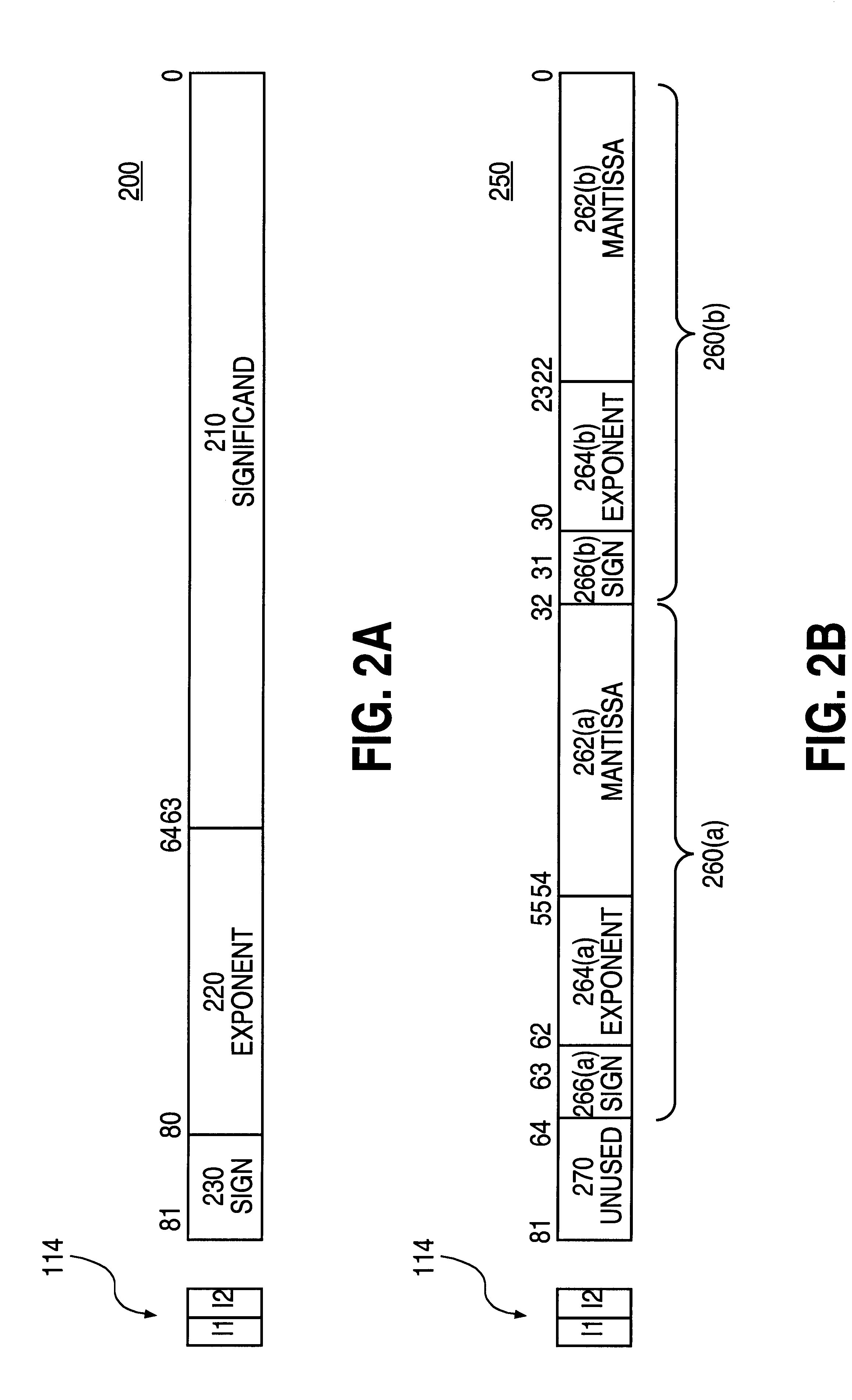
A system for processing SIMD operands in a packed data format includes a scalar FMAC and a vector FMAC coupled to a register file through an operand delivery module. For vector operations, the operand delivery module bit steers a SIMD operand of the packed operand into an unpacked operand for processing by the first execution unit. Another SIMD operand is processed by the vector execution unit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Shared FP and SIMD 3D multiplier
InactiveUS6490607B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationComputerized systemTheoretical computer science
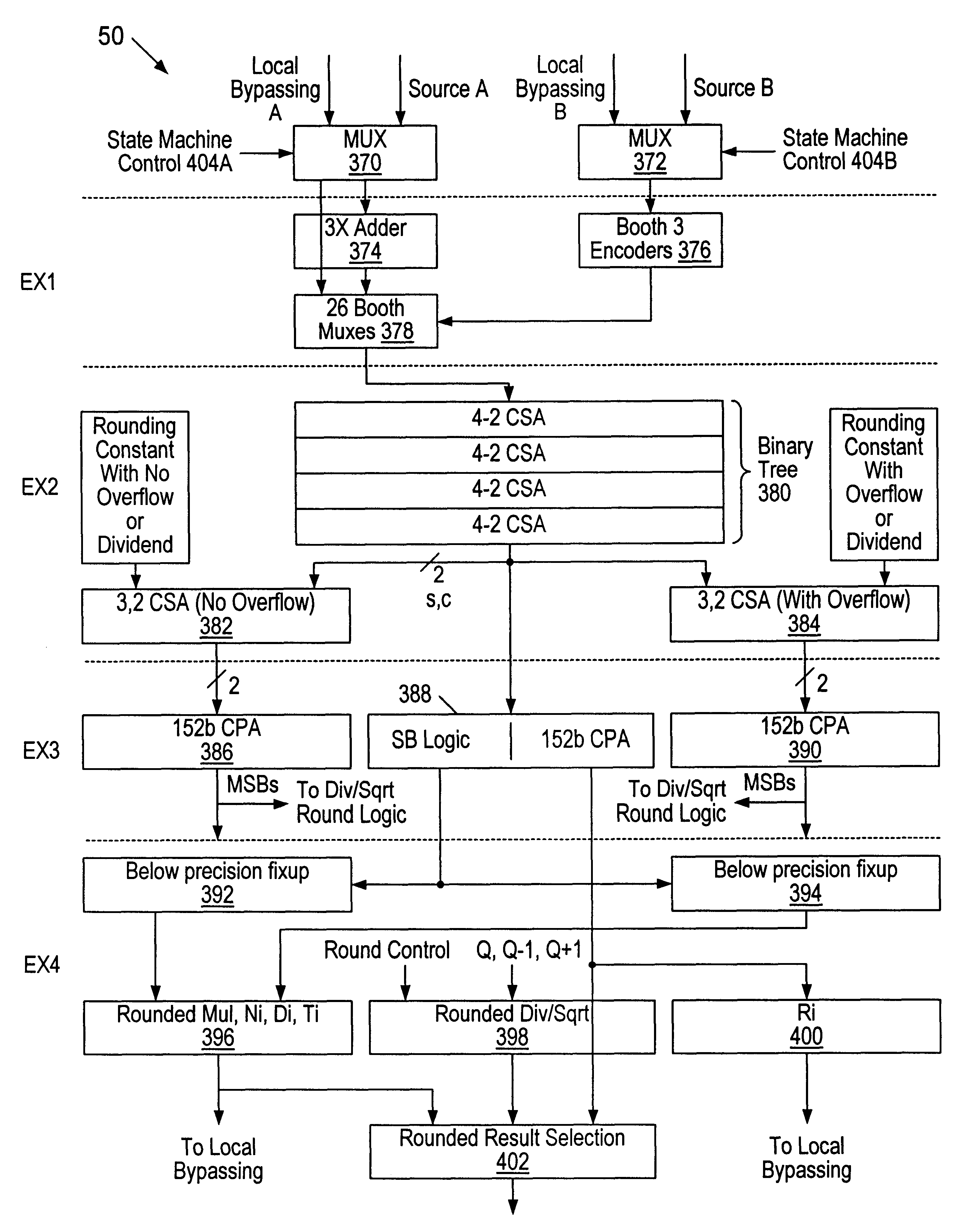
A multiplier configured to perform multiplication of both scalar floating point values (XxY) and packed floating point values (i.e., X1xY1 and X2xY2). In addition, the multiplier may be configured to calculate XxY-Z. The multiplier comprises selection logic for selecting source operands, a partial product generator, an adder tree, and two or more adders configured to sum the results from the adder tree to achieve a final result. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative multiplication operations to implement such arithmetical operations such as division and square root. The multiplier may be configured to generate two versions of the final result, one assuming there is an overflow, and another assuming there is not an overflow. A computer system and method for performing multiplication are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
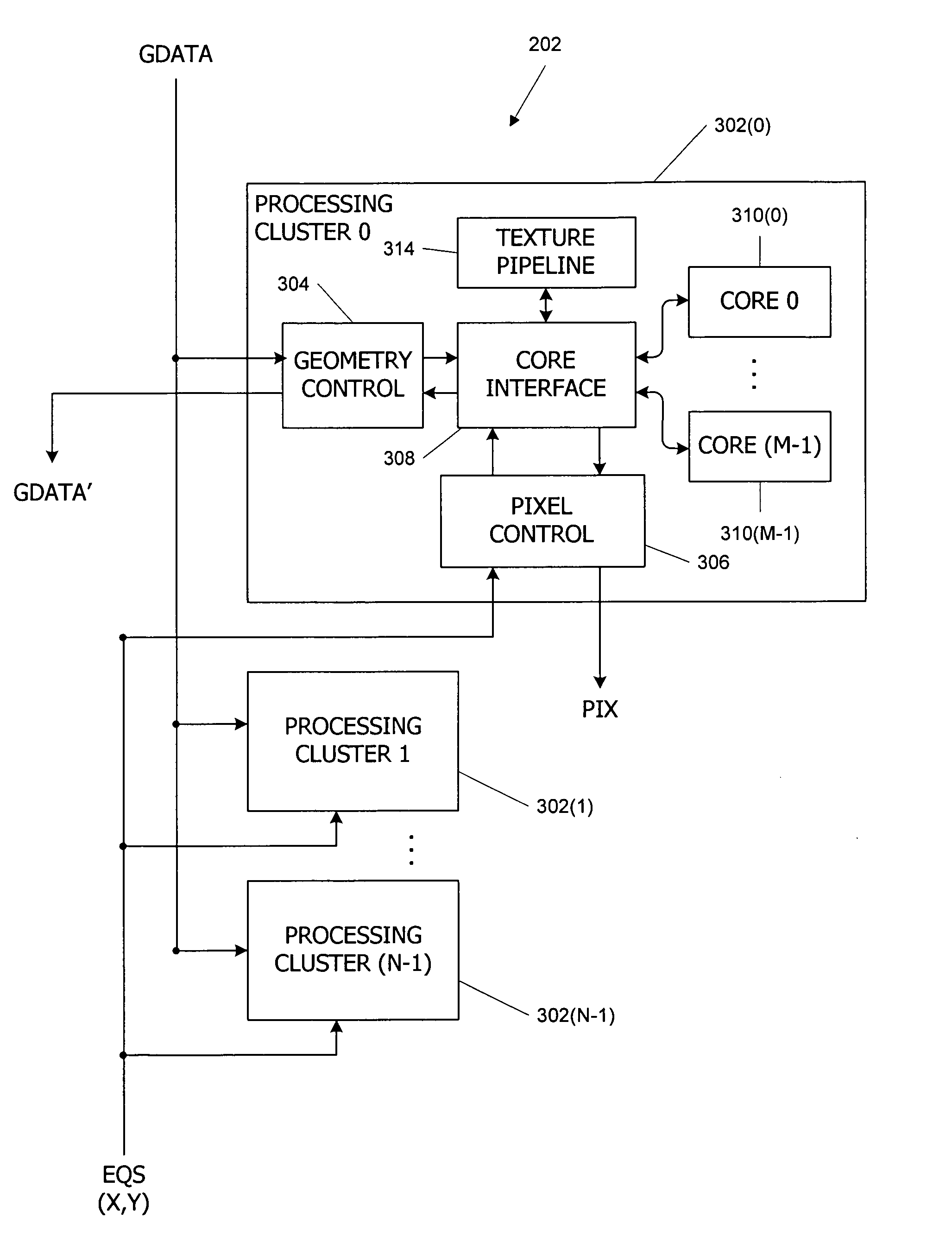
Parallel data processing systems and methods using cooperative thread arrays and SIMD instruction issue
ActiveUS7584342B1Facilitate rapid launchingEliminate needProgram synchronisationArchitecture with multiple processing unitsData processing systemData set
Parallel data processing systems and methods use cooperative thread arrays (CTAs), i.e., groups of multiple threads that concurrently execute the same program on an input data set to produce an output data set. Each thread in a CTA has a unique identifier (thread ID) that can be assigned at thread launch time and that controls various aspects of the thread's processing behavior, such as the portion of the input data set to be processed by each thread, the portion of the output data set to be produced by each thread, and / or sharing of intermediate results among threads. Where groups of threads are executed in SIMD parallelism, thread IDs for threads in the same SIMD group are generated and assigned in parallel, allowing different SIMD groups to be launched in rapid succession.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
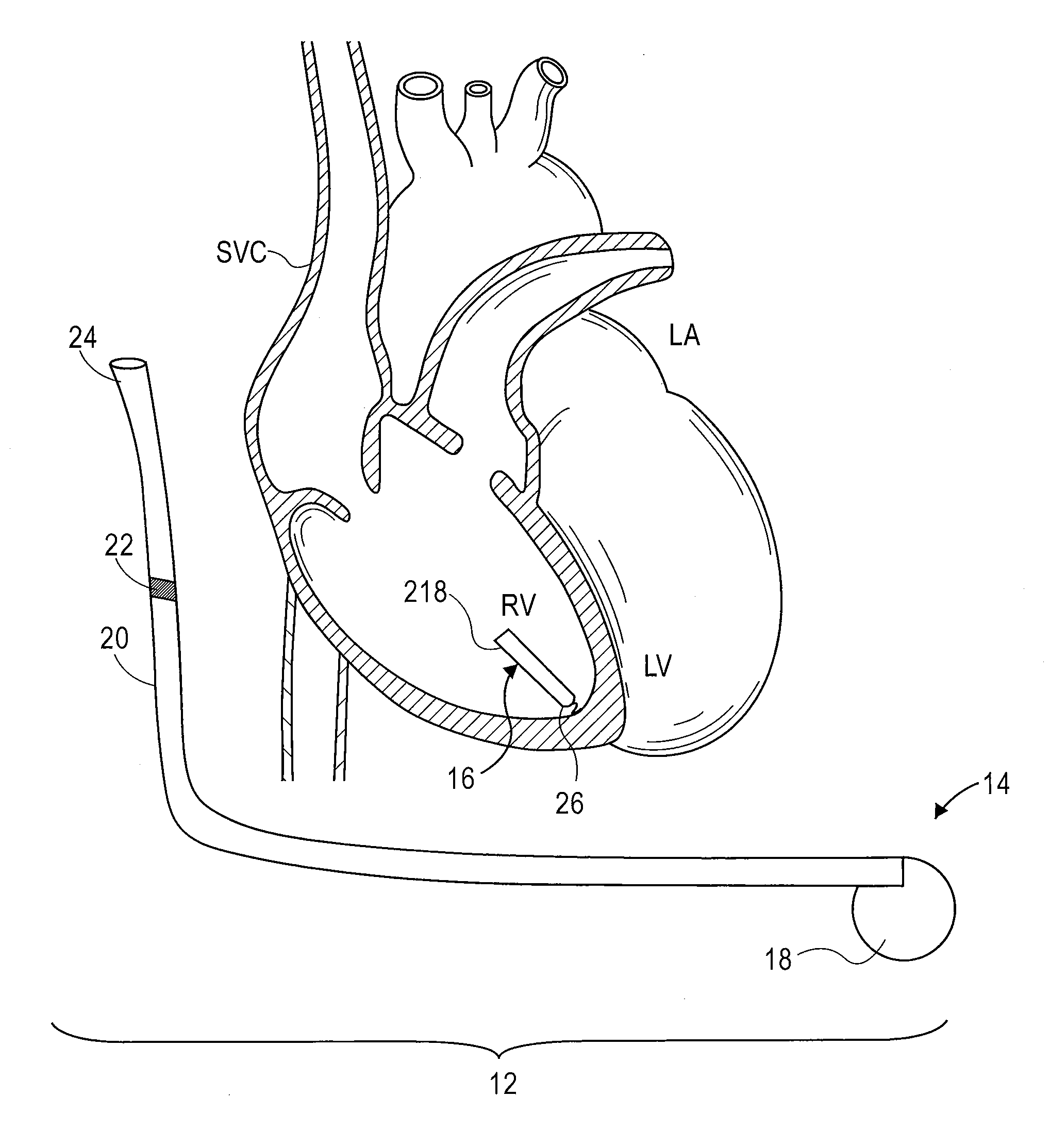
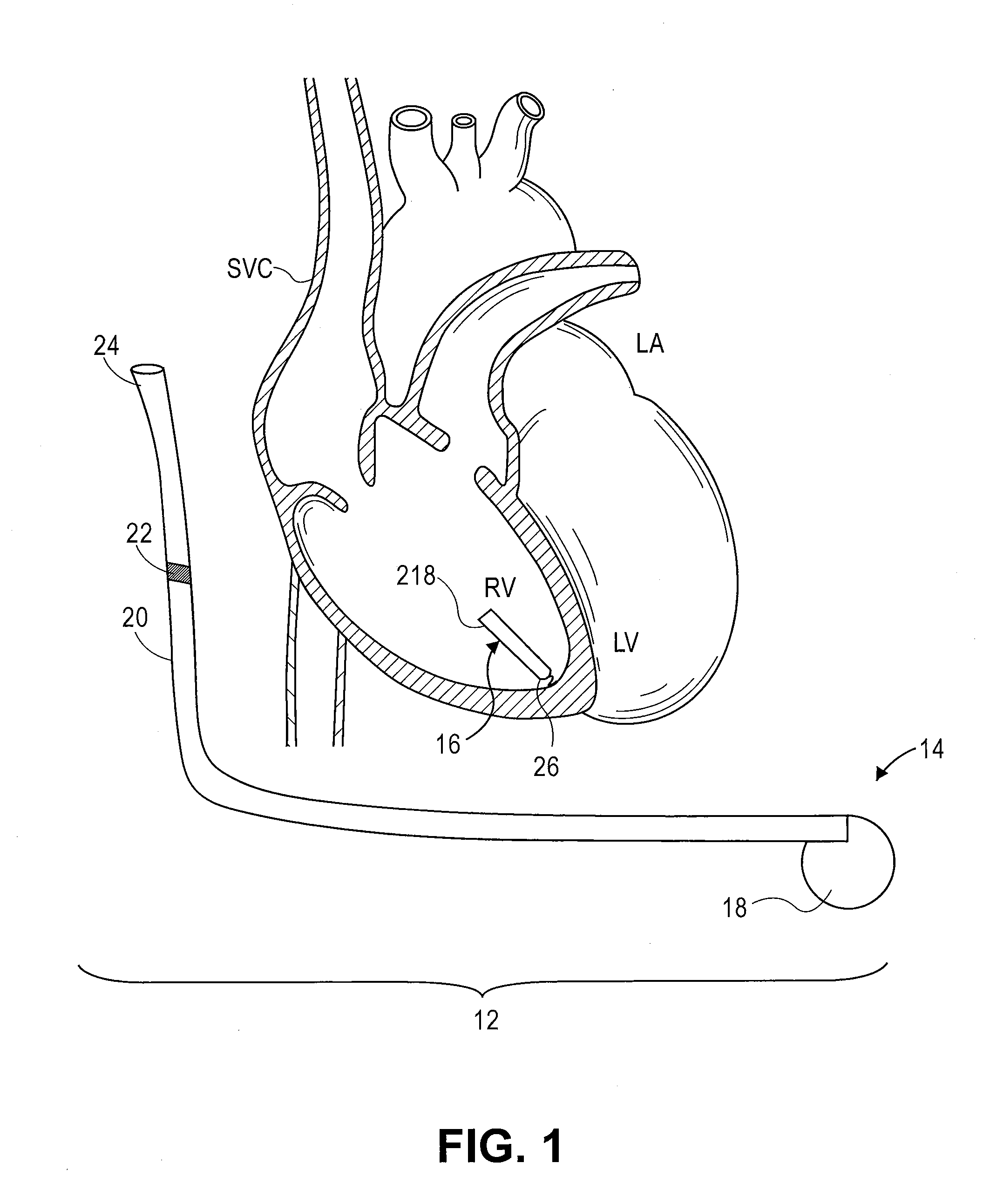
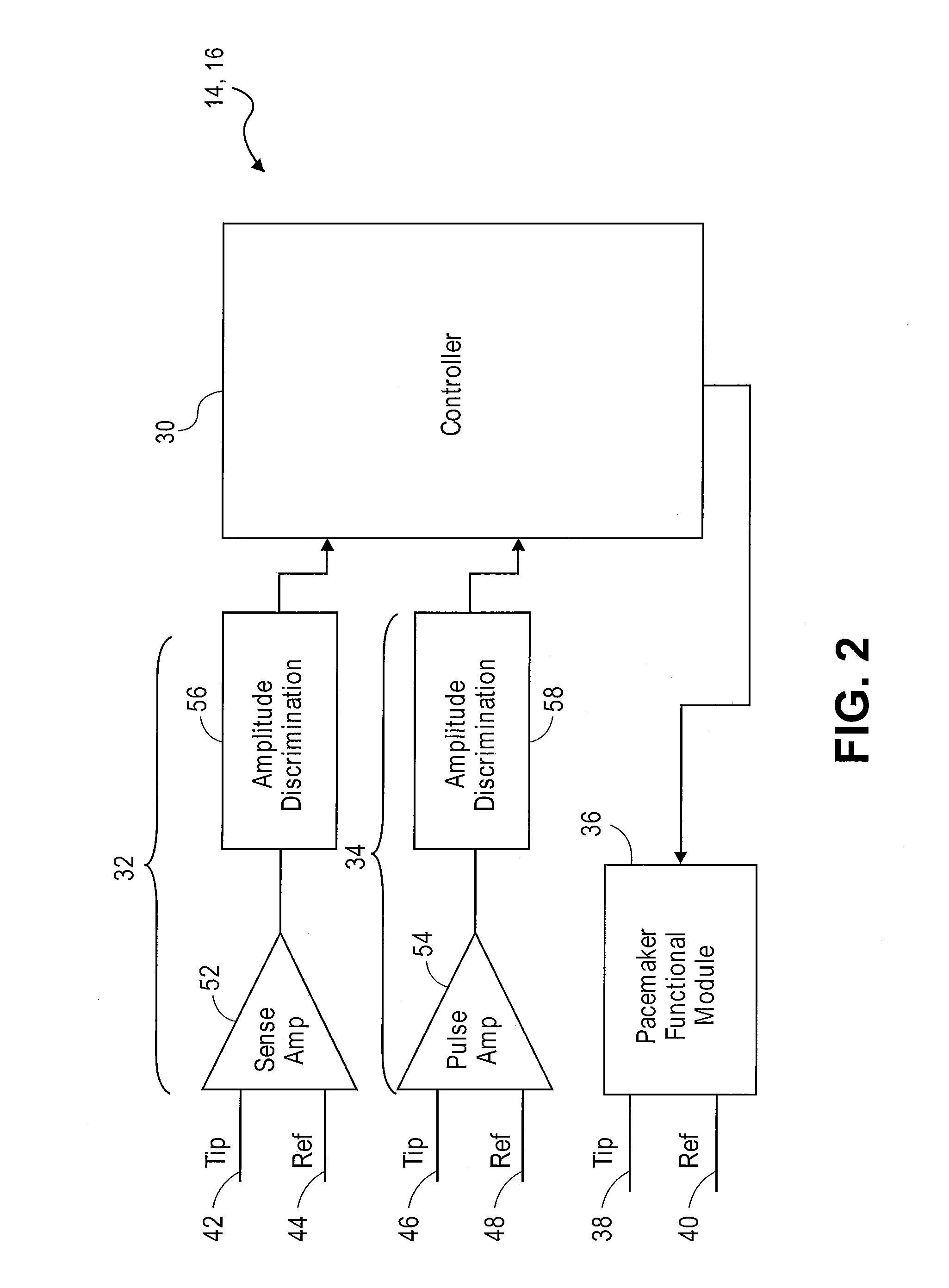
Method and system for tracking events of interest between leadless and subcutaneous implantable cardioverter devices
