Patents
Literature
506 results about "Flowering time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Early flowering in genetically modified plants
InactiveUS20070199107A1Other foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesNucleotideEctopic expression
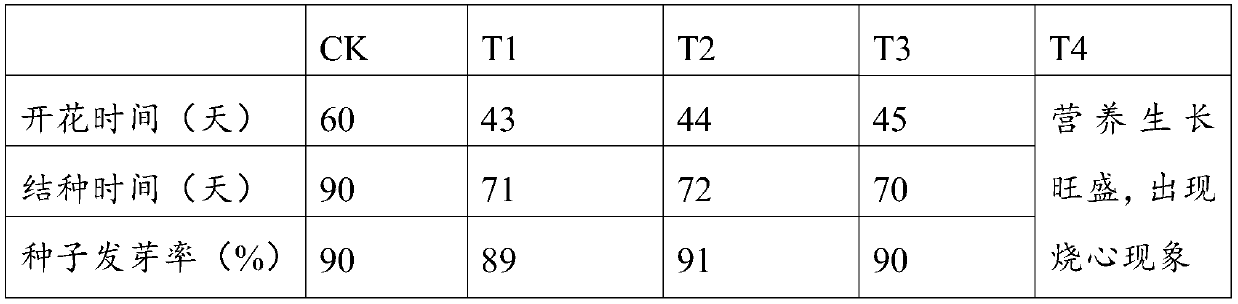
The present invention provides polynucleotides encoding CCAAT-binding transcription factor polypeptides that modulate the onset of reproductive development in plants. Polynucleotides encoding functional CCAAT-binding transcription factors were incorporated into expression vectors, introduced into plants, and ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention significantly shortened the time to flower development in the transgenic plants, as compared to the flowering time of control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
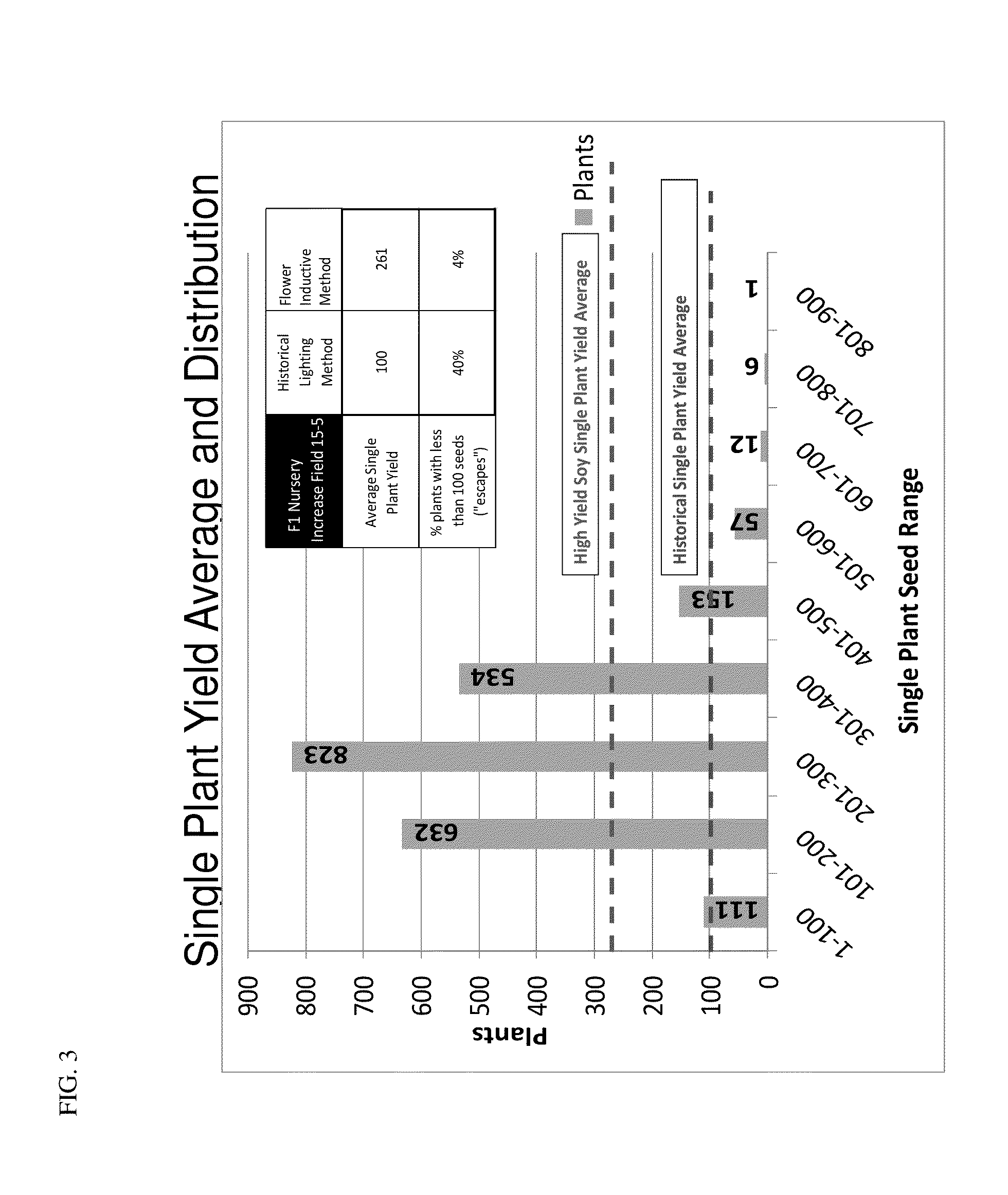
Methods for modifying flowering time and seed yield in field crops
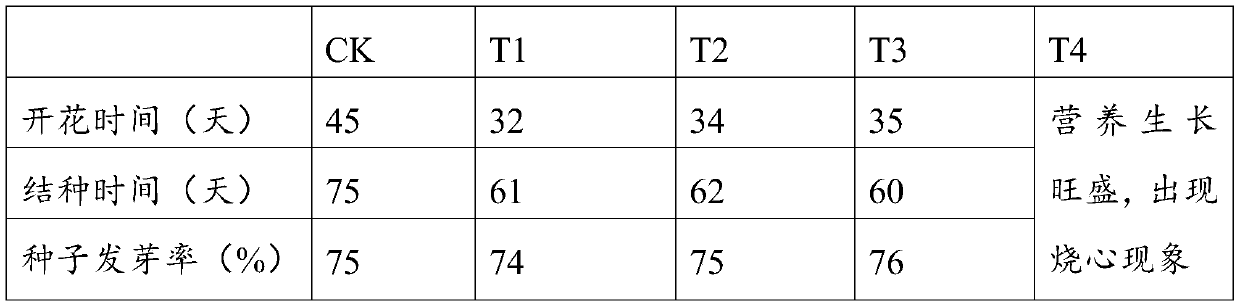
Methods for manipulating yield and generation time of short day plants grown in a field environment are provided. The methods comprise manipulating external signals such as photoperiod in order to increase the per plant seed yield. Also provided are methods for synchronizing the flowering times of plants in different maturity groups.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Flowering time adjustment and control method for enabling peony to blossom in winter
The invention discloses a flowering time adjustment and control method for enabling a peony to blossom in winter. The method comprises the steps of variety and plant selection, forced dormancy, root growth promoting and flower forcing treatment, so that a purpose of manually advancing the flowering time of the peony is achieved. The flowering time of the peony is advanced by performing low-temperature treatment on the peony in summer for breaking the dormancy; a purpose of effectively controlling the flowering time is achieved by controlling the temperature and illumination during flower forcing; the treated peony is large and bright-colored; a peony plant is robust; the flowering time is longer; and an ornamental value is high.
