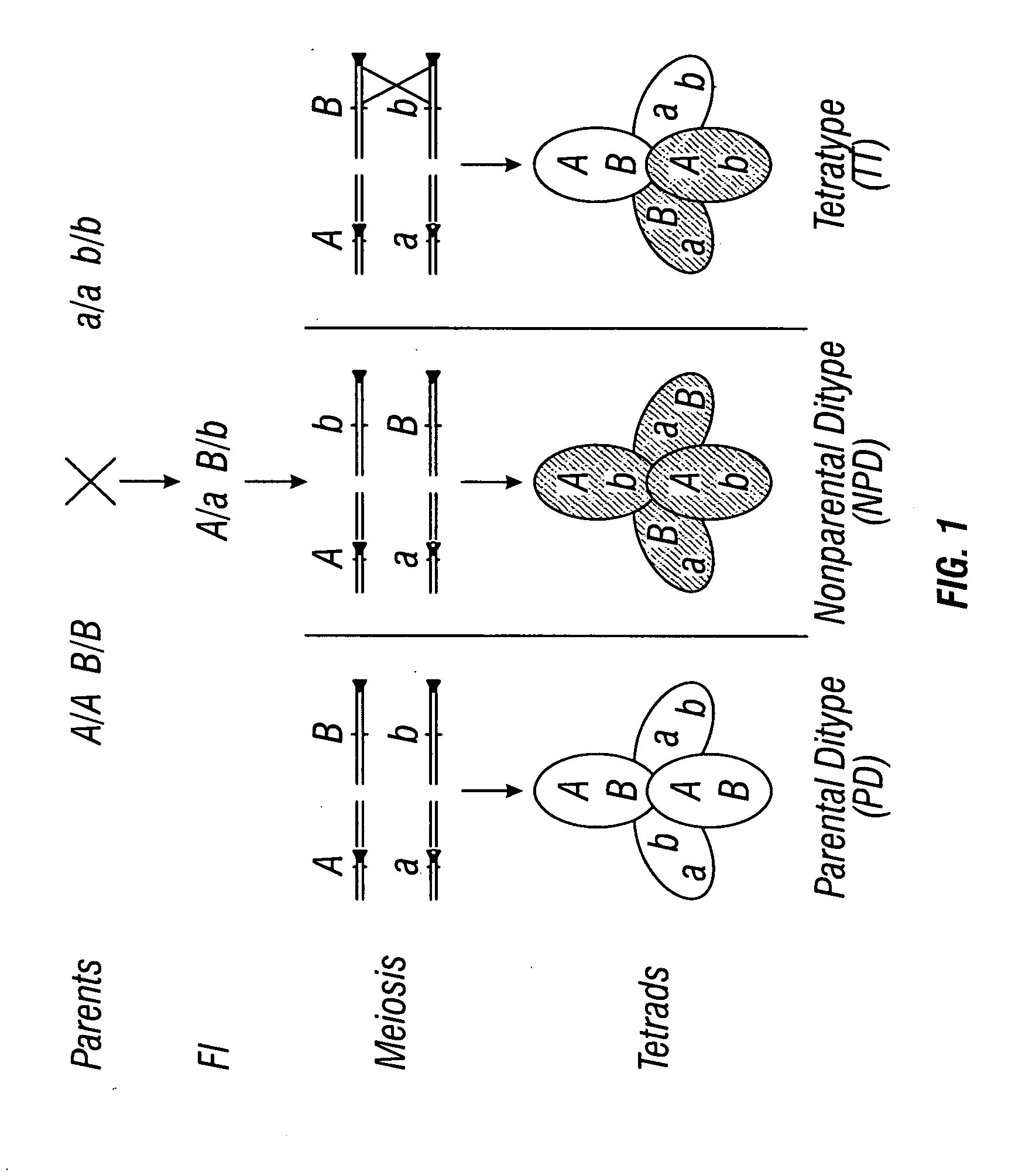
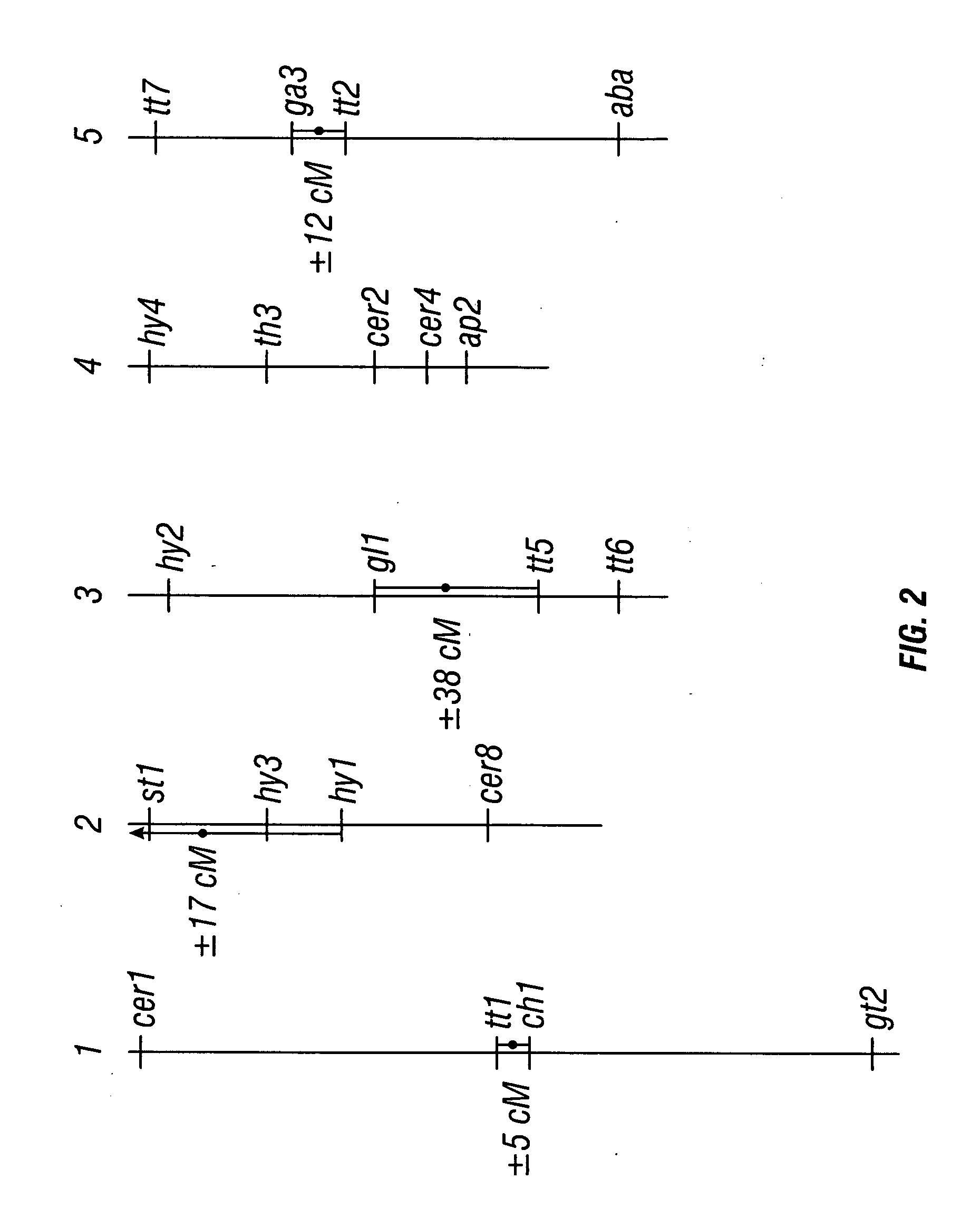
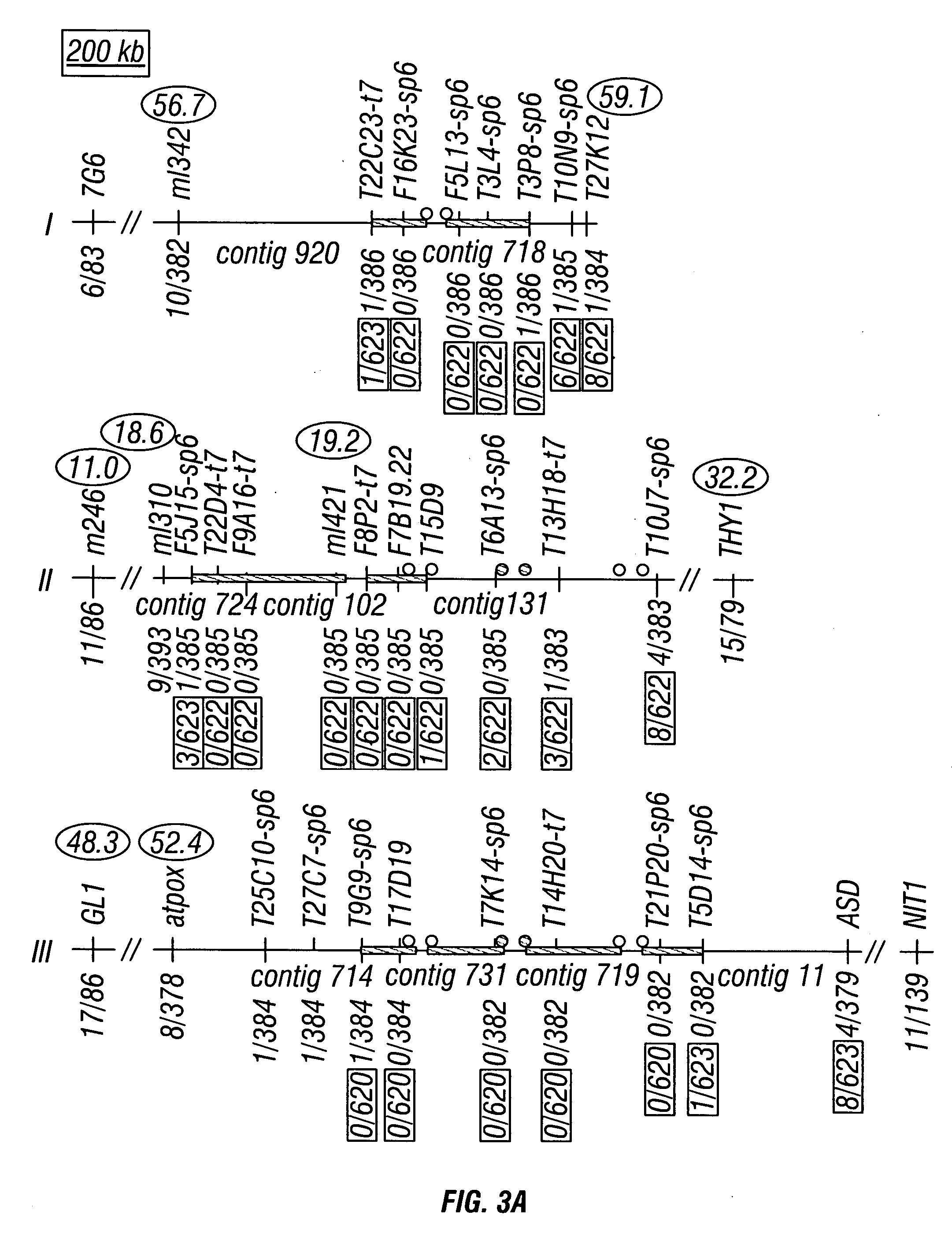
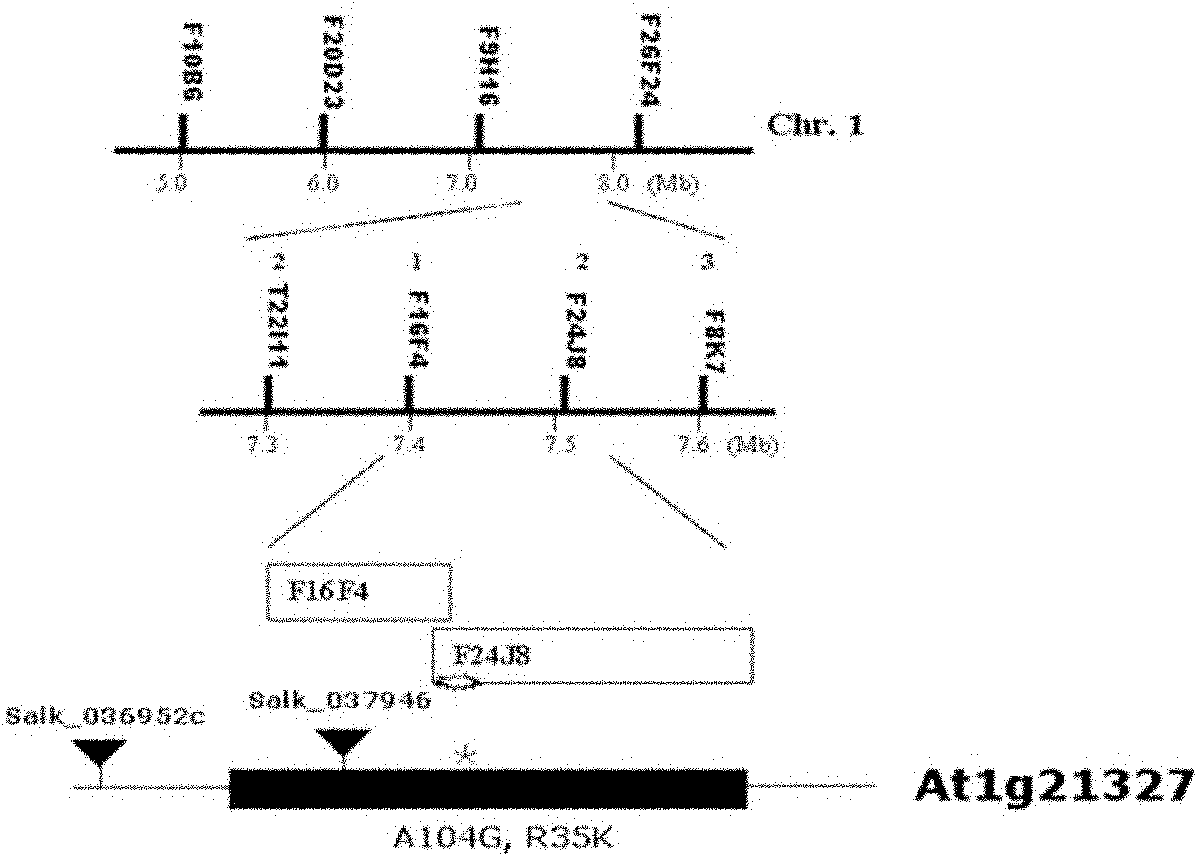
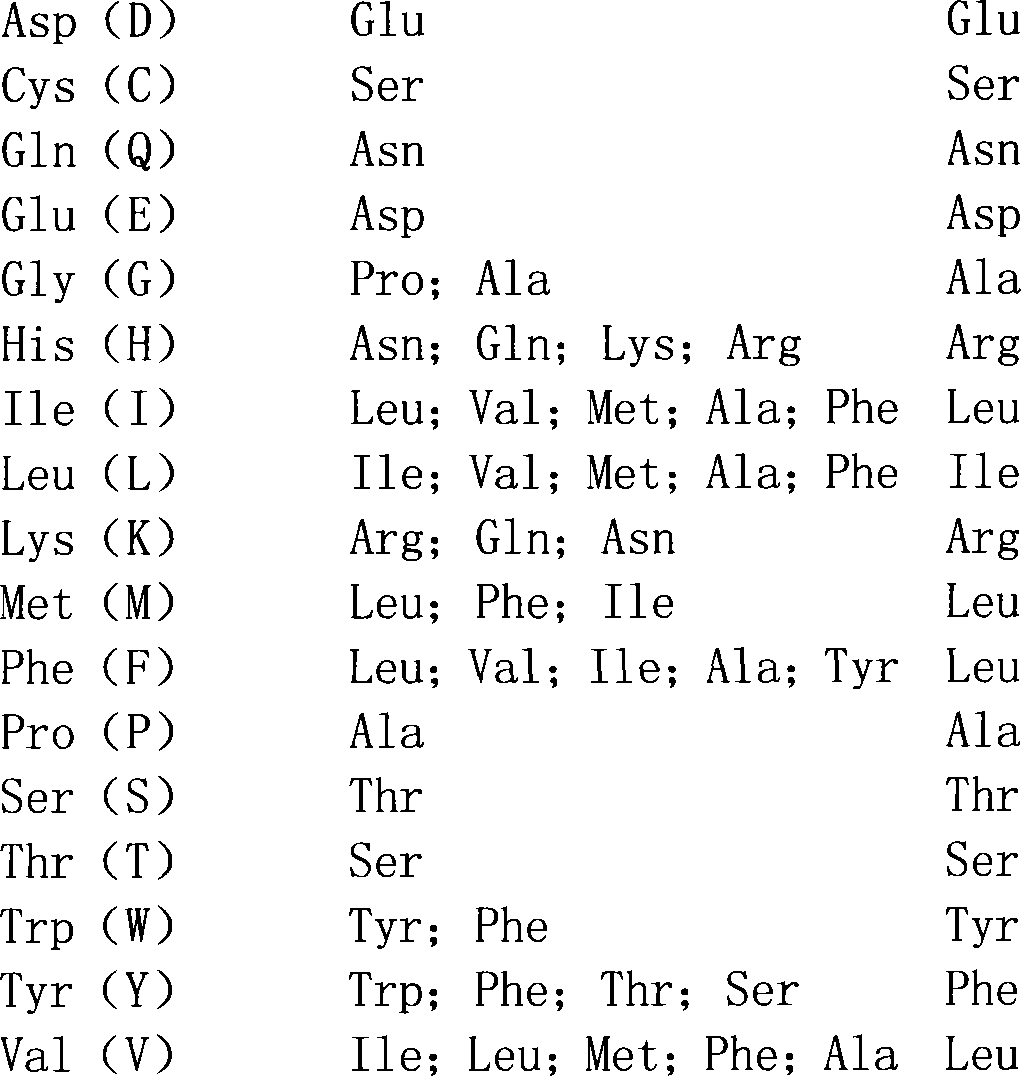
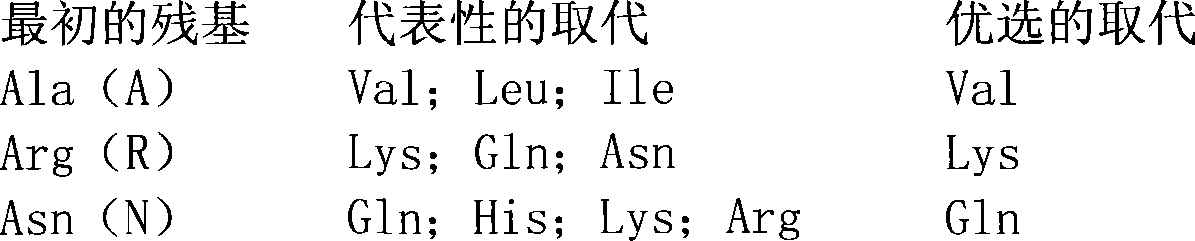Patents
Literature
725 results about "Arabidopsis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arabidopsis (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), one of the model organisms used for studying plant biology and the first plant to have its entire genome sequenced. Changes in thale cress are easily observed, making it a very useful model.
