Patents
Literature
448results about "Handling data according to predetermined rules" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
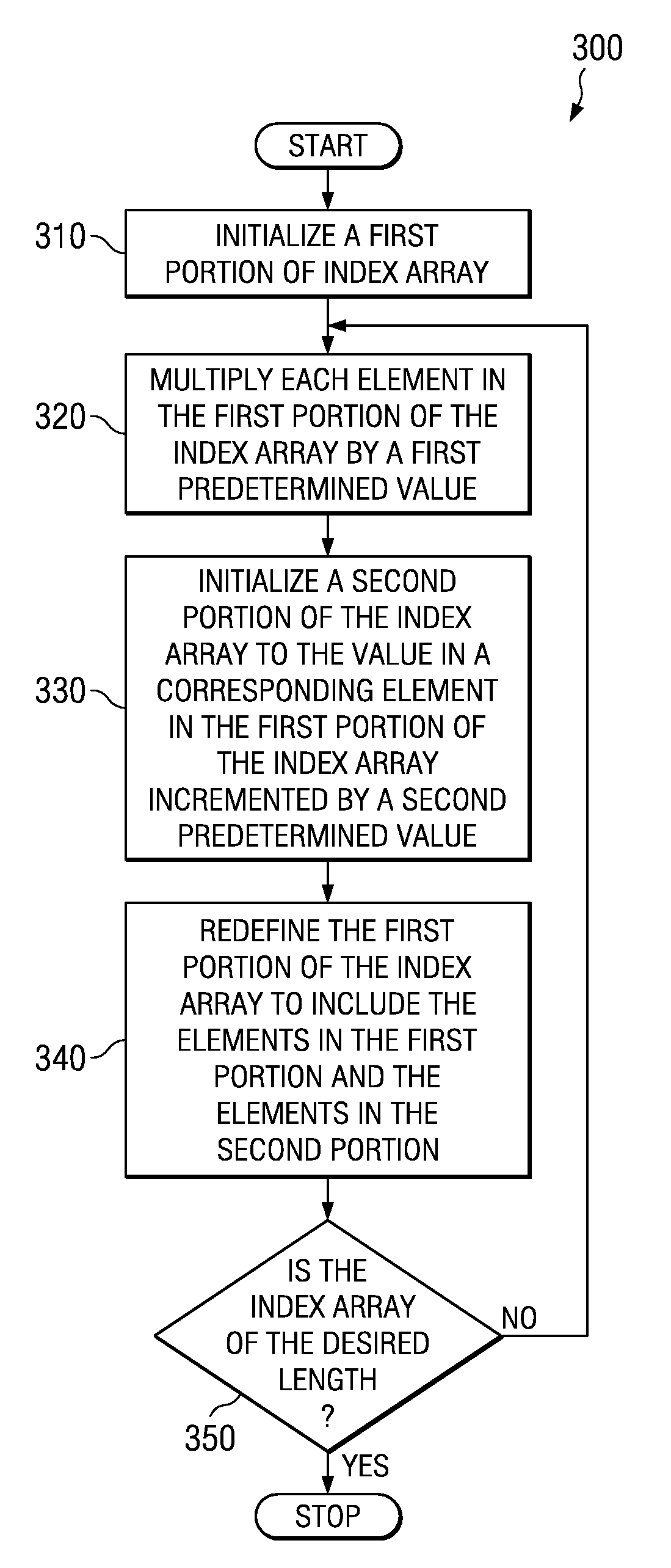
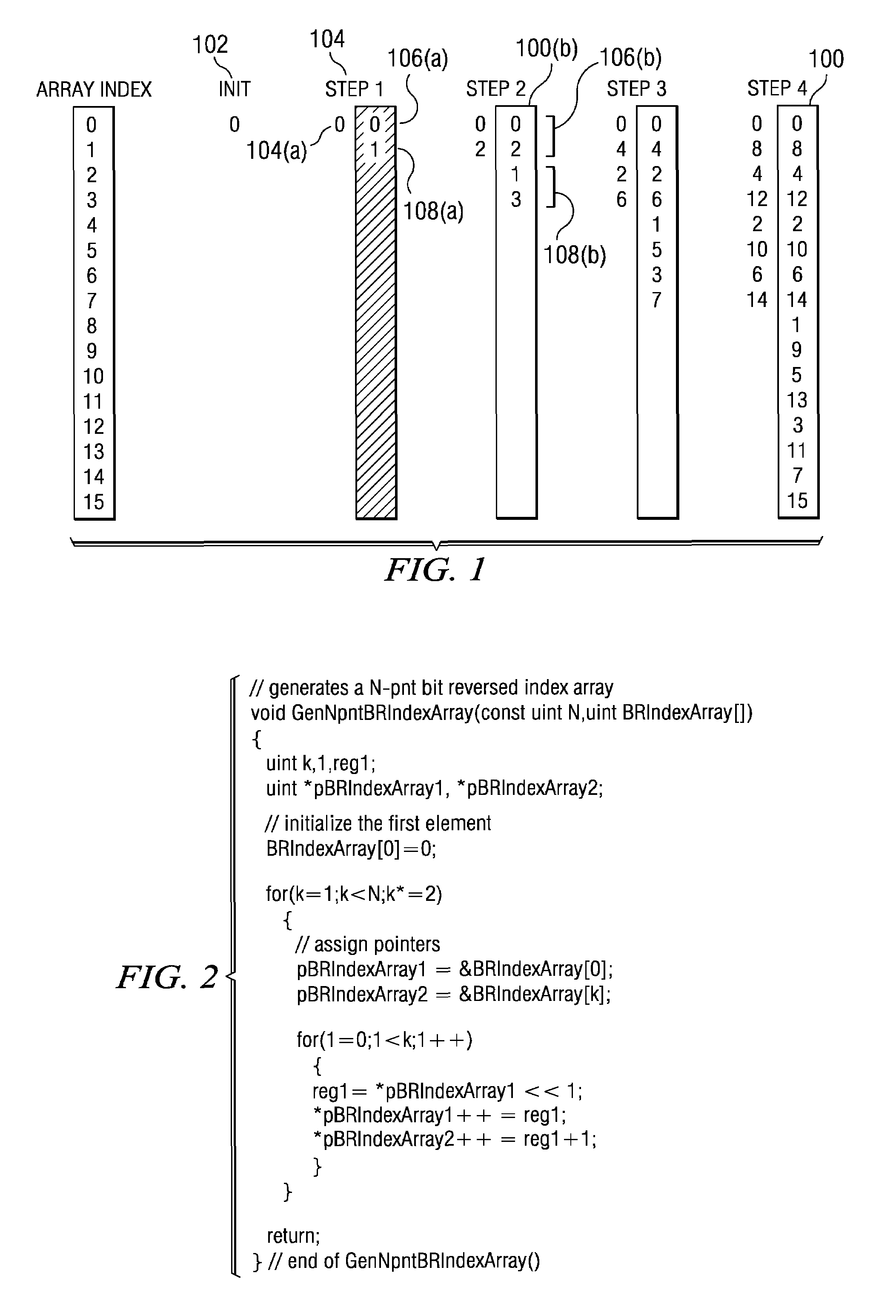
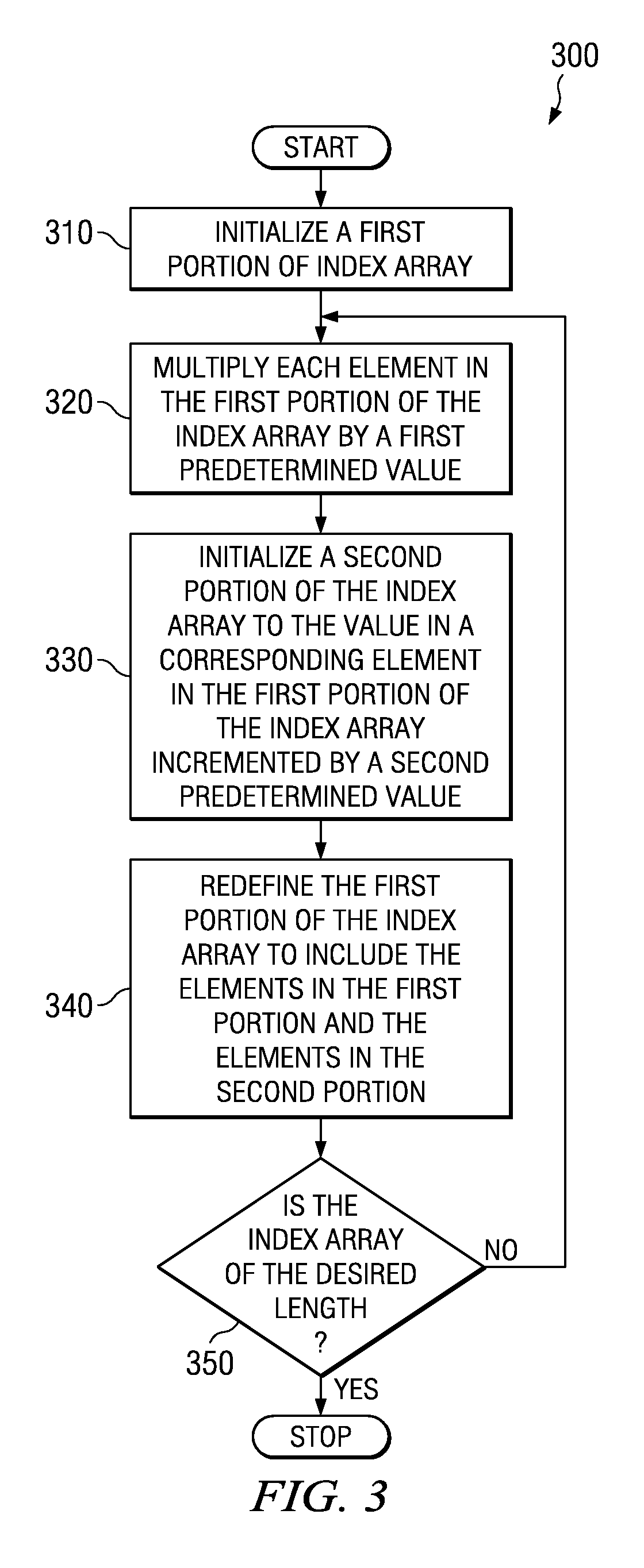
Method of generating a cycle-efficient bit-reverse index array for a wireless communication system
ActiveUS7406494B2Efficient hardwareGenerate efficientlyDigital computer detailsHandling data according to predetermined rulesCommunications systemReverse index
An efficient method of generating a bit-reverse index array in real time without performing any bit manipulation for a wireless communication system.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
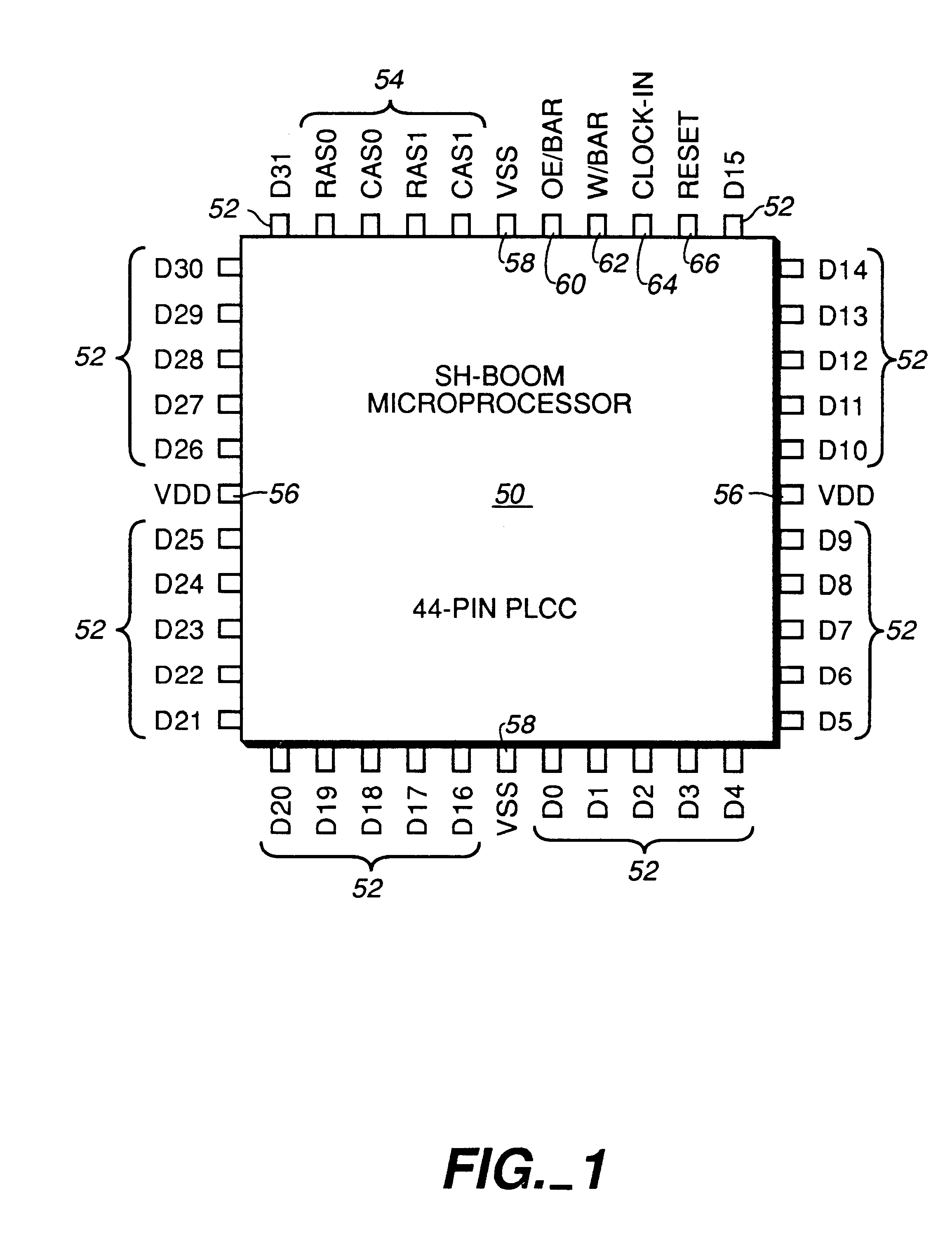
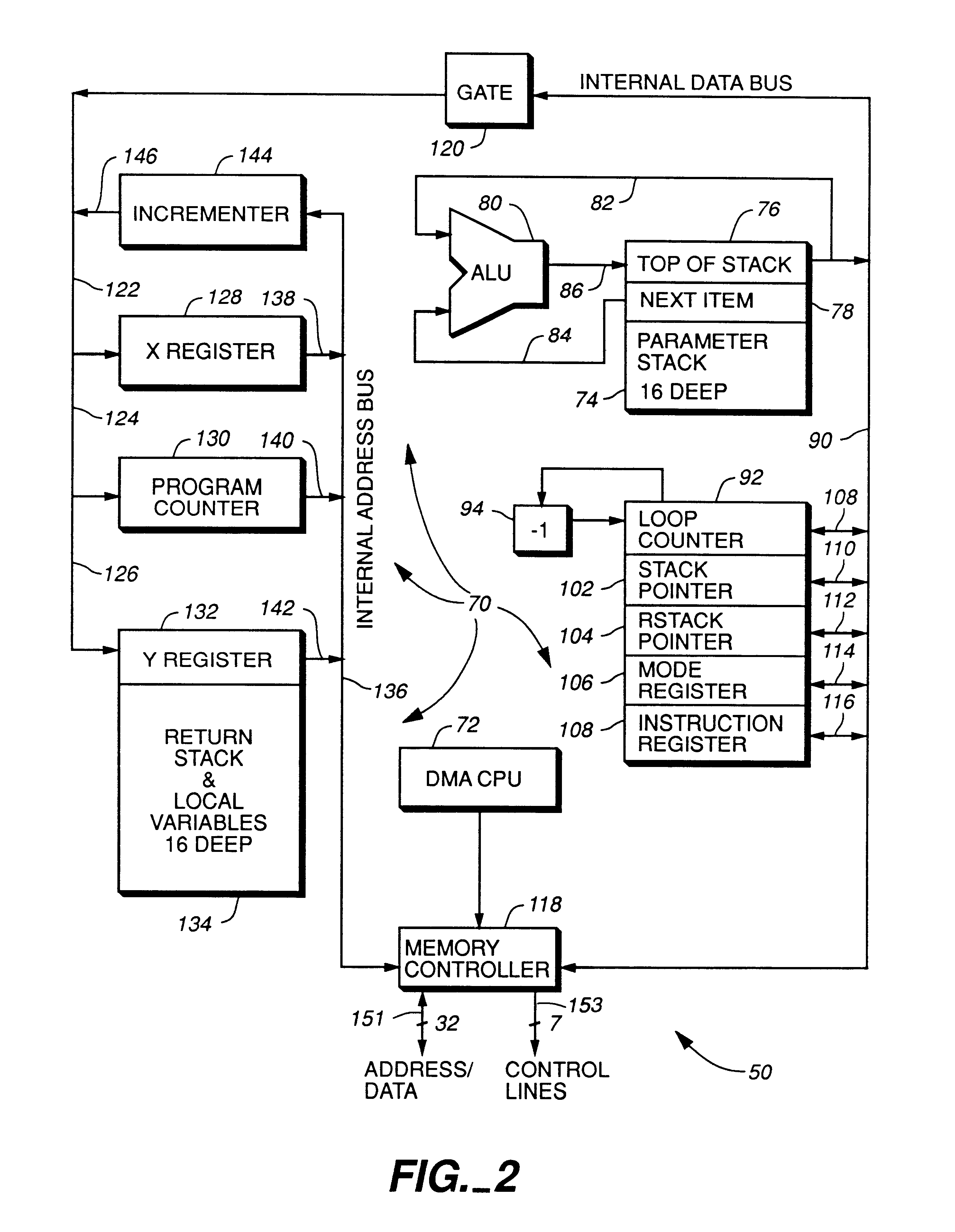
Microprocessors
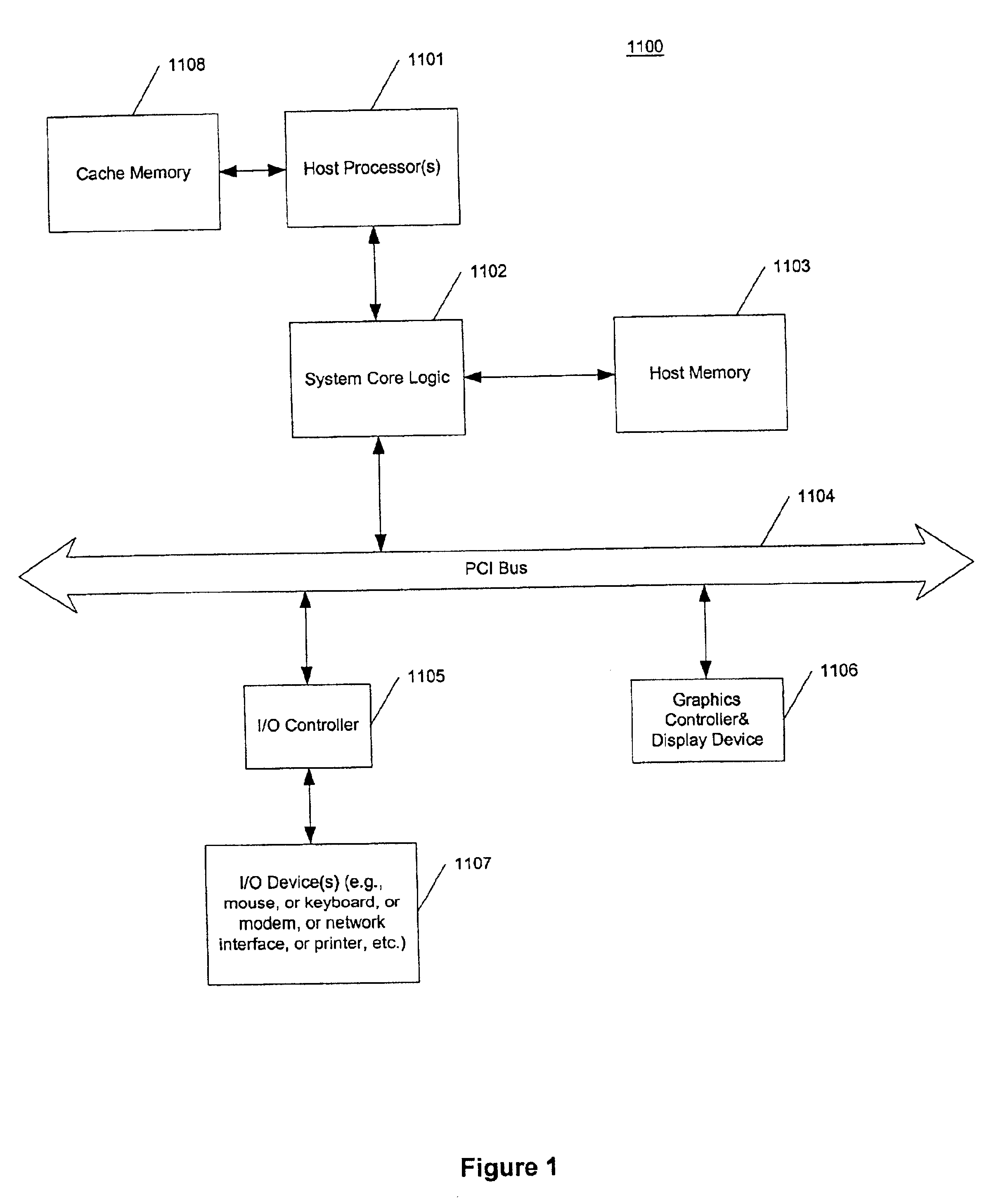
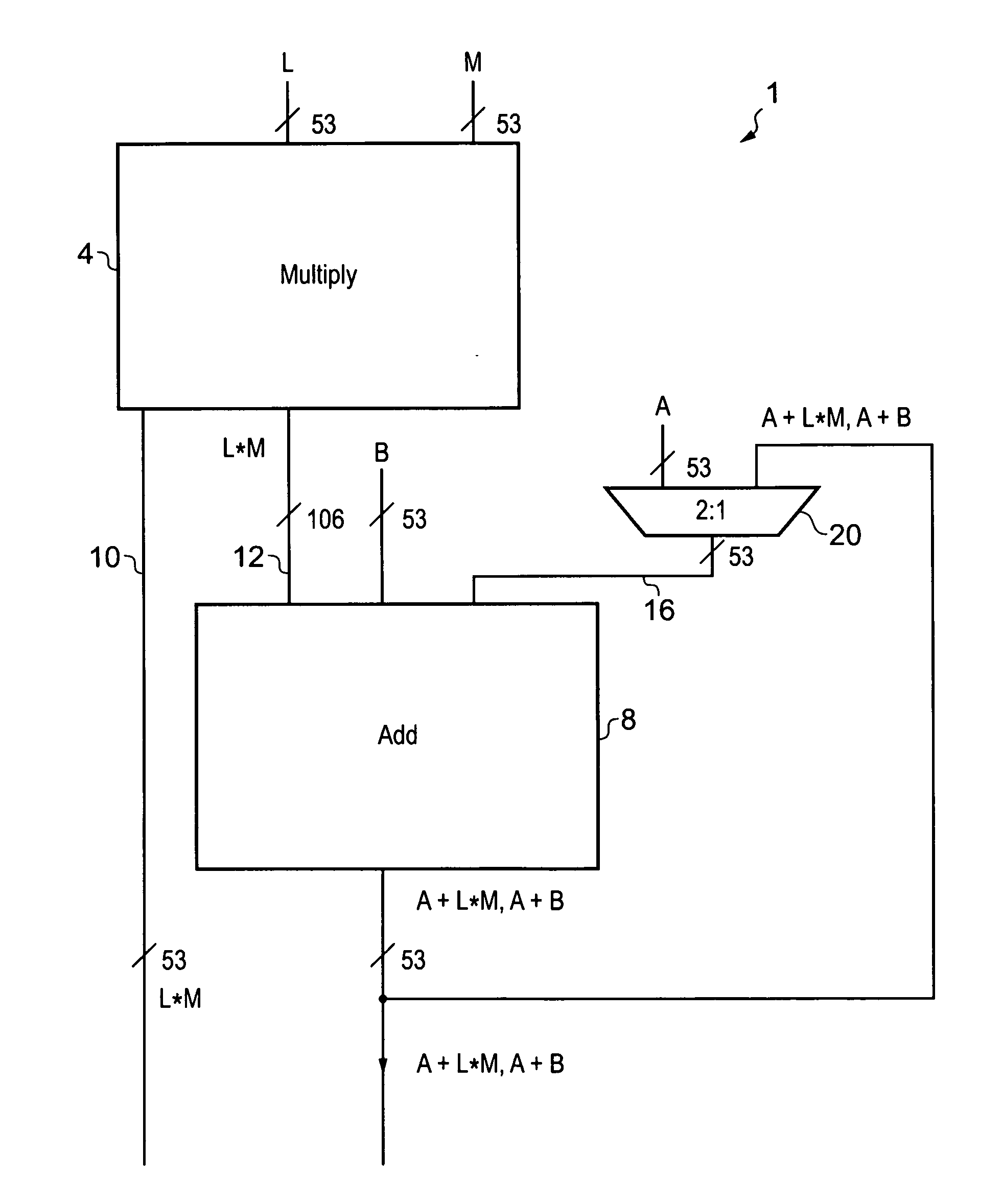
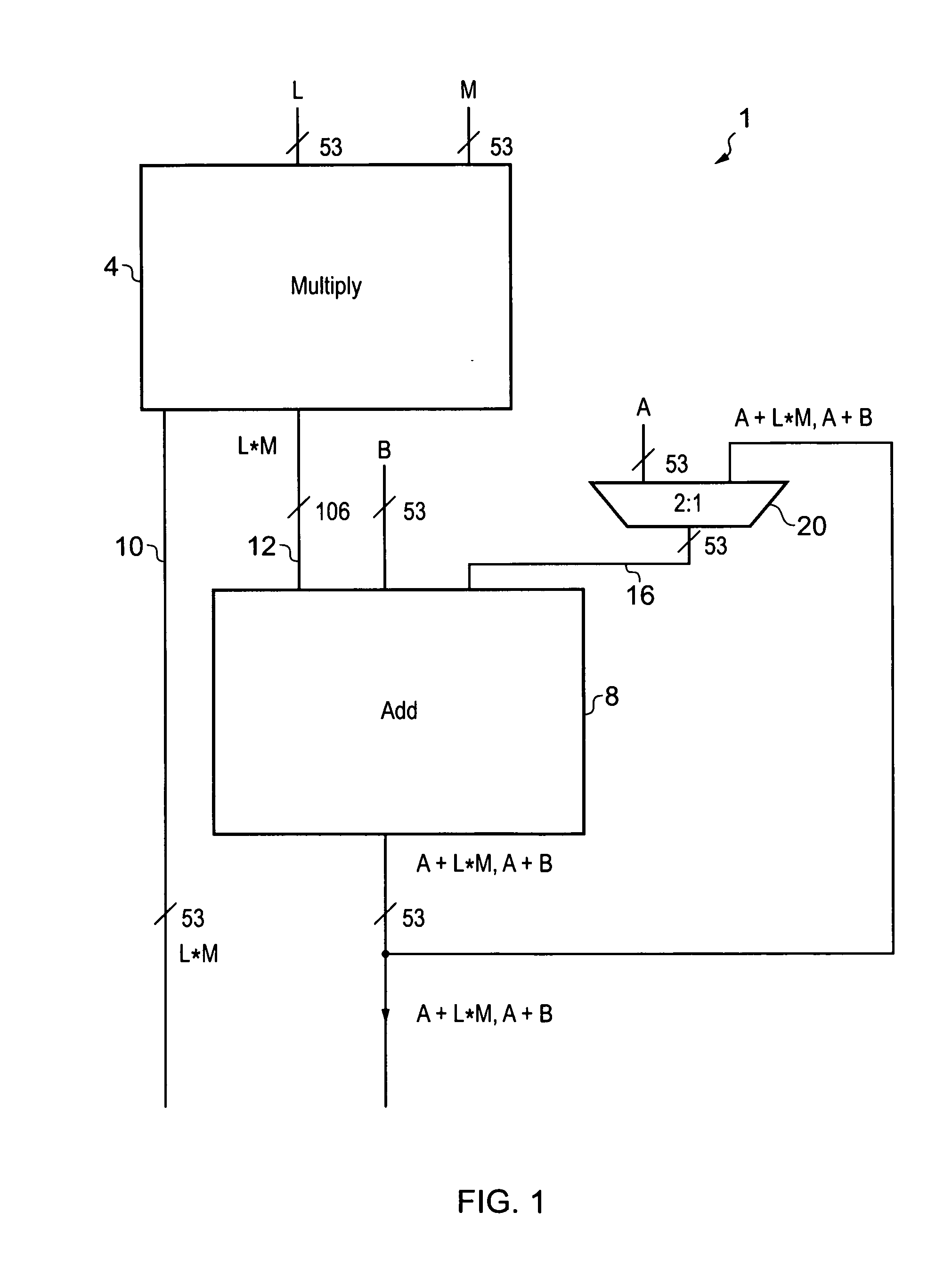
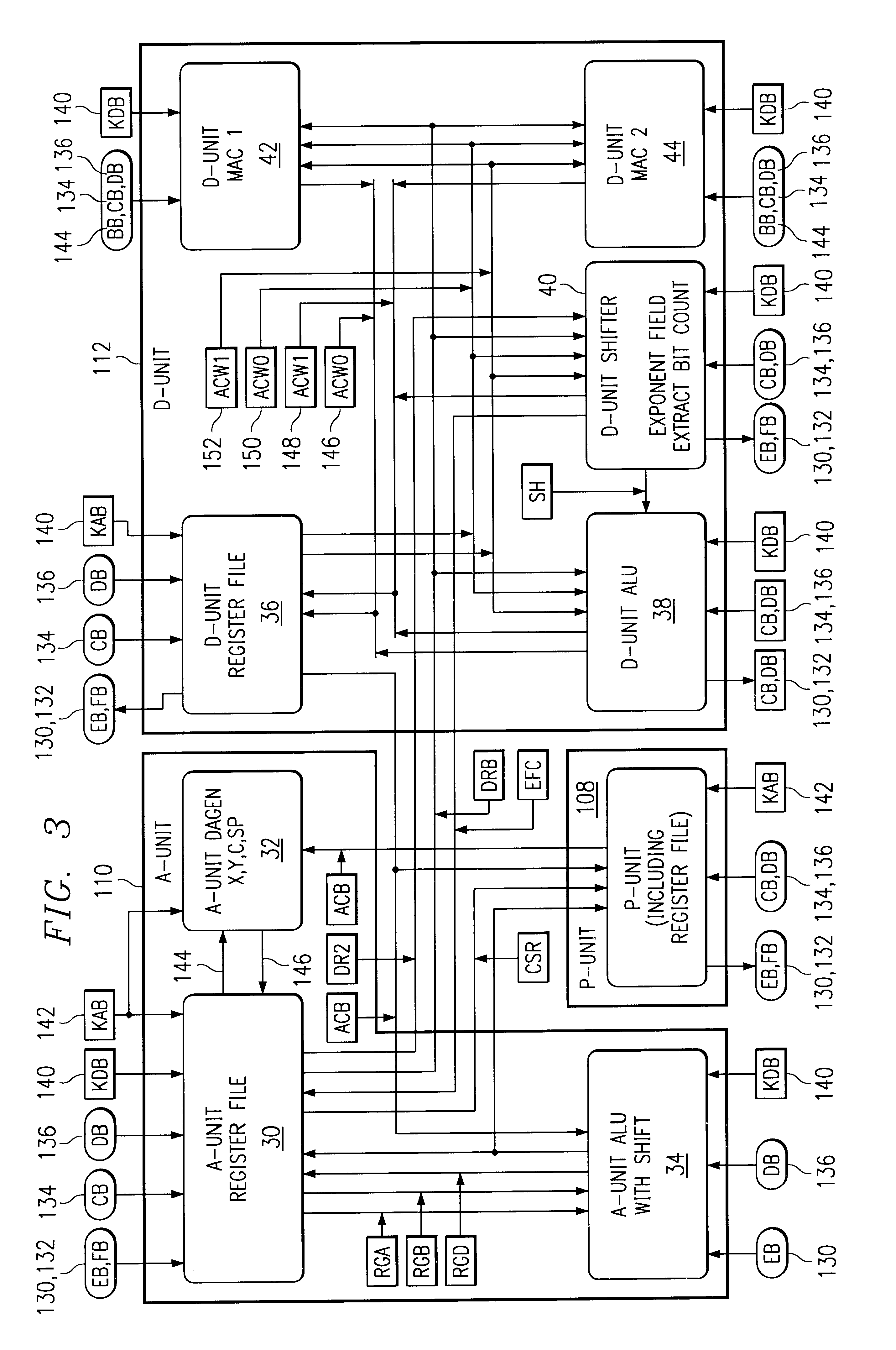
A processor (100) is provided that is a programmable fixed point digital signal processor (DSP) with variable instruction length, offering both high code density and easy programming. Architecture and instruction set are optimized for low power consumption and high efficiency execution of DSP algorithms, such as for wireless telephones, as well as pure control tasks. The processor includes an instruction buffer unit (106), a program flow control unit (108), an address / data flow unit (110), a data computation unit (112), and multiple interconnecting busses. Dual multiply-accumulate blocks improve processing performance. A memory interface unit (104) provides parallel access to data and instruction memories. The instruction buffer is operable to buffer single and compound instructions pending execution thereof. A decode mechanism is configured to decode instructions from the instruction buffer. The use of compound instructions enables effective use of the bandwidth available within the processor. A soft dual memory instruction can be compiled from separate first and second programmed memory instructions. Instructions can be conditionally executed or repeatedly executed. Bit field processing and various addressing modes, such as circular buffer addressing, further support execution of DSP algorithms. The processor includes a multistage execution pipeline with pipeline protection features. Various functional modules can be separately powered down to conserve power. The processor includes emulation and code debugging facilities with support for cache analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High performance microprocessor having variable speed system clock
InactiveUS6598148B1Improve performanceWithout sacrificing microprocessor speedRandom number generatorsInstruction analysisComputer architectureStatic random-access memory
A microprocessor integrated circuit including a processing unit disposed upon an integrated circuit substrate is disclosed herein. The processing unit is designed to operate in accordance with a predefined sequence of program instructions stored within an instruction register. A memory, capable of storing information provided by the processing unit and occupying a larger area of the integrated circuit substrate than the processing unit, is also provided within the microprocessor integrated circuit. The memory may be implemented using, for example dynamic or static random-access memory. A variable output frequency system clock, such as generated by a ring oscillator, is also disposed on the integrated circuit substrate.
