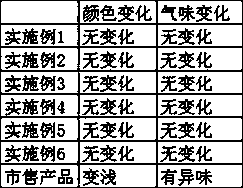
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Betula platyphylla" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
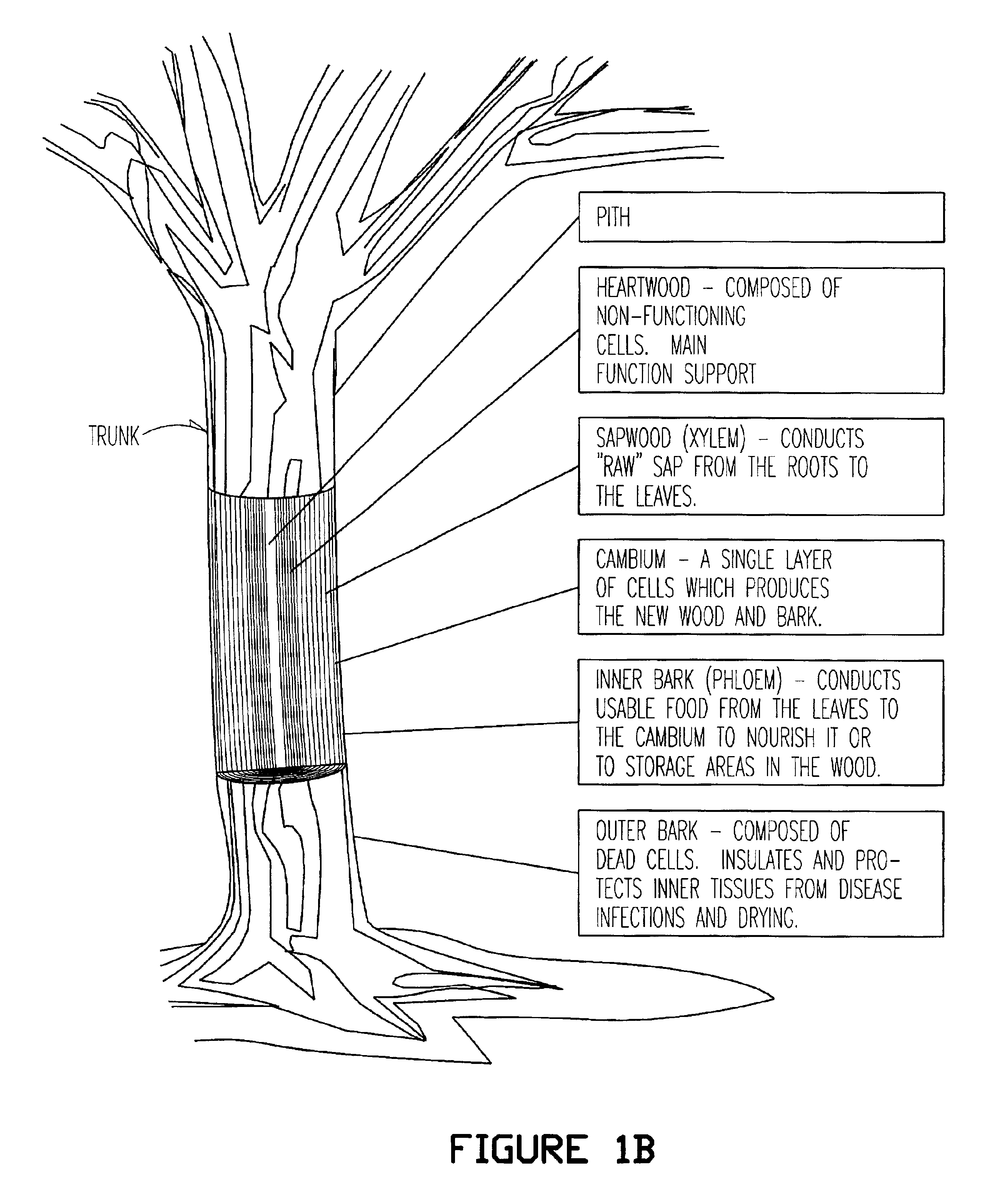
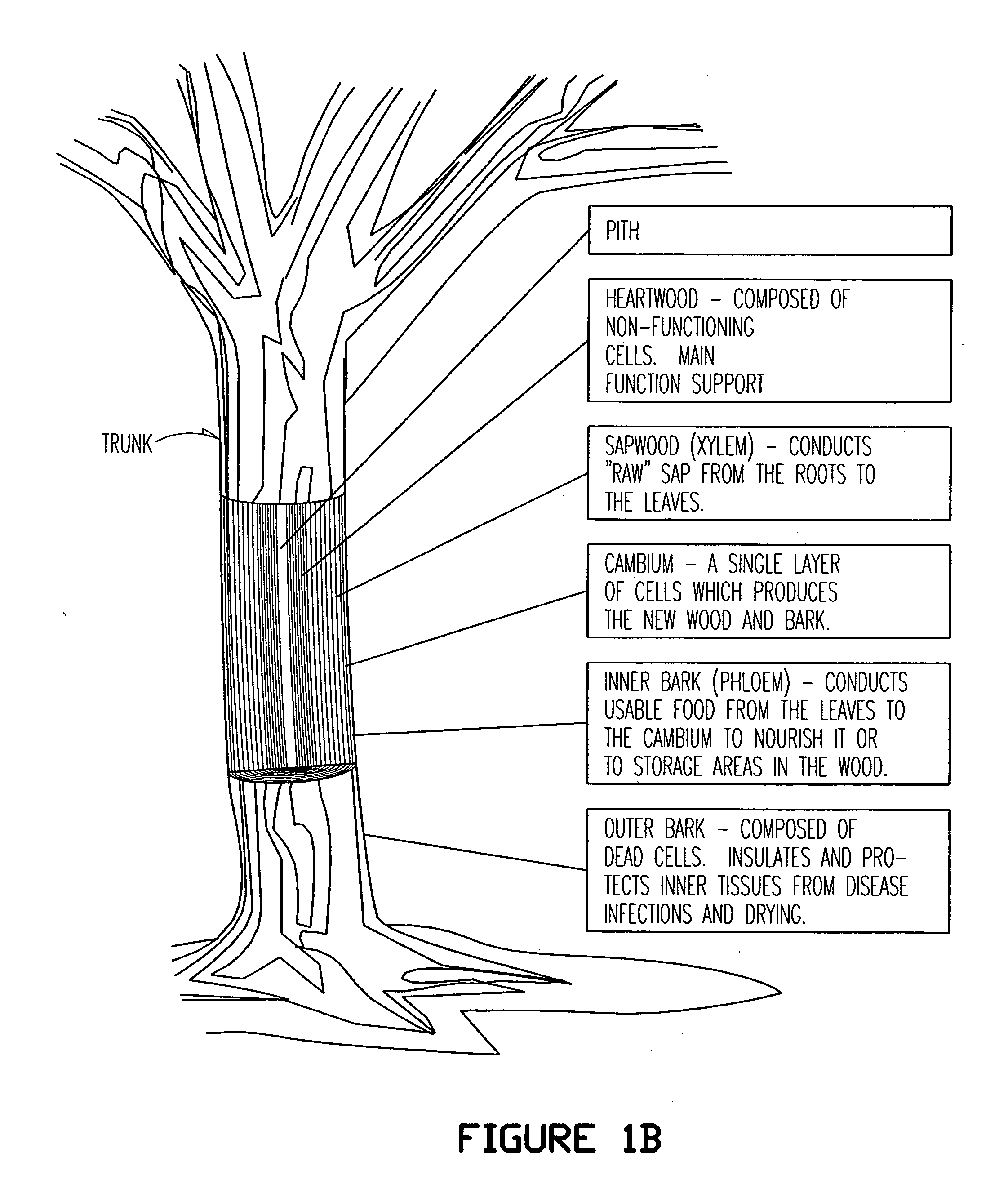
Betula platyphylla, the Japanese white birch or Siberian silver birch, is a tree species belonging to the genus Betula. It can be found in temperate or subarctic places of Asia: Japan, China, Korea and Siberia. The Japanese White Birch can grow to be 20 m to 30 m tall.
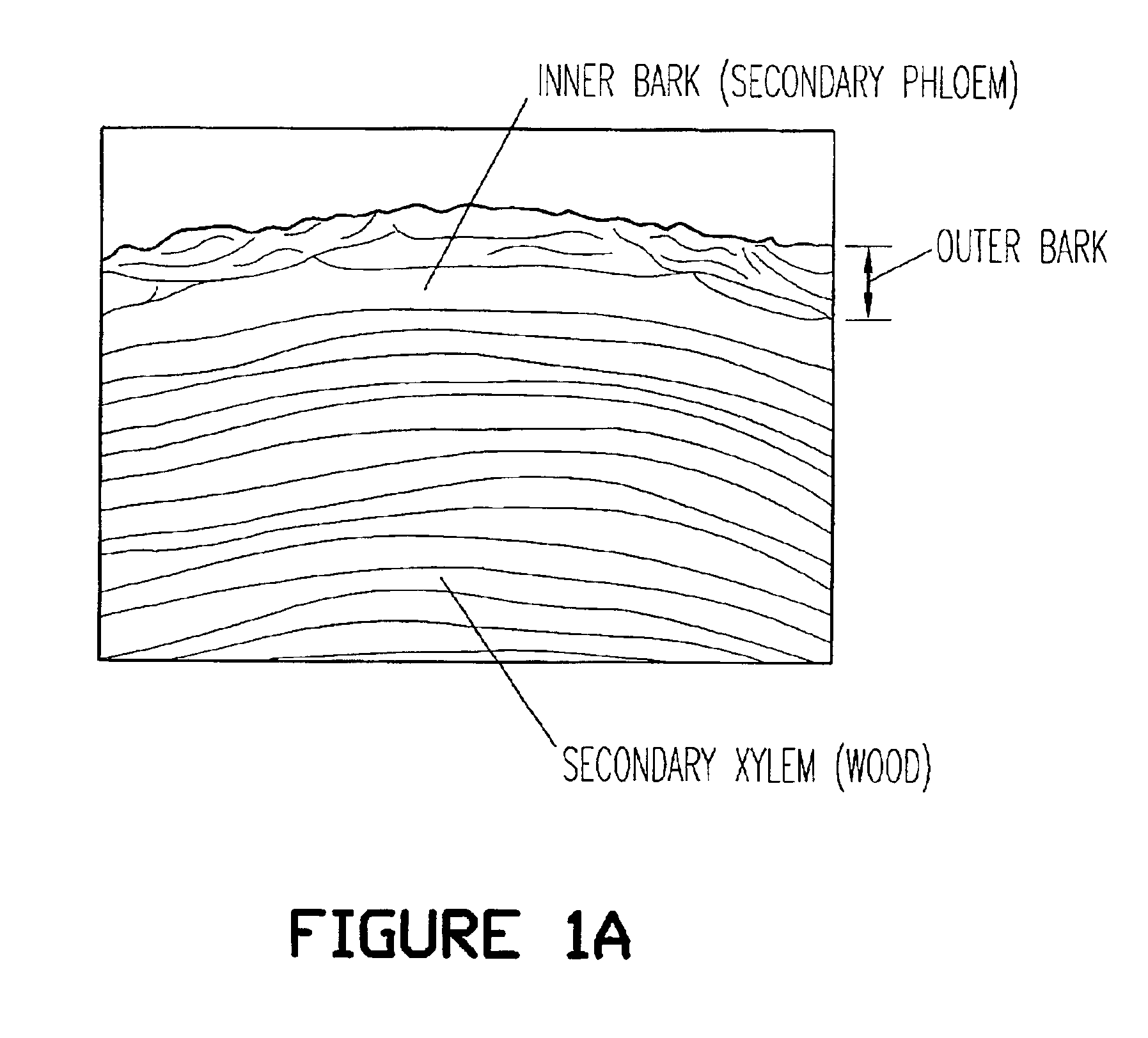
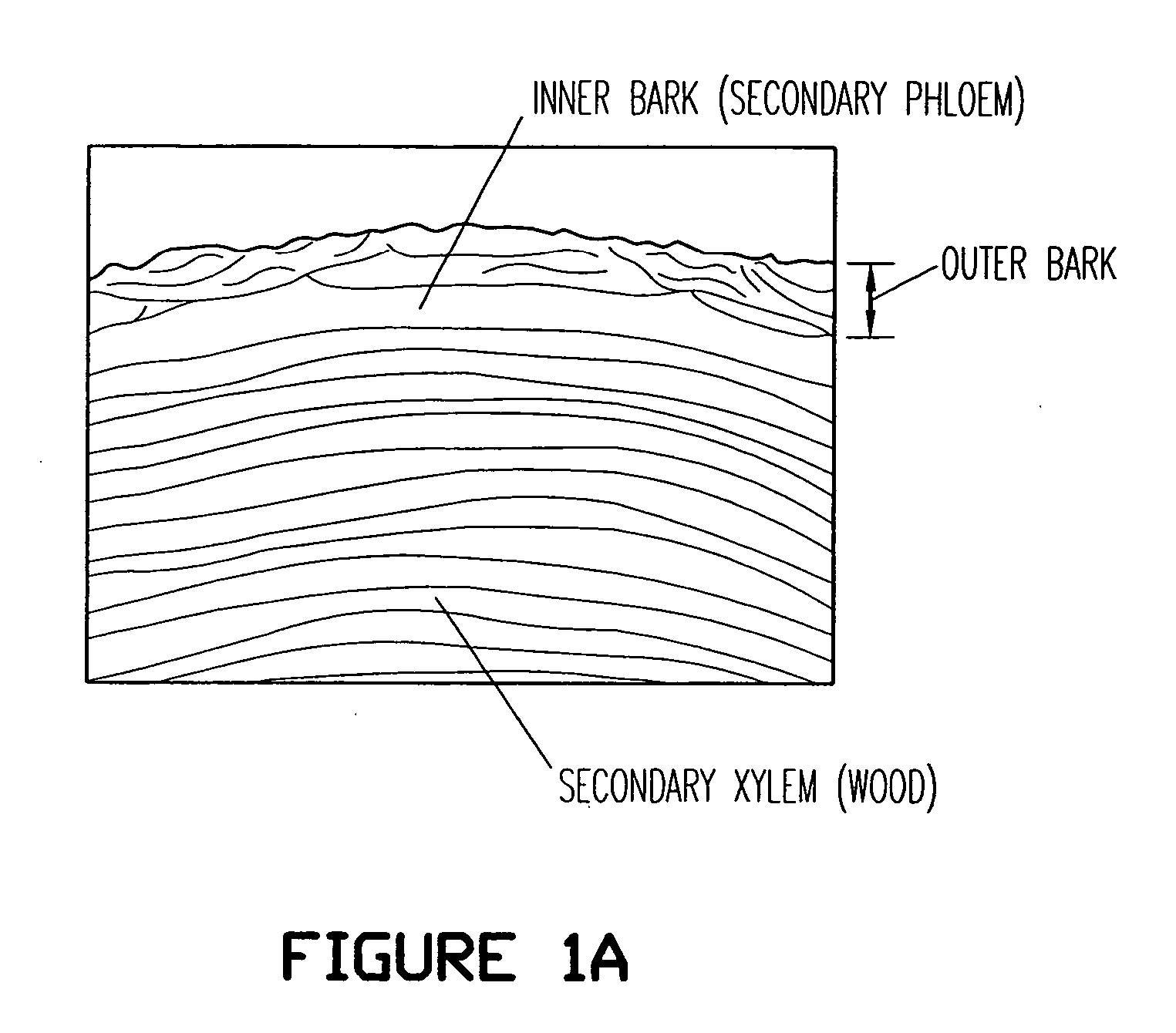
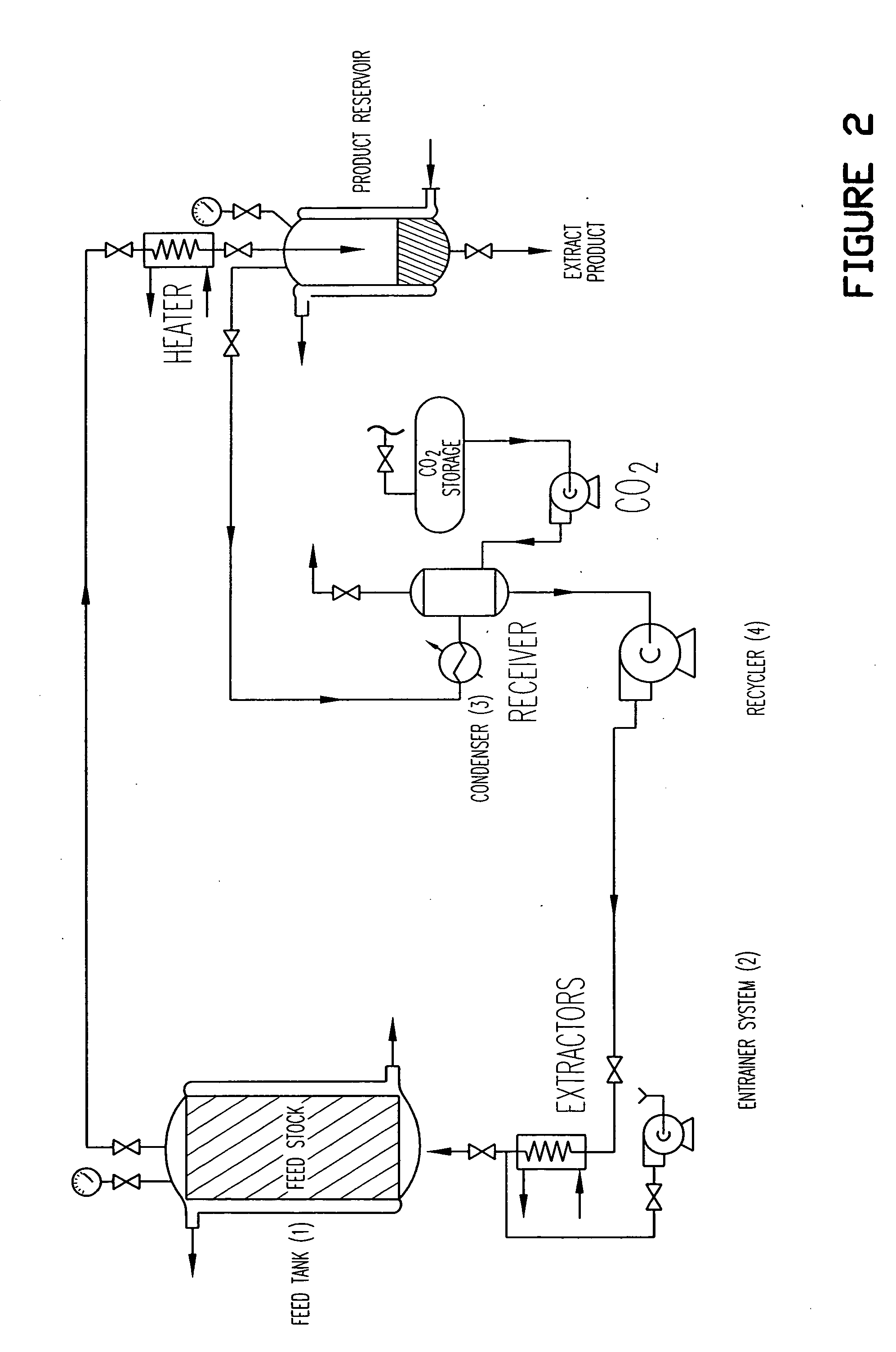
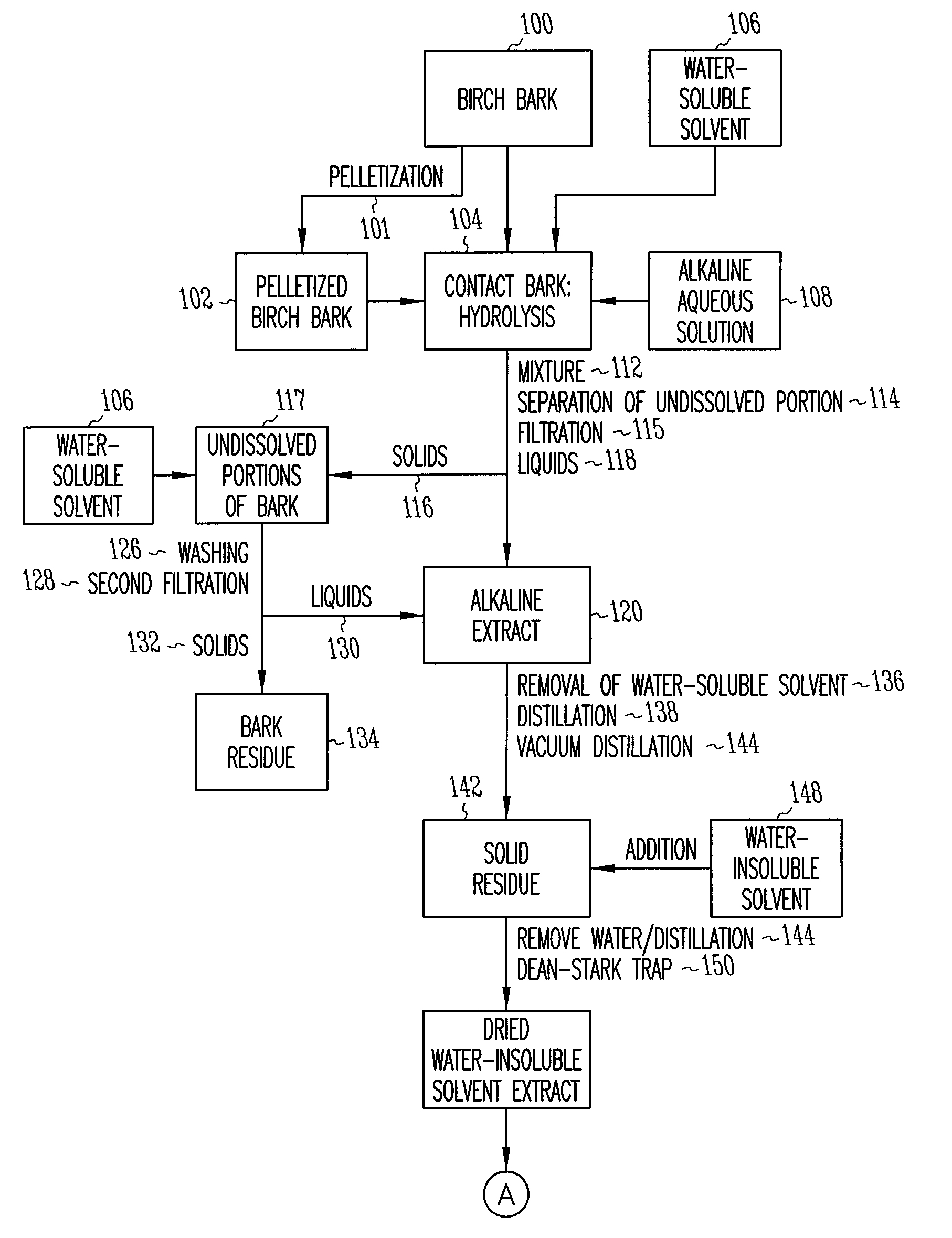
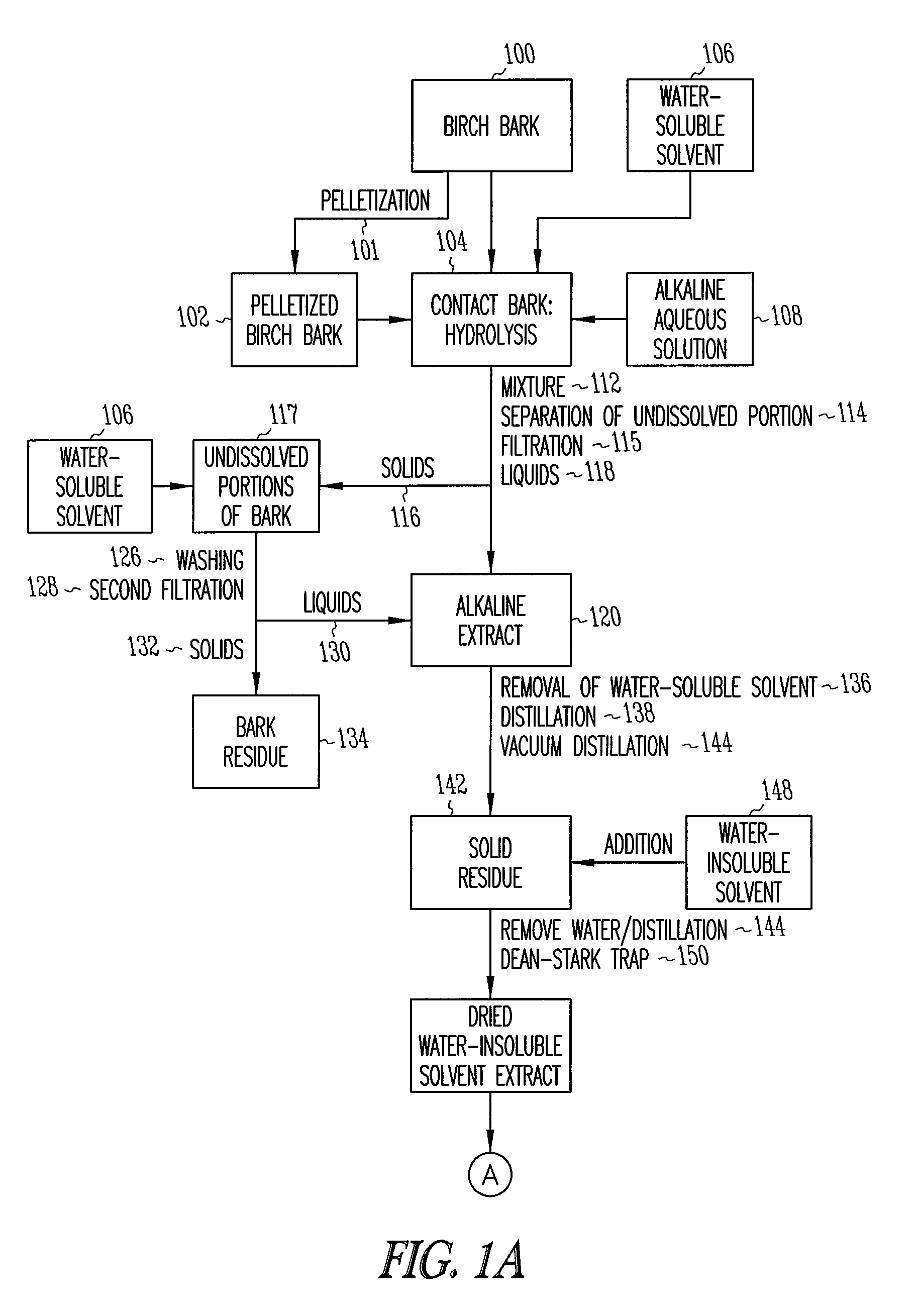
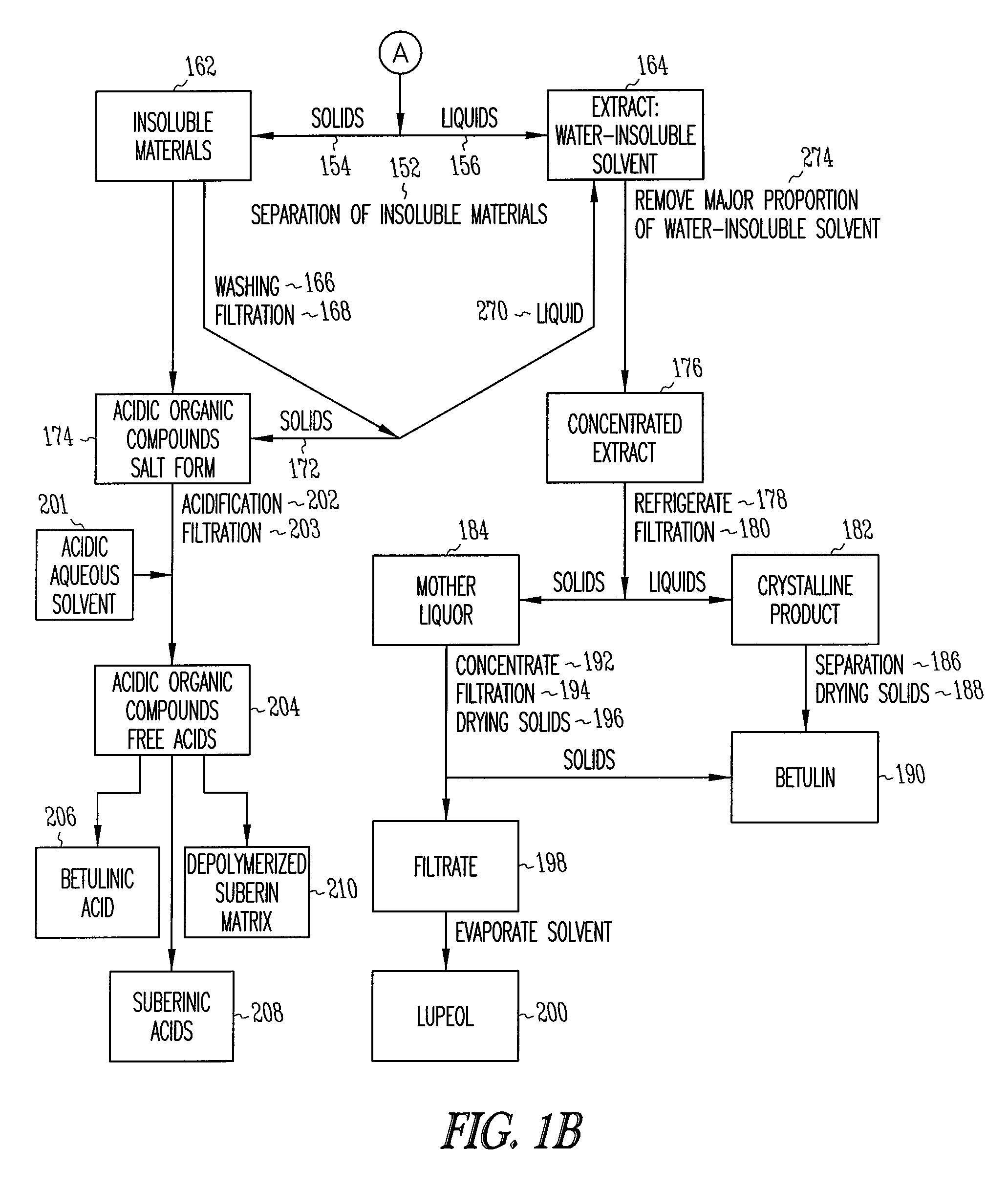
Birch bark processing and the isolation of natural products from birch bark
InactiveUS6815553B2Not costly and lengthy and dangerous procedureEasy to handleSolvent extractionOrganic compound preparationNatural productBetula platyphylla