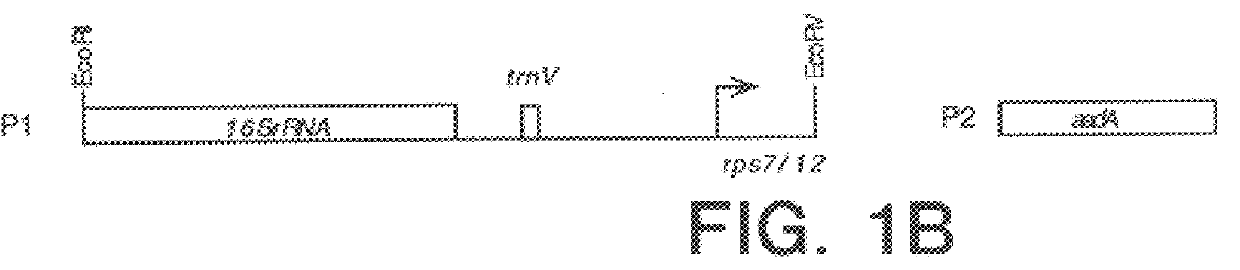
Solely pollen-specific promoter
ActiveUS7141424B2Regulate the time of trait expressionAvoid problemsSugar derivativesFused cellsDevelopmental stageHybrid seed
Owner:HANBAT NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Compositions for maintaining and restoring normal urogenital flora
A composition and methods for maintaining and restoring normal urogenital flora in humans. The composition includes one or more bacteria selected from the group consisting of Lactobacillus iners, all clones with at least 97% sequence similarity to Lactobacillus iners, Atopobium spp, and all clones with at least 90% sequence similarity to Atopobium spp as determined by sequences from 16S rRNA genes. The method for maintaining includes administering a safe and effective amount of the composition. The method for restoring includes administering a safe and effective amount of an antibiotic and subsequently administering a safe and effective amount of the composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Plant artificial chromosome compositions and methods
InactiveUS6900012B1Confer susceptibilityEnhanced advantageOther printing matterMicrobiological testing/measurementStructure and functionArabidopsis
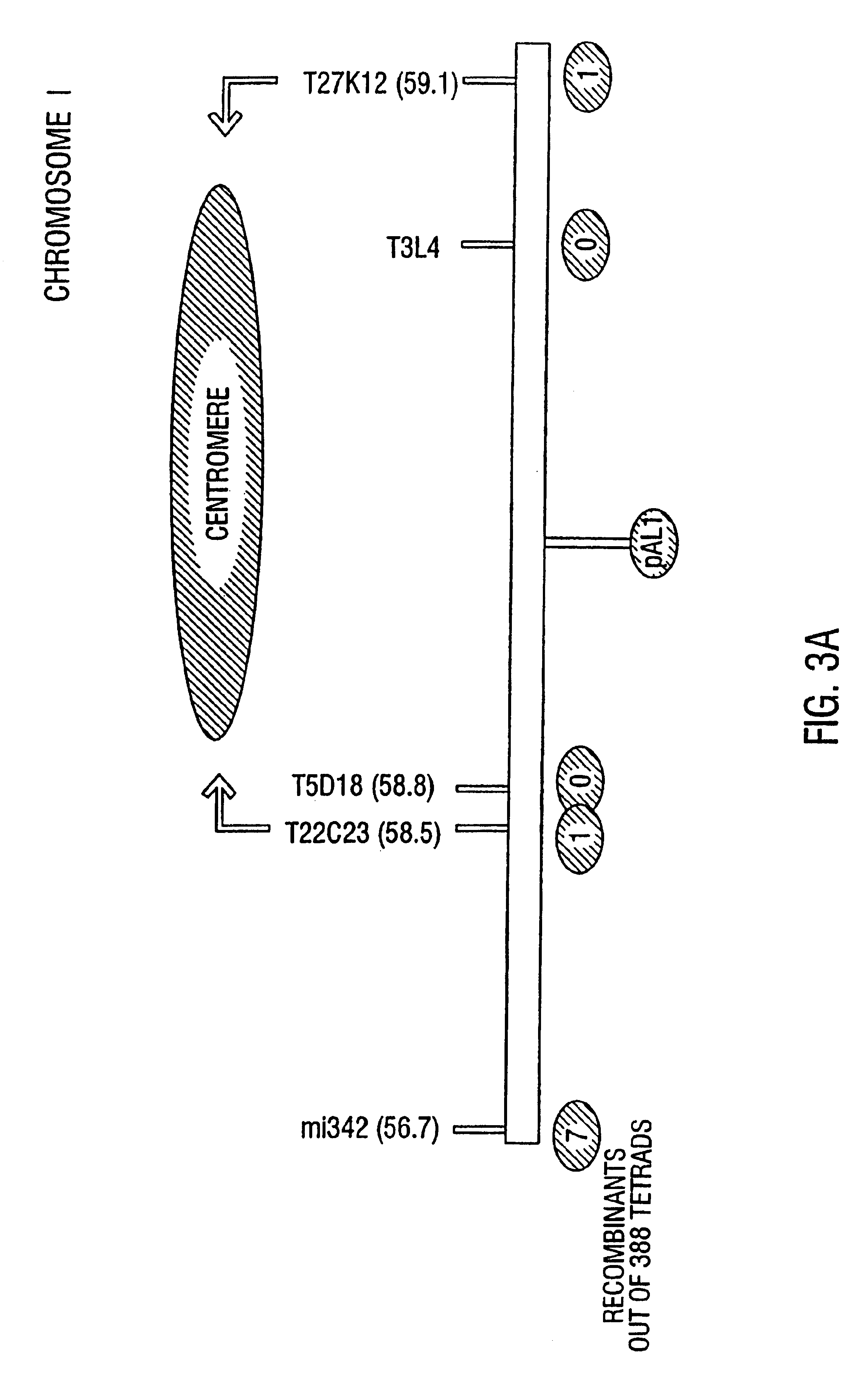
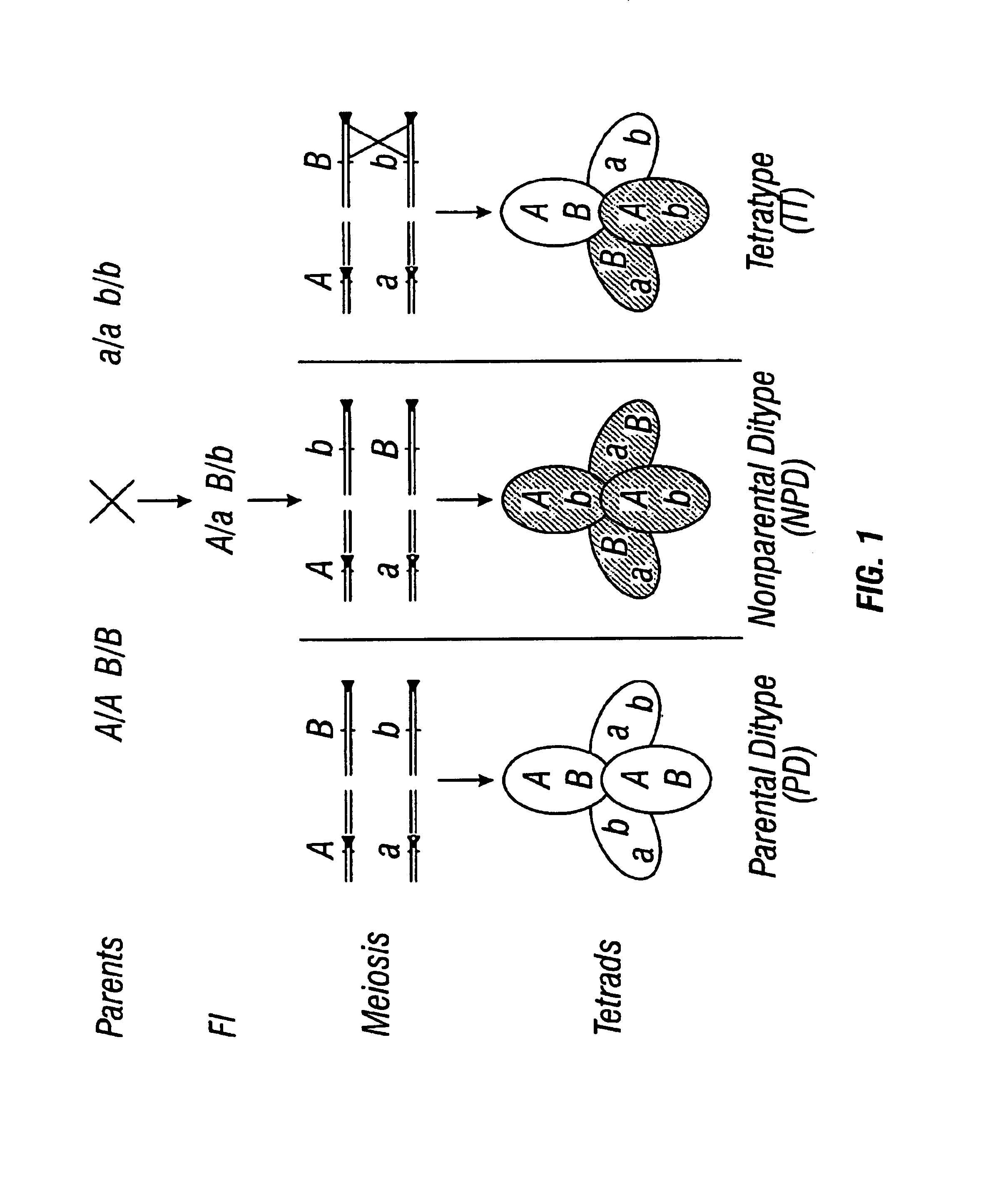
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited plant artificial chromosomes (PLACs) which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Transcriptional factor relevant to resistant adversity from Arabidopsis thaliana, coded gene, and application
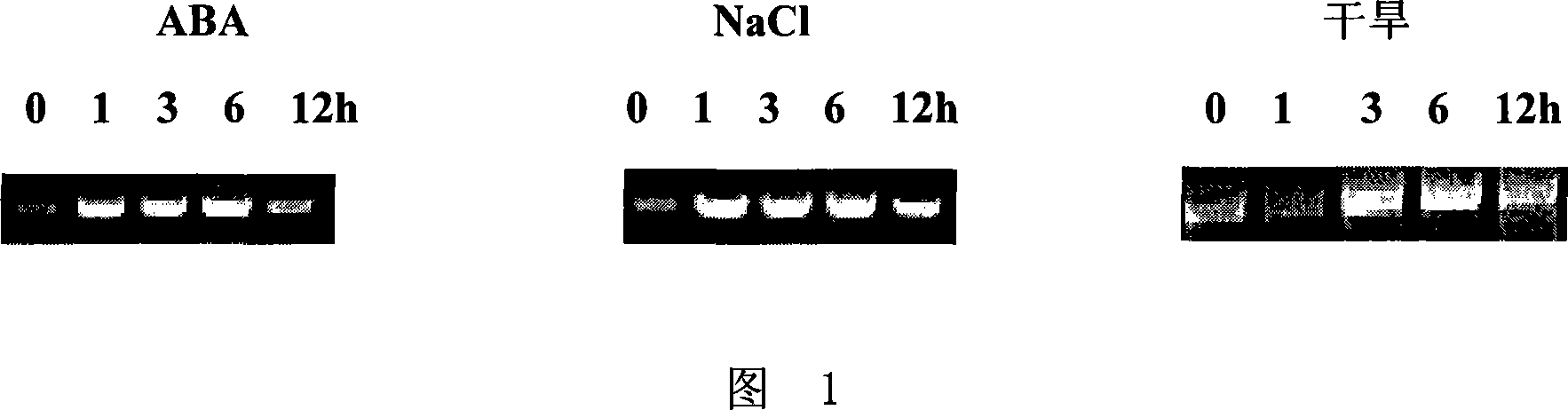
This invention discloses stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor, its coding gene and application. The stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor is derived from Arabidoesis thaliana, and can be applied in culturing stress-tolerant plants that can resist abscisic acid, high salt and draught. The transcription factor is one of the following amino acid residue sequences: (1) SEQ ID NO.1; (2) protein by substituting, deleting or adding 1-10 amino acid residues of SEQ ID NO.1, which can regulate the stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have important meaning to research on plant stress-tolerant mechanism, and method for improving draught, salt and stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have potential application in stress-tolerant genetic engineering of plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plant chromosome compositions and methods
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Plastid transformation in Arabidopsis thaliana
InactiveUS6376744B1High expressionImprove stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyEtioplasts
