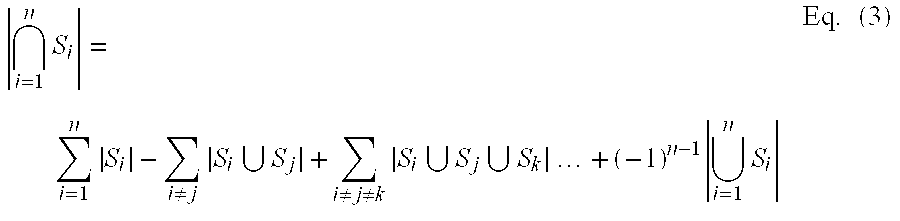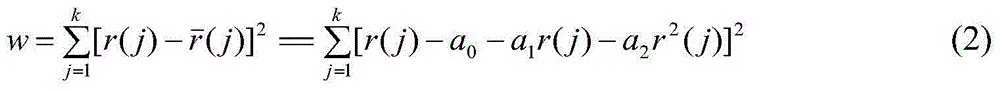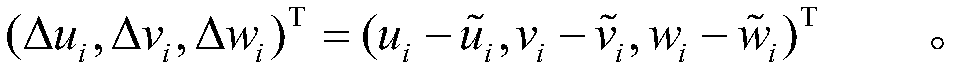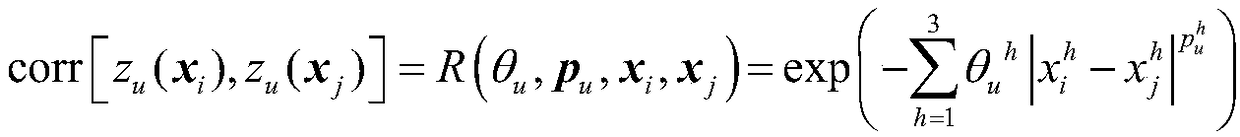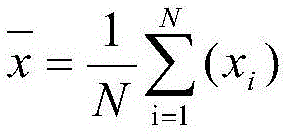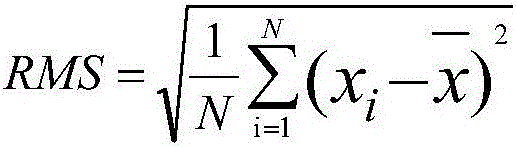Patents
Literature
469 results about "Square error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition: The mean square error is equal to the square of the bias plus the variance of the estimator. If the sampling method and estimating procedure lead to an unbiased estimator, then the mean square error is simply the variance of the estimator.
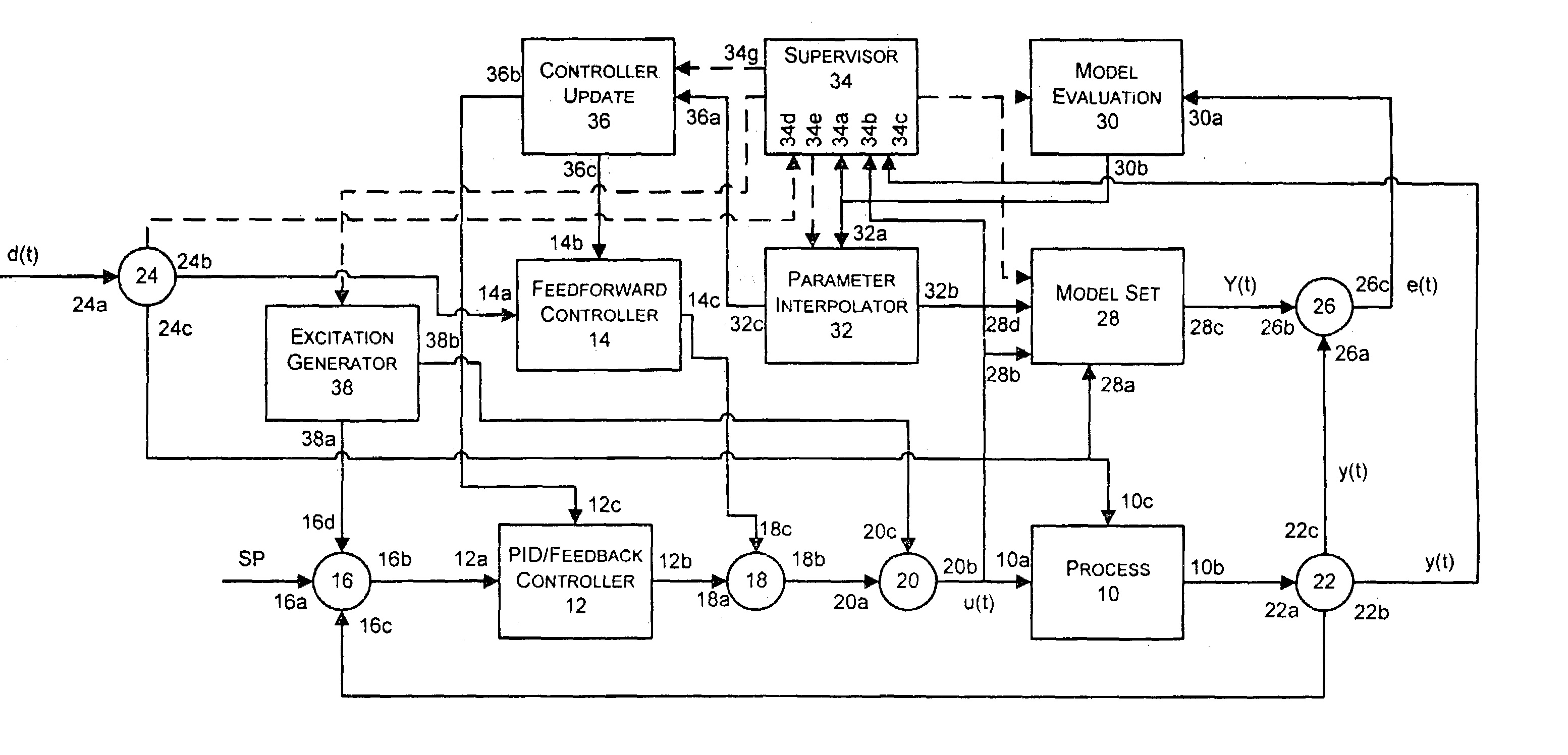
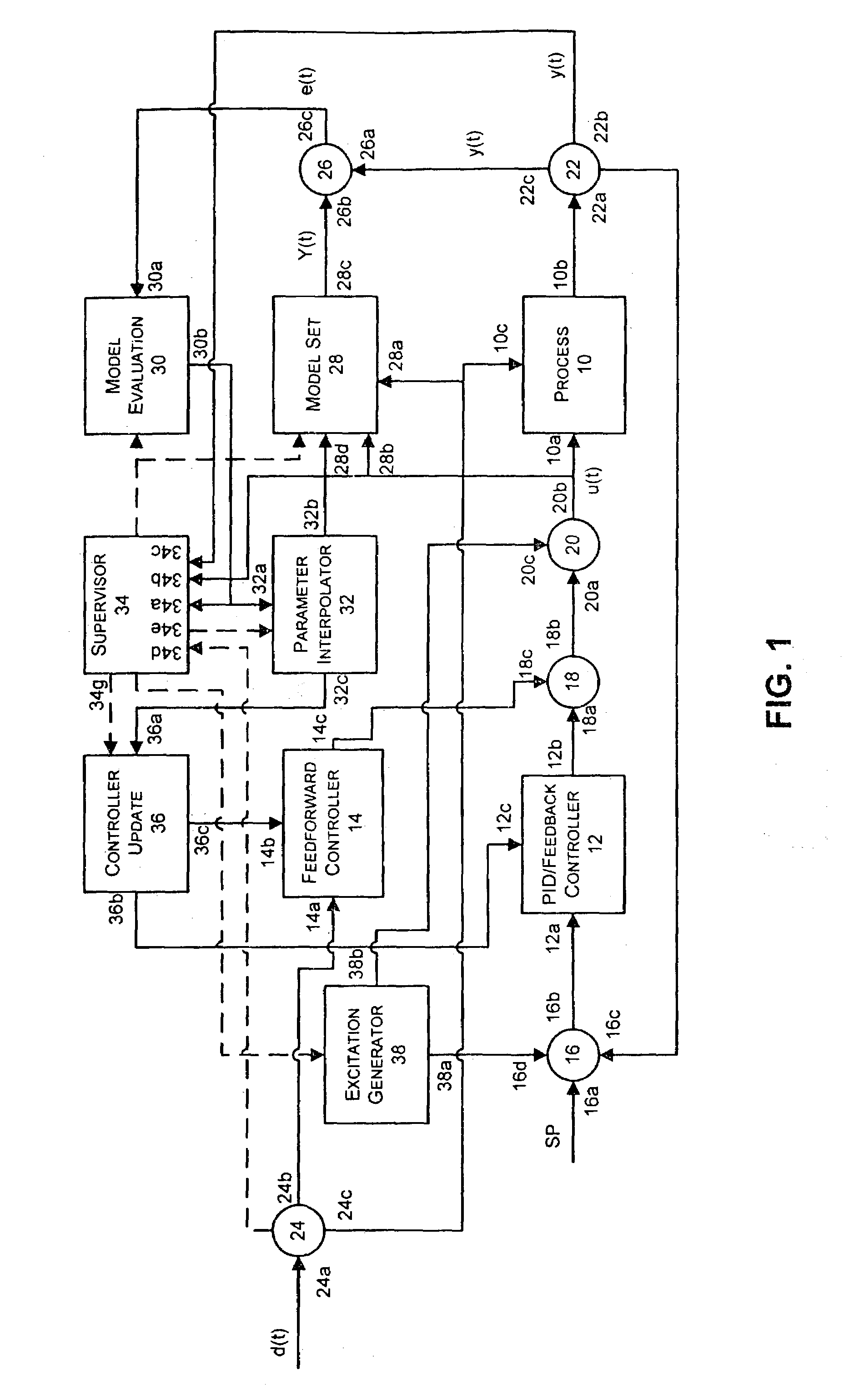
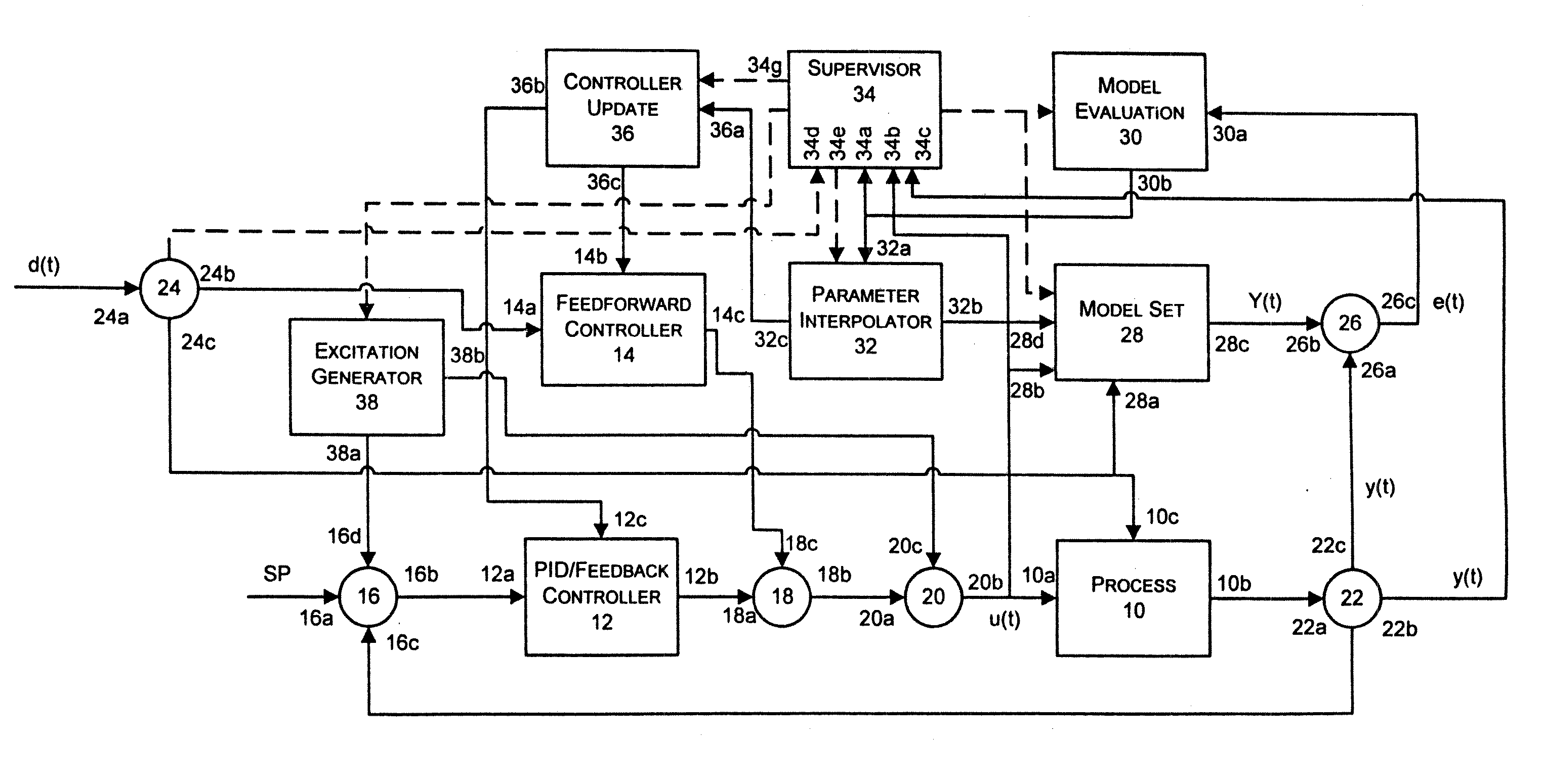
State based adaptive feedback feedforward PID controller
InactiveUS7113834B2Simulator controlControllers with particular characteristicsSelf adaptiveComputer science
A state based adaptive PID controller includes a model set component including a plurality of process models, each process model including a plurality of parameters. An error generator generates a model error signal representative of a difference between a model output signal and a process output signal. A model evaluation component computes a model squared error based on the model error signal. A parameter interpolator calculates an adaptive parameter value based on the model squared error. A controller update component updates adaptive controller parameter values based on adaptive parameter values.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
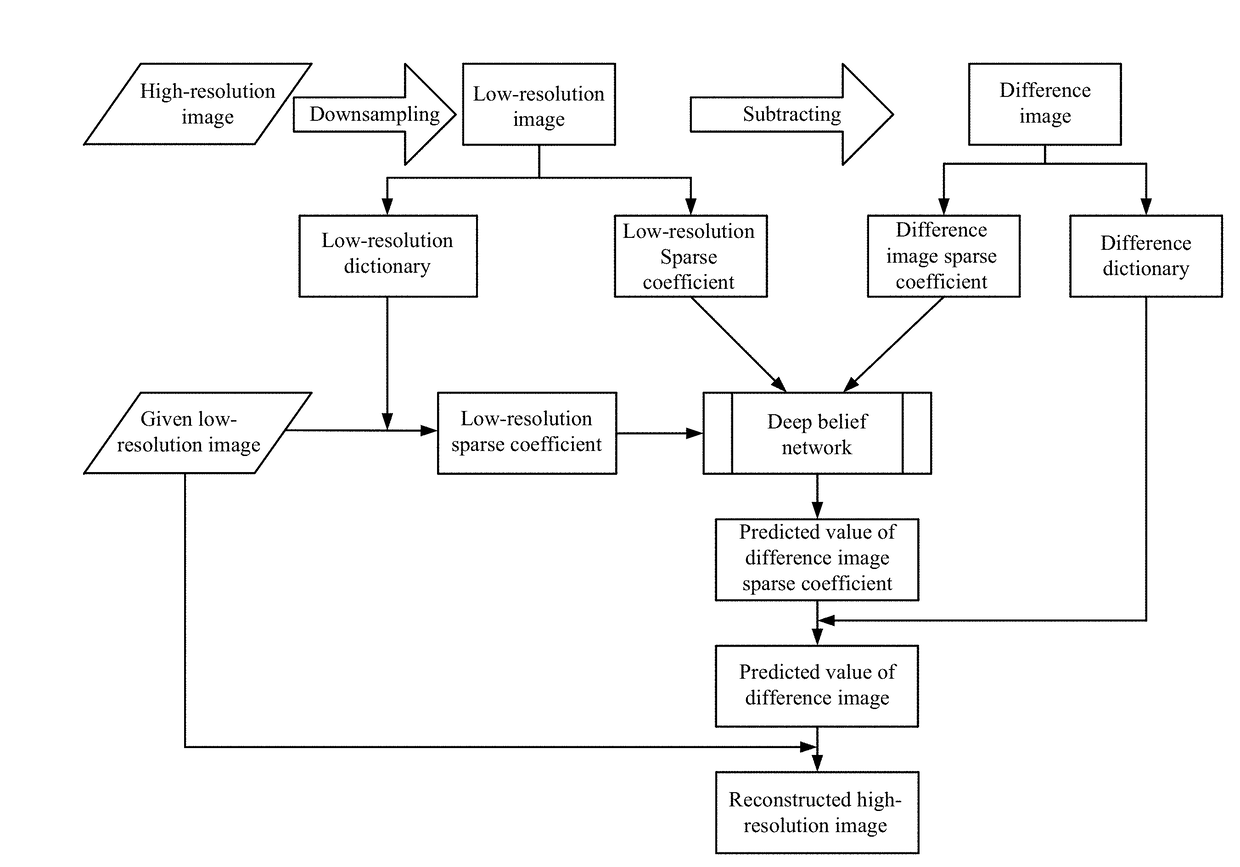
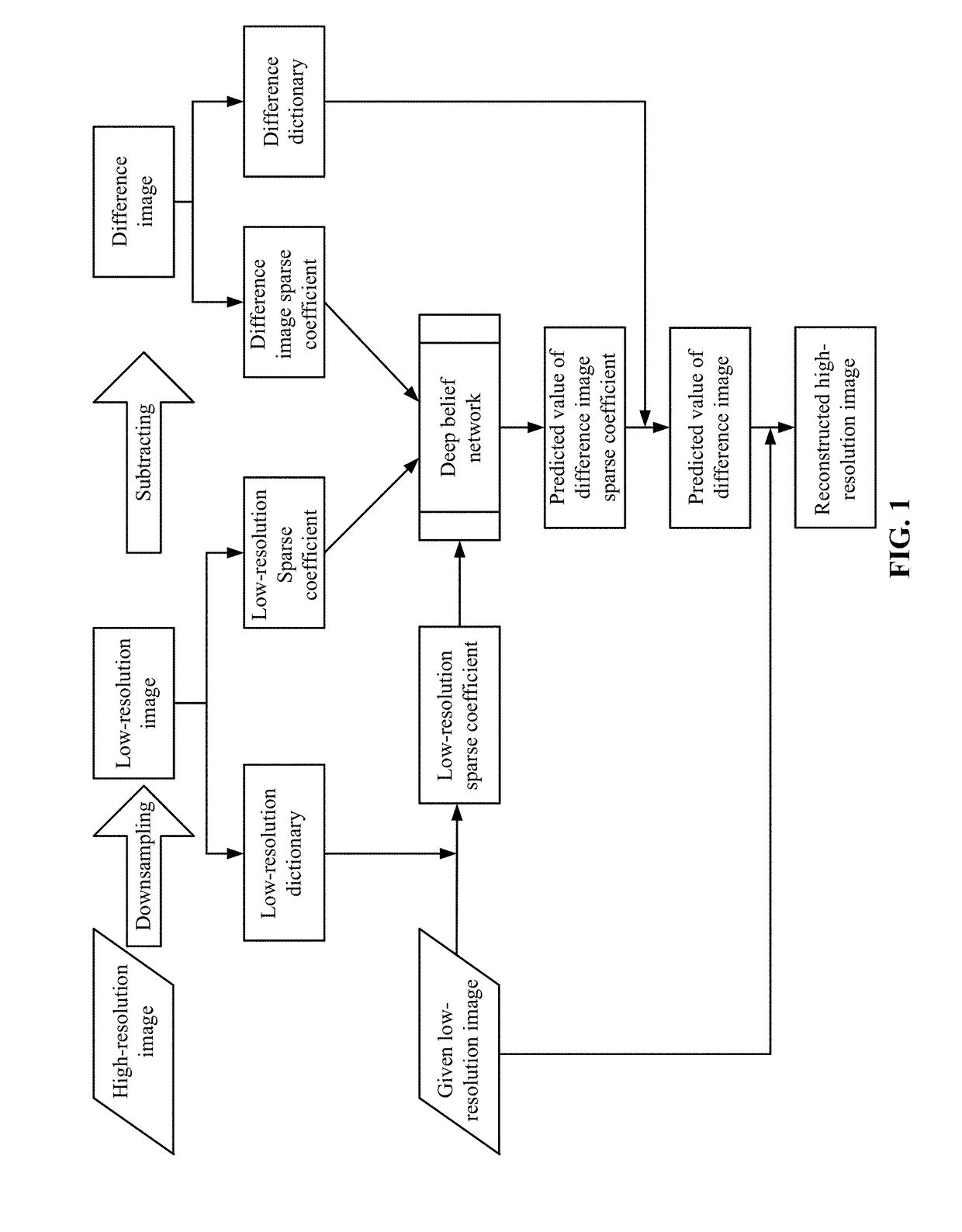
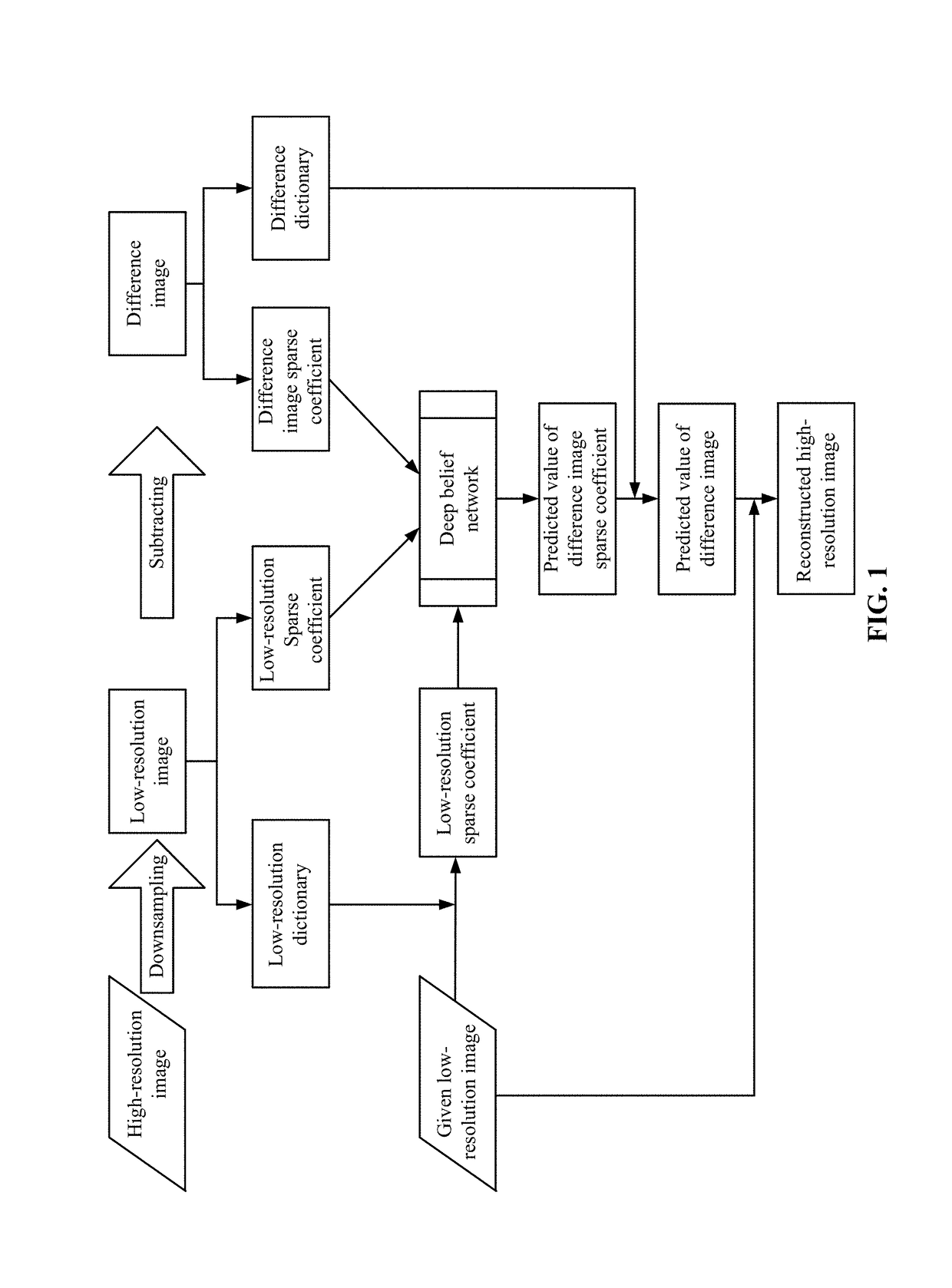
Method and system for reconstructing super-resolution image
ActiveUS20170293825A1Minimize cost functionMinimize loss functionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTest sample
A method for reconstructing a super-resolution image, including: 1) reducing the resolution of an original high-resolution image to obtain an equal low-resolution image, respectively expressed as matrix forms yh and yl; 2) respectively conducting dictionary training on yl and yhl to obtain a low-resolution image dictionary Dl; 3) dividing the sparse representation coefficients αl and αhl into training sample coefficients αl_train and αhl_train and test sample coefficients αl_test and αhl_test; 4) constructing an L-layer deep learning network using a root-mean-square error as a cost function; 5) iteratively optimizing network parameters so as to minimize the cost function by using the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_train as the input of the deep learning network; 6) inputting the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_testas the test portion into the trained deep learning network in 5), outputting to obtain a predicted difference image sparse coefficient {circumflex over (α)}hl_test, computing an error between the {circumflex over (α)}hl_test.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
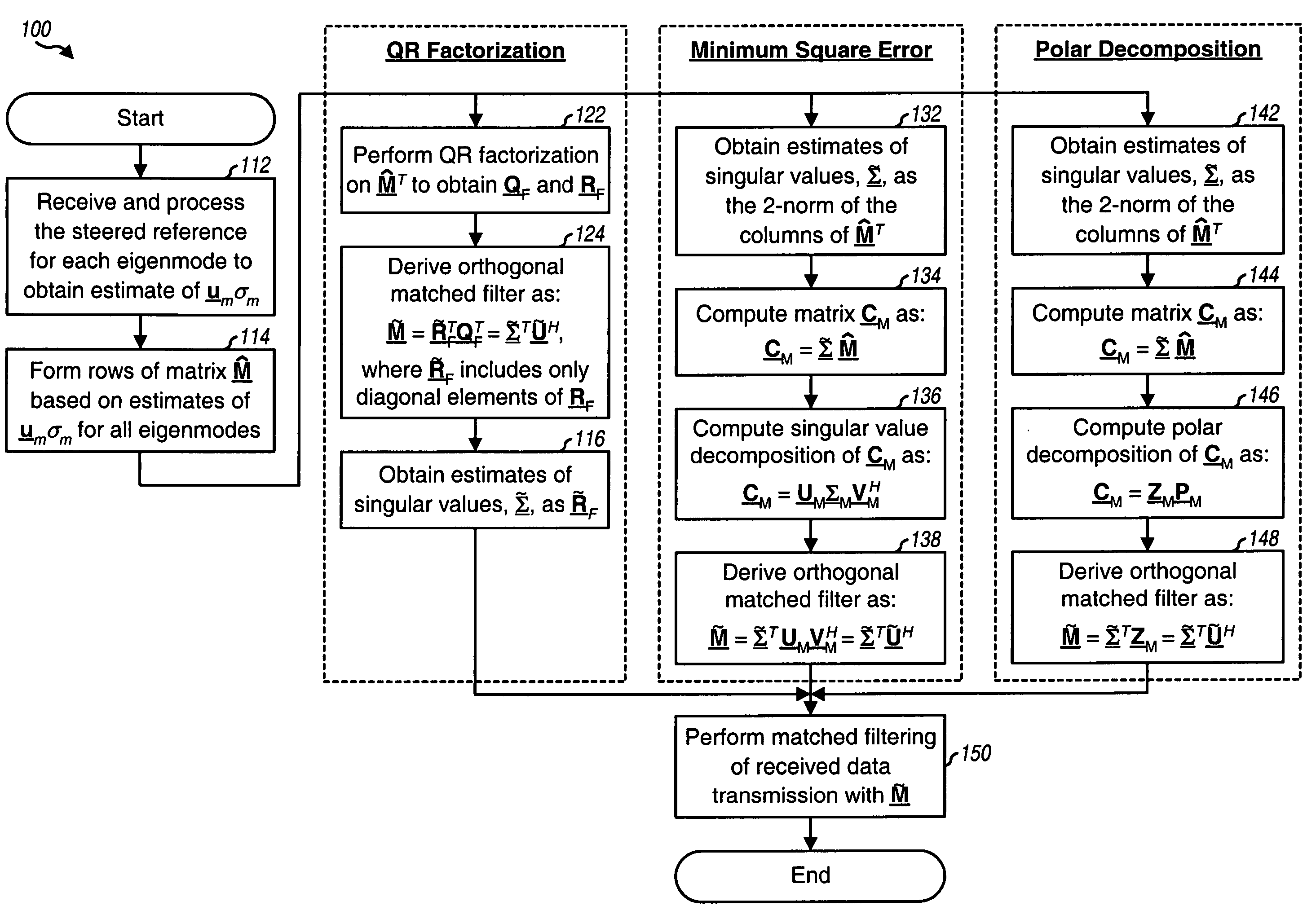
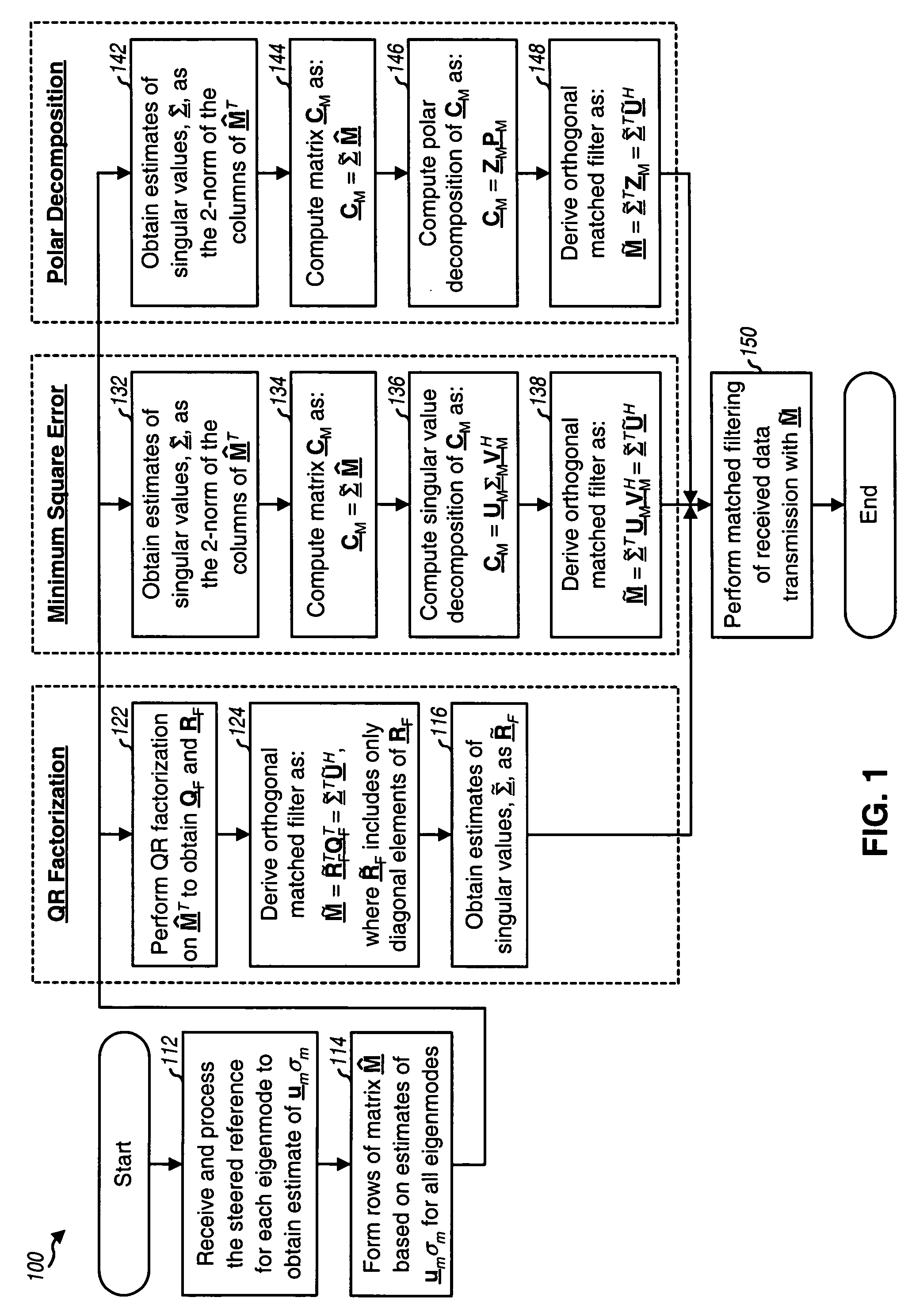
Derivation of eigenvectors for spatial processing in MIMO communication systems
Techniques for deriving eigenvectors based on steered reference and used for spatial processing. A steered reference is a pilot transmission on one eigenmode of a MIMO channel per symbol period using a steering vector for that eigenmode. The steered reference is used to estimate both a matrix Σ of singular values and a matrix U of left eigenvectors of a channel response matrix H. A matrix Ũ with orthogonalized columns may be derived based on the estimates of Σ and U, e.g., using QR factorization, minimum square error computation, or polar decomposition. The estimates of Σ and U (or the estimate of Σ and the matrix Ũ) may be used for matched filtering of data transmission received via a first link. The estimate of U or the matrix Ũ may also be used for spatial processing of data transmission on a second link (for reciprocal first and second links).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
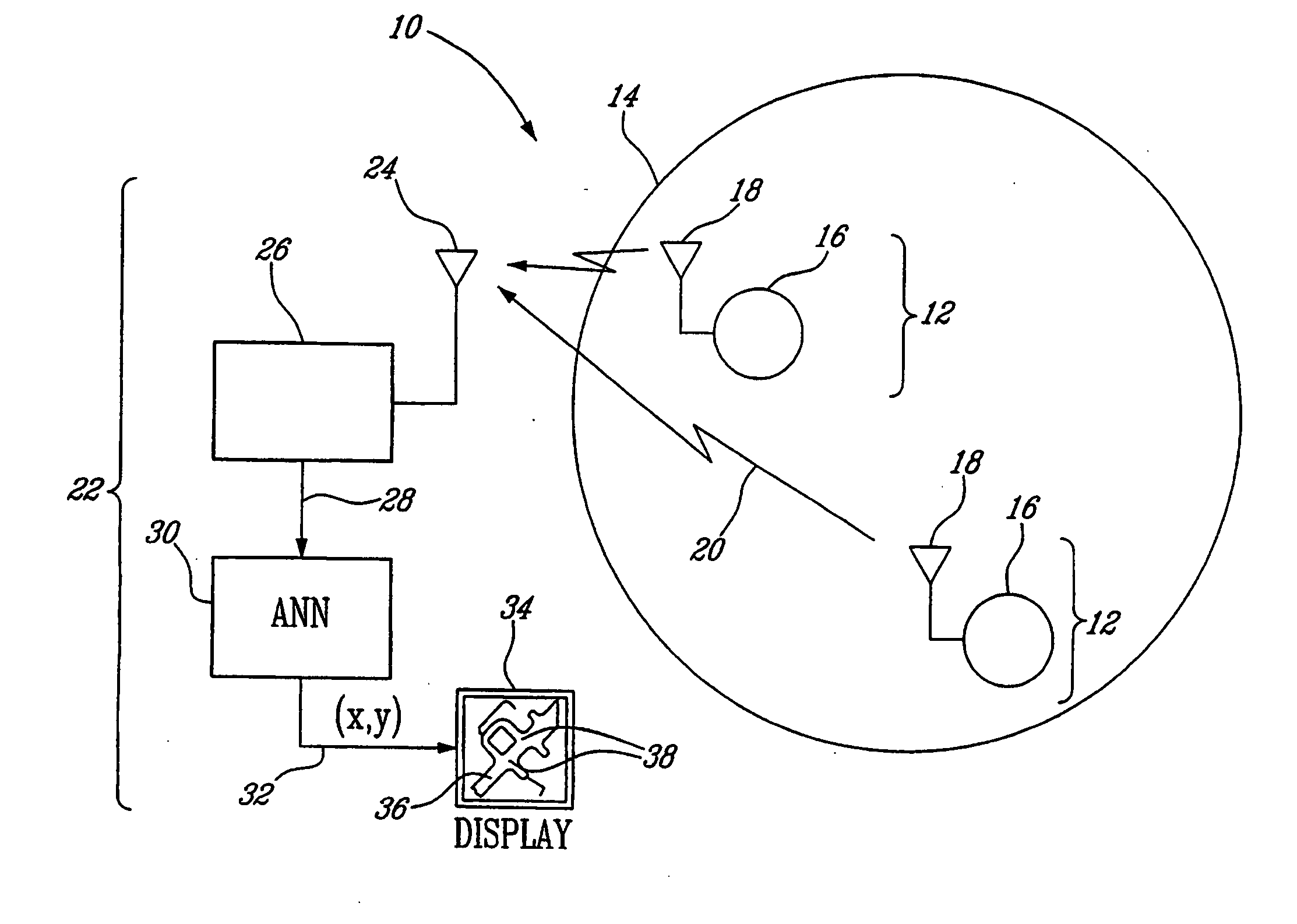
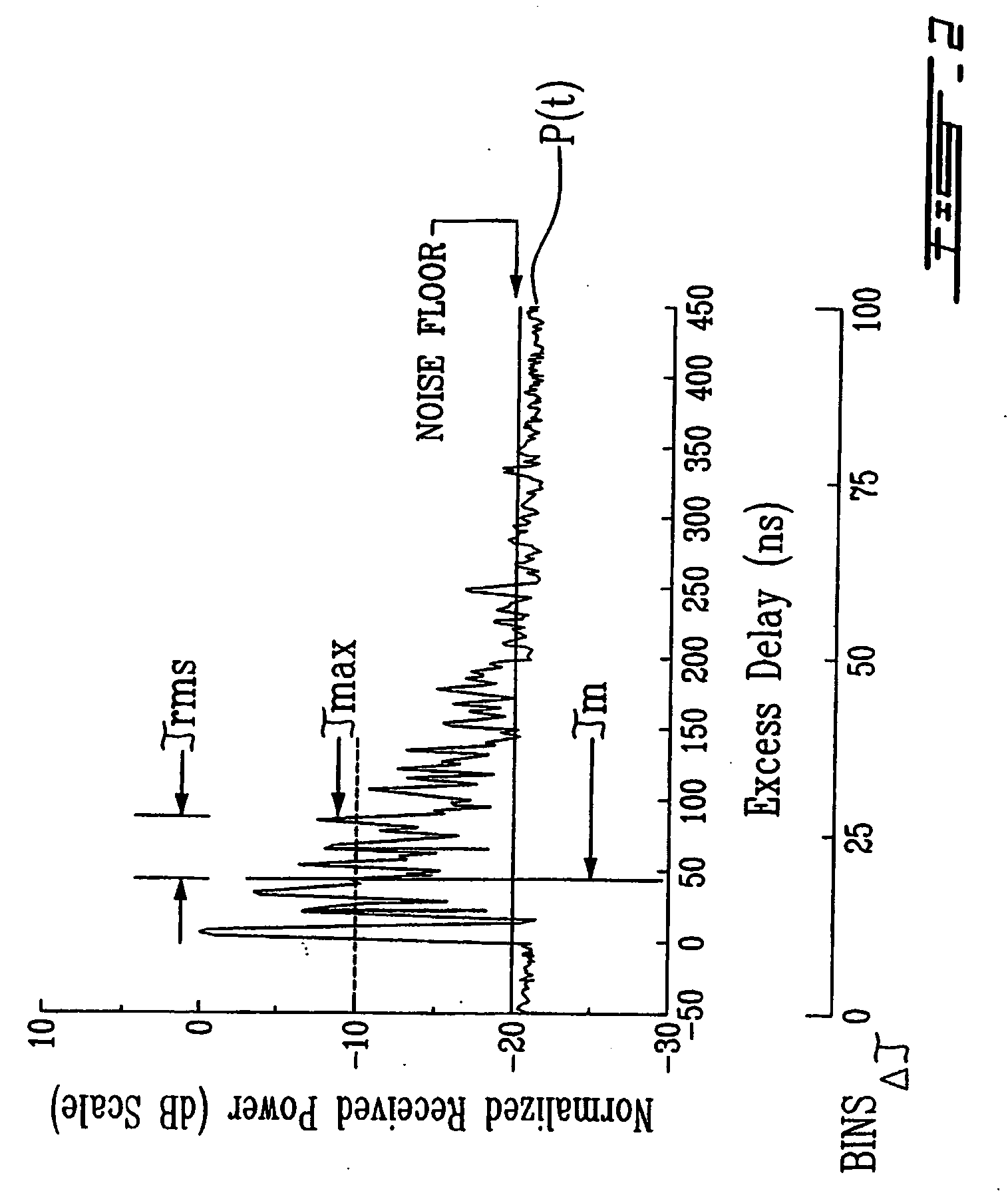
Method and system for indoor geolocation using an impulse response fingerprinting technique
ActiveUS20070010956A1Minimize error functionPolarisation/directional diversityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionData setIndoor geolocation
A system and method for predicting the location of a transmitter in an indoor zone of interest, including fixed receiver for receiving a signal from the transmitter, the receiver deriving a fingerprint from the received signal, and a trained neural network. The trained neural network predicts the transmitter location from the fingerprint. The method includes receiving a signal transmitted from the transmitter at a fixed-location receiver, deriving a fingerprint from the received signal, supplying the fingerprint to a trained neural network, and reading the predicted location from the neural network. The artificial neural network may further be trained and include a plurality of weights and biases is also shown. The method may include collecting a training data set of fingerprints and corresponding locations, inputting the training data set to the neural network, and adjusting the weights and biases by minimising a sum of squares error function.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE +1
