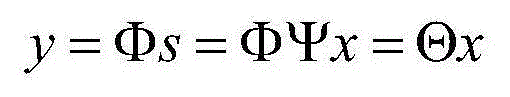Patents
Literature
426 results about "Random matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability theory and mathematical physics, a random matrix is a matrix-valued random variable—that is, a matrix in which some or all elements are random variables. Many important properties of physical systems can be represented mathematically as matrix problems. For example, the thermal conductivity of a lattice can be computed from the dynamical matrix of the particle-particle interactions within the lattice.
Method and system for statistical filters and design of statistical filters
InactiveUS7184938B1Less dataLess signalDigital variable displayNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementFrequency spectrumFilter system
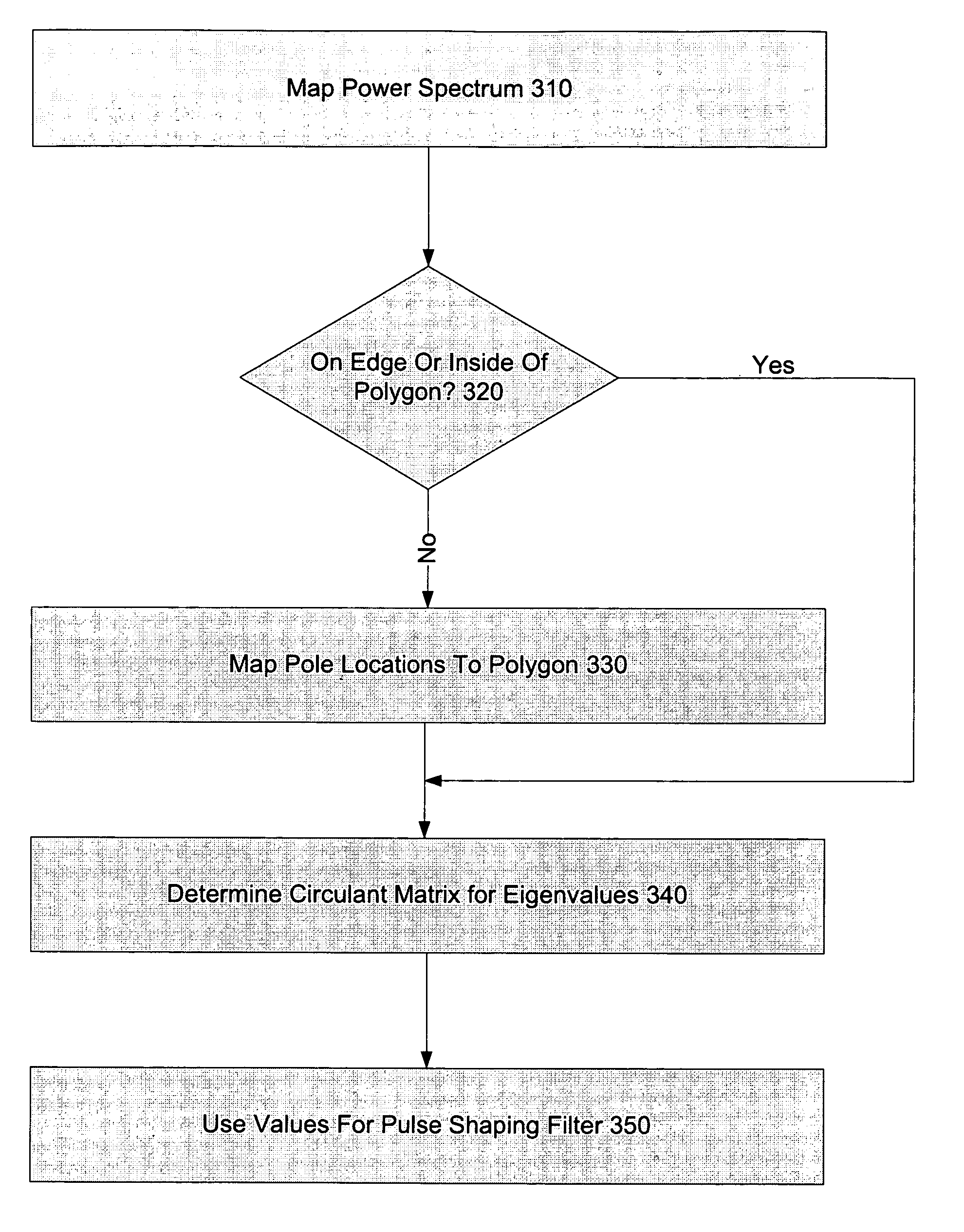
Systems and methods for the design or implementation of statistical filters for use in the spectral shaping of transmissions are disclosed. A desired power spectrum may be mapped to find pole locations that approximate the desired spectrum. These pole locations may then be mapped to the edge or inside of an equilateral polygon lying inside a unit circle, the equilateral polygon having the same number of sides as the order of the statistical filter desired and one vertex mapped to unity, to yield a set of eigenvalues. These eigenvalues may be the eigenvalues of a stochastic matrix the elements of which may be the Markov transition probabilities for use in a statistical filter designed to achieve the desired power spectrum. Use of a statistical filter employing these Markov transition values may be utilized to shape UWB or other signals to achieve the desired power spectrum.
Owner:ALEREON
Efficient Homomorphic Encryption Scheme For Bilinear Forms
InactiveUS20110243320A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
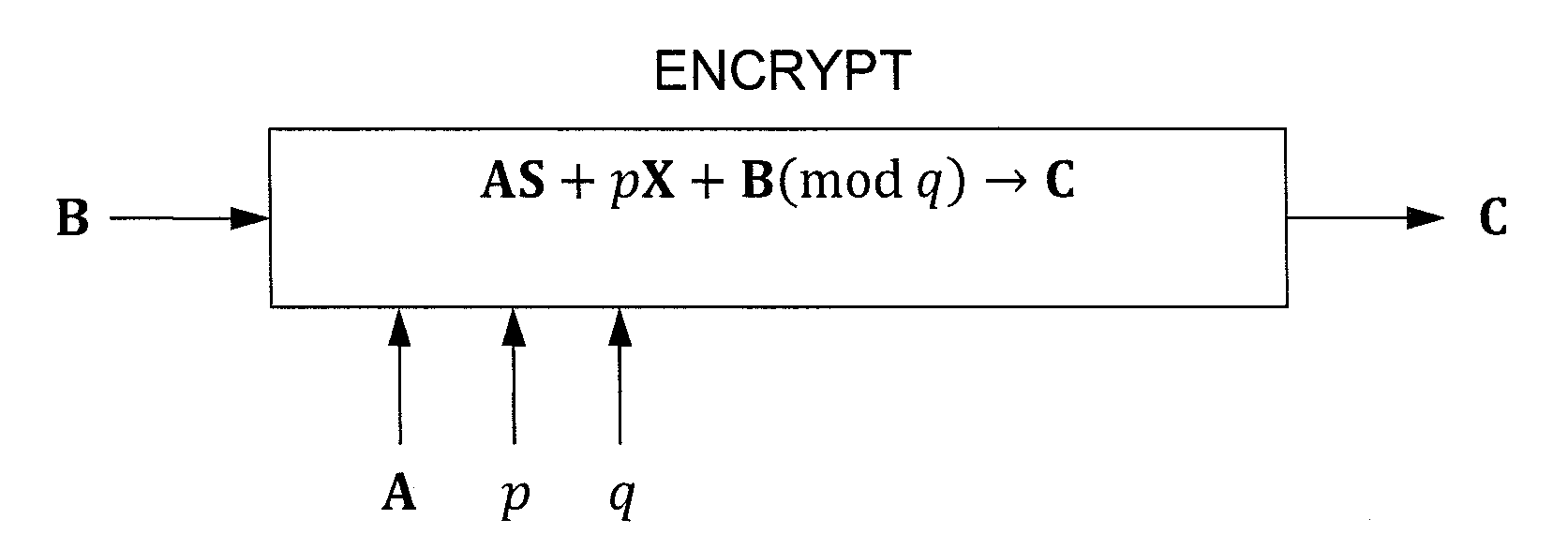
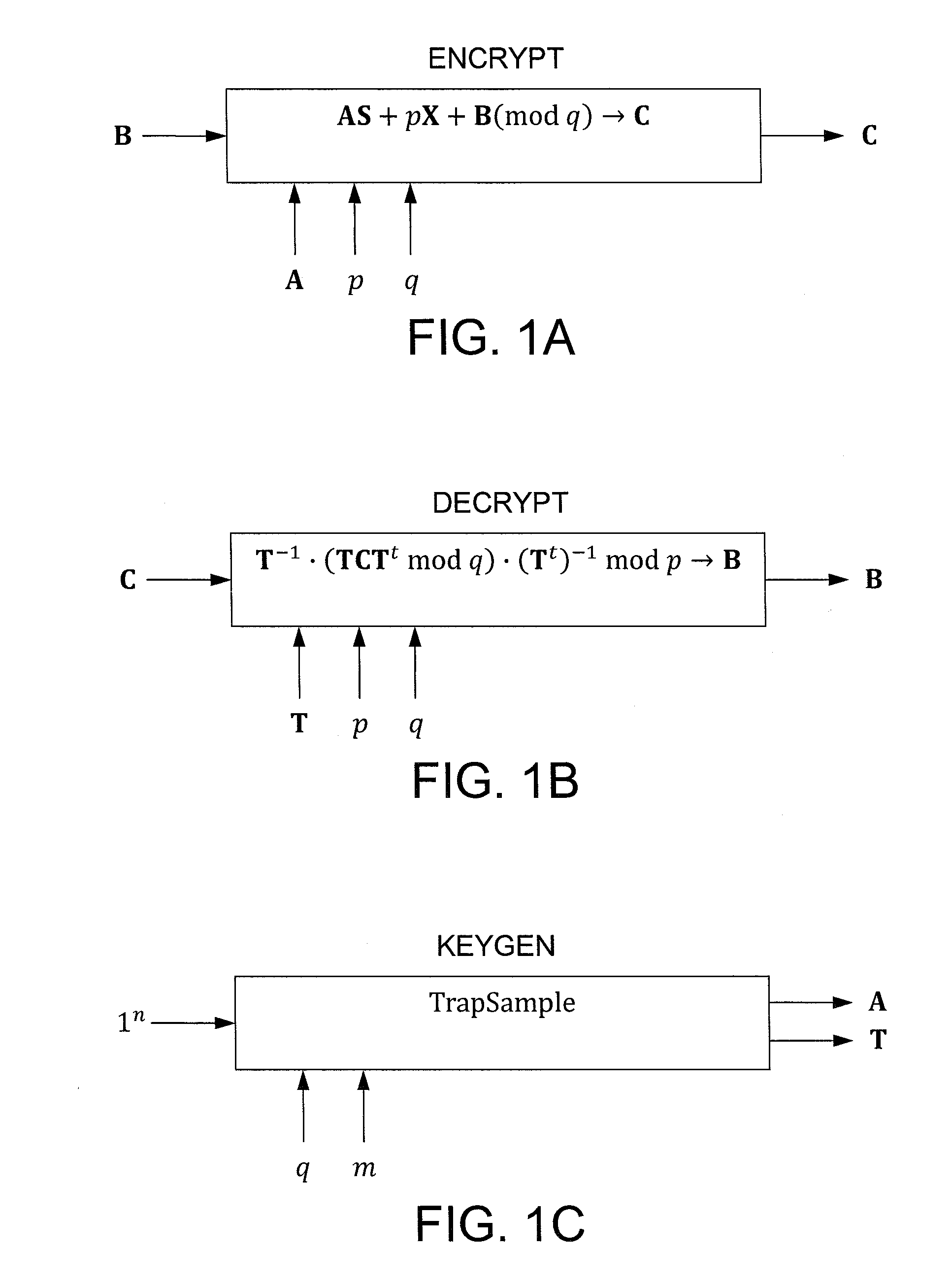
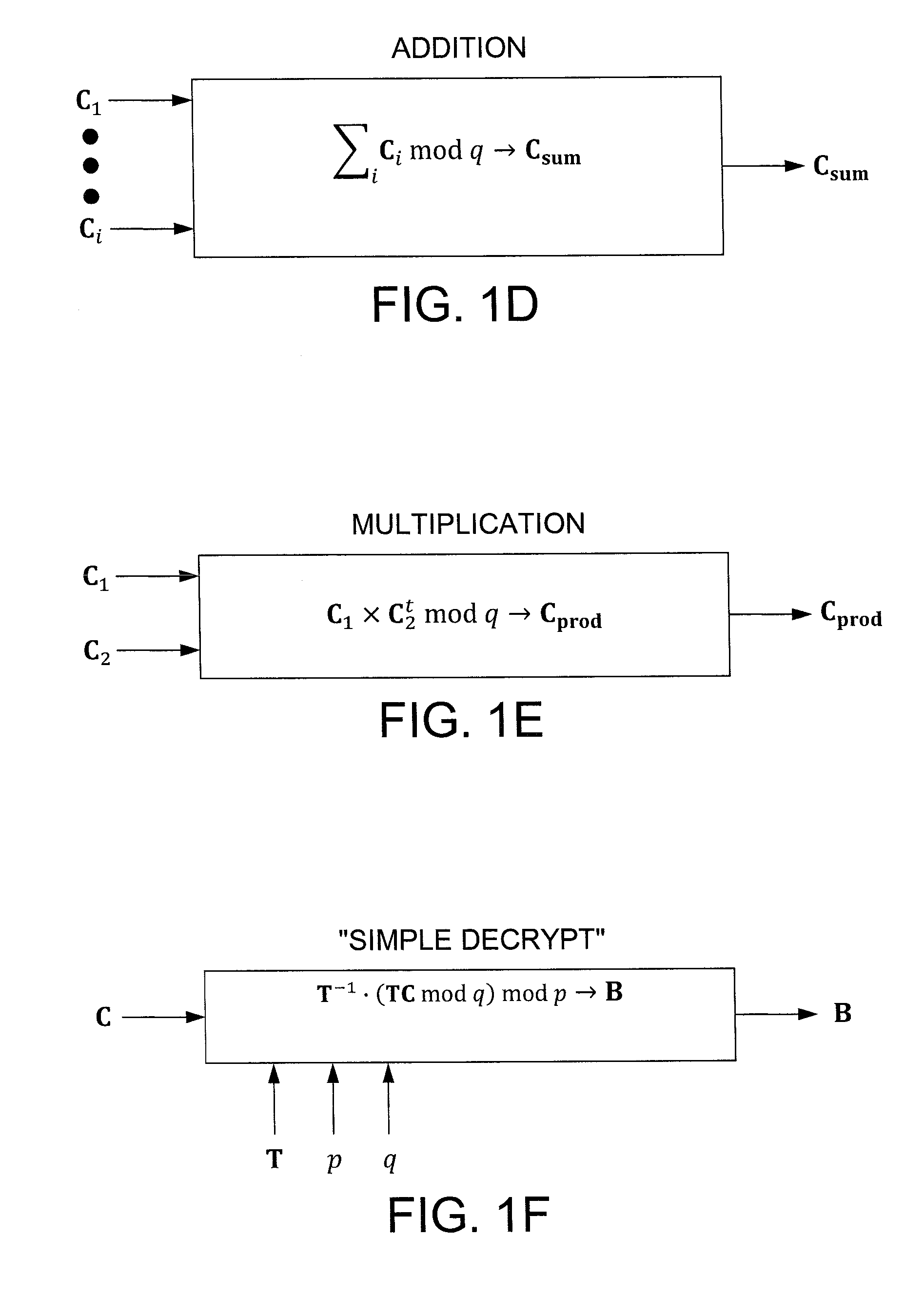
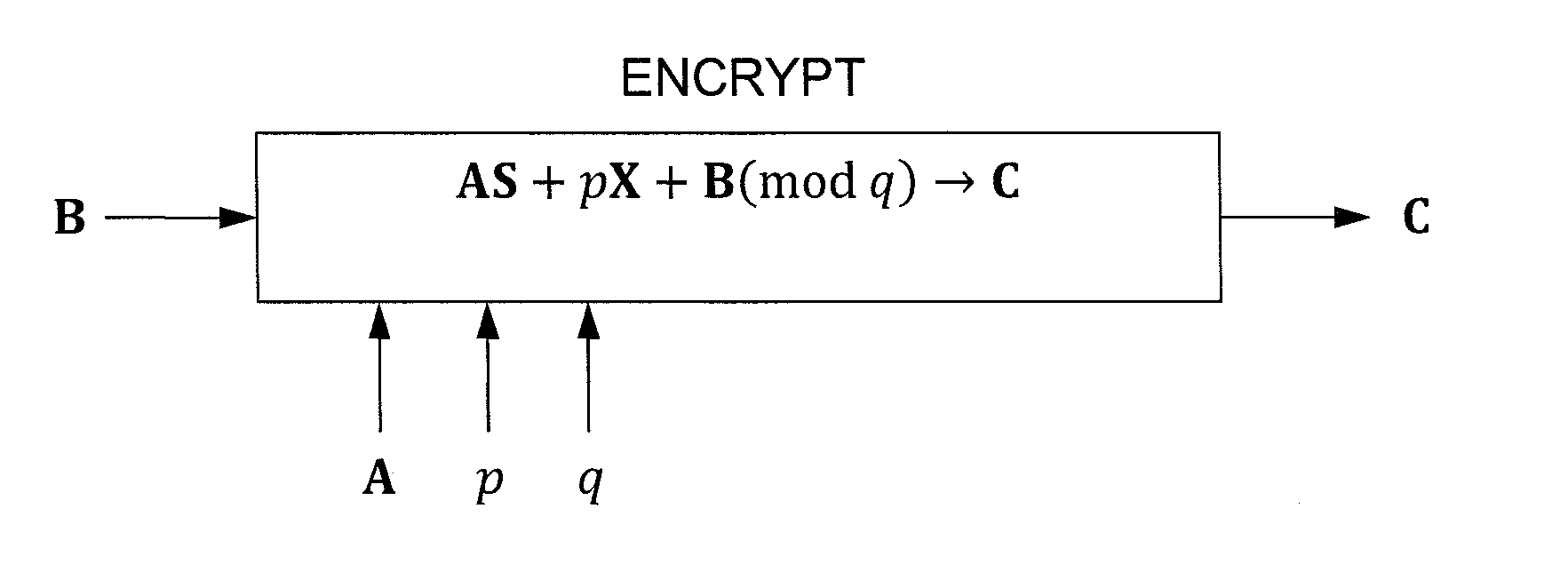
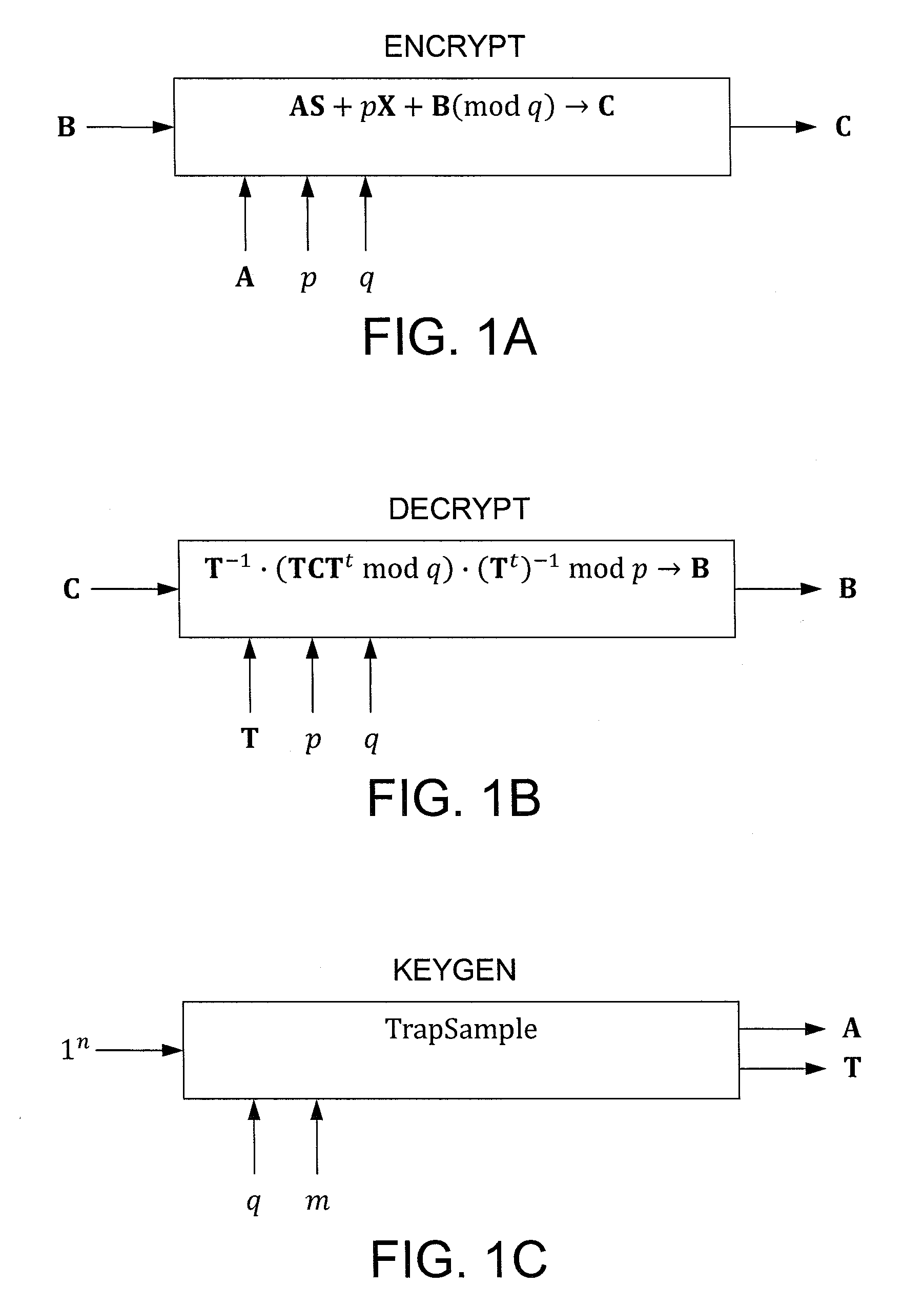
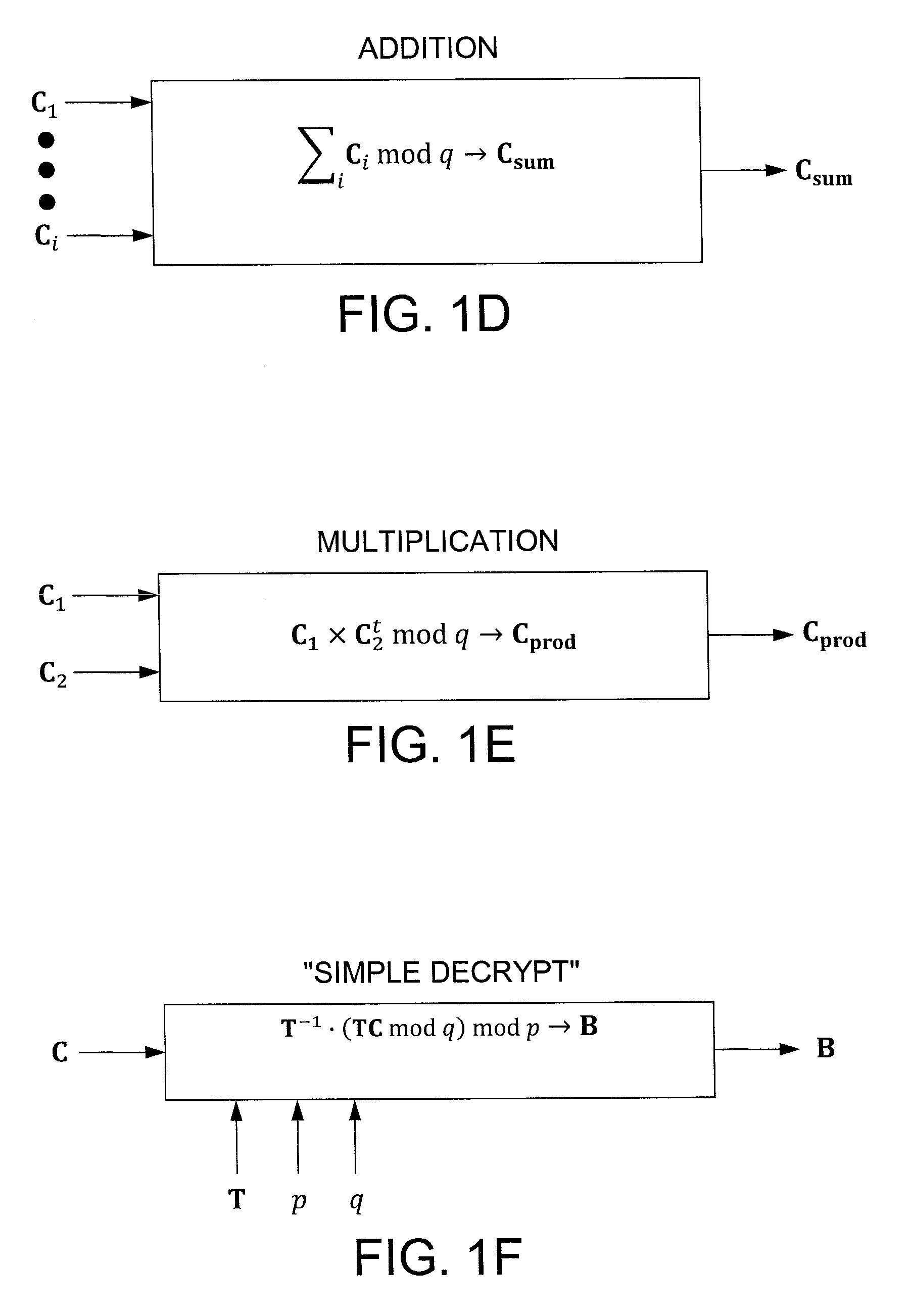
In one exemplary embodiment, a computer readable storage medium tangibly embodying a program of instructions executable by a machine for performing operations including: receiving information B to be encrypted as a ciphertext C in accordance with an encryption scheme having an encrypt function; and encrypting B in accordance with the encrypt function to obtain C, the scheme utilizes at least one public key A, where B, C, and A are matrices, the encrypt function receives as inputs A and B and outputs C as C→AS+pX+B (mod q), S is a random matrix, X is an error matrix, p is in integer, q is an odd prime number. In other exemplary embodiments, the encryption scheme includes a decrypt function that receives as inputs at least one private key T (a matrix) and C and outputs B as B=T−1·(TCTt mod q)·(Tt)−1 mod p.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electric transmission and transformation device state abnormity detection method
ActiveCN105353256ATake advantage ofImplement anomaly detectionElectrical testingElectric power transmissionComputer science
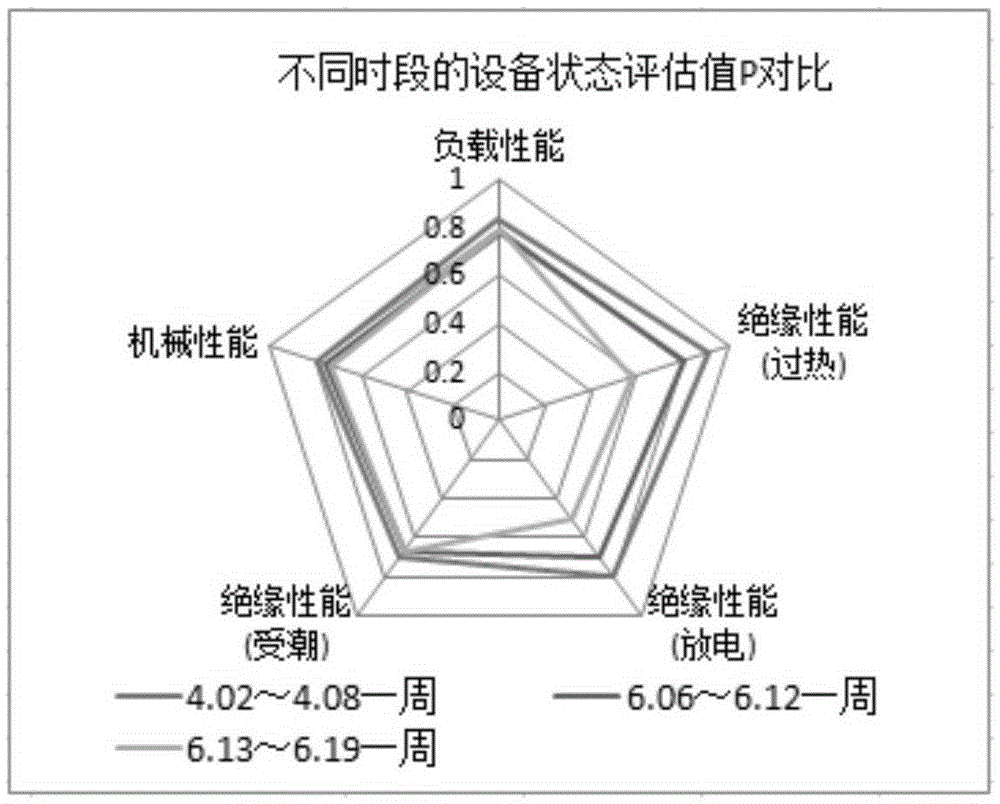
The invention discloses an electric transmission and transformation device state abnormity detection method, comprising steps of installing an on-line comprehensive monitoring device at a transformer station to monitor state quantity, determining a corresponding relation between the state quantity and the device state, performing representation on a time sequence of device state quantity data by utilizing a high dimension random matrix, analyzing spectral distribution and circular ring rate of state data in various time quantum in an operation history in the operation history, converting the device state into a state evaluation value P through quantification, comparing a device state evaluation value P with a device state evaluation value threshold P to determine whether the device state matrix has abnormity and to detect the device state abnormity, and obtaining an abnormal state and an abnormal time according to the normality detection of a residual sequence matrix.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Video target detecting and tracking method based on optical flow features
InactiveCN106709472AAvoid driftingOvercoming cavitationScene recognitionPositive sampleParticle filtering algorithm
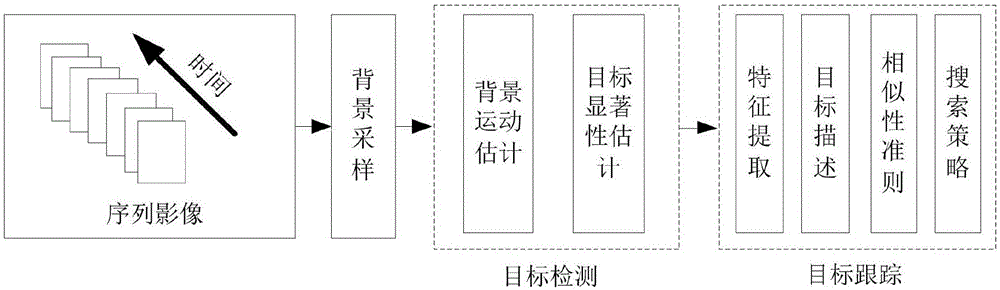
The invention provides a video target detecting and tracking method based on optical flow features. According to the technical scheme of the method, during the first step, an input image frame sequence is subjected to background sampling, and the optical flow vector of each pixel point after the sampling process is calculated. Meanwhile, the background motion is estimated based on the Mean Sift algorithm, and then the overall significance of a target is estimated. Finally, a threshold value is set according to the detection result of the target significance detection, so that a target region and a background region are separated. During the second step, the tracking of a video target is conducted: firstly, the target region is selected as a positive sample, and the background region is selected as a negative sample. The target is described based on the Haar features and the global color features of the target. Meanwhile, original features are subjected to sampling and compressing in the random matrix manner. Based on the bayesian criterion, the similarity between the target and a target of a previous frame is judged. Finally, the target is continuously tracked based on the particle filtering algorithm. In this way, multiple features including the target motion saliency, the color, the texture and the like are fused together, so that the success rate of target detection is improved. Therefore, the target can be quickly, effectively and continuously tracked.