The invention provides methods and compositions for obtaining transplastomic Arabidopsis plants. Specifically, the method provides culturing protocols and compositions that facilitate the regeneration of transformed plants following delivery of exogenous DNA molecules.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
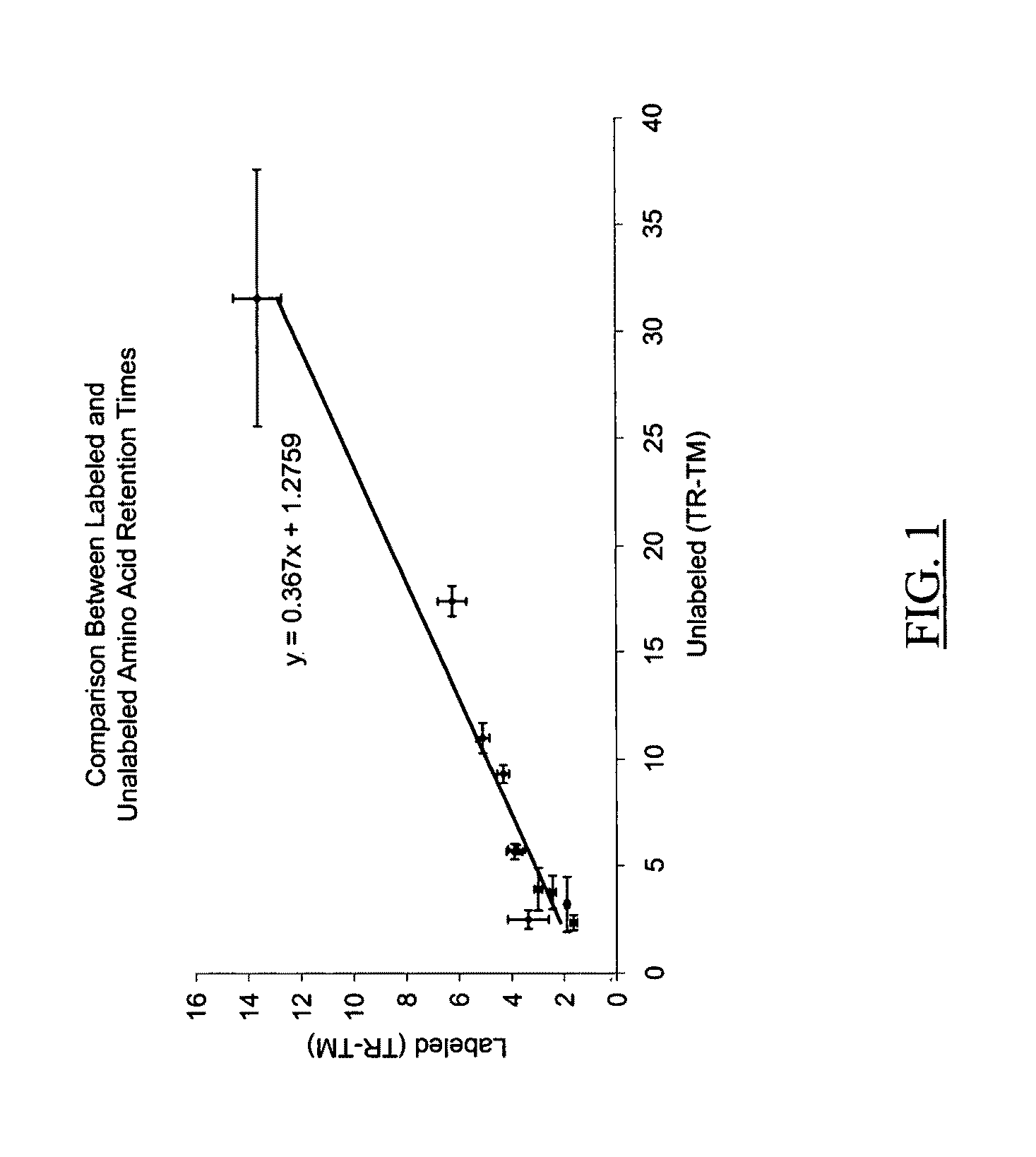
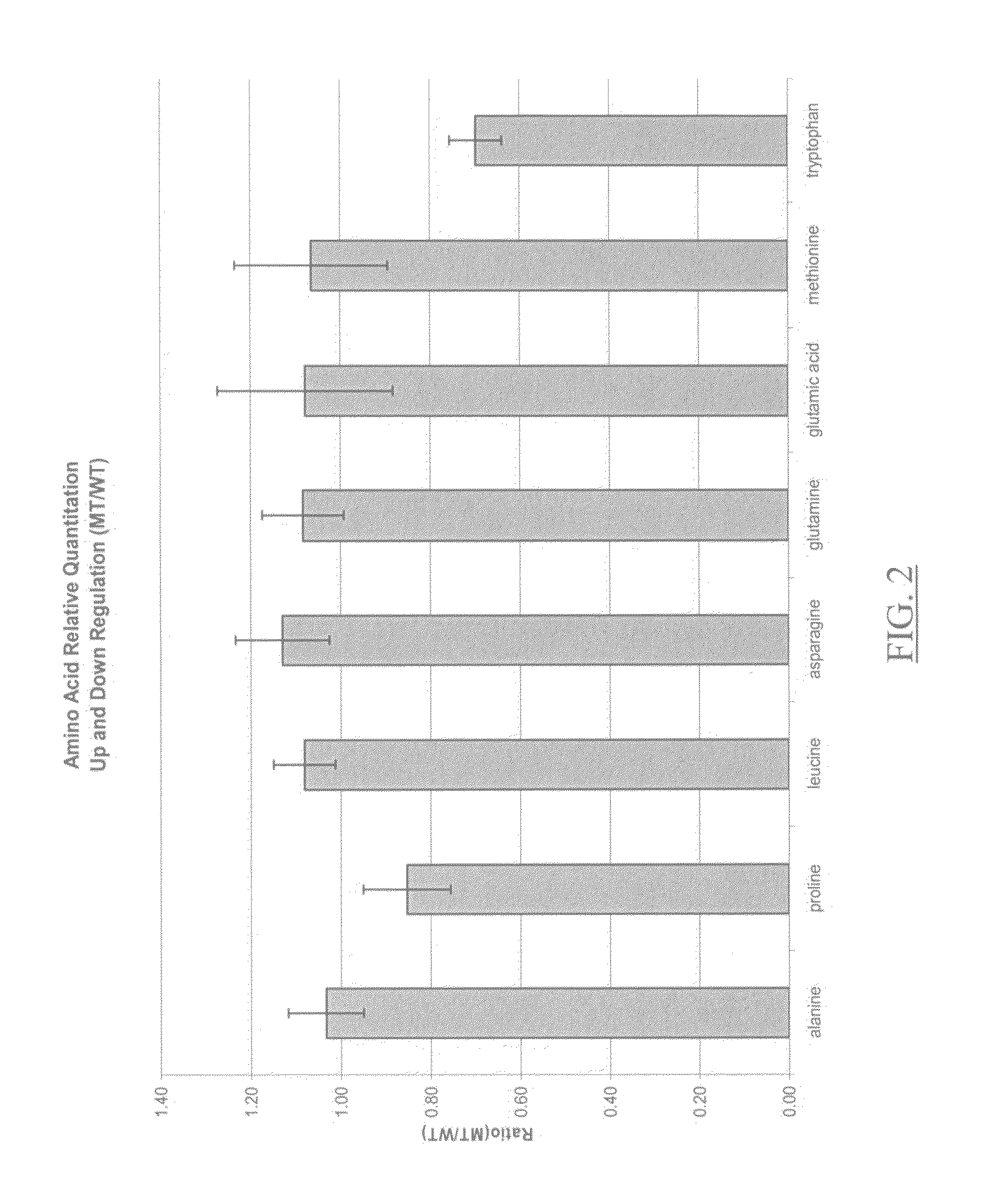
Ionizable isotopic labeling reagents for relative quantification by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20080050833A1Improve ETD analysisConvenient charging statusOrganic compound preparationComponent separationMetaboliteIsotopic labeling
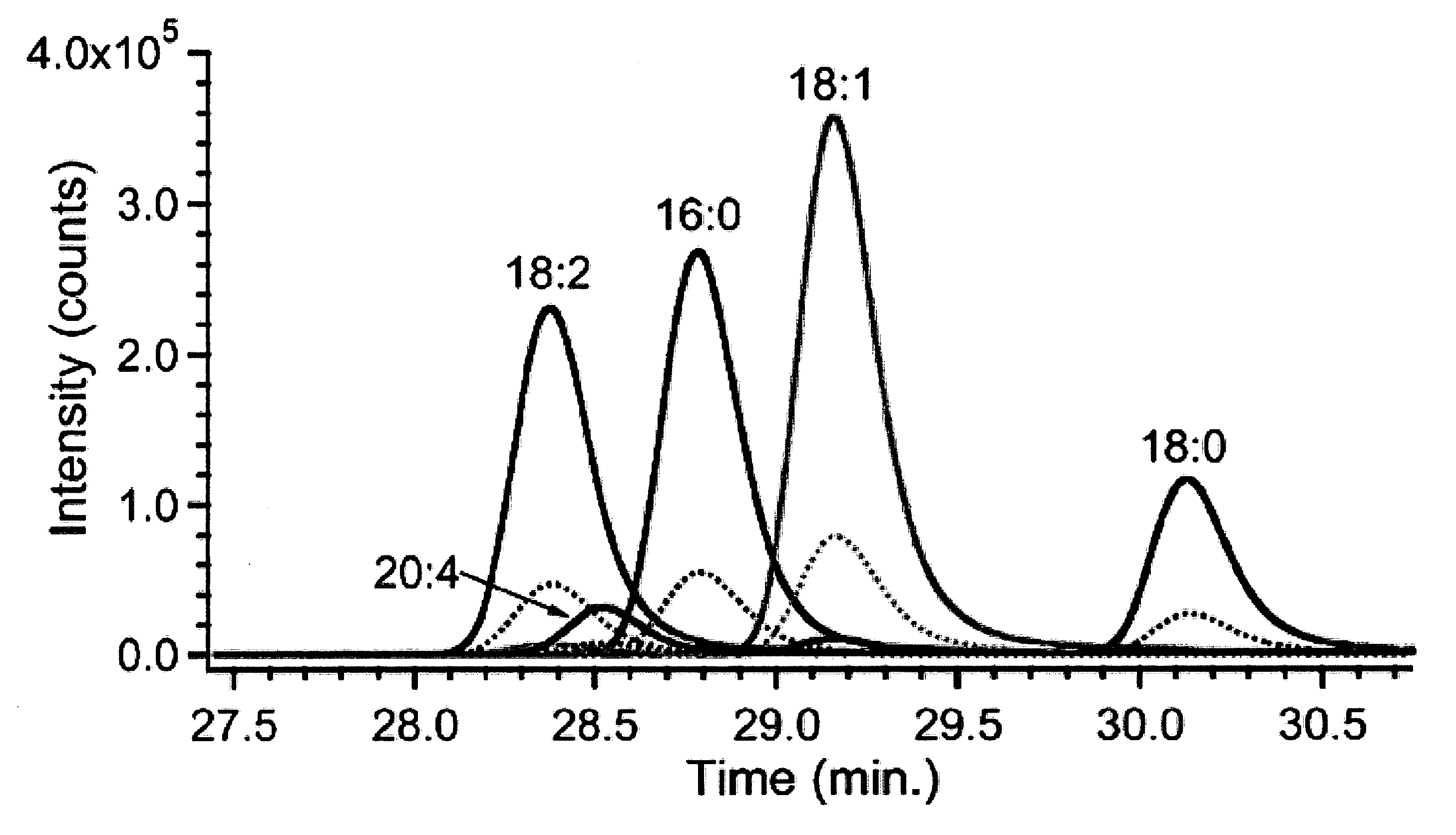
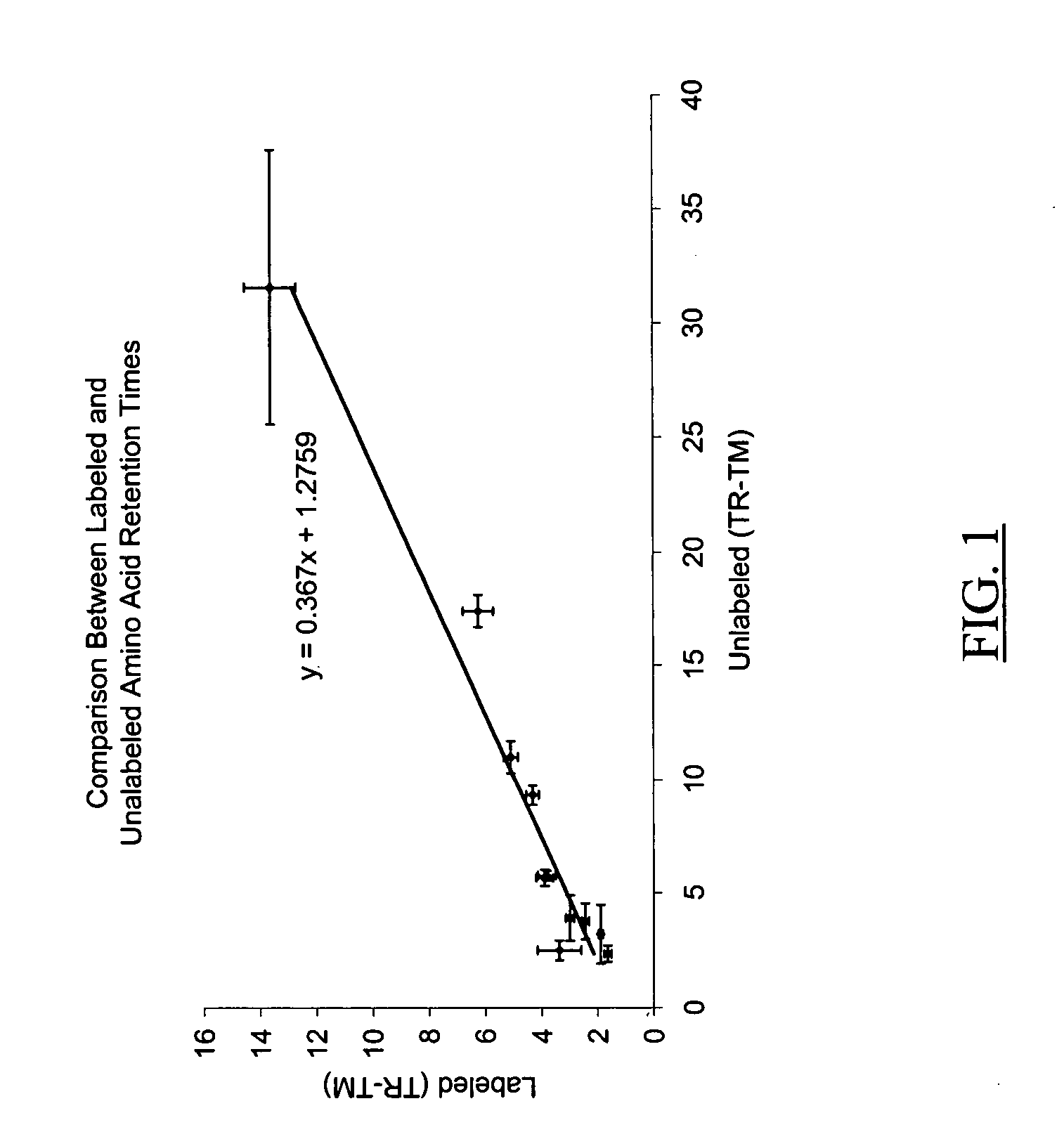
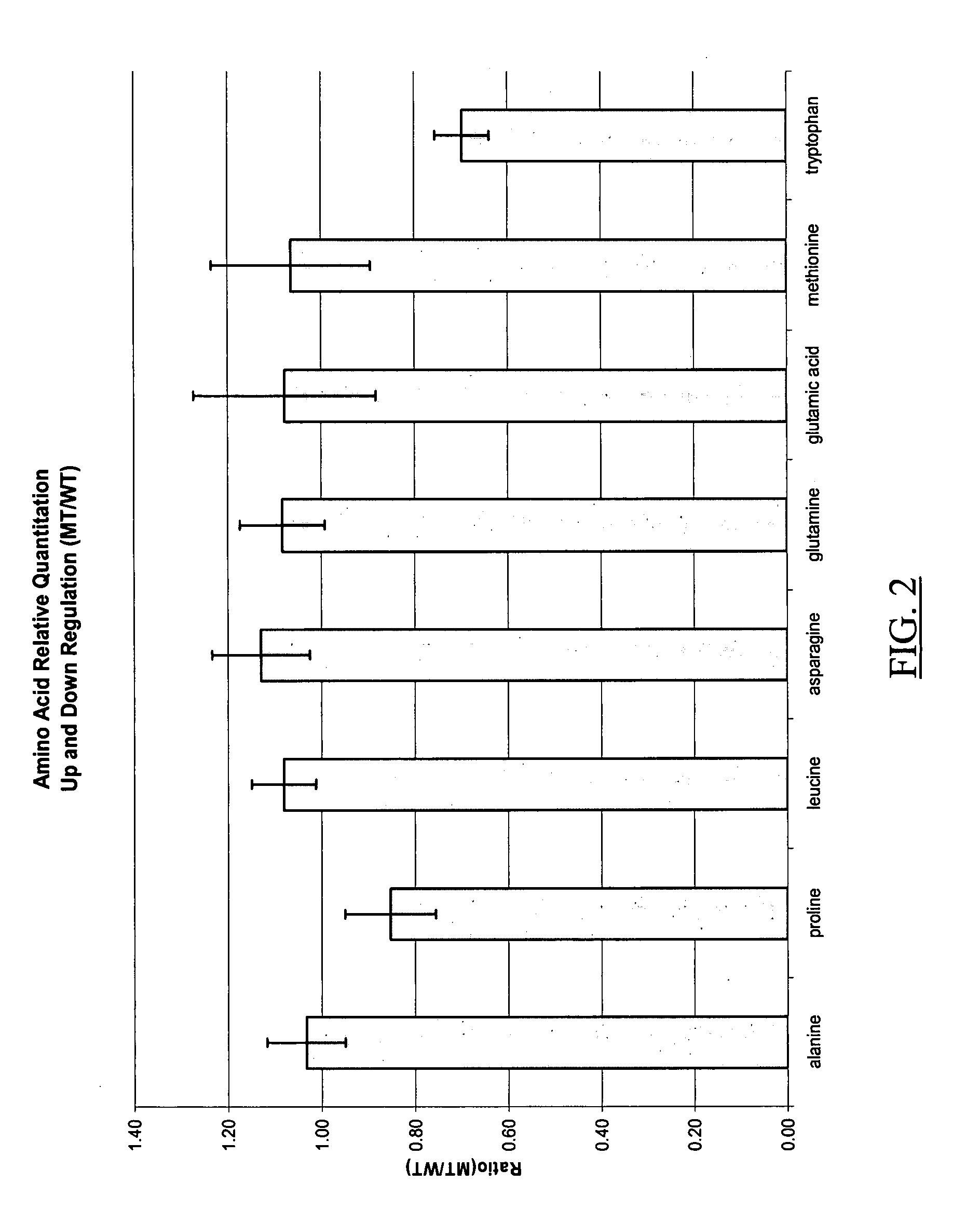
Relative quantification of metabolites by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) requiring a mechanism for simultaneous analysis of multiple analytes in two or more samples. Labeling reagents that are reactive to particular compound classes and differ only in their isotopic kit facilitating relative quantification and providing tangible evidence for the existence of specific functional groups. Heavy and light isotopic forms of methylacetimidate were synthesized and used as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing molecules, such as biological samples. Heavy and light isotopic forms of formaldehyde and cholamine were also synthesized and used independently as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing and carboxylic acid-containing molecules, such as found in biological samples. Advantageously, the labeled end-products are positively charged under normal acidic conditions involving conventional Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC / MS) applications. Labeled primary and secondary amine and carboxylic acid end-products also generated higher signals concerning mass-spectra than pre-cursor molecules and improved sensitivity. Improved accuracy concerning relative quantification was achieved by mixing heavy and light labeled Arabidopsis extracts in different ratios. Labeling strategy was further employed to ascertain differences in the amounts of amine-containing metabolites for two strains of Arabidopsis seeds.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Expressed sequences of arabidopsis thaliana
Isolated nucleotide compositions and sequences are provided for Arabidopsis thaliana genes. The nucleic acid compositions find use in identifying homologous or related genes; in producing compositions that modulate the expression or function of its encoded protein, mapping functional regions of the protein; and in studying associated physiological pathways. The genetic sequences may also be used for the genetic manipulation of cells, particularly of plant cells. The encoded gene products and modified organisms are useful for screening of biologically active agents, e.g. fungicides, insecticides, etc.; for elucidating biochemical pathways; and the like.