Owner:MOORE CHARLES H TTE UTD 03 21 2006 THE EQUINOX TRUST
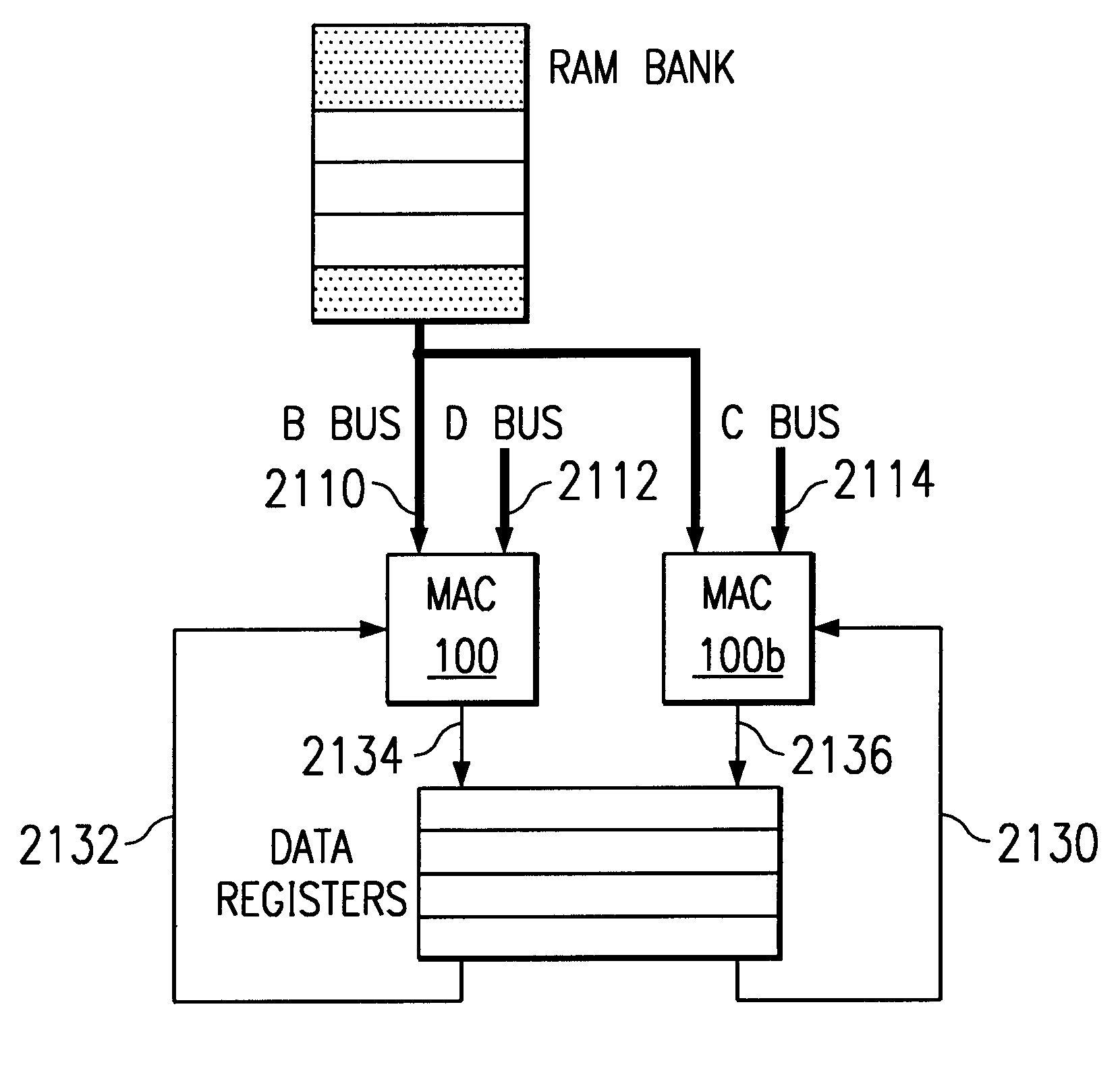
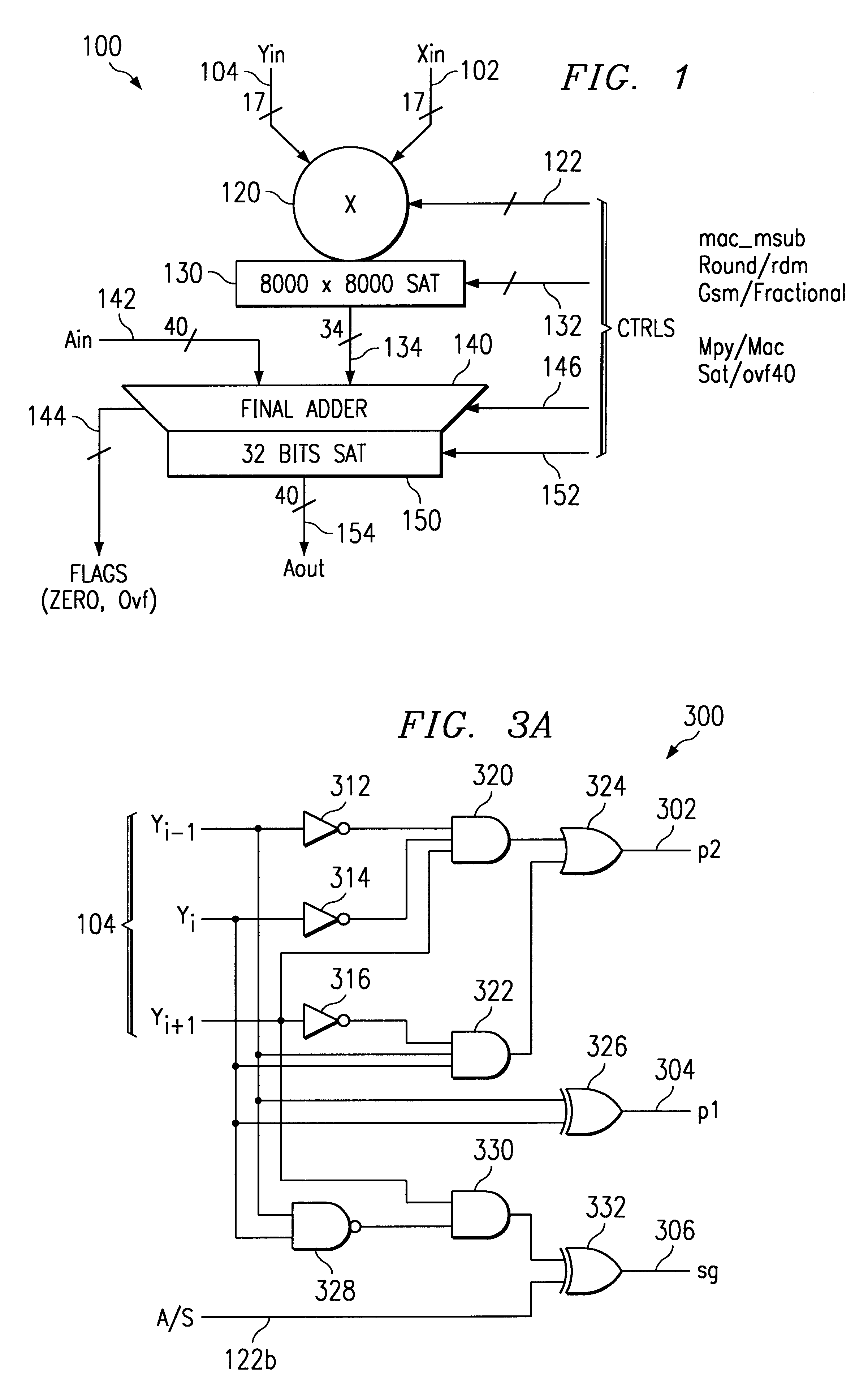
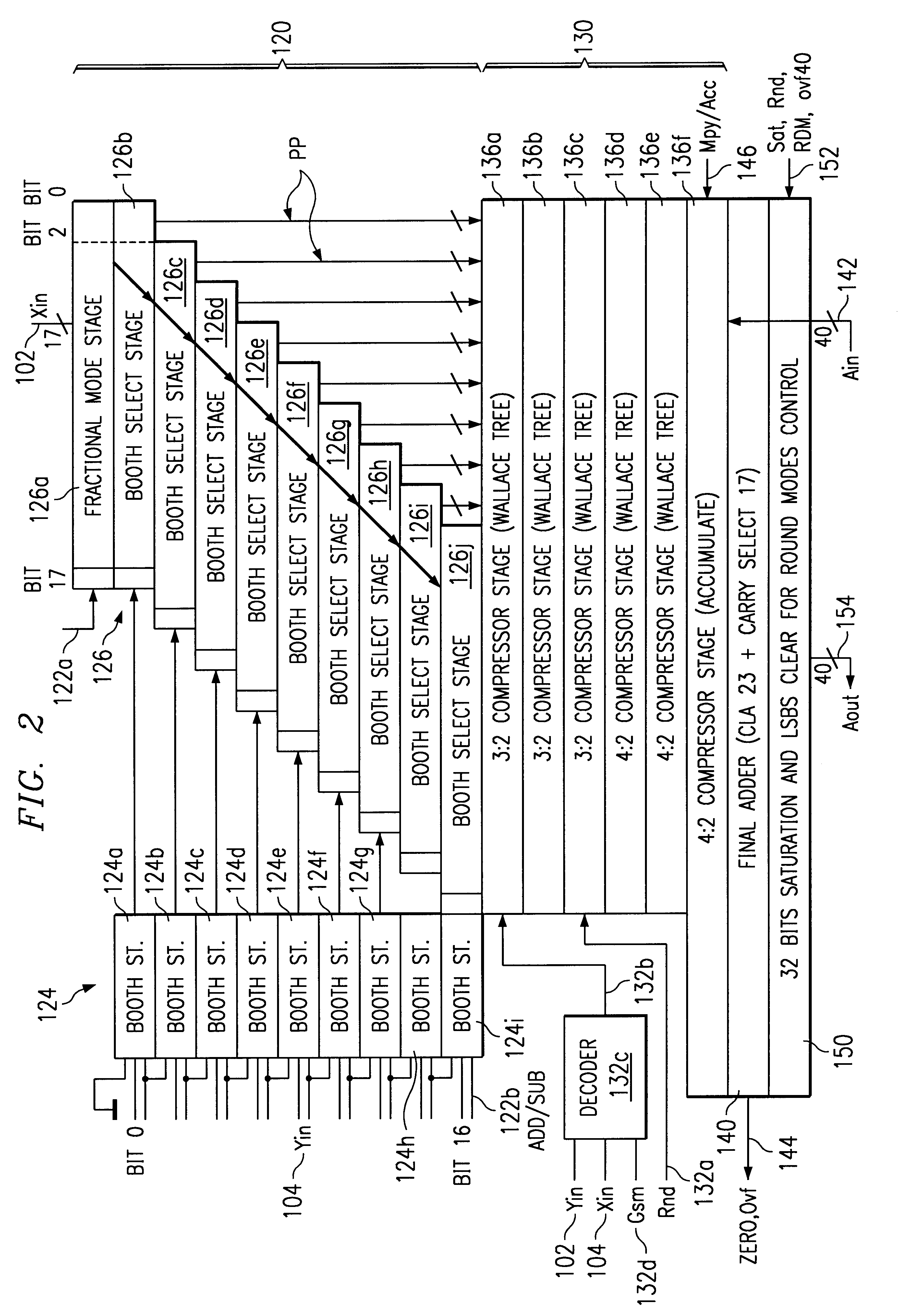
Multiplier accumulator circuits
A multiply-accumulate (MAC) unit, having a first binary operand X, a second binary operand Y, a third binary operand, Booth recode logic for generating a plurality of partial products from said first and second operands, a Wallace tree adder for reducing the partial products and for selectively arithmetically combining the reduced partial products with said third operand, a final adder for generating a final sum, and a saturation circuitry for selectively rounding or saturating said final sum is provided. A dual MAC unit is also provided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
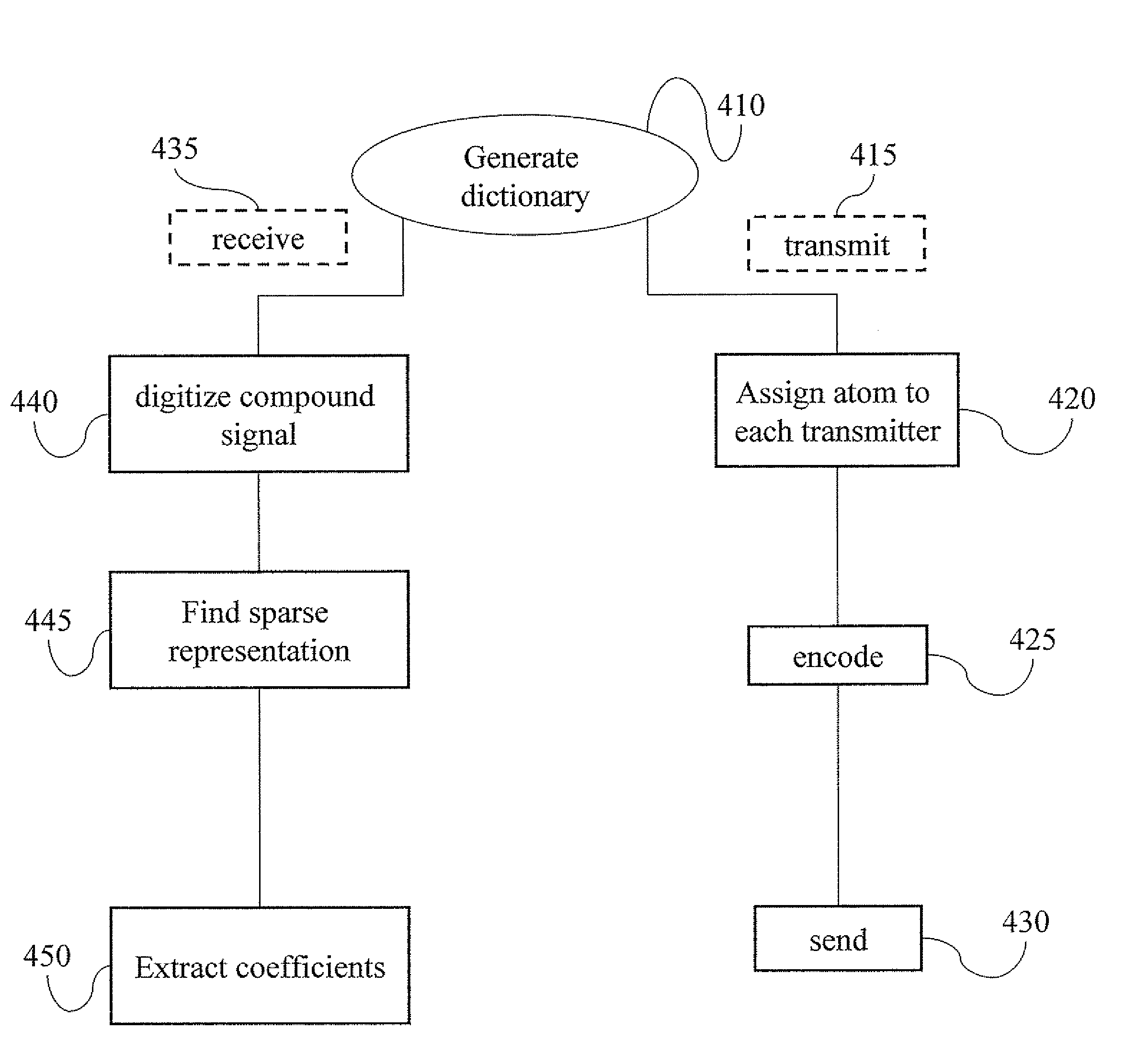
Finite harmonic oscillator
InactiveUS20090204627A1Code conversionHandling data according to predetermined rulesFeature vectorData set
A dictionary at least partially spans a set of discrete q-length signals. The atoms of the dictionary are eigenvectors of a representation of a commutative subgroup of a finite symplectic group. The dictionary may be used for interpreting a radar signal, denoising a signal, compressing data, finding a sparse representation, deblurring at a signal finding a sparse representation of a signal, encoding a signal for communication, encoding a symbol for CDMF communication, classifying a data set and generating a random number.