A distributed leadless implantable system and method are provided that comprise a leadless implantable medical device (LIMD). The LIMD comprises a housing having a proximal end configured to engage local tissue of interest in a local chamber, cardiac sensing circuitry to sense cardiac signals; and a controller configured to analyze the cardiac signals and, based thereon, to produce a near field (NF) event marker indicative of a local event of interest (EOI) occurring in the local chamber. The system and method further comprise a subcutaneous implantable medical device (SIMD). The SIMD comprises cardiac sensing circuitry to sense cardiac signals, a controller configured to identify a candidate EOI from the cardiac signals, and pulse sensing circuitry to detect the NF event marker from the LIMD. The SIMD controller is configured to declare the candidate EOI as a valid EOI or an invalid EOI based on the NF event marker.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
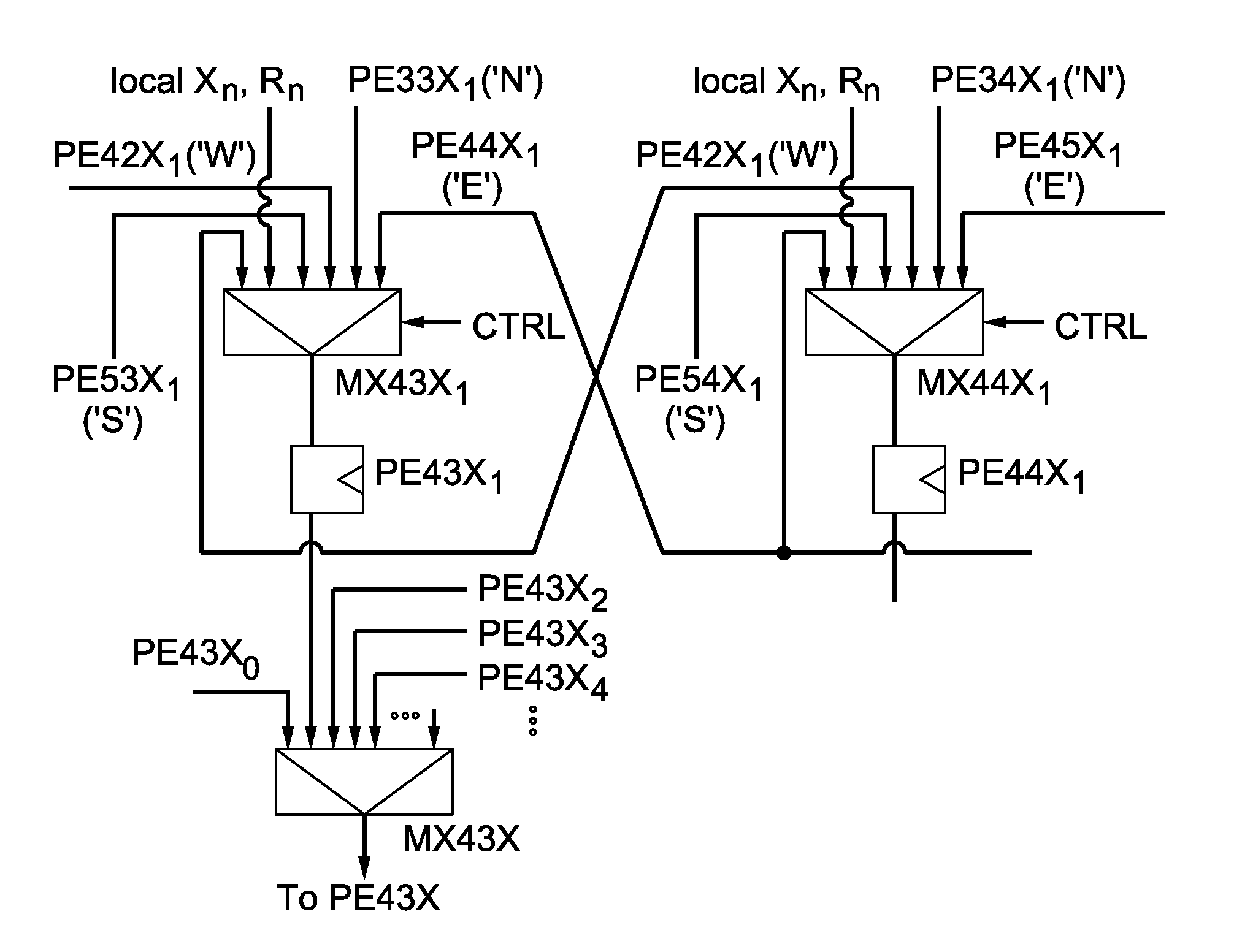
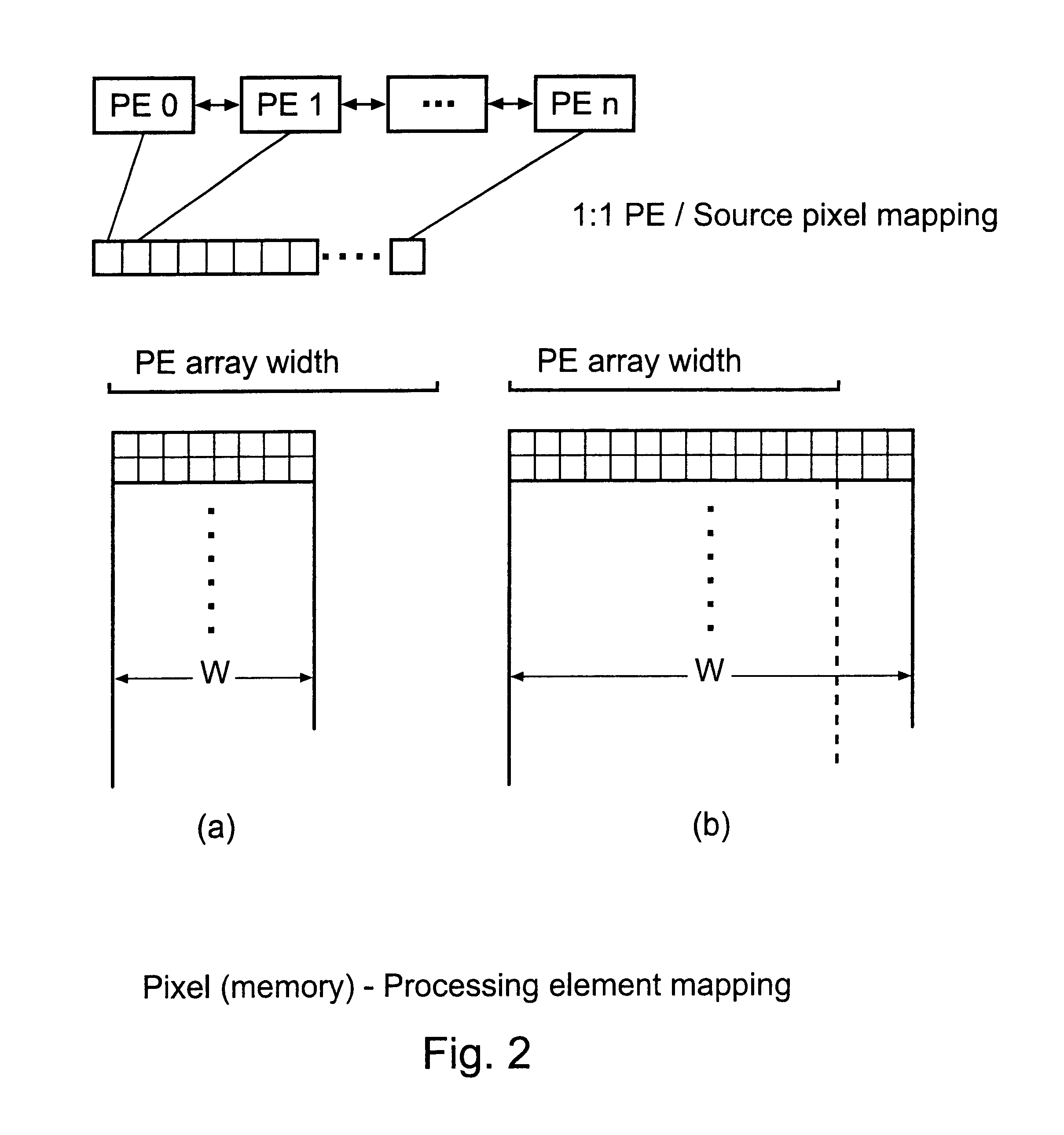
Array of processing elements with local registers
InactiveUS7941634B2Reduce loadSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsImage memory managementArray data structureImaging processing
Specialized image processing circuitry is usually implemented in hardware in a massively parallel way as a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) architecture. The invention prevents long and complicated connection paths between a processing element and the memory subsystem, and improves maximum operating frequency. An optimized architecture for image processing has processing elements that are arranged in a two-dimensional structure, and each processing element has a local storage containing a plurality of reference pixels that are not neighbors in the reference image. Instead, the reference pixels belong to different blocks of the reference image, which may vary for different encoding schemes. Each processing element has a plurality of local first registers for holding the reference image data: one of the first registers holds reference input data of a first search block, and some of the remaining first registers holding reference input data of further search blocks that have specified positions relative to the first search block.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Processor implementation having unified scalar and SIMD datapath
InactiveUS20030037221A1Register arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionProcessor registerDatapath
An improved processor implementation is described in which scalar and vector processing components are merged to reduce complexity. In particular, the implementation includes a scalar-vector register file for storing scalar and vector instructions, as well as a parallel vector unit comprising functional units that can process vector or scalar instructions as required. A further aspect of the invention provides the ability to disable unused functional units in the parallel vector unit, such as during a scalar operation, to achieve significant power savings.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multithreaded SIMD parallel processor with launching of groups of threads
ActiveUS7594095B1General purpose stored program computerProgram controlProcessing coreProcessor register
