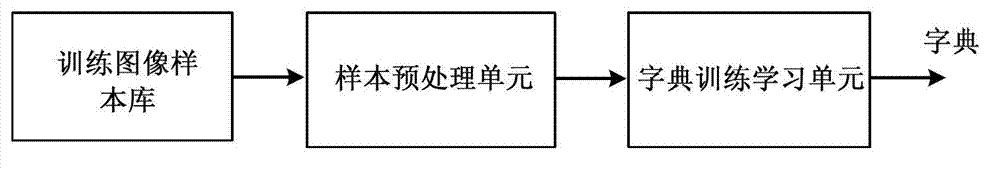
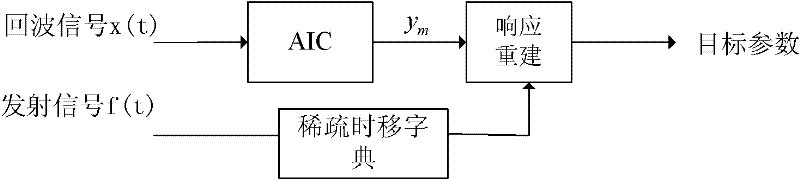
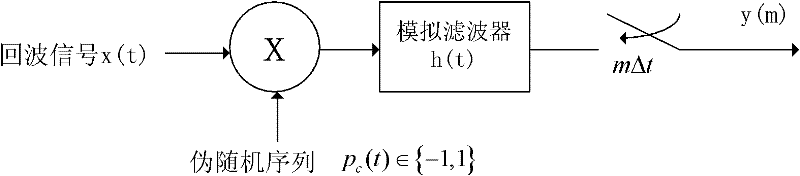
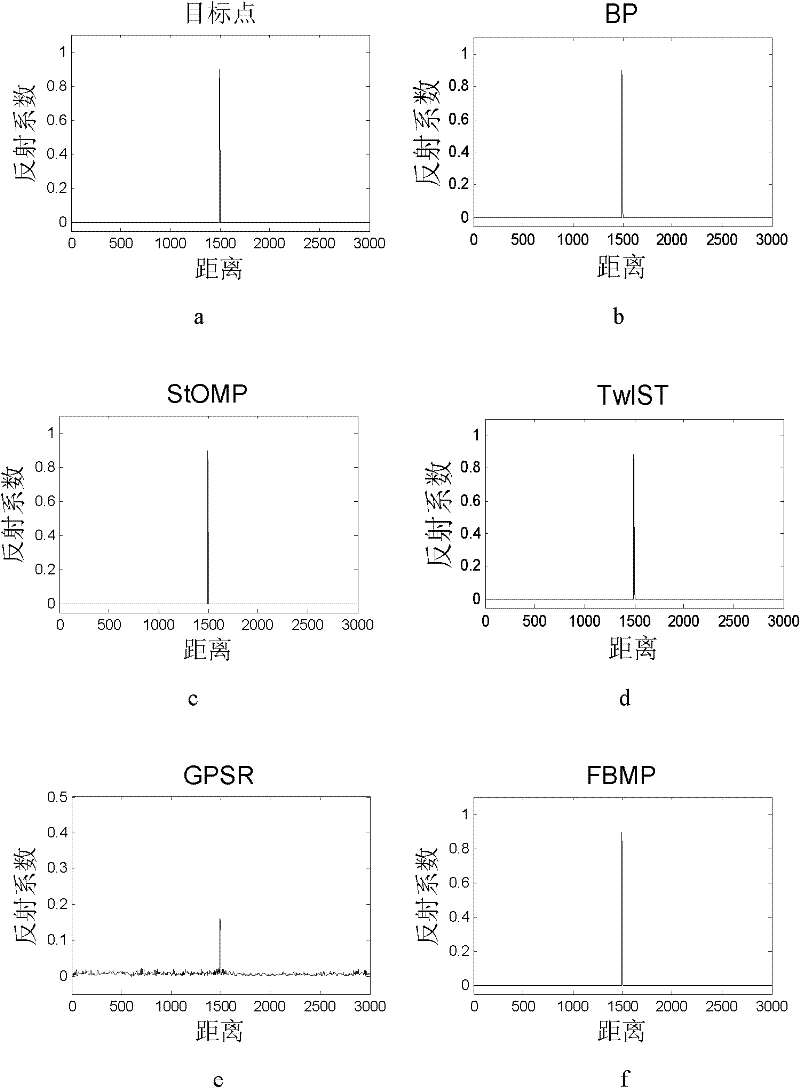
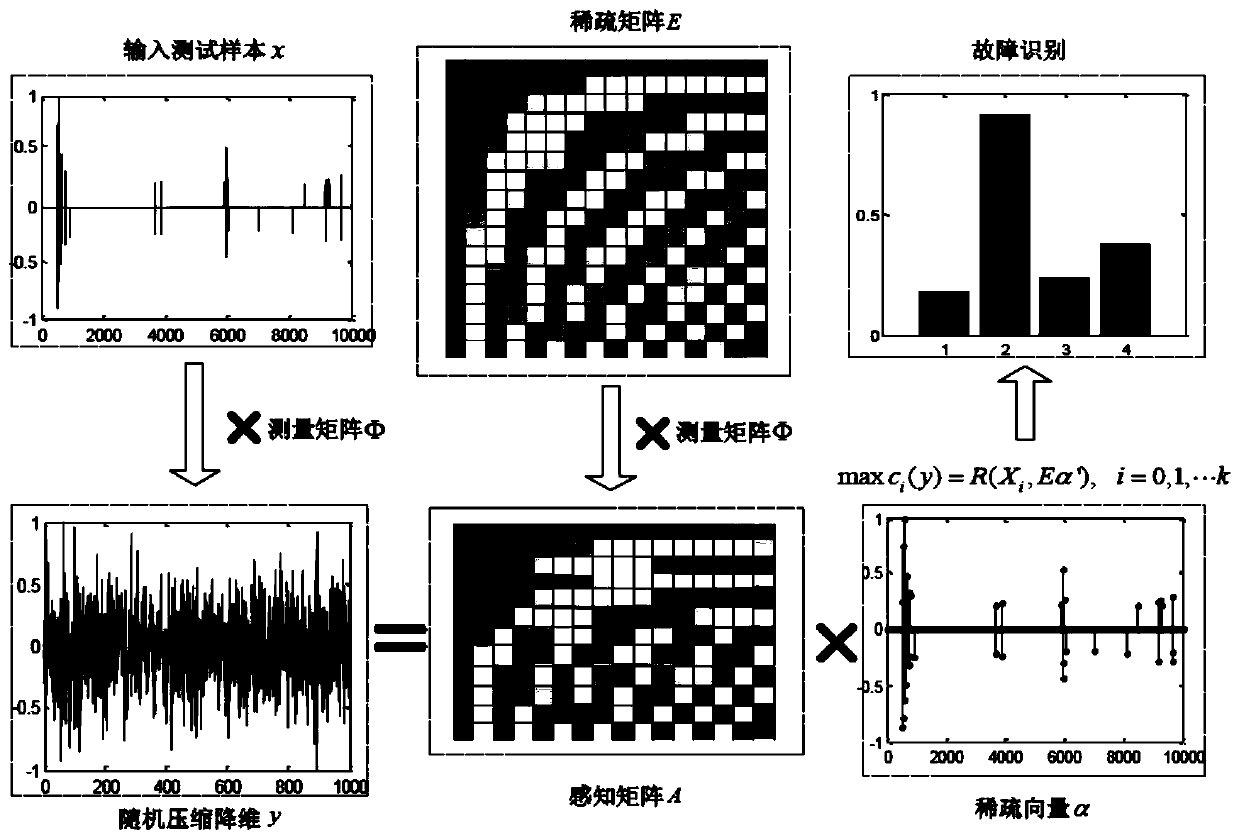
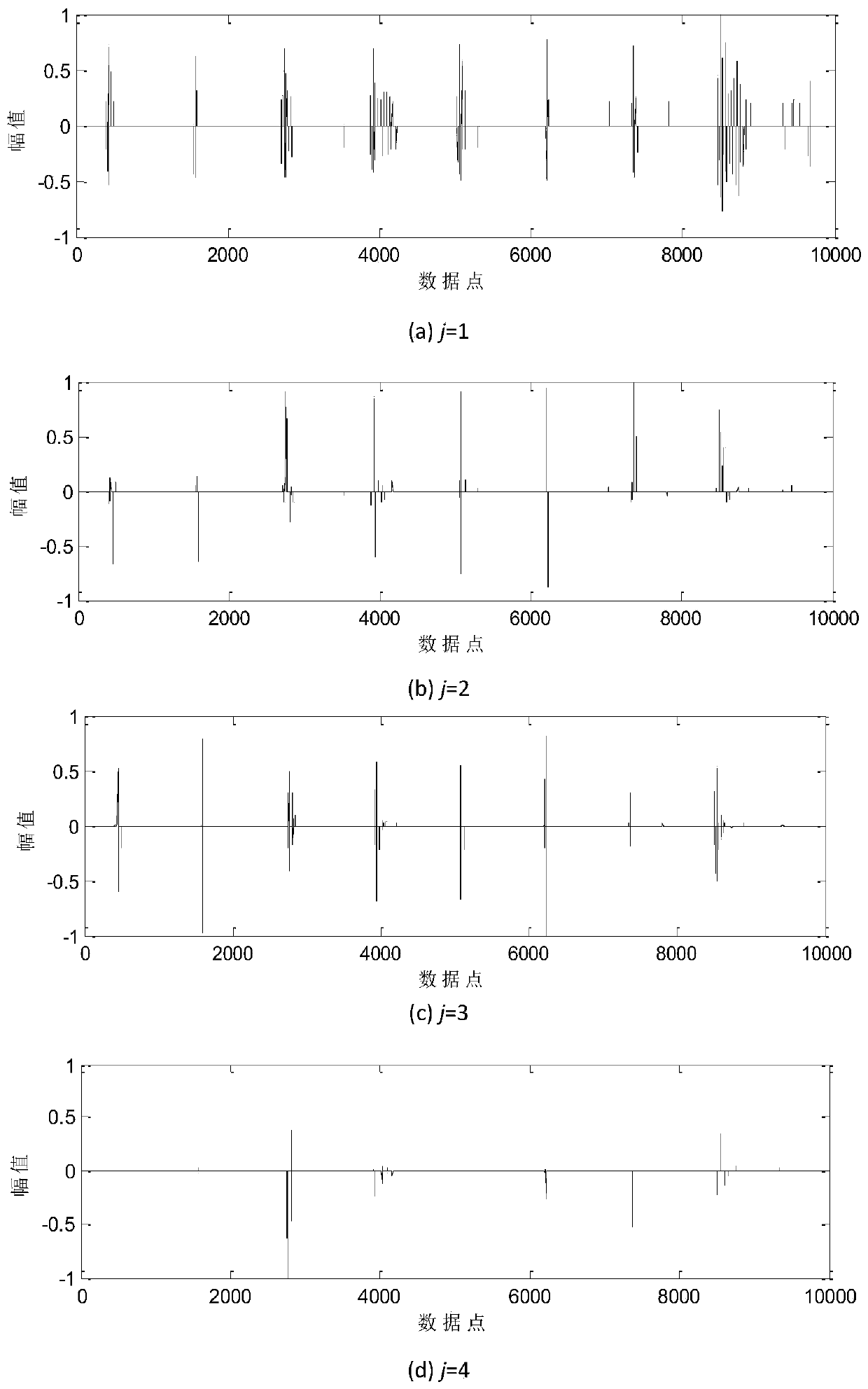
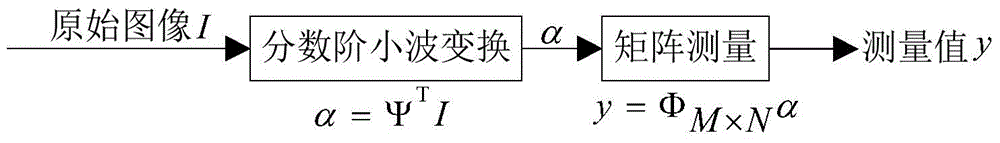
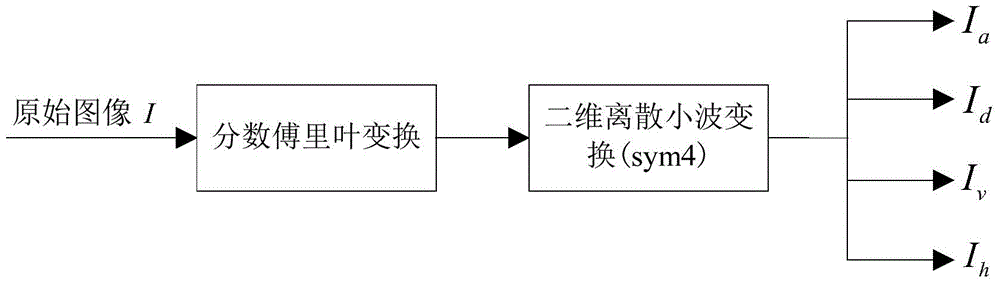
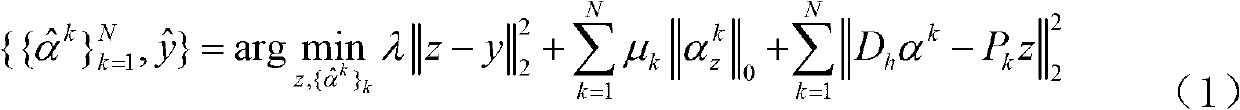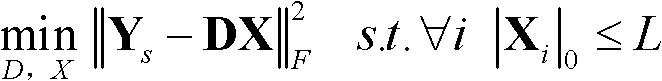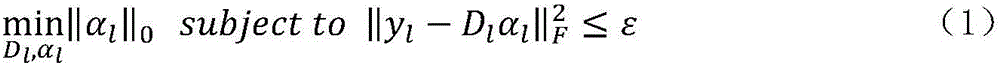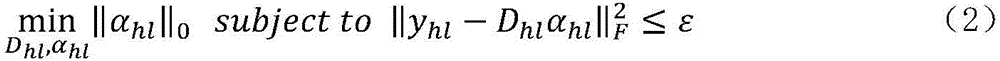Patents
Literature
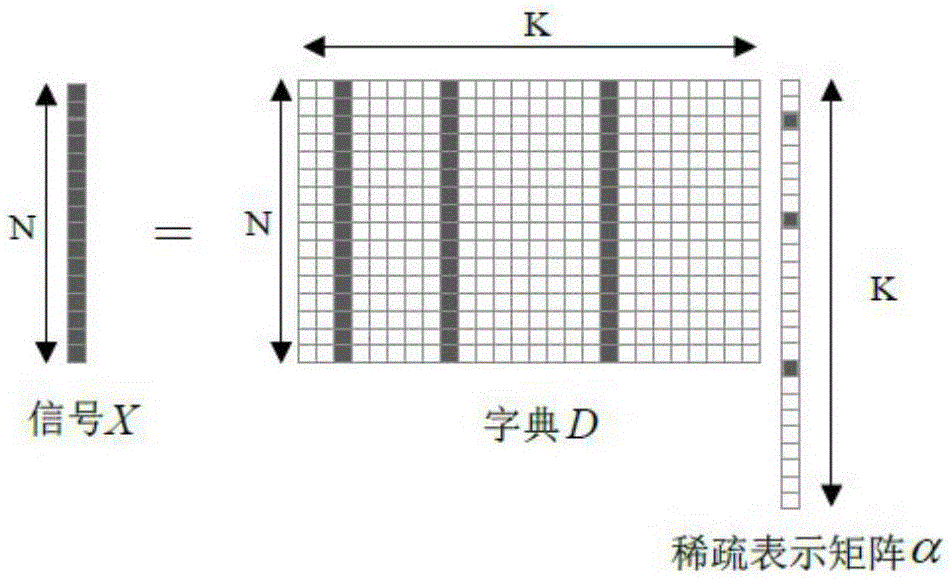
691 results about "Sparse coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
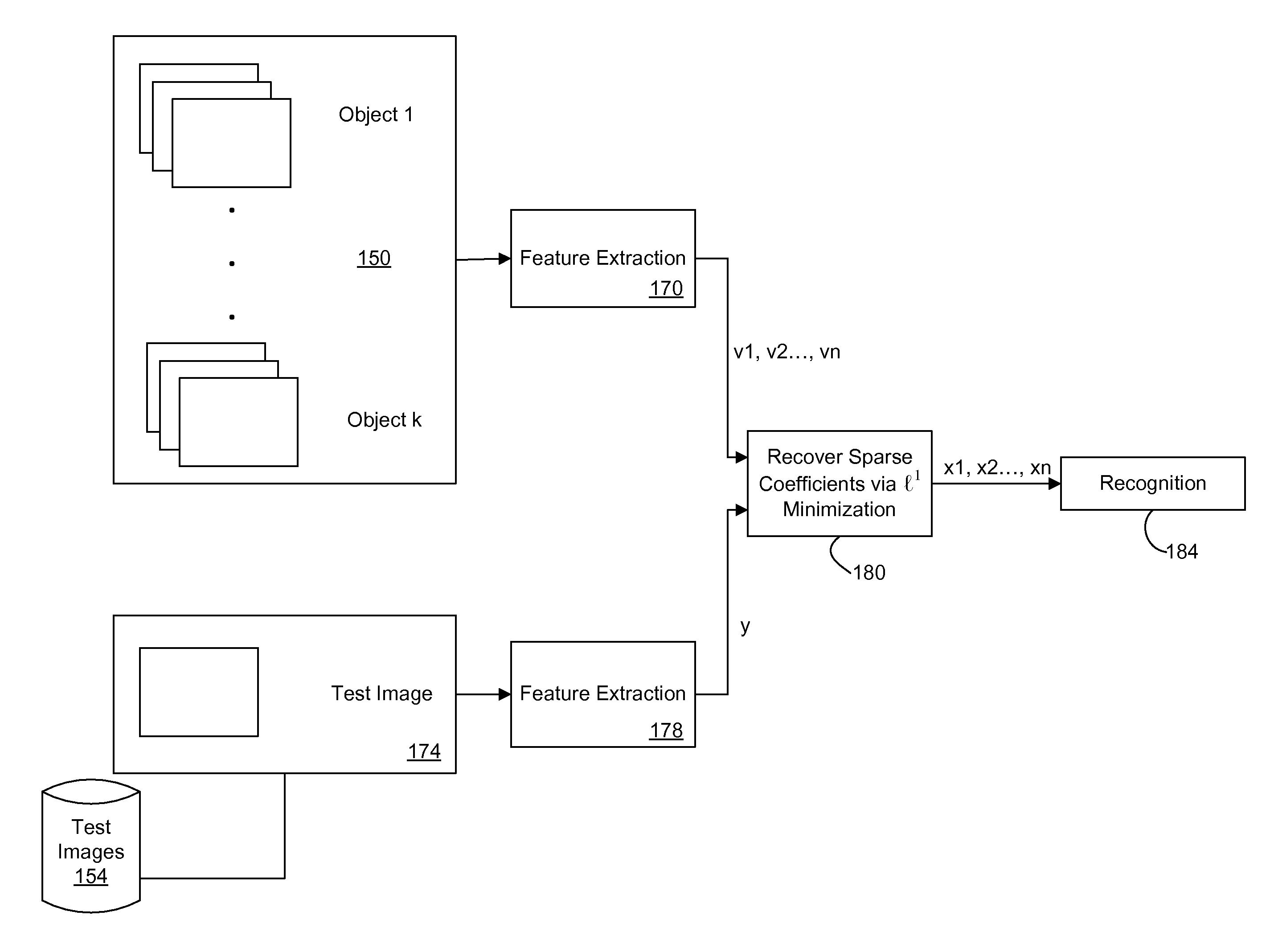
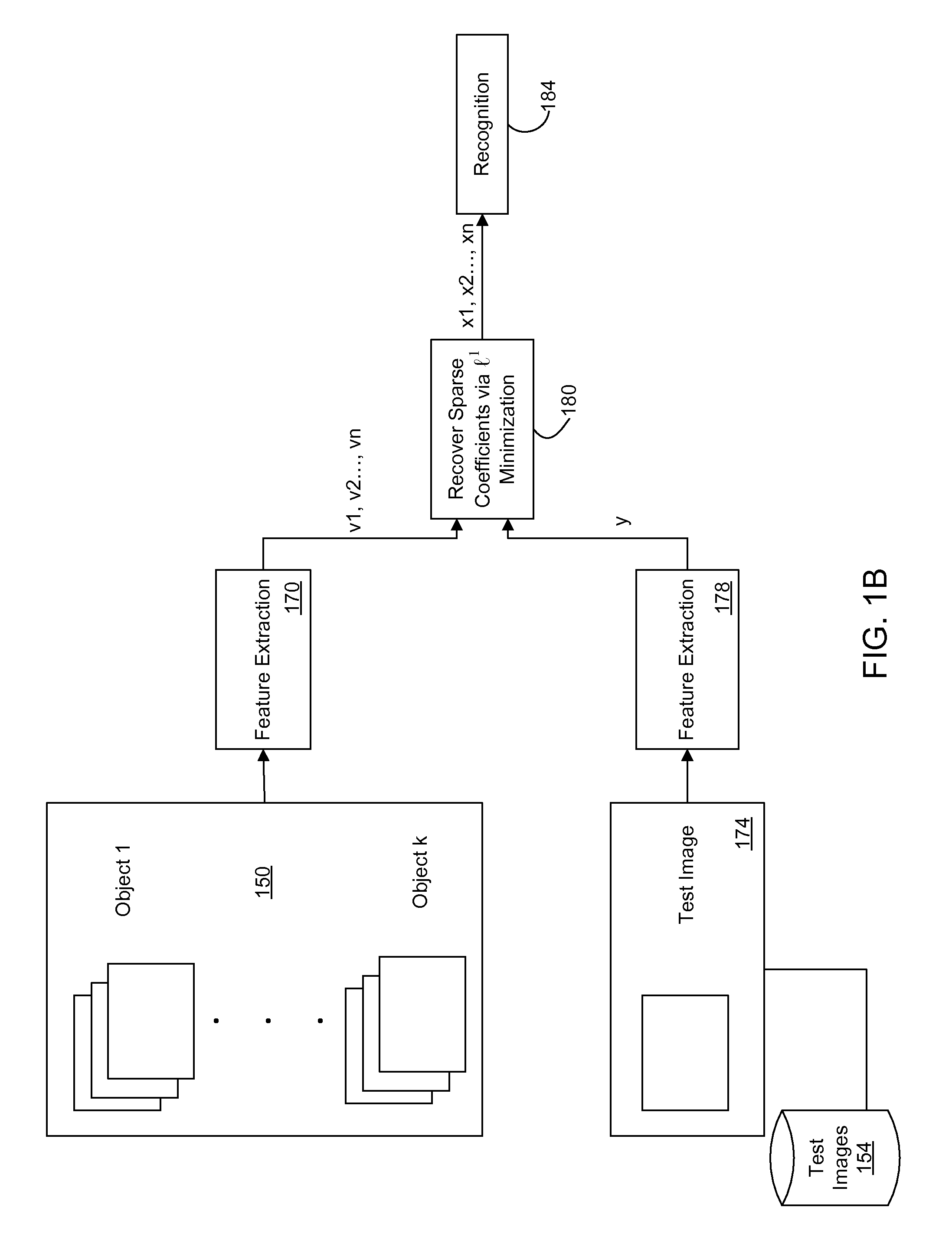
Recognition via high-dimensional data classification
ActiveUS20110064302A1Character and pattern recognitionSpeech recognitionPattern recognitionData file
A method is disclosed for recognition of high-dimensional data in the presence of occlusion, including: receiving a target data that includes an occlusion and is of an unknown class, wherein the target data includes a known object; sampling a plurality of training data files comprising a plurality of distinct classes of the same object as that of the target data; and identifying the class of the target data through linear superposition of the sampled training data files using l1 minimization, wherein a linear superposition with a sparsest number of coefficients is used to identify the class of the target data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
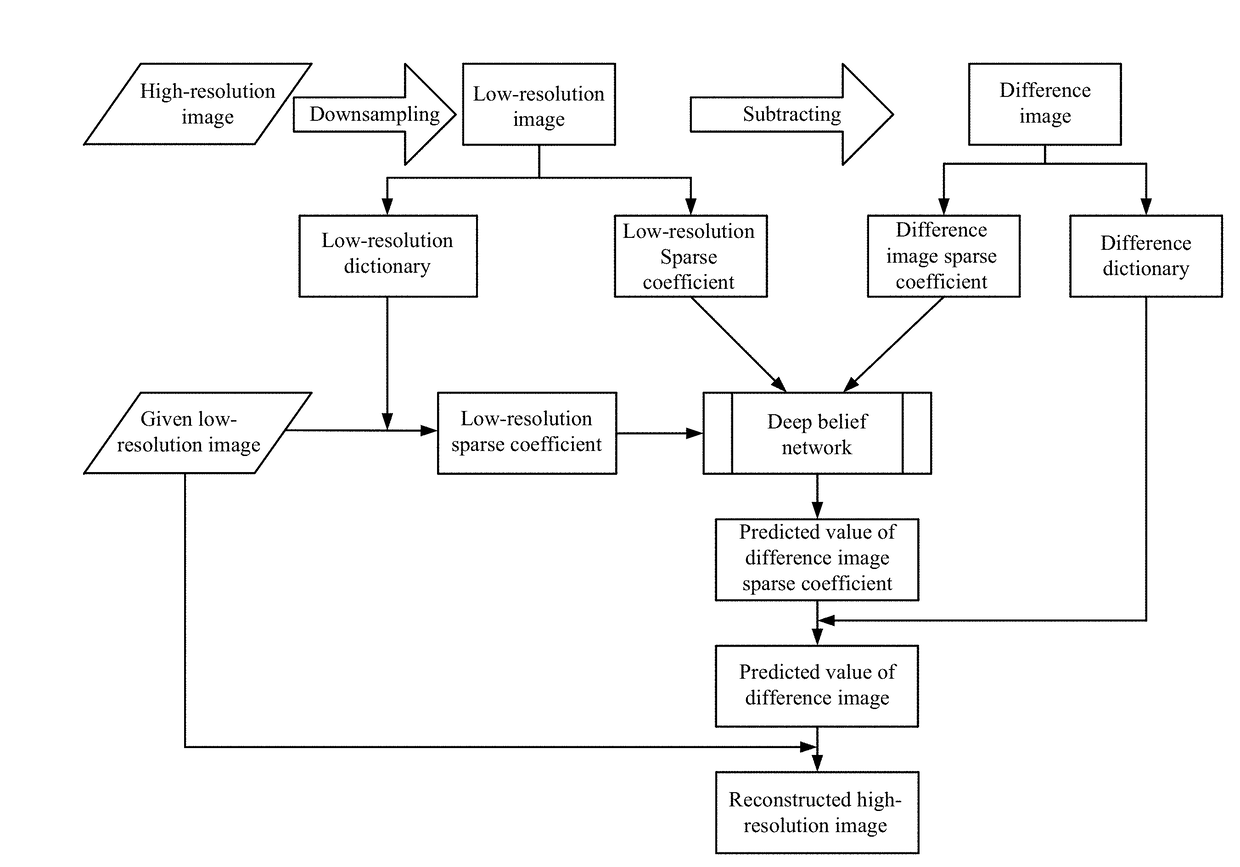
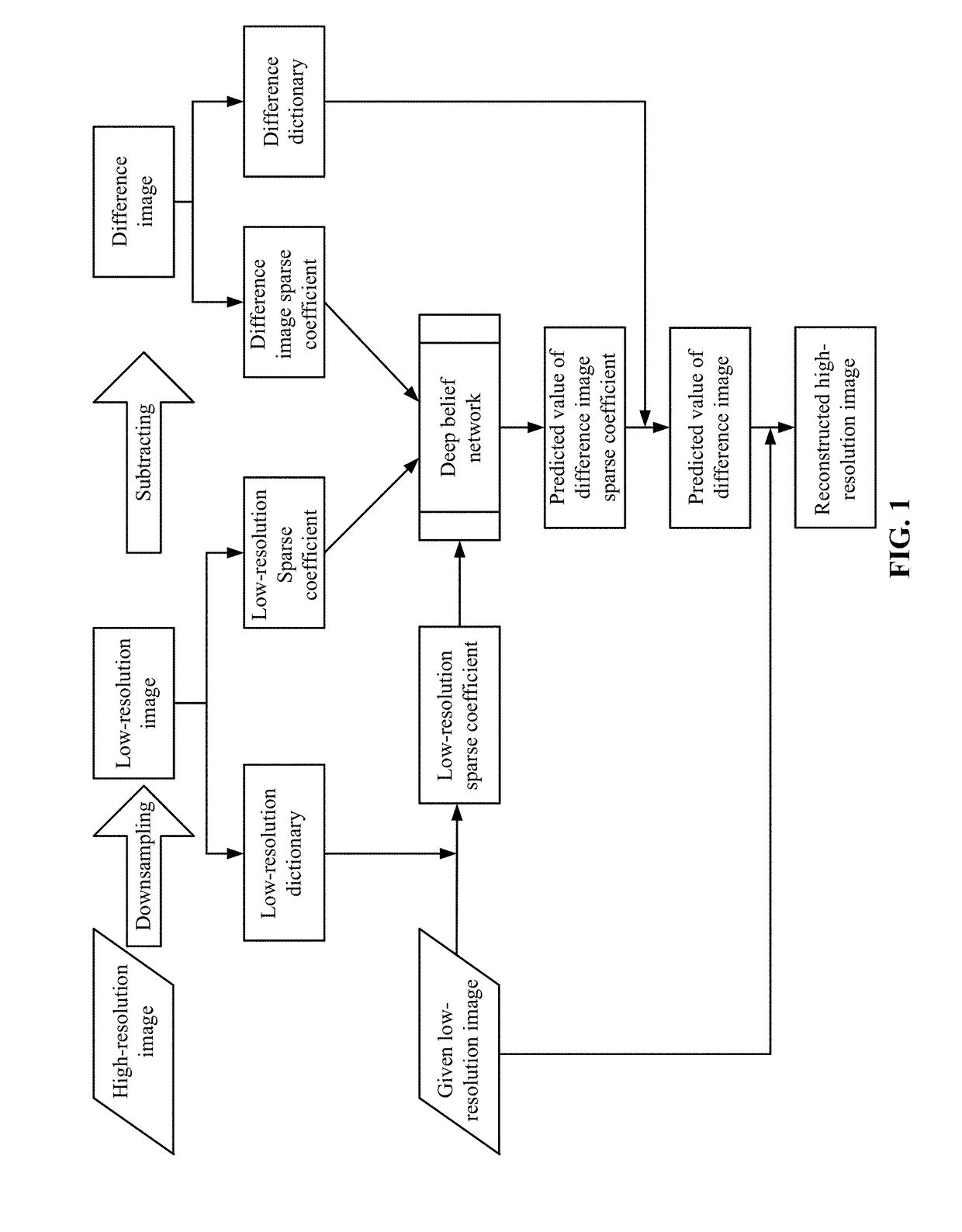
Method and system for reconstructing super-resolution image
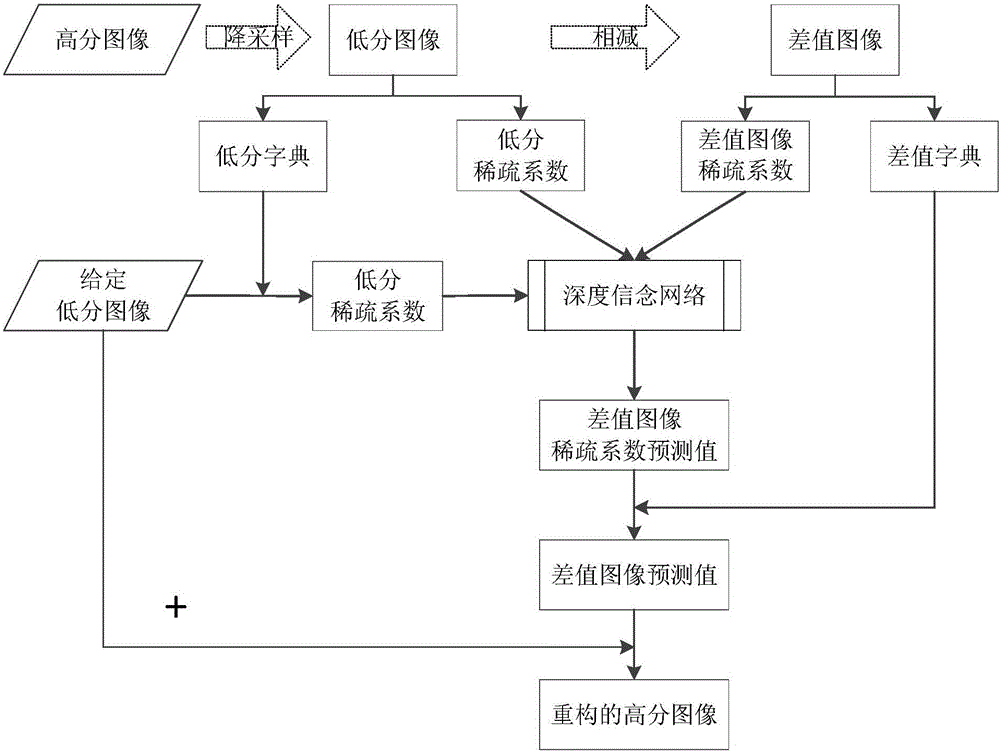
ActiveUS20170293825A1Minimize cost functionMinimize loss functionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTest sample
A method for reconstructing a super-resolution image, including: 1) reducing the resolution of an original high-resolution image to obtain an equal low-resolution image, respectively expressed as matrix forms yh and yl; 2) respectively conducting dictionary training on yl and yhl to obtain a low-resolution image dictionary Dl; 3) dividing the sparse representation coefficients αl and αhl into training sample coefficients αl_train and αhl_train and test sample coefficients αl_test and αhl_test; 4) constructing an L-layer deep learning network using a root-mean-square error as a cost function; 5) iteratively optimizing network parameters so as to minimize the cost function by using the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_train as the input of the deep learning network; 6) inputting the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_testas the test portion into the trained deep learning network in 5), outputting to obtain a predicted difference image sparse coefficient {circumflex over (α)}hl_test, computing an error between the {circumflex over (α)}hl_test.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
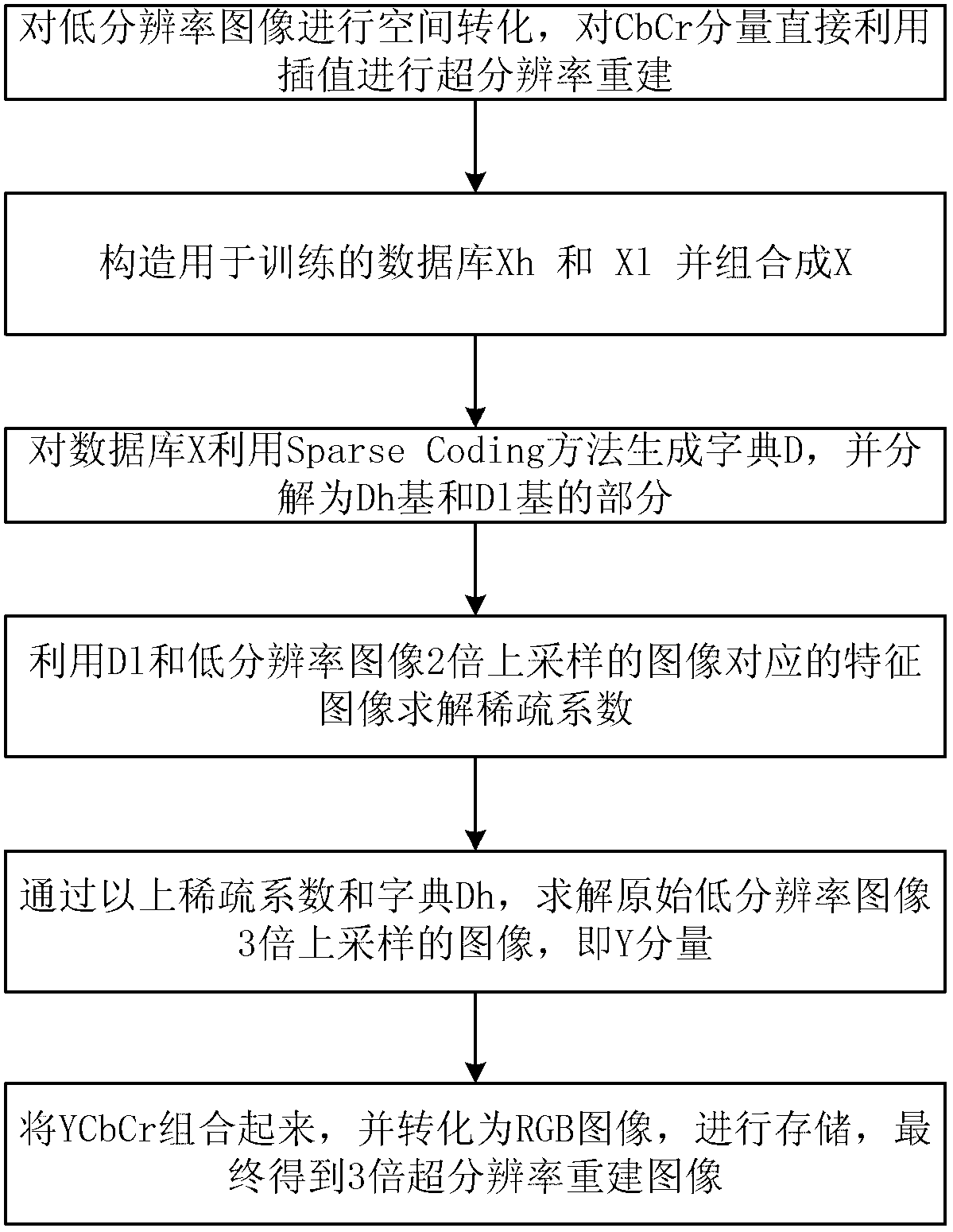
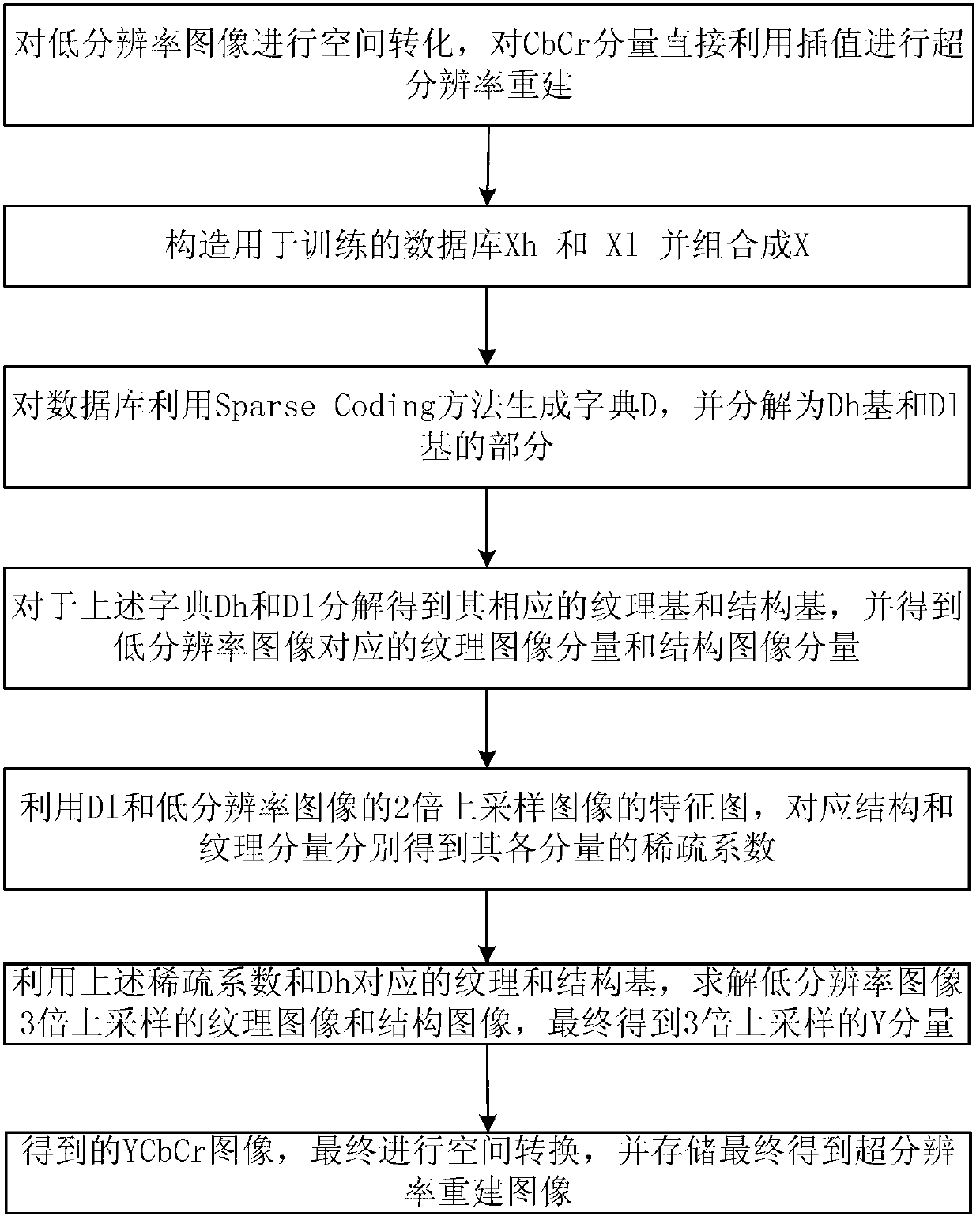
Super-resolution sparse representation method
ActiveCN102722865AHigh resolutionImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imagePattern recognition
Under the premise of no extraneous high-resolution image library, a super-resolution sparse representation method for acquiring a high-resolution image is provided. The method comprises the steps of: (1) carrying out space conversion on a given low-resolution color image to obtain the YCbCr space image of the color image, and reconstructing the constituents of Cb and Cr by using an interpolation method; (2) constructing a database used for training, namely, a high-resolution image block Xh and a low-resolution image block Xl, and combining the two image blocks into a database X; (3) generating a dictionary D from the database X by using a sparse coding method, decomposing the dictionary D into a high-resolution image dictionary Dh and a low-resolution image dictionary Dl; (4) solving a sparse coefficient by using the Dl and characteristic images corresponding to an image of upsampling the low-resolution image by 2 times; (5) solving an image of upsampling the original low-resolution image by 3 times through the sparse coefficient and the Dh; and (6) combining Y, Cb, and Cr to obtain a YCbCr image, and converting the YCbCr image into an RGB image and storing the RGB image to obtain the final super-resolution representation image.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
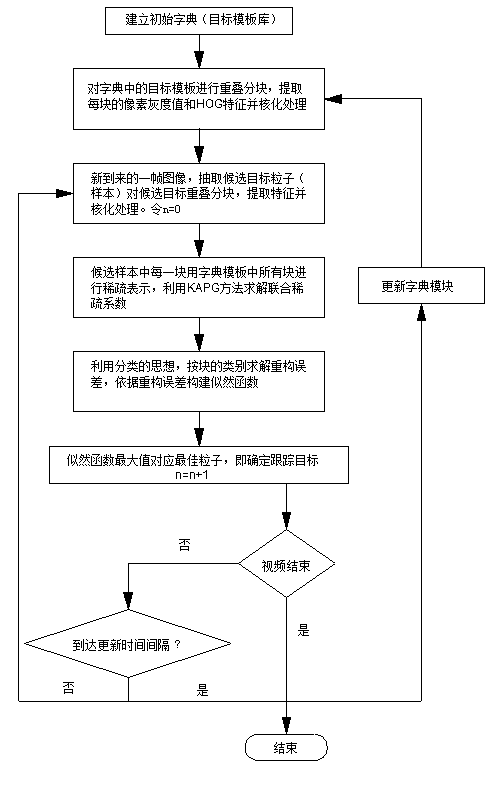
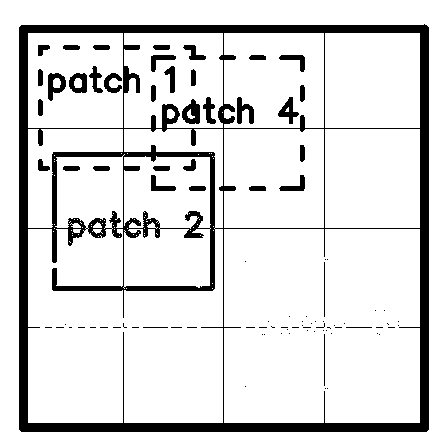
Multi-feature united sparse represented target tracking method
InactiveCN103295242AImprove robustnessAchieve precise trackingTelevision system detailsImage analysisMulti featureSparse coefficient
The invention provides a multi-feature united sparse represented target tracking method. The multi-feature united sparse represented target tracking method comprises building a primary dictionary; performing partitioning process on target modules; extracting candidate particles; extracting target characteristics; confirming the number of image characteristics and the number of block categories; performing nucleating process on the characteristics; performing block sparse representation on candidate samples in the dictionary; performing nucleus expansion; solving sparse problems; performing residual calculation on blocks; building likelihood functions; and updating template bases. The multi-feature united sparse represented target tracking method is analysis and improvement of utilized target characteristics and the traditional sparse coefficient solving method through a sparse encoding tracking device. According to the multi-feature united sparse represented target tracking method, stability of target tracking is maintained and accuracy of the target tracking device is improved under complex conditions that the illumination influence is large and the target is seriously shielded, and the accuracy of the algorithm and stability of the tracking are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