Owner:SOCHEN NIR ASHER +2
Methods and apparatus for two-dimensional main memory
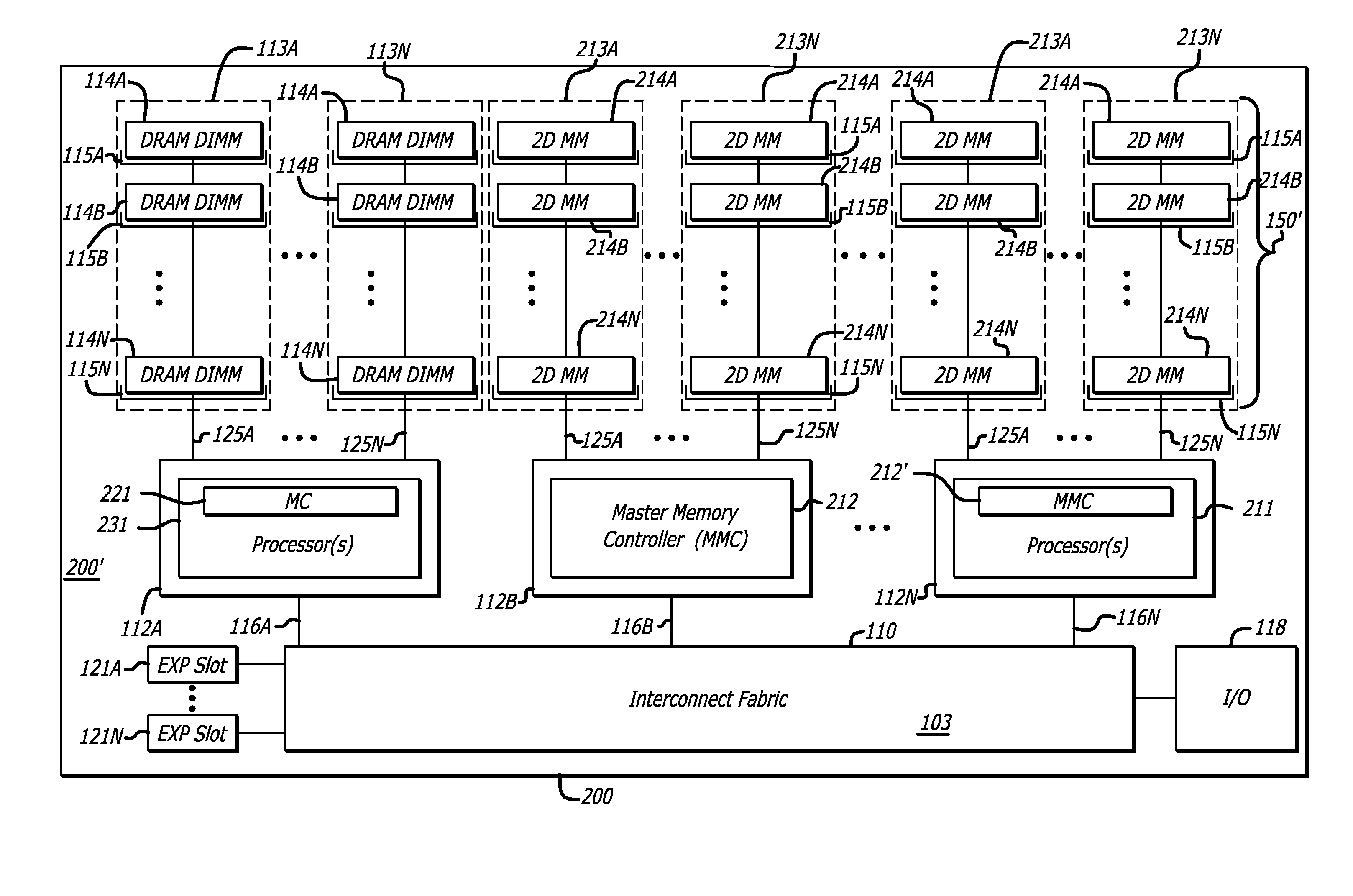
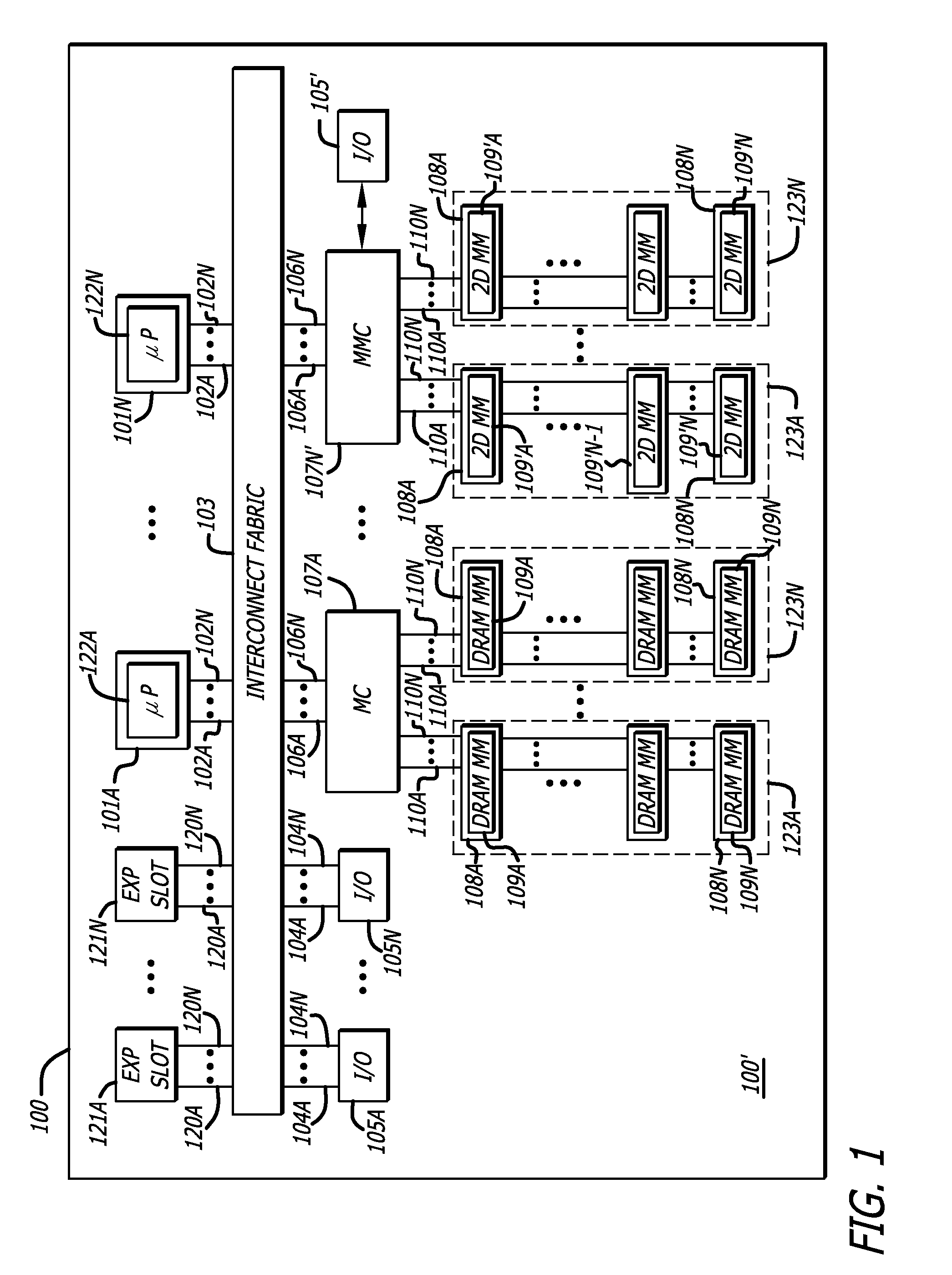
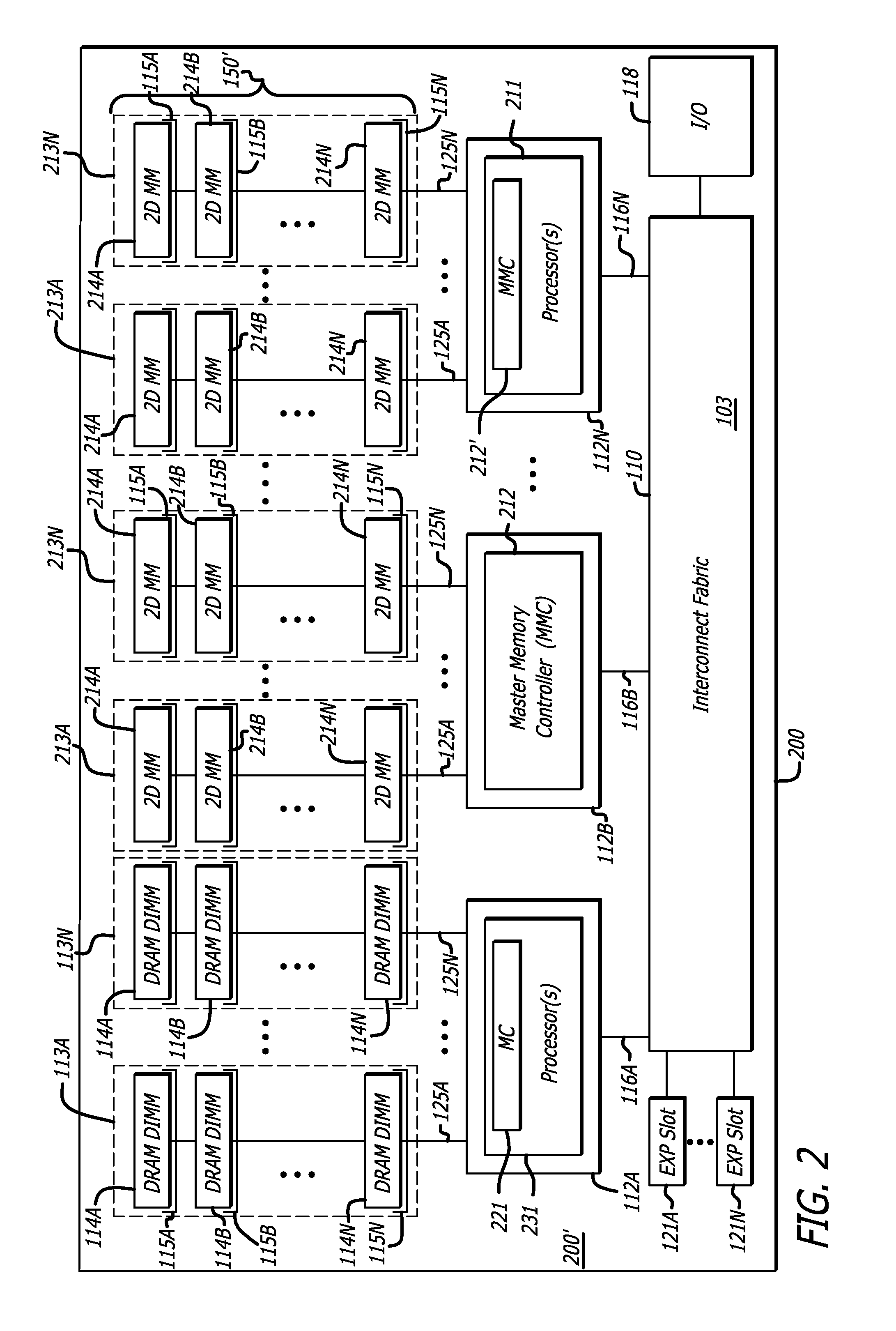
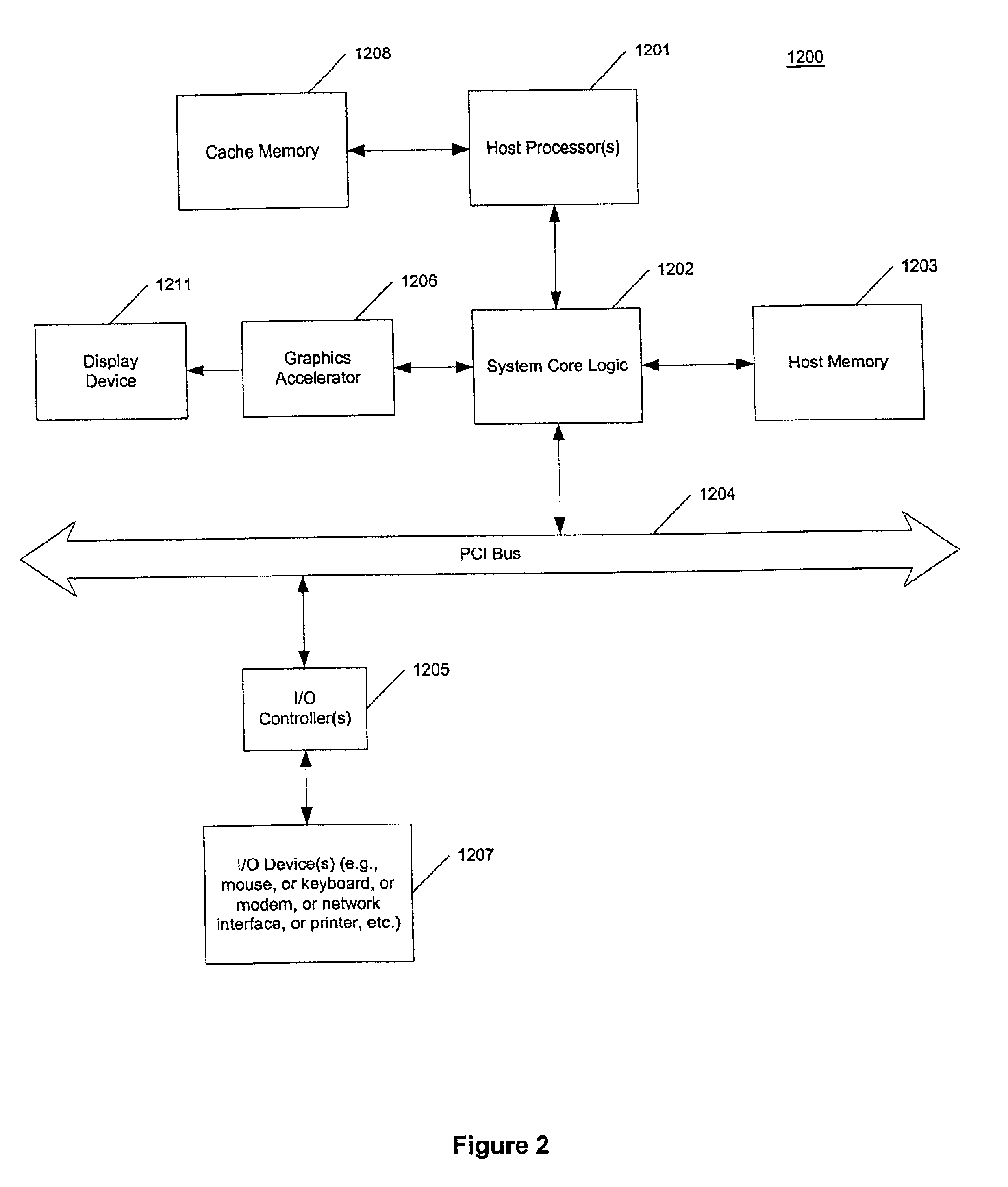
ActiveUS20090254689A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMemory controllerAddress control
In one embodiment of the invention, a memory module is disclosed including a printed circuit board with an edge connector; an address controller coupled to the printed circuit board; and a plurality of memory slices. Each of the plurality of memory slices of the memory module includes one or more memory integrated circuits coupled to the printed circuit board, and a slave memory controller coupled to the printed circuit board and the one or more memory integrated circuits. The slave memory controller receives memory access requests for the memory module from the address controller. The slave memory controller selectively activates one or more of the one or more memory integrated circuits in the respective memory slice in response to the address received from the address controller to read data from or write data into selected memory locations in the memory integrated circuits.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Concurrent shared object implemented using a linked-list with amortized node allocation
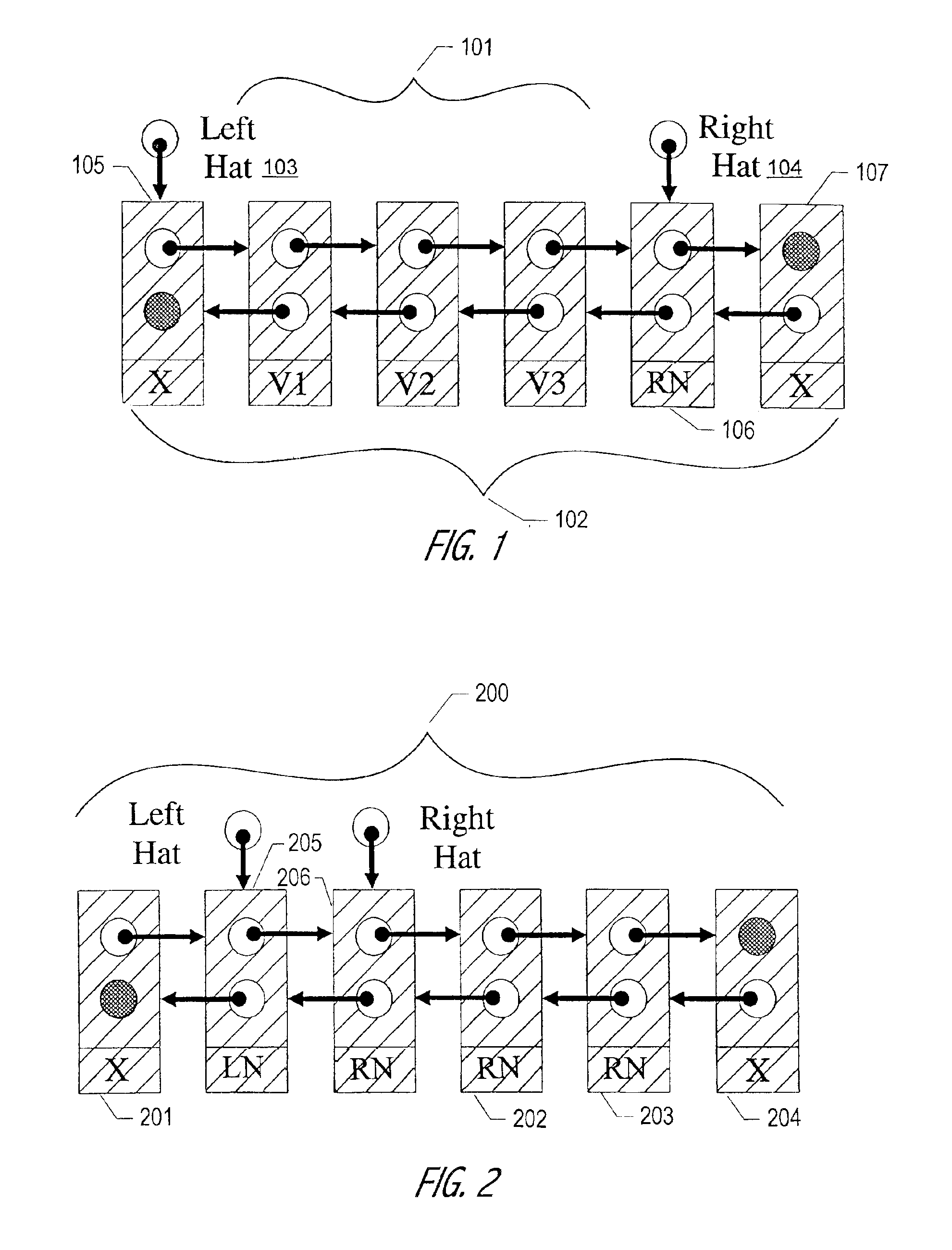
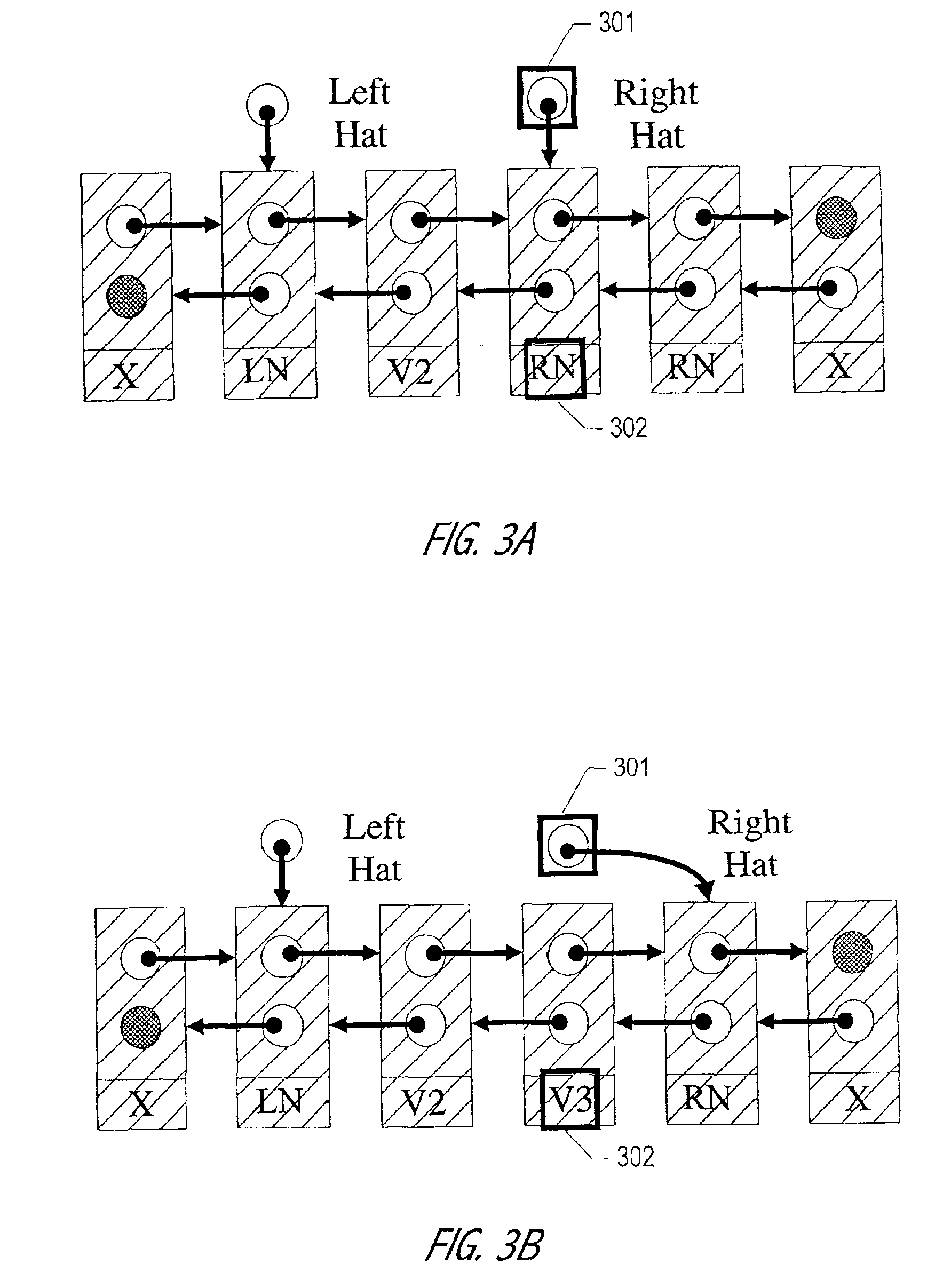
InactiveUS20010047361A1Useful for promotionHandling data according to predetermined rulesMultiprogramming arrangementsGranularityWaste collection
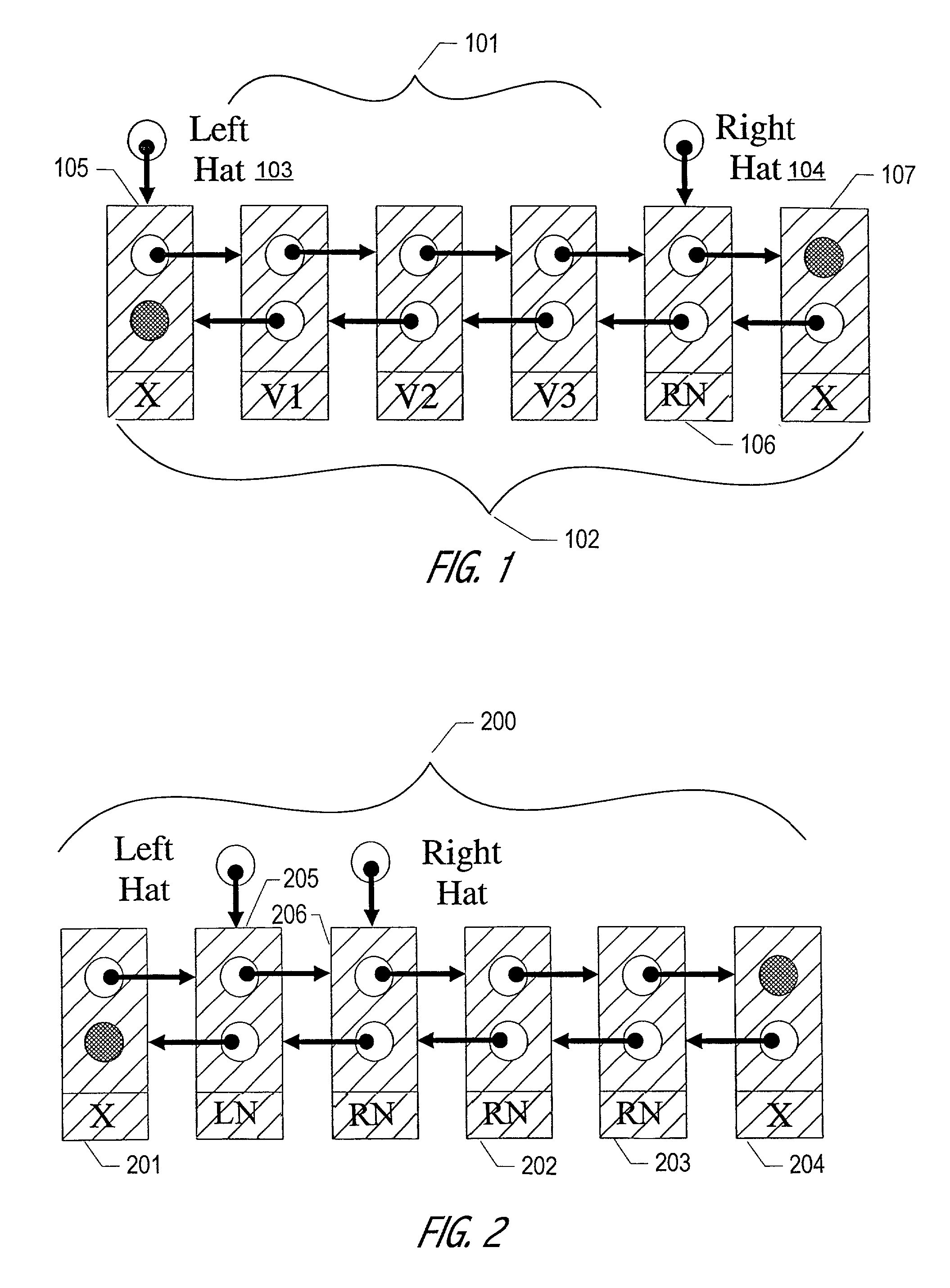
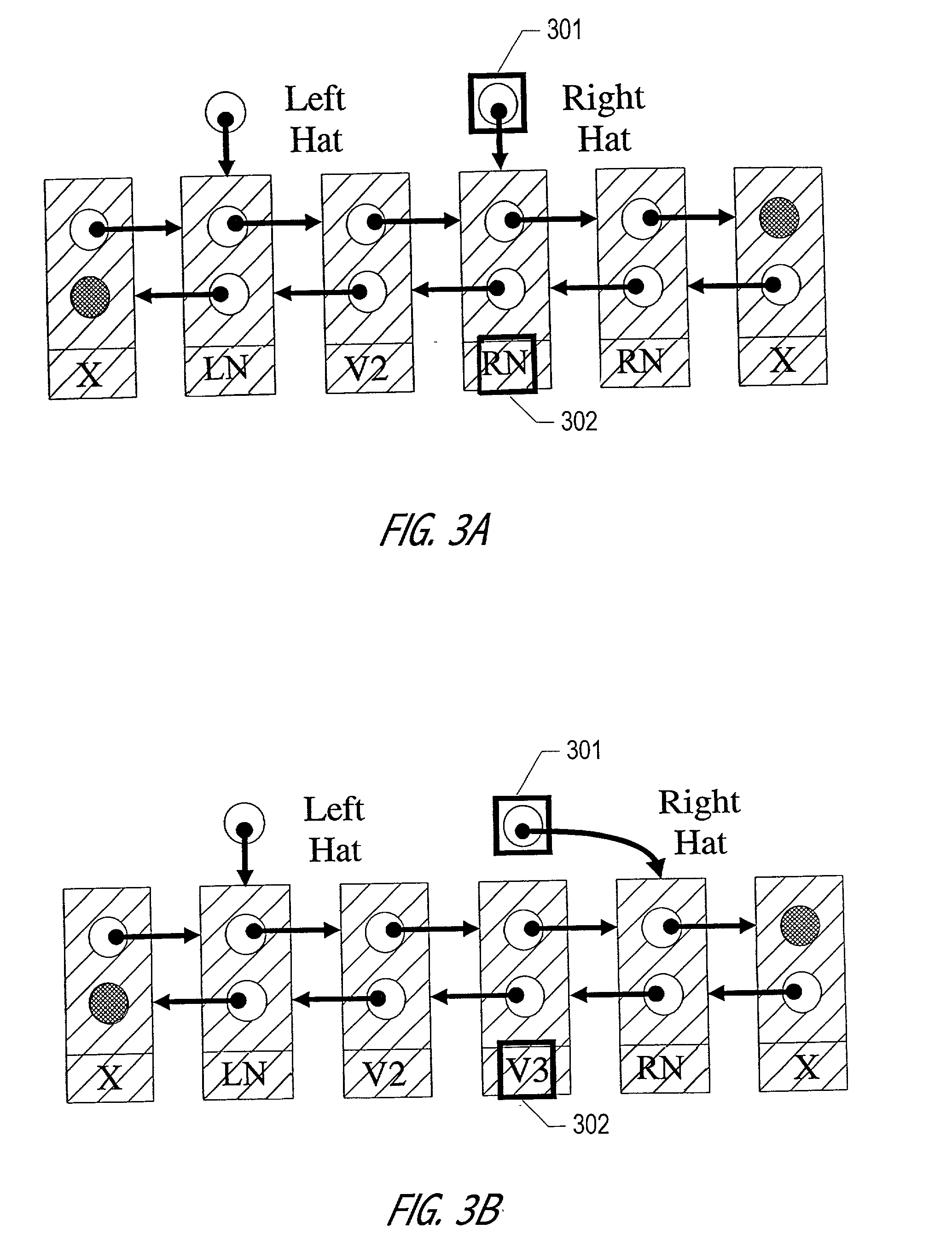
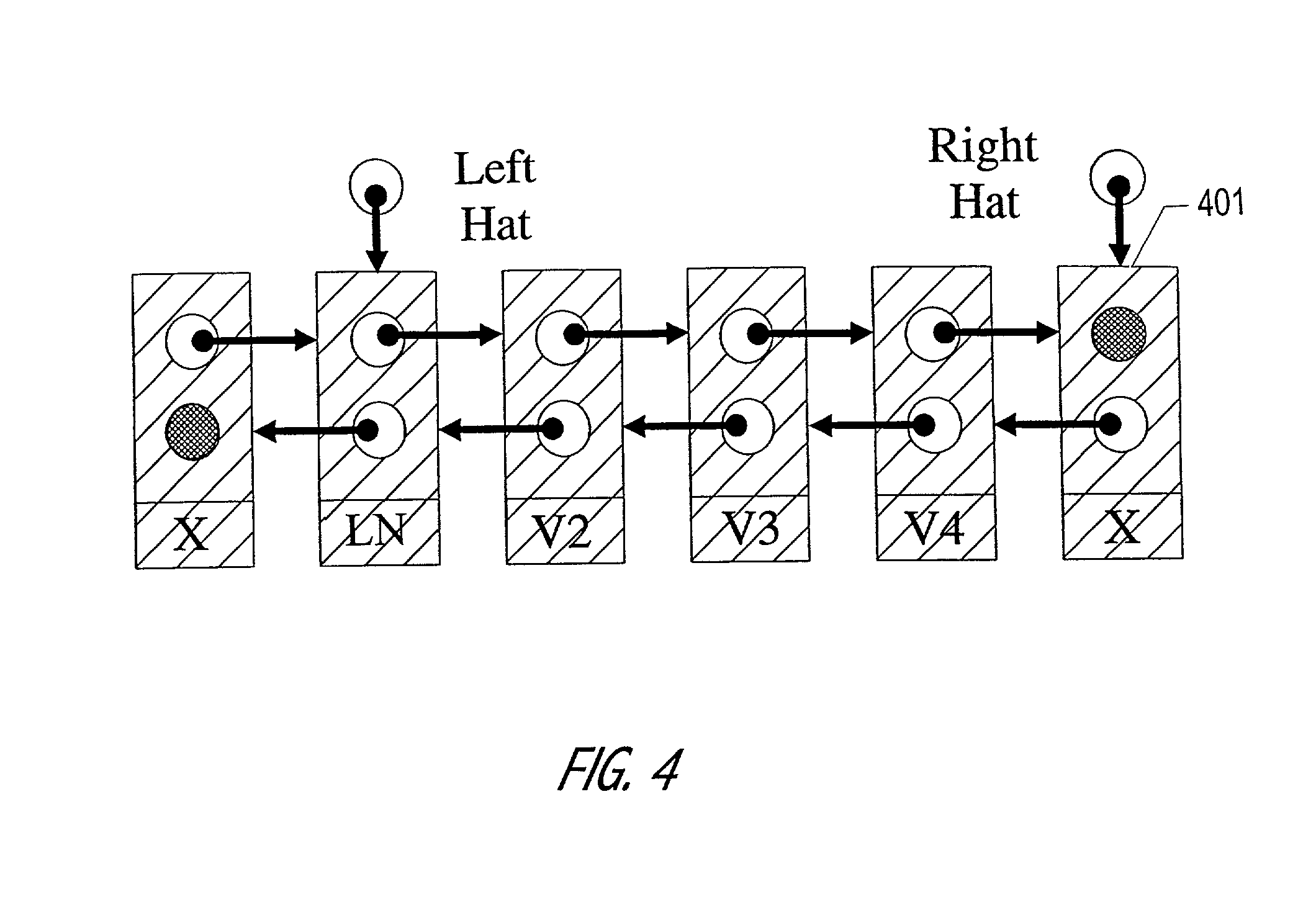
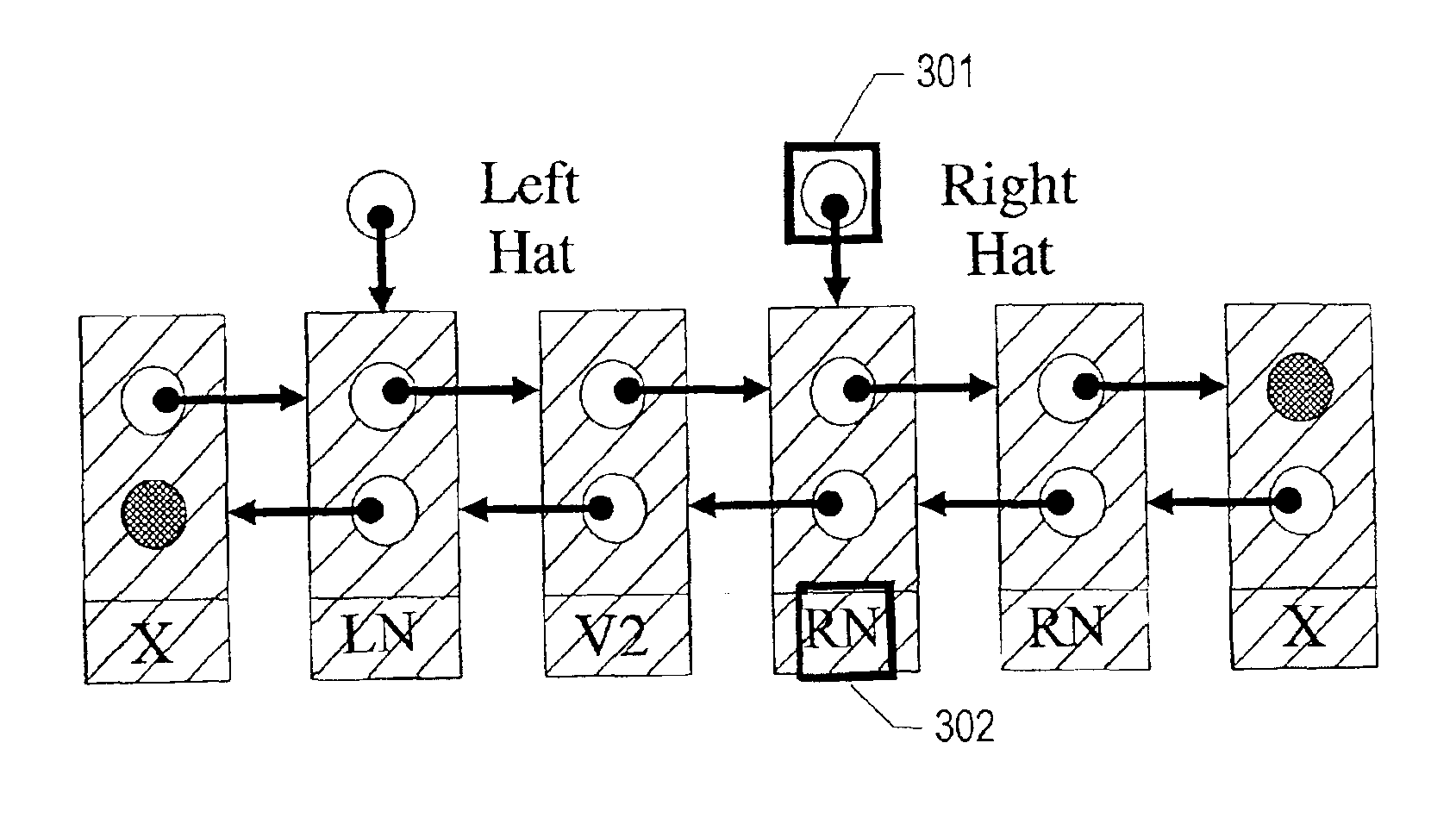
The Hat Trick deque requires only a single DCAS for most pushes and pops. The left and right ends do not interfere with each other until there is one or fewer items in the queue, and then a DCAS adjudicates between competing pops. By choosing a granularity greater than a single node, the user can amortize the costs of adding additional storage over multiple push (and pop) operations that employ the added storage. A suitable removal strategy can provide similar amortization advantages. The technique of leaving spare nodes linked in the structure allows an indefinite number of pushes and pops at a given deque end to proceed without the need to invoke memory allocation or reclamation so long as the difference between the number of pushes and the number of pops remains within given bounds. Both garbage collection dependent and explicit reclamation implementations are described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for matrix transposition
InactiveUS6877020B1Handling data according to predetermined rulesComplex mathematical operationsComputer scienceRotation matrix
Owner:APPLE INC
Video manager and organizer
ActiveUS20080172615A1Large inventoryTelevision system detailsMetadata video data retrievalHyperlinkWeb page
