Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Minimize loss function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
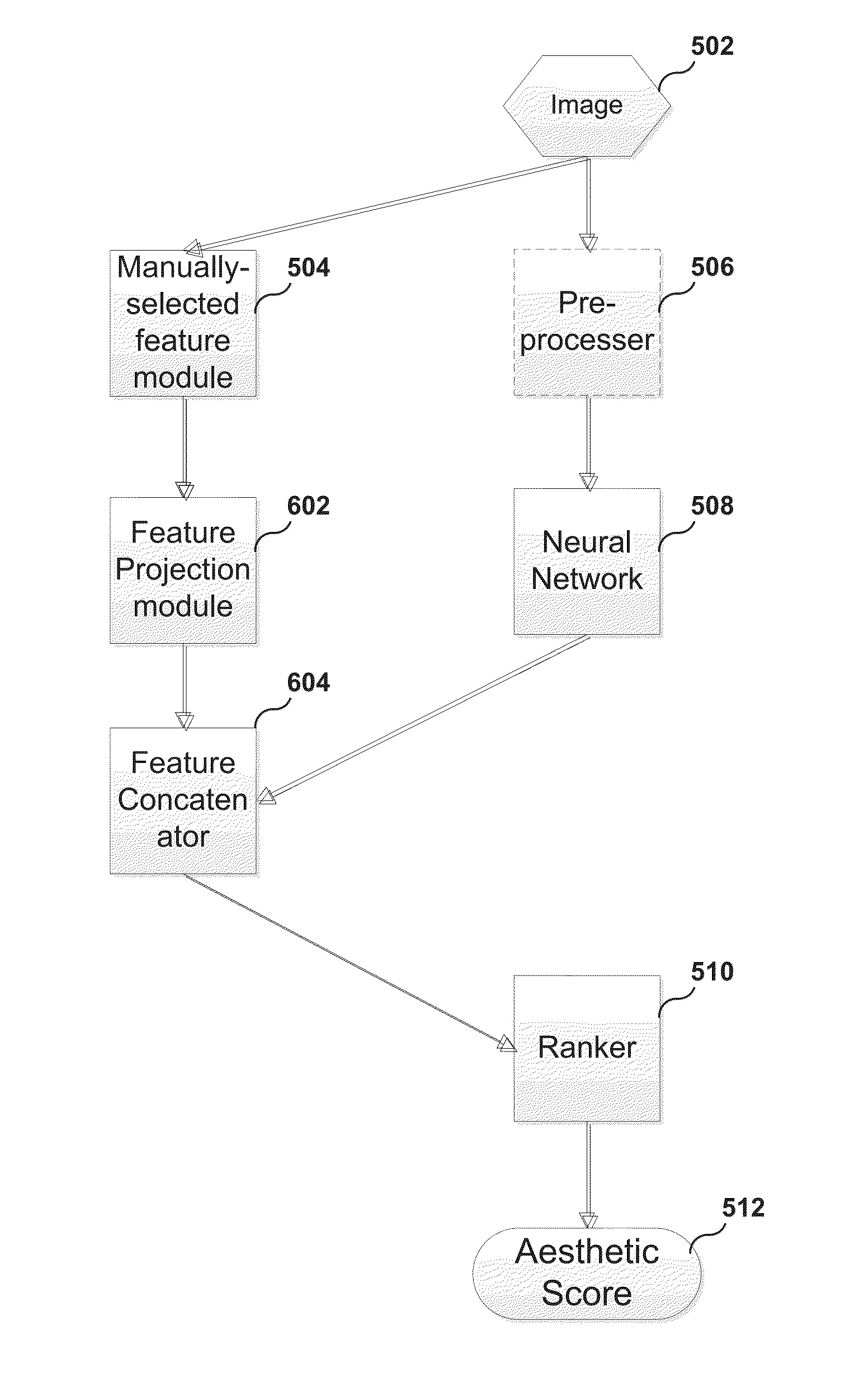
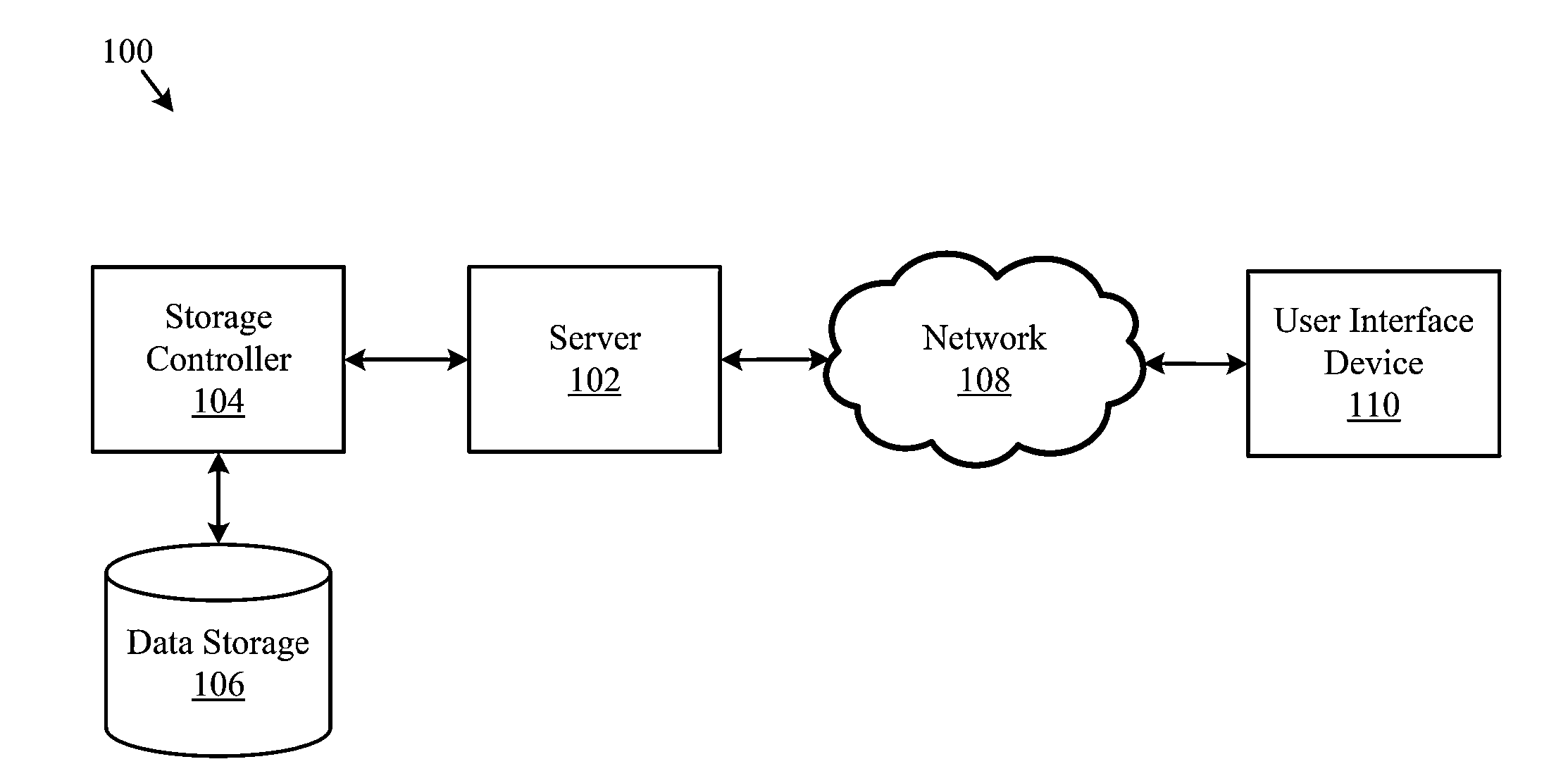
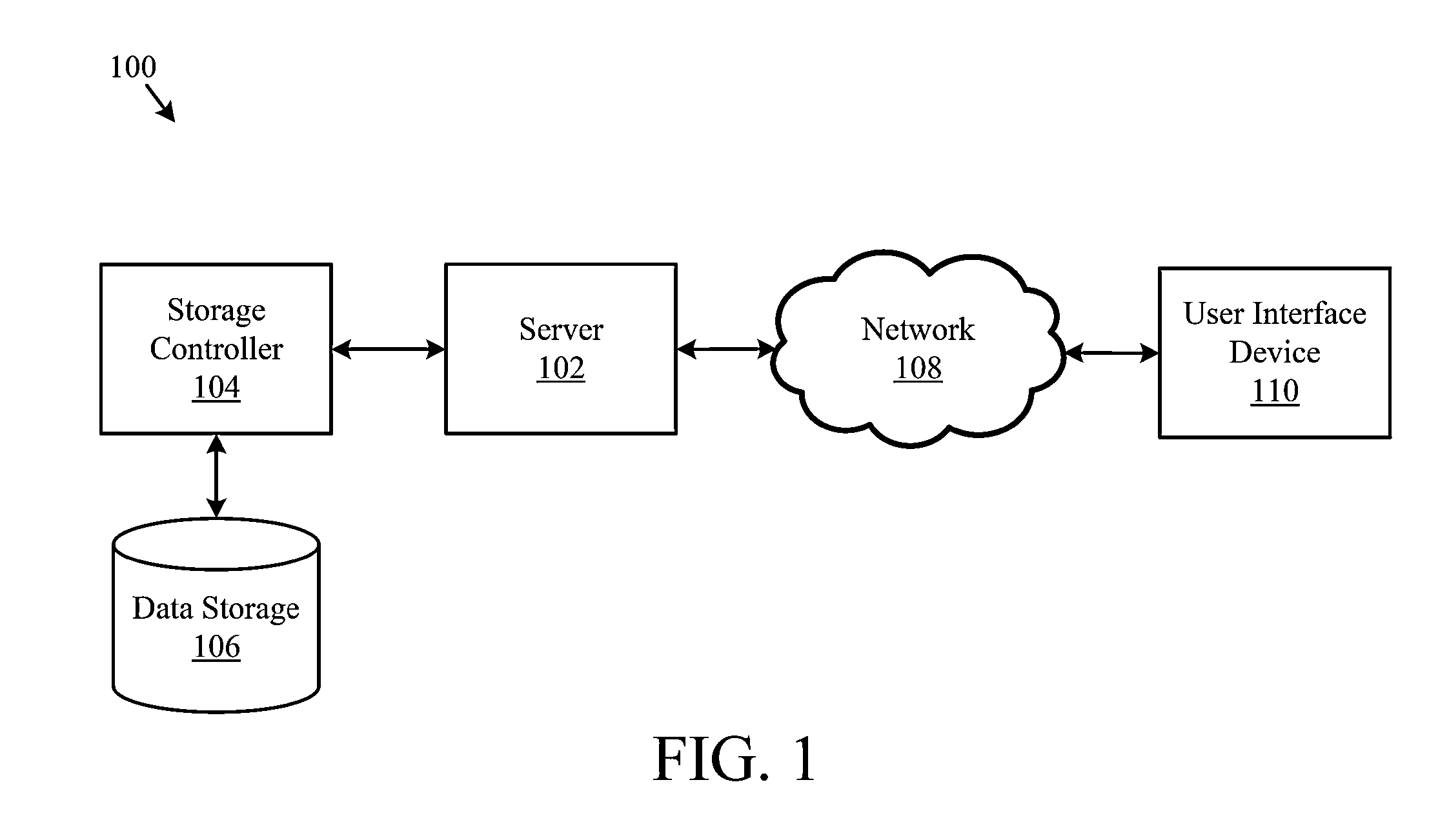
Systems, methods, and computer program products for searching and sorting images by aesthetic quality
ActiveUS20160098844A1Minimize loss functionImage enhancementDigital data information retrievalNetwork onComputer vision
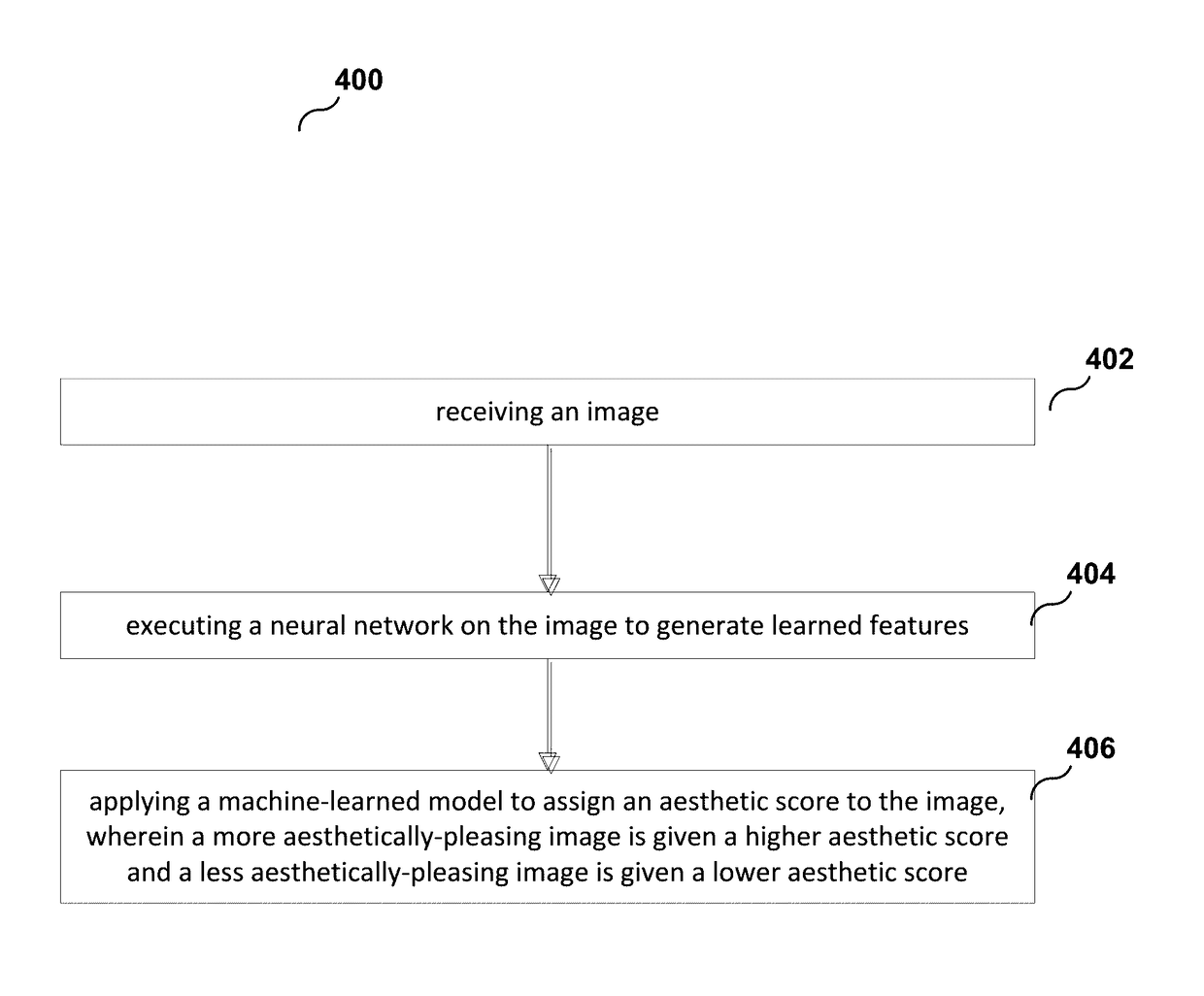
A system, method, and computer program product for assigning an aesthetic score to an image. A method of the present invention includes receiving an image. The method further includes executing a neural network on the image to generate learned features. The method further includes applying a machine-learned model to assign an aesthetic score to the image, where a more aesthetically-pleasing image is given a higher aesthetic score and a less aesthetically-pleasing image is given a lower aesthetic score. The learned features are inputs to the machine-learned model.
Owner:EYEEM MOBILE
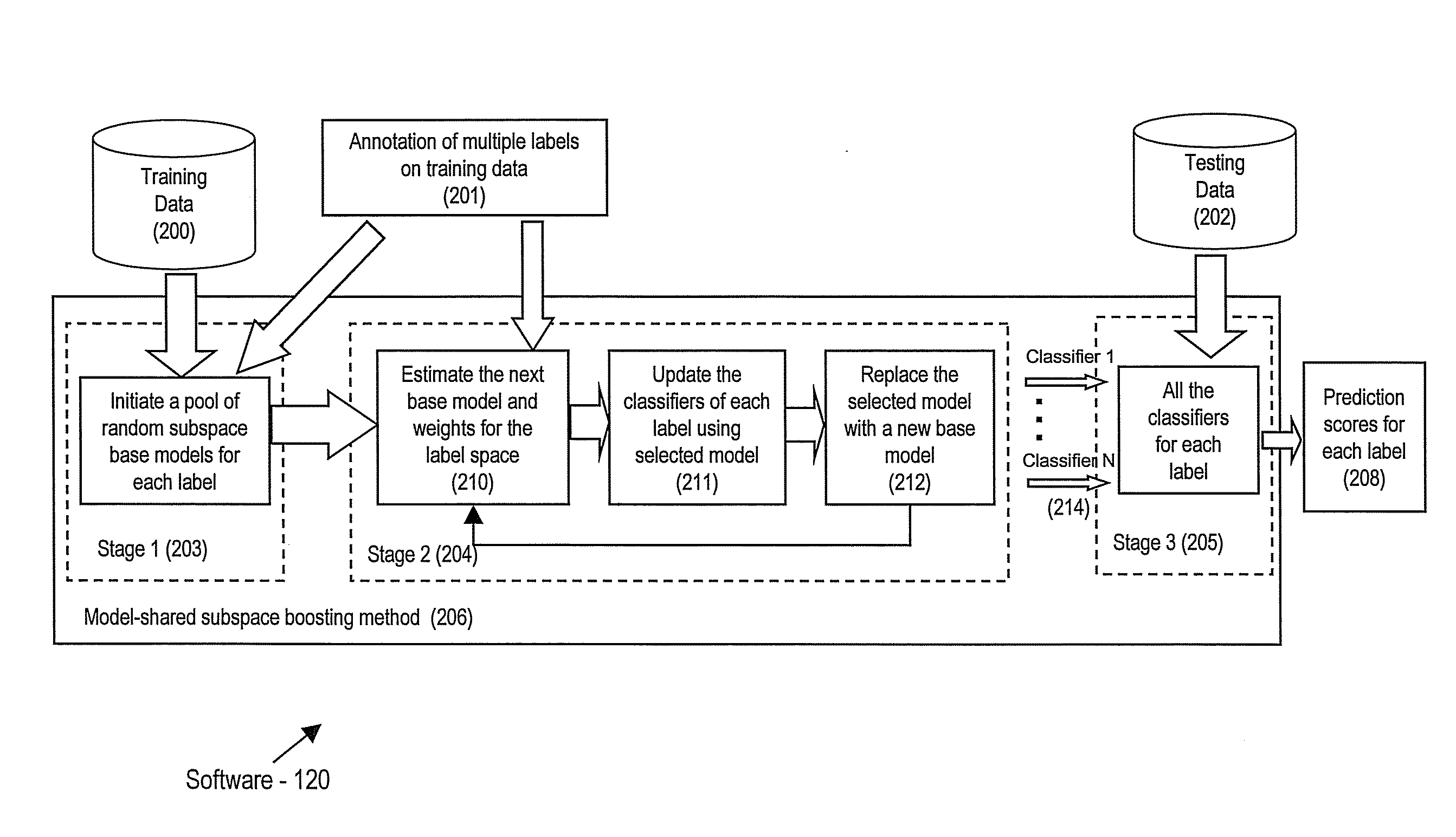
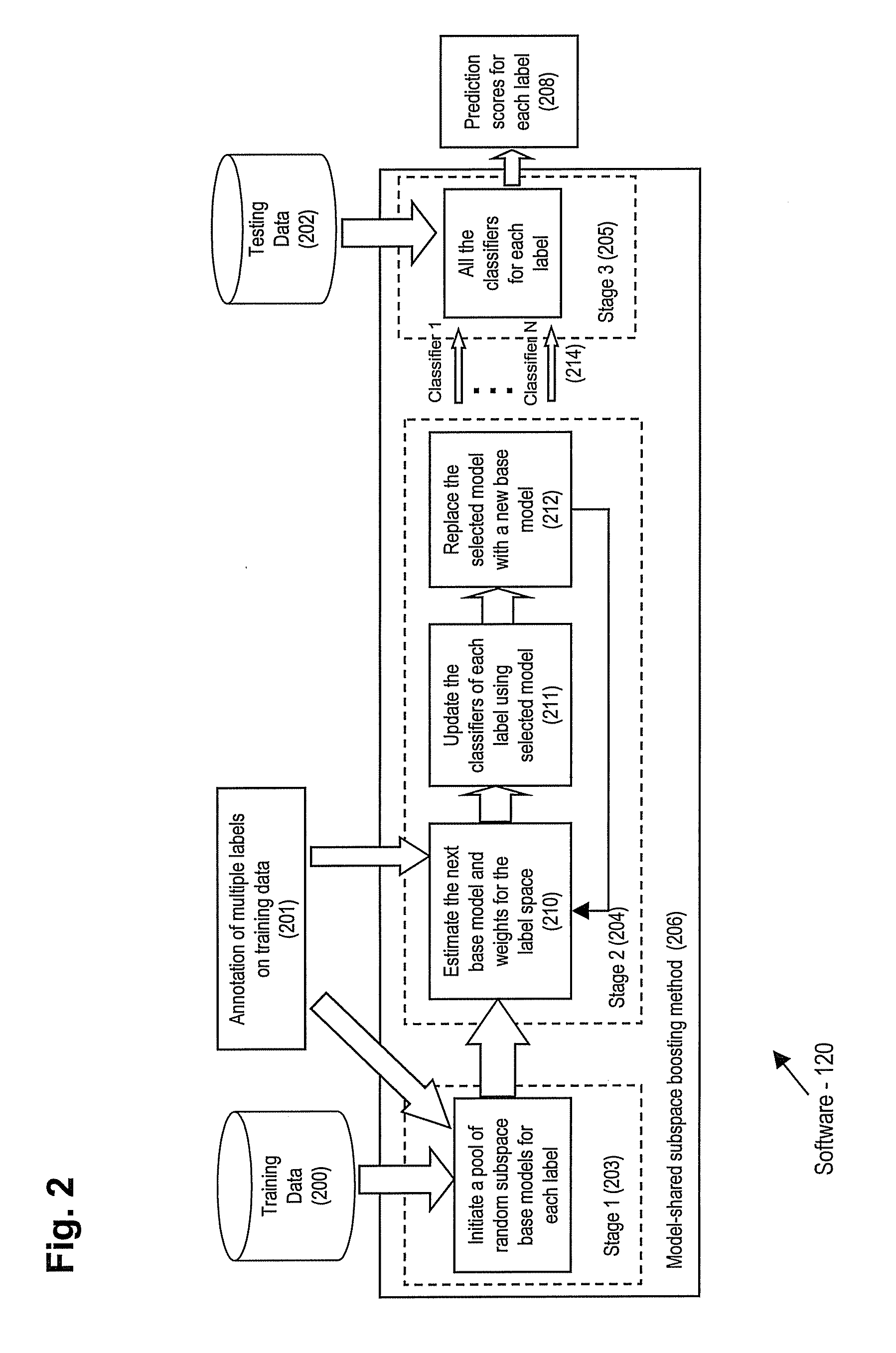
Method and apparatus for model-shared subspace boosting for multi-label classification
ActiveUS20090157571A1Minimize loss functionDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti-label classificationComputerized system
A computer program product includes machine readable instructions for managing data items, the instructions stored on machine readable media, the product including instructions for: initializing a plurality of base models; minimizing a joint loss function to select models from the plurality for a plurality of labels associated with the data items; and at least one of sharing and combining the selected base models to formulate a composite classifier for each label. A computer system and additional computer program product are provided.