In a multithreaded processing core, groups of threads are launched in parallel for single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) execution by a set of parallel processing engines. Thread-specific input data for threads in a new SIMD group can be loaded directly into the local register files used by the parallel processing engines, or the data can be accumulated in a buffer until a launch condition is satisfied. When the launch condition is satisfied, the entire group is launched. Various launch conditions can be defined, including but not limited to full population of the SIMD group, a change in data processing conditions, or a timeout.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
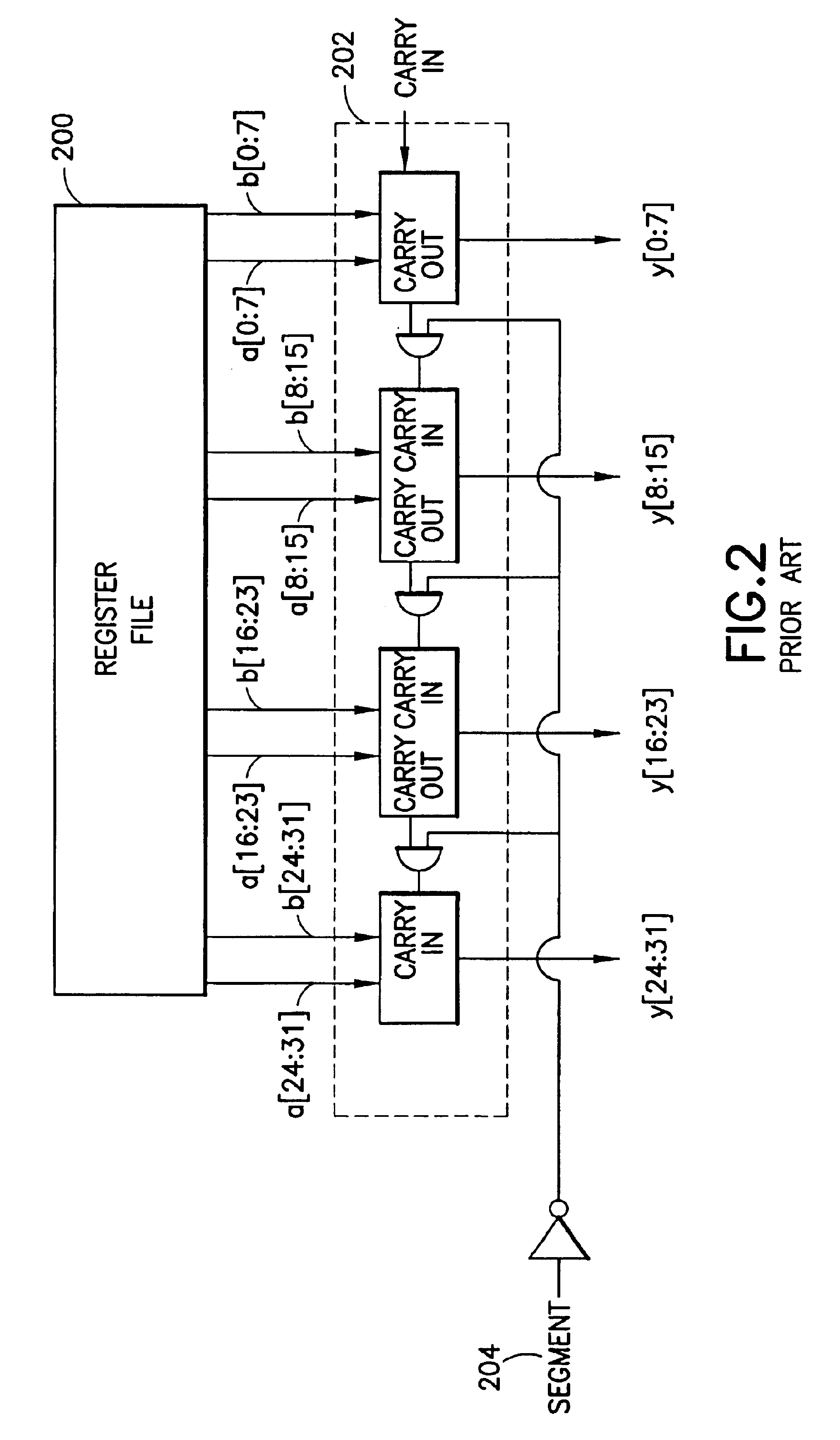
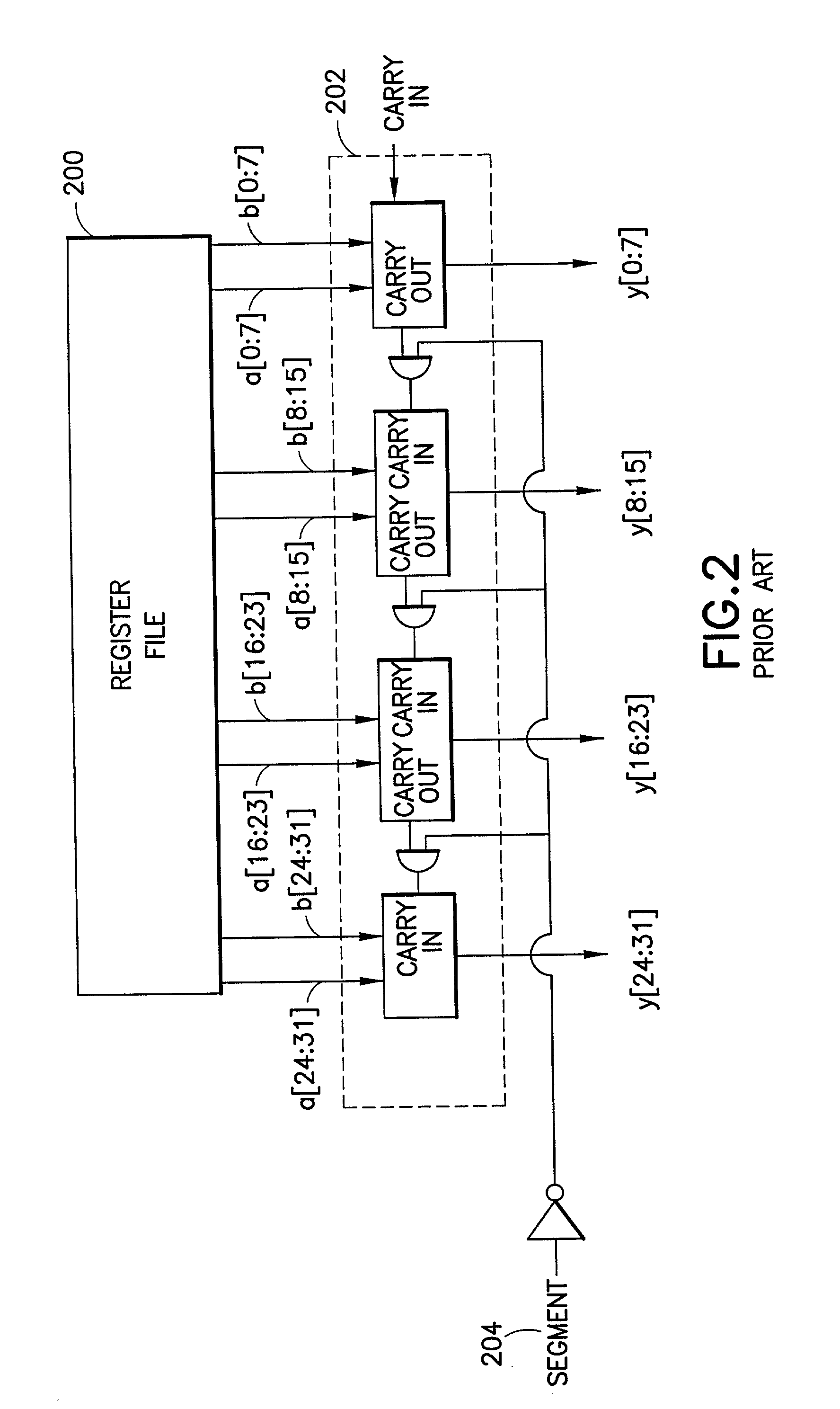
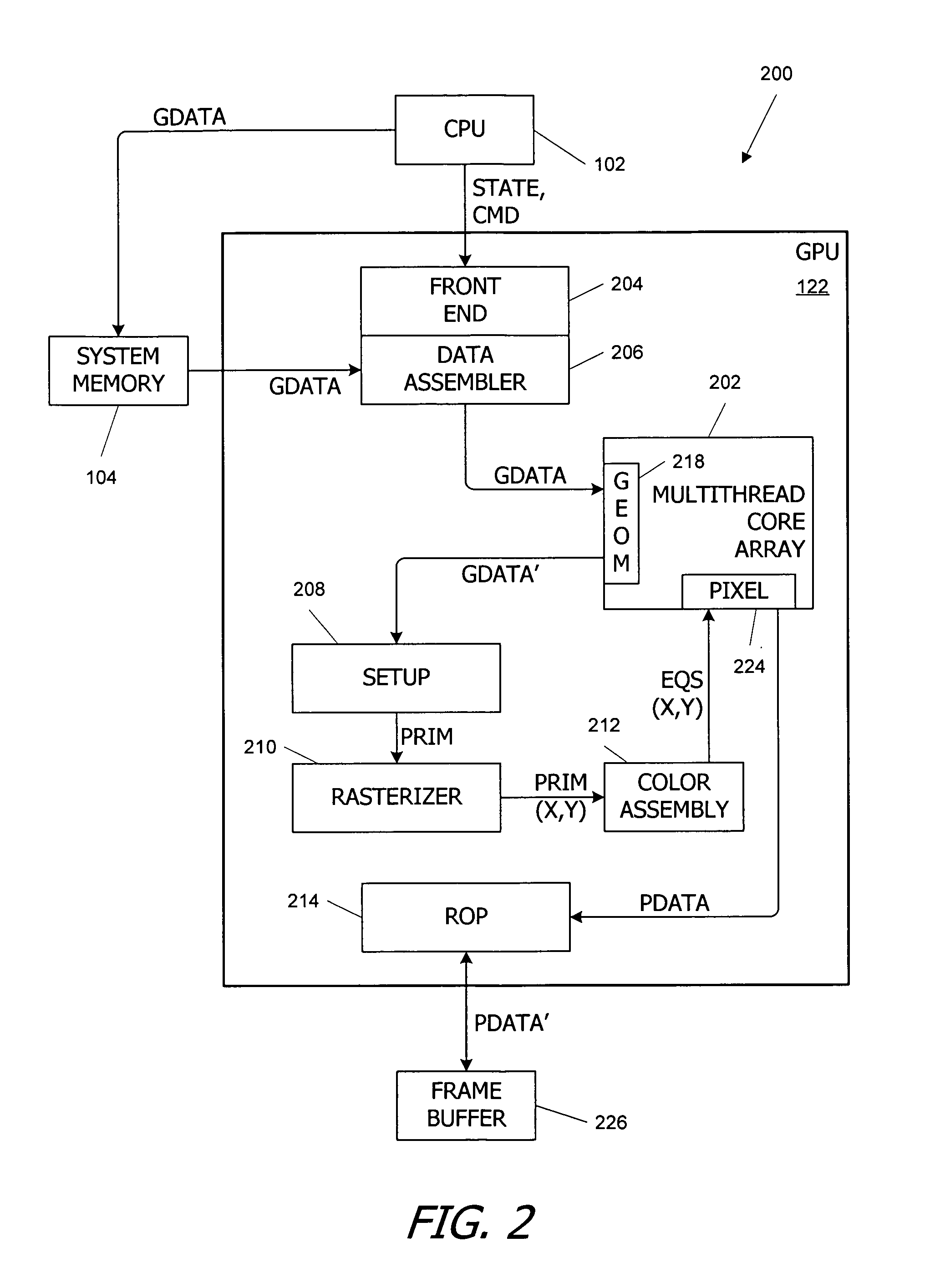
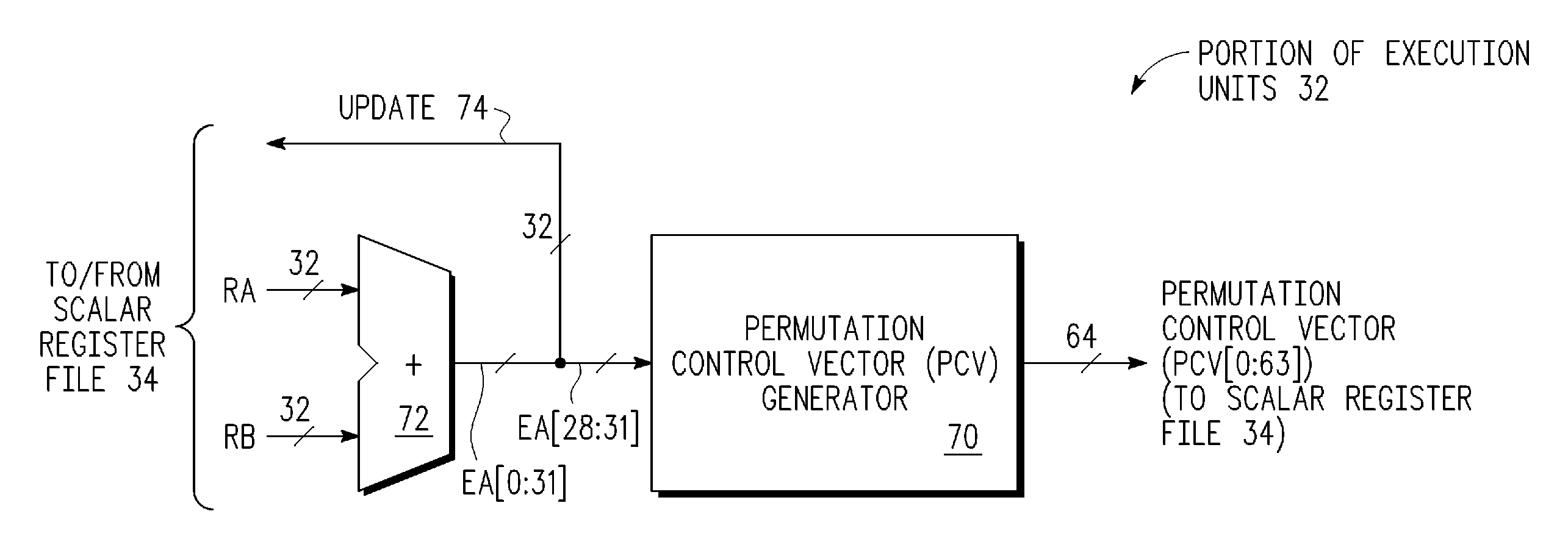
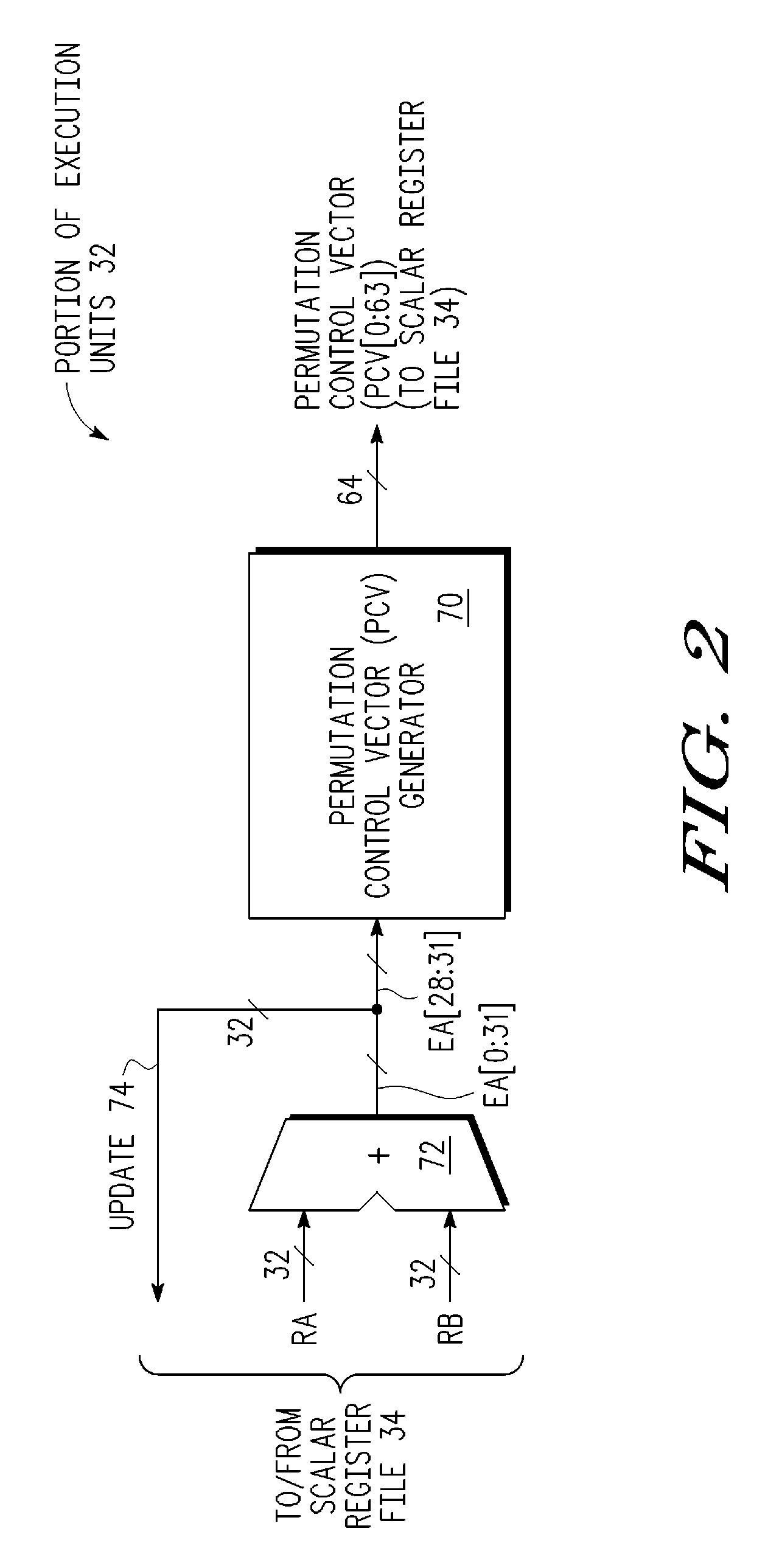
Circular buffer support in a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) data processsor
A method is provided for generating a control vector. The method comprising: providing a circular buffer having a plurality of storage elements that are arranged sequentially from a designated first storage element to a designated last storage element, and when the designated last storage element of the plurality of storage elements is accessed, the access continuing in a sequential order continuing with the designated first storage element; determining a beginning storage element of the plurality of storage elements to be accessed; and generating a control vector, the control vector comprising a plurality of index values, each of the plurality of index values corresponding to one of the plurality of storage elements of the circular buffer to be accessed in the sequential order from the beginning storage element to an ending storage element.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
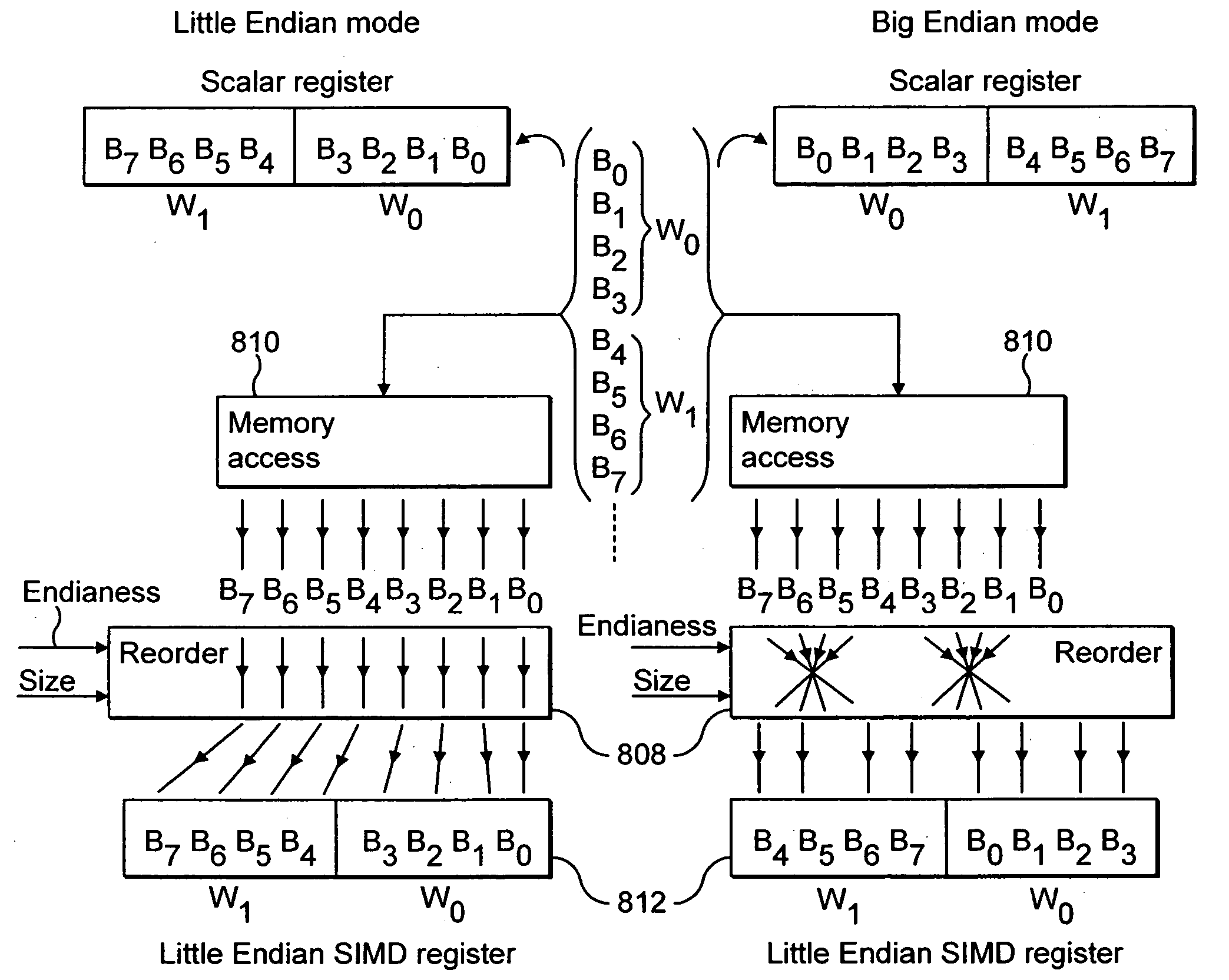
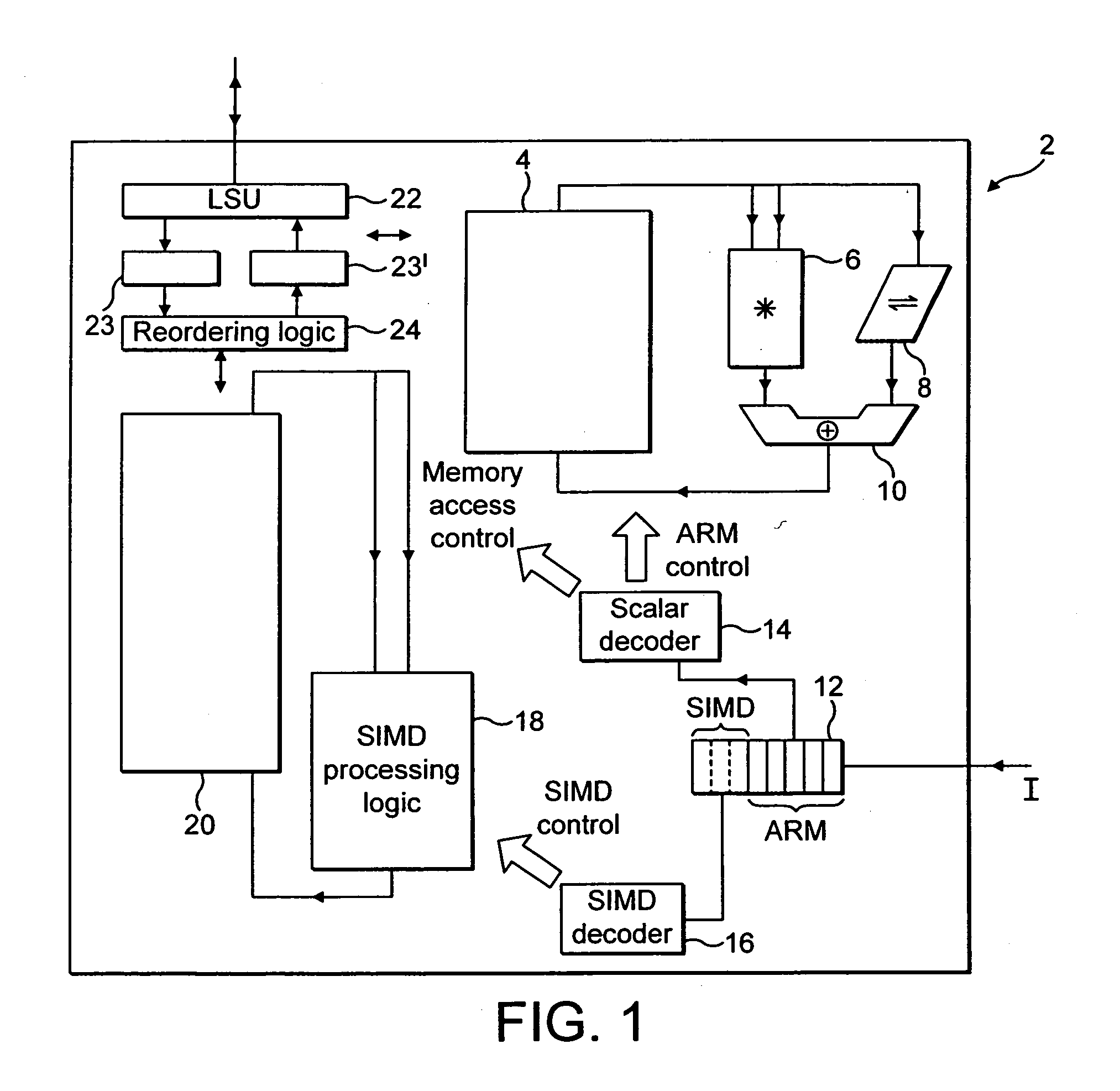
Endianess compensation within a SIMD data processing system
InactiveUS20050125647A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsHandling data according to predetermined rulesData processing systemEndianness
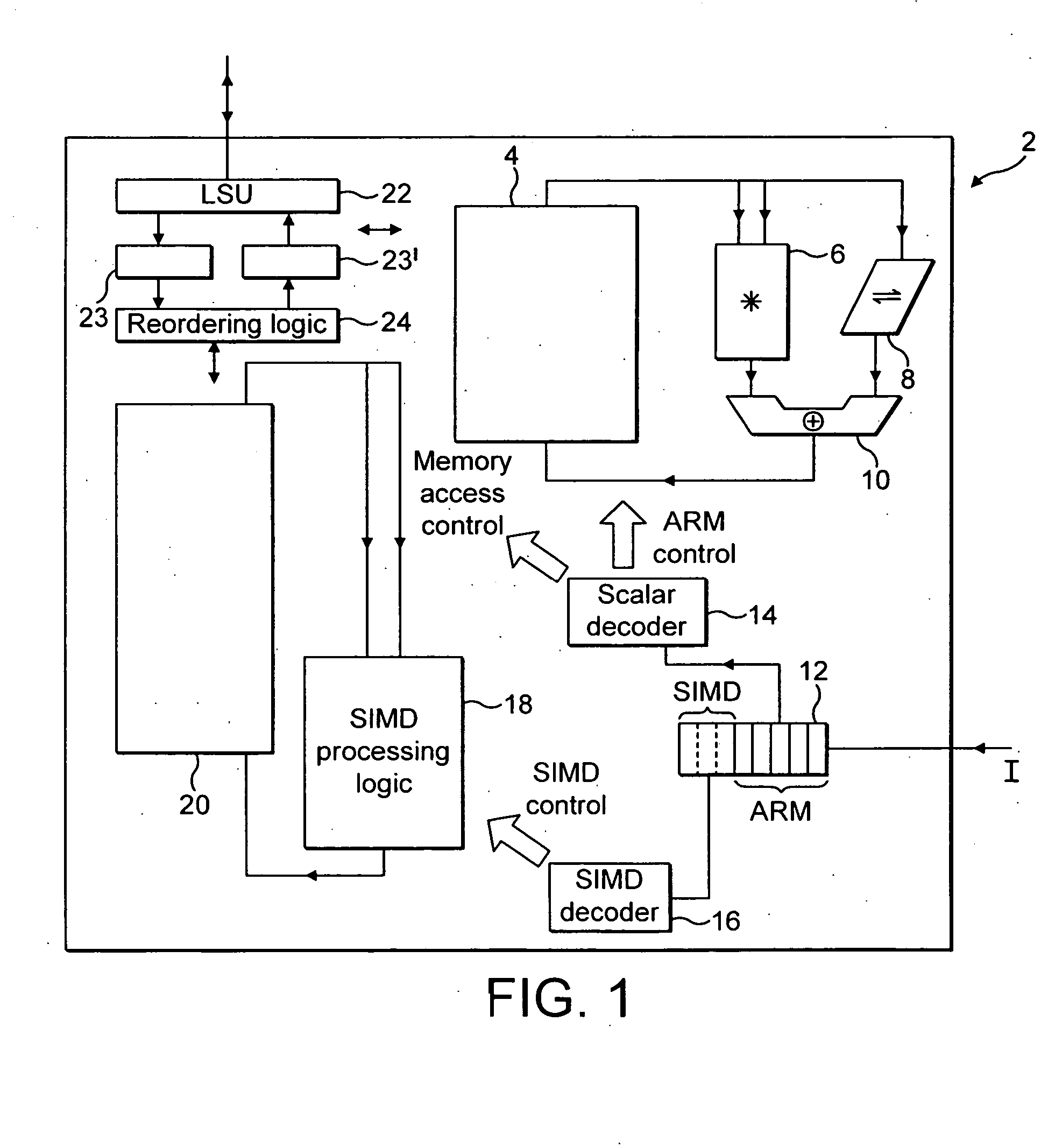
A memory system can store data in either a big endian mode or a little endian mode. Memory accessing logic 810 utilises byte invariant addressing to retrieve multiple data elements from that memory to be stored within a SIMD register 812. Data element reordering logic 808 is responsive to an endianess mode specifying signal and a data element size specifying signal to reorder retrieved bytes such that the data elements when stored within the SIMD registers 812 are invariant irrespective of the endianess mode being used by the memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
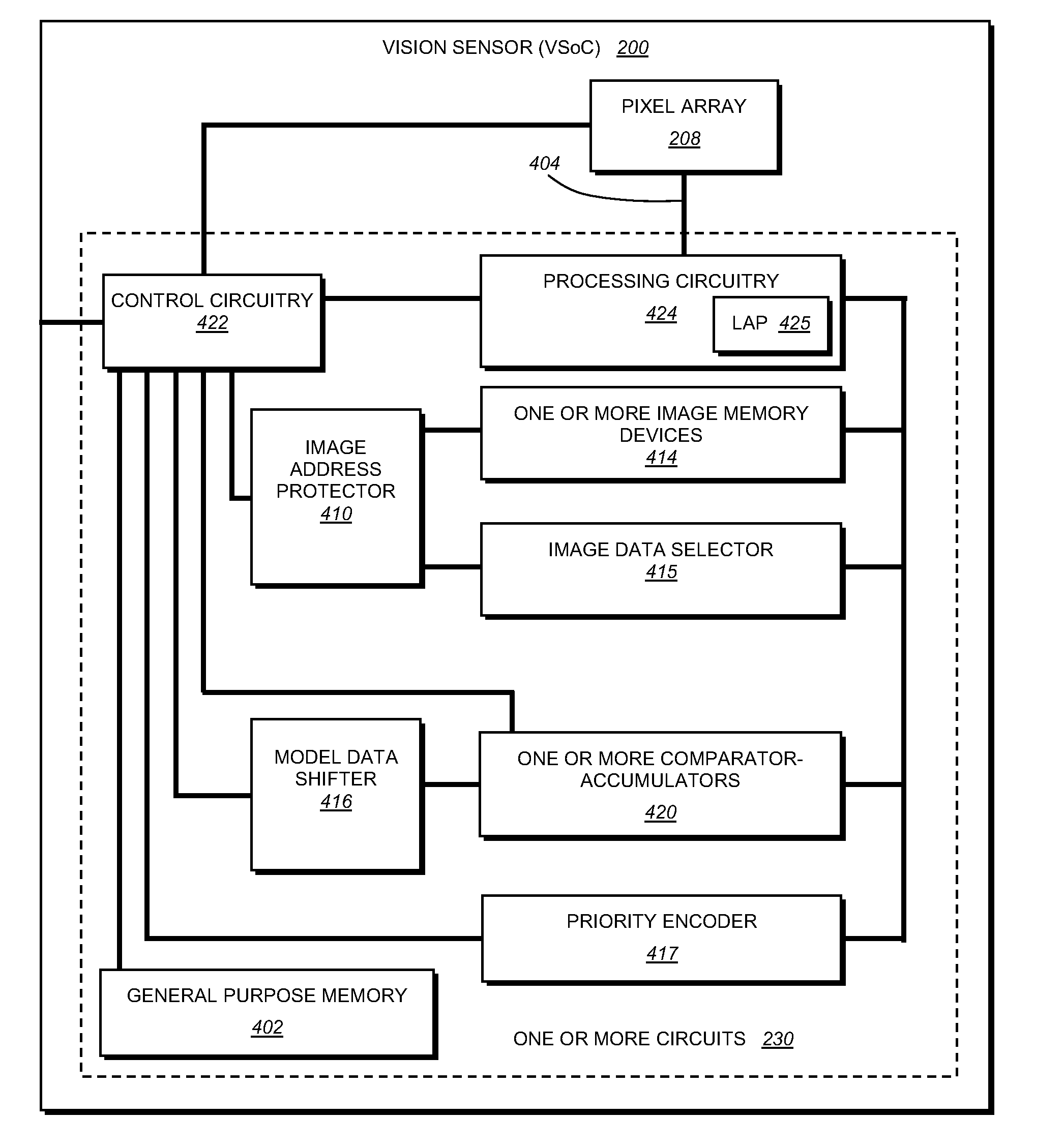
System and method for capturing and detecting symbology features and parameters
ActiveUS20100200660A1Overcome disadvantagesSensing by electromagnetic radiationSymbolic SystemsFeature set