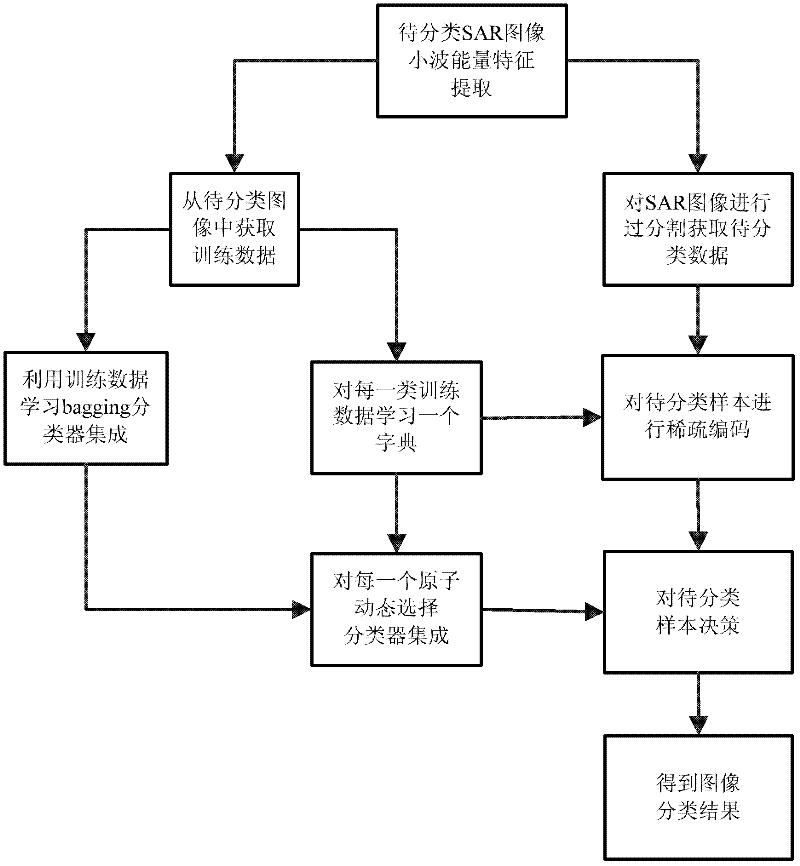
Sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image terrain classification method
ActiveCN102651073AExpress abilityImprove classification effectCharacter and pattern recognitionEnsemble selectionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image terrain classification method, which mainly solves the problem that the speed of the conventional dynamic ensemble selection algorithm and the conventional dynamic classifier selection algorithm for terrain classification in SAR images is low. The implementation process of the sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR image terrain classification method is as follows: (1) a wavelet energy feature is extracted from an SAR image to be classified; (2) training data is acquired from the SAR image to be classified; (3) the SAR image to be classified is regionalized to obtain data to be classified; (4) training samples are utilized to learn ensemble systems; (5) a dictionary is learnt for each class of training data, and a synthetic dictionary is obtained; (6) dynamic ensemble selection is carried out on each atom in the synthetic dictionary; (7) samples to be classified are sparsely coded; (8) the samples to be classified are marked according to a sparse coefficient and classifier ensembles corresponding to the atoms; (9) the marks of the samples to be classified are mapped onto pixels in the SAR image, so that a terrain classification result is obtained. The sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR image terrain classification method has the advantages of high speed and good classification effect, and can be used for SAR image target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Single-frame super-resolution reconstruction method and device based on sparse domain reconstruction
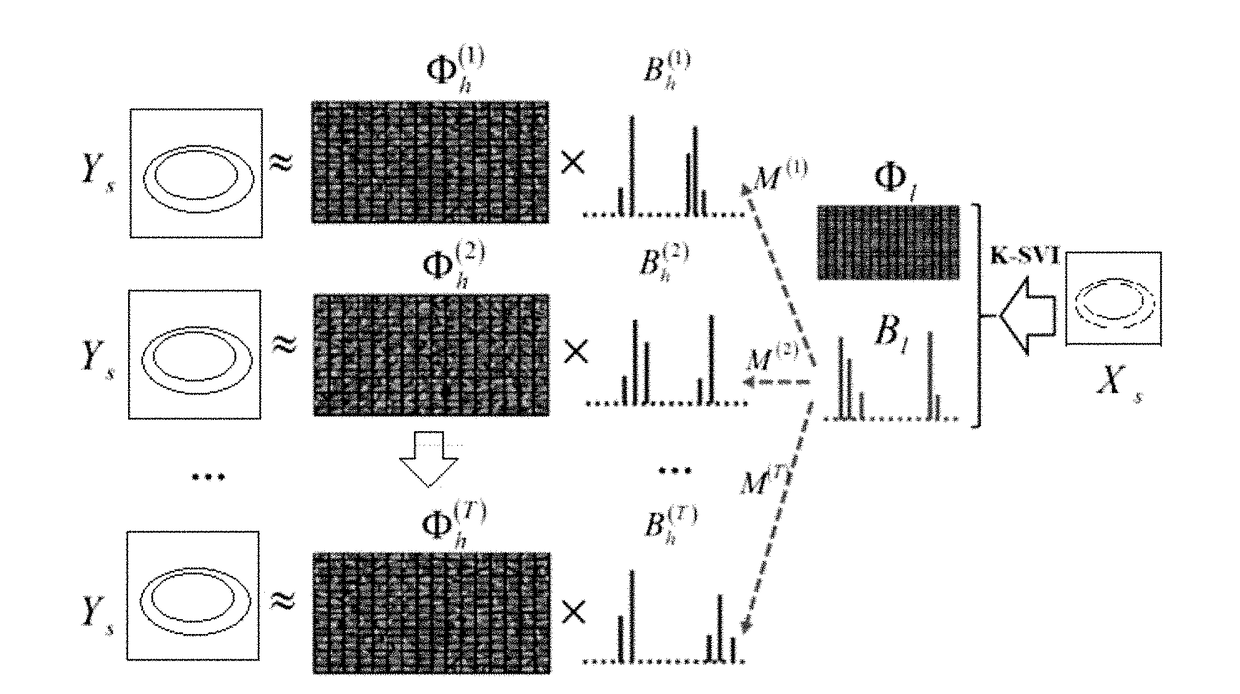
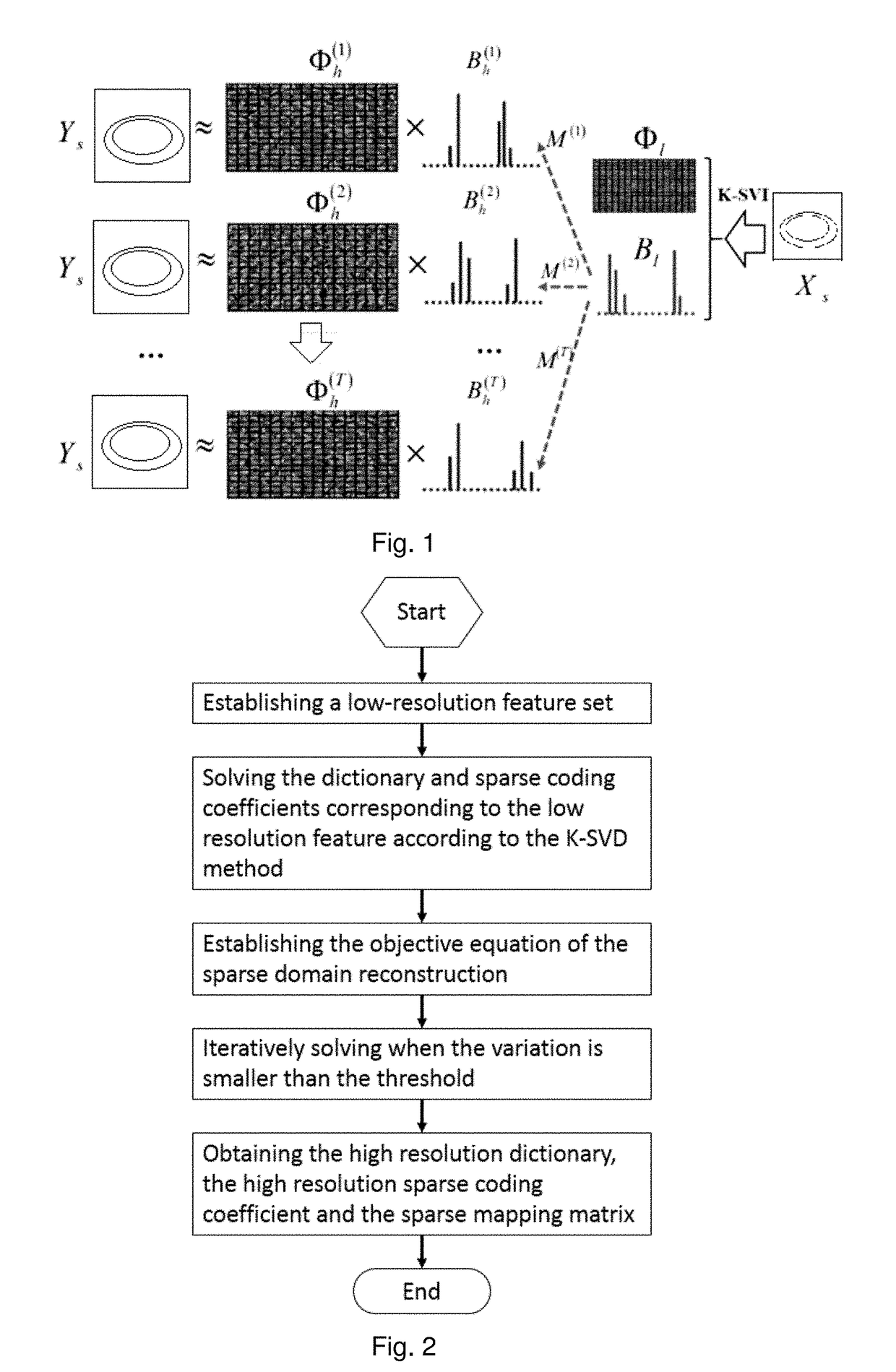
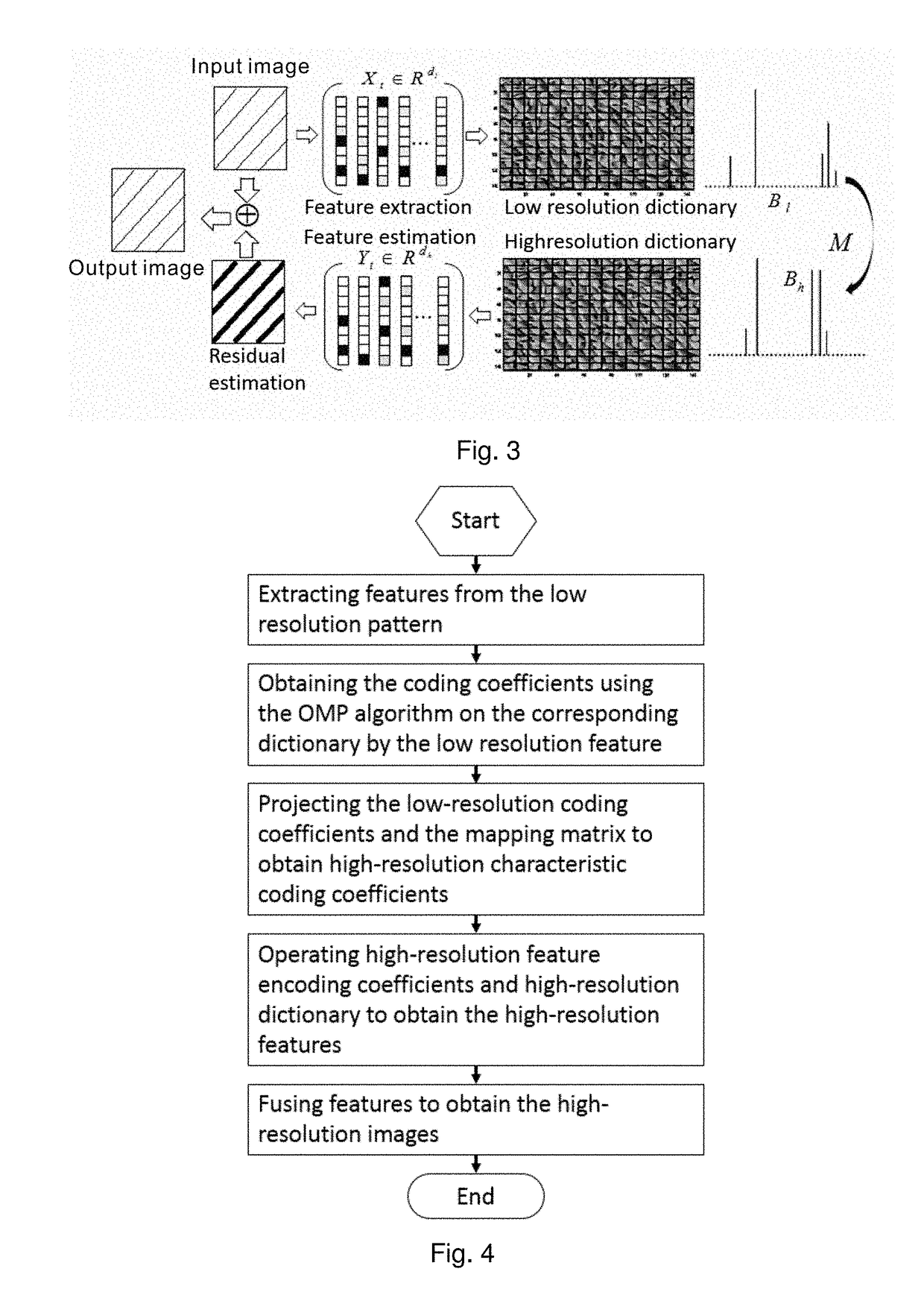
InactiveUS20180225807A1Improve mapping accuracyReduce the impactImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsImage resolution
The disclosure relates to a method and a device for single frame super resolution reconstruction based on sparse domain reconstruction, The disclosure mainly solves the technical problem in the prior art that the reconstructed image with high quality cannot be obtained by selecting the appropriate interpolation function according to the prior knowledge of the image. The disclosure adopts the first paradigm of the example mapping learning to train the mapping M of the low resolution feature on the sparse domain Bl to the high resolution feature on the sparse domain Bh and the mapping of the high resolution feature on the sparse domain Bh to the high resolution feature YS, equalizing the mapping error and the reconstruction error to the mapping operator M, the reconstructed high-resolution dictionary Φh and the reconstructed high-resolution sparse coefficient Bh, the better solution to the problem, can be used for graphics processing.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Matching dictionary and compressive sensing based radar range profile object identification method
The invention belongs to the technical field of automatic radar HRRP (high resolution range profile) object identification and particularly relates to compressive sensing based range profile object identification. Range profile object identification includes the steps: constructing a matching dictionary according to a radar echo model, selecting an appropriate test matrix for compressive sensing of a training sample range profile and to-be-identified test sample range profile which are known in type information so as to achieve data dimension reduction; then, subjecting data subjected to compressive sensing to sparse reconstruction so as to obtain sparse coefficients of the training sample range profile and the test sample range profile under the matching dictionary; utilizing the sparse coefficient of the training sample range profile as a pattern vector, and identifying the test sample range profile according to a nearest neighbor method. By the aid of compressive sensing based range profile object identification, since sparse coefficient characteristics of objects under the dictionary are extracted, redundancy is avoided, calculating amount is decreased and unnecessary noise is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
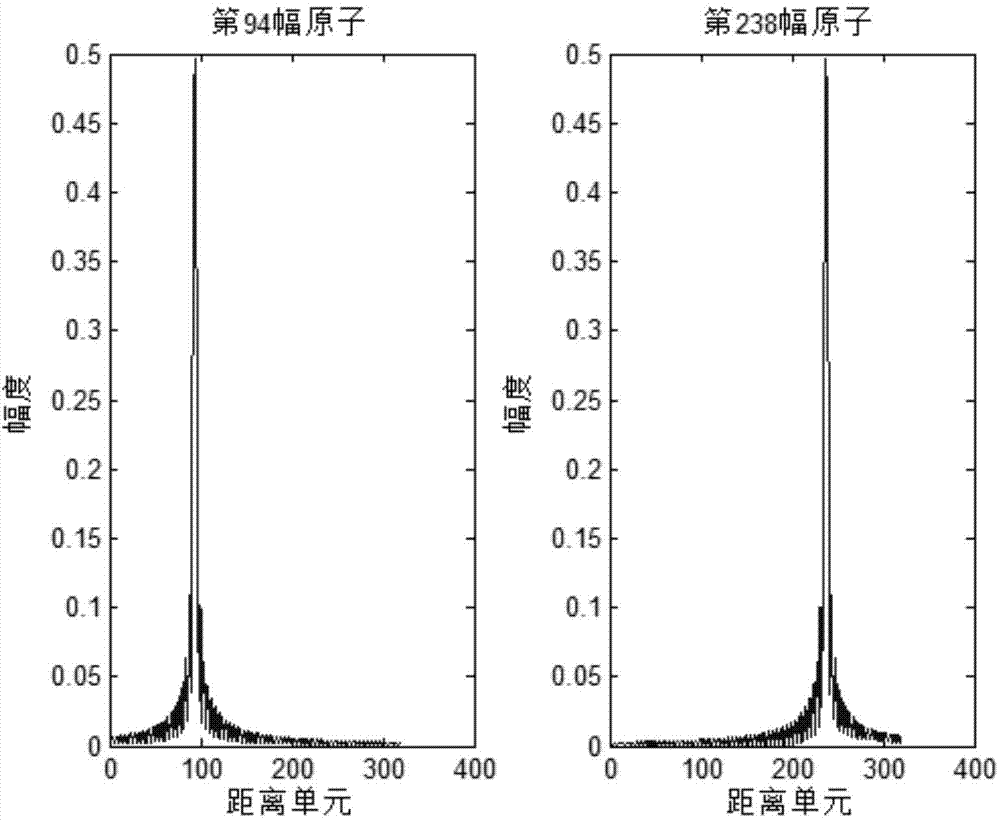
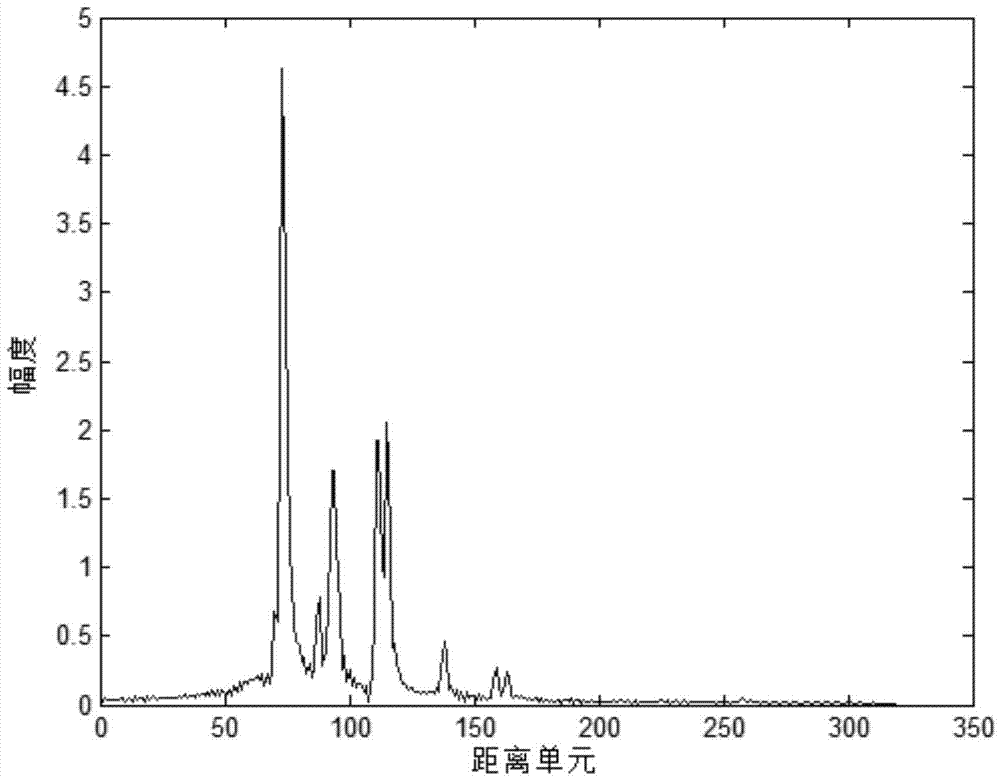
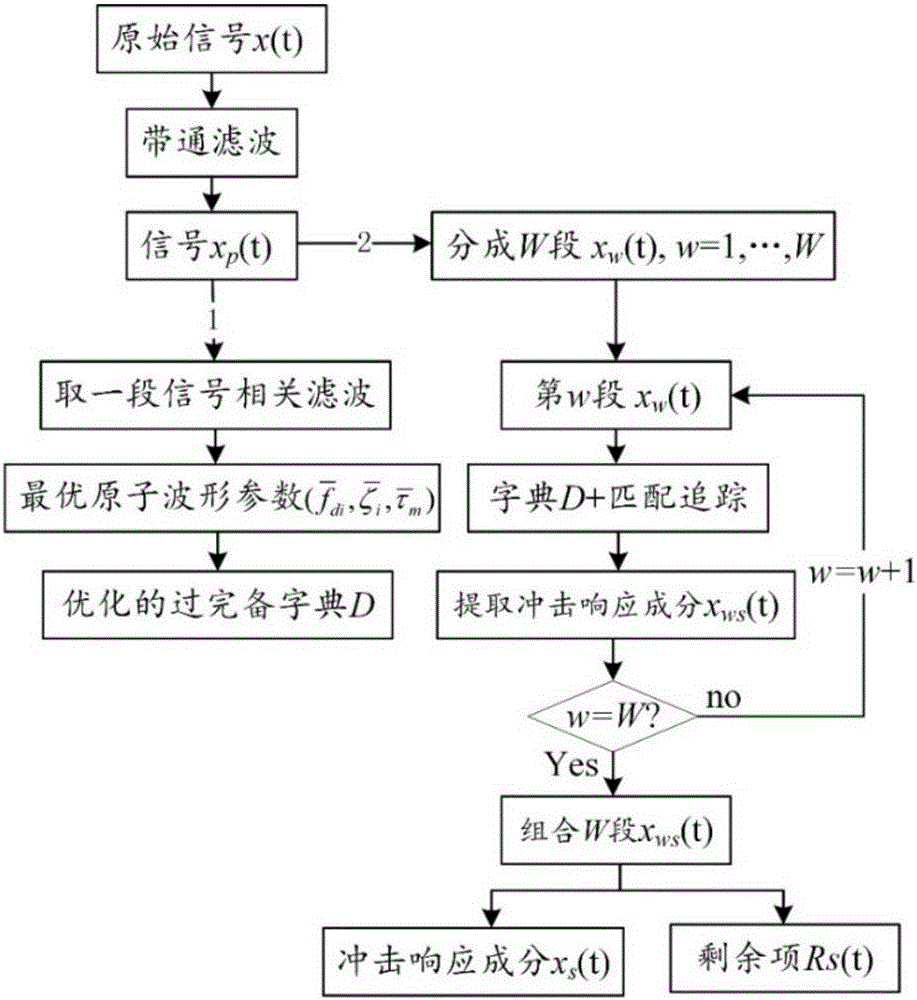
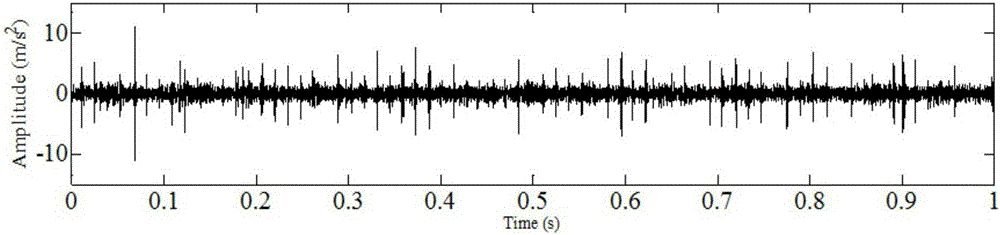
Rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on signal sparse representation theory
InactiveCN105241666AWide versatilityReduce pointsMachine bearings testingDamping ratioAdaptive method