Owner:PARADIGM GENETICS
Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46 and application thereof
InactiveCN101760439AGood control effectPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46, which is preserved in CGMCC with preservation date as November 2, 2009, and preservation number as CGMCC No.3378. The Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46 CGMCC No.3378 in the invention is a biological control bacillus separated from grass root surrounding soil near Namco Lake in Tibet, which can grow at 10 DEG C, is favorable for exerting growth promotion and biological control effects, can restrain soybean root pythium myriotylum and saccharomycetes, can boost growth of Arabidopsis and soybean, has a prevention and control effects on soybean root pythium myriotylum as high as 85%, can increase yield of soybean to 24%, and has good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING HOUJI BIO TECH
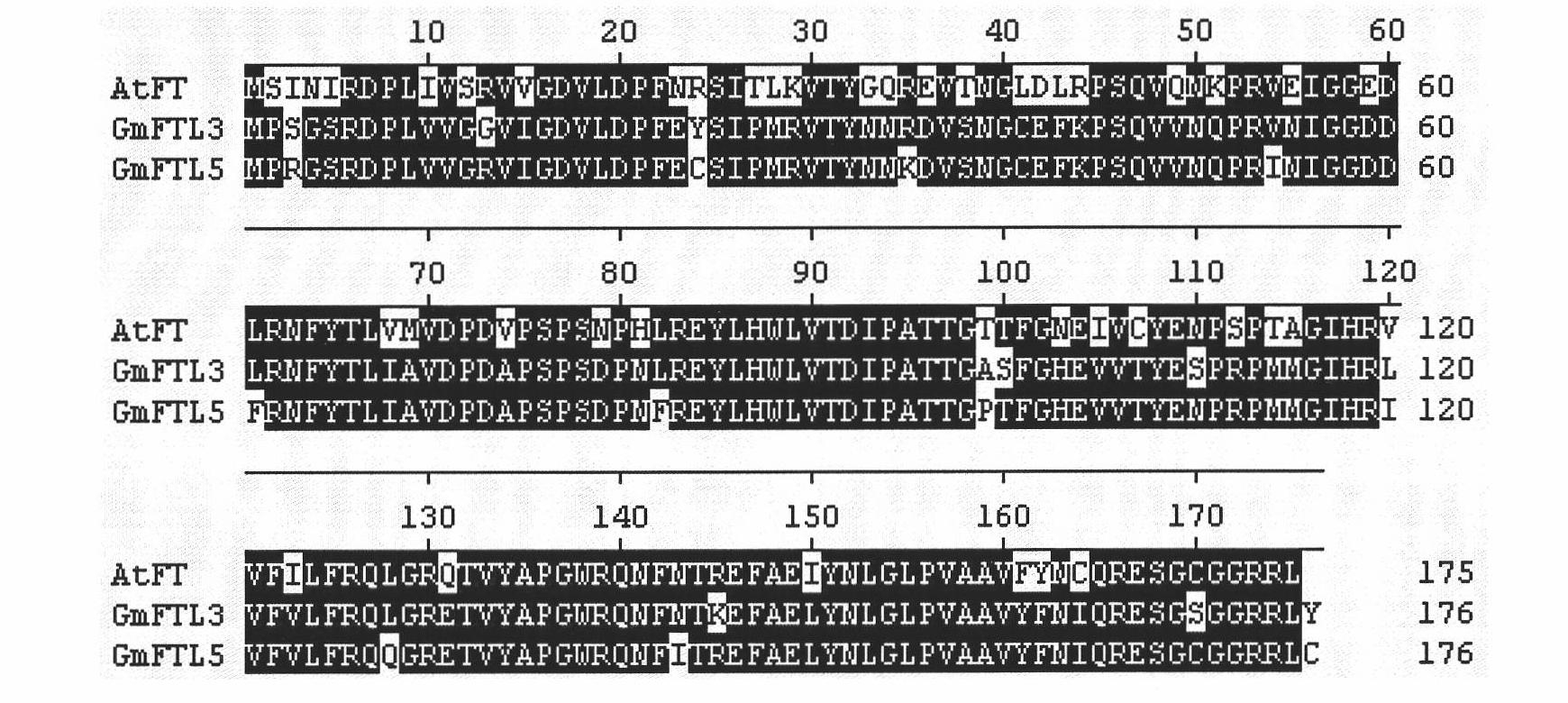
Soybean GmFTL3 protein and soybean GmFTL5 protein as well as applications thereof
ActiveCN102146124AShortened reproductive periodPromote floweringFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyArabidopsis
The invention discloses a soybean GmFTL3 protein and a soybean GmFTL5 protein which have the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 and the amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.2 respectively or the sequences which are separately obtained through replacing, deleting or adding one or more of amino acid residues and have the same functions. The GmFTL3 and GmFTL5 which are capable of overexpressing soybean flowering genes are used for obviously promoting the flowering of plant (Arabidopsis thaliana), thus the flowering time can be shortened and the growth period can be shortened. The proteins can be used for solving the problem of flowering asynchronism in the hybridization breeding process, the growth period control problems of various crops, vegetable, fruits and flowers, the problem of photoperiod sensitivity and the introduction problem.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
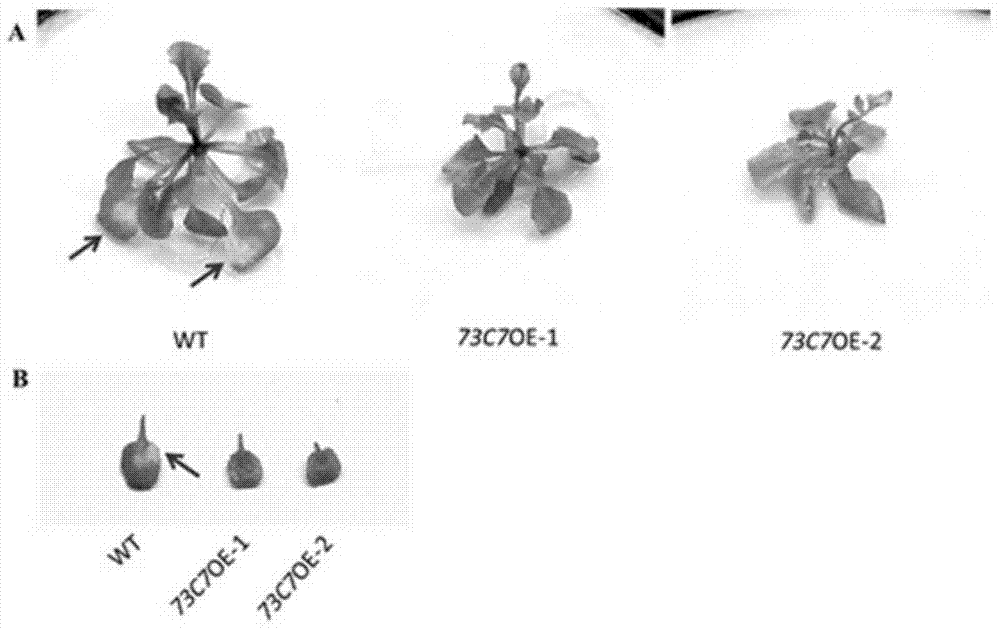
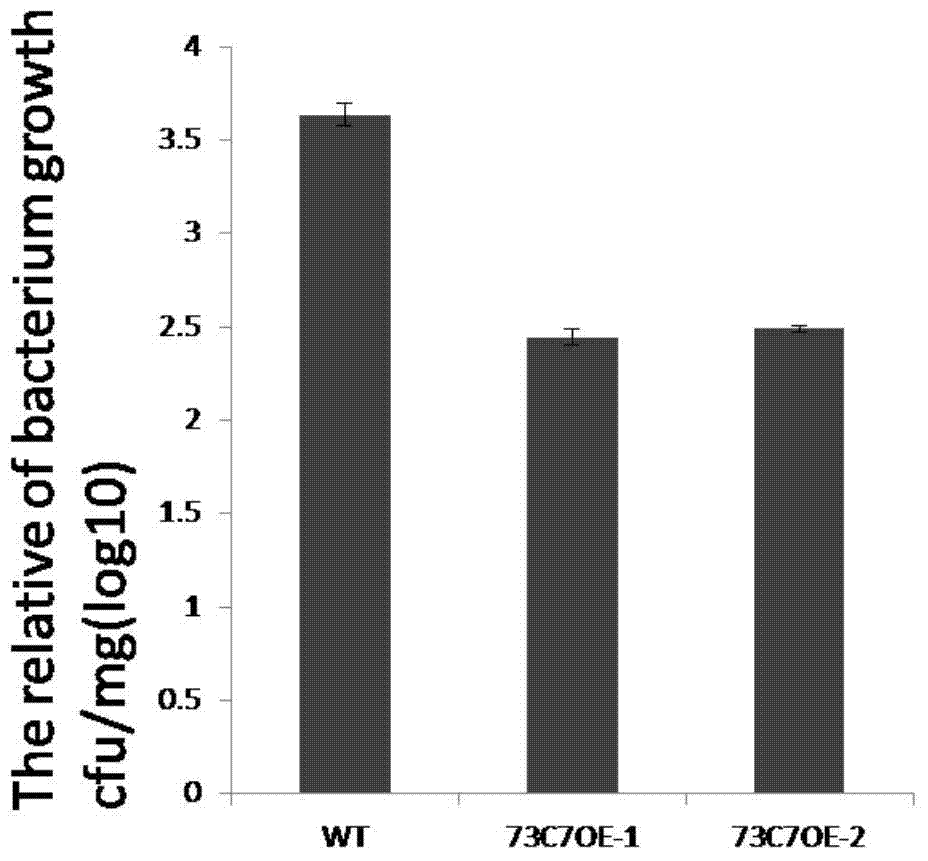
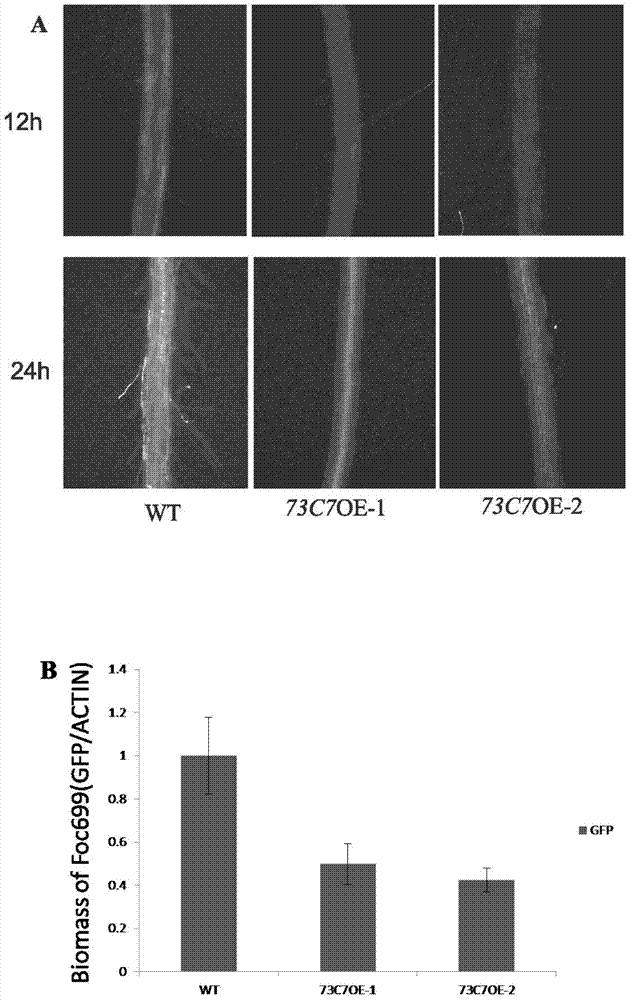
Application of Arabidopsis glycosyltransferase gene UGT73C7 in improving plant disease resistance
InactiveCN104845990AImprove disease resistanceIncrease varietyGenetic engineeringFermentationNucleotideArabidopsis
The invention discloses an application of Arabidopsis glycosyltransferase gene UGT73C7 in improving plant disease resistance, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the glycosyltransferase gene UGT73C7 is shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and is cloned by RT-PCR from Arabidopsis thaliana. The ene UGT73C7 is used to construct a plant overexpressing vector for plant transgene operation, so as to obtain the transgenic plants. The detection results show that the disease resistance of the transgenic plants is significantly improved, suggesting that new disease-resistant plants can be created after the implementation of the application disclosed by the invention, and the application can be used for the subsequent crop variety improvement and has great significance for China's agricultural production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
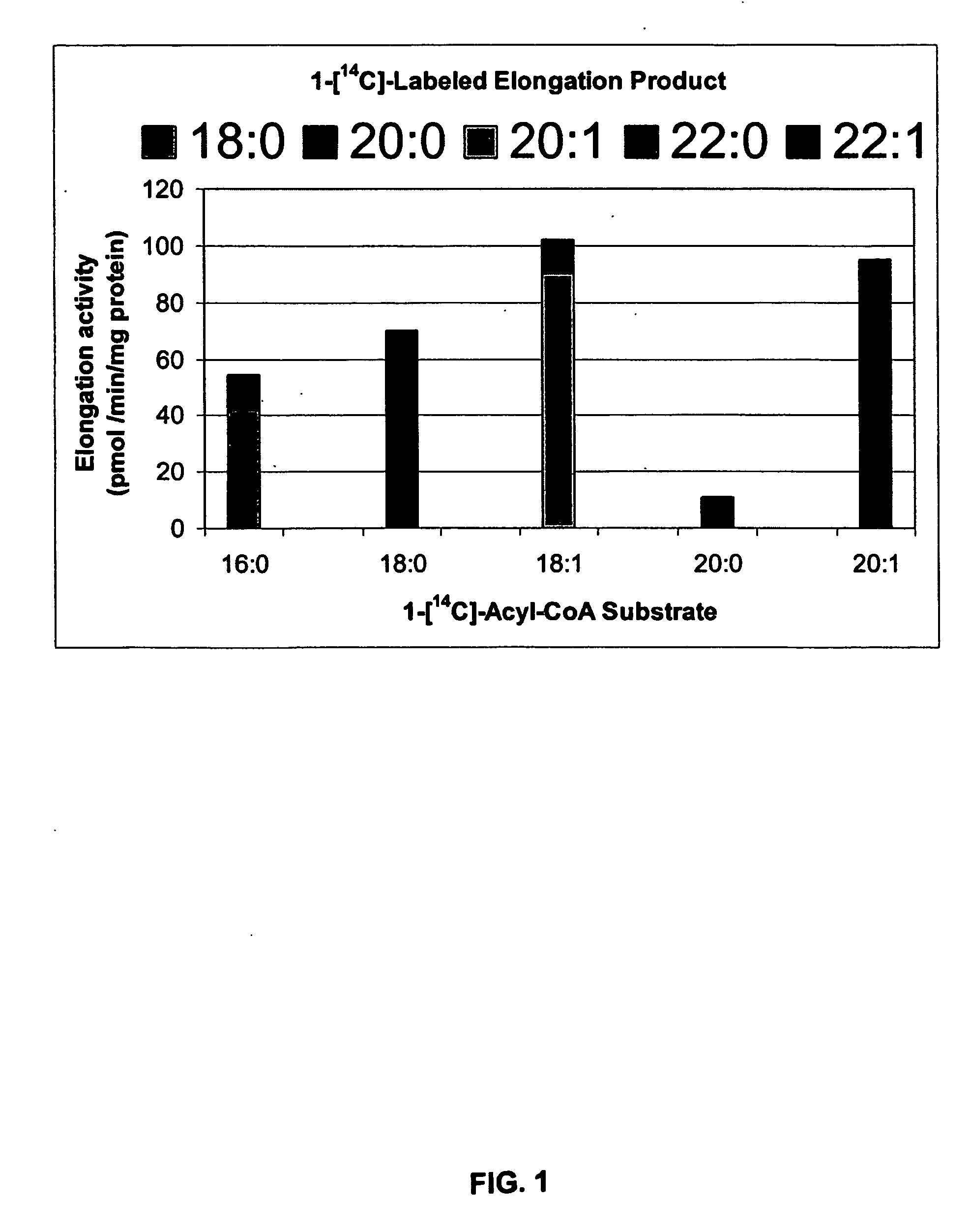
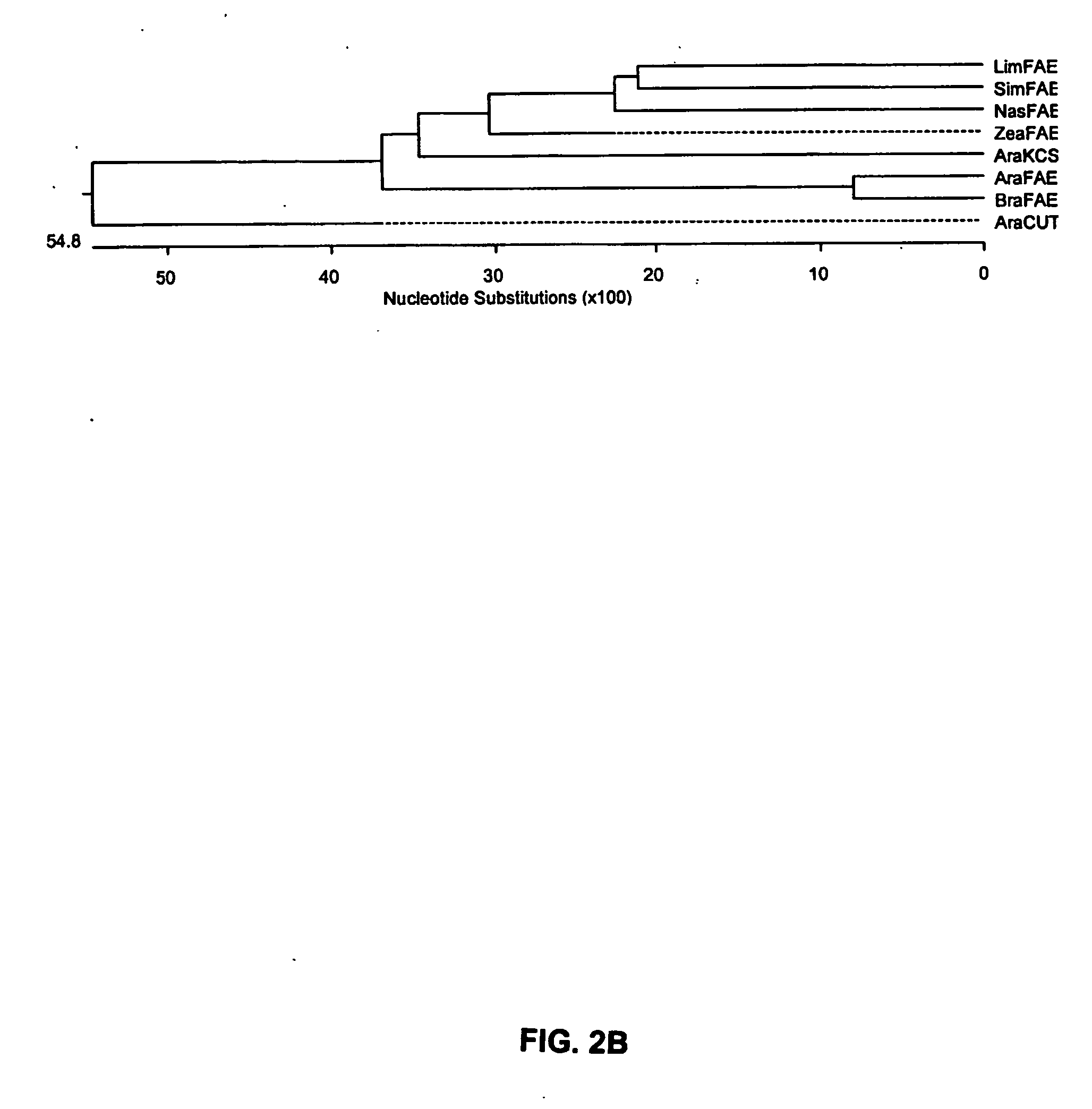
Fatty Acid Elongase (Fae) Genes And Their Utility In Increasing Erucic Acid And Other Very Long-Chain Fatty Acid Proportions In Seed Oil.
