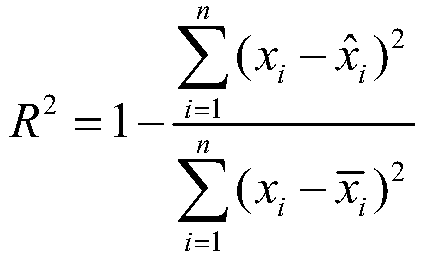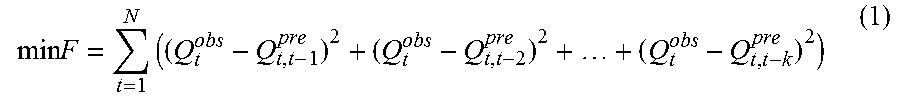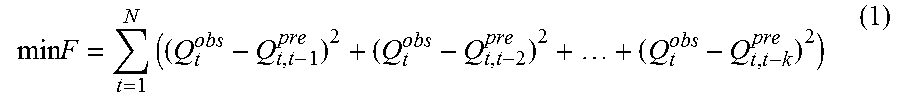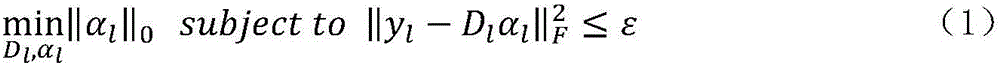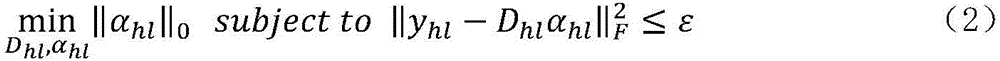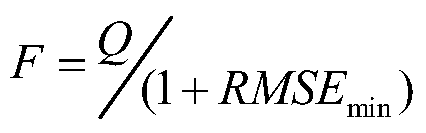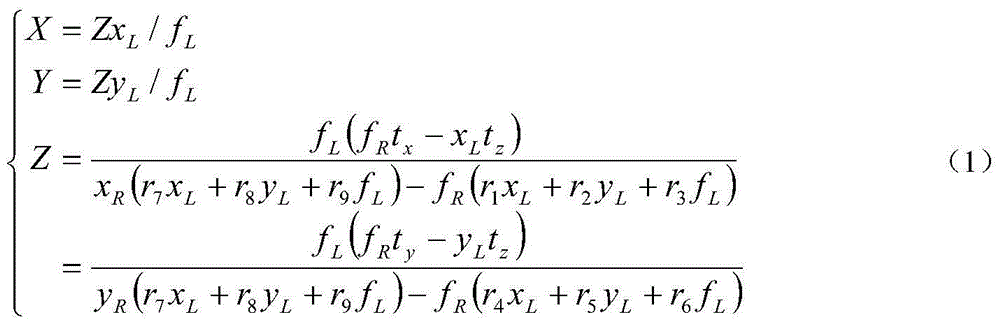Patents
Literature
819 results about "Root-mean-square deviation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) or root-mean-square error (RMSE) (or sometimes root-mean-squared error) is a frequently used measure of the differences between values (sample or population values) predicted by a model or an estimator and the values observed. The RMSD represents the square root of the second sample moment of the differences between predicted values and observed values or the quadratic mean of these differences. These deviations are called residuals when the calculations are performed over the data sample that was used for estimation and are called errors (or prediction errors) when computed out-of-sample. The RMSD serves to aggregate the magnitudes of the errors in predictions for various times into a single measure of predictive power. RMSD is a measure of accuracy, to compare forecasting errors of different models for a particular dataset and not between datasets, as it is scale-dependent.
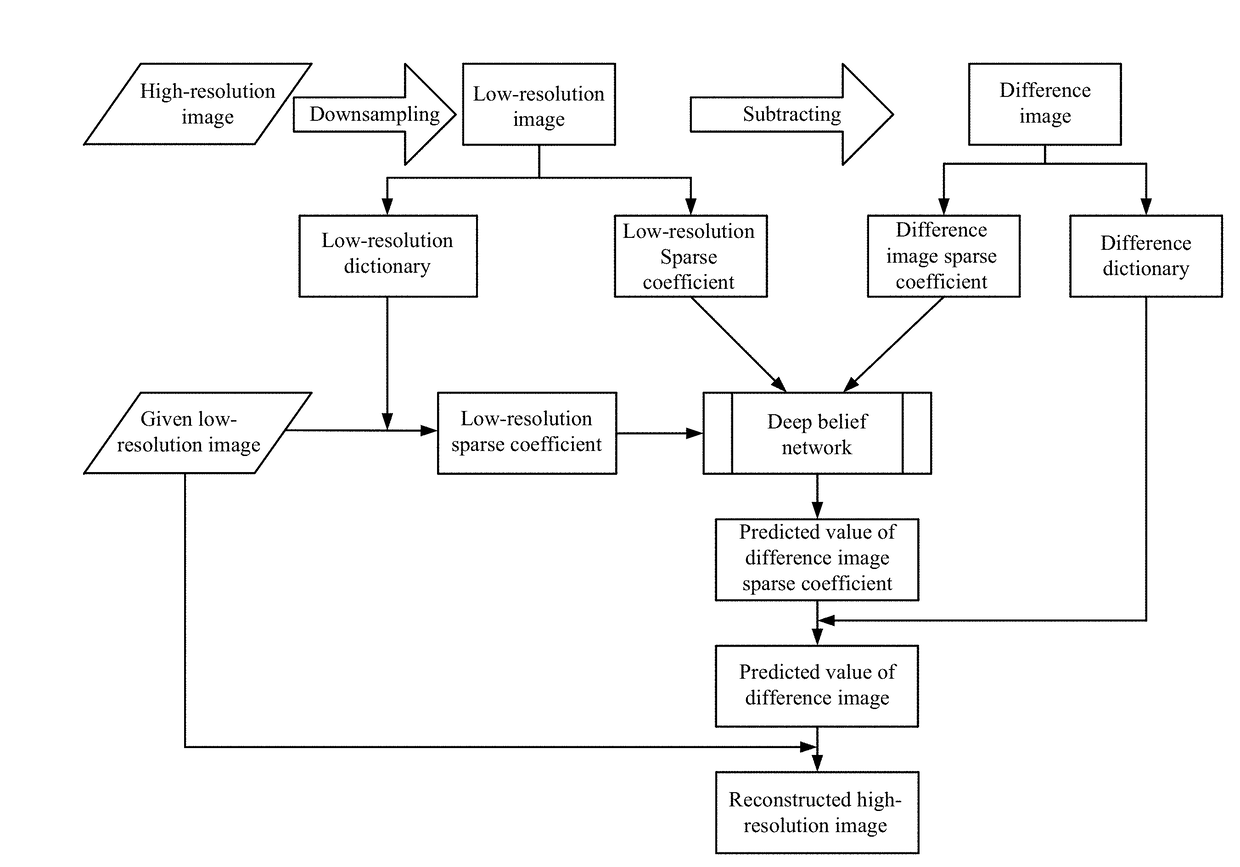
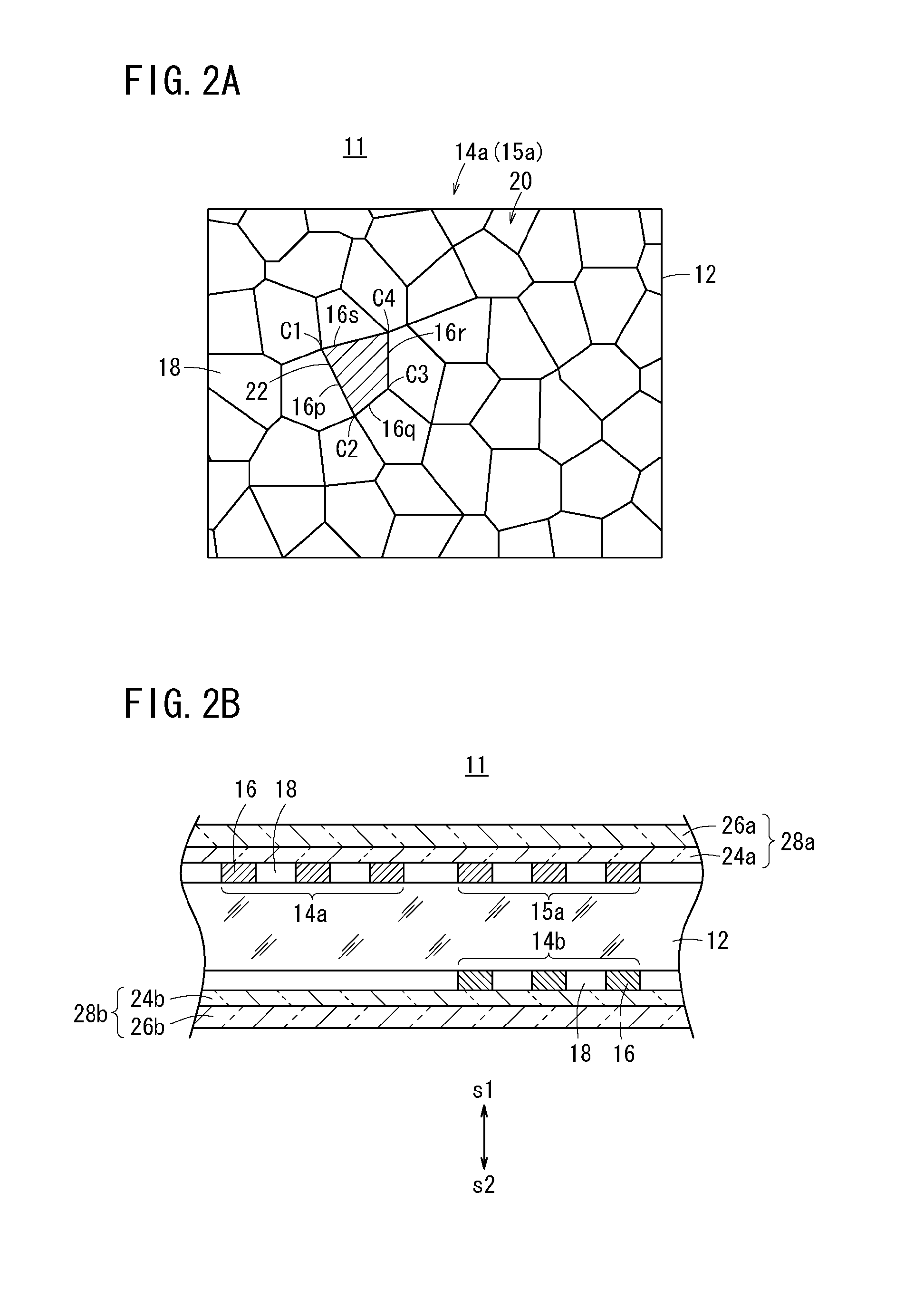
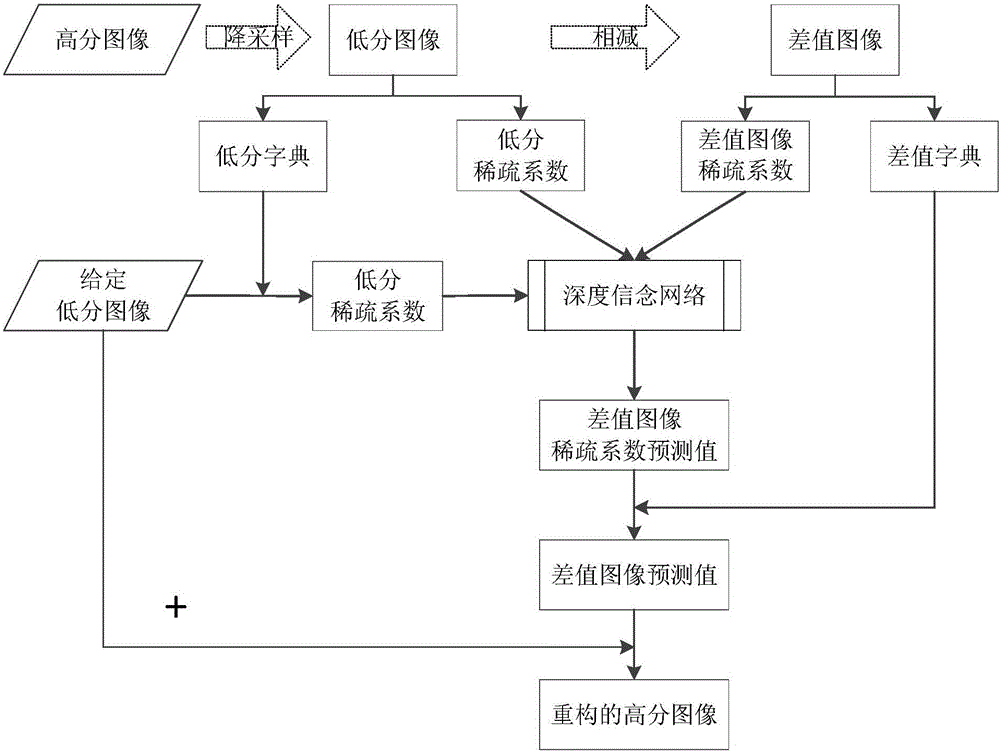
Method and system for reconstructing super-resolution image
ActiveUS20170293825A1Minimize cost functionMinimize loss functionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTest sample
A method for reconstructing a super-resolution image, including: 1) reducing the resolution of an original high-resolution image to obtain an equal low-resolution image, respectively expressed as matrix forms yh and yl; 2) respectively conducting dictionary training on yl and yhl to obtain a low-resolution image dictionary Dl; 3) dividing the sparse representation coefficients αl and αhl into training sample coefficients αl_train and αhl_train and test sample coefficients αl_test and αhl_test; 4) constructing an L-layer deep learning network using a root-mean-square error as a cost function; 5) iteratively optimizing network parameters so as to minimize the cost function by using the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_train as the input of the deep learning network; 6) inputting the low-resolution image sparse coefficient αl_testas the test portion into the trained deep learning network in 5), outputting to obtain a predicted difference image sparse coefficient {circumflex over (α)}hl_test, computing an error between the {circumflex over (α)}hl_test.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
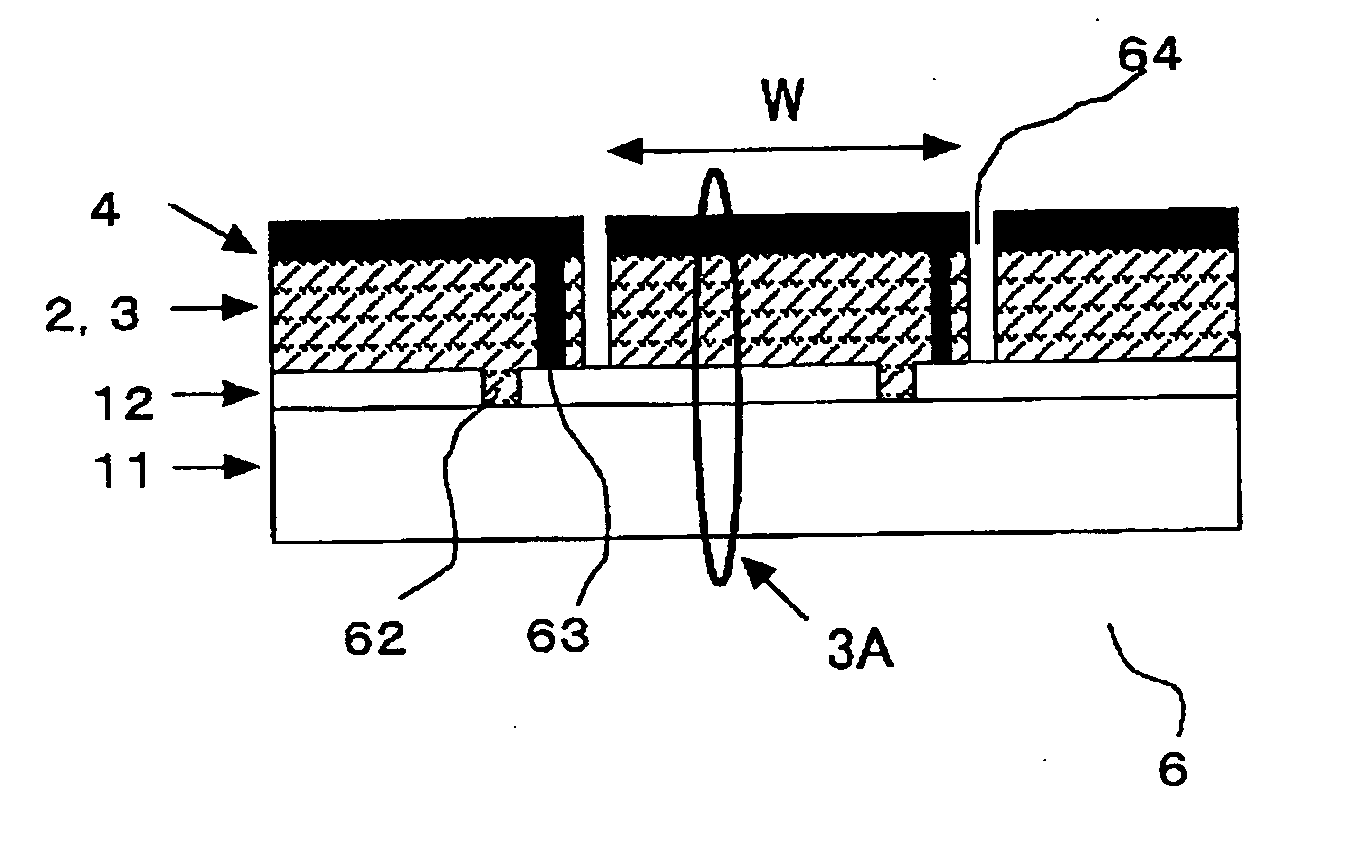
Substrate for thin-film solar cell, method for producing the same, and thin-film solar cell employing it
InactiveUS20070169805A1Improve unevennessGood light trapping effectPV power plantsSolid-state devicesTrappingLight source
An inexpensive substrate for thin film solar cells having improved performance of a thin film solar cell, and a manufacturing method thereof are provided by increasing light trapping effect due to effective increase in unevenness of a substrate for thin film solar cells. Furthermore, a thin film solar cell having improved performance using the substrate is provided. A substrate for thin film solar cells of the present invention has a transparent insulating substrate and a transparent electrode layer deposited thereon including at least zinc oxide (ZnO), the transparent insulating substrate has a fine surface unevenness having a root-mean-square deviation of the surface (RMS) 5 to 50 nm in an interface by a side of the transparent electrode layer, a projected area thereof consists of a curved surface, and furthermore a haze ratio or a ratio of a diffuse transmittance to a total transmittance as an index of unevenness of a substrate may be set at not less than 20% measured using a C light source. And thereby light trapping effect may effectively occur to improve performance of the thin film solar cell.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
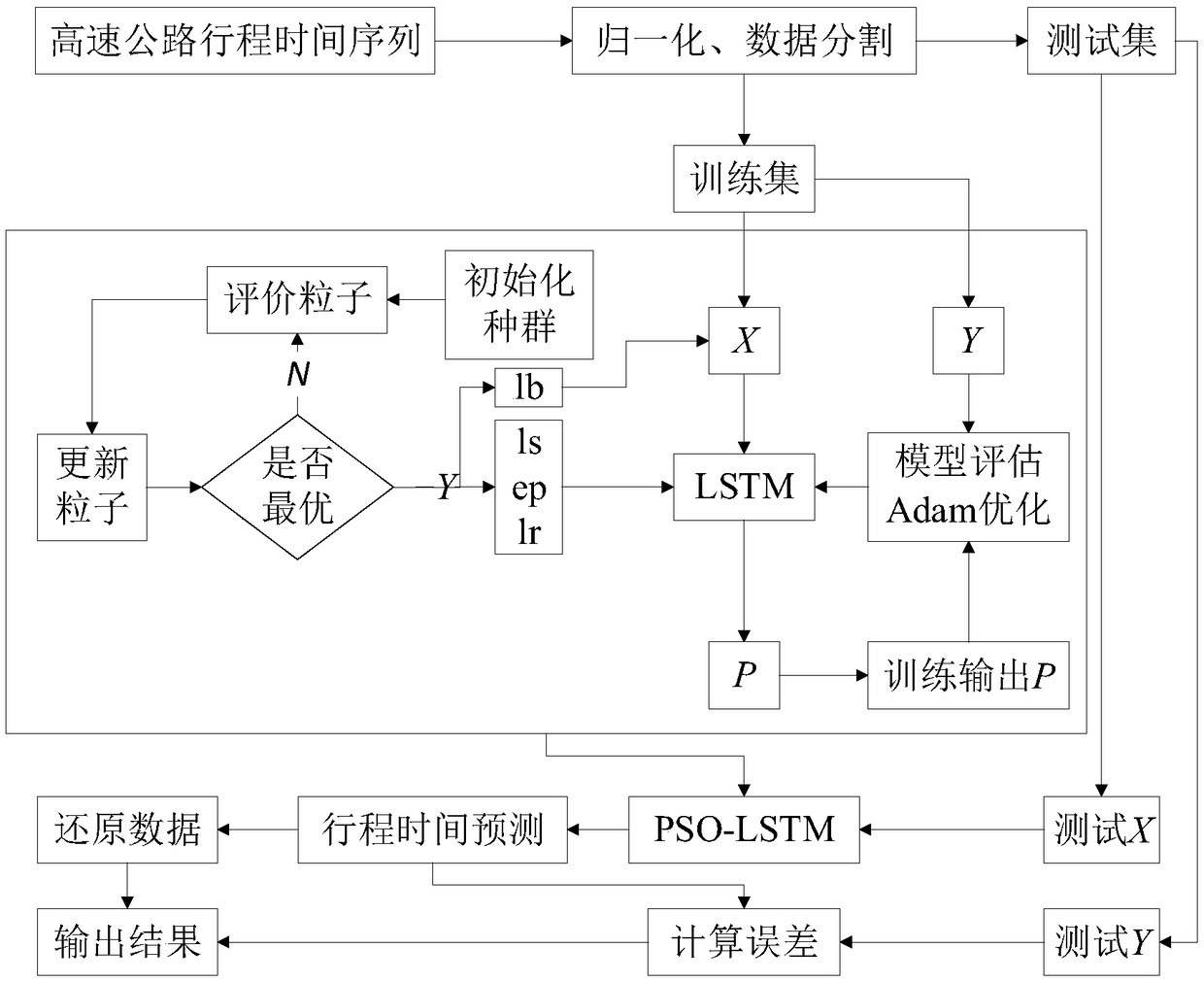
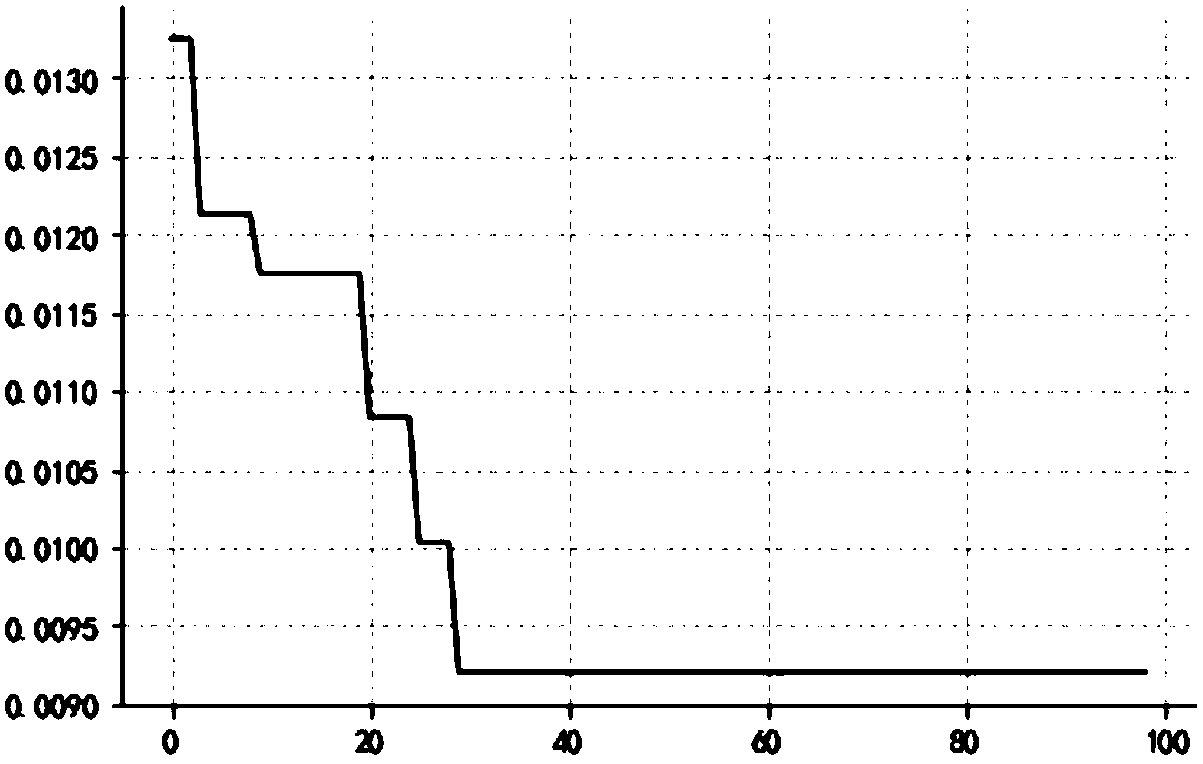
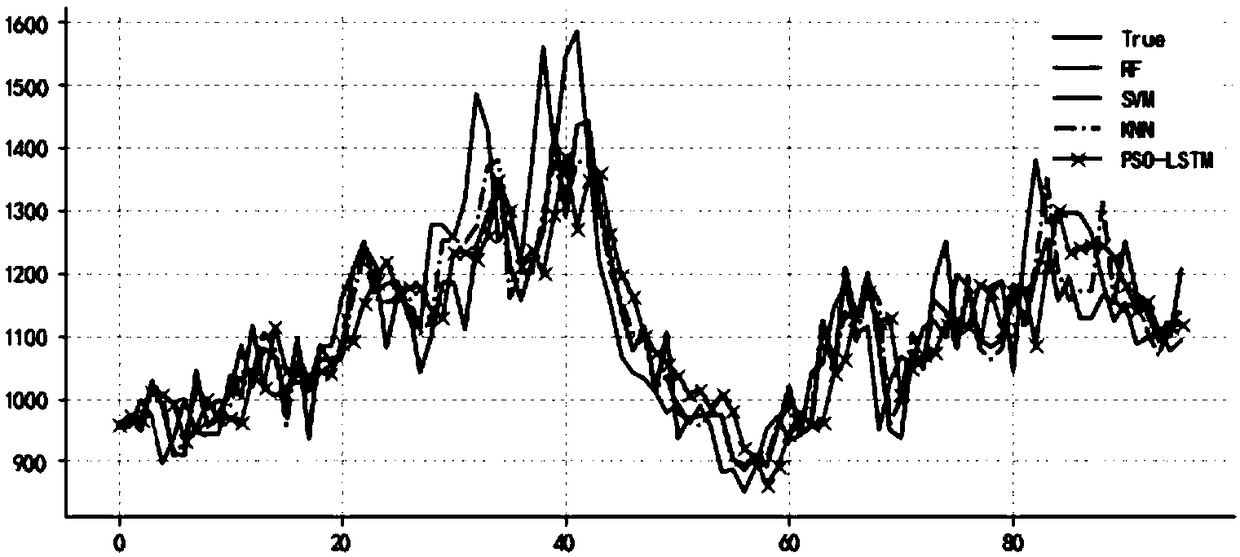
Travel time prediction method for optimizing LSTM neural network through particle swarm optimization algorithm
ActiveCN108986470AImprove forecast accuracyImprove applicabilityDetection of traffic movementNeural architecturesPrediction algorithmsNetwork model