Owner:SINOEAST CONCEPT
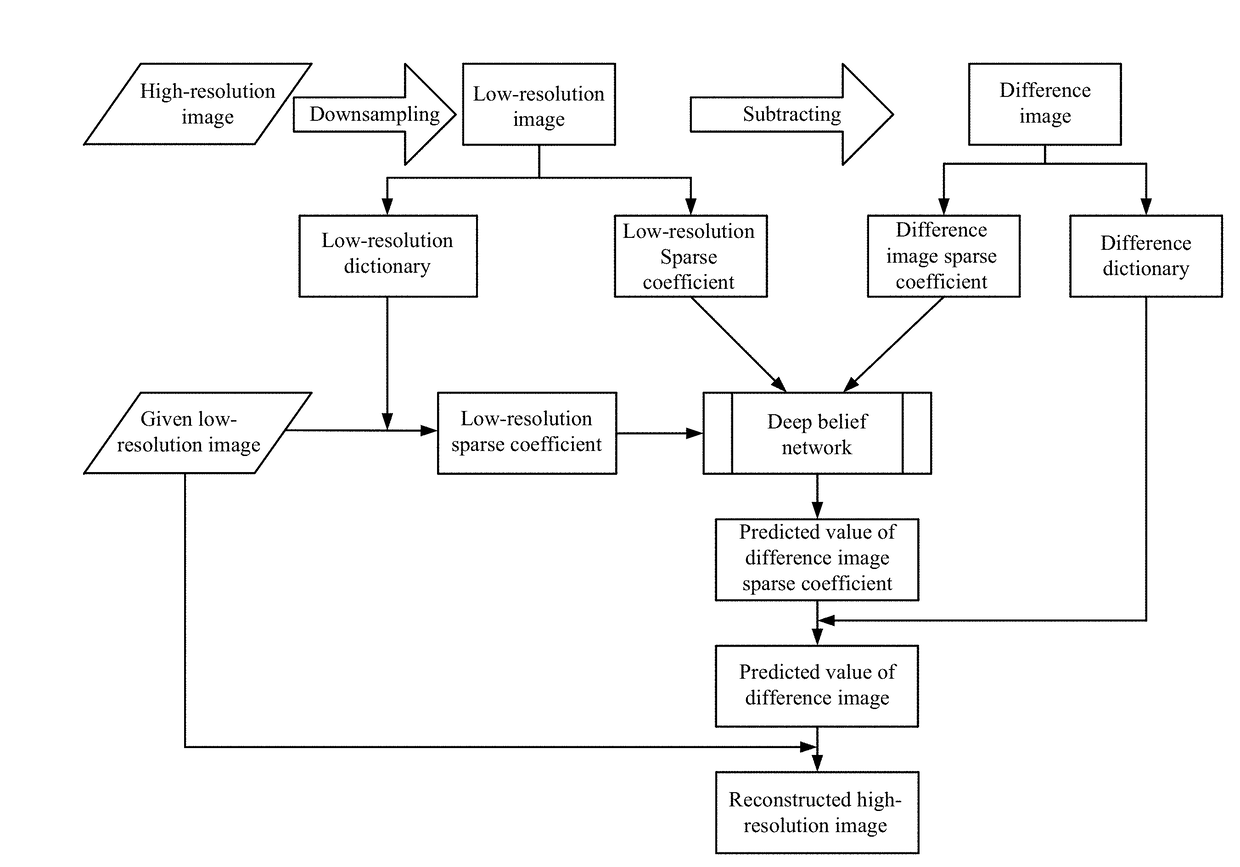
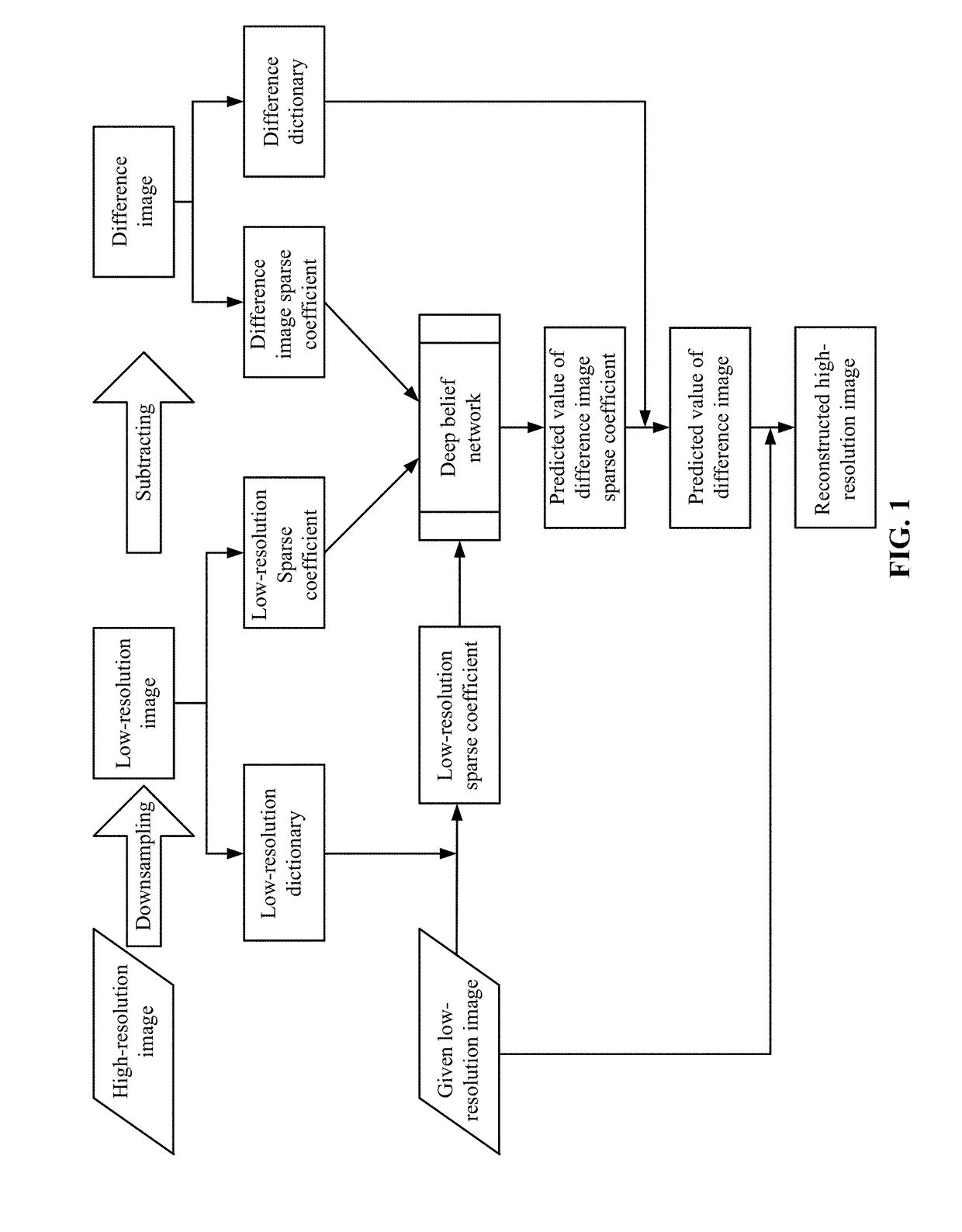
Method and system for reconstructing super-resolution image
ActiveUS20170293825A1Minimize cost functionMinimize loss functionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTest sample
A method for reconstructing a super-resolution image, including: 1) reducing the resolution of an original high-resolution image to obtain an equal low-resolution image, respectively expressed as matrix forms yh and yl; 2) respectively conducting dictionary training on yl and yhl to obtain a low-resolution image dictionary Dl; 3) dividing the sparse representation coefficients αl and αhl into training sample coefficients αl_train and αhl_train and test sample coefficients αl_test and αhl_test; 4) constructing an L-layer deep learning network using a root-mean-square error as a cost function; 5) iteratively optimizing network parameters so as to minimize the cost function by using the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_train as the input of the deep learning network; 6) inputting the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_testas the test portion into the trained deep learning network in 5), outputting to obtain a predicted difference image sparse coefficient {circumflex over (α)}hl_test, computing an error between the {circumflex over (α)}hl_test.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
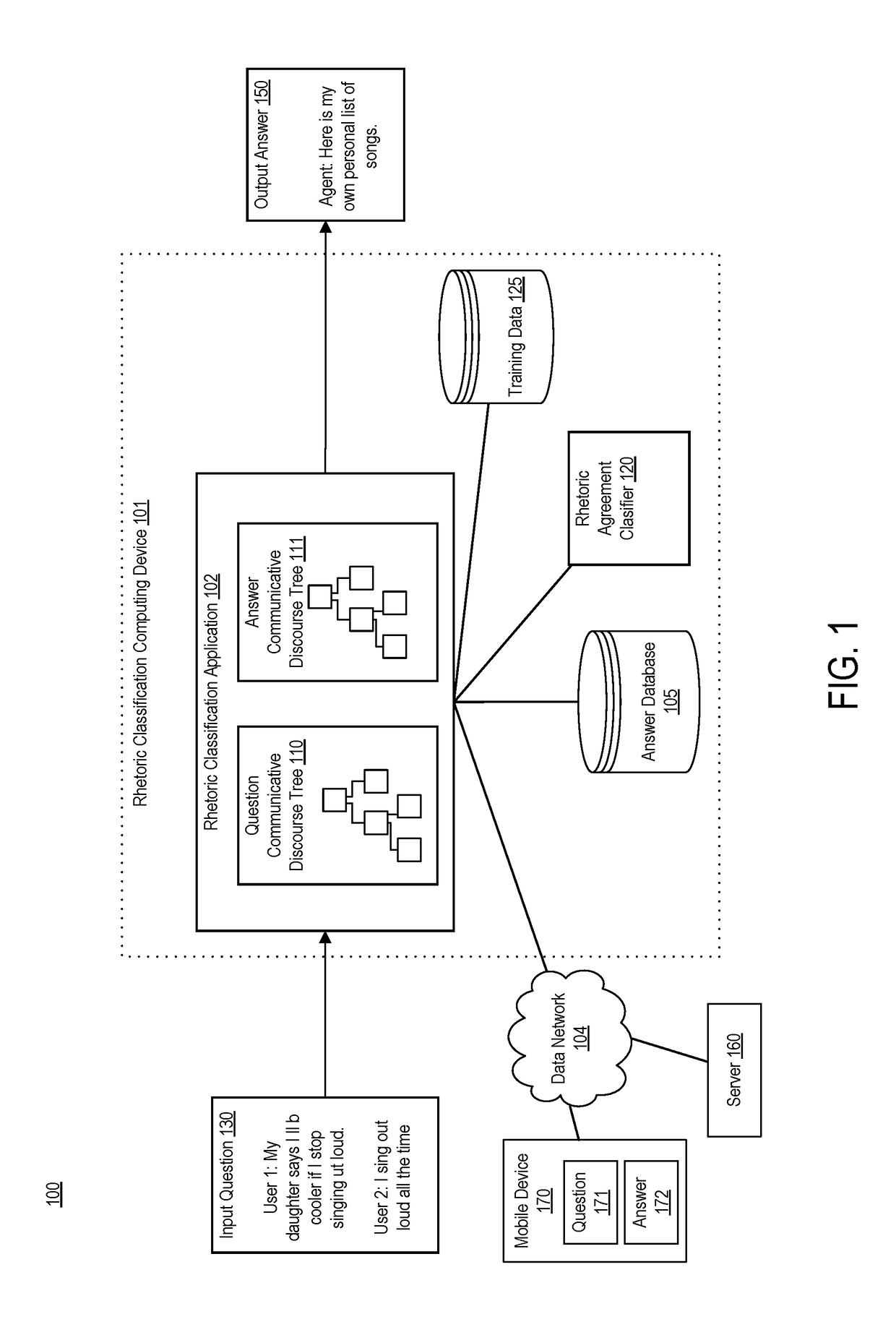
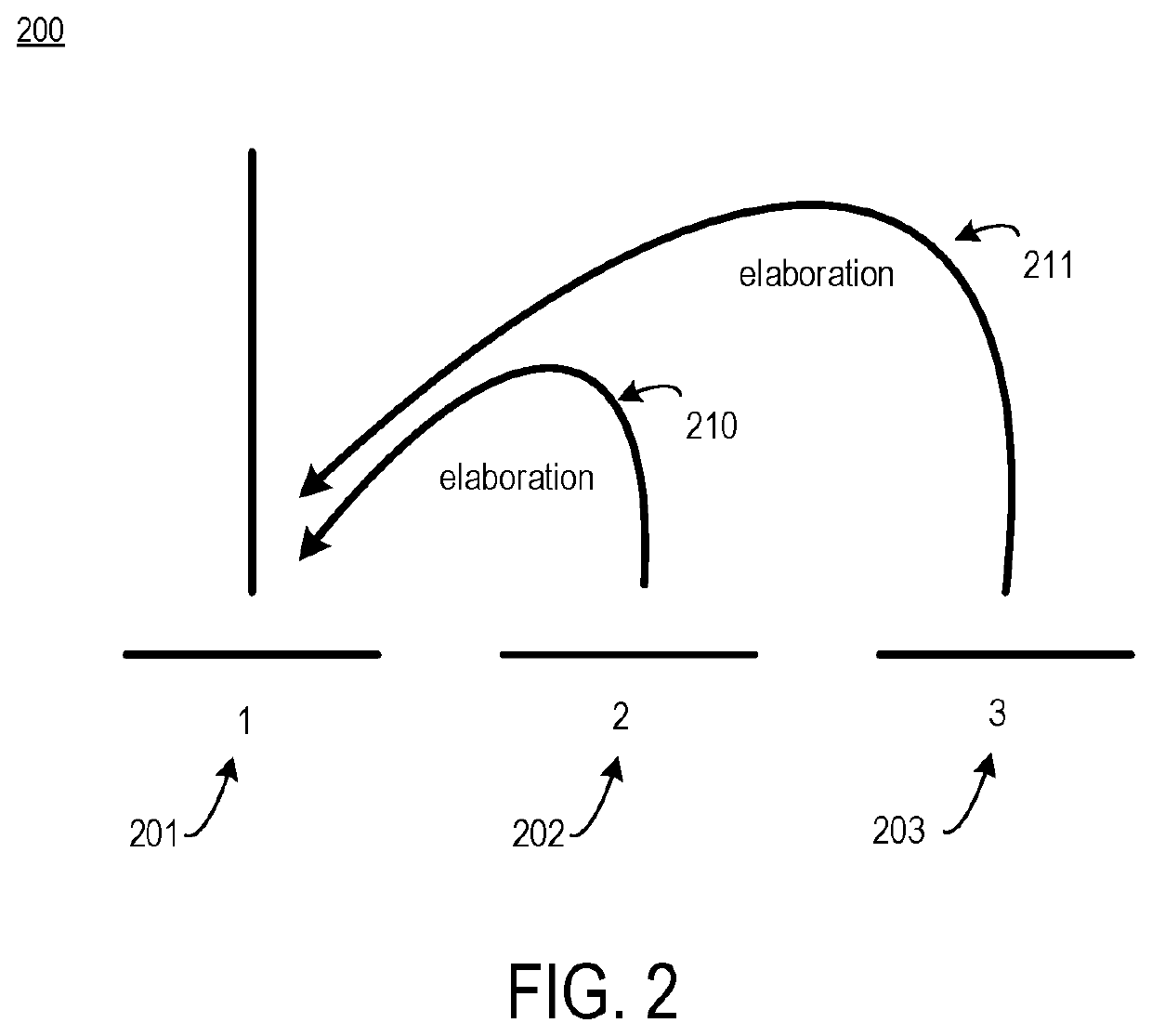
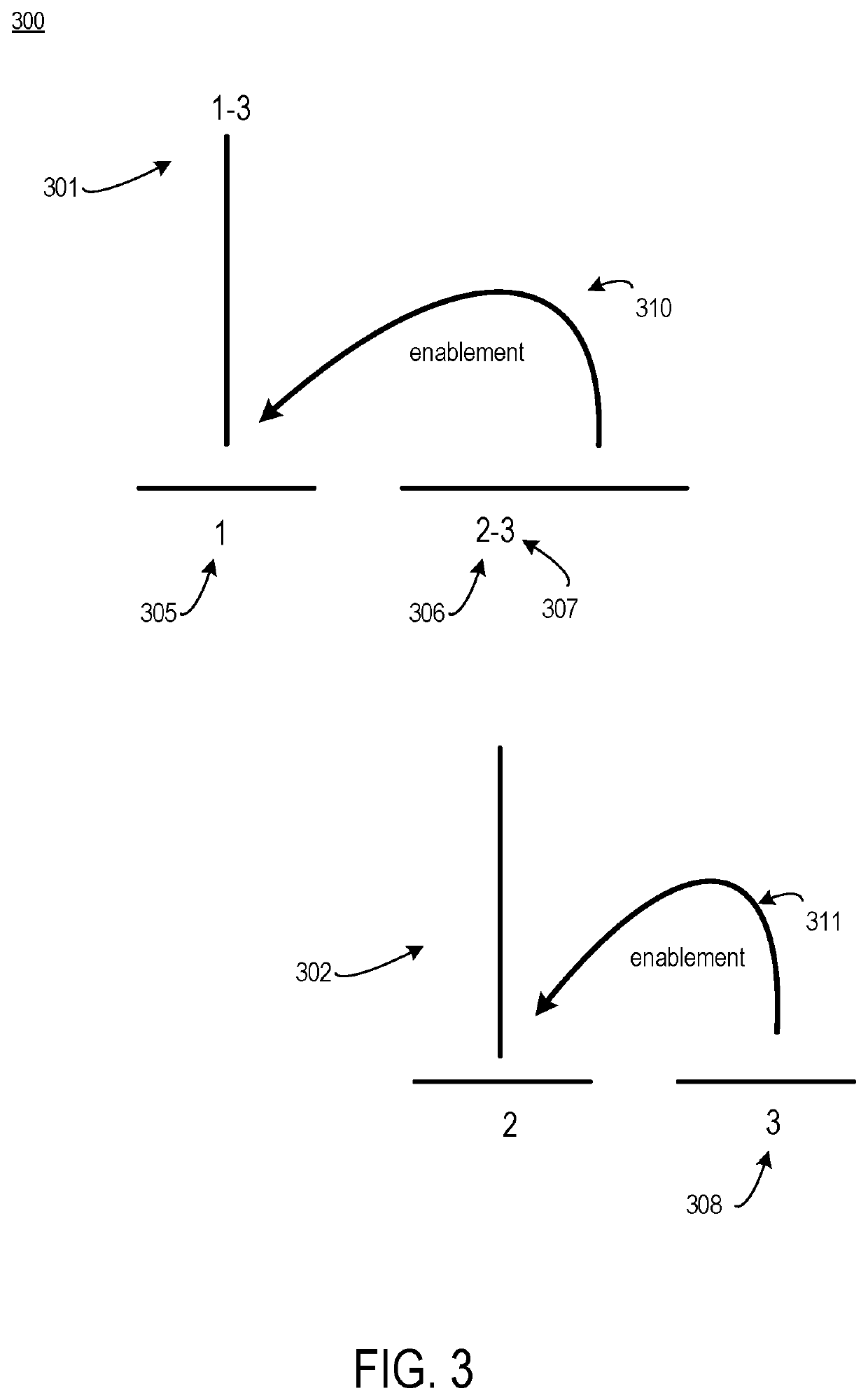
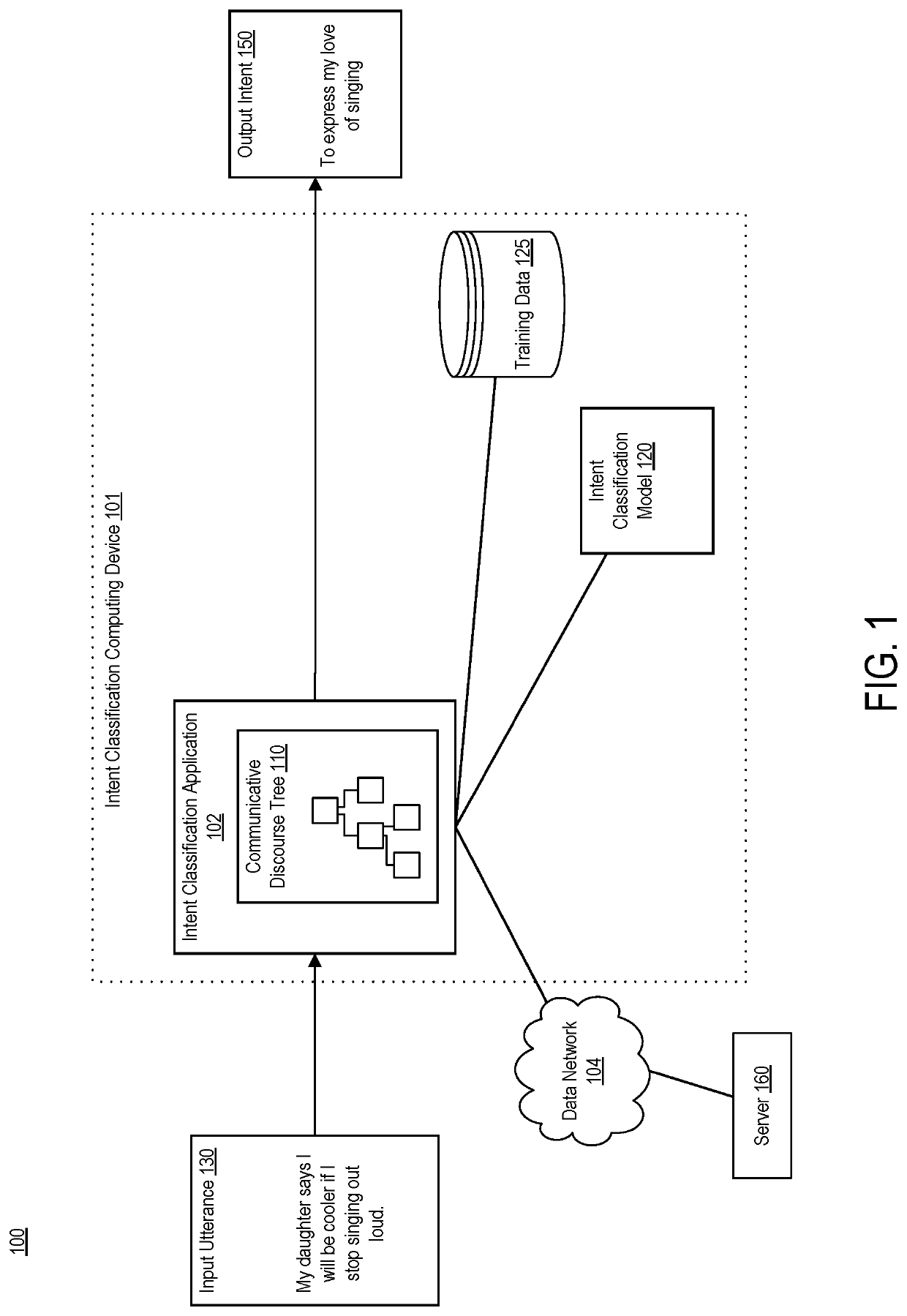
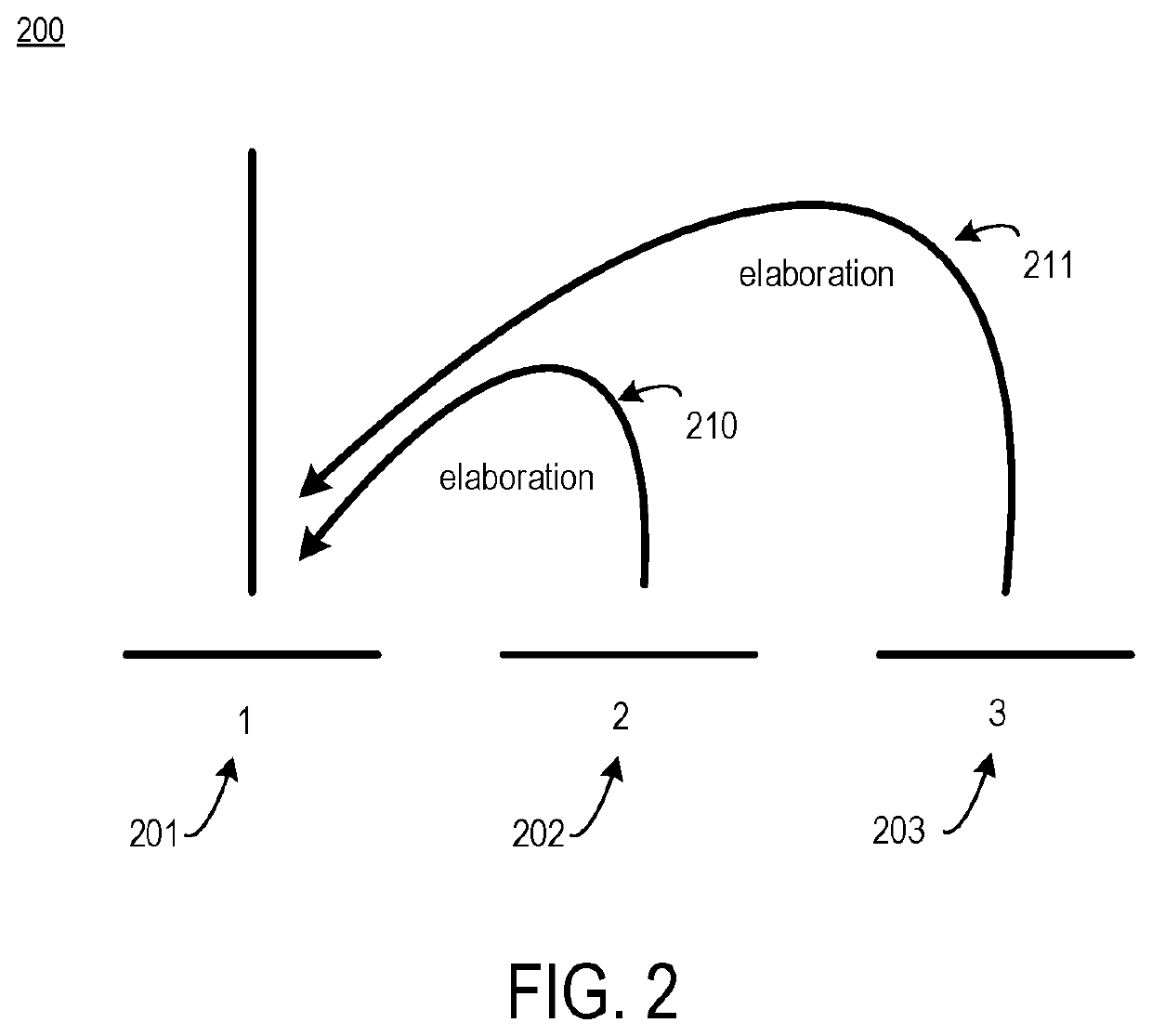
Tree kernel learning for text classification into classes of intent
ActiveUS20180365228A1Minimize loss functionSemantic analysisKernel methodsText categorizationAlgorithm
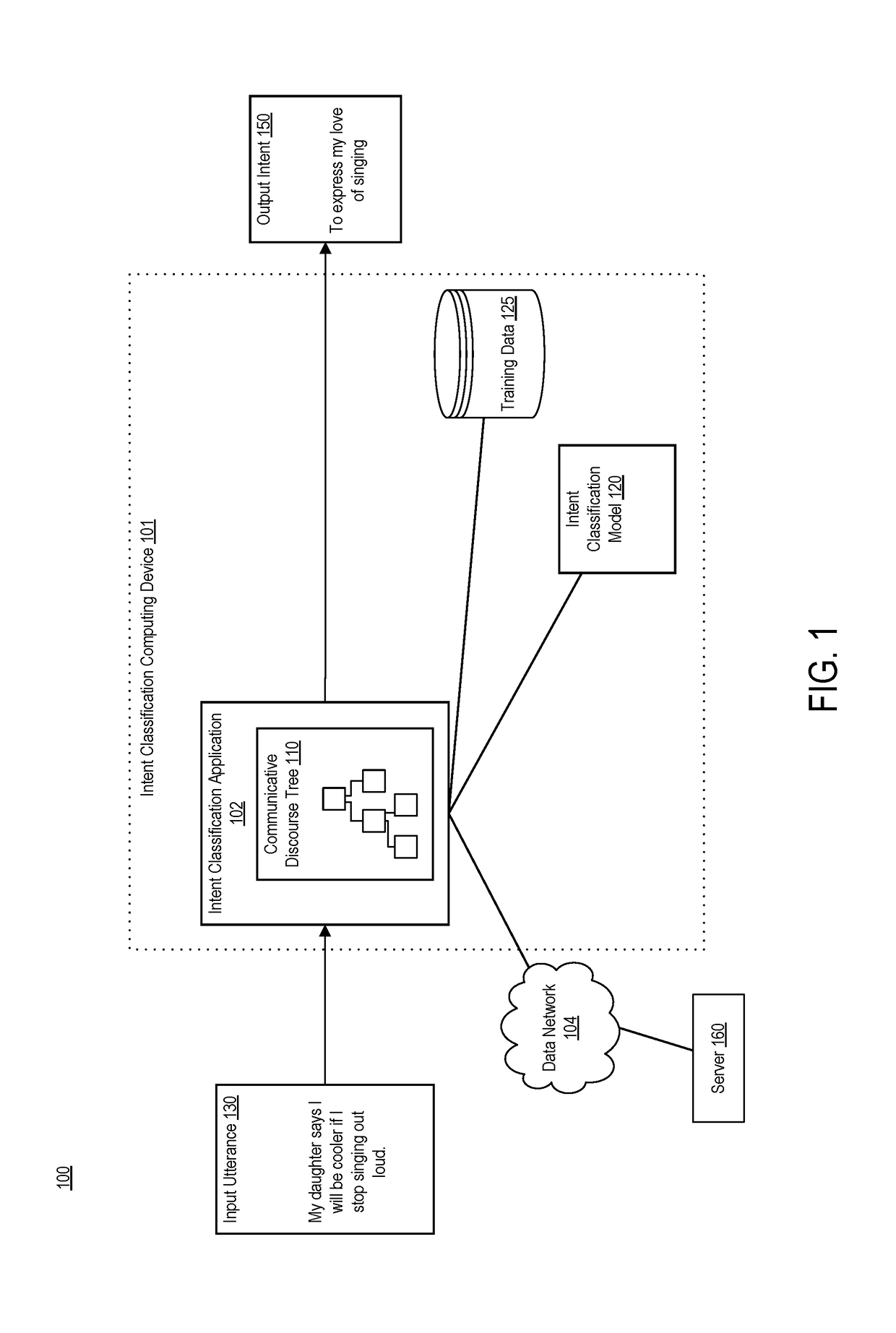
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention are related to determining an intent of an utterance. For example, an intent classification application accesses a sentence with fragments. The intent classification application creates a parse tree for the sentence. The intent classification application generates a discourse tree that represents rhetorical relationships between the fragments. The intent classification application matches each fragment that has a verb to a verb signature, thereby creating a communicative discourse tree. The intent classification application creates a parse thicket by combining the communicative discourse tree and the parse tree. The intent classification application determines an intent of the sentence from a predefined list of intent classes by applying a classification model to the parse thicket.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Large-scale real-time traffic flow prediction method based on fuzzy logic and deep LSTM
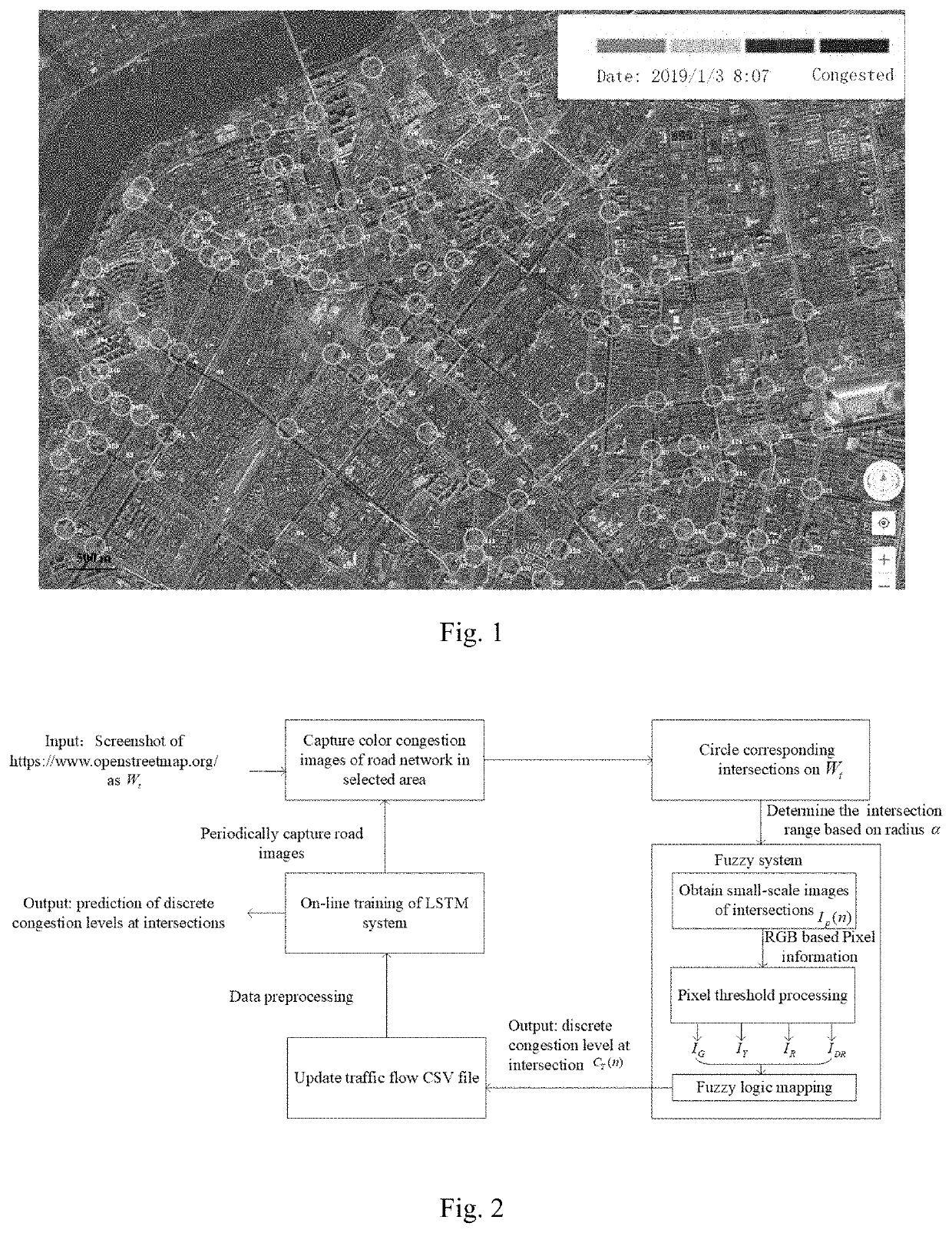