Owner:湖南优象科技有限公司
Laser radar imaging device based on compressed sensing and imaging method
ActiveCN105223582ASolve problems in signal processing capabilitiesEffective combinationElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging qualitySignal on
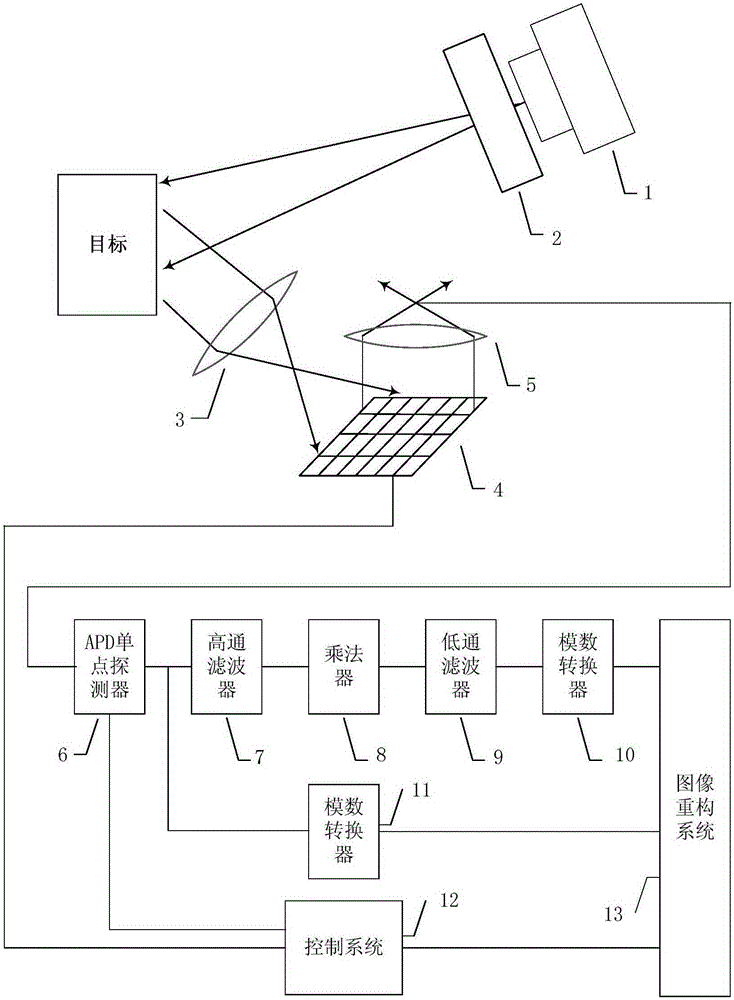
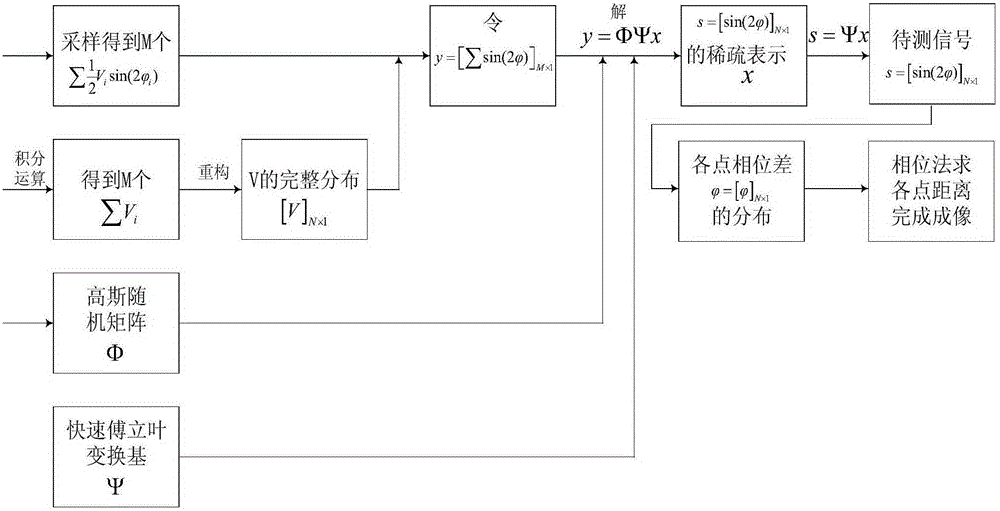
A laser radar imaging device based on compressed sensing and an imaging method are disclosed. The device comprises an amplitude modulation laser light source, a beam expanding apparatus, two lenses, a DMD digital micro-mirror, an APD photoelectric detector, a high-pass filter, a multiplier, a low pass filter, two AD analog-digital converters, a control system and an image reconstruction system. After being emitted, the laser is scattered by an imaging object and then is projected to a surface of the DMD digital micro-mirror. Reflected light is focused by another lens, then is received by an APD single point detector and then is converted into an amplified voltage signal. High-pass filtering, mixing and low-pass filtering are successively performed on the voltage signal on one parallel branch and the signal penetrates into the reconstruction system after analog-digital conversion. Simultaneously, the voltage signal directly penetrates into the reconstruction system on another parallel branch after the analog-digital conversion. According to input signals of the two branches and a random matrix corresponding to a DMD control device, a certain reconstruction algorithm is combined so that the reconstruction system can complete imaging. By using the device and the method of the invention, an imaging rate and imaging quality are increased to a great extent.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
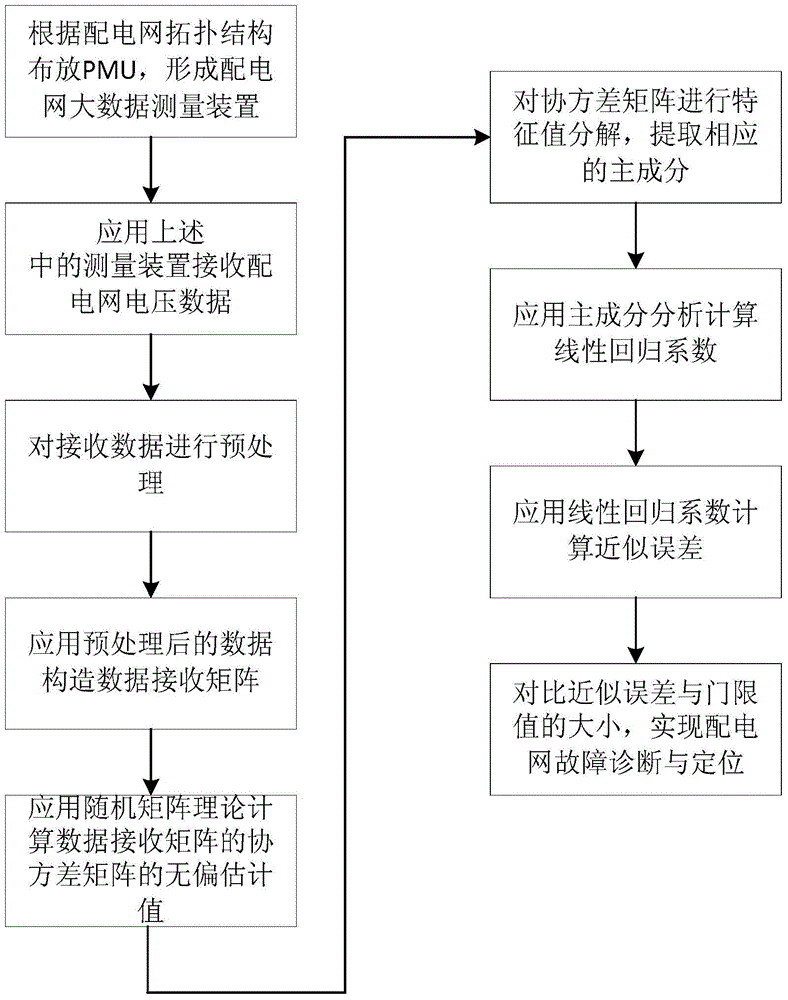
Big data fault detection and positioning method for power distribution network
ActiveCN105699804AOvercoming the problem of large estimation biasImprove applicabilityFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesPrincipal component analysisSmart grid
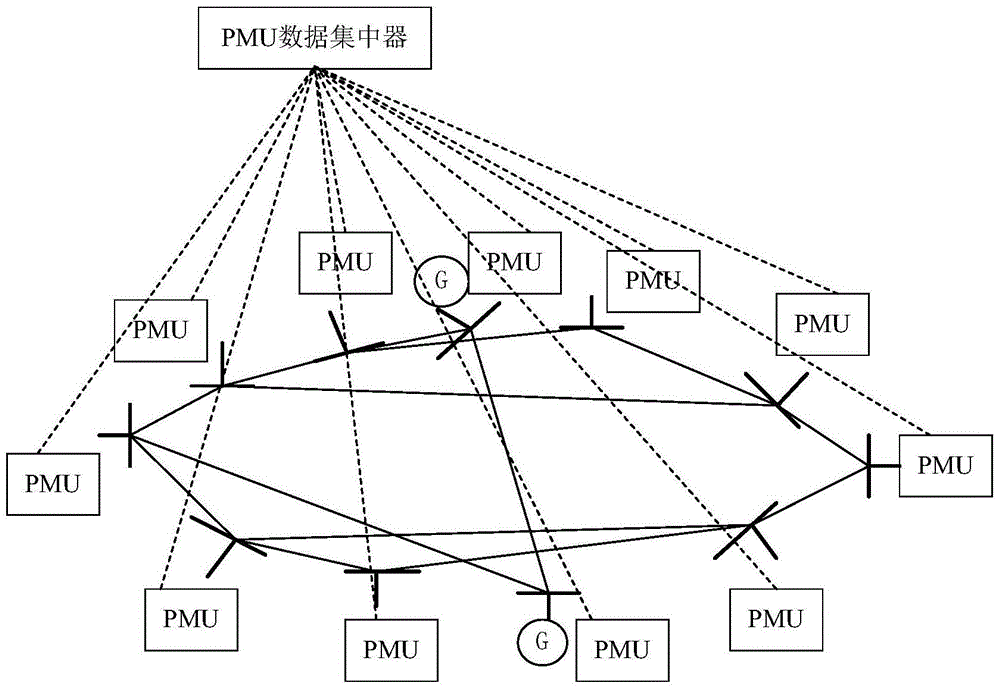
The invention provides a big data fault detection and positioning method for a power distribution network, and belongs to the field of intelligent power grids. The method comprises the steps: receiving voltage sampling data of the power distribution network through employing PMUs (Phasor Measurement Units); carrying out the preprocessing of voltages received by all PMUs, and constructing a receiving matrix; obtaining an unbiased estimated value of a receiving data covariance matrix through employing a random matrix theory; carrying out the eigenvalue decomposition of the covariance matrix, and obtaining a corresponding principal component; calculating a linear regression coefficient through employing PCA (Principal Component Analysis); comparing a relative approximation error and a threshold value, and achieving the fault detection and positioning of the power distribution network. The method provided by the invention solves a problem that the conventional covariance matrix estimation is biased under the measurement of a plurality of PMUs, and can achieve the real-time fault detection and positioning of the power distribution network.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
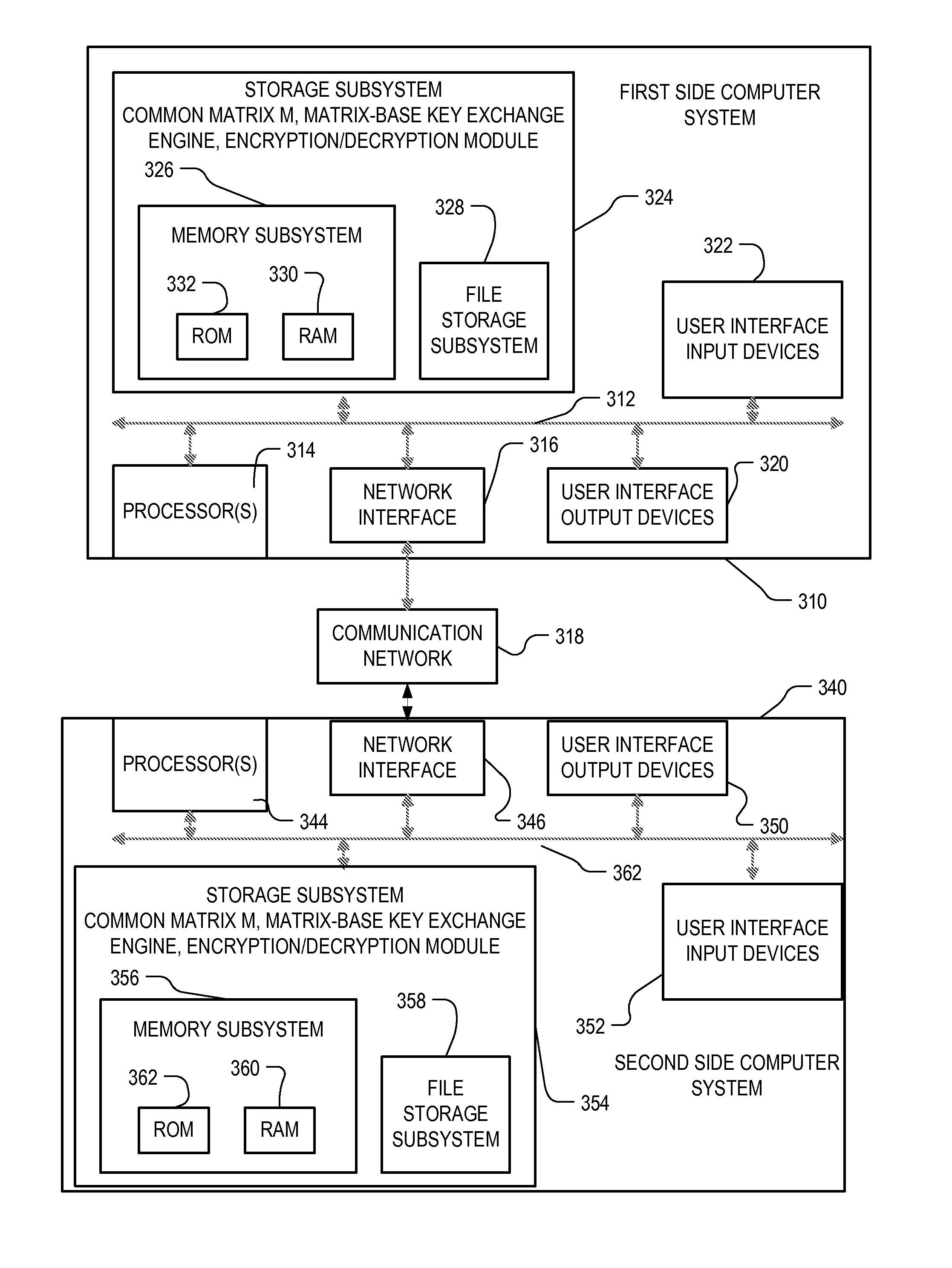
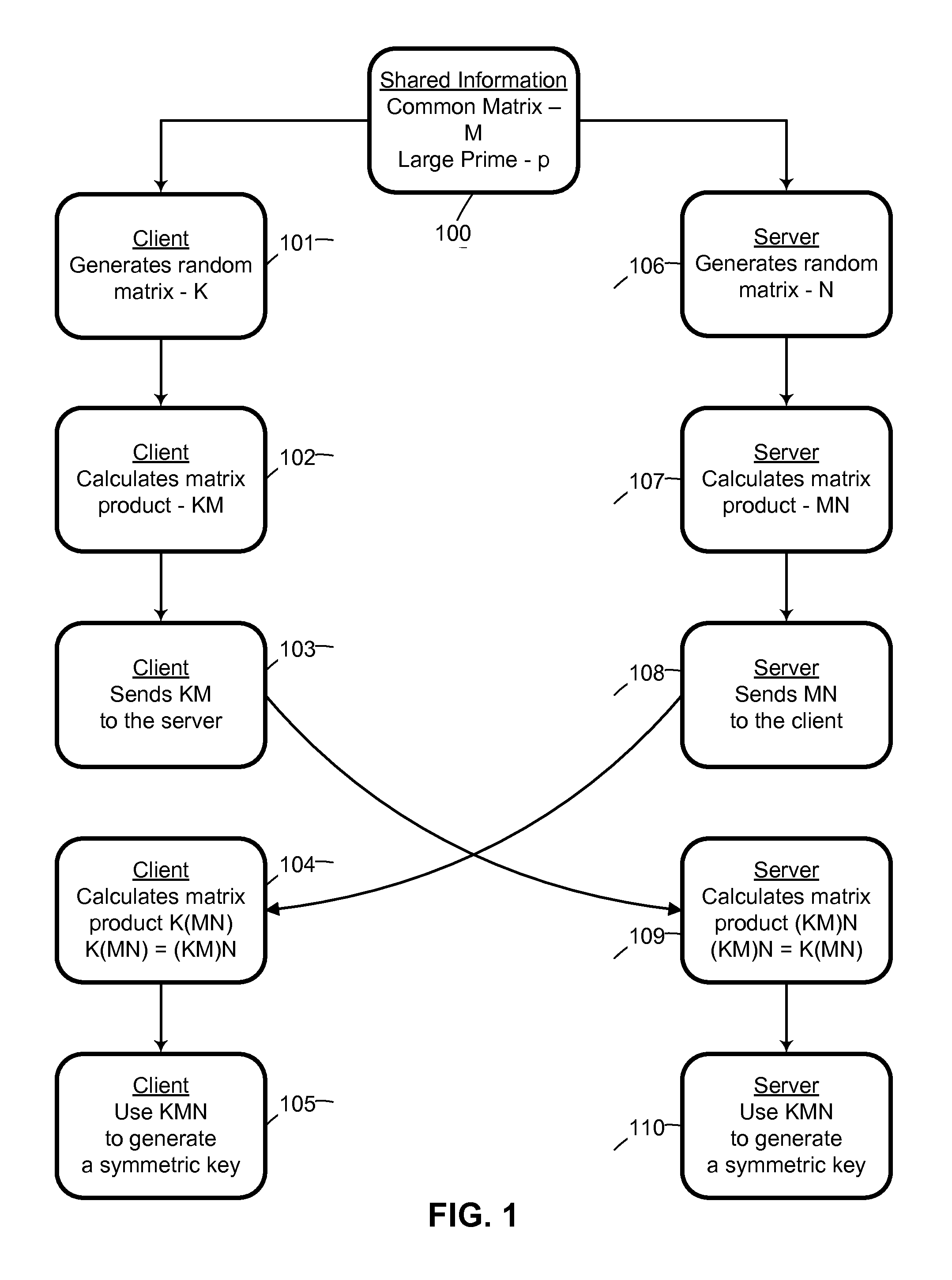
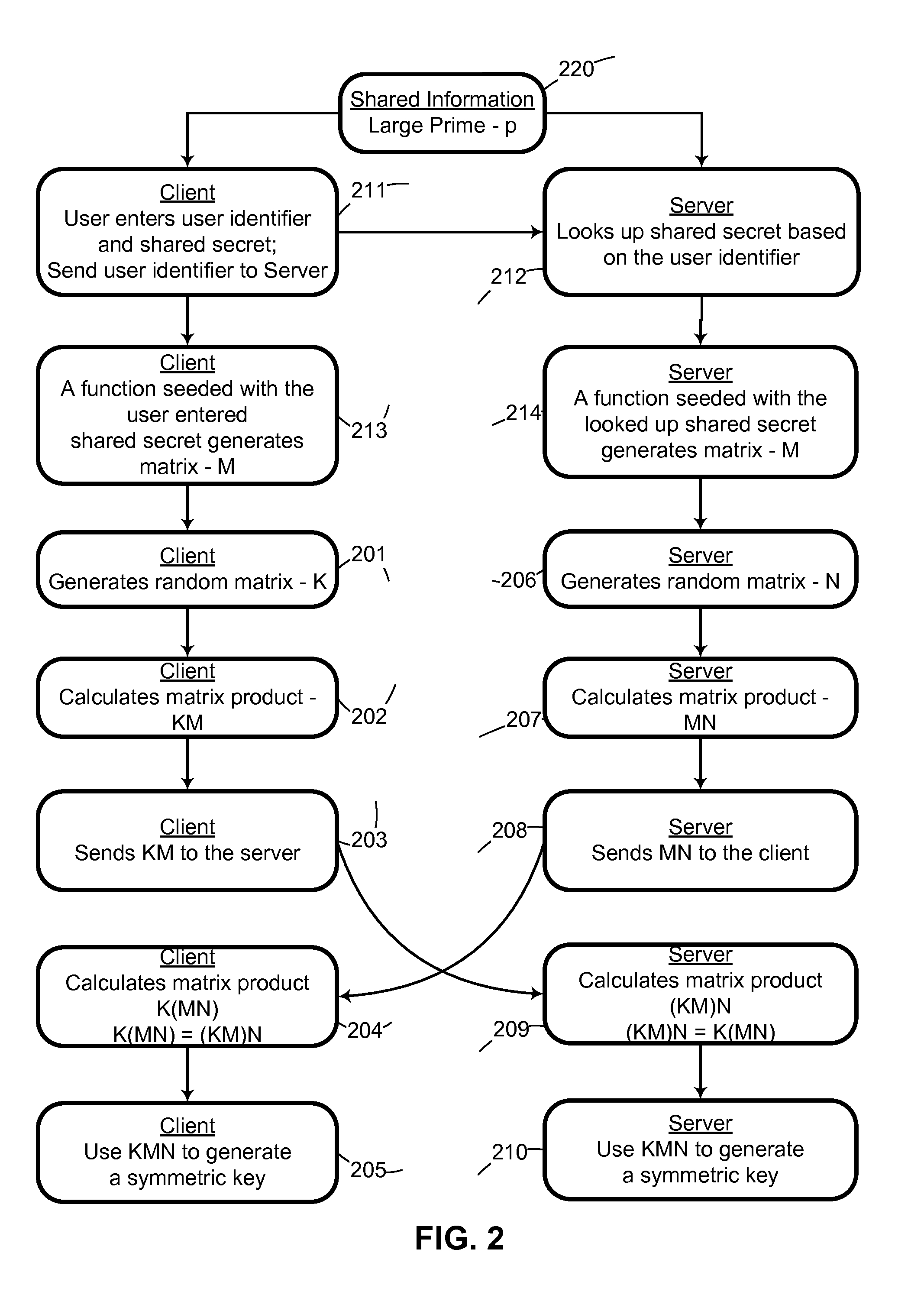
System and method for cryptographic key exchange using matrices
ActiveUS20120166809A1Improve performanceUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationThird partySecure communication
Two parties can establish a cryptographic key using a matrix based key exchange protocol, for secure communications without any prior distribution of secret keys or other secret data, and without revealing said key to any third party who may have access to all of the transmissions between them. A common matrix M, shared in advance, is multiplied by a random matrix K on the sending side, and a different random matrix N on the receiving side. The matrix product KM is sent from the sending side to the receiving side, and the matrix product MN is sent from the receiving side to the sending side. Both sides produce the common matrix product KMN, and use it for producing a symmetric key for encrypted communications.
Owner:AUTHERNATIVE INC
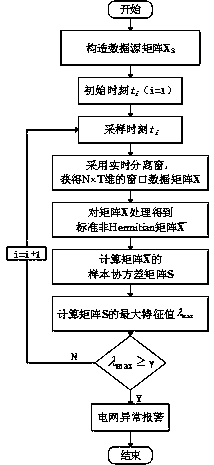
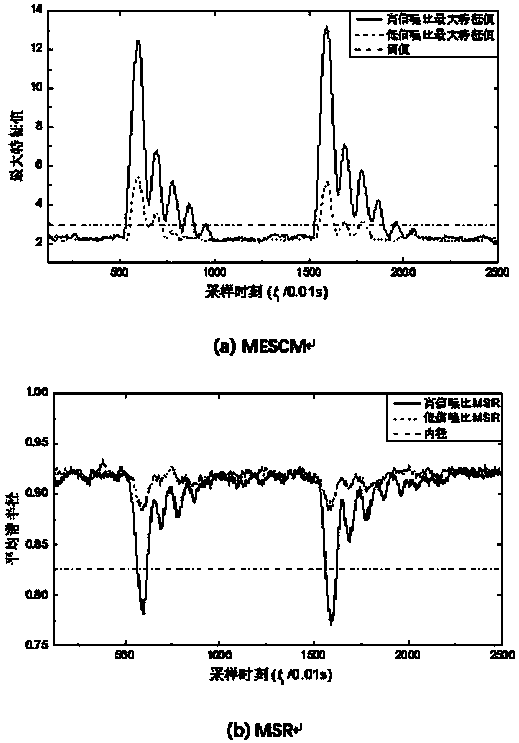
Power grid abnormal state detecting method based on maximum feature value of sample covariance matrix