The invention discloses a travel time prediction method for optimizing an LSTM neural network through a particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting travel time data, performing data normalization, and dividing the data into a training set and a test set proportionally; S2, optimizing each parameter of an LSTM neural network prediction model by using the particle swarm optimization algorithm; S3, inputting the parameters, optimized through the particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the training set, and performing the iterative optimization of the LSTM neural network prediction model; S4, predicting the test set through the trained LSTM neural network model, and evaluating a model error. The method is quick in optimization. Compared with a random forest, SVM and KNN in the traditional prediction algorithm, the method of the invention has the least mean square error and square error for the data prediction, and the model reducesthe calculation burden, so the method shows better prediction performance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
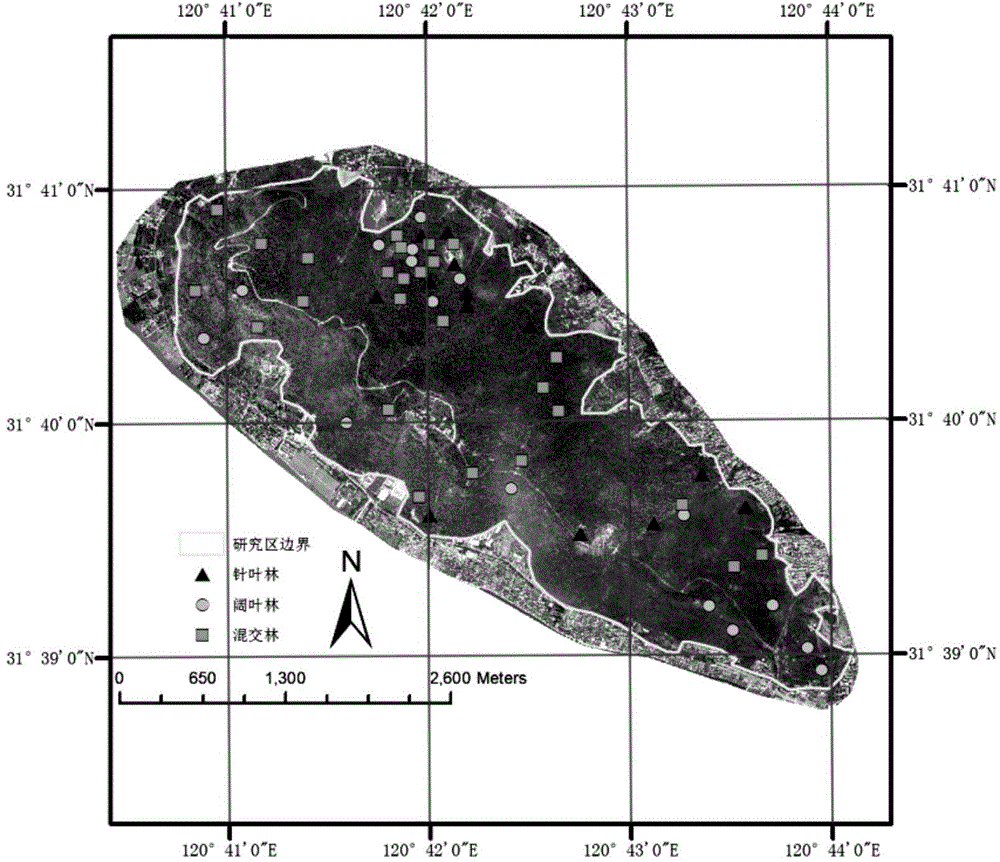
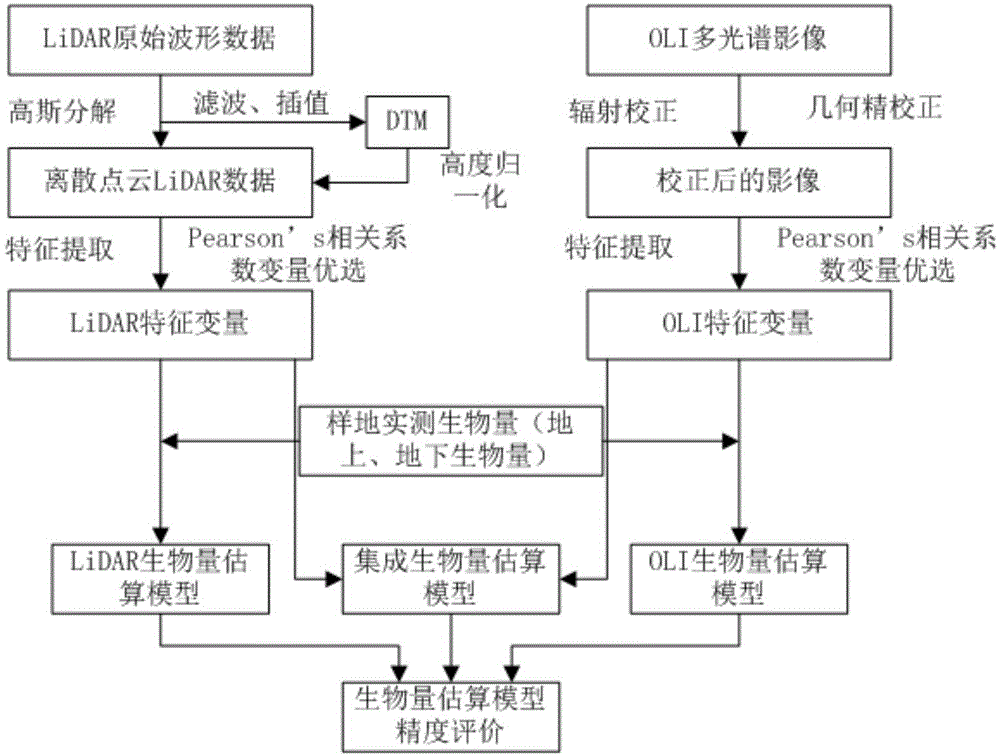
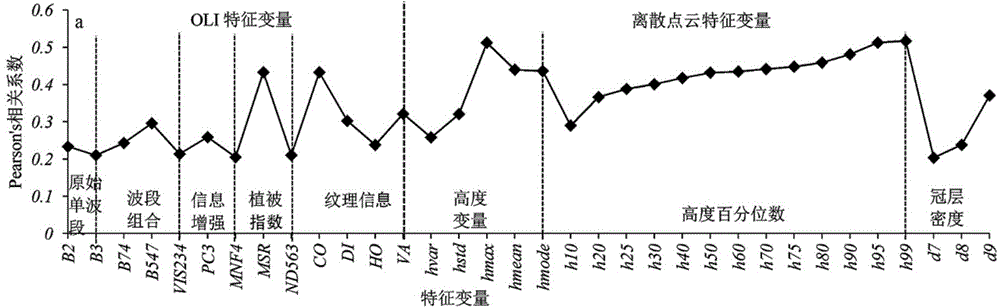
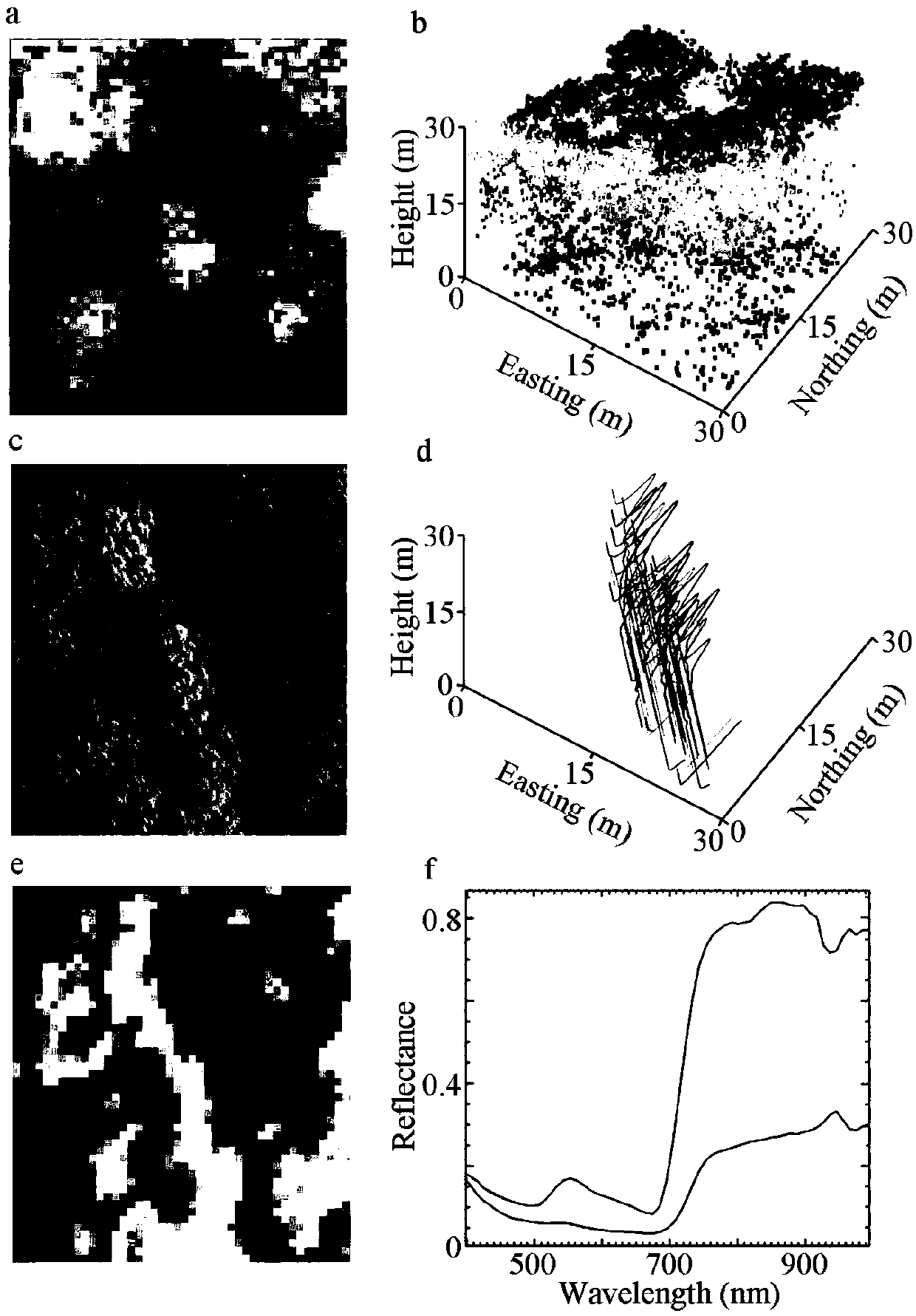
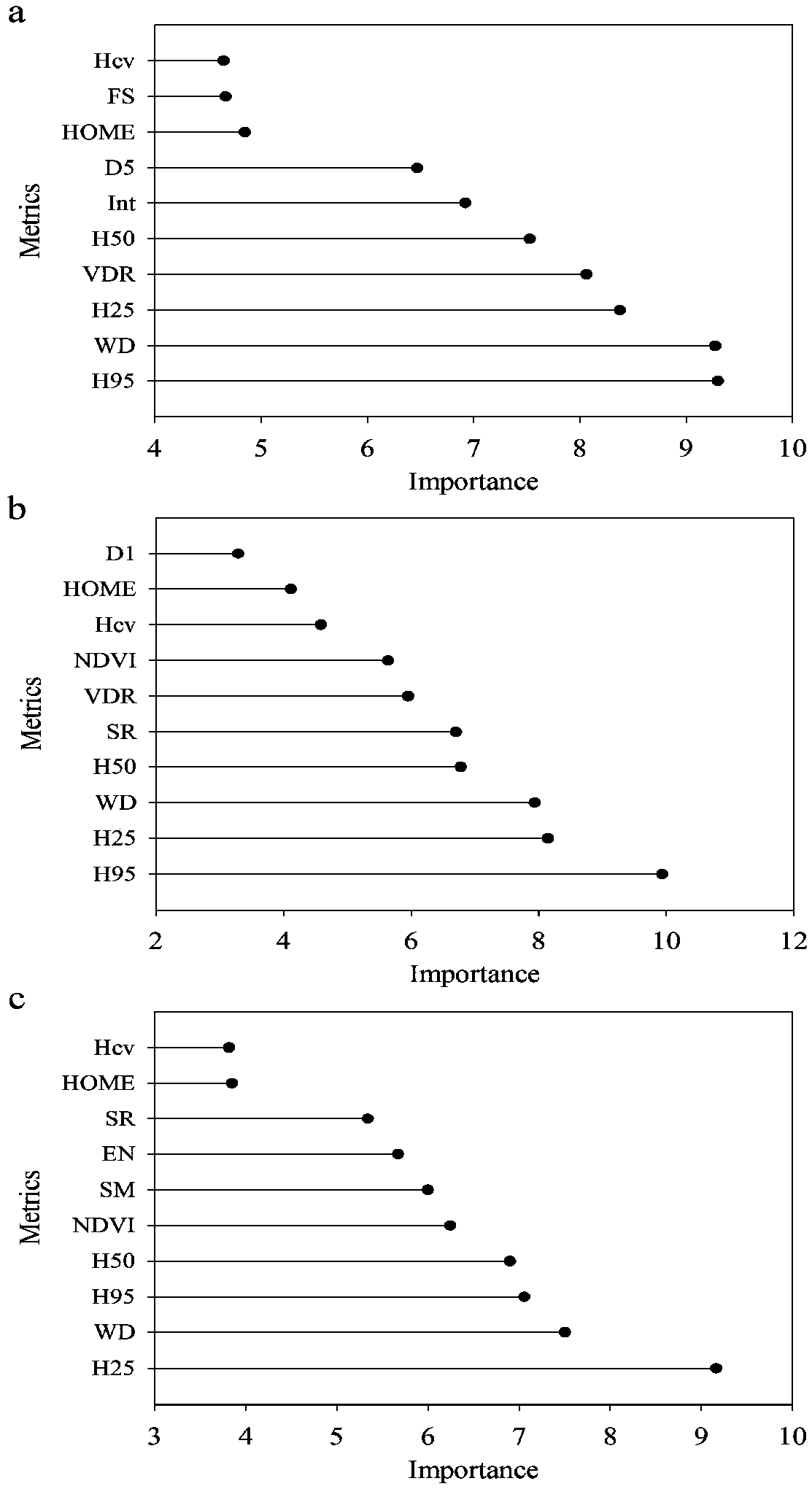
Method for inverting remote sensing forest biomass
ActiveCN104656098AGood for mechanism explanationFacilitate method portabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationSustainable managementCorrelation analysis
The invention discloses a method for inverting remote sensing forest biomass. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of remote sensing data pretreatment, extracting characteristic variables of a vegetation canopy from a LiDAR point cloud (comprising canopy three-dimensional space information) and multispectrum (comprising spectrum information on the upper surface of the canopy) data respectively; screening the characteristic variables of the LiDAR point cloud and the multispectrum through correlation analysis, and inverting overground and underground biomass by combining the ground actually measured biomass information through a stepwise regression model. Through the adoption of the optimized inverting model of northern subtropical forest biomass, constructed by method, the 'determination coefficient' R<2> of the model can be increase by 3-24%; the forest biomass can be estimated in high precision, and the 'relative root-mean-square error' (rRMSE) can be reduced by 2-10%. The method can be applied to the fields of forestry investigation, forest resource monitoring, forest carbon reserve evaluation, forest ecosystem research and the like, and provides quantitative data support for forest sustainable management and forest resource comprehensive utilization.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
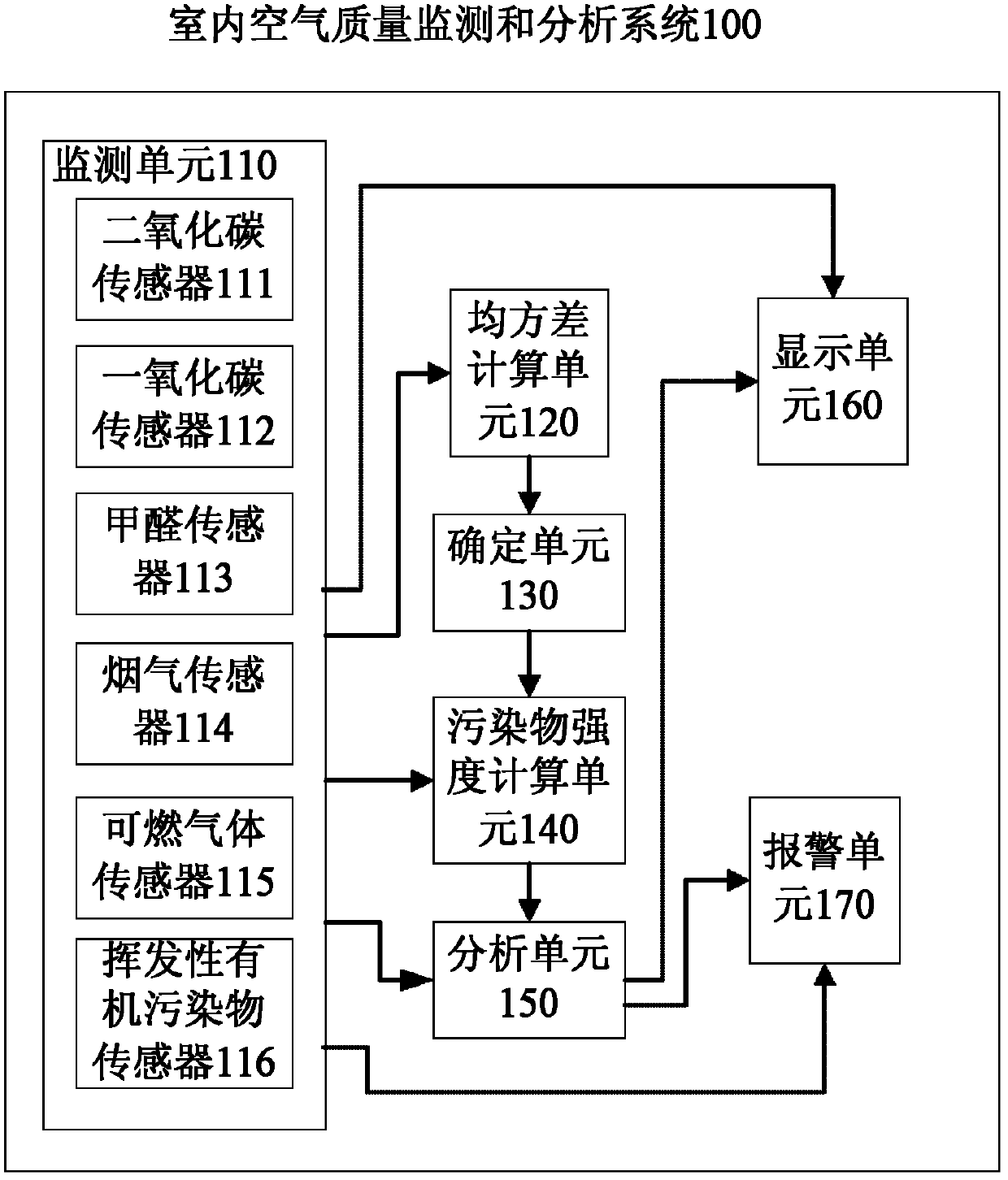
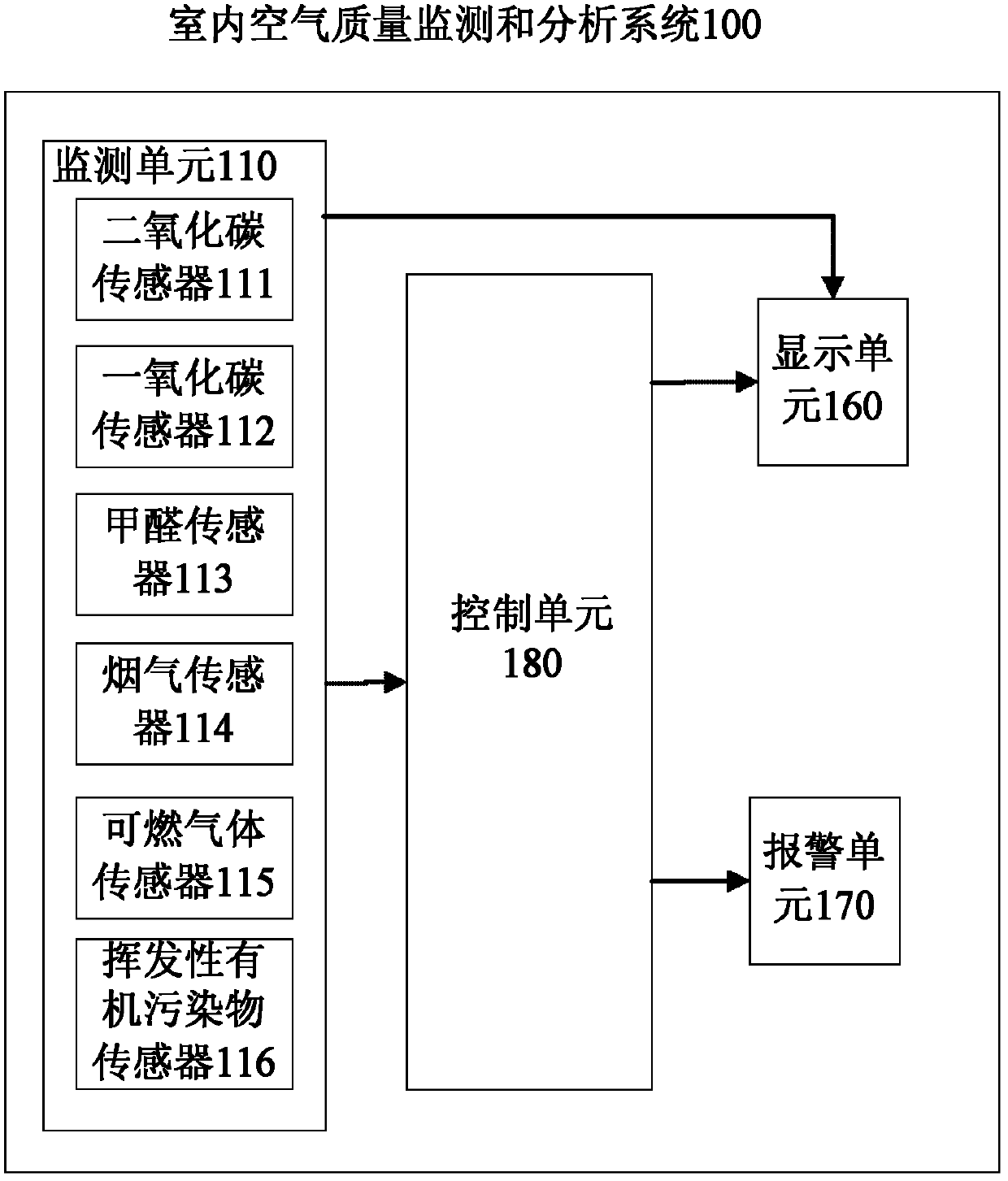
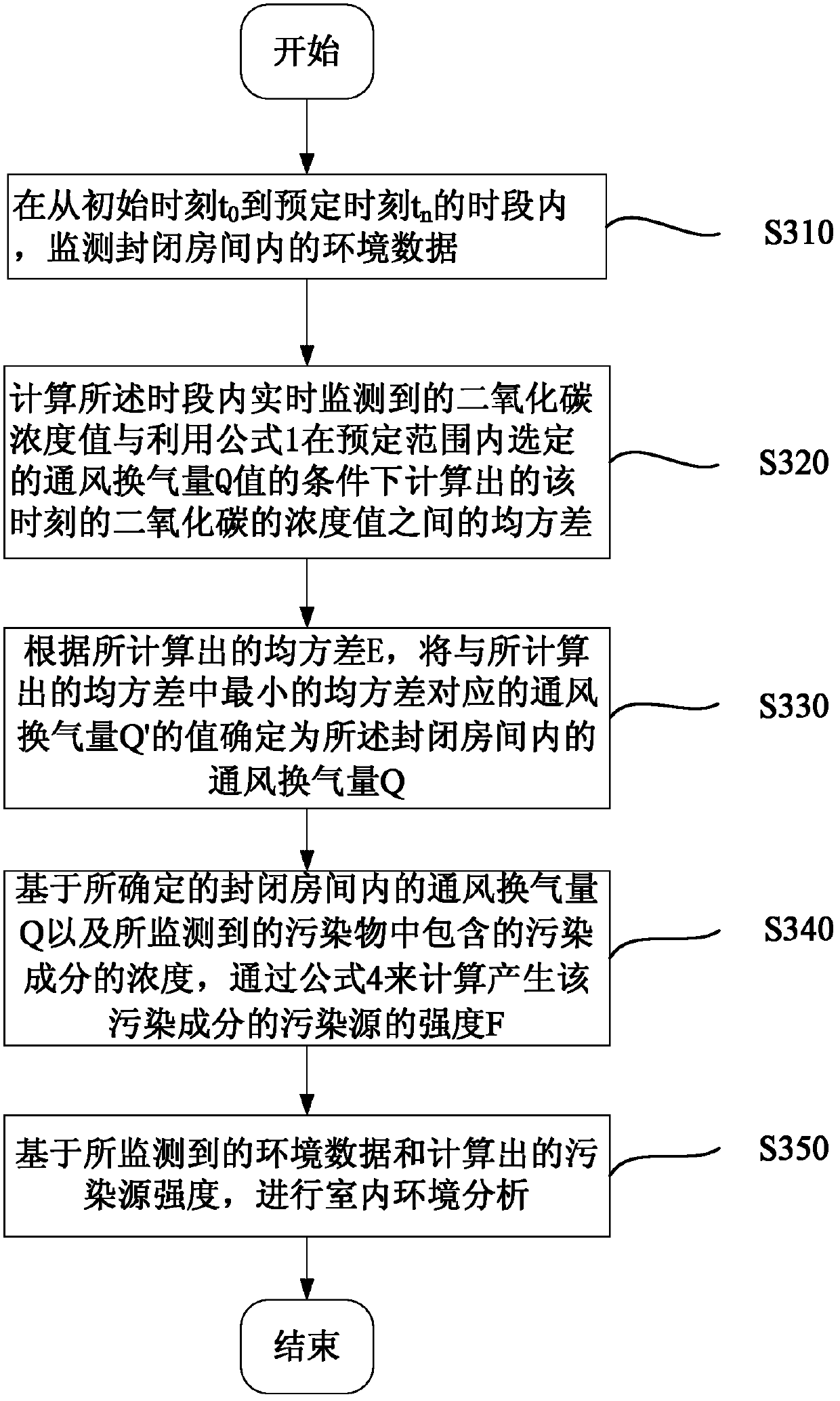
Method for evaluating indoor air quality and system for monitoring and analyzing indoor air quality
InactiveCN102353751ARealize real-time monitoringSimple interfaceAir quality improvementMaterial analysisMean squareIndoor air quality
The invention discloses a method for evaluating indoor air quality and a system for monitoring and analyzing indoor air quality. The method comprises the following steps of: monitoring environmental data in an enclosed room; computing mean square deviations between carbon dioxide concentration values measured in real time within a preset period of time and carbon dioxide concentration values at the same moments computed with a formula 1 under the condition of the value of a ventilation rate Q selected within a preset range; determining the value of a ventilation rate Q' which corresponds to a minimum mean square deviation in the computed mean square deviations as a ventilation rate Q in the enclosed room; computing the intensities F of polluting sources which produce polluting components based on the determined ventilation rate Q and the concentrations of the polluting components contained in monitored pollutants; and analyzing the indoor environment based on the monitored environmental data and the computed intensities of the polluting sources. By adopting the method and the system, the concentrations of a plurality of polluting sources in the indoor environment can be monitored in real time, and the air quality can be evaluated and analyzed according to monitoring data.