Owner:CHANGSHU JIASHENG AGRI SCI & TECH DEV
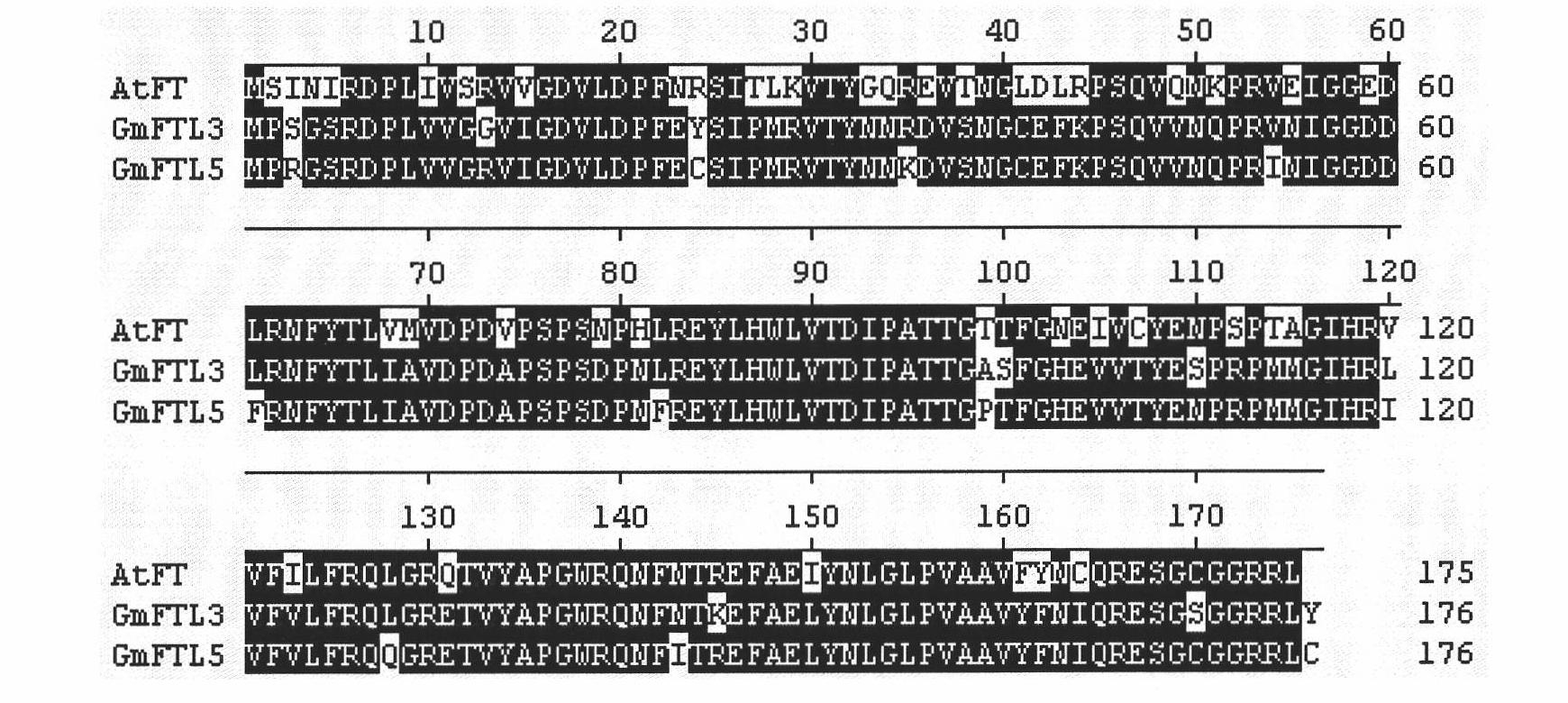
Soybean GmFTL3 protein and soybean GmFTL5 protein as well as applications thereof
ActiveCN102146124AShortened reproductive periodPromote floweringFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyArabidopsis
The invention discloses a soybean GmFTL3 protein and a soybean GmFTL5 protein which have the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 and the amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.2 respectively or the sequences which are separately obtained through replacing, deleting or adding one or more of amino acid residues and have the same functions. The GmFTL3 and GmFTL5 which are capable of overexpressing soybean flowering genes are used for obviously promoting the flowering of plant (Arabidopsis thaliana), thus the flowering time can be shortened and the growth period can be shortened. The proteins can be used for solving the problem of flowering asynchronism in the hybridization breeding process, the growth period control problems of various crops, vegetable, fruits and flowers, the problem of photoperiod sensitivity and the introduction problem.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Liquid medicine for prolonging flowering time of wild rhododendron delavayi and spraying method thereof
InactiveCN102197813AProlong flowering periodAchieve manual regulationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMedicineRhododendron delavayi
The invention discloses a liquid medicine for prolonging flowering time of wild rhododendron delavayi. The liquid medicine is obtained by adding water to gibberellin and 2,4-dichlorphenoxyacetic acid and blending, and the proportion is that 40-80 mg of gibberellin and 50-150 mg of 2,4-dichlorphenoxyacetic acid are blended with each kilogram of water. When the wild rhododendron delavayi is sprayed by the liquid medicine provided by the invention, the liquid medicine is sprayed by the following ways: spraying parts: uniformly spraying the liquid medicine on the leaves of the wild rhododendron delavayi; spraying time: spraying at the blossom bud developmental phase; spraying period: spraying for one time every seven days; and spraying frequency: spraying for five times in all. The liquid medicine disclosed by the invention has the advantages of freedom from limits of natural conditions, easiness in application in a large scale, simpleness of operation, low cost and capability of really achieving the aim of manually regulating and controlling the flowering time of the wild rhododendron delavayi. By utilizing the liquid medicine disclosed by by the invention, the flowering time of the rhododendron delavayi can be prolonged by about 10 days so that the aim of prolonging the flowering time of the wild rhododendron delavayi can be realized.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Air pineapple flowering time regulation method
The invention relates to an air pineapple flowering time regulation method. According to the method, an air pineapple is induced to flower by the aid of plant growth regulator ethephon. The method includes the steps: (1) forcing flowers of plants; (2) performing floral induction; and (3) accelerating flower bud development. By the aid of the air pineapple flowering time regulation method, the flowering rate of the air pineapple can reach more than 90%, ornamental value and commercial value of the air pineapple are greatly improved, agent cost is low, and an operating method is simple and easy.
Owner:中林绿苑江苏生态环境有限公司 +1
Fertilizer special for roses
InactiveCN106278538AFaster and more thorough ripeningFacilitates the ripening processCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingRare-earth elementFlowering time
A fertilizer special for roses comprises a base fertilizer and a foliar fertilizer. The base fertilizer comprises, by mass parts, 45-60 parts of nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium mixed fertilizer, 3-10 parts of medium elements, 0.5-5 parts of microelements, 0.1-0.4 part of compound inhibitor, 0.01-0.05 part of rare earth elements, 120-150 parts of organic fertilizer and 50-60 parts of zeolite powder. The ratio of the available nitrogen content, the available phosphorus content and the available potassium content of the nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium mixed fertilizer is (1.5-2):(2.5-3):(1-1.5); the foliar fertilizer comprises, by mass parts, 10-15 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 5-10 parts of potassium sulfate, 2.5-4.0 parts of borax, 1-1.6 parts of magnesium sulfate, 2.0-3.2 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1.2-1.8 parts of zinc sulfate, 0.5-0.8 part of sodium selenite, 0.5-0.8 part of sodium molybdate, 45-60 parts of amino acid, 1.8-3.0 parts of Chinese herbal medicine extracting liquid, 0.5-1.0 part of glycerinum, 0.1-0.5 part of growth regulator, 0.01-0.03 part of surfactant, 0.01-0.03 part of potassium permanganate and 0.01-0.03 part of aspirin. The fertilizer special for the roses can meet nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium requirements of the roses, have good slow release characteristics and prolong flowering time of the roses.
Owner:左邦庆
Method for planting malus halliana
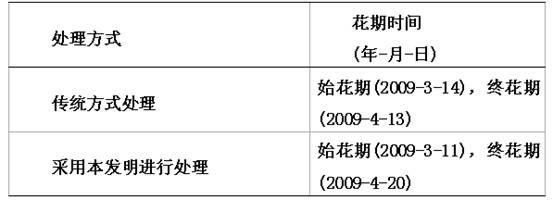
The invention discloses a method for planting malus halliana. The method comprises the steps of seedbed preparation, cutting selection, a cuttage method, seedling management, field transplanting, field management, pruning, shaping and harvesting. The method for planting the malus halliana is low in planting cost and low in investment risk, the survival rate is high after transplanting, growing vigour of plants is strong, the cultivation period is short, high technological practicality is achieved, and the method is suitable for large-area popularization and planting. Meanwhile, compared with a traditional planting method, the flowering time is eight to ten days earlier, the flowering phase is prolonged by 15 days to 20 days, the flowering number is increased, the enjoying effect of the malus halliana is effectively improved, good foundations are provided for improving the manual large-scale planting of the malus halliana and enhancing product competitiveness, and good economic benefits and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:XUANWEI SANYOU AGRI TECH DEV
Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase gene
InactiveUS6500670B1High activityImprove availabilitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBrassicaceaePlanting seed
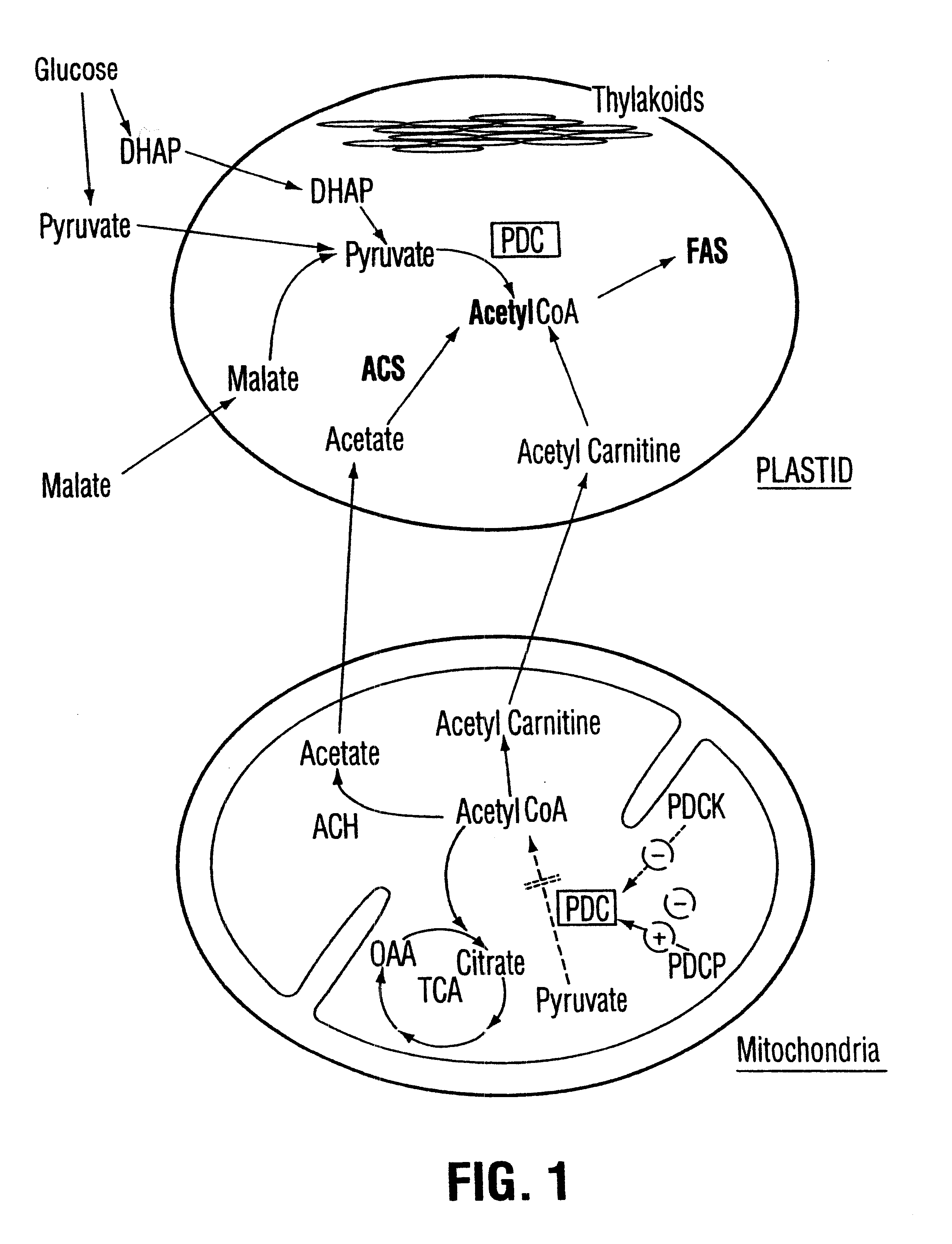
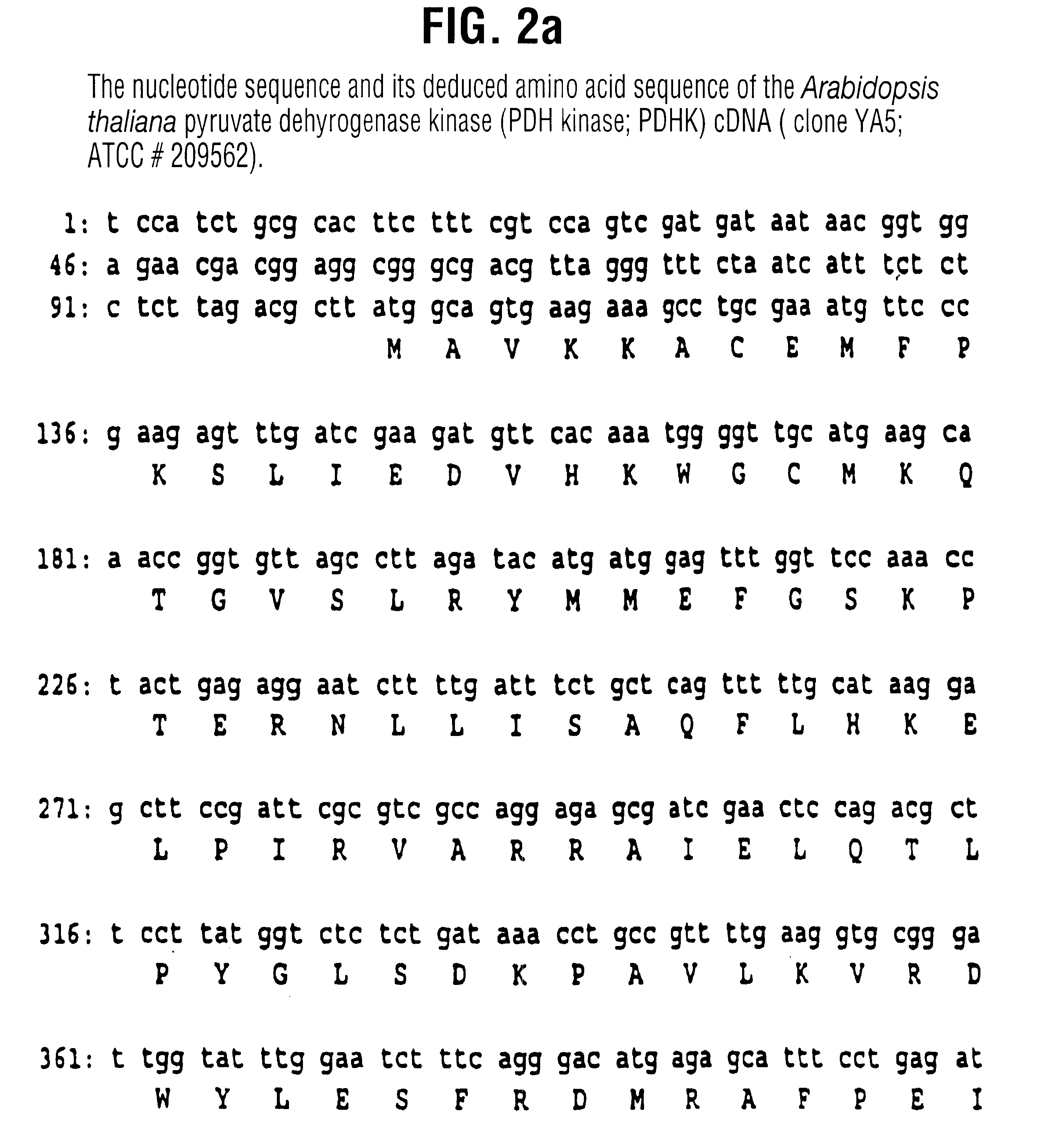
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of a mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDHK) gene [SEQ ID NO:1](pYA5; ATCC No 209562) from the Brassicaceae (specifically Arabidopsis thaliana). The invention includes isolated and purified DNA of the stated sequence and relates to methods of regulating fatty acid synthesis, seed oil content, seed size / weight, flowering time, vegetative growth, respiration rate and generation time using the gene and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO:1; or a part of SEQ ID NO:1 characterized in that said sequence has been introduced into an antisense or sense orientation, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds. The invention also relates to substantially homologous DNA sequences from plants encoding proteins with deduced amino acid sequences of 25% or greater identity, and 50% or greater similarity, isolated and / or characterized by known methods using the sequence information of SEQ ID NO:1, and to parts of reduced length that are still able to function as inhibitors of gene expression by use in an anti-sense, co-suppression or other gene silencing technologies.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method for adjusting flowering time of loquats
InactiveCN102204498AControl pumpingGood ventilation and light transmissionCultivating equipmentsCataphyllLoquat Tree
The invention discloses a method for adjusting the flowering time of loquats. The method for adjusting the flowering time of loquat comprises the steps of: A. after fruit picking, appropriately removing over-dense branches of crowns of loquat trees planted in ecoregions of dry-hot valleys of the Jinsha River, and cutting the side shoots of dense branches with more than 2 shoots on the periphery of the crowns; shearing off cross and overlaid branches and weak branches; back cutting slim and fragile braches to a large extent, and back cutting strong bearing branches slightly; and back cutting the branches with young shoots at the connecting part of the old shoots and young shoots; B. heavily applying organic fertilizer within 5 to 7 days after shearing, and watering in time; and C. applying 25 to 40 kilograms of phosphatic fertilizer, 8 to 12 kilograms of potash fertilizer, 6 to 8 kilograms of nitrogenous fertilizer per 667 square meters of field from June to July, and spraying leaf fertilizer twice or three times in the period when the summer shoots and leaves turn green; and simultaneously, bending or cutting vertical branches, the diameter of which is larger than 1.5 centimeters, in a twisting way. The method for adjusting the flowering time of loquats can be used for delaying the flowering time of loquats planted in the ecoregions of dry-hot valleys of the Jinsha River, preventing the loquats from flowering in June or before June, and enabling the spikes to blossom in July to August concentratedly, the flowering ratio and fruiting rate to be high, the fruit quality to be high, and the fruit to be supplied on the market in a fruit off-season relatively concentratedly.
Owner:SICHUAN AAS HORTICULTURE RES INST
Soybean abloom time adjusting gene GAL2 and application thereof
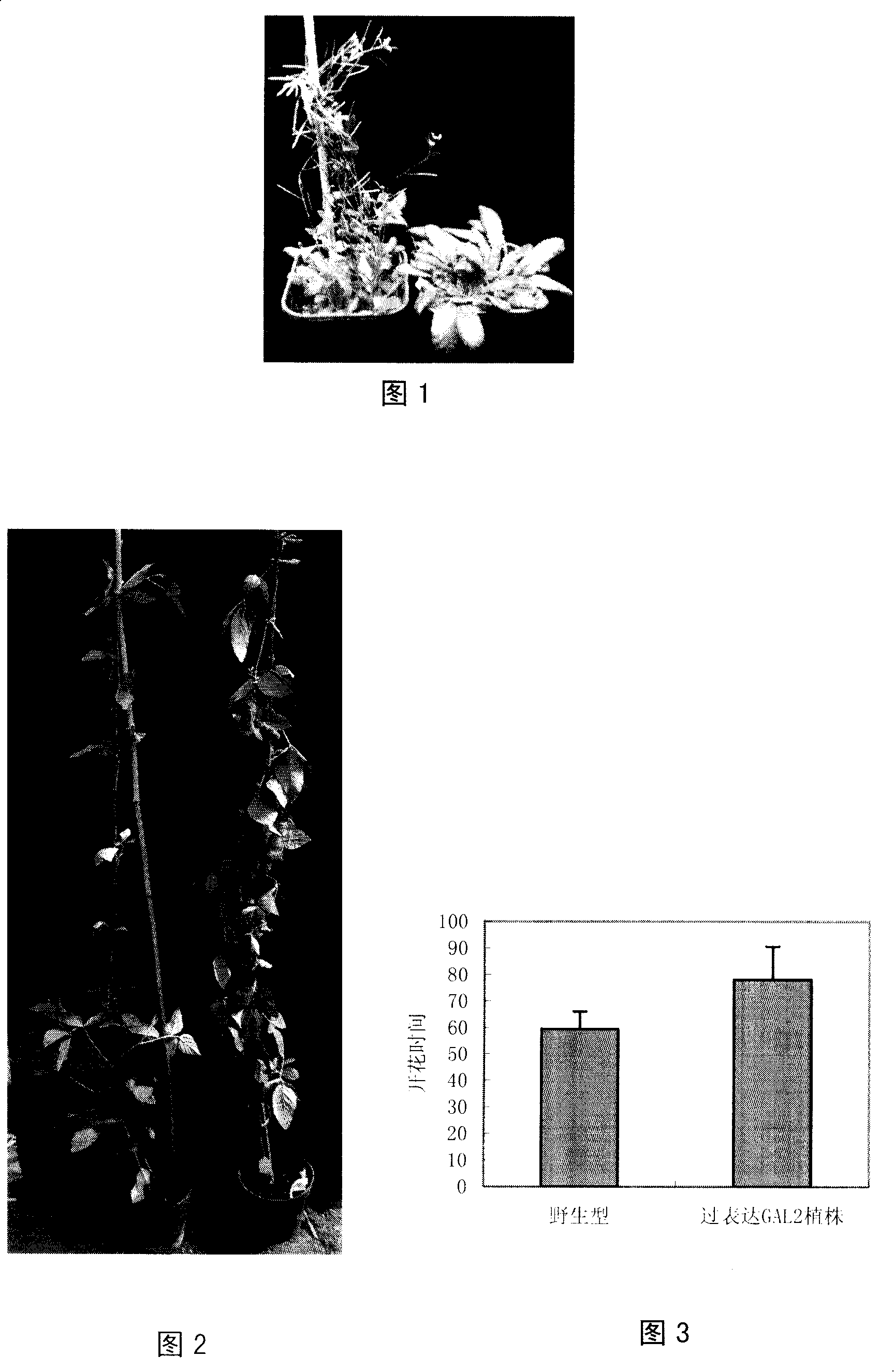
InactiveCN101148672AProlong reproductive periodIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyRegulator gene
The present invention provides one kind of soybean flowering time regulating gene GAL2 and its separating and cloning process and application. The soybean flowering time regulating gene GAL2 codes protein with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2 or the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 2 through the substitution, deletion or addition of one or several amino acids and with the same function. Over expressing the gene can postpone the soybean flowering time to prolong the growth period of soybean extremely, best utilize the natural conditions and increase the yield. In addition, the present invention makes it easy to cultivating new soybean variety.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for regulating flowers and spikes of Feizixiao litchis
InactiveCN102132666ADelayed formation timeDelayed floweringCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsGrowth retardantFruit set
The invention relates to a method for regulating flowers and spikes of Feizixiao litchis, belonging to the field of application of litchi production technology. The best method for gaining high and stable yields is to reduce the number of flowers and delay the time of flowering as the Feizixiao litchi variety is easy to flower, the number of flowers is great, the flowering needs to consume a great deal of nutrition and influence the rate of bearing fruit, and the fruit bearing is influenced by weather; the method comprises the steps: when spikes of Feizixiao litchis grows by differentiation to be 10-15 cm long in January and February, a growth retardant uniconazol with concentricity of 50-100ppm is used for postponing the growth of the spikes and restraining the premature growth of the spikes of Feizixiao litchis; after the method is adopted to treat the spikes, the premature growth of the spikes can be restrained to lead the spikes to become short and strong and greatly reduce the number of flowers, thus omitting heavy and nervous work for flower thinning for the Feizixiao litchis; and the flowering time of the Feizixiao litchis is postponed at about spring equinox, thus achieving the purpose of one-time flowering and bearing fruit, greatly improving rate of bearing fruit, and being compact in spikes, uniform in size of fruits and consistent in mature period.
