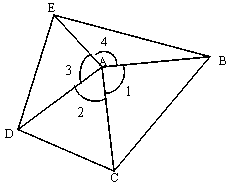
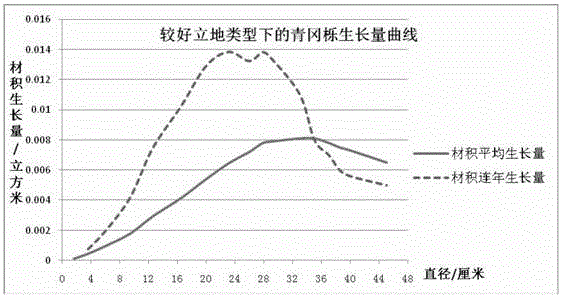
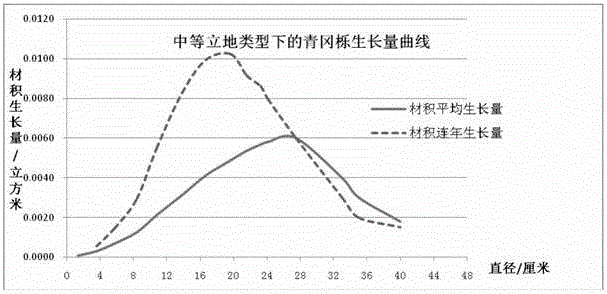
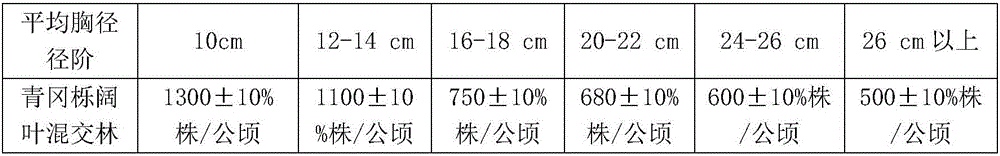
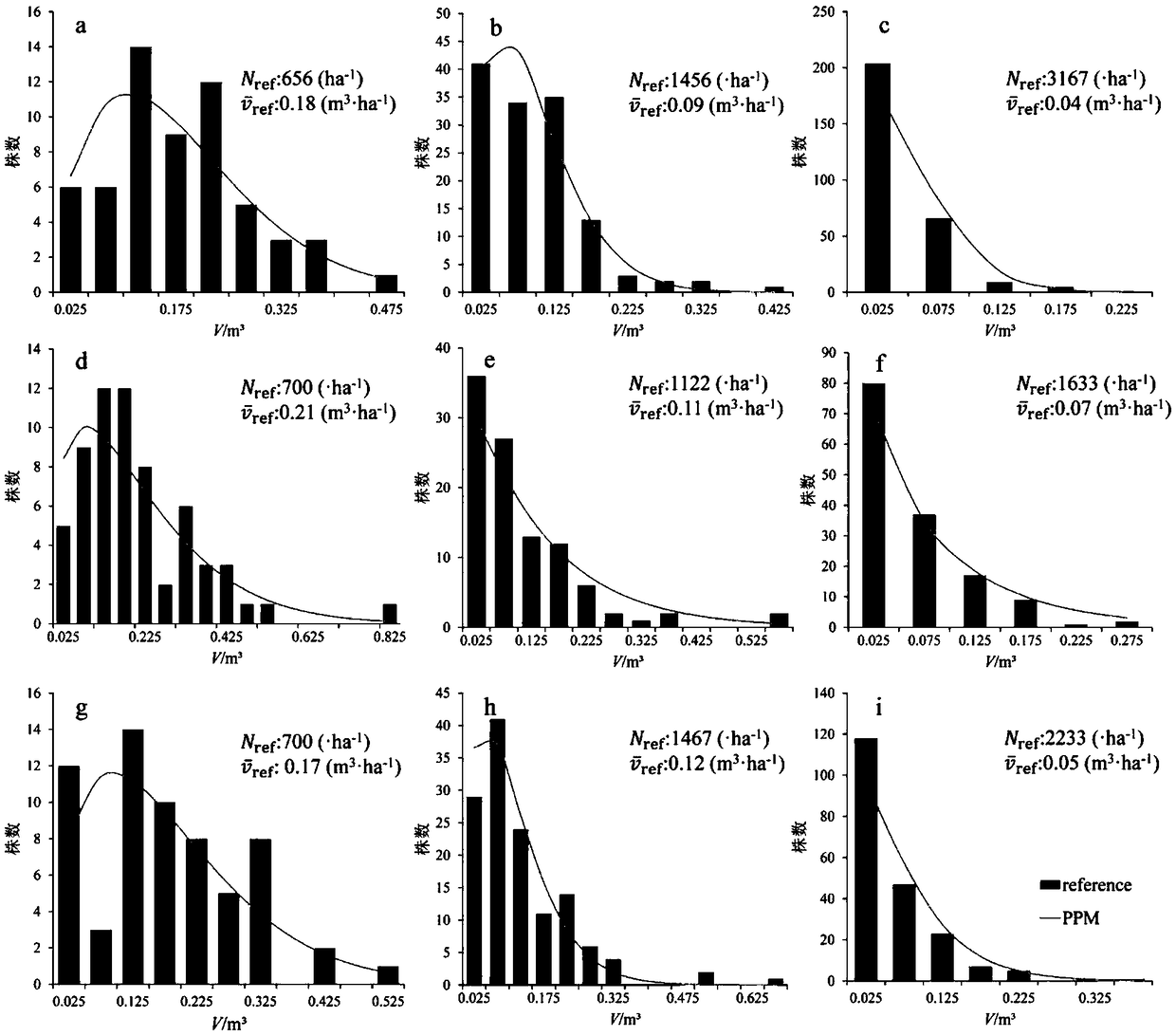
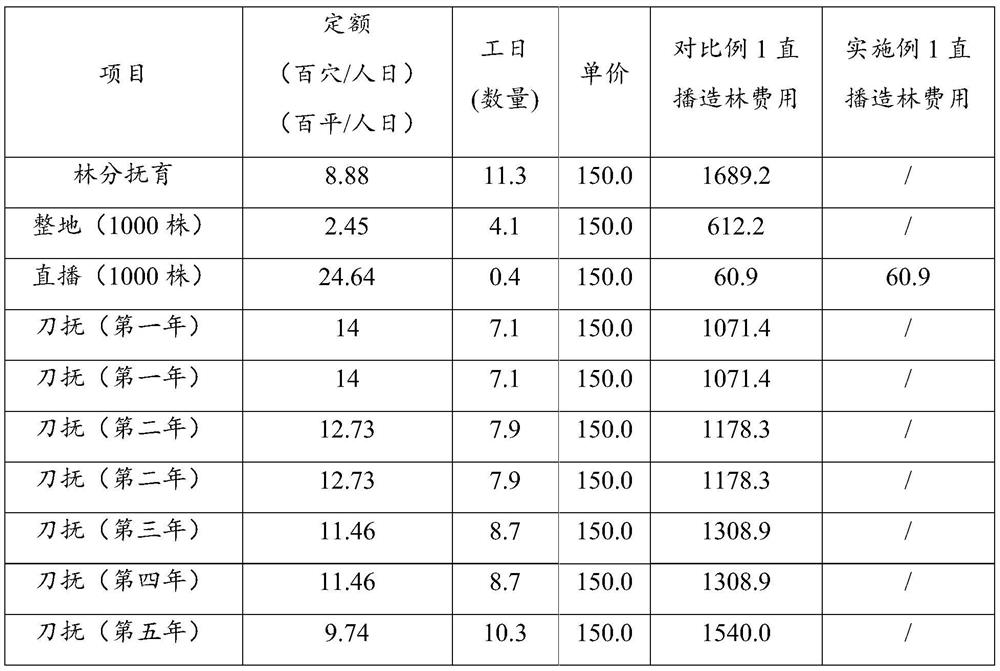
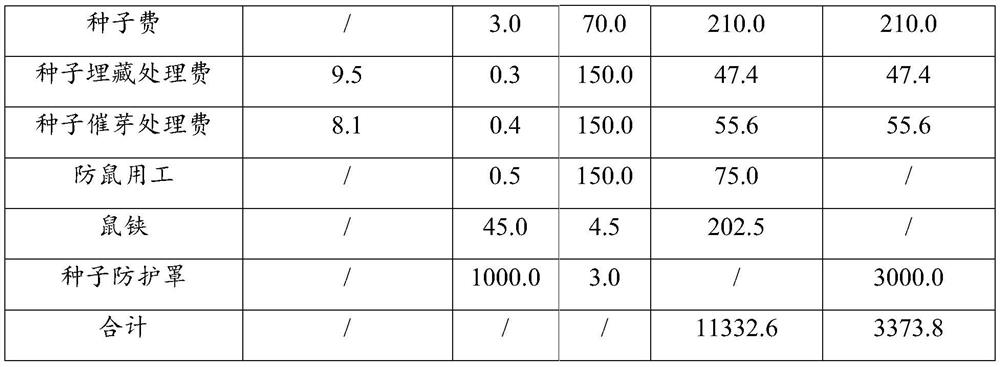
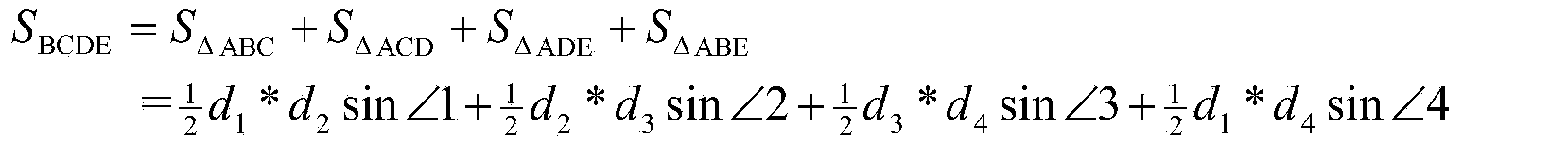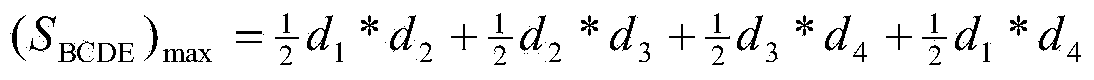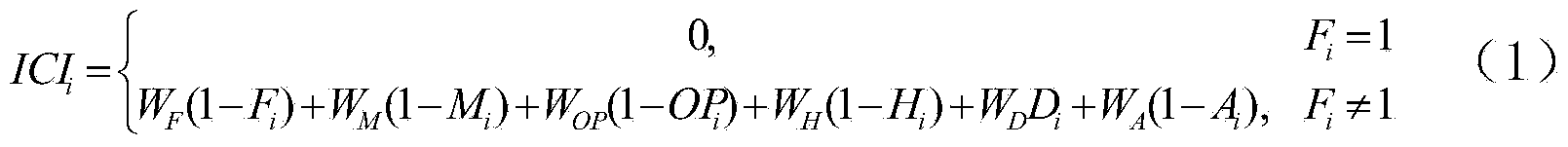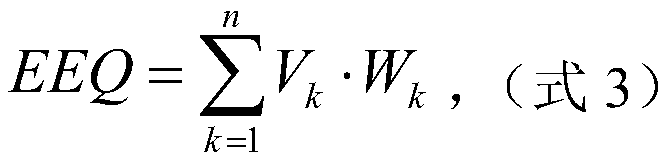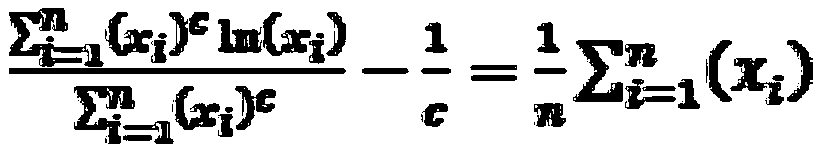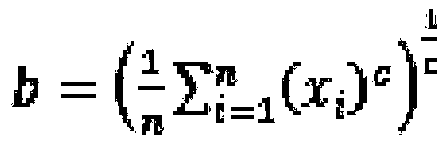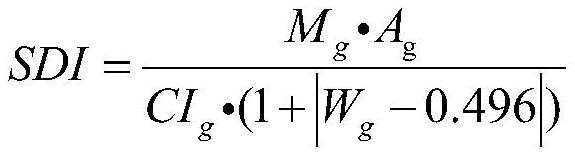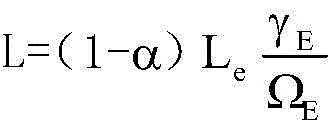Patents
Literature
41 results about "Secondary forest" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A secondary forest (or second-growth forest) is a forest or woodland area which has re-grown after a timber harvest, until a long enough period has passed so that the effects of the disturbance are no longer evident. It is distinguished from an old-growth forest (primary or primeval forest), which has not recently undergone such disruption, and complex early seral forest, as well as third-growth forests that result from harvest in second growth forests. Secondary forest regrowing after timber harvest differs from forest regrowing after natural disturbances such as fire, insect infestation, or windthrow because the dead trees remain to provide nutrients, structure, and water retention after natural disturbances. However, often after natural disturbance the timber is harvested and removed from the system, in which case the system more closely resembles secondary forest rather than complex early seral forest.
