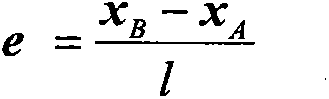Patents
Literature
180 results about "Transpose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
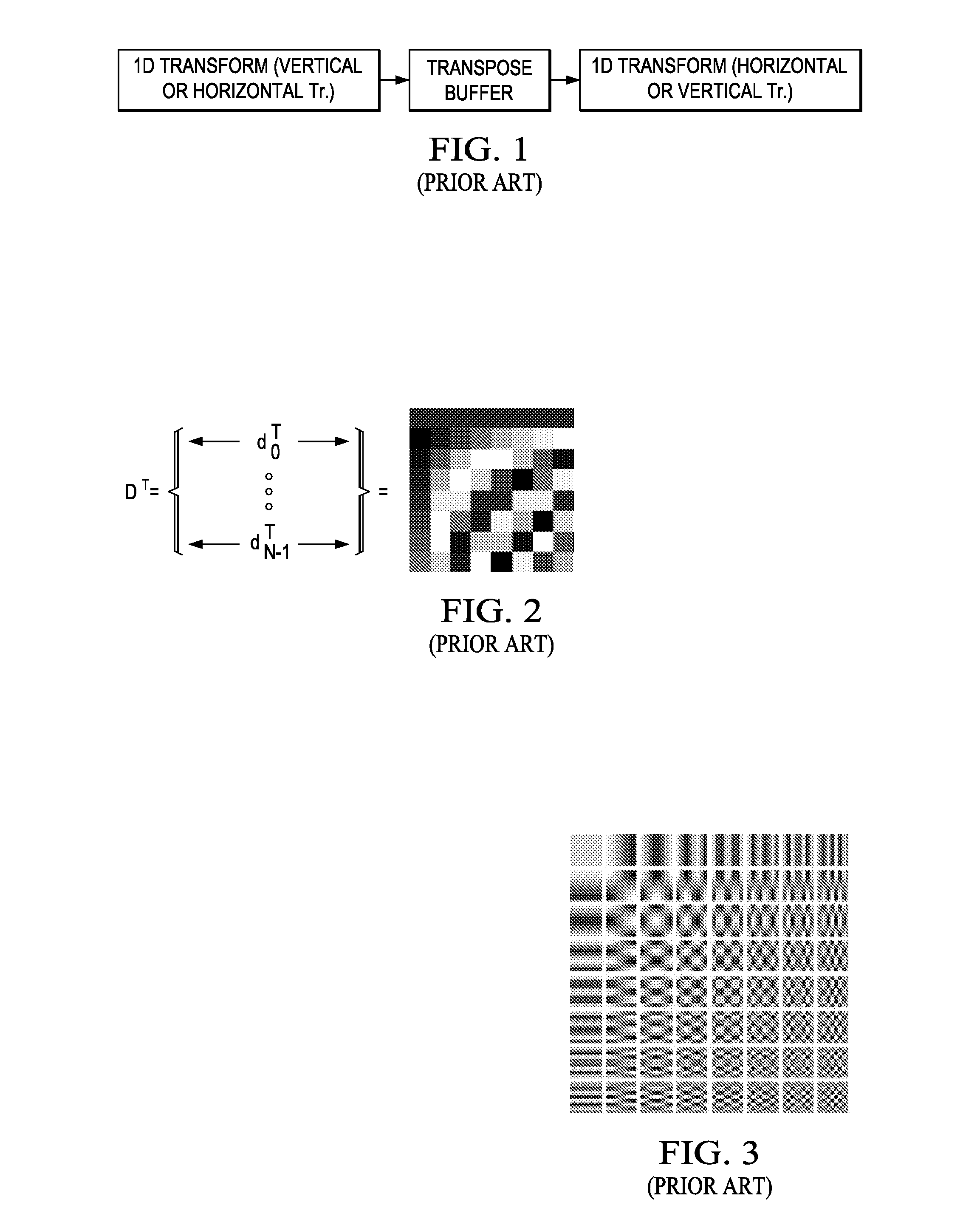
In linear algebra, the transpose of a matrix is an operator which flips a matrix over its diagonal, that is it switches the row and column indices of the matrix by producing another matrix denoted as Aᵀ (also written A′, Aᵗʳ, A or Aᵗ). It is achieved by any one of the following equivalent actions: reflect A over its main diagonal (which runs from top-left to bottom-right) to obtain Aᵀ, write the rows of A as the columns of Aᵀ, write the columns of A as the rows of Aᵀ.
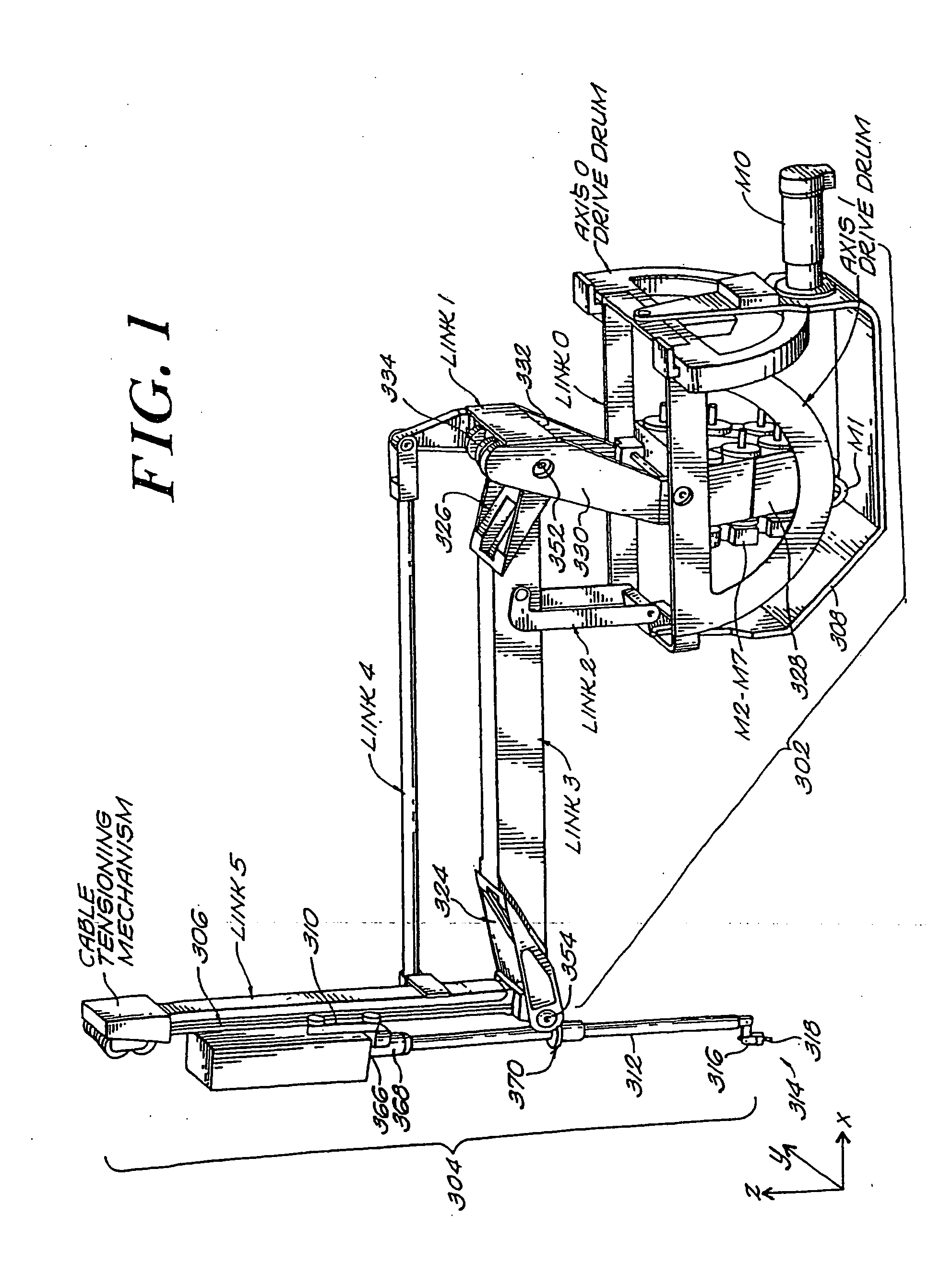
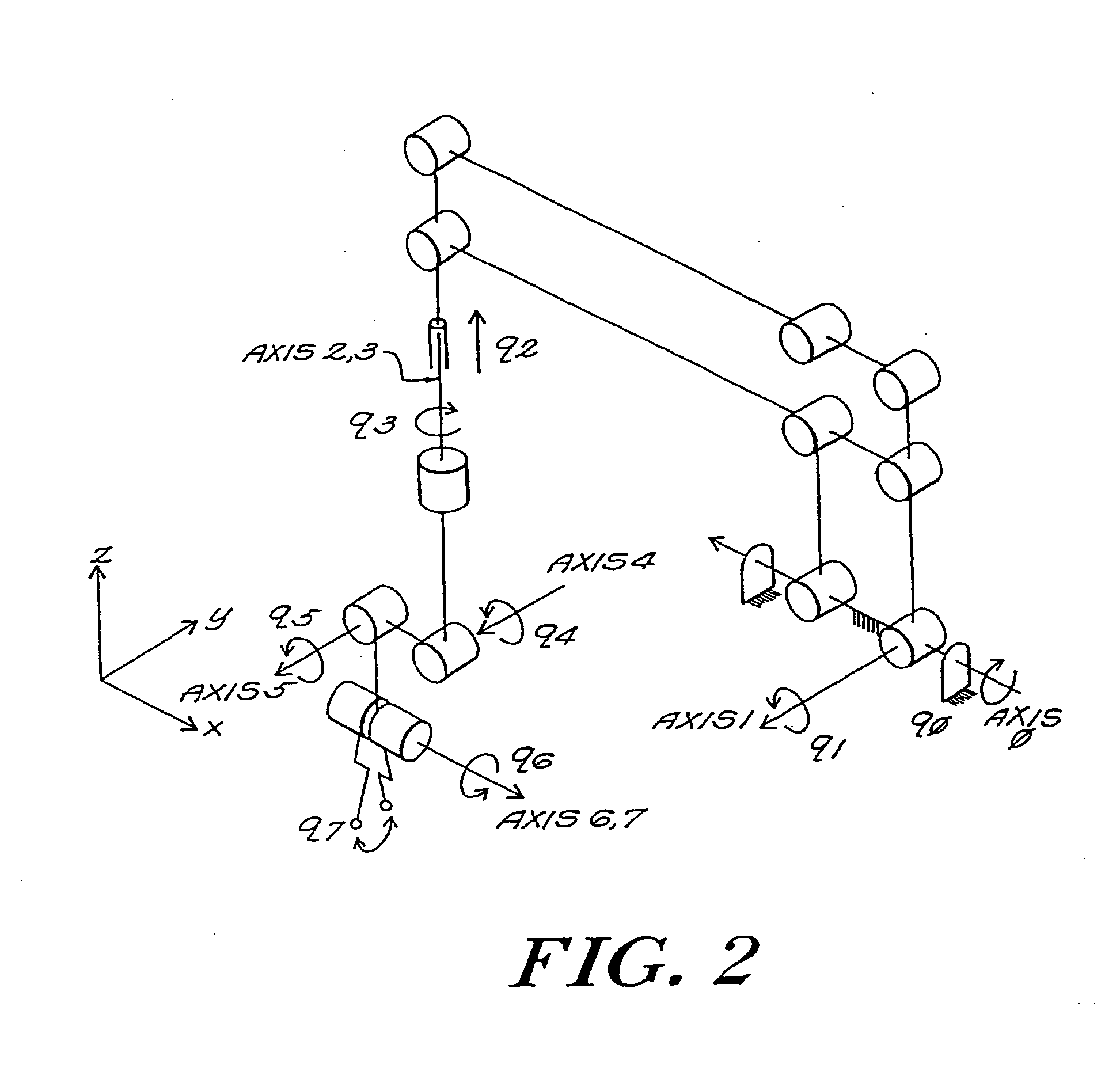
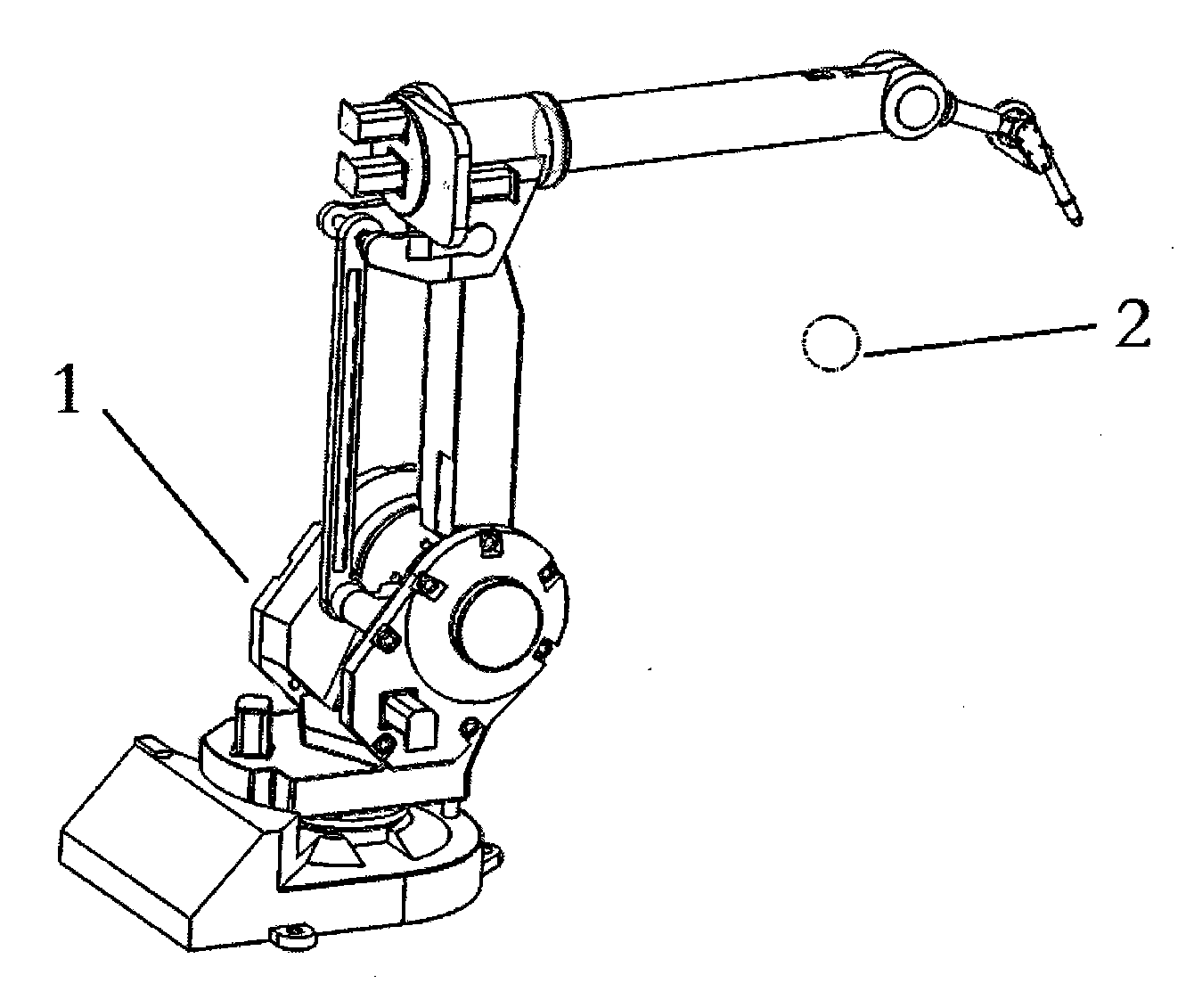
Robotic apparatus
InactiveUS20090012534A1Minimize cost functionProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsRobot end effectorEngineering
A robotic apparatus has eight actuators (M0-M7) and a linkage (LINK 0-LINK 5) that actuates an end effector. Three serial macro freedoms have large ranges of motion and inertias. Four serial micro freedoms have small ranges of motion and inertias. Translation of the end effector in an y direction is actuated by at least one micro joint and at least one macro joint. The apparatus can be part of a master and slave combination, providing force feedback without any explicit force sensors. The slave is controlled with an Inverse Jacobian controller, and the mater with a Jacobian Transpose controller. A slave having more degrees of freedom (DOFs) than the master can be controlled. A removable effector unit actuates its DOFs with cables. Beating heart surgery can be accomplished by commanding the slave to move with a beating heart and cancelling out any such motion in the motions perceived by the master.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
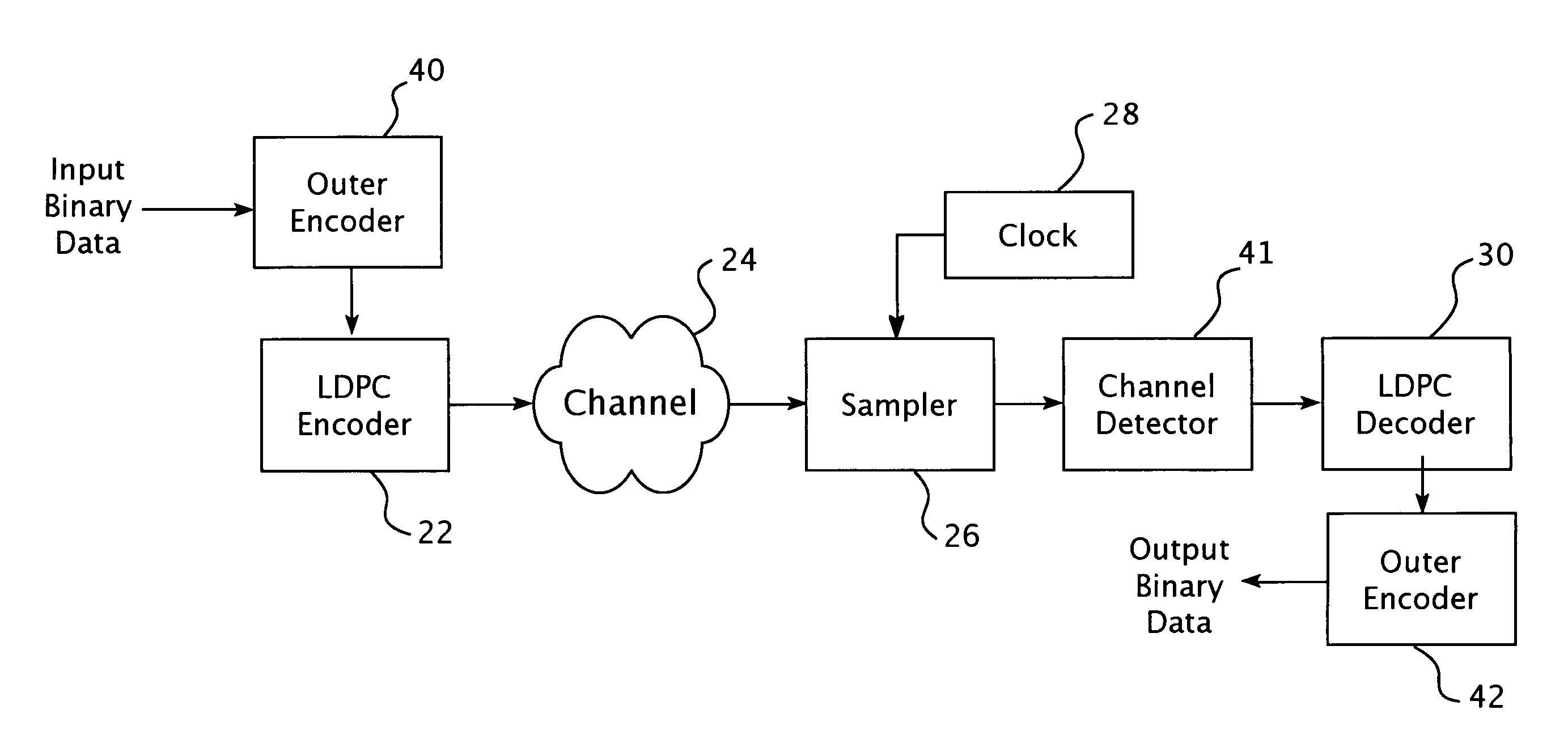
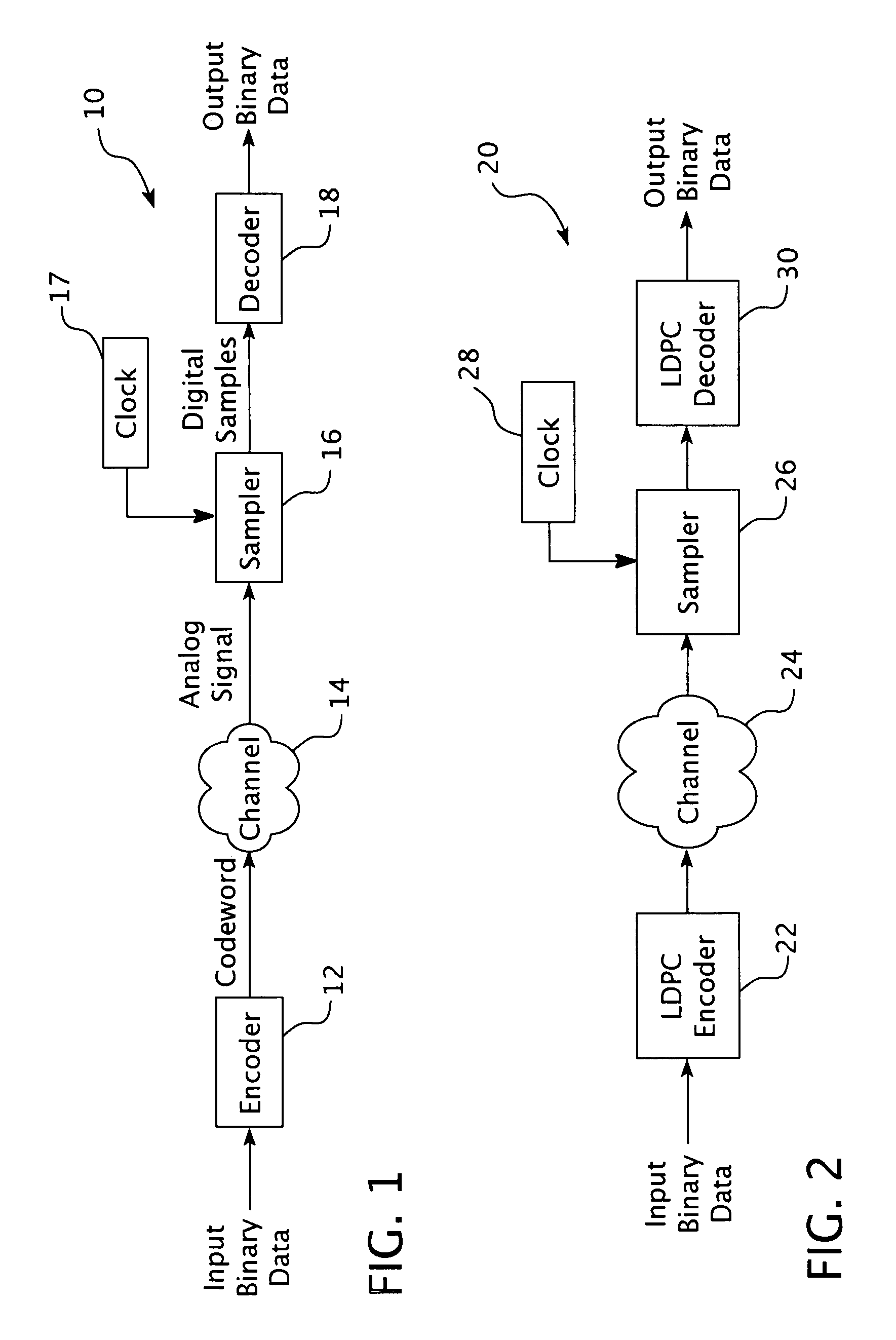
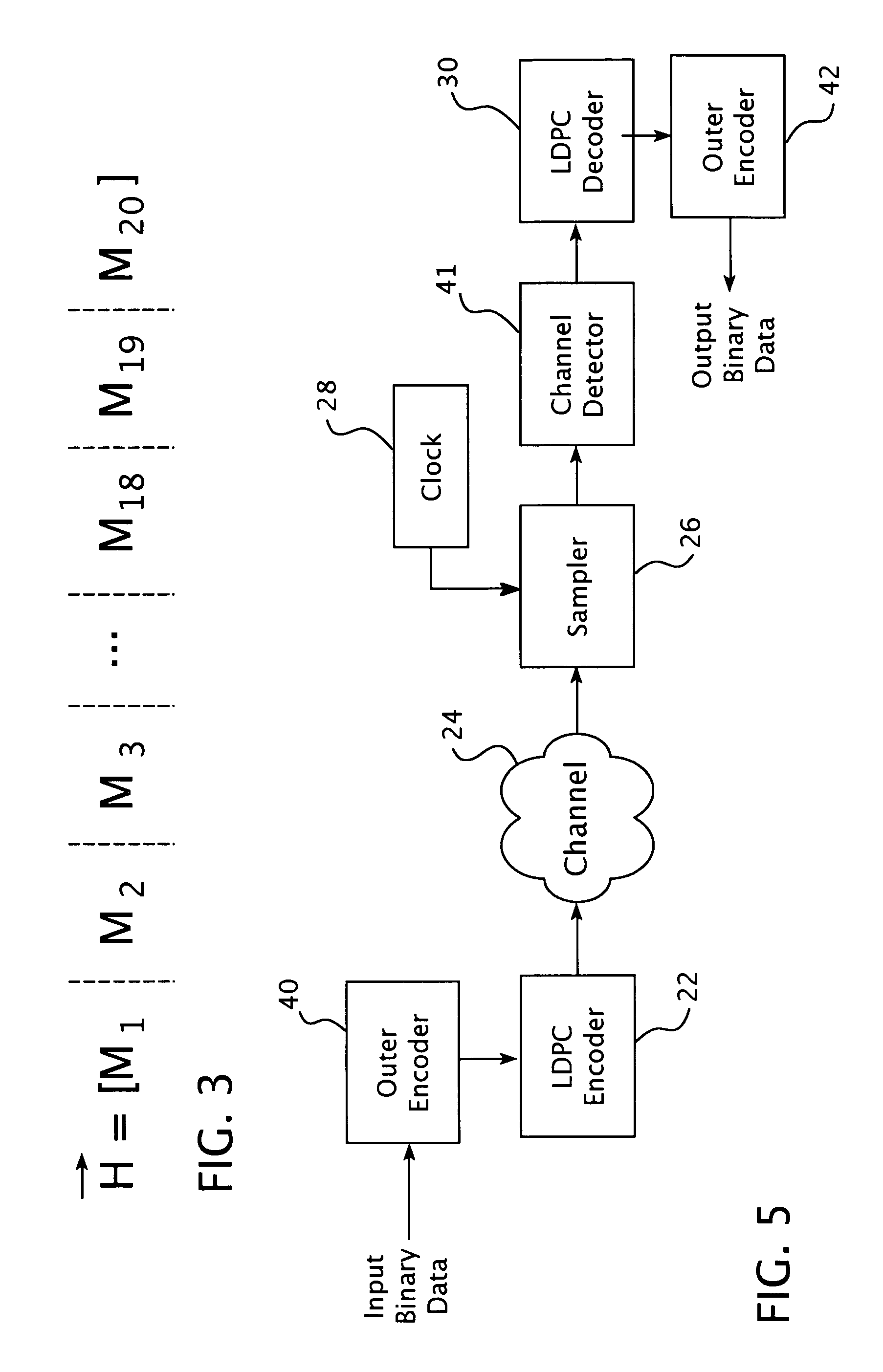
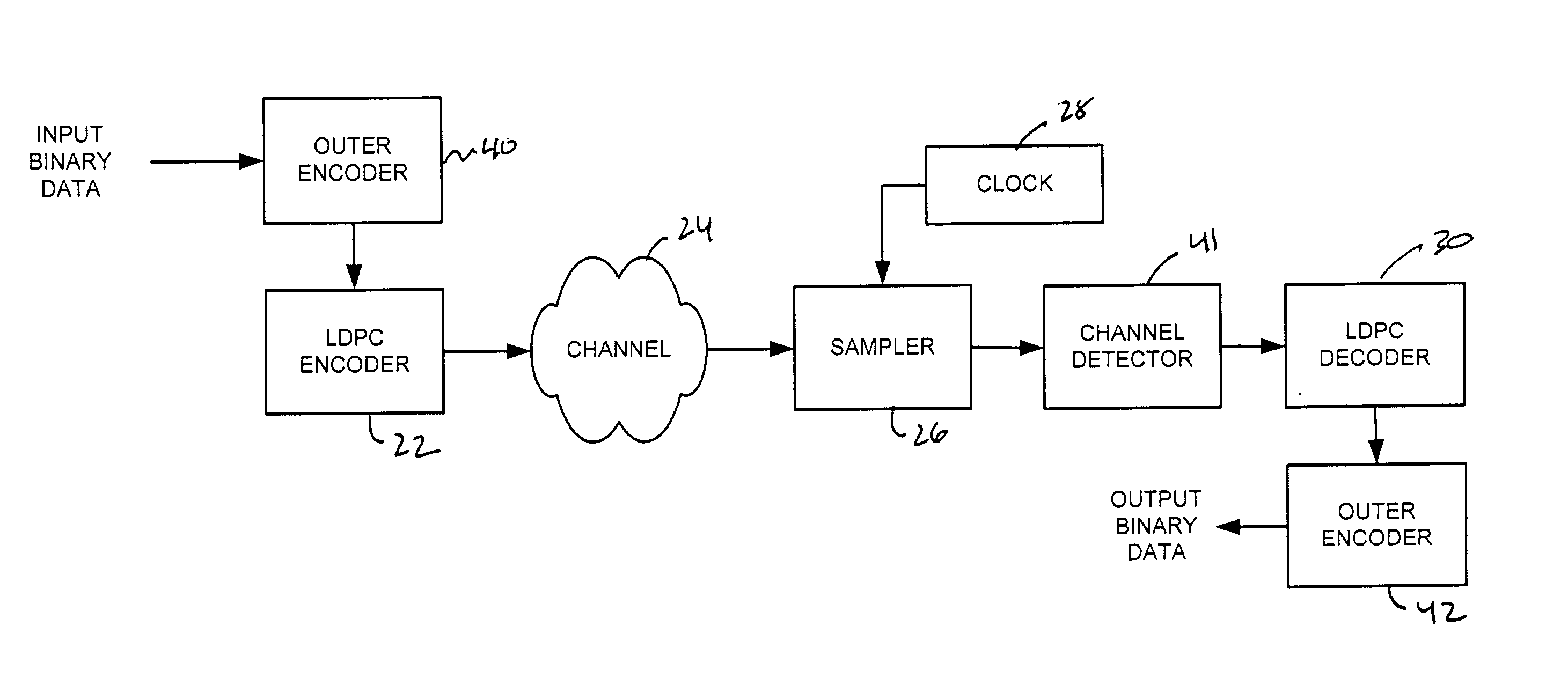
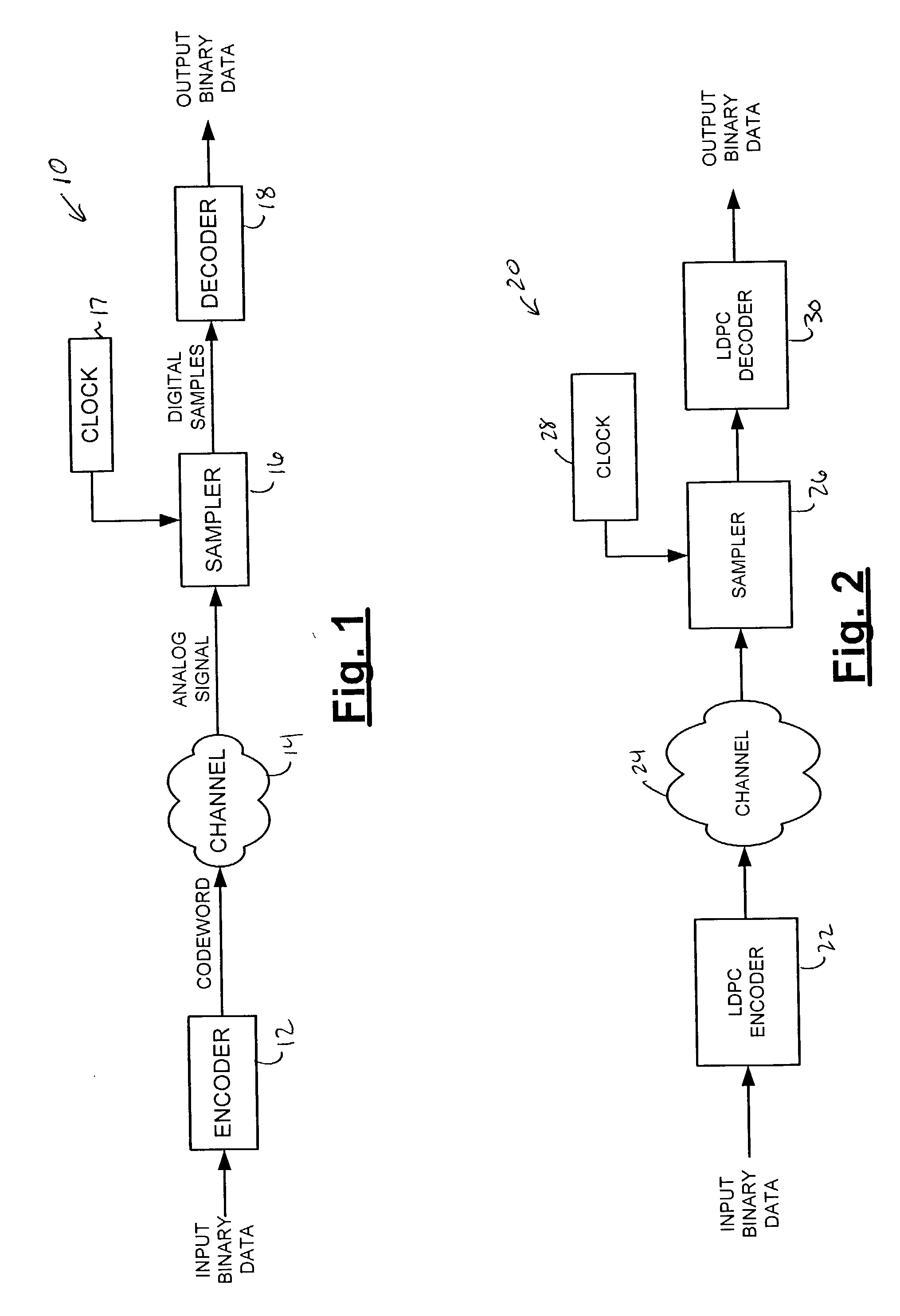
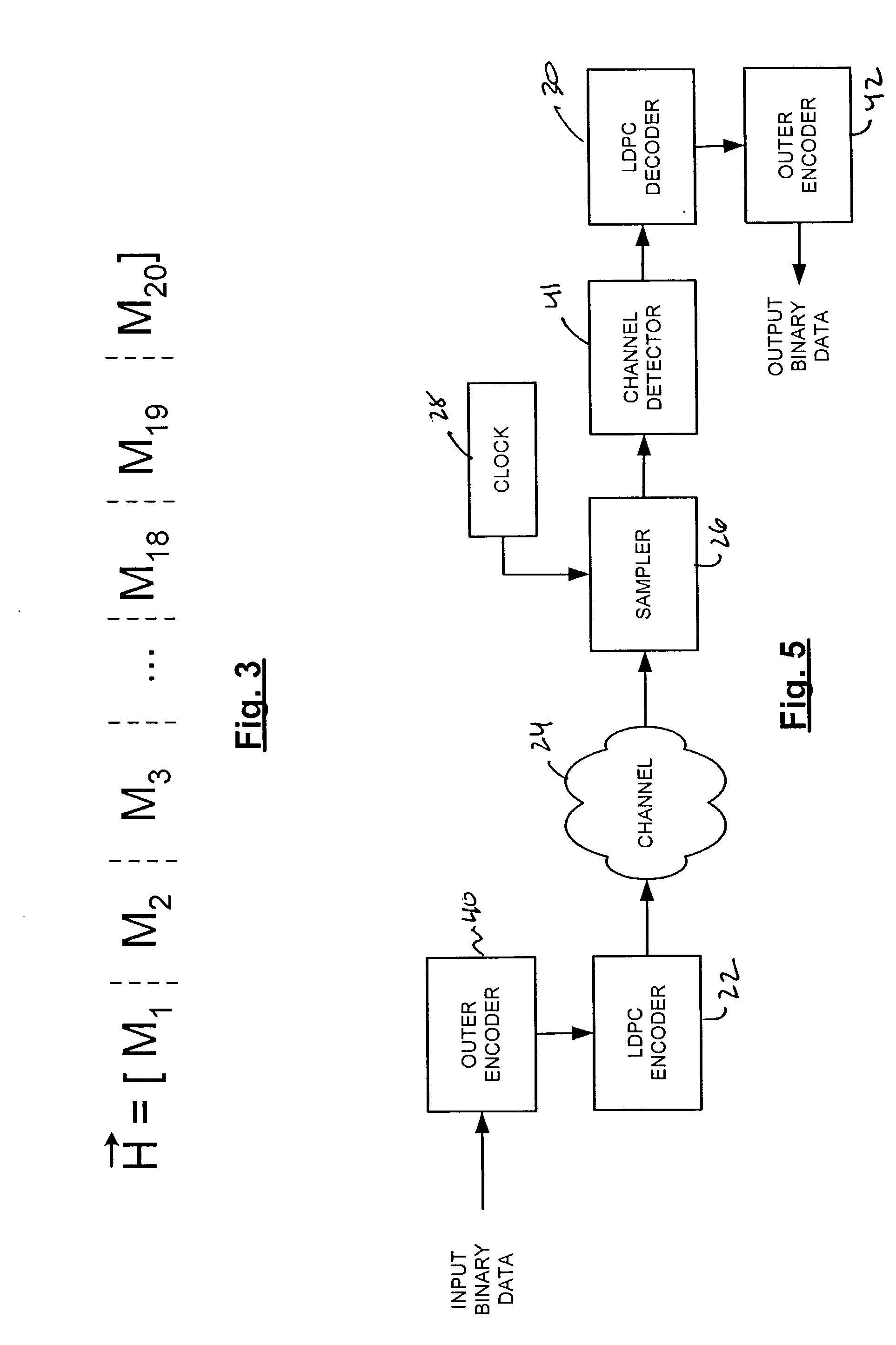
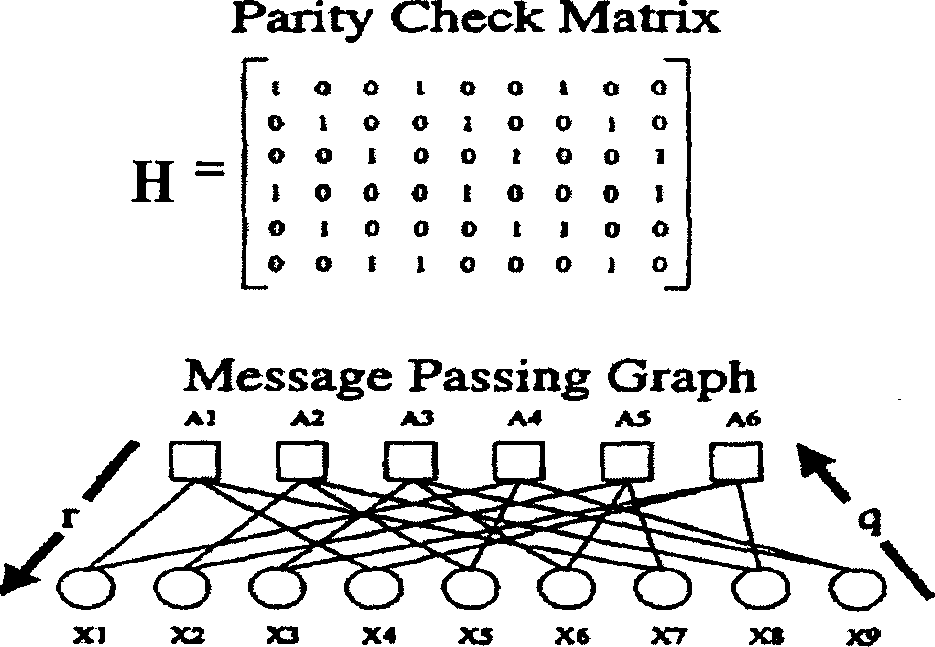
Encoding method using a low density parity check code with a column weight of two
ActiveUS7058873B2Facilitate the processOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTanner graphCommunications system
A method for communicating binary data and a digital communication system are presented. According to one embodiment, the method includes encoding a message word by multiplying the message word with a generator matrix, wherein the generator matrix multiplied by the transpose of a parity check matrix for a low density parity check code yields a null set, and wherein the parity check matrix has a column weight of two. Additionally disclosed is an encoding scheme based on a three-tier Tanner graph having a girth of twelve.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
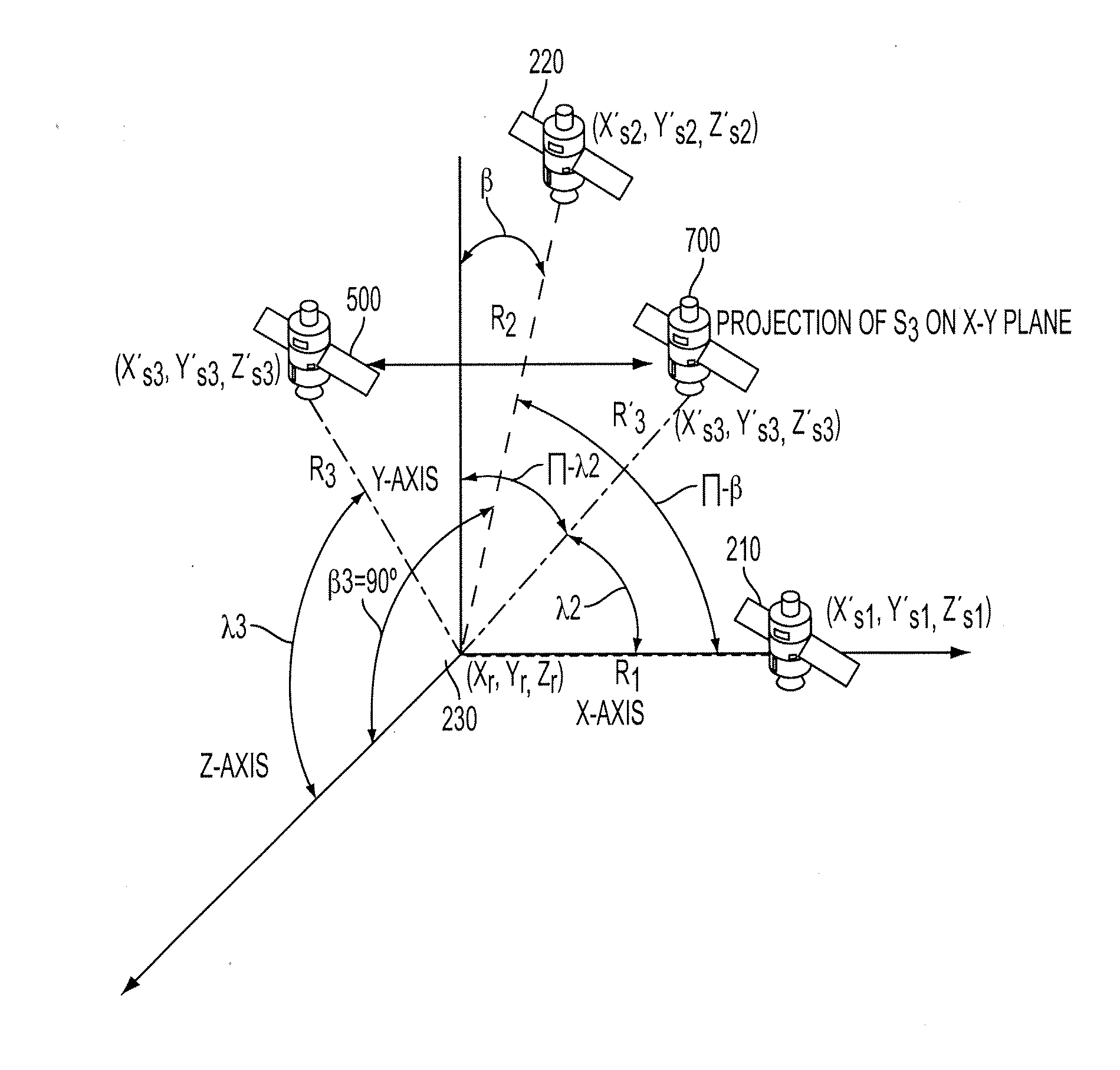
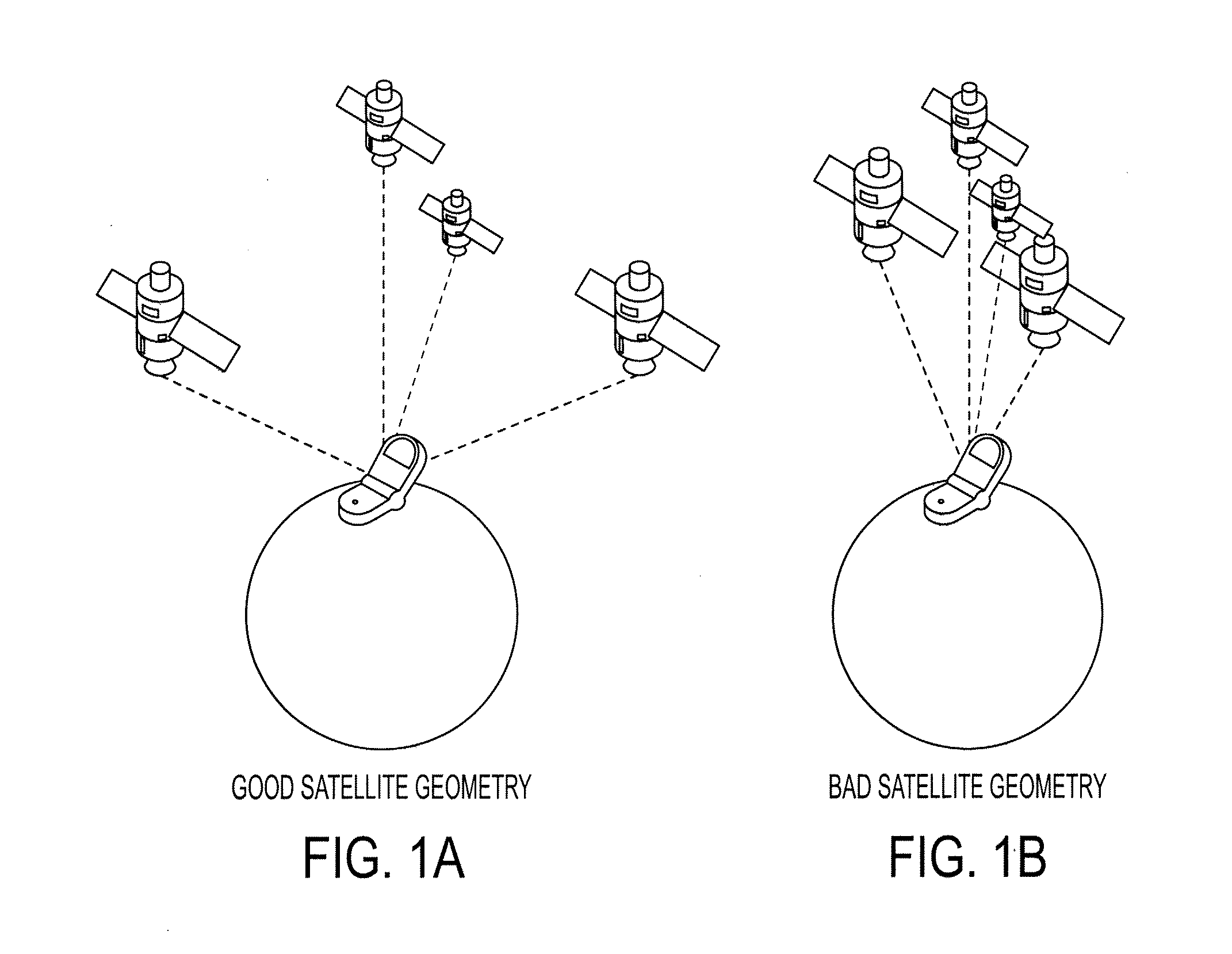
Determining A Dilution of Precision Metric Using Two or Three GPS Satellites