ActiveUS20210209939A1Improve forecast accuracyEfficient learning processImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageData set
A large-scale real-time traffic flow prediction method of the present invention is based on fuzzy logic and deep LSTM, which relates to a technical field of urban intelligent traffic management. The method includes steps of: selecting an urban road network scene to collect color images of real-time traffic flow congestion information; obtaining congestion levels of multiple intersections according to the color images, which are used in a data training set; and forming a data sensing end of FDFP through a fuzzy mechanism; establishing a deep LSTM neural network, performing deep learning on the training data set, and constructing a prediction end of the FDFP; construct a graph of road intersections and formulate a k-nearest neighbors-based discounted averaging for obtaining congestion on the edges; and inputting real-time traffic information received from a server into an FDFP model.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
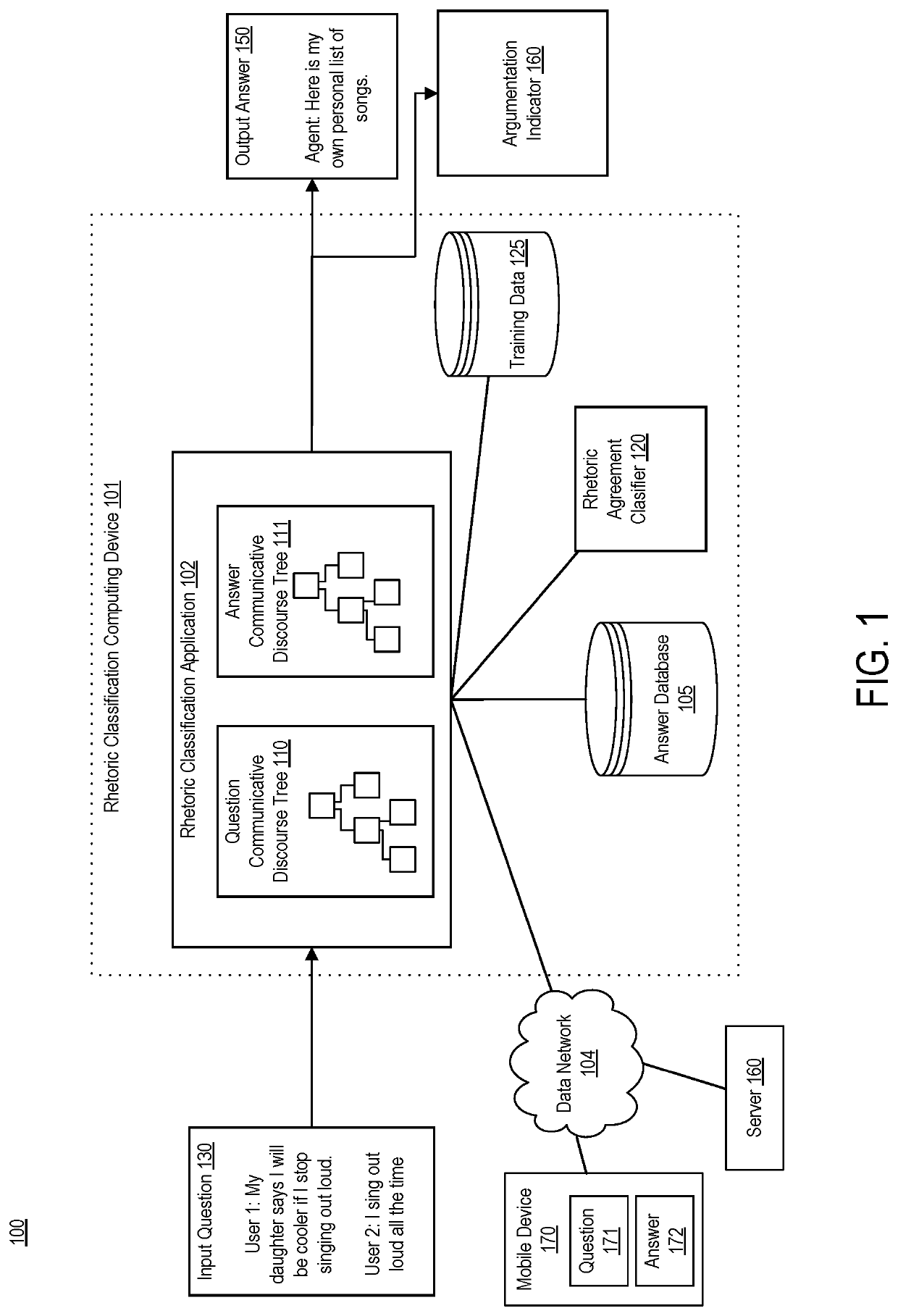
Enabling chatbots by detecting and supporting argumentation
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention detect argumentation in text. In an example, an application executing on a computing device accesses text comprising fragments. The application creates a discourse tree from the text. The discourse tree includes nodes, each nonterminal node representing a rhetorical relationship between two of the fragments and each terminal node of the nodes of the discourse tree is associated with one of the fragments. The application matches each fragment that has a verb to a verb signature, thereby creating a communicative discourse tree. The application determines whether the communicative discourse tree represents text that includes argumentation by applying a classification model trained to detect argumentation to the communicative discourse tree.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
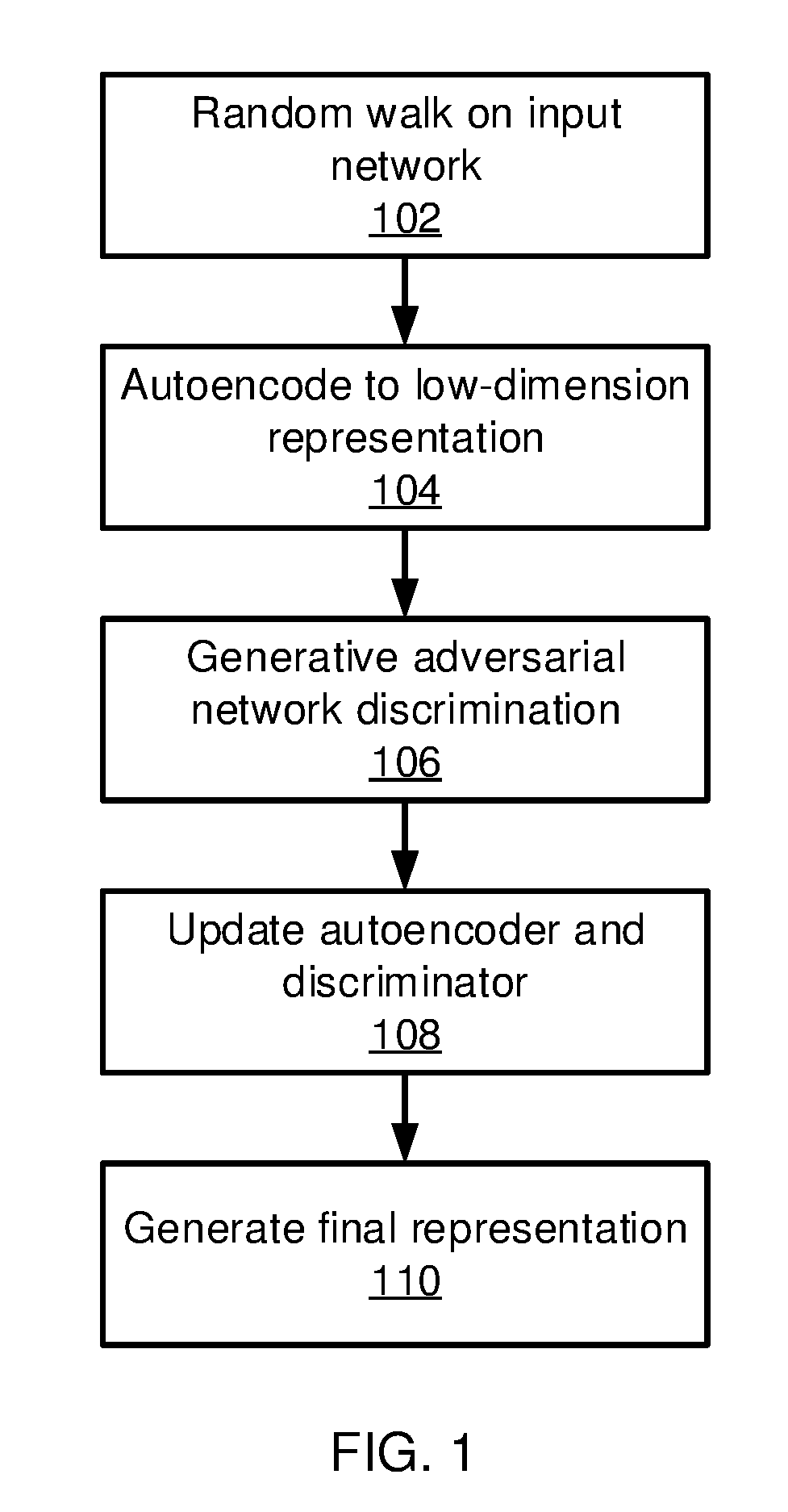
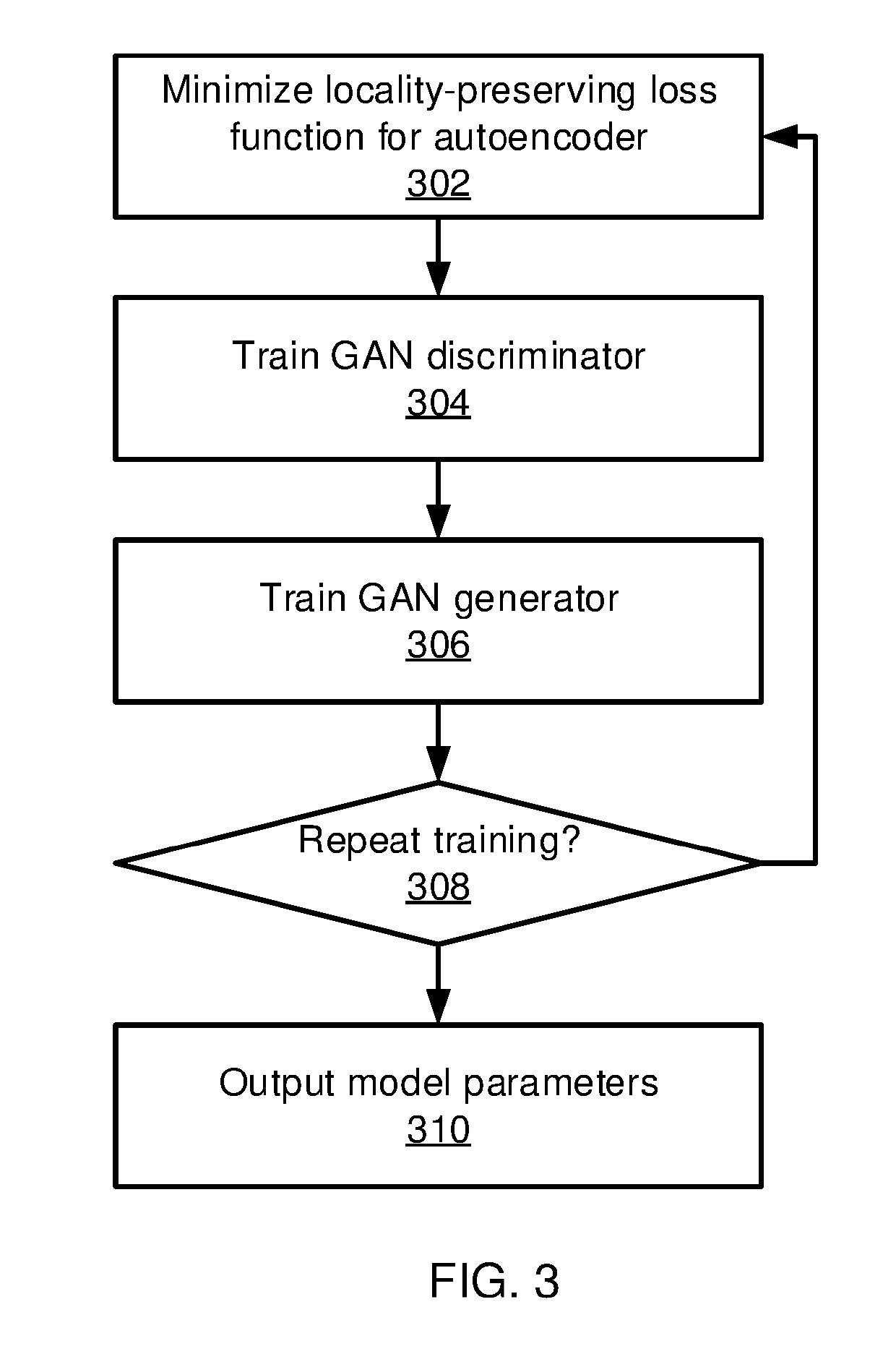
Deep Network Embedding with Adversarial Regularization
ActiveUS20190130212A1Minimize loss functionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDiscriminatorAlgorithm
Methods and systems for embedding a network in a latent space include generating a representation of an input network graph in the latent space using an autoencoder model and generating a representation of a set of noise samples in the latent space using a generator model. A discriminator model discriminates between the representation of the input network graph and the representation of the set of noise samples. The autoencoder model, the generator model, and the discriminator model are jointly trained by minimizing a joint loss function that includes parameters for each model. A final representation of the input network graph is generated using the trained autoencoder model.