Corresponding period double high resolution remote sensing image-based forest biomass estimation method
InactiveCN105913017AAccurate estimateHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionSecondary forestEstimation methods
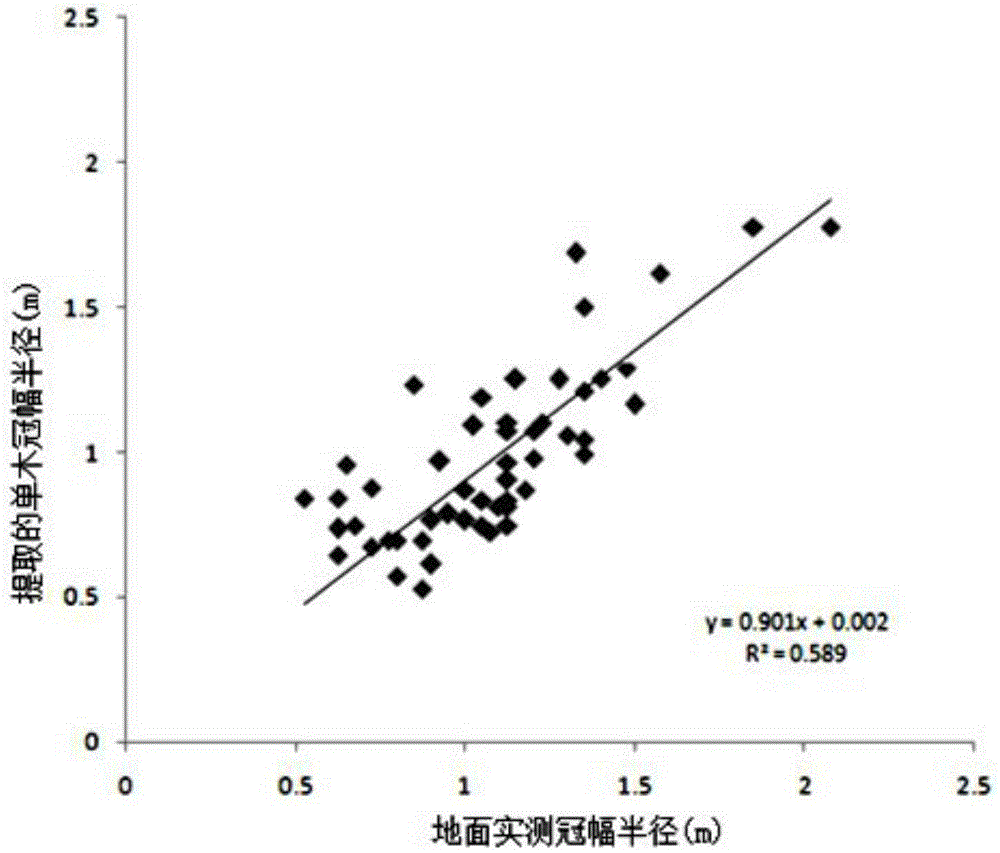
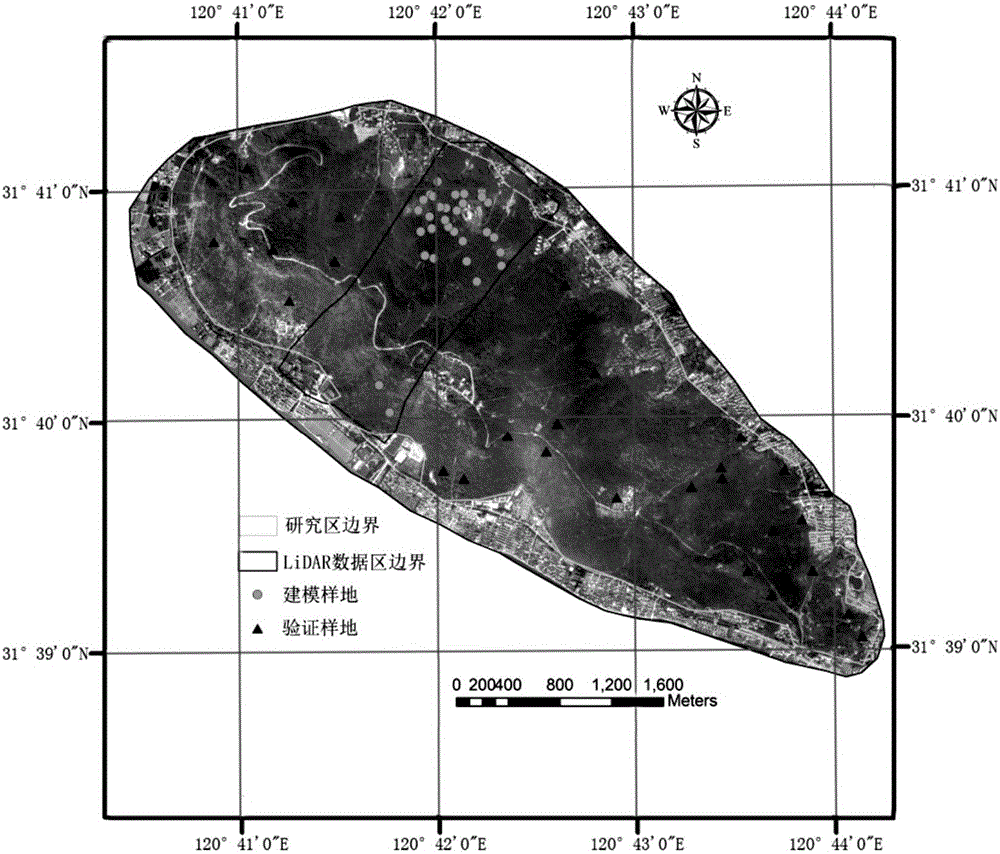
The invention discloses a corresponding period double high resolution remote sensing image-based forest biomass estimation method which comprises the following steps: the method is applied to a subtropical zone natural secondary forest in a hilly area in southern Jiangsu Province; based on double high resolution remote sensing image data obtained in a corresponding period, single tree crown breadth is extracted via an object-oriented segmentation method, five groups of hyperspectrum characteristic variables and seven single tree crown breadth structure statistical variables are extracted, biomass estimation is conducted via multiple regression model construction, and model precision is evaluated via a cross validation method. According to the method, when model parameters are determined, one of all sample areas is chosen randomly as a validation sample area, and the rest of the sample areas are used for modeling, a model obtained via fitting operation can be used for validating the sample area which is randomly chosen, the above steps are repeated in cycles till all sample areas are validated, and therefore forest biomass estimation accuracy can be improved while corresponding period double high resolution remote sensing image characteristics are fully discovered.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for joint inversion of forest aboveground biomass by integrating three data sources
ActiveCN108921885AImprove inversion accuracyImprove the inversion effectImage enhancementImage analysisTerrainAtmospheric correction
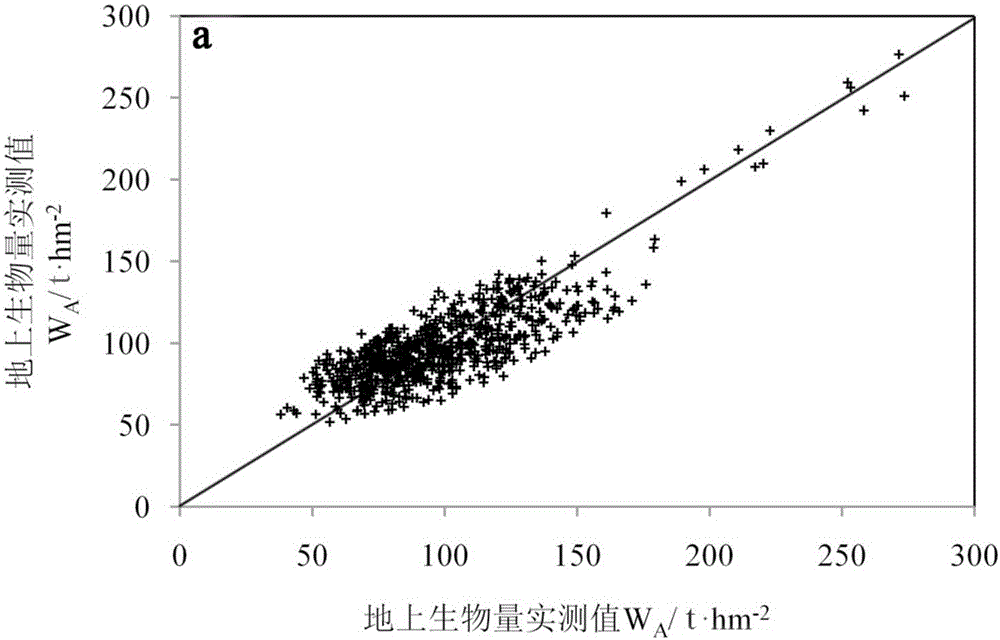
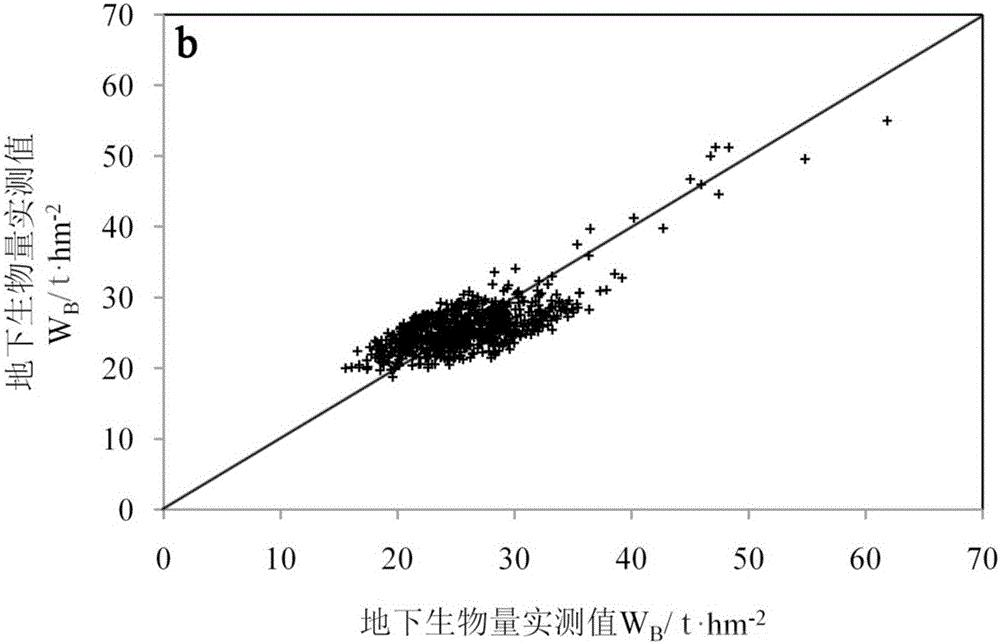
The invention discloses a method for joint inversion of forest aboveground biomass by integrating high-resolution CCD data, hyperspectral image data and laser radar point cloud data. According to themethod, first, geometric correction and stitching preprocessing are performed on airborne high-resolution CCD images, geometric correction and atmospheric correction preprocessing are performed on hyperspectral images, filtering and interpolation are performed on the laser radar point cloud data to generate a digital terrain model, and the point cloud data is normalized; second, texture features,spectral features and point cloud structural features are extracted based on three data sources obtained after preprocessing respectively; and last, models are constructed respectively in combinationwith ground measured data and extracted feature variables to predict the forest aboveground biomass. Through the method, the forest aboveground biomass of a subtropical natural secondary forest is extracted; and compared with aboveground biomass estimation results obtained by using other approximate remote sensing methods, the relative root-mean-square error of the method is lowered by 10% or above.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Tree species classification method based on multi-source simultaneous high-resolution remote sensing data
ActiveCN105354534ARefined Classification HierarchyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing dataSecondary forest
The present invention discloses a tree species classification method based on multi-source simultaneous high-resolution remote sensing data. High-resolution and hyperspectral data simultaneously acquired by an integrated sensor is utilized; firstly, coronal breadth identification is carried out based on the high-resolution data and an object-oriented method, then tree species classification is carried out based on spatial details and spectral features, which are extracted by the hyperspectral data, by combining a BP neural network classifier, and finally, the accuracy is verified by a confusion matrix. According to the tree species classification method disclosed by the invention, based on an edge detection multi-scale segmentation method, segmentation grades with different scales are established from multiple levels and multiple patterns and segmentation and information extraction are carried out layer by layer, so that the classification accuracy of tree species and forest types of subtropical natural secondary forests are promoted.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Natural planting method of mushroom
InactiveCN102084782AQuality improvementIncrease productionHorticultureGround temperatureSecondary forest
The invention discloses a natural planting method of a mushroom, solving the problems of low quality and easiness of manual pollution because the traditional mushroom planting technology is limited in the room. The natural planting method comprises the following steps of: 1, culturing a strain: separating a field-planted sporocarp to obtain a patent seed, culturing the patent seed according to the conventional expanding propagation method, continuously culturing a breeder seed to obtain a planting strain; 2, culturing a mycelium; 3, selecting a natural environment for planting: selecting an original forest, a secondary forest and an artificial forest with the ground temperature of 4-15 DEG C, the air humidity of 42-88 percent, the soil pH value of 6-7 and the forest land and grassland canopy density of 0.3-0.7; and 4, managing fruiting. The mushroom is cultured and planted by using the natural environment, and the mushroom sporocarp grows and develops under a natural and wild condition to ensure that the growth environment of the mushroom is more excellent and the product quality is better.
Owner:XINZHOU CITY HUIHENG AGRI FORESTRY & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY OVERALL DEV
Tending method for promoting western sichuan subalpine natural secondary forest to restore by utilizing reserved trees
InactiveCN105613205AShorten the timeReduce lossesCultivating equipmentsForestrySecondary forestBetula albosinensis
The invention discloses a tending method for promoting western sichuan subalpine natural secondary forest to restore by utilizing reserved trees. The method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting abies faxoniana, dragon spruce, hemlock, red birch and white birch as target tree species which need restoring in the secondary forest; S2, selecting the reserved trees; when the target tree species are the abies faxoniana, the dragon spruce or the hemlock, controlling the diameters at breast heights of the reserved trees to be more than or equal to 25cm; when the target tree species are the red birch or the white birch, controlling the diameters at breast heights of the residual trees to be more than or equal to 35cm; S3, dividing the restoration stage of the natural secondary forest according to the importance value of dominant tree species of community, wherein the restoration stage of the natural secondary forest is divided into a bushwood stage, a birch broad-leaved forest stage and a mixed broadleaf-conifer forest stage; S4, tending at the bushwood stage, tending at the birch broad-leaved forest stage and tending at the mixed broadleaf-conifer forest stage. In the restoration process of the western sichuan subalpine natural secondary forest, the reserved trees are fully utilized to tend and manage the secondary forest, so that the adverse effects of felling to the service function of a forest ecosystem can be slowed down, update is promoted, and the time for enabling the secondary forest to be restored into a forest after felling is shortened.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Strip LiDAR data upscaling-based forest biomass estimating method