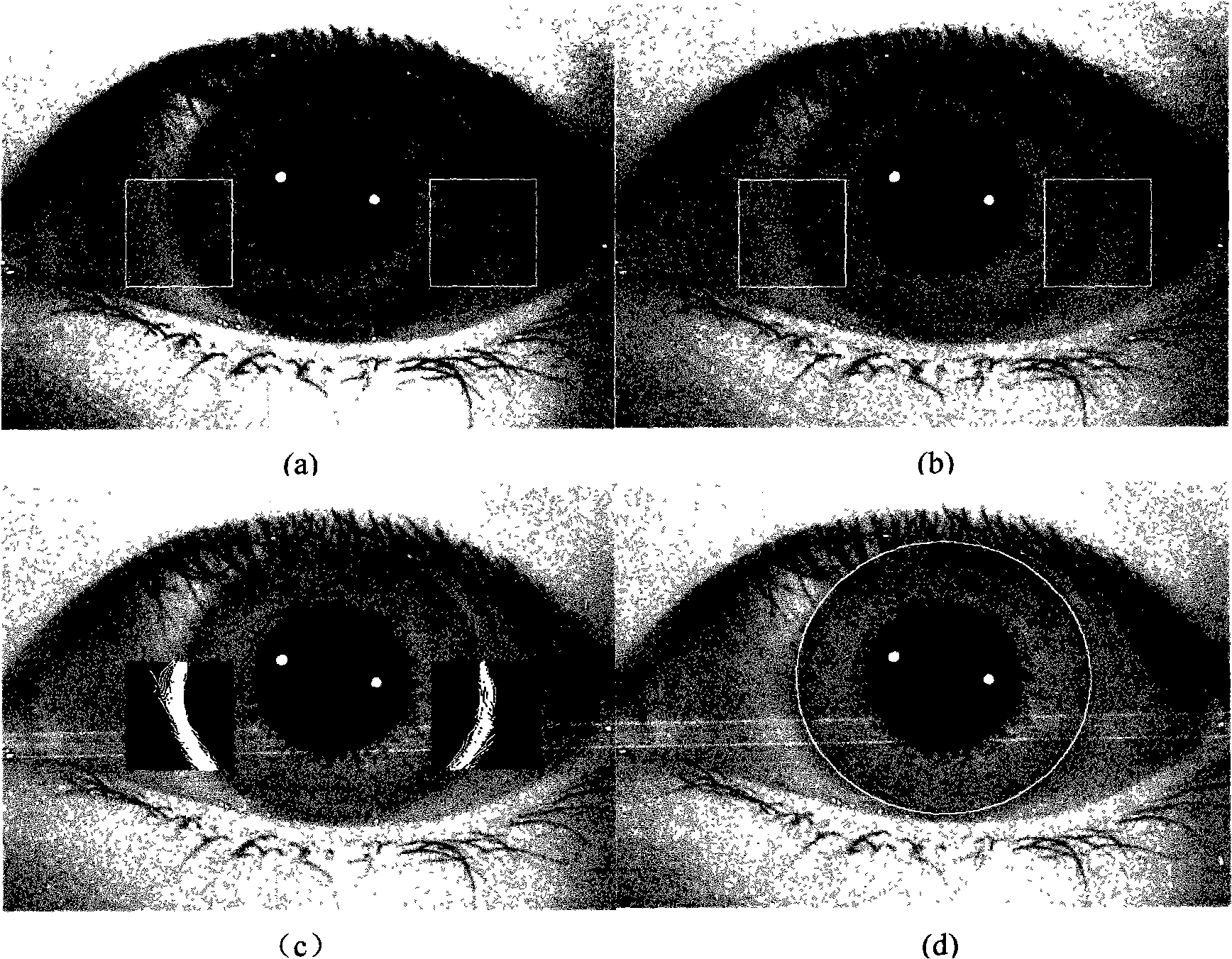
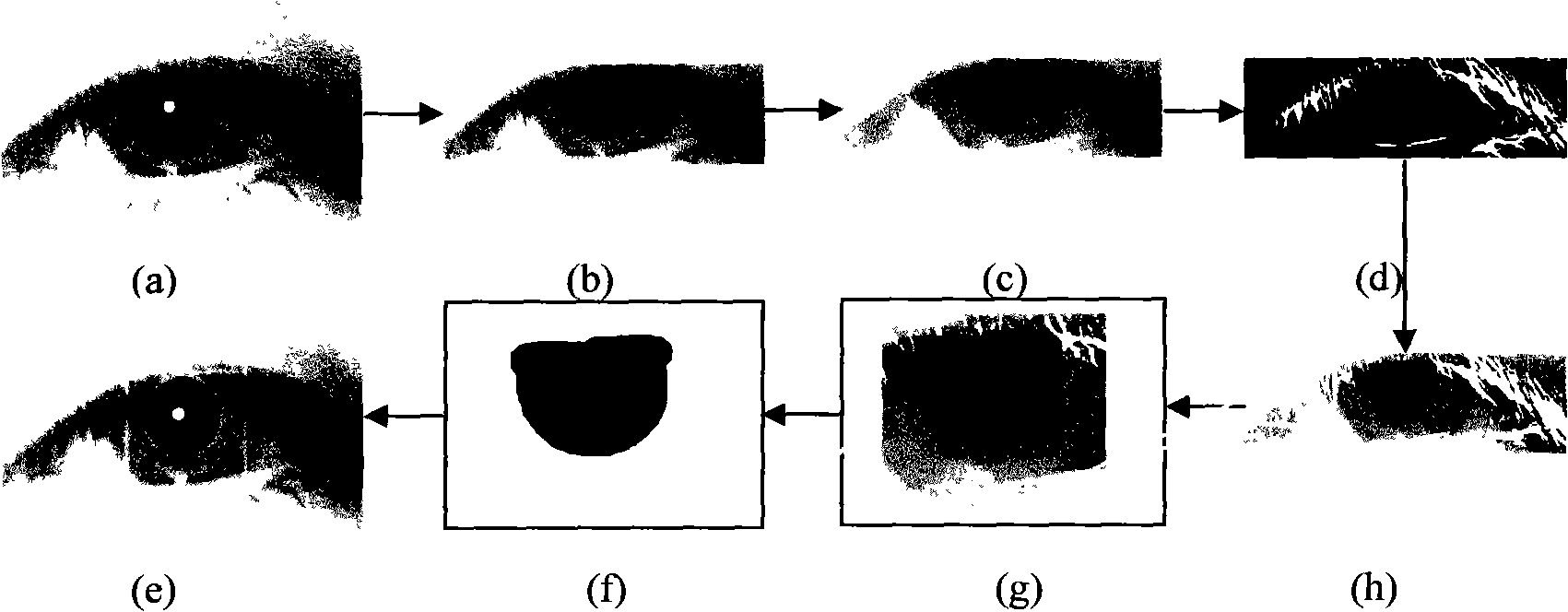
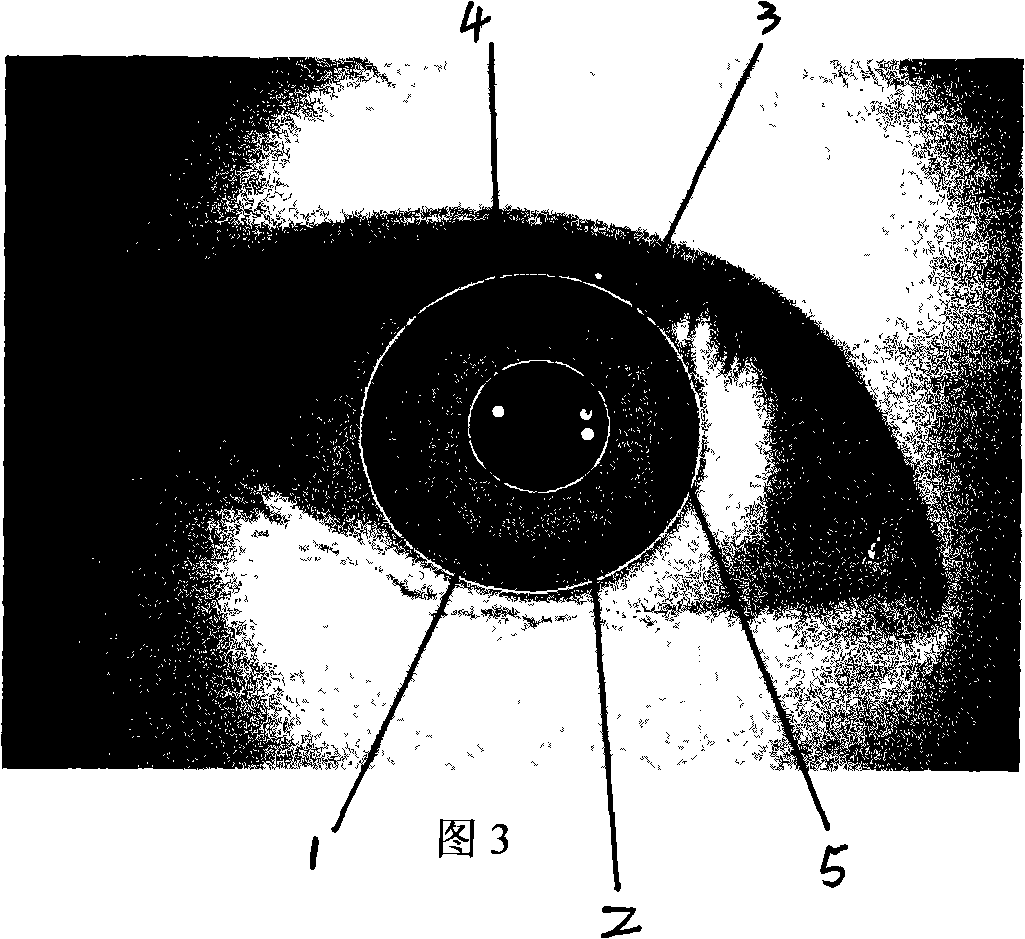
Iris positioning method based on Maximum between-Cluster Variance and gray scale information
InactiveCN101359365AFast positioning timeMeet the requirements of real-time processingCharacter and pattern recognitionCurve fittingKnowledge extraction
The invention adopts the between-class square error and the gray scale information to realize the rapid positioning of the inside and outside boundaries of the iris. Firstly, the interested pupil region is extracted through blocking; the between-class square error is adopted to obtain the pupil binary threshold for the extracted pupil region; then the inside boundary of the iris is positioned accurately through the searching of the boundary points and the curve fitting; the interested region of the iris outside boundary is extracted according to the prior knowledge and the pupil position parameter; the selected region is processed with median filtering and first-order gradient conversion; the iris outside boundary is determined through the local gradient integration method; finally, the iris outside boundary parameter is determined through the circle fitting. The method avoids the image binary from depending on the histogram; the image positioning time is greatly improved because only the interested region is processed; the whole image is not processed; the experiment indicates that the robustness and the positioning efficiency of the algorithm can satisfy the real-time processing requirement of the image.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA ZHONGSHAN INST
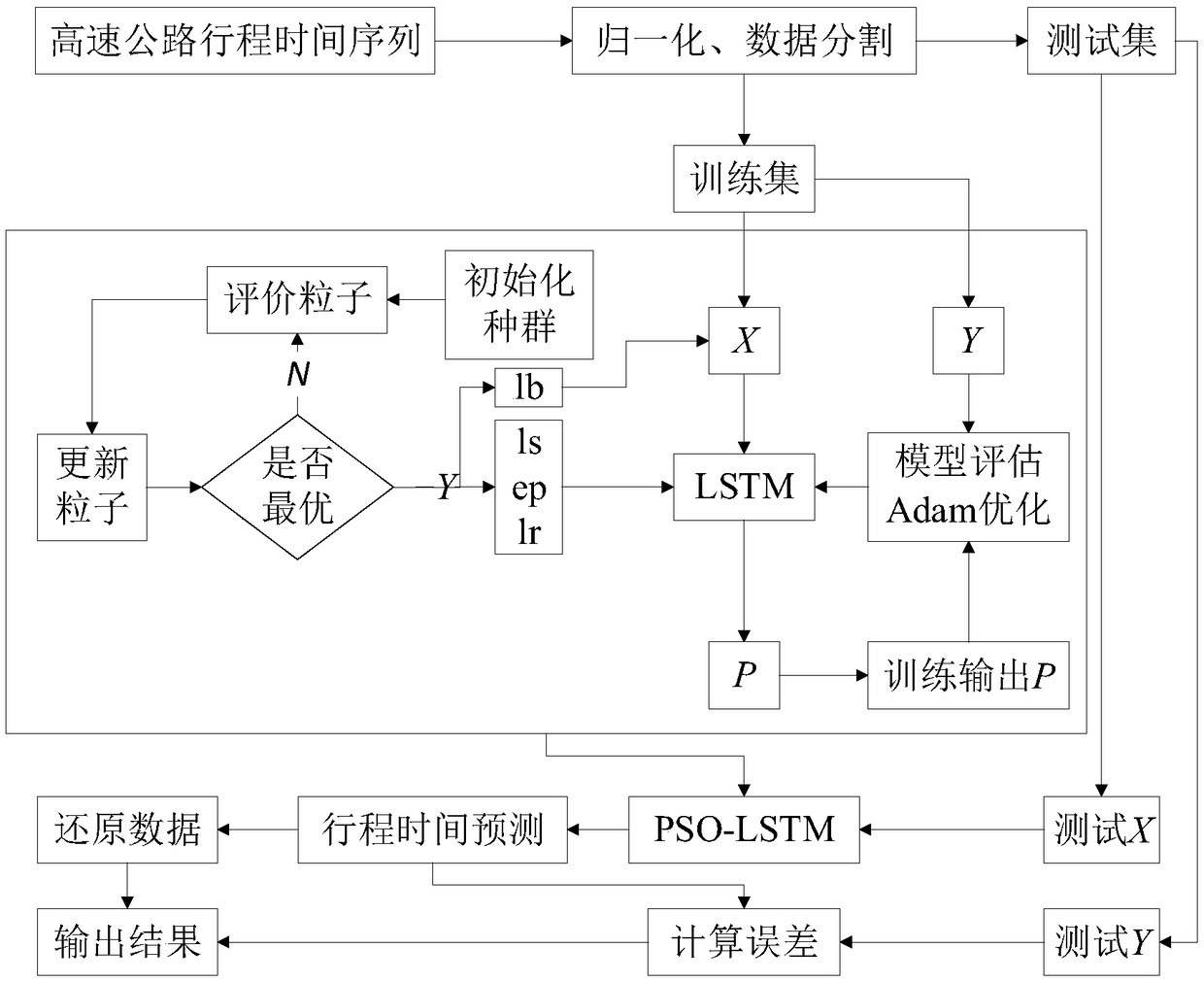
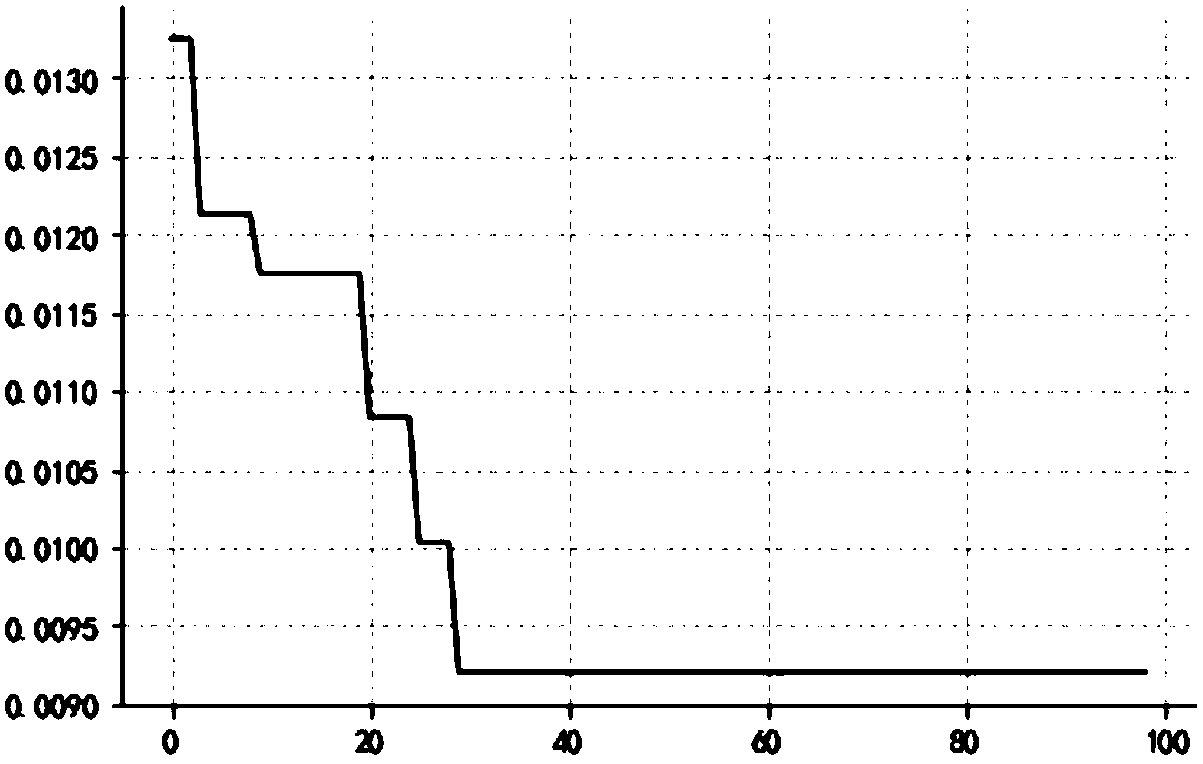
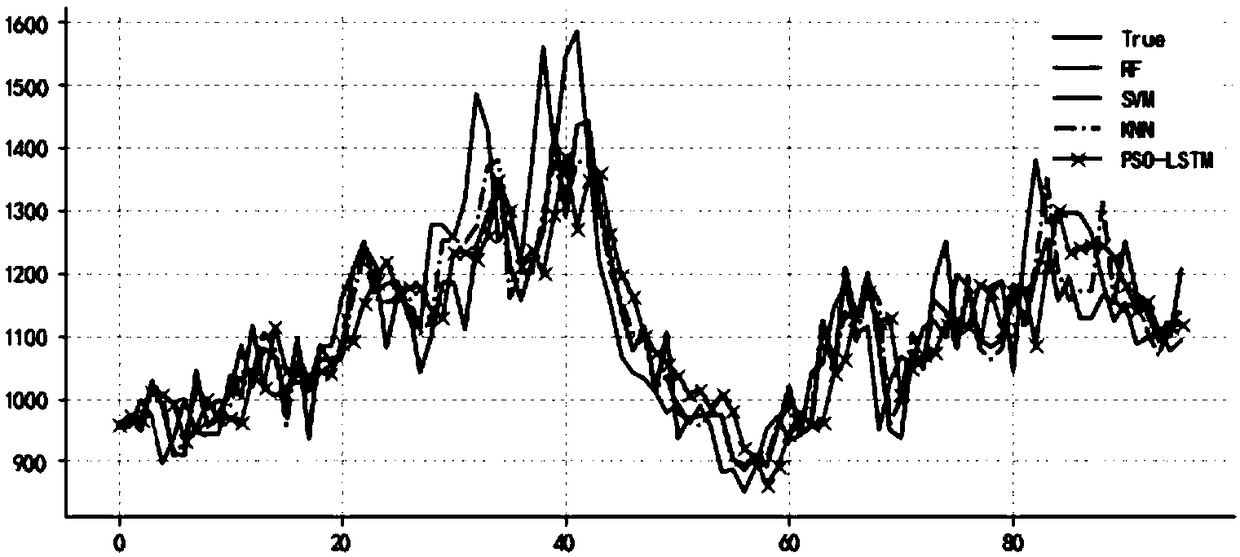
Travel time prediction method for optimizing LSTM neural network through particle swarm optimization algorithm
ActiveCN108986470AImprove forecast accuracyImprove applicabilityDetection of traffic movementNeural architecturesPrediction algorithmsNetwork model
The invention discloses a travel time prediction method for optimizing an LSTM neural network through a particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting travel time data, performing data normalization, and dividing the data into a training set and a test set proportionally; S2, optimizing each parameter of an LSTM neural network prediction model by using the particle swarm optimization algorithm; S3, inputting the parameters, optimized through the particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the training set, and performing the iterative optimization of the LSTM neural network prediction model; S4, predicting the test set through the trained LSTM neural network model, and evaluating a model error. The method is quick in optimization. Compared with a random forest, SVM and KNN in the traditional prediction algorithm, the method of the invention has the least mean square error and square error for the data prediction, and the model reducesthe calculation burden, so the method shows better prediction performance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Radar imaging system and method
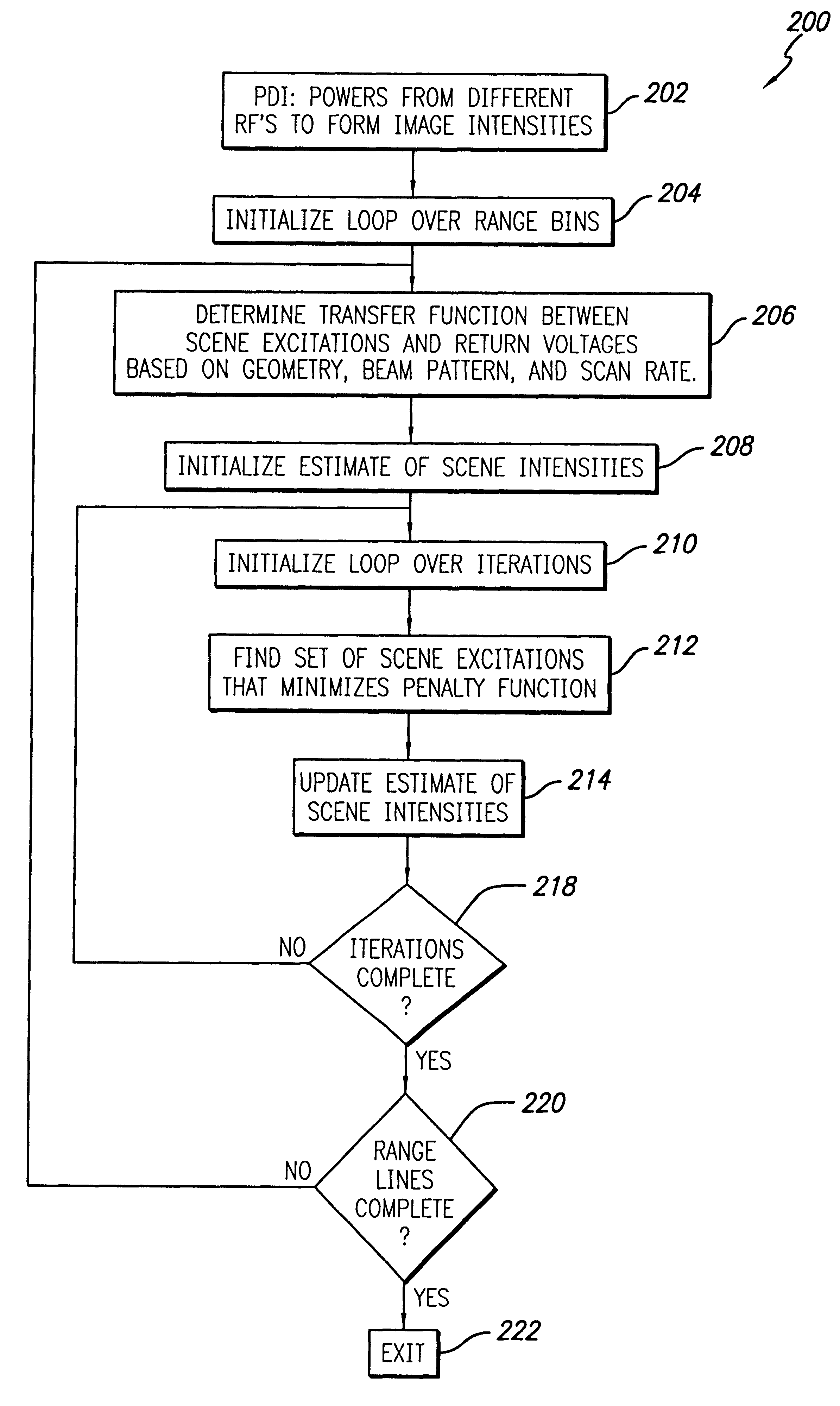
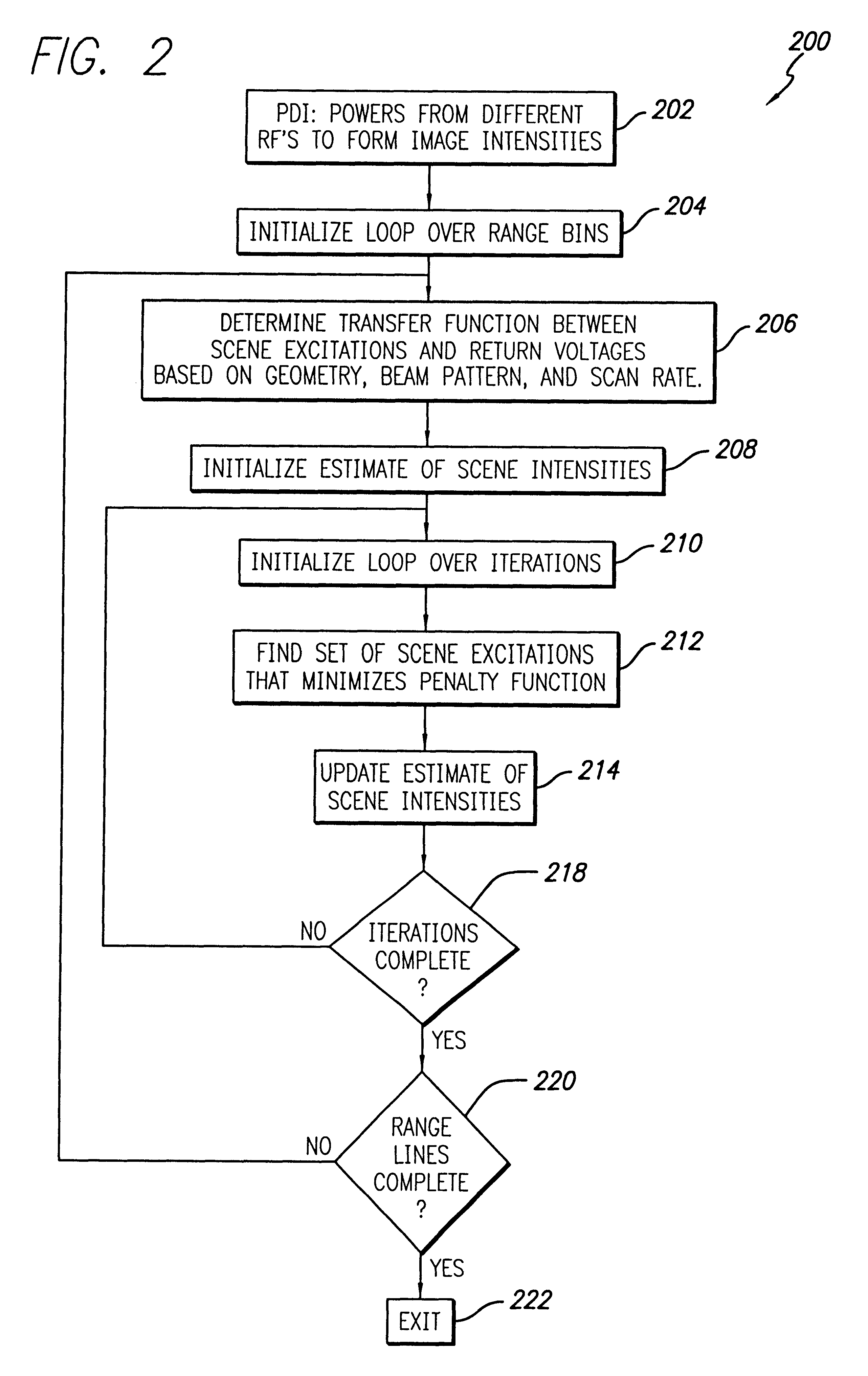
An imaging processing system and method. In accordance with the invention, the illustrative method includes the steps of providing a transfer function between scene excitations and voltage returns based on geometry, beam pattern and / or scan rate; ascertaining a set of scene excitations that minimize a penalty function of the transfer function; and ascertaining a set of scene intensities based on the scene excitations, and a set of optimal weights for the penalty function based on the scene reflectivities. The inventive method provides significantly enhanced image sharpening. In the illustrative embodiment, the inventive method uses an iterative convergence technique which minimizes a penalty function of the sum of square errors between the scene excitations corrupted by the radar system (i.e. the antenna pattern and processing) and the radar voltage returns. The innovation significantly enhances radar imagery by iteratively deriving a best scene solution, which reduces corruption introduced by the radar system. The novel technique for enhanced discrimination by the radar imagery is an iterative technique, which models the true scene signal corruption and derives a solution for the scene intensities, which minimizes the errors in the derived image. The novel technique finds the scene scatterer powers, which best match the original image pixel powers. The effect of the antenna pattern is taken into consideration when computing the derived image, which is matched against the original image. The constraint is implemented iteratively by adding a weighted sum of scene powers to the penalty function. The weights are adjusted at each iteration.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
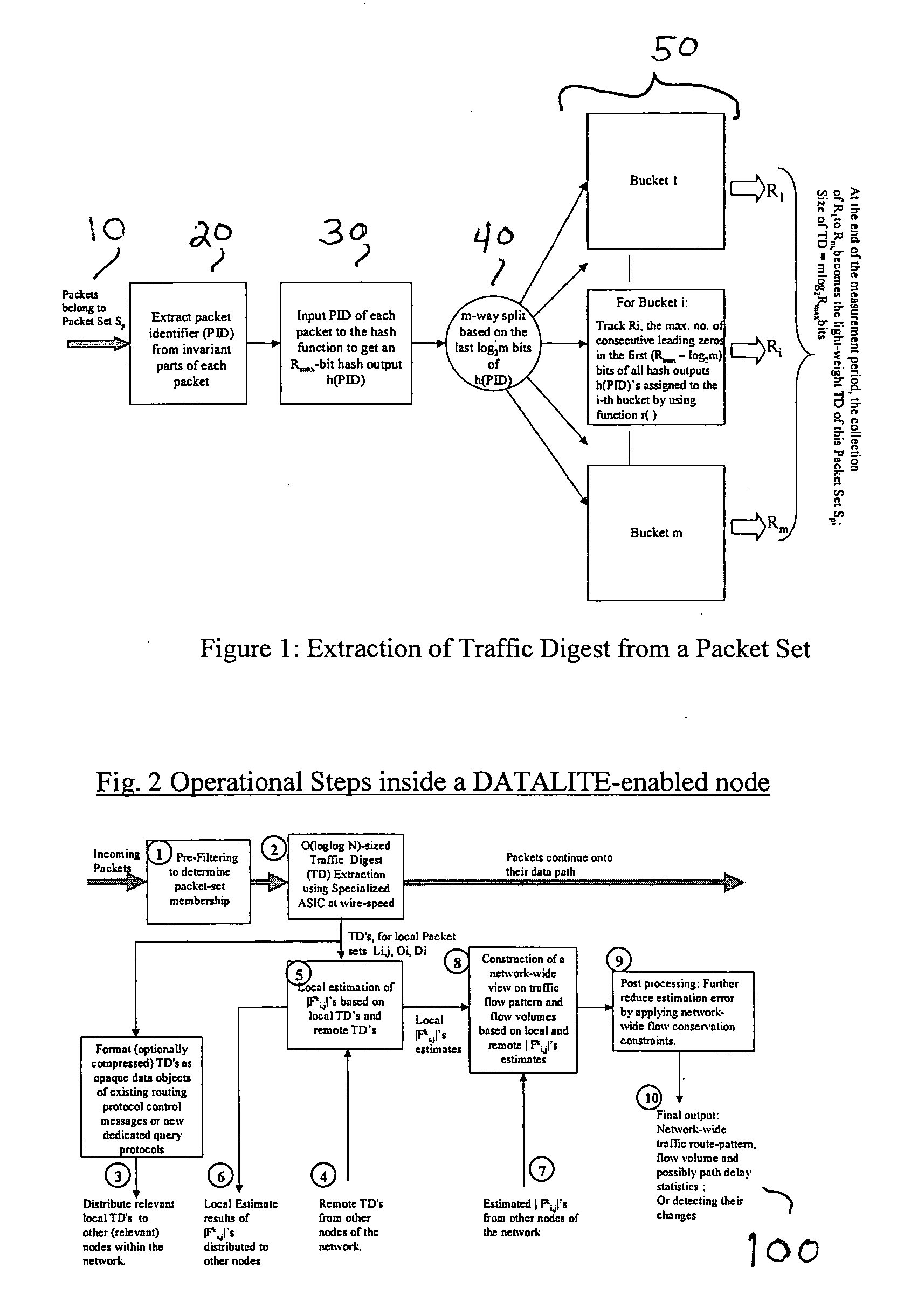
High-speed traffic measurement and analysis methodologies and protocols