Owner:北京清风康华科技有限公司
Conductive sheet, touch panel, and display device
ActiveUS20140218325A1Increase awarenessSuppress generationPrinted circuit aspectsSynthetic resin layered productsCommon logarithmDisplay device
In the mesh pattern of the conductive sheet of the invention in which openings having different shapes are arrayed in plan view, a standard deviation of an area of each of the openings is equal to or greater than 0.017 mm2 and equal to or less than 0.038 mm2, in a two-dimensional distribution of centroid positions of the openings; a standard deviation for a root mean square deviation of each of the centroid positions which are disposed along a predetermined direction, with respect to a direction perpendicular to the predetermined direction is equal to or greater than 15.0 μm; or a standard deviation over a radial direction of a value expressed by a common logarithm of a standard deviation along an angular direction in a power spectrum of the mesh pattern is equal to or greater than 0.965 and equal to or less than 1.065.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
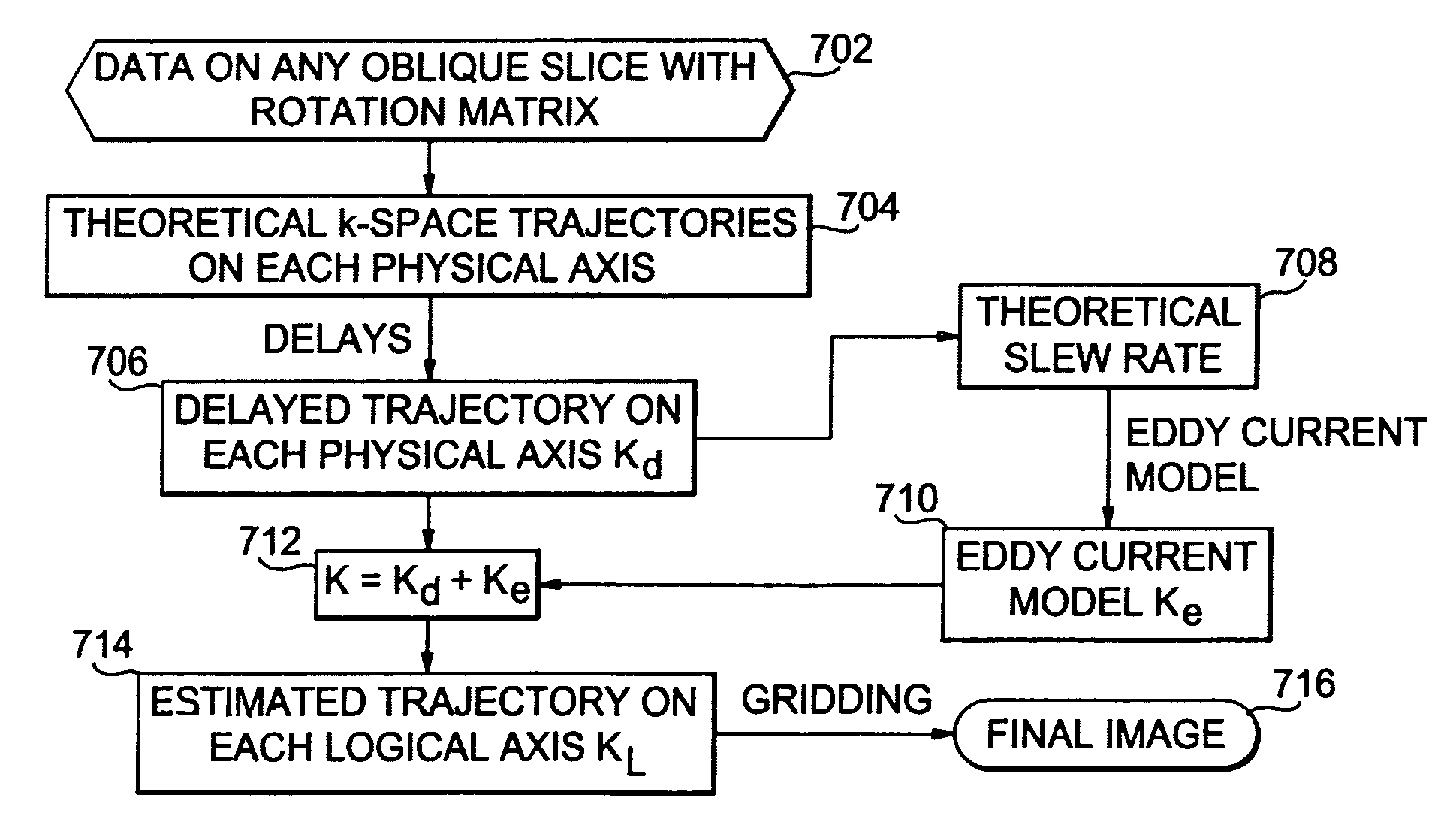
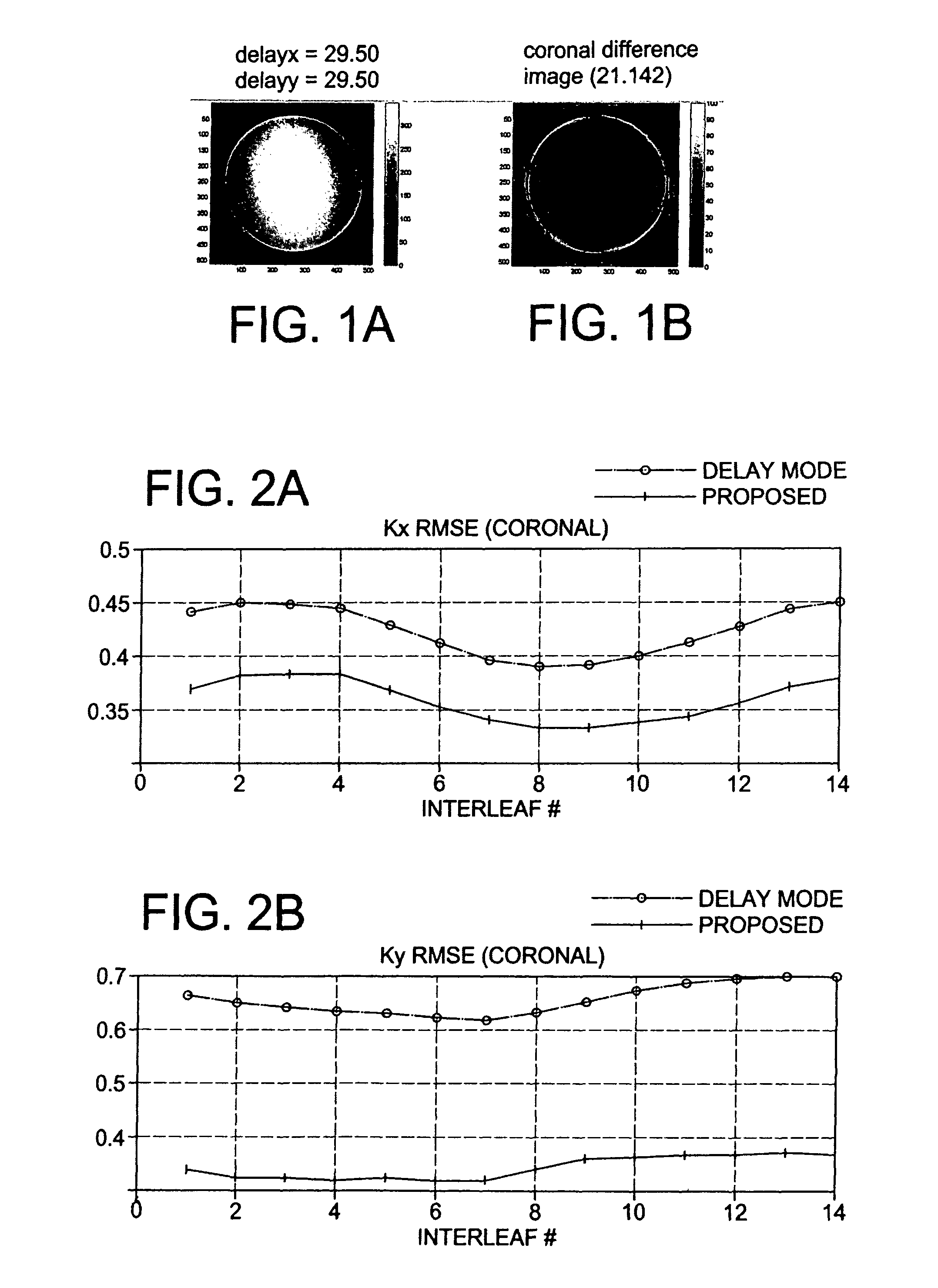
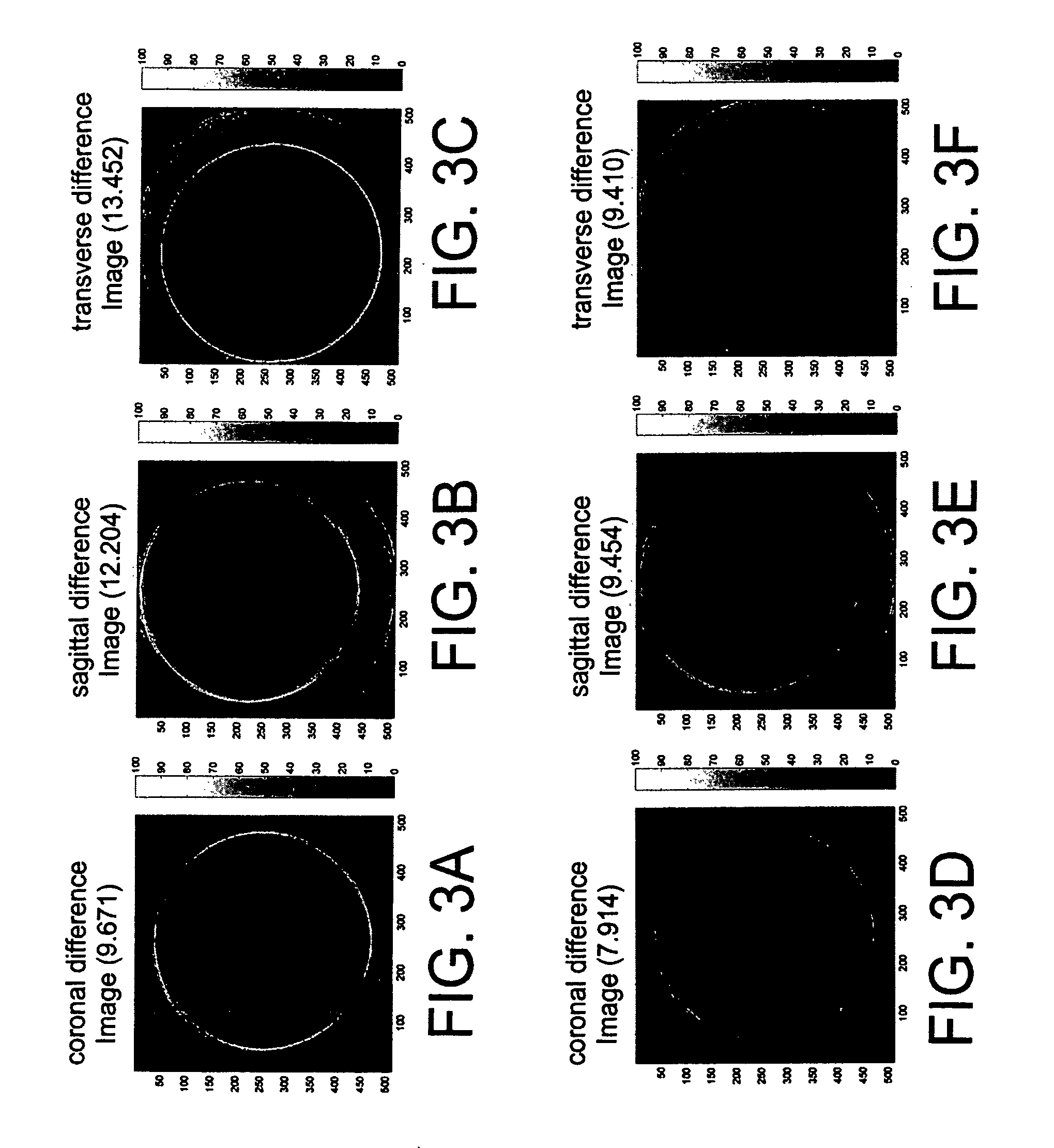
K-space trajectory estimation in spiral MRI system and related method thereof
ActiveUS7888935B1The process is simple and effectiveReduce errorsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionBaseline dataK space trajectory
First, benchmark data are collected on two thin slices of an object to get measured k-space trajectories. To find delays on different physical gradients, the root mean square error between estimated and measured k-space trajectories is minimized for different delays. To reduce the error further, an eddy current compensation is introduced along each physical gradient axis. A more accurate estimation of the k-space trajectory can be obtained to image the object.
Owner:VIRGINIA UNIV OF
Method for joint inversion of forest aboveground biomass by integrating three data sources
ActiveCN108921885AImprove inversion accuracyImprove the inversion effectImage enhancementImage analysisTerrainAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a method for joint inversion of forest aboveground biomass by integrating high-resolution CCD data, hyperspectral image data and laser radar point cloud data. According to themethod, first, geometric correction and stitching preprocessing are performed on airborne high-resolution CCD images, geometric correction and atmospheric correction preprocessing are performed on hyperspectral images, filtering and interpolation are performed on the laser radar point cloud data to generate a digital terrain model, and the point cloud data is normalized; second, texture features,spectral features and point cloud structural features are extracted based on three data sources obtained after preprocessing respectively; and last, models are constructed respectively in combinationwith ground measured data and extracted feature variables to predict the forest aboveground biomass. Through the method, the forest aboveground biomass of a subtropical natural secondary forest is extracted; and compared with aboveground biomass estimation results obtained by using other approximate remote sensing methods, the relative root-mean-square error of the method is lowered by 10% or above.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
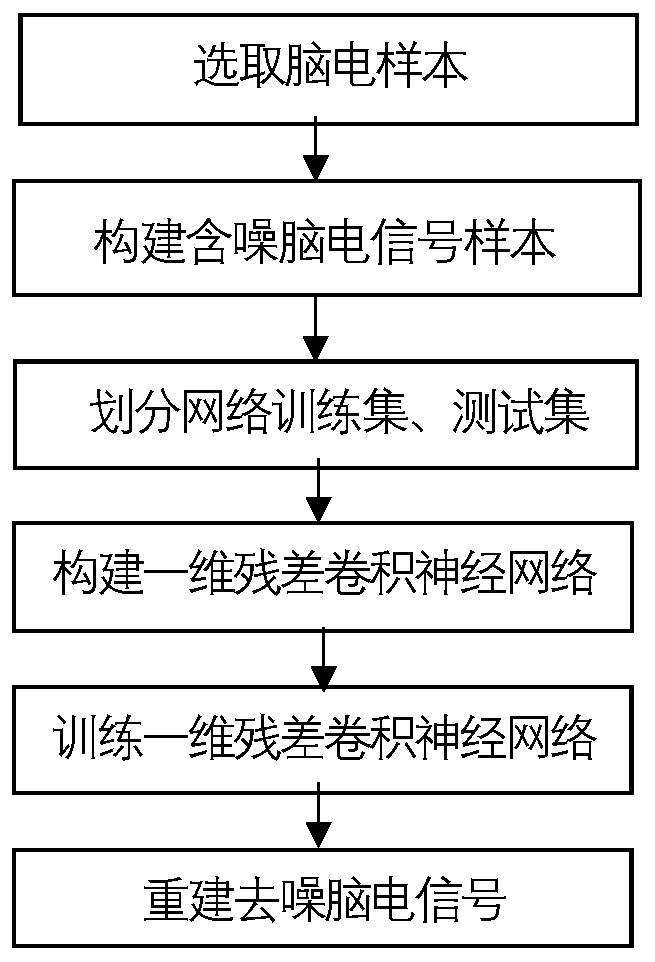
Electroencephalogram signal denoising method based on one-dimensional residual convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109784242AImprove learning effectImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkNetwork connection
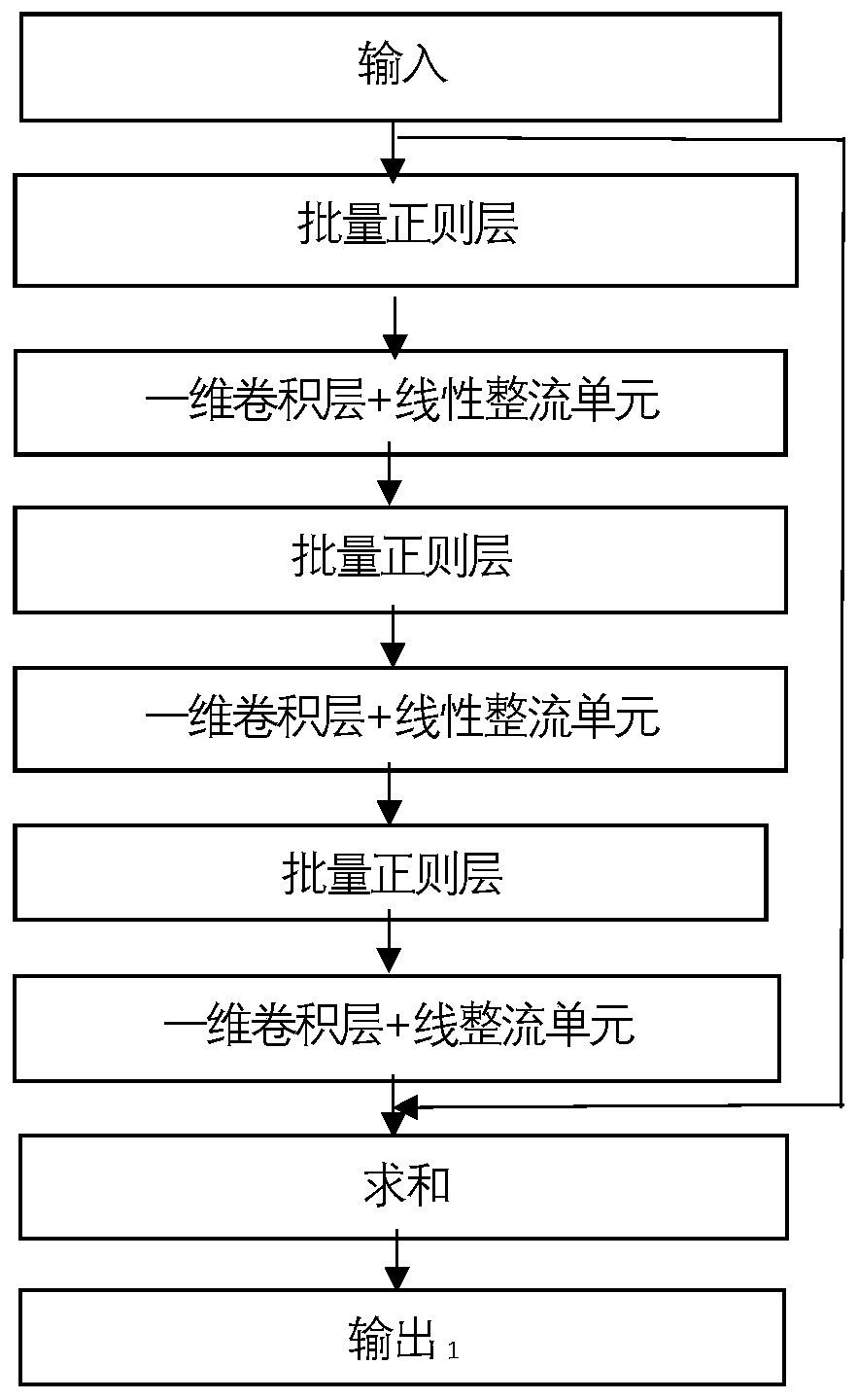
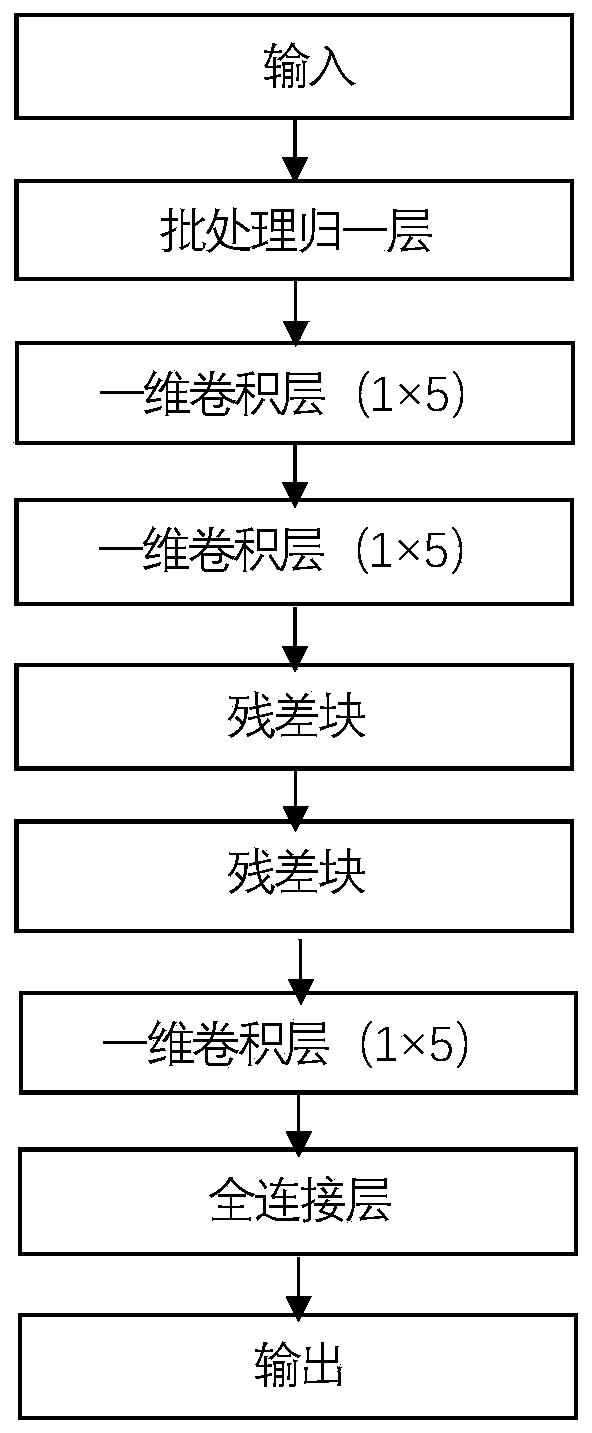
The invention discloses an electroencephalogram signal denoising method based on a one-dimensional residual convolutional neural network. The electroencephalogram signal denoising method comprises thesteps of selecting an electroencephalogram sample, constructing a noisy electroencephalogram signal sample, dividing a network training set and a test set, constructing the one-dimensional residual convolutional neural network, training the one-dimensional residual convolutional neural network and reconstructing a denoised electroencephalogram signal; according to the invention, a one-dimensionalresidual convolutional neural network formed by connecting residual networks is constructed; a convolutional layer and an activation layer are introduced, so that the learning ability of a neural network is enhanced, accurate mapping and real-time denoising of noise signals to brain signals are established, neurons smaller than 0 are removed by using a linear rectification unit layer function after the convolutional layer, effective characteristics are screened out, and the defect of gradient explosion is avoided; signal de-noising is divided into a model training process and a de-noising process, the signal-to-noise ratio and the root-mean-square error of signal de-noising are improved, the de-noising time is shortened, the de-noising efficiency and quality of electroencephalogram signals are improved, and the method can be applied to the technical field of signal processing preprocessing and de-noising processing.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
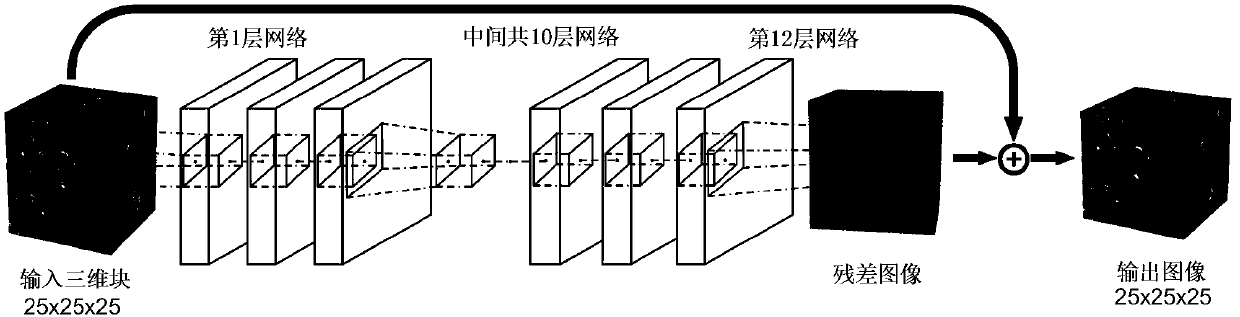
Core CT image super-resolution reconstruction method based on three-dimensional convolutional neural network
ActiveCN108898560AImprove performanceHigh-resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisAdaptive learningReconstruction method