InactiveCN105913016AReduce estimated costsImprove estimation accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSecondary forestSensing data
The invention discloses a strip LiDAR data upscaling-based forest biomass estimating method. A method implementation object is a subtropical natural secondary forest at a hilly area of southern Jiangsu Province; 9 characteristic variables are extracted from LiDAR strip data and are combined with ground estimated biomass to invert biomass continuous distribution information in a strip, sampling operation is conducted in a strip inverting result zone, samples are combined with Landsat OLI image characteristic variables covering a whole research zone, and biomass of the whole research zone can be estimated in an upscaling manner. Based on full acquisition of remote sensing data characteristic information, forest farm level biomass estimation cost is lowered via strip LiDAR data, and biomass estimating precision of a remote sensing method on the scale is improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for determining intermediate cutting intensity of natural secondary forest
The invention discloses a method for determining the intermediate cutting intensity of a natural secondary forest. The method for determining the intermediate cutting intensity of the natural secondary forest comprises the following steps of (1) building a competitive structure unit; (2) determining the minimum number of plants which are reserved; (3) building a function between a competitive structure unit area maximum value and a competitive structure unit average crown radius; (4) carrying out statistics on stand density N reality of the natural secondary forest, obtaining an average crown radius of the natural secondary forest, using the average crown radius as an R, calculating the minimum reservation density N minimum of the forest stand where a sample plot is located through the formula (1), if the N minimum is larger than the N reality, planting forest trees in the natural secondary forest in a supplement mode, wherein the N minimum minus the N reality is equal to the minimum number of the supplemented forest trees, and if the N minimum is smaller than the N reality, carrying out intermediate cutting, wherein the N reality minus the N minimum is equal to the maximum number of plants of intermediate cutting. The method for determining the intermediate cutting intensity of the natural secondary forest is simple, easy and convenient to operate, easy to master and free of cutting analytic trees, intermediate cutting can be rapidly achieved, and unwanted forest resource waste can be avoided.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Cyclobalanopsisglaucoides seed direct seeding forestation method
ActiveCN105145278AEasy to operateLow facility requirementsClimate change adaptationAfforestationSecondary forestObserved Survival
The invention discloses a cyclobalanopsisglaucoides seed direct seeding forestation method comprising the following steps: 1, seed harvesting; 2, seed screening; 3, seed storage; 4, direct seeding forestation. The method can realize a forestation survival rate above 81%; the method is simple in operation, less in facility requirements, low in management cost, simple in technical requirement, easy to promote and in application, and has important application popularization values on cyclobalanopsisglaucoides seed direct mountain seeding forestation, secondary forest reconstruction and mine ecology recovery.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for selecting natural secondary forest intermediate cutting object woods
InactiveCN103593563AOvercome the Difficulty of Selecting the Target Trees for Tendance and ThinningReasonable parenting planSpecial data processing applicationsSecondary forestHealth index
The invention discloses a method for selecting secondary forest intermediate cutting object woods. The method includes the steps of in cooperation with secondary forest characteristics and operation targets, selecting quantitative indexes, such as the freedom degree, the mixture degree, the health indexes, the purpose tree species characteristic indexes, the space density indexes and the open odds, which influence the probability that the woods in a secondary forest are determined as intermediate cutting objects, solving the weights of the six quantitative indexes with an analytic hierarchy process, analyzing correlations between the indexes which serve as independent variables and the intermediate cutting indexes which serve as dependent variables according to biological significances of the indexes for building the ICIi of the woods, and enabling the ICIi of the woods to be sort in a descending mode to determine the prior intermediate cutting object woods. The method is convenient to use, easy to operate and high in efficiency, and the accuracy can meet the requirement.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for promoting natural updating of secondary forest of fir in Minjiang River in western Sichuan
InactiveCN110122253ANatural Renewal BoostPromote growthCultivating equipmentsForestrySecondary forestSeedling
The invention discloses a method for promoting natural updating of a secondary forest of fir in the Minjiang River in western Sichuan. The method comprises steps as follows: 1) selection of high-quality seed trees of the tree layer, 2) tending of the tree layer, 3) clearing of trees on the lower layer; 4) seeding supplementing and planting supplementing. By means of the method for promoting natural updating of the secondary forest of the fir in the Minjiang River in western Sichuan, natural updating of the red birch-MinJiang River fir is promoted with a human assistance measure, naturally updated seedlings are kept, the culturing cycle is shortened, growth of trees is promoted, the soil environment and the forest stand structure of the forest are changed, the defects of limitation of natural conditions to natural updating and poor updating effect are overcome, and the natural evolution process from existing forest stand to efficient dark coniferous forests is accelerated.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Plantation method for pseudo-ginseng under trees
The invention relates to a plantation method for commercial crops and in particular relates to a plantation method under trees. The method comprises the following steps of dressing seeds, immersing seeds, selecting primary or secondary forest in an area of Northern latitude of 21 to 28 degrees and altitude of 1600 to 2300 as a plantation wood land, eliminating weeds and undershrubs for the plantation wood land, and conducting nursing work such as removing bend woods and remaining straight woods, removing weak but remaining strong woods, and eliminating weeds and pruning and cutting branches for the plantation wood land from February to April of each year from a time period ranging from two years after under-tree pseudo-ginseng seed fixed plantation or / and one year after annual seed bar fixed plantation to the harvest. Forest canopy density of the plantation area is maintained to be as high as 90%; under-tree pseudo-ginseng seeds processed in the second step is broadcast in the under-tree land or annual seed bars are fixedly planted; plant spacing distance is no less than 30cm x 30cm; and in the fifth step, the forest canopy density of the plantation area can is kept around 50 to 80%. Deficiencies of the prior art can be overcome; precious land occupation and damage by pseudo-ginseng plantation can be greatly reduced; damage to the environment by fertilizer chemicals and white pollutions can be reduced; and resource and energy consumption and loss can be reduced.