This invention provides a system and method for capturing, detecting and extracting features of an ID, such as a 1D barcode, that employs an efficient processing system based upon a CPU-controlled vision system on a chip (VSoC) architecture, which illustratively provides a linear array processor (LAP) constructed with a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) architecture in which each pixel of the rows of the pixel array are directed to individual processors in a similarly wide array. The pixel data are processed in a front end (FE) process that performs rough finding and tracking of regions of interest (ROIs) that potentially contain ID-like features. The ROI-finding process occurs in two parts so as to optimize the efficiency of the LAP in neighborhood operations—a row-processing step that occurs during image pixel readout from the pixel array and an image-processing step that occurs typically after readout occurs. The relative motion of the ID-containing ROI with respect to the pixel array is tracked and predicted. An optional back end (BE) process employs the predicted ROI to perform feature-extraction after image capture. The feature extraction derives candidate ID features that are verified by a verification step that confirms the ID, creates a refined ROI, angle of orientation and feature set. These are transmitted to a decoding processor or other device.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Accelerated ray tracing using shallow bounding volume hierarchies
InactiveUS20100053162A1Increasing arityReduce memory requirementsImage data processing detailsImage generationAlgorithmBounding volume hierarchy
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program code (software) products enable acceleration of ray tracing by using acceleration data structures with high arity to enable processing of nodes using streaming SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) instructions with reduced memory requirements.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
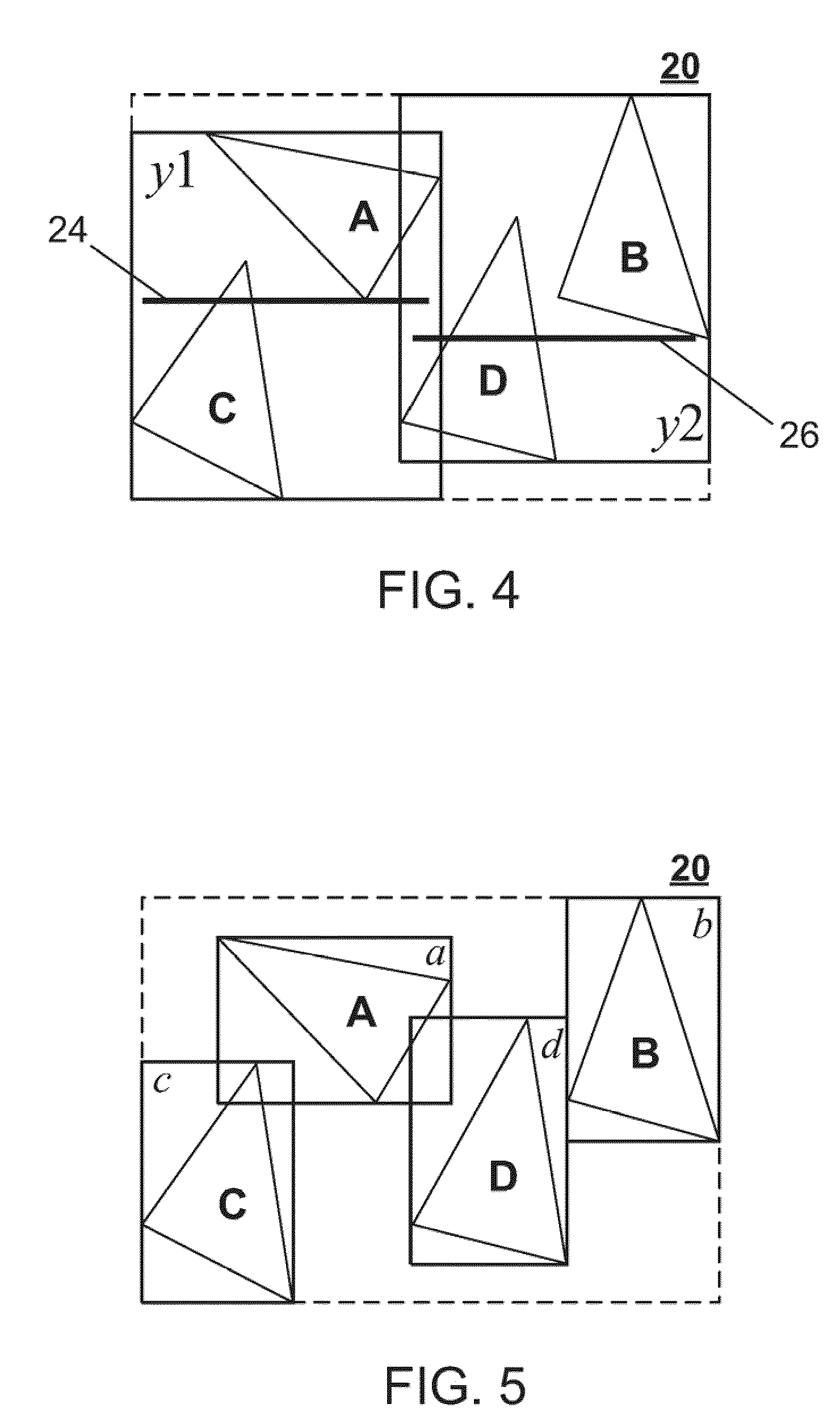
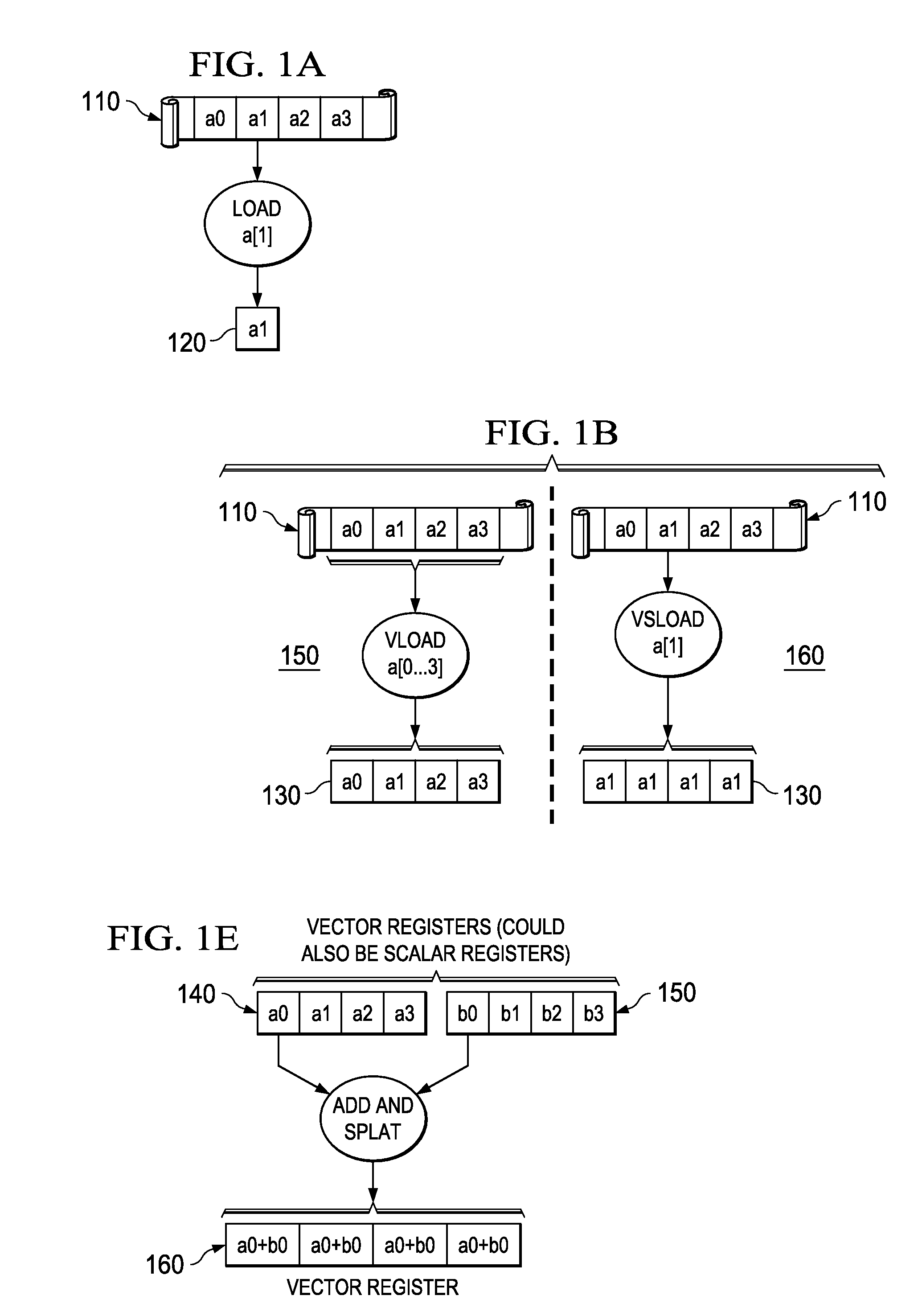
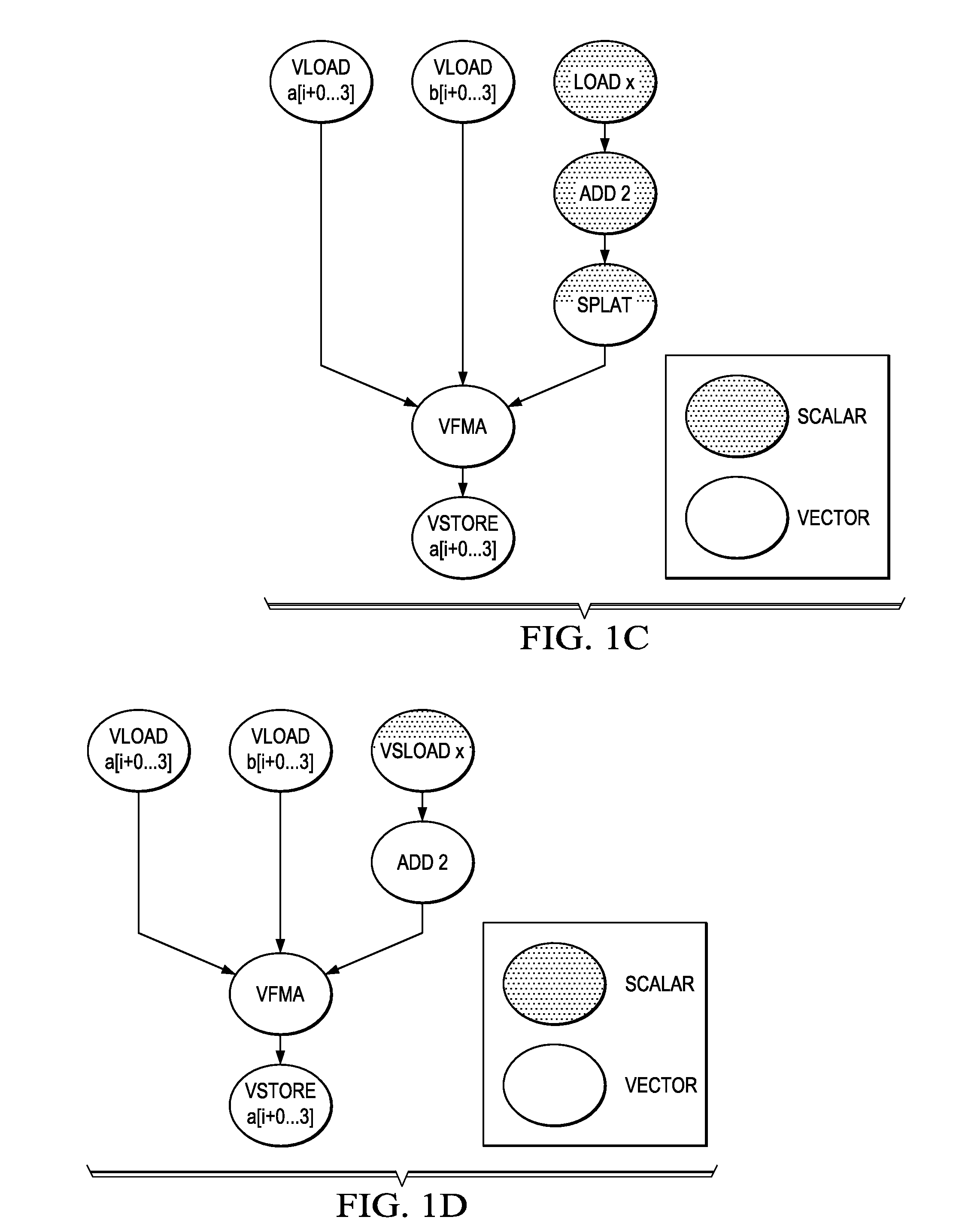
Optimized Scalar Promotion with Load and Splat SIMD Instructions
InactiveUS20090307656A1General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsSIMDVector operations
Mechanisms for optimizing scalar code executed on a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) engine are provided. Placement of vector operation-splat operations may be determined based on an identification of scalar and SIMD operations in an original code representation. The original code representation may be modified to insert the vector operation-splat operations based on the determined placement of vector operation-splat operations to generate a first modified code representation. Placement of separate splat operations may be determined based on identification of scalar and SIMD operations in the first modified code representation. The first modified code representation may be modified to insert or delete separate splat operations based on the determined placement of the separate splat operations to generate a second modified code representation. SIMD code may be output based on the second modified code representation for execution by the SIMD engine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data processing apparatus and method for performing arithmetic operations in SIMD data processing