InactiveUS20070204370A1High homologyIncrease synthesisMicroorganismsTransferasesHeterologousVery long chain fatty acid
This invention relates to seeds of plant, plants themselves and cells of such plants which comprise a heterologous gene coding for a plant (such as nasturtium (Tropaeolum majus) or Crambe abyssinica) fatty acid elongase (FAE) gene or allelic variant thereof, or combinations of one or both of these FAE genes with an Arabidopsis fatty acid elongase 1 (FAE1) gene, in co-transformation, in reading frame alignment with a promoter capable of increasing expression of said gene(s), when said transformed plant cell is in a seed, said plant cell or seed being capable of producing an increase in proportion of a very long chain monounsaturated or saturated fatty acids when compared with the proportions of said fatty acids in a control plant cell or seed lacking said heterologous FAE gene or genes. The invention also relates to combinations of these fatty acid elongase genes by traditional crossing, sufficient to increase the proportion of very long chain monounsaturated or saturated fatty acids in the seed oil of the progeny compared to the proportion of said fatty acids in either of the parental lines.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT (Asparatate AminoTransferase) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides hitherto unknown ASPAT-encoding nucleic acids and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for increasing various plant yield-related traits by increasing expression in a plant of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a MYB91 like transcription factor (MYB91 ) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having increased expression of a nucleic acid sequence encoding an MYB91 polypeptide, which plants have increased yield- related traits relative to control plants. The invention additionally relates to nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and plants containing said nucleic acid sequences. Even furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA (Gibberellic Acid-Stimulated Arabidopsis). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. Yet furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an AUX / IAA (auxin / indoleacetic acid) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding IAA polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising AUX / IAA-encoding nucleic acids, useful in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
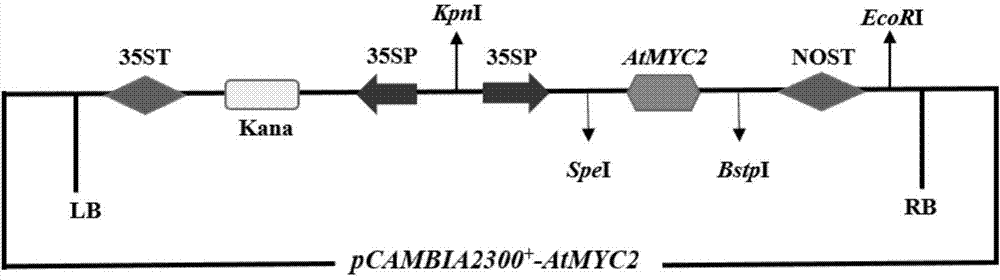
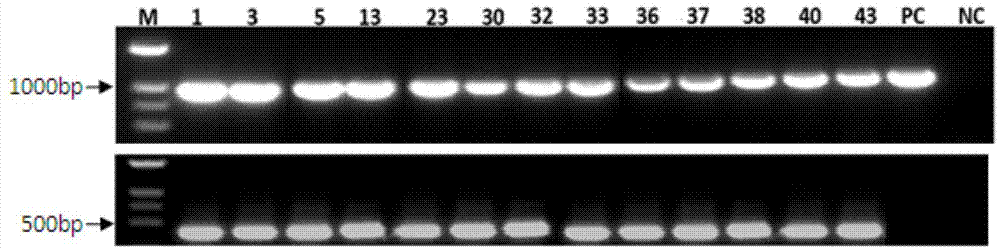
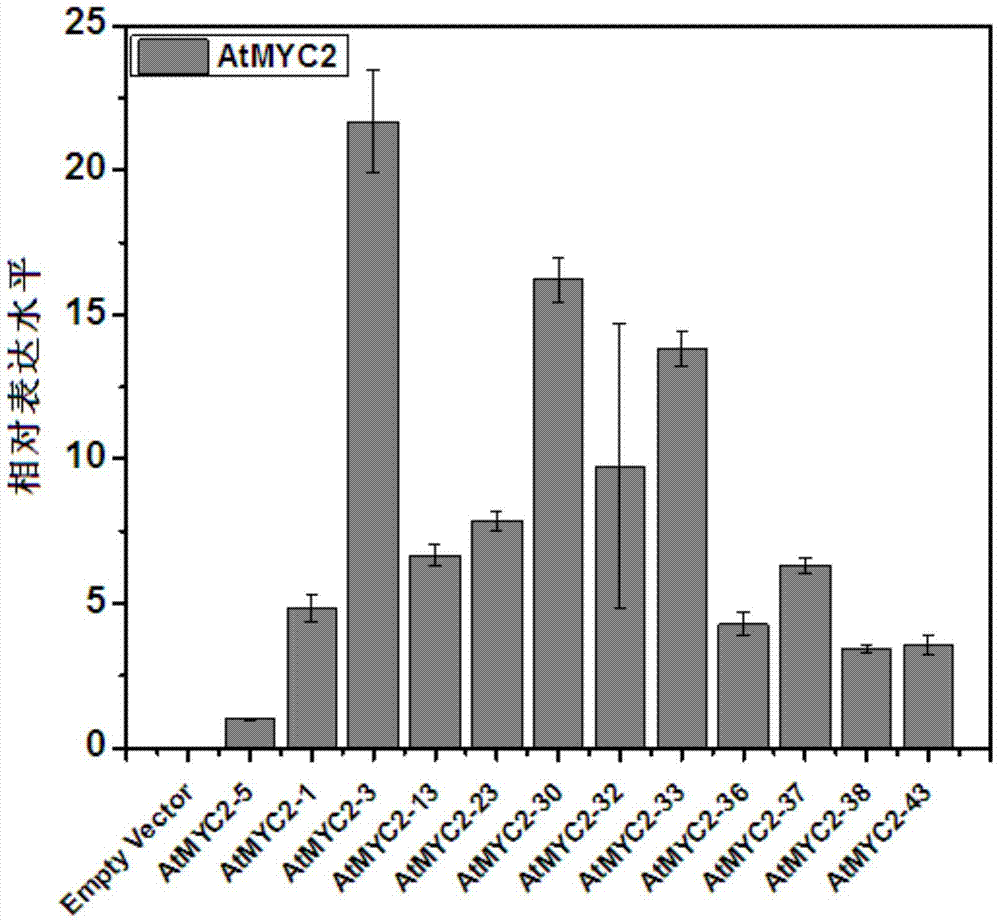
Method for increasing contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using transgene AtMYC2
InactiveCN104726485AIncrease contentGood effectFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSalvianolic acidBiology
The invention relates to a method for increasing the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in a salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a transgene AtMYC2, belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the steps of constructing a high-efficiency expression vector of a plant by using an arabidopsis transcription factor AtMYC2, and carrying out genetic transformation on salvia miltiorrhiza leaves to obtain a gene AtMYC2 overexpressed transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root; analyzing the expression of AtMYC2 in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root and related genes in biosynthetic pathways of tanshinone and salvianolic acid through qRT-PCR; measuring the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); and measuring the antioxidant activity of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a DPPH free radical scavenging method. The invention provides the method for simultaneously increasing the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root and also provides a novel high-quality raw material for producing tanshinone and salvianolic acid with important clinic demands so as to have the positive promoting significance and application value for relieving the problem that the drug resources of tanshinone and salvianolic acid are short.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
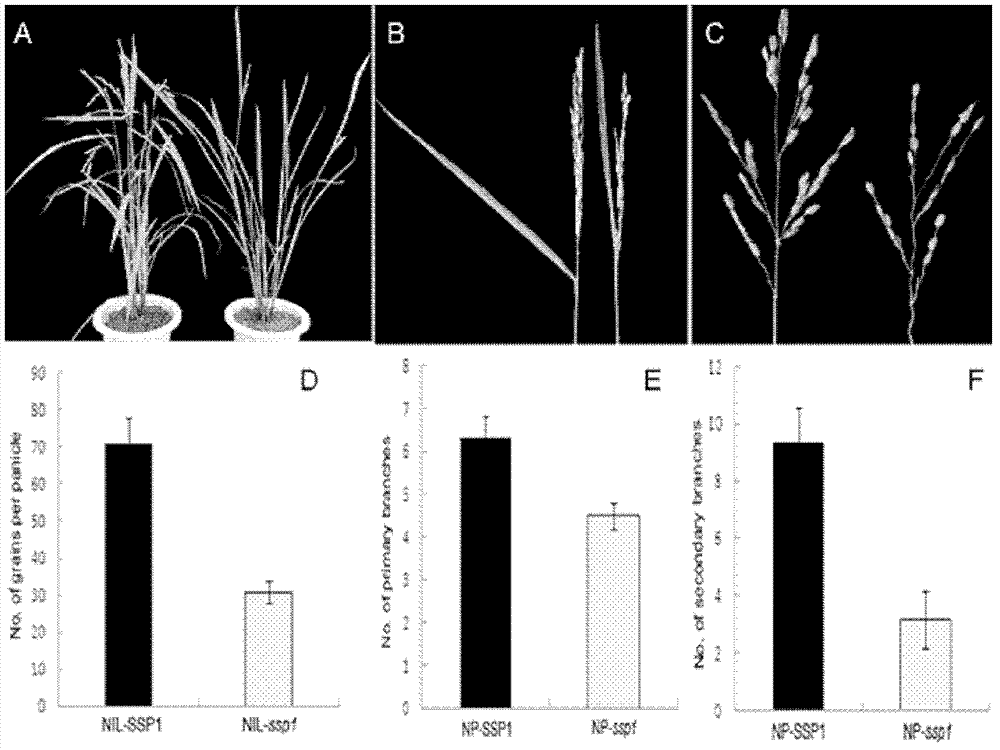
Panicle size controlling gene, mutant and application thereof
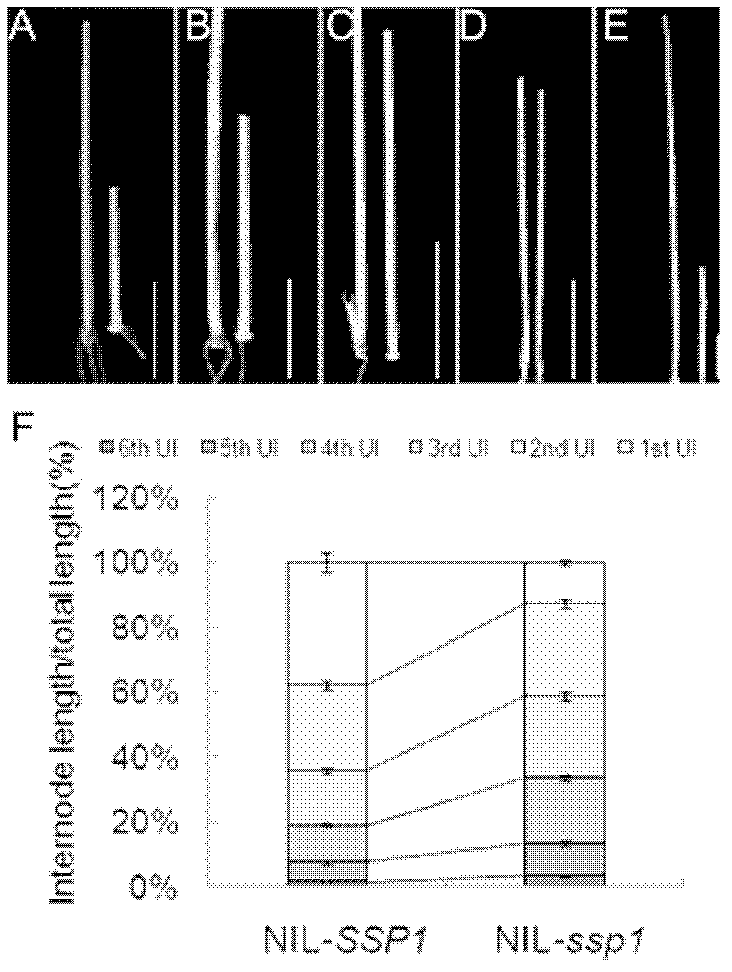
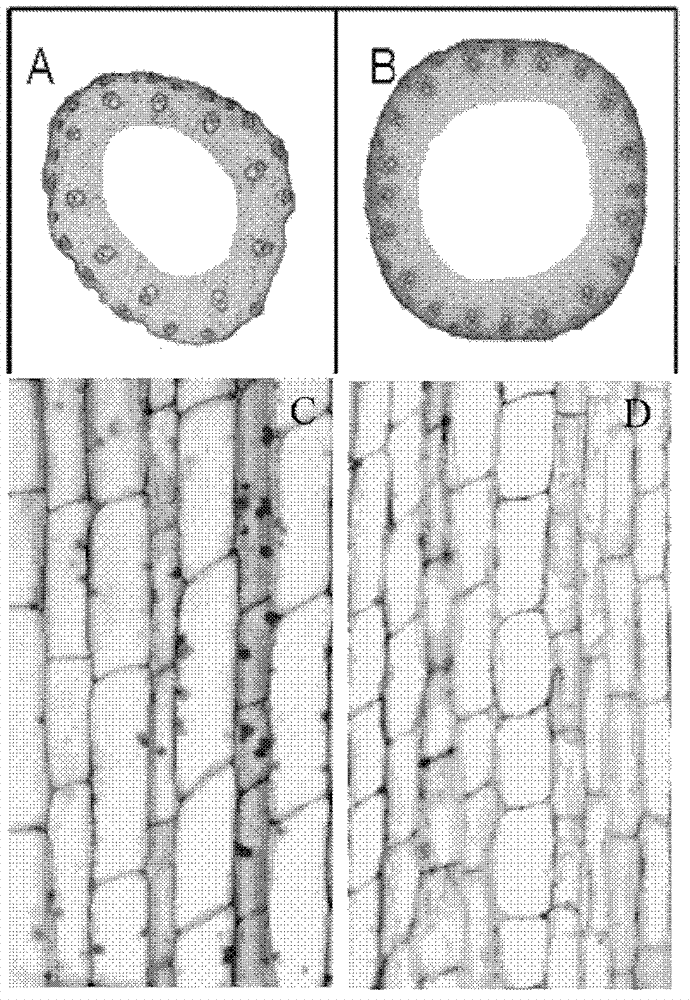
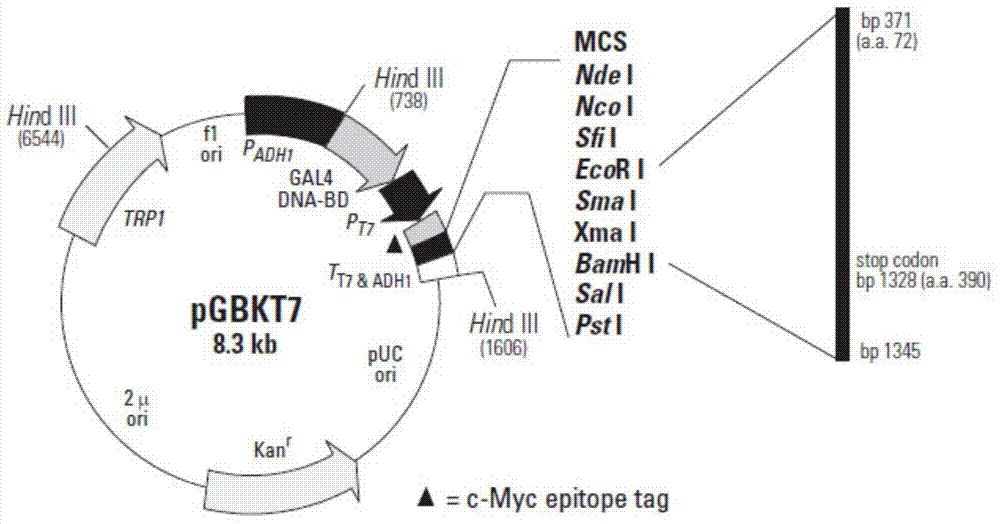
The invention relates to a panicle size controlling gene SSP1 (Small and Sheathed Panicle 1) and a mutant gene ssp1 thereof, and action mechanism thereof in regulating plant height, leaf included angle and panicle size, and provides a gene sequence SEQ IDNO: 3 from the panicle size controlling gene mutant ssp1. The invention also relates to homologous genes of the panicle size controlling gene mutant ssp1 in barley, wheat, maize, corn, sorghum, soybean, cotton, rape, arabidopsis and other plants. The above mentioned genes are all referred to as panicle size controlling genes. The invention also relates to applications of the SSP1 gene and the mutant ssp1 gene in controlling plant height, improving lodging resistance, reducing leaf angle to improve photosynthetic efficiency, changing gibberellin response, suppressing panicle sprouting and breeding.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Soybean salt-tolerant gene GmCIPK2 and application thereof
ActiveCN104726476AImprove salt toleranceGenetic engineeringFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a soybean salt-tolerant gene GmCIPK2 and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of cDNA of the soybean salt-tolerant gene GmCIPK2 is shown in SEQ ID No.1. According the application, a yeast two-hybrid system of Clontech is firstly utilized for constructing a yeast cDNA library of soybean 371005, soybean salt-tolerant gene GmCBL3 is cloned, a bait protein is constructed, and an interacting protein GmCIPK2 of a protein GmCBL3 is obtained by virtue of a yeast two-hybrid method; then a gateway is utilized for carrying out BP reaction on the gene GmCIPK2 to link the gene GmCIPK2 to pDONR221, massive cloning is carried out in escherichia coli DH5alpha by virtue of a conversion method, and then LR reaction is carried out to link the gene GmCIPK2 to an expression vector pK2GW7; the expression vector pK2GW7 is transferred into Arabidopsis by virtue of agrobacterium mediation, so that the salt tolerance of transgenic plants is obviously improved.