InactiveCN108196165AImprove noise immunityReduce computing timeFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesMaximum eigenvalueSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a power grid abnormal state detecting method based on a maximum feature value of a sample covariance matrix. The power grid abnormal state detecting method based on the maximumfeature value of the sample covariance matrix comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing a data source matrix Xs; step 2, acquiring a sliding window matrix X; step 3, standardizing the sliding window matrix X; step 4, acquiring a sample covariance matrix S; step 5, solving a maximum feature value as shown in specification of the sample covariance matrix; step 6, power grid state abnormalout-of-limit judgment: judging whether the maximum feature value as shown in specification is greater than a threshold value as shown in specification, if the maximum feature value is greater than the threshold value, determining that the state of a power grid is abnormal, and giving an alarm, and if the maximum feature value is not greater than the threshold value, determining that the abnormalstate does not exist at present, and returning to step 2 to continue carrying out a state abnormity detecting flow. The potential invalidation problem caused when a traditional mean spectral radius method detects the abnormal state of the power grid in a low signal-to-noise ratio scene is solved, meanwhile, calculation consumed time of a traditional method for detecting the abnormal state of the power grid on the basis of a random matrix theory is saved by simplifying a calculating link, and the calculating efficiency is improved remarkably.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Secret sharing technique with low overhead information content
InactiveUS20100008505A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHat matrixAlgorithm
An apparatus and method for sharing a secret comprising the steps of generating a first random matrix, generating a first projection matrix from the first random matrix, and determining a first remainder matrix from the first projection matrix and the first secret matrix. The first secret matrix may be determined using the remainder matrix and a plurality of distributed vector shares.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
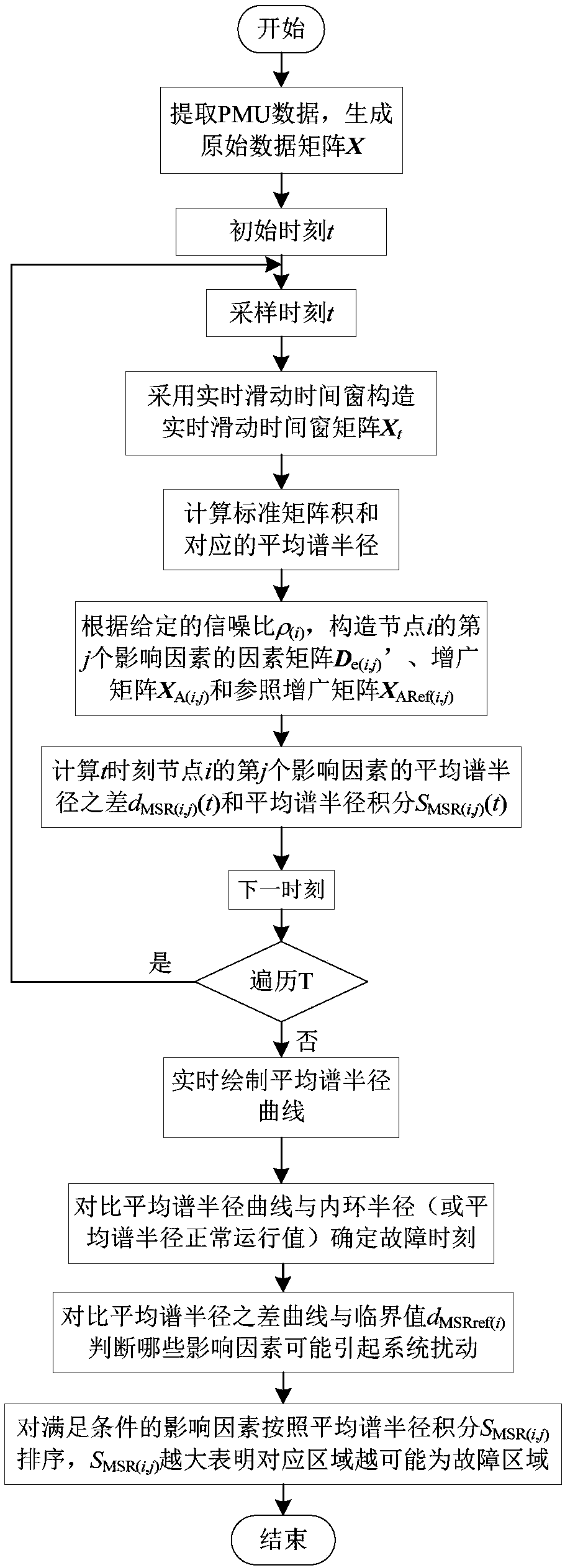
Fault moment determining and fault region location method based on random matrix theory
InactiveCN108152675APrecise positioningHelps to troubleshootFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Electric power system
The invention discloses a fault moment determining and fault region location method based on a random matrix theory, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the PMU data and signal to noise ratio of each node in a power system in a time period T, obtaining an original data matrix according to the PMU data of each node, carrying out the standardization processing of the original data matrix,and then obtaining the mean spectral radius at each moment of the time period T through a monocyclic theorem; obtaining an augmented matrix and a reference augmented matrix of each node according to the signal to noise ratio and the original data matrix, obtaining the mean spectral radius difference and mean spectral radius integral of the augmented matrix and the reference augmented matrix of each node in the time period T through the monocyclic theorem, wherein the moment when the mean spectral radius at each moment of the time period T is less than a normal operation value of the mean spectral radius is determined as a fault moment, and a node with the largest mean spectral radius in the nodes with the difference of the mean spectral radiuses of all nodes in the time period T being greater than a critical value is determined as a fault region. The method cannot be affected by bad data.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
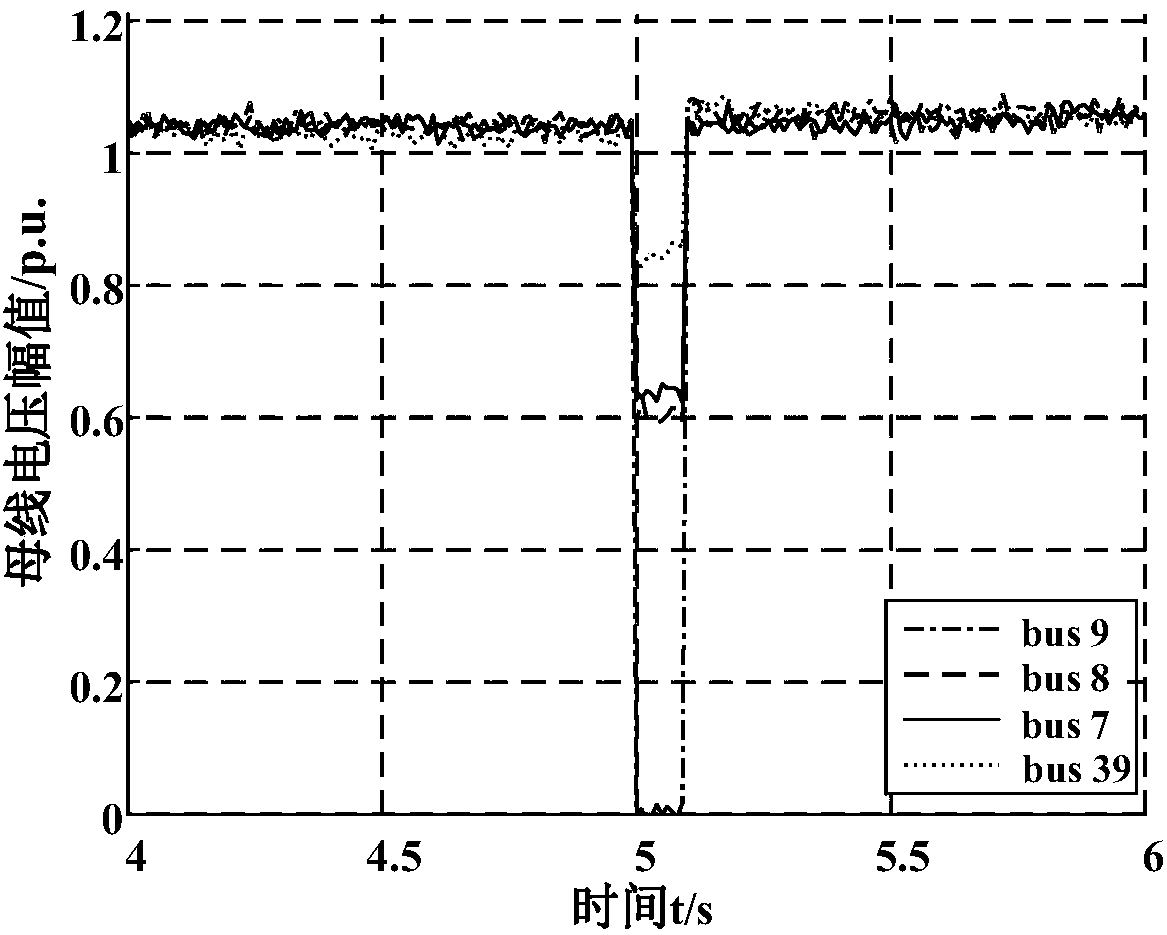
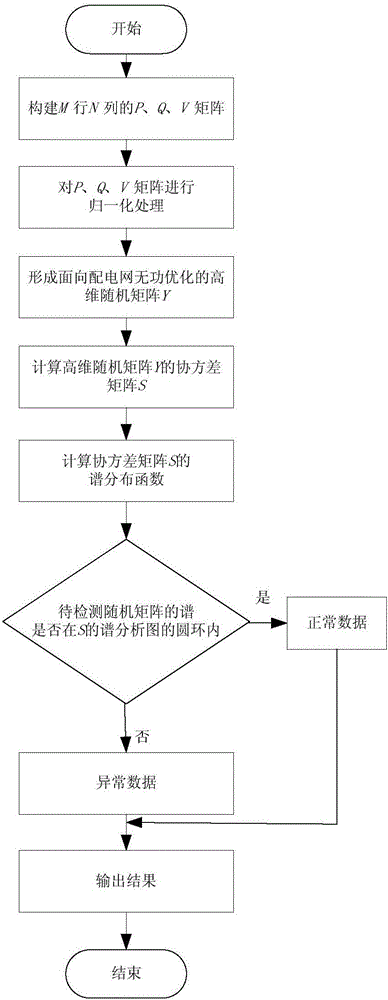
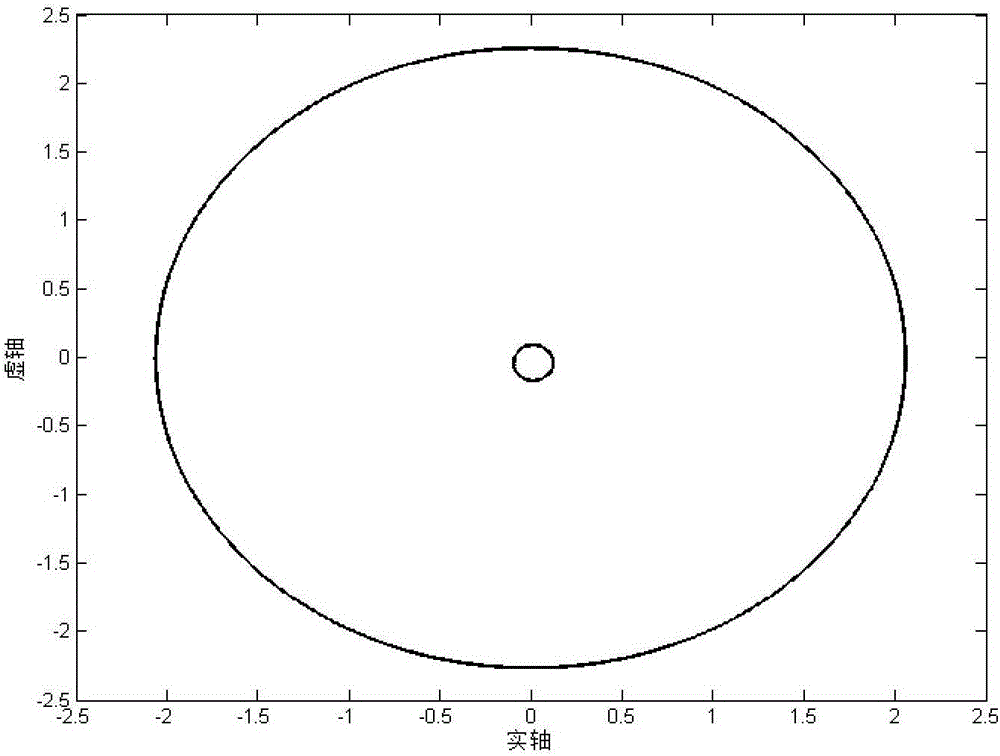
Abnormal data detection method for power distribution network based on high dimensional random matrix
The invention provides an abnormal data detection method for a power distribution network based on a high dimensional random matrix. The method comprises: constructing a high dimensional random matrix according to historical data; normalizing the high dimensional random matrix; defining a covariance matrix and obtaining the characteristic root of the covariance matrix; determining the spectral distribution function of the covariance matrix; and using the spectral distribution and ring rate to detect data anomalies. The invention provides the novel method for abnormal data detection of reactive optimization of the power distribution network. The method can accurately calculate abnormal data within any time period, is highly practical, and is high in detection efficiency.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Efficient homomorphic encryption scheme for bilinear forms
InactiveUS8861716B2Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareEncrypted function
In one exemplary embodiment, a computer readable storage medium tangibly embodying a program of instructions executable by a machine for performing operations including: receiving information B to be encrypted as a ciphertext C in accordance with an encryption scheme having an encrypt function; and encrypting B in accordance with the encrypt function to obtain C, the scheme utilizes at least one public key A, where B, C, and A are matrices, the encrypt function receives as inputs A and B and outputs C as C→AS+pX+B (mod q), S is a random matrix, X is an error matrix, p is in integer, q is an odd prime number. In other exemplary embodiments, the encryption scheme includes a decrypt function that receives as inputs at least one private key T (a matrix) and C and outputs B as B=T−1·(TCTt mod q)·(Tt)−1 mod p.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for detecting fault of power transmission line based on random matrix