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Efficient culture method of tree type honeysuckle
The invention discloses an efficient culture method of tree type honeysuckle. The efficient culture method comprises the following steps that: the varieties of the tree type honeysuckle suitable for the local climate are selected, loose sand soil convenient to drain and irrigate is selected, a planting garden is built, and deep cultivation, fine rake and ridge cultivation are carried out; the transplanting is carried out in autumn, base fertilizers are applied before the transplanting, the soil filling and the compact pedaling are carried out, root fixing water is watered, and film covering or soil covering is carried out in winter according to the air temperature conditions to prevent the freezing and preserve soil moisture; intertillage is irregularly carried out for weeding while watering after the germination in spring; leaf fertilization is carried out after flower picking in each time; slight shearing to a proper degree is carried out after flower picking in each time, and the tree form is trimmed after the tree body dormancy in winter until the early sprouting period in spring; harvesting is carried out in a bud period, and the baking is carried out in a baking room after the harvesting. Other commercial crops and other medical materials such as white paeony roots can be interplanted between ridges in the first three years. When the method provided by the invention is adopted, the tree type honeysuckle can enter the full-bloom period one year in advance, so the yield per mu in the full-bloom period reaches more than 150kg, and the flowering time is shortened by morethan 5 days in the whole year.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
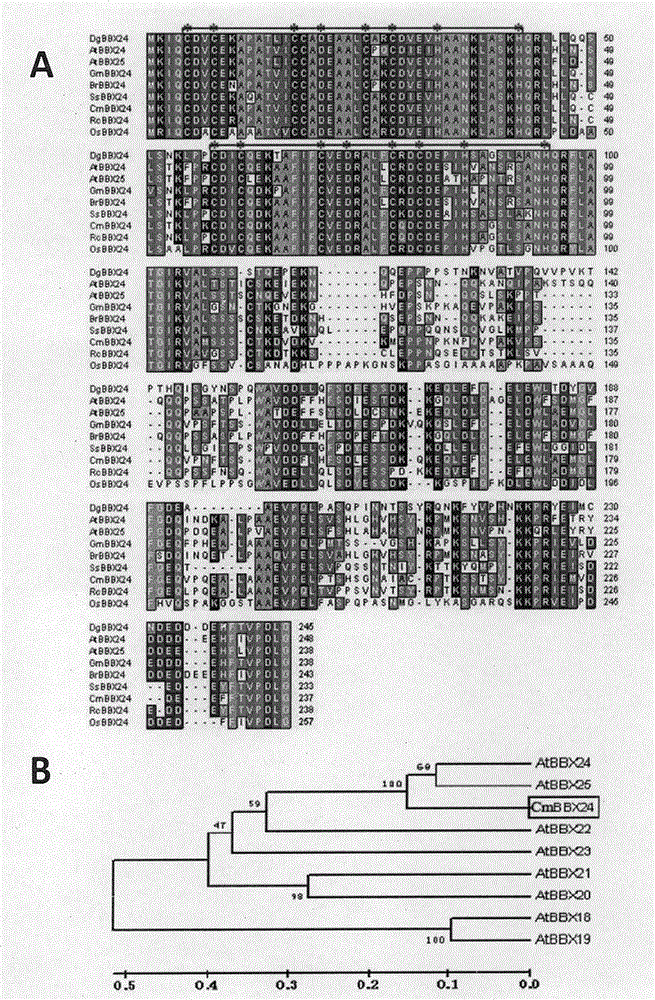
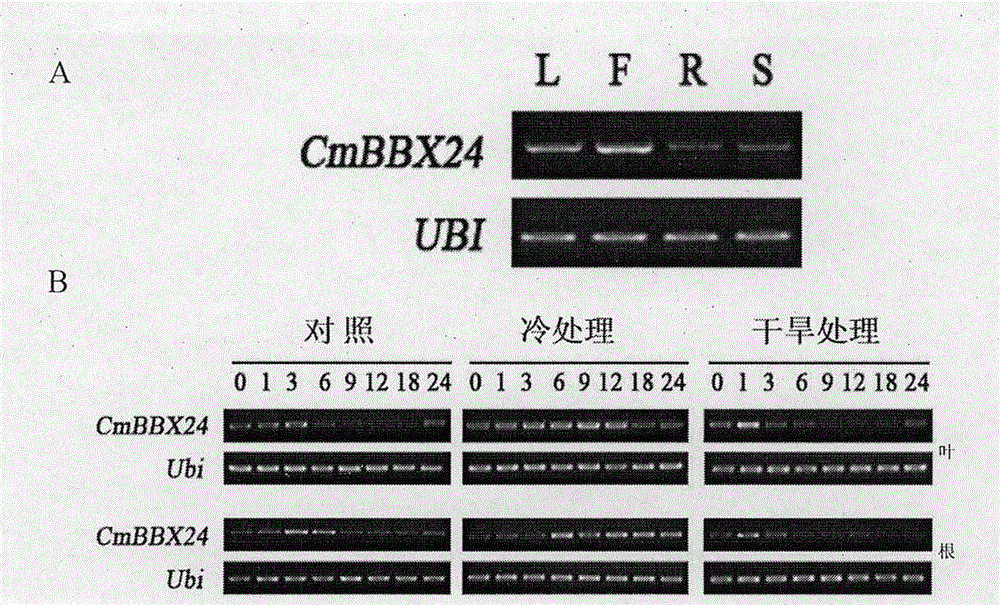
Gene with zinc finger protein structure BBX24 and application thereof
InactiveCN104004070AImprove abiotic stress toleranceIncreased tolerance to abiotic stressMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyProtein structure
The invention provides a gene with a zinc finger protein structure BBX24 and application thereof. The invention also provides a nucleotide sequence encoded with a zinc finger protein transcription factor and application in regulation of plant flowering time and abiotic stress tolerance. The gene silencing of the zinc finger protein transcription factor on chrysanthemum shows insensitivity to a photoperiod, can obviously make the flowering time of short-day chrysanthemum ahead of schedule under a long sunshine condition, and the overexpression on chrysanthemum shows enhanced tolerance to low temperature and drought. Therefore, the gene has unique advantages in the application of regulating plant flowering time and abiotic stress tolerance.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for adjusting flowering period of paphiopedilum micranthum
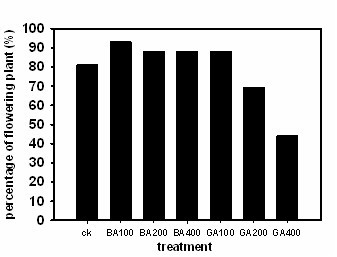
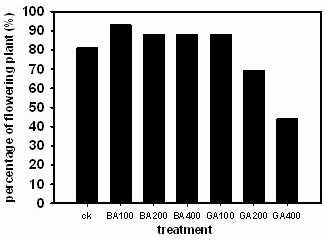
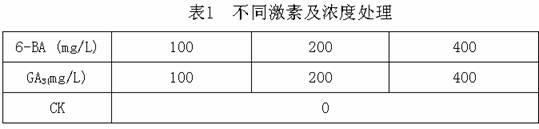
ActiveCN102197768AImprove flowering rateEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPaphiopedilum micranthumGibberellin