The invention discloses a rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on the signal sparse representation theory, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing an over-complete dictionary representing local damages of a rolling bearing through employing a multi-stage inherent frequency unit impulse response function; recognizing the multi-stage inherent frequency and damping ratio of the rolling bearing and a sensor system from a vibration response signal through a related filtering method, and obtaining an optimized dictionary; solving a sparse coefficient through employing a matching tracking algorithm, and improving the solving speed and precision through reasonable segmentation; reconstructing an impact response signal of each segment, and obtaining the sparse representation of a fault feature signal; carrying out time domain index statistic characteristic analysis of time intervals of adjacent impact response components in a sparse signal, and diagnosing the type of a fault through combining a mean value and a mean square deviation value. The method has the advantages of an analytical method and an adaptive method, improves the precision of waveform features, and can iron out the defects that a conventional method based on Fourier transform is not suitable for rotating speed fluctuation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
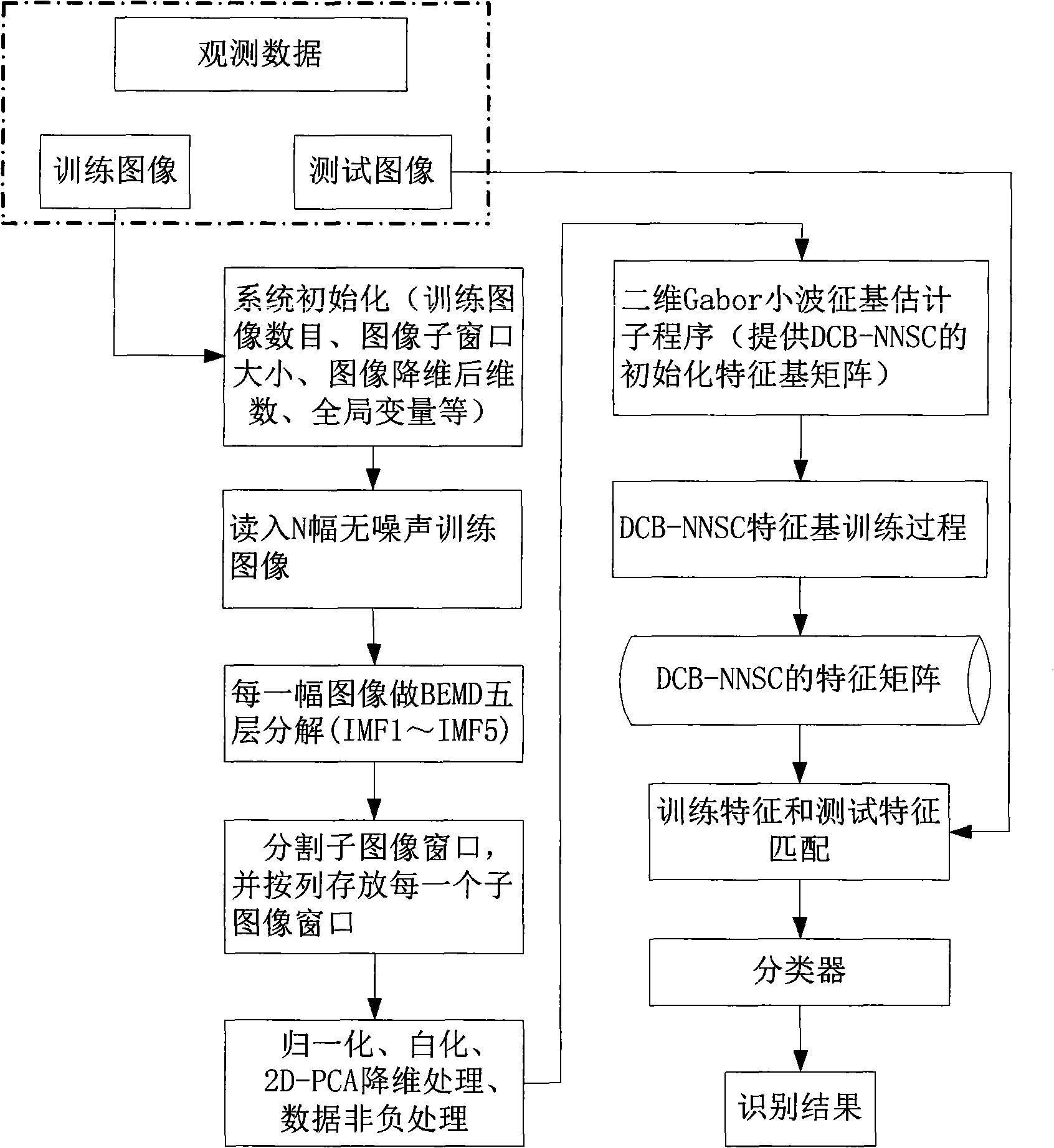
Method for extracting characteristic of natural image based on dispersion-constrained non-negative sparse coding
InactiveCN101866421AAggregation tightEfficient extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionNerve cells
The invention discloses a method for extracting the characteristic of a natural image based on dispersion-constrained non-negative sparse coding, which comprises the following steps of: partitioning an image into blocks, reducing dimensions by means of 2D-PCA, non-negative processing image data, initializing a wavelet characteristic base based on 2D-Gabor, defining the specific value between intra-class dispersion and extra-class dispersion of a sparsity coefficient, training a DCB-NNSC characteristic base, and image identifying based on the DCB-NNSC characteristic base, etc. The method has the advantages of not only being capable of imitating the receptive field characteristic of a V1 region nerve cell of a human eye primary vision system to effectively extract the local characteristic of the image; but also being capable of extracting the characteristic of the image with clearer directionality and edge characteristic compared with a standard non-negative sparse coding arithmetic; leading the intra-class data of the characteristic coefficient to be more closely polymerized together to increase an extra-class distance as much as possible with the least constraint of specific valuebetween the intra-class dispersion and the extra-class dispersion of the sparsity coefficient; and being capable of improving the identification performance in the image identification.
Owner:SUZHOU VOCATIONAL UNIV
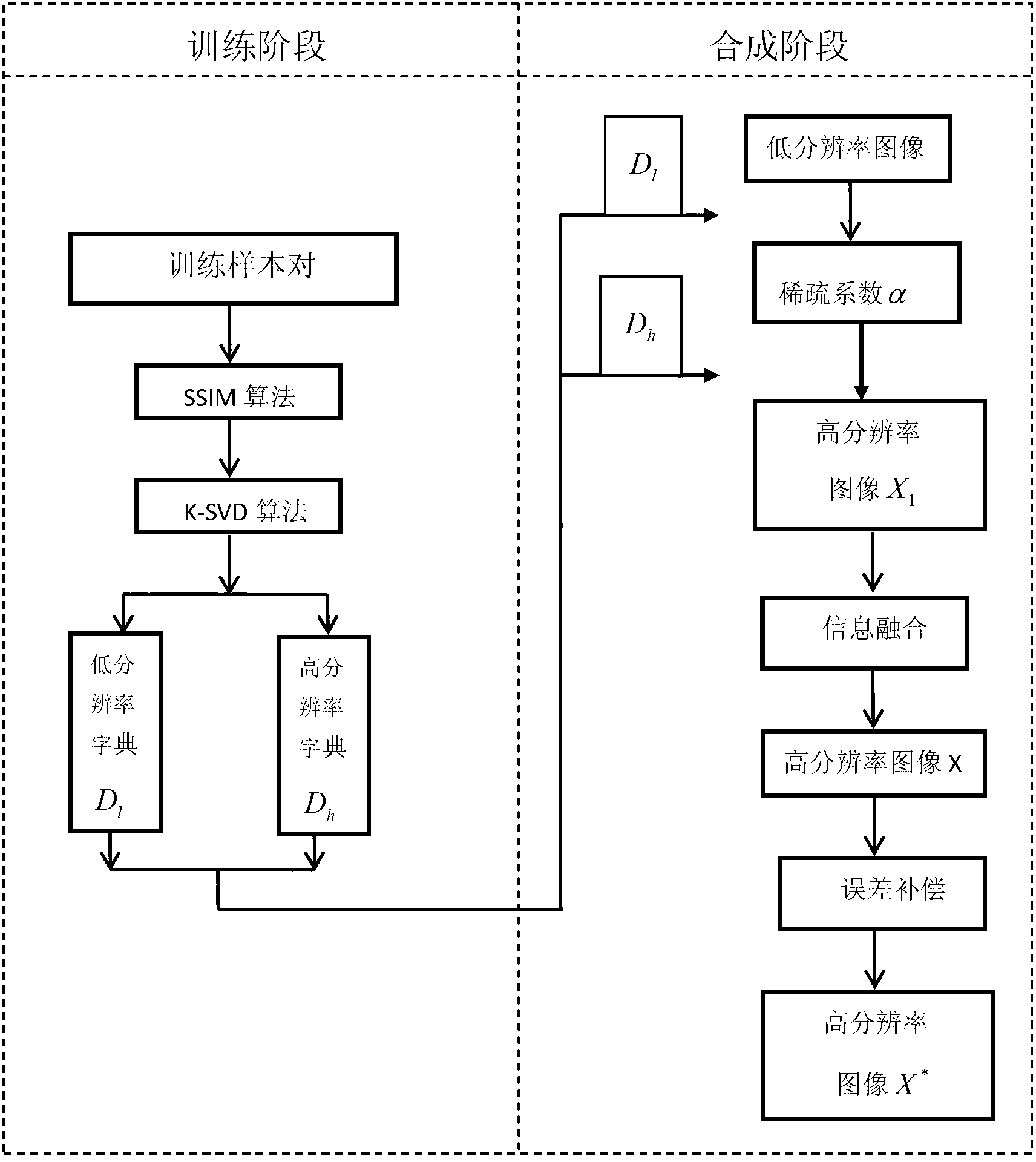
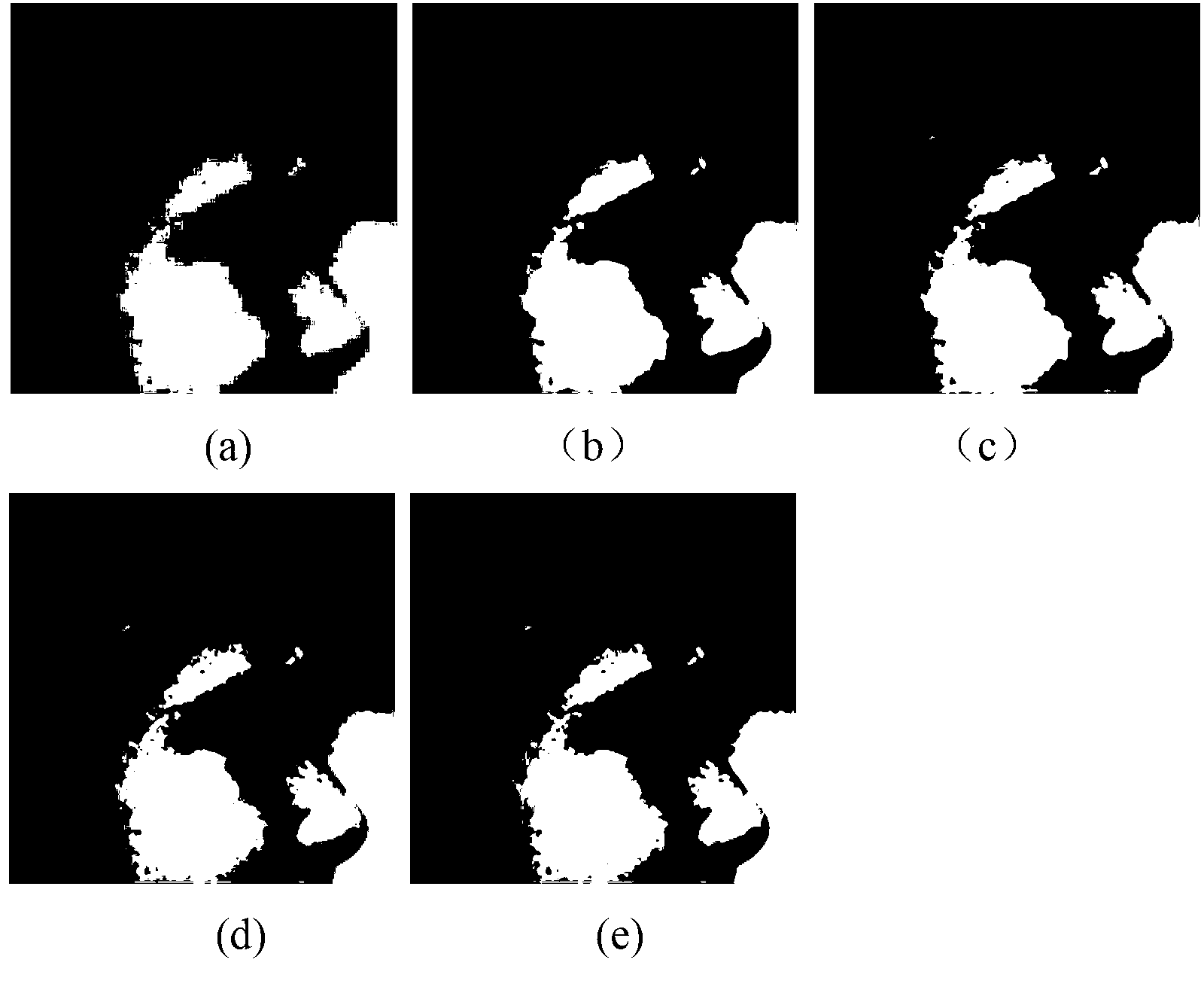
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure similarity
ActiveCN103077511ASparse coefficients are accurateReasonably high resolution dictionaryImage enhancementK singular value decompositionReconstruction method
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure similarity, mainly solving the problem that a reconstructed image based on the prior art has a fuzzy surface and a serious marginal sawtooth phenomenon. The image super-resolution reconstruction method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) acquiring a training sample pair; (2) learning a pair of high / low-resolution dictionaries by using structural similarity (SSIM) and K-SVD (K-Singular Value Decomposition) methods; (3) working out a sparse expression coefficient of an input low-resolution image block; (4) reestablishing a high-resolution image block Xi by using the high-resolution dictionaries and the sparse coefficient; (5) fusing the high-resolution image block Xi to obtain a high-resolution image X'I subjected to information fusion; (6) obtaining a high-resolution image X according to the high-resolution image X'I; and (7) carrying out high-frequency information enhancement on the high-resolution image X through error compensation to obtain a high-resolution image subjected to high-frequency information enhancement. A simulation experiment shows that the image super-resolution reconstruction method has the advantages of clear image surface and sharpened margin and can be used for image identification and target classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Sparse representation-based blind restoration method of broad image
ActiveCN102354395AReduced ringingPrevent morbidityImage enhancementPattern recognitionRestoration method
The invention relates to a sparse representation-based blind restoration method of a broad image, aiming at solving the technical problem that an image restored by the existing broad image blind restoration method is bad in effect. The method has the technical scheme that the broad image is sparsely represented by a fuzzy dictionary and a brilliant image is rebuilt by a brilliant dictionary to restore the image due to the characteristic that the sparse coefficient of the broad image under the fuzzy redundancy dictionary is coincident with that of the brilliant image under the brilliant redundancy dictionary. The illcondition during deconvolution can be avoided, the ringing effect at a high edge during image restoration can be reduced, and the image which is more brilliant can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
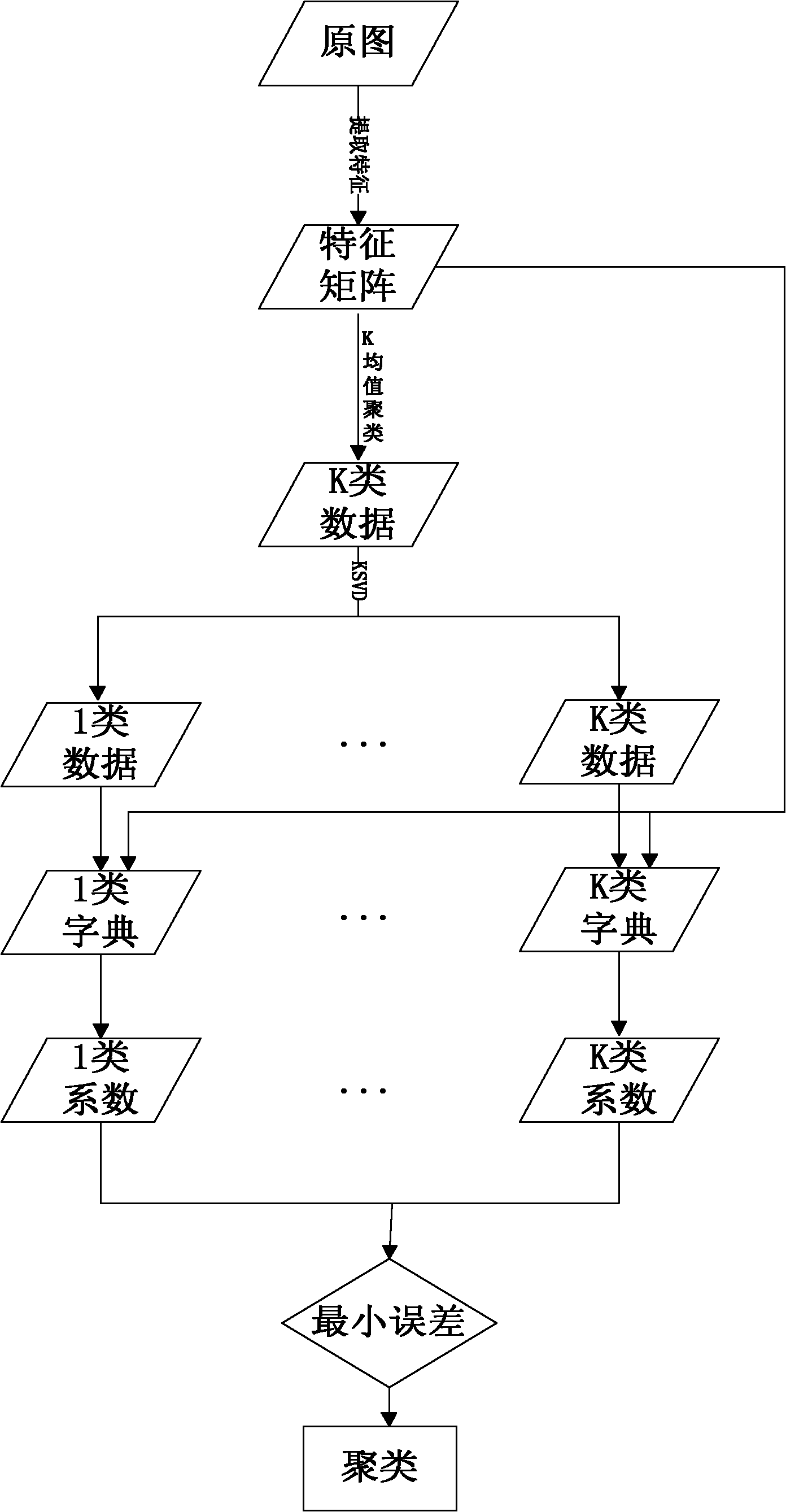
Method for segmenting images by utilizing sparse representation and dictionary learning
ActiveCN102096819AThe image segmentation effect is stableThe segmentation result is accurateCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningSingular value decomposition