Owner:韩颖
Method for analyzing type and community characteristics of small-khingan stigma-broadleaf mixed forest based on carbon reserves
InactiveCN111340643AImprove the accuracy of carbon sink capacity estimationIncrease richnessTechnology managementResourcesSecondary forestSample plot
The invention relates to the technical field of forest analysis. The invention and particularly relates to a method for analyzing the type and community characteristics of a small-khingan stigma-broadleaf mixed forest based on carbon reserves. The method comprises the following steps of sSelecting an original forest in a top-level state; using secondary forests formed by mixed forests of felling forests and over-felling forests and natural renewal succession are used as analysis objects; setting the method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing raw materials; standard sample plots setting, adopting a sample method and an arbor positioning method are adopted. The method comprises the following steps: to carry outcarrying out variety identification, listing and positioning on arbor andsmall arbor plant individuals, measuring the tree height, diameter at breast height, height under branches and crown breadth, calculating the biomass of each measured arbor by using a biomass method,calculating the carbon reserve, and analyzing sample plot population distribution through a vertical projection area, a mixing degree, an angular scale and a competition index by using a statisticalmethod. According to the method, tThe influence of the carbon reserves on the forest stand structure is analyzed by taking the carbon reserve difference shown by different forest stand structures as an entry point, and a theoretical basis is provided for correctly evaluating the carbon sequestration capability of the stigma-broadleaf mixed forest in the region and scientifically managing forest resources.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF FORESTRY
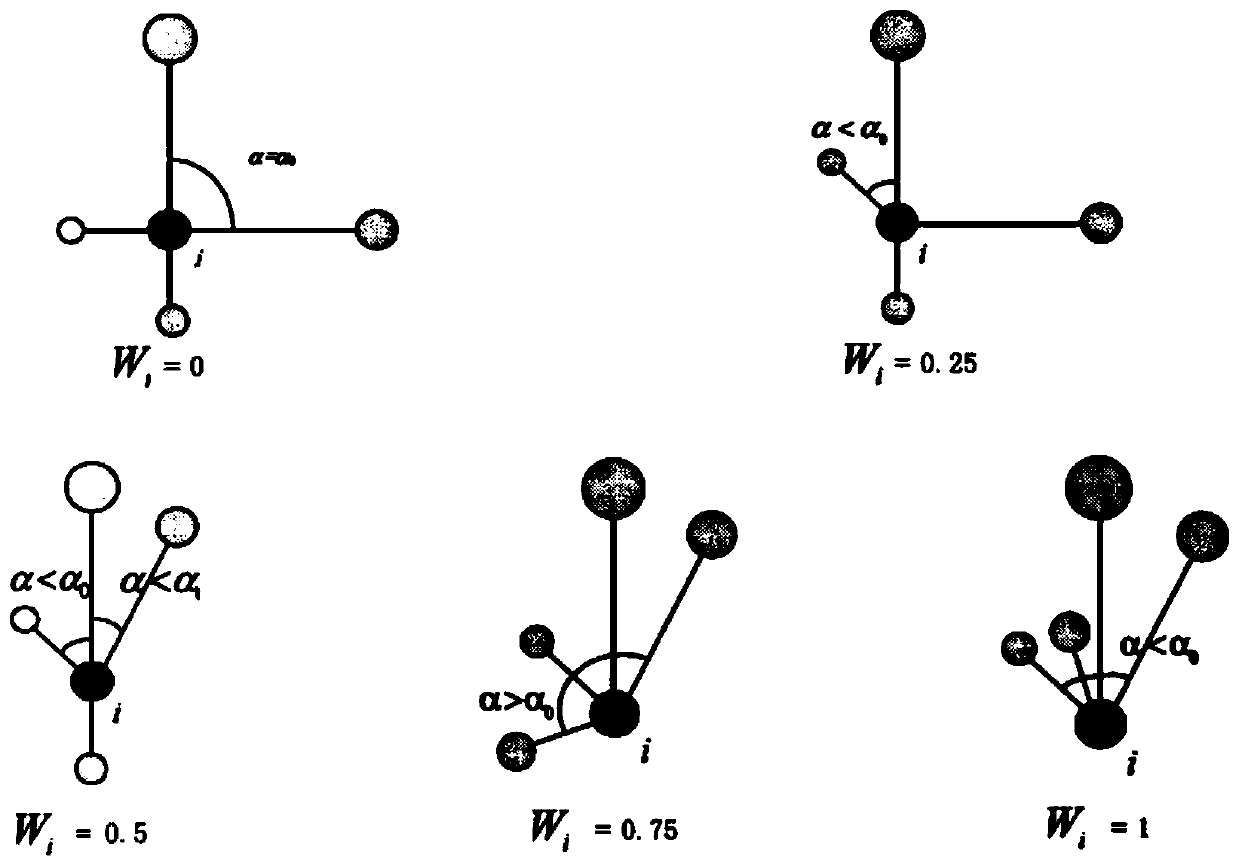
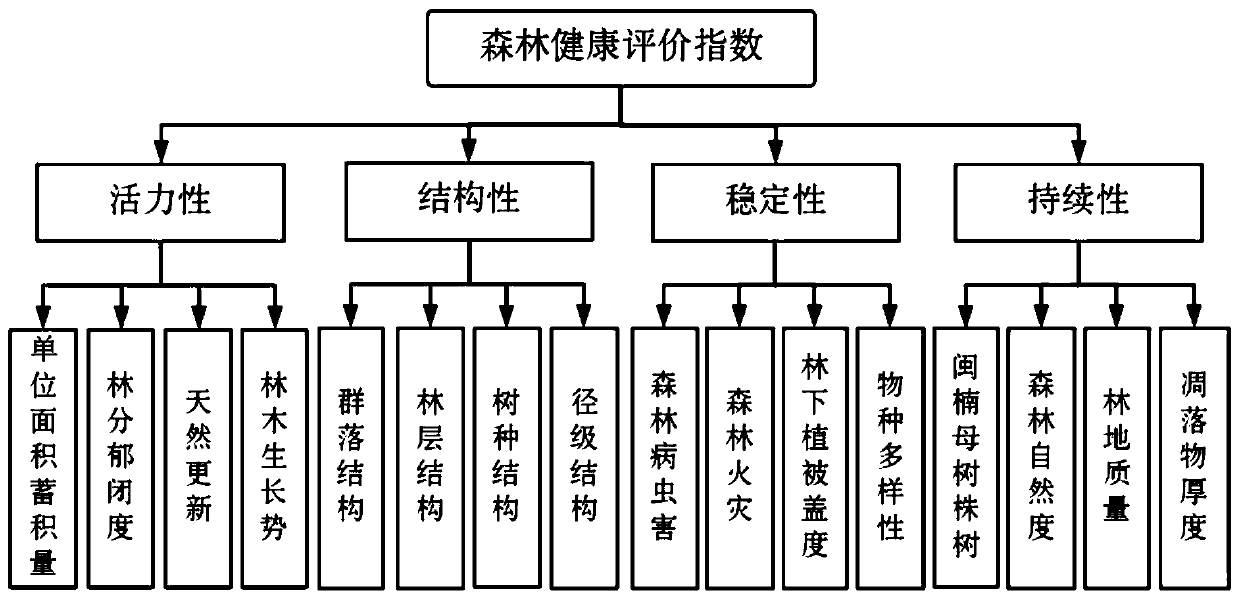
Phoebe bournei natural secondary forest health evaluation model and health evaluation method
The invention provides a Phoebe bournei natural secondary forest health evaluation model. In the health evaluation model, H is a forest health index and represents a comprehensive evaluation value of a health condition; Bj represents a value of a jth index after dimensionalization; Wj represents a total sorting weight value of the jth index; and n is the total index number; and each index comprises unit area accumulation amount, forest stand canopy density, natural updating, forest growth vigor, community