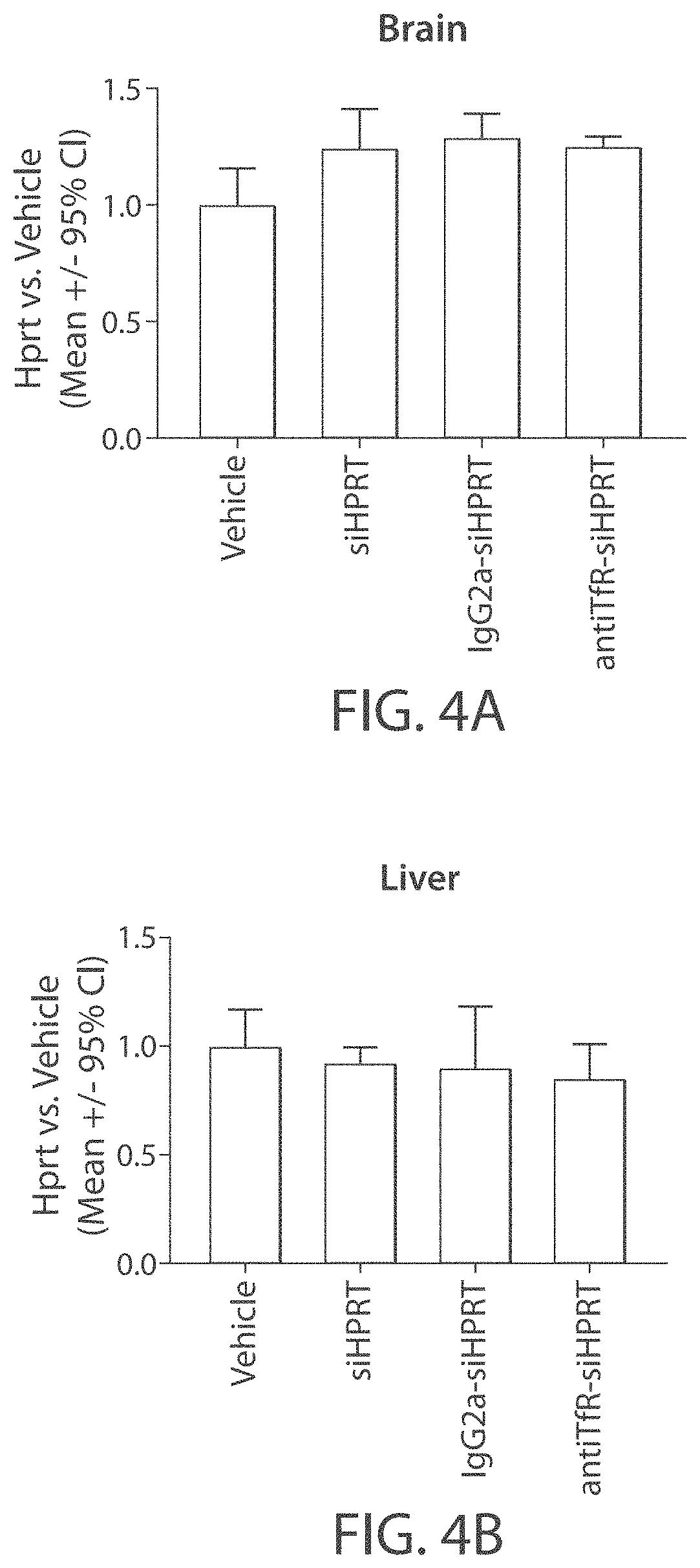
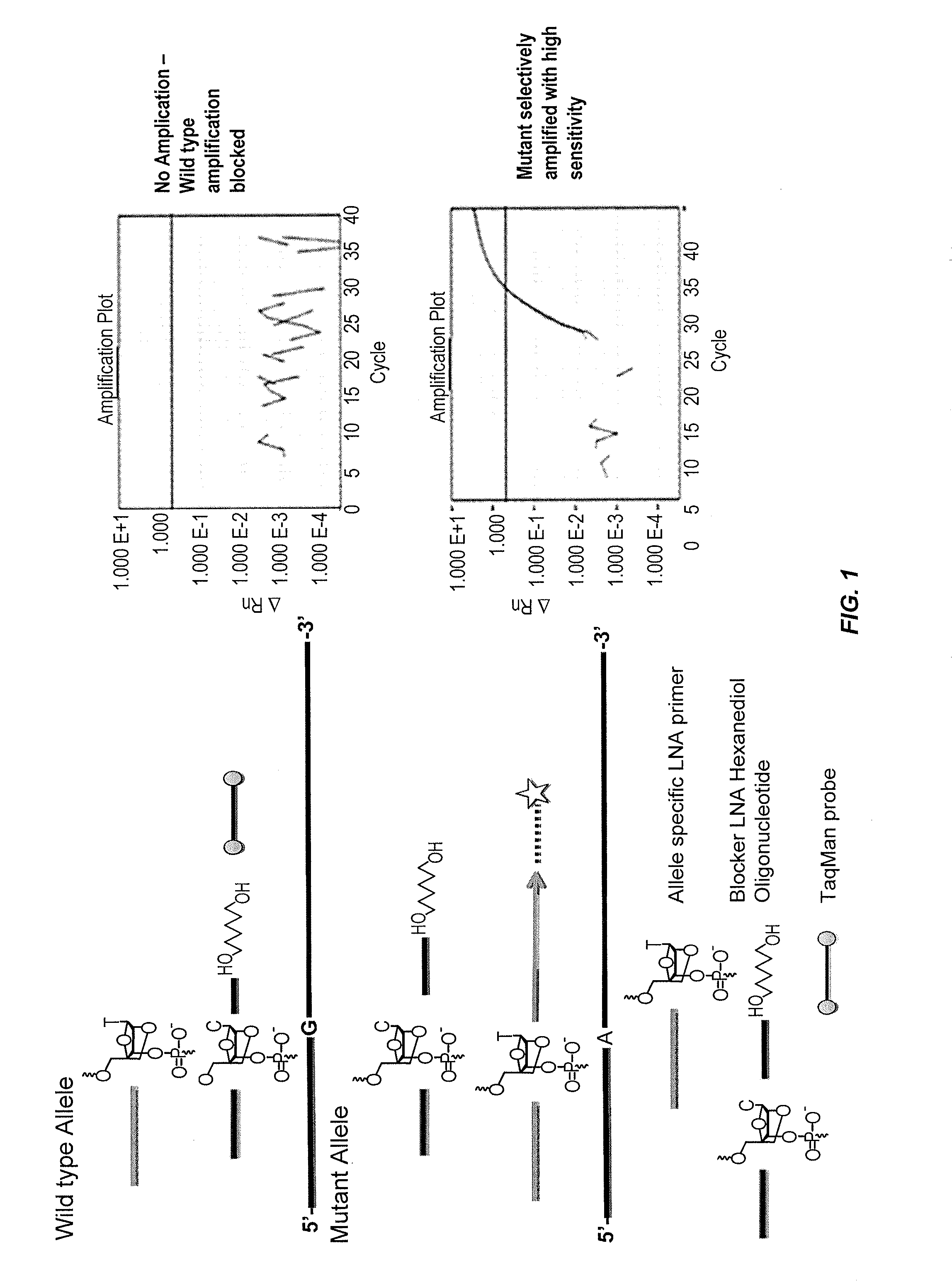
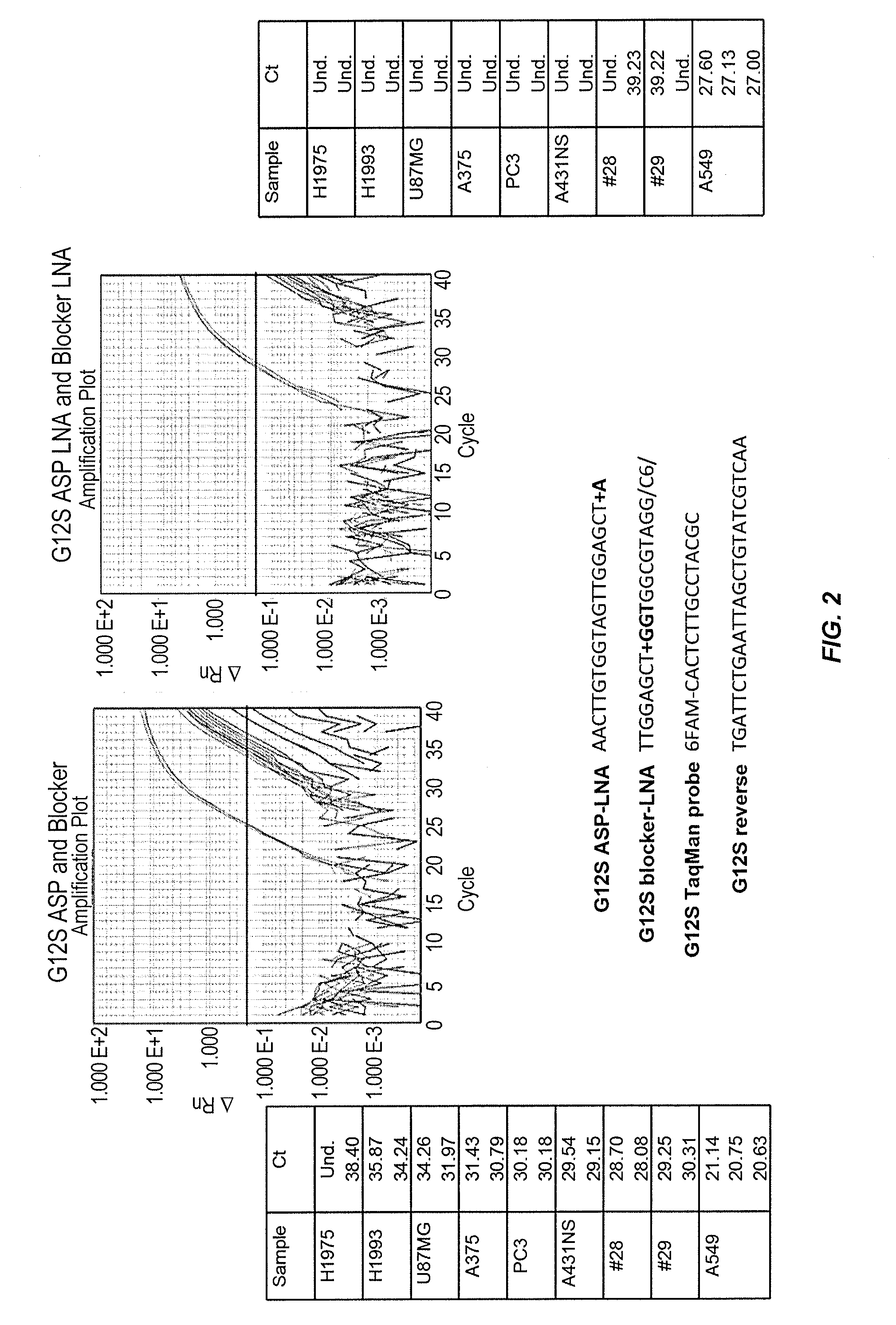
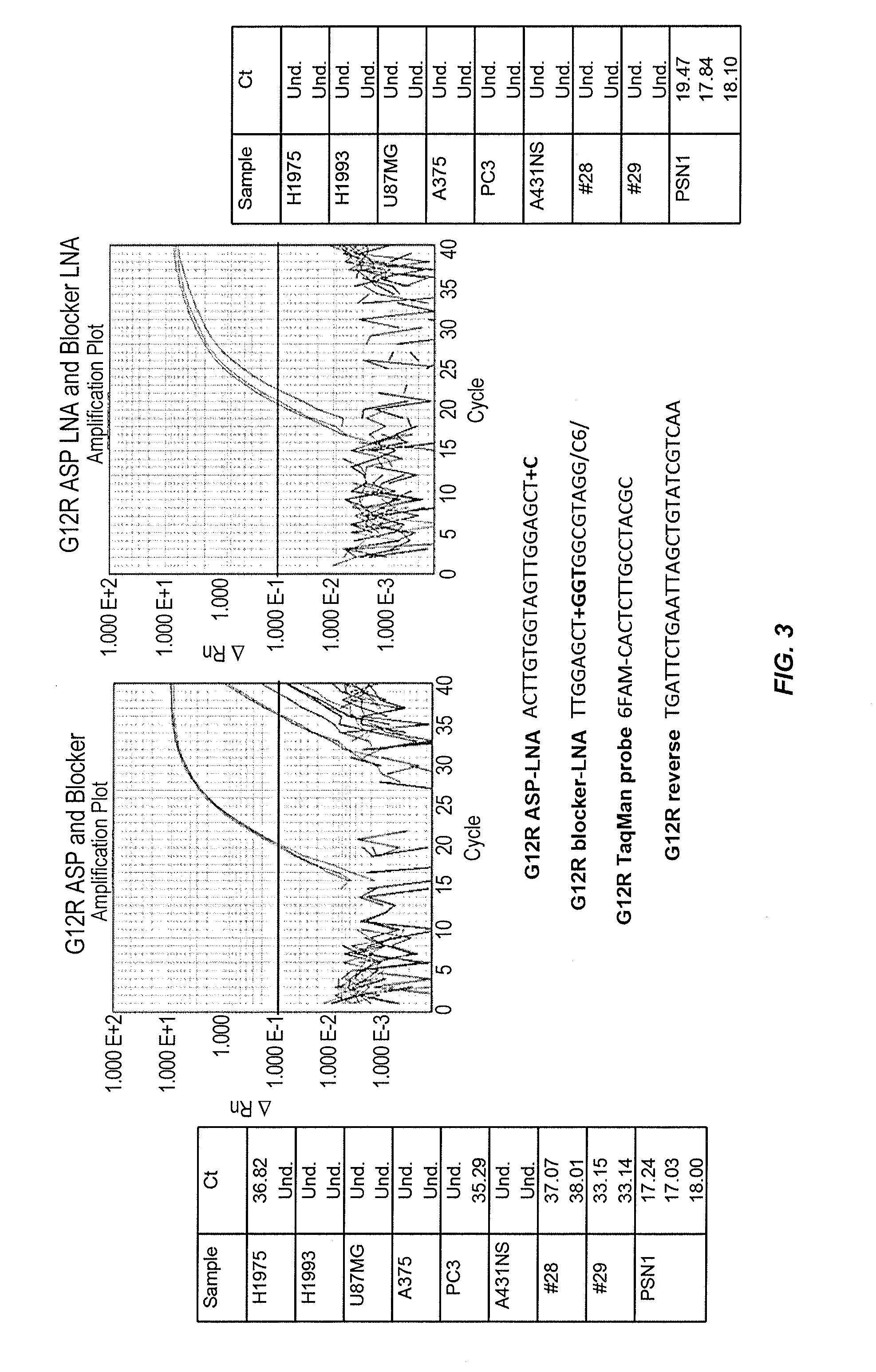
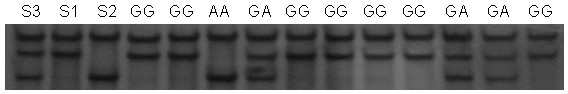Patents
Literature
196 results about "Mutant allele" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mutation …a gene is called a mutant allele. A gene is typically composed of a regulatory region, which is responsible for turning the gene’s transcription on and off at the appropriate times during development, and a coding region, which carries the genetic code for the structure of a functional molecule, generally….
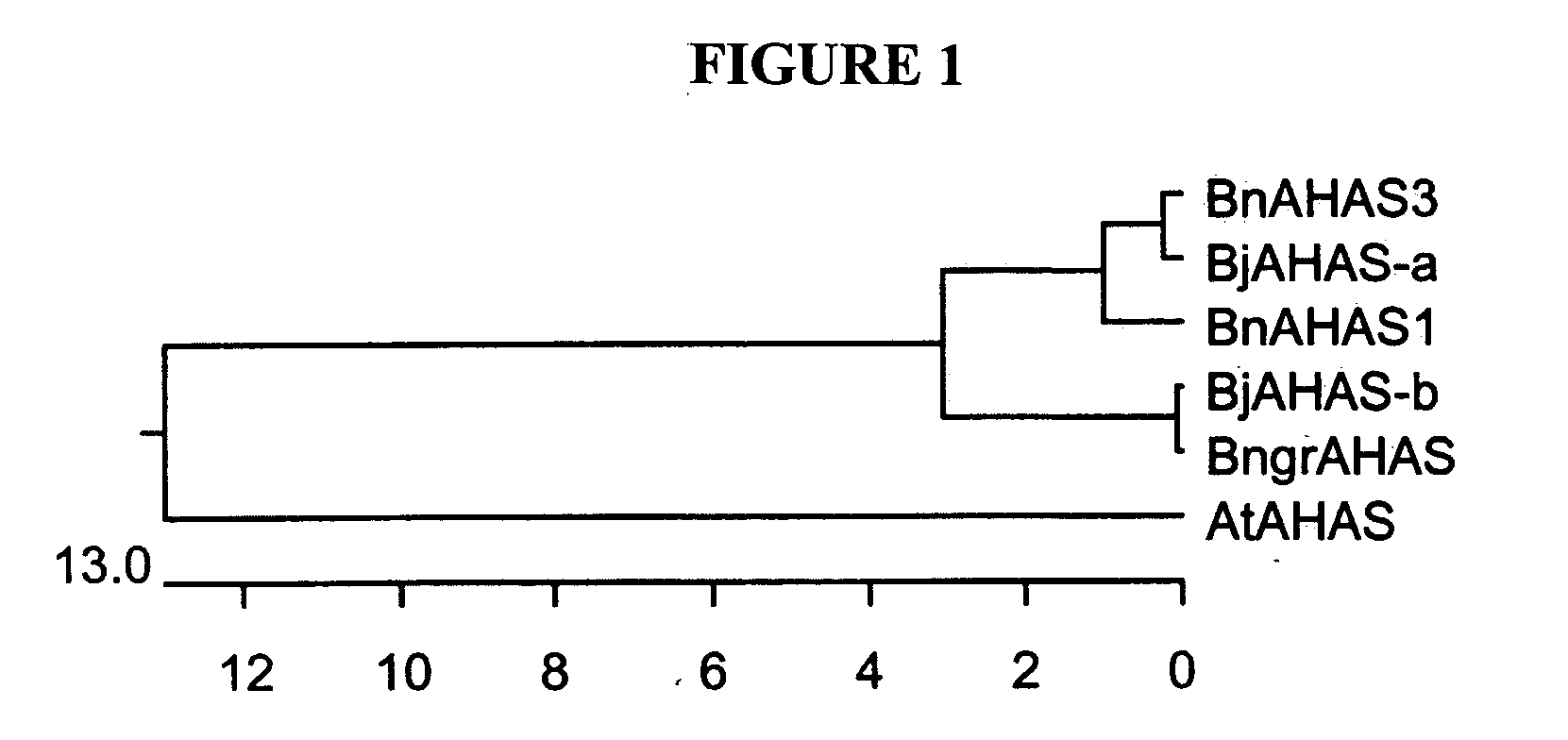
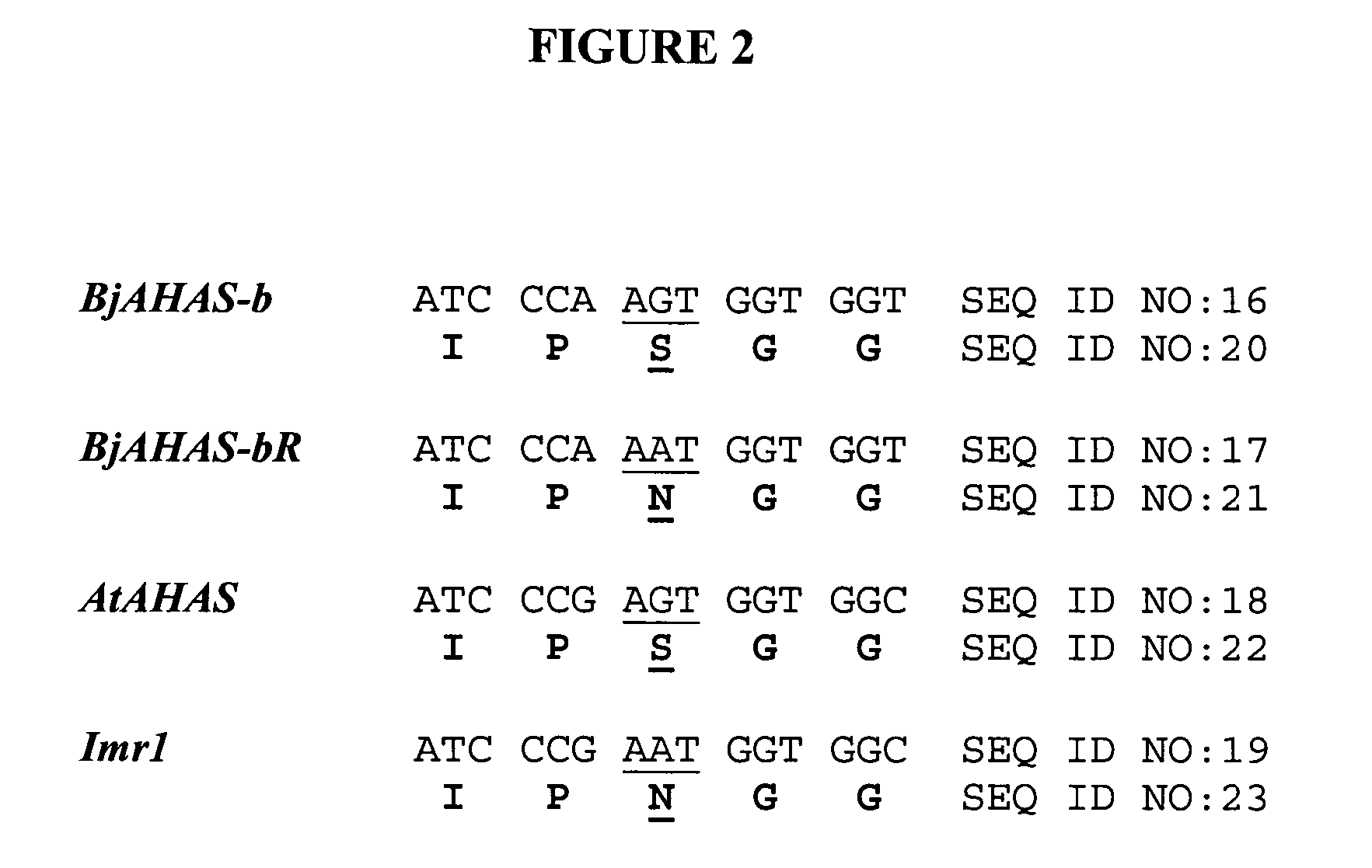
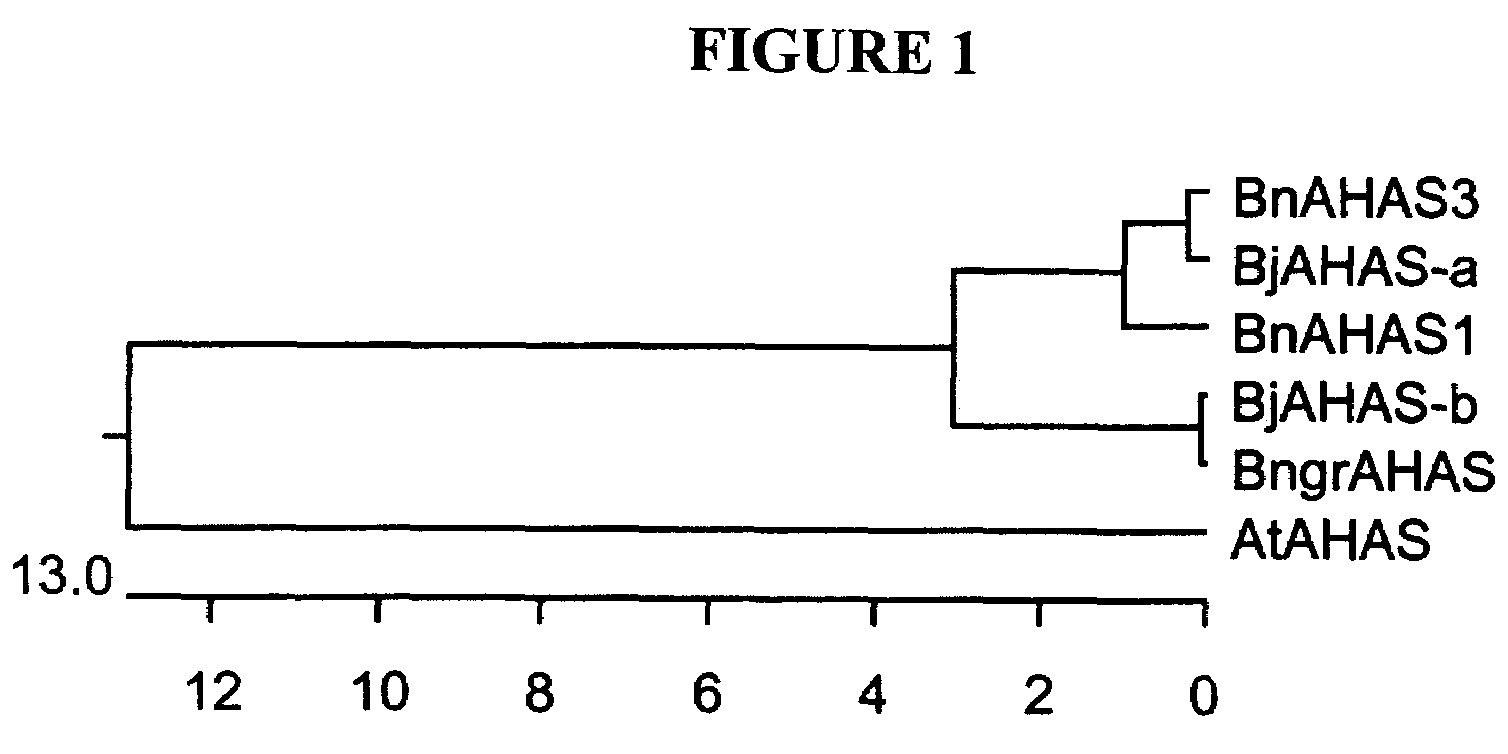
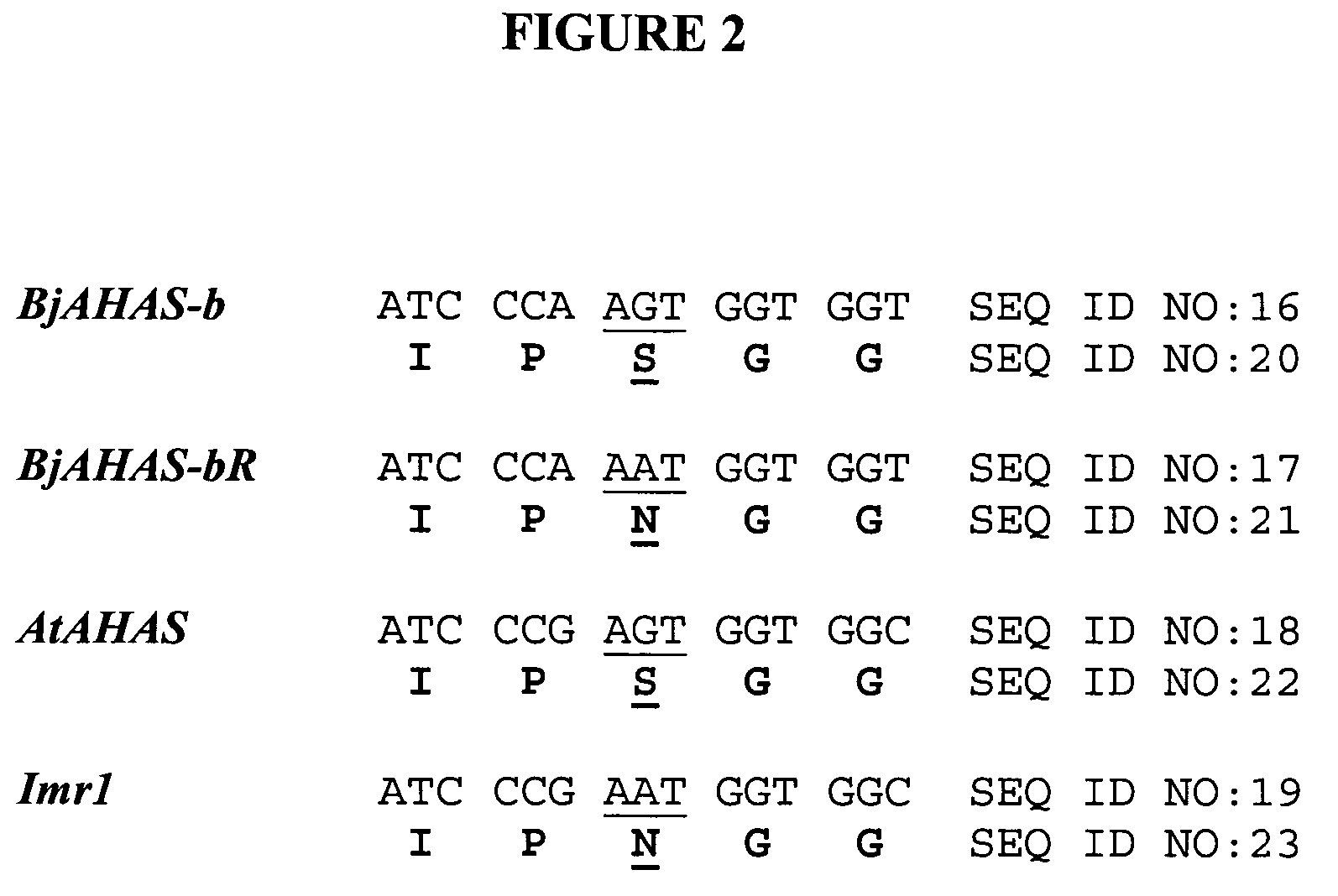
Brassica AHAS genes and gene alleles that provide resistance to imidazolinone herbicides
Plants, plant parts and plant seeds that are resistant to imidazolinone herbicides are provided. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in an AHAS gene. Specifically, plants are disclosed that contain a mutant AHAS gene allele of the Brassica juncea B genome. Two B. juncea AHAS gene sequences (BjAHAS-a and BjAHAS-b) and one B. nigra AHAS gene sequence (BngrAHAS) are disclosed. The sequence of the mutant allele, BjAHAS-bR, is also disclosed. Various methods are disclosed that include creation of mutant B. juncea lines, selection for herbicide resistant lines and determining the presence of the BjAHAS-bR mutant allele after crosses.