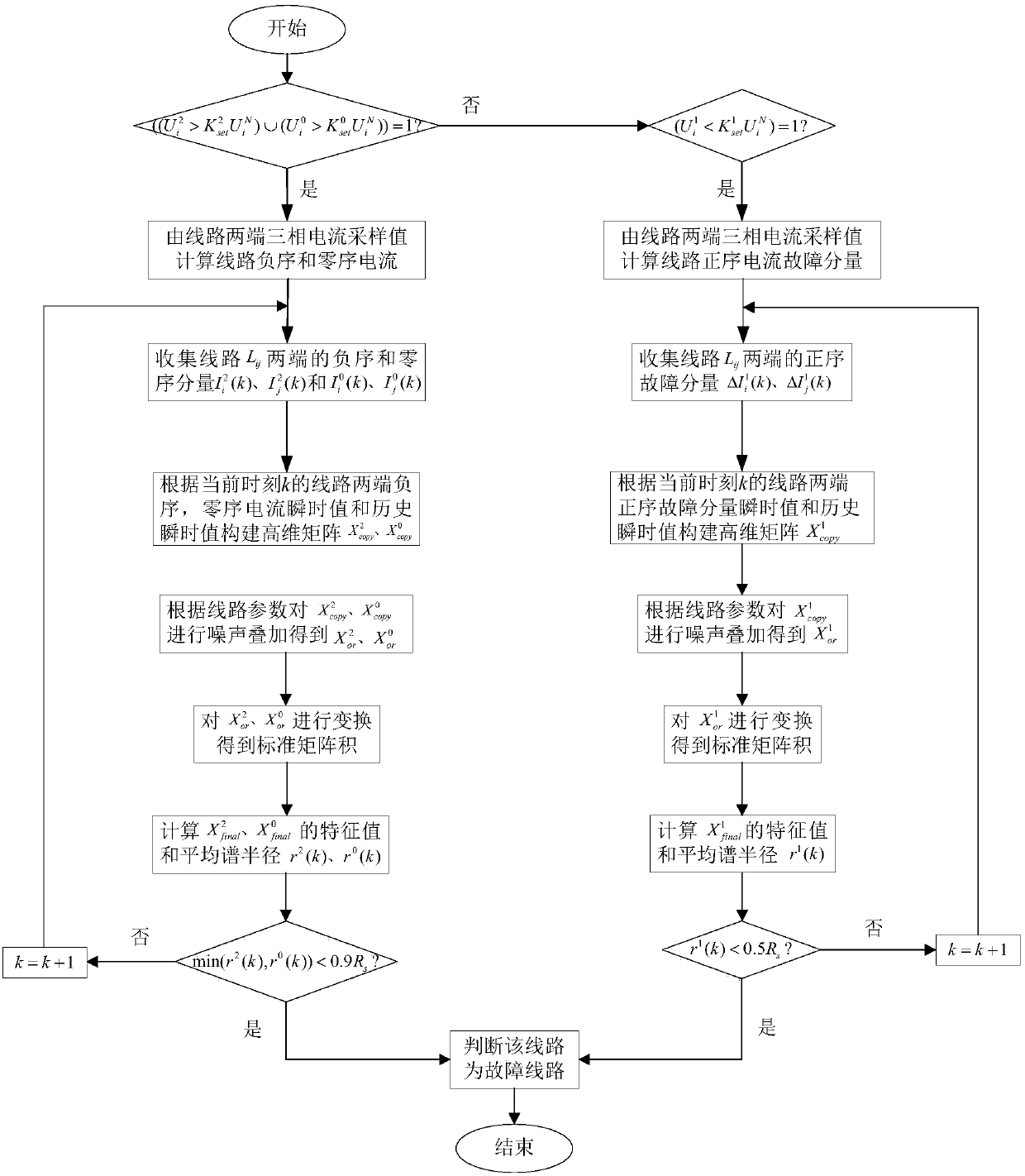
ActiveCN108828405AStrong anti-transition resistanceAccurate detectionFault location by conductor typesHigh resistanceOperation mode
The invention discloses a method for detecting a fault of a power transmission line based on a random matrix, and the method comprises the steps: respectively obtaining three-phase currents of n sample values at two ends of the line, calculating and obtaining a sequences of positive sequence current fault components, negative sequence components and zero sequence components; respectively performing copying and translation processing of each sequence, and carrying out the expansion to form a matrix of each sequence, and then performing the superimposition of a noise matrix to form an original random matrix of each sequence; employing the random matrix theory for transforming the original random matrixes into a standard matrix product; calculating a complex eigenvalue of the standard matrixproduct, calculating and obtaining the average spectral radius of the current component sequence of the line according to the eigenvalue; constructing two criteria for fault detection of the power transmission line, determining a threshold value, and determining that the line whose average spectral radius is less than the threshold value as a faulty line. The method can accurately detect the faulty line, is not affected by the position of the fault point, the fault type, a system operation mode, power flow shift and the system oscillation, can identify a high-resistance ground fault, and has better resistance to abnormal data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
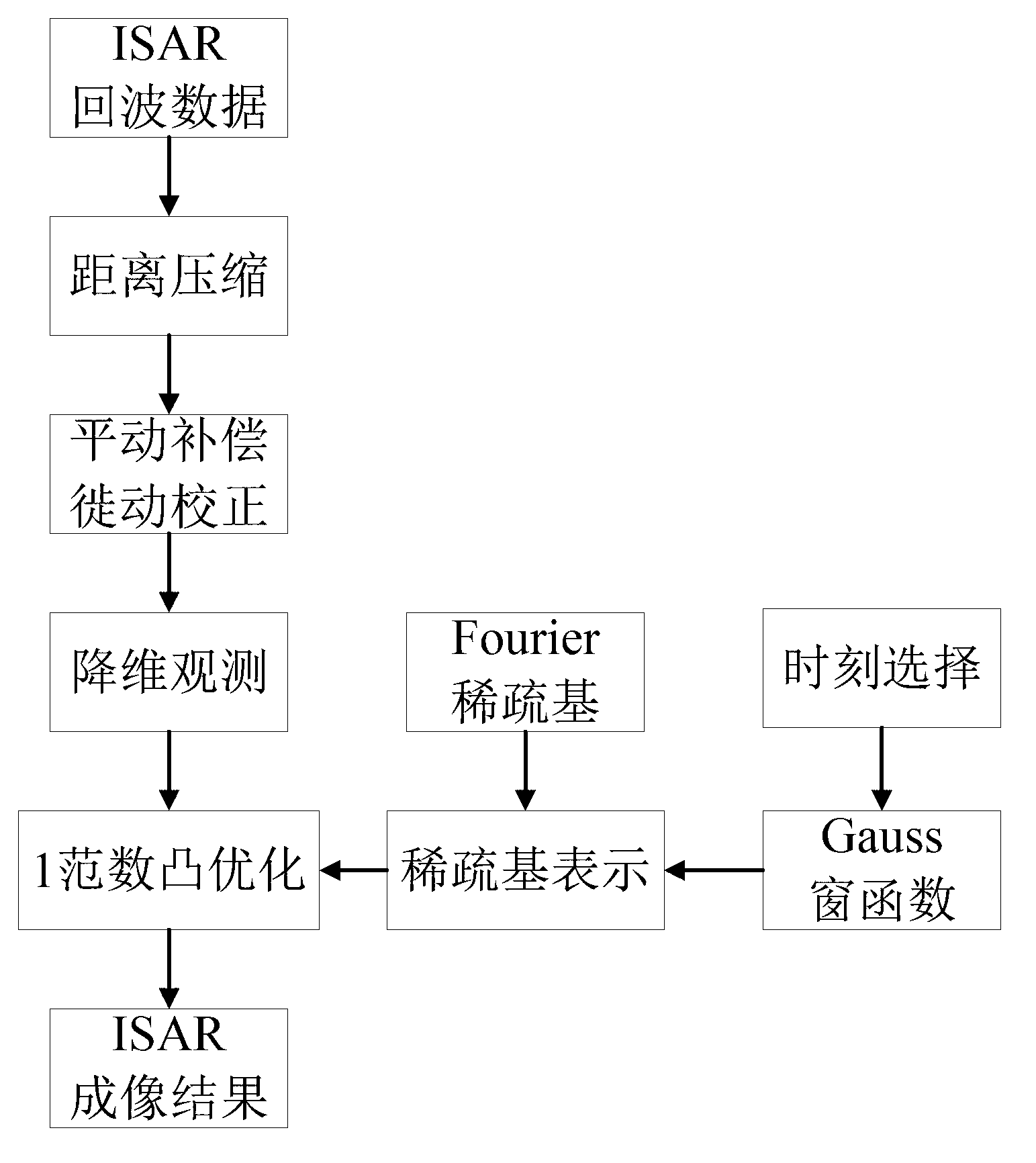
Maneuvering target ISAR imaging method utilizing compressed sensing
InactiveCN102841350AReduced Echo Sampling Rate RequirementsImprove imaging effectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging qualityDimensionality reduction
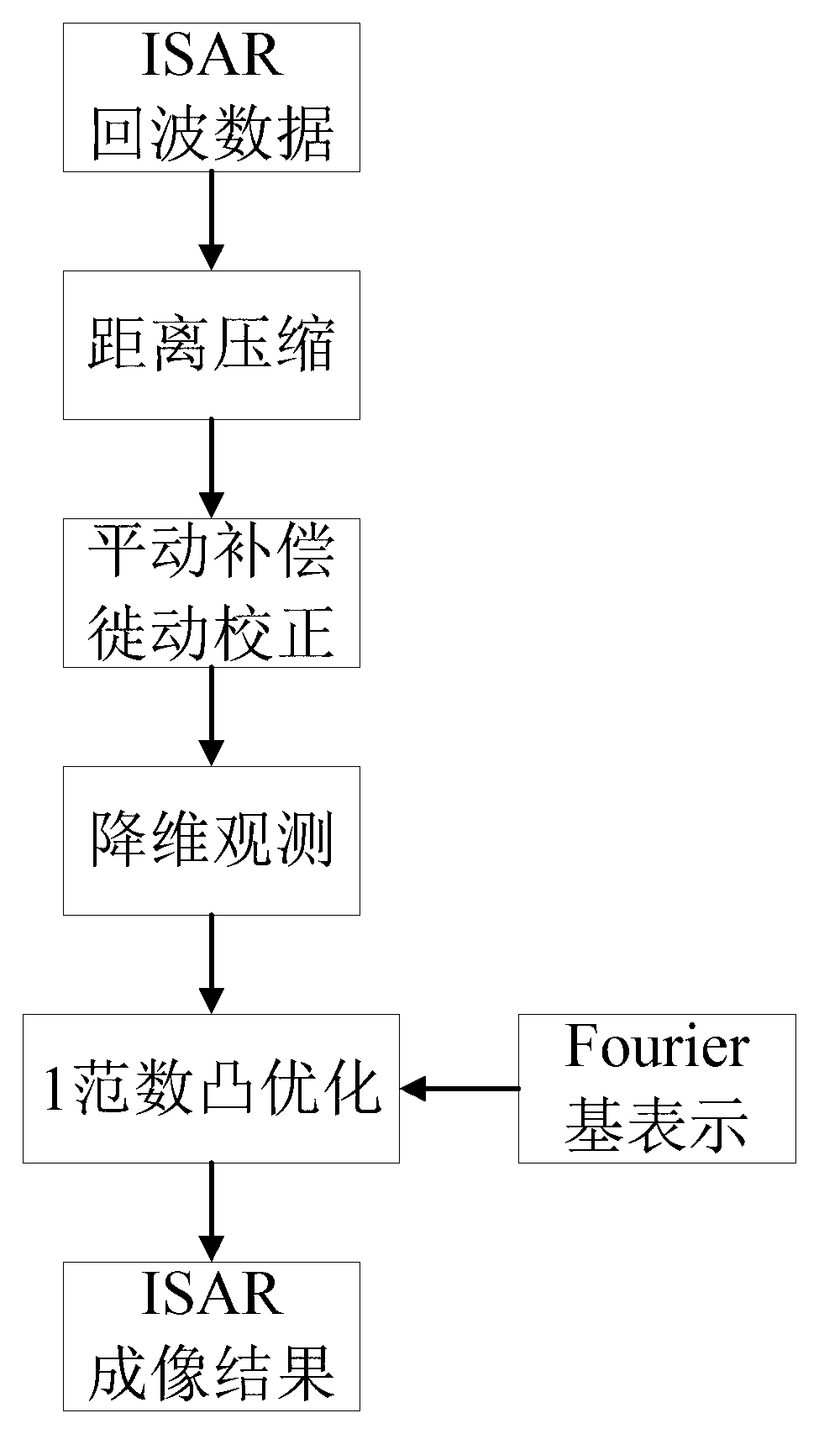
The invention provides a maneuvering target ISAR (Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method utilizing compressed sensing. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining ISAR return wave data, and allowing the return wave data to be subjected to distance compression, motion compensation and migration correction so as to obtain a complex matrix Sd; generating a Gaussian random matrix Phi, and allowing the Sd to be subjected to reduced-order observation so as to obtain a matrix Y; obtaining a sparse basis matrix of ISAR to-be-imaged times ti; solving each column of the matrix Y through a 1-norm convex optimization equation so as to obtain ISAR image results of times ti; and traversing all imaging times, so as to realize the ISAR imaging of a maneuvering target at all periods. The imaging method lowers the requirement on imaging return wave sampling rate, realizes free imaging of the maneuvering target at all imaging times, and improves no only the azimuth imaging effect of the maneuvering target, but also the ISAR imaging quality.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
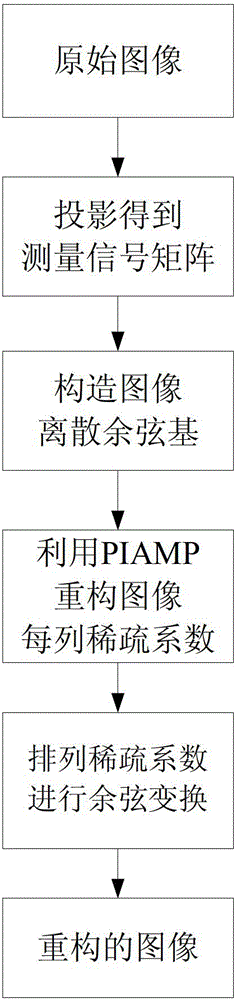
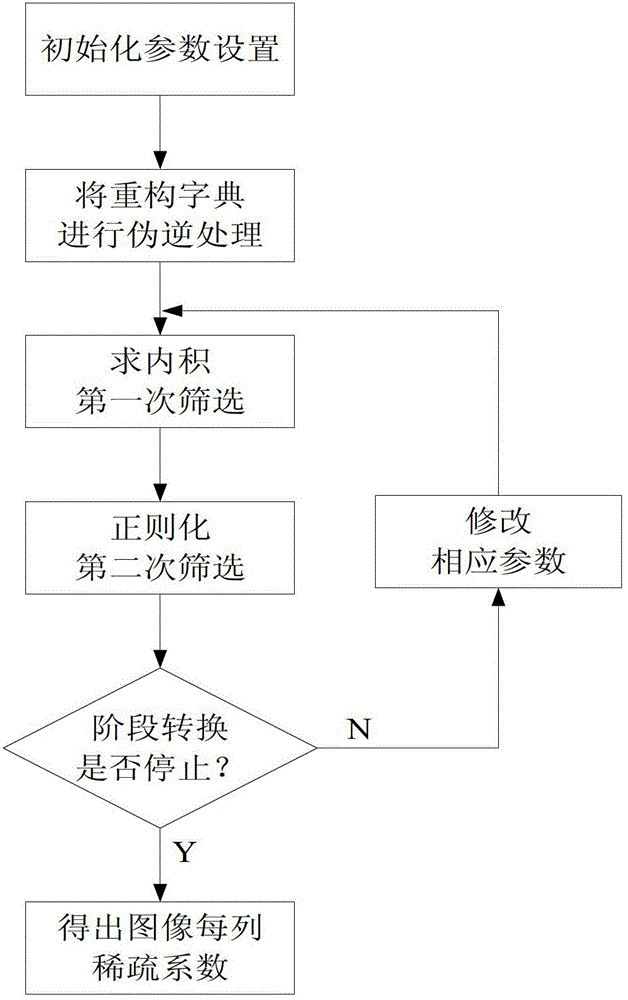
Compressive sensing reconstruction method based on pseudo-inverse adaptive matching pursuit
ActiveCN103337087AReduce relevanceLight in mass2D-image generationPattern recognitionReconstruction method
The invention relates to a compressive sensing image reconstruction method based on a pseudo-inverse adaptive matching pursuit (PIAMP), which is characterized by comprising the steps that a gauss random matrix is selected for projecting an image to form a measurement signal matrix; an image sparse base is constructed; each column of the measurement signal matrix is reconstructed by adopting the PIAMP to form a sparse coefficient of each column of the image; and the sparse coefficients of the columns of the image are arrayed and subjected to cosine transformation to form a reconstruction image. The method particularly takes account of the dictionary relevance, iteration stage division and the like in a sparse coefficient reconstruction process, so that selection of the sparse coefficients is more accurate, and the precision of image reconstruction is higher.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
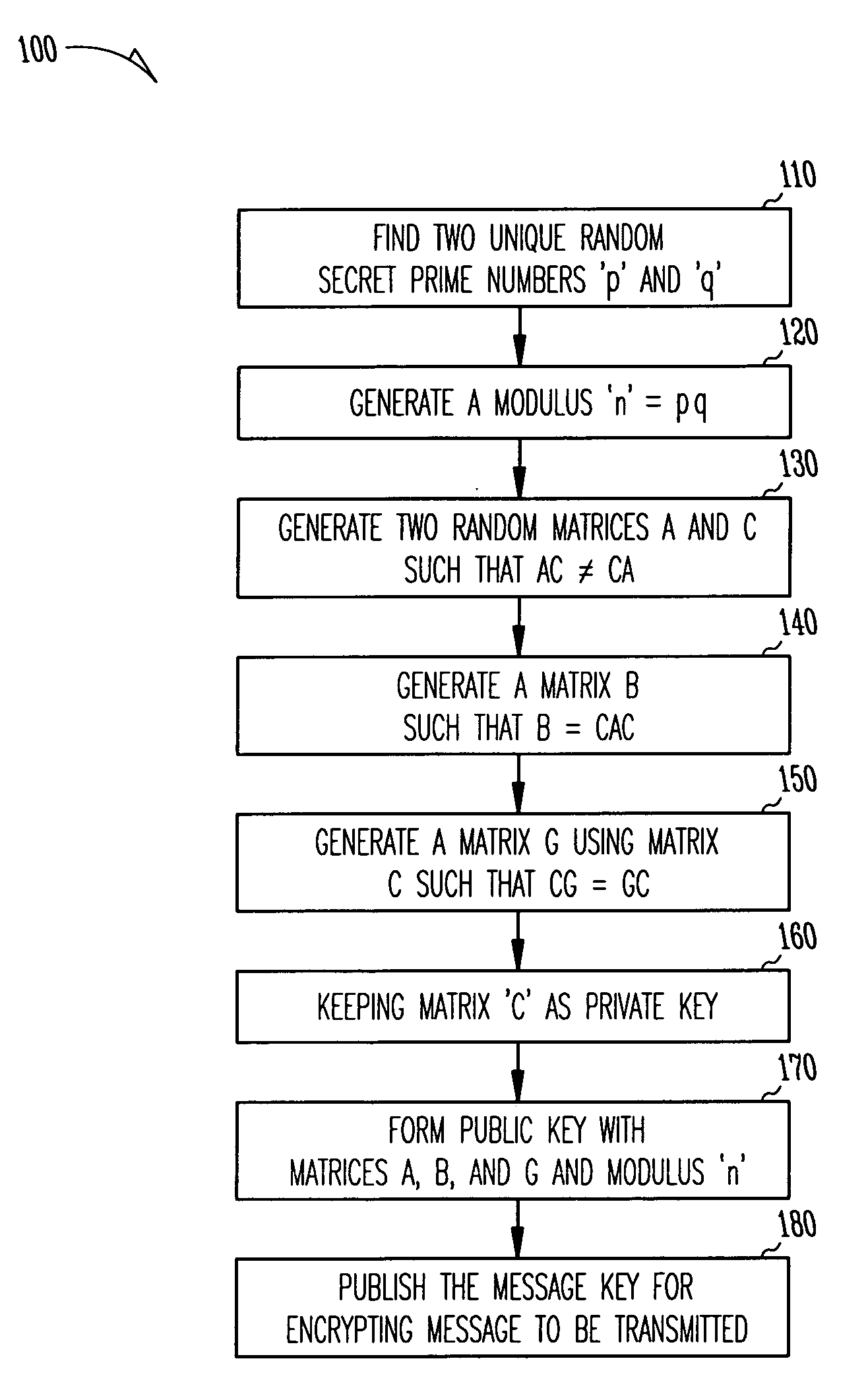
Public key cryptography using matrices
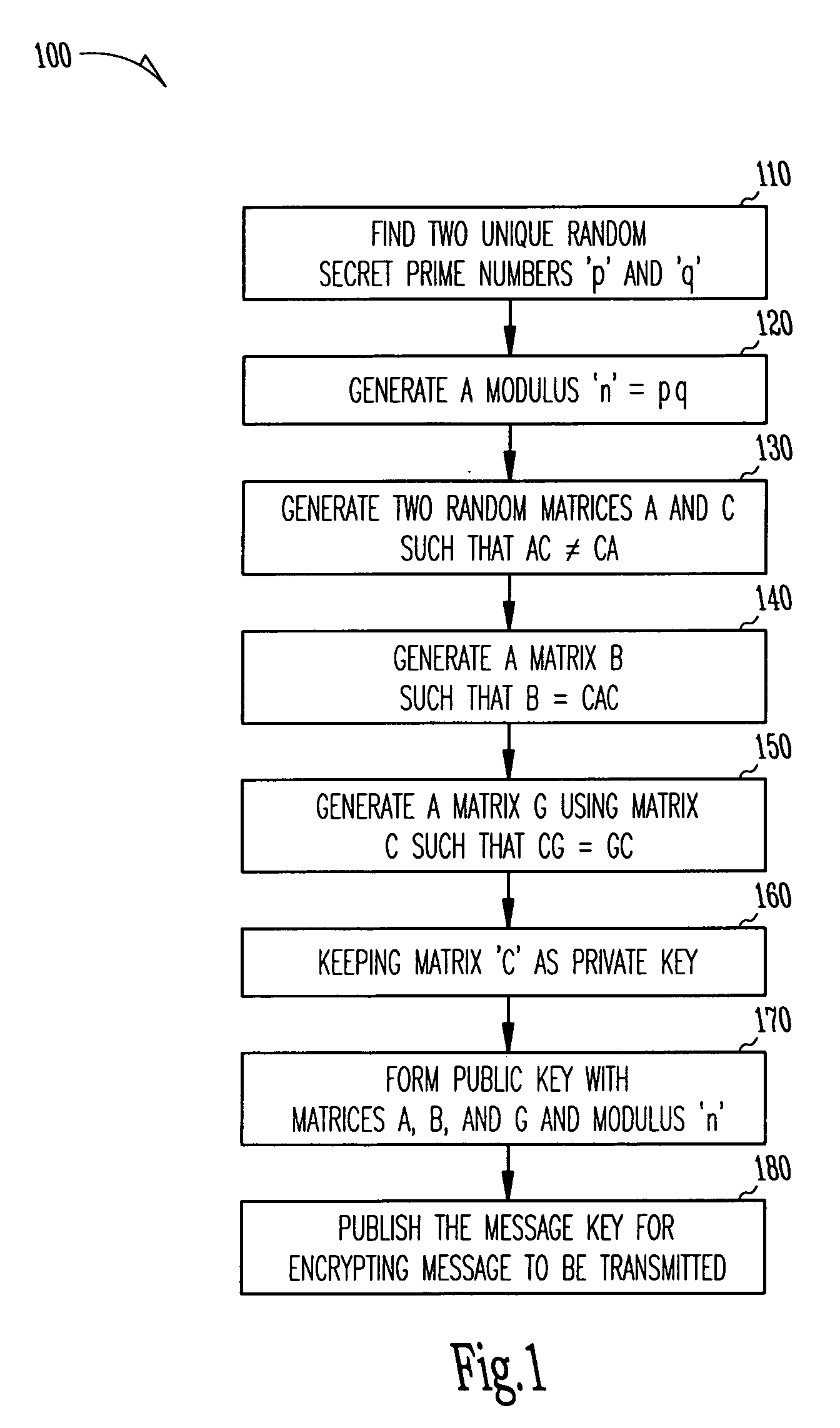
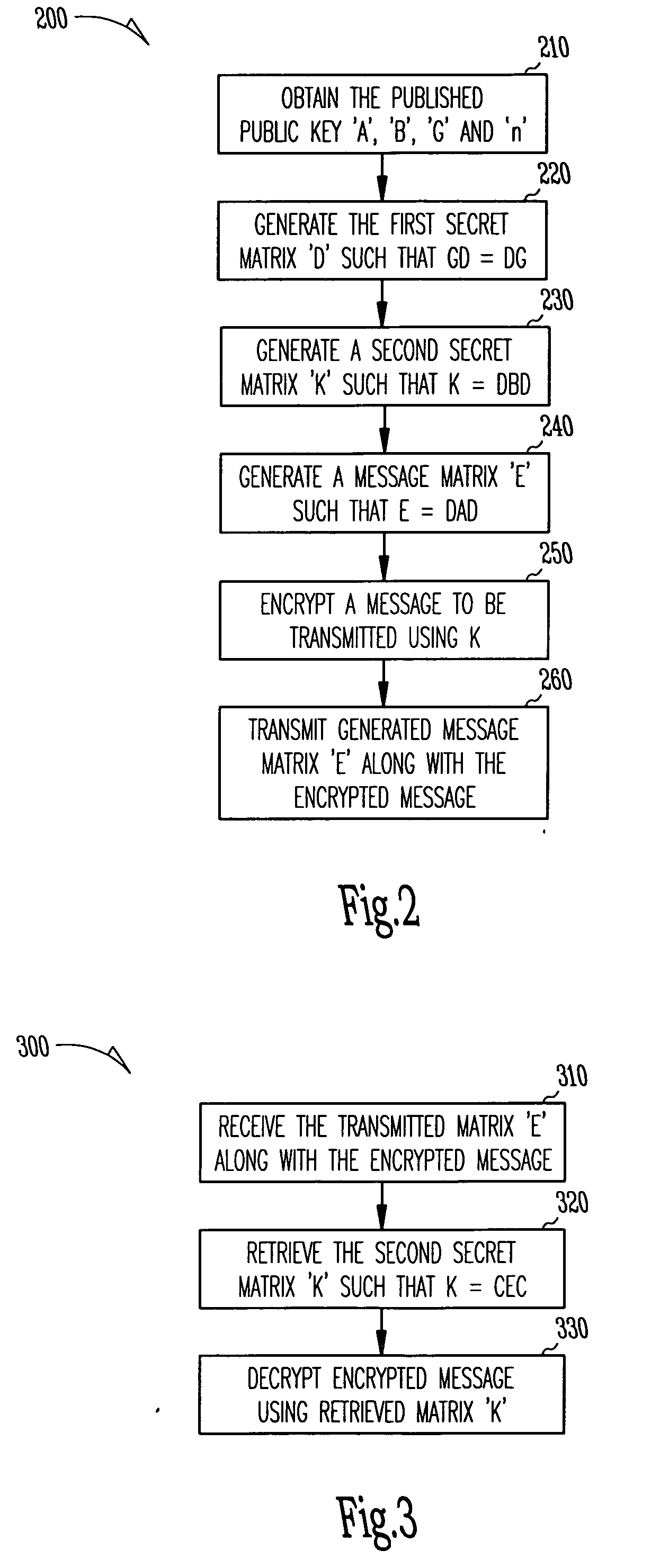
InactiveUS20080037774A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationRandom matrixComputer security
The invention provides techniques for secure messages transmission using a public key system to exchange secret keys. A first entity creates public and private keys by generating a product n of two large, randomly chosen prime numbers, and then generating random matrices {A, C}, in the group GL(r,Zn) with a chosen matrix rank r such that AC is not equal to CA, and then generating a matrix B=CAC, and finding a matrix G that commutes with C. Matrices A, B, G and the integers n and r are then published as the public key and matrix C is then kept as the private key. A second entity then obtains the public key and calculates a secret matrix D that commutes with G, and further calculates the matrices K=DBD and E=DAD. The message to be sent is then encrypted using matrix K as the secret key and then sent to the first entity with matrix E. First entity then retrieves secret matrix K using K=CEC and then decrypts the received encrypted message using the retrieved secret matrix K.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Power grid abnormality quick detection method based on random matrix spectral radius method