The invention discloses a method for segmenting images by sparse representation and dictionary learning, and the method is mainly used for solving the problem of unstable division result under the condition of no sample label in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting an image to be segmented, and extracting the gray co-occurrence features and wavelet features of the image to be segmented; (2) carrying out K-means clustering on the image to be segmented by utilizing the features so as to obtain K-feature points; (3) acquiring K dictionaries corresponding to the K-feature points by an KSVD (K-clustering with singular value decomposition) method; (4) carrying out sparse decomposition on all the features of the K dictionaries by a BP (back propagation) algorithm to obtain a sparse coefficient matrix; (5) calculating the sparse representation error of each dictionary according to each feature point, and dividing the point corresponding to the feature to the type with the smallest dictionary error; and (6) repeating the step (5) until all the points have label values, and finishing final segmentation. Compared with the prior art, the method can be used for significantly improving the image stability and the segmentation performance, and can be used for target detection and background separation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Face identification method based on multiscale weber local descriptor and kernel group sparse representation
InactiveCN102722699AEfficient extractionImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionTest sampleDirection information
The invention discloses a face identification method based on multiscale weber local descriptor and kernel group sparse representation. The face identification method comprises the following steps: firstly normalizing the size of face images and smoothing the images by utilizing a gaussian filter; extracting differential excitation ingredients of the multiscale weber local descriptor of the images and extracting direction information by utilizing an Sobel operator; extracting the multiscale weber local descriptor of the face images according to the multiscale differential excitation and the direction information and mapping the multiscale weber local descriptor to a kernel space by utilizing a histogram intersection kernel; then with a kernel matrix obtained by a training sample as a sparse dictionary, calculating group sparse representation coefficients of a kernel vector obtained by a test sample; and finally reconstructing a multiscale weber local descriptor vector of the test sample according to the group sparse representation coefficients and distinguishing the test sample by utilizing the minimum reconstruction error. According to the face identification method, the multiscale weber local descriptor and the kernel group sparse representation algorithm are fused for face identification, and the identification accuracy rate is greatly improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Sparse representation and dictionary learning-based bearing fault classification method
ActiveCN107368809AEnhance expressive abilityQuality assuranceCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningDecomposition
The invention discloses a sparse representation and dictionary learning-based bearing fault classification method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preprocessing acquired history bearing vibration signals to obtain vibration signals under different working states, respectively constructing corresponding sub-dictionaries and combining the sub-dictionaries into a redundant dictionary; and online acquiring a bearing vibration signal by using a sensor, solving a sparse coefficient of the signal under the redundant dictionary by using a generalized orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm, and classifying the vibration signal through a reconstruction error so as to identify the bearing working state. According to the method, relatively good classification effect can be obtained, the dictionary training process can be accelerated and the ability, of being adapted to target signals, of the dictionary is improved, so that the method is capable of realizing the sparse decomposition of complex vibration signals more efficiently and is used for fault identification.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
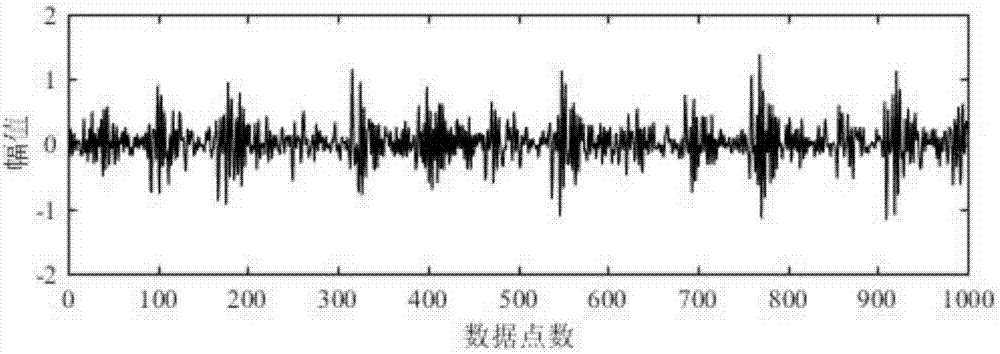
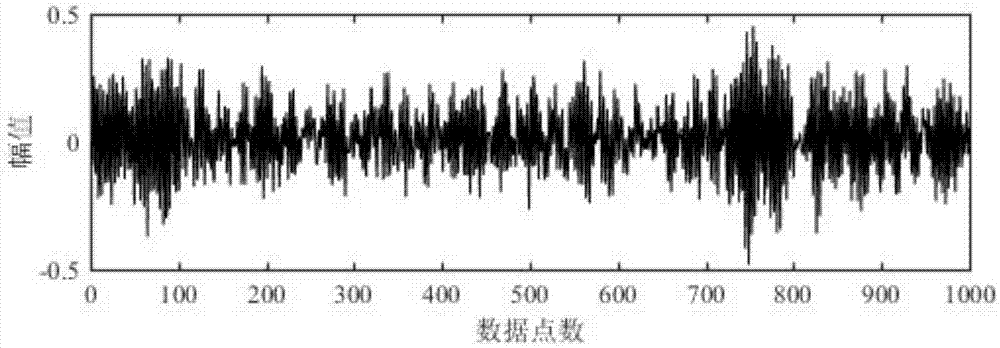
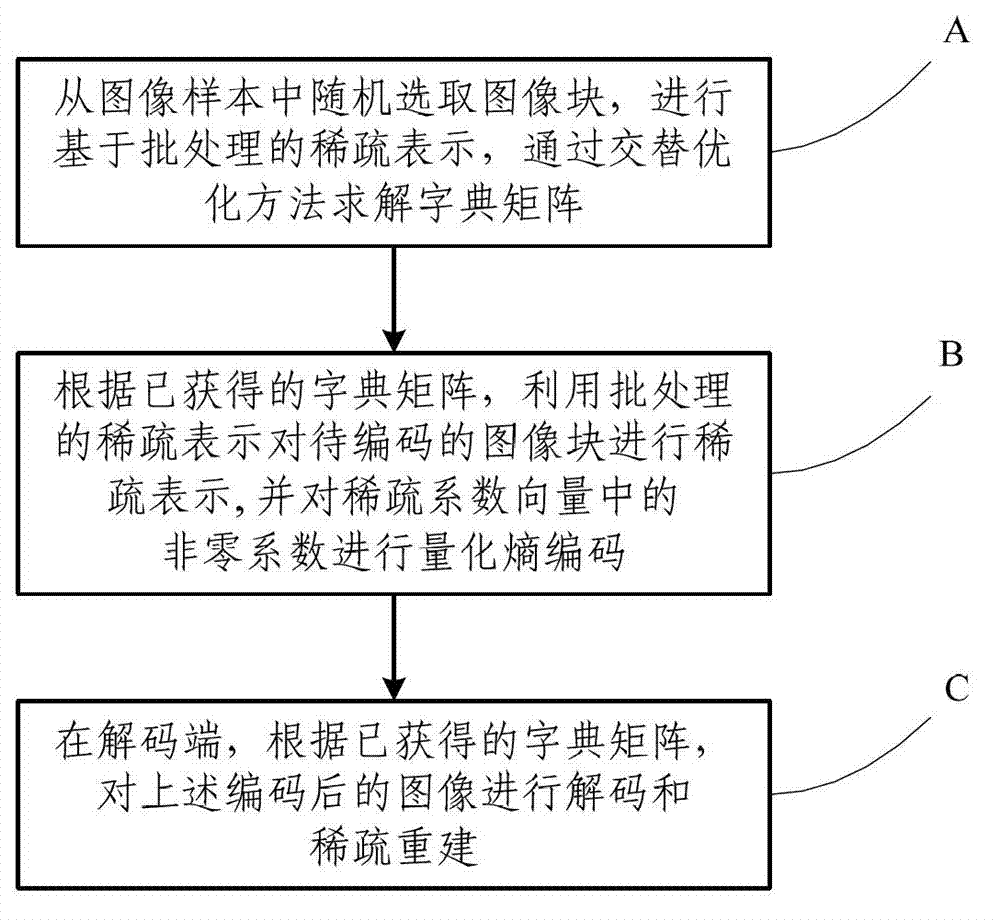
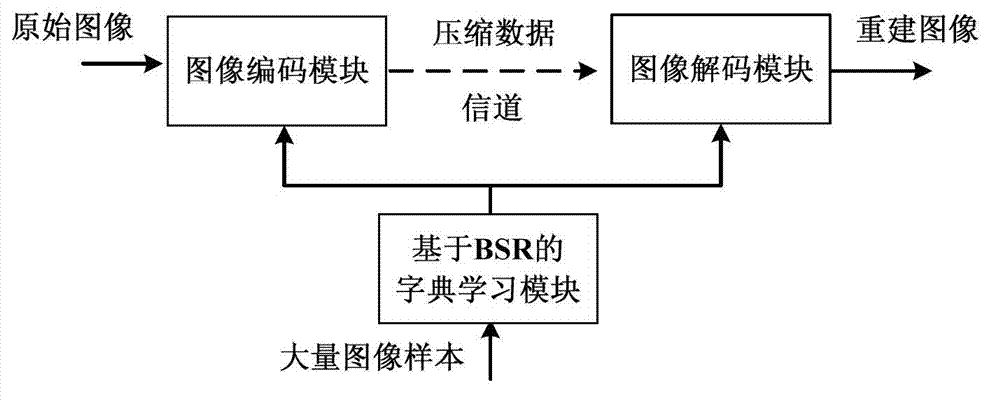
Image coding method and system based on dictionary learning
InactiveCN103489203AIn line with subjective feelingsExcellent rate-distortion compression performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingDictionary learningNonzero coefficients
The invention discloses an image coding method and system based on dictionary learning. The method comprises the steps that image blocks are randomly selected from an image sample to carry out sparse representation based on batch processing, and a dictionary matrix is solved through an alternative optimization method; according to the obtained dictionary matrix, the sparse representation processed in batch is utilized to carry out sparse representation on the image blocks to be coded, and quantification entropy coding is carried out on nonzero coefficients in sparse coefficient vectors; decoding and sparse reconstruction are carried out on the coded image at a decoding end according to the obtained dictionary matrix. The system comprises a dictionary learning module of sparse representation based on batch processing, an image coding module and an image decoding module. According to the method and system, the problem that the training sample in dictionary learning is large in scale is resolved, meanwhile reconstruction errors of the image sample are reduced, and rate-distortion performance of image compression is significantly promoted.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Radar Target Parameter Estimation Method Based on AIC Compressed Information Acquisition and FBMP