An online video search system, including a tag discoverer including a web encyclopedia crawler for (i) accessing a web encyclopedia to find web pages related to at least one designated reference topic, and (ii) retrieving a plurality of web pages by performing an n-level depth recursive traversal of the web pages found, and web pages that are hyper-linked thereto, a concept extractor for extracting important concepts founds in the retrieved plurality of web pages, and a user interface for providing at least of the important concepts extracted by the web page processor to an online video search engine. A method and a computer-readable storage medium are also described and claimed.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
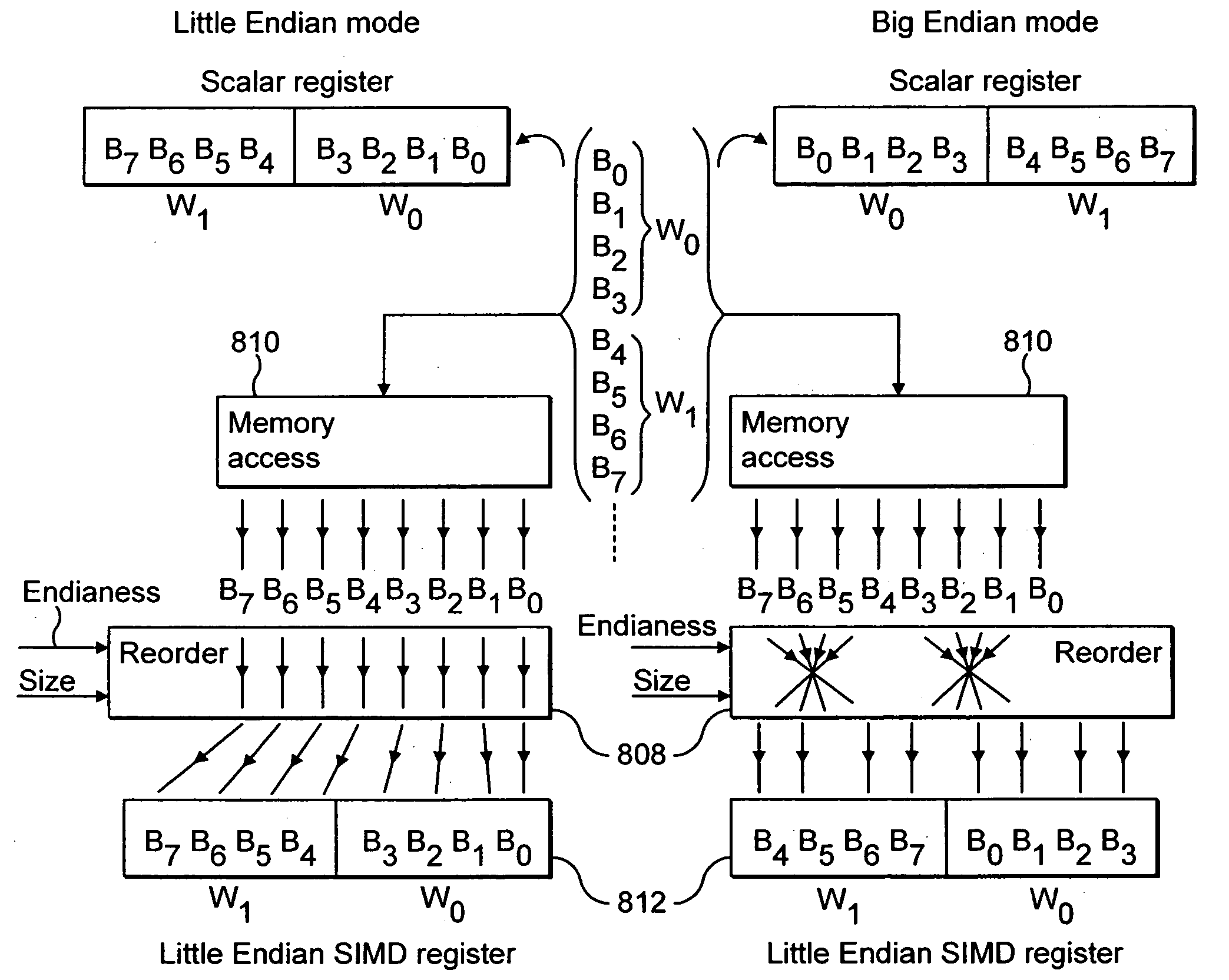
Endianess compensation within a SIMD data processing system
InactiveUS20050125647A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsHandling data according to predetermined rulesData processing systemEndianness
A memory system can store data in either a big endian mode or a little endian mode. Memory accessing logic 810 utilises byte invariant addressing to retrieve multiple data elements from that memory to be stored within a SIMD register 812. Data element reordering logic 808 is responsive to an endianess mode specifying signal and a data element size specifying signal to reorder retrieved bytes such that the data elements when stored within the SIMD registers 812 are invariant irrespective of the endianess mode being used by the memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
Apparatus and method used for executing matrix multiplication operation
ActiveCN107315574ADigital computer detailsHandling data according to predetermined rulesMatrix multiplicationControl unit
The invention discloses an apparatus and a method used for executing matrix multiplication operation. The apparatus is characterized by comprising a storage unit used for storing matrix data related with a matrix operation instruction, a register unit used for storing scalar data related with the matrix operation instruction, a control unit used for decoding the matrix operation instruction and controlling an operation process of the matrix operation instruction, and a matrix operation unit used for performing the matrix multiplication operation on an input matrix according to the decoded matrix operation instruction, wherein the matrix operation unit is a customized hardware circuit.
Owner:ANHUI CAMBRICON INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for producing an index vector for use in performing a vector permute operation
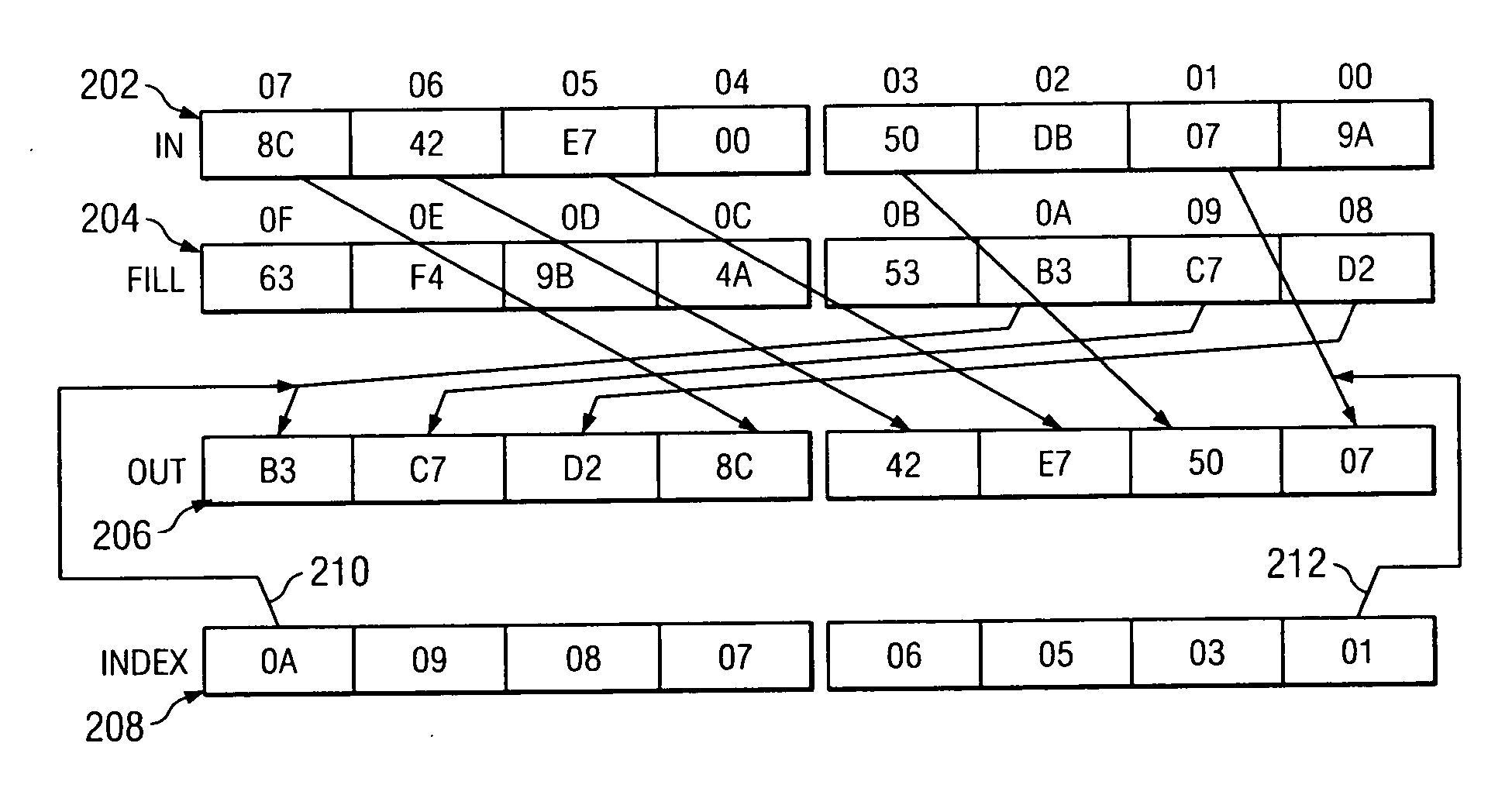
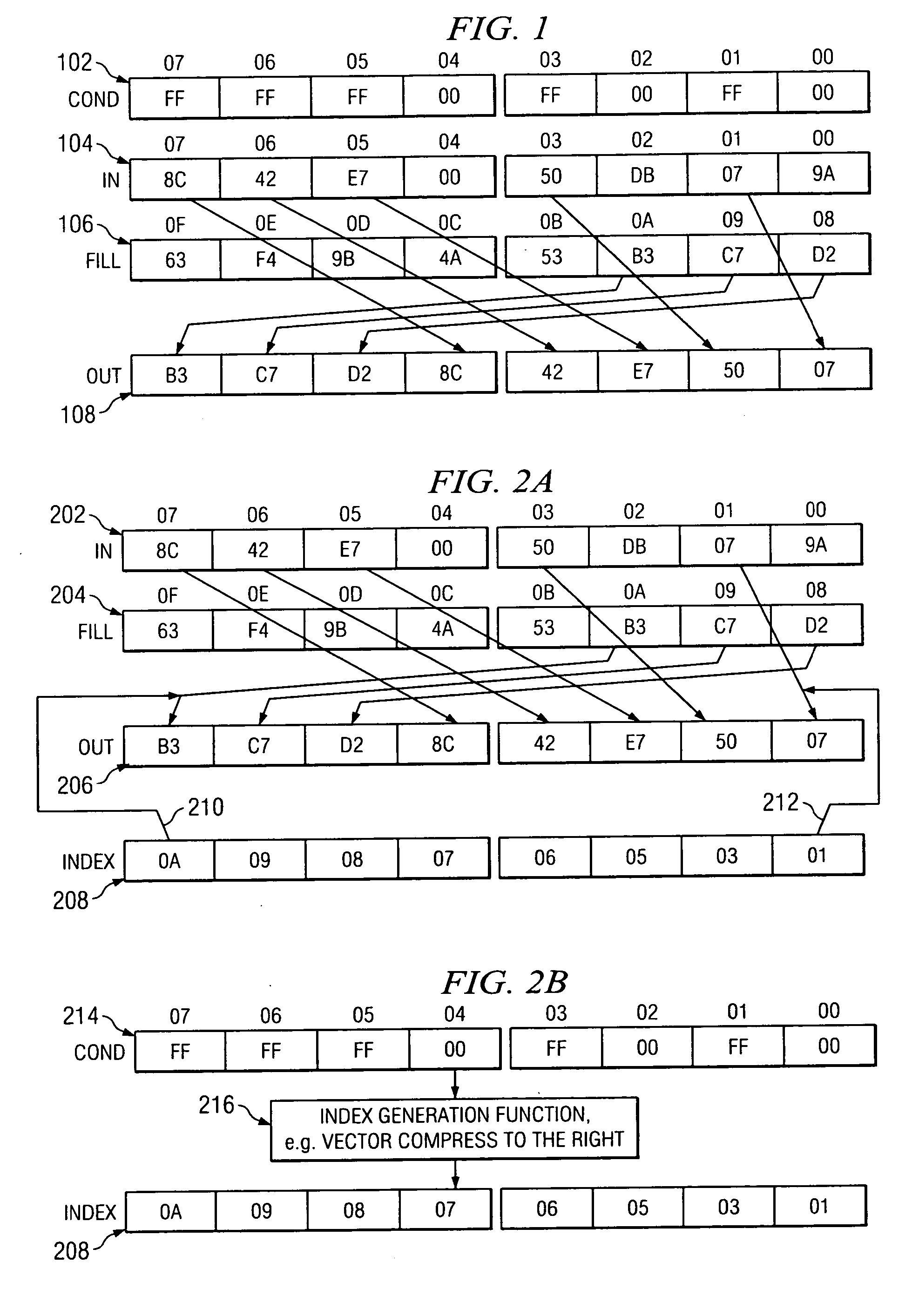
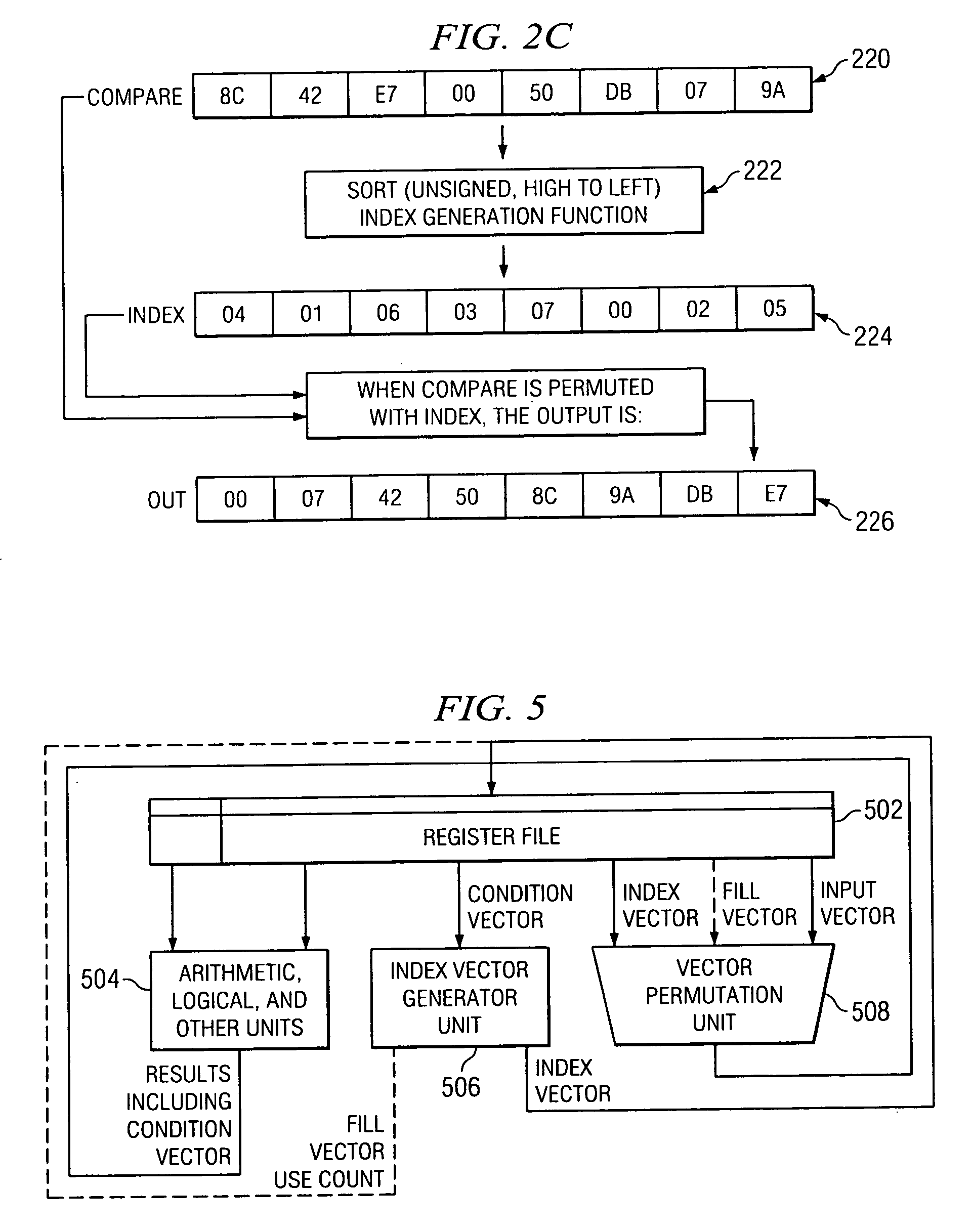
ActiveUS20060184765A1Handling data according to predetermined rulesGeneral purpose stored program computerTheoretical computer scienceVector generation