InactiveCN107132454AImprove exception analysisEasy to handleData processing applicationsFault location by conductor typesData acquisitionPower grid
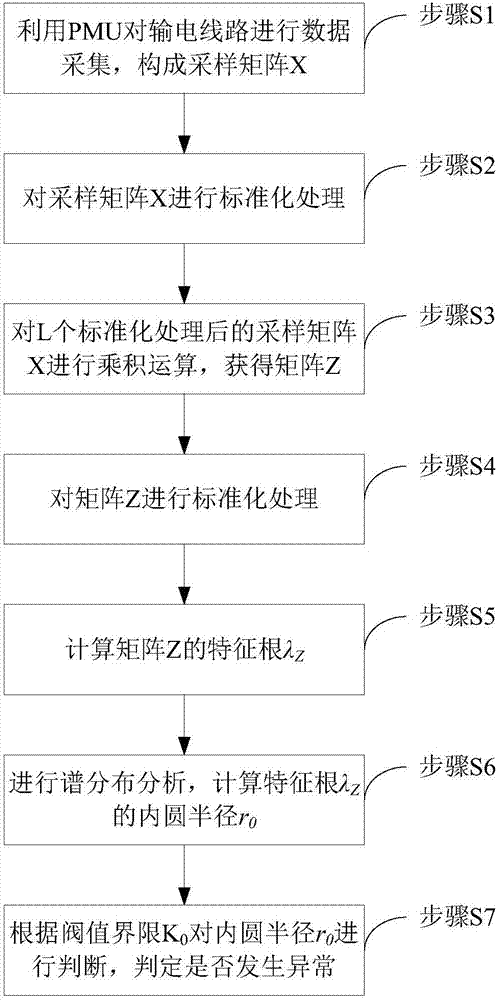
The invention discloses a power grid abnormality quick detection method based on a random matrix spectral radius method, and the detection method comprises the steps: carrying out the data collection of a power transmission line through a PMU, constructing sampling matrixes X, carrying out the standardization processing of the sampling matrixes X, carrying out the multiplying operation of L sampling matrixes X after standardization processing, obtaining a matrix Z, carrying out the standardization processing of the matrix Z, calculating the characteristic root of the matrix Z, carrying out the spectral distribution analysis, calculating the inner circle radius of the characteristic root, carrying out the judgment of the inner circle radius according to a threshold value boundary, and judging whether there is an abnormality or not. According to the invention, the method achieves the real-time quick global processing of data collected by the PMU, can accurately distinguish an abnormal weak signal, is high in sensitivity, enables the detection time to be remarkably ahead of the abnormality occurrence time, and can greatly improve the abnormality analysis and processing level of a power grid.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
Overall situation reconstitution optimization model construction method for image block compressed sensing
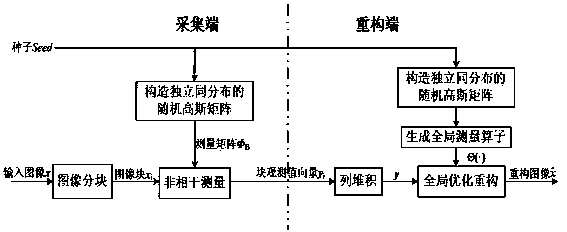
InactiveCN103440675AAvoid defectsSmall sparsity2D-image generationImage codingEngineeringRaster scan
The invention discloses an overall situation reconstitution optimization model construction method for image block compressed sensing. The procedures of a collecting end include that firstly, an image x is divided into n B*B small blocks xi, wherein x and xi are pulled to be column vectors in a raster scanning manner; secondly, an independent identically distributed gauss random matrix phi B with the size of MB*B2 is generated; thirdly, incoherent measuring is performed on each block xi to obtain observed value vectors yi which is equal to phi B xi; fourthly, the observed value vectors yi and a seed for generating the gauss random matrix are sent to a reconstruction end. The procedures of the reconstruction end include that firstly, the received observed value vectors yi of all the blocks are accumulated to be y=[yi; y2;..., yn] in columns; secondly, an overall situation reconstitution measurement operator theta ( ) is constructed, wherein the input of the overall situation reconstitution measurement operator is an image x, the corresponding output of the overall situation reconstitution measurement operator is y, and the overall situation reconstitution measurement operator is composed of a block measurement matrix set phi and a ranking operator P ( ); thirdly, an overall optimization reconstitution model is set up, and the image is recovered with a corresponding compressed sensing reconstitution algorithm. The overall situation reconstitution optimization model construction method for image block compressed sensing can effectively eliminate the block effect in the prior art, and strong robustness on variation of the block size B is achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
SAR image transmission method based on compressed sensing and channel self-adaption
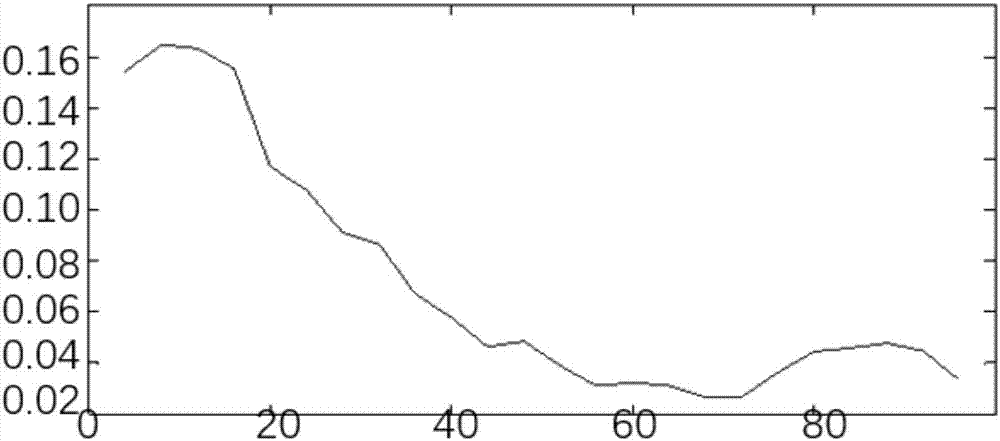
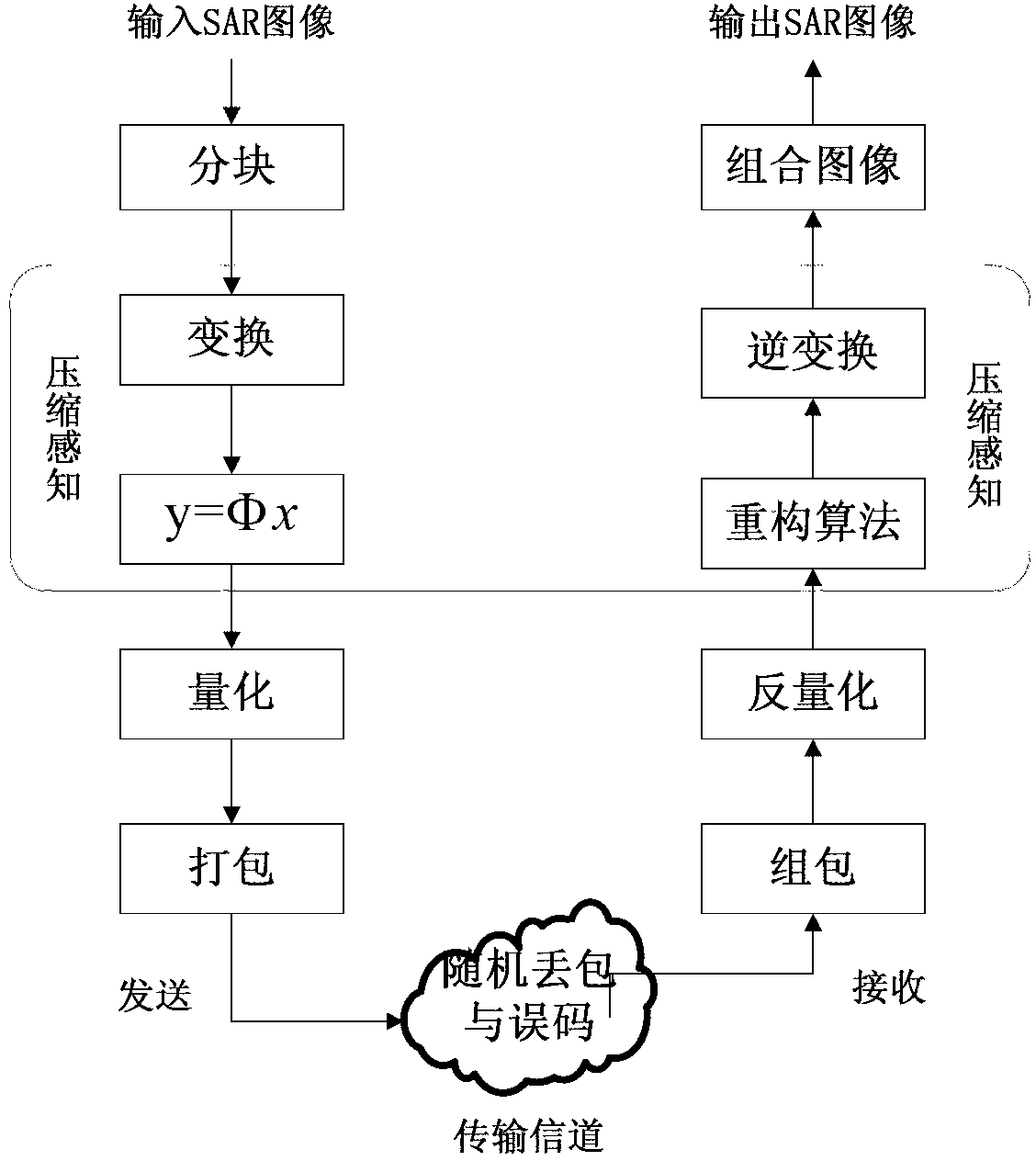
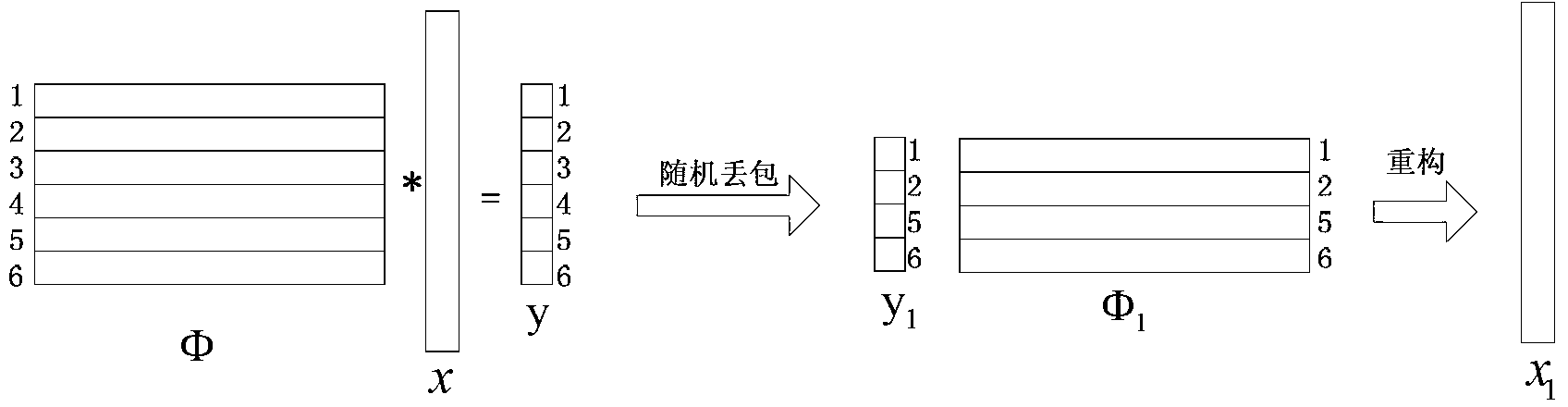
ActiveCN103327326ASimple codingSolve the problem of complex codingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSmall amplitudeTransmission channel
The invention discloses an SAR image transmission method based on compressed sensing and channel self-adaption. The SAR image transmission method comprises the steps that first, input SAR images are divided into small images with the same size; direction elevating and wavelet transformation are conducted on each small image; zero setting is conducted on coefficients with small amplitude values, only large coefficients in a small proportion are reserved, and then random measurement is conducted on a wavelet coefficient by a random matrix; then quantization is conducted on measurement values. Sampling values after being quantized are packaged before transmission. Random drop and error codes are added in a simulation transmission channel. The inverse operation of the above steps, namely, packaging, inverse quantization, wavelet coefficient reconstruction, wavelet inverse transformation and image combination, are conducted at a receiving end. According to the SAR image transmission method based on the compressed sensing and channel self-adaption, compressed sensing is used as an encoder of the SAR images, only two times of matrix multiplication are needed in the encoding process, and encoding of the SAR images is made to be simple. Due to the fact that an encoding end of the SAR images is placed in flight equipment such as an unmanned plane generally, the encoder is as simple as possible. The compressed sensing is introduced to be used as the compression encoder of the SAR images, and the problem that encoding of the SAR images is complex is solved.