The invention discloses a method for adjusting flowering period of paphiopedilum micranthum. The method for adjusting flowering period of paphiopedilum micranthum comprises the steps of treating a grown plant of paphiopedilum micranthum with gibberellins GA3 and 6-benzylpurine 6-BA of different concentrations; when the gibberellins GA3 is used for treatment, the concentrations are respectively 100mgL-1, 200mgL-1 and 400mgL-1; and when the 6-benzylpurine 6-BA is used for treatment, the concentrations are respectively 100mgL-1, 200mgL-1 and 400mgL-1. According to the market demand, different hormones of different concentrations are used for adjusting the flowering rate, the flowering time, the flowering period and the length of scape, and the method speeds up flowering of the paphiopedilum micranthum by 54 to 70 days. The flowering period adjusting method of paphiopedilum micranthum disclosed by the invention is characterized by high operability, obvious control effect and the like, canprovide operable technical support for commercial flower production of paphiopedilum micranthum.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing short-day strawberry flowering seedlings in central region of Yunnan province
ActiveCN104115732AIncrease costImprove reproductive efficiencyCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationFragariaBEACH STRAWBERRY
The invention discloses a method for producing short-day strawberry flowering seedlings in the central region of Yunnan province. The method comprises the steps of variety selecting, stock plant field planting curing, seedling breeding and short-day flowering processing. The short-day strawberry variety with the properties that the number of flowers in simple inflorescence is more than 20, the flowering time of a single flower in the same inflorescence is scattered, and the flowering time of the simple inflorescence lasts for one or more months is selected; the stock plant field planting curing, the seedling breeding and short-day flowering processing are carried out in the central region of Yunnan province with the altitude ranging from 1,600 meters to 1,900 meters; a nutrient solution including 100-150 milligrams per liter of N, 20-25 milligrams per liter of P and 80-100 milligrams per liter of K is used for watering the seedlings during the stock plant curing period, the seedlings are processed for 10 hours in the short day and processed for 30-35 days under the natural temperature condition, and flower bud differentiation is achieved in more than 90 percent of seedlings. The flowering cost is low, the flowering seedling supply time is early, 30-40 seedlings can be harvested in each stock plant in the middle ten days of June, the fresh autumn short-day strawberries can be produced, and normal winter and spring fresh strawberry production can be guaranteed.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
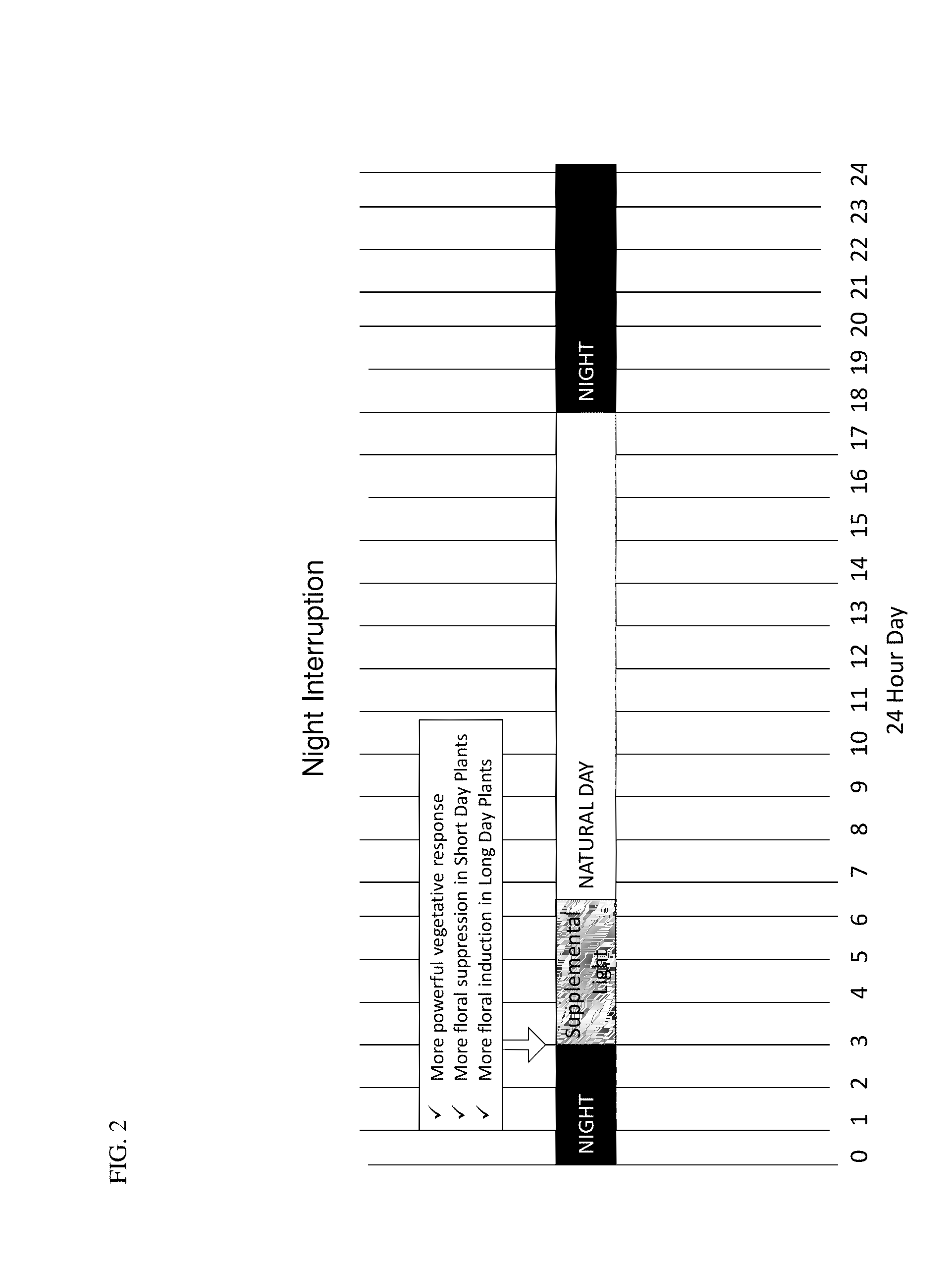
Illumination method for regulating reproductive development of plants
ActiveCN110495318AConsistent germinationShorten the breeding cycleSaving energy measuresHorticulture methodsLeafy vegetablesSeedling
The invention relates to the technical field of plant lighting, in particular to an illumination method for regulating the reproductive development of plants. Seeds are subjected to germination acceleration, germinated vegetable seedlings are continuously illuminated by first LED plant lamps, and the PPFD on the leaves of the vegetable seedlings, the illumination quantity, the temperature, the relative humidity and the CO2 concentration are controlled; the seedlings with excellent growth vigor are planted in a field and intermittently illuminated by second LED plant lamps, and the duty cycle of intermittent light