structure, forest layer structure, tree species structure, diameter level structure, forest pest and disease damage, forest fire, under-forest vegetation coverage, species diversity, Phoebe bournei mother tree plant number, forest naturalness, forest land quality and litter thickness. According to the Phoebe bournei natural secondary forest health evaluation model, a health evaluation index system and a health evaluation model of the Phoebe bournei natural secondary forest are constructed; the Phoebe bournei natural secondary forest in Jiangxi Province is evaluated; a main countermeasure for promoting health operation is provided according to an evaluation result; and a scientific basis is provided for protection and sustainable operation of the Phoebe bournei natural secondary forest.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
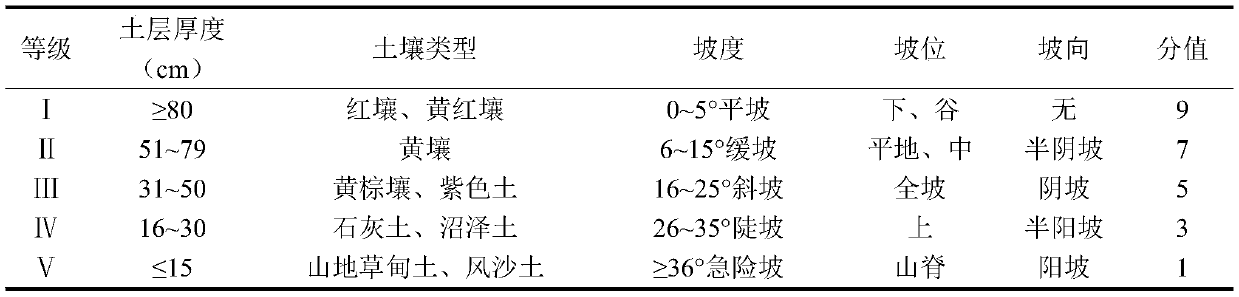
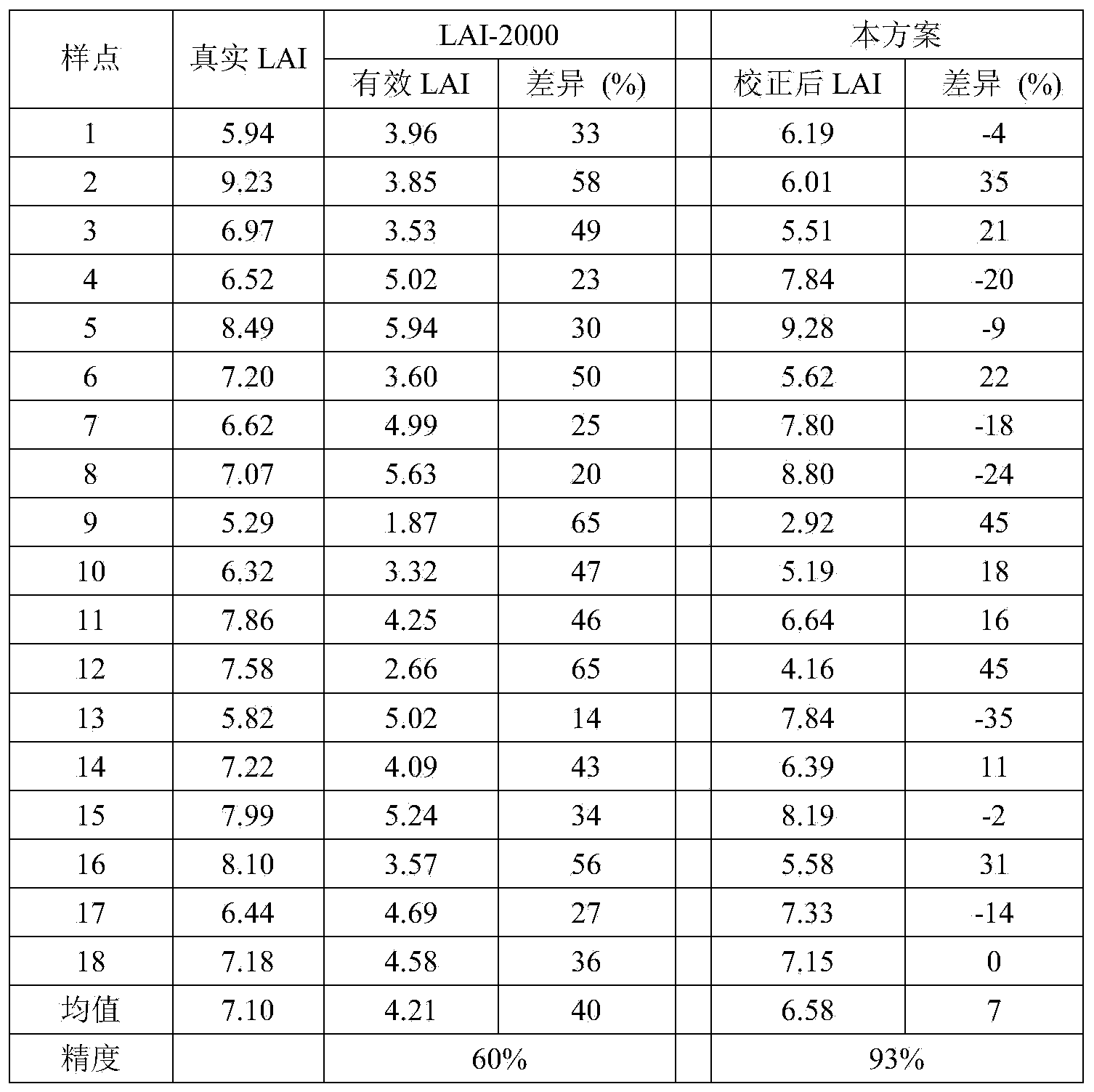
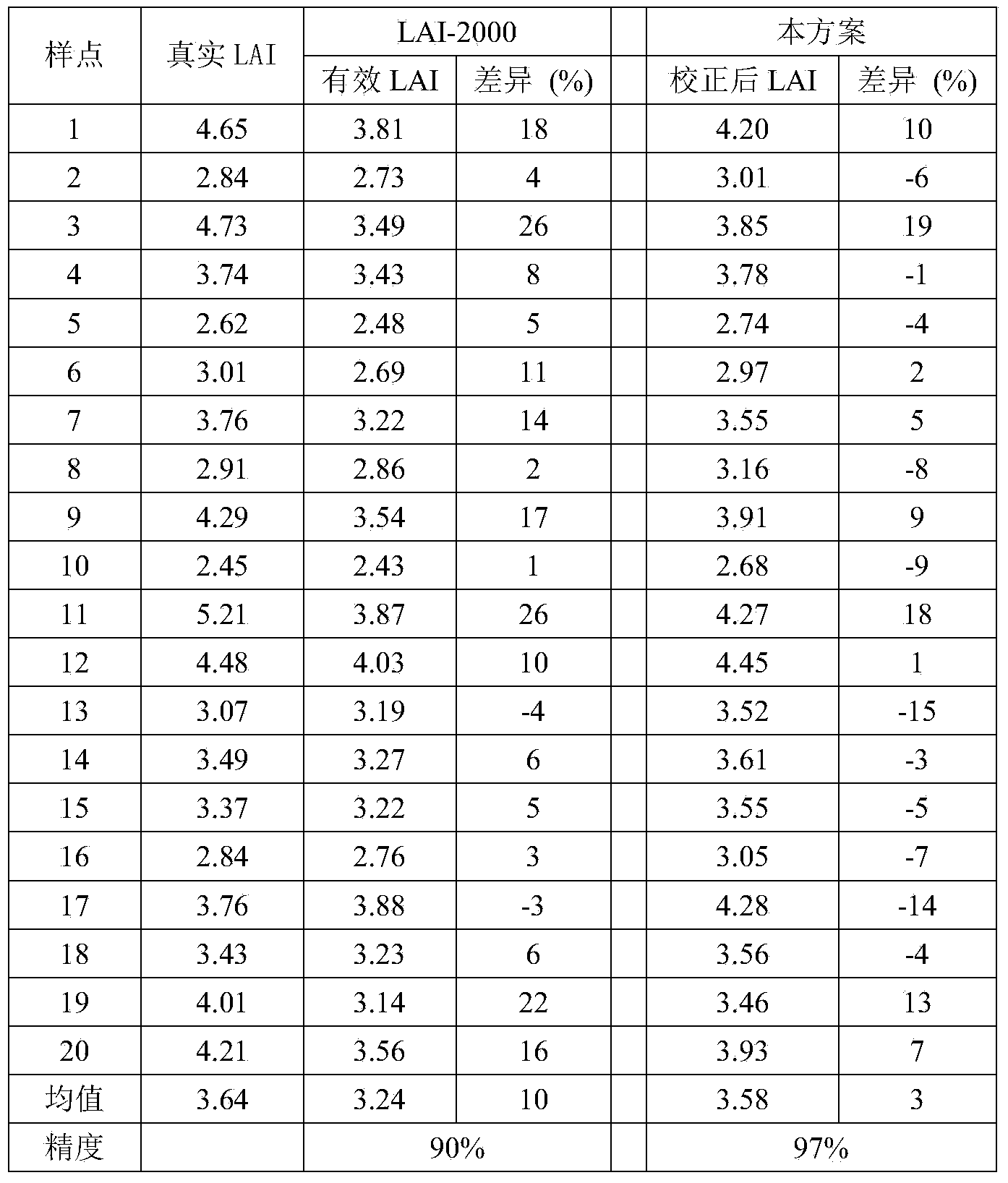
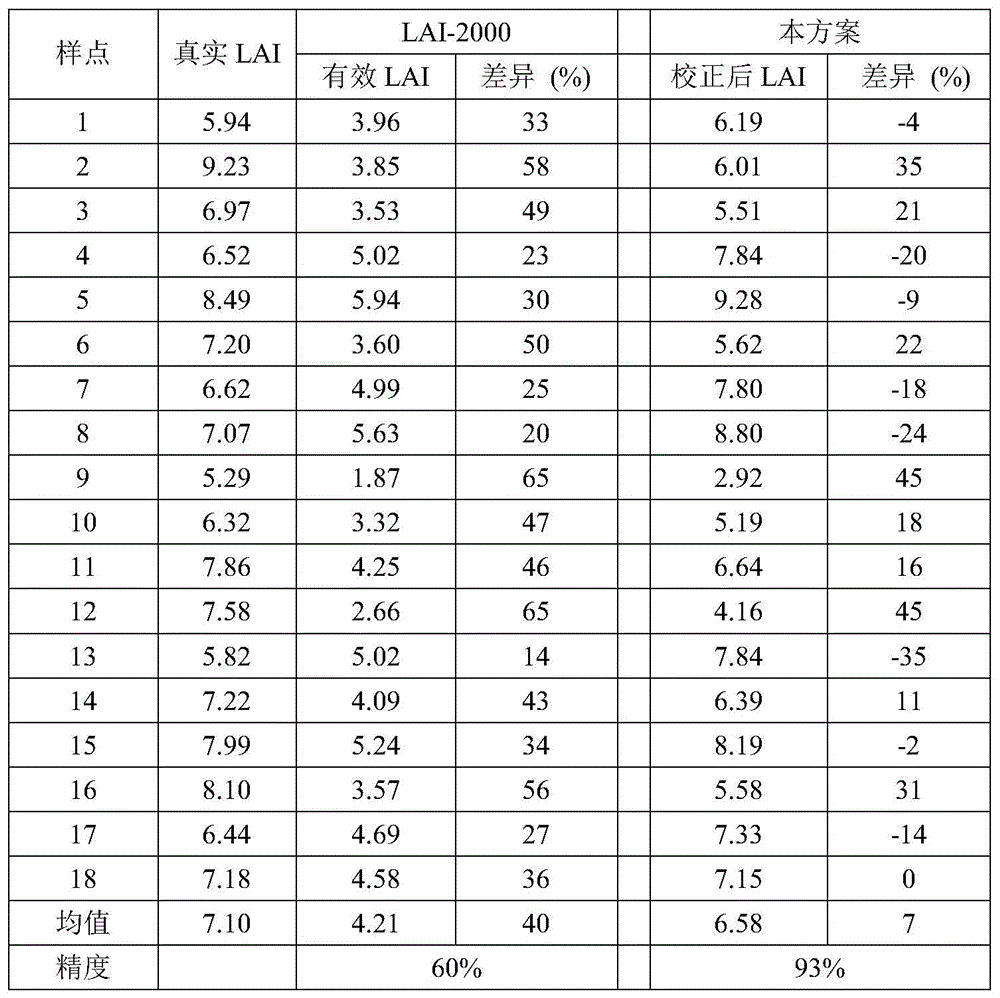
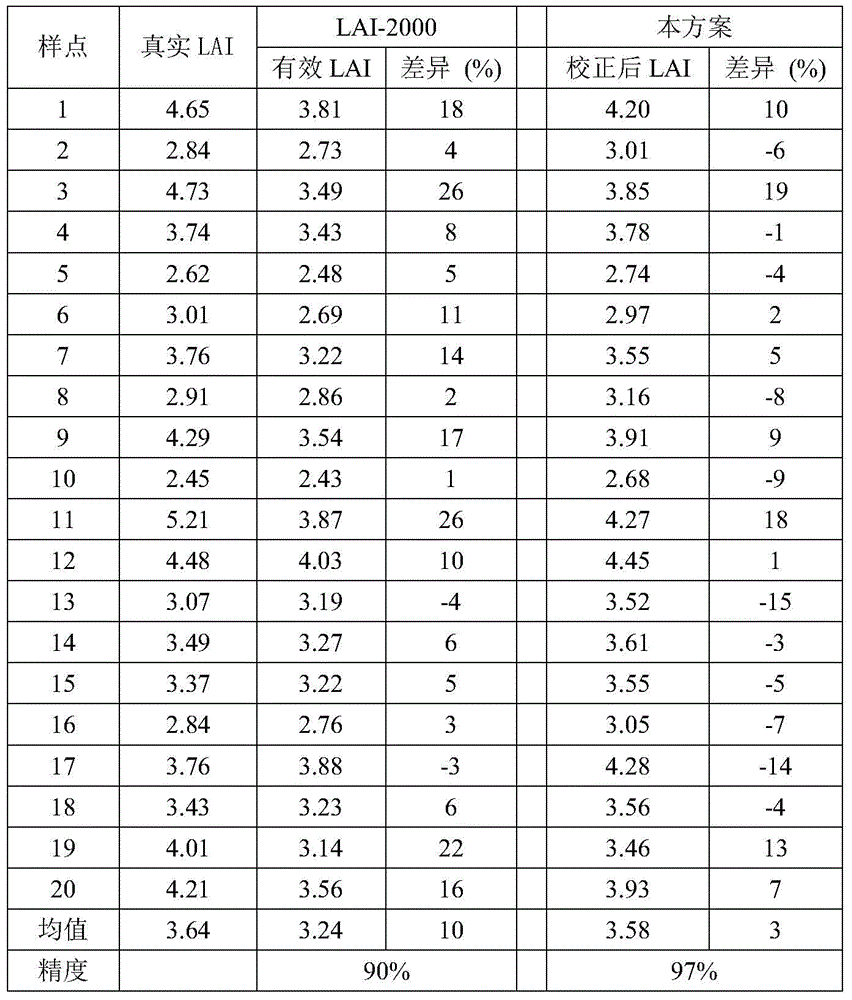
Correction method for measuring leaf area index by use of plant canopy analyzer
ActiveCN104330058AHigh measurement accuracyHigh precisionUsing optical meansSecondary forestBetula platyphylla
The invention provides a correction method for measuring a leaf area index by use of a plant canopy analyzer, relates to a correction method for measuring the leaf area index and aims at solving the problem that the existing measuring method by use of the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer is limited and low in leaf area index estimation accuracy. The correction method is used for obtaining an LAI value by use of the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer; correction is based on a formula as shown in the description; in the formula, L represents the LAI numerical value after correction and Le represents the LAI numerical value before correction; alpha, omega E and gamma E in the formula are correction coefficients, wherein alpha is the proportion of a lignin index in the total LAI, and the values of alpha of an artificial Korean pine forest and a betula platyphylla secondary forest are 0.03 and 0.04, respectively; omega E is a crowding index, and the values of omega E of the artificial Korean pine forest and the betula platyphylla secondary forest are 0.95 and 0.87, respectively; gamma E is a needle-cluster ratio. The correction method for measuring the leaf area index by use of the plant canopy analyzer takes the influence of the crowding effect into account and is comprehensive in the range of consideration, and the obtained data are true and reliable.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Medium-site-based cyclobalanopsis glauca broadleaved mixed forest cutting method