Owner:苏州协同创新智能制造装备有限公司
Method and Apparatus for Public Key Encryption Scheme RLCE and IND-CCA2 Security
InactiveUS20180176015A1Improve security levelKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationPlaintextMcEliece cryptosystem
Owner:WANG YONGGE
Method for identifying SAR target under shielding conditions
ActiveCN103425998AReduce interferenceImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionDecompositionDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a method for identifying an SAR target under shielding conditions. The method mainly solves the problem that the identification performance of an existing identification technology is lowered under shielding conditions. The method is achieved through the steps that logarithmic transformation and median filtering are performed on a training image sequentially, image column vectorization is performed, premultiplication random matrix dimensionality reduction and energy normalization are performed on the training image as pre-processing, and pre-processed data are used for constructing a data dictionary D; logarithmic transformation, median filtering and image column vectorization are performed on the image to be tested sequentially, the premultiplication random matrix dimensionality reduction and energy normalization are performed on the image to be tested as pre-processing, and a non-negative sparse representation is constructed through test data after the pre-processing and the data dictionary D; a non-negative sparse decomposition coefficient is acquired after optimization, and various reconstruction errors are calculated through the non-negative sparse decomposition coefficient; a target identification result is acquired according to the minimum reconstruction error criterion. The method has the advantages of being high in identification rate and stable in performance even when the target to be tested is shielded, and is applicable to SAR target identification when the target may be shielded.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
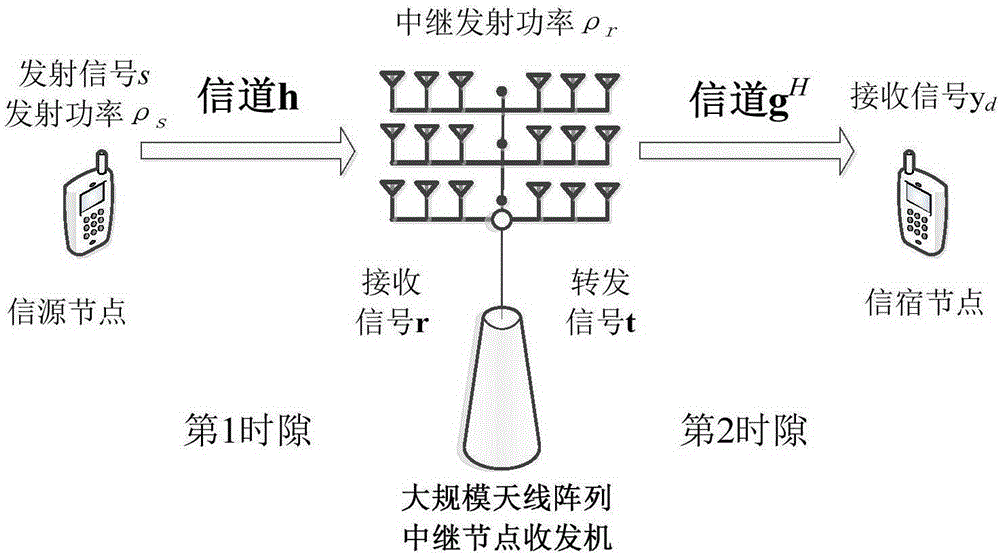
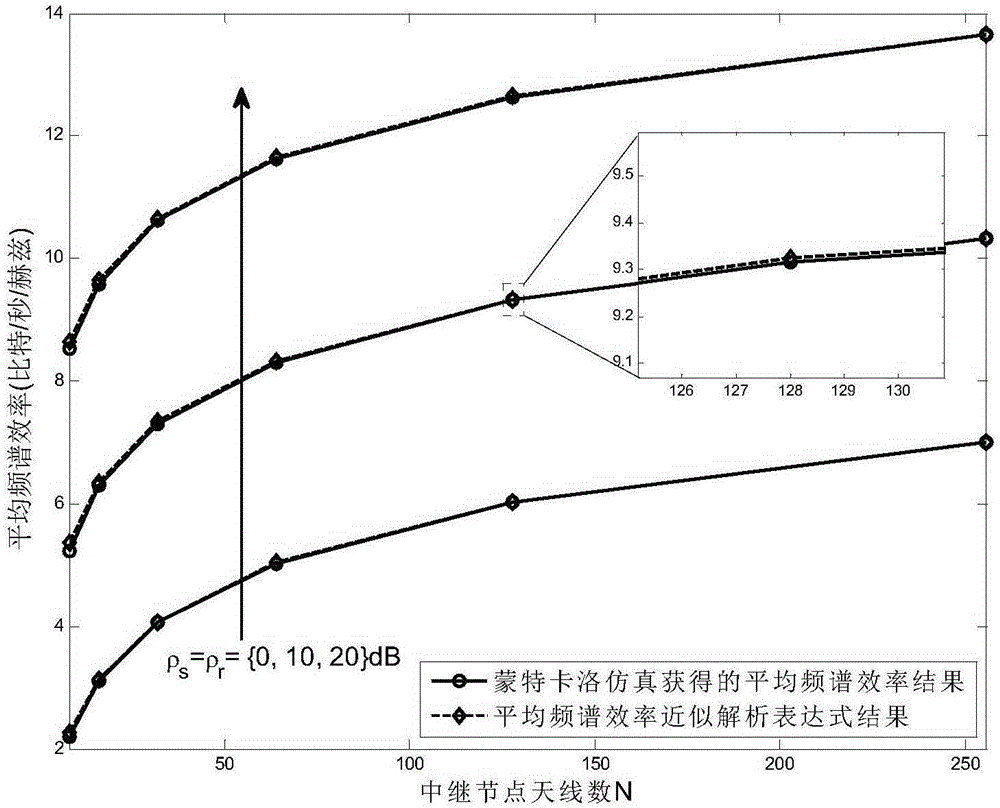
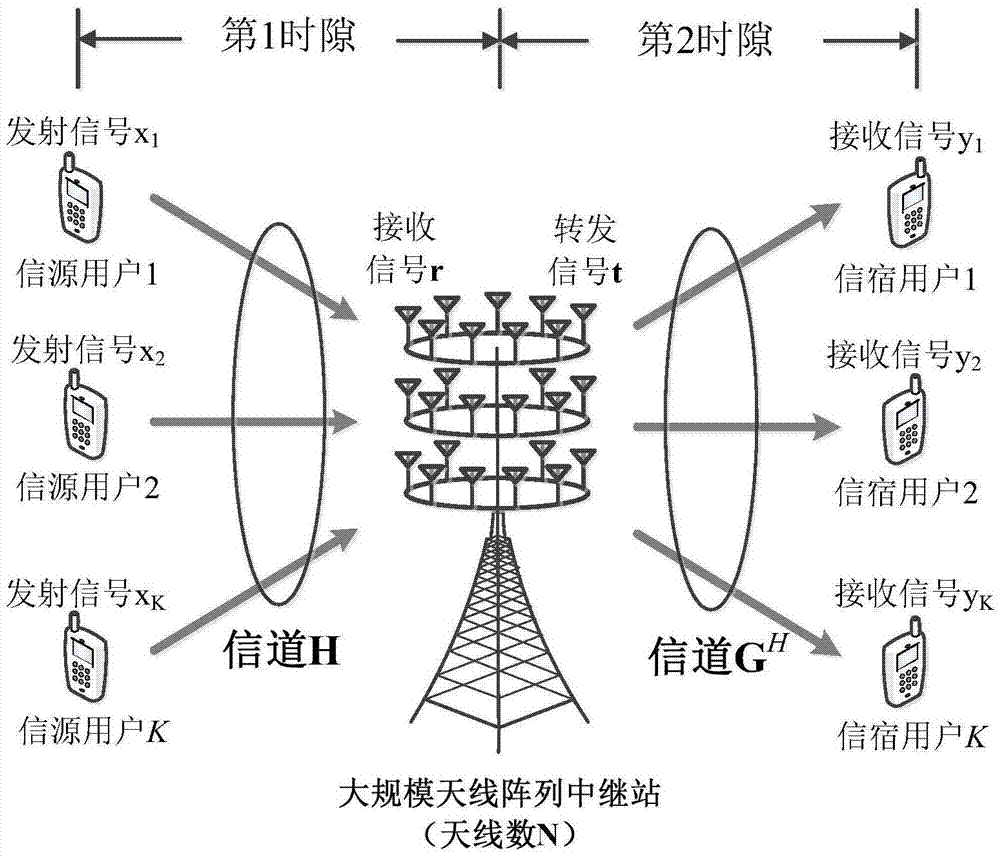
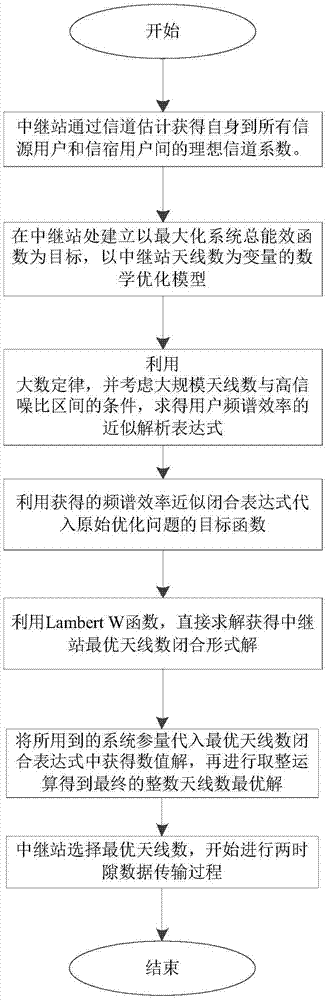
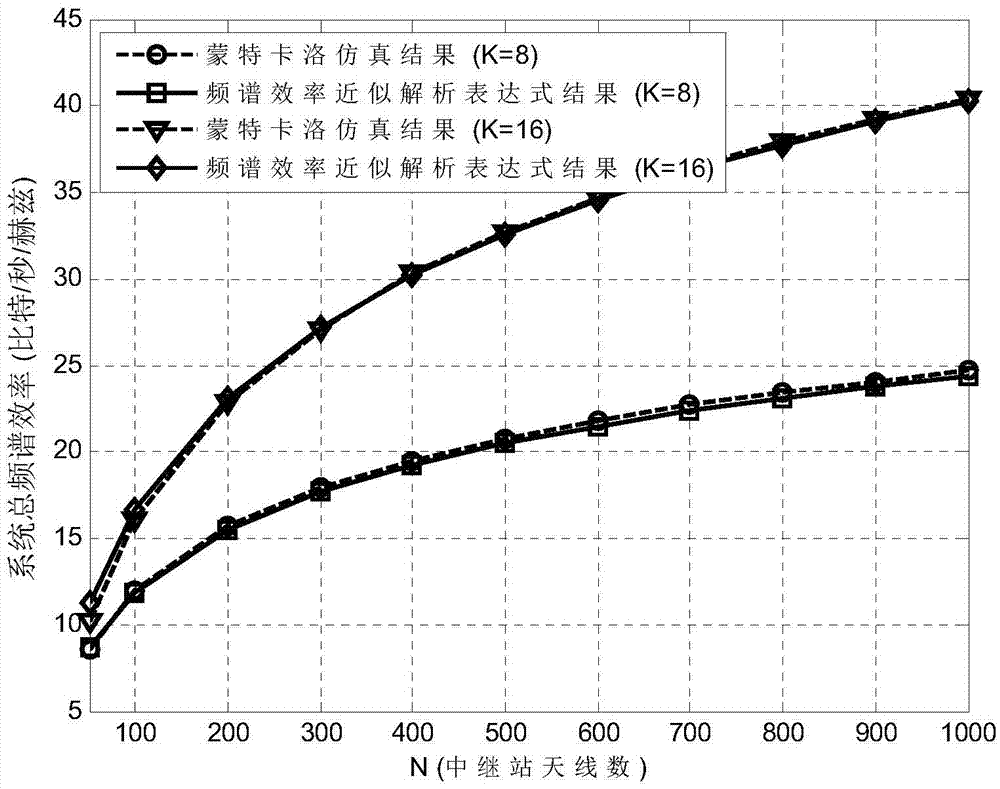
Single-user large-scale antenna relay system power allocation method based on energy efficiency optimization
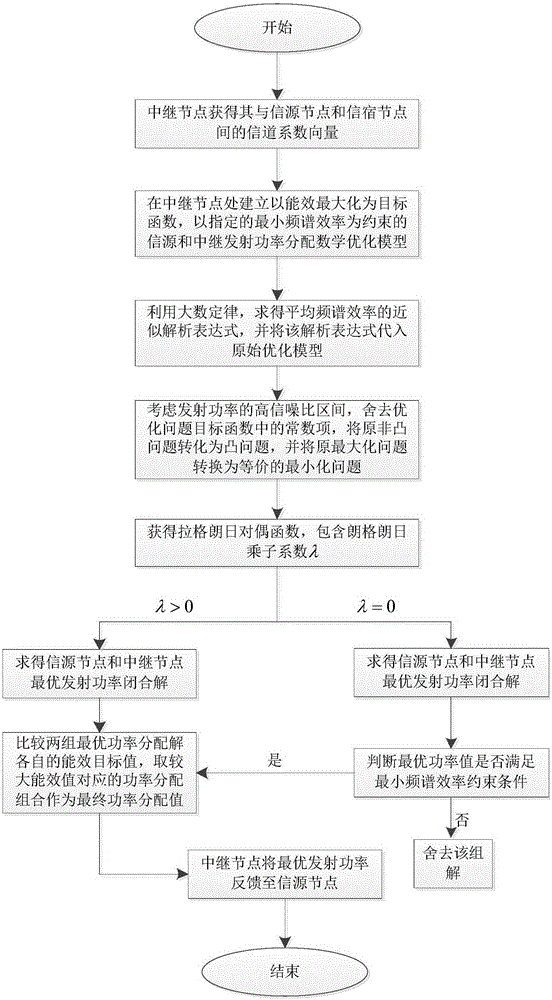
ActiveCN105246142AReduce overheadReduce processing complexityPower managementTransceiverOptimization problem
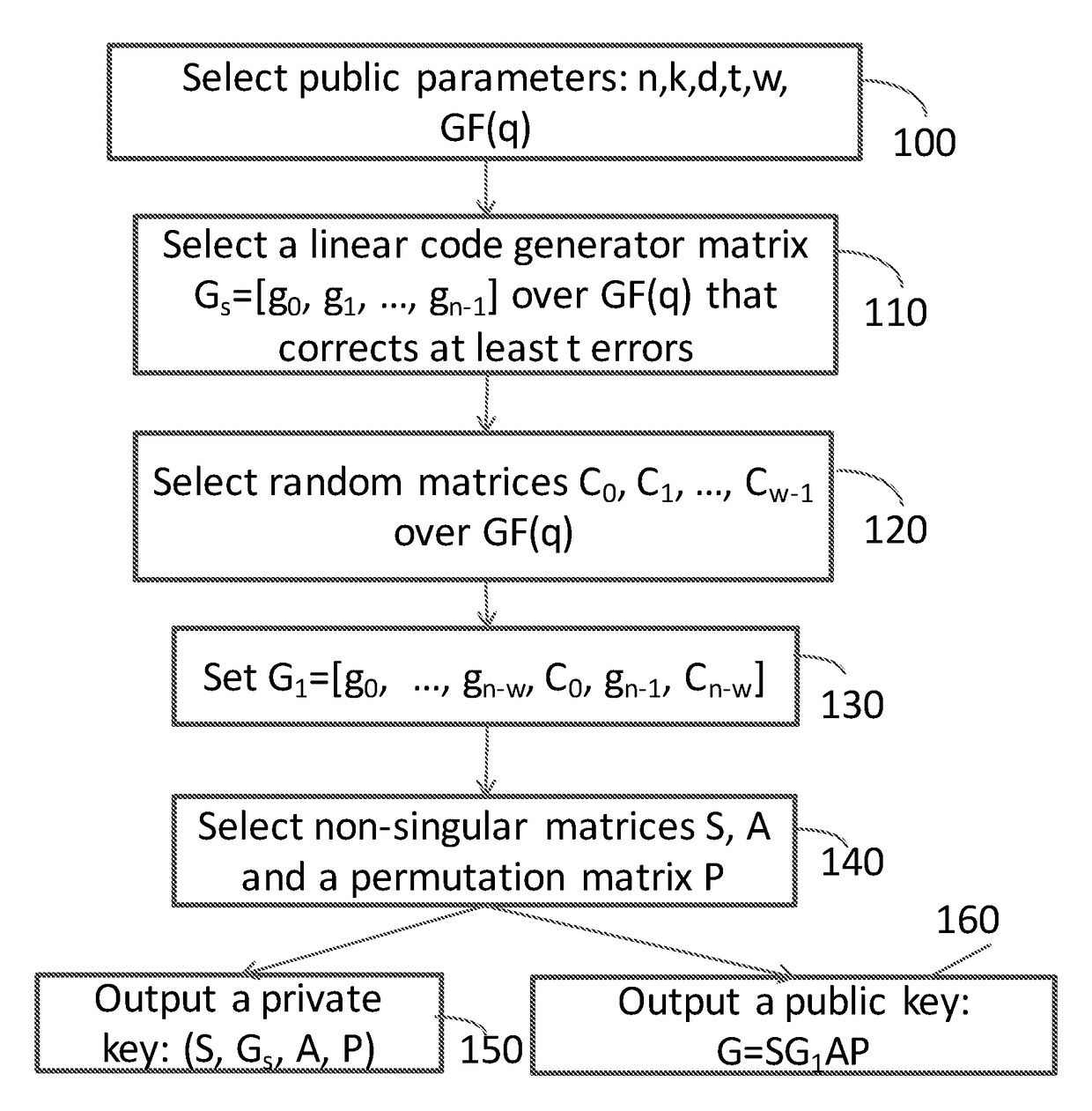
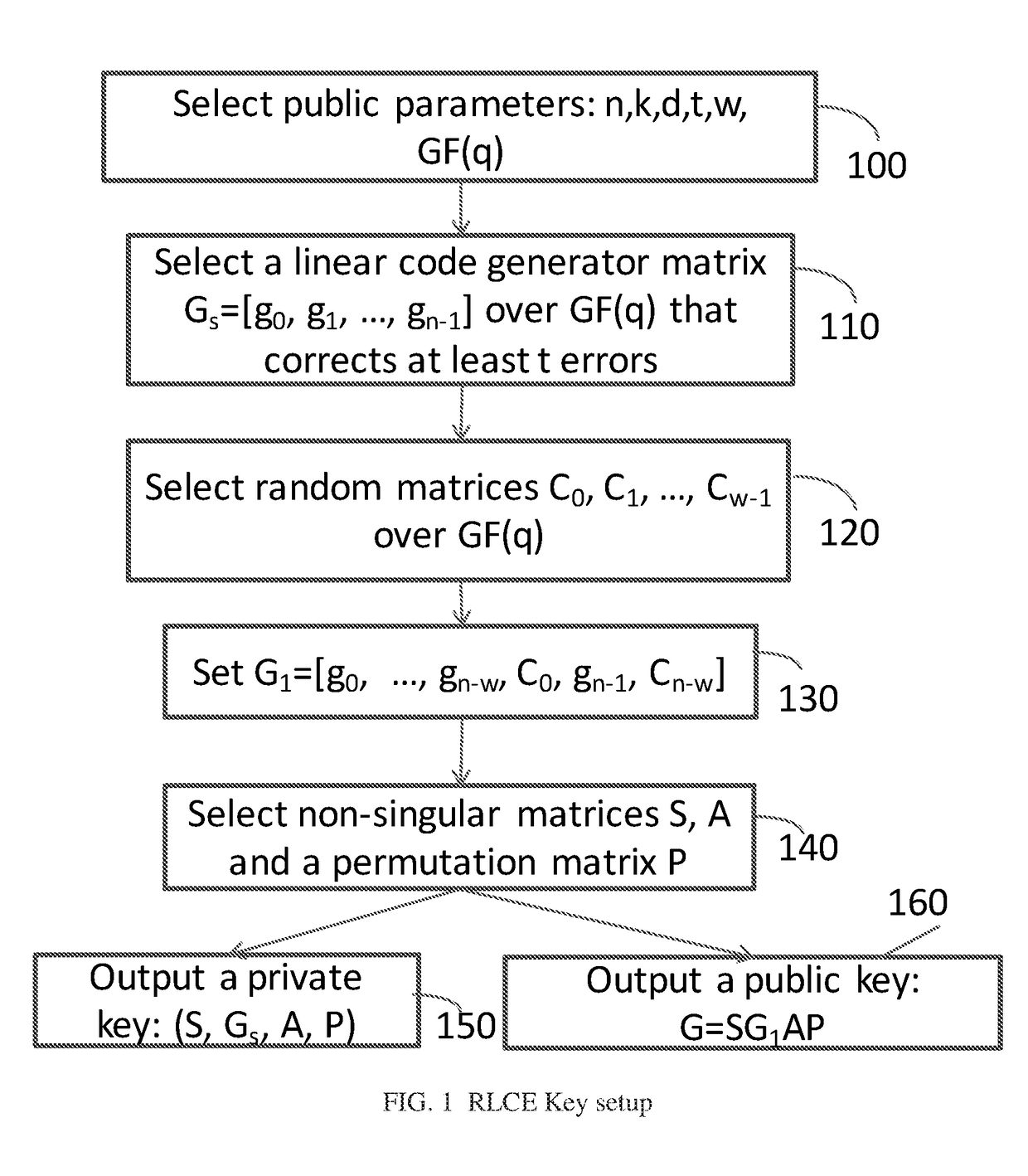
The invention discloses a single-user large-scale antenna relay system power allocation method based on energy efficiency optimization. A communication system consists of a single antenna information source node, a single antenna information sink node, and a relay node transceiver configured with a large scale of antennas, and is shown in accompanying drawings in the summary. According to the method, a mathematical optimization model taking transmitting powers of the information source node and a relay node as design variables is built specific to a design objective of system energy efficiency maximization under a constraint condition of satisfying specified system quality of service (QoS). Since an accurate analytical expression is unavailable for an objective function in an optimization problem, an accurate approximate analytical expression of the objective function is obtained by means of a law of large numbers in a large-dimension random matrix theory. Then, a non-convex objective function is transformed into a convex function through interval approximation equivalence with a large signal-to-noise ratio. Through a Lagrange dual function convex optimization algorithm, a closed-form solution of a power allocation scheme is obtained finally by means of a Lambert W function, so that solving of the optimization problem with an alternate iteration method is avoided.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for consitituting sparse generative matrix and method for coding low-density block check code
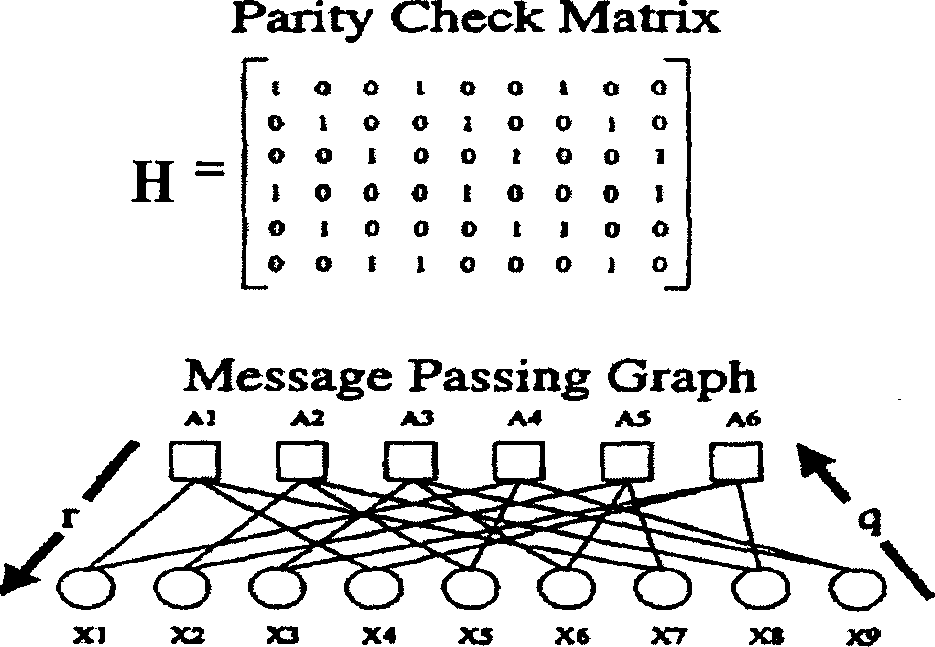
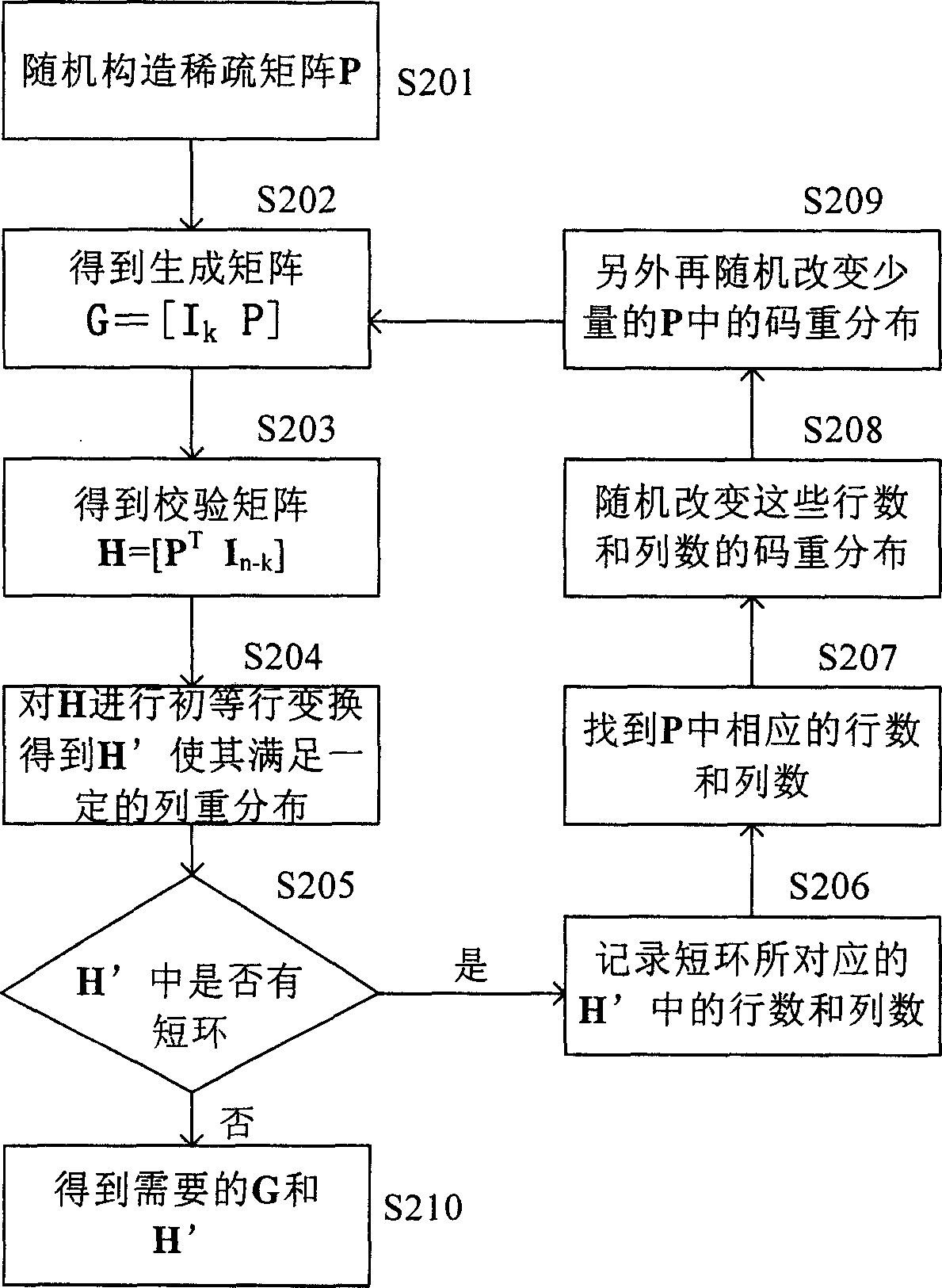
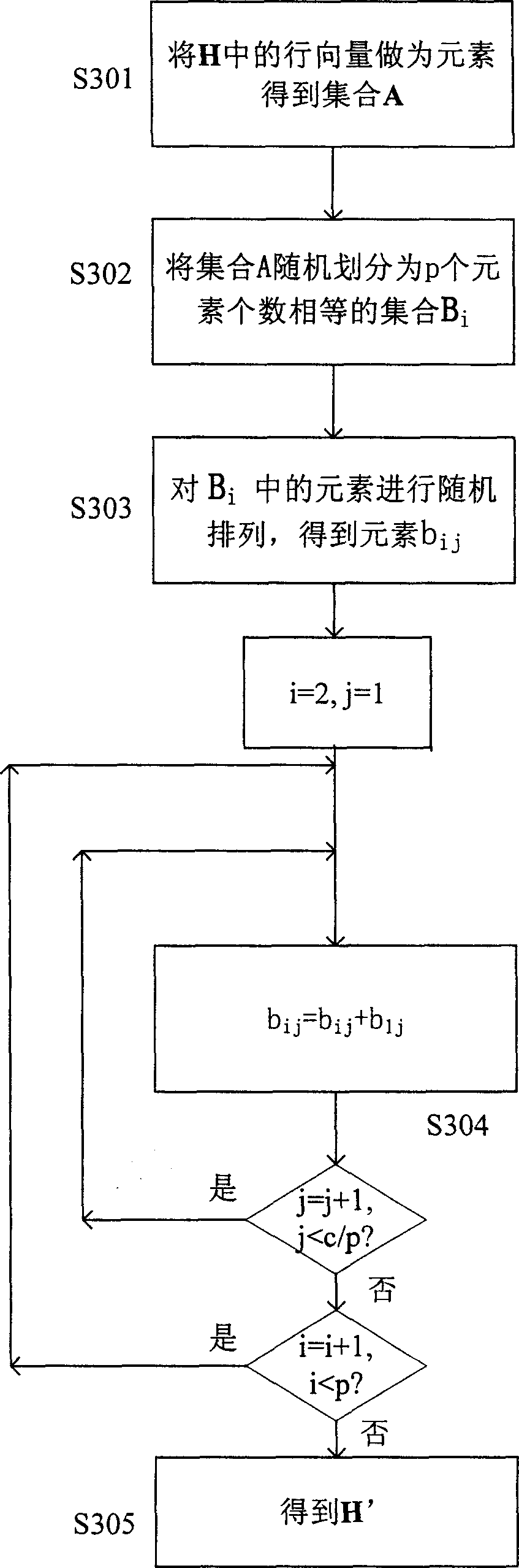
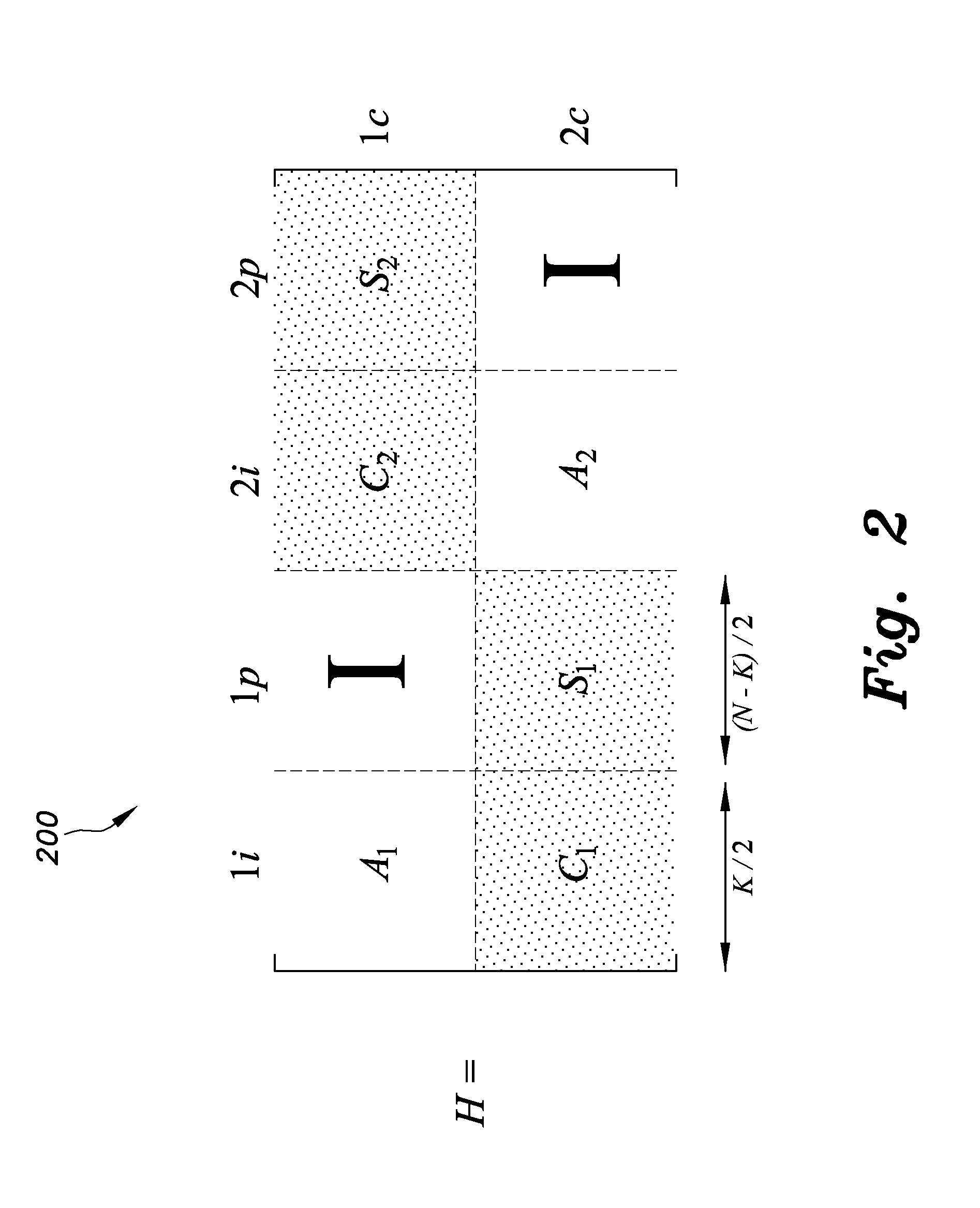
InactiveCN1889367ASimple codingError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsPartition of unityAlgorithm
This invention discloses a method for generating matrixes including: a, randomly generating a sparse matrix P of k lines and n-k columns, b, getting a generated matrix G=[Ik P] from said sparse matrix P, checking the matrix H=[PT In-k], in which, Ik is the unit matrix of k lines and k columns, the PT is the transposed matrix of P, c, carrying out initial transformation to said checked matrix H to let it meet the preset re-distribution of columns to get the transformed check matrix H, d, checking if there are short rings in the matrix H, e, recording the corresponding lines and columns of the short rings in H to further get the numbers corresponding to said short rings in H so as to further find out numbers corresponding to those in the random matrix P and H, f, regulating the code re-distribution corresponding to said line and column number in P, g, repeating said step b to f and short rings do not exist in H.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Encryption protection system and method for neural network model relating to iteration and random encryption