A method for generating a permutation index vector includes receiving a condition vector and performing an index generation function using the condition vector in order to generate the permutation index vector. An index vector generation circuit is also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
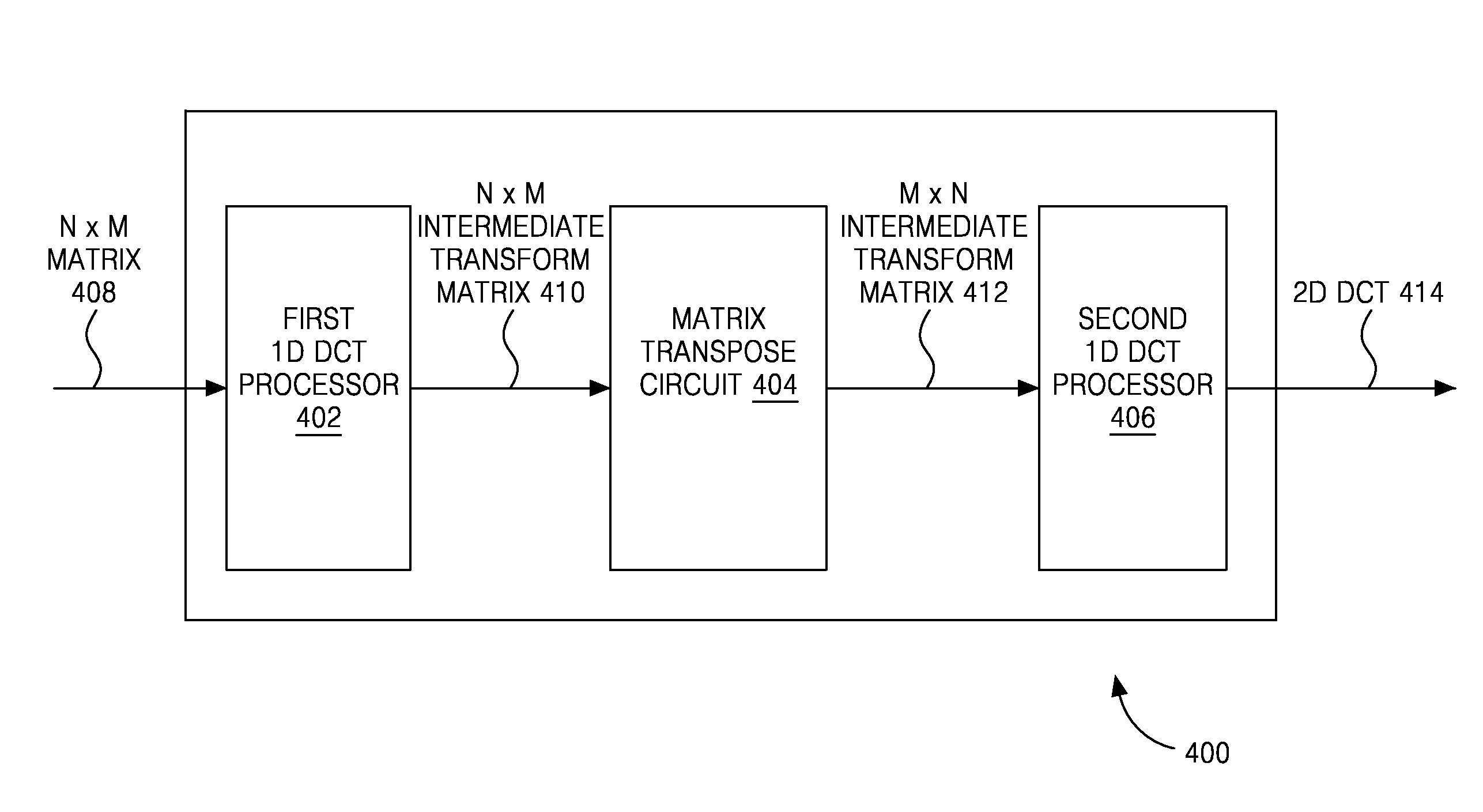
Matrix transposition in a computer system
ActiveUS7031994B2Improves speed and parallelabilityEasy transpositionHandling data according to predetermined rulesGeneral purpose stored program computerAlgorithmComputerized system
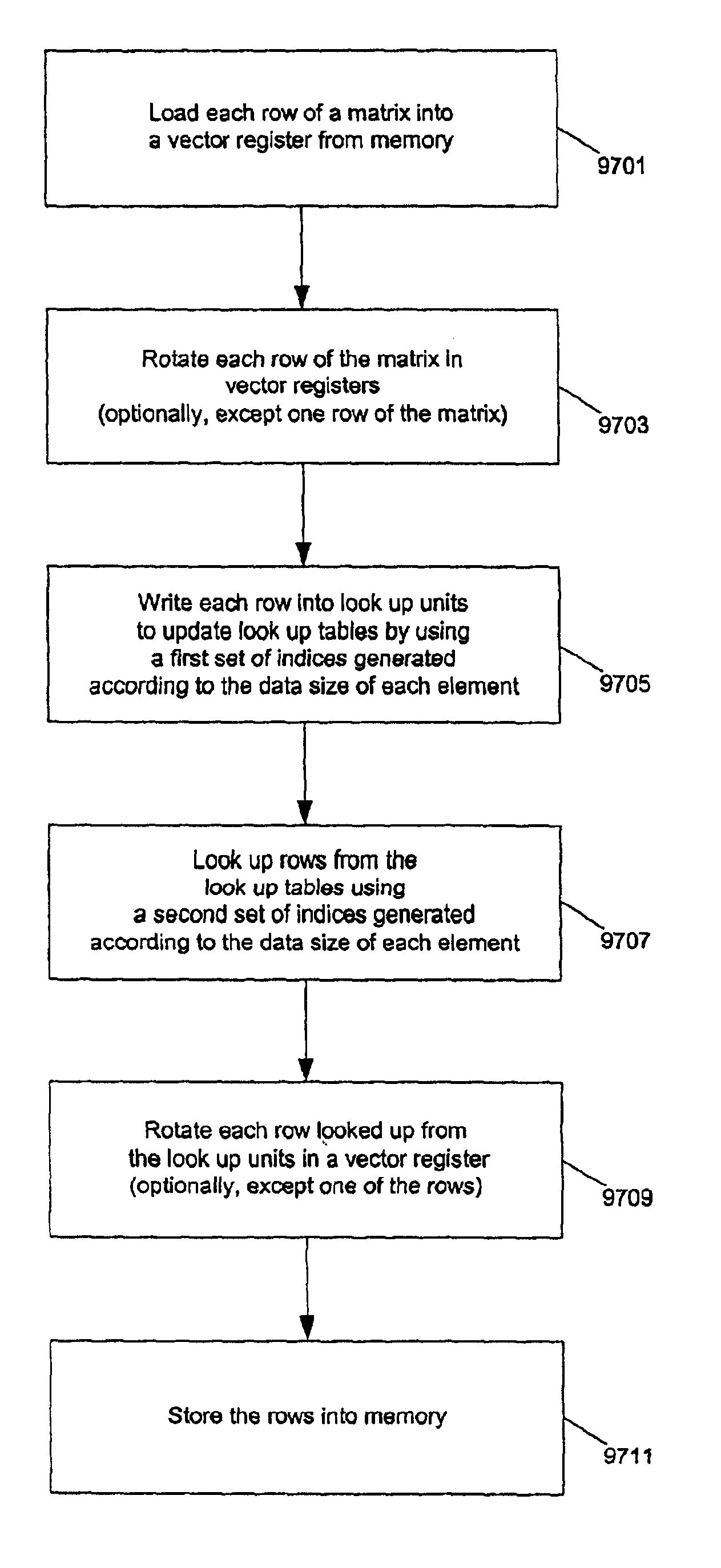
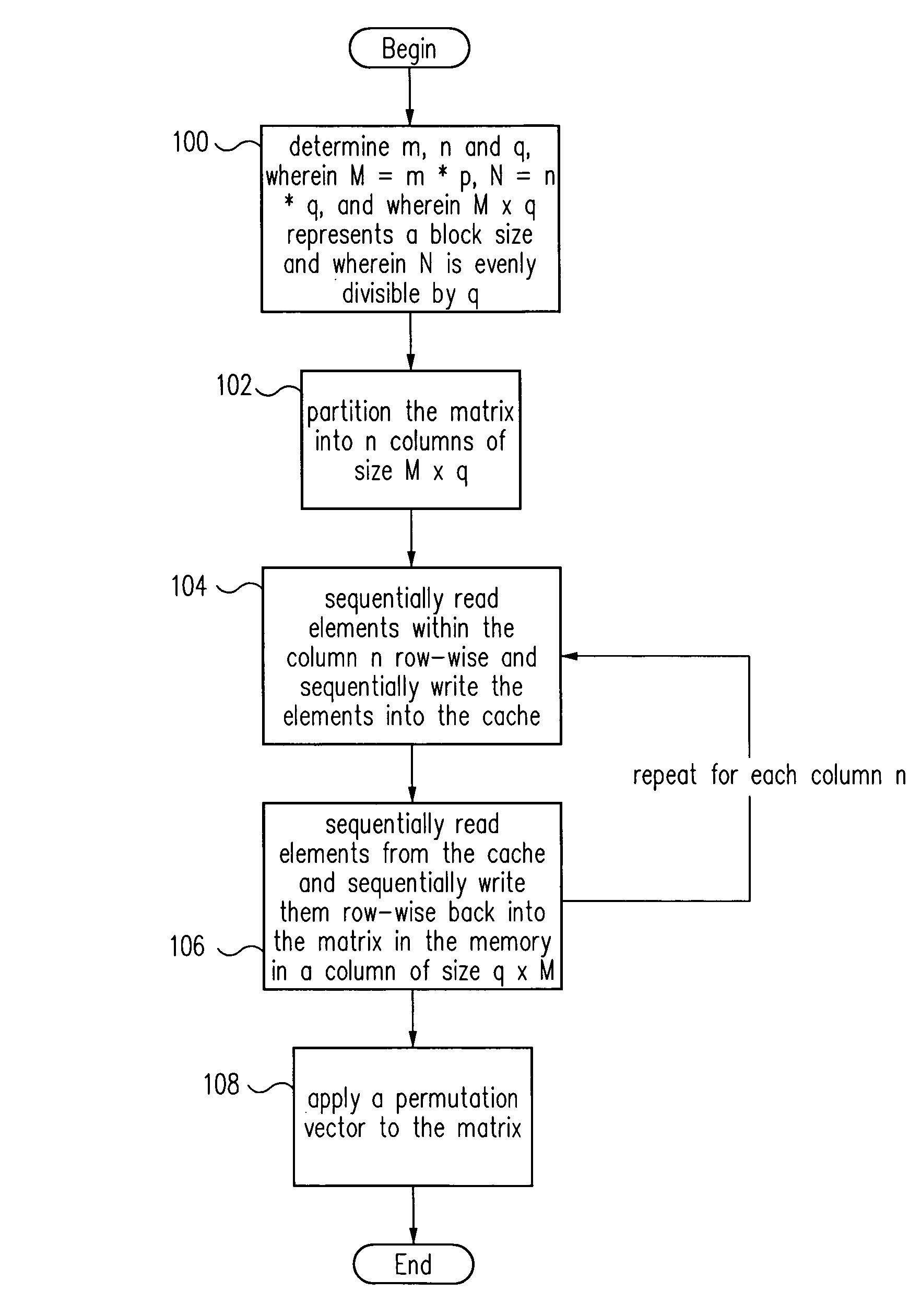
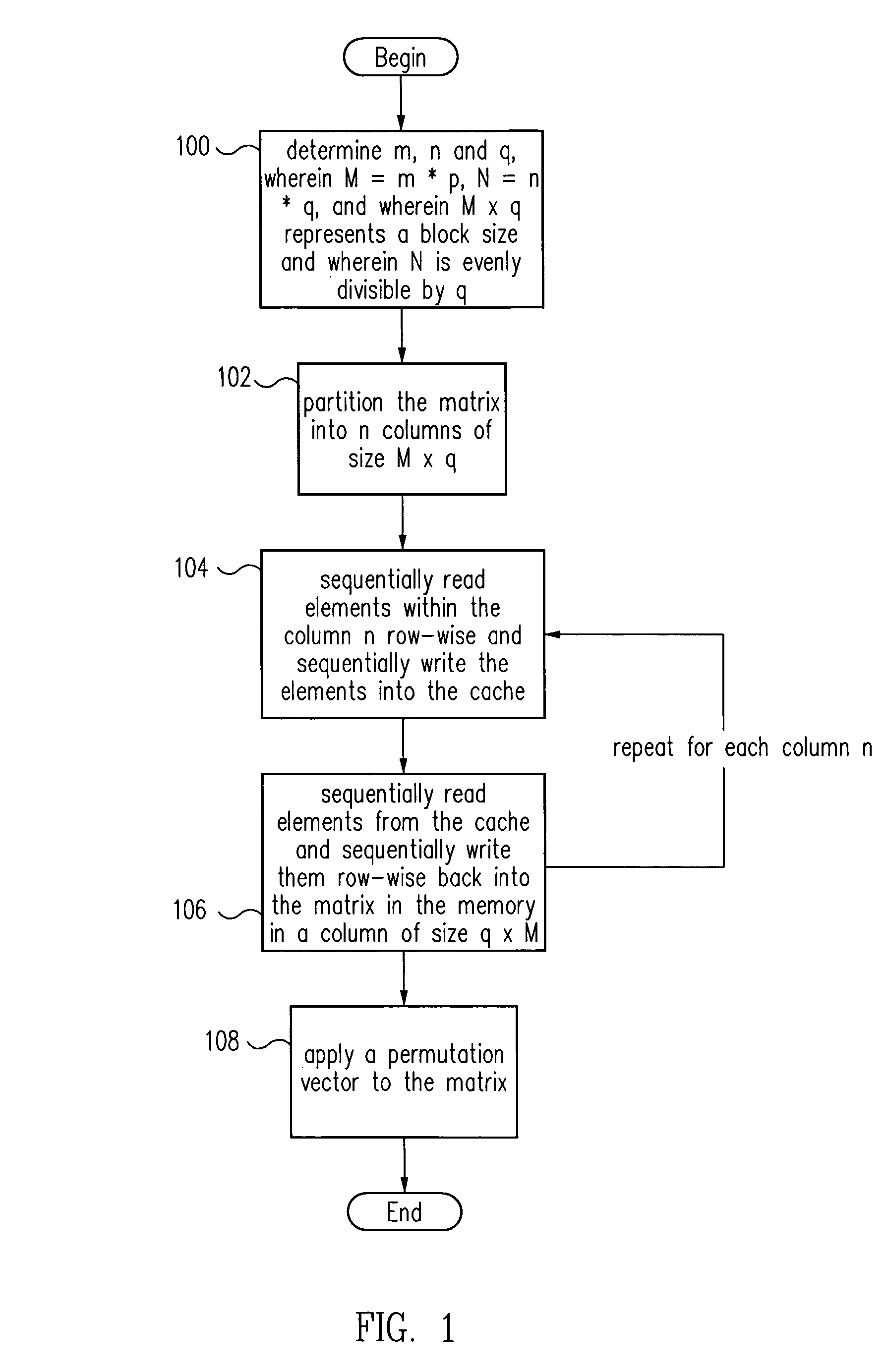
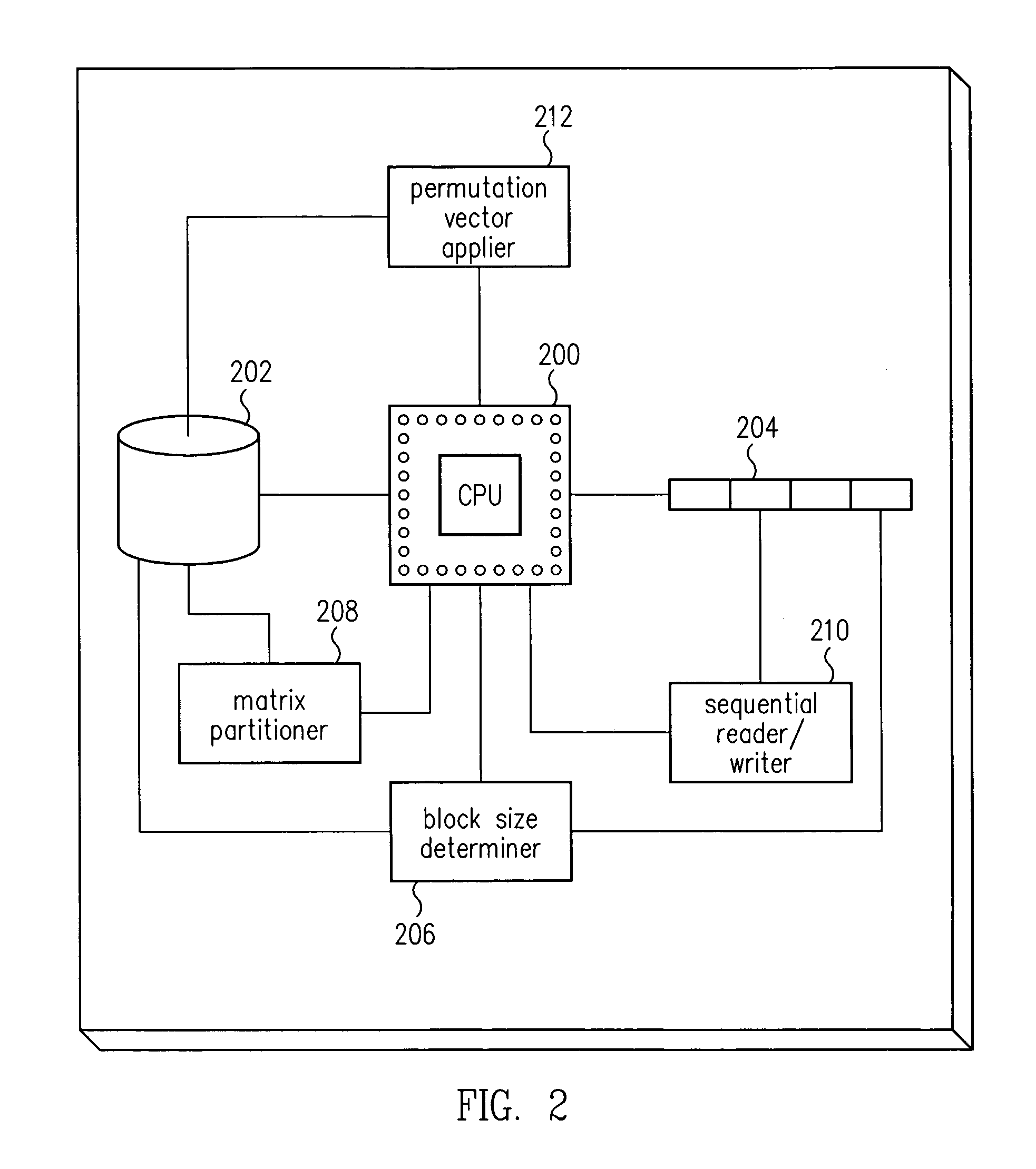
Improved transposition of a matrix in a computer system may be accomplished while utilizing at most a single permutation vector. This greatly improves the speed and parallelability of the transpose operation. For a standard rectangular matrix having M rows and N columns and a size M×N, first n and q are determined, wherein N=n*q, and wherein M×q represents a block size and wherein N is evenly divisible by p. Then, the matrix is partitioned into n columns of size M×q. Then for each column n, elements are sequentially read within the column row-wise and sequentially written into a cache, then sequentially read from the cache and sequentially written row-wise back into the matrix in a memory in a column of size q×M. A permutation vector may then be applied to the matrix to arrive at the transpose. This method may be modified for special cases, such as square matrices, to further improve efficiency.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Unmanned device utilization methods and systems
Owner:ELWHA LLC
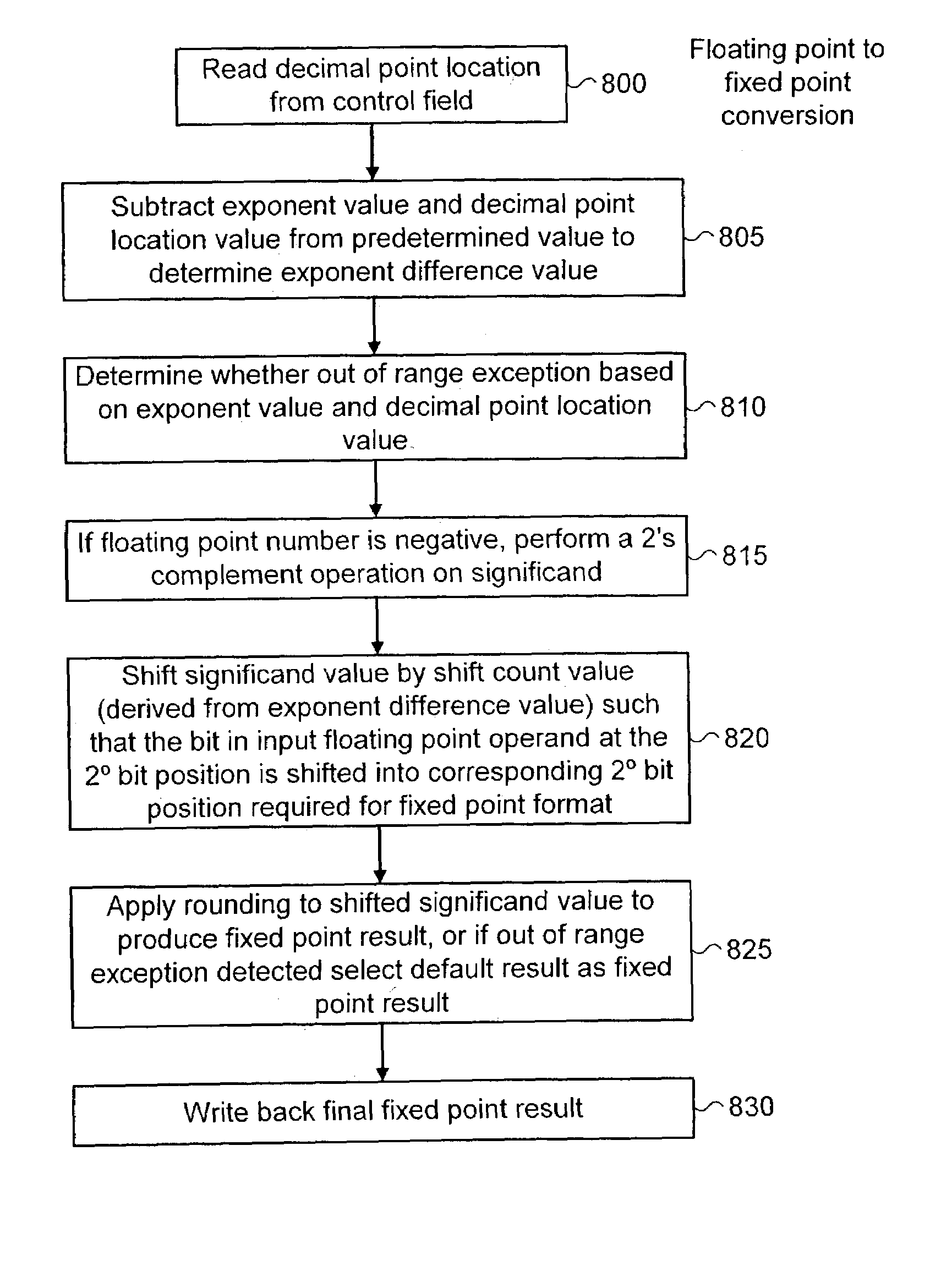
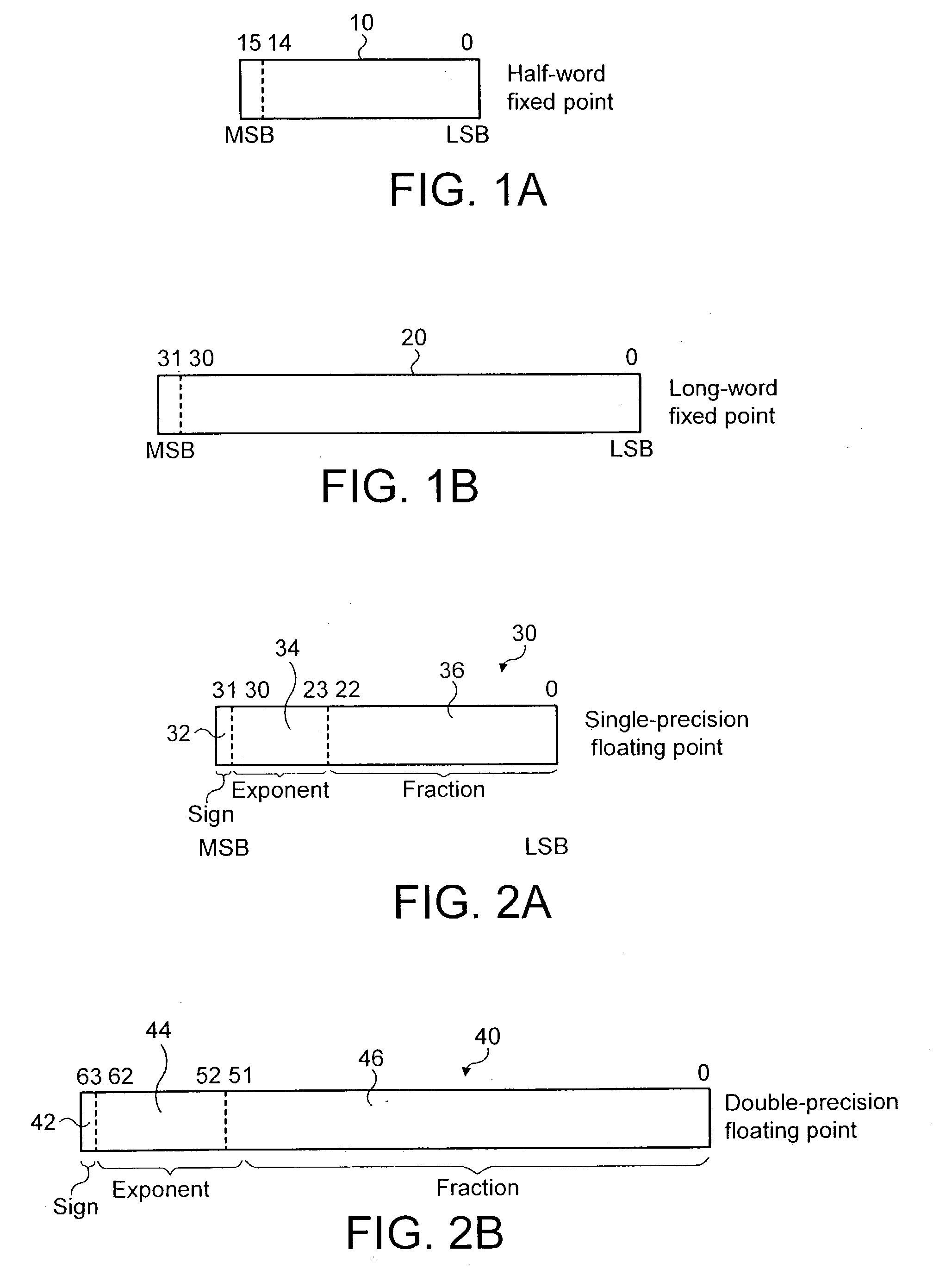
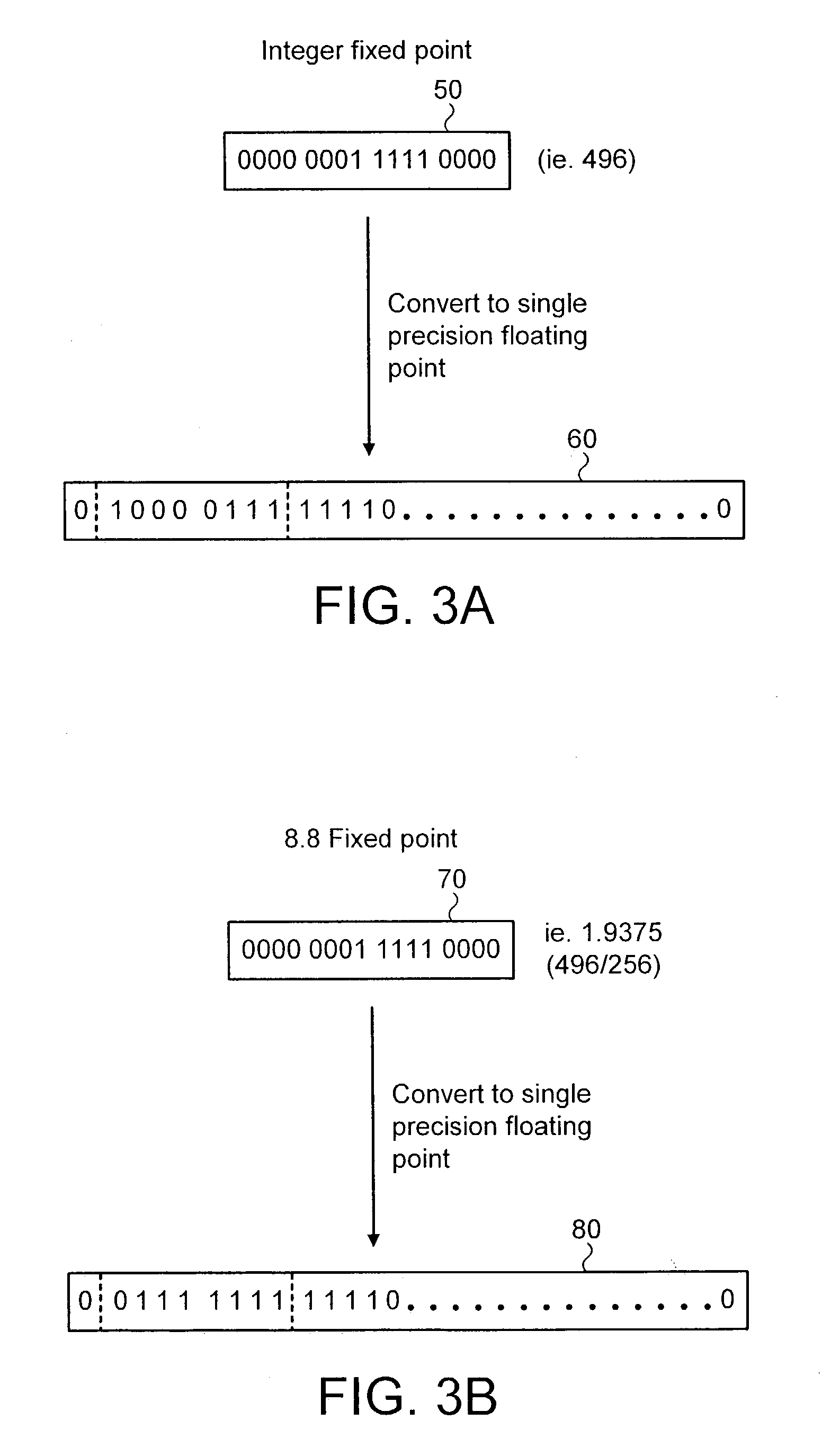
Data processing apparatus and method for converting a number between fixed-point and floating-point representations
ActiveUS7236995B2Efficient storageCost effectiveCode conversionDigital computer detailsParallel computingFloating point
A data processing apparatus and method for converting a number between fixed-point and floating-point representations. More particularly, the data processing apparatus includes a data processing unit operable to execute instructions, with the data processing unit being responsive to a format conversion instruction to apply a format conversion operation to a number to perform a conversion between the fixed-point representation of the number and the floating-point representation of the number. Furthermore, a control field is provided which is arranged to provide a programmable value specifying a decimal point location within the fixed-point representation of the number, and the data processing unit is operable to reference the control field and to control the formal conversion operation in accordance with the programmable value. This enables a single instruction to be used to directly convert between fixed-point formats (where the position of the decimal point may be programmable varied) and floating-point representations.