Owner:PIONEER OVERSEAS
Ho/ll canola with resistance to clubroot disease
This disclosure concerns a plant of the genus, Brassica, or parts thereof, which comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of high oleic acid content, low linolenic acid content, increased herbicide resistance, restorer of cytoplasmic male sterility, and increased clubroot disease (Plasmodiophora brassicae) resistance, compared to a wild-type plant of the same species. This disclosure further relates to wild-type and mutant alleles of genes involved in these traits, molecular markers linked thereto, and methods of their use.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
High oleic acid Brassica juncea
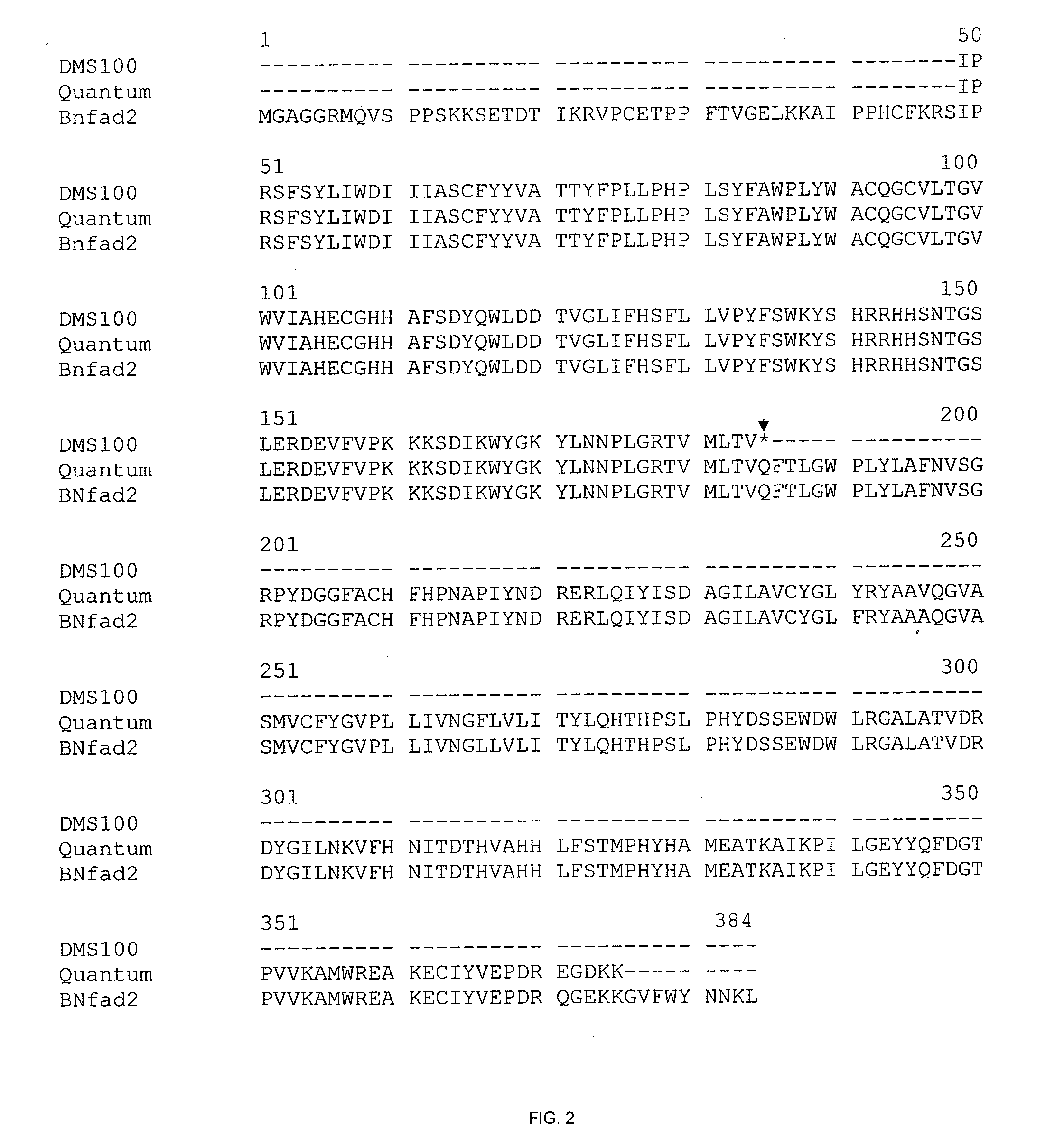
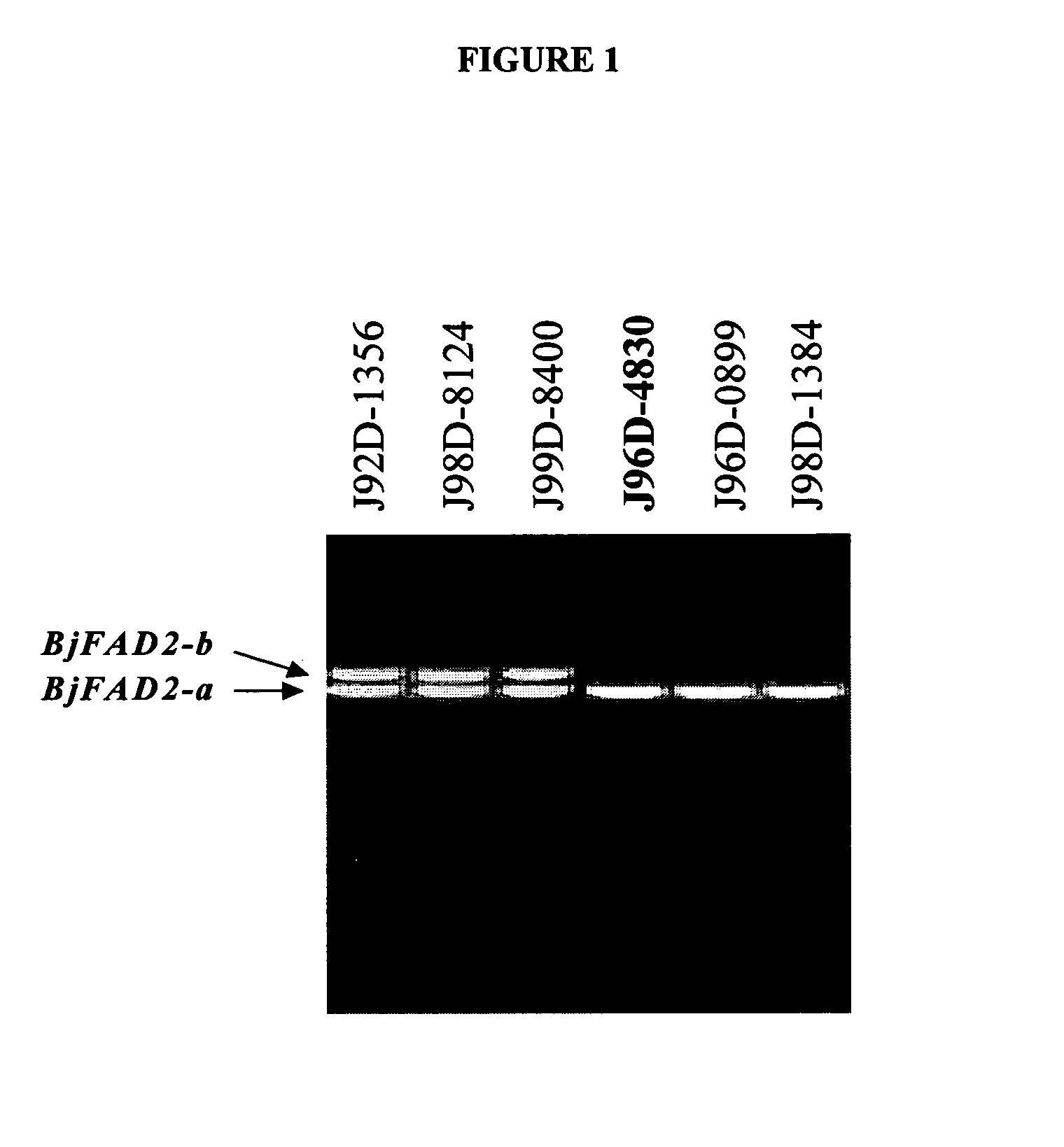
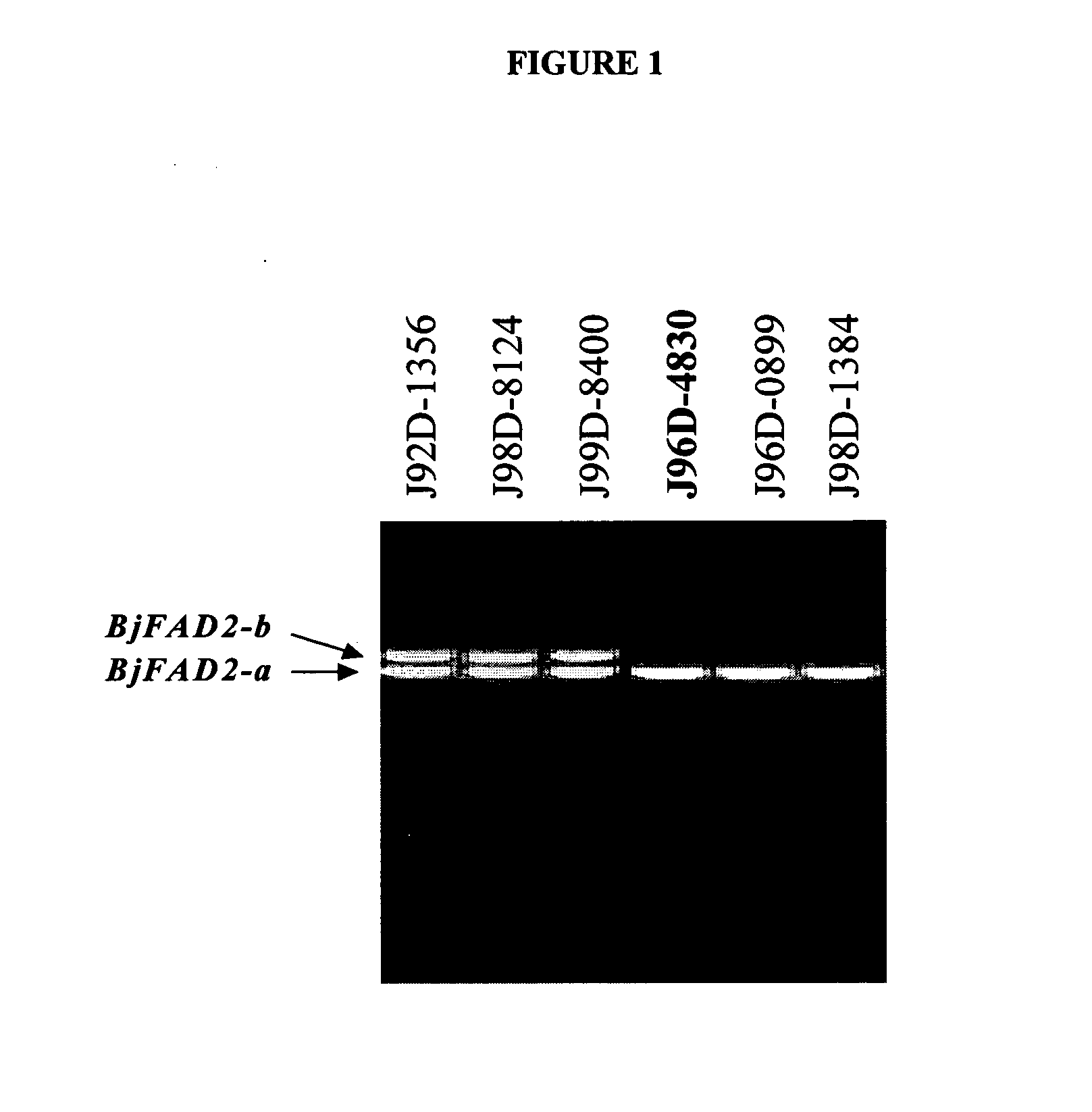
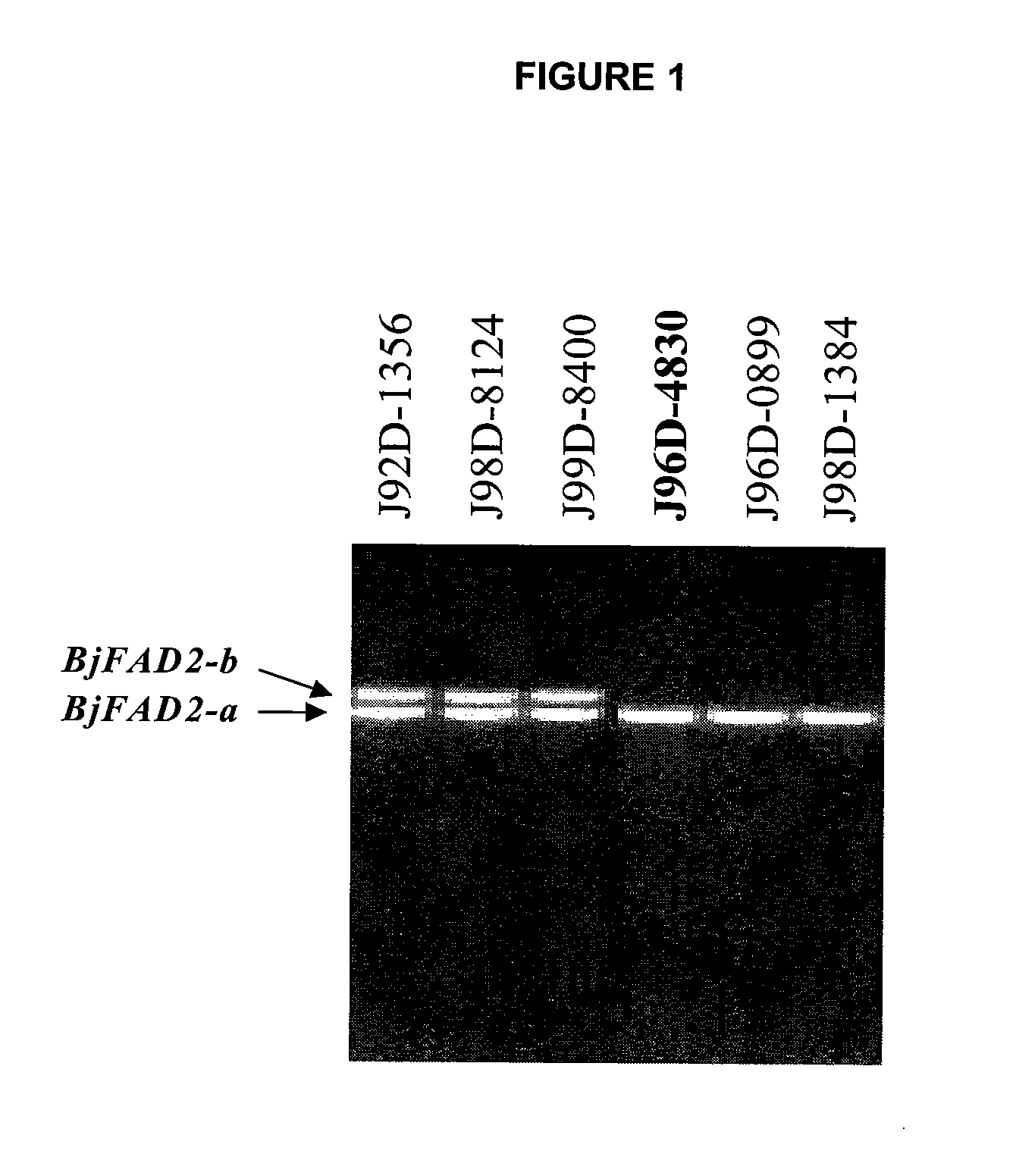
In various aspects, the invention provides Brassica juncea plants, seeds, cells, nucleic acid sequences and oils. Edible oil derived from plants of the invention may have significantly higher oleic acid content than other B. juncea plants. In one embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-086-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-086-3 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a premature stop codon, so that there are no functional copies of the FAD2 gene in MJ02-086-3 plants. Seeds from MJ02-086-3 plants may for example yield an oil having oleic acid content of greater than about 70% by weight.