ActiveCN108898028AGuaranteed performanceKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the field of artificial neural network protection mechanism, and particularly relates to an encryption protection system and method for a neural network model relating to iterative and random encryption. The system comprises a data input module, an encryption module and an encryption data input module, an artificial neural network model module and a data output module; theencryption module comprises a structure conversion module and an iterative processing module; the iterative processing module comprises a password generation module, a password embedding module and asingle-layer convolution neural network model module; the password generation module comprises a fixed matrix generation module and a random matrix generation module. According to the invention, theprotective password can be embedded in the artificial neural network model under the condition that the calculation amount is not significantly increased and the performance of the artificial neural network is maintained, so that after the artificial neural network model is released, any copying, secondary development or modification cannot influence the protective password, and destroying the protective password can lead to a reduction in the performance of the artificial neural network model or may cause an effective output.
Owner:CHENGDU PANOAI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Optimal energy efficiency-based antenna selection method for multi-user and large-scale antenna relay system
InactiveCN105450275AReduce power overheadReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityHigh level techniquesMathematical modelPairwise coupling
The present invention discloses an optimal energy efficiency-based antenna selection method for a multi-user and large-scale antenna relay system. The system comprises a plurality of information source users, a plurality of information sink users and a relay station, wherein the number of the information source users is equal to the number of the information sink users. The information source users and the information sink users are pairwise coupled and the information transmission between the information source users and the information sink users is realized via the relay station within two time slots. All information source users and information sink users in the system are respectively provided with a single antenna. The relay station is provided with an antenna array of a large-scale number illustrated in the drawings of the abstract. According to the technical scheme of the invention, in order to realize that the energy efficiency of the system is maximal, the antenna number of the relay station is adopted as an optimization variable for the establishment of a mathematical model. Since no clear analytical expression is available for a target function of the above optimization problem, an approximately accurate analytical expression for the target function of the optimization problem is figured out firstly based on the law of large numbers in the large dimensional random matrix theory. After that, based the quasi-concave characteristics of the optimization variable in the analytical expression, an optimal antenna number closed-form solution for realizing the optimal energy efficiency is finally solved out by means of the Lambert W function at the same time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for secure communication on a compound channel
InactiveUS20160365977A1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationLeft half
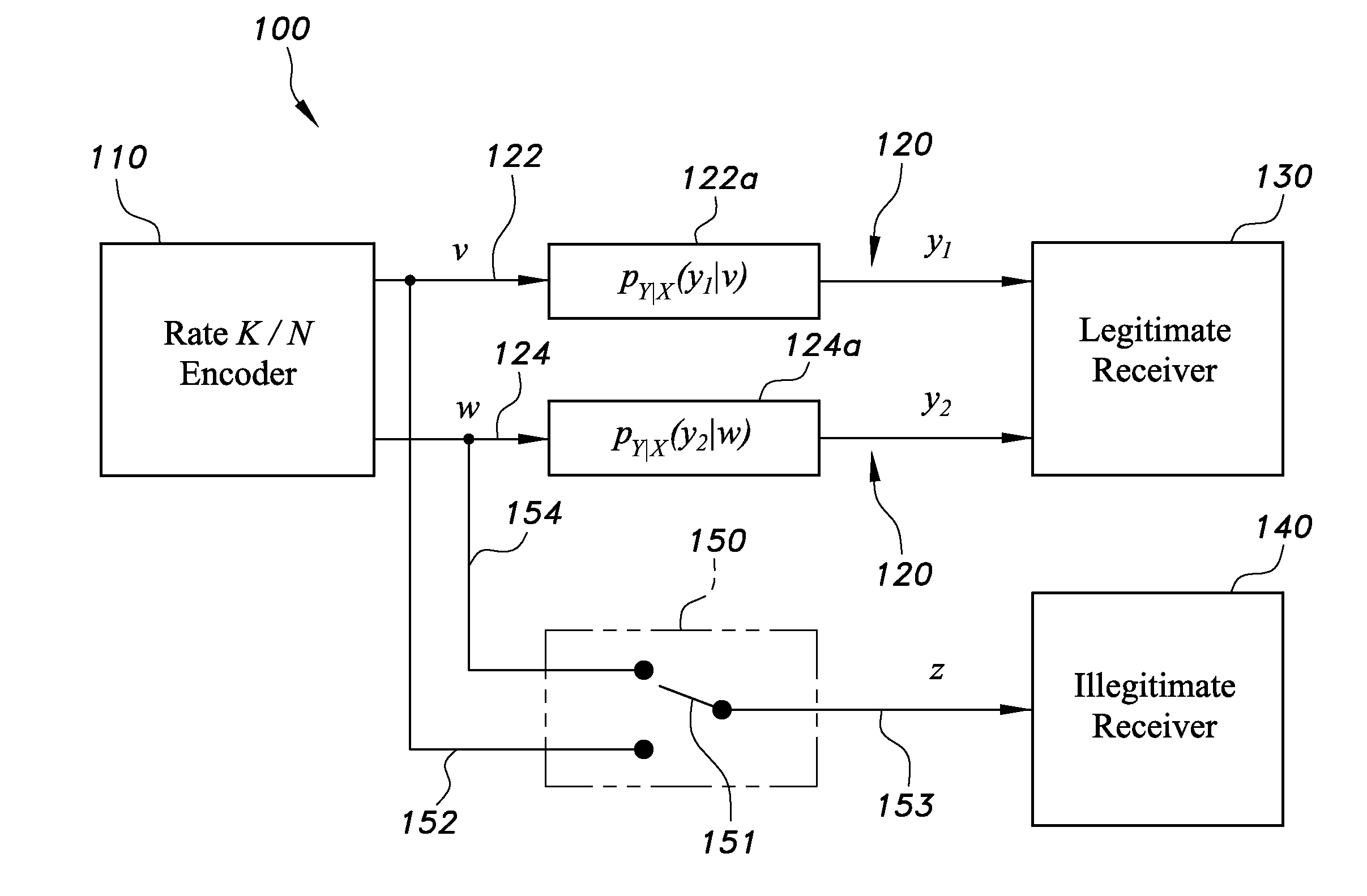
The anti-diversity concept for secure communication on a two-link compound channel provides secure communication over two parallel communication channels. The message is split into two separate bit sequences by a source splitter. An error correction encoder (110) is applied to the two bit sequences to provide two code words for two channels (122, 124), such that left and right halves of an error correction code matrix respectively corresponds to the two parallel signal channels (122, 124). For the left half of the error correction code matrix, an upper left matrix block is a random permutation matrix, an upper right block is the identity matrix, and the bottom right matrix block is a random matrix of column and row weight greater than or equal to one. The bottom left matrix block is a column permutation of the bottom right, random matrix block. The right half error correction code matrix is a similar, symmetric structure.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Apparatus for coding low density parity check code and method thereof
InactiveUS20060123314A1Increase speedError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDevice formTheoretical computer science
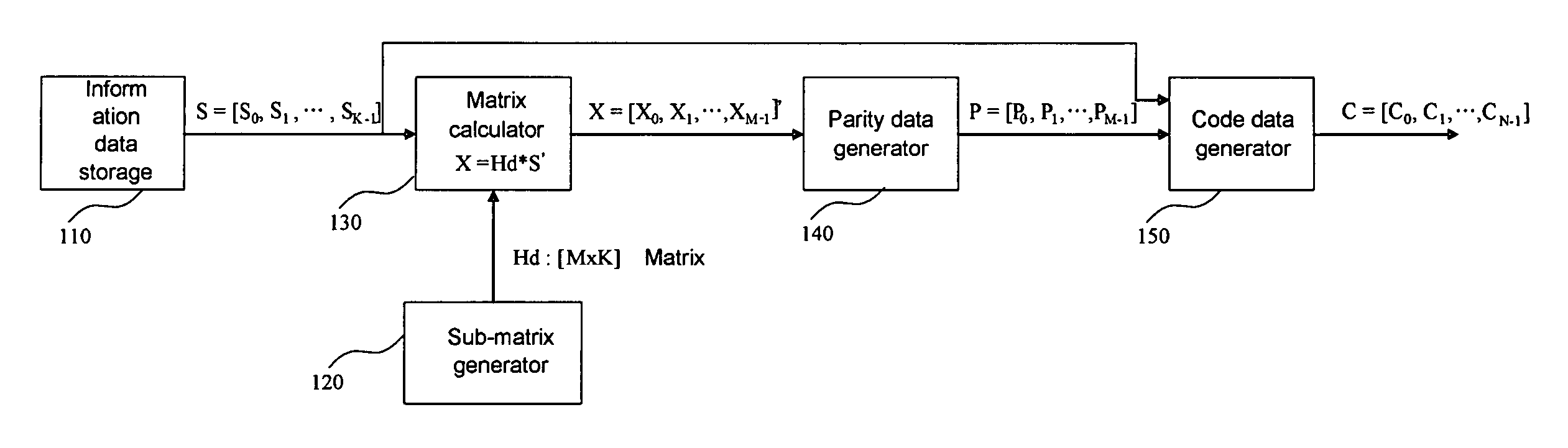
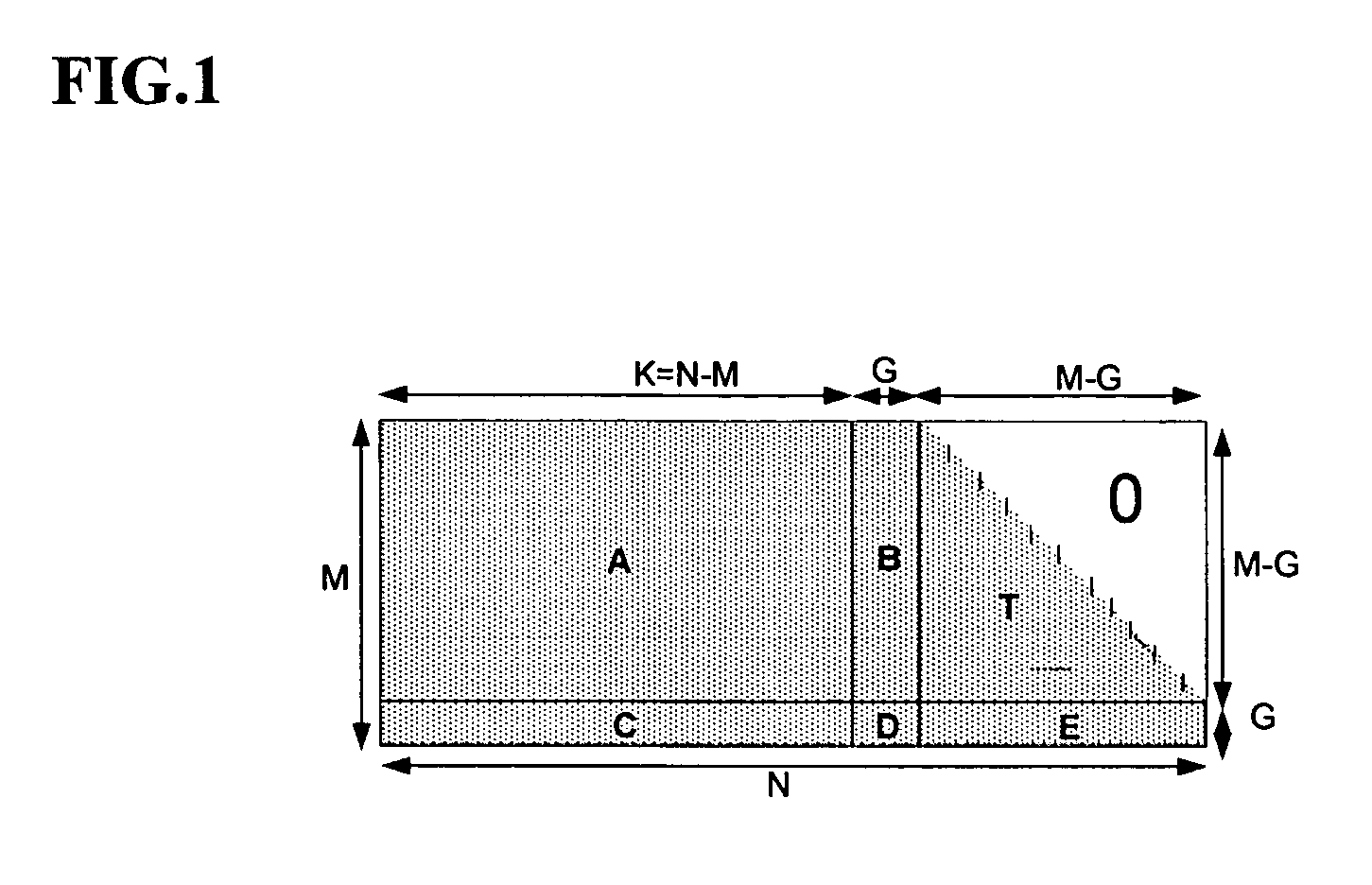
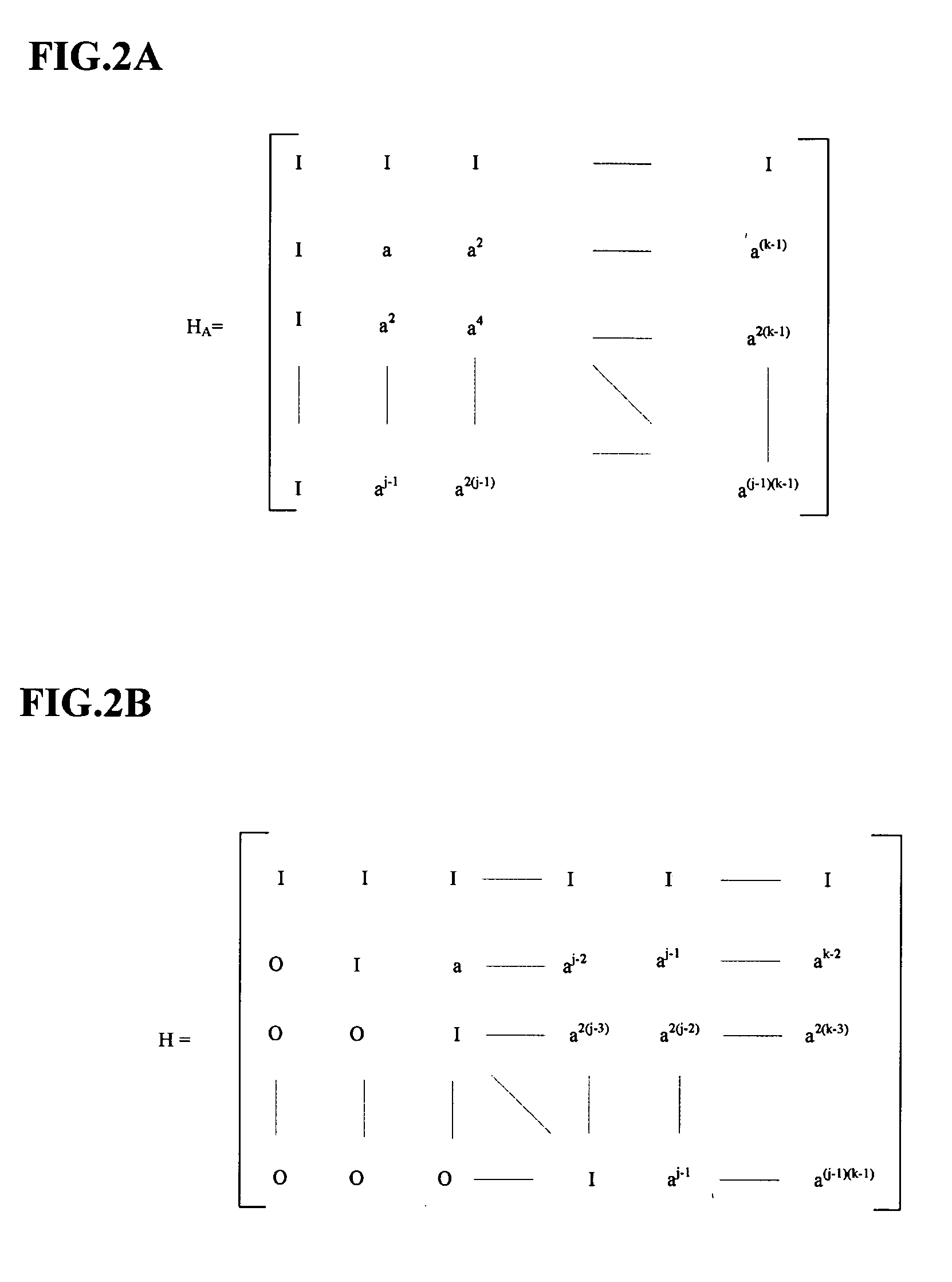