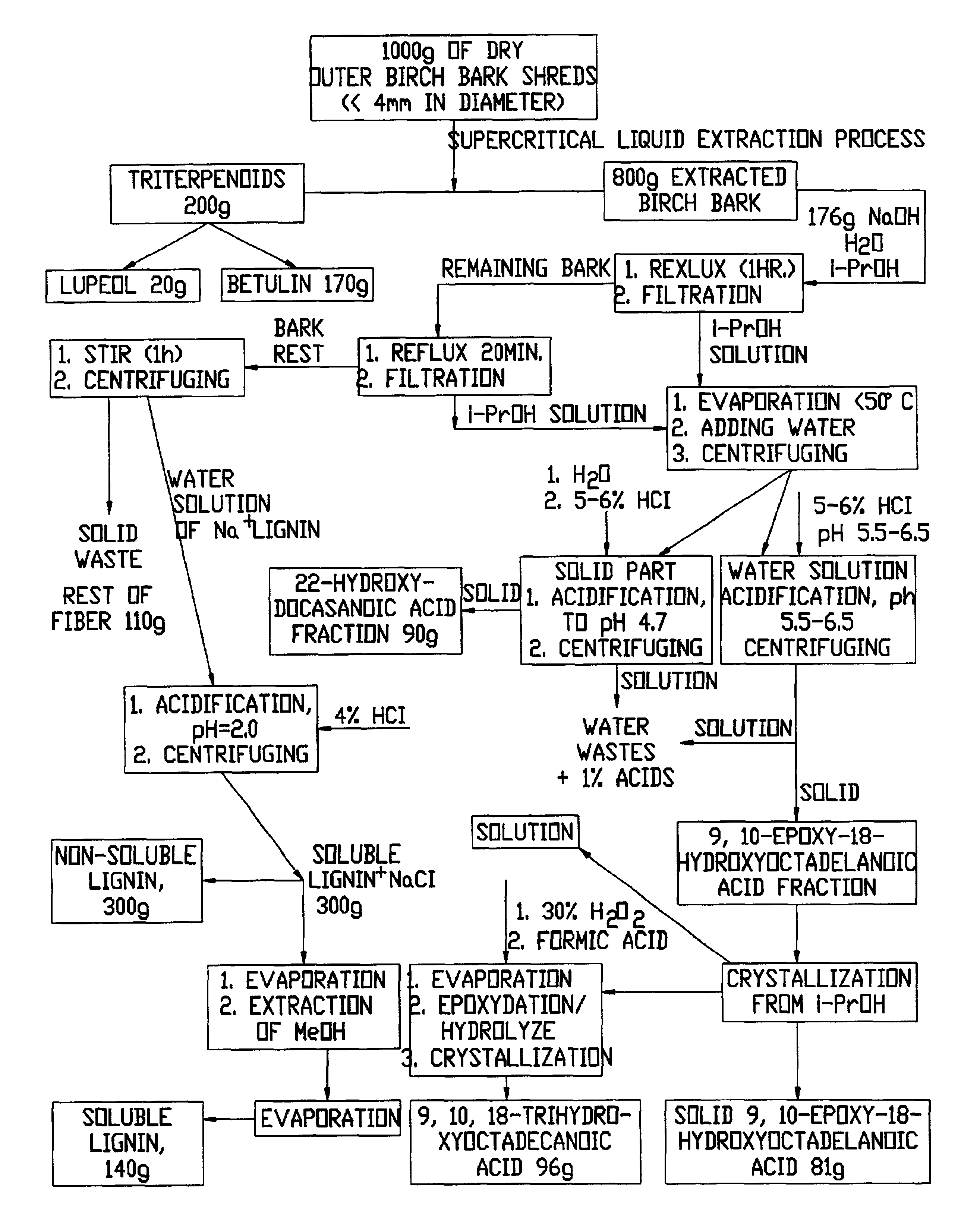
The invention provides methods for separating outer birch bark from inner birch bark. The invention also provides methods for isolating betulin; lupeol; betulinic acid; 9,10-epoxy-18-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid; 9,10,18-trihydroxyoctadecanoic acid; polyphenolic polymers and fatty acids from birch bark.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Birch bark processing and the isolation of natural products from birch bark
InactiveUS20050158414A1Not costly and lengthy and dangerous procedureEasy to handleBiocideSolvent extractionNatural productBetula platyphylla
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Healthy chili milk candy
InactiveCN105795081AAbundant raw materialsRich ingredients, rich tasteConfectionerySweetmeatsVegetable oilGalactooligosaccharide
The present invention discloses healthy chili milk candy. The healthy chili milk candy is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 42-44 parts of white granulated sugar, 35-37 parts of galactooligosaccharides, 12-14 parts of chilies, 11-13 parts of condensed milk, 3-5 parts of anhydrous cream, 3-4 parts of hydrogenated vegetable oil, 3-4 parts of skim milk, 1.6-1.8 parts of locust bean gum, 1.4-1.6 parts of chili leaves, 0.6-0.8 part of longan leaf, 1.1-1.3 parts of soybean pods, 1.1-1.3 parts of eleusine indica, 0.6-0.8 part of equisctum ramosissimum, 0.6-0.8 part of rorippa globosa, 0.4-0.6 part of gymnema sylvestre, 0.4-0.6 part of tangerine leaf, 0.4-0.6 part of betula alba juice, 0.4-0.6 part of edible salt and 0.6-0.8 part of lactobacillus delbrueckii. The provided healthy chili milk candy is crisp in texture, sweet, sour and palatable, rich in flavor, balanced in nutrition and easy to absorb, and can protect the heart and brain blood vessels, increase resistance, promote metabolism, delay aging, beautify features and lose weight.