InactiveUS20050220023A1Minimal communication overheadMore bandwidth is requiredError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNODALWire speed
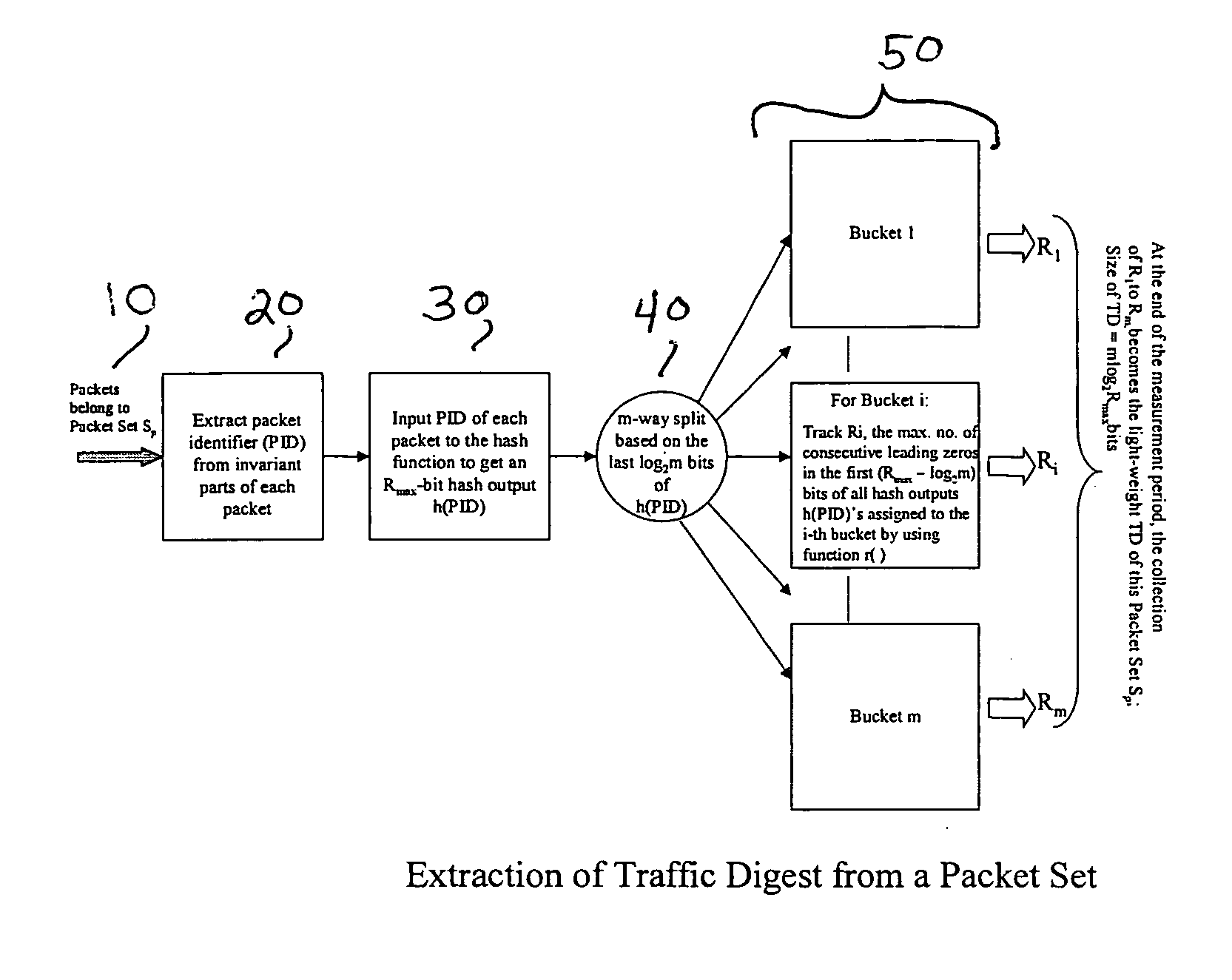
We formulate the network-wide traffic measurement / analysis problem as a series of set-cardinality-determination (SCD) problems. By leveraging recent advances in probabilistic distinct sample counting techniques, the set-cardinalities, and thus, the network-wide traffic measurements of interest can be computed in a distributed manner via the exchange of extremely light-weight traffic digests (TD's) amongst the network nodes, i.e. the routers. A TD for N packets only requires O(loglog N) bits of memory storage. The computation of such O(loglog N)-sized TD is also amenable for efficient hardware implementation at wire-speed of 10 Gbps and beyond. Given the small size of the TD's, it is possible to distribute nodal TD's to all routers within a domain by piggybacking them as opaque data objects inside existing control messages, such as OSPF link-state packets (LSPs) or I-BGP control messages. Once the required TD's are received, a router can estimate the traffic measurements of interest for each of its local link by solving a series of set-cardinality-determination problems. The traffic measurements of interest are typically in form of per-link, per-traffic-aggregate packet counts (or flow counts) where an aggregate is defined by the group of packets sharing the same originating and / or destination nodes (or links) and / or some intermediate nodes (or links). The local measurement results are then distributed within the domain so that each router can construct a network-wide view of routes / flow patterns of different traffic commodities where a commodity is defined as a group of packets sharing the same origination and / or termination nodes or links. After the initial network-wide traffic measurements are received, each router can further reduce the associated measurement / estimation errors by locally conducting a minimum square error (MSE) optimization based on network-wide commodity-flow conservation constraints.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
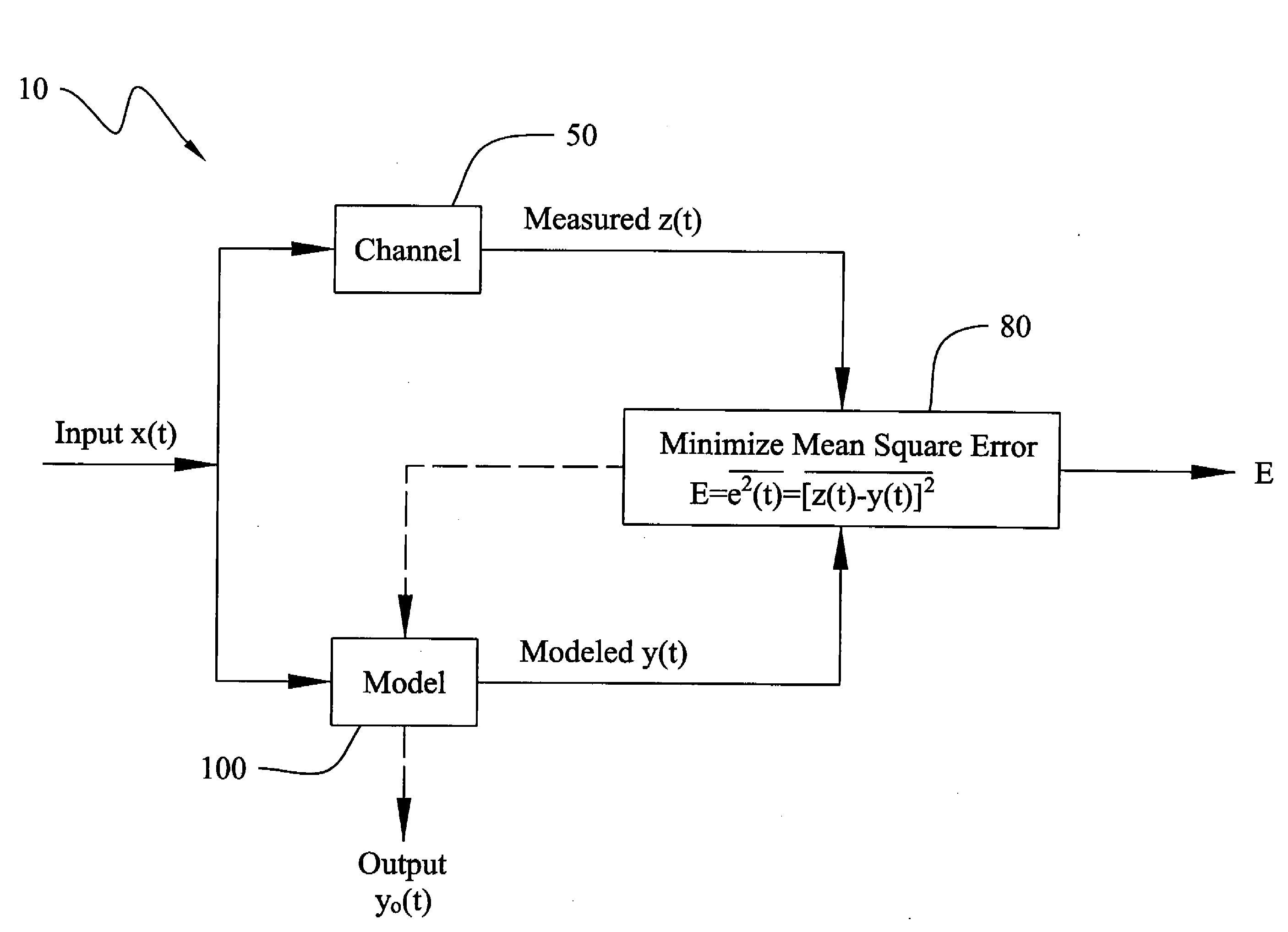
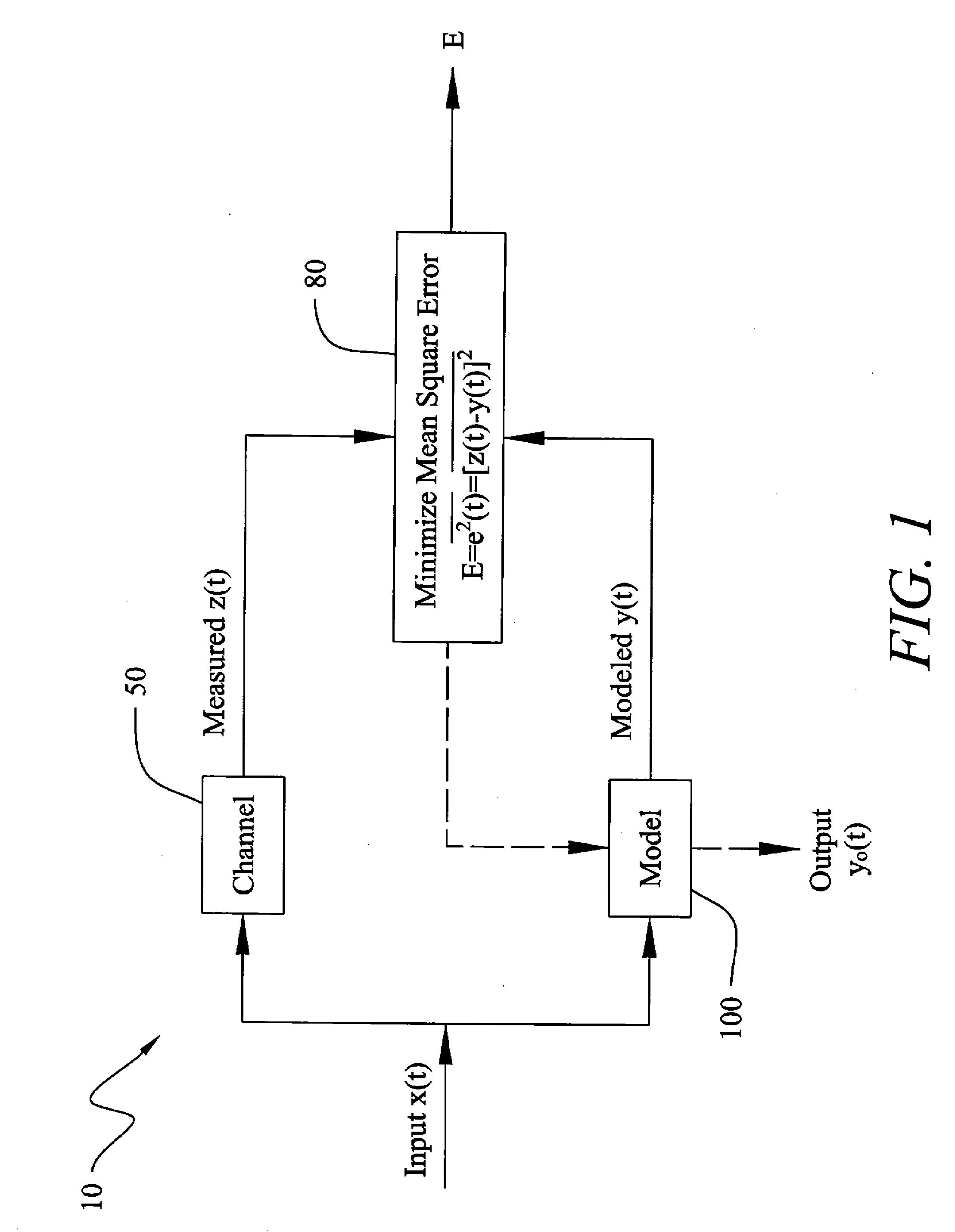
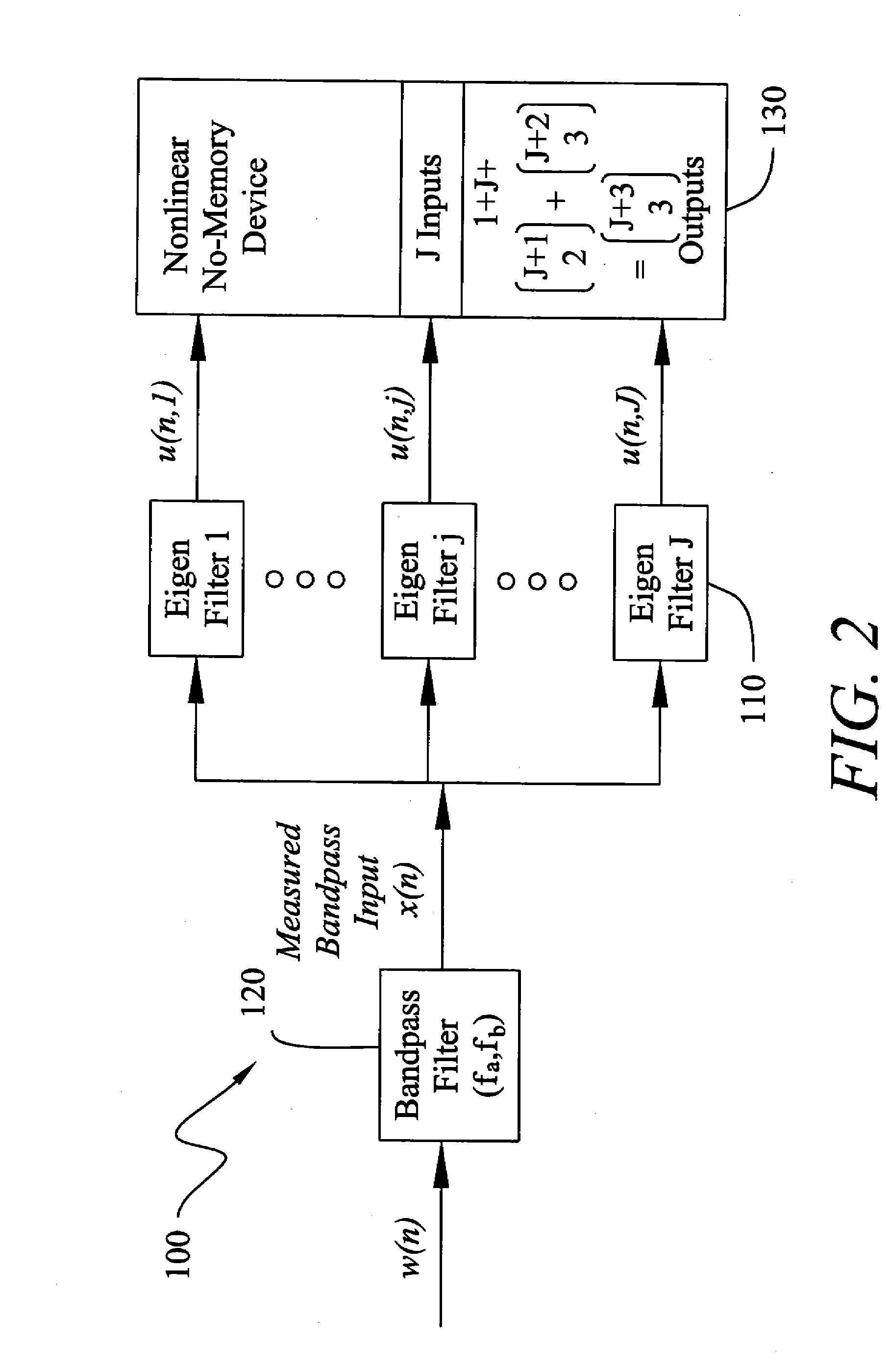
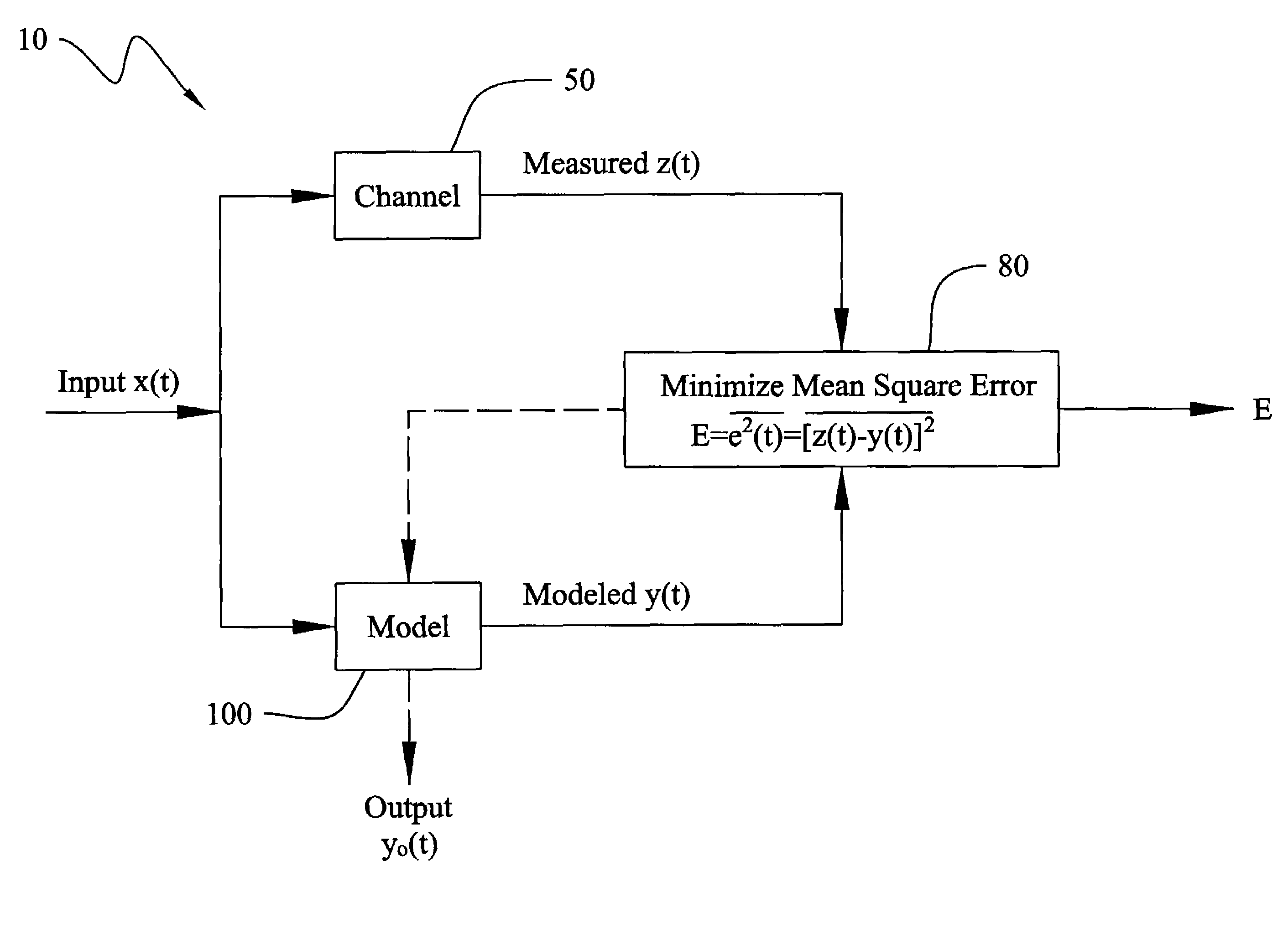
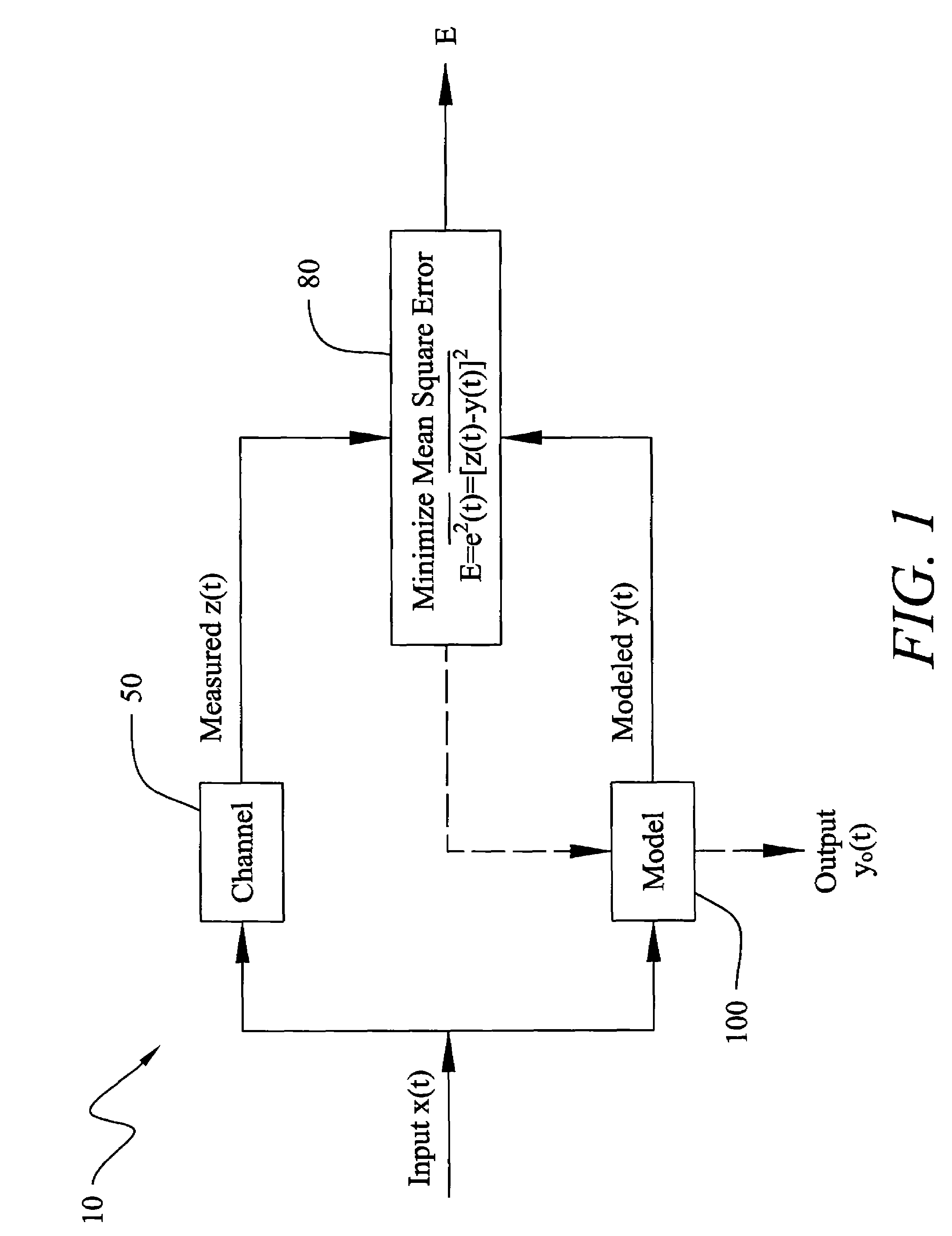
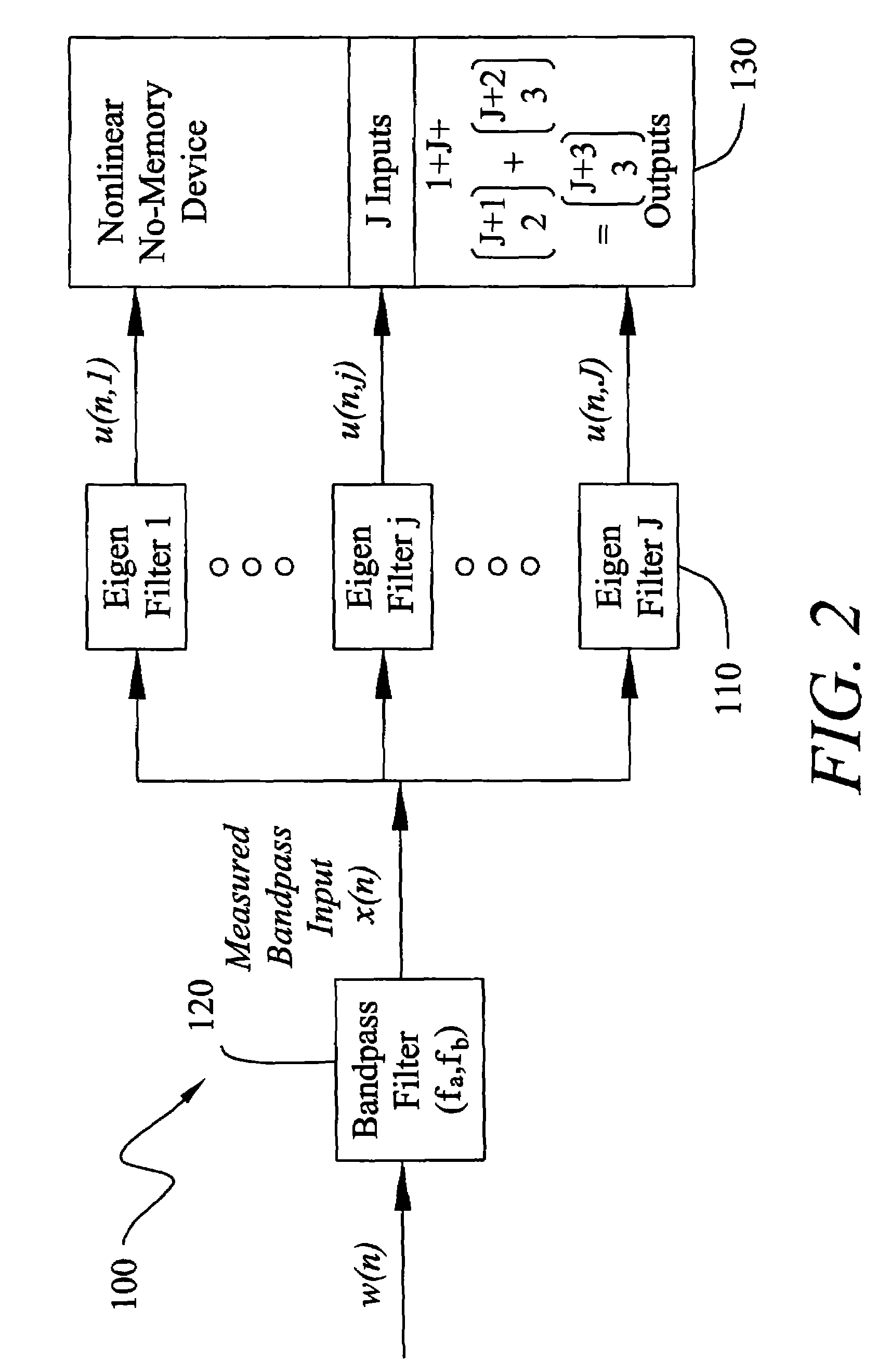
Method and Apparatus for Improved Active Sonar Using Singular Value Decomposition Filtering
InactiveUS20090003134A1Excellent performance resultGuarantee linear independenceAcoustic wave reradiationSingular value decompositionSonar
The invention is a method for improved active sonar using a singular value decomposition filtering and a Volterra-Hermite Basis Expansion to model real active sonar measurements. The fitting model minimizes the sum of the squared errors between a measured channel response, z(t), and model response, y(t), which is a fitted Volterra Series solution. The model requires as input an excitation waveform, x(t), to which is fitted the model response, y(t). A contracted broadband cross-ambiguity function is used to correct the excitation waveform for Doppler and range effects. Once completed, the modeled response can be used to determine the linearity or non-linearity of the channel effects. Appropriate measures can be utilized to reduce these effects on the measured channel response.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENT DIV NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL THE
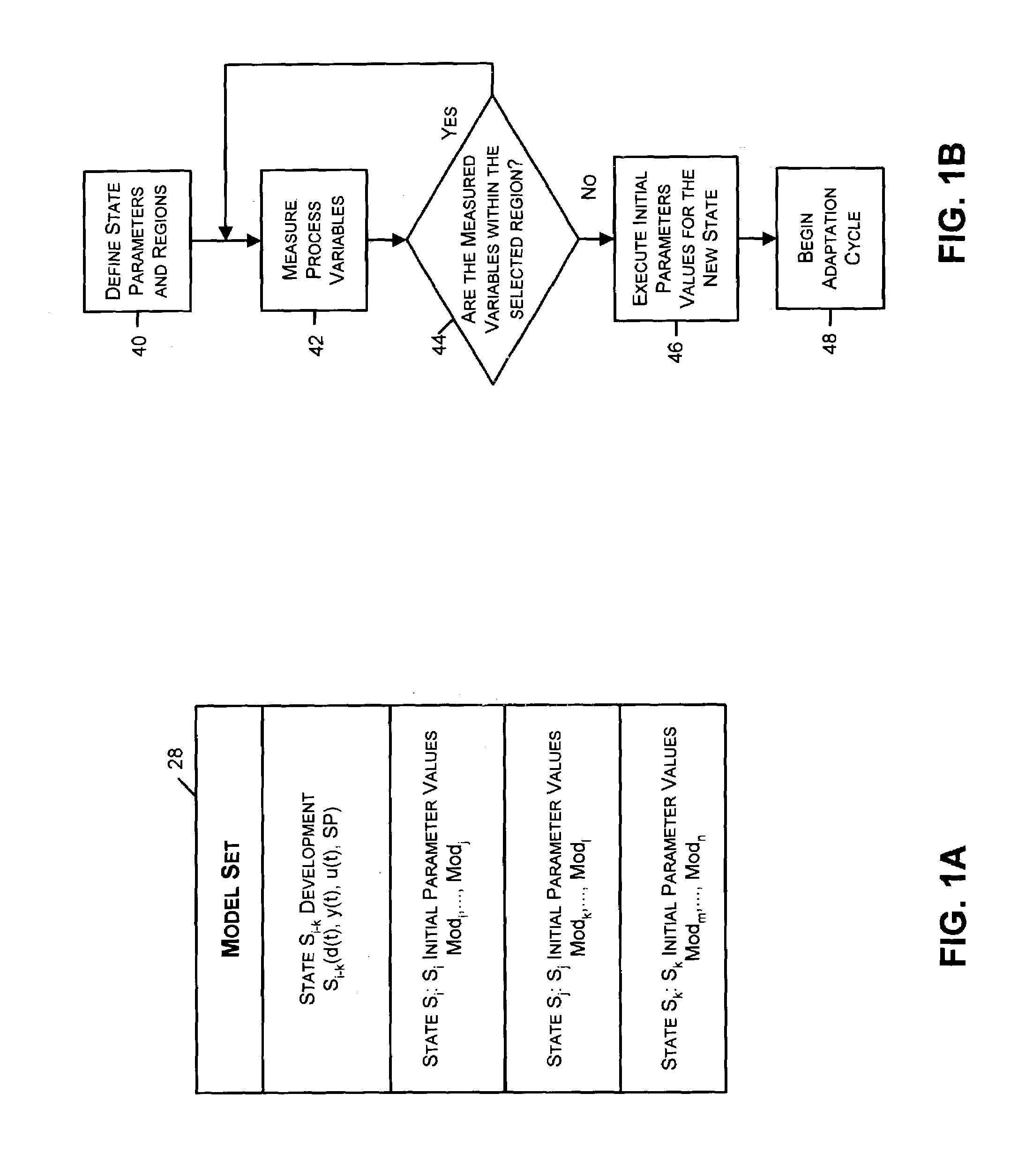
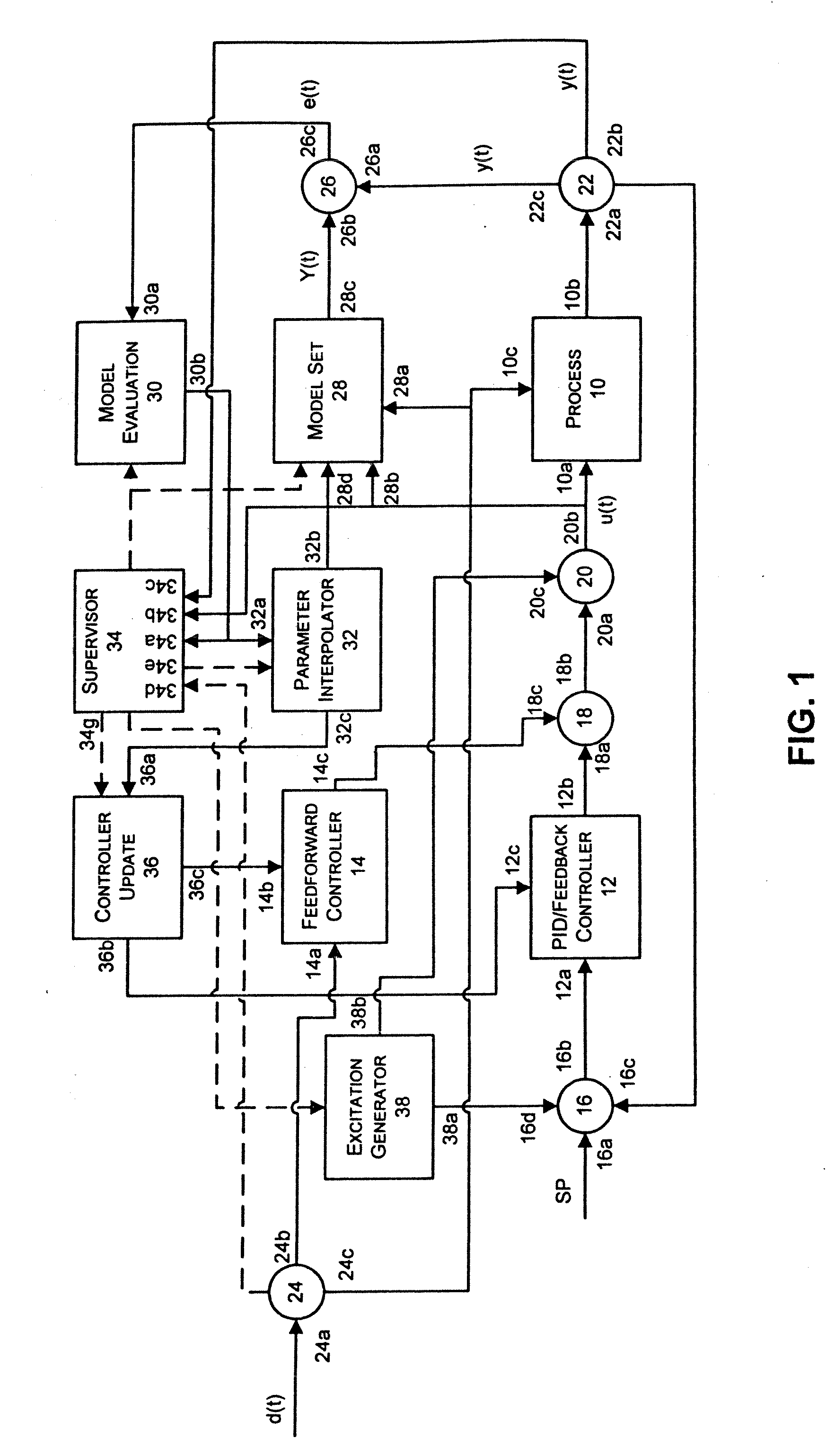
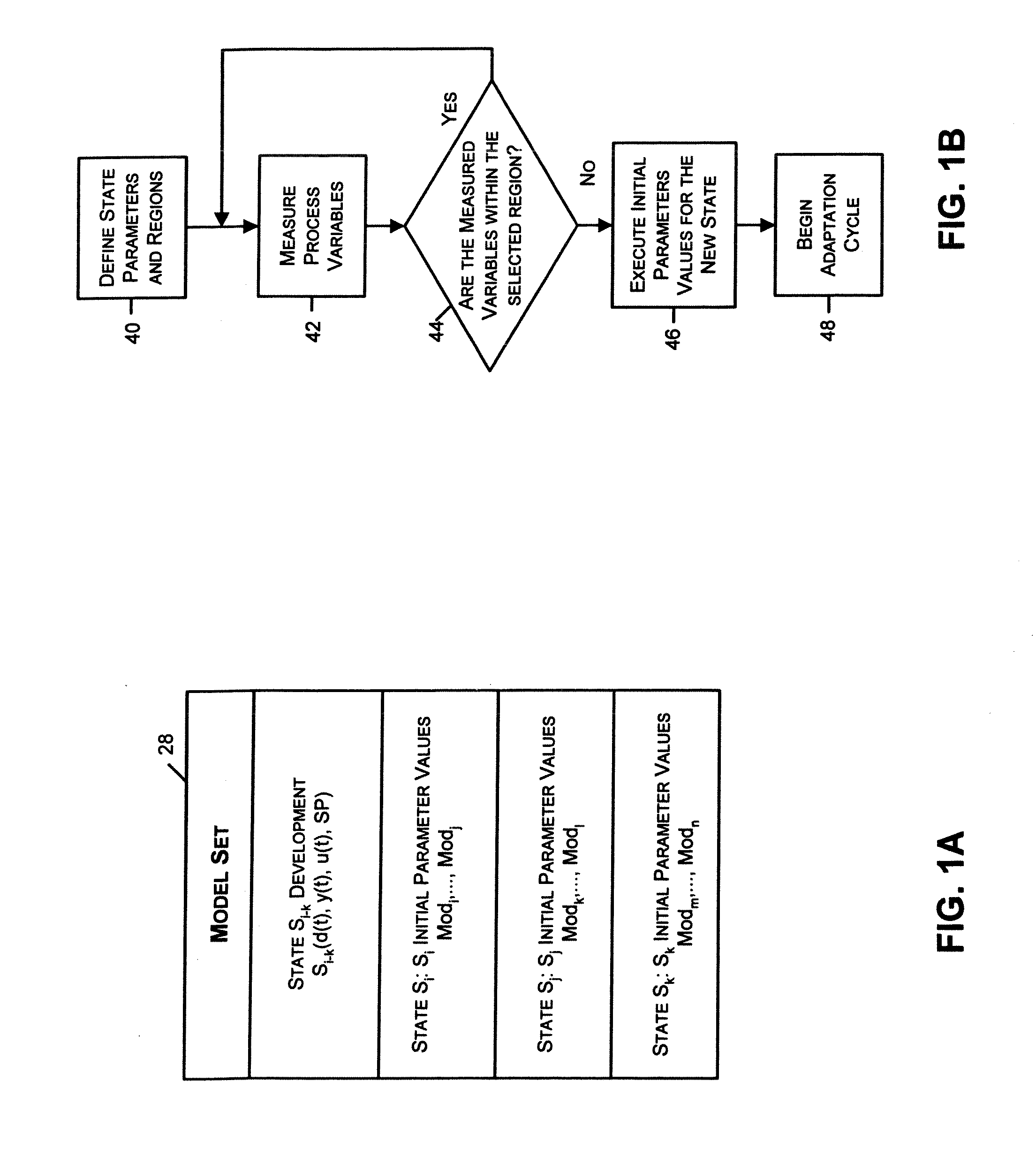
State Based Adaptive Feedback Feedforward PID Controller
InactiveUS20070021850A1Simulator controlComputation using non-denominational number representationState variableProcess region
A state based adaptive feedback / feedforward PID controller includes a model set component, communicatively coupled to a process input, having a state variable defining a number of process regions, and a number of models grouped into the process regions. Each of the grouped models includes a plurality of parameters having a value selected from a set of predetermined initial values assigned to the respective parameter. The adaptive controller further includes an error generator communicatively coupled to the model set component and a process output. The error generator configured to generate a model error signal representative of the difference between a model output signal and a process output signal. The error generator, communicatively coupled to a model evaluation component, is configured to compute a model squared error corresponding to a model and correlating the model squared error to parameter values represented in the model. The adaptive controller further includes a parameter interpolator communicatively coupled to the model evaluation component for calculating a respective adaptive parameter value for parameters represented in the model and a controller update component, communicatively coupled to the parameter interpolator, for updating the controller in response to adaptive parameter values upon conclusion of an adaptation cycle.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