The present invention provides a coding device of a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code for simply coding information data without generating a code generator matrix. The coding device forms a parity-check matrix having two sub-matrixes. At this time, the first sub-matrix is a random matrix or a structural matrix. The second sub-matrix is a structural matrix having two 1s in each column. Parity data is calculated by using the structural second matrix without calculating an inverse matrix of the second matrix when temporary data is generated by using the first sub-matrix with reference to the information data. Code data is generated from the parity data and the information data and is transmitted.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Ultra-sensitive spectral imaging astronomical telescope based on second-order compressed sensing and method
InactiveCN103968945ASolve the problem of insufficient dimensionalityHigh resolutionSpectrum investigationTelescopesSpatial light modulatorSpectral bands
The invention relates to an ultra-sensitive spectral imaging astronomical telescope based on second-order compressed sensing, which comprises an optical unit and an electric unit, wherein the optical unit comprises an astronomical telescope lens, a first spatial light modulator, a collimation part, a spectrometric part, a spectral convergence part, a second spatial light modulator and a collection part; the electric unit comprises a single-photon point detector, a counter, a random number generator, a control module, a data packet memory and a compressed sensing module; a celestial image is collected through the astronomical telescope lens, and is imaged to the first spatial light modulator; a randomly modulated light beam is collimated into parallel light, and the parallel light forms a spectral band through the spectrometric part; the spectral band is secondarily randomly modulated through the second spatial light modulator, and is finally collected in the single-photon point detector; and a compressed sensing algorithm is used for obtaining an astronomical target spectral image according to a photon count value and two groups of random matrixes.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Distribution network fault line selection method based on random matrix and Hausdorff distance
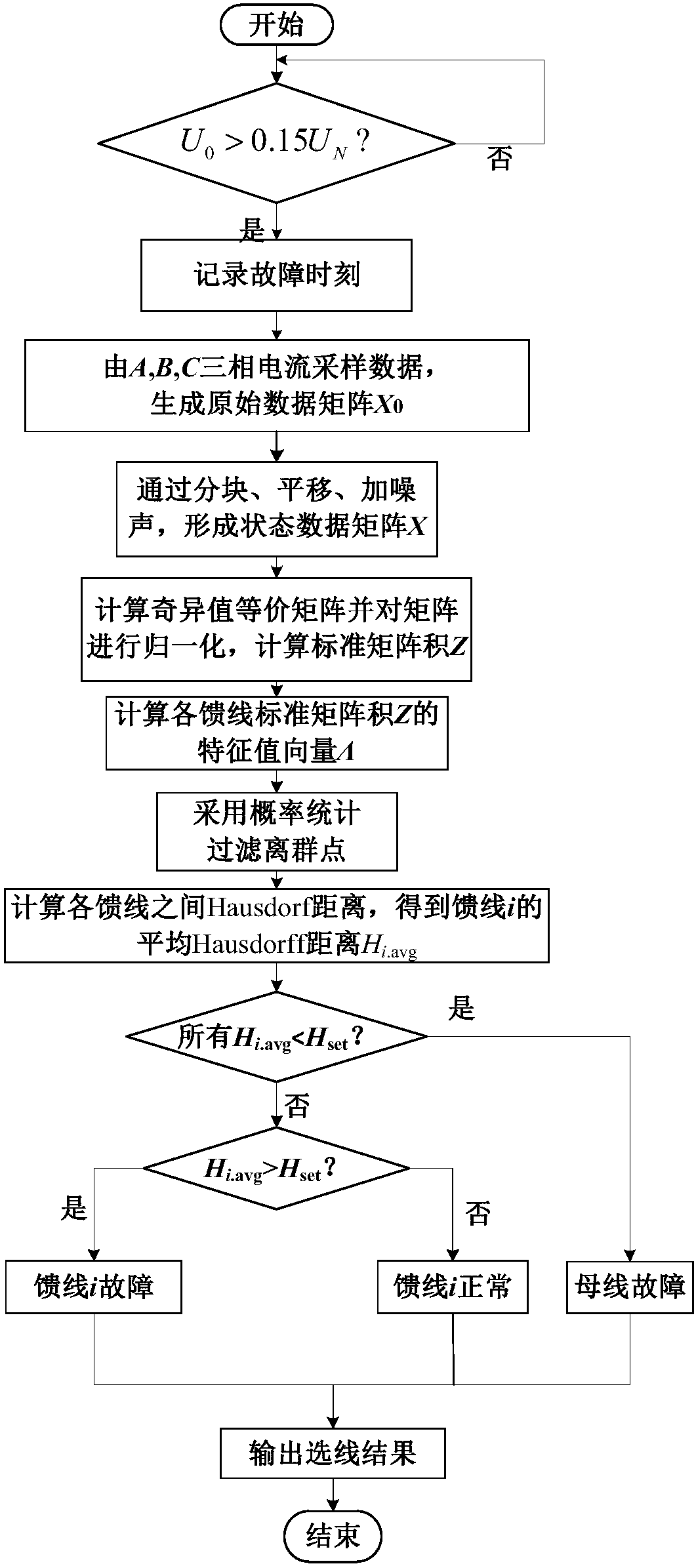
ActiveCN108572303AThe fault line selection result is accurateImprove reliabilityFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemEuclidean vectorData Matrix
The invention discloses a distribution network fault line selection method based on a random matrix and a Hausdorff distance. Three-phase current sampling values of a feeder line before and after fault are selected, through blocking and translation processing, white Gaussian noise is added, a state data matrix is generated, a product matrix is obtained by using equivalent transformation of singular values of the random matrix, a standard matrix product is obtained by normalization, eigenvalue vectors are acquired, probability statistics is carried out, eigenvalue vectors with the probabilitiesP to be smaller than 10% are used as outliers to be filtered, a Hausdorff distance algorithm is adopted, the Hausdorff distances between the eigenvalue vector of a certain feeder line and the eigenvalue vectors of other feeder lines are calculated, the maximum value is removed, averaging is carried out to obtain an average Hausdorff distance of the feeder line, if the average distance is larger than a threshold, fault of the feeder line is judged, and if the average Hausdorff distance of each feeder line is smaller than the threshold, fault of a connected bus is judged. A fault feeder line and a fault bus can be judged accurately, the judgment does not rely on a distribution network model and is not influenced by a fault location, transition resistance, an initial phase angle and a line type, and the practicability is good.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
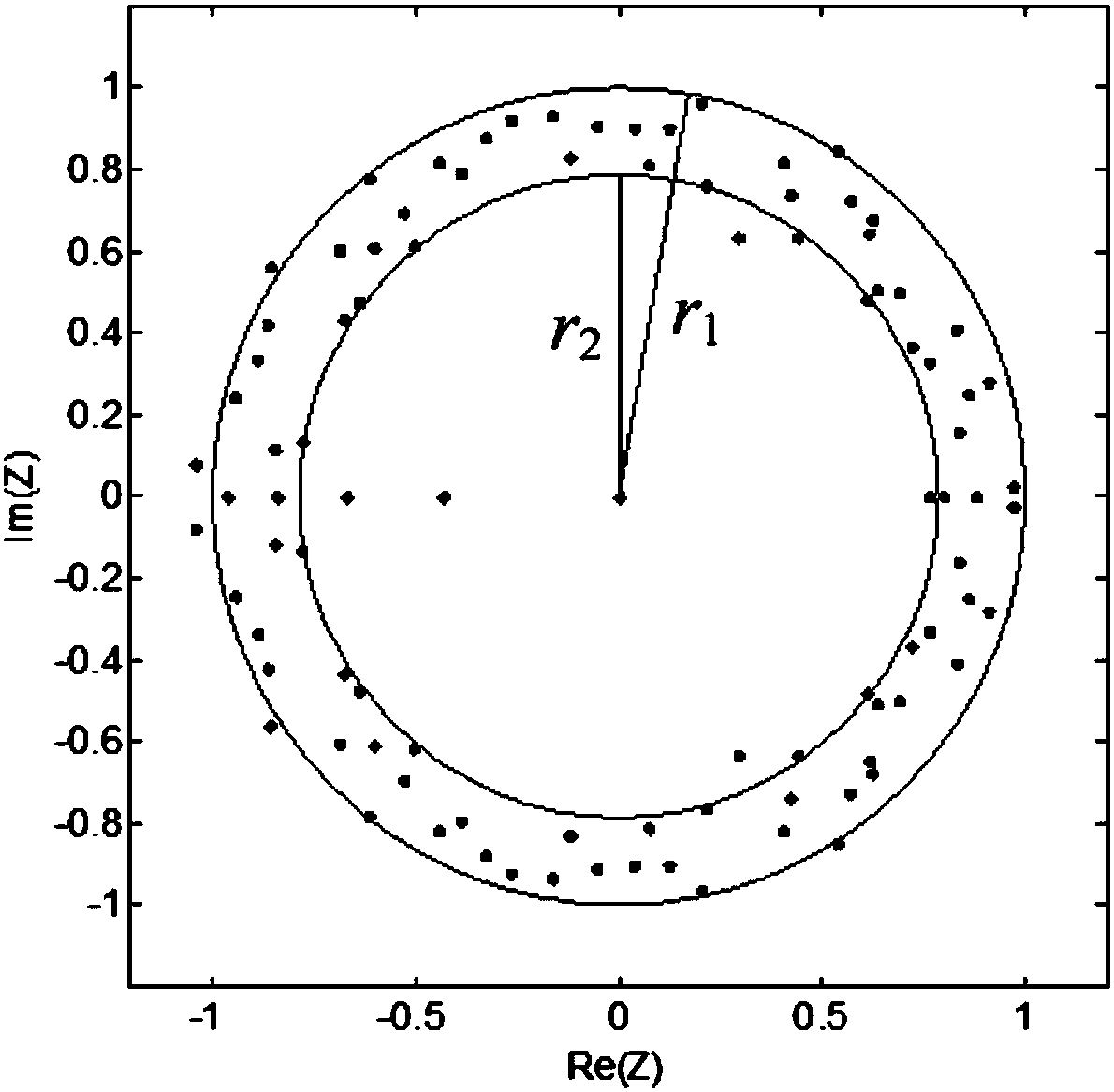
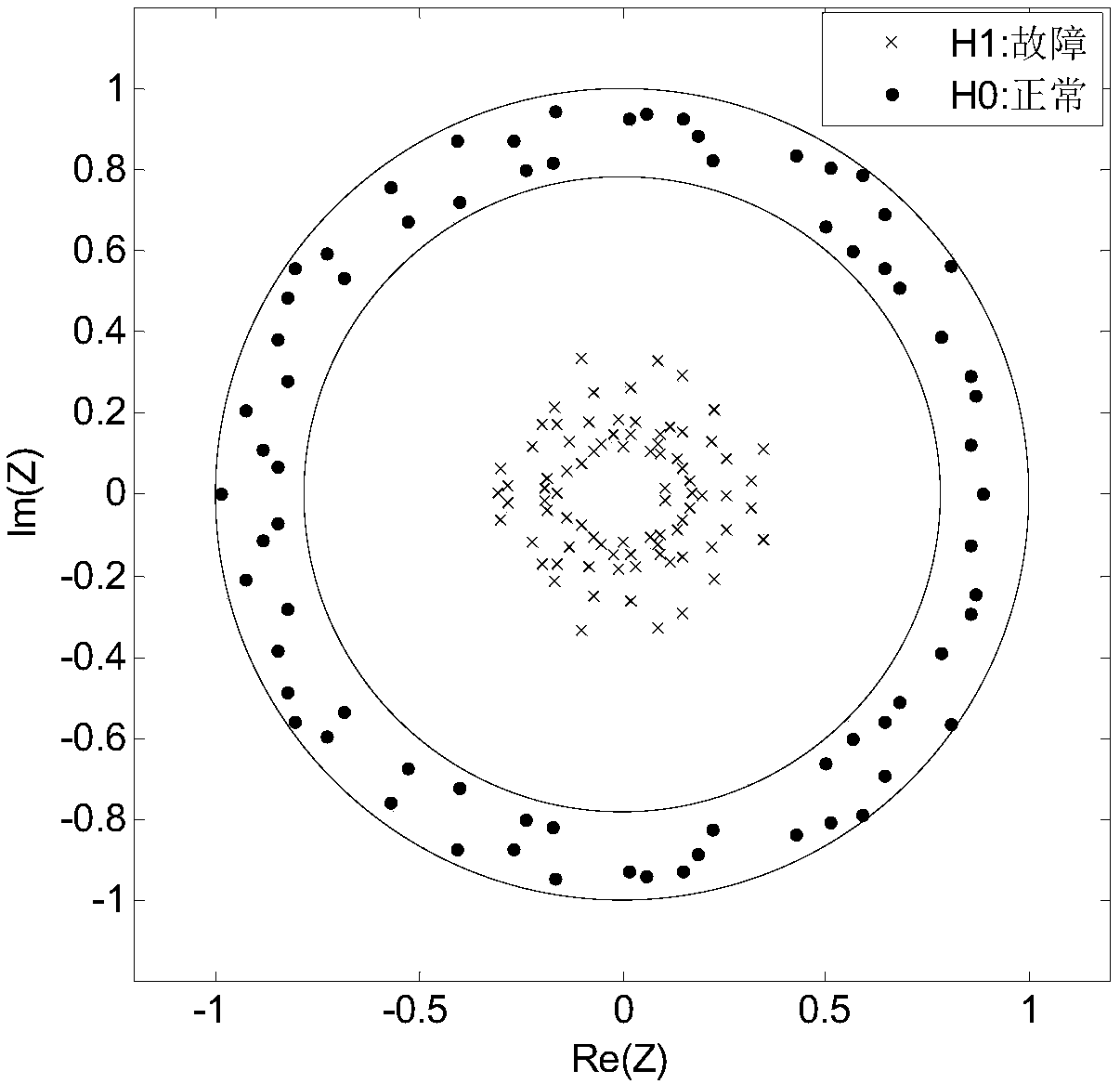
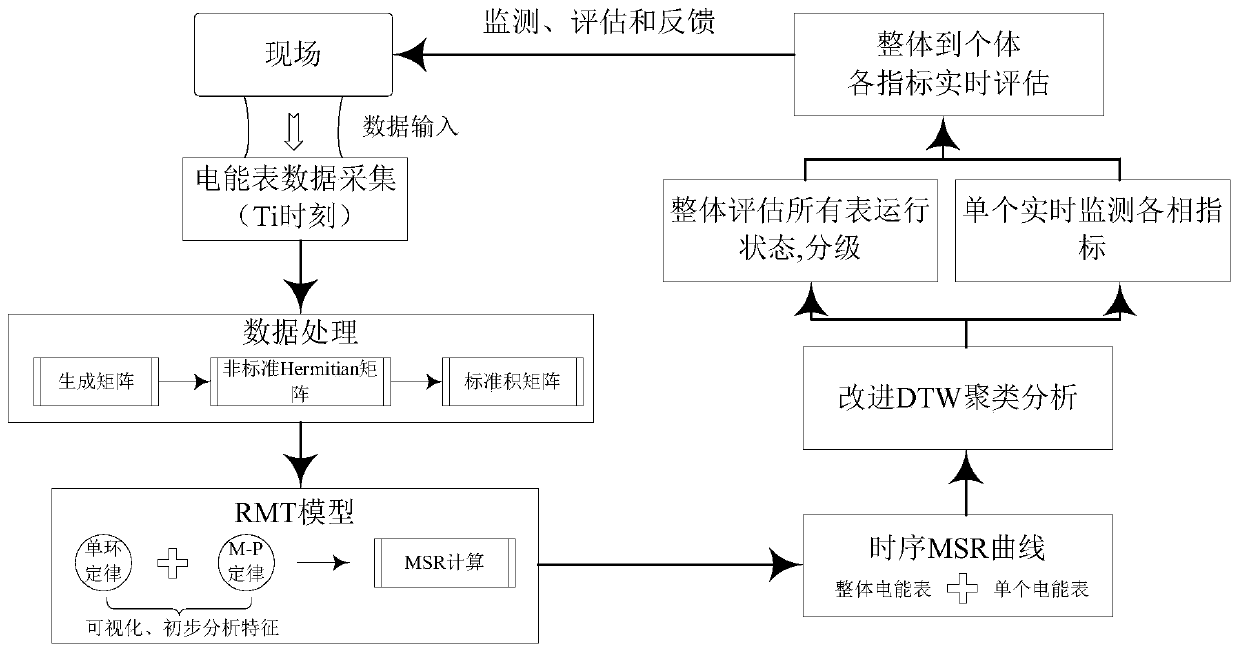
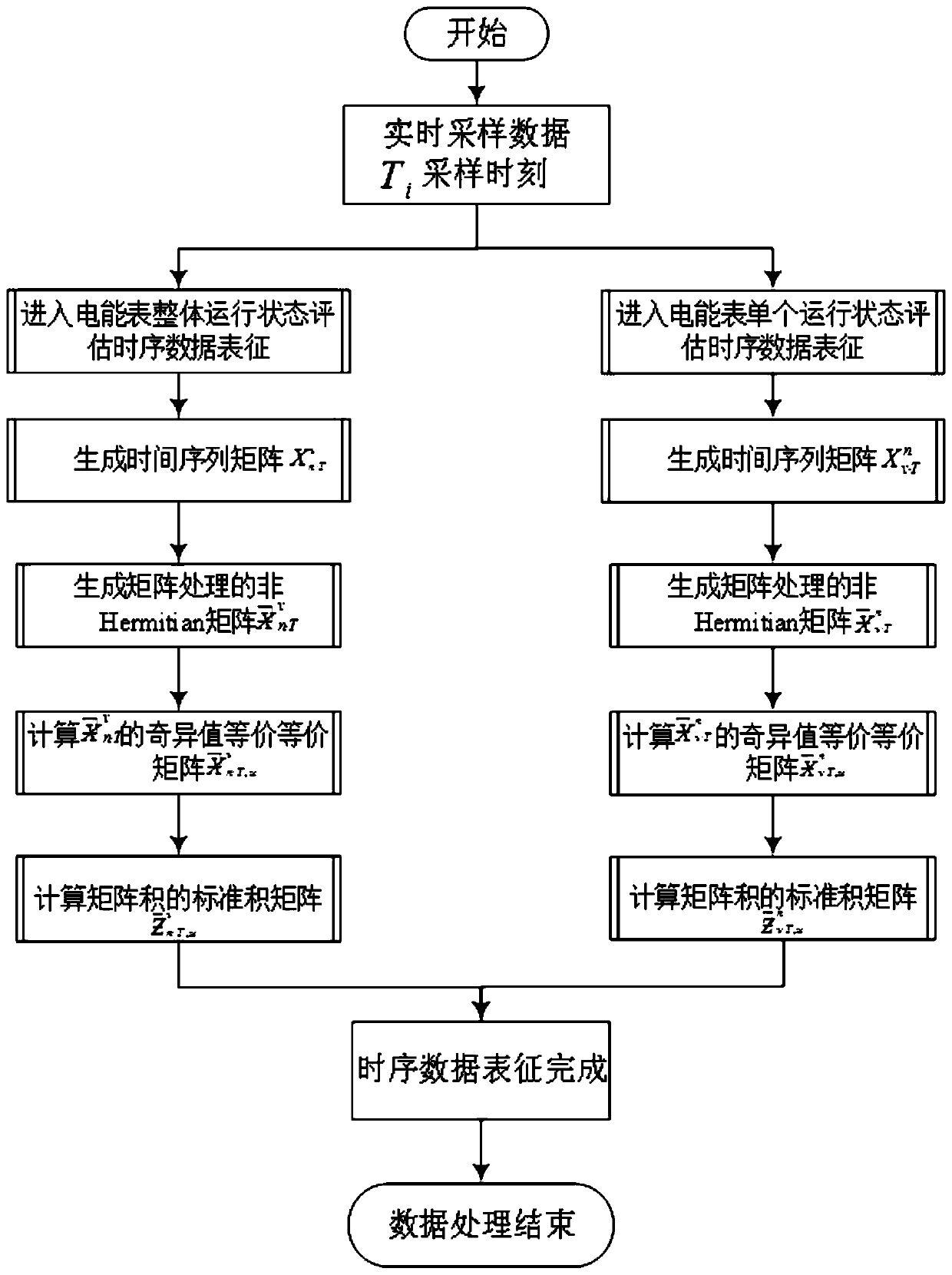
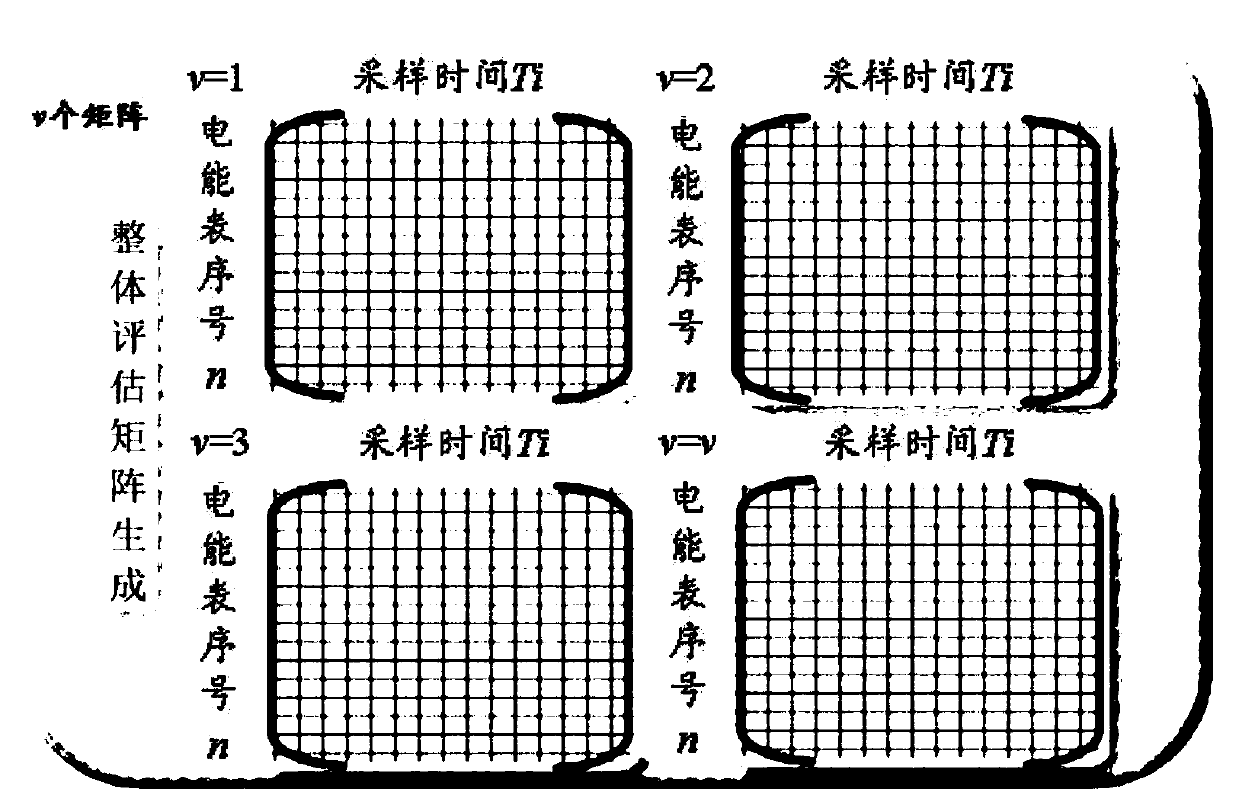
Method and device for evaluating operation state of electric meter
ActiveCN110488218ARobustImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrical measurementsCluster algorithmSpacetime
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric power metering and inspection and particularly relates to a method and device for evaluating an operation state of an electric meter. The method is characterized in that firstly, unified pre-processing of each indicator data of an electric meter is performed to complete characterization of time series data; secondly, the real-time separationwindow technology is utilized to integrate the time series data, based on the random matrix theory, real-time calculation and analysis of statistical time-series characteristics of the multi-dimensional meter time series data are performed; thirdly, the DTW clustering algorithm is utilized to calculate similarity of the time series data, so the random matrix statistics are clustered and ranked; and lastly, the clustering result is analyzed to obtain the range of the electric meter operation state evaluation level, and real-time operation state evaluation of the electric meter is completed. The method is advantaged in that states are classified not dependent on scores but on similarity between sequences, good noise resistance and timeliness are achieved, state intervals can be more accurately divided, moreover, spatiotemporal characteristics of the data have better applicability.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com