Owner:SASKATCHEWAN WHEAT POOL +1
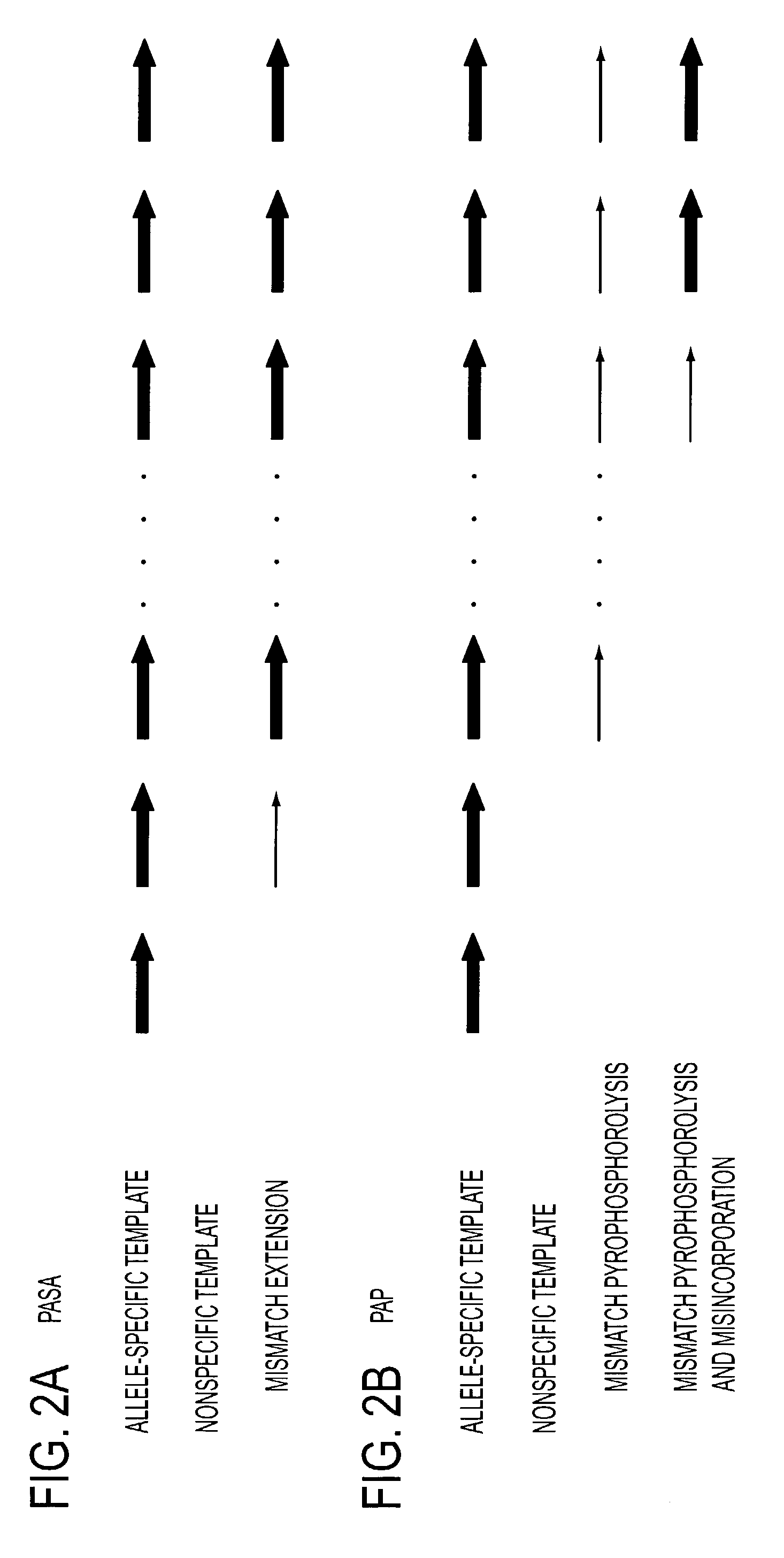
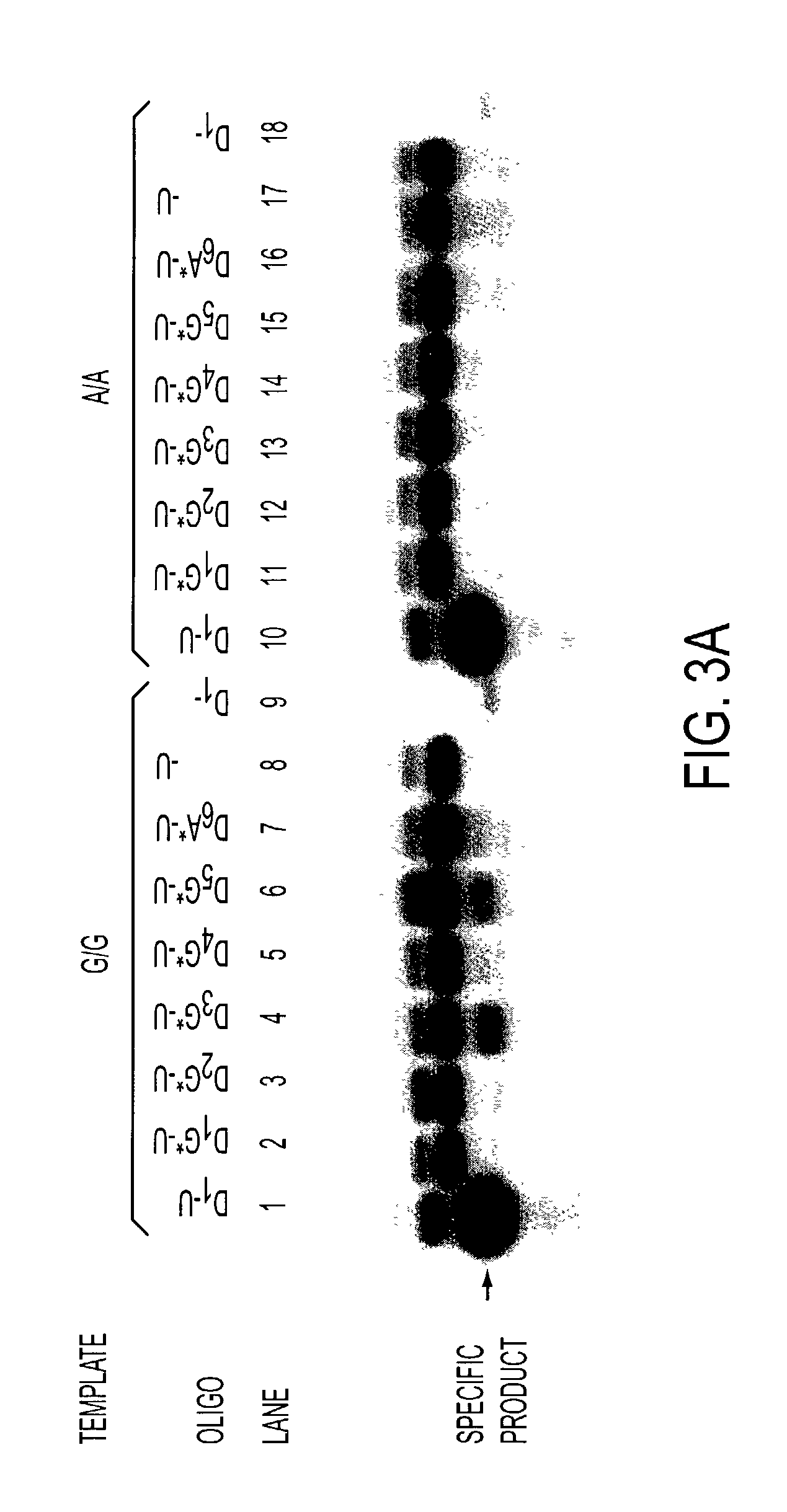
Pyrophosphorolysis activated polymerization (PAP)
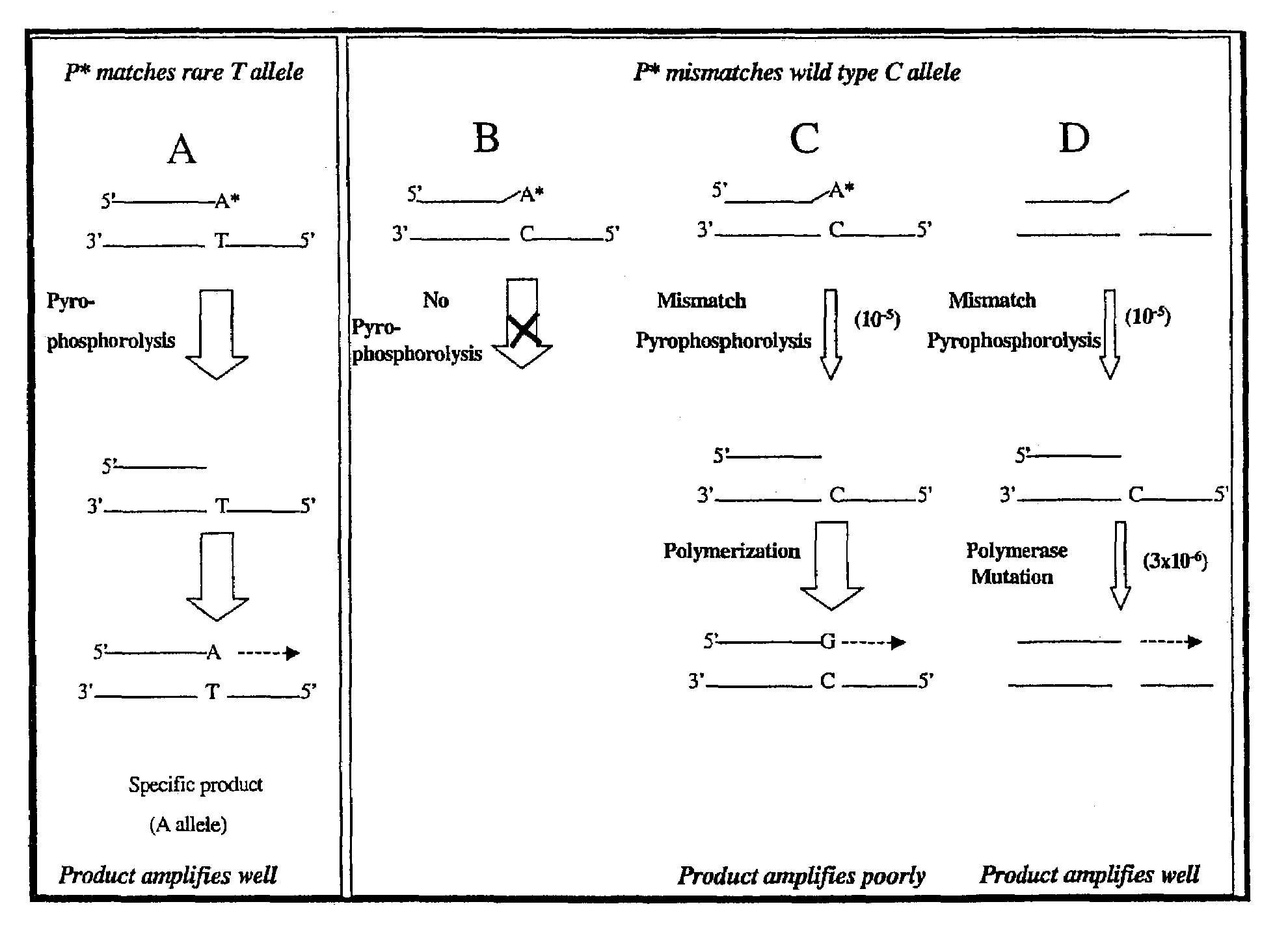
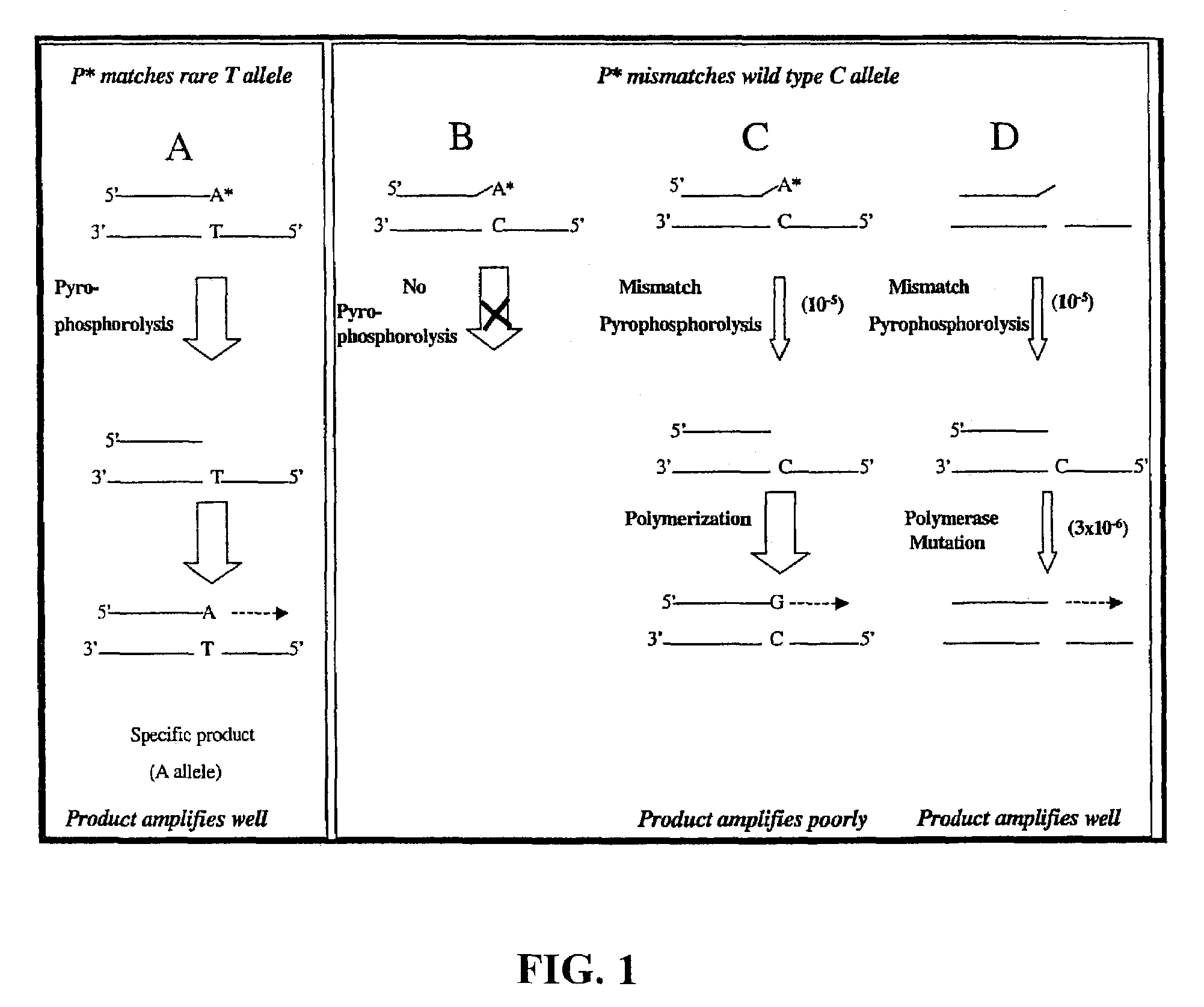
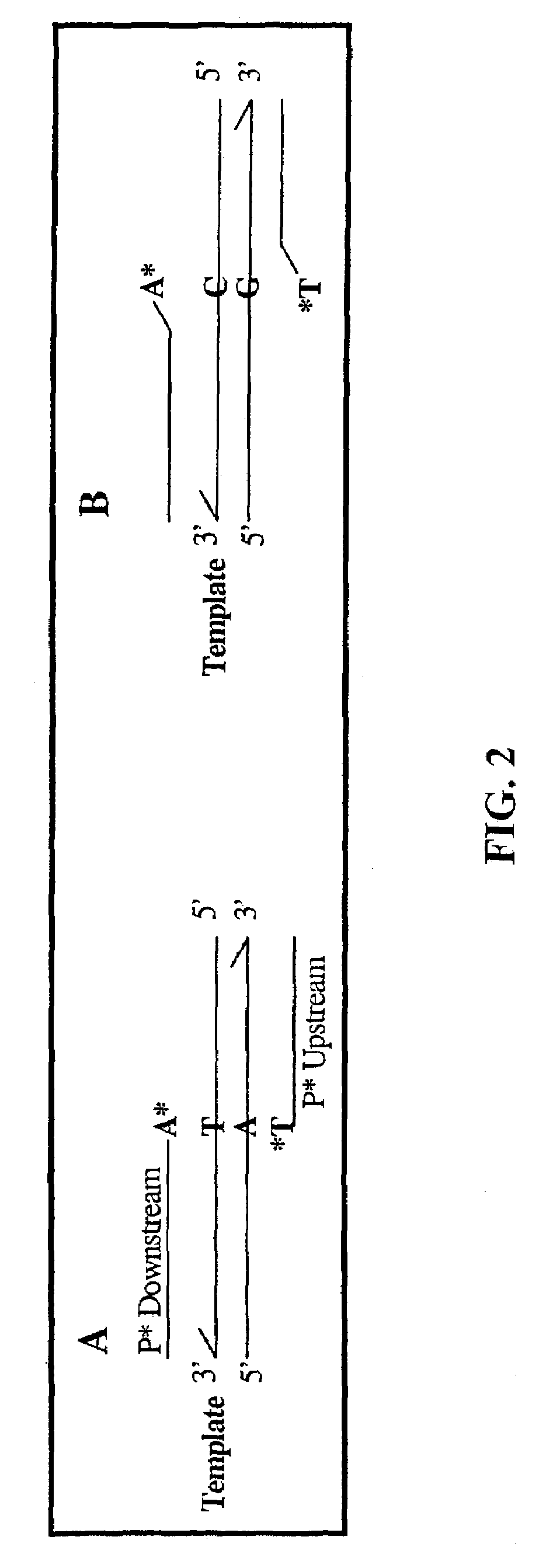
InactiveUS7033763B2Eliminate errorsMost efficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
A novel method of pyrophosphorolysis activated polymerization (PAP) has been developed. In PAP, pyrophosphorolysis and polymerization by DNA polymerase are coupled serially for each amplification by using an activatable oligonucleotide P* that has a non-extendible 3′-deoxynucleotide at its 3′ terminus. PAP can be applied for exponential amplification or for linear amplification. PAP can be applied to amplification of a rare allele in admixture with one or more wild-type alleles by using an activatable oligonucleotide P* that is an exact match at its 3′ end for the rare allele but has a mismatch at or rear its 3′ terminus for the wild-type allele. PAP is inhibited by a mismatch in the 3′ specific sequence as far as 16 nucleotides away from the 3′ terminus. PAP can greatly increase the specificity of detection of an extremely rare mutant allele in the presence of the wild-type allele. Specificity results from both pyrophosphorolysis and polymerization since significant nonspecific amplification requires the combination of mismatch pyrophosphorolysis and misincorporation by the DNA polymerase, an extremely rare event. Using genetically engineered DNA polymerases greatly improves the efficiency of PAP.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Ho/ll canola with resistance to clubroot disease
ActiveUS20130298279A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyMutant allele
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
High oleic acid Brassica juncea
ActiveUS20050039233A1High oleic acid contentOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyPremature Stop Codon
In various aspects, the invention provides Brassica juncea plants, seeds, cells, nucleic acid sequences and oils. Edible oil derived from plants of the invention may have significantly higher oleic acid content than other B. juncea plants. In one embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-086-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-086-3 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a premature stop codon, so that there are no functional copies of the FAD2 gene in MJ02-086-3 plants. Seeds from MJ02-086-3 plants may for example yield an oil having oleic acid content of greater than about 70% by weight.
Owner:SASKATCHEWAN WHEAT POOL +1
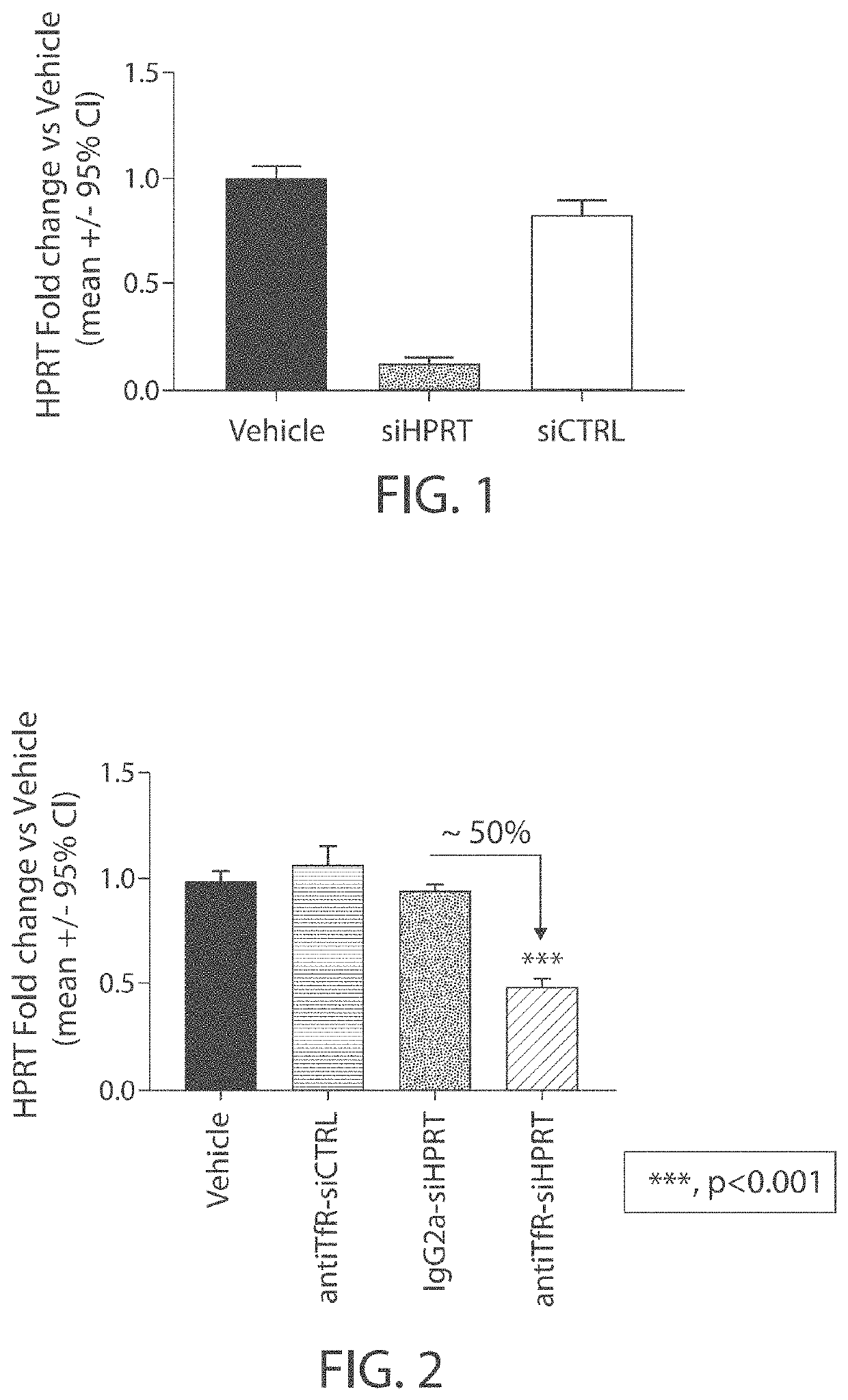
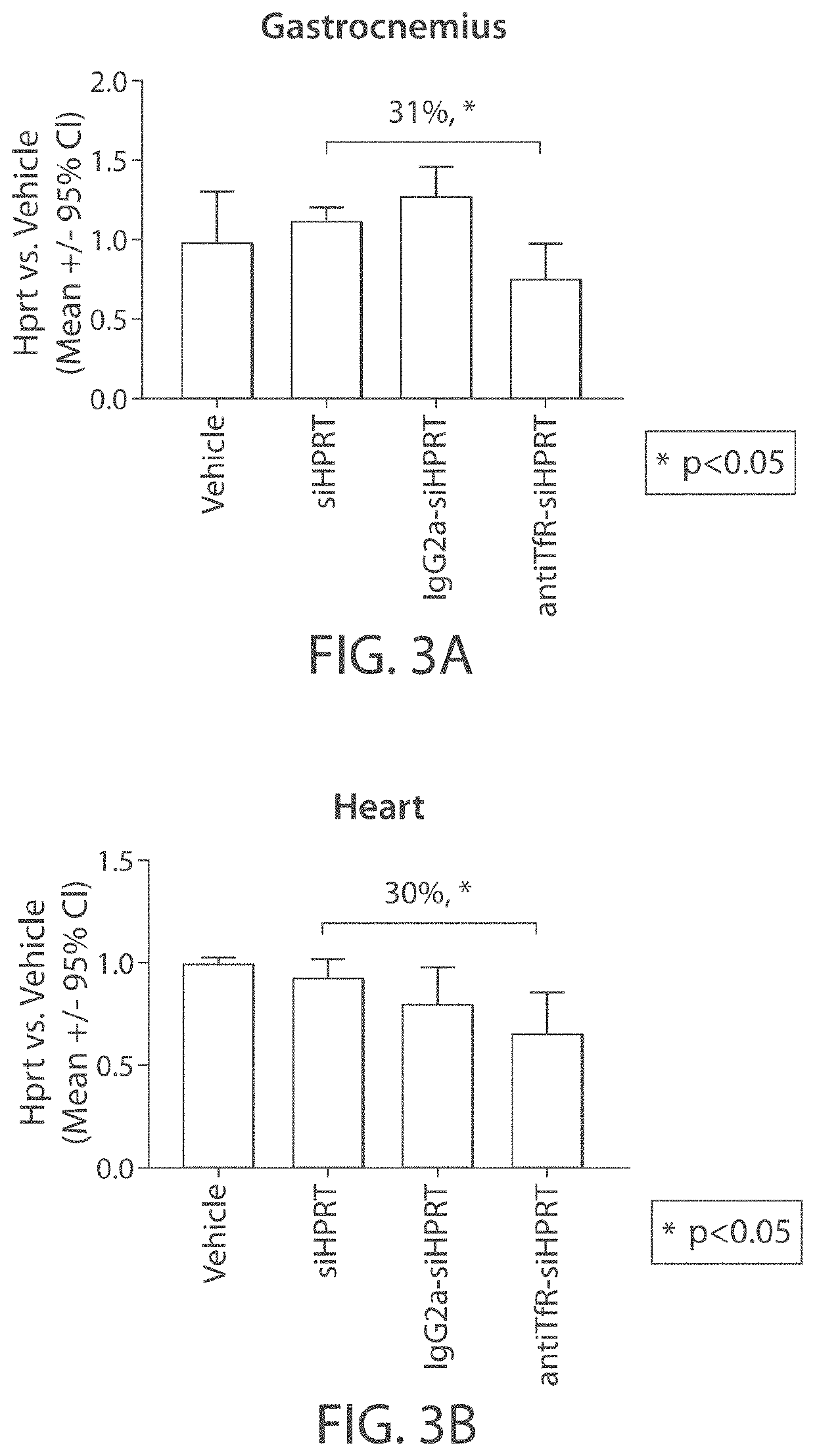
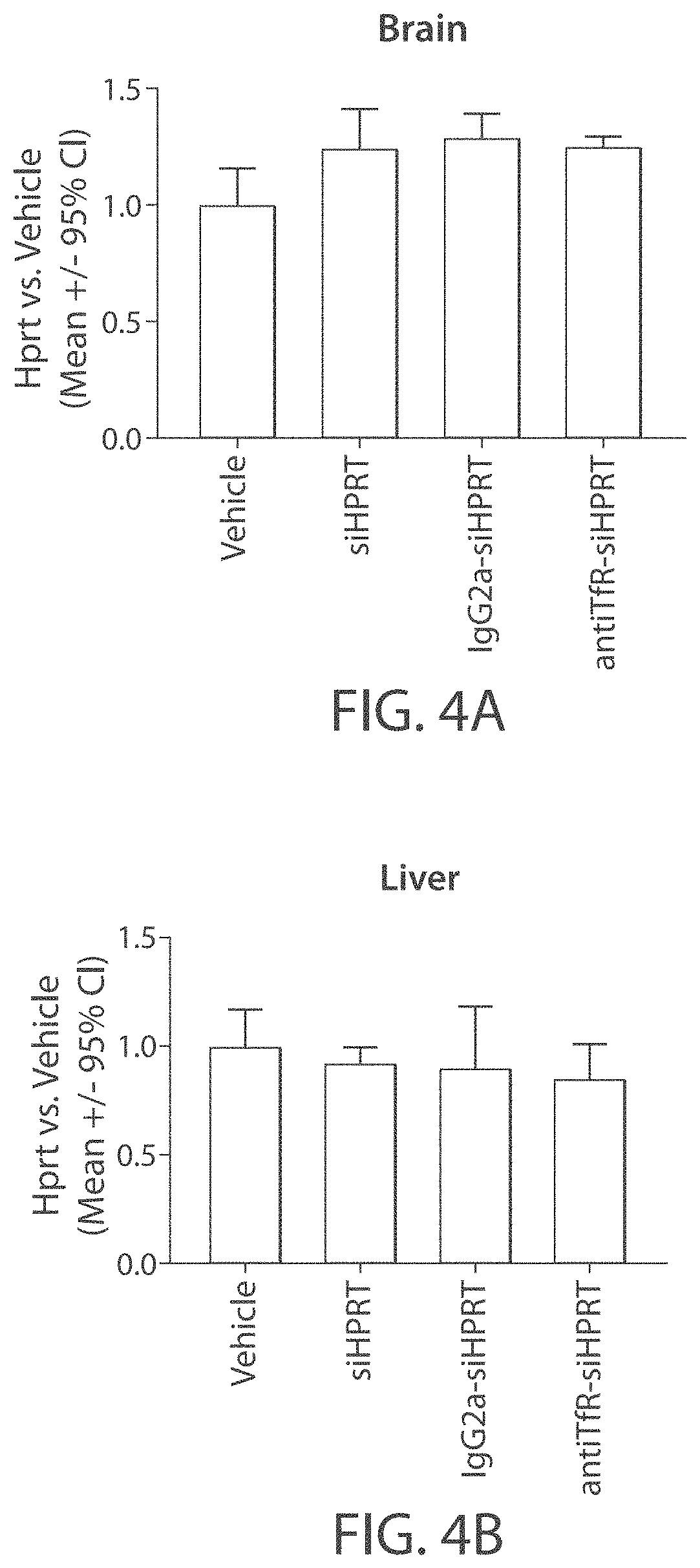
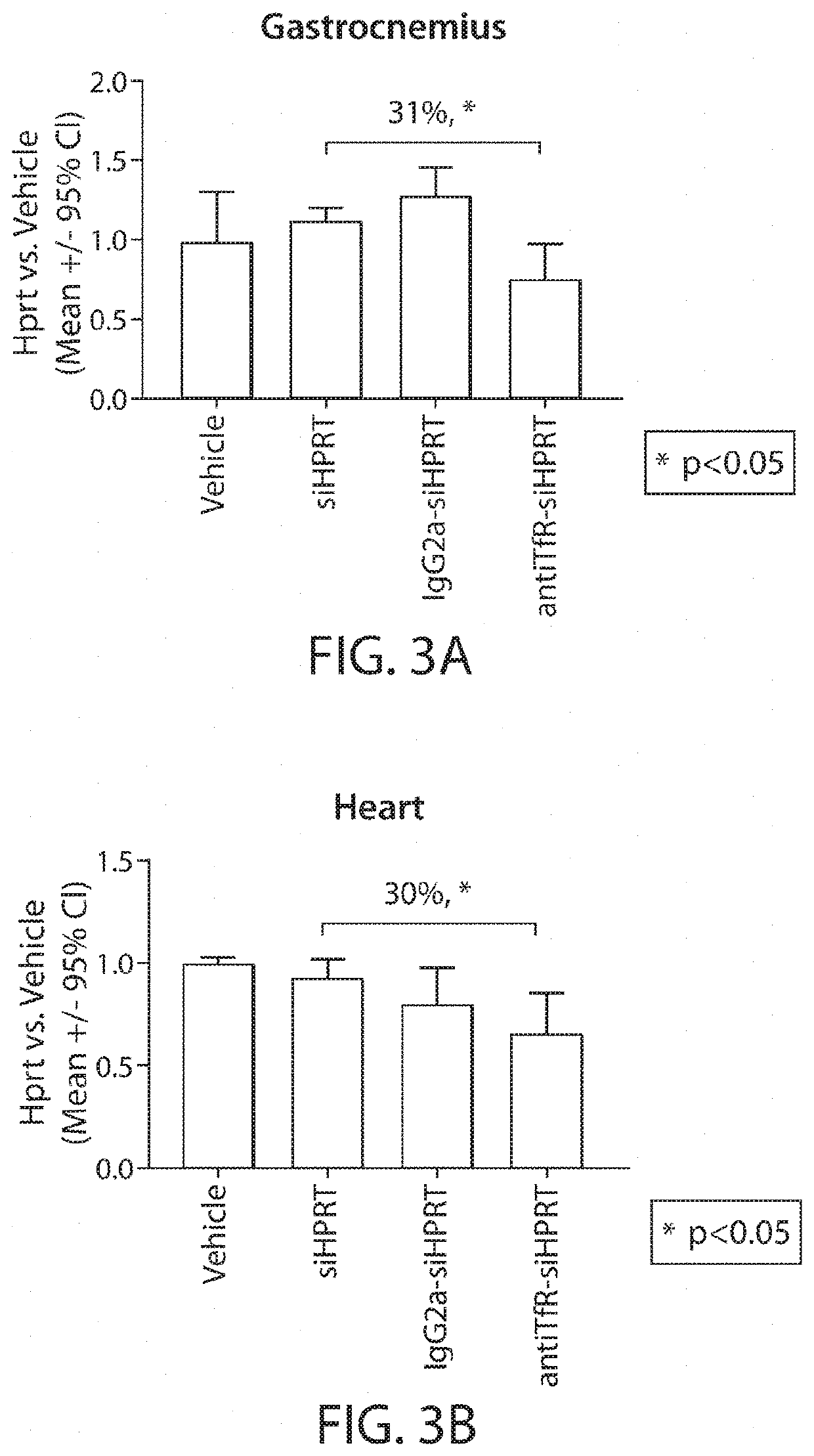
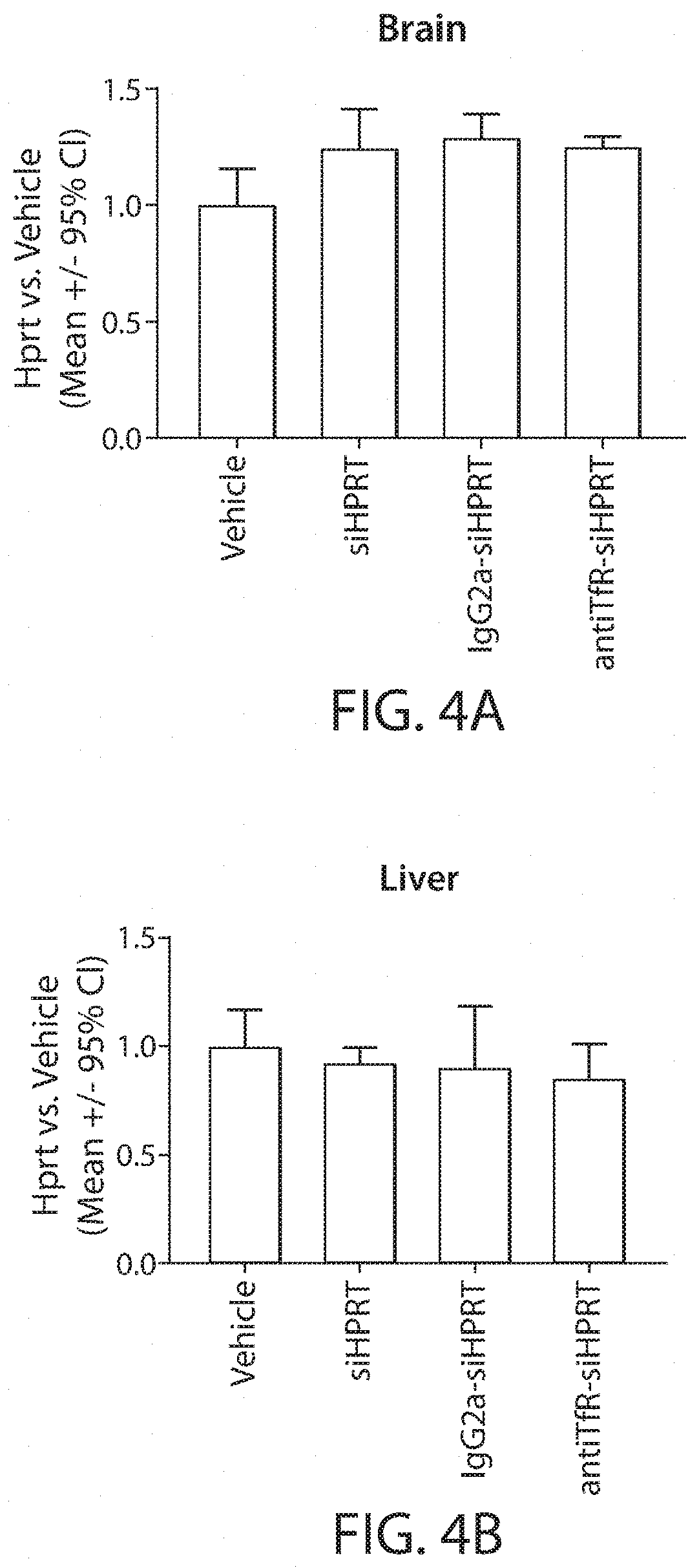