The invention discloses a core three-dimensional image super-resolution method, which comprises the following steps: (1) sending an image in a training set to a three-dimensional convolutional neuralnetwork proposed by the method, wherein the first layer of the network performs low-frequency feature extraction; (2) allowing the second to eleventh layers of the network to be responsible for learning a mapping relationship between low frequency and high frequency features; (3) allowing the twelfth layer of the network to use the learned mapping relationship to map the low frequency features into the high frequency features; (4) using a residual learning method to calculate a root mean square error, and accelerating the training by using the momentum gradient descent method; (5) using the adaptive learning rate and a gradient cutting method to optimize the training process during the process of training, and using the training configurations in (1) to (5) to perform continuous iterativetraining; and (6) using the trained network model to complete the reconstruction. The invention can improve the resolution of a rock CT three-dimensional image, restore more structure and details, andprovide clearer image samples for the next step of geology-petroleum research.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
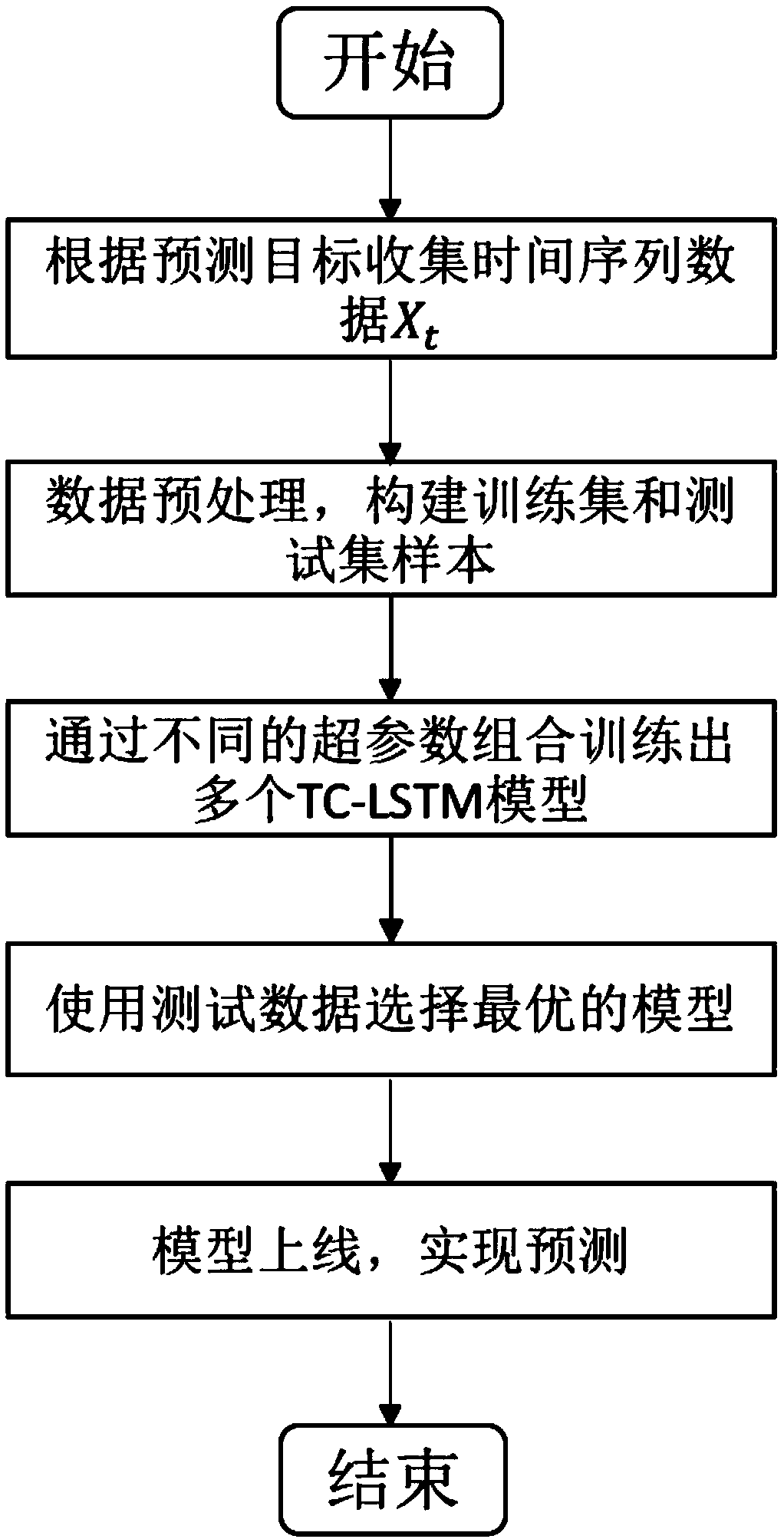
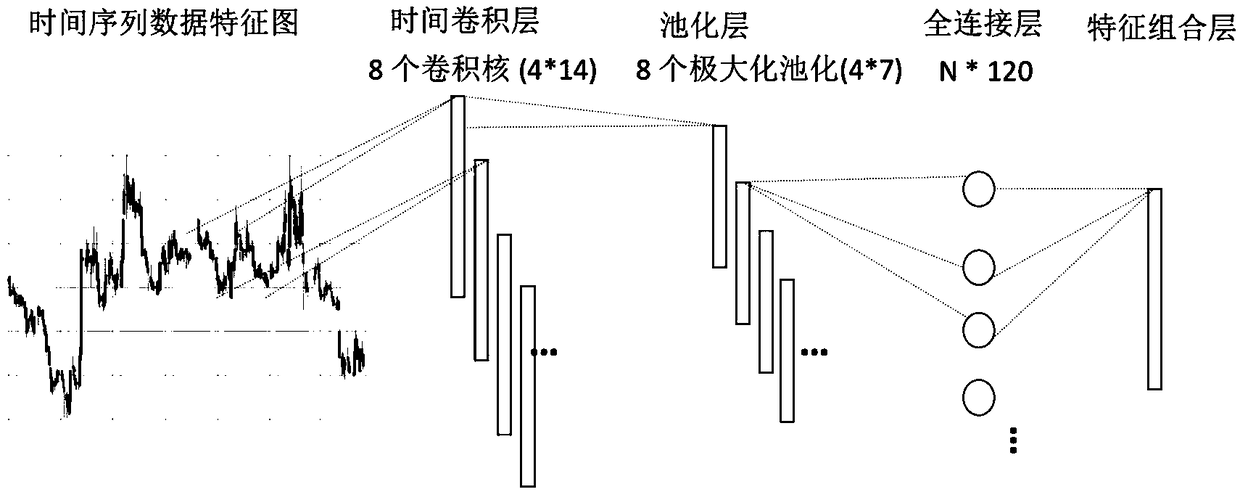
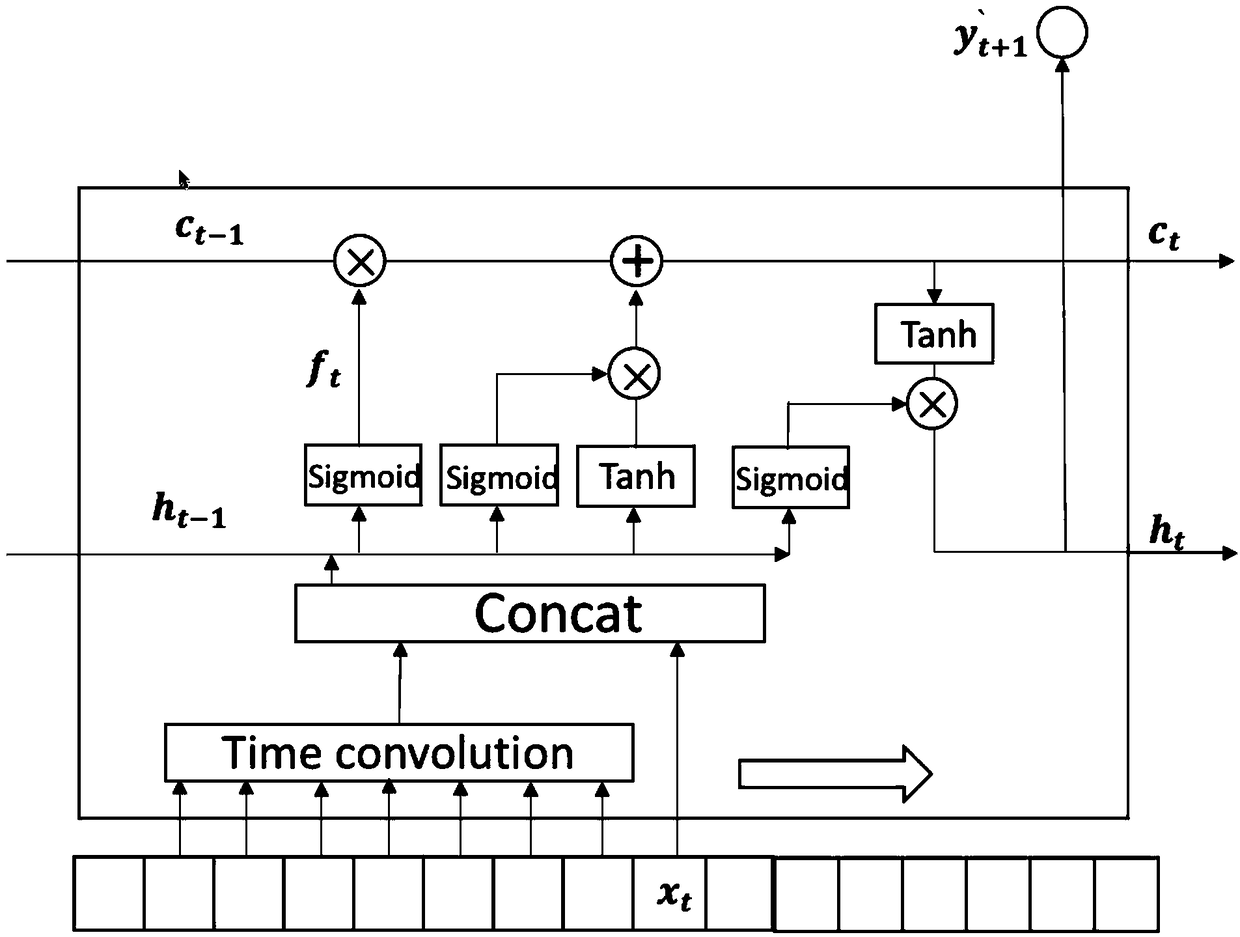
Time sequence prediction method based on time convolution and LSTM
InactiveCN108764460AHigh precisionEasy to digForecastingNeural architecturesHyperparameterRoot-mean-square deviation
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
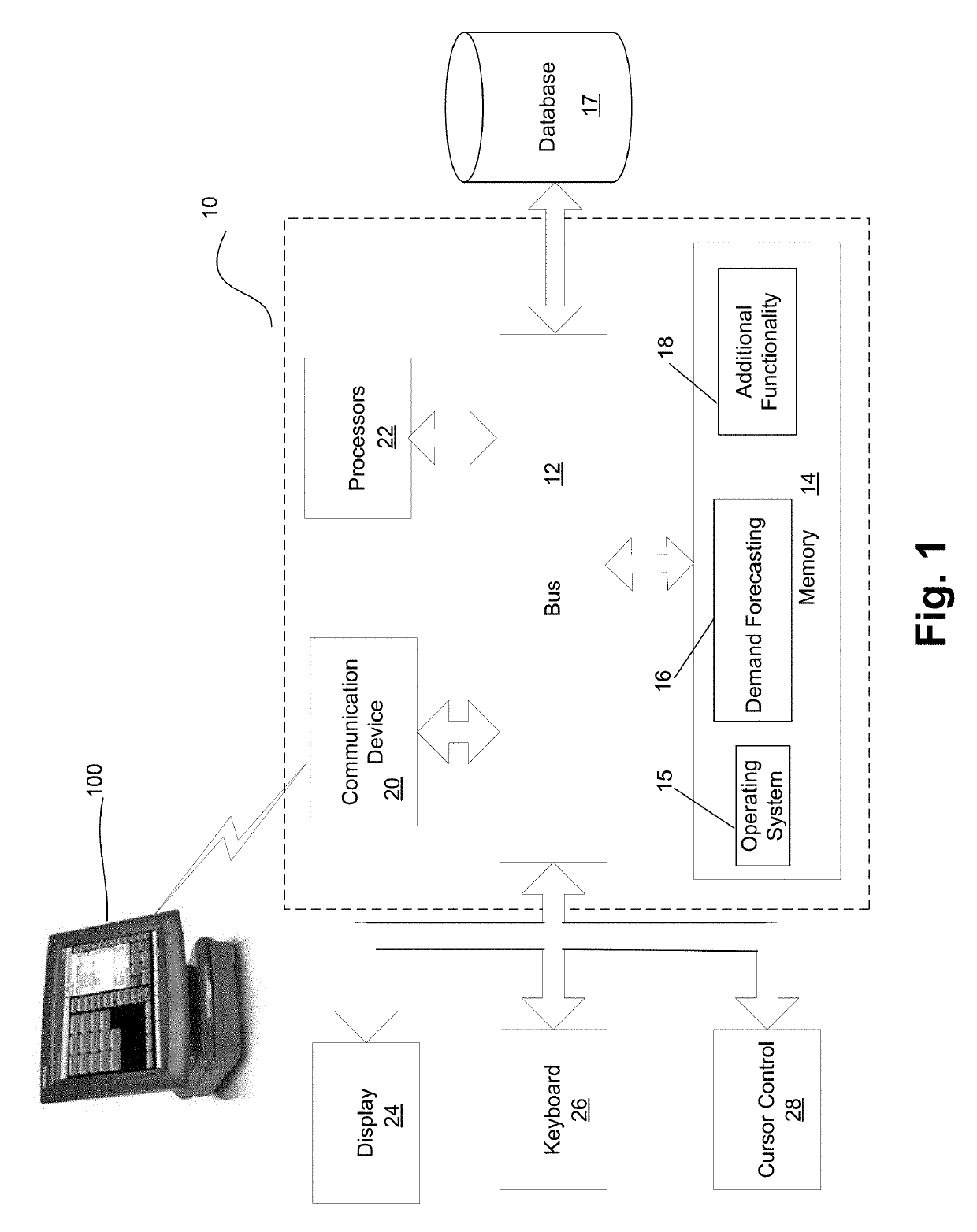
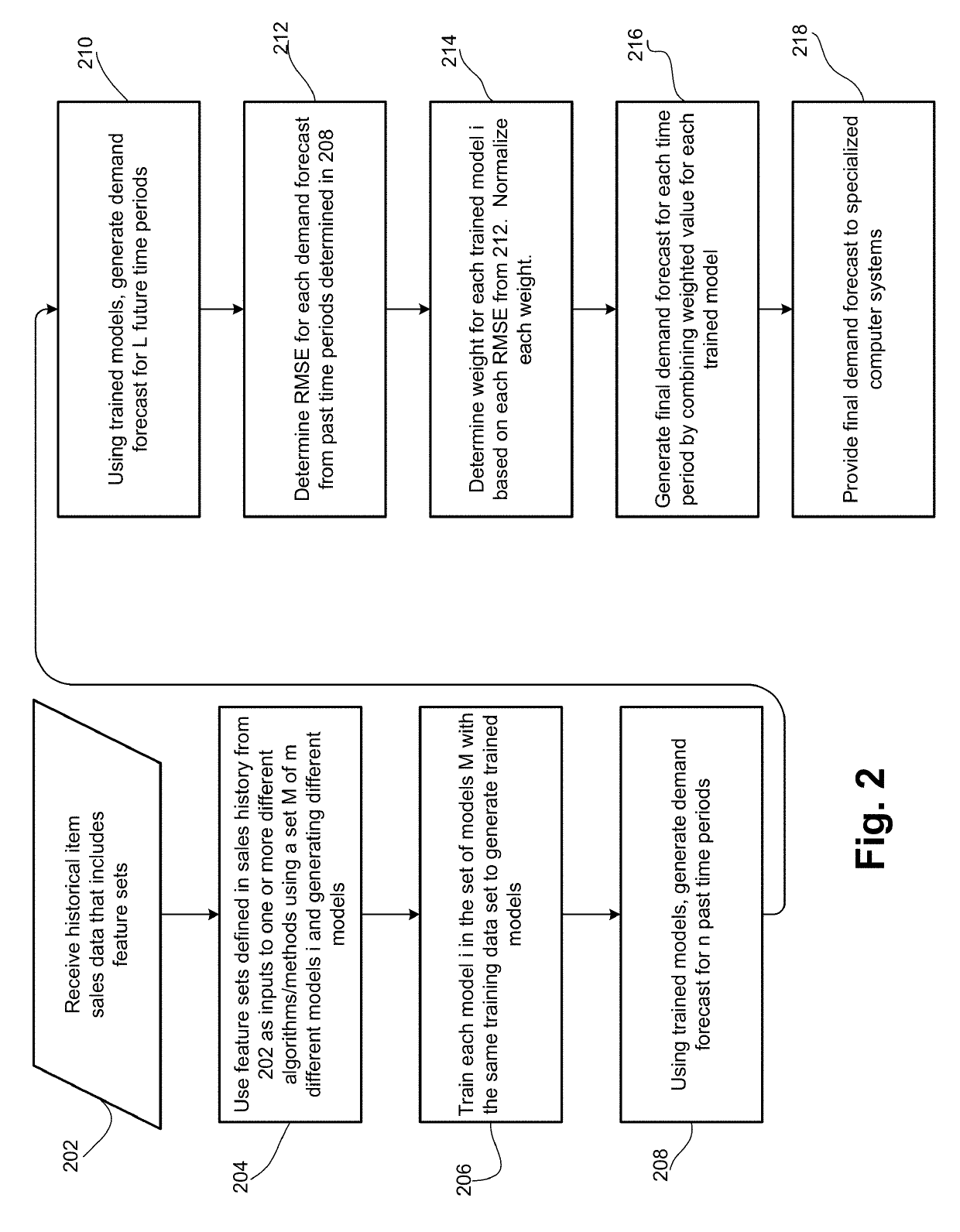
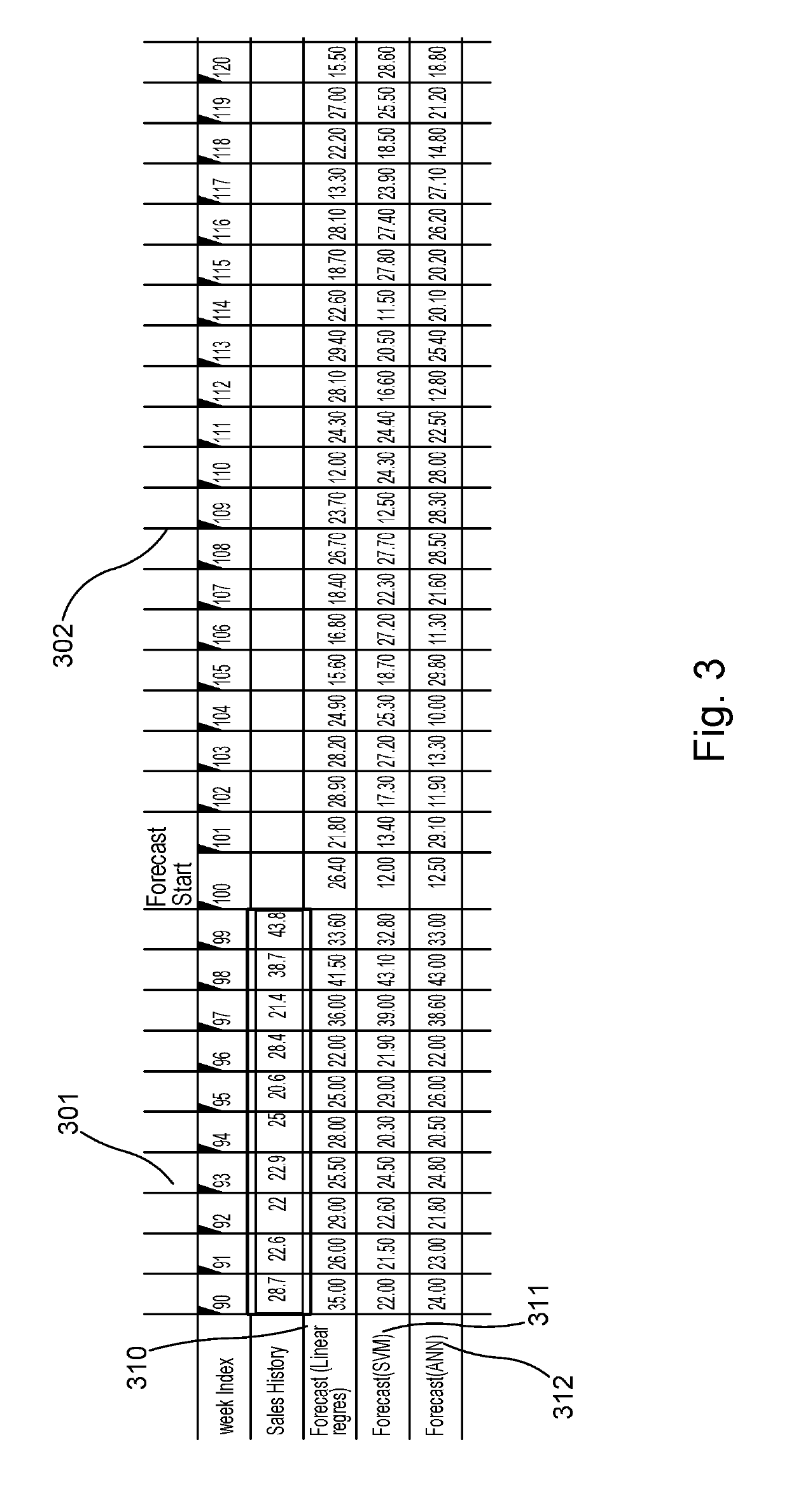
Demand forecasting using weighted mixed machine learning models
Embodiments forecast demand of an item by receiving historical sales data for the item for a plurality of past time periods including a plurality of features that define one or more feature sets. Embodiments use the feature sets as inputs to one or more different algorithms to generate a plurality of different models. Embodiments train each of the different models. Embodiments use each of the trained models to generate a plurality of past demand forecasts for each of some or all of the past time periods. Embodiments determine a root-mean-square error (“RMSE”) for each of the past demand forecasts and, based on the RMSE, determine a weight for each of the trained models and normalize each weight. Embodiments then generate a final demand forecast for the item for each future time period by combining a weighted value for each trained model.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
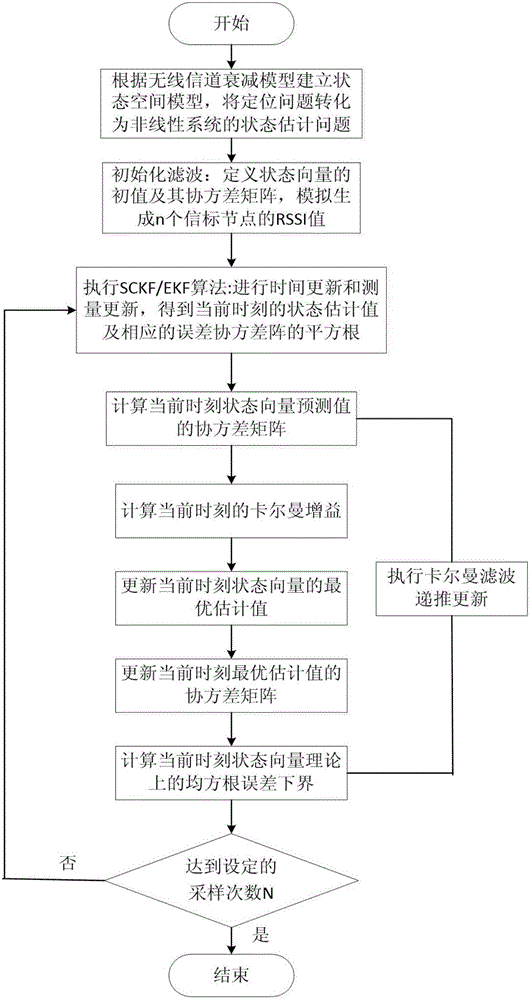
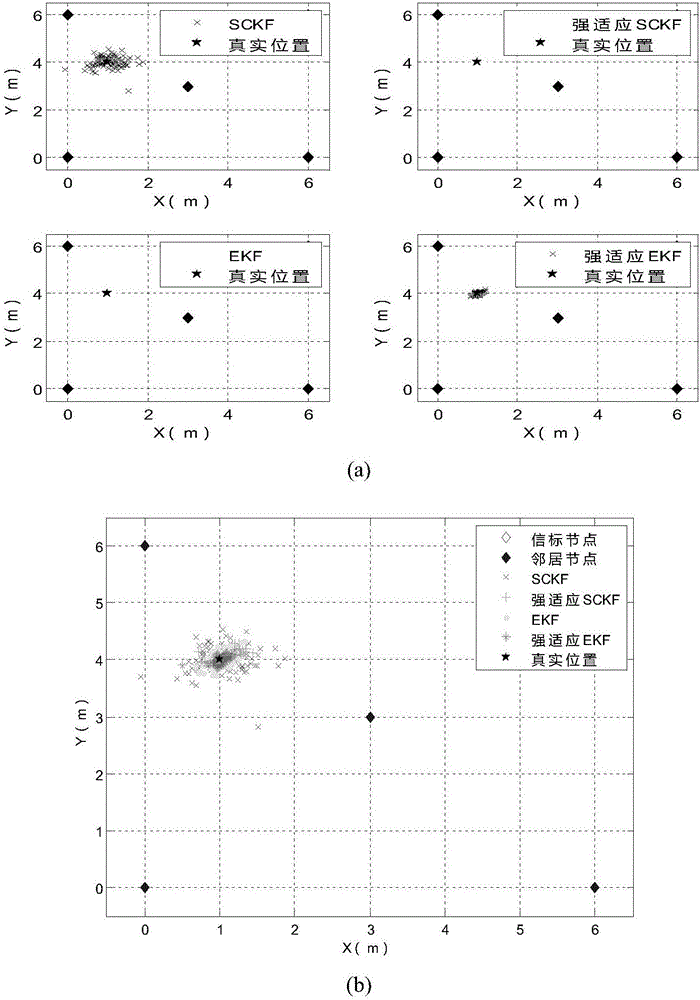
Nonlinear system state estimation method based on Kalman filtering positioning
ActiveCN106646356AImprove stabilityNo divergent failurePosition fixationNonlinear filterChannel parameter
The invention discloses a nonlinear system state estimation method based on Kalman filtering positioning, and proposes a strongly adaptive Kalman filtering mechanism which combines a nonlinear filtering algorithm and Kalman filtering. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the simultaneous estimation of node positions and channel parameters through employing an RSSI state estimation algorithm based on square root volume Kalman filtering, and obtaining the estimation value of a state vector; employing the Kalman filtering for further processing according to the linear change of a state equation, obtaining optimal estimation, and building a strongly adaptive square root volume Kalman filtering algorithm; giving the design steps of the strongly adaptive square root volume Kalman filtering algorithm; and calculating a theoretical square root error lower bound under a state space model based on the RSSI state estimation. The method enables an estimation result to be improved, and improves the precision. The method does not need to excessively depend on improper initial conditions, can be well adapted to a highly nonlinear system, and is not liable to enable the algorithm to be divergent and ineffective.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
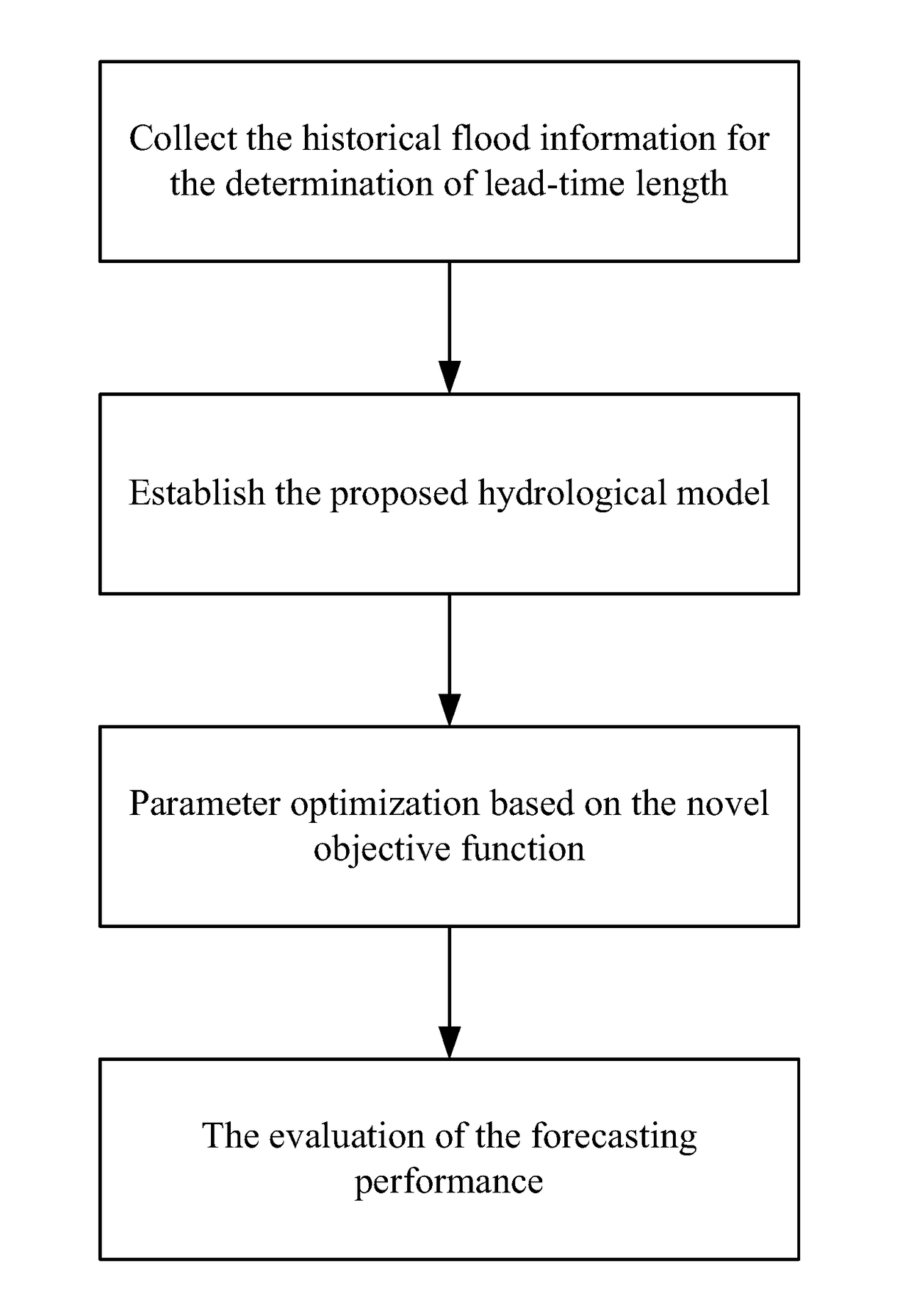
Method for forecasting floods for multiple lead times
InactiveUS20170168195A1Improve abilitiesImprove forecast accuracyWeather condition predictionClimate change adaptationEvaporationModel parameters
A method for forecasting flood, the method including: 1) collecting historical flood information, estimating a mean concentration time of a basin, and determining a length of a lead time; 2) establishing hydrological models, inputting hydrological variables including precipitation and evaporation to the hydrological models while neglecting the precipitation within lead times; 3) determining an objective function, which is a sum of squared errors between a forecasted streamflow and an observed streamflow within multiple lead times, and utilizing optimized algorithms to calibrate hydrological model parameters; and 4) selecting criteria to evaluate forecasting performance of the hydrological model including a Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency, a root mean square error, a water balance index, a qualified rate of peak flow, and a qualified rate of a peak time.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Joint sparse representation and deep learning-based image super resolution method and system
ActiveCN105931179AHigh precisionHigh super-resolution reconstruction accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage resolution