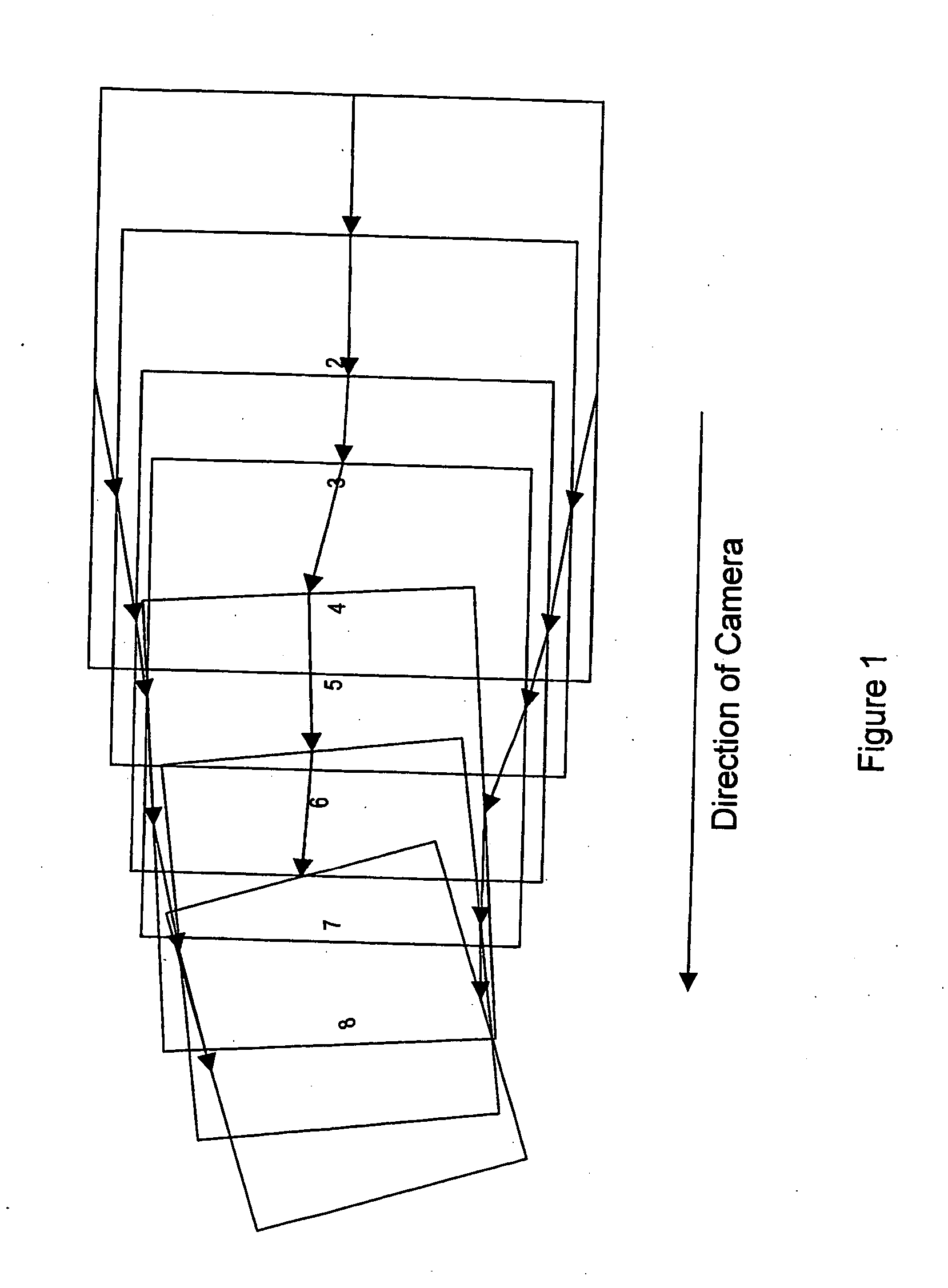
Method and system for estimating global motion in video sequences
ActiveUS20060072663A1Ensure correct executionOvercome the noiseColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorInterframe coding
The invention relates to estimating the global motion between frames of a motion-compensated inter-frame encoded video sequence, directly from the motion vectors encoded within the frames. For any particular frame, the motion vectors are first decoded, and a finite number of sets of vectors are selected. An affine or other geometrical transform is then used to generate a motion estimation for each set, and then the least median squared error present in each motion estimation is calculated for each estimation. The motion estimation with the smallest least median squared error is then selected as being representative of the global motion in the image of the frame. A panoramic image generating method and system which makes uses of the global motion estimations thus obtained is also described
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
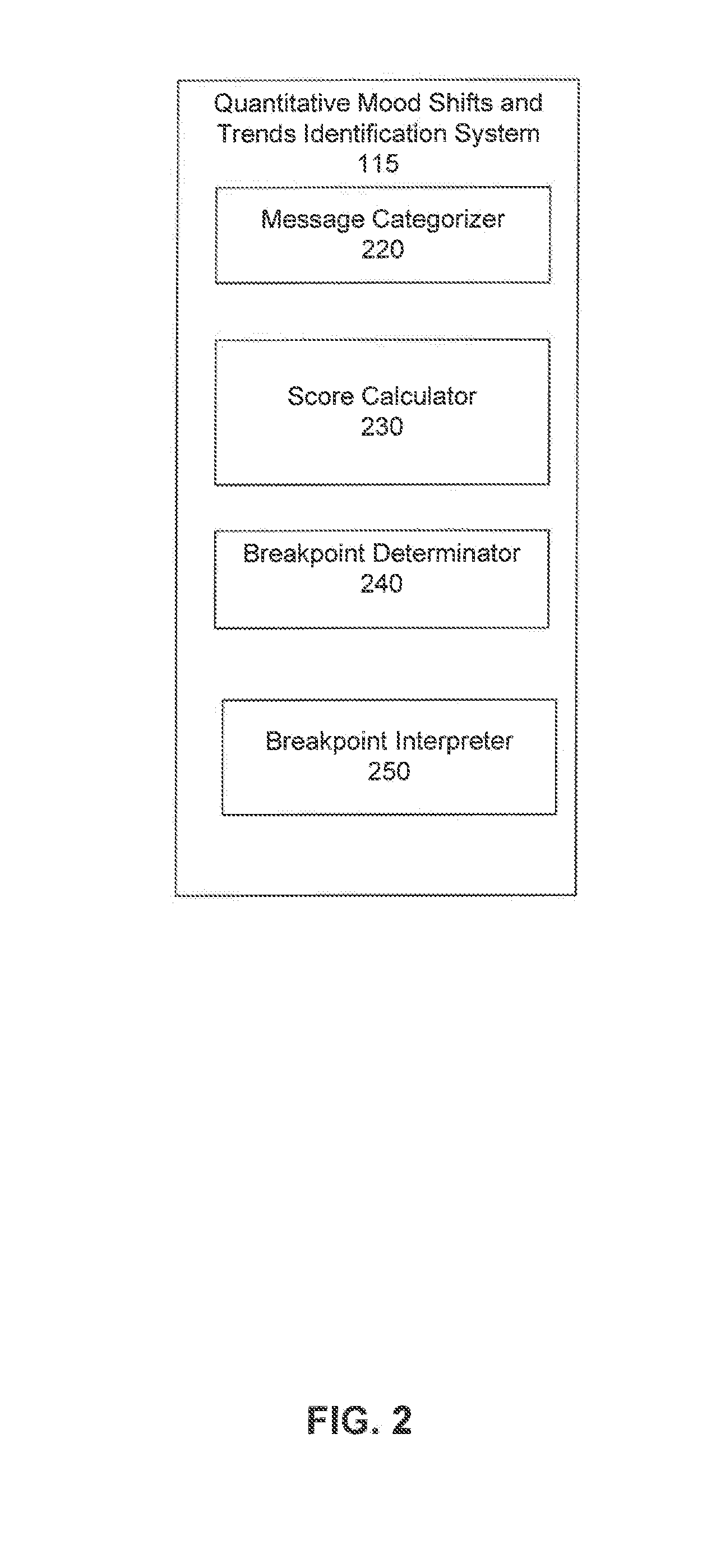
Identifying and Forecasting Shifts in the Mood of Social Media Users
ActiveUS20130275352A1Minimize sumDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingSocial mediaComputer science
Quantitatively identifying and forecasting shifts in a mood of social media users is described. An example method includes categorizing the textual messages generated from the social media users over a selected period of time into a plurality of word categories, with each word category containing a set of words associated with the mood of social media users. A score indicating an intensity of the mood of the social media users is calculated for each word category, wherein a value of the score and its corresponding time point define a data point for the word category. Subsequently, breakpoints in the mood of social media users are determined so that the breakpoints minimize a sum of square errors representing a measurement of a consistency of all data points from inferred values of the scores of the data points derived using the breakpoints over the selected period of time. Further, space of all possible breakpoints for the word categories are searched to identify a defined number and locations of the breakpoints. Finally the breakpoints over the selected period of time are interpreted to identify the shifts in the mood of social media users and trends between breakpoints.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
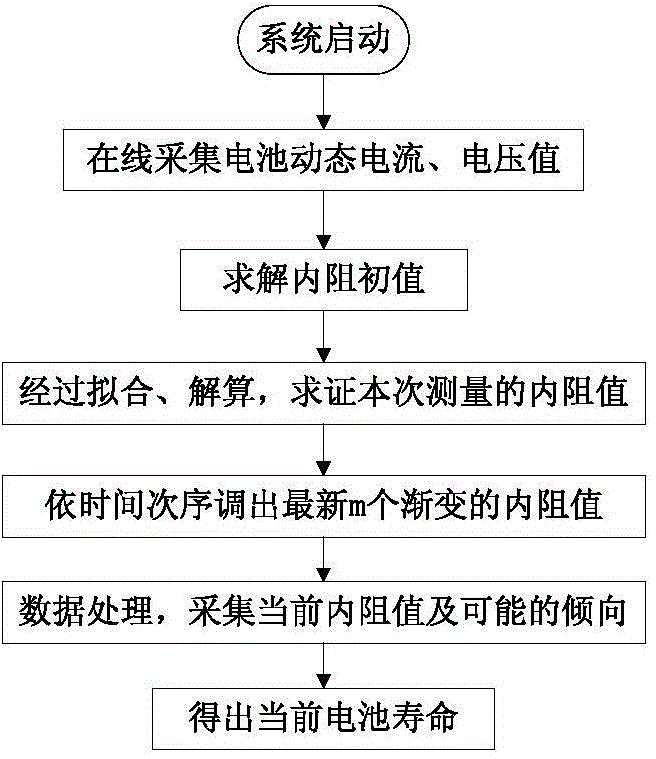
Power battery service life monitoring method based on on-line internal resistance testing
ActiveCN104678320AImprove accuracyOvercoming the disadvantages of "false value"Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingStart timeInternal resistance
The invention discloses a power battery service life monitoring method based on on-line internal resistance testing, and aims to solve the technical problem that the conventional power battery service life testing method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, the power battery service life monitoring method comprises the following steps: under the condition of rated load, testing a voltage-primary discharge current value of a power battery, thereby obtaining a present operation state value of the power battery; on the basis of continuous testing, calculating a primary value of the internal resistance of the power battery; subsequently, meeting optimization target which meets 'minimum square error' by using a least square fit method, and working out a primary tested value R (i) of the internal resistance of the power battery; testing for multiple times, thereby obtaining as string of progressive charge sequence {R(i)} i=1, 2, ..., m which can reflect the change rule of the internal resistance of the power battery within a relatively long period; finally, with the combination of historical records such as the service starting time and the utilization rate of the power battery, implementing data processing so as to obtain the present service life state of the power battery, and predicting the change and the available degree of the service life of the power battery in a future period. The power battery service life monitoring method is simple and practical, and avoids off-line measurement.
Owner:西安正中德信息科技有限公司
An Imaging Method of Nonlinear Frequency Modulation Scaling for Synthetic Aperture Radar
InactiveCN102288961ALow orthogonalityRelatively small errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarFrequency modulation
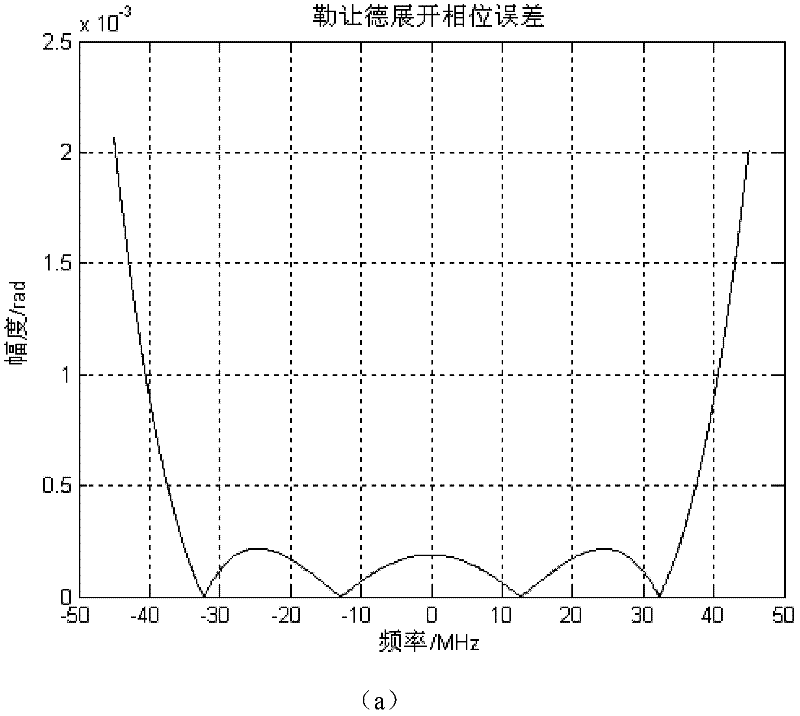
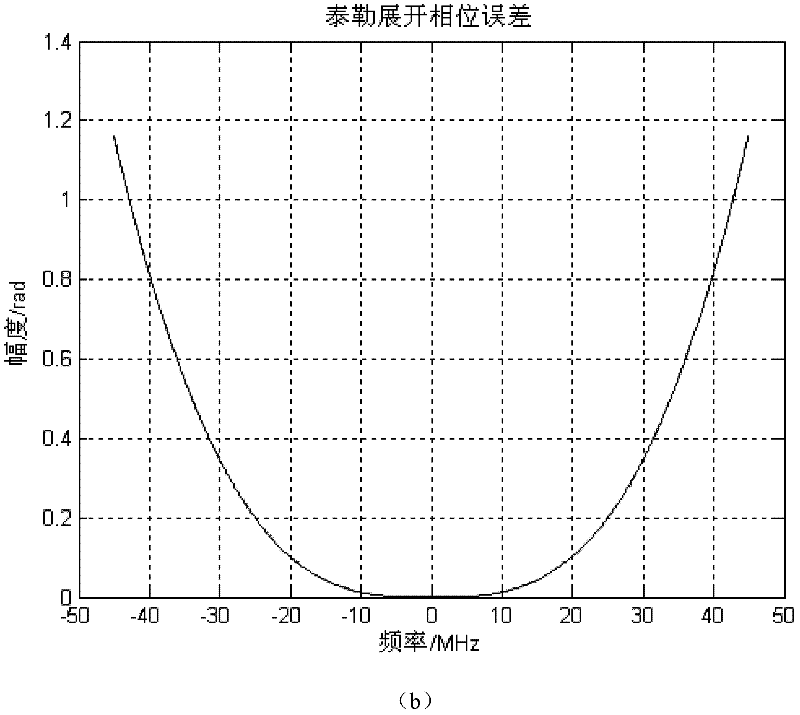