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating dystrophinopathies
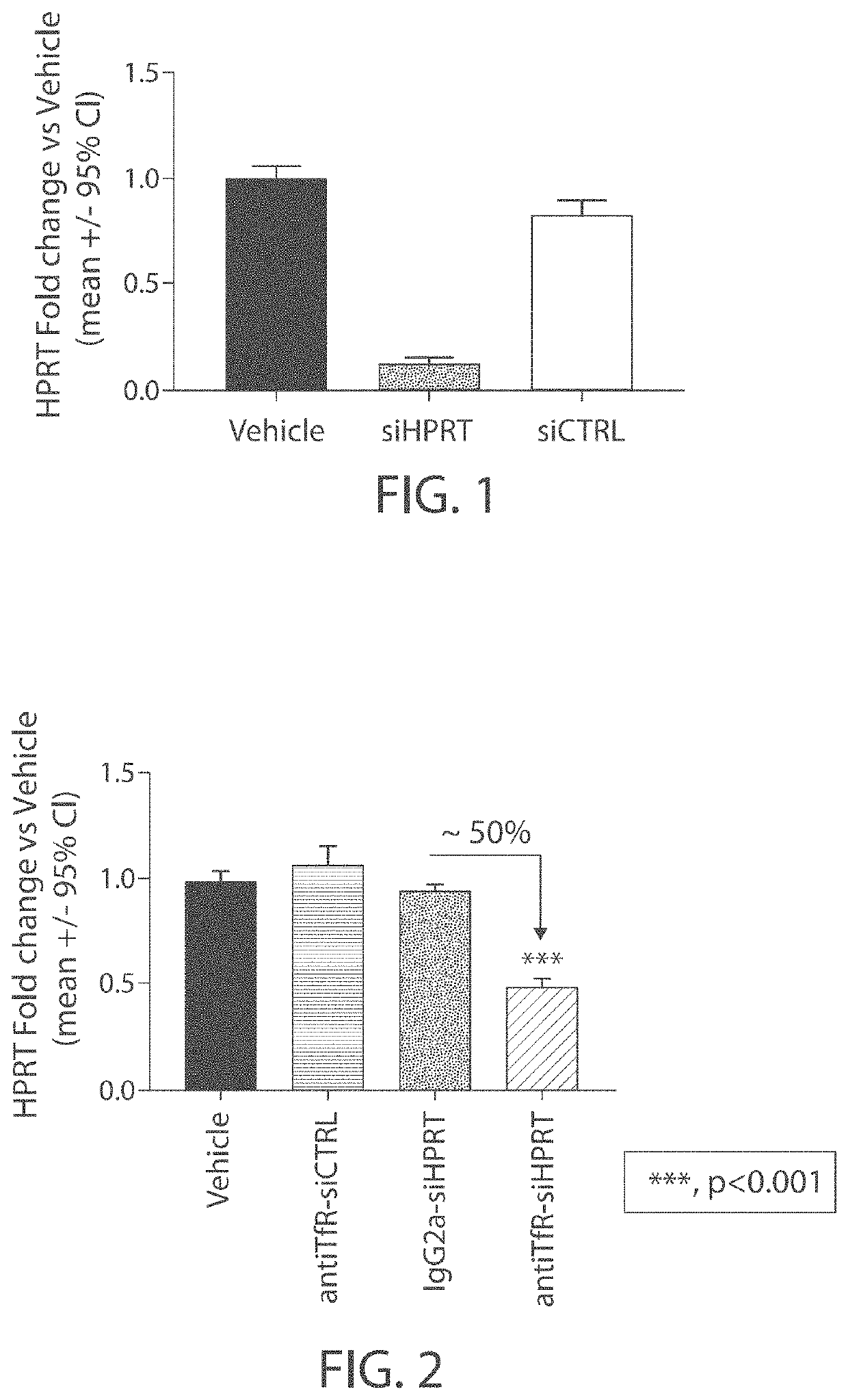
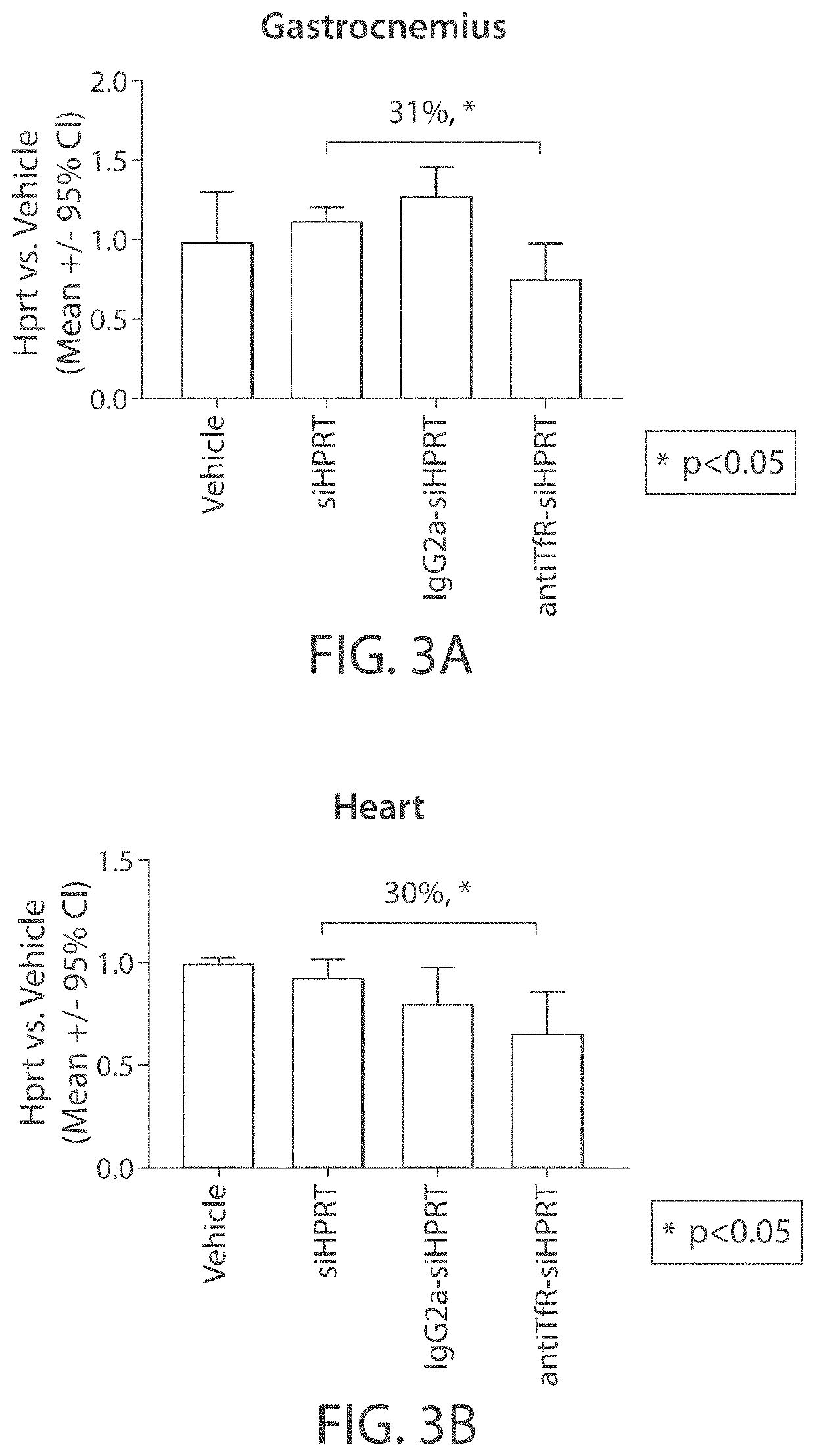
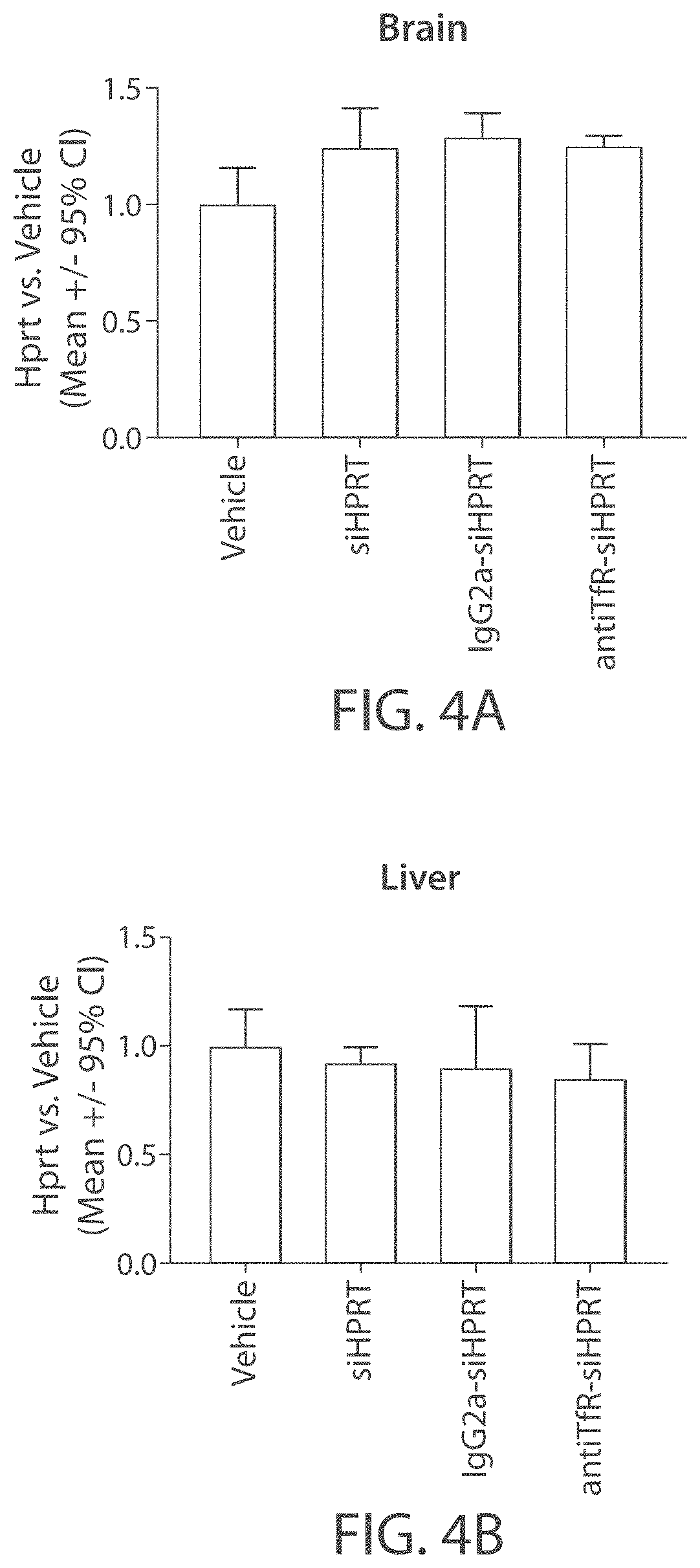
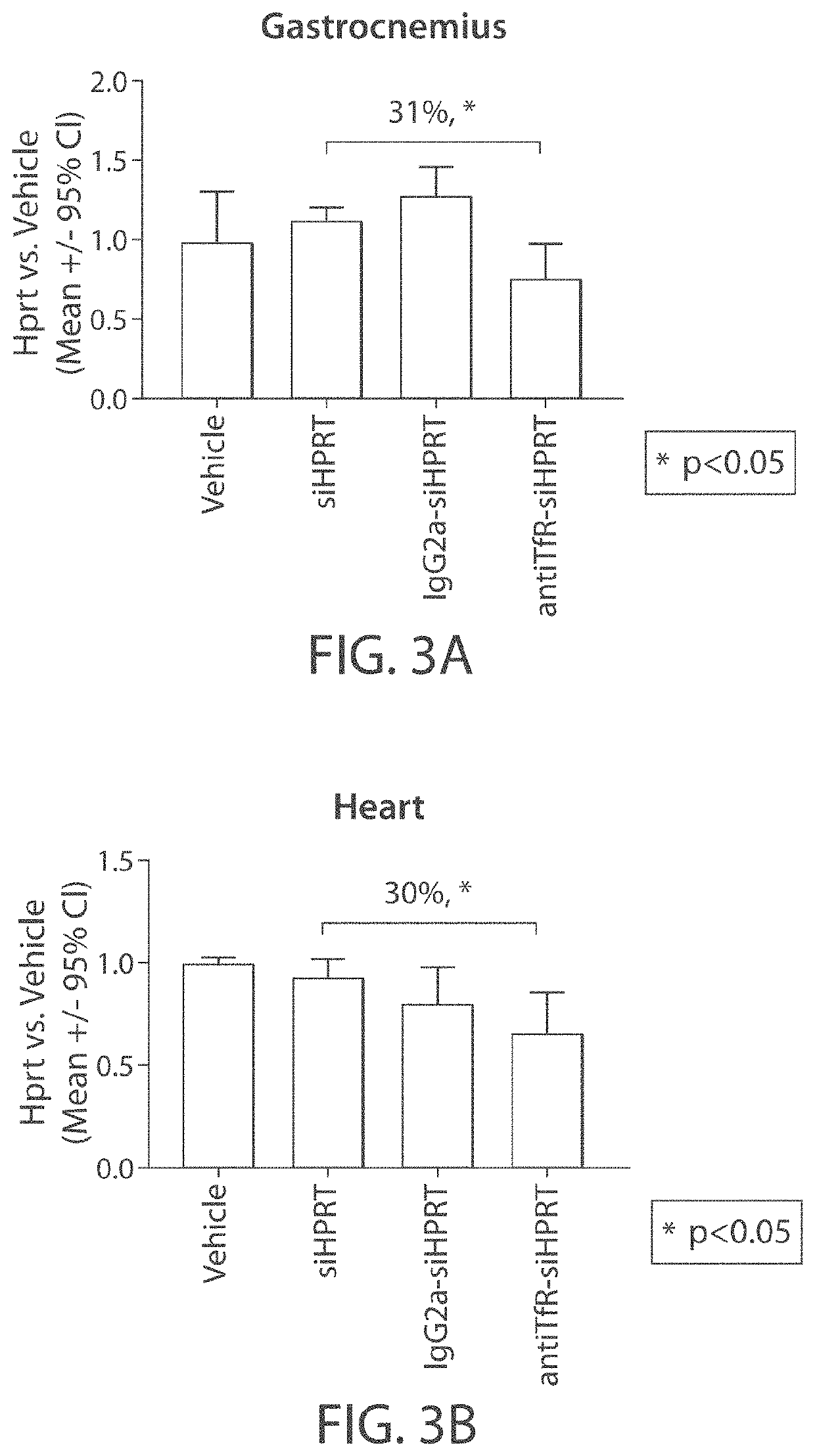
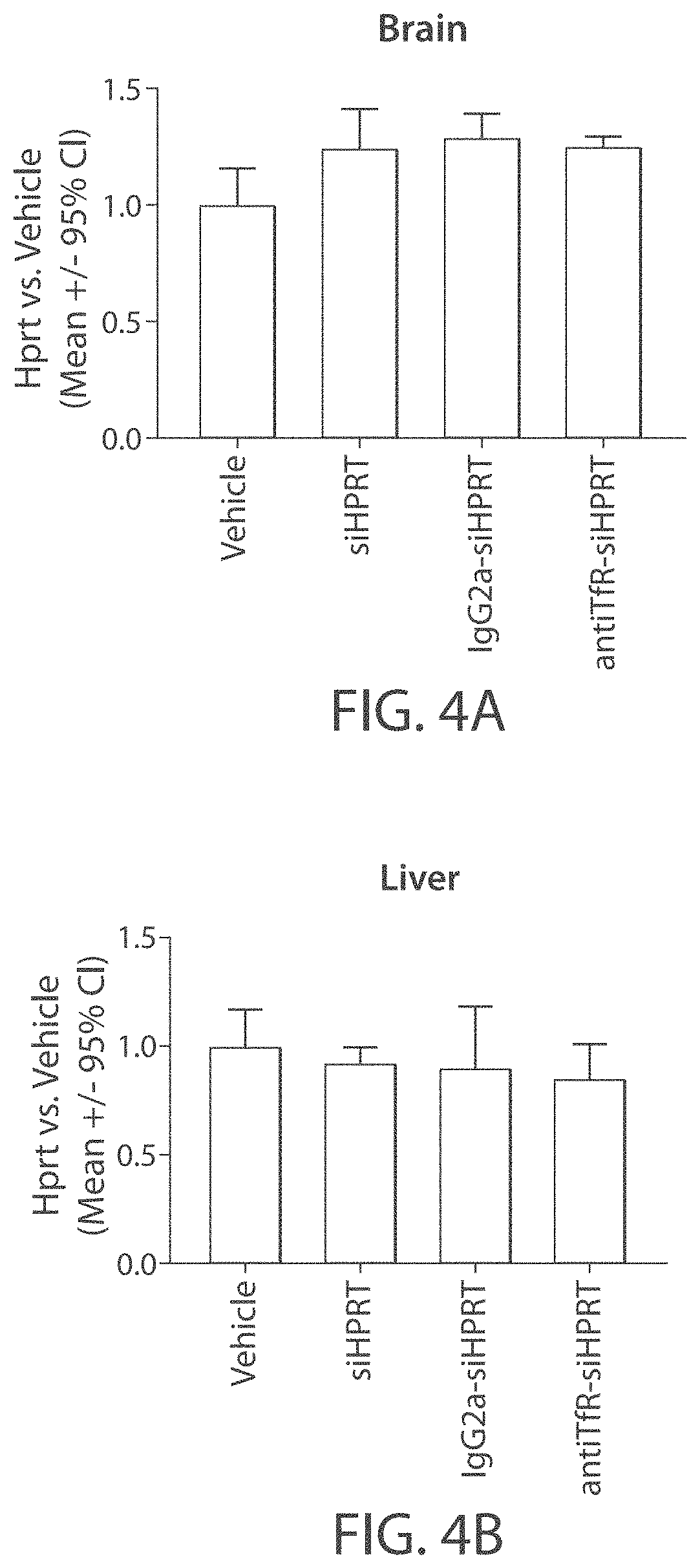
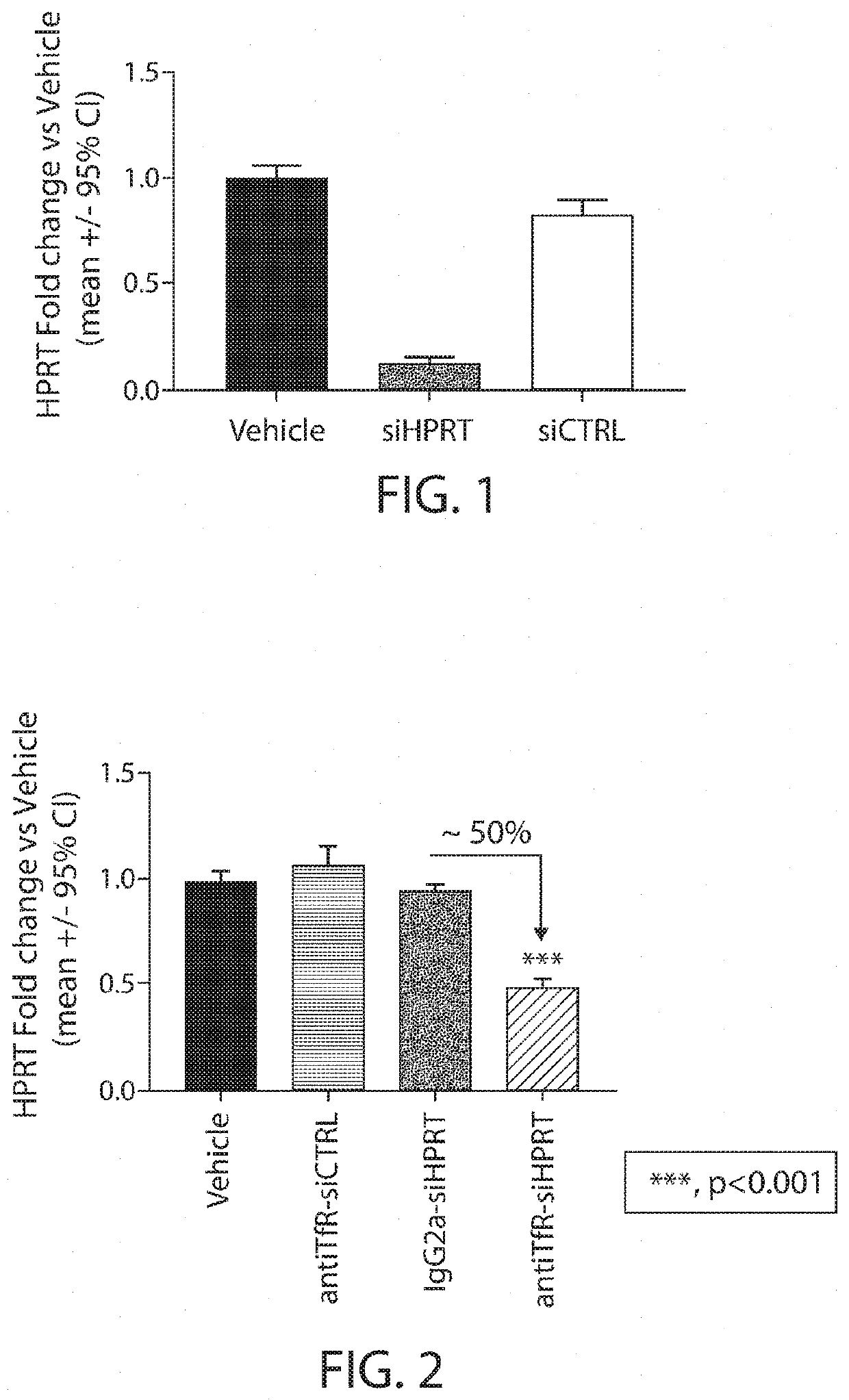
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload promotes the expression or activity of a functional dystrophin protein. In some embodiments, the molecular payload is an oligonucleotide, such as an antisense oligonucleotide, e.g., an oligonucleotide that causes exon skipping in a mRNA expressed from a mutant DMD allele.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
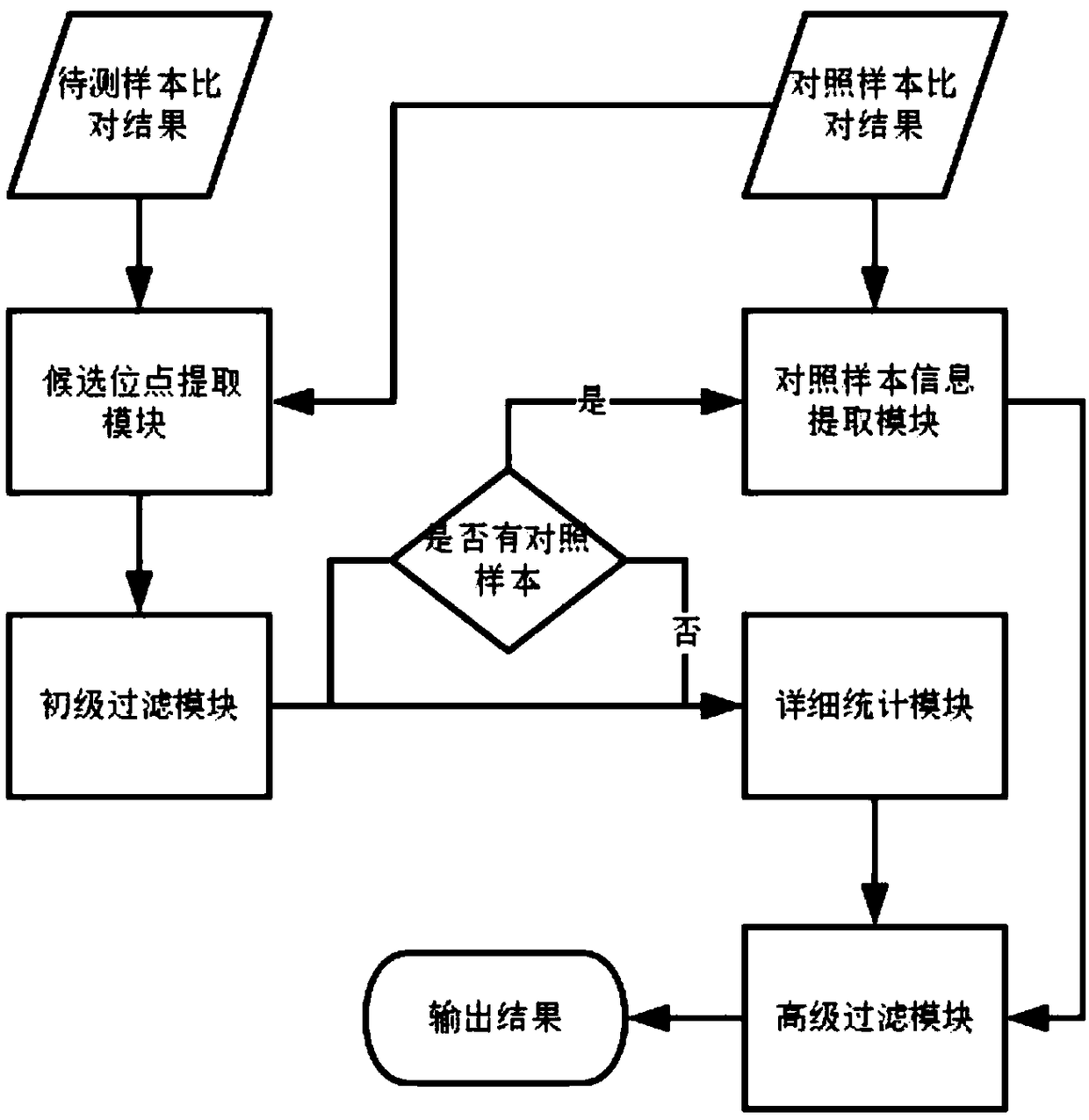
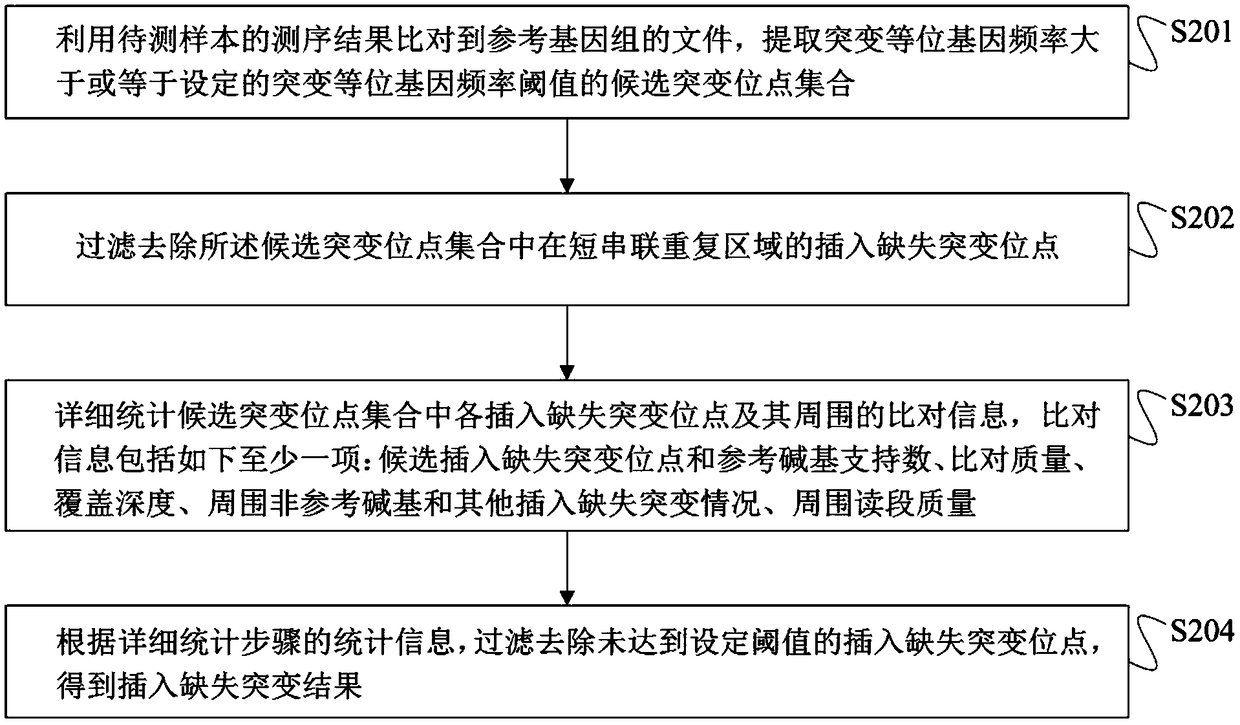
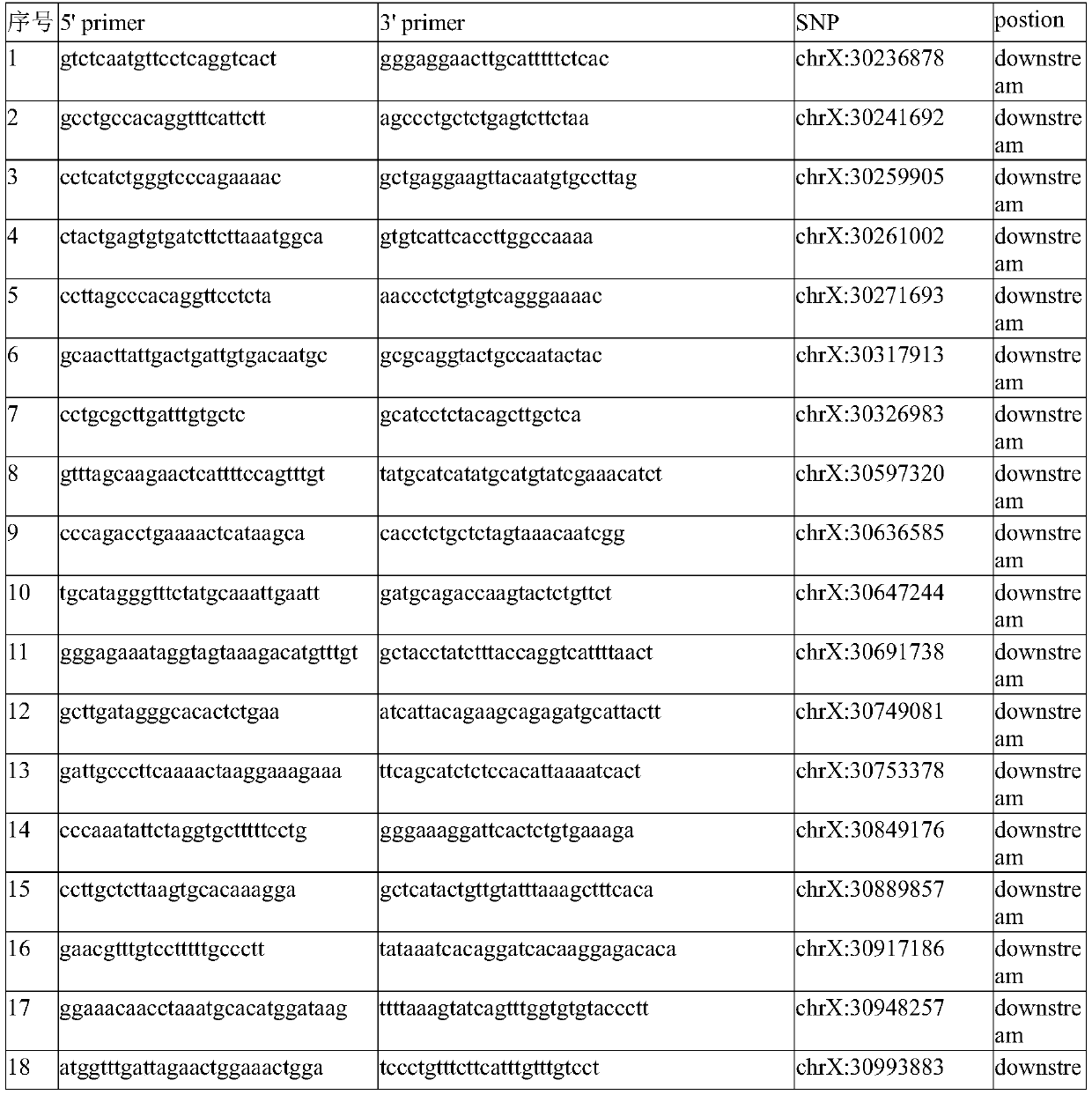
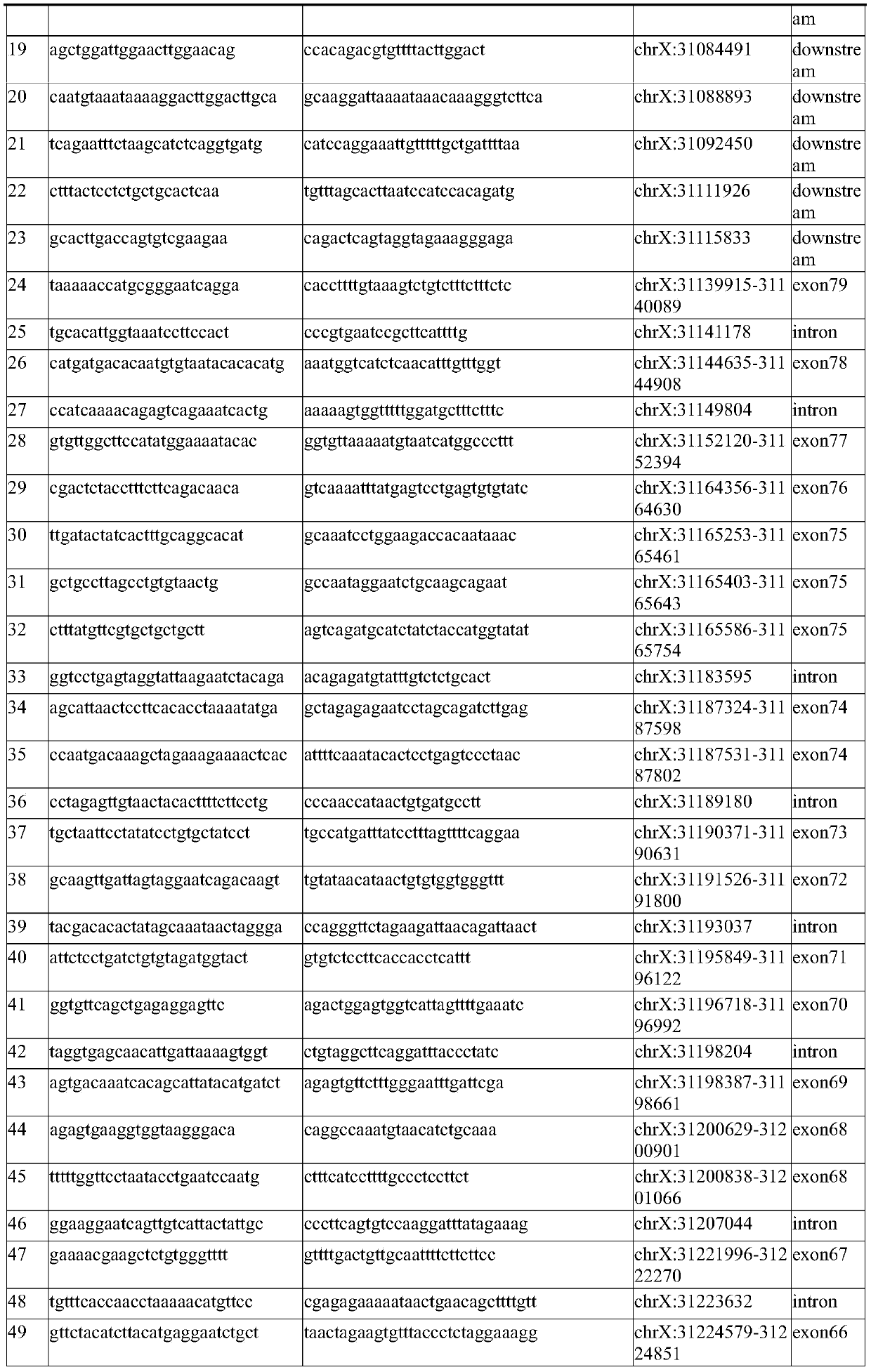
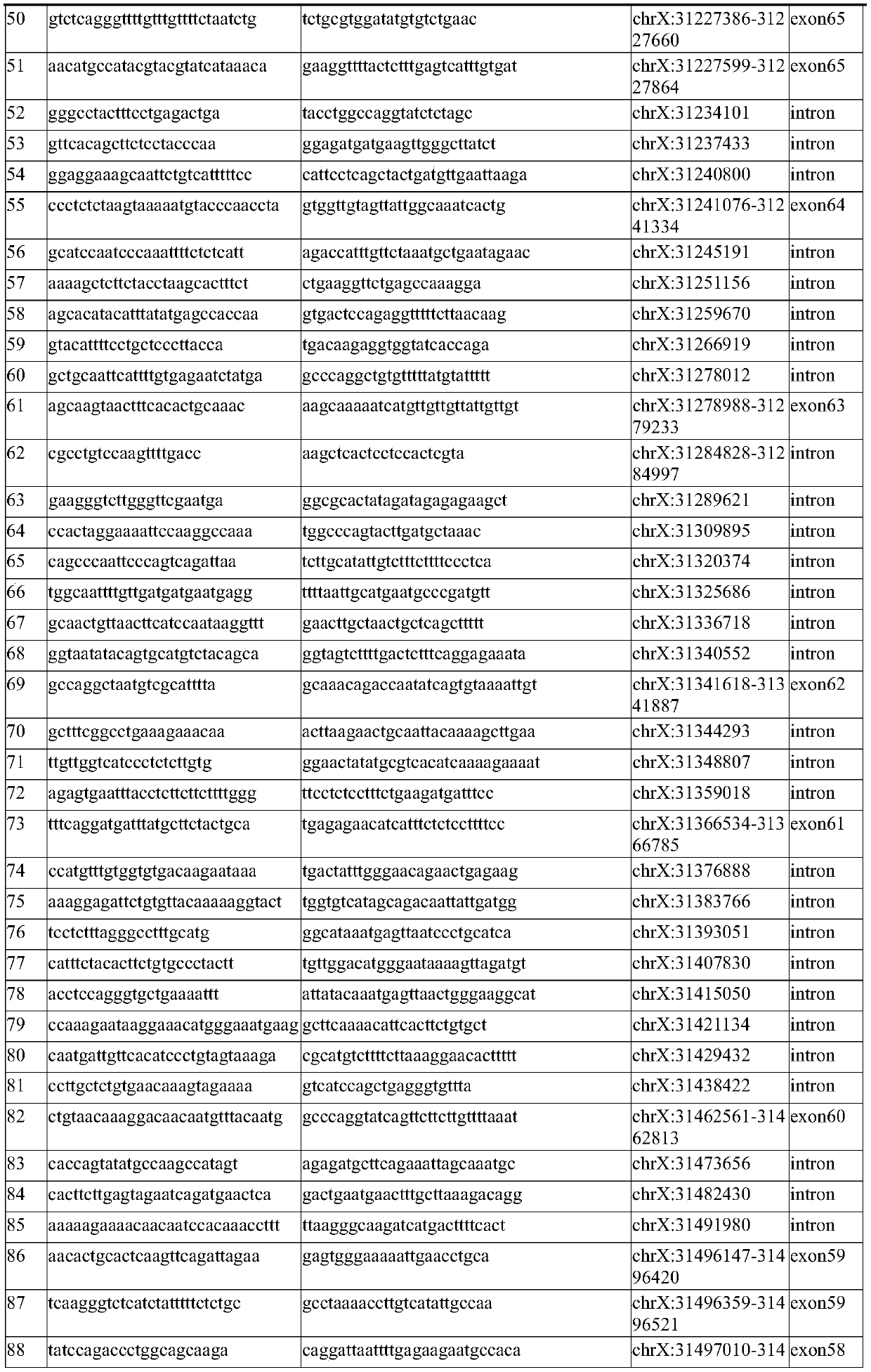
Method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, device and storage medium
ActiveCN108690871AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsInsertion deletionAllele frequency
The present application discloses a method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, a device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps:comparing a sample to be tested with a file of a reference genome to extract a set of candidate mutation sites with mutation allele frequency being greater than or equal to a threshold; filtering to remove sites in a short tandem repeat region; making detail statistics of comparison information of the mutation sites and comparison information surrounding the mutation sites, wherein the comparisoninformation includes InDel site and reference base support number, comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non-reference base and other insertion deletion mutations, surrounding read quality;and filtering to remove sites that do not reach the set threshold according to statistical information to obtain mutation results. The method does not require partial assembly, and filters second-generation sequencing data in advance to quickly eliminate most of false positive results caused by the comparison, reduces detection running time and computing resources, improves detection efficiency, has strong sensitivity and specificity, and can quickly and accurately detect InDel mutations.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
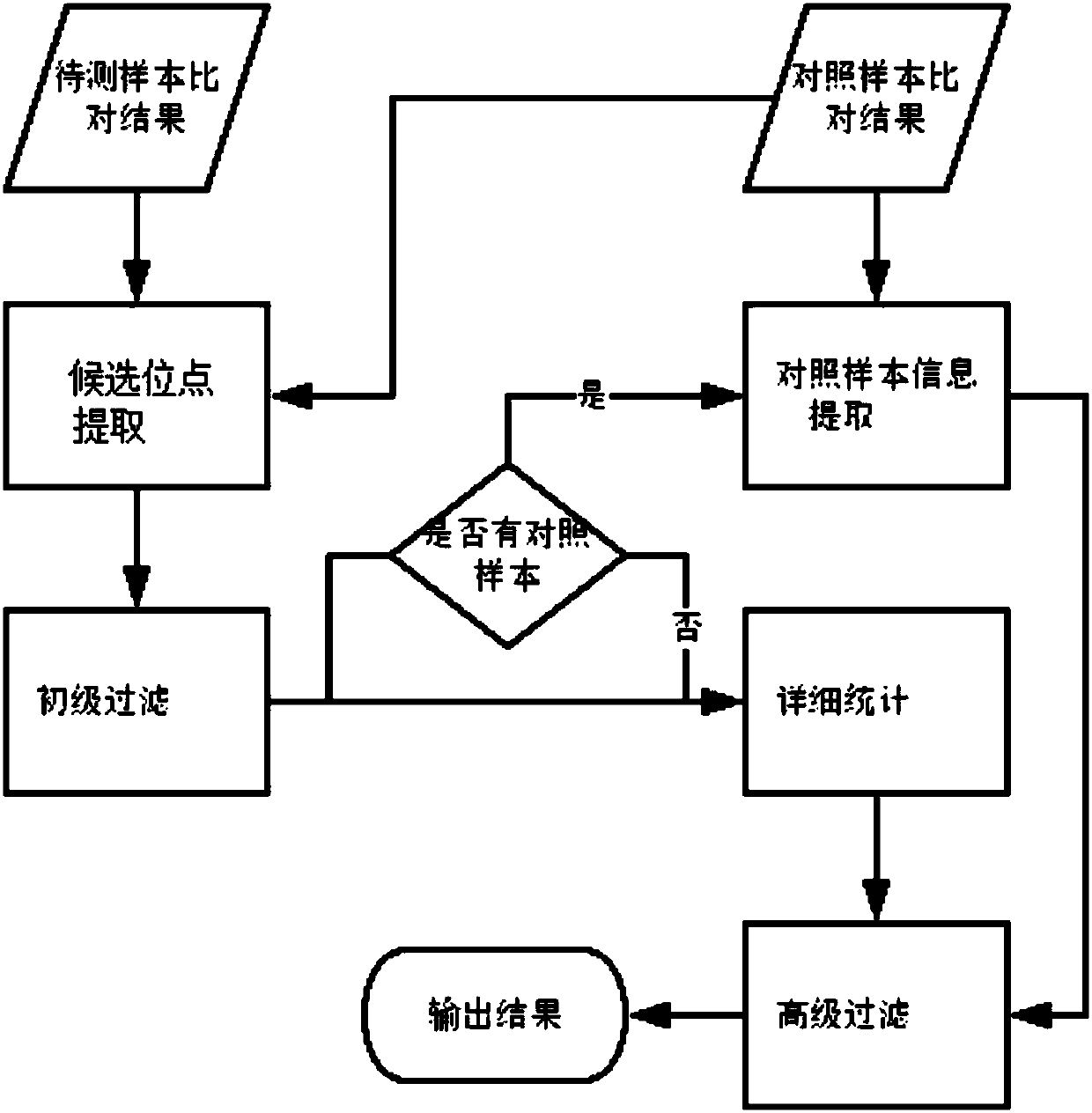
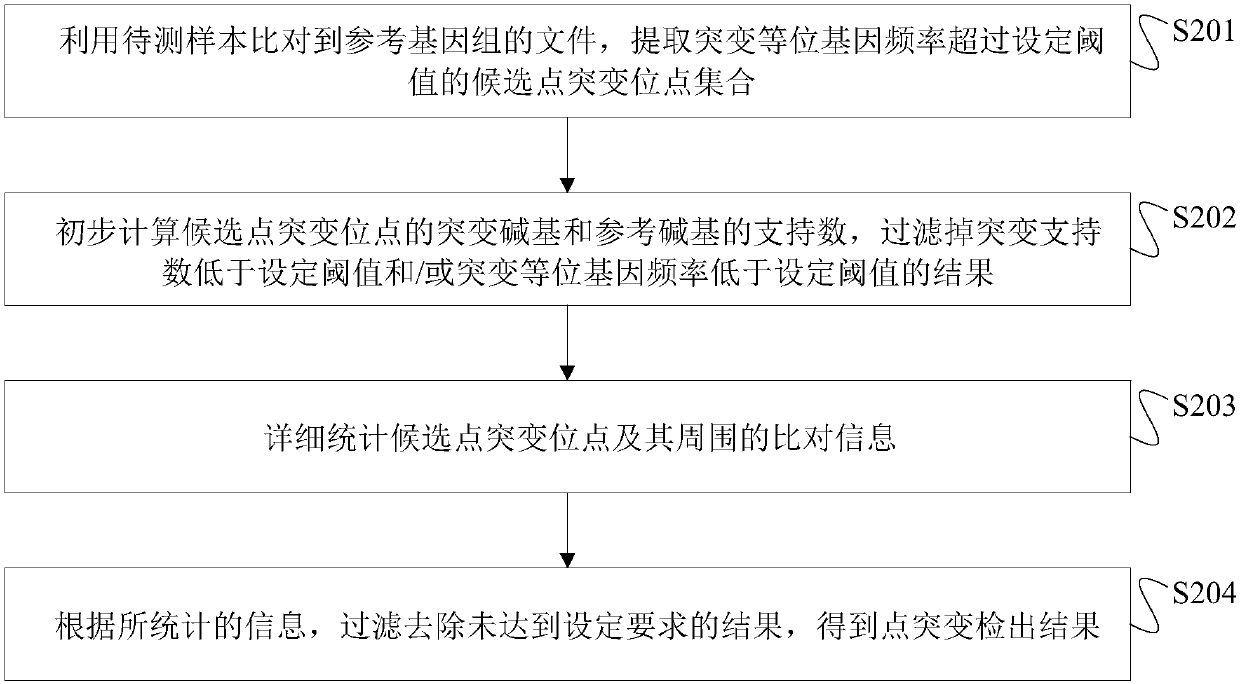
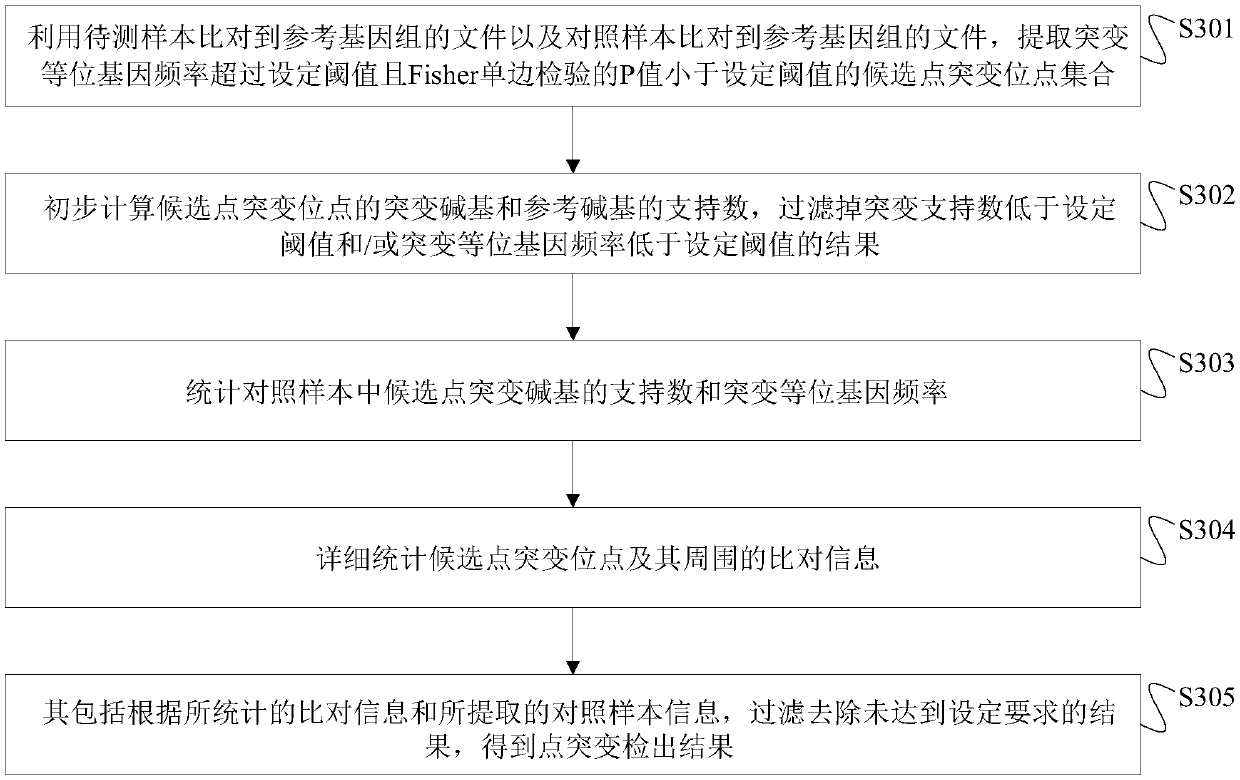
Next generation sequencing-based point mutation detection filtering method and apparatus, and storage medium