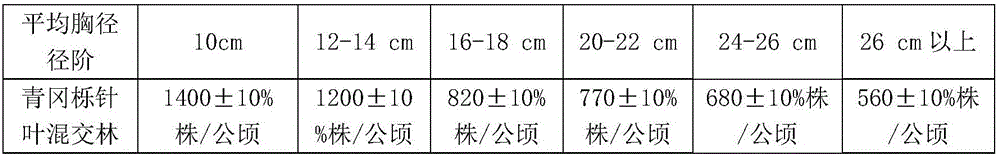
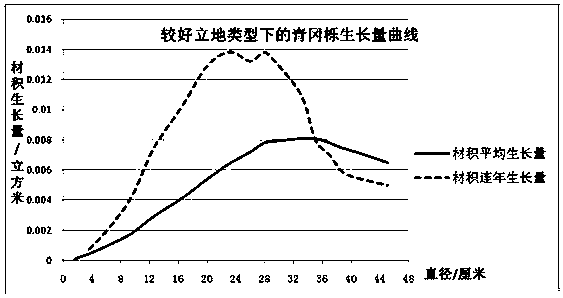
ActiveCN106472243AThe method of measuring breast diameter is simpleThe method of measuring breast diameter is accurateForestrySecondary forestCyclobalanopsis glauca
The invention relates to a secondary forest harvesting method, in particular to a medium-site-based cyclobalanopsis glauca broadleaved mixed forest cutting method. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: (1) investigating a selectively cut standing forest to determine that the standing forest has trees of which the diameters at breast height are 18 cm or above and reach a cutting target diameter and can be cut; (2) making statistics about trees of which the diameters at breast height are 5 cm or above in the standing forest to be cut, and calculating an average diameter at breast height; (3) preliminarily marking the trees reaching the cutting target diameter; (4) making statistics about the number of reserved trees, and calculating the average diameter at breast height of the reserved trees; (5) selecting the reasonable number of the reserved trees after cutting according to the following table; (6) regulating the trees to be cut reaching the target diameter at breast height to make the number of the reserved trees consistent with standards in the table, and performing cutting. The method is applied to cutting of a medium site cyclobalanopsis glauca broadleaved mixed forest, and is easy to operate and accurate, and forest resource waste can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Technical project for building fell and secondary forest organic orchard
The technical proposal for building organic fruit garden on barren hills and in secondary forests belongs to crop technical field, which particularly relates to reasonable reconstruction and utilization of barren hills and secondary forests. The technical proposal for building organic fruit garden on barren hills and in secondary forests comprises: 1. Building gardens on barren hills; 2. Pumping contour groove; 3. Moving vegetation grooves; 4. Arranging plants in short distance and between wide rows; 5. Operating in an organic way. The invention is a new exploration mode in building gardens on barren hills and in secondary forest. The implementation of the invention can improve the ecological environment of the barren hills, secondary forests and barren slopes in a reasonable way and bring obvious ecological and economic benefits.