ActiveCN102288951AHigh precisionReduce time costWave based measurement systemsEstimation methodsRadar imaging
The invention discloses a radar target parameter estimation method based on AIC (automatic information center) compression information acquisition and FBMP (fast Bayesian matching pursuit), which mainly solves the problem that the existing compression sensing radar target parameter estimation method cannot simultaneously improve estimation precision and reduce time cost. The method comprises the implementation steps that low-dimension compression observation of radar echo signals is realized by AIC; a time shift sparse dictionary is designed on the basis of transmitted signals, so the radar echo signals can obtain sparse presentation on the time shift sparse dictionary; observation matrices needed in a compression sensing reconstruction theory are constructed according to AIC sampling sequences and the time shift sparse dictionary; sparse coefficient vectors of the radar echo signals are solved by a fast Bayesian matching pursuit FBMP algorithm so as to realize radar target parameterestimation. The invention has advantages that the number of non-zero coefficients in the sparse coefficient vectors of signals to be reconstructed is determined adaptively, the reconstruction precision can be improved when the time cost is reduced, and the method can be used for radar target recognition and radar imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Joint sparse representation and deep learning-based image super resolution method and system
ActiveCN105931179AHigh precisionHigh super-resolution reconstruction accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage resolution
The invention relates to a joint sparse representation and deep learning-based image super resolution method and a joint sparse representation and deep learning-based image super resolution system. The method includes the following steps that: resolution reduction is performed on an original high-resolution image, so that a low-resolution image of which the size is the same as the original high-resolution image, and the difference value part of the original high-resolution image and the low-resolution image is obtained; a low-resolution image dictionary, a difference value image dictionary and corresponding sparse representation coefficients are obtained; a deep learning network with root-mean-square error adopted as a cost function is constructed, and network parameters are optimized iteratively, so that the cost function can be minimum, a trained deep learning network can be obtained; and the sparse coefficient of the low-resolution image, which is adopted as a test part, is inputted into the deep learning network, when error is smaller than a given threshold value, a corresponding high-resolution image can be reconstructed according to the low-resolution image of which the resolution is to be improved. According to the method and system of the invention, defects of an existing method according to which a joint dictionary training mode is utilized to make a high-resolution image and a low-resolution image share a sparse representation coefficient can be eliminated, and deep learning is utilized to fully learn the mapping relationship between the low-resolution image sparse representation coefficient and the difference value image sparse representation coefficient, and therefore, a high-resolution reconstruction result with higher precision can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
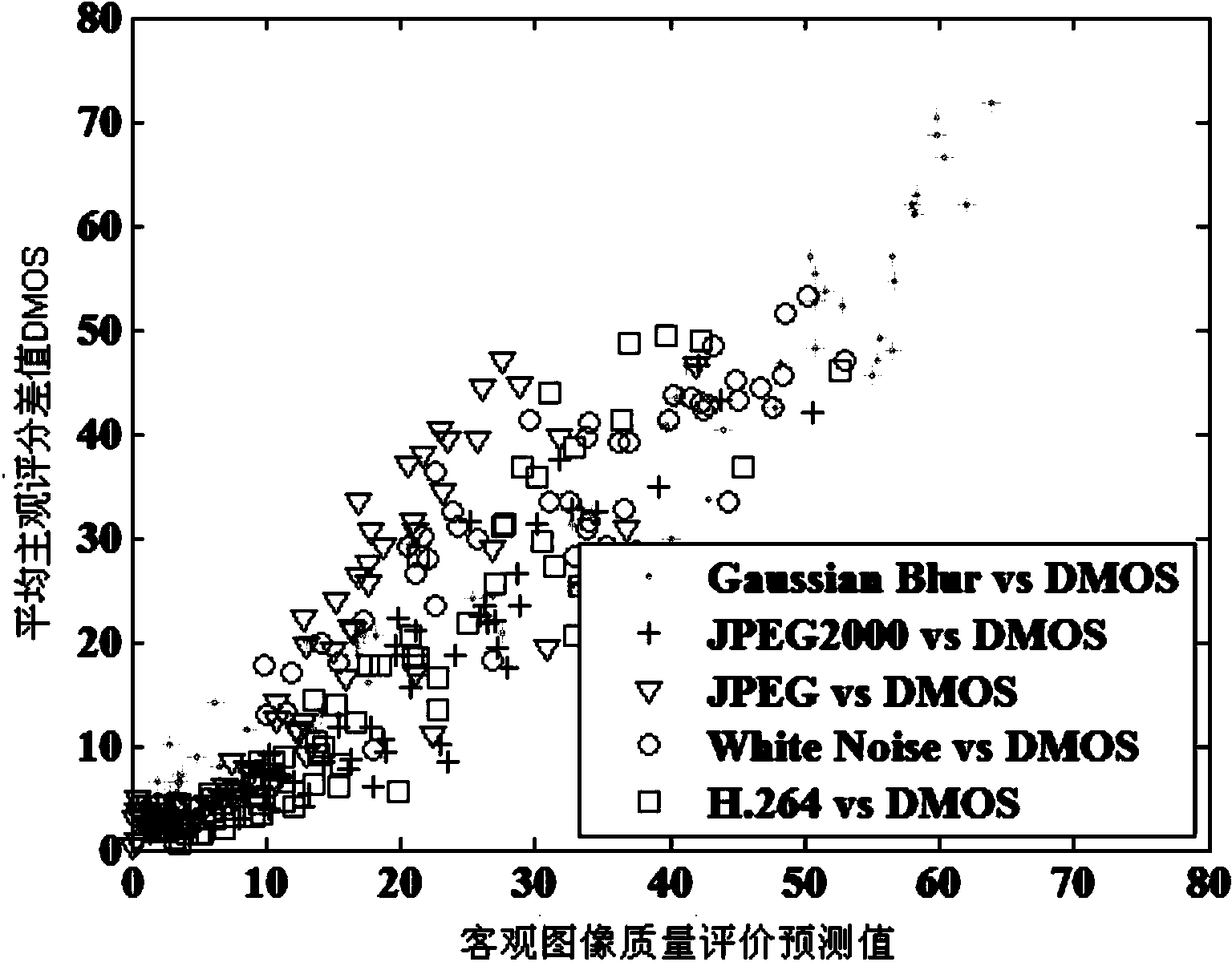
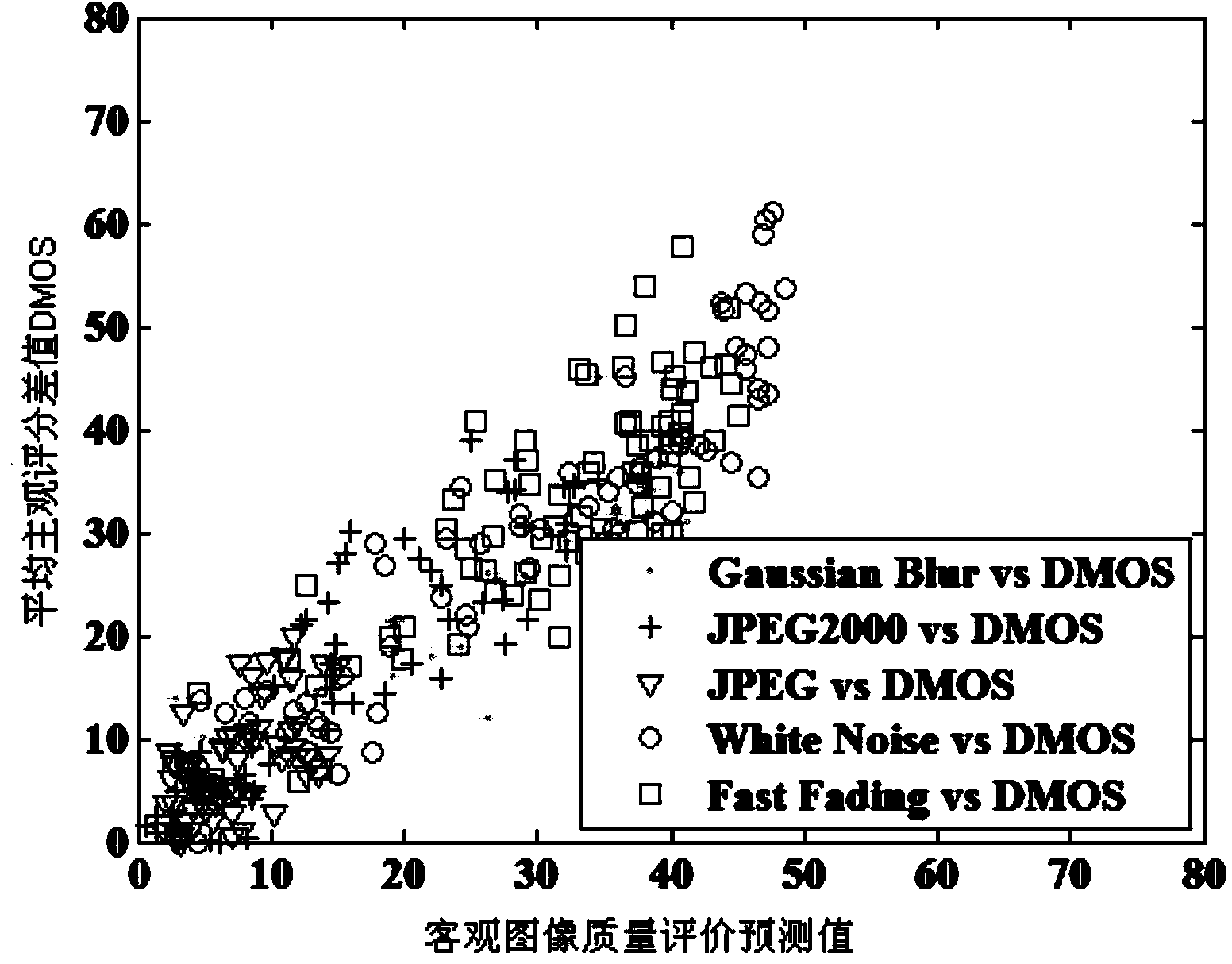
Three-dimensional image quality objective evaluation method based on sparse representation
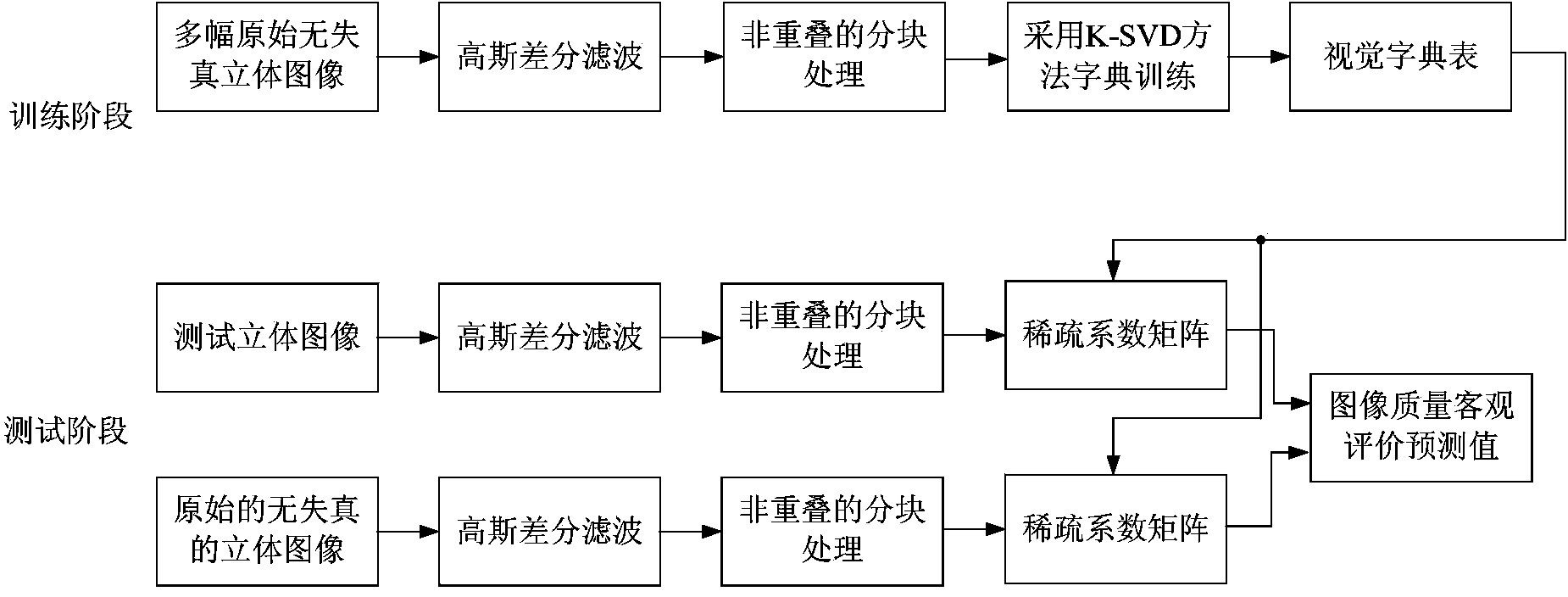
ActiveCN104036501AAvoid learning the training processReduce computational complexityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionViewpoints
The invention discloses a three-dimensional image quality objective evaluation method based on sparse representation. According to the method, in a training stage, left viewpoint images of a plurality of original undistorted three-dimensional images are selected for forming a training image set, Gaussian difference filtering is adopted for carrying out filtering on each image in the training image set to obtain filtered images in different scales, and in addition, a K-SVD method is adopted for carrying out dictionary training operation on a set formed by all sub blocks in all of the filtered images in different scales for constructing a visual dictionary table; and in a test stage, the Gaussian difference filtering is performed on any one tested three-dimensional image and the original undistorted three-dimensional image to obtain filtered images in different scales, then, the filtered images in different scales is subjected to non-overlapped partition processing, and an image quality objective evaluation prediction value of the tested images is obtained. The three-dimensional image quality objective evaluation method has the advantages that a complicated machine learning training process is not needed in the training stage; and the in the test stage, the image quality objective evaluation prediction value only needs to be calculated through a sparse coefficient matrix, and in addition, the consistency with the subjective evaluation value is better.
Owner:创客帮(山东)科技服务有限公司
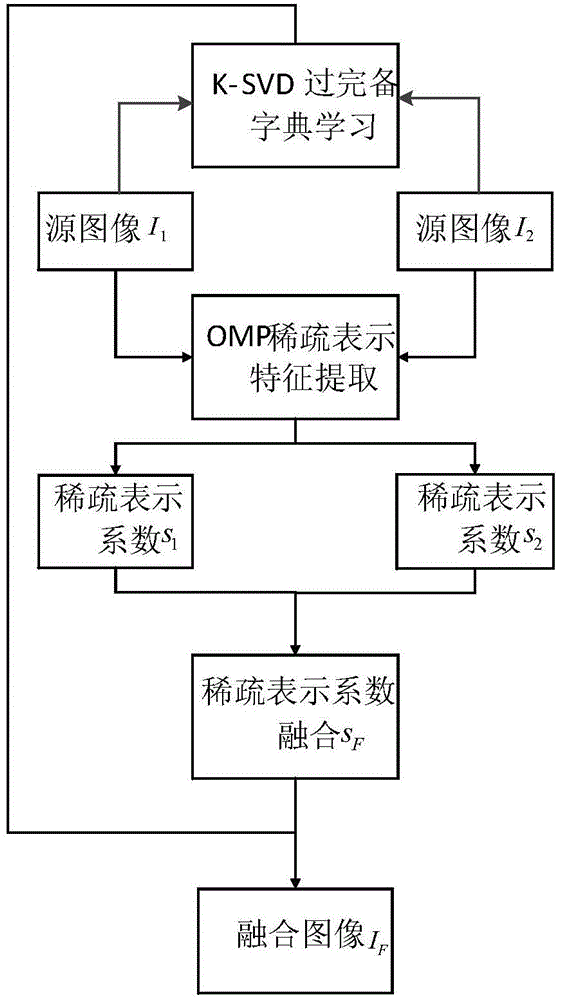
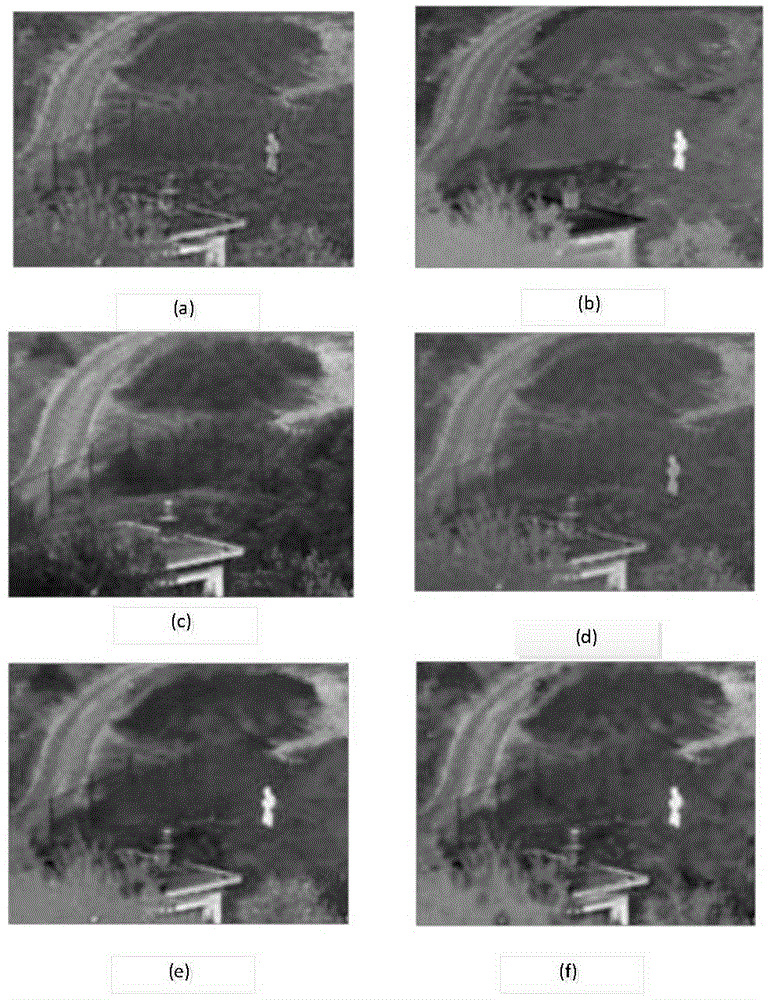
Infrared and visible image fusion method based on sparse representation