Owner:YINGSHANG HAOYUAN FOOD
Micro-propagation method for white birch with purple leaf
InactiveCN101502237AShort reproductive cycleImprove efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBetula platyphyllaObserved Survival
The present invention relates to a micropropagation method of purple-leaf birch, and relates to a micropropagation method. The invention settles the problems of long breeding cycle, long propagation efficiency, high cost and low survival rate. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1. sterilizing the explant; 2. cutting the explant to stem segment, and then executing induction cultivation for obtaining micro-branch; 3. cutting the micro-branch to stem segment and proliferating in the culture medium; and 4. executing invigoration culture to the proliferated micro-branch, sticking into a rooting substrate for executing rooting culture for finishing the micropropagation of purple-leaf birch. The micropropagation method of purple-leaf birch of the invention has the advantages of short propagation period, high efficiency and excellent genetic stability. The propagation efficiency is that the purple-leaf birch propagates for 30-40 times every 30-40 days. The method of the invention also has the advantages of simple operating technique, labor saving, time saving and low cost. The cost is saved by 30%-50% compared with the prior art. Furthermore the rooting rate and survival rate of seedling propagation equally can obtain 100%.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
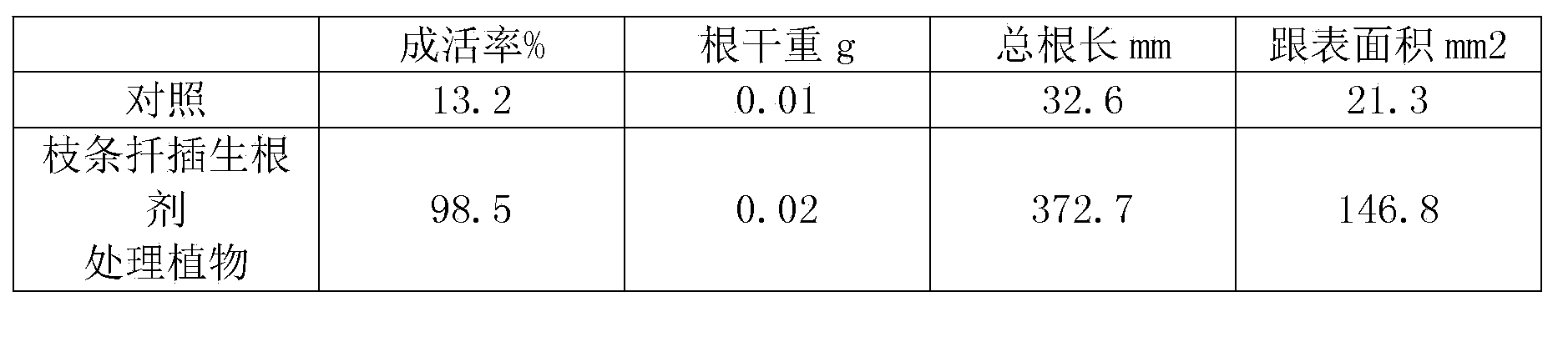
White birch branch cuttage method and special cuttage rooting agent thereof
InactiveCN103570436AIncrease rootingFast rootingHorticultureFertilizer mixturesGrowth plantBetula platyphylla
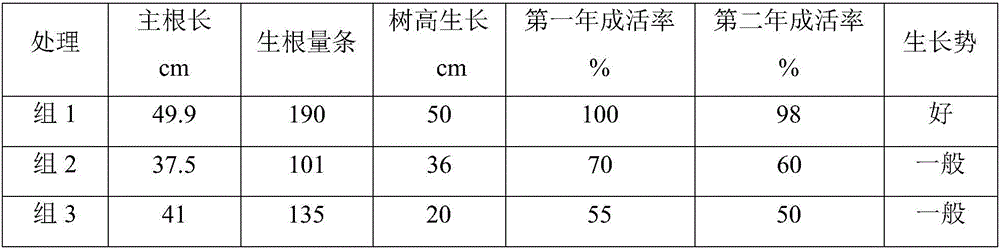
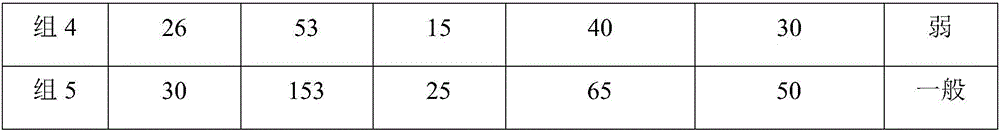
The invention discloses a white birch branch cuttage method and a special cuttage rooting agent thereof, relates to a white birch plantation method and belongs to the technical field of agriculture. The special cuttage rooting agent is obtained by compounding of assistants, shortens root differentiation time and improves a root amount, a rooting rate and a cuttage survival rate of white birch branches. A plant-growth regulator and micronutrients related to root development are used as main agents and the main agents and the assistants are compounded into powder or a solution, the special cuttage rooting agent can shorten root differentiation time, improve a root amount and a rooting rate of white birch branches and improve a cuttage survival rate of white birch branches to above 95%, the problems of the existing white birch branch cuttage technology are solved thoroughly, white birch branch cuttage technology research and industrial application are promoted, and the white birch branch cuttage method has an important effect in white birch seedling soilless-cultivation, industrialized seedling production and seed resource preservation.
Owner:刘平
Pharmaceutical agent containing birch extract as an effective ingredient and its use
ActiveCN101023915APromote productionKeep moistCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNatural productAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a new filaggrinogen or fibrous polyprotein generation accelerator, mantellum protein generation accelerator, cholesterol generation accelerator and cell-activating agent from natural product, which use sap of Betula platyphylla Sukatchev var.japonica Hara as effective constituents.
Owner:KOBAYASHI KOSE CO LTD
Method for promoting accumulation of triterpene in betula platyphylla suk. suspension cell by utilizing endophytic fungi elicitor
InactiveCN101824459ASimple processShort cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFungus protein
The invention provides a method for promoting accumulation of triterpene in betula platyphylla suk. Suspension cell by utilizing endophytic fungi elicitor. The method utilizes endophytic fungi separated from betula latyphylla suk. bark, the endophytic fungi is prepared into fungi elicitor, appropriate concentration of fungi elicitor is added in appropriate stage of betula platyphylla suk. suspension cell growth, after induction is carried out for a period of time, cells are collected, and endophytic fungi capable of effectively improving accumulation of triterpene is screened out as phomopsis sp. On the basis, induction effect of polysaccharide elicitor and protein elicitor prepared by the fungi is further optimized; 40Mug / ml of polysaccharide elicitor is added on the eighth day of betula platyphylla suk. cell culture, triterpene content in cell after induction for one day reaches up to 29.47mg / g, being 1.78 times that of the control group; 80Mug / ml of fungus protein elicitor is added on the eighth day of betula platyphylla suk. cell culture, induction culture is carried out for four days, and triterpene content in cell reaches up to 34.49mg / g, being 2.47 times that of the control group. In the invention, the type and concentration of the added elicitor, growth stage of betula platyphylla suk. suspension cell added with appropriate elicitor and induction time of elicitor are determined, induction technology of effectively improving accumulation of triterpene in betula platyphylla suk. suspension cell is formed, and important theory and technical basis are laid for betula platyphylla suk. triterpene production by utilizing cell engineering technology, thus the invention has wide application potential and promotion prospect.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
Method suitable for treating plateau stony desertification under photovoltaic panels
InactiveCN106386094AReduce churnReduce degradationSuperphosphatesClimate change adaptationPlateauFestuca ovina
The invention discloses a method suitable for treating plateau stony desertification under photovoltaic panels. Festuca ovina l. is planted within the scope 10m away from the photovoltaic panels and under the photovoltaic panels; the plantation mode of festuca ovina l. is seed sowing; sweet osmanthus or tea trees are planted in the scope from 10 to 20m away from the photovoltaic panels, wherein the plantation mode of sweet osmanthus or tea trees is seedling planting, and Betula platyphylla is planted at the place 20m beyond the photovoltaic panels; before seed sowing or seedling growing, 80 to 600g / m2 fertilizer is applied on the soil surface; before seed sowing or seedling growing, the seed sowing and seedling growing areas are watered. According to the method of the invention, fertilizer is applied before planting, well-adapted and drought tolerant sweet osmanthus or tea trees, festuca ovina l. and Betula platyphylla are selected and forestation modes of directed seeding or seedling growing are adopted to recover the land surface vegetation, reduce soil loss and land degeneration, increase survival rate of seedlings, and block fierce wind and severe cold; multiple tree species three-dimensional mixed pattern is formed to treat the plateau stony desertification under photovoltaic panels; the method is suitable for large-scale promotion.
Owner:云南云创数字生态科技有限公司
Birch efficient transgenic method
InactiveCN103146749AIncreased resistance to Agrobacterium infectionImprove infection abilityGenetic engineeringFermentationBetula platyphyllaTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a birch efficient transgenic method and relates to a plant transgenic method. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for solving the problems of low transformation efficiency and complex bacteria removing process of the existing birch transgenic method. The method is carried out through the following steps: step one, carrying out rooting culture twice for sub-cultured seedlings without root and selecting healthy leaves applied to agrobacterium infection; step two, infecting via agrobacterium; step three, co-culturing; and step four, finally acquiring transgenic plants through callus culture, differentiation culture, subculture and rooting culture. The method can be used for enhancing the agrobacterium infection-resisting capability of the leaves and speeds up the wound infection risk by selecting explants in the appropriate physiological state; the number of times for removing bacterium is reduced from the original 20-25 to 7-10; and the birch transgenic efficiency is increased by 2.32-3 times. The method can be applied to the birch transgenic field.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for treating birch bark
InactiveCN104942939AAvoid crackingGuaranteed toughnessWood treatment detailsThermal wood treatmentPotassium nitrateBetula platyphylla
The invention relates to a method for treating birch bark. The method comprises the following steps: (1) peeling fresh birch bark, cleaning the surface, suffocating for 1.5-2 hours by a steamer, and then cooling naturally; (2) preparing a treatment solution, mixing 3.2-4 parts of polyethylene glycol, 6-8 parts of glycerinum, 4.5-6.8 parts of potassium nitrate, 1-1.8 parts of pine-seed oil, 1.5-2.4 parts of chlorinated paraffin and 25 parts of water evenly so as to prepare the treatment solution; (3) putting birch bark treated in the step (1) into the treatment solution prepared in the step (2), soaking for 2-3 days, flushing clean with clear water after treating is completed, then suffocating for 0.5 hour by the steamer, taking out, cooling to normal temperature at the cooling speed of 2 DEG C / min. The method for treating birch bark for bark pictures is simple, and is convenient to use; the treated birch bark is good in stability and is easy to color.