ActiveUS20050125476A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantityInstruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerData memory
A data processing apparatus, method and a computer program product. A data processing apparatus comprising: a register data store operable to store data elements; an instruction decoder operable to decode an arithmetic returning high half instruction; a data processor operable to perform data processing operations controlled by said instruction decoder wherein: in response to said decoded arithmetic returning high half instruction, said data processor is operable to specify within said register data store, one or more source registers operable to store a plurality of source data elements of a first size, and one or more destination registers operable to store a corresponding plurality of resultant data elements of a second size, said second size being half the size of said first size; and to perform the following operations in parallel on said plurality of source data elements to produce said corresponding plurality of resultant data elements: perform an arithmetic operation on said source registers specified by said instruction to produce a plurality of corresponding intermediate result data elements; form said resultant data elements from information derived from a high half of a corresponding one of said plurality of intermediate result data elements; store said resultant data elements in said destination register.
Owner:ARM LTD
SIMD four-data element average instruction
InactiveUS20050216545A1Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesData averagingLeast significant bit
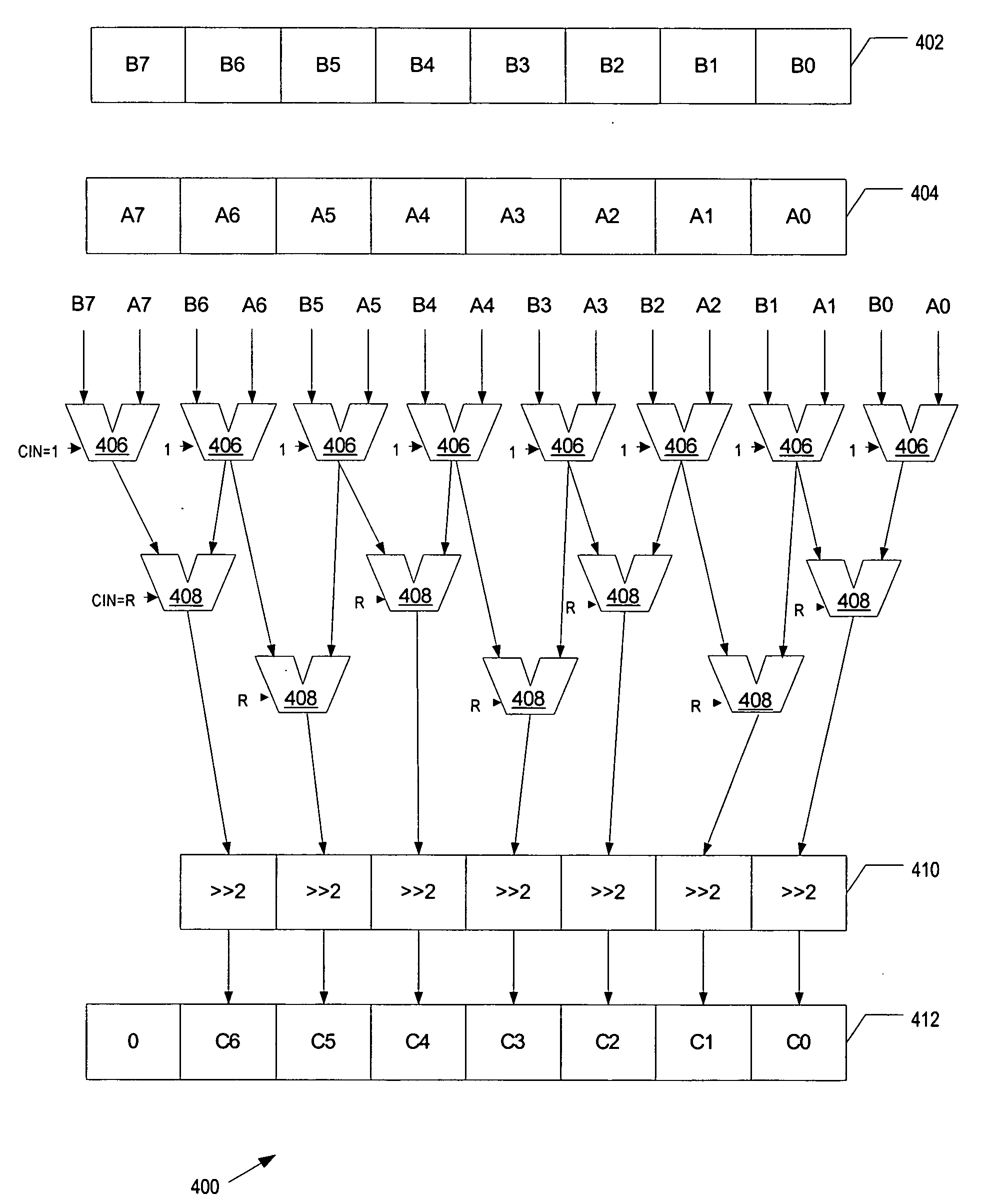
According to some embodiments, a Single-Instruction / Multiple-Data averaging operation is presented. The averaging operation averages multiple sets of data elements, for example, two data elements each from a first source and a second source, producing a set of averages. In at least one embodiment, in a first adder stage, a first plurality of data elements are added to a second plurality of data elements, generating a plurality of intermediate results. In a second adder stage, multiple different combinations of the plurality of intermediate results are added together, generating a plurality of sum results. The two least significant bits of each sum result are discarded.
Owner:INTEL CORP
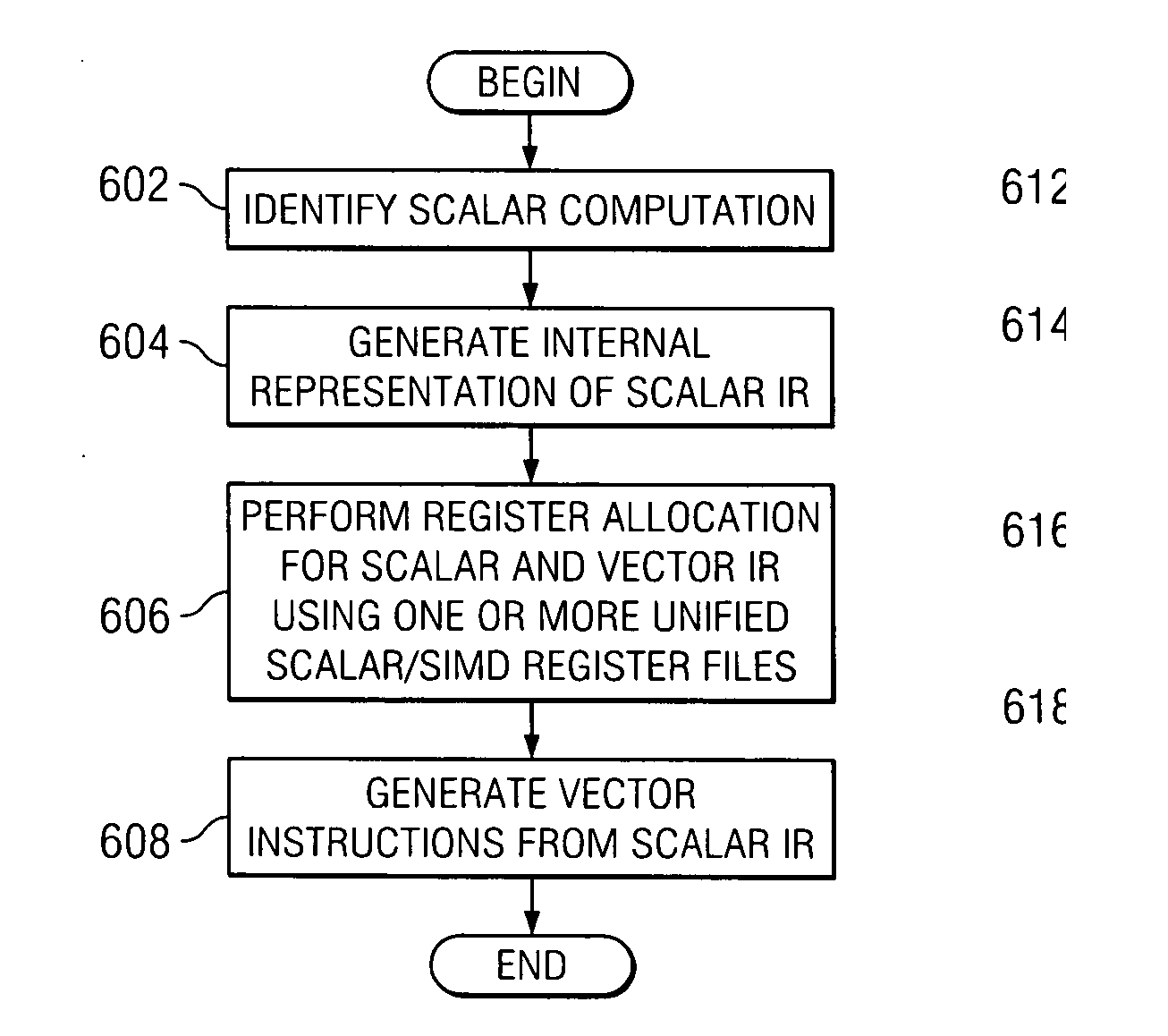
Compilation for a SIMD RISC processor
InactiveUS20070124722A1Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemScalar Value
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and computer usable code are provided for generating code to perform scalar computations on a Single-Instruction Multiple-Data (SIMD) Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) architecture. The illustrative embodiments generate code directed at loading at least one scalar value and generate code using at least one vector operation to generate a scalar result, wherein all scalar computation for integer and floating point data is performed in a SIMD vector execution unit.