Owner:NEC CORP
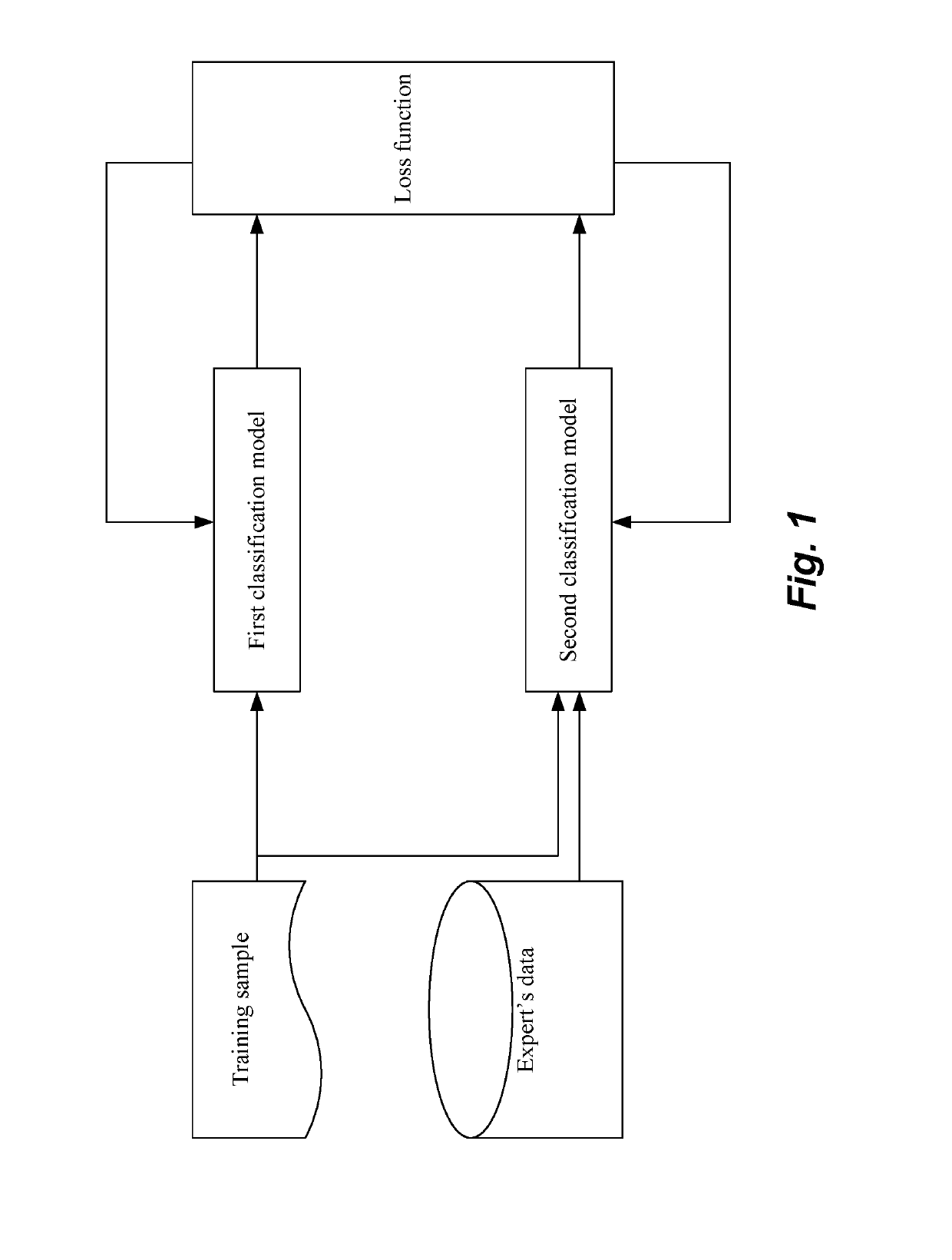
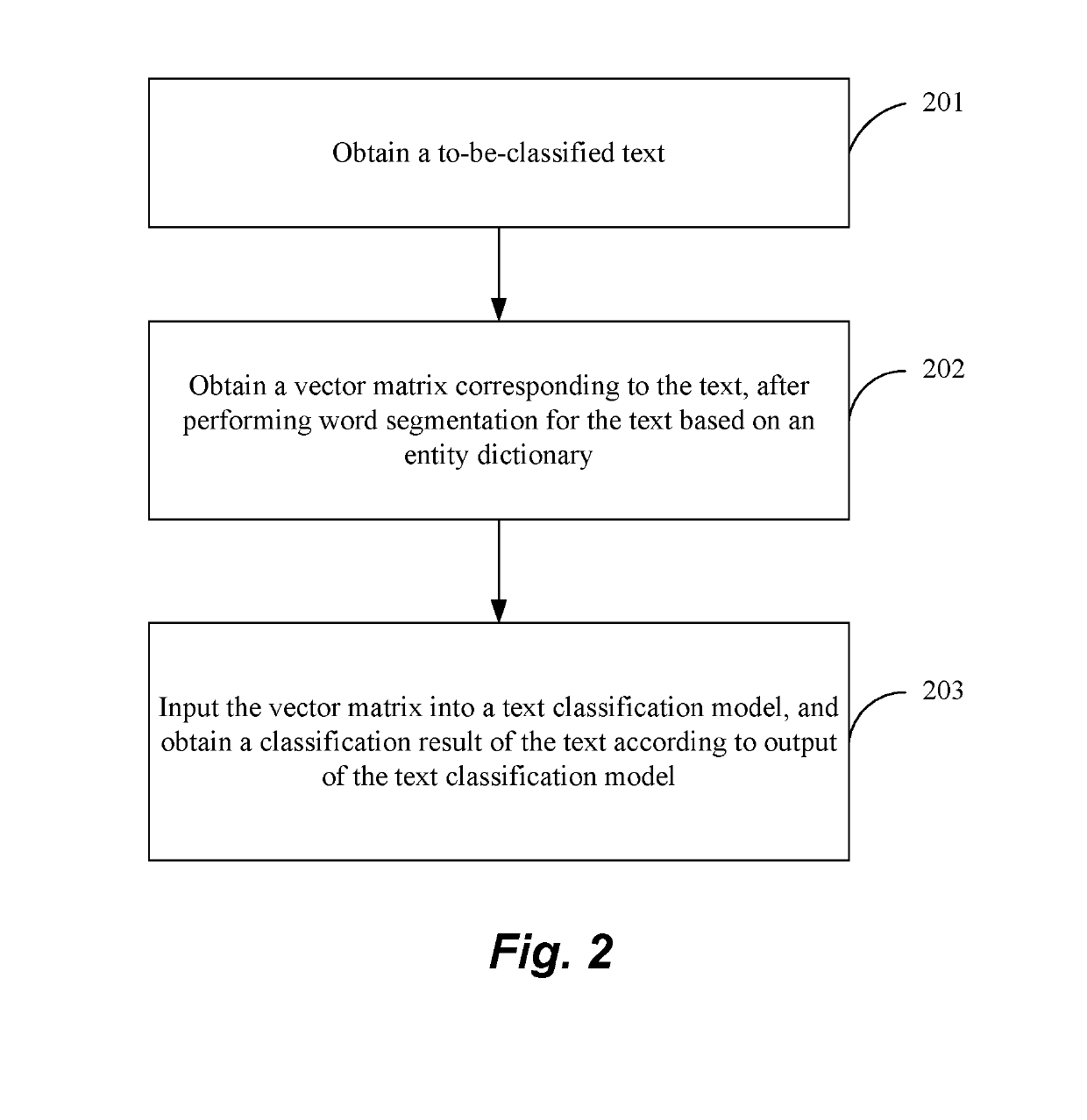
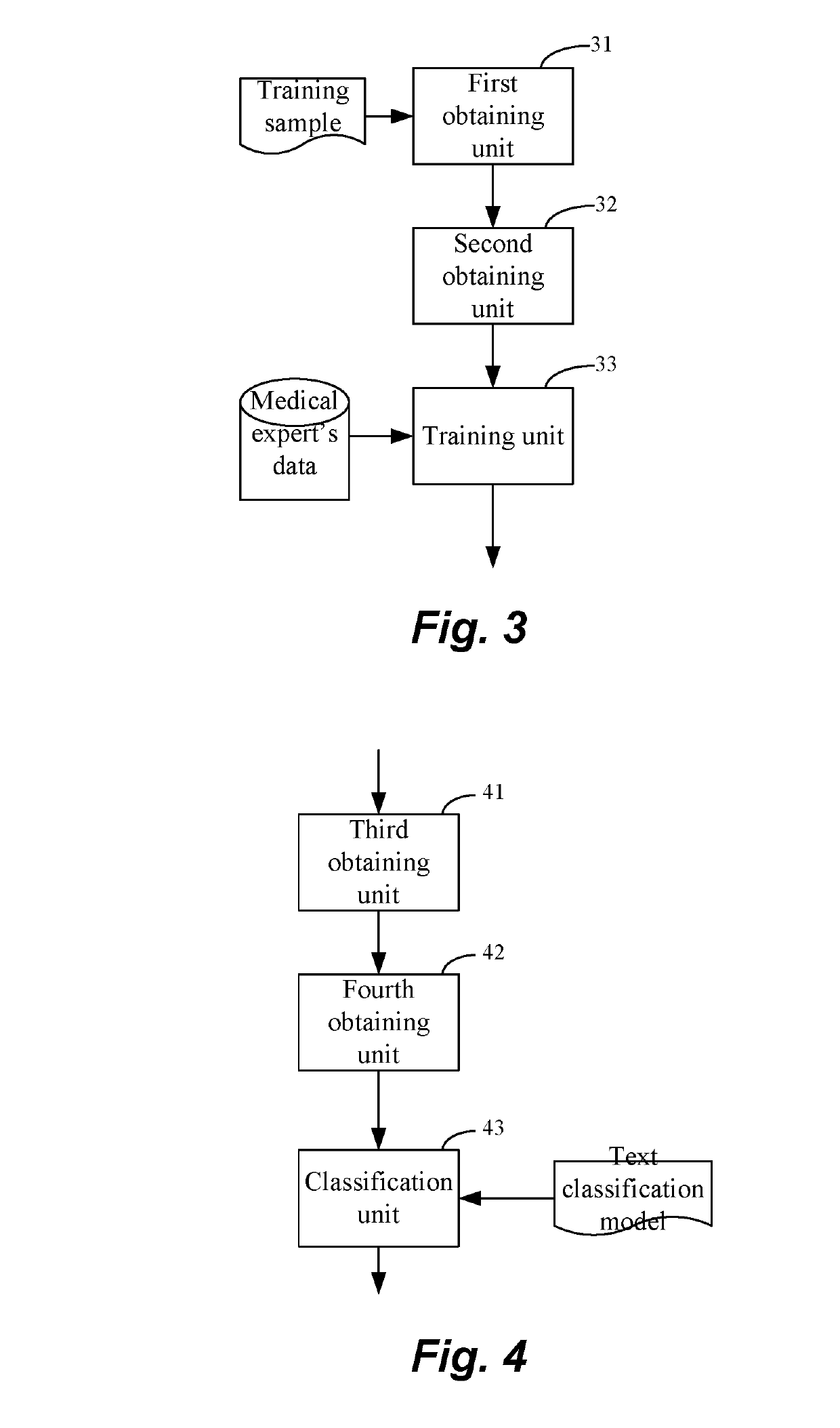
Method and apparatus for building text classification model, and text classification method and apparatus
ActiveUS20190095432A1Improving text classification effectImprove classification performanceNatural language translationSemantic analysisText categorizationAlgorithm
The present disclosure provides a method and apparatus for building a text classification model, and a text classification method and apparatus. The method of building a text classification model comprises: obtaining a training sample; obtaining a vector matrix corresponding to the text, after performing word segmentation for the text based on an entity dictionary; using the vector matrix corresponding to the text and a class of the text to train a first classification model and a second classification model respectively; during the training process, using a loss function of the first classification model and a loss function of the second classification model to obtain a loss function of the text classification model, and using the loss function of the text classification model to adjust parameters for the first classification model and the second classification model, to obtain the text classification model formed by the first classification model and the second classification model. The text classification method comprises: obtaining a to-be-classified text; obtaining a vector matrix corresponding to the text, after performing word segmentation for the text based on an entity dictionary; inputting the vector matrix into a text classification model, and obtaining a classification result of the text according to output of the text classification model. The text classification effect can be improved through the technical solutions of the present disclosure.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Utilizing discourse structure of noisy user-generated content for chatbot learning
ActiveUS20180357221A1Minimize loss functionSemantic analysisKernel methodsUser-generated contentParse tree
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention uses noisy-robust discourse trees to determine a rhetorical relationship between one or more sentences. In an example, a rhetoric classification application creates a noisy-robust communicative discourse tree. The application accesses a document that includes a first sentence, a second sentence, a third sentence, and a fourth sentence. The application identifies that syntactic parse trees cannot be generated for the first sentence and the second sentence. The application further creates a first communicative discourse tree from the second, third, and fourth sentences and a second communicative discourse tree from the first, third, and fourth sentences. The application aligns the first communicative discourse tree and the second communicative discourse tree and removes any elementary discourse units not corresponding to a relationship that is in common between the first and second communicative discourse trees.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data loss prevention system for cloud security based on document discourse analysis
ActiveUS20180365593A1Avoid spreadingMinimize loss functionMathematical modelsEnsemble learningVerbnounData loss
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention are related to determining a document classification. For example, a document classification application generates a set of discourse trees, each discourse tree corresponding to a sentence of a document and including a rhetorical relationship that relates two elementary discourse units. The document classification application creates one or more communicative discourse trees from the discourse trees by matching each elementary discourse unit in a discourse tree that has a verb to a verb signature. The document classification application combines the first communicative discourse tree and the second communicative discourse tree into a parse thicket and applies a classification model to the parse thicket in order to determine whether the document is public or private.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Automated 3D root shape prediction using deep learning methods
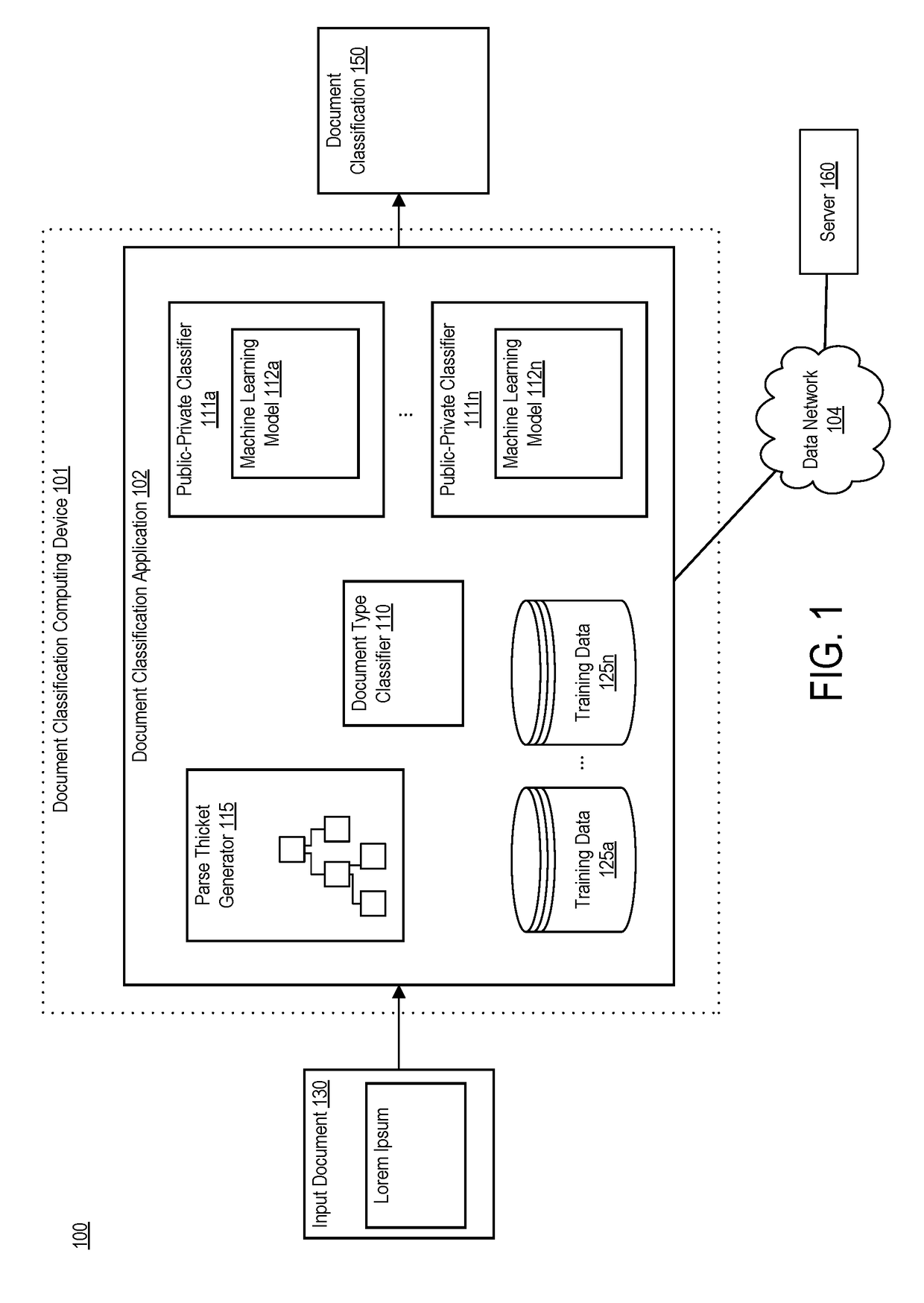
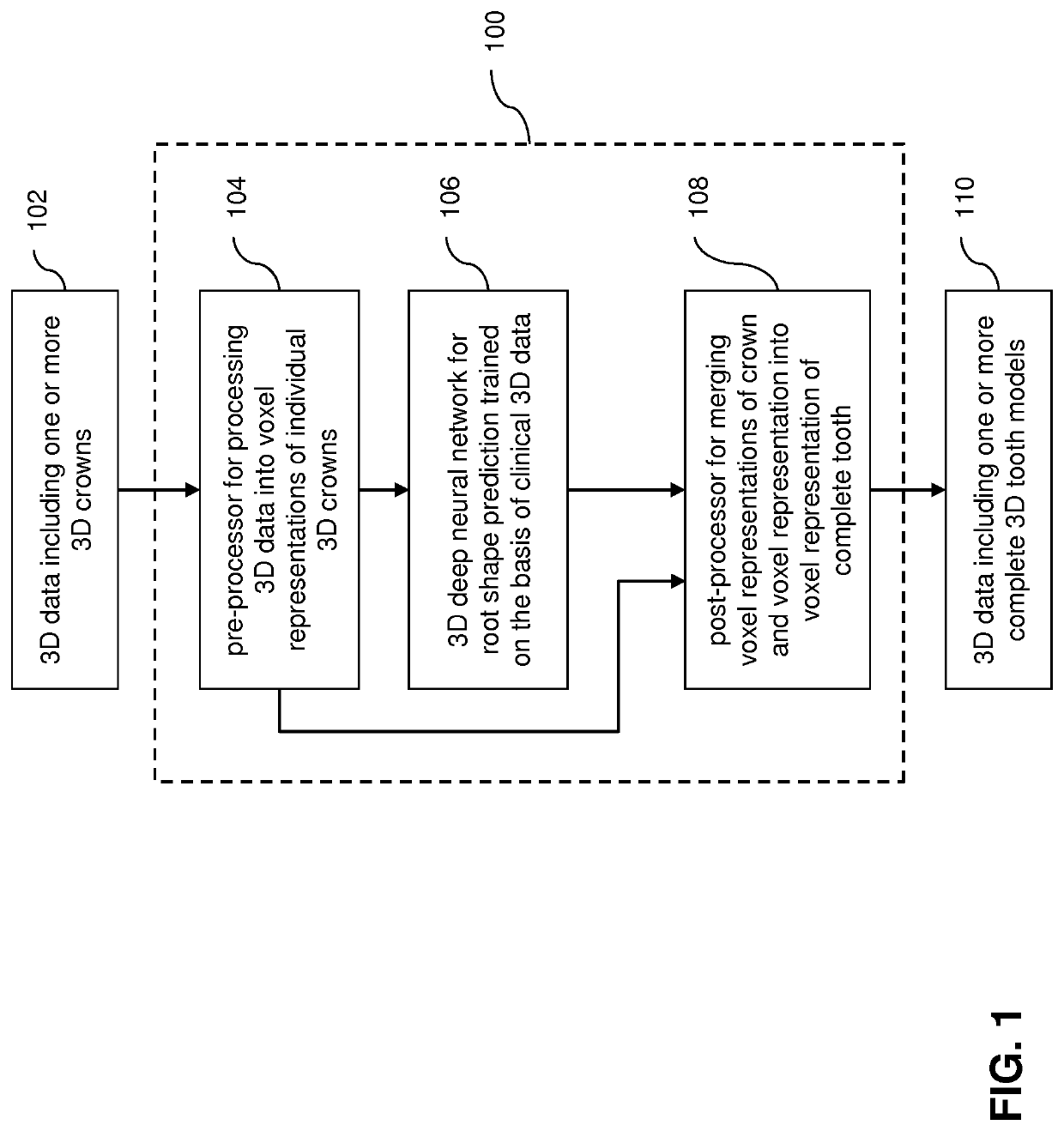
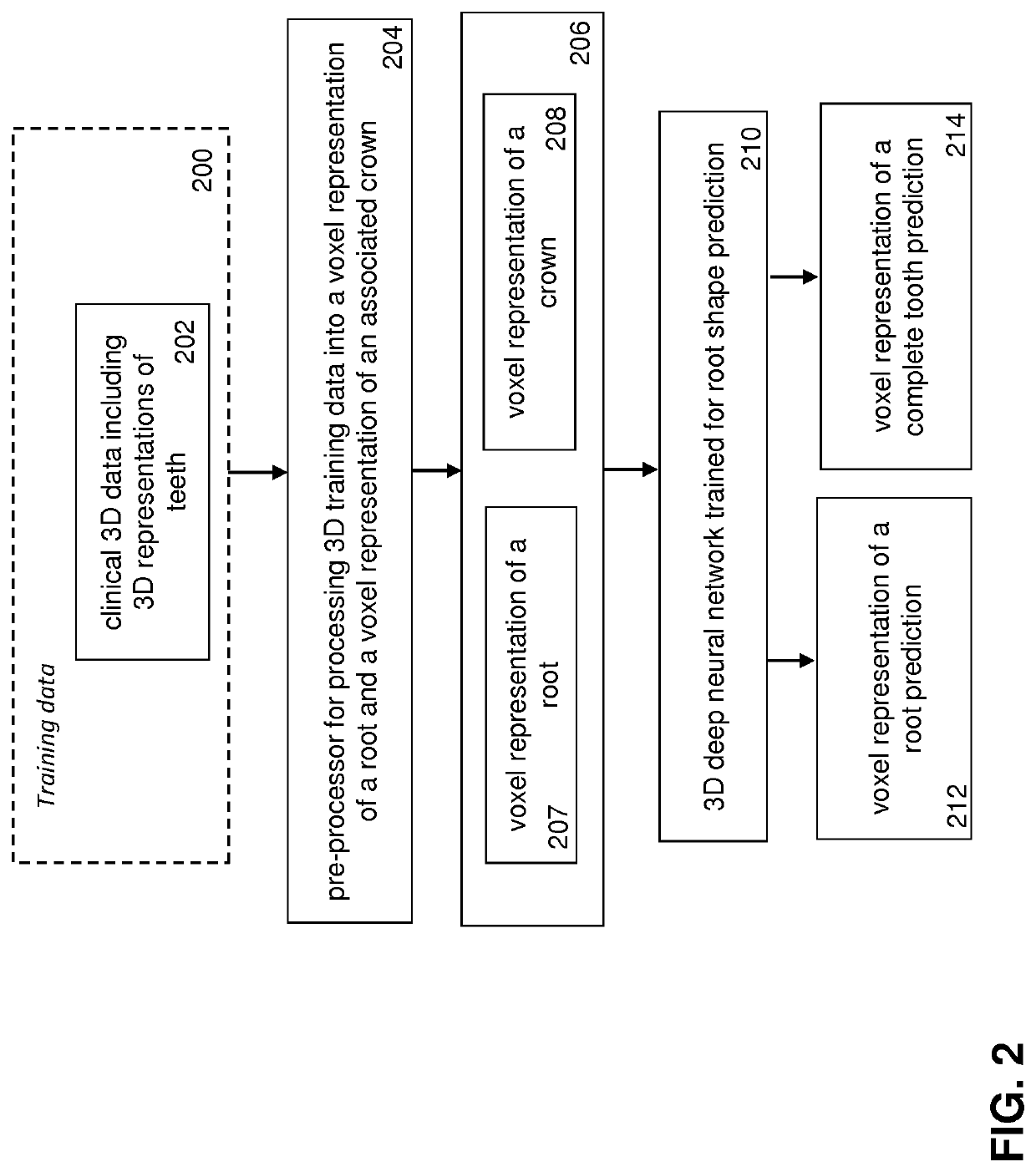
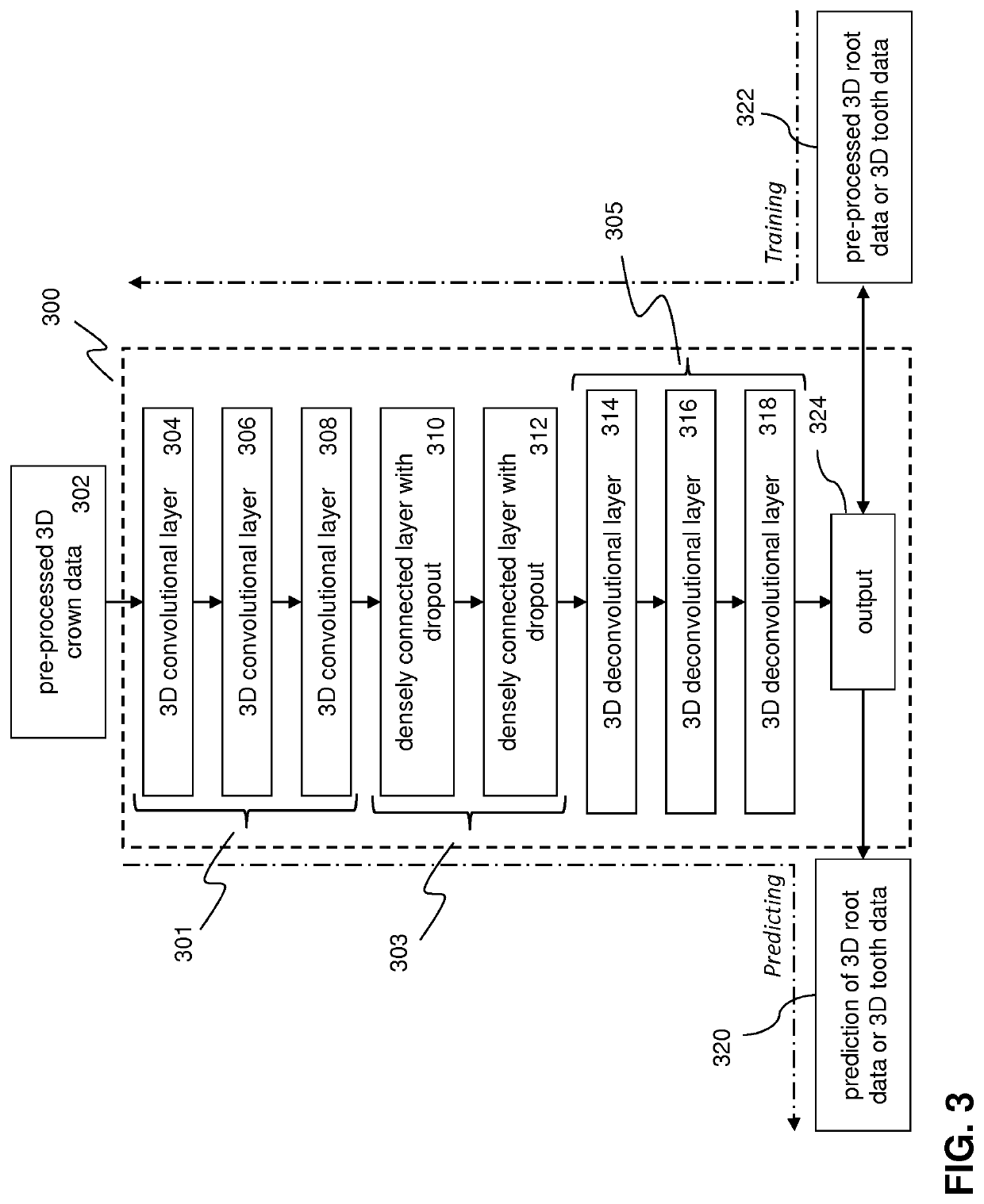
ActiveUS20210082184A1Minimize loss functionEfficient use ofImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsTooth crownData transformation
A computer-implemented method for automated 3D root shape prediction comprising: receiving data defining at least one 3D representation of a tooth and processing the data including: transforming at least part of the data into a voxel representation of a crown; a pre-processor providing the representation of the crown to the input of the neural network trained on clinical representations of real teeth; the first neural network generating a representation of a root or a tooth from the crown, wherein the generation of the representation of the root or tooth includes: determining voxel activations in a voxel space of the output of the deep learning network, each activation representing a probability measure defining the probability that a voxel is part of the root or the tooth; and, determining whether a voxel activation is part of the root or the tooth by comparing the voxel activation with a voxel activation threshold value.
Owner:PROMATON HLDG BV
Systems, methods, and computer program products for searching and sorting images by aesthetic quality
ActiveUS9659384B2Minimize loss functionDigital data information retrievalImage codingNetwork onComputer vision
A system, method, and computer program product for assigning an aesthetic score to an image. A method of the present invention includes receiving an image. The method further includes executing a neural network on the image to generate learned features. The method further includes applying a machine-learned model to assign an aesthetic score to the image, where a more aesthetically-pleasing image is given a higher aesthetic score and a less aesthetically-pleasing image is given a lower aesthetic score. The learned features are inputs to the machine-learned model.