The invention provides an infrared and visible image fusion method based on sparse representation. The fusion method includes the steps that images are chunked, a dictionary is trained, sparse coefficients of the two source images are respectively solved, the sparse coefficient of a fused image is obtained through a module value maximax return rule, and the fusion result image is obtained through reconstruction. The fusion method can adapt to the own characteristics of the infrared and visible images, and compared with a traditional method, the extracted representation coefficients of the source images are better in sparsity and characteristic retentivity and can reflect substantive characteristics and internal structures of signals better, so that the fusion effect of the infrared and visible images is effectively improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
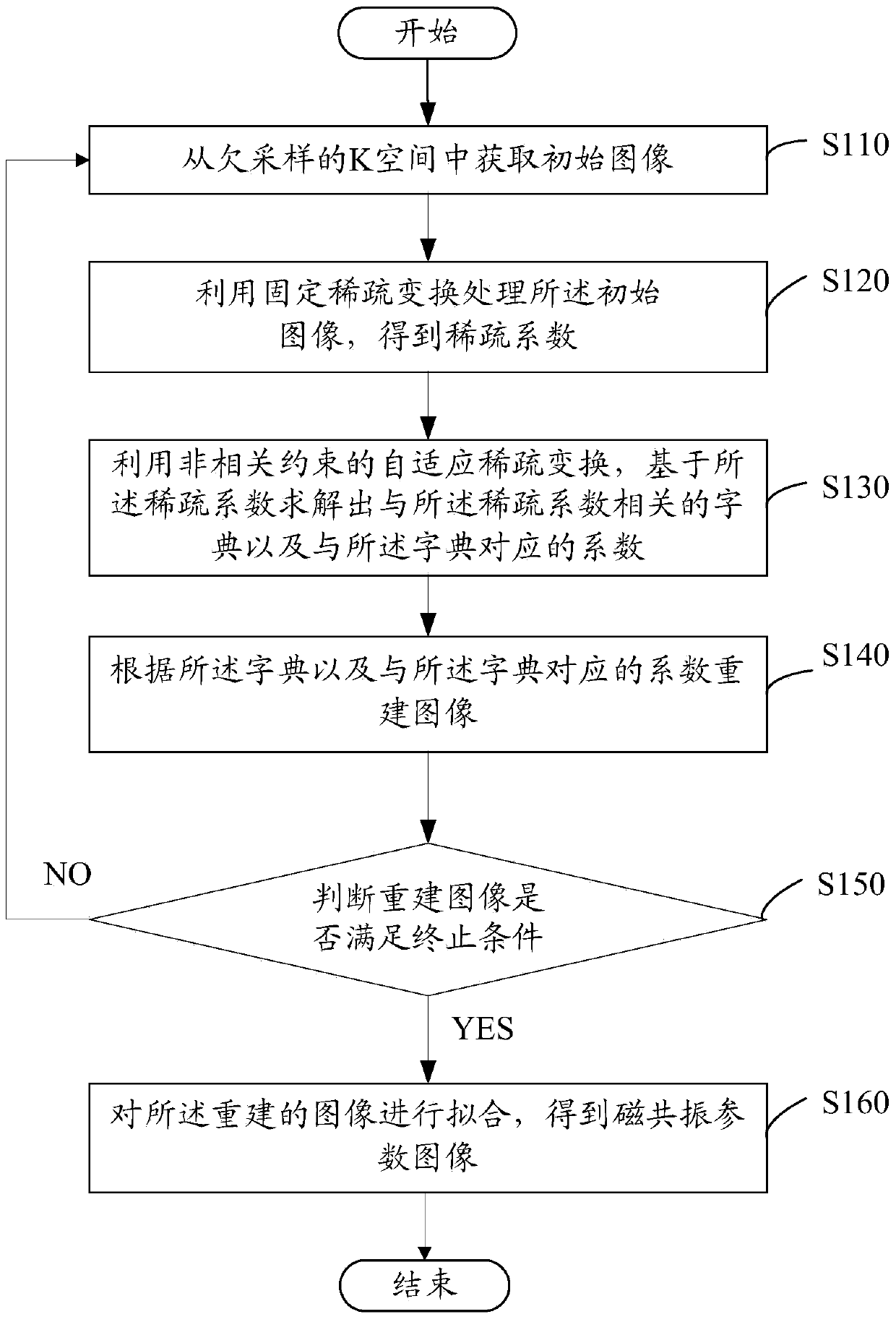
Magnetic-resonance fast imaging method and system thereof
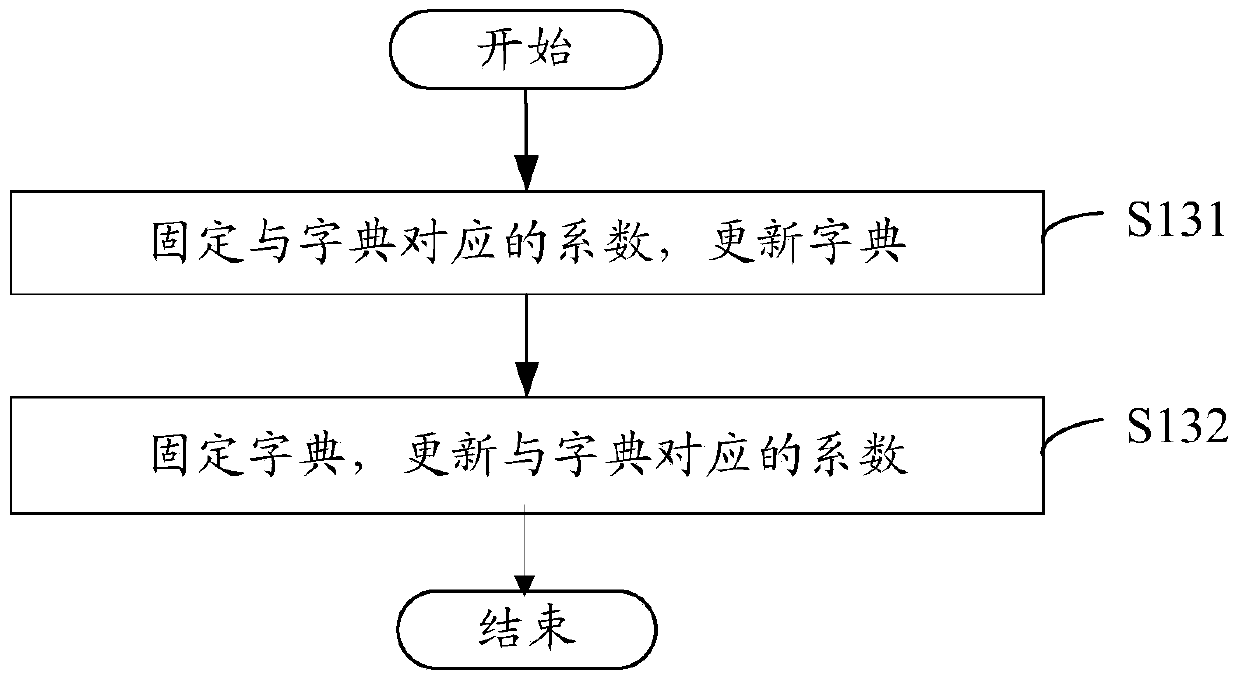
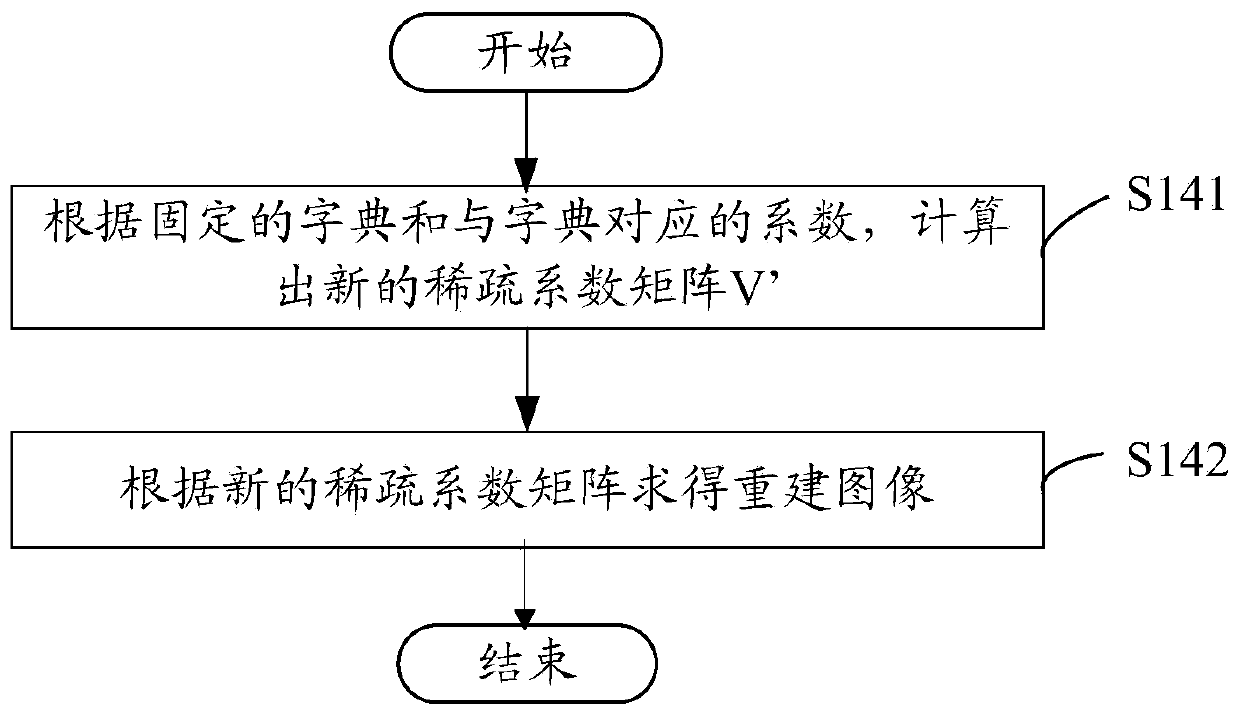
ActiveCN103472419AGood non-correlationHigh precisionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceSelf adaptive
The invention relates to a magnetic-resonance fast imaging method. The magnetic-resonance fast imaging method comprises the following steps: (a) acquiring an initial image from an undersampled K space; (b) performing treatment on the initial image by fixed sparse conversion to get a sparse coefficient; (c) acquiring a dictionary related to the sparse coefficient and a coefficient corresponding to the dictionary based on the sparse coefficient and by virtue of non-related constraint self-adaptive sparse conversion; (d) reconstructing an image according to the dictionary and the coefficient corresponding to the dictionary; (e) updating data in the K space and judging whether the reconstructed image meets a termination condition or not, and if so, implementing the step (f), otherwise, returning to the step (a); and (f) fitting the reconstructed image to get a magnetic resonance parameter image. By adopting the magnetic-resonance fast imaging method, the precision in reconstruction of the image is improved to a certain extent. Simultaneously, the invention further provides a magnetic-resonance fast imaging system applying the magnetic-resonance fast imaging method. The system can obtain reconstructed images with high precision.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Compressed sensing-based FPM (Fourier ptychographic microscopy) algorithm
ActiveCN104200449AImprove reconstruction effectImage enhancementImage resolutionOptimization problem
Disclosed is a compressed sensing-based FPM algorithm. The algorithm comprises the steps of 1) utilizing an FPM platform to collect a low-resolution image ri (x, y) under different illuminations; 2) based on images obtained under illumination of different angles, actually, obtained by translating images under normal illumination in a frequency domain, establishing a constraint for the collected image ri (x, y), and based on the constraint, solving the optimization problem of an optimal problem according to a compressed sensing structure; 3) solving the optimization problem through iteration to obtain a sparse coefficient a, and multiplying the a with an over-complete dictionary to obtain a final result. According to the compressed sensing-based FPM algorithm, by taking advantage of the compressed sensing technology, mathematical abstraction is performed on an original FPM algorithm, a frequency domain iteration method is abstracted into an optimal solution solving method, the image super-resolution reconstruction problem is solved from a new angle, and the algorithm reconstruction effects can be enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on sparse representation and non-local similarity
InactiveCN104063886AReduce blockinessPromote reconstructionImage enhancement2D-image generationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceReconstruction method
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on sparse representation and non-local similarity, and mainly aims to improve the reconstruction quality of a nuclear magnetic resonance image. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, sampling a Fourier transform coefficient corresponding to the nuclear magnetic resonance image by adopting a variable-density random down-sampling method, and performing Fourier inversion on sampled data to obtain an initial reference image for reconstructing; secondly, blocking the reference image to obtain similar structural characteristics of each type of image sub-blocks and obtain corresponding dictionaries of each type of image sub-blocks and sparse representation coefficients of the image sub-blocks; lastly, estimating the original image by using the non-local similarity of the image sub-blocks, restraining the sparse coefficients of the image sub-blocks, combining the sparsity of the image in a wavelet domain, and performing iterative reconstruction through a hybrid regular term solving model. By adopting the method, the non-local similarity of the image is fully utilized, complex textures in the image can be effectively reconstructed, and the quality of a reconstructed quality is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
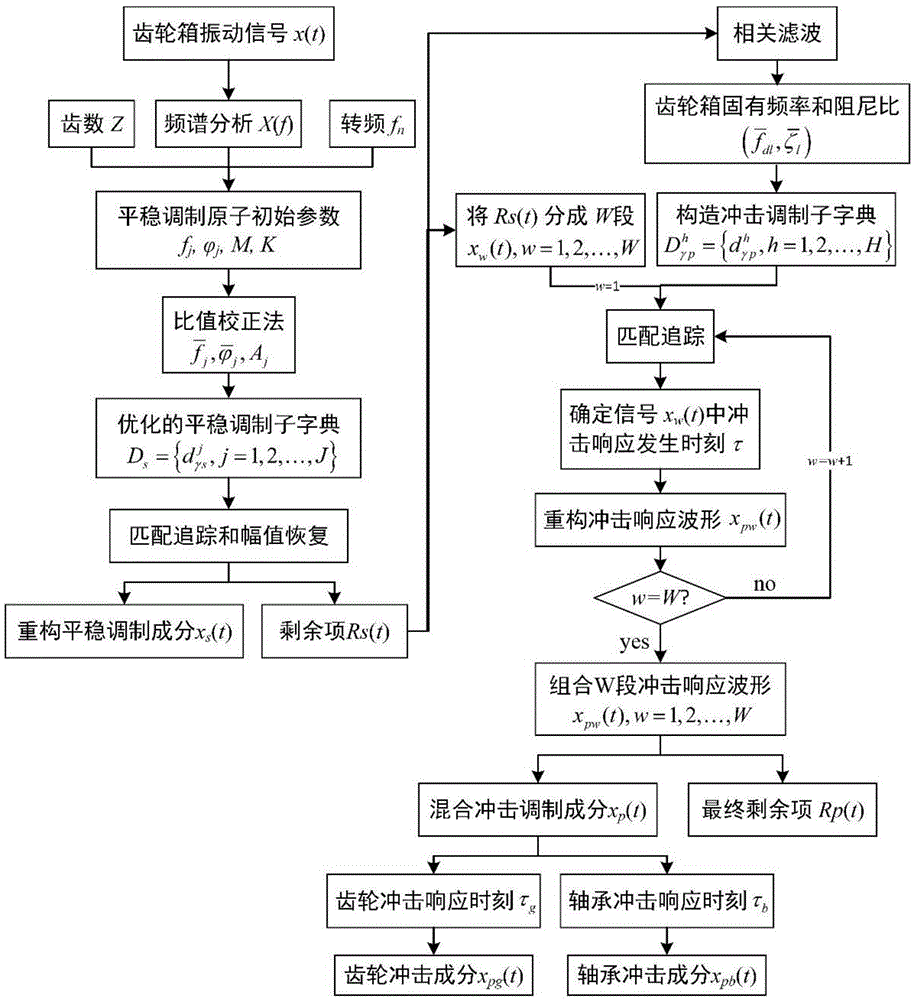
Sparse-decomposition-based hybrid fault feature extraction method of gear wheel and bearing
ActiveCN105424359AWide versatilityEffectively identify distributed faultsMachine gearing/transmission testingMachine bearings testingFrequency spectrumFeature extraction