The invention discloses a next generation sequencing-based point mutation detection filtering method and apparatus, and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of performing comparison with files of a reference genome by utilizing a to-be-detected sample, and extracting candidate point mutation site sets with variant allele frequencies exceeding a set threshold; preliminarily calculatingsupport numbers of mutant bases and reference bases of candidate point mutation sites, and filtering results with the mutant support numbers lower than the set threshold and / or the variant allele frequencies lower than the set threshold; performing detailed statistics on the candidate point mutation sites and surrounding comparison information, wherein the information comprises at least one of thefollowing information: the support numbers of the mutant bases and the reference bases of the candidate point mutation sites, base and comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non reference base and insertion / deletion statuses, and surrounding read quality; and according to the statistical information, filtering the results which do not meet set requirements to obtain a point mutation detection result. While the resource demands and the detection speed are optimized, the sensitivity and specificity of point mutation detection are improved.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating dystrophinopathies
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Brassica Juncea Lines With High Oleic Acid Profile In Seed Oil
In various aspects, the invention provides Brassica juncea plants, seeds, cells, nucleic acid sequences and oils. Edible oil derived from plants of the invention may have significantly higher oleic acid content than other B. juncea plants. In one embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-357-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-313-1 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a single base-pair change (a G to A substitution in the ORF at position 281 in reference to the first ATG start codon) relative to the wild type sequence. The change is predicted to encode a Glycine-94 Aspartic acid mutation in the sequence of the predicted BjFAD2-a protein. In another embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-357-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-357-3 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a single base-pair change (a C to T substitution in the ORF at position 647 in reference to the first ATG start codon) relative to the wild type sequence. The change is predicted to encode a Proline-216 Leucine mutation in the sequence of the predicted BjFAD2-a protein. As a result of these mutations, it can be predicted that the function of the BjFAD2-a proteins are negatively affected in Brassica juncea lines MJ02-313-1 and MJ357-3 as reflected in the increased levels of oleic acid in seed oil in comparison with the wild-type line J96D-4830. Seeds from MJ02-313-1 and MJ02-357-3 plants may for example yield an oil having oleic acid content of greater than 70% by weight.