The invention belongs to an imaging method for nonlinear frequency modulation label change in the synthetic aperture radar imaging technology, which comprises the steps of two-dimensional frequency domain unfolding, filtering processing, nonlinear frequency modulation label change, distance compression, distance migration correction, rest phase compensation and position compression. In the method of the invention, the characteristics of orthogonality and minimum square error of the Legendre polynomials are utilized for carrying out three-order unfolding on the two-dimensional frequency domain signals of the obtained echo signals according to the Legendre orthogonality polynomials, and then, the focusing imaging on targets is realized through carrying out filtering processing and the like on three-order phase items in echo signal two-dimensional frequency domain expression. When the method of the invention is adopted, the maximum phase error under the same condition is less than 0.2 percent of the maximum phase error in the prior art, so the assurance is provided for the high-precision imaging under the large-inclination view angle condition. Therefore, the method of the invention has the characteristics that the phase error in the imaging process can be effectively reduced, the imaging processing of the large-inclination view angle is realized, in addition, the imaging effect is good, the imaging processing efficiency and the precision are high, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radiographic apparatus and an image processing method therefore
ActiveUS20140205058A1Securing convergence accuracySpeedReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingImaging processingTomography
Initial values Â1P̂1M̂1 . . . ÂnP̂nM̂n of parameters representing a geometric relationship between an X-ray tube, a stage and a flat panel X-ray detector are estimated, a least squares solution (p̂w)i of characteristic point three-dimensional coordinates is estimated, and only limited parameters are updated until reprojection square errors converge. Thus, based on known radiographic conditions, initial values of the parameters are estimated, and a nonlinear optimization operation is carried out on only the parameters considered, in view of mechanisms and drive characteristics of the apparatus, to have large errors between the initial values of the parameters and the parameters at a time when radiography is actually carried out. As a result, the calculation can be speeded up, while securing the convergence accuracy of the nonlinear optimization operation, by using the radiographic conditions, i.e. information on tomography.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Surface defect detection method based on visual saliency map and support vector machine
ActiveCN104198497AAccurate visual salient areaImprove classification accuracyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSupport vector machineVisual saliency
The invention discloses a surface defect detection method based on a visual saliency map and a support vector machine. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating the visual saliency map of a surface image sample of a product to be detected by using a GBVS (Graph-based Visual Saliency) model, carrying out adaptive threshold segmentation on the visual saliency map through a method of maximum classes square error, extracting a visual saliency region, calculating the average gray-values of the visual saliency map and the average gray-values of the visual saliency region in the visual saliency map, and respectively carrying out normalization processing to form two-dimensional features, then taking the obtained two-dimensional features of the visual saliency map as training samples of the support vector machine, selecting two dimensions to classify the optimal classification line, based on the optimal classification line, classifying the two-dimensional features, thereby distinguishing whether the product in the map has defects or not. The surface defect detection method disclosed by the invention can effectively save labor, lower the labor intensity and improve the work efficiency and has high identification accuracy.
Owner:苏州佳赛特智能科技有限公司
Demodulation and timing synchronization combined method for GFSK (Gauss Frequency Shift Key)
InactiveCN102170414ASimplify complexityReduce overheadSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-modulated carrier systemsLoop filterFilter tuning
The invention relates to a demodulation and timing synchronization combined method for a GFSK (Gauss Frequency Shift Key). In the invention, an oversampling signal is used as an input of a demodulation and synchronization loop; after a phase of the sampling signal is adjusted by an interpolation filter, conjugate multiplication is carried out on the sampling signal by every two continuous sampling values to obtain a phase difference; and the phase difference is used as an input of timing error detection. With a difference between front and back phase values as a direction of error adjustment,a middle phase value of every three continuously calculated phase values is used as a size of the error adjustment. A timing error is fed back to the interpolation filter after passing through a loopfilter, and a new sampling value is adjusted again and again. By using the invention, the realization complicatedness of hardware is simplified and the use of a square error detection algorithm is avoided under an oversampling situation; and the demodulation and timing synchronization combined method for the GFSK, provided by the invention, has the advantages of small hardware cost and good timing detection performance.