The invention relates to a joint sparse representation and deep learning-based image super resolution method and a joint sparse representation and deep learning-based image super resolution system. The method includes the following steps that: resolution reduction is performed on an original high-resolution image, so that a low-resolution image of which the size is the same as the original high-resolution image, and the difference value part of the original high-resolution image and the low-resolution image is obtained; a low-resolution image dictionary, a difference value image dictionary and corresponding sparse representation coefficients are obtained; a deep learning network with root-mean-square error adopted as a cost function is constructed, and network parameters are optimized iteratively, so that the cost function can be minimum, a trained deep learning network can be obtained; and the sparse coefficient of the low-resolution image, which is adopted as a test part, is inputted into the deep learning network, when error is smaller than a given threshold value, a corresponding high-resolution image can be reconstructed according to the low-resolution image of which the resolution is to be improved. According to the method and system of the invention, defects of an existing method according to which a joint dictionary training mode is utilized to make a high-resolution image and a low-resolution image share a sparse representation coefficient can be eliminated, and deep learning is utilized to fully learn the mapping relationship between the low-resolution image sparse representation coefficient and the difference value image sparse representation coefficient, and therefore, a high-resolution reconstruction result with higher precision can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
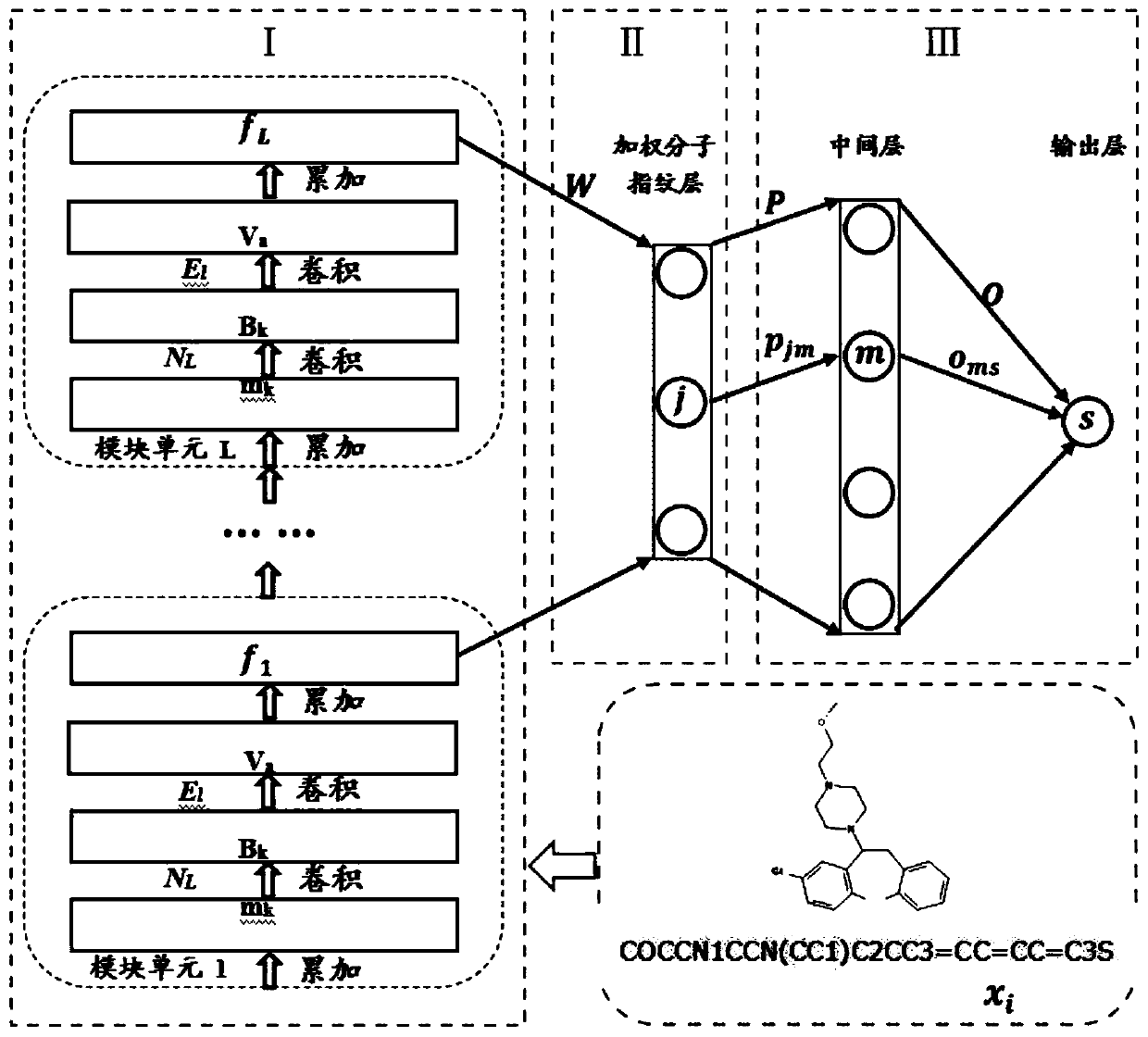
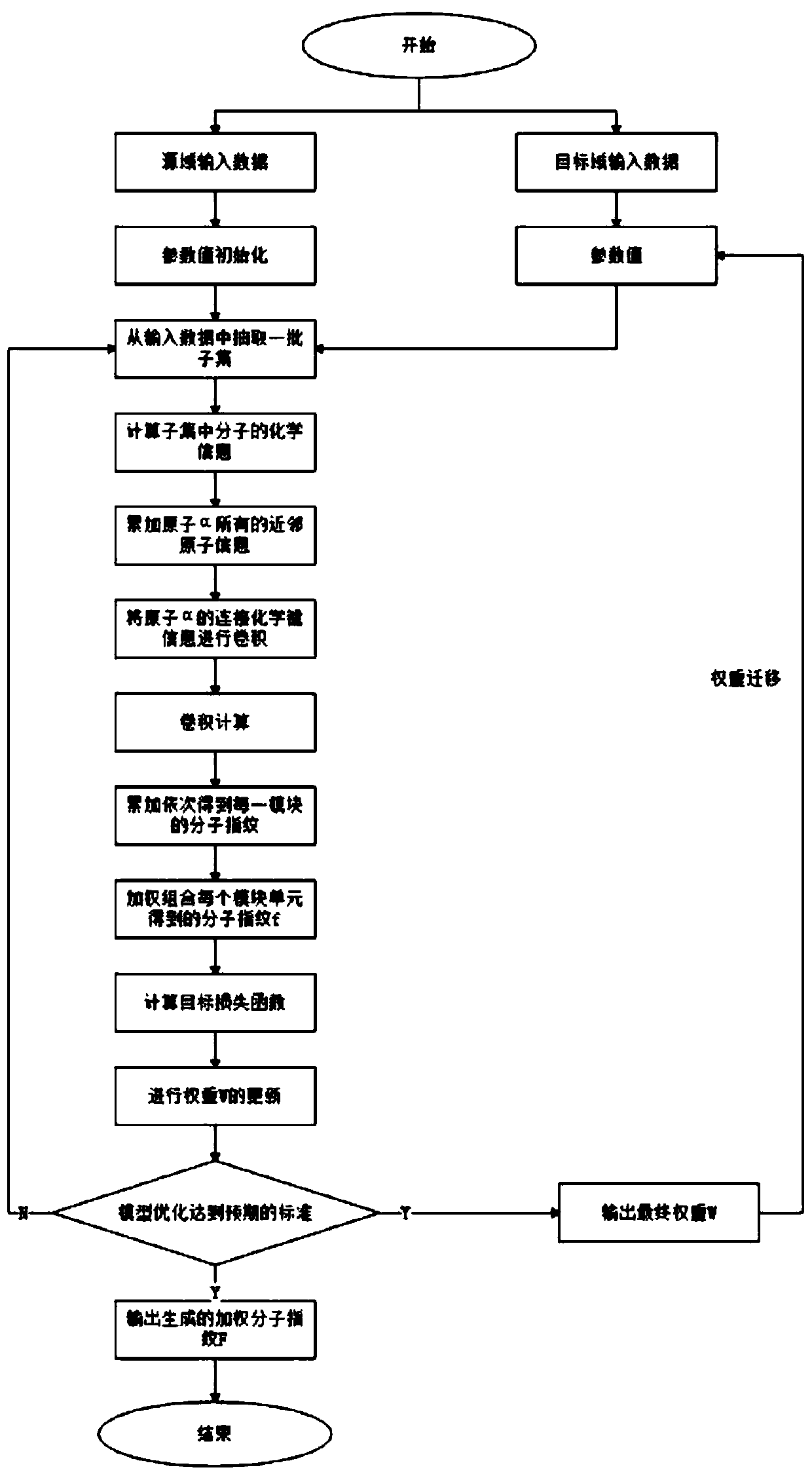
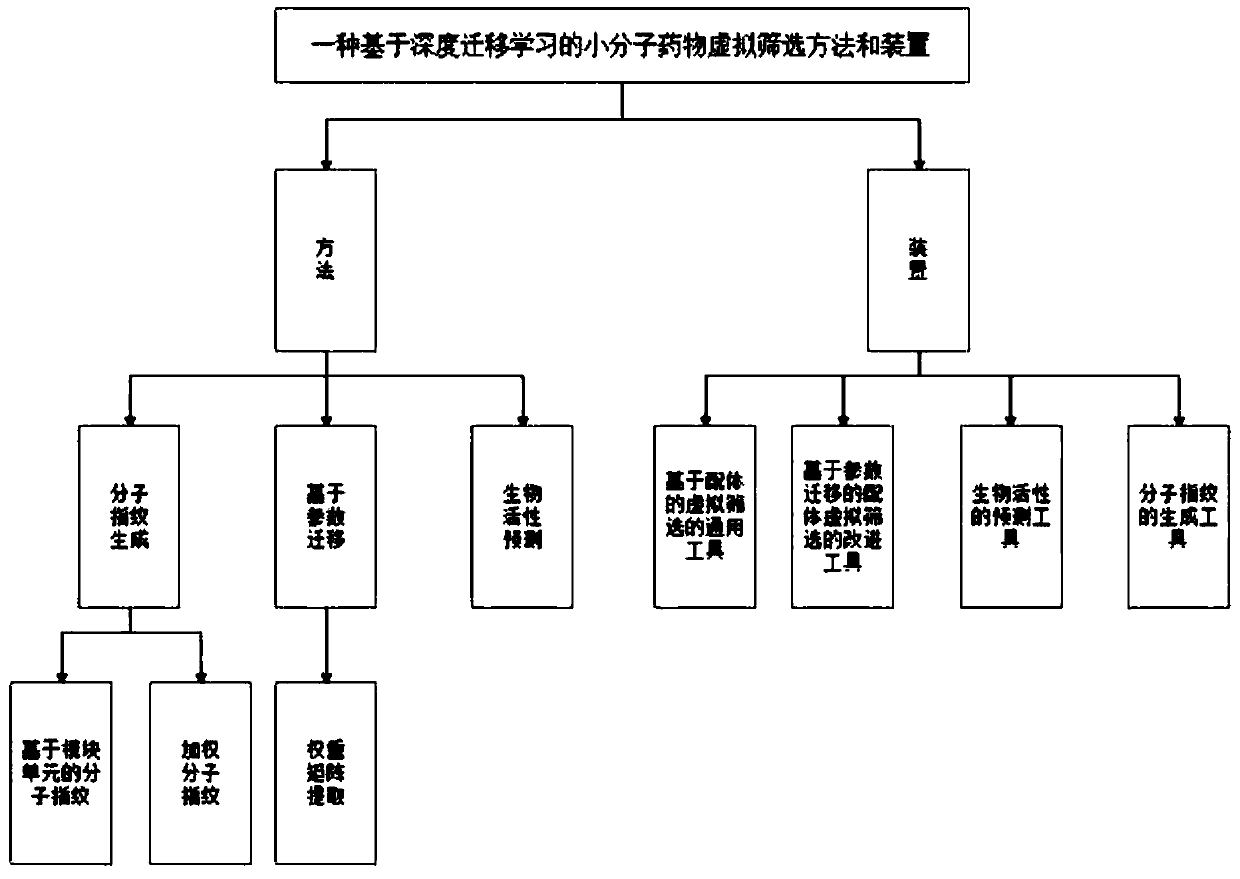
Small molecule drug virtual screening method based on deep migration learning and application thereof
ActiveCN110459274AImplement the buildMolecular designChemical machine learningDrug targetDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a small molecule drug virtual screening method based on deep migration learning and application thereof. A source domain is used as an input to be trained, converged and derived to obtain a weight matrix; a target domain is input into an improvement tool to serve as the initialization weight of the target domain; fine adjustment, training and convergence are conducted on the initialization weight and data in the target domain sequentially; a biological activity value of interaction of a lead compound and a drug target in the target domain is predicted, a target domain molecular fingerprint and a predicted value are obtained, and an evaluation index root mean square error and a correlation coefficient of a predicted result are output; the target domain is subjected to fine adjustment by repeating above steps, and the weight matrix of the source domain helps the target domain build a model. According to the small molecule drug virtual screening method and the application thereof, the effective virtual screening model can still be obtained under the condition that the information of a known active ligand sample is insufficient, and does not need to rely on a large number of data samples.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
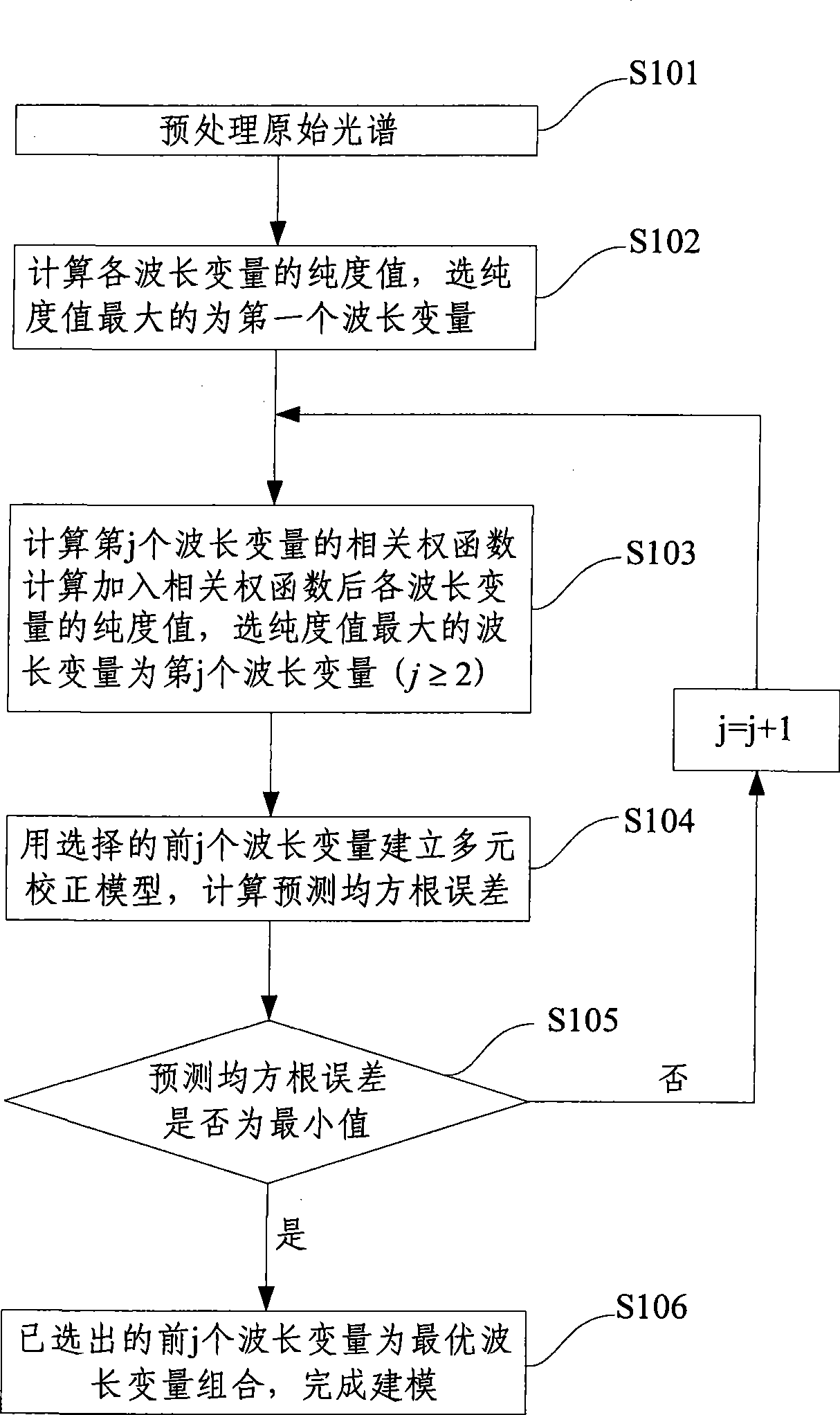
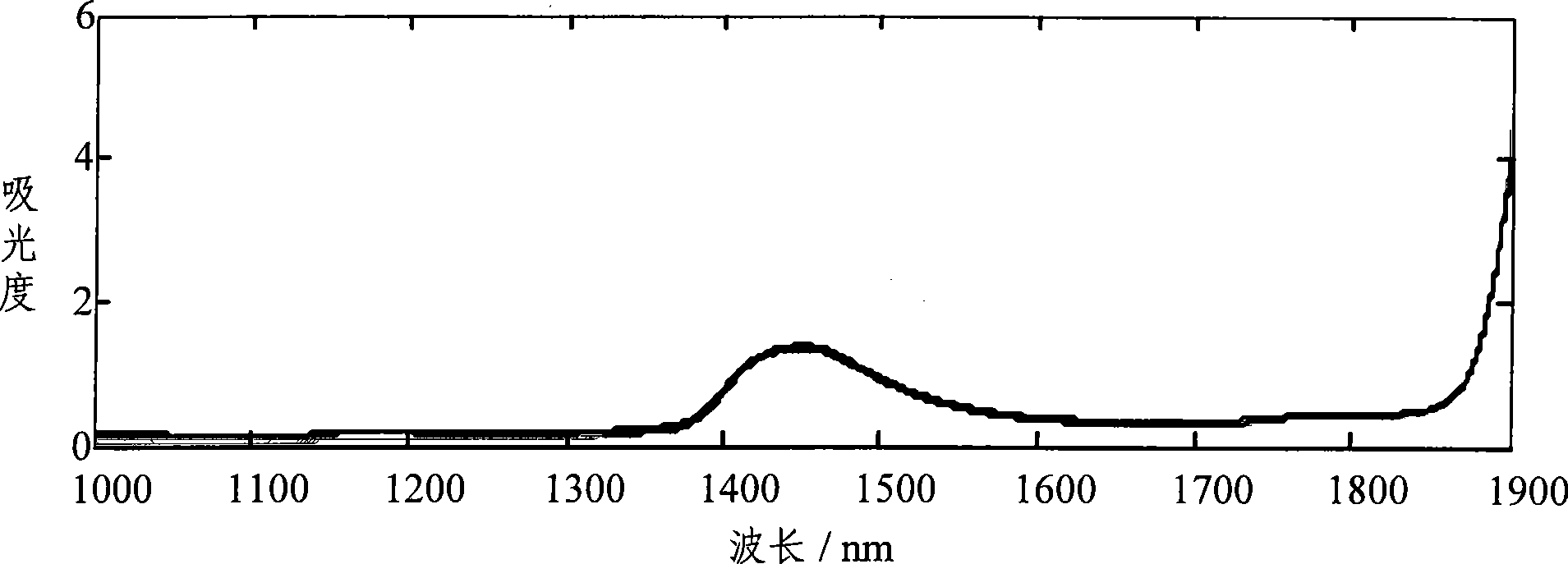
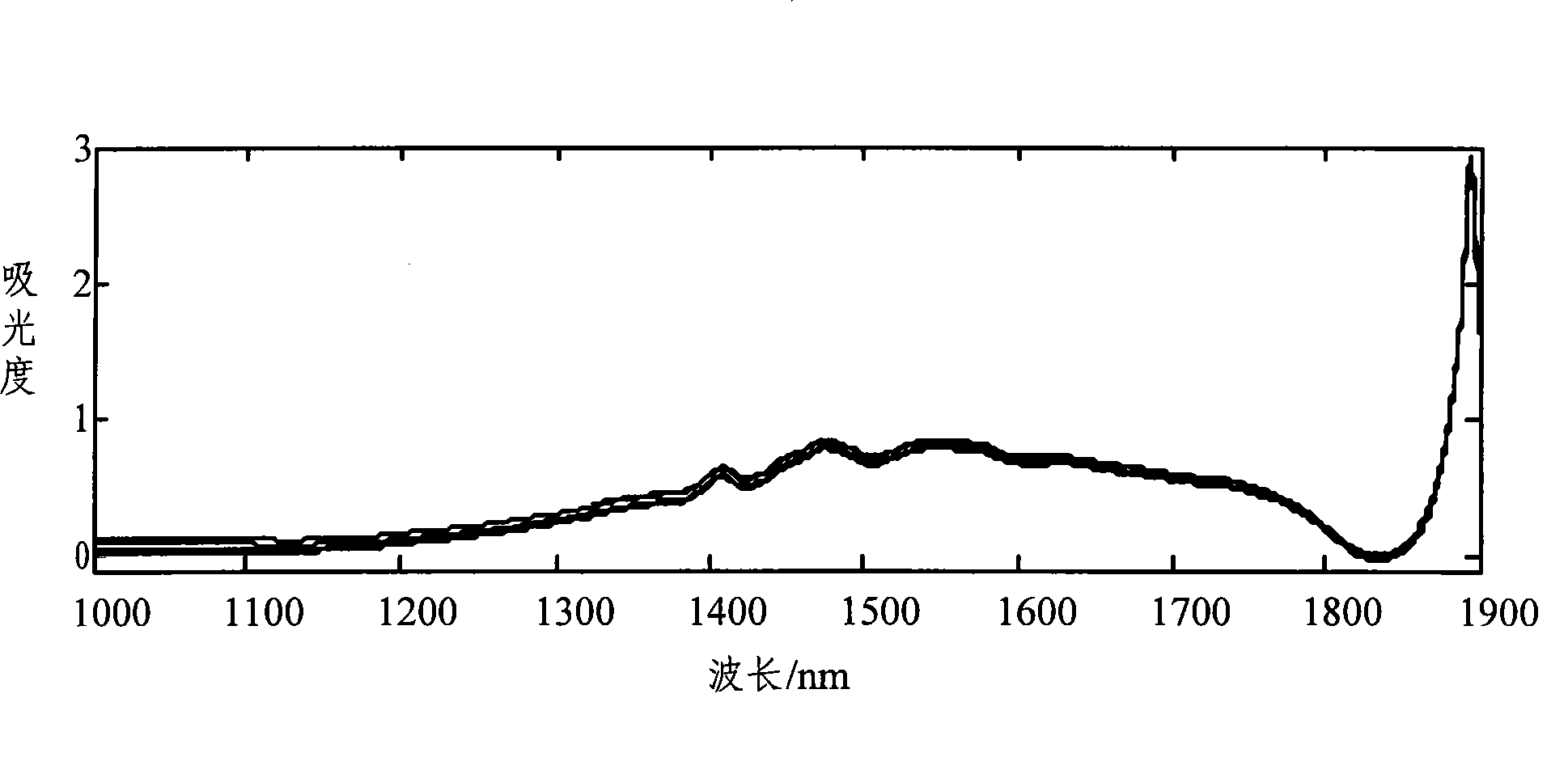
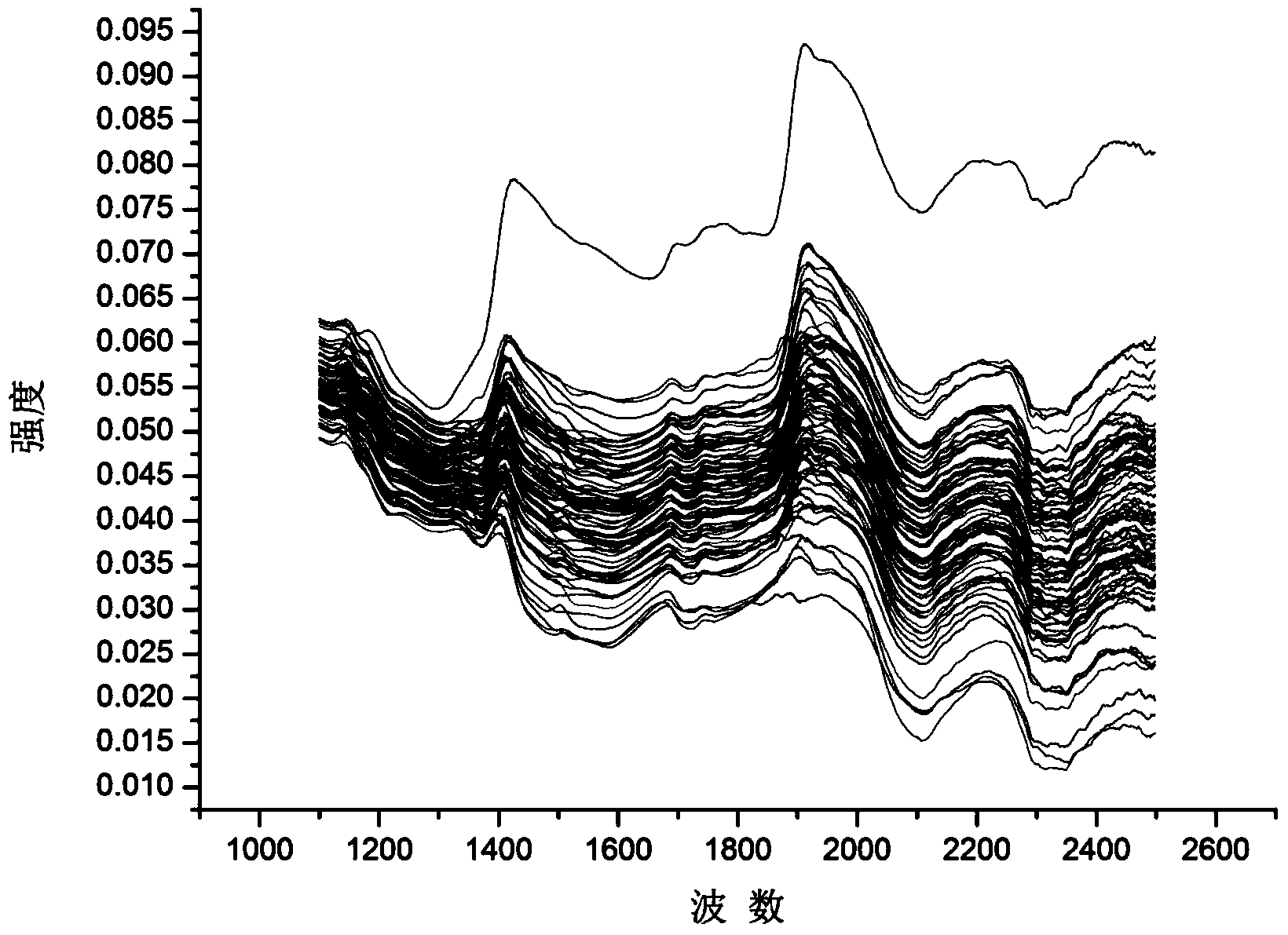
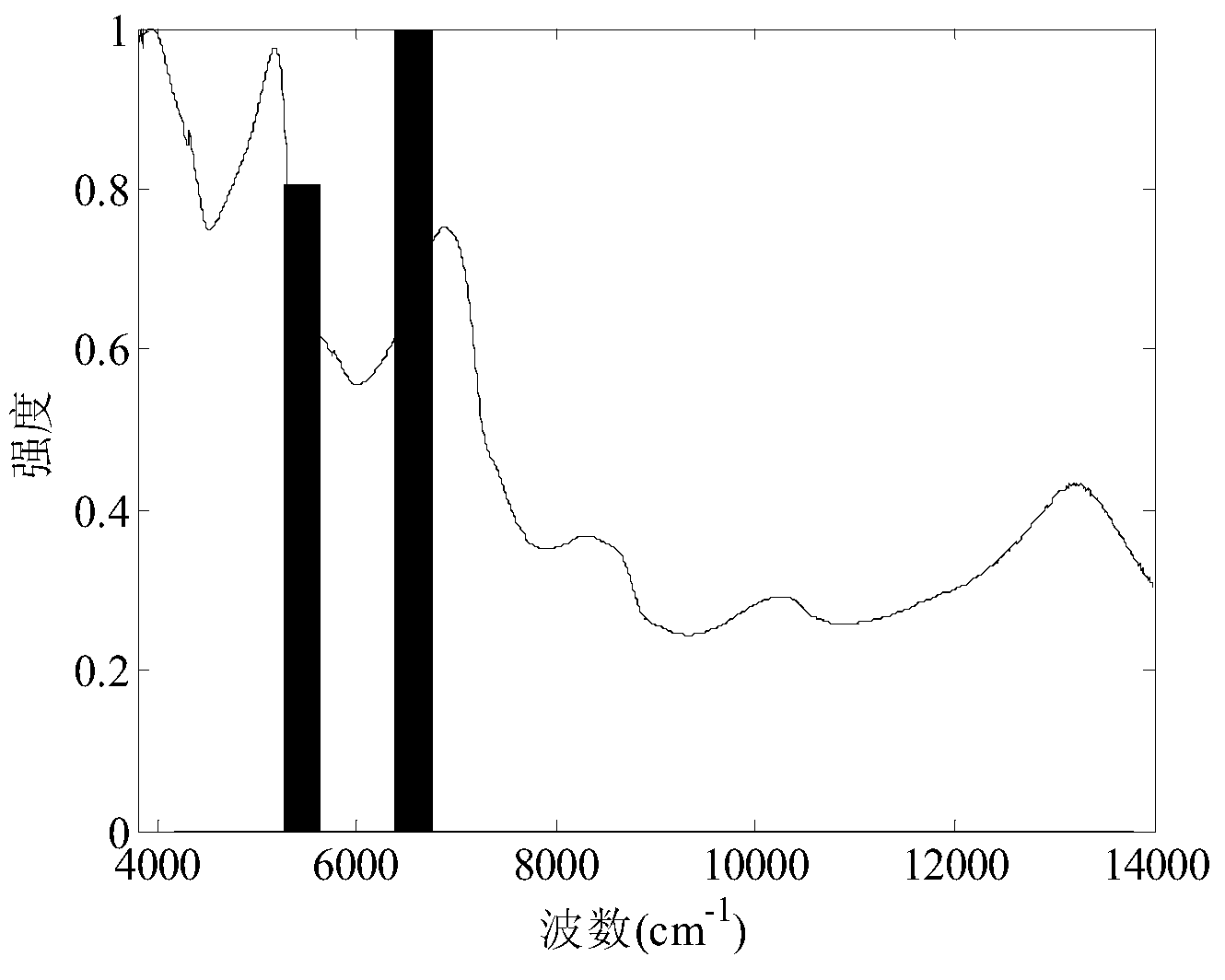
Wavelength variable optimization method in spectrum analysis
InactiveCN101430276AOvercoming complex setup challengesGood repeatabilityAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsPredicted RMRLength wave
The invention discloses a method for optimizing wavelength variable in spectral analysis. The method comprises the steps as follows: obtained original spectrum is pretreated to obtain a spectral array with useless information eliminated; the purity value of each wavelength variable is calculated in the obtained spectral array to select the wavelength variable with maximum purity value as a first wavelength variable; the relative weighting function of no. j wavelength variable and selected (j-1) wavelength variables is calculated, and the purity value of each wavelength variable after the relative weighting function is added is calculated; the wavelength variable with the maximum purity value is selected as no. j wavelength variable, wherein, j is the integral more than or equal to 2; partial least square regression modeling is carried out by optimized different quantities of the wavelength variables, and predicted root mean square error is calculated; when the predicted root mean square error is minimum, the wavelength variable combination selected for modeling is the optimized wavelength variable combination. The quantity of the wavelength variables selected by the method is small, and the method can minimize redundant information and can improve modeling speed and efficiency obviously.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
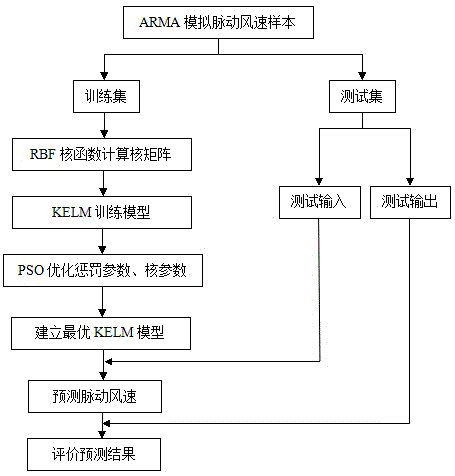
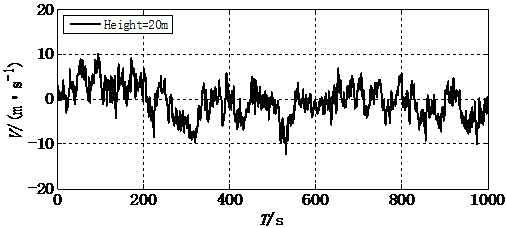
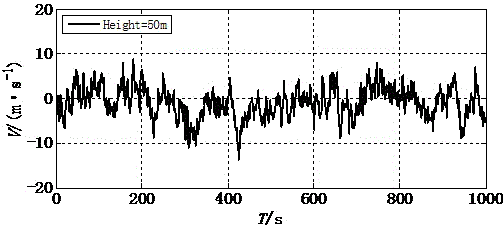
Fluctuation wind speed prediction method based on extreme learning machine
InactiveCN105354363ASolve the problem of random initializationFast learningSpecial data processing applicationsLearning machineRoot mean square
The present invention provides a fluctuation wind speed prediction method based on an extreme learning machine. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1: using an ARMA model to perform simulation to generate fluctuation wind speed samples of vertical spatial points, and dividing the fluctuation wind speed sample of each spatial point into two parts of a training set and a test set; step 2: giving training samples, setting a Gaussian kernel function as a kernel function, and calculating a kernel function matrix K of the training samples; step 3: establishing a limit learning machine algorithm model of the kernel function; and step 4: comparing test samples with results of prediction of fluctuation wind speed by KELM, calculating a mean absolute error, a root-mean-square error and a correlated coefficient of a predicted wind speed and an actual wind speed, and evaluating the effectiveness of the method. The invention provides a prediction method for a complete wind speed time-history curve needed for wind resistance design, thereby reducing a great deal of time costs.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Ultrashort-term slide prediction method for wind power