Owner:EYEEM MOBILE
Data loss prevention system for cloud security based on document discourse analysis
ActiveUS11100144B2Avoid spreadingMinimize loss functionEnsemble learningKernel methodsVerbnounData loss
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention are related to determining a document classification. For example, a document classification application generates a set of discourse trees, each discourse tree corresponding to a sentence of a document and including a rhetorical relationship that relates two elementary discourse units. The document classification application creates one or more communicative discourse trees from the discourse trees by matching each elementary discourse unit in a discourse tree that has a verb to a verb signature. The document classification application combines the first communicative discourse tree and the second communicative discourse tree into a parse thicket and applies a classification model to the parse thicket in order to determine whether the document is public or private.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
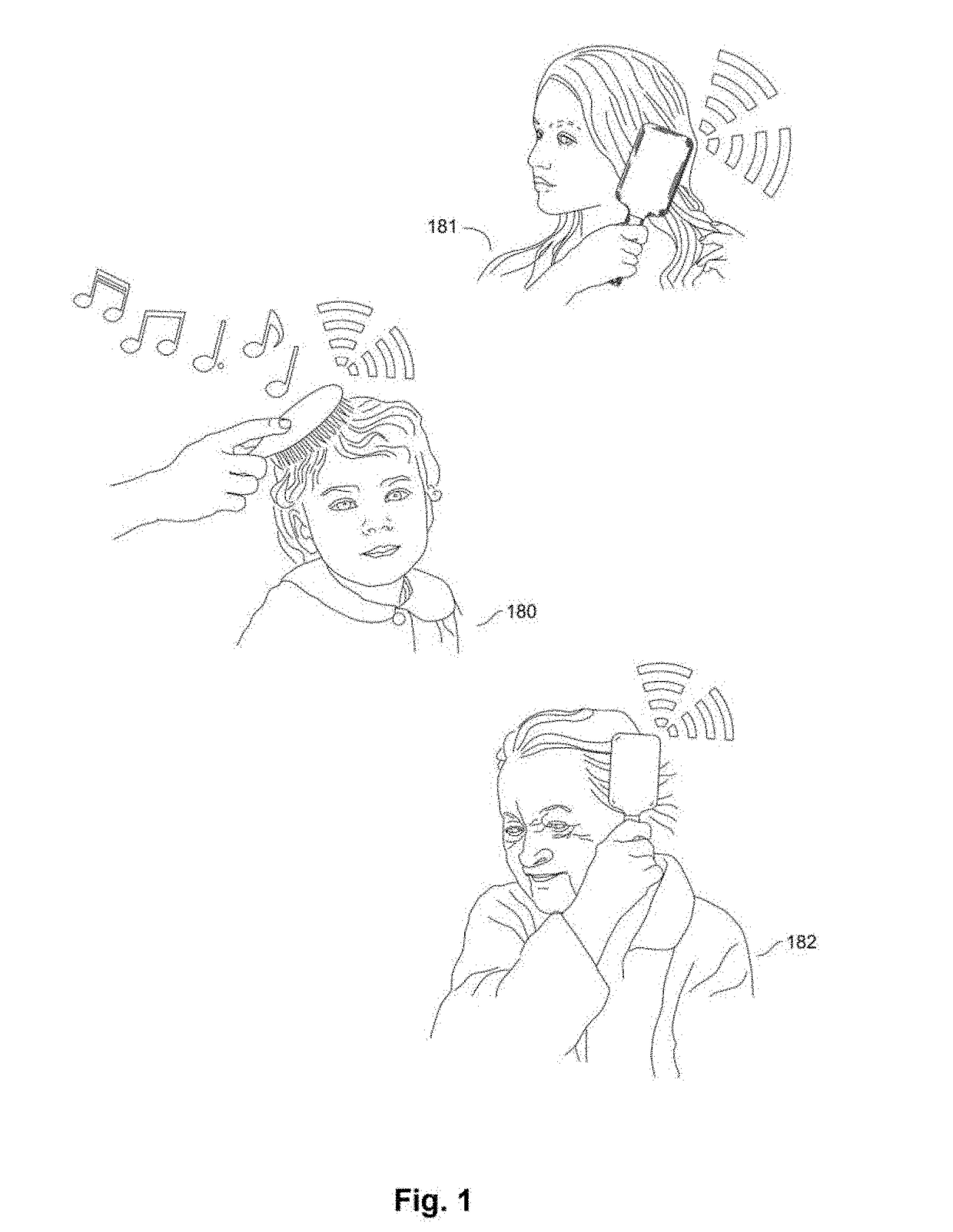
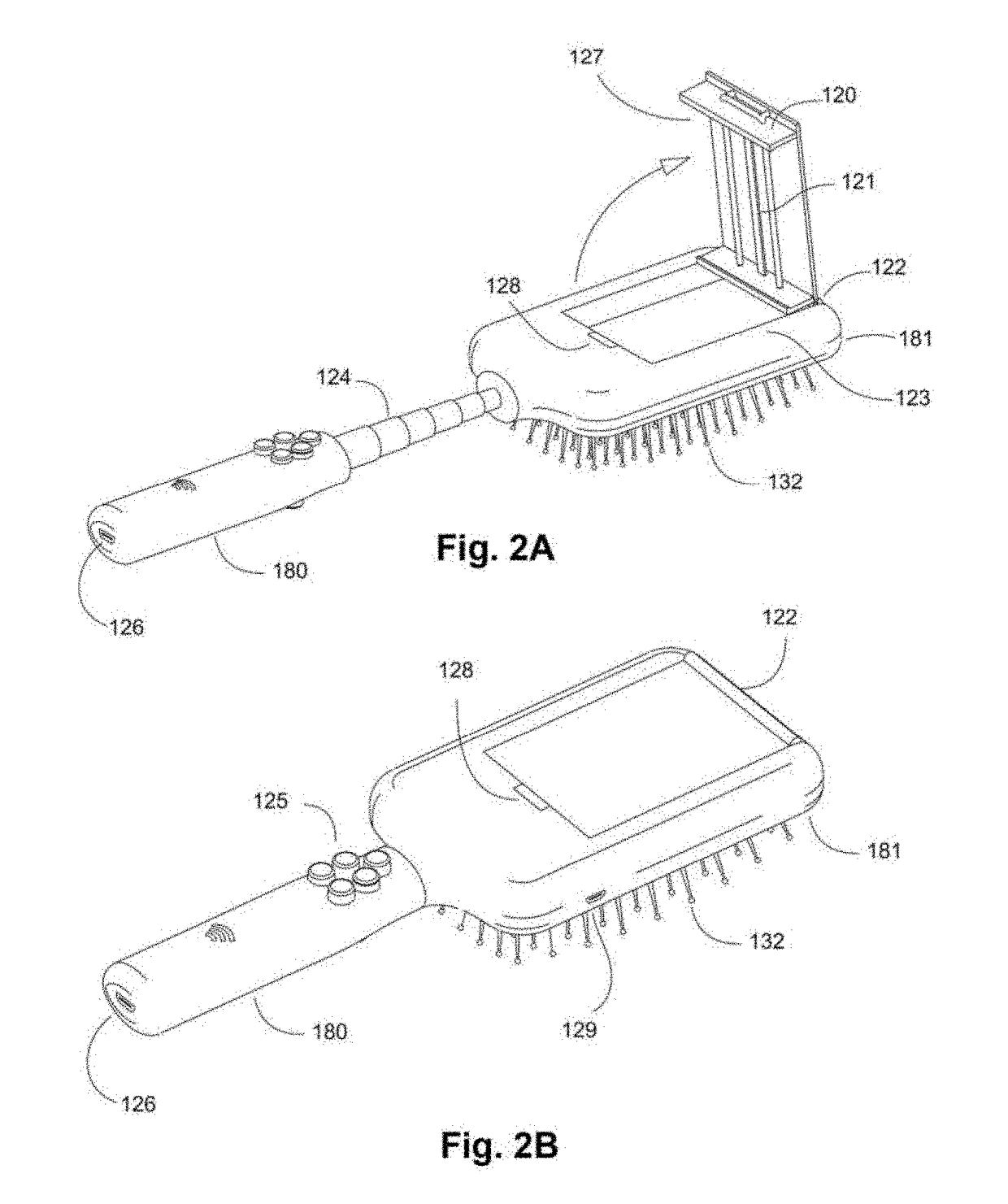
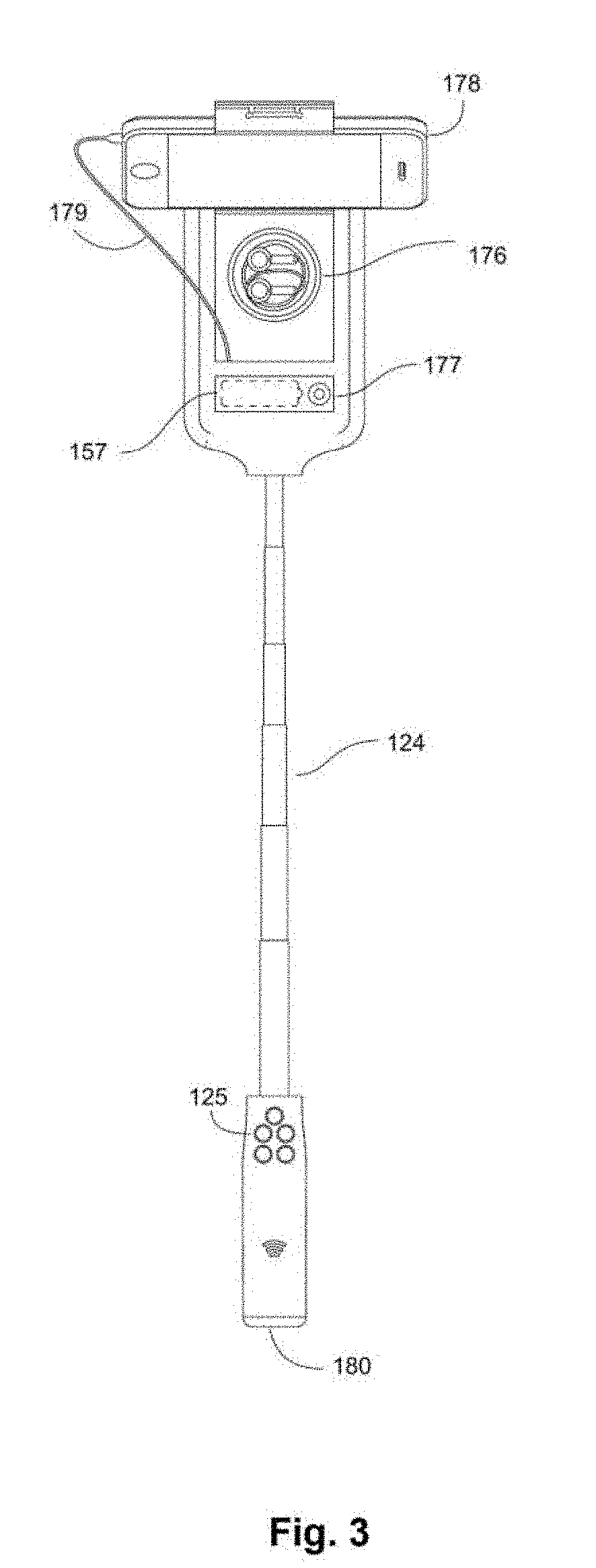
Smart Brushes and Accessories Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20190075922A1Optimize dataReliable and inexpensive and accurateTelevision system detailsBrush bodiesModem deviceElectrical battery
The present invention comprises systems and methods for using a specialized styling device, such as a smart hairbrush, smart comb, or accessories, which allow for the collection of data from the devices, and for users to interact over a wireless network. The devices may including a wireless radio frequency modem connected to the internet and a battery to power components, including lights, speakers, cameras, microphones, and sensors. A smart brush may allow for computations through processors, memory, system-on-a-chip, applications, batteries, operating systems, and wired or wireless communication interfaces. It is also possible for the smart brush to connect with other electronic devices, including phones, tablets, and cameras in order to share electrical power and communicate over one or more interfaces. A smart brush may operate as an independent mobile device or within a smart home or other system with multiple computing devices, appliances, and sensors connected together within a network.
Owner:RIVERA MANOLO FABIO
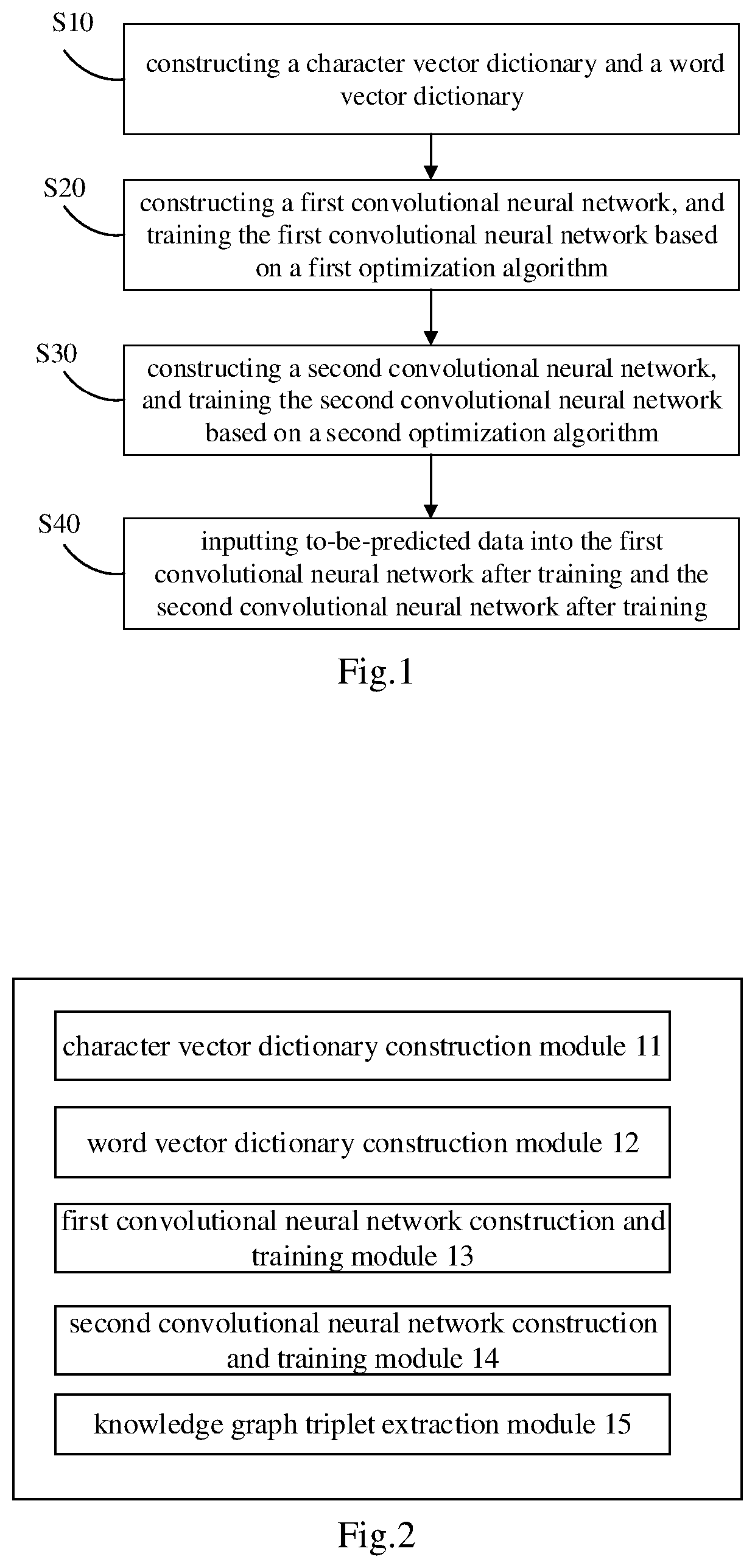
Method, equipment, computing device and computer-readable storage medium for knowledge extraction based on textcnn
ActiveUS20210216880A1Improve model training efficiencyImprove computing efficiencySemantic analysisKernel methodsAlgorithmKnowledge extraction
The application discloses a method for knowledge extraction based on TextCNN, comprising: S10, collecting first training data, and constructing a character vector dictionary and a word vector dictionary; S20, constructing a first convolutional neural network, and training the first convolutional neural network based on a first optimization algorithm, the first convolutional neural network comprises a first embedding layer, a first multilayer convolution, and a first softmax function connected in turn; S30, constructing a second convolutional neural network, and training the second convolutional neural network based on a second optimization algorithm, the second convolutional neural network comprises a second embedding layer, a second multilayer convolution, a pooling layer, two fully-connected layers and a second softmax function, the second embedding layer connected in turn; S40, extracting a knowledge graph triple of the to-be-predicted data according to an entity tagging prediction output by the first trained convolutional neural network and an entity relationship prediction output by the second trained convolutional neural network.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
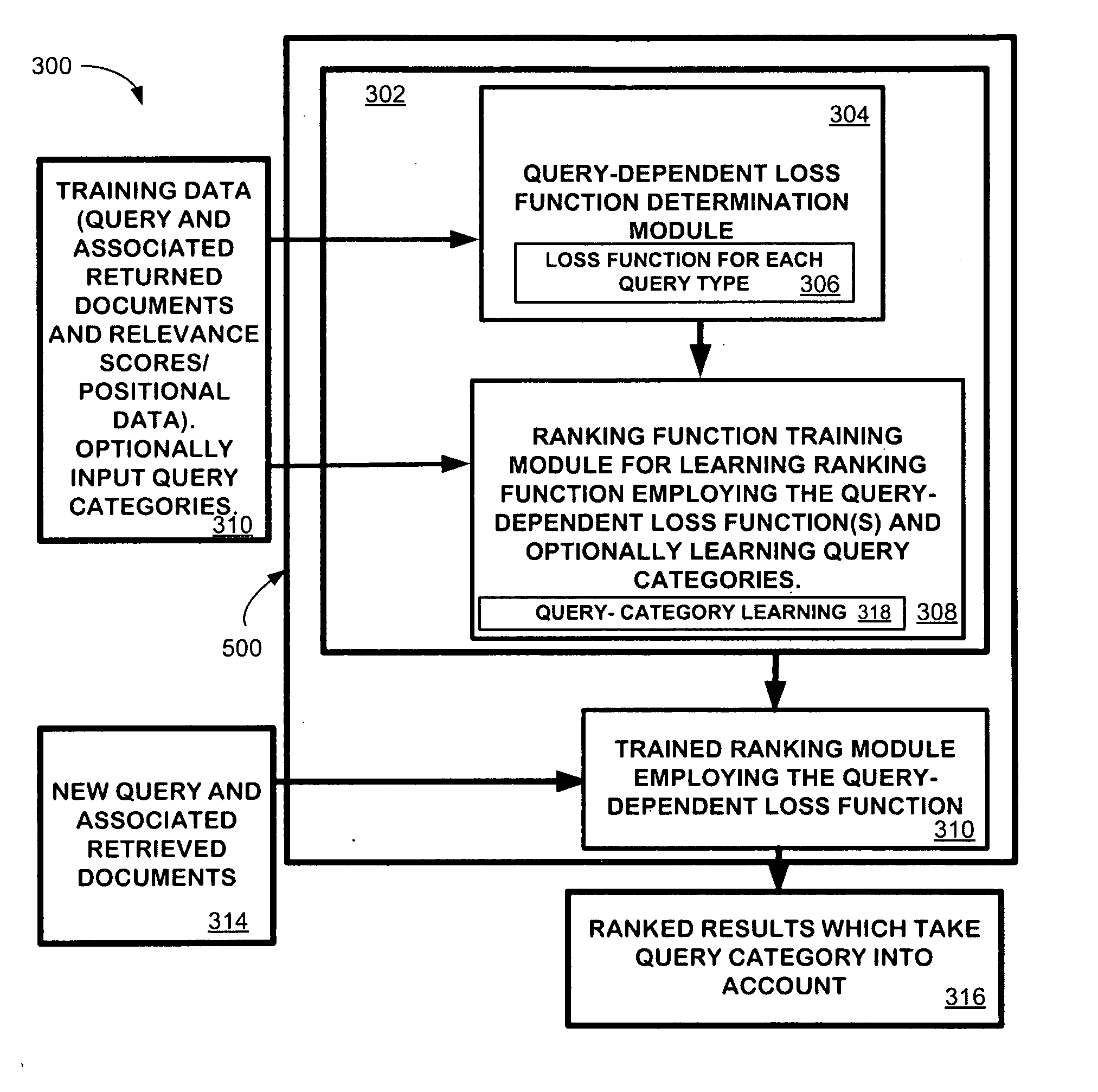
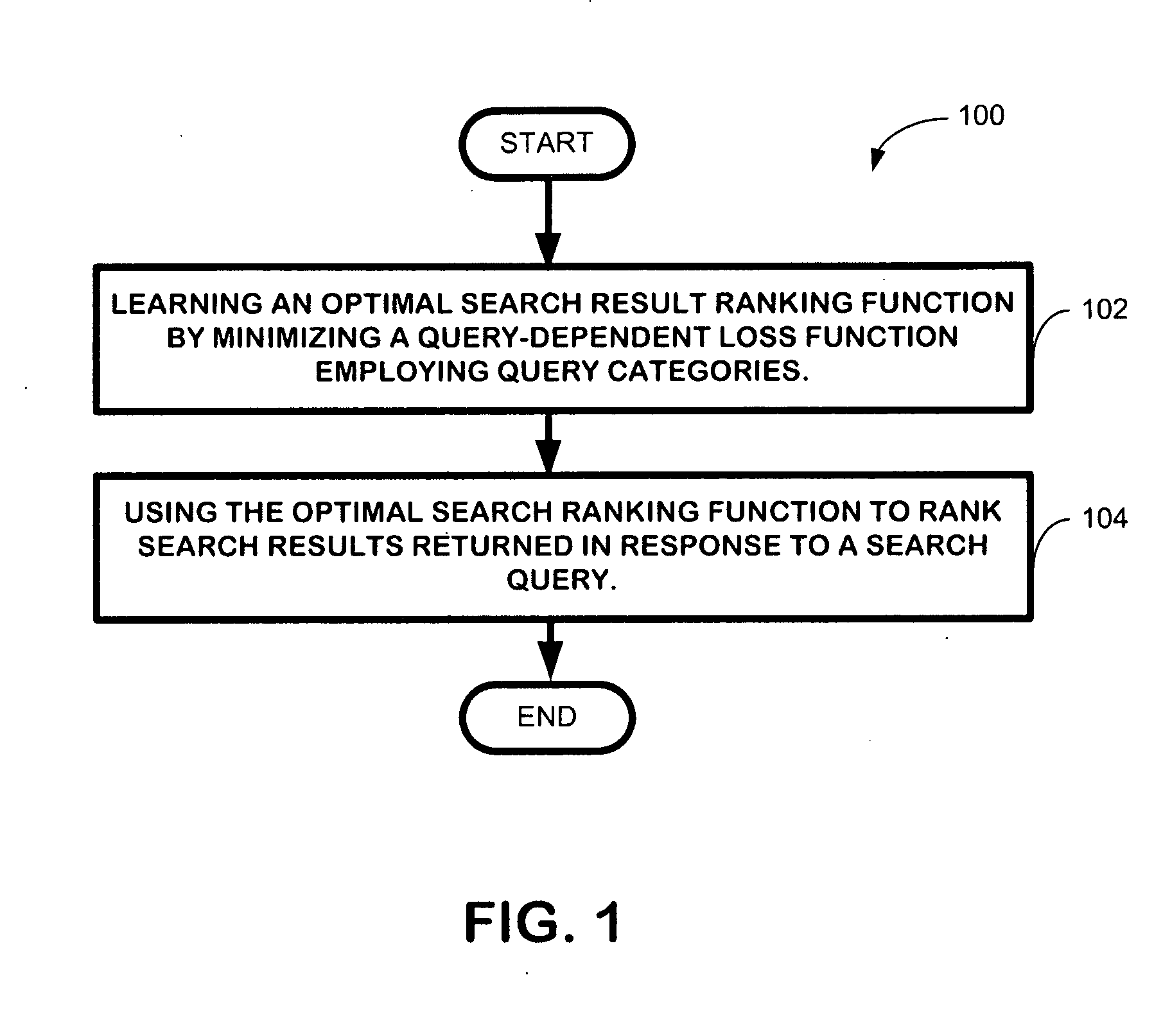
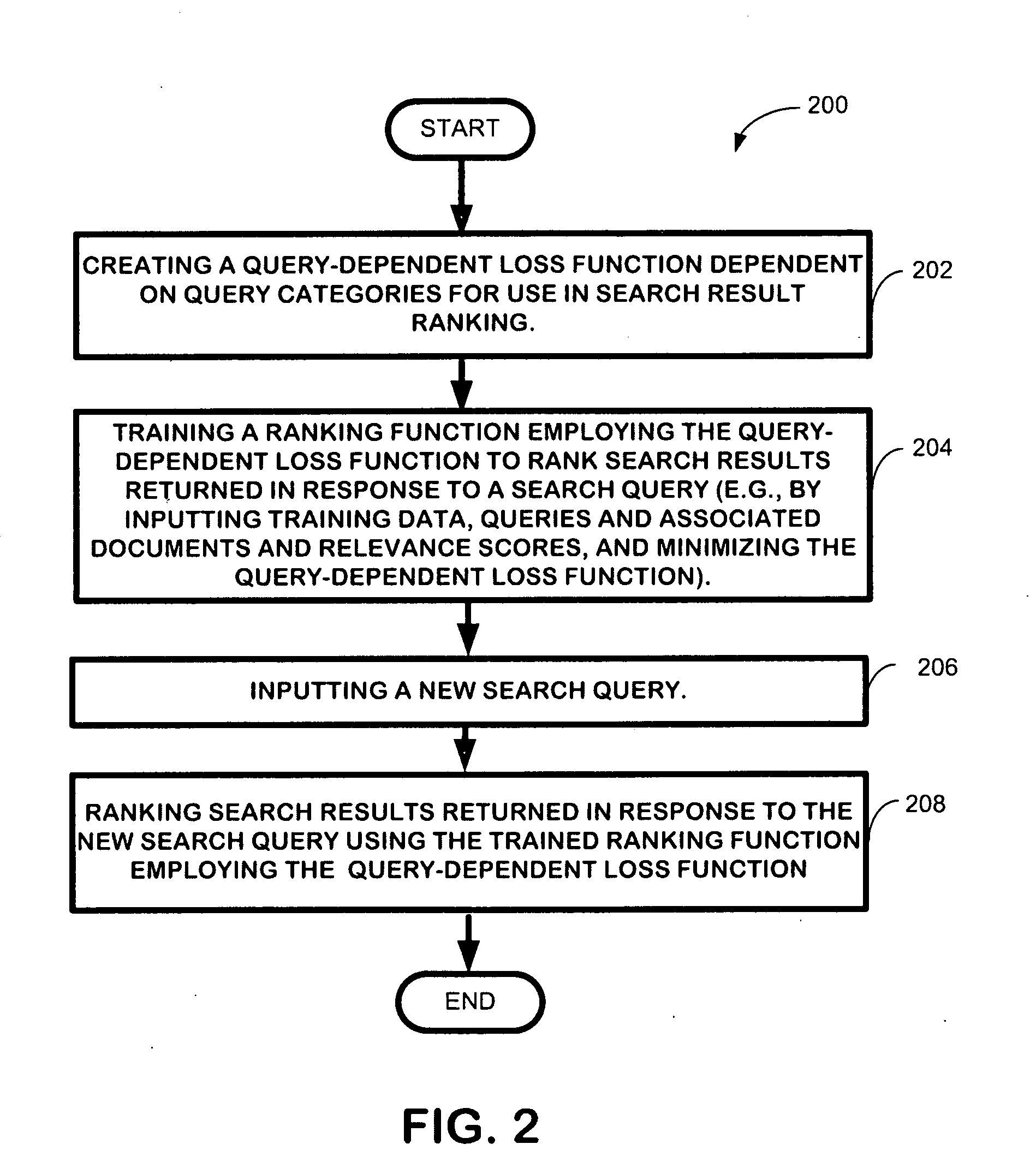
Learning to rank using query-dependent loss functions
InactiveUS20100257167A1Minimize loss functionTuning of ranking models theoretically sound and practically effectiveDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsFactoidLearning to rank