Owner:浙江瑞讯微电子有限公司
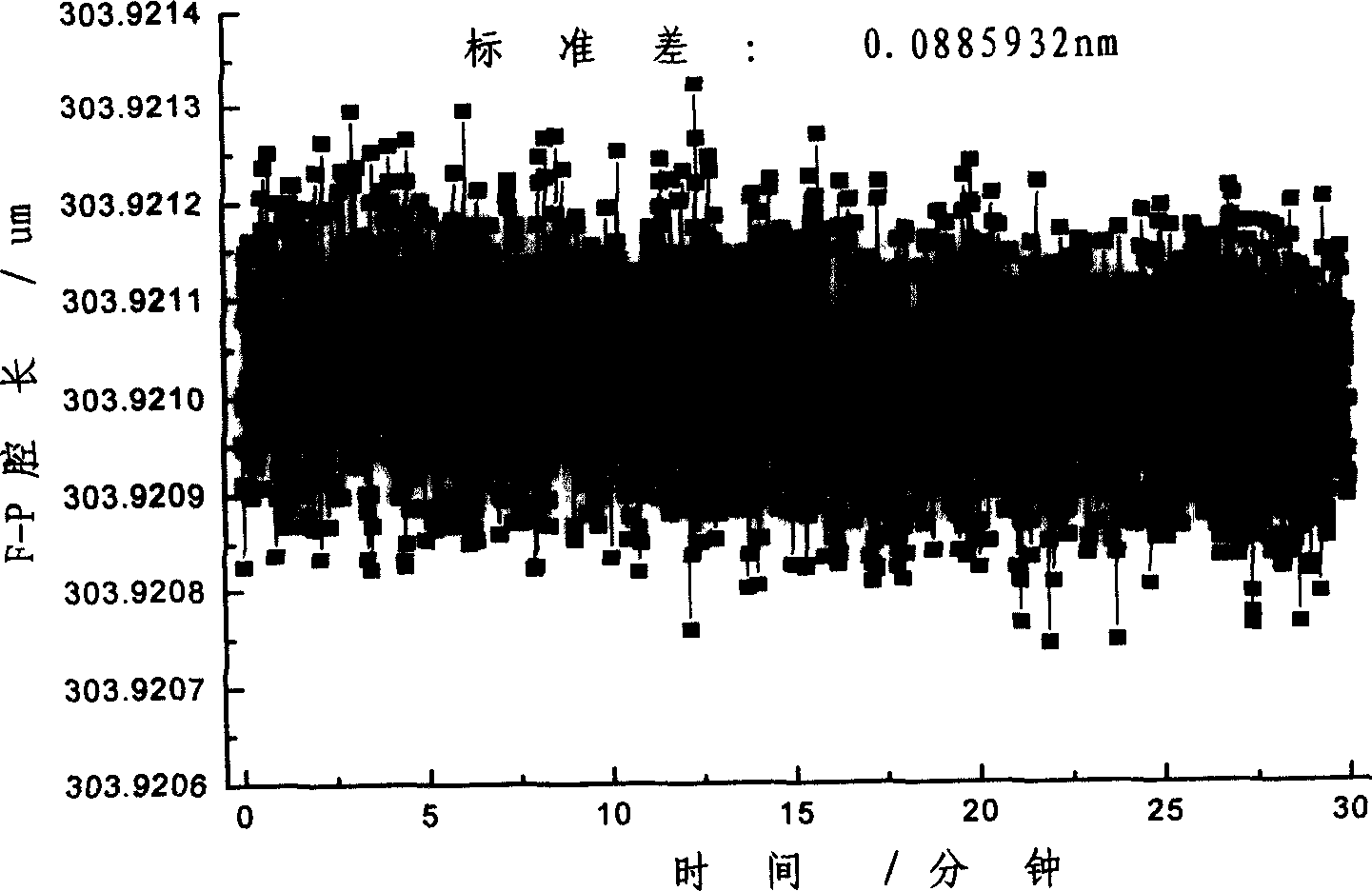
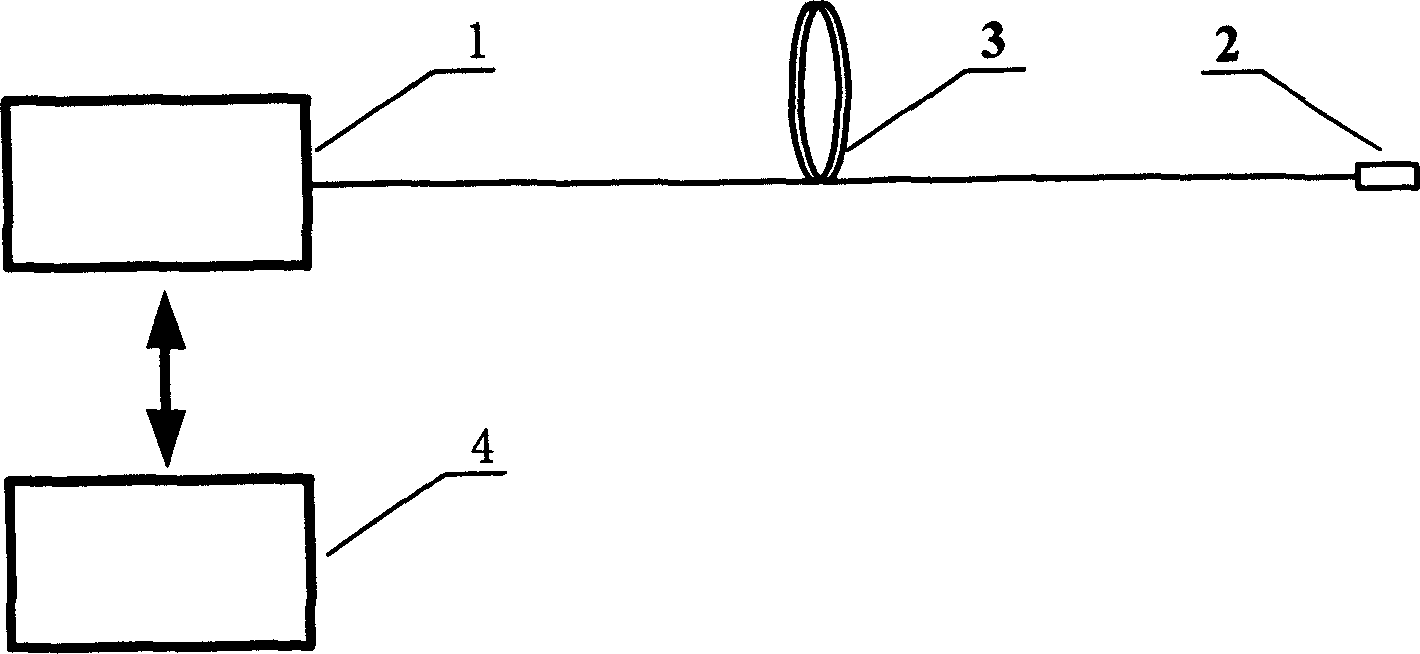
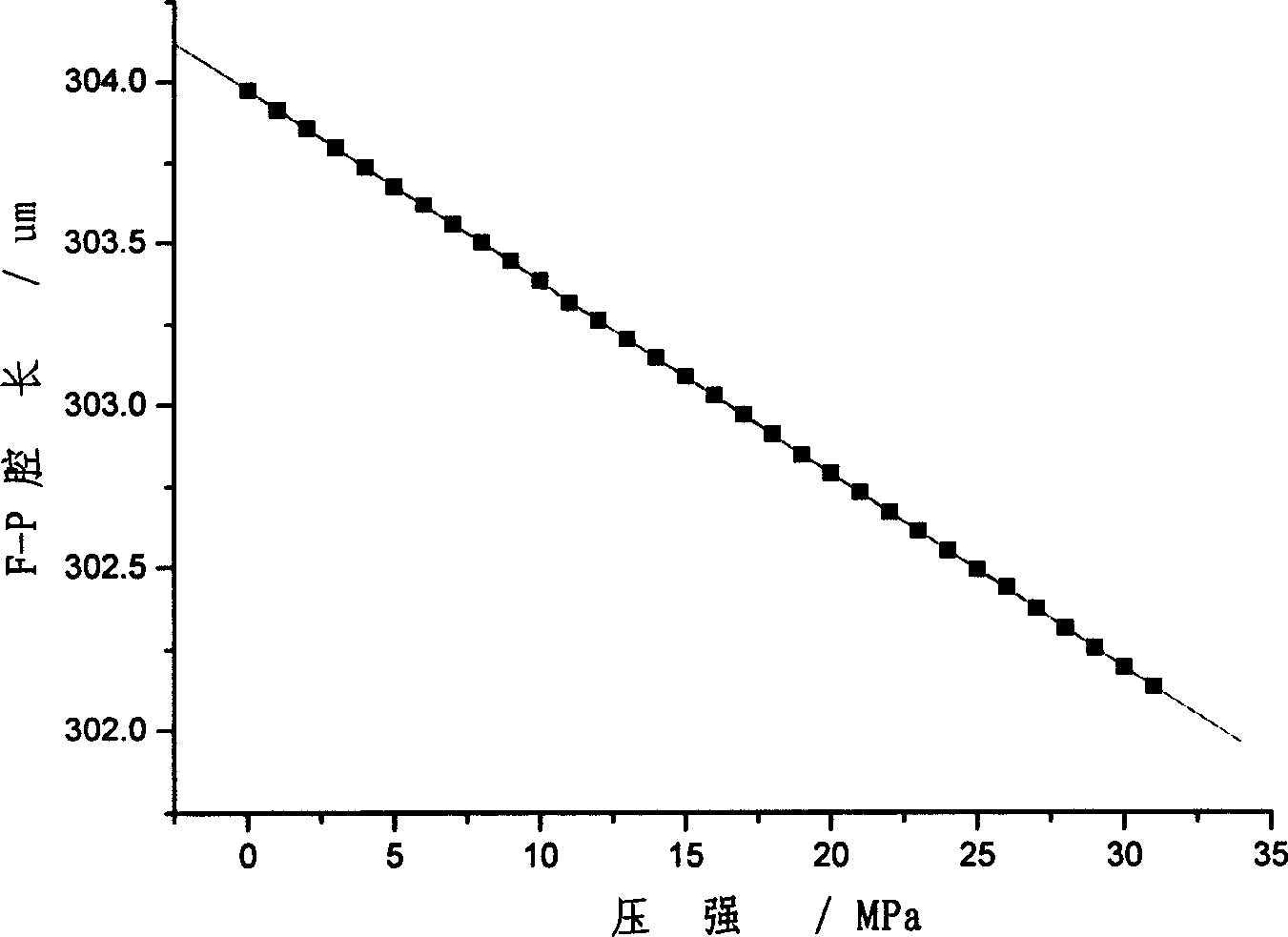
Cavity length demodulating algorithm of fibre-optical F-P sensor
InactiveCN1831485AHigh cavity length resolutionLarge dynamic rangeFibre transmissionConverting sensor output opticallyGratingLong-period fiber grating
A demodulation - algorithm of optical fiber F-P transducer cavity length includes calculating out a group of ideal spectrum sequence for reasonable estimation element according to transfer function of optical fiber F-P sensing head, calculating out a group of mean - square error value according to calculated out ideal spectrum sequence and measured spectrum sequence, using estimation element corresponding to minimum mean - square error as optimum estimation element of actual cavity length.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
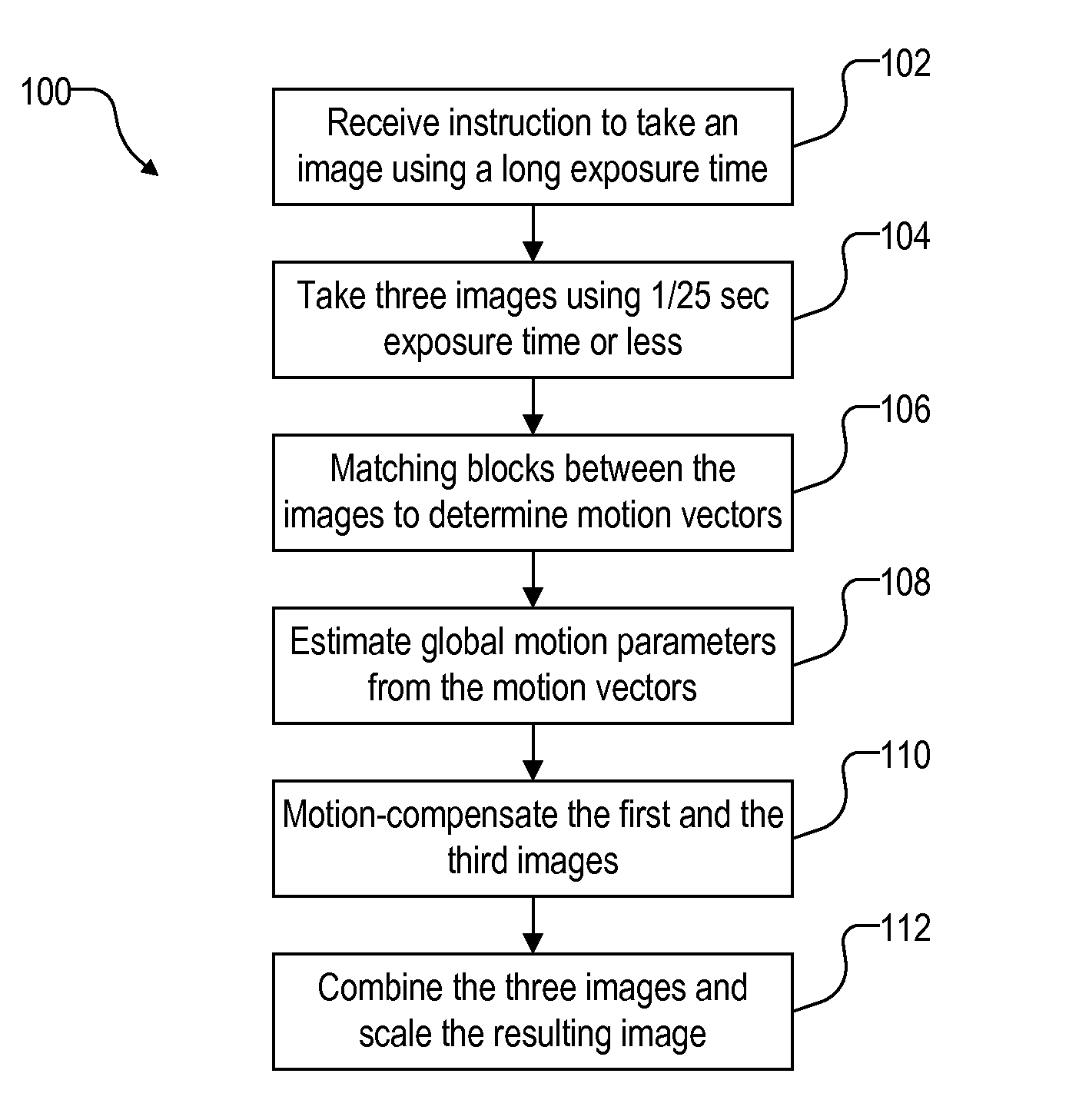
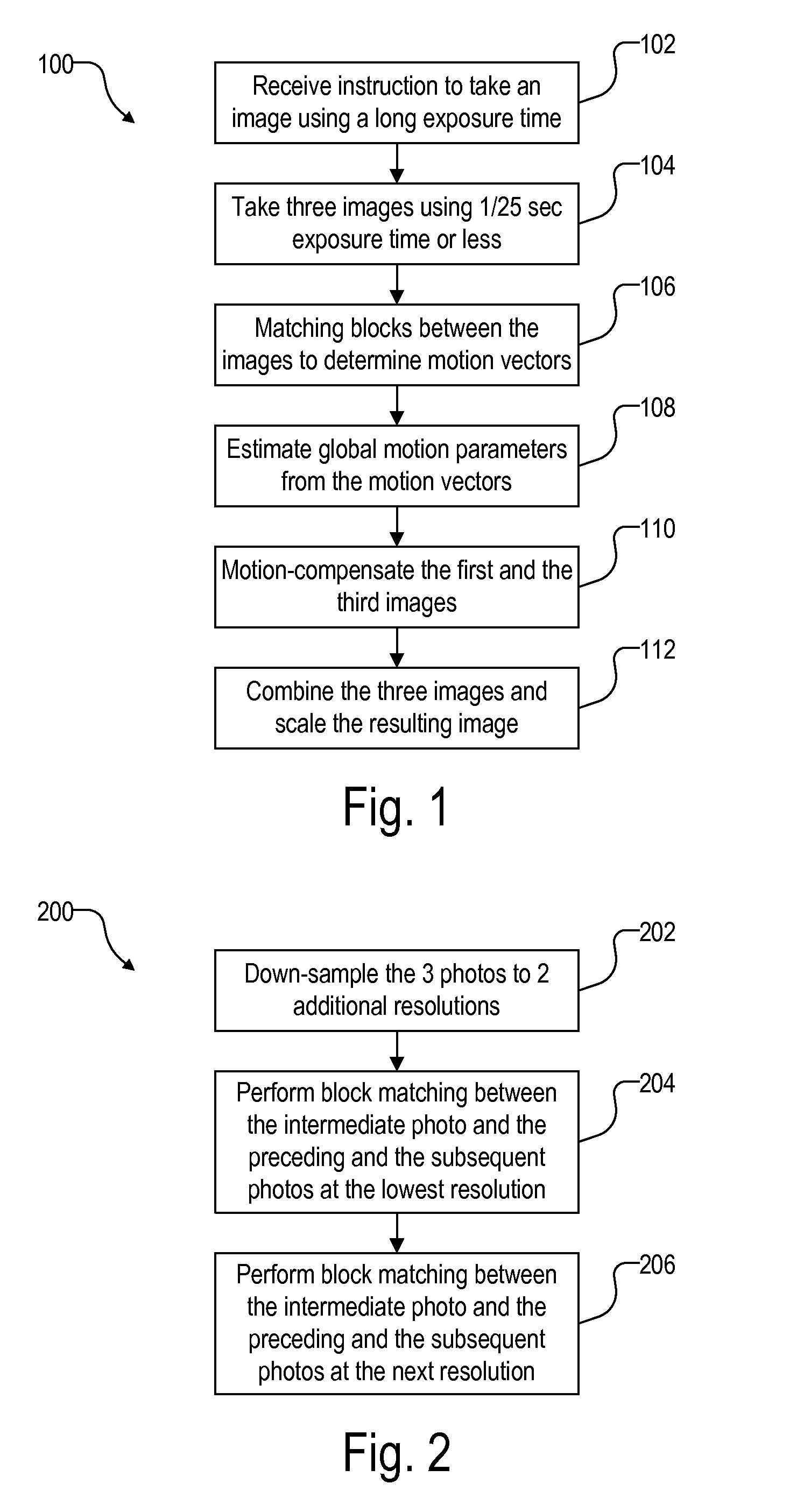
Algorithm description on non-motion blur image generation project
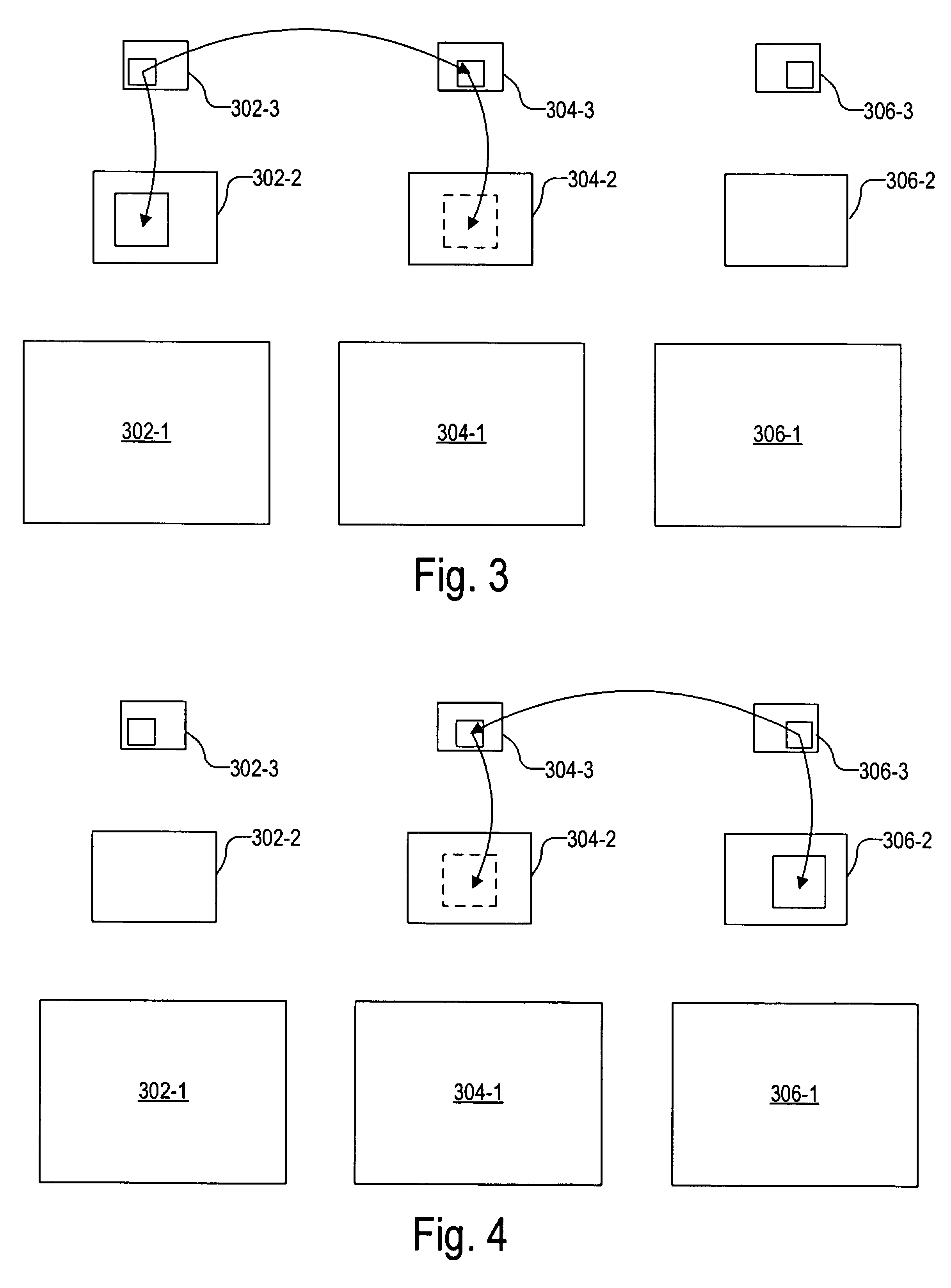
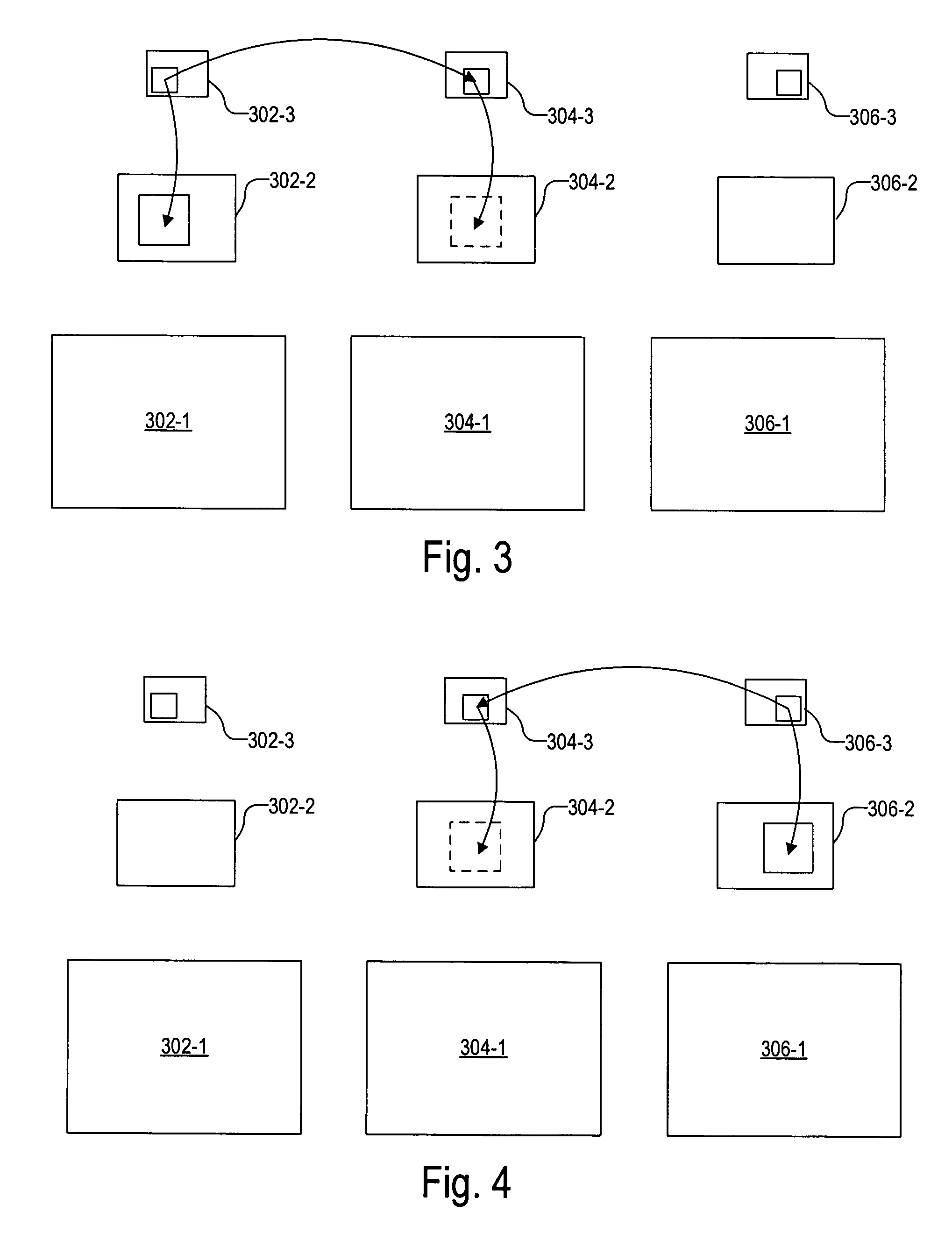
A method for simulating an image captured at a long exposure time (“simulated image”), includes (1) capturing each of first, second, and third images at a short exposure time, (2) determining a first relative motion between the first and the second images, (3) transforming the first image to remove the first relative motion, (4) determining a second relative motion between the third and the second images, (5) transforming the third image to remove the second relative motion, and (6) combining the first, the second, and the third images to form the simulated image. Relative motions between images are determined by matching blocks at multiple resolutions to determine corresponding points between the images. Transformation to remove relative motion is determined by fitting corresponding points between the images using a minimum square error (MSE) algorithm in a random sample consensus (RANSAC) framework.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Algorithm description on non-motion blur image generation project
A method for simulating an image captured at a long exposure time (“simulated image”), includes (1) capturing each of first, second, and third images at a short exposure time, (2) determining a first relative motion between the first and the second images, (3) transforming the first image to remove the first relative motion, (4) determining a second relative motion between the third and the second images, (5) transforming the third image to remove the second relative motion, and (6) combining the first, the second, and the third images to form the simulated image. Relative motions between images are determined by matching blocks at multiple resolutions to determine corresponding points between the images. Transformation to remove relative motion is determined by fitting corresponding points between the images using a minimum square error (MSE) algorithm in a random sample consensus (RANSAC) framework.