The disclosed subject matter relates to a method for determining a Dilution of Precision Metric (DOP) with less than four satellites in a hybrid positioning system. In some embodiments, the method includes determining an initial position estimate of a device using a non-satellite positioning system, obtaining satellite measurements from less than four satellites, wherein the measurements include each satellite's position with respect to the initial position estimate, constructing a geometry matrix corresponding to the measurements from the less than four satellites using each satellite's position and the initial position estimate, multiplying the geometry matrix by its transpose to construct an H matrix, determining an inverse of the H matrix, and determining the DOP based on a sum of the diagonal elements of the inverse H matrix. In some embodiments, the non-satellite positioning system is a WLAN positioning system.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Matrix transposition in a computer system
ActiveUS7031994B2Improves speed and parallelabilityEasy transpositionHandling data according to predetermined rulesGeneral purpose stored program computerAlgorithmComputerized system
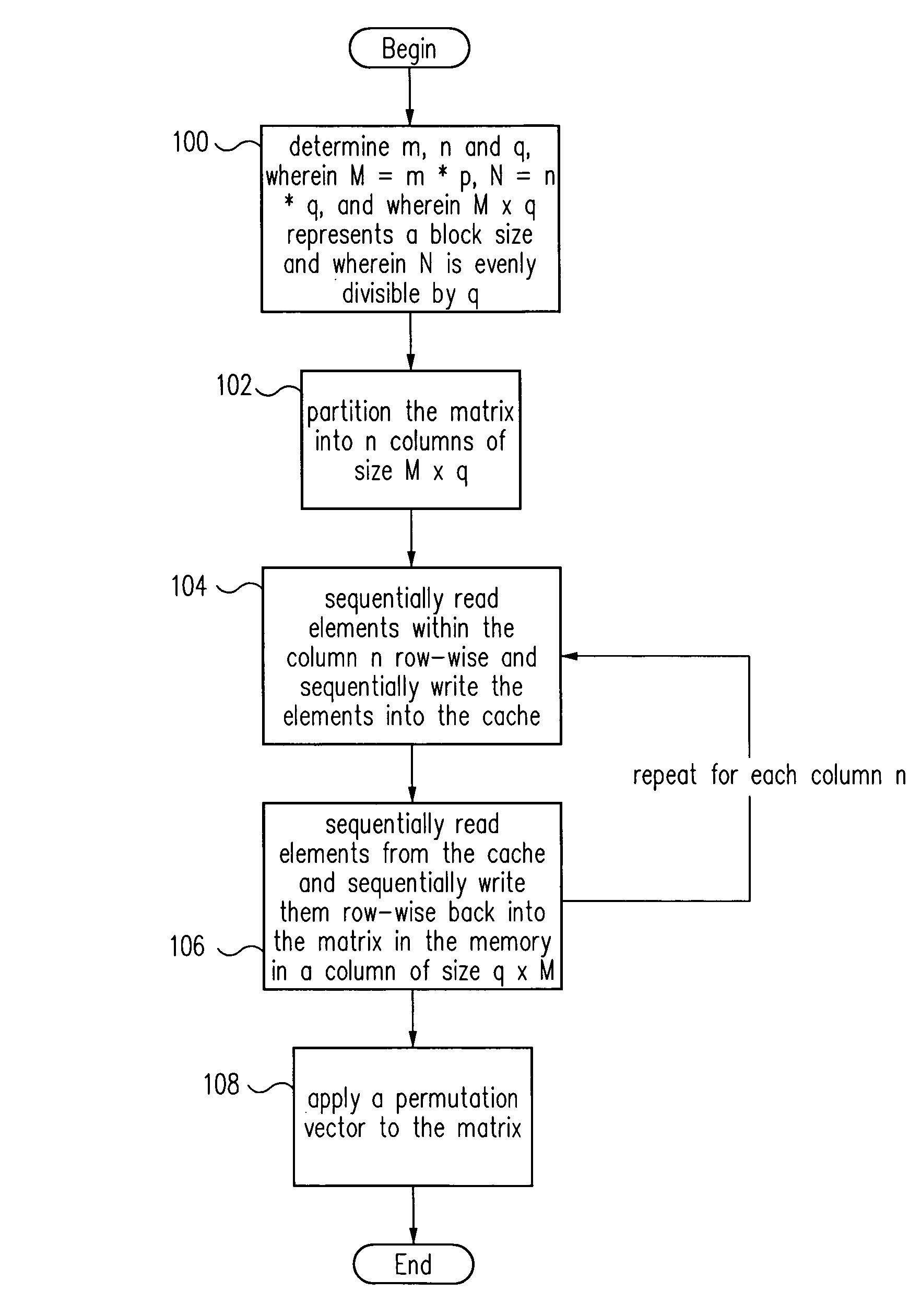
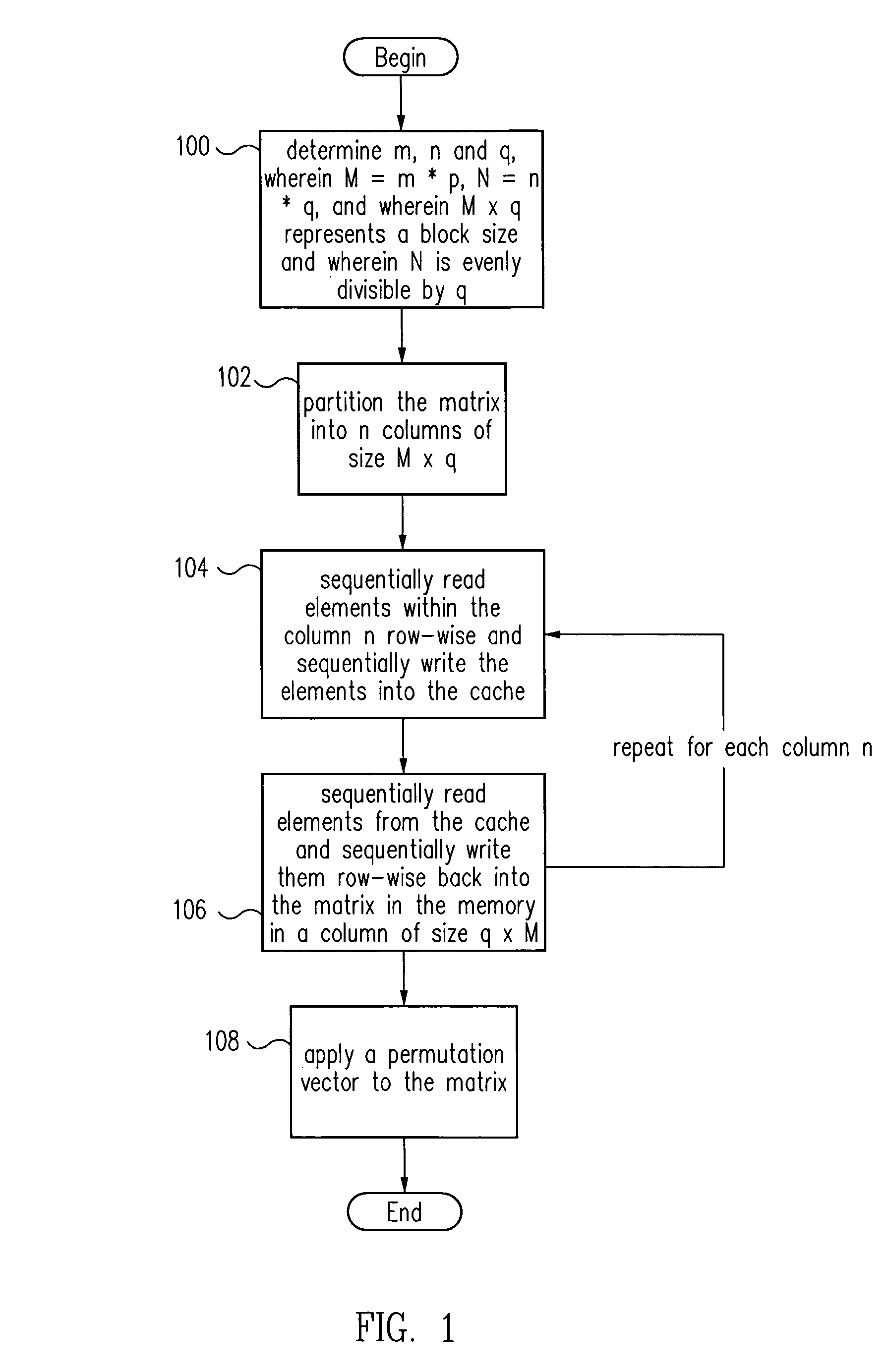
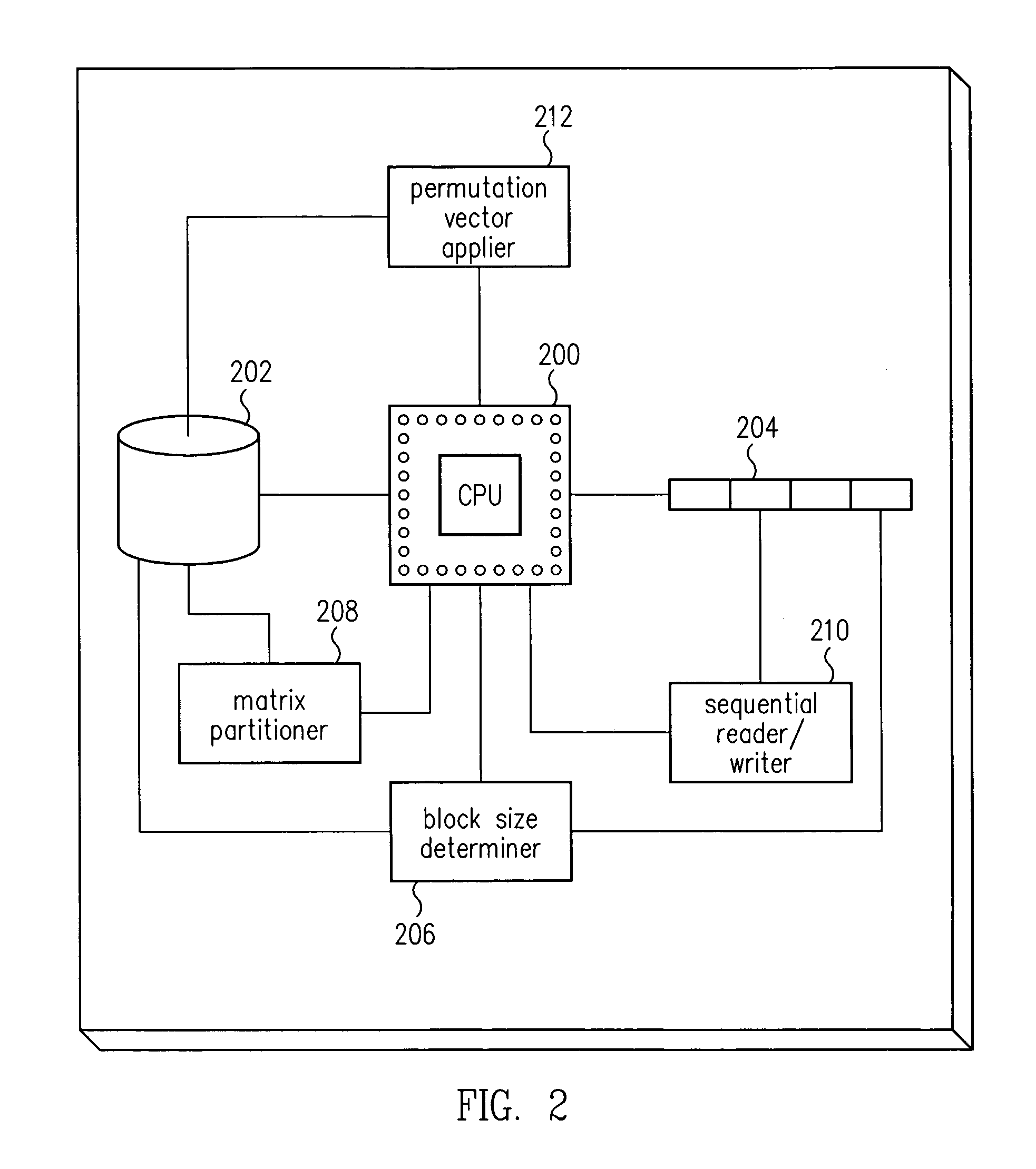
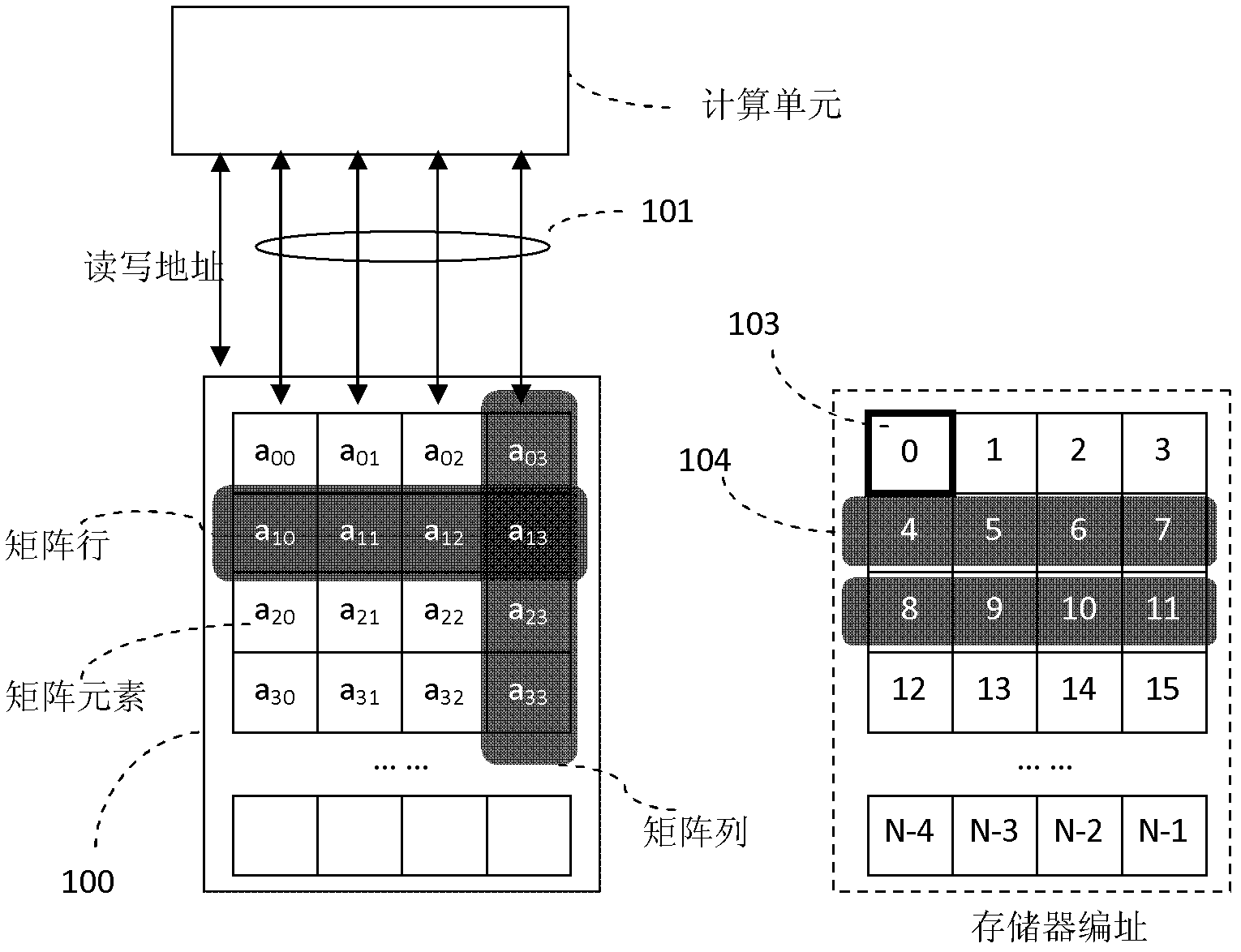
Improved transposition of a matrix in a computer system may be accomplished while utilizing at most a single permutation vector. This greatly improves the speed and parallelability of the transpose operation. For a standard rectangular matrix having M rows and N columns and a size M×N, first n and q are determined, wherein N=n*q, and wherein M×q represents a block size and wherein N is evenly divisible by p. Then, the matrix is partitioned into n columns of size M×q. Then for each column n, elements are sequentially read within the column row-wise and sequentially written into a cache, then sequentially read from the cache and sequentially written row-wise back into the matrix in a memory in a column of size q×M. A permutation vector may then be applied to the matrix to arrive at the transpose. This method may be modified for special cases, such as square matrices, to further improve efficiency.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Encoding method using a low density parity check code with a column weight of two
ActiveUS20040093549A1Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTanner graphCommunications system
A method for communicating binary data and a digital communication system are presented. According to one embodiment, the method includes encoding a message word by multiplying the message word with a generator matrix, wherein the generator matrix multiplied by the transpose of a parity check matrix for a low density parity check code yields a null set, and wherein the parity check matrix has a column weight of two. Additionally disclosed is an encoding scheme based on a three-tier Tanner graph having a girth of twelve.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
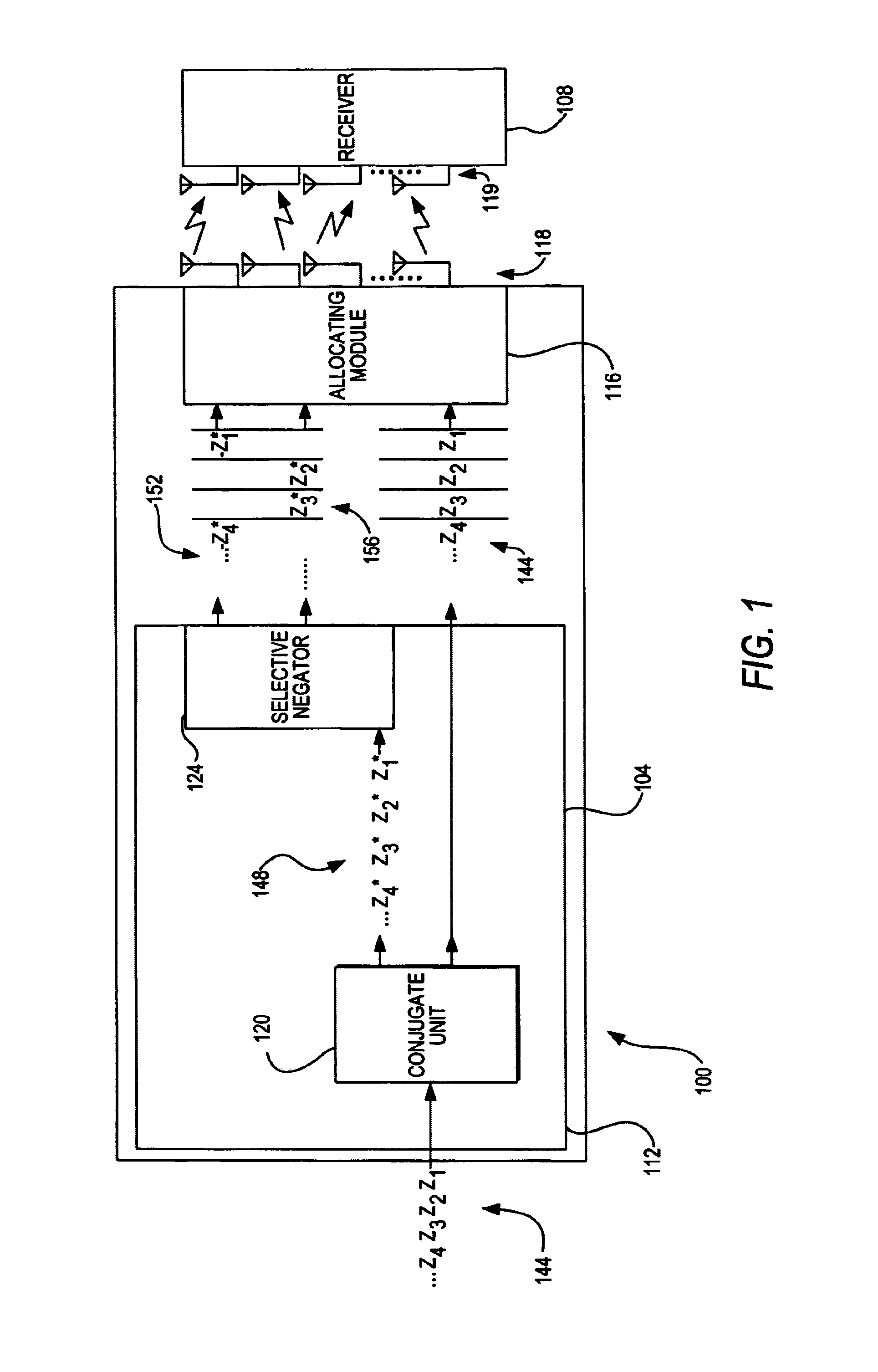
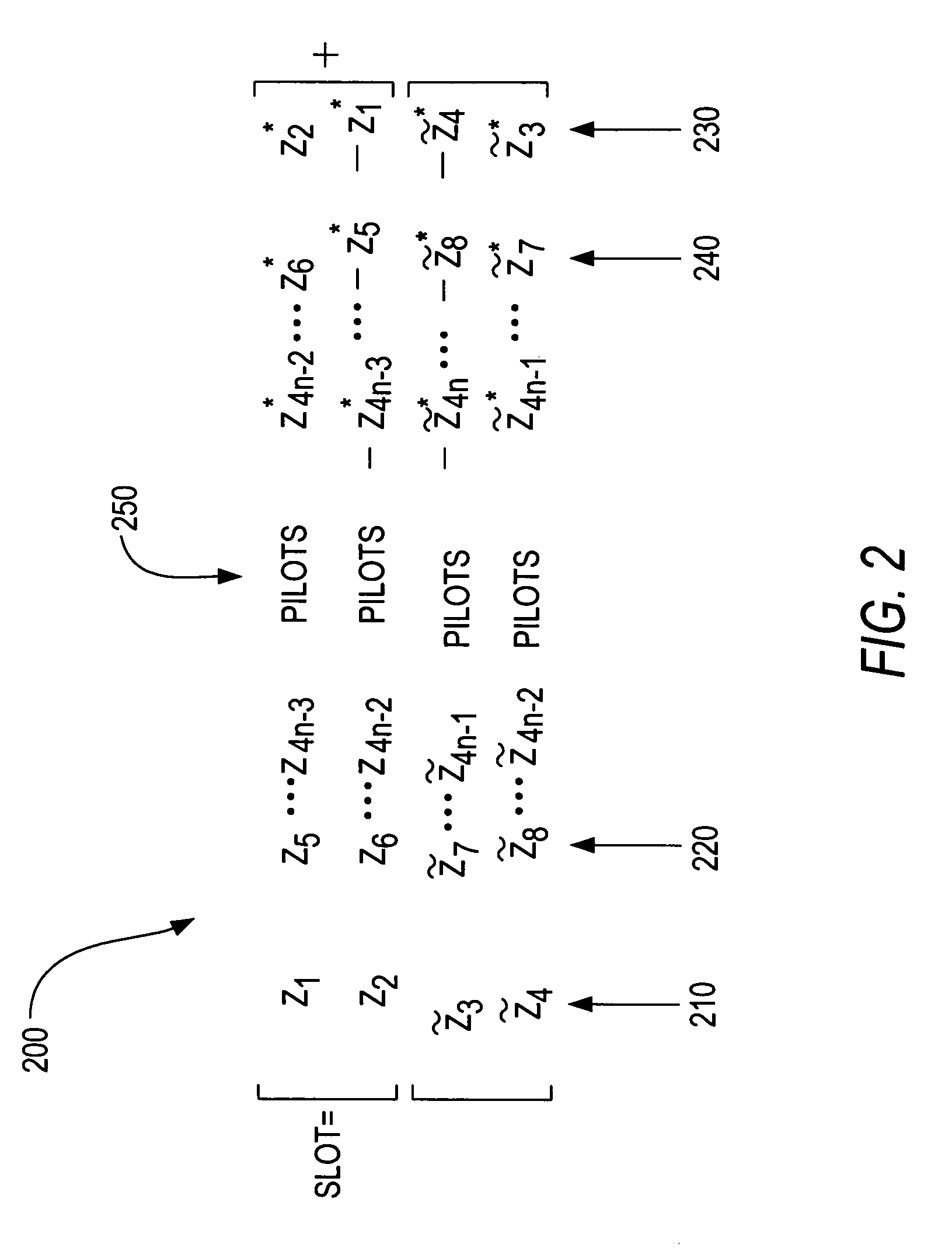
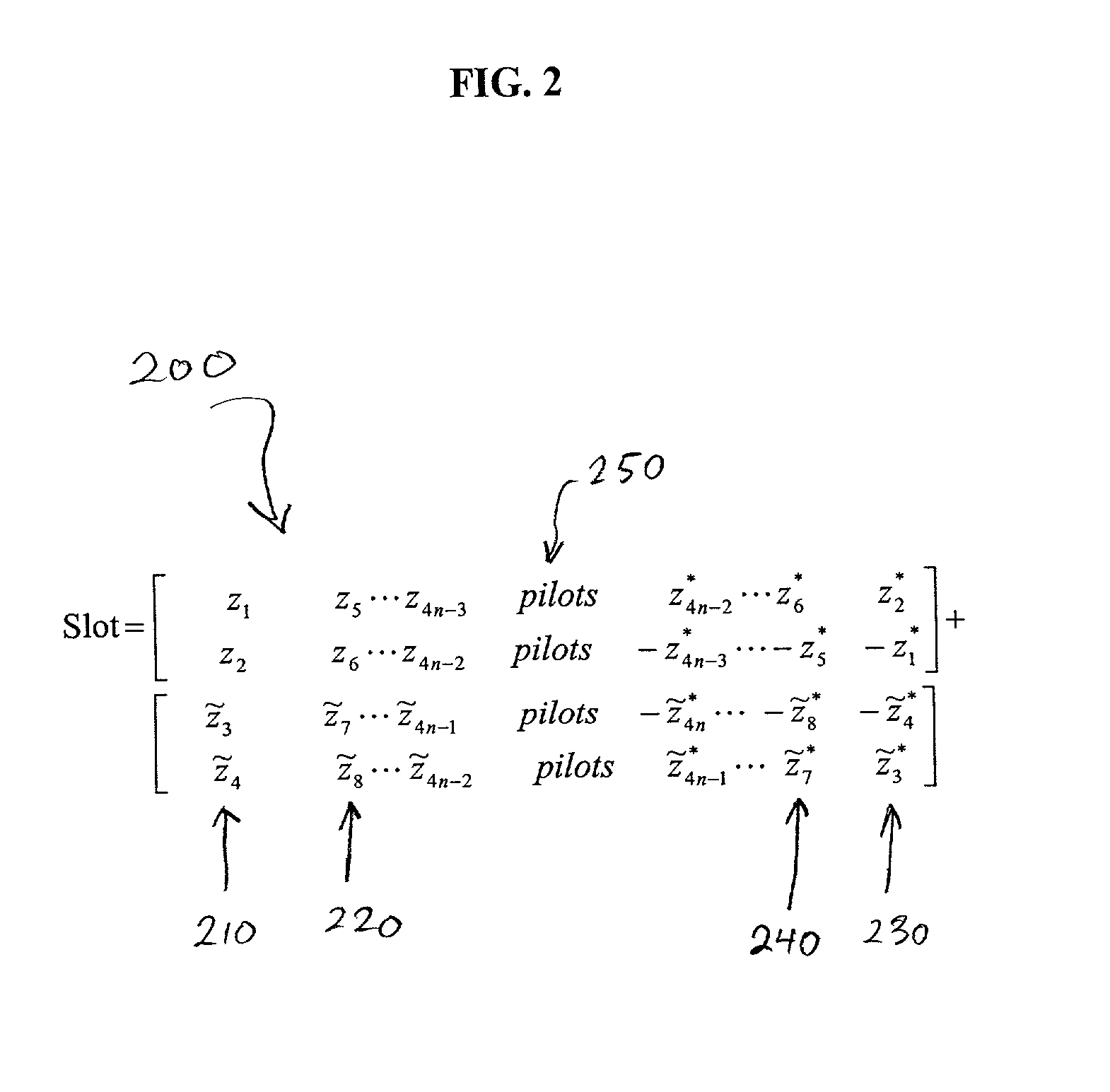
ISI-robust slot formats for non-orthogonal-based space-time block codes
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
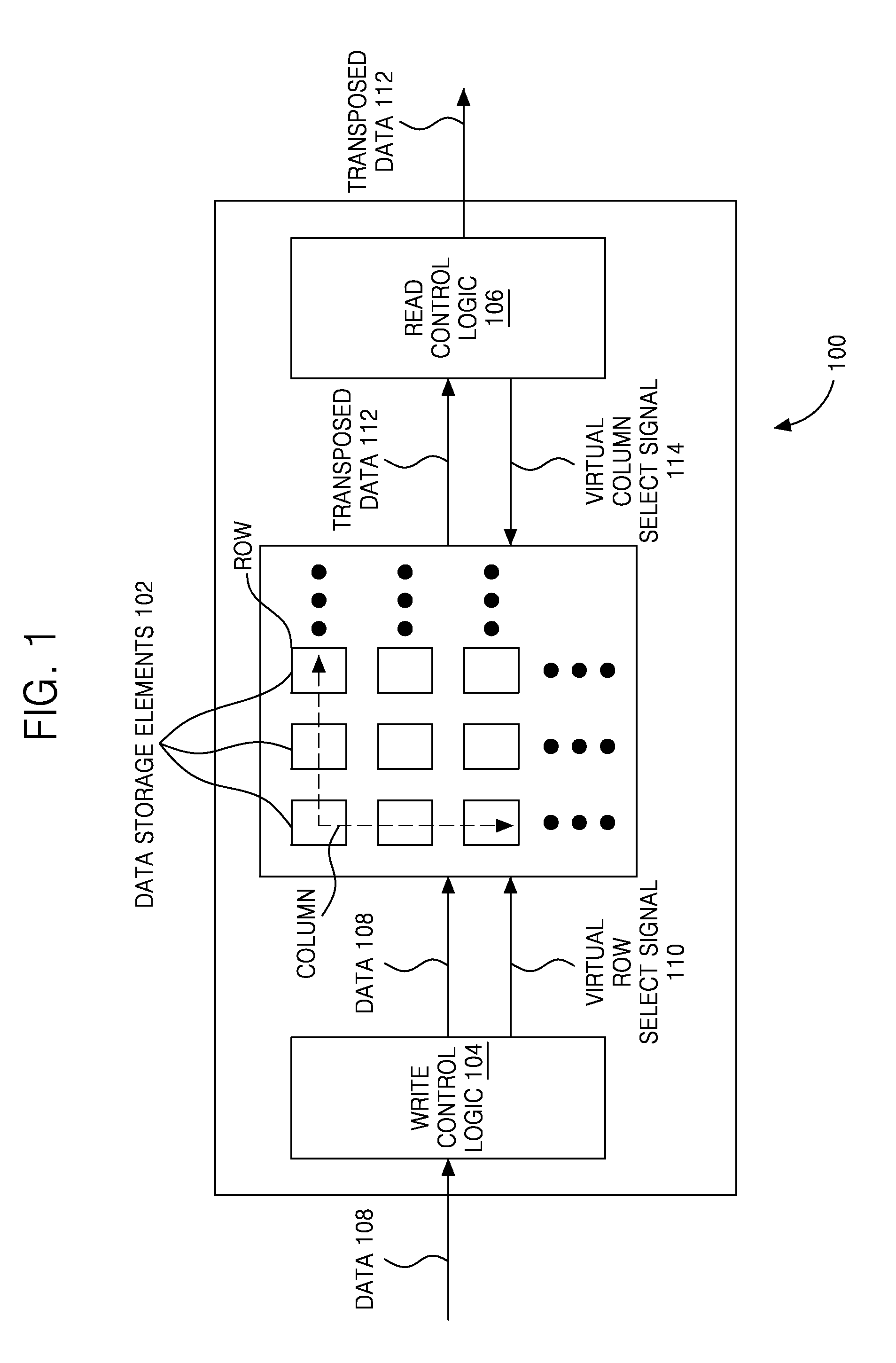
System and method for successive matrix transposes
InactiveUS20110264723A1Handling data according to predetermined rulesData mergingComputer architectureTranspose