Owner:ARM LTD
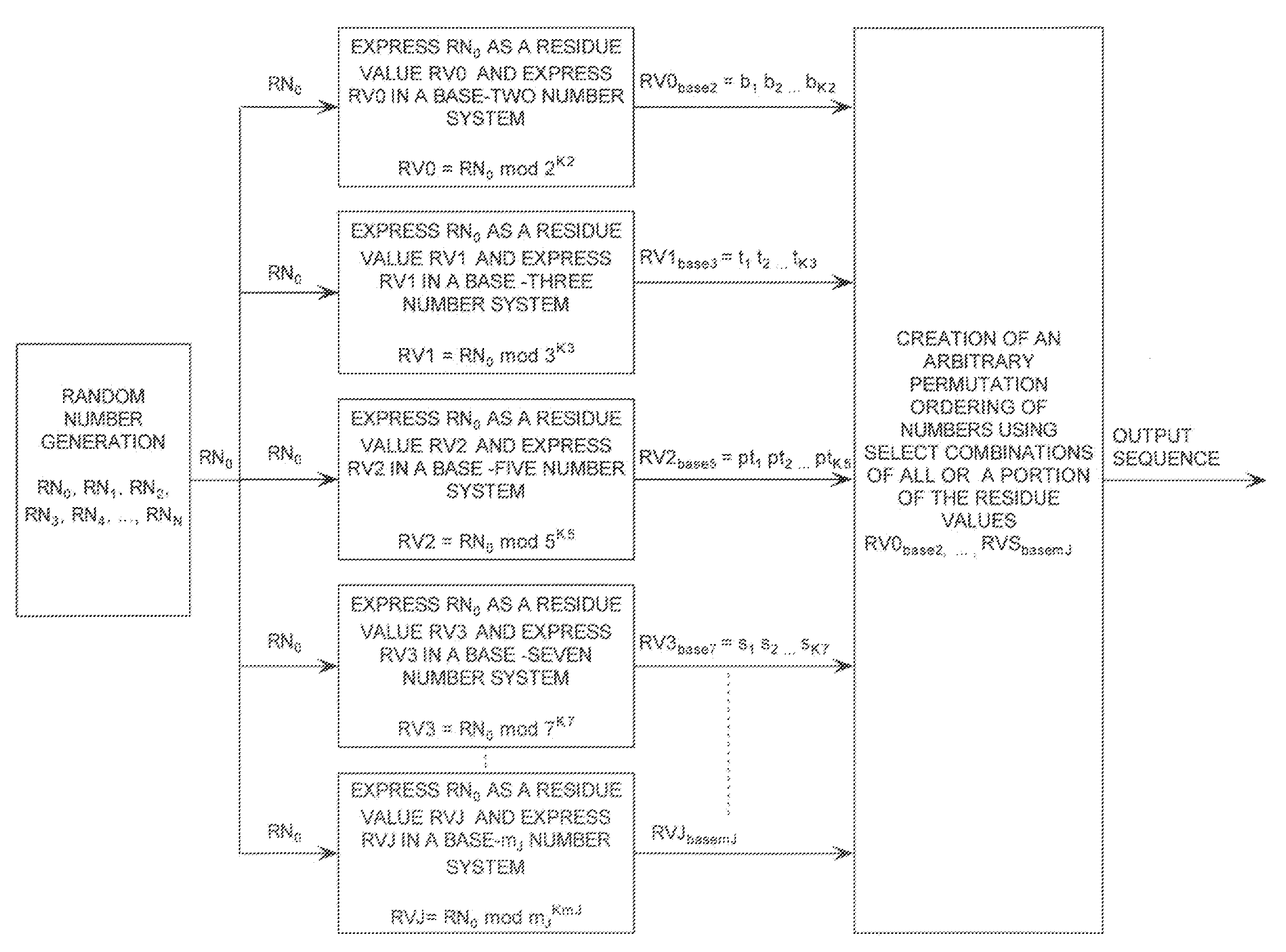
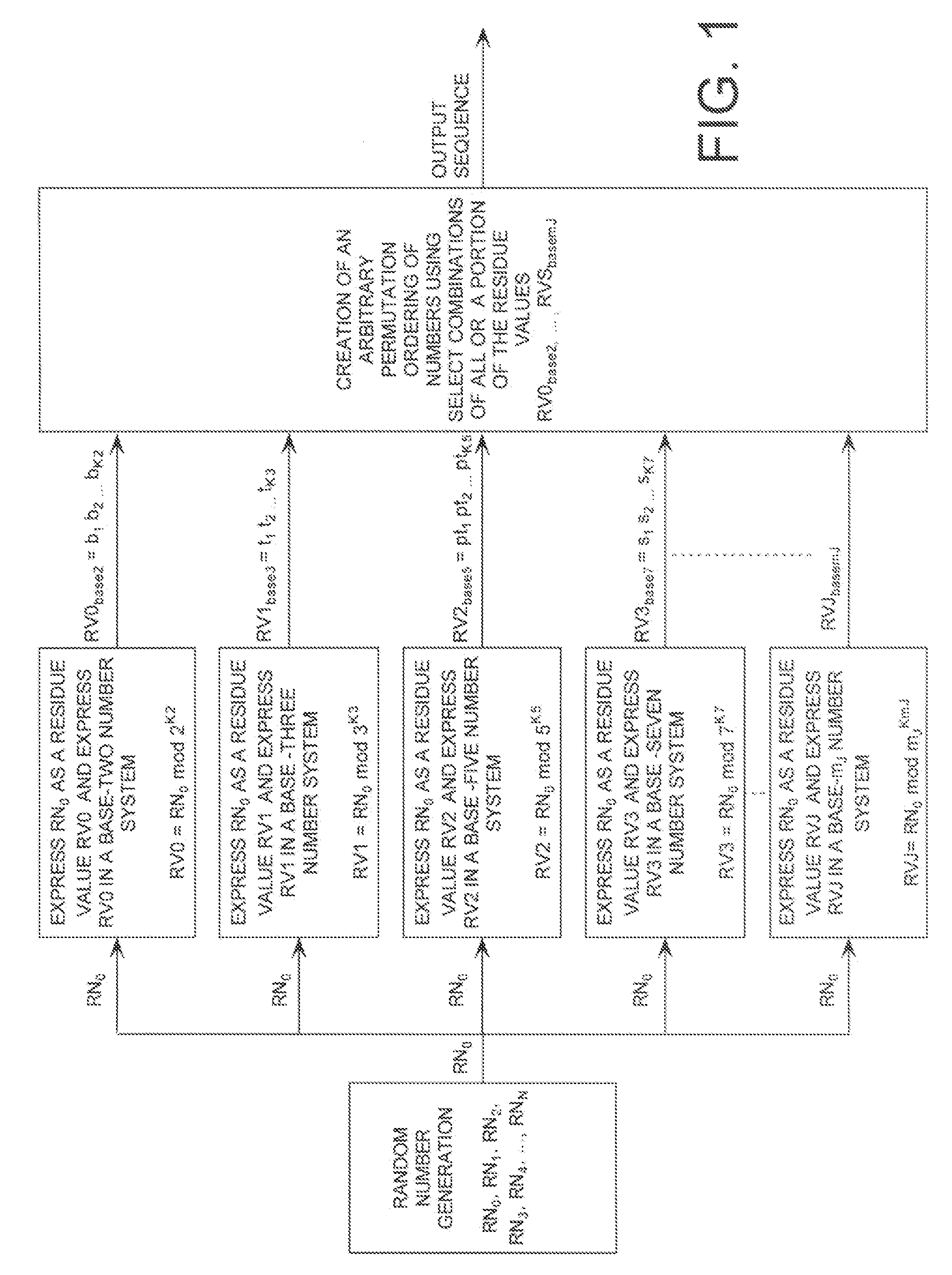
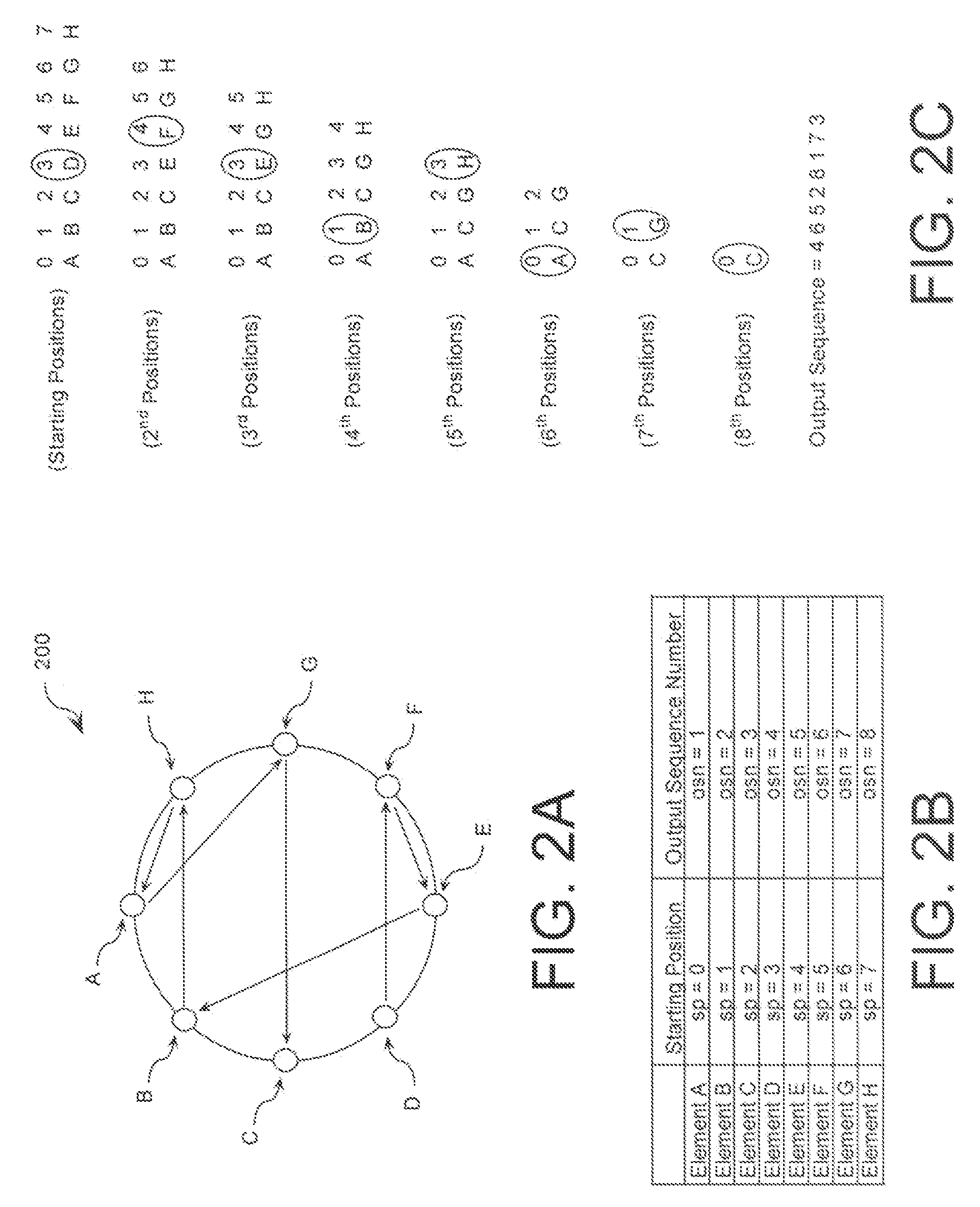
Extending a Repetition Period of a Random Sequence
ActiveUS20080294710A1Extended maintenance periodRandom number generatorsHandling data according to predetermined rulesNumber generatorComputer science
A method is provided for extending a sequence repetition period of a random number generator in systems based on the availability of random sequences. The method includes performing RNS arithmetic operations to express a random number in a sequence as RNS residue values. Each generated random number has a value between zero and n!−1. The method also includes converting each of the RNS residue values to a relatively prime base number system so that each of the RNS residue values includes at least one digit. The method further includes generating an arbitrary permutation ordering of output sequence numbers using a select combination of digits associated with each of the RNS residue values. The arbitrary permutation ordering is applied to a cyclic structure having n elements. Each of the n elements has an associated output sequence number.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Integrated circuit device and electronic instrument
InactiveUS20070016700A1Handling data according to predetermined rulesDigital storageElectronic instrumentData memory
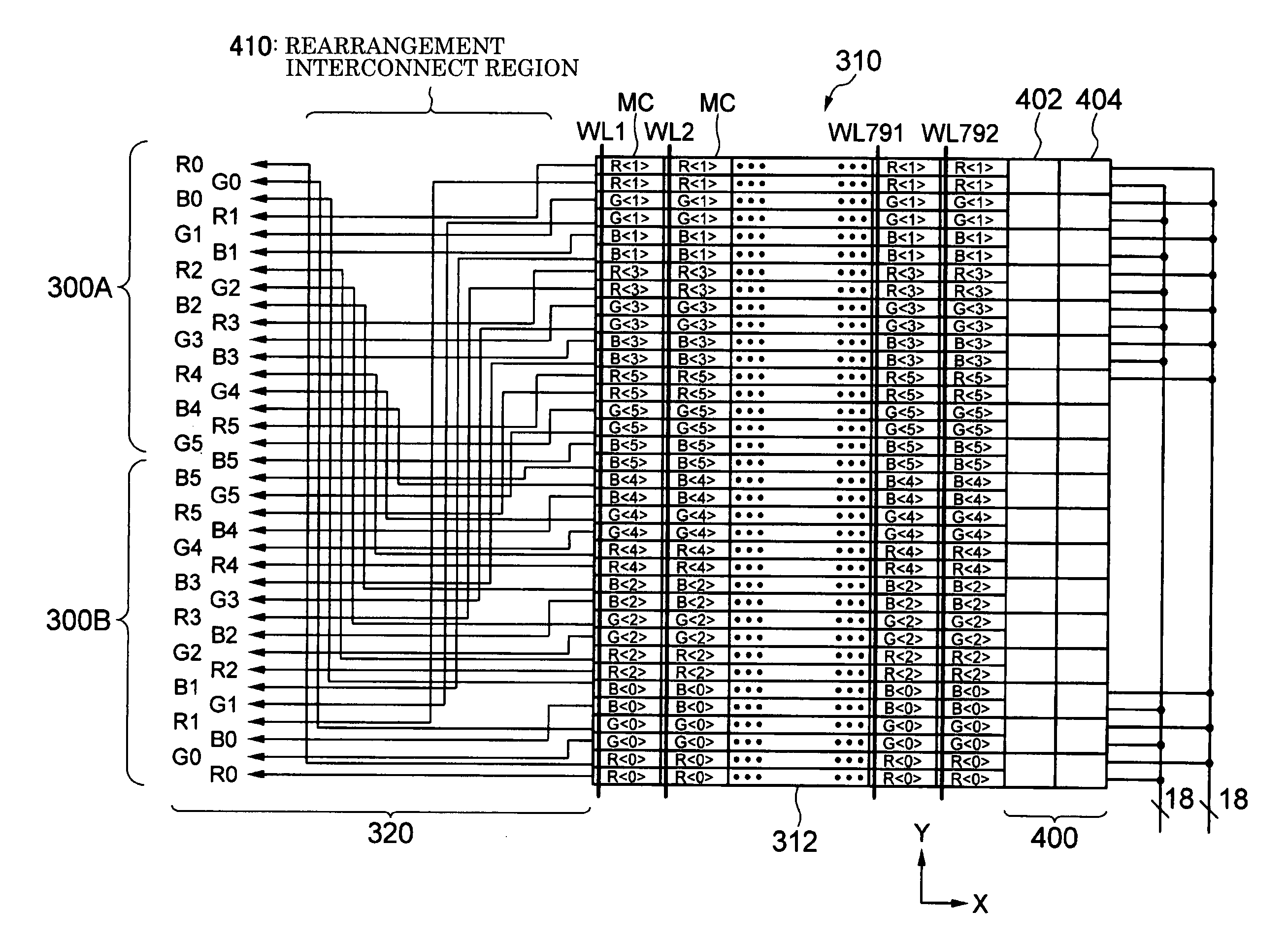
An integrated circuit device has a data memory including a memory cell array which includes a plurality of wordlines, a plurality of bitlines, and a plurality of memory cells, and a memory output circuit. The data read order in the memory cell array corresponding to the arrangement of the bitlines differs from the data output order from the memory output circuit. The integrated circuit device includes a rearrangement interconnect region in a region of the memory output circuit. The rearrangement interconnect region rearranges data input in the data read order using interconnects and outputs the data in the data output order.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Concurrent shared object implemented using a linked-list with amortized node allocation
InactiveUS7017160B2Useful for promotionInterprogram communicationHandling data according to predetermined rulesGranularityWaste collection
The Hat Trick deque requires only a single DCAS for most pushes and pops. The left and right ends do not interfere with each other until there is one or fewer items in the queue, and then a DCAS adjudicates between competing pops. By choosing a granularity greater than a single node, the user can amortize the costs of adding additional storage over multiple push (and pop) operations that employ the added storage. A suitable removal strategy can provide similar amortization advantages. The technique of leaving spare nodes linked in the structure allows an indefinite number of pushes and pops at a given deque end to proceed without the need to invoke memory allocation or reclamation so long as the difference between the number of pushes and the number of pops remains within given bounds. Both garbage collection dependent and explicit reclamation implementations are described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Apparatus and method for performing floating point addition
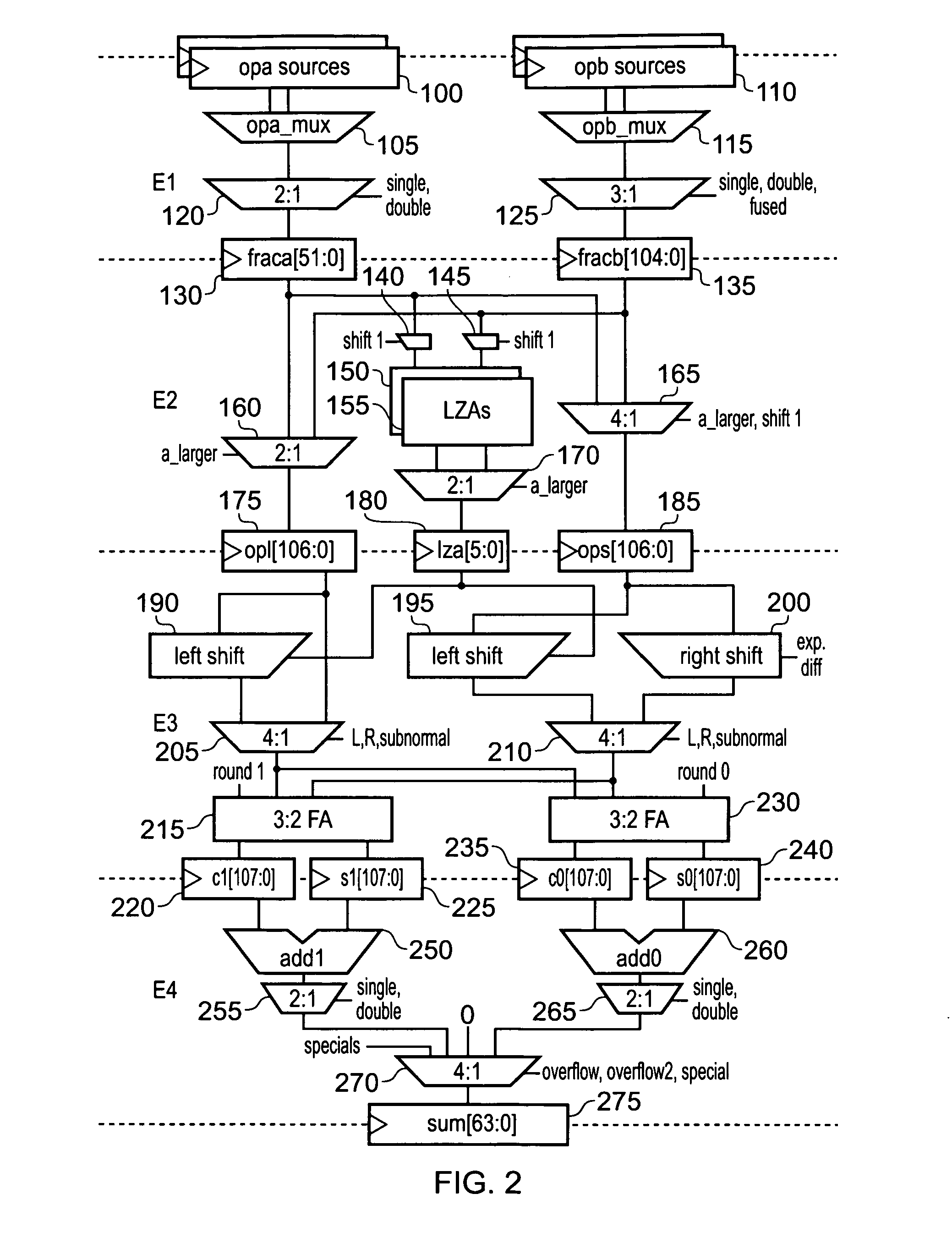
ActiveUS20120215823A1Small and simpleSignificant comprehensive benefitsComputations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsOperandLeading zero
An apparatus and method are provided for performing an addition operation on operands A and B in order to produce a result R, the operands A and B and the result R being floating point values each having a significand and an exponent. The apparatus comprises prediction circuitry for generating a shift indication based on a prediction of the number of leading zeros that would be present in an output produced by subjecting the operands A and B to an unlike signed addition. Further, result pre-normalization circuitry performs a shift operation on the significands of both operand A and operand B prior to addition of the significands, this serving to discard a number of most significant bits of the significands of both operands as determined by the shift indication in order to produce modified significands for operands A and B. Operand analysis circuitry detects, with reference to the exponents of operands A and B, the presence of a leading bit cancellation condition, and addition circuitry is configured, in the presence of the leading bit cancellation condition, to perform an addition of the modified significands for operands A and B, in order to produce the significand of the result R. Such an approach provides a particularly simple and efficient apparatus for performing addition operations.
Owner:ARM LTD
Dynamic Data Driven Alignment and Data Formatting in a Floating-Point SIMD Architecture
InactiveUS20100095087A1Minimizing amount of dataQuantity minimizationProgram control using stored programsHandling data according to predetermined rulesControl vectorProcessor register
Mechanisms are provided for dynamic data driven alignment and data formatting in a floating point SIMD architecture. At least two operand inputs are input to a permute unit of a processor. Each operand input contains at least one floating point value upon which a permute operation is to be performed by the permute unit. A control vector input, having a plurality of floating point values that together constitute the control vector input, is input to the permute unit of the processor for controlling the permute operation of the permute unit. The permute unit performs a permute operation on the at least two operand inputs according to a permutation pattern specified by the plurality of floating point values that constitute the control vector input. Moreover, a result output of the permute operation is output from the permute unit to a result vector register of the processor.
Owner:IBM CORP
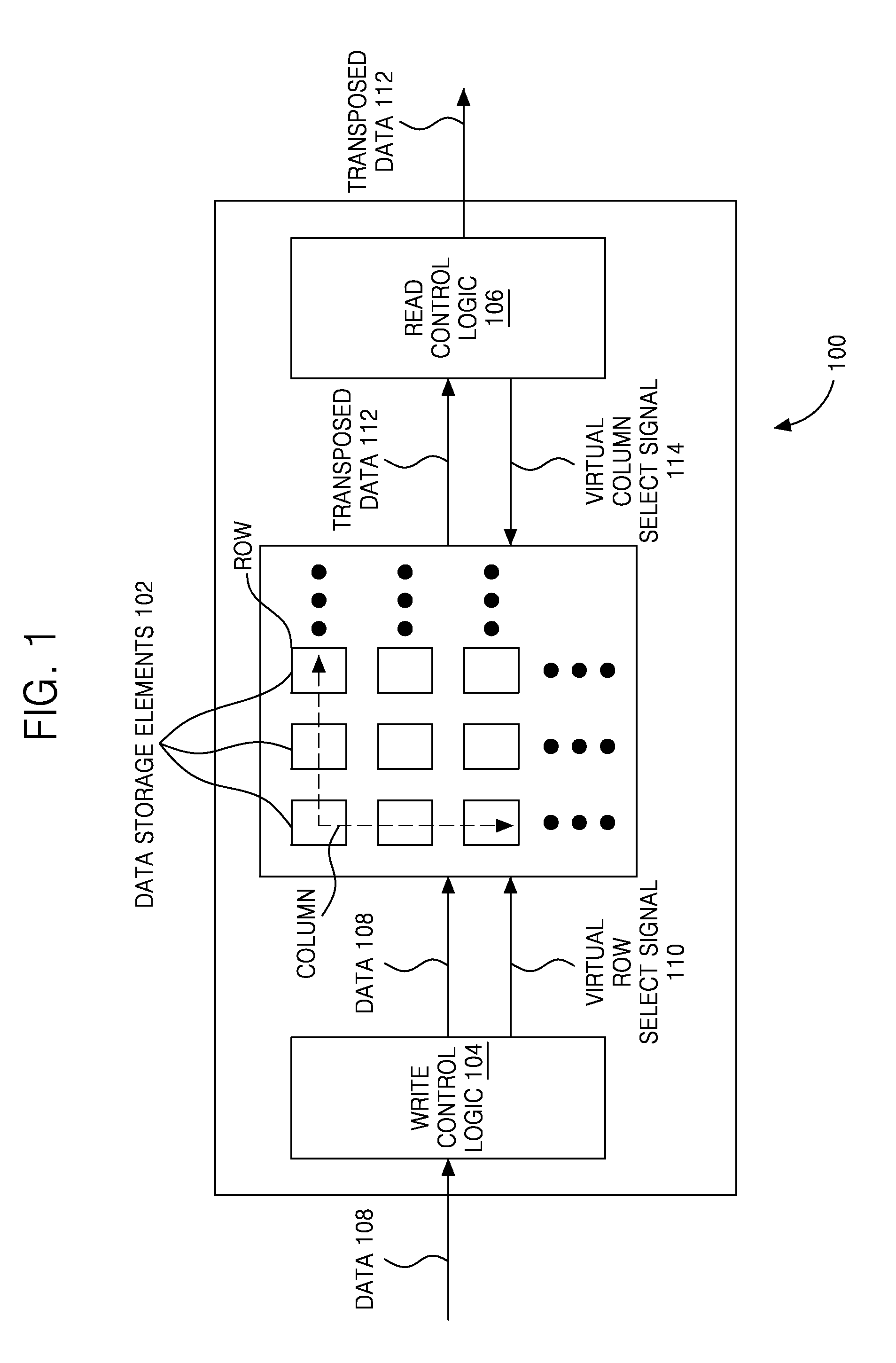
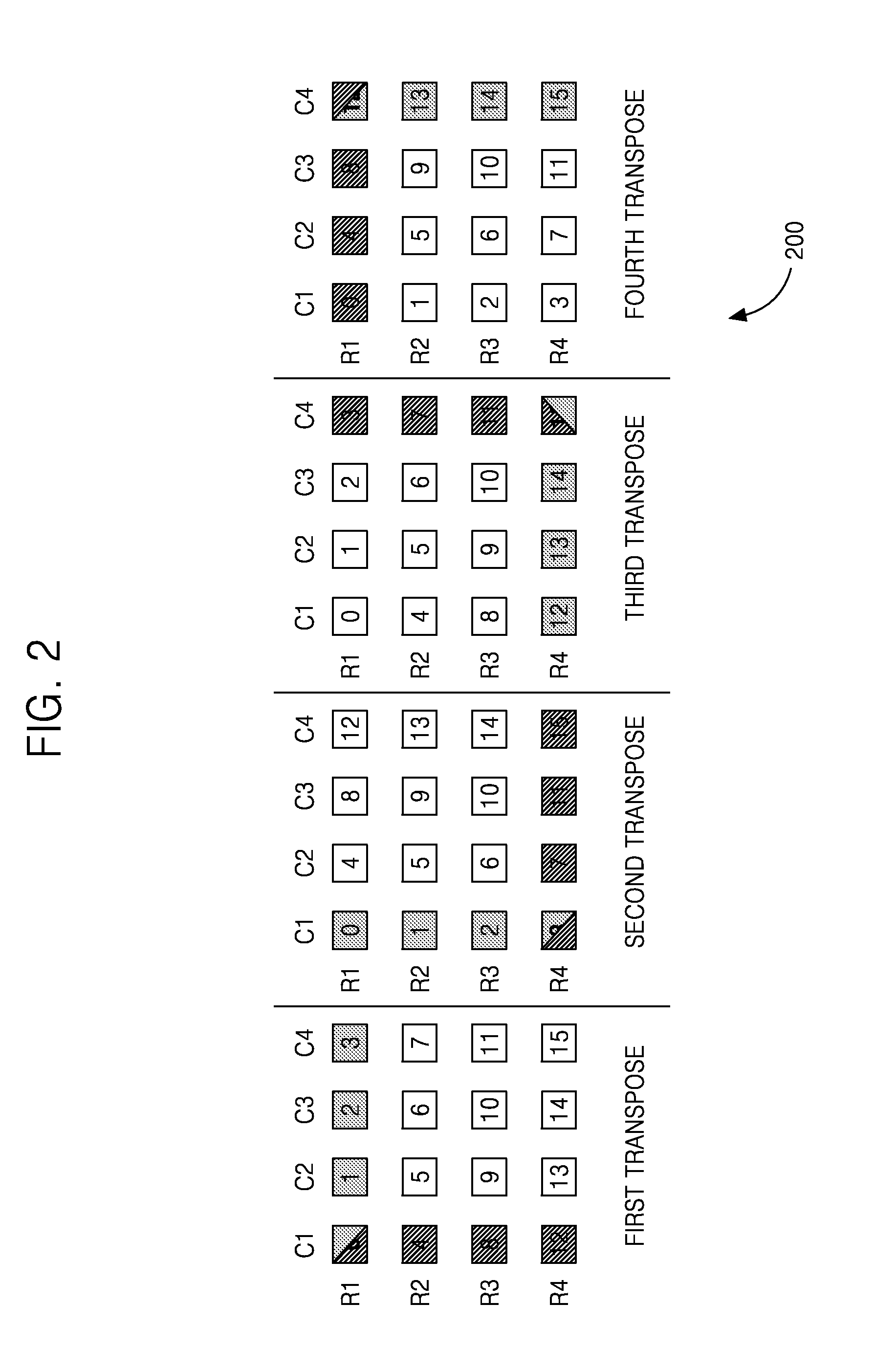
System and method for successive matrix transposes
InactiveUS20110264723A1Handling data according to predetermined rulesData mergingComputer architectureTranspose
A system and method for successively transposing a matrix is disclosed. The device includes a plurality of data storage elements arranged as a two dimensional (2D) structure including X rows and Y columns. The device further includes write control logic coupled to the input of plurality of data storage elements for writing data in at least one virtual row. The device also includes read control logic coupled to the output of the plurality of data storage elements for reading the data from at least one virtual column, where the data write to the at least one virtual row and the data read from the at least one virtual column are performed substantially simultaneously during each cycle of operation such that the 2D structure is transposed successively with zero cycle delay between successive transposes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Context-based cloud security assurance system
ActiveUS20160156661A1Increased level of assuranceImprove the level ofNumber-allocation/character-counting for messagesHandling data according to predetermined rulesSystem configurationContext based
A cloud infrastructure is enhanced to provide a context-based security assurance service to enable secure application deployment. The service inspects network and cloud topologies to identify potential security capabilities and needs. Preferably, these options are then surfaced to the user with easy-to-understand, pre-configured templates representing security assurance levels. When a template (e.g., representing a pre-configured assurance level) is selected by the user, the system then applies specific capabilities and controls to translate the user-selected generalized specification (e.g., “high security”) into granular requirements for a specific set of security resources. Preferably, the identification of these security resources is based on system configuration, administration, and information associated with the pre-configured template.