The invention discloses a sparse-decomposition-based hybrid fault feature extraction method of a gear wheel and a bearing, wherein the method can be used for diagnosing a hybrid fault formed by a distributed gear wheel fault and a local gear wheel and bearing fault in a gear case. When a steady modulation dictionary is constructed, atomic parameter optimization is carried out by using a discrete frequency spectrum correction technology, thereby improving precision of steady modulation component separation. When an impact modulation dictionary is constructed, an over-complete dictionary using a multi-stage inherent-frequency unit impulse response function as an atom is established and the inherent frequency and the damping ratio are identified in a self-adapting mode from a fault vibration signal, so that an impact response waveform caused by local faults of the gear wheel and the bearing can be represented well. After optimization of the steady modulation dictionary and the impact modulation dictionary, the dictionary redundancy is substantially reduce; and with a segmented matching tracking method, the point number of inner product calculation during the sparse coefficient solving process is reduced. On the basis of the two kinds of measures, the speed of signal sparse decomposition is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
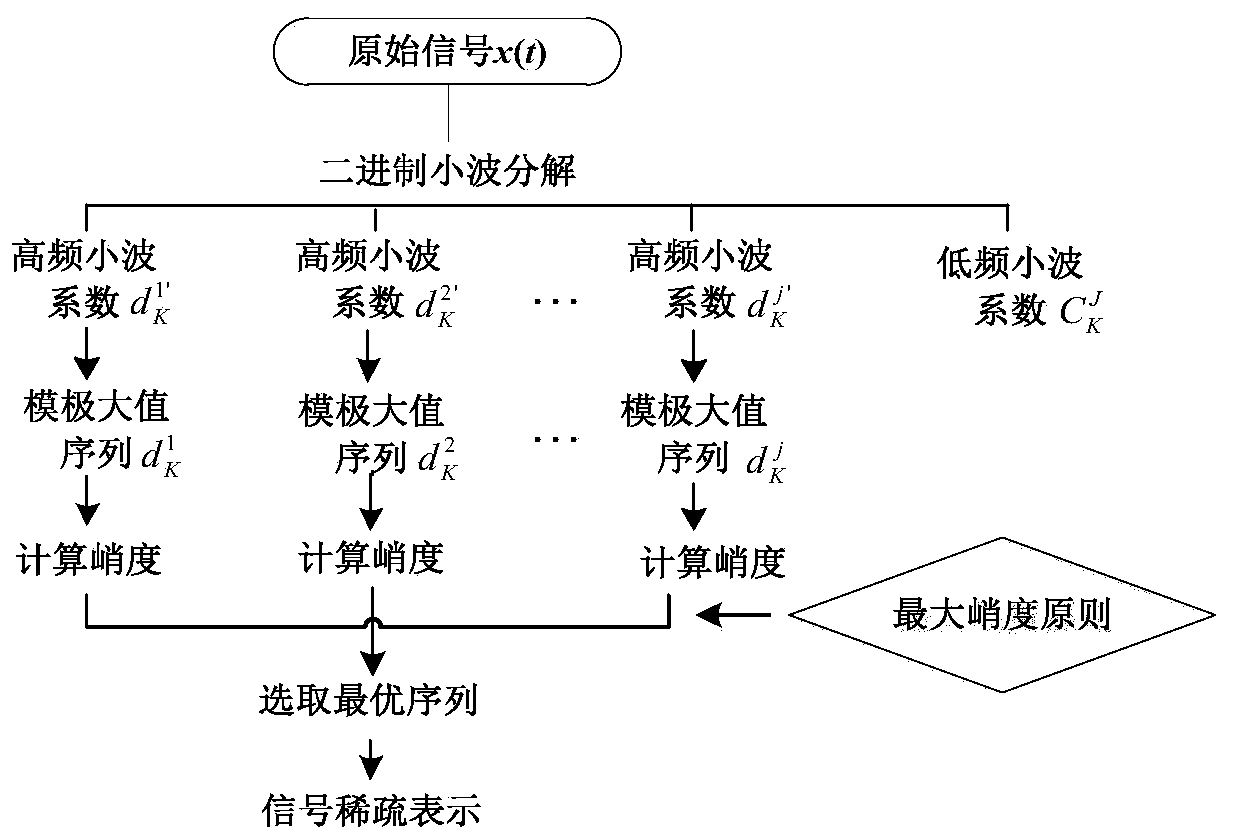
Improved self-adaptive sparse sampling fault classification method
InactiveCN109993105AReduce redundant informationReduce complexityMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsTime shifting
An improved self-adaptive sparse sampling fault classification method belongs to the technical field of fault diagnosis. A traditional sparse classification method is improved. Firstly, a wavelet module maximum value and a kurtosis method are used for carrying out feature enhancement processing on signals, and on the premise that signal sparsity is guaranteed, a unit matrix is adopted to replace aredundant dictionary. Secondly dimension reduction is carried out on data by adopting a Gaussian random measurement matrix, thereby reducing redundant information in the signal, and reserving effective and small amount of data. Then, a sparse coefficient is solved by adopting a sparsity adaptive matching pursuit (SAMP) algorithm, and the compressed signal is reconstructed; and finally, a cross correlation coefficient is adopted as a judgment basis of the category of the fault, so that an improved adaptive sparse sampling fault classification method is provided. Experimental verification proves that redundant information in signals is effectively reduced, the influence of time shift deviation on fault type judgment is avoided, meanwhile, the operation complexity is reduced, and the calculation speed and the reconstruction precision are improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
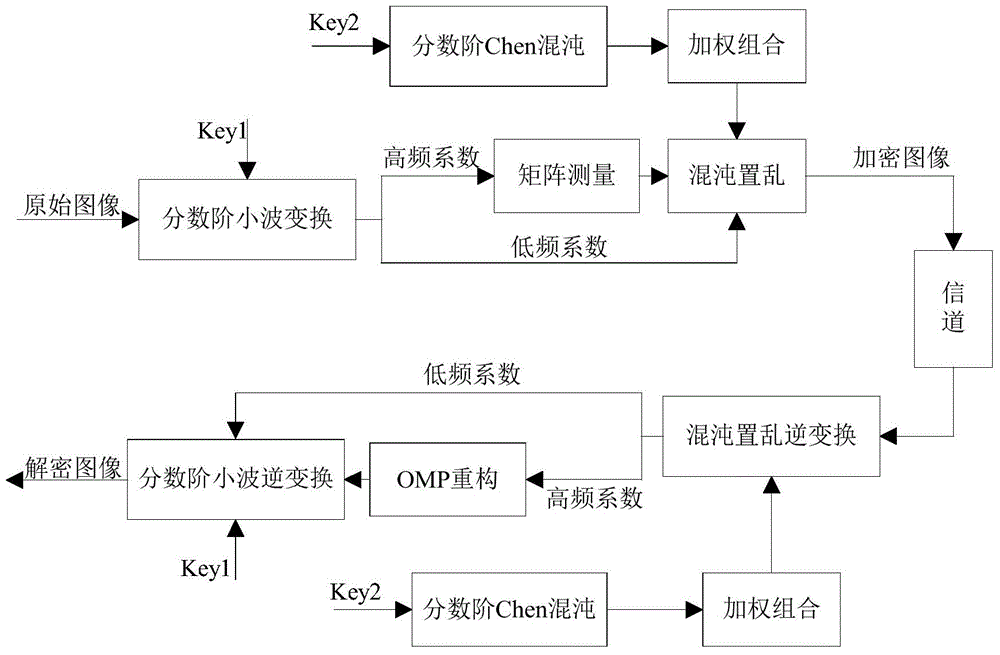
Image compression sensing and image encrypting method based on sparse matrix control
InactiveCN104463765AImprove scrambling effectImprove securityImage data processing detailsImage transferCiphertext
The invention provides an image compression sensing and image encrypting method based on sparse matrix control. An order is used as a secret key for controlling generation of a fraction wavelet transformation sparse matrix, and then the sparse matrix is used for carrying out sparse expression for an image to obtain a low-frequency coefficient matrix and a high-frequency coefficient matrix of the image; measurement matrixes of the number of corresponding measurement times are constructed according to the sparseness of the coefficient matrixes, and sparse coefficients are measured to obtain a compressed and encrypted image. In order to improve the safety of an encryption algorithm, fraction Chen chaos sequences of a weighted array are used for scrambling measurement values to obtain a ciphertext. The fraction wavelet transformation and fraction Chen chaos scrambling are combined, and the non-linear characteristic of the fraction order property and the fraction chaos sequences is fully utilized. The image is encrypted while being compressed, the difficulty of the large data size when the image is transmitted can be effectively overcome, and image information leakage is prevented.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
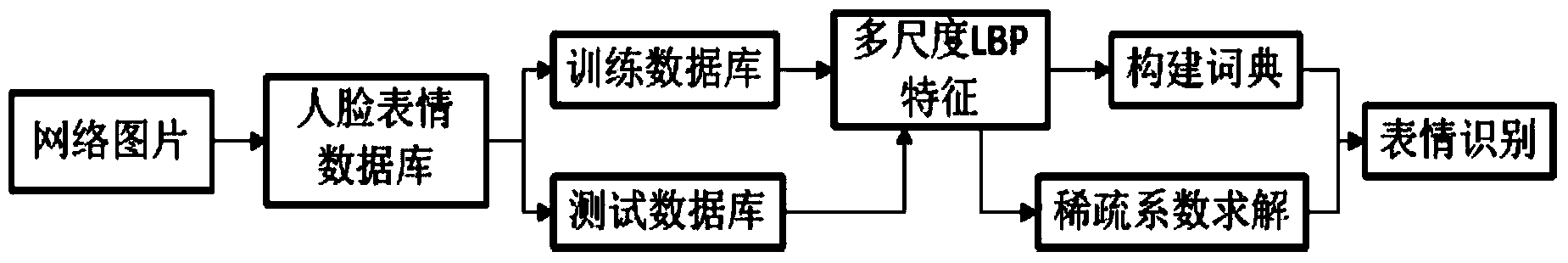
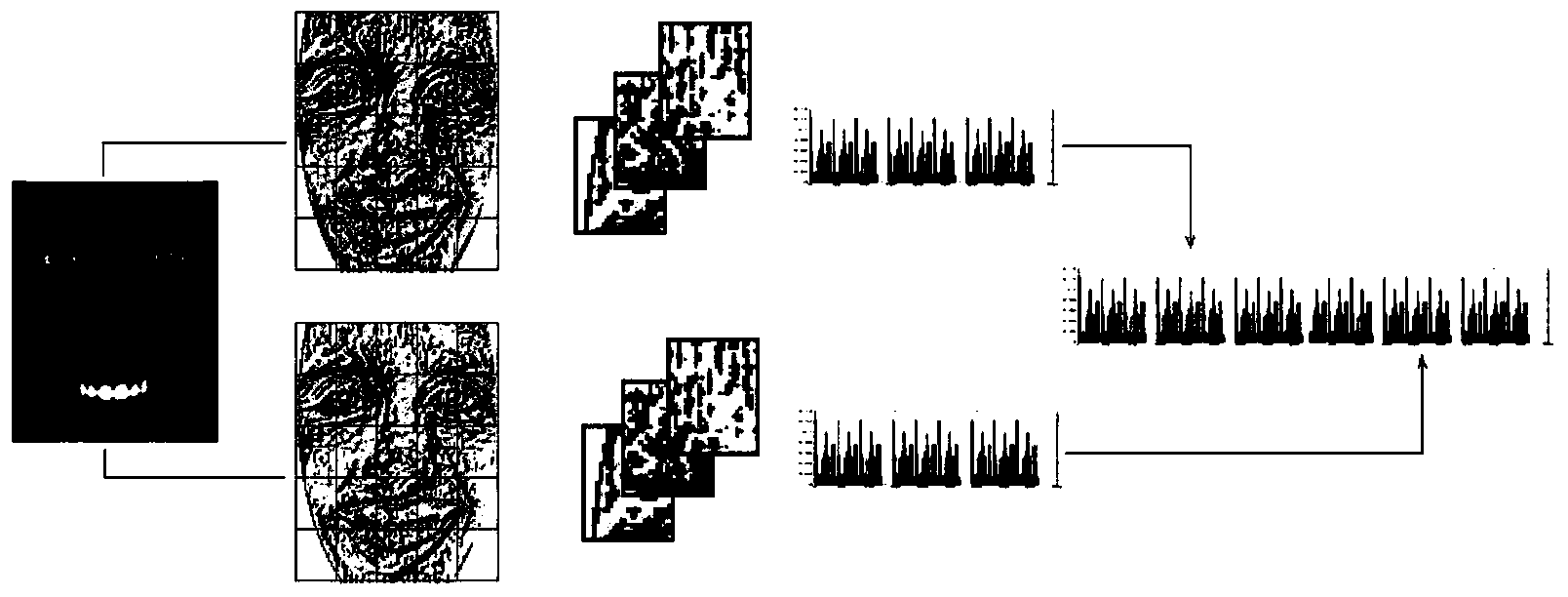
Large-scale facial expression recognition method based on multiscale LBP and sparse coding
InactiveCN103971095ASolve the sparsity problemVerify validityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer science
The invention provides a large-scale facial expression recognition method based on a multiscale LBP and sparse coding. The method comprises the steps that a large-scale facial expression database is built firstly, a training database and a testing database are generated based on a random sampling technology, then facial expression features are expressed through multiscale LBP features, then a dictionary needed in a sparse coding method is generated, a new expression sample is solved to obtain an optimal sparse coefficient, and the sparse coefficients of different expressions are accumulated to recognize the expression samples. According to the method, a high-robustness feature expressing mode is obtained through the multiscale LBP features, the sparse problem in large-scale facial expression recognition is solved through sparse coding, and the effectiveness of the large-scale facial expression recognition method based on the multiscale LBP and sparse coding is verified.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Sorting method based on non-supervision feature selection
ActiveCN103942568AImprove classification speedImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorCurse of dimensionality
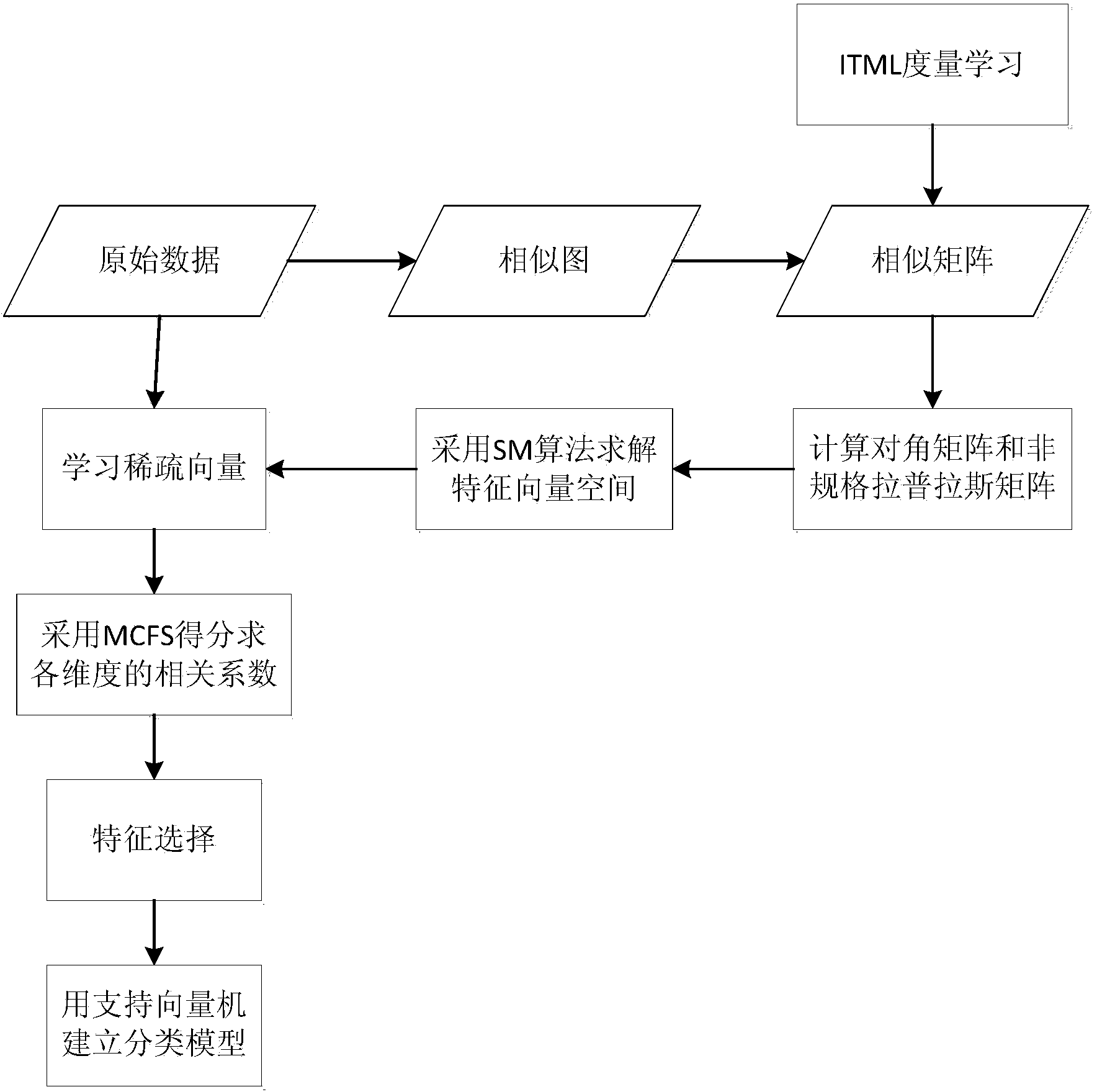
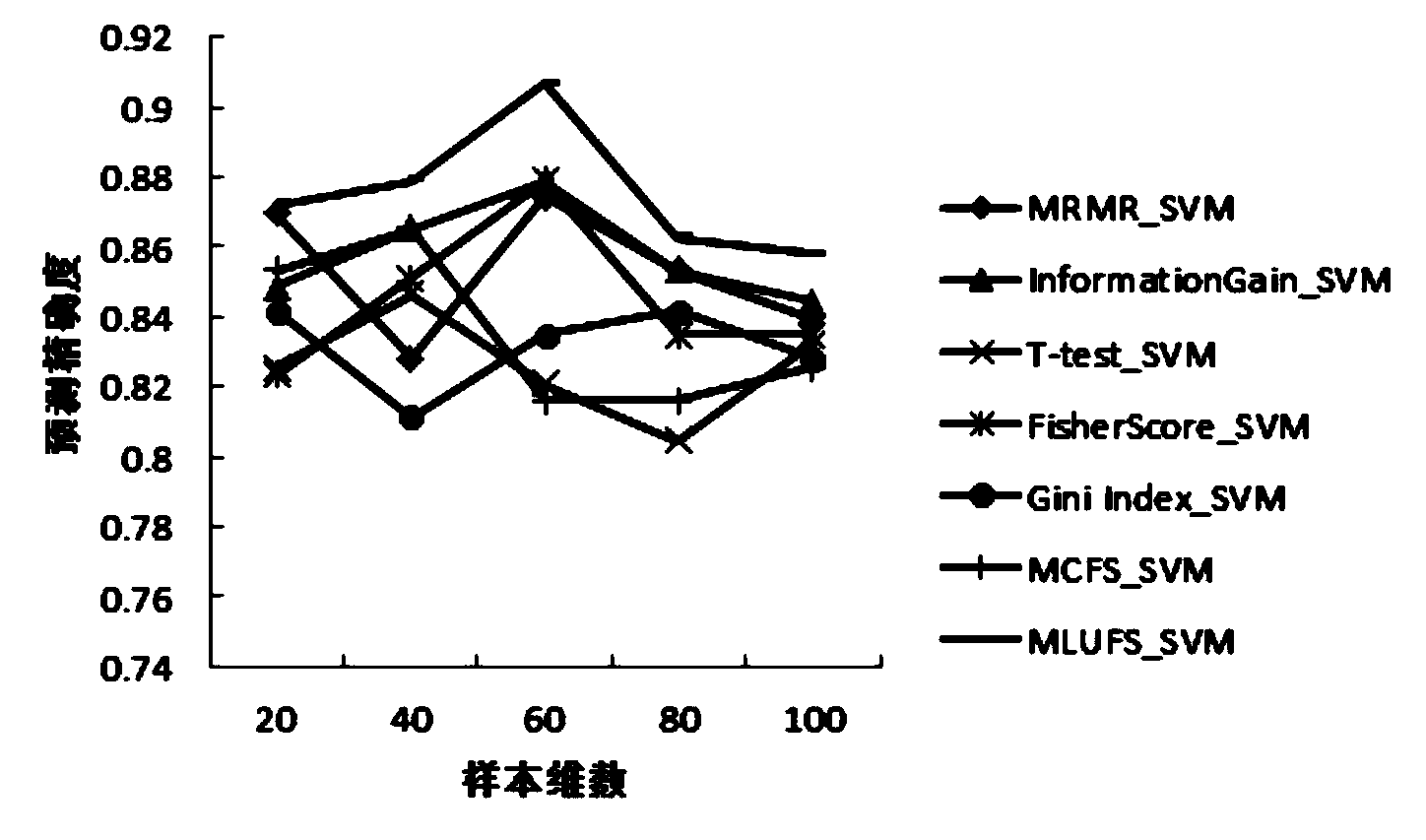