A system and method for successively transposing a matrix is disclosed. The device includes a plurality of data storage elements arranged as a two dimensional (2D) structure including X rows and Y columns. The device further includes write control logic coupled to the input of plurality of data storage elements for writing data in at least one virtual row. The device also includes read control logic coupled to the output of the plurality of data storage elements for reading the data from at least one virtual column, where the data write to the at least one virtual row and the data read from the at least one virtual column are performed substantially simultaneously during each cycle of operation such that the 2D structure is transposed successively with zero cycle delay between successive transposes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
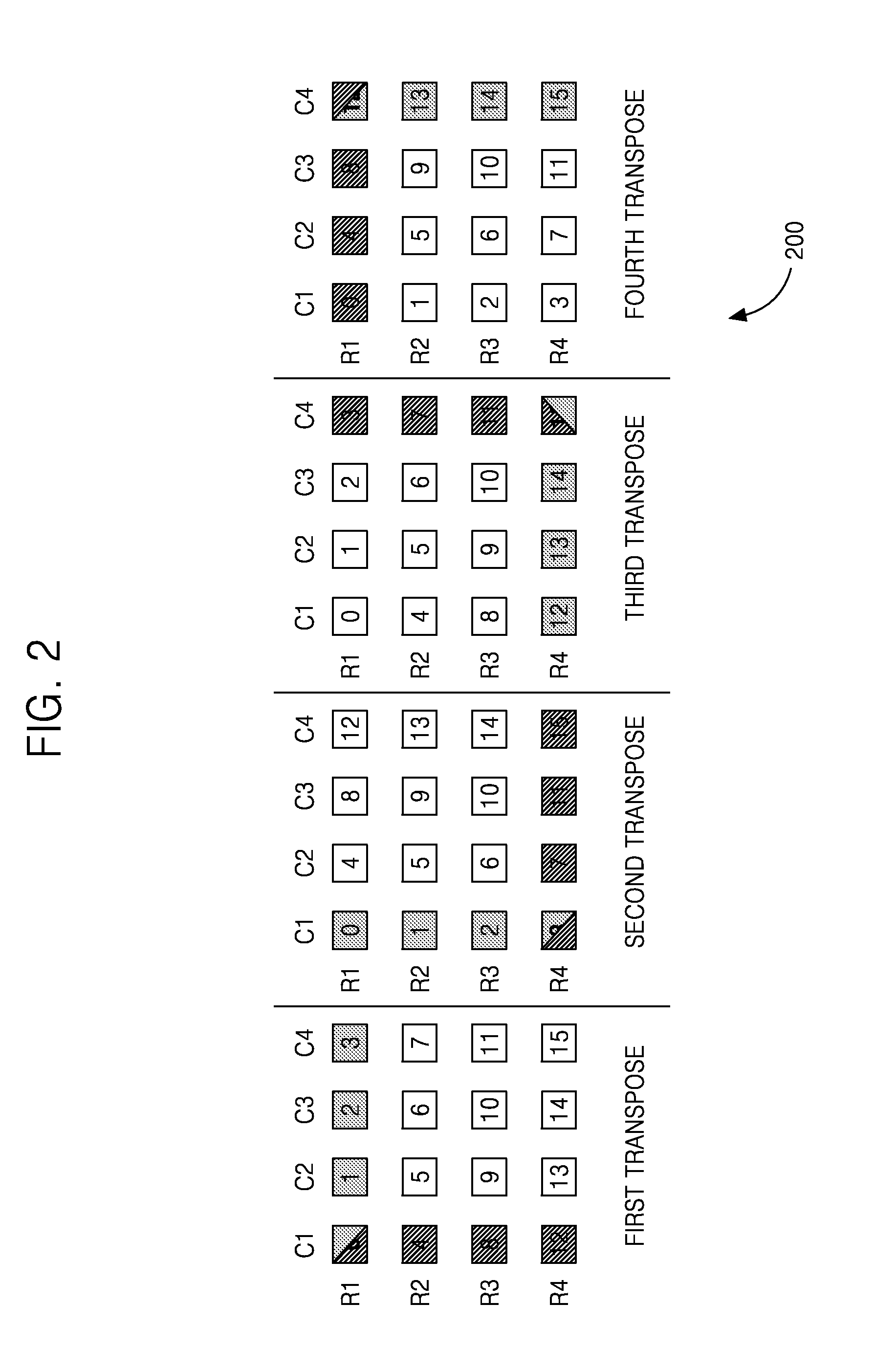
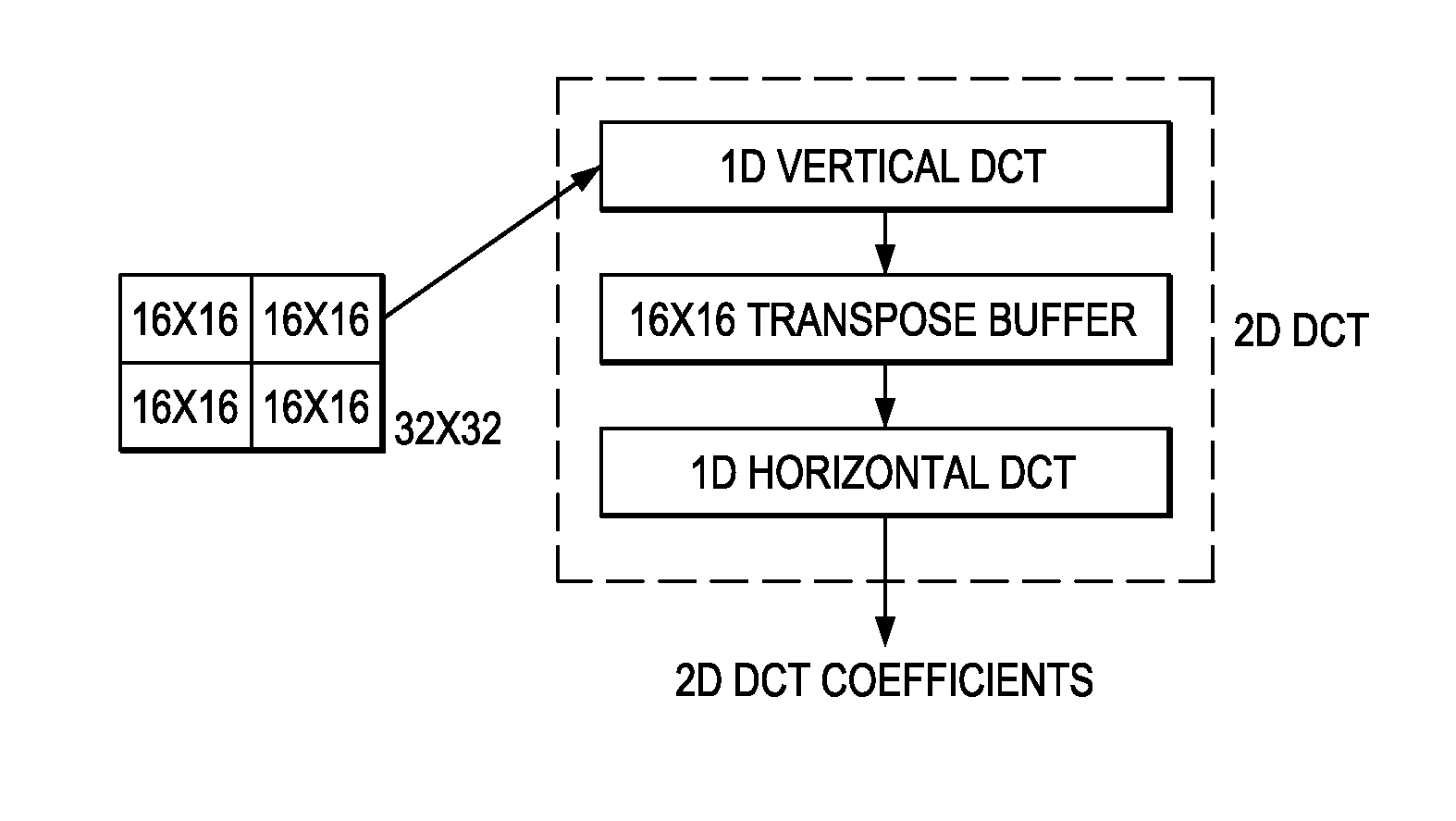
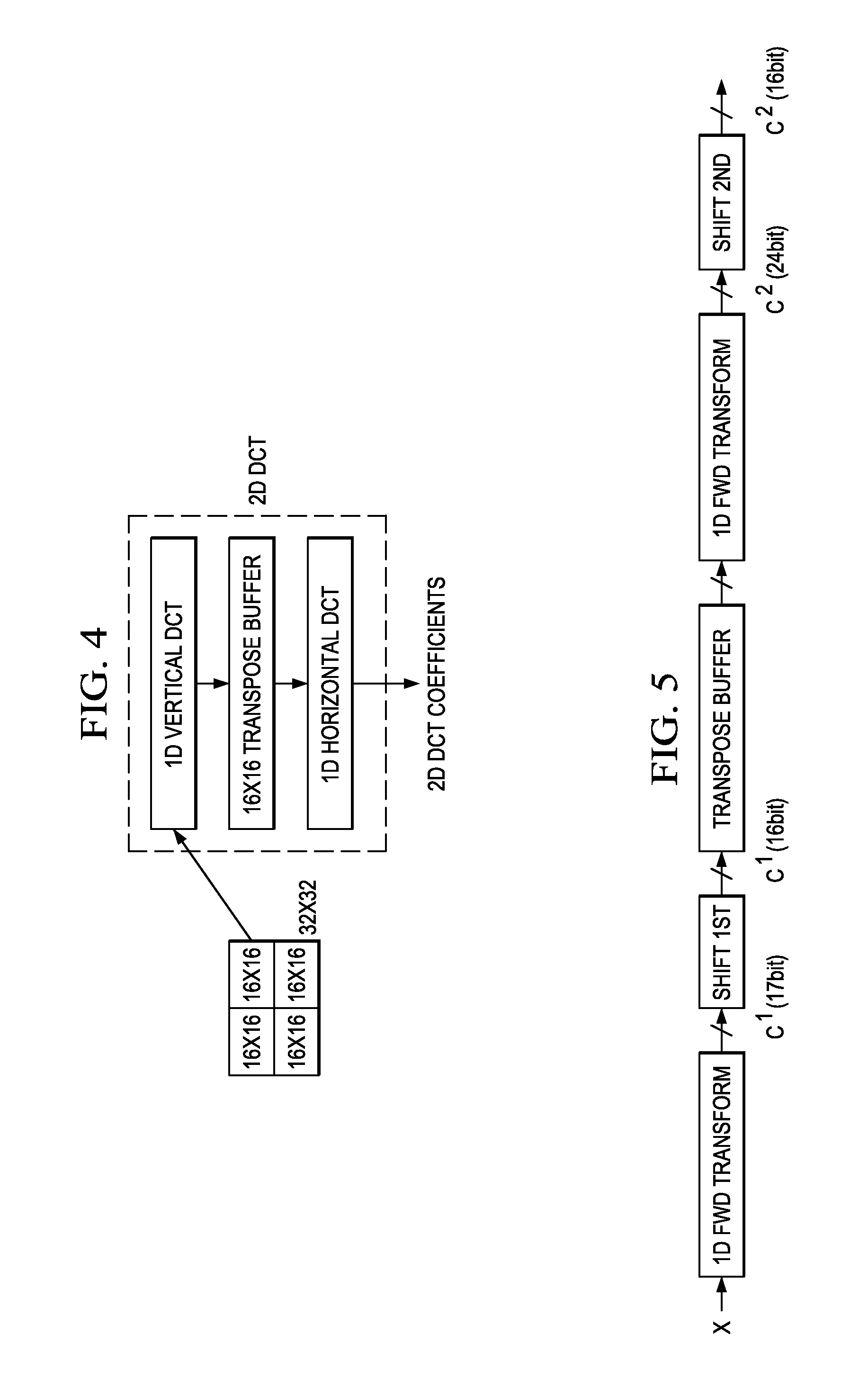
Low-Complexity Two-Dimensional (2D) Separable Transform Design with Transpose Buffer Management
ActiveUS20130243083A1Reduce bit widthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel computingTranspose
Methods are provided for reducing the size of a transpose buffer used for computation of a two-dimensional (2D) separable transform. Scaling factors and clip bit widths determined for a particular transpose buffer size and the expected transform sizes are used to reduce the size of the intermediate results of applying the 2D separable transform. The reduced bit widths of the intermediate results may vary across the intermediate results. In some embodiments, the scaling factors and associated clip bit widths may be adapted during encoding.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
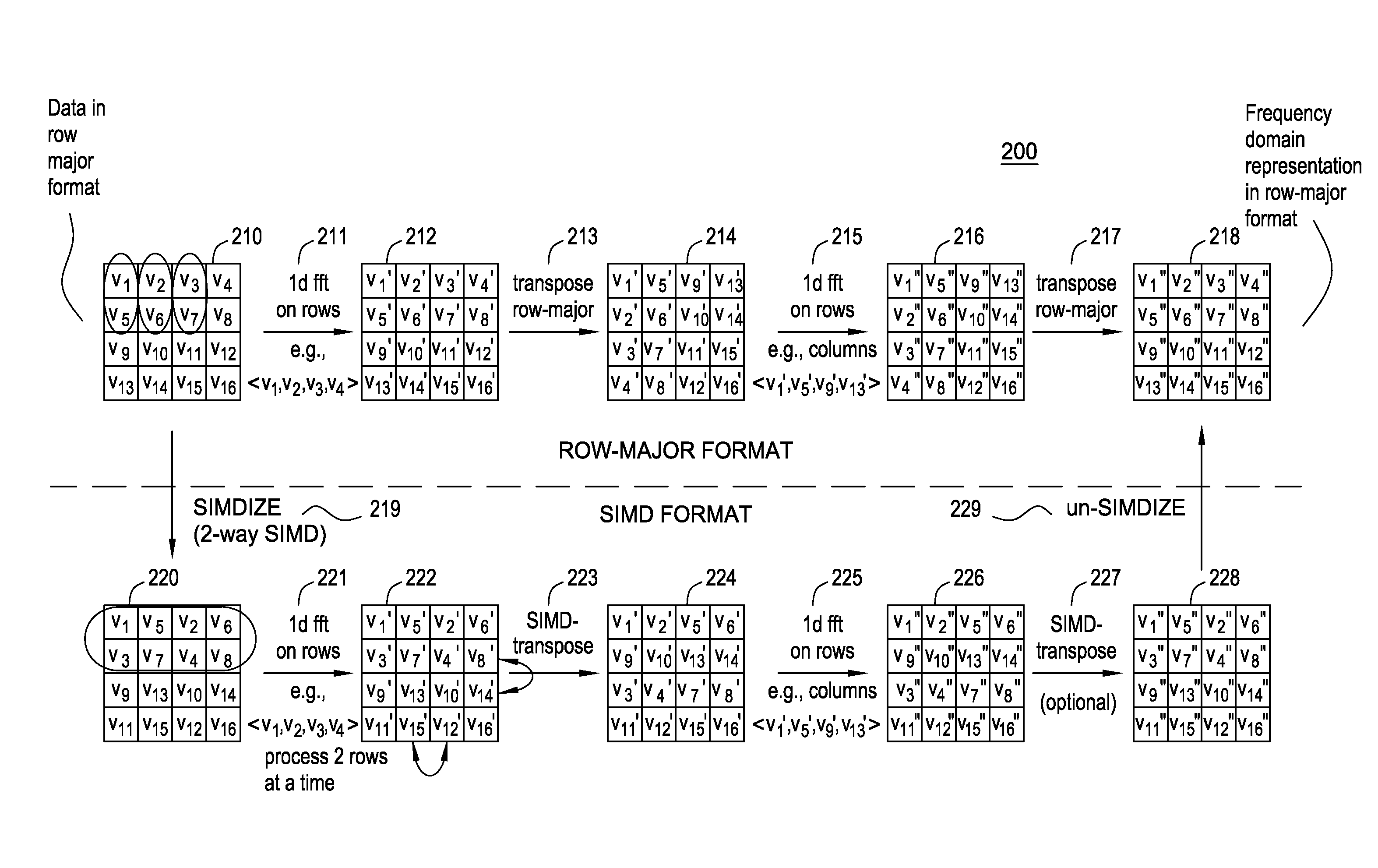
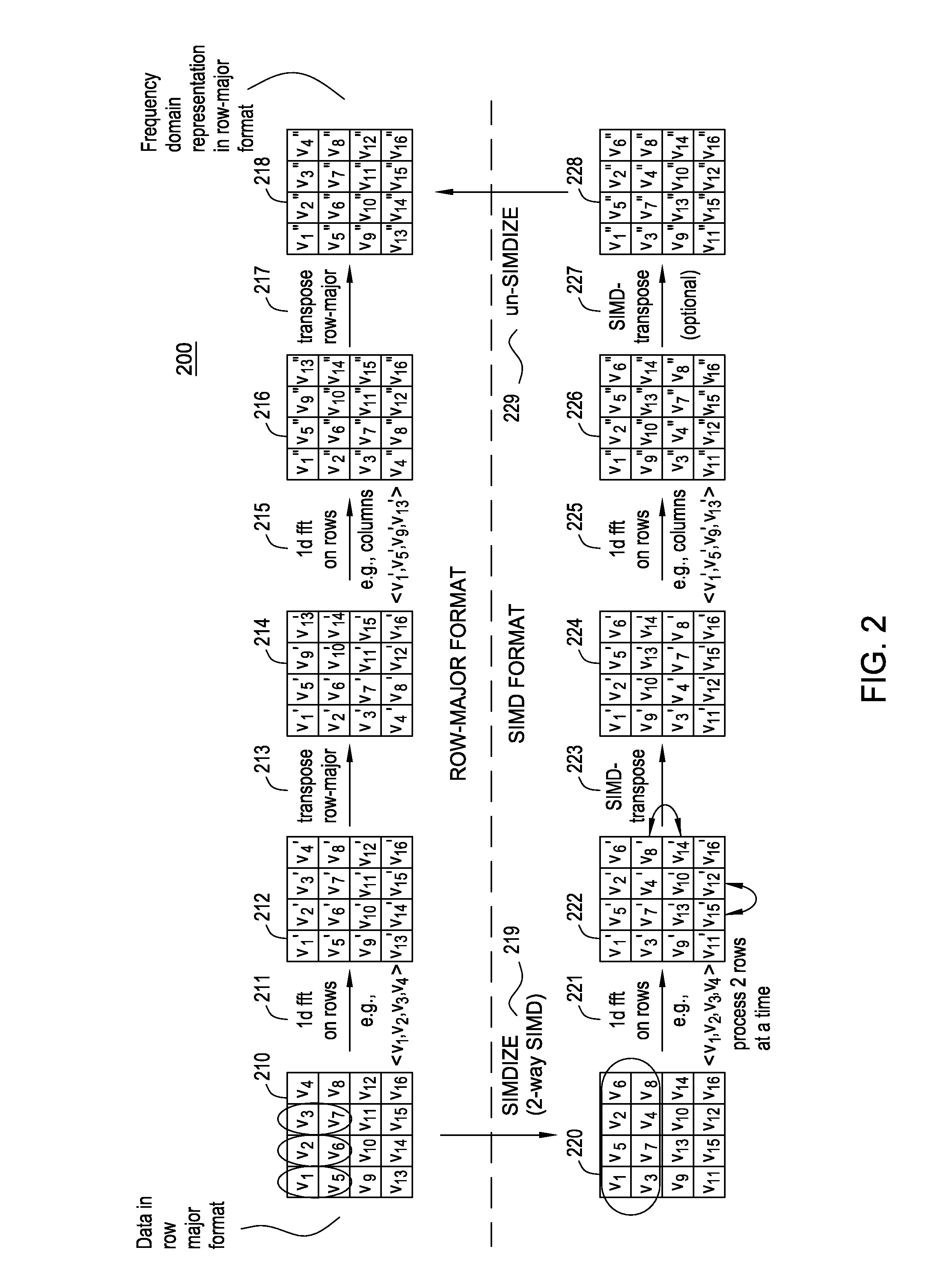
Transposing array data on simd multi-core processor architectures
InactiveUS20110107060A1Program control using stored programsDigital data processing detailsOn columnTranspose
Systems, methods and articles of manufacture are disclosed for transposing array data on a SIMD multi-core processor architecture. A matrix in a SIMD format may be received. The matrix may comprise a SIMD conversion of a matrix M in a conventional data format. A mapping may be defined from each element of the matrix to an element of a SIMD conversion of a transpose of matrix M. A SIMD-transposed matrix T may be generated based on matrix M and the defined mapping. A row-wise algorithm may be applied to T, without modification, to operate on columns of matrix M.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-grain parallel storage system and storage
ActiveCN102541774AImprove execution efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingTranspose
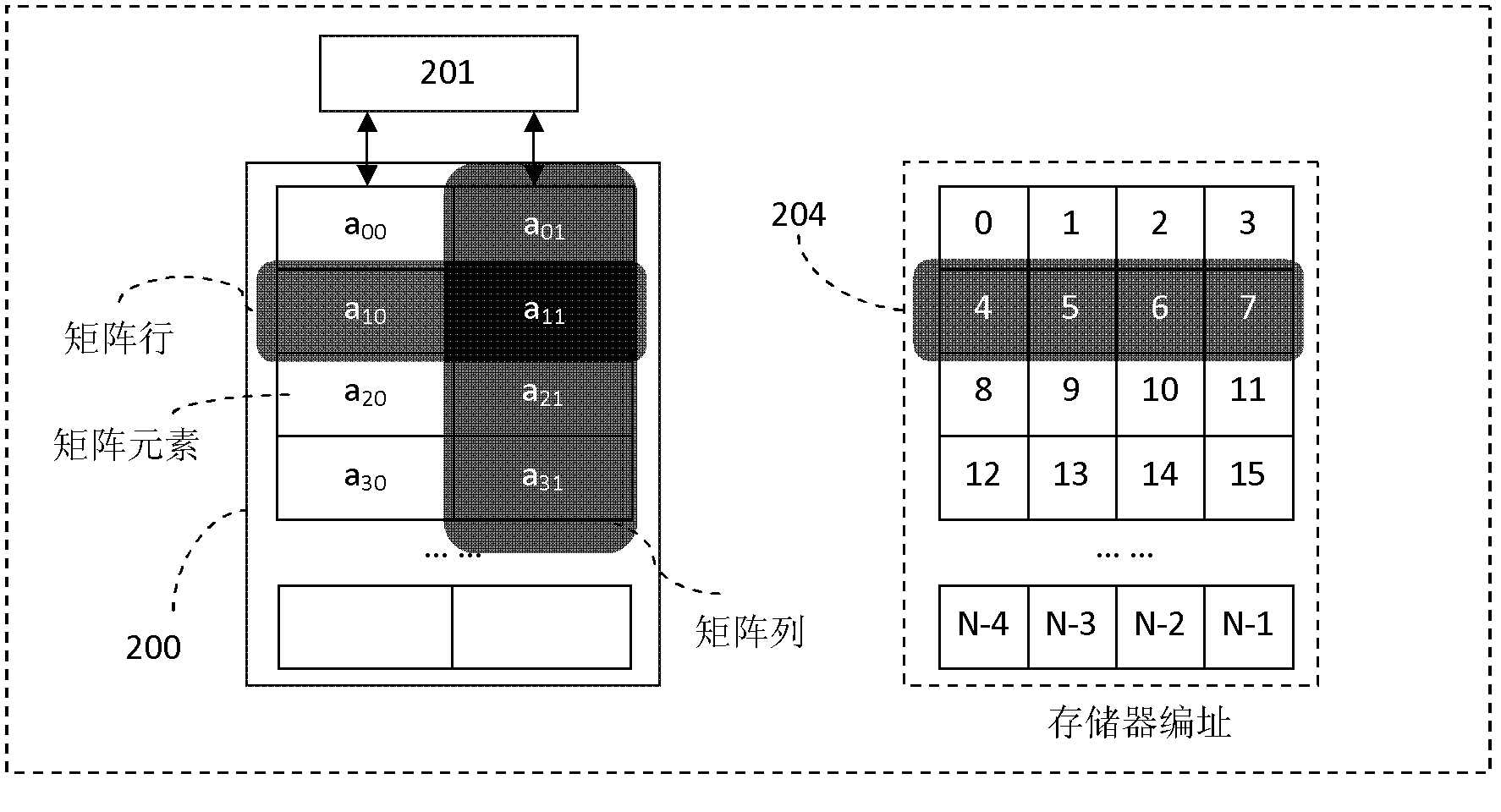
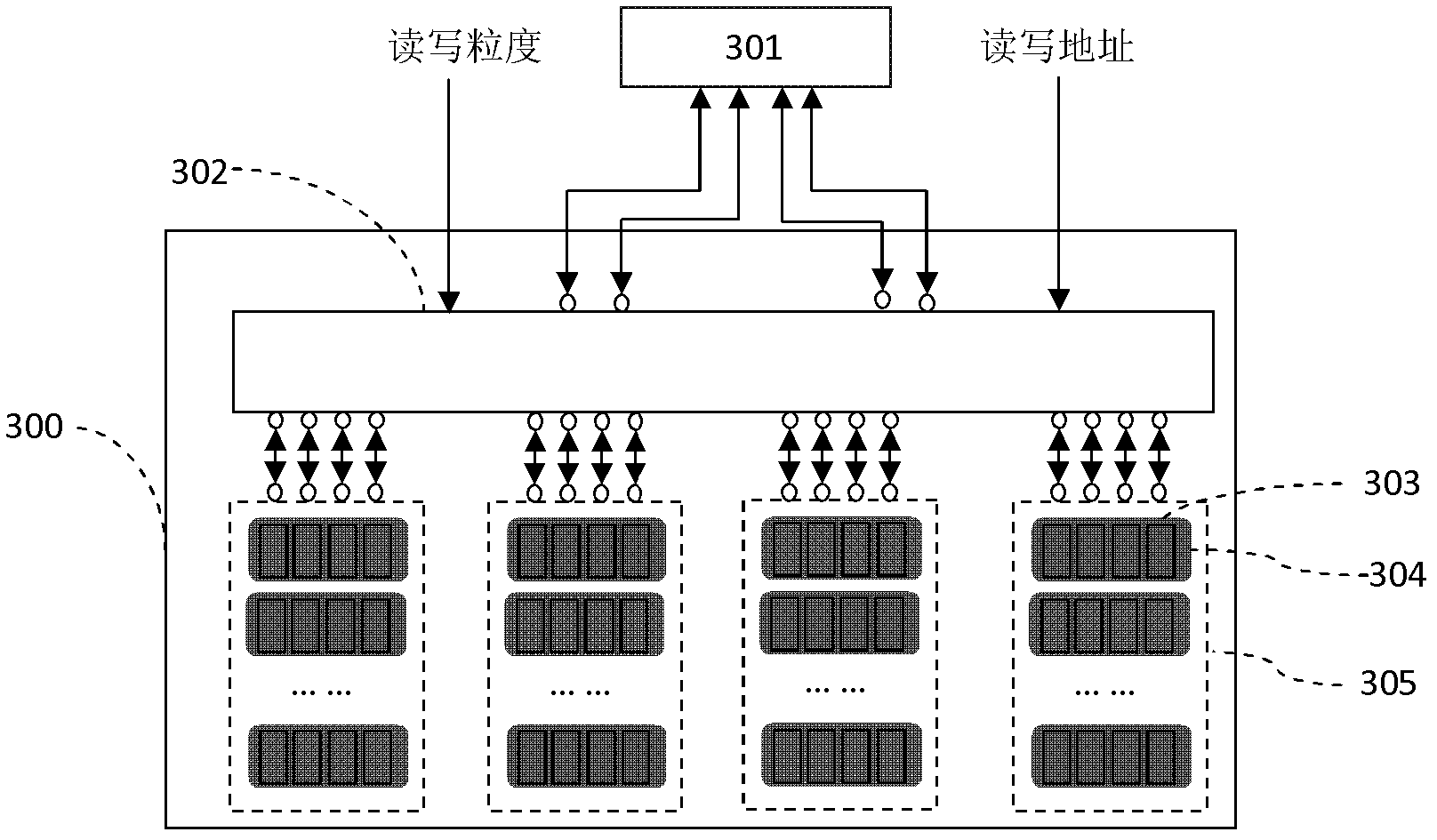
The invention discloses a multi-grain parallel storage system and a storage (300) supporting array multi-grain parallel reading and writing. The storage system includes a reading and writing port (301) and the storage (300); the storage comprises W storage blocks (305) and a data strobe network (302); each storage block (305) is a two-dimensional array comprising a plurality of storage units (303); each storage line (304) in the two-dimensional array includes W storage units (303); each storage block can read and write one storage line (304) once; and w is 2 to the power of n, and n is a natural number. The storage system provided by the invention can support different data types of matrix array data parallel reading at the same time, thereby radically clearing the transpose operation requirement in the signal processing algorithm, and improving the executing efficiency of the signal processing algorithm.