Owner:IBM CORP
Rounding mechanisms in processors
InactiveUS7047272B2Efficient hardware implementationComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsRoundingAlgorithm
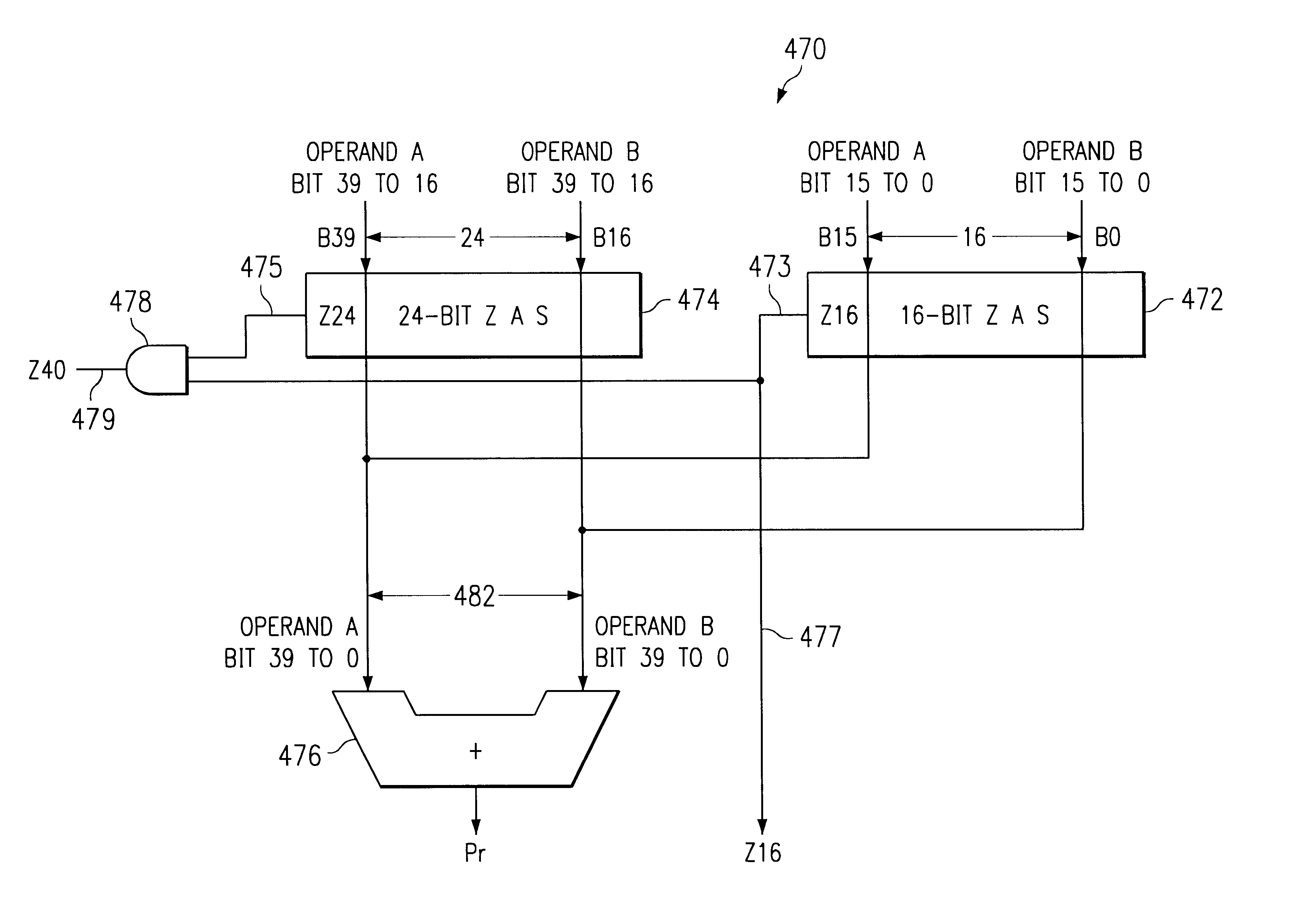
An arithmetic unit, for example a multiply and accumulate (MAC) unit 42, for a processing engine includes a partial product reduction tree 480. The partial product reduction tree will generate carry results and provides a final output to a final adder 470 connected to the partial production reduction tree. Unbiased rounding logic 476 is provided. A carry propagation tree is responsive to the carry results for anticipating a zero on each of N least significant bits of the final adder. When zero is anticipated on each of N least significant bits of the final adder, the carry propagation tree is operable to generate an output signal 477 which is used by the unbiased rounding stage to force the (N+1)th least significant bit of the final adder to zero. Through the use of a carry propagation tree to predict, or anticipate zeros on the N least significant bits, unbiased rounding can be effected without a time penalty in that a carry propagation tree can be configured to be at least a rapid as the carry propagation of the final adder. Where a zero anticipation function is provided, this can also be mapped onto the carry propagation tree, thus providing an efficient hardware implementation through sharing of that hardware between functions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Maintaining a double-ended queue as a linked-list with sentinel nodes and delete flags with concurrent non-blocking insert and remove operations using a double compare-and-swap primitive
InactiveUS7000234B1Interprogram communicationHandling data according to predetermined rulesSentinel nodeDouble compare-and-swap
A linked-list-based concurrent shared object implementation has been developed that provides non-blocking and linearizable access to the concurrent shared object. In an application of the underlying techniques to a deque, the linked-list-based algorithm allows non-blocking completion of access operations without restricting concurrency in accessing the deque's two ends. The new implementation is based at least in part on a new technique for splitting a pop operation into two steps, marking that a node is about to be deleted, and then deleting it. Once marked, the node logically deleted, and the actual deletion from the list can be deferred. In one realization, actual deletion is performed as part of a next push or pop operation performed at the corresponding end of the deque. An important aspect of the overall technique is synchronization of delete operations when processors detect that there are only marked nodes in the list and attempt to delete one or more of these nodes concurrently from both ends of the deque.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
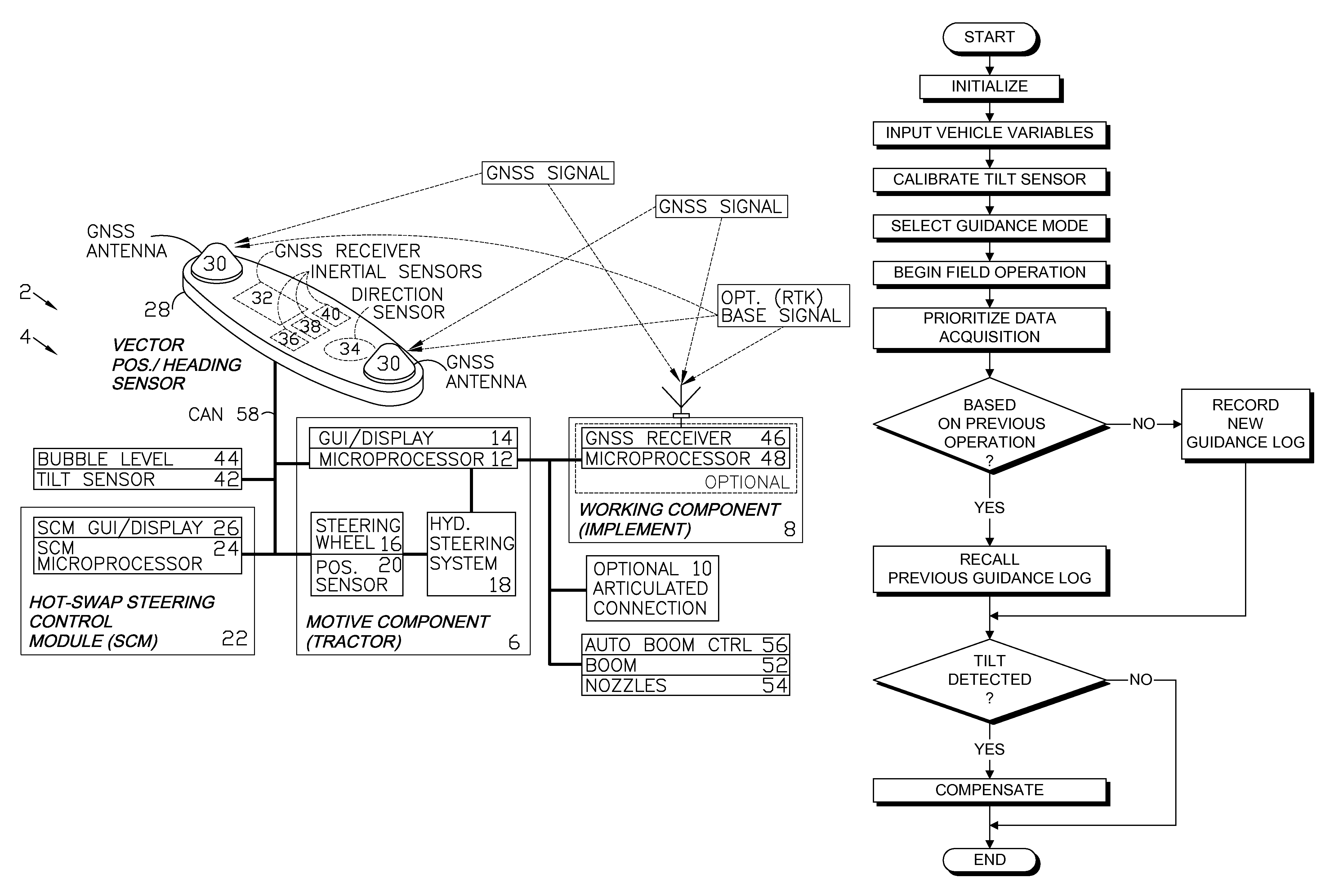
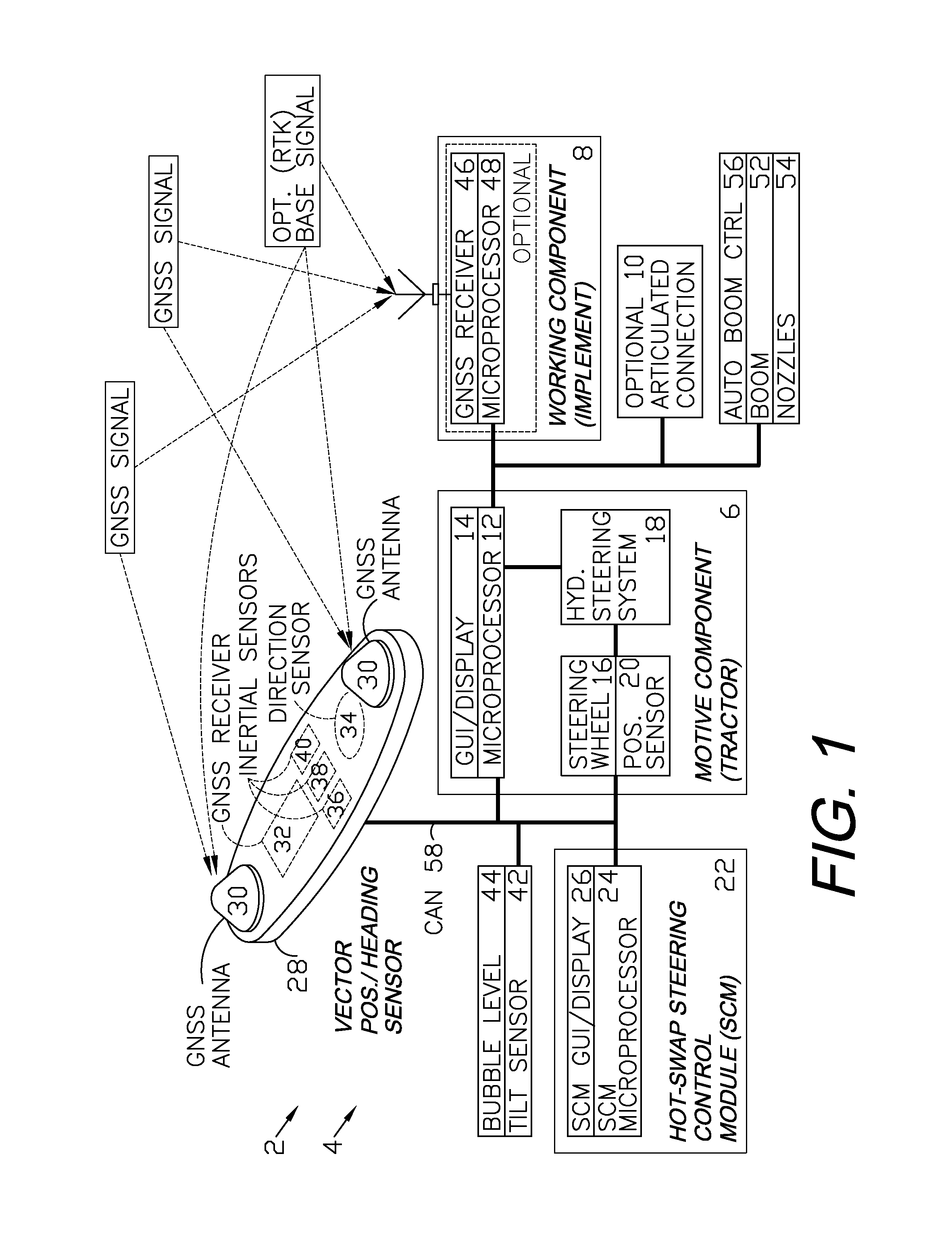
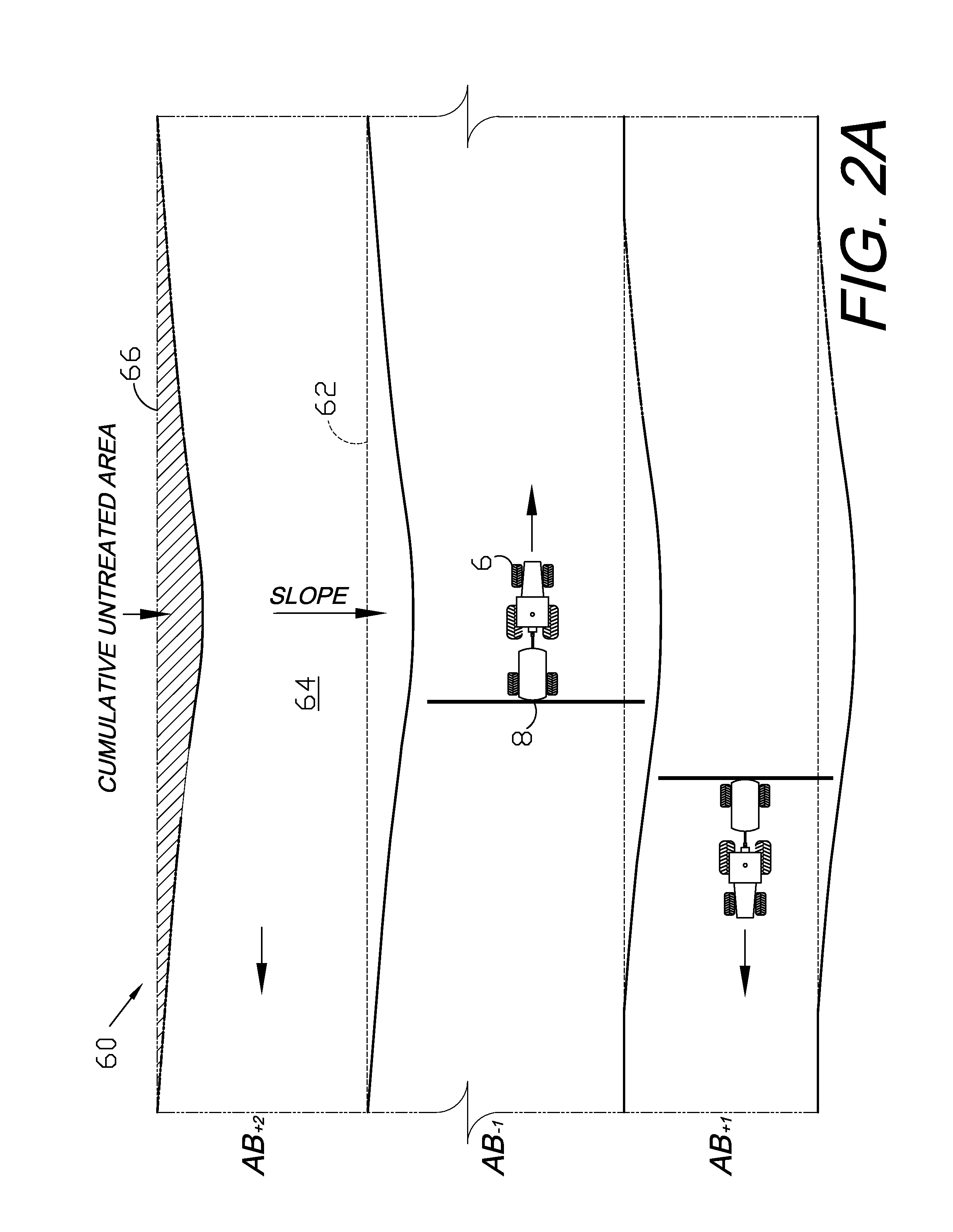
GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS7885745B2Instruments for road network navigationAnalogue computers for trafficControl systemSteering control
A GNSS control system and method are provided for guiding, navigating and controlling a motive component, such as a tractor, and a working component, such as an implement. A vector position / heading sensor is mounted on the motive component and includes multiple antennas connected to a GNSS receiver. The sensor also includes inertial sensors and a direction sensor, which are connected to a microprocessor of a steering control module (SCM). The SCM can be hot swapped among different vehicles and can interface with their respective original, onboard control systems. The implement can be provided with an optional GNSS antenna, receiver or both, and can be guided independently of the motive component. The SCM can be preprogrammed to guide the vehicle over a field in operating modes including straight line, contour, concentric circle and point+direction. A spray boom with multiple nozzles can be installed on the implement and the nozzles can be independently activated based upon a location of the implement as determined from a log of GNSS data.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
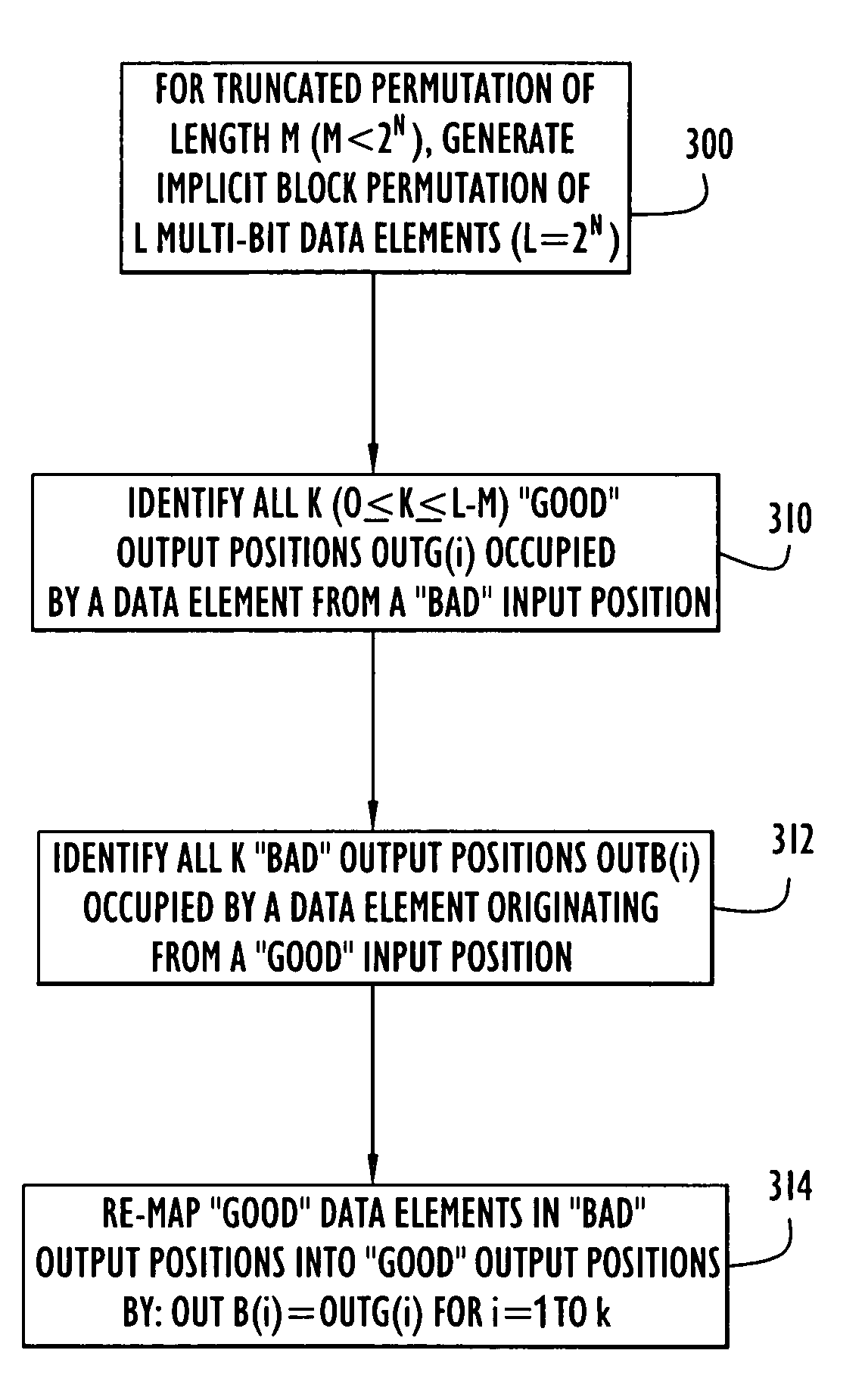
Method and apparatus for generating random permutations
InactiveUS6934388B1Reducing hardwareReduce processing requirementsRandom number generatorsHandling data according to predetermined rulesTheoretical computer scienceProcessor register
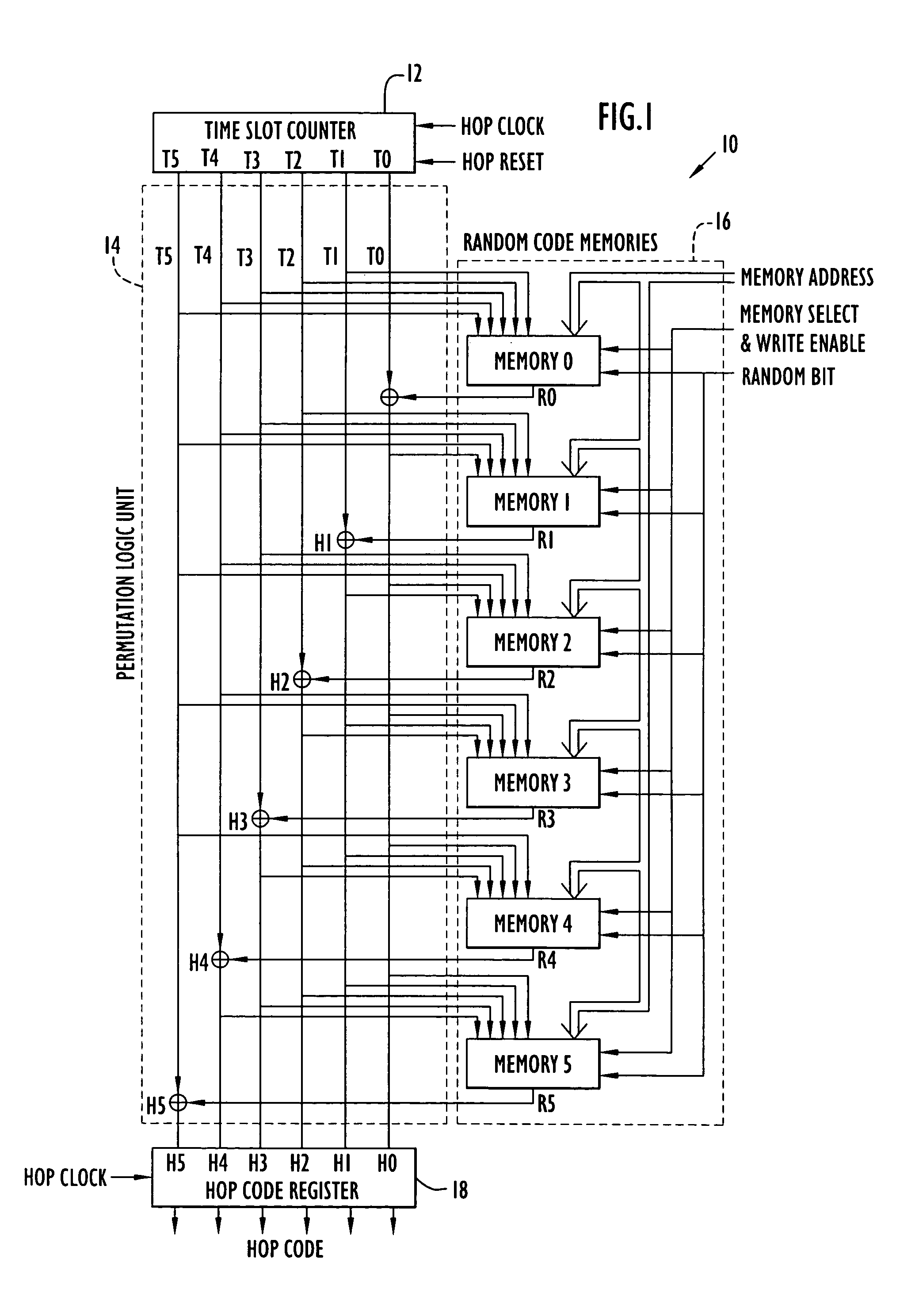
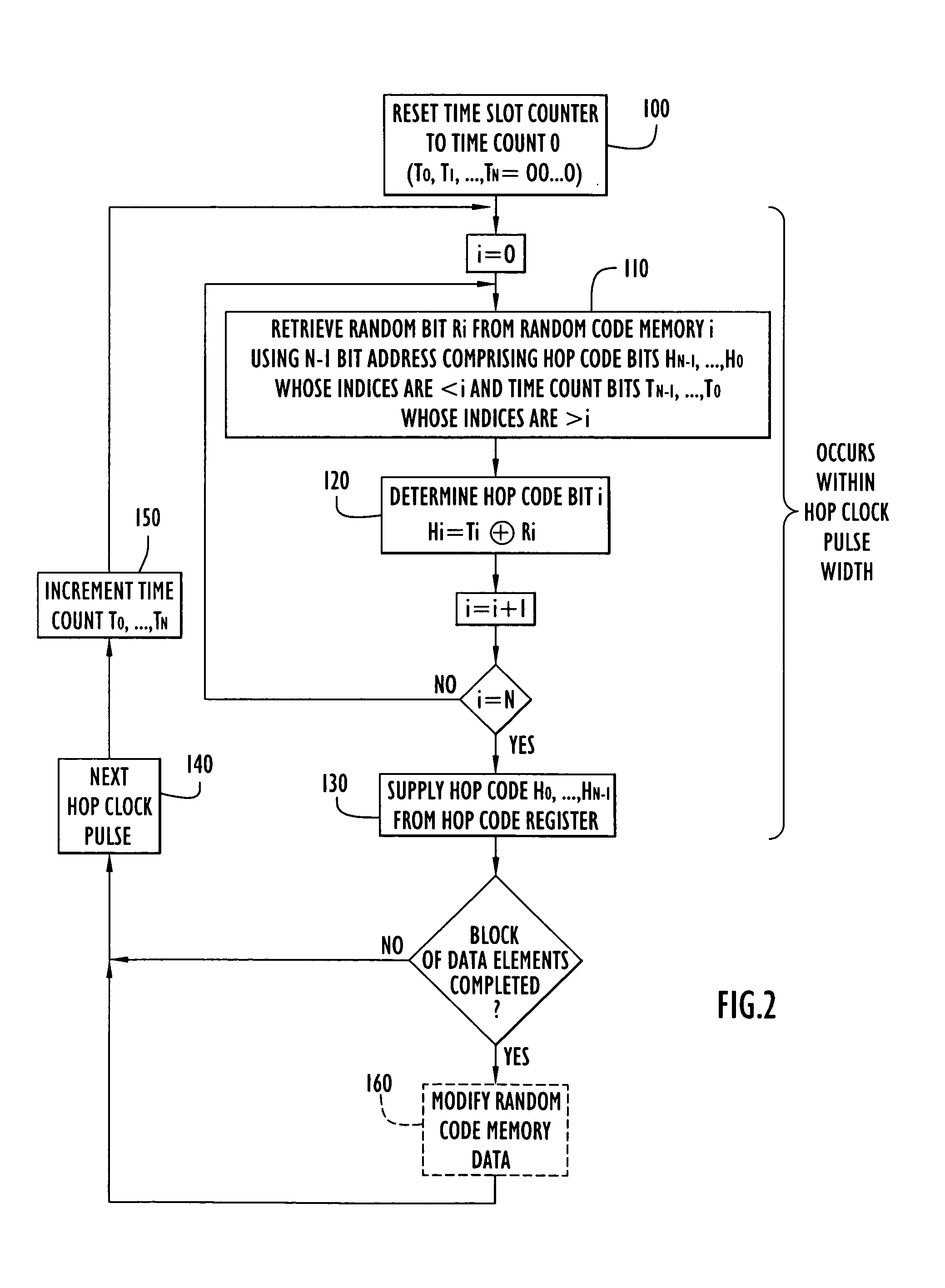
An apparatus (10) for generating a sequence of blocks of randomly permuted multi-bit data elements includes an input register (12) that produces a repeating block of distinct input data elements from which output blocks of permuted data elements are generated. A permutation logic unit (14) forms an output data element from each input data element in accordance with random data stored in random code memories (16). The output data element produced by the permutation logic unit is supplied to an output register (18). The manner in which the random data is selected and applied by the permutation logic unit ensures that each of the data elements in the input block will be mapped into an output position in the output block.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Rearranging data between vector and matrix forms in a SIMD matrix processor
ActiveUS6898691B2Register arrangementsHandling data according to predetermined rulesAlgorithmProcessor register
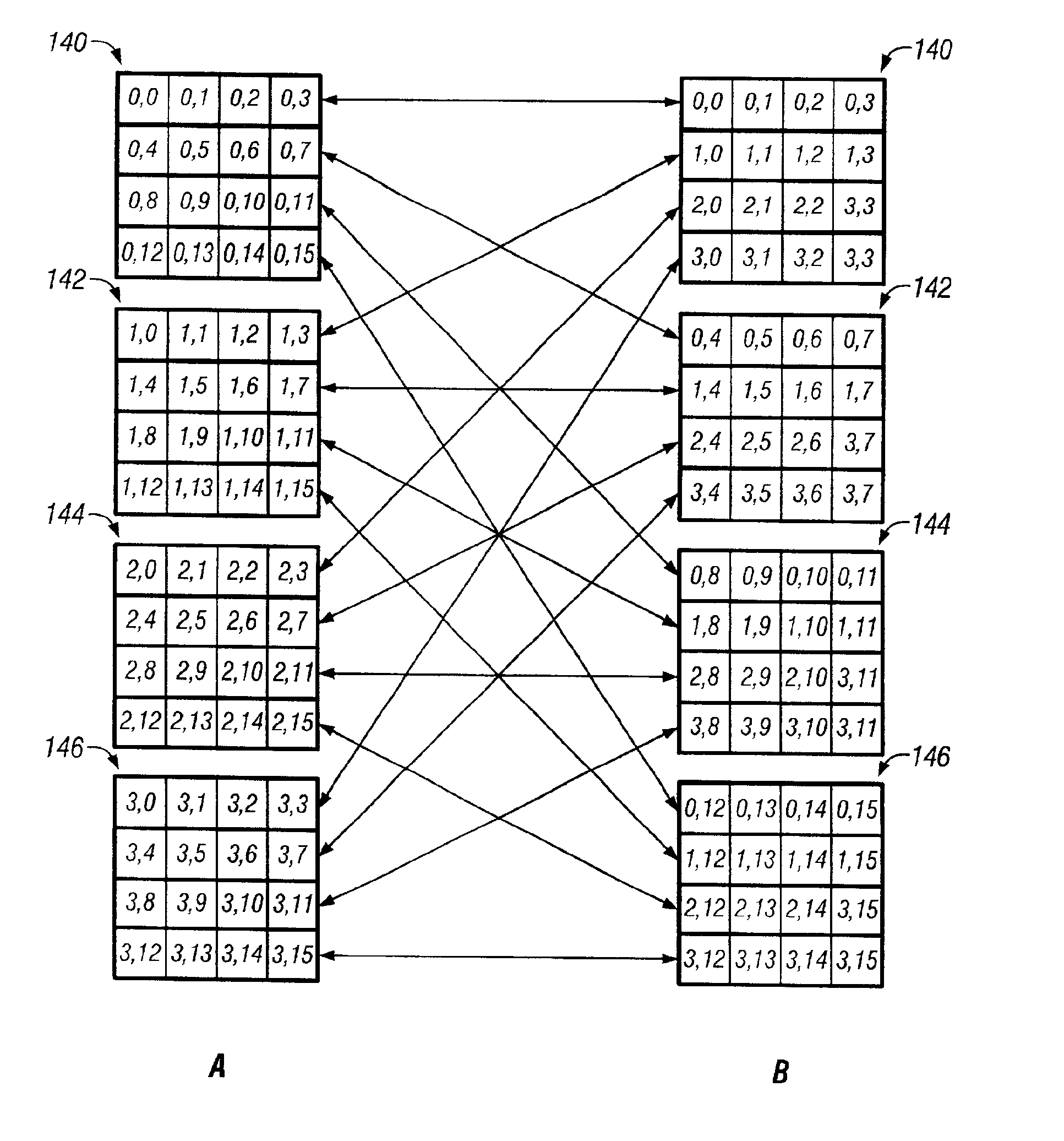