The invention discloses a sorting method based on non-supervision feature selection. By means of the method, high dimensional data are expressed in similar diagrams, distances between sample points are obtained through the ITML, and a similar matrix of the original high dimensional data is set up; then the SM algorithm is executed on the similar matrix and a diagonal matrix corresponding to the similar matrix to achieve mapping of original sample sets to feather vector space; then through learning of sparse coefficient vectors and MCFS scores, weight coefficients of all attributes in the original sample set are obtained, and the attribute which can best express the original sample information is selected out; finally a support vector machine is used for setting up a sorting model of the selected data to predict fatigue states of a driver. The method selects features of the high dimensional data under the condition of maintaining data aggregate structures before the sorting model is set up, and the negative effect of curse of dimensionality on data sorting is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compressed sensing image reconstructing method based on prior model and 10 norms
InactiveCN102148987AReduce computational complexityShort runtimeImage codingTelevision systemsImmune genetic algorithmComputation complexity
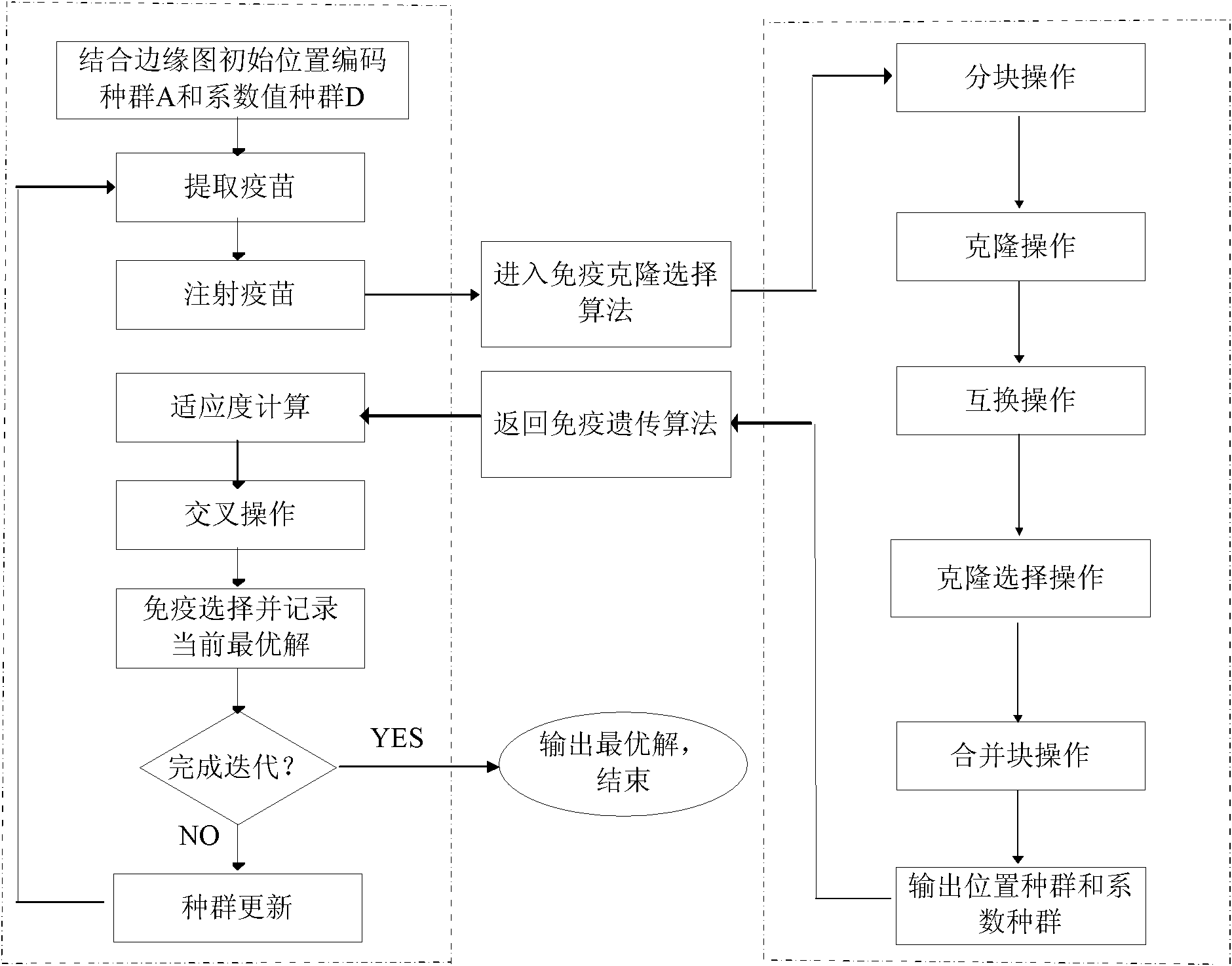
The invention discloses a compressed sensing image reconstructing method based on a prior model and 10 norms, mainly used for solving the defects of poor visual effect and long operation time existing in image reconstruction in the prior art. In the technical scheme of the invention, a compressed sensing image reconstruction frame with 10 norms is optimized by utilizing a prior model; and the positioning of sparsity coefficient and solution of the sparsity coefficient value are achieved through two effective steps: step 1, establishing the prior model, and carrying out low frequency coefficient inverse wavelet transform so as to obtain an image with a fuzzy edge, determining the position of the edge by edge detection, and searching the position of wavelet high frequency subband sparsity coefficient through an immunization genetic algorithm by using the prior model of which the wavelet coefficient has inter-scale aggregation; and step 2, solving a corresponding high frequency subband by using an improved clone selective algorithm, and then carrying out the inverse wavelet transform so as to obtain a reconstructed image. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of good visual effect and low calculation complexity, and can be used in the fields of image processing and computer visual.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Compressive sensing reconstruction method based on pseudo-inverse adaptive matching pursuit
ActiveCN103337087AReduce relevanceLight in mass2D-image generationPattern recognitionReconstruction method
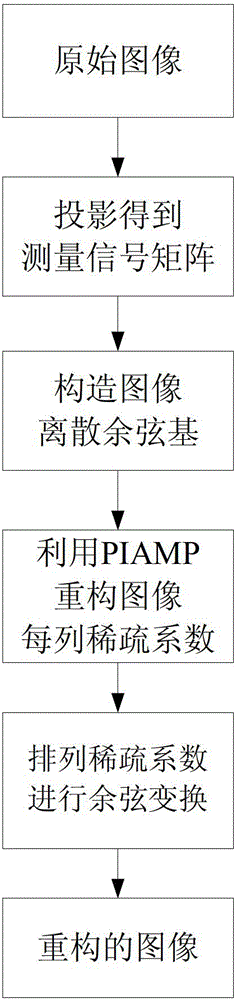
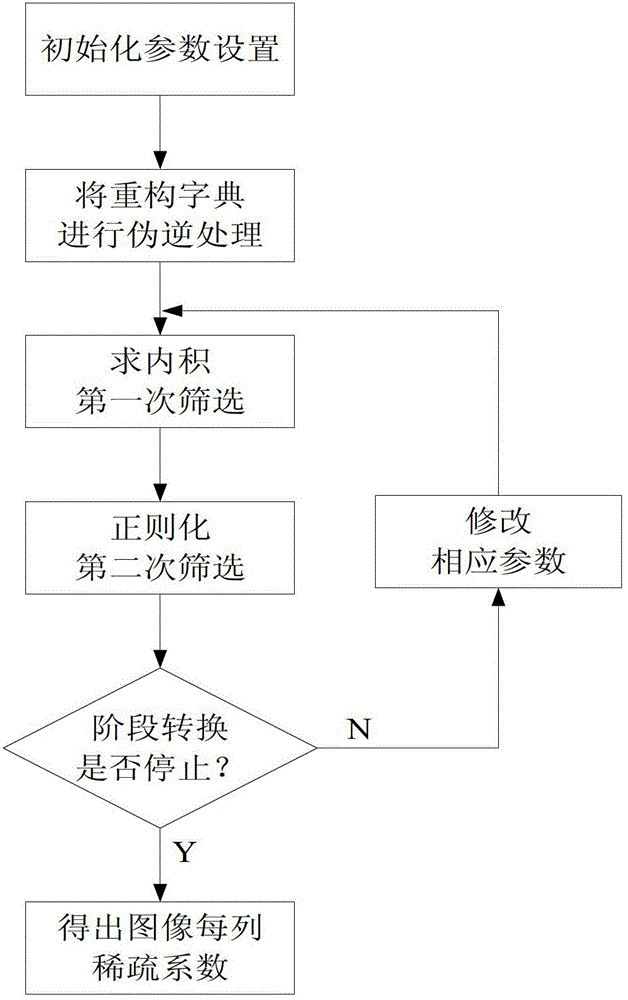
The invention relates to a compressive sensing image reconstruction method based on a pseudo-inverse adaptive matching pursuit (PIAMP), which is characterized by comprising the steps that a gauss random matrix is selected for projecting an image to form a measurement signal matrix; an image sparse base is constructed; each column of the measurement signal matrix is reconstructed by adopting the PIAMP to form a sparse coefficient of each column of the image; and the sparse coefficients of the columns of the image are arrayed and subjected to cosine transformation to form a reconstruction image. The method particularly takes account of the dictionary relevance, iteration stage division and the like in a sparse coefficient reconstruction process, so that selection of the sparse coefficients is more accurate, and the precision of image reconstruction is higher.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Three-dimensional CT core image super-resolution reconstruction method
ActiveCN105006018AHigh-resolutionThe pore structure features are clear and obviousGeometric image transformationComputerised tomographsThree dimensional ctFeature extraction
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional core image super-resolution reconstruction method. The method comprises the steps of: performing degradation on a three-dimensional CT core image, and performing decomposition and feature extraction on the degraded three-dimensional image to obtain a feature block 2; performing dictionary training on an extraction feature application algorithm to obtain a low-resolution dictionary Dl and a sparse coefficient alpha; performing decomposition and feature extraction on the input three-dimensional image to obtain a feature block 1; according to the feature block 1 and the sparse coefficient alpha, obtaining a high-resolution dictionary Dh of the input three-dimensional CT core image; according to the feature block 1 and the low resolution dictionary Dl, obtaining a new sparse coefficient beta; according to the high-resolution dictionary Dh and the new sparse coefficient beta, obtaining a three-dimensional high-resolution image block; performing up-sampling on the three-dimensional CT core image by using an interpolation algorithm and obtaining an enlarged three-dimensional image; and filling the enlarged three-dimensional image with the three-dimensional high-resolution image blocks to obtain an enlarged three-dimensional core sample model. According to the three-dimensional core image super-resolution reconstruction method, the problem of a contradiction between the resolution of the three-dimensional CT image and the sample dimension is solved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com