Owner:SHANDONG CROP GERMPLASM CENT
Salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat and coding protein as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102234653AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention particularly relates to a salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat and coding protein as well as application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological gene engineering. The salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat is a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table. The invention has the beneficial effects that an MYB transcription factor gene TaMYB33 of wheat is obtained by cloning for the first time, and a mediation method of agrobacterium tumefaciens is used for transferring the gene into arabidopsis. The comparative analysis proves that compared with a wild arabidopsis plant, the salt tolerance and drought resistance of a transgenic arabidopsis plant containing the gene TaMYB33 provided by the invention are obviously improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN +1
Plant chromosome compositions and methods
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
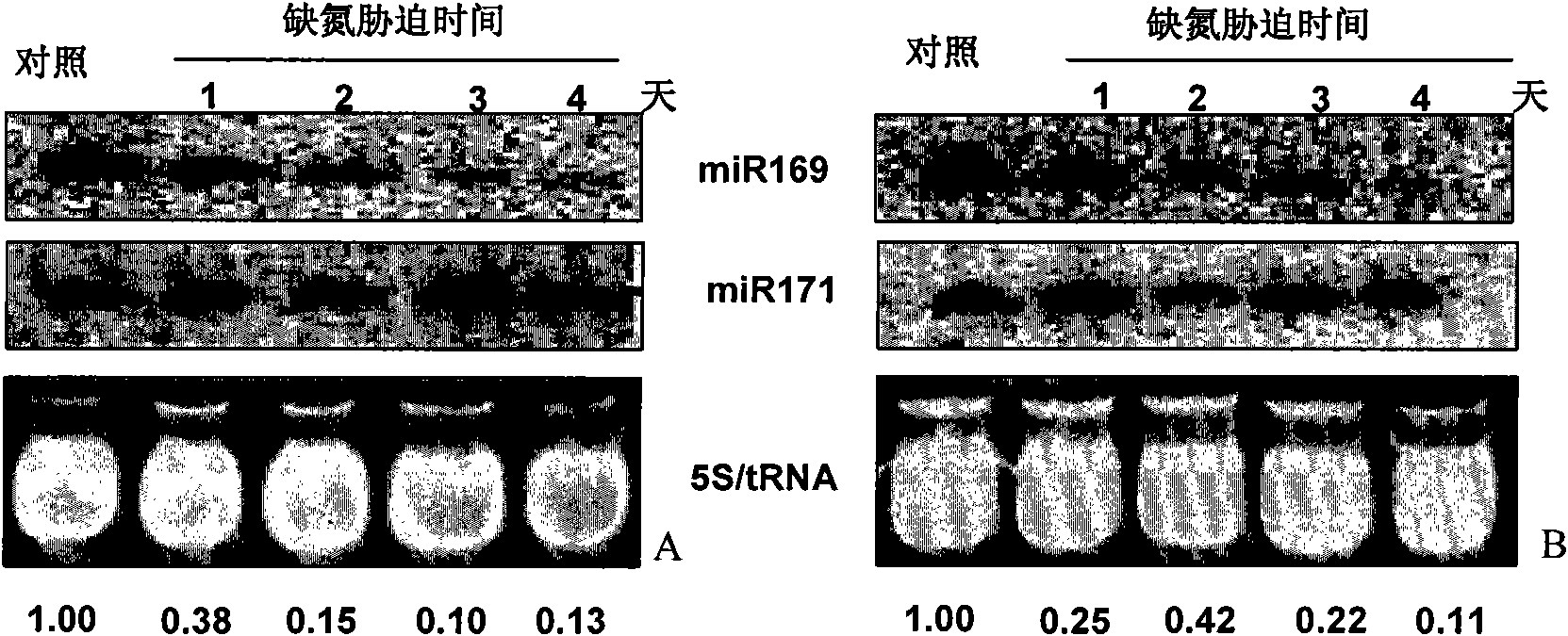
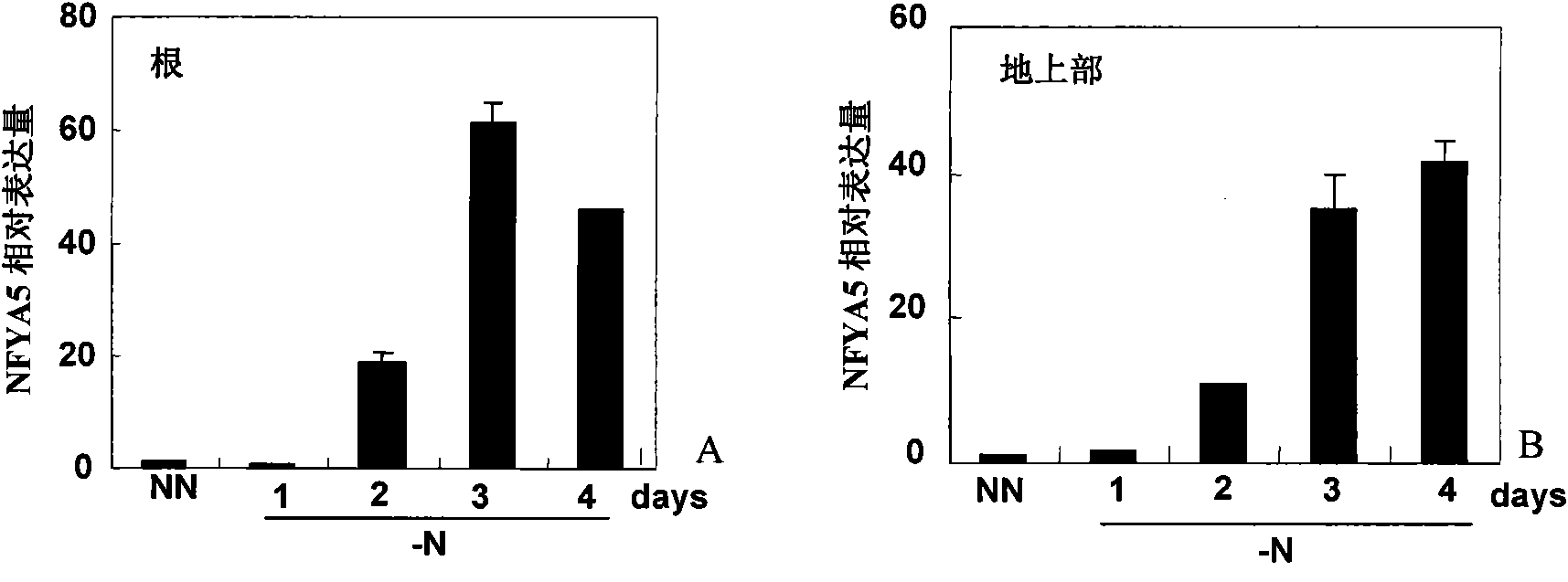
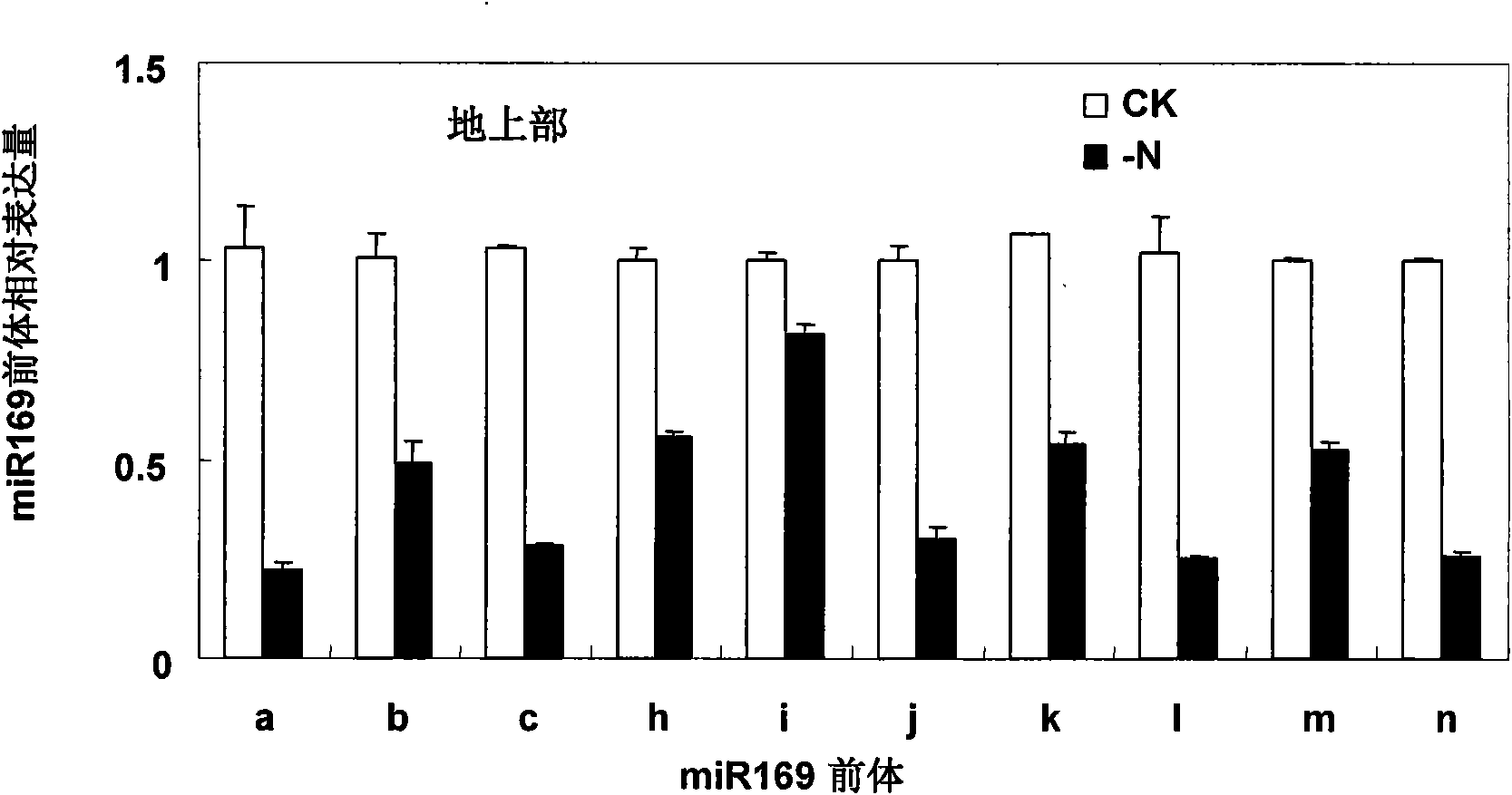
Application of miR169 or target genes NFYA5 thereof in nitrogen stress adaptation of plants
InactiveCN101955970AIncreased sensitivityEnhanced ability to tolerate low nitrogen stressFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNitrogen stressLow nitrogen
The invention discloses application of small RNA miR169 or target genes NFYA5 thereof related to nitrogen metabolism in the nitrogen stress adaptation of plants, which is characterized in that miR169 is excessively expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh to increase the sensitivity of the Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh on nitrogen deficiency stress; and the target genes NFYA5 of miR169 is correspondingly excessively expressed to reduce the sensitivity of the Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh on the nitrogen deficiency stress and enhance the capability of the Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh on low nitrogen stress resistance. The invention can ensure that the analysis and the deeply knowledge of the complicated regulate and control network can be further applied to the cultivation of crops of high-efficiency nitrogen.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
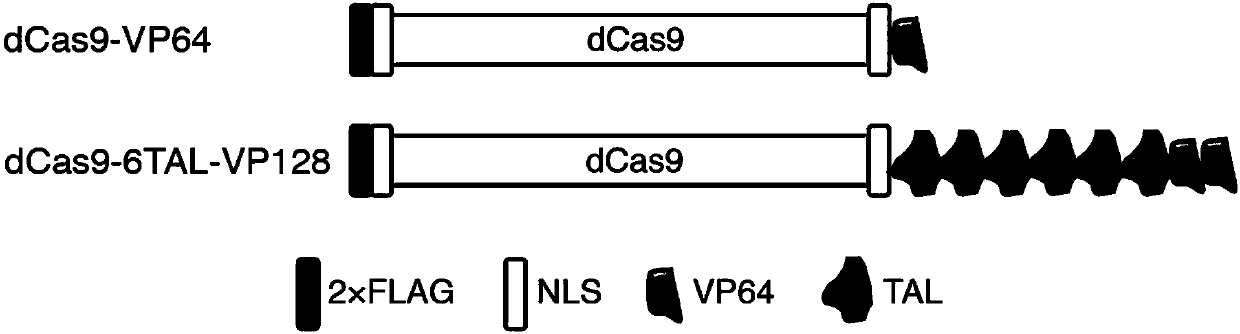
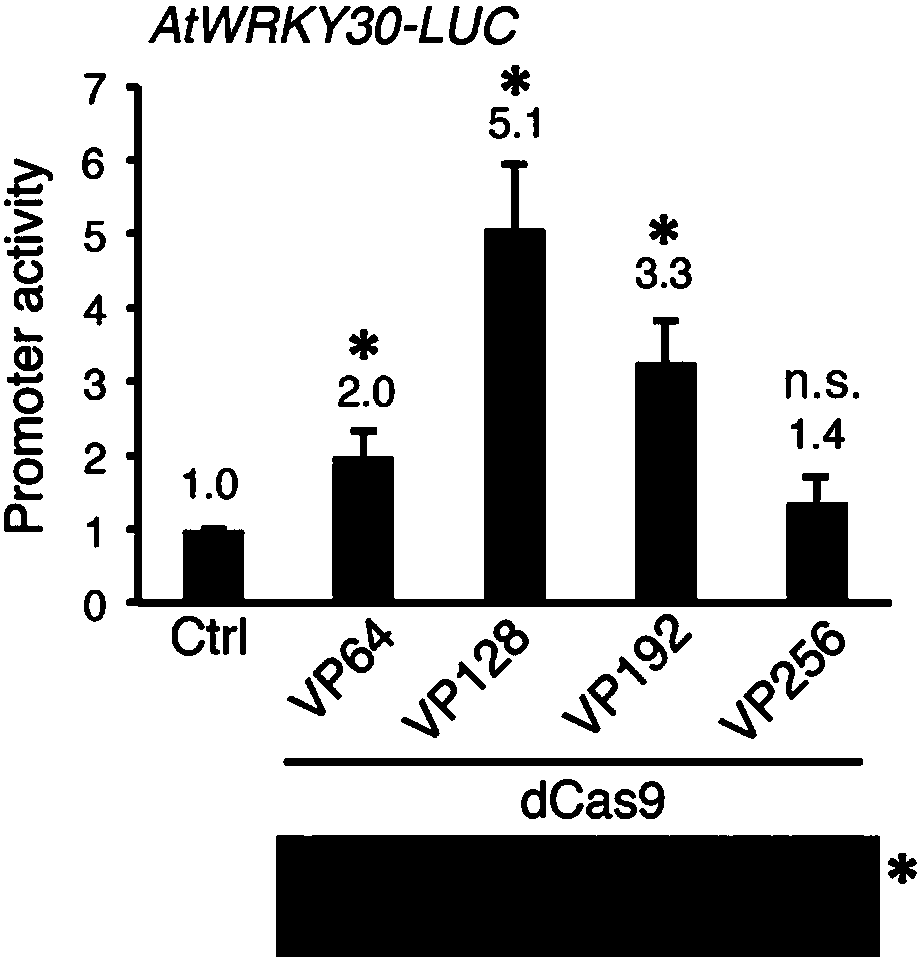
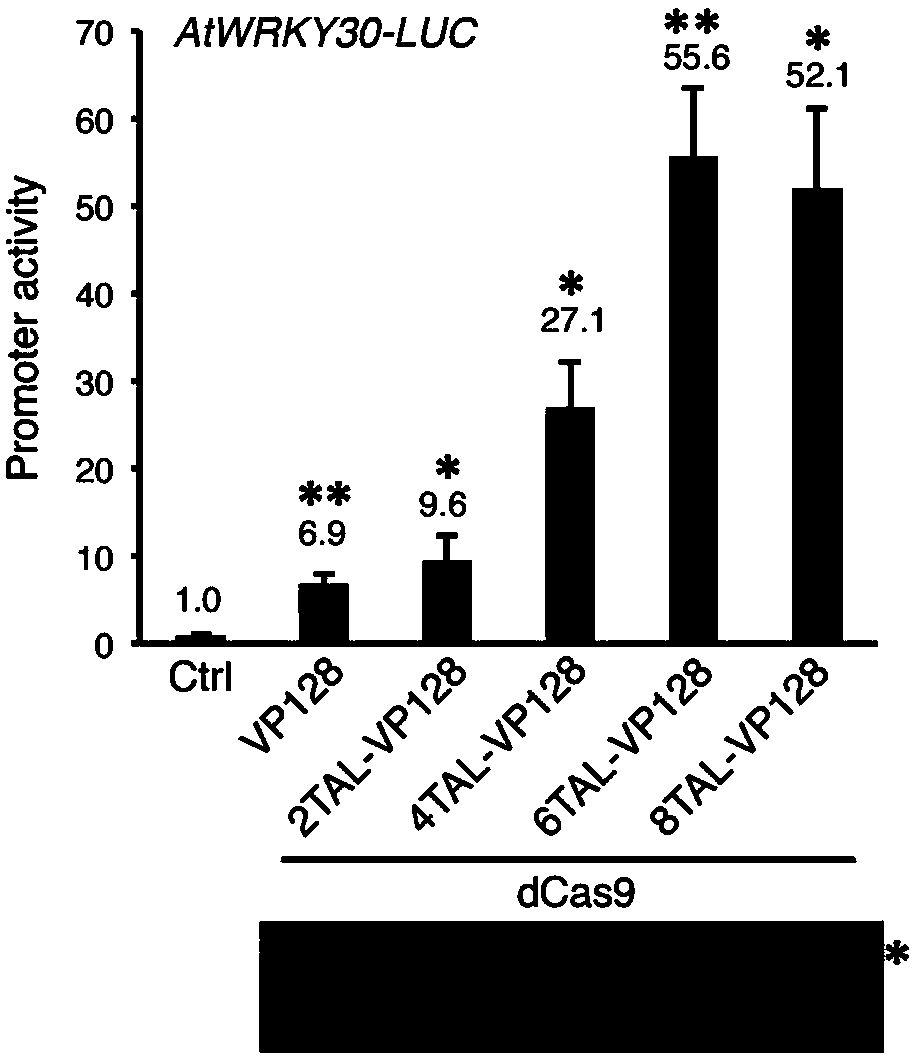
High-efficiency artificial activating transcription factor dCas9-TV, and coding gene and applications thereof
ActiveCN107722125ATranscriptional activationEliminate the need for cloningHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMetaboliteBiological activation
The invention relates to a high-efficiency artificial activating transcription factor dCas9-TV, and a coding gene and applications thereof. According to a construction method, the carboxyl terminal ofnuclease inactivated Cas9 protein (dCas9) is connected with a plurality of copies of VP64 and TAL transcription-activating domains so as to obtain a series of novel artificial activating transcription factors, and obtain dCas9-TV with the best transcriptional activation activity via screening. When only one guide RNA (gRNA) is adopted for targeting a specific gene promoter, dCas9-TV is capable ofrealizing high efficiency activating of transcription of endogenous genes of Arabidopis thaliana and paddy rice; when a plurality of gRNA are adopted for targeting a plurality of target genes, dCas0-TV is capable of realizing transcription activation of a plurality of genes. In addition, it is confirmed that dCas9-TV possesses the same high efficiency targeting transcription activation activity in human cells. An in vitro assembled dCas9-TV / gRNA ribonucleoprotein compound can be adopted for transcription activation of Arabidopis thaliana and paddy rice endogenous genes. The high-efficiency artificial activating transcription factor dCas9-TV can be adopted in the fields such as genome genetic screening, metabolite biosynthesis pathway reconstruction, and crop improvement.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
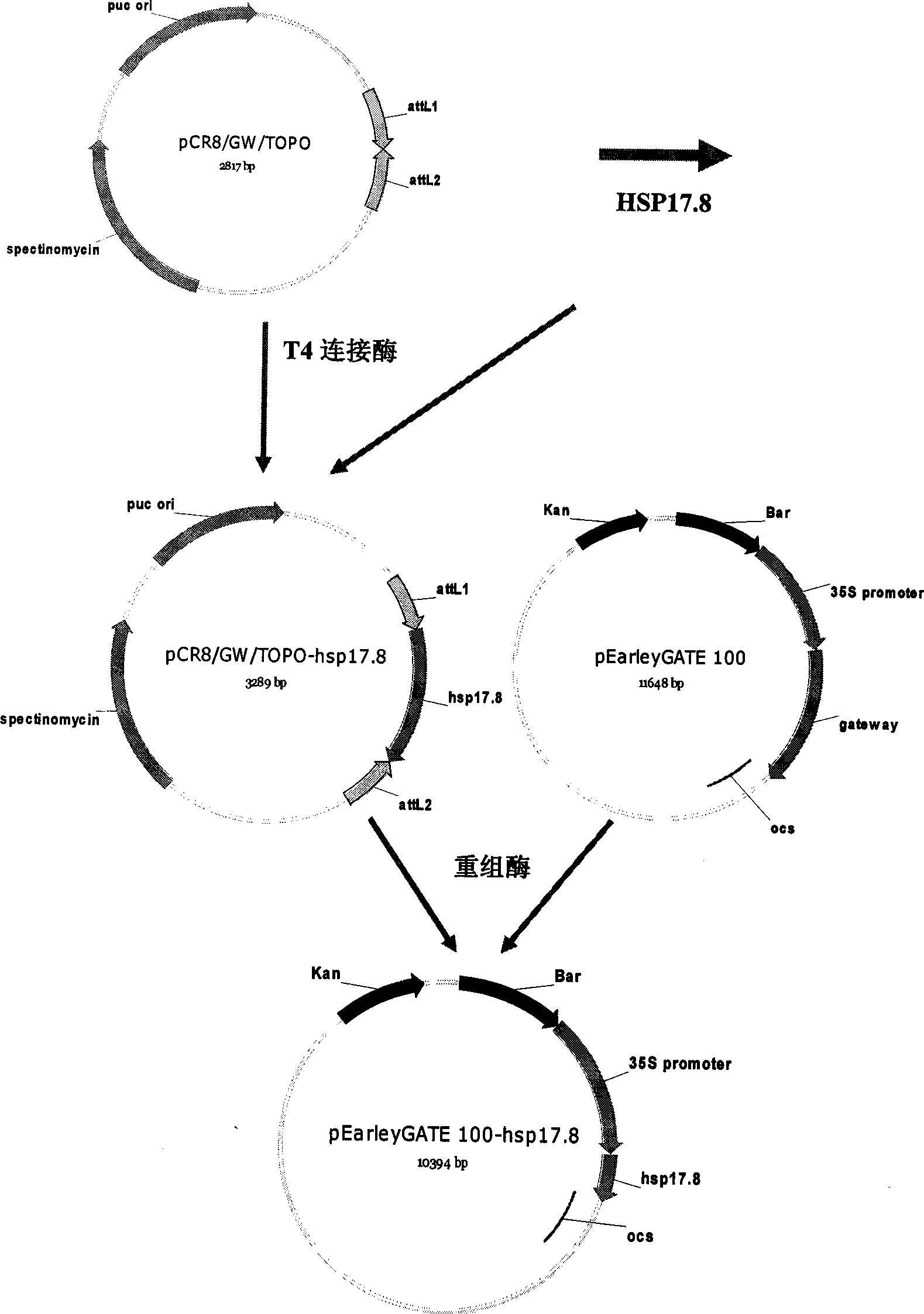
Rape heat shock protein gene HSP17.8 and application thereof
InactiveCN101544983AImprove heat resistanceReduce harmPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
The invention discloses a rape heat shock protein gene HSP17.8 and application thereof. The invention provides a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the gene, gene sequences which at least have 70 percent homology with a DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in other crops, and mutant alleles or derivatives produced by adding, substituting, inserting or deleting one or more nucleotides. At the same time, the heat shock protein gene also proves that the overexpression of the heat shock protein gene strengthens the heat resistance of arabidopsis at high temperature by means of model plant, namely the arabidopsis through transgenic technology, increases the yield of seeds at high temperature, and improves the yield of the arabidopsis under high temperature stress, so the heat shock protein gene has good application prospect in heat-tolerance breeding of crops.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
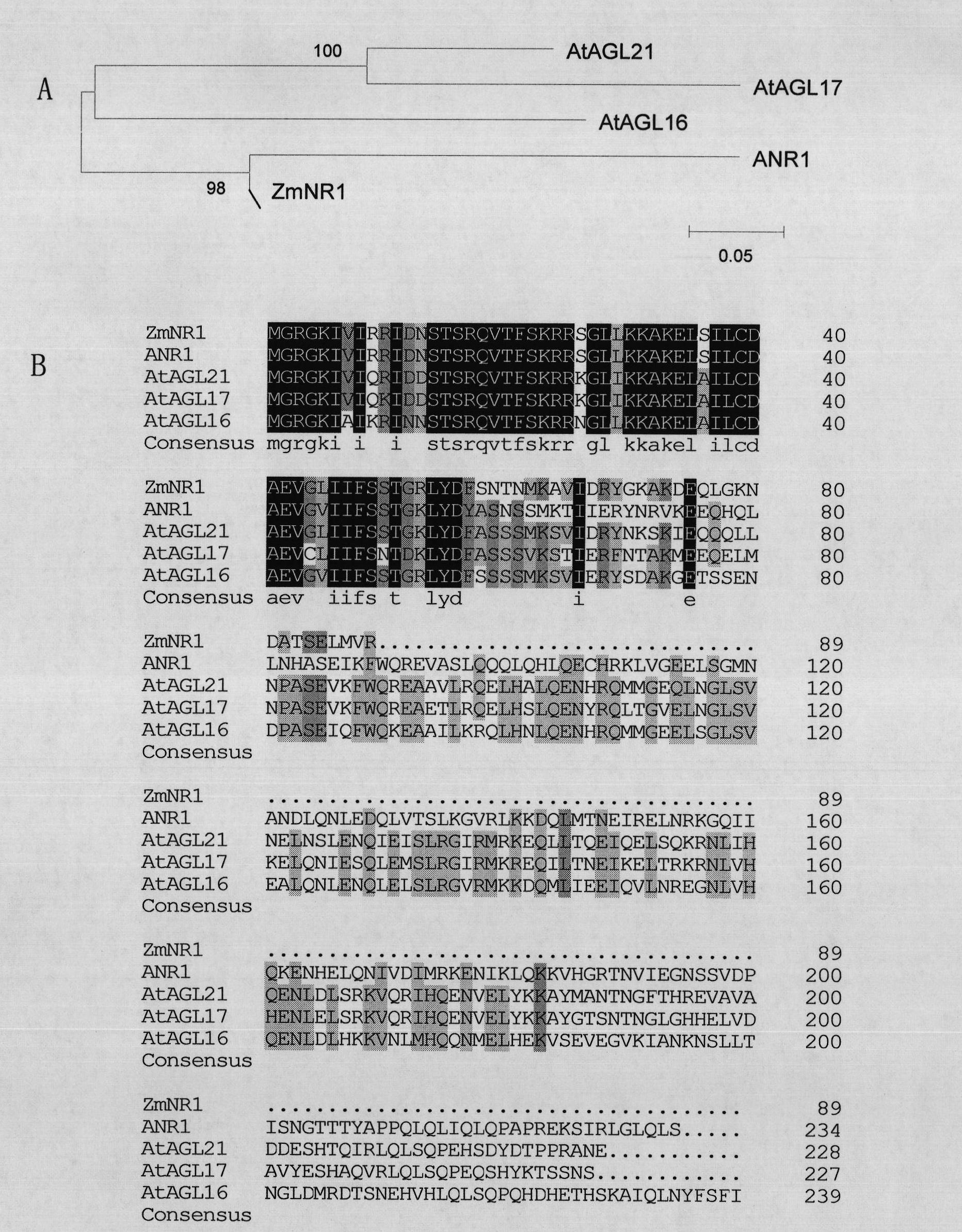