Owner:HUBEI ZHIMIN AGRI
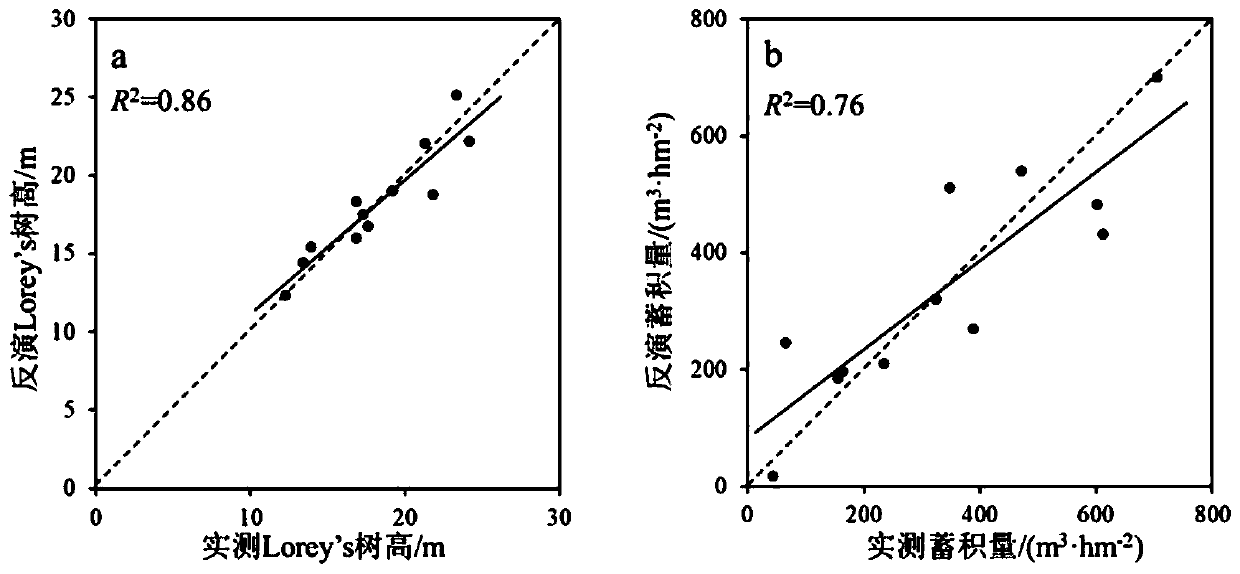
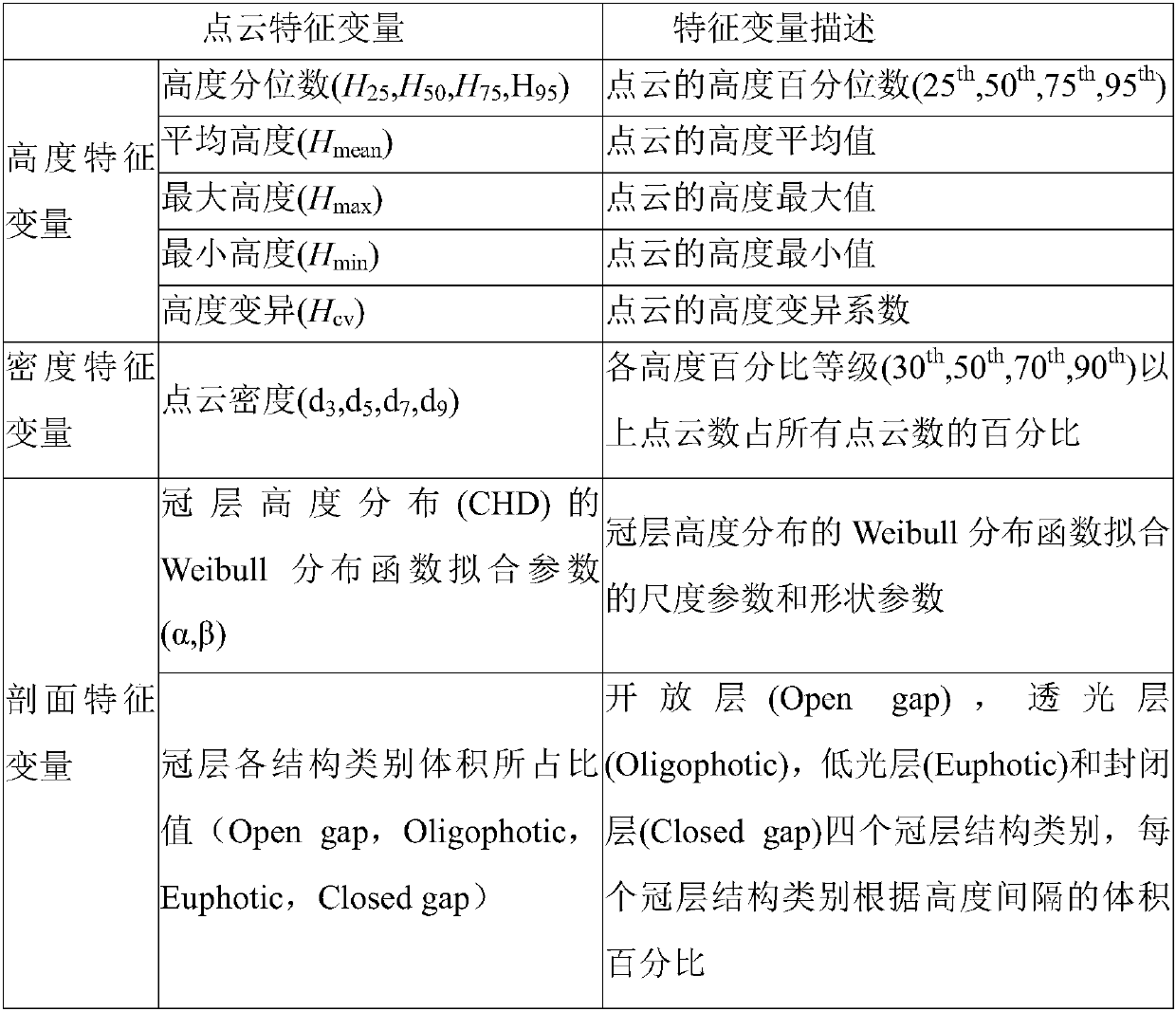
Forest stock volume distribution prediction method based on airborne laser radar data
InactiveCN109164460AEasy accessImprove abilitiesElectromagnetic wave reradiationSecondary forestSustainable management
The invention discloses a forest stock volume distribution prediction method based on onboard laser radar data, and belongs to the field of the forest resource monitoring, forest sustainable management control and ecological factor investigation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing normalization processing on laser radar point cloud data, and extracting characteristic variables from the normalized point cloud data; performing optimization on the laser radar characteristic variables and inverting a Weibull scale parameter and a Weibull shape parameter by resolving the Weibull scale parameter and the Weibull shape parameter by adopting a maximum likelihood method; and finally predicting the forest stock volume distribution by using a two-parameter Weibull distribution parameter. Compared with other similar estimation method, total precision of the estimation method of the forest stock volume distribution disclosed by the invention is improved by 5% and more, themethod not only is beneficial to mechanism explanation of the characteristic variables, but also can be used for the natural forest and the secondary forest.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Logging method for Cyclobalanopsis glauca coniferous mixed forest based on good site
InactiveCN106408429AThe method of measuring breast diameter is simpleThe method of measuring breast diameter is accurateData processing applicationsSecondary forestMixed coniferous forest
The invention relates to a logging method for a secondary forest, in particular to a logging method for a Cyclobalanopsis glauca coniferous mixed forest based on a good site. The logging method comprises the steps of: (1) investigating a culled forest, determining that a forest stand has woods with diameters at breast height (DBH) of 24 cm or more and reaching a logging target DBH, and performing selective cutting operation, (2) counting woods with DBH of 5 cm or more in the forest stand to be logged, and calculating an average DBH; (3) marking the woods reaching the logging target DBH preliminarily; (4) counting a number of reserved trees and calculating an average DBH of the reserved trees; (5) and selecting a number of reasonably reserved trees after logging according to the average DBH of the reserved trees on the basis of a table shown in description; (6) adjusting the to-be-logged woods reaching the logging target DBH according to the step (3), so that the number of the reserved trees meets standards in the table, and logging the woods. The logging method is used for logging the Cyclobalanopsis glauca coniferous mixed forest in the good site, is simple and accurate in operation, and can reduce the waste of a large amount of forest resources.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Secondary forest structure parameter inversion method based on unmanned aerial vehicle stereo photogrammetry point cloud
ActiveCN110554406AHigh quality inversionHigh precisionElectromagnetic wave reradiationInternal combustion piston enginesTerrainMeasurement point
The invention discloses a secondary forest structure parameter inversion method based on unmanned aerial vehicle stereo photogrammetry point cloud, and belongs to the fields of forest resource monitoring, ecological factor investigation, biodiversity research and the like. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring image data of a secondary forest by virtue of an unmanned aerial vehicle,and performing image matching and image splicing on the image data to obtain sparse point cloud; encrypting the sparse point cloud to obtain an encrypted point cloud; normalizing the encrypted point cloud by means of a digital terrain model obtained by a laser radar carried by the unmanned aerial vehicle, and obtaining normalized photogrammetric point cloud data; extracting point cloud characteristic variables from the normalized photogrammetric point cloud data; optimally selecting point cloud characteristic variables, establishing a multiple regression model by means of ground measured datato invert forest stand characteristics, and achieving high-quality inversion of forest structure parameters.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A harvesting method based on medium-site Quercus qinggang broad-leaved mixed forest
ActiveCN106472243BThe method of measuring breast diameter is simpleThe method of measuring breast diameter is accurateForestrySecondary forestCyclobalanopsis glauca
The invention relates to a secondary forest harvesting method, in particular to a medium-site-based cyclobalanopsis glauca broadleaved mixed forest cutting method. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: (1) investigating a selectively cut standing forest to determine that the standing forest has trees of which the diameters at breast height are 18 cm or above and reach a cutting target diameter and can be cut; (2) making statistics about trees of which the diameters at breast height are 5 cm or above in the standing forest to be cut, and calculating an average diameter at breast height; (3) preliminarily marking the trees reaching the cutting target diameter; (4) making statistics about the number of reserved trees, and calculating the average diameter at breast height of the reserved trees; (5) selecting the reasonable number of the reserved trees after cutting according to the following table; (6) regulating the trees to be cut reaching the target diameter at breast height to make the number of the reserved trees consistent with standards in the table, and performing cutting. The method is applied to cutting of a medium site cyclobalanopsis glauca broadleaved mixed forest, and is easy to operate and accurate, and forest resource waste can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
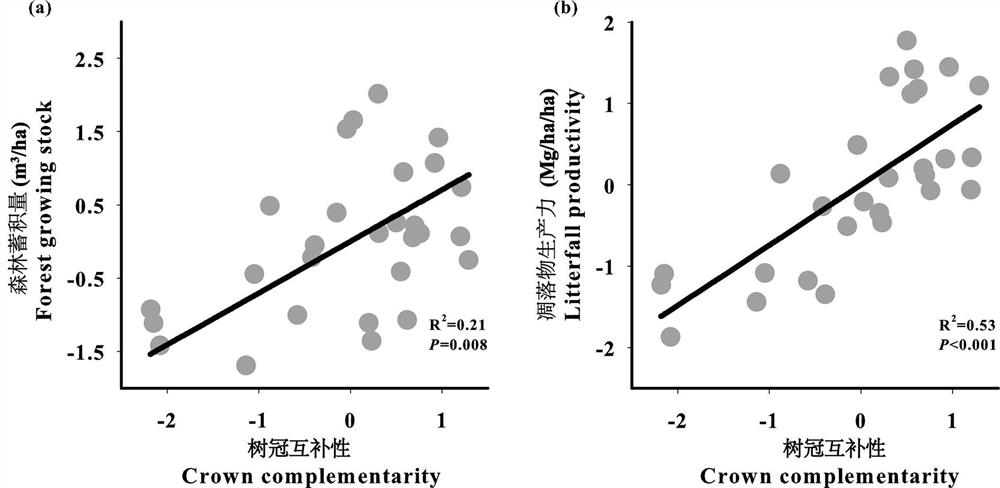
Method for improving forest productivity based on crown complementarity
ActiveCN112329976AIncrease diversityRich diversityClimate change adaptationForecastingSecondary forestSample plot
The invention discloses a method for improving the forest productivity based on crown complementarity, which comprises the following steps of: selecting bushes, secondary forests and protoplasts withdifferent soil nutrient and moisture gradients, and quantifying the non-overlapping degree of the crown volume of a tree individual in the vertical direction through standard sample plot investigationto obtain a community horizontal crown complementarity index; reflecting community productivity by using the total amount of forest stand annual litters, establishing a regression relationship between the community productivity and crown complementary indexes, screening community types with high species richness, strong crown complementarity and high productivity, and sorting the crown complementarity indexes according to tree species individuals; selecting an individual pair greater than the average value of the community as a species pairing combination with high crown complementarity; meanwhile, according to the community multi-degree proportion of the species combination of the type, determining the number proportion, integrating the planting method, and forming community afforestation schemes with different site high productivity. The forest productivity can be remarkably improved by accurately optimizing the forest stand space structure, and the method can be widely applied to afforestation, tending, forest stand transformation and large-diameter wood cultivation.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Secondary forest thinning method based on stand development index
ActiveCN113575348BPromote positive successionGuaranteed accuracyForestrySecondary forestEnvironmental resource management
The invention relates to the technical field of secondary forest thinning, in particular to a secondary forest thinning method based on a stand development index. The composition of tree species, determine the flora and the succession stage, and divide the tree species in the plot according to the top tree species, associated tree species, pioneer tree species and exotic tree species; C. Build a multi-objective model based on the stand development index; D. Use improvement The genetic algorithm was used to solve the multi-objective model to obtain the optimal tending and thinning plan for the secondary forest. The invention uses the stand development index to construct a multi-objective model for tending and thinning of the secondary forest, uses the improved genetic algorithm to perform global optimization, quickly obtains the reasonable thinning intensity and the spatial position of the thinning tree, ensures the accuracy and rationality of the thinning plan, and improves the forest efficiency. quality, and promote the positive succession of secondary forests.