Owner:ARCSOFT
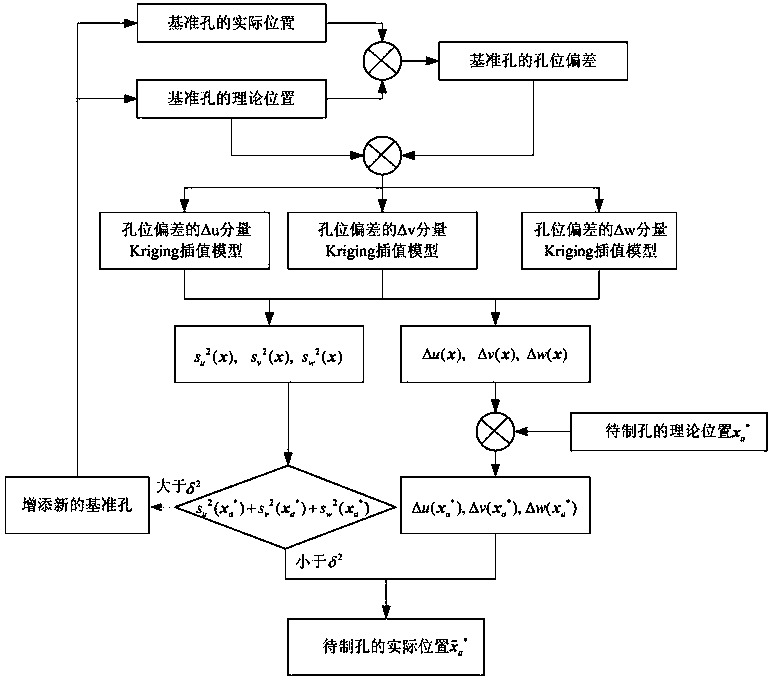
Hole position correcting method of automatic hole forming system
ActiveCN109318050AGood nonlinear function fitting characteristicsImprove calculation accuracyAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusMean squareDelta-v
The invention provides a hole position correcting method of an automatic hole forming system. The method comprises the following steps: a three-dimensional model of a workpiece to be punched is built;theoretical positions of a reference hole and a hole to be formed are marked; an actual position of the reference hole is machined and measured; a hole position deviation of the reference hole is calculated; based on a Kriging model, response functions delta u (x), delta v (x) and delta w (x) of the hole position deviation and mean square error functions su2 (x), sv2 (x) and sw2 (x) are obtained;three components of the hole position deviation of the hole to be formed are calculated according to the theoretical position of the hole to be formed and the three response functions; correspondingmean square errors are calculated according to the theoretical position of the hole to be formed and the three mean square error functions; and an actual position of the hole to be formed is obtained.The mean square errors of the hole position deviation of any one hole to be formed calculated through the method are determined by the hole position deviation of reference holes at two ends and the hole position deviation of multiple adjacent holes, so that the calculating precision of the hole position deviation of the hole to be formed is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
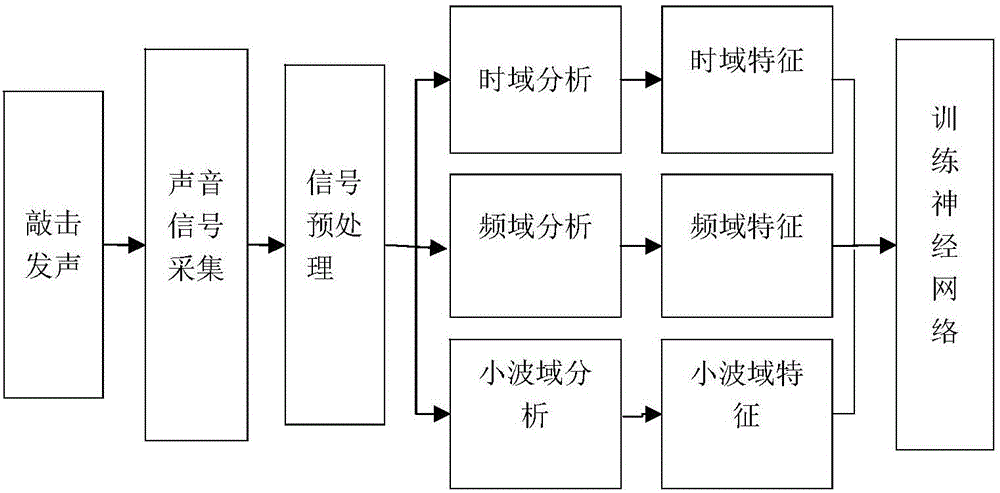
Neural network-based acoustic glass defect detection method
InactiveCN106841403AImprove discriminationAccurate and efficient completionProcessing detected response signalHidden layerNODAL
The invention discloses a neural network-based acoustic glass defect detection method which comprises the following steps: acquiring a knocking signal of a glass sample through a pickup in an actual production environment; preprocessing the knocking signal; performing feature extraction on the pure knocking signal; setting initial parameters of a BP neutral network: taking an extracted feature as the input of the neutral network, setting the number of nodes on an input layer of the BP neutral network to be 7, setting the number of nodes on a hidden layer of the BP neutral network to be 15, setting the number of nodes on an output layer of the BP neutral network to be 2, and setting an output result to be (0, 1) which indicates that the glass sample has a defect, and to be (1, 0) which indicates that the glass sample is defect-free; training the BP neutral network, setting the learning rate of the BP neutral network to be 0.1, setting a target square error value to be 0.1, training the BP neutral network through a LeVenberg-Marquardt algorithm, and stopping training if an error of the neutral network is less than the set target square error value. A signal feature extracted through the method is high in distinction degree, and can complete a glass defect detection task more accurately and efficiently.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Device and method for measuring non-isoplanatism wave-front errors and turbulence characteristic parameters of atmosphere turbulence
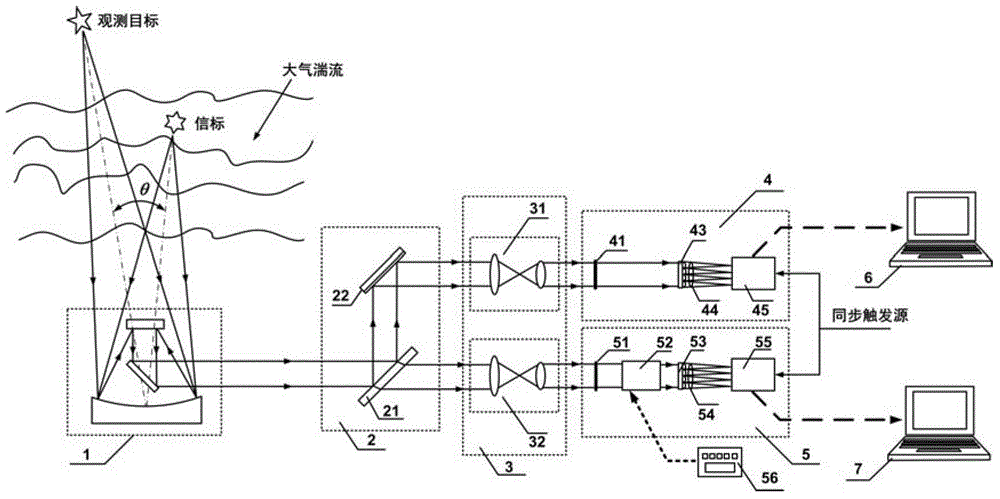
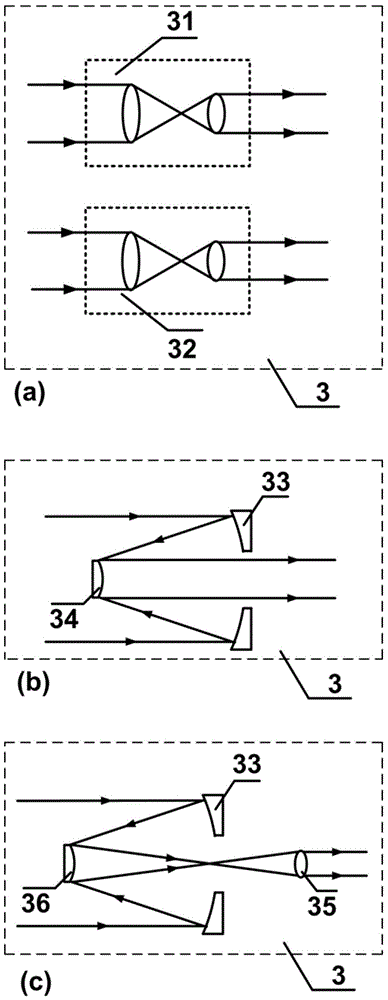
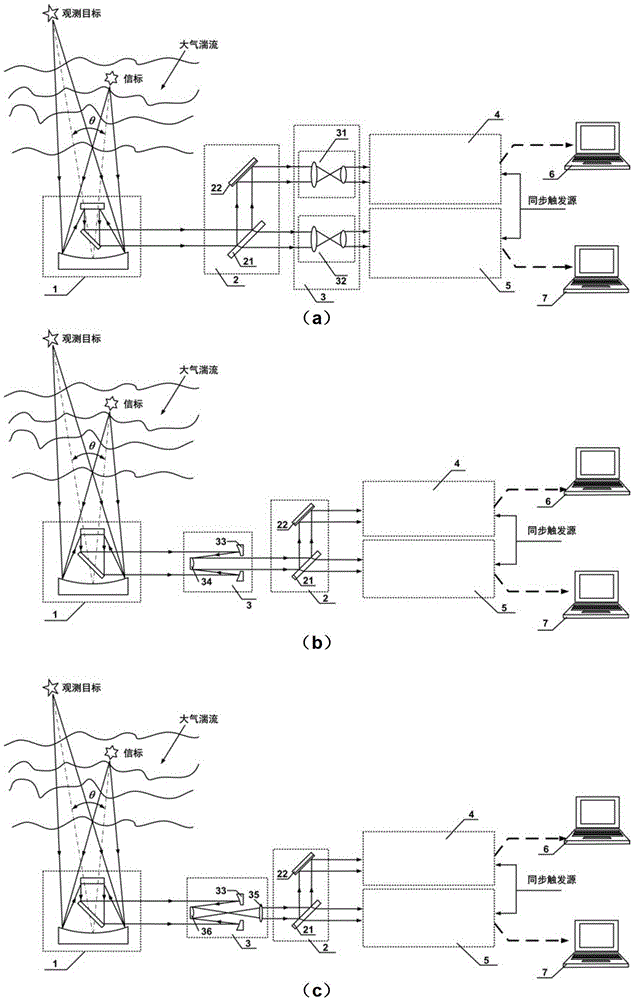
ActiveCN103335950AReduce the effect of jitterSimple structureMaterial analysis by optical meansObservational errorMeasurement device
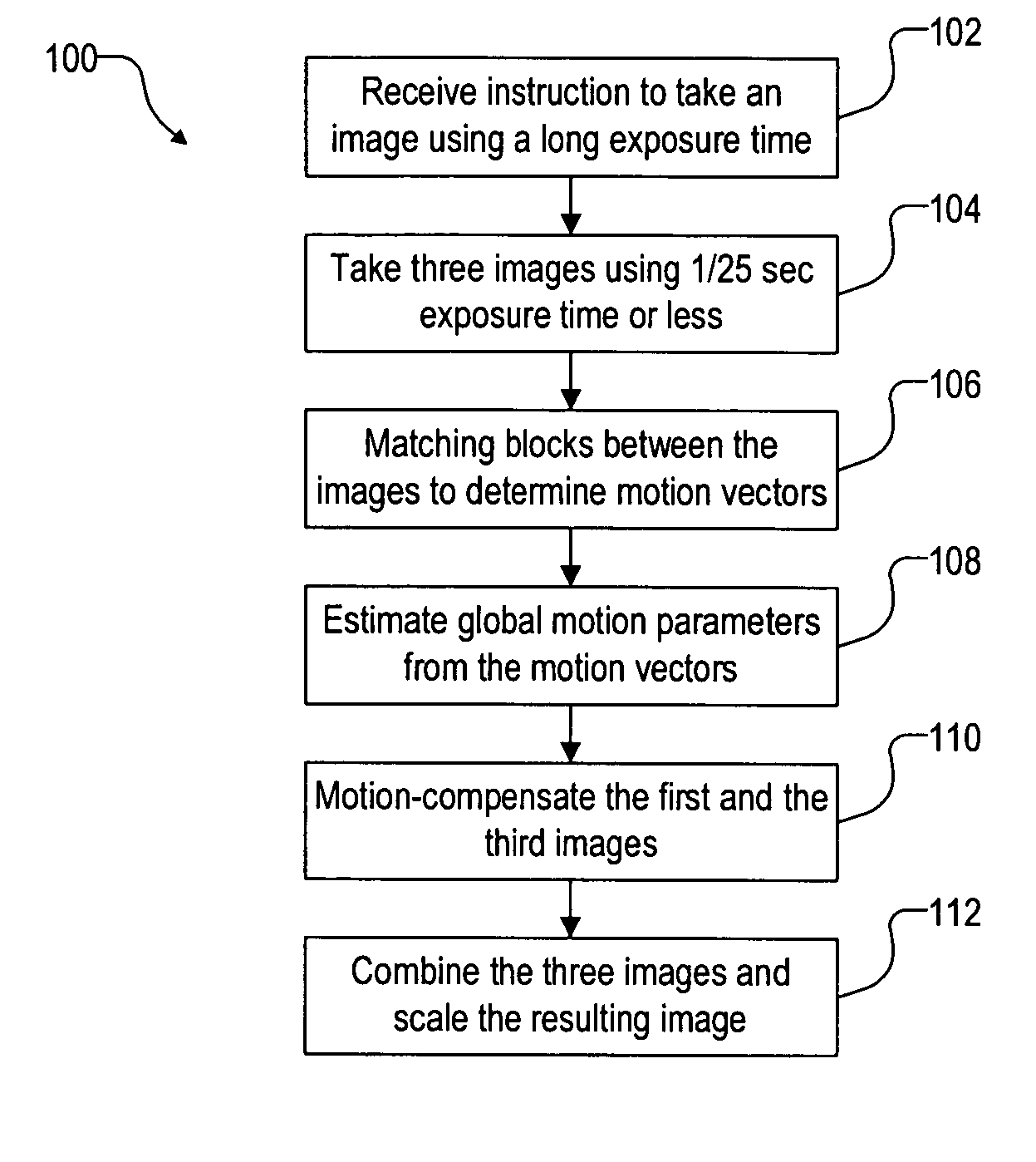
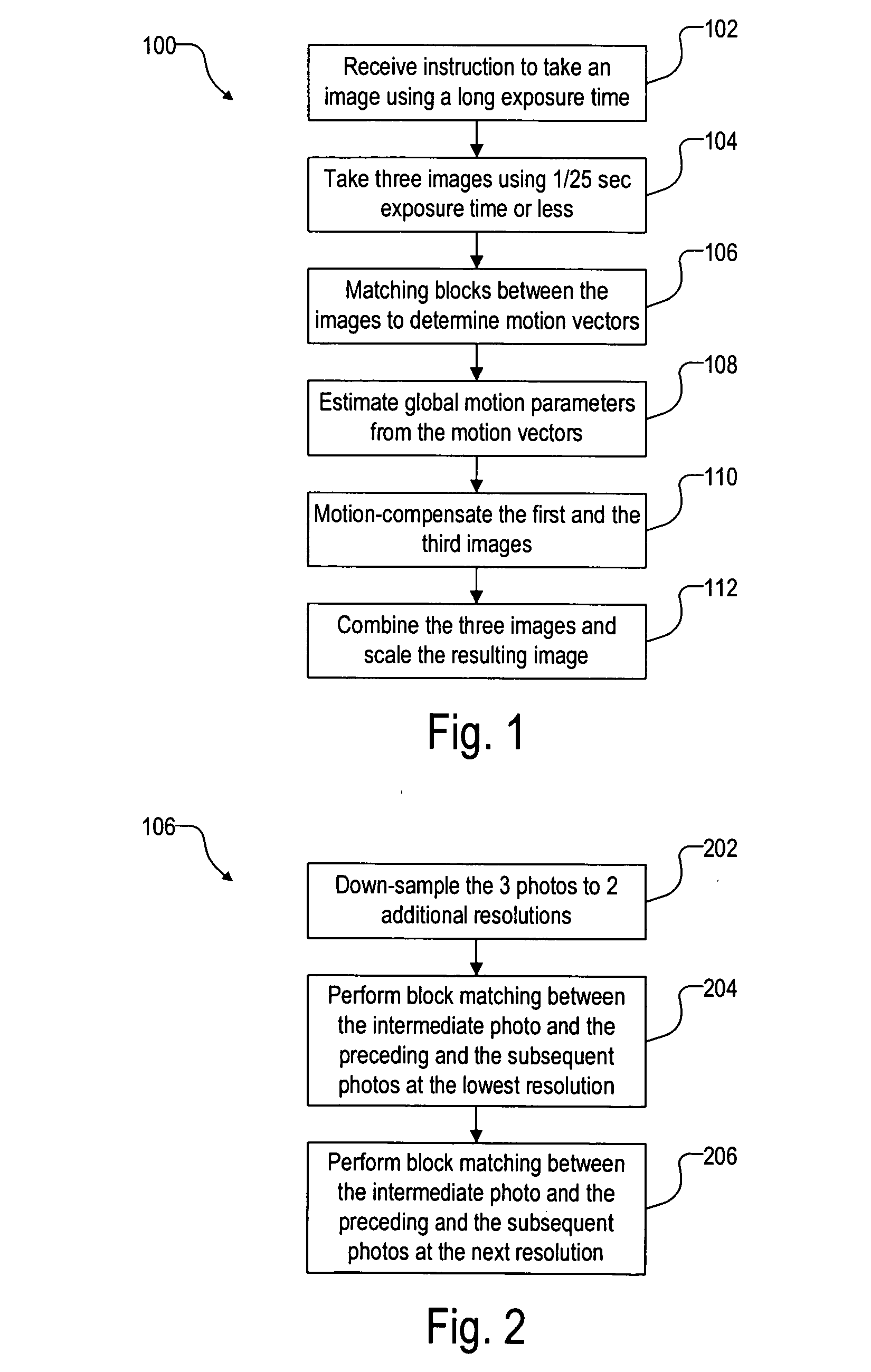
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring non-isoplanatism wave-front errors and turbulence characteristic parameters of an atmosphere turbulence. The method comprises the following steps: setting a beacon Hartmann sensor focusing distance according to a beacon mode; respectively receiving a target light wave imaging light spot pattern and a beacon light wave imaging light spot pattern by utilizing a target Hartmann sensor and a beacon Hartmann sensor; controlling a target Hartmann sensor CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a beacon Hartmann sensor CCD to synchronously collect by an external synchronous triggering source; calculating an average slope of a time sequence target light wave and a beacon light wave in a sub-hole diameter of a micro-lens set, and carrying out difference operation by utilizing a wave-front processor; carrying out recovery on a difference average slope and a target light wave average slope and expanding a Zernike mode by utilizing a recovering algorithm to obtain counting characteristics including non-isoplanatism wave-front errors, target turbulence wave-front two-dimensional distribution, wave-front square errors, a P-V value, Zernike mode square errors, non-isoplanatism relative errors and the like, as well as the turbulence characteristic parameters including the coherence length, an isoplanatic angle, the beacon equivalent diameter and the like. The device and method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of high light energy utilization rate, small measurement errors and wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
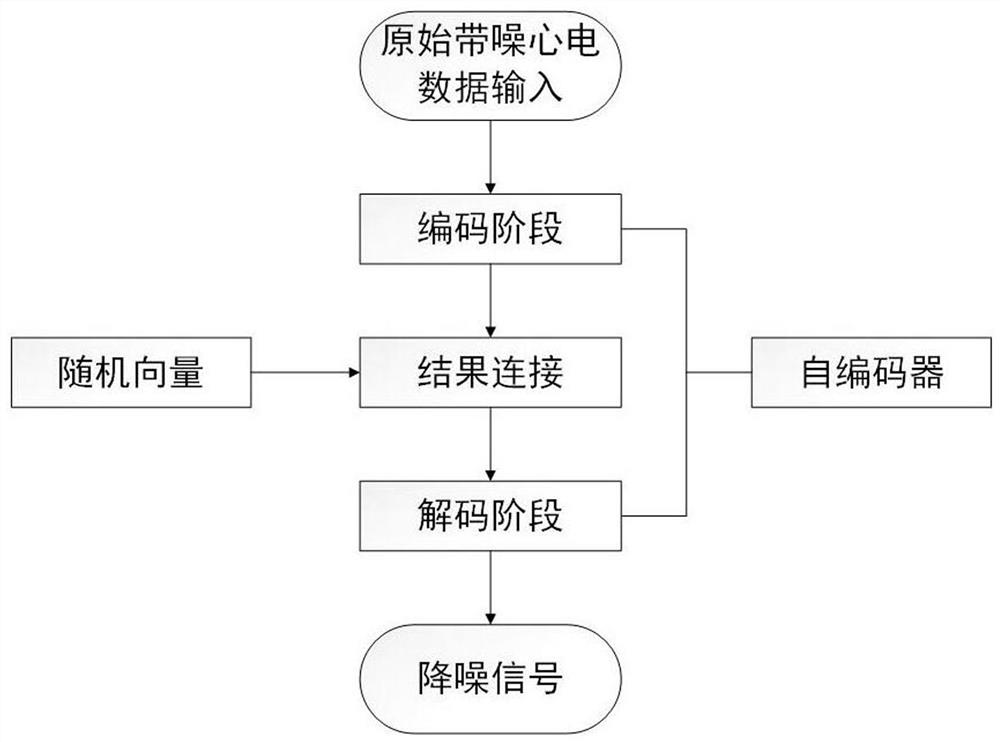
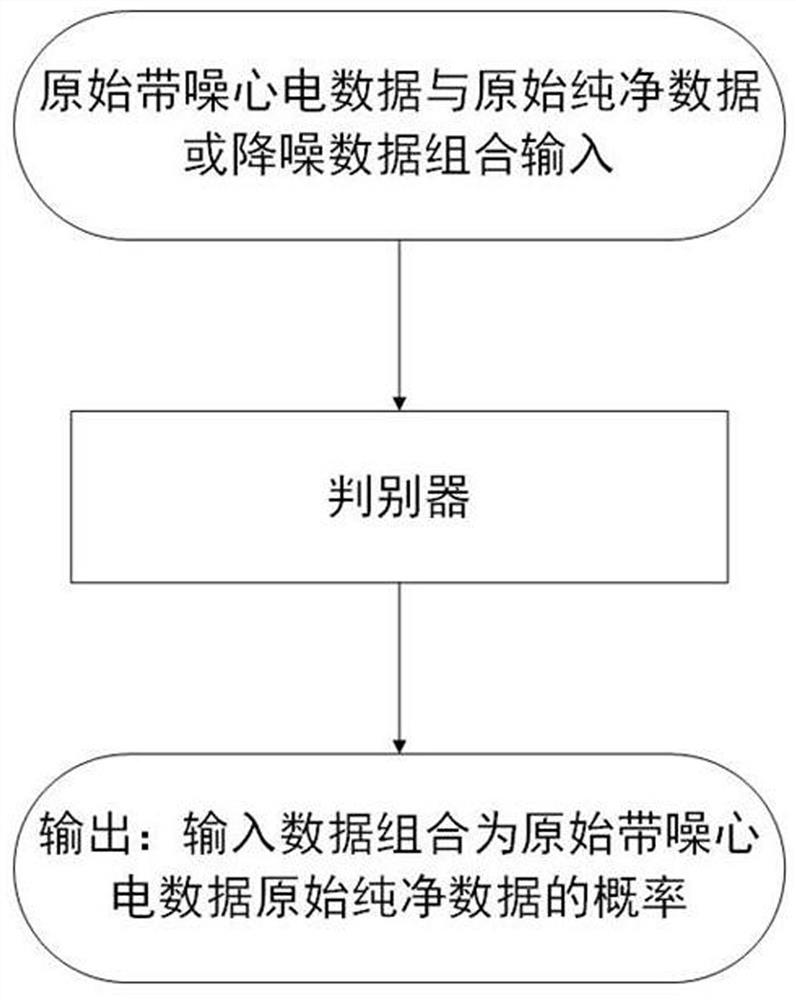
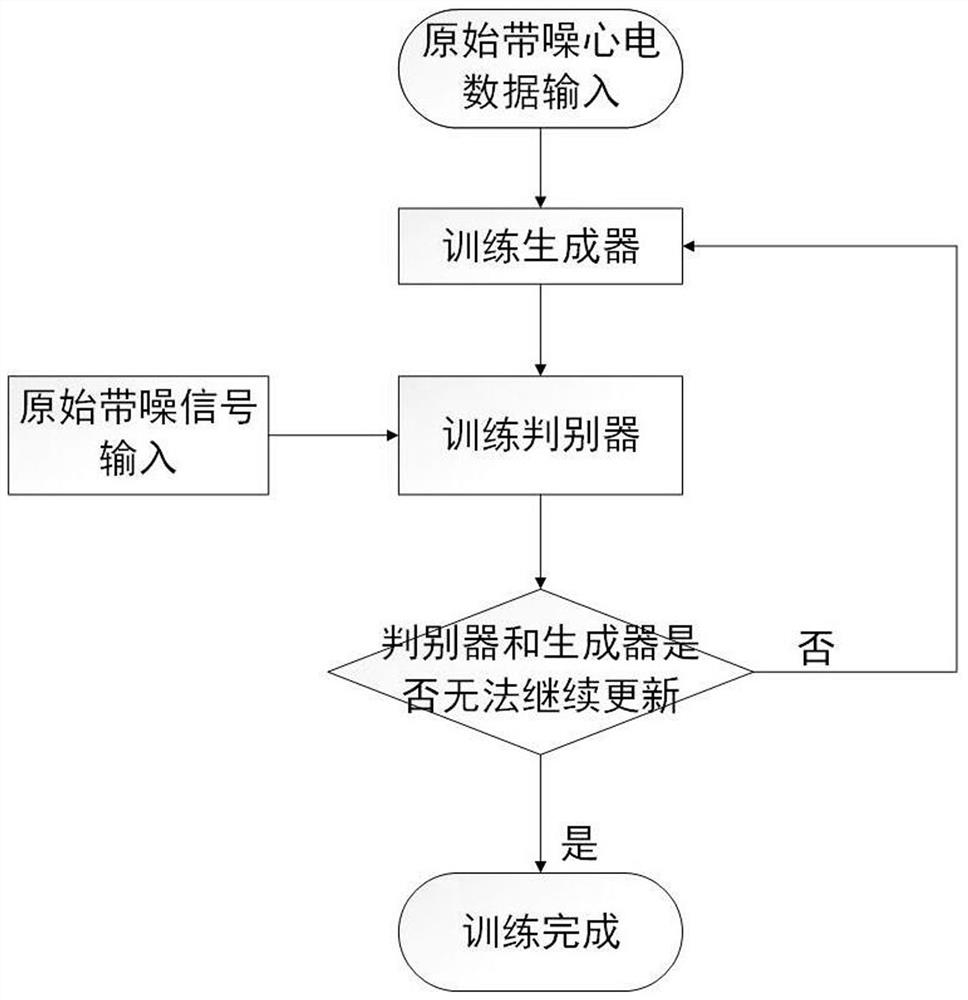
Electrocardiosignal noise reduction method based on adversarial generative network
ActiveCN111814656AGuaranteed directionalityGuaranteed compatibilityCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalGenerative adversarial network
According to the electrocardiosignal noise reduction method based on the generative adversarial network, the conditional generative adversarial network is used, so that the directionality of generateddata and the matching performance of a signal after noise reduction and a noisy signal are ensured, and the generalization ability of a model is improved. In the training process, uncertain noise mixed data is used for training, so that the model can perform noise reduction on various noise mixed signals without pre-judgment, and the complexity of the method is simplified. Design of an improved loss function is realized, the resistance in the original loss function of the CGAN is reserved, the root-mean-square error and the noise-to-signal power ratio are increased, the increase of the root-mean-square error enables the model to capture the local features of the signal and maintain the useful medical features of the signal, and the increase of the noise-to-signal power ratio enables the model to capture the global features of the signal, so that the training process is stable.