Owner:阜南佳利工艺品股份有限公司
Depolymerization extraction of compounds from birch bark
ActiveUS20090182158A1Increase productionHigh yieldBiocideCosmetic preparationsSimple Organic CompoundsDepolymerization
The invention provides improved processes for the extraction of betulin, lupeol, betulinic acid, suberinic acids, and / or other organic compounds and compositions from birch bark. In some embodiments, the birch bark can be physically processed prior to the extraction process, which can further improve the yield of the extraction. The bark processing can include, but is not limited to, one or more of pelletizing the bark, baling the bark, pucking the bark, or compressing the bark, to a form that is more dense per volume unit than prior to the processing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
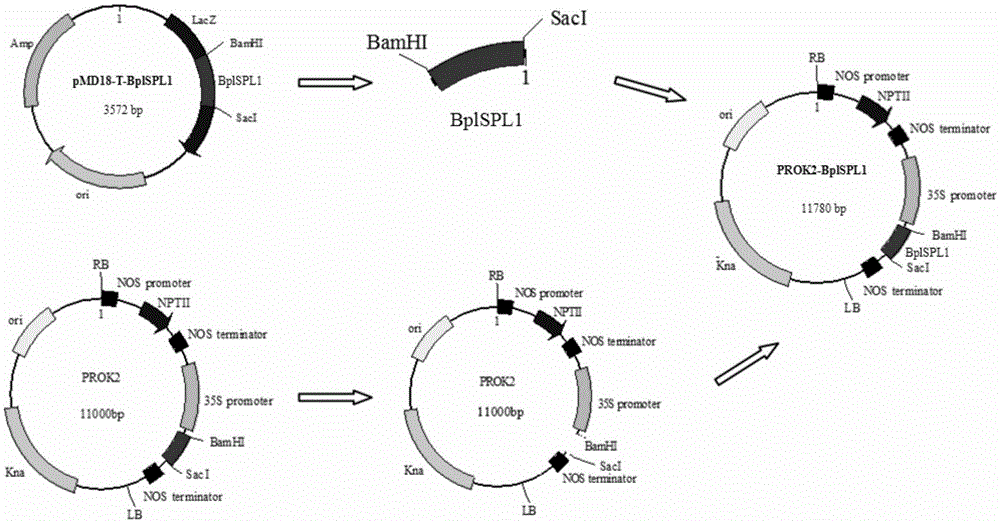
Betula platyphylla BplSPL1 gene for promoting precocious flowering and encoded protein thereof
InactiveCN106591320AEarly floweringShorten flowering timePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringGenetic engineeringFlowering time
Belonging to the field of gene technology in molecular biology, the invention relates to a betula platyphylla BplSPL1 gene for promoting precocious flowering and an encoded protein thereof. The invention is characterized in that the betula platyphylla BplSPL1 gene for promoting precocious flowering has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table, and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The invention provides the betula platyphylla flowering gene BplSPL1 and applies the gene to construction of a BplSPL1 gene's plant expression vector, and the constructed plant expression vector is subjected to agrobacterium impregnation of an arabidopsis thaliana plant so as to obtain a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant and achieve precocious flowering. Therefore, the gene has the function of inducing precocious flowering of arabidopsis thaliana and can regulate plant leaf development. The gene provided by the invention utilizes genetic engineering technology to regulate betula platyphylla flowering time and leaf development, provides gene resources and theoretical basis, and has great application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +3
A BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., an encoding protein thereof and applications of the gene
InactiveCN106868018AImprove the ability to resist adversity and stressHigh activityPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringHalotoleranceBetula platyphylla
The invention relates to a BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., an encoding protein thereof and applications of the gene and discloses the BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., the encoding protein thereof and the applications of the gene. The objective of the invention is to provide the BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., the encoding protein thereof and the applications of the gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table, and an amino sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence table. The gene can enhance adversity stress resistance of plants. An agrobacterium-tumefaciens-mediated leaf disc transformation method is utilized to perform genetic transformation of the betula platyphylla Suk., obtained transgenic betula platyphylla Suk. plants are subjected to salt resistance and drought tolerance analysis, and results show that the gene can enhance salt resistance and drought tolerance of the betula platyphylla Suk.. Through the gene, the encoding protein and the applications, a novel BpSPL9-transgenic betula platyphylla Suk. variety that is salt-resistant and drought-tolerant can be cultivated. The gene, the encoding protein and the applications are applied in the field of forest tree molecular breeding.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
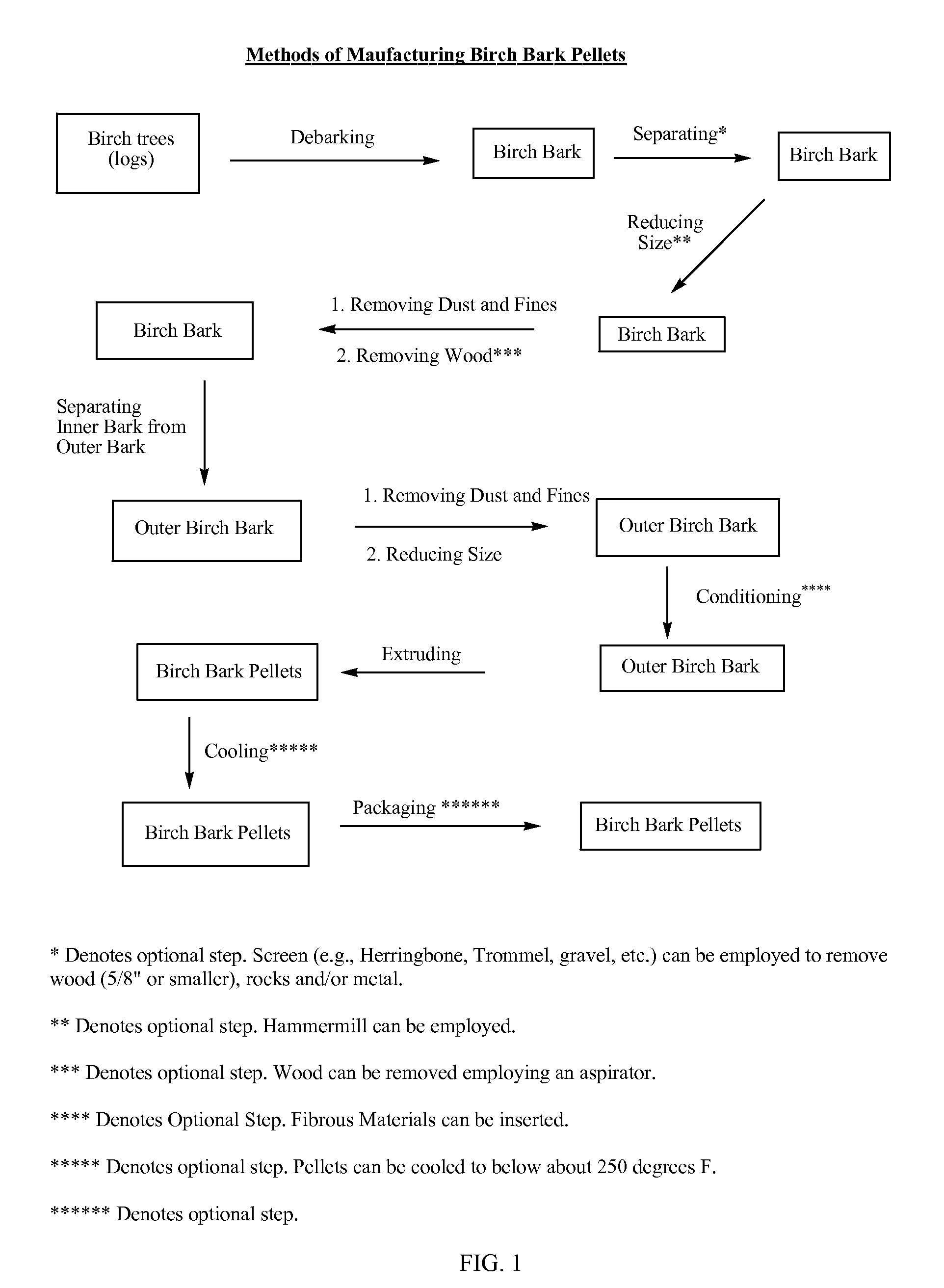
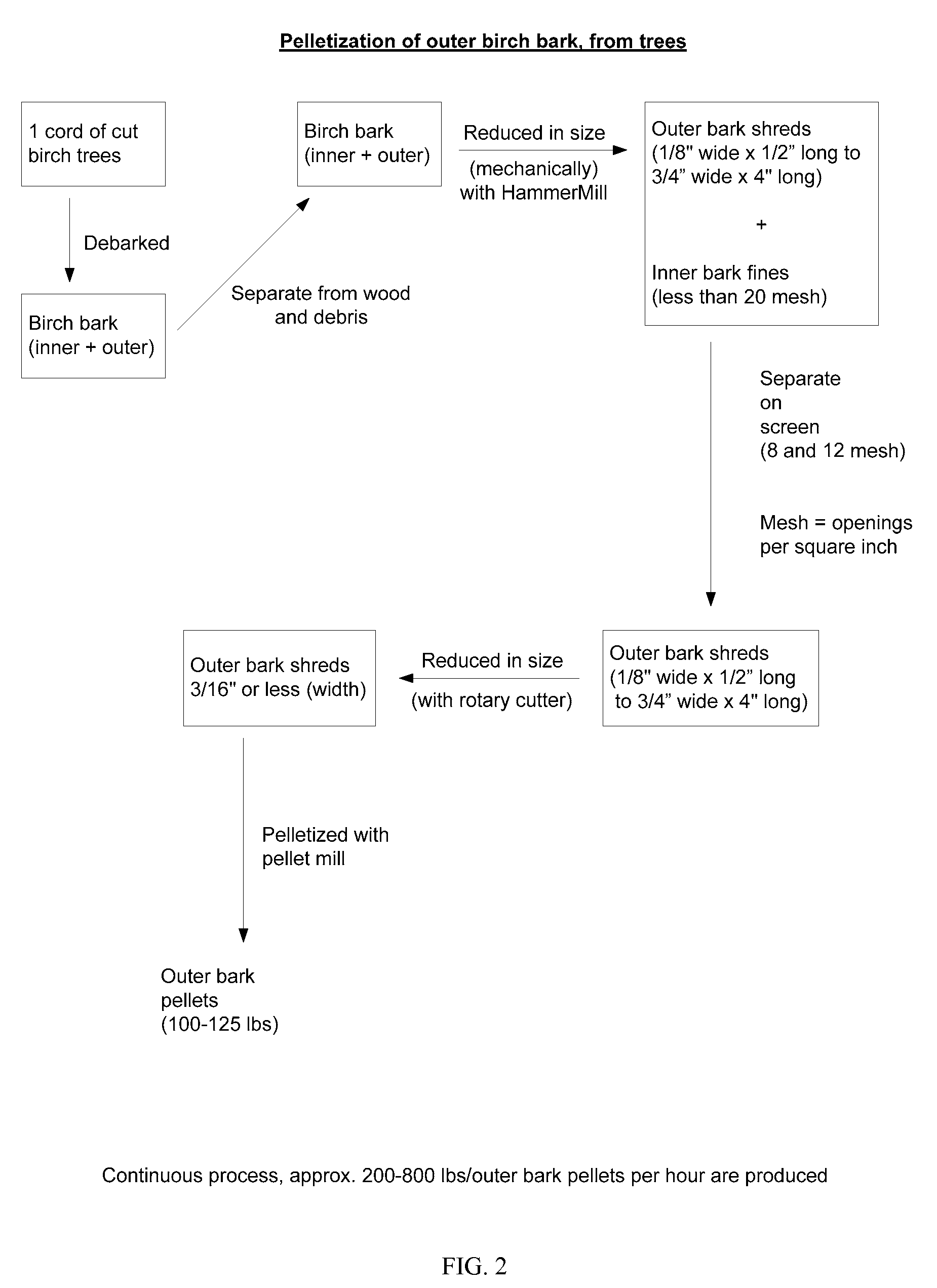
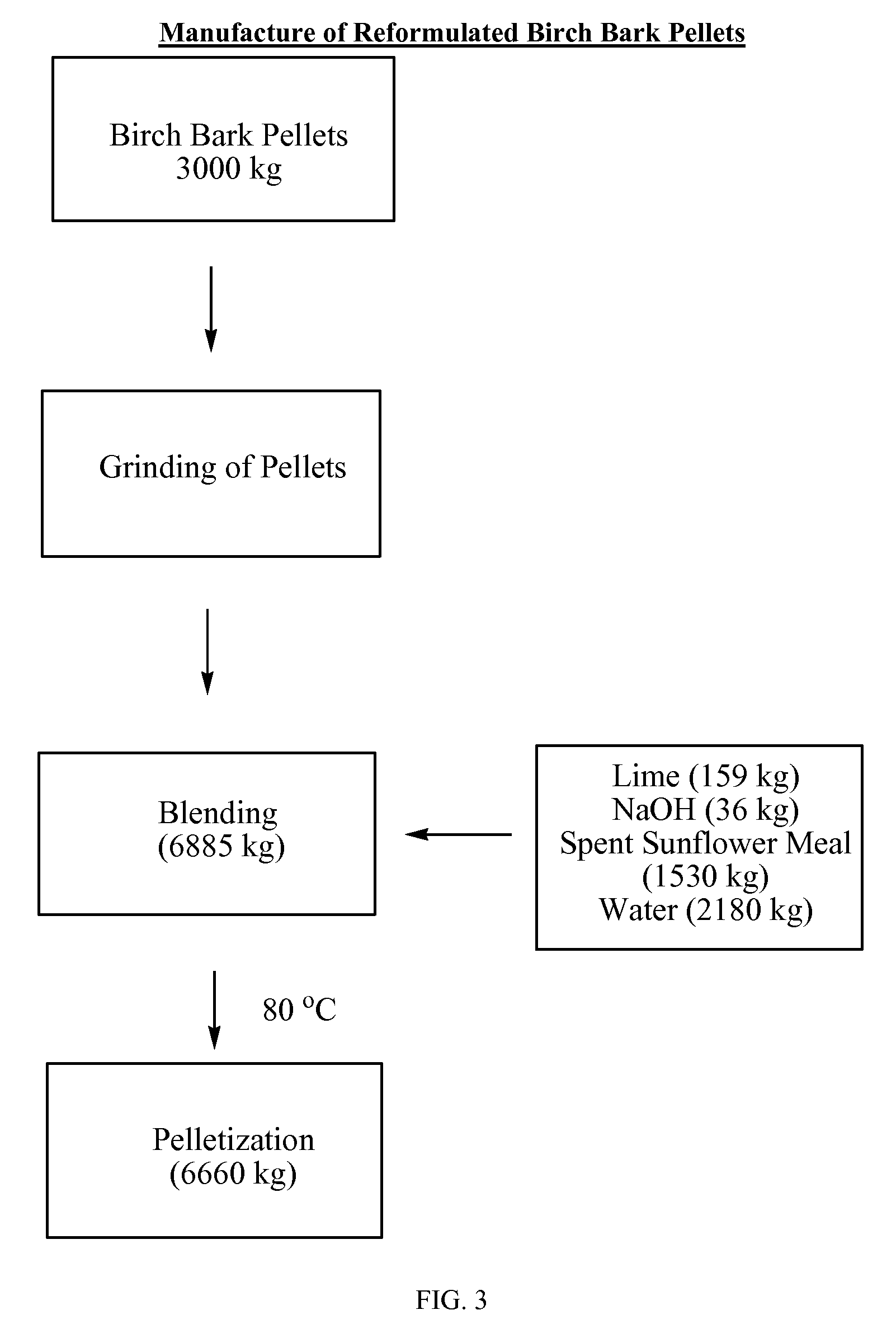
Birch bark pelletization and methods for obtaining natural products from birch bark pellets
InactiveUS20090253943A1Reduce shippingReduce processing costsDischarging arrangementMouldsNatural productMedicine