Owner:NUTRIEN AG SOLUTIONS (CANADA) INC
Brassica AHAS genes and gene alleles that provide resistance to imidazolinone herbicides
Owner:PIONEER OVERSEAS
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating dystrophinopathies
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload promotes the expression or activity of a functional dystrophin protein. In some embodiments, the molecular payload is an oligonucleotide, such as an antisense oligonucleotide, e.g., an oligonucleotide that causes exon skipping in a mRNA expressed from a mutant DMD allele.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
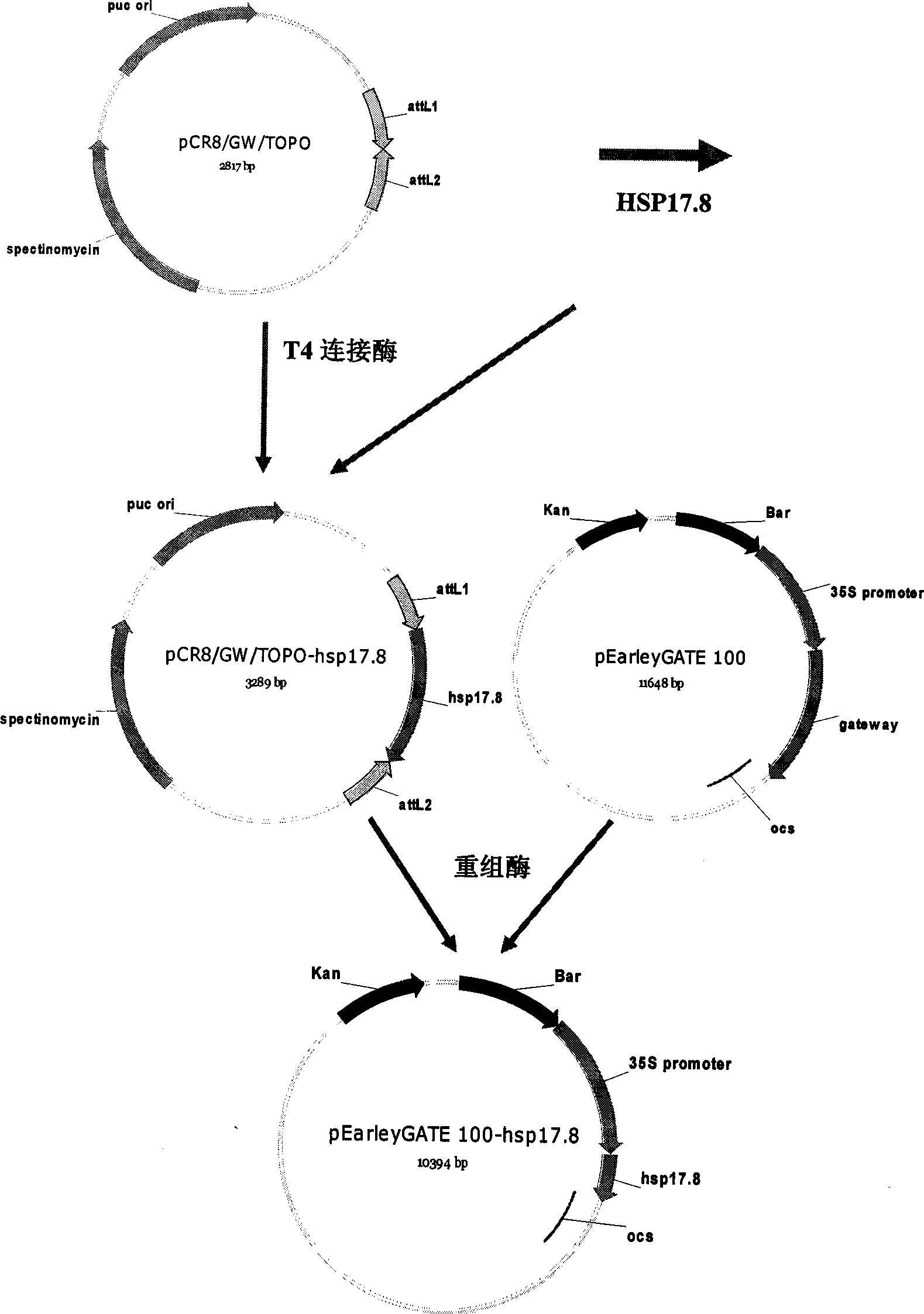
Rape heat shock protein gene HSP17.8 and application thereof
InactiveCN101544983AImprove heat resistanceReduce harmPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
The invention discloses a rape heat shock protein gene HSP17.8 and application thereof. The invention provides a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the gene, gene sequences which at least have 70 percent homology with a DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in other crops, and mutant alleles or derivatives produced by adding, substituting, inserting or deleting one or more nucleotides. At the same time, the heat shock protein gene also proves that the overexpression of the heat shock protein gene strengthens the heat resistance of arabidopsis at high temperature by means of model plant, namely the arabidopsis through transgenic technology, increases the yield of seeds at high temperature, and improves the yield of the arabidopsis under high temperature stress, so the heat shock protein gene has good application prospect in heat-tolerance breeding of crops.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating dystrophinopathies
PendingUS20210308273A1High activityHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMutant alleleInternalization
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload promotes the expression or activity of a functional dystrophin protein. In some embodiments, the molecular payload is an oligonucleotide, such as an antisense oligonucleotide, e.g., an oligonucleotide that causes exon skipping in a mRNA expressed from a mutant DMD allele.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
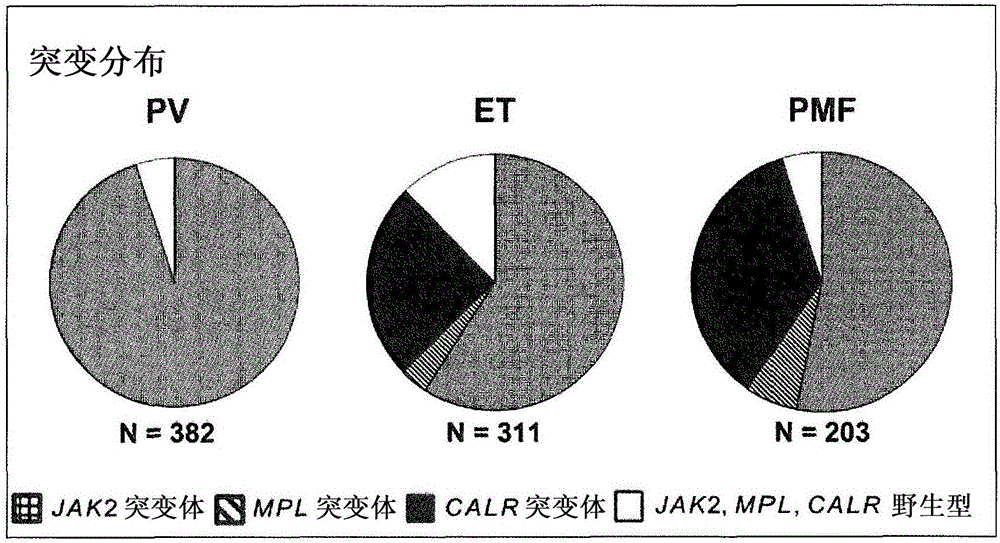
Mutant calreticulin for the diagnosis of myeloid malignancies
PendingCN105916876AMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMutant alleleADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing myeloid malignancy comprising determining the presence of a mutant allele of the calreticulin gene. Also genomic sequences, cDNA sequences, mRNA sequences and protein sequences of the mutant calreticulin are subject of the present invention. Further, the invention relates to medical uses of inhibitors of mutant calreticulin.
Owner:CEMM FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR MOLEKULARE MEDIZIN
Serial coupling of restriction cleavage and extension for nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS7105298B2Improve efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyExact matchMutant allele
A novel method of pyrophosphorolysis activated polymerization (PAP) has been developed. In PAP, pyrophosphorolysis and polymerization by DNA polymerase are coupled serially for each amplification by using an activatable oligonucleotide P* that has a non-extendable 3′-deoxynucleotide at its 3′ terminus. PAP can be applied for exponential amplification or for linear amplification. PAP can be applied to amplification of a rare allele in admixture with one or more wild type alleles by using an activatable oligonucleotide P* that is an exact match at its 3′ end for the rare allele but has a mismatch at or near its 3′ terminus for the wild type allele. PAP is inhibited by a mismatch in the 3′ specific subsequence as far as 16 nucleotides away from the 3′ terminus. PAP can greatly increase the specificity of detection of an extremely rare mutant allele in the presence of the wild type allele. Specificity results from both pyrophosphorolysis and polymerization since significant nonspecific amplification requires the combination of mismatch pyrophosphorolysis and misincorporation by the DNA polymerase, an extremely rare event. Using genetically engineered DNA polymerases greatly improves the efficiency of PAP.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating dystrophinopathies
ActiveUS20220025066A1High activityHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMutant alleleInternalization
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload promotes the expression or activity of a functional dystrophin protein. In some embodiments, the molecular payload is an oligonucleotide, such as an antisense oligonucleotide, e.g., an oligonucleotide that causes exon skipping in a mRNA expressed from a mutant DMD allele.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods for detecting allelic variants
ActiveUS20140248612A1Increase the differenceLow efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant alleleGenetics
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for discriminating sequence variation between different alleles. More specifically, in some embodiments, the present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for determining the presence and / or level (e.g., quantitating) of rare (e.g., mutant) allelic variants, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or nucleotide insertions or deletions, in samples comprising abundant (e.g., wild-type) allelic variants with high sensitivity and / or specificity. As such, in certain embodiments, the present invention provides a highly selective method for the detection of somatic mutations, e.g., in samples containing abundant levels of a wild-type allele compared to very low levels of a mutant allele.
Owner:PROMETHEUS BIOSCI INC
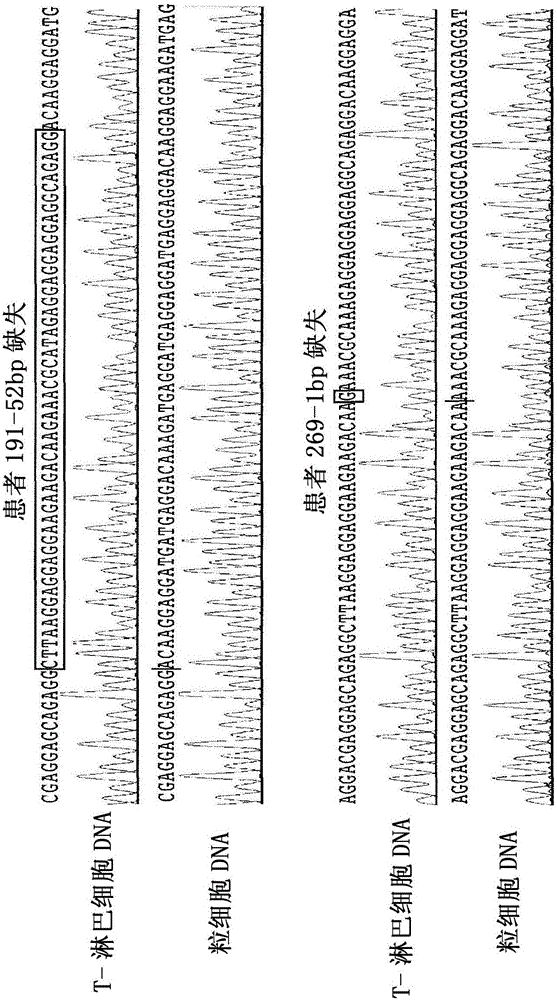
Method and kit for detecting Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene defects, and primer composition
ActiveCN110541025AImprove general performanceImprove diagnosis rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDuchenne muscular dystrophyGene defect
The invention relates to a method and a kit for detecting Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene defects, and a primer composition. For the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene defects, a pre-embryo implantation genetic detection method which is strong in universality, high in diagnosis rate and low in cost is established in a second-generation sequencing platform. According to the method, multiple PCR is carried out on a detected sample for a coding region locus and a target SNP locus of a Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene, and a library is built; then a multiplex PCR product is subjected to high-throughput sequencing analysis, and a haplotype of a mutant allele is constructed by combining with family information, so that a genotype of an embryo is judged; and finally a Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene defect detection result of an offspring is determined. According to the scheme, a cell level pre-experiment is omitted; and based on a high-throughput sequencing technology, different label sequences can be added to samples, so that a large number of samples can be analyzed at one time, and the average sequencing depth can reach more than 100X.
Owner:REPRODUCTIVE & GENETIC HOSPITAL OF CITIC XIANGYA CO LTD +1
Methods for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms
InactiveUS7223536B2Low efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
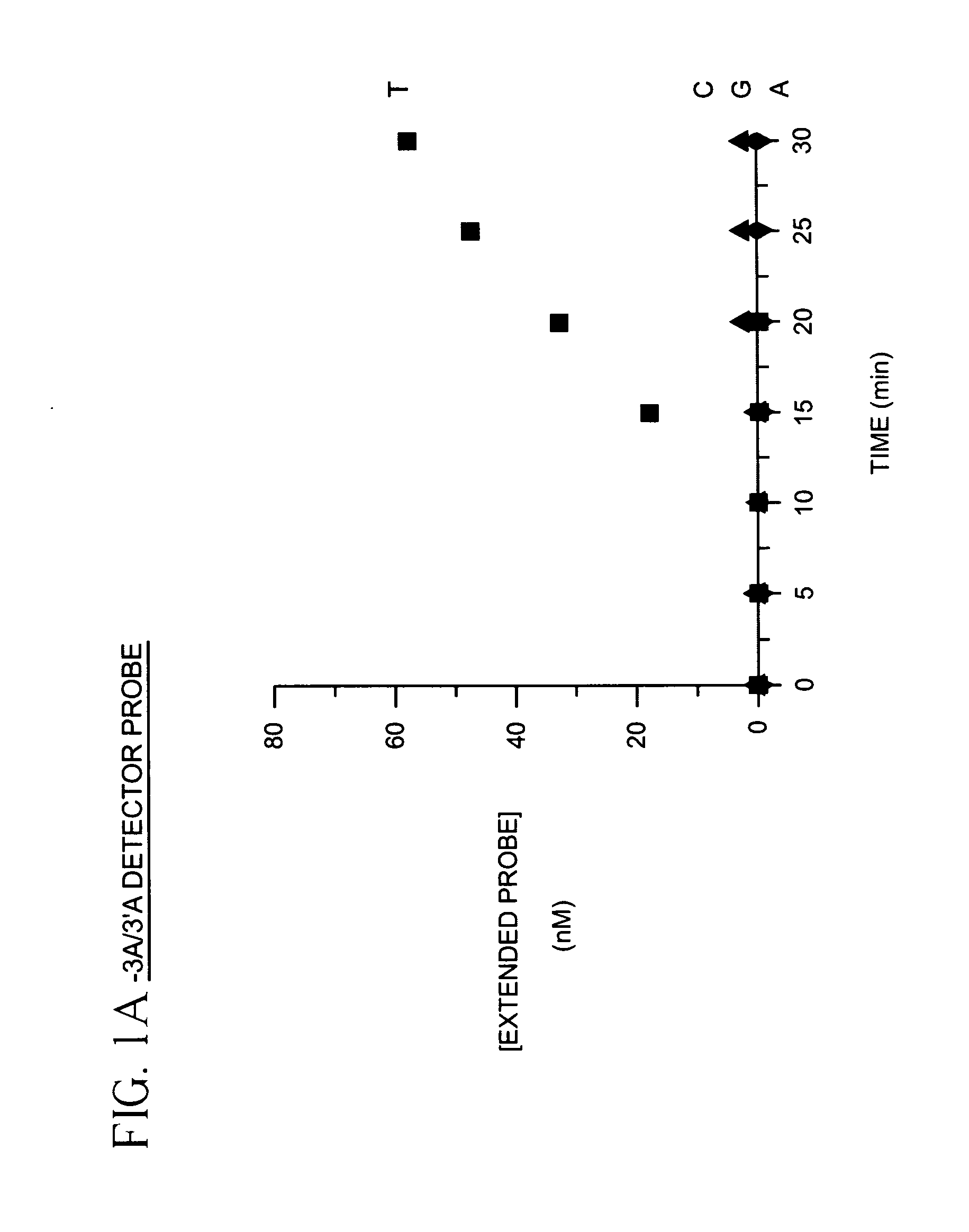
The present invention provides methods for detecting and identifying sequence variations in a nucleic acid sequence of interest using a detector primer. It has been found that the reduced efficiency of primer extension by DNA polymerases when the 3′ end of a primer does not hybridize perfectly with the target can be adapted for use as a means for distinguishing or identifying the nucleotide in the target which is at the site where the diagnostic mismatch between the detector primer and the target occurs. The detector primer hybridizes to the sequence of interest and is extended with polymerase. The efficiency of detector primer extension is detected as an indication of the presence and / or identity of the sequence variation in the target. The inventive methods make use of nucleotide mismatches at or near the 3′ end of the detector primer to discriminate between the nucleotide sequence of interest and a second nucleotide sequence which may occur at that same site in the target. The methods are particularly well suited for detecting and identifying single nucleotide differences between a target sequence of interest (e.g., a mutant allele of a gene) and a second nucleic acid sequence (e.g., a wild type allele for the same gene).