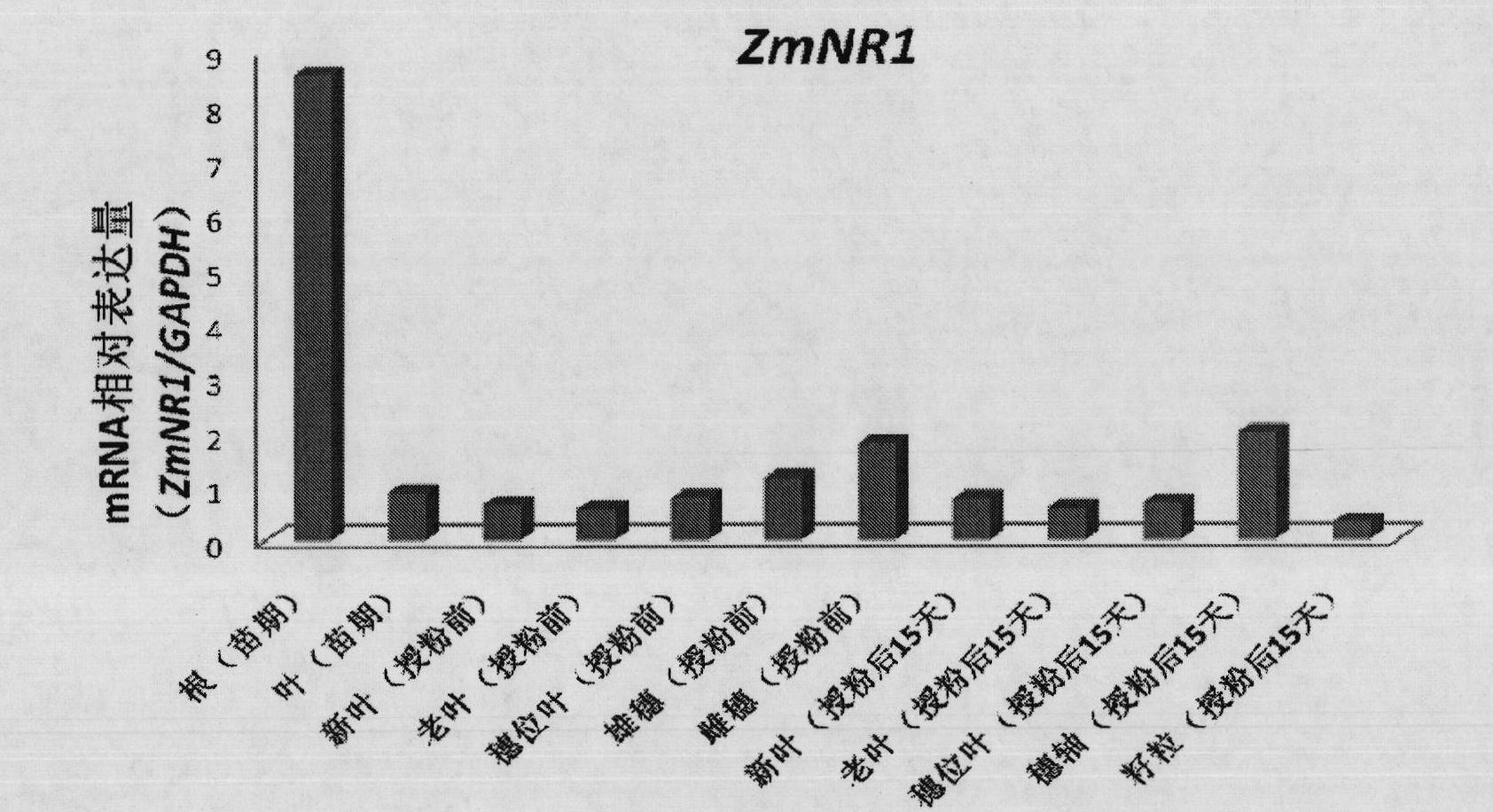
Plant root development related protein ZmNR1 and coding gene thereof
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Ionizable isotopic labeling reagents for relative quantification by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7982070B2Improve ETD analysisConvenient charging statusComponent separationOrganic compound preparationMetaboliteIsotopic labeling
Relative quantification of metabolites by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) requiring a mechanism for simultaneous analysis of multiple analytes in two or more samples. Labeling reagents that are reactive to particular compound classes and differ only in their isotopic kit facilitating relative quantification and providing tangible evidence for the existence of specific functional groups. Heavy and light isotopic forms of methylacetimidate were synthesized and used as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing molecules, such as biological samples. Heavy and light isotopic forms of formaldehyde and cholamine were also synthesized and used independently as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing and carboxylic acid-containing molecules, such as found in biological samples. Advantageously, the labeled end-products are positively charged under normal acidic conditions involving conventional Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC / MS) applications. Labeled primary and secondary amine and carboxylic acid end-products also generated higher signals concerning mass-spectra than pre-cursor molecules and improved sensitivity. Improved accuracy concerning relative quantification was achieved by mixing heavy and light labeled Arabidopsis extracts in different ratios. Labeling strategy was further employed to ascertain differences in the amounts of amine-containing metabolites for two strains of Arabidopsis seeds.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Method for detecting profile phenotype of arabidopsis
InactiveCN103471523ADoes not affect normal growthRealize non-destructive testingUsing optical meansImage calibrationRgb image
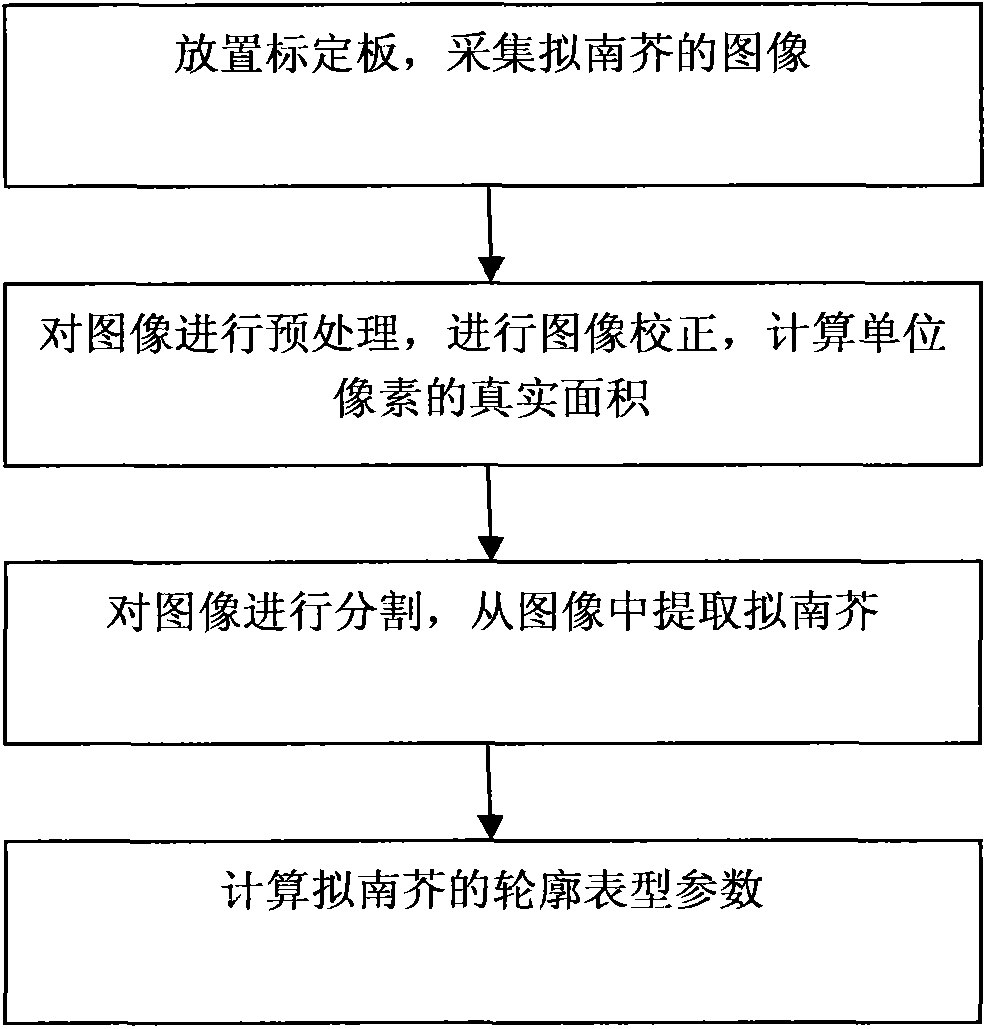
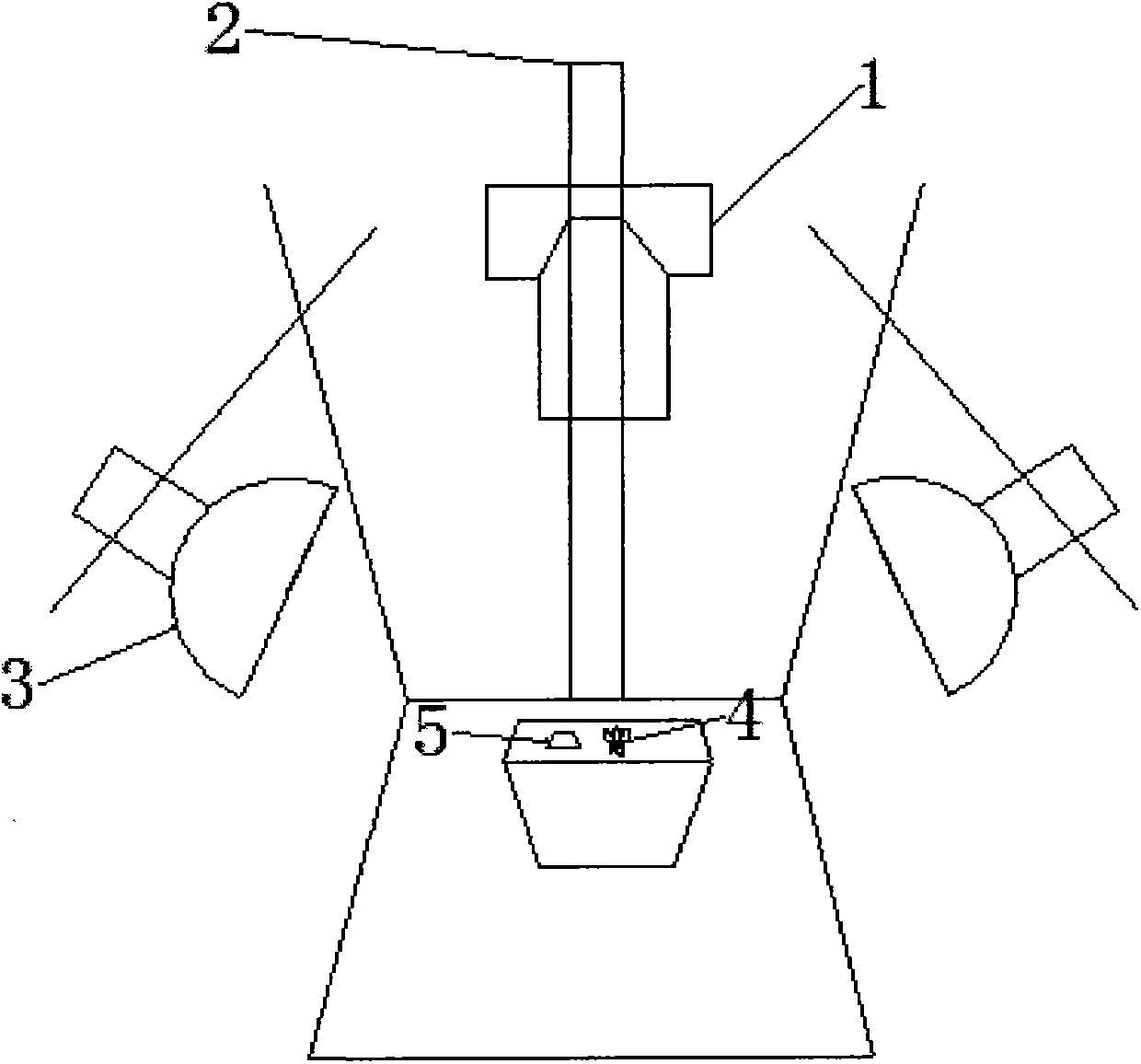
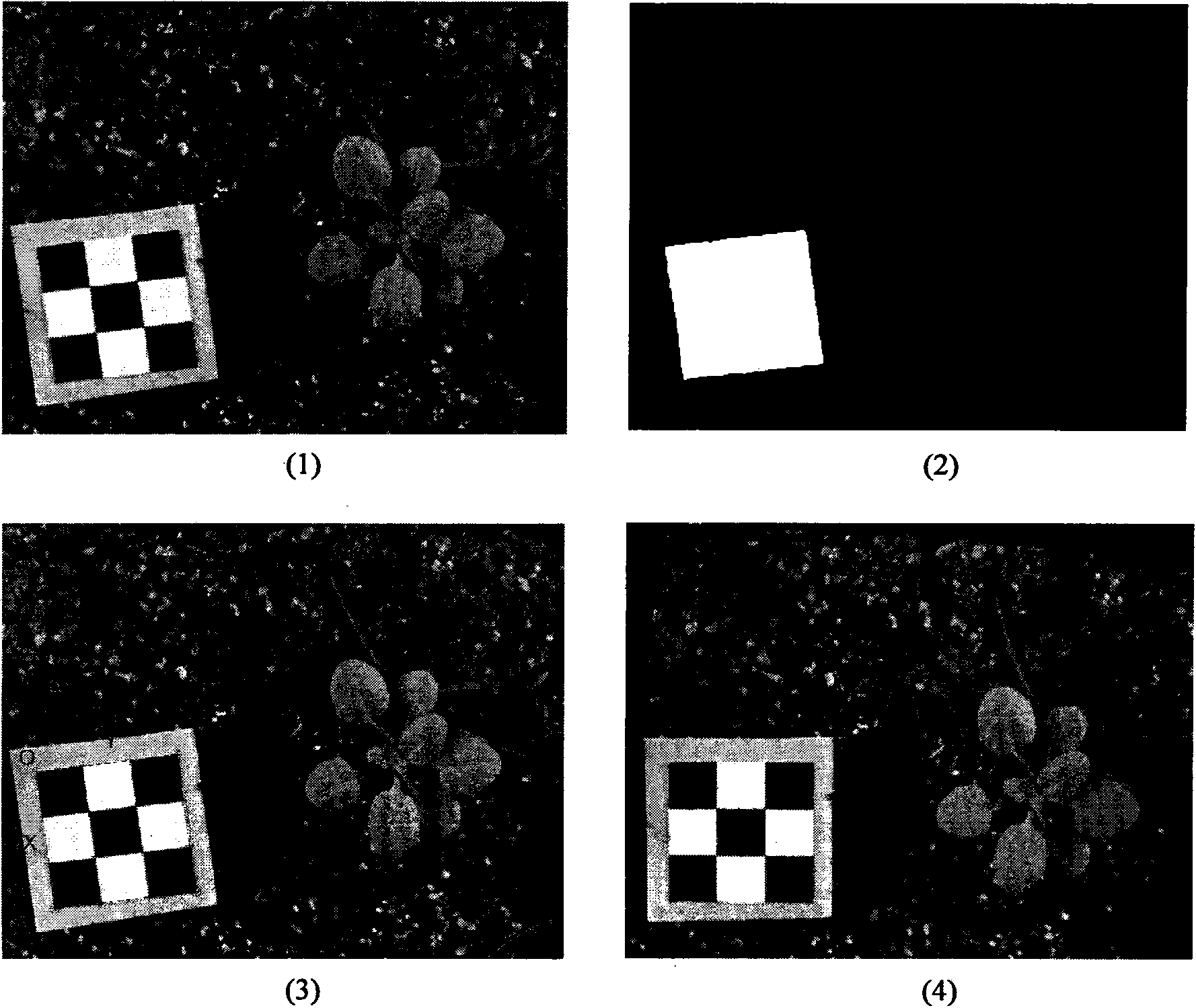
Provided is a method for detecting a profile phenotype of arabidopsis. The method includes the steps that a calibration board is placed in a planting pot of the arabidopsis, an RGB image of the arabidopsis is collected through a camera, the collecting image is preprocessed, automatic correction and calibration of the image are achieved, image correction is used for correcting deformation of the image, image calibration is used for obtaining a real size of a unit pixel, the preprocessed image is divided, the arabidopsis is separated from the background and extracted from the image, after the arabidopsis image is separated, a profile phenotype parameter of the arabidopsis is extracted, and an overall profile of the arabidosis is quantitatively described through an oval Fourier descriptor. The differences of the overall profile and growth orientation of the arabidopsis with different genes can be described through analysis of the profile phenotype parameters, and accordingly the function of different genes and influences of the different genes on the arabidopsis can be concluded.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
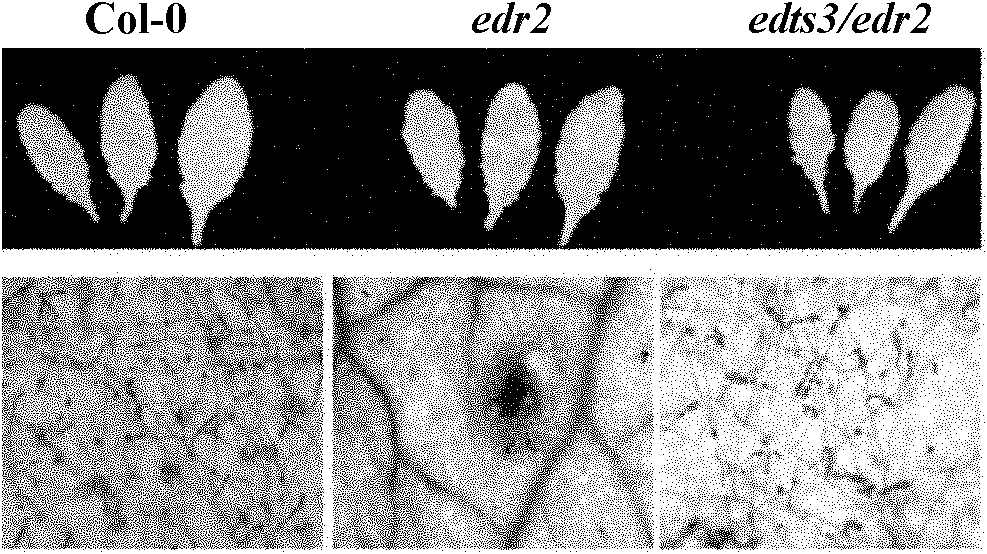
Cloning and application of arabidopsis oidium disease resistance suppressor gene EDTS3
InactiveCN102586268AImprove disease resistanceHigh expressionPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringSuppressorGenetics
The invention relates to separated cloning, functional verification and application of arabidopsis oidium disease resistance suppressor gene EDTS3, and further relates to a mutant gene of the EDTS3 gene, protein encoded by the EDTS3 gene and application of the EDTS3 gene.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving cold resistance of zoysia
The invention discloses a method for improving the winter resistance of Japanese lawngrass. This method includes converting transcription activation factor CBF1 / DREB1b of quasi-mustard induction gene into Japanese lawngrass embryonal callus to improve the winter resistance of Japanese lawngrass, which can include the following steps: 1) disseminating the Japanese lawngrass embryonal callus with agricillin liquor carrying CBF1 / DREB1b; 2) placing the disseminated Japanese lawngrass embryonal callus onto the coculture medium to perform coculture; 3) placing the cocultured embryonal callus onto the screening culture medium for screening; 4) placing the screened embryonal callus onto the differentiated culture medium for differentiation culture; 5) placing the differentiated and germinated young plant onto the rooted culture medium for radication; 6) placing the plant which can produce root onto strong-plant screening culture medium for screening the Japanese lawngrass strong-plant which has improved winter resistance. The invention has important theoretical and operation significance for culturing new species of Japanese lawngrass with improved cold resistance and extended green period and has a wide application foreground.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT +1
Expressed sequences of arabidopsis thaliana
Isolated nucleotide compositions and sequences are provided for Arabidopsis thaliana genes. The nucleic acid compositions find use in identifying homologous or related genes; in producing compositions that modulate the expression or function of its encoded protein, mapping functional regions of the protein; and in studying associated physiological pathways. The genetic sequences may also be used for the genetic manipulation of cells, particularly of plant cells. The encoded gene products and modified organisms are useful for screening of biologically active agents, e.g. fungicides, insecticides, etc.; for elucidating biochemical pathways; and the like.