InactiveCN103117546ASparse decomposition effectReduce the absolute mean errorSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsDecompositionAlgorithm
The invention relates to an ultrashort-term slide prediction method for wind power. An atomic sparse decomposition method with quite high non-stable signal tracking and prediction capacity is used as a front decomposition method of a neural network. A wind power time sequence is decomposed into an atomic component and a residual error component, the atomic component is automatically predicted, the residual error component is predicted by the neural network, atomic decomposition results are updated by adding the latest wind power real-time data, and further the wind power of a next moment is slidably predicted. Actual wind field data prove that the model can effectively avoid non-stability of the wind power, sparser decomposition effects are achieved, and statistical intervals of absolute average error and root mean square error computation values can be remarkably reduced. Therefore, the ultrashort-term slide prediction method has the advantages that non-stability of the wind power can be effectively avoided, the sparser decomposition effects are achieved, and the statistical intervals of the absolute average error and root mean square error computation values can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption substances
ActiveCN103324861ALow costSimple and fast operationSpecial data processing applicationsPerturbateurs endocriniensDrug biological activity
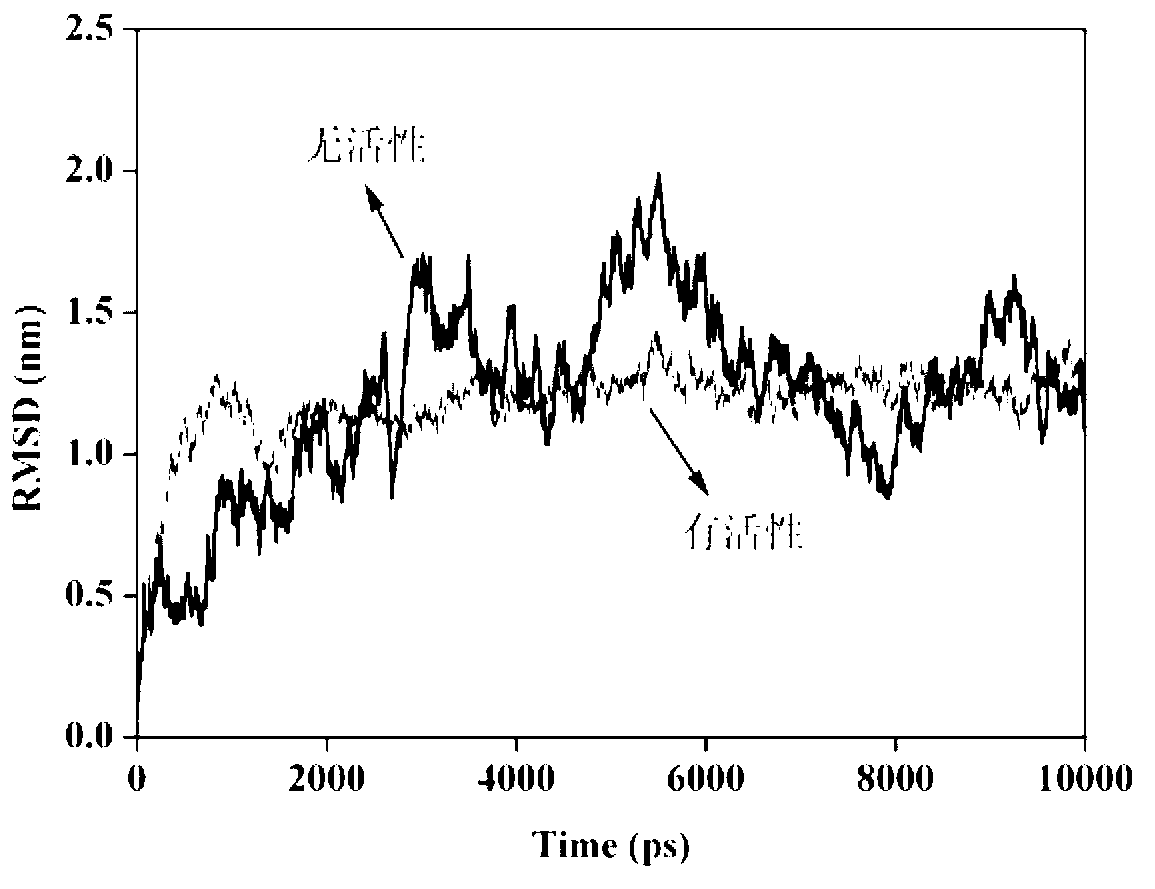
The invention discloses a molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption substances, and belongs to the field of virtual screening and activity prediction of environmental suspicious endocrine disruption substances. The molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method includes the steps of carrying out butt joint on a receptor file obtained by the fact that optimization and testing or homology modeling are / is carried out on tested small molecules to form a compound, and then using a GROMACS software package to carry out molecular dynamics simulation. Motion trail analysis is carried out on a twelfth helix of a receptor, pollutants with the activity of the receptor are identified through a changing curve of root-mean-square deviation analysis of a space position along with time changes, within the required time, a corresponding helix is regarded to be located to a determined position when the curve tends to be stable, and the receptor has the biological activity. In addition, the located position is inspected to judge whether the activity is fitting or resistance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Three-dimensional reconstruction method for indoor dynamic scene based on RGBD camera
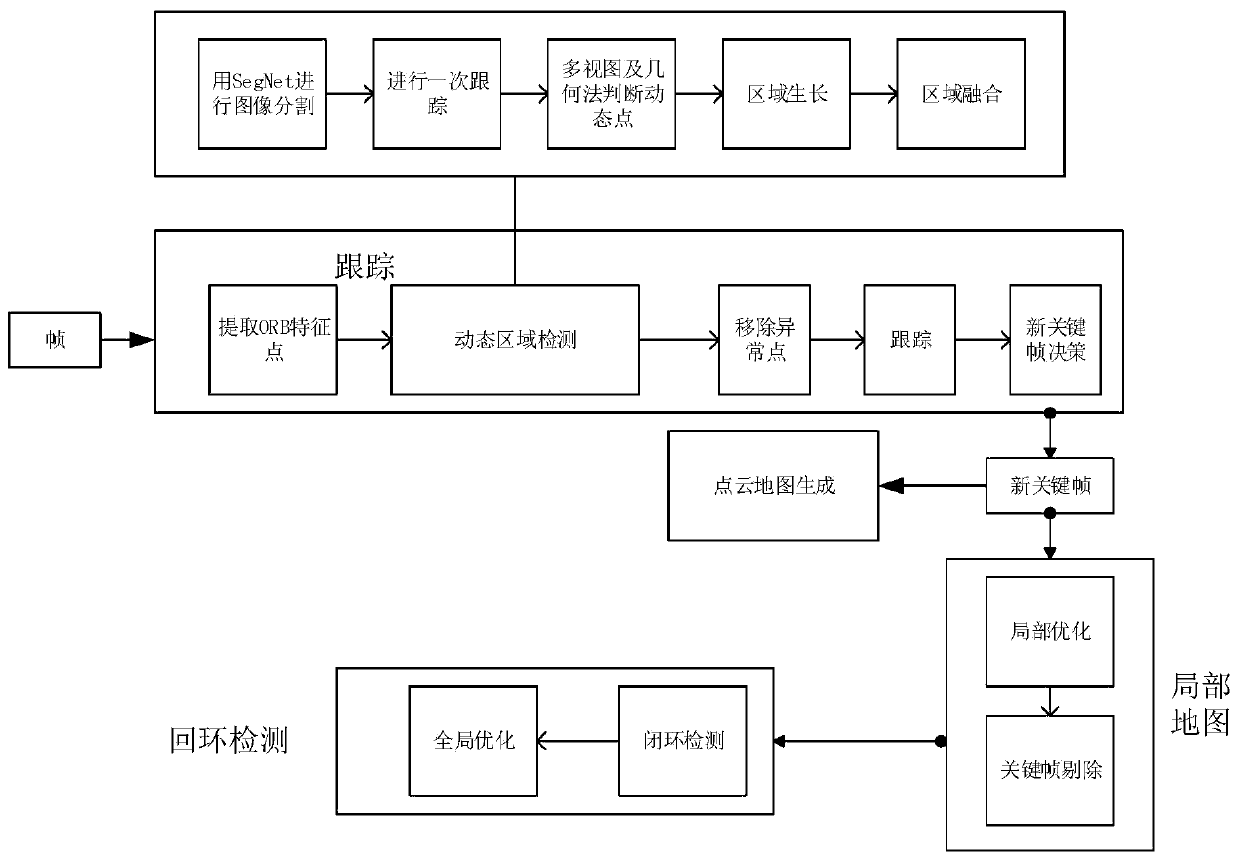
ActiveCN110349250AOptimize BAResolve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData setReconstruction method
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method for an indoor dynamic scene based on an RGBD camera. The three-dimensional reconstruction method comprises the steps of RGBD camera calibration, scene image acquisition, feature point extraction, dynamic point detection and elimination, elimination of dynamic points by using a mode of combining a convolutional neural network and a multi-view geometric method, tracking, new key frame insertion, local map optimization, loop detection and the like. By using the three-dimensional reconstruction method, the problems of inaccurate camera pose estimation and dynamic object ghosting of three-dimensional reconstruction in a dynamic scene are effectively solved, and the dynamic region detection step is optimized in time, and the effect of real-time reconstruction can be achieved. A camera track absolute error is used for measurement on a TUM data set, and the root-mean-square error of the camera track absolute error is increased to 0.025 from the previous 0.752.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
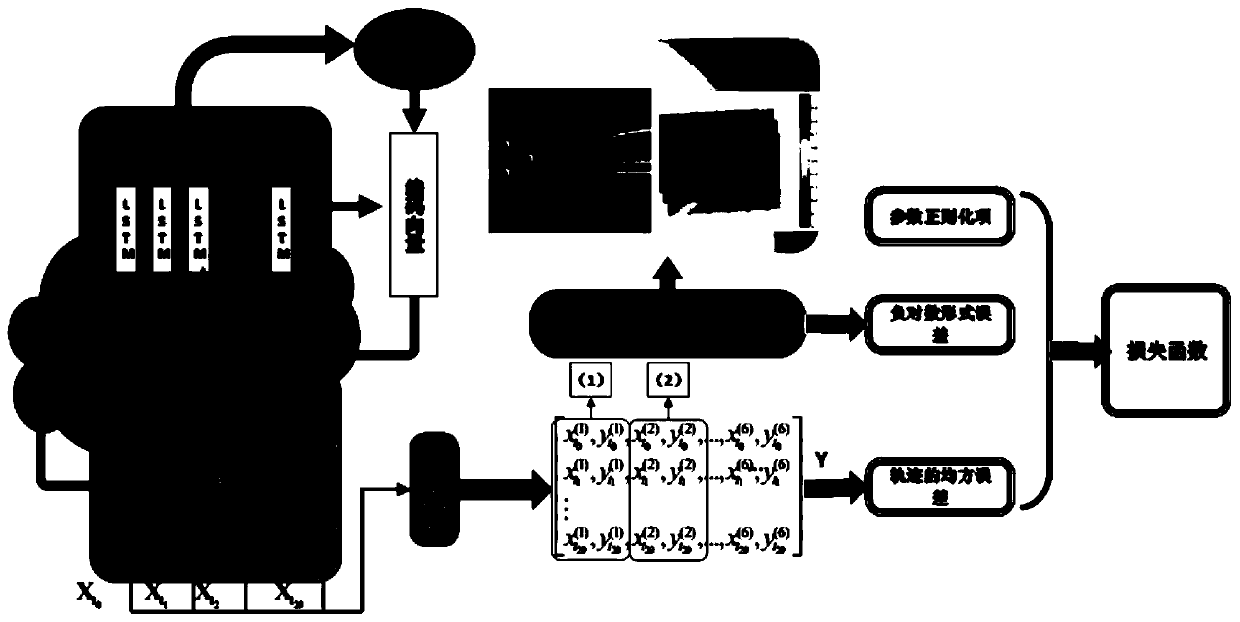
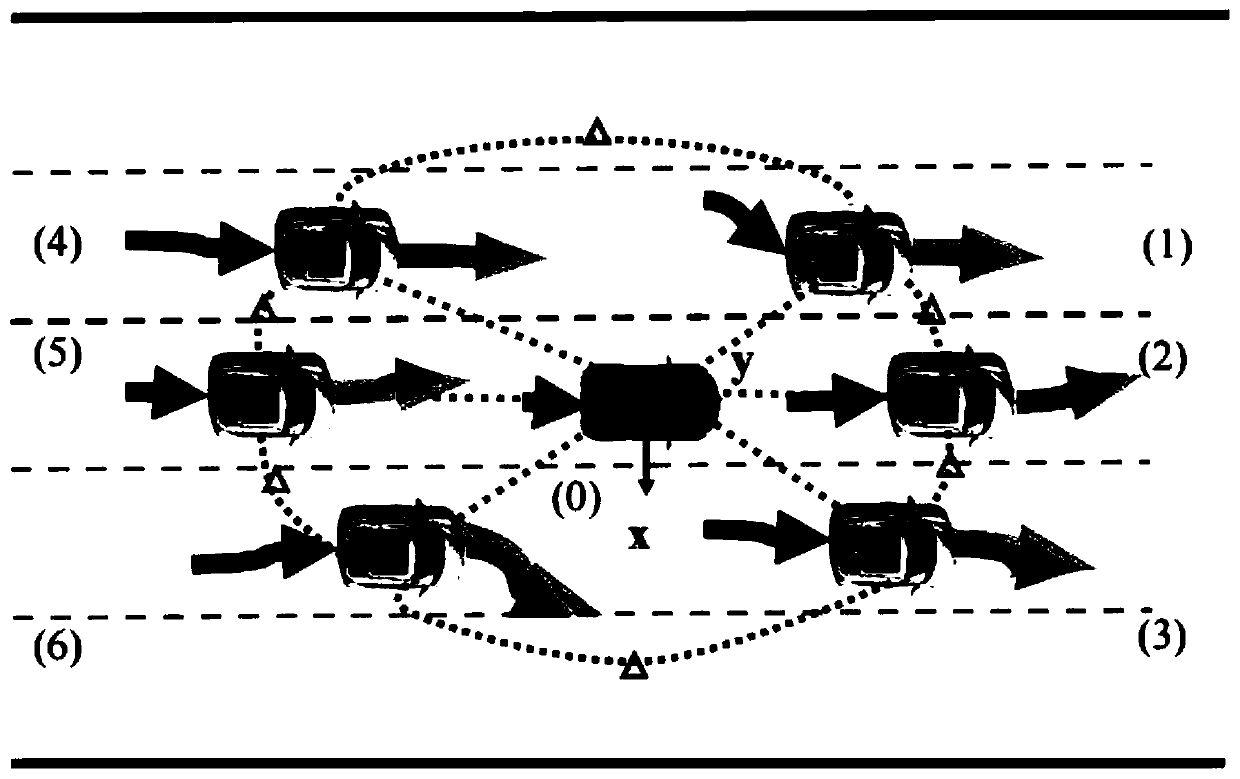
Multiple vehicle trajectory prediction method based on long-short memory network
The invention discloses a multiple vehicle trajectory prediction method based on a long-short memory network, and the method comprises the steps of taking the historical trajectories of a main vehicleand an adjacent vehicle as the input, and fully considering the mutual impact between the positions of the vehicles and the driving behaviors; encoding and decoding through a network; further inputting the outputted future track of the adjacent vehicle into a hybrid density network; estimating the probability distribution of the vehicle positions; at every training, combining the error of a hybrid density network, a root-mean-square error of the trajectory result and the parameter regularization item of an encode-decoder network to form a loss function; and guiding the update of the network parameters, so that the prediction accuracy of the network can be improved. According to the method, the trained neural network can predict the probabilistic position information of the adjacent vehicles, and the position information forms a continuous track according to the time sequence, so that the main vehicle can be assisted to make decisions and plan.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
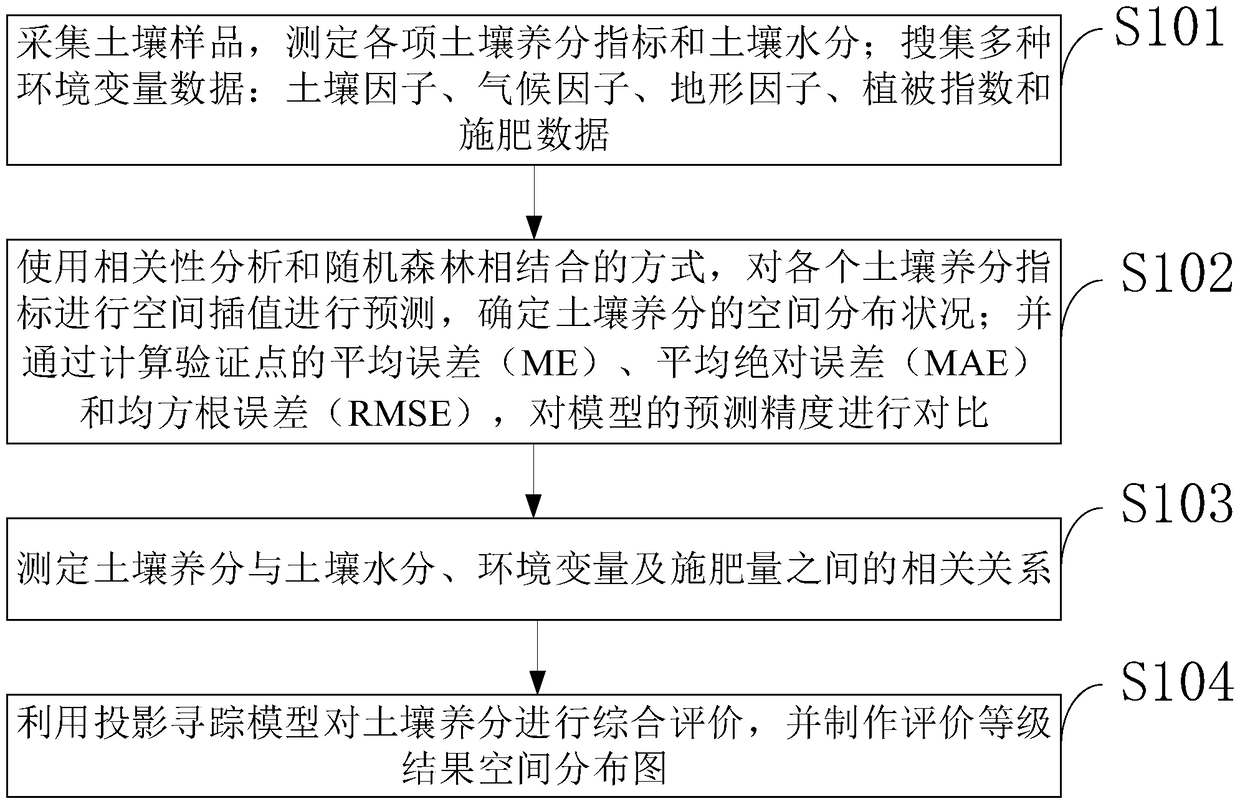
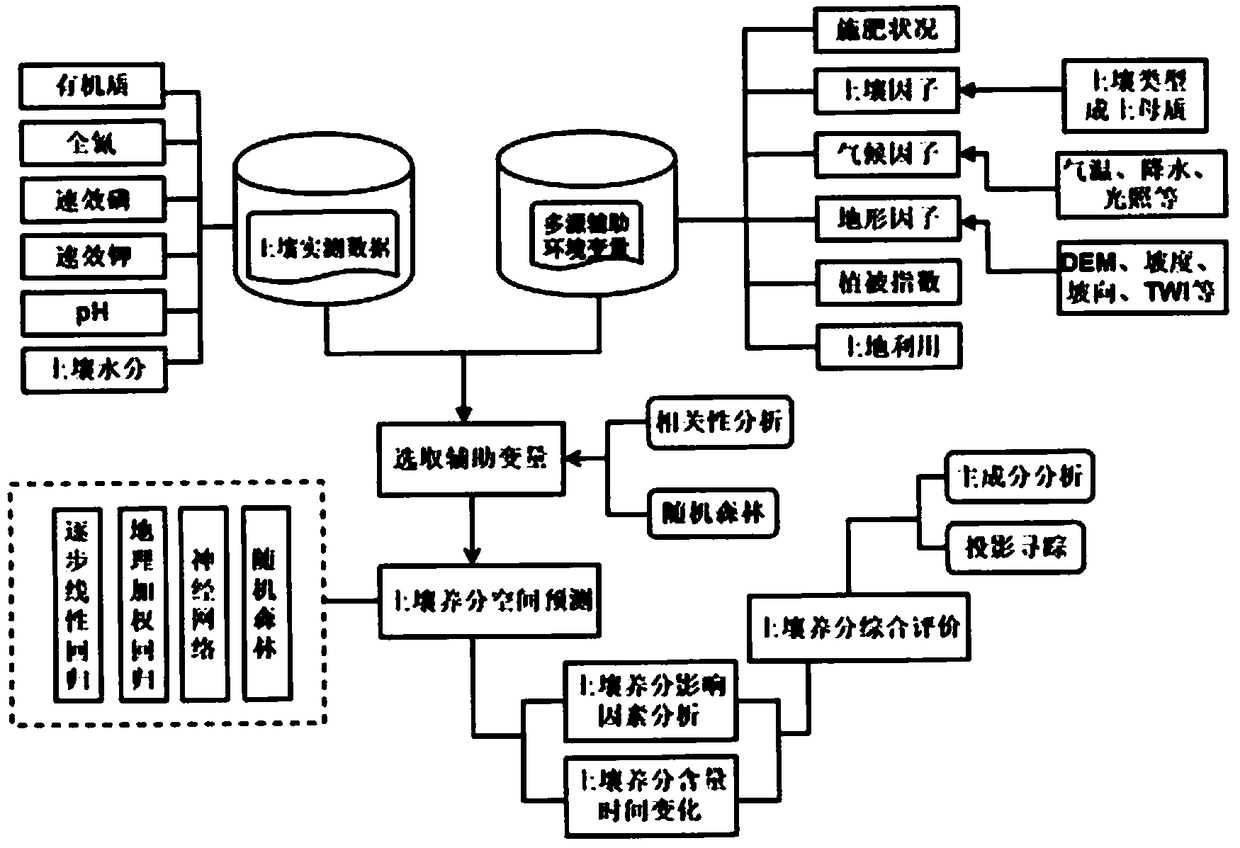
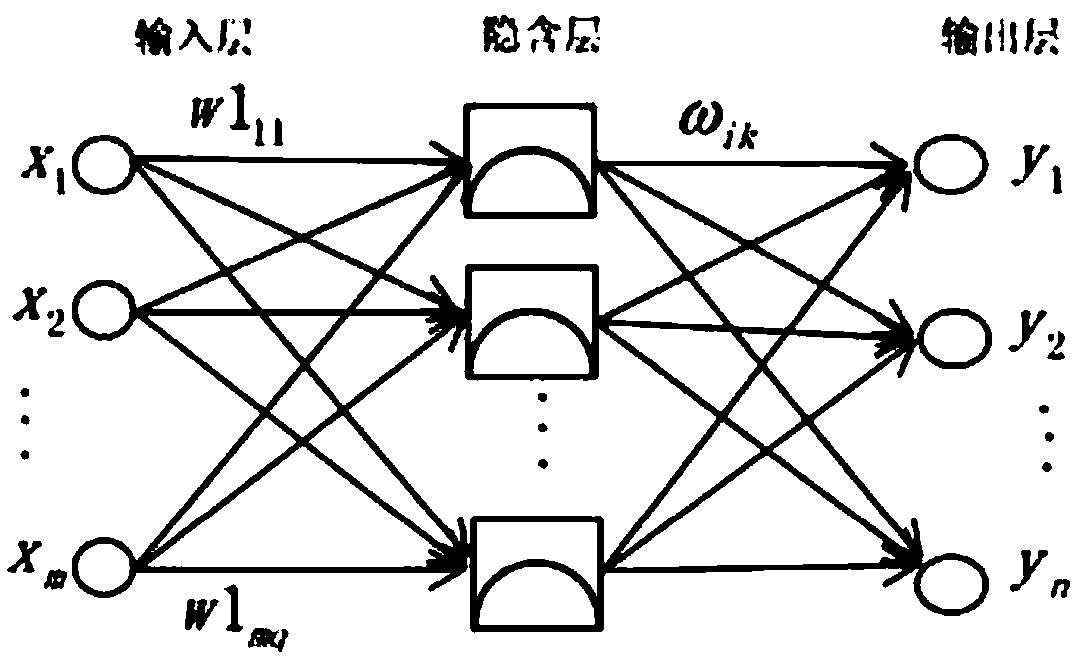
Soil nutrient prediction and comprehensive evaluation method based on machine learning algorithm
PendingCN109374860AReduce correlationImprove relevanceEarth material testingCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrelation analysisMoisture