Owner:RES INST OF FOREST RESOURCE INFORMATION TECHN CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
Pinus koraiensis direct seeding afforestation method
PendingCN112753519AImprove the conservation rate of afforestationImprove work efficiencyClimate change adaptationAfforestationSecondary forestPinus koraiensis
The invention provides a pinus koraiensis direct seeding afforestation method, and belongs to the technical field of forestry. The pinus koraiensis direct seeding afforestation method comprises the steps that a secondary forest or over-cut forest stand with canopy density of 0.7-0.9 is selected, the lower portion of a closed canopy formed by broad-leaved tree crowns in the forest stand is selected as a direct seeding point, after forest is cleared, a land preparation operation link is omitted, small holes are directly formed in the direct seeding point of a forest land for seeding pinus koraiensis seeds, and a special protective cover is used for protection. According to the pinus koraiensis direct seeding afforestation method, through the forest stand selection and the direct sowing point selection, pinus koraiensis seedlings subjected to direct sowing afforestation are sheltered by the broad-leaved tree crowns, the pinus koraiensis seedlings are prevented from being sealed by dense shrub and grass by inhibiting over-development of ground weeds, shrubs and vines under the forest, a young forest tending operation link is omitted, and meanwhile the preservation rate after five years of the afforestation is increased. The pinus koraiensis direct seeding afforestation method is simple to operate and easy to popularize, and compared with the prior art, the preserving rate after 10 years of the afforestation is increased by 287.5%, and the afforestation cost is reduced by 70%.
Owner:黑龙江省林业科学院伊春分院
A Calibration Method for Measuring Leaf Area Index Using Plant Canopy Analyzer
ActiveCN104330058BHigh measurement accuracyHigh precisionUsing optical meansSecondary forestBetula platyphylla
The invention provides a correction method for measuring a leaf area index by use of a plant canopy analyzer, relates to a correction method for measuring the leaf area index and aims at solving the problem that the existing measuring method by use of the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer is limited and low in leaf area index estimation accuracy. The correction method is used for obtaining an LAI value by use of the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer; correction is based on a formula as shown in the description; in the formula, L represents the LAI numerical value after correction and Le represents the LAI numerical value before correction; alpha, omega E and gamma E in the formula are correction coefficients, wherein alpha is the proportion of a lignin index in the total LAI, and the values of alpha of an artificial Korean pine forest and a betula platyphylla secondary forest are 0.03 and 0.04, respectively; omega E is a crowding index, and the values of omega E of the artificial Korean pine forest and the betula platyphylla secondary forest are 0.95 and 0.87, respectively; gamma E is a needle-cluster ratio. The correction method for measuring the leaf area index by use of the plant canopy analyzer takes the influence of the crowding effect into account and is comprehensive in the range of consideration, and the obtained data are true and reliable.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Magnolia officinalis planting method
InactiveCN112449960APlant high qualityHigh quality and high qualityCultivating equipmentsSecondary forestForest management
The invention discloses a magnolia officinalis planting method, belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicinal material planting, and aims to solve the problem that under the background of large-scale magnolia officinalis artificial cultivation at present, scientific transformation research of magnolia officinalis low-efficiency forests becomes social attention due to low environmental, ecological and economic benefits and severe loss caused by low-efficiency artificial forests and secondary forests. In the past, deep research and effective methods for transformation of the magnolia officinalis forest are lacked, and the magnolia officinalis forest grows, develops and renovates mainly through forest conservancy protection, or the forest is transformed through artificial afforestation after comprehensive intermediate cutting or high-strength cutting is carried out. According to the magnolia officinalis planting method, large-scale planting is conducted through measuresof base construction, seed selection and seedling raising, transplanting, forest management and pest control, and magnolia officinalis planting achieves high quality and high yield through reasonablelayout, reasonable positions, reasonable weather and high-quality seedlings.
Owner:袁学亮
Soil layer structure contrastive analysis method and reconstruction method thereof
PendingCN113447638ASimple structureImprove ecological levelEarth material testingCultivating equipmentsSecondary forestStructure analysis
The invention discloses a soil layer structure contrastive analysis method and a reconstruction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of forestry soil layer structure analysis and reconstruction. The soil layer structure contrastive analysis method comprises the following steps: (1) measuring a soil layer structure Z of a target area; (2) according to a target tree species, searching an original forest or a natural secondary forest which has the same climatic zone as the target region, is close to the target region in geographic position and grows with the target tree species; (3) measuring a soil layer structure N in the original forest or the natural secondary forest at a position near a naturally updated sapling of the target tree species; and (4) comparing the difference between the soil layer structure Z and the soil layer structure N. Through a relatively simple technical means, the ecological interaction between the forest trees and the soil is fully utilized under the minimum human intervention, the positive effect of plant growth on the environment and the land and the positive feedback of the land on the plants are exerted, and the naturally maintained ecological balance of the trees and the soil can be realized within the shortest time.
Owner:自然林(北京)科技有限公司
A Tree Species Classification Method Based on Multi-source Simultaneous High Resolution Remote Sensing Data
ActiveCN105354534BRefined Classification HierarchyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpectroscopyClassification methods
The invention discloses a tree species classification method based on multi-source simultaneous high-resolution remote sensing data, using the high-resolution and hyperspectral data acquired by an integrated sensor at the same time, firstly based on the high-resolution data and an object-oriented segmentation method for crown width identification, Then based on the spatial details and spectral features extracted from the hyperspectral data and combined with the BP neural network classifier, the tree species is classified, and finally the accuracy is verified by the confusion matrix. The invention is based on a multi-scale segmentation algorithm based on edge detection, establishes segmentation levels of different scales from multiple layers and multiple patterns, performs segmentation and information extraction layer by layer, and improves the classification accuracy of subtropical natural secondary forest tree species and forest types.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Torreya grandis base reconstruction technology using gaps
InactiveCN107347564AEnsure normal growth and developmentProtected growthCultivating equipmentsForestrySecondary forestEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a Torreya grandis base reconstruction technology using gaps, in particular to reasonable rebuilding and utilization of gaps of a Torreya grandis base. The Torreya grandis base reconstruction technology using the gaps comprises the steps of selection of secondary forest gaps, gap management and subsequent transplantation of the gaps. The technology provides construction of the Torreya grandis base with a new explore mode, and the quality and yield of Torreya grandis can be maintained without affecting an original forest; by means of the technology, considerable ecological and economic benefits can be brought to the Torreya grandis base, and popularization is worthwhile for Torreya grandis planting industry.
Owner:GUIZHOU BOTANICAL GARDEN (GUIZHOU INST OF HORTICULTURAL SCI GUIZHOU INST OF BOTANY)
A Method of Inverting Forest Aboveground Biomass by Combining Three Types of Data Sources
ActiveCN108921885BImprove inversion accuracyImprove the inversion effectImage enhancementImage analysisAtmospheric correctionImaging data
The invention discloses a method for combining high-resolution CCD data, hyperspectral image data and laser radar point cloud data to jointly invert forest aboveground biomass. Geometric correction, splicing preprocessing, geometric correction and atmospheric correction preprocessing of hyperspectral images, filtering of lidar point cloud data, interpolation to generate digital terrain models, and normalization of point cloud data; and then based on the preprocessed The texture features, spectral features and point cloud structure features are extracted from the three data sources; finally, a method for predicting forest aboveground biomass is constructed by combining the ground measured data and the extracted feature variables to construct models respectively. The invention extracts the aboveground biomass of the subtropical natural secondary forest, and compared with the aboveground biomass estimation results using other similar remote sensing methods, the relative root mean square error is reduced by more than 10%.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A method for direct seeding afforestation of Qinggang yunnanensis
ActiveCN105145278BEasy to operateLow facility requirementsClimate change adaptationAfforestationCyclobalanopsis glaucoidesSecondary forest
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com