The present invention provides birch bark pellets that include outer birch bark. The present invention also provides methods of manufacturing birch bark pellets from outer birch bark. The present invention also provides methods for obtaining a natural product from birch bark pellets. The birch bark pellets are manufactured from outer birch bark that includes relatively low amounts of inner birch bark and wood. The birch bark pellets meet the requirement for extraction, to obtain e.g., betulin and / or lupeol from the pellets.
Owner:MYREXIS INC
Application of betula platyphylla suk. bHLH9 protein in regulation of synthesis of triterpenoids
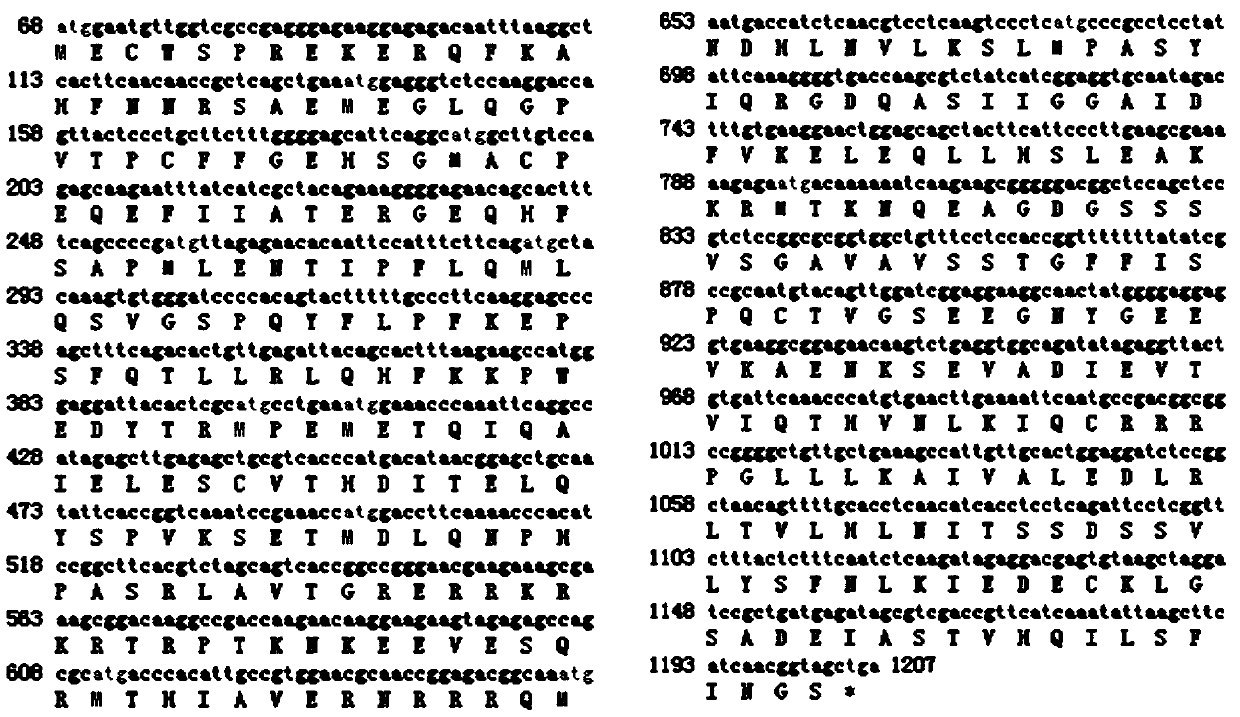
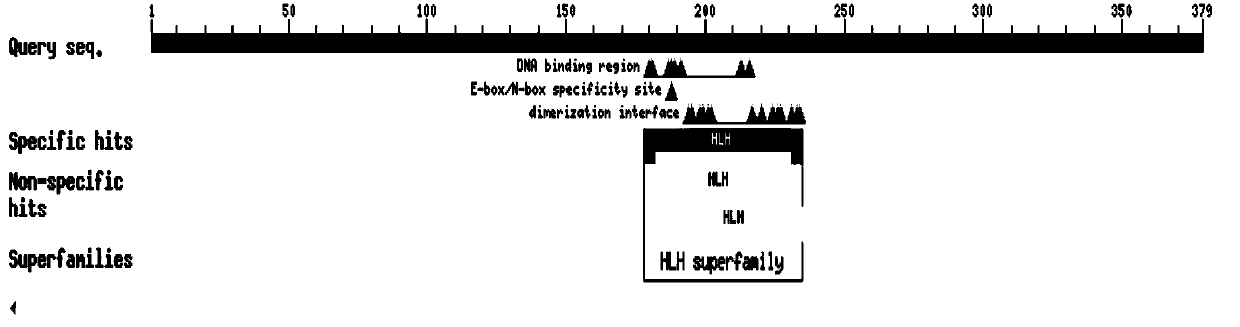
The invention discloses an application of a betula platyphylla suk. bHLH9 protein and related biomaterials in regulation of synthesis of triterpenoids. Experiments prove that over expression of a BpbHLH9 gene can increase the content of triterpenoids and triterpenoid precursors in transgenic yeast and transgenic betula platyphylla suk., wherein improvement of the content of oleanolic acid is the most significant. The relative expression quantities of triterpenoid pathway key enzyme genes in the transgenic betula platyphylla suk. are all up-regulated to a different extent. The results show thatthe BpbHLH9 gene is involved in the synthesis of the betula platyphylla suk. triterpenoids, and the expression of the triterpenoid pathway key enzyme genes and the content of the triterpenoids such as oleanolic acid, betulinic acid and betulin can be effectively improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Witchhazel after-sun repair composition and application
InactiveCN108434036APromote whiteningImprove facial shineCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMedicineHamamelis mollis
The invention discloses a witchhazel after-sun repair composition and application. The composition comprises, by weight, 1-10 parts of anthemis nobilis flower extracts, 1-10 parts of white birch barkextracts and 1-10 parts of witchhazel extracts. According to the witchhazel after-sun repair composition, the anthemis nobilis flower extracts, the white birch bark extracts and the witchhazel extracts are compounded, can have a synergistic effect and can improve oily faces, supplement water and relieve the symptoms of redness, swelling, coarse pores and couperose skin; the composition is high inlight stability, lasting in repair and capable of promoting tenderness and whiteness of skin.
Owner:江西登云健康美业互联有限公司 +1
Conditioning cream prepared by Chinese herb medicine extract superfine powder and with functions of acne removing and whitening and preparation method of conditioning cream
InactiveCN105342952APromote blood circulationImprove internal environmentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCentella asiatica extractBletilla striata
The invention discloses a conditioning cream prepared by Chinese herb medicine extract superfine powder and with functions of acne removing and whitening and a preparation method of the conditioning cream. The effective constituents of the conditioning cream comprise, by weight, 20-65 parts of azalea leaf extract, 18-60 parts of hamamelis virginiana extract, 15-55 parts of fructus rubi extract, 10-40 parts of white willow bark extract, 10-45 parts of betula platyphylla bark extract, 10-35 parts of centella asiatica extract, 8-30 parts of herba leonuri extract, 8-30 parts of radix glycyrrhizae extract, 6-20 parts of bletilla striata extract, 6-20 parts of radix ampelopsis extract, 5-15 parts of tribulus terrestris extract, 4-15 parts of salviae miltiorrhizae extract, 4-15 parts of fructus gardeniae and 5-12 parts of pearl powder. The conditioning cream prepared by the Chinese herb medicine extract superfine powder and with the functions of acne removing and whitening has the advantages that the conditioning cream is good in effect, safe and practical, raw material particle size is decreased evidently to allow the particle size to be 3.1-12.5 micrometers, namely 400-1000 mesh by performing superfine grinding on the coarse powder of Chinese herbal medicine extract, sufficient percutaneous absorption is achieved, and an ideal effect is brought into play.