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil detection, and discloses a soil nutrient prediction and comprehensive evaluation method based on machine learning algorithm. The method includes collecting a soil sample and measuring various soil nutrient indexes and soil moisture; collecting various environmental variable data; conducting spatial interpolation on each soil nutrient index for prediction by combining correlation analysis with random forests to determine the spatial distribution of soil nutrients; comparing the prediction accuracy of a model by calculating an average error, amean absolute error and a root mean square error of a verification point; determining the correlation between the soil nutrient and the soil moisture and between environmental variables and fertilization amount; utilizing a projection seeking model to comprehensively evaluate the soil nutrient and making a spatial distribution map of evaluation grade results. The method attempts to provide a newidea for soil nutrient evaluation from a non-linear perspective by the relationship between nutrient grades and evaluation indexes.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Module transfer method based on multiscale modeling
InactiveCN103854305AImprove efficiencyImprove performanceColor/spectral properties measurements3D modellingMultiscale decompositionMultivariate calibration
The invention discloses a module transfer method based on multiscale modeling. The method comprises the following steps: collecting original spectra of a host instrument and a slave instrument; by combining the characteristic of wavelet basis and the characteristic of the original spectrum of a sample, selecting the optimal wavelet basis to carry out wavelet multiscale decomposition on the spectrum to obtain wavelet coefficient; reconstructing the wavelet coefficient; respectively performing multivariate calibration on each layer of reconstructed spectrum; setting up a prediction model based on partial least squares method and leaving one cross-validation method for the spectrum after performing multivariate calibration to obtain a cross-validation root-mean-square error of the prediction model; performing model fusion on the prediction model by using weight number, and calculating the prediction root-mean-square error and related coefficient to evaluate the model transfer effect. Compared with a conventional model transfer method, the method greatly improves the model transfer efficiency and performance, and can be widely applied to fields of near-infrared and Raman spectrum.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
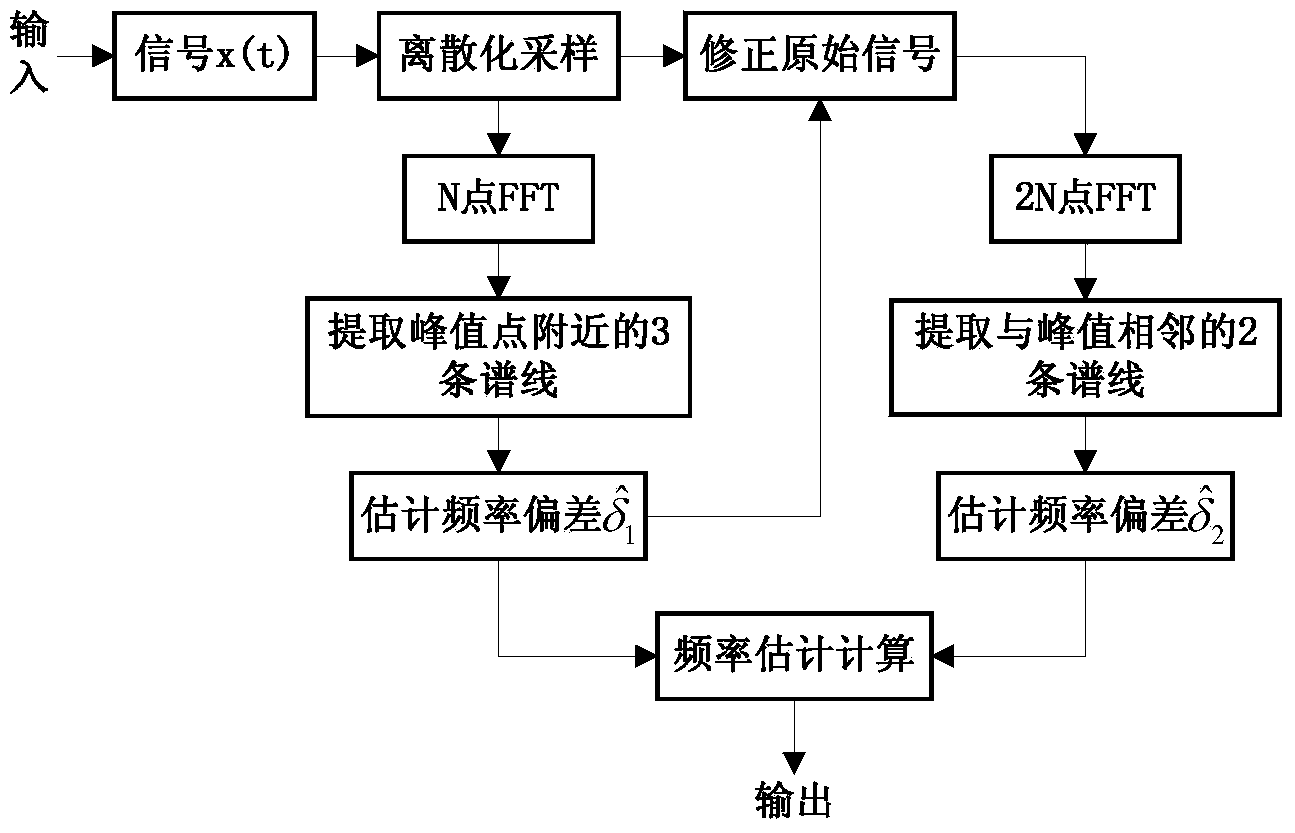
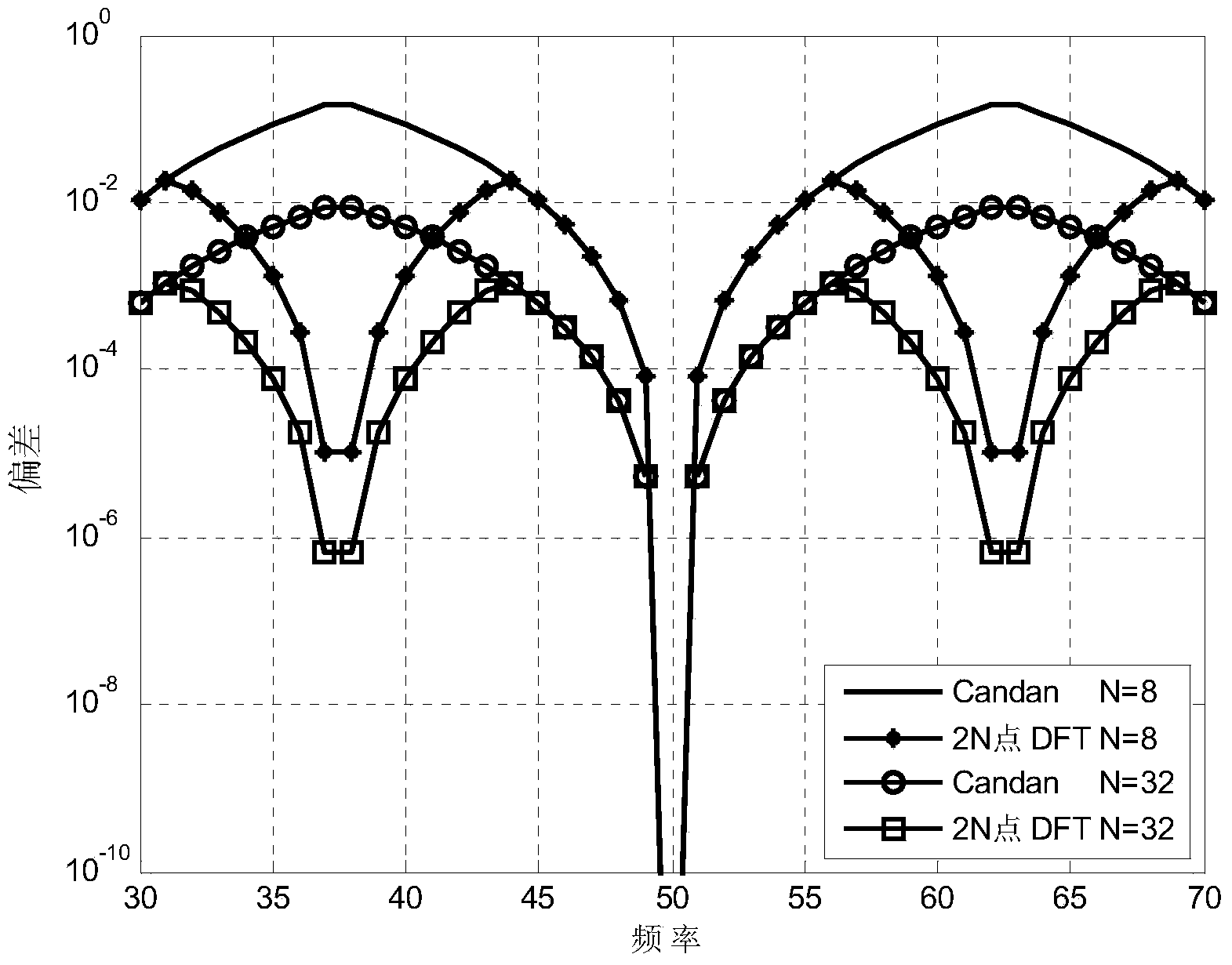
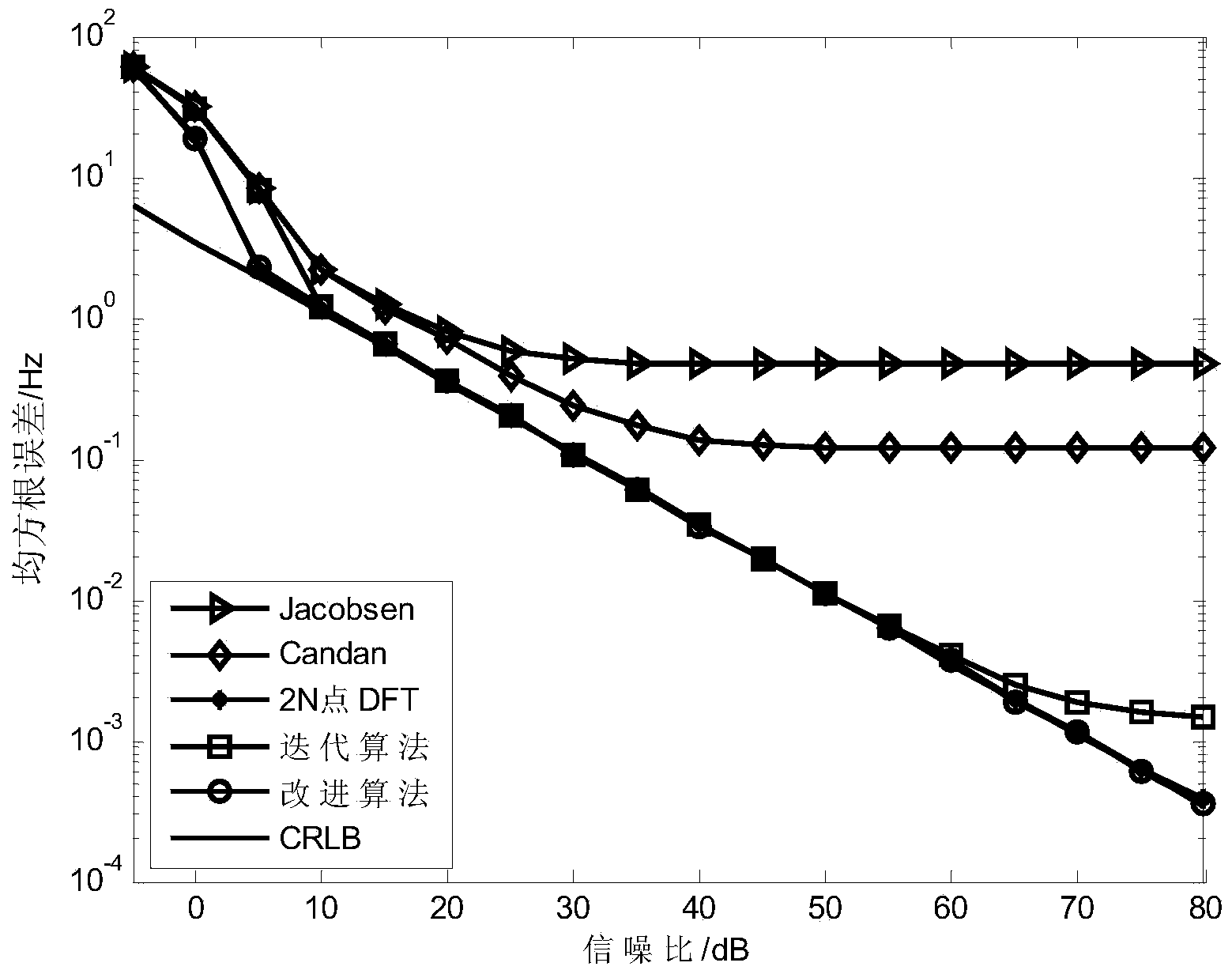
Method for estimating sinusoidal signal frequency based on DFT
InactiveCN103941089ASimple calculationImprove performanceFrequency measurement arrangementLower limitAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for estimating the sinusoidal signal frequency based on DFT. The method aims to achieve that root-mean-square errors of frequency estimation are all similar to a cramer-rao lower limit when relative frequency deviation is an arbitrary value, and the estimation performance of the method is superior to that of an existing frequency estimation algorithm. Through analysis of the performance of a Candan algorithm and the performance of a 2N point DFT algorithm, after necessary discretization preprocessing is conducted on original signals, frequency deviation is estimated through the Candan algorithm in the coarse estimation stage, and the frequency of the original signals is corrected through the frequency deviation; then fine estimation is conducted on the corrected original signals through the 2N point DFT algorithm. The step for correcting the frequency of the original signals is added, the advantages of the Candan algorithm and the advantages of the 2N point DFT algorithm are exerted, and the method is very suitable for application occasions with high estimation accuracy requirements.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Fluctuating wind velocity simulation method based on data driving
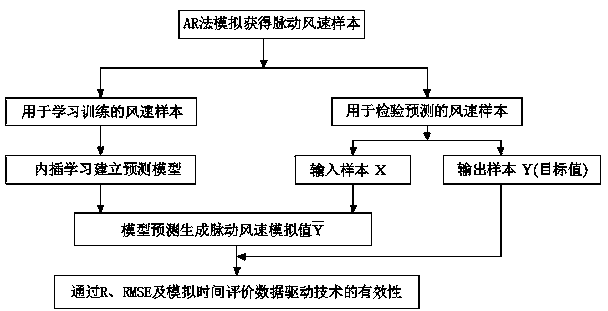
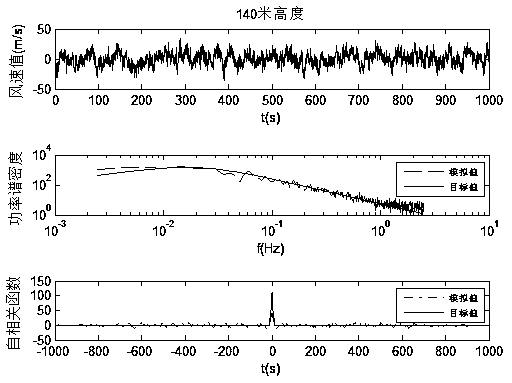
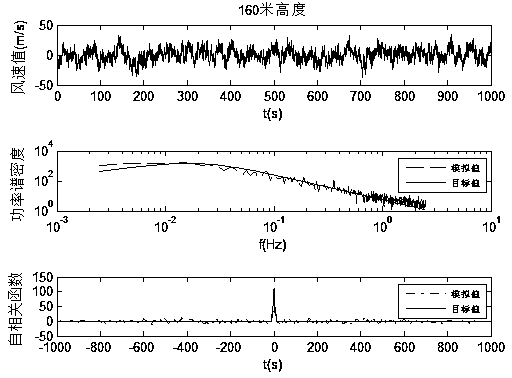
InactiveCN104376214ARelevant geometric interpretationPerfect mathematical formBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientOriginal data
The invention provides a fluctuating wind velocity simulation method based on a data driving technology. The method comprises the steps that first, a certain number of fluctuating wind velocities, distributed in the height direction, of a super high-rise building are obtained with an AR method through numerical simulation and serve as sample data, then, three technological methods based on data driving including a BP neural network, an SVM and an LS-SVM are used for learning and training the sample data in some height areas with an interpolation method, a regression forecasting model is built, and the fluctuating wind velocities of other height areas are simulated and predicted. The correlation coefficient of a prediction simulation value and a target value (original data), a root-mean-square error and the time needed by simulation are adopted as evaluation indexes. Through comparison between the evaluation indexes, the result shows that the BP neural network is short in consumed time but poor in simulation accuracy; the SVM is high in simulation accuracy but high in time consumption; the LS-SVM is high in accuracy and short in consumed time.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Characteristic spectrum area selection method for near infrared spectrum
ActiveCN103308463AImprove robustnessSolve the problem of low precision and poor applicabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsRoot mean squareNear-infrared spectroscopy
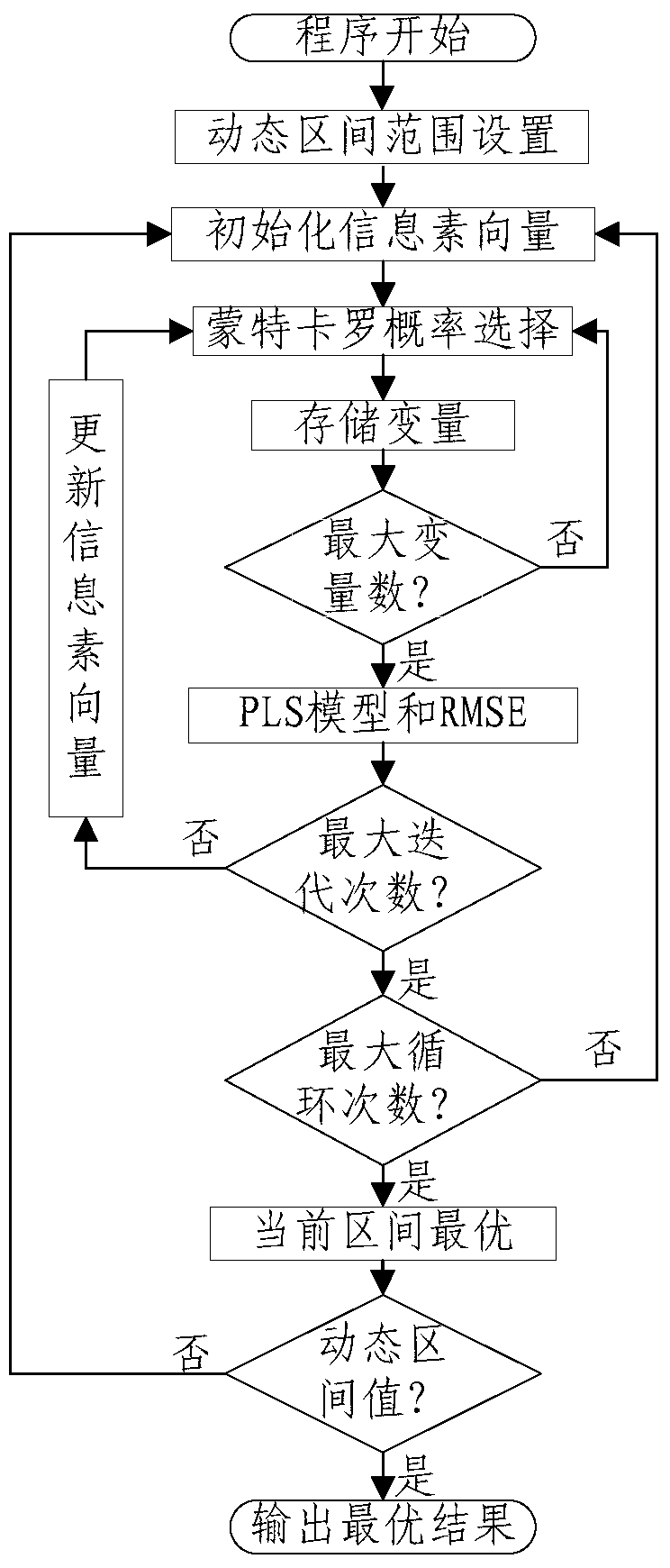