Owner:上海思朗科技有限公司
Method and device for detecting transmission signal with division detection
InactiveUS20100042666A1Reduce complexityComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsQR decompositionAlgorithm
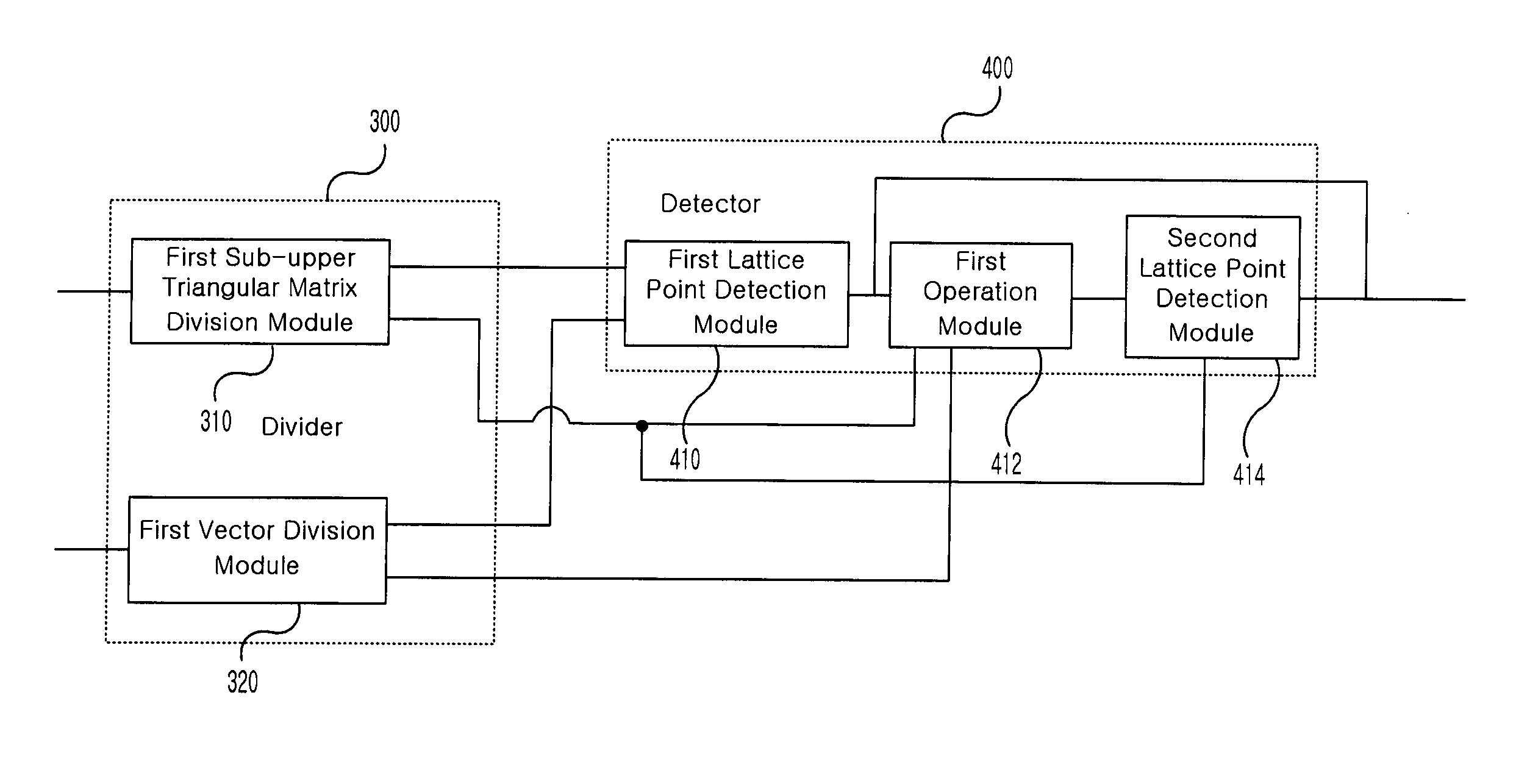
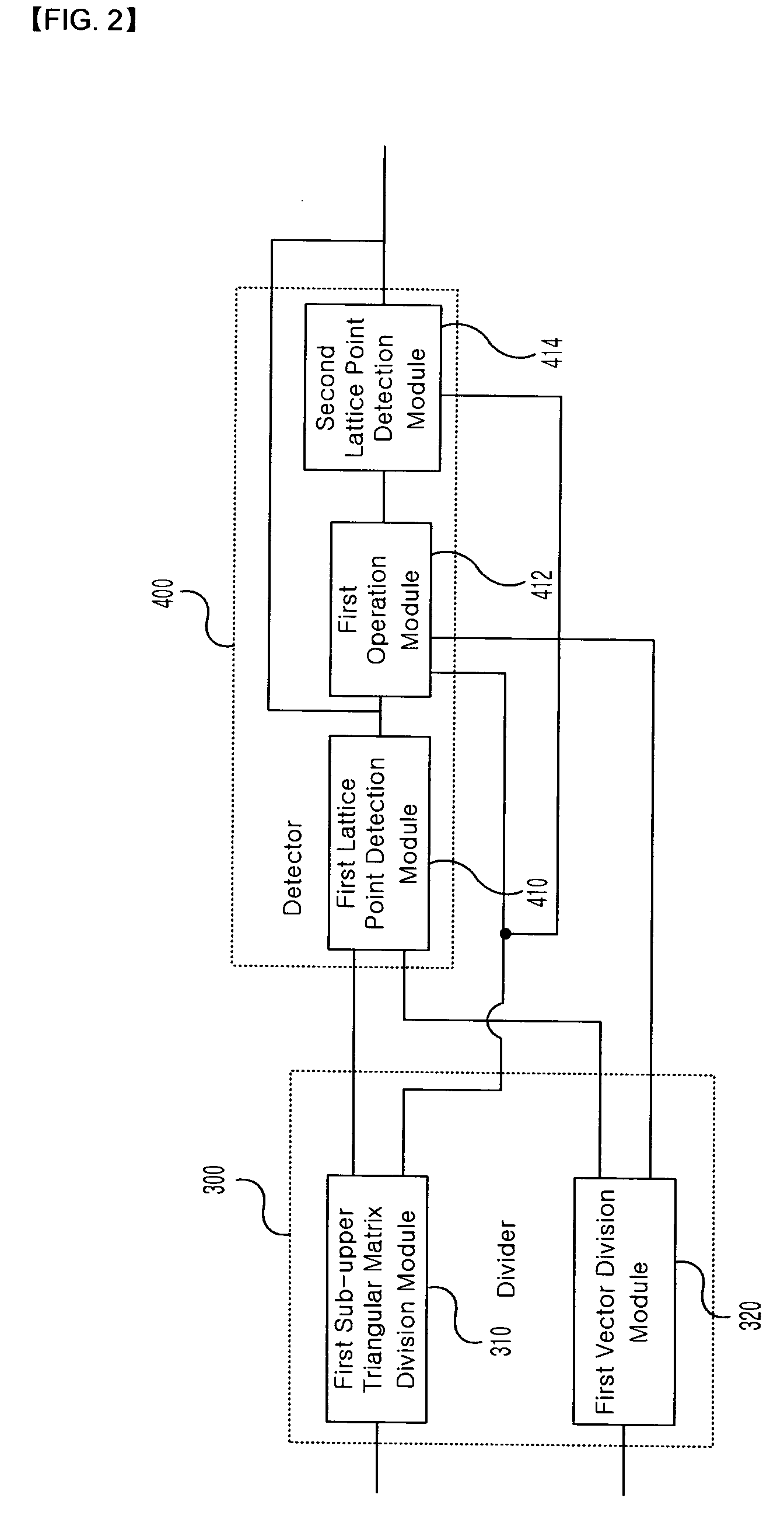
The present invention relates to a method and device for detecting a transmission signal on the basis of a received signal by applying a division and detection algorithm. An embodiment of the invention provides a method of detecting a transmission signal including: obtaining a unitary matrix and an upper triangular matrix by performing a sorted QR-decomposition algorithm with respect to a matrix indicating a channel state; calculating a vector y by multiplying a transpose matrix of the unitary matrix by the received signal Y; dividing the upper triangular matrix R into a plurality of sub-upper triangular matrices and dividing the calculated vector y into a plurality of sub-vectors so as to correspond to the divided plurality of sub-upper triangular matrices; and detecting a lattice point corresponding to each of the divided sub-vectors using the divided plurality of sub-upper triangular matrices.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
ISI-robust slot formats for non-orthogonal-based space-time block codes
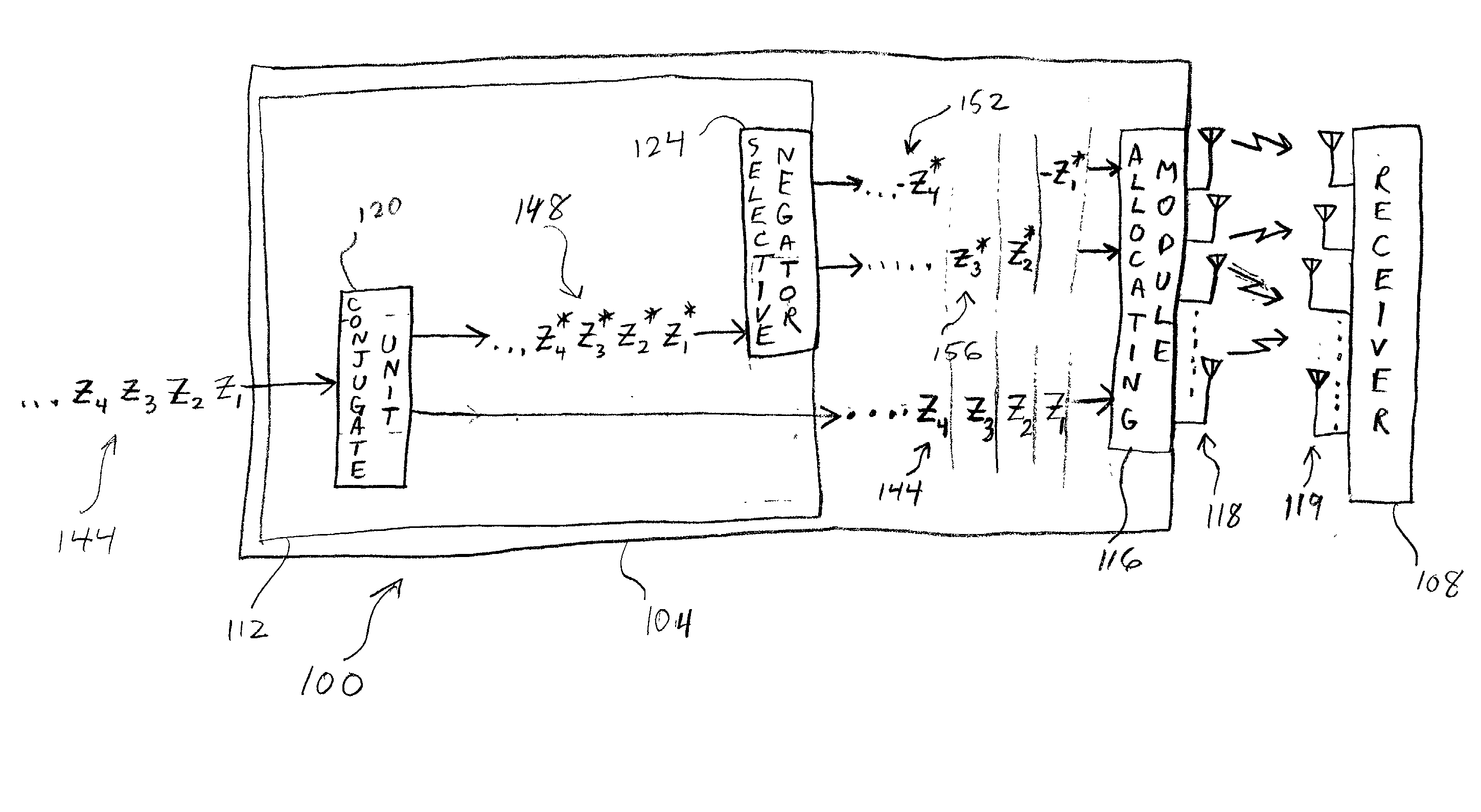
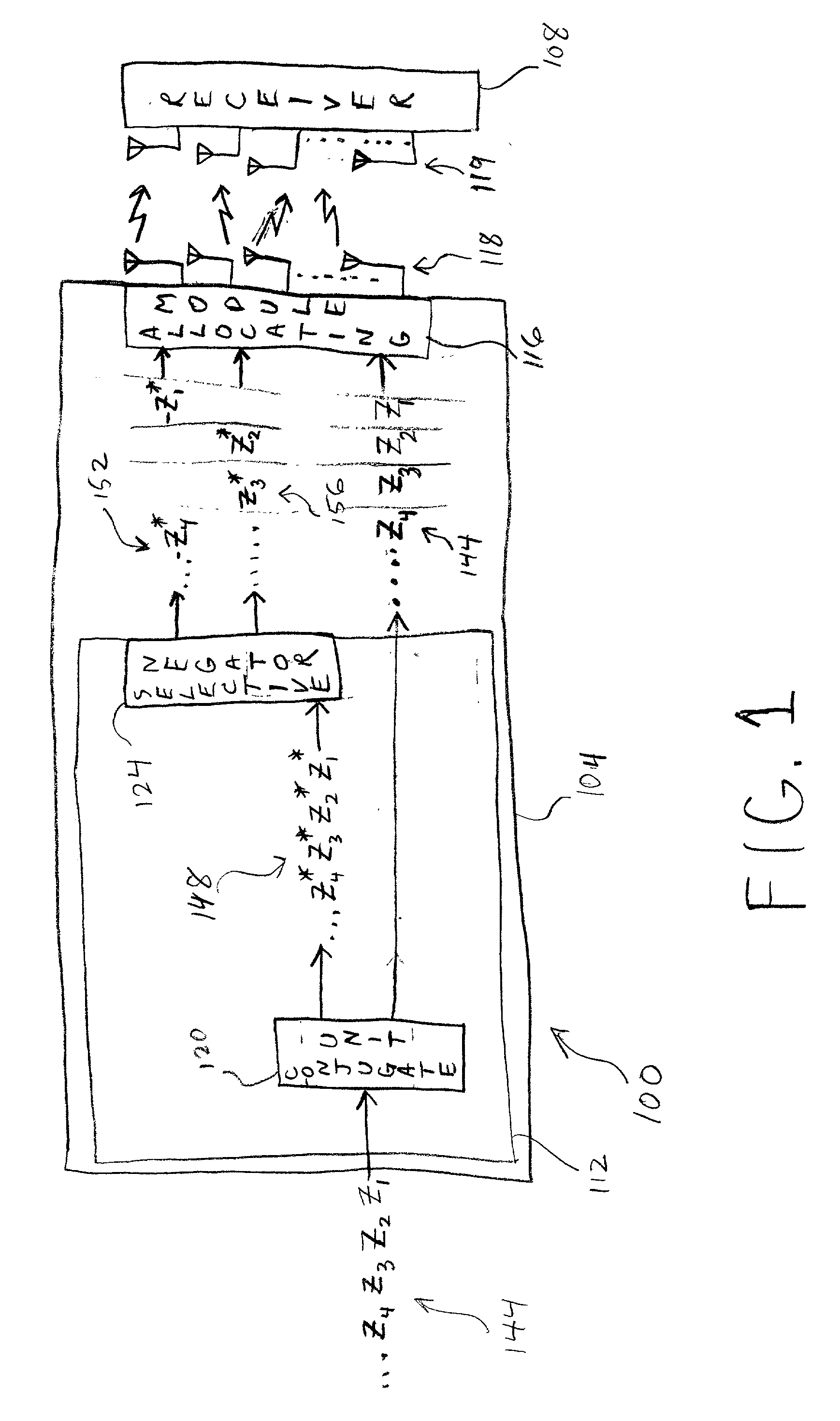
InactiveUS20020126648A1Modulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionSymbol of a differential operatorTranspose
The transmit diversity and symbol rate in a wireless mobile system are increased by allocating the complex symbols to be transmitted in accordance with a time-space slot format that incorporates non-orthogonal-based matrices, defined as matrices whose format is such that the product of the matrix and its Hermitian transpose is other than the identity matrix times a real number other than unity. The non-orthogonal-based matrices are indexed by antenna and by symbol period. Copies and complex conjugates (or negative complex conjugates) of the same symbol that are transmitted from different antennas are mutually separated into non-adjacent parts of the slot. Each non-orthogonal-based "space-time" matrix is composed of orthogonal-based matrices, i.e., matrices other than non-orthogonal-based matrices. Preferably, sequences of complex conjugates are time-reversed in the slot.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
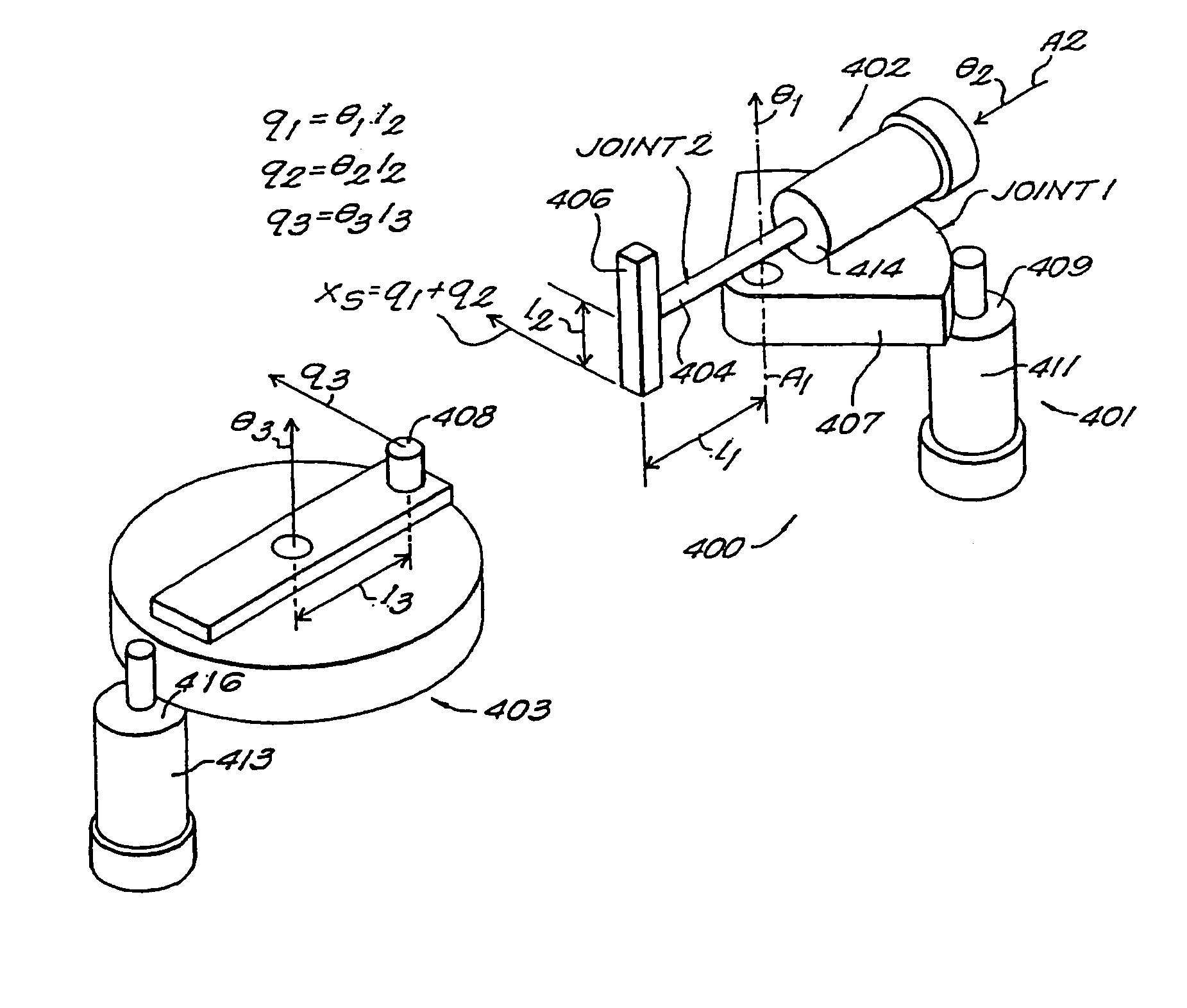
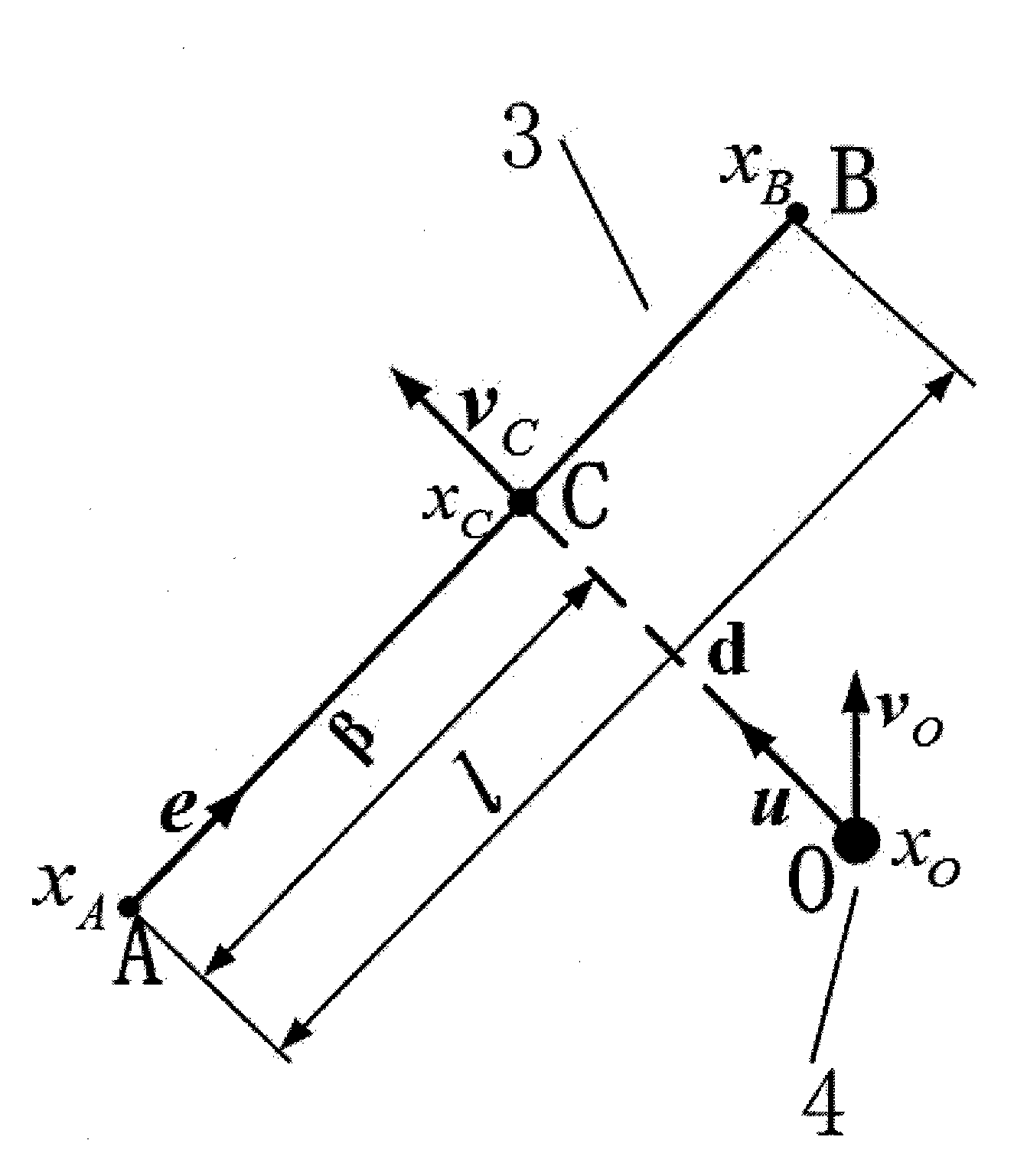
Redundant mechanical arm moving obstacle avoiding algorithm
InactiveCN104392081AAvoid realizationSolving for dodging speedSpecial data processing applicationsTransposeControl theory
The invention provides a redundant mechanical arm moving obstacle avoiding algorithm. According to the algorithm, the relative position relationship of a redundant mechanical arm and a moving obstacle is used to obtain a prediction collision point of the obstacle relative to each rod element of the mechanical arm; then, the shortest prediction distance obtained by using the moving speed of the obstacle is used, and in addition, the avoiding speed of each rod element is obtained according to the relationship between the distance value and the safety threshold; the avoiding speed is converted into an angle speed variable corresponding to each joint of the mechanical arm by a Jacobian transpose matrix, finally, the angle speed variable is introduced into a gradient projection method to obtain the angle speed of each joint, and the avoiding on the moving obstacle is realized. The algorithm provided by the invention has the advantages that the accurate tracking on the tail track of the mechanical arm is ensured, the avoidance on the moving obstacle is realized, and the important significance is realized on improving the safety of an industrial mechanical arm.