Owner:金建文
Functional skin care lotion with effects of whitening and freckle removing
InactiveCN106361653AAvoid harmNo allergic reactionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycyrrhiza glabra RootVaccinium macrocarpon
The invention discloses a functional skin care lotion with the effects of whitening and freckle removing. The functional skin care lotion is characterized by being prepared from, by weight, 5%-8% of Asian betula platyphylla juice, 4.5%-6.5% of other functional skin care product additives, 10%-12% of glycerin, 1.5%-2% of ceramide 3, 0.8%-1.5% of sodium hyaluronate, 1.5%-2.5% of polysorbate-20, 0.5%-1% of carbomer and 70%-76.2% of water, wherein the other functional skin care product additives are prepared from, by weight, 4-6 parts of a glycyrrhiza glabra root extract, 4.5-7.5 parts of an euterpe oleracea fruit extract, 3-7 parts of arbutin, 2-5 parts of a vaccinium macrocarpon fruit extract and 2-5 parts of a strawberry extract. The functional skin care lotion with the effects of whitening and freckle removing has the good whitening, freckle removing and oxidation resisting effect trial process and is suitable for being used by people with various skin types in the age group that freckles are prone to grow.
Owner:珀蒂珍(广东)健康产品有限公司
Rapid propagation method of wild betula platyphylla suk
ActiveCN106171996AEasy to rootStrong resistance to diseases and insect pestsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureShootBetula platyphylla
The invention provides a rapid propagation method of wild betula platyphylla suk. The rapid propagation method comprises the following steps: 1) obtainment of the stem explant of the wild betula platyphylla suk; 2) inducing culture of the stem explant of the wild betula platyphylla suk; 3) enrichment culture of clustered shoots of the wild betula platyphylla suk; 4) rooting culture of the wild betula platyphylla suk: at the first stage, firstly culturing single shoots cut from the clustered shoots in a first rooting culture medium, putting the single shoots under 2800-3000Lux and illuminating the single shoots for 20 hours everyday to culture the single shoots until the single shoots root for 8-10 days; at the second stage, transferring the single shoots to a second rooting culture medium to be cultured for 20-30 days until good root systems grow; 5) hardening and transplanting of wild betula platyphylla suk tissue culture seedlings: carrying out hardening under normal temperature for 7-10 days and then transplanting the seedlings to a substrate to be cultured for 30-35 days, thus obtaining rapid propagation seedlings of the wild betula platyphylla suk; 6) transplanting: transplanting the seedlings to planting sites. The problems that the wild betula platyphylla suk is difficult in tissue culture and rooting and has low rooting rate are solved by adopting the rapid propagation method.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Potted cultivation method for centella asiatica
InactiveCN105409525AGuaranteed hydrophobicityGuaranteed water retentionAnimal corpse fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersAspirinBetula platyphylla
The invention relates to the technical field of planting industry and particularly relates to a potted cultivation method for centella asiatica. The method comprises the steps of scissoring creeping stems of wild centella asiatica in March every year, adding 2-5 parts of glucose, 0.01-0.03 part of magnesium sulfate and 3-5 parts of aspirin into every 100 parts of silver birch juice so as to obtain a rooting solution, soaking cuts of the creeping stems of the wild centella asiatica in the rooting solution for 10-15 days, mixing garden soil, coarse sand, sawdust, humus soil, egg-shell meal, feather meal and plant ash according to the weight ratio of 5: 1: 1: 3: 1: 1: 1 so as to obtain soil for cultivation, spreading the soil for cultivation and sphagnum moss, which are in the volume ratio of 4: 0.5, into each cultivation pot in a layered manner from bottom to top sequentially, planting the creeping stems of the wild centella asiatica in cultivation pots according to a ring shape in a manner that the spacing among rings is 5-7cm and 5-10 creeping stems of the wild centella asiatica are subjected to stem planting per 0.01 square meter, and placing the cultivation pots at a shady place with the cultivation shade rating of 50-70% after stem planting.
Owner:QUANJIAO TAOHUAWAN FRUIT & VEGETABLE PLANTATION SPECIALIZED COOP
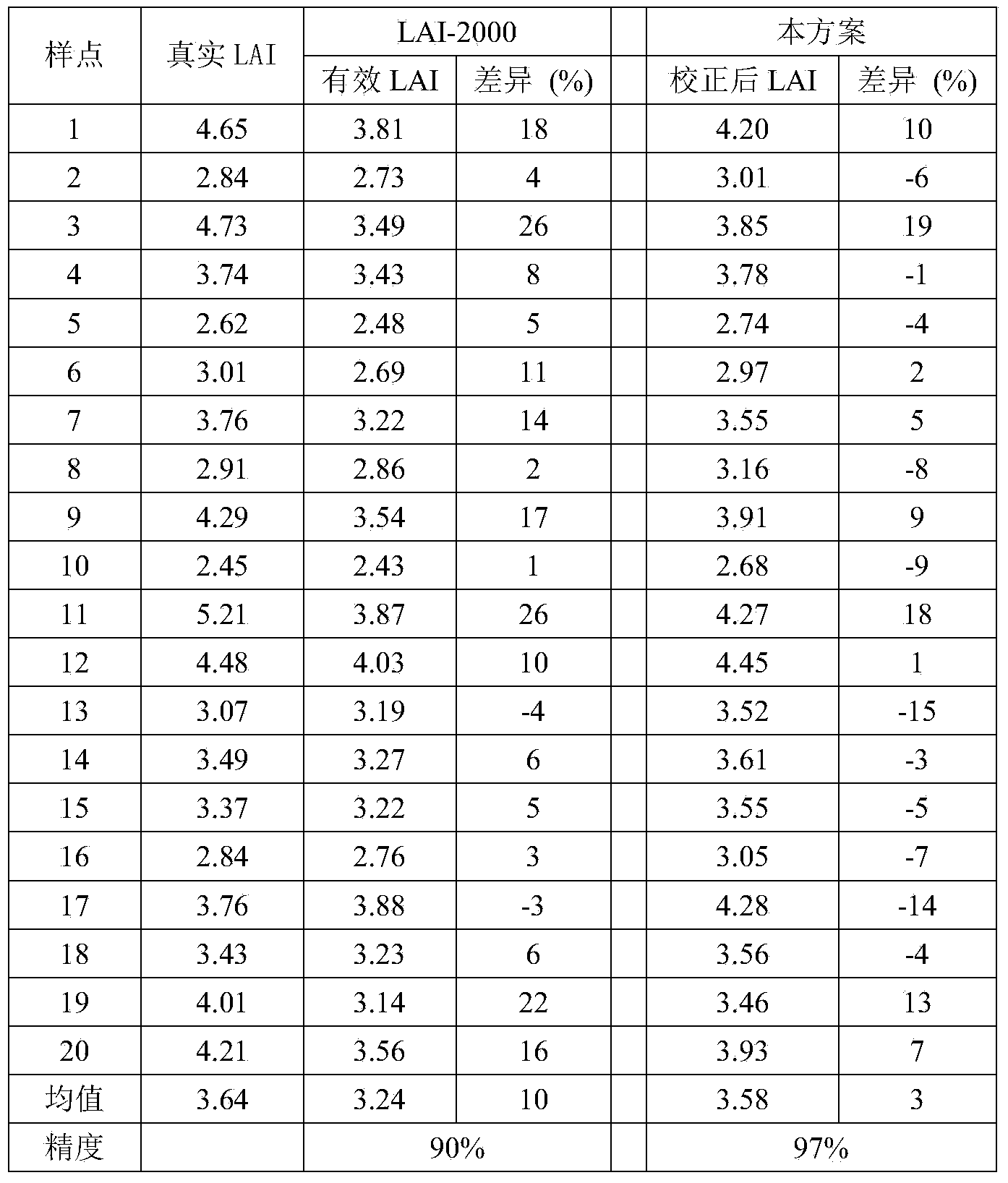
Correction method for measuring leaf area index by use of plant canopy analyzer
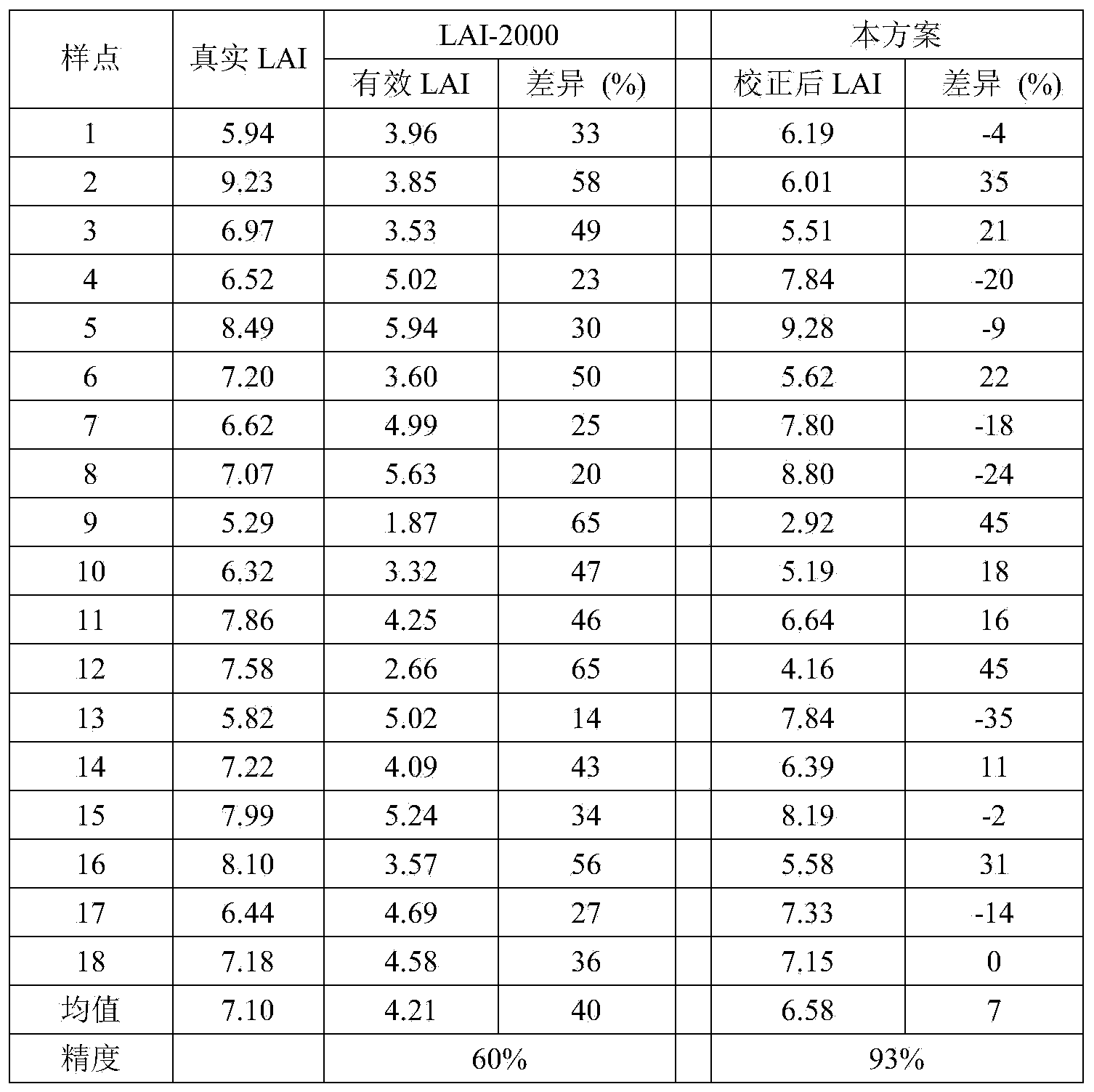
ActiveCN104330058AHigh measurement accuracyHigh precisionUsing optical meansSecondary forestBetula platyphylla
The invention provides a correction method for measuring a leaf area index by use of a plant canopy analyzer, relates to a correction method for measuring the leaf area index and aims at solving the problem that the existing measuring method by use of the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer is limited and low in leaf area index estimation accuracy. The correction method is used for obtaining an LAI value by use of the LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer; correction is based on a formula as shown in the description; in the formula, L represents the LAI numerical value after correction and Le represents the LAI numerical value before correction; alpha, omega E and gamma E in the formula are correction coefficients, wherein alpha is the proportion of a lignin index in the total LAI, and the values of alpha of an artificial Korean pine forest and a betula platyphylla secondary forest are 0.03 and 0.04, respectively; omega E is a crowding index, and the values of omega E of the artificial Korean pine forest and the betula platyphylla secondary forest are 0.95 and 0.87, respectively; gamma E is a needle-cluster ratio. The correction method for measuring the leaf area index by use of the plant canopy analyzer takes the influence of the crowding effect into account and is comprehensive in the range of consideration, and the obtained data are true and reliable.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Base fertilizer for root reinforcing at betula platyphylla plantation initial stage
InactiveCN105399527APromote rapid growthPromote reproductionExcrement fertilisersNitrogenous fertilisersManganeseBoer goat
The invention provides a base fertilizer for root reinforcing at betula platyphylla plantation initial stage and relates to the betula platyphylla plantation technology field. The base fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials: fresh betula platyphylla leaves, banana peels, manganese sulfate, zinc sulfate, boric acid, inositol, vitriol thiamine, glycine, citric acid, green tea, honey, pig dung, Boer goat dung, bagasse and amino acids. The raw materials of the prepared base fertilizer are easily available, the usage effects are good, rapid growth of roots can be promoted, root breeding is accelerated, and the plantation survival rate and the disease-resistant rate are raised.