Owner:IBM CORP
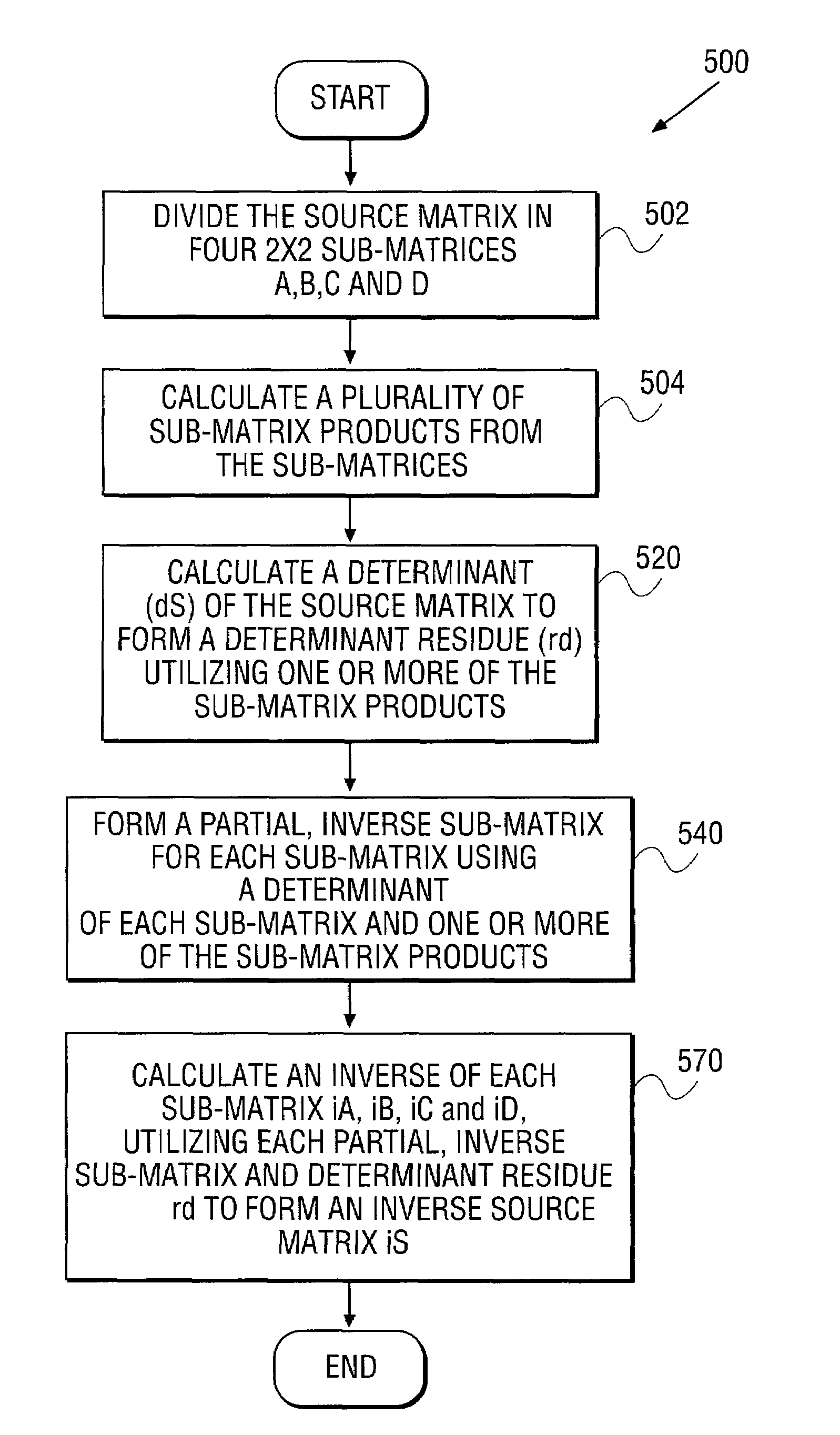
Apparatus and method for inverting a 4x4 matrix
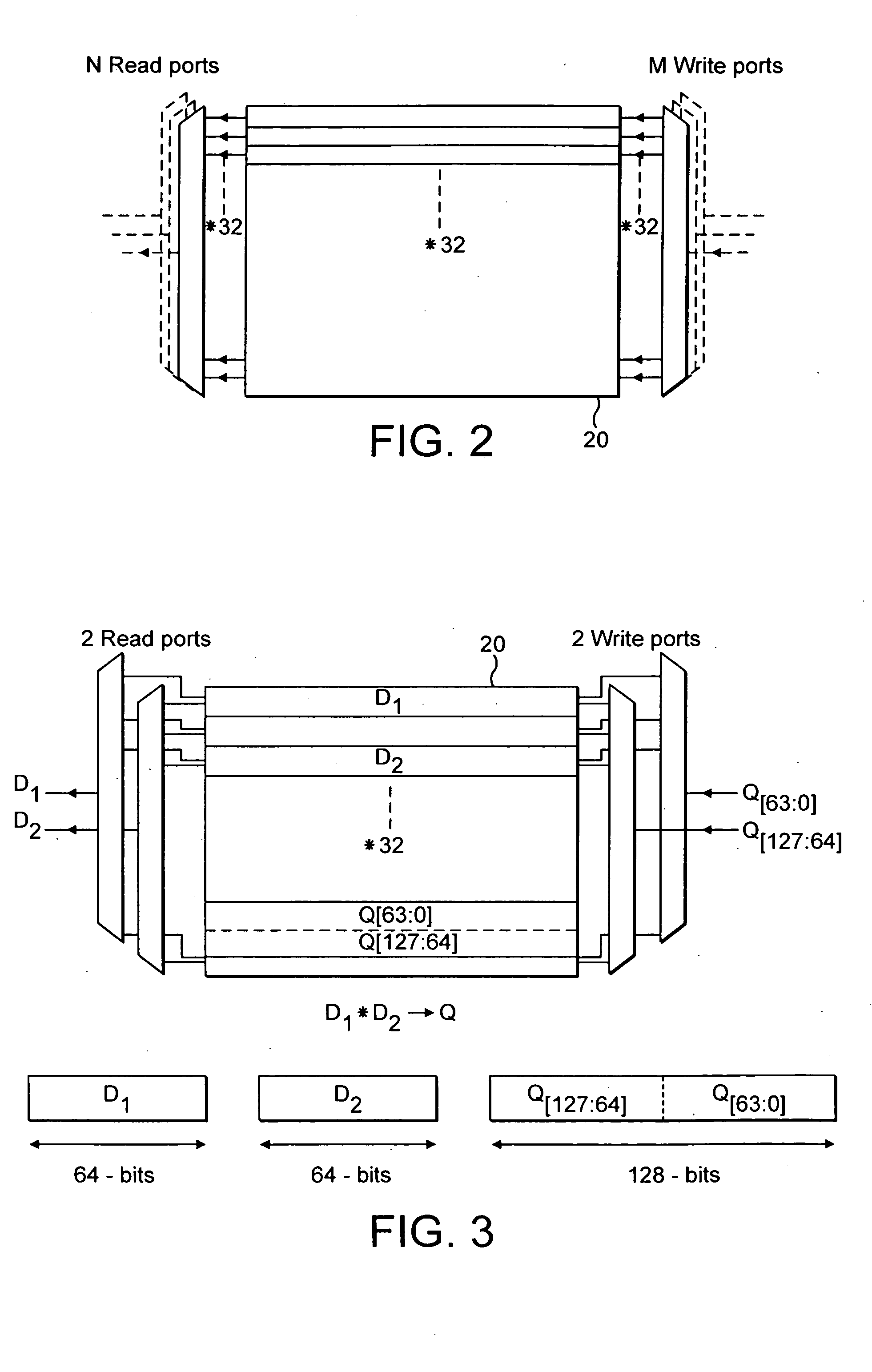
An apparatus and method for inverting a 4×4 source matrix. A source matrix is divided into four 2×2 sub-matrices. A plurality of sub-matrix products are subsequently calculated from the sub-matrices. Next, a determinant of the source matrix is calculated to form a determinant residue utilizing the previously computed sub-matrix products. Calculation of partial inverse for each sub-matrix is next performed, using the sub-matrix products and determinants of the sub-matrices. Finally, an inverse of each sub-matrix is calculated, utilizing the partial inverse sub-matrices and the determinant residue to form an inverse of the 4×4 source matrix. The article allows processors to store two floating-point elements within a Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) register. Accordingly, a sub-matrix is represented using two SIMD registers, resulting in improved computational locality and efficiency. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Bitstream buffer manipulation with a SIMD merge instruction
ActiveUS20050108312A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsRegister arrangementsVariable lengthSIMD
Method, apparatus, and program means for performing bitstream buffer manipulation with a SIMD merge instruction. The method of one embodiment comprises determining whether any unprocessed data bits for a partial variable length symbol exist in a first data block is made. A shift merge operation is performed to merge the unprocessed data bits from the first data block with a second data block. A merged data block is formed. A merged variable length symbol comprised of the unprocessed data bits and a plurality of data bits from the second data block is extracted from the merged data block.
Owner:INTEL CORP
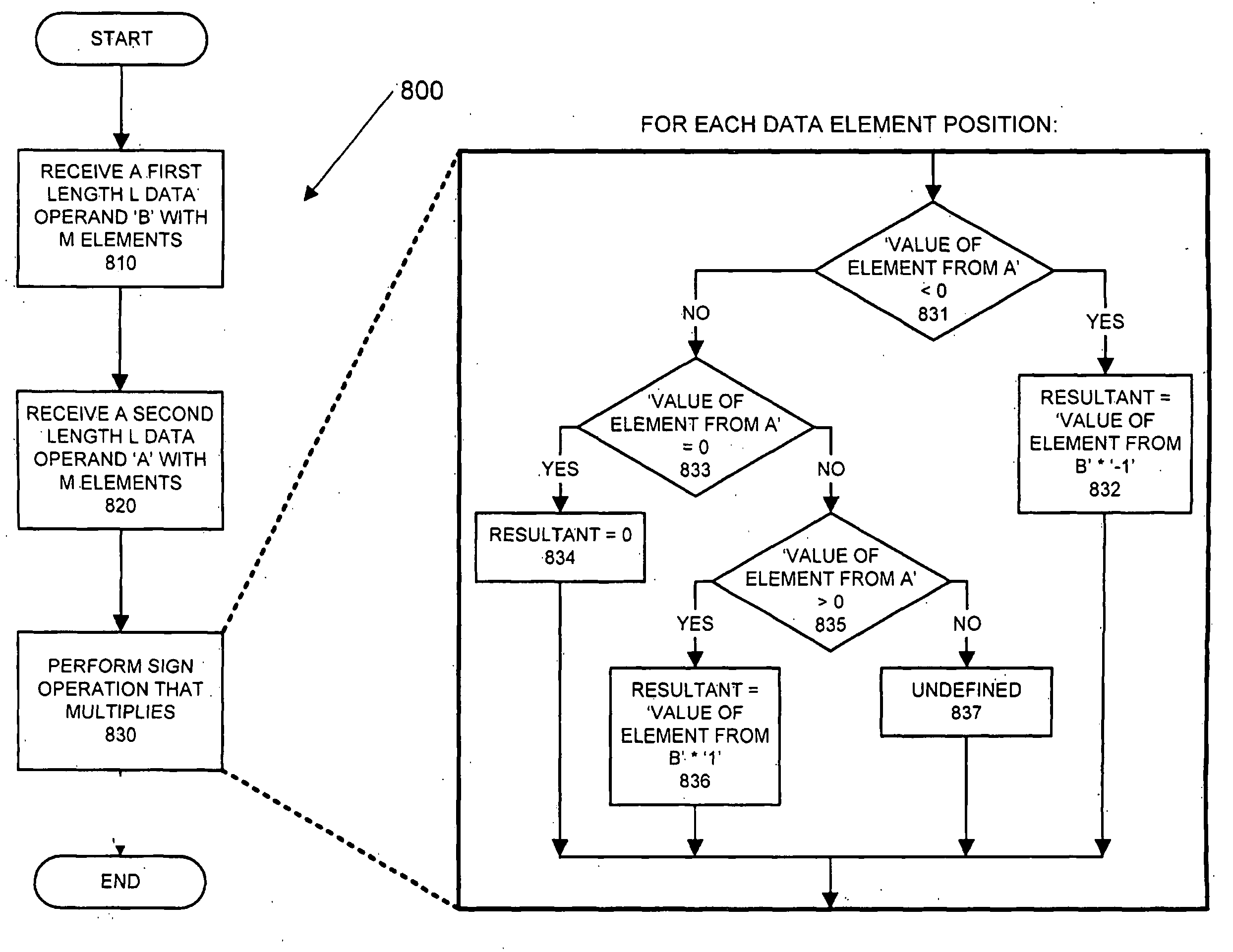
Nonlinear filtering and deblocking applications utilizing SIMD sign and absolute value operations
ActiveUS20090077143A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsInstruction analysisNonlinear filterNonlinear filtering
Method, apparatus, and program means for nonlinear filtering and deblocking applications utilizing SIMD sign and absolute value operations. The method of one embodiment comprises receiving first data for a first block and second data for a second block. The first data and said second data are comprised of a plurality of rows and columns of pixel data. A block boundary between the first block and the second block is characterized. A correction factor for a deblocking algorithm is calculated with a first instruction for a sign operation that multiplies and with a second instruction for an absolute value operation. Data for pixels located along said block boundary between the first and second block are corrected.
Owner:INTEL CORP
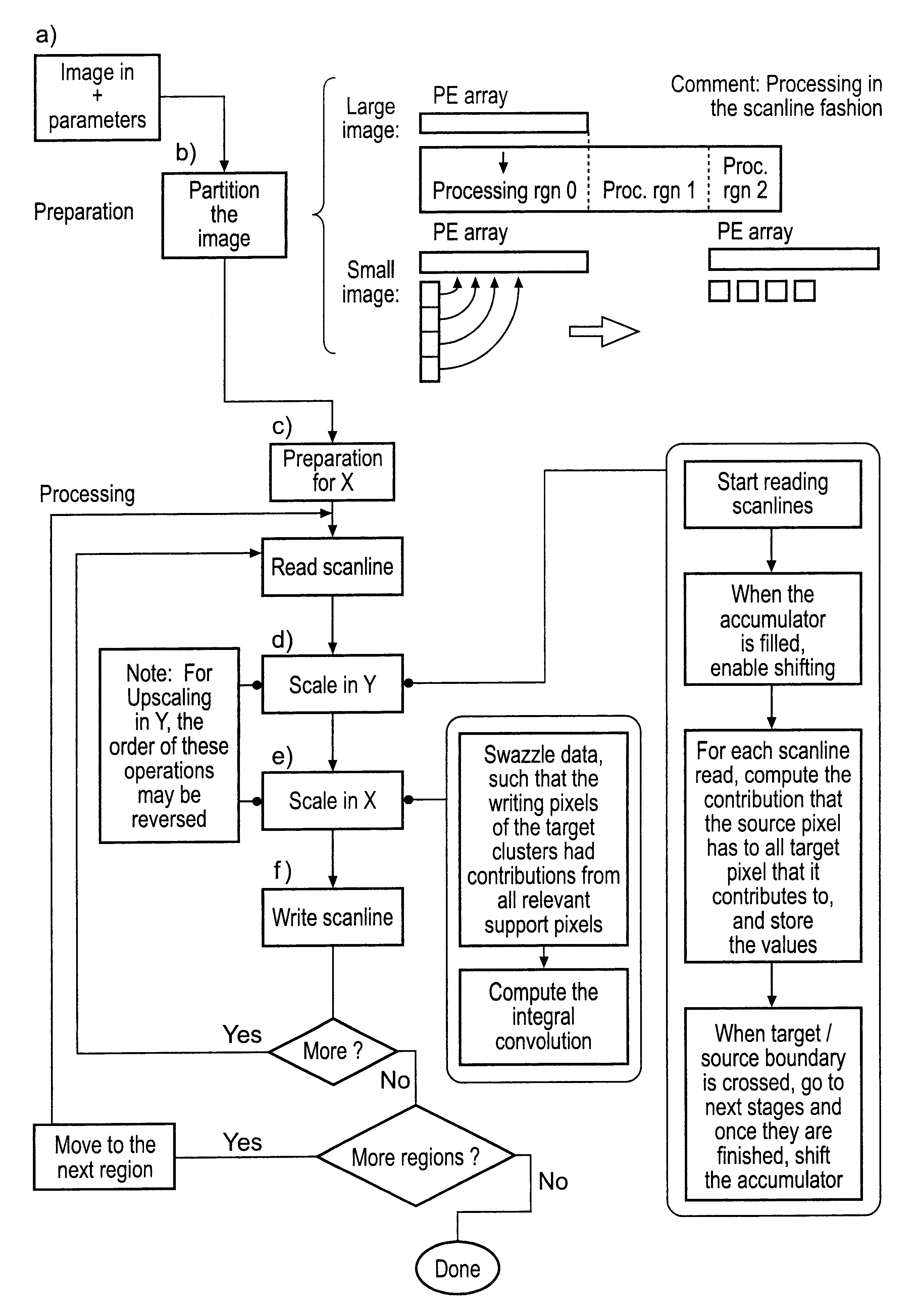
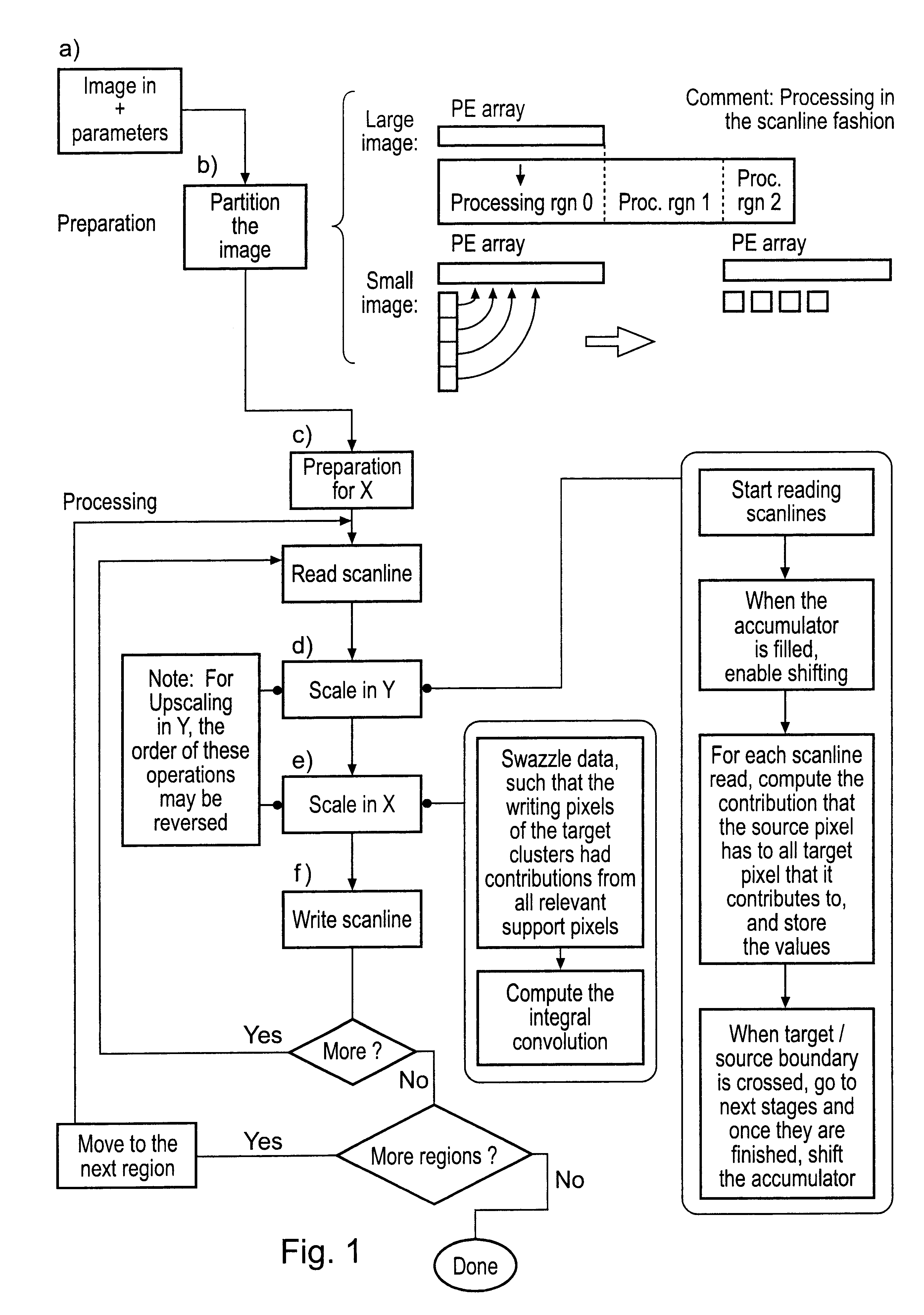
Image scaling
InactiveUS6825857B2Exceeding performanceFast imagingGeometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionDigital filter
Owner:RAMBUS INC
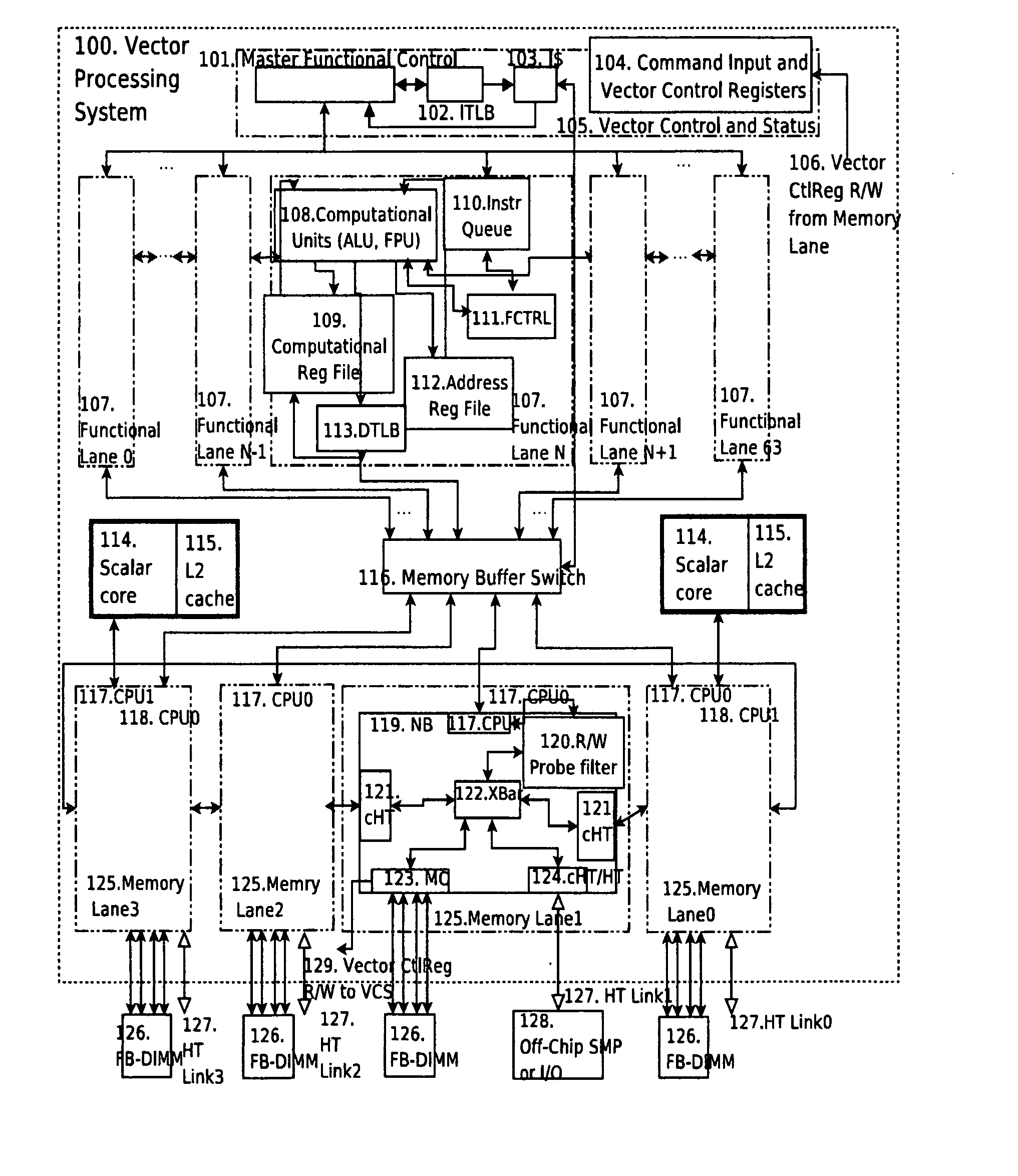
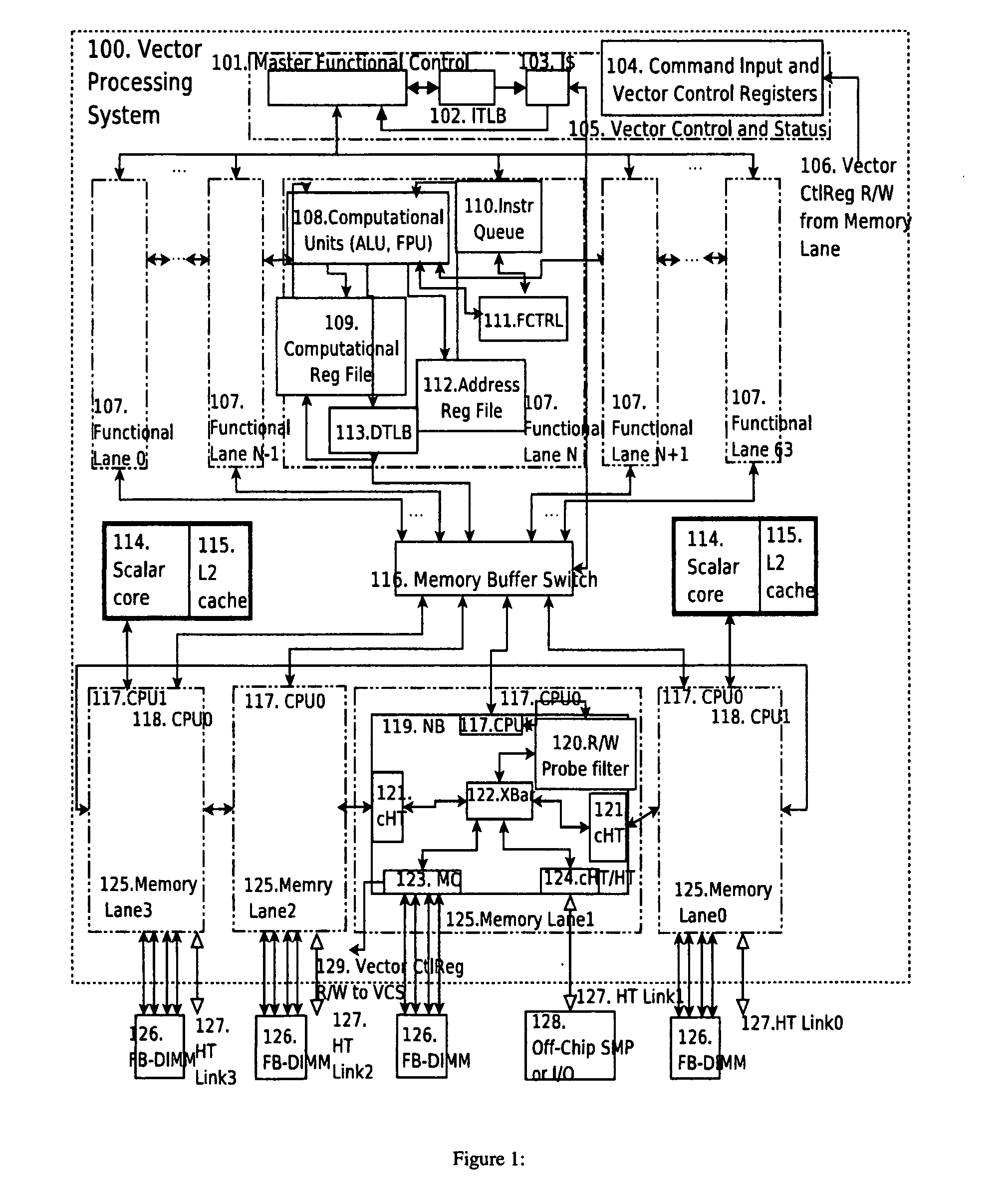
Vector processor