and an illumination duration within a gap illumination cycle, the PPFD on the vegetable leaves, the illumination quantity, the temperature, the relative humidity and the CO2 concentration are controlled. According to the method, by regulating different light environment parameters and illumination modes in the seedling raising period and the cultivation period in the leafy vegetable breeding process, the conversion of vegetables from vegetative growth to reproductive growth is effectively promoted, the flowering time is shortened by one fifth or above, and the seed collection cycle is greatly shortened.
Owner:FUJIAN SANAN SINO SCI PHOTOBIOTECH CO LTD
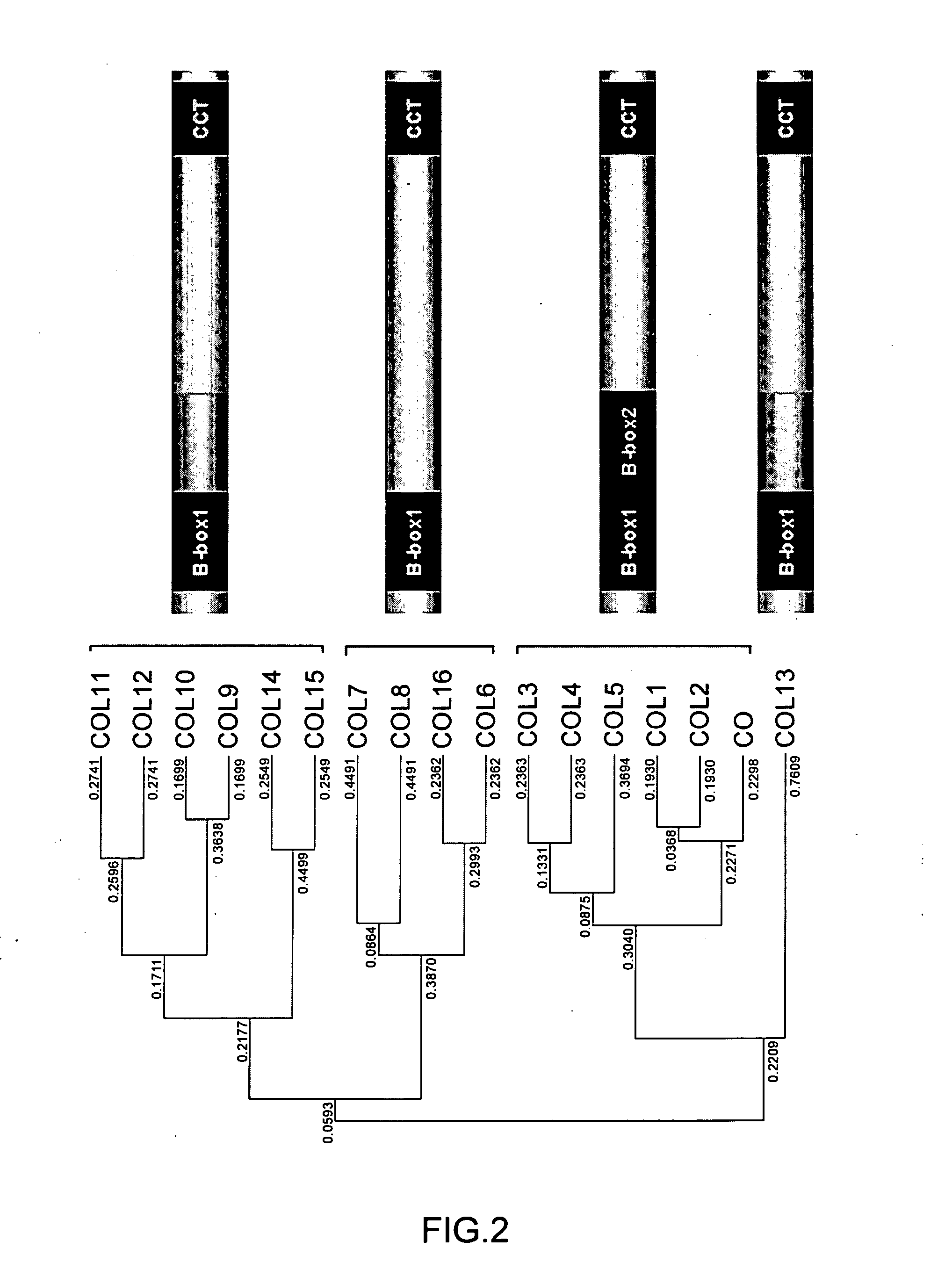
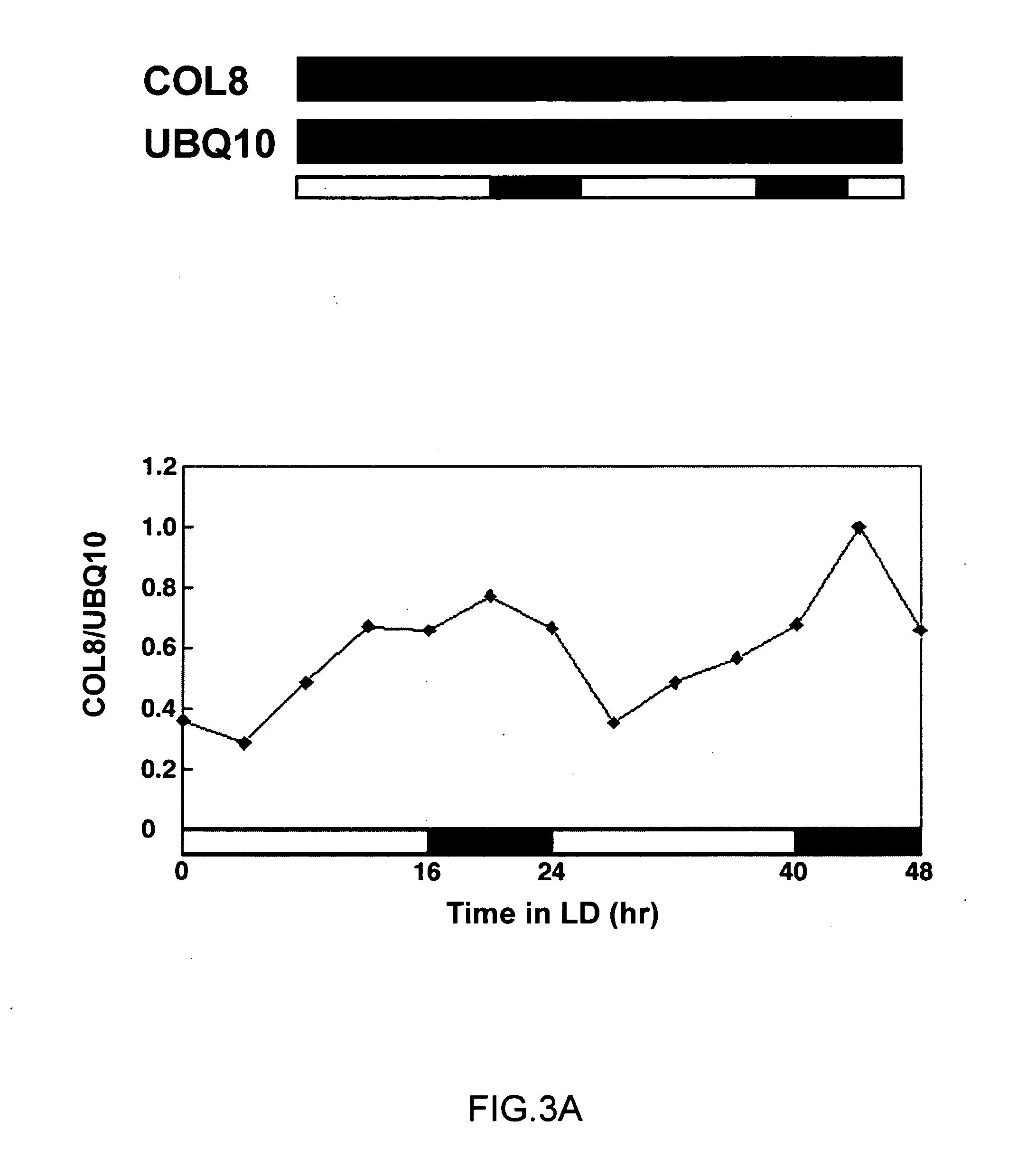
Control of hypocotyllength and flowering time by COL8 gene
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid including a nucleotide sequence encoding COL8, which controls hypocotyl length and flowering time in a plant. It is found that plants over-expressing COL8 under long day conditions show slight hypocotyl elongation and delayed flowering in comparison with the wild type. In addition, COL8 and FKF1, which is a circadian-clock related gene, are found to be localized at the same site in a plant cell, indicating the existence of an interaction between the two.
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY
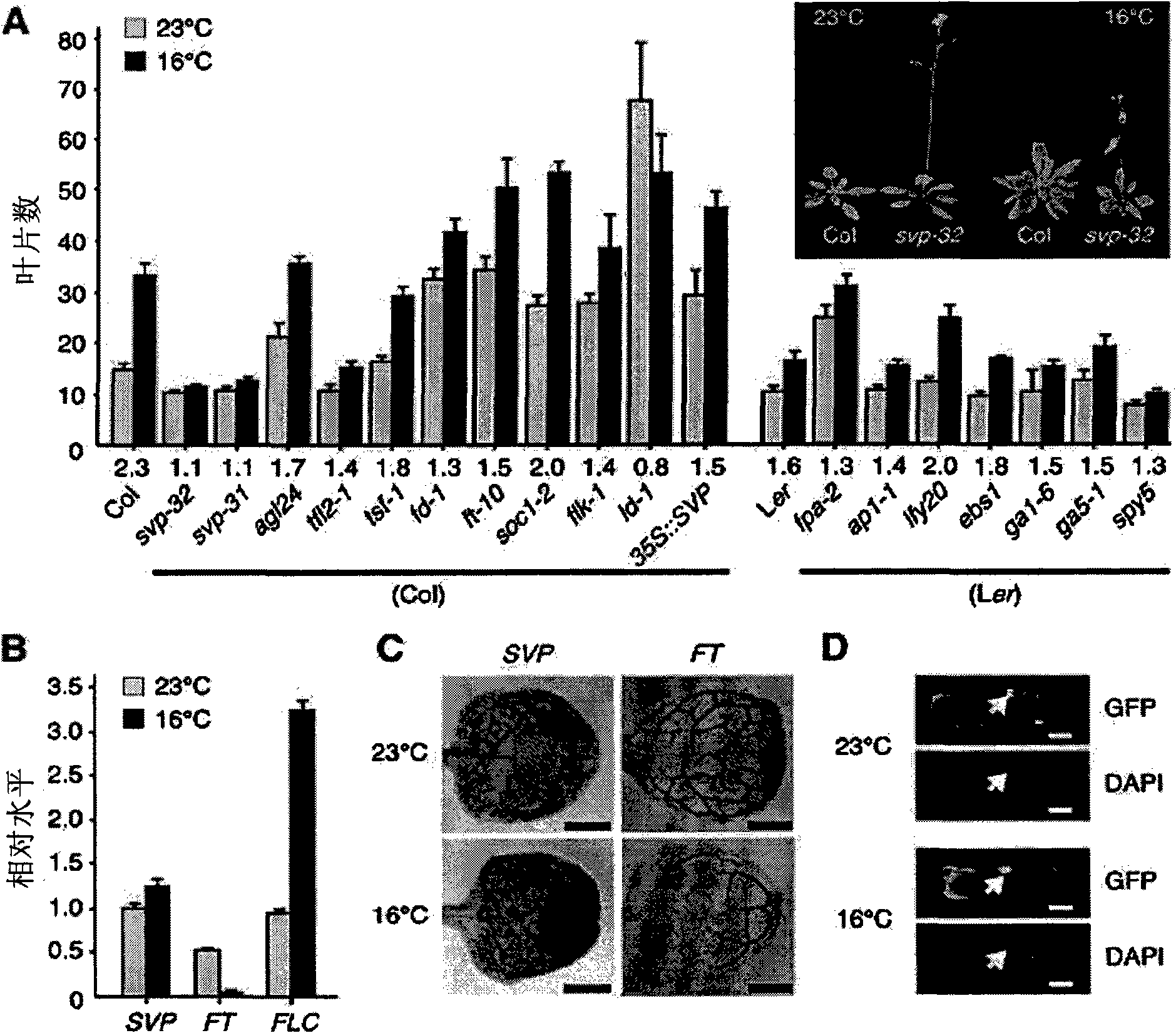
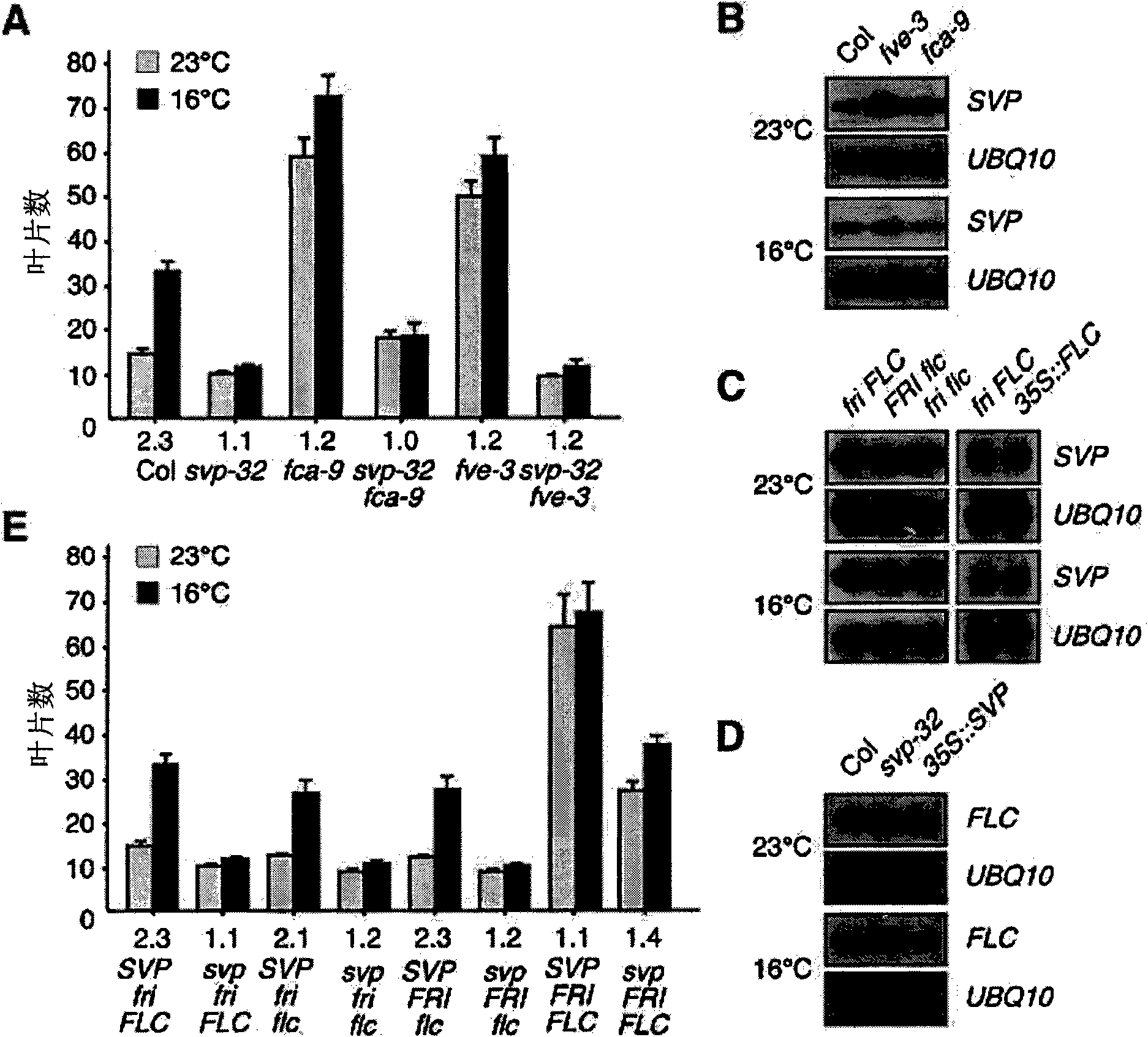
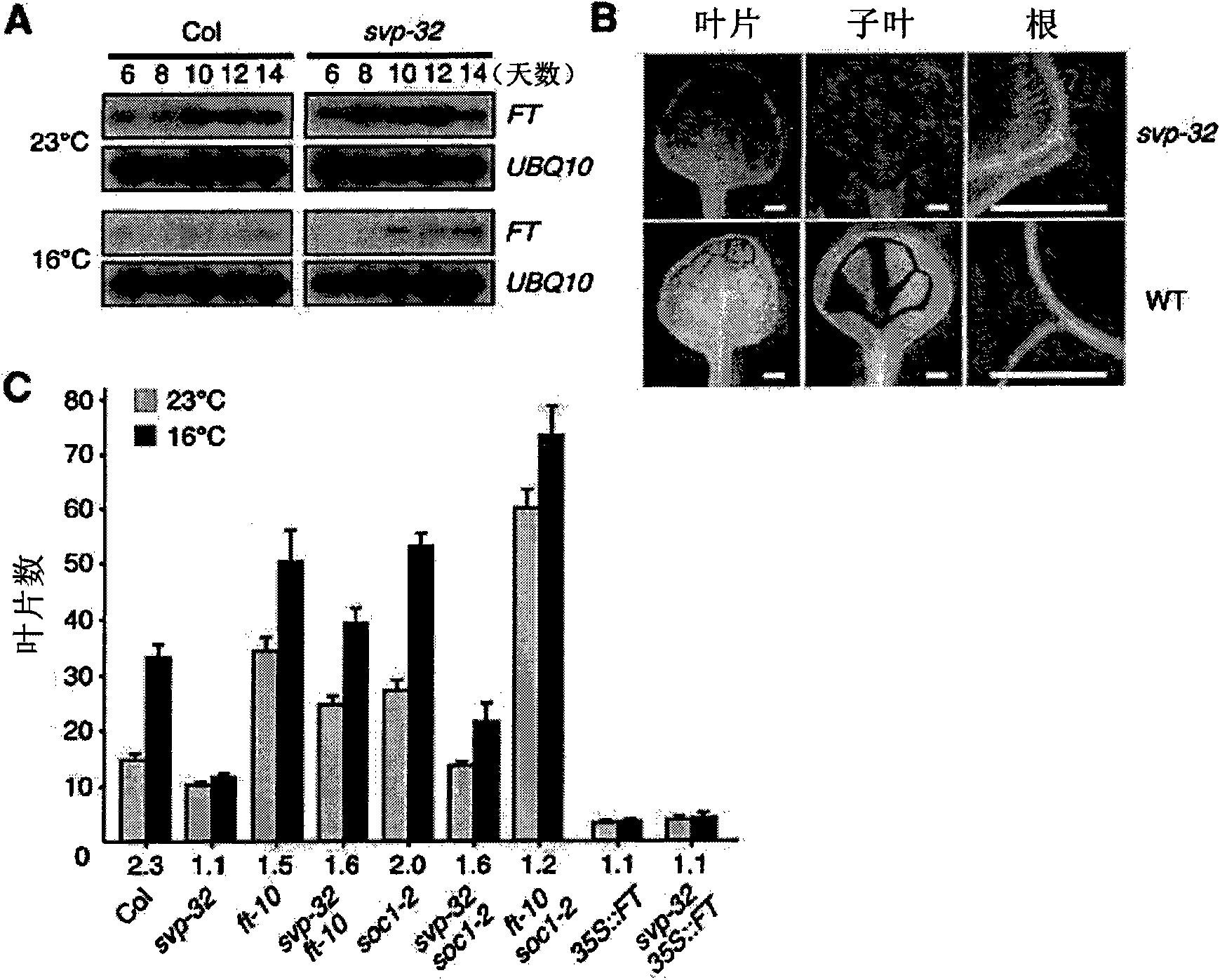
SVP gene controlling flowering time of plants
The present invention relates to SVP protein which controls the flowering time of plants originating from Arabidopsis, a gene encoding SVP protein, a recombinant vector comprising said gene, a plant transformed with said recombinant vector, a method of controlling flowering time of plants by using said gene, and a method of searching a protein or a gene which controls the flowering time of plantsby using said SVP protein or said gene encoding the same.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Schimacrenata crossbreeding method
InactiveCN104885923AGreat market potentialImprove the quality of hybrid parentsPlant genotype modificationFruit setHybrid seed
The invention discloses a schimacrenata crossbreeding method. The schimacrenata crossbreeding method comprises selecting forest stand and select trees, carrying out grafted seedling cultivation, dividing a select tree asexual system into 3-5 subsystems according to schimacrenata asexual system flowering periods comprising early, middle and later periods and according to schimacrenata select tree producing areas and flowering time, and carrying out hybrid seed production by a scheme comprising that breeding parents of each one of the subsystems are subjected to single crossing, a hybridized composition is determined and hybridization does not occur between subsystems so that schimacrenata seeds with a mature period of 2 years are obtained. Through hybrid seed production, a novel schimacrenata seed is produced so that a high-quality breed is obtained. According to different breeding parent combination, a fruit-setting ratio is 95%. The schimacrenata crossbreeding method provides a technical support for ecological forest planting.
Owner:FUJIAN ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for controlling flowering time of plant
InactiveUS20110257013A1Efficient productionPrevention of gene leakageBiocidePlant growth regulatorsHeterologousCopper