Queries describe users' search needs and therefore they play a role in the context of learning to rank for information retrieval and Web search. However, most existing approaches for learning to rank do not explicitly take into consideration the fact that queries vary significantly along several dimensions and require different objectives for the ranking models. The technique described herein incorporates query difference into learning to rank by introducing query-dependent loss functions. Specifically, the technique employs query categorization to represent query differences and employs specific query-dependent loss functions based on such kind of query differences. The technique employs two learning methods. One learns ranking functions with pre-defined query difference, while the other one learns both of them simultaneously.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Training saliency
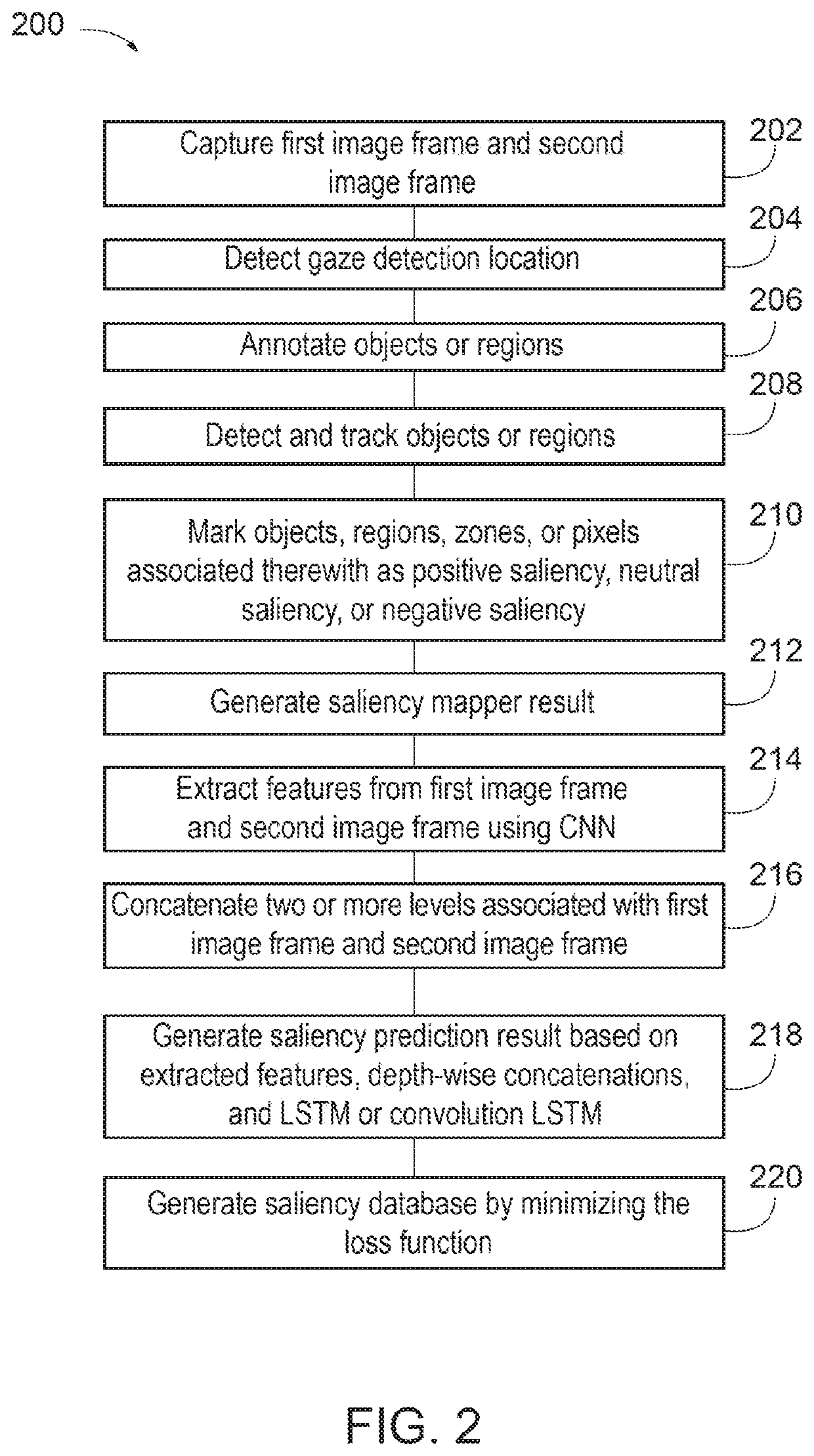
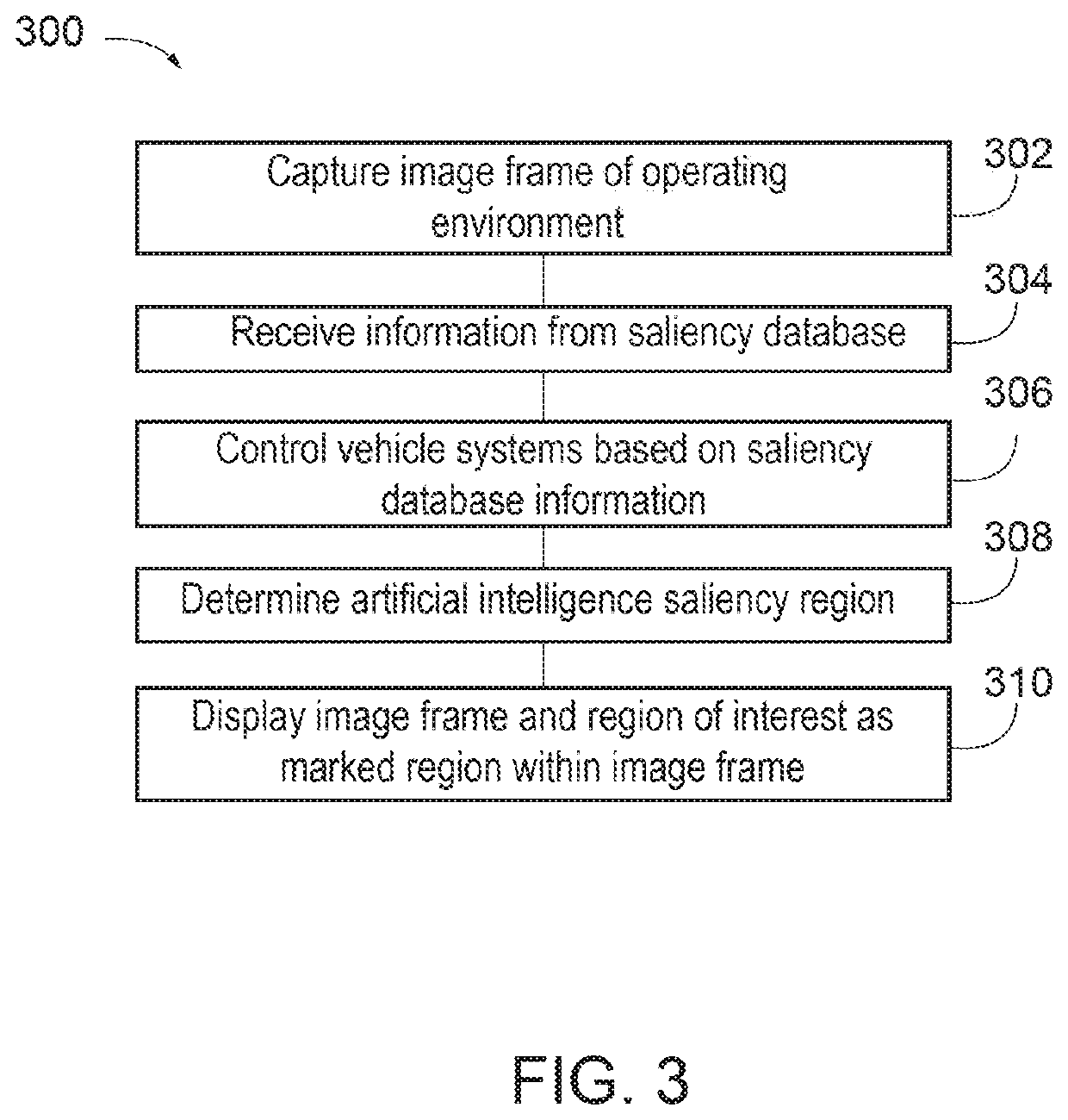
ActiveUS20200097754A1Minimize loss functionAutonomous decision making processCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorEnvironmental geology
Saliency training may be provided to build a saliency database, which may be utilized to facilitate operation of an autonomous vehicle. The saliency database may be built by minimizing a loss function between a saliency prediction result and a saliency mapper result. The saliency mapper result may be obtained from a ground truth database, which includes image frames of an operation environment where objects or regions within respective image frames are associated with a positive saliency, a neutral saliency, or a negative saliency. Neutral saliency may be indicative of a detected gaze location of a driver corresponding to the object or region at a time prior to the time associated with a given image frame. The saliency prediction result may be generated based on features extracted from respective image frames, depth-wise concatenations associated with respective image frames, and a long short-term memory layer or a recurrent neural network.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for extracting video preview, device and computer storage medium
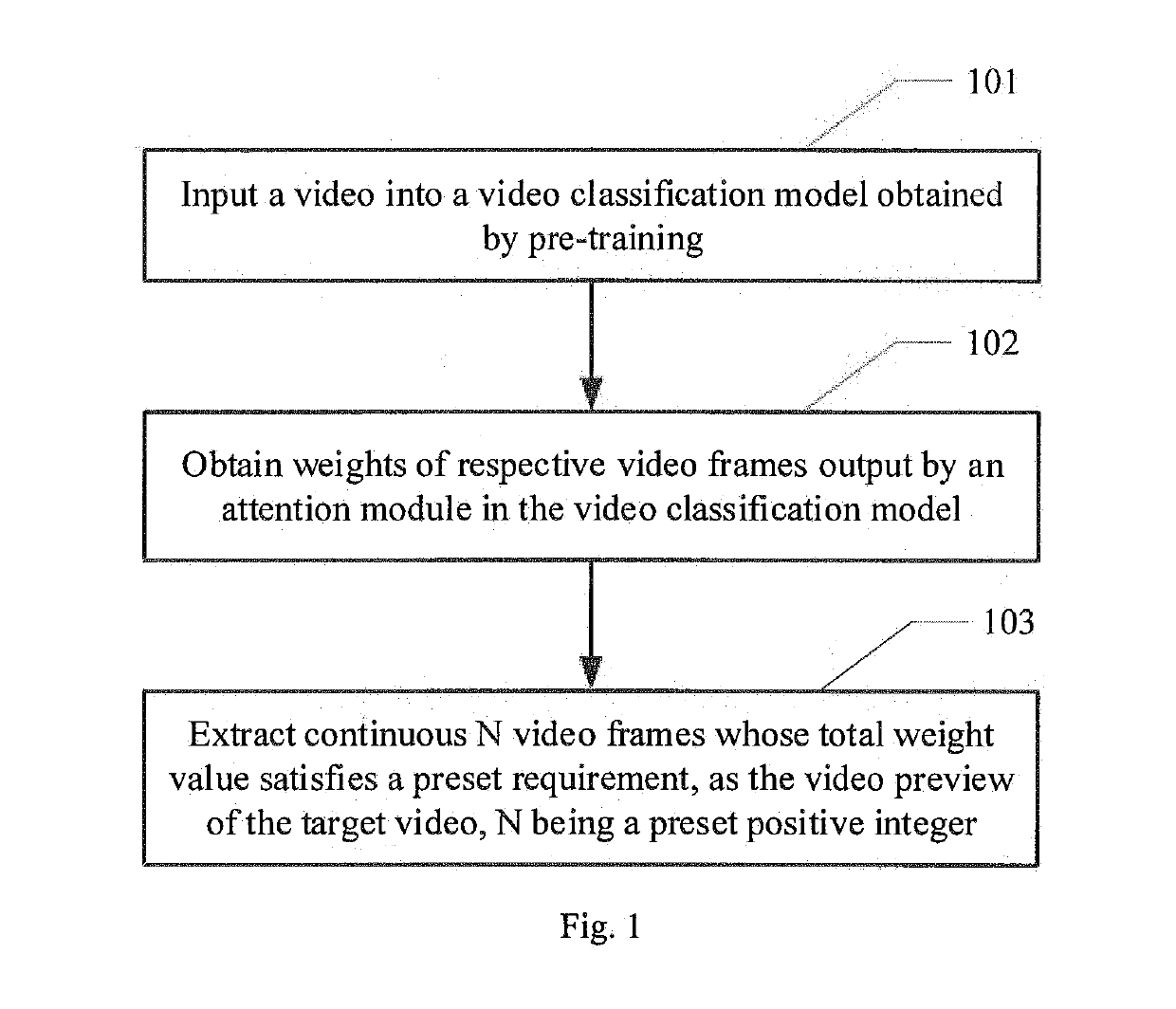
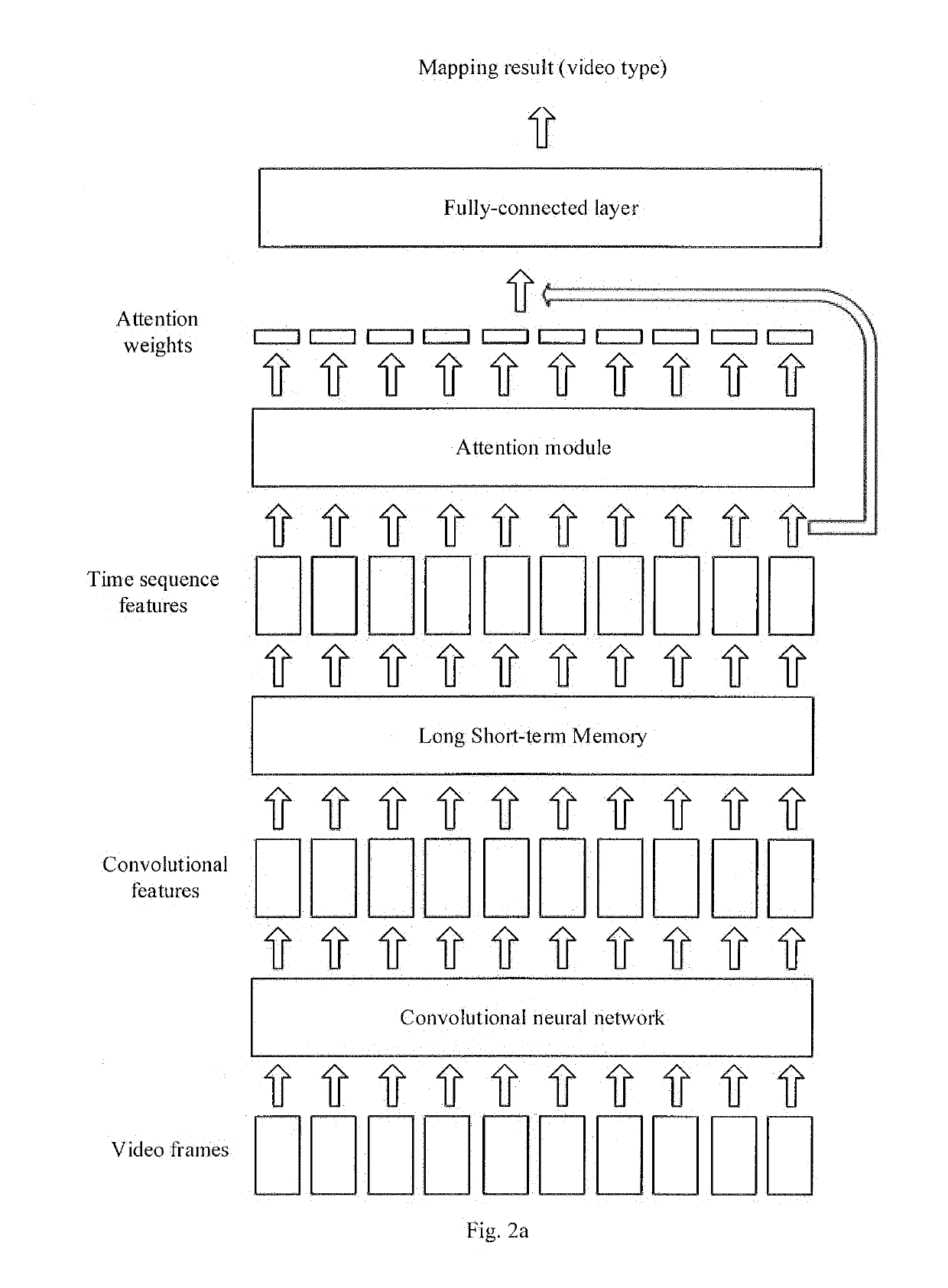
ActiveUS20190163981A1Reduce labor costsEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionSelective content distributionPattern recognitionComputer module
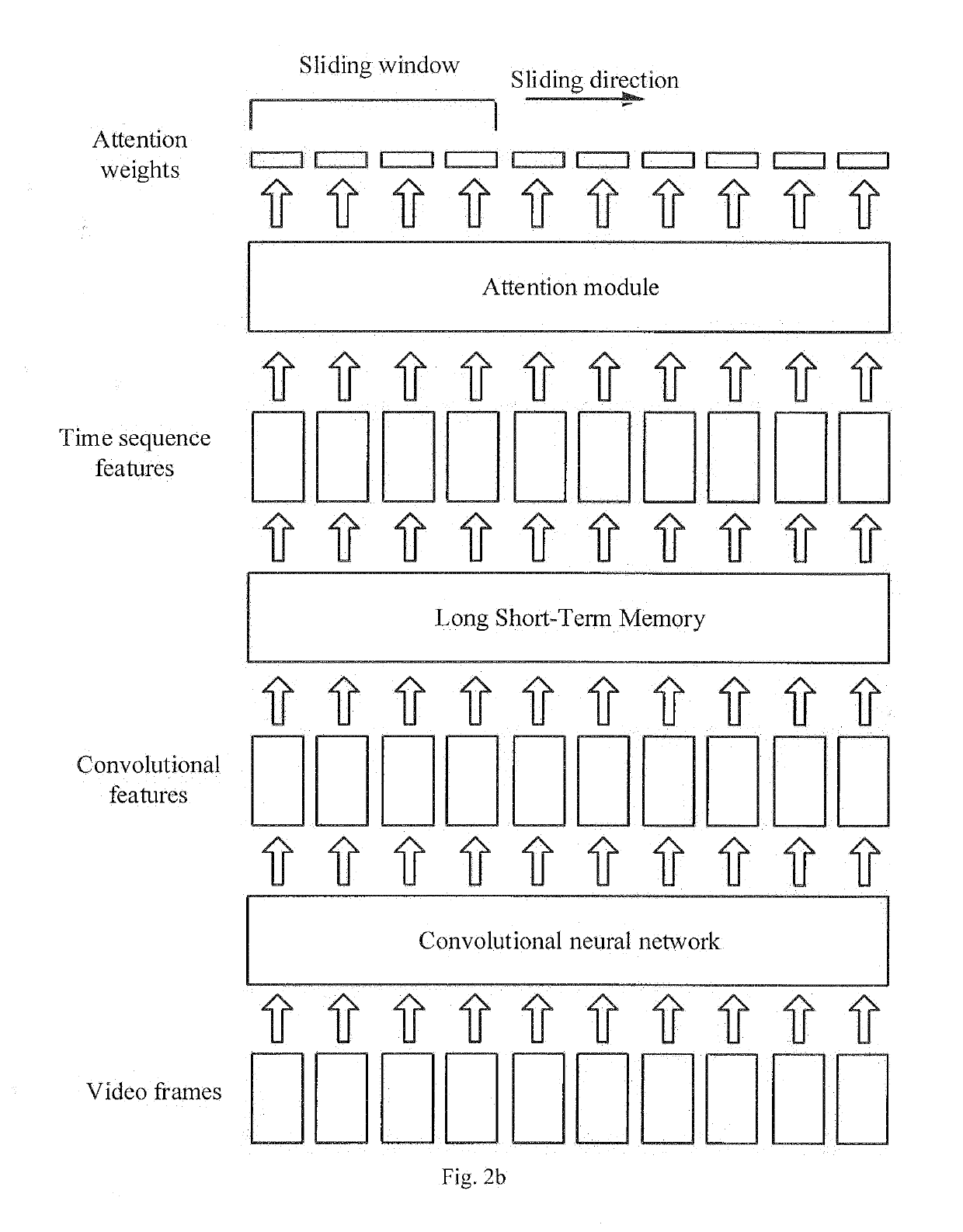
The present disclosure provides a method and apparatus for extracting a video preview, a device and a computer storage medium. The method comprises: inputting a video into a video classification model obtained by pre-training; obtaining weights of respective video frames output by an attention module in the video classification model; extracting continuous N video frames whose total weight value satisfies a preset requirement, as the video preview of the target video, N being a preset positive integer. It is possible to, in the manner provided by the present disclosure, automatically extract continuous video frames from the video as the video preview, without requiring manual clipping, and with manpower costs being reduced.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Neural network learning device and neural network learning method
InactiveUS20200012926A1Reduce weightReduce stepsImage codingDigital video signal modificationLearning unitNeural network learning
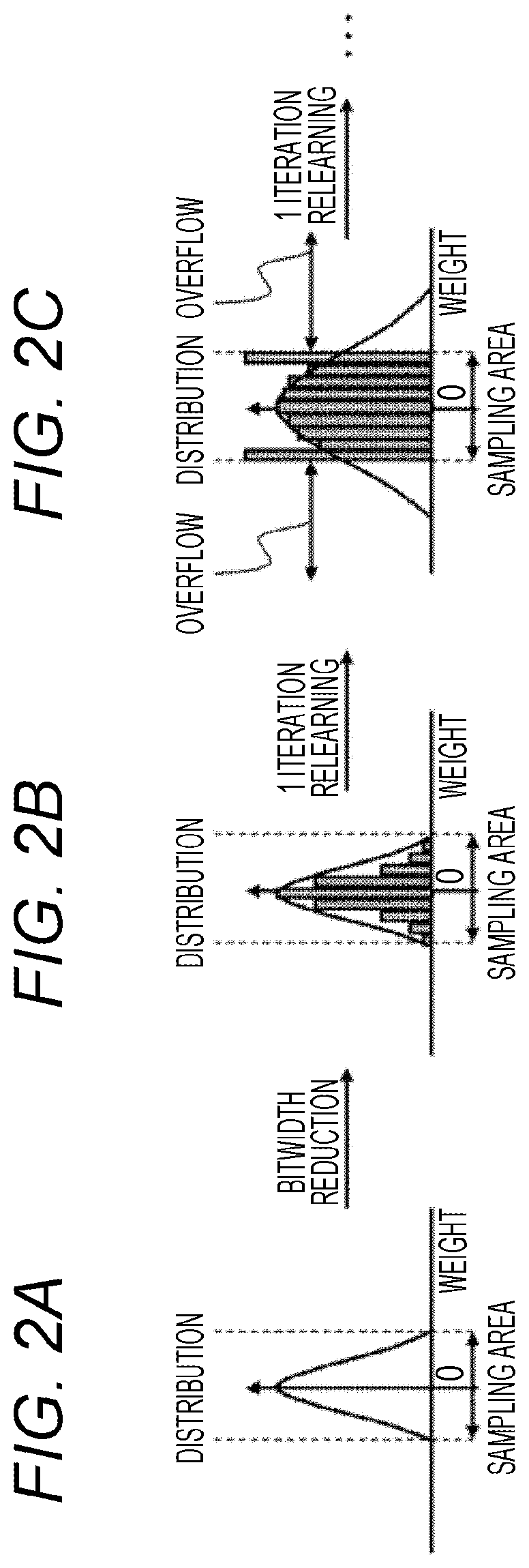
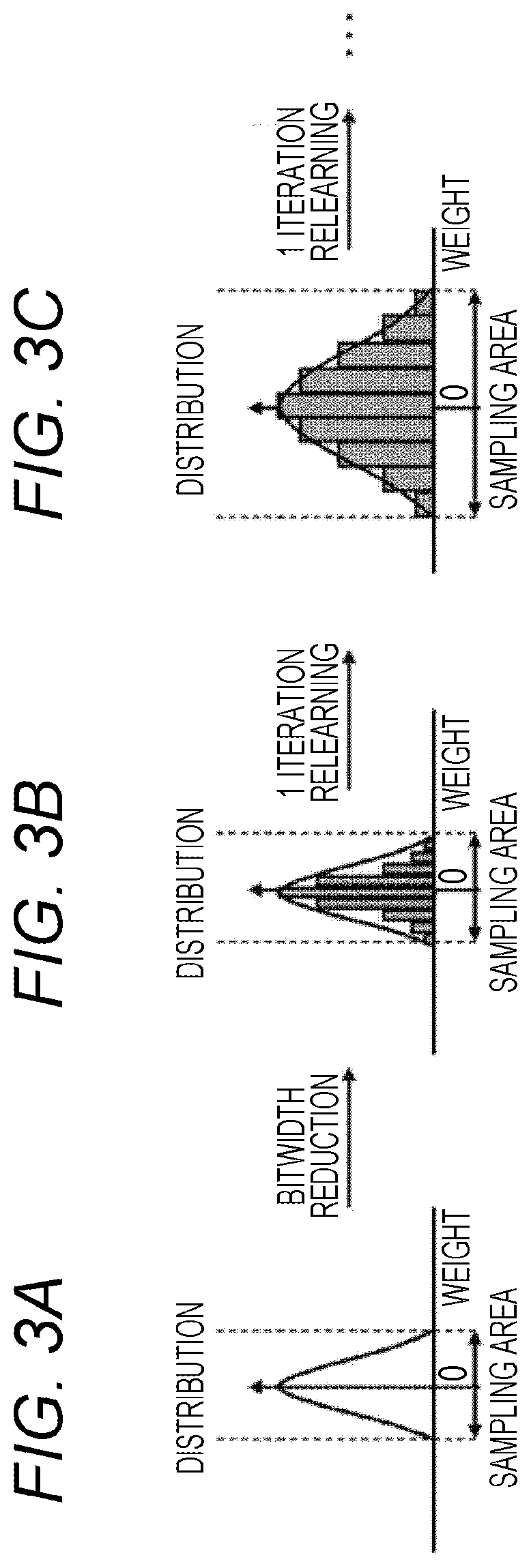
Provided is a learning device of a neural network including a bitwidth reducing unit, a learning unit, and a memory. The bitwidth reducing unit executes a first quantization that applies a first quantization area to a numerical value to be calculated in a neural network model. The learning unit performs learning with respect to the neural network model to which the first quantization has been executed. The bitwidth reducing unit executes a second quantization that applies a second quantization area to a numerical value to be calculated in the neural network model on which learning has been performed in the learning unit. The memory stores the neural network model to which the second quantization has been executed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Learning Method of Generative Adversarial Network with Multiple Generators for Image Denoising
ActiveUS20220092742A1Accelerate network trainingImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingAlgorithm
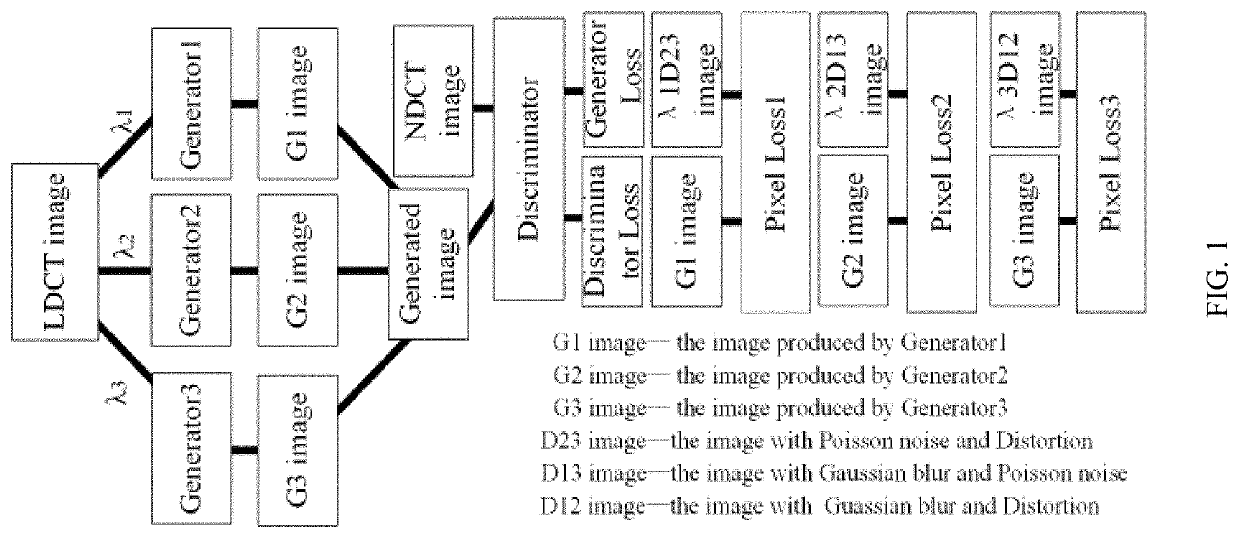
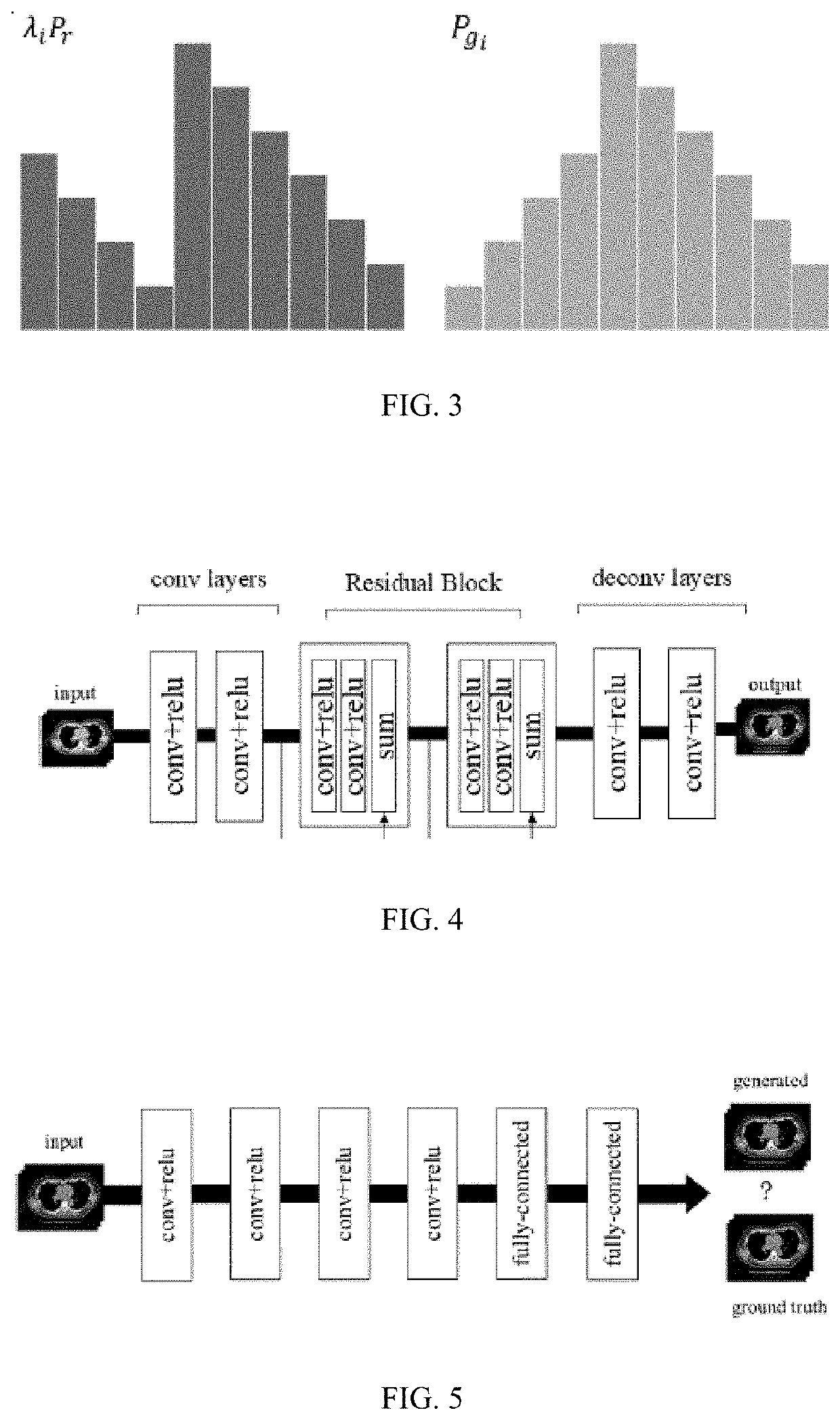