The invention provides a characteristic spectrum area selection method for a near infrared spectrum. The characteristic spectrum area selection method comprises the following steps of: applying a Monte Carlo probability selection combined ant colony optimization algorithm to a characteristic spectrum area selection problem of the near infrared spectrum; setting a dynamic section range and initializing algorithm parameters to obtain each spectrum section of an object to be taken as an equivalent searching point; establishing a partial least square analyzing model by taking the quality or characteristics of the object to be detected as a standard reference; predicating a root-mean-square error by the model to repeatedly carry out weighting calculation to update pheromone vectors according to the predicated root-mean-square error; carrying out iterative computation and searching to obtain the optimal characteristic spectrum area of the near infrared spectrum; and carrying out multiple circulating calculation and automatically judging to obtain the optimal characteristic spectrum area of the near infrared spectrum. The characteristic spectrum area selection method disclosed by the invention combines the wholeness of Monte Carlo probability selection and ant colony optimization algorithm positive feedback so as to effectively avoid the disadvantages of experience selection in a modeling process and data redundancy of all selections, rapidly obtain a global optimum characteristic spectrum area, and improve the precision and the stability of modeling.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
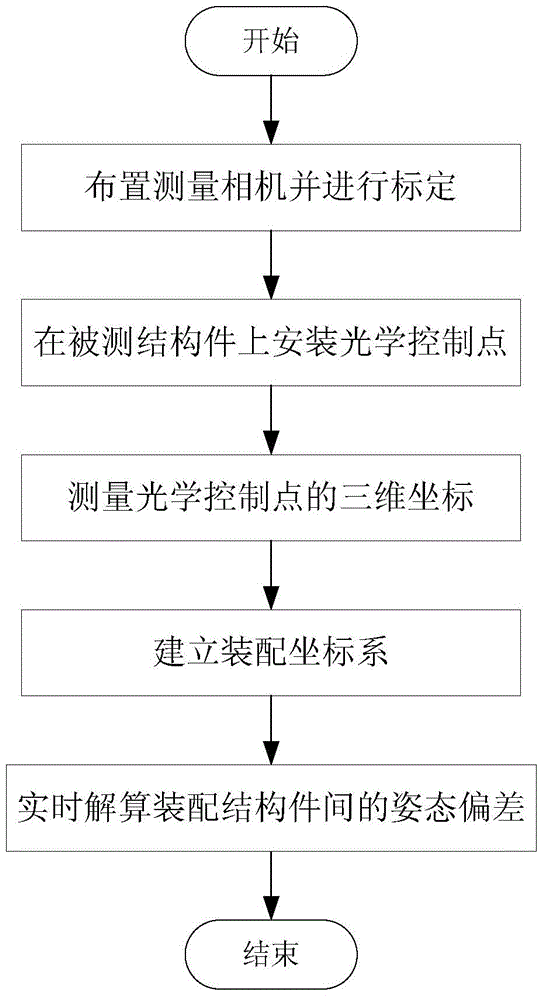
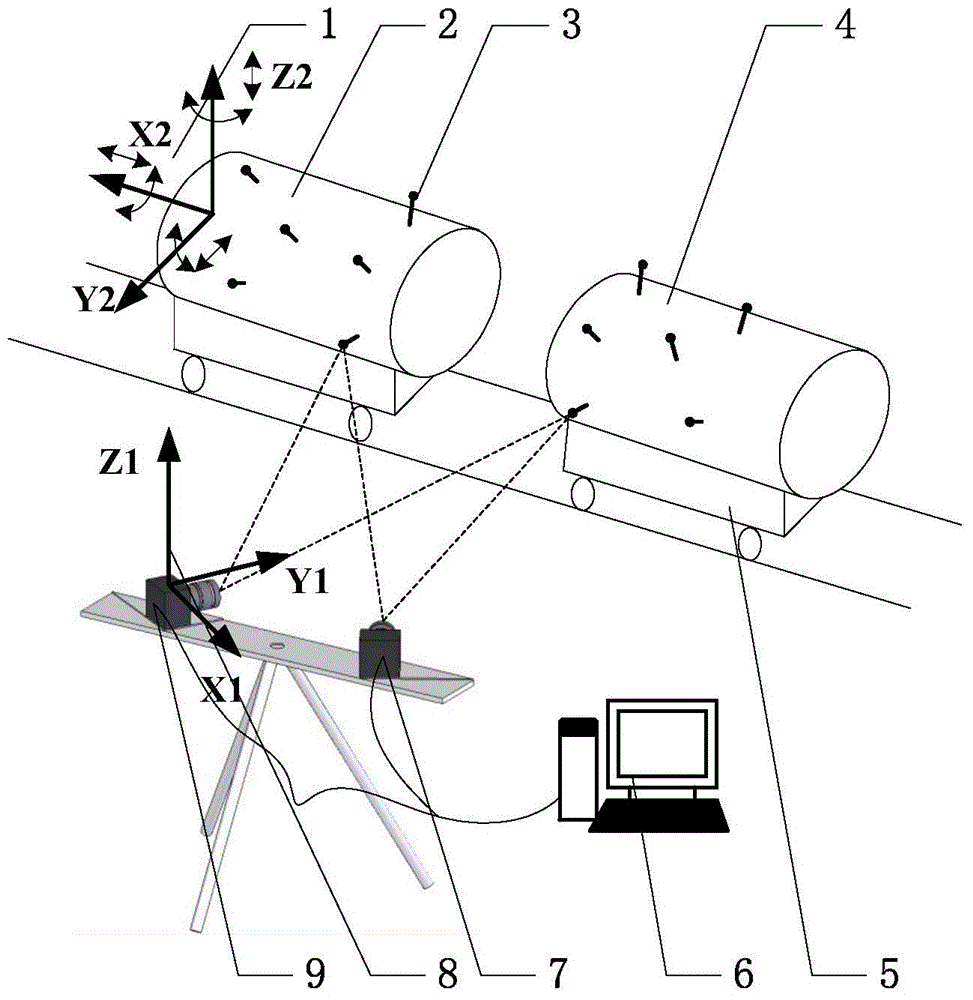
Large-scale structural component assembly joining measurement method based on visual principle
InactiveCN105627917ASolve the problem of online measurement of six degrees of freedom attitude deviationLow costUsing optical meansManufacturing technologyEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of mechanical assembly manufacturing technology, in particular relates to large-scale structural component assembly joining measurement method based on the visual principle, and aims to solve the problems of either high cost or large errors of conventional large-scale structural component assembly joining measurement. The method comprises the steps of setting and calibrating a measurement camera, mounting optical control points on structural components to be measured, measuring three-dimensional coordinates of the optical control points, establishing an assembly coordinate system and solving the attitude deviation among the assembled structural components. The method solves the problems of online measurement of the six-degree of freedom attitude deviation in the large-scale structural component assembly joining process by using the stereoscopic visual principle of a dual camera. The method is simple in equipment measurement, low in cost, and capable of detecting elastic deformation of large-scale structural components. Experimental results show that when the assembly measurement space is 5m*5m*5m and the number of adopted feature light spots reaches 5, the root-mean-square error of the attitude measurement method maintains within 0.05 degrees, the refresh rate reaches 200 frames per second, and the data are accurate and reliable.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST FOR METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT TECH +1
Shaped surface-oriented quick determination method for adjustment quantity of active panel of large parabolic antenna
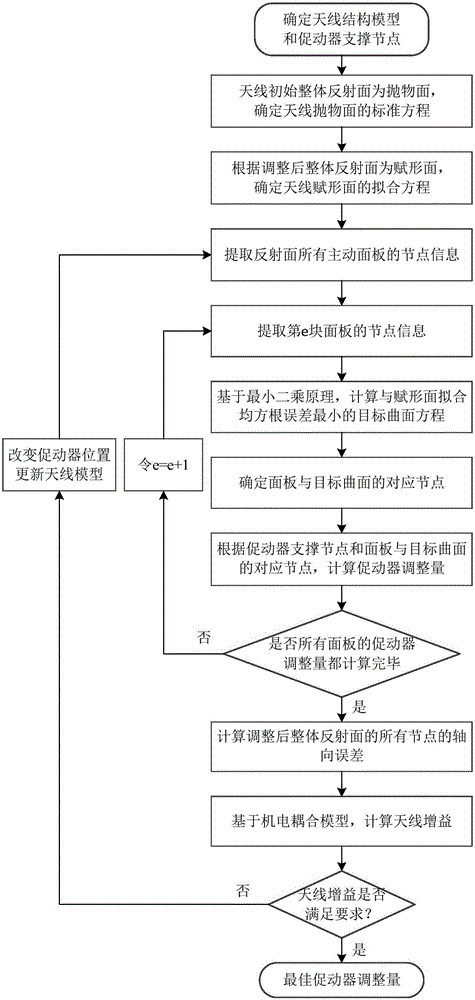
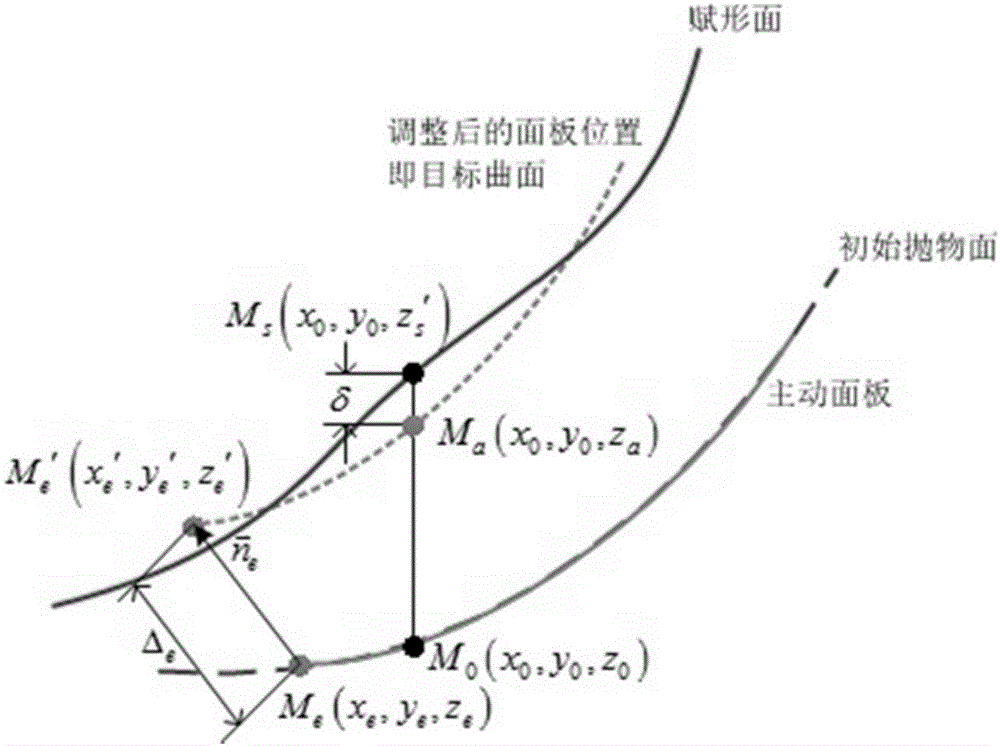
ActiveCN105977649AShort total travelGuarantee the electrical performance of the antennaDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityAntenna gain
The invention discloses a shaped surface-oriented quick determination method for adjustment quantity of an active panel of a large parabolic antenna. The method comprises the steps of determining an antenna structure model and an actuator supporting node; determining an overall reflection surface shape of the large parabolic antenna under two working modes, and determining a fitting equation of a shaped surface; extracting node information of the active panel on the refection surface; calculating a target curved surface with minimum fitting root mean square error with the shaped surface; determining corresponding nodes of the panel and the target curved surface, and calculating an actuator adjustment quantity; calculating axial errors of all nodes of the adjusted overall reflection surface; calculating an antenna gain using an electromechanical coupling, judging whether the antenna gain meets the requirement, and outputting an optimal actuator adjustment quantity. By adopting the method, the optimal adjustment quantity of the active panel actuator of the antenna can be directly and accurately adjusted, so that the adjusted overall reflection surface of the antenna is closer to the shaped surface, the electric performance of the antenna can be obviously improved, and an accurate surface shape conversion function of the large parabolic antenna under two working modes is realized.
Owner:西安电子科技大学工程技术研究院有限公司
Method of Positioning RFID Tags
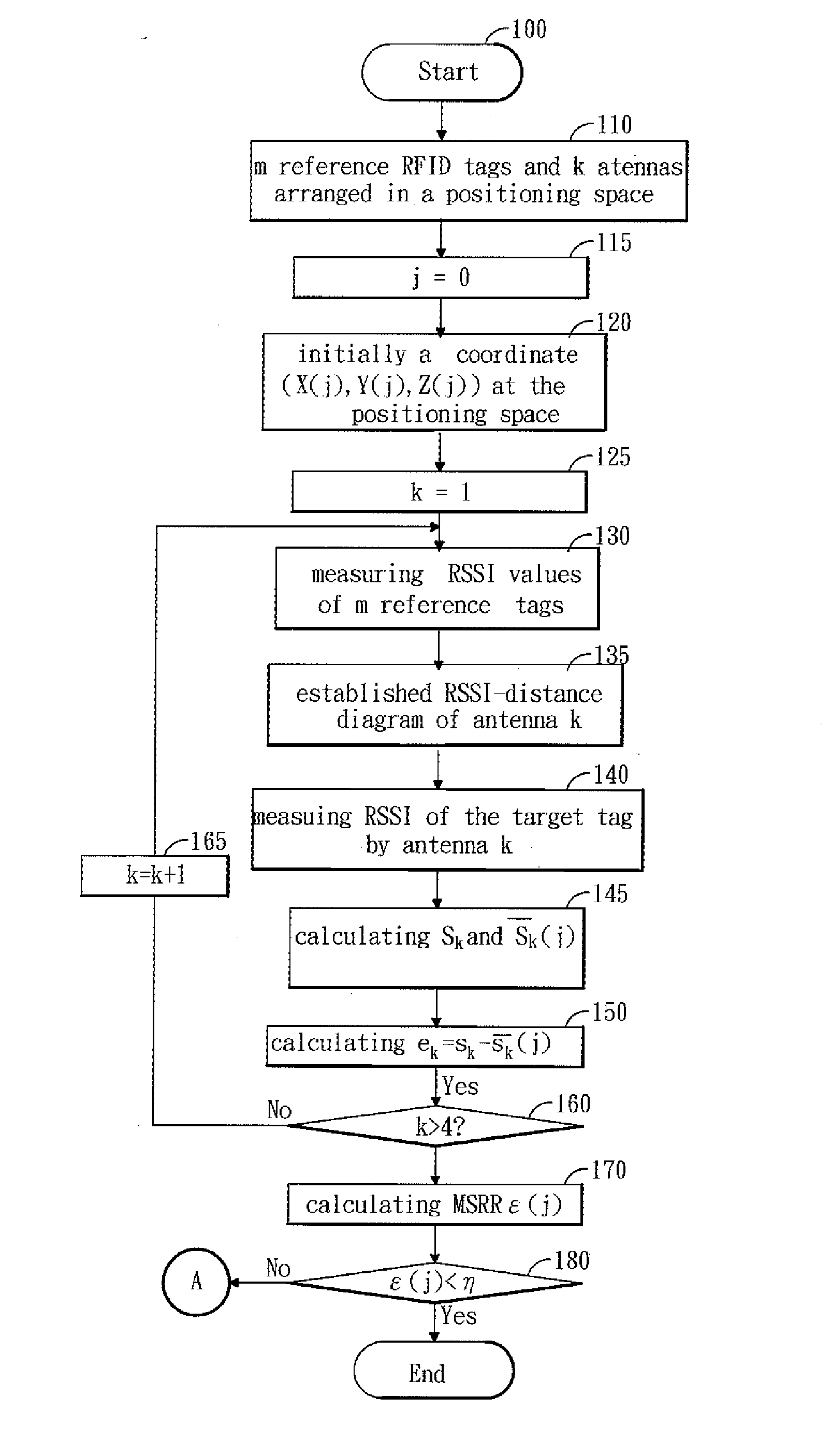
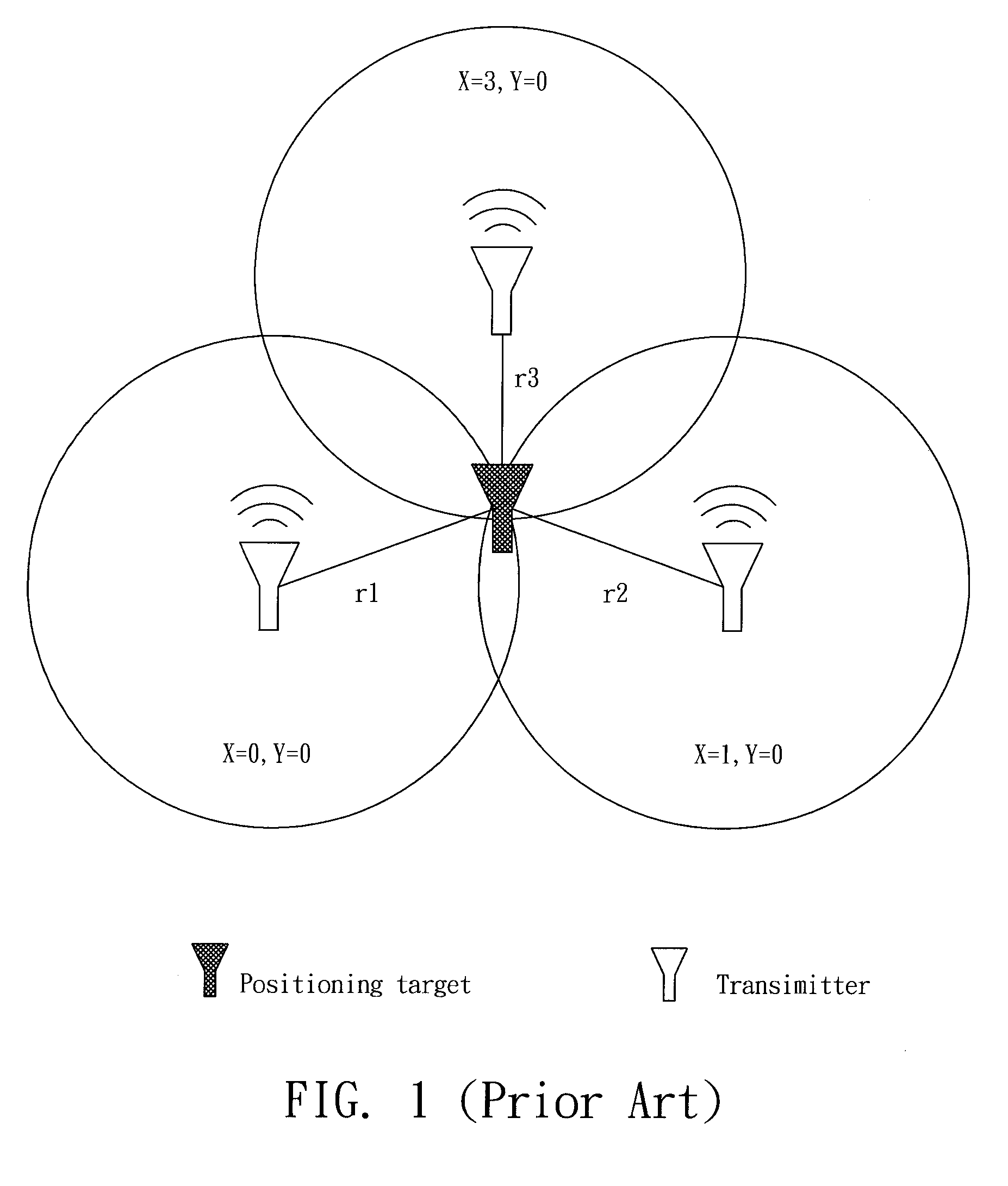
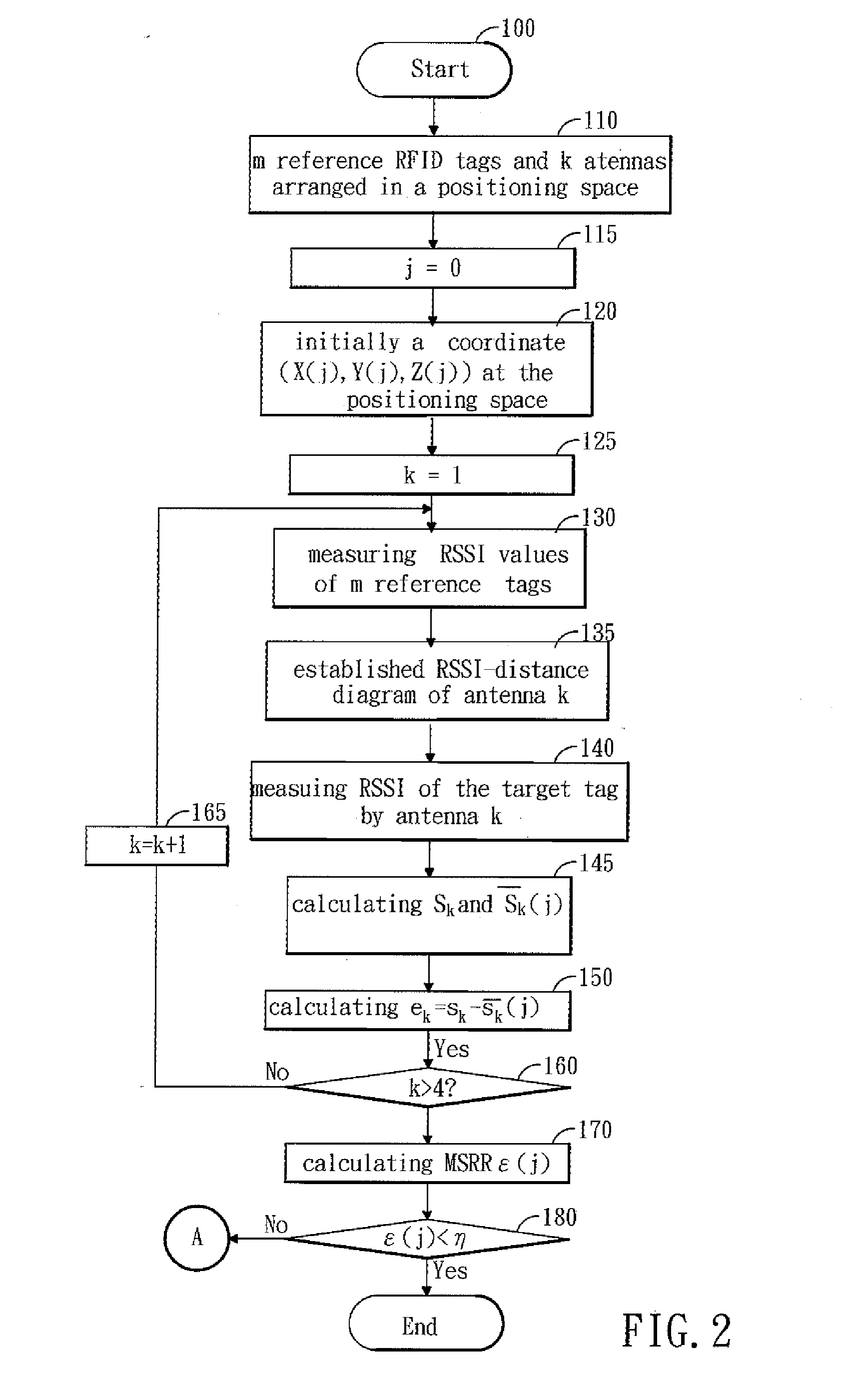
InactiveUS20110057840A1Save iteration timeSave the iteration time for positioningDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationEngineeringComputer science
A method of positioning a RFID tag by using four antennas associated with an algorithm is disclosed. A diagram is depicted, which is about relationships between the RSSI and distance according to environment of the space. Next, four antennas are arranged in the space. Four measured distances analyzed from the RSSI curve are measured. Thereafter, a position of the RFID tag is assumed at the center of space. The position is served as an initial coordinate. Subsequently, the root mean square error (RMSE) is determined. If the RMSE is small than or equal to termination criteria, the coordinate is regarded as the position of the RFID tag, otherwise the initial 3-D coordinate is updated by adding some correcting values at each measuring weight. This process is repeated till the RMSE meets the assigned condition.
Owner:NAT PINGTUNG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com