Owner:管小清 +1
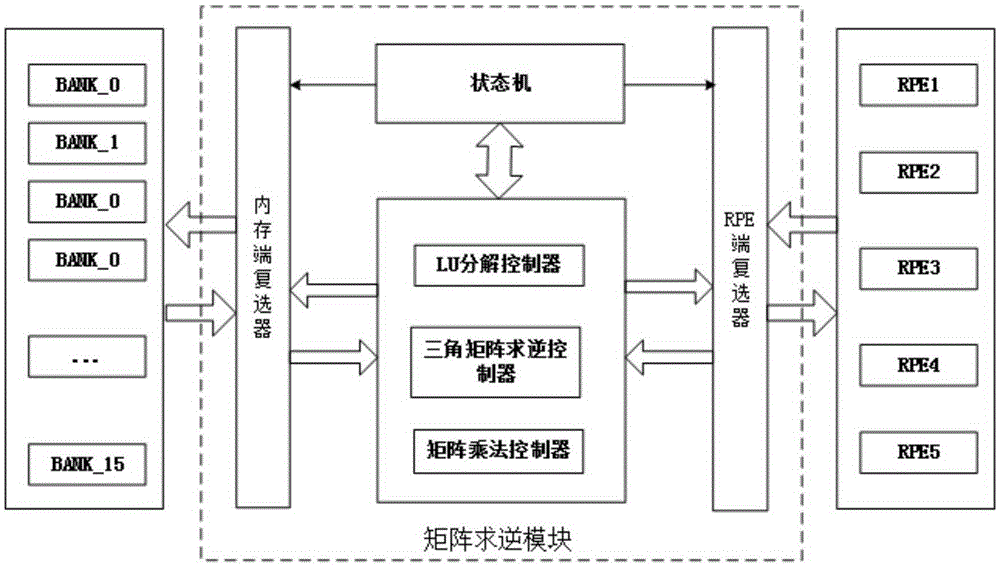
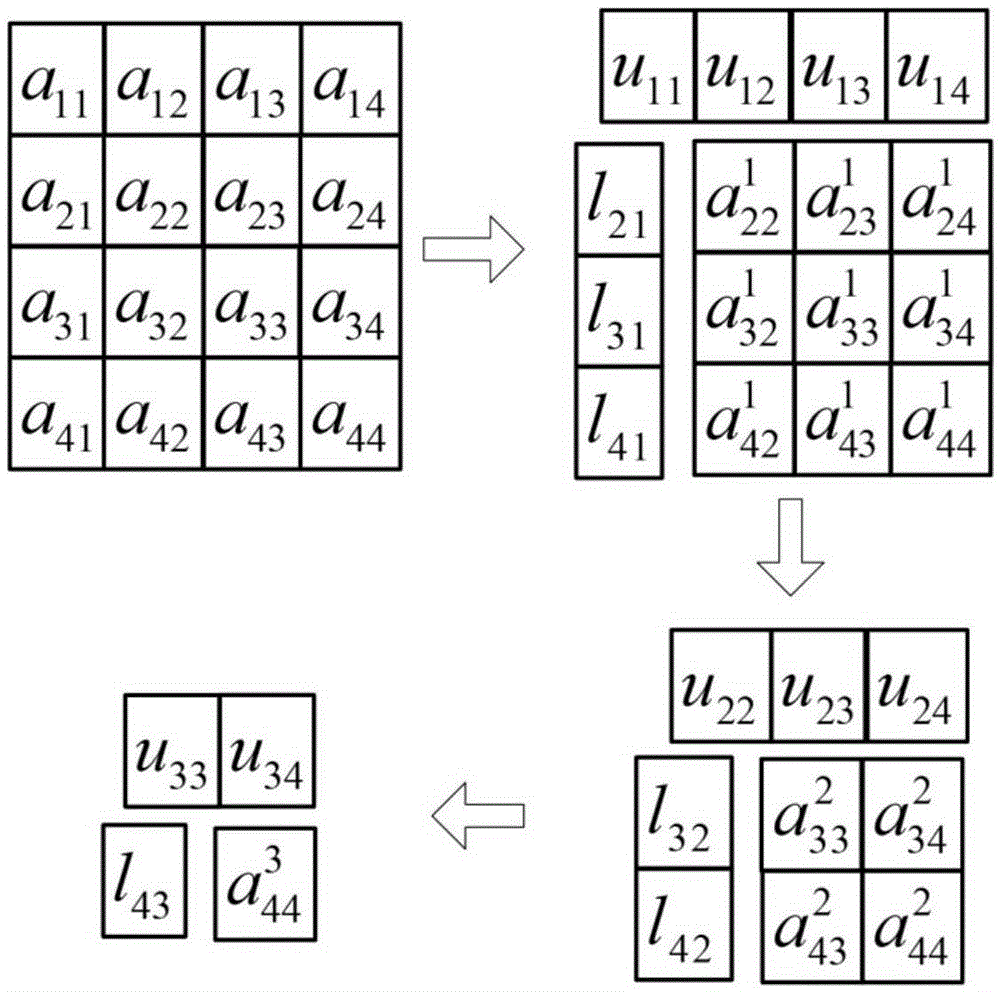
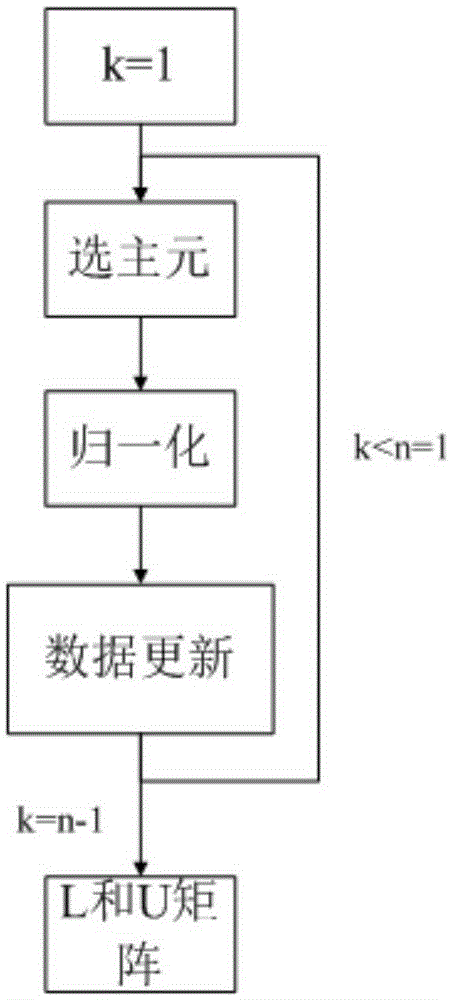
Matrix inverse operation method
InactiveCN105426345AImplement the inverse operationMeet performance needsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix inverseLU decomposition
The invention relates to a matrix inverse operation method. The method comprises the steps of 1, conducting column pivoting LU decomposition, wherein a source matrix A is decomposed into a unit lower triangular matrix L, an upper triangular matrix U and a permutation matrix P according to the formula PA=LU; 2, conducting triangular matrix inversion, wherein the inverse matrix L-1 of the matrix L is obtained through matrix inversion, and matrix inversion is conducted on the transposed matrix of the matrix U and then transposition is conducted to obtain U-1; 3, finally conducting matrix multiplication, wherein the matrix U-1 and the matrix L-1 are multiplied, and column transformation is conducted on the matrix multiplication result according to the permutation matrix P to obtain a source matrix A-1. The method has the advantages that by using the column pivoting LU decomposition algorithm, the time complexity of the matrix inversion algorithm is effectively reduced, parallelizability of matrix inversion operation is improved, time for matrix inversion operation is shortened, matrix inversion operation of any order can be conducted, and the number of hardware resources can be increased or reduced according to count requirements of operation so that practical application requirements can be better met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Modeling Light Transport In Complex Display Systems
InactiveUS20070171382A1Easy to useTime consumingProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionTransposeComputer vision
An image created by a first projector is recreated using a second projector by relating the two projectors to a common point of view, preferably as viewed from a camera. A first transport matrix T1 is captured to relate the first projector to the camera. A second transport matrix T2 is then capture to relate the second projector to the camera. To have a first image p1, as projected by the first projector, reproduced by the second projector, the second projector projects a distorted image defined as (T2−1)(T1)p1. The inverse of T2, as used in this equation is an estimation defined by first creating an intermediate matrix {hacek over (T)} of equal size as T2. If a column in T2 is denoted as Tr and a corresponding column in {hacek over (T)} is denoted as {hacek over (T)}r, then the construction and population of {hacek over (T)} is defined as {hacek over (T)}r=Tr / (∥Tr∥)2, and the inverse of T2 is estimated as the transpose of {hacek over (T)}.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
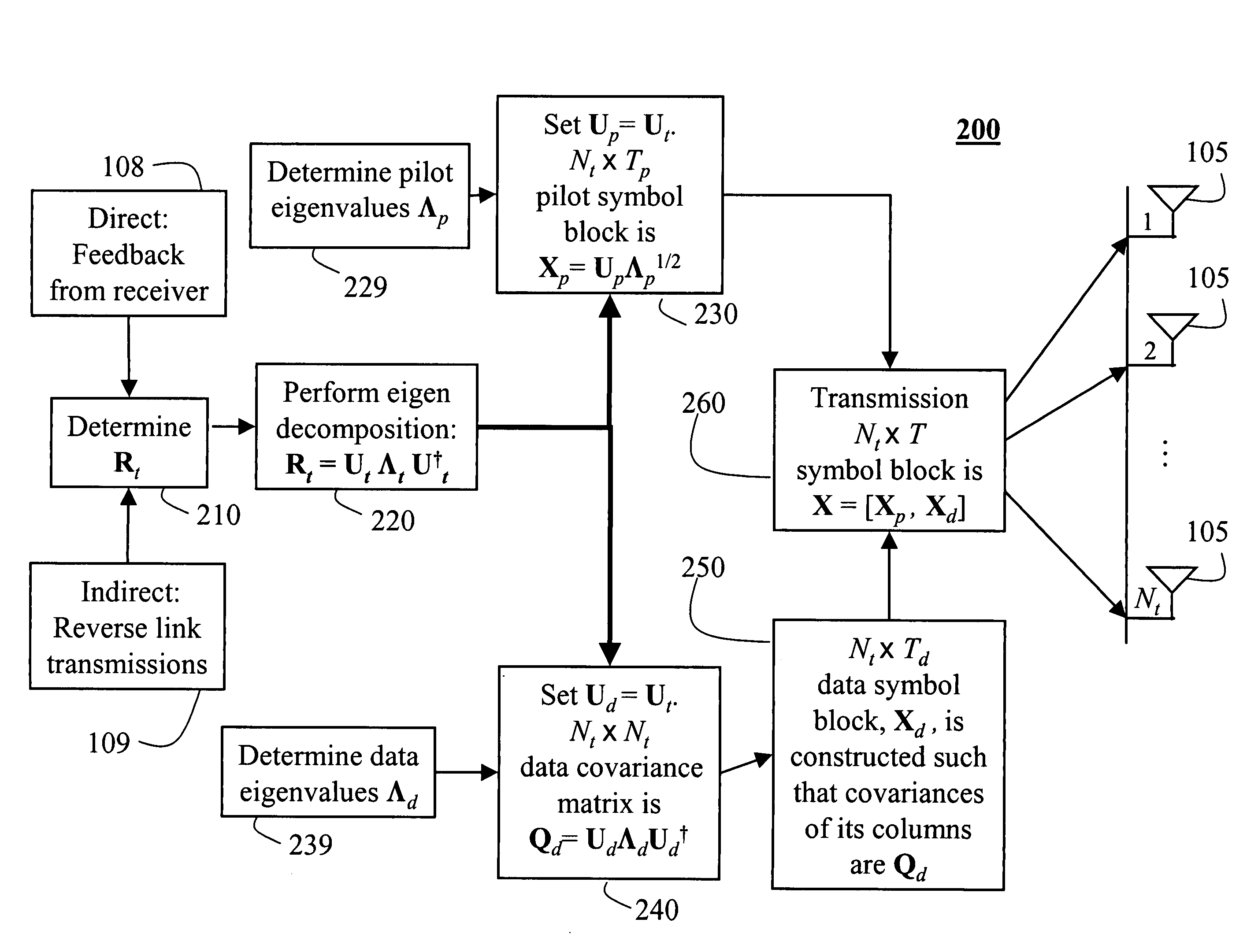
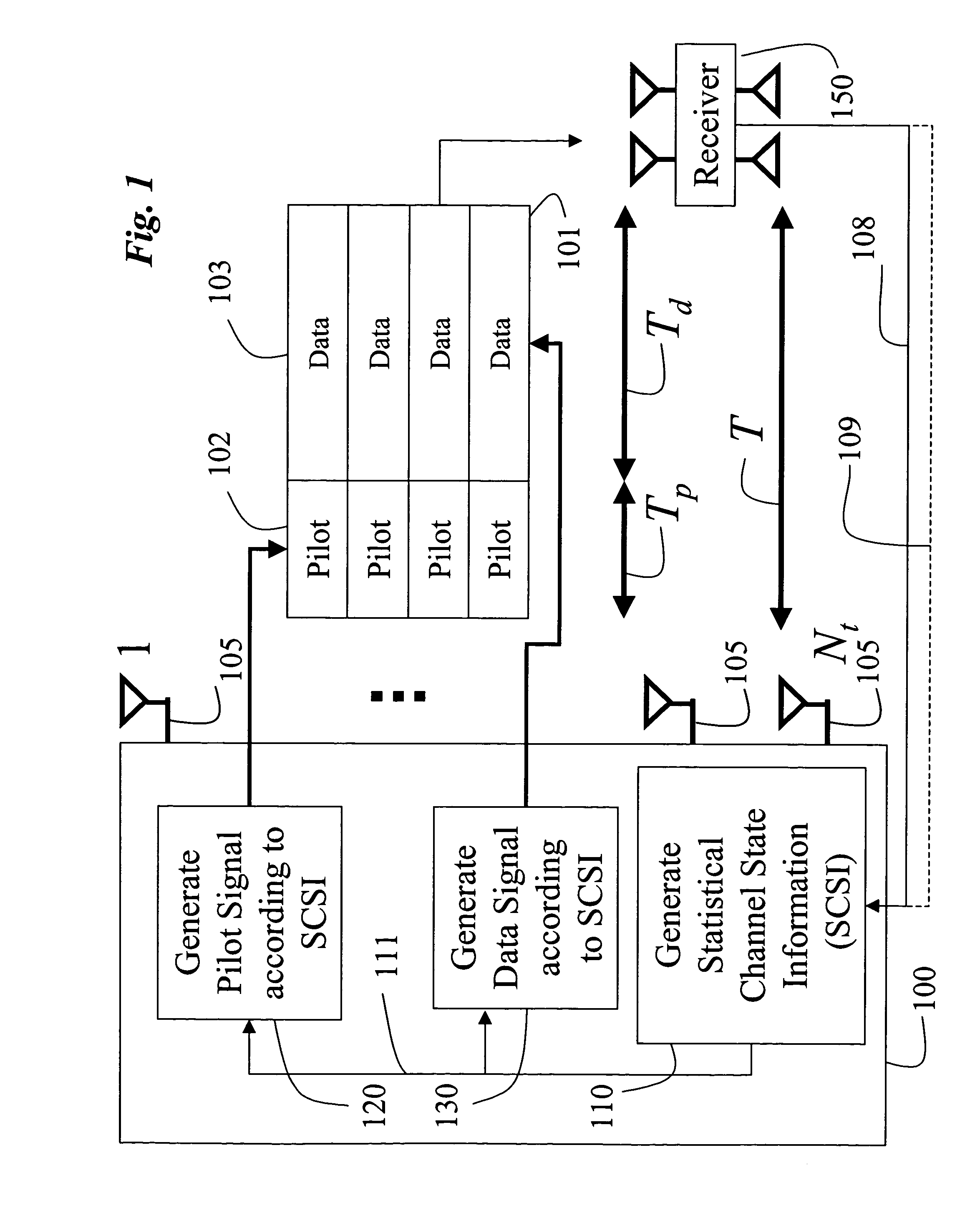
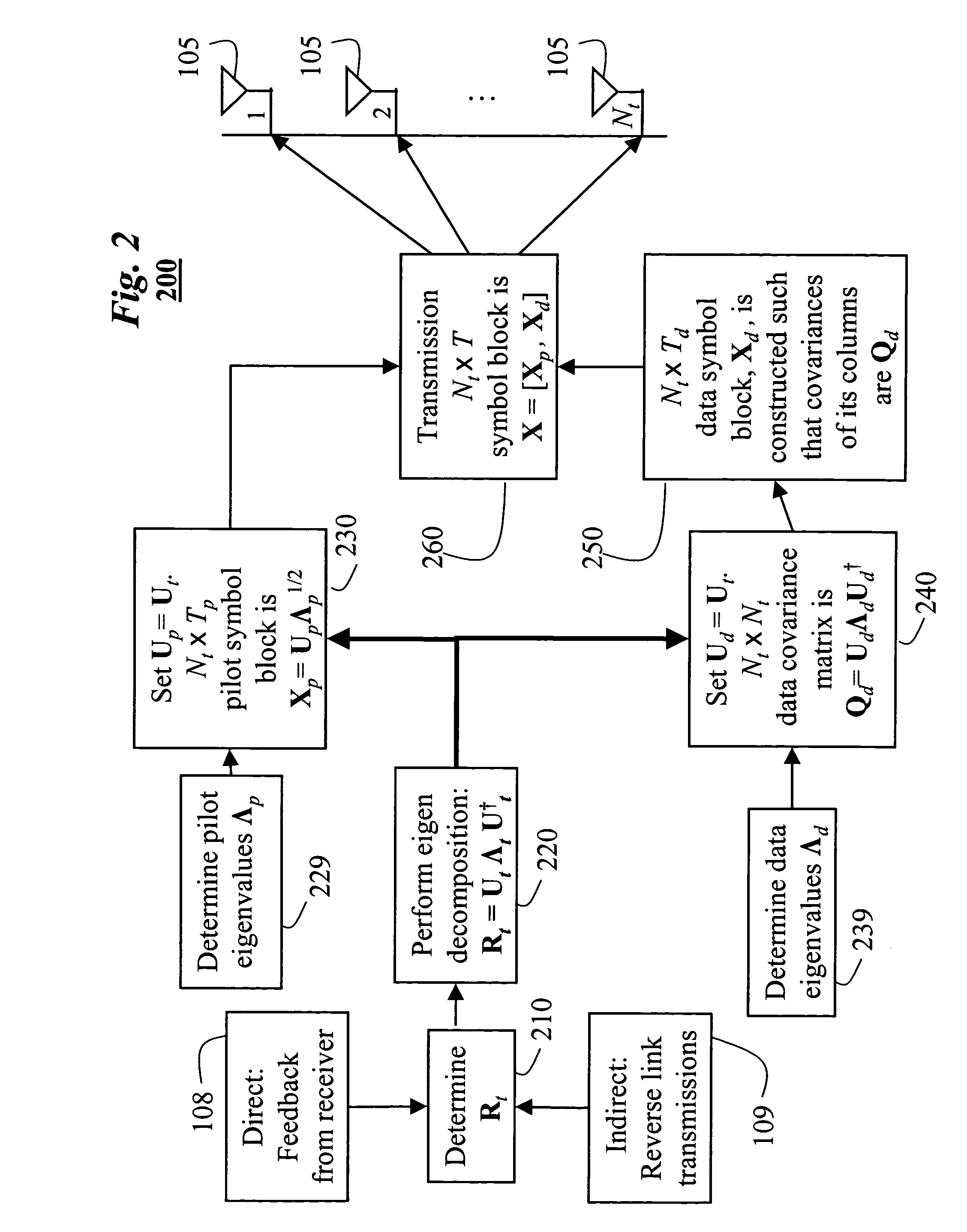
Pilot and data signals for MIMO systems using channel statistics
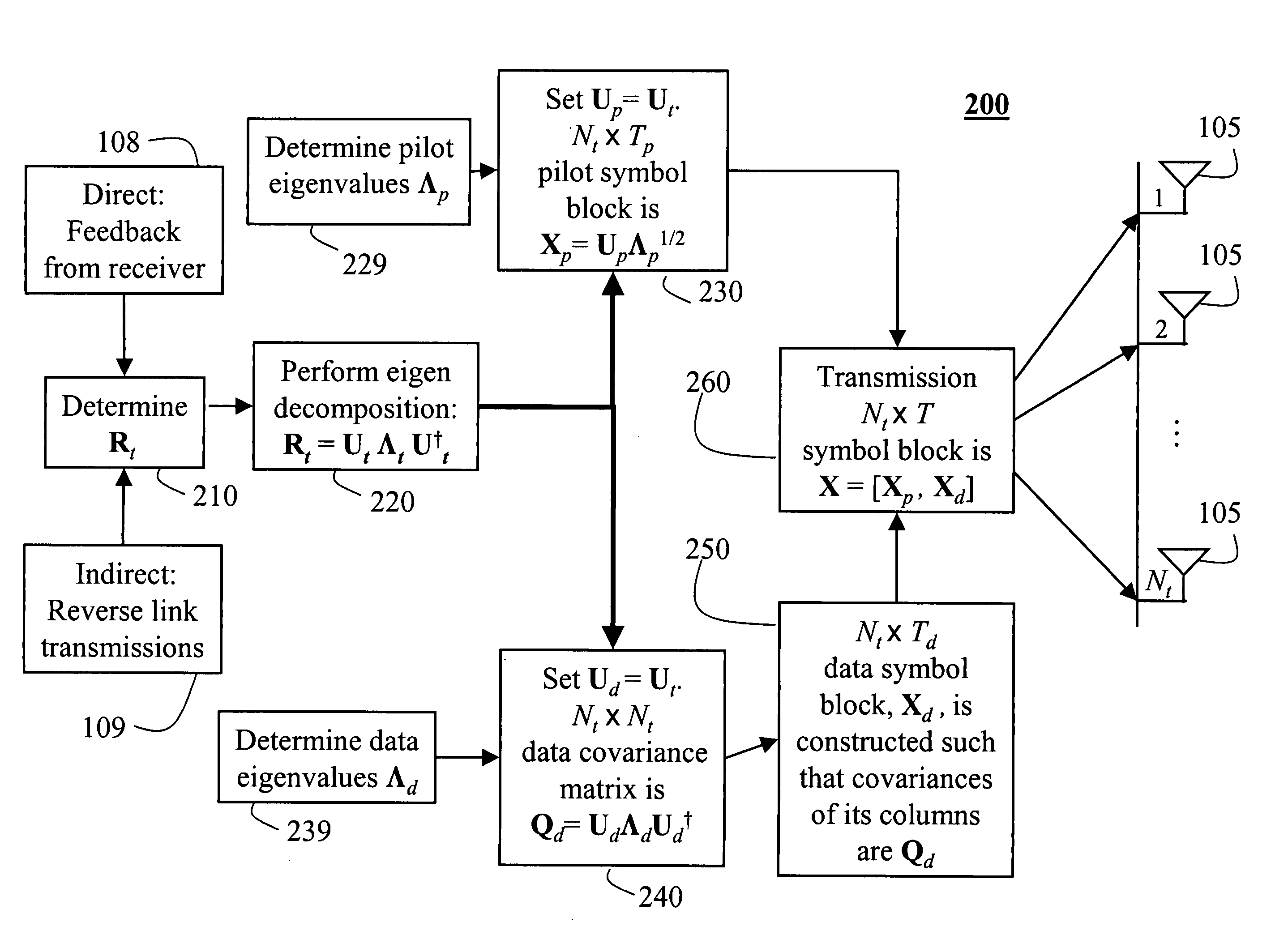
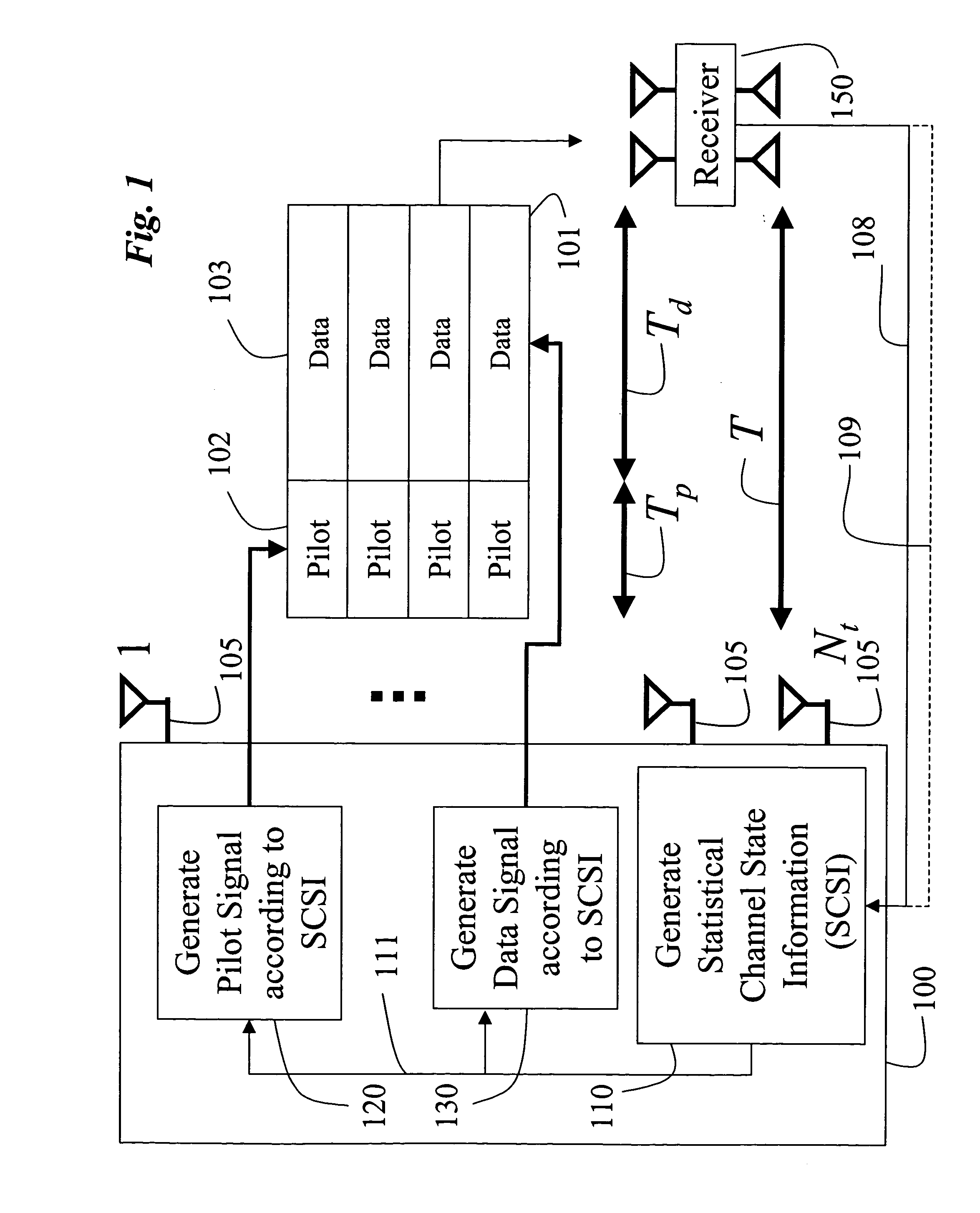
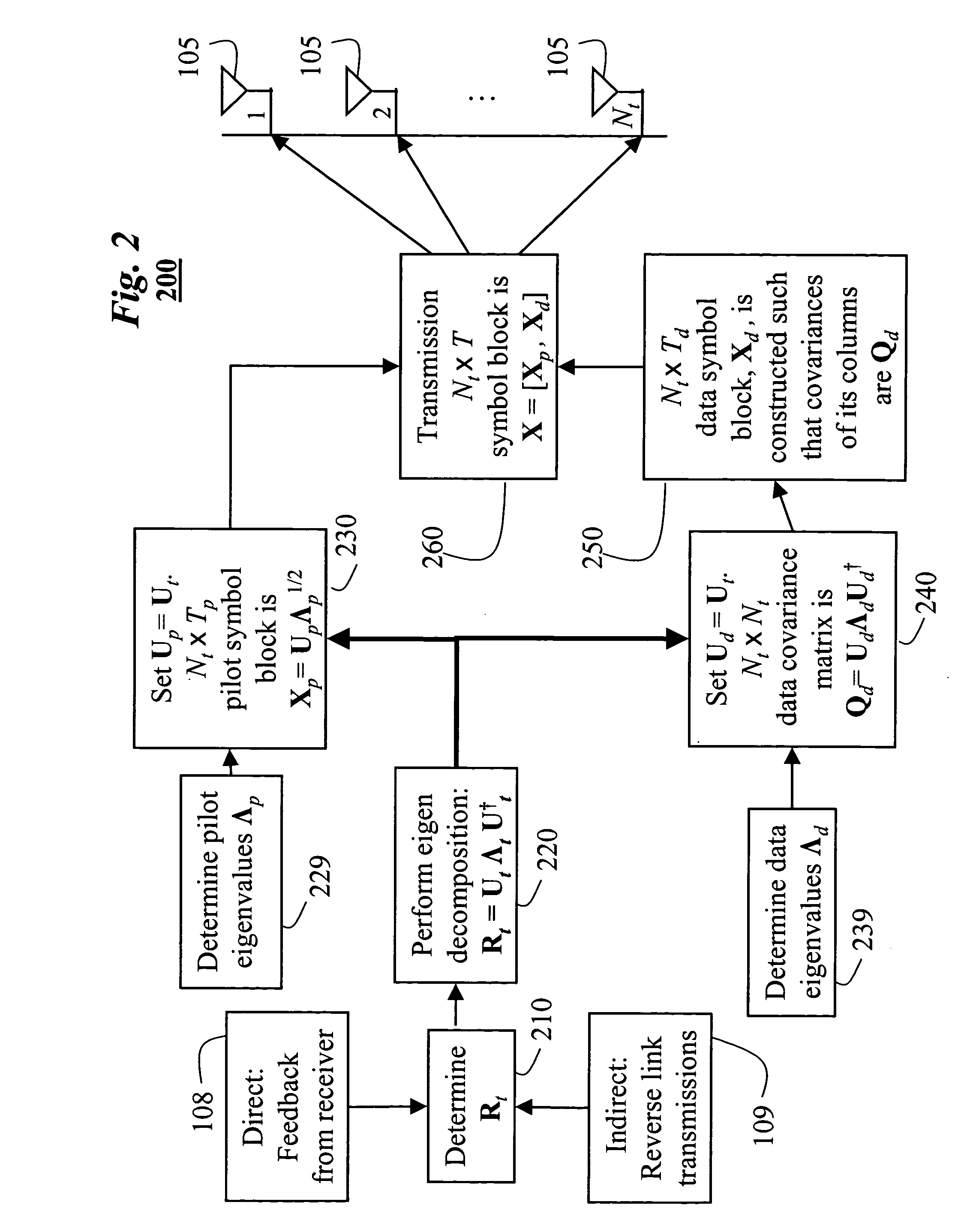
InactiveUS20060018402A1Improve data transfer rateSimplify complexityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemChannel statistics
A method generates signals in a transmitter of a multiple-input, multiple-output wireless communications system. The transmitter includes Nt transmit antennas. A transmit covariance matrix Rt determined using statistical state information of a channel. The transmit covariance Rt matrix is decomposed using transmit eigenvalues Λt to obtain a transmit eigenspace Ut according to Rt=UtΛtU†t, where † is a Hermitian transpose. A pilot eigenspace Up is set equal to the transmit eigenspace Ut. A Nt×Tp block of pilot symbols Xp is generated from the pilot eigenspace Up and pilot eigenvalue Λp according to Xp=UpΛp1 / 2. A data eigenspace Ud is set equal to the transmit eigenspace Ut. In addition, a Nt×Nt data covariance matrix Qd is generated according to UdΛdU†d, where Λd are data eigenvalues. A Nt×Td block of data symbols is generated, such that an average covariance of each of the columns in the block of data symbols Xd equals the data covariance matrix Qd. The block of pilot and data symbols form the signals to be transmitted.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
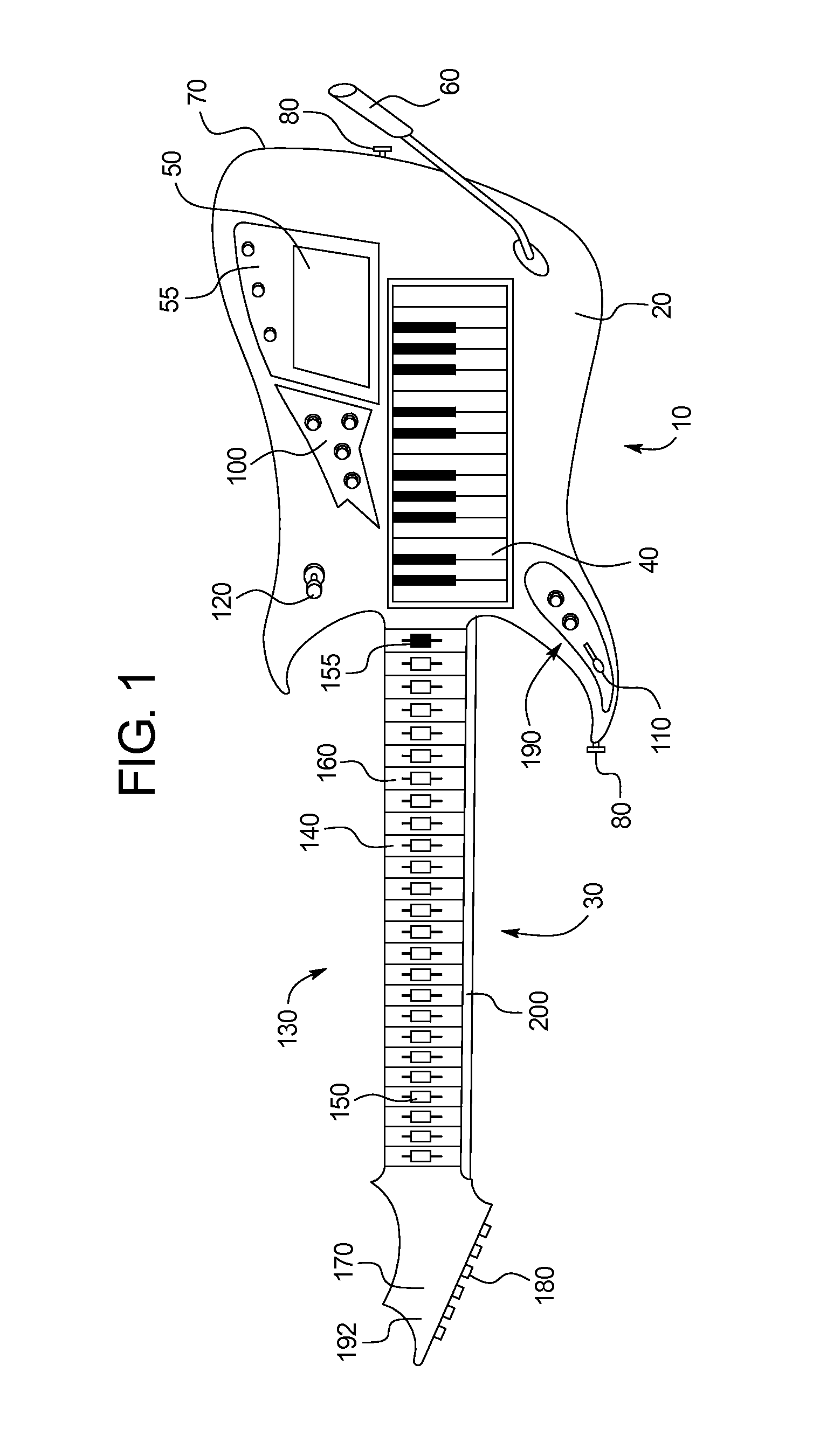
Keyboard guitar including transpose buttons to control tuning
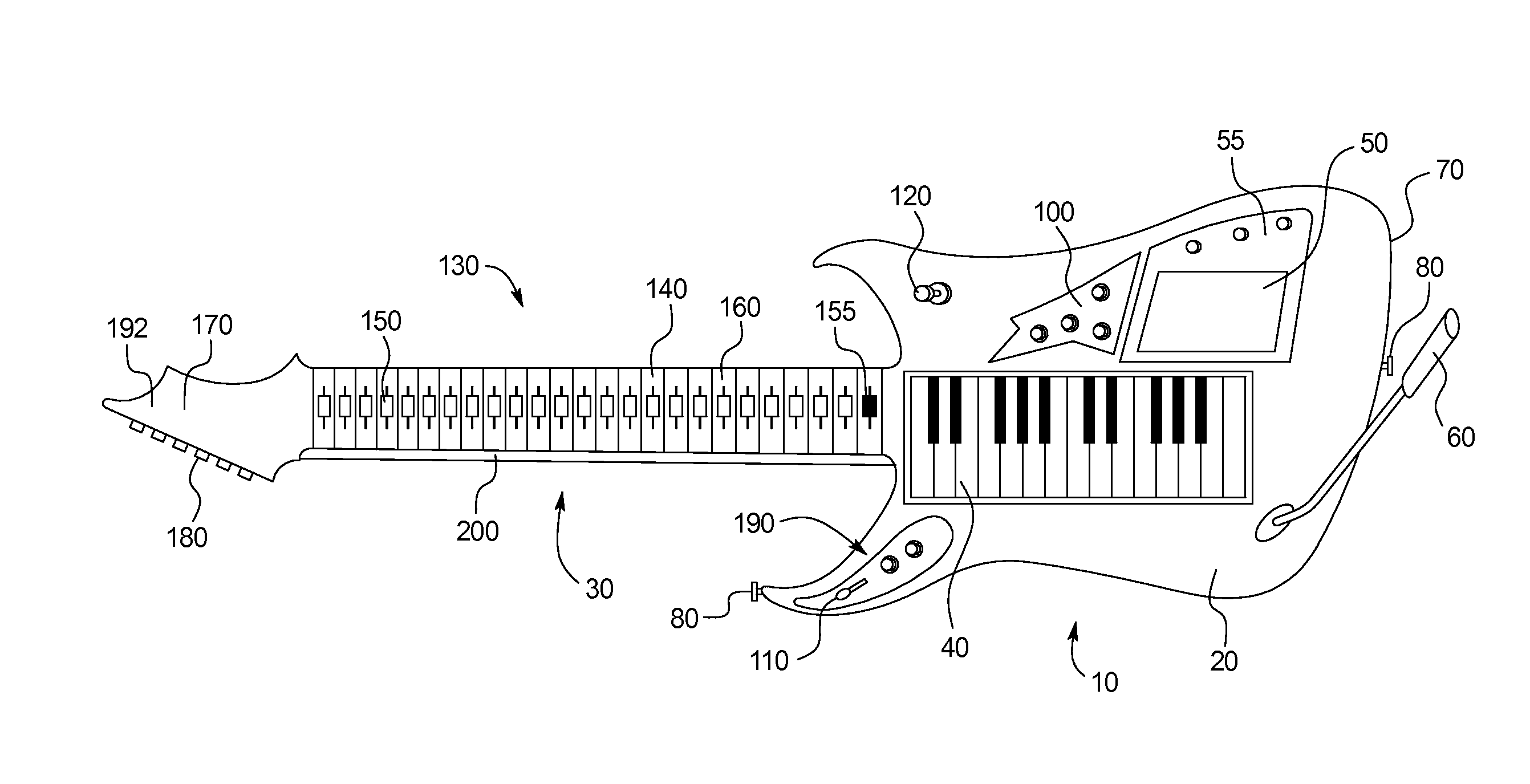
ActiveUS20130255474A1Changing chordSit downElectrophonic musical instrumentsElongated neckEngineering
A musical instrument includes: a body including a keybed having a plurality of keys, wherein activation of each key creates an electrical signal at an output, wherein said electrical signal represents a pitch associated with a musical note; an elongated neck connected to the body; and a plurality of transpose buttons located along the length of the neck, wherein the transpose buttons of the fretboard are configured to control the tuning of the keys in the keybed such that activation of each of the transpose button alters the pitch represented by the electrical signal that is output by of each of the keys.