This invention discloses a group of instructions, block4 and block4v, in a matrix processor 16 that rearranges data between vector and matrix forms of an A×B matrix of data 120 where the data matrix includes one or more 4×4 sub-matrices of data 160-166. The instructions of this invention simultaneously swaps row or columns between the first 140, second 142, third 144, and fourth 146 matrix registers according to the instructions that perform predefined matrix tensor operations on the data matrix that includes one of the following group of operations: swapping rows between the different individual matrix registers, or swapping columns between the different individual matrix registers. Additionally, successive iterations or combinations of the block4 and or block4v instructions perform standard tensor matrix operations from the following group of matrix operations: transpose, shuffle, and deal.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for efficiently implementing a last-in first-out buffer
InactiveUS6892278B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationHandling data according to predetermined rulesArray data structureComputer science
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that implements a last-in first-out buffer. The system includes a plurality of cells arranged in a linear array to form the last-in first-out buffer, wherein a given cell in the interior of the linear array is configured to receive get and put calls from a preceding cell in the linear array, and to make get and put calls to a subsequent cell in the linear array. If the given cell contains no data items, the given cell is configured to make a get call to retrieve a data item from the subsequent cell. In this way the data item becomes available in the given cell to immediately satisfy a subsequent get call to the given cell without having to wait for the data item to propagate to the given cell from subsequent cells in the linear array. If the given cell contains no space for additional data items, the given cell is configured to make a put call to transfer a data item to the subsequent cell. In this way, space becomes available in the given cell to immediately satisfy a subsequent put call to the given cell without having to wait for data in the given cell to propagate to subsequent cells in the linear array.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for processing vectorized data
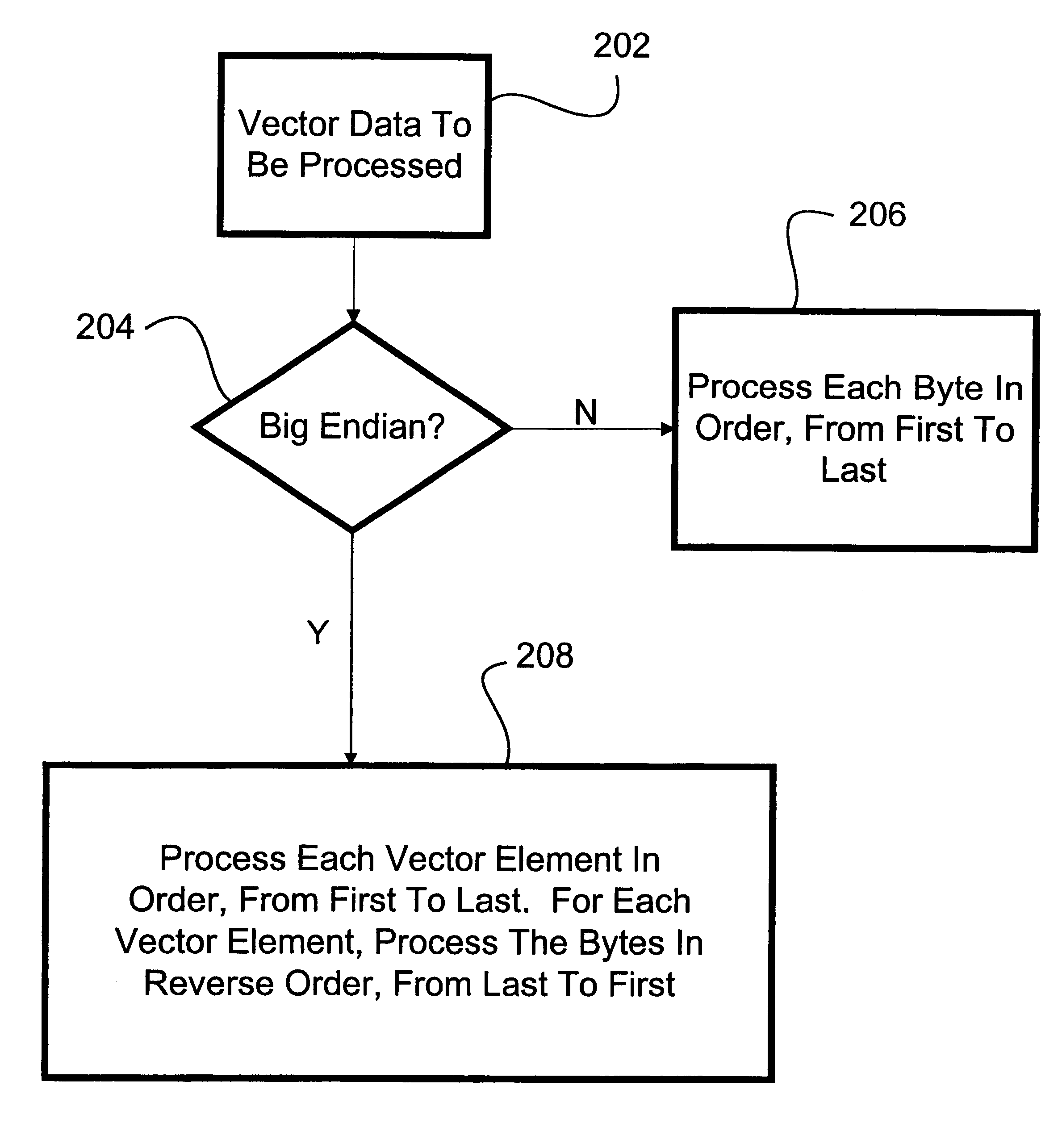
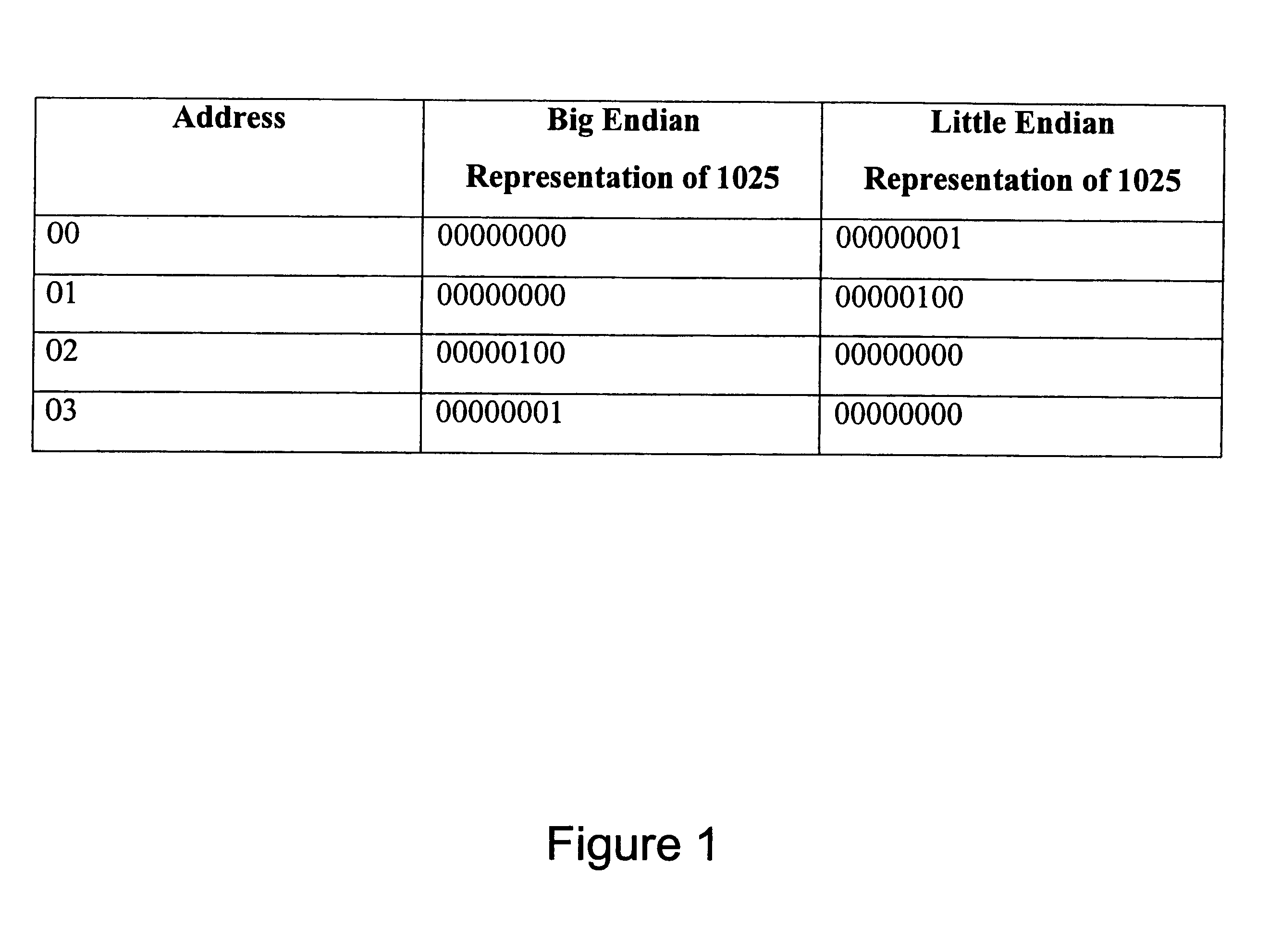
InactiveUS6728874B1Handling data according to predetermined rulesGeneral purpose stored program computerReverse orderVector element
A method and system for correctly processing both big endian and little endian vector data. If the vector has a little endian data order, each piece of data (such as a byte) within the vector is processed in order. If the vector has a big endian data order, each vector element is processed in order, but each piece of data within each vector element is processed in reverse order.
Owner:III HLDG 6
Method and system for performing permutations with bit permutation instructions
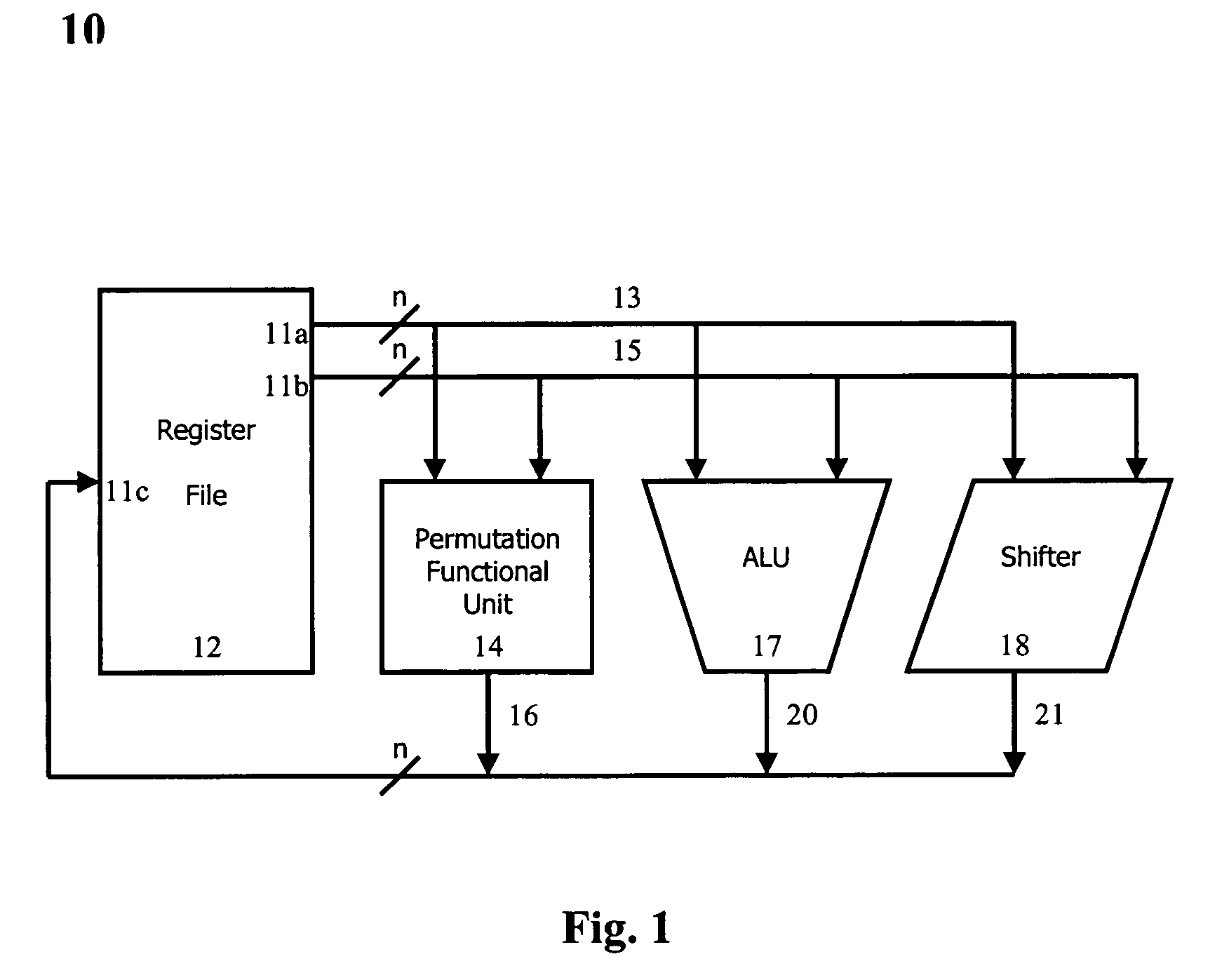
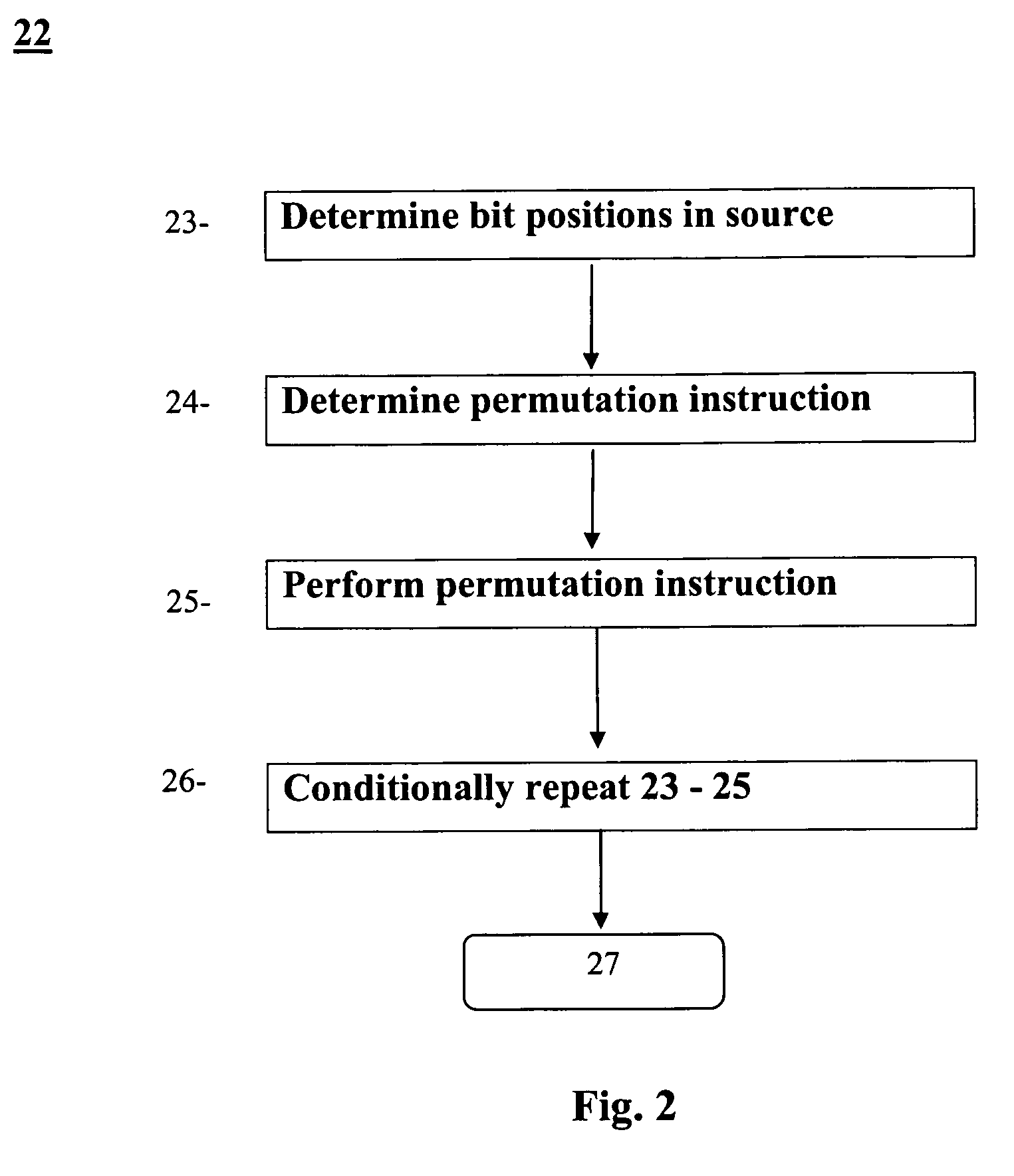
InactiveUS20050149590A1Fast cryptographyEasy to handleDigital computer detailsHandling data according to predetermined rulesParallel computingInstruction sequence
The present invention provides permutation instructions which can be used in software executed in a programmable processor for solving permutation problems in cryptography, multimedia and other applications. PPERM and PPERM3R instructions are defined to perform permutations by a sequence of instructions with each sequence specifying the position in the source for each bit in the destination. In the PPERM instruction bits in the destination register that change are updated and bits in the destination register that do not change are set to zero. In the PPERM3R instruction bits in the destination register that change are updated and bits in the destination register that do not change are copied from intermediate result of previous PPERM3R instructions. Both PPERM and PPERM3R instruction can individually do permutation with bit repetition. Both PPERM and PPERM3R instruction can individually do permutation of bits stored in more than one register. In an alternate embodiment, a GRP instruction is defined to perform permutations. The GRP instruction divides the initial sequence in the source register into two groups depending on control bits. The first group is combined with the second group to form an intermediate sequence toward the desired final permutation. The total number of GRP instructions for a bit level permutation of n bits is not greater than 1gn. The GRP instruction can be used to permute k-bit subwords packed into an n bits word, where k can be 1, 2, . . . , or n bits, and k*r=n. At most 1gr permutation instructions are used in the permutation instruction sequence, where r is the number of k-bit subwords to be permuted. The GRP instruction can also be used to permute 2n bits stored in two n-bit registers. The total number of instructions for bit permutation of 2n bits is 21gn+4, and two of those instructions are SHIFT PAIR instruction.
Owner:TELEPUTERS
Popular searches
Current supply arrangements Number-of-one counters Specific program execution arrangements Computation using denominational number representation Next instruction address formation Concurrent instruction execution Power supply for data processing Memory systems Data conversion Architecture with single central processing unit
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com