Owner:SHANDONG ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE INST
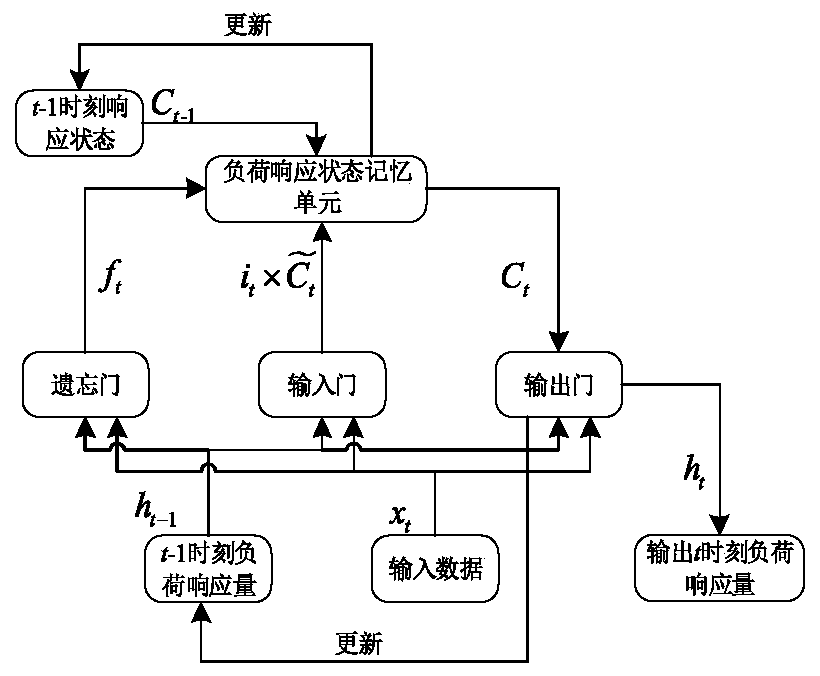
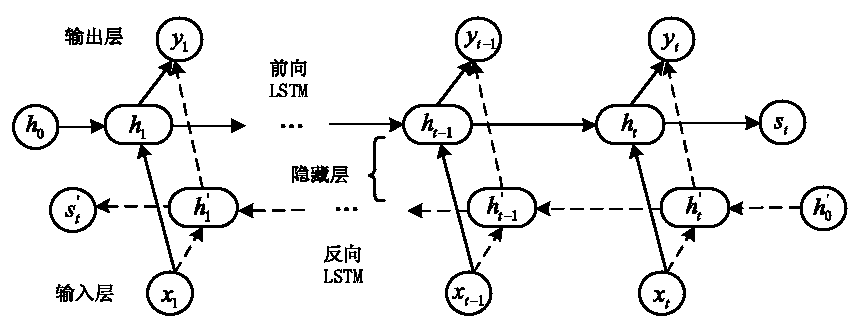
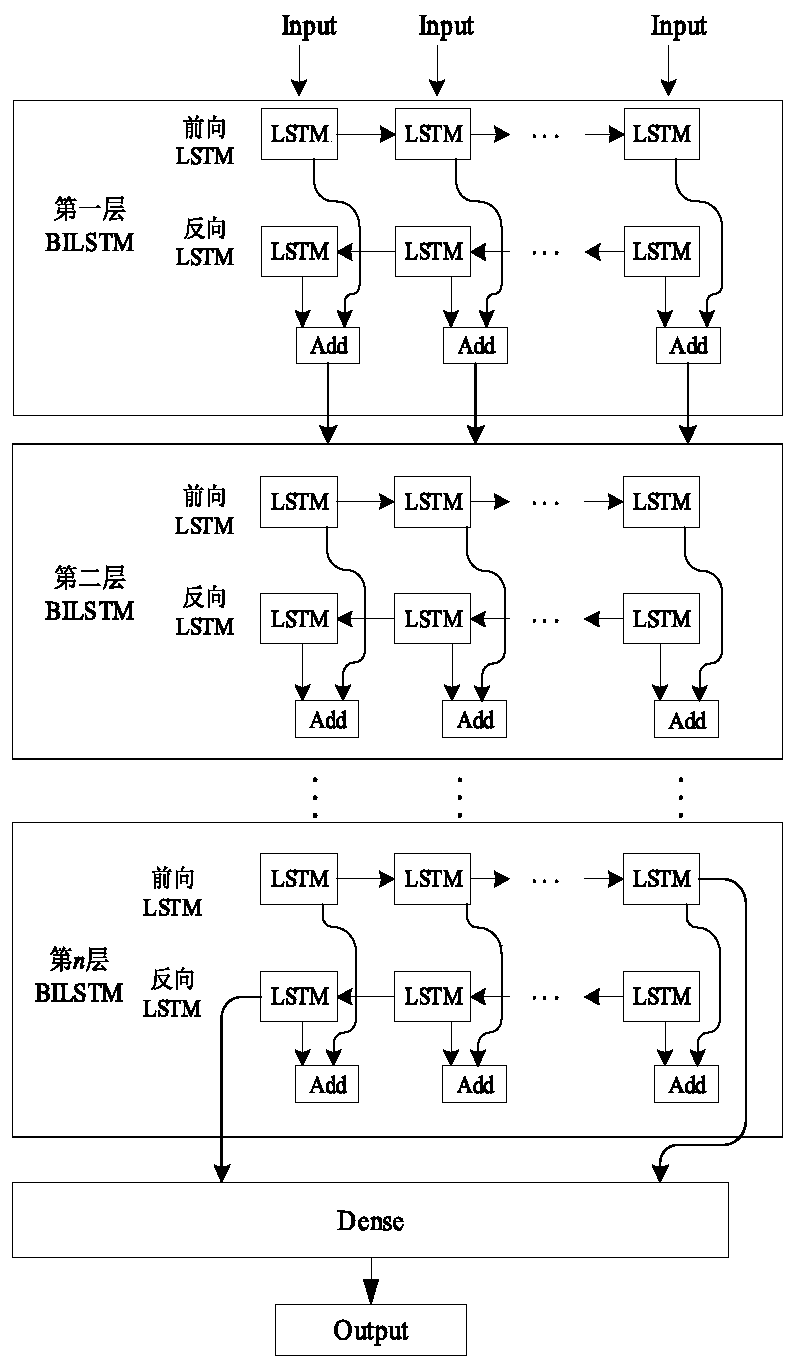
Multi-factor short-term load prediction method based on PCA-DBILSTM
PendingCN111027772AReduce data dimensionalityImprove forecast accuracyForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionLoad forecastingPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a multi-factor short-term load prediction method based on PCA-DBILSTM (Principal Component Analysis-DBILSTM). Firstly, normalization and One hot encoding are carried out on original input data to obtain a multi-dimensional matrix, principal component extraction is carried out on the multi-dimensional matrix by utilizing a PCA method, and then prediction is carried out by utilizing a DBILSTM network prediction model. Compared with a traditional power load prediction method, the method has the advantages that the average absolute percentage error (MAPE) and the root-mean-square error (RMSE) are both reduced, and the result shows that the method has high prediction precision.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
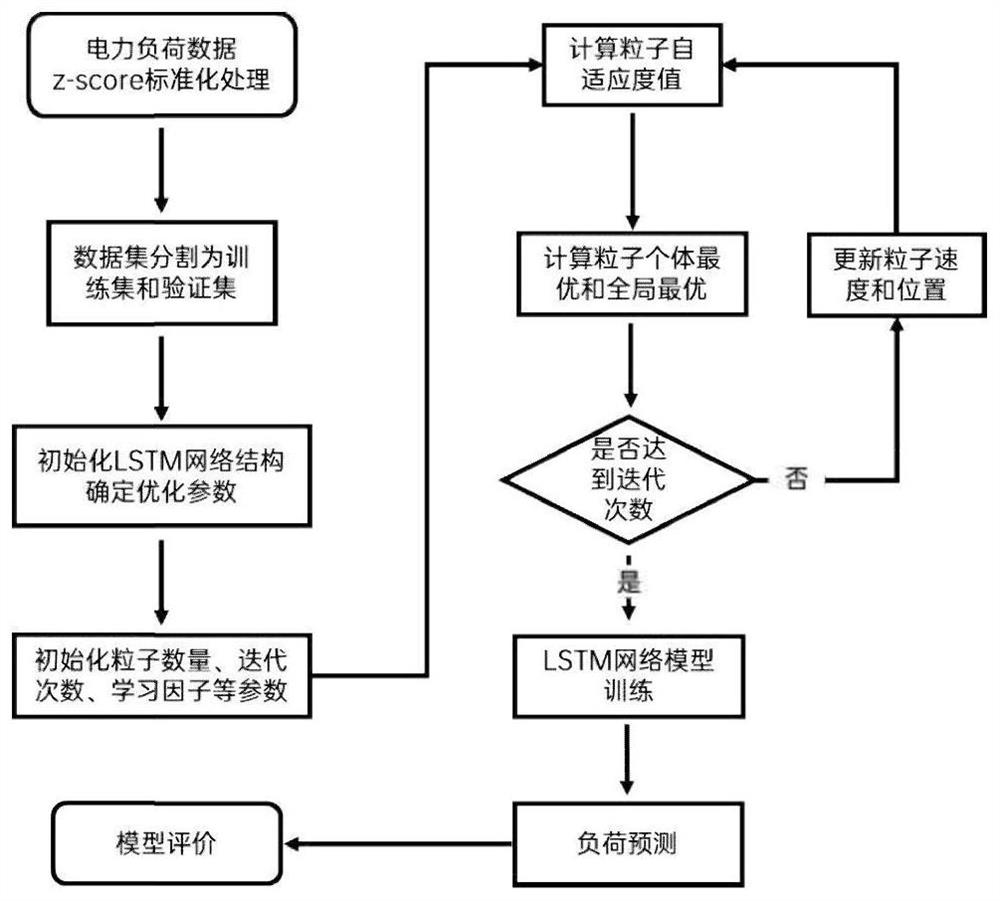
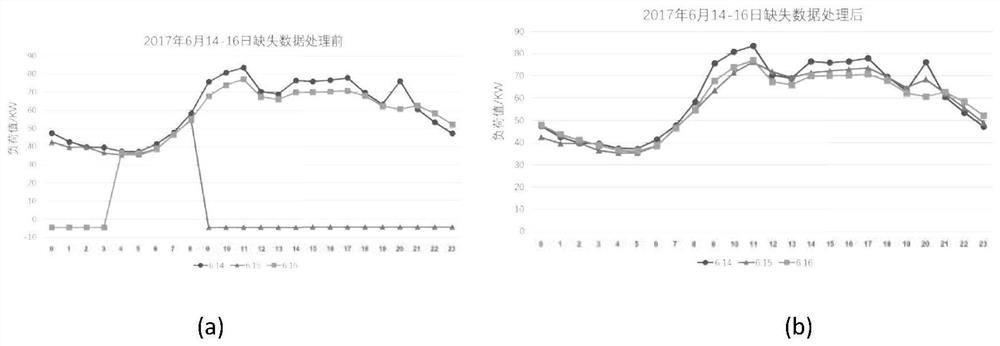
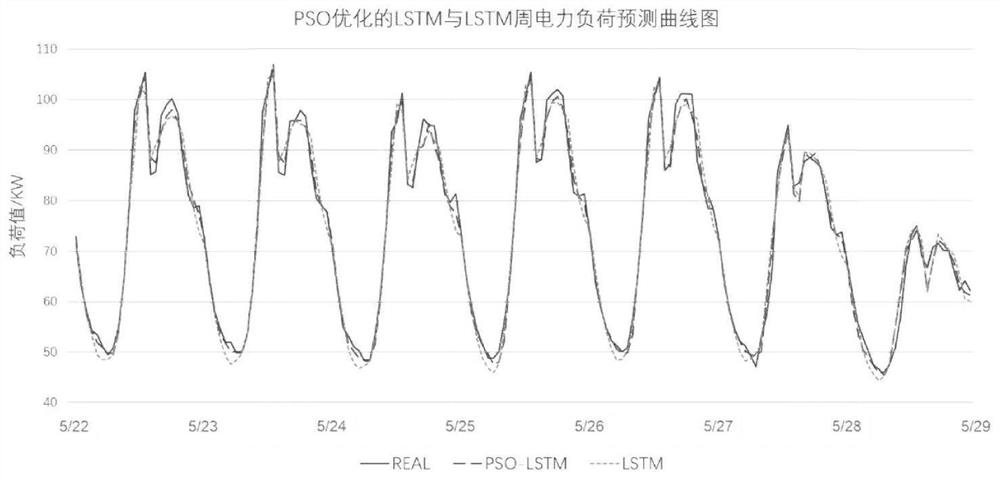
Method for seven-day prediction of 24-point power load values based on optimized LSTM network
PendingCN111783953AOvercoming Data Source HeterogeneityOvercome the defect of large dimension differenceForecastingArtificial lifeData setData acquisition
The invention provides a method for seven-day prediction of 24-point power load values based on an optimized LSTM network. The method comprises data acquisition, data analysis and data preprocessing.The method comprises the following concrete steps: dividing a data set into a training set and a verification set; based on the training set, conducting parameter optimization on a long-term and short-term memory neural network (LSTM) by using a particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO); determining optimal values of three parameters, namely the number of hidden layer nodes, a learning rate andthe number of iterations, of the LSTM network suitable for 24-point power load prediction; and with the training set as input, predicting 24-point power load values in the future 7 days based on the optimized LSTM network, comparing power load data output by a model with the verification set, and determining the prediction accuracy of the model by further taking two indexes, namely a mean absoluteerror (MAE) and a root-mean-square error (RMSE) into consideration. By means of the prediction method, prediction accuracy and timeliness are improved, and the prediction effect is better than the prediction effect of an existing power load prediction method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and system for reconstructing super-resolution image
ActiveUS10181092B2Overcome defectsFully learnImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionTest sample
A method for reconstructing a super-resolution image, including: 1) reducing the resolution of an original high-resolution image to obtain an equal low-resolution image, respectively expressed as matrix forms yh and yl; 2) respectively conducting dictionary training on yl and yhl to obtain a low-resolution image dictionary Dl; 3) dividing the sparse representation coefficients αl and αhl into training sample coefficients αl_train and αhl_train and test sample coefficients αl_test and αhl_test; 4) constructing an L-layer deep learning network using a root-mean-square error as a cost function; 5) iteratively optimizing network parameters so as to minimize the cost function by using the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_train as the input of the deep learning network; 6) inputting the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_test as the test portion into the trained deep learning network in 5), outputting to obtain a predicted difference image sparse coefficient {circumflex over (α)}hl_test, computing an error between the {circumflex over (α)}hl_test.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for improved active sonar using singular value decomposition filtering
InactiveUS7929375B2Guarantee linear independenceAvoid poor resultsAcoustic wave reradiationSingular value decompositionSonar
The invention is a method for improved active sonar using a singular value decomposition filtering and a Volterra-Hermite Basis Expansion to model real active sonar measurements. The fitting model minimizes the sum of the squared errors between a measured channel response, z(t), and model response, y(t), which is a fitted Volterra Series solution. The model requires as input an excitation waveform, x(t), to which is fitted the model response, y(t). A contracted broadband cross-ambiguity function is used to correct the excitation waveform for Doppler and range effects. Once completed, the modeled response can be used to determine the linearity or non-linearity of the channel effects. Appropriate measures can be utilized to reduce these effects on the measured channel response.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENT DIV NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL THE
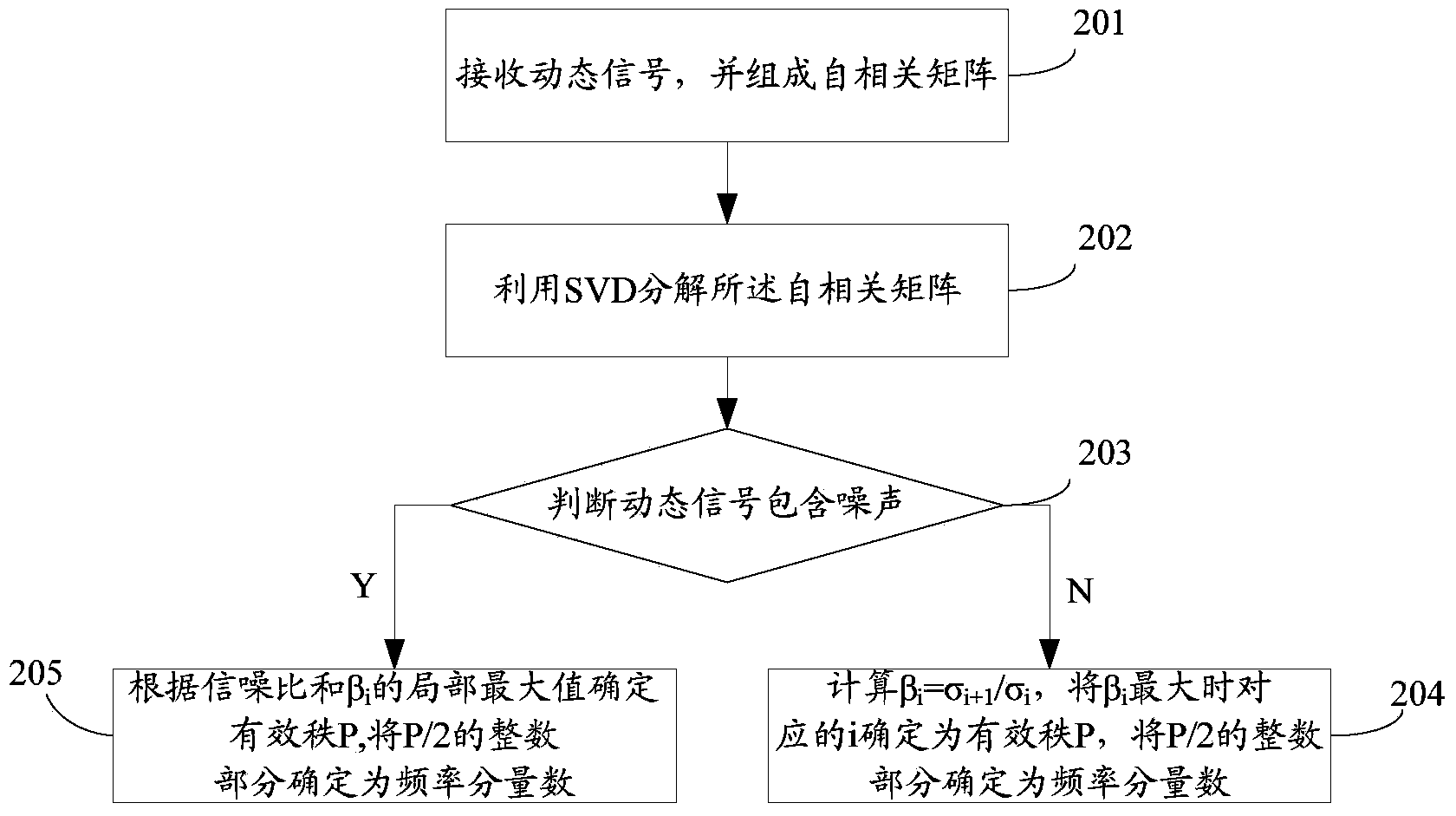
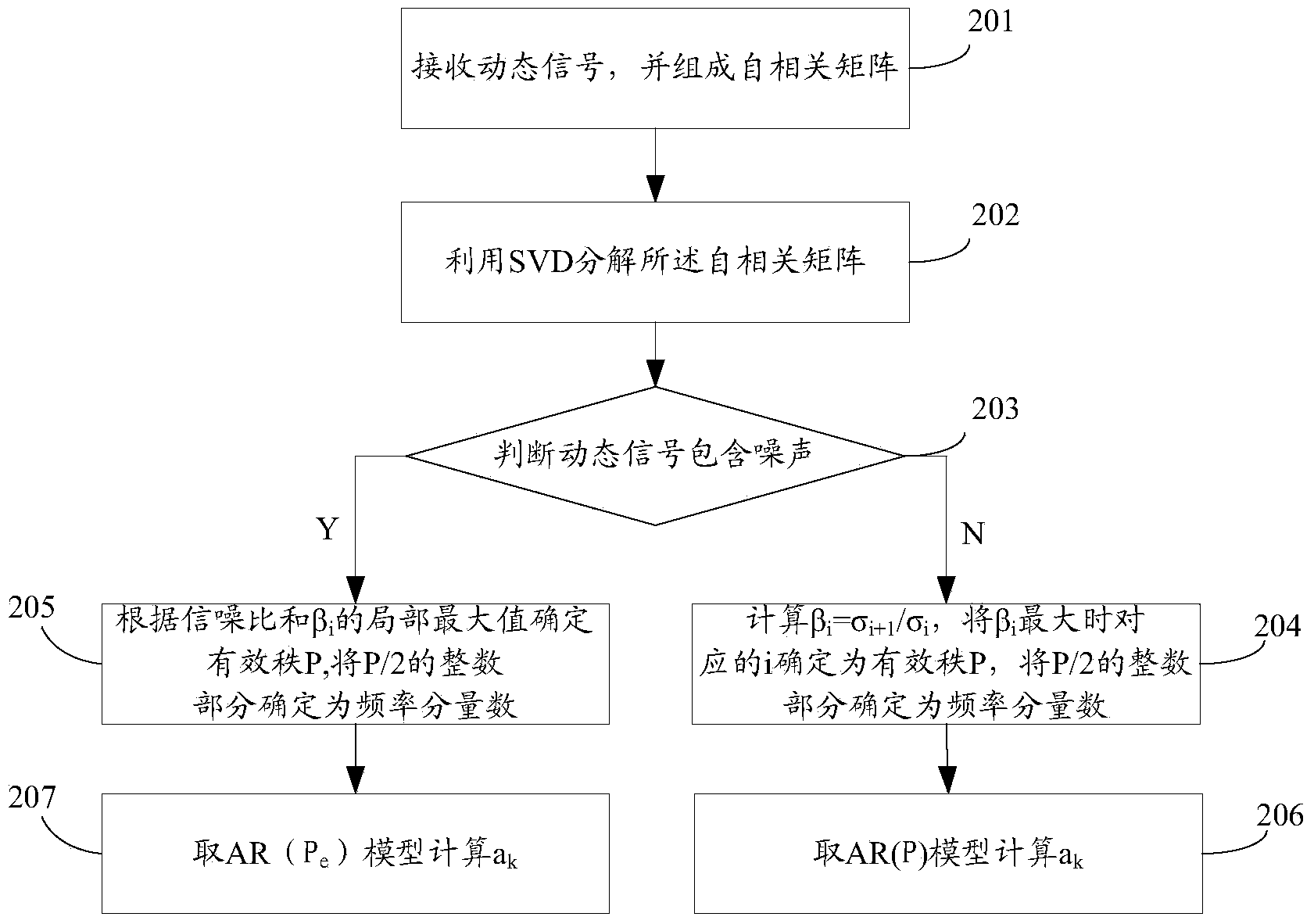
Dynamic signal parameter acquisition method
ActiveCN103630742ASimple calculationThe calculation result is accurateSpectral/fourier analysisComputation processPower grid
The application discloses a dynamic signal parameter acquisition method, comprising the steps of selecting dynamic sampling signal sequences of a power grid to form an autocorrelation matrix; determining an effective rank of the autocorrelation matrix and frequency components of the dynamic sampling signal sequence; establishing an auto-regressive (AR) model, and resolving a model parameter of the AR model; through a Prony algorithm, determining a dynamic sampling signal expression and a complex sequence, wherein the dynamic sampling signal sequence is expressed by the complex sequence under a condition of satisfying square error minimization; and introducing a characteristic polynomial root corresponding to the model parameter into the complex sequence, and resolving various parameters of the dynamic sampling signal sequence. The application, instead of directly solving parameters in the Prony algorithm, regards a current moment signal as a linear combination of original various moment signals through an AR parameter model thought, and converts a nonlinear problem into a linear estimation problem, so that the computing process is simpler and computing result is more accurate.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
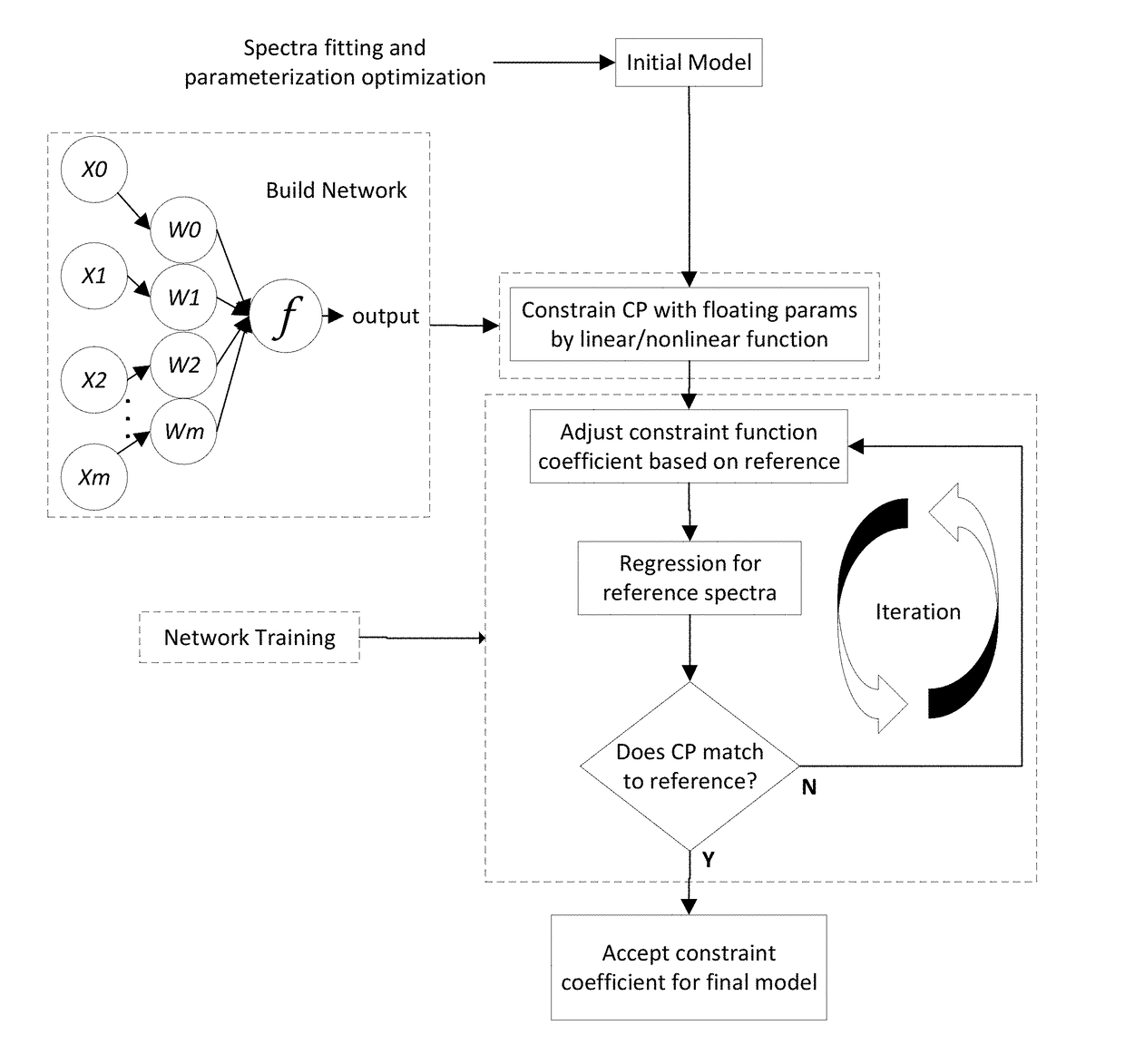
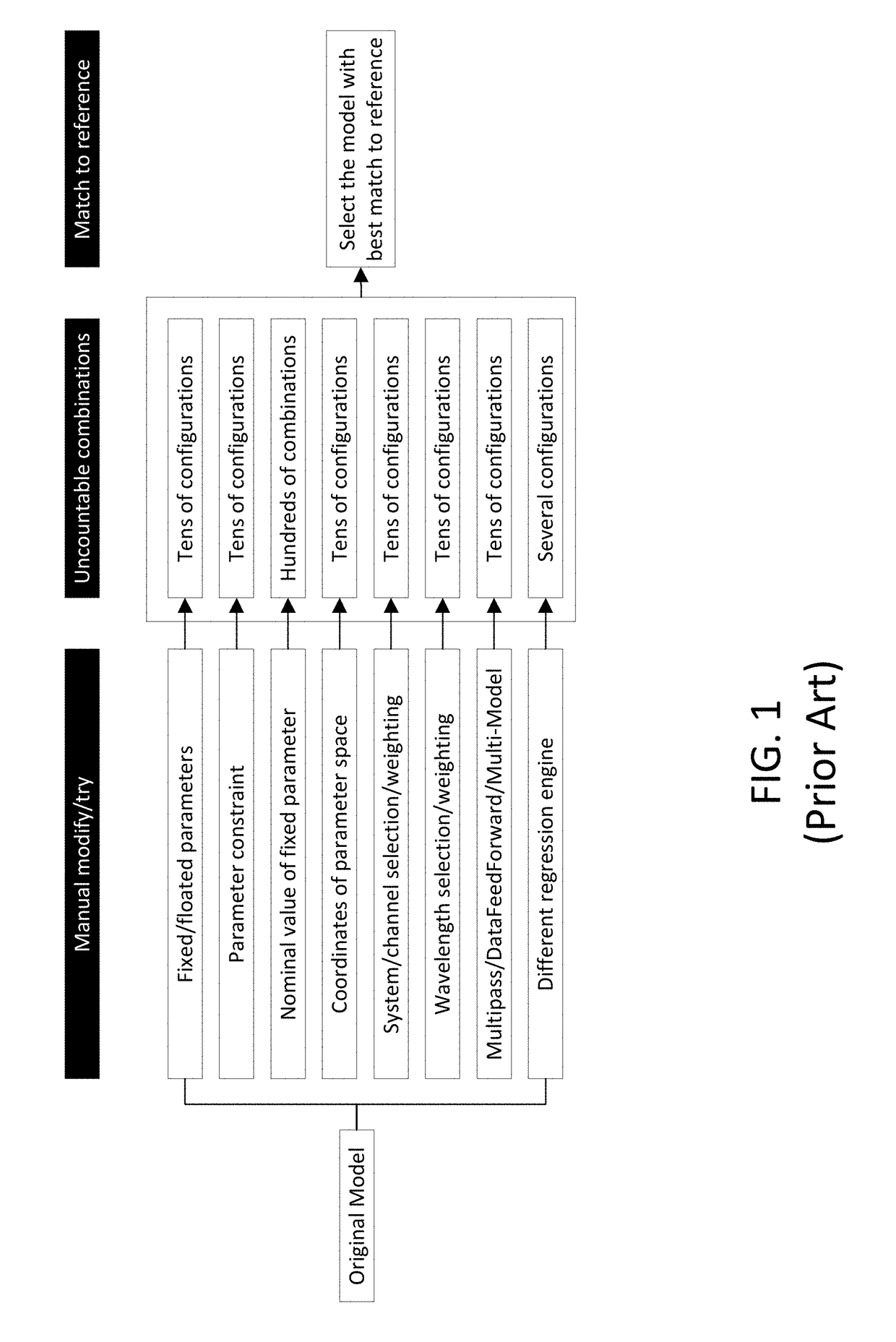
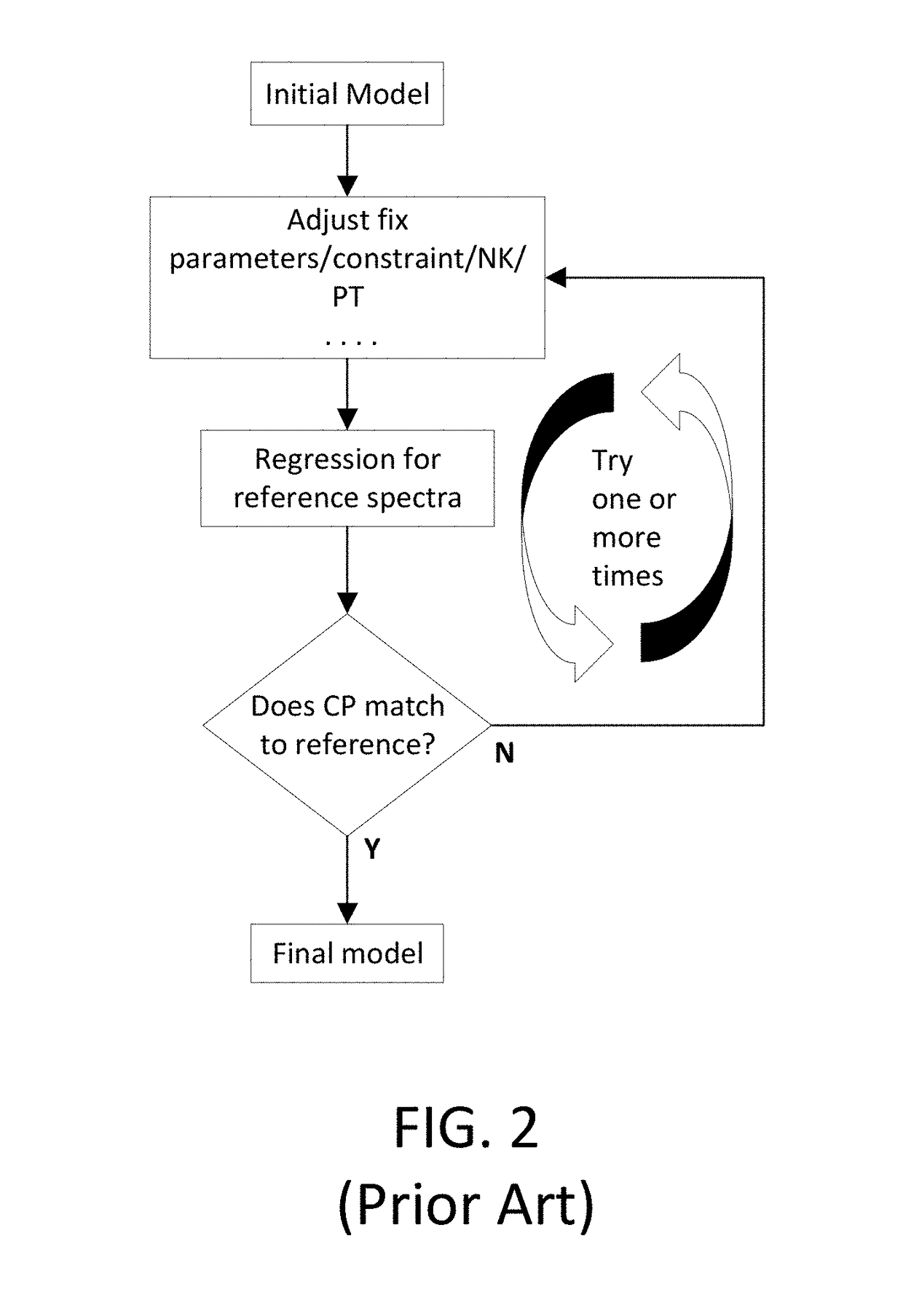
Automated Accuracy-Oriented Model Optimization System for Critical Dimension Metrology
ActiveUS20180232630A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusMetrologyAlgorithm
Techniques and systems for critical dimension metrology are disclosed. Critical parameters can be constrained with at least one floating parameter and one or more weight coefficients. A neural network is trained to use a model that includes a Jacobian matrix. During training, at least one of the weight coefficients is adjusted, a regression is performed on reference spectra, and a root-mean-square error between the critical parameters and the reference spectra is determined. The training may be repeated until the root-mean-square error is less than a convergence threshold.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com