Owner:HANKS MICHAEL S
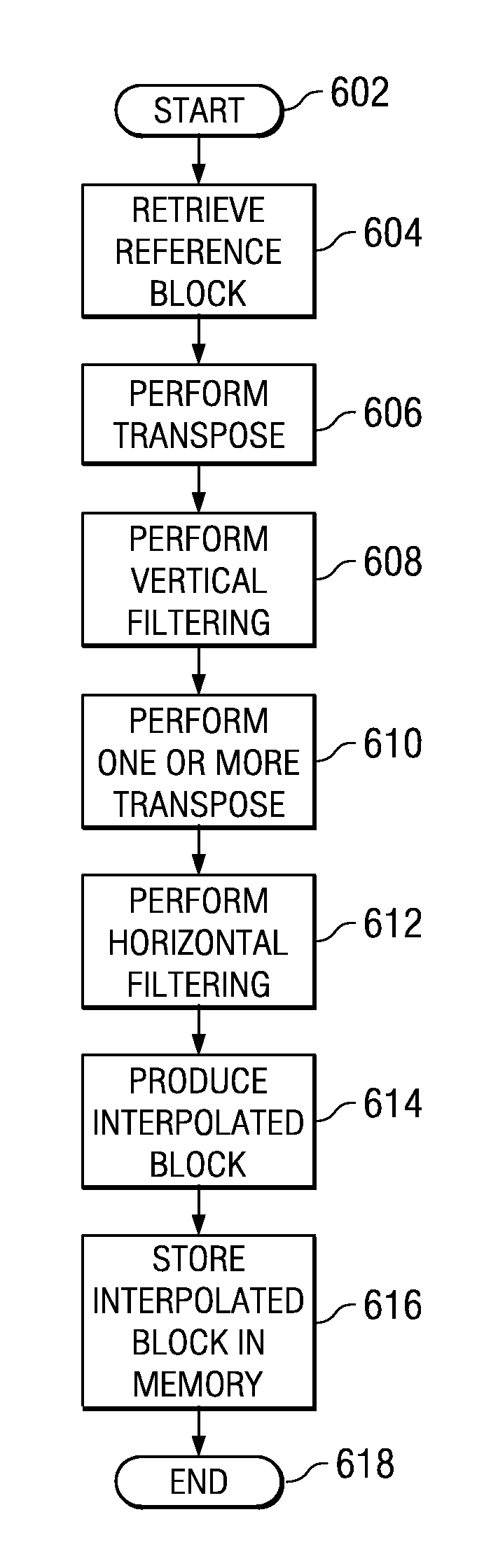
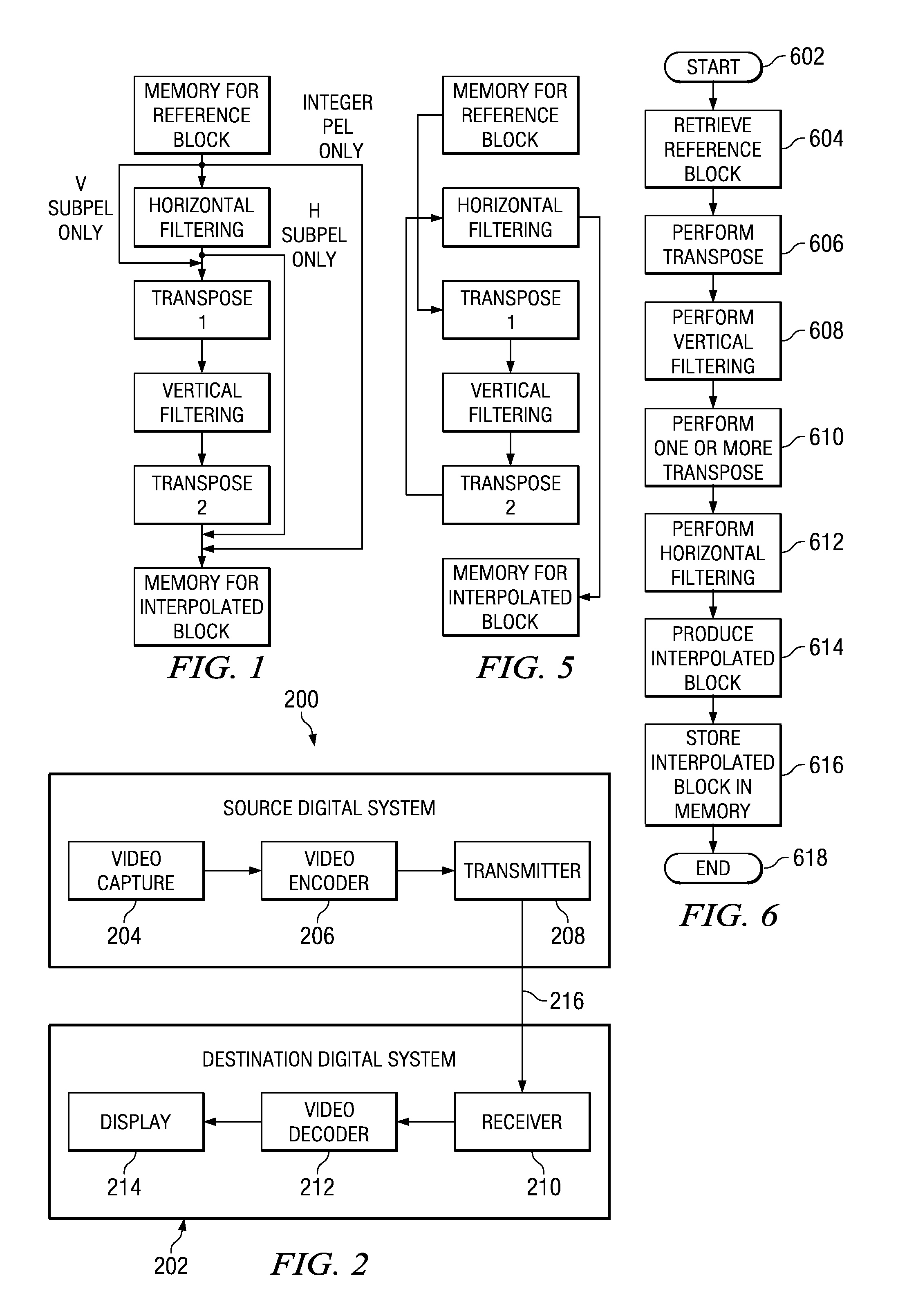
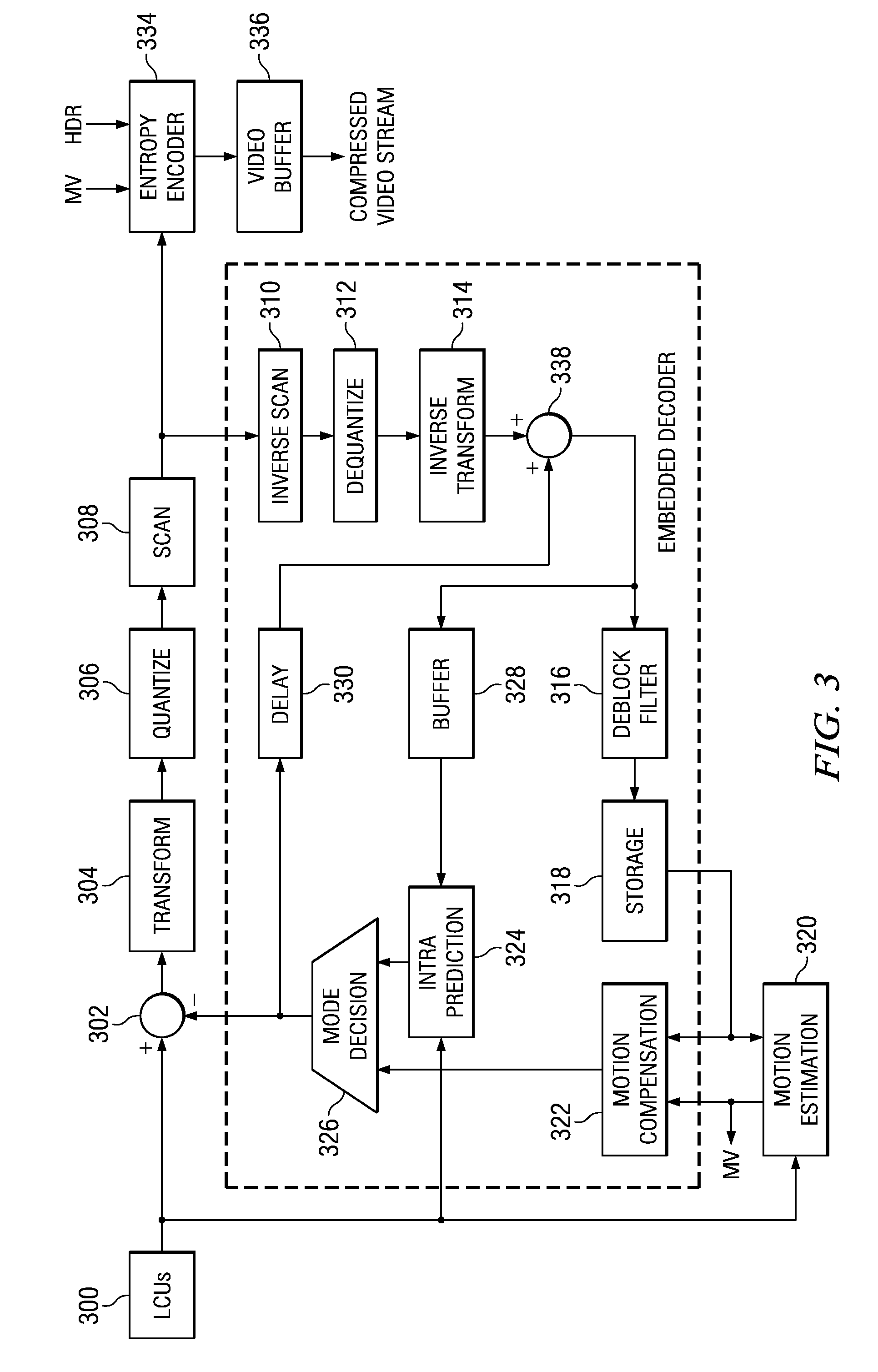
Method and Apparatus for Prediction Unit Size Dependent Motion Compensation Filtering Order
A motion compensation method and apparatus. The method includes retrieving data relating to a reference bock, performing a transpose on the retrieved data, performing vertical filtering on the transposed retrieved data, performing one or more transpose on the vertically filtered data, performing horizontal filtering on the transposed vertically filtered dad, and generating an interpolated bock and storing the interpolated block.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pilot and data signals for MIMO systems using channel statistics
InactiveUS7443925B2Improve data transfer rateSimplify complexityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemChannel statistics
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Limiting feedback method and device for large-scale antenna system
InactiveCN104539335AReduce the burden onReduce processing complexitySpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsDimensionality reductionEngineering
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY +1
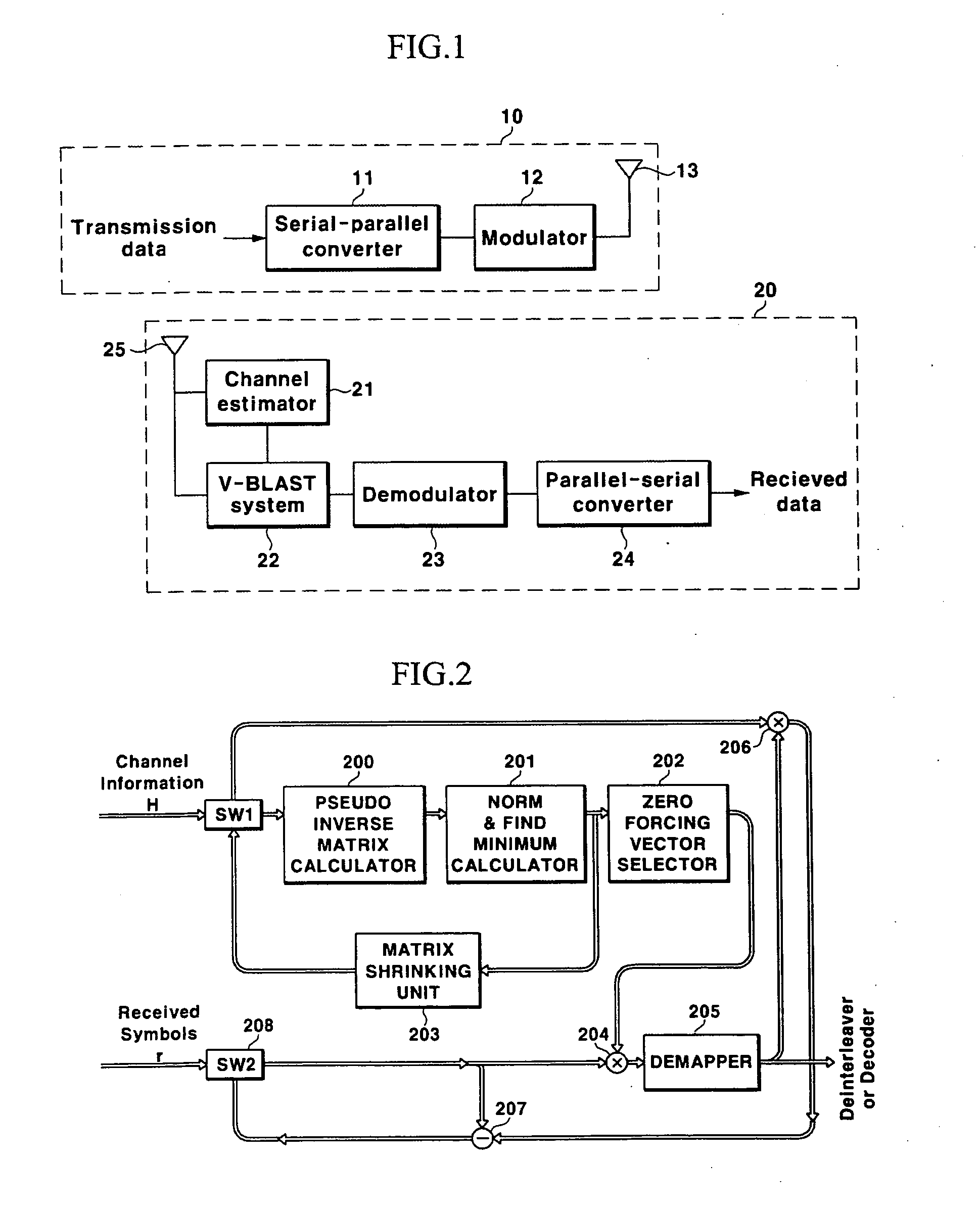
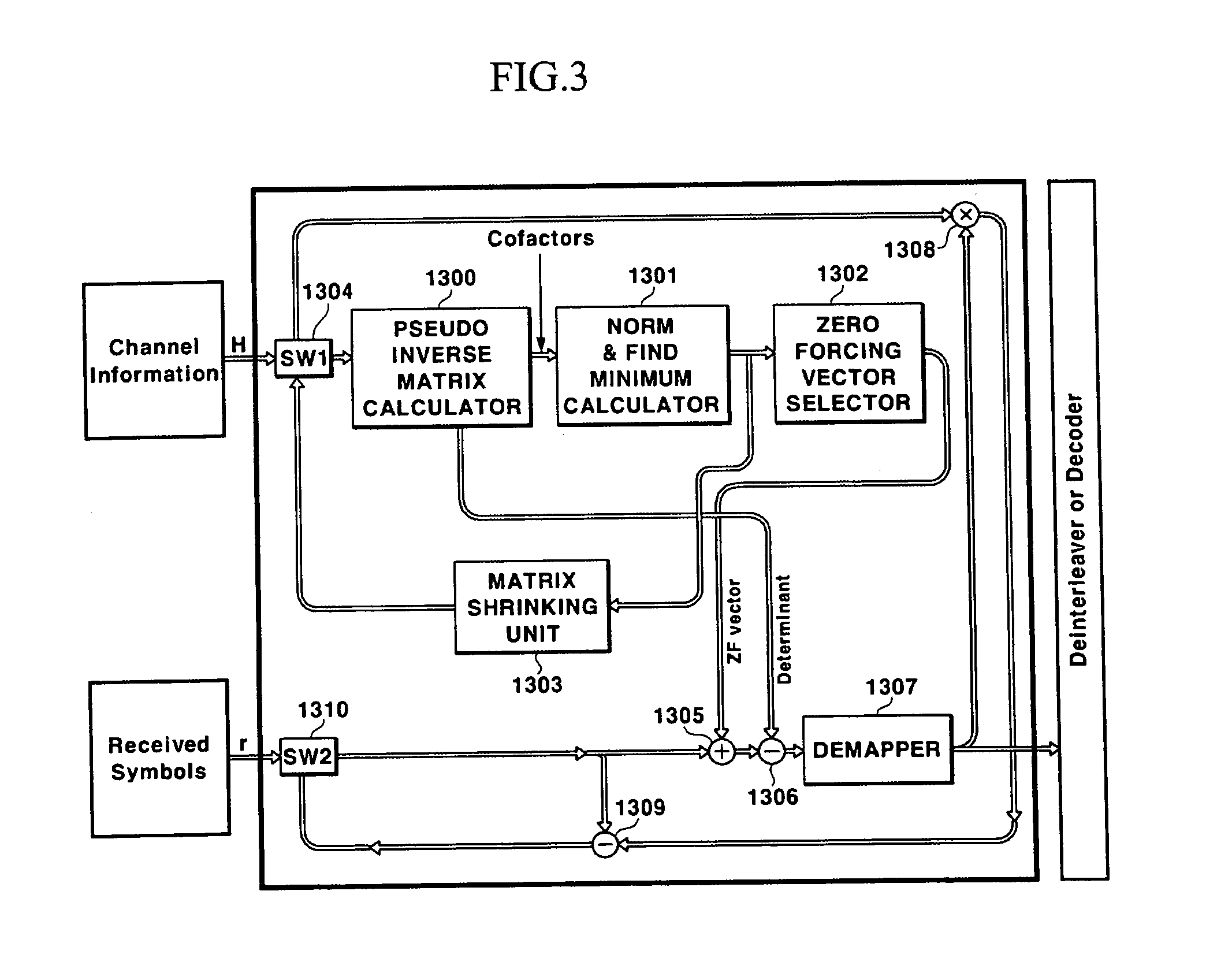
Processing device for a pseudo inverse matrix and V-BLAST system
InactiveUS20050149596A1Effective functionEfficient processingBaseband system detailsComputation using non-contact making devicesTransfer function matrixCommunications system
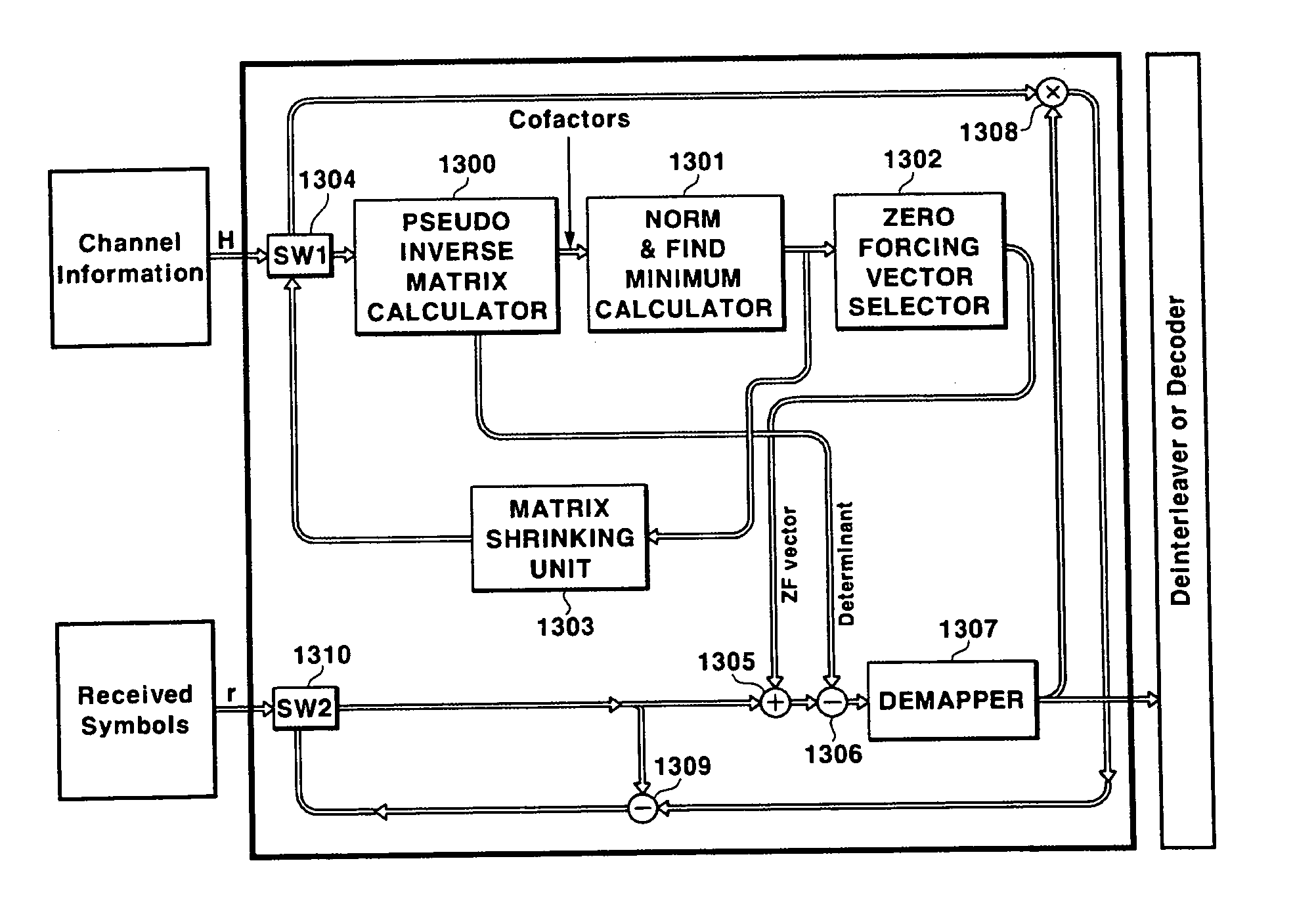
Disclosed is a V-BLAST system for a MIMO communication system. In the V-BLAST system for a MIMO communication system, a pseudo inverse matrix calculator receives a channel transfer function matrix including channel information and produces a cofactor matrix and a determinant for a pseudo inverse matrix. A norm & minimum calculator calculates a minimum index for the cofactor matrix outputted from the pseudo inverse matrix calculator, a weight vector selector selects a row vector having the minimum index and calculates a transposed matrix for the row vector; an adder adds the transposed matrix to a received input symbol, and a subtractor subtracts the determinant to the output. A demapper performs a determined function operation to the output and produces estimated information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
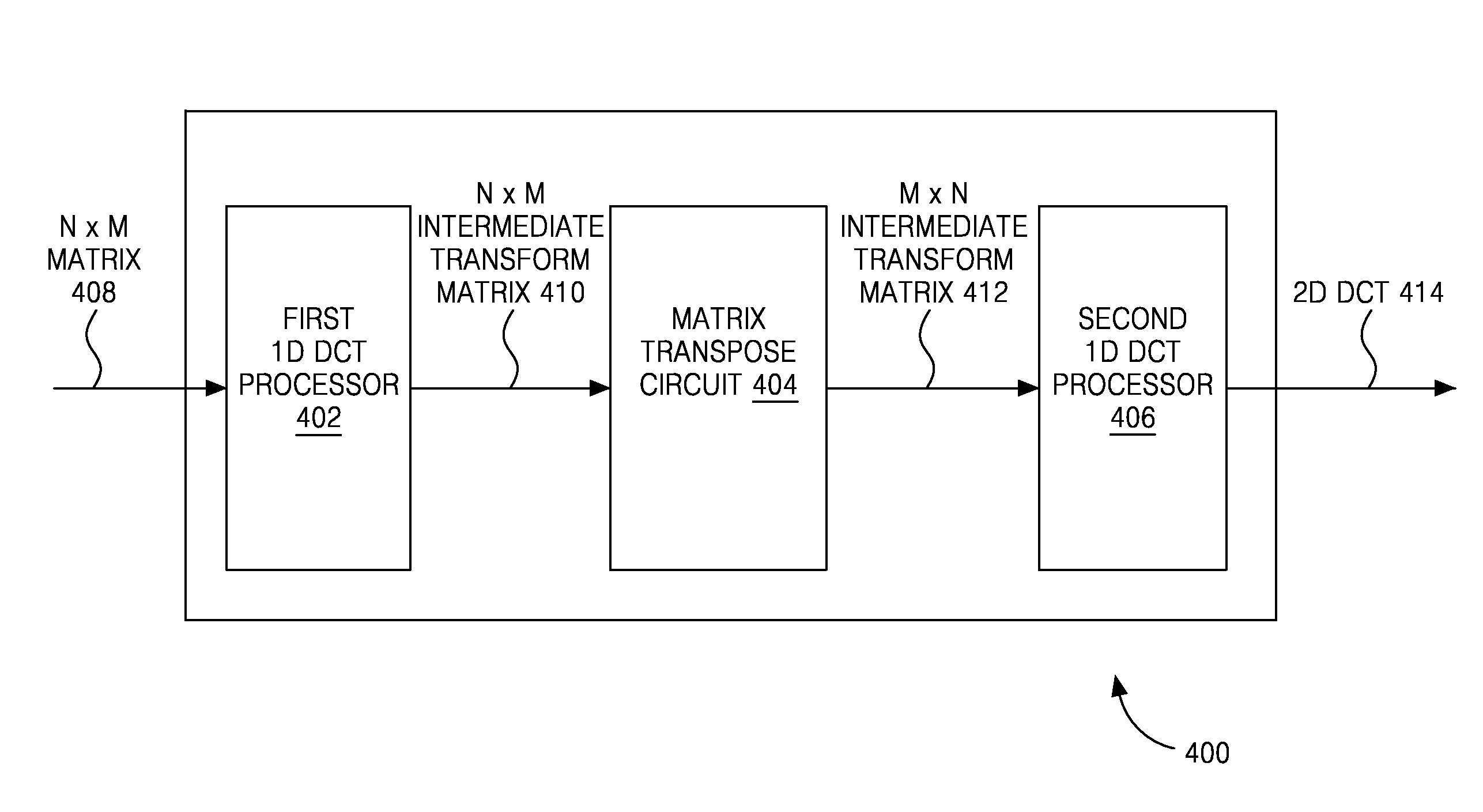
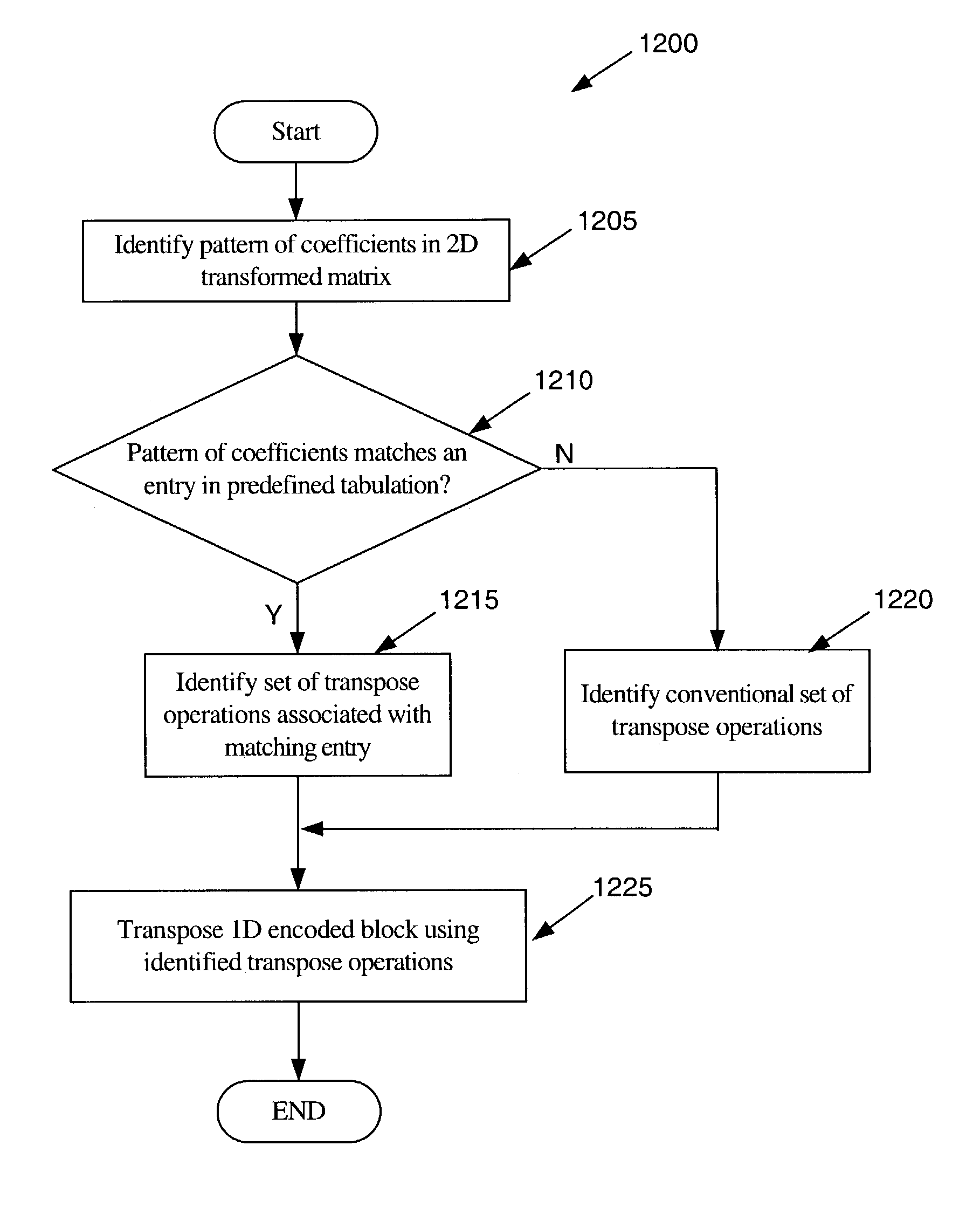
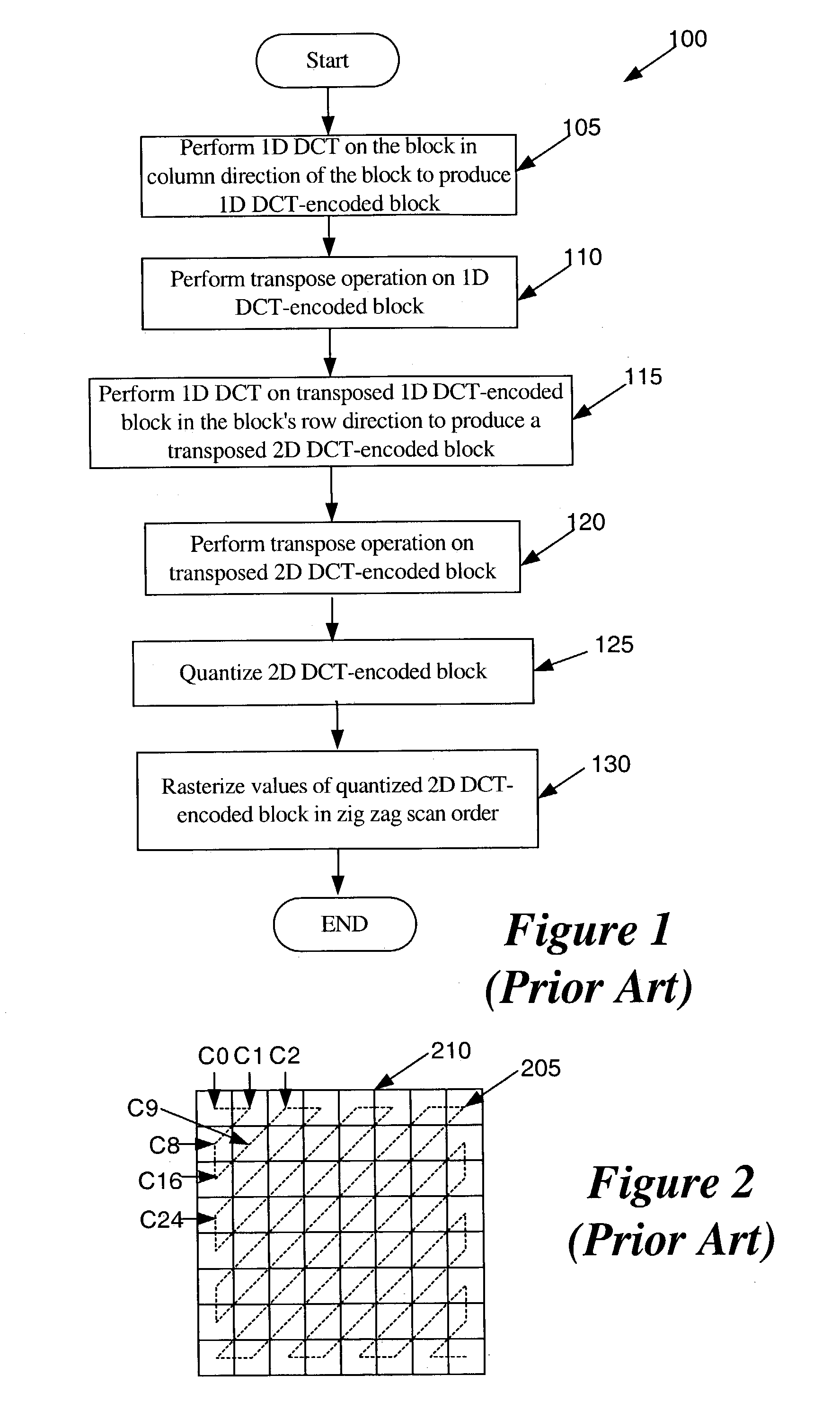
Video encoding and decoding
InactiveUS7376280B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamArray data structure
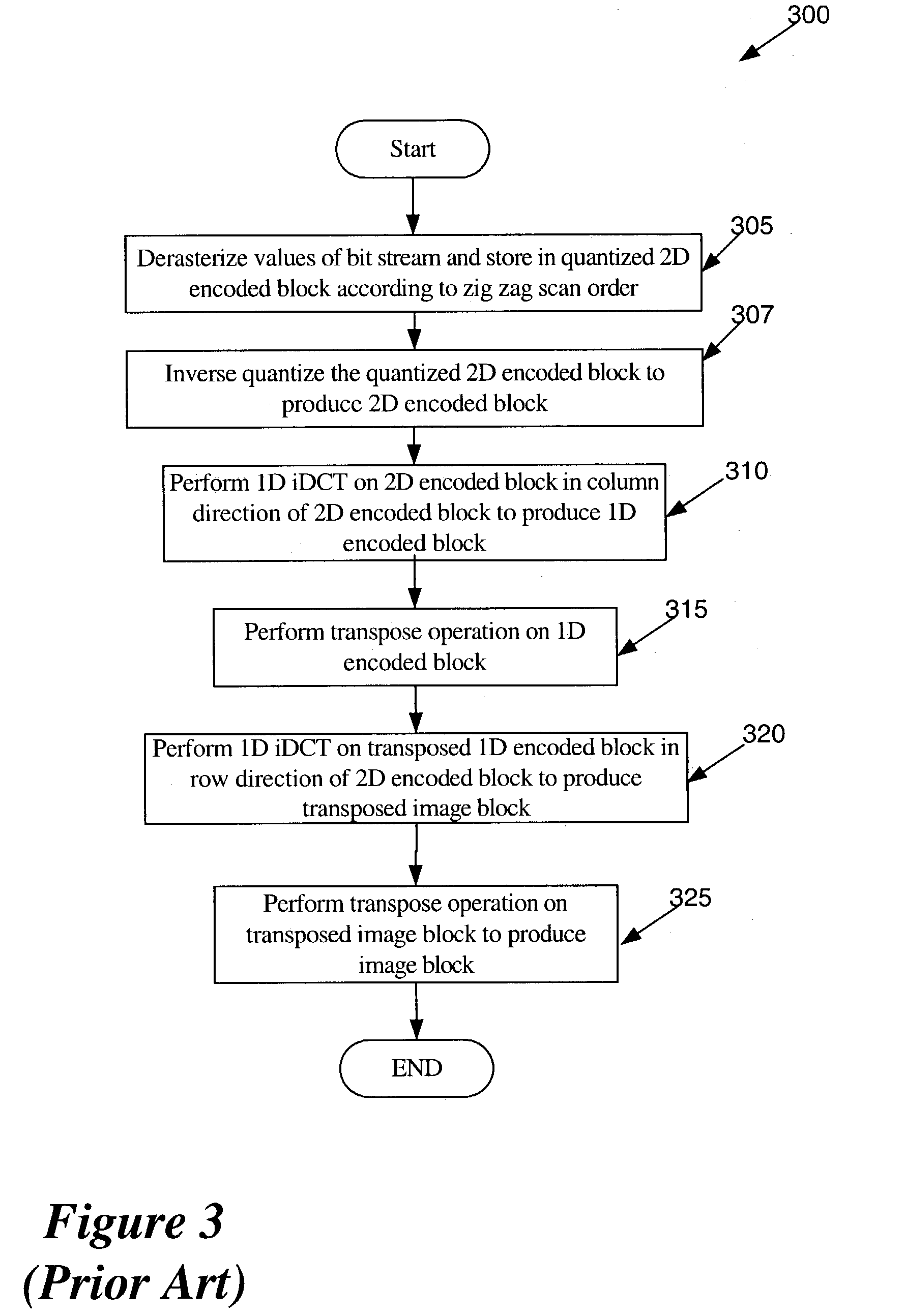
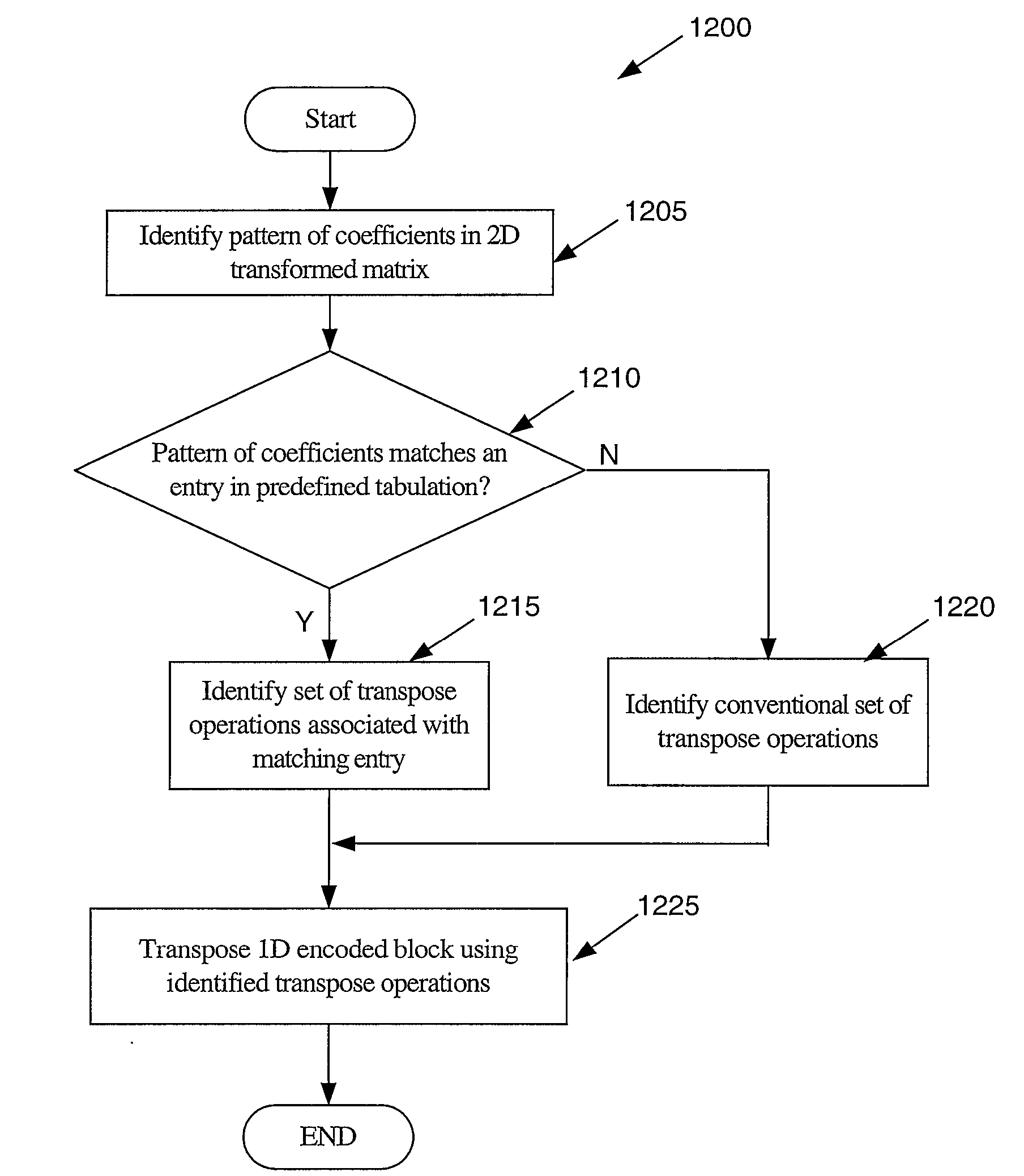
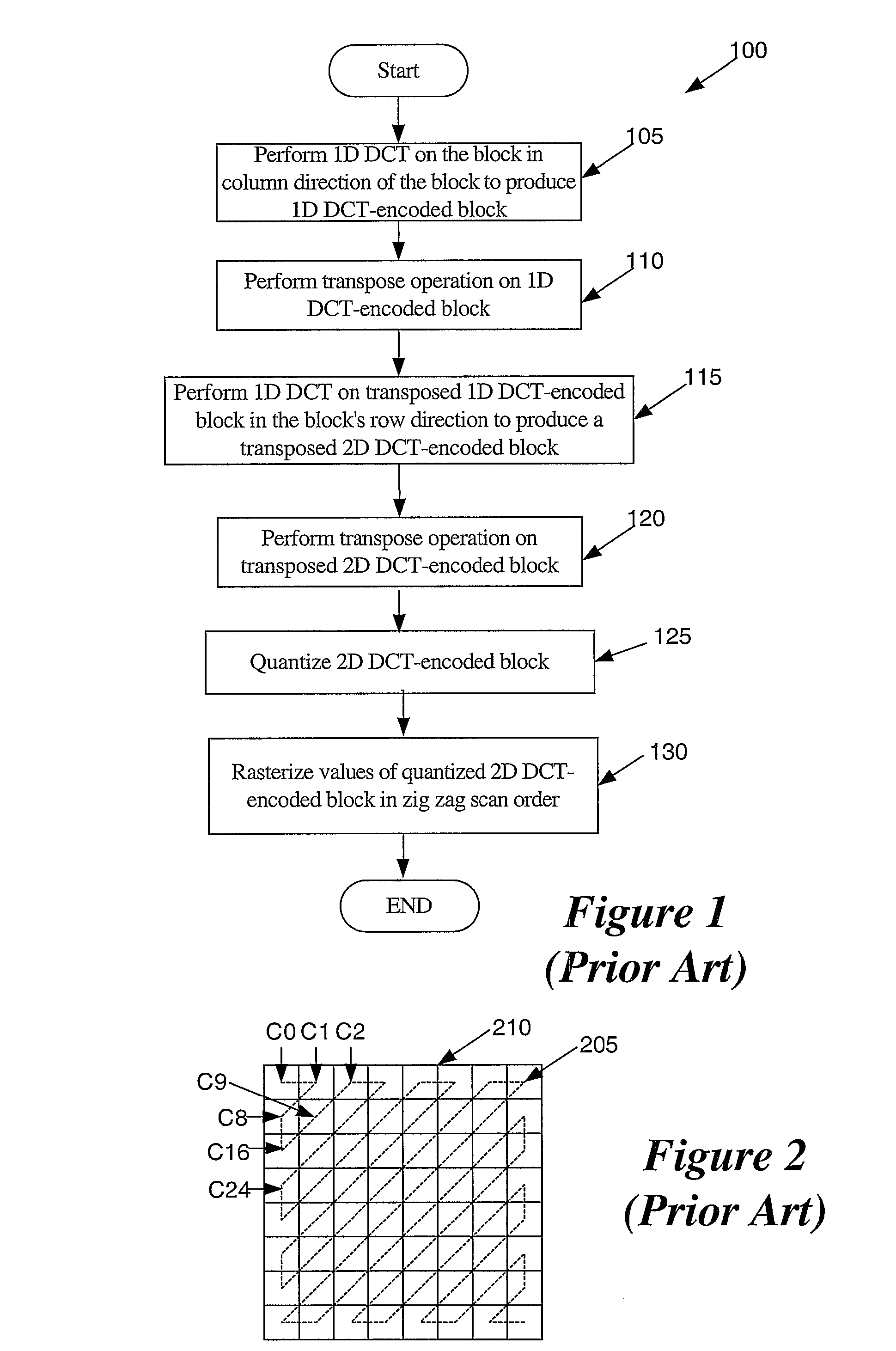
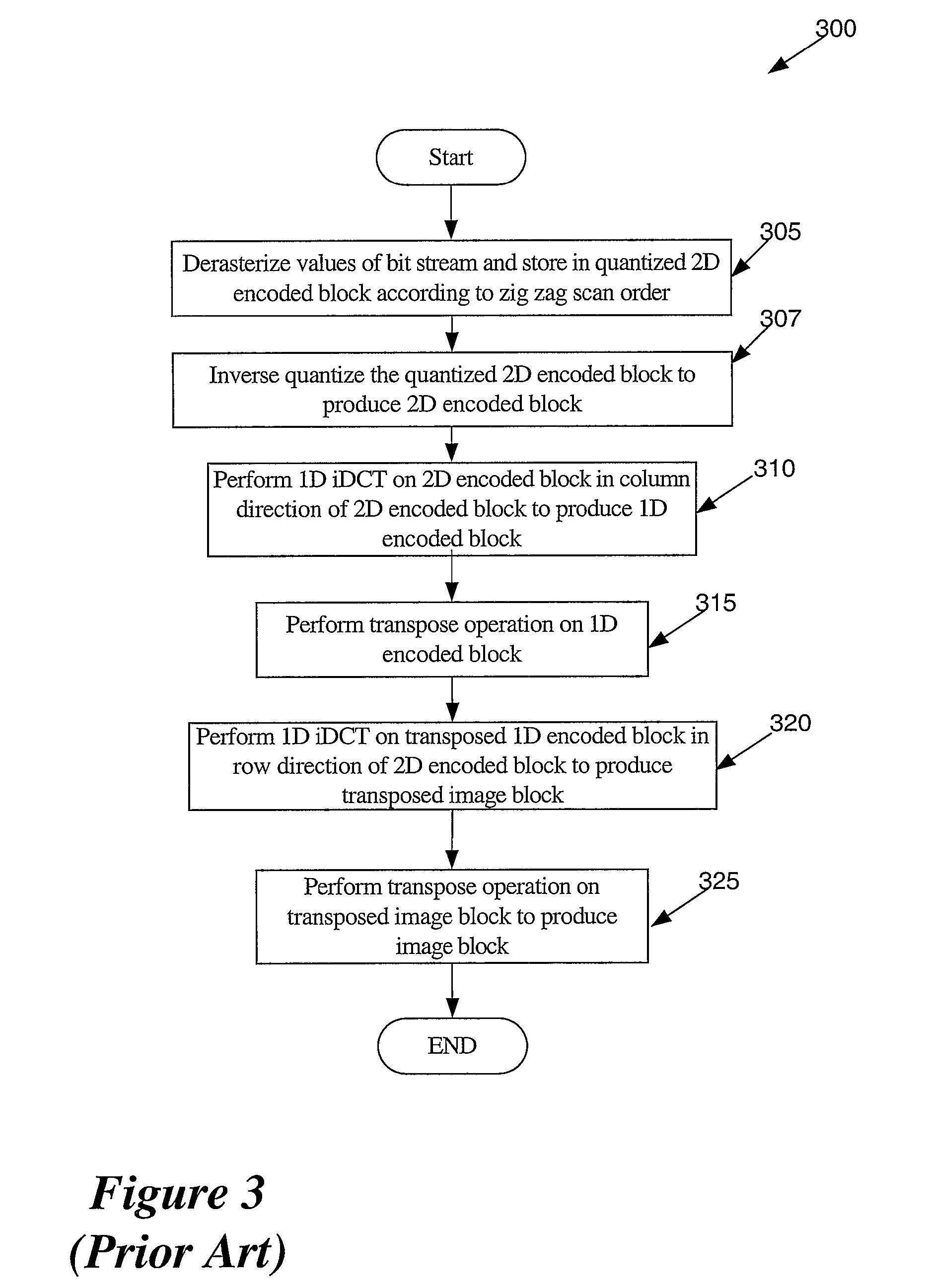
A method for encoding video with a two-dimensional (2D) transform separable to two one-dimensional (1D) transforms. The method receives an array of values for a sub-section of an image, performs a first 1D-transform of the array, transposes the resulting array, and performs a second 1D-transform of the array resulting from the transpose. The method, without performing another transpose, generates a data stream using a transposed scan order based on the values of the array resulting from the second transform. A method for decoding video encoded by a 2D transform, which separable to two 1D transforms. The method receives a data stream containing encoded values for an image, parses out the values into an array using a transposed scan order, performs a first 1D-inverse transform on the array, transposes the resulting array, and performs a second 1D-inverse transform of the array resulting from the transpose to produce a decoded output.
Owner:APPLE INC
Graphics processing unit based matrix transpose optimization method
ActiveCN103761215AImplement parallel processingIncrease computing speedConcurrent instruction executionProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsArray data structure