Owner:PARADIGM GENETICS
Protein coded sequence of cucumber TTG1-like gene
The invention relates to a protein coding sequence of a cucumber TTG1-like gene in the technical field of genetic engineering, which comprises: encoding a nucleotide sequence of polypeptide which has the activity of cucumber TTG1-like protein, wherein the nucleotide sequence has the homology 70% of a 160-1158th nucleotide sequence from nucleotide in SED ID NO.3, or the nucleotide sequence can be hybridized with the 160-1158th nucleotide sequence from the nucleotide in the SED ID NO.3 under the condition that the temperature is 45-55DEG C. A gene which is homologous with TTG1 which determines the initiation of epidermal hair by arabidopsis thaliana is cloned in cucumbers, which is not only beneficial for understanding a molecular mechanism which is built by plant epidermal hair form, but also helpful for recognizing the molecular mechanism which is formed by cucumber fruit thorn which is an important quality gene, theoretical foundation is provided for breeding the cucumber quality, and the variety breeding process is accelerated. The protein coding sequence of the invention also plays an important role of improving plant flower color and has great application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for changing nitrogen utilization efficiency in plants
InactiveUS20110010797A1Promote plant growthImproved nitrate remobilizationImmunoglobulinsFermentationNitrogenArabidopsis
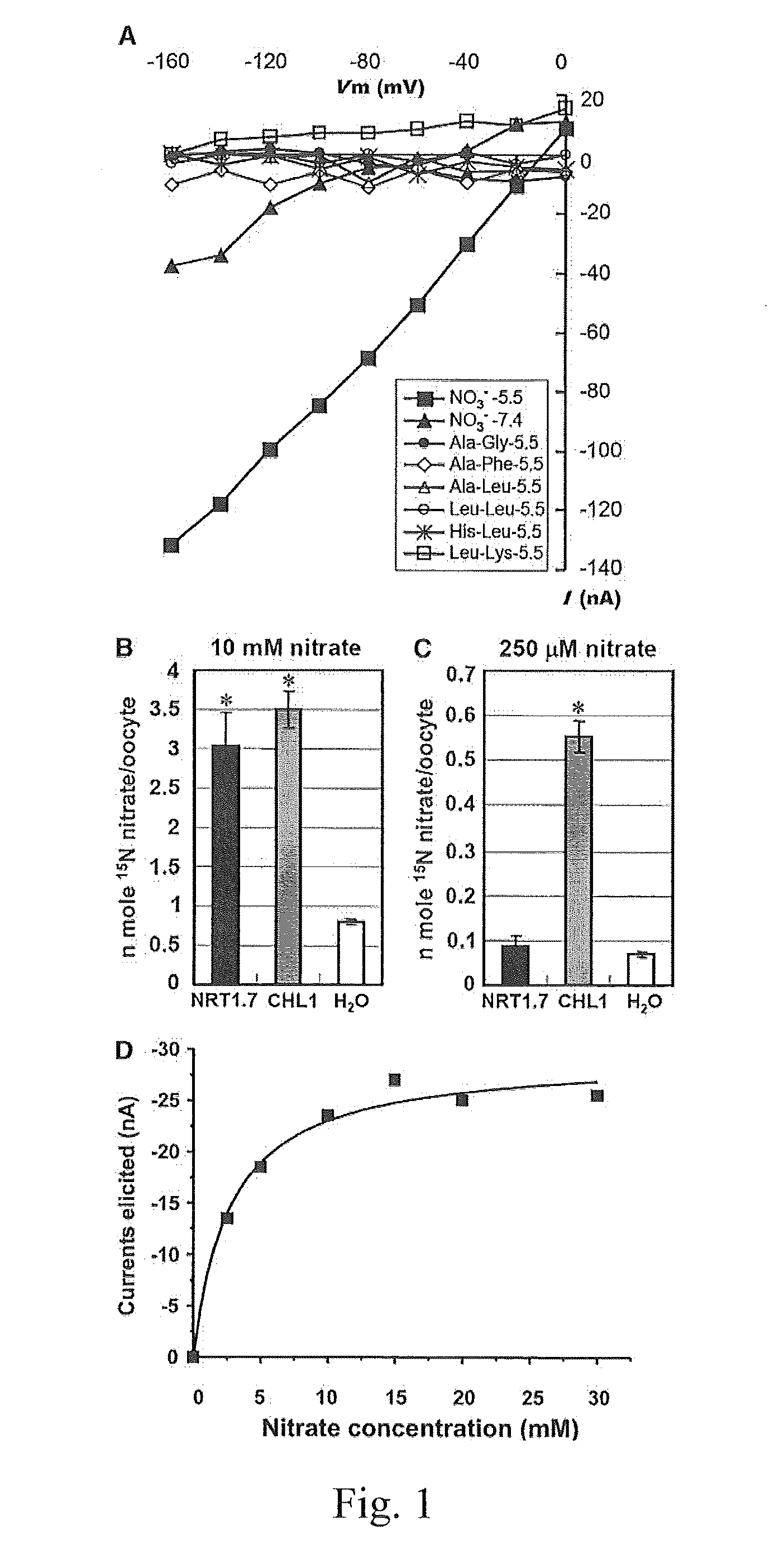
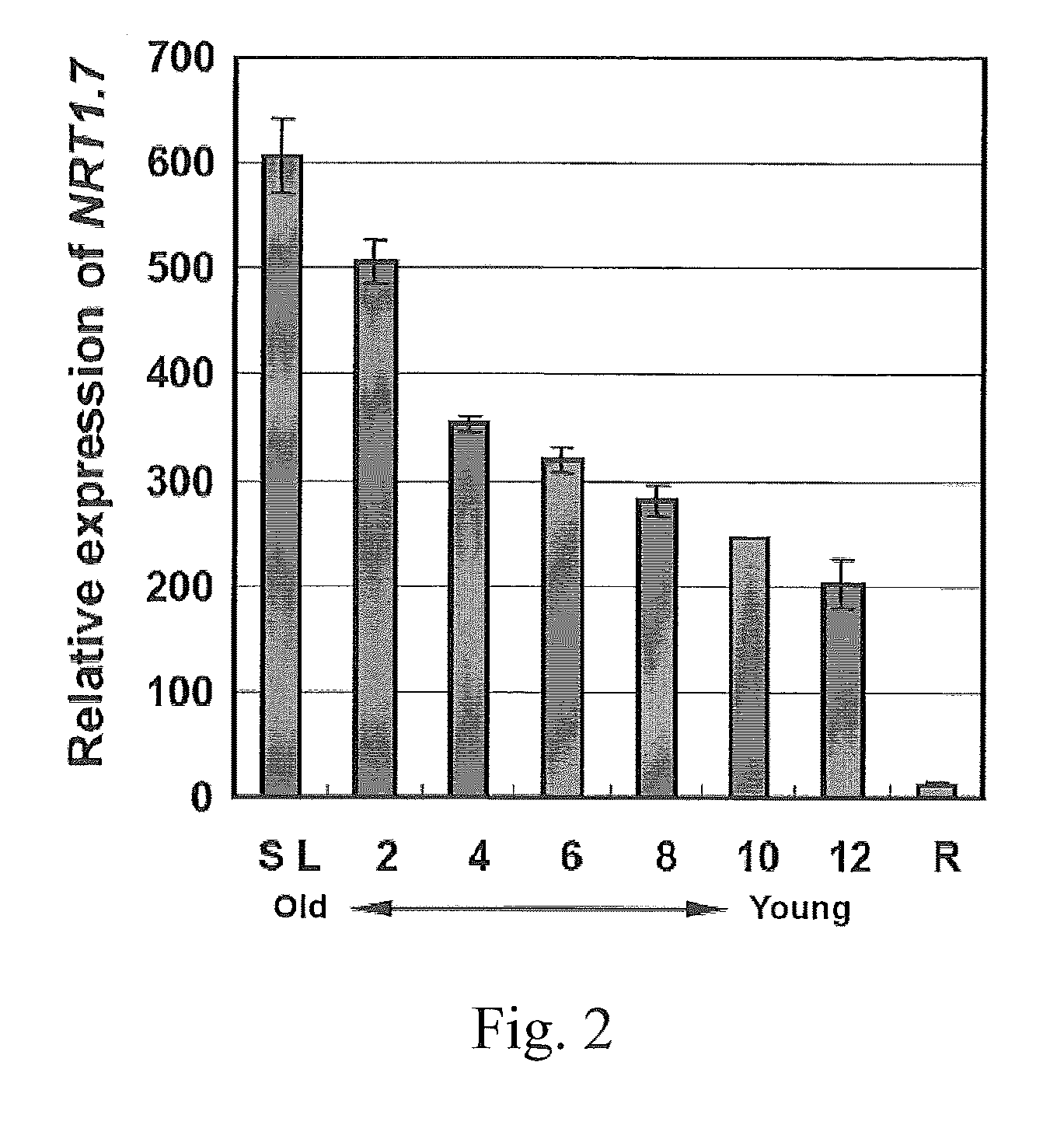
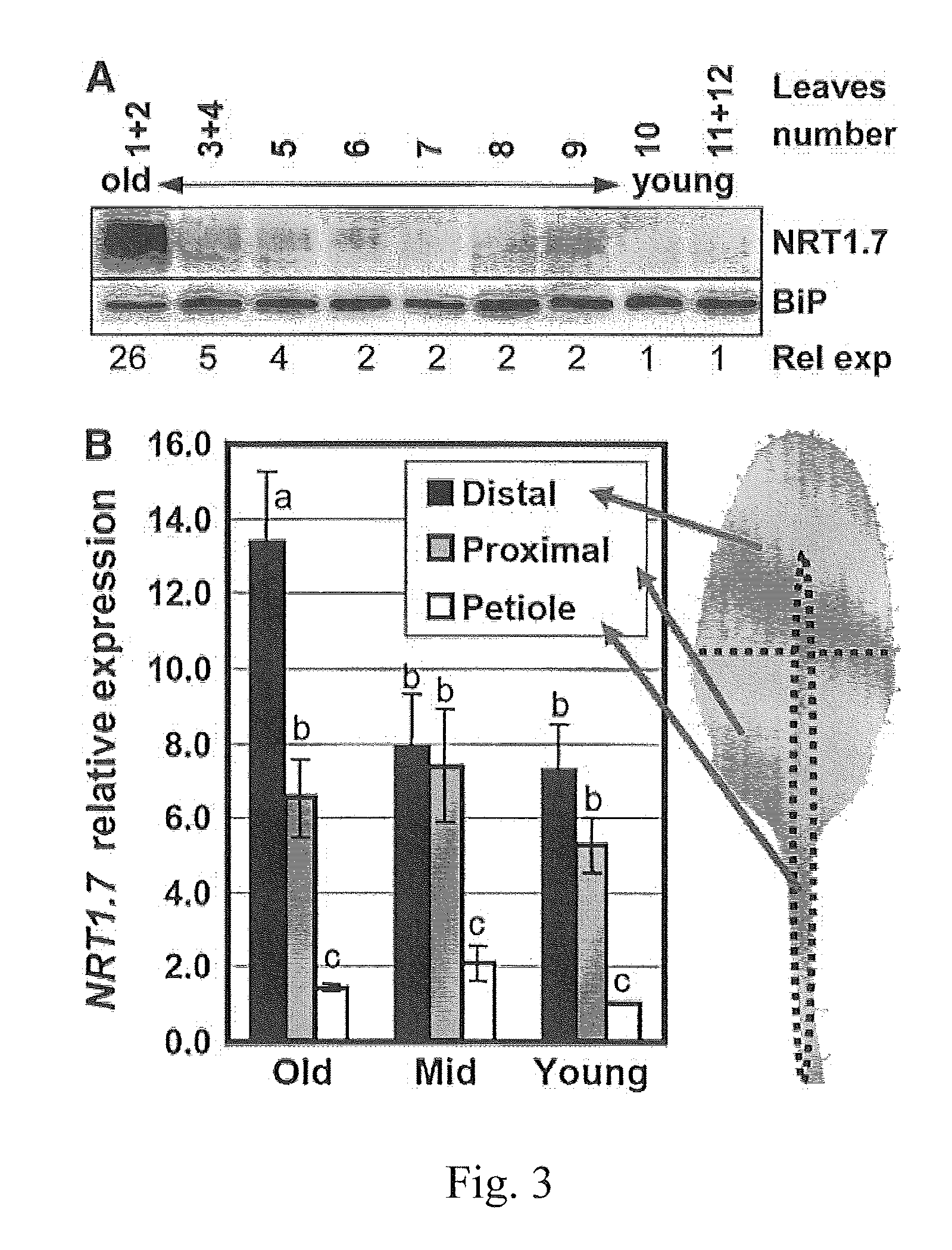
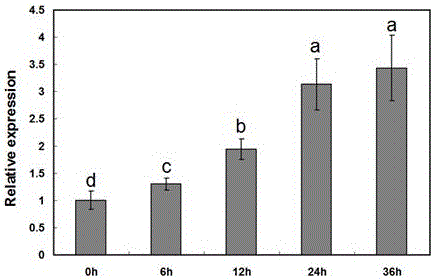
The present invention provides a method for changing nitrogen utilization efficiency in a plant comprises regulating the expression of Arabidopsis NRT 1.7 or an orthologue thereof so that the nitrate remobilization from older leaves to young leaves in the plant is regulated, thereby the nitrogen utilization efficiency is changed. The present invention also provides a transgenic plant obtainable by transforming a plant with an expression construct with a high or low level of expression of NRT 1.7. On the other hand, the present invention yet provides a chimera nitrate transporter, a DNA molecule coding for this chimera transporter and an expression vector thereof.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
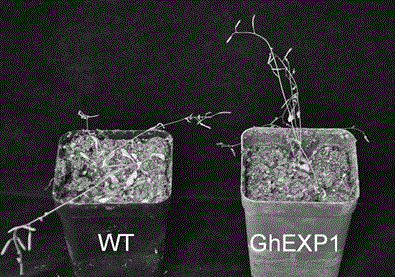
Cotton drought resistant gene GhEXP1 and applications thereof
InactiveCN104988159AReduced drought toleranceEasy to understandPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention relates to a cotton drought resistant gene GhEXP1 and applications thereof, and belongs to the biology technical field. The related gene GhEXP1 is a cotton expansin gene and is reported for the first time. The gene is cloned from an upland cotton draught resistant species (Ao 3503), and through RT-PCR analysis, people find that the expression of GhEXP1 is up-regulated after a drought treatment. The drought resistant performance of strains containing silenced GhEXP1 gene is obviously reduced. The living rate of GhEXP1 transgene arabidopsis plants is 80% after a 30-day drought treatment; while the living rate of referential wild arabidopsis is 10%; and the result shows that the GhEXP1 gene can prominently improve the drought resistant performance of plants. The GhEXP1 gene is advantageously used for improving the plant drought resistance and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com