The present invention relates to a method for controlling flowering time of a transgenic plant in a copper ion-inducible manner, wherein a heterologous gene which controls flowering time has been introduced to the plant.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
EjAGL17 protein for regulating and controlling eriobotrya japonica flowering time as well as coding gene and application of gene
InactiveCN110669119APromote early floweringPromote early resultsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the field of plant molecular biology, and particularly relates to an EjAGL17 gene related to eriobotrya japonica flowering time regulation and control and an application of the EjAGL17 gene. The full length of the sequence of a coding region of cDNA of the EjAGL17 gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein coded by the EjAGL17 gene is shown asSEQ ID No.2. The EjAGL17 gene disclosed by the invention is transiently expressed in tobacco leaf cells and is positioned at a cell nucleus, so that the protein coded by the gene has typical transcription factor characteristics; meanwhile, the expression of the gene has significant difference in different stages of eriobotrya japonica flower development; the EjAGL17 gene overexpression vector istransferred into wild type arabidopsis thaliana through an agrobacterium mediated inflorescence dip dyeing method, and results show that overexpression of the EjAGL17 gene in the wild type arabidopsisthaliana can promote flowering time of the arabidopsis thaliana by about 14 days; and a transgenic plant material obtained by using the EjAGL17 gene overexpression vector can obviously advance the flowering phase of a plant and further promote the fruiting time to be advanced, can be used for directional breeding of early blossoming and early maturing varieties of the plant, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Cultivation method for flowering phases of azaleas
InactiveCN104737741AImprove permeabilitySimple structureGrowth substratesFertilising methodsSoil treatmentPeat
The invention provides a cultivation method for the flowering phases of azaleas. The cultivation method comprises the first step of soil treatment, wherein peat soil, humus soil, pine needle leaf mold and clay are stirred evenly to obtain cultivation soil; sulphur powder is splashed on the cultivation soil to be evenly stirred, and the cultivation soil stands for one day and used for cultivation of the azaleas; the second step of illumination management, wherein the rate of shading of a sunshade net is adjusted to be 70-75% from 9:30 am to 4:30 pm in summer and 60-65% from 10:30 am to 3:30 pm in autumn; the third step of clipping and shaping, wherein the tree bodies of the azaleas are clipped in May and are subjected to rejuvenation, sick branches are erased, and part of side branches and branches growing excessively are cut off; the fourth step of water and fertilizer management, wherein the azaleas are watered once every morning from March to May and is watered once in the morning and night everyday from June to September, the leaf surfaces of the azaleas are sprayed with water at noon, and the azaleas are watered once every two days from October to November; the fifth step of prolonging the flowering time; the sixth step of pest control. The method can effectively improve the flowering rate and abloom rate of the azaleas, prolongs the flowering phases of the azaleas and meets the higher and higher market requirements.