The invention relates to a graphics processing unit based matrix transpose optimization method. The method includes: converting an R-line S-column input matrix into a one-dimensional array, allocating storage spaces and copying data; setting a two-dimensional index space; computing global identifiers, workgroup identifiers and local identifies of work items; partitioning the matrix, and corresponding matrix partitions to workgroups; applying for local memories in the workgroups, copying the data into the local memories and synchronously waiting for completion of data copying; computing column and line indexes of the transposed data in a global memory; computing locations of output data in the global memory and local memories; assigning the data of the local memories to the one-dimensional array in the global memory to realize conflict-free memory consolidation access; and copying the one-dimensional array to the memories to form an S-line R-column superposed matrix. By the method, parallel computation of consolidation access and matrix transpose is realized, and execution efficiency of programs is improved.
Owner:北京新松佳和电子系统股份有限公司
Method for consitituting sparse generative matrix and method for coding low-density block check code
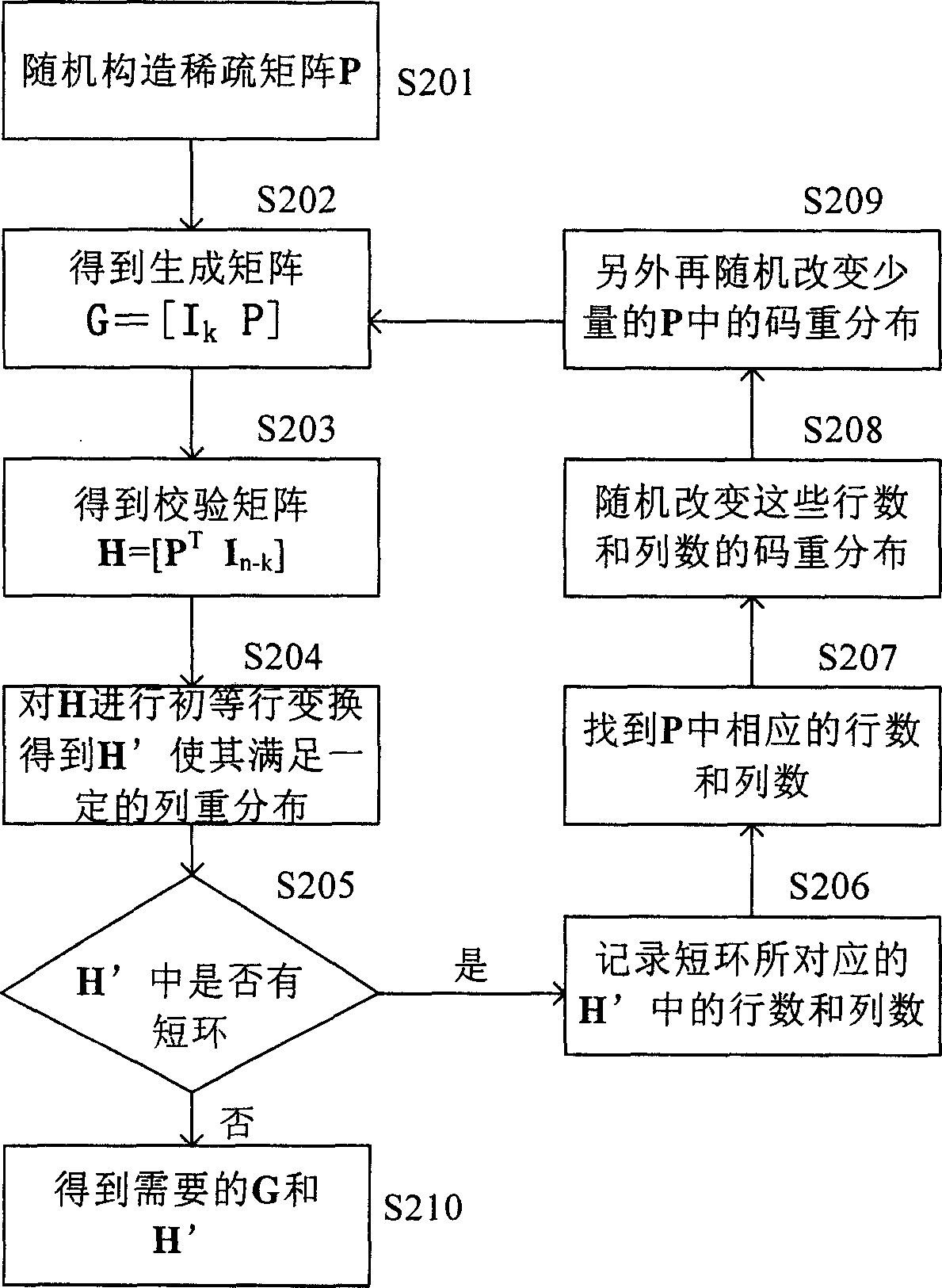
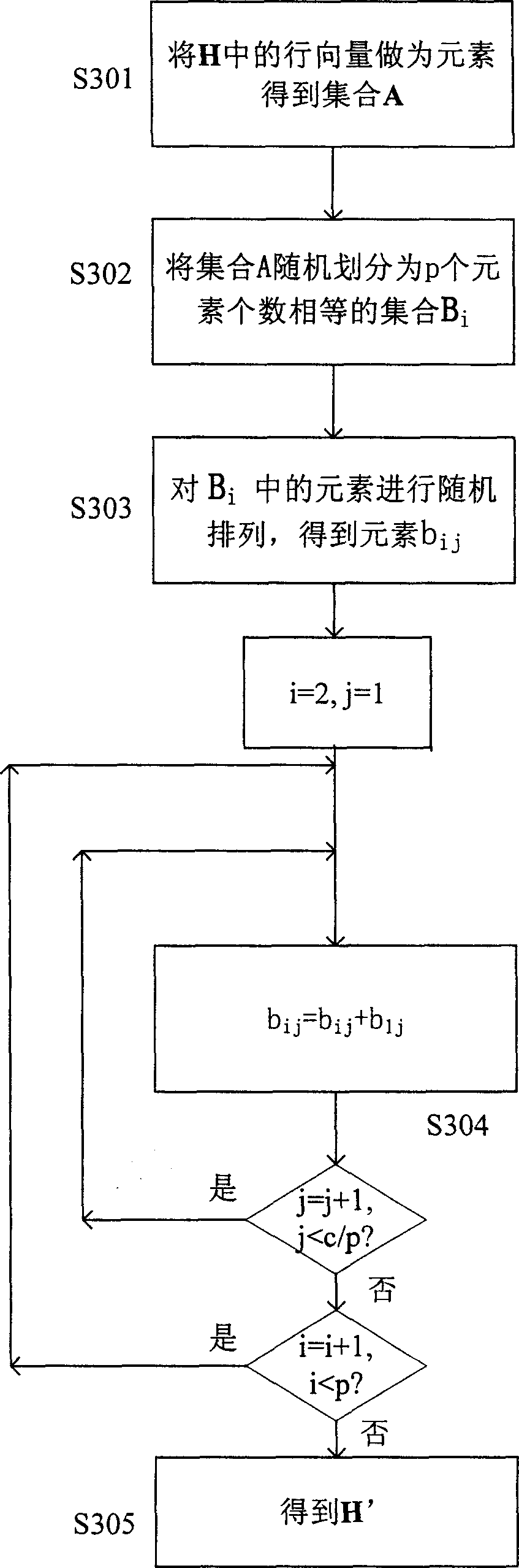
InactiveCN1889367ASimple codingError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsPartition of unityAlgorithm
This invention discloses a method for generating matrixes including: a, randomly generating a sparse matrix P of k lines and n-k columns, b, getting a generated matrix G=[Ik P] from said sparse matrix P, checking the matrix H=[PT In-k], in which, Ik is the unit matrix of k lines and k columns, the PT is the transposed matrix of P, c, carrying out initial transformation to said checked matrix H to let it meet the preset re-distribution of columns to get the transformed check matrix H, d, checking if there are short rings in the matrix H, e, recording the corresponding lines and columns of the short rings in H to further get the numbers corresponding to said short rings in H so as to further find out numbers corresponding to those in the random matrix P and H, f, regulating the code re-distribution corresponding to said line and column number in P, g, repeating said step b to f and short rings do not exist in H.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
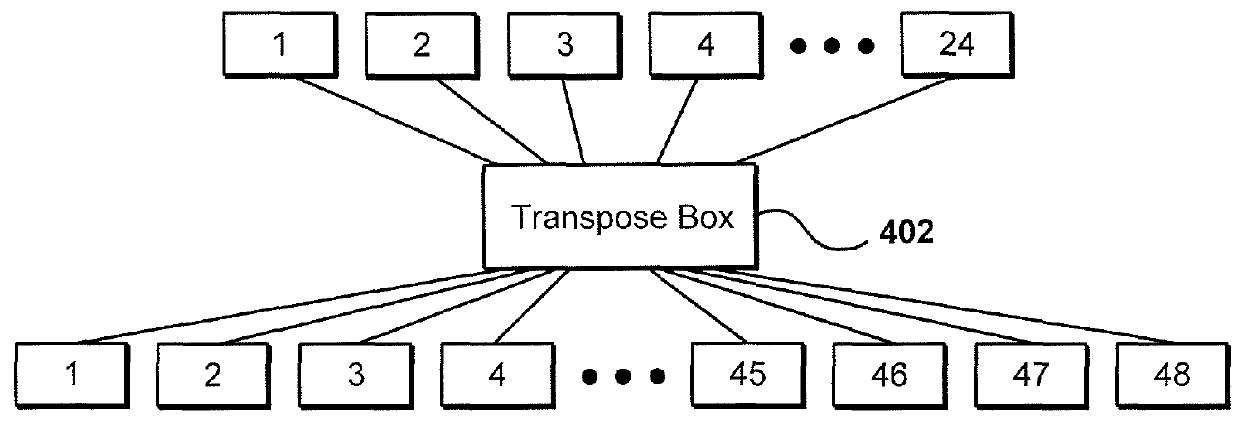
Logical switches
The deployment and scaling of a network of electronic devices can be improved by utilizing one or more network transpose boxes. Each transpose box can include a number of connectors and a meshing useful for implementing a specific network topology. Different tiers of a network can be connected to one or more of the network transpose boxes, and operated as a logical switch. A control server can be used to manage the control plane operations of the logical switch.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
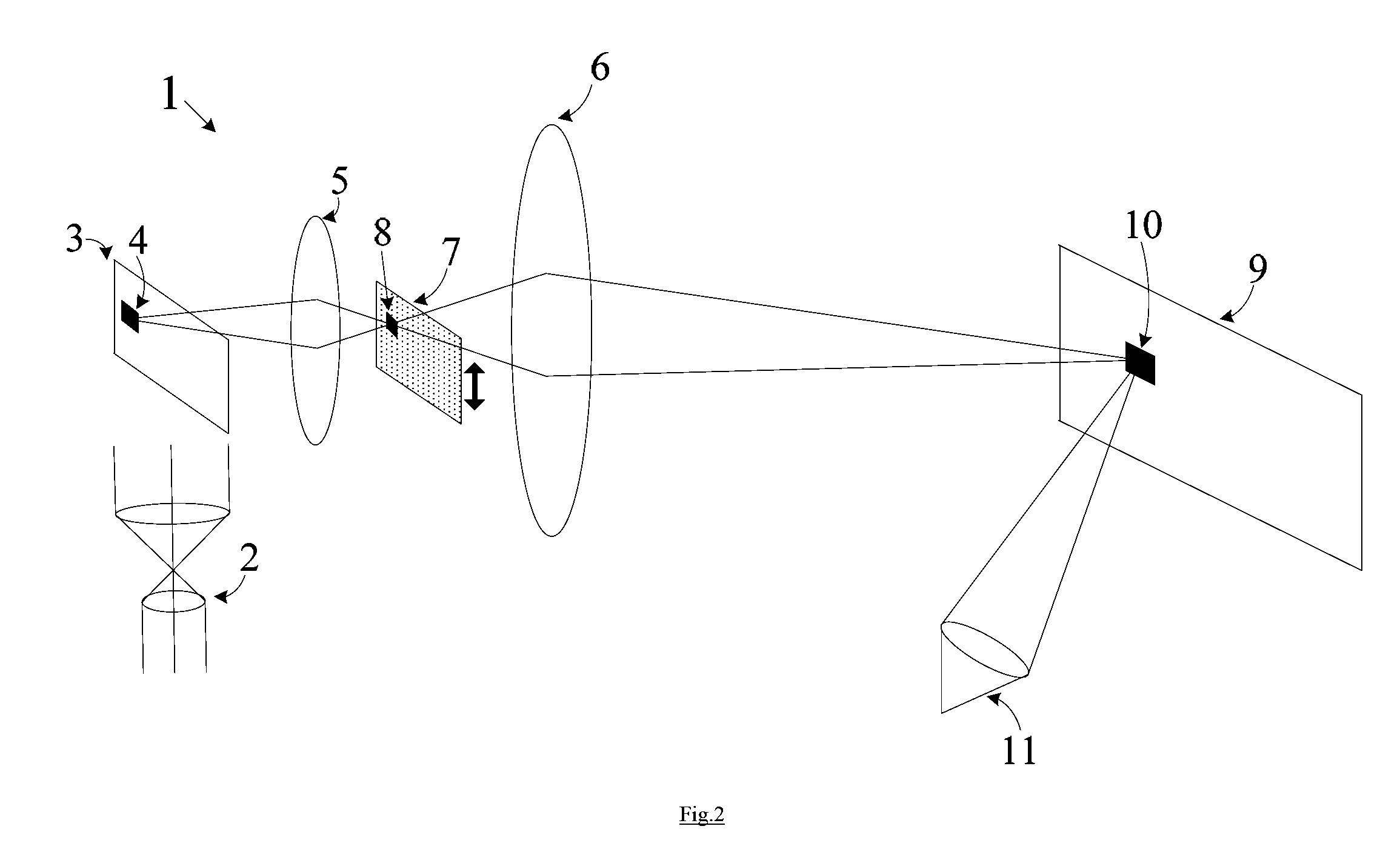
Speckle reduction
ActiveUS20110216390A1Eliminate needIncrease flexibilityDiffusing elementsPhotomechanical apparatusTransposeSpeckle reduction
Speckle reduction apparatus includes a radiation path and a mask arranged within the radiation path. The mask includes an array of electrically controllable cells configured to form a pattern on the mask that varies with time. The speckle reduction mask includes a first linear array including first parallel lines arranged to change the phase of incident radiation, and a second linear array including second parallel lines arranged to change the phase of incident radiation and further arranged such that cells are formed at the intersections of the first parallel lines and the second parallel lines. The speckle reduction mask includes a N1×N2 array of cells, A, formed according to:ATA=βδk,l,where AT is the transpose of A, β is a real and positive constant, dk,l is Kronecker delta and N1≠N2.