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
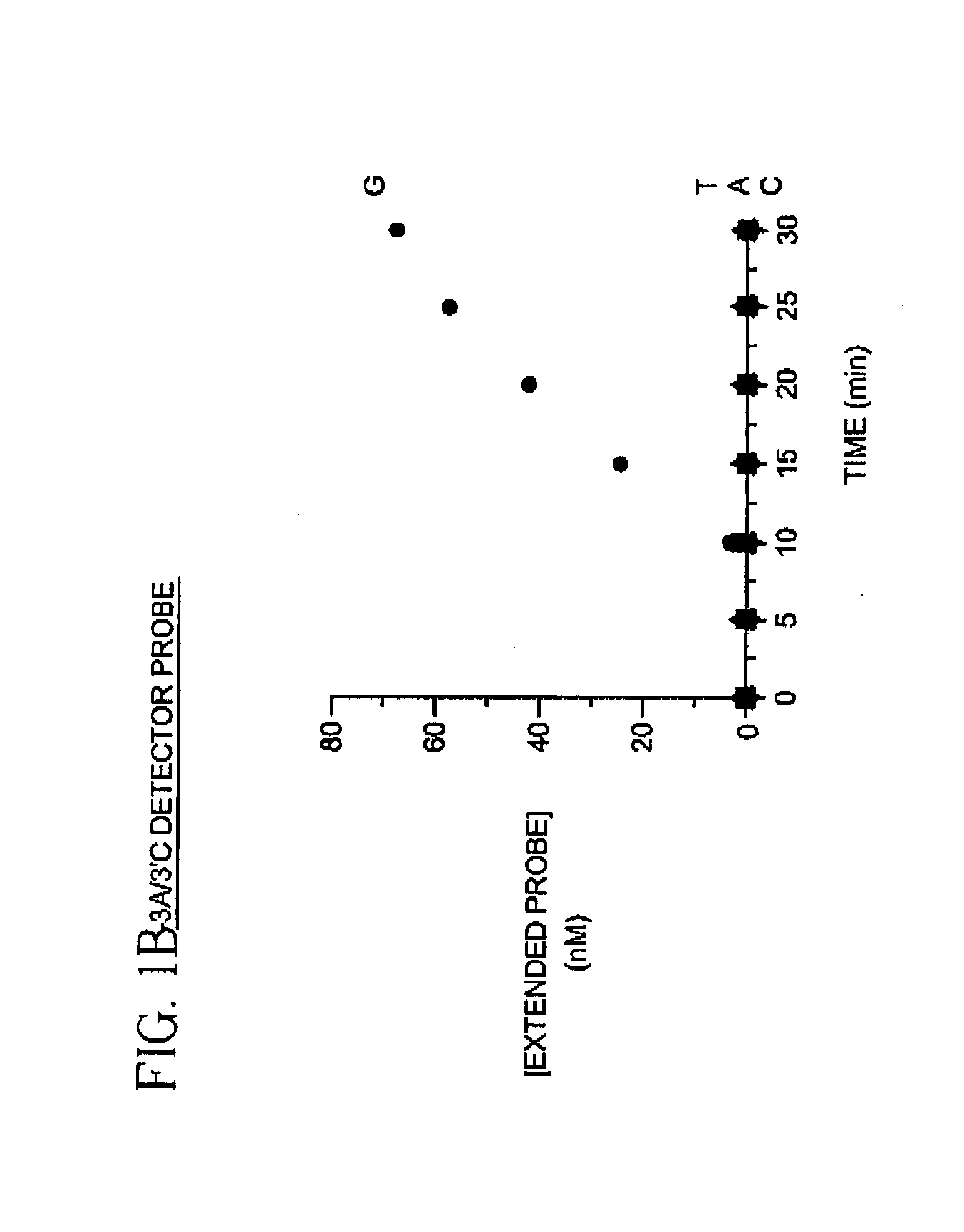
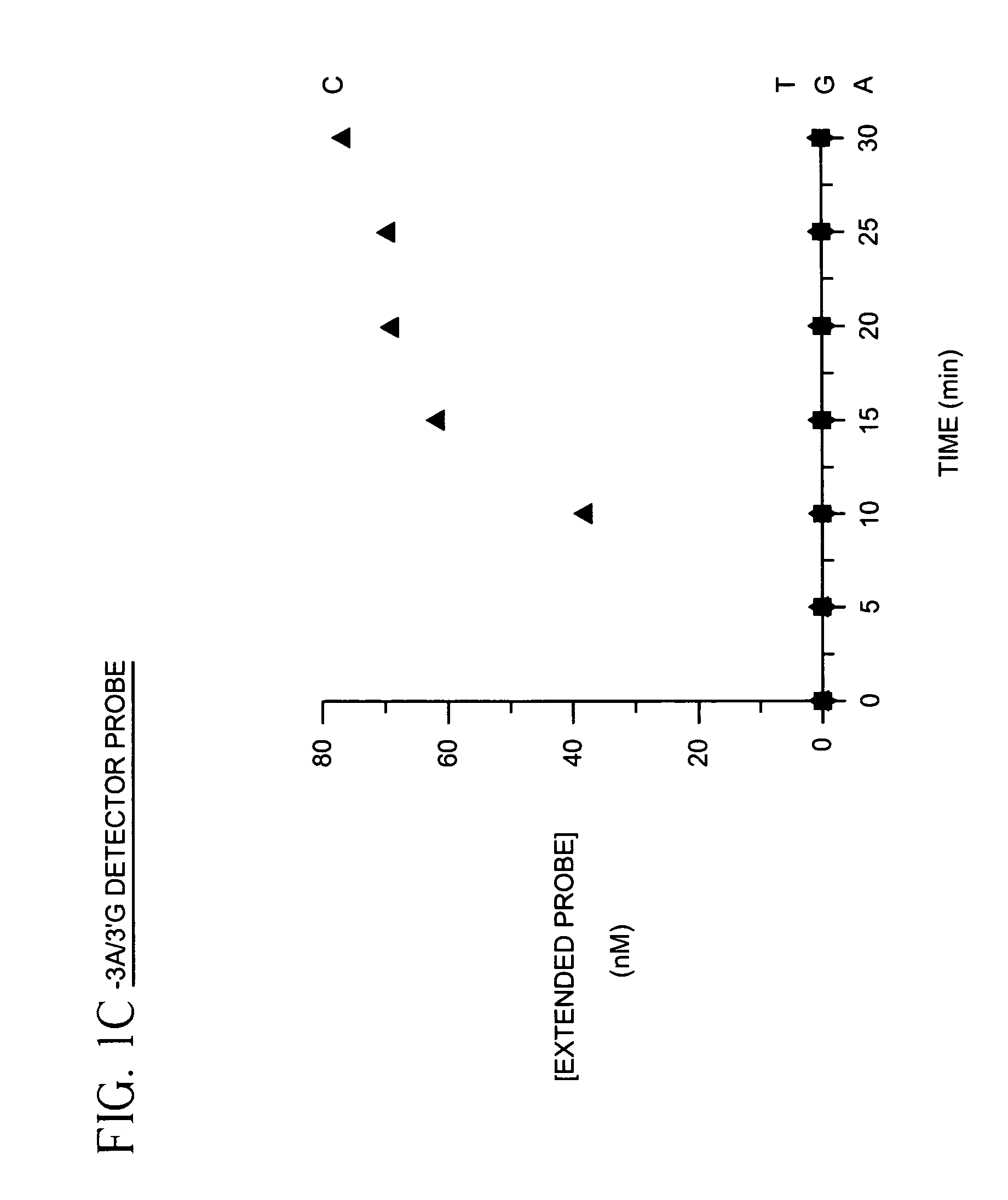
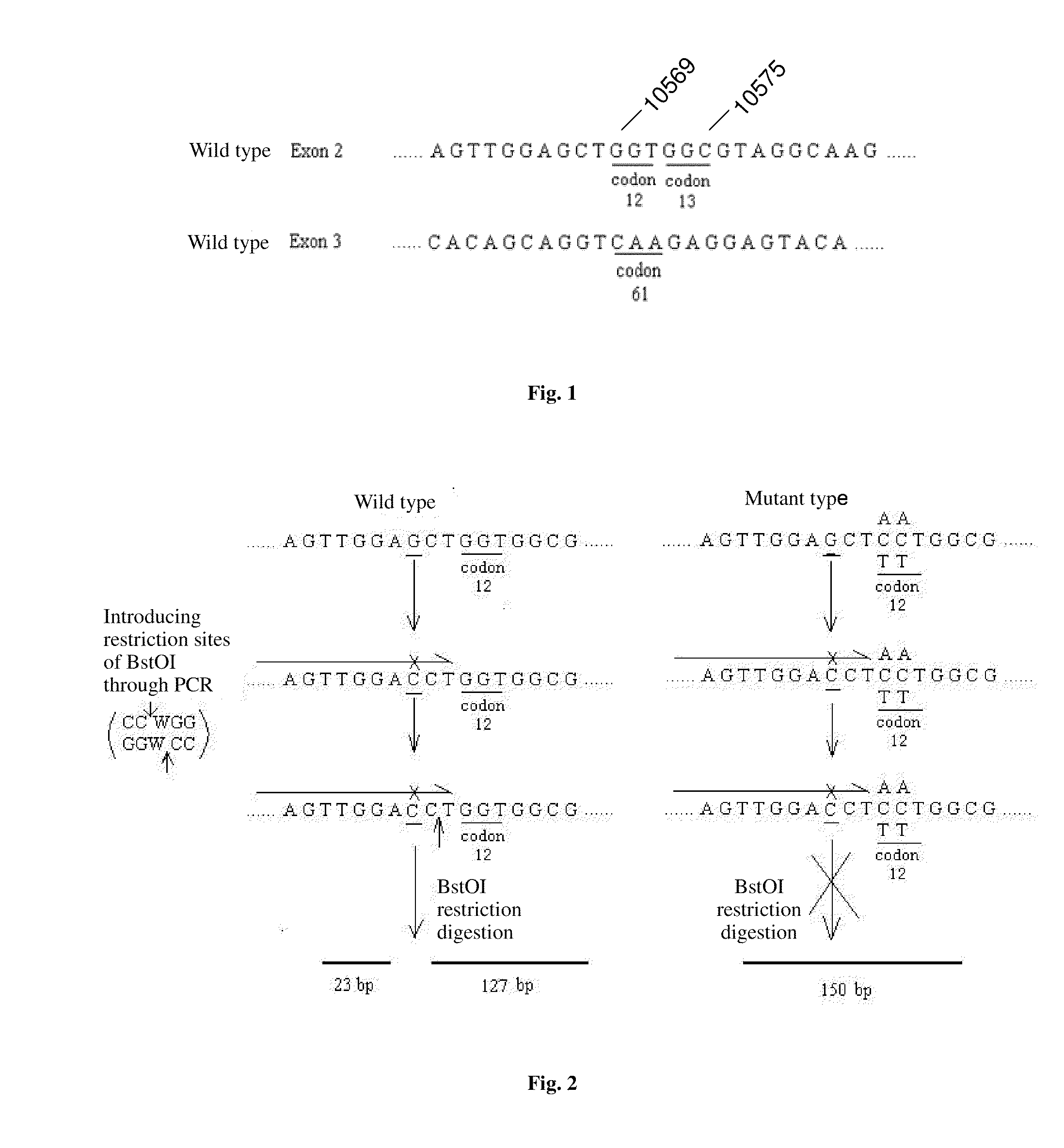
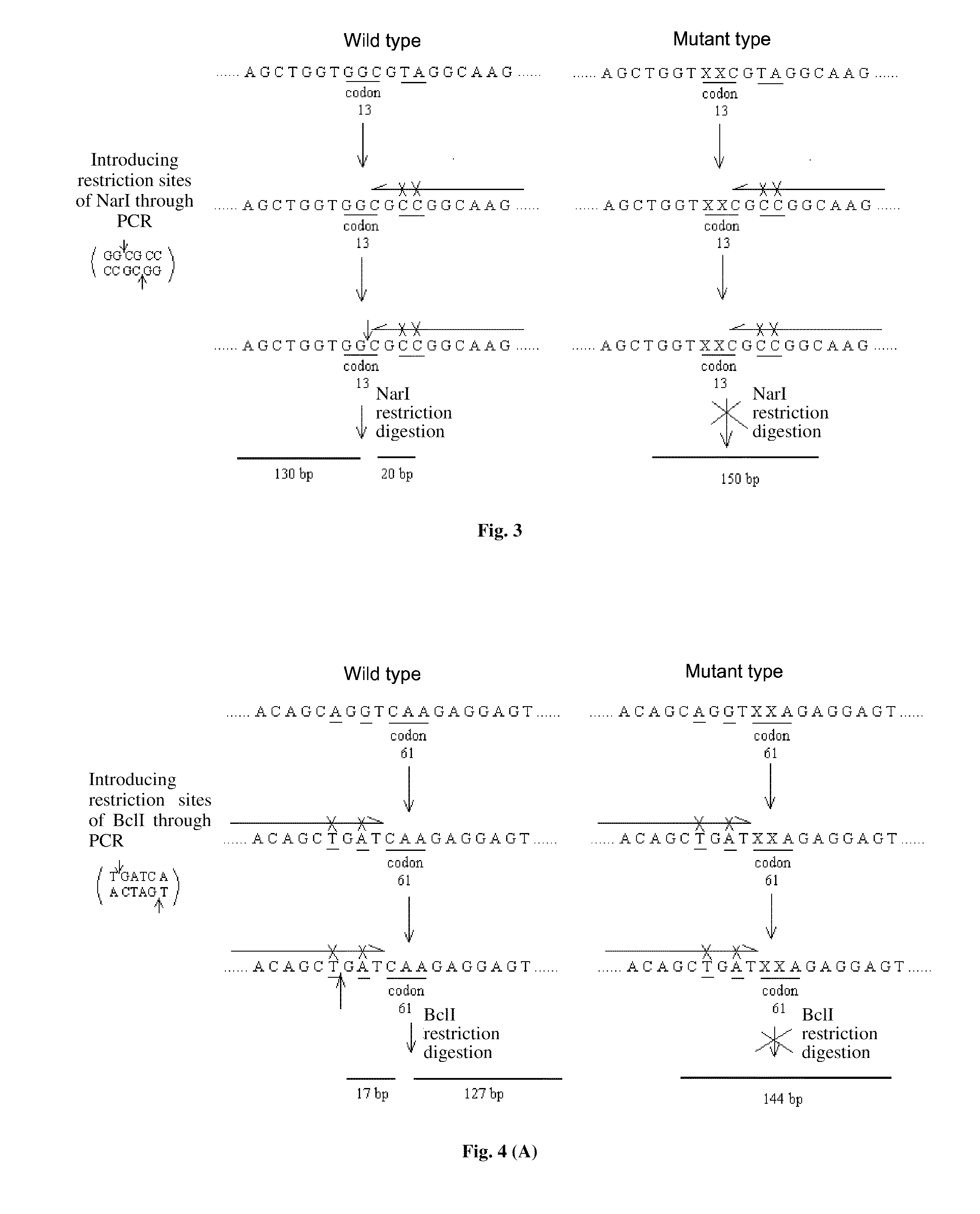
PROBES FOR DETECTING MUTATIONS OF kRas GENE, LIQUICHIP AND DETECTION METHODS THEREOF
InactiveUS20110269640A1Steric hindrance is reducedImprove efficiencySugar derivativesNucleotide librariesMicrosphereMutant allele
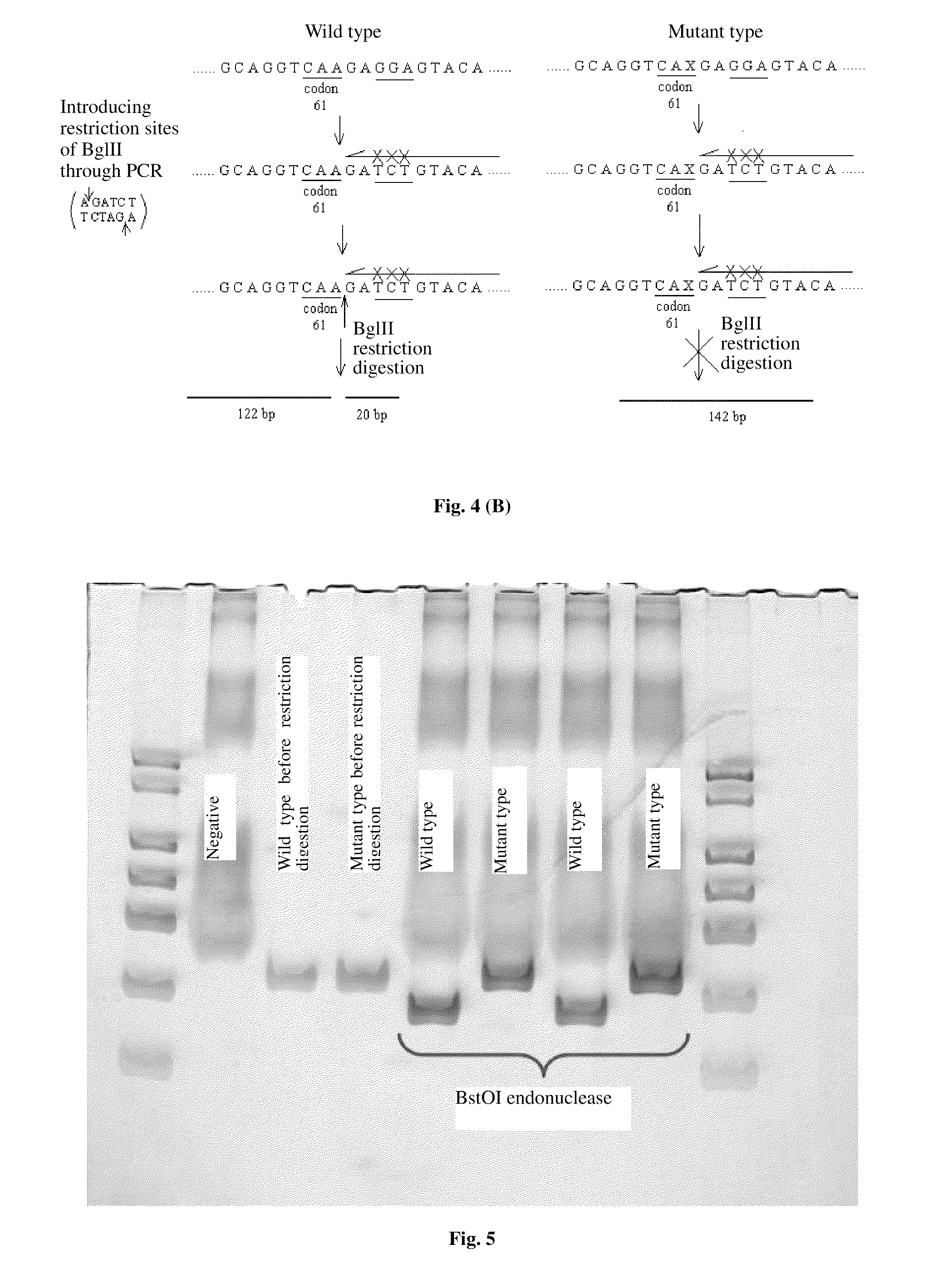
Nucleic acid probes for detecting kRas gene mutations, liquid chips and detection methods thereof are provided. The liquid chips for detecting kRas gene mutations comprise: microspheres coupled with wild-type and mutant-type probes, each of which is amino-substituted at 5′-terminal, specific for kRas codons 12, 13 and / or 61, and primers for amplifying the target sequence biotin-labeled at the terminal which are enriched with mutant alleles of kRas codons 12, 13 and / or 61 to be detected. The detection methods are rapid and accurate, and the processes of the methods are easy to perform. The liquid chip can be used to detect mutations of kRas as assistance to early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, and can be used to prognose efficiency of the molecular targeted therapy to choose right medicine accurately clinically and avoiding economic loss and time loss caused by unnecessary treatment.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Method and kit for detecting correlated mutation allele of total farrow number of sow as well as application
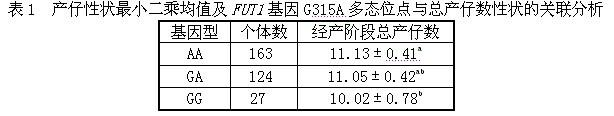
InactiveCN101892318AIncrease in total litter sizeAccurate genotypingMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismGene type
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting the correlated mutation allele of a total farrow number of a sow as well as the application. The method adopts a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)-SSCP (Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism) method, PCR augmentation comprises a section from 315-bit deoxyribonucleotide at the 5' terminal of Gen Bank Accession Number AX752829, PCR augmentation products are detected by gel electrophoresis, and the gene type of the sow to be detected is confirmed according to an electrophoresis result: the gene type of the sow to be detected can be GG or AA which means a homozygote if the electrophoresis result presents two straps, and the gene type of the sow to be detected can be GA which means a heterozygote if the electrophoresis result presents three straps. The detection method of the invention has simple operation, low expense and high accuracy, can realize the automatic direct detection and has higher practical breeding application values. The method and the kit of the invention can be applied to breed grices, early select grices to be selected, effectively solve the problem of long time for selecting excellent grices in practical production, decrease the breeding expense, increase the total sow farrow number and improve the economic benefits.
Owner:BEIJING HEILIU ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TECH
Reverse two-hybrid system for identification of interaction domains
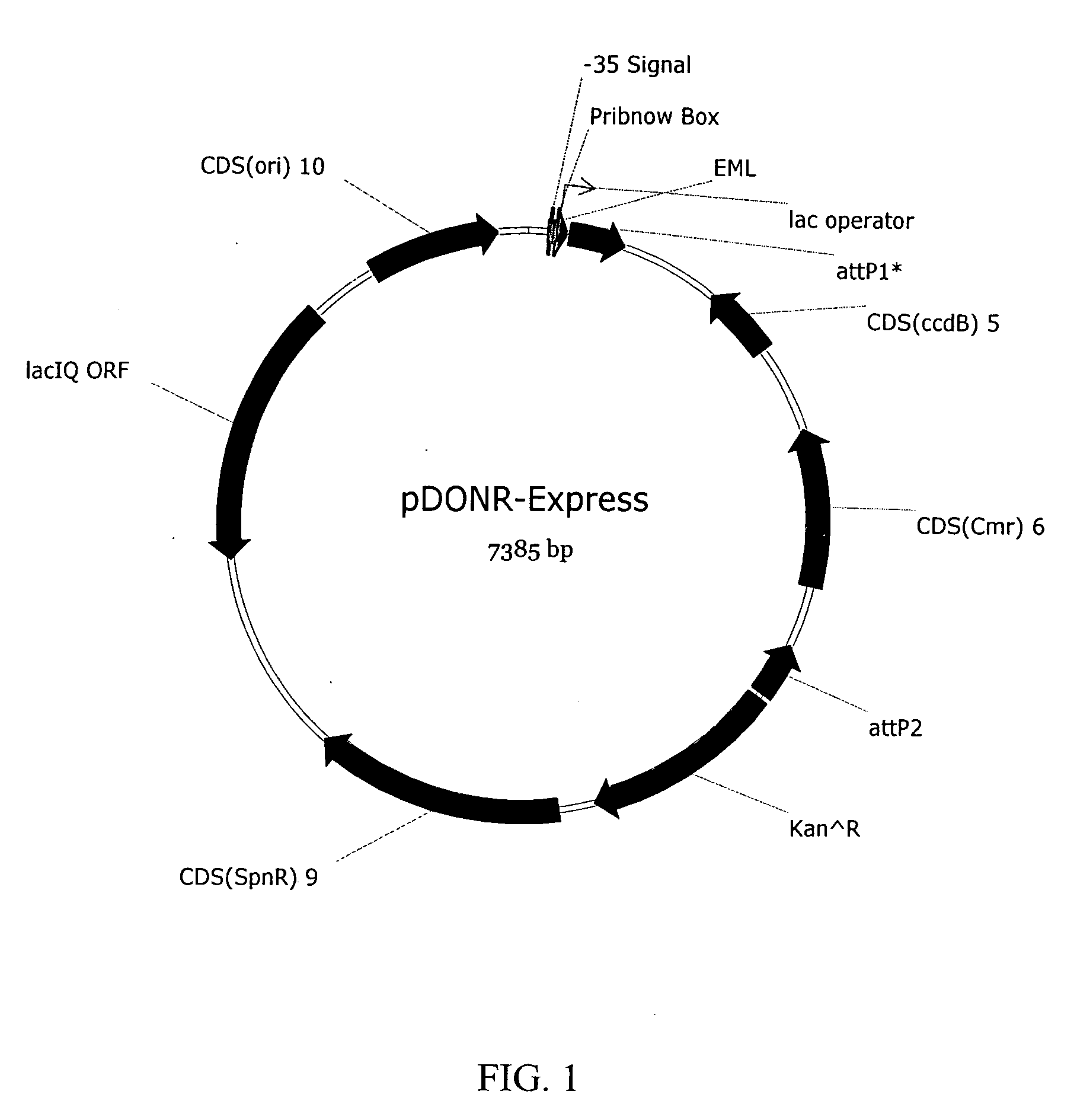
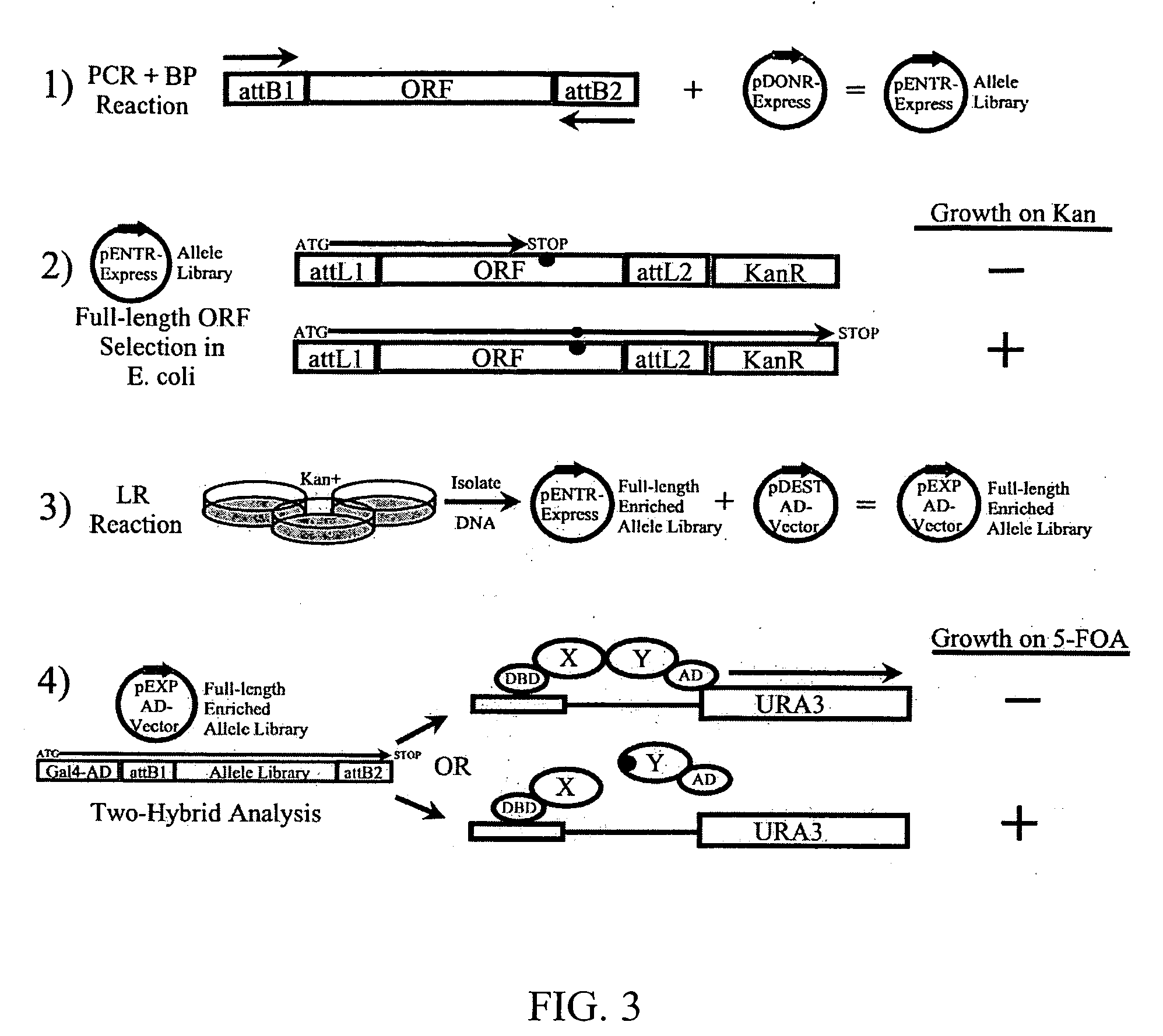
The present invention provides methods for producing allele libraries and vectors for producing these libraries. The present invention also provides methods of identifying interaction domains between proteins. The vectors, kits, and methods of the present invention suitably utilize recombinational cloning to efficiently generate and screen full-length mutant alleles of target sequences of interest.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Depression gene
InactiveUS7410944B1Avoid depressionImprove disease symptomsPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesGermline mutationGenetics human
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
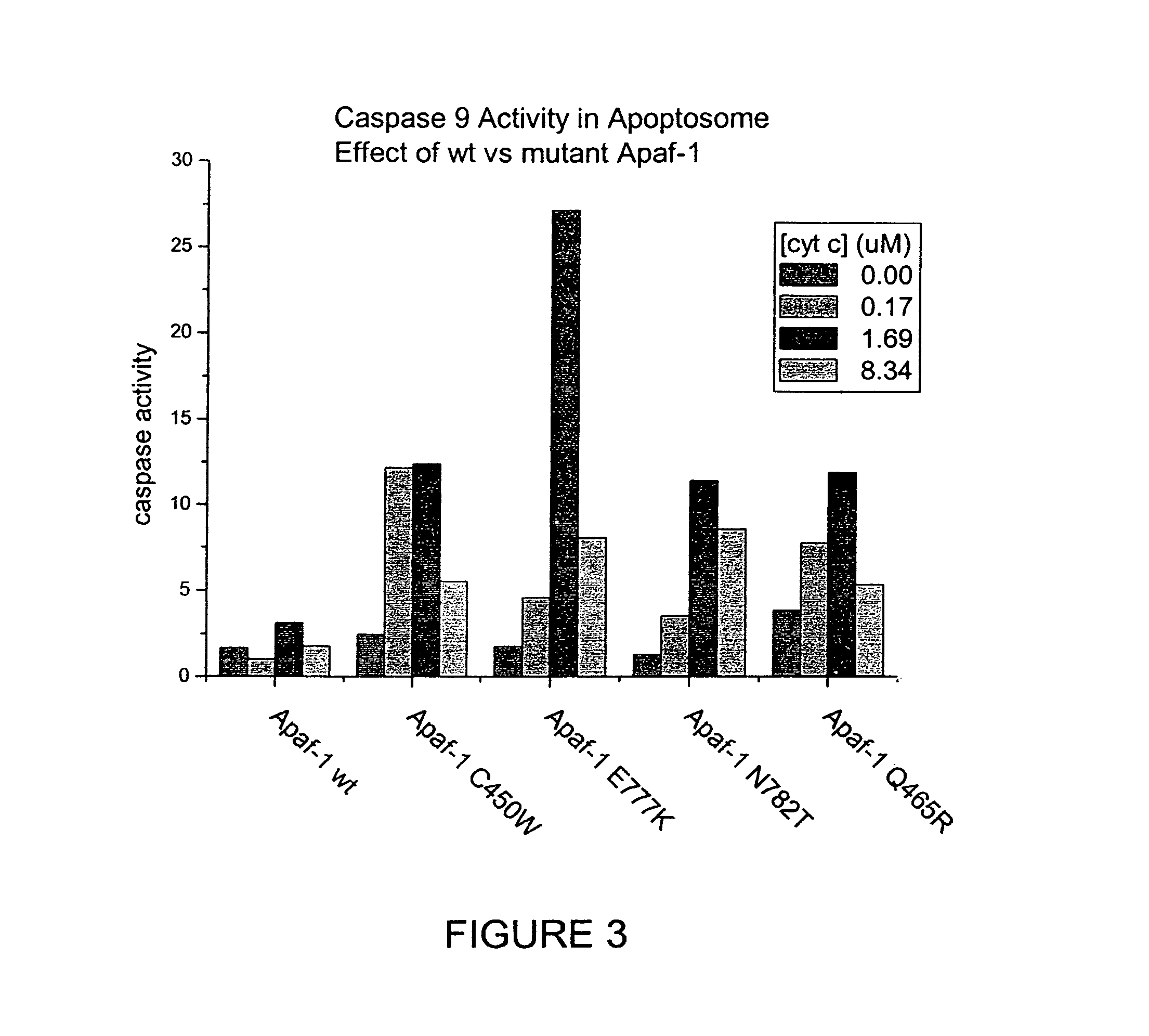
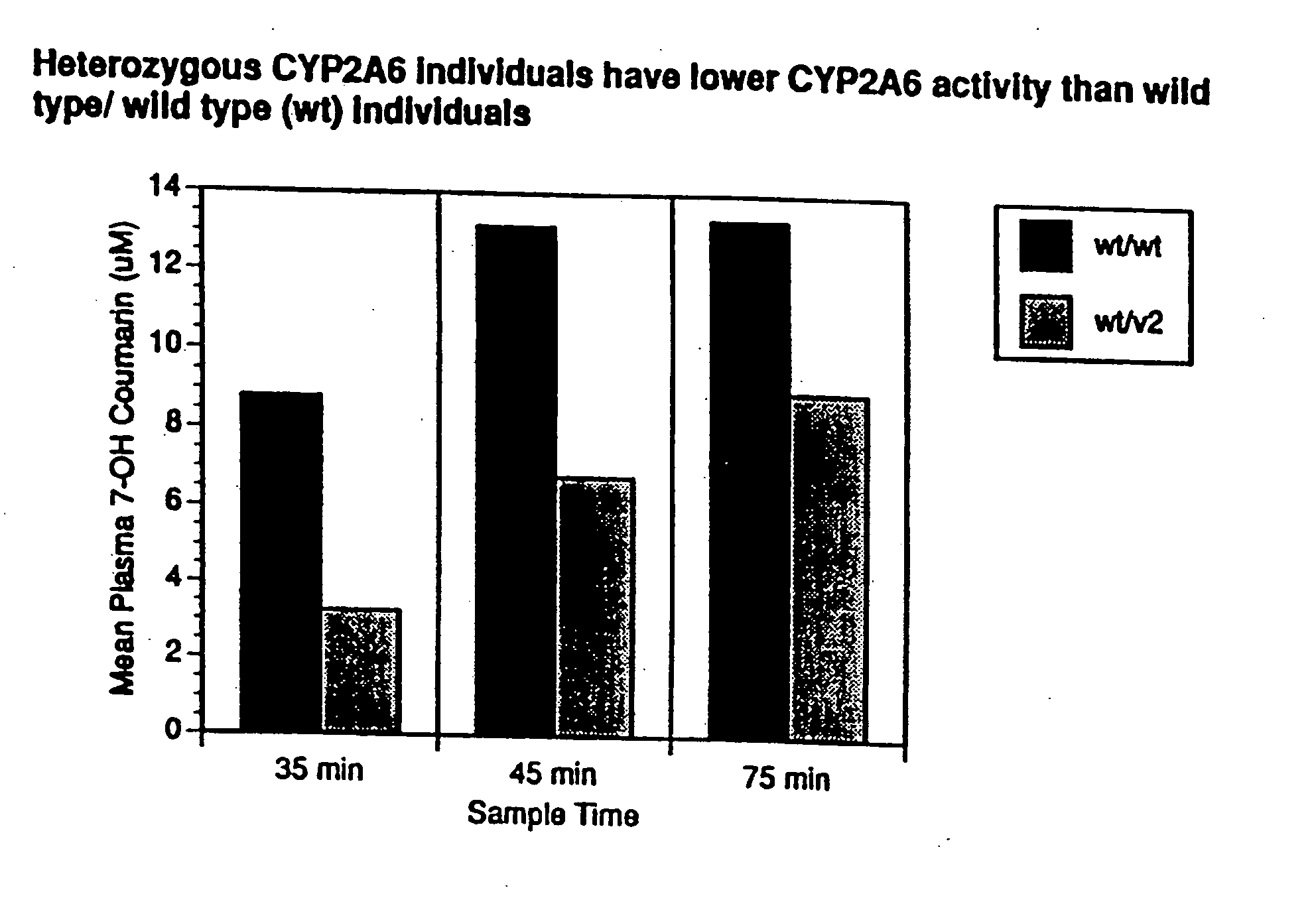
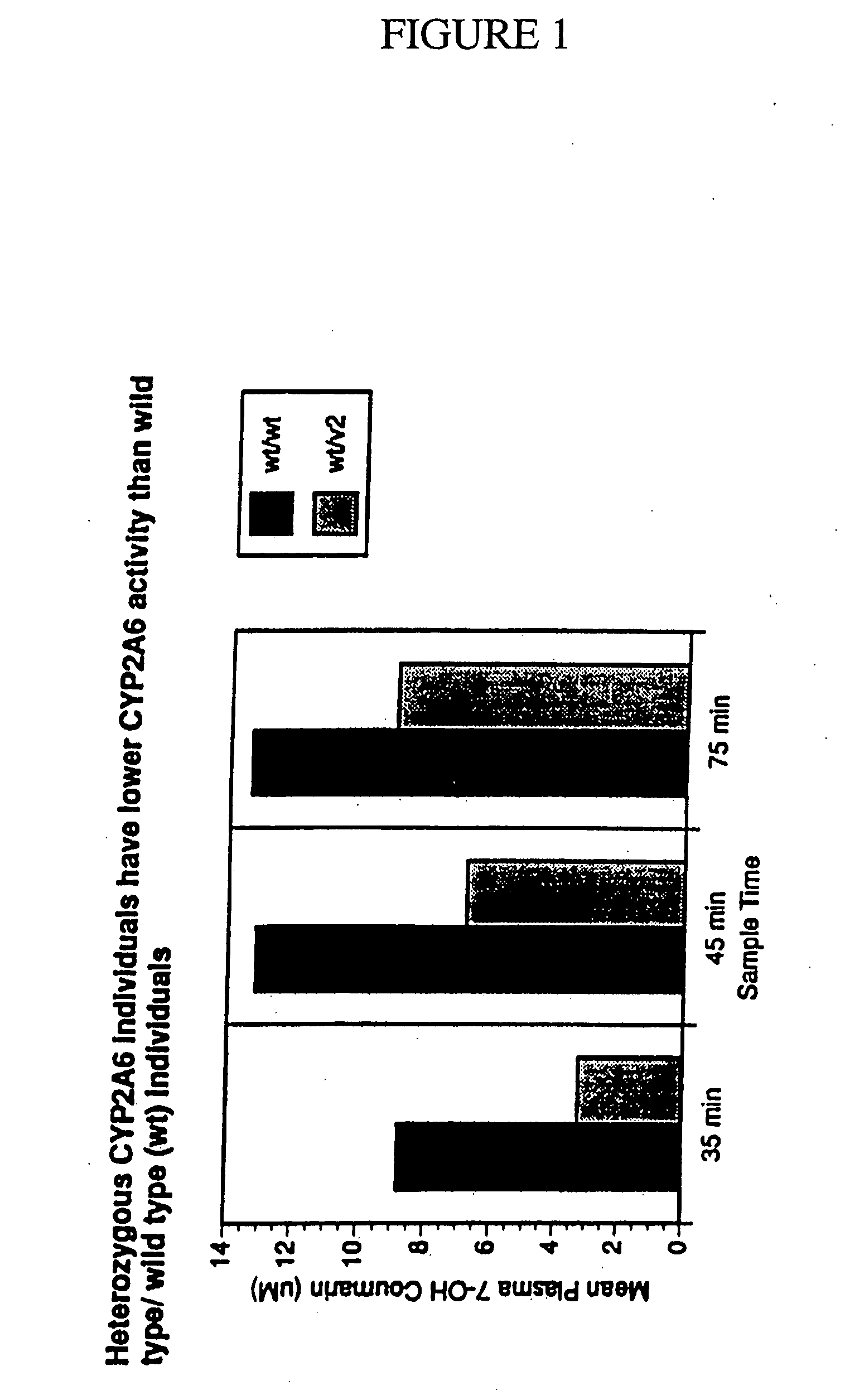
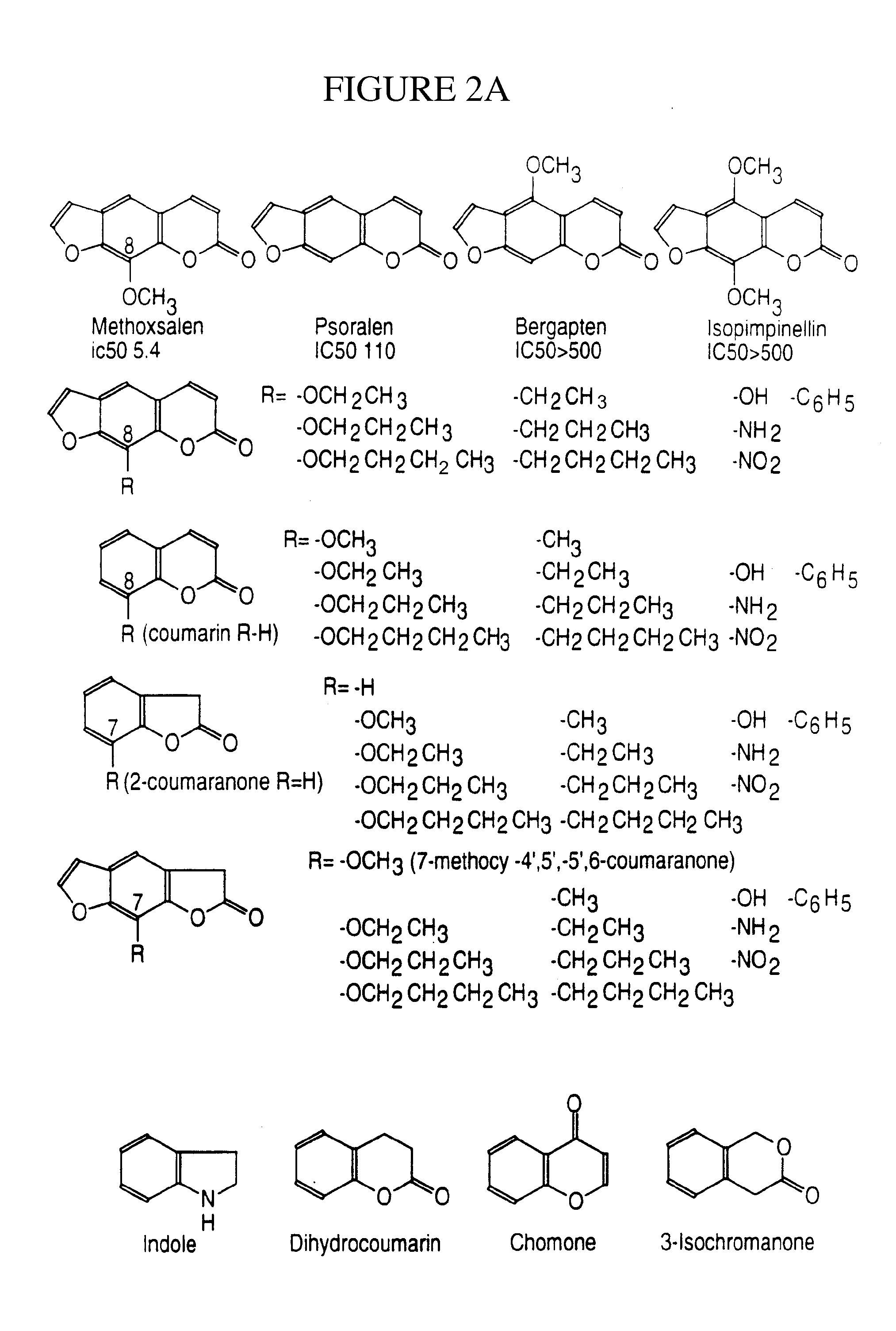
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on cyp2a enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Method to Screen Plants for Genetic Elements Inducing Parthenogenesis in Plants
InactiveUS20130180005A1Fertilization of will not be preventedPromote generationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