Owner:陈林美
Method for breeding corn inbred line by using hybridizing induction of haploids
The invention discloses a method for breeding a corn inbred line by using the hybridizing induction of haploids, and belongs to the field of crop breeding methods. The method comprises the following steps: pollinating basic population or cenospecies according with breeding targets by using JASS31, and selecting aleurone layer top purple and purple-free embryonic tip labeled grains; naturally or artificially doubling the obtained material, and inbreding; and selecting non-separated head progeny rows realizing consistent progenies as a new inbred line. The method has a high haploid inductivity reaching above 13%, and has the advantages of obvious selection labeling, easy screening and high accuracy; and additionally, the JASS31 used in the invention has a moderate height, a long flowering time and a large pollen amount, and natural pollination induction of haploids can be carried out, so the artificial pollination can be avoided, labor saving is realized, and it is suitable for the large scale population operation. The method also has the characteristics of high breeding efficiency, simple operation and fast breeding speed.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Protein related to flowering time of plant, and coding gene and application thereof
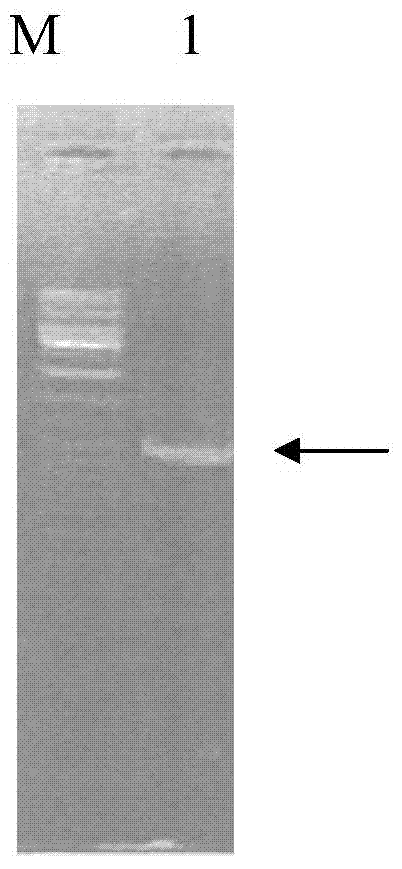
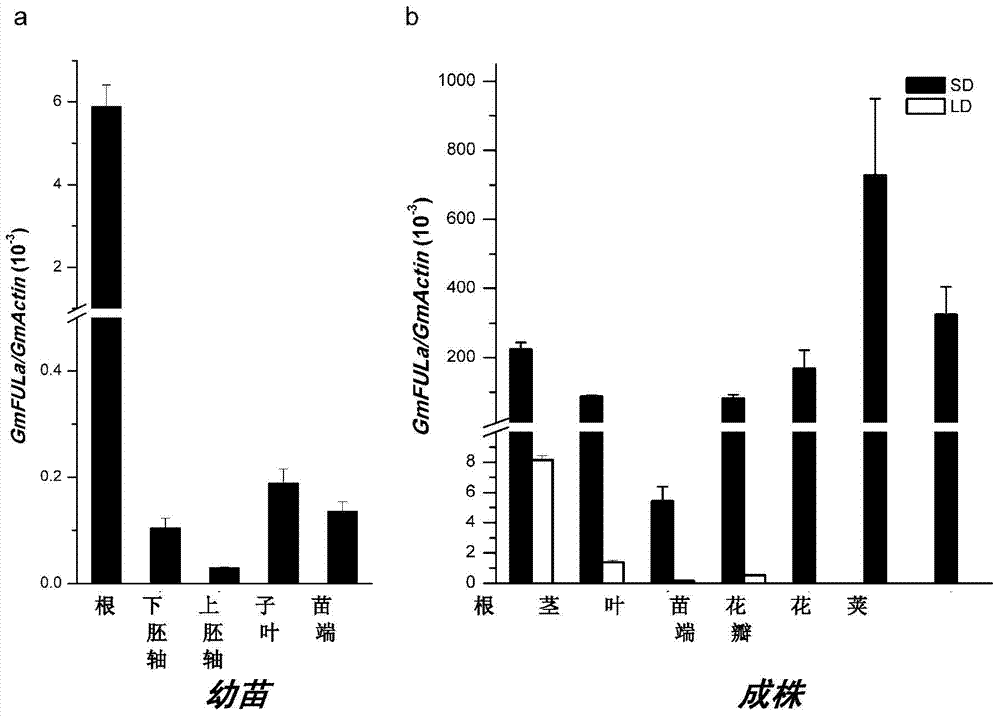
The invention discloses a protein related to flowering time of a plant, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is protein 1) or 2), wherein 1) is a protein composed of an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table, and 2) is a protein related to the flowering time of the plants and derived from the sequence 2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table. Experimental results of the invention prove that a gene GmFULa is found in soybean and overexpressed in arabidopsis so as to obtain a, and the flowering time of the transgenic plant is earlier than the flowering time of a non-transgenic wild plant; thus, it is observed that the gene or the protein expressed by the gene plays a role in promoting earlier flowering of plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of wheat TaMADS6 gene in regulation of plant spike and grain development as well as flowering time
InactiveCN110804623AHigh expressionIncrease the number of spikeletsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to the technical field of plant molecular biology, and specifically relates to application of a wheat TaMADS6 gene in regulation of plant spike and grain development as well as flowering time. It is discovered by the invention that a TaMADS6 protein has the functions of regulating plant flowering as well as spike and grain developing; and moreover, number of spikelets, numberof spikelet stalks and grain number per spike are significantly increased with flowering time obviously delayed by increasing expression of the TaMADS6 protein in plants. The TaMADS6 has relatively high application values, and can be applied to genetic breeding and germplasm resource improvement of the wheat; and thus, gene resources and new ideas are provided for cultivation of high-yield plants. Therefore, the TaMADS6 is of great significance to agricultural production.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Major QTL site for flowering time-related traits of brassica napus, SNP molecular markers and application
ActiveCN110592251AHigh contribution rateAccelerate the breeding process during the growth periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrassica
The invention provides a major QTL site for flowering time-related traits of brassica napus. The major QTL site is located between the 6143445th base and the 7287910th base of an A02 chromosome of thebrassica napus, and preferably has a contribution rate of 15.43 percent for the flowering time-related traits of the brassica napus. The major QTL site is closely linked with a first SNP molecular marker which is located on the 6143445th base and is A or C, and the mutation causes polymorphism; the major QTL site is closely linked with a second SNP molecular marker which is located on the 7287910th base and is A or G, and the mutation causes polymorphism; and the major QTL site is closely linked with a peak SNP molecular marker which is located on the 6330026th base and is C or G, and the mutation causes polymorphism. The invention further provides related SNP molecular markers and application. The major QTL site for the flowering time-related traits of brassica napus has a high contribution rate for the flowering time-related traits of the brassica napus, has a key effect on regulation of the flowering time-related traits of brassica napus, can be used as map-based cloning and molecular marker assisted selection and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Sucrose preservative for flower arrangement
The invention discloses a sucrose preservative for flower arrangement, which belongs to the field of plant preservatives, and aims to overcome the defects in the existing flower arrangement that because water in a flower vase for arranging flowers is malnourished, the lives of the arranged flowers are too short; and the capillary clogging caused by the putrefaction of incisions due to funguses in the water results in that the water absorbing capacity of arranged fresh flowers is reduced, and the fresh flowers are wilted. The sucrose preservative for flower arrangement comprises the following components in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of sucrose, 2 parts of citric acid, 0.2 part of sodium chloride and 50-60 parts of water. The method for preparing the preservative comprises the following steps: weighing the sucrose, the citric acid and the sodium chloride, dissolving in water, and stirring to completely dissolve the components; heating the solution to 100 DEG C, and cooling to room temperature; and filtering the solution, and filling the filter liquor into a vessel to obtain the sucrose preservative for flower arrangement. The invention has the advantages that the preservative keeps the arranged flowers bright, prolongs the flowering time of the fresh flowers, increases the nutrition of the arranged flowers, and promotes the growth of the arranged flowers; and the preservative is easy to produce, convenient to use, low in cost, and convenient to store and transport.
Owner:SHANGHAI DETONG ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method for regulating flowering period of phalaenopsis tissue culture seedlings
InactiveCN109362545AFlowering period controllablePromote formationGrowth substratesSaving energy measuresPhalaenopsisBud
The invention discloses a method for regulating the flowering period of phalaenopsis tissue culture seedlings. The method comprises the following steps that 1, roots of the phalaenopsis seedlings arewrapped in sphagna, placed in a 1.5 L nutrient bowl and cultivated in a greenhouse until new roots grow out, and then fertilization is conducted; 2, when the roots are completely wound in sphagna, the1.5 L nutrient bowl is replaced with a 3.5-inch nutrient bowl, and 10 days after bowl replacement, fertilization is conducted once every 10 days; 3, an abscisic acid solution is adopted for wateringthe roots of phalaenopsis plants to promote dormancy of the phalaenopsis plants; 4, 120 days before expected marketing and selling, flower buds are induced, a GA3 solution and a KH2PO4 solution are adopted for watering the roots of the phalaenopsis plants in the early stage of flower bud induction, a compound fertilizer solution is adopted for watering the roots of the phalaenopsis plants in the later stage of the flower bud induction, and after natural illumination in this stage is completed, a combined LED red-blue light source is adopted for illuminating phalaenopsis; 5, in a flower bud differentiation period, a 6-BA solution is adopted for watering the roots of the phalaenopsis plants. The method is adopted for regulating the flowering period of the phalaenopsis tissue culture seedlings to obtain phalaenopsis which has a controllable flowering time and neater and brighter flowers.
Owner:GUANGXI ECO ENG VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Method for controlling late-maturing litchi to bloom earlier
The invention belongs to the technical field of litchi cultivation and management, and particularly discloses a method for controlling late-maturing litchis to bloom earlier. The method comprises the following steps: by taking an early-maturing litchi variety as a scion and a late-maturing litchi variety as a rootstock, after a late-maturing litchi plant grows for 2-4 years, grafting the scion of the early-maturing litchi variety into a twig of the late-maturing litchi variety in April, continuously cutting off buds or young shoots growing from the lower end of the graft union after grafting, and stopping cutting the buds or the young shoots in the middle of September; managing the scion at the upper part of the graft union, culturing 1-2 new shoots on the survival grafted scion, controlling a final shoot to be mature at early September, and implementing shoot control treatment, wherein buds of the late-maturing litchi variety at the lower part of the graft union are germinated and flowers grow out. By adopting a grafting technique, the late-maturing litchi variety can bloom as early as the early-maturing litchi variety, the blooming time can be brought ahead for 2-3 months, and the method is breakthrough of a litchi flowering time regulation and control technique.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com