Owner:HGSKOLEN I BUSKERUD OG VESTFOLD
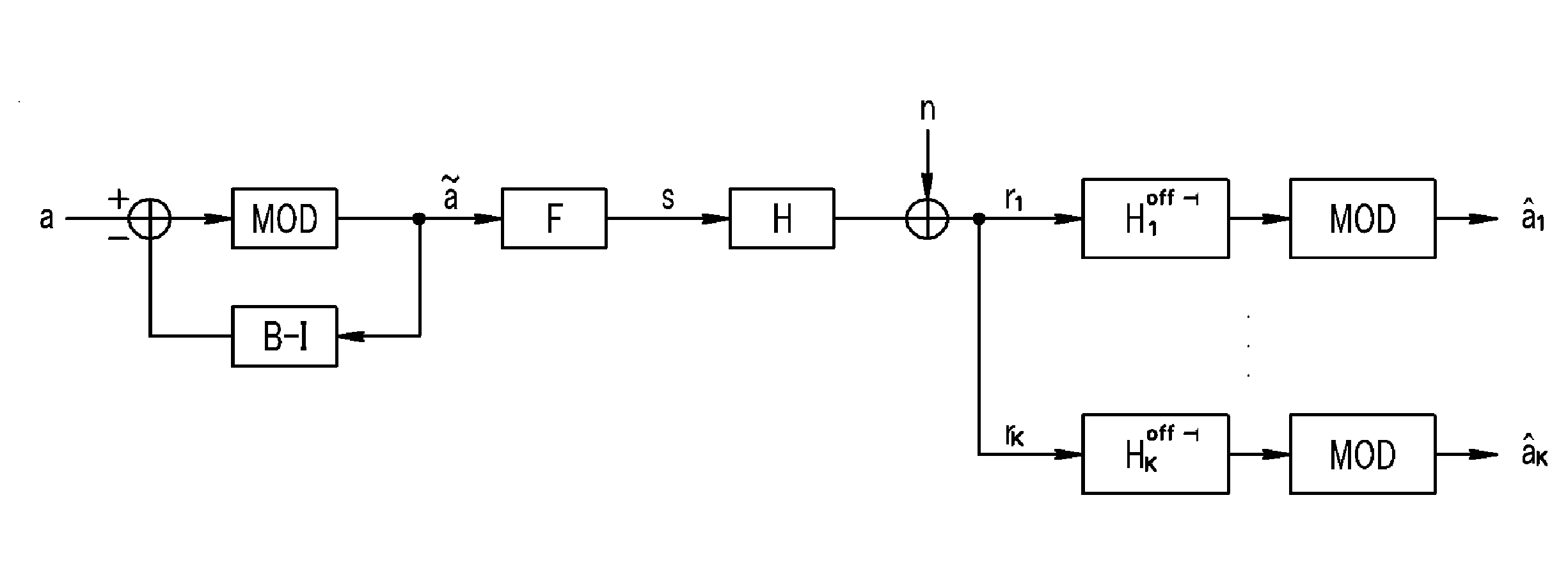
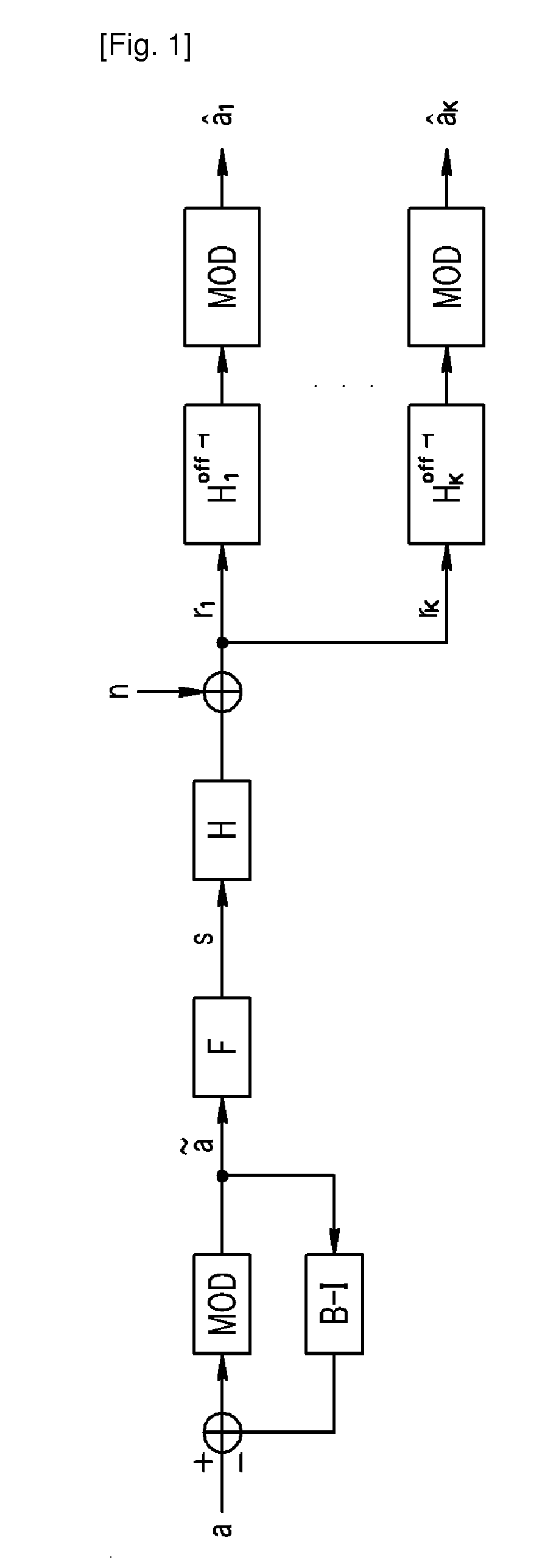
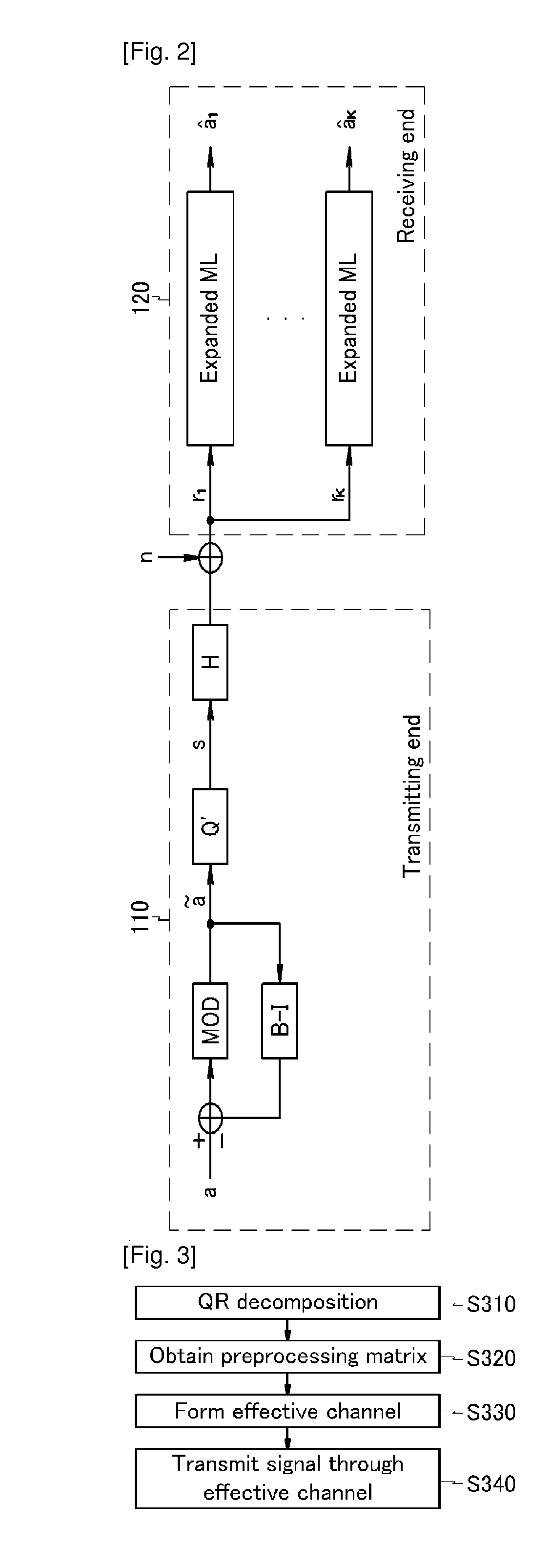
Transmitting/receiving method for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output system
ActiveUS20100310001A1Increase data rateImprove error performanceDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationQR decompositionTriangulation
Disclosed is a transmitting / receiving method in a multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) channel. The transmitting method includes: performing QR decomposition on a Hermitian transpose matrix of a channel matrix to obtain a first matrix and a second matrix as a triangular matrix; obtaining a preprocessing matrix by using the first matrix; and forming an effective channel based on the preprocessing matrix by a block triangulation technique.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Video encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20080232475A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamArray data structure
A method for encoding video with a two-dimensional (2D) transform separable to two one-dimensional (1D) transforms. The method receives an array of values for a sub-section of an image, performs a first 1D-transform of the array, transposes the resulting array, and performs a second 1D-transform of the array resulting from the transpose. The method, without performing another transpose, generates a data stream using a transposed scan order based on the values of the array resulting from the second transform. A method for decoding video encoded by a 2D transform, which separable to two 1D transforms. The method receives a data stream containing encoded values for an image, parses out the values into an array using a transposed scan order, performs a first 1D-inverse transform on the array, transposes the resulting array, and performs a second 1D-inverse transform of the array resulting from the transpose to produce a decoded output.
Owner:APPLE INC
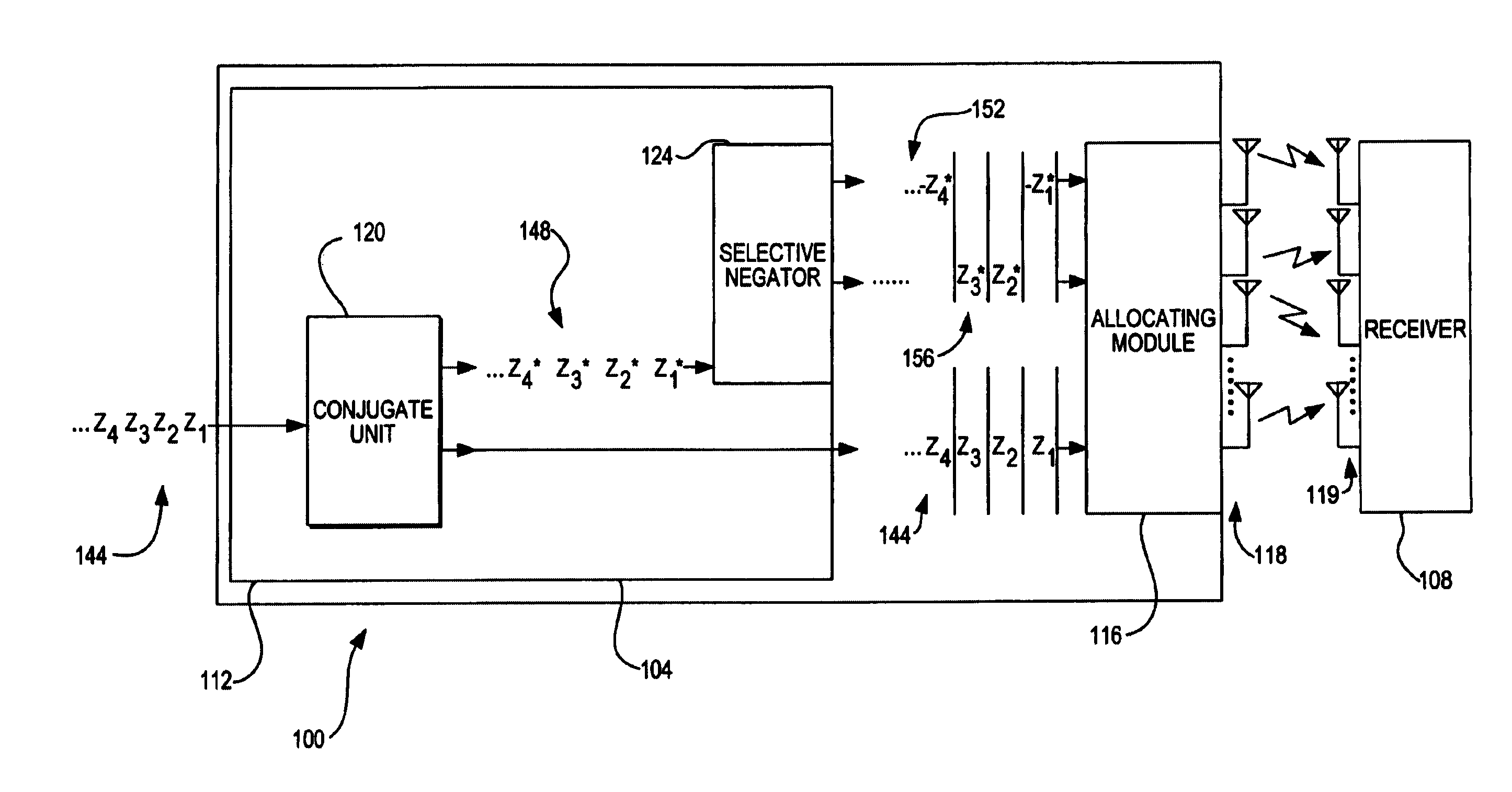
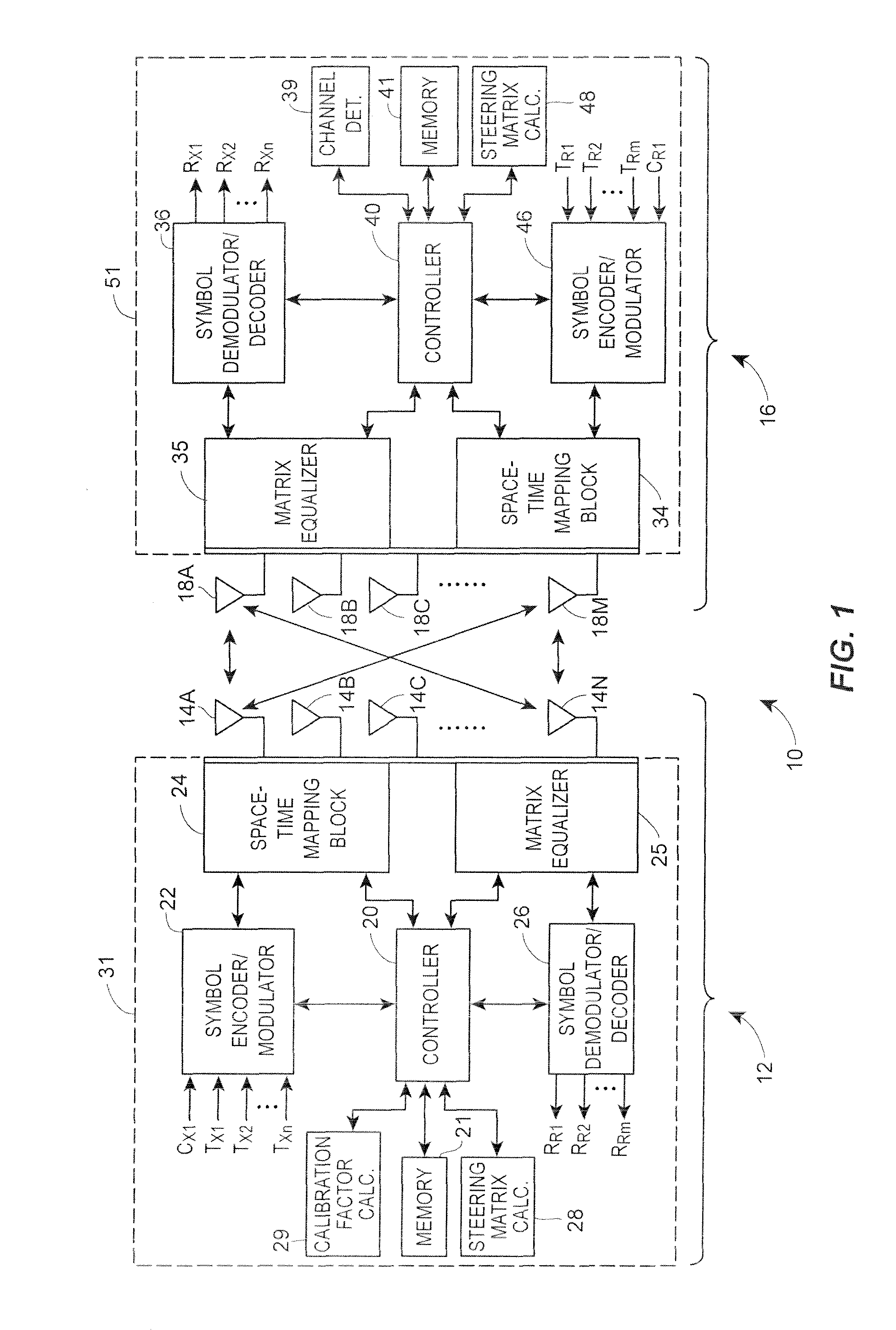
Calibration correction for implicit beamforming in a wireless MIMO communication system
ActiveUS8340597B1Promote resultsTransmitters monitoringDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemEngineering
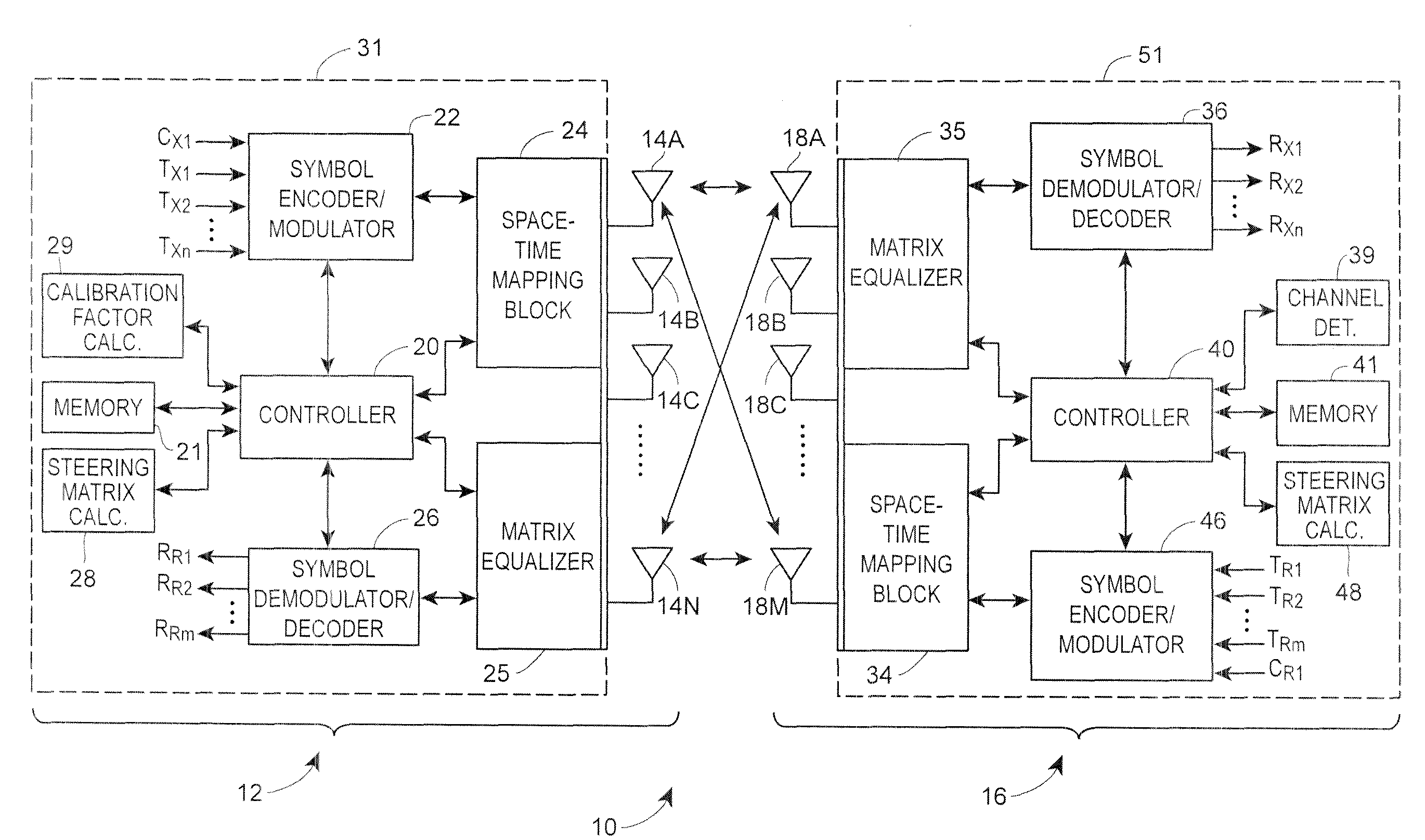
A transmitter beamforming technique for use in a MIMO wireless communication system determines a calibration factor and then applies the calibration factor to a transmit beamforming steering matrix developed using implicit beamforming, i.e., using an estimate of a forward channel disposed between a transmitter and a receiver based on a measurement of the reverse channel disposed between the receiver and the transmitter. The beamforming technique first determines descriptions of both the forward and reverse channels, determines an estimate of the forward channel from the description of the reverse channel, determines right singular matrixes which model the forward channel and the estimated forward channel and then develops a calibration factor from the determined right singular matrixes. The beamforming technique then applies the determined calibration factor to a steering matrix which is calculated using a standard implicit beamforming technique, i.e., assuming that the forward channel can be described as the transpose of the reverse channel. The use of this beamforming technique provides superior beamforming results when using implicit beamforming without having to take the necessary steps to determine a description of the actual forward channel each time a new steering matrix is to be calculated.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Matrix transposition method in SAR imaging system based on DSP chip
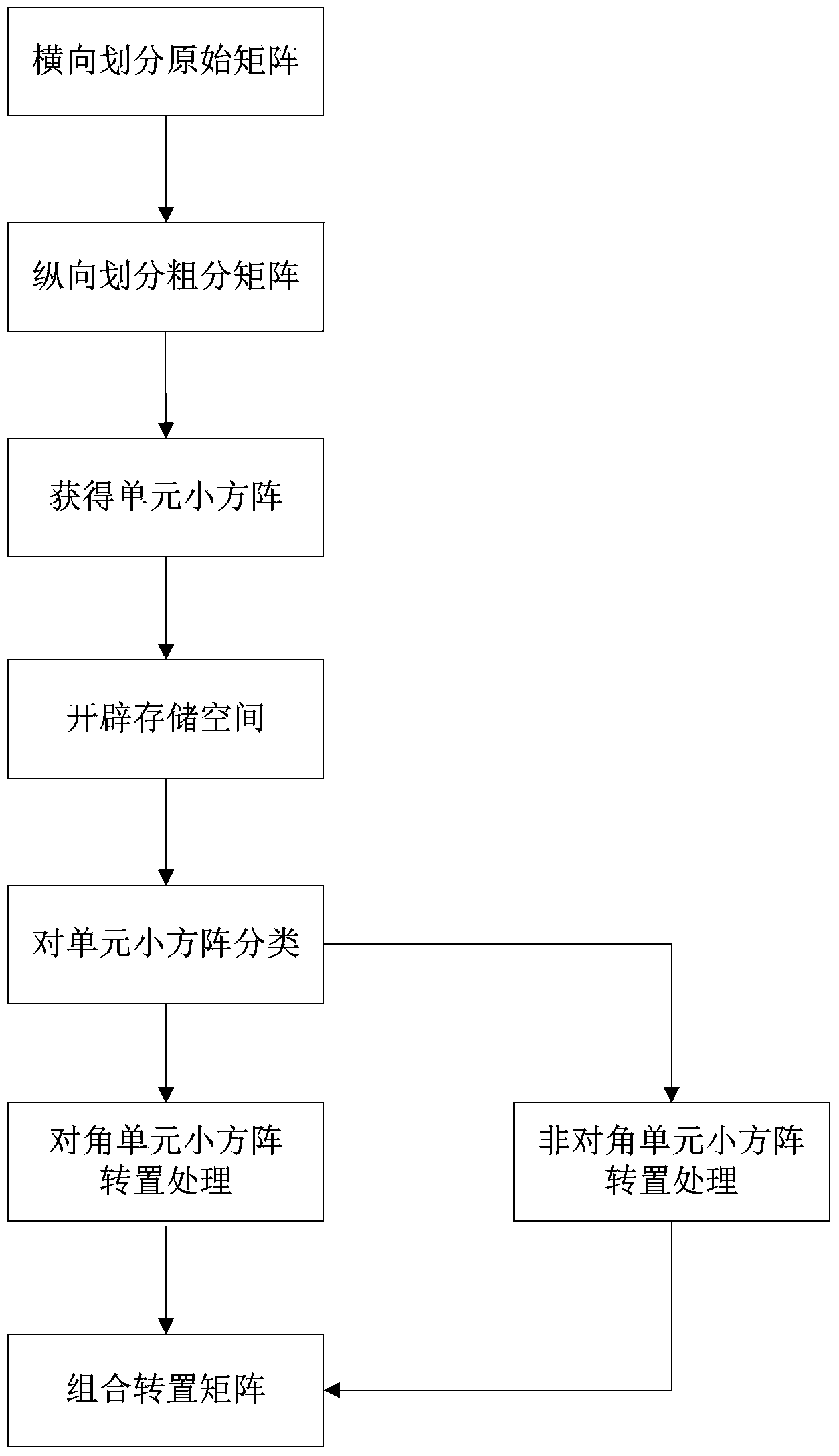
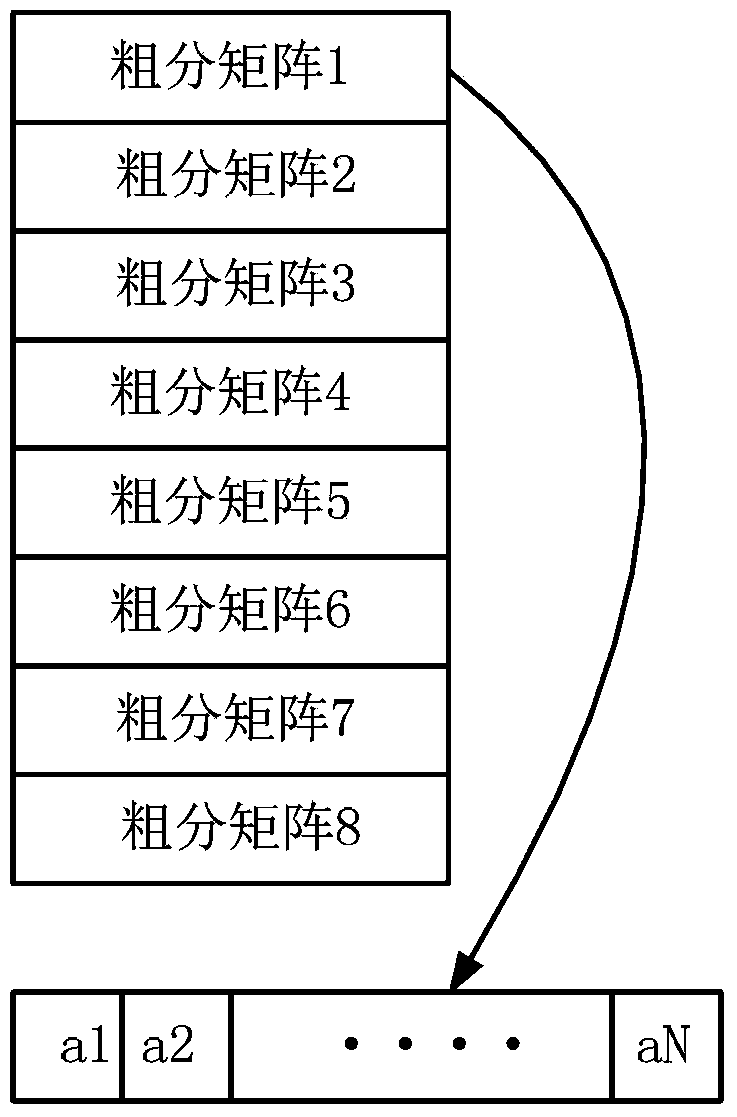
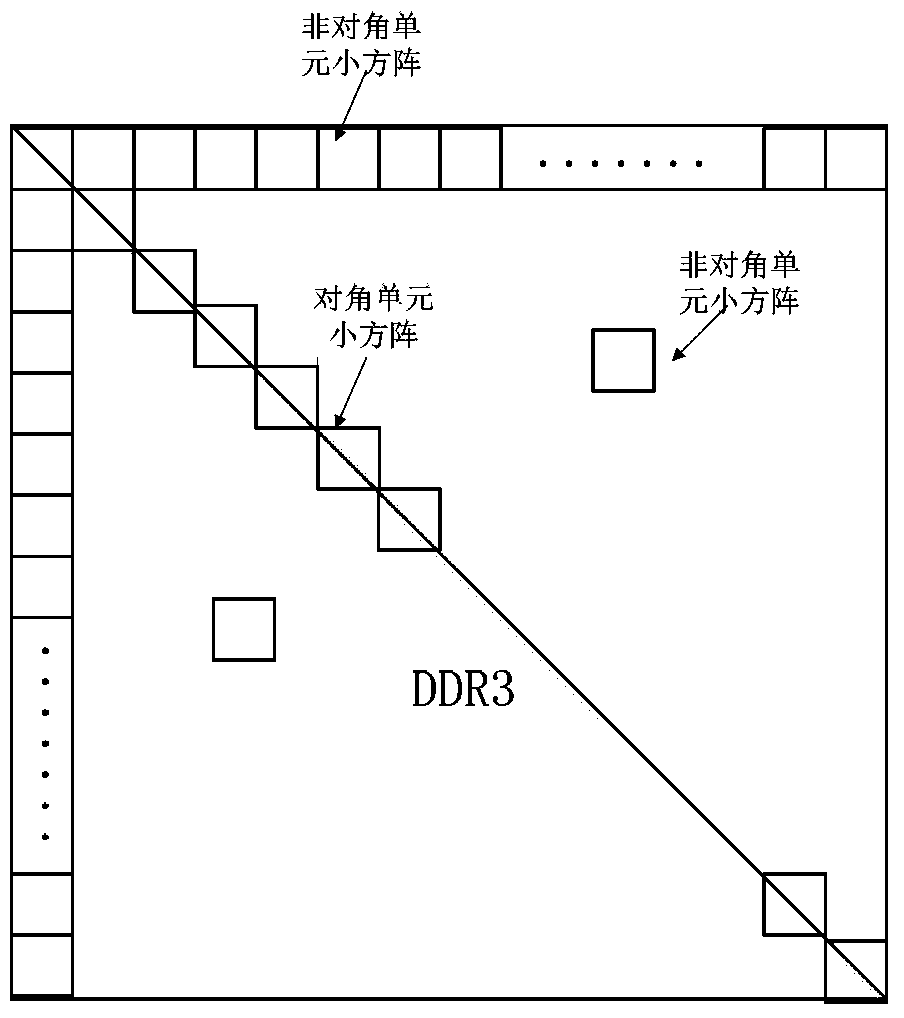
InactiveCN103412284ASave storage spaceOvercome the disadvantage of taking a lot of time to moveRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarAlgorithm
The invention discloses a matrix transposition method in an SAR imaging system based on a DSP chip. The problems that radar real-time imaging storage space is small, and the requirement for real-time performance is high are mainly solved. The implementation process of the matrix transposition method comprises the steps that (1) an original matrix is transversely divided; (2) a rough classification matrix is longitudinally divided; (3) small unit matrixes are obtained; (4) storage space is created; (5) the small unit matrixes are classified; (6) transposition is carried out on the small diagonal unit matrixes; (7) transposition is carried out on the small non-diagonal unit matrixes; (8) the transpositioned matrixes are combined. The matrix transposition method aims at the transposition operation of a large-scale radar return original data matrix, the large matrix is roughly and finely divided into two classes of small unit matrixes, different transposition methods are applied to processing the matrixes, a large amount of storage space is saved, and operation efficiency is improved. The matrix transposition method is simple, easy to implement and suitable for the transposition operation of various radar real-time imaging systems and other systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com