The present invention relates to a learning method of generative adversarial network (GAN) with multiple generators for image denoising, and provides a generative adversarial network with three generators. Such generators are used for removing Poisson noise, Gaussian blur noise and distortion noise respectively to improve the quality of low-dose CT (LDCT) images; the generators adopt the residual network structure. The mapped short connection used in the residual network can avoid the vanishing gradient problem in a deep neural network and accelerate the network training; the training of GAN is always a difficult problem due to the unreasonable measure between the generative distribution and real distribution. The present invention can stabilize training and enhance the robustness of training models by limiting the spectral norm of a weight matrix.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
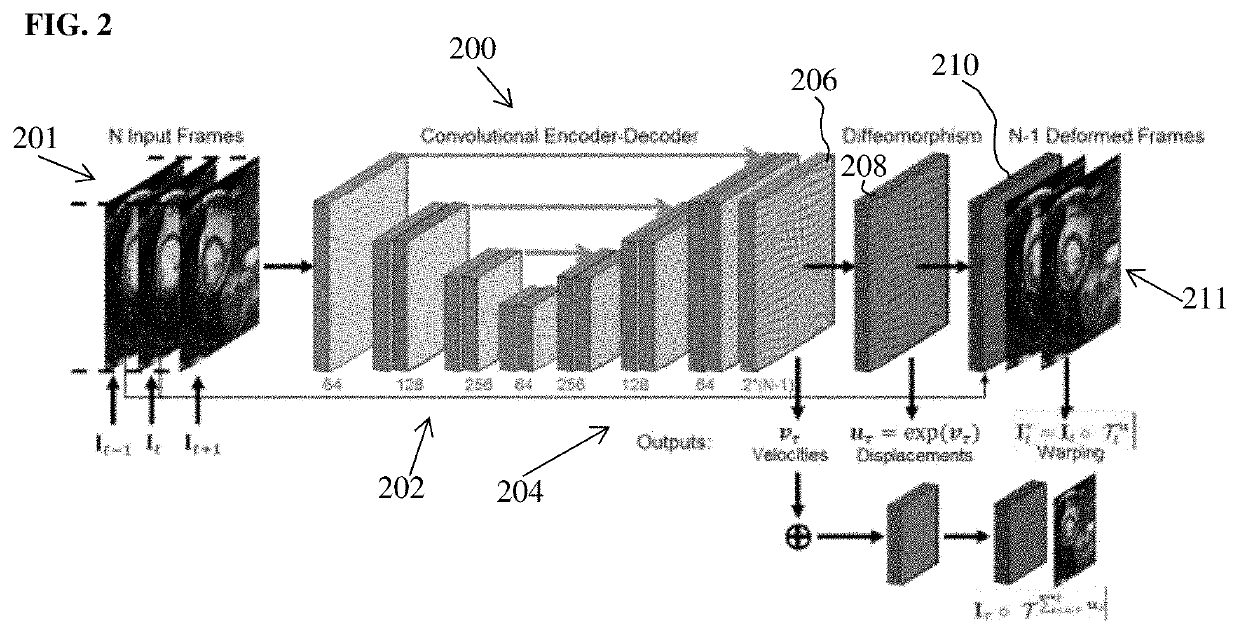
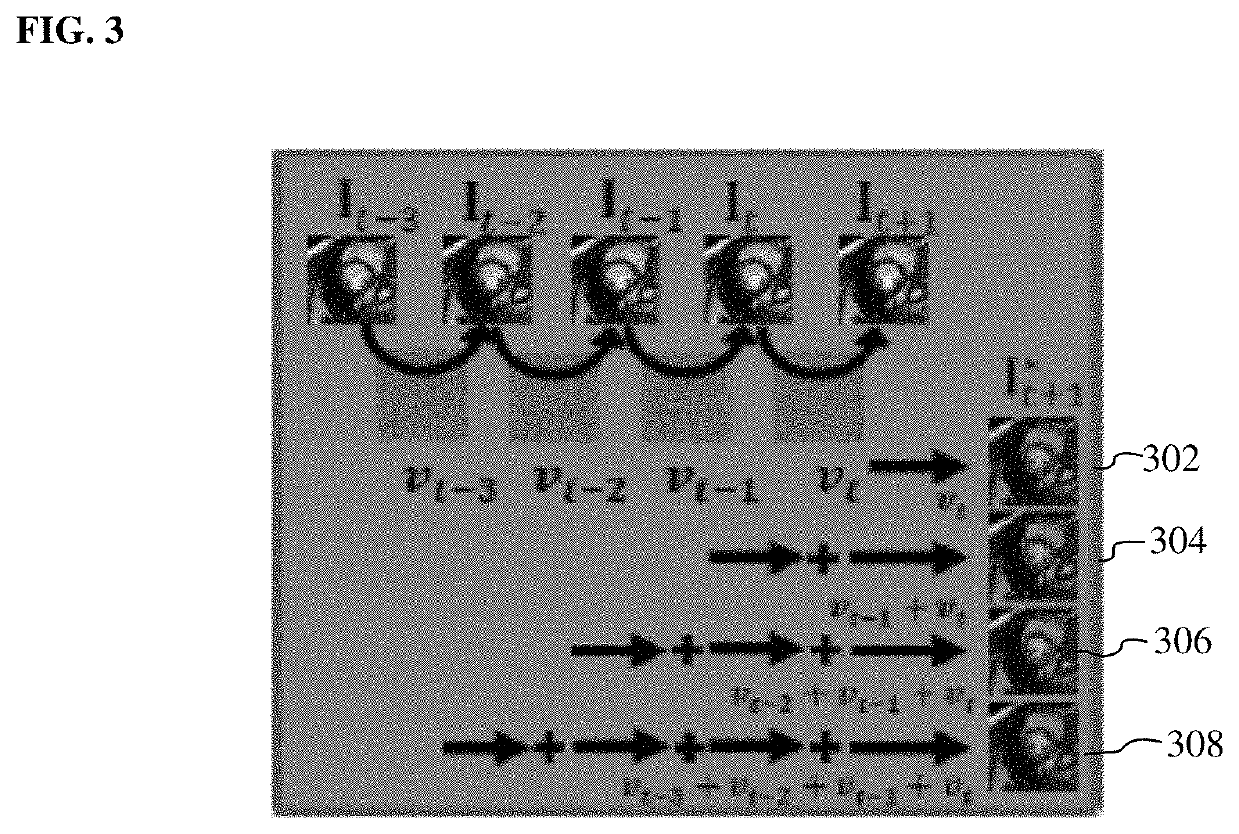
Method and System for Deep Motion Model Learning in Medical Images
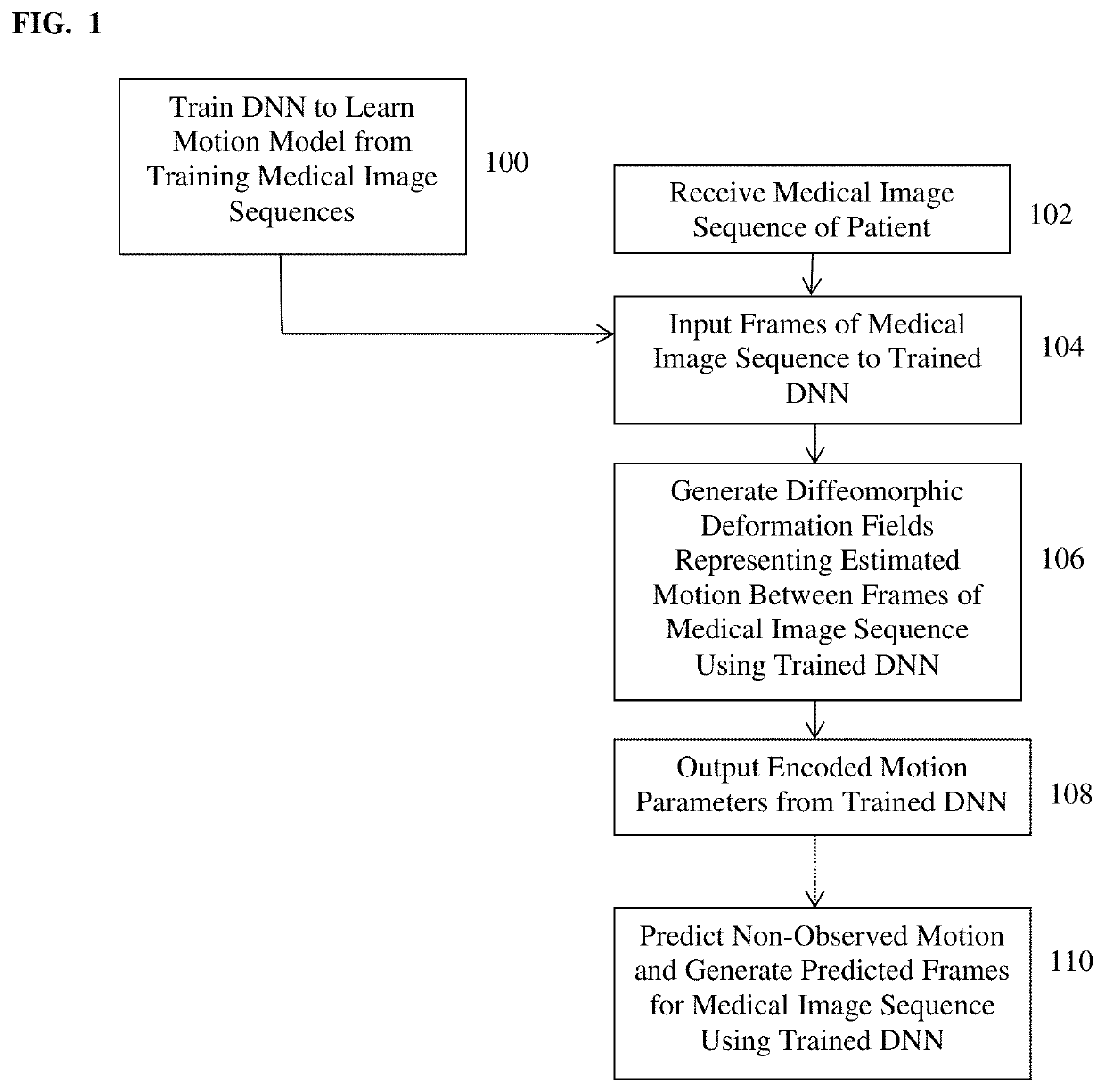
ActiveUS20200090345A1Minimize loss functionImage enhancementImage analysisComputer basedModel learning
A method and system for computer-based motion estimation and modeling in a medical image sequence of a patient is disclosed. A medical image sequence of a patient is received. A plurality of frames of the medical image sequence are input to a trained deep neural network. Diffeomorphic deformation fields representing estimated motion between the frames of the medical image sequence input to the trained deep neural network are generated. Future motion, or motion between frames, is predicted from the medical image sequence and at least one predicted next frame is generated using the trained deep neural network. An encoding of the observed motion in the medical image sequence is also generated, which is used for motion classification (e.g., normal or abnormal) or motion synthesis to generate synthetic data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
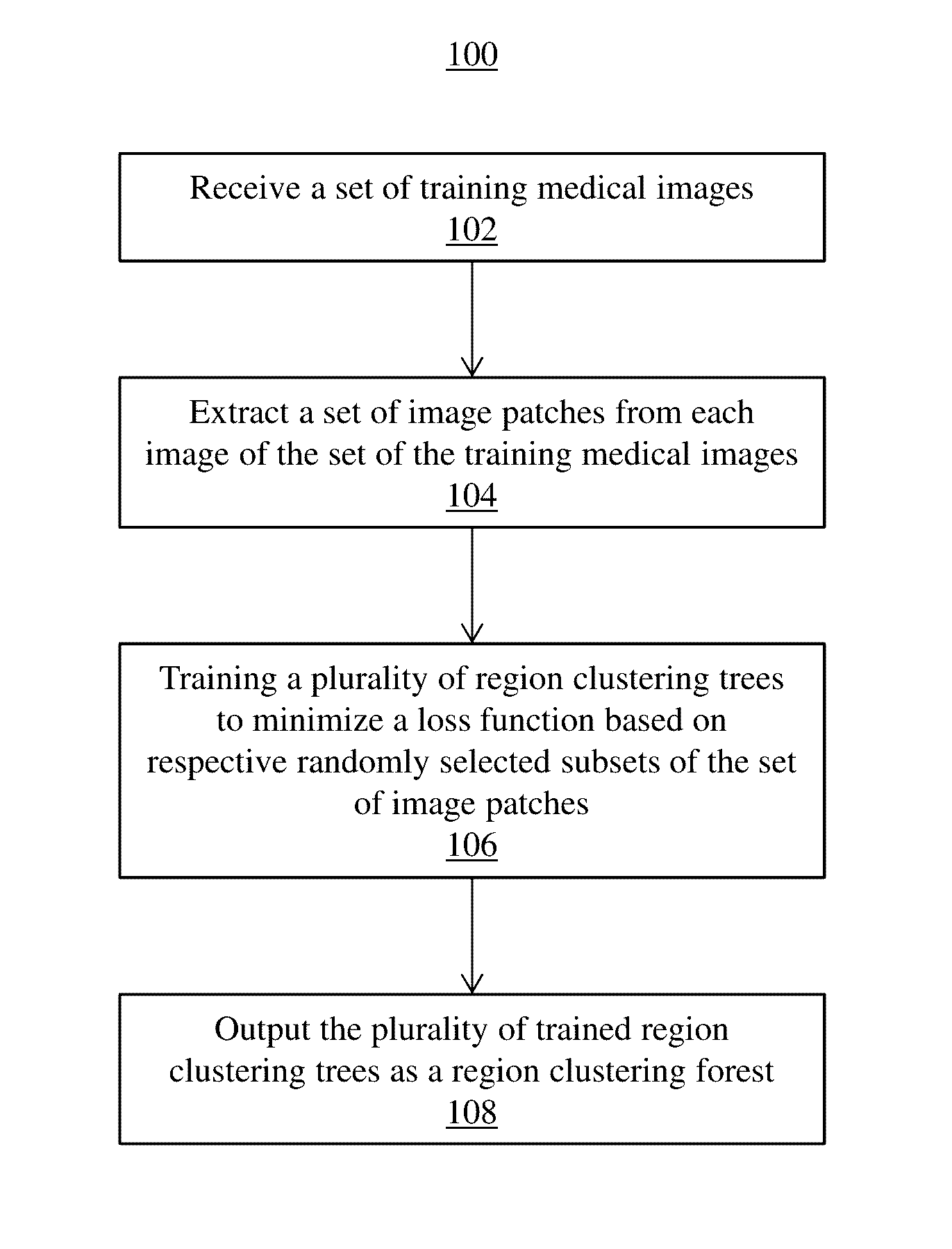
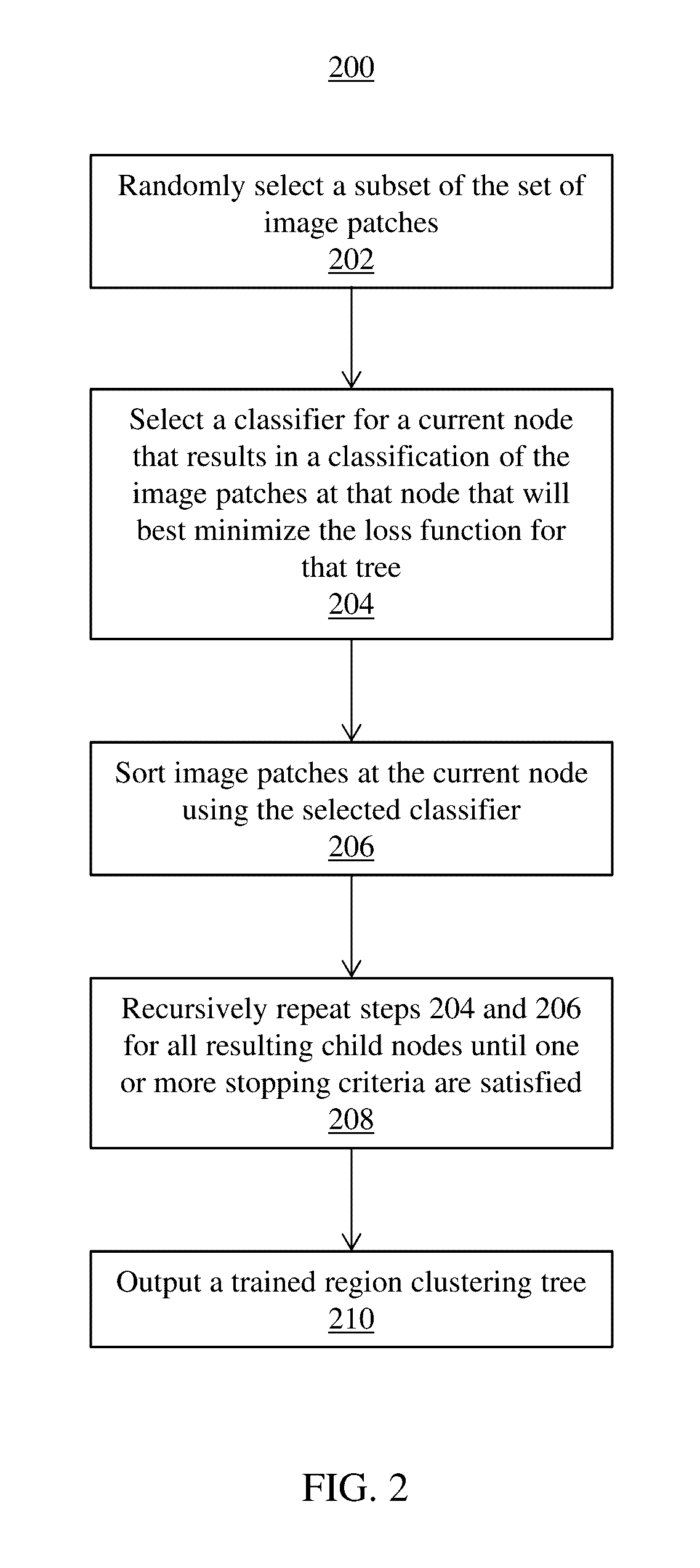
Region Clustering Forest for Analyzing Medical Imaging Data
ActiveUS20160328841A1Minimize loss functionImage enhancementImage analysisMedical imaging dataTree clustering
Systems and methods for training a region clustering forest include receiving a set of medical training images for a population of patients. A set of image patches is extracted from each image in the set of medical training images. A plurality of region clustering trees are generated each minimizing a loss function based on respective randomly selected subsets of the set of image patches to train the region clustering forest. Each of the plurality of region clustering trees cluster image patches at a plurality of leaf nodes and the loss function measures a compactness of the cluster of image patches at each leaf node in each of the plurality of region clustering trees.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Video displaying method and apparatus, device and computer storage medium
ActiveUS20190163336A1Improve abilitiesConveniently and effectively viewCharacter and pattern recognitionSelective content distributionComputer graphics (images)
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Methods and Systems for Automated Text Correction
InactiveUS20140163963A2Minimize loss functionNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceData science
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Enabling chatbots by detecting and supporting affective argumentation
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention detect affective argumentation in text. In an example, an application executing on a computing device accesses text comprising fragments. The application creates a discourse tree from the text. The discourse tree includes nodes, each nonterminal node representing a rhetorical relationship between two of the fragments and each terminal node of the nodes of the discourse tree is associated with one of the fragments. The application matches each fragment that has a verb to a verb signature, thereby creating a communicative discourse tree. The application determines whether the communicative discourse tree represents text that includes affective argumentation by applying a classification model trained to detect affective argumentation to the communicative discourse tree.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Tree kernel learning for text classification into classes of intent
ActiveUS10839161B2Minimize loss functionDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisText categorizationVerbnoun