Compositions and methods for producing a plant population lacking sexually derived embryos are provided. Compositions include suppression cassettes encoding polynucleotides and promoters resulting in parthenogenesis. Further provided are parthenogenesis genetic elements used to prevent sexual reproduction in self-reproducing plants.Methods include: utilizing maternal embryo defective recessive mutations which are maintained as a sterile inbred maintenance system, allowing generation of populations that are homozygous for recessive mutant alleles, but transgenically complemented. Methods include utilizing a toxin genes expressed via egg-cell specific promoters, creating a dominant, embryo-less phenotypes, non-transmittable through female gametes. Resultant hemizygous plants are transformed with egg-cell promoters driving the antidote, a pollen ablation PTU and a seed color marker for identification of transgenic seed. The generation of a plants 50% female fertile, having seed which when grown in the next generation will yield plants with 50% viable transgenic seed, and 50% non-viable embryo-less seed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Leaf lettuce mutant allele
InactiveUS20140259210A1Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic MaterialsMutant allele
The present invention is directed toward leaf lettuce varieties containing mutant allele VSTMA1 that exhibit tan seed color. The invention relates to the seeds, plants and plant parts of lettuce plants containing mutant allele VSTMA1 and to methods for producing a lettuce plant by crossing lettuce plants containing mutant allele VSTMA1 with itself or another lettuce cultivar. The invention further relates to methods for producing a lettuce plant containing mutant allele VSTMA1 containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic lettuce plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to lettuce cultivars or breeding cultivars and plant parts derived from lettuce plants containing mutant allele VSTMA1, to methods for producing other lettuce cultivars, lines or plant parts derived from lettuce plants containing mutant allele VSTMA1 and to the lettuce plants, varieties, and their parts derived from the use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid lettuce seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing lettuce plants containing mutant allele VSTMA1 with another lettuce cultivar.
Owner:SAKATA SEED AMERICA
Diabetes gene
InactiveUS6902888B1Preventing and treating diabetesReduce and prevent gene expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin dependent diabetesDiabetes Therapy
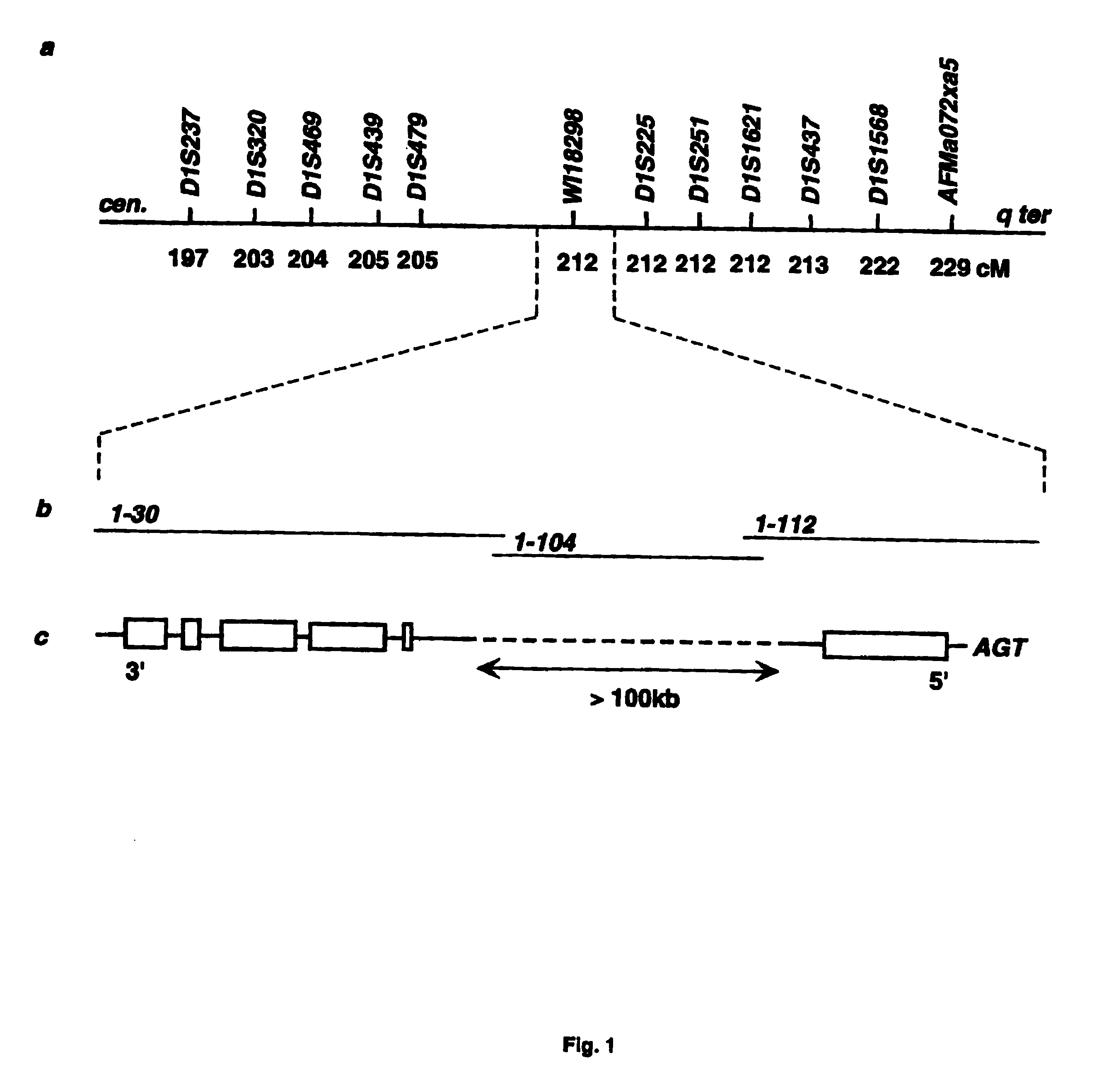
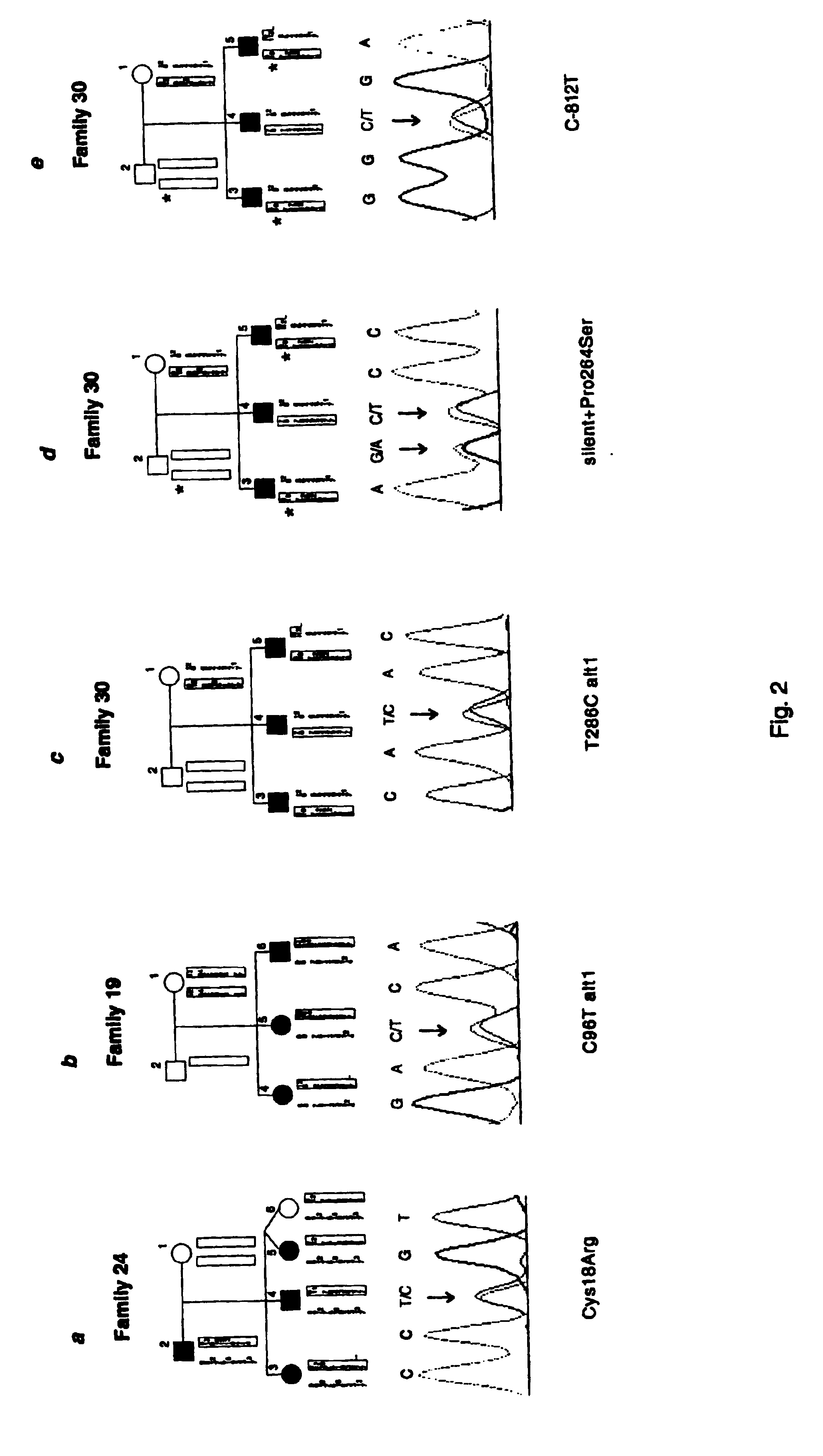
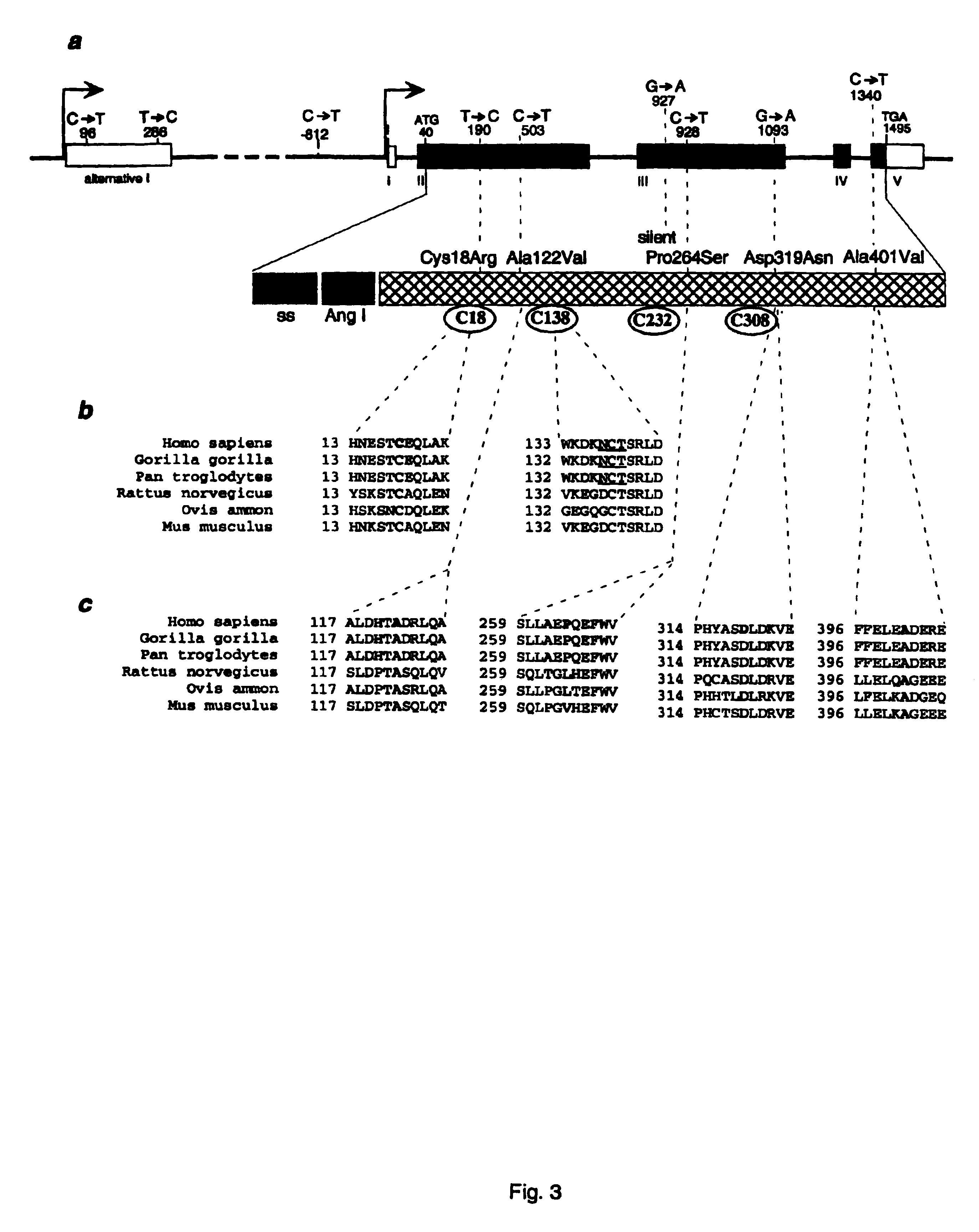
The present invention relates generally to the field of human genetics. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods and materials used to isolate and detect human diabetes mellitus predisposing gene, specifically the angiotensinogen (AGT) gene, some mutant alleles of which cause susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). More specifically, the invention relates to gernline mutations in the AGT gene and their use in the diagnosis of predisposition to diabetes. The invention also relates to the prophylaxis and / or therapy of diabetes associated with a mutation in the AGT gene. The invention further relates to the screening of drugs for diabetes therapy. Finally, the invention relates to the screening of the AGT gene for mutations, which are useful for diagnosing the predisposition to diabetes.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
Rice Mutant Allele
InactiveUS20100132062A1Increase productionControl spreadImmunoglobulinsPlant genotype modificationNucleotideMutant allele
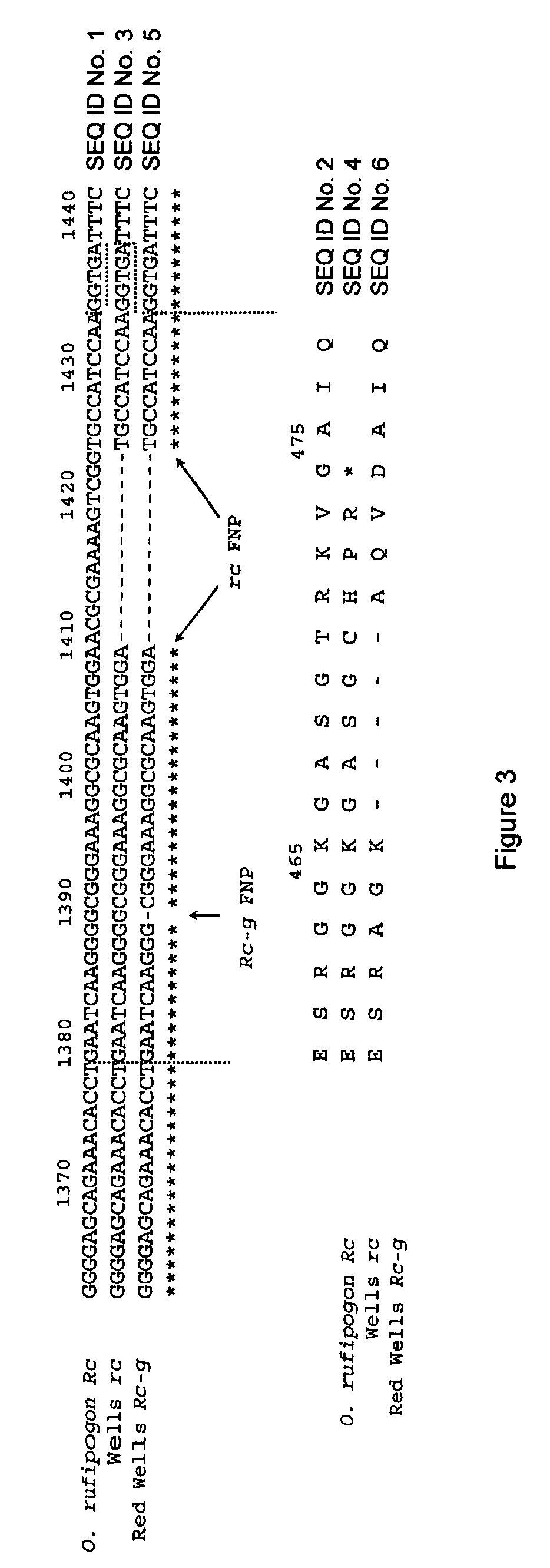
A rice mutant allele designated Rc-g is disclosed. The invention relates to the Rc-g nucleotide sequence, the amino acid sequence, rice seeds containing the mutant allele Rc-g, to rice plants containing the mutant allele Rc-g and to methods for producing a rice plant containing the mutant allele Rc-g produced by crossing a rice plant containing allele Rc-g with itself or another rice variety. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds and hybrid rice plants containing mutant allele Rc-g.
Owner:DEREN CHRISTOPHER W +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com