Owner:安徽和合园林绿化工程有限公司
Effective externally-applied composition containing betula platyphylla extract
InactiveCN107837224AAccelerates the injury healing processNo scarsCosmetic preparationsAntimycoticsDiseaseBletilla striata
The invention provides an effective externally-applied composition containing a betula platyphylla extract; the composition is composed of the following raw materials: bletilla striata, moutan bark, carboxymethyl cellulose, radix angelica sinensis, the betula platyphylla extract, cassia bark, ginseng, a hamamelis mollis extract and butanediol. Compared with the prior art, the composition has the following beneficial effects that with comprehensive utilization of combined efficacies of drug effects of betula platyphylla with other components, the composition is used as a skin care additive, supplements nutrition for damaged skin, can help treatment of acne and wound healing, accelerates the healing process of injury, makes scars and pigments not remain, can be used for treating psoriasis, eczema, skin lacerated wound or blistering, mosquito bites, varicose veins, hemorrhoids and other diseases, and has a curative effect on all skin incised wounds, bruises and sunburn.
Owner:珀蒂珍(广东)健康产品有限公司
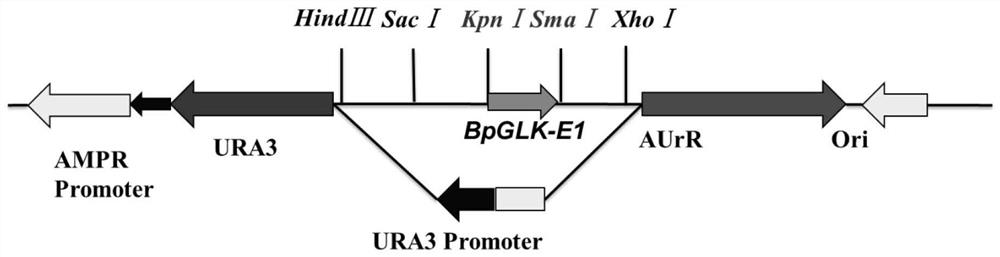
CRISPR/Cas9 system for targeted knockout of GLK gene and application of CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN112941077ARich varietyOther foreign material introduction processesAngiosperms/flowering plantsRibosomal proteinCallus
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 system for targeted knockout of a GLK gene and application of the CRISPR / Cas9 system, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the invention, through design, construction and screening, some efficient gRNA and target site sequences which are based on a CRISPR / Cas9 system and can target a Betula platyphylla GLK gene at the same time are finally provided, specifically, the Betulinic GLK gene is used as an editing target gene, and the externally-purified Cas9 protein and the GLK-gRNA are mixed to obtain the ribosomal protein complex RNP; the Betula platyphylla callus is bombarded through particles; the T-DNA-free insertion gene editing technology is preliminarily established; the Betula platyphylla yellow leaf plant is obtained by utilizing the gene editing technology; and a new idea is provided for enriching the Betula platyphylla variety and rapidly creating the Betula platyphylla plant mutant.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Efficient betula platyphylla root transgenic method
PendingCN114836468AImprove conversion efficiencyShort conversion cycleAfforestationFermentationBiotechnologyBetula platyphylla
The invention relates to an efficient betula platyphylla root transgenosis method, and belongs to the technical field of plant transgenosis. In order to solve the problems of long culture period, long transformation period and low efficiency of explants of an existing betula platyphylla transgenosis system, the invention provides an efficient betula platyphylla root transgenosis method which comprises the following steps: selecting betula platyphylla roots with root tiller reproductive capacity as a transgenosis material; the method comprises the following steps: culture of white birch roots, genetic transformation of agrobacterium carrying a target gene, induction of callus formation through co-culture, induction of adventitious bud formation through resistance screening, and finally formation of a complete plant through induction. Compared with an existing betula platyphylla transgenosis method, the method has the advantages that the transformation period is shortened, the transformation efficiency is improved, the difficulty in explant selection is avoided, the genetic background of transgenic offspring plants is unified, the utilization rate of materials is improved, and the problem of difficulty in degerming is further solved. The efficient betula platyphylla root transgenic method provided by the invention is simple to operate and easy to master.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Botanical formulation derived from birch bark
ActiveUS20120223157A1Reduce swellingPainful pressureBiocideNervous disorderPain syndromeBetula platyphylla
A formulation and method of mitigation of symptoms of patients suffering from a neurocutaneous pain syndrome by topical application of the formulation. The formulation is obtained by steeping the bark of a tree from the genus Betula in an aqueous acidified solution and then subsequent filtering, packaging and sterilization.
Owner:RADENTZ LESLIE MARIE
Culture medium for betula platyphylla embryogenic callus induction, method for embryogenic callus induction and cultivation method for tissue culture seedlings
InactiveCN110313403AReduce contactA large amountPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSucroseSaccharum
The invention provides a culture medium for betula platyphylla embryogenic callus induction, a method for embryogenic callus induction and a cultivation method for tissue culture seedlings, and belongs to the technical field of plant tissue culture. The provided culture medium for betula platyphylla embryogenic callus induction takes an MS culture medium as a basic culture medium and comprises 2 mg / L of 2,4-D, 0.2 mg / L of NAA, 5.5 g / L of agar and 40 g / L of saccharose, and the pH value of the culture medium for betula platyphylla embryogenic callus induction is 5.8. By using the culture medium,the callus induction rate is 90% or above, and the embryogenic callus induction rate is 19% or above.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
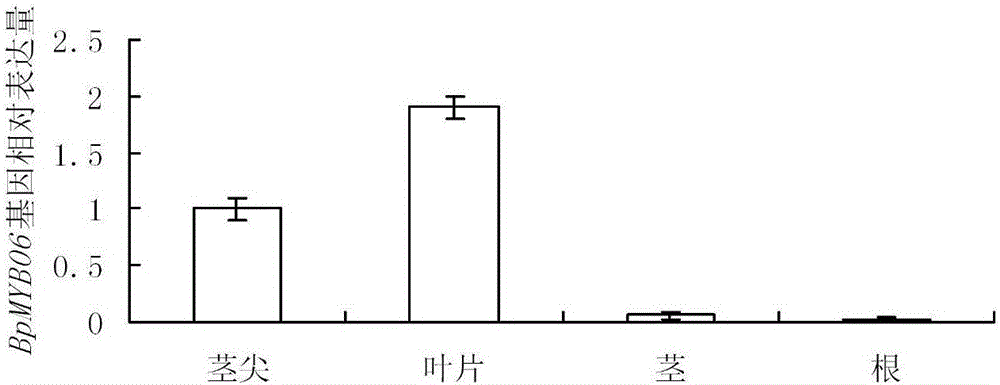
BpMyB106 gene in Betula platyphylla and amino acid sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN104962563AIncrease speedIncrease growth ratePlant peptidesFermentationYeastCis-regulatory element
The invention relates to and aims at providing a BpMyB106 gene in Betula platyphylla and an amino acid sequence and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the BpMyB106 gene in Betula platyphylla is show in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.1; the amino acid sequence thereof is shown in a sequence list SEQ ID NO.2. The BpMyB106 gene helps improve expressive abundance of photosynthesis related genes. The yeast one-hybrid technique shows that a BpMyB106 transcription factor is capable of directly controlling photosynthetic genes to increase the photosynthetic speed and growth speed of Betula platyphylla by the combination with photosynthesis related cis-acting elements; a new variety of Betula platyphylla with the trans-BpMYB106 gene, which is high in luminous effect and growth speed, can be cultivated with the BpMyB106 gene; the BpMyB106 gene is applicable to the field of molecular breeding of trees.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Rooting powder for cutting and cultivating white birches
The invention discloses rooting powder for cutting and cultivating white birches. The rooting powder is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-4 parts of sodium selenite, 48-50 parts of furfural residues, 34-37 parts of traditional Chinese medicine residues, 1-2 parts of myo-inositol, 3-4 parts of sodium glutamate, 8-11 parts of agar, 9-13 parts of gelatin powder, 42-45 parts of potassium humate, 4-5 parts of ferrous sulfate, 33-37 parts of green haws, 50-52 parts of fresh smoked plums, 83-87 parts of wrinkling Chinese flowering quinces and an appropriate amount of water. When the rooting powder disclosed by the invention is used, the divergence time of short roots can be shortened, the rooting quantity, rooting speed and cutting survival rate of branches of the white birches are improved; the myo-inositol, the sodium glutamate and the like are added, so that the vitality and the ATP enzyme activity of the root system can be obviously improved, the development of the root system is promoted, and the dry weight of the root system is increased. The rooting powder disclosed by the invention has important effects on the respects of the industrial seedling culture, afforestation and timber processing of the white birches.
Owner:郭道槐
Potted plant nutritional soil
InactiveCN106565326AImprove breathabilityStable pHGrowth substratesCulture mediaBetula platyphyllaPeat
The invention discloses a potted plant nutritional soil which is composed of the following ingredients by mass: 50-60 parts of garden soil, 5-7 parts of quick lime, 30-40 parts of rice chaff ash, 15-25 parts of peat, 10-12 parts of white birch bark, 30-32 parts of plant ash, 40-42 parts of fluffy soil, 25-35 parts of pine bark and 150-250 parts of water. The potted plant nutritional soil is rich in nutrient elements, good in soil permeability, stable in soil acid-base property, has waste turned into treasure, and has a broad market development space.
Owner:张帅
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com