ActiveUS20070255894A1General purpose stored program computerDigital storageProcessing InstructionScalar processor
A vector processing system provides high performance vector processing using a System-On-a-Chip (SOC) implementation technique. One or more scalar processors (or cores) operate in conjunction with a vector processor, and the processors collectively share access to a plurality of memory interfaces coupled to Dynamic Random Access read / write Memories (DRAMs). In typical embodiments the vector processor operates as a slave to the scalar processors, executing computationally intensive Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) codes in response to commands received from the scalar processors. The vector processor implements a vector processing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) including machine state, instruction set, exception model, and memory model.
Owner:HESSEL RICHARD +1
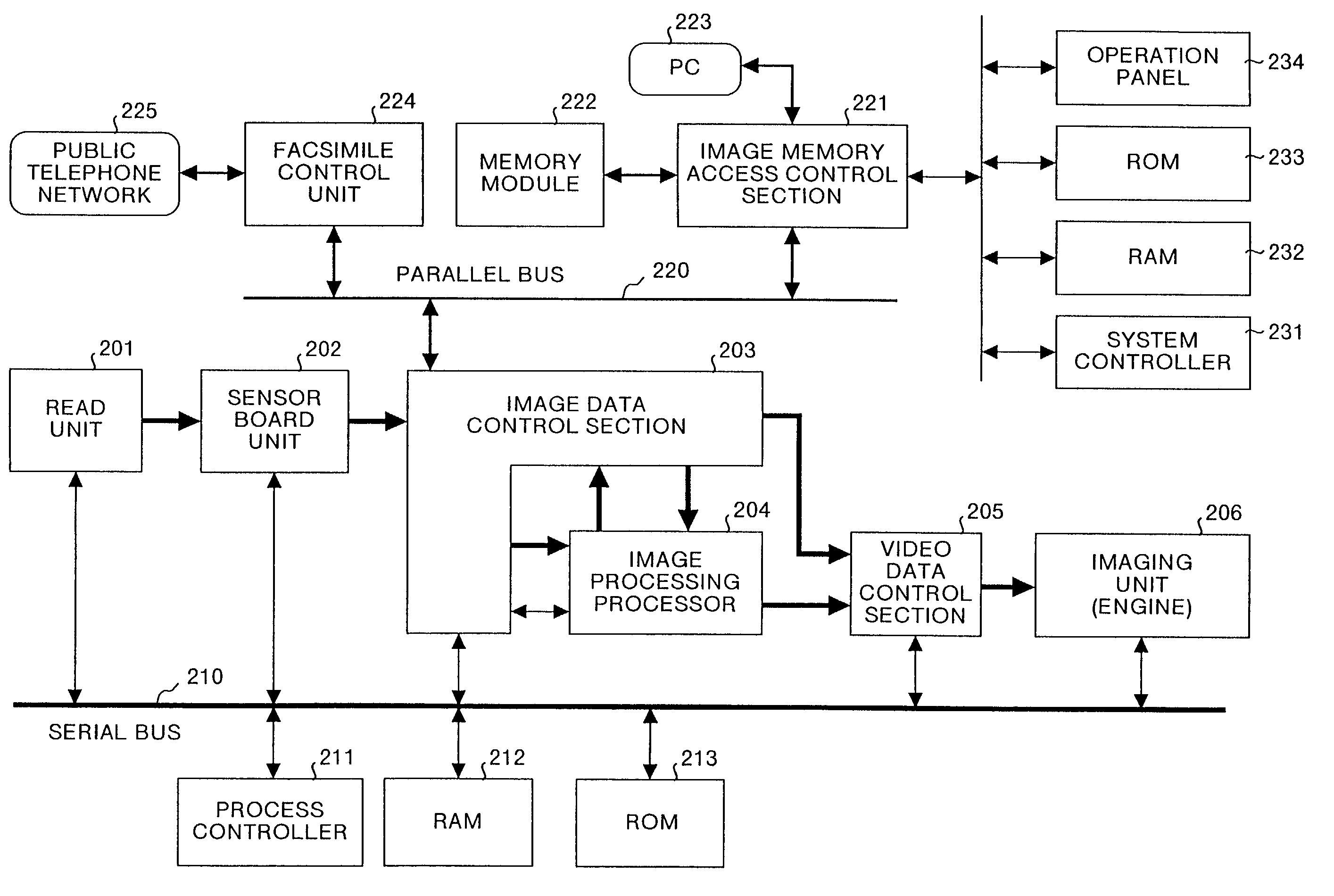
Method and apparatus for image processing, and a computer product
InactiveUS7200287B2Efficiently perform image processingSimple processImage memory managementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingProcessor register
The image processing apparatus is provided with a plural memory controllers, each of which controls a RAM. The memory controllers are connected to an SIMD type arithmetic processing section. A control register is connected to the memory controllers. The control register controls transfer of image data between the RAMs and the SIMD type arithmetic processing section.
Owner:RICOH KK
Floating Point Only Single Instruction Multiple Data Instruction Set Architecture
InactiveUS20100095097A1General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsData processing systemProcessor register
Mechanisms for implementing a floating point only single instruction multiple data instruction set architecture are provided. A processor is provided that comprises an issue unit, an execution unit coupled to the issue unit, and a vector register file coupled to the execution unit. The execution unit has logic that implements a floating point (FP) only single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instruction set architecture (ISA). The floating point vector registers of the vector register file store both scalar and floating point values as vectors having a plurality of vector elements. The processor may be part of a data processing system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Field-programmable gate array based accelerator system
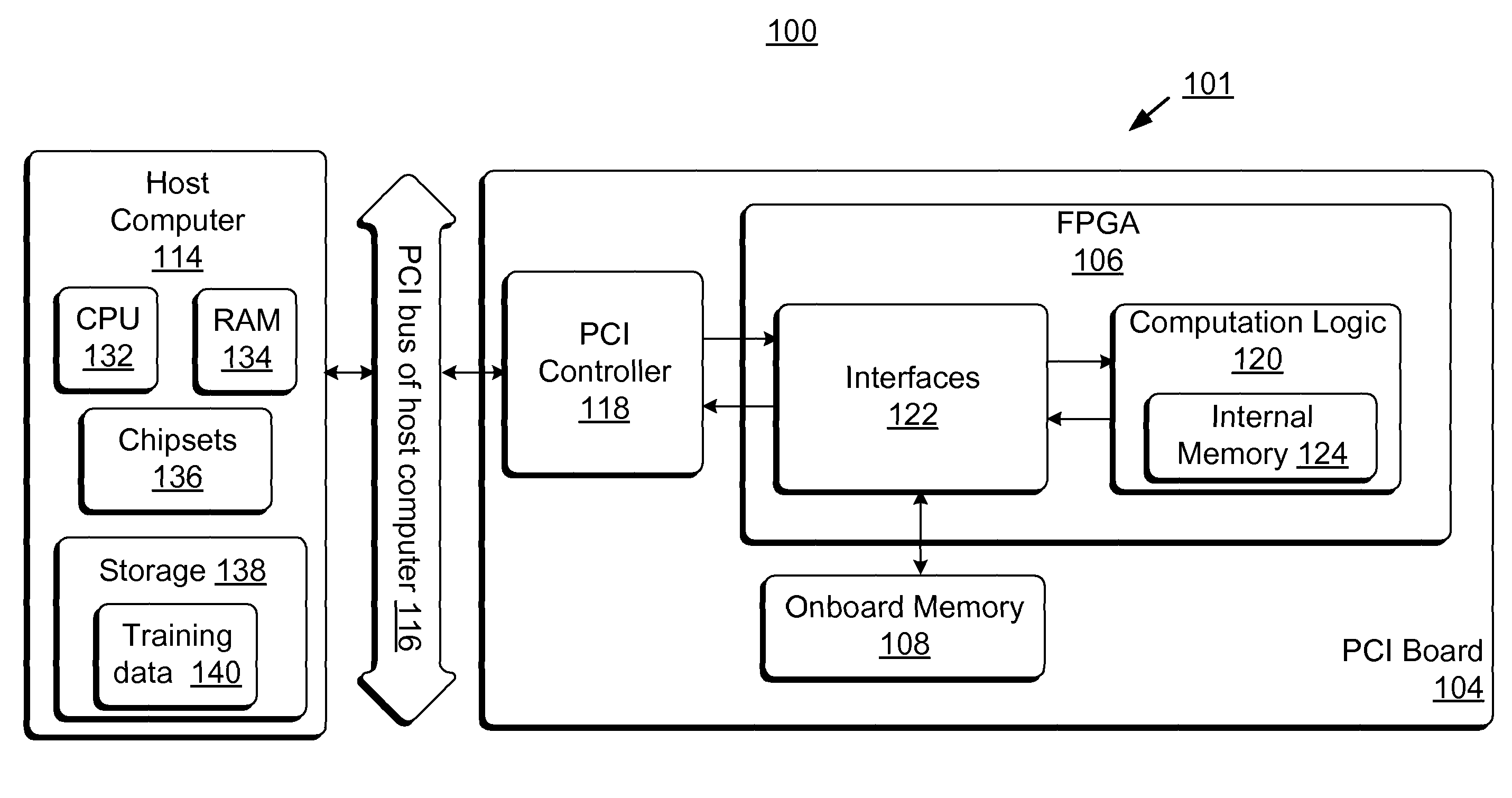
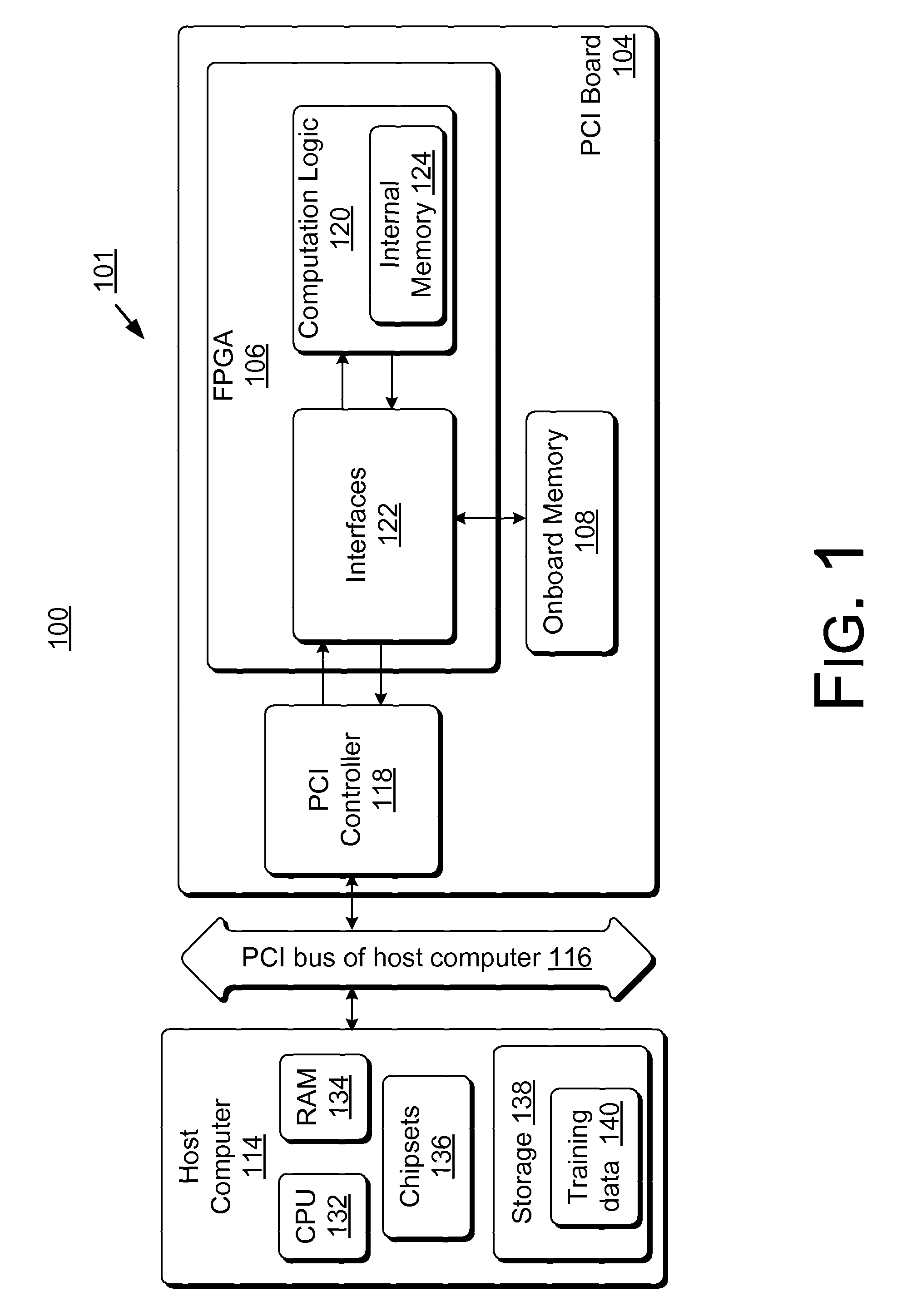
ActiveUS8131659B2Less timeLess costDigital computer detailsDigital dataHidden layerArithmetic logic unit
Accelerator systems and methods are disclosed that utilize FPGA technology to achieve better parallelism and processing speed. A Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) is configured to have a hardware logic performing computations associated with a neural network training algorithm, especially a Web relevance ranking algorithm such as LambaRank. The training data is first processed and organized by a host computing device, and then streamed to the FPGA for direct access by the FPGA to perform high-bandwidth computation with increased training speed. Thus, large data sets such as that related to Web relevance ranking can be processed. The FPGA may include a processing element performing computations of a hidden layer of the neural network training algorithm. Parallel computing may be realized using a single instruction multiple data streams (SIMD) architecture with multiple arithmetic logic units in the FPGA.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