Systems, devices, and methods of the present invention are related to determining an intent of an utterance. For example, an intent classification application accesses a sentence with fragments. The intent classification application creates a parse tree for the sentence. The intent classification application generates a discourse tree that represents rhetorical relationships between the fragments. The intent classification application matches each fragment that has a verb to a verb signature, thereby creating a communicative discourse tree. The intent classification application creates a parse thicket by combining the communicative discourse tree and the parse tree. The intent classification application determines an intent of the sentence from a predefined list of intent classes by applying a classification model to the parse thicket.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Artificial neural network and method of training an artificial neural network with epigenetic neurogenesis
ActiveUS20200125930A1Minimize loss functionCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeHidden layerNeurogenesis
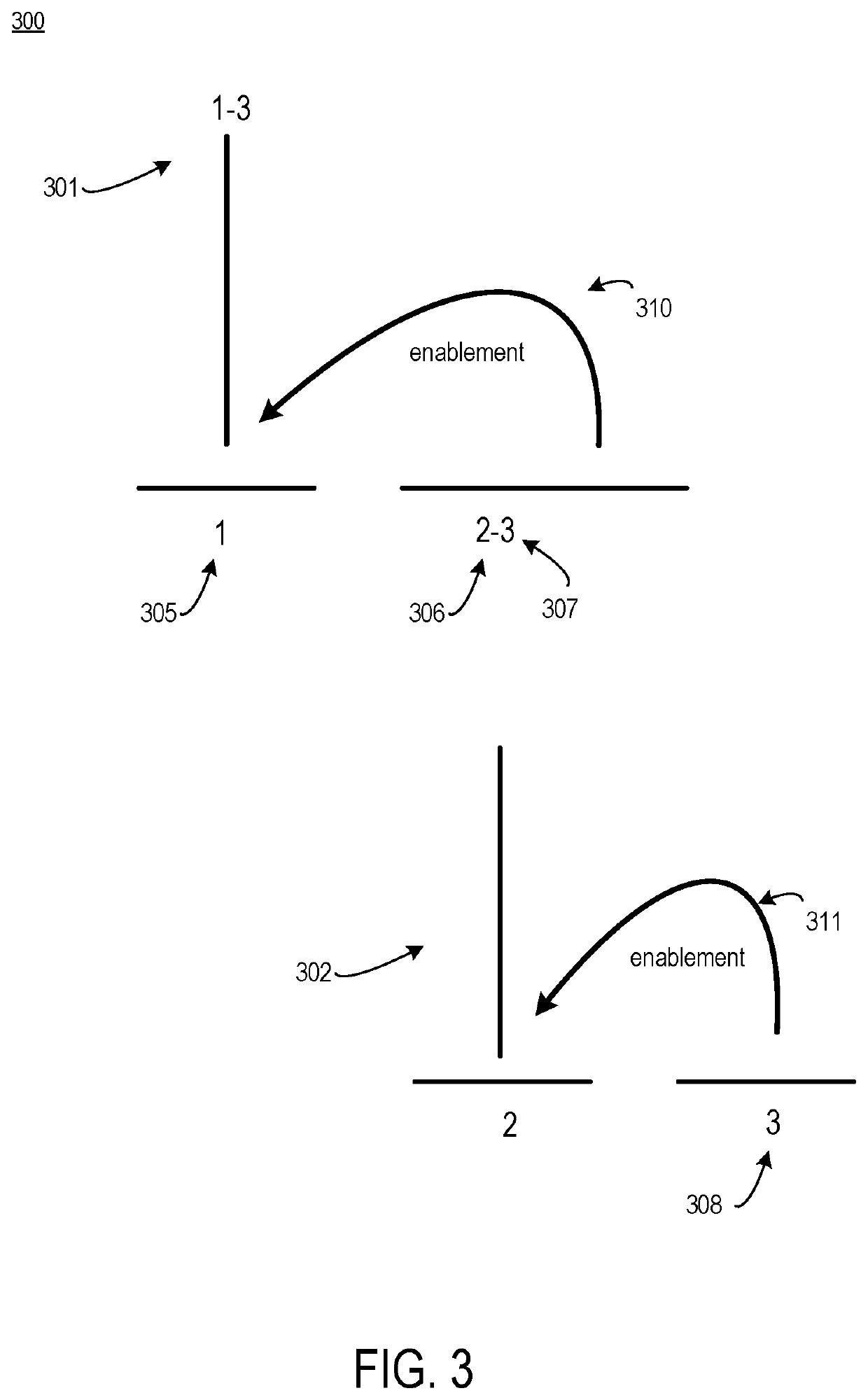
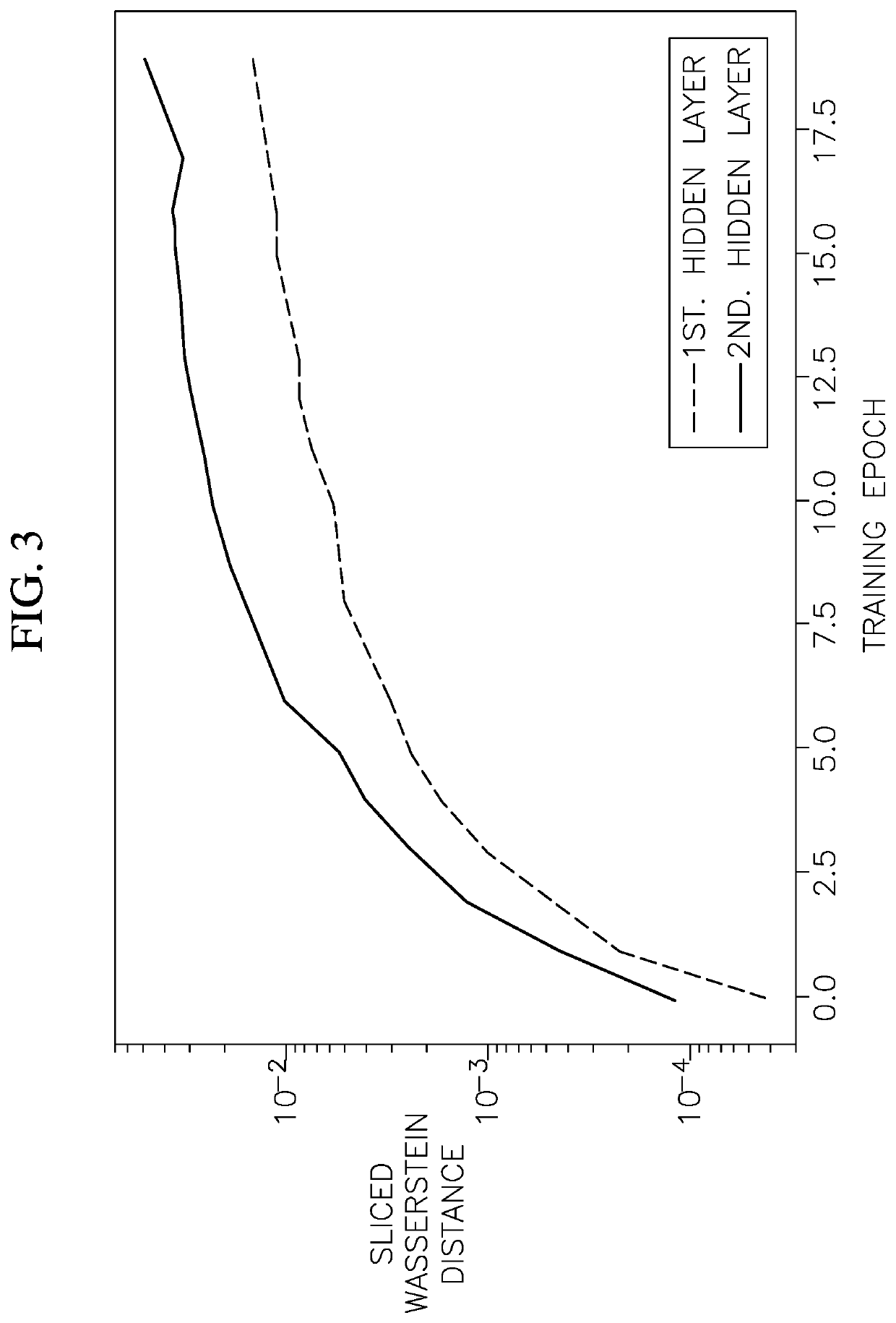
A method for retraining an artificial neural network trained on data from an old task includes training the artificial neural network on data from a new task different than the old task, calculating a drift, utilizing Sliced Wasserstein Distance, in activation distributions of a series of hidden layer nodes during the training of the artificial neural network with the new task, calculating a number of additional nodes to add to at least one hidden layer based on the drift in the activation distributions, resetting connection weights between input layer nodes, hidden layer nodes, and output layer nodes to values before the training of the artificial neural network on the data from the new task, adding the additional nodes to the at least one hidden layer, and training the artificial neural network on data from the new task.
Owner:HRL LAB
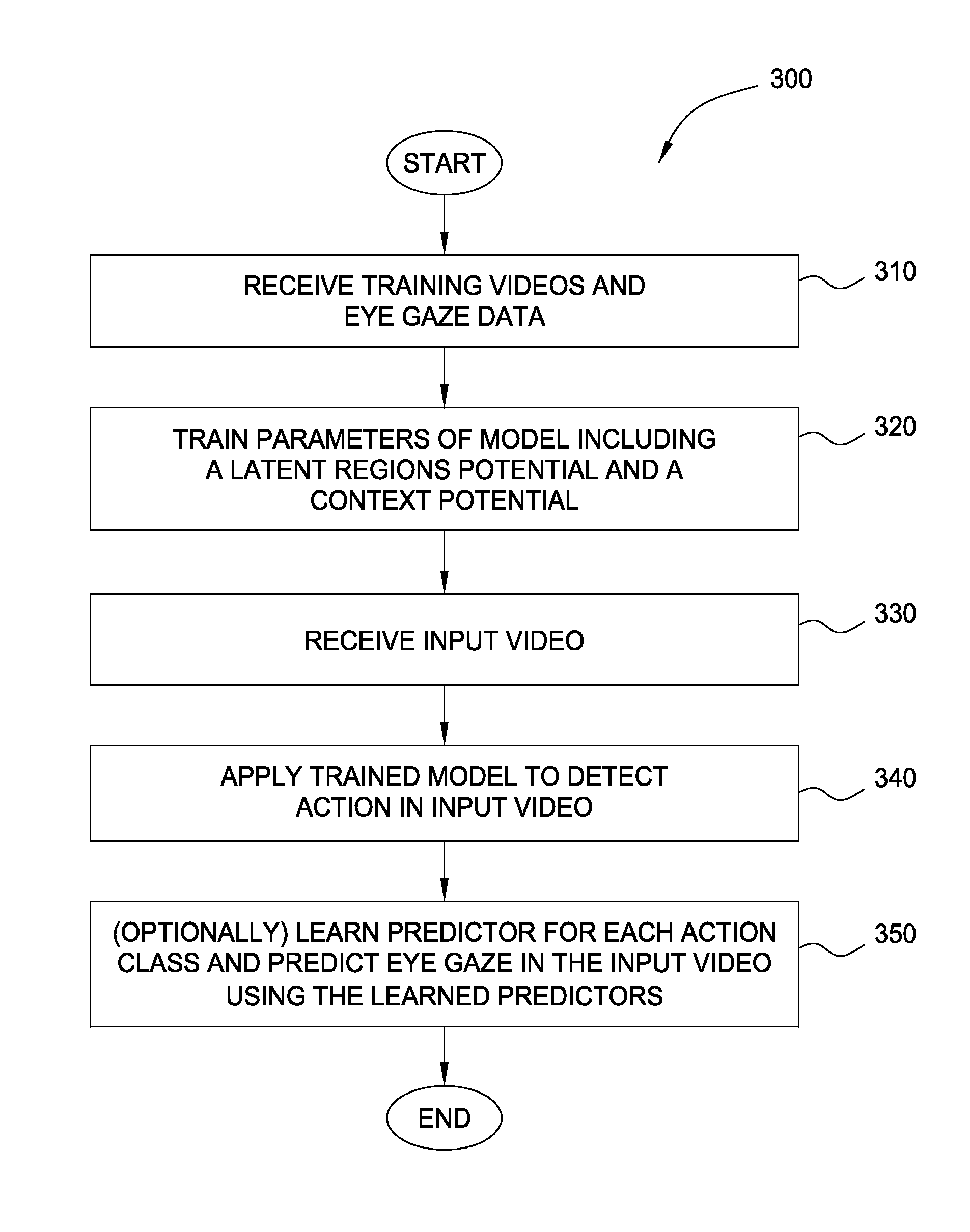
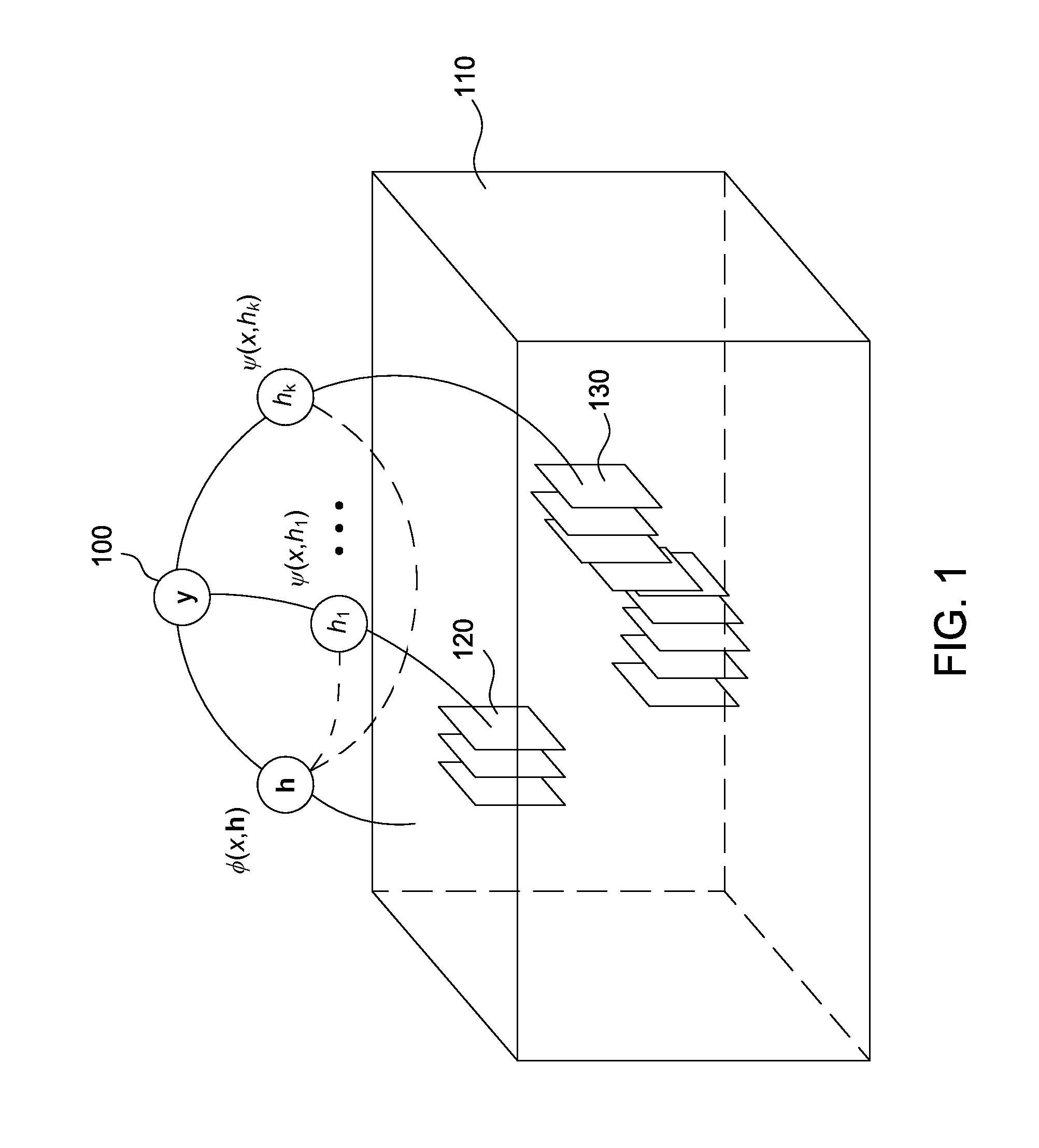
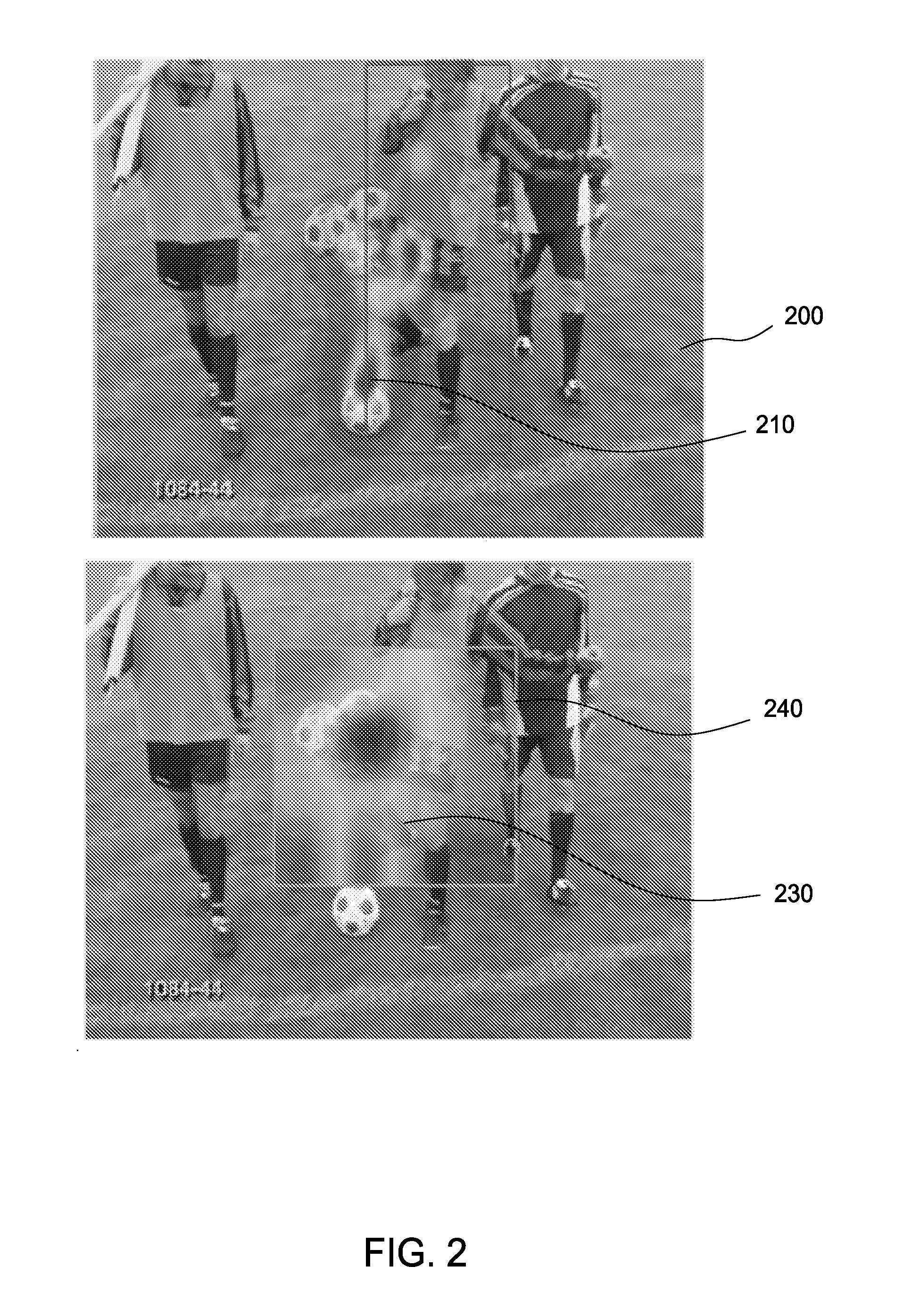
Eye gaze driven spatio-temporal action localization
ActiveUS9514363B2Minimize loss functionPenalizes misclassification of actionAcquiring/recognising eyesPattern recognitionTemporal Regions
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Stop word data augmentation for natural language processing
PendingUS20210082400A1Minimize loss functionSemantic analysisSpeech recognitionNatural languageUtterance
Techniques for stop word data augmentation for training chatbot systems in natural language processing. In one particular aspect, a computer-implemented method includes receiving a training set of utterances for training an intent classifier to identify one or more intents for one or more utterances; augmenting the training set of utterances with stop words to generate an augmented training set of out-of-domain utterances for an unresolved intent category corresponding to an unresolved intent; and training the intent classifier using the training set of utterances and the augmented training set of out-of-domain utterances. The augmenting includes: selecting one or more utterances from the training set of utterances, and for each selected utterance, preserving existing stop words within the utterance and replacing at least one non-stop word within the utterance with a stop word or stop word phrase selected from a list of stop words to generate an out-of-domain utterance.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Employing abstract meaning representation to lay the last mile towards reading comprehension
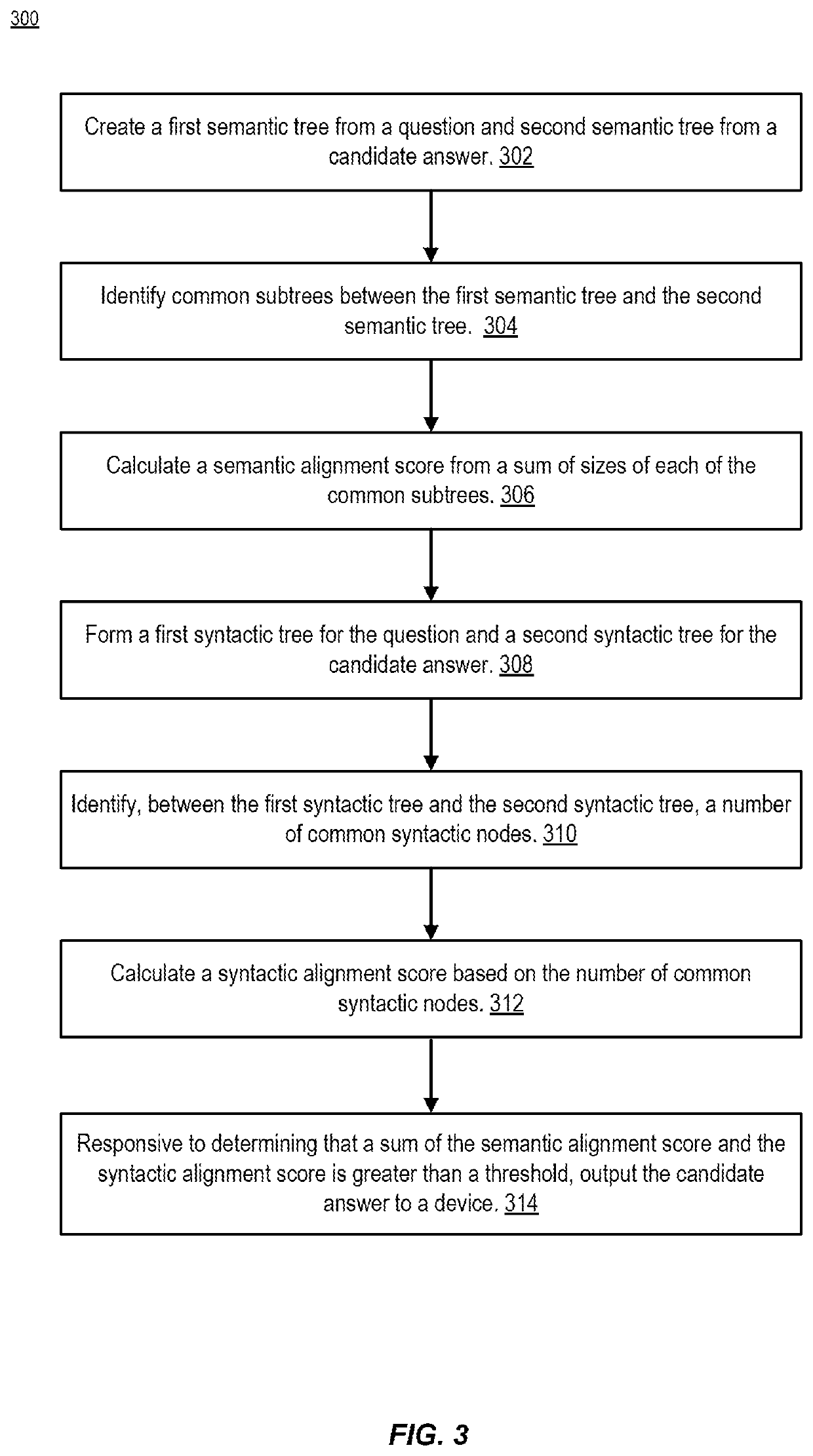
ActiveUS20210150152A1Minimize loss functionNatural language translationDigital data information retrievalSemantic treeSemantic alignment
An autonomous agent creates a first semantic tree from a question and second semantic tree from a candidate answer. The agent identifies, between the first semantic tree and the second semantic tree, common subtrees and calculates a semantic alignment score from a sum of sizes of each of the common subtrees. The agent forms a first syntactic tree for the question and a second syntactic tree for the candidate answer. The agent identifies a number of common syntactic nodes between the first syntactic tree and the second syntactic tree. The agent calculates a syntactic alignment score based on the number of common syntactic nodes. Responsive to determining that a sum of the semantic alignment score and the syntactic alignment score is greater than a threshold, the agent outputs the candidate answer to a device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com