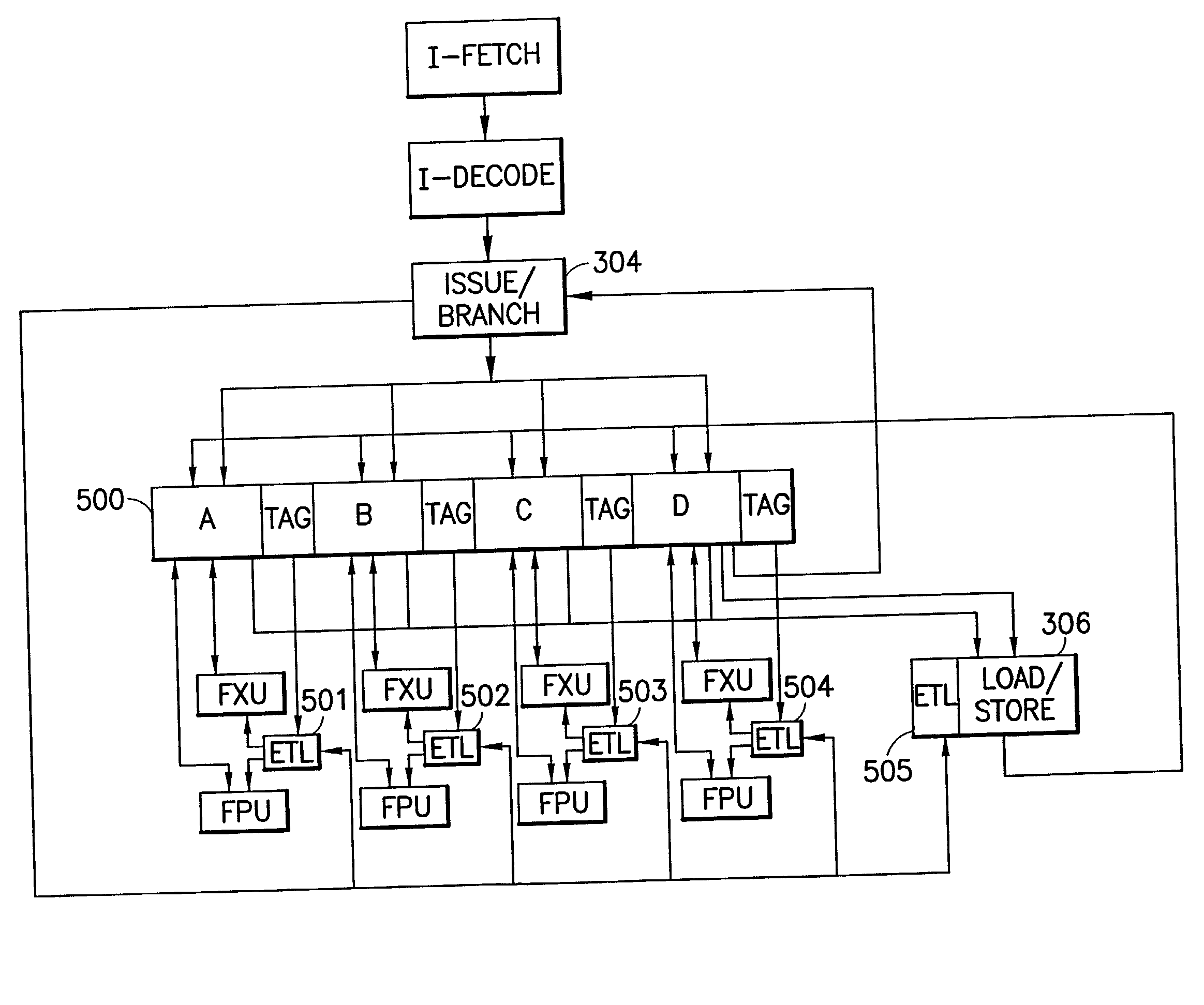
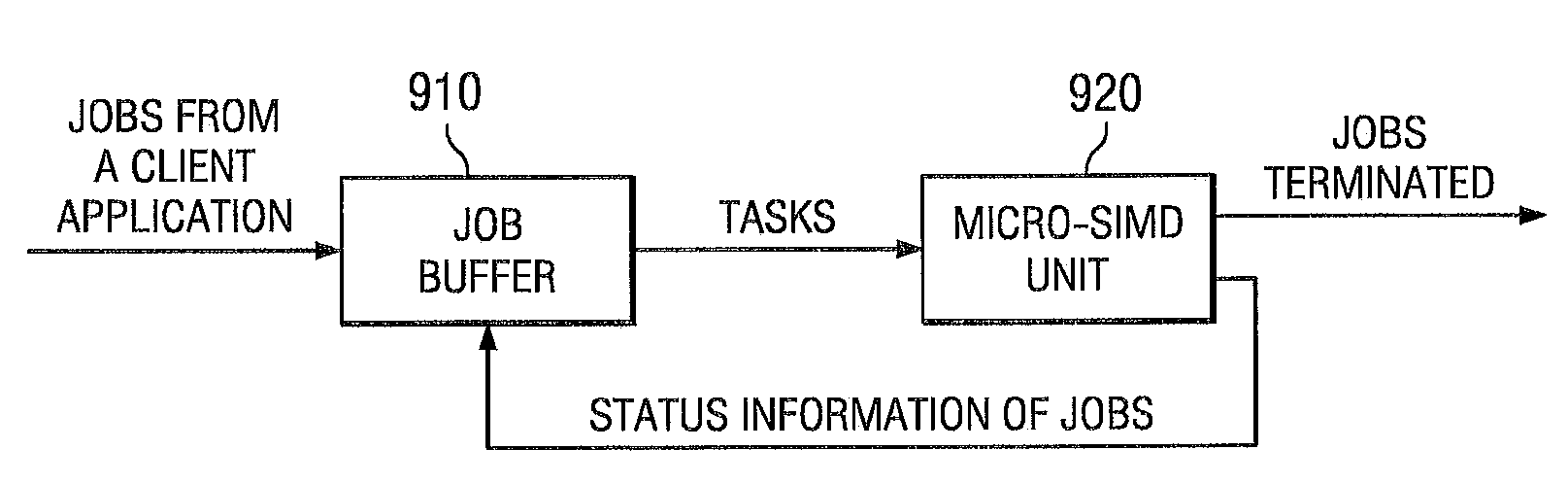
System and method for efficiently executing single program multiple data (SPMD) programs
ActiveUS7904905B2Data efficientProgram initiation/switchingGeneral purpose stored program computerControl flowData stream
A system and method is disclosed for efficiently executing single program multiple data (SPMD) programs in a microprocessor. A micro single instruction multiple data (SIMD) unit is located within the microprocessor. A job buffer that is coupled to the micro SIMD unit dynamically allocates tasks to the micro SIMD unit. The SPMD programs each comprise a plurality of input data streams having moderate diversification of control flows. The system executes each SPMD program once for each input data stream of the plurality of input data streams.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Source adaptive system and method for 2D iDCT
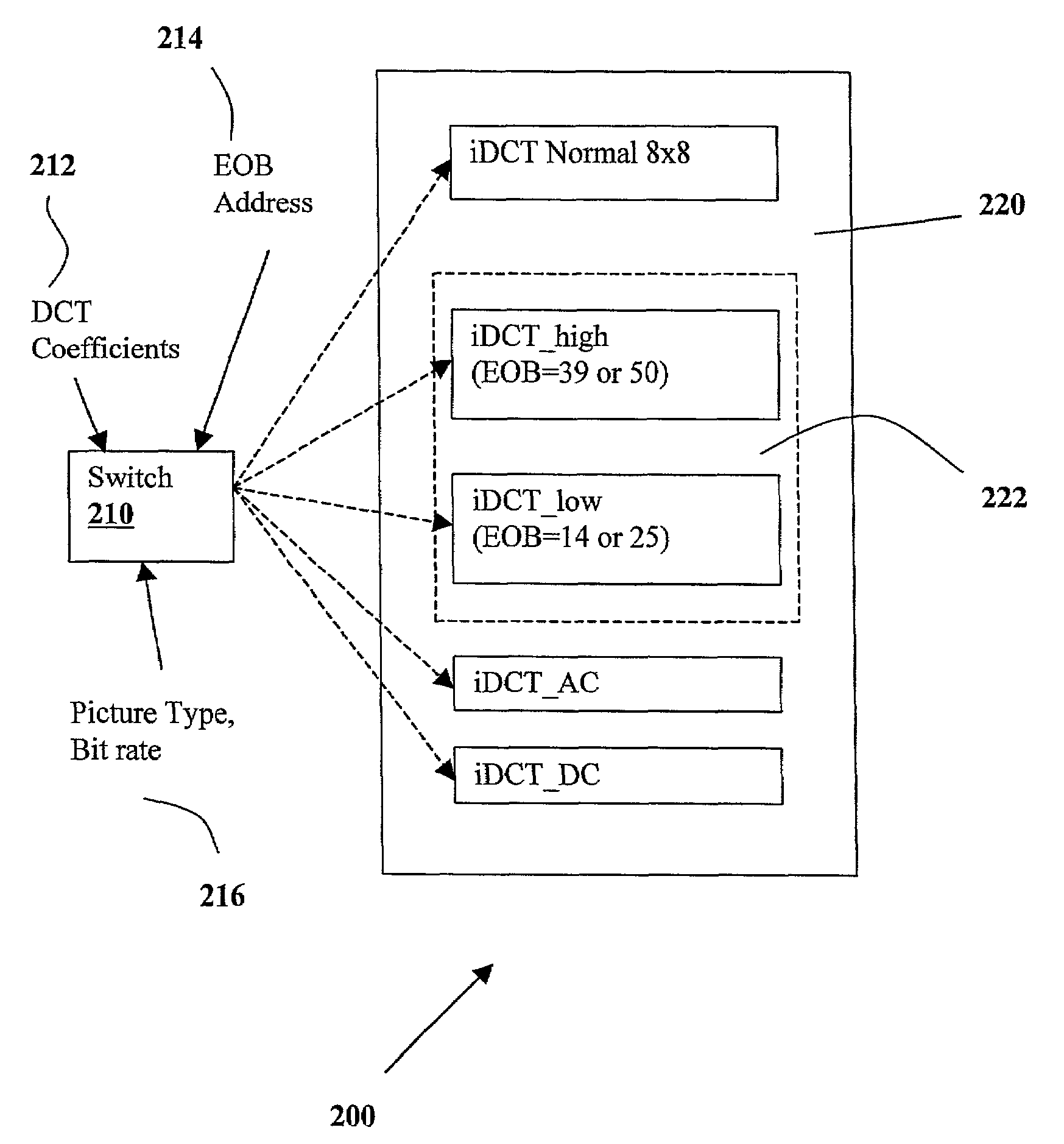
InactiveUS7366236B1Reduction of iDCT execution timeReduced execution timeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSource statisticsVideo quality
This invention discloses a fast two-dimensional inverse Discrete Cosine Transform (iDCT) that adapts to compressed video source statistics to reduce execution time. iDCT algorithms for sparse blocks eliminate calculations for some zero coefficients and are implemented with quad-word parallel single-instruction-multiple-data (SIMD) multimedia instructions. It is observed that end-of-block marker value histograms vary little within single shots. An adaptive control mechanism is proposed that selects the optimal set of iDCTs to prepare for an entire shot from its first frames (to reduce software overheads and penalties). This introduces no degradation of decoded video quality as compared with a conventional SIMD 8×8 iDCT implemented with Intel MMX instructions.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
Aliasing data processing registers
ActiveUS20050172106A1Reduce needHighly flexible accessRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisData processing systemProcessor register
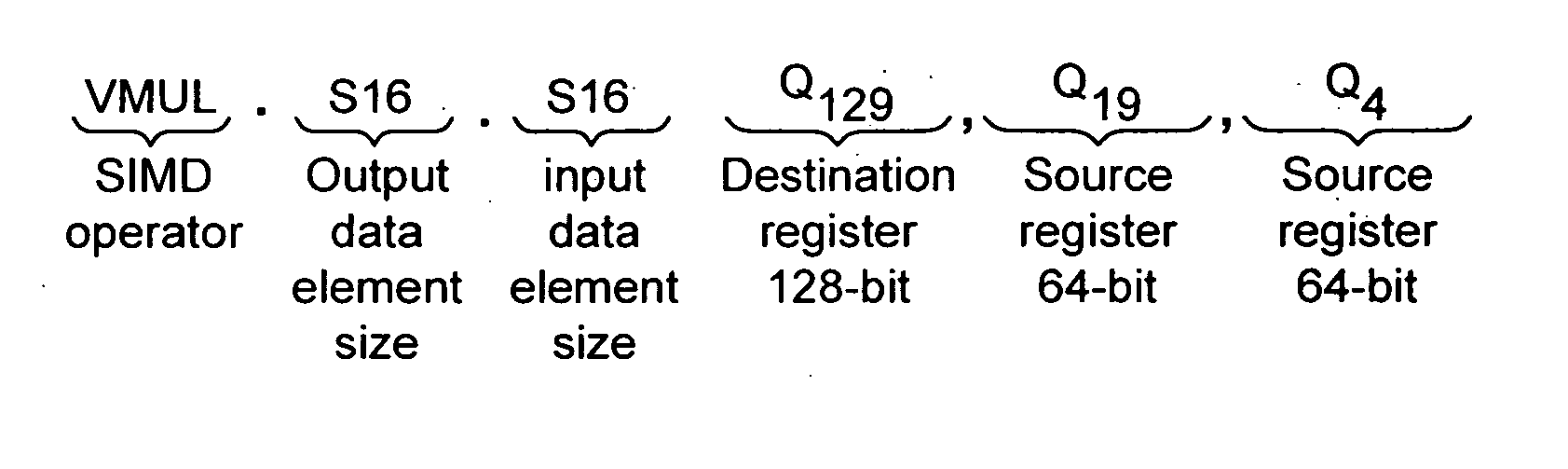
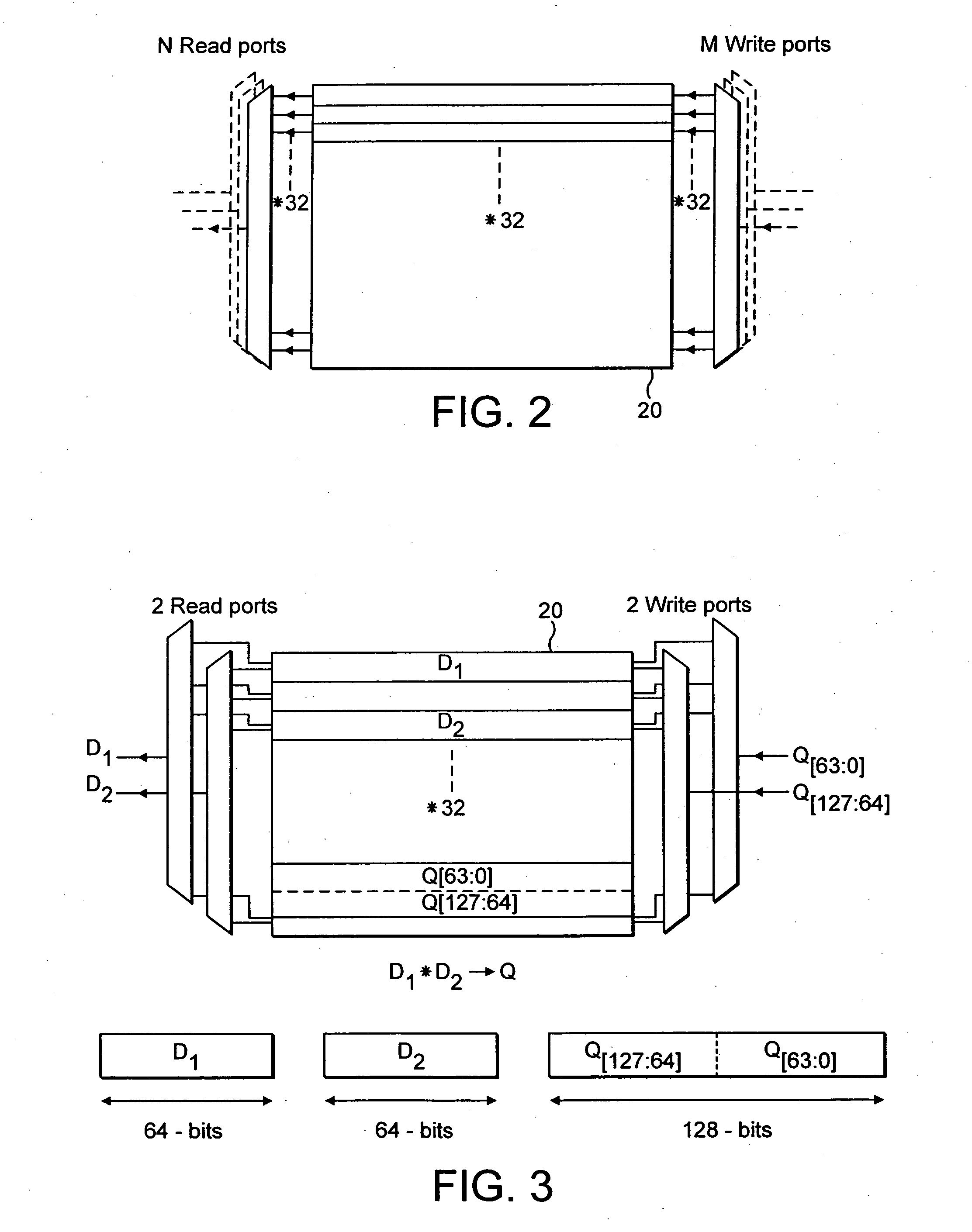
A register data store 20 is provided within a data processing system 2. The register data store 20 may be accessed via registers for which a data processing instruction specifies a register size Q, D and a data element size S16, S8 for the multiple SIMD data elements to be manipulated by that data processing instruction. A given data processing element may be accessed via different registers depending upon the mapping between the register specifier, the register size and the data element size to a particular location within the register data store 20.
Owner:ARM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com